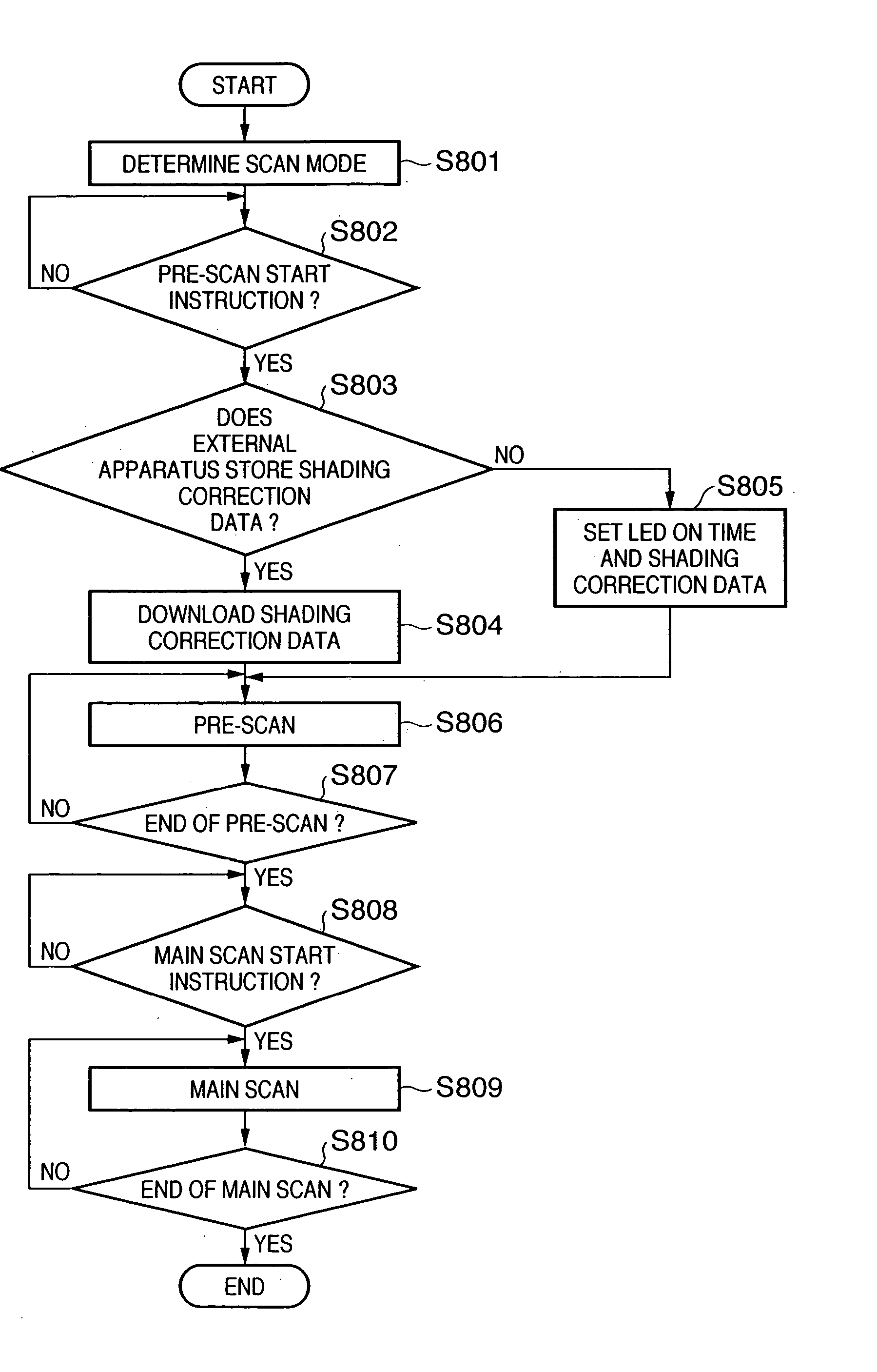
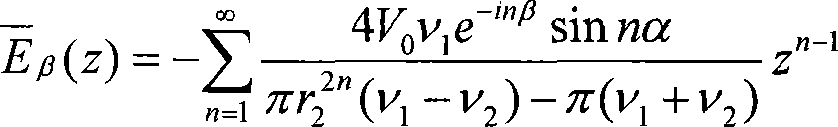Patents
Literature
184 results about "Sensitivity distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
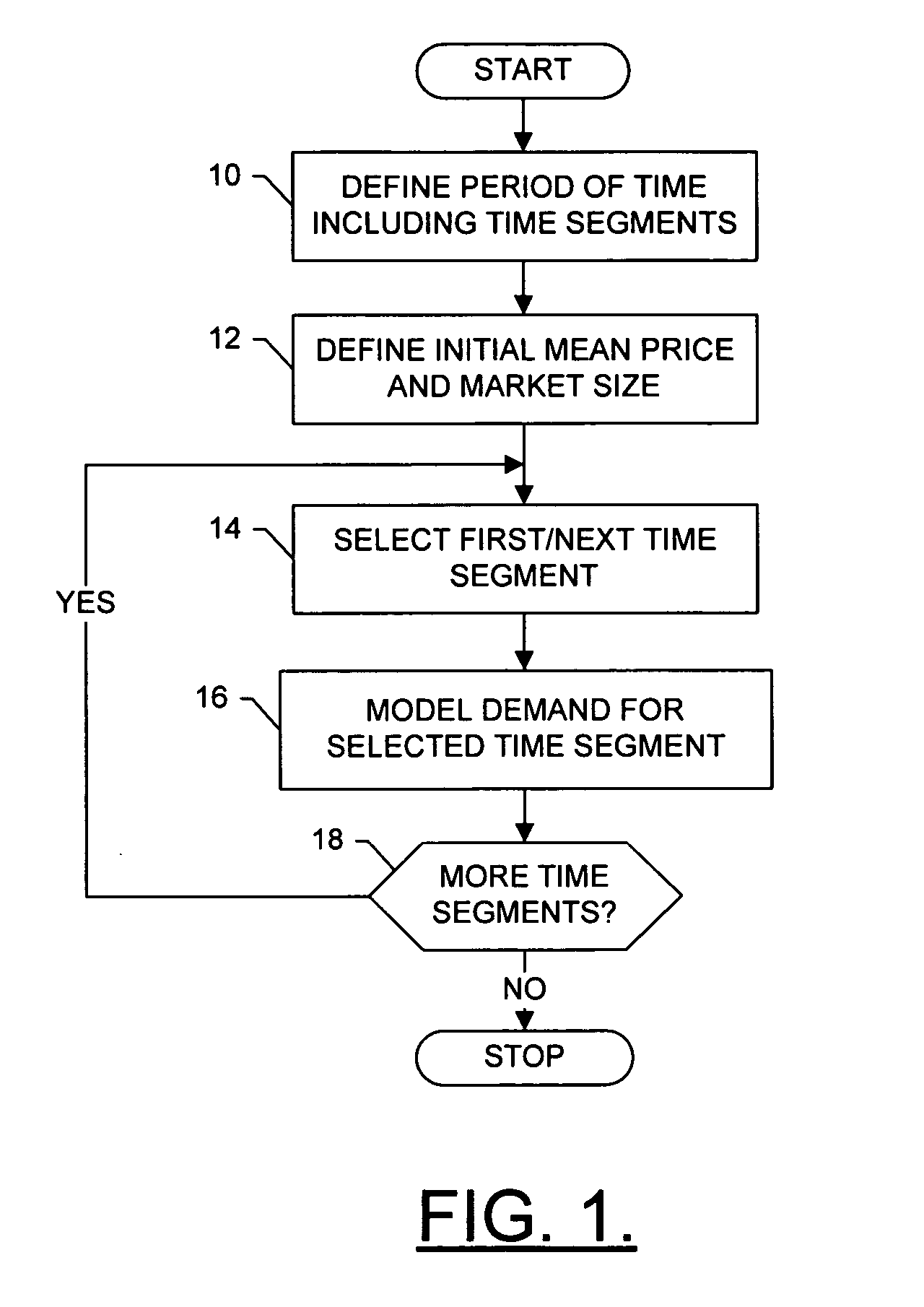
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
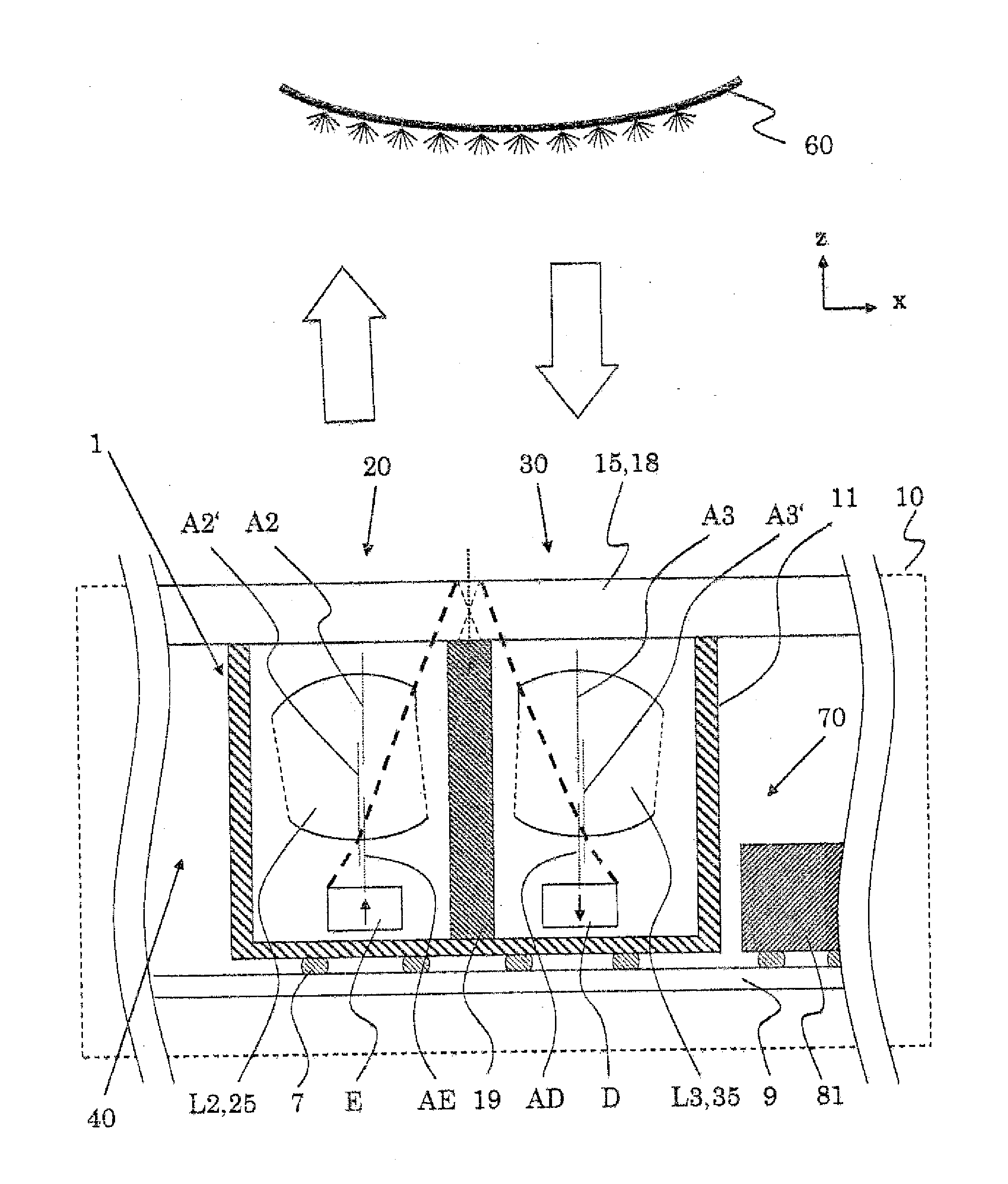
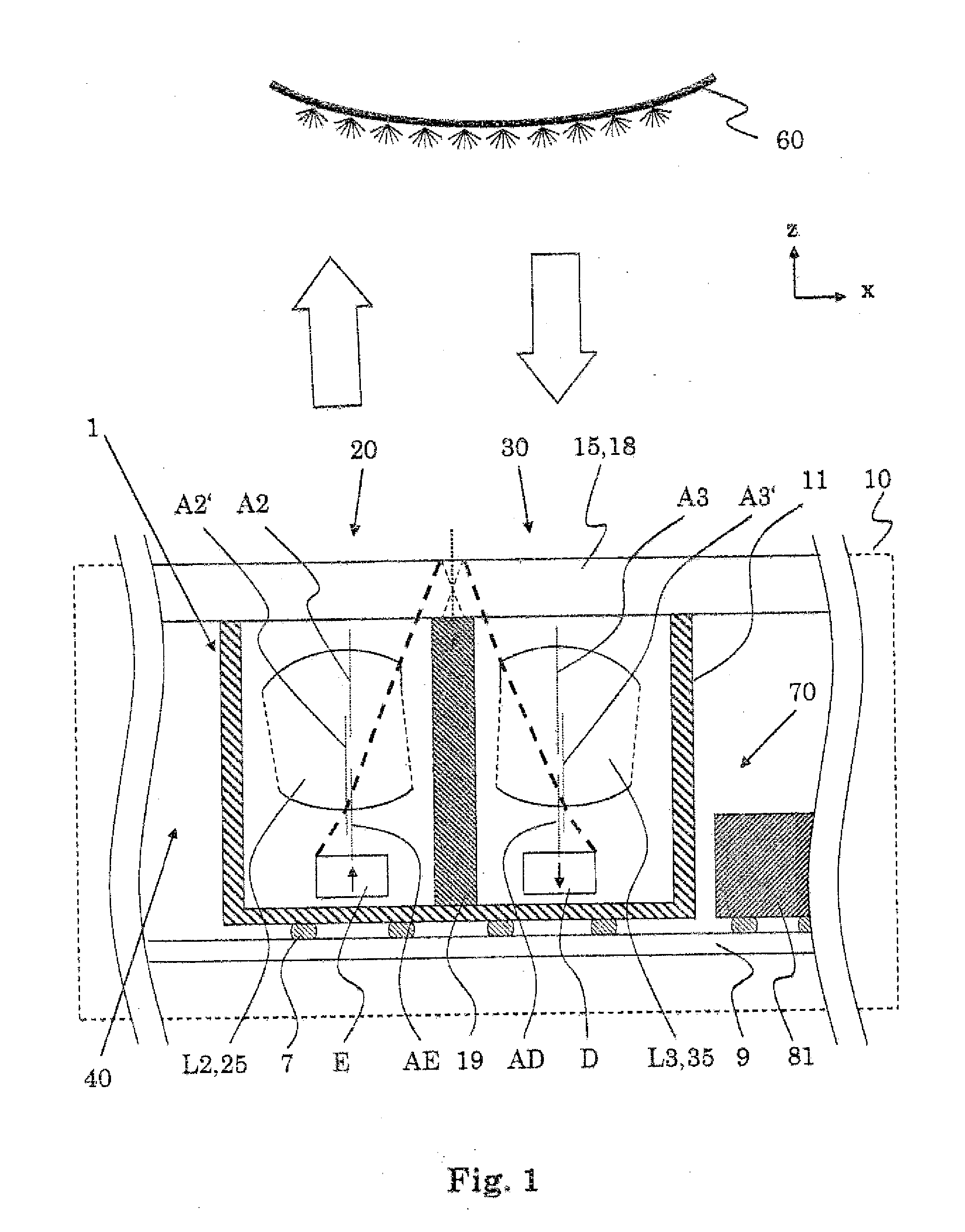
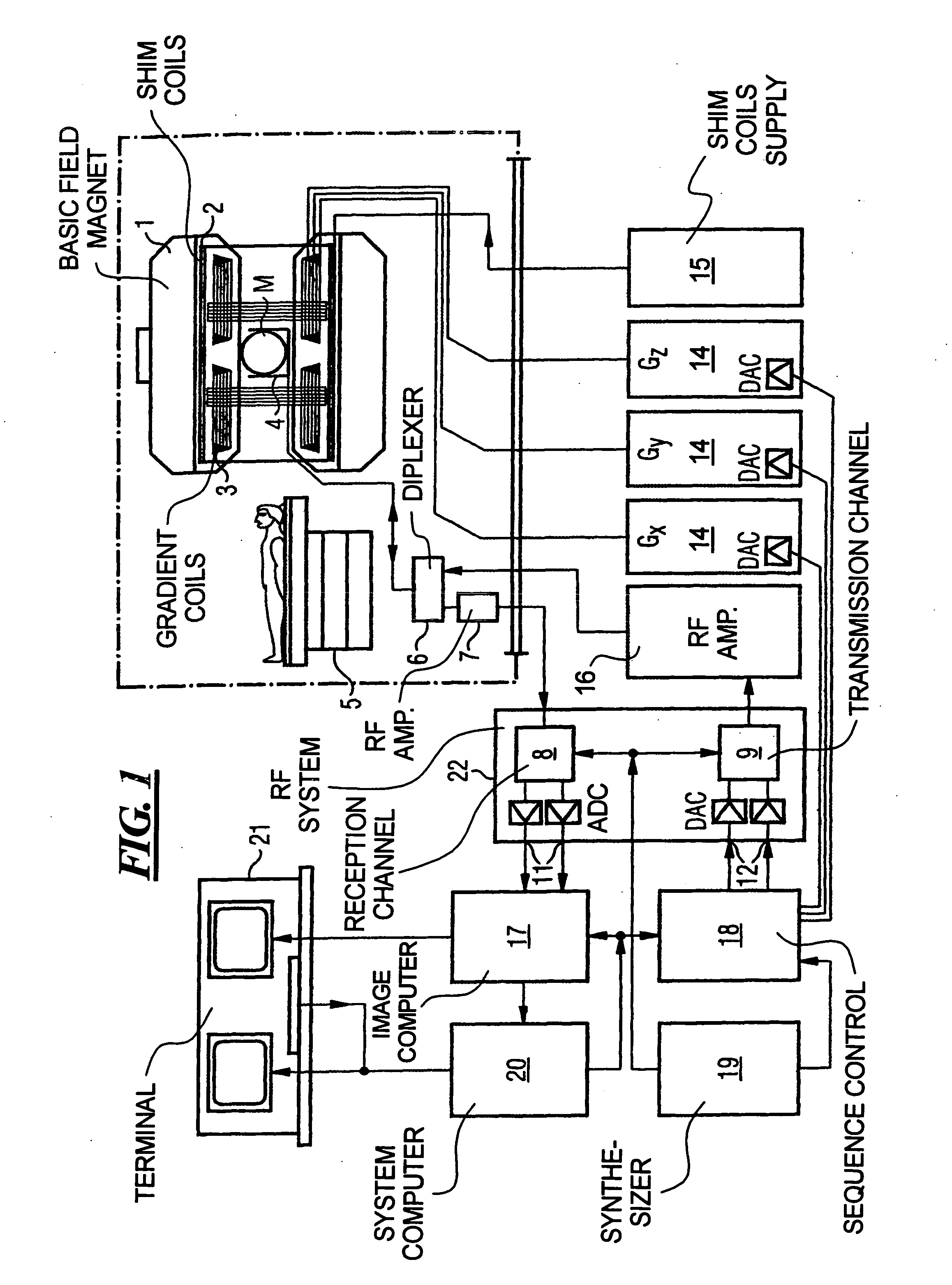
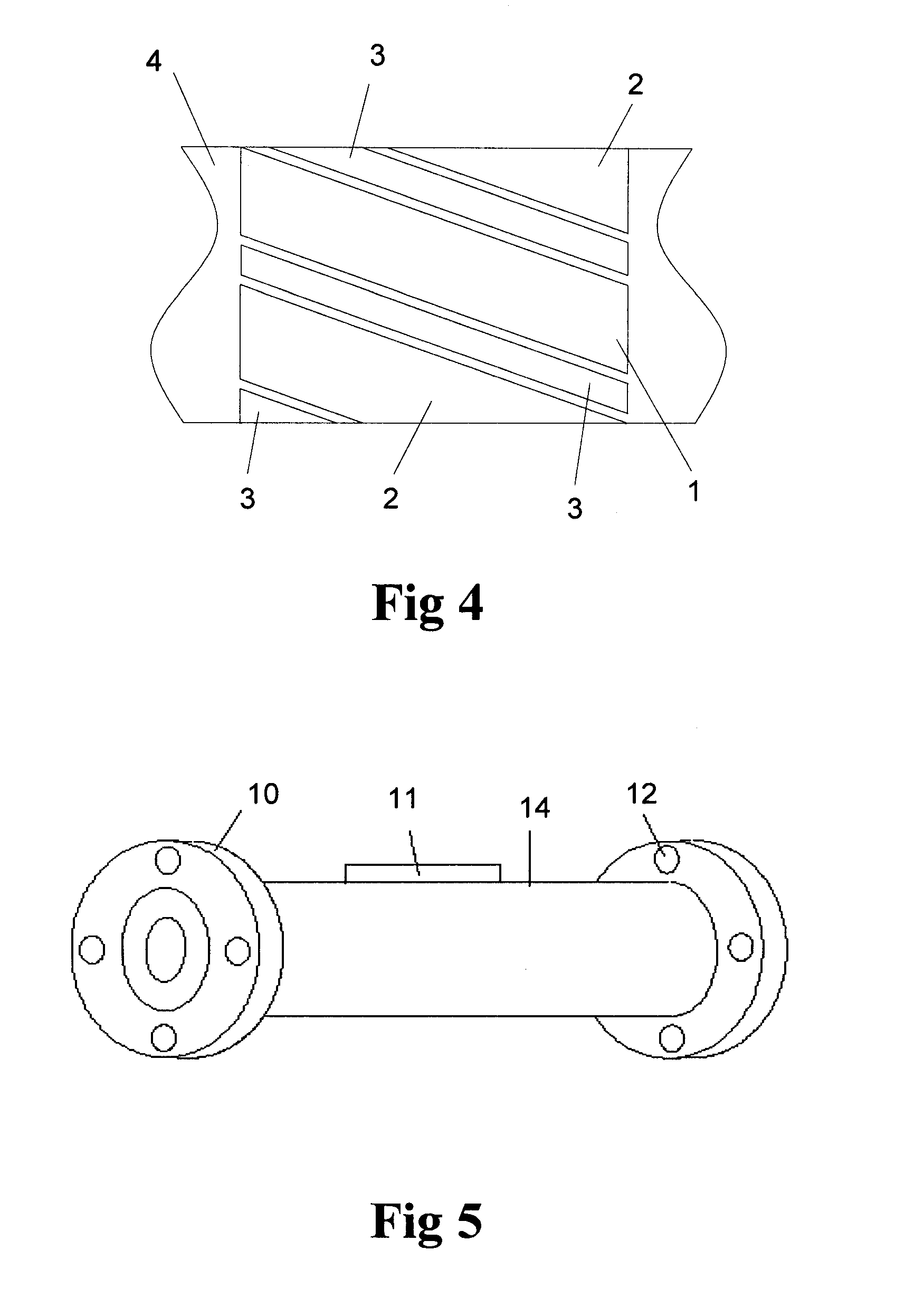
A. Sensitivity Distribution. The sensitivity distribution of an impedance measurement gives a relation between the impedance Z (and change in it) caused by a given conductivity distribution (and its change). It describes how effectively each region is contributing to the measured impedance signal.
Opto-electronic module and devices comprising the same
ActiveUS20130153772A1Safely proximityPredictable and safe operationRadiation pyrometryPhotometryEmission channelingDistribution characteristic
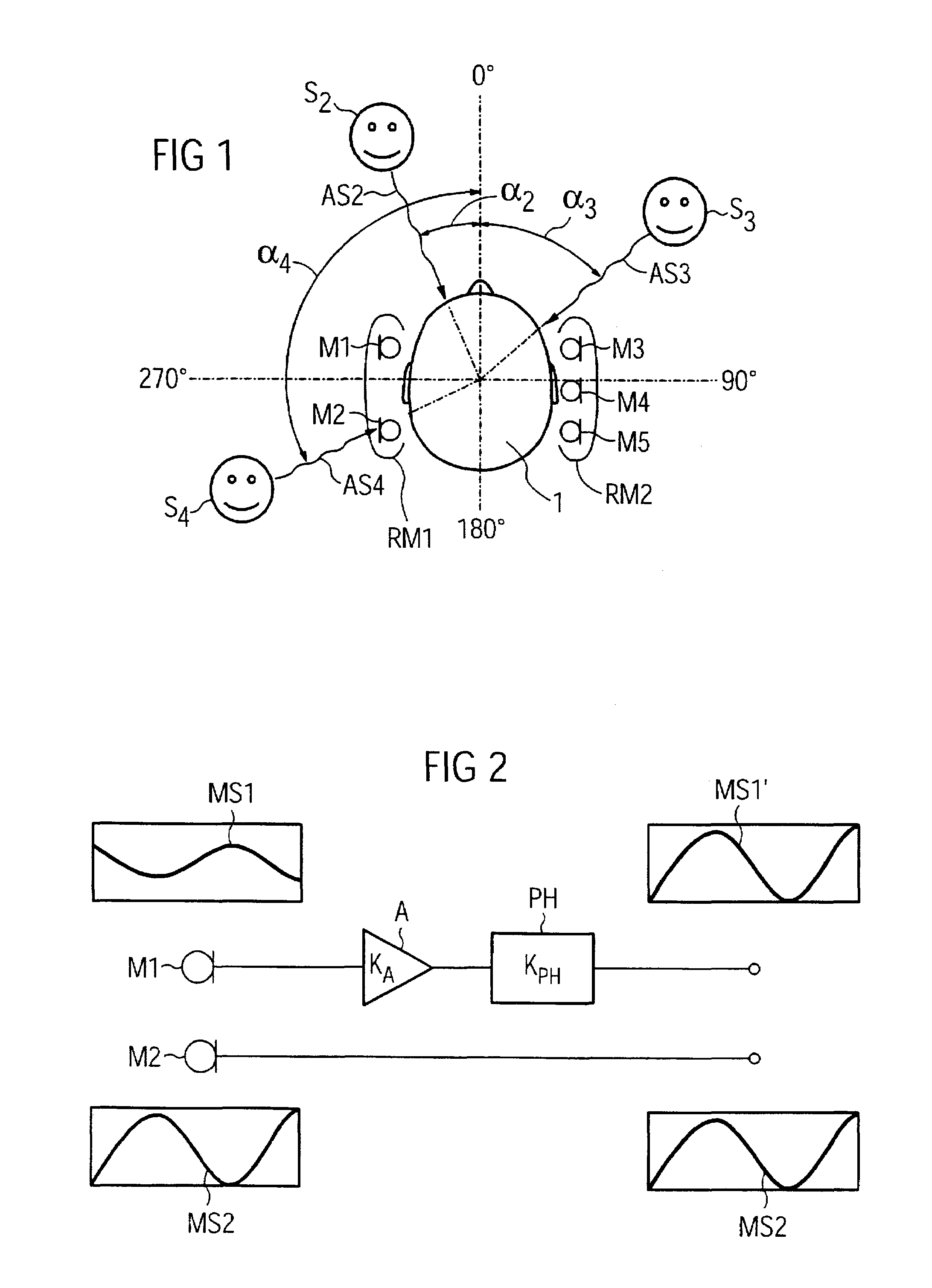
An opto-electronic module includes a detecting channel comprising a detecting member for detecting light and an emission channel comprising an emission member for emitting light generally detectable by said detecting member. Therein, a radiation distribution characteristic for an emission of light from said emission channel is non rotationally symmetric; and / or a sensitivity distribution characteristic for a detection in said detecting channel of light incident on said detection channel is non rotationally symmetric; and / or a central or main emission direction for an emission of light from said emission channel and a central or main detection direction for a detection of light incident on said detection channel are aligned not parallel to each other; and / or at least a first one of the channels comprises one or more passive optical components.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
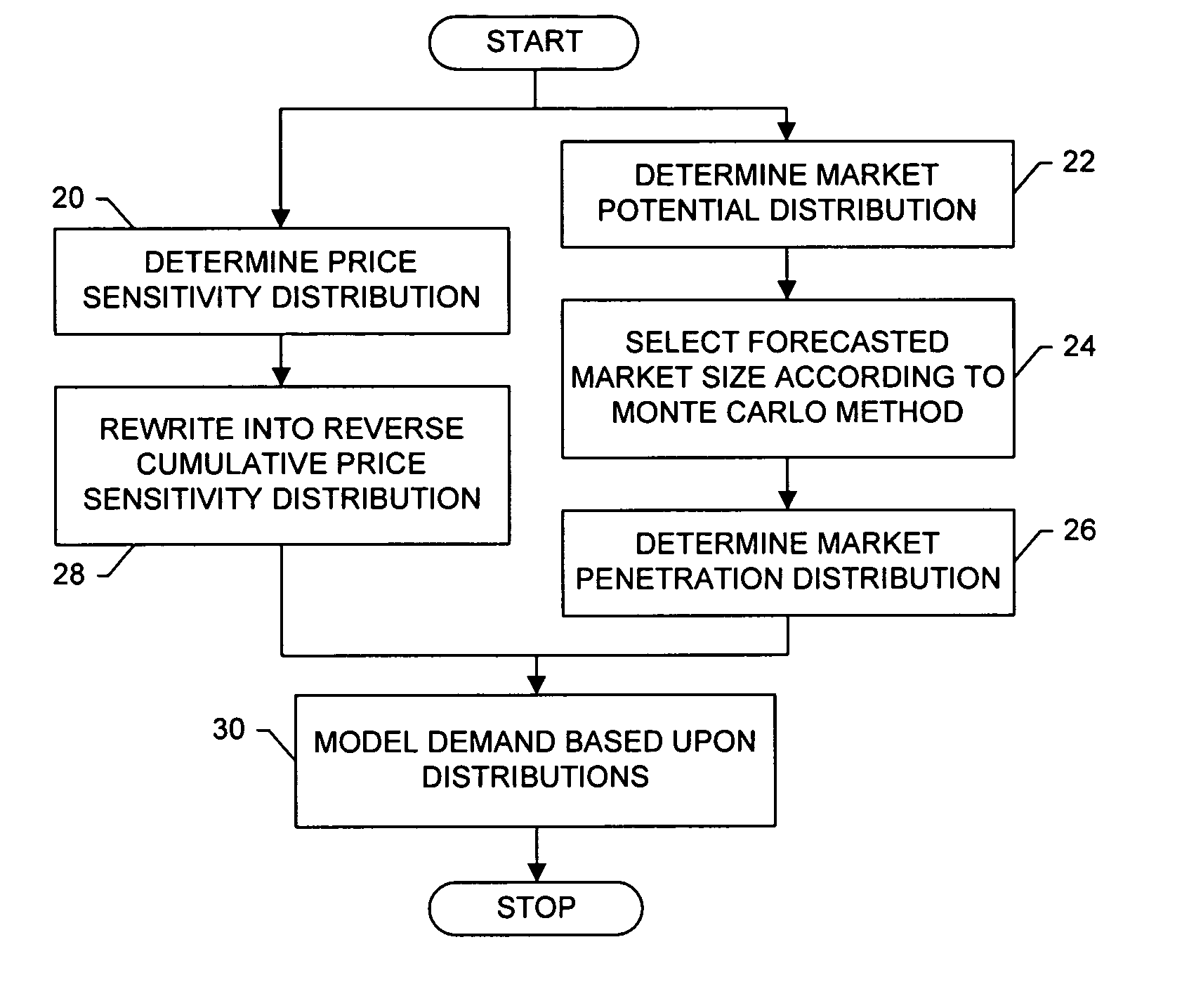
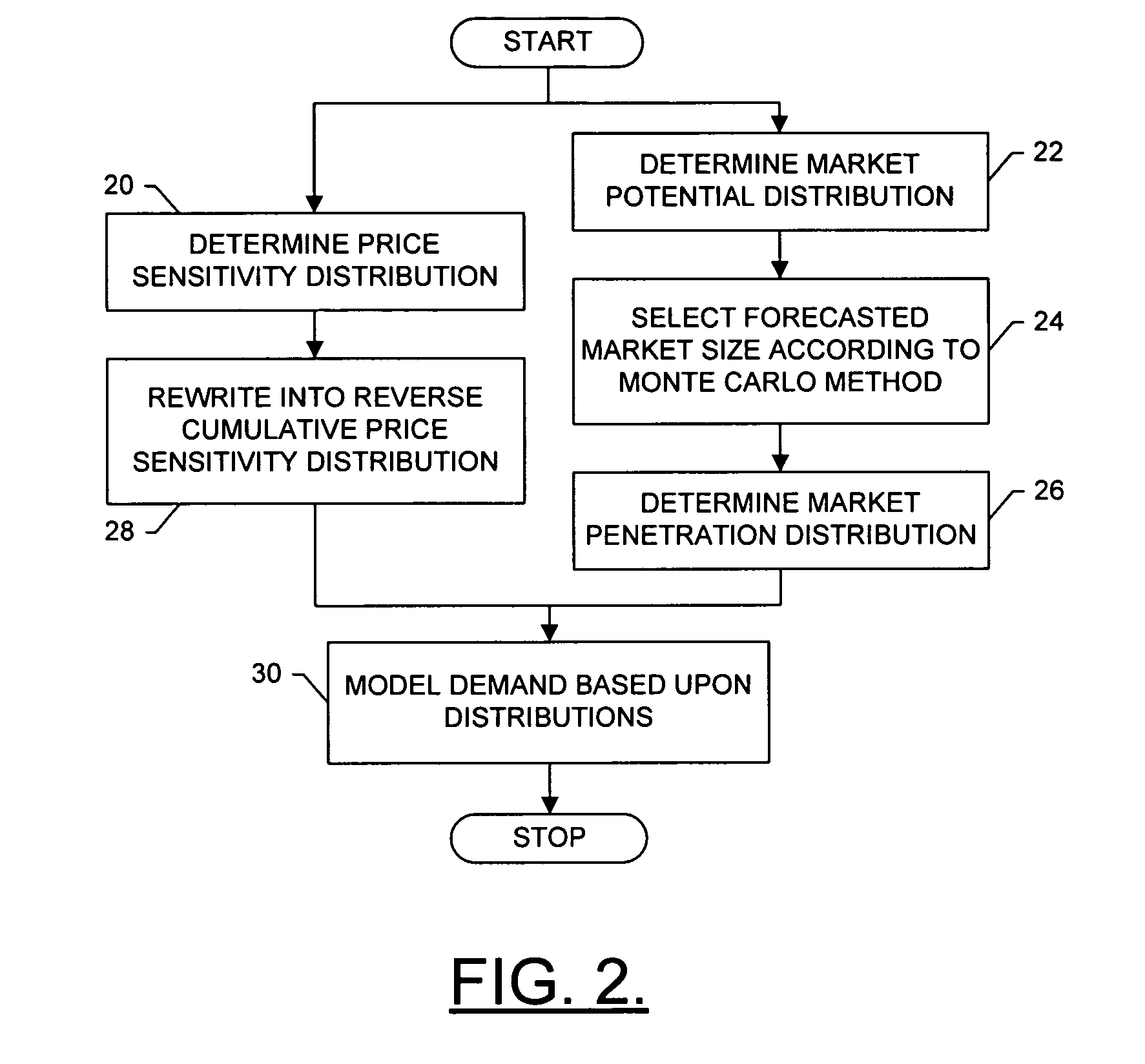
Systems, methods and computer program products for modeling demand, supply and associated profitability of a good in an aggregate market
InactiveUS20050273415A1Easy to understandIncrease variabilityFinanceResourcesRequirements modelEngineering
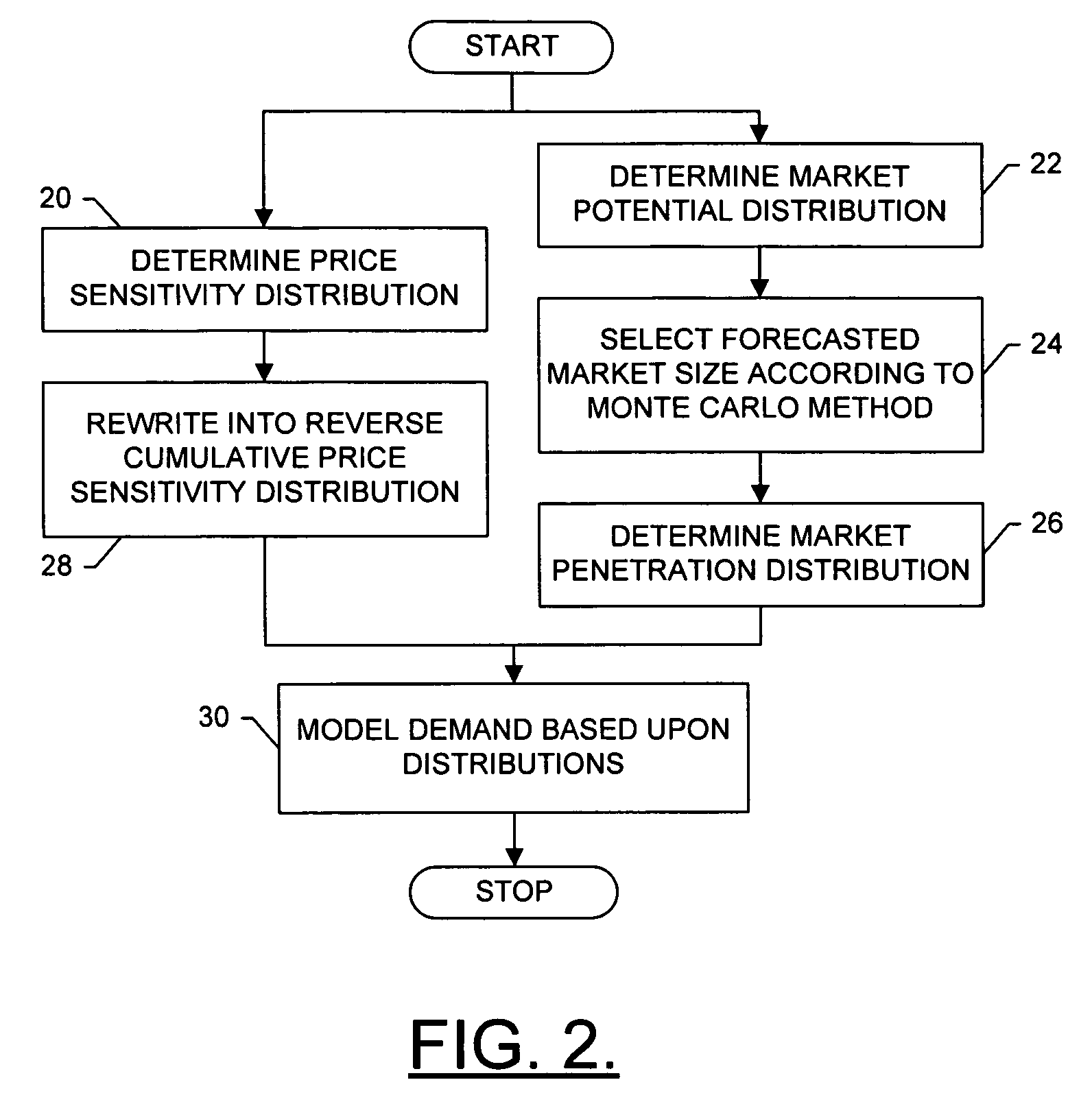
A method is provided that includes defining a plurality of independent component markets for a good. In accordance with the method, each component market can be defined a respective price sensitivity distribution of a unit purchase of the good, as well as a market potential distribution of a number of units of the good. The demand and / or supply in the aggregate market can thus then be modeled based upon the price sensitivity distributions and market potential distributions of the component markets. The method can further include modeling cost and / or profitability of the good in an aggregate market. Profitability can be modeled based upon the demand model and the cost model for the aggregate market.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
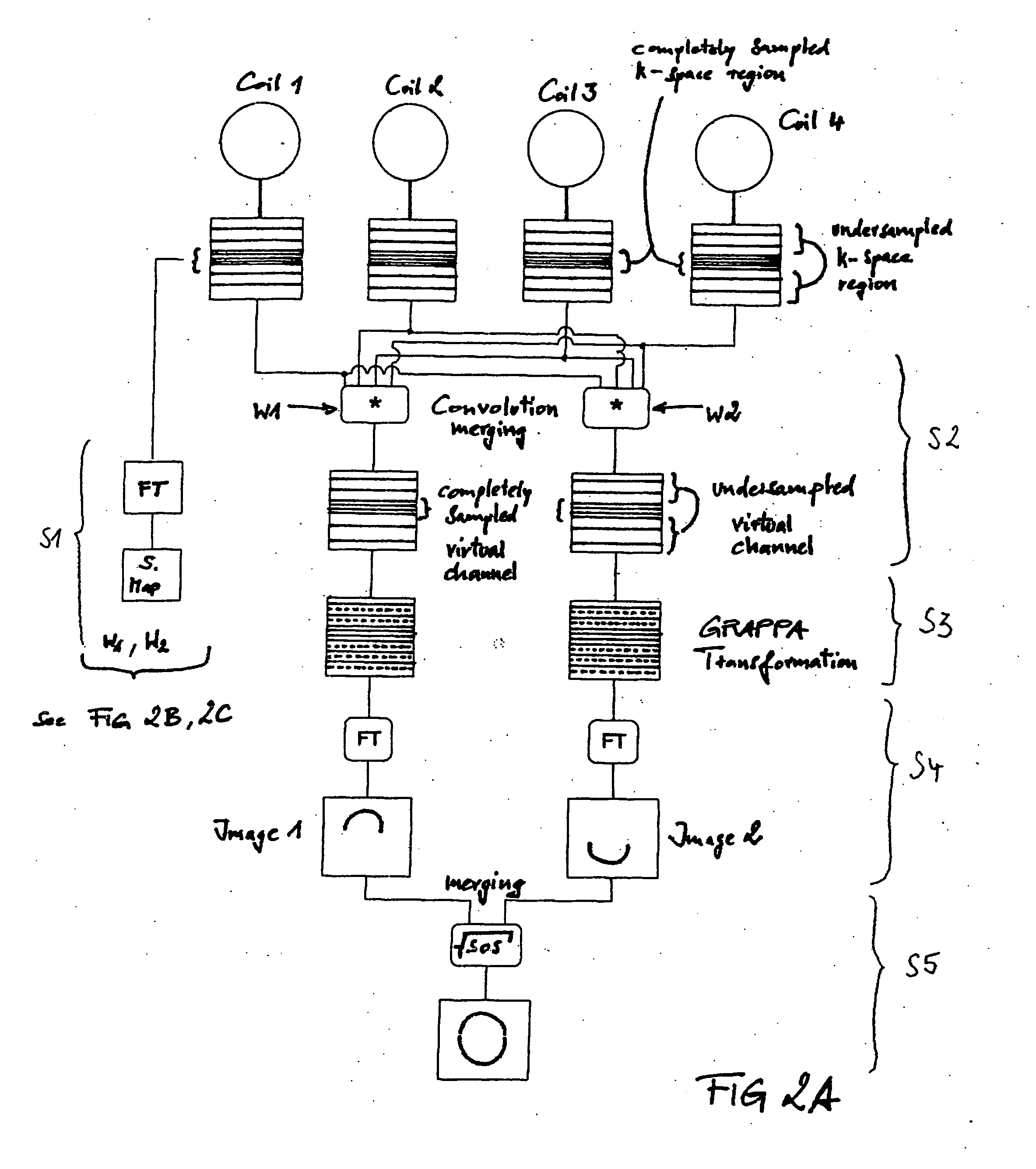
Parallel collection image reconstruction method and device
InactiveCN101308202AImprove SNRMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
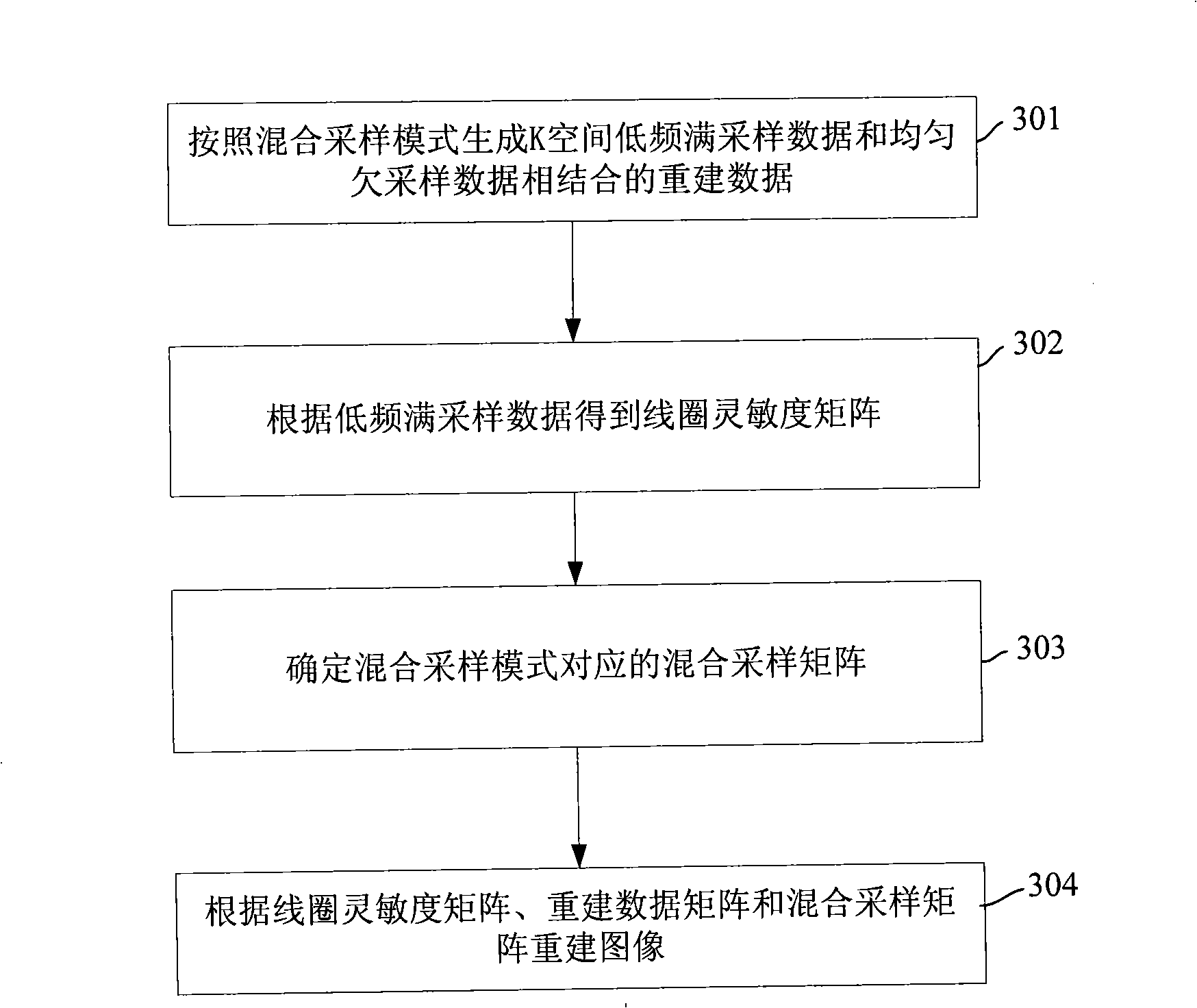
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing a parallel-acquired image, comprising: generating reconstruction data by combining uniformly under-sampled data and low-frequency fully-sampled data in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) K-space according to a hybrid sampling mode; calculating the sensitivity distribution of a coil according to the low-frequency fully-sampled data; and reconstructing an image according to the reconstruction data, the sensitivity distribution of the coil and the hybrid sampling mode. The invention also discloses an apparatus for reconstructing the parallel-acquired image. The method and the apparatus are adopted to generate reconstruction data by combining uniformly under-sampled data and low-frequency fully-sampled data in K-space according to the hybrid sampling mode and take the hybrid sampling mode into account during the image reconstruction, and the signal to noise ratio of the reconstructed image is effectively improved by using the reconstruction data combined with the low-frequency fully-sampled data in reconstructing the image since the low-frequency fully-sampled data contains more useful information.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Data correction apparatus, data correction method, magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20070198203A1Data unificationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementResonanceX-ray
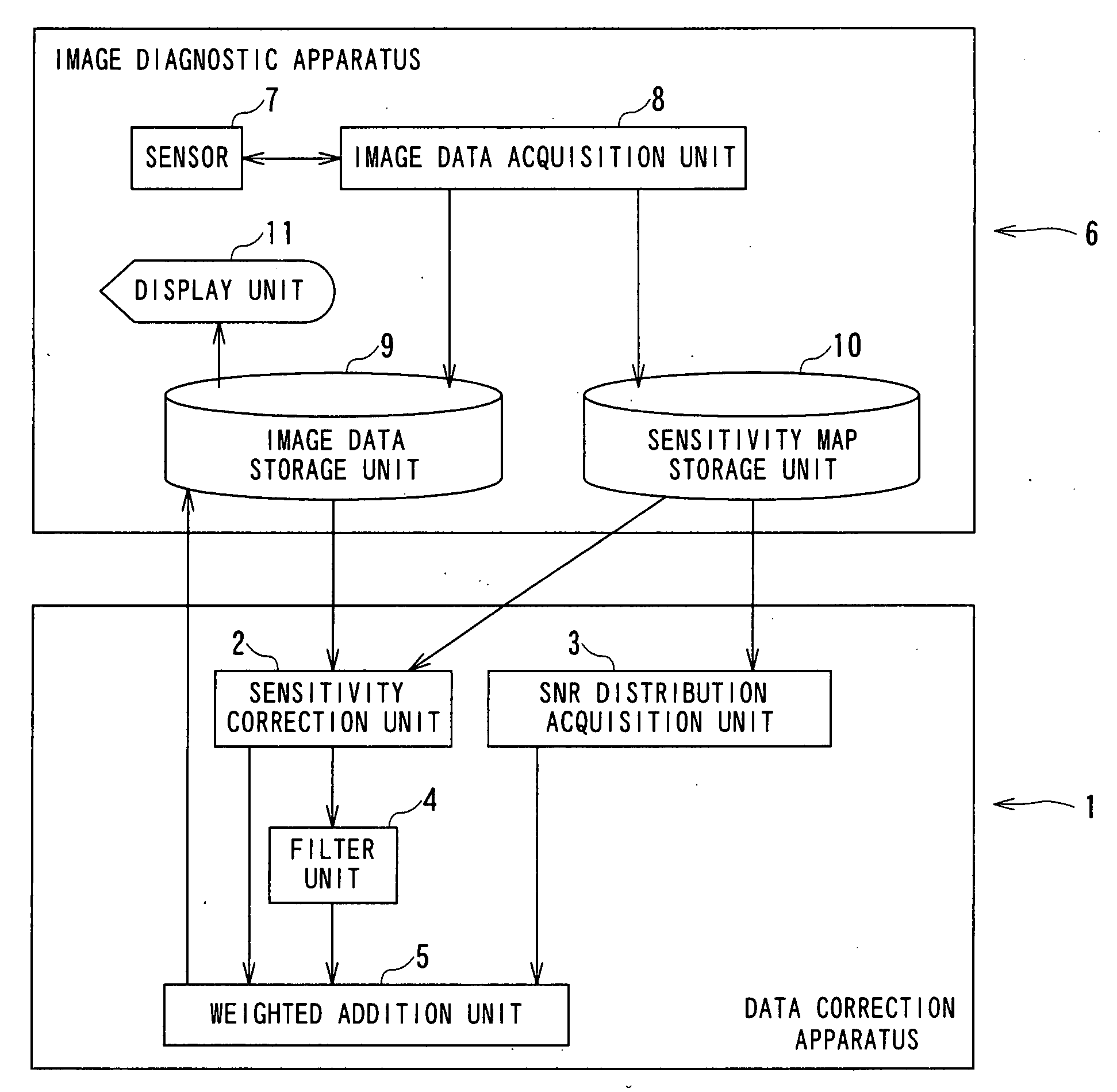
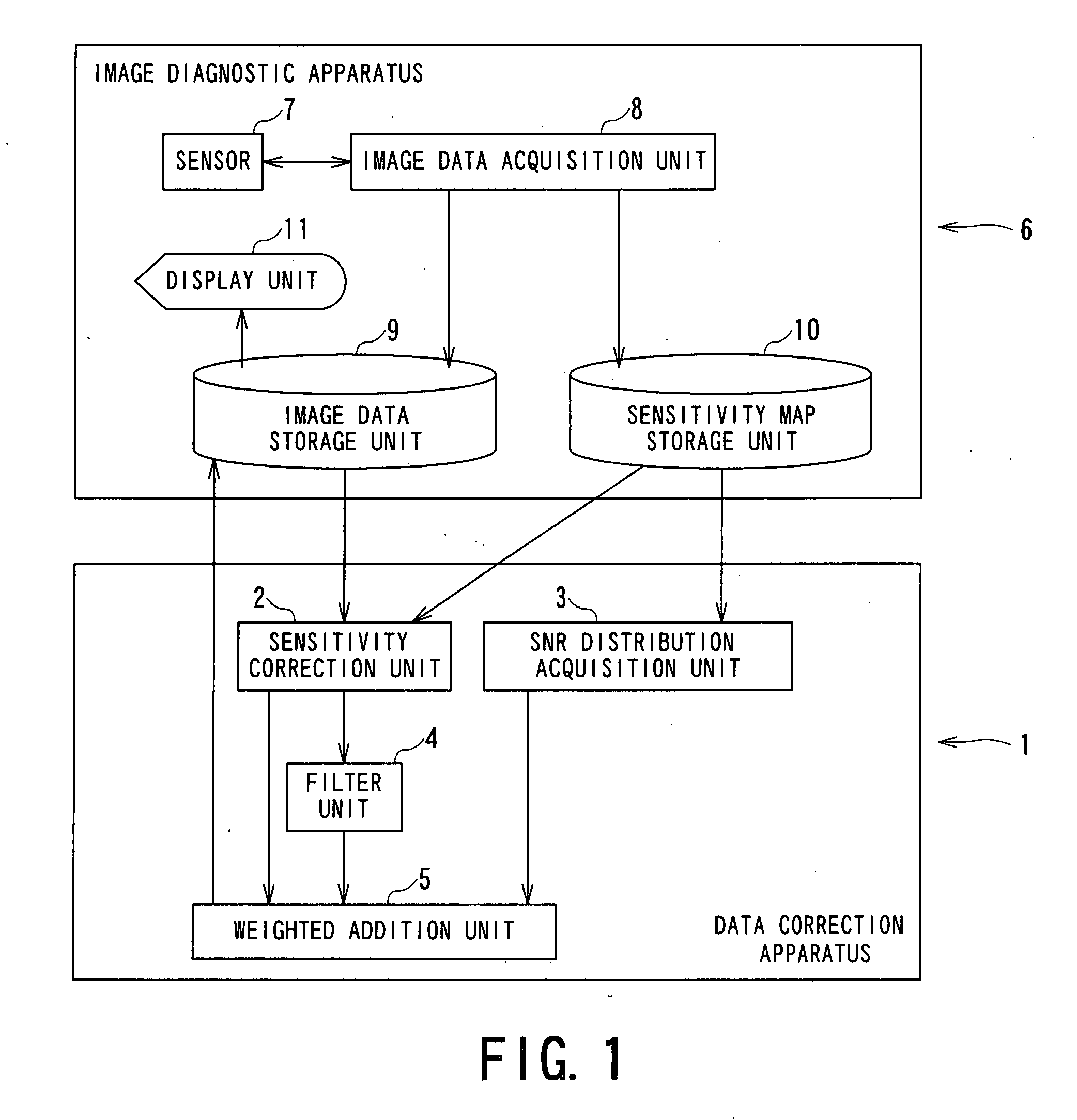
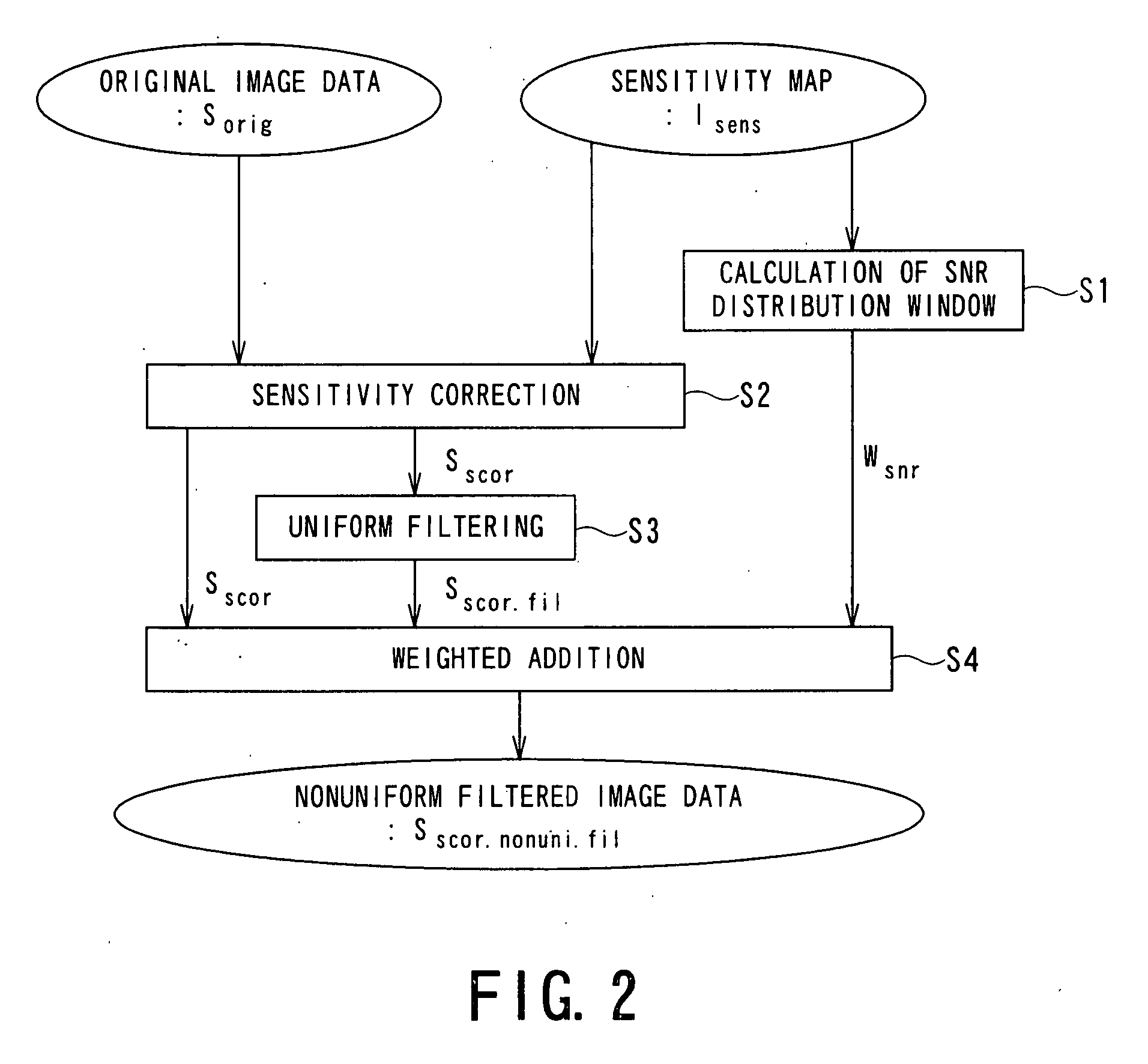
A data correction apparatus includes a sensitivity correction unit and an SNR distribution correcting unit. The sensitivity correction unit produces first processed data by performing sensitivity correction to first objective data obtained based on correction objective data using ununiform sensitivity distribution of a sensor for acquiring the correction objective data. The SNR distribution correcting unit produces pieces of component data each subjected to corresponding weighting depending on an SNR distribution and corresponding filtering having a mutually different intensity using second objective data obtained based on the correction objective data to produce second processed data by compounding the pieces of the component data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Parallel MR imaging using high-precision coil sensitivity map
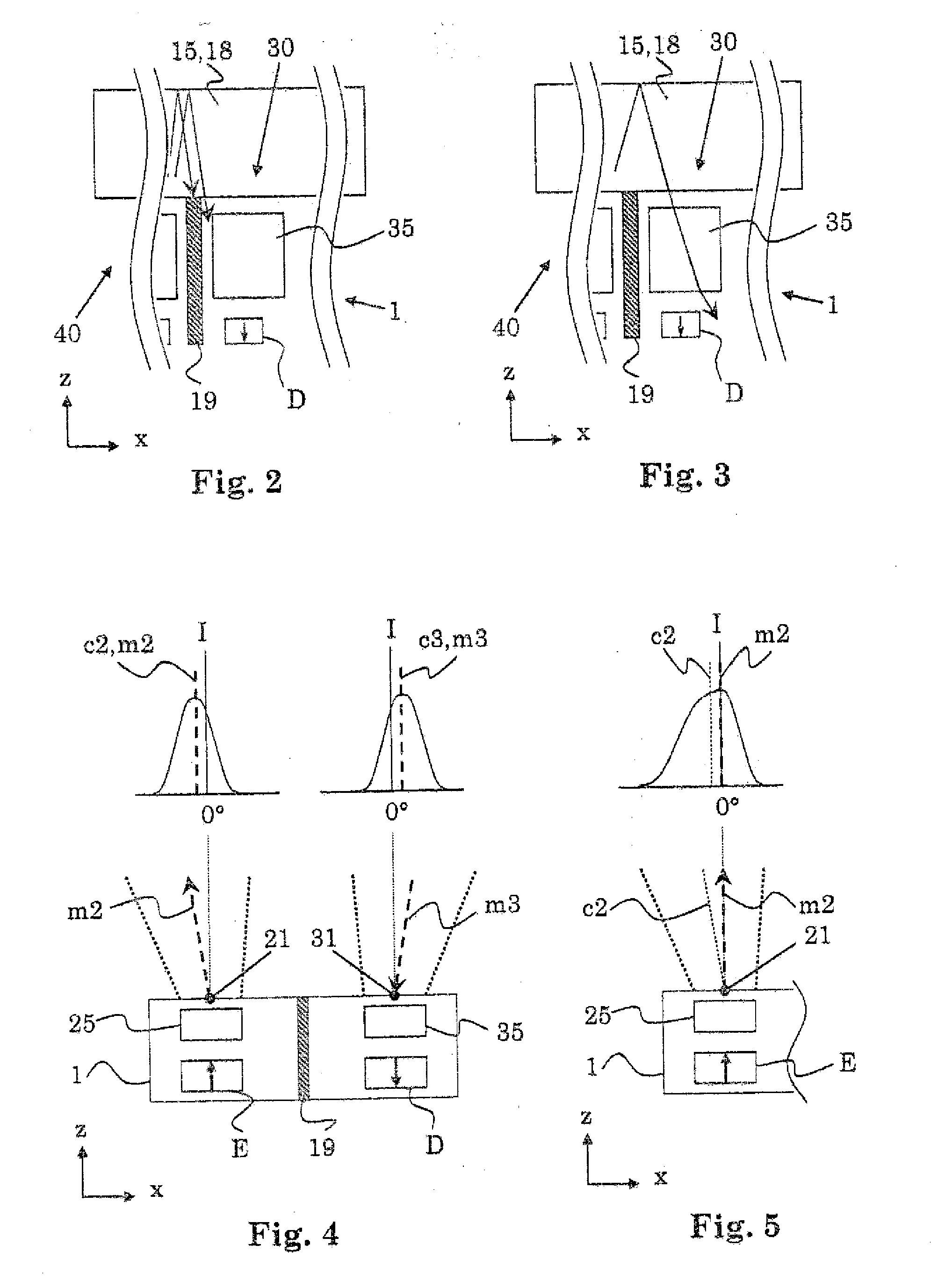
InactiveUS6949928B2Improve accuracyHigh precision estimationDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRapid imagingSensitivity distribution
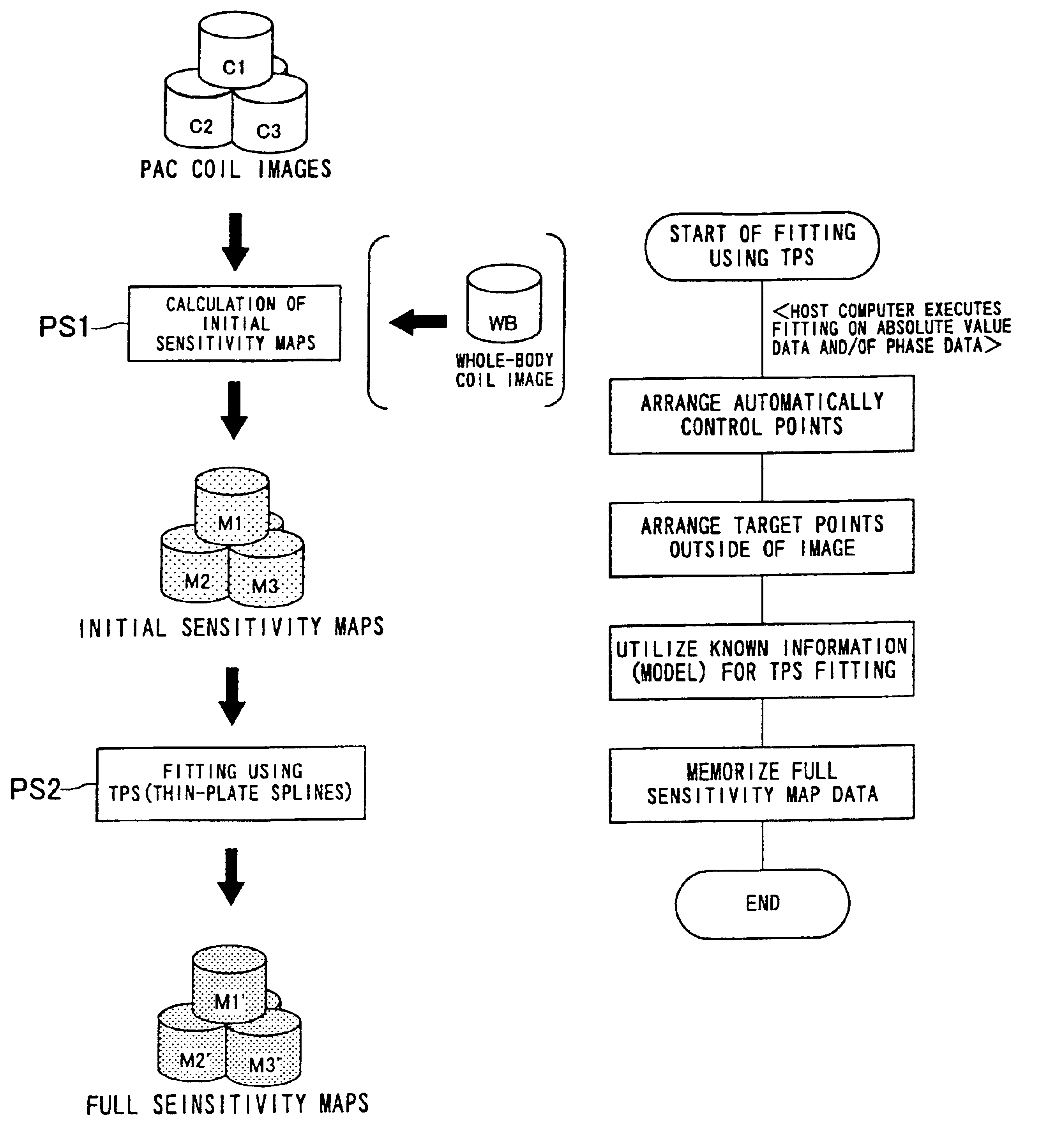
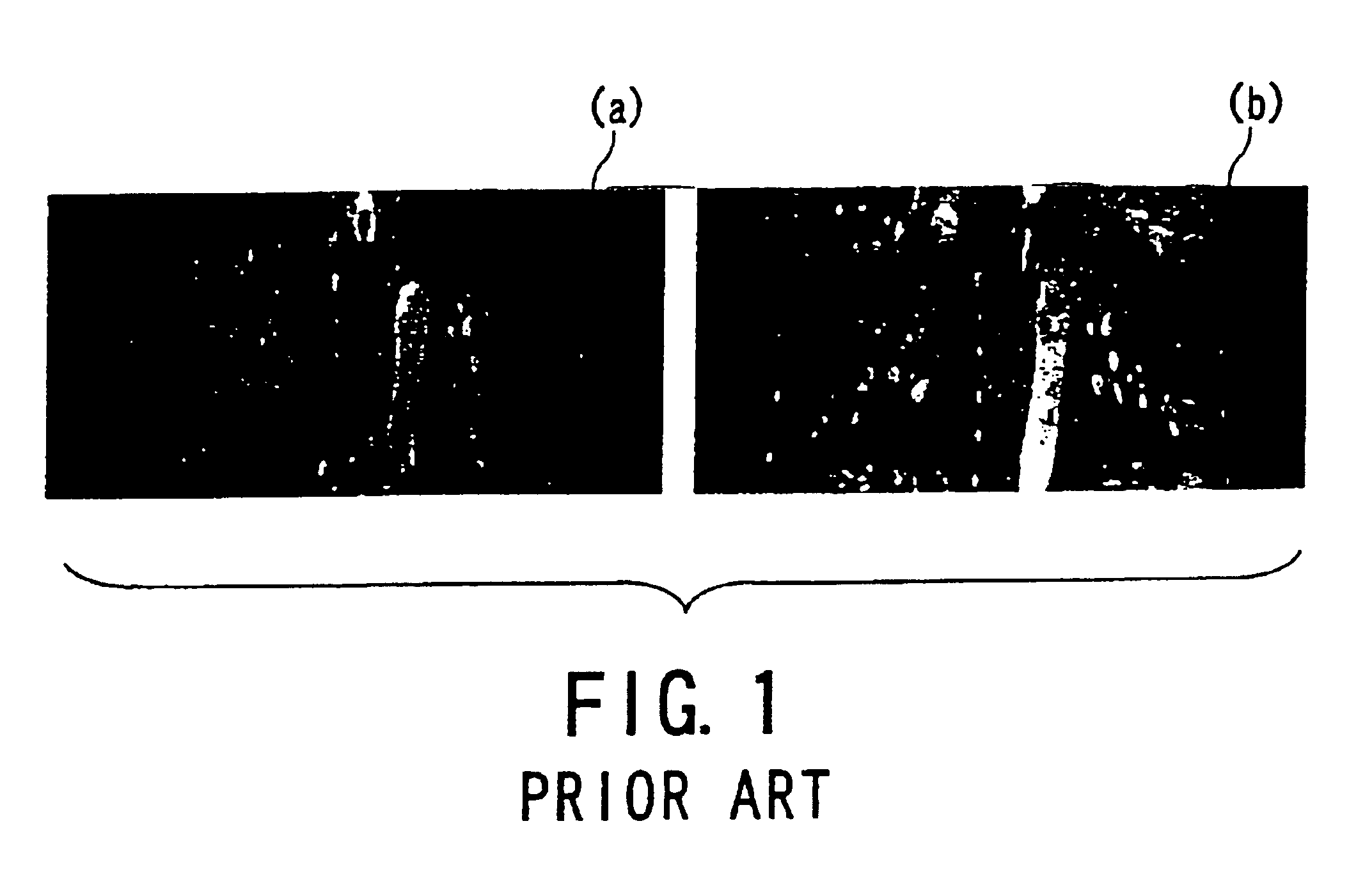
A sensitivity distribution is estimated for a multicoil used in multicoil fast imaging. Initial sensitivity maps M1 to M3 are produced respectively from images C1 to C3 acquired from the plurality of RF coils in the multicoil. By fitting TPS (thin-plate splines) to the initial sensitivity maps M1 to M3 used as target data, sensitivity maps M1′ to M3′ for unfolding are estimated. In fitting the TPS, functions are activated, such as automatic arrangement of control points, addition of target points to the outside of an image, use of a known model, and fitting to at least either absolute value components of MR data or phase components of the MR data. Thus, even if only coarse echo data is acquired from the region to be imaged, a sensitivity map of each element coil of the multicoil is estimated with high precision.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Non-contact type electric impedance sensor and image rebuilding method based on the sensor
InactiveCN101241094AQuick responseLow costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRapid imagingBreakdown strength
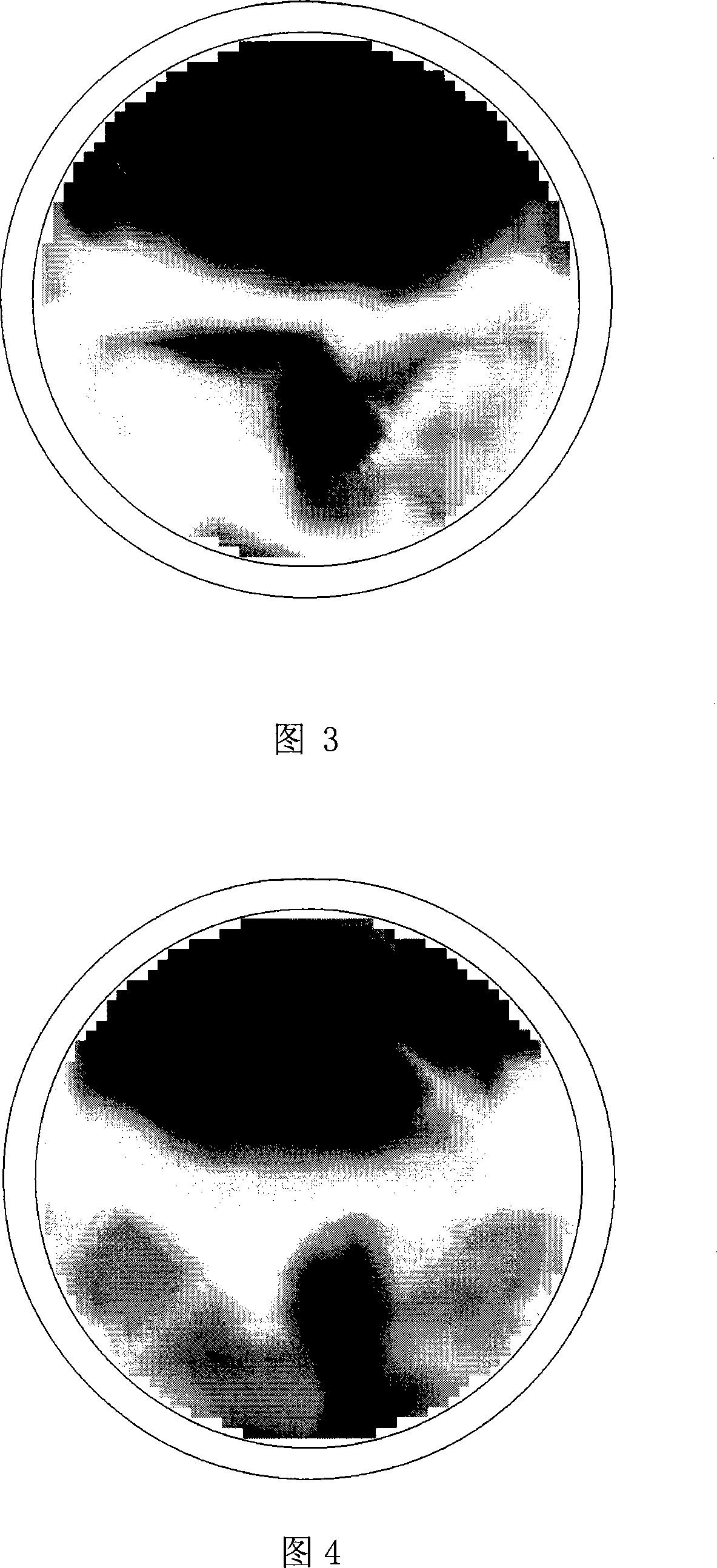
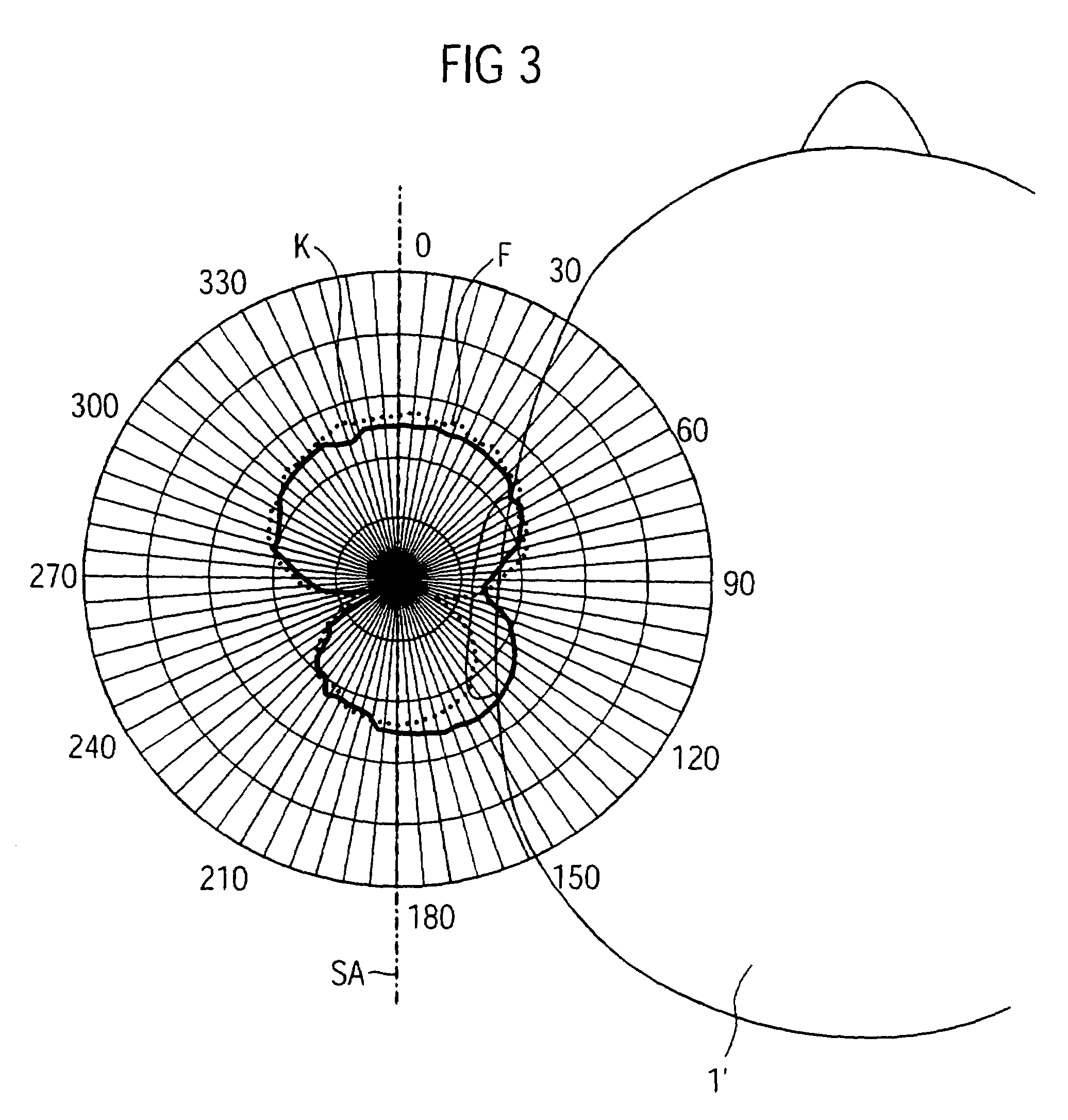
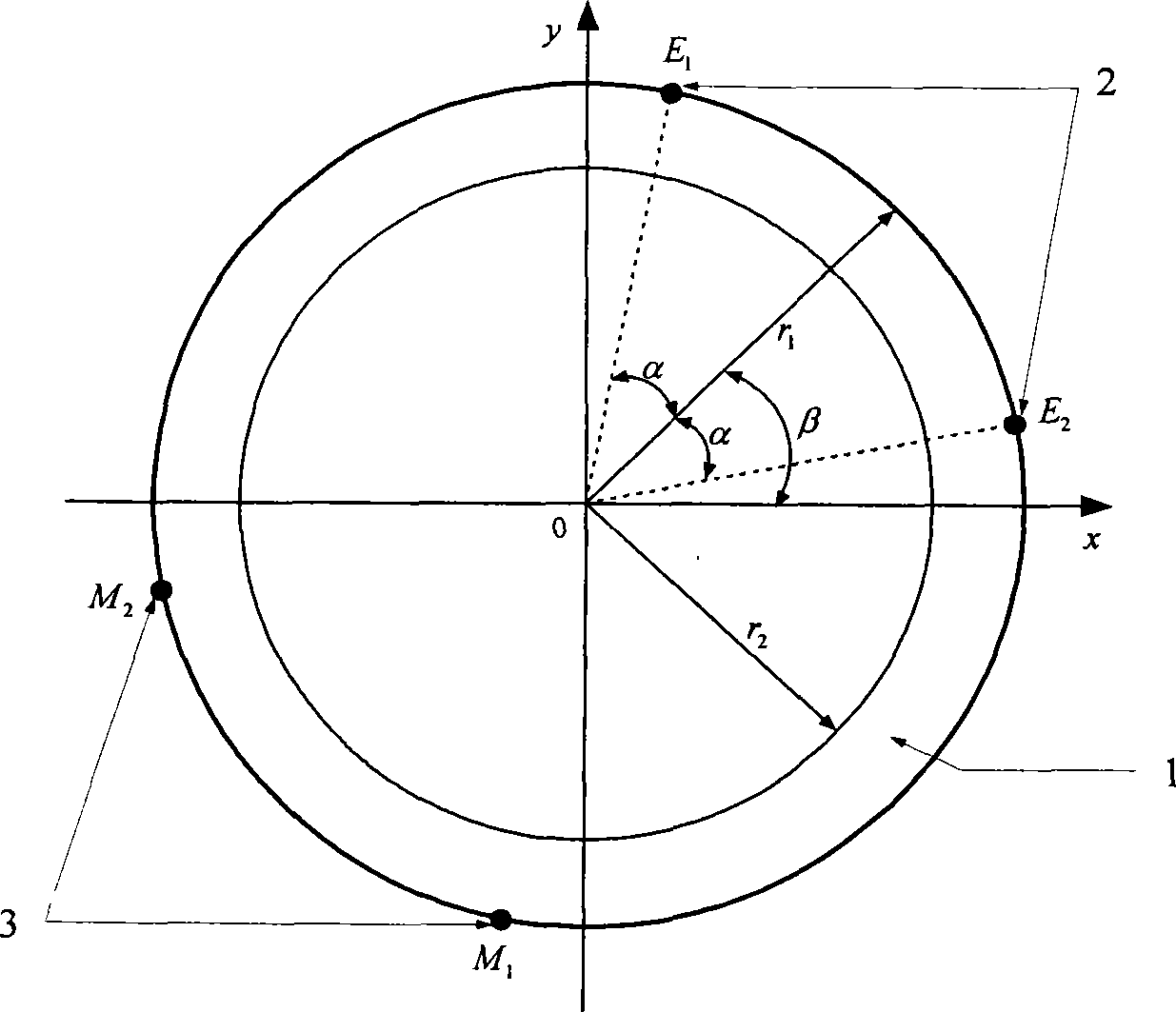
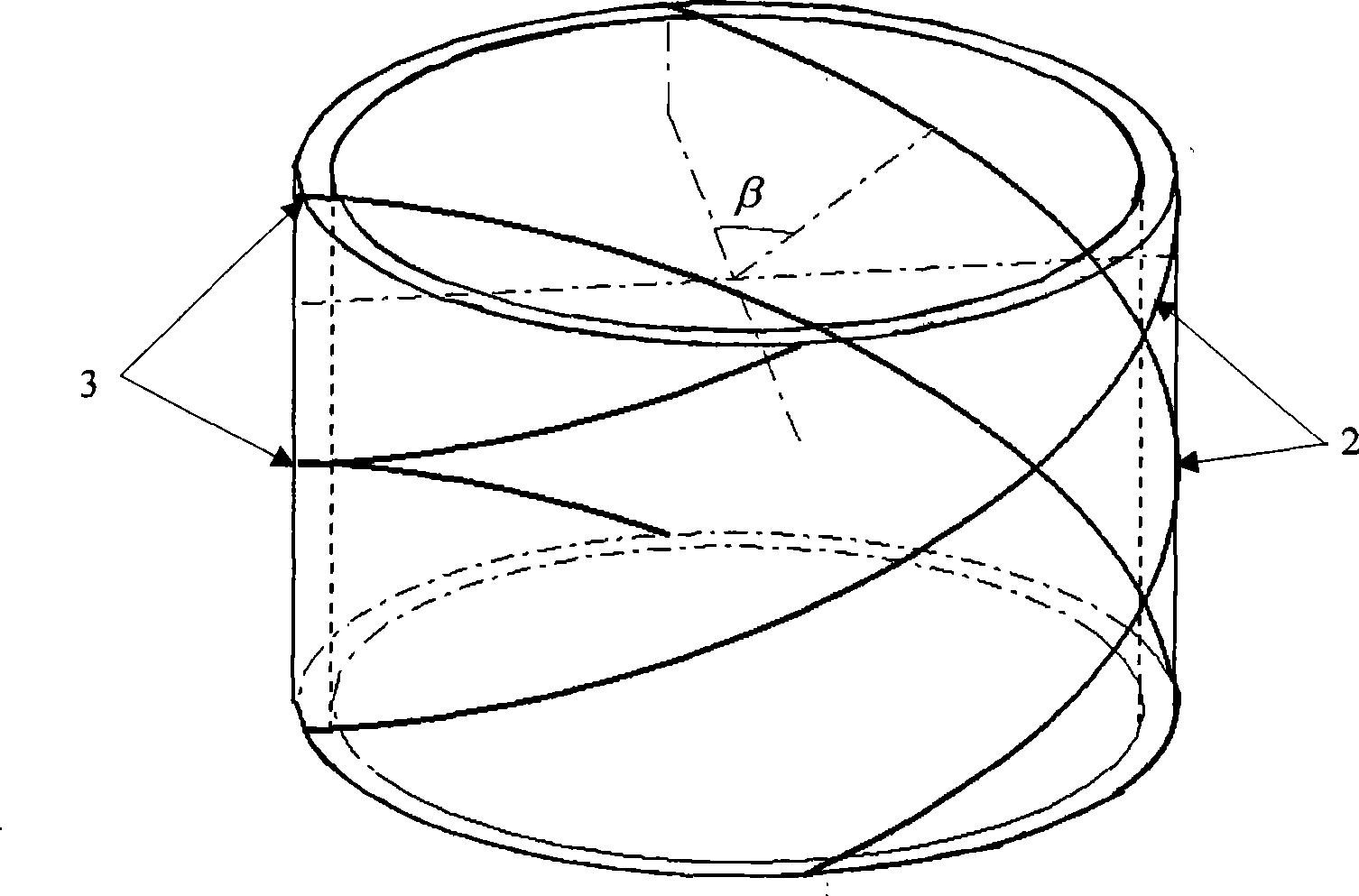
The present invention provides a non-contact impedance sensor which is mounted on measuring region, the radial section structure of the sensor comprises of four layers, metal tube layer, insulation material layer, electrode array layer and insulation ring layer from outside to inside in turn. At least two electrodes are distributed in one circle on the insulation ring layer whose thickness is less than 1% of external diameter, and electric field intensity between electrode array and metal tube layer is less than breakdown strength of insulation layer. The electrode array is separated with measuring region by insulation ring layer. Two image reconstruction algorithms to realize electrical impedance tomography based on the said sensor are also provided. The present invention provides analytical medel, corresponding sensitivity distribution expression and two rapid imaging methods, the sensor can measuring synchronous same-positional dual-mode impedance, advance mutual fusion of real parts and imaginary part information of impedance distribution, predigest the design and implement of software and hardware of dual-mode measuring system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and apparatus for image mosaicing
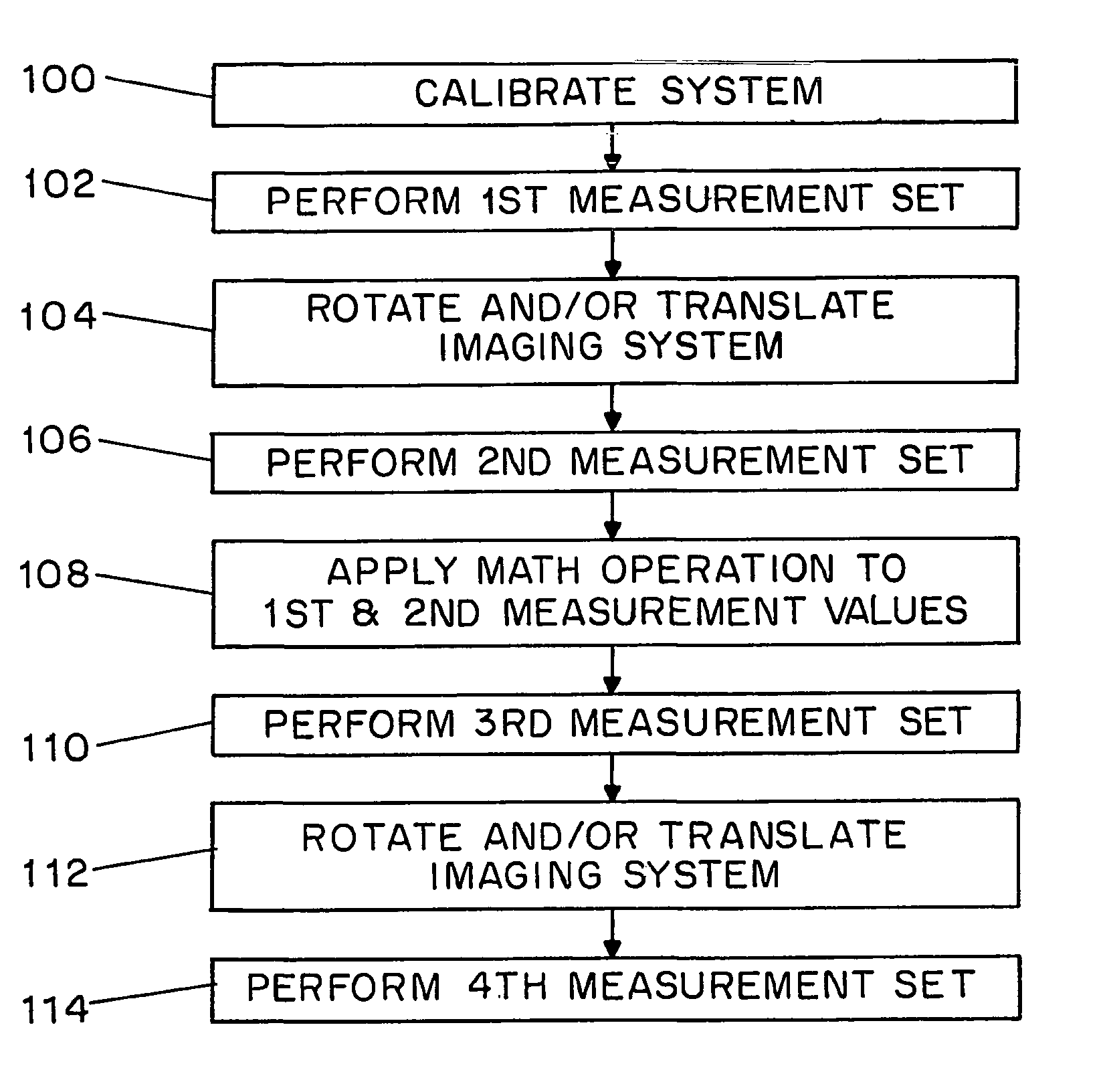
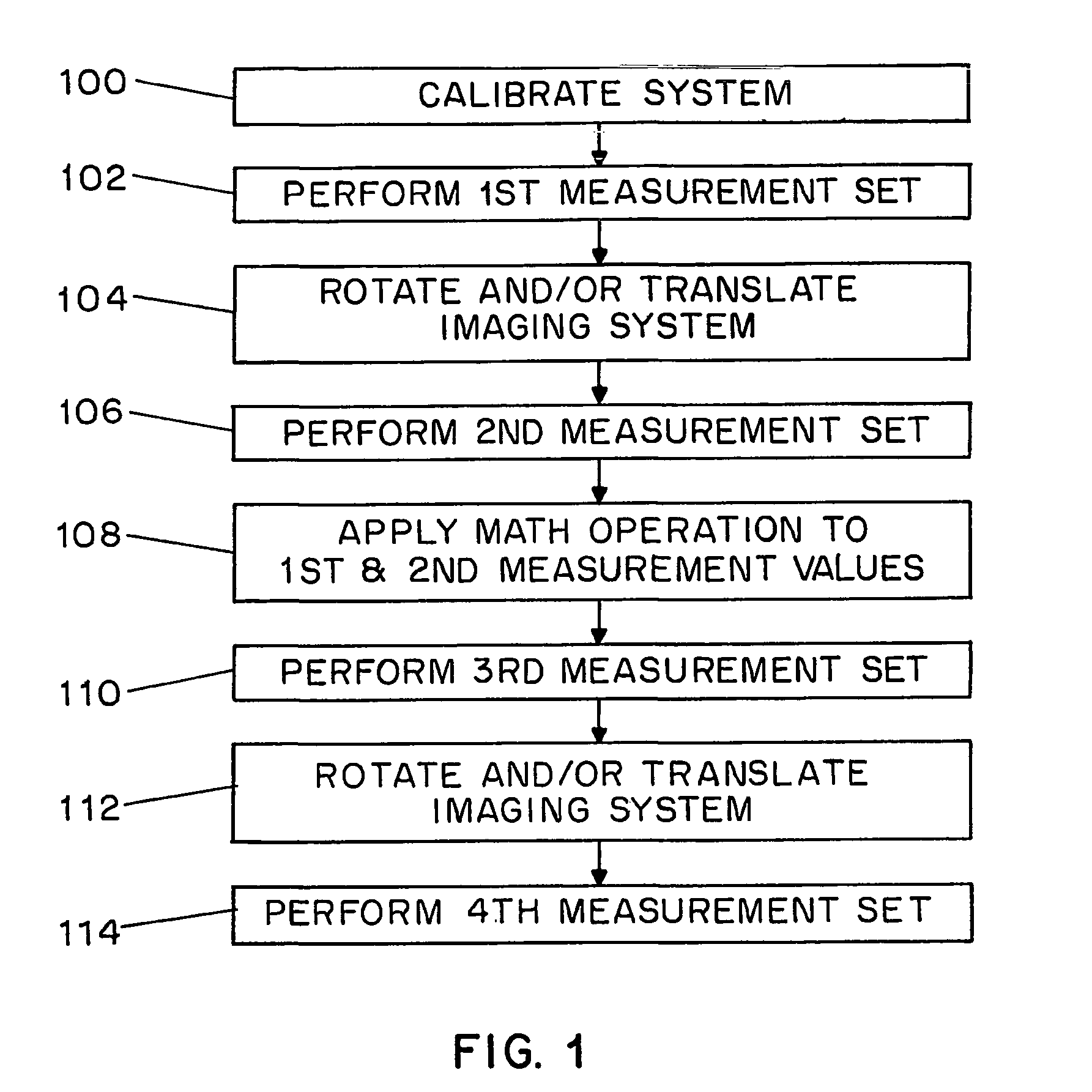
ActiveUS7440637B2Expand field of viewEnhanced brightness dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage detectionSensitivity distribution
A method and apparatus is provided for capturing images using a camera or other imager having imaging sensitivity characteristics which vary across the imager's viewing angle. The imager's characteristics can be non-uniform with respect to exposure, color sensitivity, polarization sensitivity, focal distance, and / or any other aspect of image detection. The imager is rotated or translated in order to capture different portions of the scene being imaged. Because the imager is in multiple positions when the respective scene portions are captured, each scene portion is imaged by multiple portions of the imager's sensitivity profile.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Systems, methods and computer program products for modeling uncertain future demand, supply and associated profitability of a good
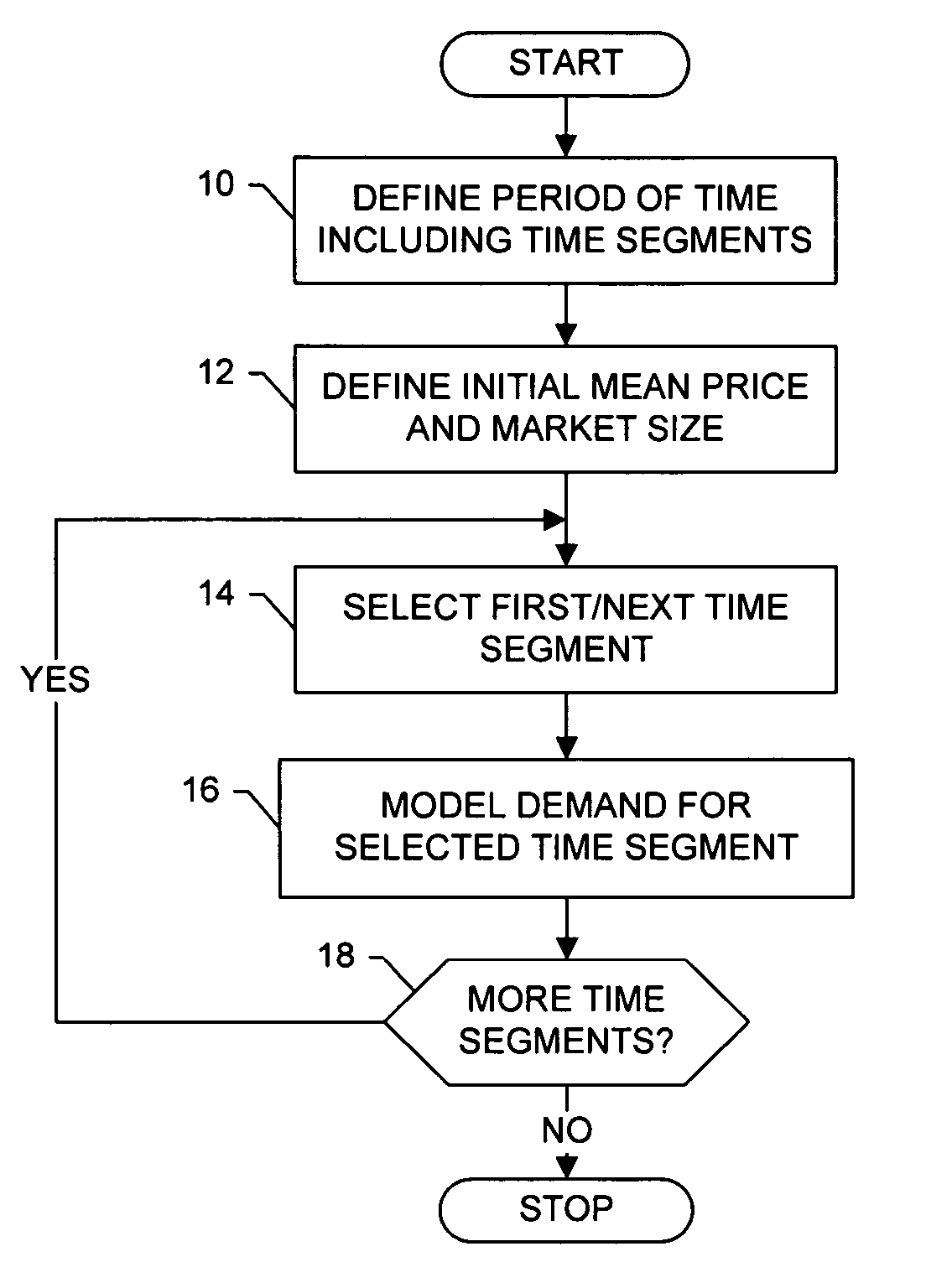
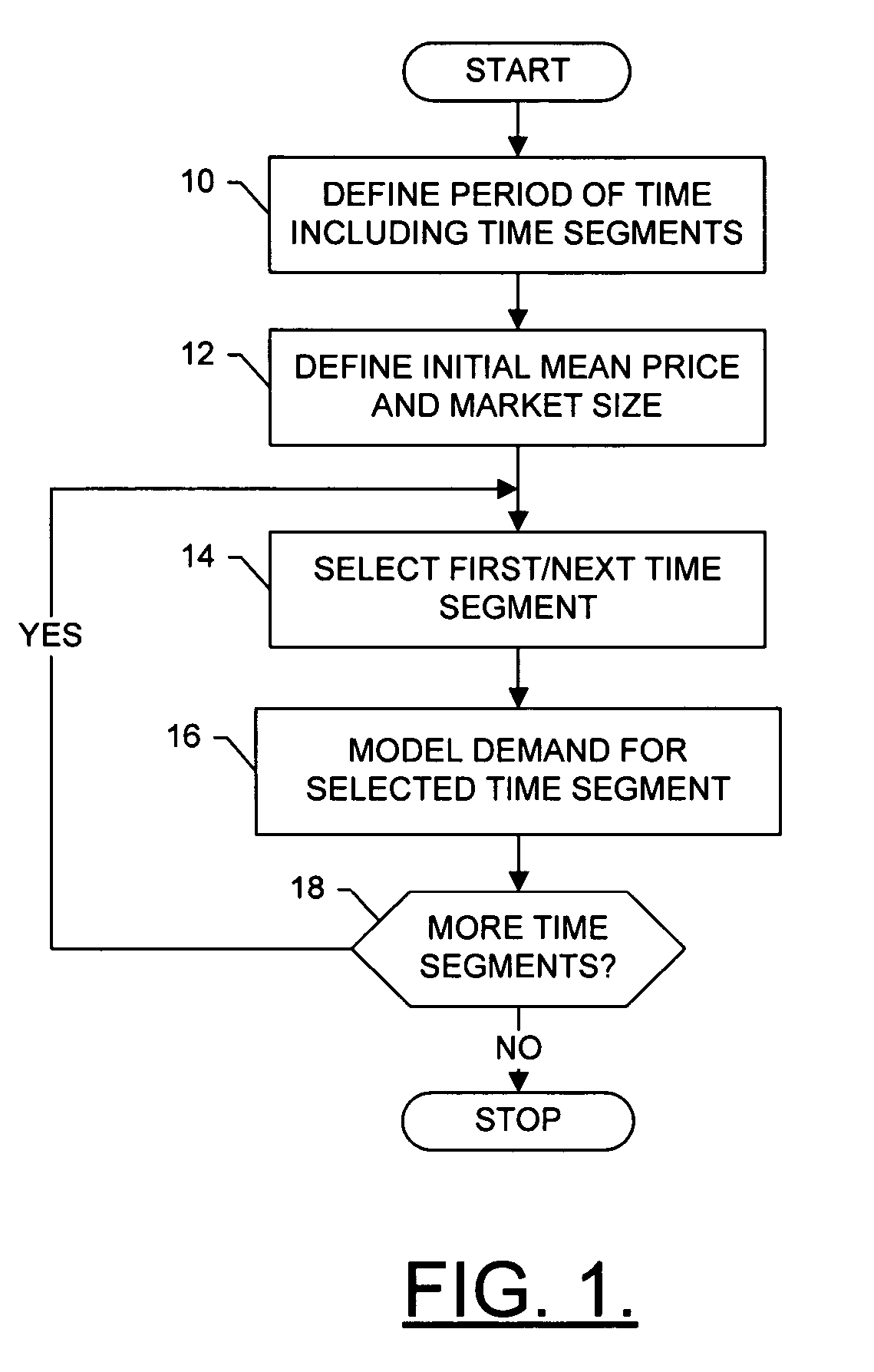
InactiveUS7769628B2Easy to understandEasy to shapeMarket predictionsCash registersRequirements modelTime segment
A method is provided that includes modeling future demand and / or future supply for a good at one or more segments of a period of time. In accordance with the method, future demand / supply at a respective time segment is modeled based upon a price sensitivity distribution of a unit purchase of the good, as well as a market potential distribution of a number of units of the good in a market associated with the good, during the respective time segment. The price sensitivity distribution and / or the market potential distribution for a respective time segment is based upon a growth rate and an uncertainty for the respective time segment. The method can further include modeling cost and / or profitability of the good at a respective time segment. Profitability can be modeled based upon the demand model and the cost model for the respective time segment.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
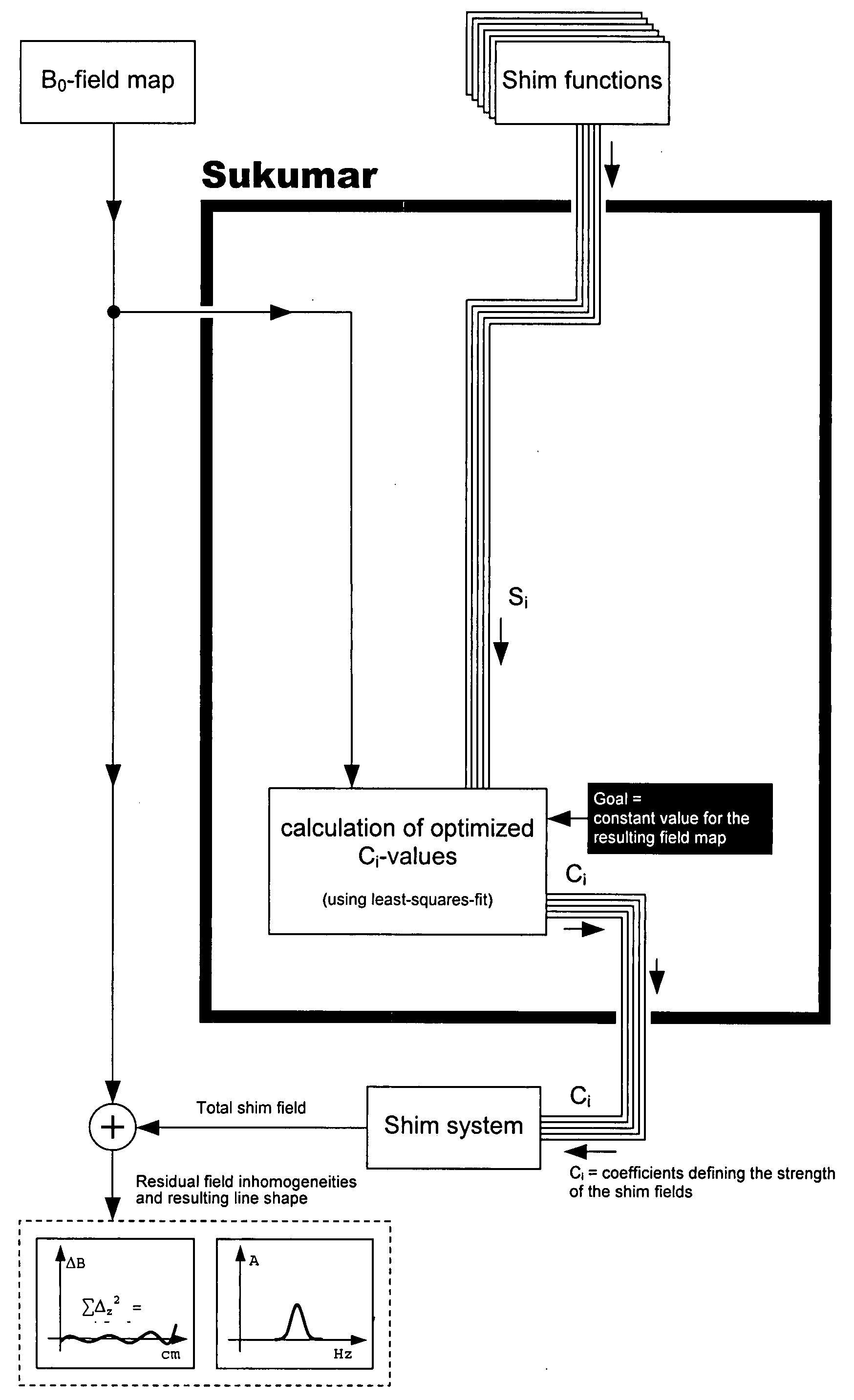
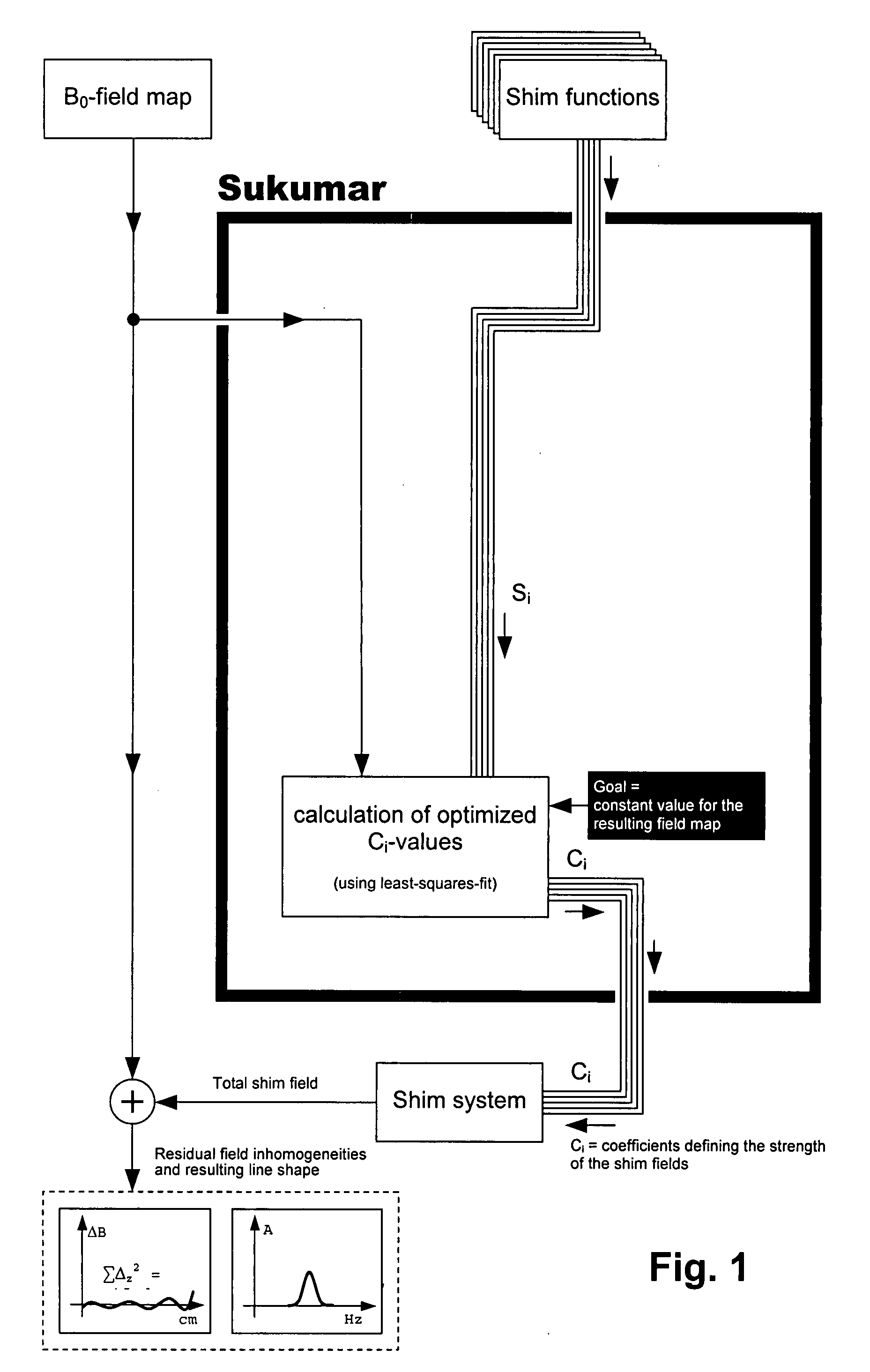
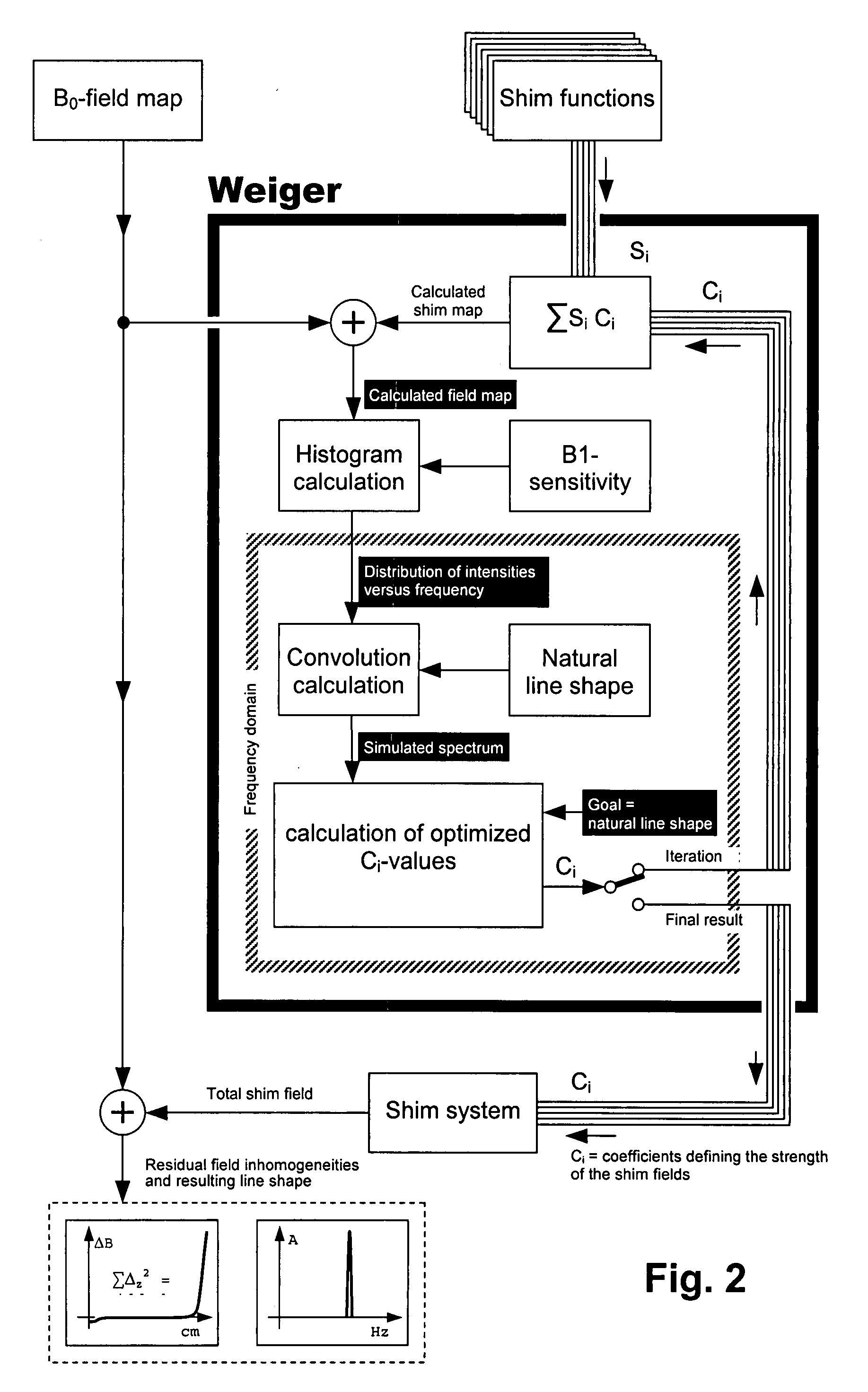
Method for automatic shimming for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080116894A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumResonance
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
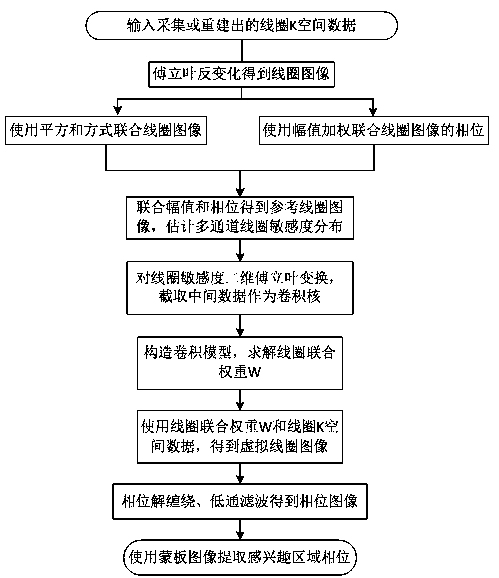
Phase processing method for parallel magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN104749538AAvoid noiseAvoid the effects of aliasing artifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage domainMR - Magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a phase processing method for parallel magnetic resonance imaging. The phase processing method comprises the following steps of performing Fourier inverse transformation on K spacial data acquired by multi-channel coils in the parallel magnetic resonance imaging to obtain amplitudes and phases of all coil images; constructing a reference coil image, and estimating the spatial sensitivity distribution of all the coils in multiple channels; performing two-dimensional Fourier transformation on the spatial sensitivity distribution of the reference coil image, and intercepting an intermediate matrix as a convolution kernel; constructing a K spacial data convolution model, and solving a joint weight W of the coils; obtaining a K spacial value of a virtual coil and performing Fourier inverse transformation to obtain a virtual coil image; unwrapping a phase and removing the phase of the background of the virtual coil image; extracting the phase of a region of interest by using a mask image. According to the phase processing method disclosed by the invention, phase information of the image is acquired by combining K space with coil data, and the phenomenon that a phase information acquisition algorithm based on an image domain is influenced by noise and aliasing artifact in the reconstruction of the parallel magnetic resonance imaging under the condition of accelerated sampling is avoided.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Touch panel device
InactiveUS20110254805A1Reduce noiseMinimize unevenness in positional distributionTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingRC time constantEngineering
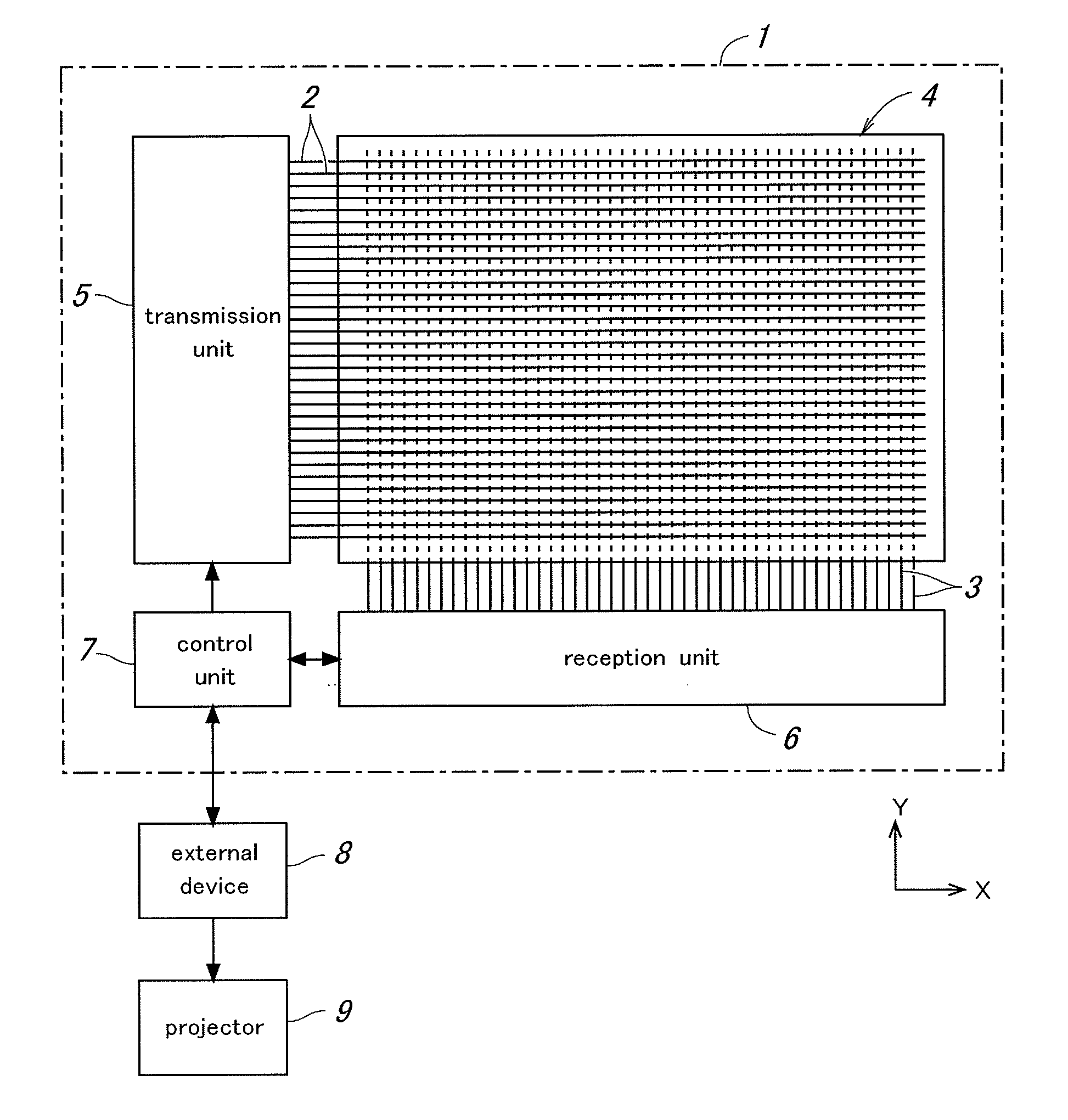
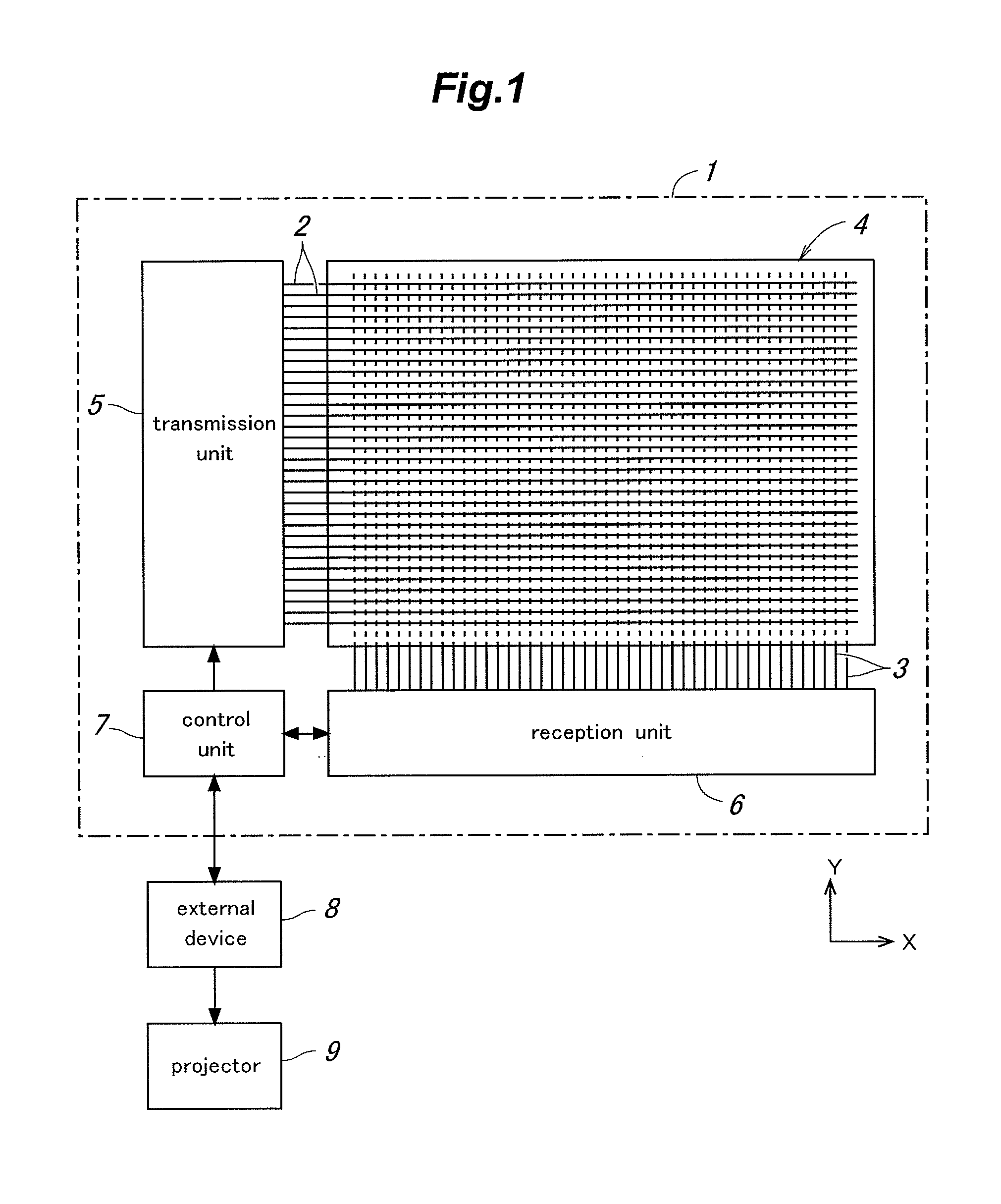
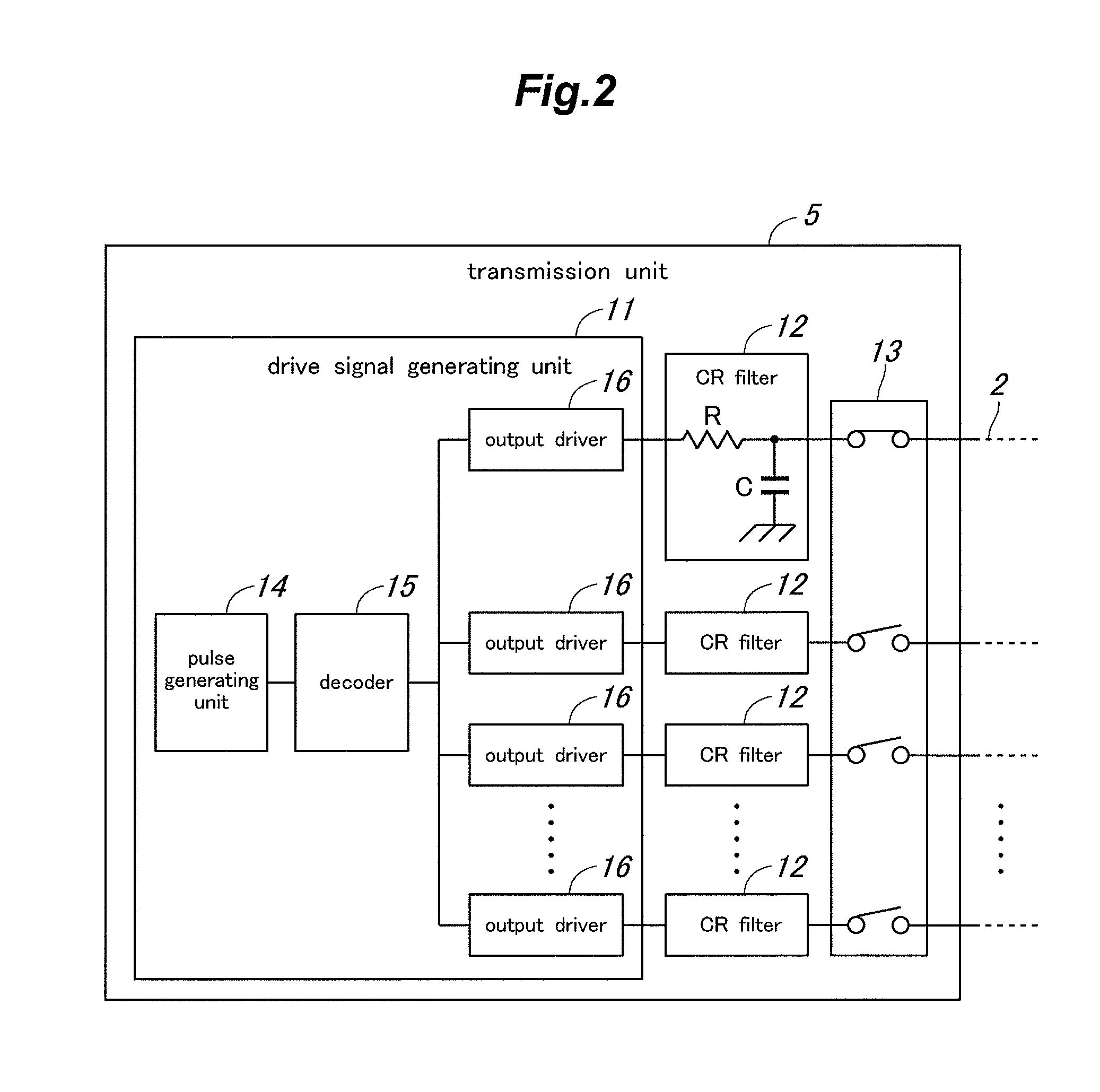
In a touch panel device comprising a panel main body (4) including a grid array of transmission electrodes (2) and reception electrodes (3) and defining a touch surface (51), the transmission electrodes are connected to a transmission unit (5) for sequentially applying a drive signal to the transmission electrodes. A time constant element is connected to each transmission electrode via the corresponding lead wire to adjust an overall time constant of the transmission electrode, the time constant of each time constant element being selected to be greater as the length of the lead wire for the corresponding transmission electrode increases. Thereby, the induction noises induced in the reception electrodes owing to the drive signal conducted through the lead wires leading to the transmission electrodes can be minimized and homogenized among the different transmission electrodes, and the positional variations in the distribution of the sensitivity of touch position detection owing to the variations in the lengths of the lead wires leading to the transmission electrodes can be minimized.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
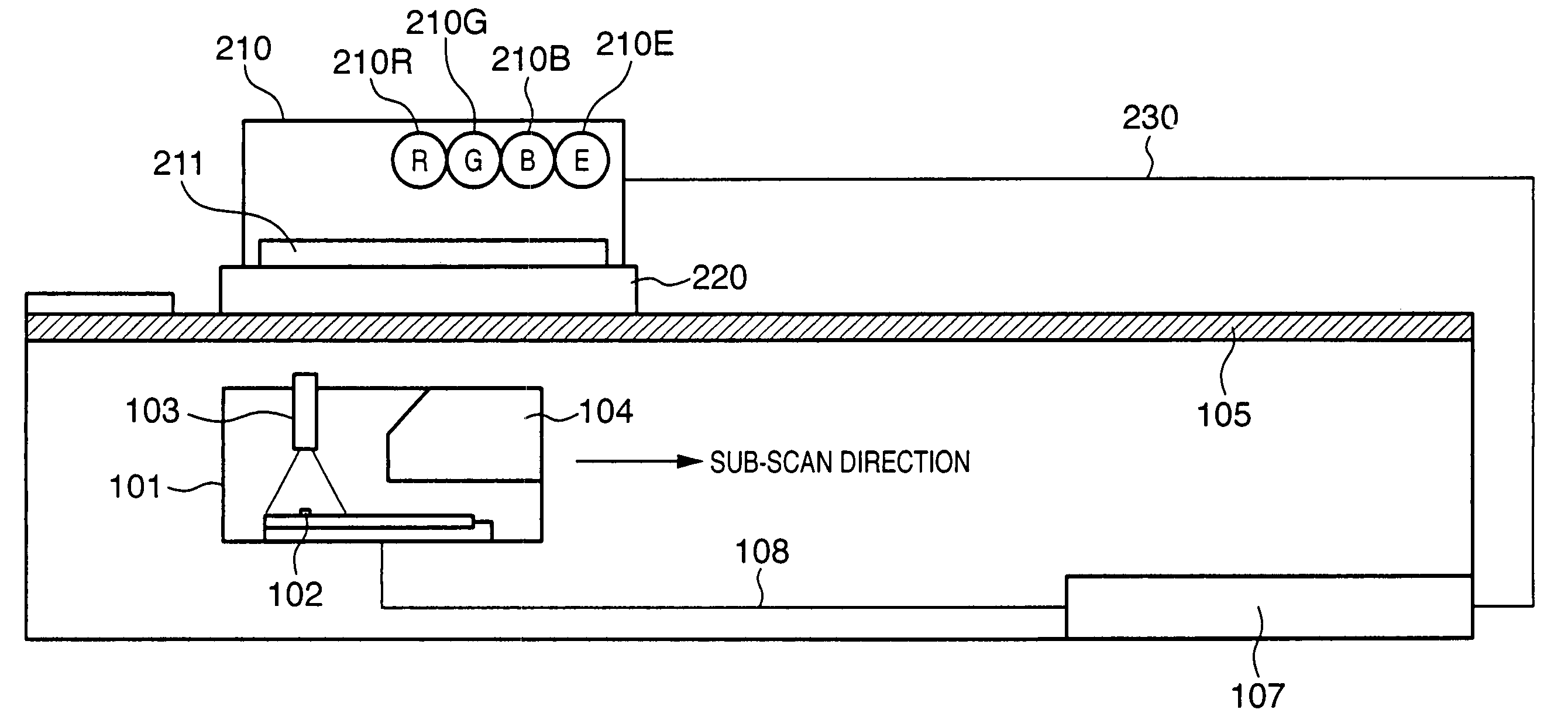
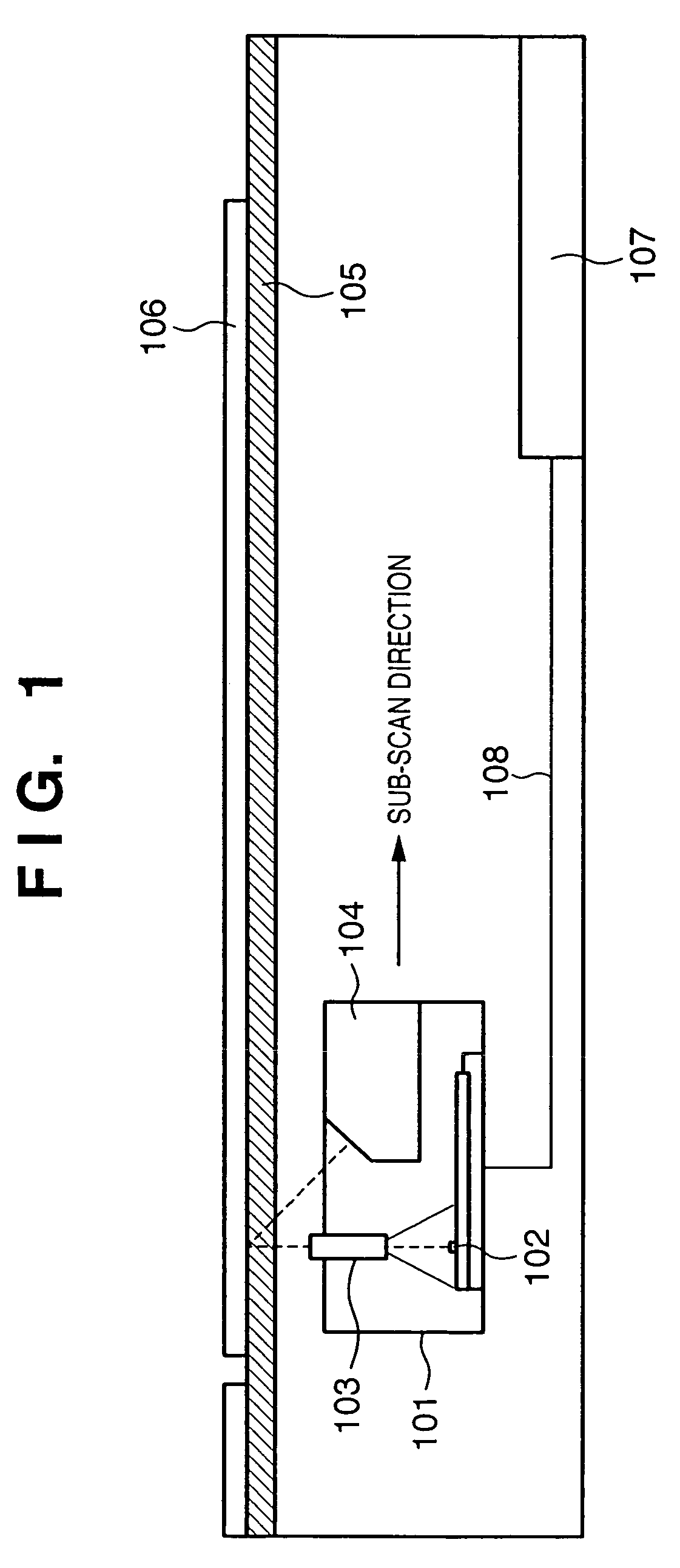
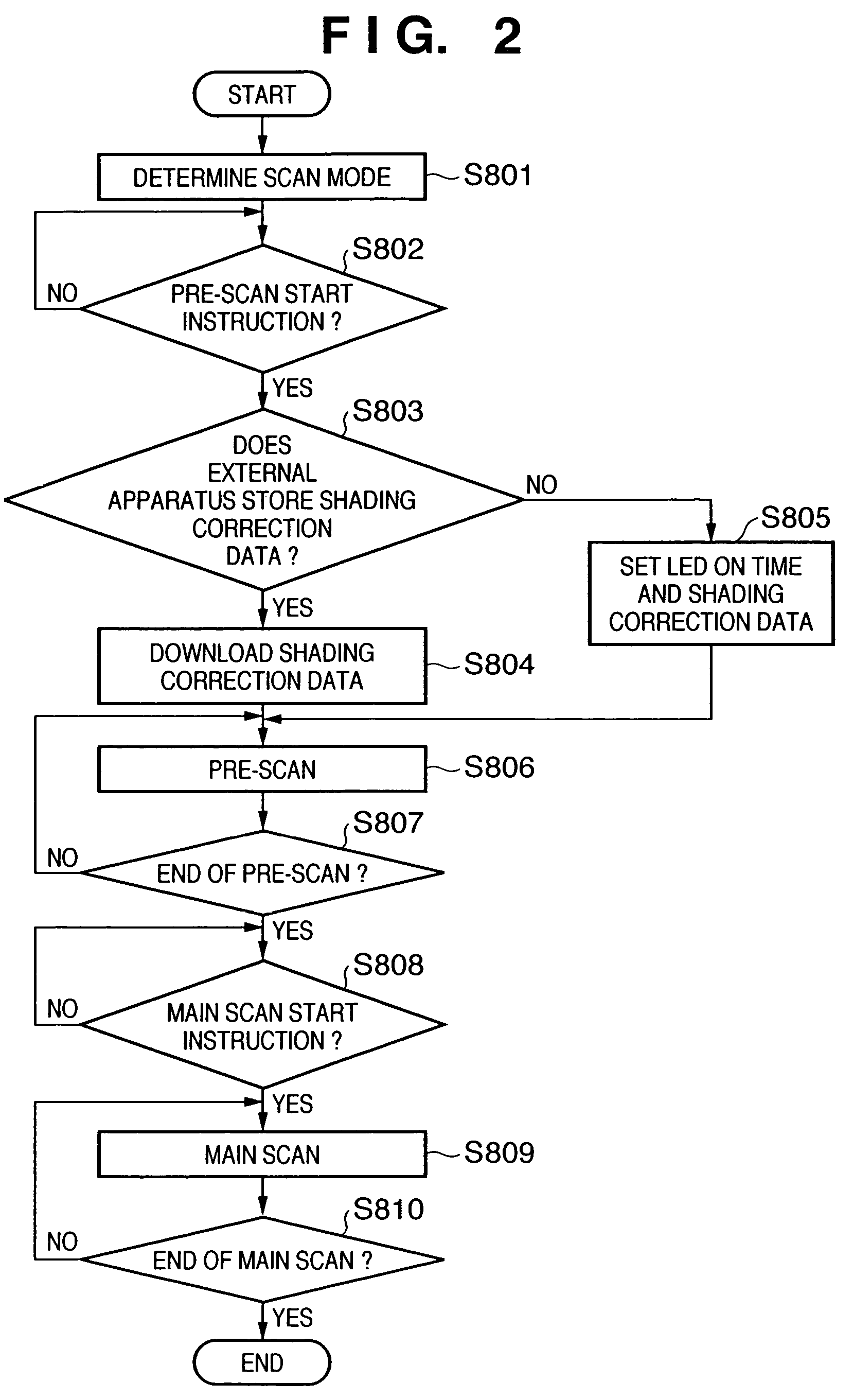
Image scanning device and its control method
InactiveUS20050174610A1Faithful color reproductionConvenient ArrangementColour-separation/tonal-correctionSolid-state device signal generatorsPaper documentLength wave
This invention provides a technique which allows more faithful color reproduction by a relative simple arrangement. To this end, according to this invention, by time-divisionally driving R, G, B, and E LEDs respectively having dominant emission wavelengths of 630 nm, 525 nm, 470 nm, and 500 nm, a common monochrome line image sensor (102) scans a document image. Scanned image data of respective color components undergo correction equivalent to that attained by shifting the barycentric positions of respective wavelength distributions so as to become closer to the CIE-RGB sensitivity distributions.
Owner:CANON KK
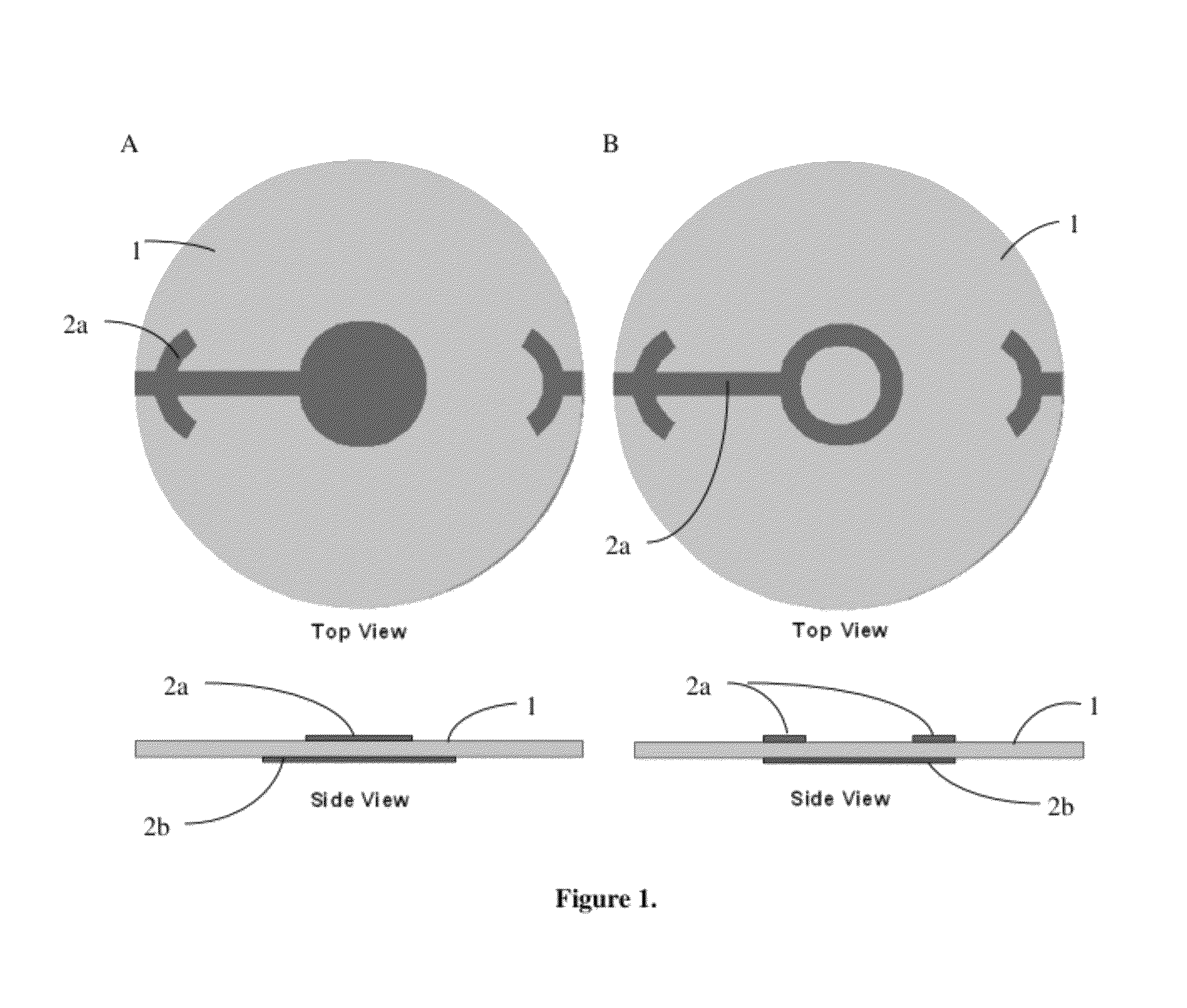
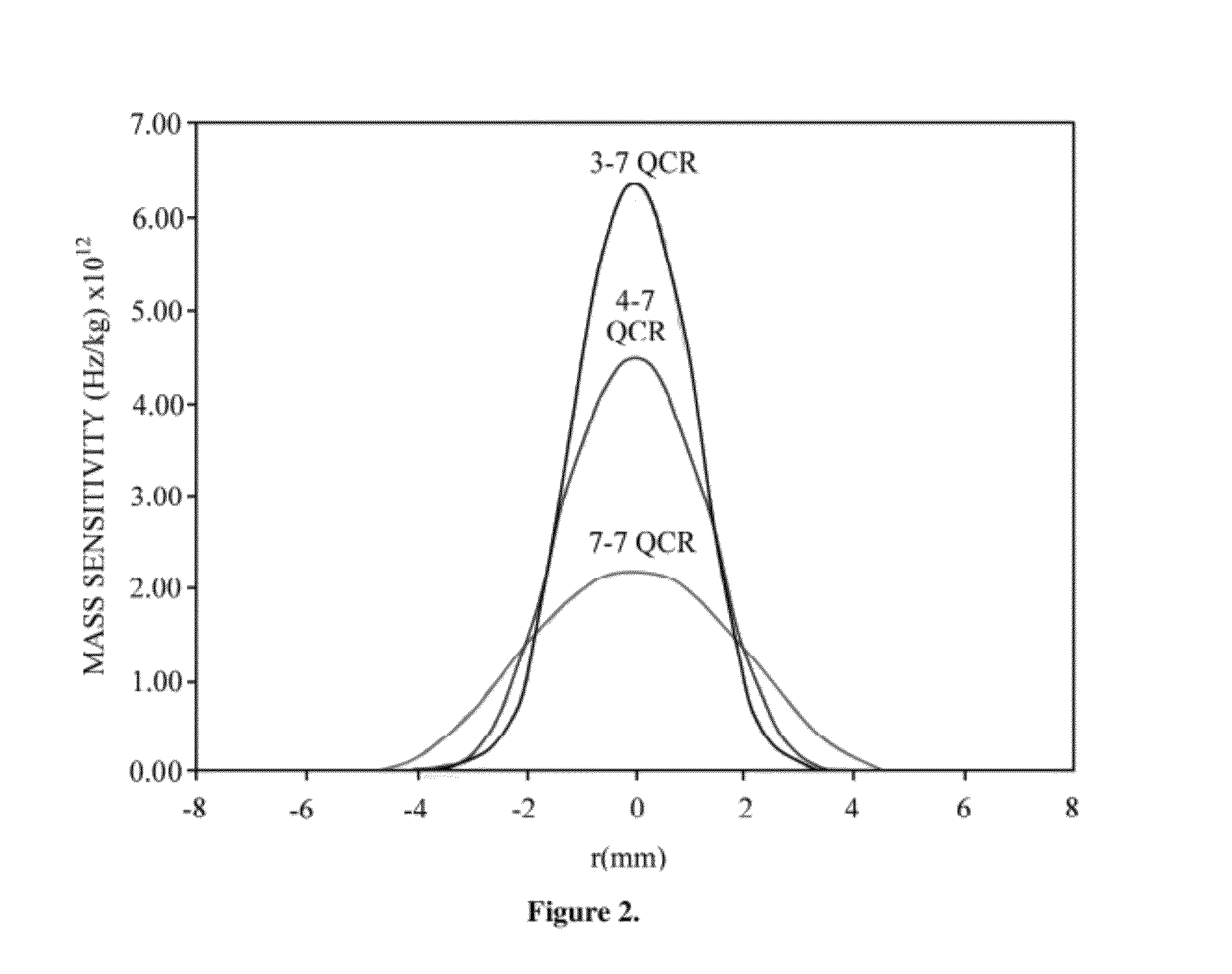
Uniform mass sensitivity thickness shear mode quartz resonator
ActiveUS8215171B1Accurate and inexpensive characterizationUniform sensitivityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersMass loadingSensitivity distribution
A ring electrode design that produces a uniform mass sensitivity distribution across a TSM device is presented. A new technique and apparatus to measure this mass sensitivity distribution is also presented. Novel electrode geometries on thickness shear mode (TSM) quartz resonators achieve radial uniformity of mass sensitivity, how receptive the device is to mass loadings, and high frequency stability across the active sensing area of the sensor device. The device allows for absolute mass measurement down to the nanogram level. Fabricated devices utilizing model predictions were tested using this apparatus, and good agreement between theory and experiment is found.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP +1
Image scanning device and its control method
InactiveUS7529003B2Faithful color reproductionConvenient ArrangementColour-separation/tonal-correctionSolid-state device signal generatorsSensitivity distributionLength wave
This invention provides a technique which allows more faithful color reproduction by a relative simple arrangement. To this end, according to this invention, by time-divisionally driving R, G, B, and E LEDs respectively having dominant emission wavelengths of 630 nm, 525 nm, 470 nm, and 500 nm, a common monochrome line image sensor (102) scans a document image. Scanned image data of respective color components undergo correction equivalent to that attained by shifting the barycentric positions of respective wavelength distributions so as to become closer to the CIE-RGB sensitivity distributions.
Owner:CANON KK
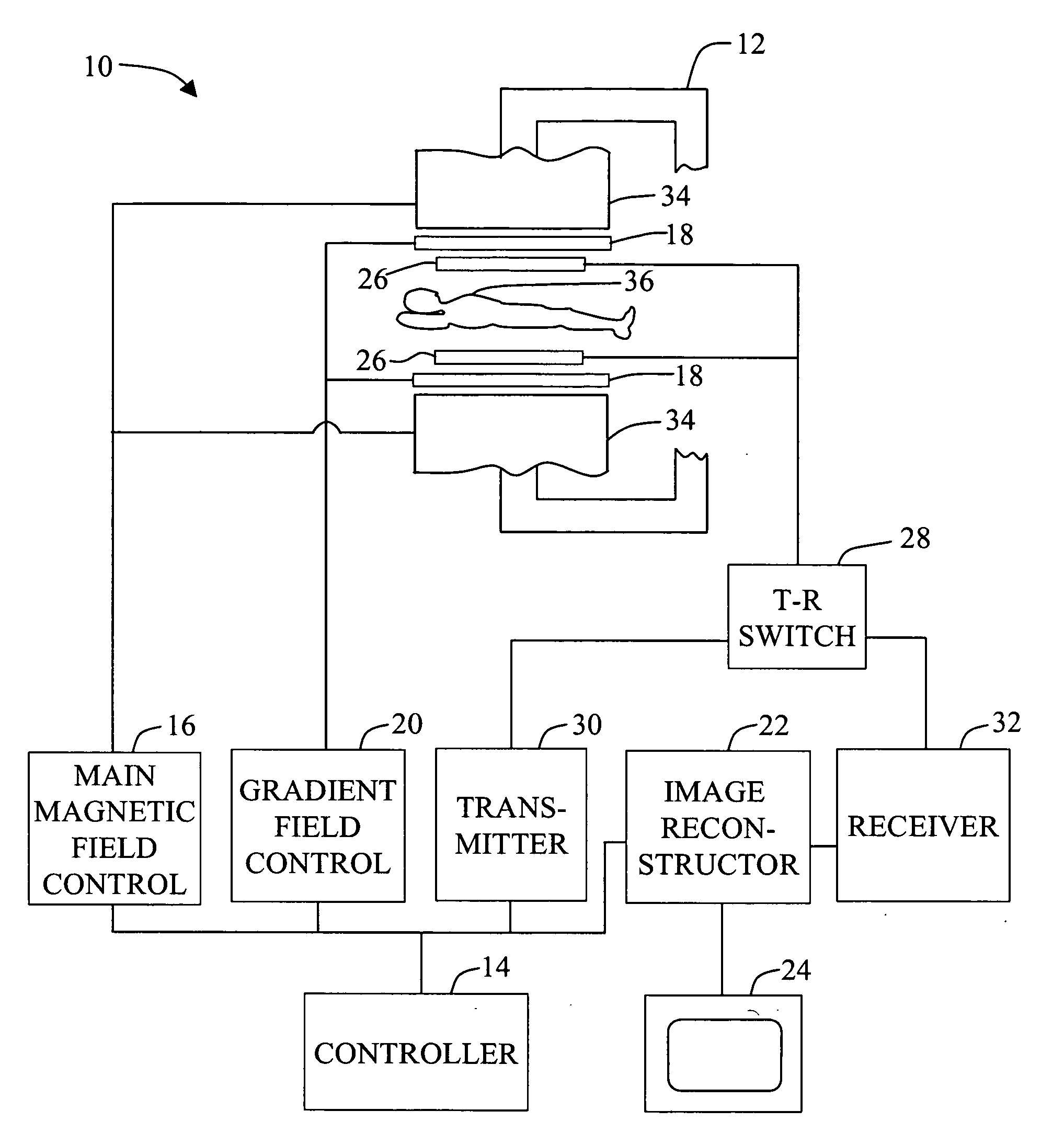
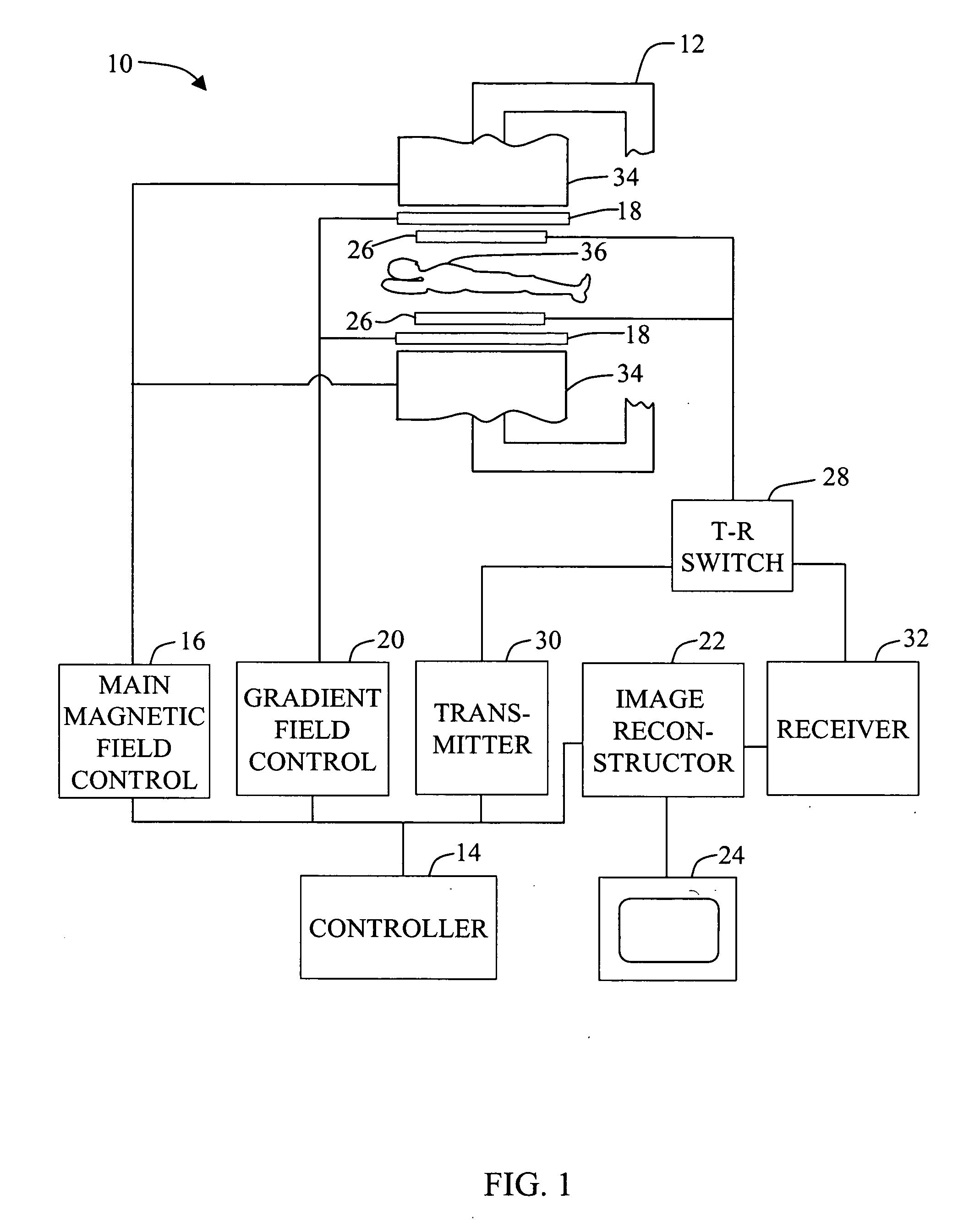
Magnetic resonance imaging method with sub-sampled acquisition
A magnetic resonance imaging method employs sub-sampled signal acquisition from a number of receiver coils such as surface coils. A full field-of-view magnetic resonance image is reconstructed on the basis of the sensitivity profiles of the receiver coils, for example on the basis of the SENSE technique. The reconstruction is carried out mathematically as an optimization, for example, requiring a minimum noise level in the magnetic resonance image. According to the invention, a priori information is also involved in the reconstruction and the a priori information is taken into account especially as a constraint in said optimization.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic resonance parallel imaging method with K-space sensitivity encoding
ActiveUS20060208731A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce Image ArtifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resonance
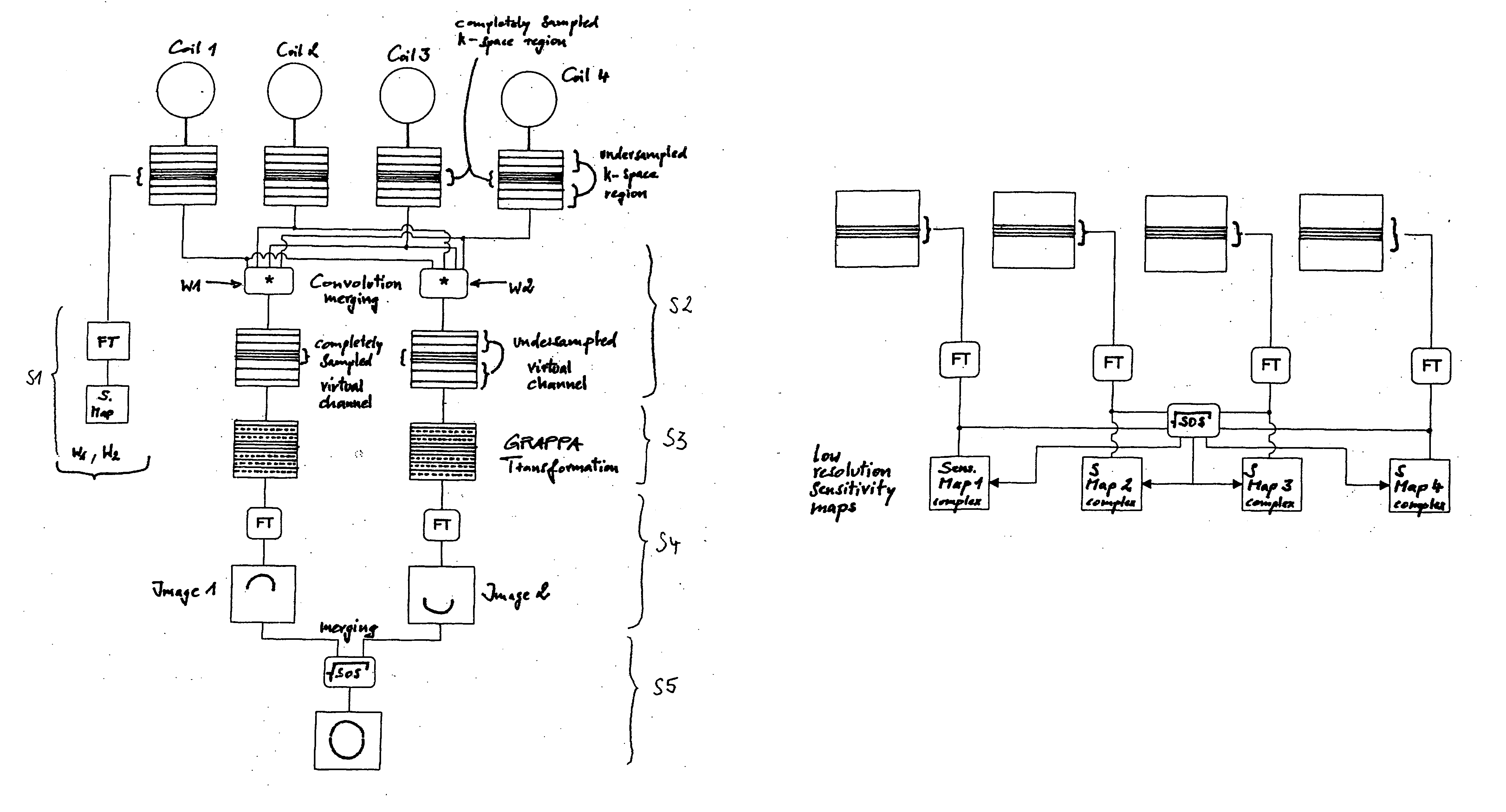
In a K-space SENSitivity Encoding (KSENSE) magnetic resonance parallel imaging method the sensitivity distribution of MR reception coils; is calculated and based on the sensitivity of the coils, signals from the respective coil merging channels are merged. The merged data are used to perform k-space data fitting and optimal fitting parameters are found. The fitting parameters are used to remove artifacts in the reconstructed image. The KSENSE method, compared to SENSE, mSENSE and GRAPPA, has the advantages of the image reconstructed by KSENSE having an optimized signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is superior to that of an image reconstructed by GRAPPA under the same conditions and approximates that when mSENSE is used, and an image reconstructed by KSENSE has relatively low residual artifacts and an artifact intensity, as a whole, that is superior to that of an image reconstructed by SENSE or the like under the same conditions and equivalent to that when GRAPPA is used, and, compared to GRAPPA that also performs operations in k-space, KSENSE has a higher reconstruction speed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for calibrating coil sensitivity profiles
InactiveUS20050096534A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensitivity distributionCoil sensitivity
A method for calibrating coil sensitivity profiles is described. The method includes generating reference sensitivity maps for each coil, imaging a subject, interleaving, with the imaging of the subject, imaging of at least one fiducial mark provided with each coil, and deriving, based on the coil positioning and coil loading, actual sensitivity maps from the reference sensitivity maps.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
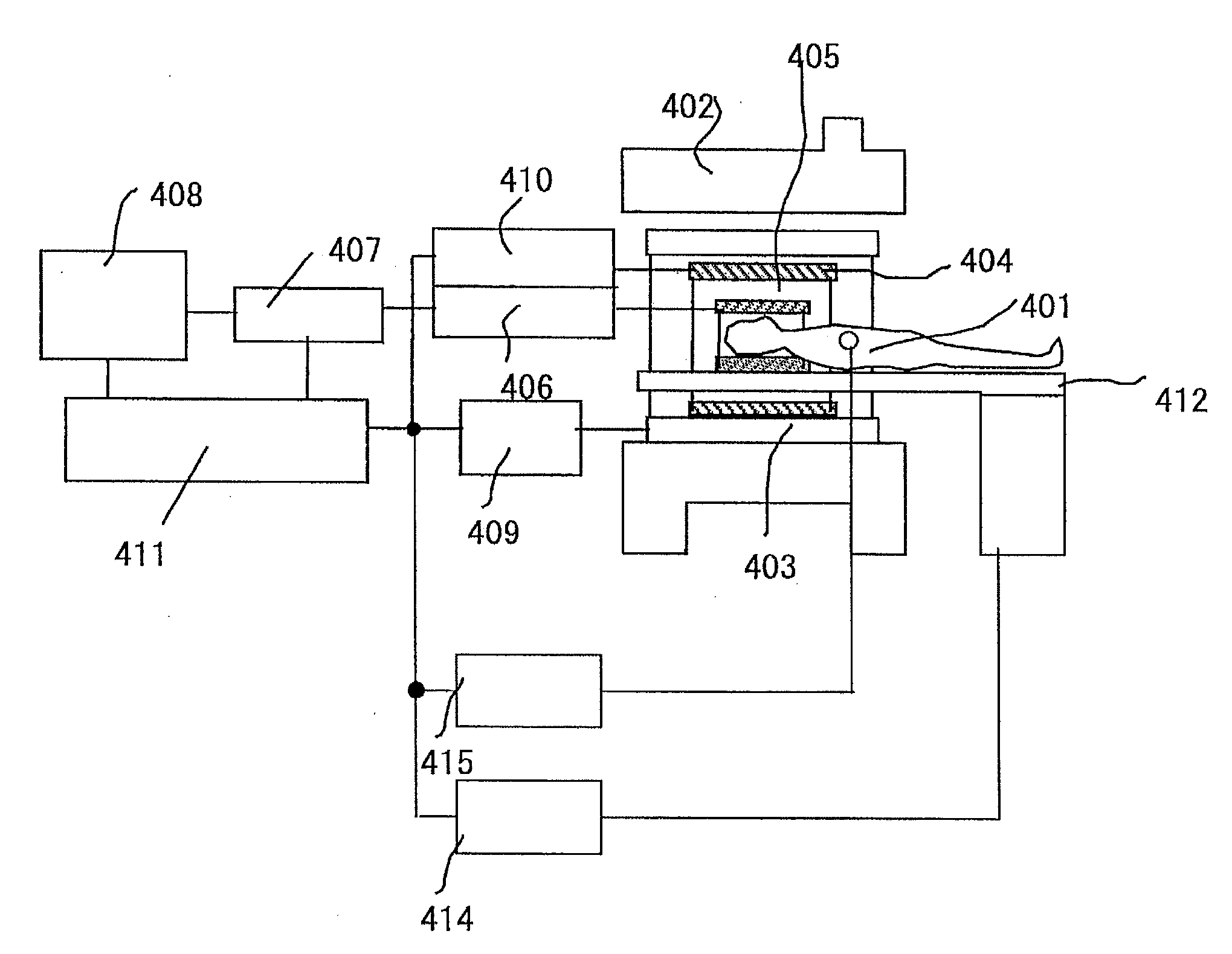
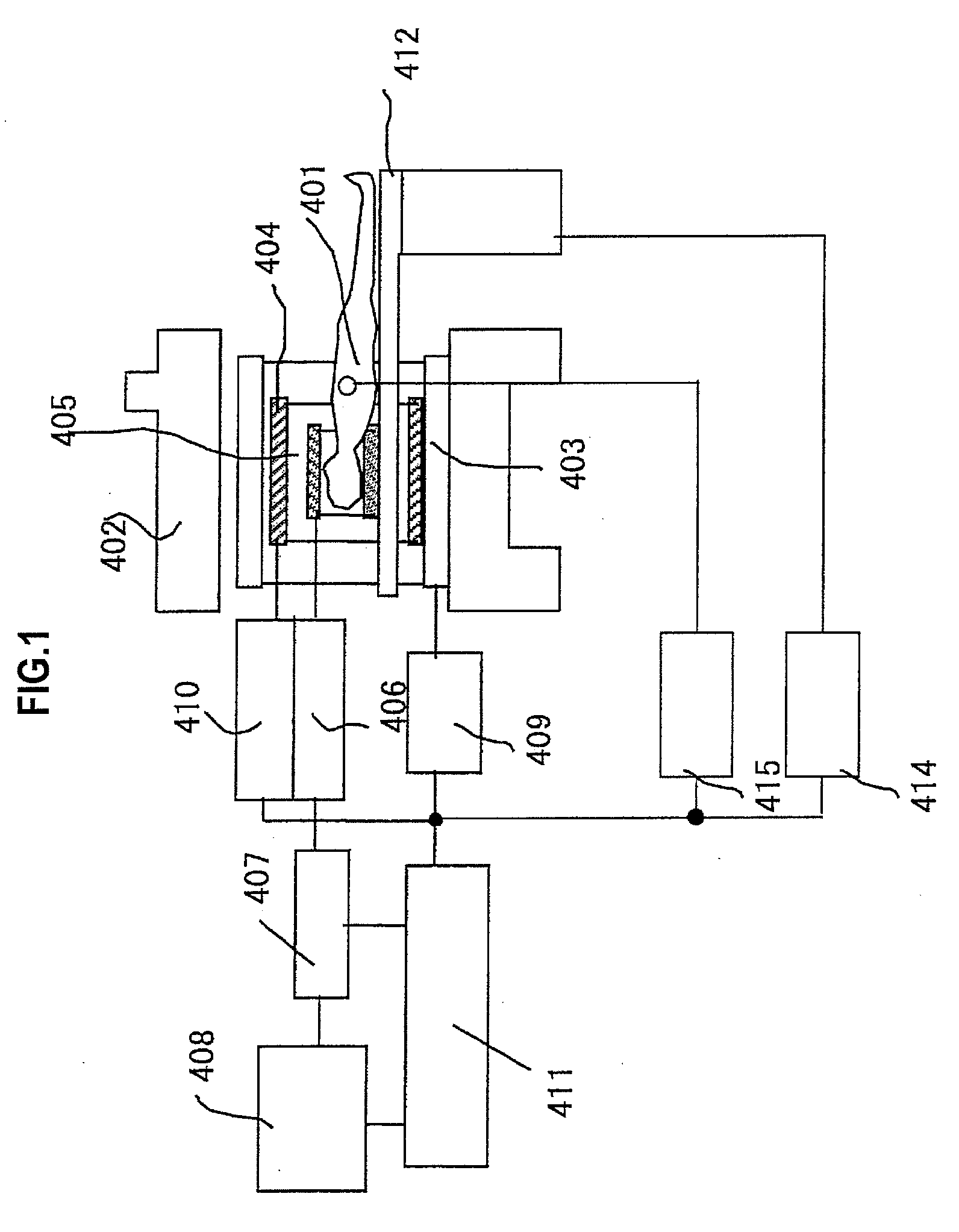
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20100039110A1Avoid it happening againReduce in quantityCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFourier transform on finite groupsReceiver coil
An MRI apparatus capable of performing a high-speed operation for removing aliasing from the data measured by non-Cartesian imaging in a real space with a small amount of operation is provided. Non-Cartesian data sampling is performed by thinning the number of data by using multiple receiver coils having different sensitivity distribution from each other. Image reconstruction means creates orthogonal data by gridding non-orthogonal data obtained by each receiver coil on a grid having an equal spatial resolution to and a narrower field of view than a target image, subjects it to Fourier transform and creates the first image data containing aliasing components. The second image data is created by using the first image data created for each receiver coil and a sensitivity distribution of each receiver coil.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
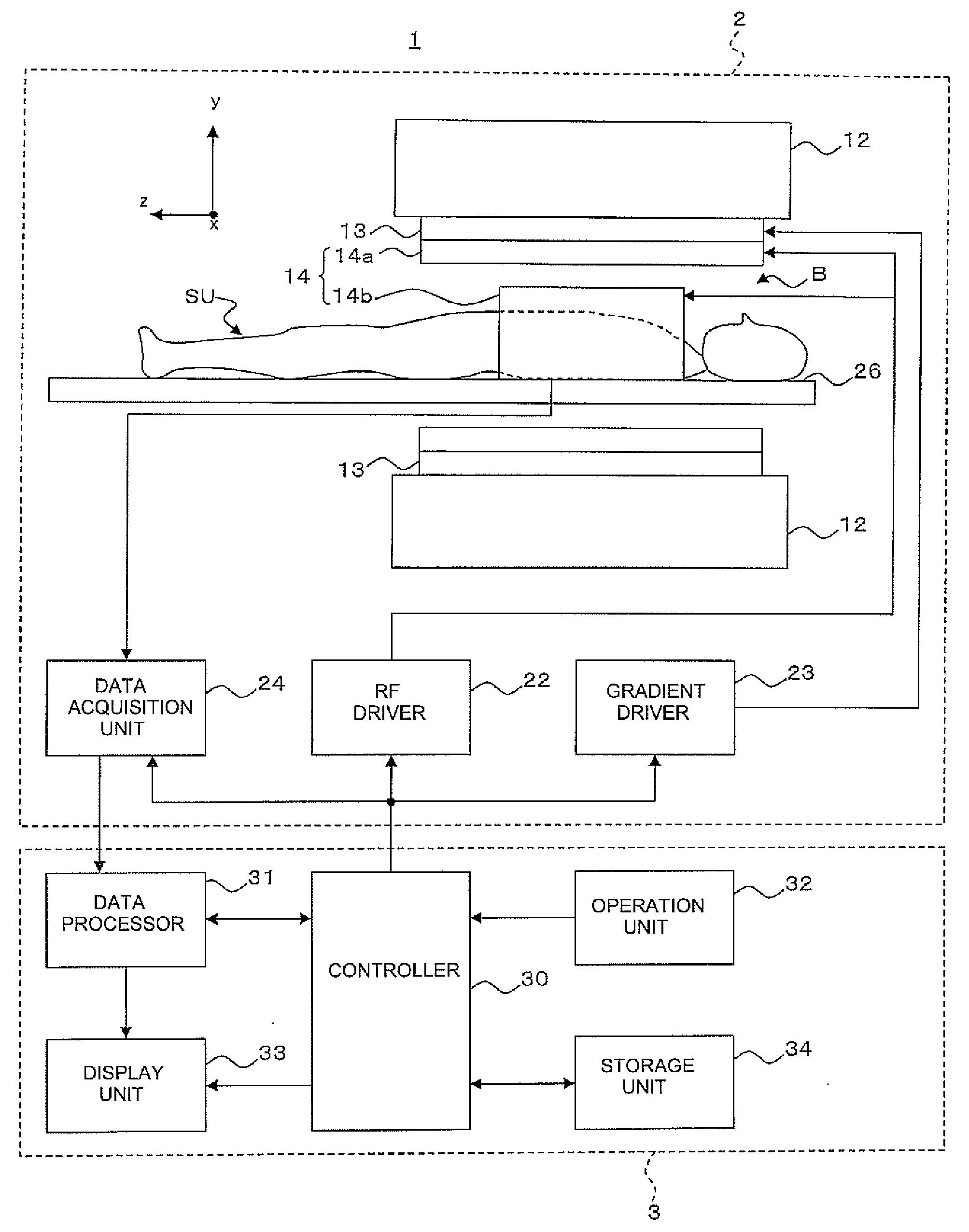
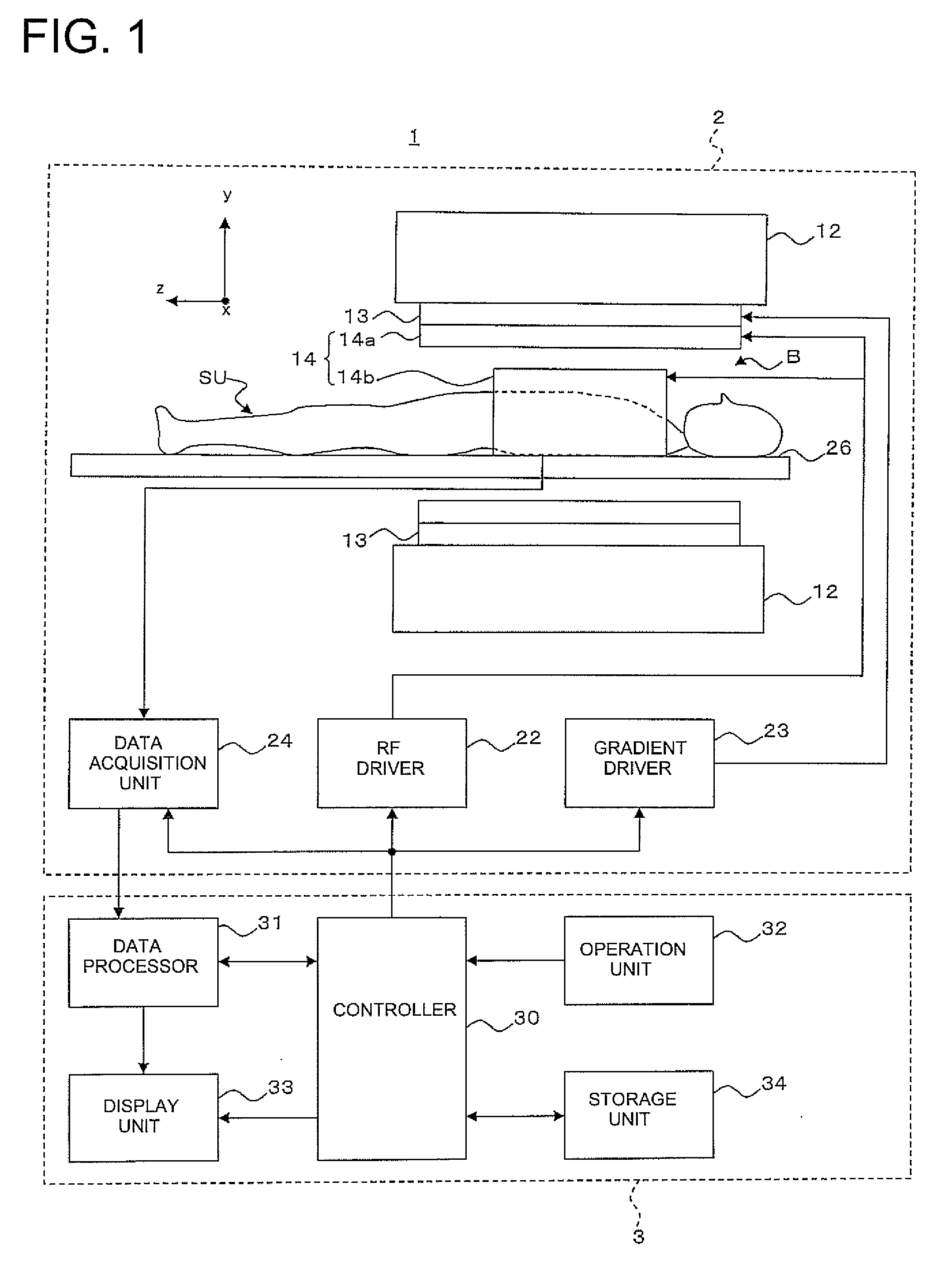
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus, magnetic resonance imaging method and sensitivity distribution measuring apparatus
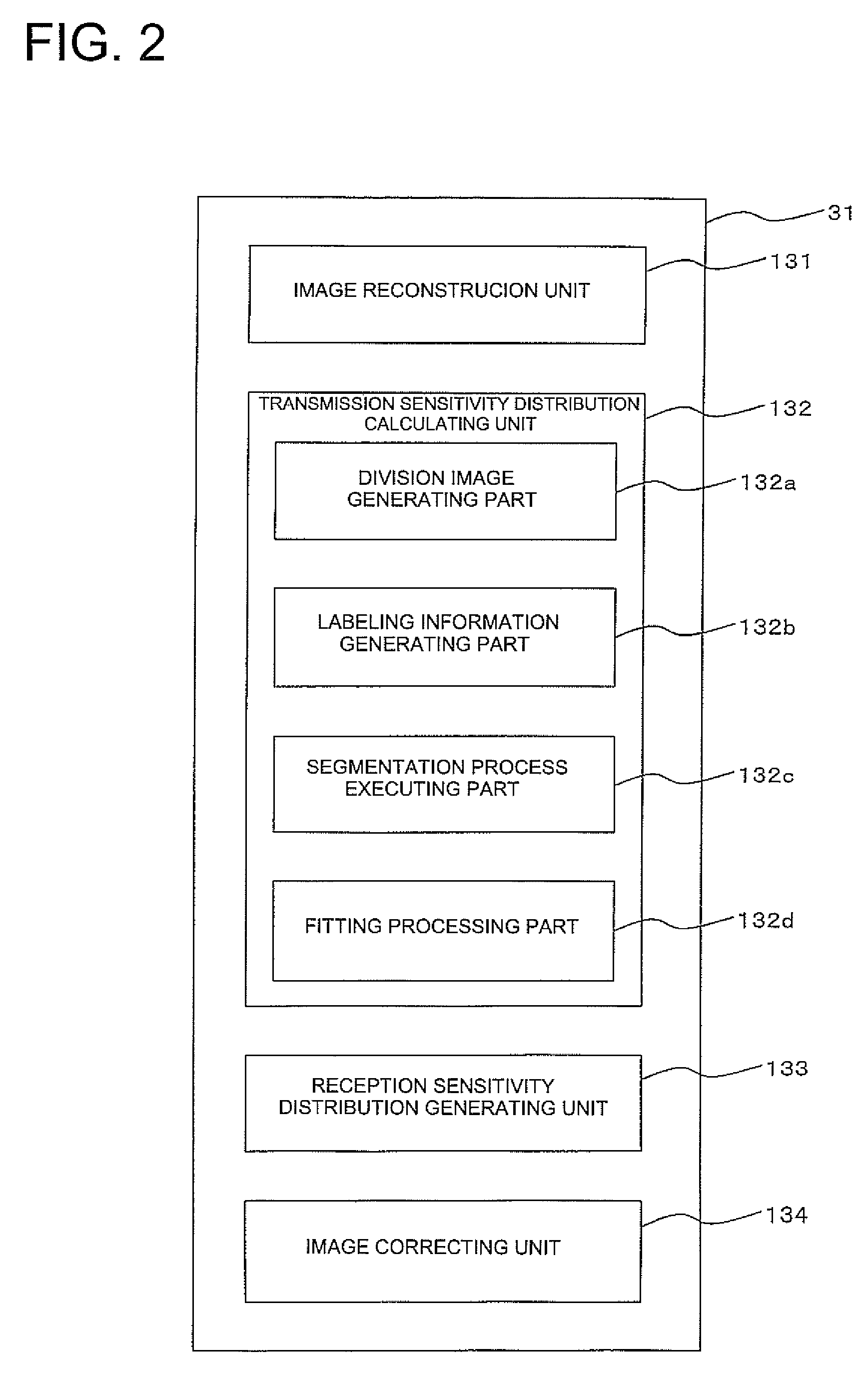
InactiveUS20080231273A1High precisionImprove image qualityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImage extractionImaging processing
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus which executes a scan for allowing an RF coil unit to transmit RF pulses to an imaging area of a subject in a static magnetic filed space and allowing the RF coil unit to acquire magnetic resonance signals generated in the imaging area, includes: a scan section which executes, as the scan, each of an actual scan for acquiring the magnetic resonance signals as actual scan data and a reference scan for acquiring the magnetic resonance signals as reference scan data; an image reconstruction unit which reconstructs an actual scan image about the imaging area, based on the actual scan data and reconstructs a reference scan image about the imaging area, based on the reference scan data; a transmission sensitivity distribution calculating unit which calculates a transmission sensitivity distribution at the transmission of the RF pulses by the RF coil unit in the imaging area, based on the reference scan image and the actual scan image; and an image correcting unit which corrects the actual scan image using the transmission sensitivity distribution, wherein the transmission sensitivity distribution calculating unit includes: a division image generating part which executes image processing for dividing the first reference image by the second reference image, thereby generating a division image; a labeling information generating part which executes a labeling process on the division image thereby to generate labeling information about the division image; a segmentation process executing part which executes a segmentation process on the actual scan image, based on the labeling information thereby to extract a plurality of segments from the actual scan image; and a fitting processing part which calculates relational expressions indicative of relationships between pixel values of pixels constituting the segments and pixel positions thereof with respect to the segments extracted from the actual scan image, by performing a process for fitting to polynomial models, and wherein the transmission sensitivity distribution is calculated based on the relational expressions calculated by the fitting processing part.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method and apparatus for identifying the direction of incidence of an incoming audio signal
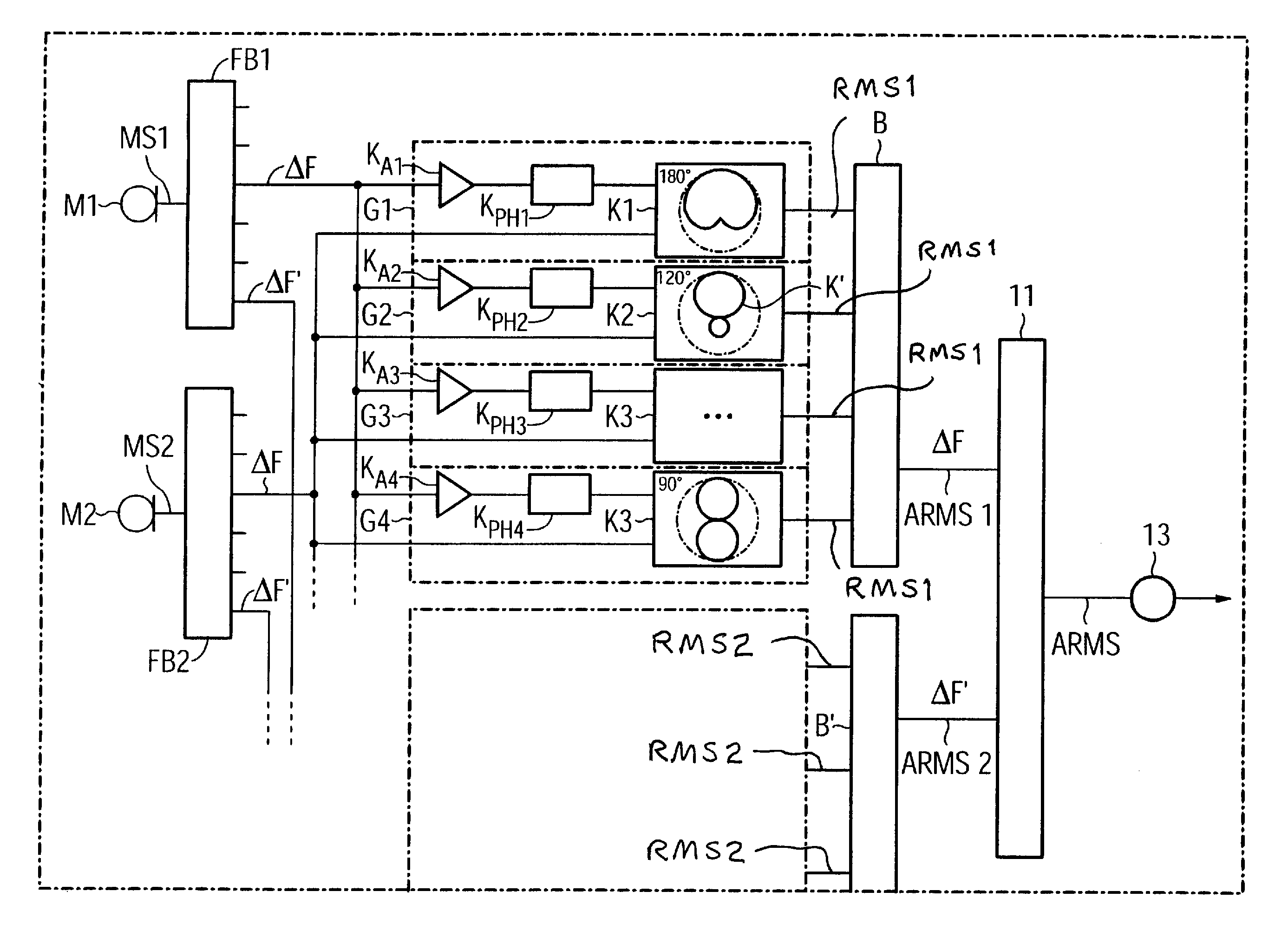
ActiveUS7561701B2Easy accessMinimizing sensitivityMicrophonesLoudspeakersSensitivity distributionSignal source
To determine the direction of incidence for a signal from an acoustic signal source using a directional microphone system, which has at least two microphones, two or more directional microphone signals are produced, each having a direction-dependent sensitivity distribution with a minimum in one direction. The directional microphone signals are assessed with regard to a quantity to determine the directional microphone signal which is most influenced by the associated direction dependent sensitivity distribution. The direction of incidence is determined as being the direction in which the minimum of the sensitivity distribution of this directional microphone signal is located.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
System, Method, And Device For Measuring Parameters Of A Two-Phase Flow
InactiveUS20100107775A1Accurate measurementMass flow measurement devicesVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsRemote controlComputerized system
A capacitive sensor for measuring flow parameters of a two-phase flow, a device for measuring phase concentration of a two-phase flow, and a system and method for measuring flow parameters of a two-phase flow is disclosed. In the capacitive sensor, at least one pair of electrodes is twisted by 180° in a common direction into a spiral shape. Edge guard electrodes are twisted in the common direction and are formed between adjacent electrode edges. Problems of non-homogeneous sensitivity distribution of a measuring field and soft field effect can be effectively addressed, thereby allowing reliable and accurate measurement of phase concentration of a two-phase flow. The system for measuring flow parameters of the two-phase flow can output signals with a current of 4˜20 mA to a PLC system or communicate with an industrial process control computer or with a remote control computer system in a operating room.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Parallel transmission by spin dynamic fingerprinting
ActiveUS20160282436A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensitivity distributionSpatial change
A general framework is for signal encoding in MRF that enables simultaneous transmit and receive encoding to accelerate the acquistion process, or improve the fidelity of the final image / parameter-map per unit scan time. The proposed method and systems capitalize on the distinct spatial variations in the sensitivity profile of each transmit-coil to reduce the acquistion time, and / or improve the fidelity of the final parameter-map per unit time.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
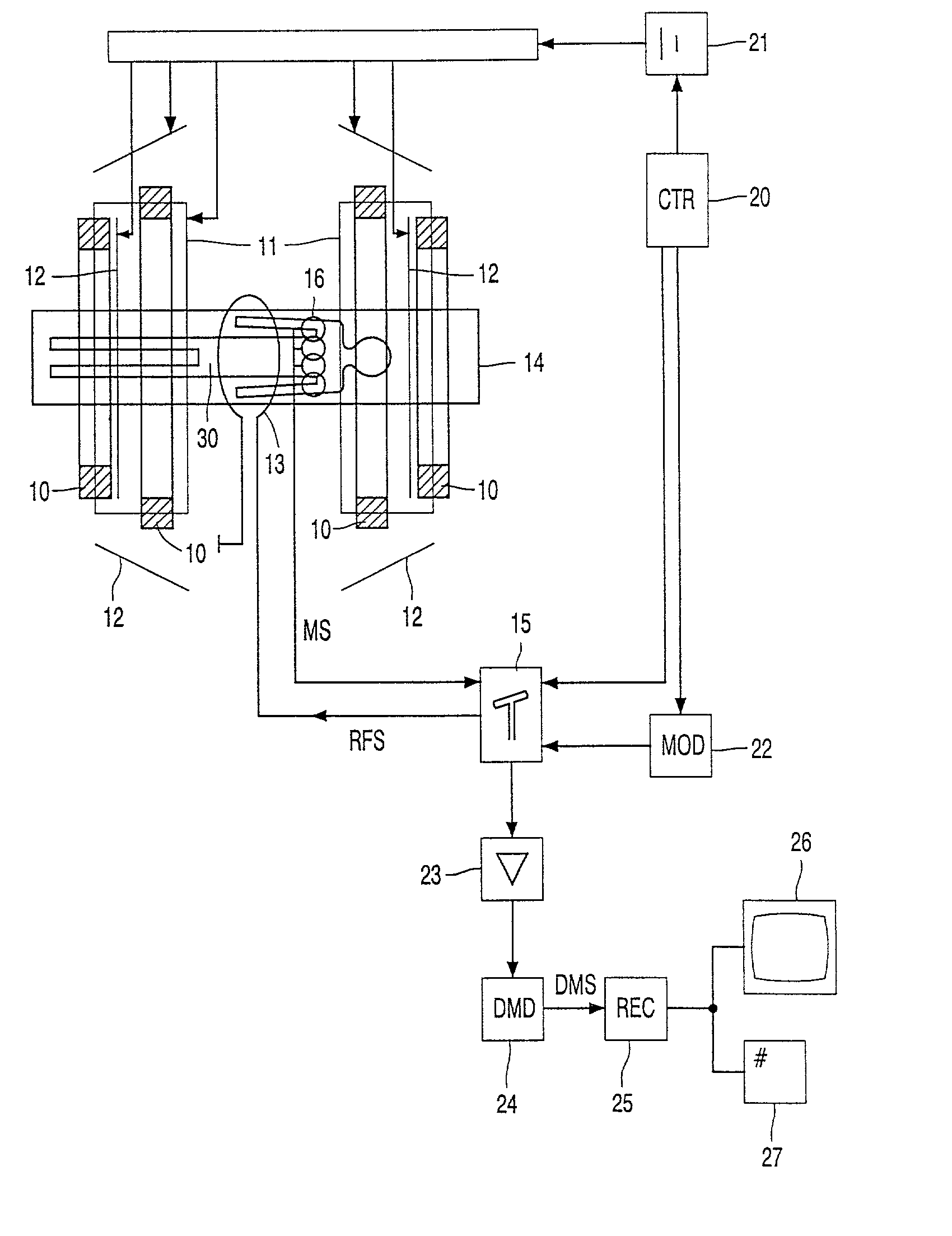
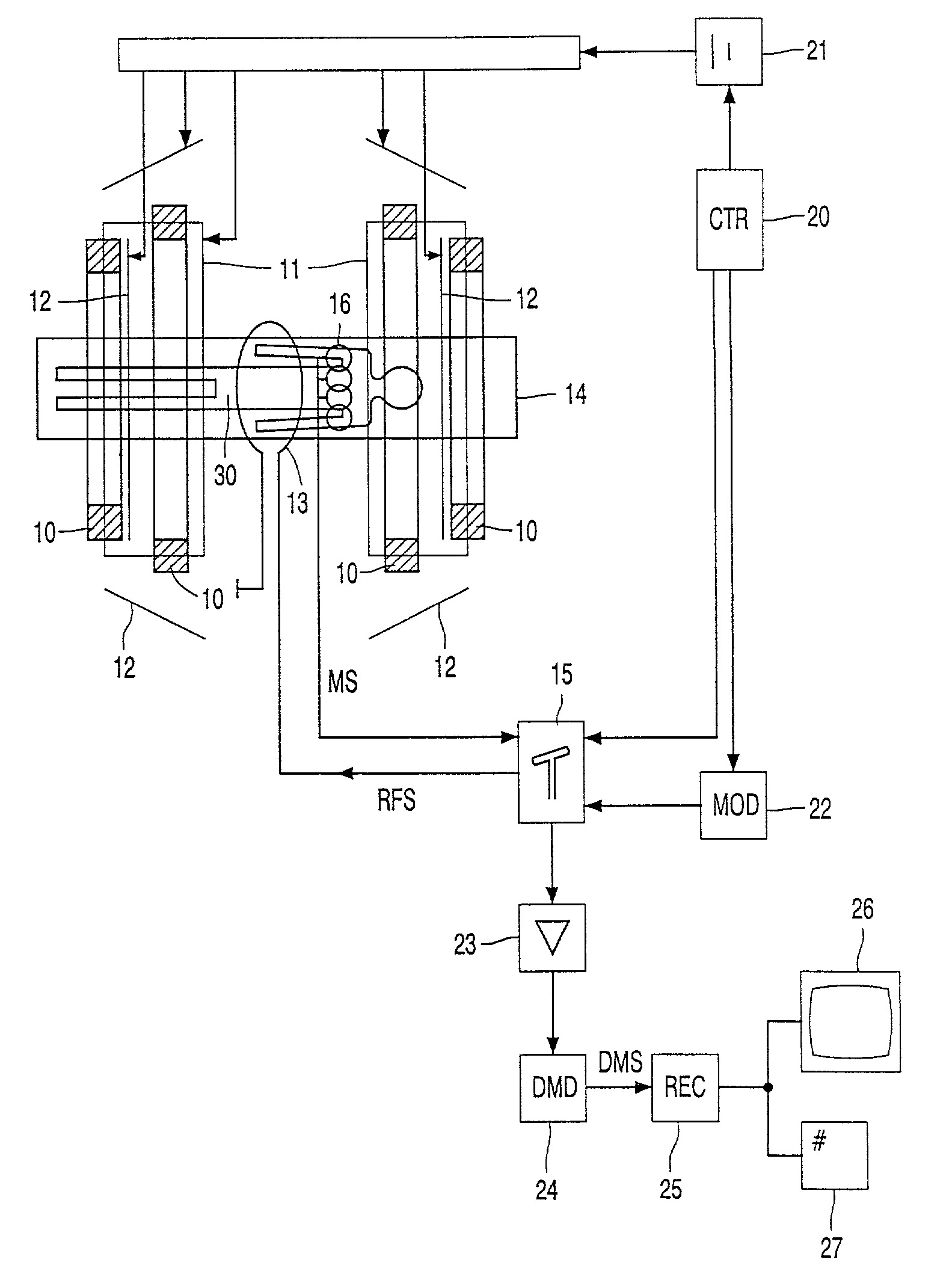
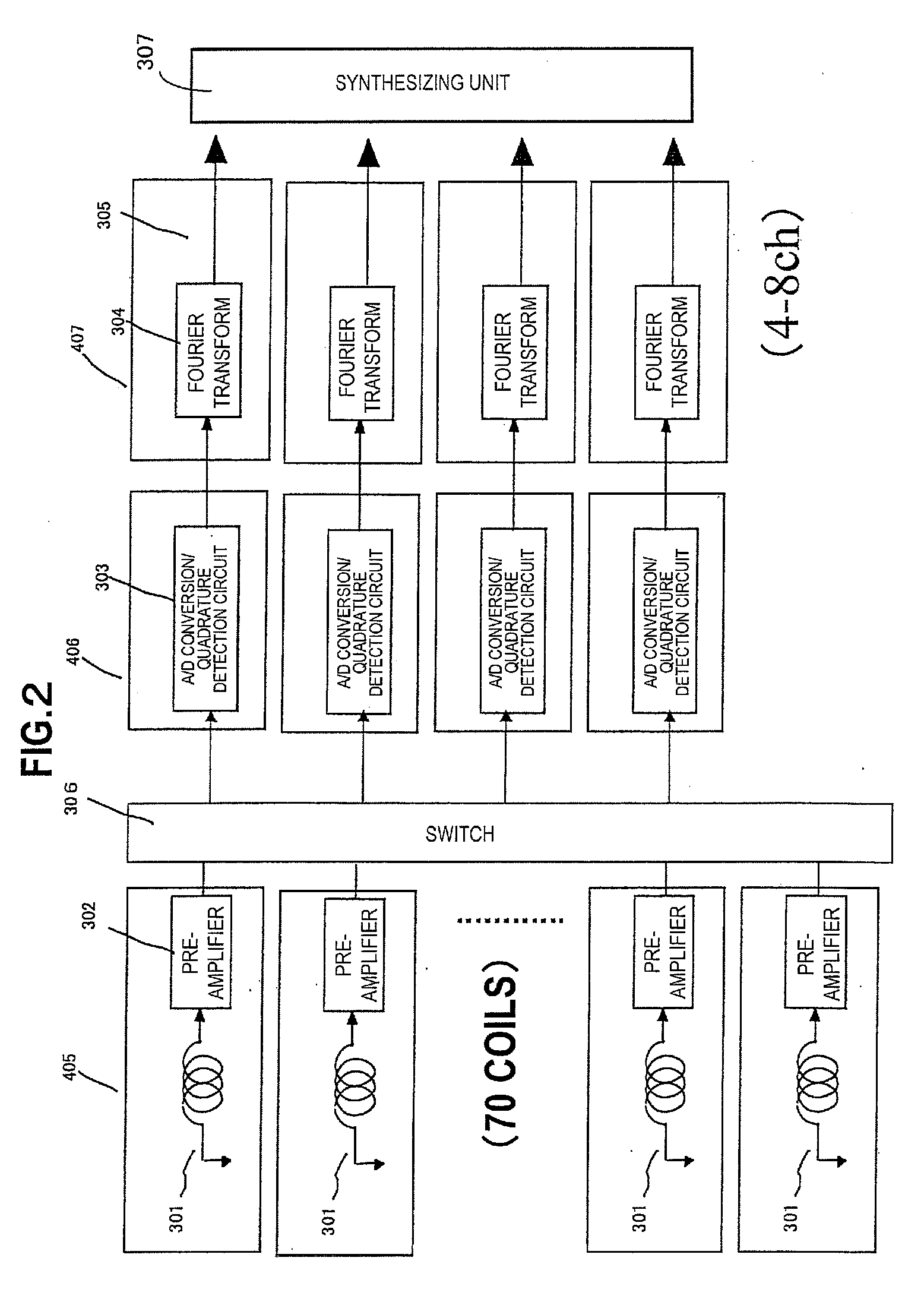
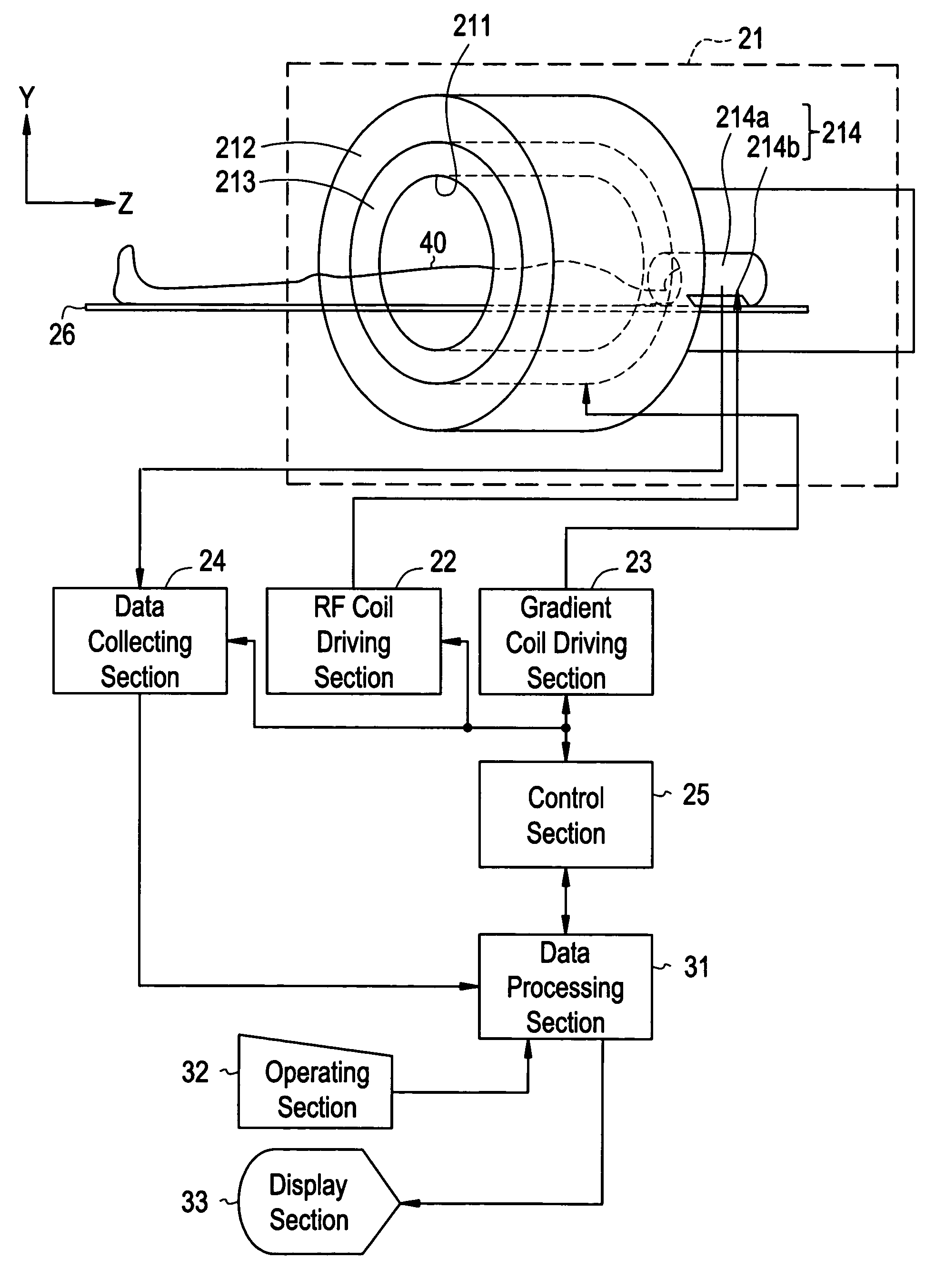
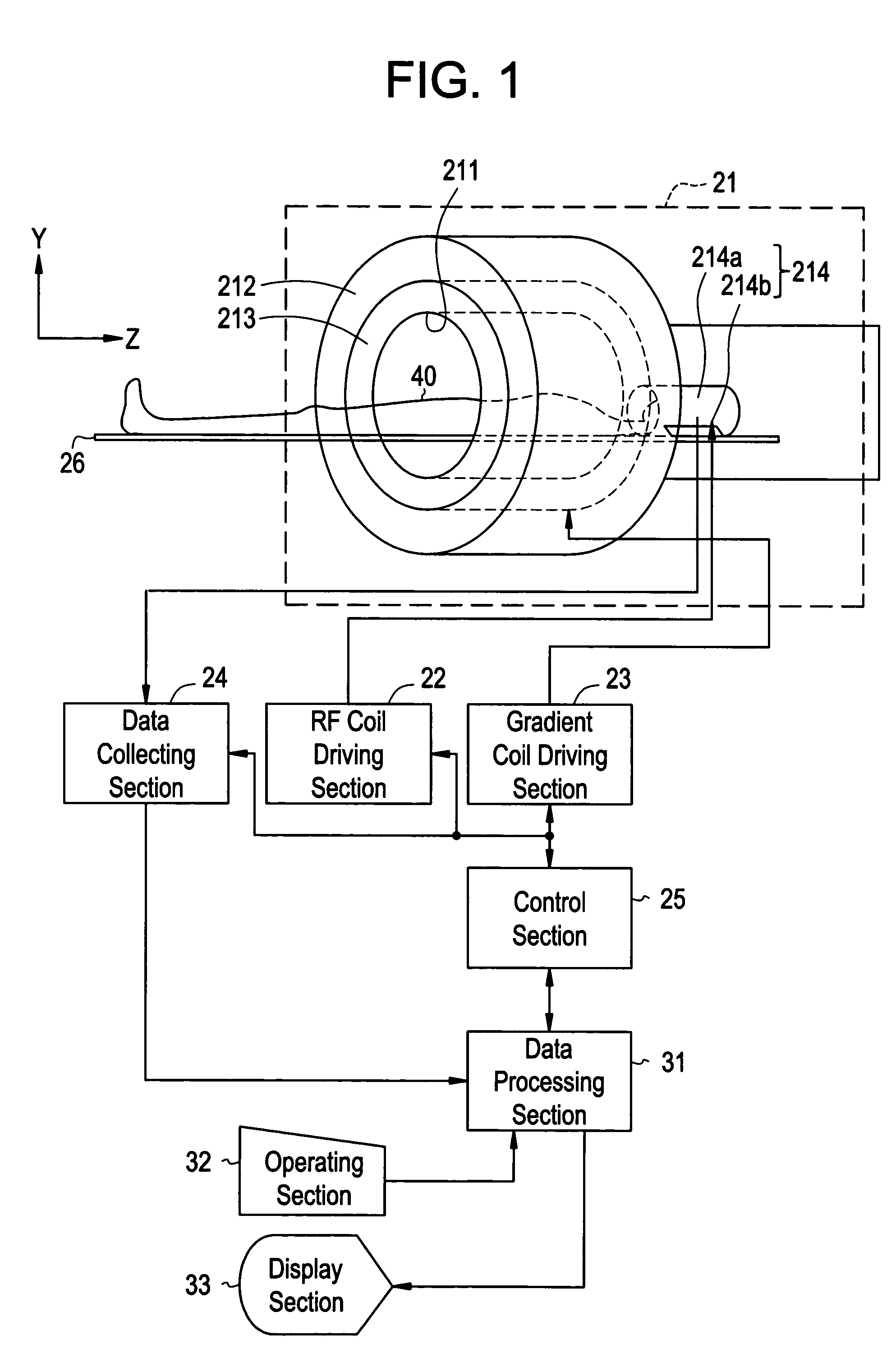
Magnetic resonance imaging system
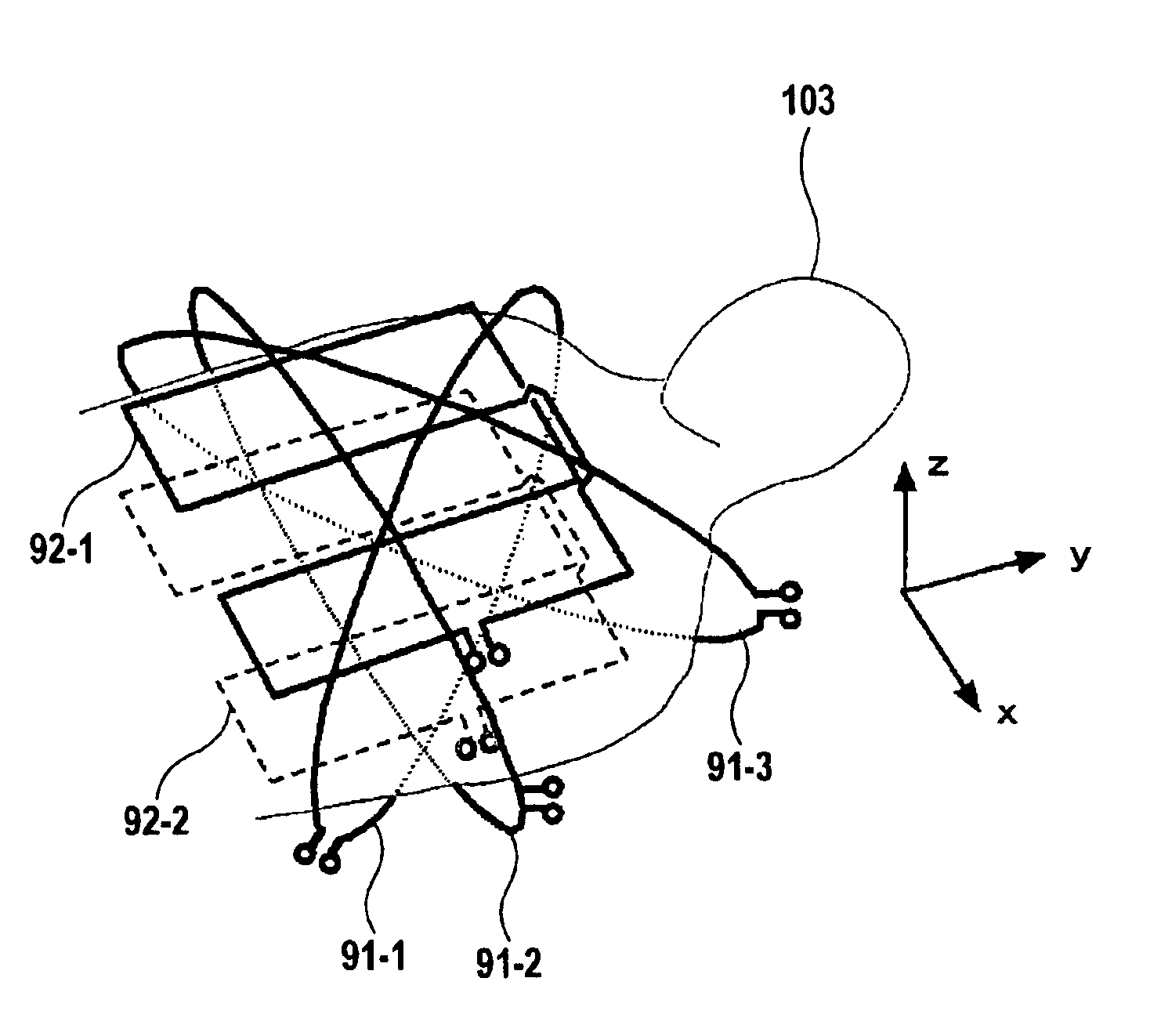
InactiveUS7061242B2Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSurface coil
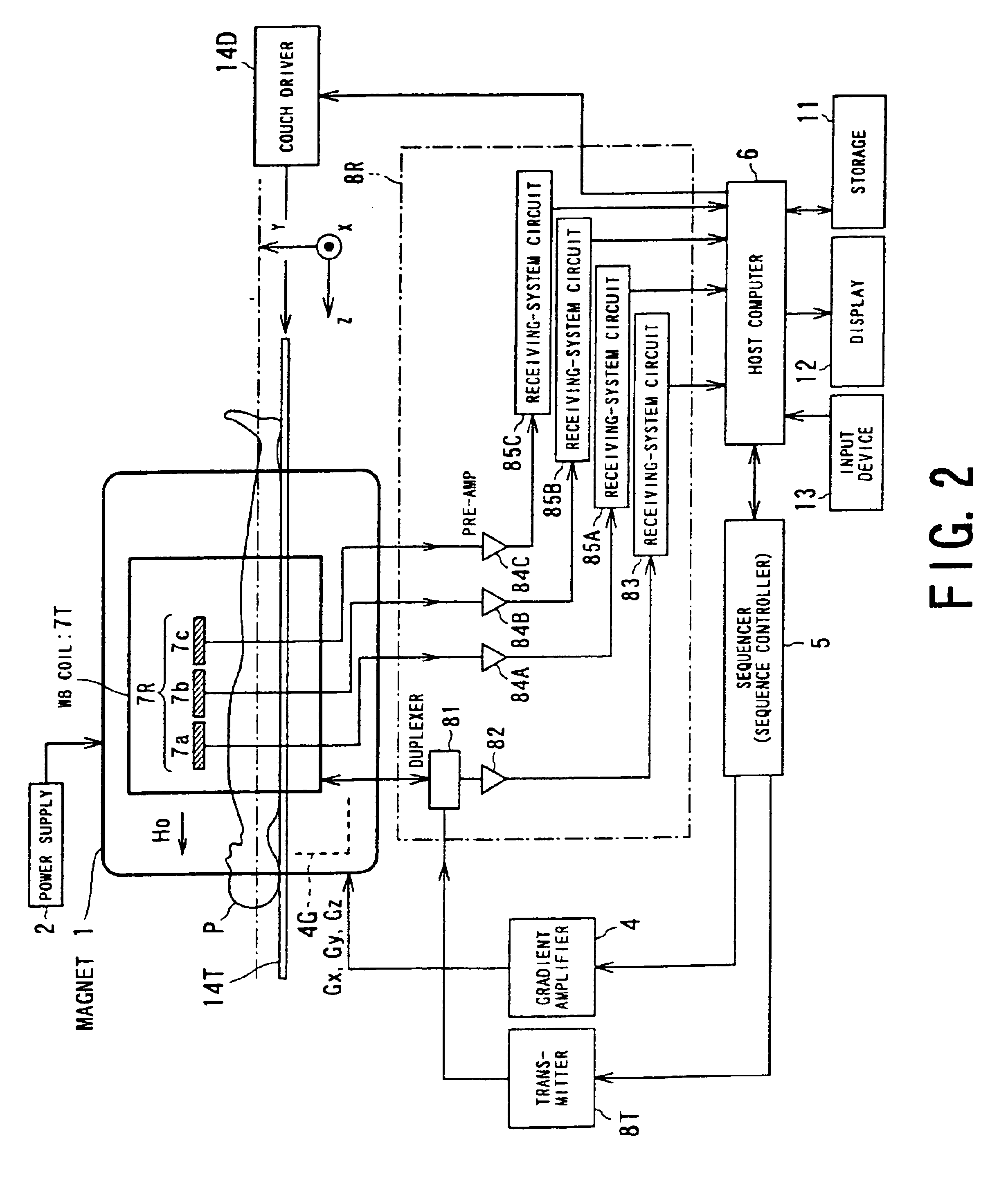
To provide a diagnostic apparatus utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance suitable for interventional MRI which is not limited as to selection of an imaging section and an phase-encoding axis, the reception coil thereof includes three loop coils arranged so as to surround an object to be examined and to be within a plane including a line segment parallel to a static magnetic field direction, and two surface coils arranged in the vicinity of the surface of the object within a plane including a line segment perpendicular to the static magnetic field direction. In the reception coil, two or more sub-coils have nonuniform sensitivity profiles along an arbitrary axis. Therefore, the reception coil configured to have sensitivity throughout the imaging areas can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Photosensitive composition, pattern forming material, photosensitive laminate, pattern forming apparatus and method of pattern formation
ActiveCN101052918AGood reproducibilityInhibition biasSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringSensitivity distribution
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS7015696B2Accurate calculationAccurate imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsProton magnetic resonanceT2 weighted
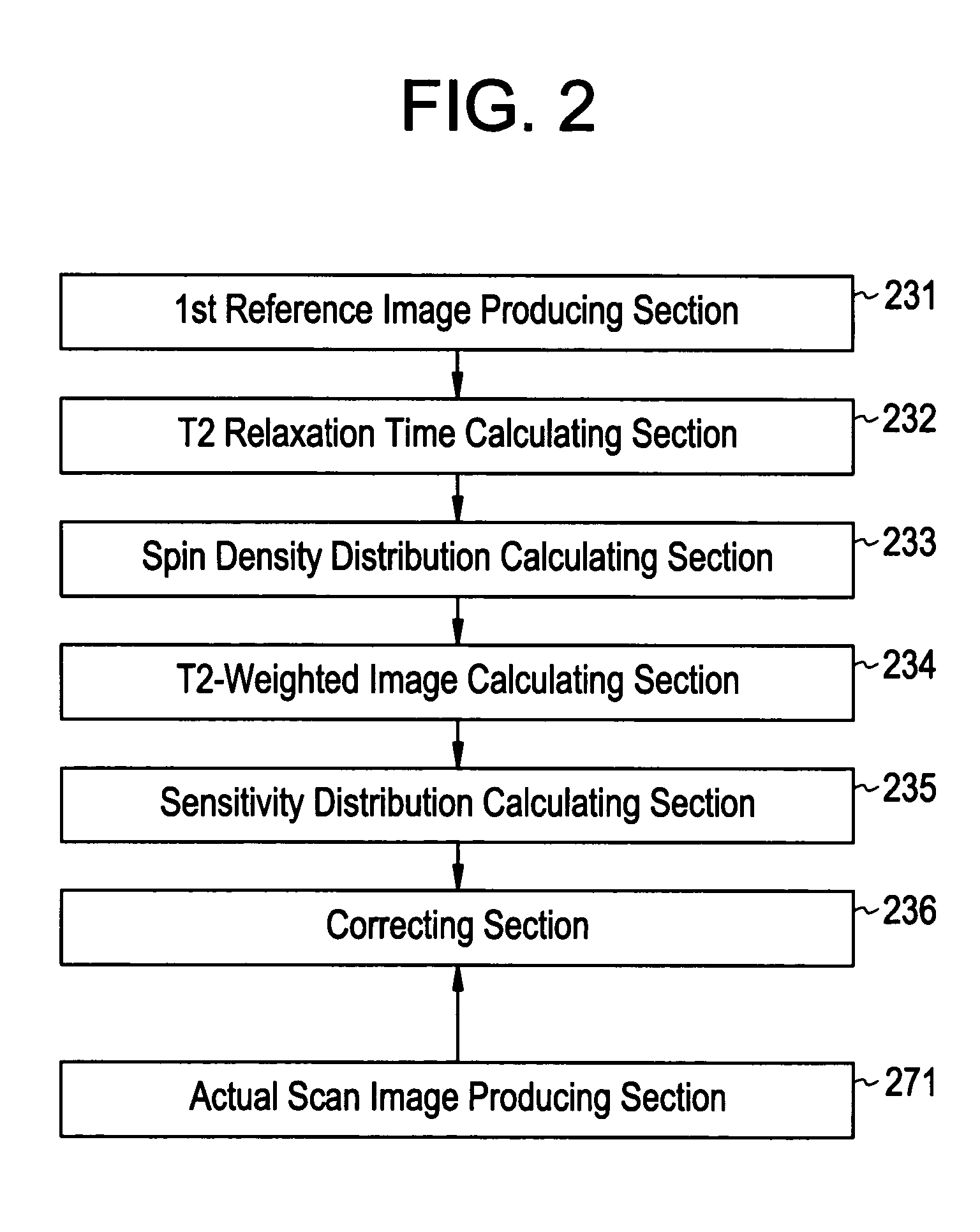
A method for calculating a sensitivity distribution of a receive coil and taking a tomographic image of a subject, based on magnetic resonance signals received by a surface coil in an imaging sequence with a plurality of different echo times TE1 and TE2 in a reference scan, a plurality of reference images are produced by a first reference image producing section; and based on the plurality of reference images, a T2 relaxation time is calculated by a T2 relaxation time calculating section. Then, based on the calculated T2 relaxation time, a T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2 is calculated by a T2-weighted image calculating section, and thereafter, based on the reference image and T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2, a sensitivity distribution is calculated by a sensitivity distribution calculating section. Based on the sensitivity distribution, a tomographic image by an actual scan is corrected by a correcting section.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
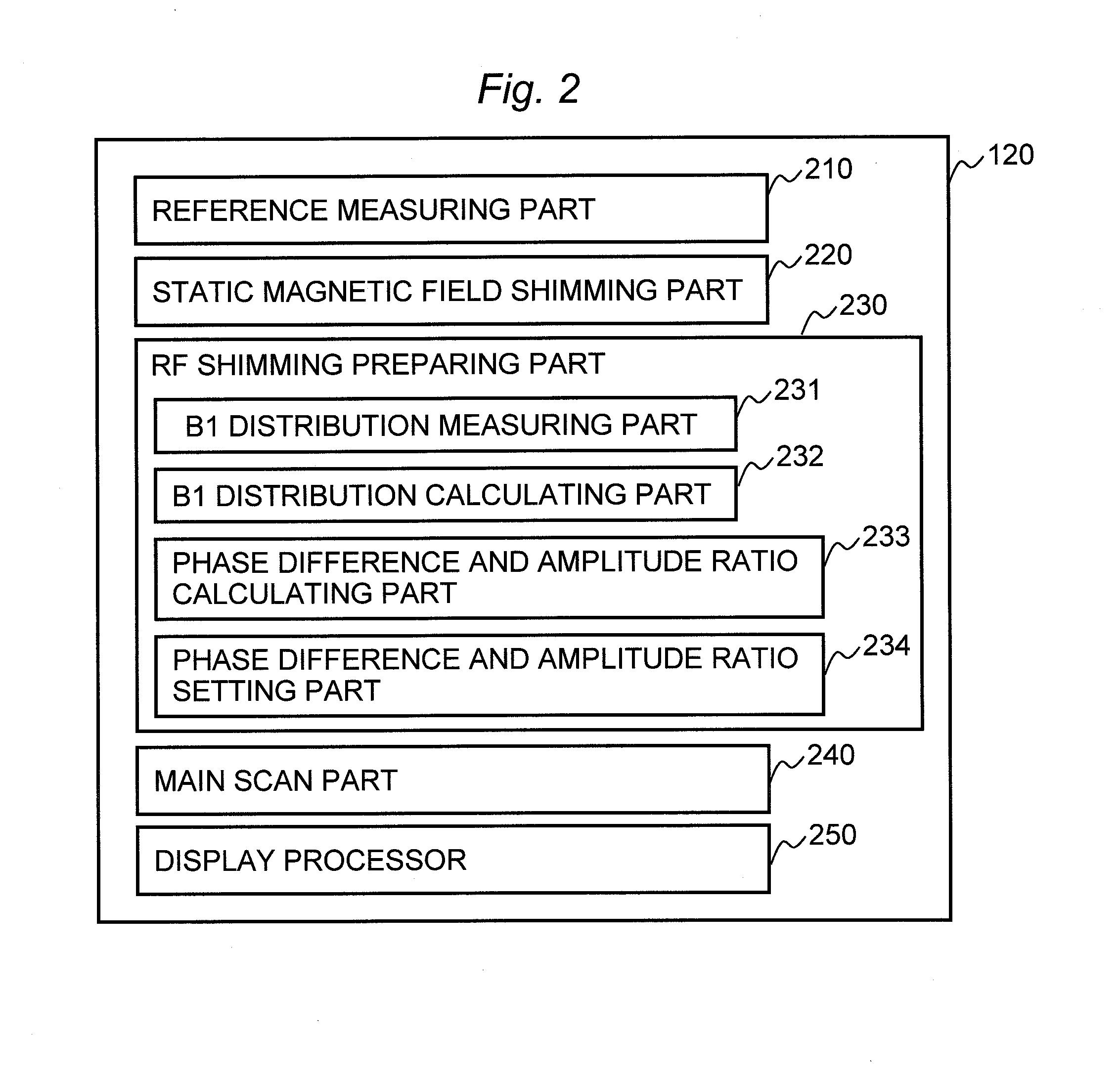
Magnetic resonance imaging device and transmitting sensitivity distribution calculation method
ActiveUS20130082708A1High quality imagingHigh precisionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase differenceReference image
B1 distribution is calculated in a short time with a high degree of precision, and a high quality image is obtained. In the RF shimming for irradiating electromagnetic waves using an RF coil having multiple channels, the absolute values of subtraction images between multiple reconstructed images are used to calculate a transmitting sensitivity distribution which is necessary for calculating inter-channel phase difference and amplitude ratio of RF pulses provided to the respective channels. Those multiple reconstructed images are obtained by executing the imaging sequence after applying a prepulse at different flip angles respectively. Assuming an image obtained with a minimum flip angle as a reference image, for instance, the subtraction images are created between the reference image and the other respective images. It is also possible that multiple subtraction images being obtained are divided by one another, and the transmitting sensitivity distribution is created on the basis of the division result.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Conductive sensor for phase seperation containing rate in two-phase stream and structure parameter optimizing method thereof
InactiveCN101419180APrevent floatingLarge measuring rangeMaterial resistanceAnalytic modelFast measurement
The invention provides a two-phase flow split rate conductive sensor. The sensor consists of a conducting ring layer, and an exciting electrode couple and a measuring electrode couple which are attached to the conducting ring layer, wherein exciting electrodes and measuring electrodes are symmetrically and spirally distributed according to an angle of 180 degrees in the radial direction of a tube wall of the conducting ring layer. At the same time, the invention also provides a structural parameter optimizing method based on the structure of the sensor. The method has the advantages of aiming at real-time measurement of two-phase flow rate, overcoming the defect of floating of a measured electrode caused by contact of a measured electrode and a non-conductive substance in the prior conductive sensor, providing a conductive electrical sensor, providing an expression of sensitivity distribution of any point on a two-dimensional sensor cross section based on an analytic model of the conductive electrical sensor, and quickly optimizing a structural parameter. The method belongs to non-intrusive quick measurement, widens measurement range, and has low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
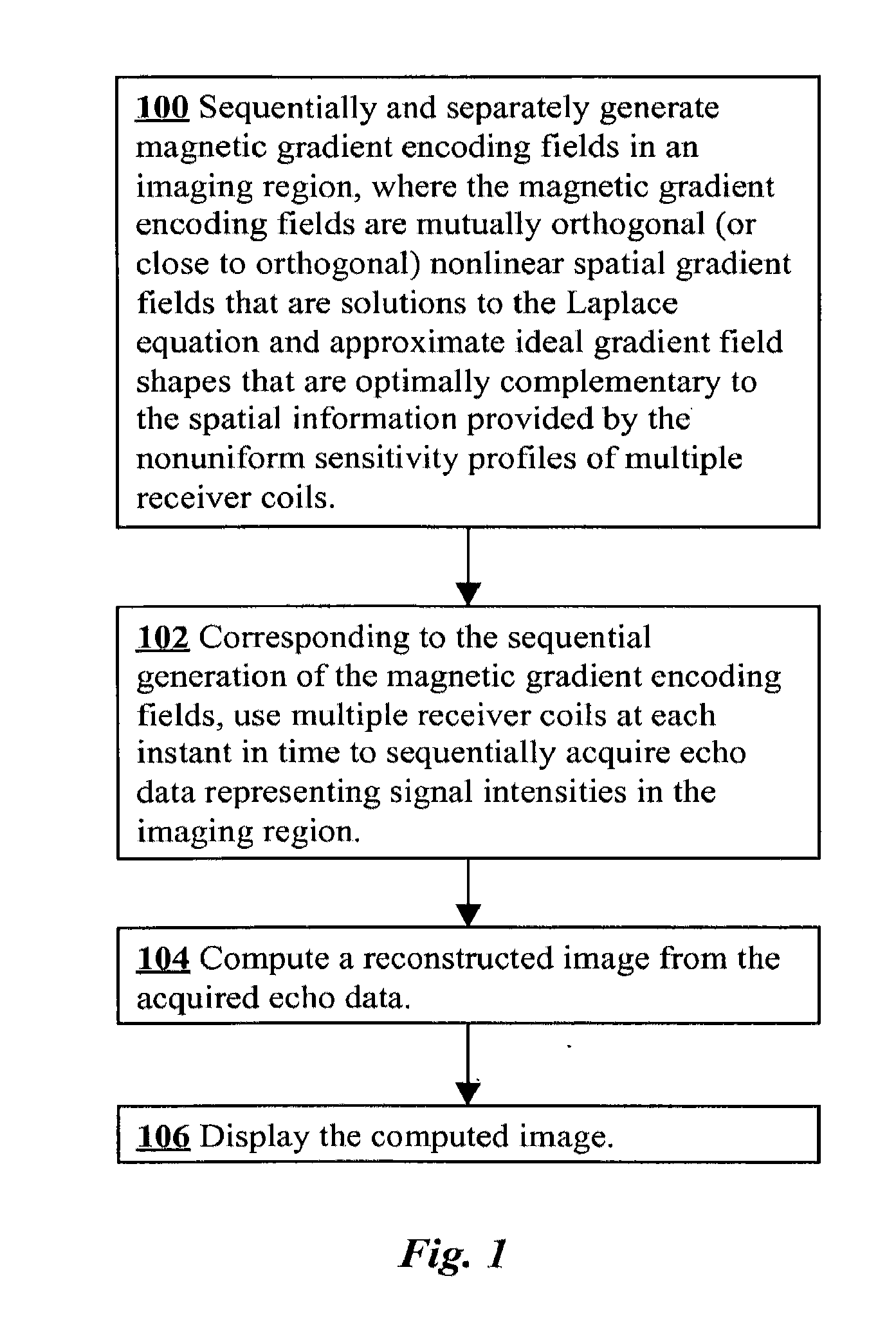
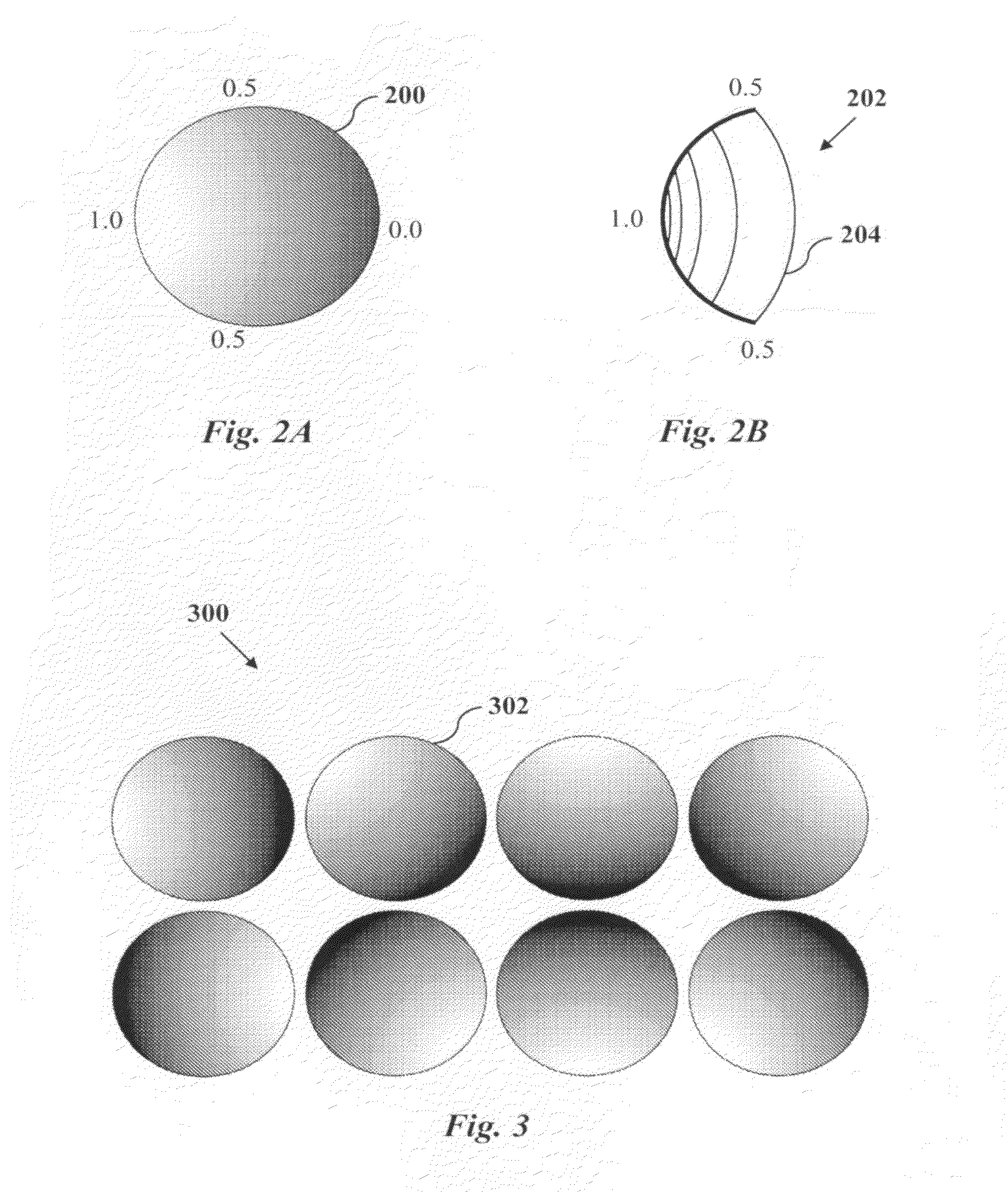
Accelerated MRI with Nonlinear Spatial Encoding Gradients
ActiveUS20120286783A1High quality imagingReduce scan timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientReceiver coil
In a method of magnetic resonance imaging, a set of nonlinear, mutually orthogonal magnetic gradient encoding fields are sequentially and separately generated in an imaging region [100]. Using multiple receiver coils having nonuniform sensitivity profiles, echo data representing signal intensities in the imaging region is sequentially acquired as the magnetic gradient encoding fields are sequentially generated [102]. A reconstructed image of the imaging region is computed from the acquired echo data [104], and the reconstructed image is then be stored and / or displayed on a display monitor [106].
Owner:YALE UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance imager and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveCN1530072AEliminate wrinkling artifactsNo loss of image qualityLaser detailsLighting and heating apparatusPhase correctionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
For the purpose of removing wraparound artifacts without degrading image quality of an image, there are provided a phase correcting section (1072) for conducting phase correction processing on received signals in an actual scan based on a reference signal as a corrective signal received by one of a plurality of receive coils (1013), without applying a gradient magnetic field Gp in a phase encoding direction, and an unfolding section (1075) for removing wraparound artifacts in an image based on the signals received by the plurality of receive coils (1013) in the actual scan and subjected to the phase correction processing by the phase correcting section (1072), and on the difference in sensitivity distribution among the plurality of receive coils (1013), so that the phase correction processing is conducted while preserving the relative phase relationship among the coils, and unfolding processing (removal processing) is conducted using the result of such phase correction processing.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Fresh water acute criteria prediction method based on quantitative structure-activity relationship for metals
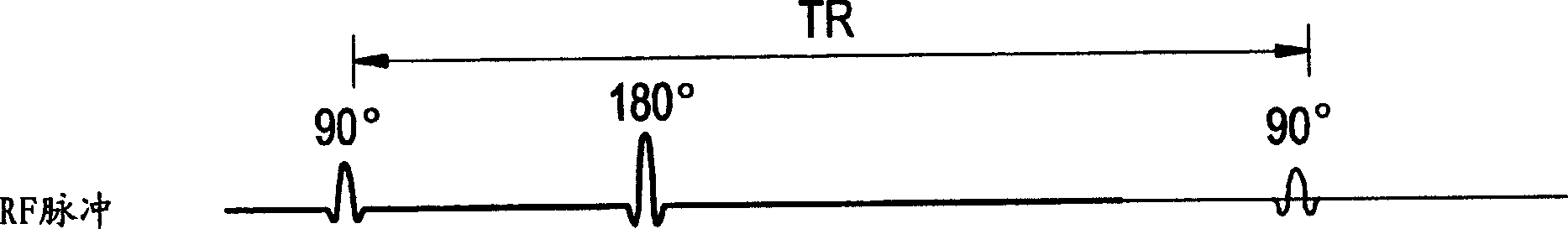
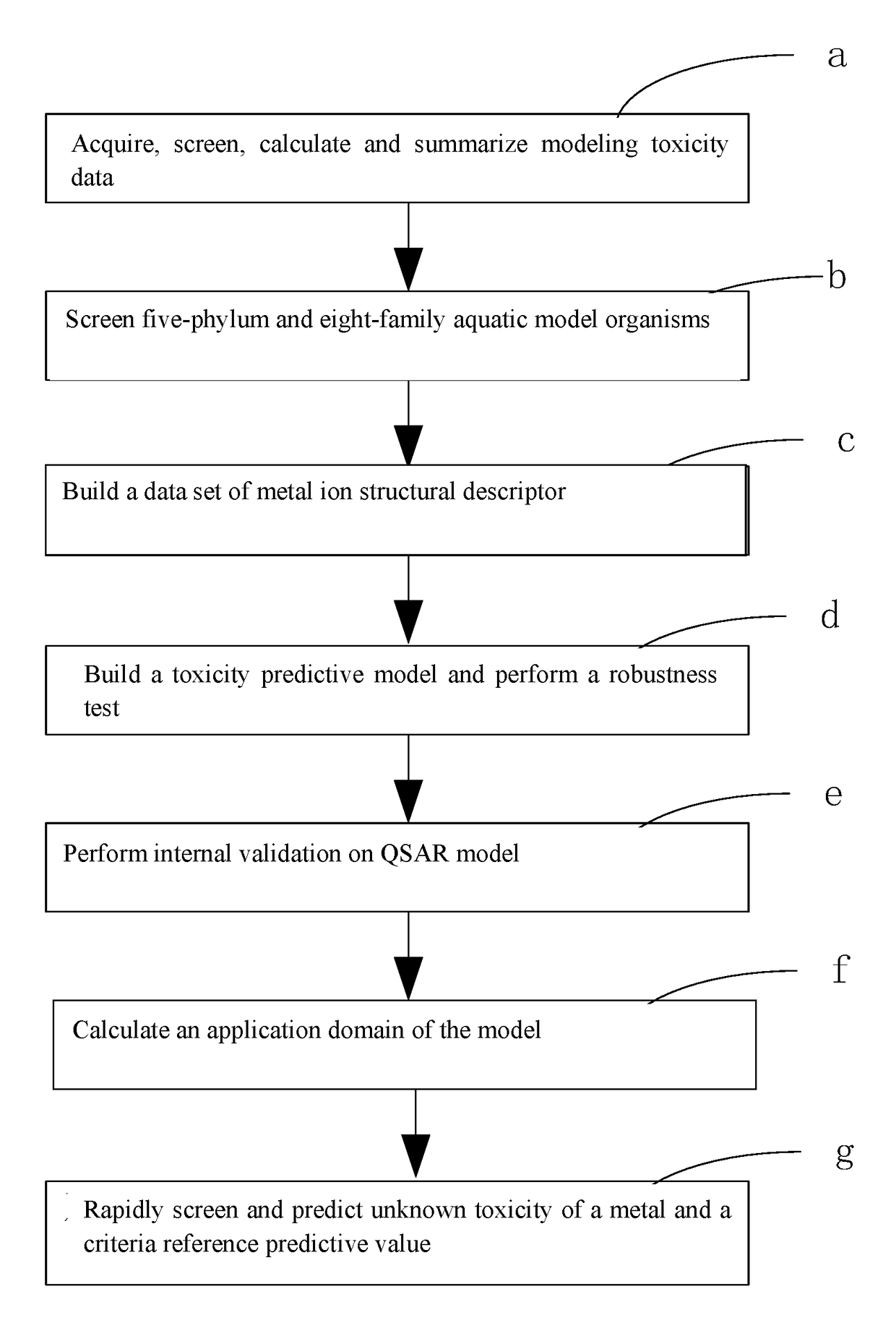
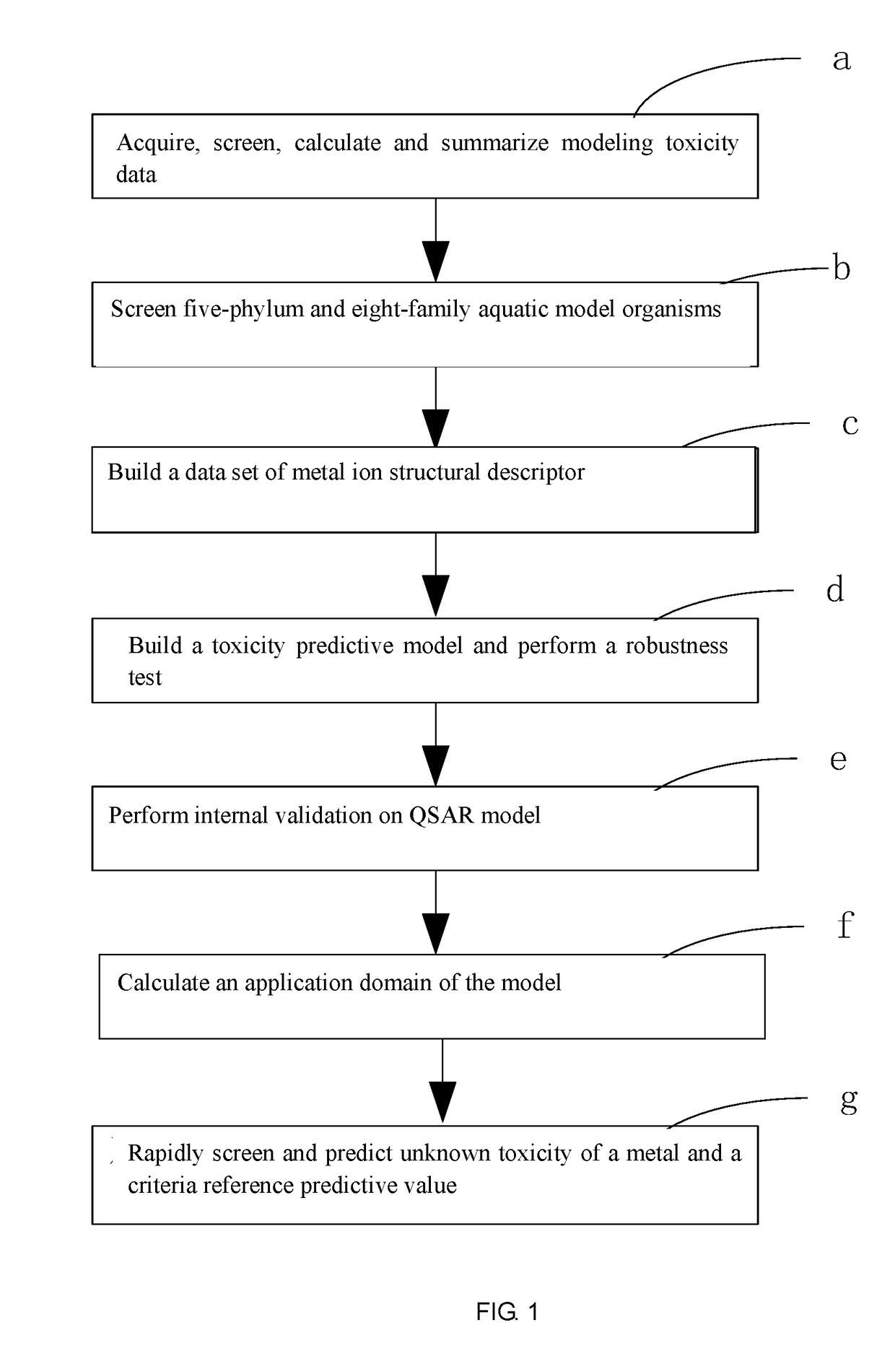
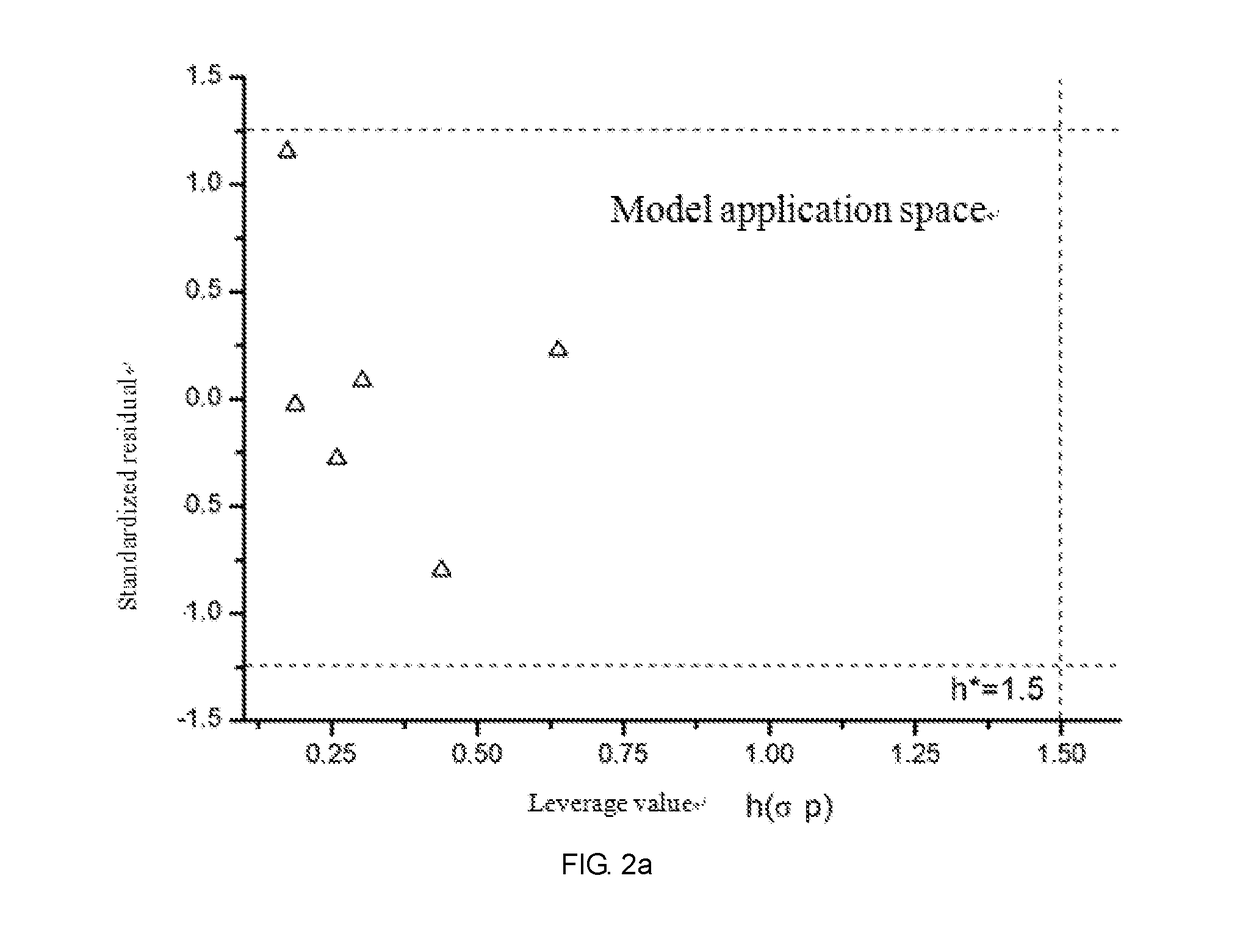
ActiveUS20170323085A1Improve precisionPredict in advanceChemical property predictionForecastingChemical structureAcute toxicity testing
The present invention relates to a fresh water acute criteria prediction method based on a quantitative structure-activity relationship for metals. An unknown toxic endpoint of a metal is predicted according to a quantitative relationship between structural characteristics of heavy metal ions and acute toxicity effects of aquatic organisms, and hazard concentrations for protecting the aquatic organisms of different proportions are derived from sensitivity distribution analysis on different species. The fresh water acute criteria prediction method is a method for establishing a metal toxicity predictive model by integrating physicochemical structural parameters of heavy metals and toxic mechanisms of different aquatic organisms and applying the metal toxicity predictive model to prediction of an unknown criteria reference value.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com