Patents
Literature
150 results about "Proton magnetic resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (proton NMR, hydrogen-1 NMR, or 1H NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules.
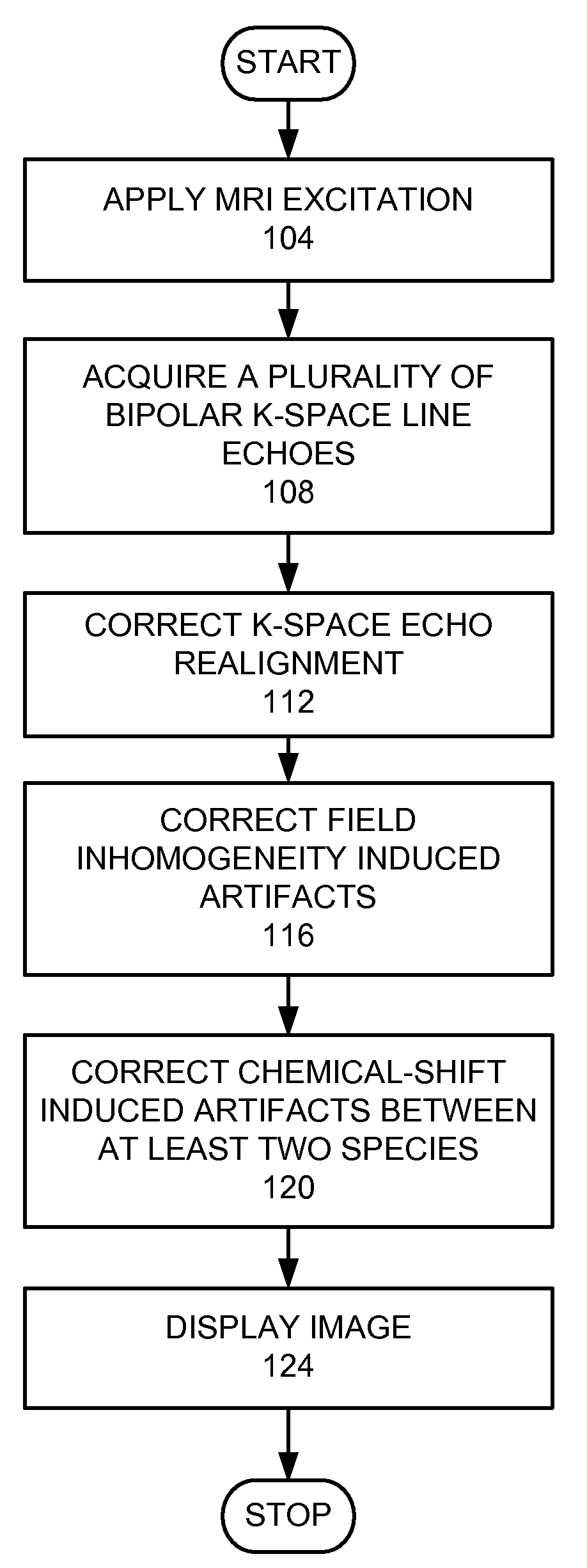
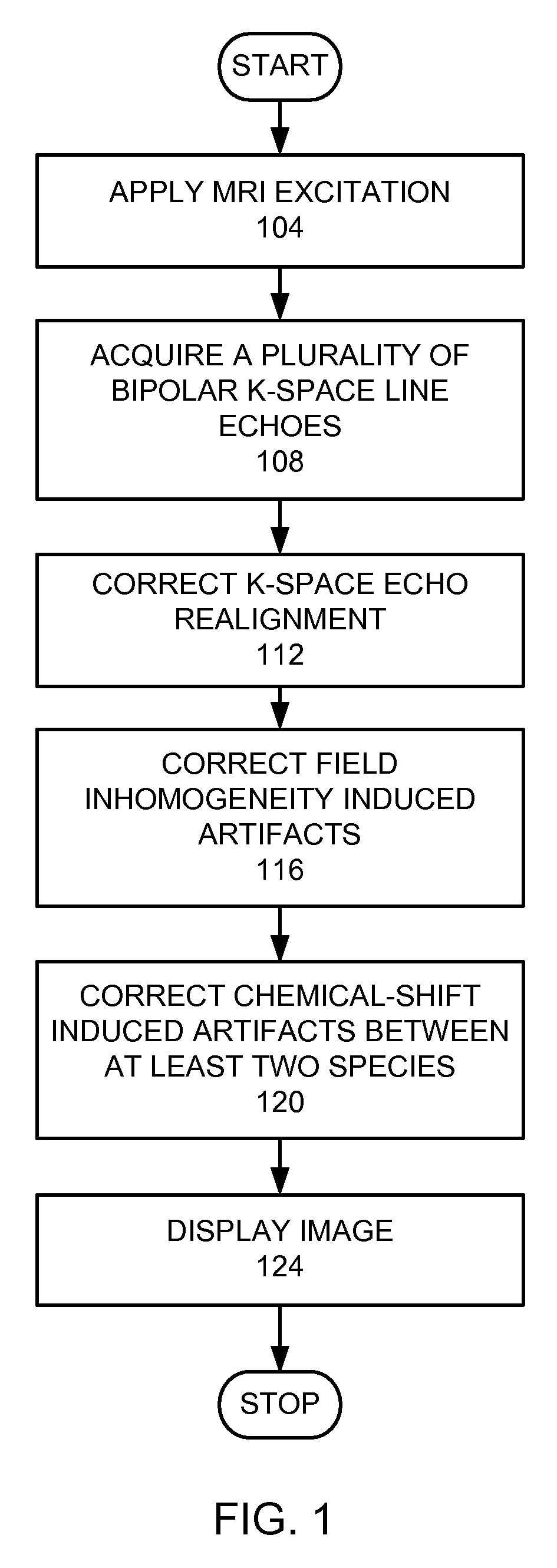
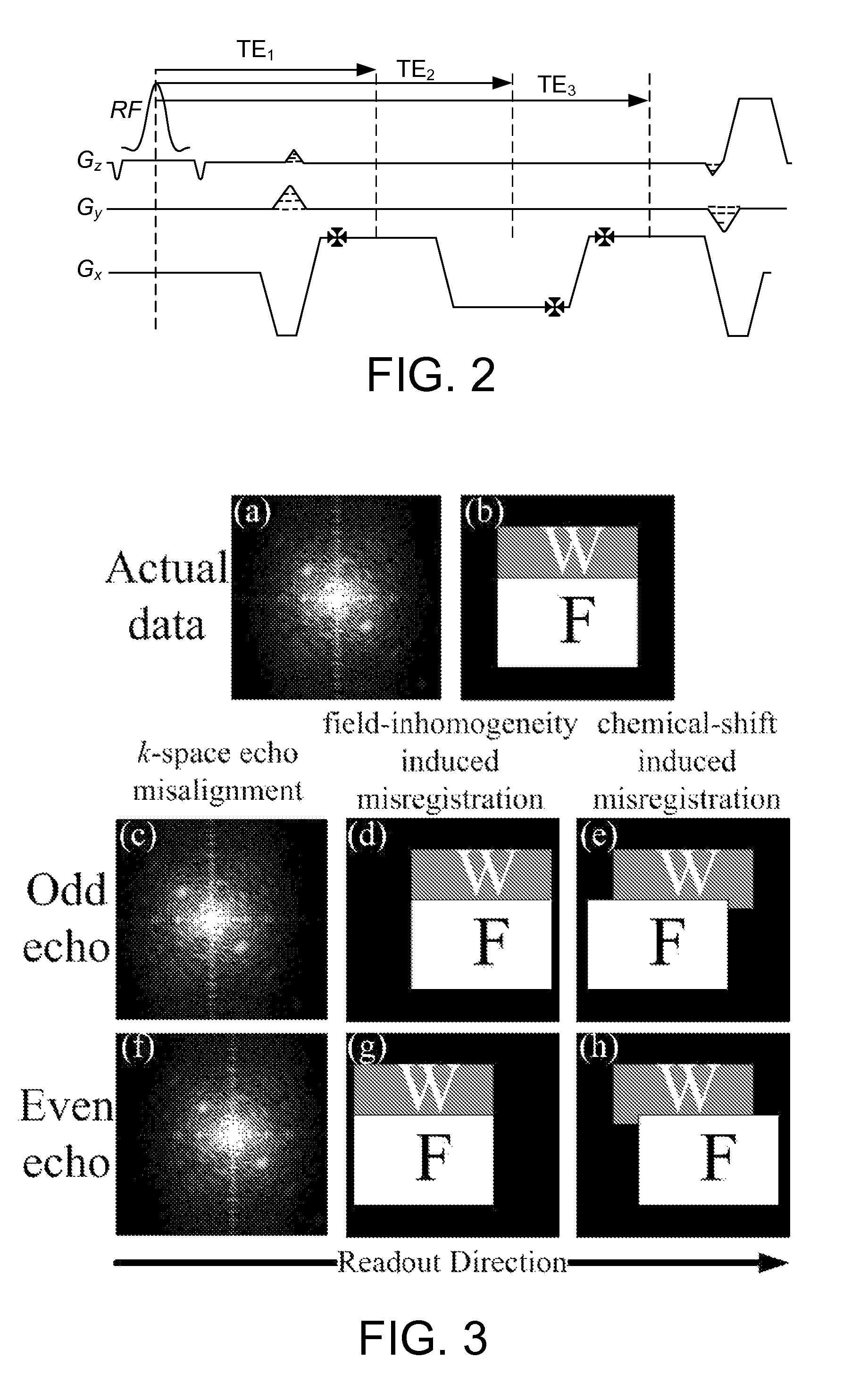
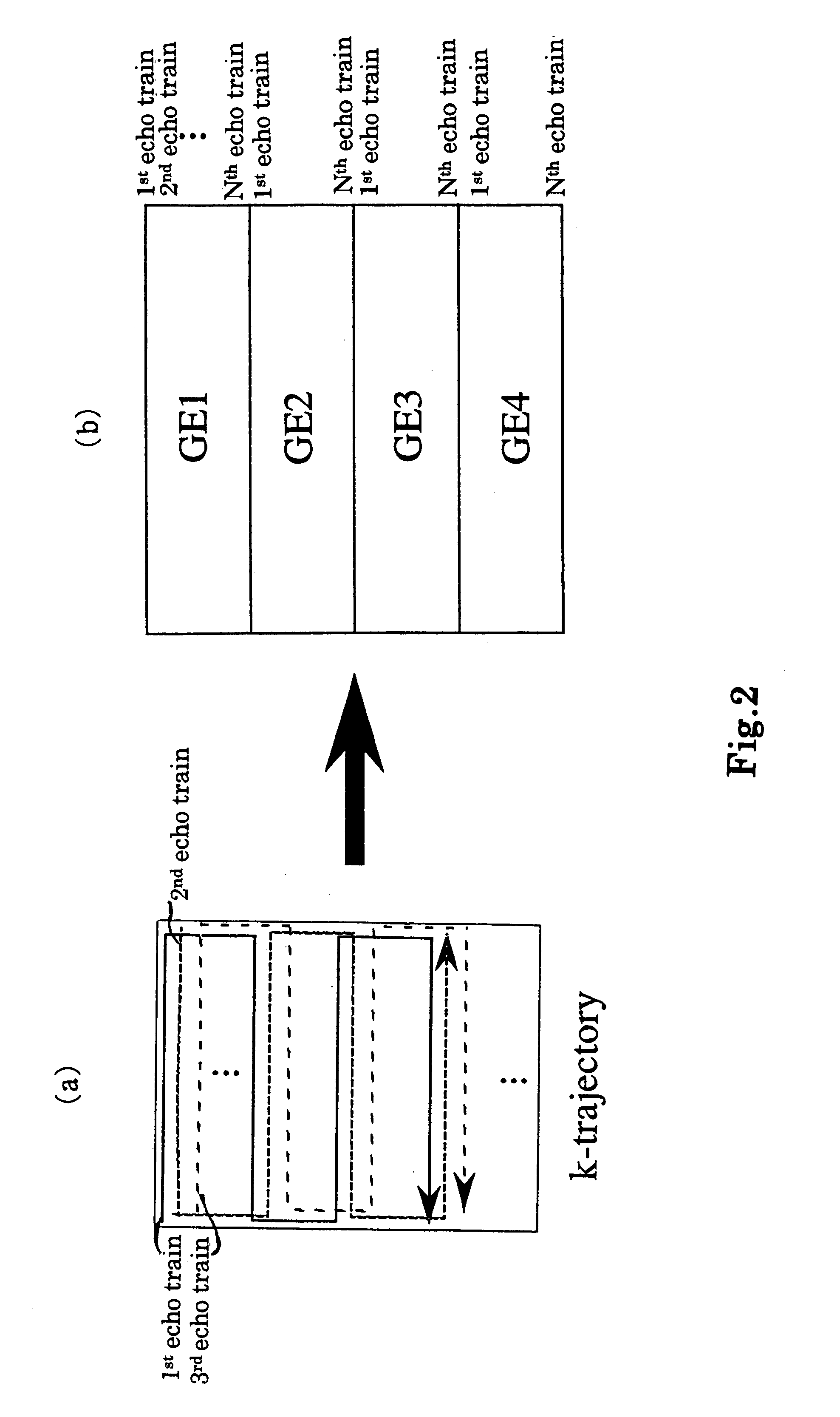
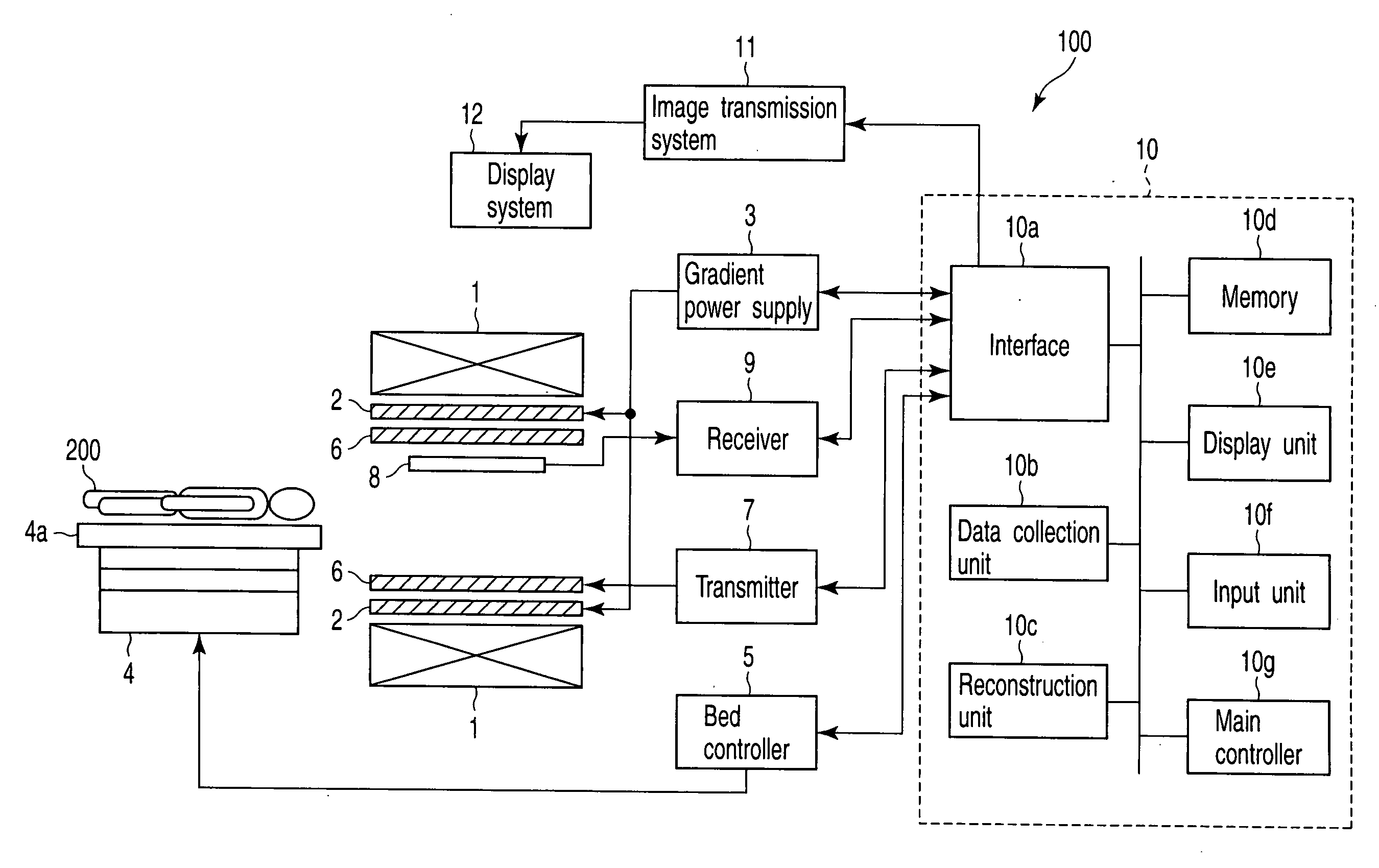
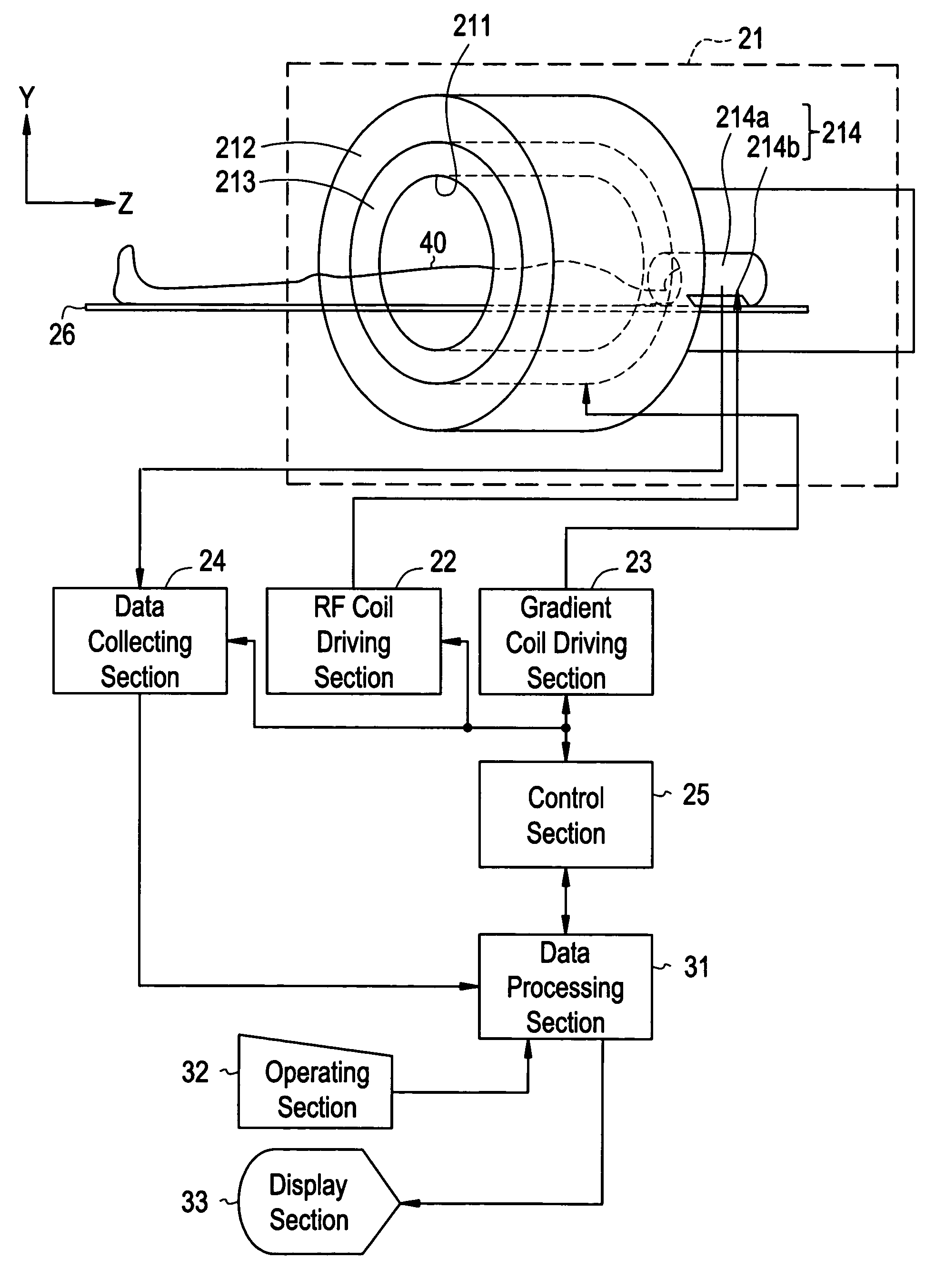
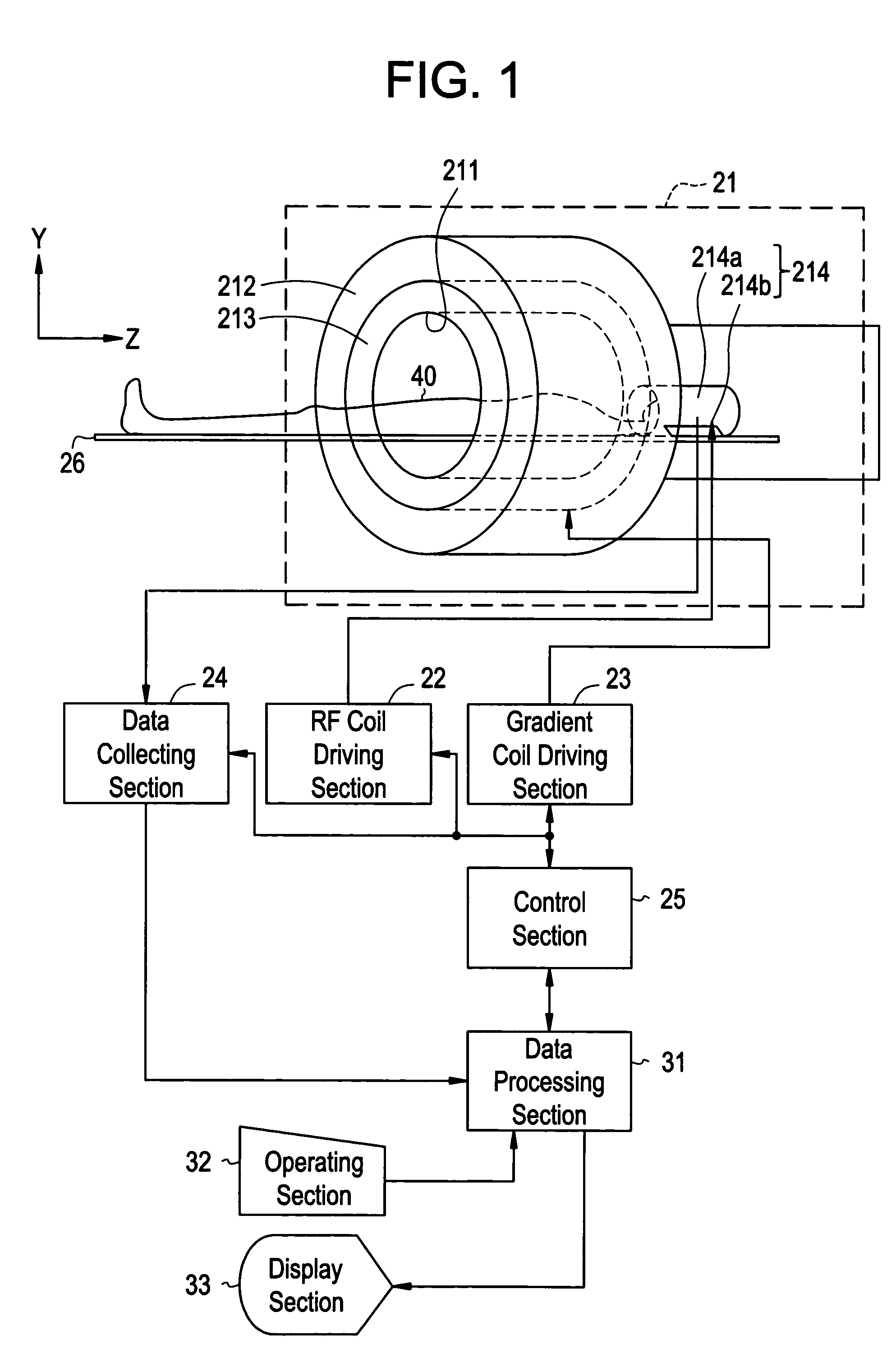
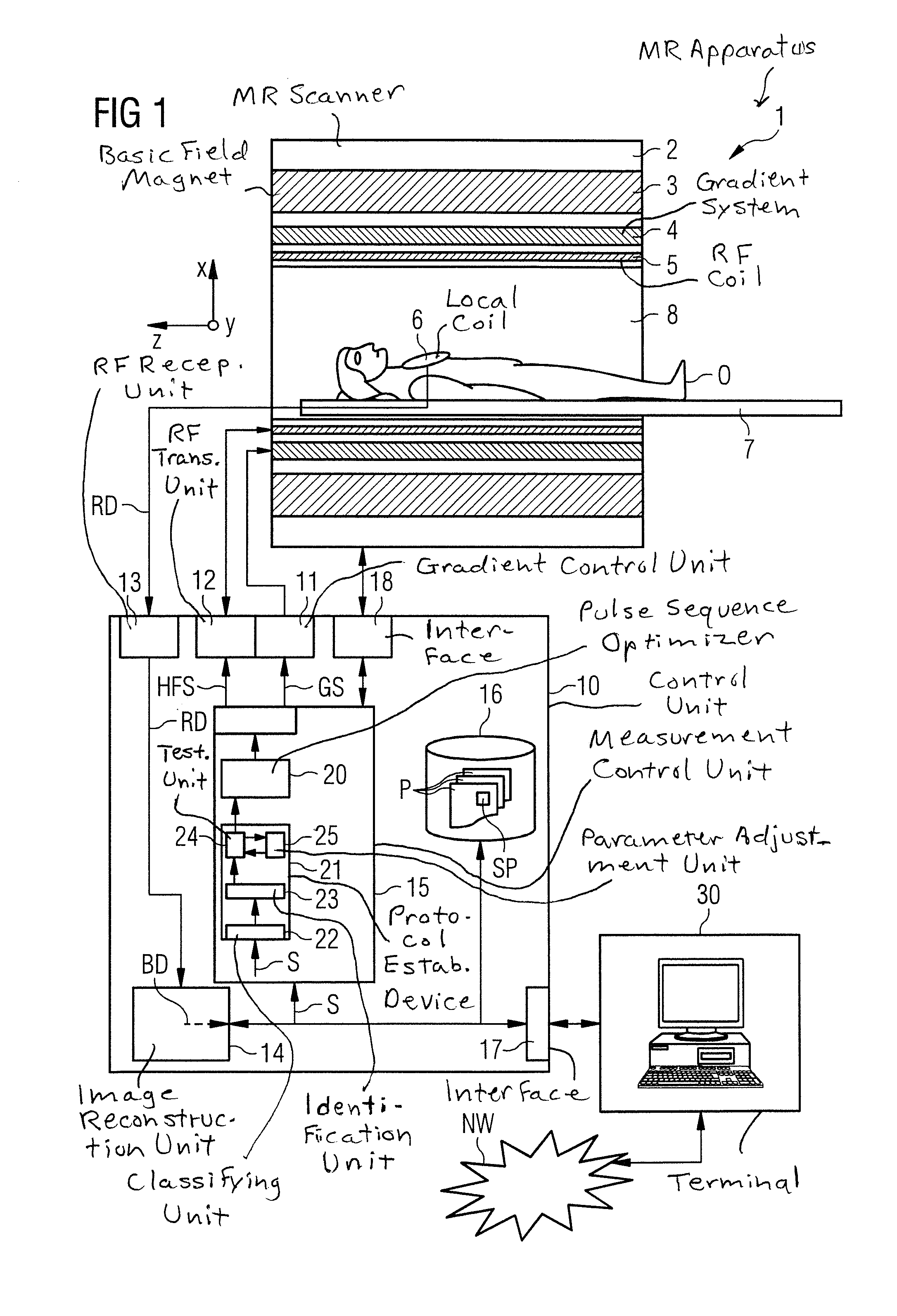
Magnetic resonance imaging with bipolar multi-echo sequences
ActiveUS7777486B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionProton magnetic resonanceResonance excitation
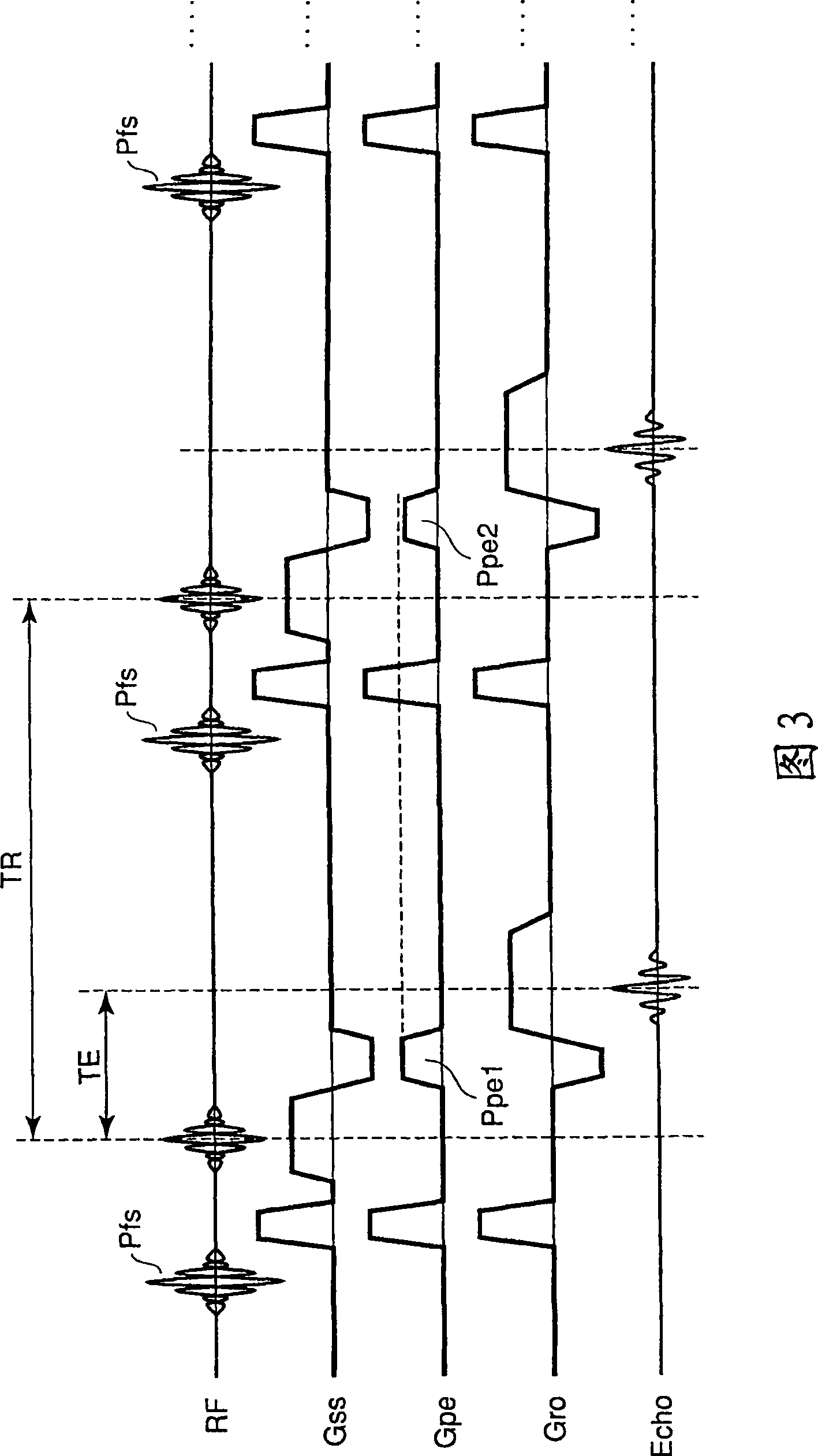
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is provided. A magnetic resonance excitation is provided. A plurality of k-space echoes is acquired bi-directionally wherein at least one echo is an even echo acquired in a first direction and at least one echo is an odd echo acquired in a second direction opposite from the first direction. K-space echo realignment is corrected between the even and odd echoes. Field inhomogeneity induced artifacts are corrected. Chemical shift induced artifacts between at least two species are corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
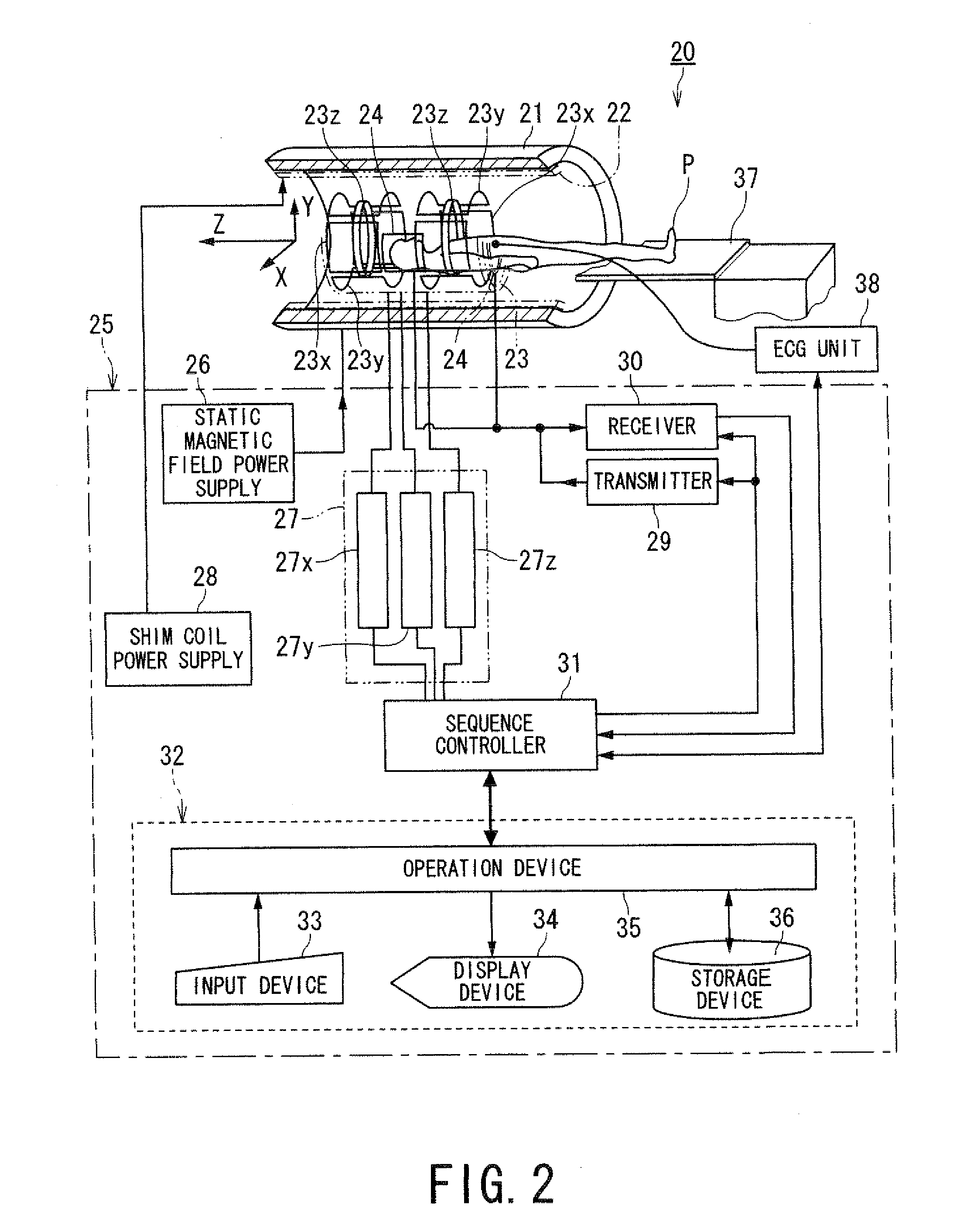
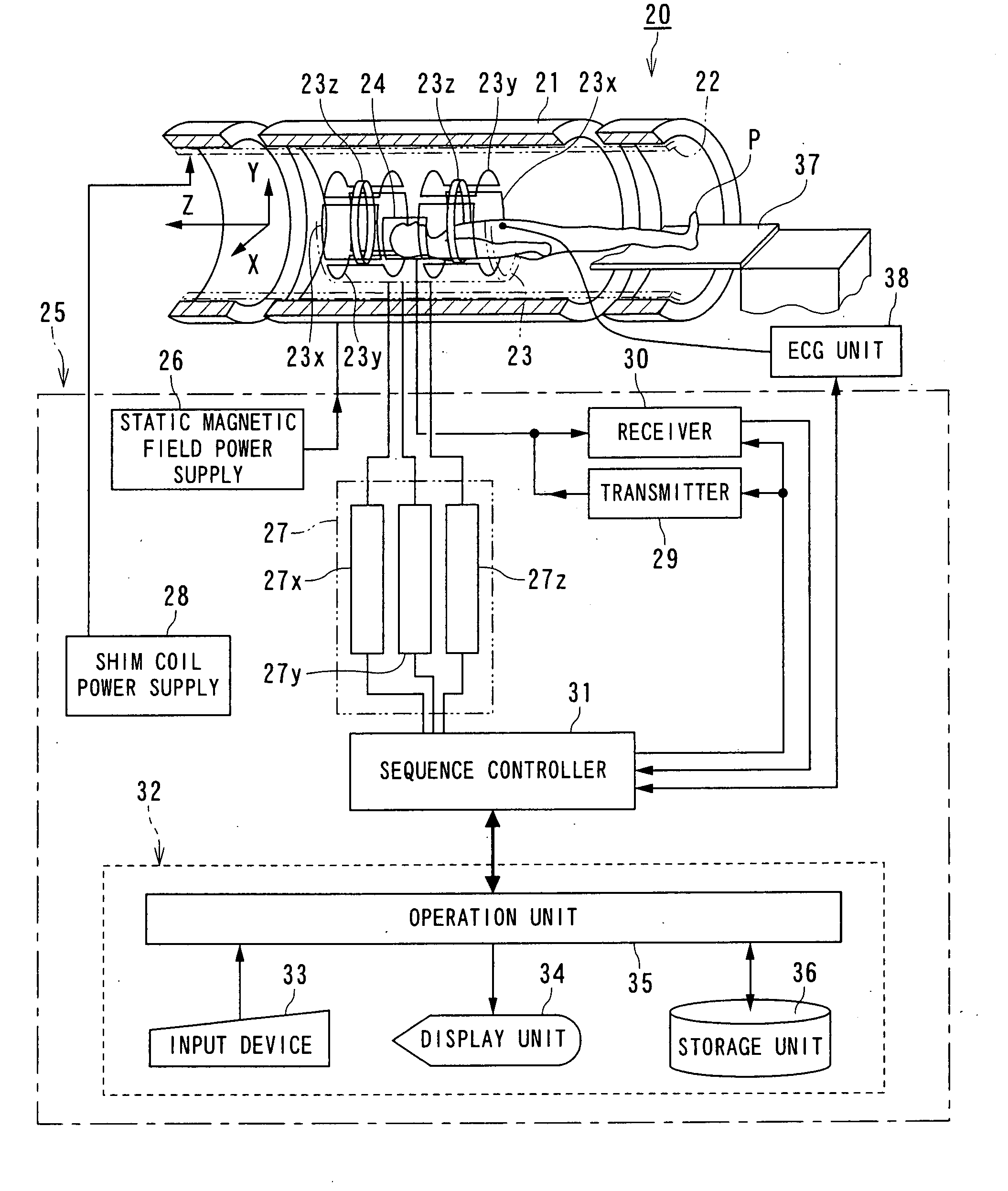
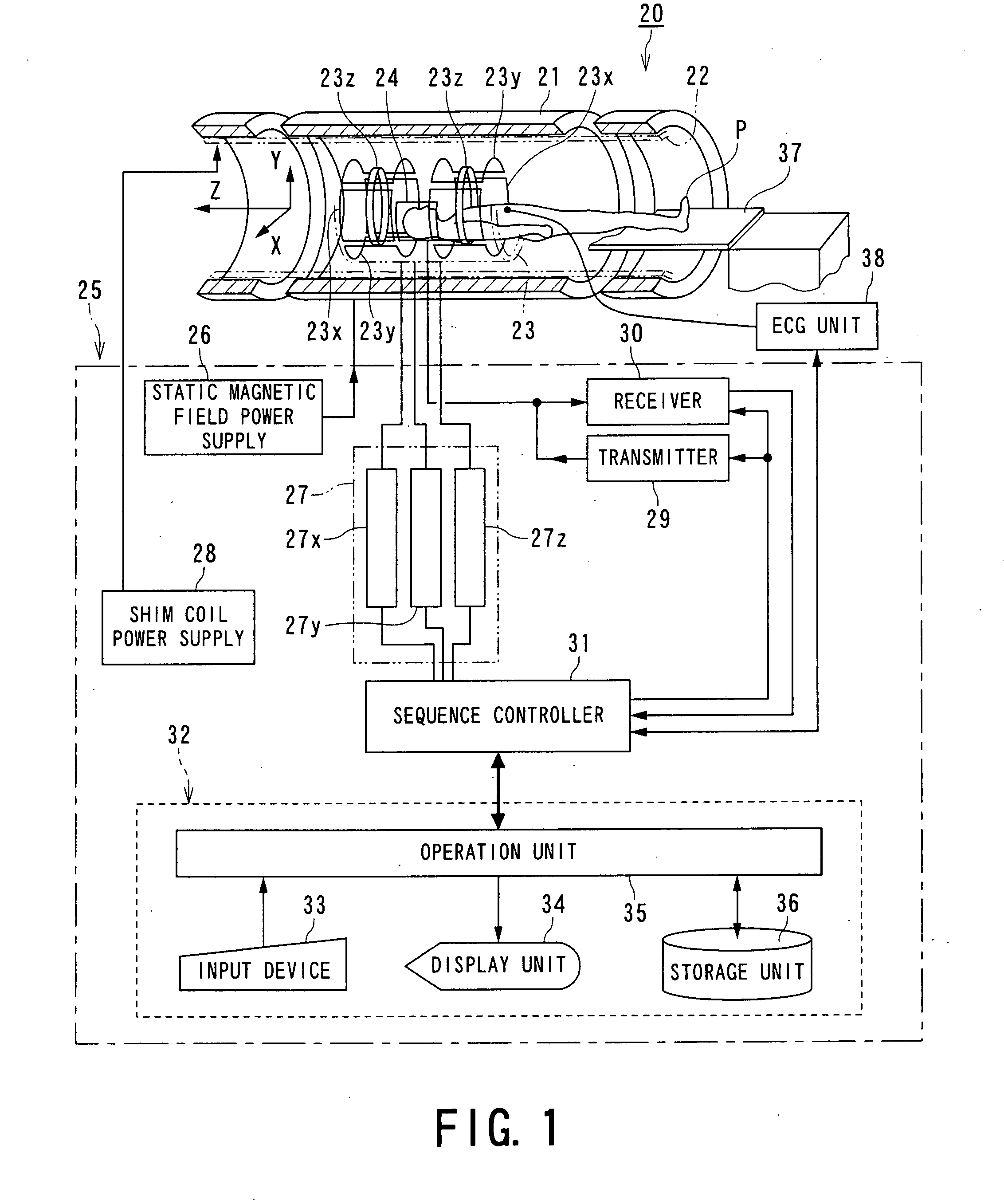
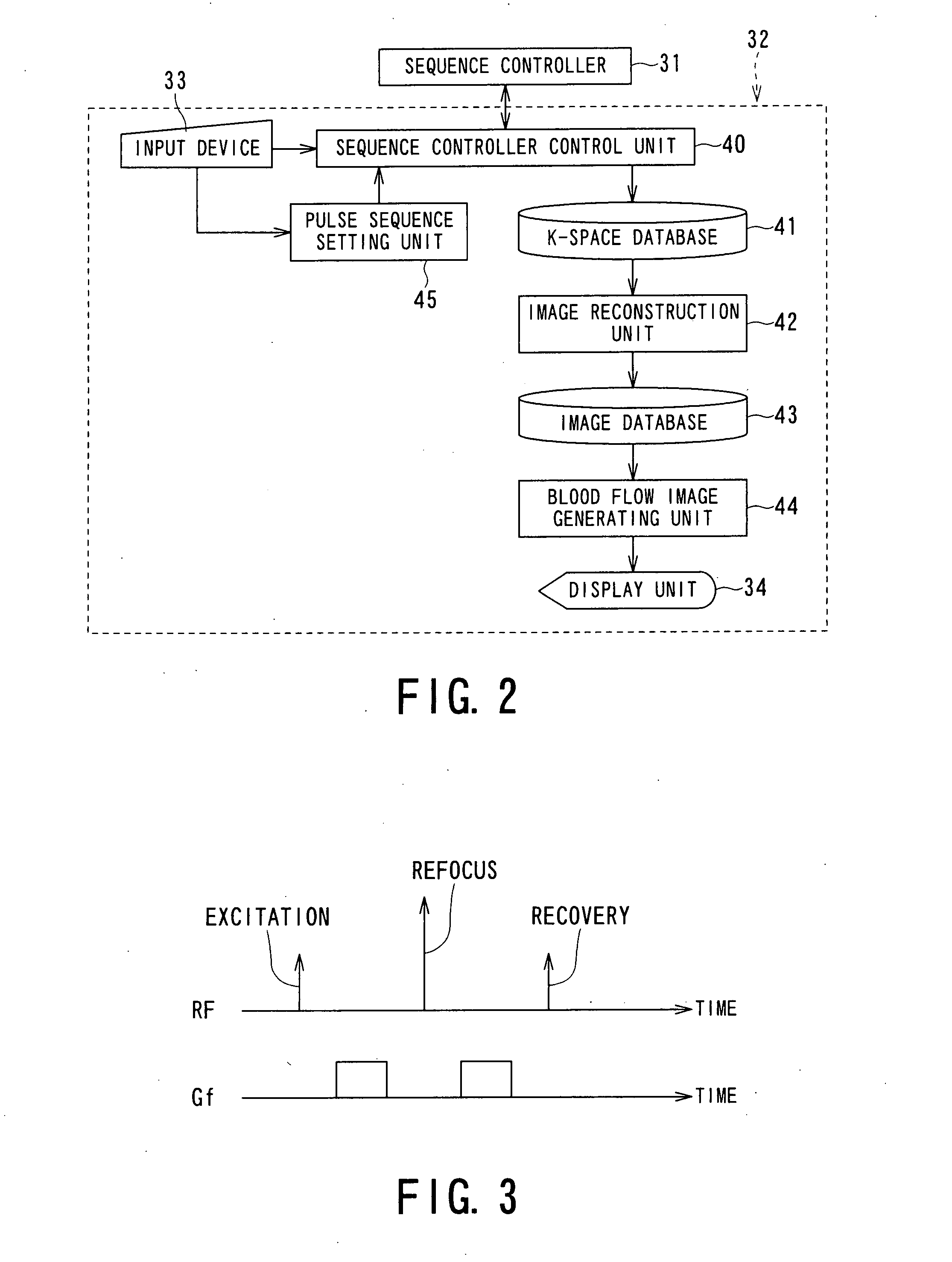
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
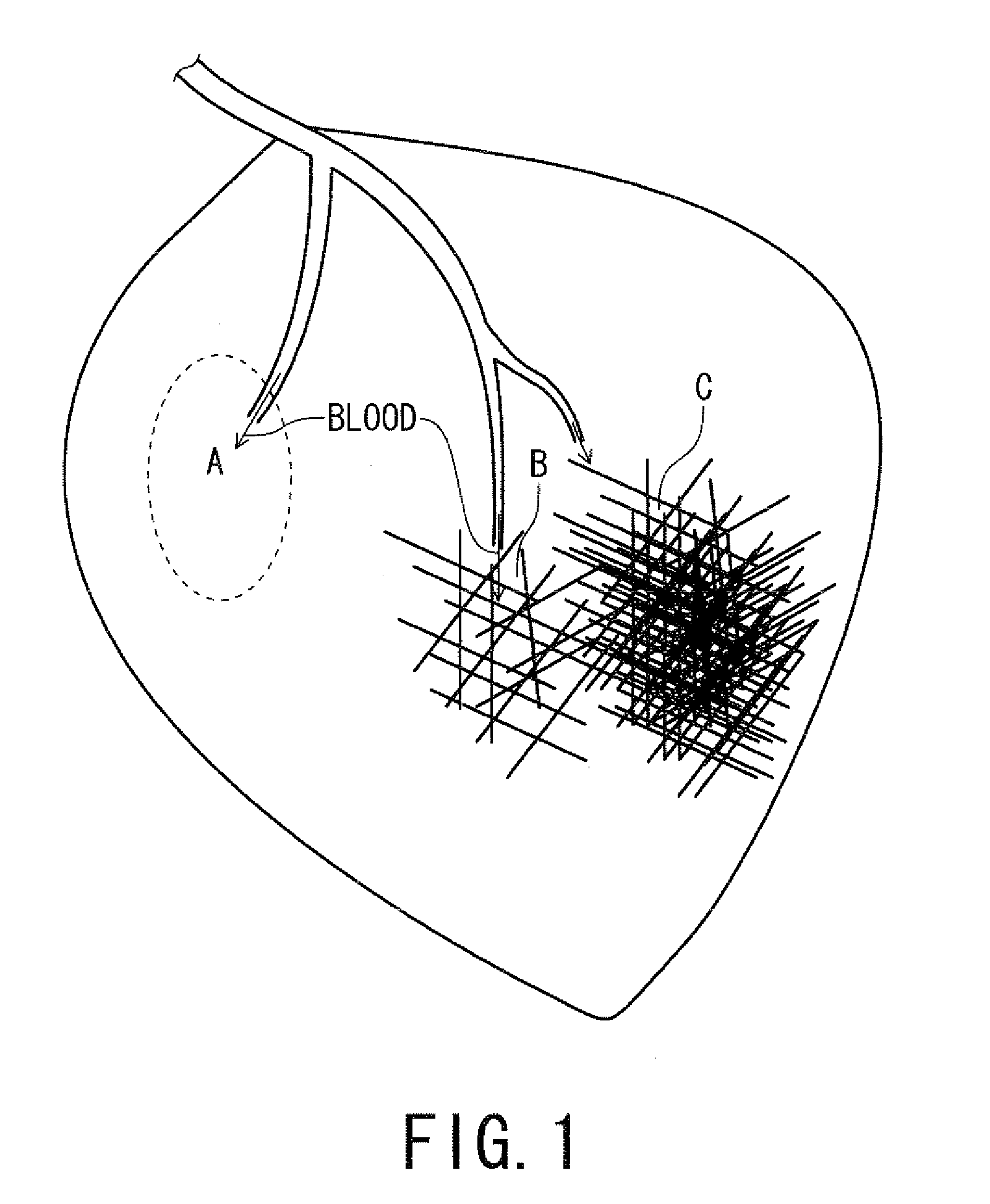
ActiveUS20110071382A1Easy accessSatisfactory resolutionMagnetic measurementsSensorsAscending aortaProton magnetic resonance
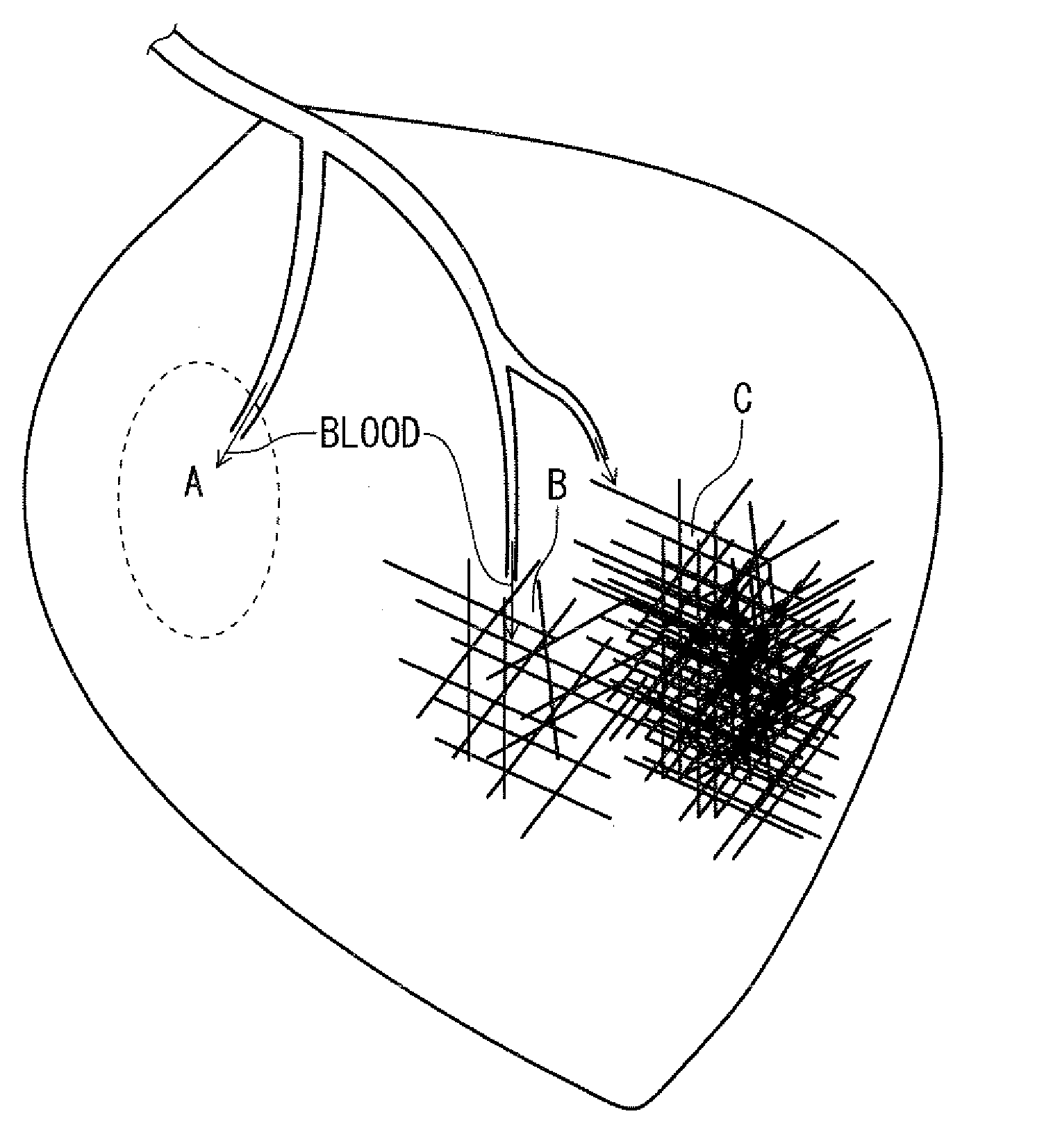
According to one of the aspects of an MRI apparatus of the present invention, the MRI apparatus includes an imaging data acquiring unit and a blood flow information generating unit. The imaging data acquiring unit acquires imaging data from an imaging region including myocardium, without using a contrast medium, by applying a spatial selective excitation pulse to a region including at least a part of an ascending aorta for distinguishably displaying inflowing blood flowing into the imaging region. The blood flow information generating unit generates blood flow image data based on the imaging data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Methods and systems of combining magnetic resonance and nuclear imaging
InactiveUS20110270078A1Reducing and minimizing mis-registration artifactReducing or minimizing mis-registration artifactsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityProton magnetic resonance
An multi-modality imaging system for imaging of an object under study that includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus and an MRI-compatible single-photon nuclear imaging apparatus imbedded within the RF coil of the MRI system such that sequential or simultaneous imaging can be done with the two modalities using the same support bed of the object under study during the imaging session.
Owner:GAMMA MEDICA
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
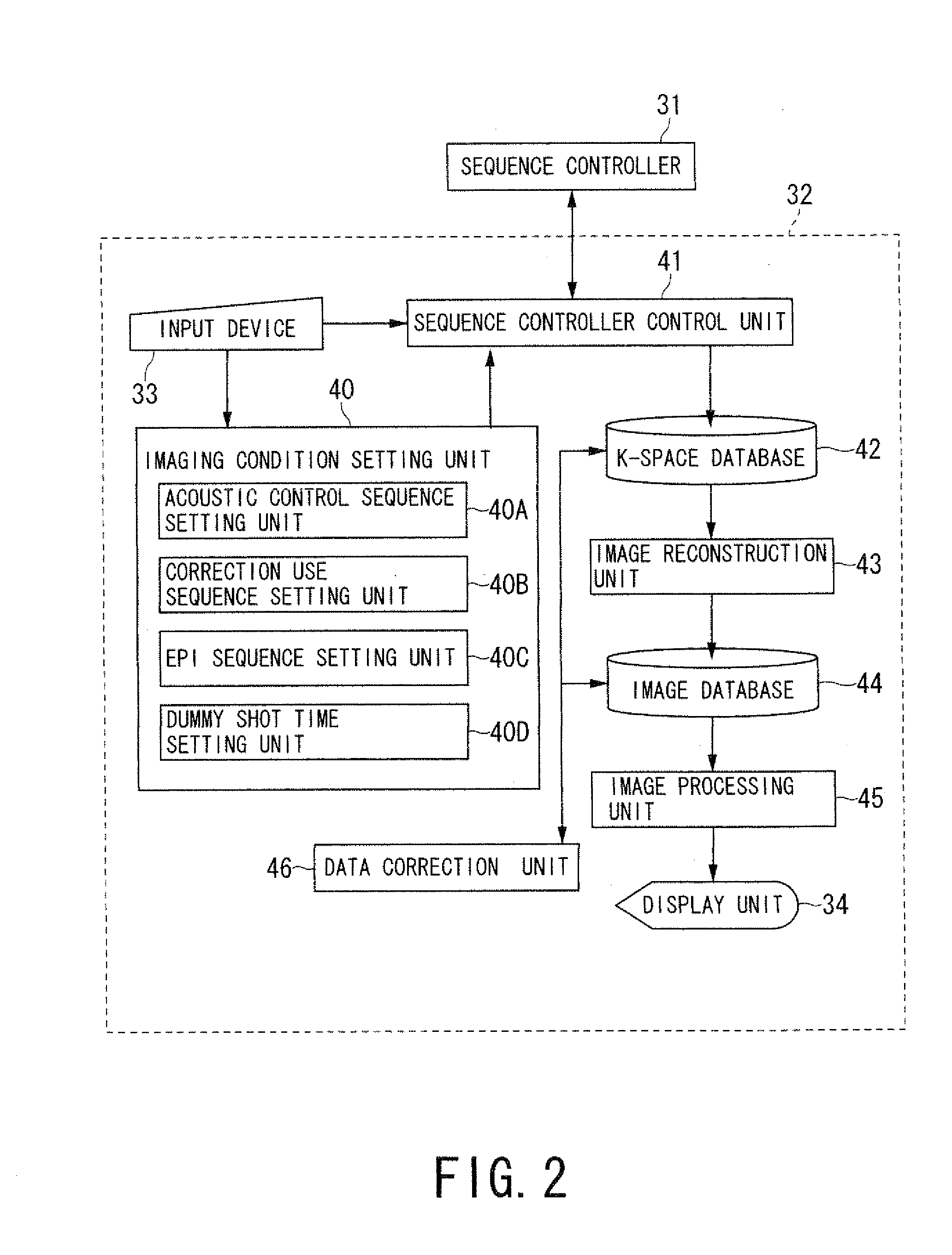
ActiveUS20080161678A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringProton magnetic resonanceImaging condition
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an imaging condition setting unit, a scan performing unit and a blood flow image generating unit. The imaging condition setting unit sets a sequence accompanying application of a motion probing gradient pulse as an imaging condition. The scan performing unit performs an imaging scan according to the sequence. The blood flow image generating unit generates a blood flow image based on data acquired by the imaging scan.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
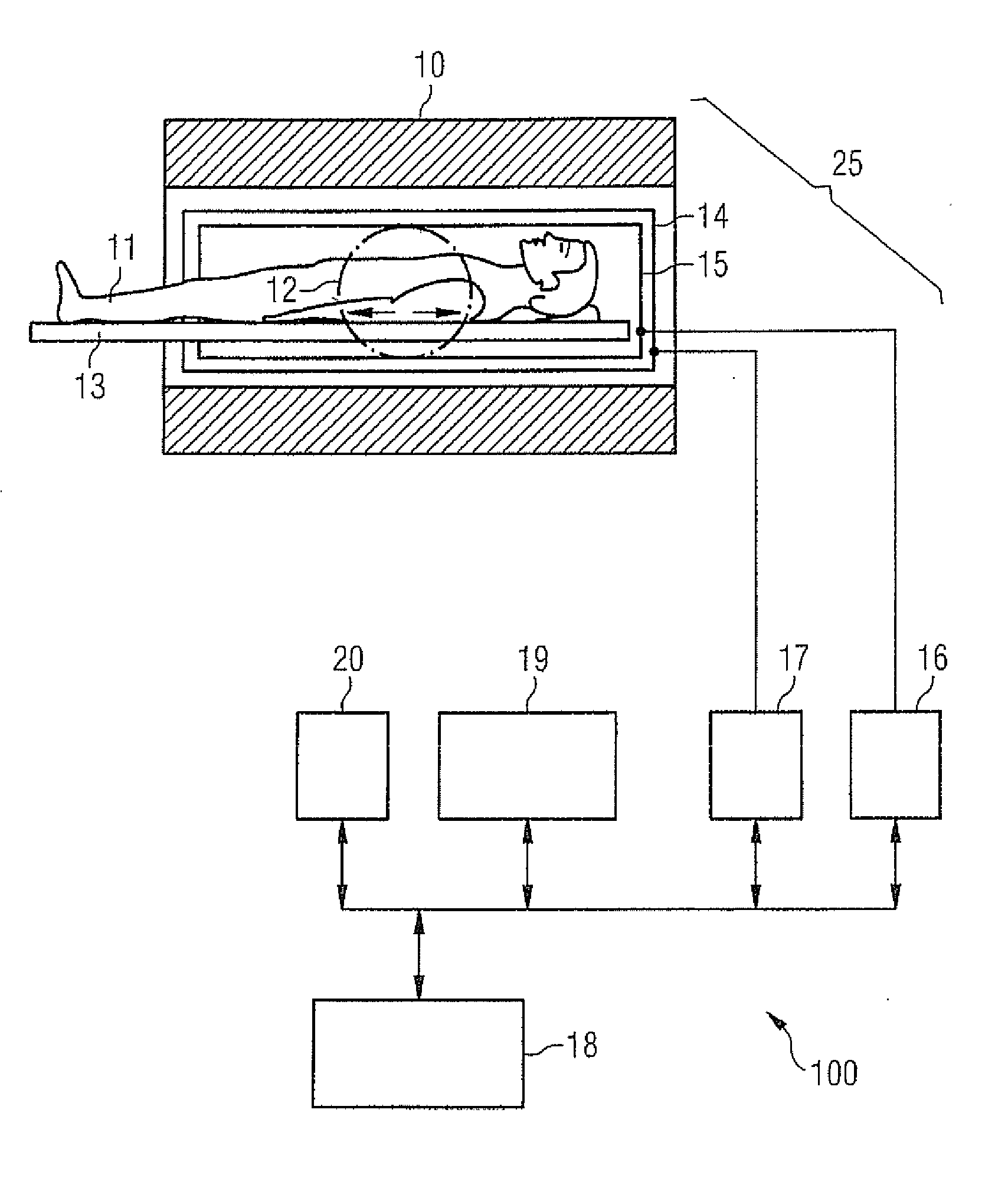
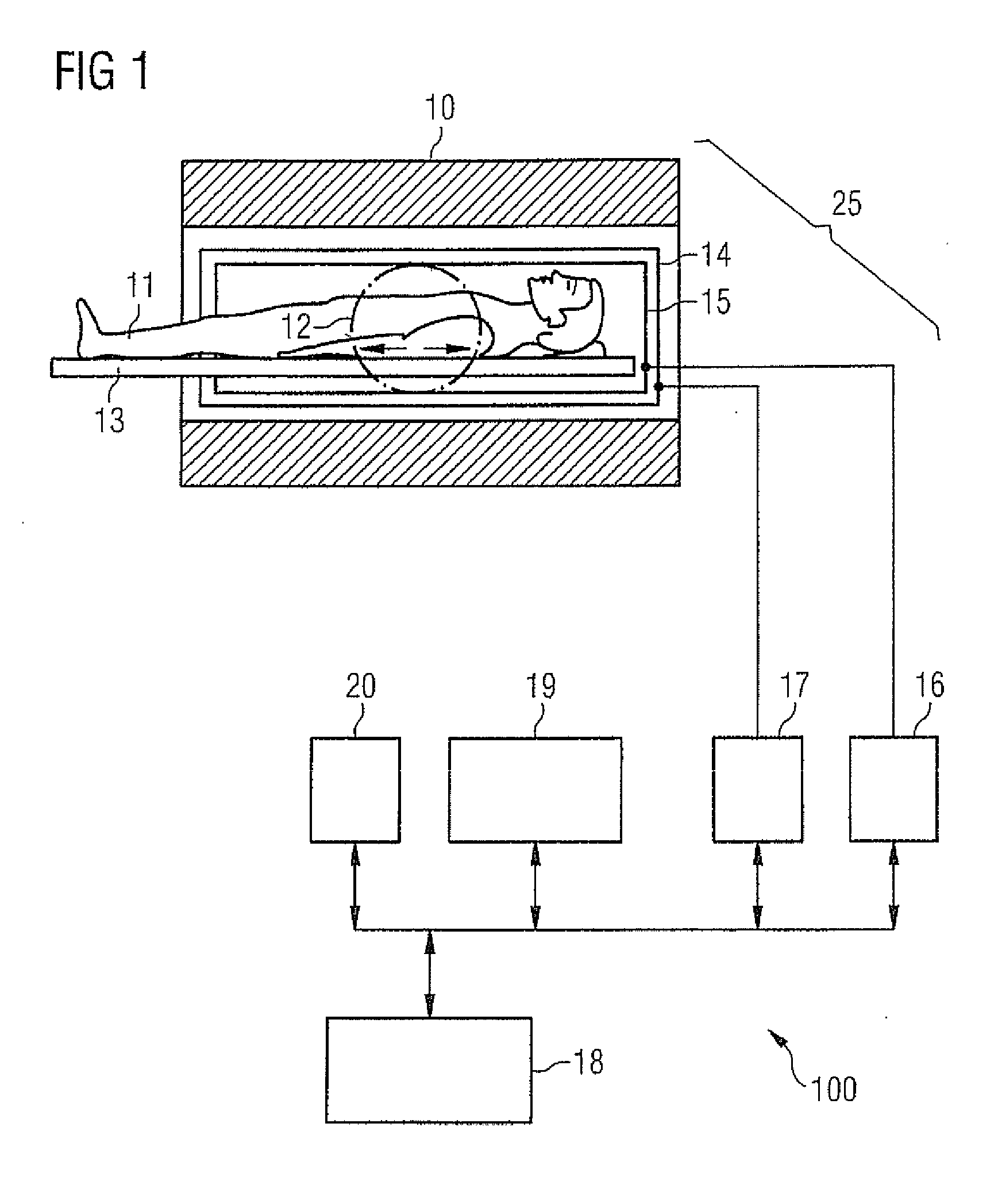
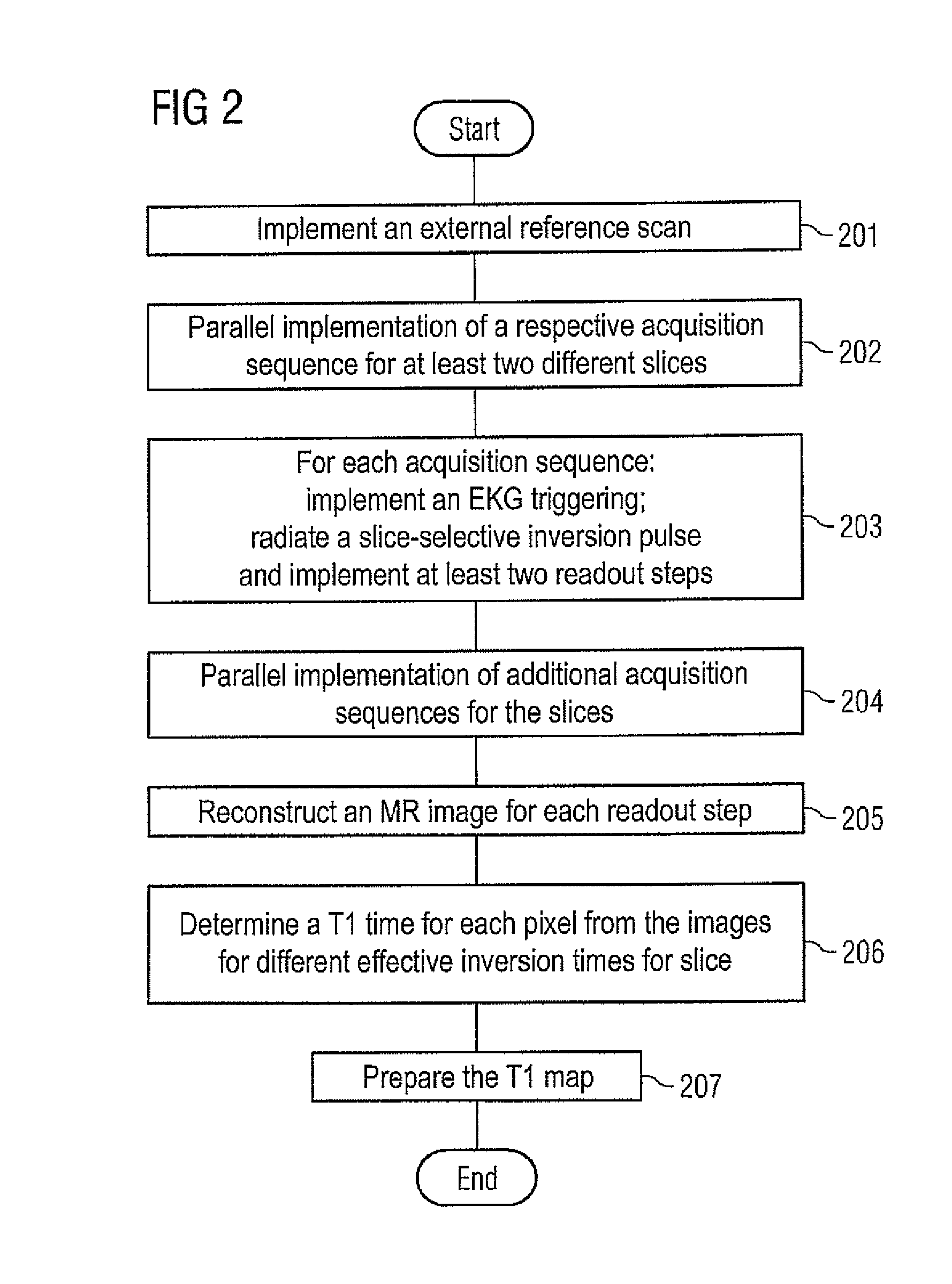
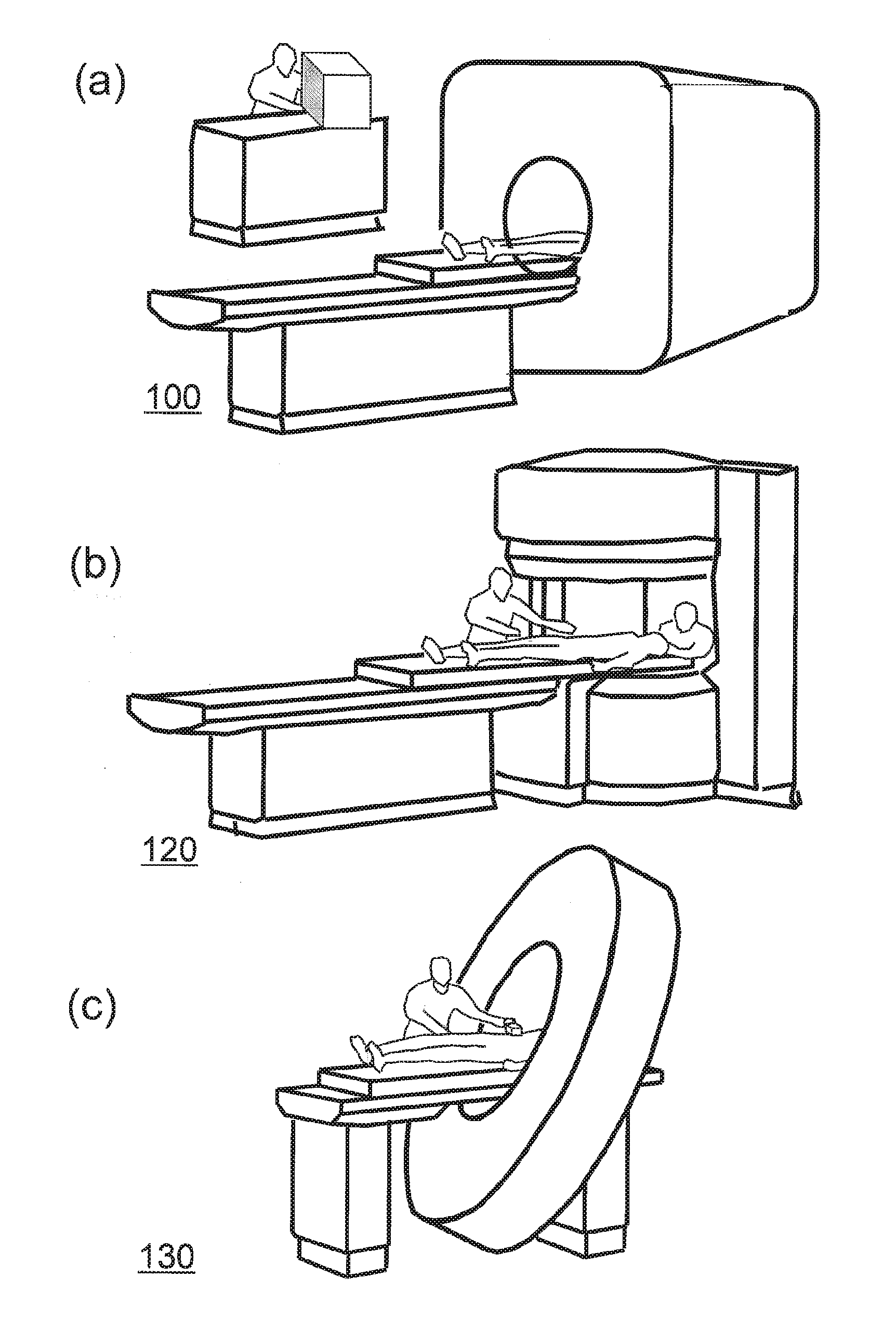
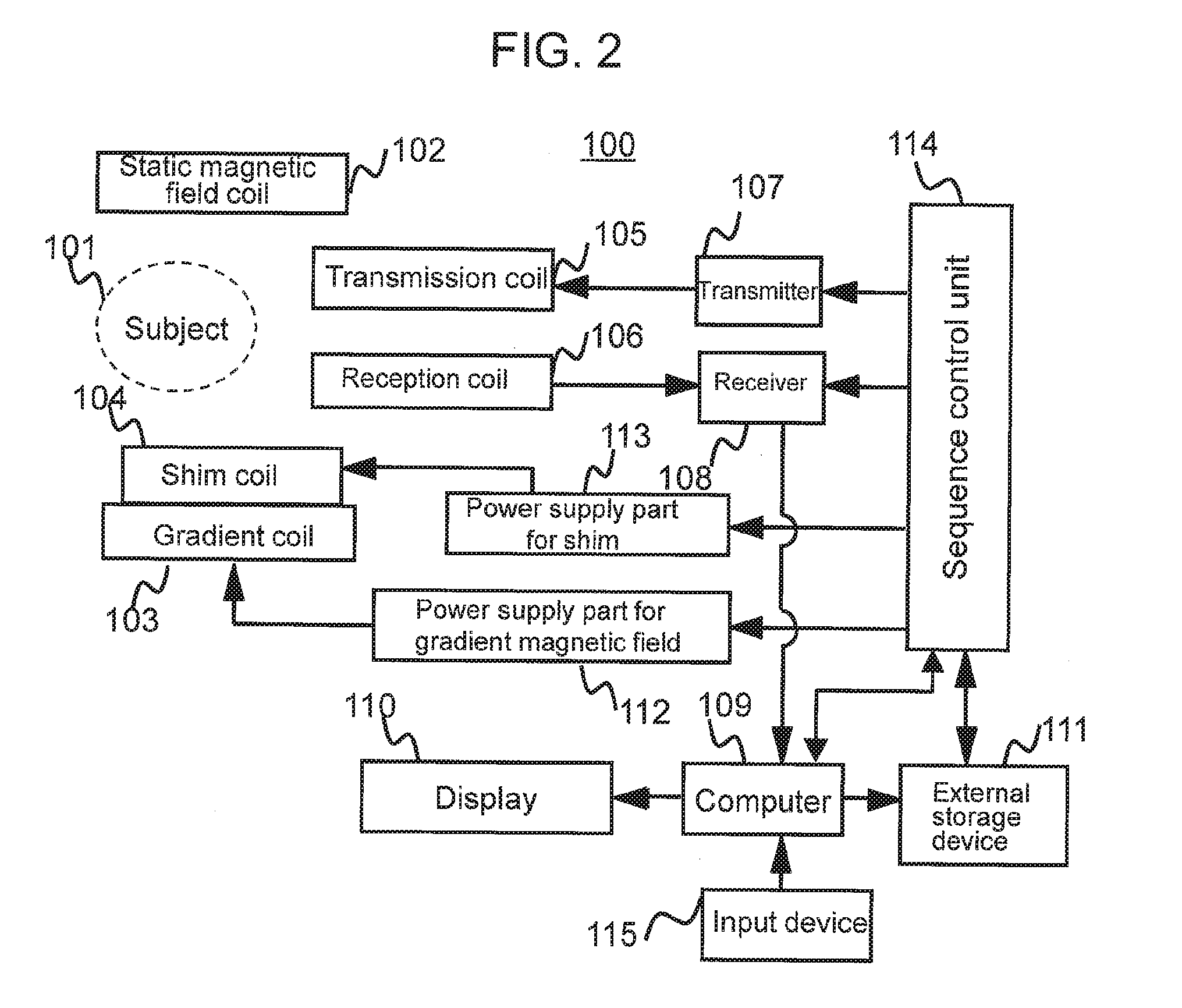
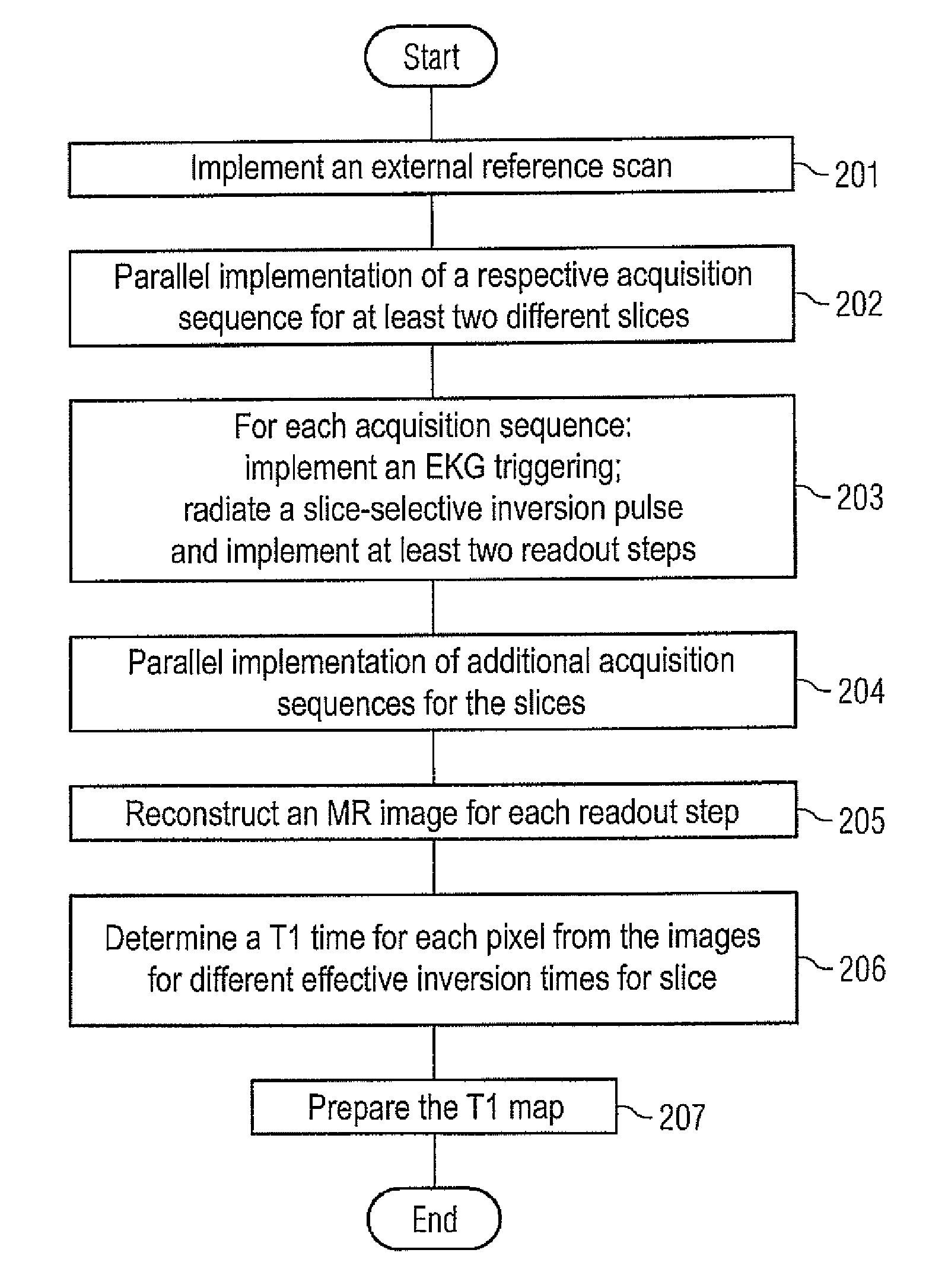
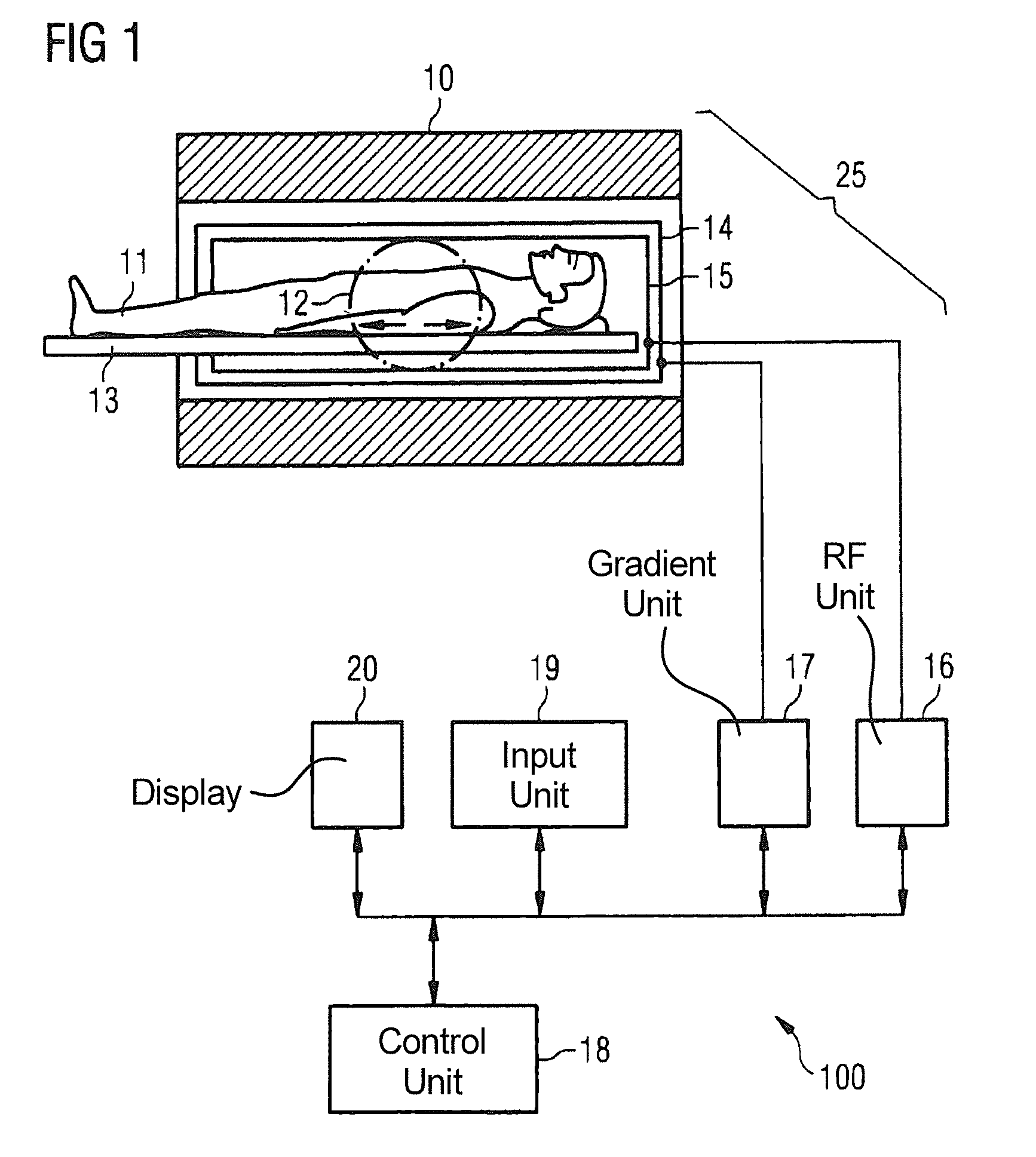
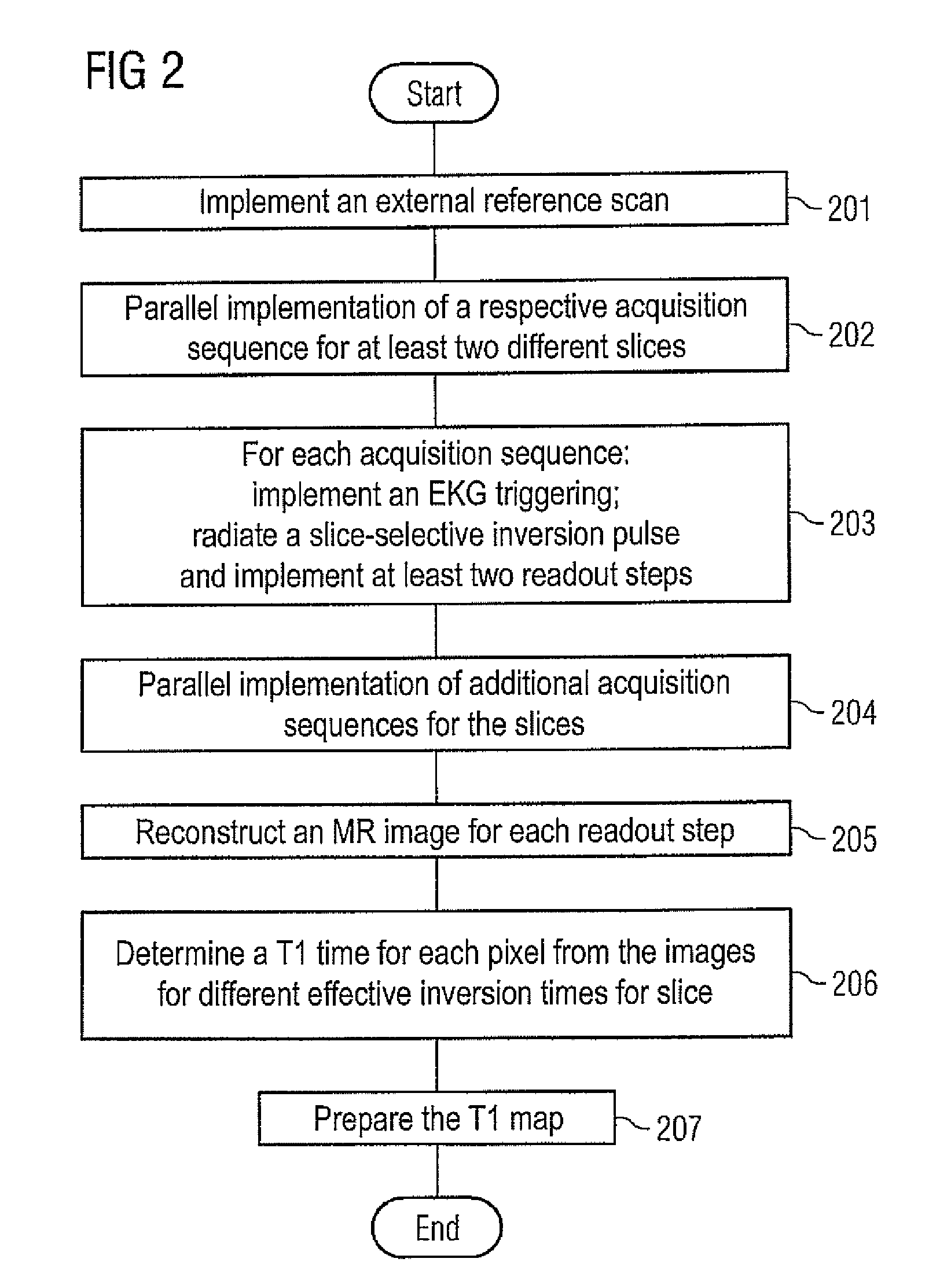
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create t1 maps
ActiveUS20110181285A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpatially resolvedProton magnetic resonance
In a method and apparatus for MR imaging, a data acquisition sequence is executed wherein at least two slices of an examination subject are imaged in parallel with a gradient echo method for spatially resolved quantification of the T1 relaxation time.At least one first acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a first slice of the examination subject and at least one second acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a second slice of the examination subject. The acquisition sequences each include an inversion pulse and at least two successive readout steps. The first and second acquisition sequences are temporally offset from one another such that they at least partially overlap.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance system and method to detect and confirm analytes
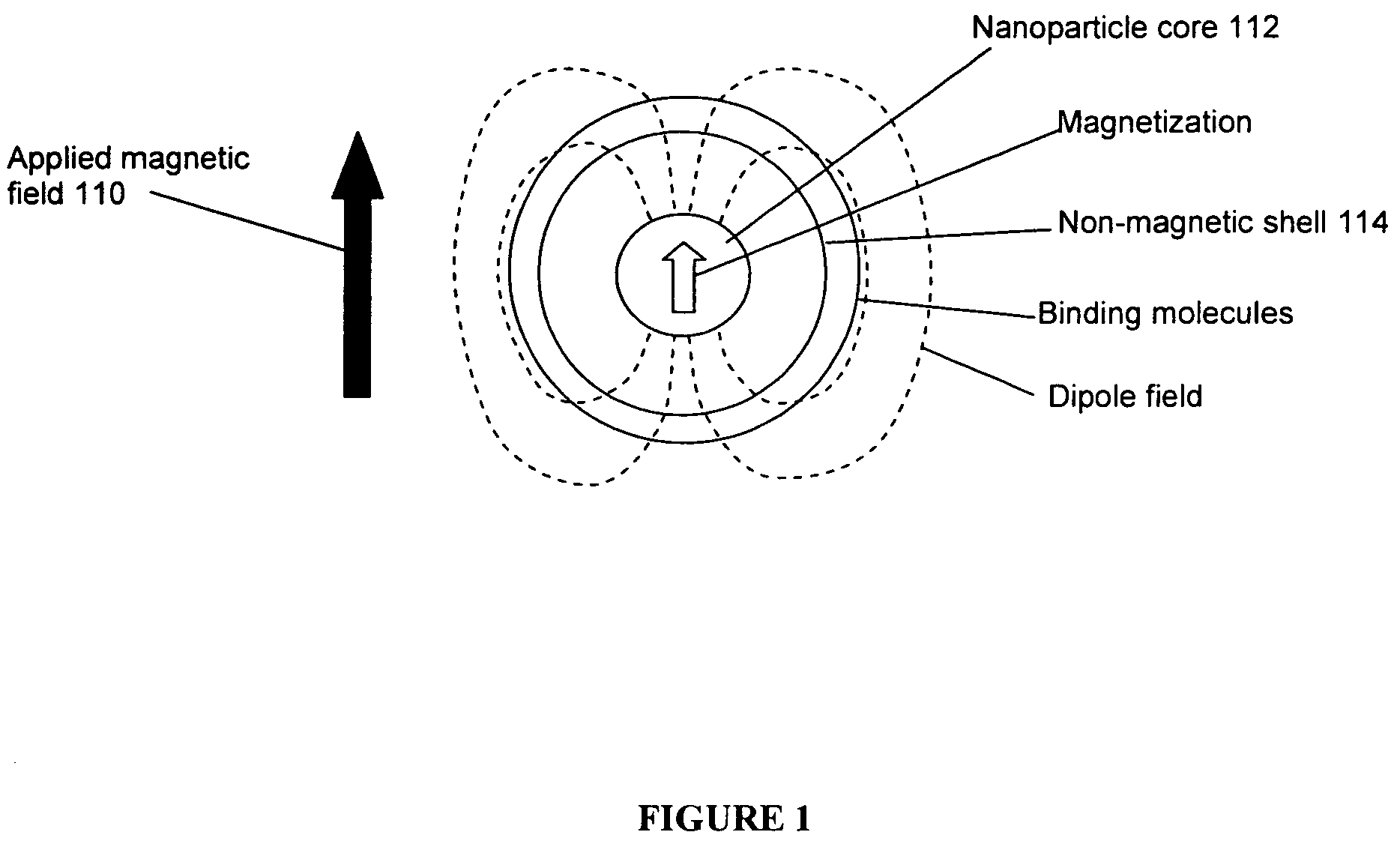
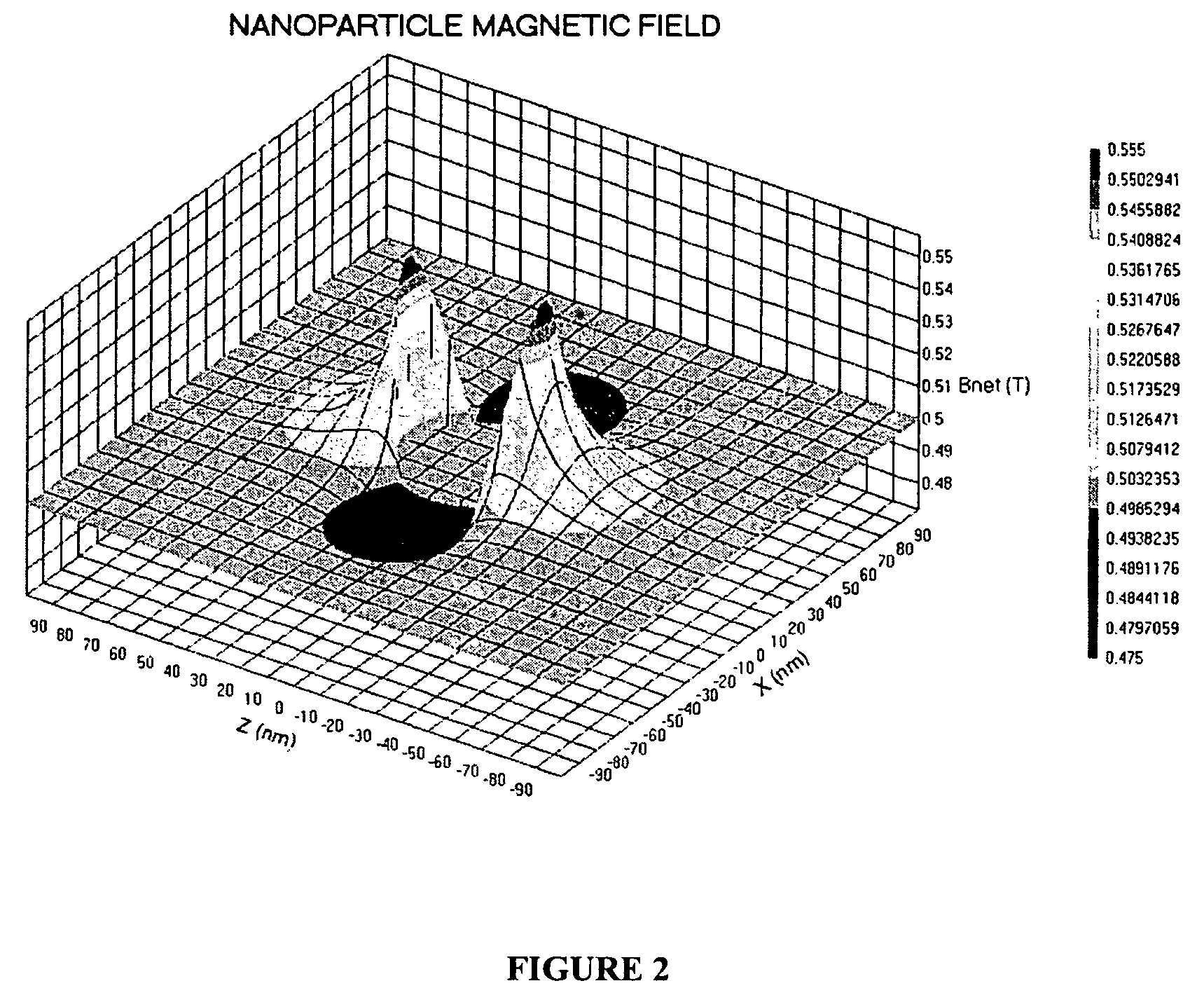
ActiveUS7781228B2Improve bindingReduce activity timeNanotechMagnetic measurementsResonance measurementProton magnetic resonance
A system and method are provided to detect target analytes based on magnetic resonance measurements. Magnetic structures produce distinct magnetic field regions having a size comparable to the analyte. When the analyte is bound in those regions, magnetic resonance signals from the sample are changed, leading to detection of the analyte.
Owner:MENON BIOSENSORS
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20090018433A1Suppress and reduce influenceMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringProton magnetic resonanceResonance
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an acoustic control unit and an image data acquisition unit. The acoustic control unit applies a gradient magnetic field for controlling a sound in synchronized with a signal representing a respiratory body motion. The image data acquisition unit acquires imaging data by imaging subsequently to controlling the sound and generates image data based on the imaging data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Coated stent assembly and coating materials
InactiveUS20060140867A1High sensitivityStrong specificityNanomedicineNMR/MRI constrast preparationsMagnetic susceptibilityProton magnetic resonance
A high magnetic susceptibility nanomagnetic material that may be attached to recognition molecules and other therapeutic biological materials so as to be targeted to specific biologic tissues, thereby enabling the presence of the targeted tissue to be detected under magnetic resonance imaging with much greater sensitivity. Also a stent coated with such nanomagnetic material to enable artifact free imaging of such stent under magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
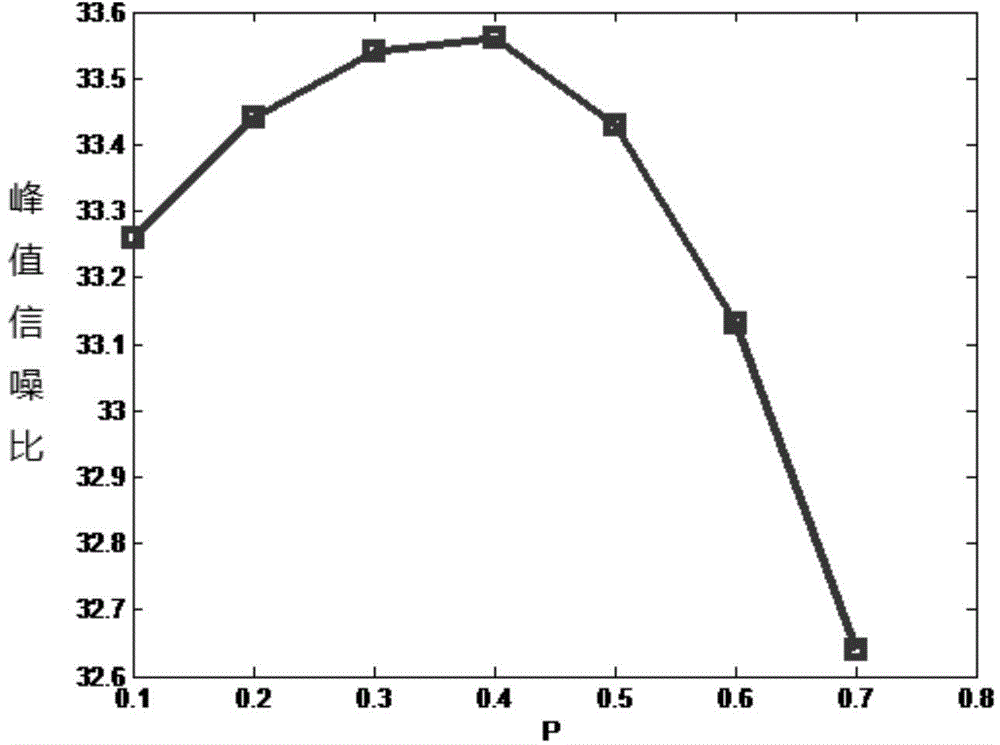
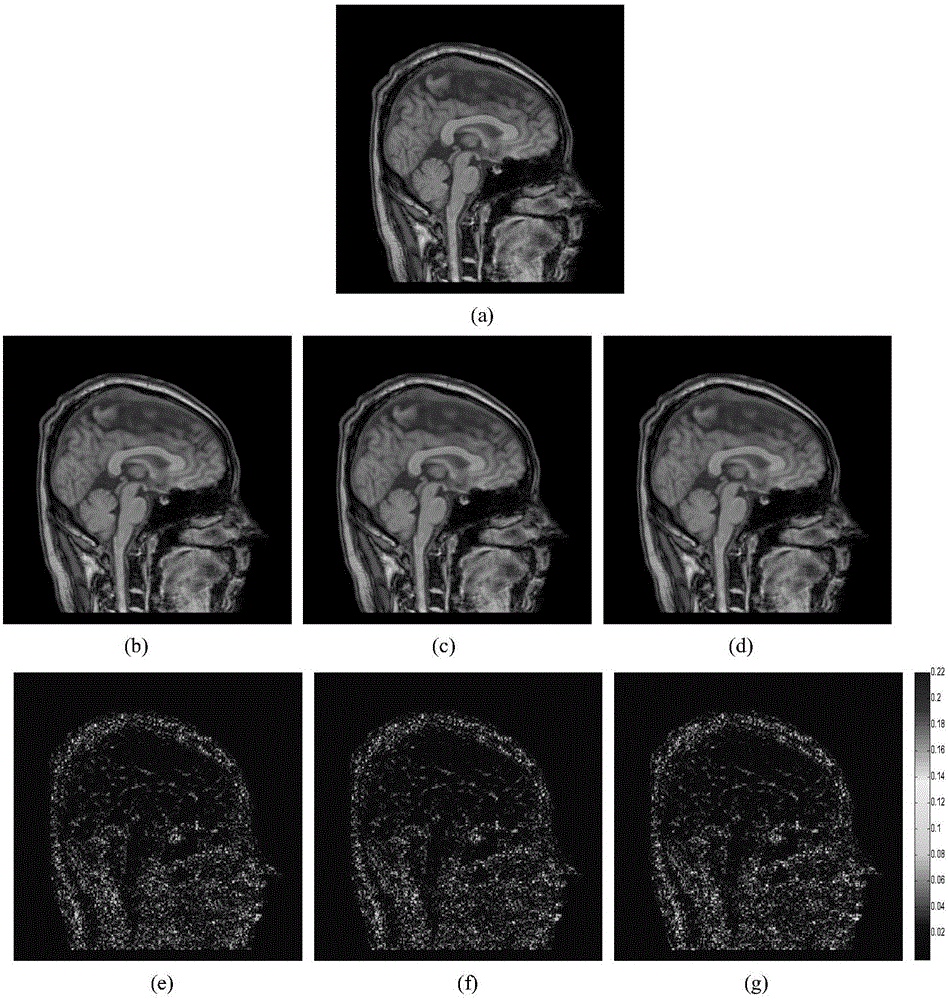
Non-convex low-rank reconstruction method for rapid magnetic resonance (MR) imaging
ActiveCN104933683AReduce complexitySimple calculationImage enhancementPattern recognitionSingular value decomposition
The invention relates to a non-convex low-rank reconstruction method for rapid MR imaging. An MR image data reconstruction mathematic model based on low-rank prior information of non-local similar image blocks is established, and iterative solution is carried out on the model in a direction alternative iteration method; a non-convex p norm of the low-rank matrix of the non-local image model with the low-rank prior information is solved by deposition and iteration of Taylor first-order approximation and the singular value, a similar image block is obtained, and a reconstruction image is solved via iteration by increasing the auxiliary variable and separating the variable. The image prior information is used to combine the non-local similarity with the low-rank characteristic of the image block, the Fourier transform and the characteristic of the low-rank matrix are used to simplify the calculation process, the complexity of algorithm is reduced, the performance of the reconstructed MRI images by part of K space data is improved, the image can be reconstructed more accurately with less scanning and measurement, pseudo shadows of the images are reduced, and rapid MRI is realized.
Owner:南昌市云影医疗科技有限公司
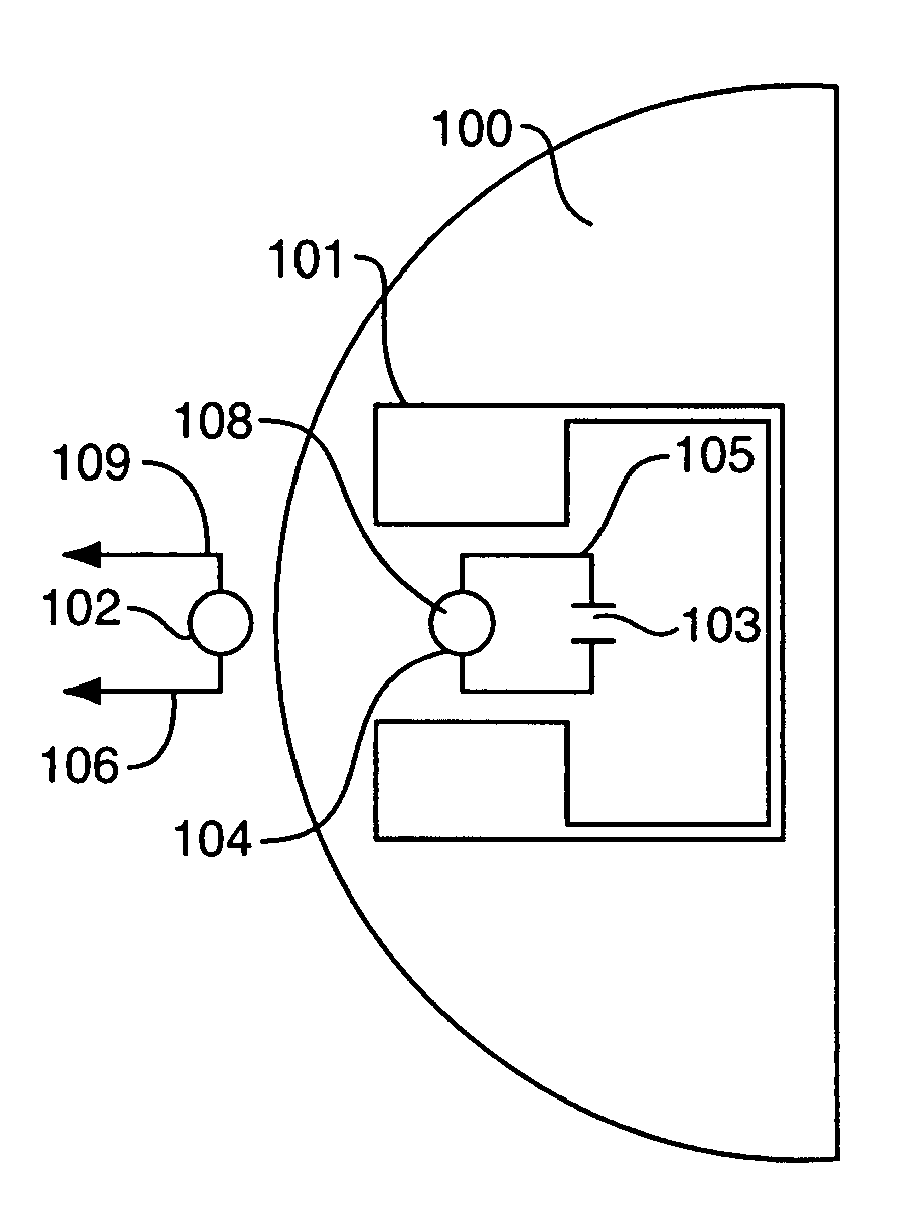
Magnetic resonance system with implantable components and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20120223705A1Diagnostic recording/measuringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance measurementProton magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance systems and methods of use thereof are provided. The systems employ implantable radiofrequency coils (105) and optionally implantable magnets (101). The systems can employ weak permanent magnets and / or permanent magnets that provide magnetic fields that are much less homogeneous than in conventional systems. This allows, for example, for inexpensive and simple probeheads for nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry with suitable biosensors. The methods of the present invention allow in-vivo magnetic resonance measurements and, in particular, monitoring of analytes and determination of medical diagnostic information, for example, based on determined magnetic resonance parameters.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and imaging method
InactiveUS6169398B1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic susceptibilityProton magnetic resonance
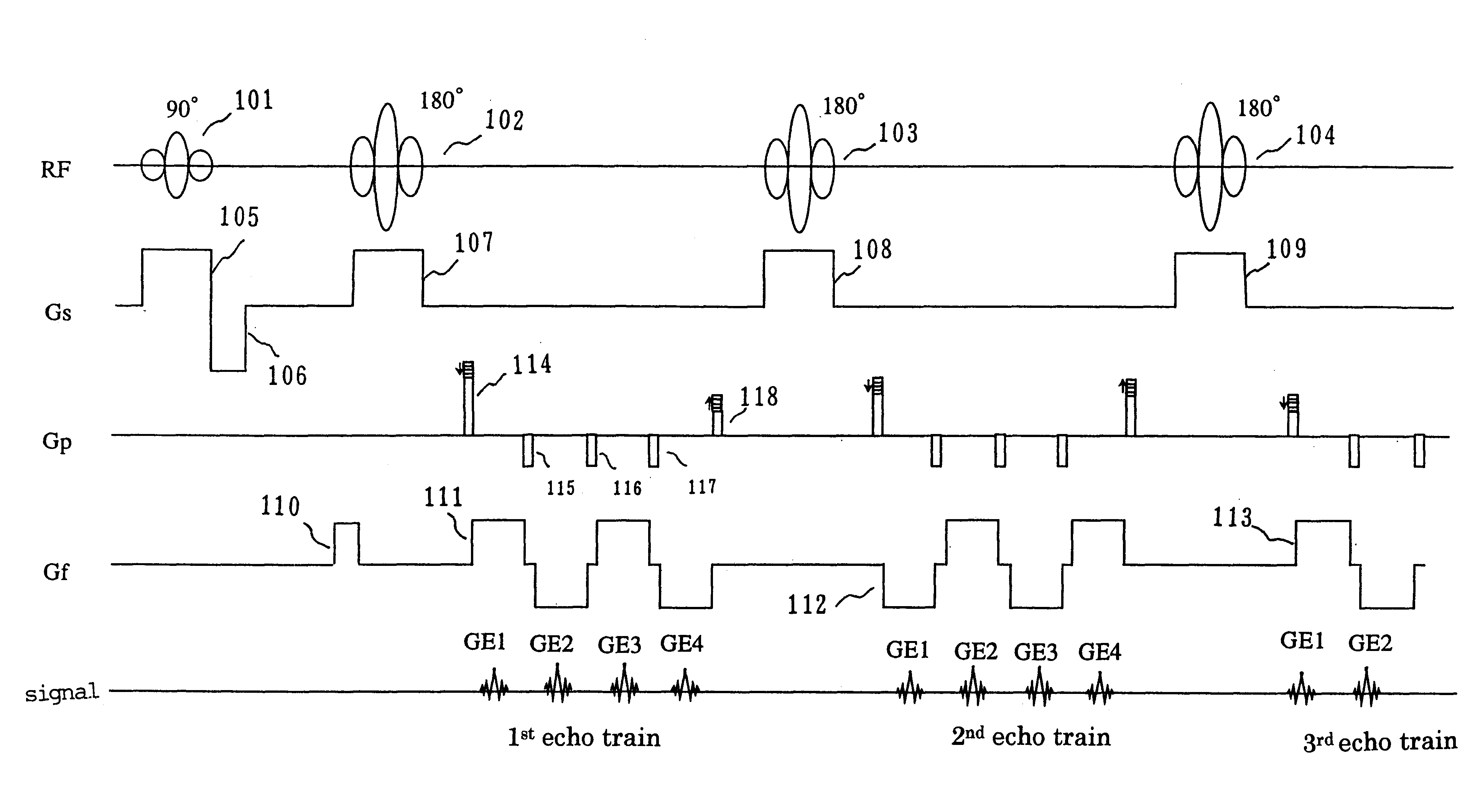
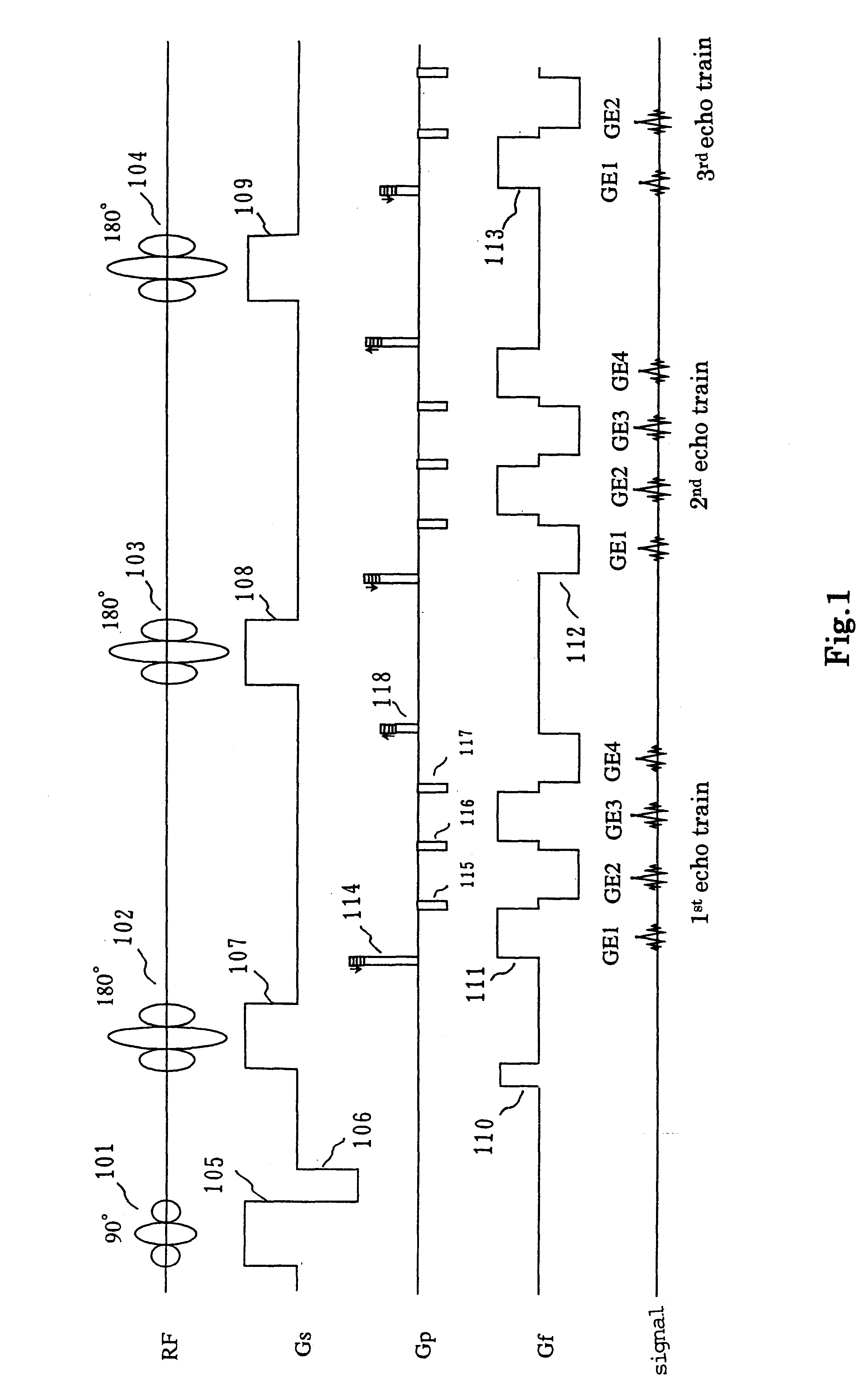
The MRI apparatus of the present invention performs a pulse sequence for applying successively 180° pulses 102, 103 . . . after application of a 90° pulse 101 at constant intervals and applying readout magnetic fields 111 during the interval between pairs of 180° pulses while the polarity of the magnetic field 111 is inverted several times to collect a plurality of gradient echo signals that are phase encoded differently. Here, the application of the readout gradient magnetic field is controlled such that generation of the gradient echo signals does ot coincide with generation of the spin echo signal. The image reconstruction is performed by using only T2* weighted gradient echo signals to obtain images reflecting difference in magnetic susceptibility and inhomogeneities in local magnetic fields.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
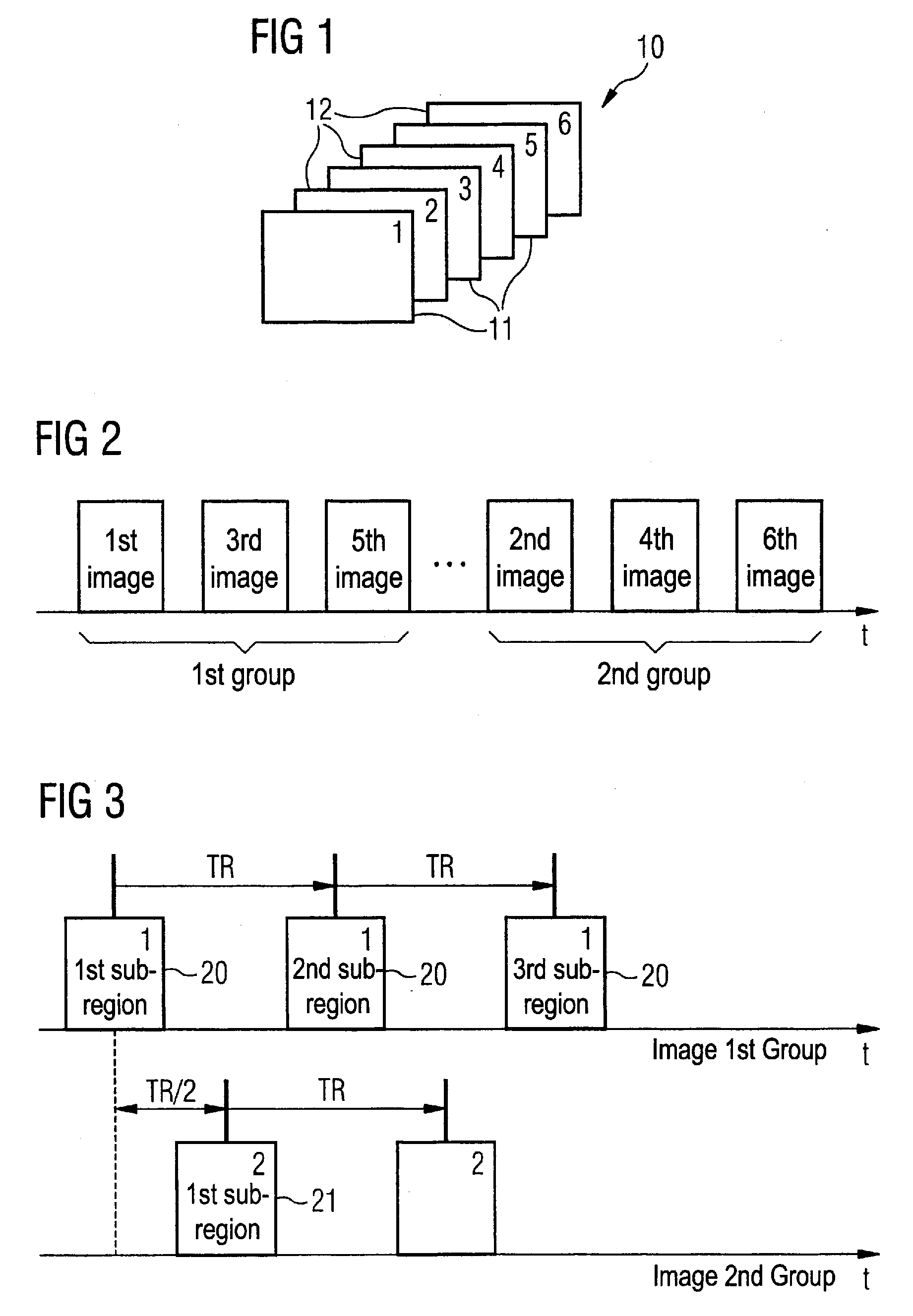
Magnetic resonance system and method for correction of movement artifacts
InactiveUS20080317315A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setProton magnetic resonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) for correction of movement in the acquisition of MR images of an examination region, wherein the movement that occurs between the acquisition of data of spatially different slices of the examination region is taken into account, data from the examination region are acquired in multiple slices that are acquired in at least two groups, with slices of a second group arranged at least partially between slices of the first group, such that at least one slice of the second group lies between slices of the first group. Correction for movement of the examination region that occurred between the acquisition of data of the slices of the first group and the acquisition of data of an intervening slice of the second group is done by reconstructing a reference data set for the intervening slice from acquired slice data of the first group for the movement correction. This reference data set is compared with data of the acquisition of the MR image of the intervening slice in order to determine and correct the occurred movement.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
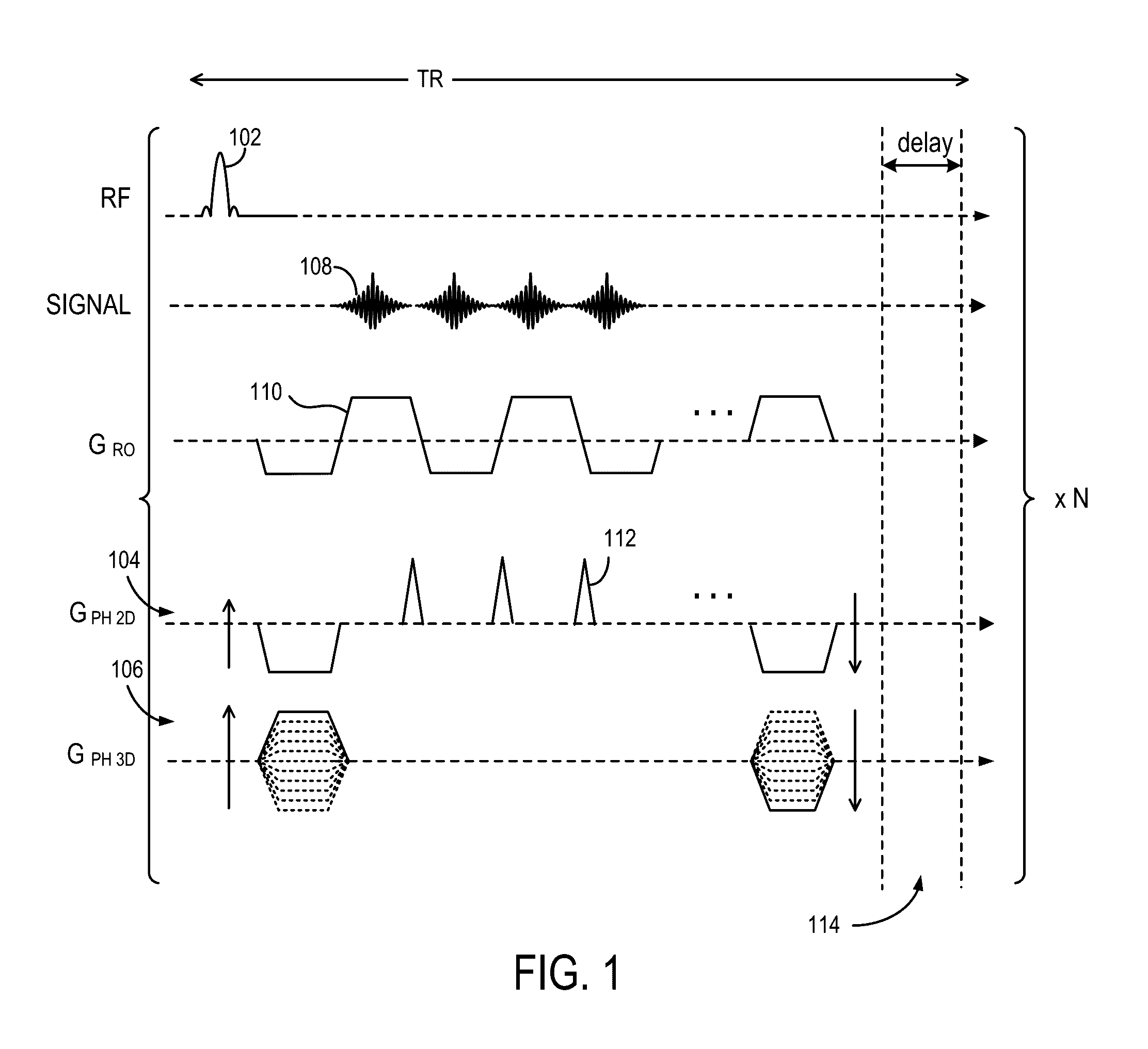
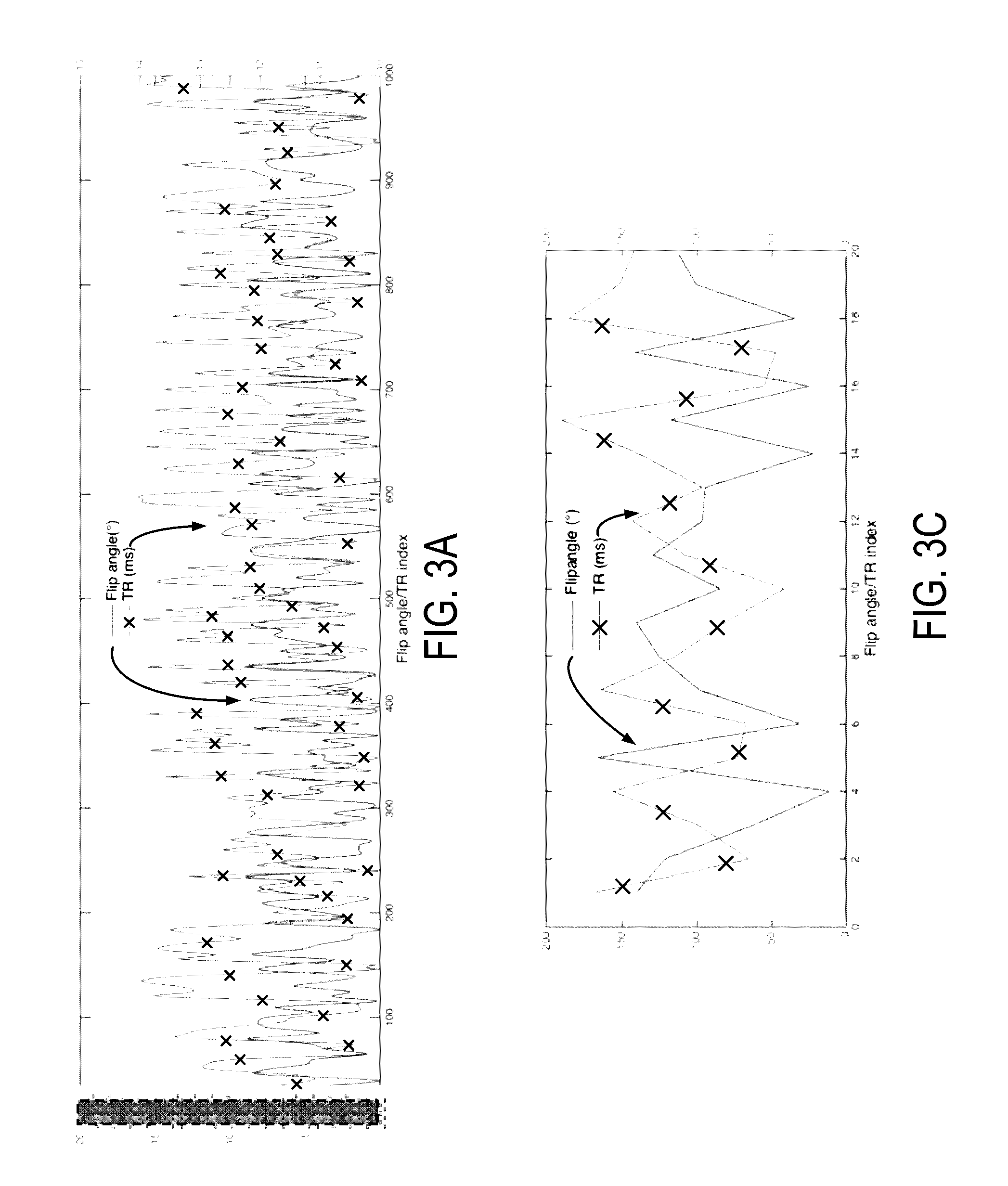
3D Balanced EPI Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting
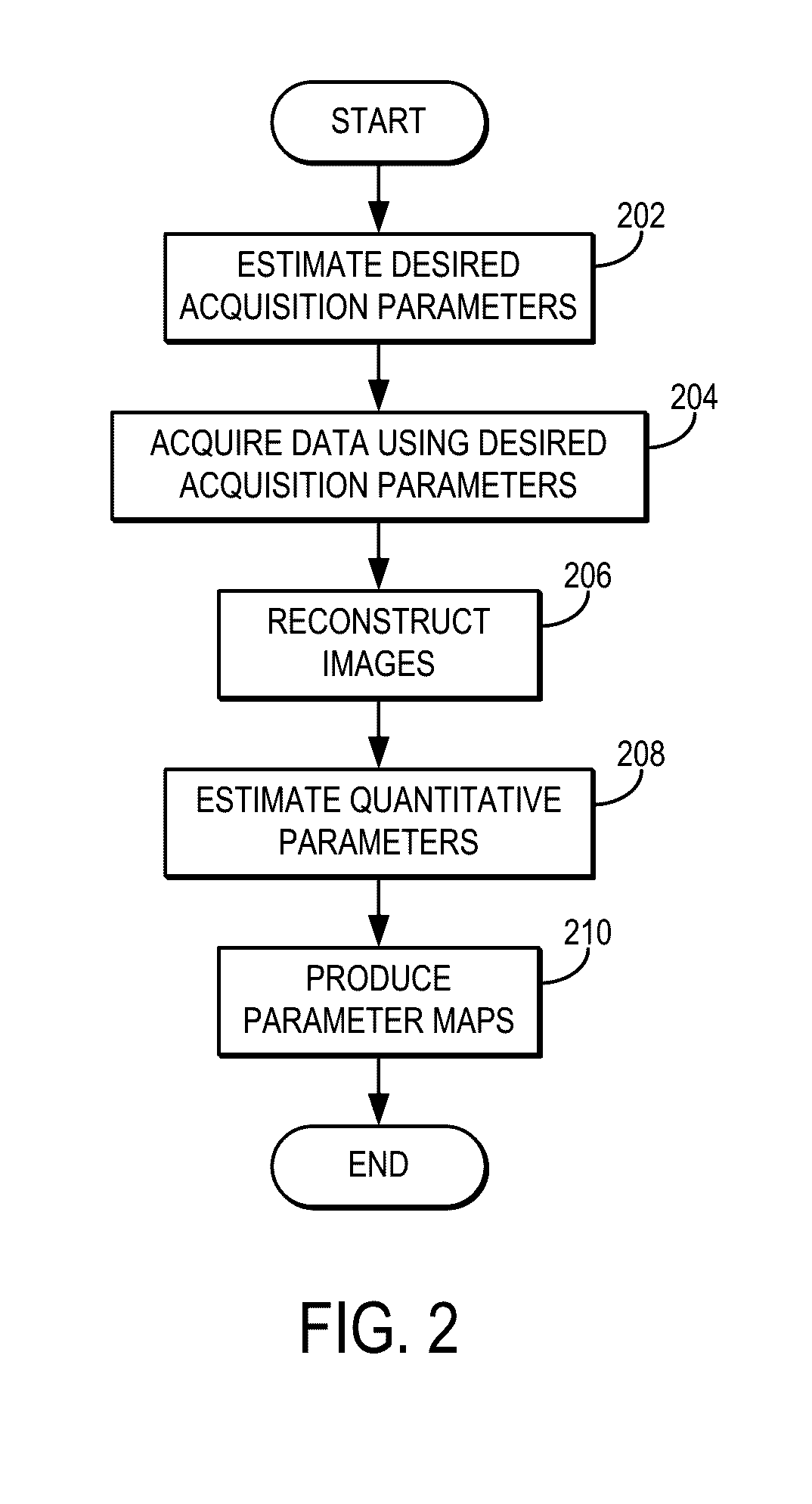
Provided is a system and method for performing a magnetic resonance fingerprinting imaging process. The process includes determining acquisition parameters including at least one of repetition time (TR) or flip angle (FA), selected to control one of a duration and a number of repetitions of for a pulse sequence that samples k-space in a Cartesian acquisition pattern by acquiring an echo train. The process also includes controlling a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system to perform the pulse sequence a plurality of times to acquire magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) data corresponding to signals from the subject excited by the pulse sequence. The process also includes estimating quantitative tissue properties of the subject by comparing the MRF data to a database and reconstructing, from the MRF data, at least one image of the subject indicating the estimated quantitative tissue properties.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
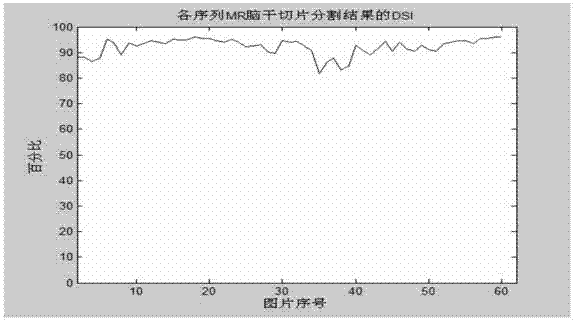
Method for partitioning brainstem areas automatically from MR (magnetic resonance) sequence images
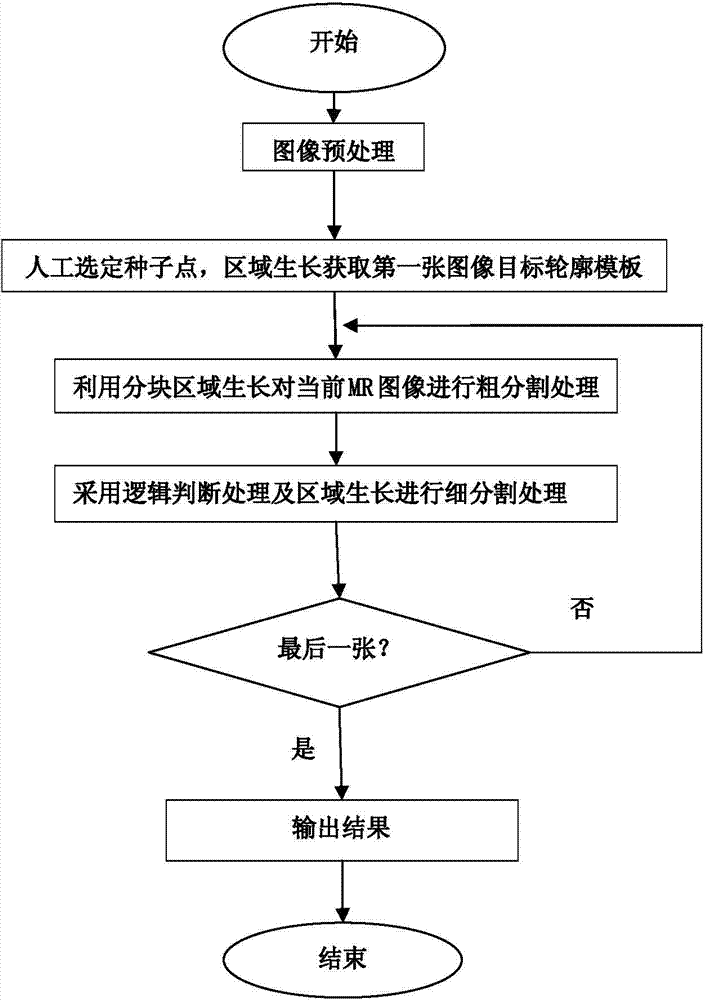
InactiveCN103489198AReduce split workloadReduce interventionImage analysisHuman bodyProton magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a method for partitioning brainstem areas automatically from MR (magnetic resonance) sequence images. The method is used for partitioning the brainstem areas automatically and continuously from the human body encephalic MR sequence images, so as to offer technological bases for reconstruction of 3D model of the encephalic tissues to doctors to judge the state of an illness of the patient efficiently and intuitively. The method comprises steps of (1) preprocessing: carrying out gray level clustering analysis on all MR nerve sequence images, and clustering the gray levels of all the MR images to be processed to be five-level gray level images; (2) selecting seed point pixel, obtaining the outline border of the brainstem area of the first MR image through a neighbor region growing algorithm based on the image area growing rate; (3) roughly partitioning the current MR image through a block region growing method; (4) repartitioning the roughly partitioned MR images through logical judgment treatment and the region growing method; and (5) repeating the step (3) and the step (4) till finishing partitioning all MR images.
Owner:钟映春
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and control method thereof
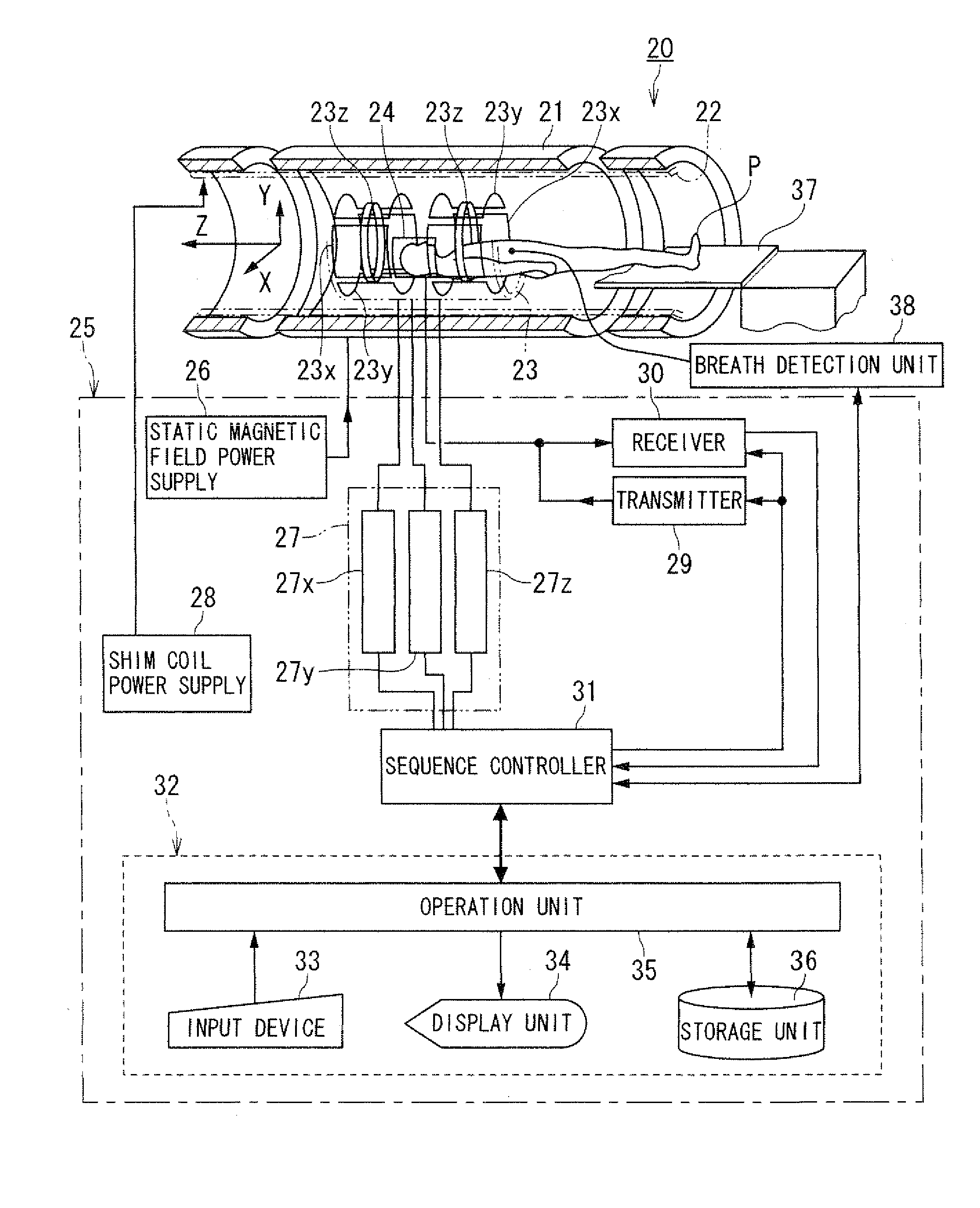
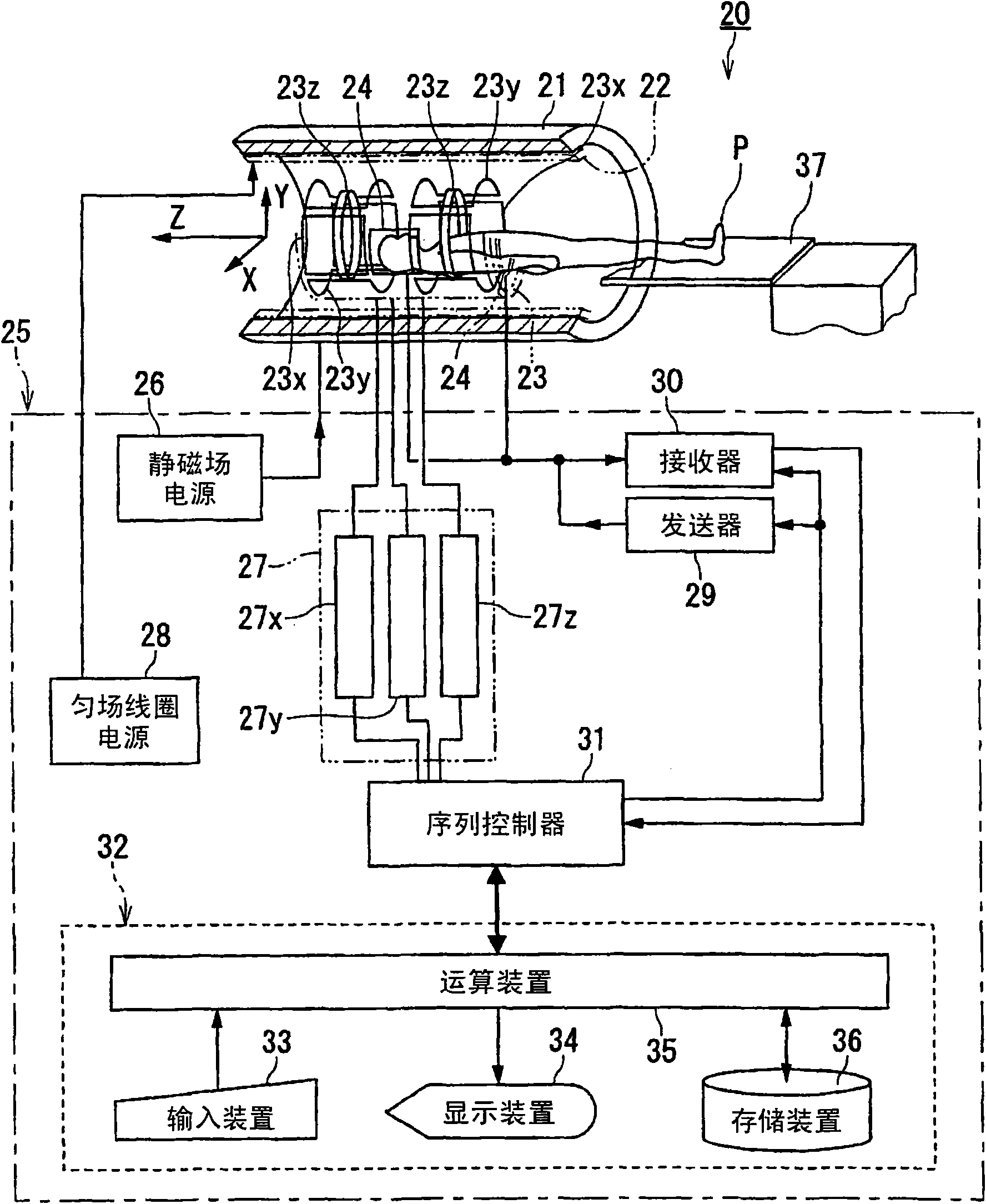
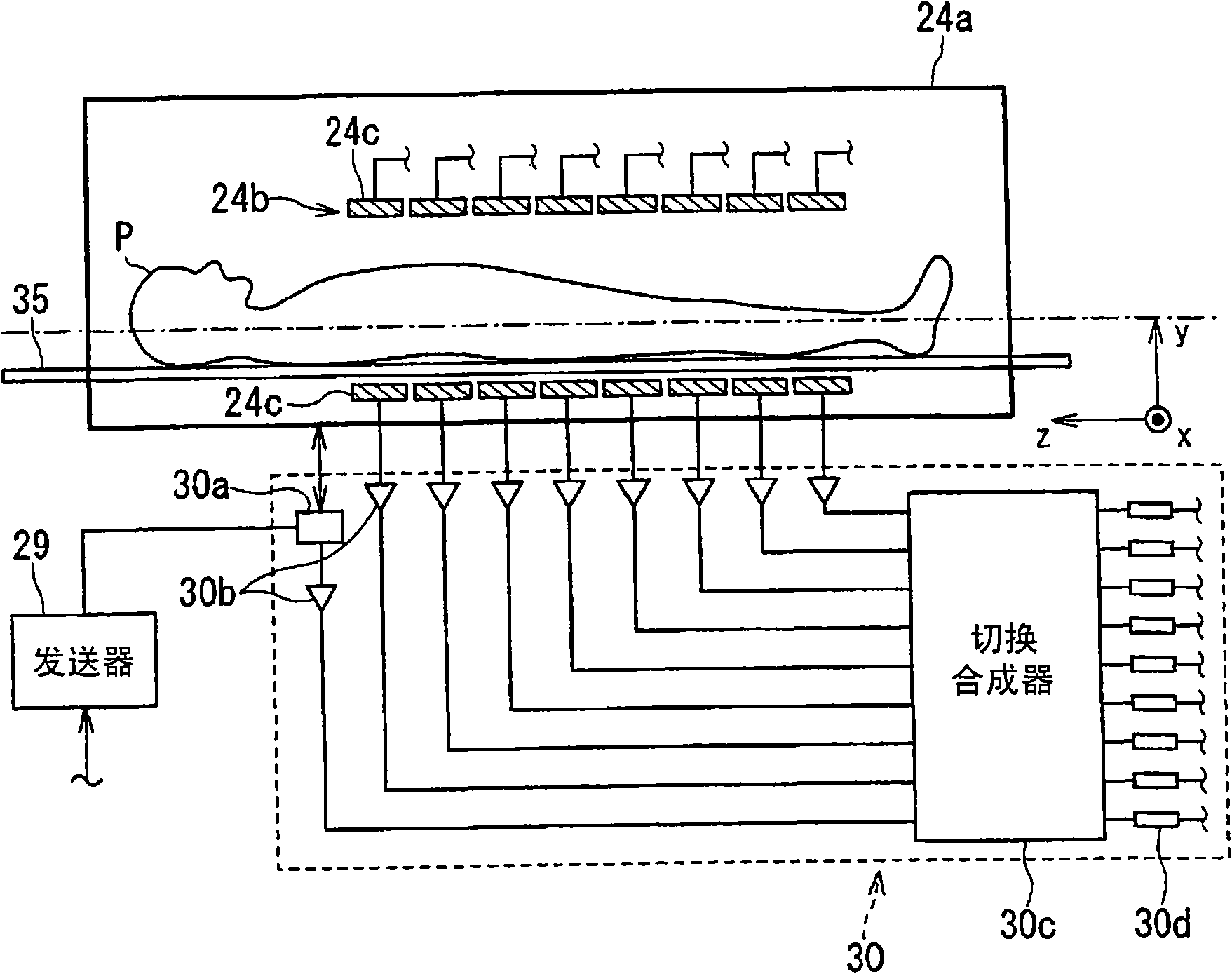
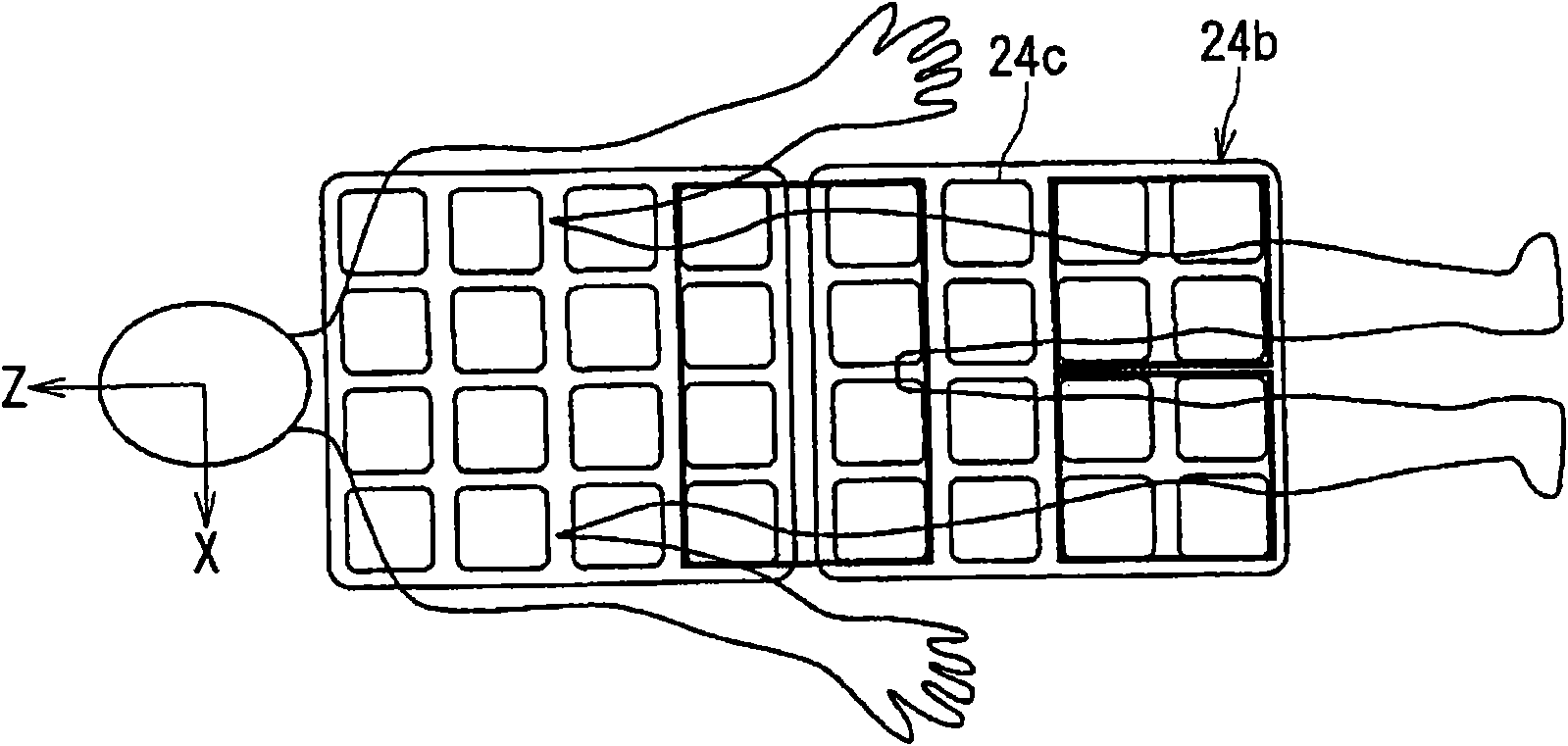
ActiveUS20080281186A1Easy to adaptMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringProton magnetic resonancePulse sequence
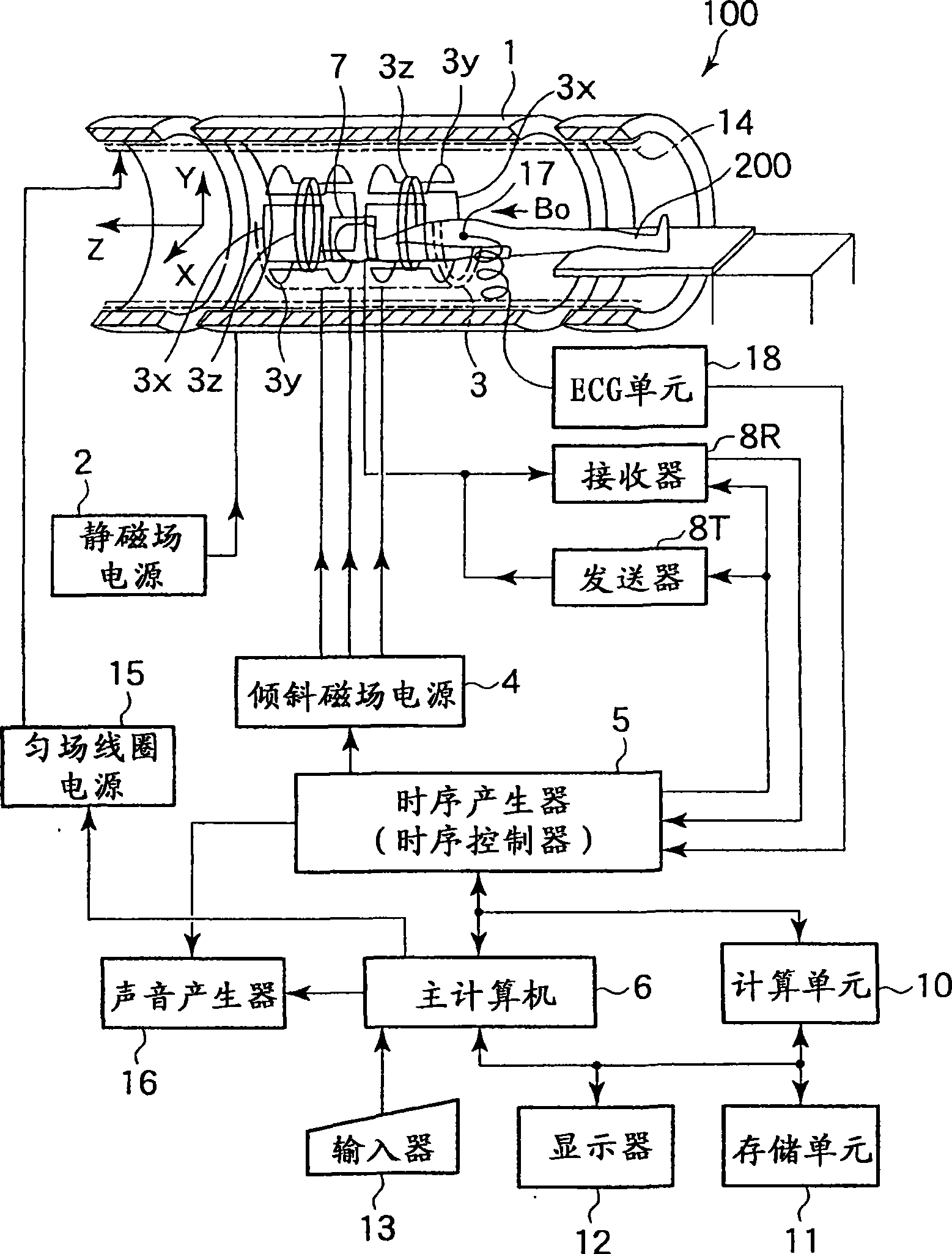
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a collection unit which applies a uniform static magnetic field to a subject and also applies a radio-frequency magnetic field and a gradient magnetic field to the subject in accordance with a predetermined pulse sequence to collect a magnetic resonance signal from the subject, a imaging unit which images the subject based on the magnetic resonance signal collected by the collection unit, a detection unit which detects a respiratory level of the subject, an informing unit which informs the subject of whether the detected respiratory level falls within an allowable range, and a unit which controls the collection unit and the imaging unit in such a manner that the magnetic resonance signal for imaging is collected and the subject is imaged based on the thus collected magnetic resonance signal for imaging when the detected respiratory level falls within the allowable range.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Lung rapid magnetic resonance imaging method based on prior knowledge and sparse sampling
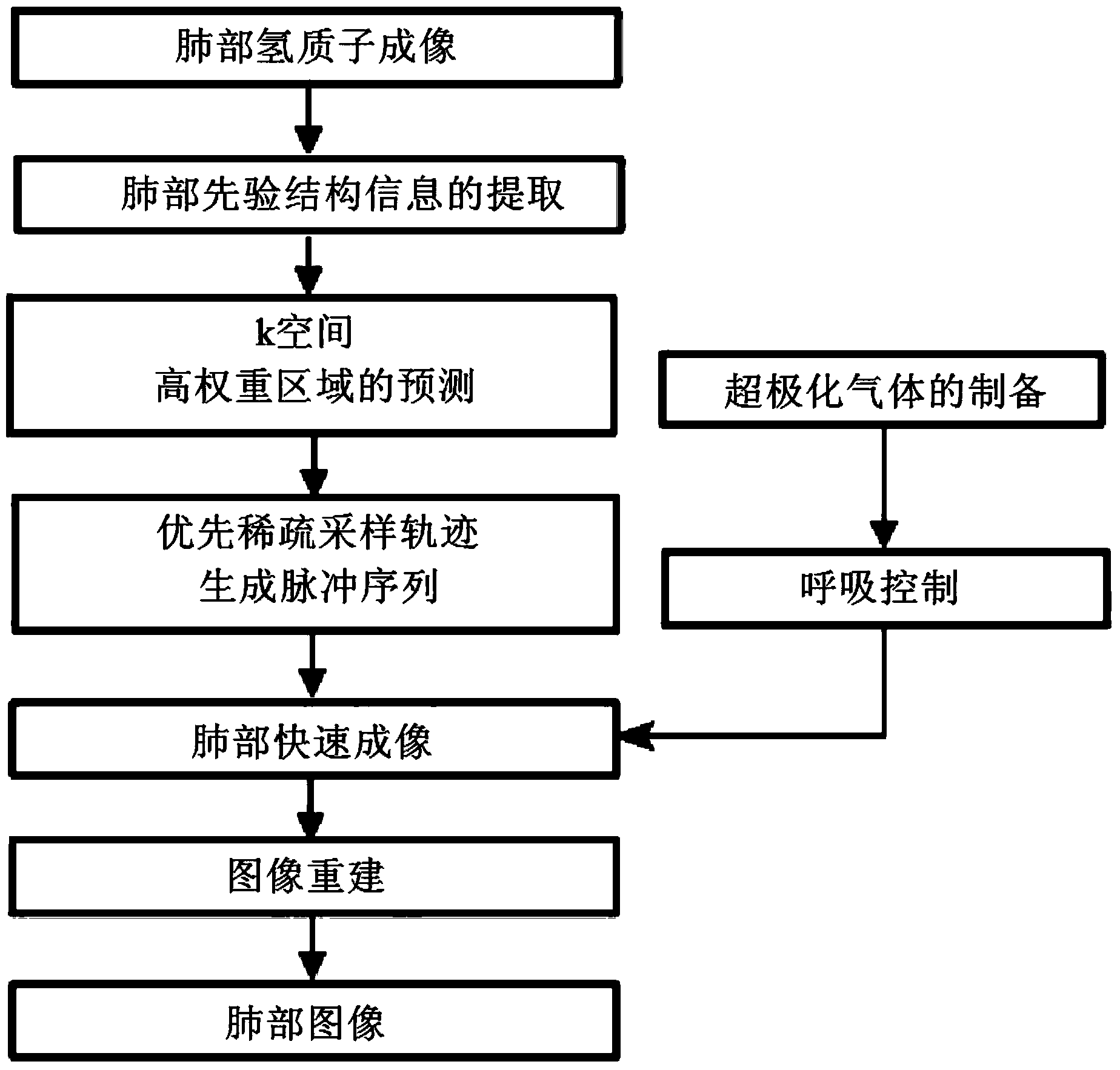
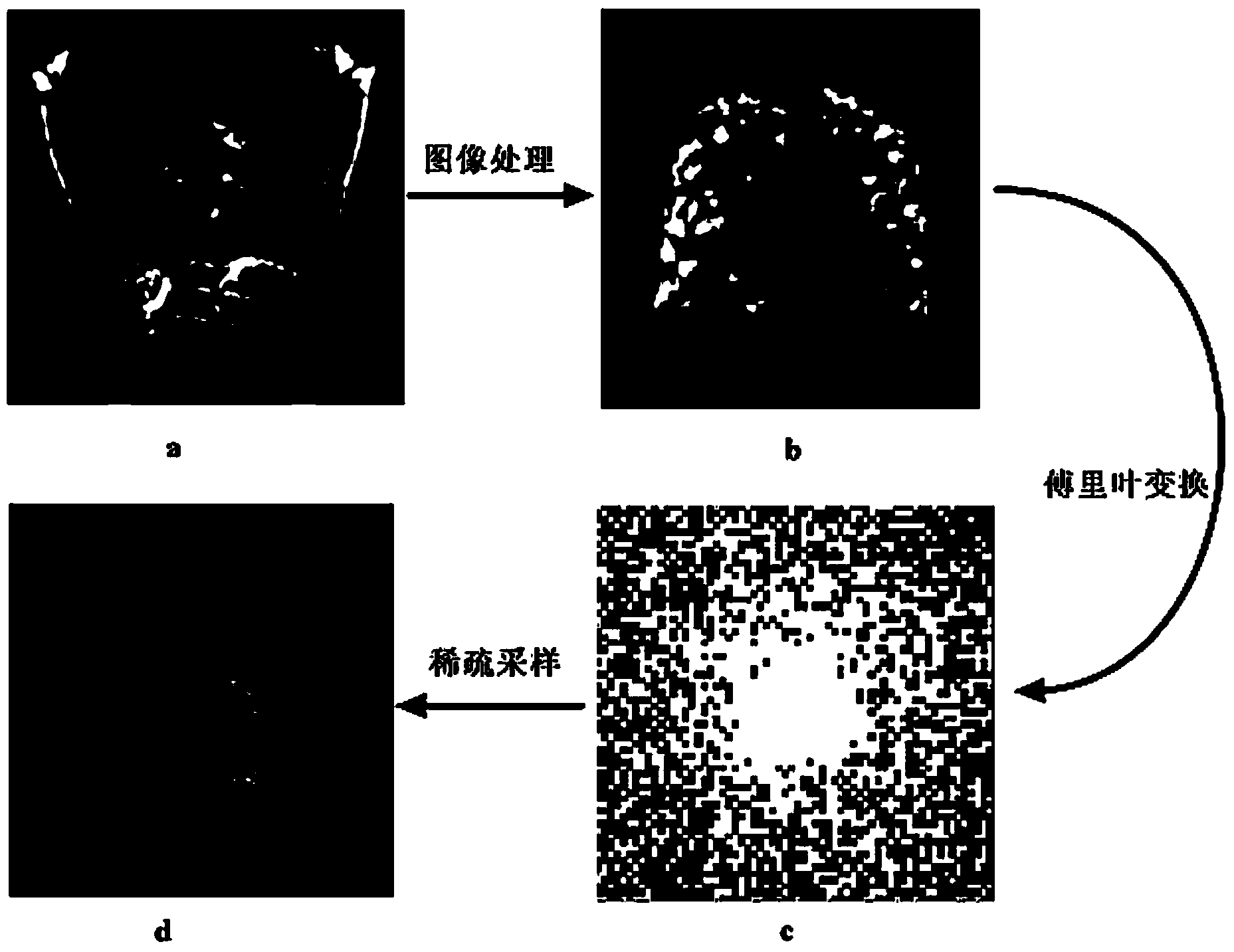
ActiveCN104027113AReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProton magnetic resonanceImaging quality
The invention discloses a lung rapid magnetic resonance imaging method based on prior knowledge and sparse sampling. A hyperpolarization gas contrast medium makes lung magnetic resonance imaging possible. In the imaging process, an imaging object needs to hold the breath to reduce generation of motion artifacts, the polarizability of hyperpolarization gas is attenuated rapidly along with the time, the signal-to-noise ratio of the image is reduced, and therefore great significance for improvement of the imaging speed is achieved. According to the lung rapid magnetic resonance imaging method, firstly hydrogen proton magnetic resonance imaging is carried out on the lung area firstly, the prior information of signal distribution of the lung area is extracted through an image processing method, a self-adapting hyperpolarization gas sparse sampling pulse sequence is generated according to the prior information, and the lung is imaged after the imaging object inhales the hyperpolarization gas. The sampling points are reduced, so that the imaging time is shortened. Due to the guidance of the prior information, the polarizability of the gas contrast medium is used more reasonably, and the image quality is equal to or better than that of a full-sampling method.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS7015696B2Accurate calculationAccurate imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsProton magnetic resonanceT2 weighted
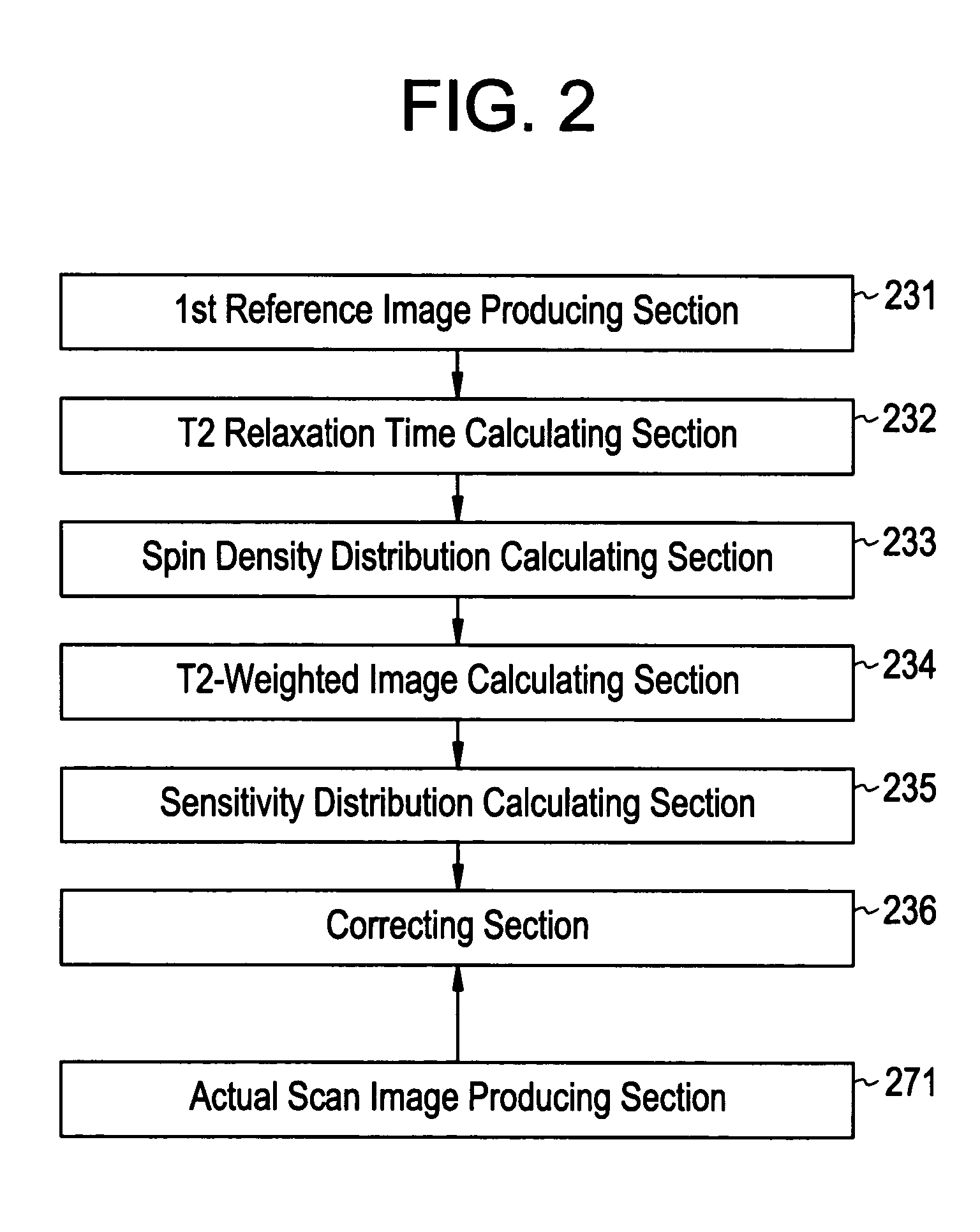
A method for calculating a sensitivity distribution of a receive coil and taking a tomographic image of a subject, based on magnetic resonance signals received by a surface coil in an imaging sequence with a plurality of different echo times TE1 and TE2 in a reference scan, a plurality of reference images are produced by a first reference image producing section; and based on the plurality of reference images, a T2 relaxation time is calculated by a T2 relaxation time calculating section. Then, based on the calculated T2 relaxation time, a T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2 is calculated by a T2-weighted image calculating section, and thereafter, based on the reference image and T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2, a sensitivity distribution is calculated by a sensitivity distribution calculating section. Based on the sensitivity distribution, a tomographic image by an actual scan is corrected by a correcting section.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Selective sampling magnetic resonance-based method for assessing structural spatial frequencies
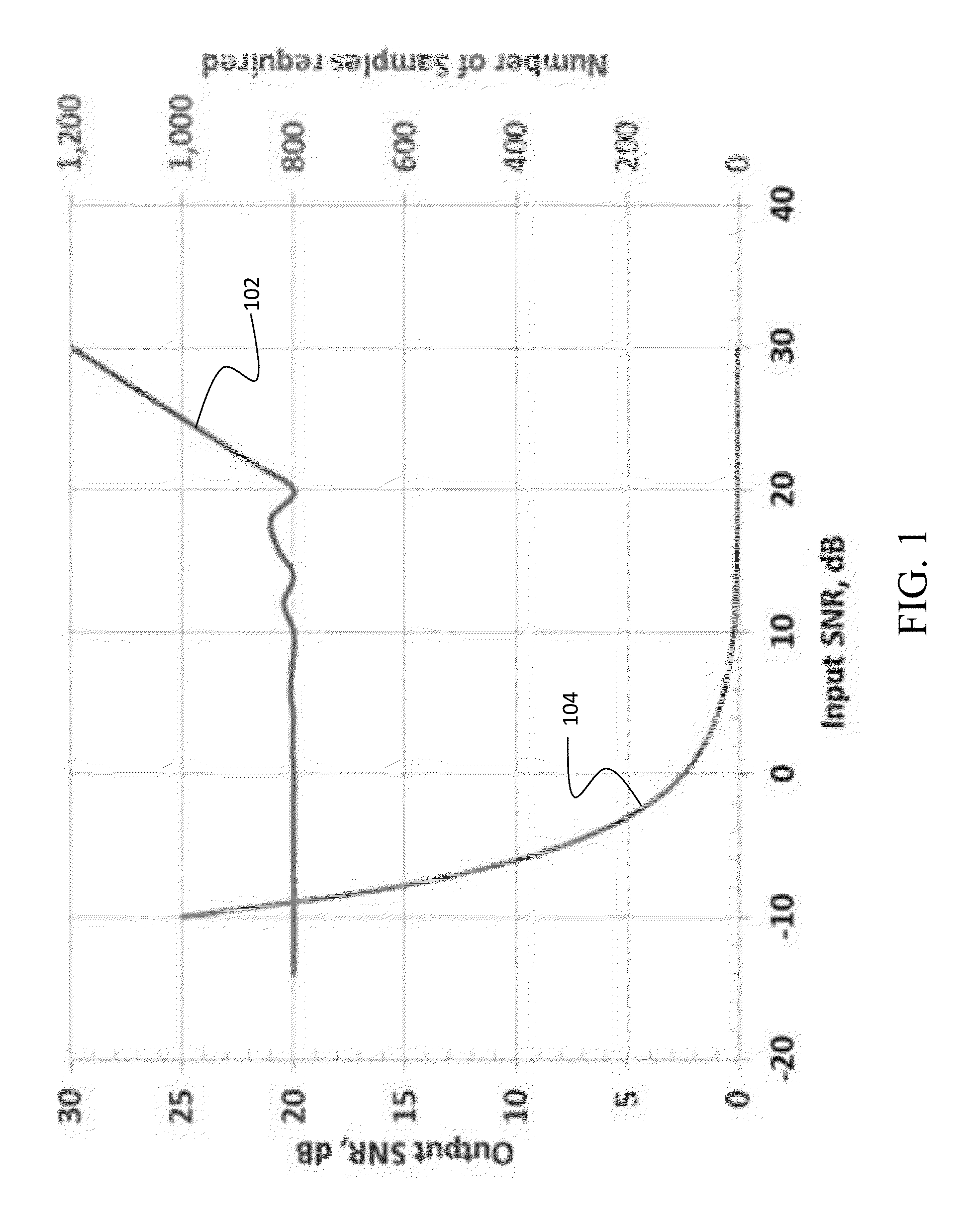
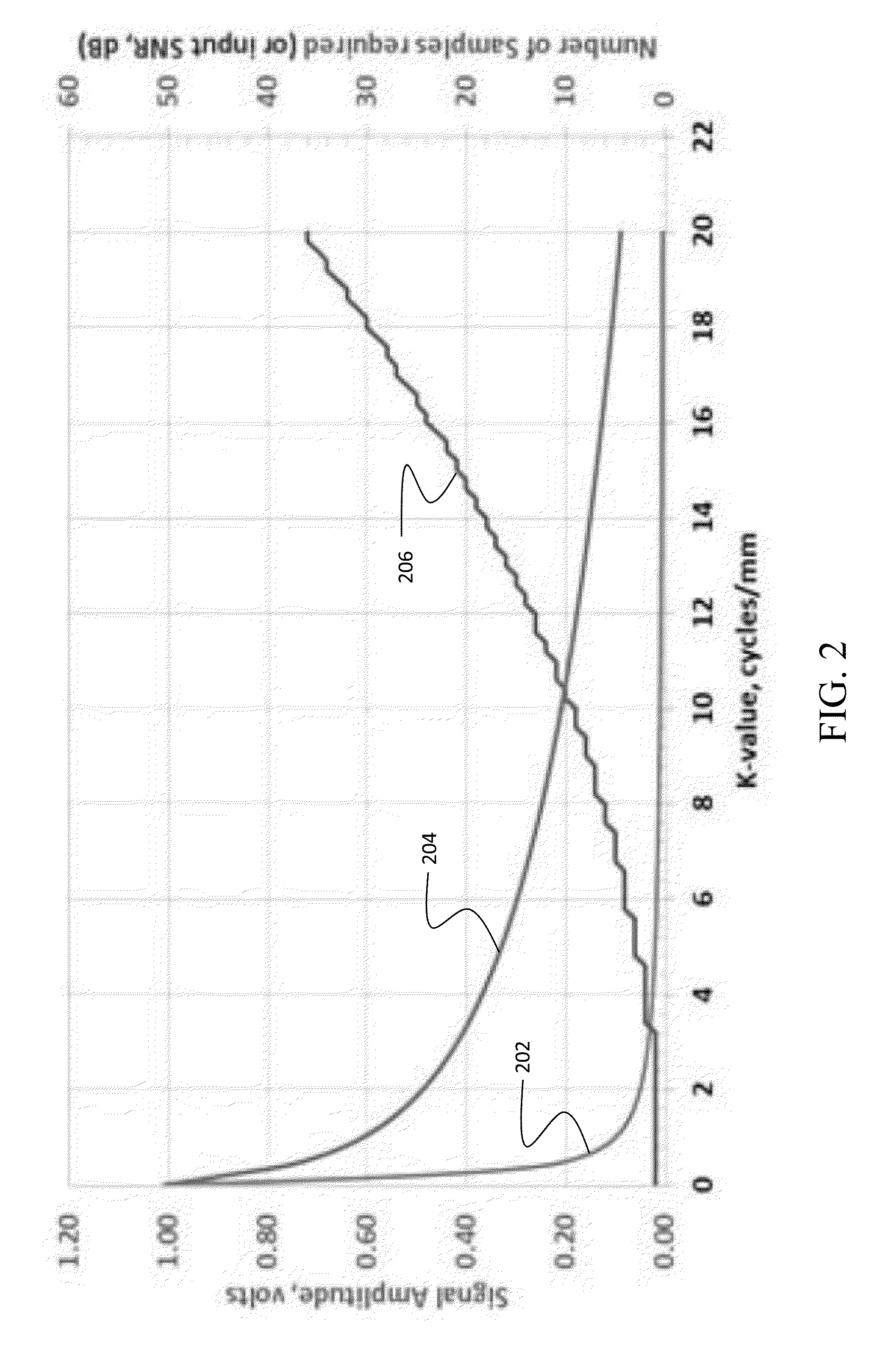
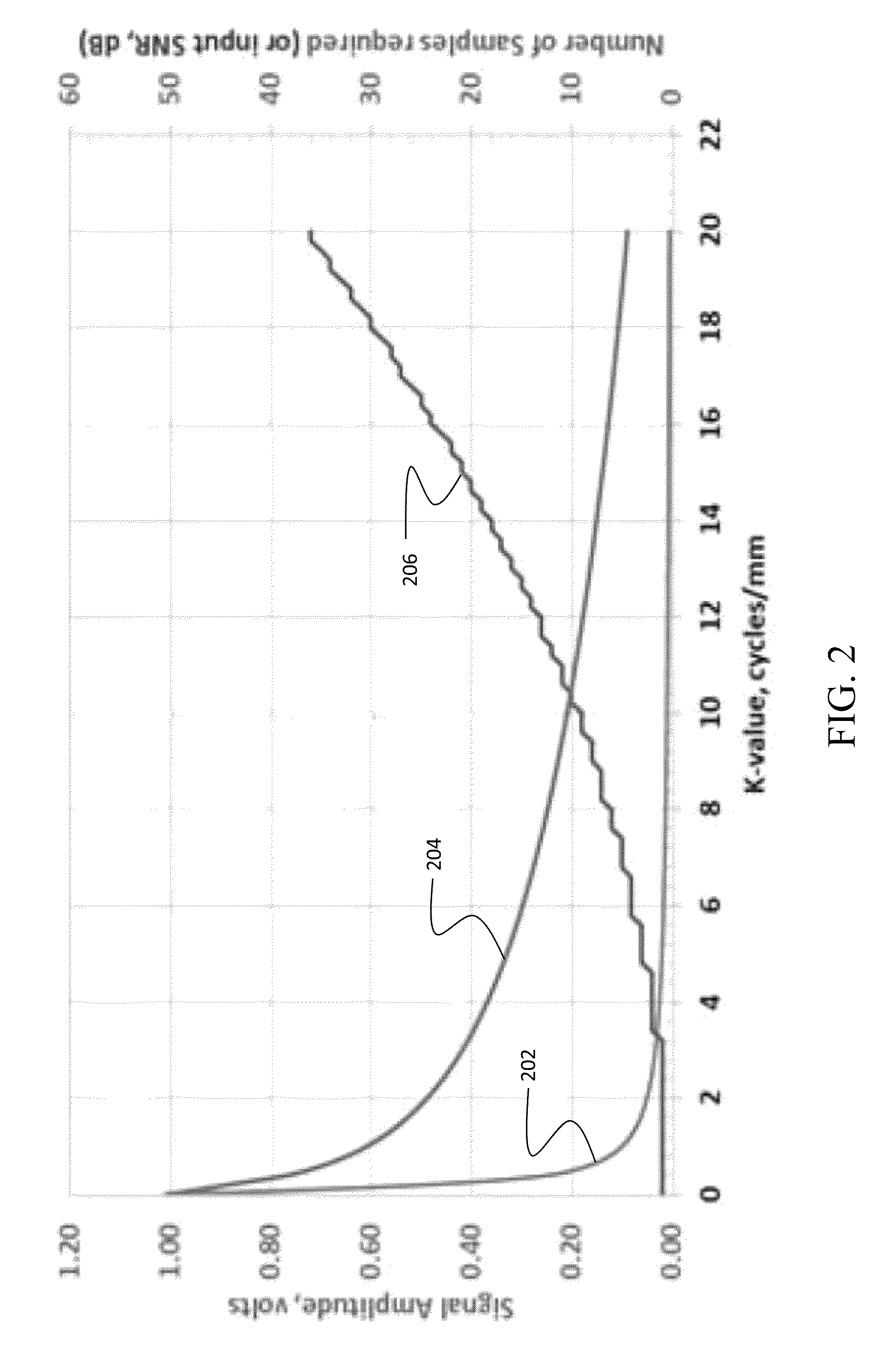
The disclosed embodiments provide a method for acquiring MR data at resolutions down to tens of microns for application in in-vivo diagnosis and monitoring of pathology for which changes in fine tissue textures can be used as markers of disease onset and progression. Bone diseases, tumors, neurologic diseases, and diseases involving fibrotic growth and / or destruction are all target pathologies. Further the technique can be used in any biologic or physical system for which very high-resolution characterization of fine scale morphology is needed. The method provides rapid acquisition of selected values in k-space, with multiple successive acquisitions of individual k-values taken on a time scale on the order of microseconds, within a defined tissue volume, and subsequent combination of the multiple measurements in such a way as to maximize SNR. The reduced acquisition volume, and acquisition of only select values in k-space along selected directions, enables much higher in-vivo resolution than is obtainable with current MRI techniques.
Owner:BIOPROTONICS
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and temperature information measurement method
InactiveUS20160192859A1High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsBiological bodyMetabolite
A technique for improving accuracy of temperature measurement in a living body using MRS / MRSI is provided. A cerebrospinal fluid suppression sequence that does not affect nuclear magnetic resonance signals of metabolite, but suppresses nuclear magnetic resonance signals of cerebrospinal fluid is executed in advance of execution of a signal measurement sequence for measuring nuclear magnetic resonance signals of water and a desired metabolite. There are thereby obtained spectra of water and the metabolite obtained from the nuclear magnetic resonance signals of water and the metabolite in which nuclear magnetic resonance signals of cerebrospinal fluid is suppressed. The obtained spectral peaks are fitted to a model function to obtain resonant frequencies of water and the metabolite, and the difference thereof is used to calculate temperature.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create T1 maps
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
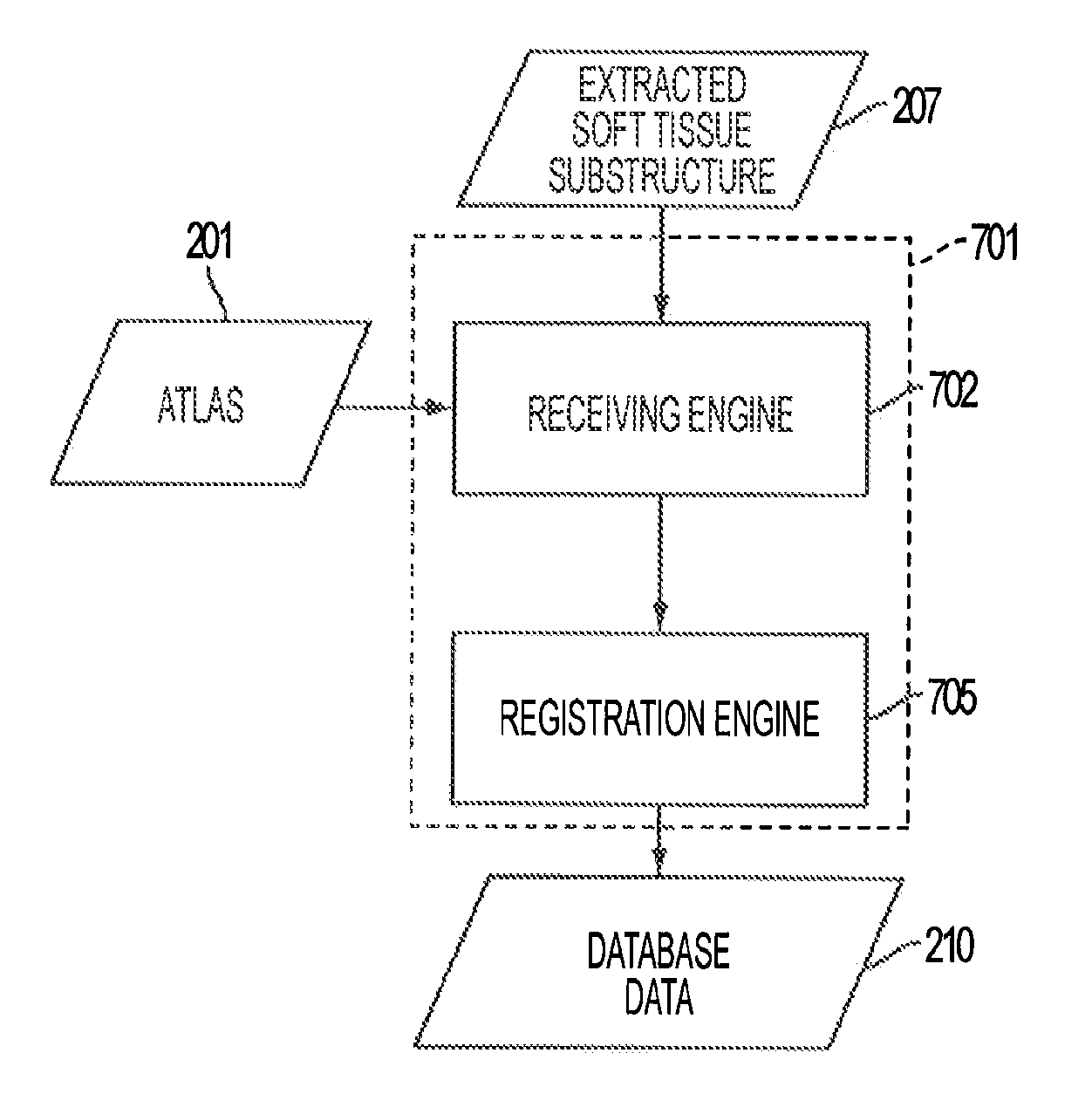
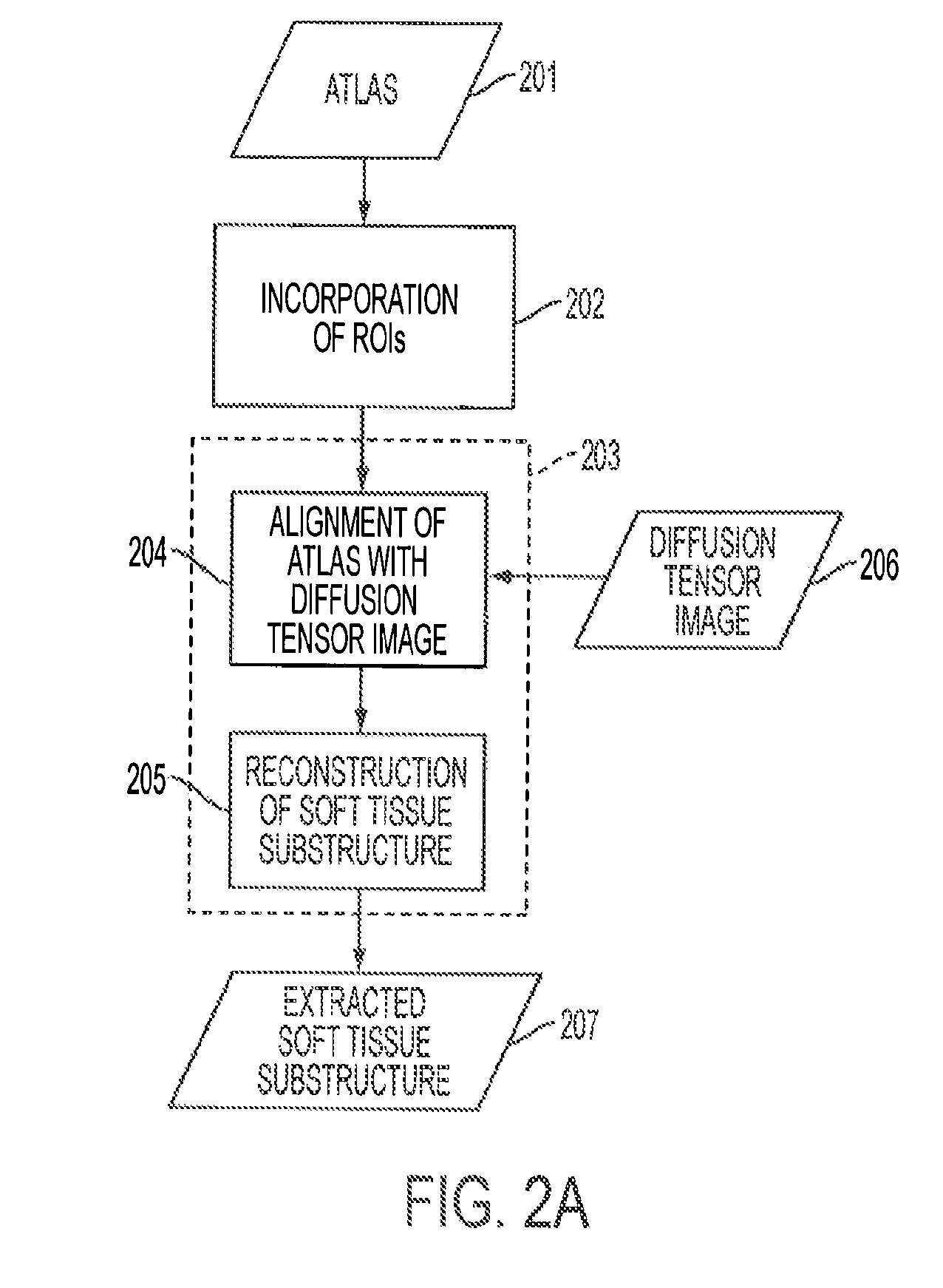
Automated fiber tracking of human brain white matter using diffusion tensor imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a MRI scanner; a signal processing system in communication with the magnetic resonance imaging scanner to receive magnetic resonance (MR) signals for forming magnetic resonance images of a subject under observations; a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit contains database data corresponding to a soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The database data includes information identifying at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The signal processing system is adapted to process MR signals received from the MRI scanner to automatically identify at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and analysis method for fat suppression effect in magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
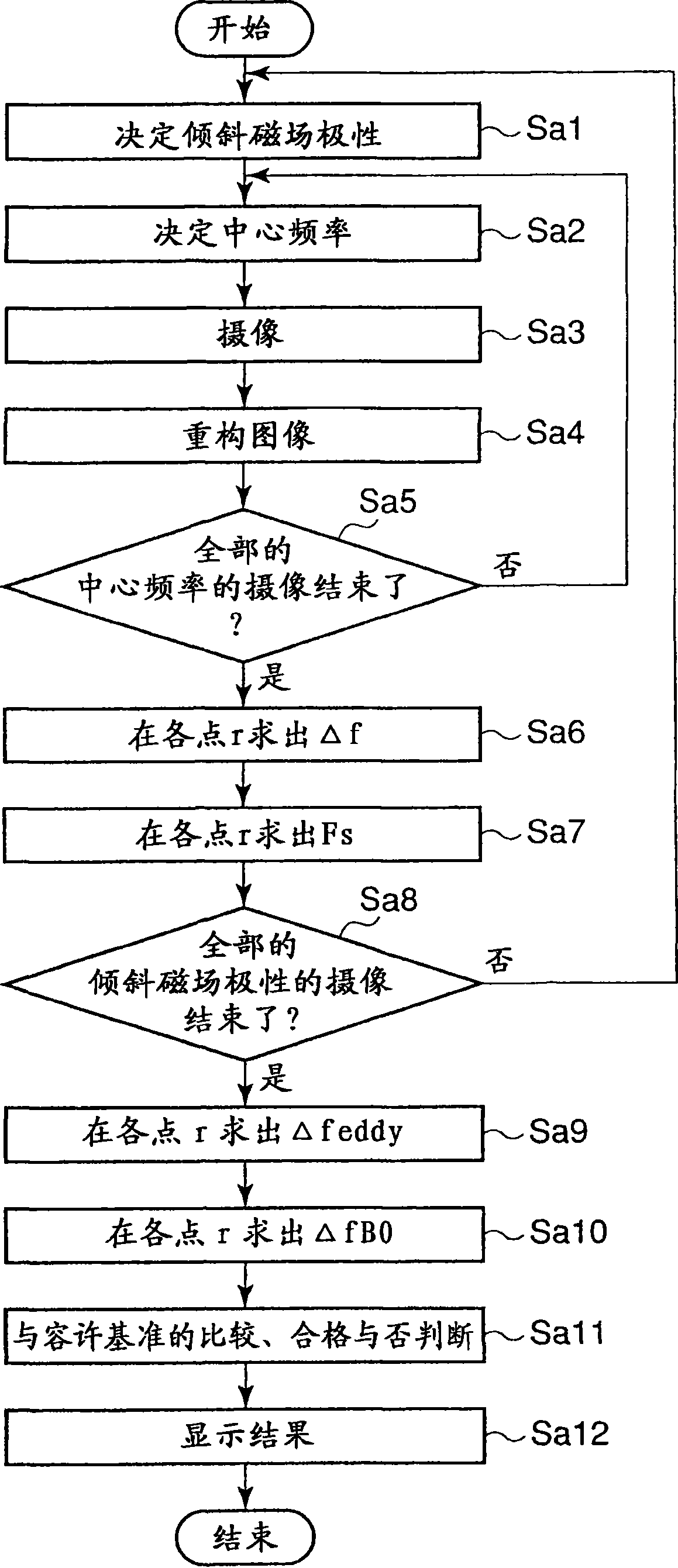
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an imaging unit which performs imaging more than once with respect to an imaging target while changing a central frequency of a fat suppression pulse, a generation unit which generates a plurality of images based on magnetic resonance signals obtained by imaging performed more than once, and a calculation unit which calculates factor information of spatial inhomogeneity of a fat suppression effect based on the plurality of images.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and magnetic resonance system to acquire mr data in a predetermined volume segment of an examination subject
ActiveUS20130249550A1Avoid impairing signalNo additional considerationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientProton magnetic resonance
In a method and a magnetic resonance (MR) system, a marked area is determined that demarcates a predetermined volume segment of the subject relative to the regions adjacent thereto. Nuclei in the predetermined volume segment are excited, or nuclei in a region adjacent thereto are saturated with an RF excitation pulse at the same time a magnetic field gradient is activated. The center frequency of a frequency range of the RF excitation pulse and the direction of the magnetic field gradient are adjusted dependent on resonant frequencies of substances present within the predetermined volume segment in order, starting from the predetermined volume segment to shift an actual excitation volume segment excited by the RF excitation pulse toward the marked area, or to shift a saturation volume saturated by the RF excitation pulse away from the marked area. MR data are then acquired from the predetermined volume segment.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
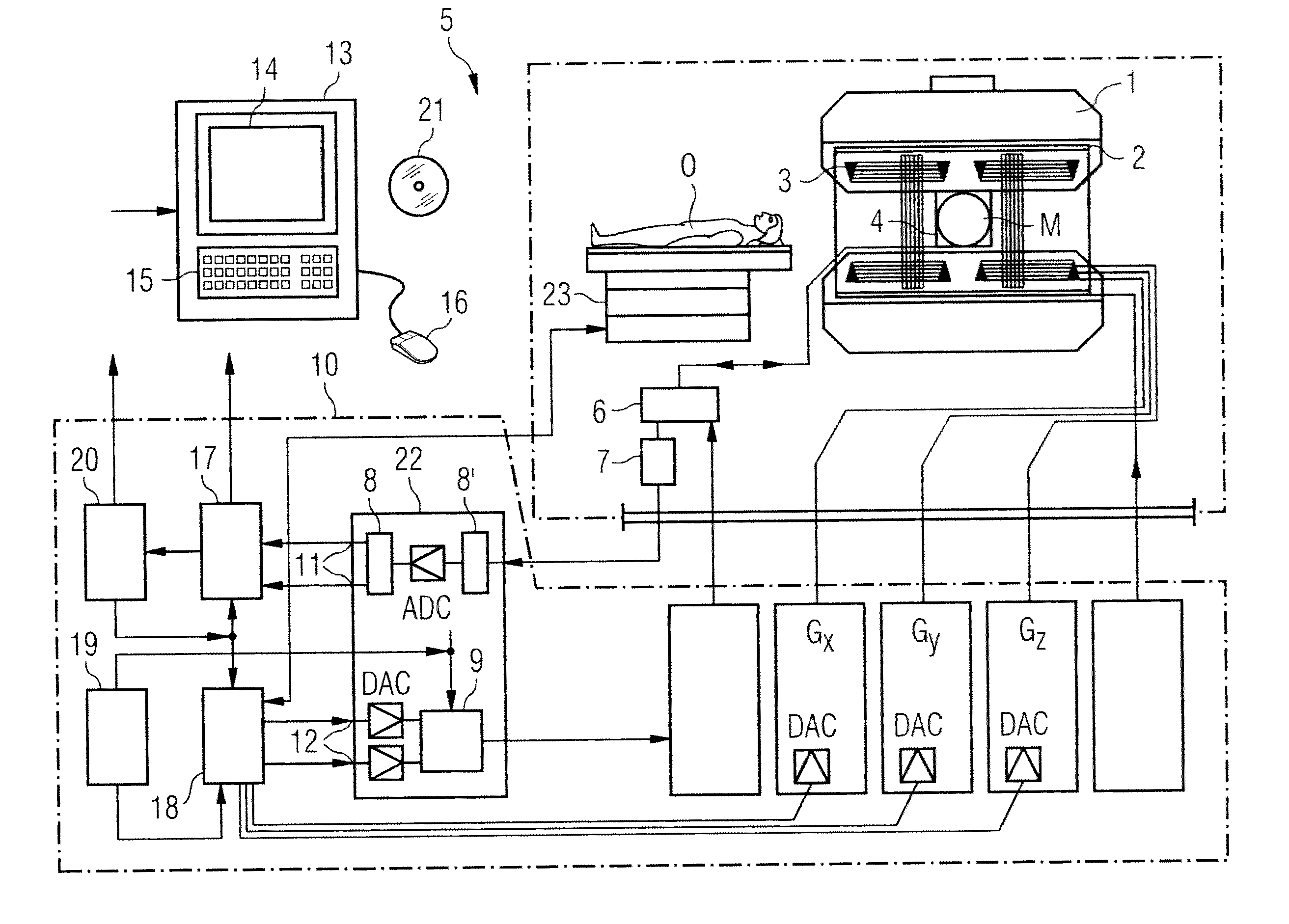
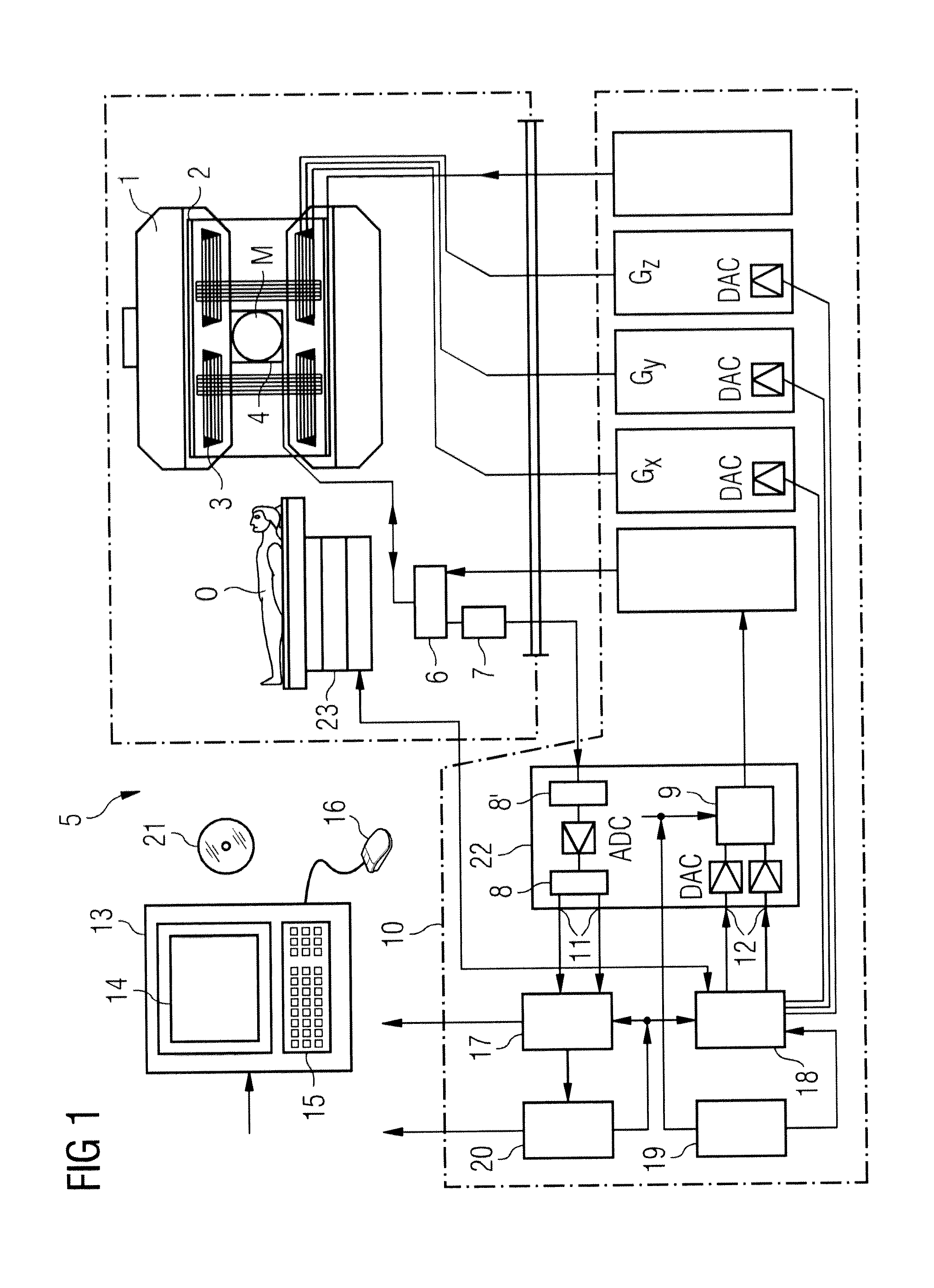
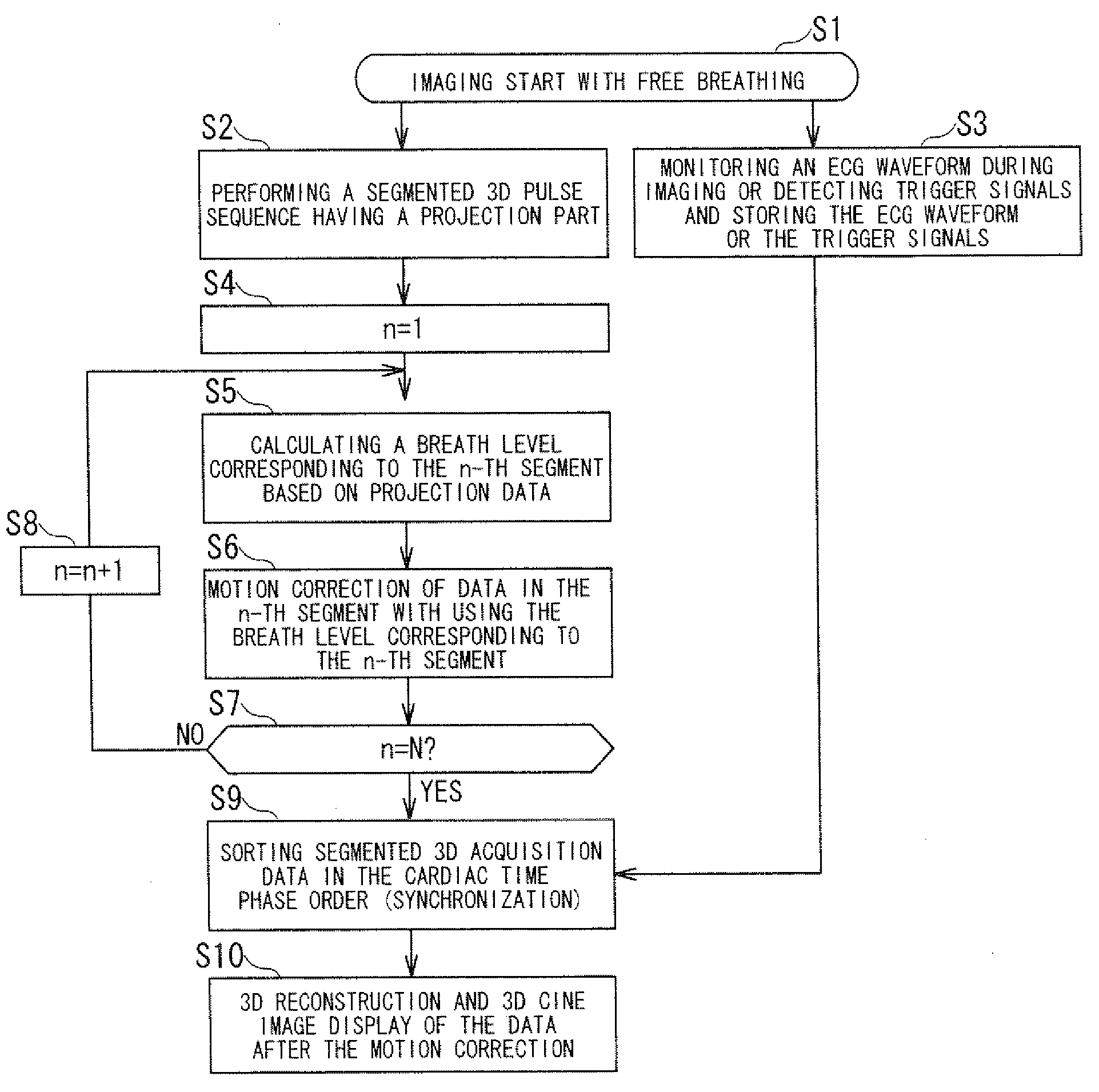
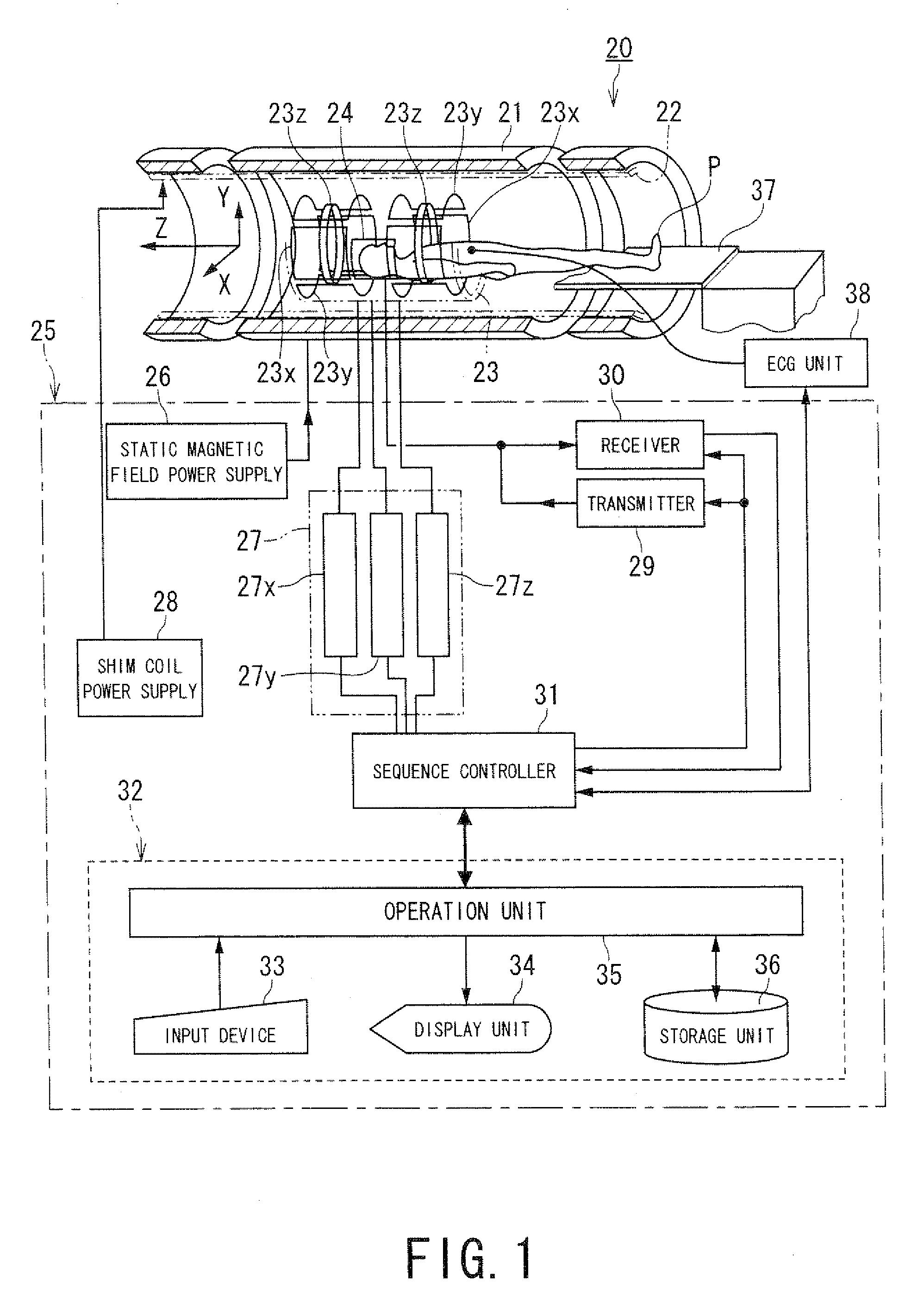
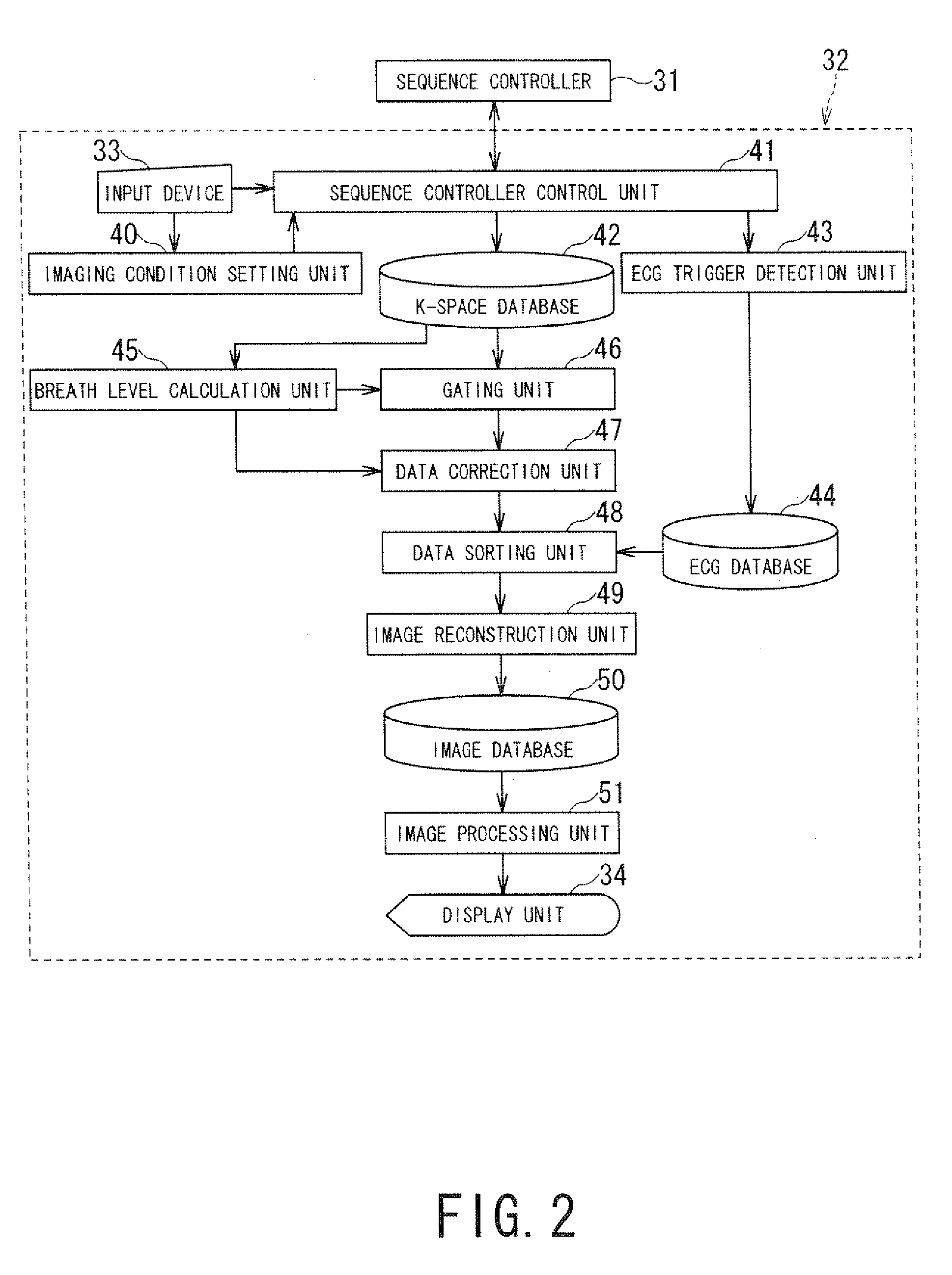
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20090148021A1High resolutionImage analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationProton magnetic resonanceResonance
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a data acquisition unit, a correction unit, a sorting unit and n image reconstruction unit. The data acquires data for imaging and projection data. The correction unit performs motion correction of the data using the breath levels obtained based on the projection data. The data sorting unit sorts the data after the motion correction into a cardiac time phase order based on electrocardiographic information. The image reconstruction unit reconstructs three dimensional image data based on the sorted data after the motion correction.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Selective sampling magnetic resonance-based method for assessing structural spatial frequencies
The disclosed embodiments provide a method for acquiring MR data at resolutions down to tens of microns for application in in-vivo diagnosis and monitoring of pathology for which changes in fine tissue textures can be used as markers of disease onset and progression. Bone diseases, tumors, neurologic diseases, and diseases involving fibrotic growth and / or destruction are all target pathologies. Further the technique can be used in any biologic or physical system for which very high-resolution characterization of fine scale morphology is needed. The method provides rapid acquisition of selected values in k-space, with multiple successive acquisitions of individual k-values taken on a time scale on the order of microseconds, within a defined tissue volume, and subsequent combination of the multiple measurements in such a way as to maximize SNR. The reduced acquisition volume, and acquisition of only select values in k-space along selected directions, enables much higher in-vivo resolution than is obtainable with current MRI techniques.
Owner:BIOPROTONICS
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
The invention provides magnetic resonace imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method. A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a trigger generating unit, a blood flow image generating unit and a control unit. The trigger generating unit acquires blood flow information of an object and generates a trigger based on the blood flow information. The blood flow image generating unit acquires imaging data with using the trigger and generates blood flow image data. The control unit controls so as to repeatedly perform a probe sequence for acquiring the blood flow information and animaging sequence for acquiring the imaging data alternately.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
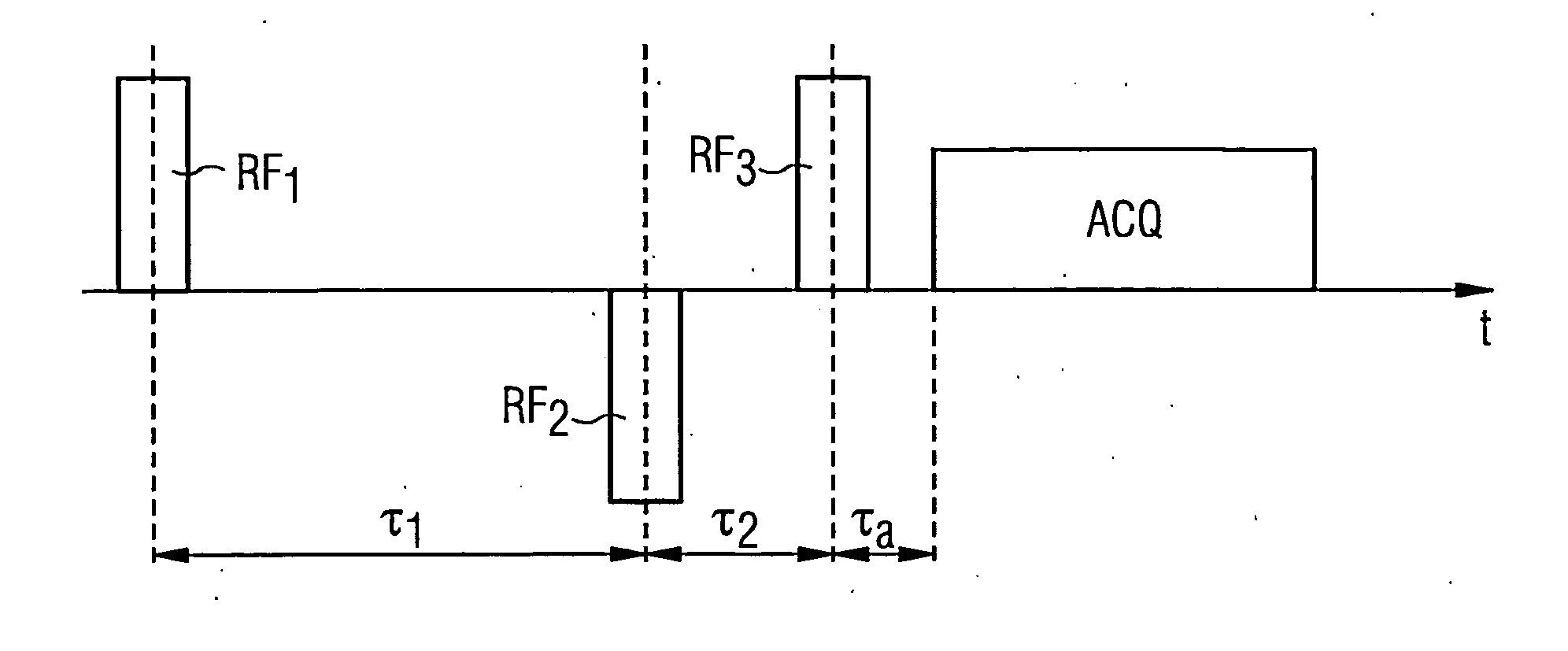
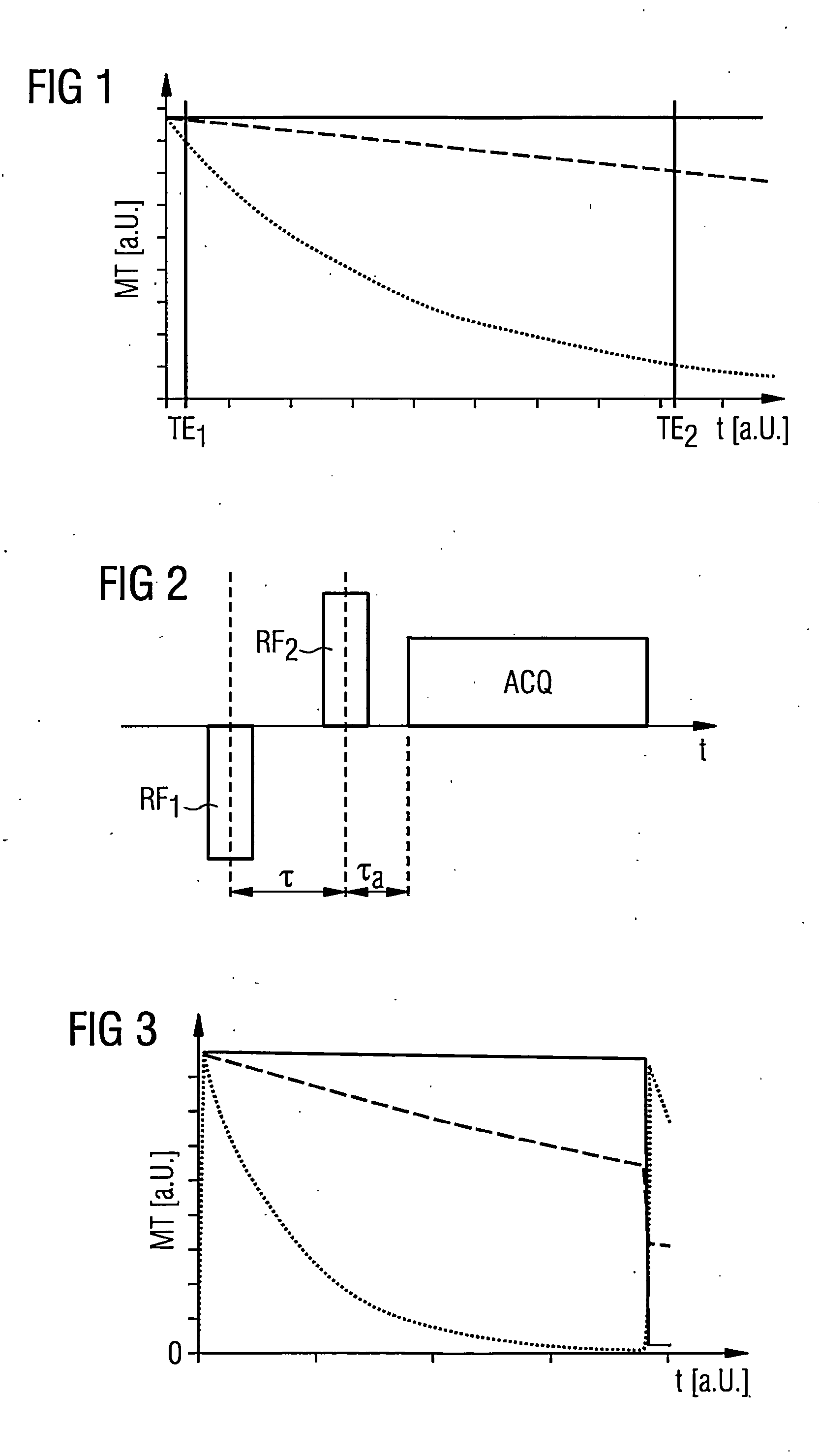
Magnetic resonance system, operating method and control device to generate t2-weighted images using a pulse sequence with very short echo times
InactiveUS20130169273A1Suppressed quickly and wellSuppressed quickly and effectivelyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProton magnetic resonanceResonance
In a method to control a magnetic resonance system to generate magnetic resonance exposures of an examination subject, a first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse with a pulse length of at most 50 μs is initially emitted in a volume region of the examination subject. At least one second magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse, whose phase is essentially rotated by 180° relative to the first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse, with a pulse length of at most 50 μs, is emitted in the same volume region of the examination subject in a predetermined time interval immediately after the first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse. An acquisition of raw data from the volume region of the examination subject then takes place. Furthermore, a control device for operating a magnetic resonance system as well as a magnetic resonance system with such a control device to implement such a method, are described.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
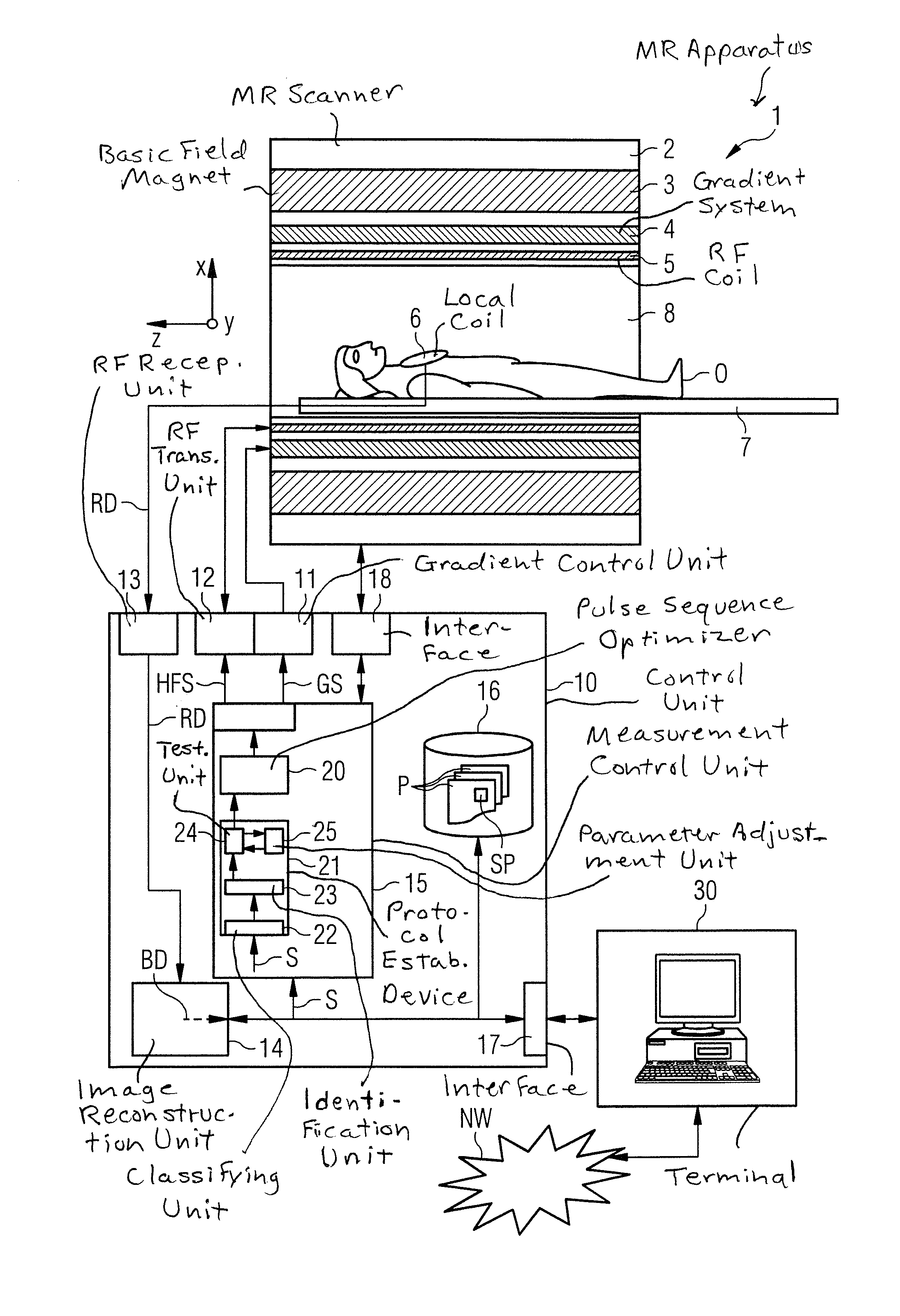
Method and device for optimizing magnetic resonance system operating sequences with respect to physiological limiting values
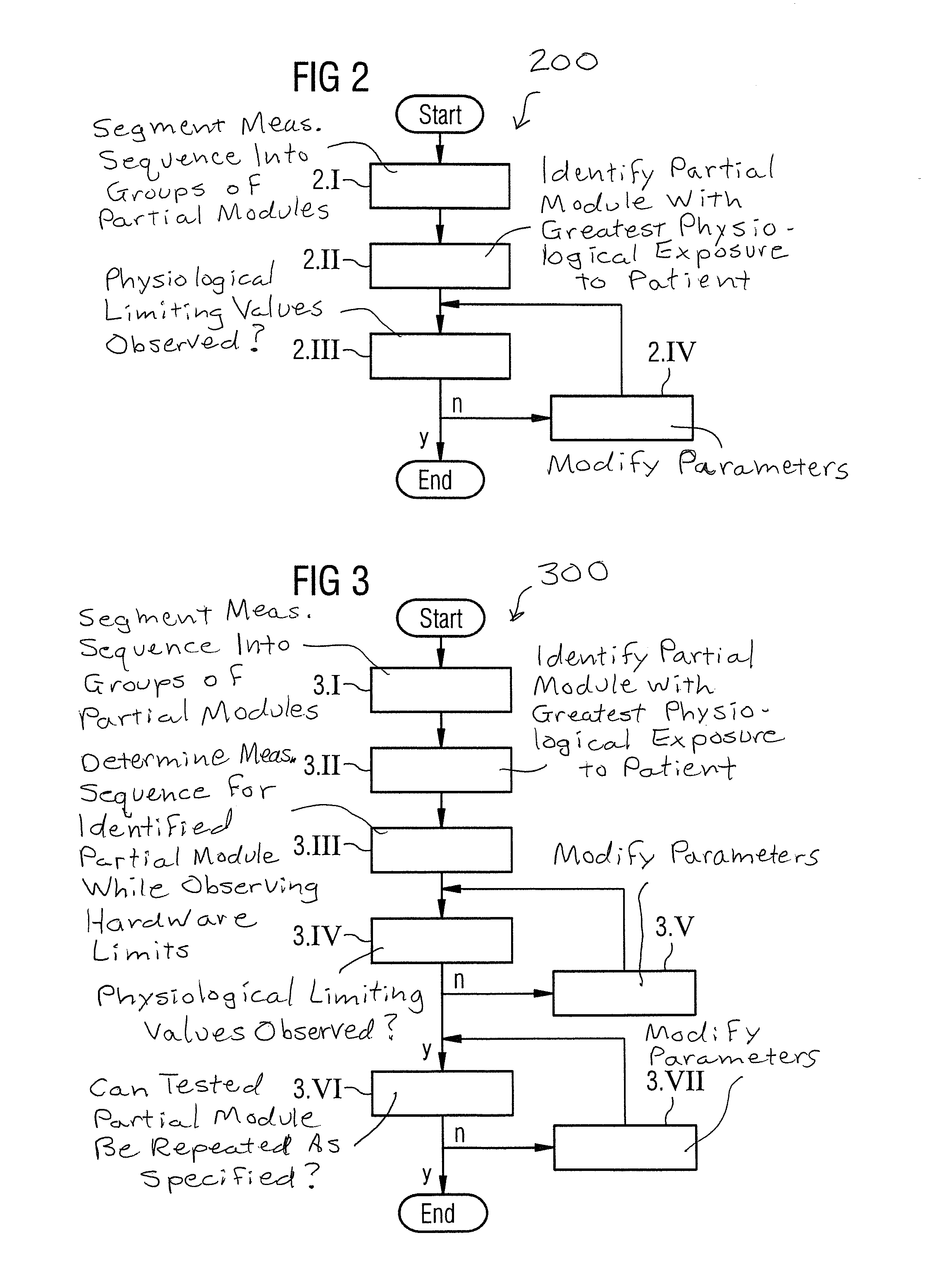
ActiveUS20150285885A1Effective and more user-friendlySimplify work proceduresSurgical instrument detailsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsProton magnetic resonanceResonance
A method and device for establishing a protocol relating to a measurement sequence for controlling a magnetic resonance tomography system, the measurement sequence is segmented into various groups of partial modules that are similar to one another. A partial module that potentially generates the greatest physiological exposure for a patient is identified. Furthermore, a test is carried out by means of a model function to determine whether physiological limiting values are being observed in the measurement sequence for the partial module. If the physiological limiting values are not being observed, parameters influencing the measurement sequence are modified and the preceding test step is repeated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Contrast agent and preparation method thereof
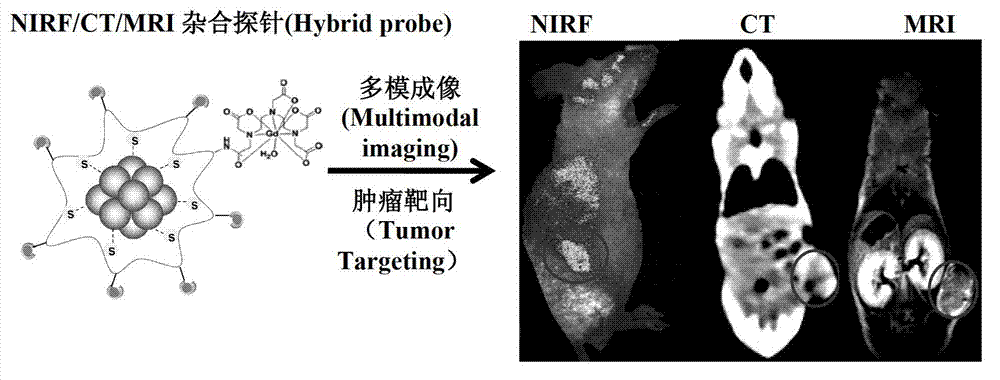
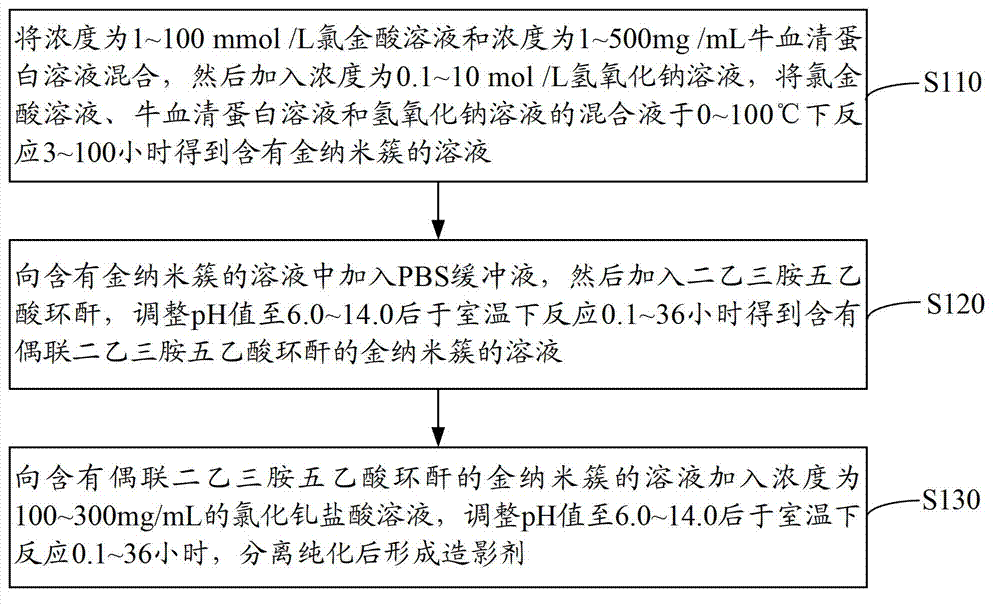
ActiveCN102813943AHigh sensitivityNot easy to swallowNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryRare-earth elementProton magnetic resonance
The invention provides a contrast agent which comprises water and nanoparticles suspending in water and with a gold nano-cluster as a core and a diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-gadolinium chelating agent as a shell. The gold nano-cluster has the functions of near infrared fluorescence (NIR) and computed tomography (CT) imaging; gadolinium is a rare earth element responsive to nuclear magnetic resonance, and the diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-gadolinium chelating agent has a magnetic resonance imaging (MIR) function; the contrast agent provided by the invention fuses the gold nano-cluster and the gadolinium chelating agent together, is capable of NIR / CT / MRI three-mode radiography and can fuse near infrared fluorescence, computed tomography imaging and magnetic resonance imaging together. Furthermore, the nanoparticles have a diameter of mere 0.9 to 1.1 nm, so the contrast agent is hardly phagocytosed by a reticuloendothelial system (RES) of a living body and has high permeability and improved radiographic sensitivity. The invention also provides a preparation method for the contrast agent.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging nano-carrier, nano drug carrier system and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108404142AGood for passive targetingActive targetingPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSide effectProton magnetic resonance
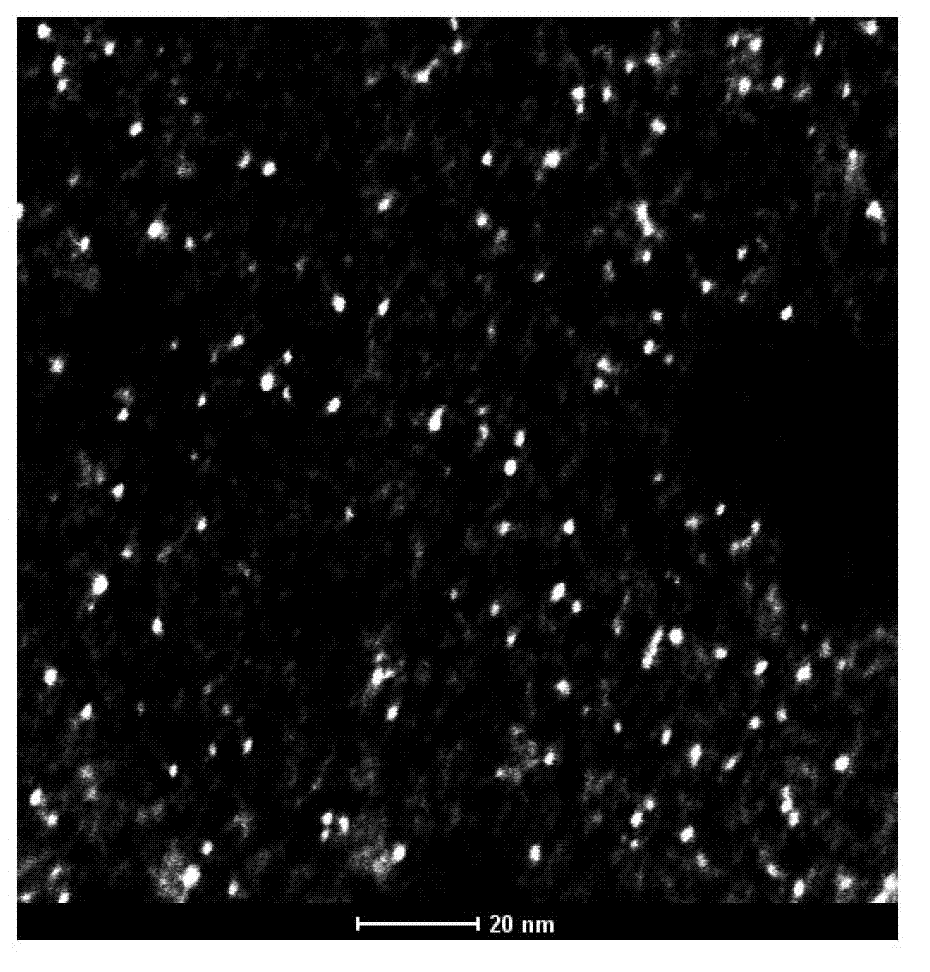
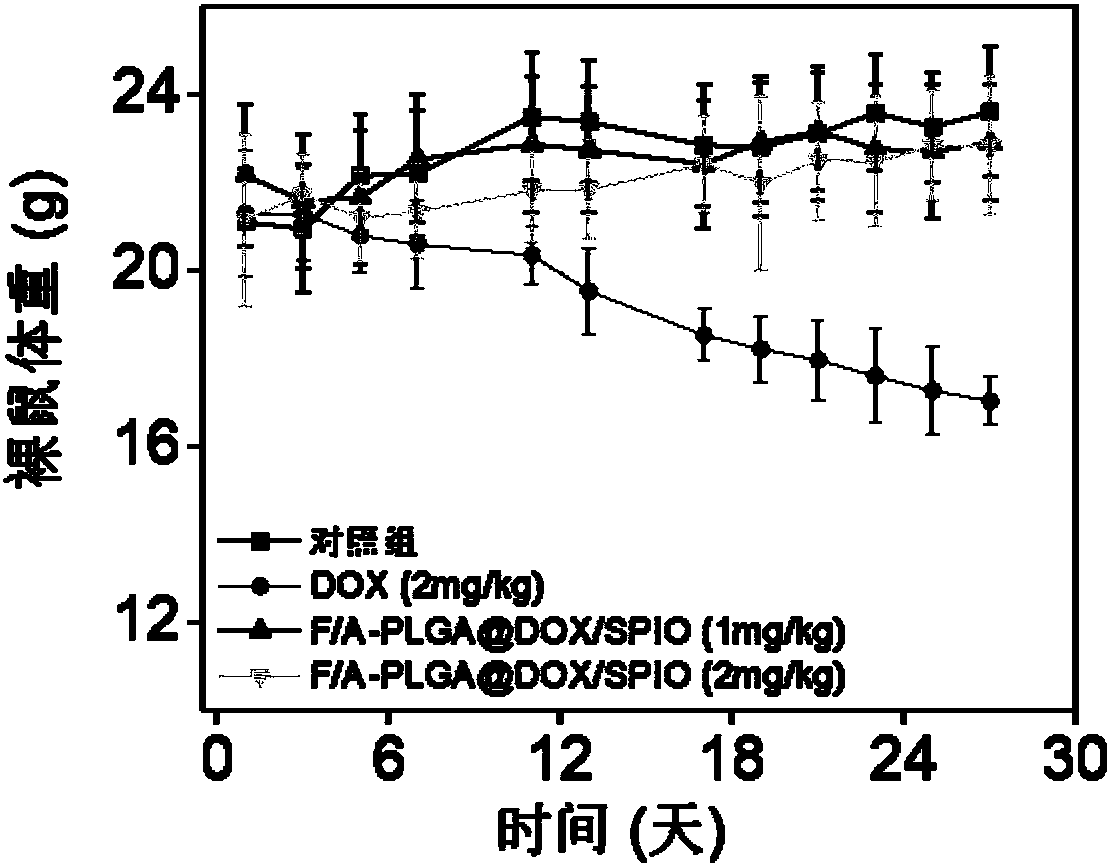
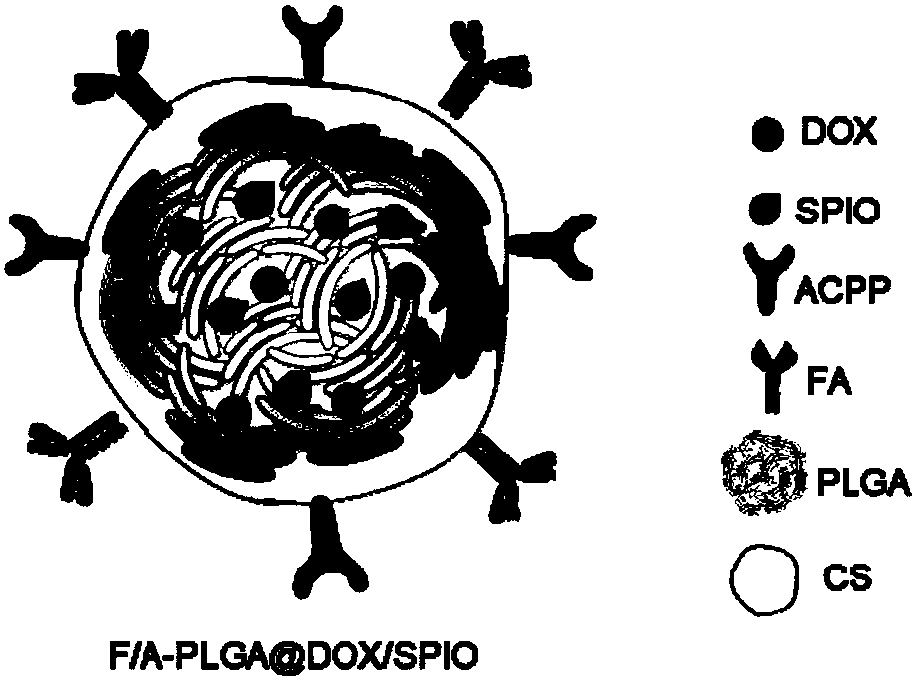
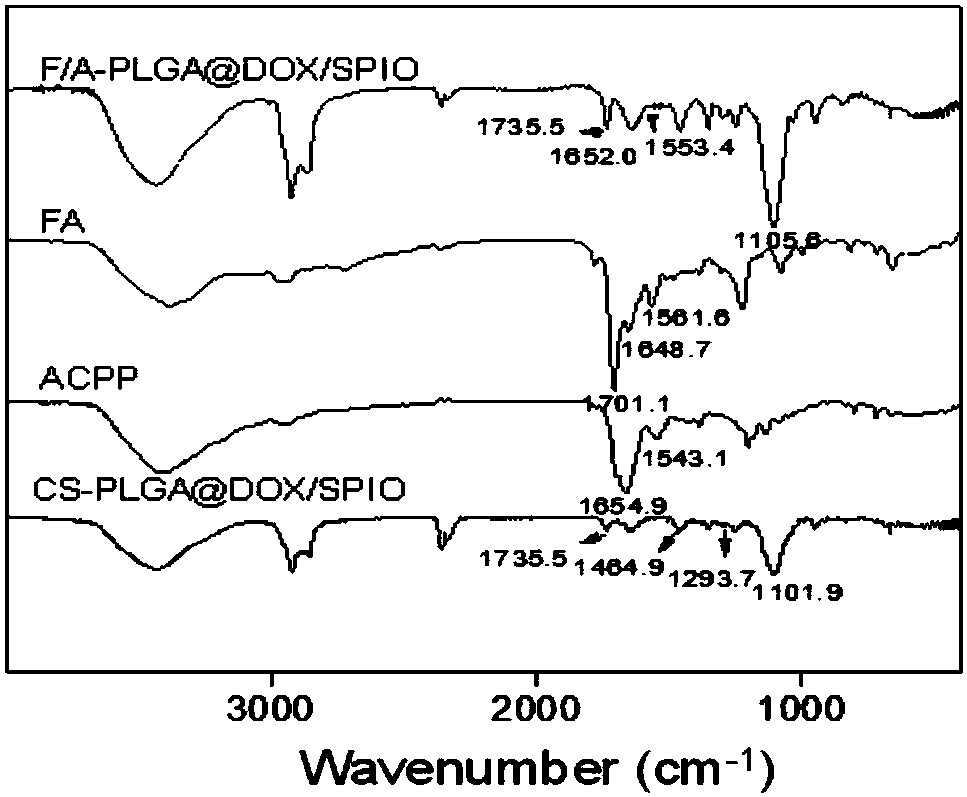
The invention belongs to the field of bio-medicine, and discloses a magnetic resonance imaging nano-carrier, a nano drug carrier system and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, two targeting molecules, namely folic acid and cell-penetrating peptide, are adopted, so that a targeting effect on tumors is improved, and meanwhile, anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo is enhanced. PLGA, which is low in toxicity and good in biocompatibility, is taken as the anti-tumor drug carrier, and the terminal of the PLGA is modified with CS, so that the functional nano-system is prepared. Meanwhile, nuclear magnetic imaging drugs and anti-tumor drugs are effectively loaded, so that the anti-tumor drugs can reach a tumor focus part in a specific mode, and tumor region nuclear magnetic localization of ferroferric oxide nanoparticles can be implemented; and meanwhile, a therapeutic effect with high selectivity and low toxicity can be achieved. With the application of the invention,shortcomings of conventional cytotoxic drugs which are poor in selectivity, relatively strong in toxic and side effects, capable of causing drug tolerance easily and the like can be overcome; and a utilization degree of the anti-tumor drugs can be improved and toxic and side effects can be reduced. The preparation method of the drug carrier system is simple and easy to implement; and the preparedproduct (the drug carrier system) is good in repeatability and stability.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com