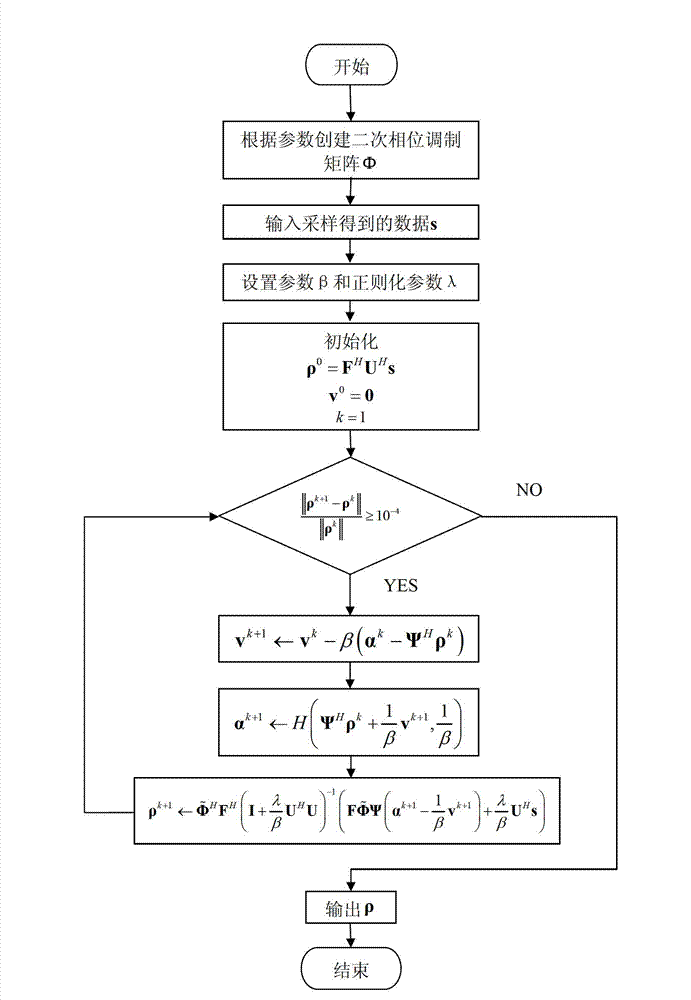
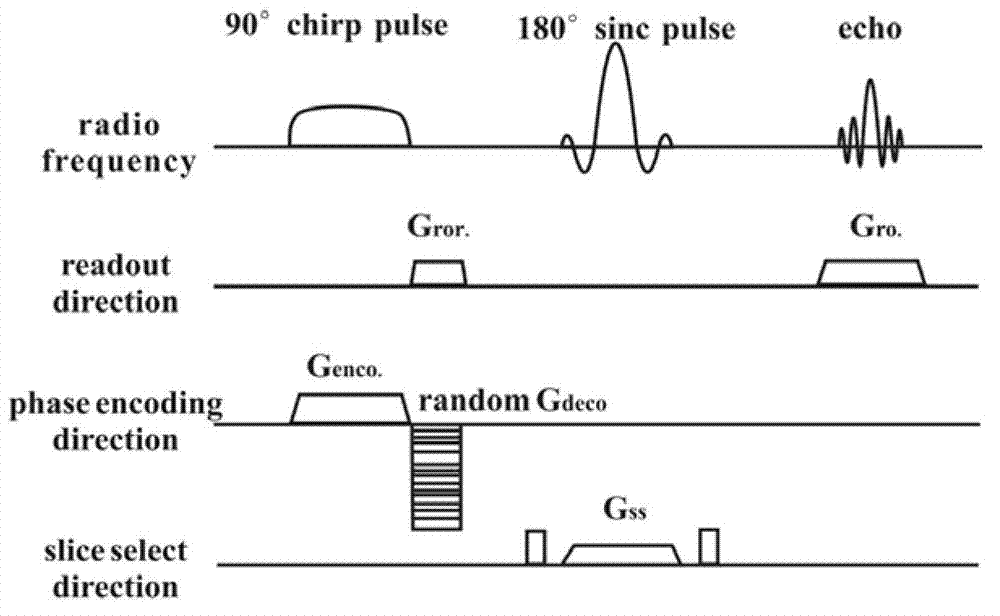
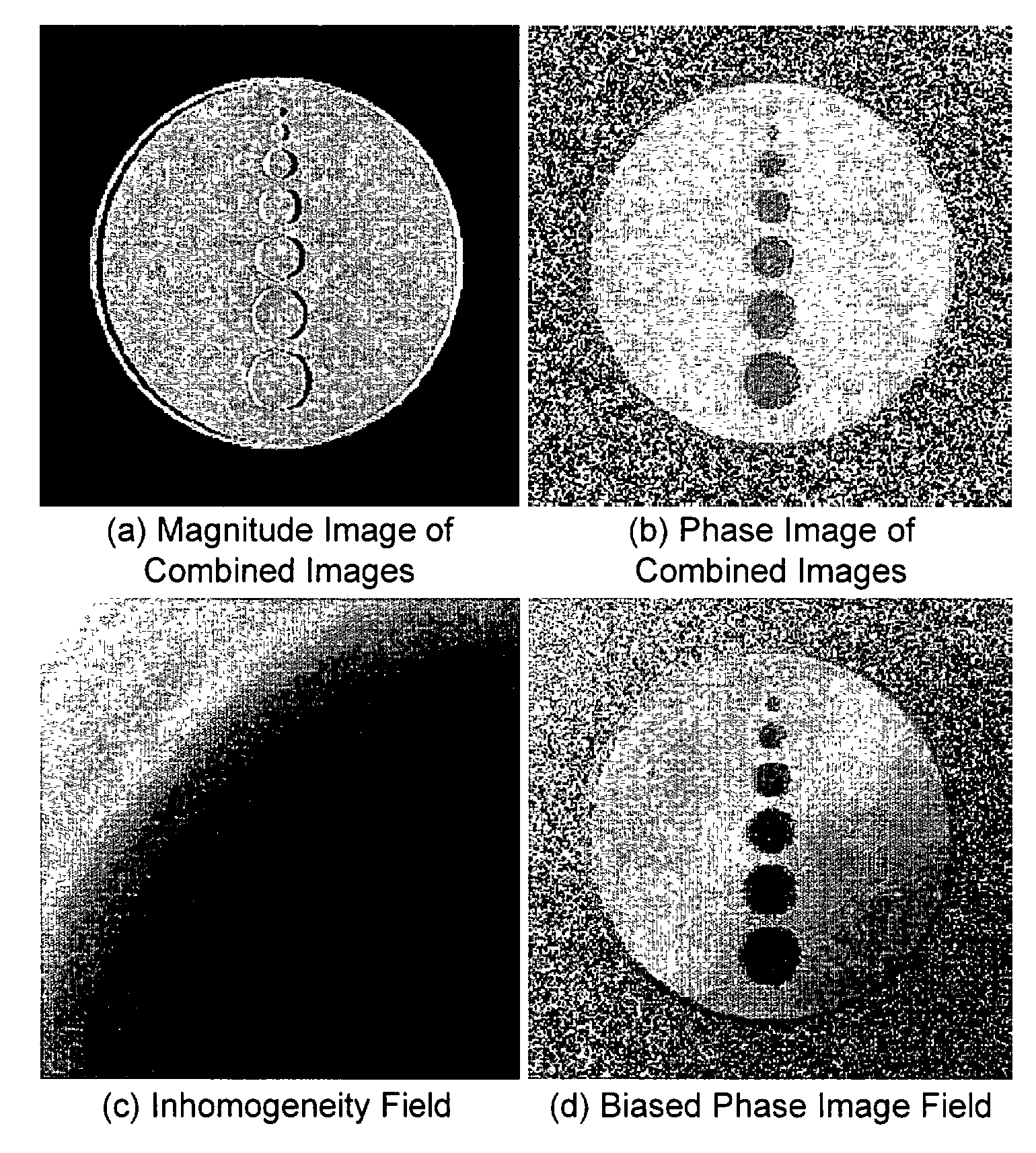
Patents
Literature
297results about How to "Reduced imaging time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
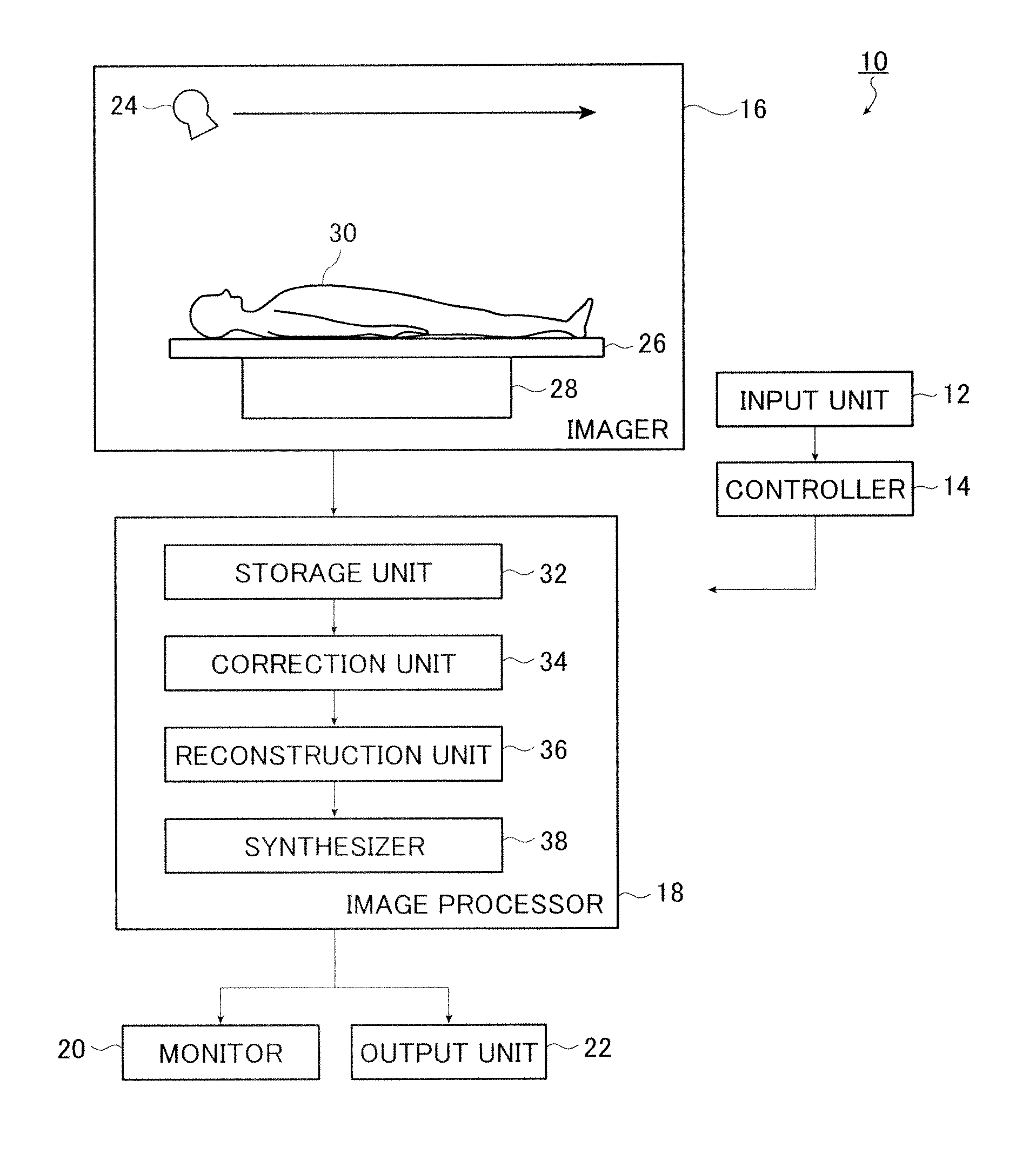
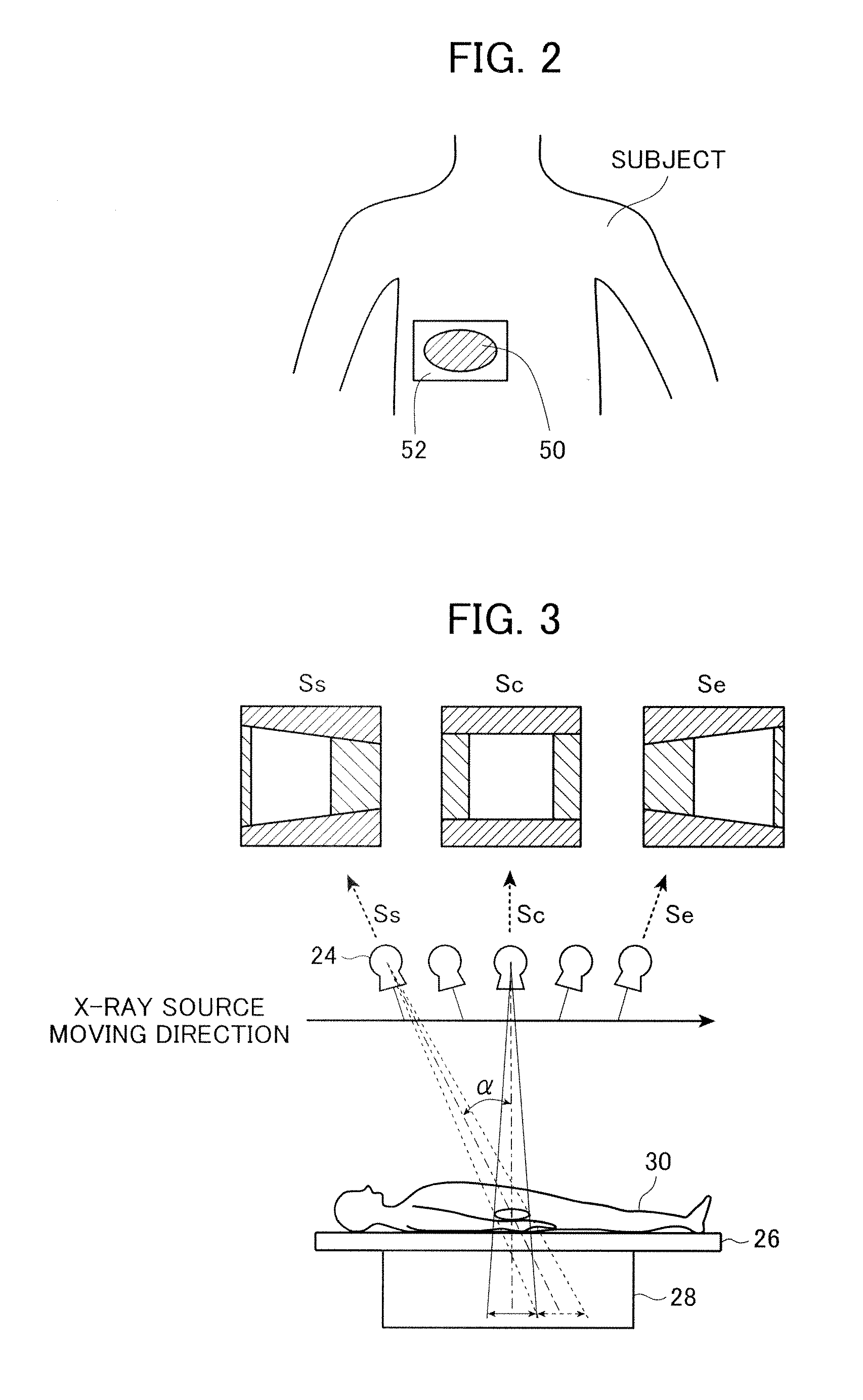
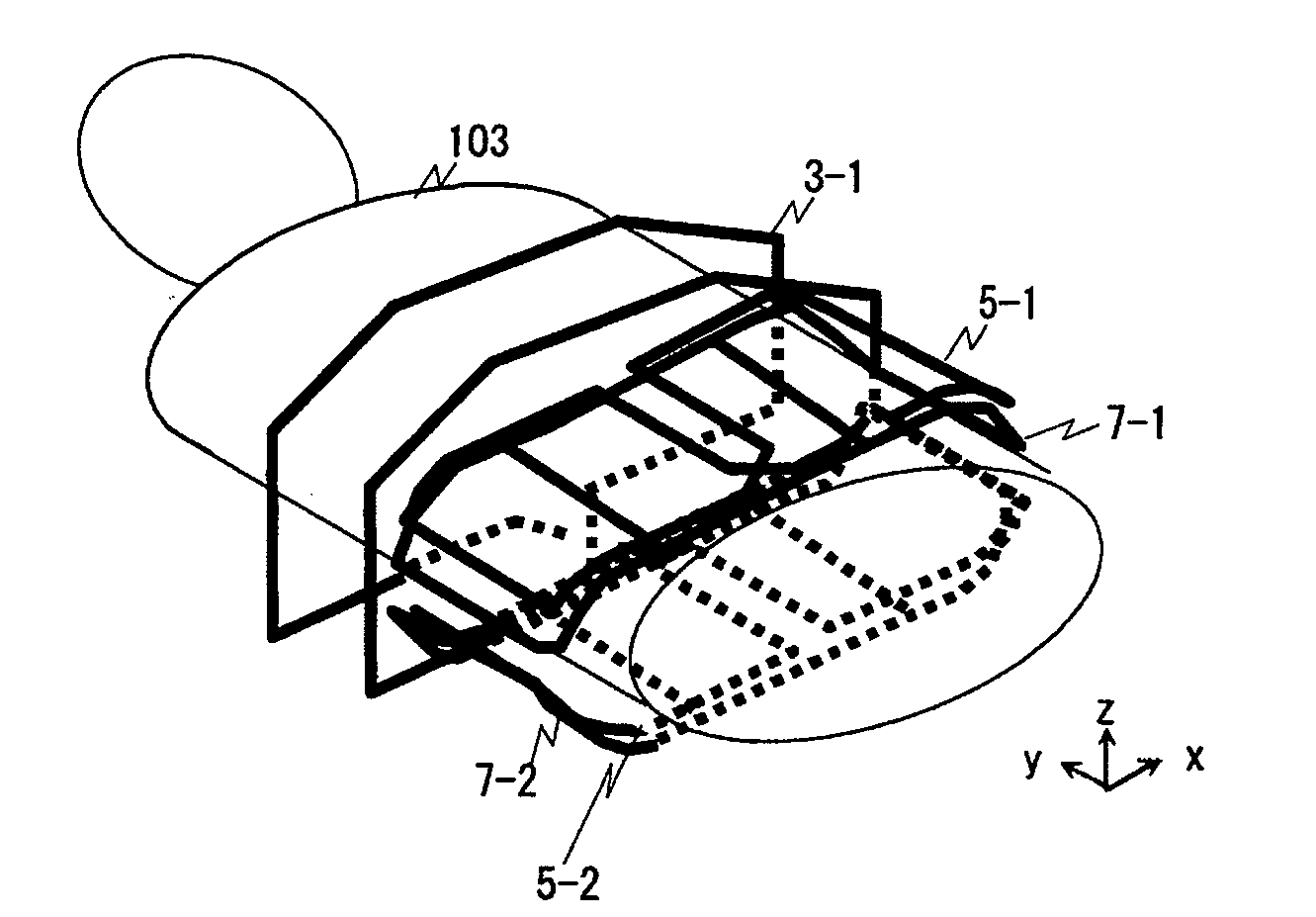
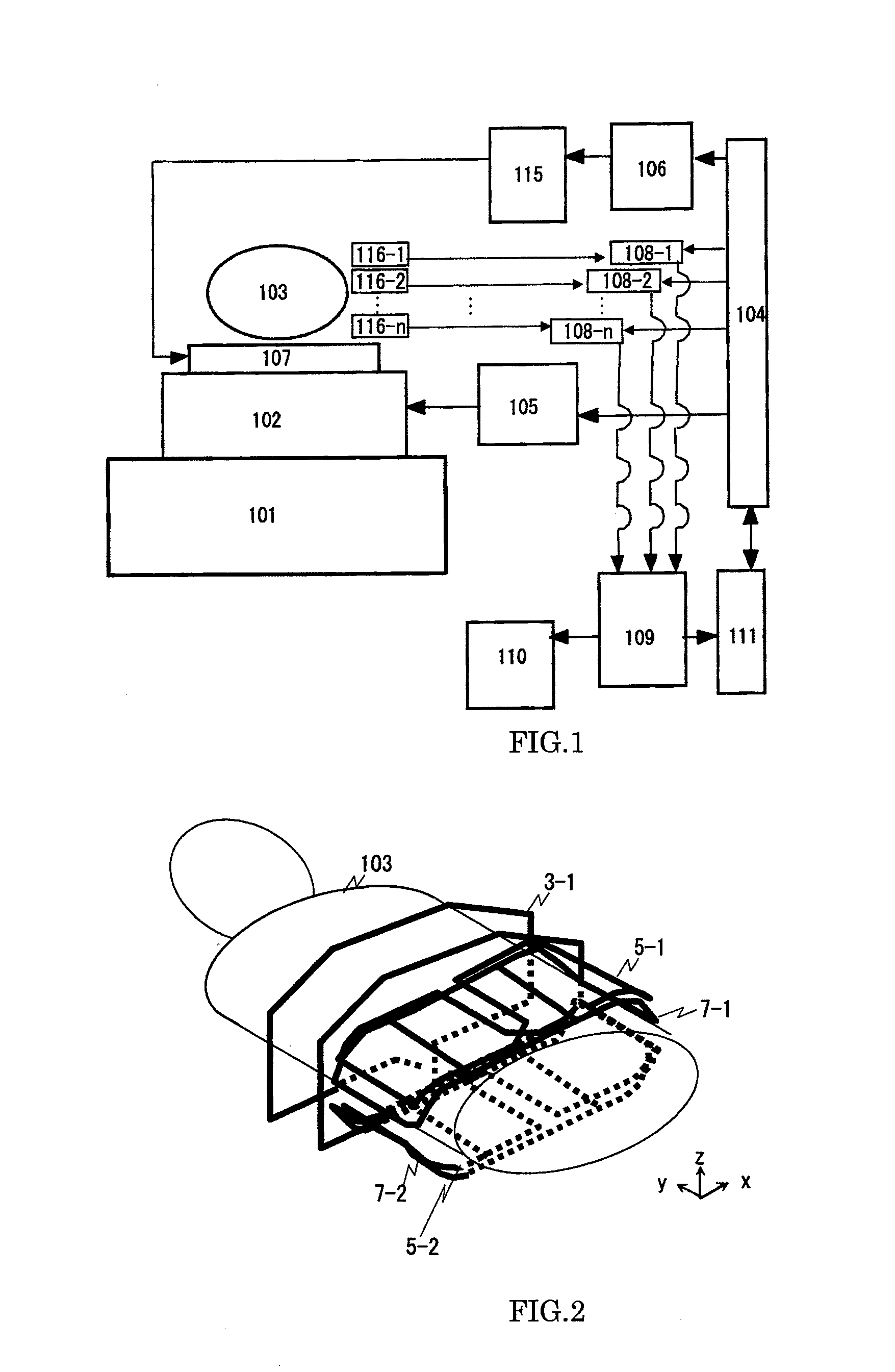
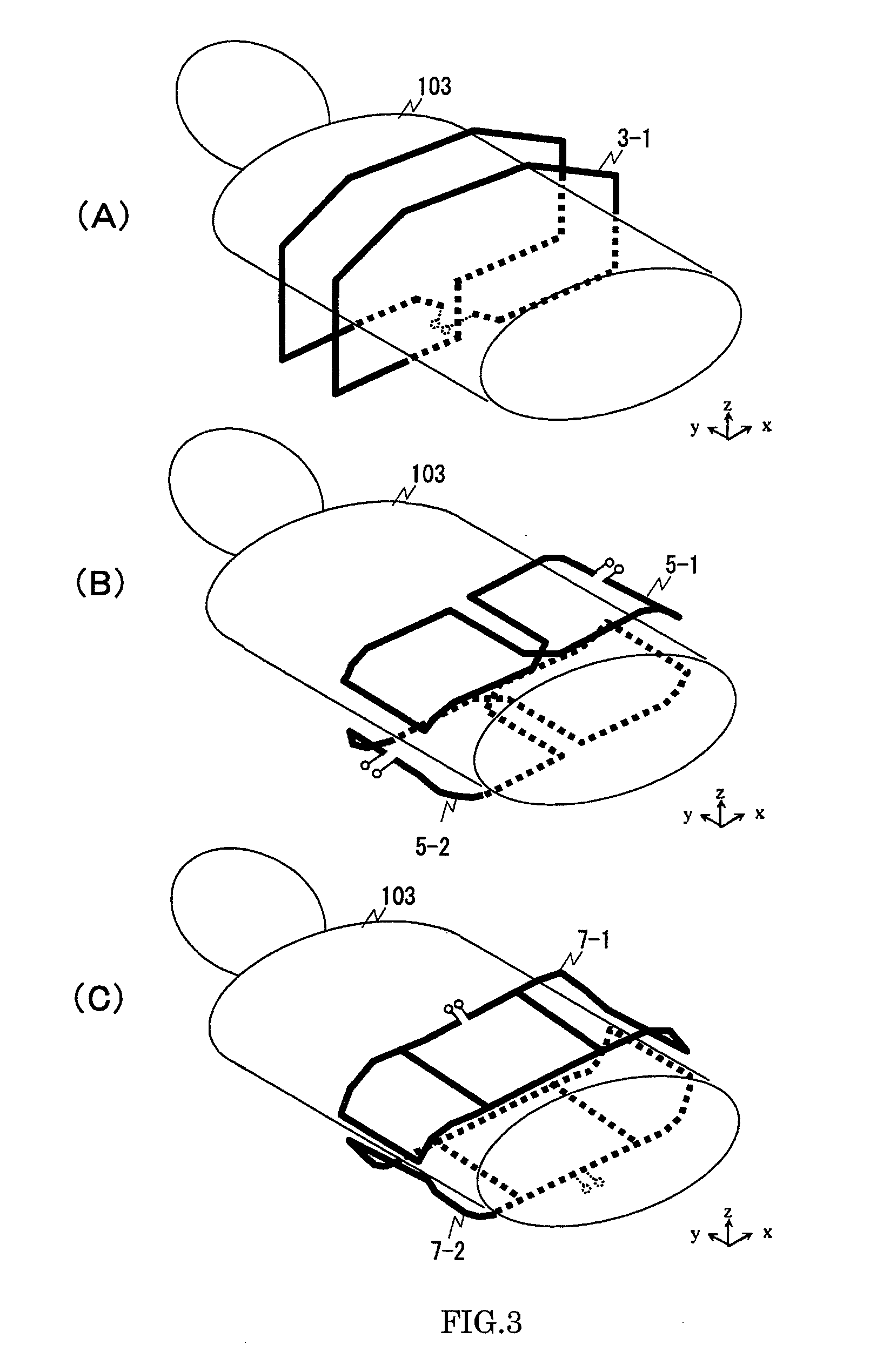
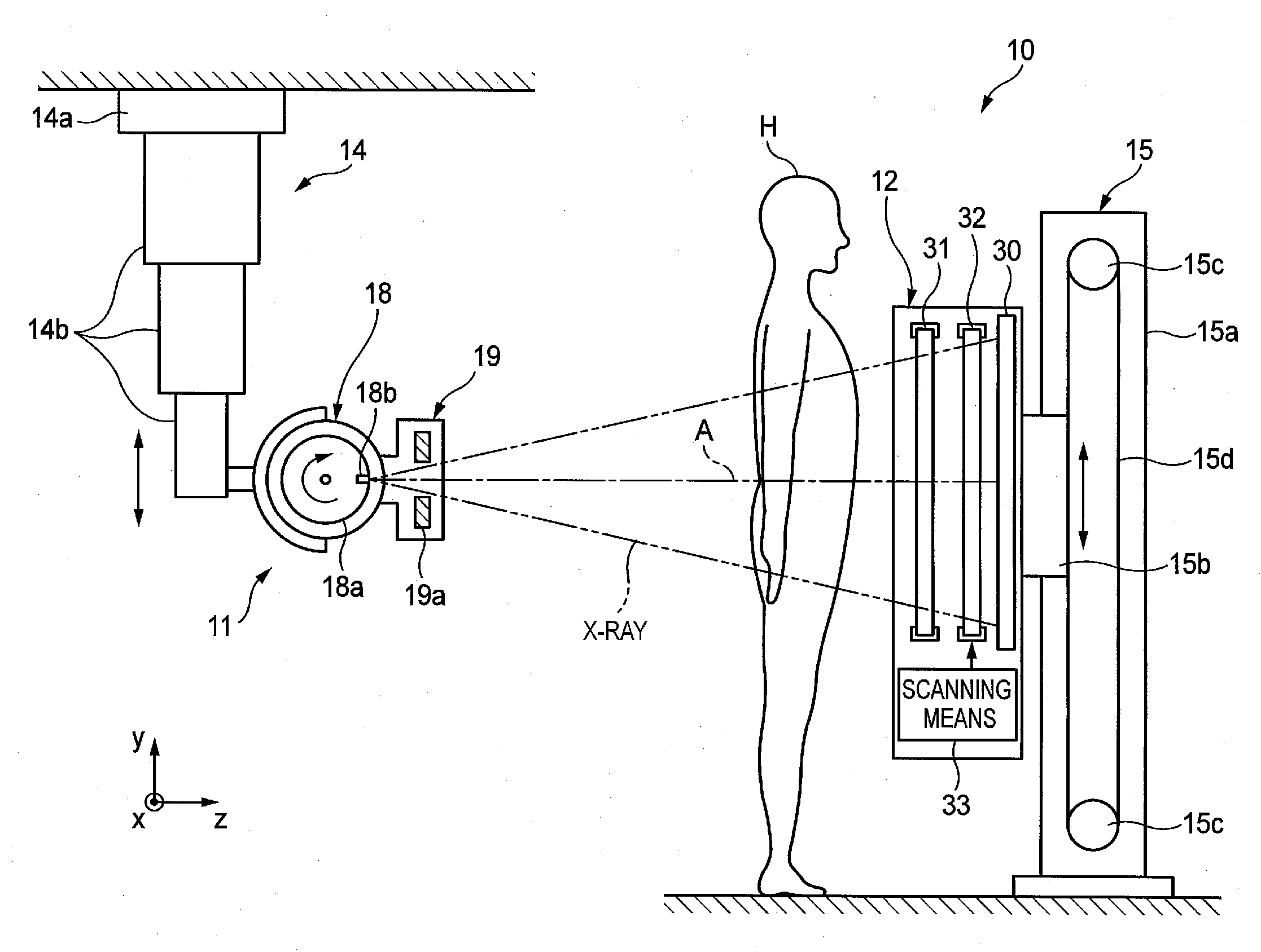
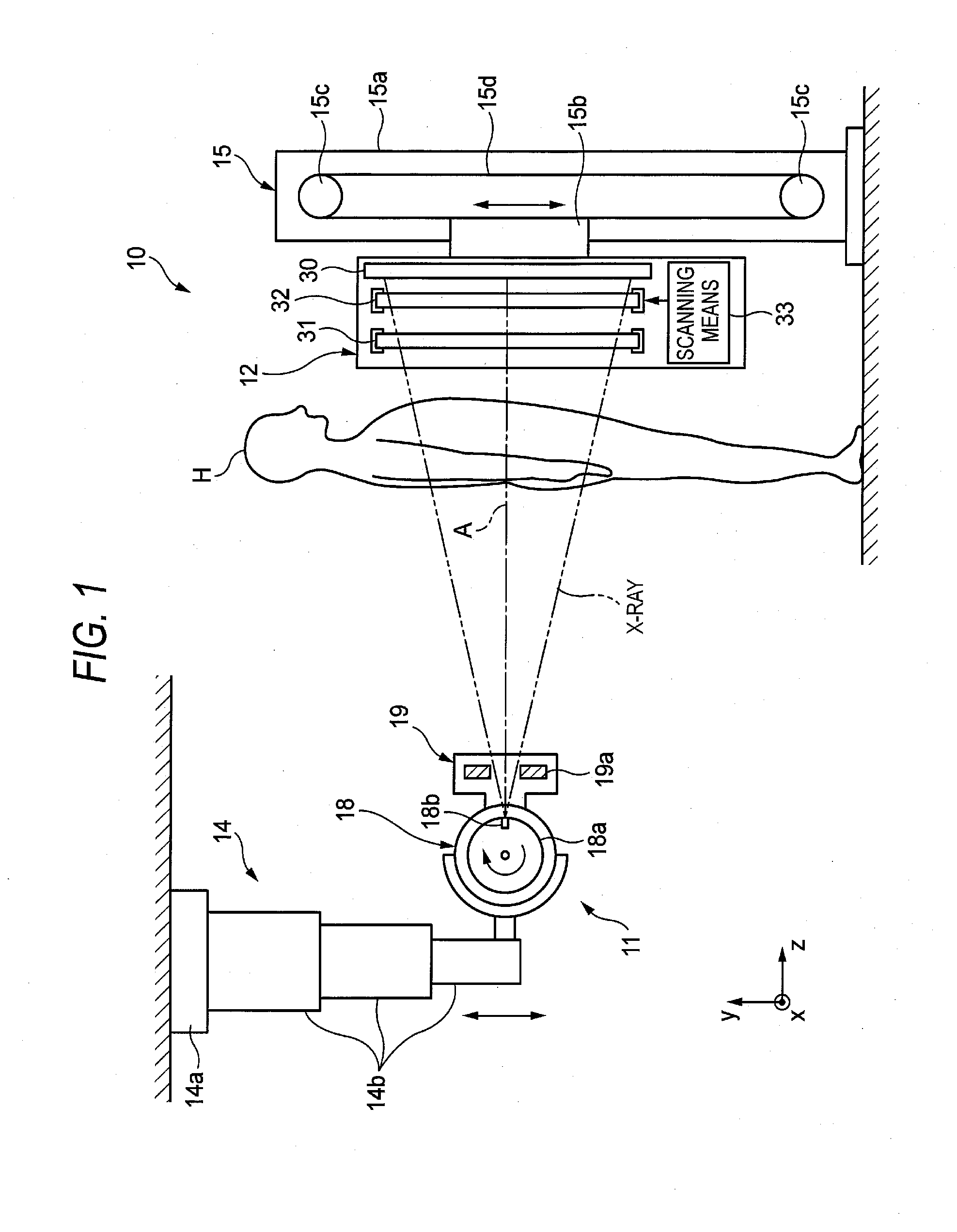
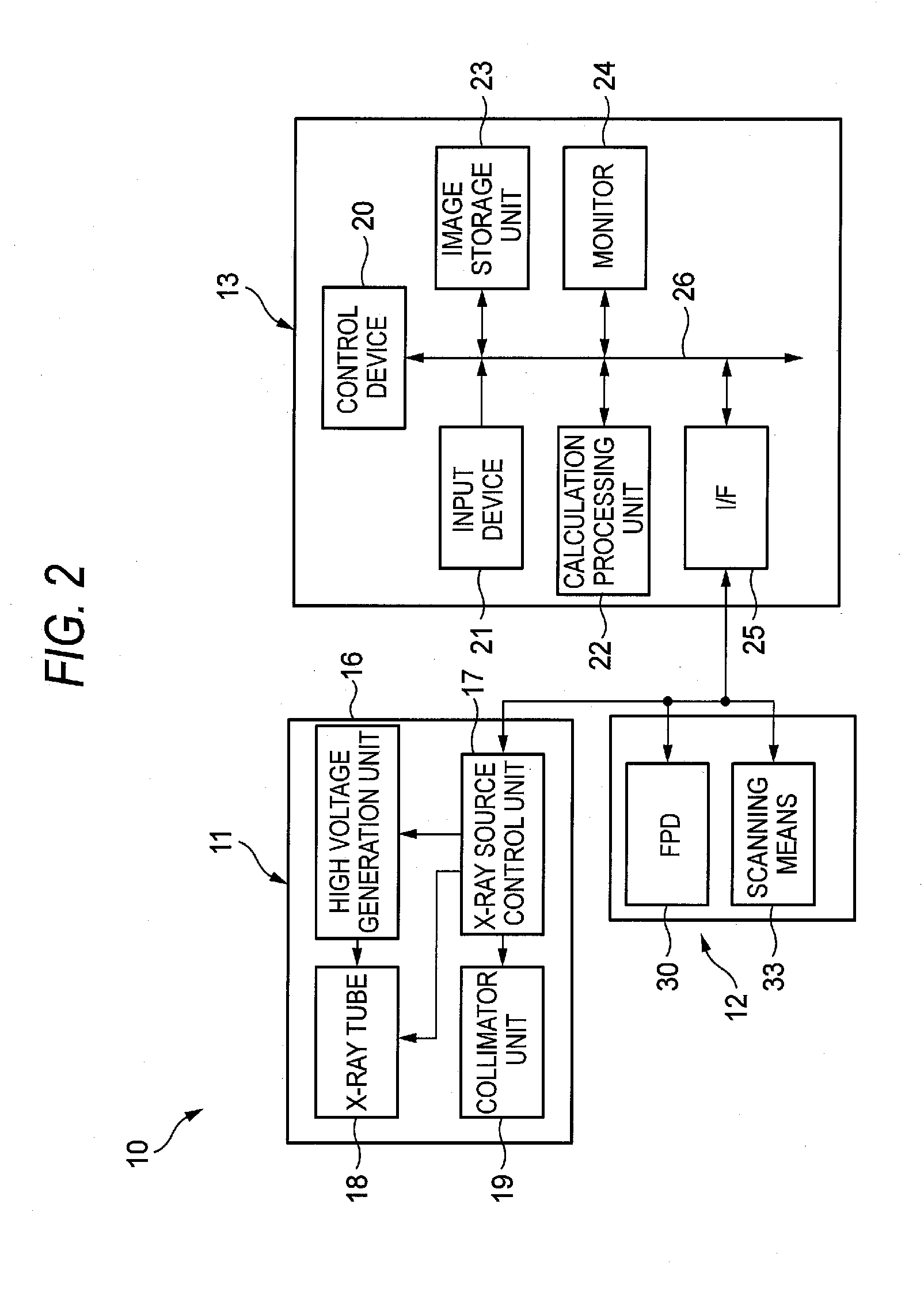
X-ray imaging system and x-ray imaging method
InactiveUS20120051498A1Reduce exposureReduced imaging timeReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayX ray image
An X-ray imaging system is for irradiating a subject with X ray from an X-ray source at a plurality of different angles to acquire X-ray images, and reconstructing an X-ray tomographic image from the X-ray images. The system comprising a region setting unit for setting a region of interest on a pre-shot image or a previously acquired X-ray tomographic image, an imaging control unit for continuously varying an aperture formed by collimator blades according to a position of the X-ray source to image the region of interest and acquiring projection data of the X-ray images in accordance with the position of the X-ray source, and an image reconstructing unit for reconstructing the X-ray tomographic image from the projection data of the X-ray images of the region of interest. The aperture formed by the collimator blades are varied so that all the X-ray images formed on the X-ray detector is rectangular regardless of the position of the X-ray source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
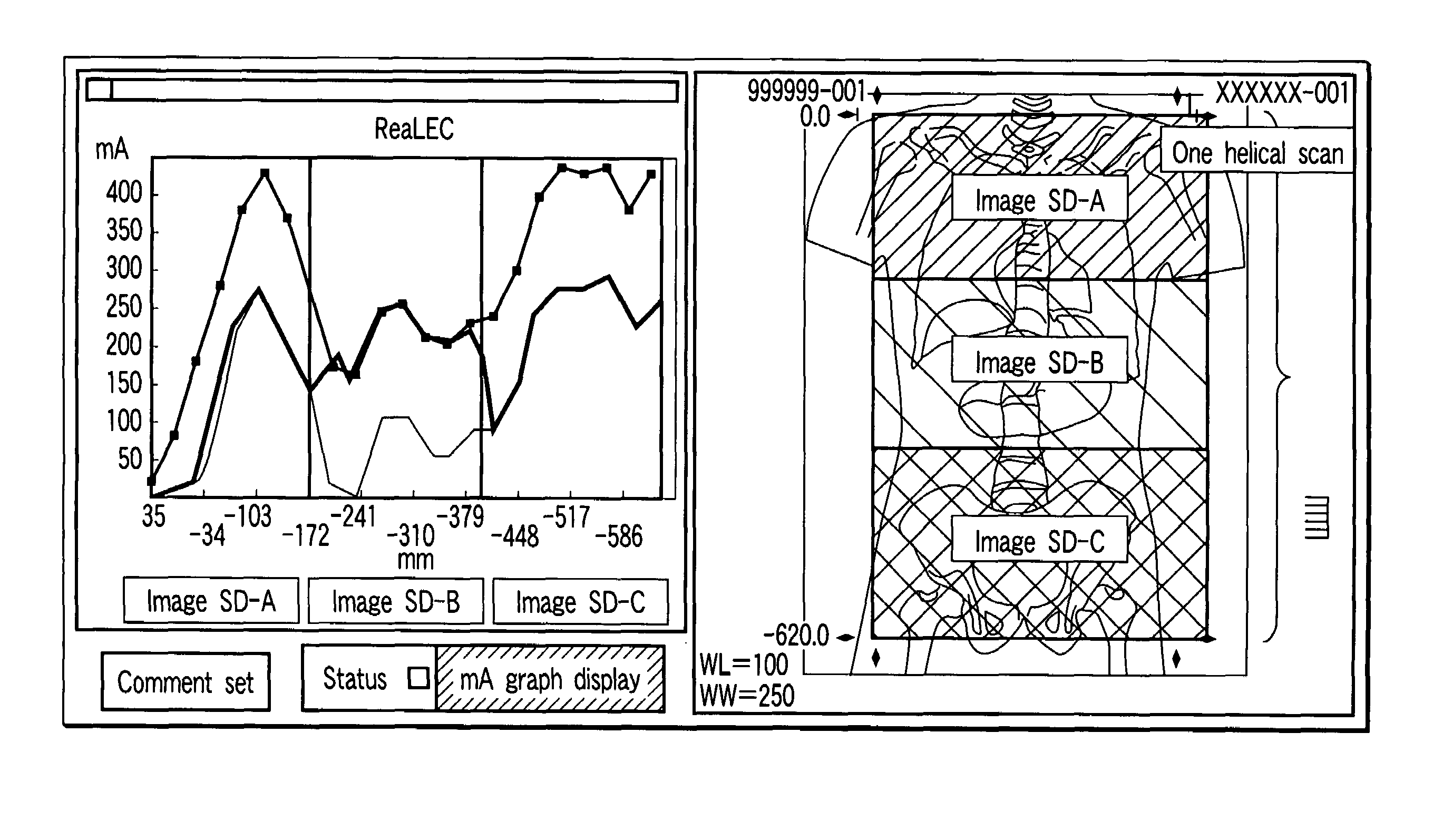
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
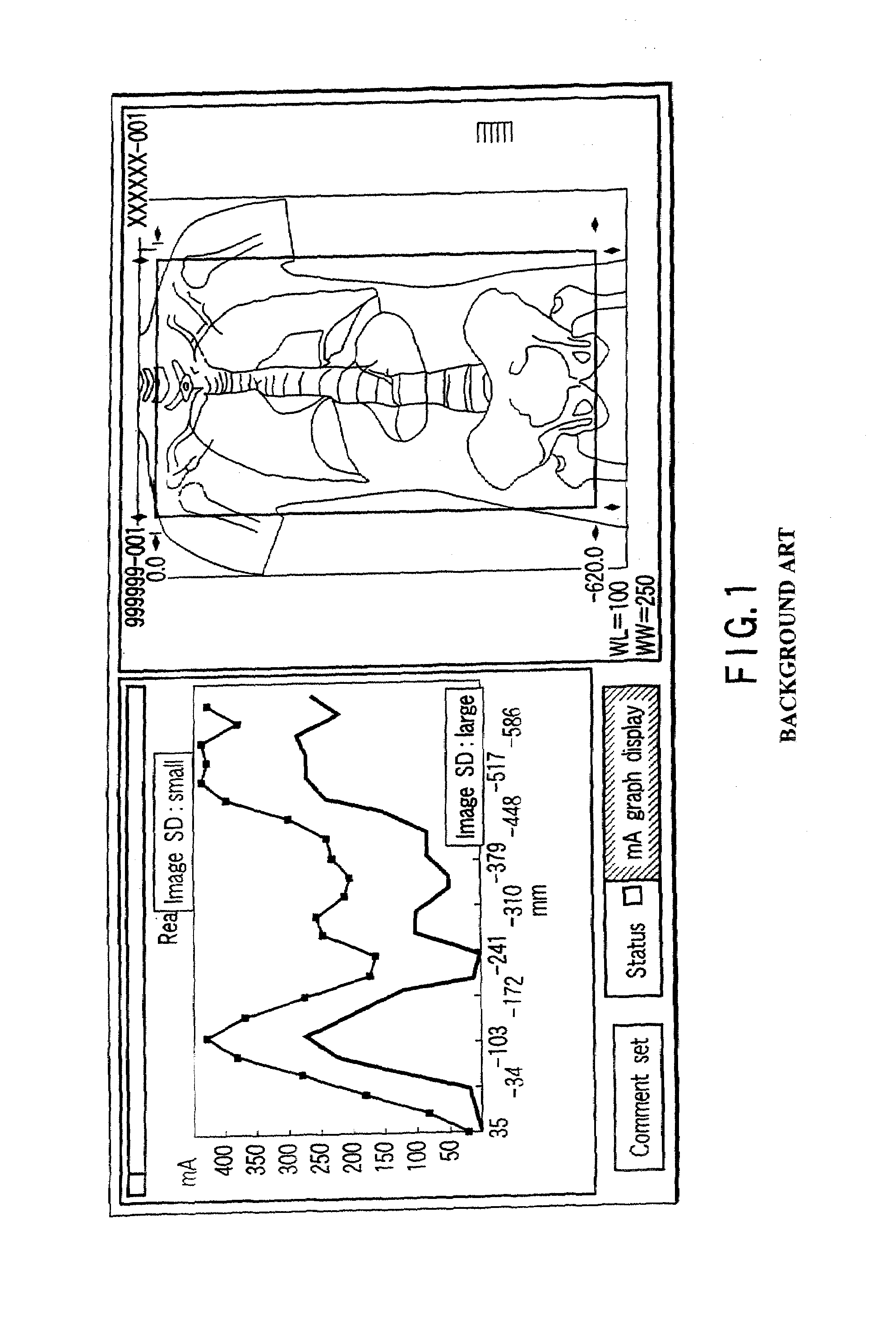
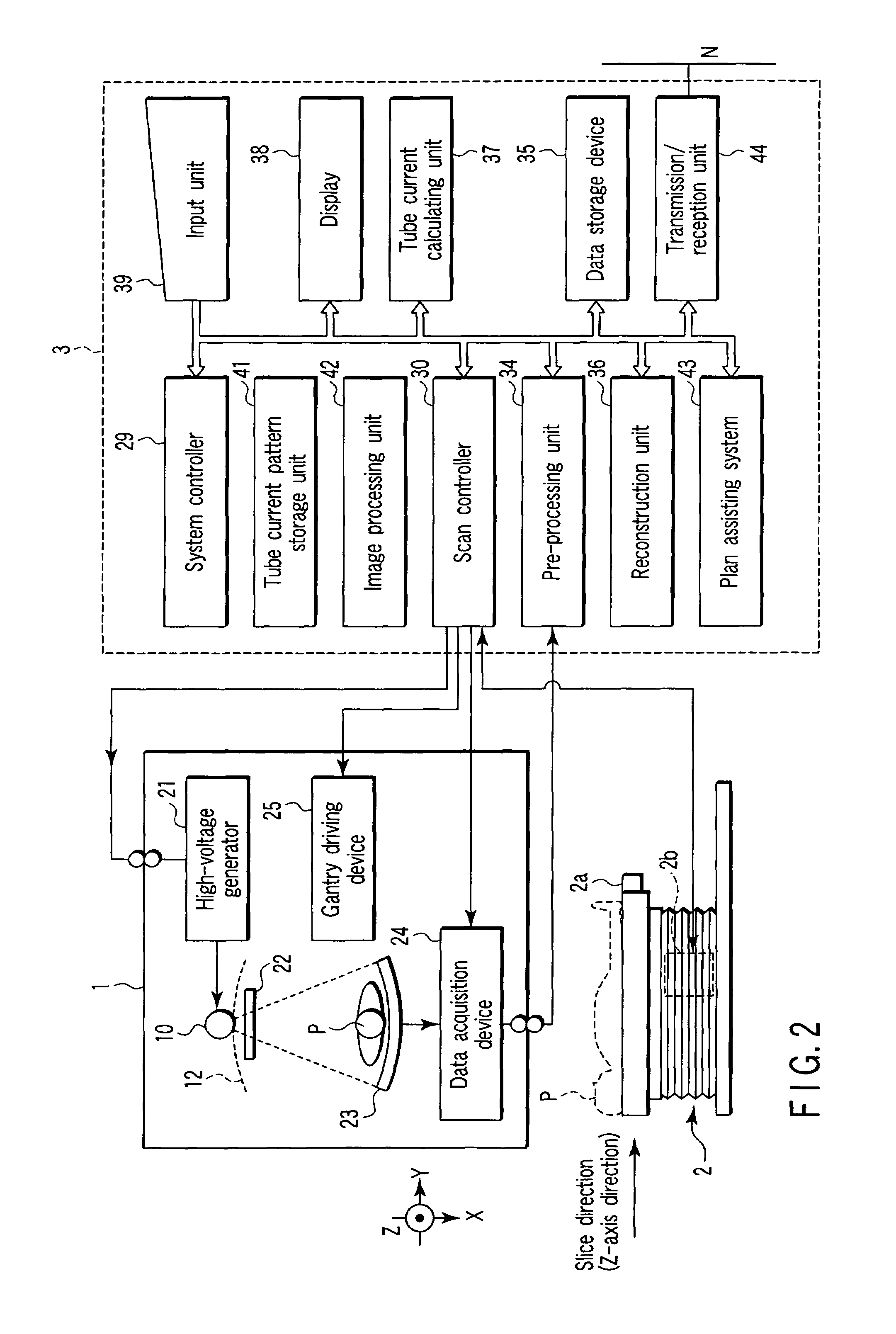
ActiveUS7215733B2Reduce operating loadReduce exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayEngineering
A plurality of region-specific areas are set on a scanogram, and an image SD value is set for each region-specific area. A tube current calculating unit calculates a tube current value at each position on the basis of a tube current pattern in a tube current pattern storage unit, an image SD value for each region-specific area, and a CT value at each position on the scanogram in each region-specific area. A scan controller controls X-ray emission in accordance with a calculated tube current value at each position.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Ophthalmologic apparatus and control method of the same
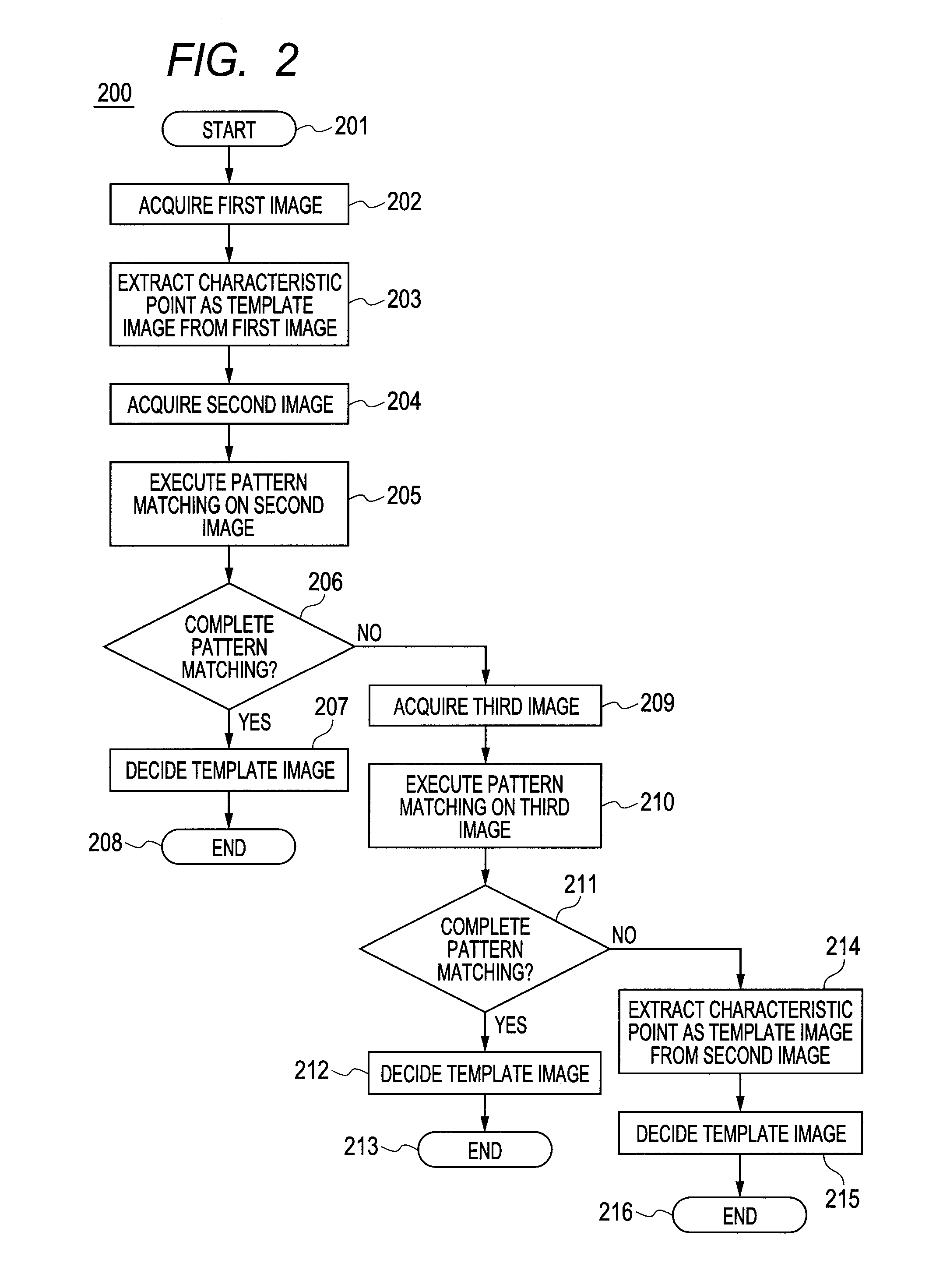
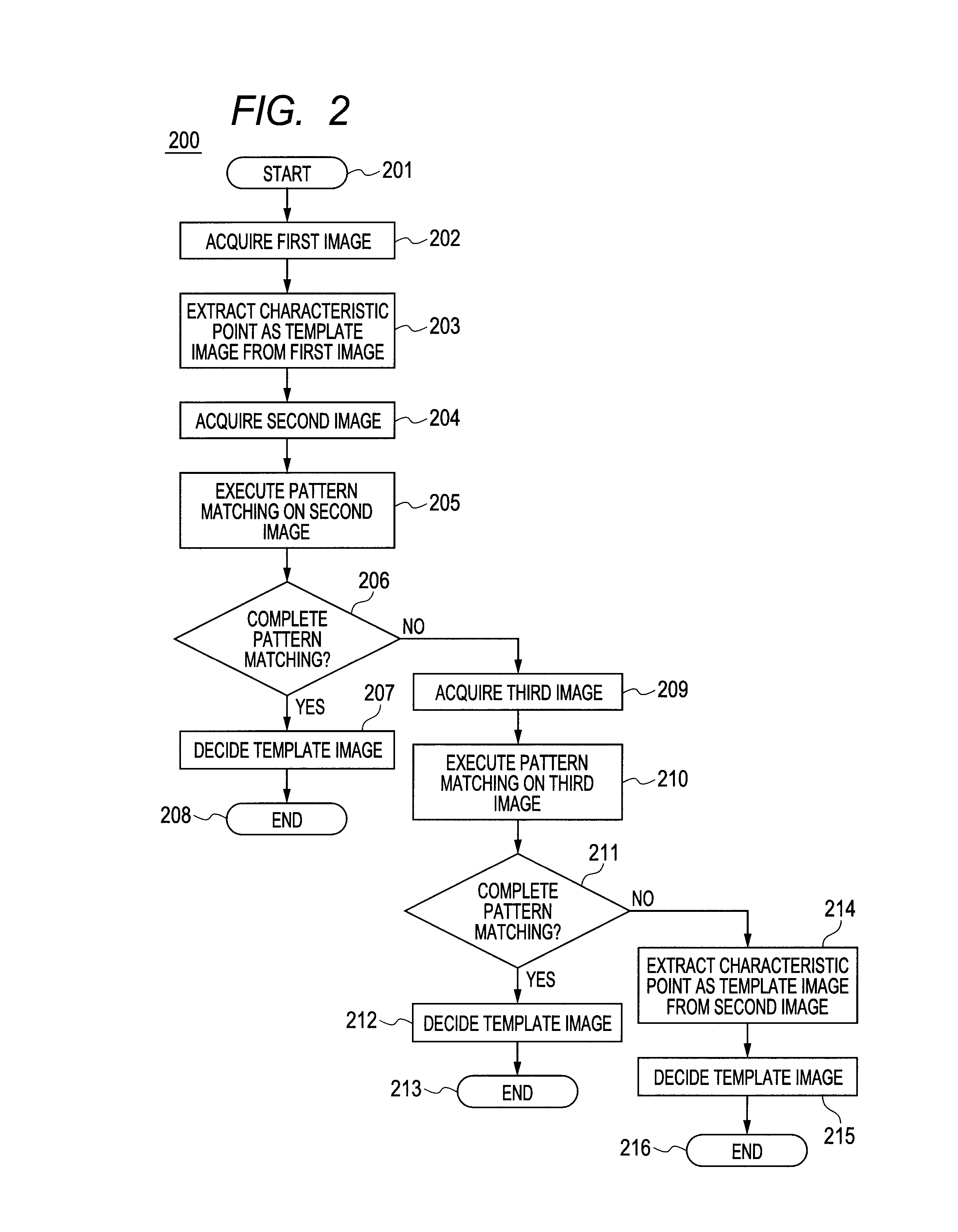
There is provided an ophthalmologic apparatus having a tracking function that can select a fundus image that is less affected by eye motion to reduce burdens on an operator / a patient in fundus imaging, wherein the ophthalmologic apparatus picks up a first fundus image (202), extracts a characteristic point as a template from the first fundus image (203), executes pattern matching on a second fundus image (205) to determine presence / absence of eye motion, and decides a tracking template image (207).
Owner:CANON KK
Millimeter wave holographic three-dimensional imaging detection system and method
InactiveCN105699494ASimple structureHigh-resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDetection using electromagnetic wavesImage resolutionData acquisition
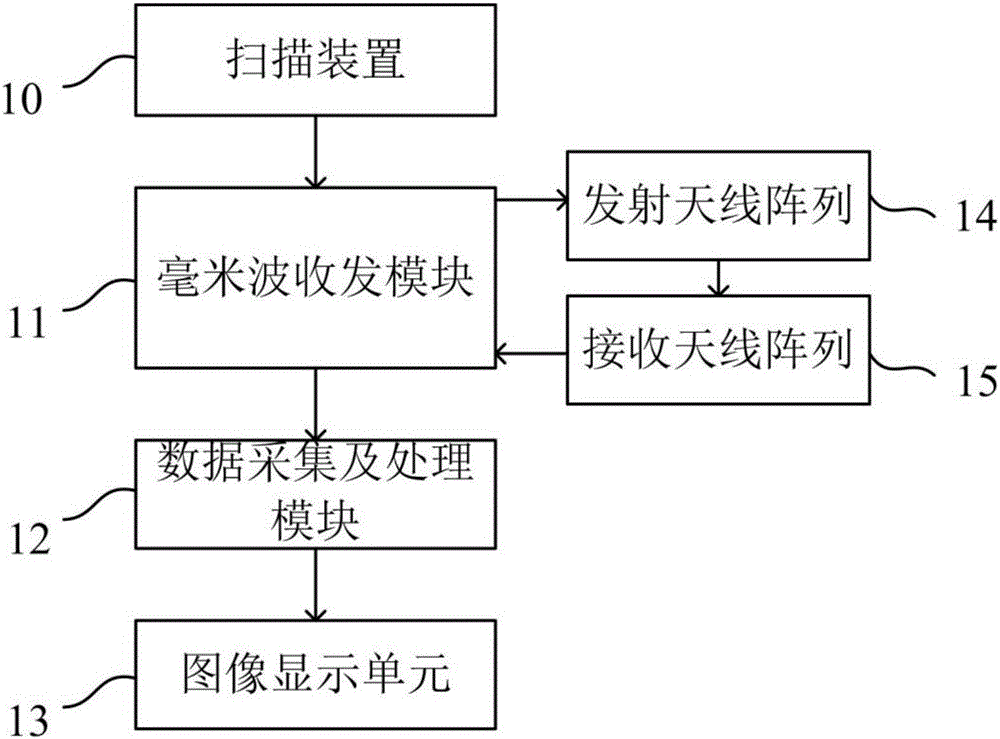
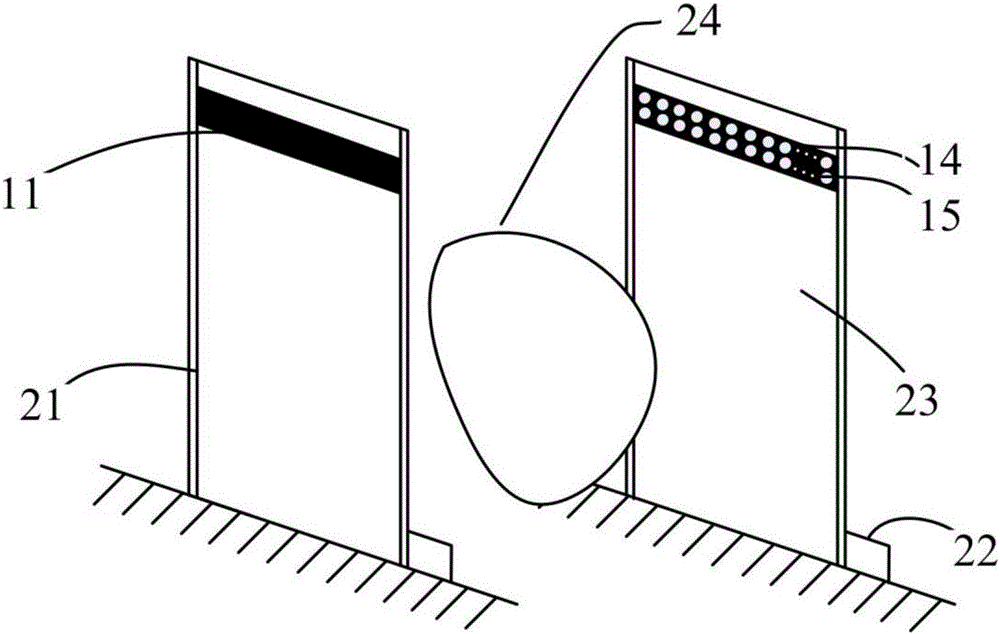
The invention provides a millimeter wave holographic three-dimensional imaging detection system. The millimeter wave holographic three-dimensional imaging detection system comprises a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna, a millimeter wave receiving / transmitting module, a scanning device, a data acquisition and processing module and an image display unit, wherein the transmitting antenna is used for transmitting a millimeter wave transmitting signal to an object to be detected; the receiving antenna is used for receiving an echo signal returned by the object to be detected; the millimeter wave receiving-transmitting module is used for generating the millimeter wave transmitting signal transmitted to the object to be detected, and receiving and processing the echo signal from the receiving antenna; the scanning device is used for fixing and moving the millimeter wave receiving-transmitting module, the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna; the data acquisition and processing module is used for acquiring and processing the echo signal output by the millimeter wave receiving-transmitting module to generate a three-dimensional image of the object to be detected; the image display unit is used for displaying the three-dimensional image generated by the data acquisition and processing module. Furthermore, the invention further provides a millimeter wave holographic three-dimensional imaging detection method of the object to be detected by utilizing the millimeter wave holographic three-dimensional imaging detection system. The millimeter wave holographic three-dimensional imaging detection system provided by the technical scheme has the advantages of simple structure, high resolution ratio, short imaging time, relatively large view field and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF TERAHERTZ TECH & INNOVATION +1
Inspection Apparatus using Magnetic Resonance and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Signal Receiver Coil
ActiveUS20100033177A1Without of S/N ratioIncrease flexibilityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectromagnetic couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
An MRI apparatus capable of selecting an optional direction as a phase encoding direction and achieving a preferable S / N, when an imaging time shortening technique is applied. A receiver coil, used as a receiver coil of a vertical magnetic field MRI apparatus, is a combination of a first coil (solenoid coil) forming a current loop around the outer circumference of a test object, second coils forming even-numbered current loops, and third coils forming odd-numbered current loops, in the direction intersecting the plane of the current loop of the first coil. The second coil and the third coil are arranged in such a manner that, as for the current loops in the array direction thereof, a position where a sensitivity of one coil is minimized approximately coincides with a position where the sensitivity of the other coil is maximized, whereby electromagnetic coupling is suppressed.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Apparatus and method for reconstructing magnetic resonance image using learning, and under-sampling apparatus method and recording medium thereof
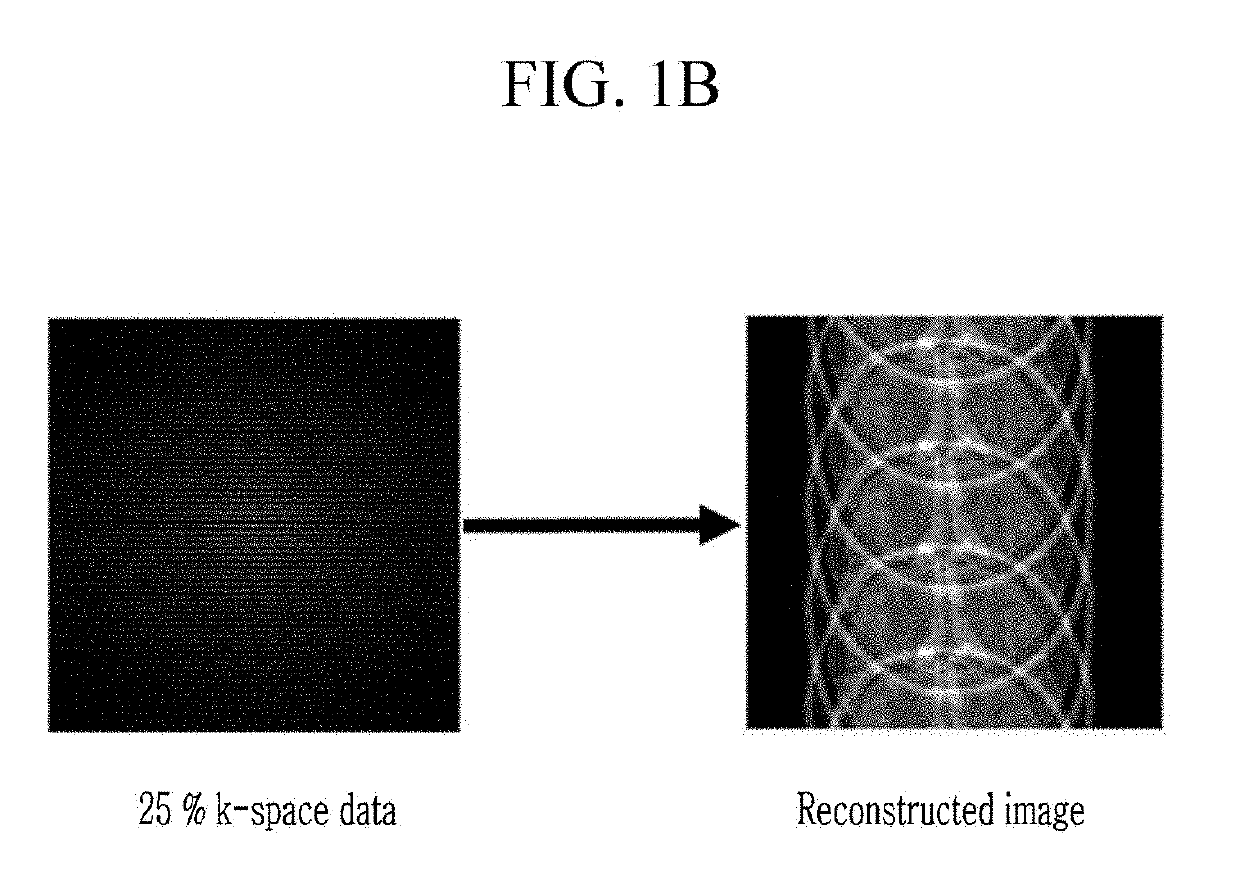
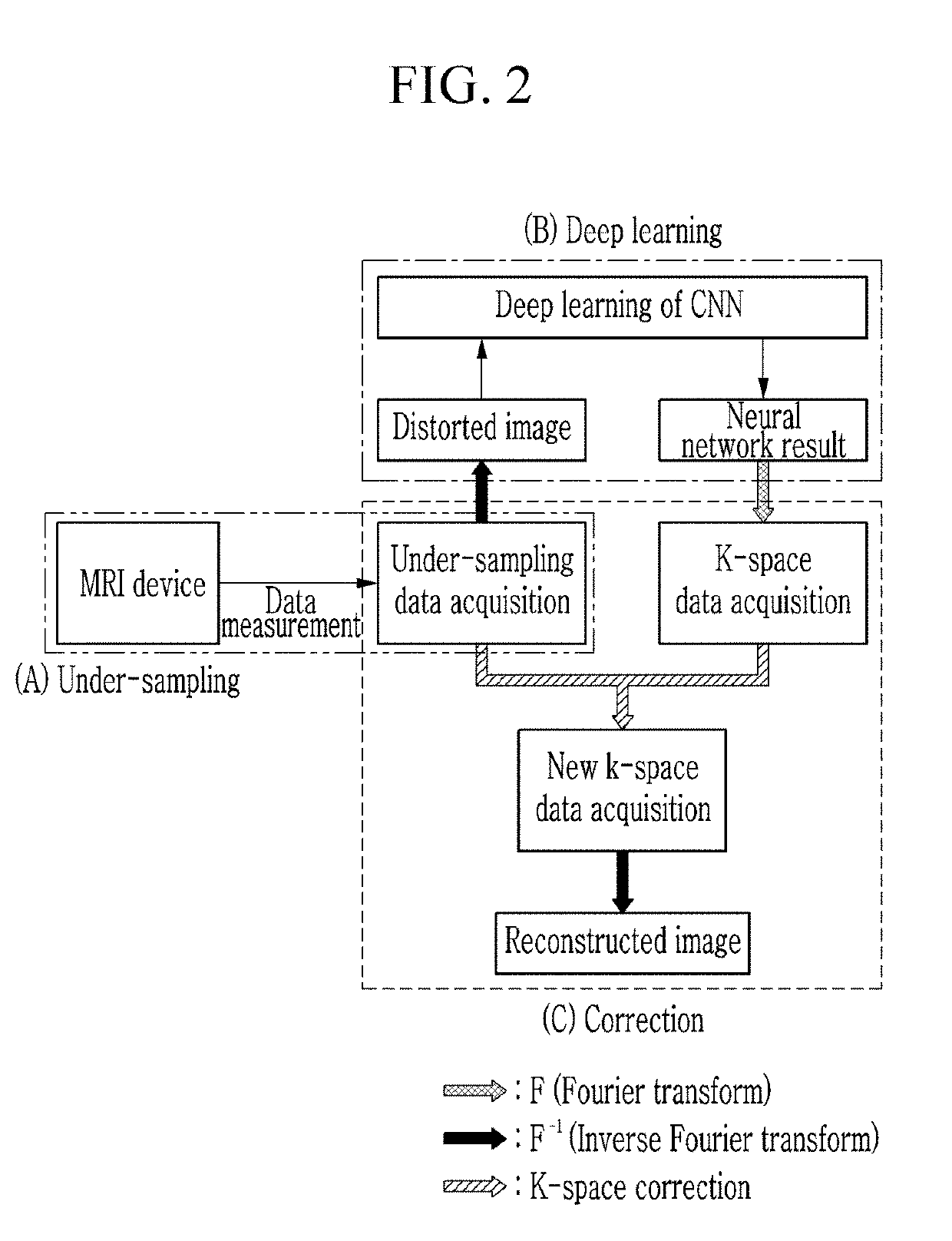
ActiveUS20190101605A1High quality reconstructionReduced imaging timeImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceFull sample
An under-sampling apparatus for MR image reconstruction by using machine learning and a method thereof, an MR image reconstruction device by using machine learning and a method thereof, and a recoding medium thereof are disclosed. The disclosed under-smapling apparatus includes: a setting portion that sets a region corresponding to a center of the k-space image as a first region and remaining regions as a second region; and an under-sampling portion that full-samples the first region and under-samples the second region, wherein in the under-sampling performed in the second region, lines are selected at regular intervals and then only the selected line is full-sampled. According to the under-sampling apparatus, a high-resolution MR image can be acquired while reducing imaing time.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Random-access vector graphics
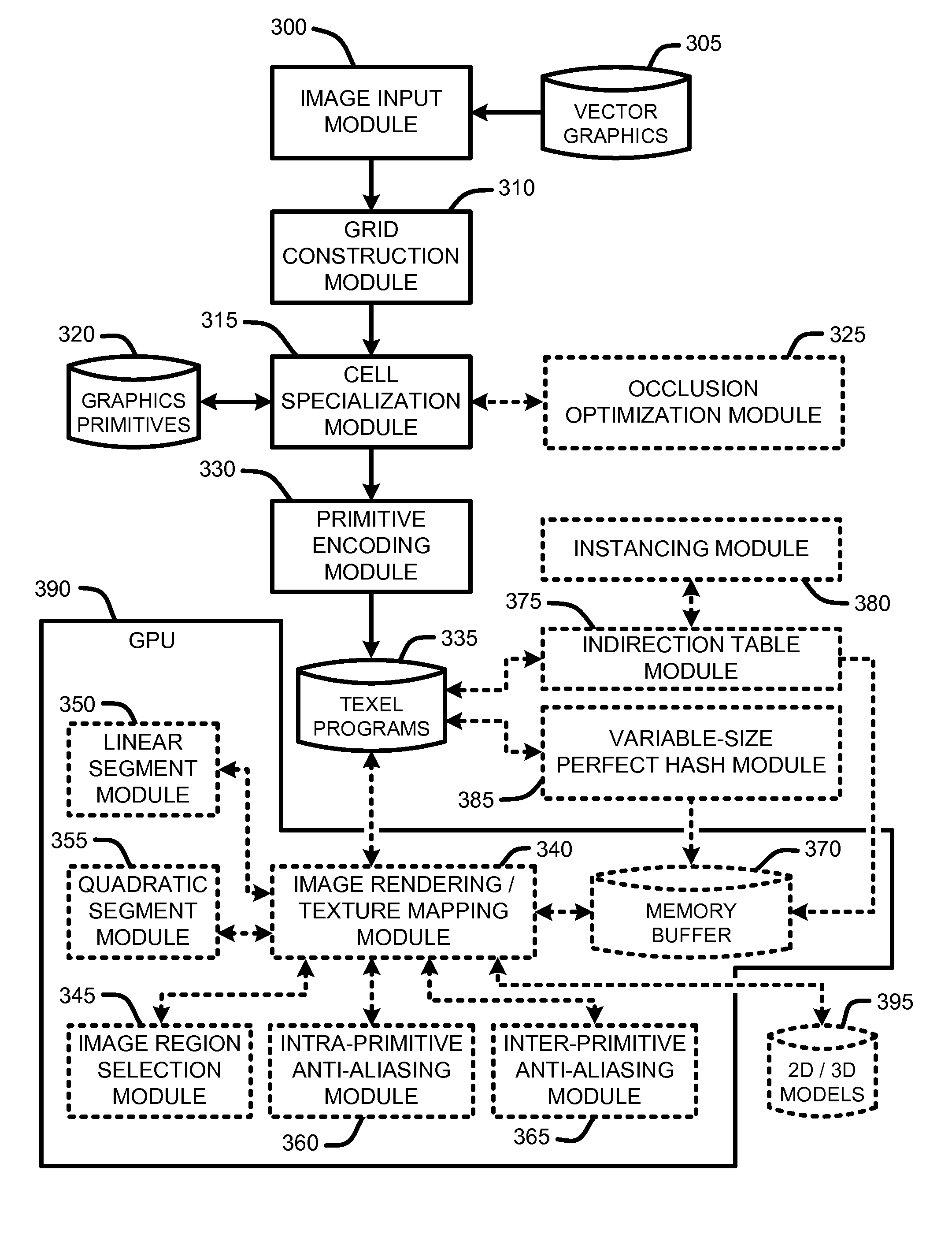
ActiveUS7872648B2Easy accessReduced imaging timeCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingComputational scienceVariable length
A “Vector Graphics Encoder” encodes vector graphics in a randomly accessible format. This encoding format enables particular portions of encoded images to be directly accessed, at any desired level of zoom, without processing or otherwise decoding the entire image. This random-access format is based on a coarse image grid of partially overlapping cells wherein each cell is defined by a “texel program.” Unlike fixed-complexity cells used by conventional vector images, each cell defined by a texel program is locally specialized without requiring global constraints on the complexity of each cell. The texel program for each cell is provided as a variable-length string of tokens representing a locally specialized description of one or more of layers of graphics primitives overlapping the cell. Images are then rendered by interpreting the texel programs defining one or more cells.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
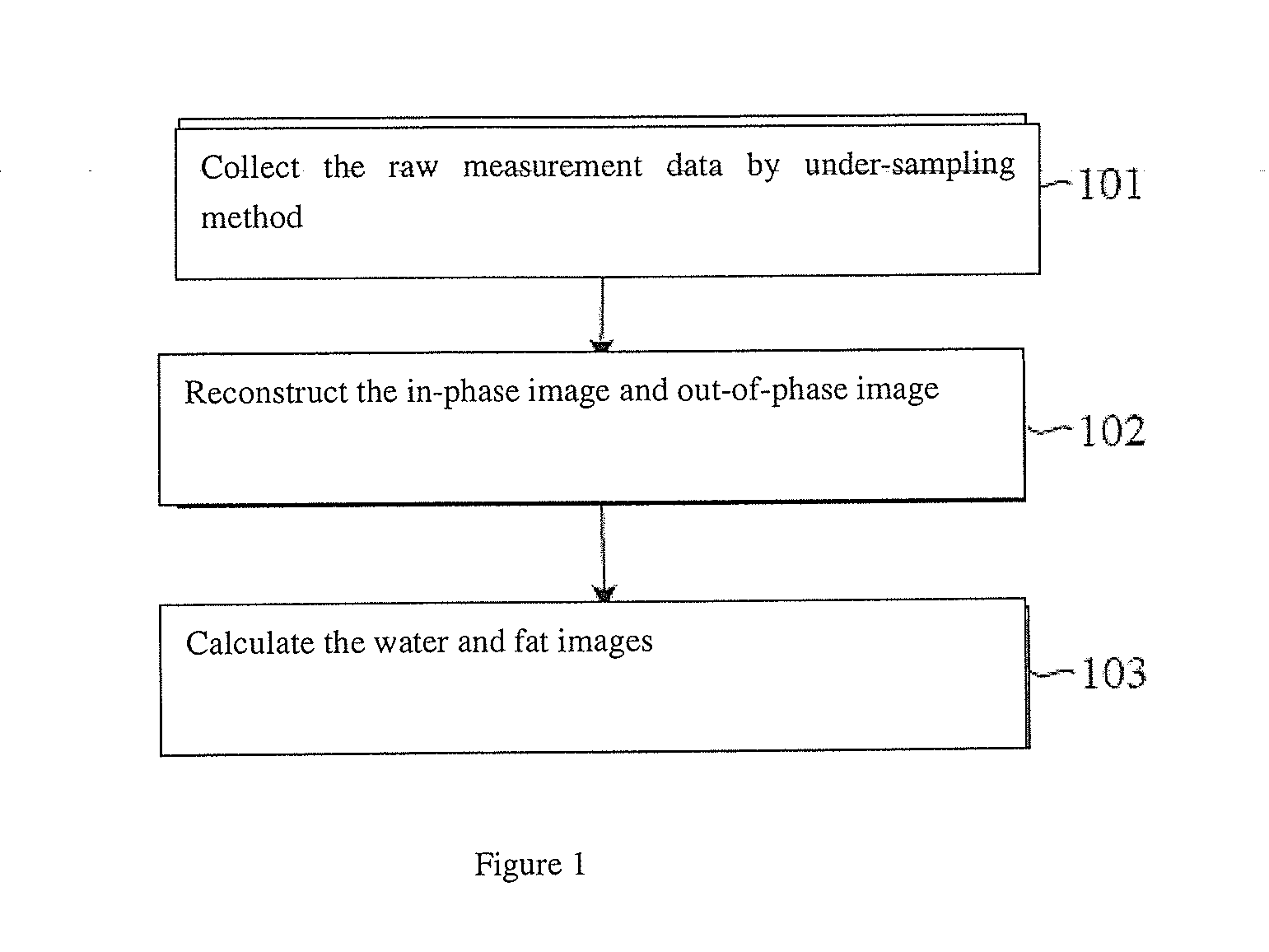
Magnetic resonance imaging water-fat separation method
ActiveUS20110267054A1Reduce MRI scan timeReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSystem matrixIterative method
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) water-fat separation method includes acquiring in-phase image raw measurement data and out-of-phase image raw measurement data with an MRI device, reconstructing an in-phase image and an out-of-phase image according to a system matrix and the raw measurement data using the penalty function regularized iterative reconstruction method, and calculating water and fat images according to the in-phase image and the out-of-phase image. The use of the penalty function regularized iterative method eliminates the need for k-space raw measurement data with a 100% sampling rate, thereby reducing the MRI scan time, shortening the entire imaging time, and improving the efficiency of the MRI device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
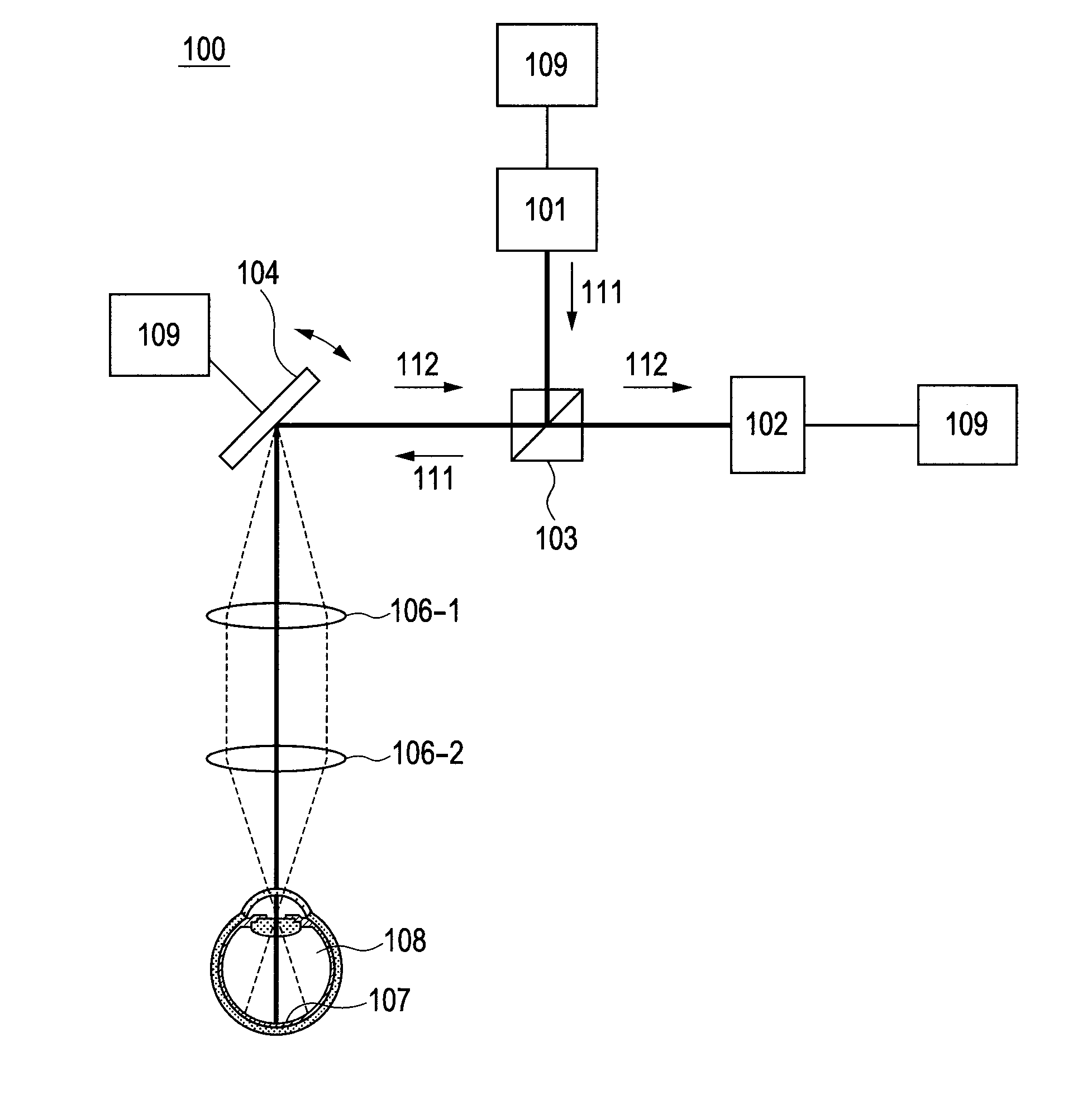
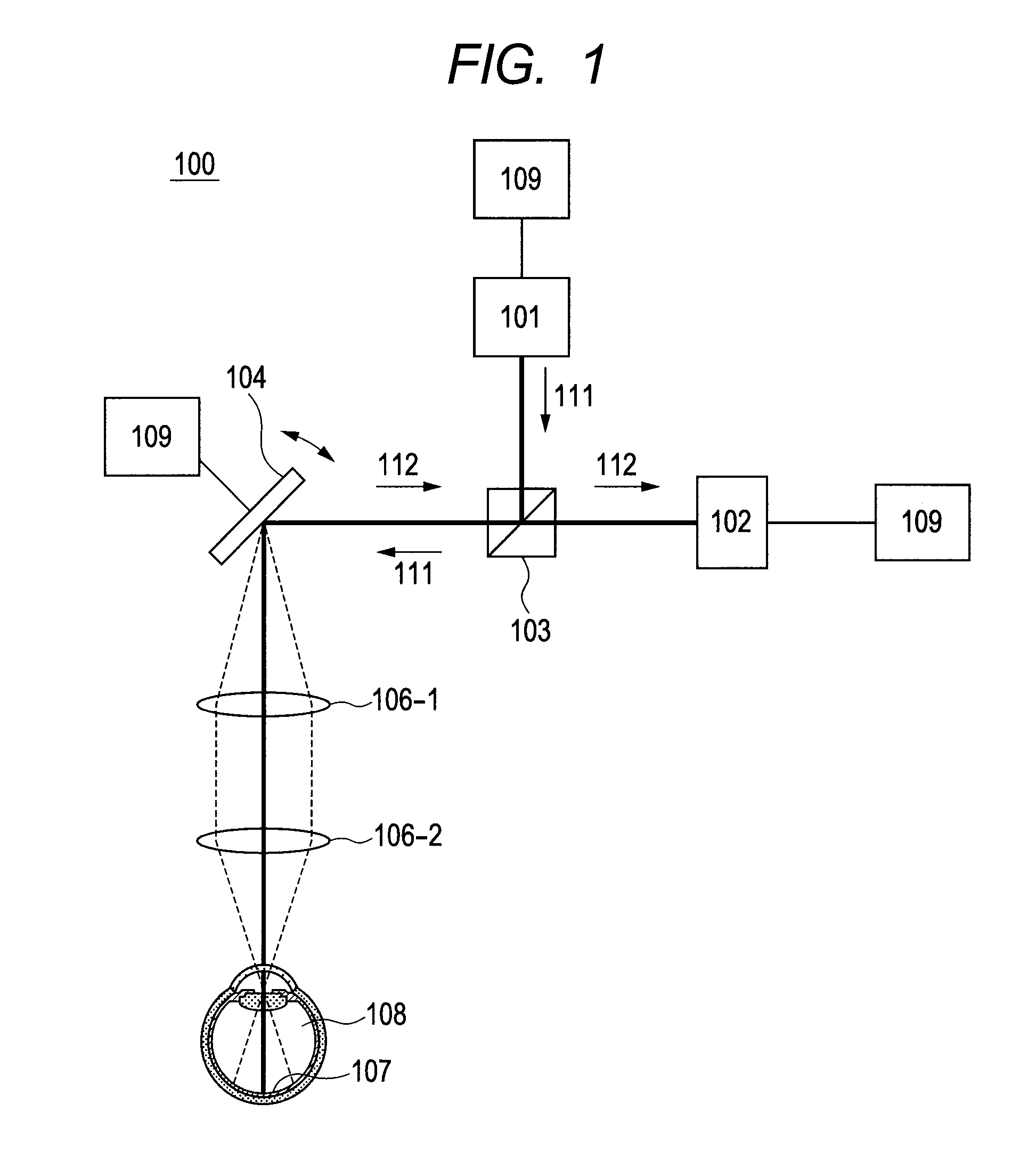
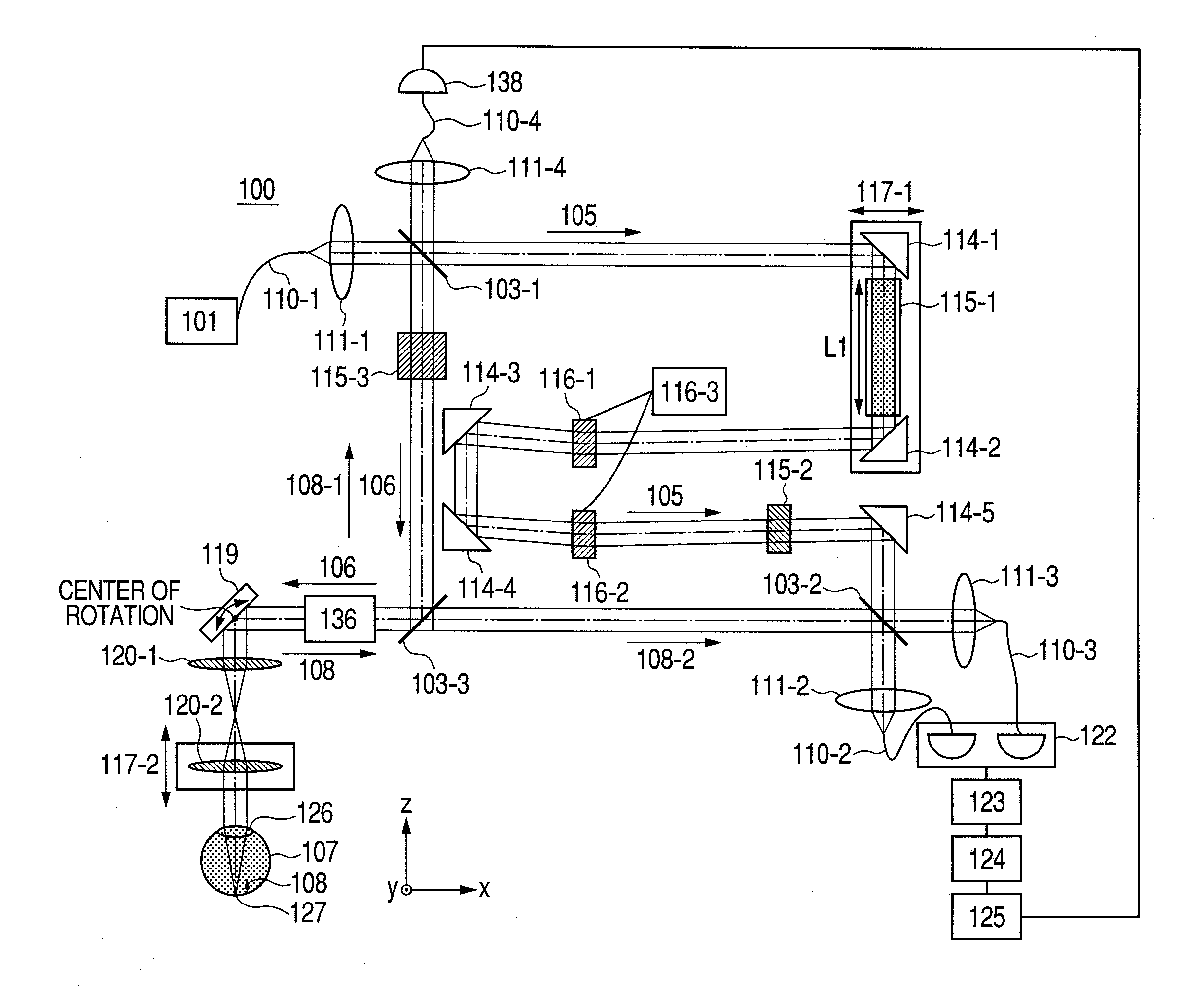
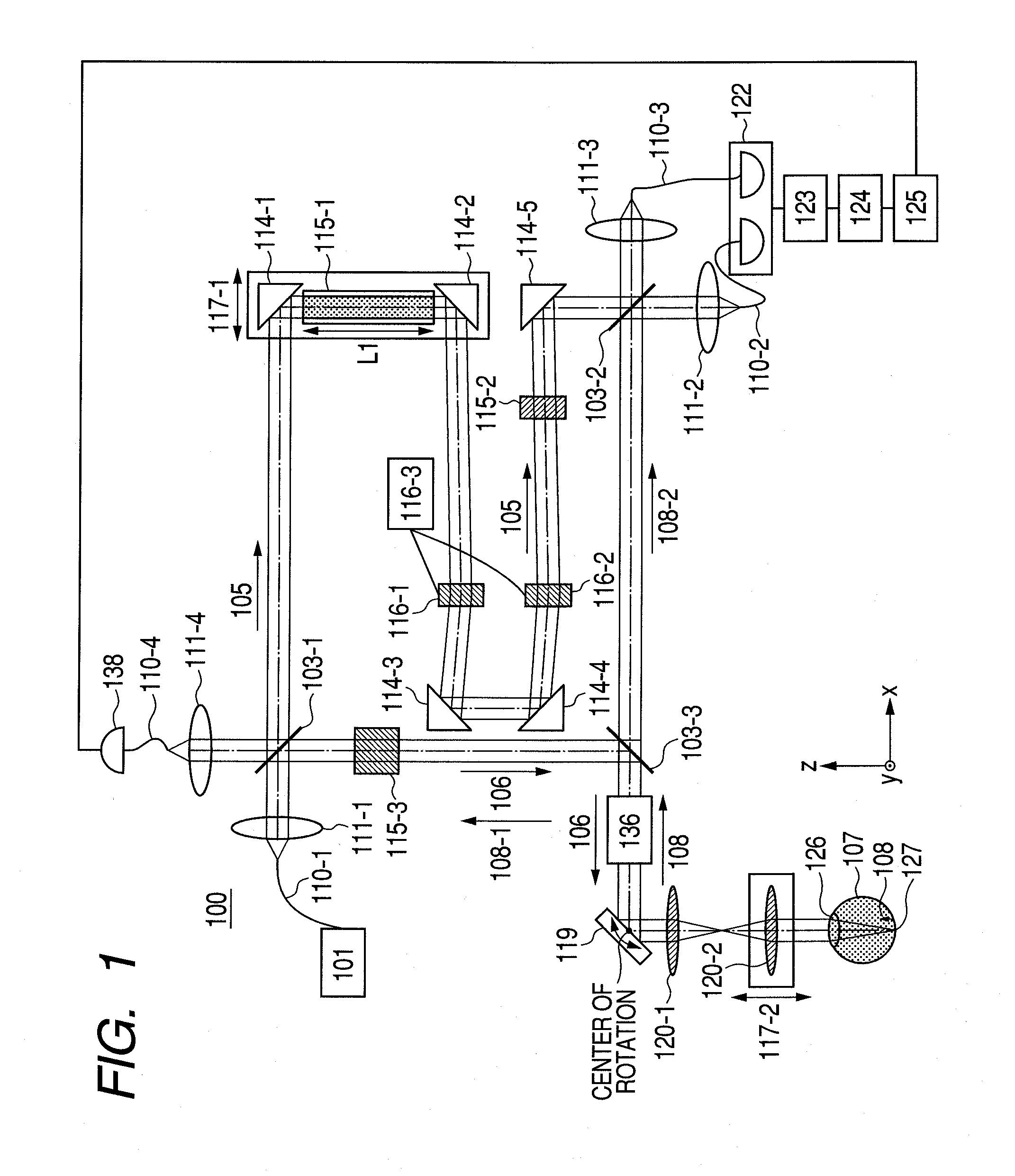
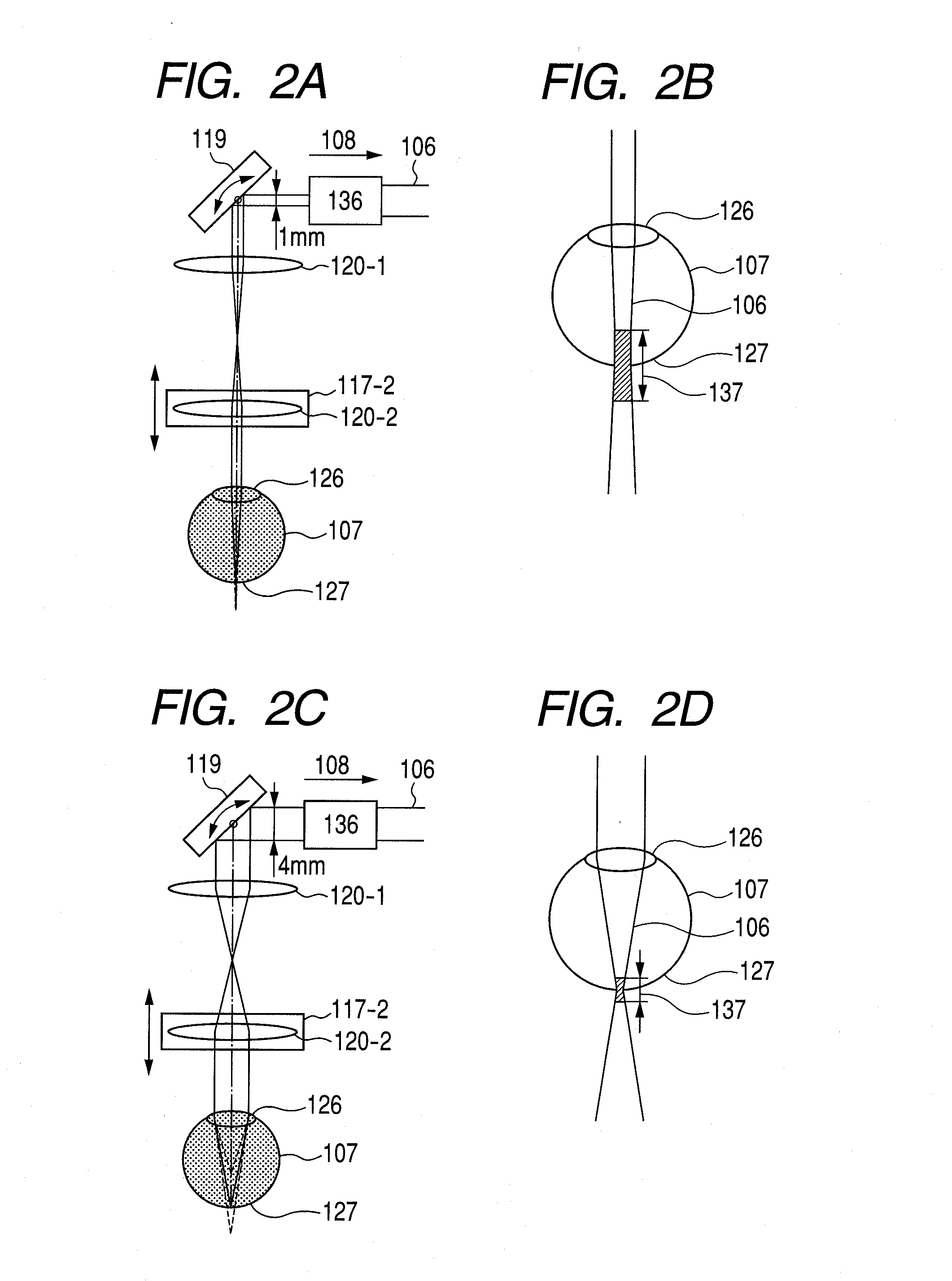
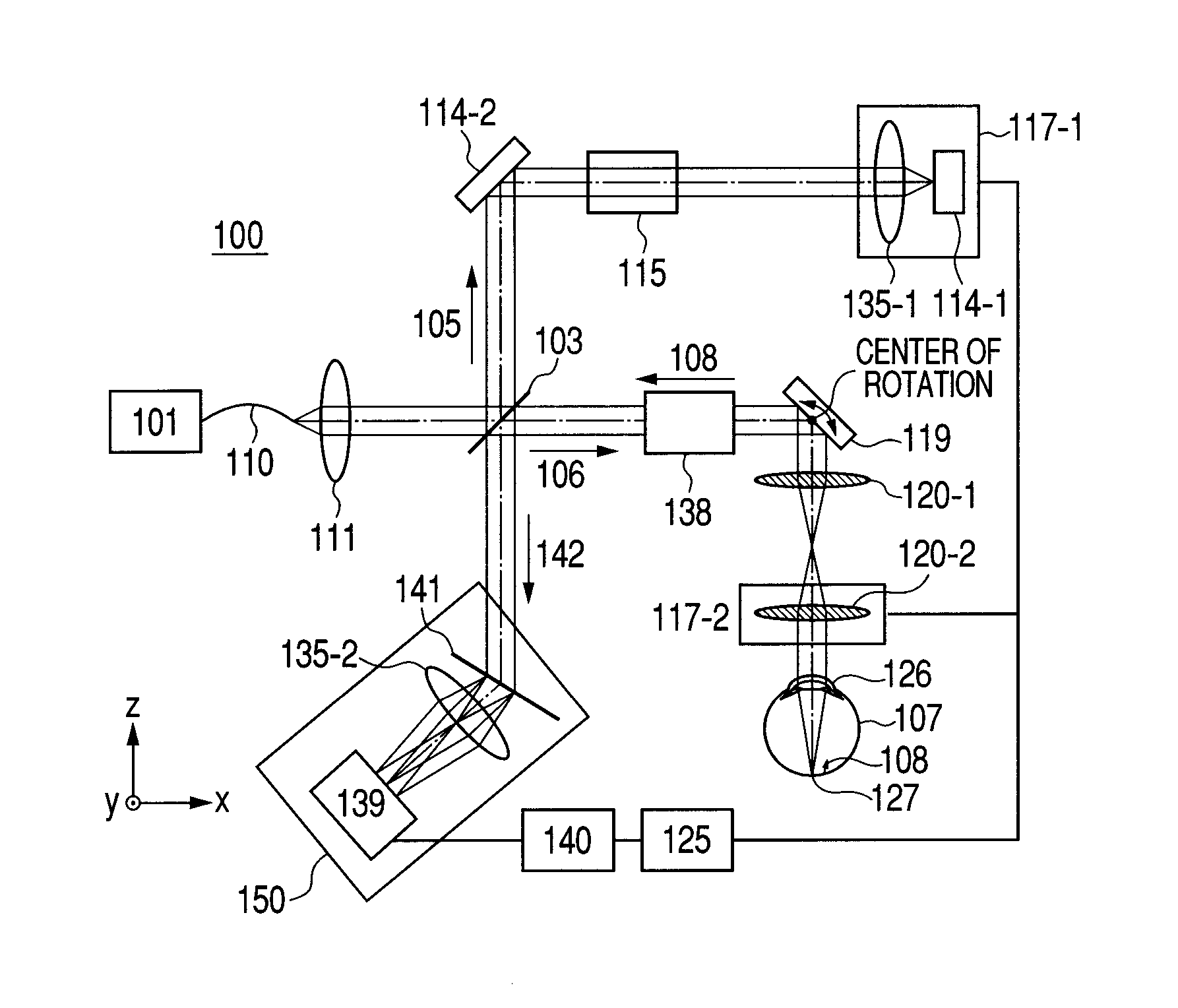
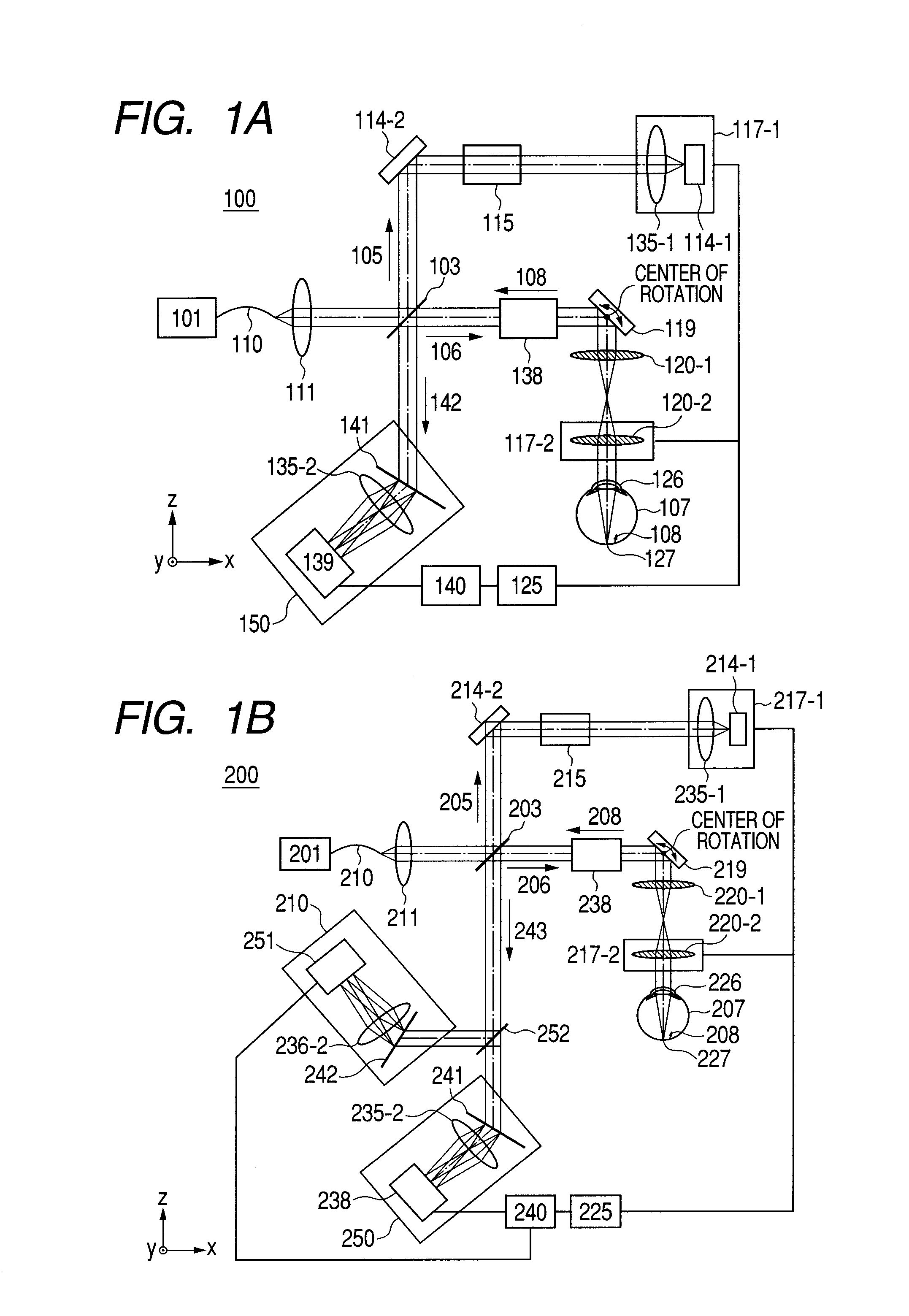
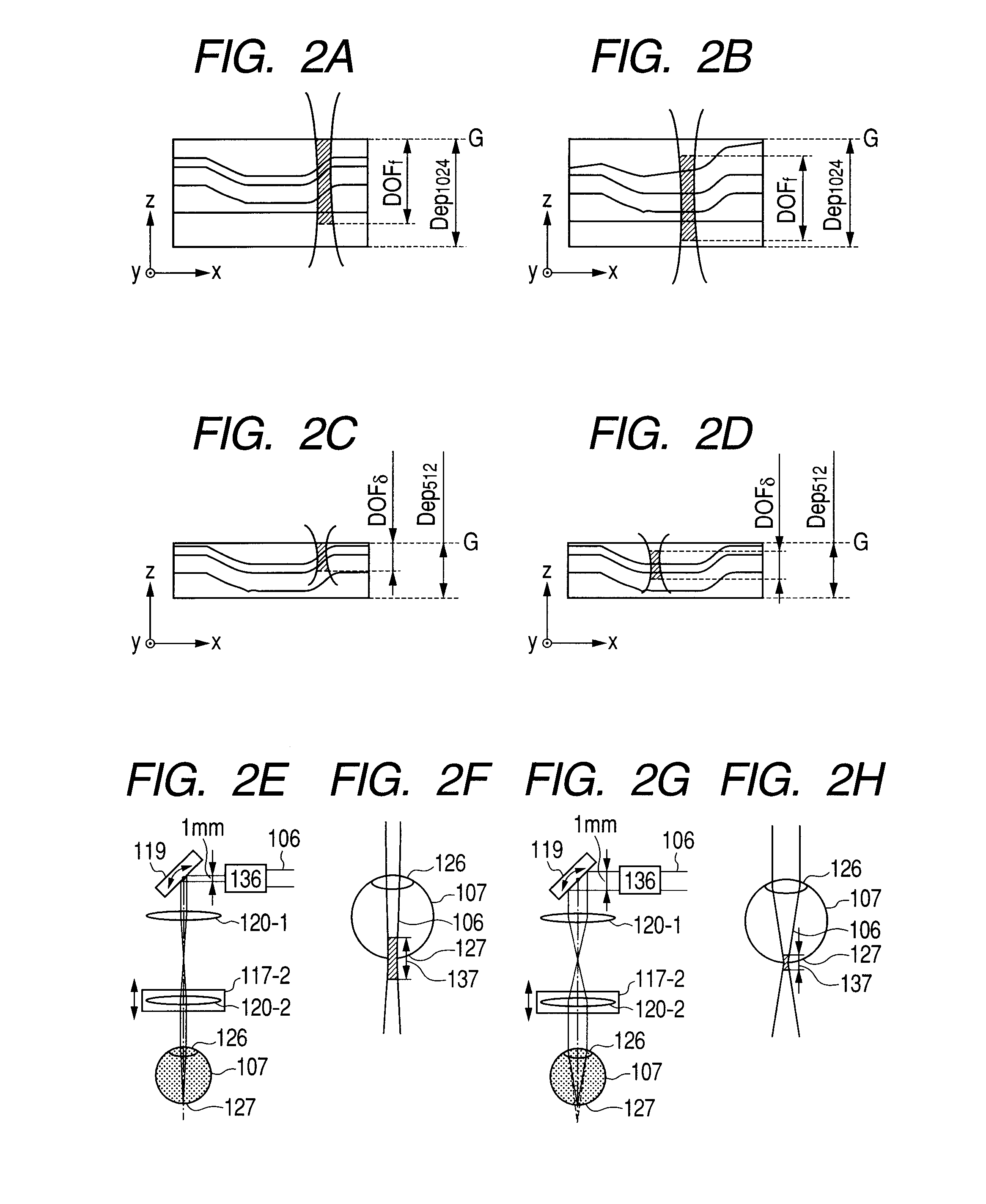
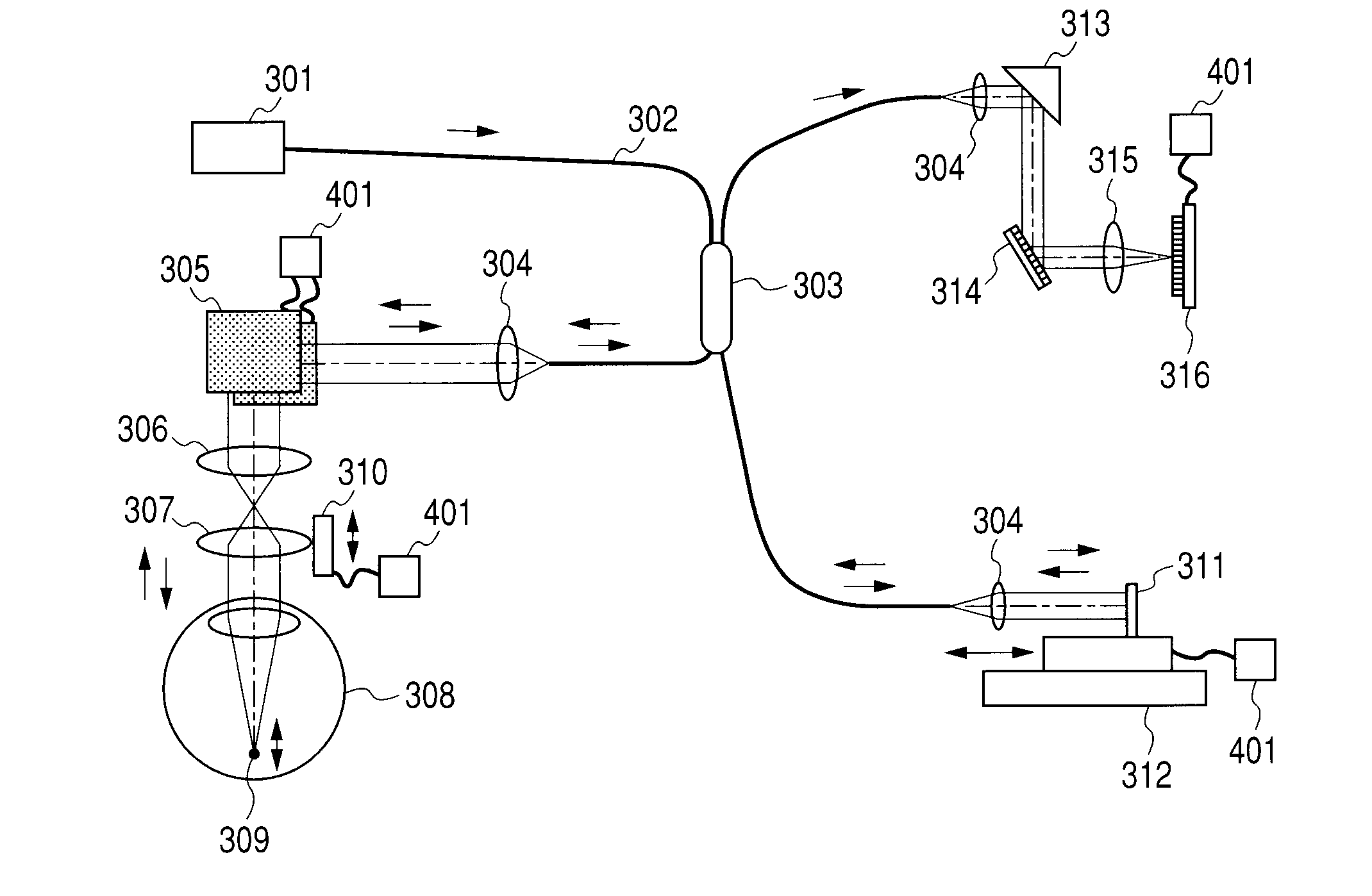
Optical coherence tomographic imaging apparatus and optical coherence tomographic imaging method
ActiveUS20100321700A1Keep for a long timeReduced imaging timeMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographyBeam diameterImage resolution
A beam diameter varying portion varies a first beam diameter of a measuring beam incident on an optical portion to a second beam diameter larger than the first beam diameter. An adjustment portion adjusts a condensing position of the measuring beam on the optical portion based on intensity information of a return beam from a position of an inspection object with the first beam diameter. The beam diameter is varied from the first to the second beam diameter by the beam diameter varying portion at the position adjusted by the adjustment portion to cause the measuring beam having the second beam diameter to be incident. A condensing position can be adjusted in a relatively short time because the measuring beam small in beam diameter is used, and a combined beam can be acquired with high transverse resolution because the measuring beam large in beam diameter is used.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical tomographic imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110026035A1Reduce the burden onReduced imaging timeRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam diameterImage resolution
An optical tomographic imaging apparatus is provided which includes a low-resolution mode for rough imaging and a high-resolution mode for obtaining detailed images. In particular, an optical tomographic imaging apparatus is provided which enables tomographic imaging during a high-resolution mode to be performed at higher speeds. An imaging apparatus according to the present invention captures an optical interference tomographic image based on a combined beam that combines a return beam from an object irradiated by a measuring beam and a reference beam corresponding to the measuring beam. The imaging apparatus according to the present invention further includes a beam diameter changing unit for changing a beam diameter of the measuring beam. Furthermore, the imaging apparatus according to the present invention includes a detection unit configured to detect the combined beam at a resolution according to the beam diameter.
Owner:CANON KK
Radiographic apparatus and radiographic system
InactiveUS20120114098A1Fast decayAvoid configurationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsGratingPhase difference
A radiographic apparatus includes a first grating, a second grating, a scanning unit, and a radiological image detector. The second grating includes a periodic form that has a period which substantially coincides with a pattern period of a radiological image formed a radiation having passed through the first grating. The scanning unit relatively displaces the radiological image and the second grating to a plurality of relative positions at which phase differences between the radiological image and the second grating are different each other. The radiological image detector detects the radiological image masked by the second grating. The scanning unit includes a driving unit that drives one of the first grating and the second grating relatively to the other in a pattern arrangement direction of the radiological image and a plurality of elastic members that has natural frequencies different from each other.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
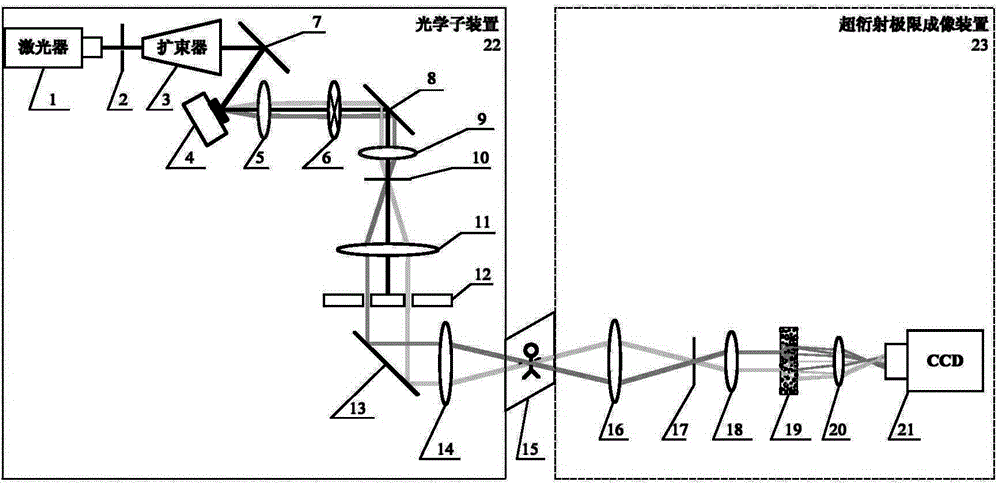
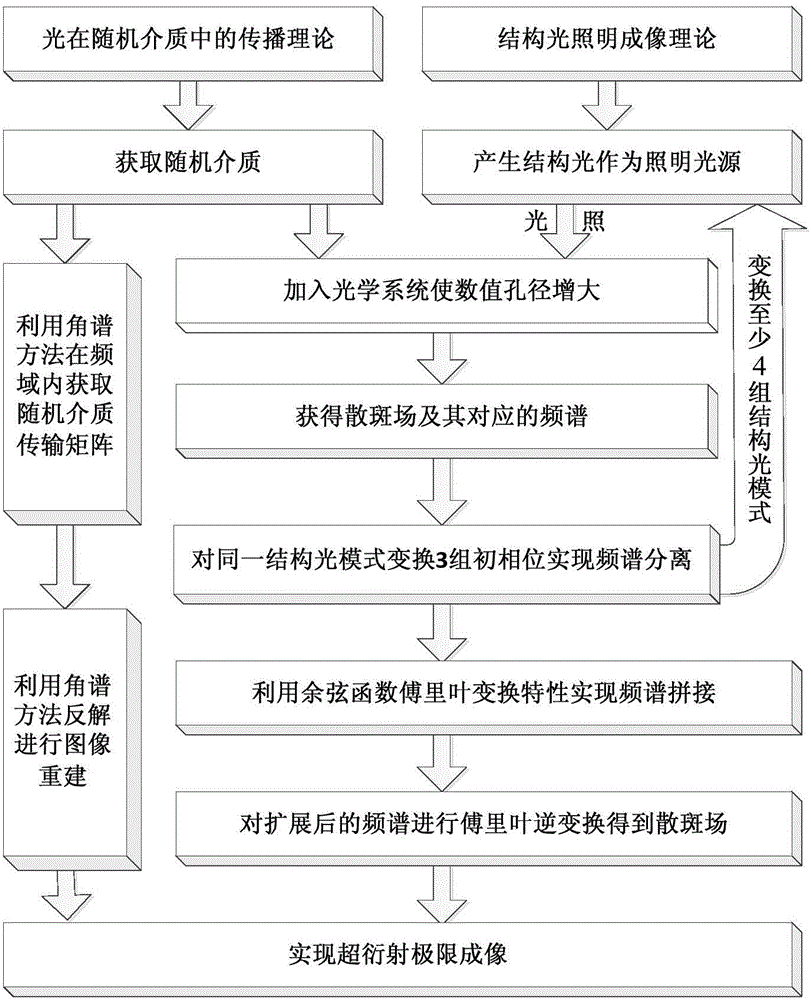
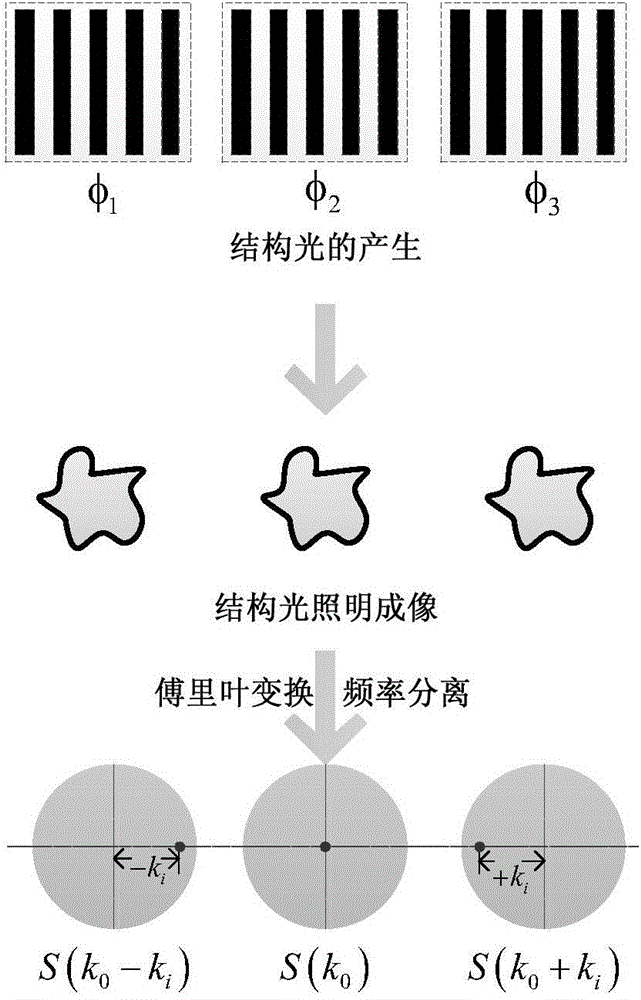
Structural illumination-based random scattering optical beyond-diffraction-limit imaging system and method
ActiveCN104102017ASimple preparation processSimple structureOptical elementsBeam expanderSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a structural illumination-based random scattering optical beyond-diffraction-limit imaging system and method. The objective of the invention is mainly to solve the problems of complicated techniques, long imaging time, difficult realization of system structure and low imaging resolution of existing similar technologies. The imaging system includes a light source, a beam expander, a spatial light modulator, a lambda / 4 wave plate, a beam expanding lens group, a light blocking plate, lenses, a random scattering medium, a convergence lens, and a CCD camera; light beams emitted by the light source are subjected to beam expansion of the beam expander and thereafter enter the spatial light modulator, so that 0-level light and + / -1-level light are obtained; the 0-level light and + / -1-level light pass through the lambda / 4 wave plate, so that circularly polarized light can be obtained; after being subjected to beam expansion of the beam expanding lens group, the circularly polarized light reaches the light blocking plate, and the + / -1-level light is reserved; the + / -1-level light is interfered when passing through the lenses, and structural light can be generated, and an observation target can be illuminated; and the illuminated observation target enters the random scattering medium, and strong scattering occurs, and light beams enter the CCD camera through the convergence lens. The structural illumination-based random scattering optical beyond-diffraction-limit imaging system of the invention has the advantages of simple structure and high imaging resolution, and can be used for optical super resolution imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for fast multi-slice mapping of myelin water fraction
InactiveUS20090312625A1Increasing volume coverageShorten the construction periodMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseMulti slice
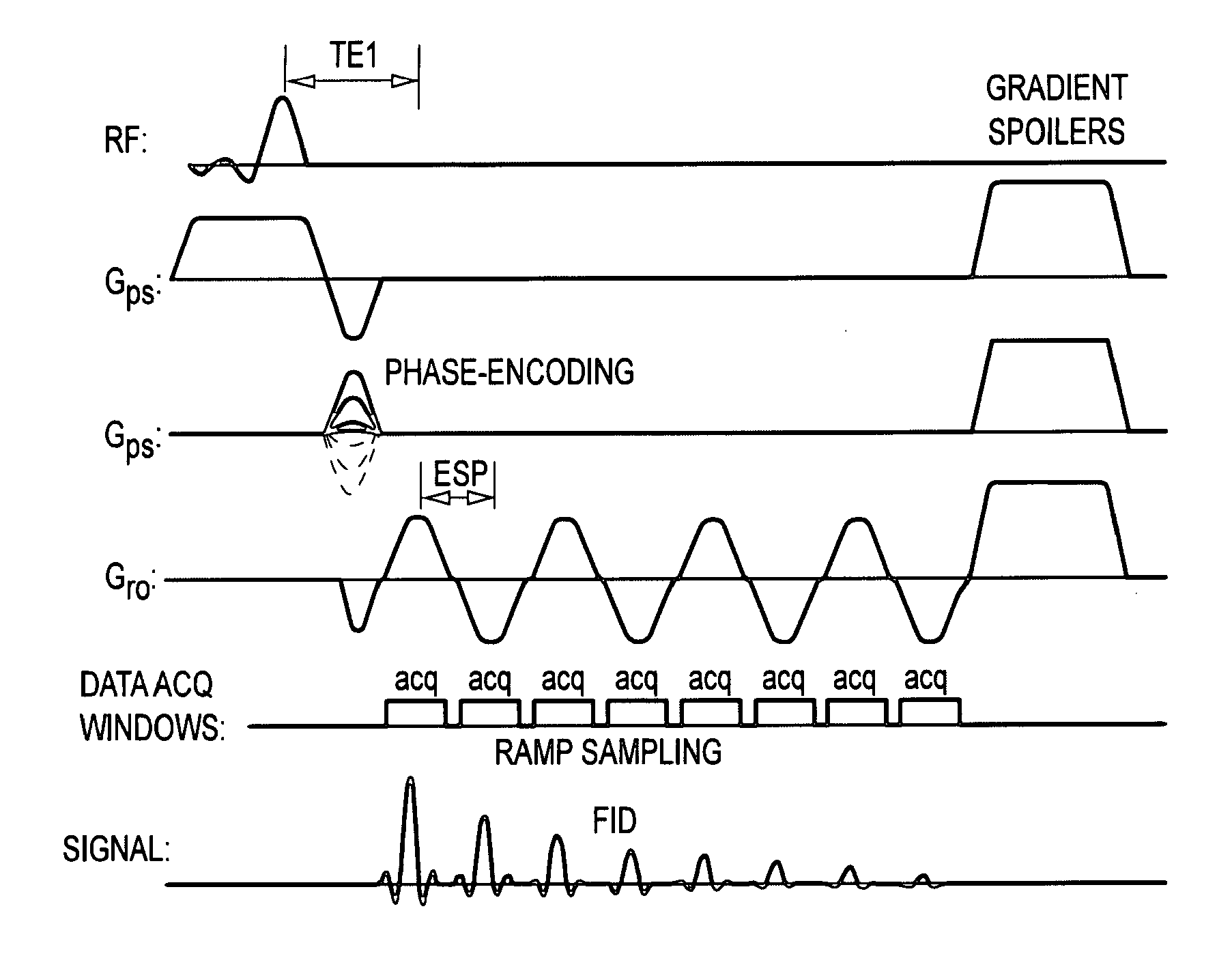
Mapping of myelin water content in white matter may provide important information for early diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and the detection of white matter abnormality in other diseases. It is disclosed here that free induction decay (FID) of each voxel at multiple slice locations is acquired in the brain using an echo-planar spectroscopic imaging (EPSI) pulse sequence. The multi-slice EPSI acquisition is designed to have a short first echo time (˜2 ms) and echo-spacing (˜1 ms) in order to acquire multiple sampling points during the fast decay of the myelin water signal. Multi-compartment analysis is then applied to the FID in each pixel using a 3-pool model of white matter to obtain quantitative maps of the myelin water fraction. Using this technique, the MR data for whole brain mapping of the myelin water can be acquired in less than 10 minutes, making this technique feasible for routine clinical applications.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Optical tomographic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100181462A1Increase influenceLarge influenceMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansFocal positionDepth direction
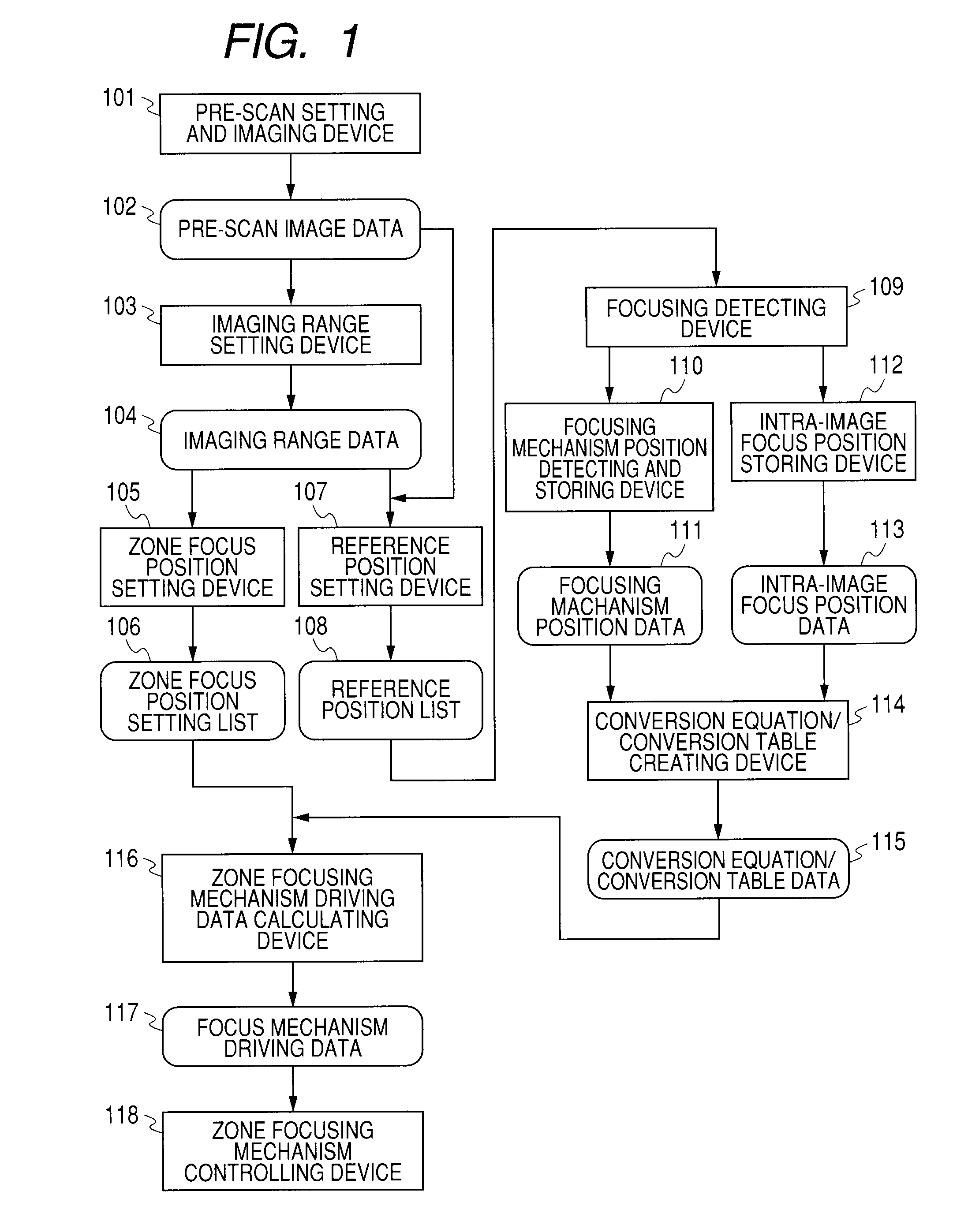
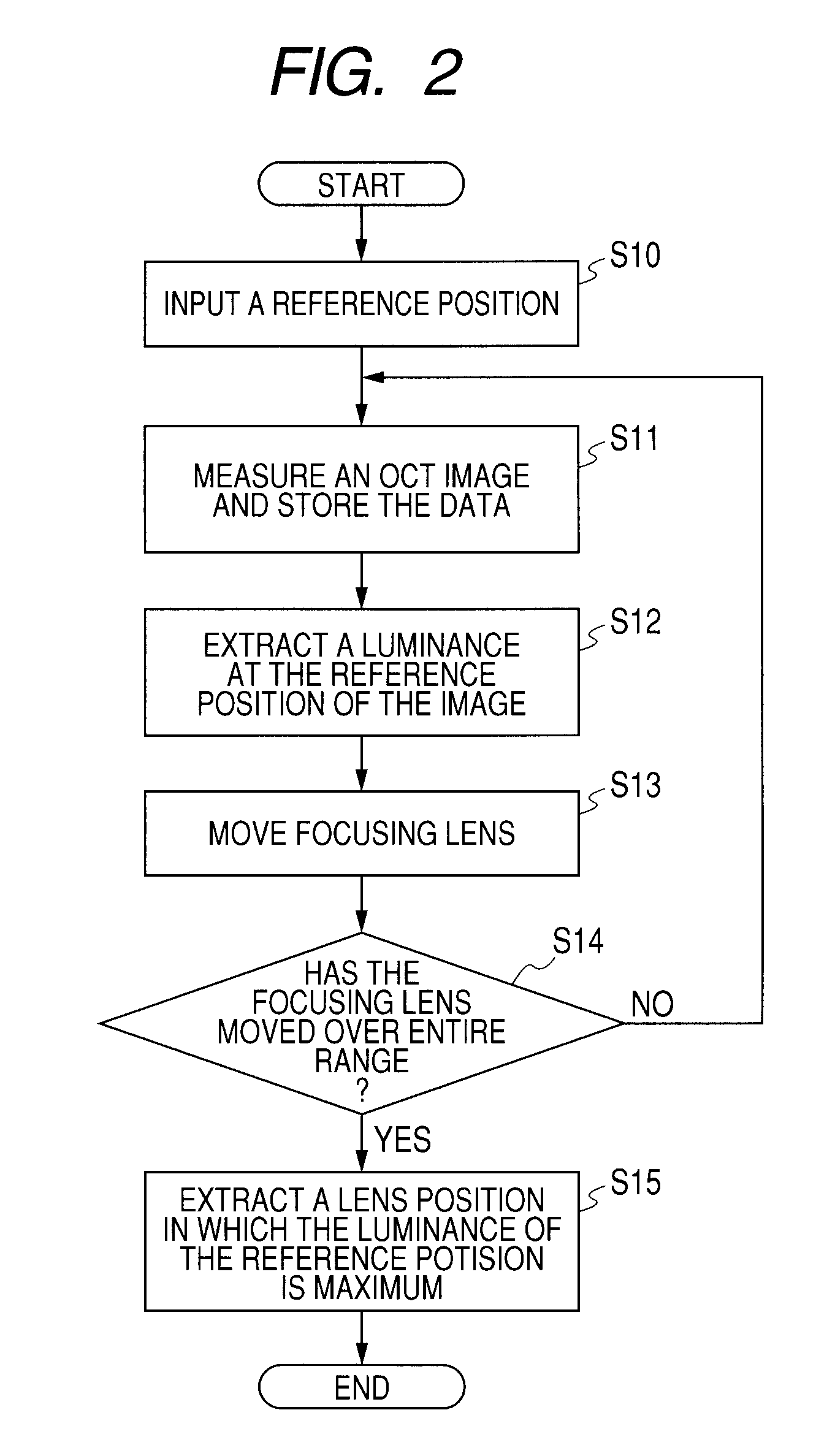
Provided is an optical tomographic imaging apparatus that is capable of shortening a period of time of focusing at multiple focus positions when images split in a depth direction are obtained by zone focusing. The optical tomographic imaging apparatus includes: a focus position setting device for splitting a zone within a predetermined imaging depth range into multiple focus zones so as to set multiple focus positions; a reference position setting device for setting at least two reference positions in an imaging depth direction within the predetermined imaging depth range; and a focus controlling device for performing focusing at the multiple focus positions sequentially based on focus position information generated by the focus position setting device and determining a focus condition of an in-focus state for the at least two reference positions set in advance by the reference position setting device.
Owner:CANON KK
CT (computed tomography) imaging method and CT imaging system based on multi-mode Scout scanning
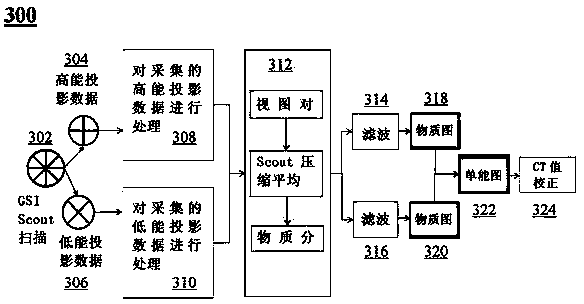
InactiveCN103892859AReduce X-ray doseReduced imaging timeComputerised tomographsTomographyLow voltageDual energy
A CT imaging method and a CT system based on a multi-mode scout scan. The CT imaging method based on a multi-mode scout scan comprises: performing an instant switching dual energy scout radiation scan on a region of interest of a subject by way of instant switching between high voltage and low voltage to collect dual energy protection data of the region of interest; and reconstructing a material decomposition image and a mono-energetic image based on the collected dual energy projection data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Deep water net cage fish school status remote real time monitoring instrument based on acoustic multi-beam
InactiveCN101334473AImprove distributionShorten the timeTransmission systemsAcoustic wave reradiationEngineeringArray element
The invention discloses an acoustic multi-beam-based remote real-time monitor of fish shoals in a deep water net cage, relating to a monitoring device. The invention provides the acoustic multi-beam-based remote real-time monitor of the fish shoals in the deep water net cage which has flexible marine operation, easy placement and strong anti-wave capability. The acoustic multi-beam-based remote real-time monitor is provided with a detection signal transmitting and echo collection device, a data analysis and image display device and a data wireless transmission device. The detection signal transmitting and echo collection device is provided with an annular transducer array and a control box, and the annular transducer array is provided with single beam transducer array elements; the control box is provided with a power supply, a controller, a detection signal generator, a power amplifier, a signal collection and preservation circuit and a signal pre-treatment circuit. The data analysis and image display device is used for realizing the remote detection and the control operations on a bank station, carrying out the analysis of the received monitoring data of the fish shoals in the net cage and carrying out the image display of the result. The data wireless transmission device is connected with the detection signal transmitting and echo collection device and the data analysis and image display device.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Photon counting laser radar based on composite pseudo-random coding
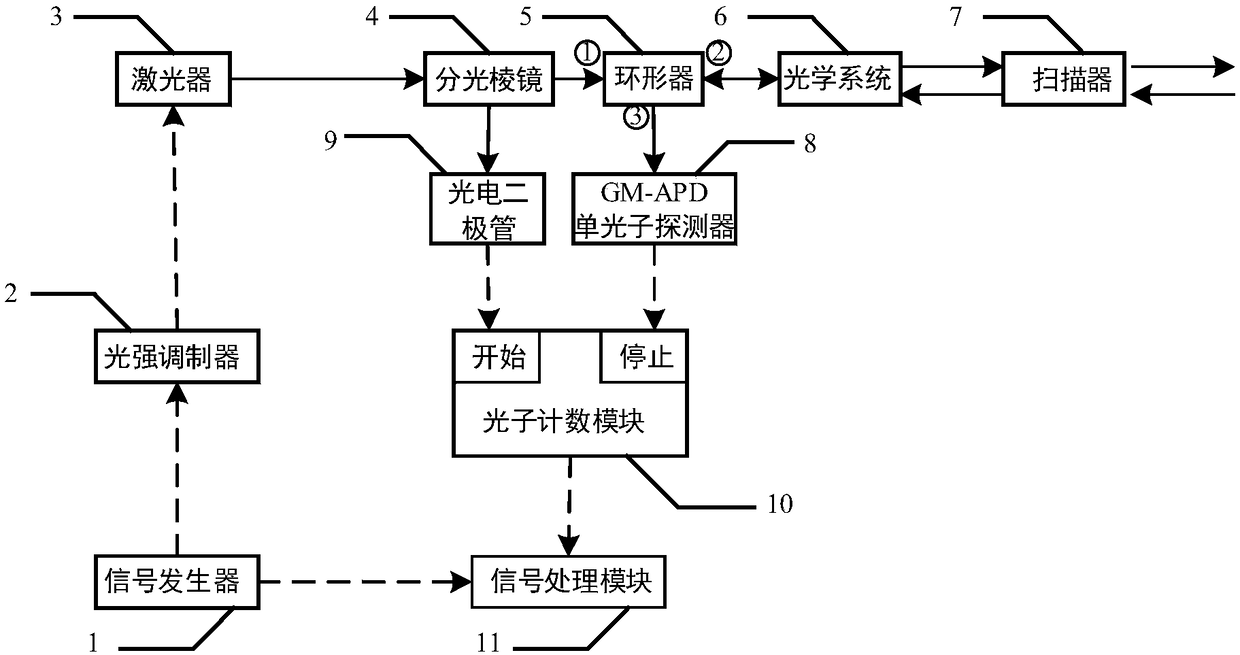
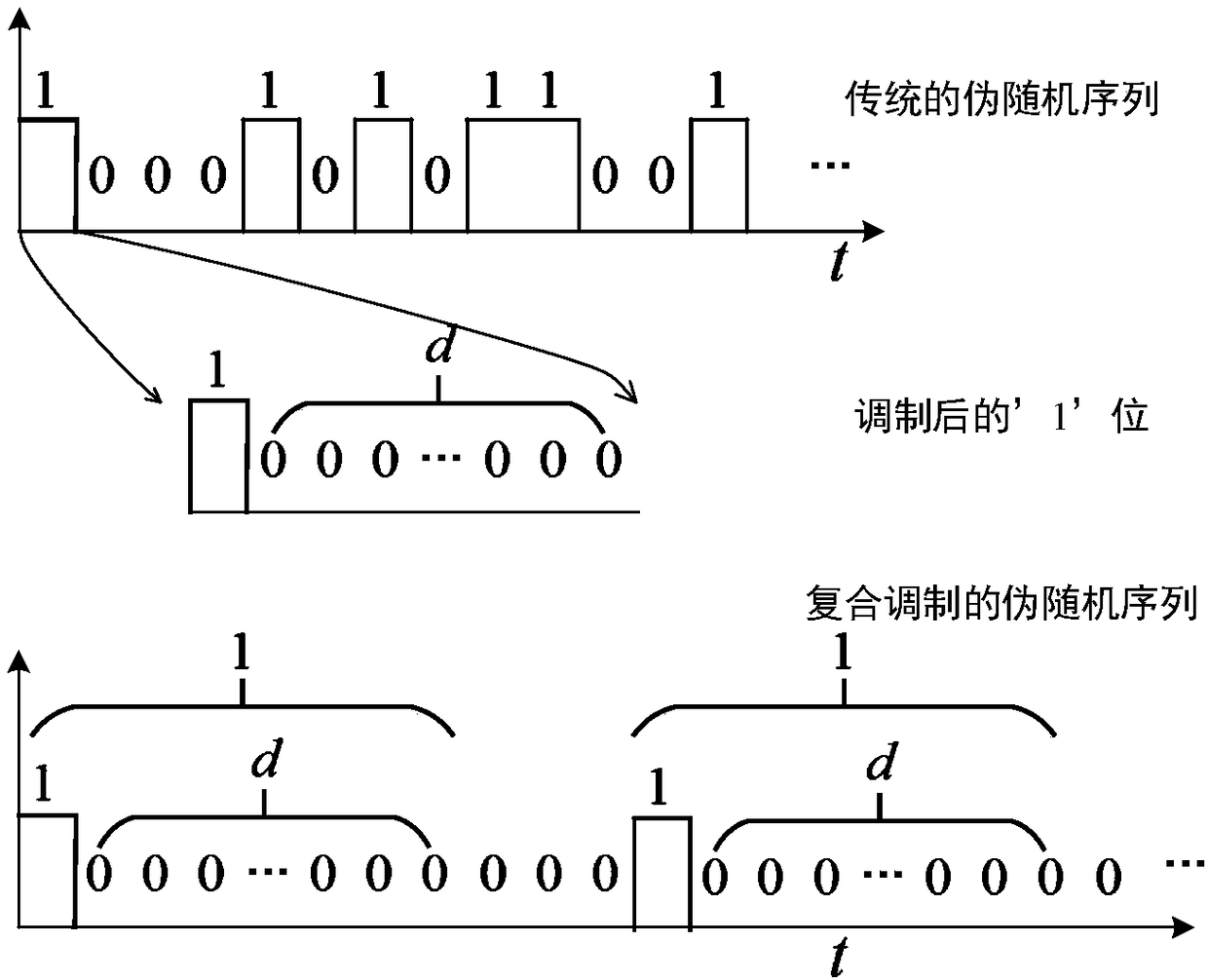
ActiveCN108089194AReduced imaging timeImprove noise immunityElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterPrism
The invention discloses a photon counting laser radar based on composite pseudo-random coding. The photon counting laser radar is composed of a signal generator, a light intensity modulation device, alaser device, a beam splitter prism, a circulator, an optical system, a scanner, a GM-APD single-photon detector, a photodiode, a photon counting module, and a signal processing module. An overall structure of a transmitting-receiving-same-path type optical reduced system is employed and a scanner is used for carry out scanning and transmitting a laser pulse string, so that the field angle of thelaser radar is extended. After processing on a laser signal transmitted by an optical system by the beam splitter prism, one part of the signal irradiates the photodiode directly to form a light trigger signal and the other part of signal is scanned by the scanner and then the scanned signal is irradiated on a target; an echo signal reflected by the target enters the scanner, the processed signalreturns to a second port of the circulator by the optical signal and enters the GM-APD single-photon detector through a third port of the circulator; the GM-APD single-photon detector records an echosequence and generates a stopping signal; and a detection result recorded by the photon counting module is transmitted to the signal processing module for follow-up processing and flight time of a pulse string is obtained.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
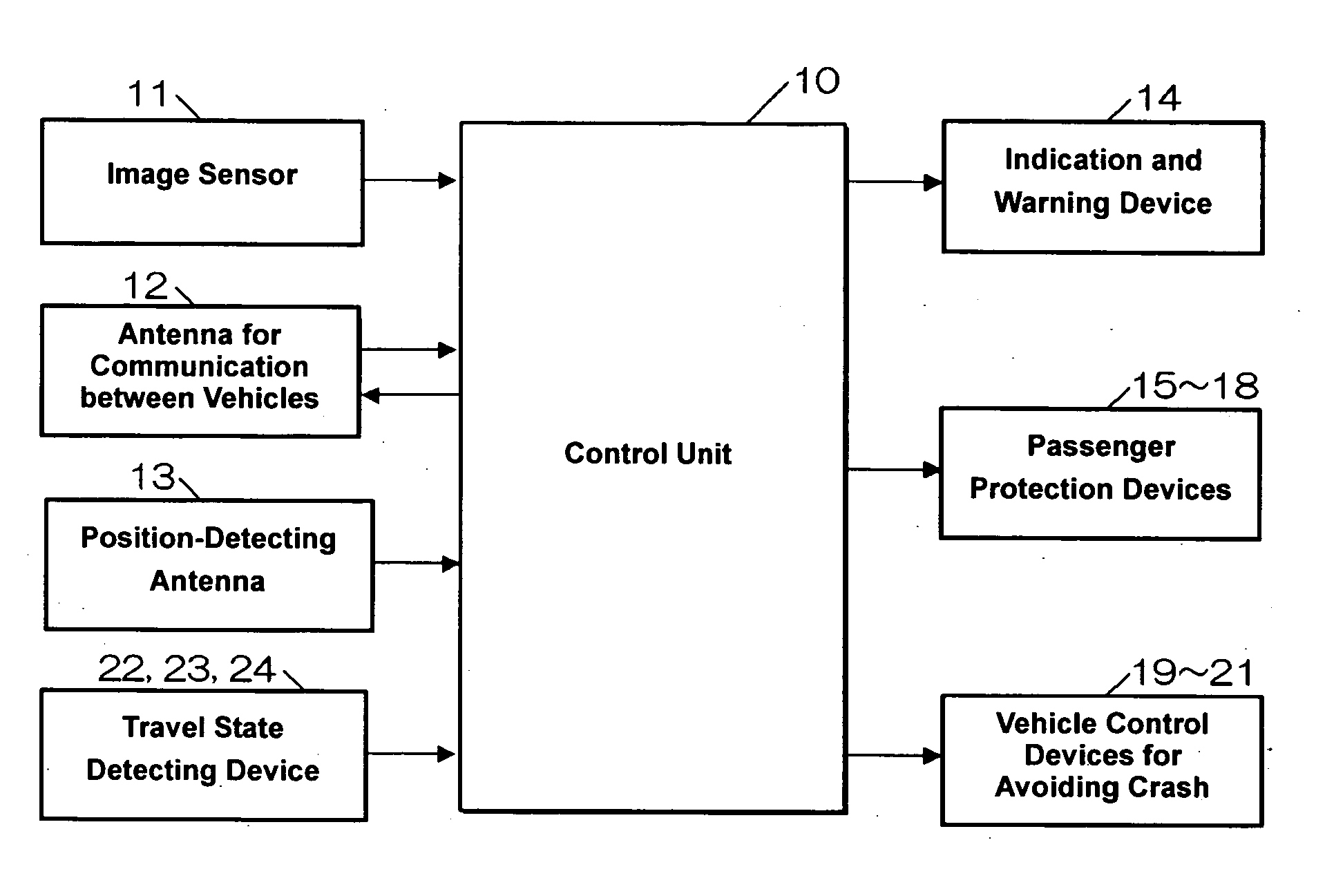
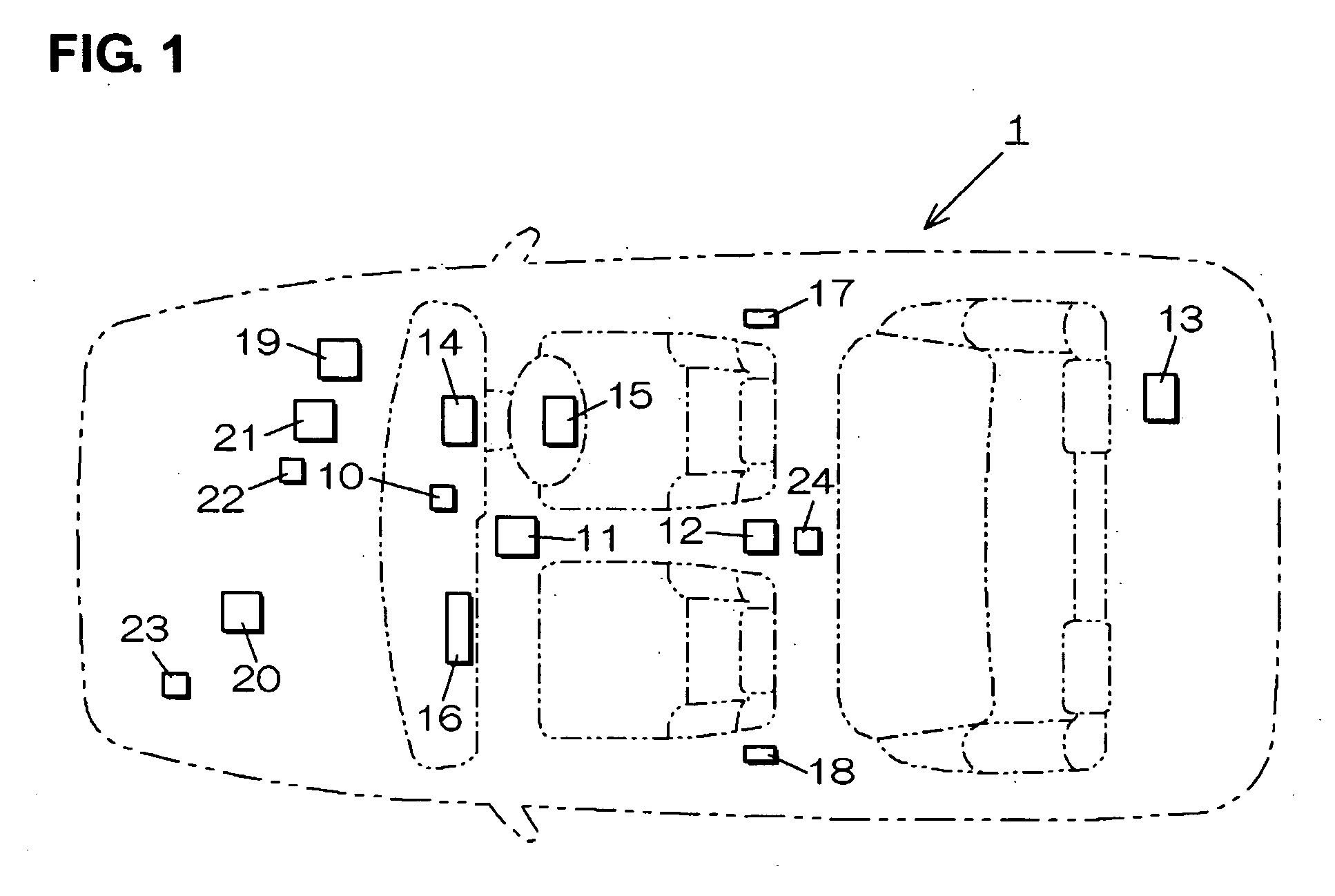
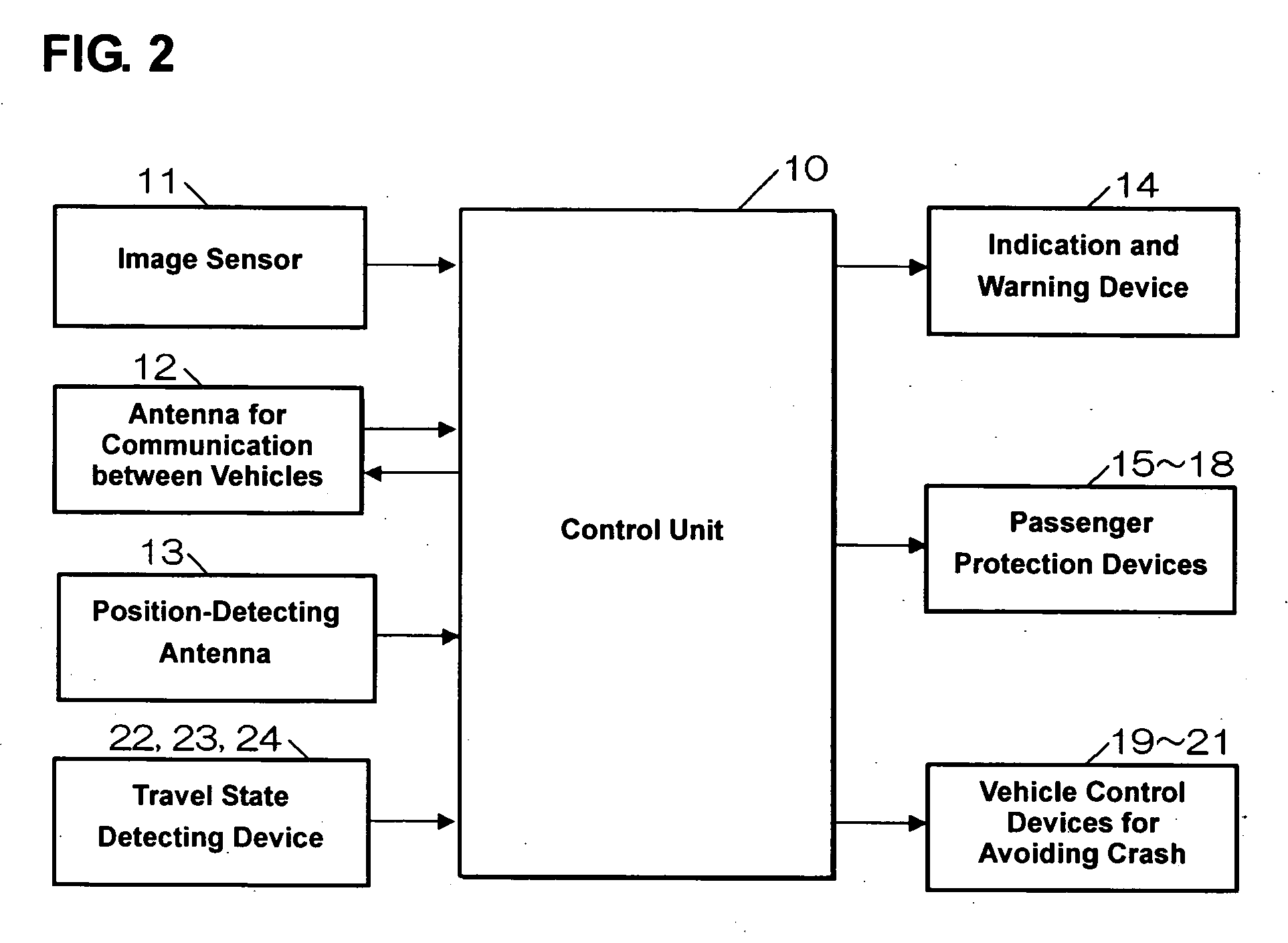
Travel assistance device for vehicle
InactiveUS20070021904A1Reduced imaging timeImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsEngineeringImage matching
The relative position of the surrounding vehicle to the traveling vehicle is determined from respective position information of the traveling vehicle and the surrounding-vehicle obtained through communication between vehicles. The processing area of the image picked up by the camera is restricted on the basis of this relative position. By comparing the template that is obtained with a scale-transfer from the previously-memorized template on the basis of the position information of the vehicle to the image of the vehicle with an image matching, the precious position of the surrounding vehicle is detected. Thereby, the passenger protection devices are operated. Accordingly, the processing time of image data picked up by the camera can be properly shortened and the accuracy of recognition of obstacles can be improved.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
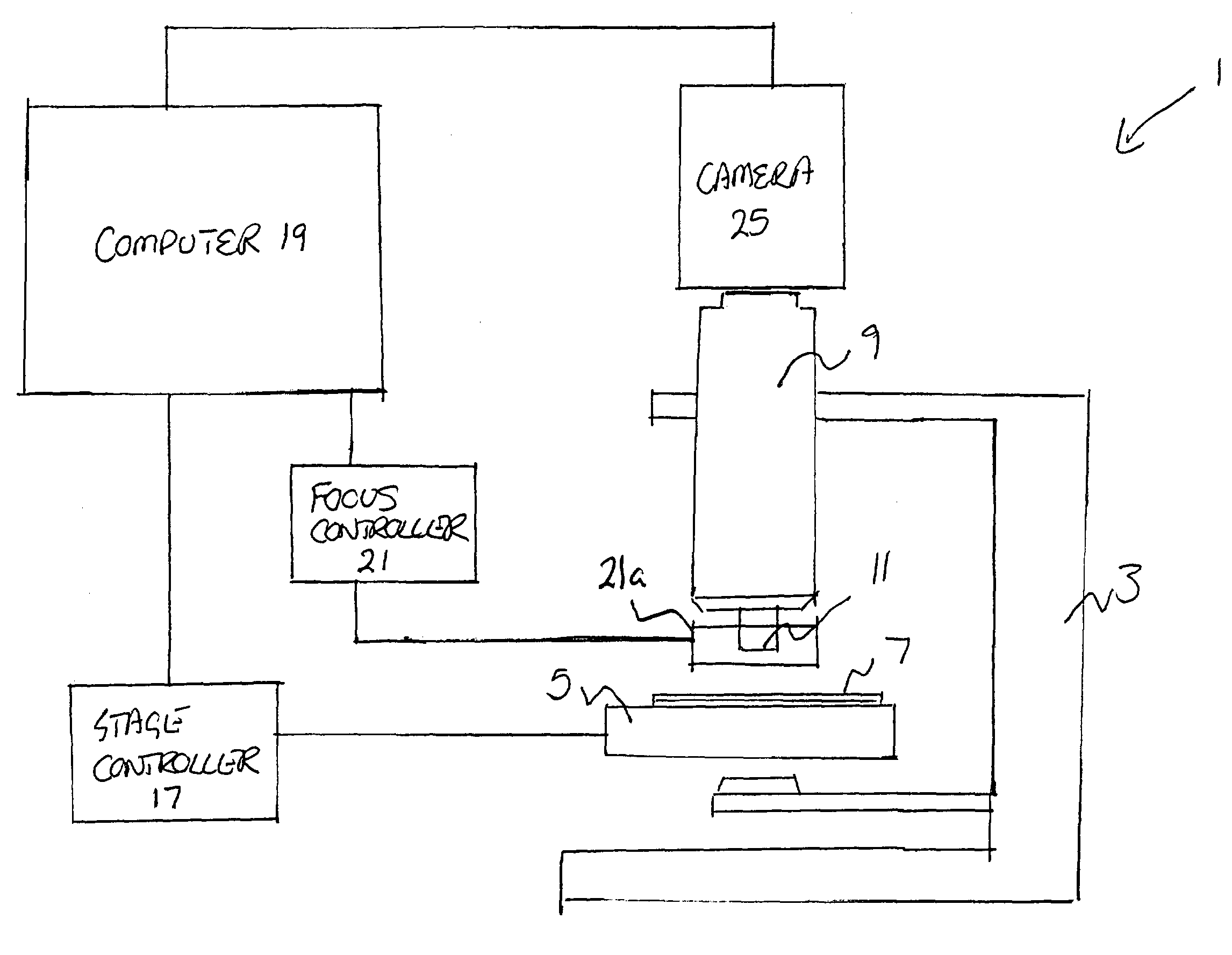
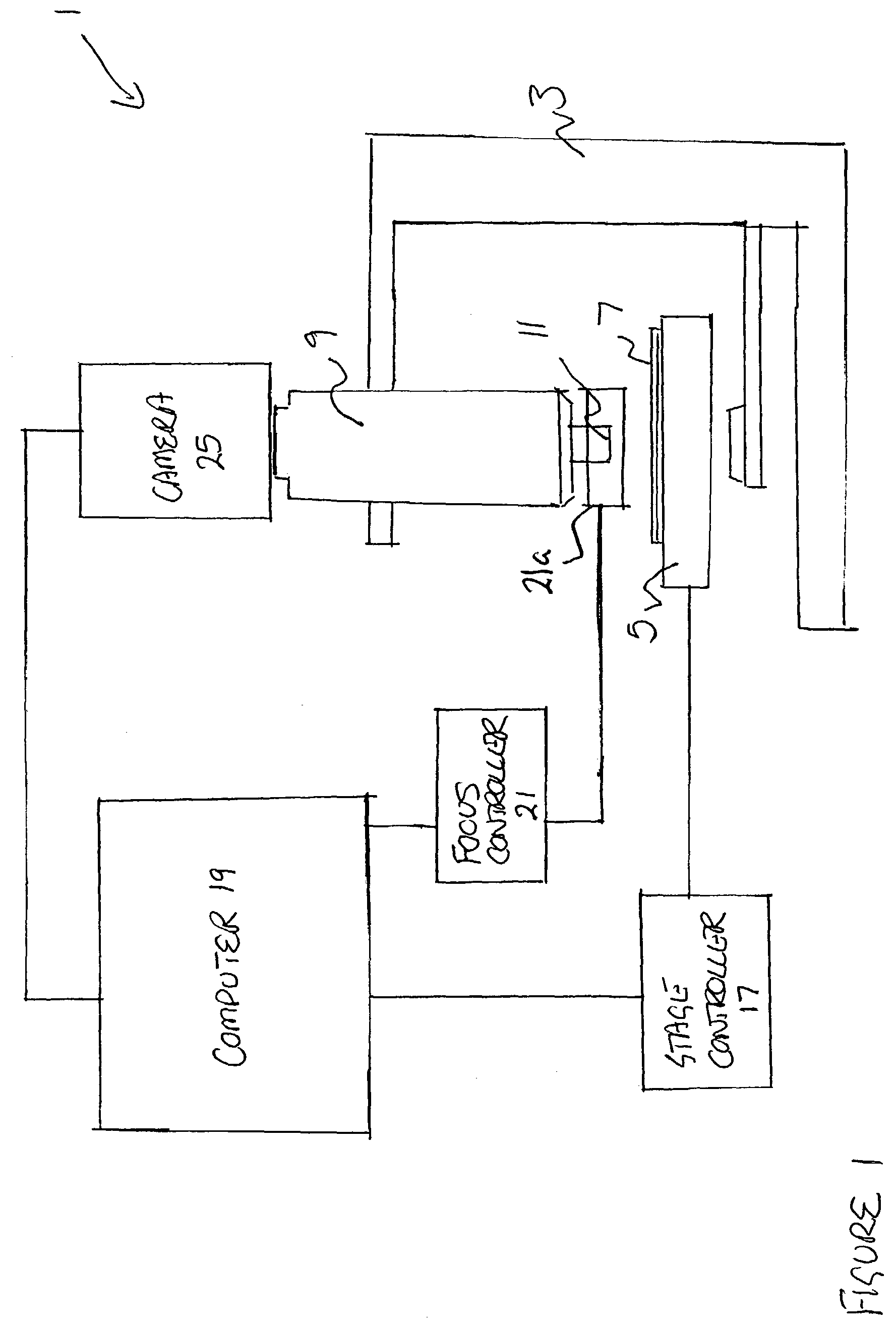
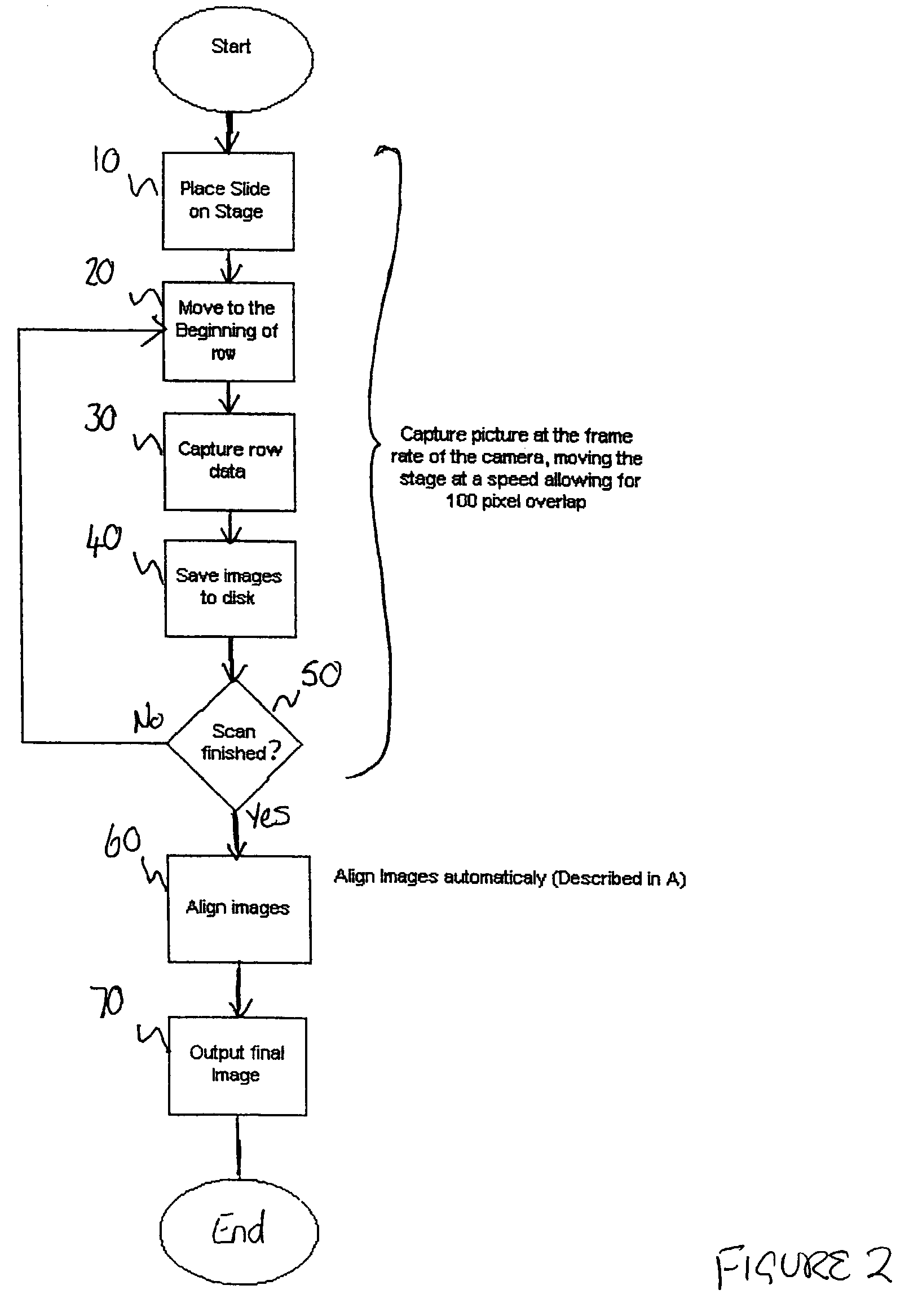
Method and apparatus for acquiring digital microscope images
InactiveUS7388599B2Reduced imaging timeColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsShutter speedImage system
A method and apparatus for acquiring digital microscope images is disclosed, in which a plurality of magnified images of a specimen are captured for tiling together to provide an overall composite image of the specimen. In accordance with the described method, the specimen is moved relative to an imaging system comprising a microscope and camera in a predetermined path whilst the plurality of magnified images are captured. In a preferred embodiment, the specimen, contained on a slide, is mounted on a movable microscope stage, and is moved beneath the microscope in the predetermined path. The velocity of the movement of the stage and the shutter speed of the camera is computer controlled to capture overlapping, clear images.
Owner:SOURCE BIOSCI
Active terahertz security inspection imaging method and system
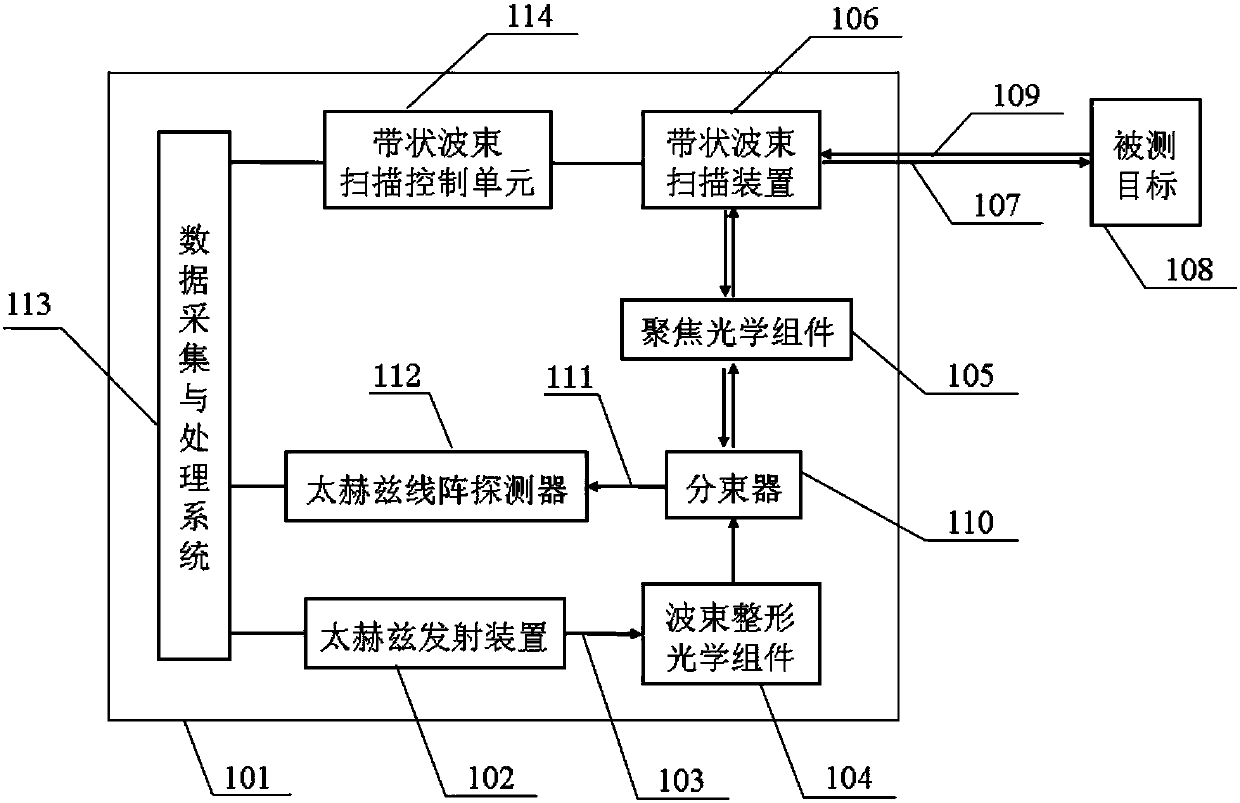
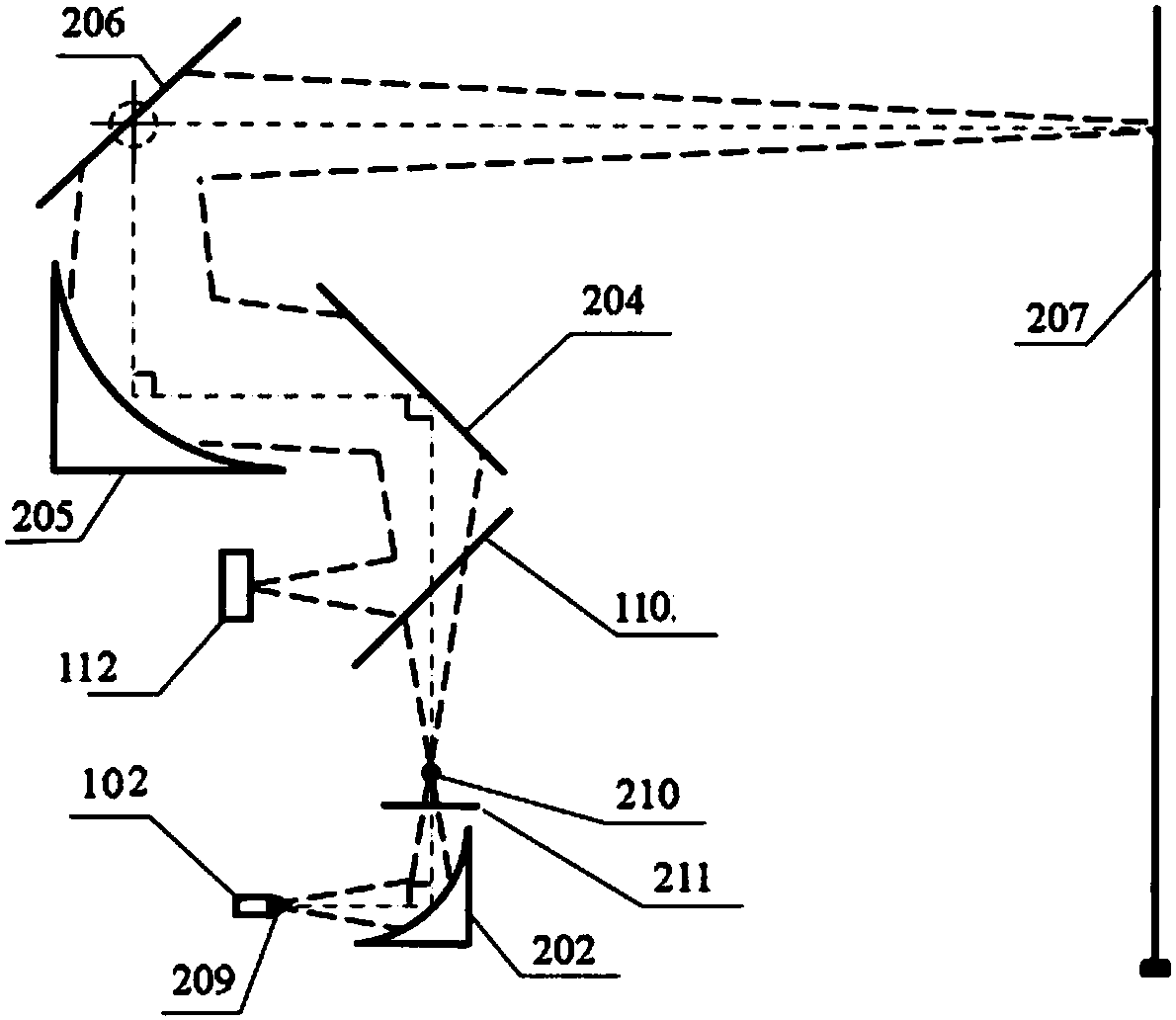
The invention, which belongs to the technical fields of security inspection equipment and image processing, discloses an active terahertz security inspection imaging method and system. The security inspection imaging system is characterized in that a data acquisition and processing system is connected with a terahertz transmitter, a terahertz linear array detector and a band-shaped beam scanning control unit respectively; a beam splitter is connected with a beam shaping optical assembly, the terahertz linear array detector and a terahertz focusing optical assembly respectively; and the band-shaped beam scanning control unit is connected with the terahertz focusing optical assembly, the band beam scanning control unit, and a tested target. In addition, according to the active terahertz security inspection imaging method, on the basis of a mode of terahertz radiation emitted by a terahertz source, one-dimensional scanning of a band-shaped beam focusing beam, and receiving by a linear array terahertz detector, irradiation and scanning of the whole target plane are completed rapidly to achieve an objective of rapid imaging and checking on a target. With the active terahertz security inspection imaging system, the imaging quality is improved. Because of the one-dimensional scanning way, the imaging time is saved; and with the array detector, the circuit system structure is simplified, the system cost is lowered, and the expenditure is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus
ActiveUS7372269B2Fast imagingReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePropeller
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Ophthalmologic apparatus and control method of the same
There is provided an ophthalmologic apparatus having a tracking function that can select a fundus image that is less affected by eye motion to reduce burdens on an operator / a patient in fundus imaging, wherein the ophthalmologic apparatus picks up a first fundus image (202), extracts a characteristic point as a template from the first fundus image (203), executes pattern matching on a second fundus image (205) to determine presence / absence of eye motion, and decides a tracking template image (207).
Owner:CANON KK
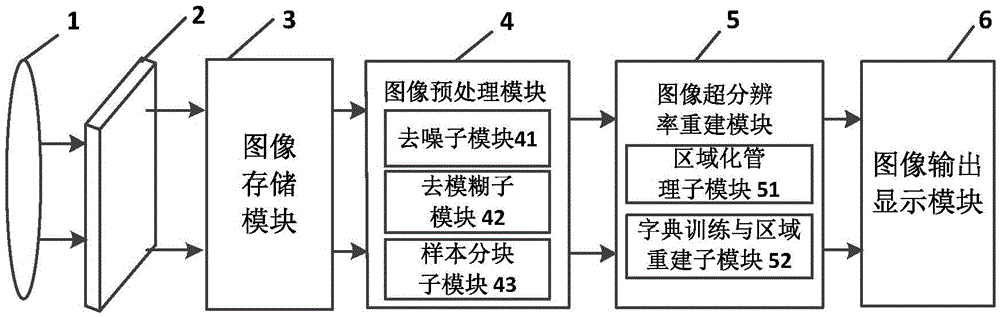
High-efficiency super-resolution imaging device and method with regional management
InactiveCN105678728AImprove super-resolutionReduced imaging timeImage enhancementImage analysisImage storageMedical imaging
The invention provides a high-efficiency super-resolution imaging device and method with regional management, and aims at solving the problem that an existing super-resolution imaging device and method is long in imaging time and low in resolution. The imaging device comprises an imaging lens group, a high-resolution detector, an image storage module, an image pre-processing module, an image super-resolution reconstruction module and an image output display module connected successively, wherein the image super-resolution reconstruction module is composed of an image regional management sub-module and a dictionary training and regional reconstruction sub-module. The imaging method comprises the following steps of obtaining optical signals of a practical scene; obtaining low-resolution images; storing the low-resolution images; preprocessing the images; carrying out regional image management; training dictionaries and reconstructing super-resolution areas, and splicing images of the reconstructed super-resolution sub-regions. The imaging device and method can be used to improve the imaging resolution effectively and shorten the imaging time, and applied to the fields including video monitoring, satellite remote-sensing imaging and medical imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Magnetic resonance imaging device
ActiveUS20060049829A1Accurately calculateShorten the timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMR - Magnetic resonanceLow frequency
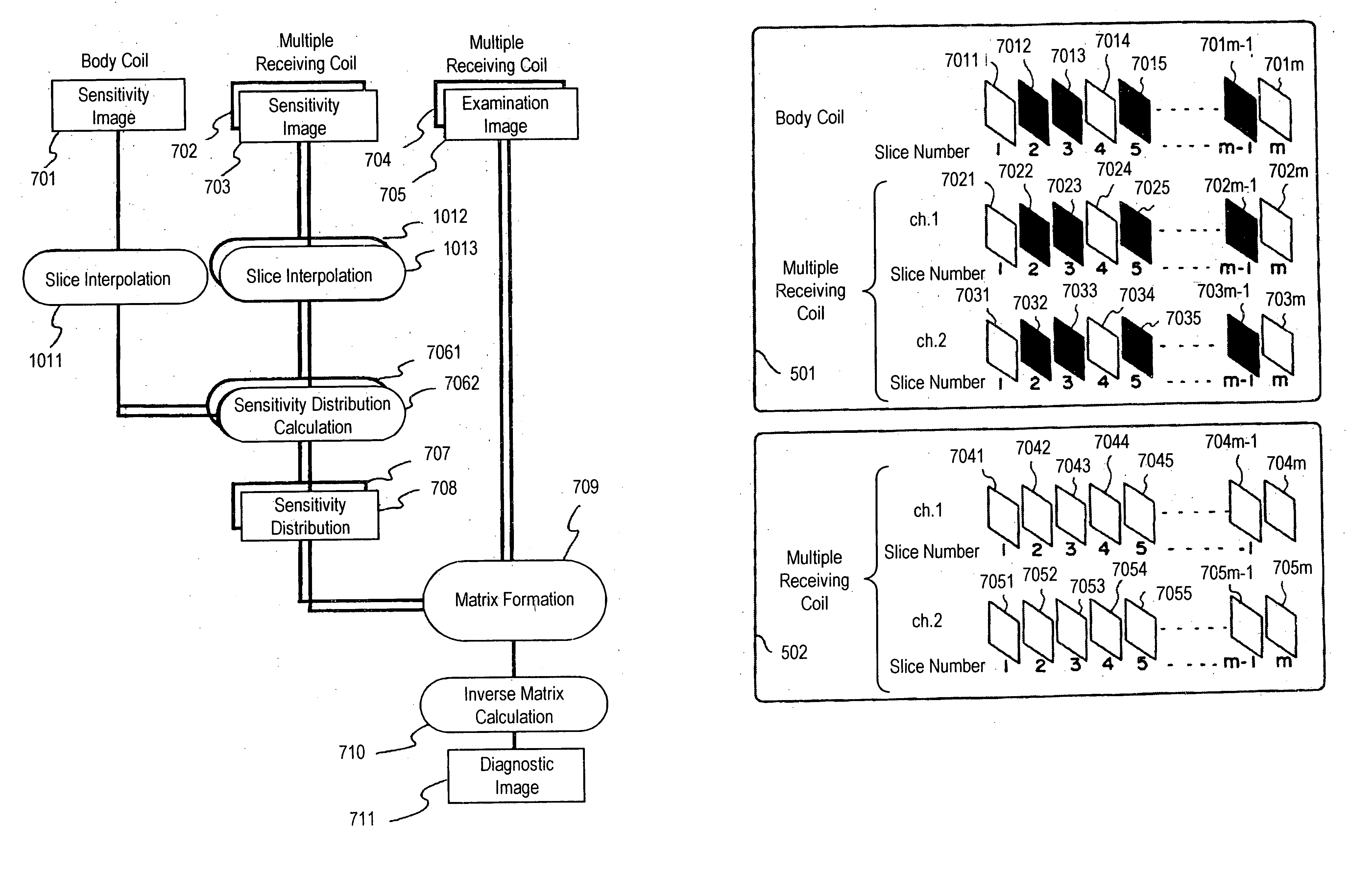
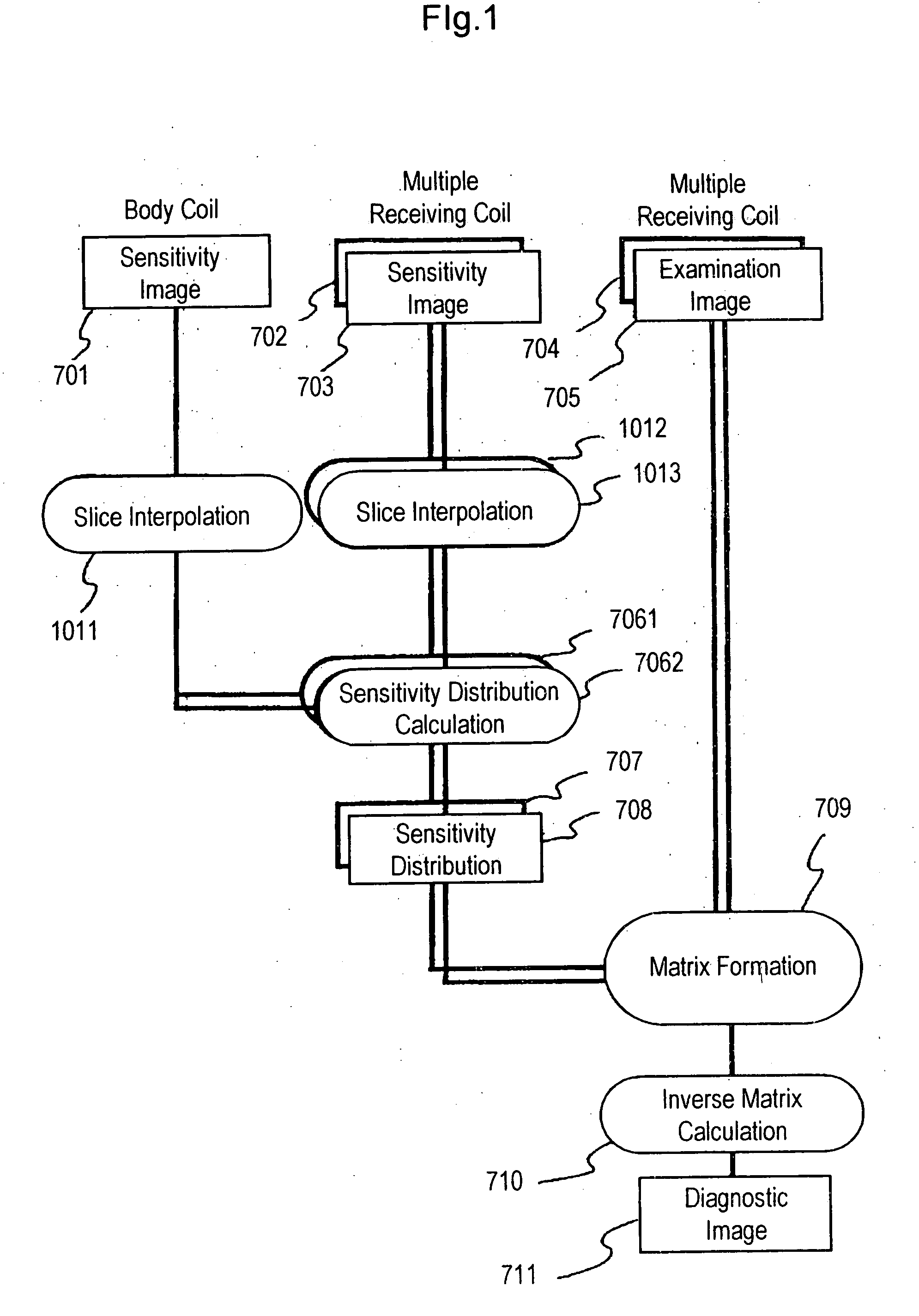
A first pulse sequence is executed on an imaging portion of an object to be examined using a multiple receiving coils including a plurality of receiving coils to obtain sensitivity images 701 to 703, each of n in number, which is smaller than the number of examination image. When those sensitivity images are calculated, NMR signals are measured only in a low-frequency region of a k space. Next, a second pulse sequence is executed while phase encoding steps are thinned out to acquire examination images 704 and 705, each of m in number (m>n), of the object with each receiving coil. When sensitivity distributions 707 and 708 are generated on the basis of sensitivity images 701 to 703, if a sensitivity distribution on a slice corresponding to examination images 704 and 705 is not yet measured, it is calculated with a slice interpolation processing on the basis of sensitivity distributions 701 to 703, and an aliasing artifact in examination images 704 and 705 are removed using sensitivity distributions 707 and 708 with a matrix calculation.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging method and device
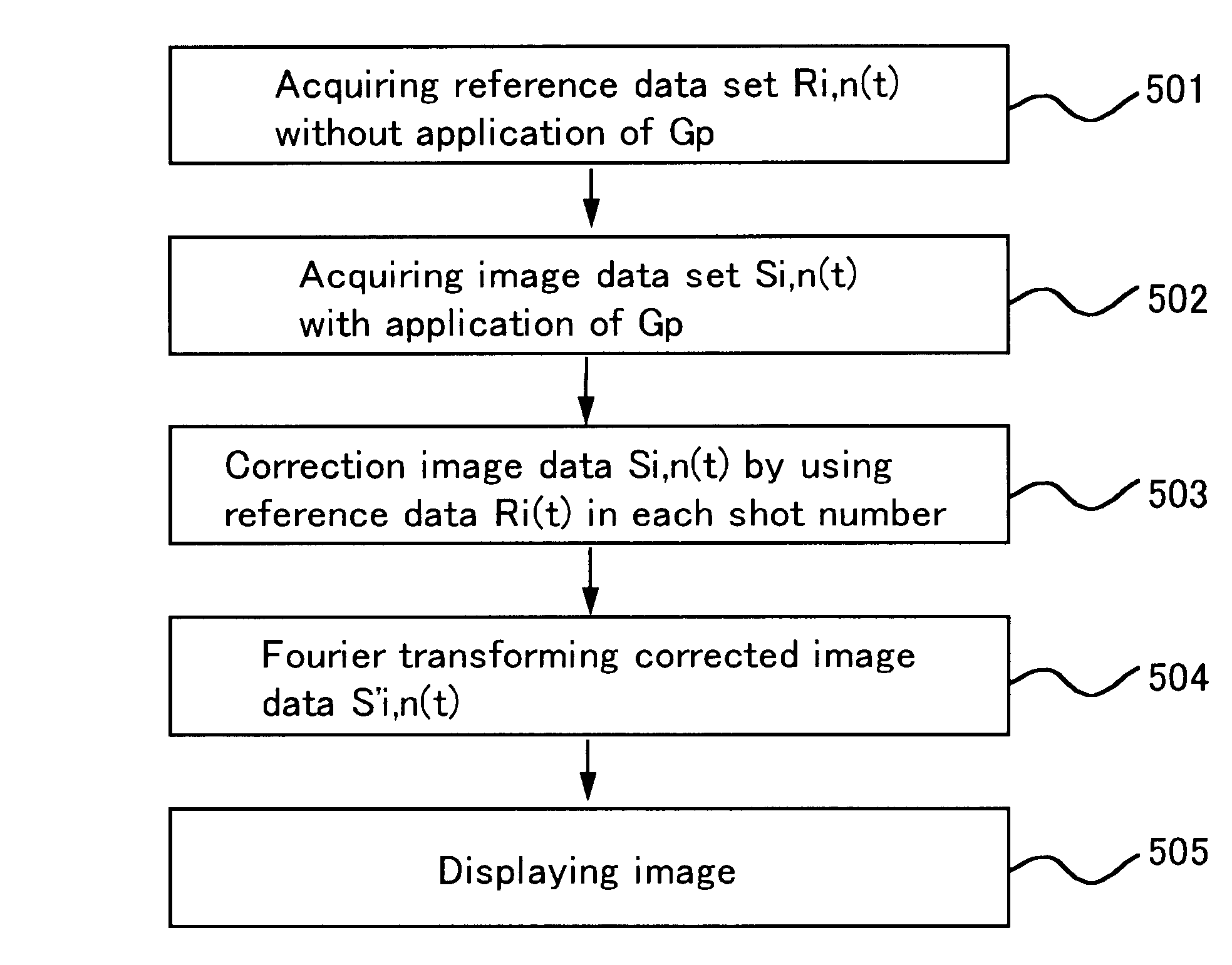
InactiveUS6728568B1Improve image qualityEnhance the imageDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionImaging quality
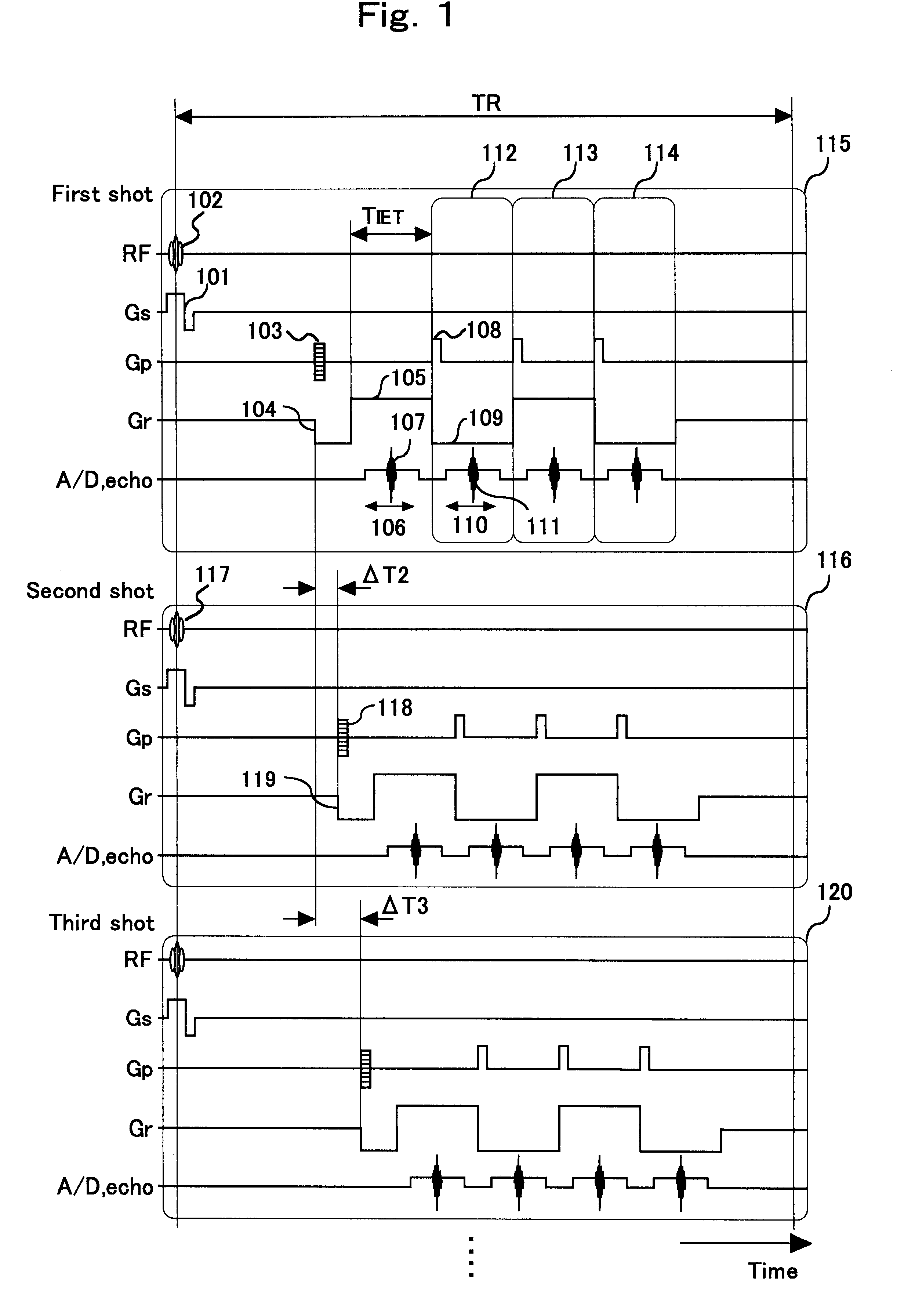
In order to improve image quality in MRI using an EPI method without extending imaging time excessively, reference data is acquired in the absence of substantial phase encoding gradients by using an EPI sequence in combination with an echo shift (ETS) method, at times related to the timing of echo signals for image data. The reference data is used for phase correcting the image data acquired with application of phase encoding. The reference data can be measured for a single shot, or a few shots, and used to estimate reference data for the rest of the shots in which imaging data is acquired.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Three-dimensional terahertz tomography system, scanning method and image reconstruction method thereof
InactiveCN107631995AReduced imaging timeTomography RealizationMaterial analysis by optical meansReconstruction methodAbsorption rate
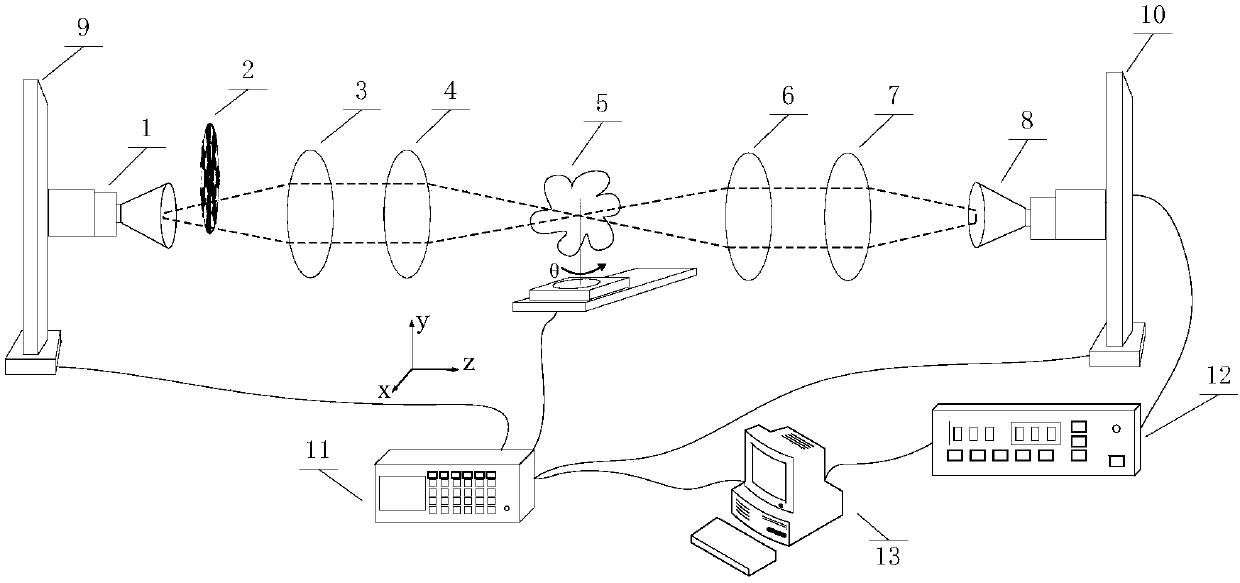
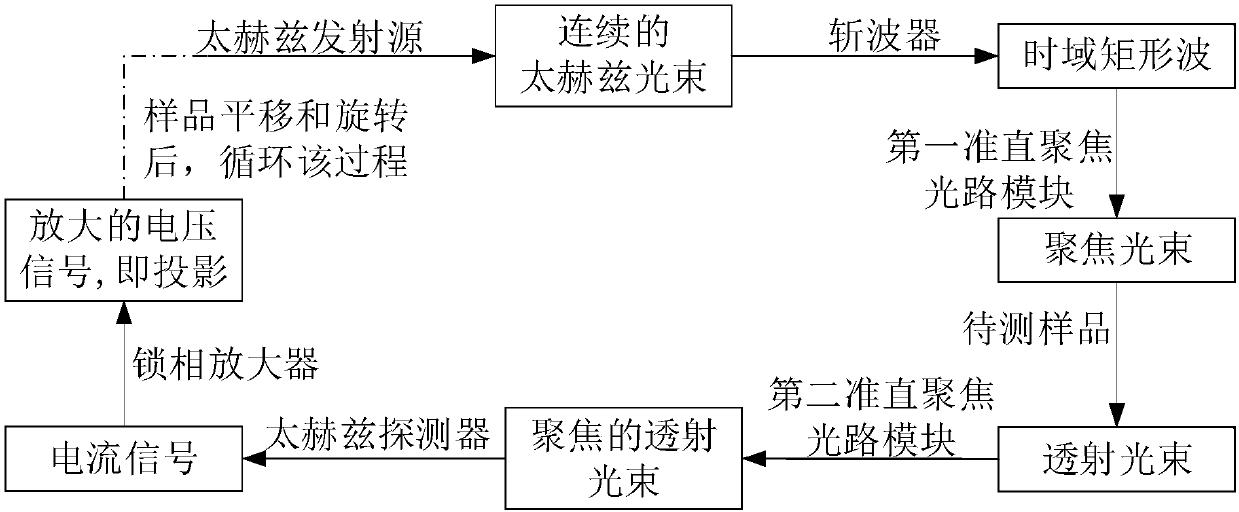
The invention discloses a three-dimensional terahertz tomography system, a scanning method and an image reconstruction method thereof. The three-dimensional terahertz tomography system comprises a terahertz emitting source, a wave chopper, a sample rotation translation table, a light beam transmission unit, a terahertz detector and a lock-in amplifier. The imaging method comprises a scanning method for acquiring projection data and an image reconstruction method. According to the present invention, when a sample is scanned by the imaging system, only the single-frequency transmitted light intensities of each detection point are required to be recorded, such that the imaging time is reduced, and the power is high so as to image the thick object; when the image reconstruction is performed according to the projection data, the absorption rate distribution of the sample at the angle according to the projection data at each angle is obtained, and the absorption rate distribution and the terahertz light beam light intensity distribution are subjected to deconvolution, such that the actual absorption rate distribution of the sample can be obtained; and with the imaging method and the system of the present invention, the problem that the light approximation on the terahertz light beam can cause the blurred image in the existing imaging technology can be effectively solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Correlated imaging system
The invention provides a correlated imaging system used for carrying out correlated imaging on an object to be imaged through a thermal light source. The correlated imaging system comprises an object arm light path and a first reference arm light path, wherein the object arm light path is internally provided with a first barrel detector and the object to be imaged; the first barrel detector samples a total light field intensity signal Sm, passing through the object to be imaged, in the object arm light path; the first reference arm light path is provided with a reference detector device for sampling the distribution information of the light field intensity of the first reference arm light path; the reference detector device comprises at least one reference detector unit; each reference detector unit comprises a timing sequence controller and a plurality of reference detectors with the spatial resolving power; the reference detectors are controlled by the timing sequence controller; the reference detectors are exposed in sequence for sampling under the control of the timing sequence controller. As the reference detectors are alternately exposed in time sequence, the exposure frame rates can be overlapped, limitation of existing reference detectors on the sampling speed is broken through, the sampling speed is greatly increased, and the imaging time is shortened.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by radio-frequency pulse
ActiveCN103033784AImprove controllabilityReduced imaging timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData spacePulse sequence
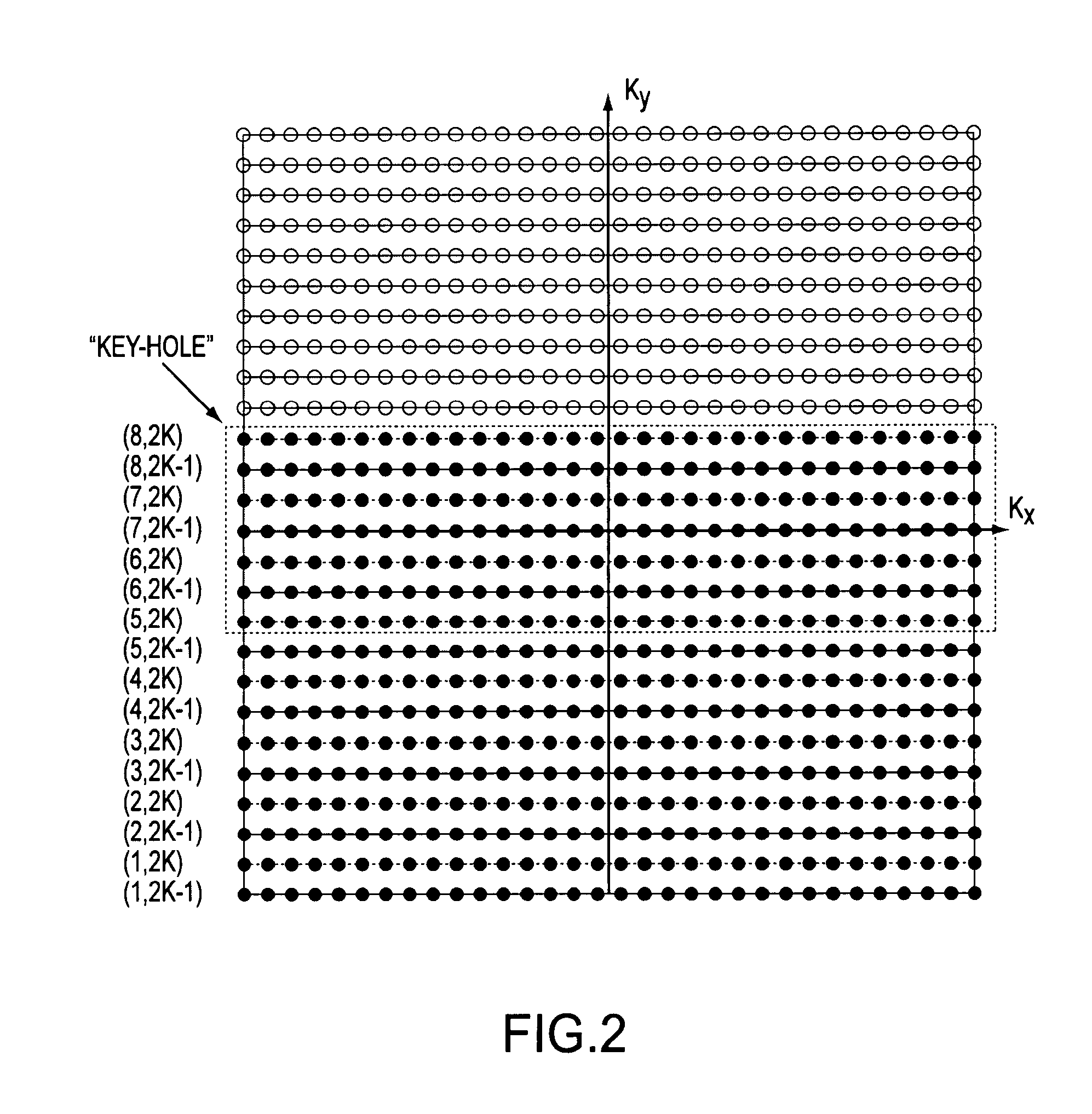
The invention discloses a compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by a radio-frequency pulse, and relates to the magnetic resonance imaging method. The invention provides the compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by the radio-frequency pulse, wherein the compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method controlled by the radio-frequency pulse is capable of controlling a space K to spread spectrum easily. The method includes the spectrum spreading to the space K from the radio-frequency pulse, undersampling at random and image reconstruction. In the magnetic resonance imaging, the radio-frequency pulse of linear frequency modulation is exerted along the phase encoding direction to control the energy diffusion of magnetic resonance imaging data space. The undersampling at random is carried out to the imaging data with spread spectrum, and sampling time is reduced. In terms of the undersampling data, suggested fast reconstruction algorithm is adopted to carry out sparse reconstruction to the imaging. Due to the fact that radio-frequency pulse sequence is utilized to carry out the spread spectrum of the space K, compared with space K with a shim coil, the controllable property of the spread spectrum of the space K is good. The purposes of reducing imaging time and accelerating the magnetic resonance imaging are achieved by adopting the methods of undersamping the magnetic resonance signal at random and the image reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fat/water separation and fat minimization magnetic resonance imaging systems and methods
ActiveUS7099499B2Reduced imaging timeEliminate needCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringExpectation–maximization algorithmWater based
Systems and methods for identifying the relative contribution of fat and water signals in a magnetic resonance (“MR”) image including an algorithm operable for selecting an image signal model, selecting a scan parameter, forming a bias field estimate, applying a bias correction to a phase image, estimating the signal fraction of fat and water at each of a plurality of voxels, and forming a fat-suppressed image, a water-suppressed image, or a combination of a fat-based image and a water-based image. The (“MRI”) fat suppression systems and methods requiring only a single image acquisition including an algorithm operable for selecting a relative phase of approximately θ=π / 2 or another suitable relative phase, employing an expectation maximization algorithm to classify the phase of the complex image, and projecting complex vectors into fat and water components to obtain fat and water images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Missile-borne SAR forward-squint imaging method based on GPU
InactiveCN104459693ALow costReduced imaging timeSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionZero paddingTime domain
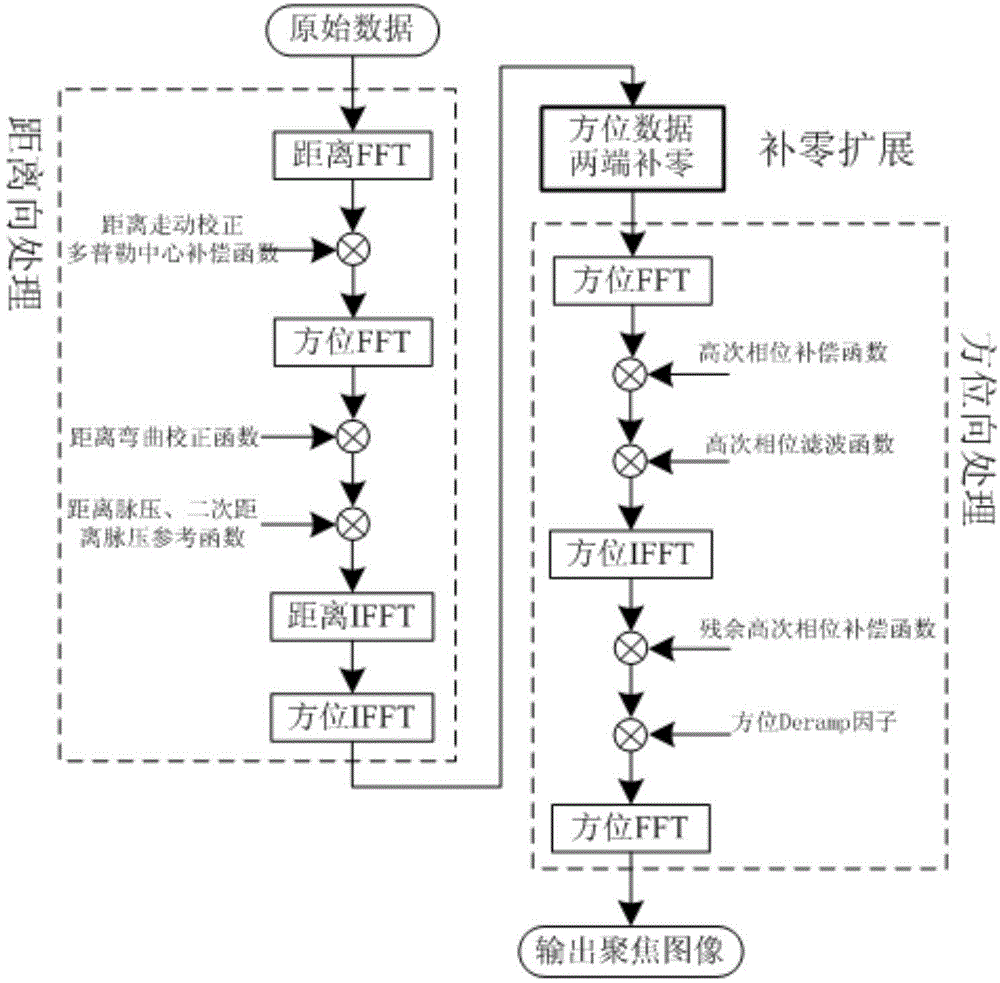
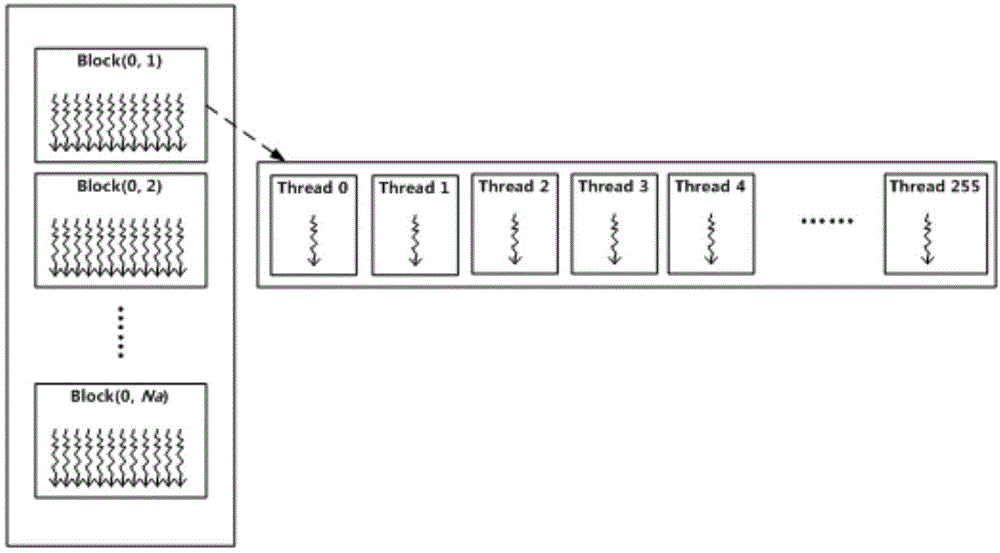
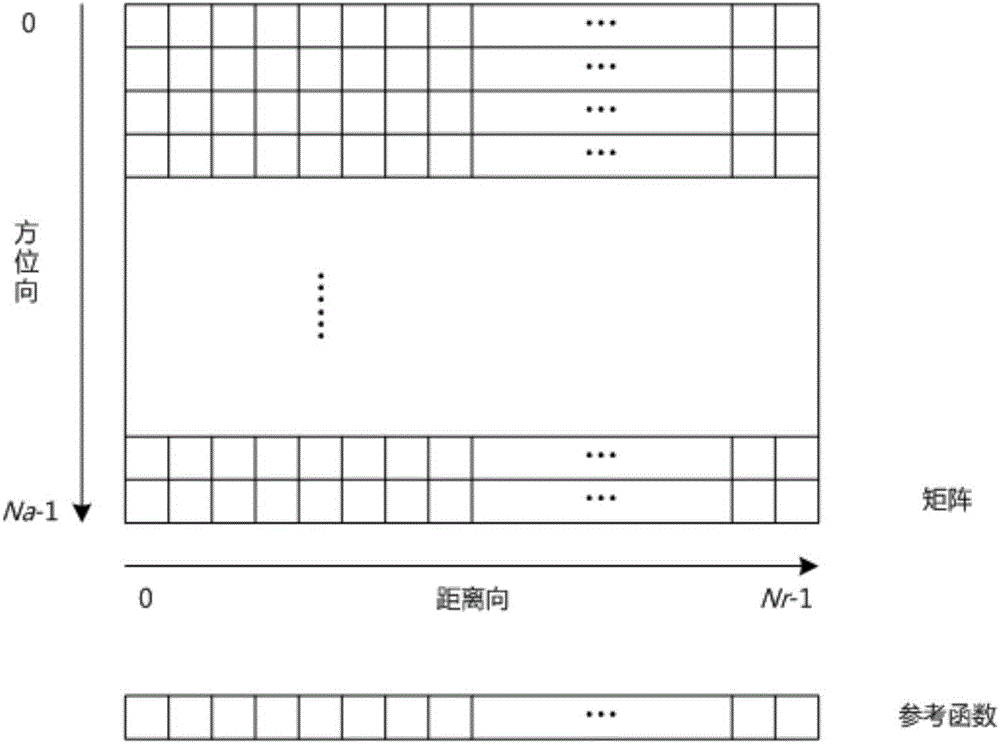
The invention belongs to the technical field of missile-borne SAR imaging, and particularly relates to a missile-borne SAR forward-squint imaging method based on a GPU. The method comprises the specific steps that the work parameter of a synthetic aperture radar is set on a GPU side, and stored in the GPU, and SAR raw echoed data are stored in the GPU in a matrix mode; on the GPU side, distance direction processing is carried out on an SAR raw echoed data matrix, and distance orientation two-dimensional time domain data are obtained; on the GPU side, zero padding expansion is carried out on a distance orientation two-dimensional time domain data matrix in the azimuth, and a distance orientation two-dimension time domain data matrix of Na'*Nr is obtained after azimuth zero padding expansion; on the GPU side, azimuth processing is sequentially carried out on the distance orientation two-dimension time domain data matrix obtained after azimuth zero padding expansion, and focused SAR image data are obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com