Patents
Literature
4327results about "Colour-separation/tonal-correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
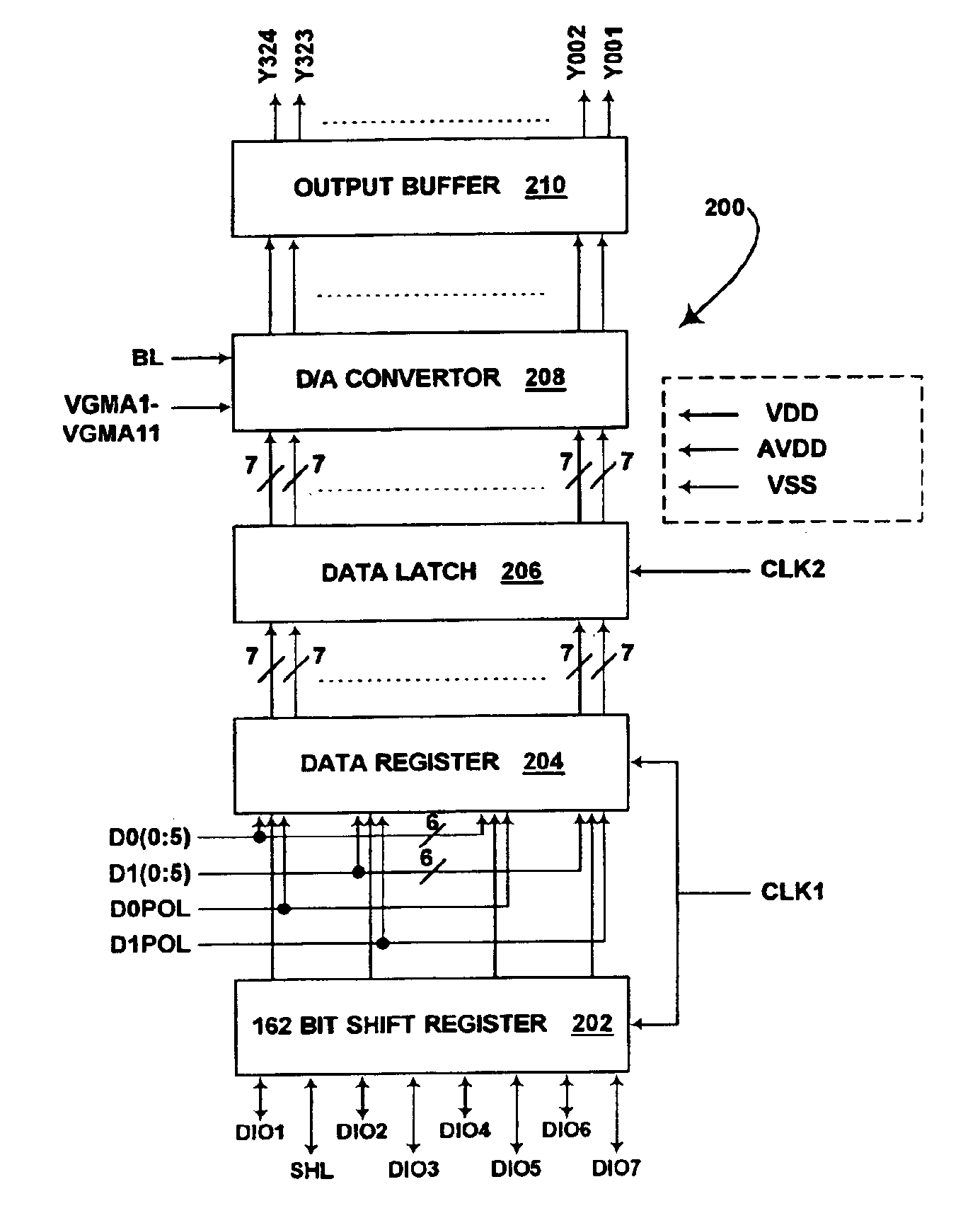
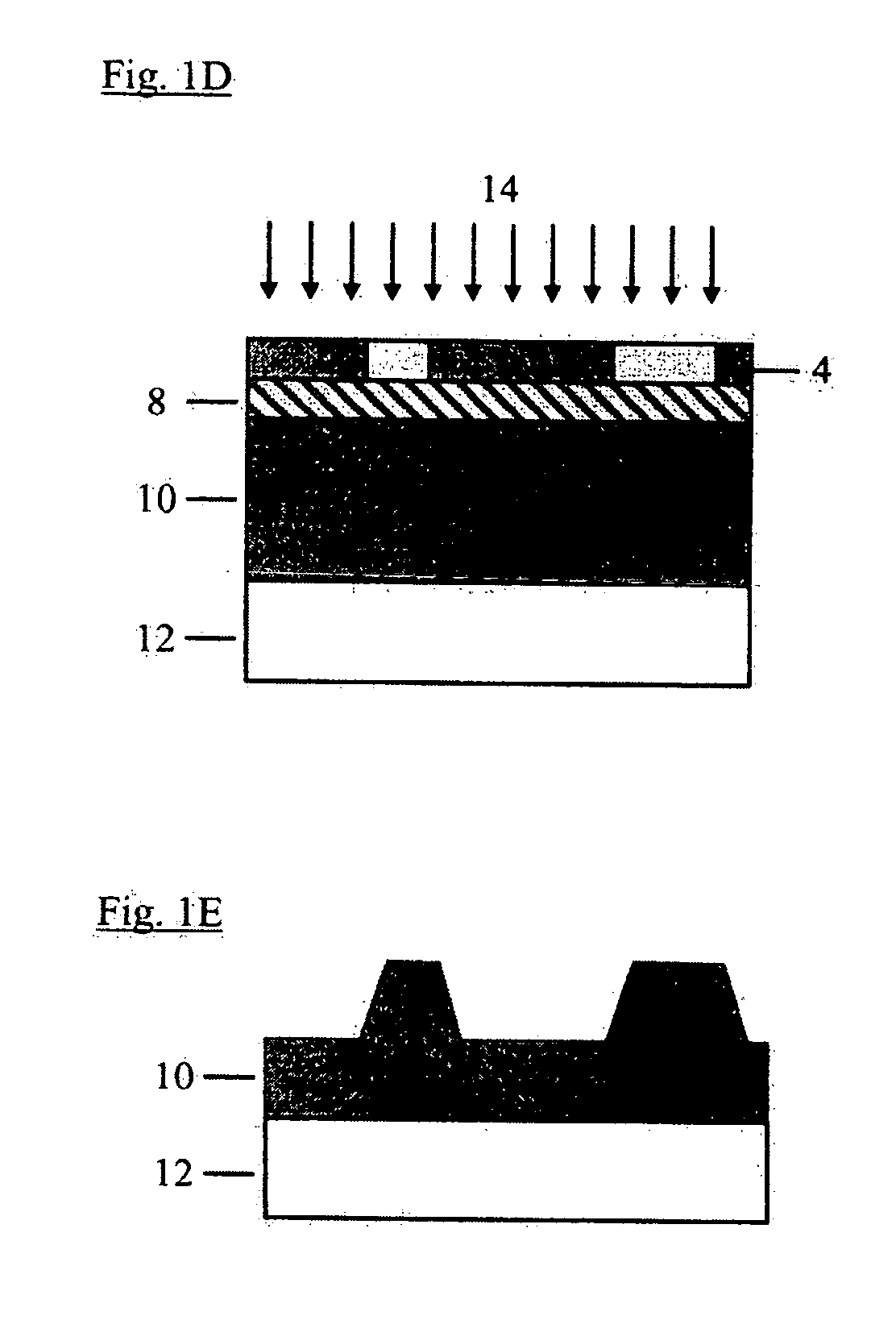
Methods for driving bistable electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS7012600B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGray levelDisplay device
A bistable electro-optic display has a plurality of pixels, each of which is capable of displaying at least three gray levels. The display is driven by a method comprising: storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary to convert an initial gray level to a final gray level; storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display; receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary to convert the initial state of said one pixel to the desired final state thereof, as determined from said look-up table. The invention also provides a method for reducing the remnant voltage of an electro-optic display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
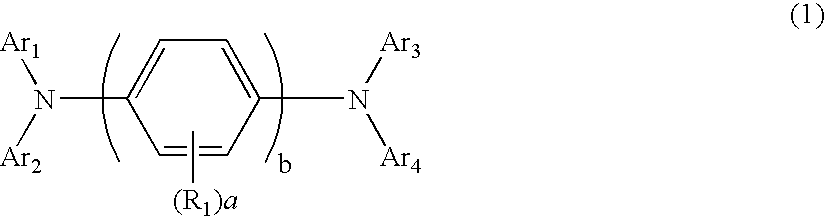
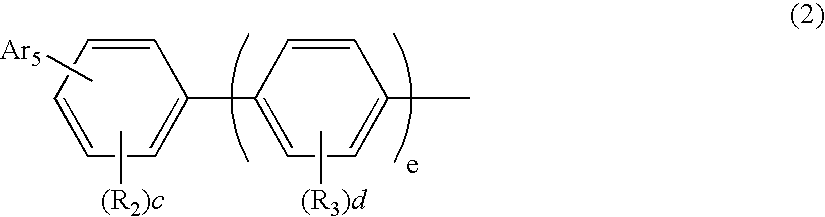
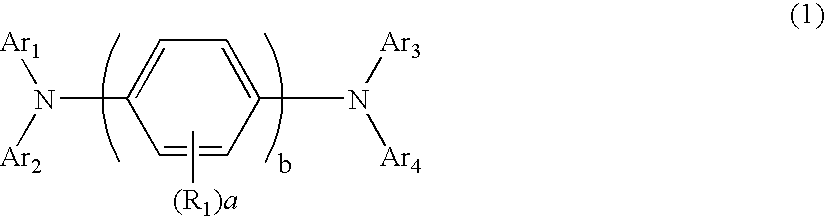
Aromatic amine derivatives and organic electroluminescence device using the same
InactiveUS20070145888A1Increase productionLong life-timeOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceAmine derivatives
Provided are: a novel aromatic amine derivative having an asymmetric structure; and an organic electroluminescence device having one or multiple organic thin film layers including at least a light emitting layer, the one or multiple organic thin film layers being interposed between a cathode and an anode. The aromatic amine derivative realizes the organic EL device capable of suppressing the crystallization of a molecule, improving yields upon production of the organic EL device, and having a long lifetime when at least one layer of the one or more multiple organic thin film layers contains the aromatic amine derivative alone or as a component of a mixture.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
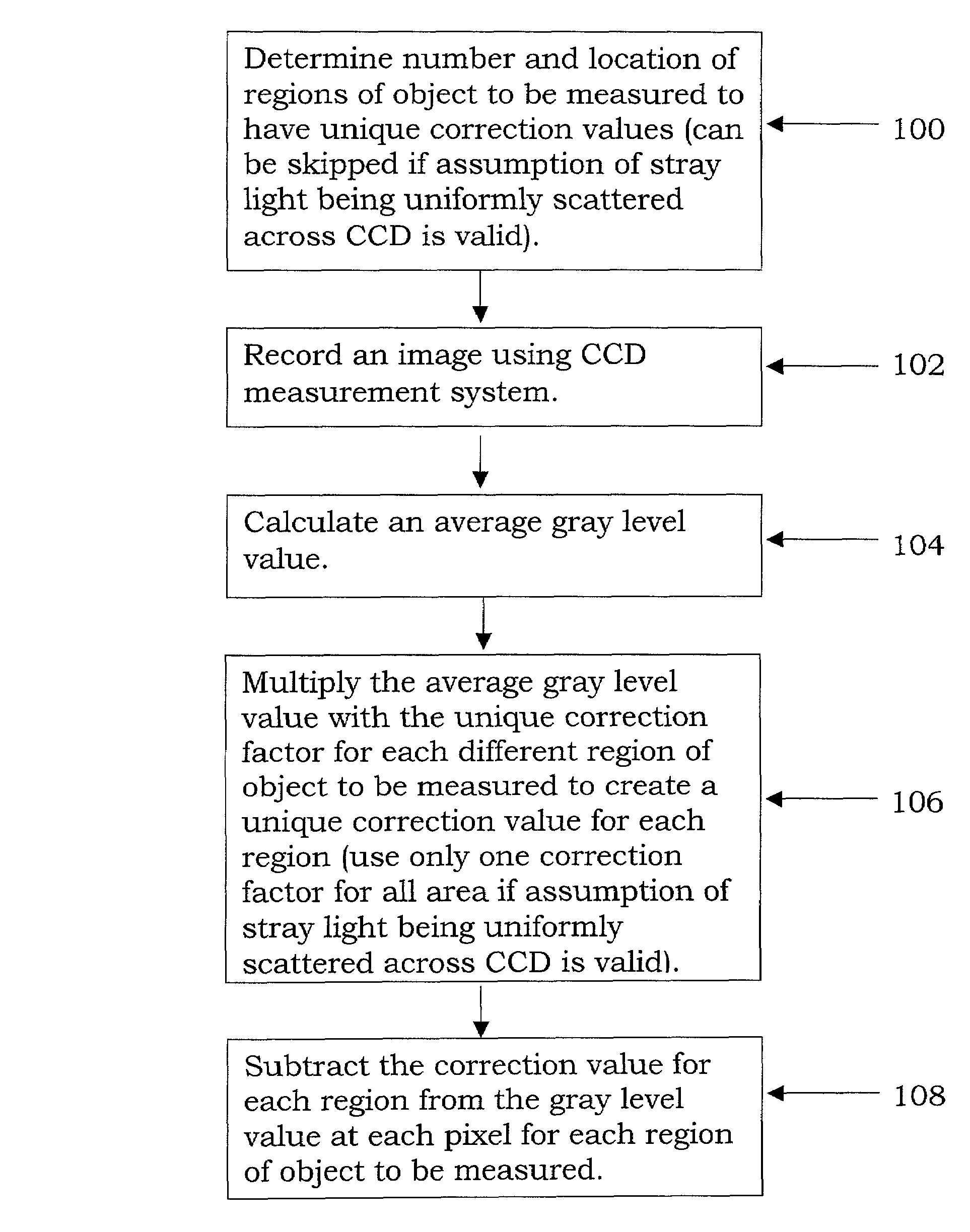
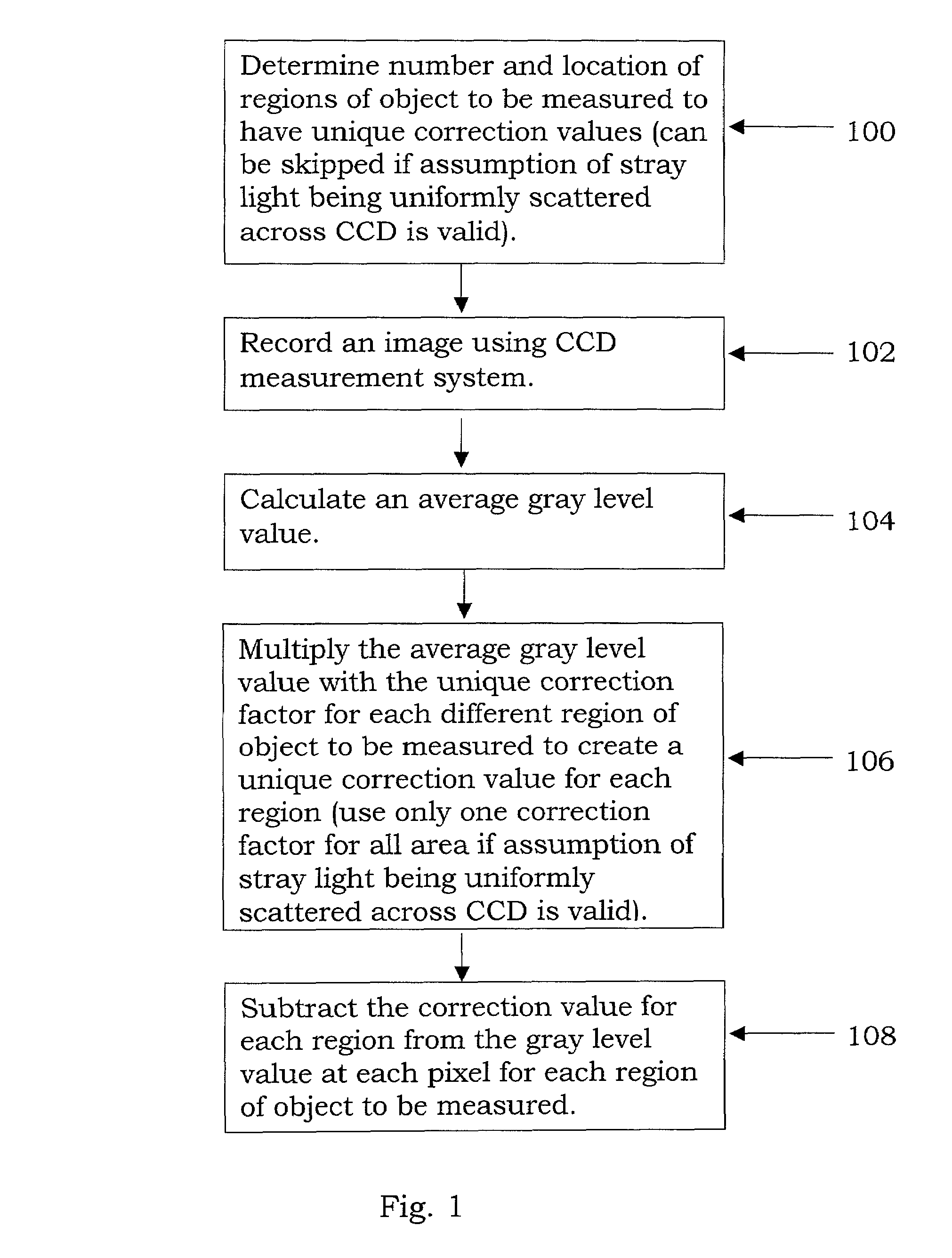
Stray light correction method for imaging light and color measurement system
ActiveUS6975775B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease grayscaleTelevision system detailsImage enhancementGray levelOptoelectronics
A stray light correction method for image light and color measurement system, uses a solid-state light detector array such as a charge-coupled device to record an image, so that a gray level value for each pixel of the solid-state light detector array is obtained. An average gray level value of the solid-state light detector array is calculated based on the gray level value for each pixel. The average gray level value is further multiplied with a stray light factor to obtain a correction value. The gray level value of each pixel is then subtracted with the correction value, such that the stray light effect can be eliminated.
Owner:RADIANT ZEMAX
Method for transforming three color input signals to four or more output signals for a color display
InactiveUS6897876B2Preserve accuracyLife expectancyColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionGamut
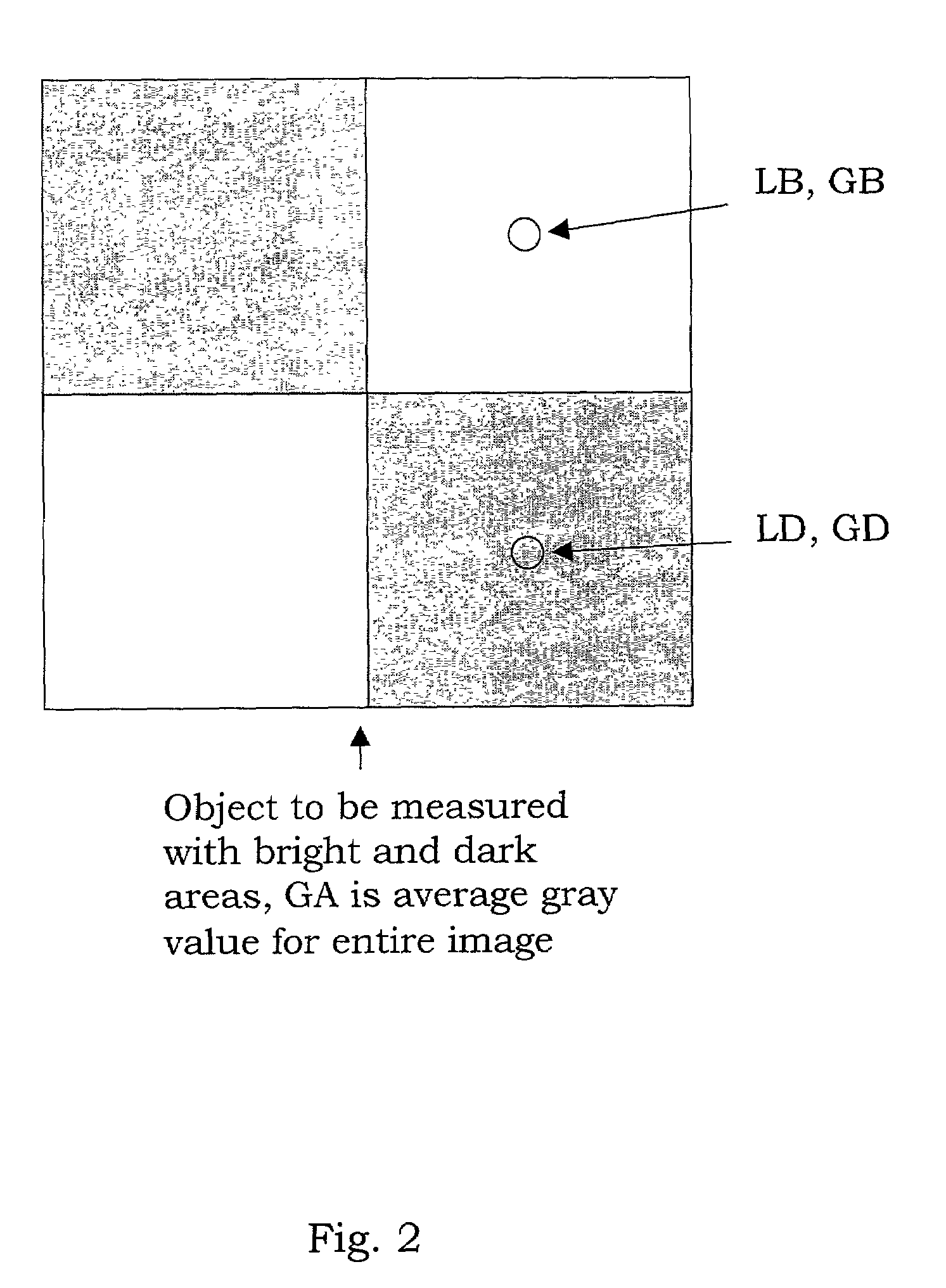
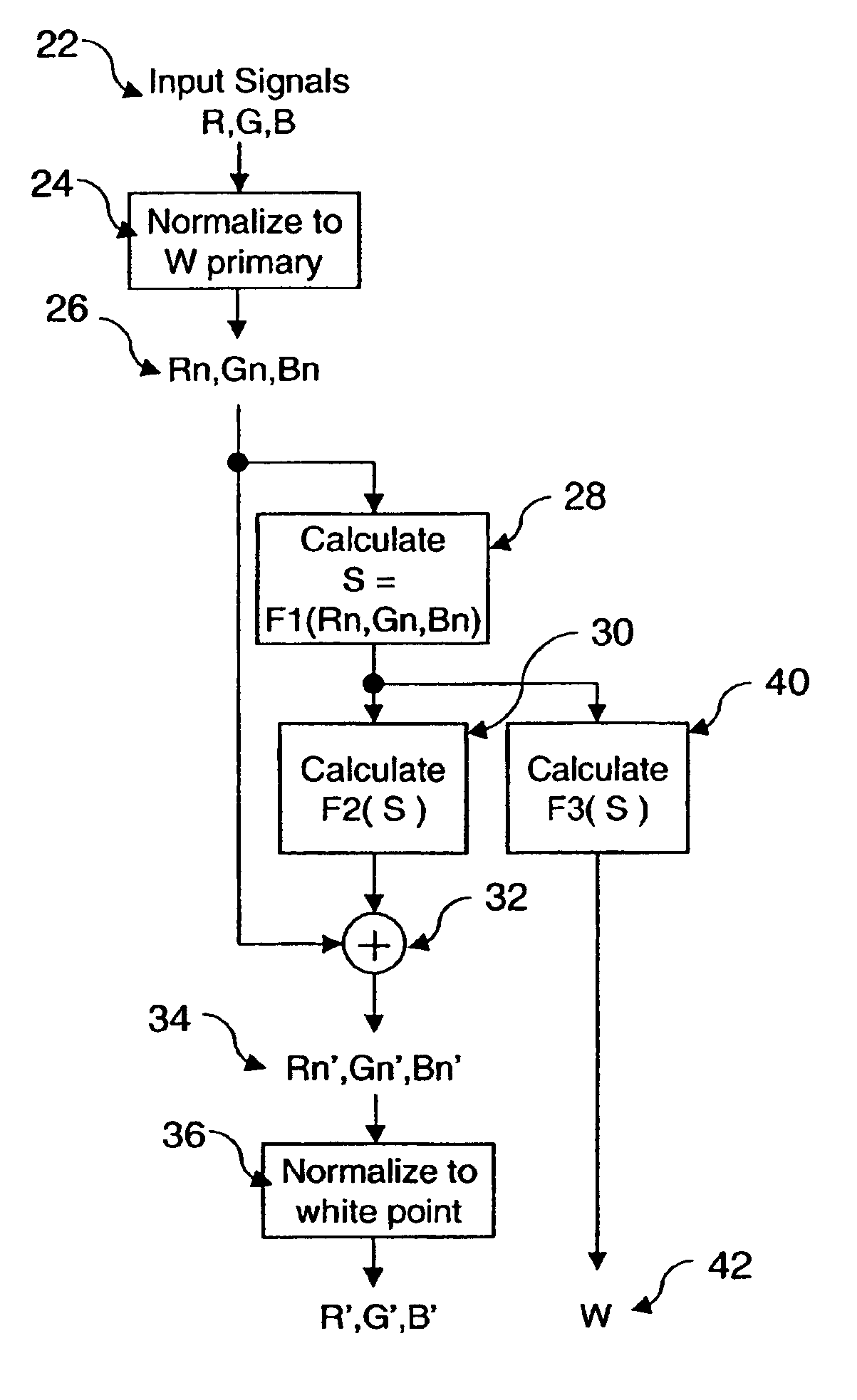
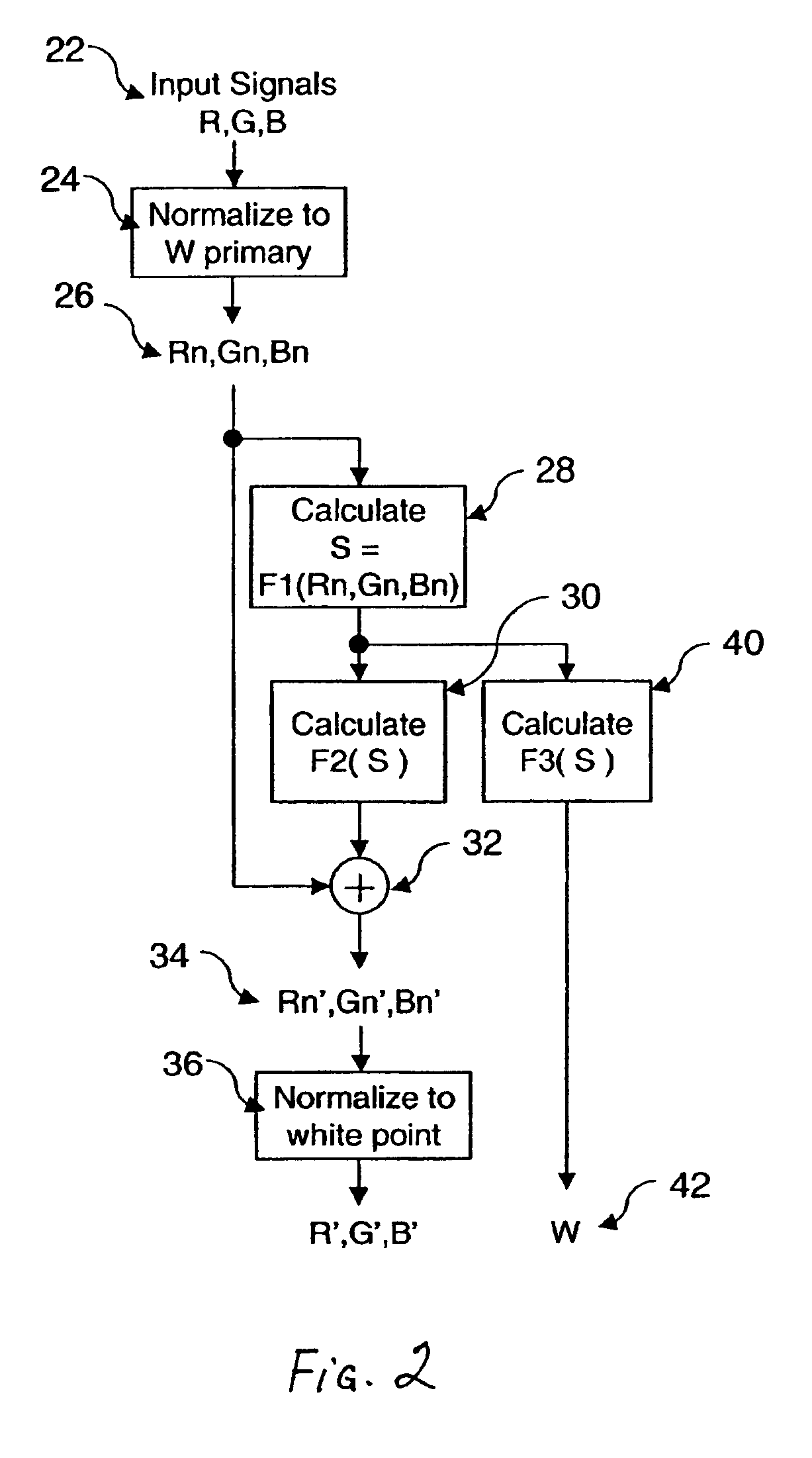
A method for transforming three color input signals (R, G, B) corresponding to three gamut defining color primaries to four color output signals (R′, G′, B′, W) corresponding to the gamut defining color primaries and one additional color primary W for driving a display having a white point different from W includes the steps of: normalizing the color input signals (R,G,B) such that a combination of equal amounts in each signal produces a color having XYZ tristimulus values identical to those of the additional color primary to produce normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn); calculating a common signal S that is a function F1 of the three normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn); calculating a function F2 of the common signal S and adding it to each of the three normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn) to provide three color signals (Rn′,Gn′,Bn′); normalizing the three color signals (Rn′,Gn′,Bn′) such that a combination of equal amounts in each signal produces a color having XYZ tristimulus values identical to those of the display white point to produce three of the four color output signals (R′,G′,B′); and calculating a function F3 of the common signal S and assigning it to the fourth color output signal W.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
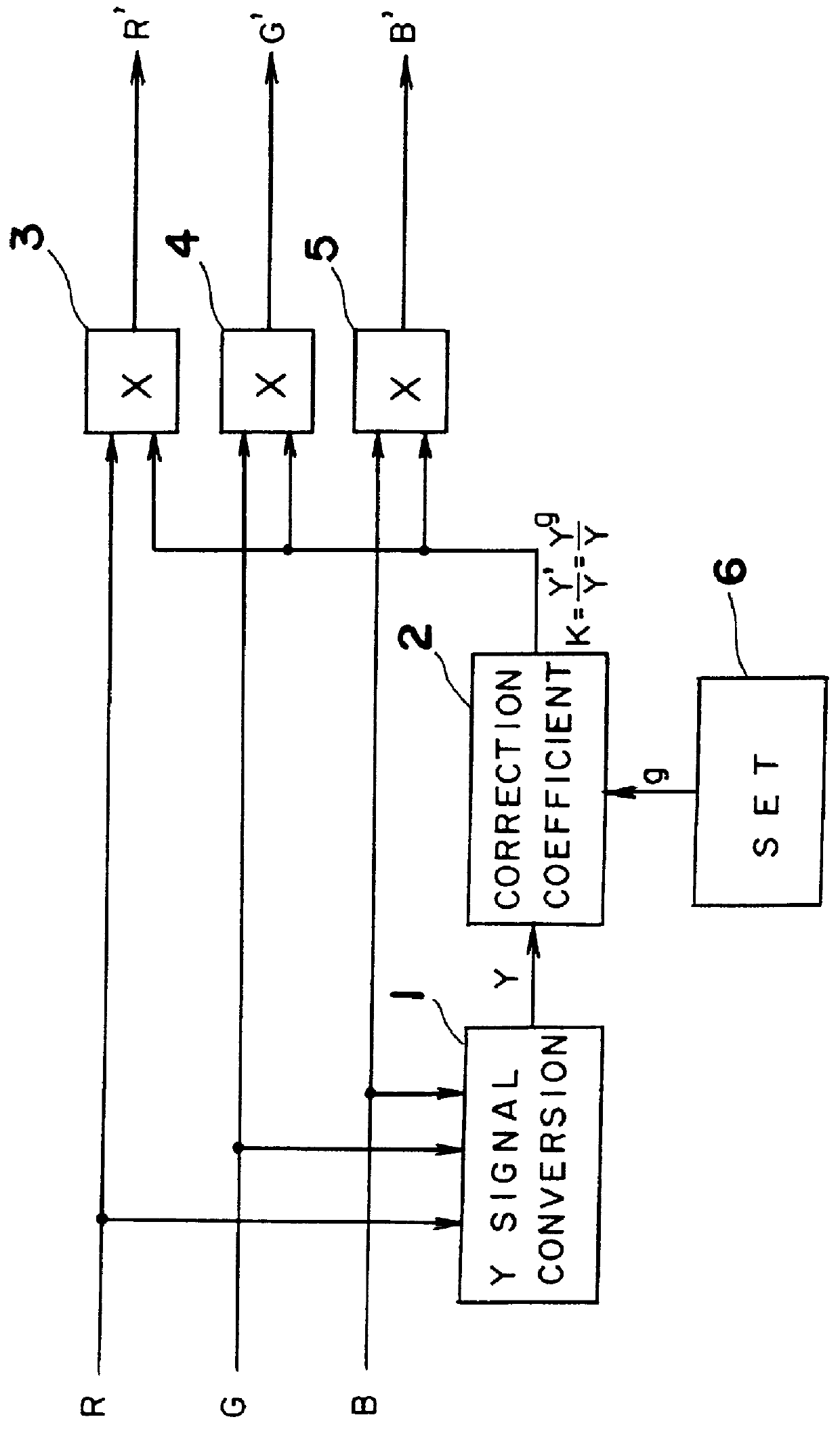
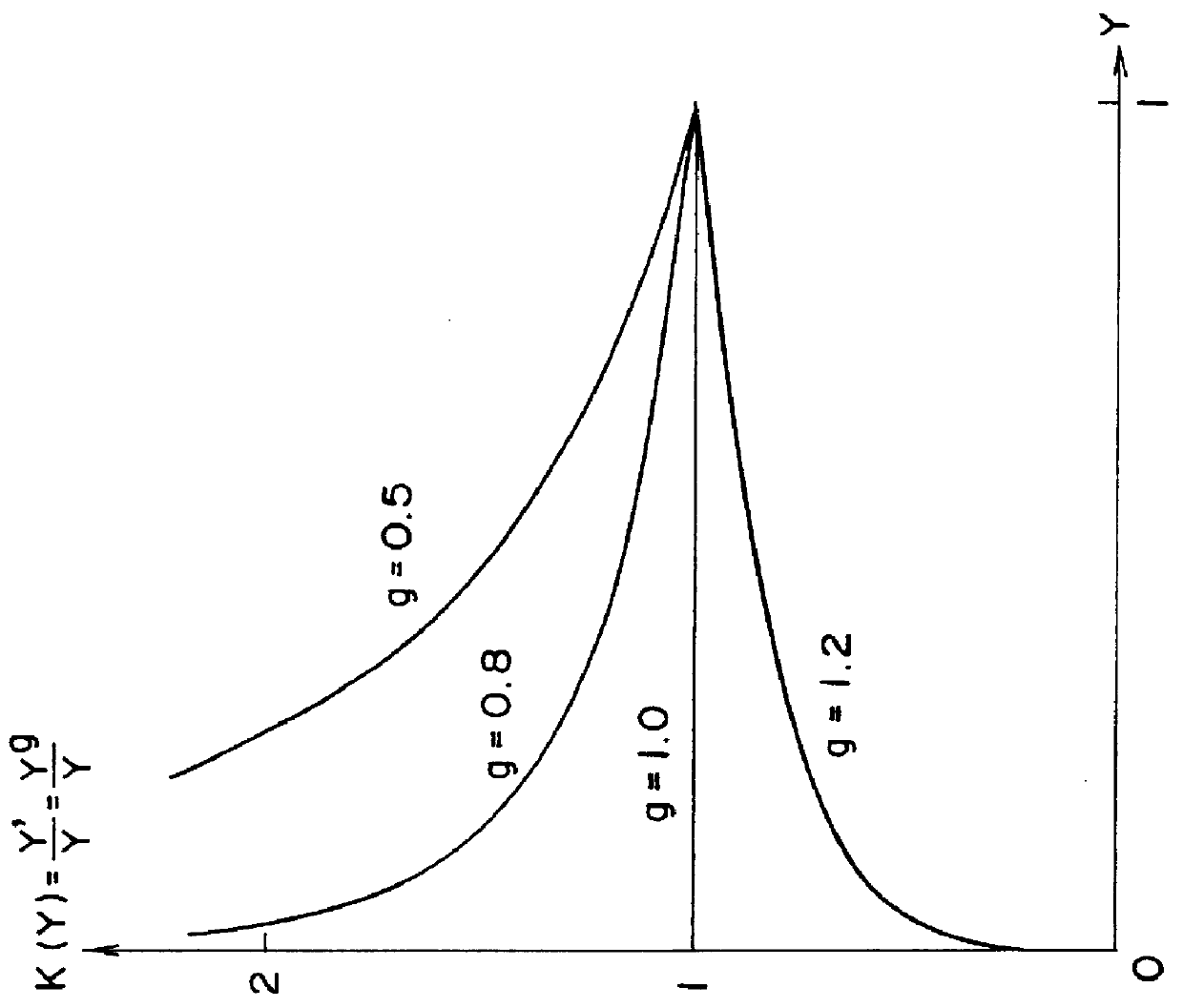
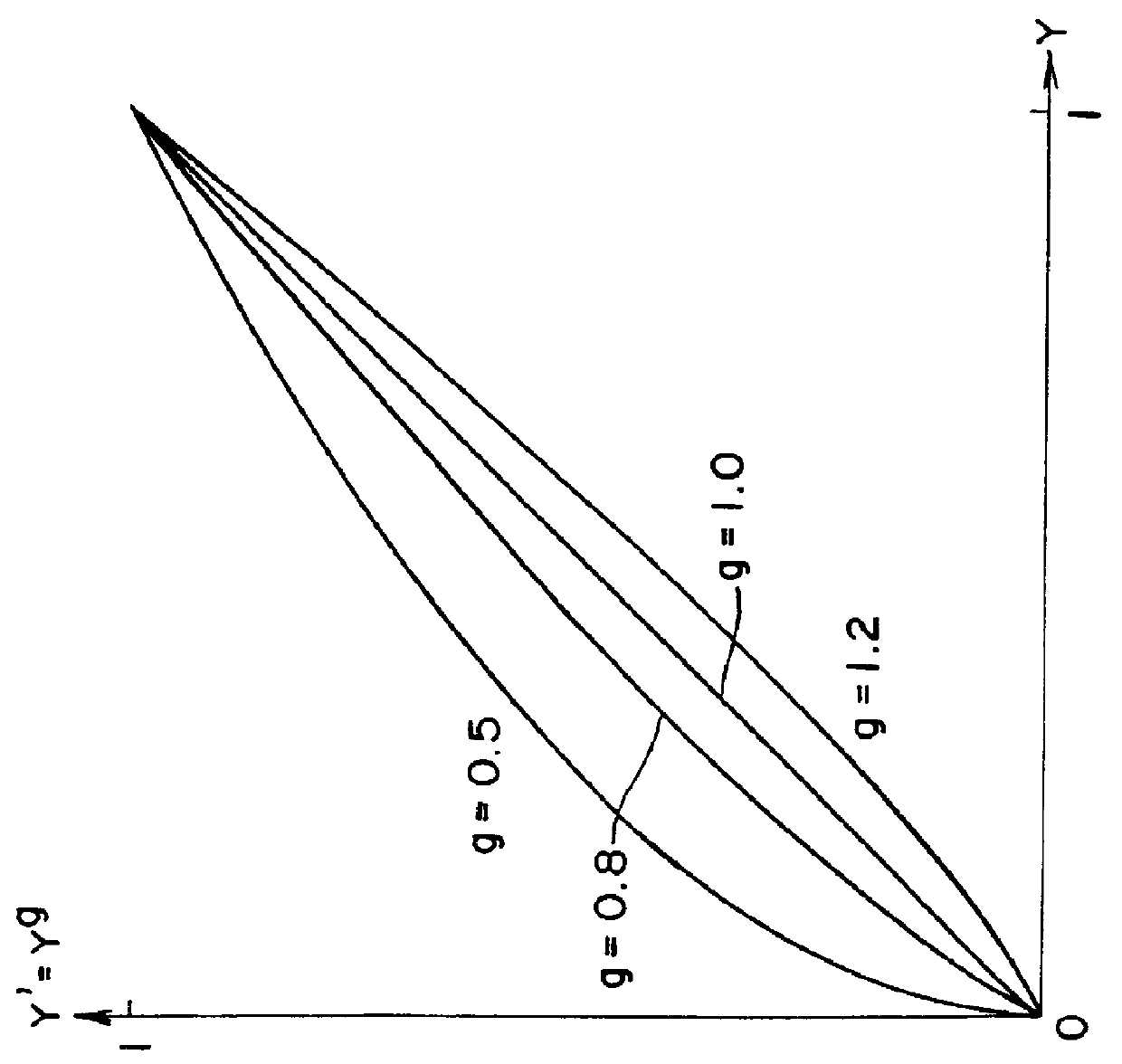
Gradation correction method and device
InactiveUS6101271AColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionHueCorrection method
The gradation correction device includes a luminance signal convertor to generate a luminance signal from the input R, G, B signals, a correction coefficient calculator which calculates the ratio to the luminance signal of the luminance signal after gamma correction to the predetermined gradation characteristics, and a multipliers to multiply the output from the correction coefficient calculator by each of the R, G, and B input signals. When the gradation correction is applied, effective brightness adjustment can be applied with no change in hue and saturation and without exceeding the dynamic range of a device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
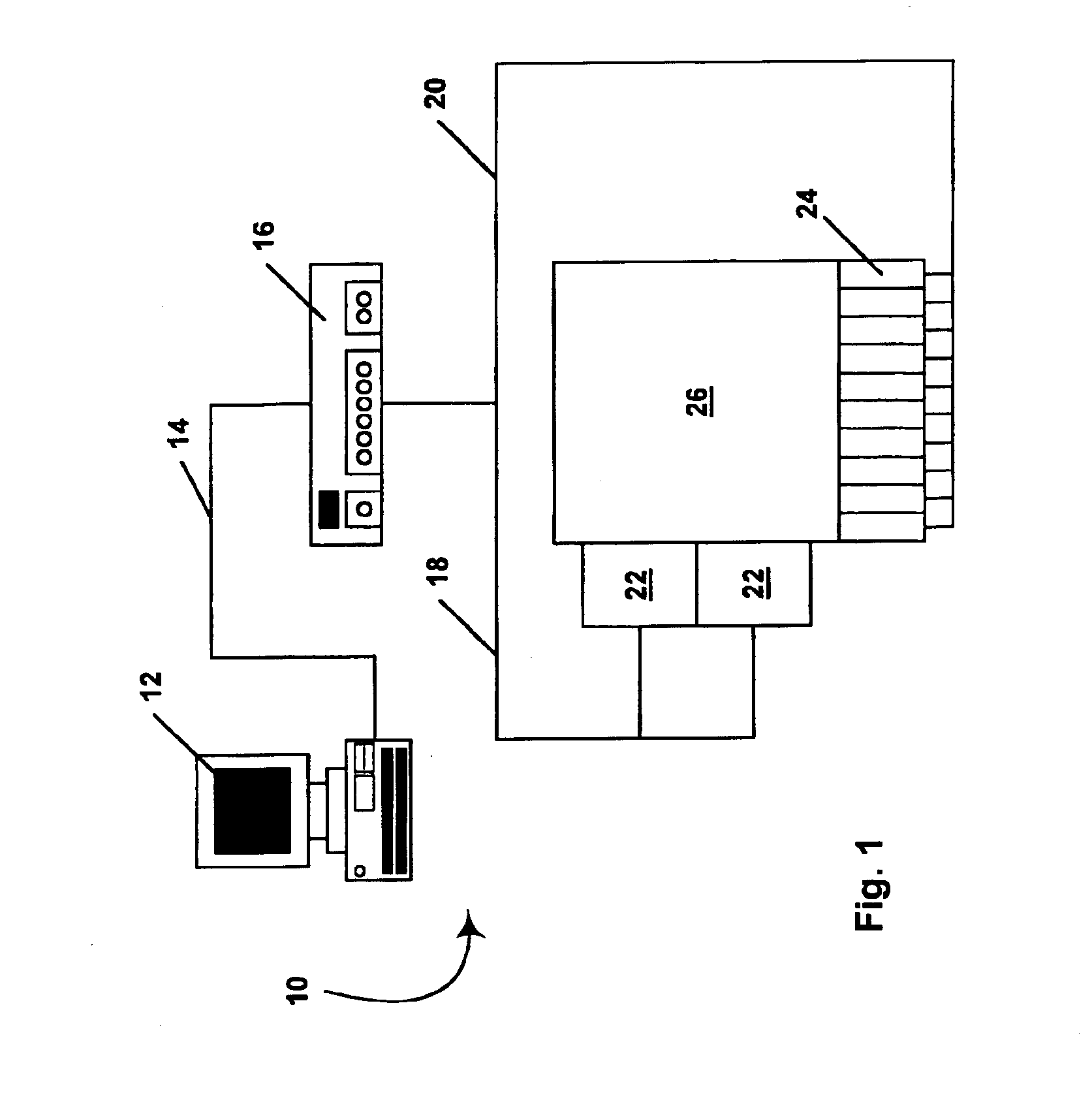
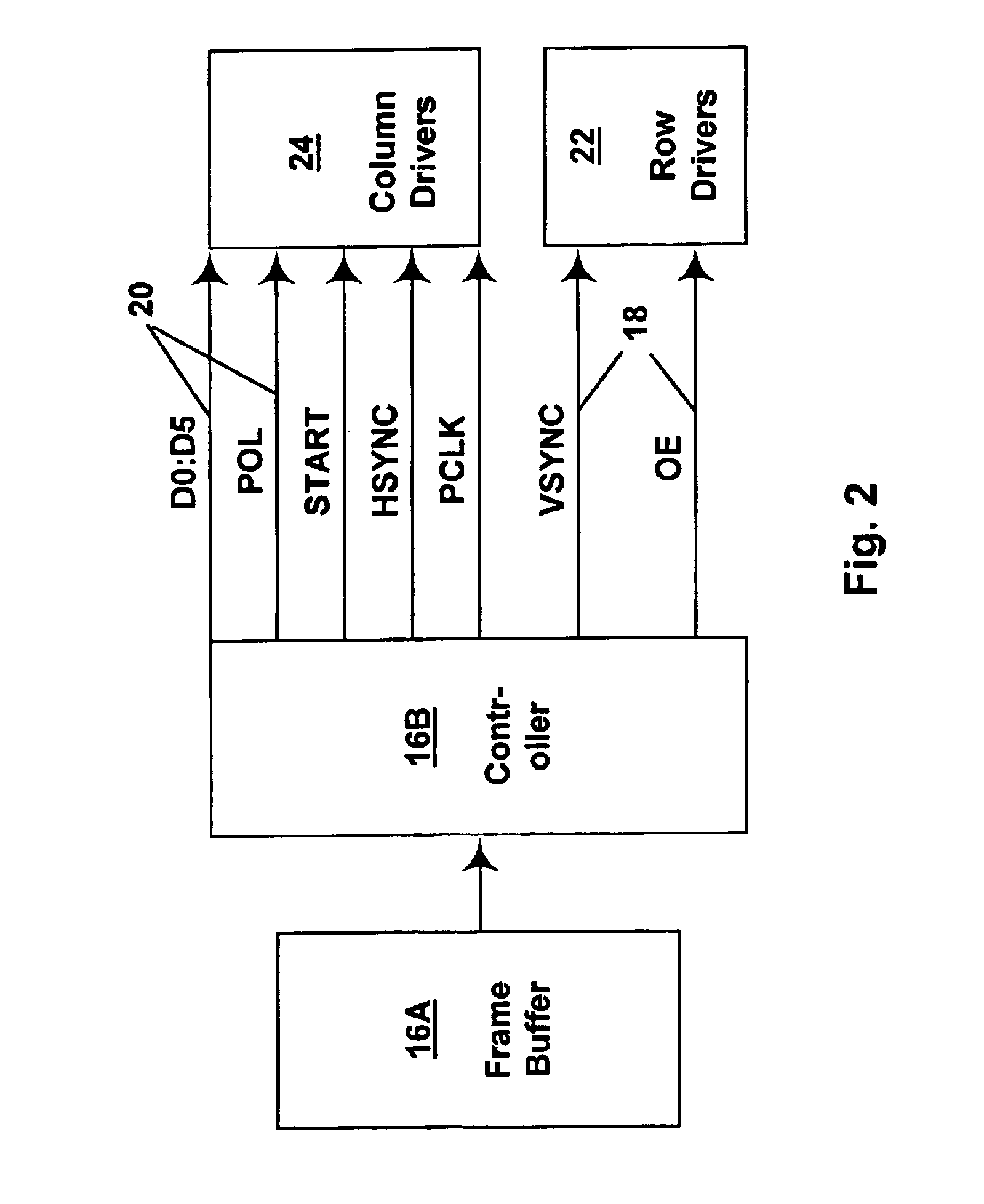
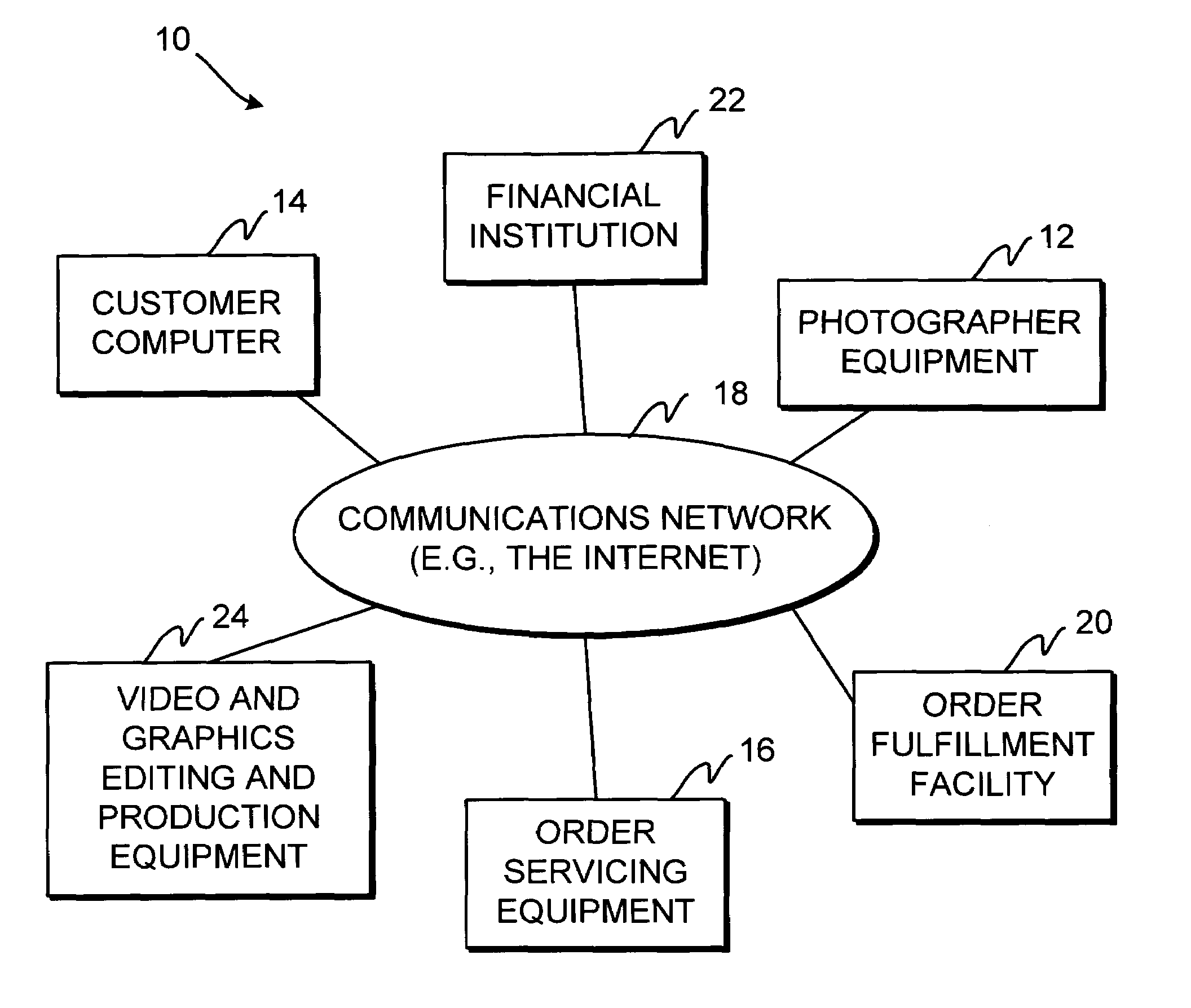
Online digital image-based product ordering system
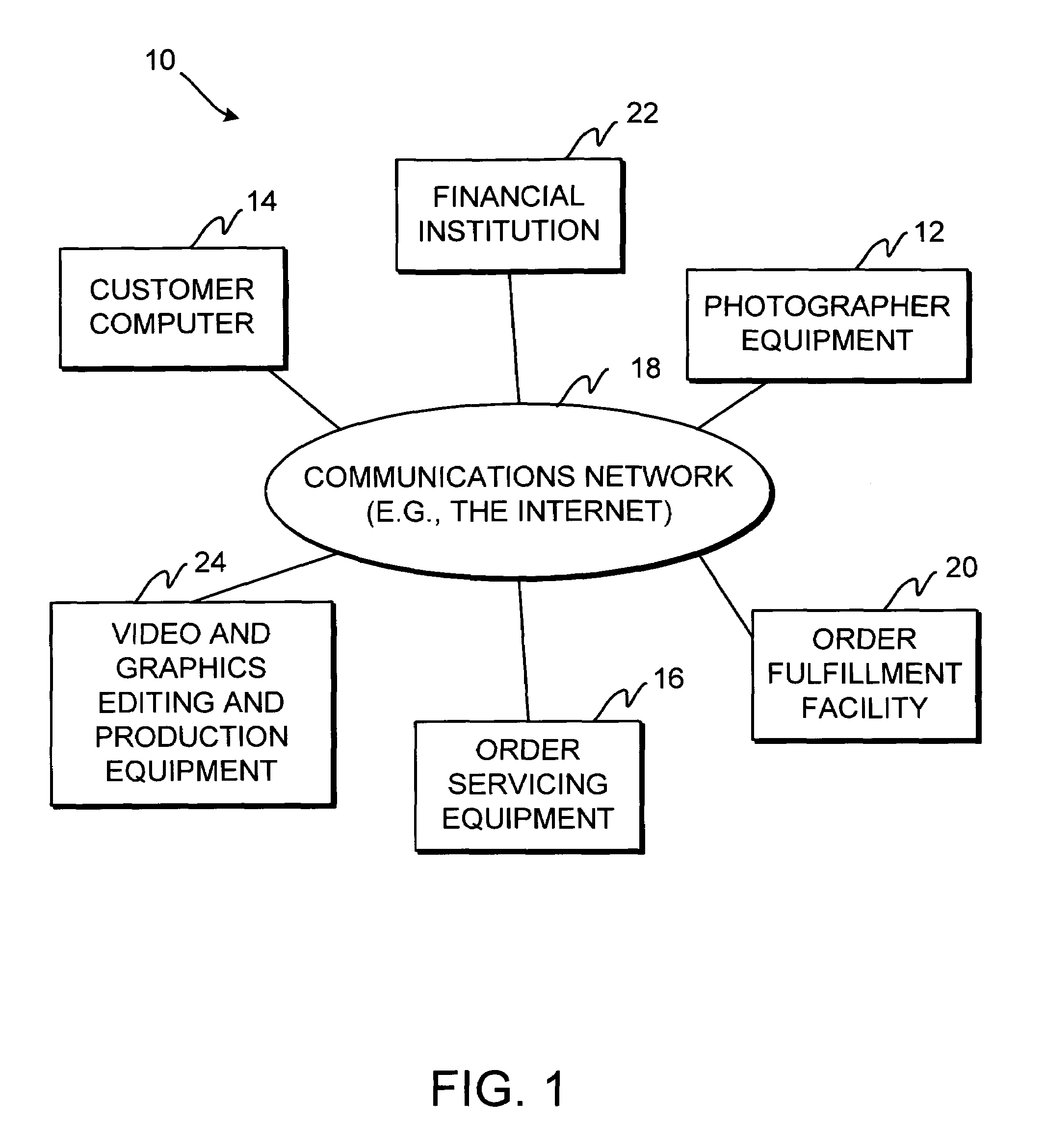
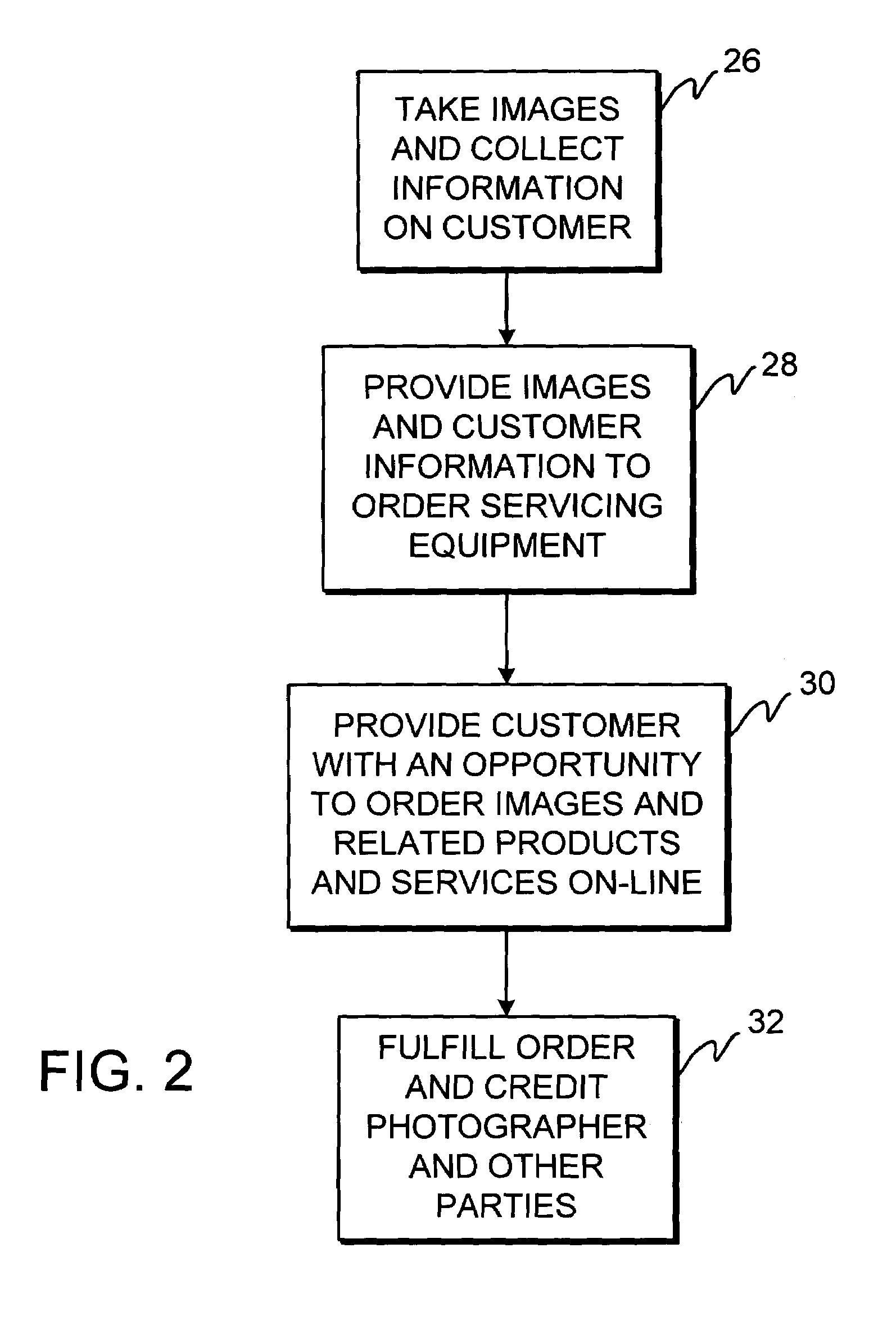
InactiveUS7343320B1Image changeProcessingVisual presentationServicing equipmentComputer graphics (images)
A system is provided that allows a photographer to take images for a customer and provide those images to order servicing equipment with which the images are placed on-line for the customer to view. The customer may place orders for the images and products and services related to the images. The order servicing equipment may credit the photographer when the customer orders images, products, or services. Images may be manipulated before images, products, or services are ordered. Images may be taken using film-based cameras or digital image acquisition equipment. Image presentation options may be selected. Content may be appended to the images. Web sites and digital albums may be created using the images. The photographer may check the status of assignments that have been submitted to the order servicing equipment and may check on account status. Different rights levels may be established for different parties. Loyalty rewards may be awarded for frequent use of the system.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Imaging device and image processing program for estimating fixed pattern noise from partial noise output of available pixel area
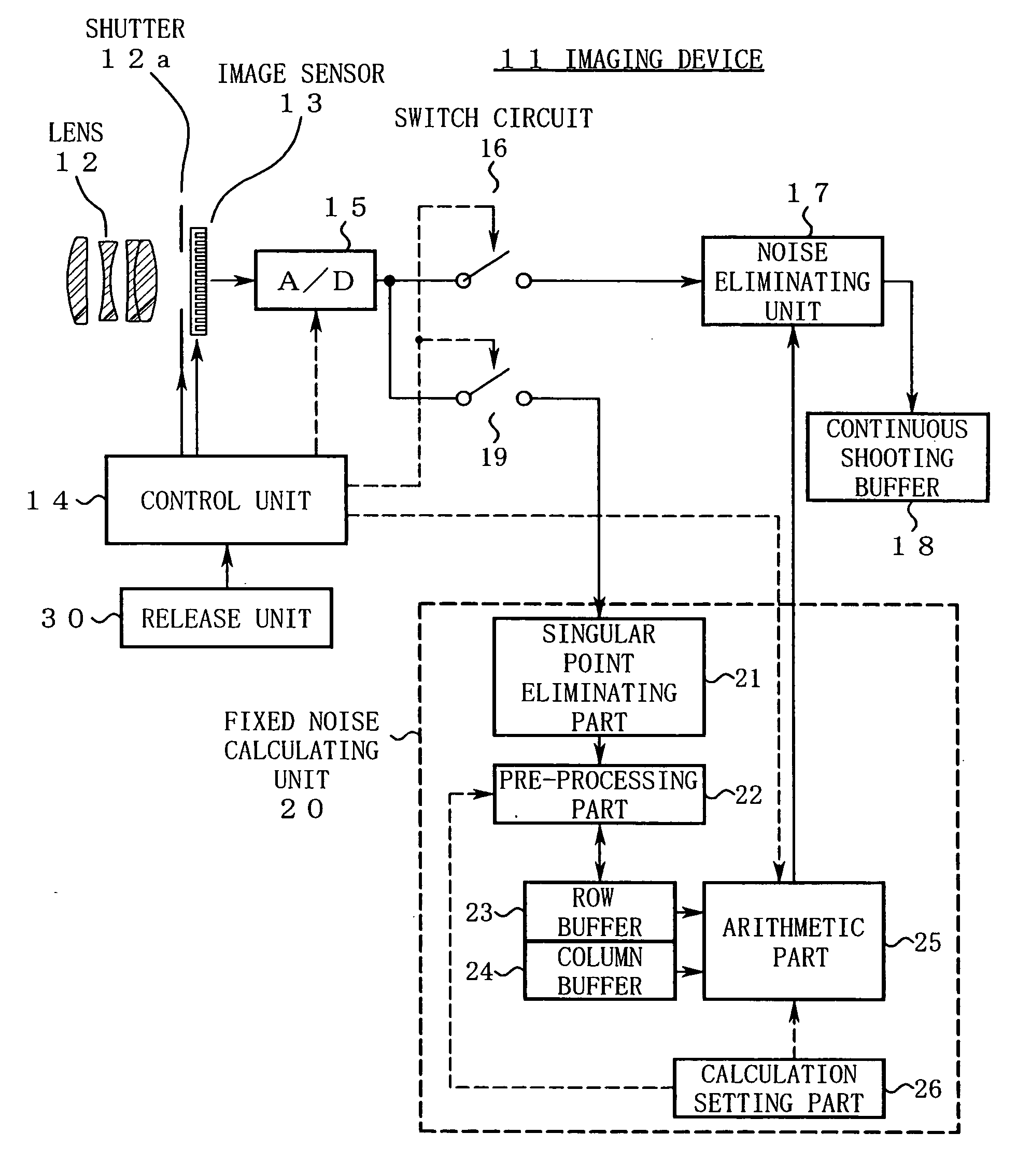
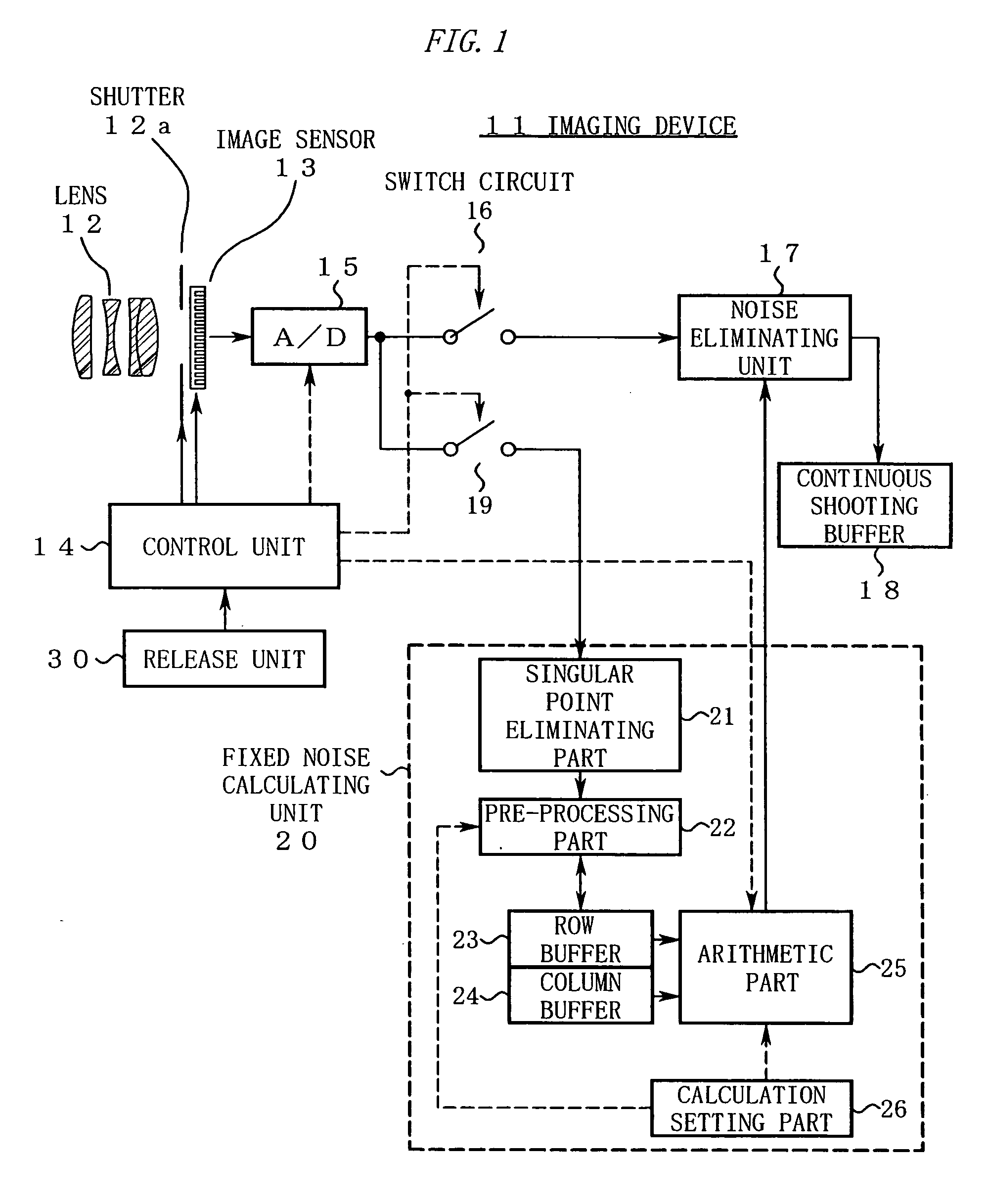
ActiveUS20060098888A1Shorten the timeTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionImaging processing
An imaging device of the present invention includes an image capturing unit, a noise obtaining unit, a fixed noise calculating unit, and a noise eliminating unit. The image capturing unit generates image data by photoelectrically converting, pixel by pixel, a subject image formed on an available pixel area of a light-receiving surface. The noise obtaining unit reads a noise output from a partial area of the available pixel area. The fixed noise calculating unit calculates an estimation of fixed pattern noise of the available pixel area based on the noise output read from the partial area. The noise eliminating unit subtracts the fixed pattern noise from the image data.
Owner:NIKON CORP
System and method for automatically altering device functionality
InactiveUS20070030539A1Avoid damagePrevent unauthorized accessMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionQuarantineEmbedded system
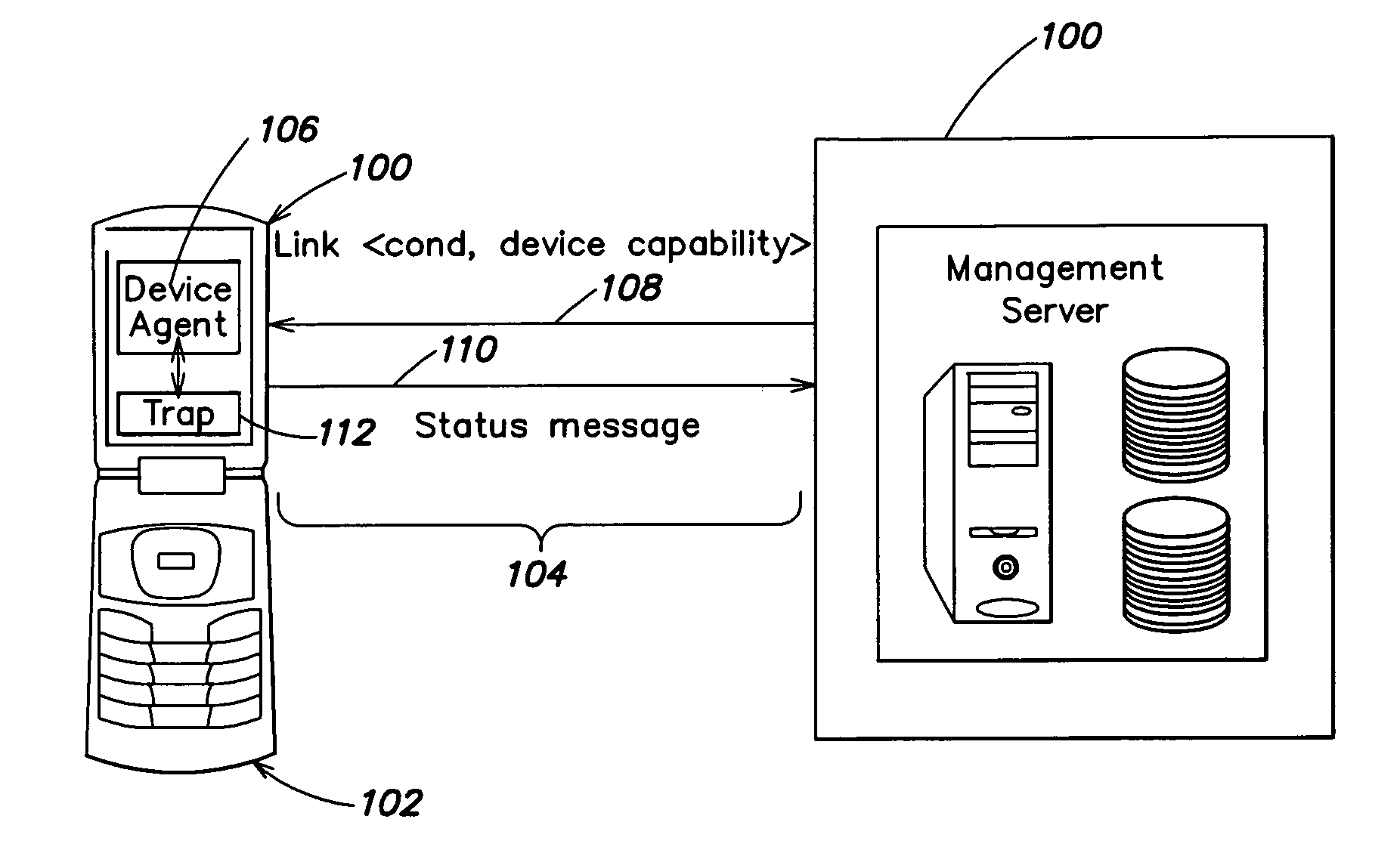
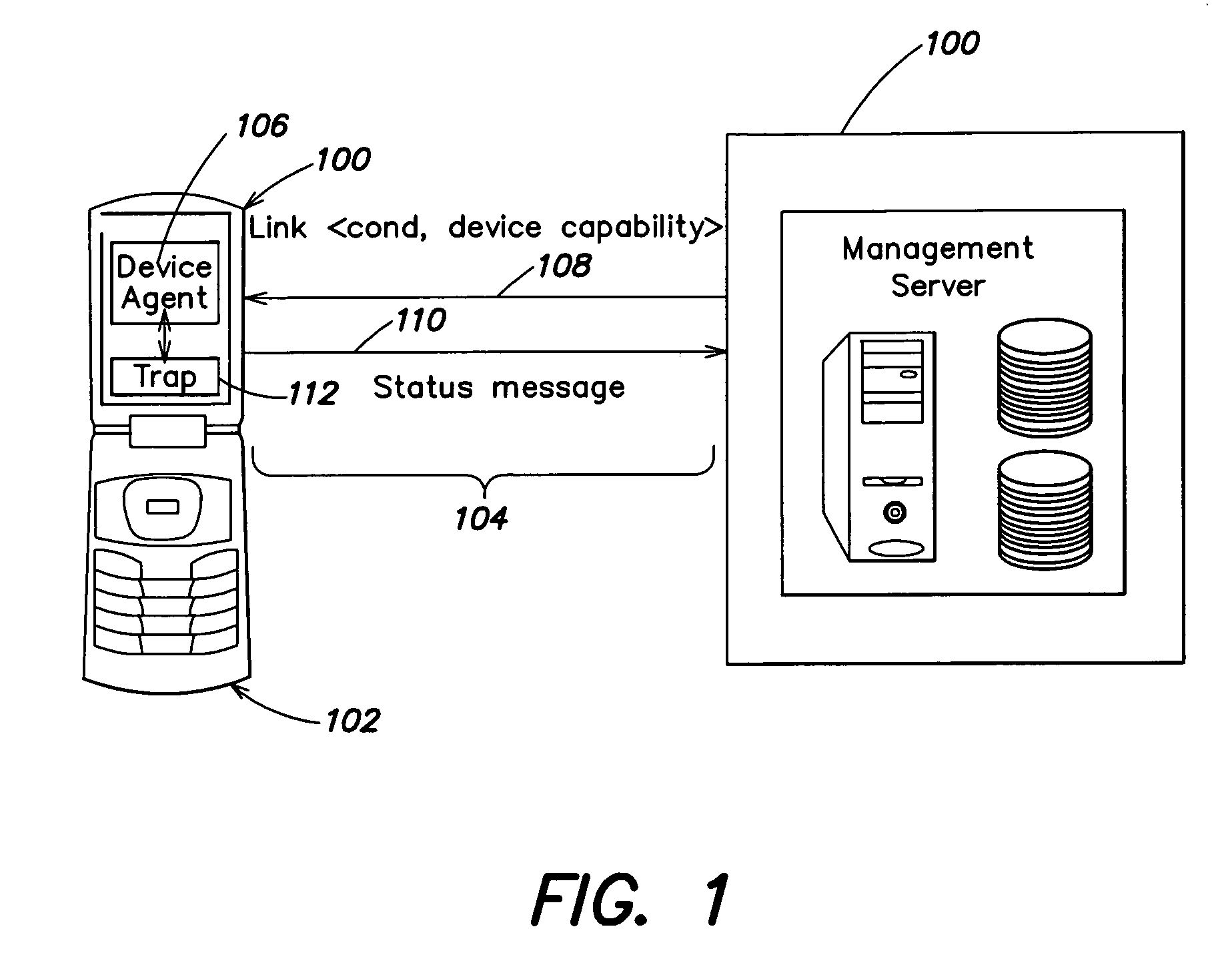
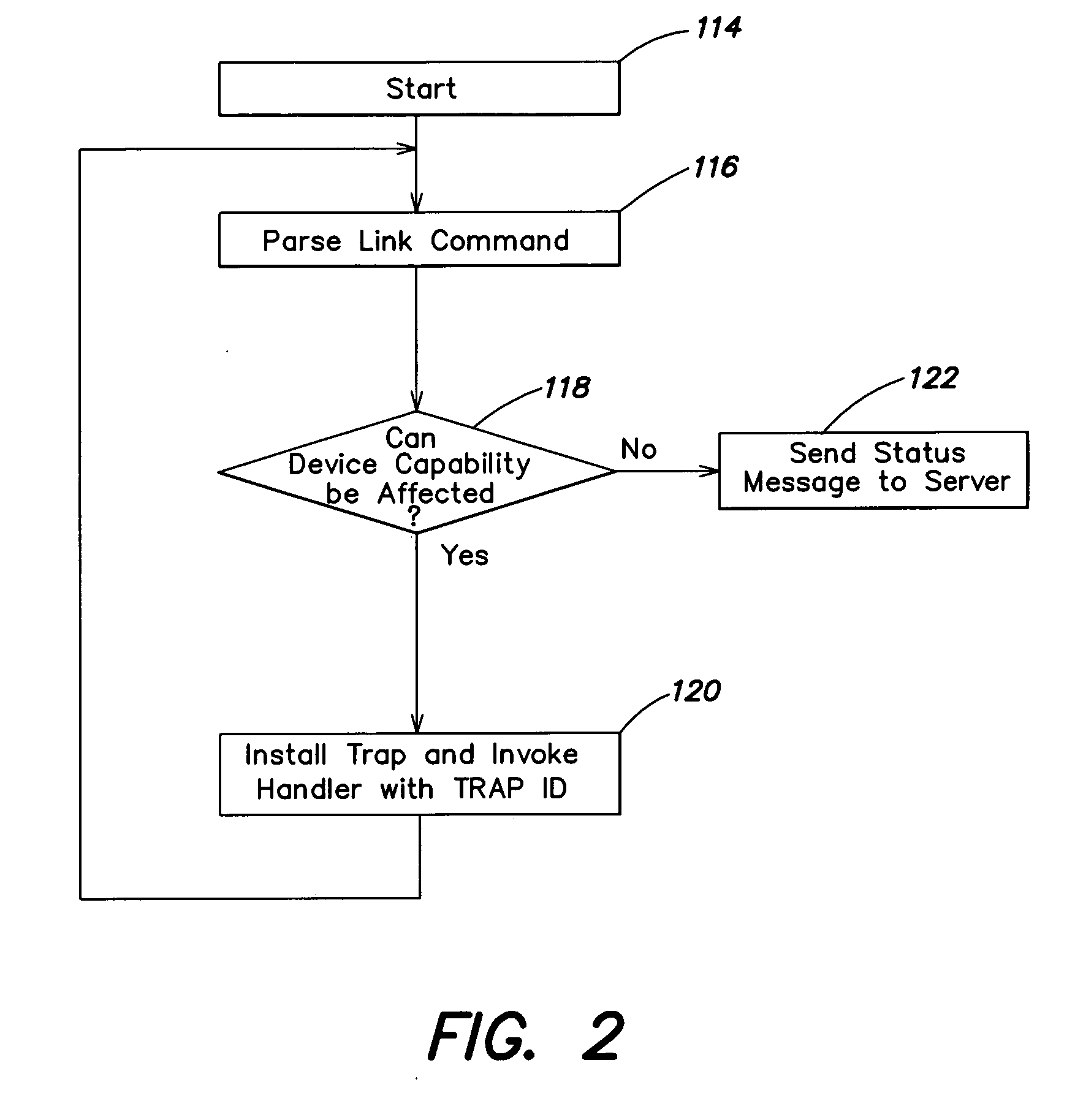
A system and method for automatically altering device functionality based on the occurrence of certain predetermined conditions. A link may be established between a device and a trusted server to provide an association between various conditions that may be detected at the device and actions that are to be taken on the device. In particular, software traps can be set up and linked to device functionality such that execution of the trap may automatically disable or enable certain device capabilities. Some aspects of the invention are directed to a system and method for remotely setting software traps for detecting software viruses and, upon execution of the traps, several methods for establishing a quarantine on infected devices.
Owner:MFORMATION +1
Multi-array sensor with integrated sub-array for parallax detection and photometer functionality
Methods and systems of imaging to correct parallax. Color information is received from multi-array sensors. Luminance information is received from a sub-array sensor arranged with the multi-array sensors. Color information received from at least one of the multi-array sensors is correlated with the luminance information received from the sub-array sensor. Color information is shifted among the multi-array sensors, based on the correlation, to correct the parallax.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
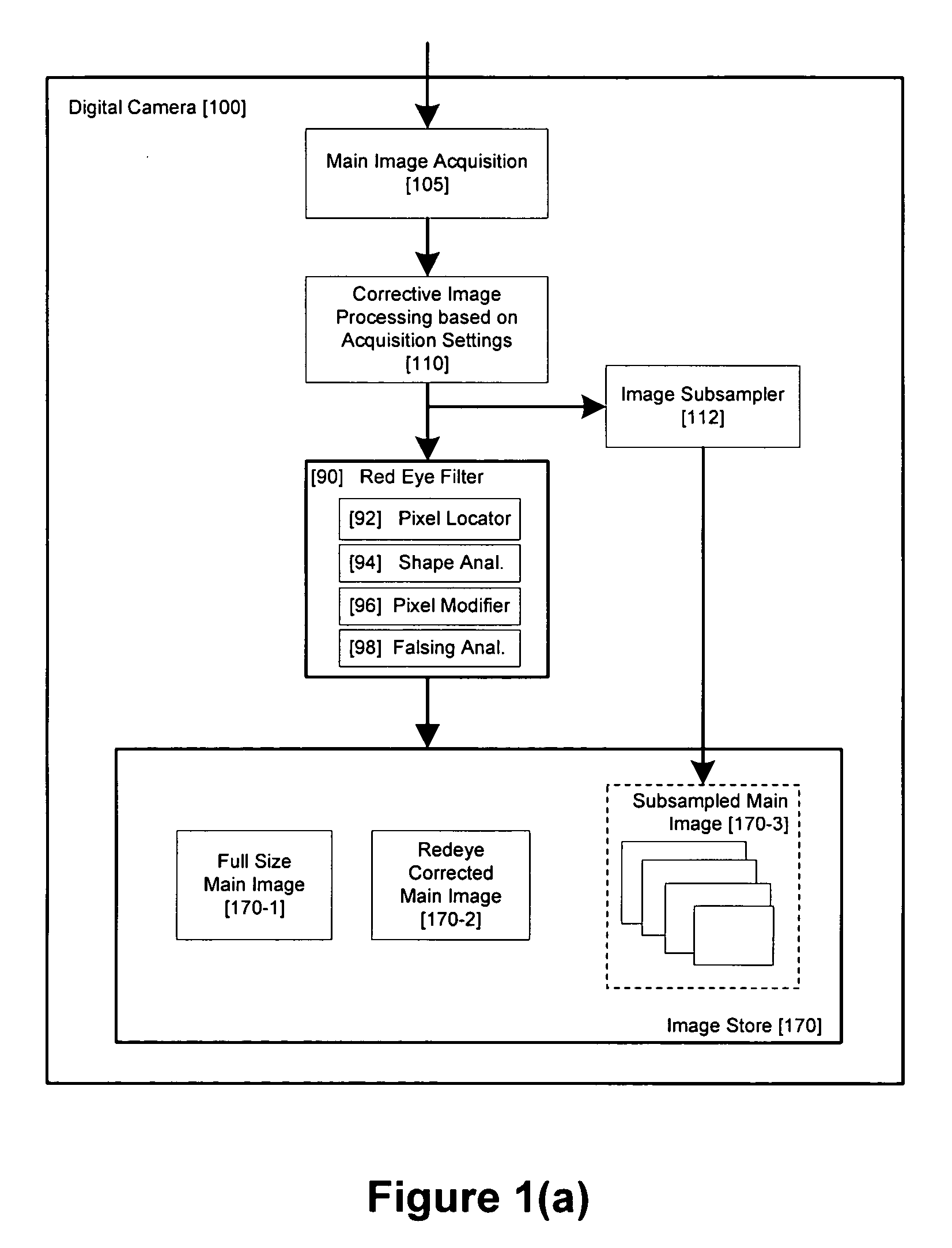
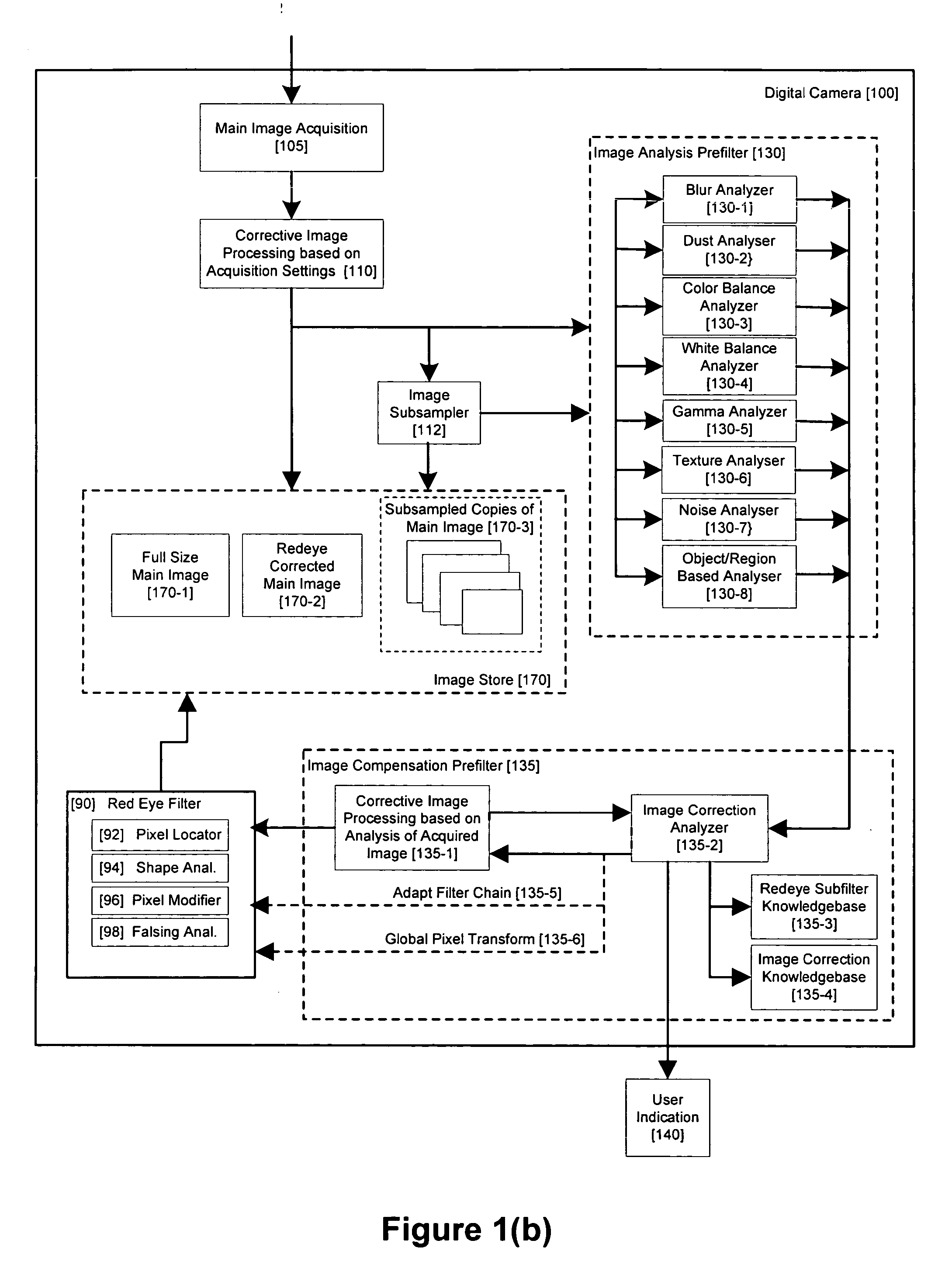
Method and apparatus for red-eye detection in an acquired digital image
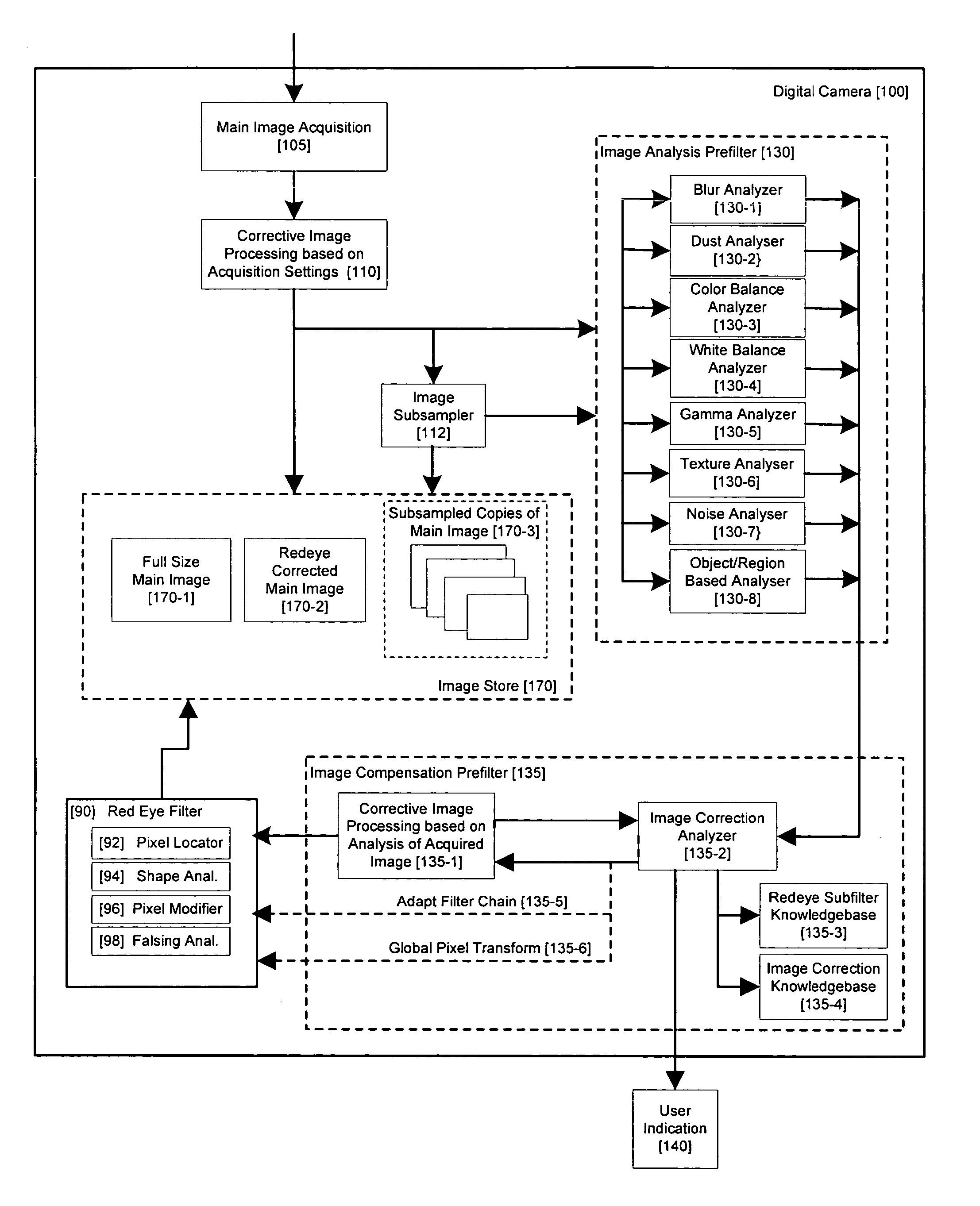
ActiveUS20060093212A1Reduction of false positiveLower requirementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging qualityDigital image
A method for red-eye detection in an acquired digital image comprises acquiring a first image and analyzing the first acquired image to provide characteristics indicative of image quality. The process then determines if one or more corrective processes can be beneficially applied to the first acquired image according to the characteristics. Any such corrective processes are then applied to the first acquired image. Red-eye defects are then detected in a second acquired image using the corrected first acquired image. Defect detection can comprise applying one or more, or a chain of two or more, red-eye filters to the first acquired image. In this case, prior to the detecting step, it is determined if the red-eye filter or red eye filter chain can be adapted in accordance with the characteristics. The red-eye filter may be adapted accordingly.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
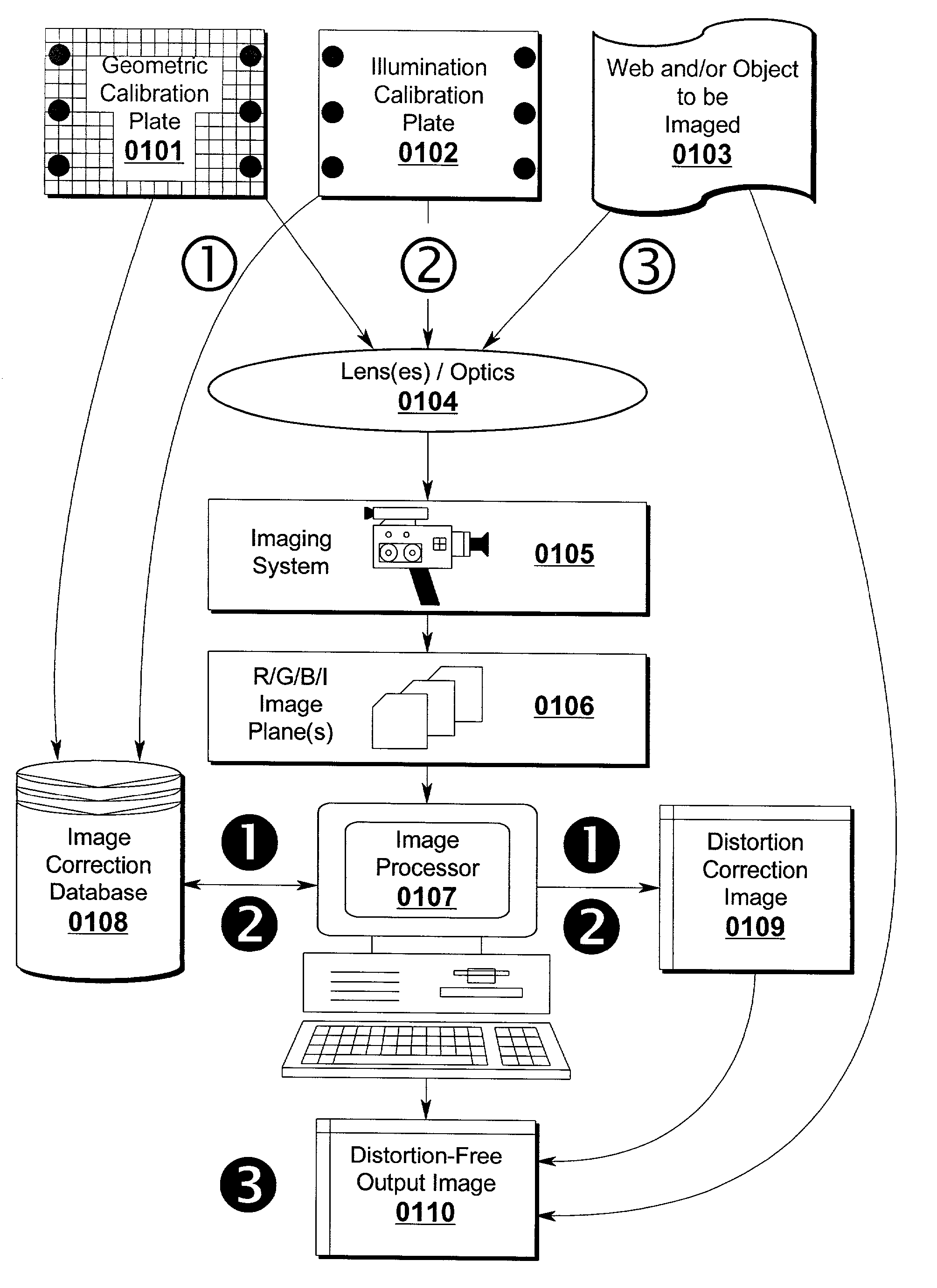
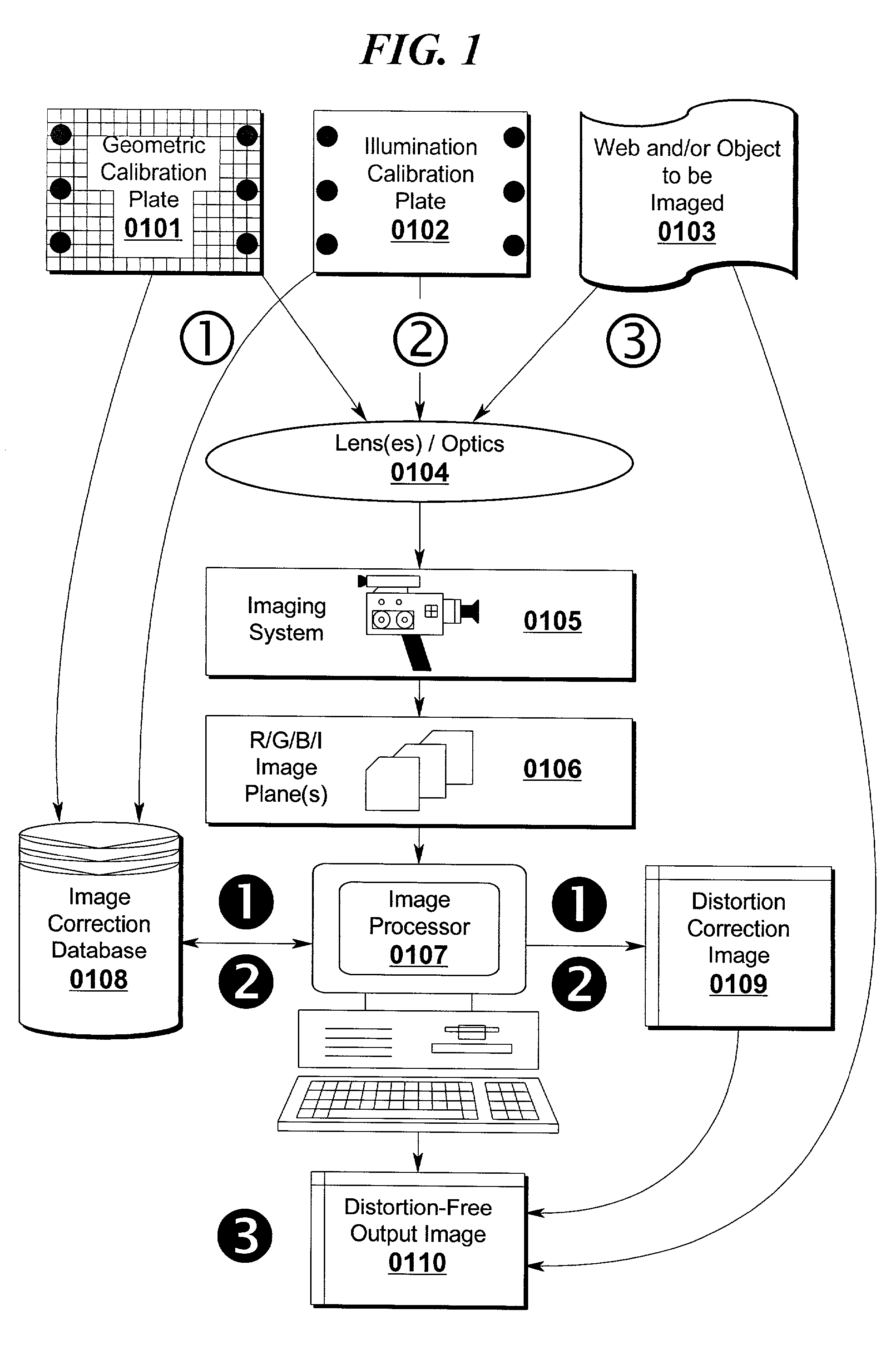
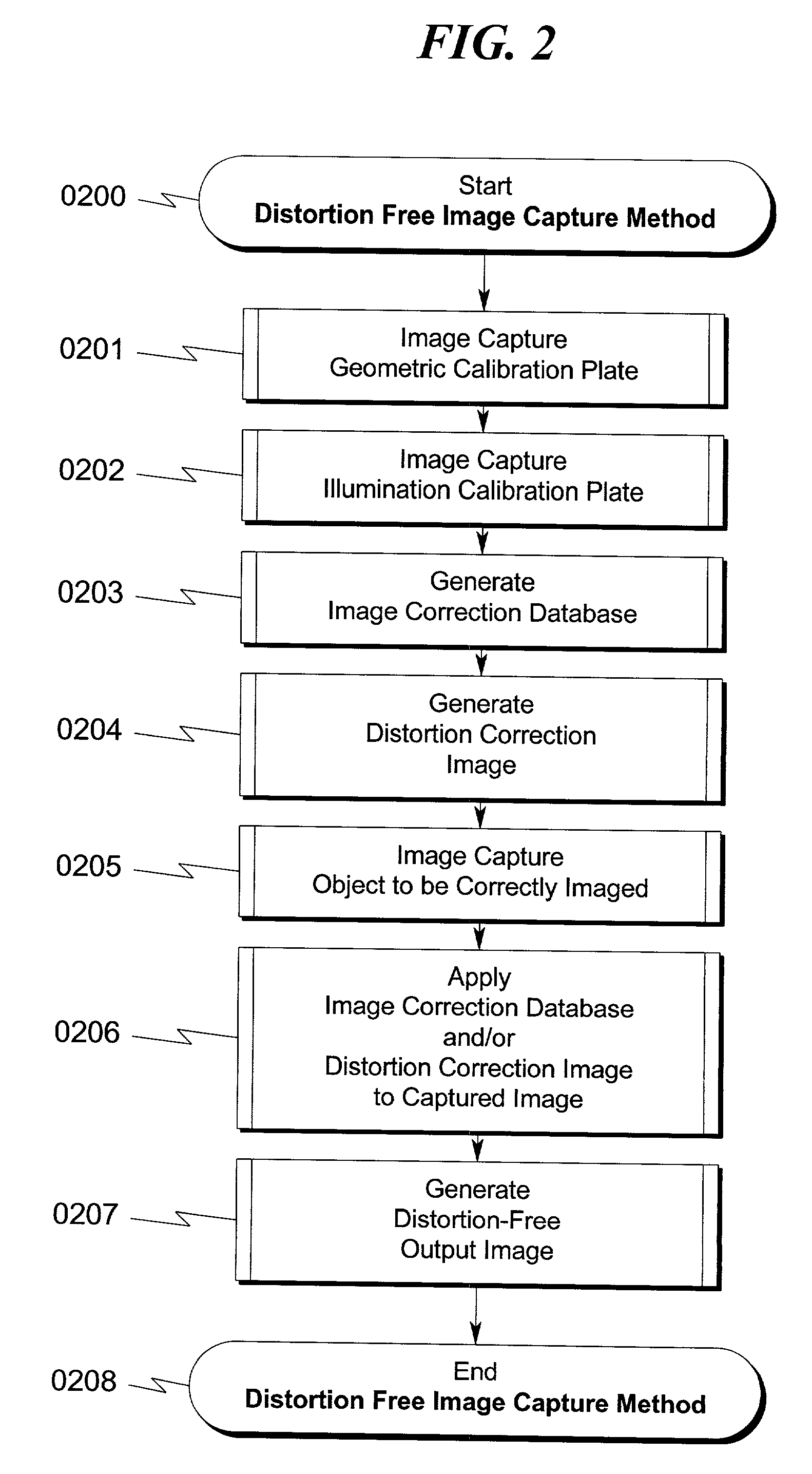
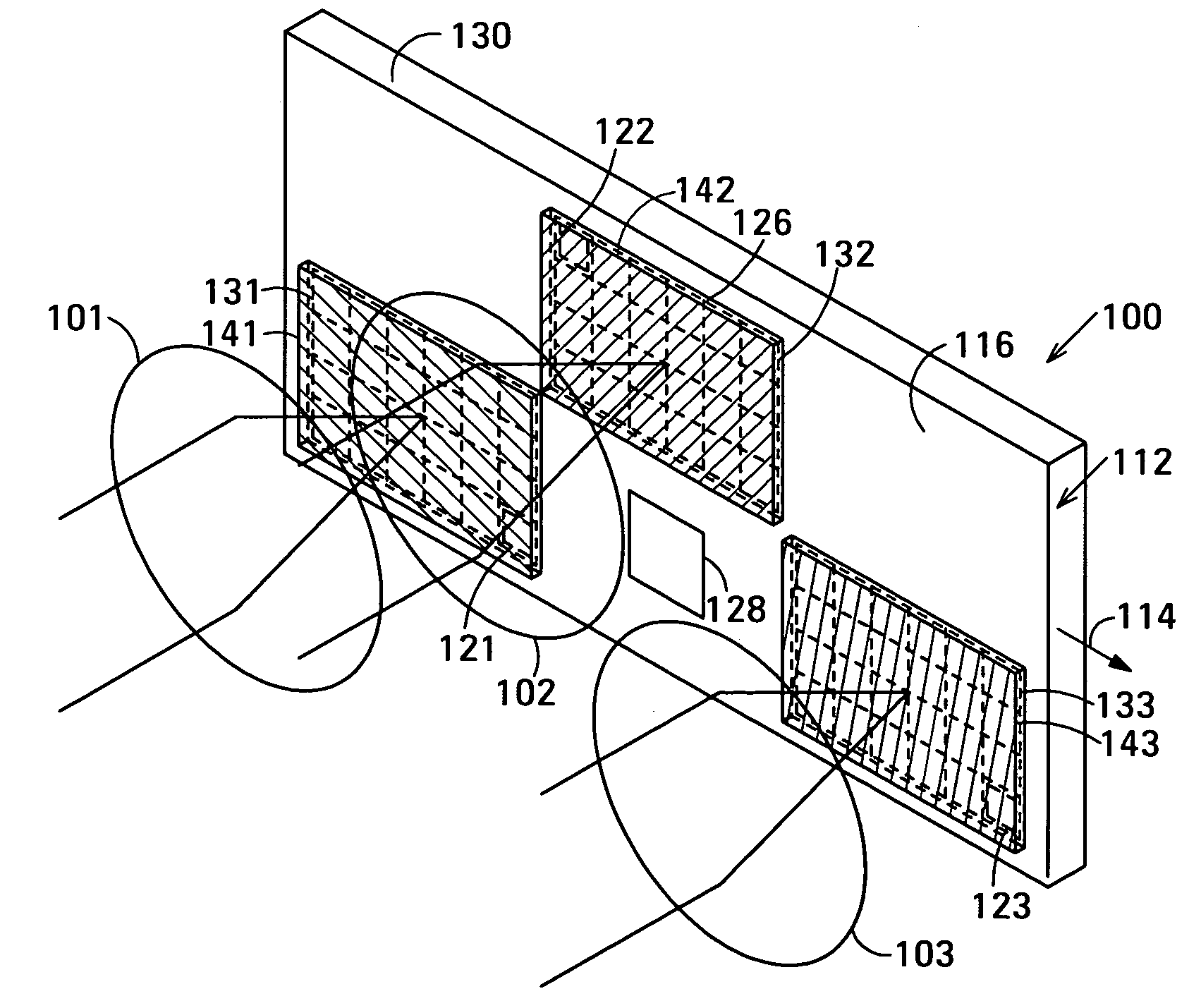
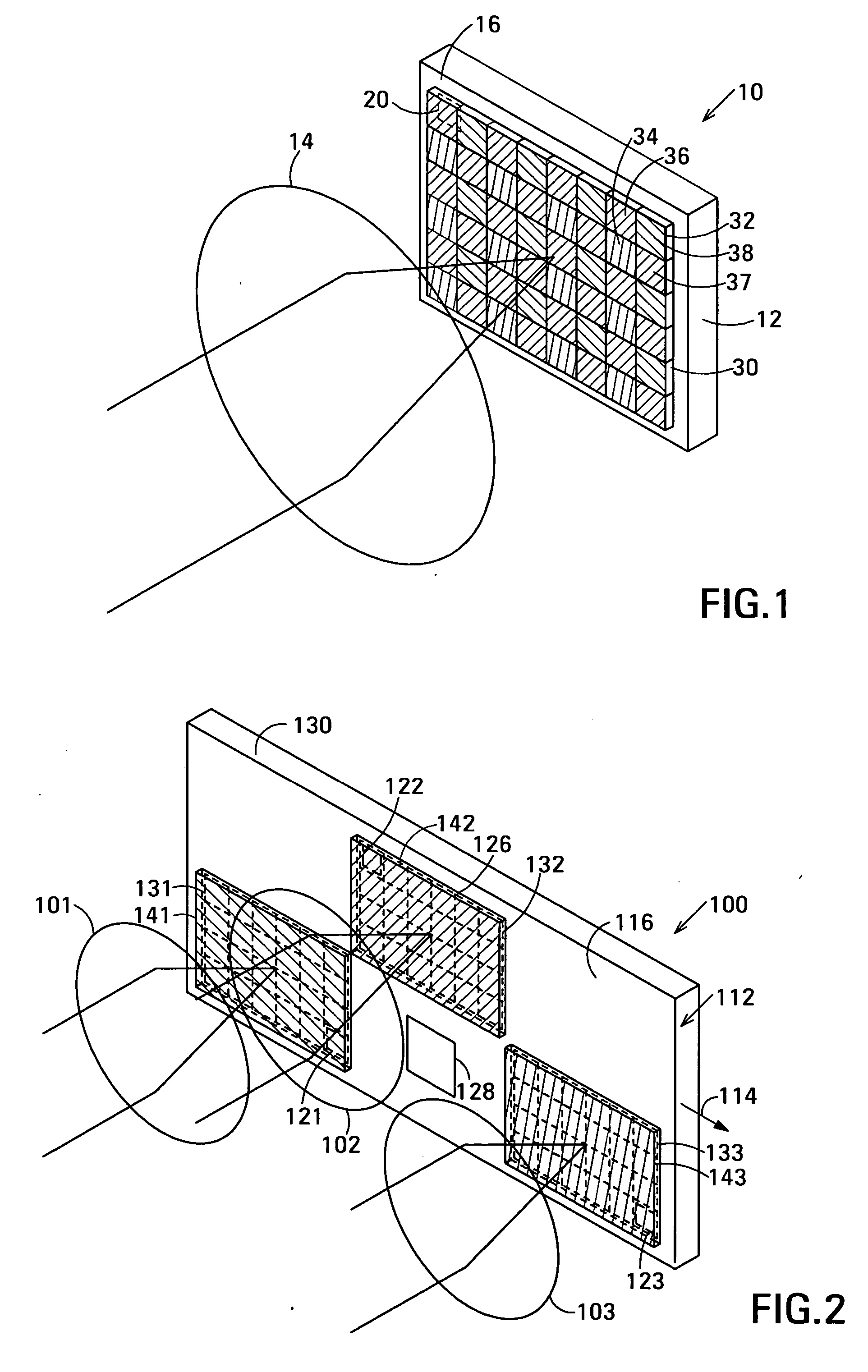
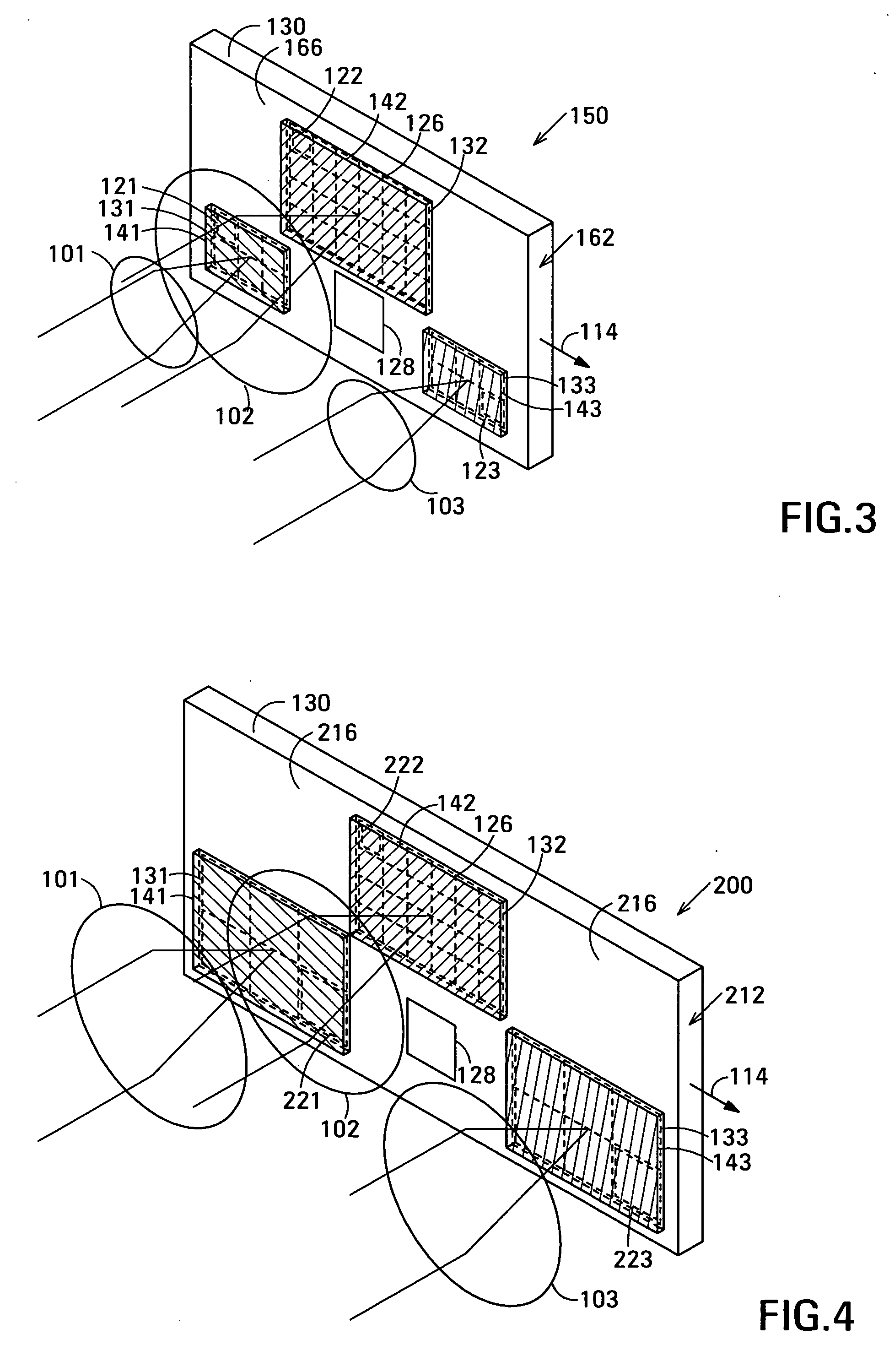
Distortion free image capture system and method
InactiveUS20020041383A1Low costImprove distortionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementOphthalmologyDistortion free
A system and method for correcting distortions that occur in image capture systems is disclosed. The present invention in some preferred embodiments includes provisions to correct or change magnification differences for all causes including position errors in zoom lens positioning mechanisms as well as those caused by chromatic aberration, CCD alignment errors, lens distortion off center variations, pincushion / barrel lens distortion, magnification distortions, camera and lens misalignment errors, and lighting variations (including flash-to-flash illumination variations). A significant feature of the present invention in contrast with the prior art is that with the use of a movable calibration plate in the present invention it is possible to image capture both the calibration plate and the input object image in a single image capture, thus permitting simultaneous compensation for a variety of lighting and illumination variations not possible with the prior art.
Owner:LEWIS JR CLARENCE A +1
Color image sensor with imaging elements imaging on respective regions of sensor elements
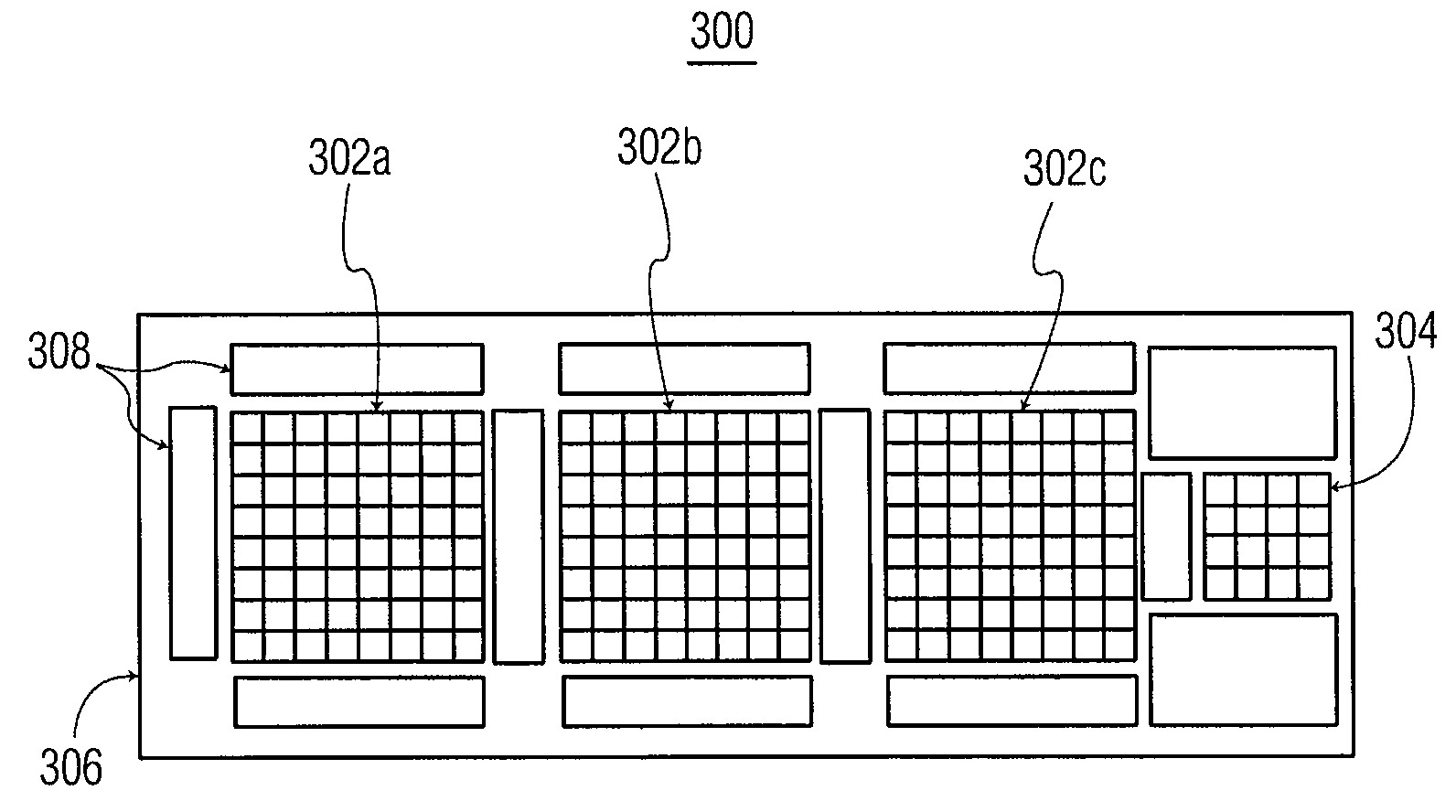
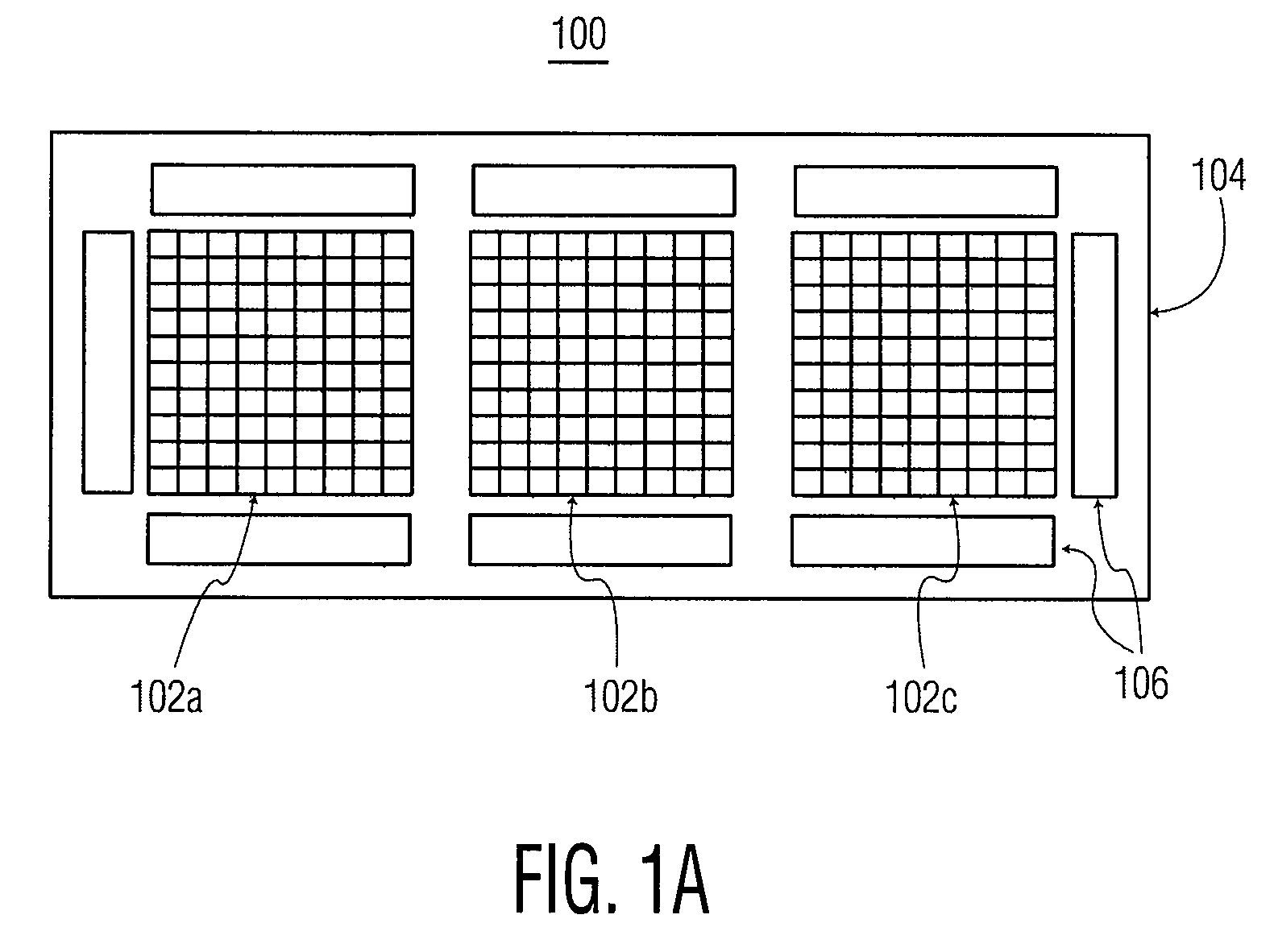
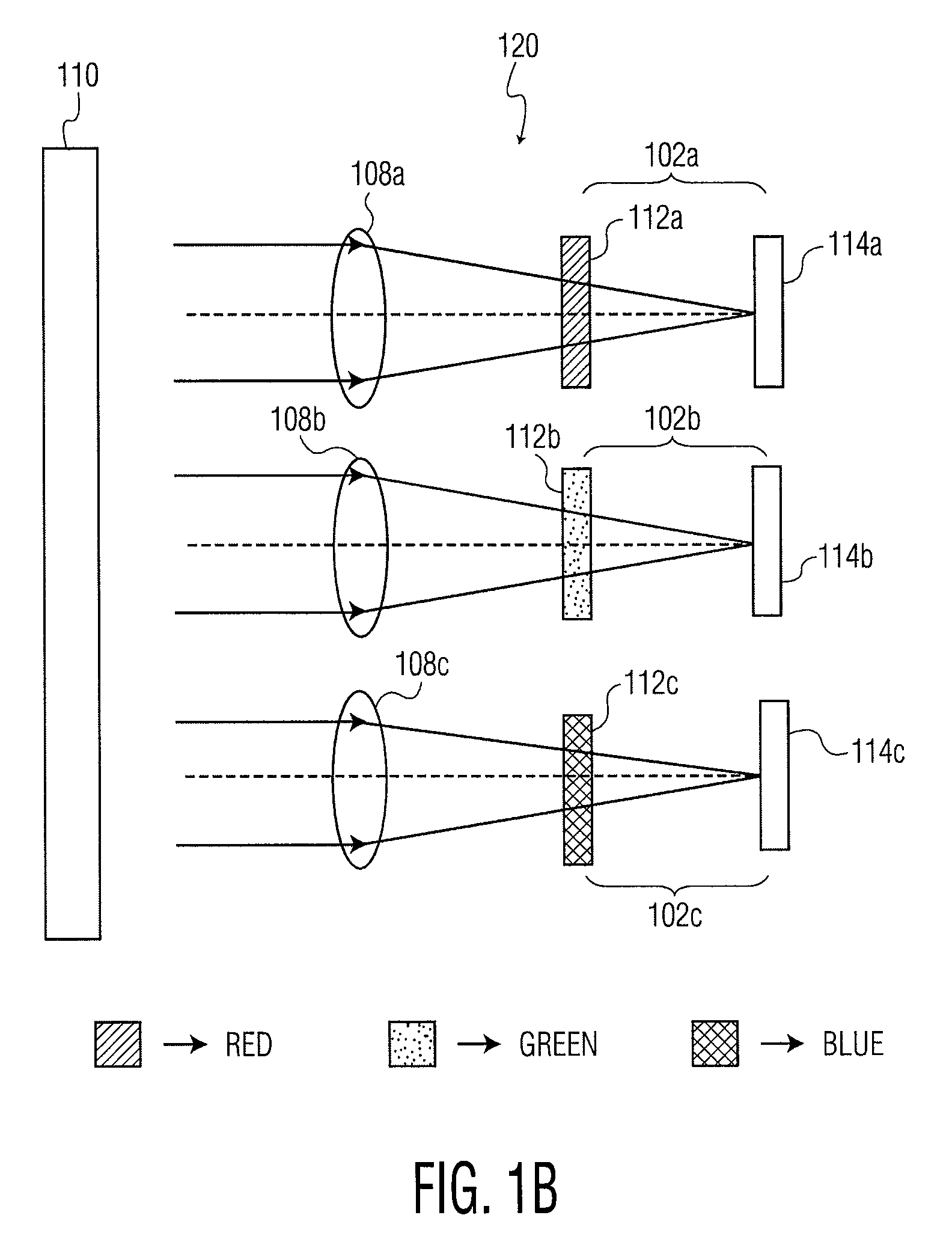
ActiveUS20050134698A1Faster read-out timeReduce areaTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageImage signal
The color image sensor generates an image signal representing a subject. The color image sensor has a light sensor and imaging elements arranged to form images of the subject in light of different colors on respective regions of the light sensor. The light sensor includes sensor elements and is operable to generate the image signal in response to light incident on it.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Producing an extended dynamic range digital image
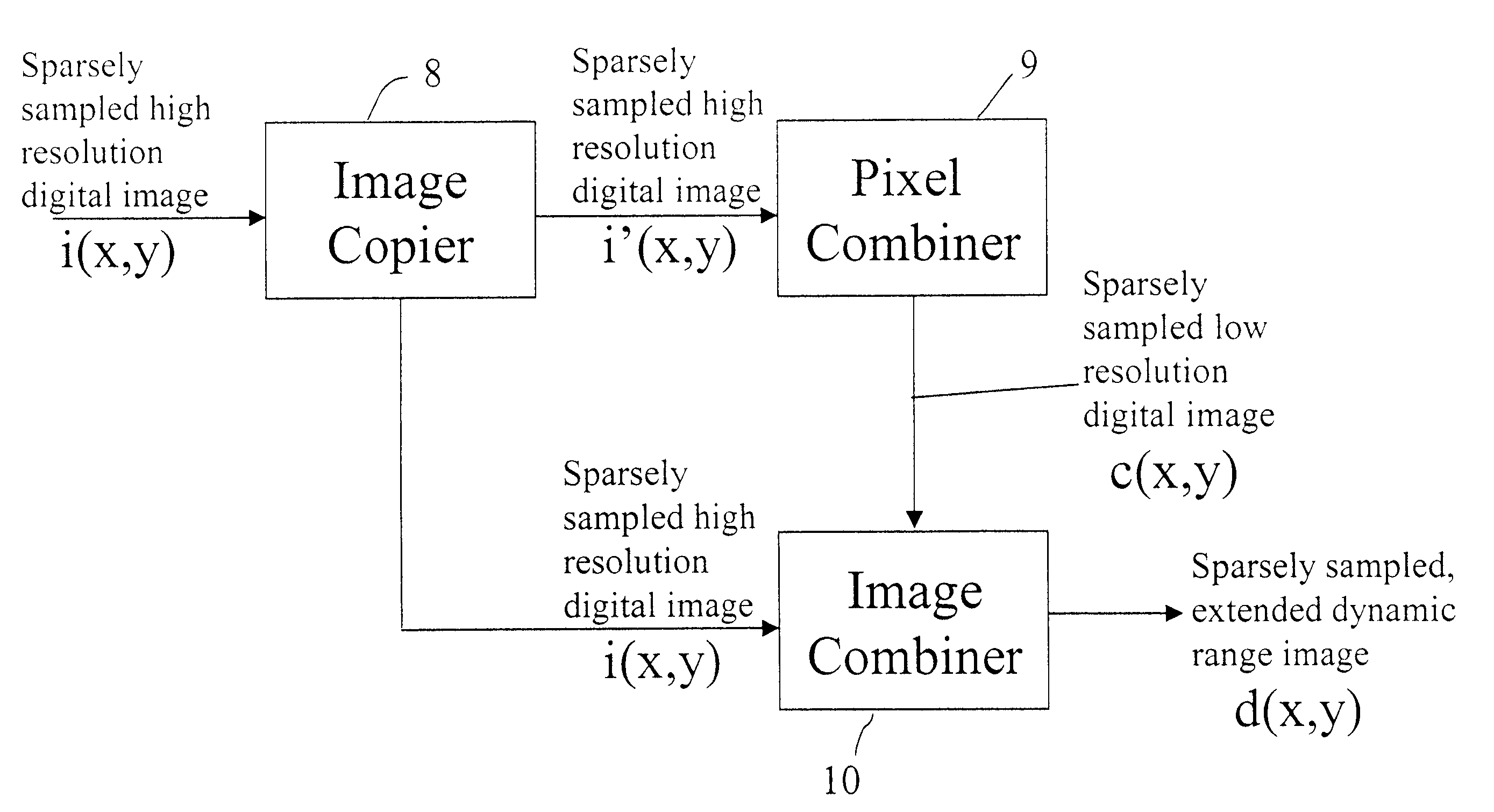
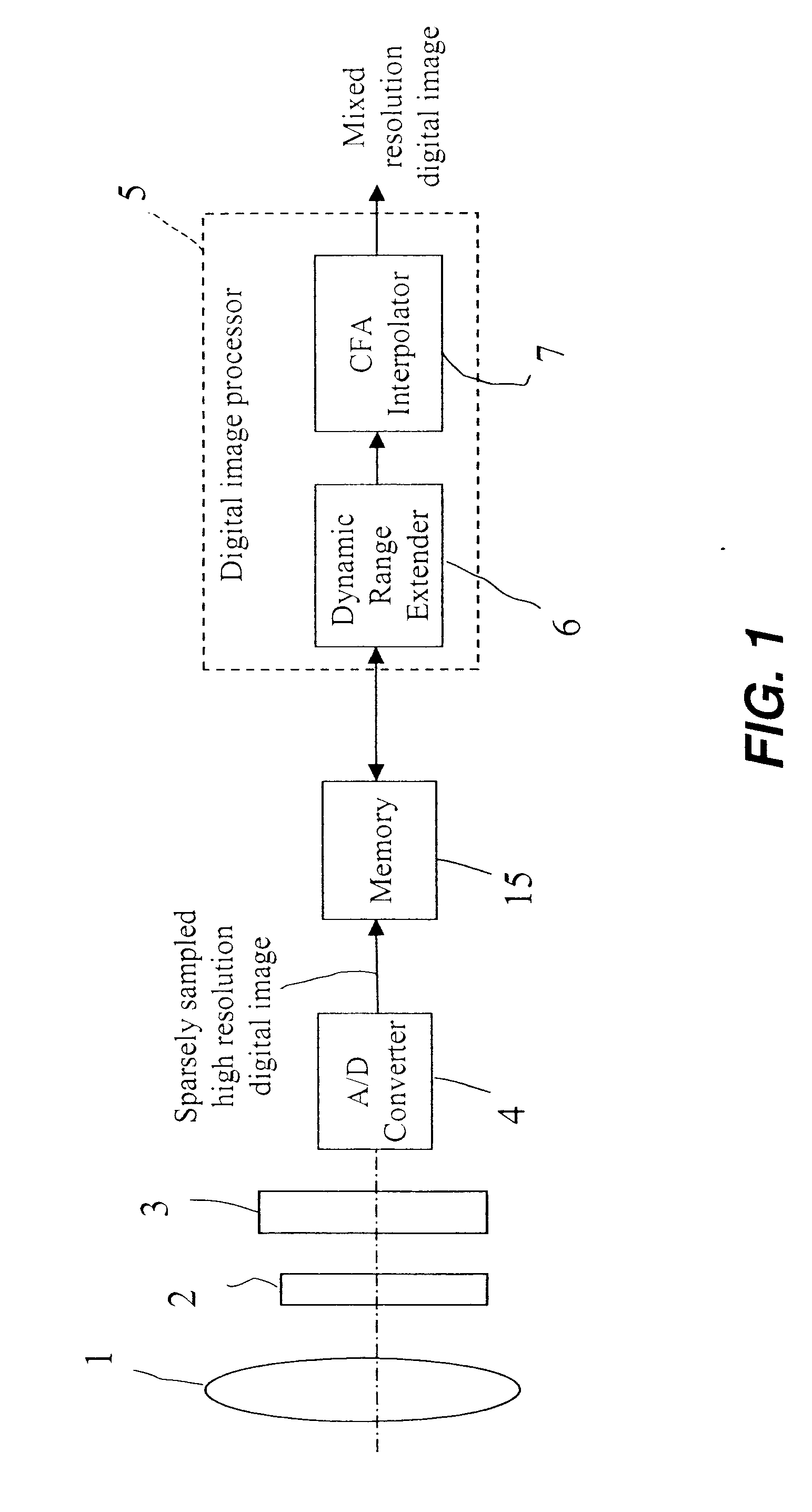
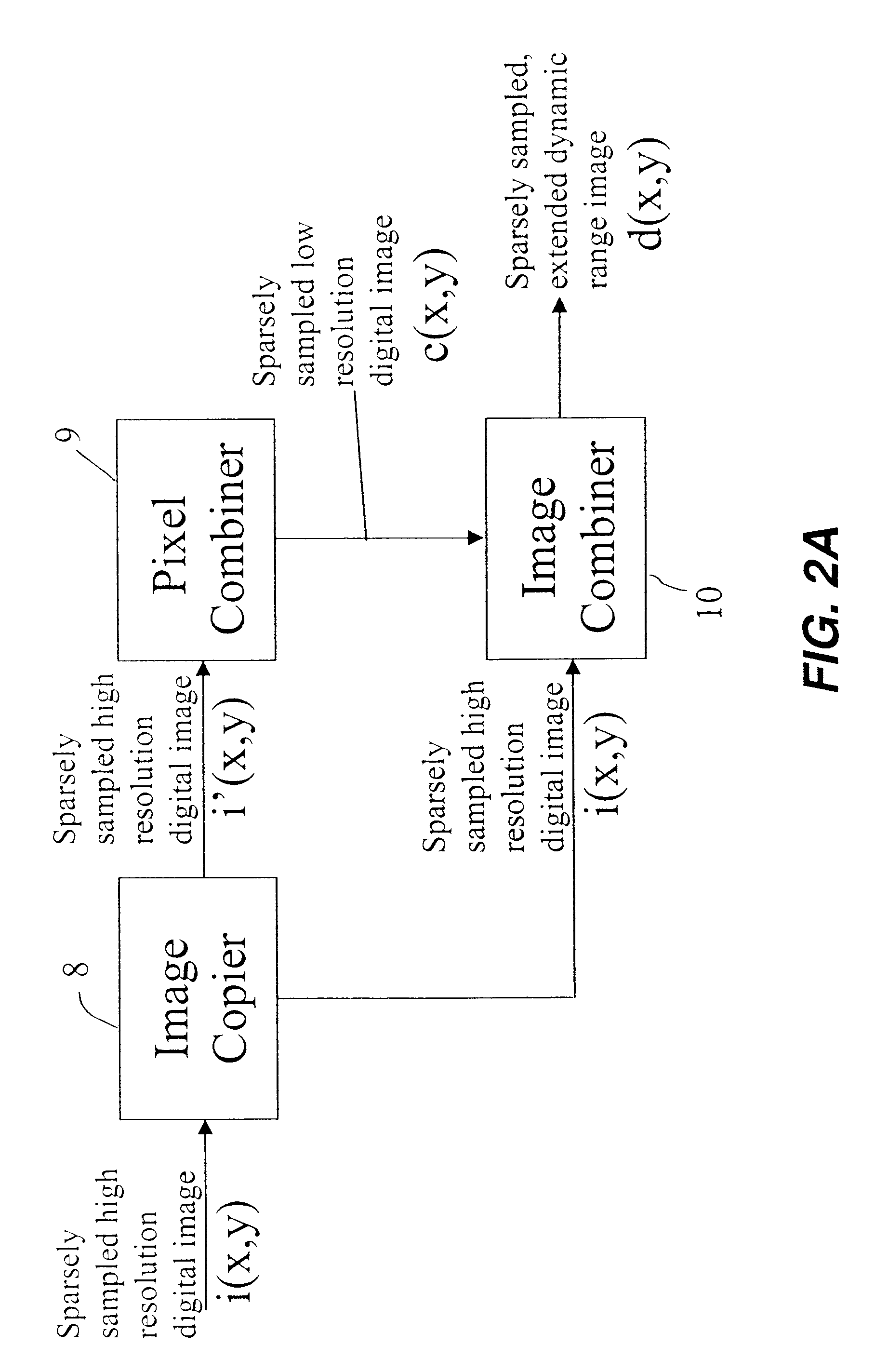
InactiveUS20080025634A1Improve dynamic rangeEnhance the imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionDigital image
A method of producing a digital image with extended dynamic range, includes capturing at least a first full resolution digital image of a scene; combining pixels of a first full resolution digital image to produce a lower resolution digital image identifying dark regions in a first full resolution digital image and replacing the dark regions in the full resolution image with corresponding regions from the brighter, lower resolution image to thereby provide a digital image with extended dynamic range.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and apparatus for processing image data
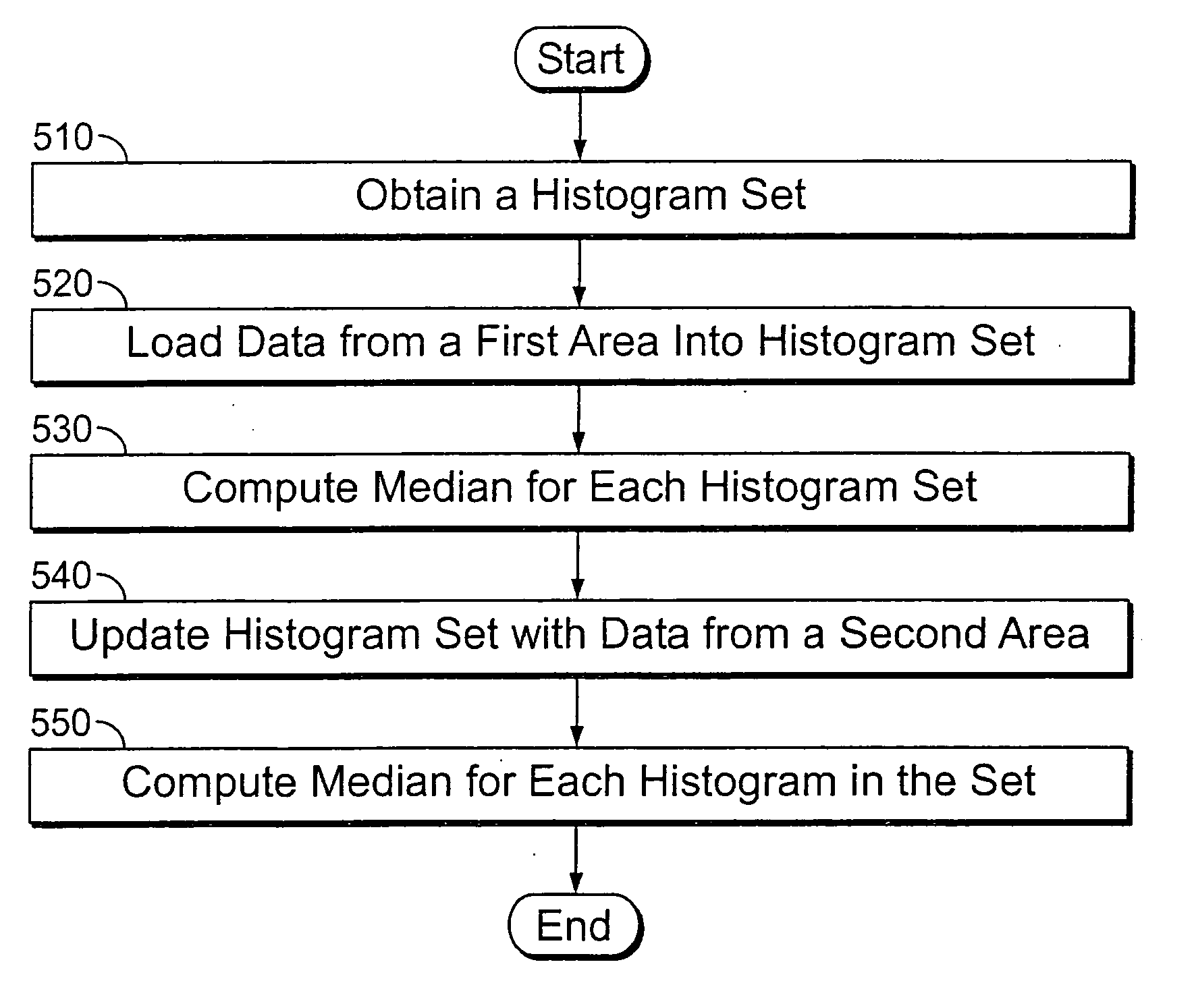
InactiveUS20060110063A1Improve executionIncrease speedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingImage resolution
The invention is a method and apparatus for improving image-processing applications. Embodiments of the invention provide methods for preserving computation results and offer intermediary computation steps to allow the processing of images at any location to take advantage of previously processed image areas. The preferred embodiment offers a method for building a median filter that significantly improves the processing speed over basic techniques. By building a histogram hierarchy, image data statistics are added and subtracted using a multiplicity of histograms from the histogram hierarchy, where each histogram describes an image area. Furthermore, a histogram hierarchy is built using multiple layers, each layer defining a level of statistical resolution.
Owner:SHELL & SLATE SOFTWARE
Image processing method and apparatus using self-adaptive binarization
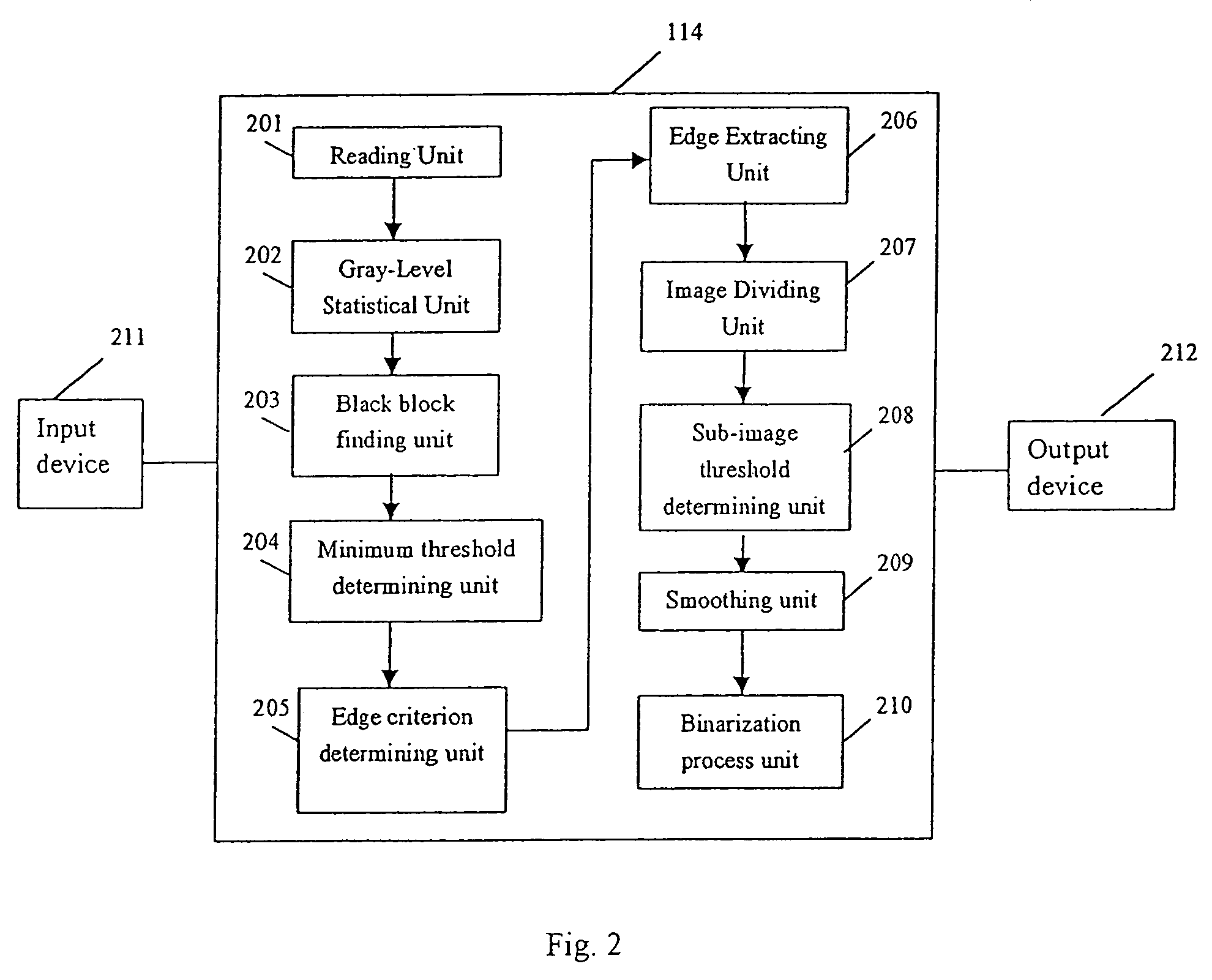
ActiveUS7062099B2Fast and effective binarization processImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
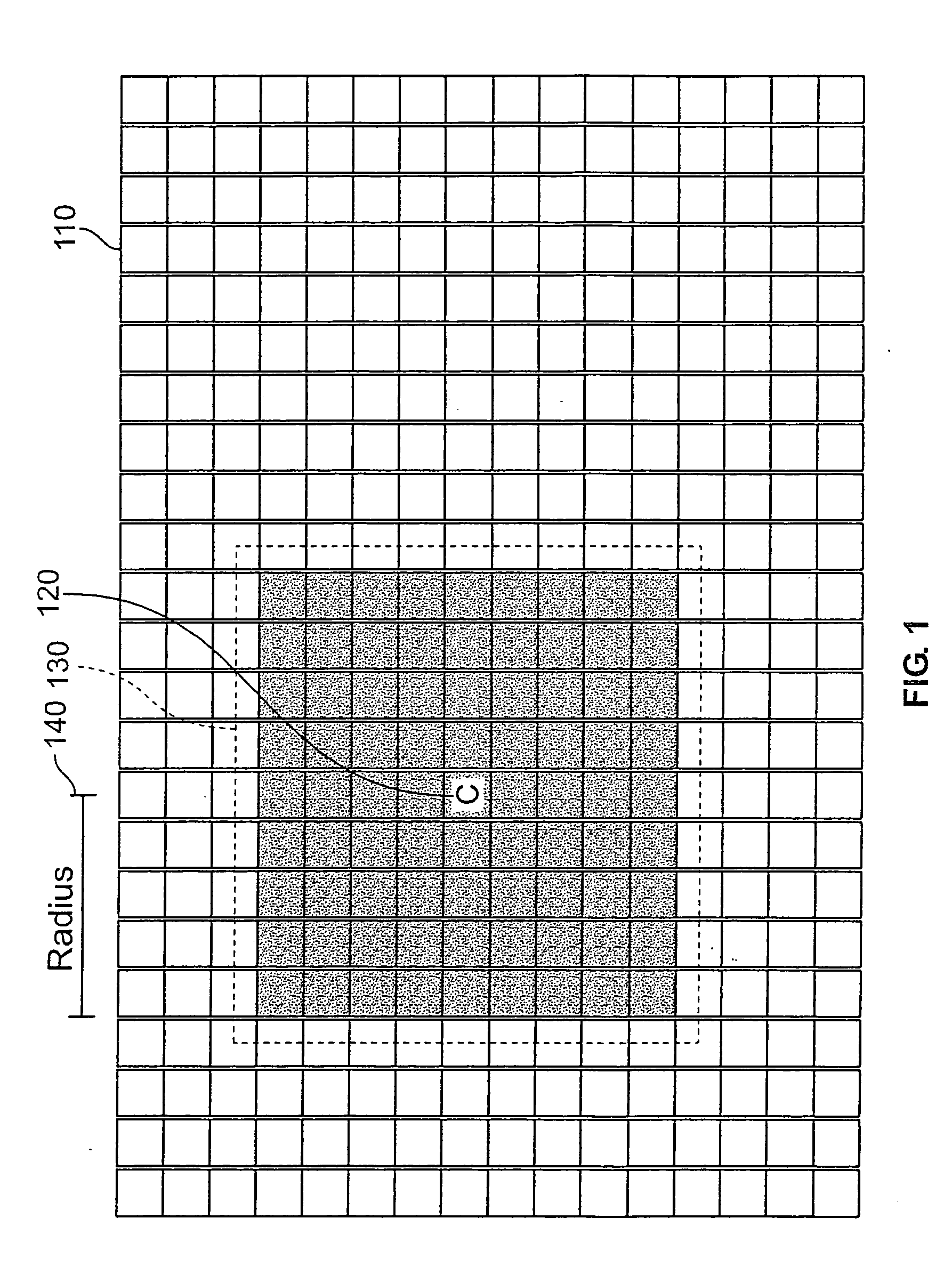
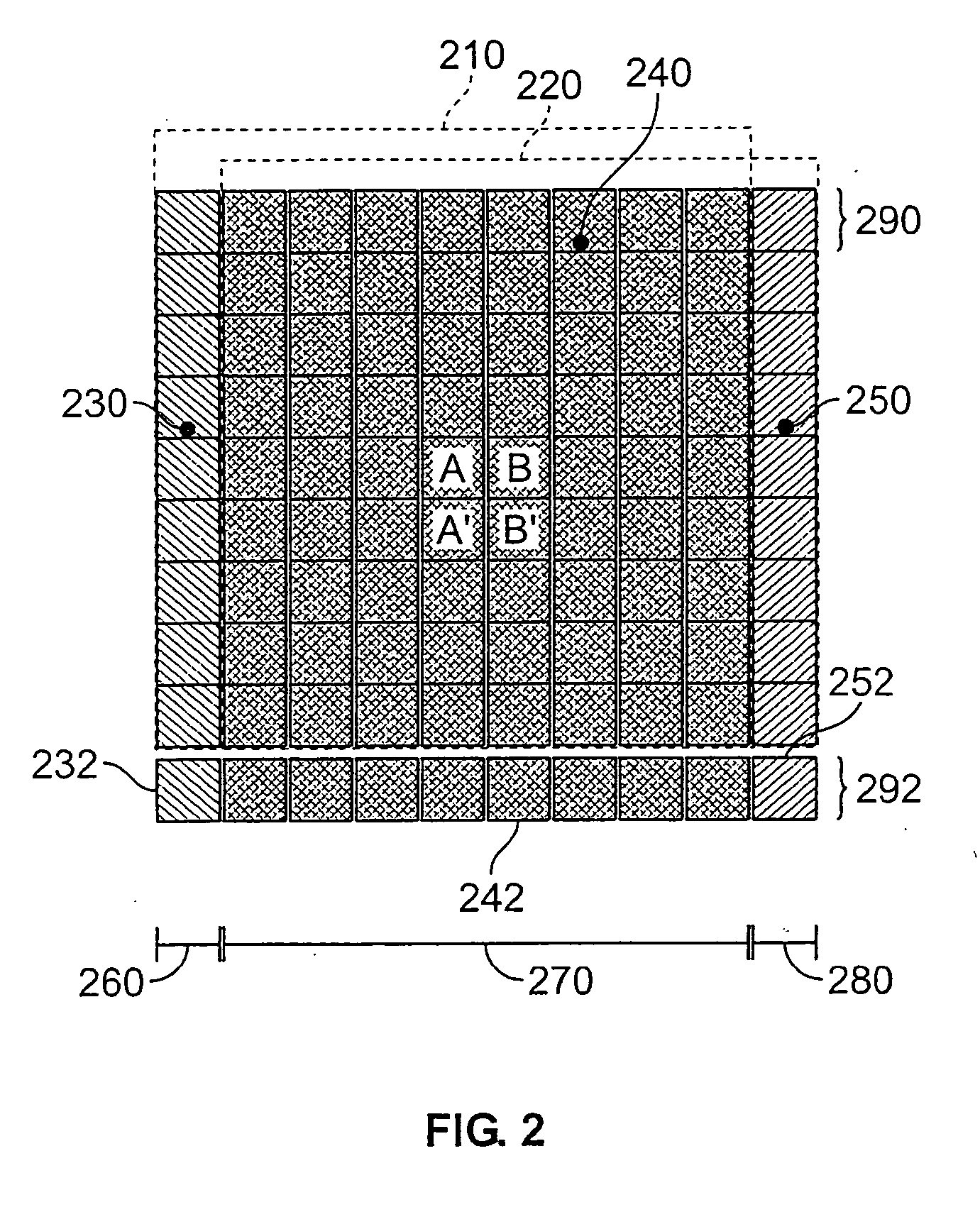
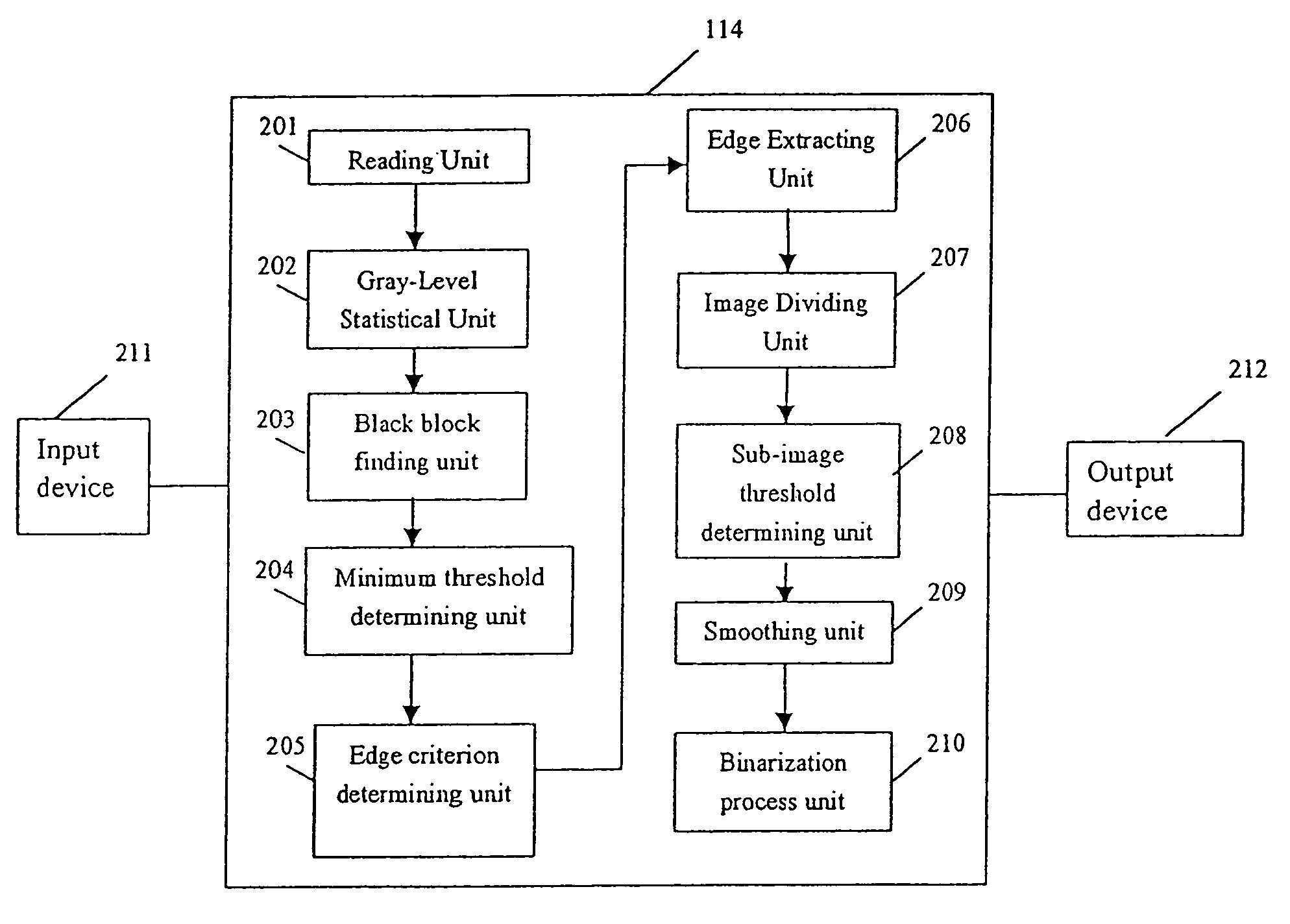
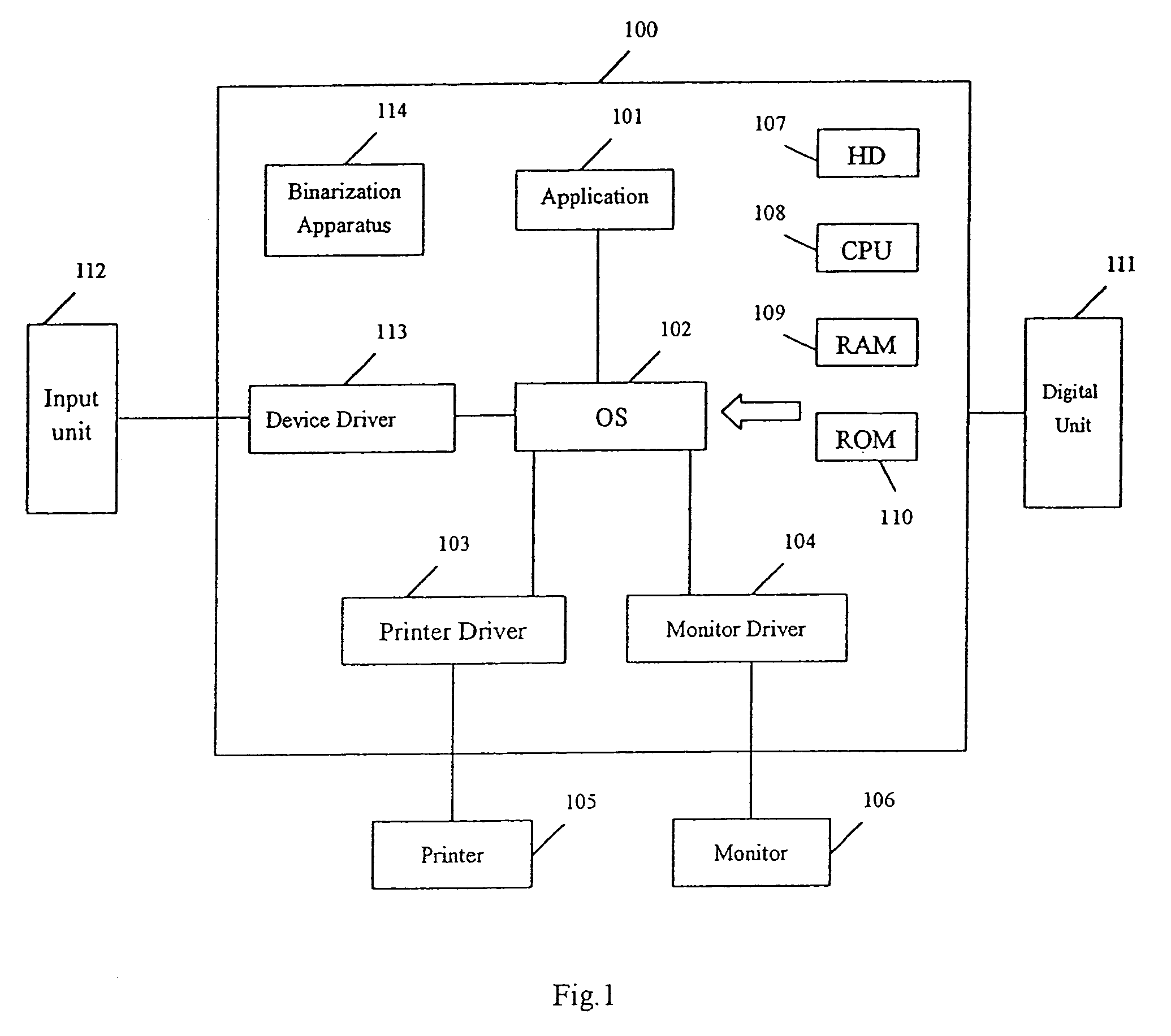
The present invention provides a unique method, apparatus, system and storage medium for image binarization process, wherein an image to be processed is divided into a plurality of sub-images and an binarization threshold for each of the sub-images is determined based on the gray-levels of the edge pixels detected in respective sub-image. The image processing method of the present invention comprises: calculating a gray-level statistical distribution of pixels of an image, detecting edge pixels in an image based on an edge criterion corresponding to the gray-level statistical distribution, dividing the image into a plurality of sub-images; determining a binarization threshold for each of the sub-images based on the gray-levels of edge pixels detected in the sub-image; and performing binarization process for each of the sub-images based on the binarization threshold of the sub-image.
Owner:CANON KK
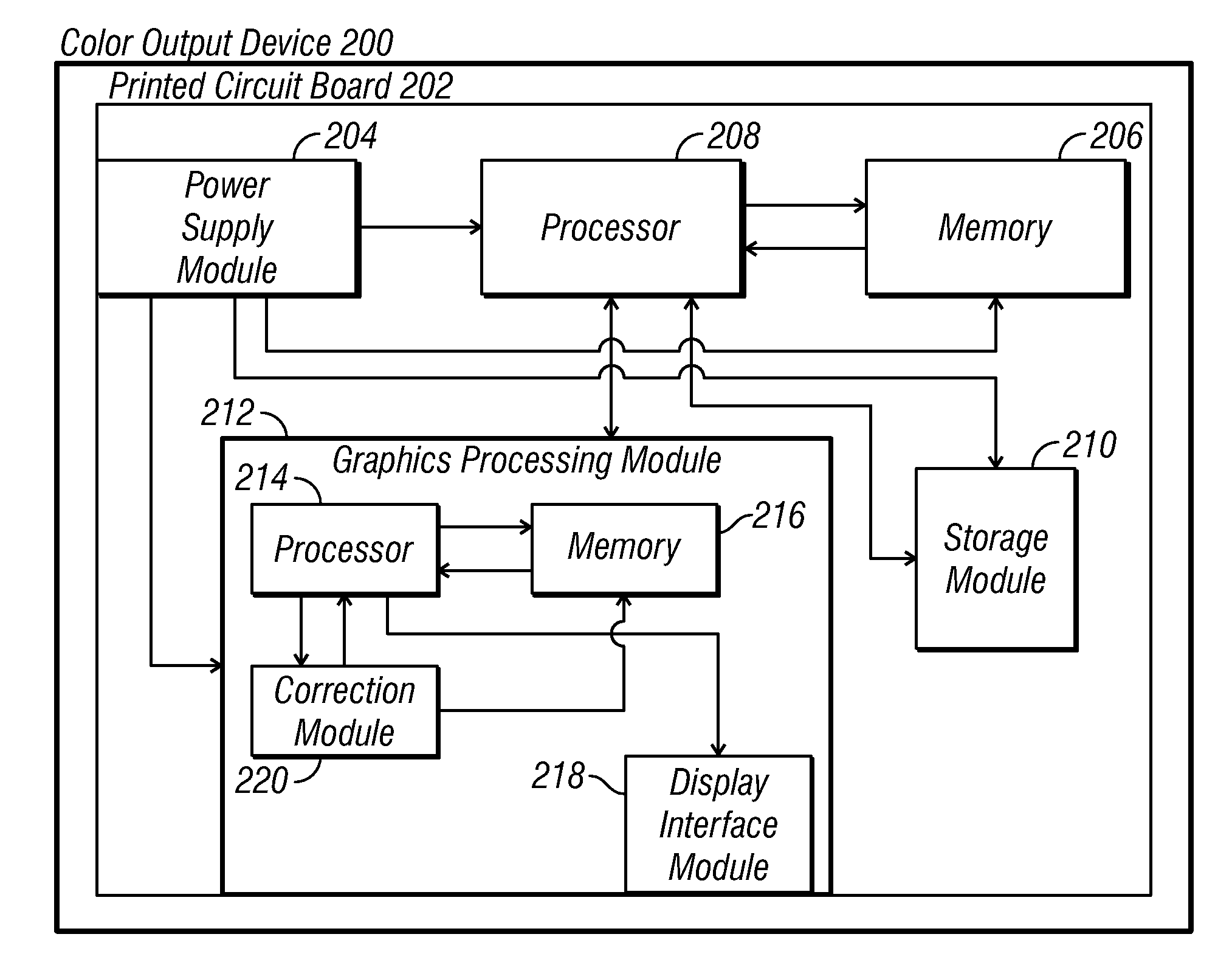
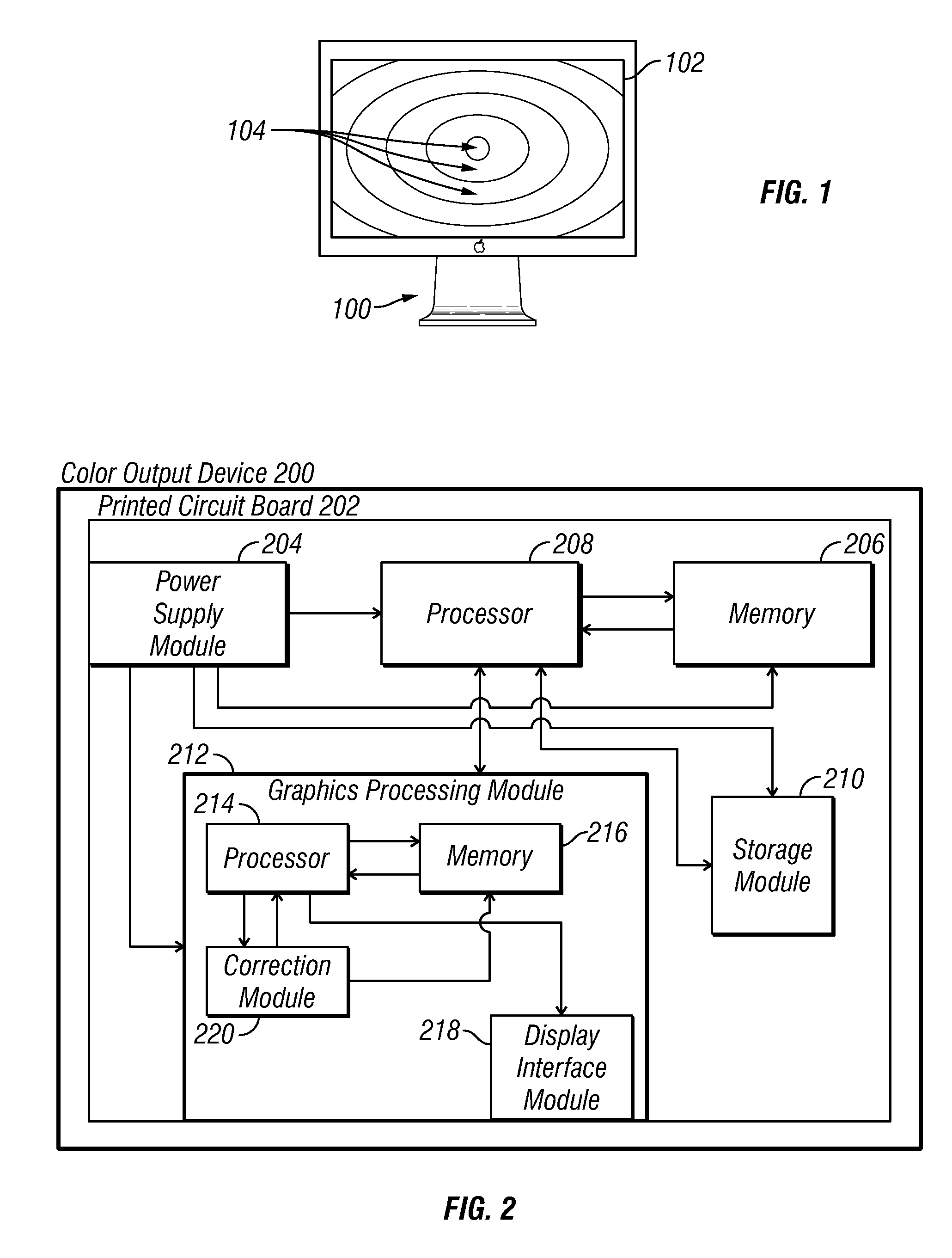
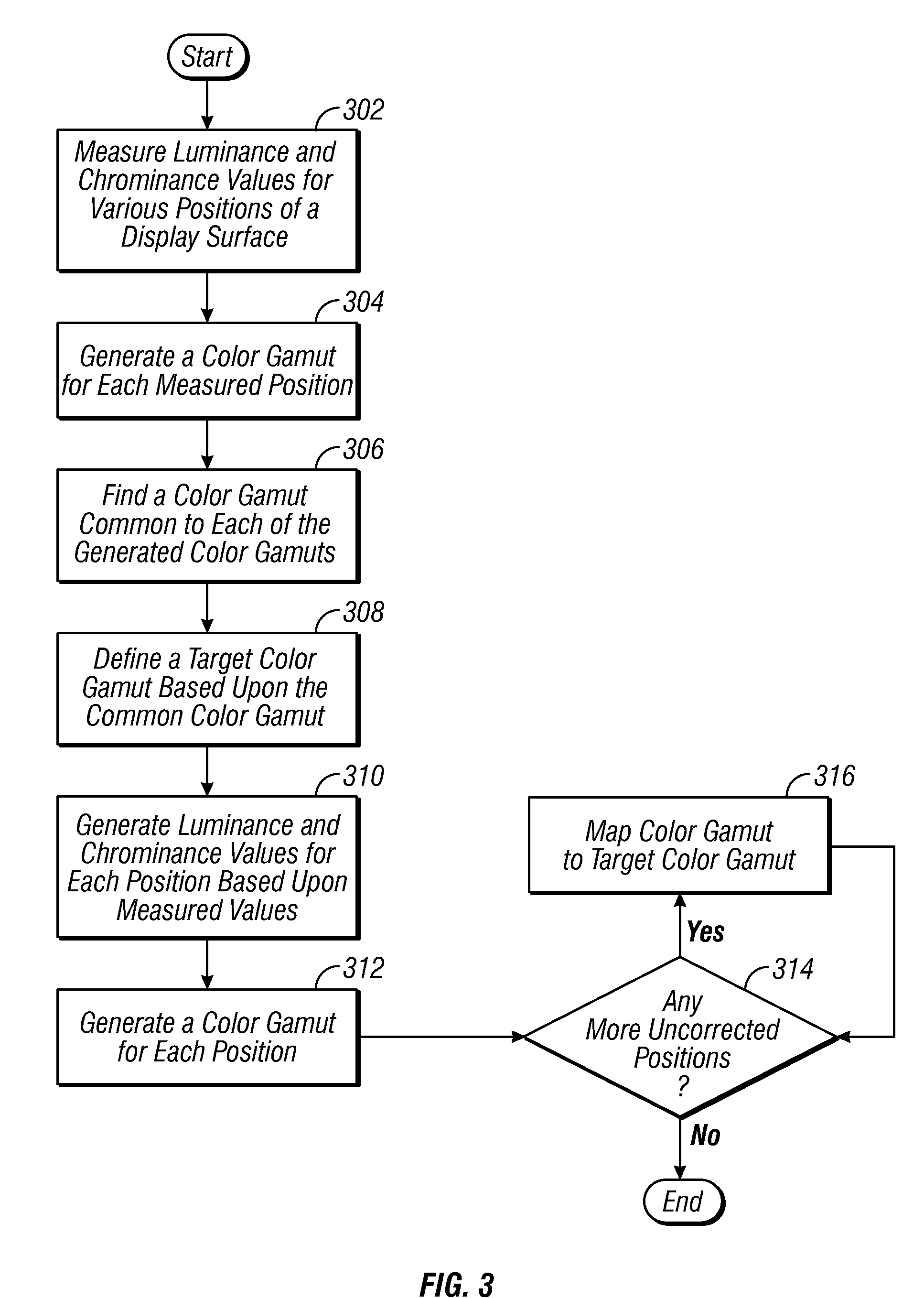
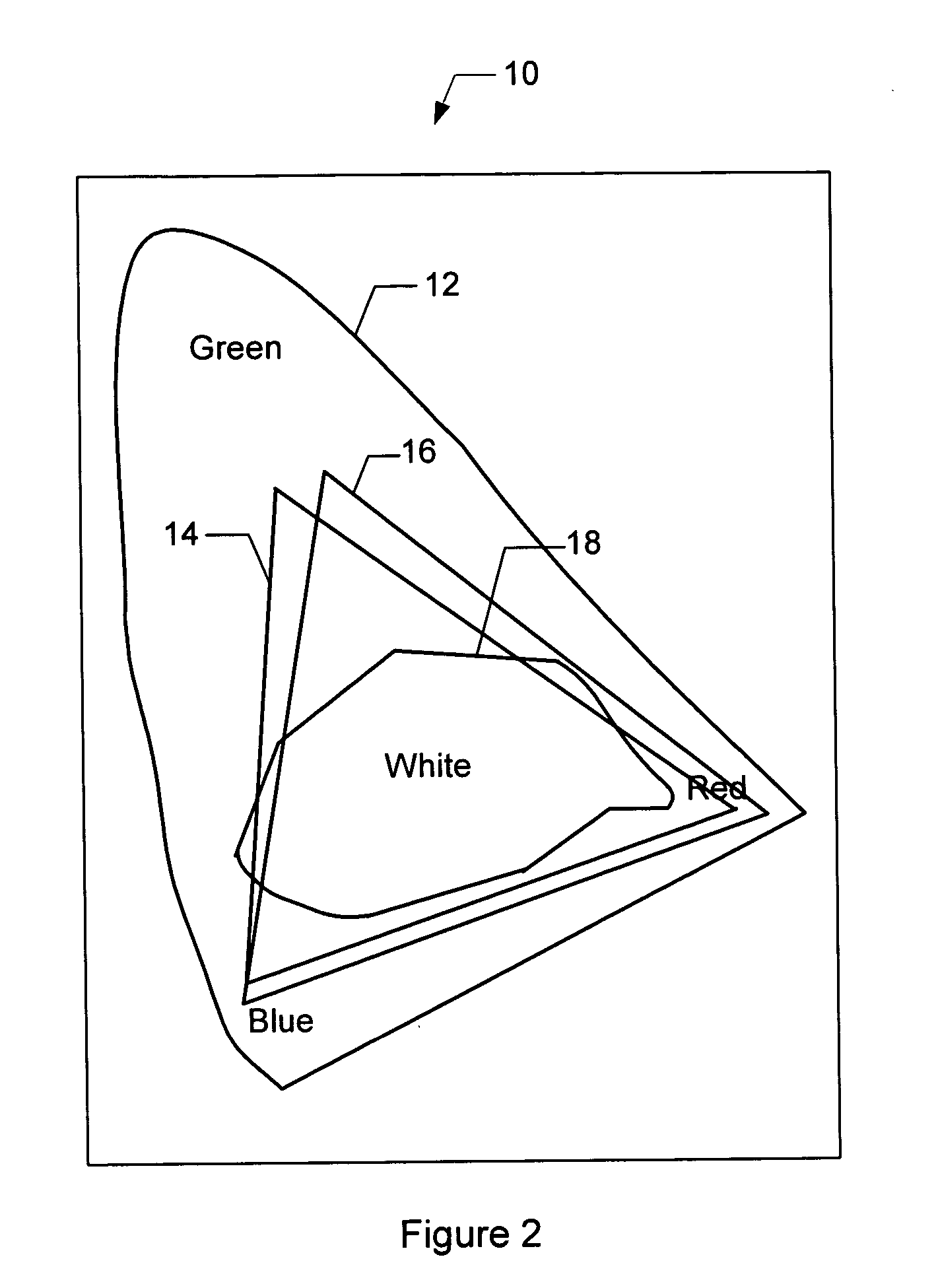
Methods and apparatus for color uniformity
Methods and apparatus for achieving color and luminance uniformity in color output devices. In one embodiment, measurements of luminance and chrominance are taken at various regions of the display surface for a range of color inputs. Using the collected data, a color volume is formed for each of the measured regions. This color volume comprises a set of all colors producible at the measured region. The color volumes for each of the measured regions are then used to generate a common color gamut, i.e., a volume of colors that are producible in each of the measured regions. A gamut mapping can then be performed for all or a portion of the positions on the display surface to a target color gamut. Input data for the gamut mapping process may be determined by conventional interpolative techniques.
Owner:APPLE INC
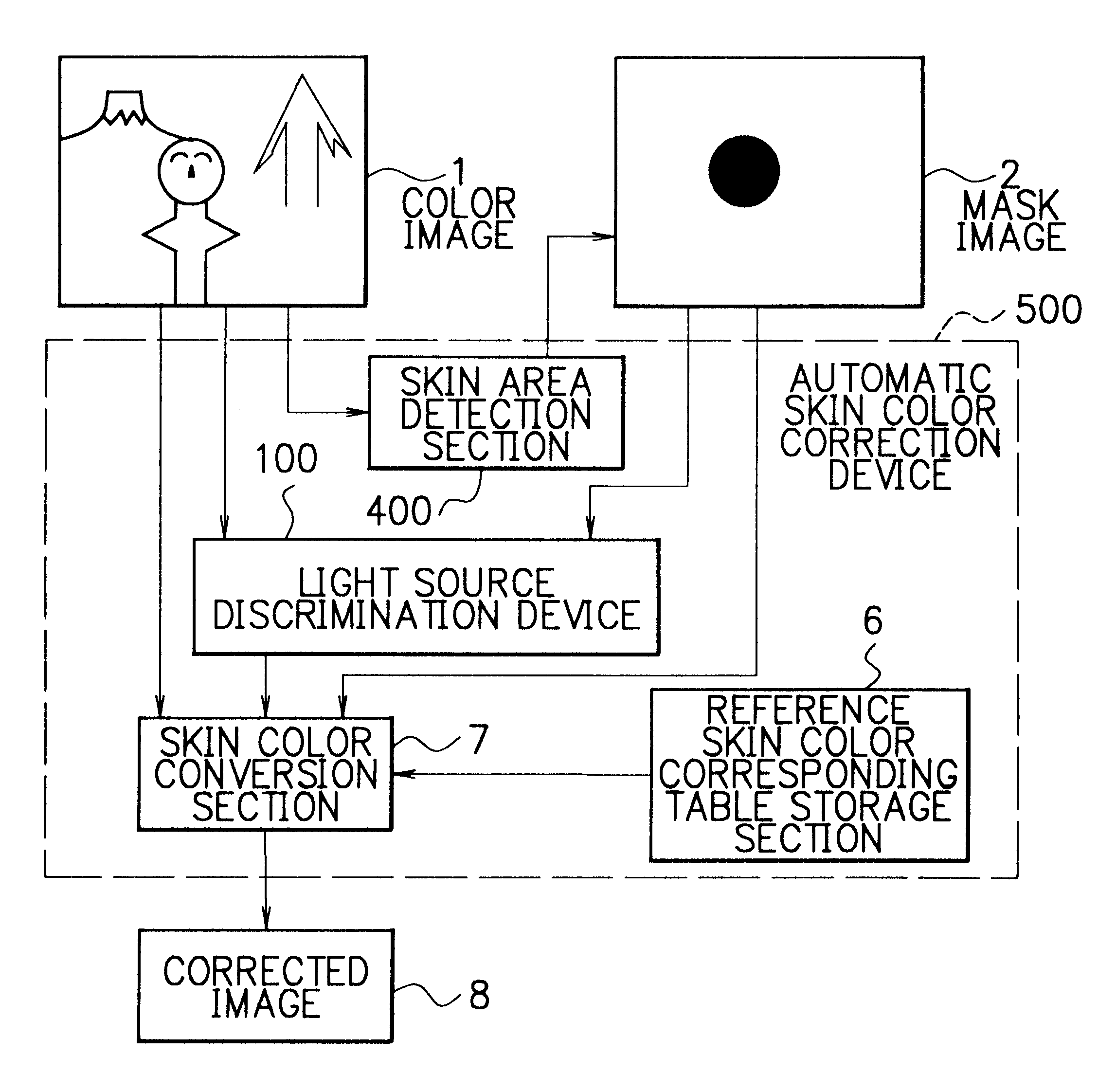
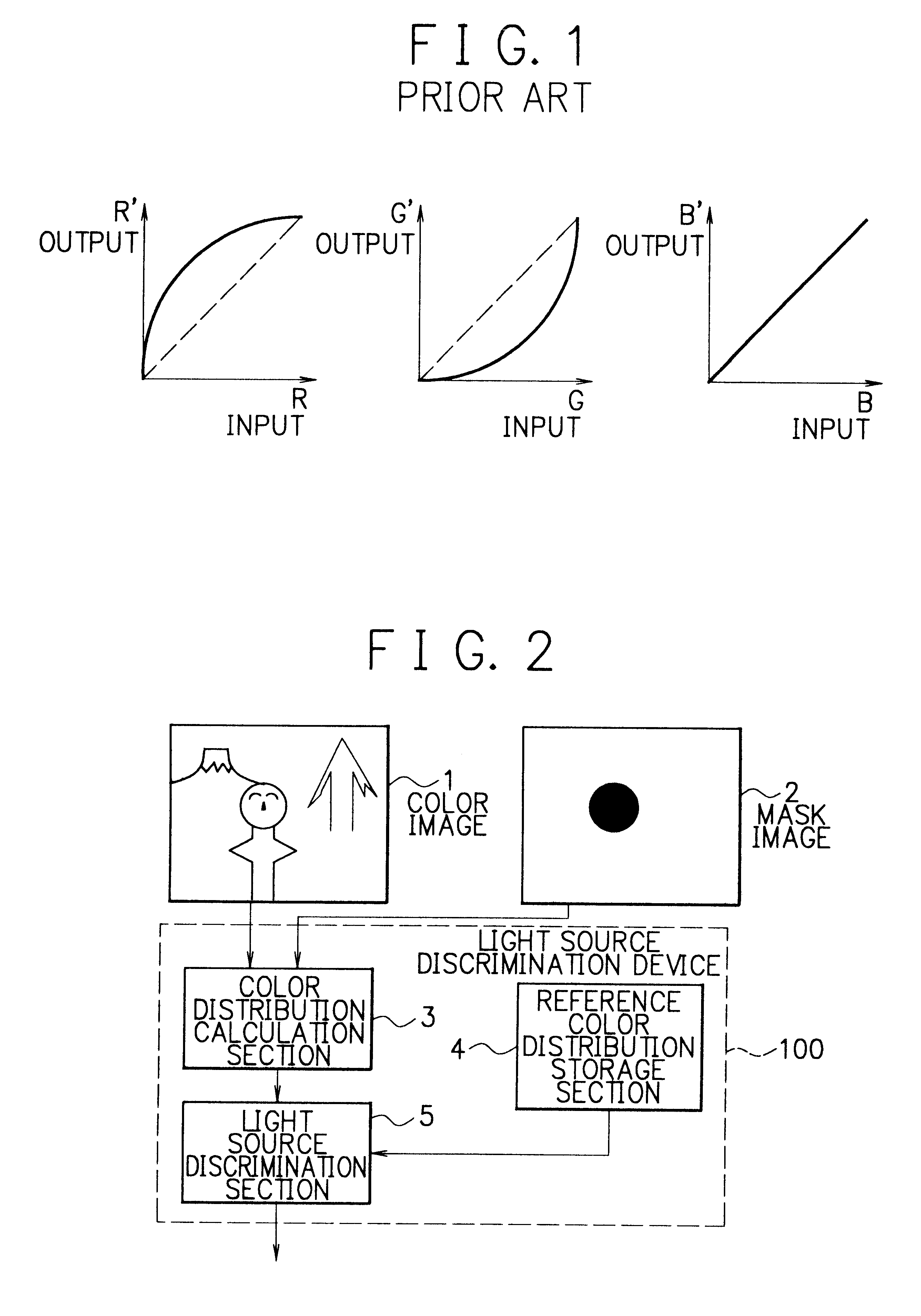
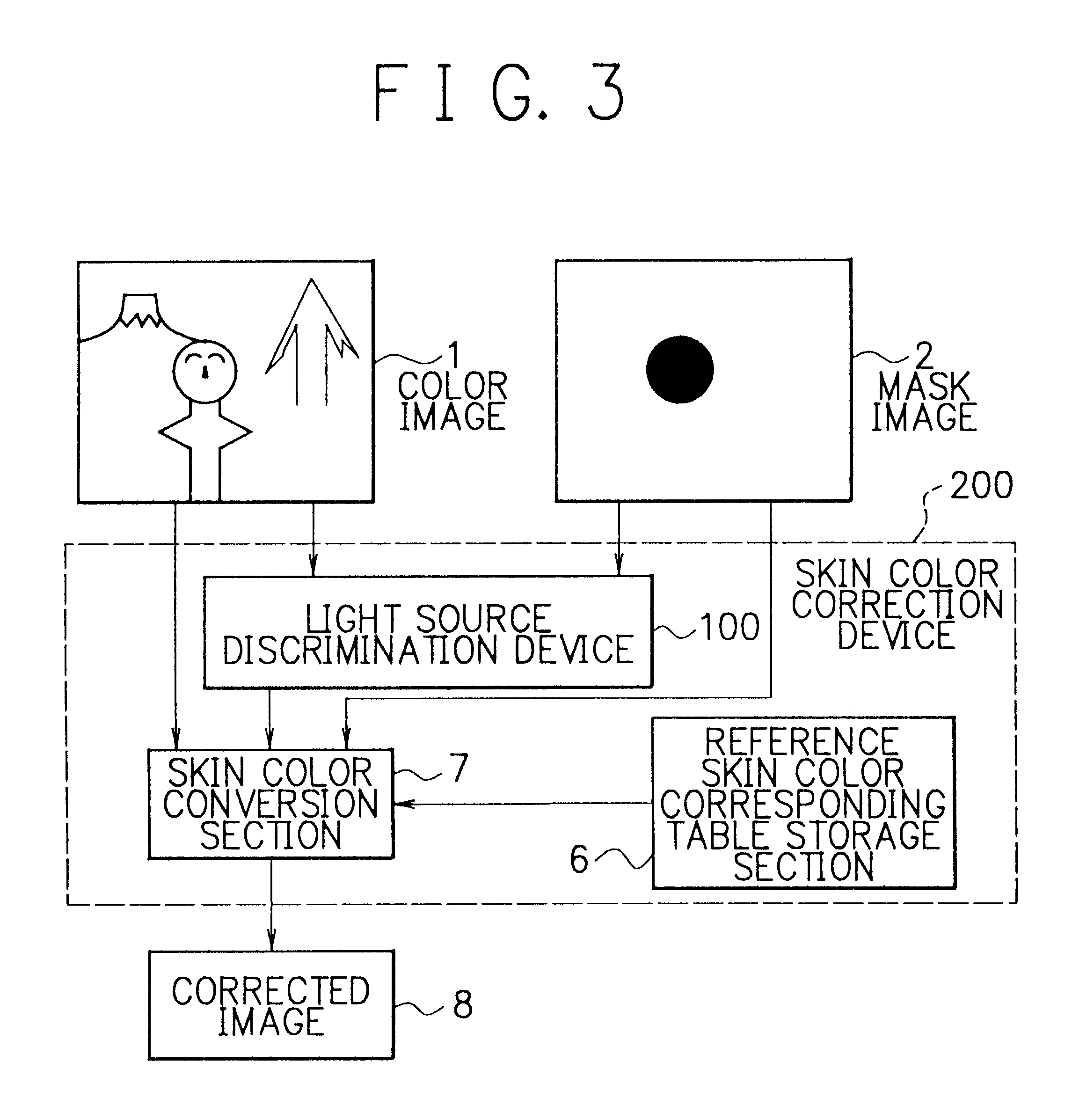
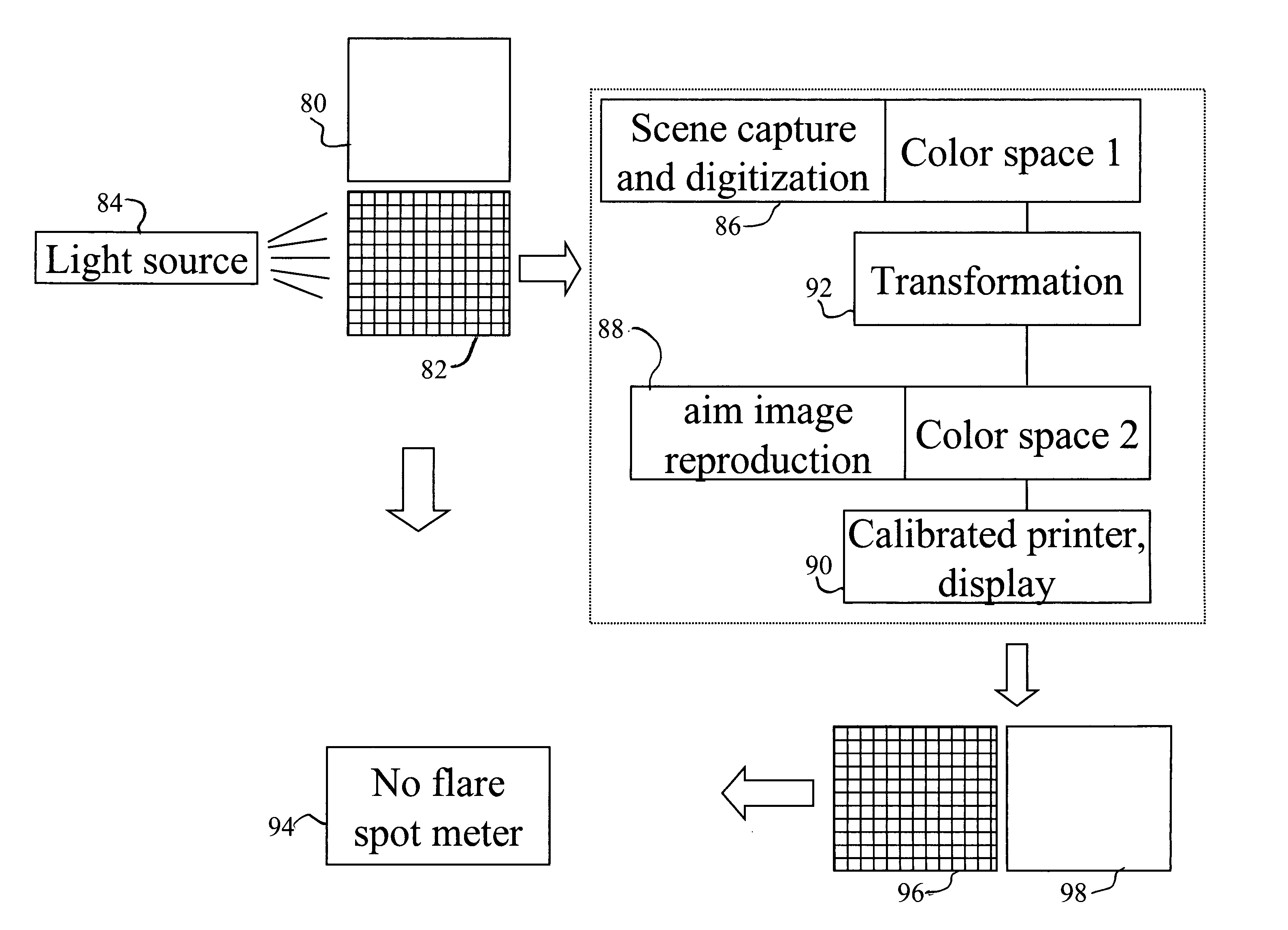
Method and device of light source discrimination, skin color correction, and color image correction, and storage medium thereof capable of being read by computer
A method and a device of light source discrimination, skin color correction, and color image correction, and storage medium thereof capable of being read by a computer always enable reproducibility, of color to be maintained highly regardless of difference of light source. There is calculated color distribution of portion of a face or skin in image by color distribution calculation section. There is compared the color distribution with distribution of skin color taken photograph under respective light sources stored in reference color distribution storage section. A light source discrimination section discriminates the light source at the time of taking photograph. There is corrected color by converting color under the light source of candidate substance into a corresponding color under standard light source.
Owner:NEC CORP
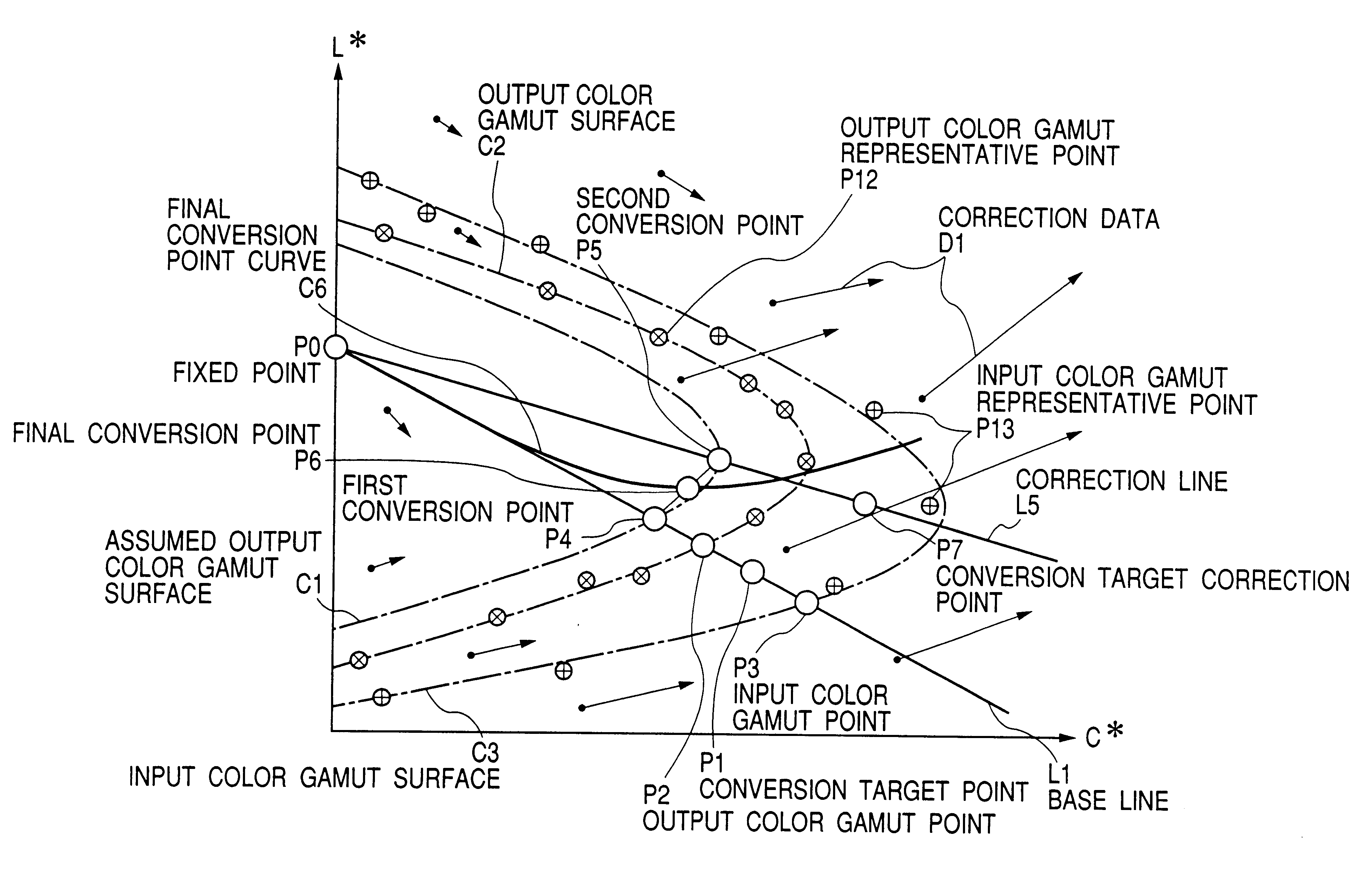
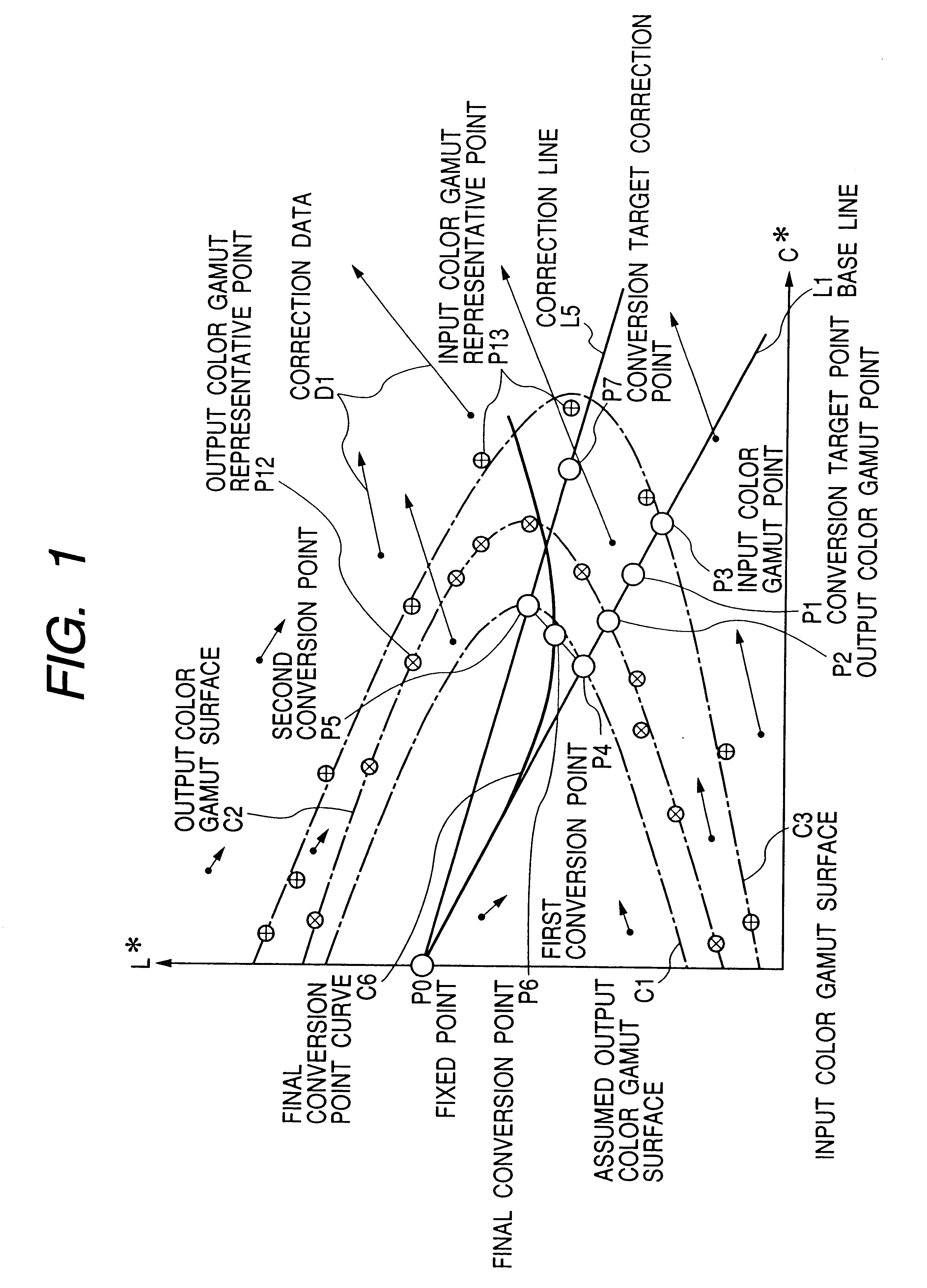
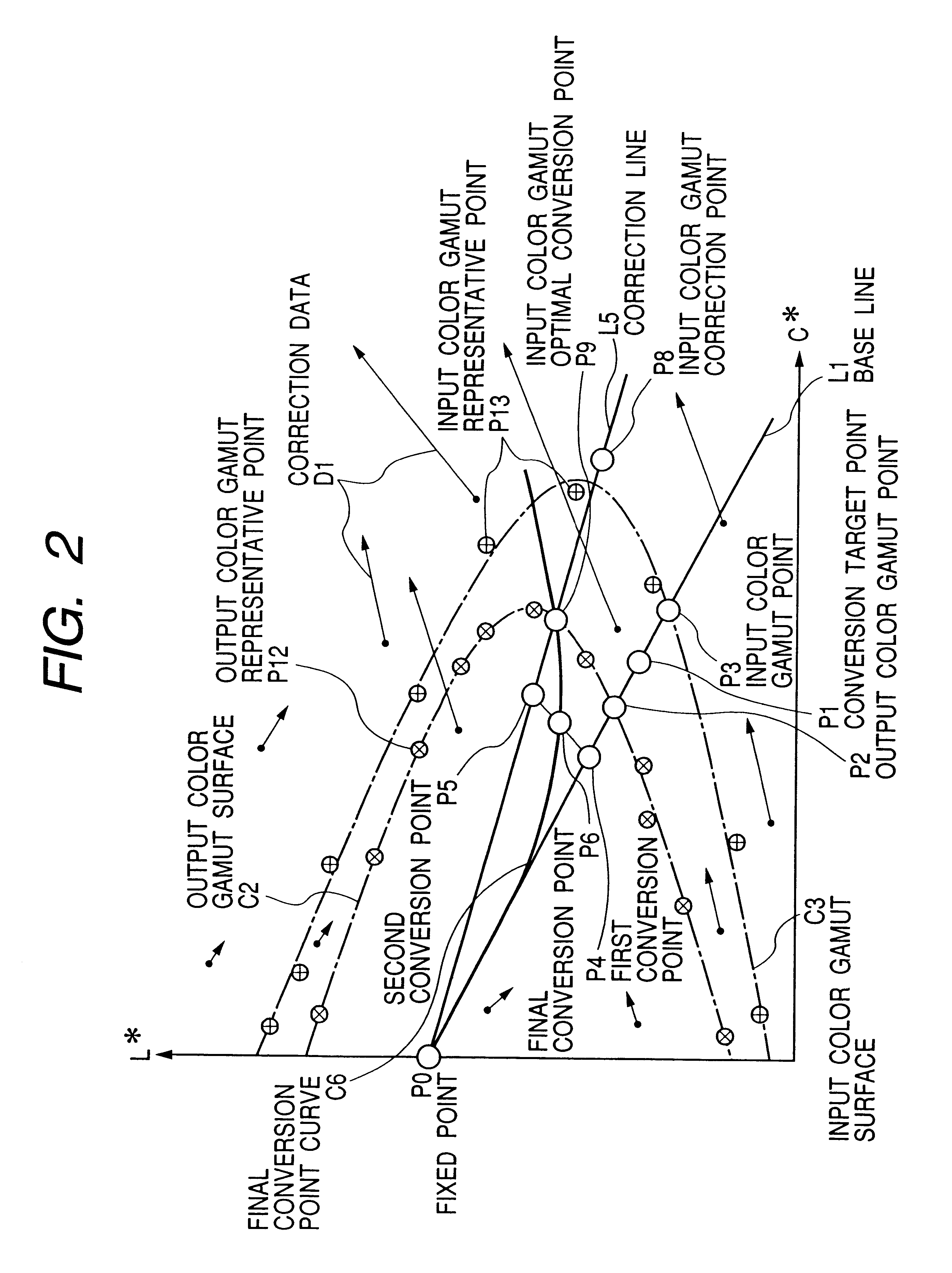
Systems, methods, and computer program products for converting between color gamuts associated with different image processing devices
InactiveUS20050185200A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingGamut
The present invention provides systems, methods, and computer program products for performing color gamut mapping between different color gamuts on a pixel basis. A set of desired parameters is initially defined representing the desired color gamut transformation to which the color values of the pixel are to be mapped. The parameters describe the best-fit lines for the portions of the curve for the gamut transform to which the specific parameters are applied. The present invention next maps the color values used for the pixel in the first color gamut and the color values used for the pixel in the second gamut to the parameters of the transform. The present invention performs mapping by isolating portions of a curve and approximating those portions of the curve with a best straight-line fit. This method of mapping from one color gamut to another color gamut is less computationally intensive than conventional methods.
Owner:ZIH CORP
Automatic white balance method and apparatus
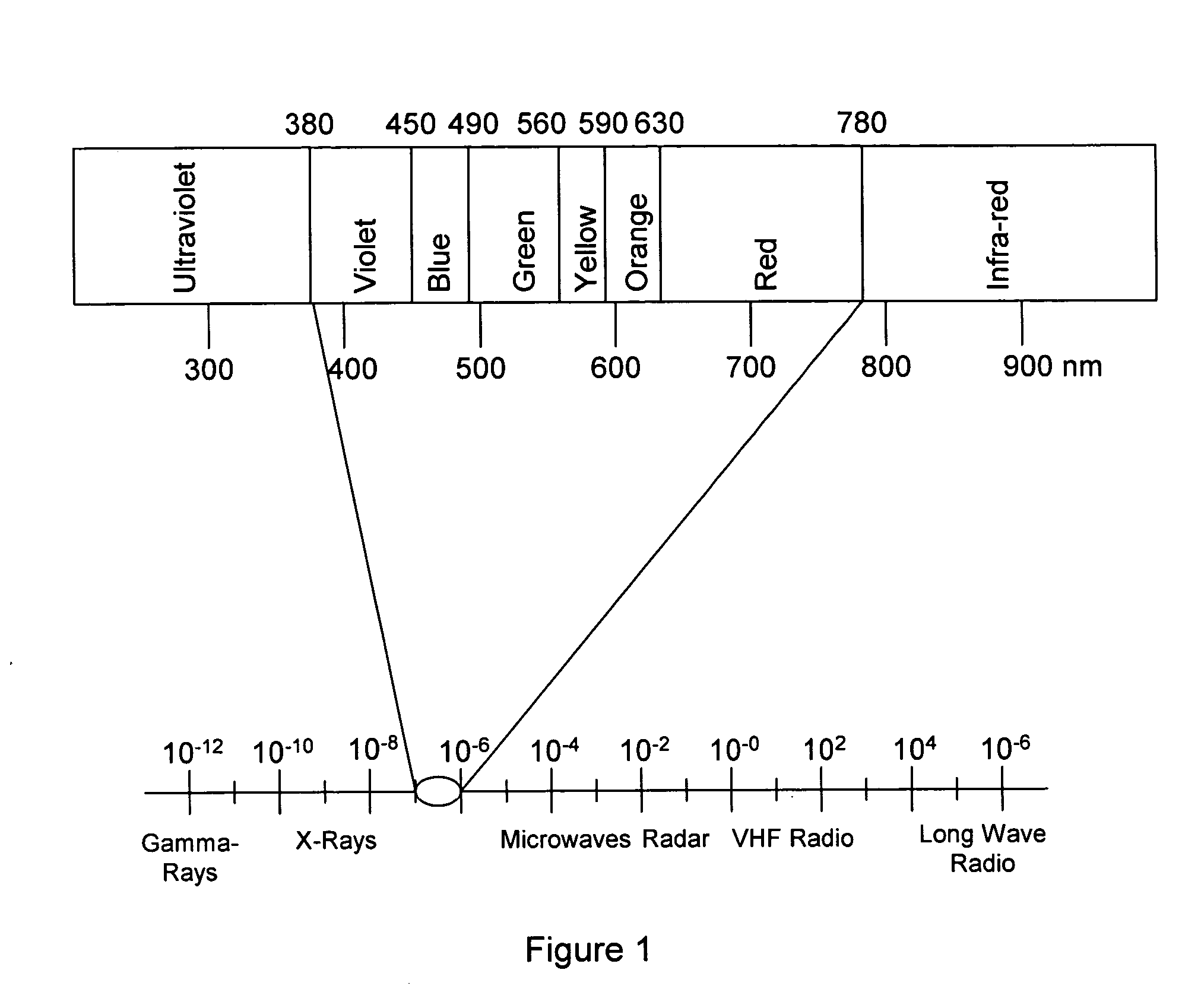
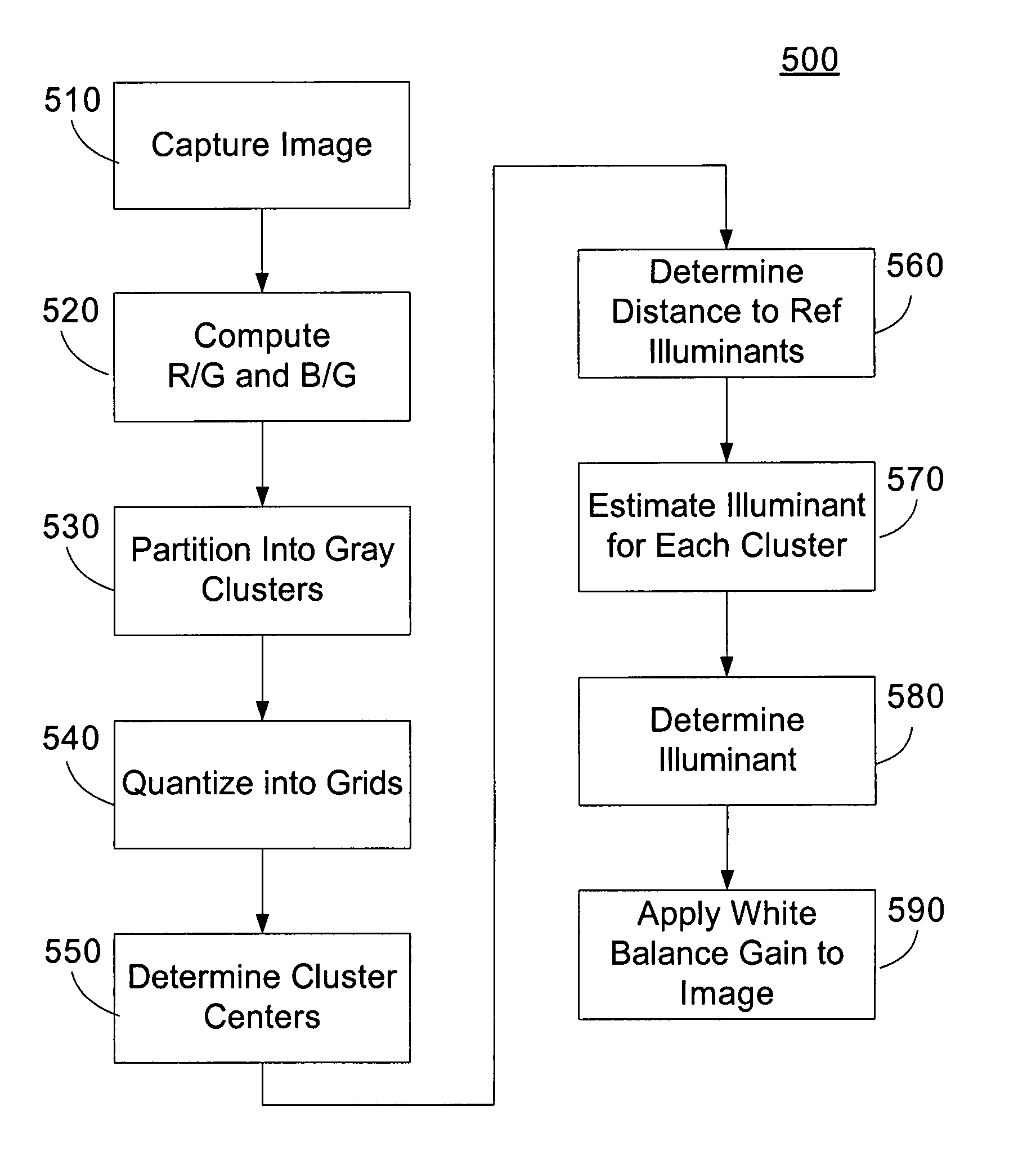
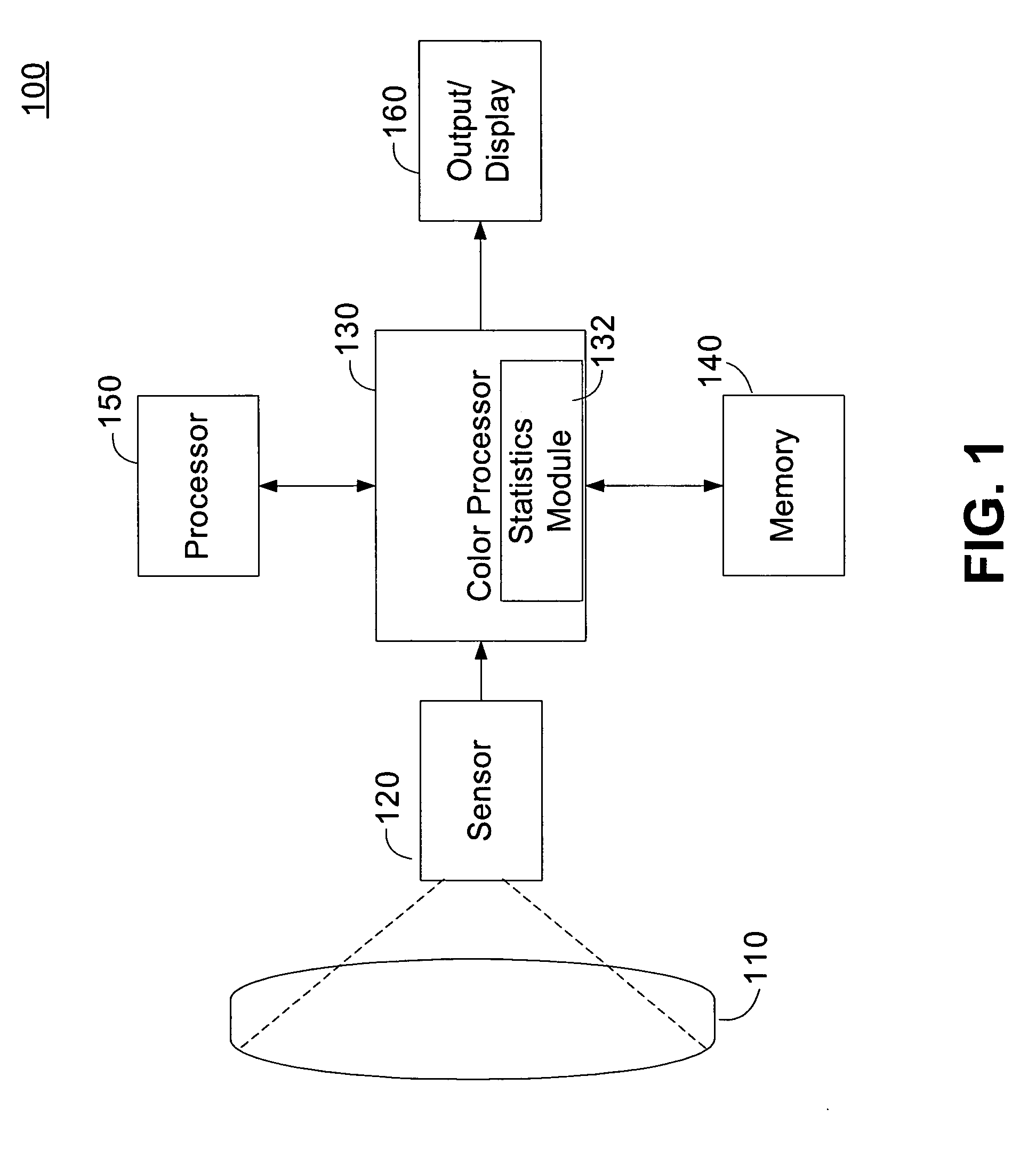
Automatic white balance of captured images can be performed based on a gray world assumption. Initially, a flat field gray image is captured for one or more reference illuminations. The statistics of the captured gray image are determined and stored for each reference illumination during a calibration process. For each subsequent captured image, the image is filtered to determine a subset of gray pixels. The gray pixels are further divided into a one or more gray clusters. The average weight of the one or more gray clusters is determined and a distance from the average weights to the reference illuminants is determined. An estimate of the illuminant is determined depending on the distances. White balance gains are applied to the image based on the estimated illuminant.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
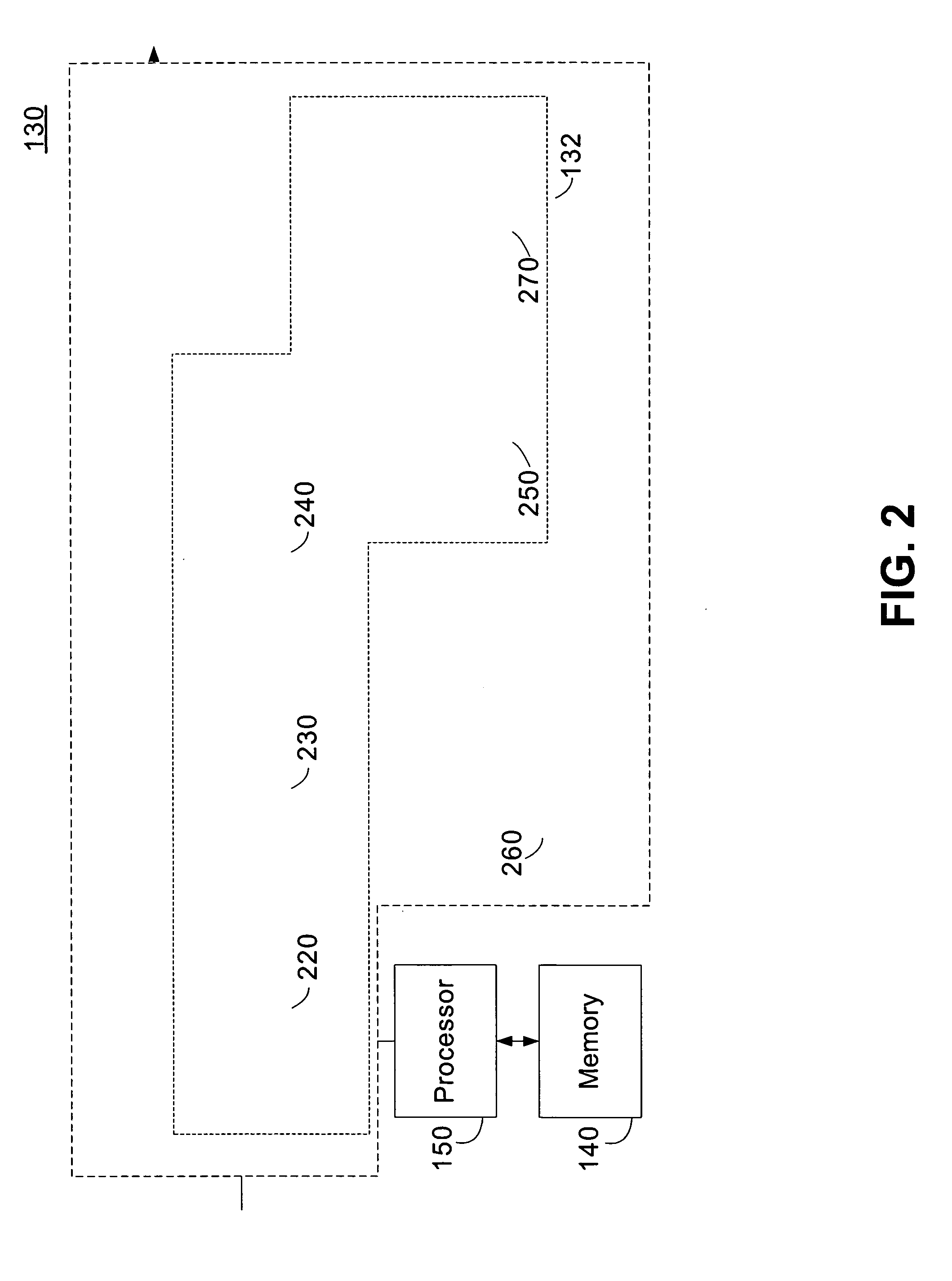
Mobile communication terminal with dual-display unit having function of editing captured image and method thereof
ActiveUS20070035616A1Conveniently editImprove the display effectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsReal time displayImage capture
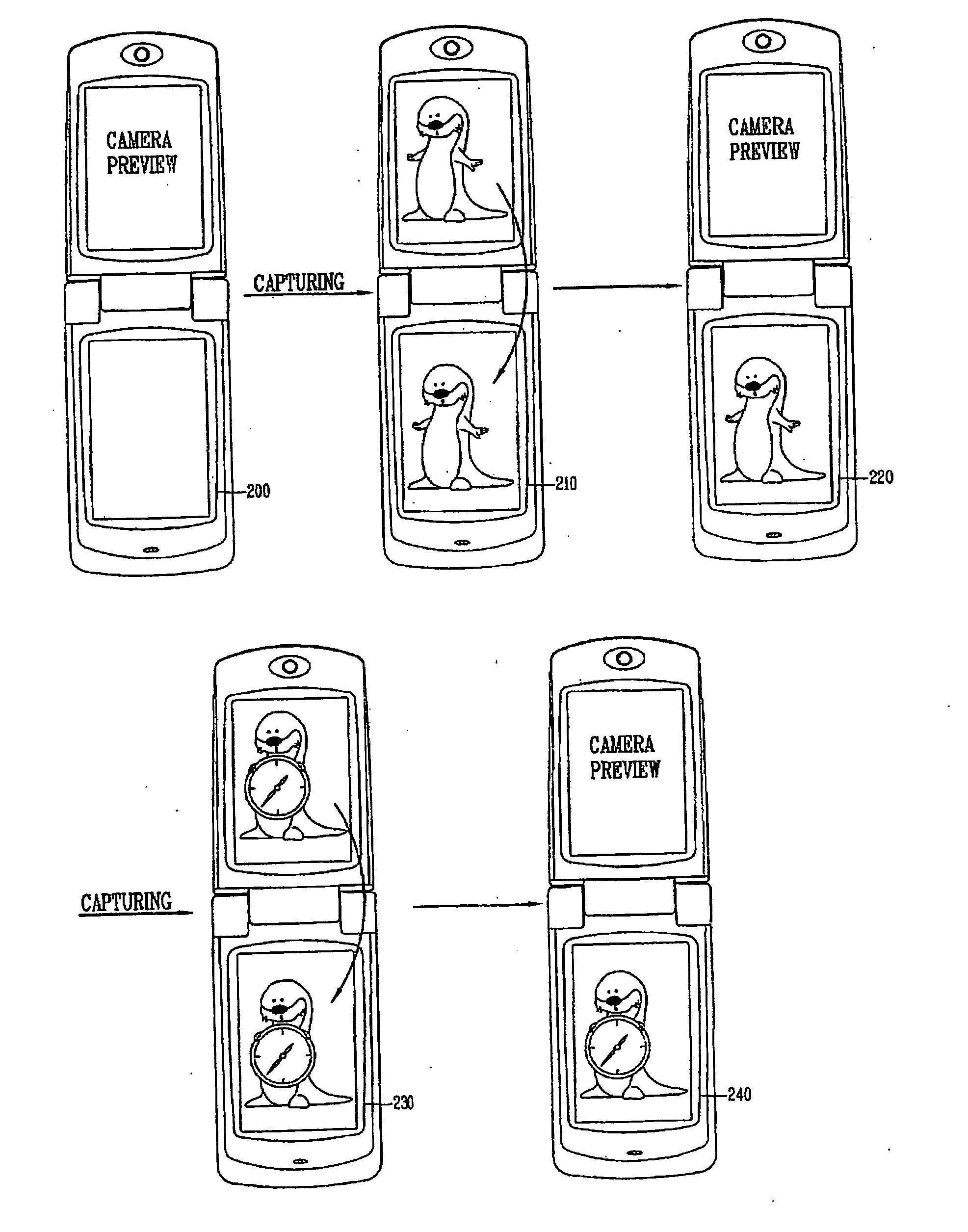
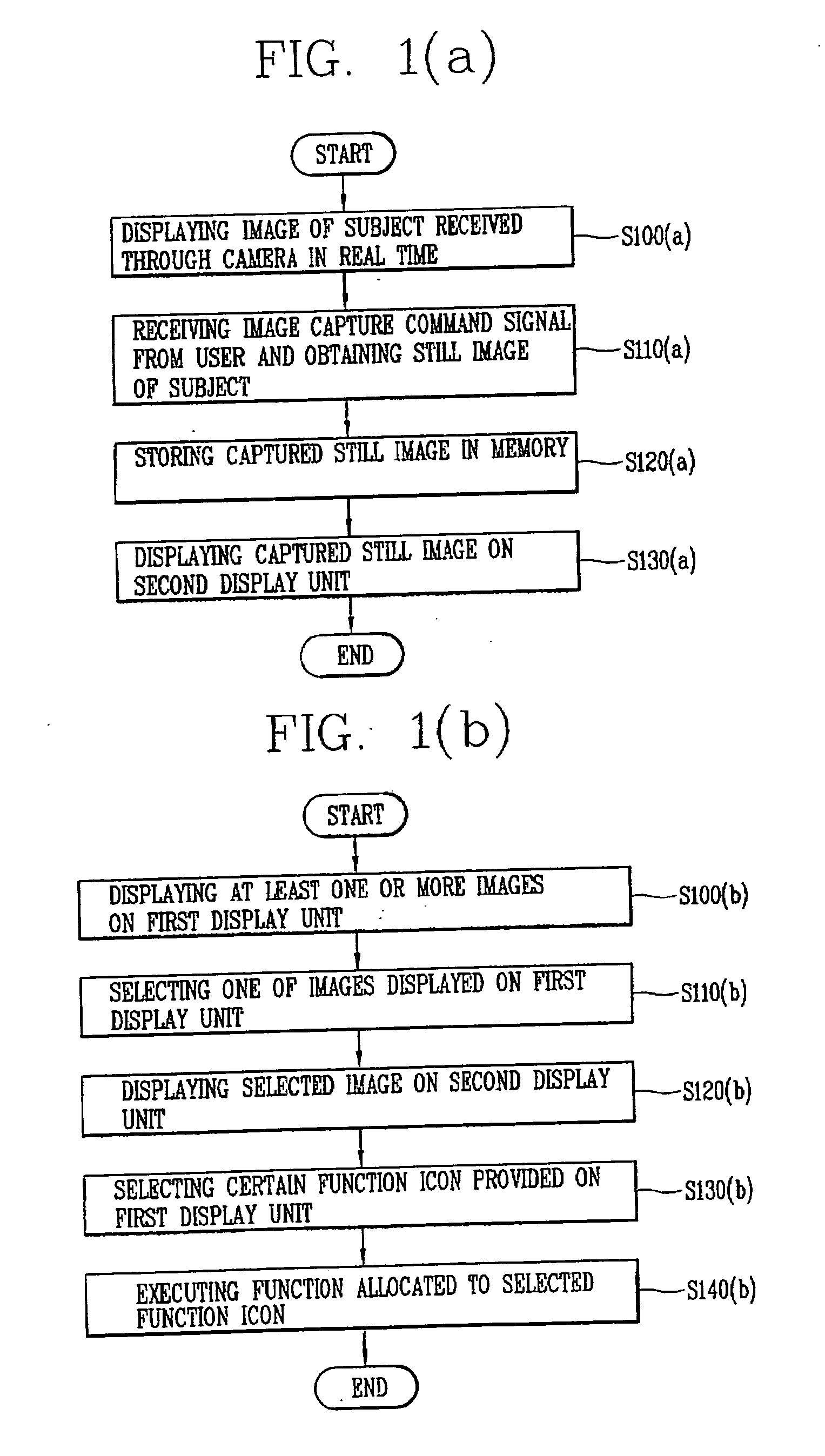
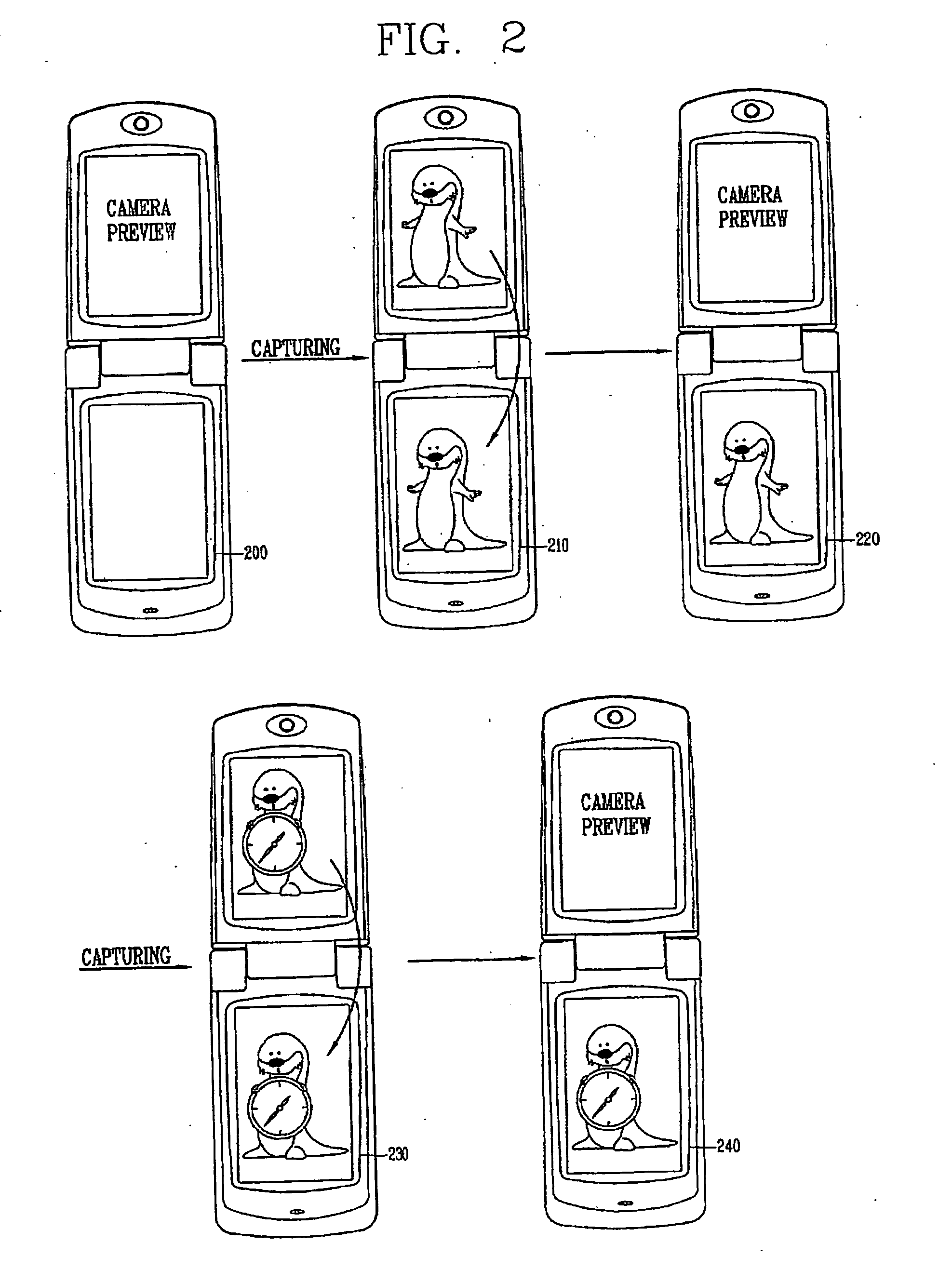
A mobile communication terminal with a camera and a dual-display unit, whereby, in an image capturing mode, a first display unit displays an image of a subject received through a camera in real time and a second display unit displays a still image of the subject captured according to an image capture command signal received from a user, and in an image editing mode, when one of at least two or more images displayed on the first display unit is selected, the selected image is displayed on the second display unit, and at the same time, when a certain function icon provided to the first display nit is selected, a function allocated to the selected function icon is executed. An image of a camera preview and a captured image are displayed on each different display unit, so a user can capture a moment an image is to be captured and check the recently captured image by naked eyes, enhancing user convenience and providing fun to users.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
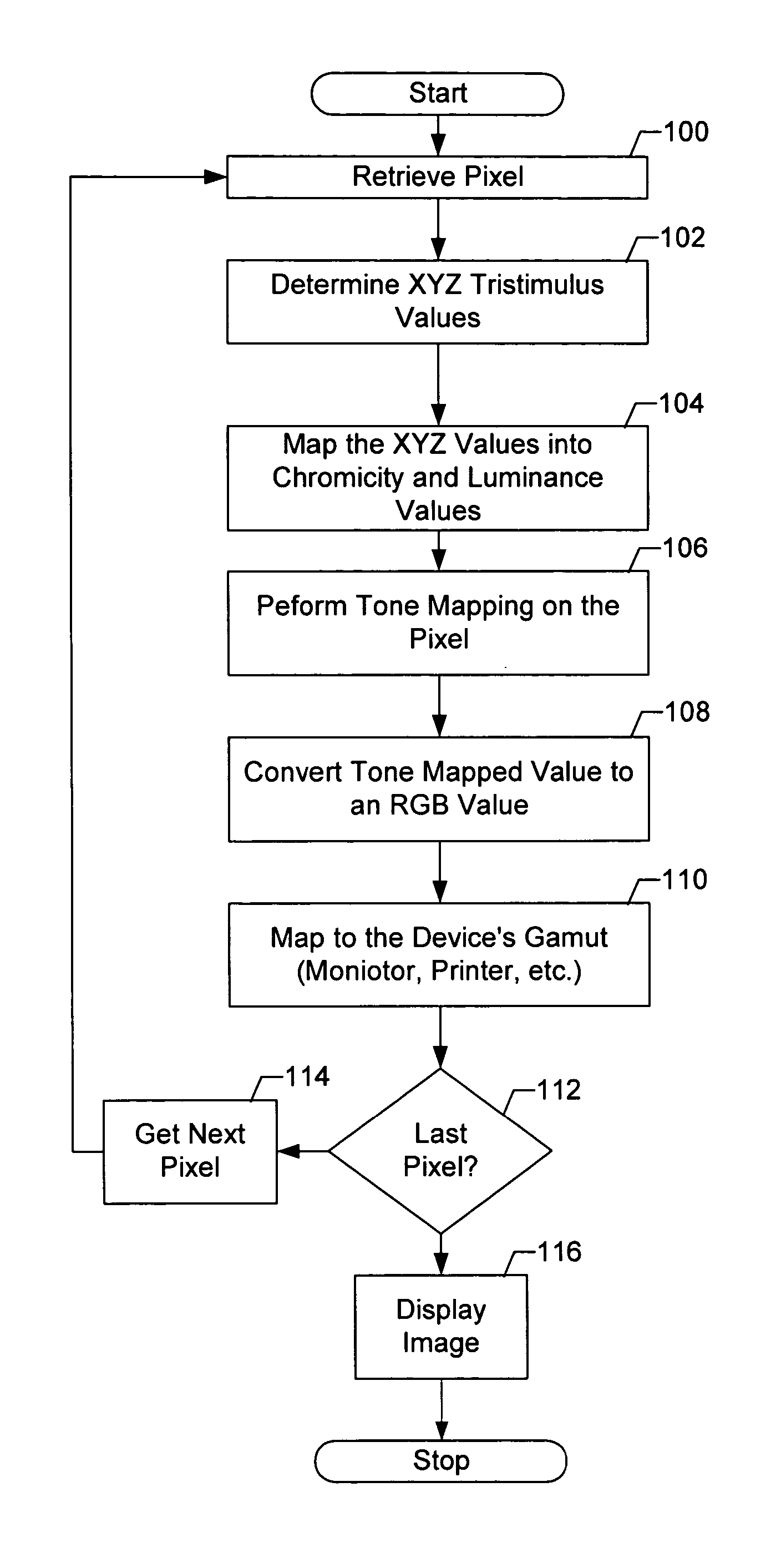
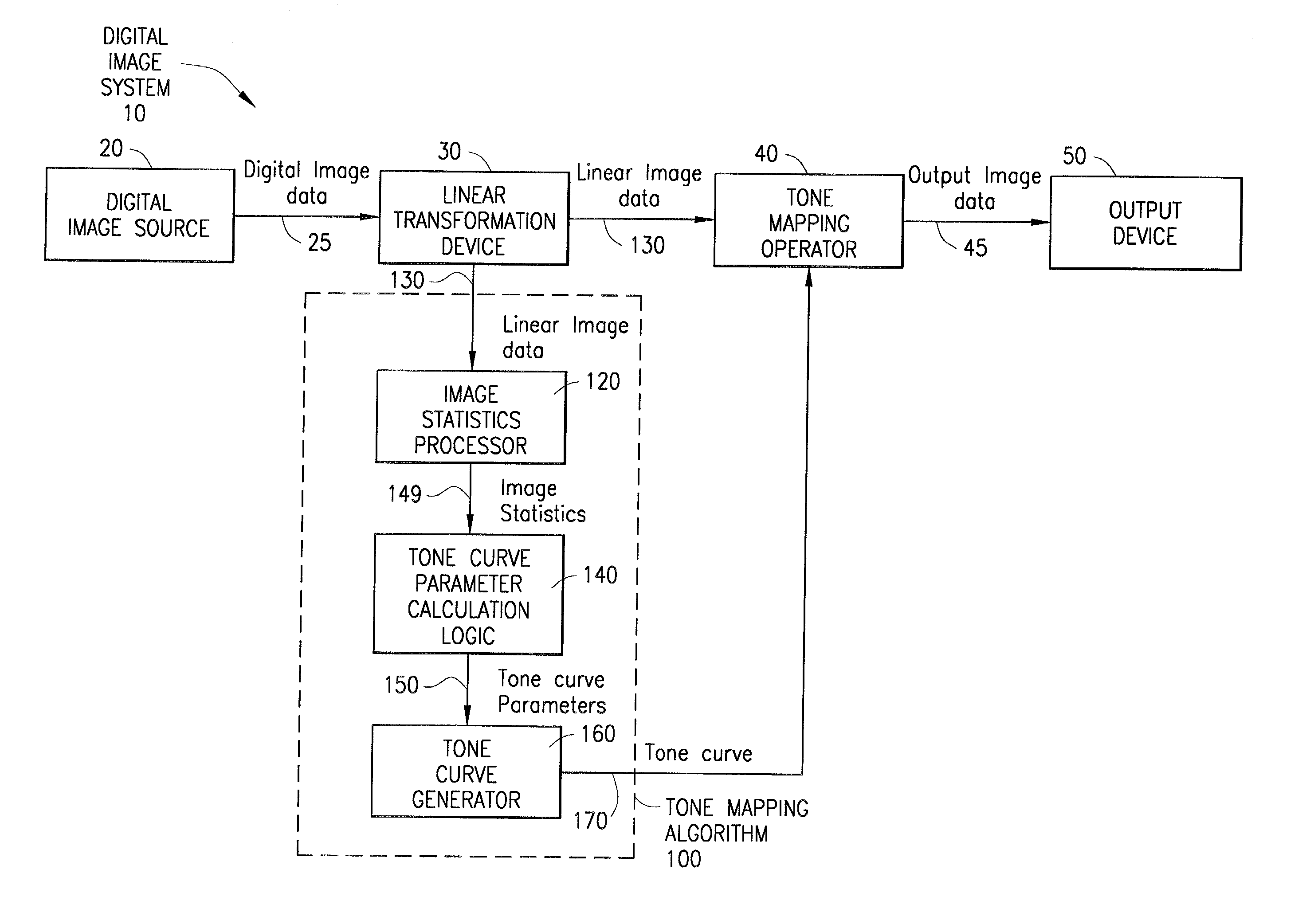
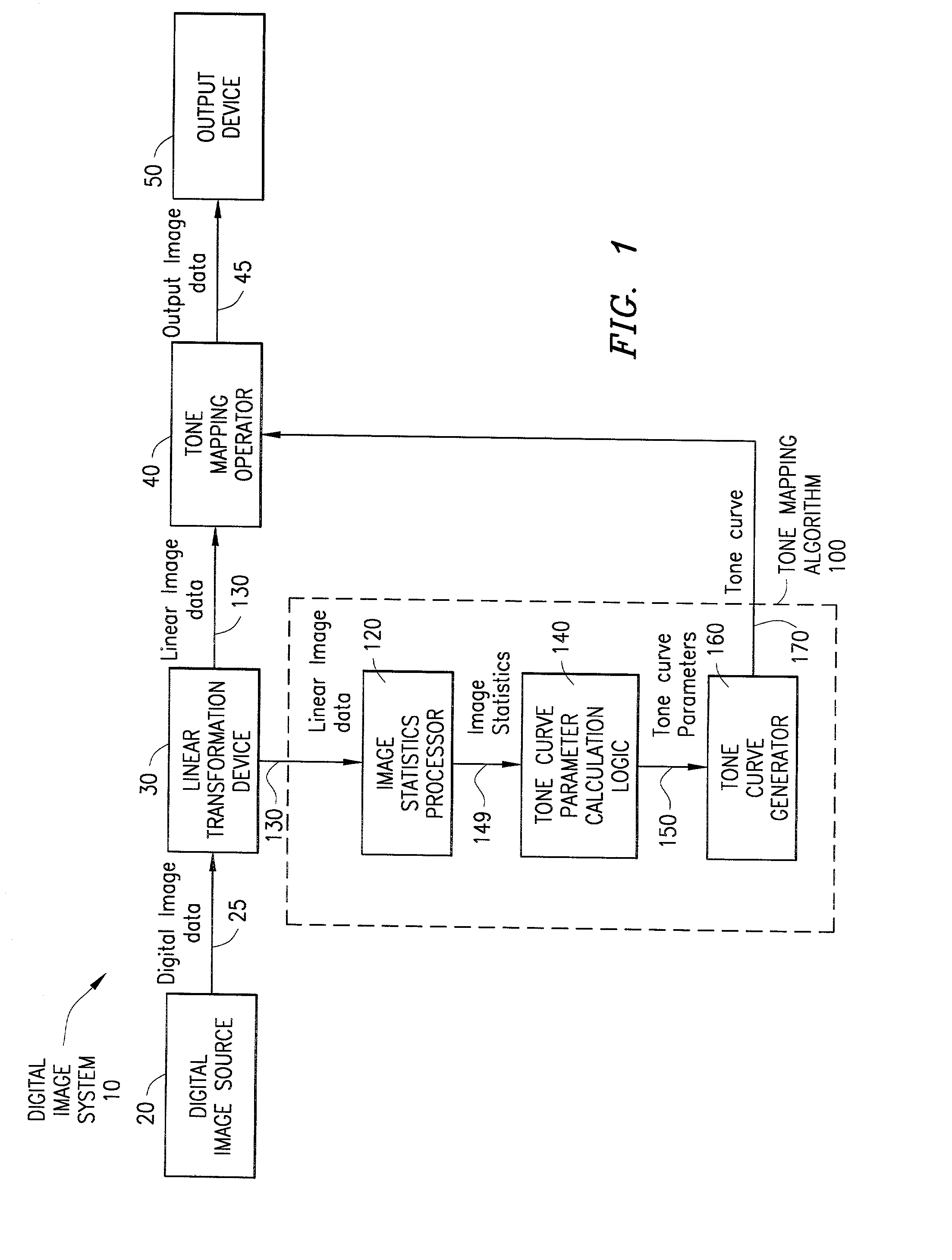
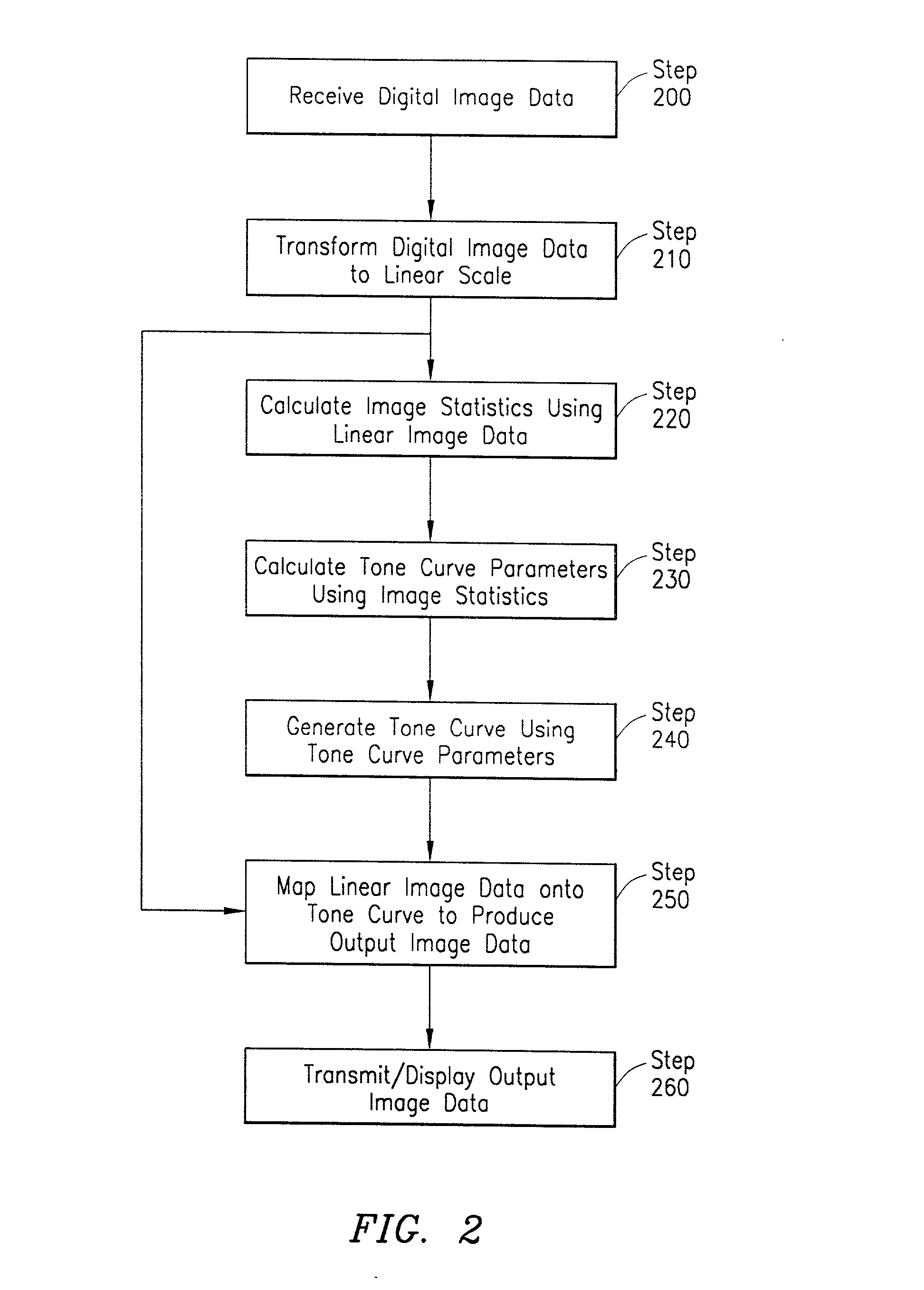
System and method for digital image tone mapping using an adaptive sigmoidal function based on perceptual preference guidelines
InactiveUS20020171852A1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersTone mappingTagged Image File Format
An adaptive image tone mapping curve based on perceptual preference guidelines is generated as a sigmoidal function, in which the sigmoidal function parameters (slope and shift) are determined by original image statistics. Tone curves generated for different images each have a smooth sigmoidal shape, so that the tone mapping process does not change the image histogram shape drastically. The sigmoidal function has the form: <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00001"> <number>1< / number> t it ( x ) = 100 1 + exp it ( - alpha it ( x / 100 - beta ) ) , <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00001" file="US20020171852A1-20021121-M00001.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00001" wi="216.027" he="18.96615" file="US20020171852A1-20021121-M00001.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> where alpha is the slope parameter and beta is the shift parameter. The input value x in the sigmoidal function varies in the range [0, 100], because the tone curve is generated on an L* scale, which has values from 0 to 100. The sigmoidal tone curve calculation can be implemented efficiently using simple arithmetic operations by pre-calculating and storing various factors used in the calculation of alpha and beta and by pre-generating a pair of fixed tone curves with two extreme slopes and interpolating between the curves.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
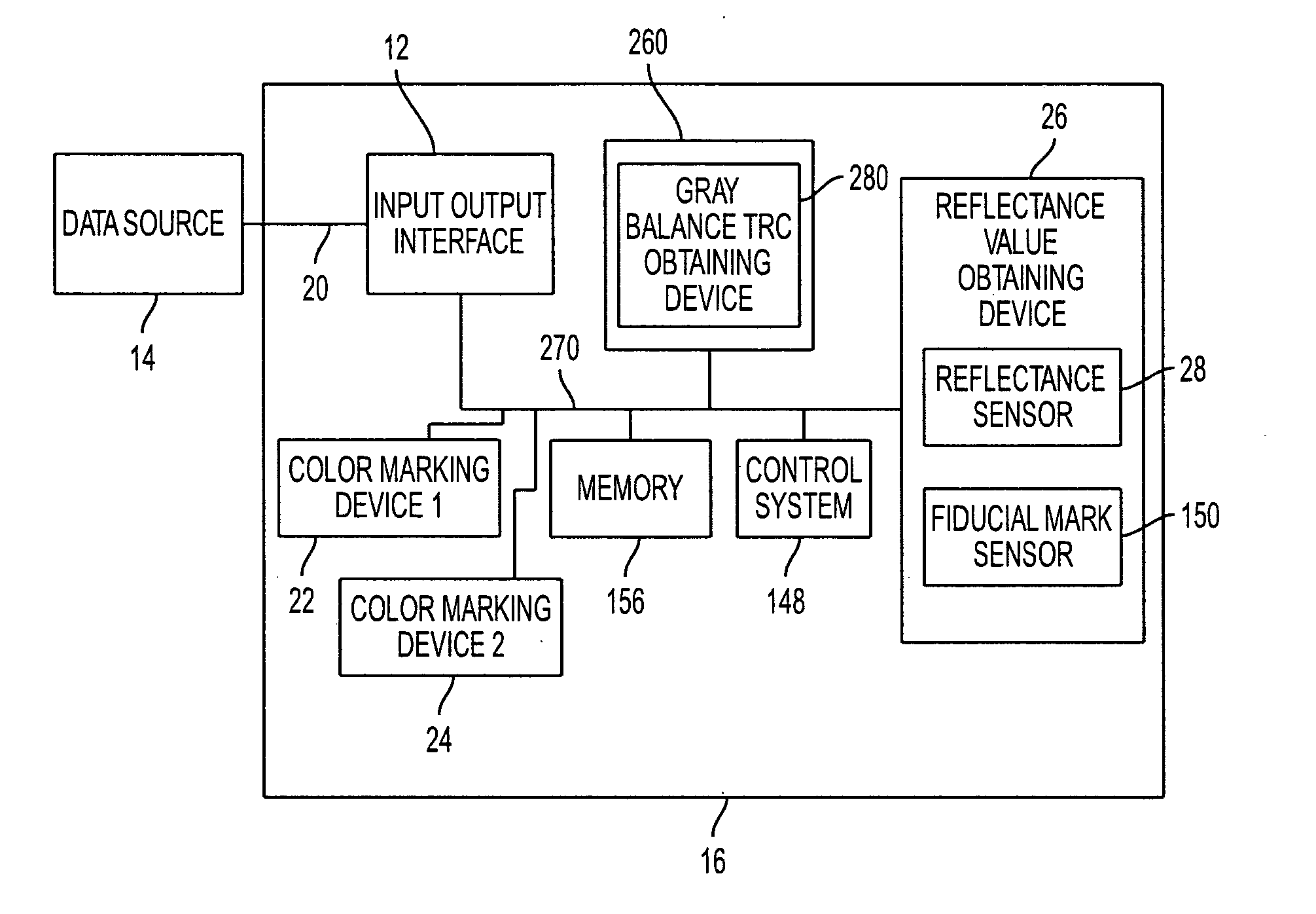
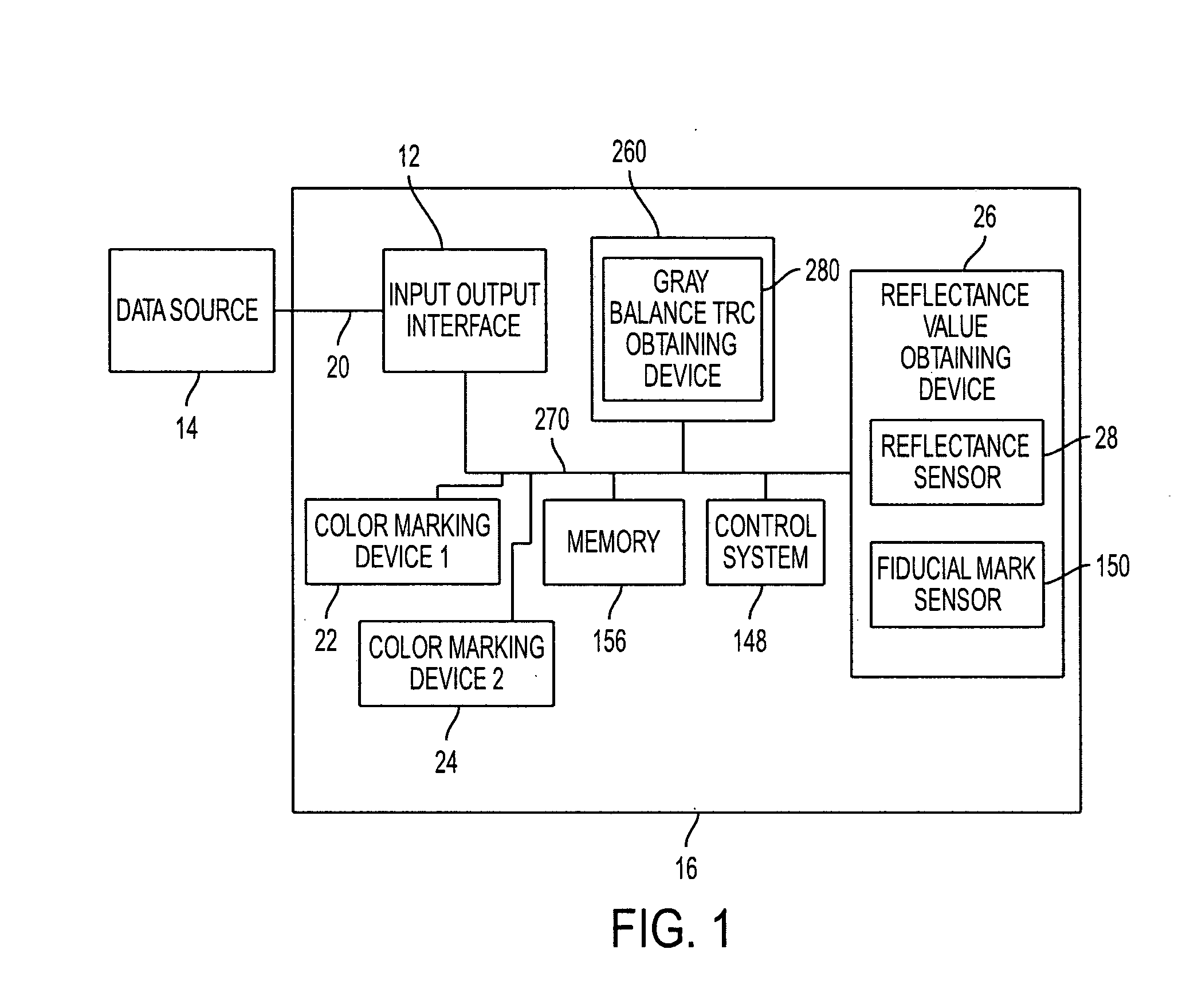
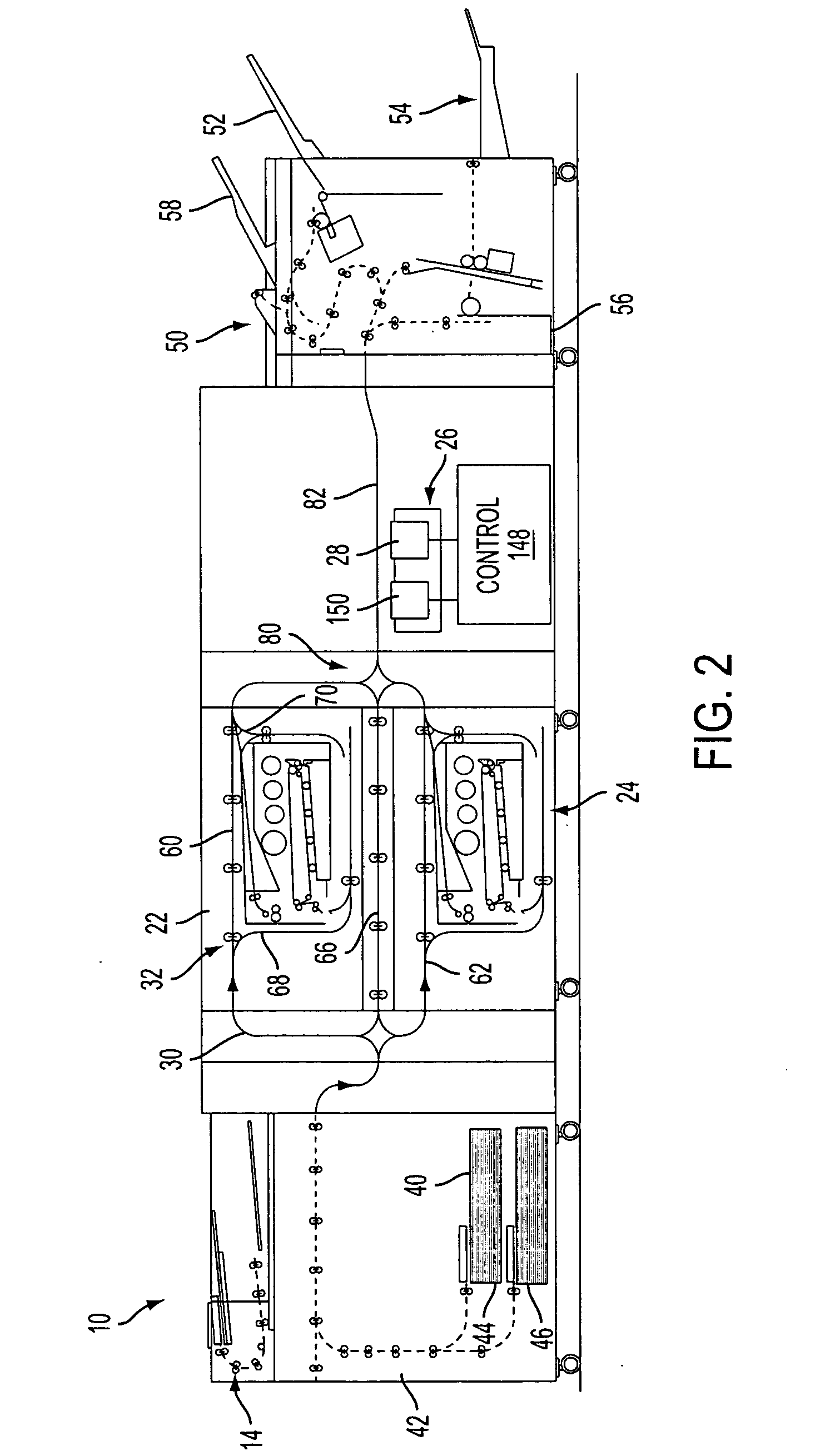
Gray balance for a printing system of multiple marking engines
InactiveUS20060197966A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsTest patchElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for calibrating a printing system including a plurality of printers includes designating one of the plurality of printers as a reference printer and defining color values for a desired response for one or more printed test patches on a control page. Through a first process aimed toward achieving the desired response, a printed control page is generated with the reference printer, the control page including one or more of the test patches which, when measured, has a measured response which approaches the desired response. Through a second process aimed toward achieving a desired response, the desired response being the measured response of the reference printer, a printed control page is generated with a second of the printers, the control page including one or more of the test patches which, when measured, has a response which approaches the measured response of the reference printer.
Owner:XEROX CORP
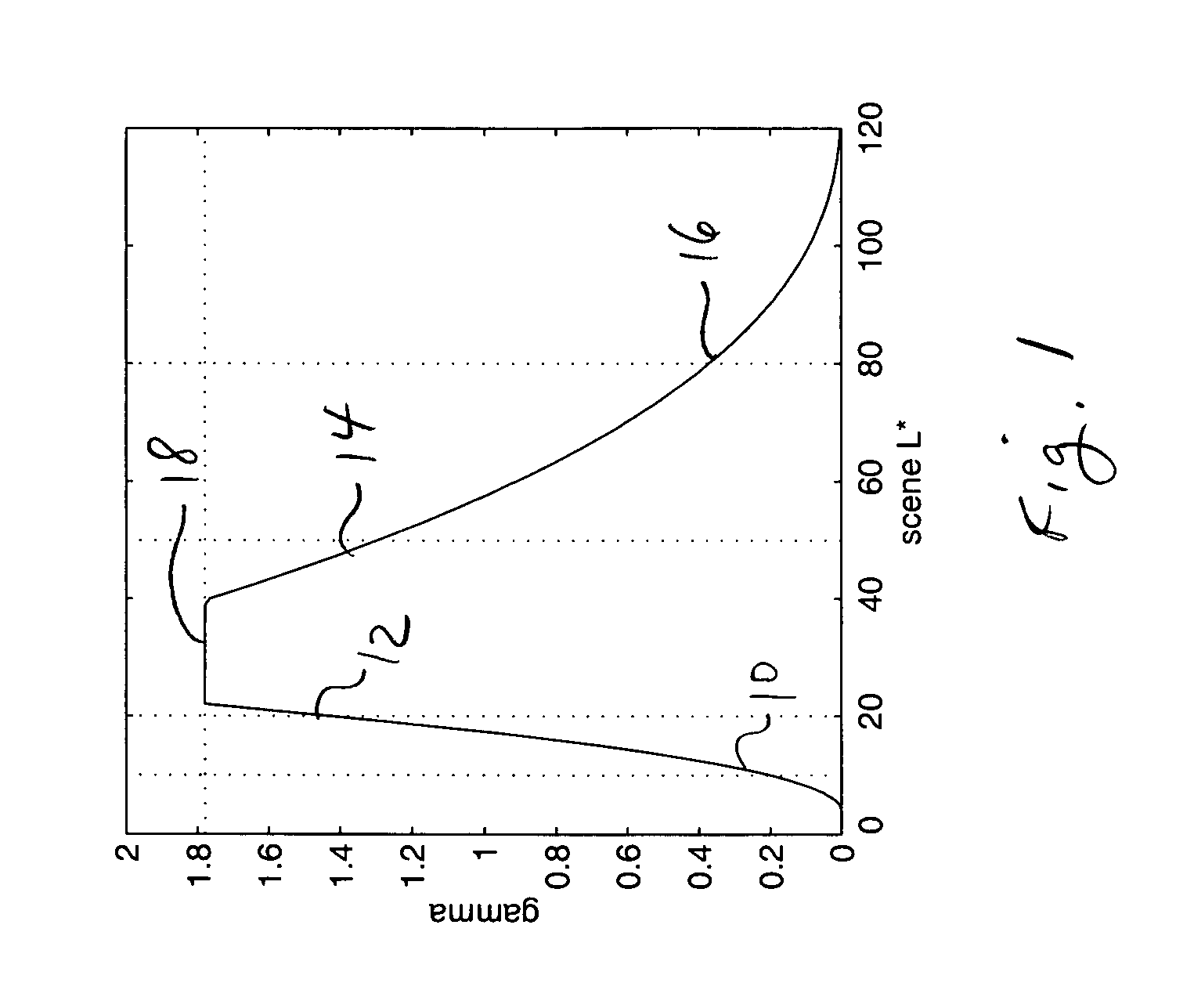
Tonescales for geographically localized digital rendition of people
InactiveUS20060077405A1Improve skinImproved rendering of peopleImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersGeolocationPlateau
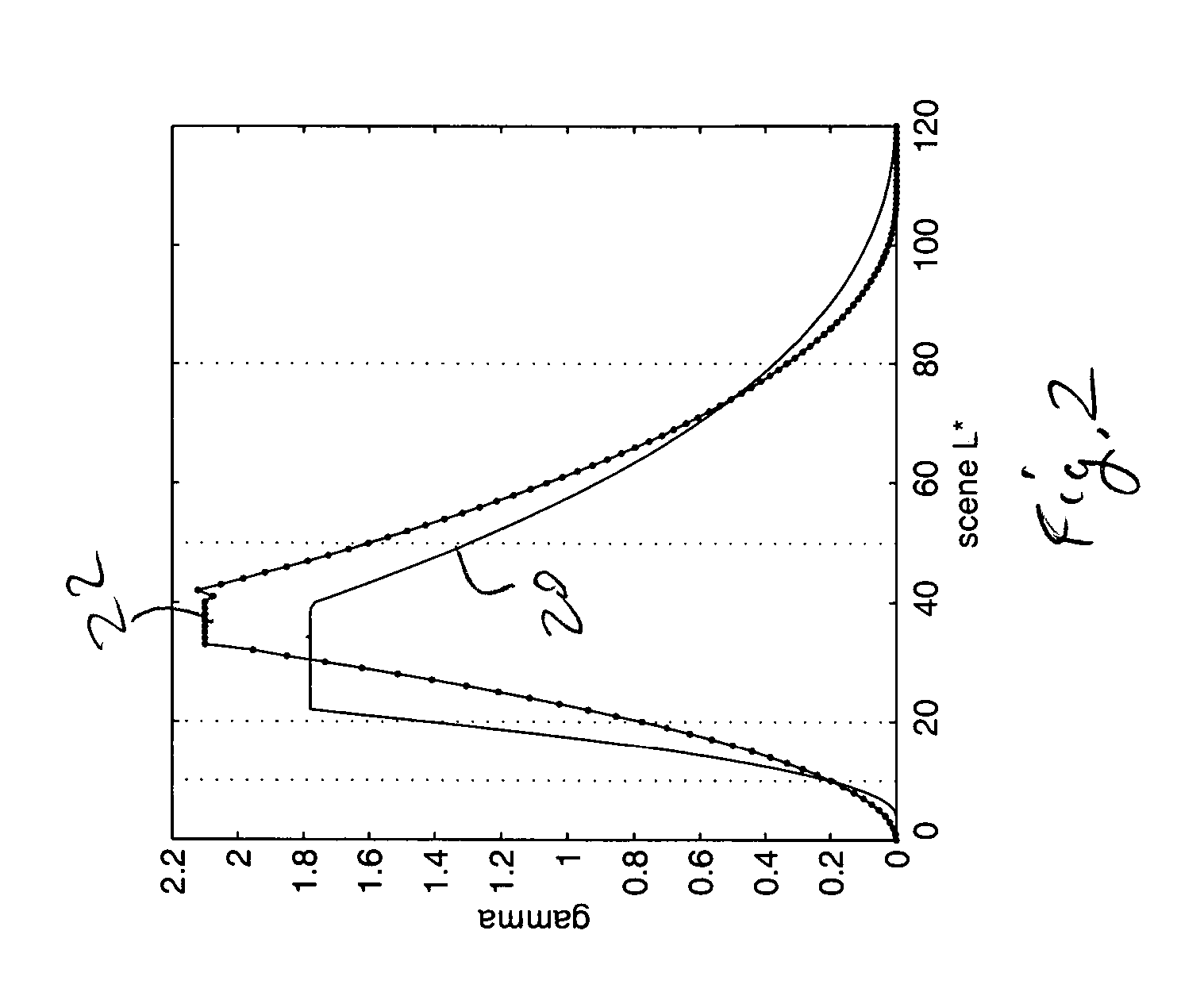
In a method and system for processing a photographic image having lightness values, L*, representing one of the colorimetric values of an original scene, the photographic image is transformed. The transformed image has a gamma as a function of CIE 1976 L*, which includes a dark region having a rising slope, a light region having a falling slope, and a plateau region having a slope constantly within 5 percent of a maximum value in said plateau region. The rising slope is at least twice as large as the absolute value of the falling slope. The plateau region is between 10 L* and 30 L* wide. Gamma is a derivative of visually perceived reproduced CIE 1976 L* versus scene CIE 1976 L*. Gamma has a maximum slope between 1.5 and 2.0.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
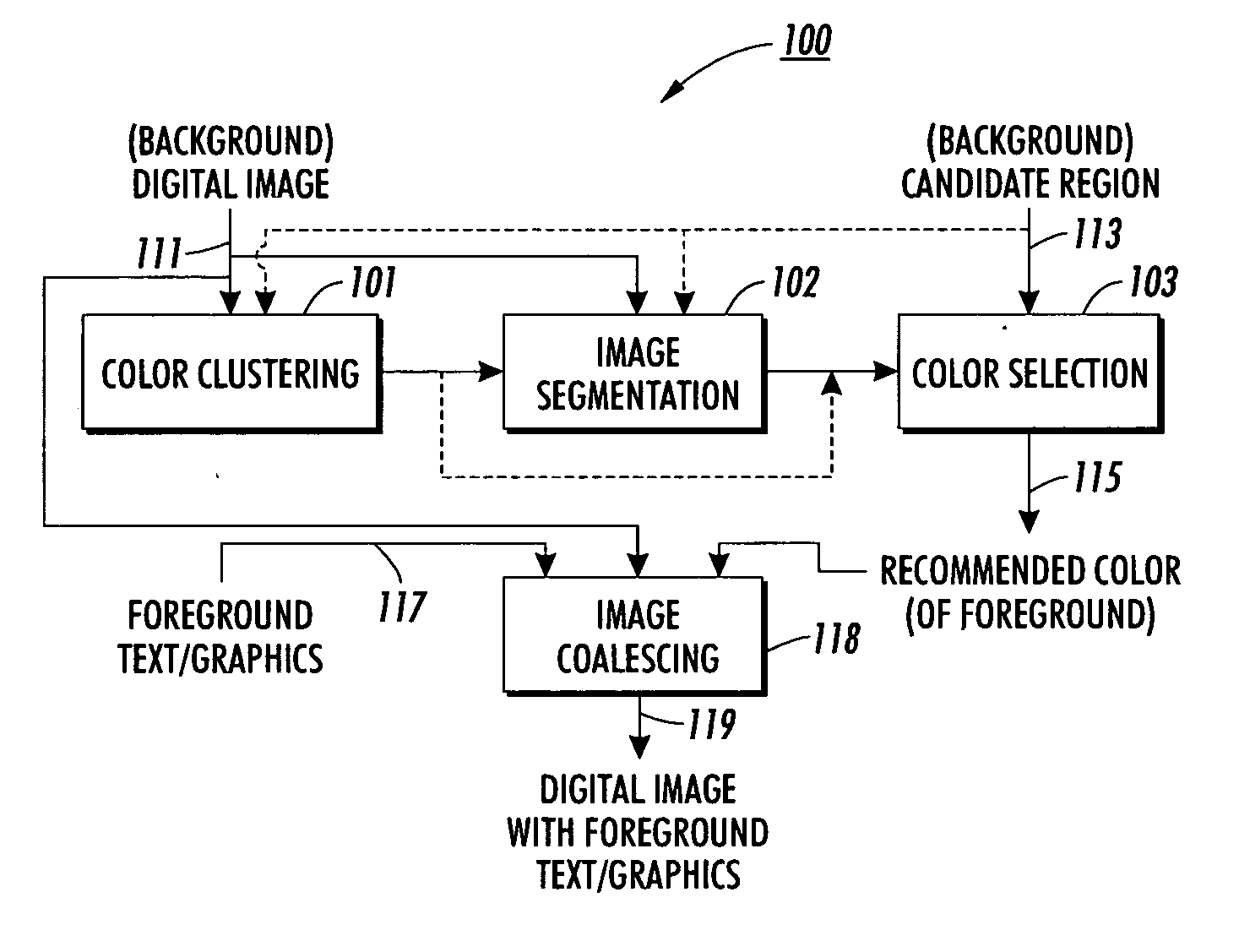
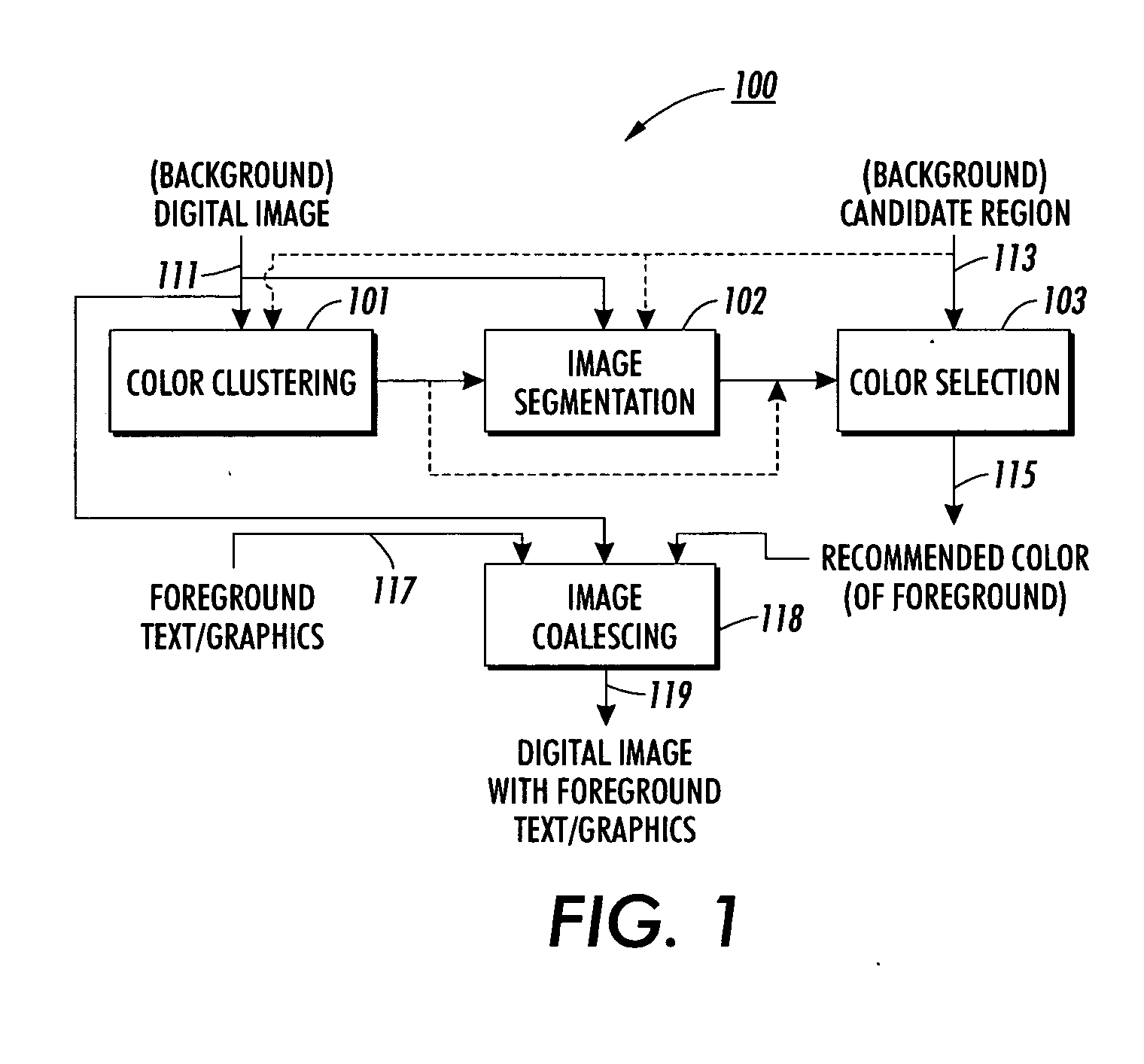
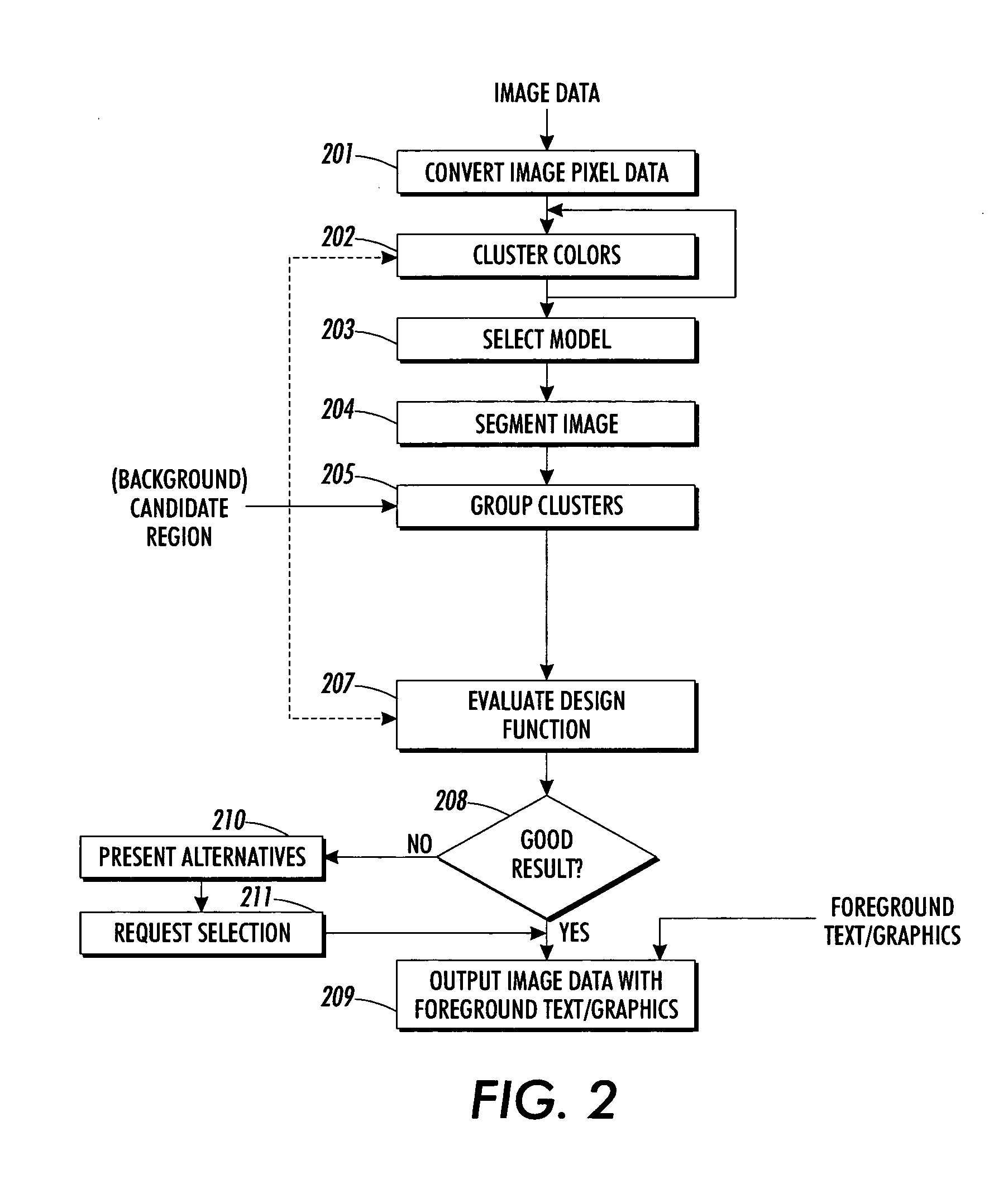
Method and apparatus for automatically determining image foreground color
ActiveUS20050157926A1Maximize functionalityReduce in quantityTexturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital imageComputer science
A foreground color for a digital image is automatically determined by dividing the colors of the pixels of at least a part of the digital image into a number of color clusters in a color space, and for at least one cluster selecting a color being related to the at least one color cluster according to predetermined criteria.
Owner:XEROX CORP
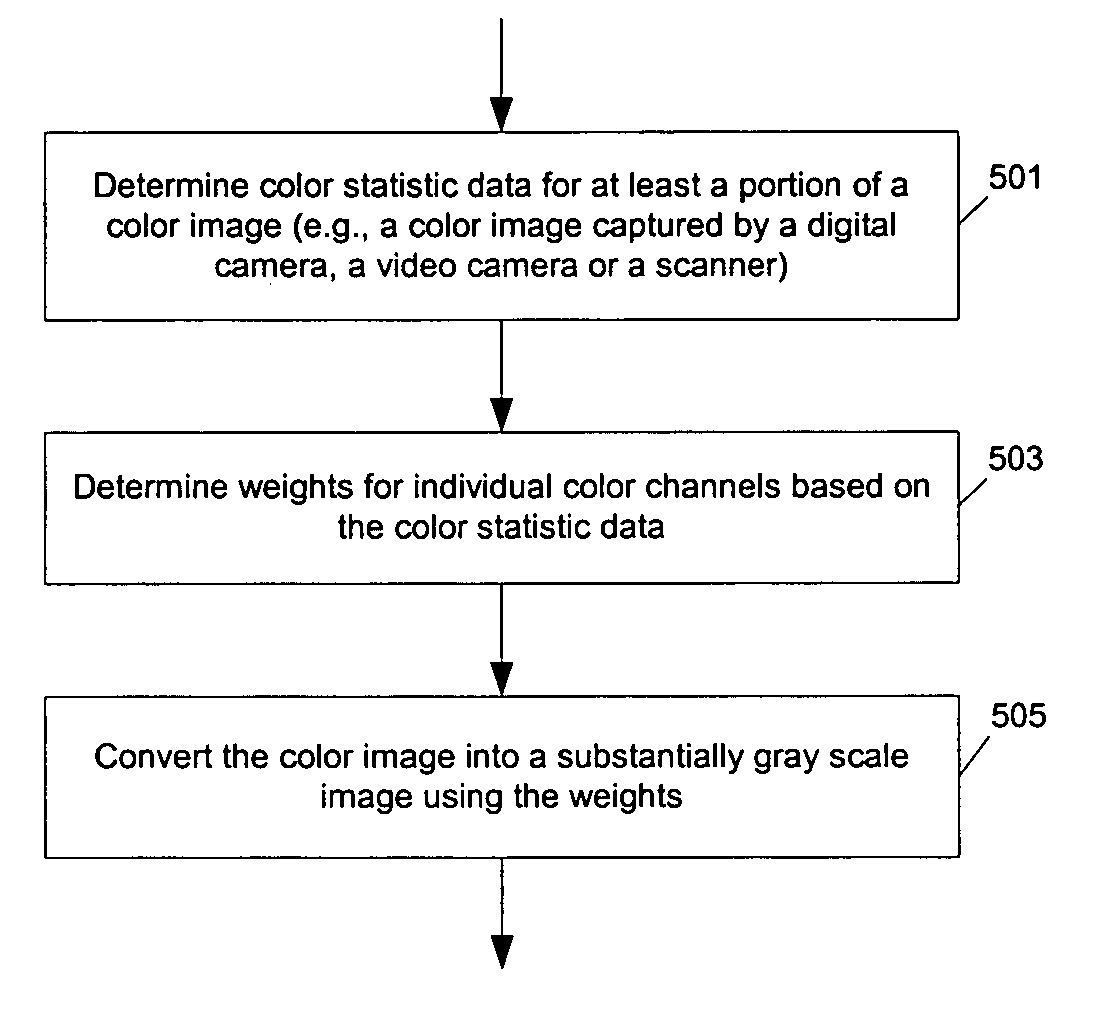
Methods and apparatuses for aesthetically enhanced image conversion
InactiveUS20060072158A1Good lookingDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsNonlinear scalingGray level
Methods and apparatuses for automated conversion of color images to aesthetically enhanced gray scale images. In one embodiment, the mix of color channels of a color image is automatically determined as a result of analysis of the image for the generation of a gray scale image. In one example, the data of a color channel (e.g., Blue) that is not suitable for a gray scale representation is not used. The adjustment strength depends on the image itself. In one example, a stronger color channel is automatically weighted less than a weaker color channel for enhancement. In one example, after the contrast is further strengthened through nonlinear scaling, the boundary portion of the image is darkened to strengthen the edges and draw attention to the center of the image. Optionally, an attractive color balance adjustment is also made according to the gray levels to further enhance the appearance.
Owner:APPLE INC
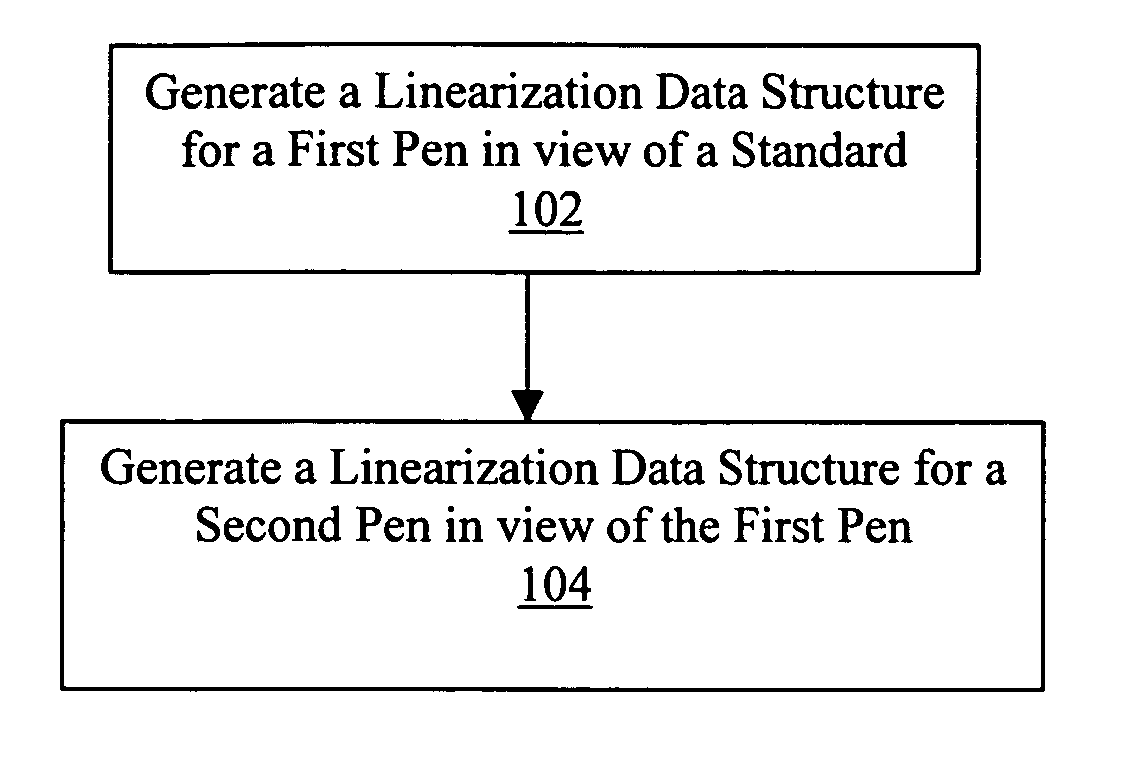
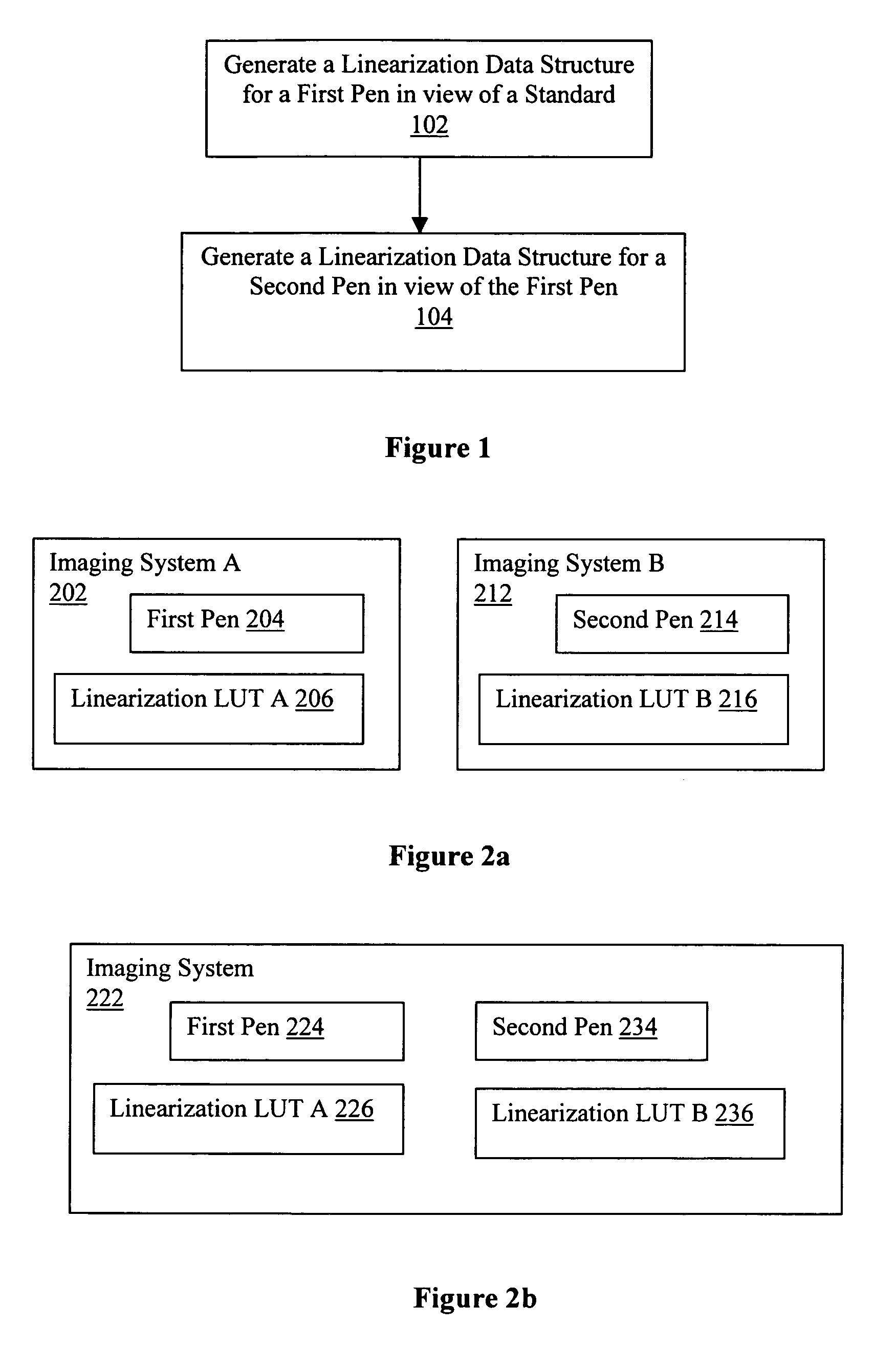
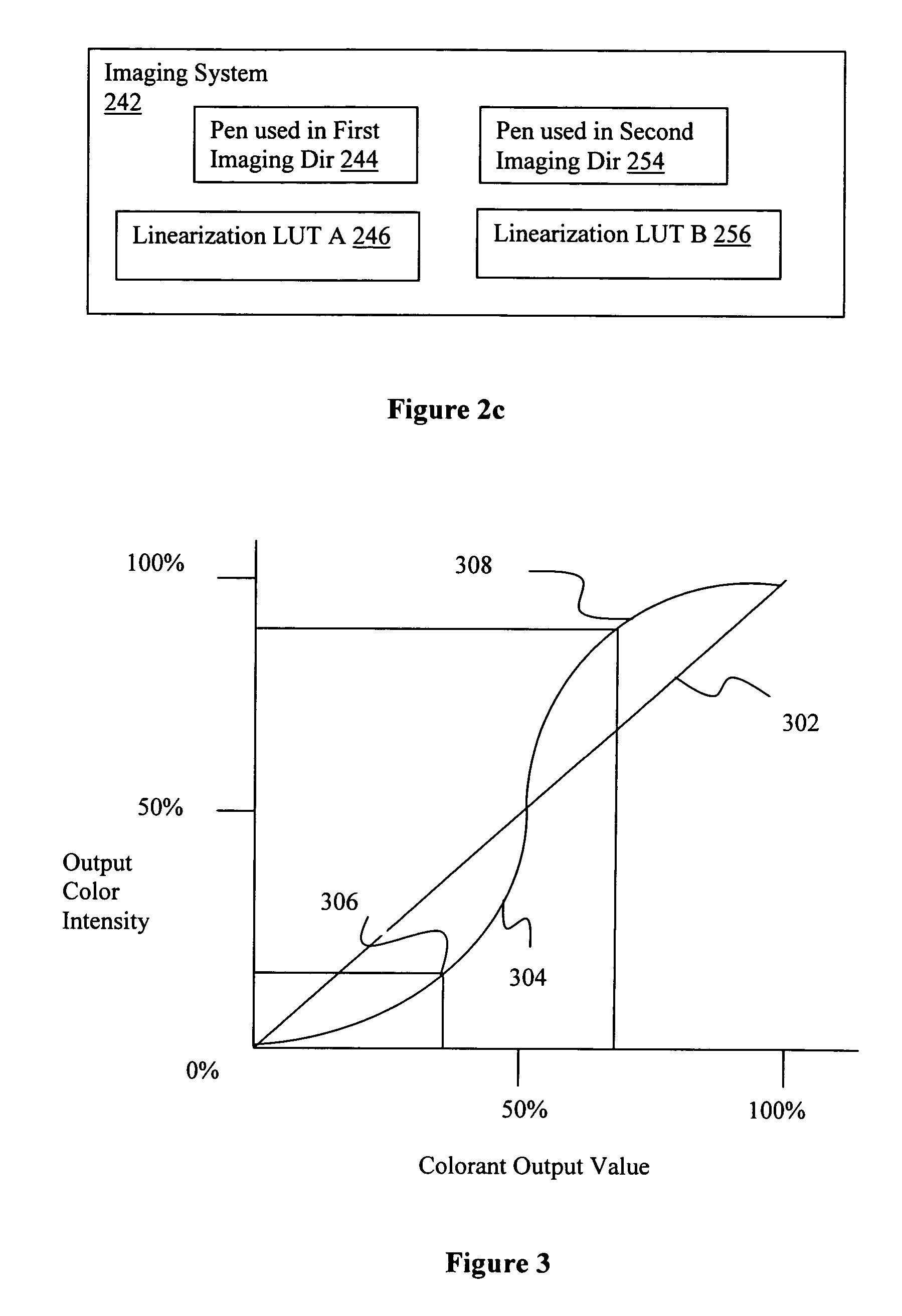
Conforming output intensities of pens
InactiveUS20050018221A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer scienceLinearization
A linearization data structure is generated for a pen, in view of another pen, for conforming output intensities of the pen to output intensities of the other pen.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method of producing a relief image for printing
ActiveUS20050227182A1Low costHigh imaging sensitivityRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRadiation
The present invention involves a method for making a relief image. A film that includes a carrier sheet and an imageable material is used to form a mask image that is opaque to a curing radiation. In one embodiment, the mask image is formed on the carrier sheet while in another embodiment, the mask image is formed on a receptor sheet. The mask image is then transferred to a photosensitive material, such as a flexographic printing plate precursor. The resulting assembly is exposed to the curing radiation resulting in exposed and unexposed areas of the photosensitive material. The carrier sheet or the receptor sheet may be removed from the mask image either before or after exposure to the curing radiation. Finally, the photosensitive material and mask image assembly is developed with a suitable developer to form a relief image.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS +1
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS6724507B1More colorColour-separation/tonal-correctionPictoral communicationColor imageColor transformation
Provided is an image processing method and a apparatus of converting a color input image or a partial region thereof in accordance with a color gamut of a color image output apparatus is provided. The method and apparatus is characterized in that only the region requiring color gamut compression can be put to color gamut compression depending on the distribution of an input image, that the direction of the color gamut compression can be controlled continuously for each of the regions; the amount of the color gamut compression can be controlled continuously including clipping, that when color gamut compression is conducted by a color converter of a multi-dimensional DLUT interpolating calculation type, an excessively unnecessary color gamut compression can be avoided particularly upon clipping, and that there is enabled correction for visual bending in iso-hue lines caused by distortion of a color space in each of the regions of the color space.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Method and system for selectively applying enhancement to an image
ActiveUS7092573B2Increase volumeAdditional artifactImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageControl signal
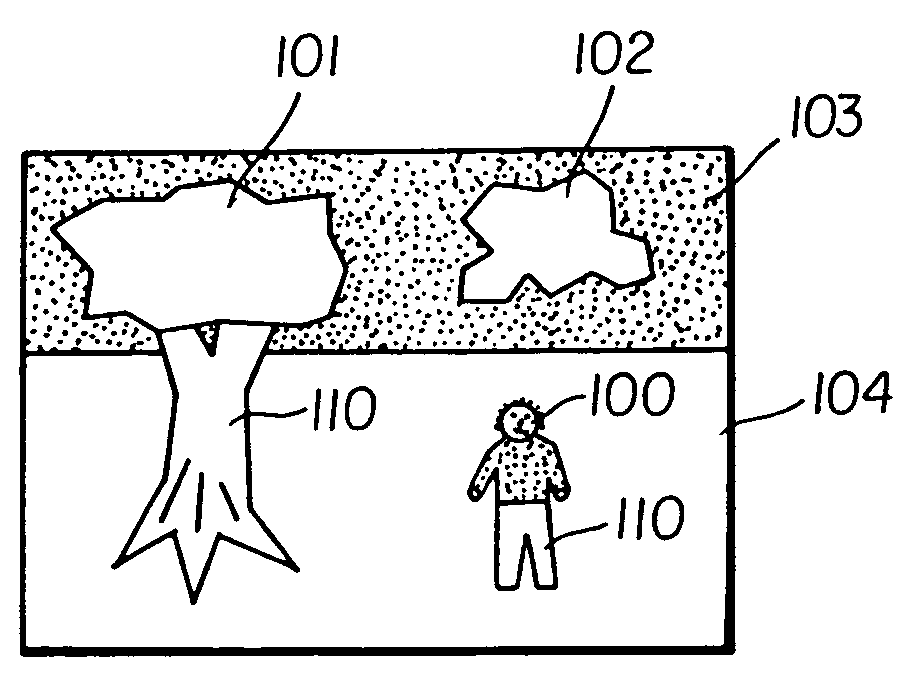
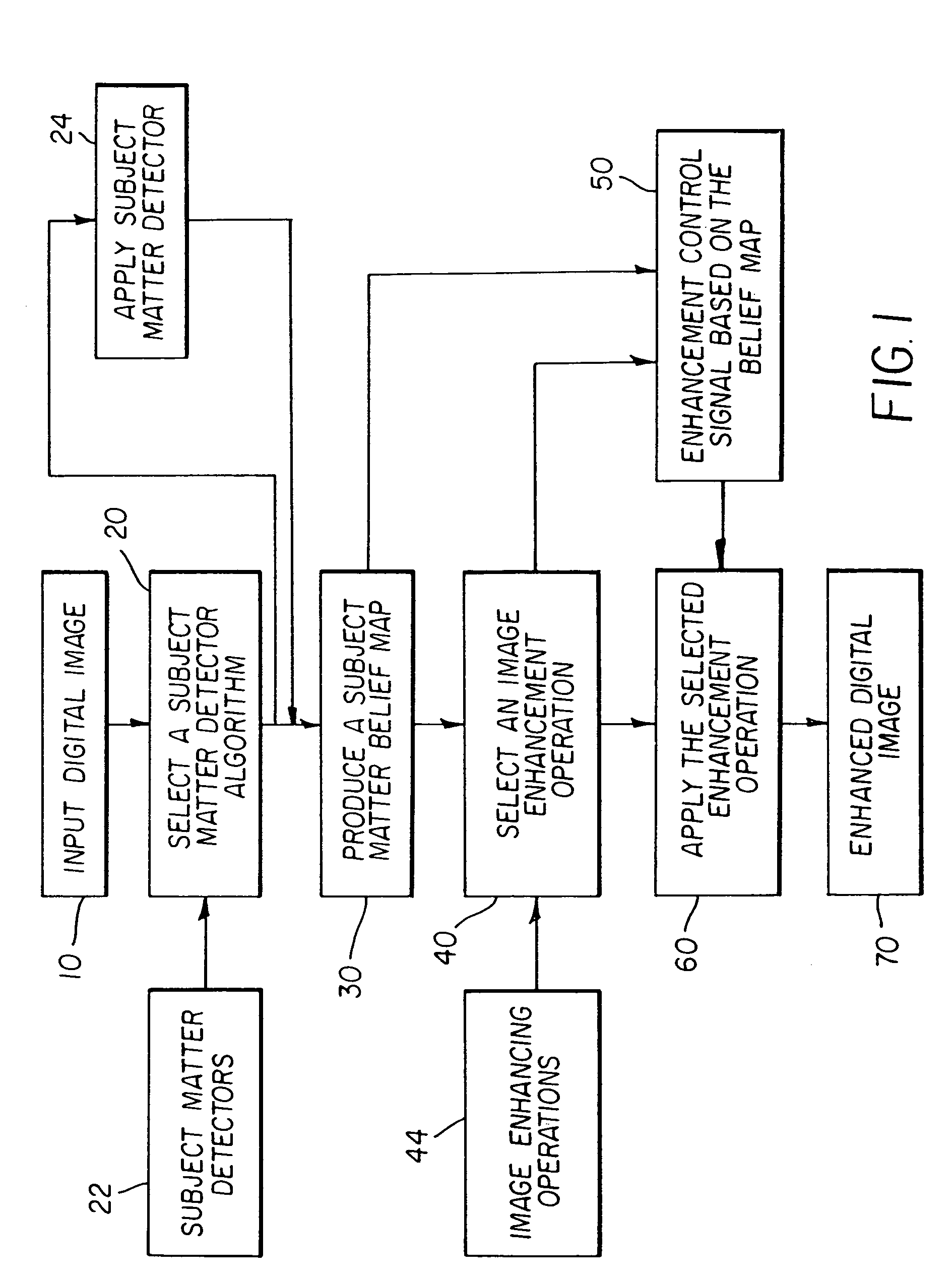
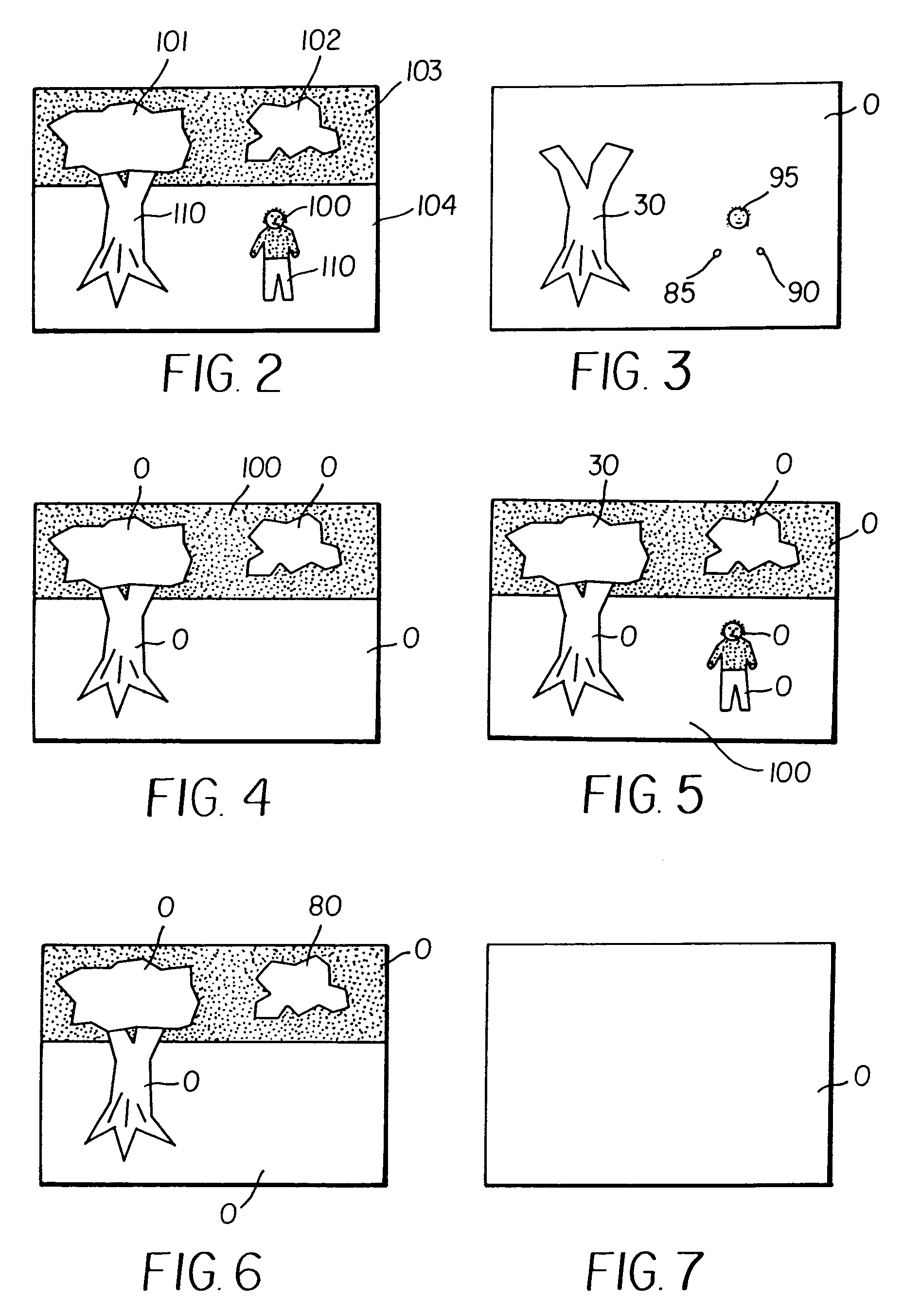
A method for processing a digital color image includes the steps of: providing a subject matter detector for distinguishing between target and background subject matters; applying the subject matter detector to the image to produce a belief map indicating the degree of belief that pixels in the image belong to target subject matter; providing an image enhancement operation that is responsive to a control signal for controlling the degree of image enhancement; and applying image enhancement to the digital image by varying the control signal according to the belief map to produce an enhanced image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
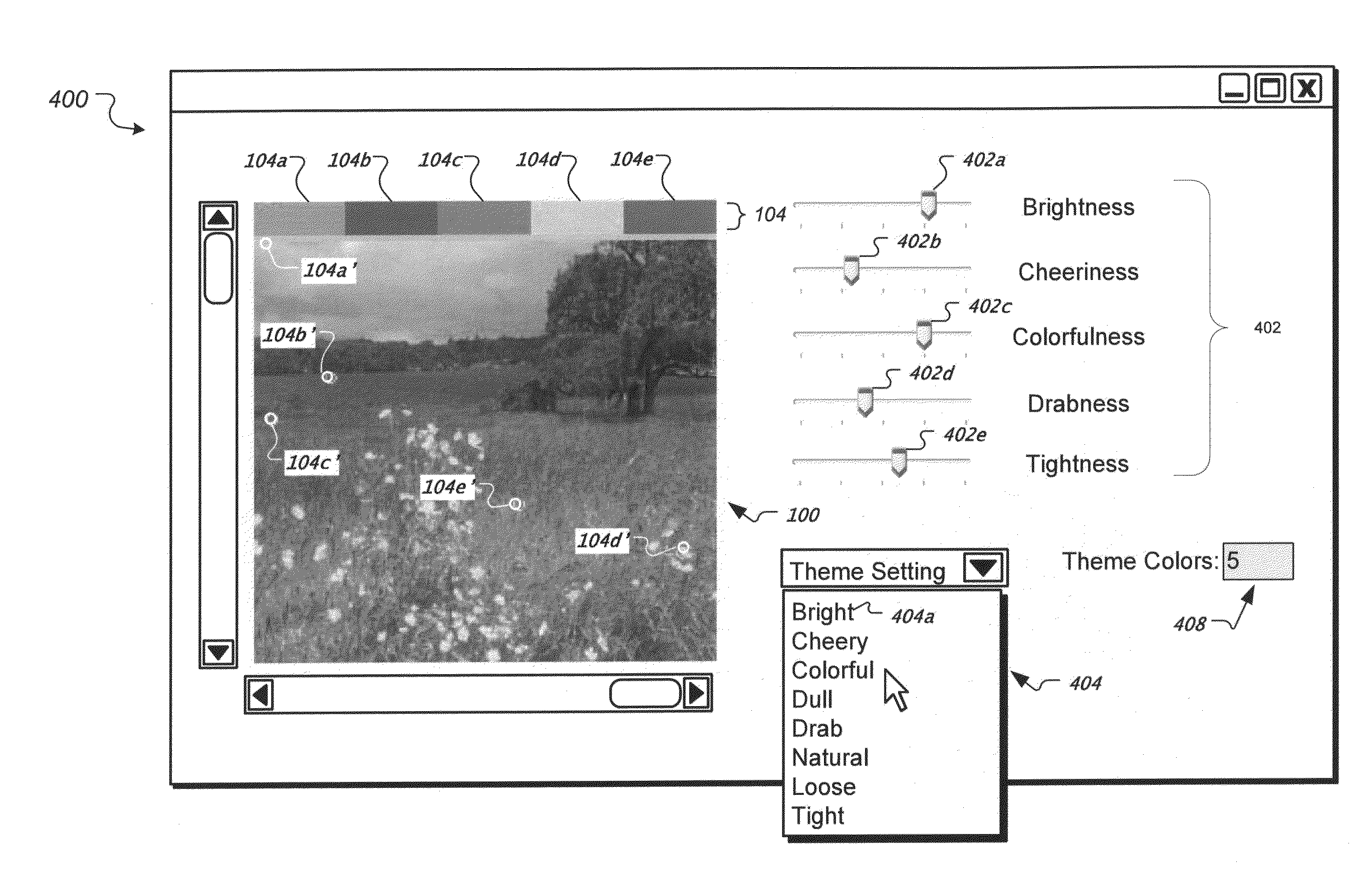
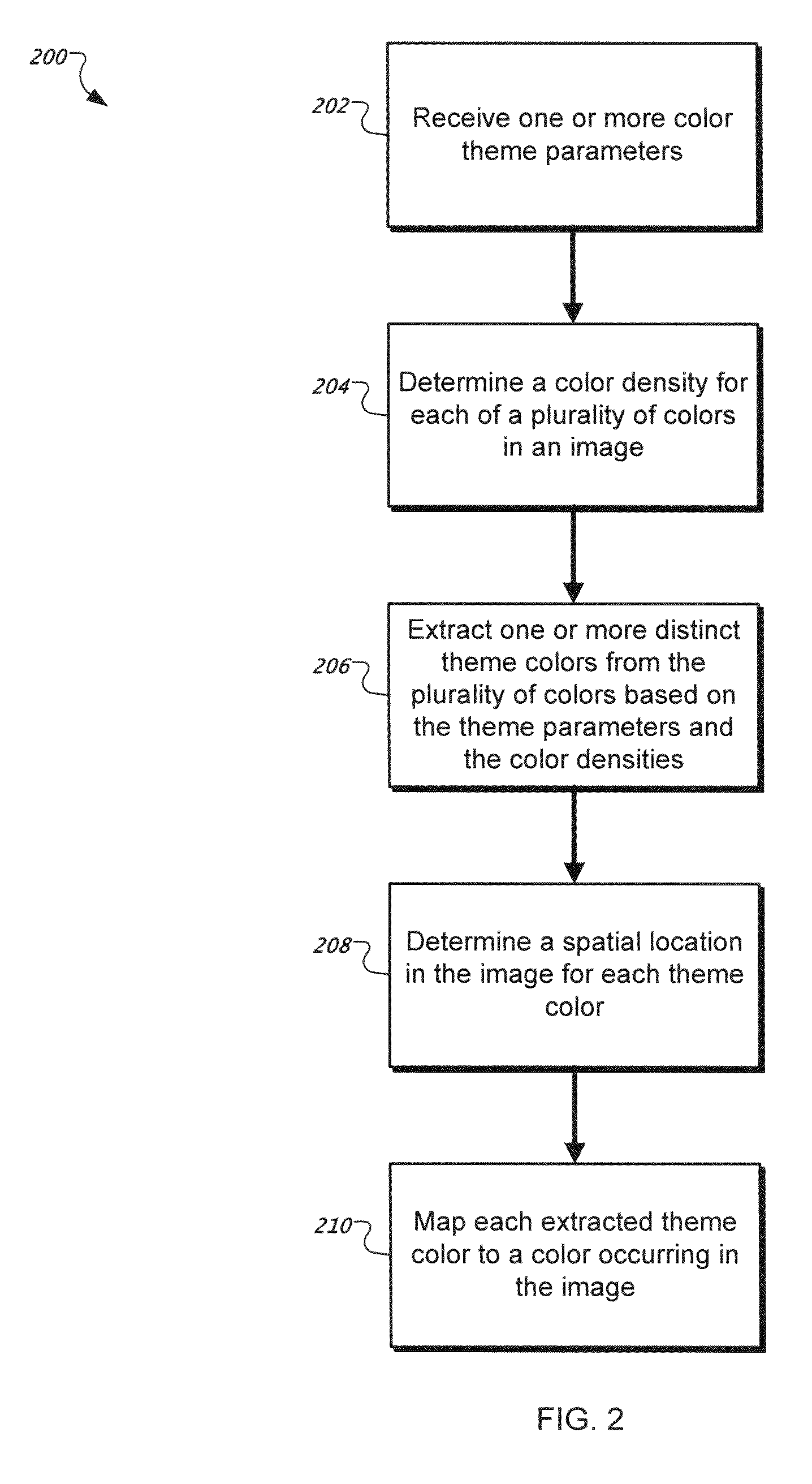
Subjective and locatable color theme extraction for images
Systems, methods, and program products for subjective and locatable color theme extraction for images. Determining a color density for each of a plurality of colors in an image where each of the plurality of colors belongs to a color space, extracting one or more distinct theme colors from the plurality of colors based on qualitative parameters and the determined color densities, and mapping each extracted theme color to a color occurring in the image where the mapping is based on a color distance between the theme color and colors occurring in the image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com