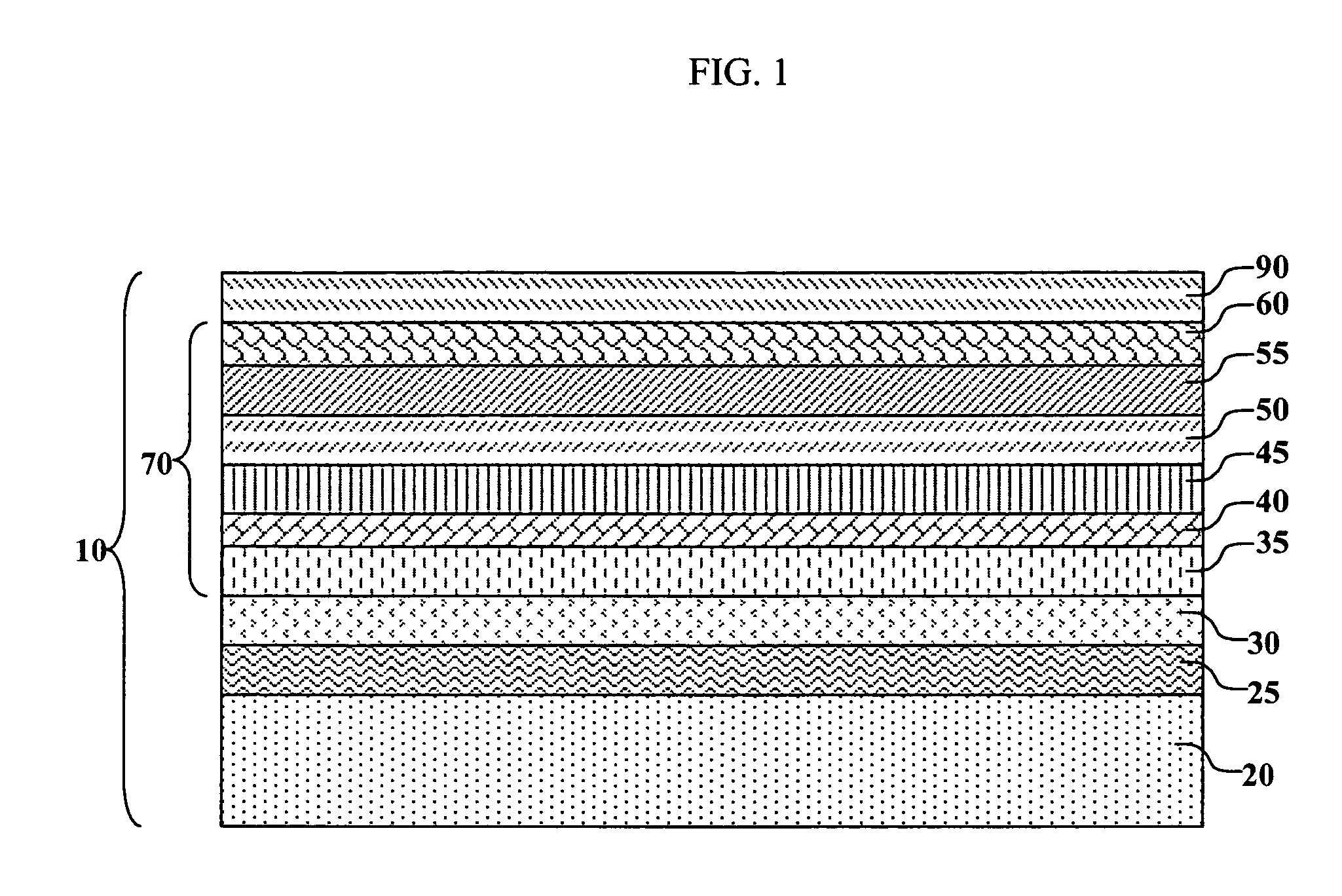
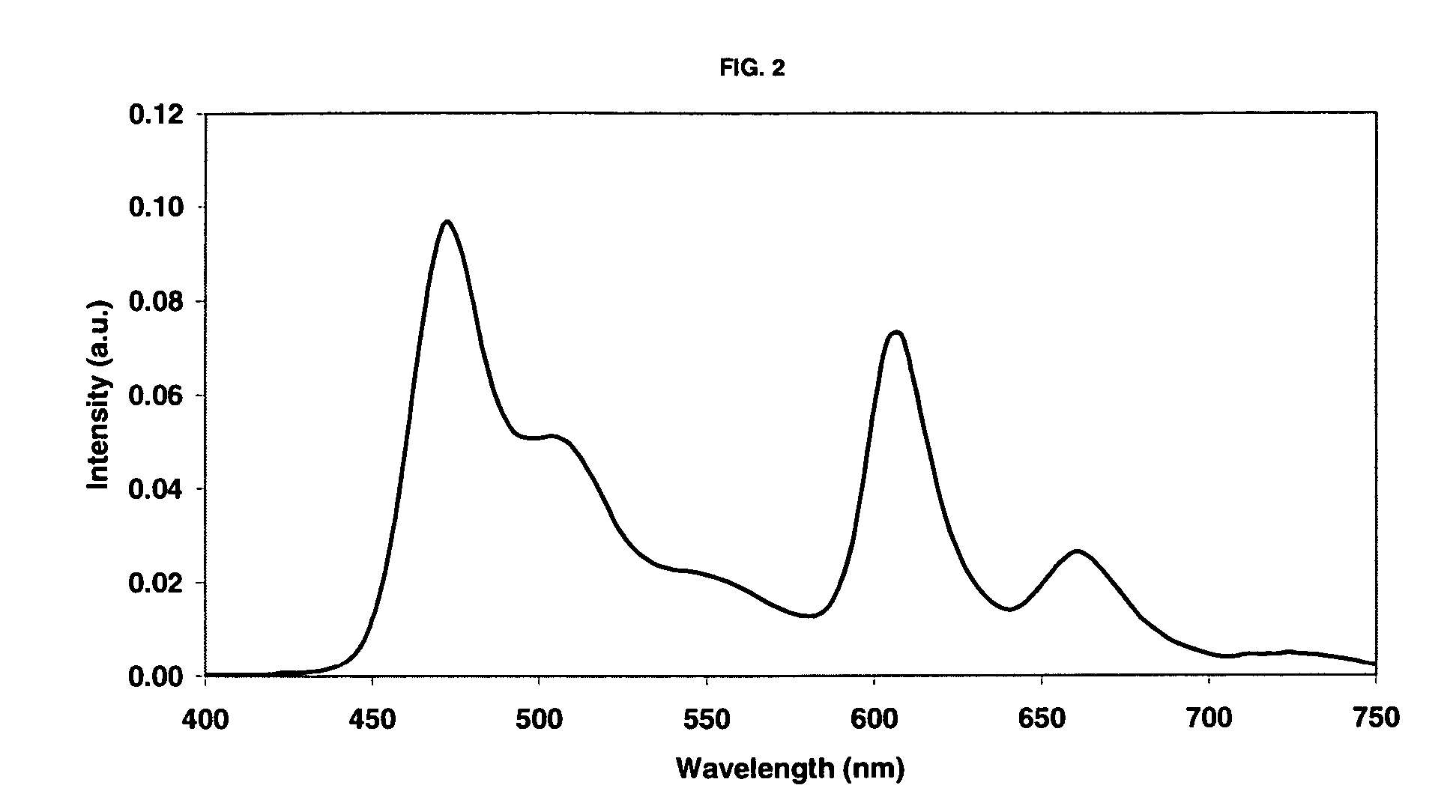
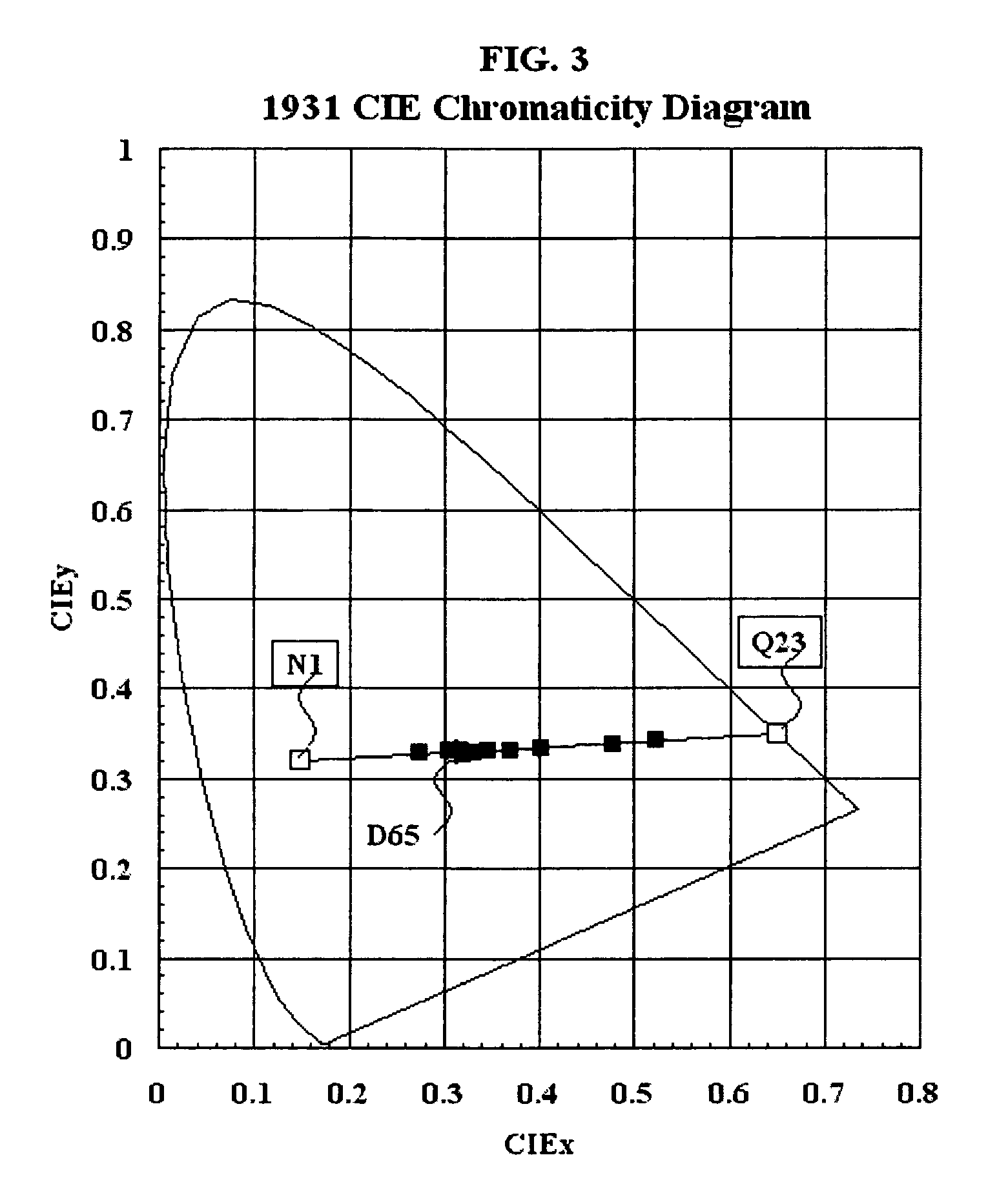
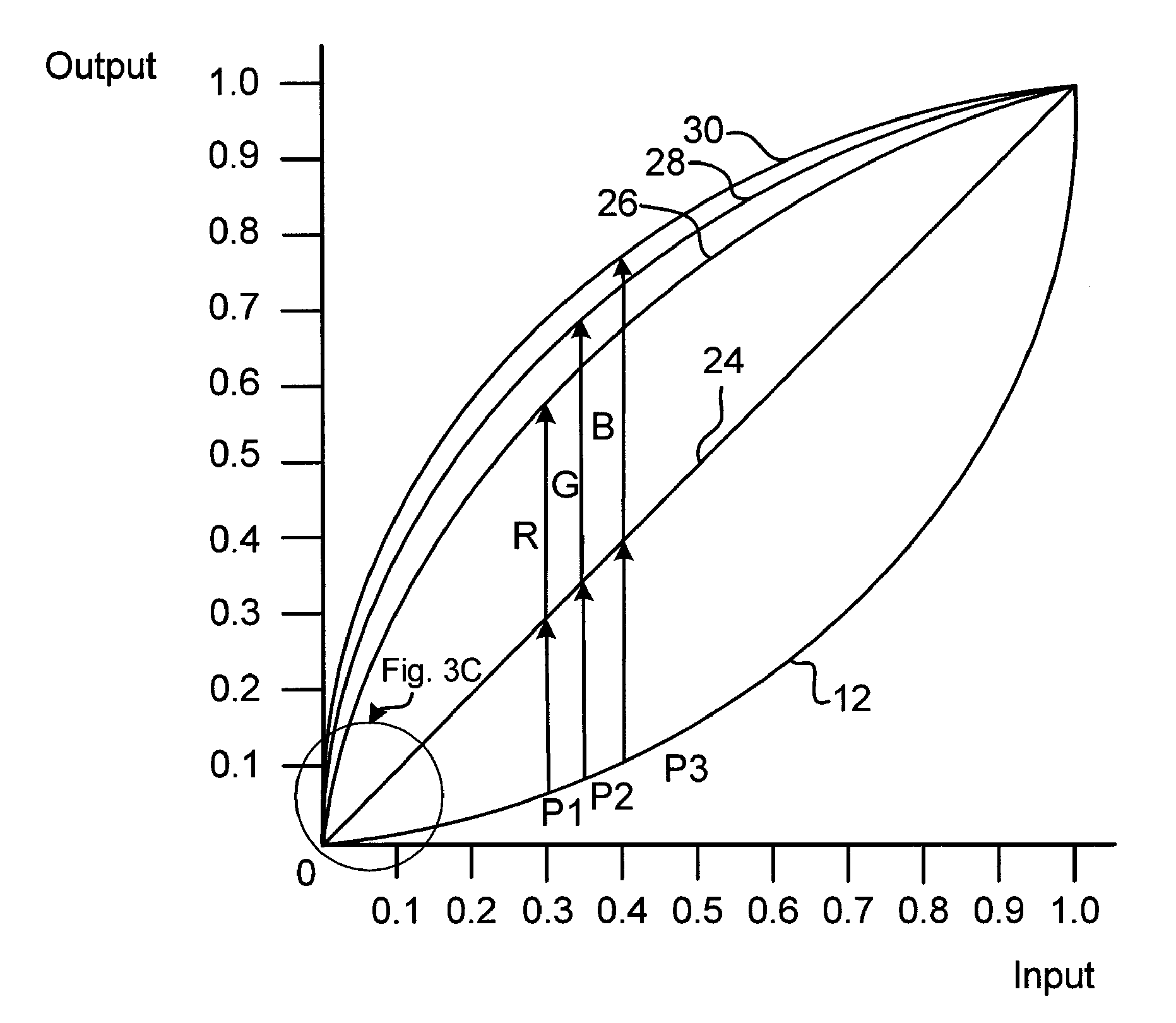
Patents
Literature
639 results about "White point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
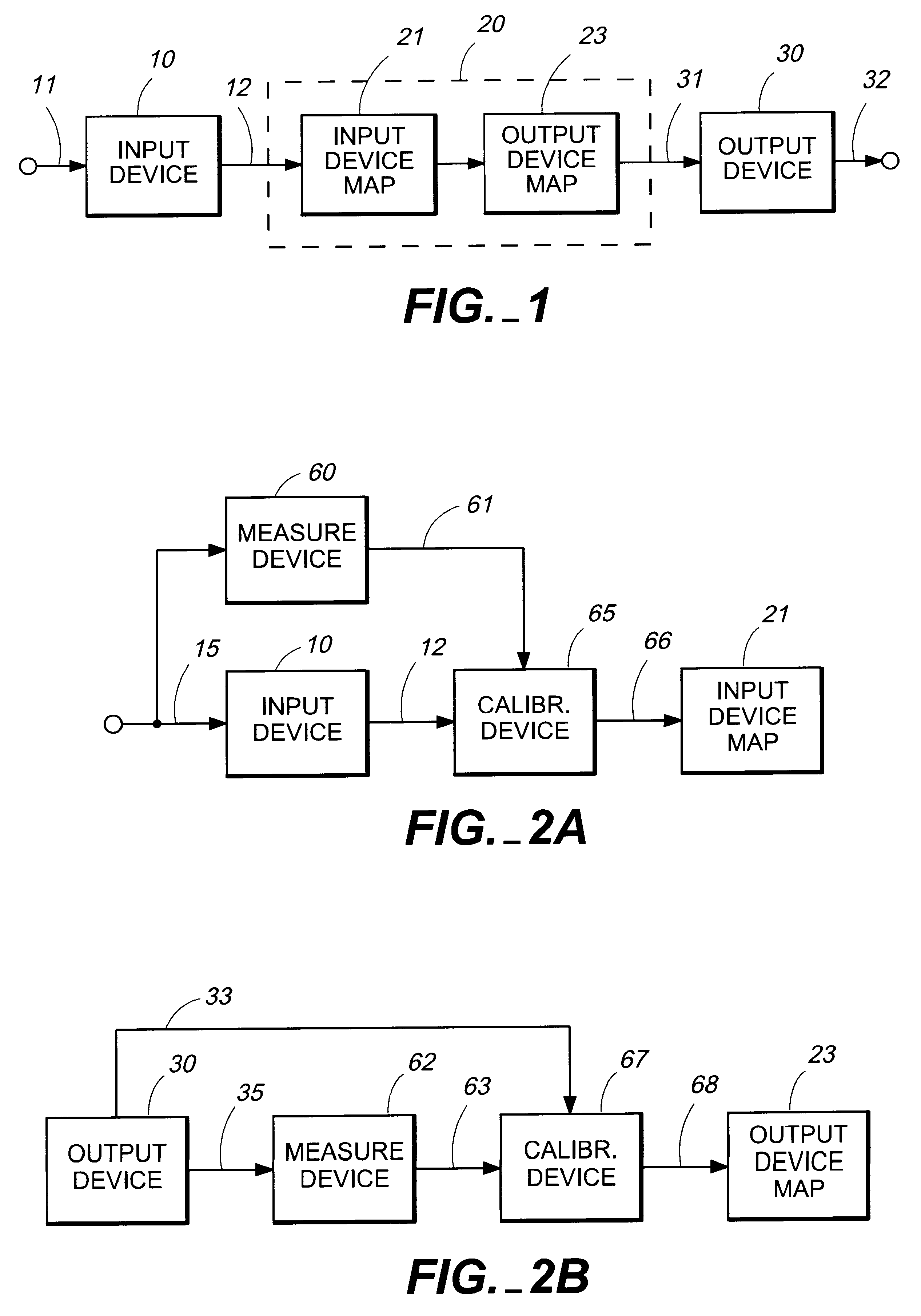
A white point (often referred to as reference white or target white in technical documents) is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results. For example, photographs taken indoors may be lit by incandescent lights, which are relatively orange compared to daylight. Defining "white" as daylight will give unacceptable results when attempting to color-correct a photograph taken with incandescent lighting.
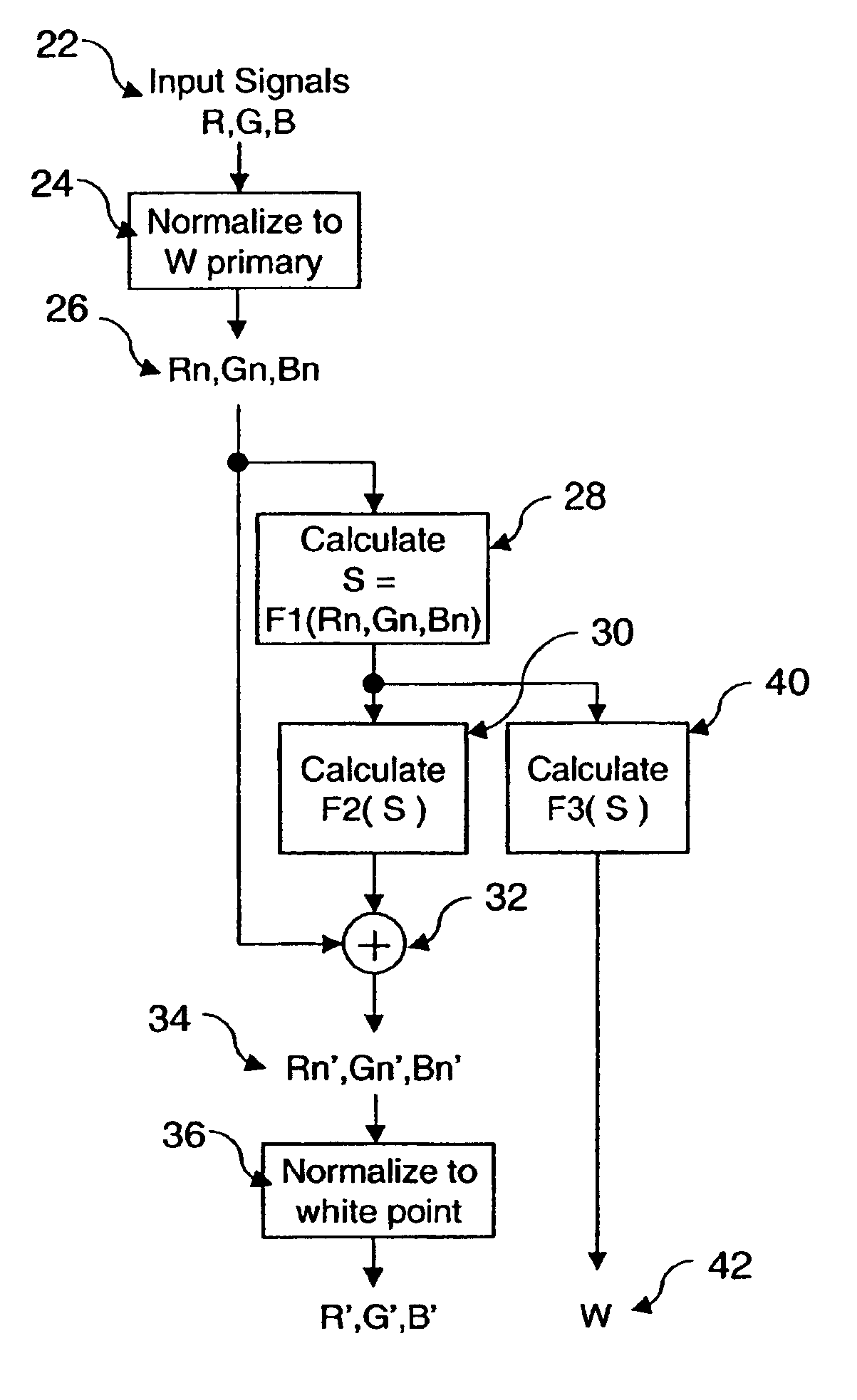
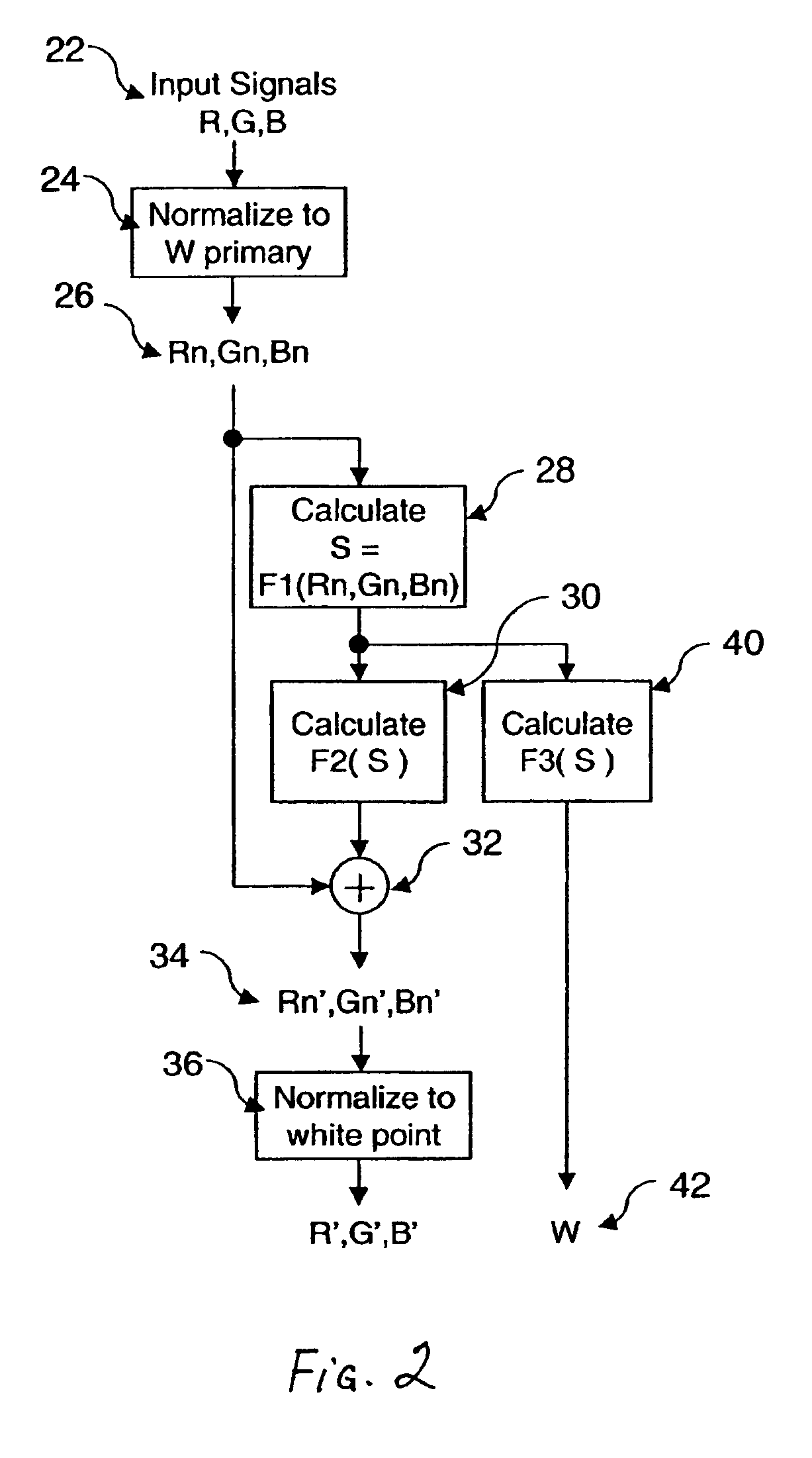
Method for transforming three color input signals to four or more output signals for a color display
InactiveUS6897876B2Preserve accuracyLife expectancyColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionGamut
A method for transforming three color input signals (R, G, B) corresponding to three gamut defining color primaries to four color output signals (R′, G′, B′, W) corresponding to the gamut defining color primaries and one additional color primary W for driving a display having a white point different from W includes the steps of: normalizing the color input signals (R,G,B) such that a combination of equal amounts in each signal produces a color having XYZ tristimulus values identical to those of the additional color primary to produce normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn); calculating a common signal S that is a function F1 of the three normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn); calculating a function F2 of the common signal S and adding it to each of the three normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn) to provide three color signals (Rn′,Gn′,Bn′); normalizing the three color signals (Rn′,Gn′,Bn′) such that a combination of equal amounts in each signal produces a color having XYZ tristimulus values identical to those of the display white point to produce three of the four color output signals (R′,G′,B′); and calculating a function F3 of the common signal S and assigning it to the fourth color output signal W.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
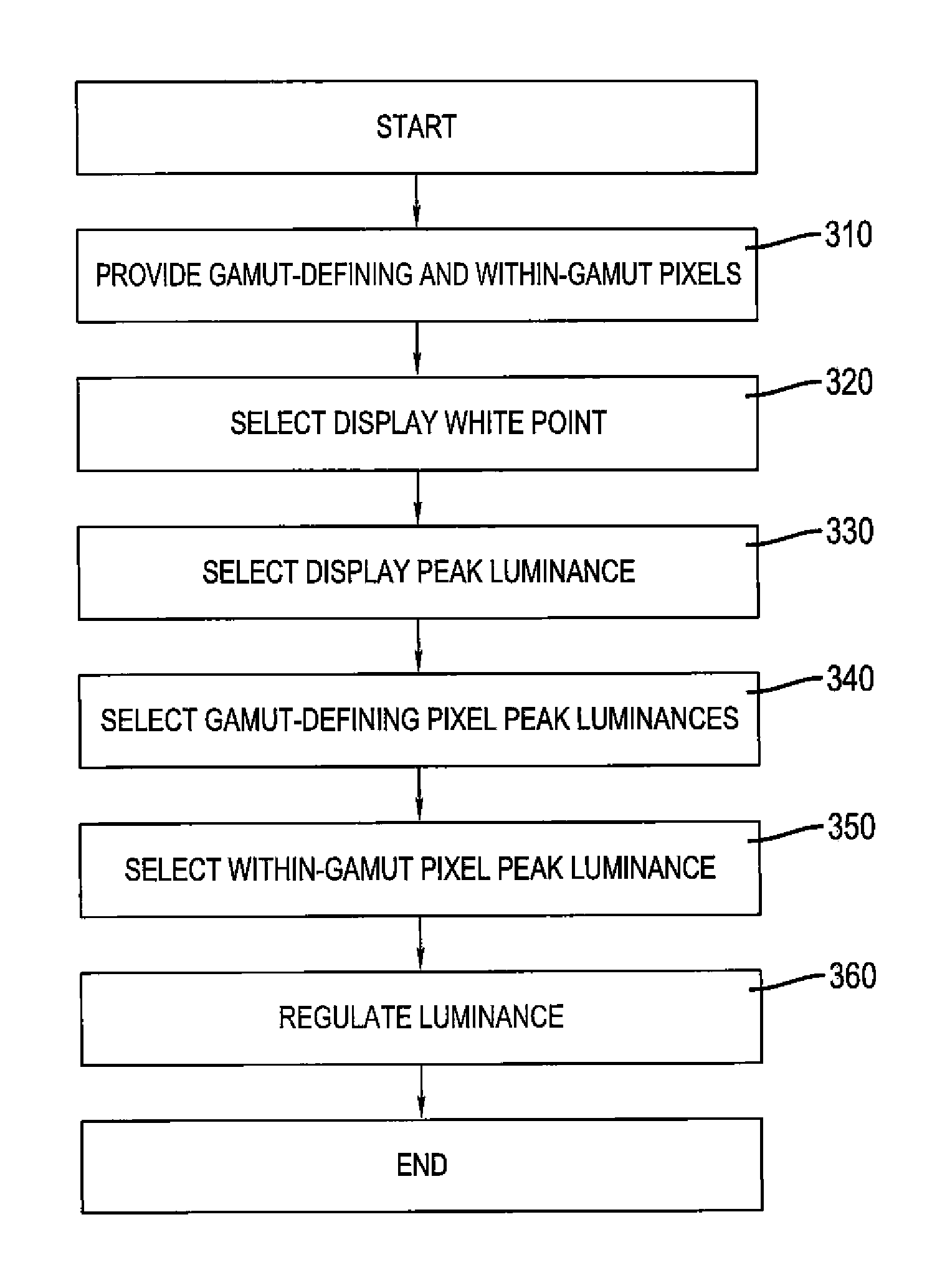
OLED display with improved power performance
An OLED display for producing a full color image, comprising a plurality of at least four different colored pixels including three different colored addressable gamut-defining pixels and a fourth addressable within-gamut pixel, each pixel having an organic light-emitting diode with first and second electrodes and one or more organic light-emitting layers provided between the electrodes; the OLED display having a selected display white point, display peak luminance, gamut-defining pixel peak luminances and within-gamut pixel peak luminance; and drive circuitry for regulating luminance of the organic light-emitting diode of each of the colored pixels wherein the sum of the gamut-defining pixel peak luminances is less than the display peak luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
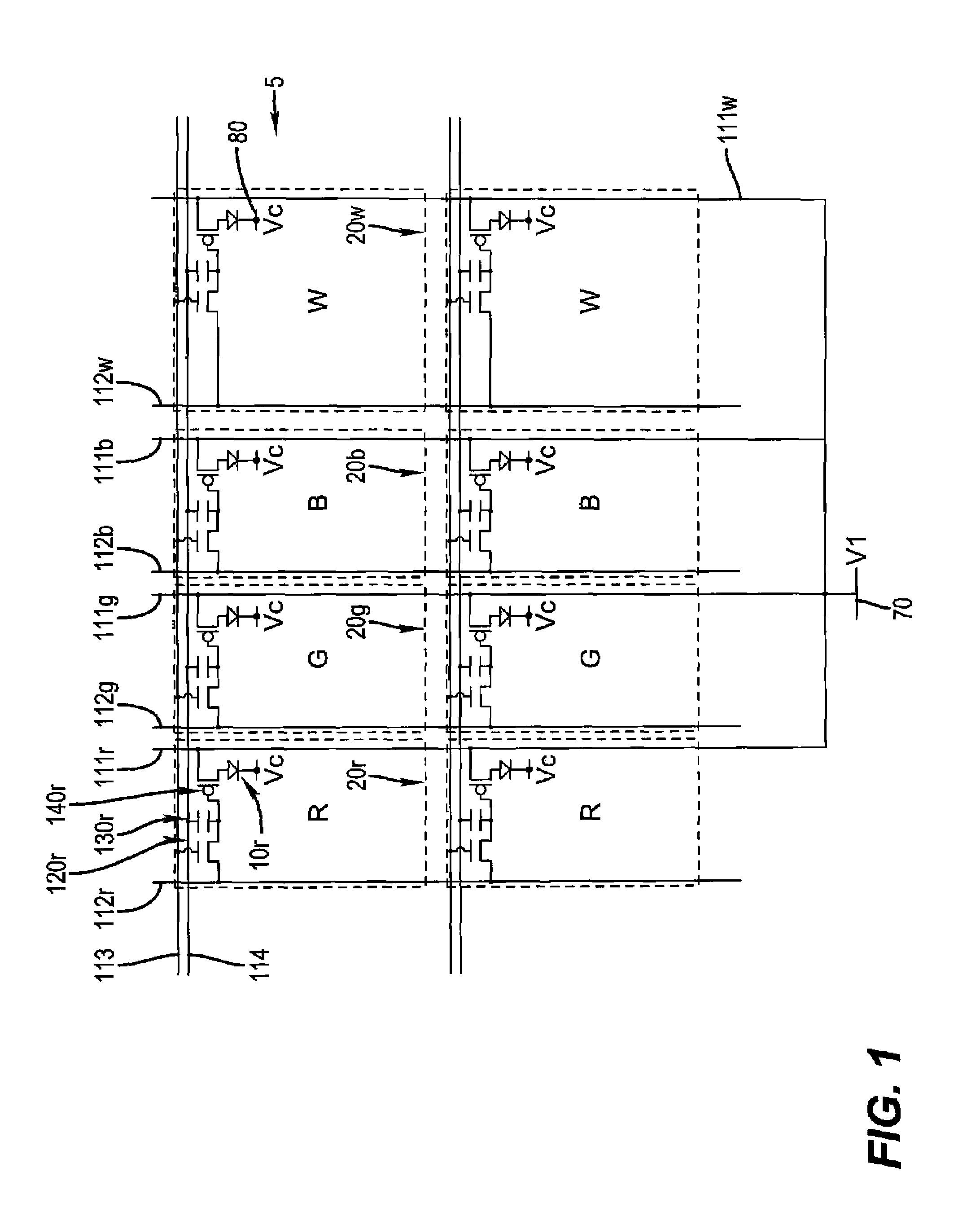
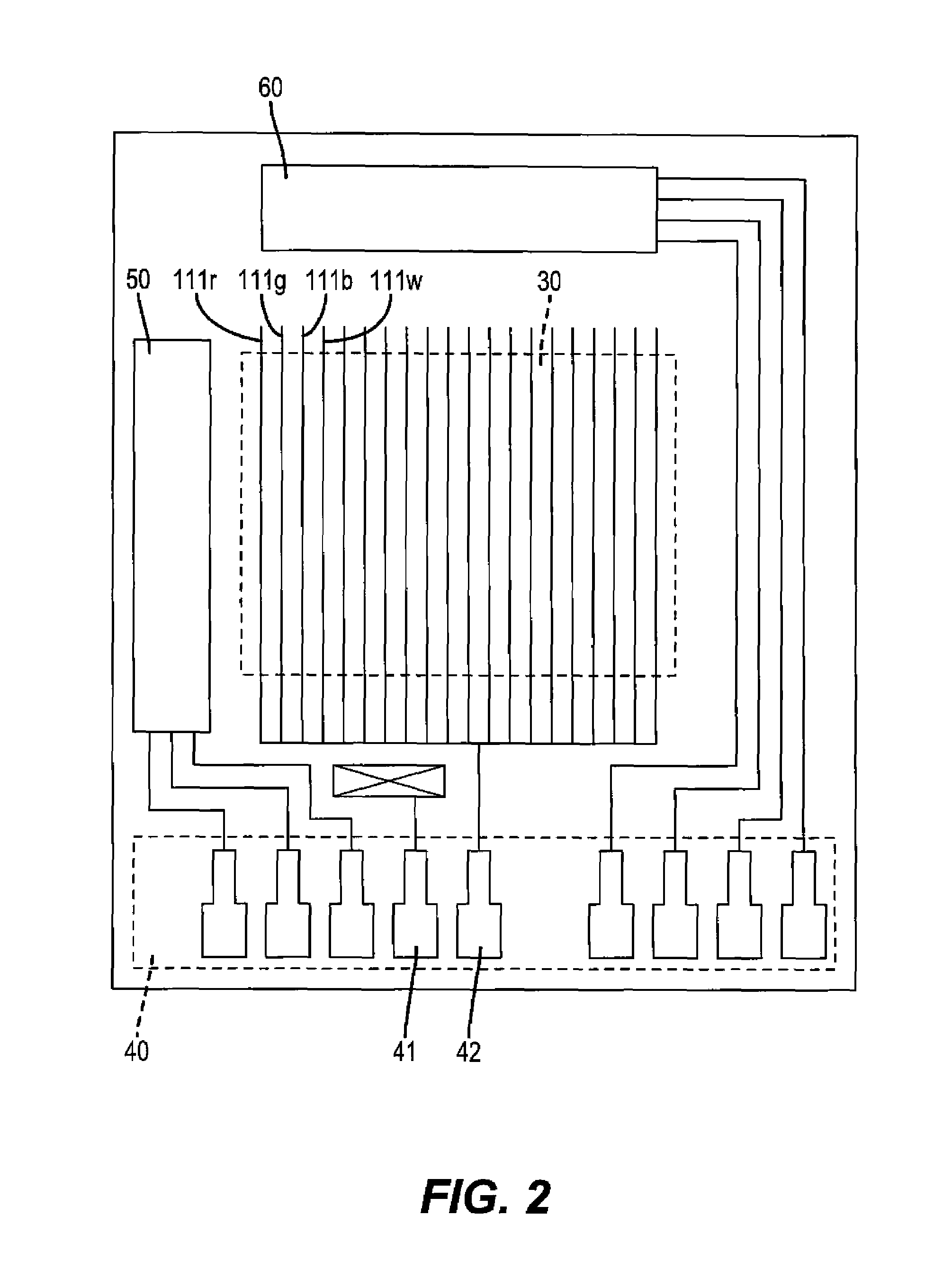
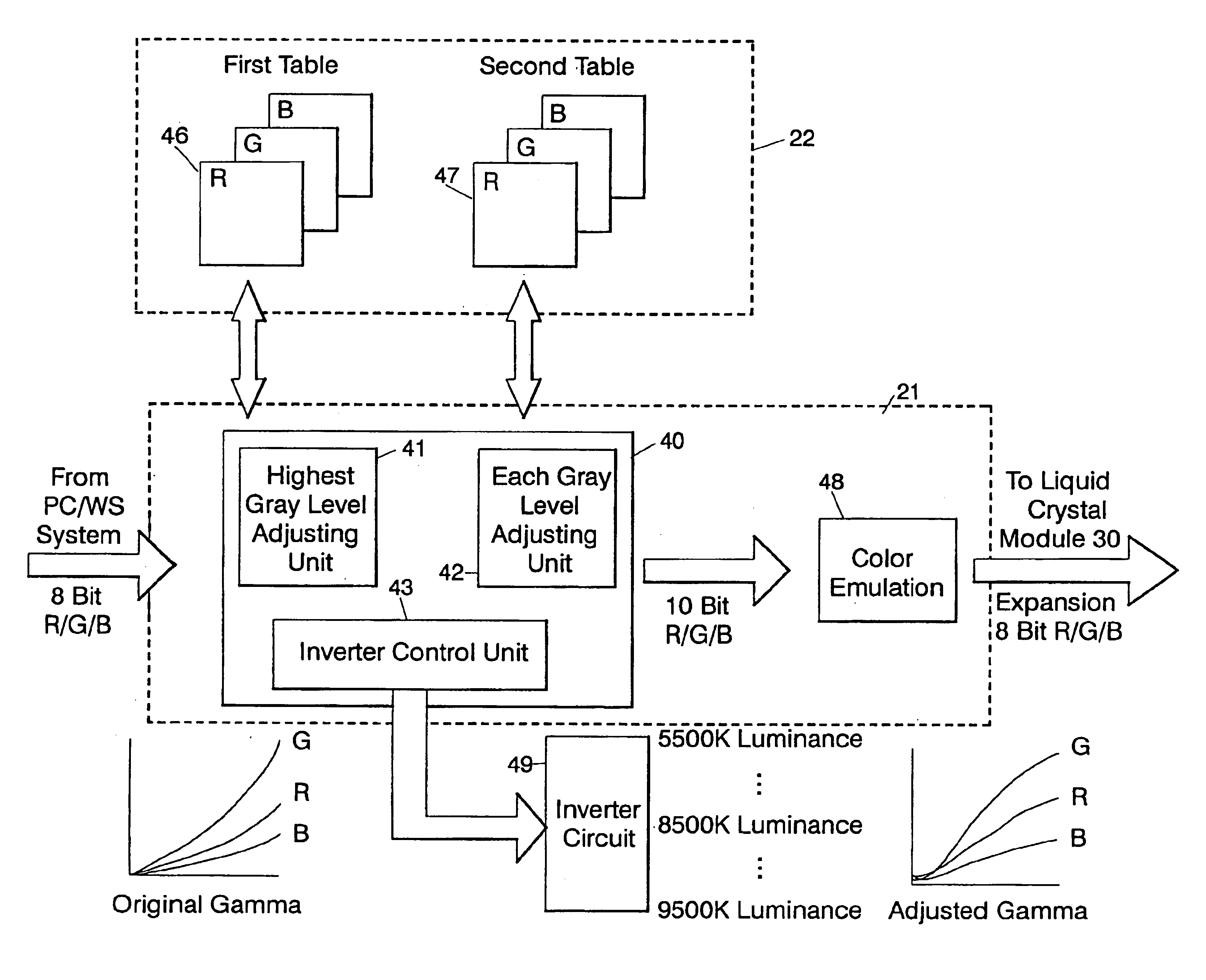
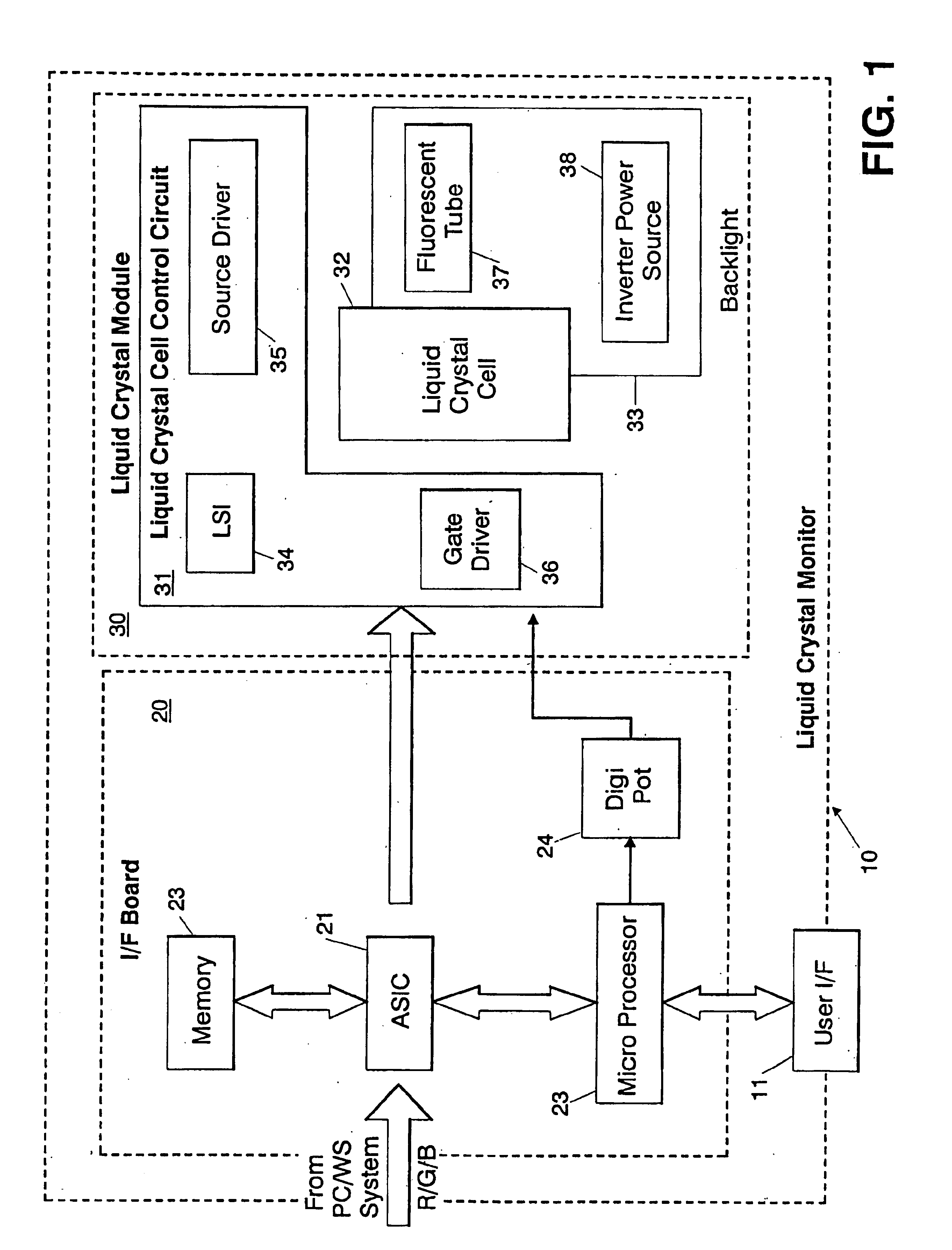
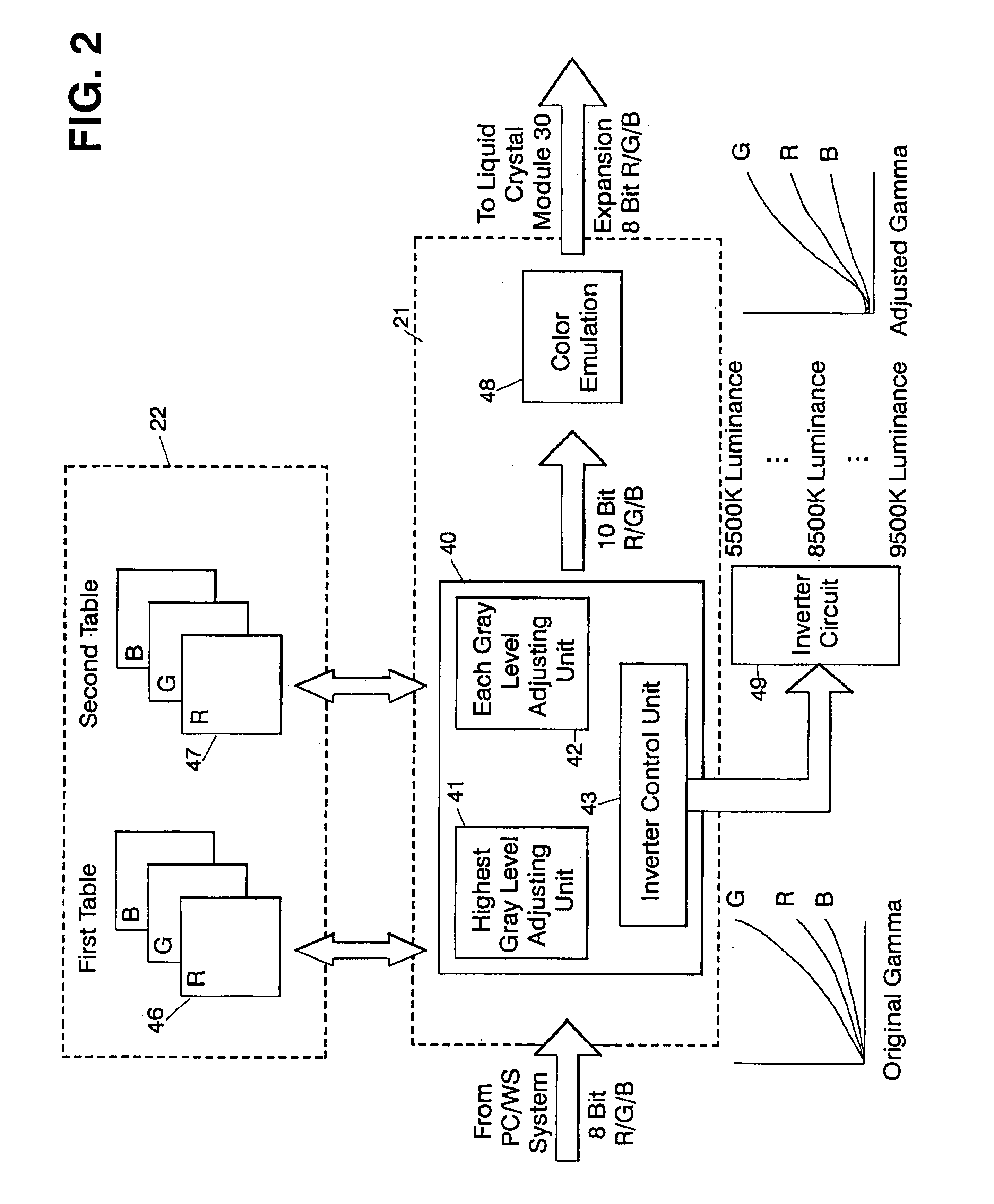
White point adjusting method, color image processing method, white point adjusting apparatus and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6862012B1Highly accurate convergenceImprove accuracyColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayComputer graphics (images)
A white point adjusting apparatus is provided to adjust an achromatic color level for an input video signal including a plurality of color signals, and display an adjusted image on a liquid crystal module. This adjusting apparatus comprises: a first table for setting a white point by deciding an offset quantity of at least one color signal from a highest gray level for each color temperature; a second table for setting an offset quantity of the color signal to converge a halftone white point for each color temperature set by the first table; and a white point adjusting unit for adding the offset quantities set by the first and second tables and to the input video signal.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
System for 3D image projections and viewing
InactiveUS20100060857A1Improve efficiencyImprove color gamutOptical filtersProjectors3d imageComplementary filter
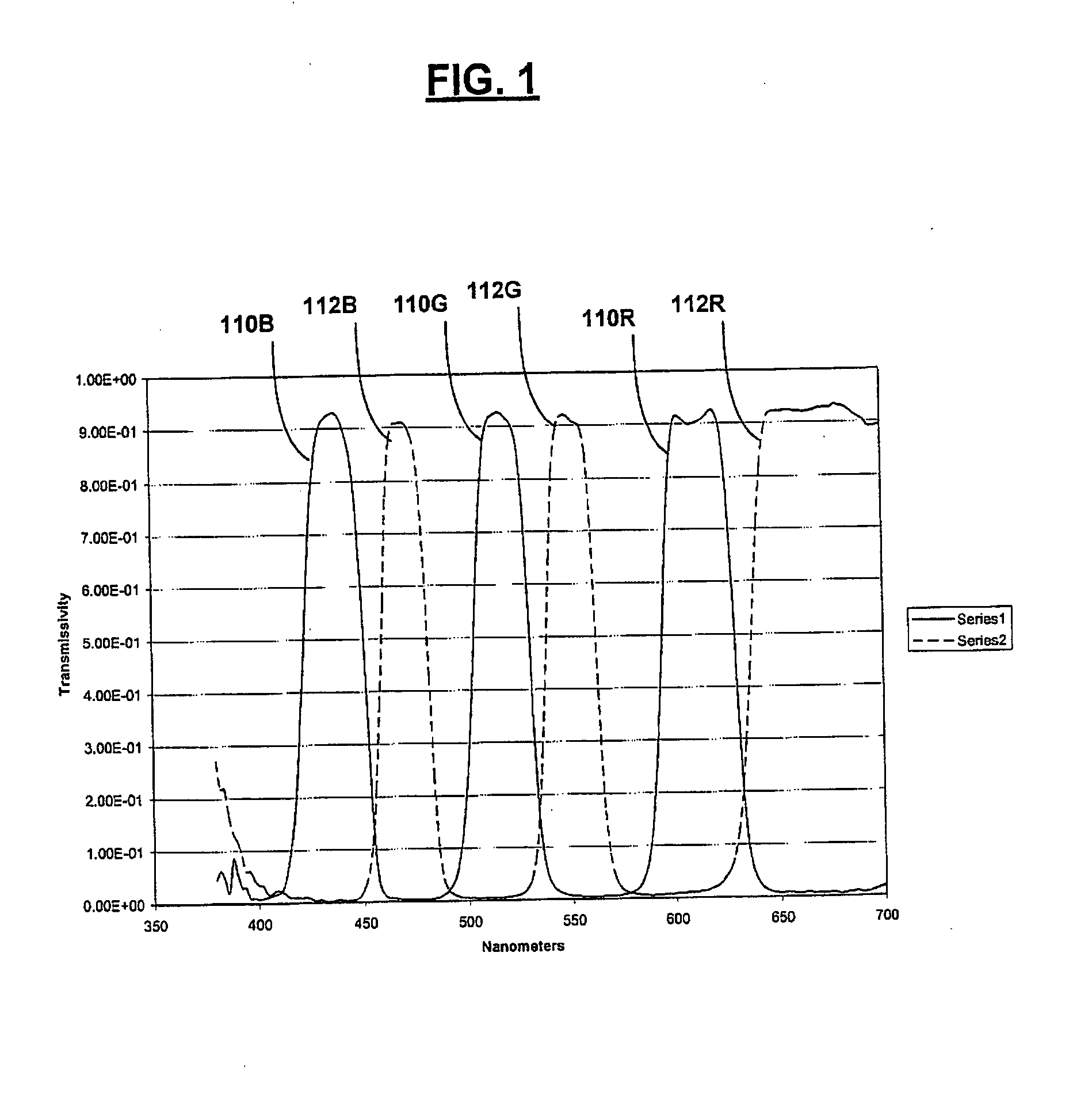
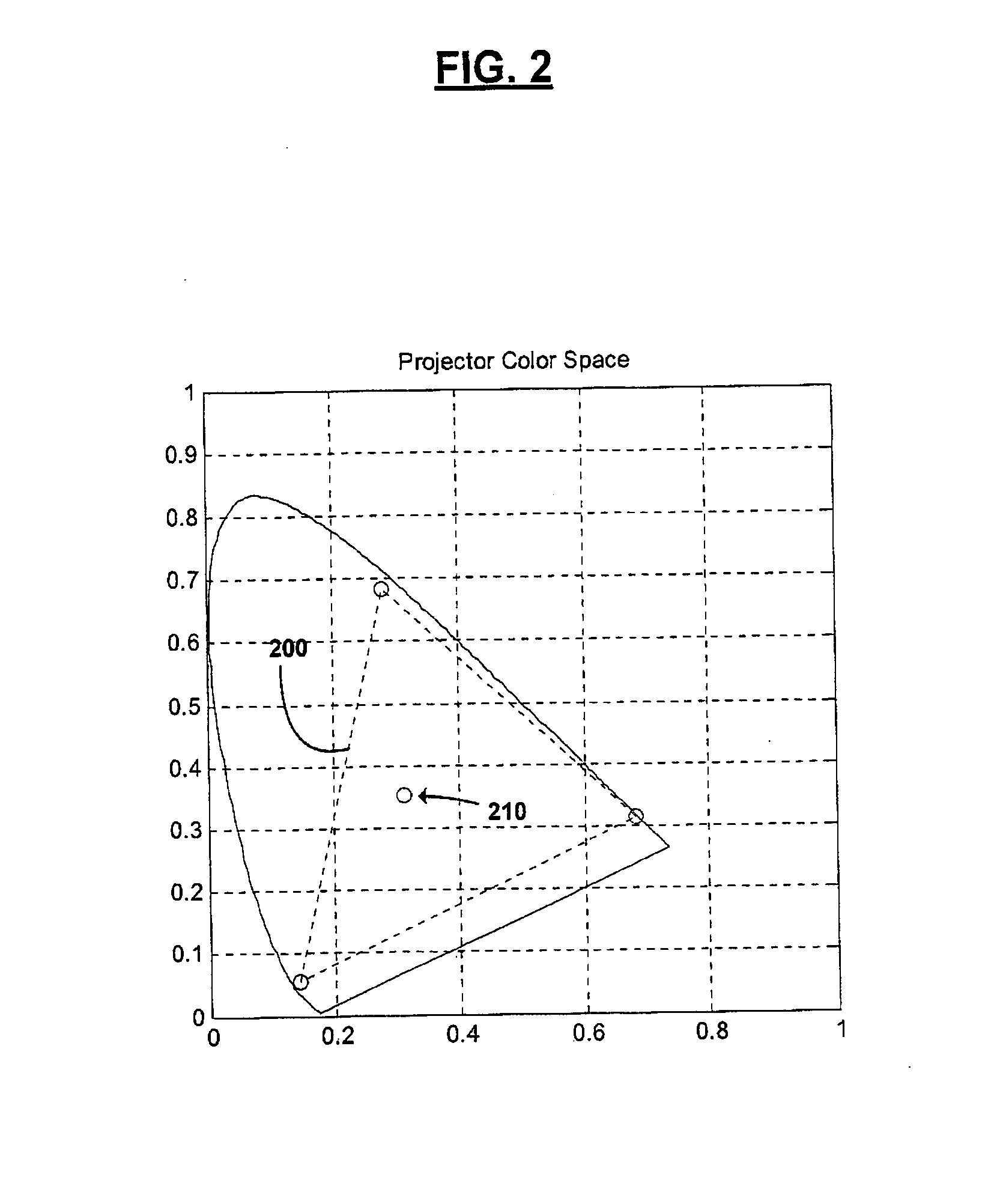
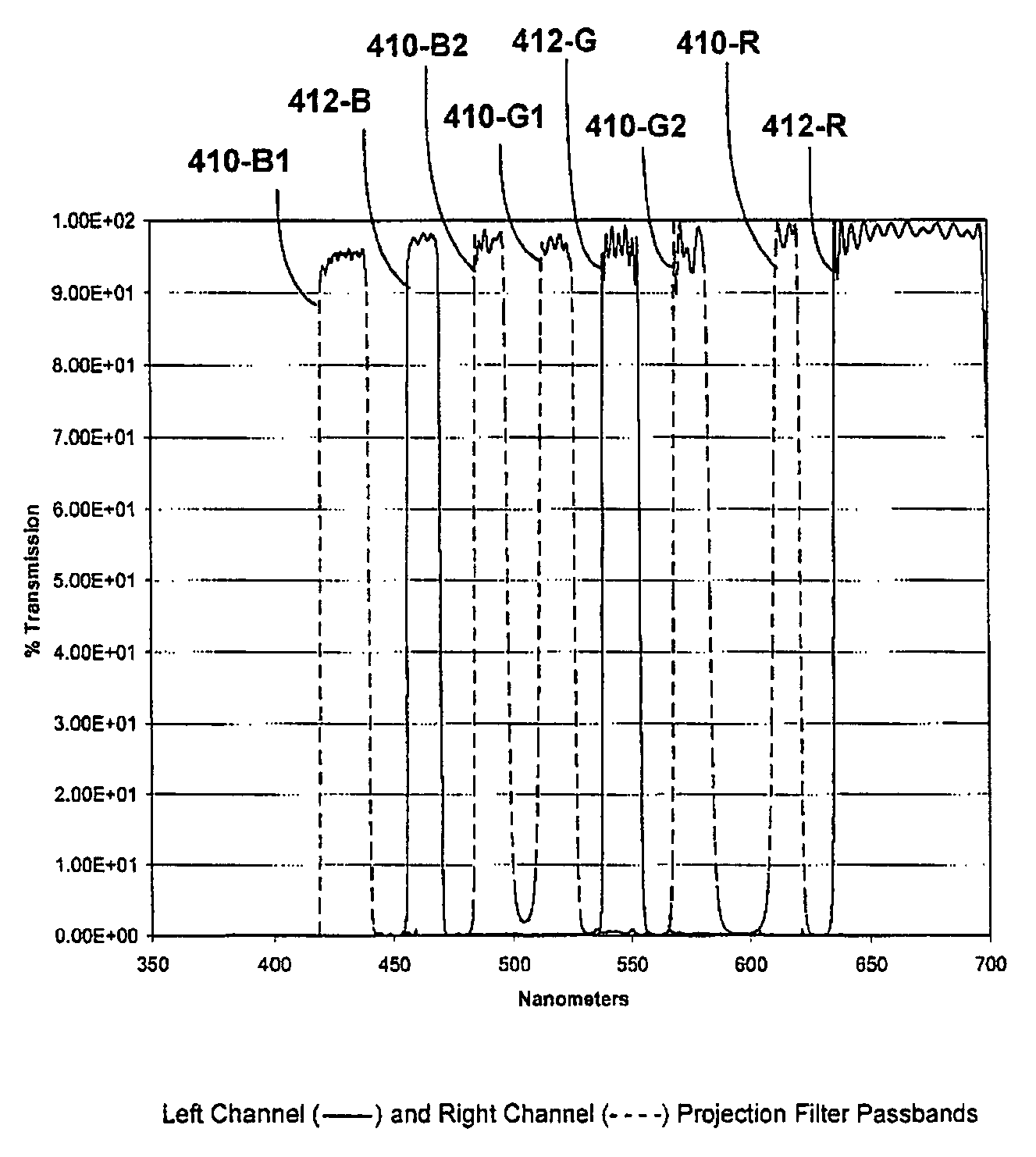
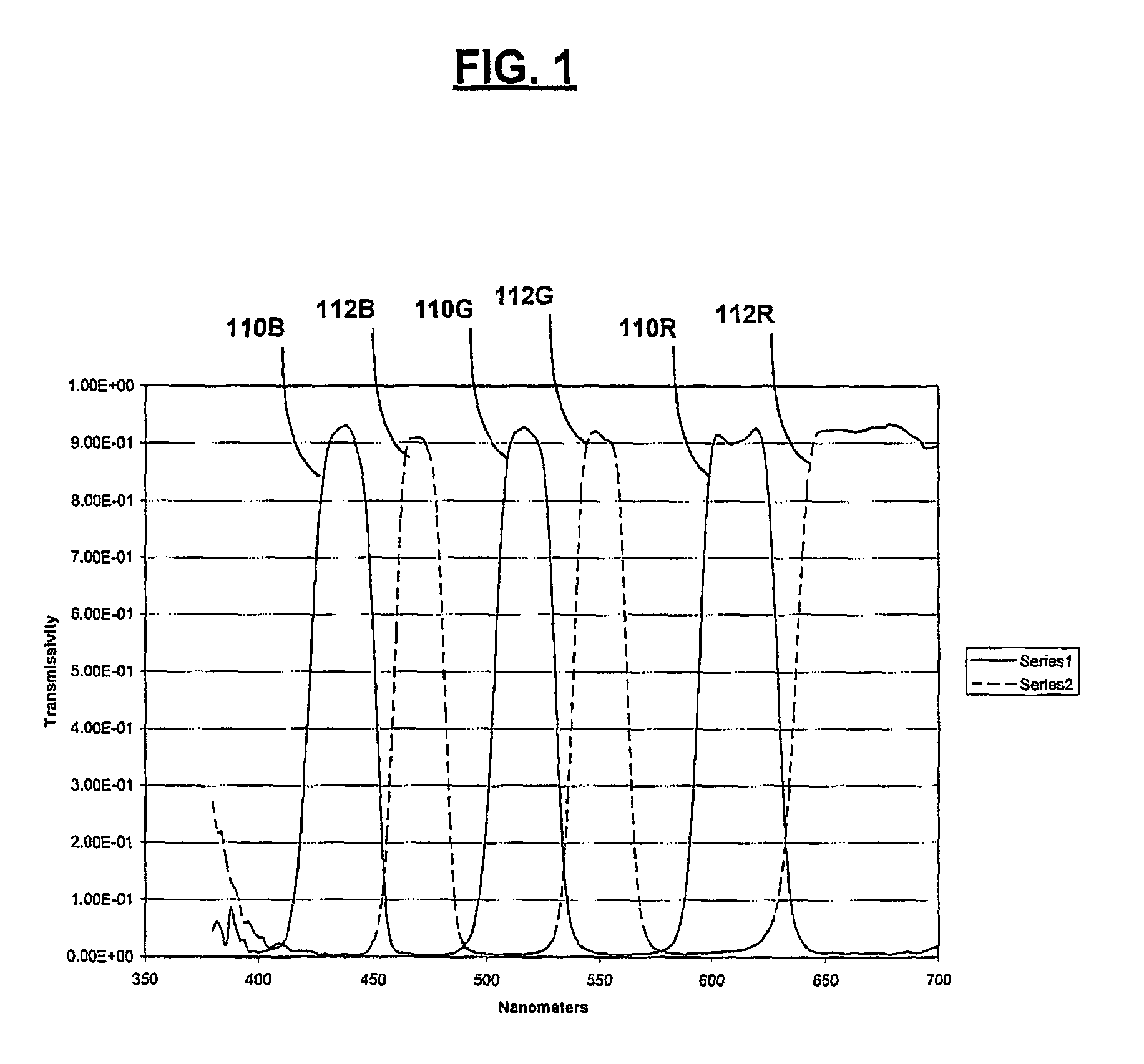
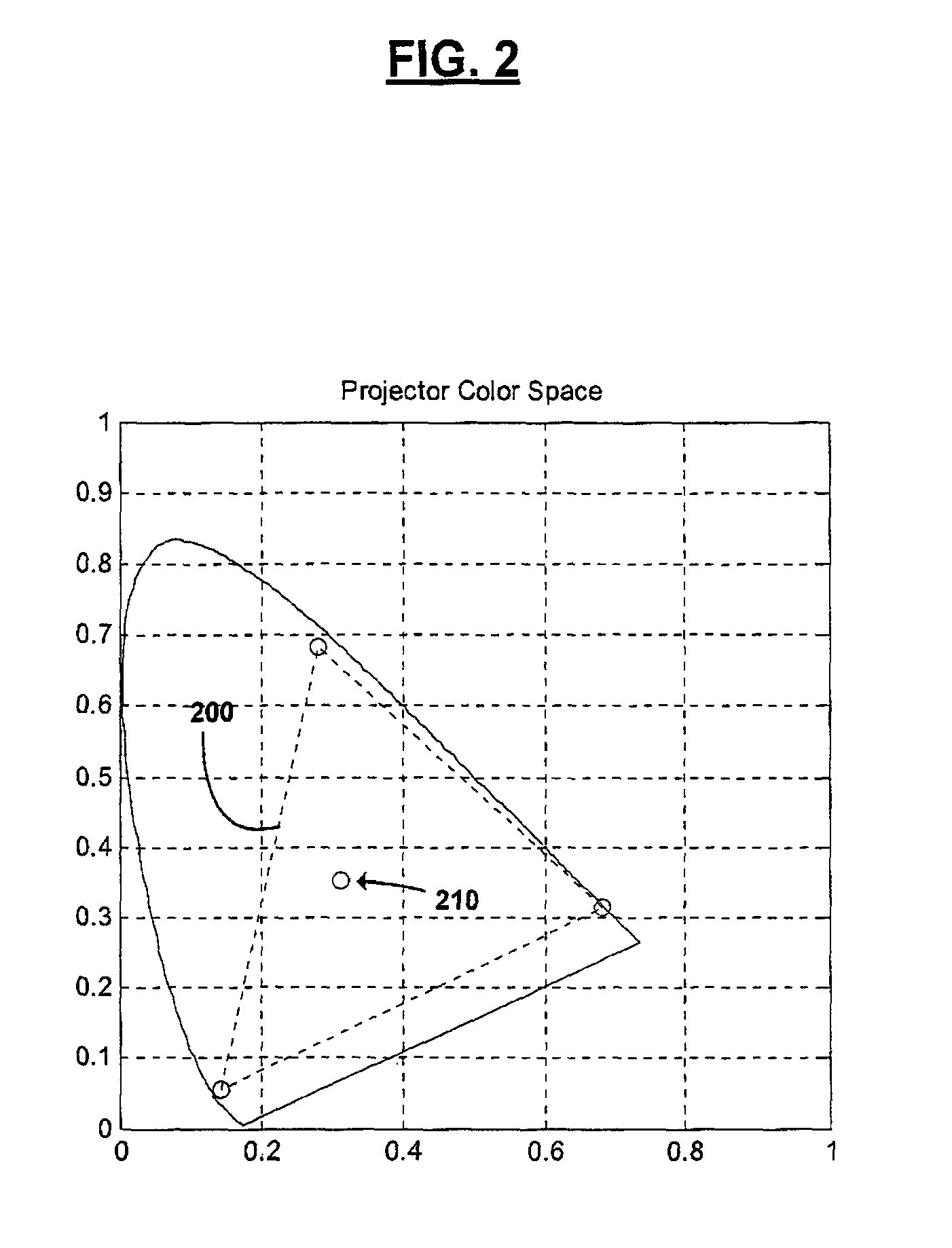
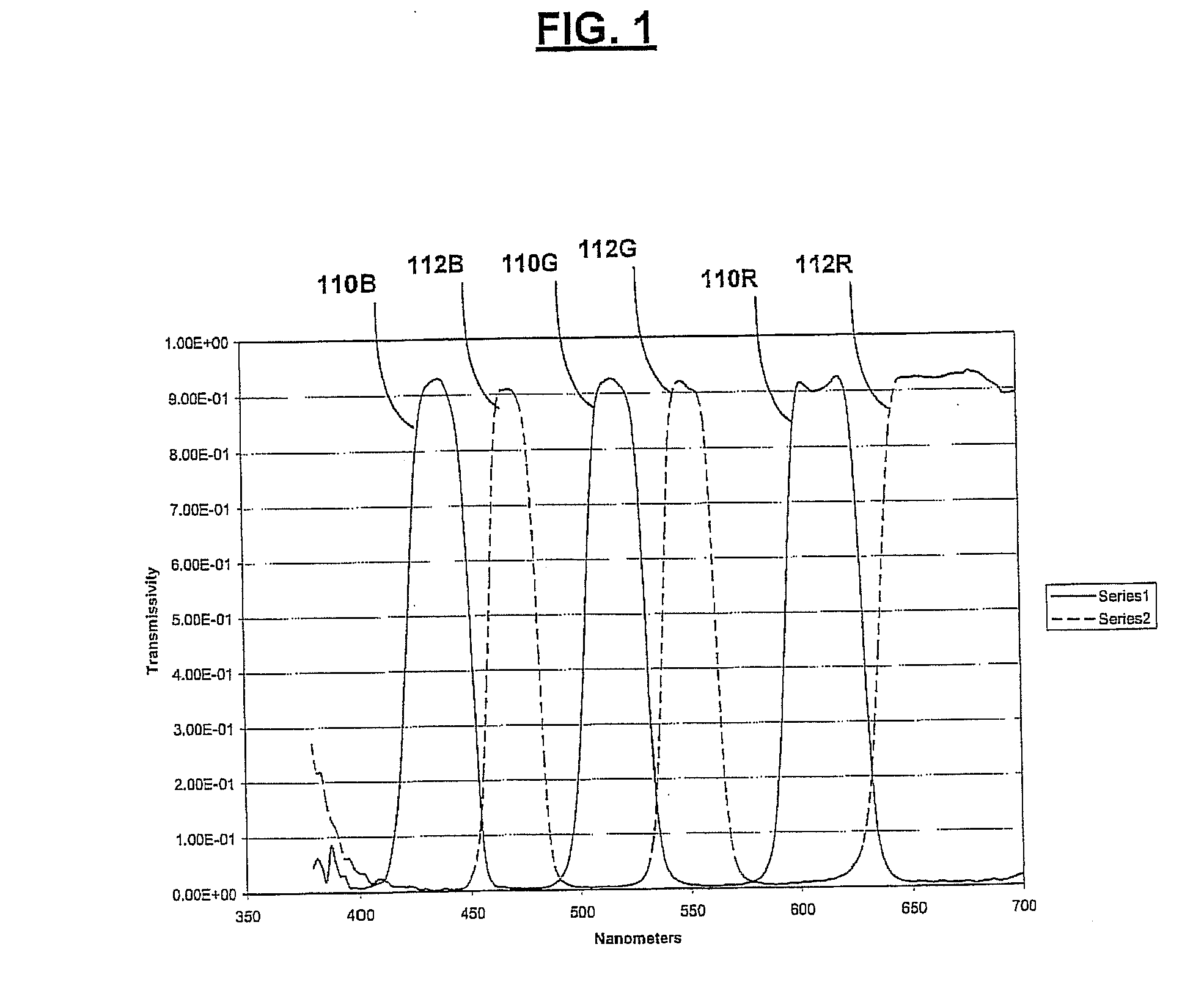
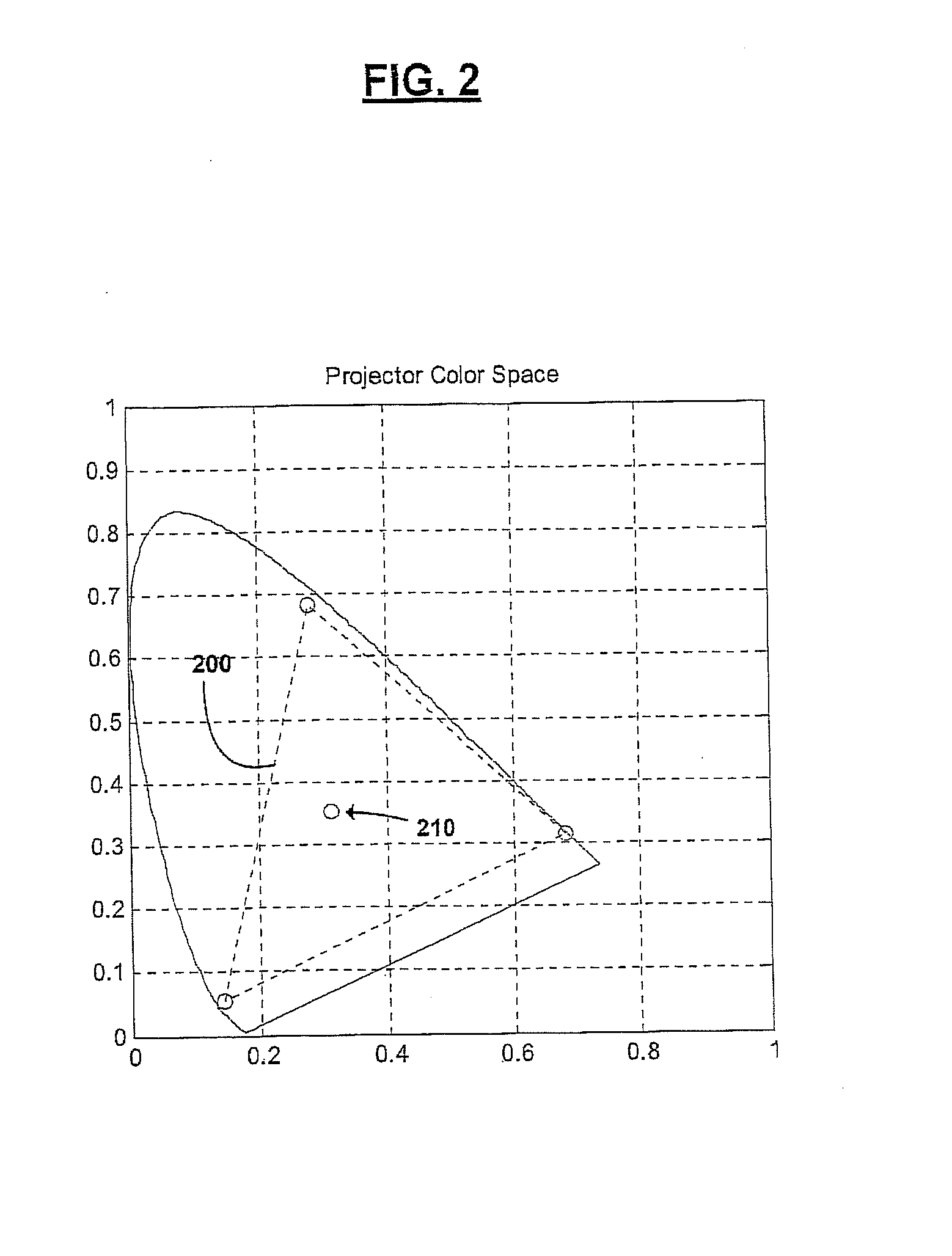
Shaped glasses have curved surface lenses with spectrally complementary filters disposed thereon. The filters curved surface lenses are configured to compensate for wavelength shifts occurring due to viewing angles and other sources. Complementary images are projected for viewing through projection filters having passbands that pre-shift to compensate for subsequent wavelength shifts. At least one filter may have more than 3 primary passbands. For example, two filters include a first filter having passbands of low blue, high blue, low green, high green, and red, and a second filter having passbands of blue, green, and red. The additional passbands may be utilized to more closely match a color space and white point of a projector in which the filters are used. The shaped glasses and projection filters together may be utilized as a system for projecting and viewing 3D images.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
OLED display with improved power performance
An OLED display for producing a full color image, comprising a plurality of at least four different colored pixels including three different colored addressable gamut-defining pixels and a fourth addressable within-gamut pixel, each pixel having an organic light-emitting diode with first and second electrodes and one or more organic light-emitting layers provided between the electrodes; the OLED display having a selected display white point, display peak luminance, gamut-defining pixel peak luminances and within-gamut pixel peak luminance; and drive circuitry for regulating luminance of the organic light-emitting diode of each of the colored pixels wherein the sum of the gamut-defining pixel peak luminances is less than the display peak luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Spectral separation filters for 3D stereoscopic D-Cinema presentation
ActiveUS20080284982A1Improve efficiencyImprove color gamutPrismsOptical filtersPattern recognition3d image
Spectral separation filters for channels of a 3D image projection incorporate passbands of primary colors. In at least one of the filters, passbands are present in more than 3 primary colors. A set of two filters include a first filter having passbands of low blue, high blue, low green, high green, and red, and a second filter having passbands of blue, green, and red. The additional primary passbands of the first filter allow for an increased color space in projections through the filters compared to filters only having red, green, and blue primaries. The added flexibility of the increased color space is utilized to more closely match a color space and white point of a projector in which the filters are used.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Spectral separation filters for 3D stereoscopic D-cinema presentation
ActiveUS7959295B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove efficiencyPrismsOptical filtersPattern recognition3d image
Spectral separation filters for channels of a 3D image projection incorporate passbands of primary colors. In at least one of the filters, passbands are present in more than 3 primary colors. A set of two filters include a first filter having passbands of low blue, high blue, low green, high green, and red, and a second filter having passbands of blue, green, and red. The additional primary passbands of the first filter allow for an increased color space in projections through the filters compared to filters only having red, green, and blue primaries. The added flexibility of the increased color space is utilized to more closely match a color space and white point of a projector in which the filters are used.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Rendering of high dynamic range images
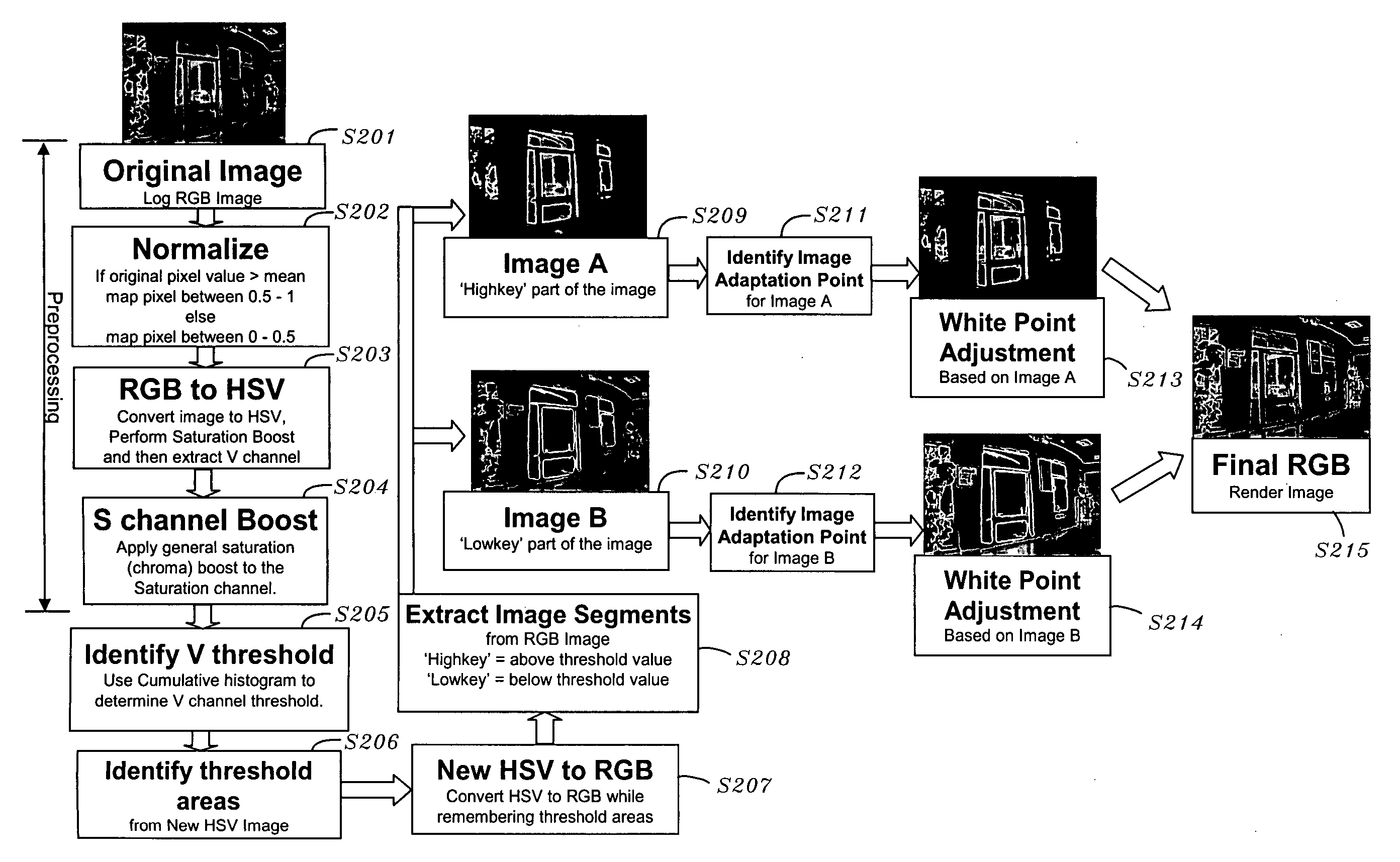
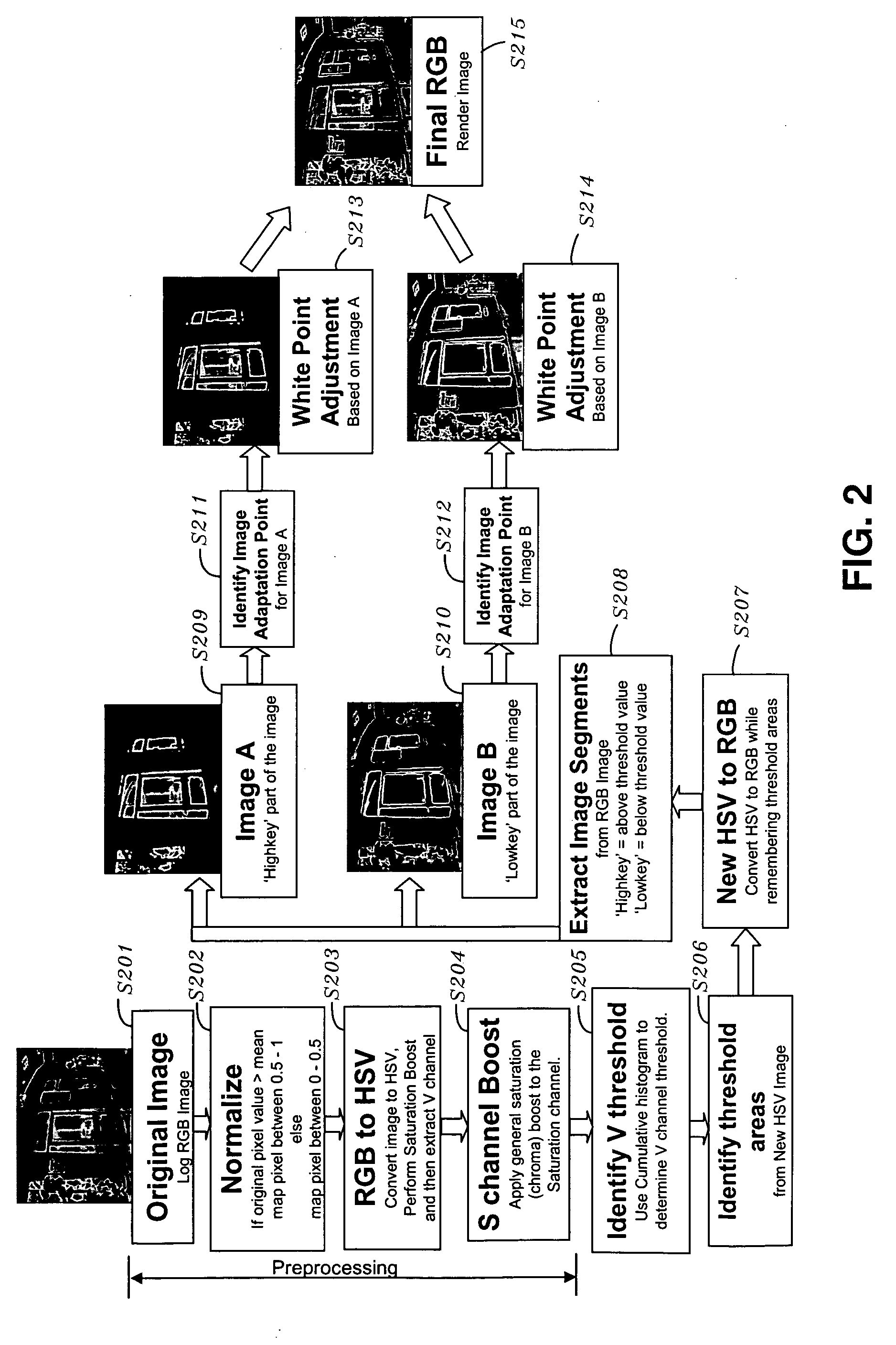
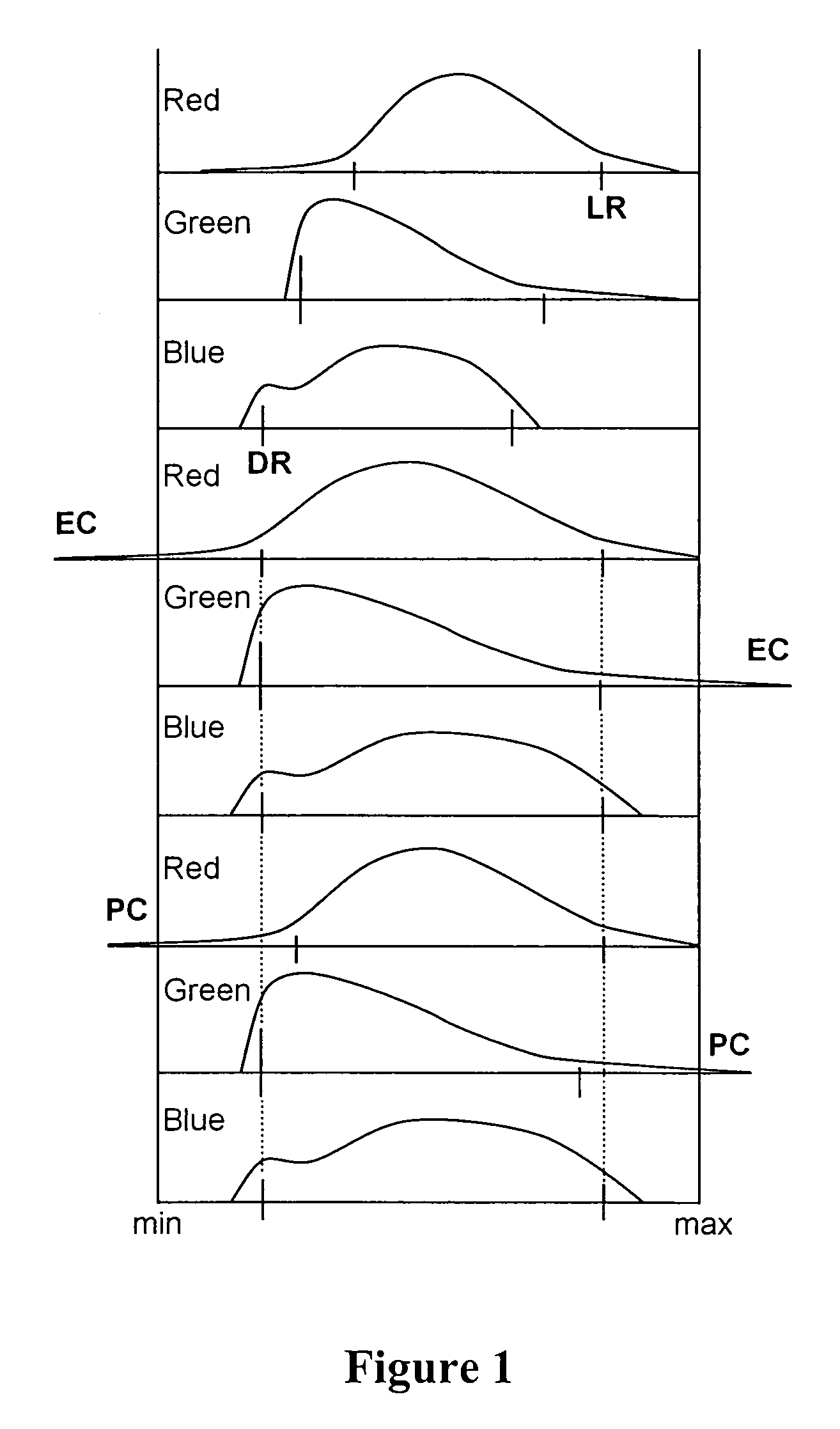
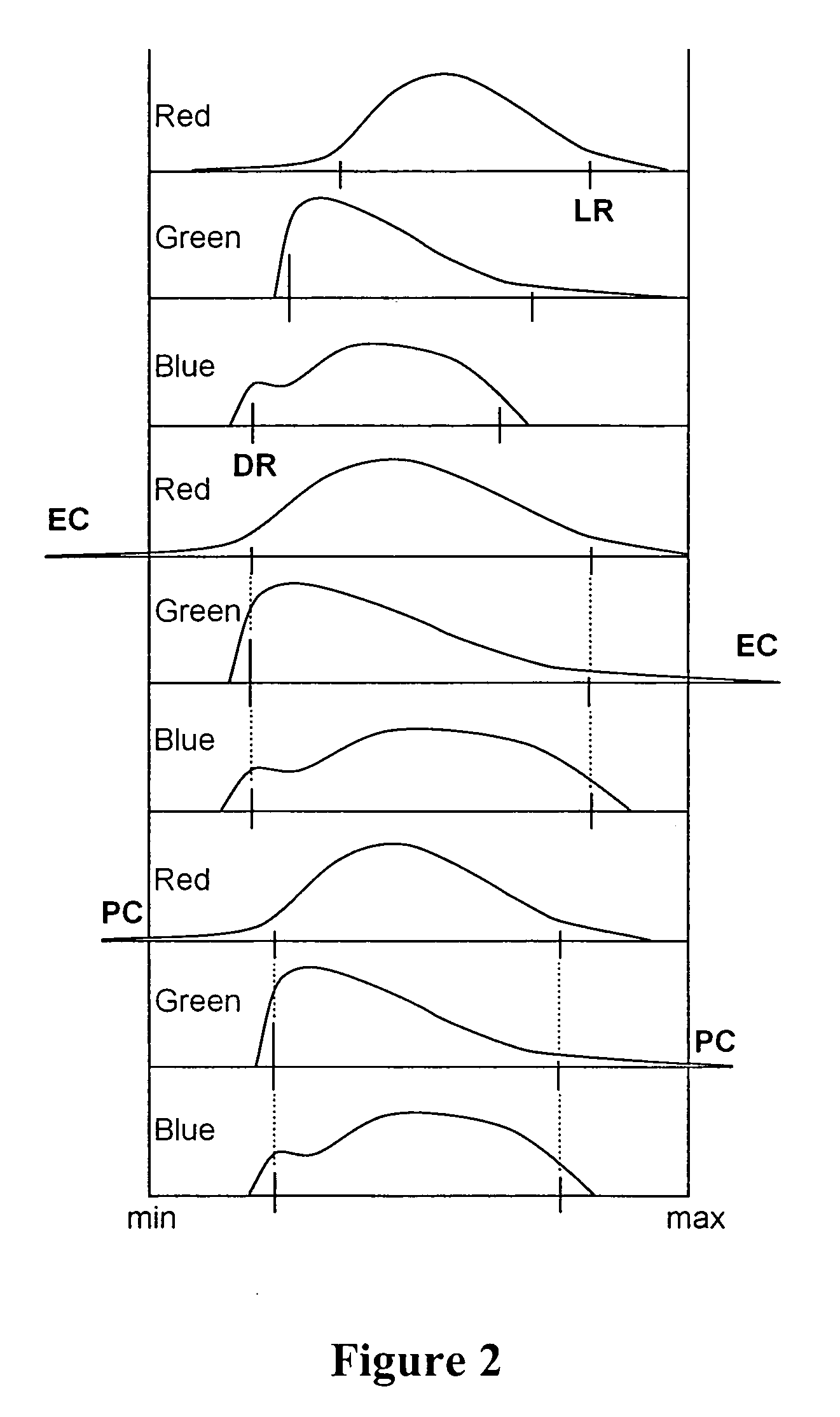
InactiveUS20060262363A1Uneven white balanceImage enhancementImage analysisWhite pointHigh dynamic range
White balance normalization of a high dynamic range image is performed by identifying a first image adaptation point for a relatively lighter portion of the image and a second image adaptation point for a relatively darker portion of the image. A first white point adjustment for the lighter portion of the image is performed using the first image adaptation point and a second white point adjustment for the darker portion of the image is performed using the second image adaptation point. Thus, multiple illumination sources can be taken into account in rendering a high dynamic range image, providing a more visually appealing rendered image.
Owner:CANON KK
Selecting white point for OLED devices
InactiveUS20060105198A1Improve equipment efficiencyReduce power consumptionIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensWhite pointWhite light
A method for selecting two different light-emitting materials for use in an OLED device, each of which produces different color light, which combine to produce white light. Each light emitting material has its own point on a chromaticity diagram, and the light-emitting materials are selected such that, when a line is drawn between the first point and the second point, it passes through a desired white area defined on a chromaticity diagram.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Accurate Color Display Device
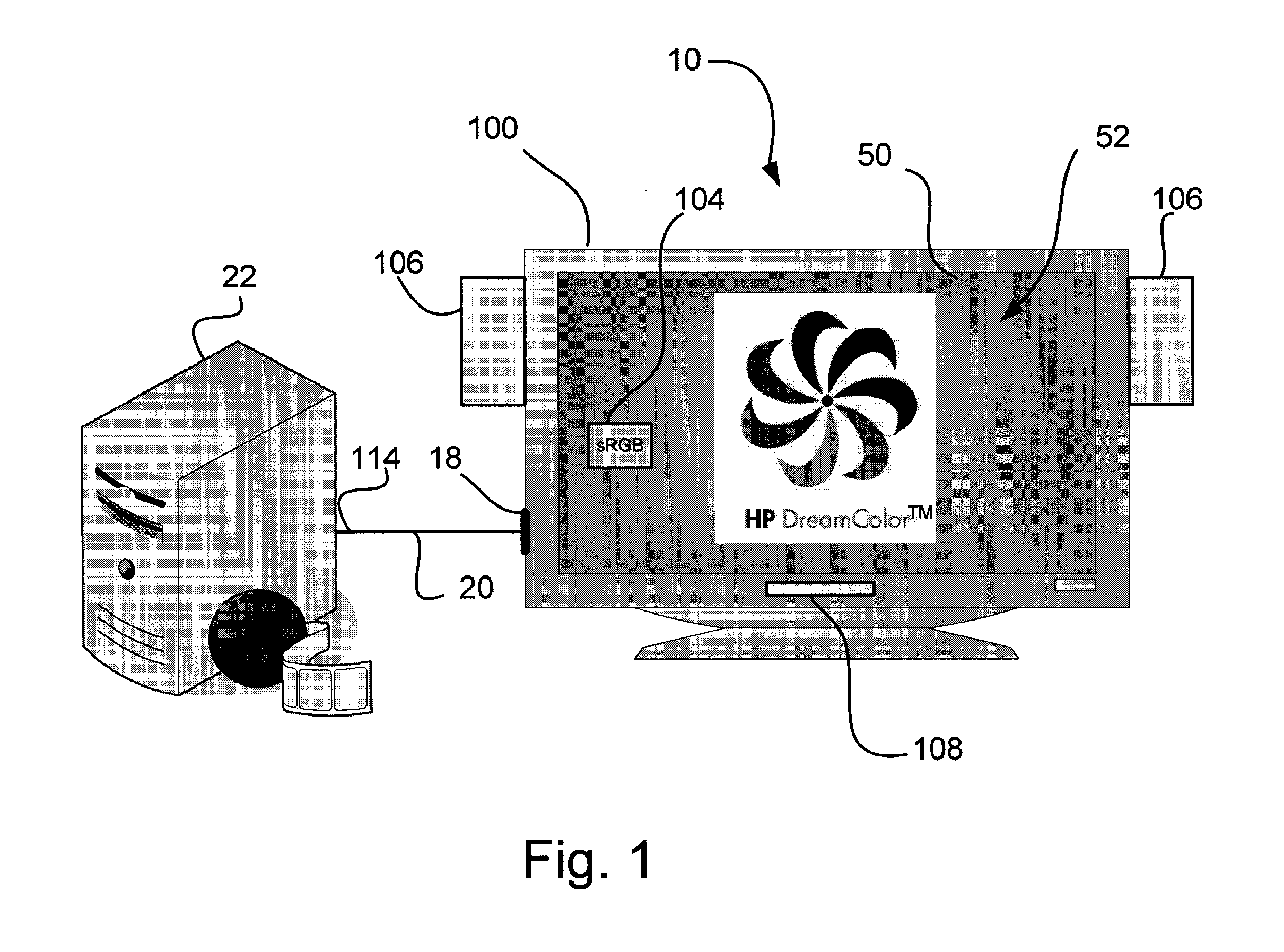
A color accurate display device is configured to receive an encoded first color space having a first gamut from a set of encoded primaries {R, G, B} and a first white point. The device includes a display panel having an active area configured for an encoded second color space having a second white point and a set of native primaries each with a characterized tone response with respect to the second color space and a measured tone response from the display panel, the primaries having a second gamut larger than and including the first gamut. Also included is a color space conversion circuit configured to convert the set of encoded primaries {R, G, B} and first white point of the first color space to the set of native primaries and second white point compensating for each characterized tone response of the second color space.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
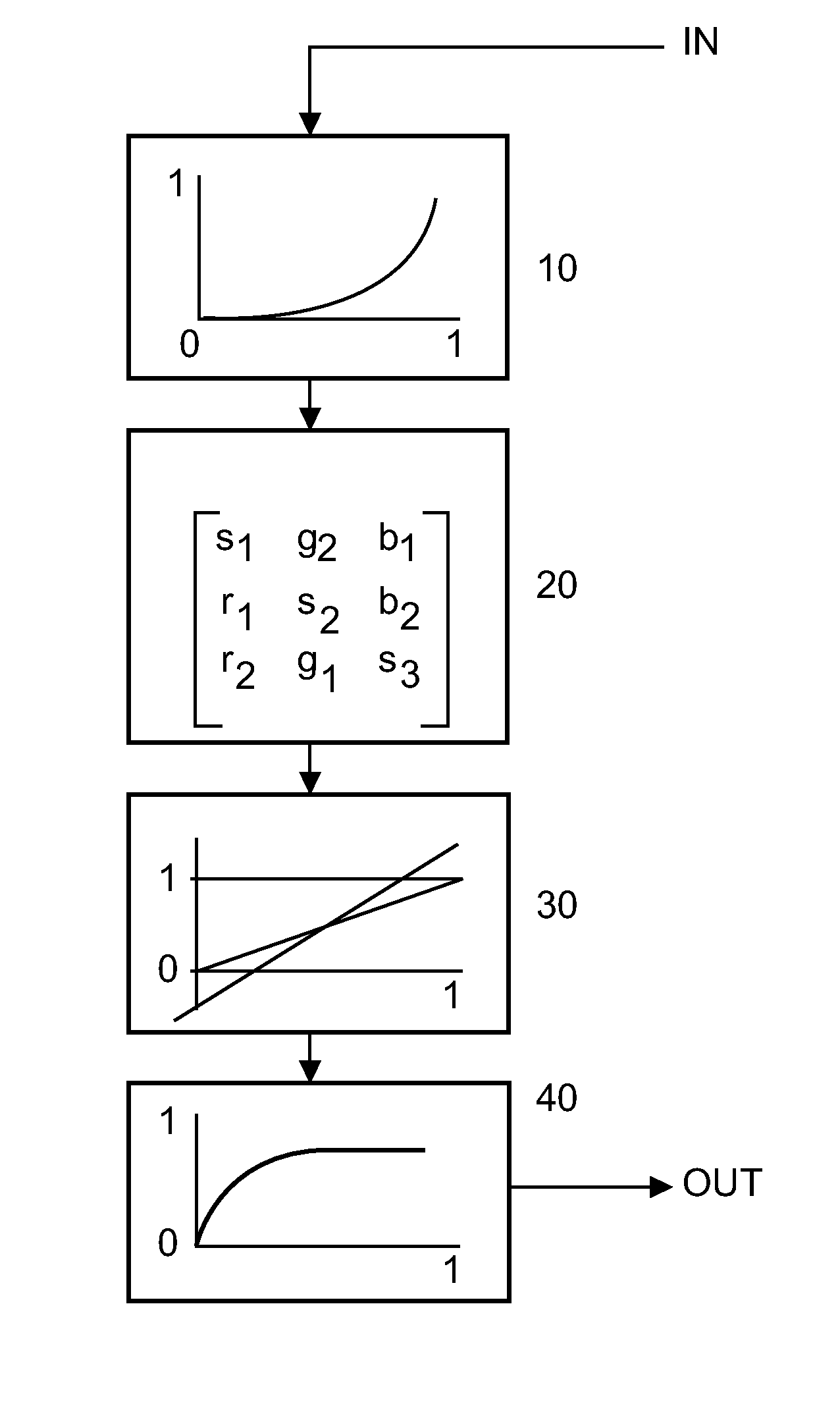
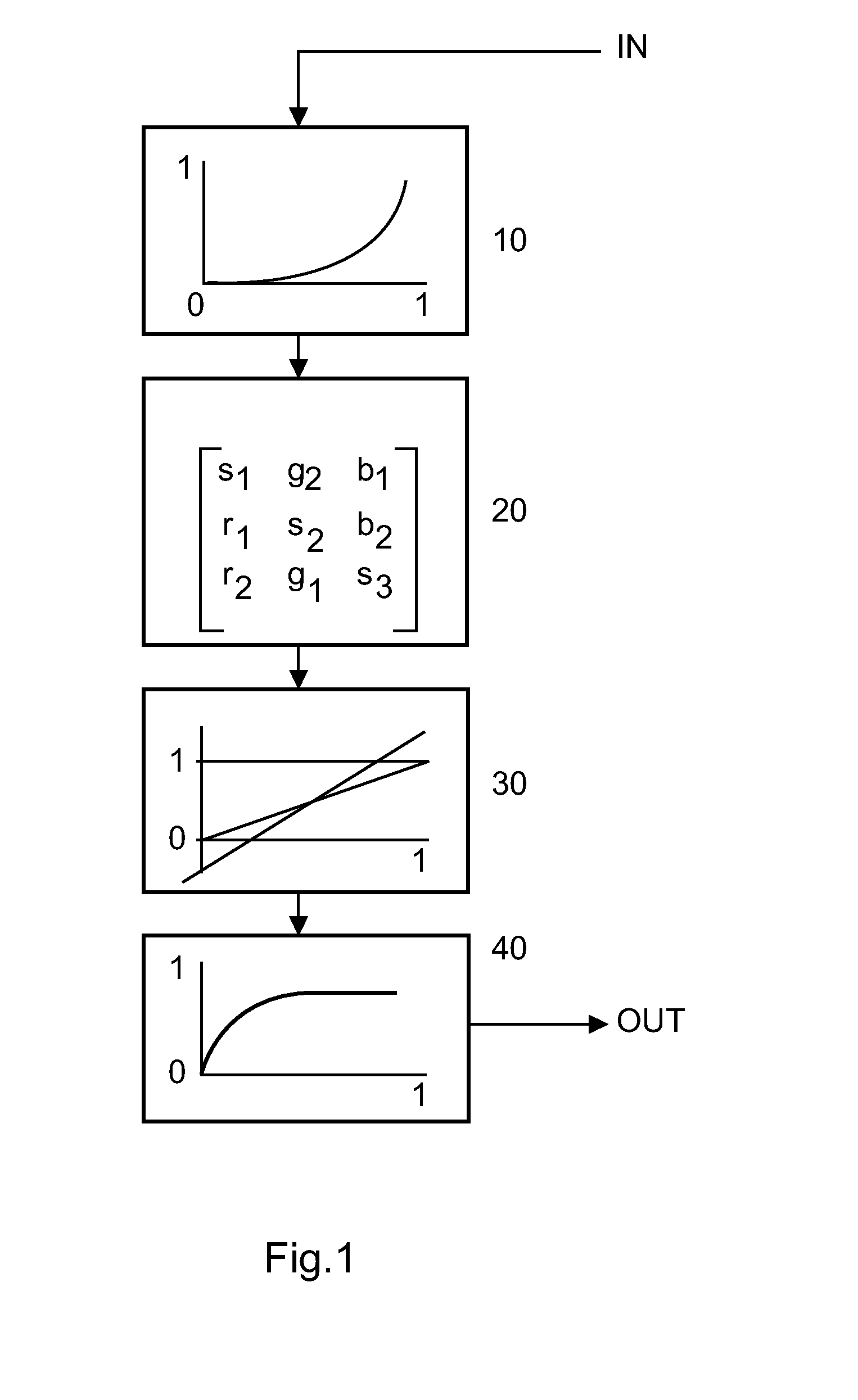
Device and method for processign color image data
InactiveUS20100020242A1Avoid severe clippingAvoid lostColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor imageGamut
The present invention relates to a video processing device comprising a luminance and saturation detector (LSHD) for detecting the luminance values (lum) and the saturation values (sat) of pixels of an input video signal (IN); and a white-point, saturation and hue modulator (WSH) for transforming luminance and saturation properties (lum, sat) of the pixels of the input video signal (IN) into white-point, saturation and hue correction factors (W, Wc; S, Sc; H, Hc). The video device also comprises a color gamut matrix generating unit (CGMG) for generating a color gamut matrix in the perception domain based on the white-point, saturation and hue correction factors (Wc, Sc, Hc) of the white-point, saturation and hue modulator (WSH); a color gamut mapping unit (20) for multiplying the pixels of the input video signal (IN) with a color gamut matrix generated by the color gamut matrix generating unit (CGMG); and a clipping unit (31) for clipping the results of the a color gamut mapping unit (20) which are out of a predefined range.
Owner:DYNAMIC DATA TECH LLC
Automatic white balance correcting method and device
ActiveCN103929632AAvoid calculationImprove color castColor signal processing circuitsPicture signal generatorsWhite pointComputer engineering
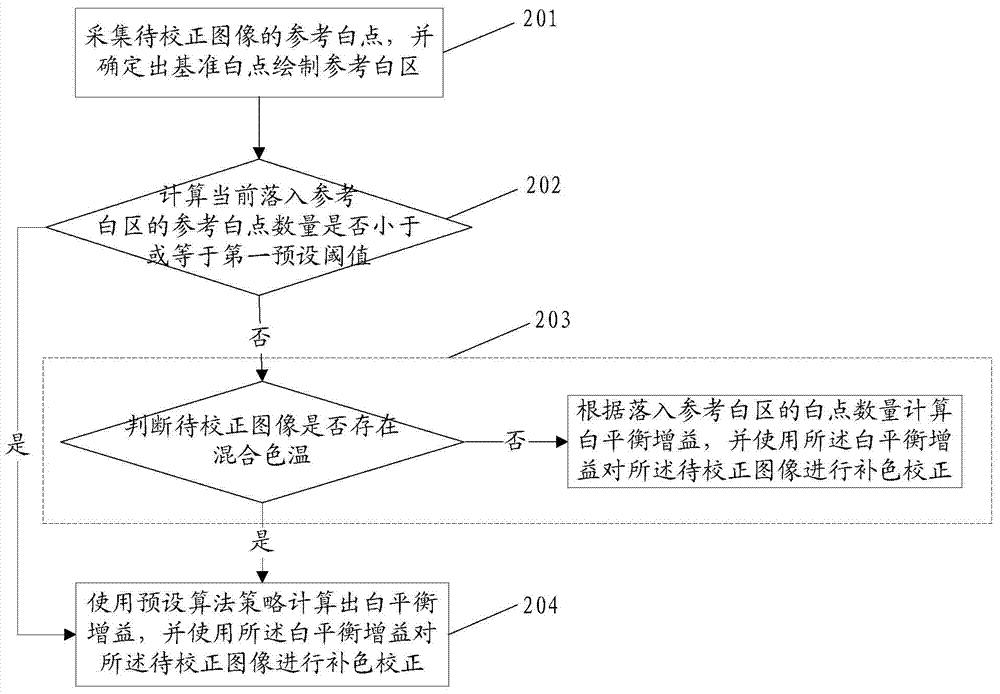
The invention provides an automatic white balance correcting method which includes the steps of collecting reference white points of an image to be corrected, determining the reference white points to draw a reference white region, calculating the number of the reference white points, currently located in the reference white region, of the image to be corrected, judging whether mixed color temperature exists in the image to be corrected or not, if the number of the reference white points is smaller than or equal to a first preset threshold value or it is judged that the mixed color temperature exists in the image to be corrected, calculating white balance gains through a preset algorithm strategy, carrying out color complementing correcting on the image to be corrected through the white balance gains, if it is judged that the mixed color temperature does not exist or the number of the reference white points is larger than the first preset threshold value, calculating the white balance gains according to the number of the white points located in the reference white region, and carrying out color complementing correcting on the image to be corrected through the white balance gains. According to the automatic white balance correcting method, the color shifting problem generated when the image is corrected through the white balance gains calculated with a reference white region table look-up method when the number of the reference white points is excessively small and the mixed color temperature exists is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVIEW TECH CO LTD
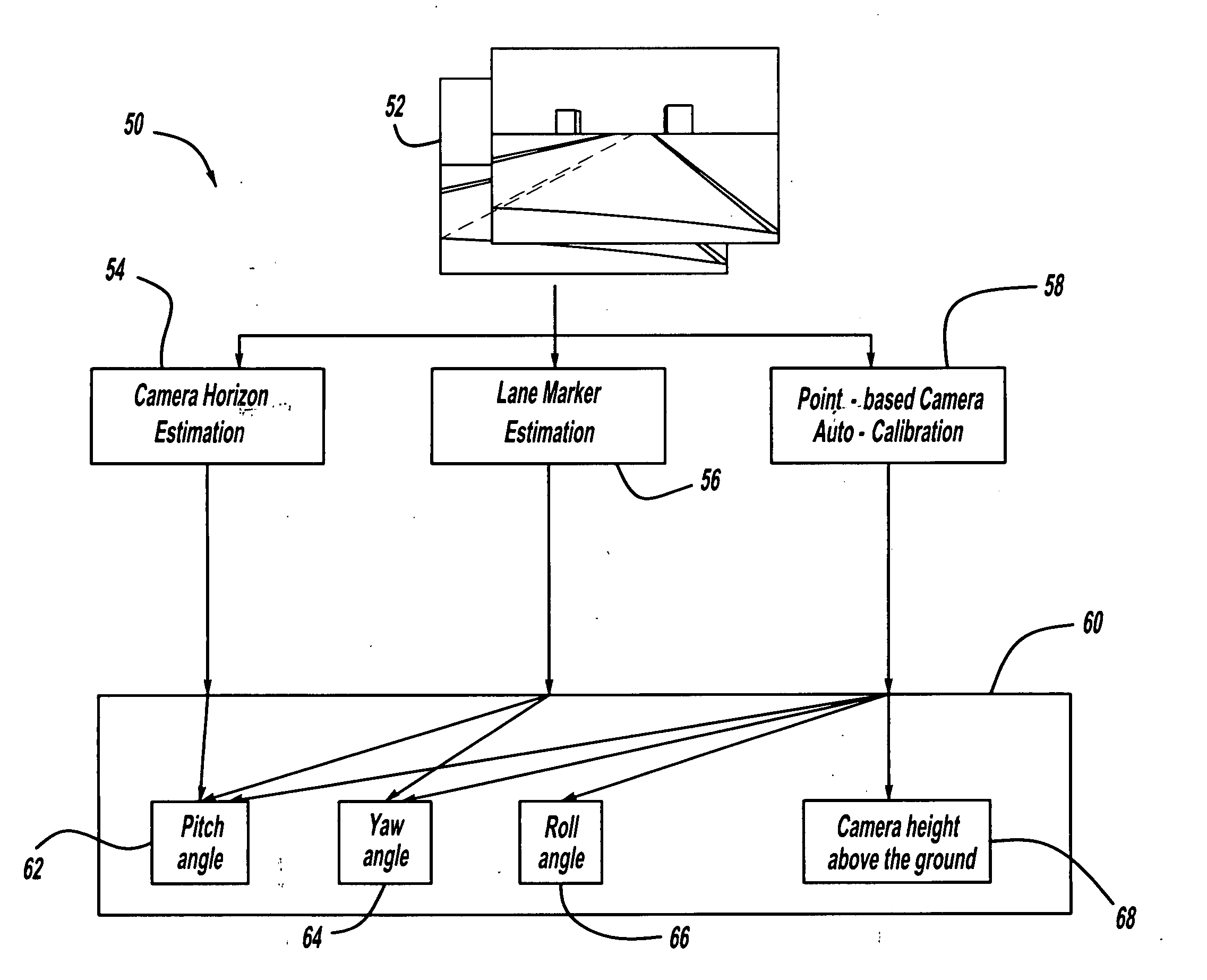
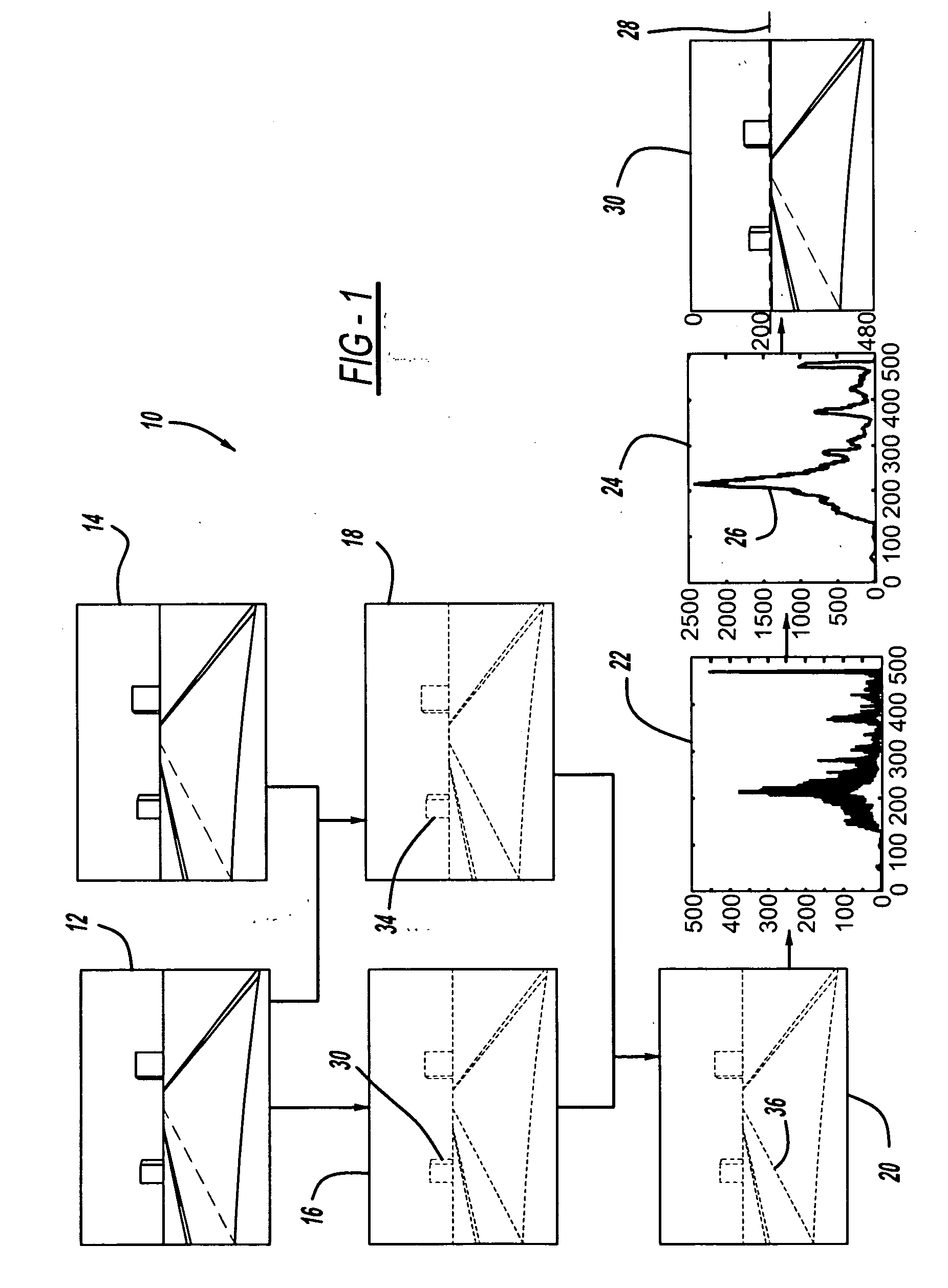
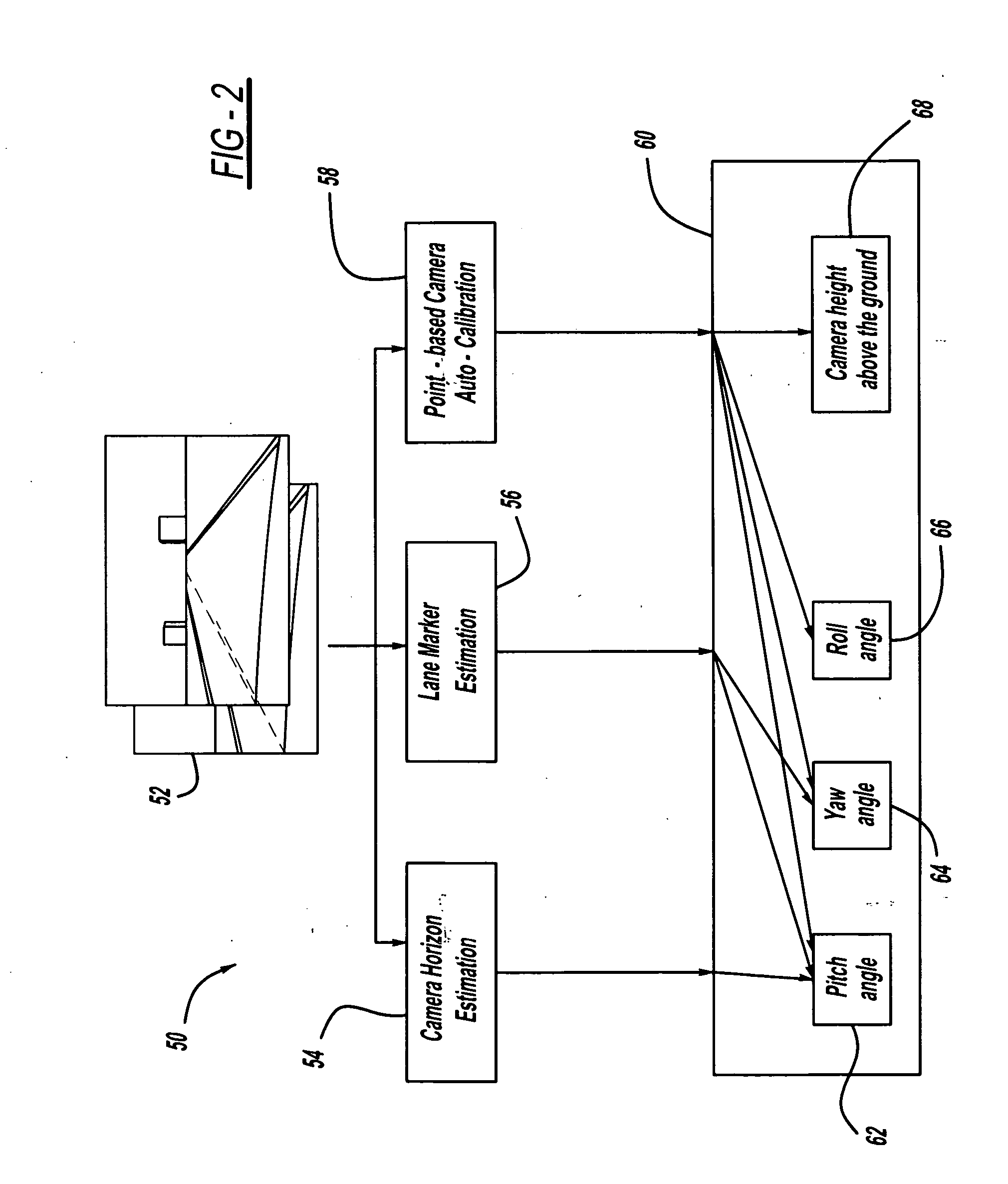
Camera auto-calibration by horizon estimation
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
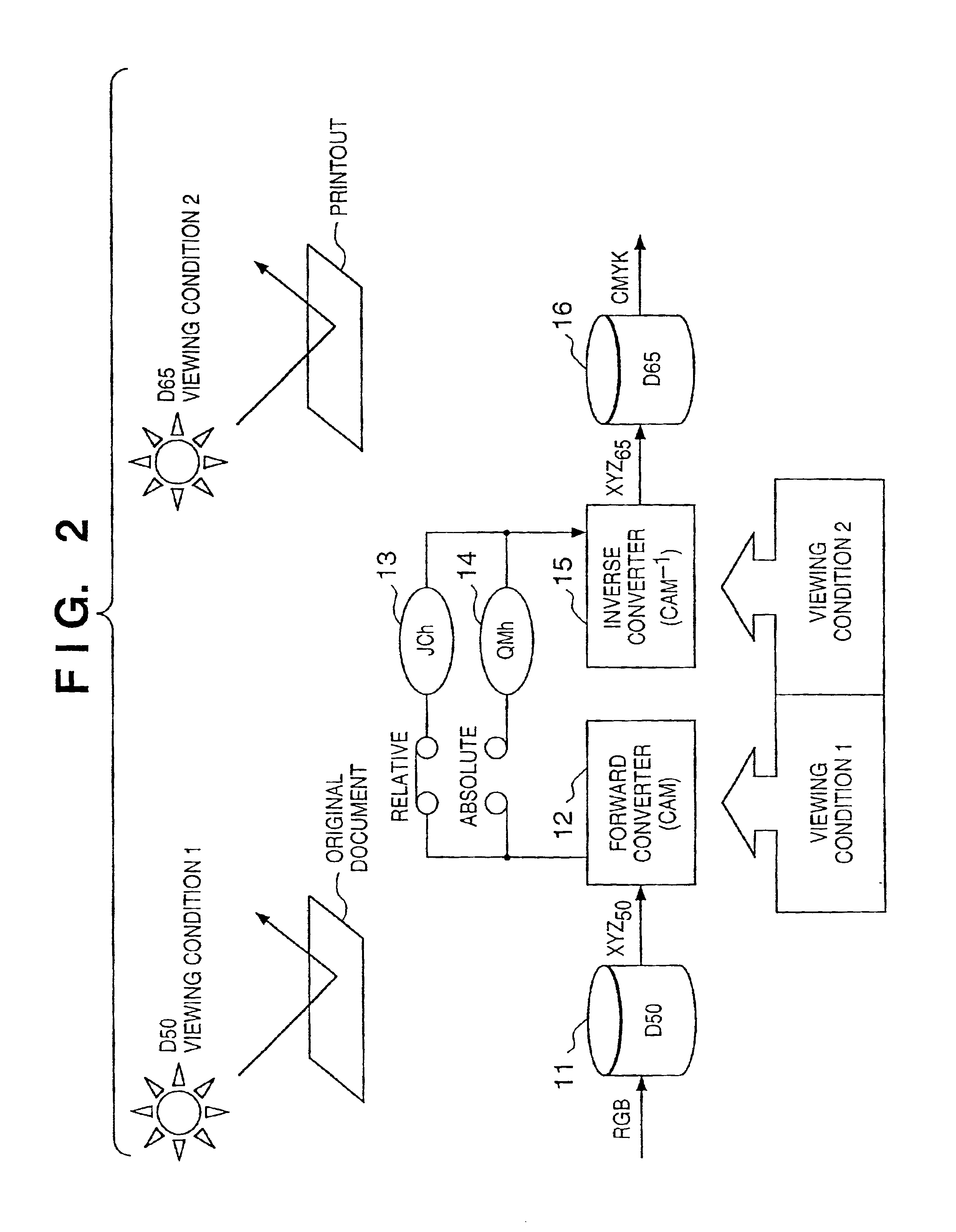
Image processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050078122A1Easy to set upColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionLab color spaceGamut
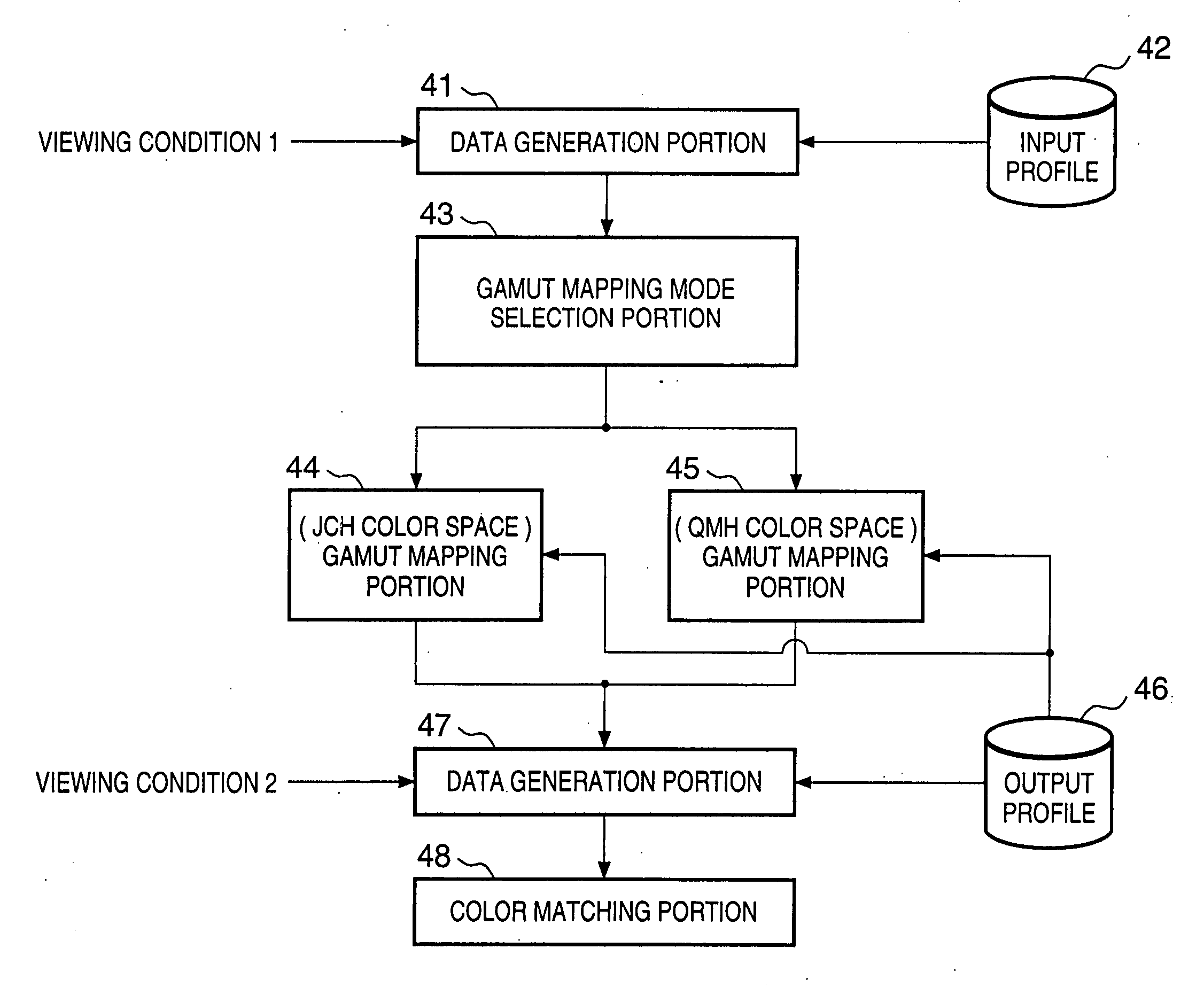
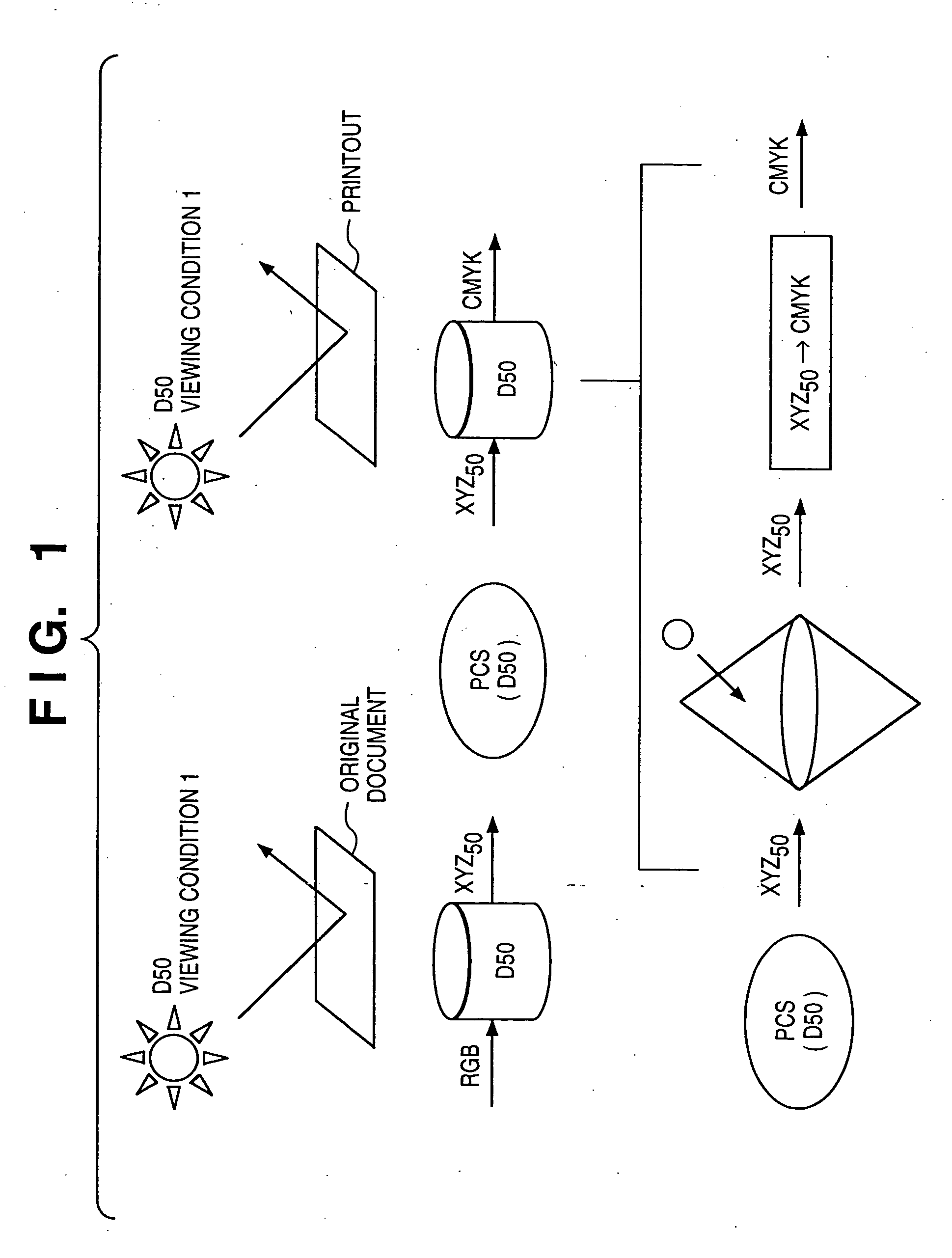
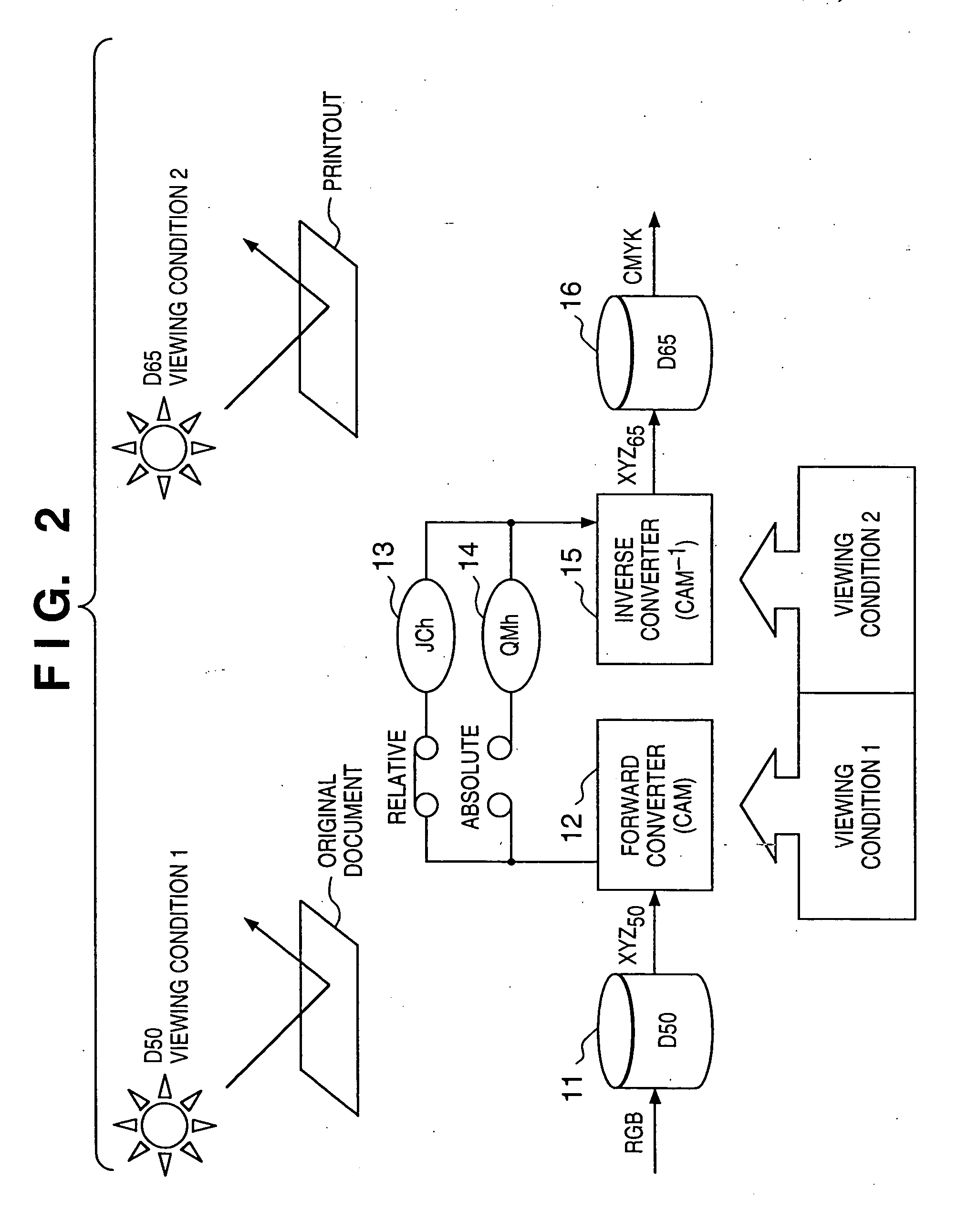
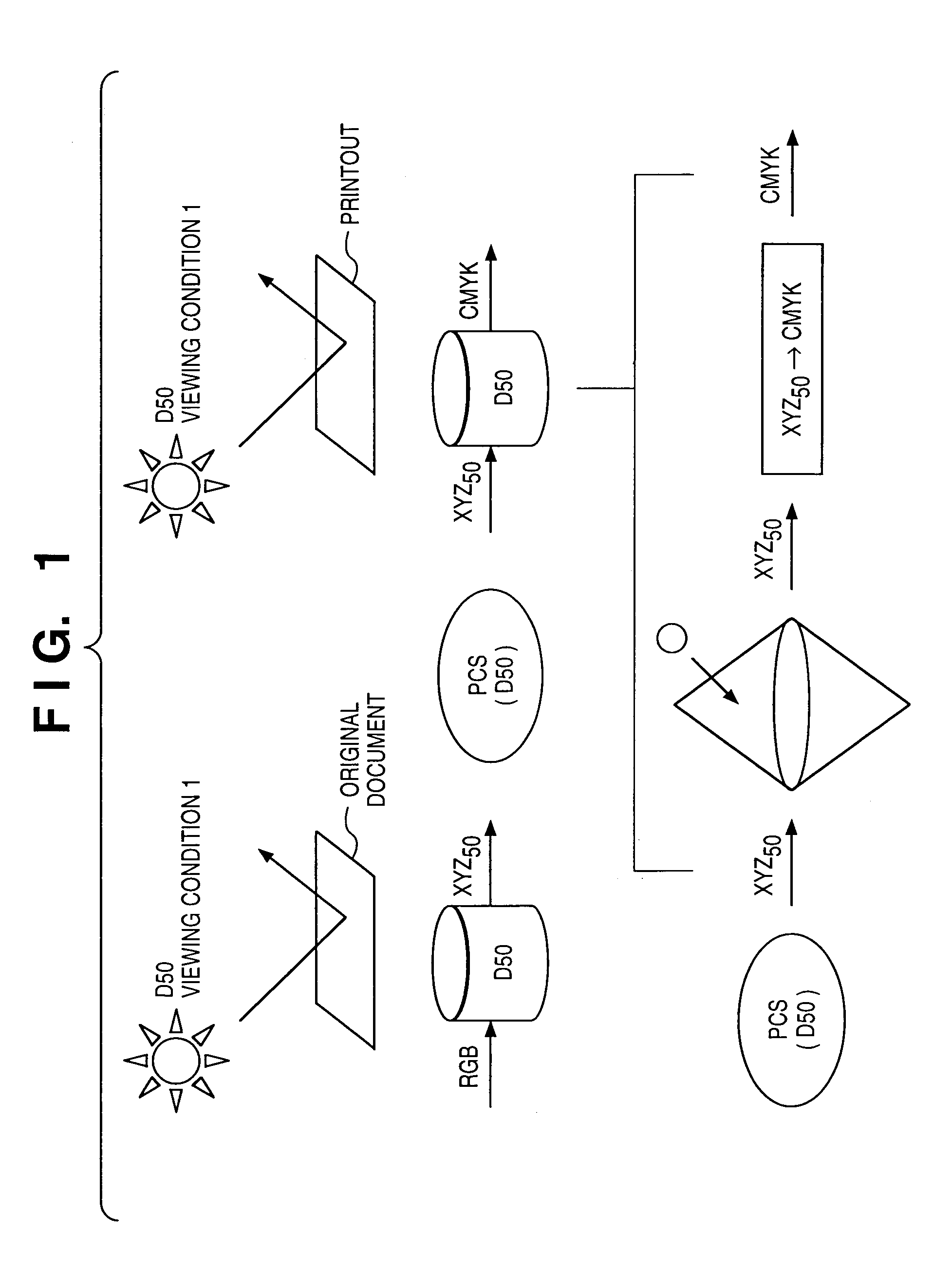
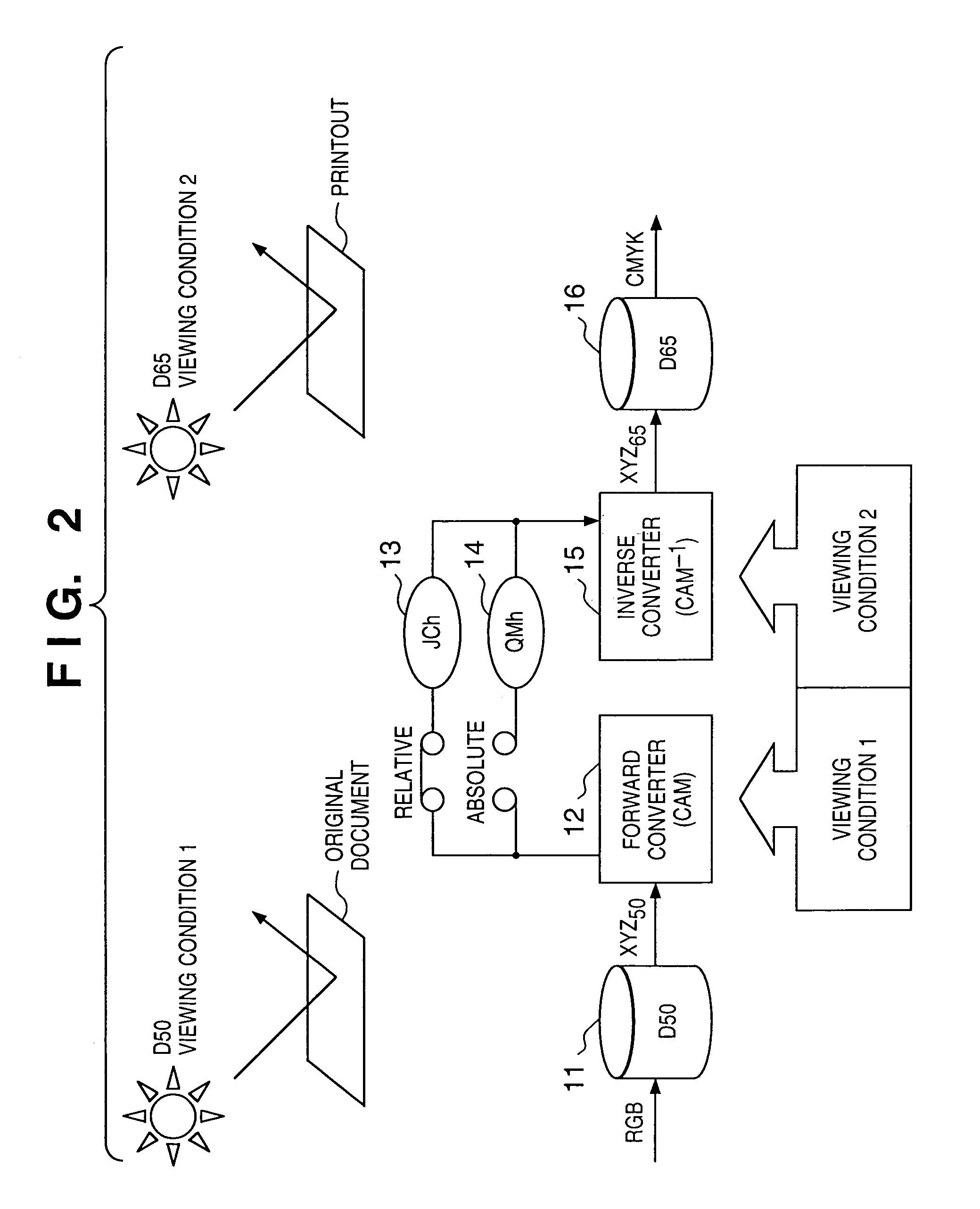
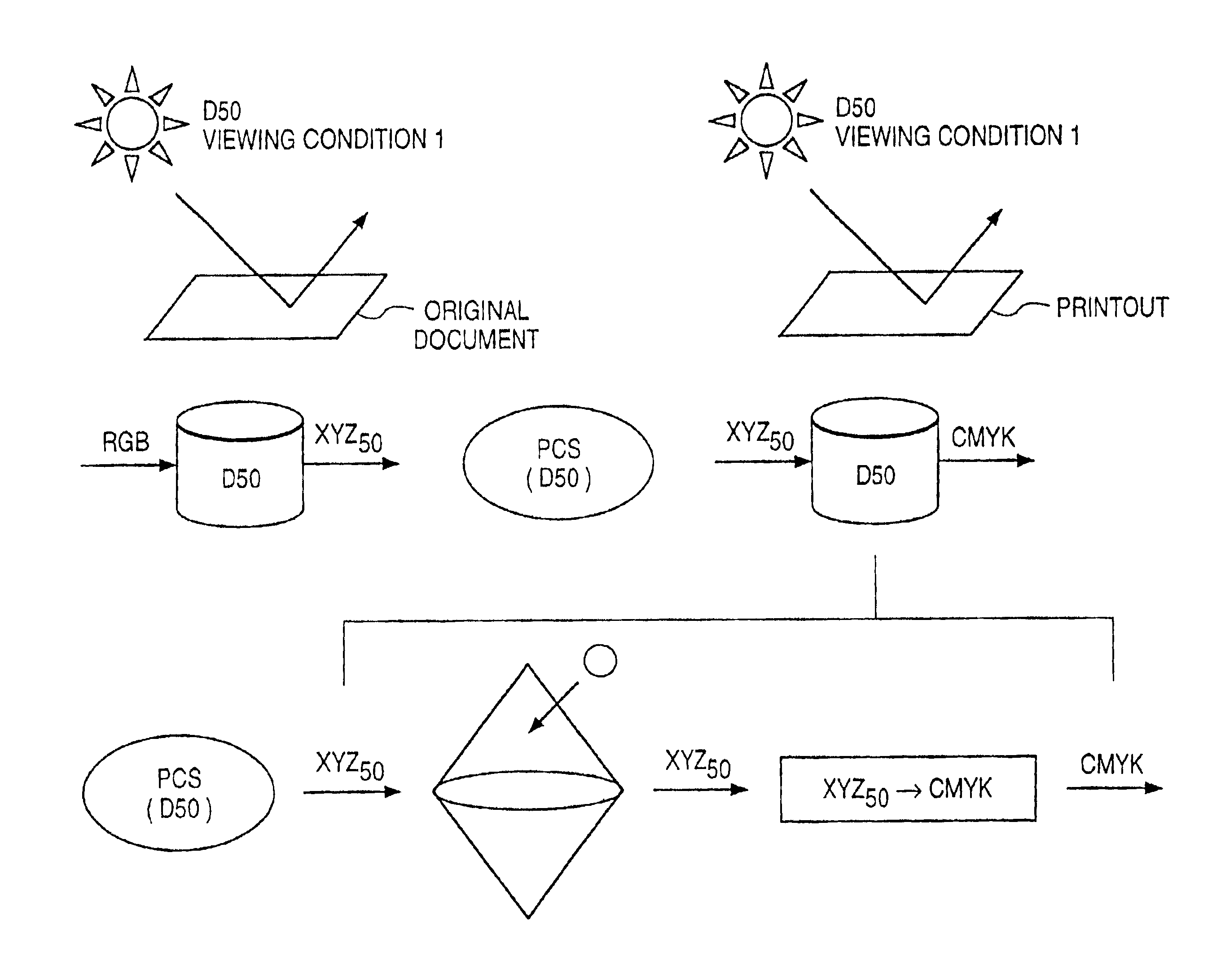
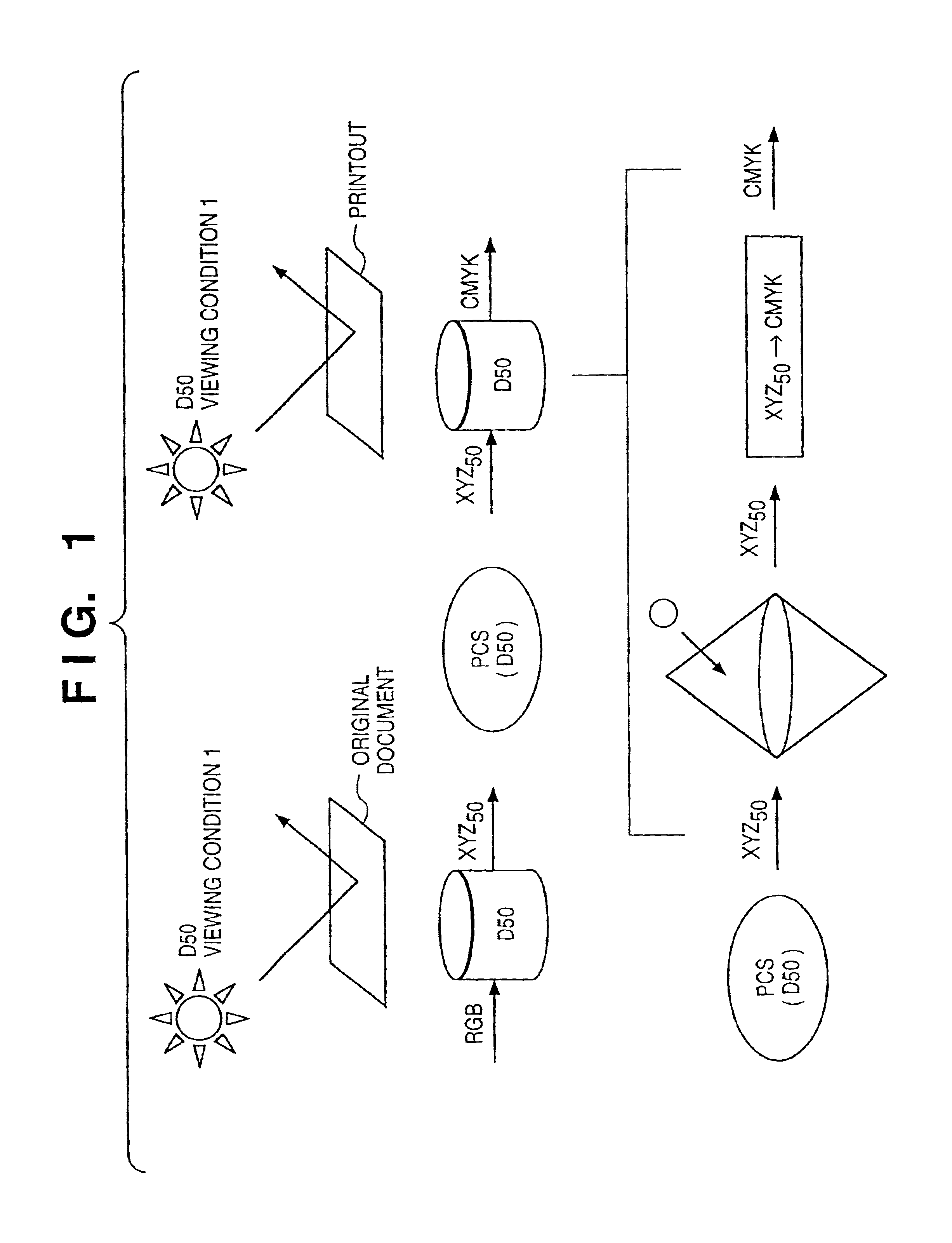
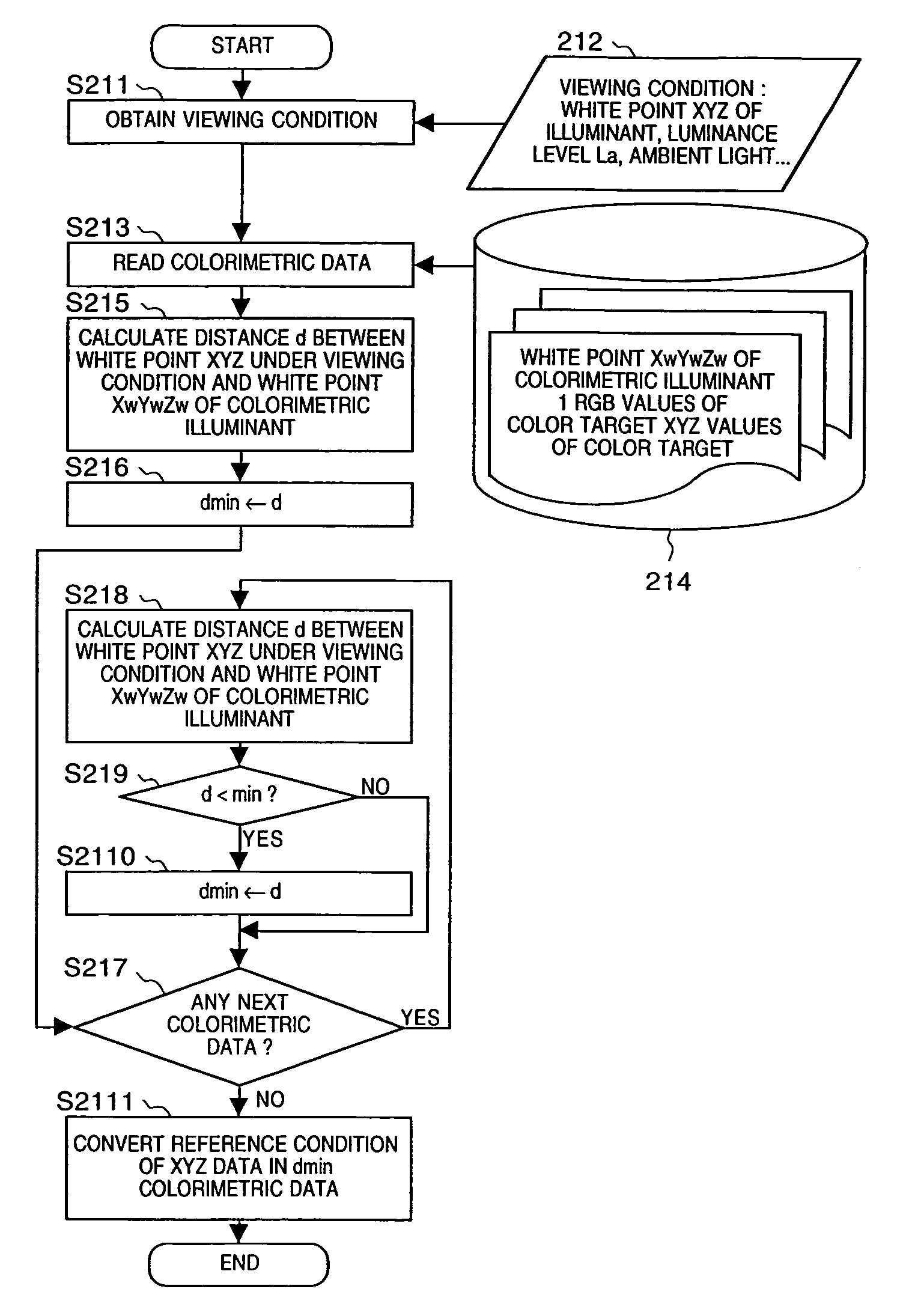
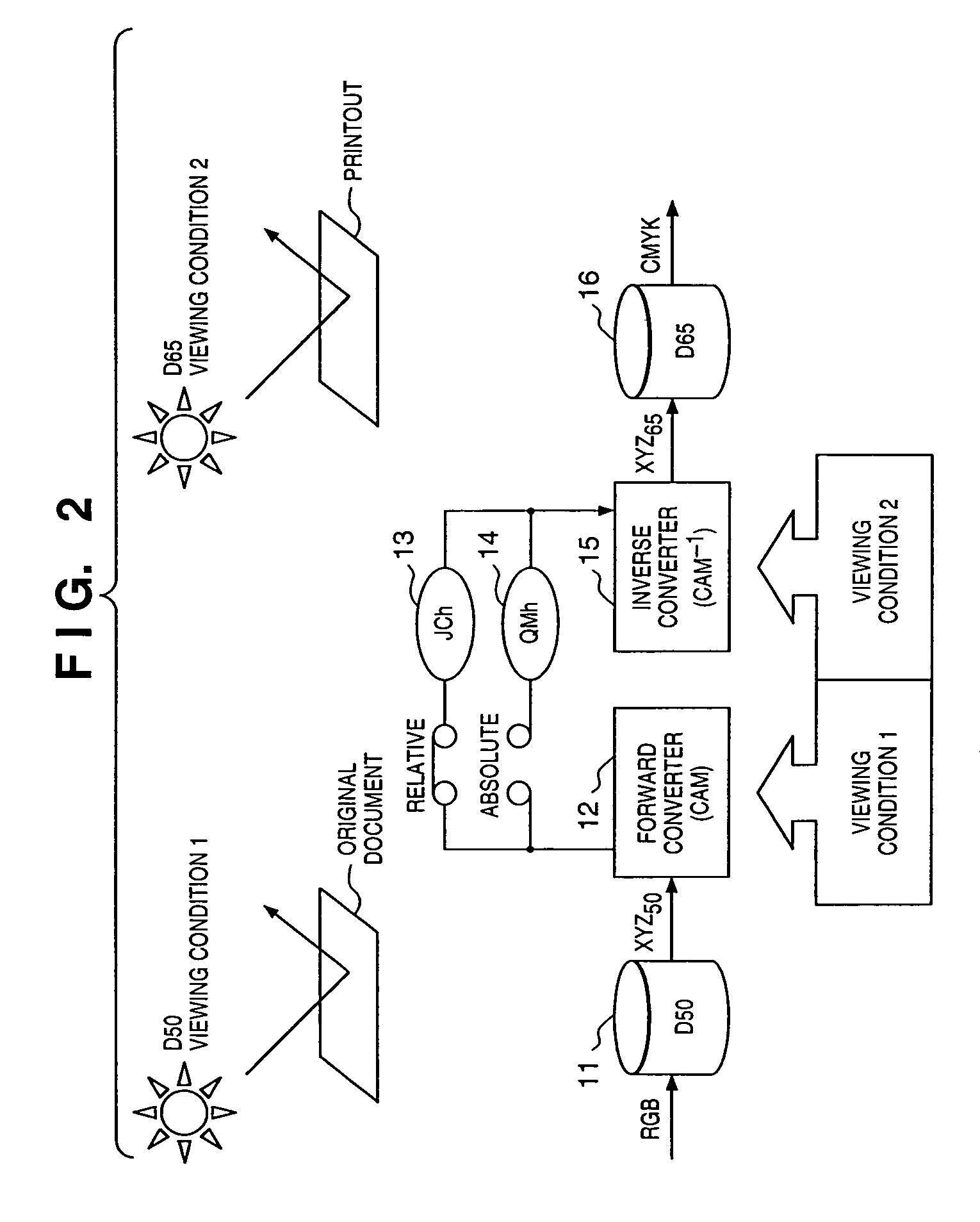
If gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by one Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
Electro-luminescent display with adjustable white point
ActiveUS20100289727A1Improve power efficiencyExtended service lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsGamutDisplay device
The present invention provides an EL display adapted to receive a three-color input image signal, including three gamut-defining EL emitters for emitting red, green, and blue colored light and two additional EL emitters for emitting at least two additional colors of light, the chromaticity coordinates of the at least two additional colors of light lying inside the gamut and near the Plankian Locus; a structure for providing a display white point; and a controller responsive, to the provided display white point and the input image signal for providing first separate drive signals for the three gamut-defining EL emitters and second separate drive signals for the two additional EL emitters, wherein the respective luminance values corresponding to the second separate drive signals are each a function of the input image signal and the distances between the display white point and the pseudo-blackbody points of the two additional colors.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Image processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7027067B1Easy to set upTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionLab color space
If gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by one Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
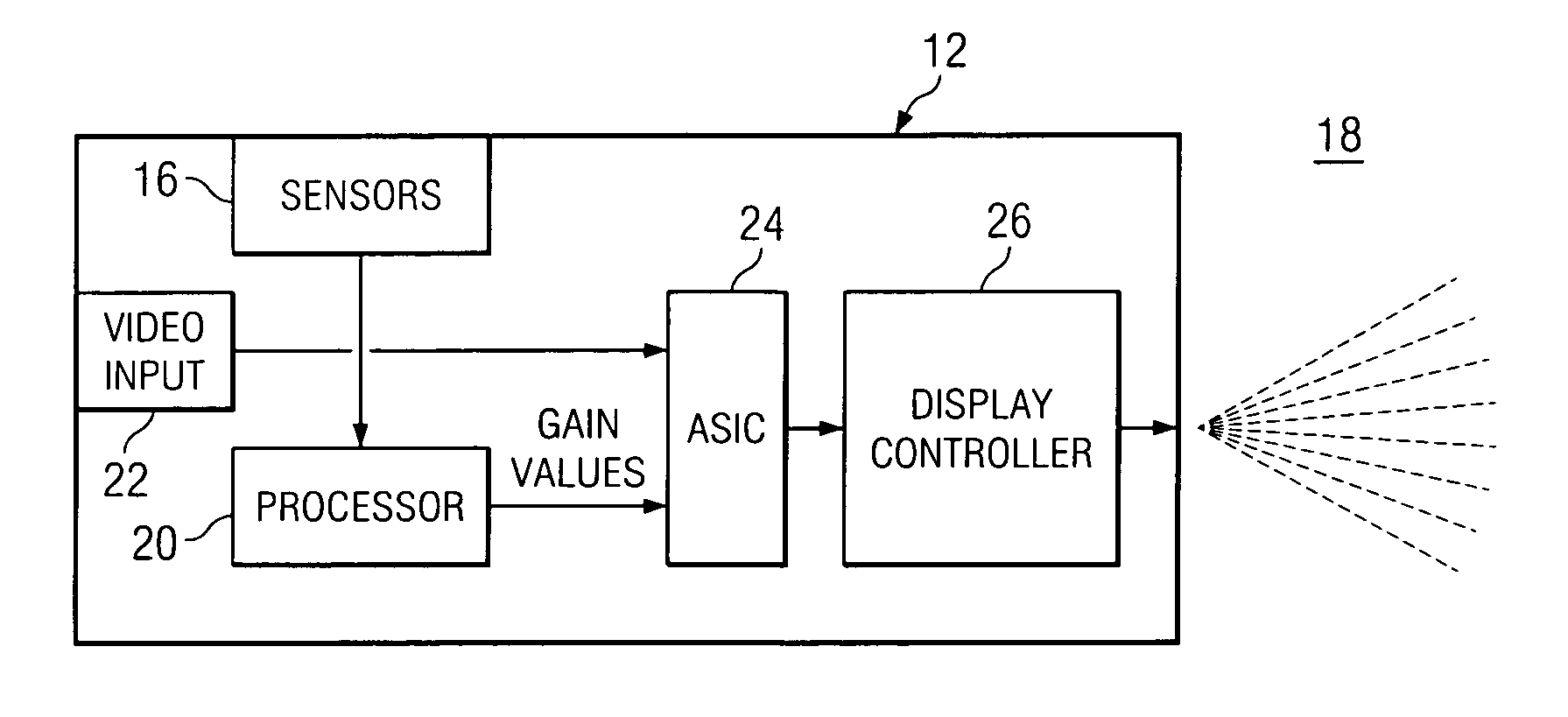
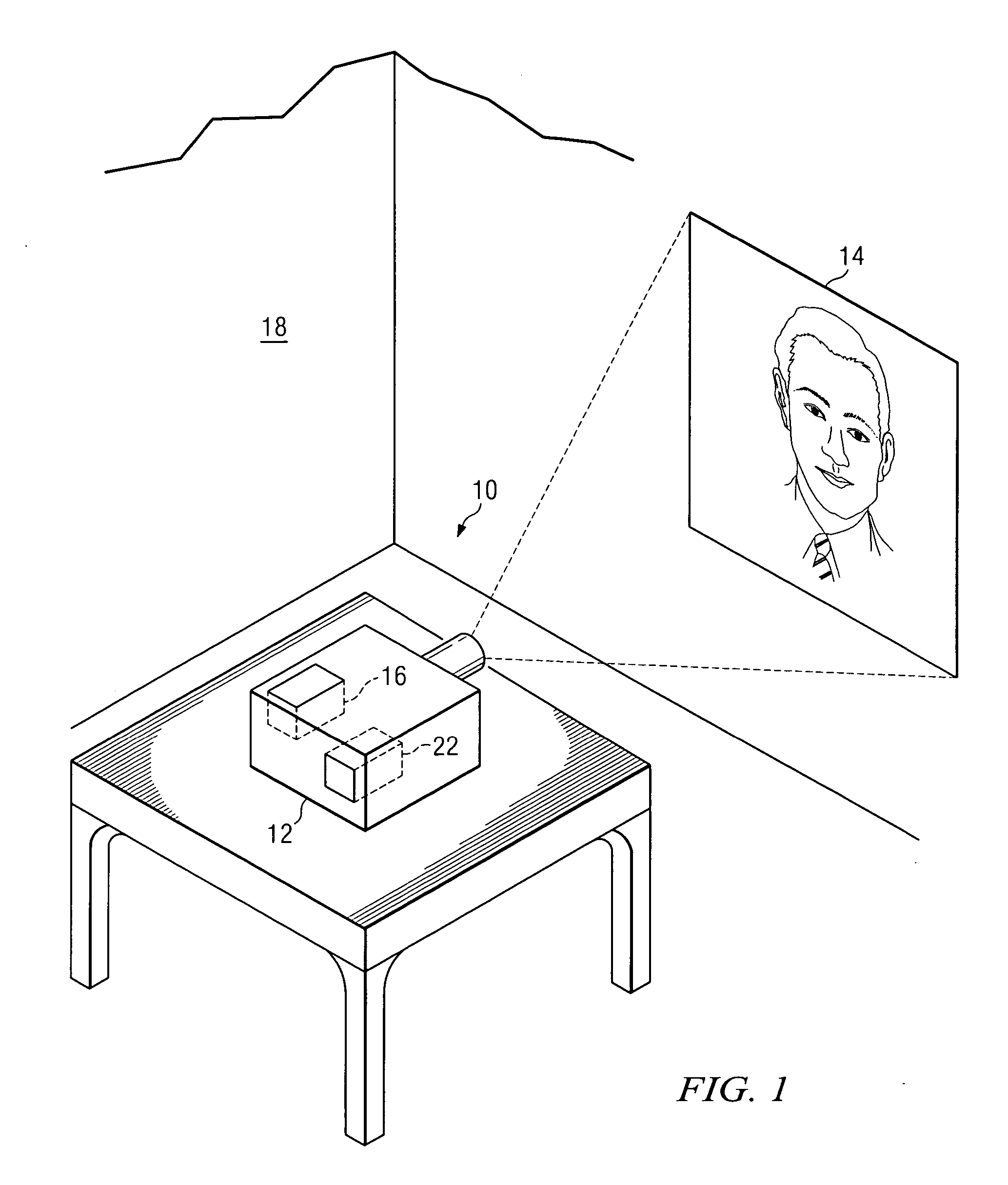
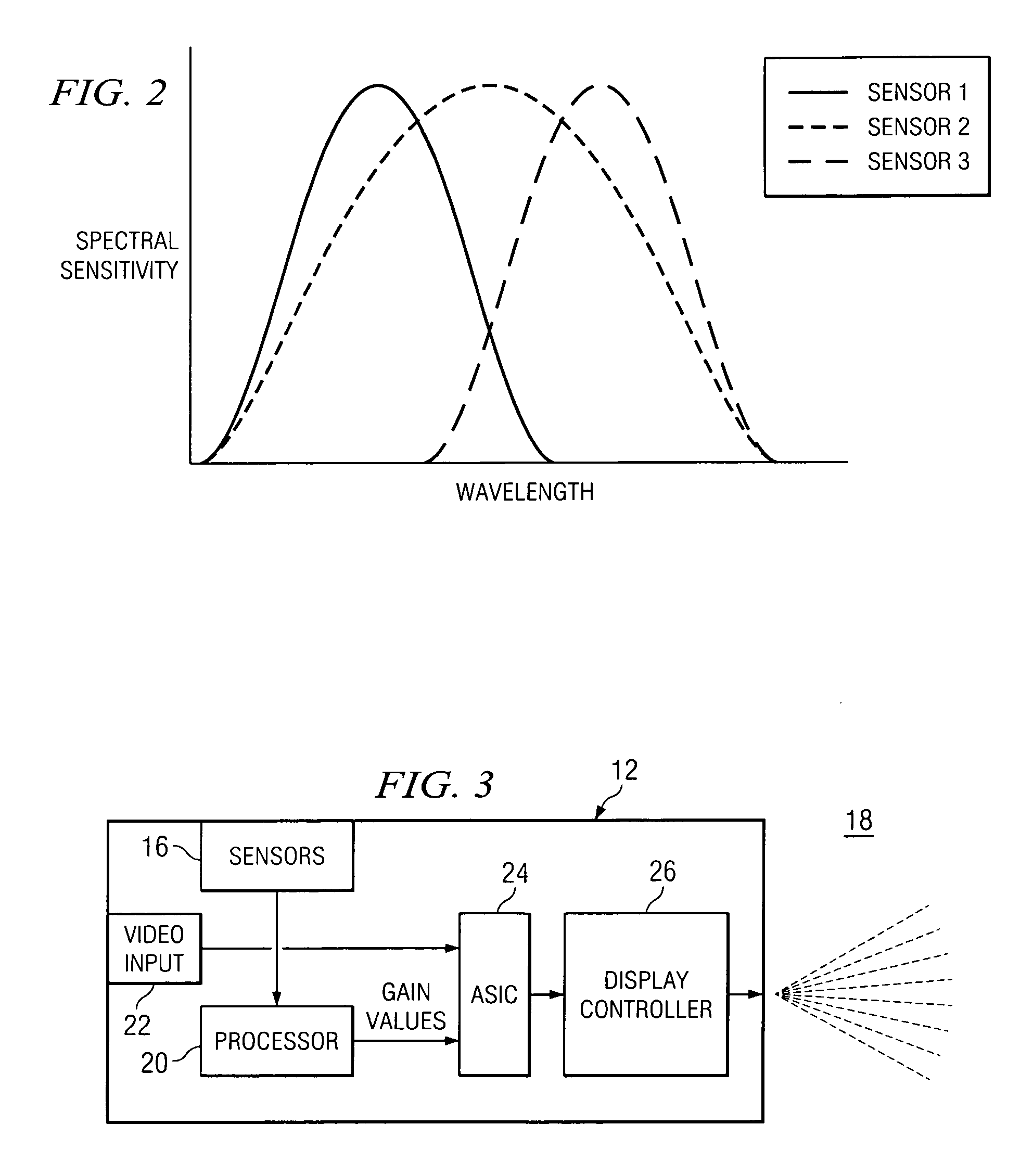
Apparatus and method for automatically adjusting white point during video display
InactiveUS20070081102A1Enhance displayed imageTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Display device
The present disclosure relates to systems and processes for automatically adjusting the white point of displayed images to account for changes in ambient light. In one embodiment, a display system includes a display device having sensors for recording the red (R), green (G) and blue (B) values for ambient light and measuring the intensity of such light. The sensors feed these values into a processor, which calculates R, G, B gain values to be applied to the video input R, G, B values. In this manner, the display device can account for changes in ambient light to adjust the perceived white point accordingly. Related methods for automatically adjusting the white point of a perceived image are also described.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
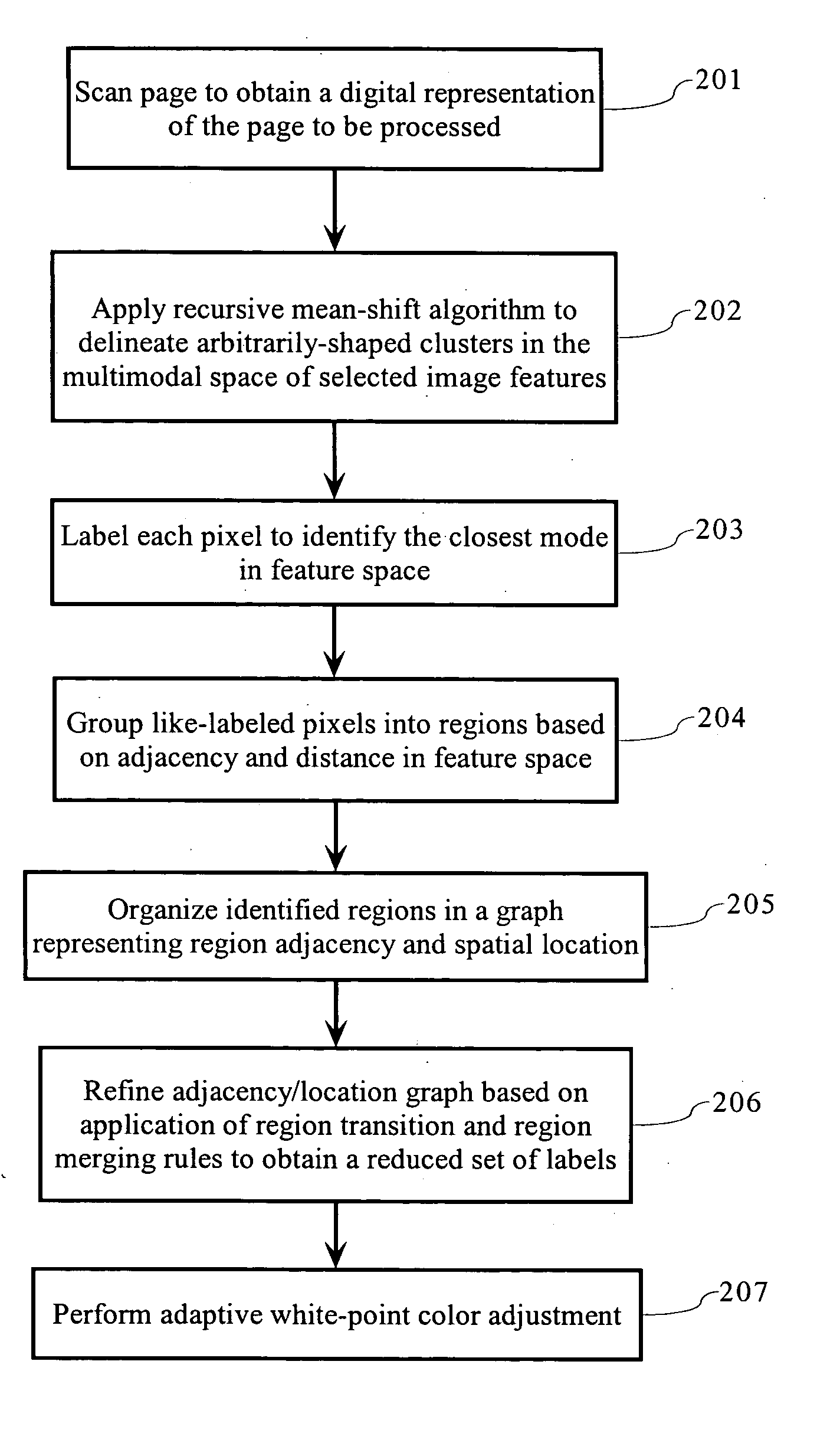
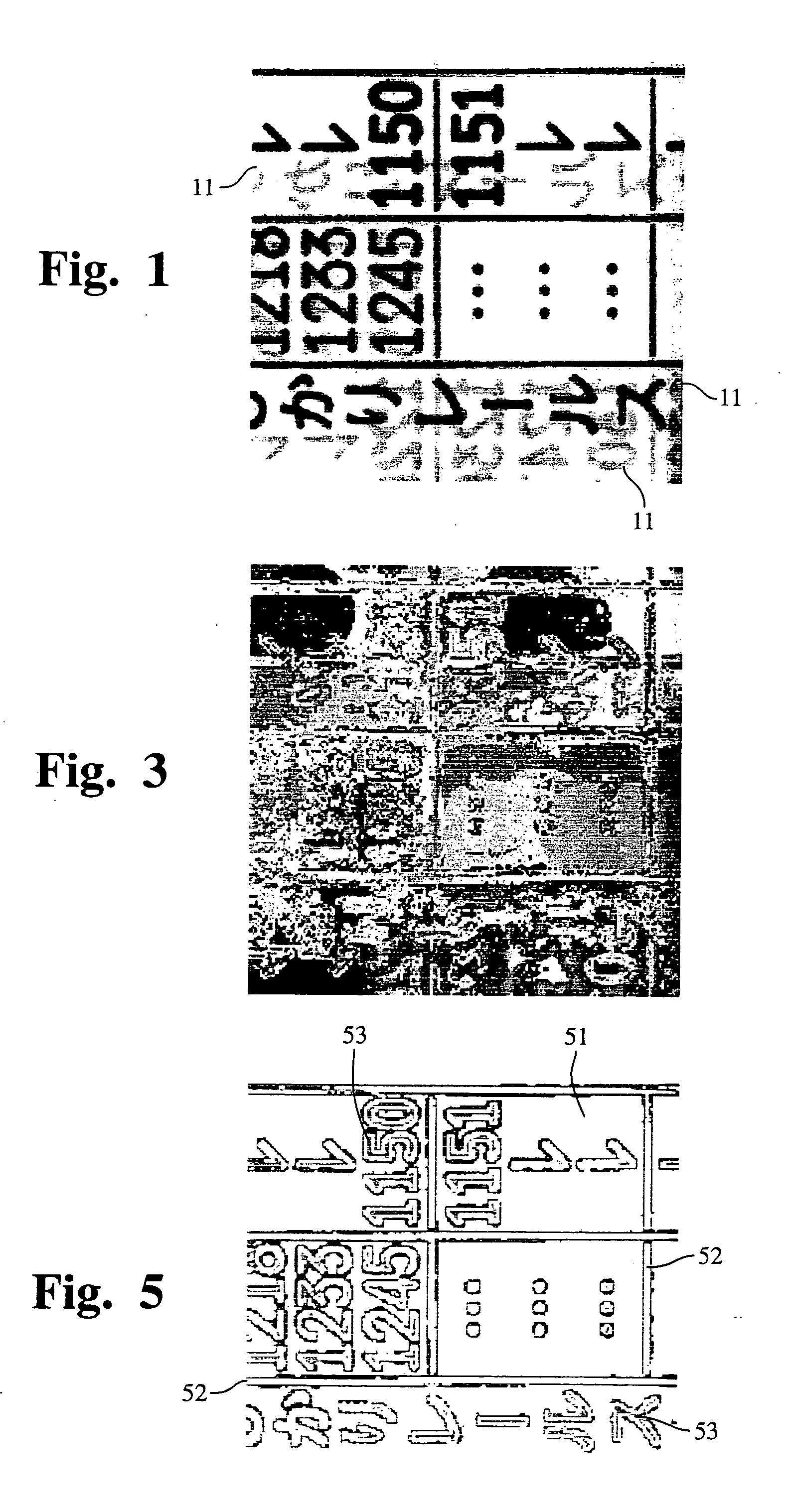
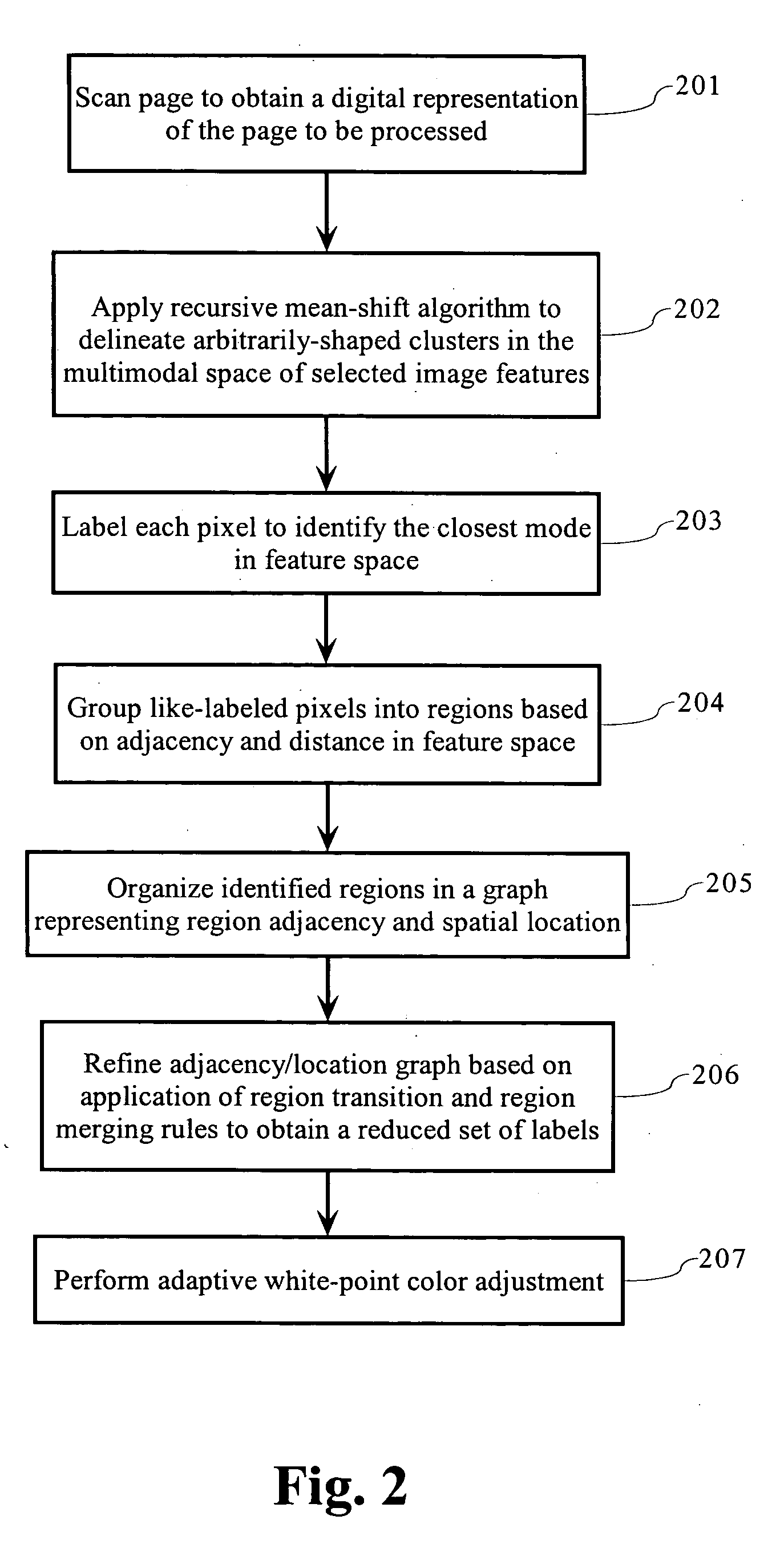
Page background estimation using color, texture and edge features
An algorithm for estimating which pixels belong to the background of a scanned page. The algorithm is particularly designed to handle situations in which the page background varies in color / intensity, as is case when bleed-through artifacts from the reverse side of the page appear in the background. In determining background regions, including properly classifying bleed-through artifacts regions as such, the algorithm uses multiple local and global criteria for making the determination. In addition to being able to find large connected pieces of background, the algorithm is also able to find isolated islands of background by analyzing transition characteristics of neighboring regions. Regions are identified on the basis of similar local features and also by the nature of transitions between foreground regions that do not directly share a boundary. An adaptive white-point adjustment technique based on identified background regions improves the perceived quality of the printed output.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Image processing apparatus and method, and profile generating method
InactiveUS6859551B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersLab color spaceGamut
If gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by one Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
OLED Display with Reduced Power Consumption
ActiveUS20120212515A1High display white point luminanceMaintaining color saturationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpectral modifiersGamutComputer graphics (images)
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method and apparatus for improved color correction
InactiveUS6844881B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionColor correction
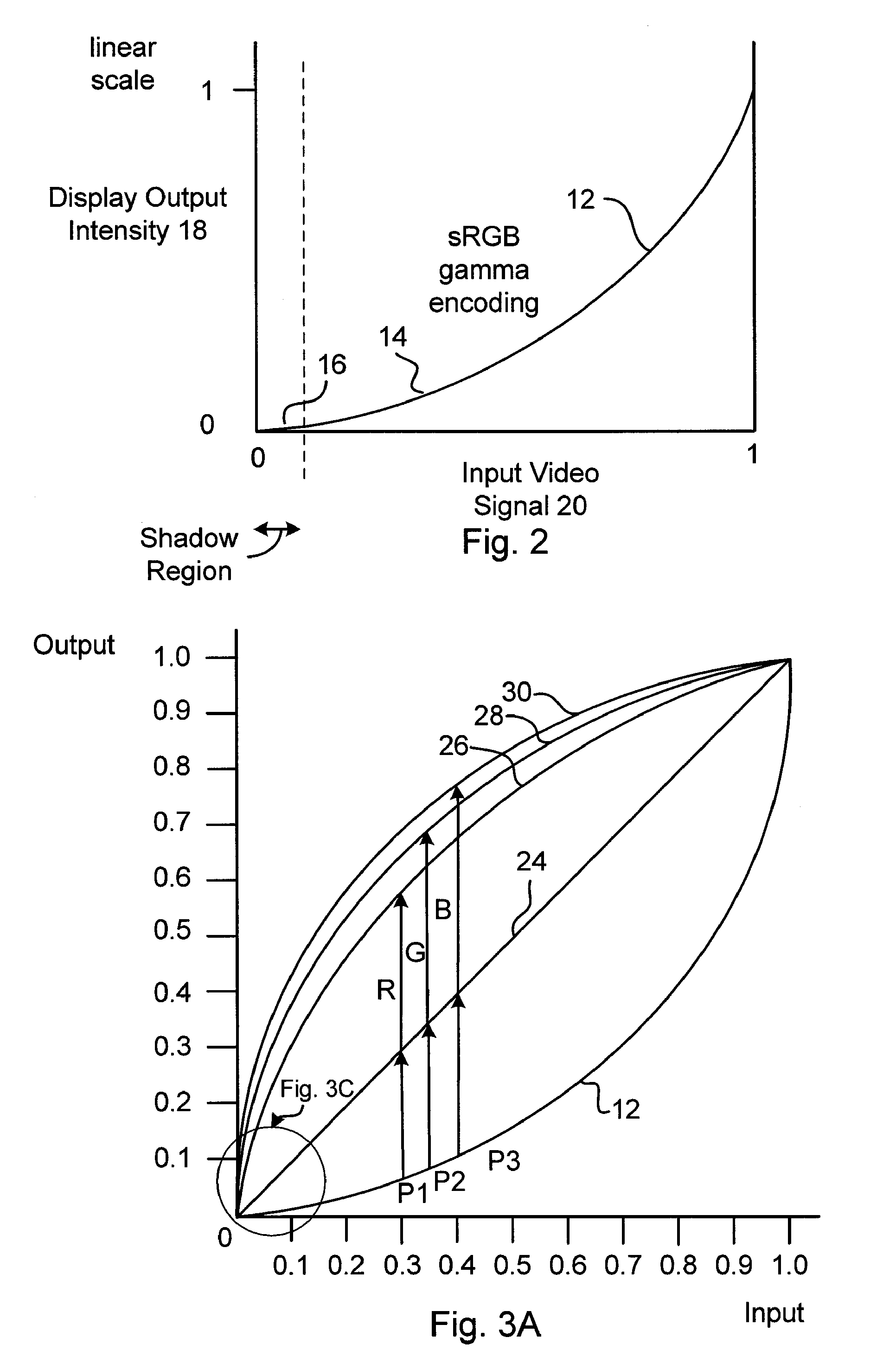
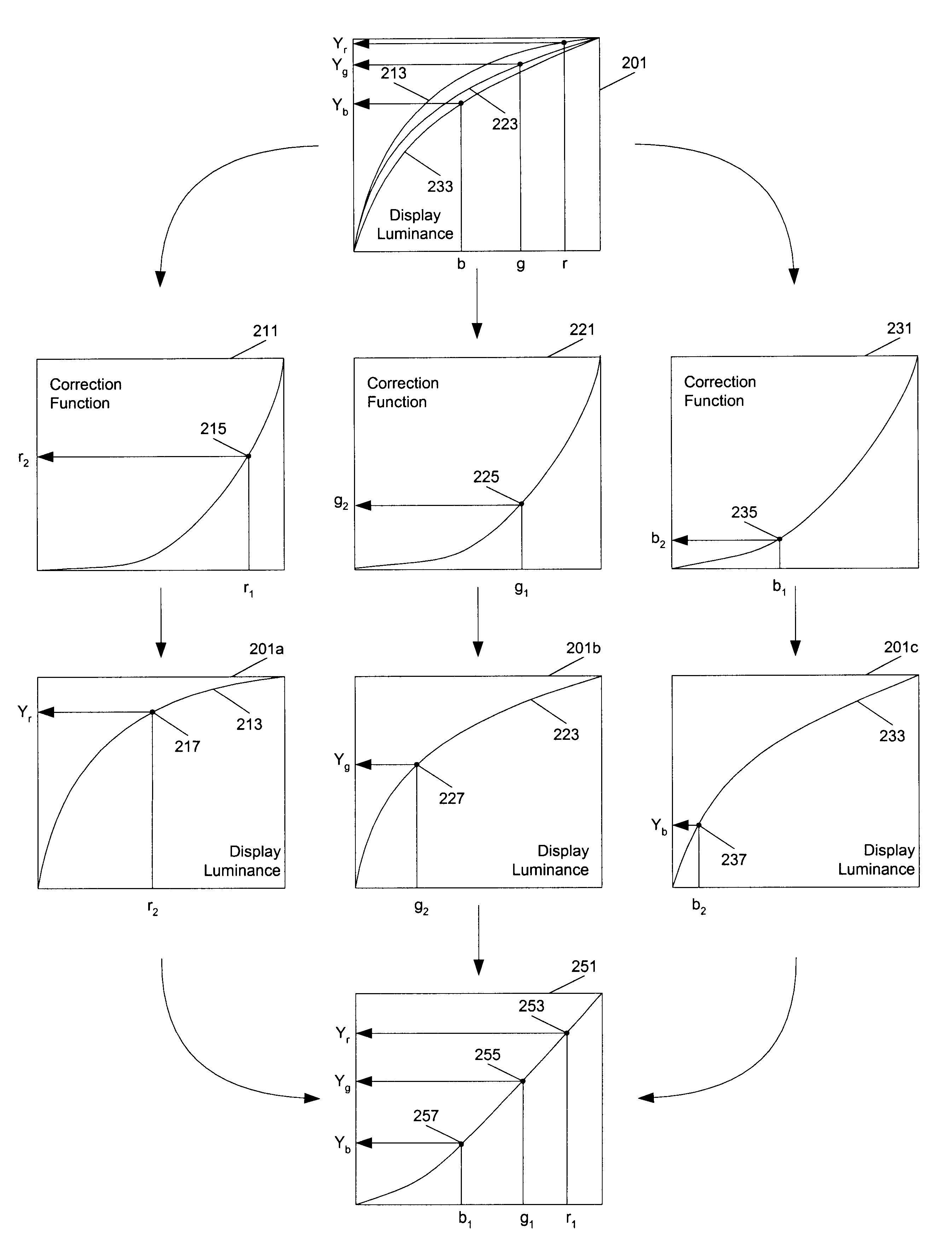
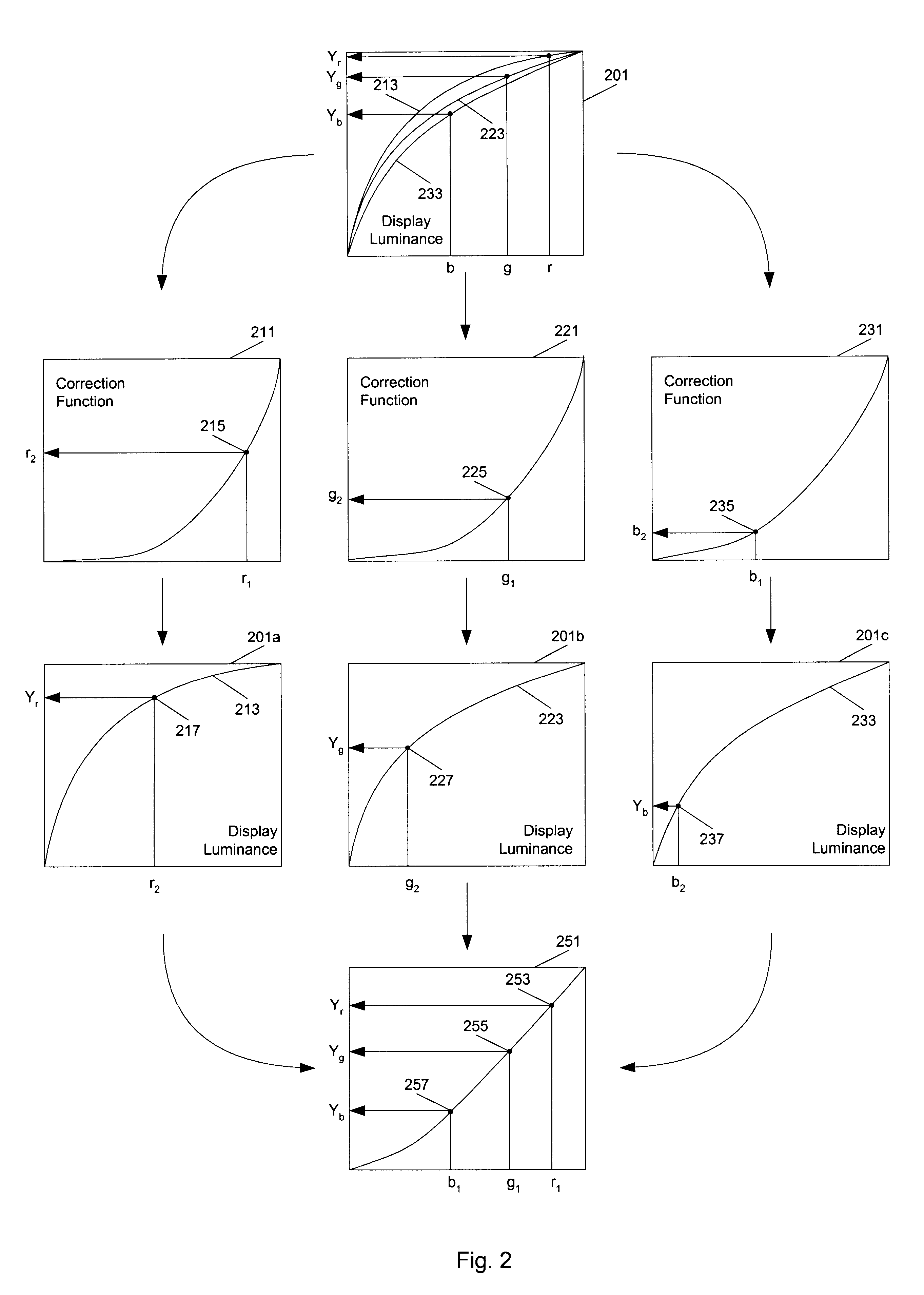
Methods and apparatuses for performing gamma corrections to maintain a plurality of colors substantially consistent with a color point. In one aspect of the present invention, a method to generate correction functions for performing color correction for a device for signals of different color components in a color space includes: generating a first correction function for a first color component in the color space; and generating second correction functions for second color components in the color space by reducing first color differences between a target white point and white points of a plurality of grays corrected by the first and second correction functions. The second color components are the color components in the color space other than the first color component. The first color differences are minimized relative to a chromaticity diagram.
Owner:APPLE INC
Device-independent and medium-independent color matching between an input device and an output device
InactiveUS6181445B1Improve accuracyImage data processing detailsColour-separation/tonal-correctionColor imageColor mapping
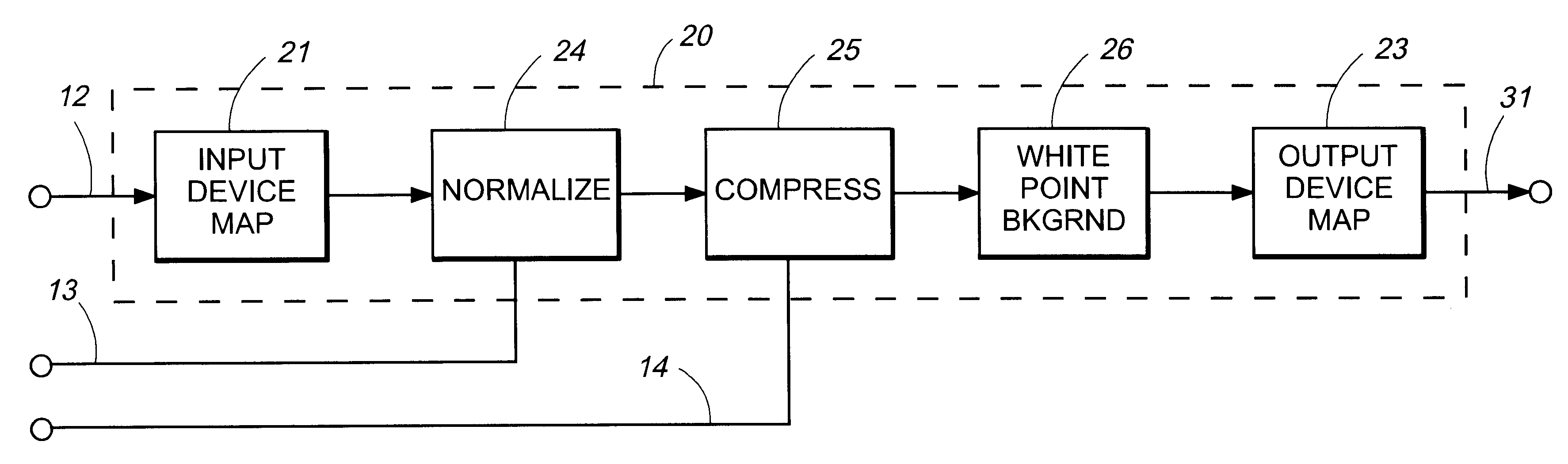
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for improving color matching between original color images and reproductions thereof. In the present invention, color space transformations are derived for a color image reproduction system comprising an input device and an output device by obtaining a first transformation for the input device that maps from colors within an input-device-dependent color space to colors within a first device-independent color space, and obtaining a normalization transformation that normalizes information obtained from the first transformation with respect to a white point in a second device-independent color space.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Single-frame image detection apparatus for vehicle queue length at road junction and its working method
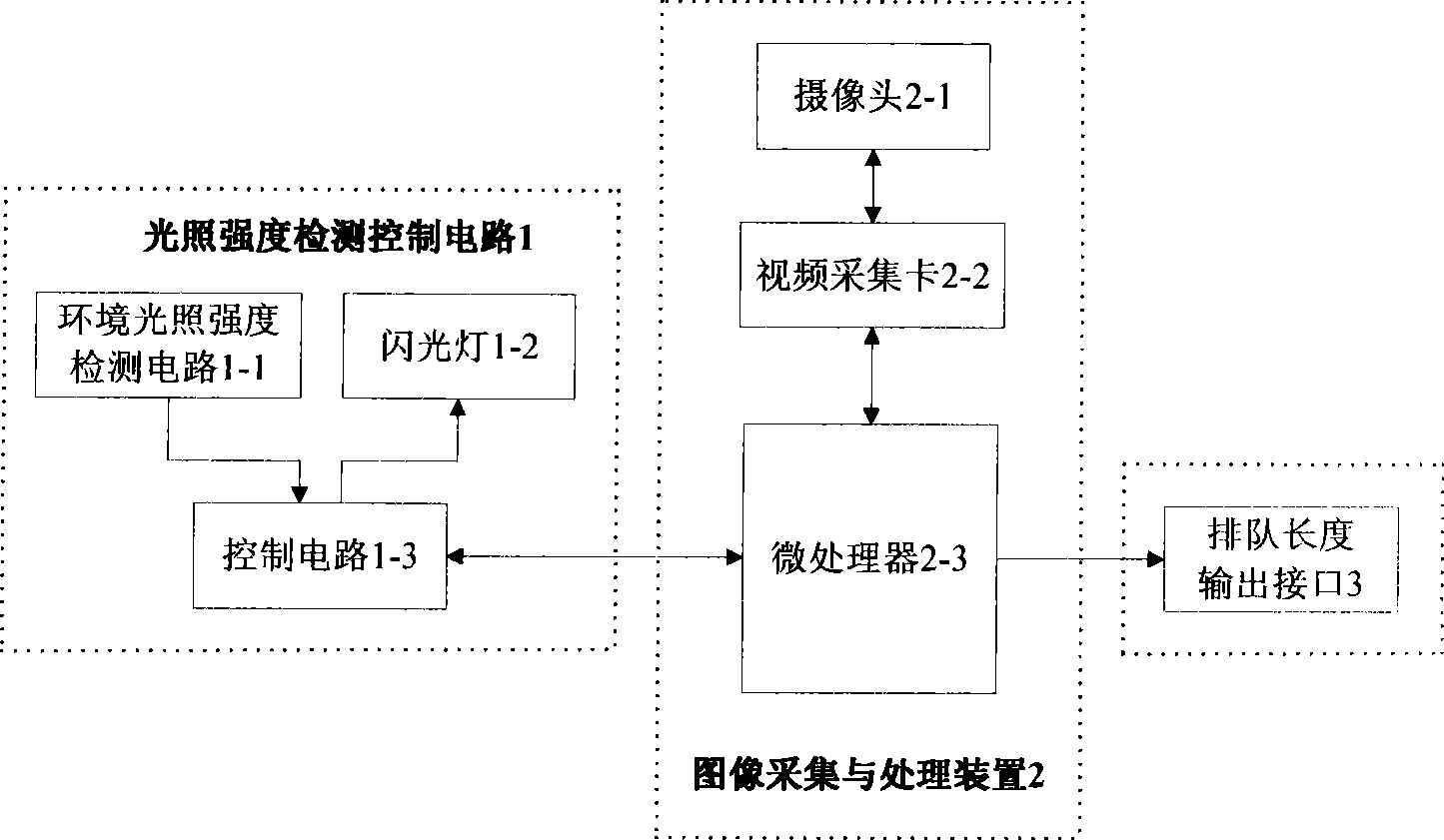
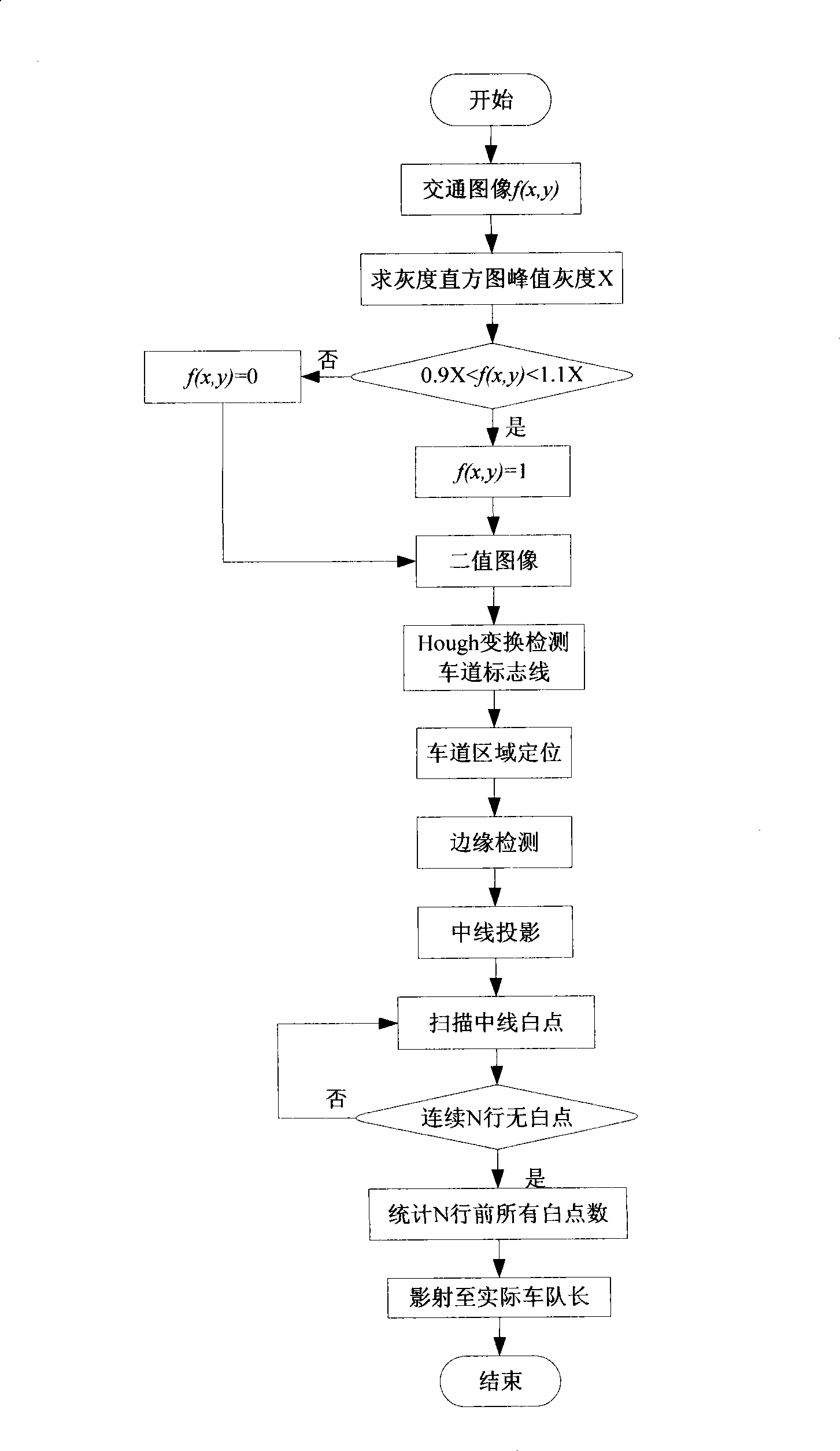
InactiveCN101469985AReduce computationReal-timeDetection of traffic movementPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryImage detectionWorking set
The invention relates to a single frame picture test device for automobile queue length at crossroad and a working method thereof. The single frame picture test device comprises an illumination intensity detection control circuit, an image collection and processing device, and a queue length output interface. The working method comprises: detecting environment illumination intensity, and automatically using a flash lamp to collect a single frame traffic image under low illumination intensity; processing binarization on the traffic image via double threshold value method; detecting lane edges via Hough transformation to define a lane region; detecting boundary to obtain the boundary image of automobiles; projecting the edge information of automobiles to the center line of the lane region; scanning the white points on the center line to determine queue tail; calculating the queue length in the image, calculating actual automobile queue length, and outputting the actual automobile queue length via an output interface. The invention overcomes the defects of video flow detection which is affected by weather, illumination, camera vibration and the like, having the advantages of simple calculation, high operation speed and high reliability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU +1
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6999617B1High color reproductionTexturing/coloringPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesLab color spaceGamut
If one gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by the Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
Automatic color balance
ActiveUS7057768B2Automatically correcting color balanceTrue colorDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsDark spotBlack point
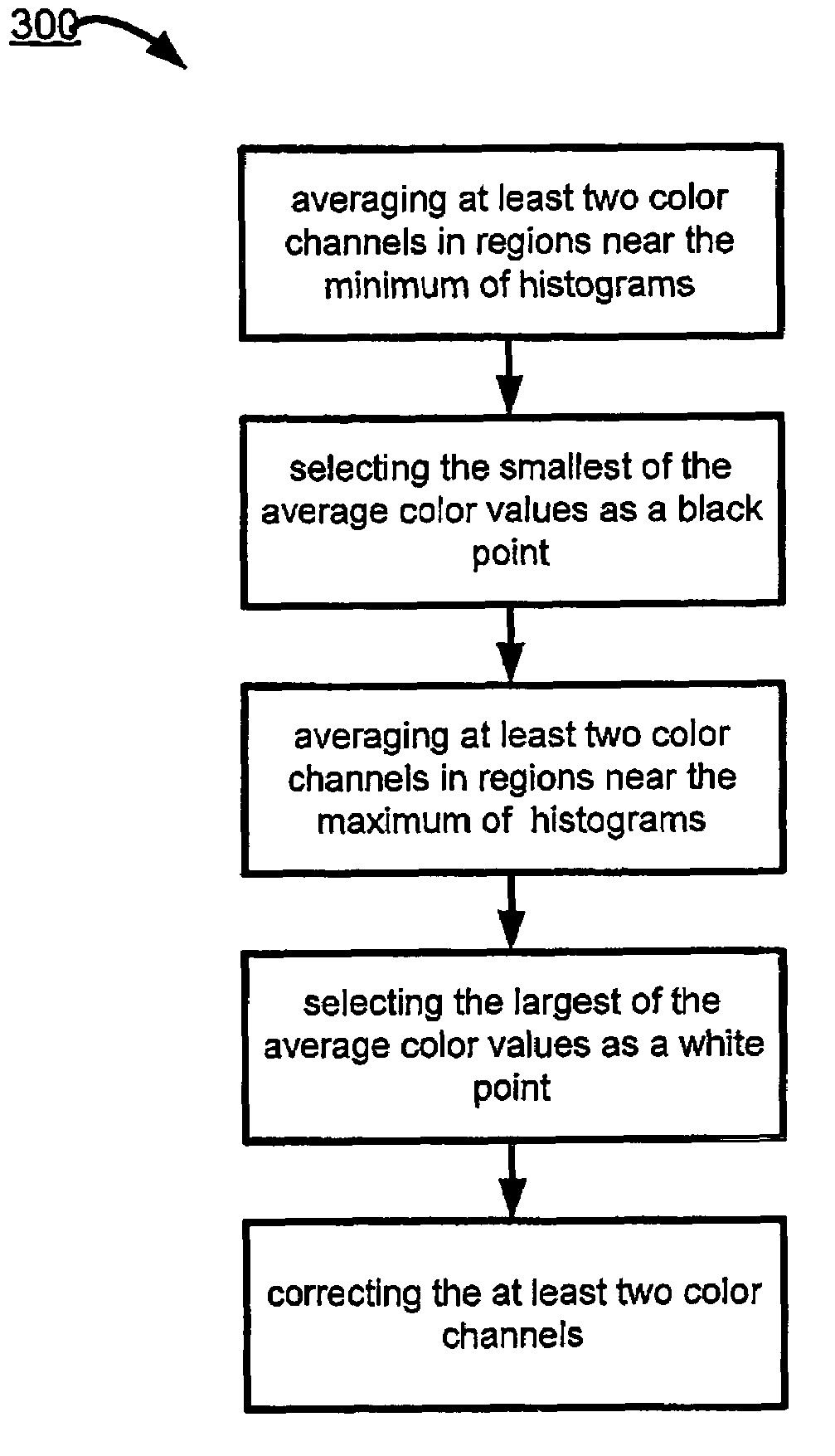
A method corrects a color image by avenging at least two color channels in regions near the minimum of histograms of the at least two color channels; selecting the smallest of the avenge color values as a black point; averaging at least two color channels in regions near the maximum of the histograms of the at least two color channels and selecting the largest of the avenge color values as the white point; and correcting the at least two color channels by adjusting the smallest and the largest color averages to respectively match the valves of the black point and the white point to form corrected image data. A preferred method limits the adjustment to a predetermined amount of clipping of the at least two color channels.
Owner:COREL CORP +1
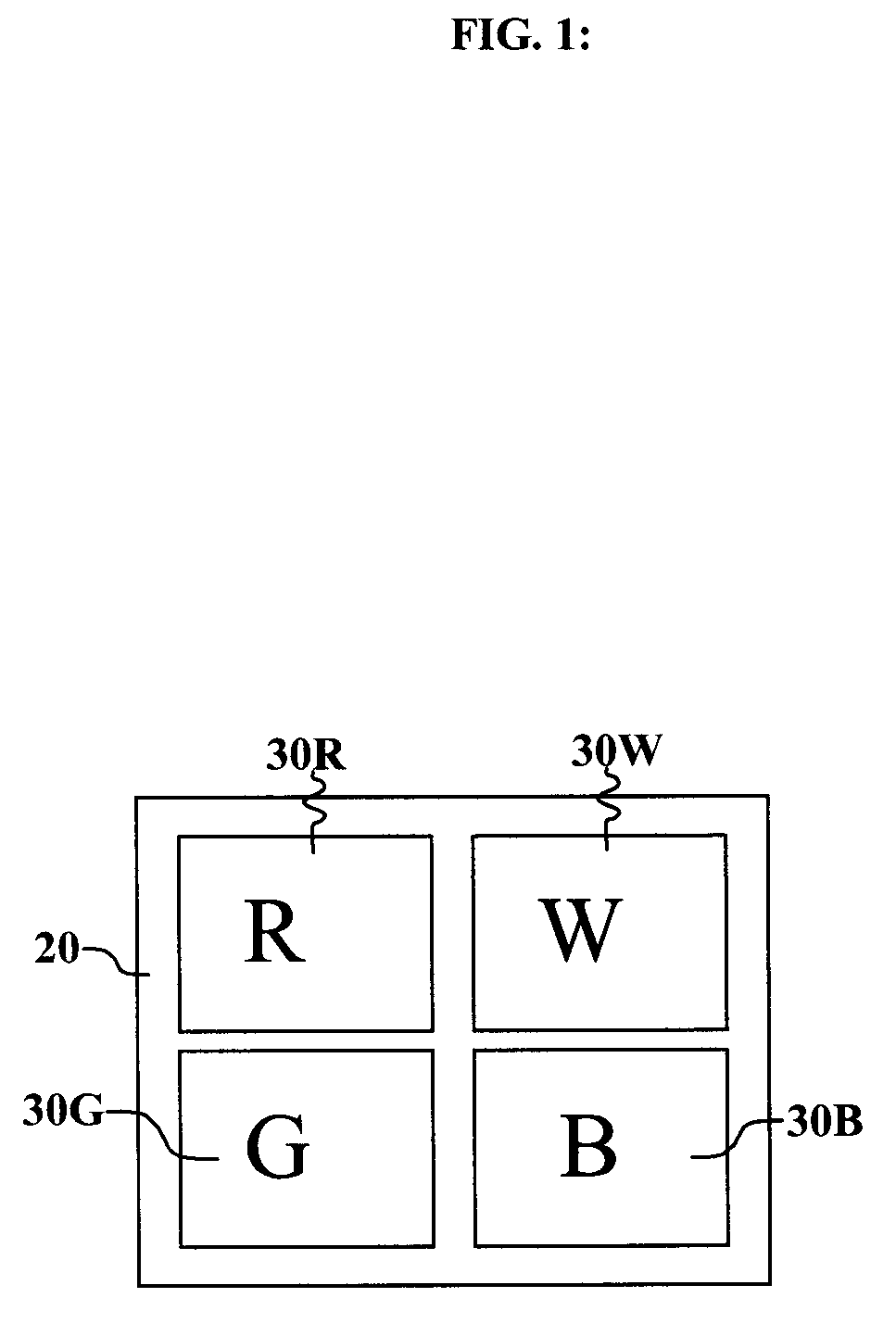
Pixel structure with optimized subpixel sizes for emissive displays
InactiveUS7176861B2Extend battery lifeStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceComputer science
A method of designing a fixed format emissive display is described using a computing device having a processor and a memory, the display comprising an array of emissive pixel elements, each pixel element comprising at least two sub-pixel elements made of different materials. The method comprises selecting areas of the at least two sub-pixel elements so that each pixel element displays white at a predetermined white point within a certain tolerance over a lifetime of the pixel, and such that the lifetimes of the sub-pixel areas are within a predetermined tolerance of each other.A display having sub-pixel elements optimized so that each pixel element displays white at a predetermined white point within a certain tolerance over a lifetime of the pixel, and such that the lifetimes of the sub-pixel areas are within a predetermined tolerance of each other is also described.
Owner:BARCO NV
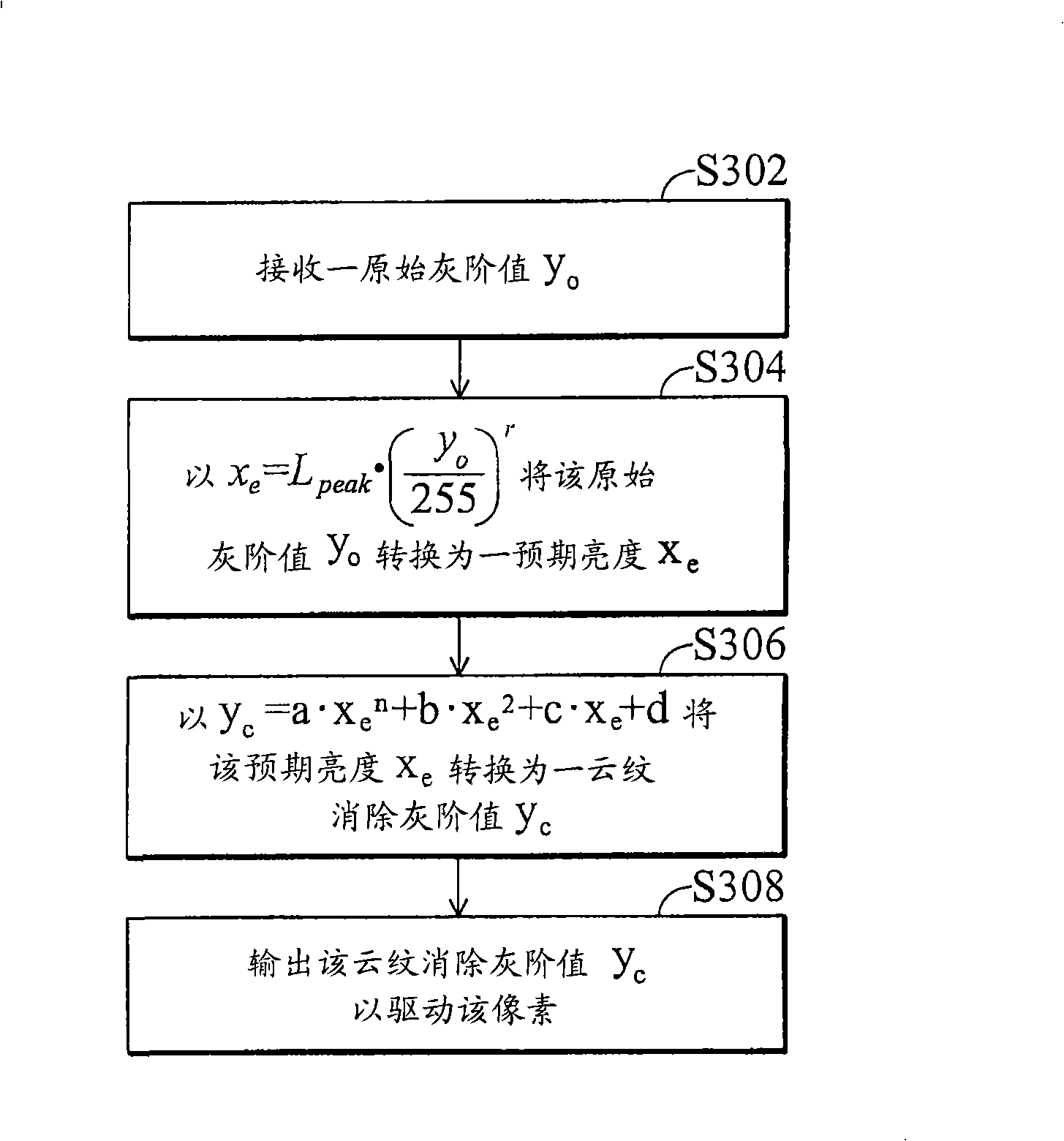
Image display system and its moire defect elimination method
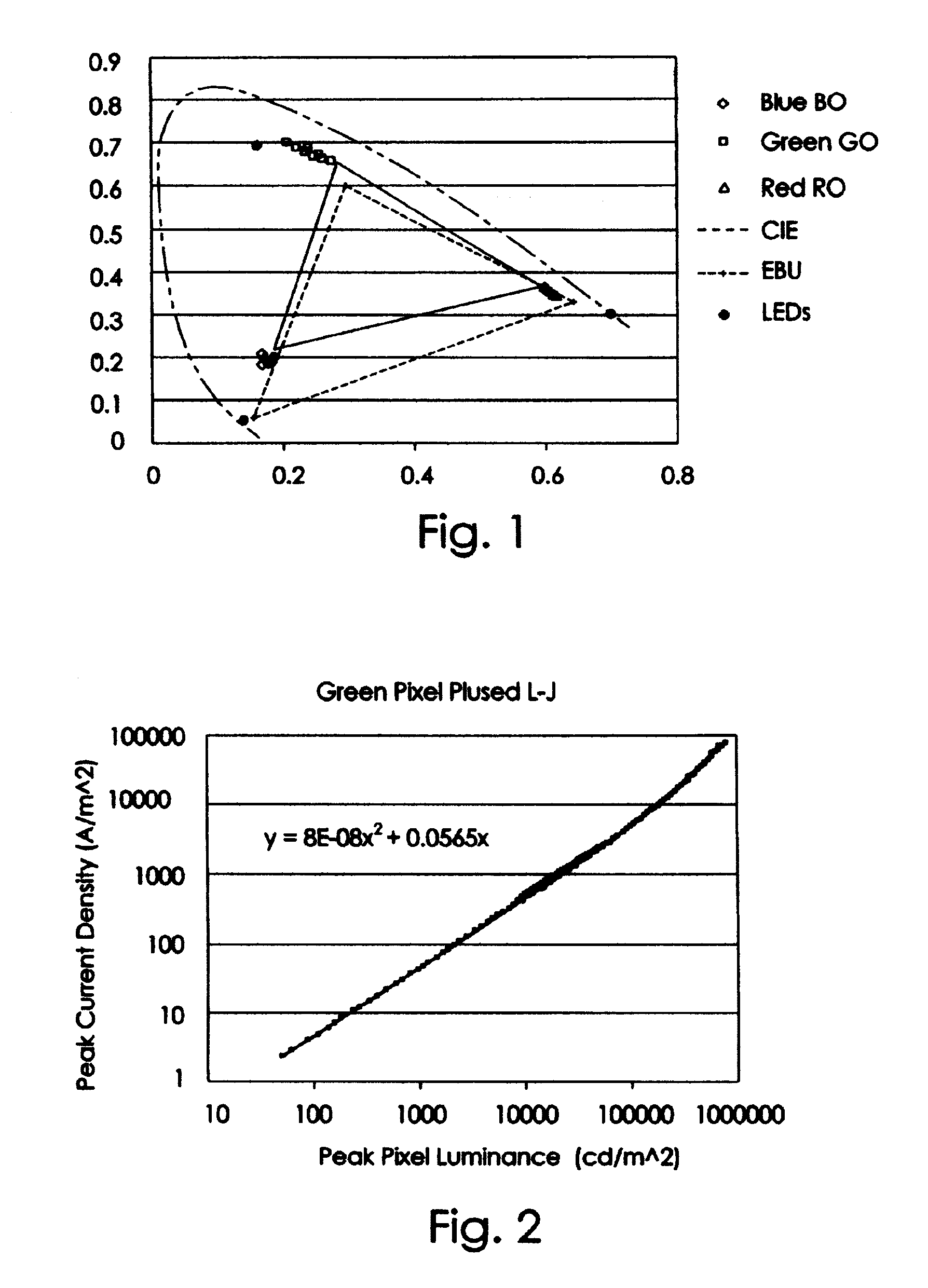
The invention provides an image display system, not only discloses a method for collecting test data but also discloses various algorithms for eliminating the defect of cloud pattern; the invention does not need to change the structure of pixel and also large storage space is not needed; while the cloud pattern is eliminated, the algorithms disclosed by the invention can carry out dynamic adjustment for gamma parameters, white point setting and peak brightness according to the requirements of different users or different using environments and the difference from the traditional technique is that adjustment is needed to be carried out for the parameters by extra processes.
Owner:TPO DISPLAY
Spectral Separation Filters For 3D Stereoscopic D-Cinema Presentation
ActiveUS20110205494A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove efficiencyOptical filtersProjectorsPattern recognition3d image
Spectral separation filters for channels of a 3D image projection incorporate passbands of primary colors. In at least one of the filters, passbands are present in more than 3 primary colors. A set of two filters include a first filter having passbands of low blue, high blue, low green, high green, and red, and a second filter having passbands of blue, green, and red. The additional primary passbands of the first filter allow for an increased color space in projections through the filters compared to filters only having red, green, and blue primaries. The added flexibility of the increased color space is utilized to more closely match a color space and white point of a projector in which the filters are used.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Calibrating rgbw displays
ActiveUS20080252653A1The calibration method is simpleFew stepsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGamutMain channel
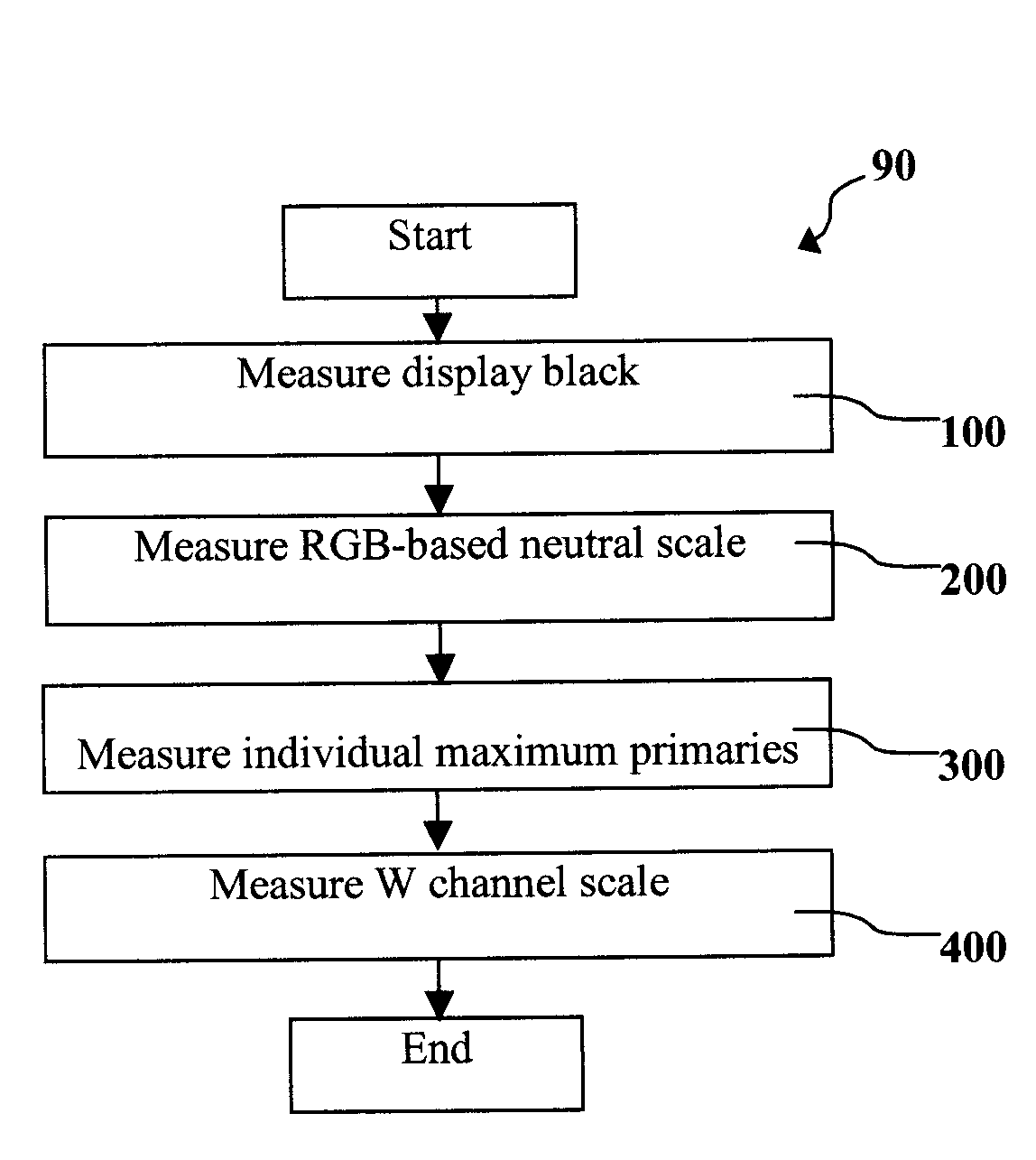
A method for calibrating a display device having four or more channels, including three main channels which include in their gamut a desired display white point, and one or more further channels, said display device also having one or more individual adjustment controls for each channel. The method uses a series of targets, which are each one or more activated display settings at which the luminance and chromaticity coordinates are measured and recorded.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Three-dimensional image display system
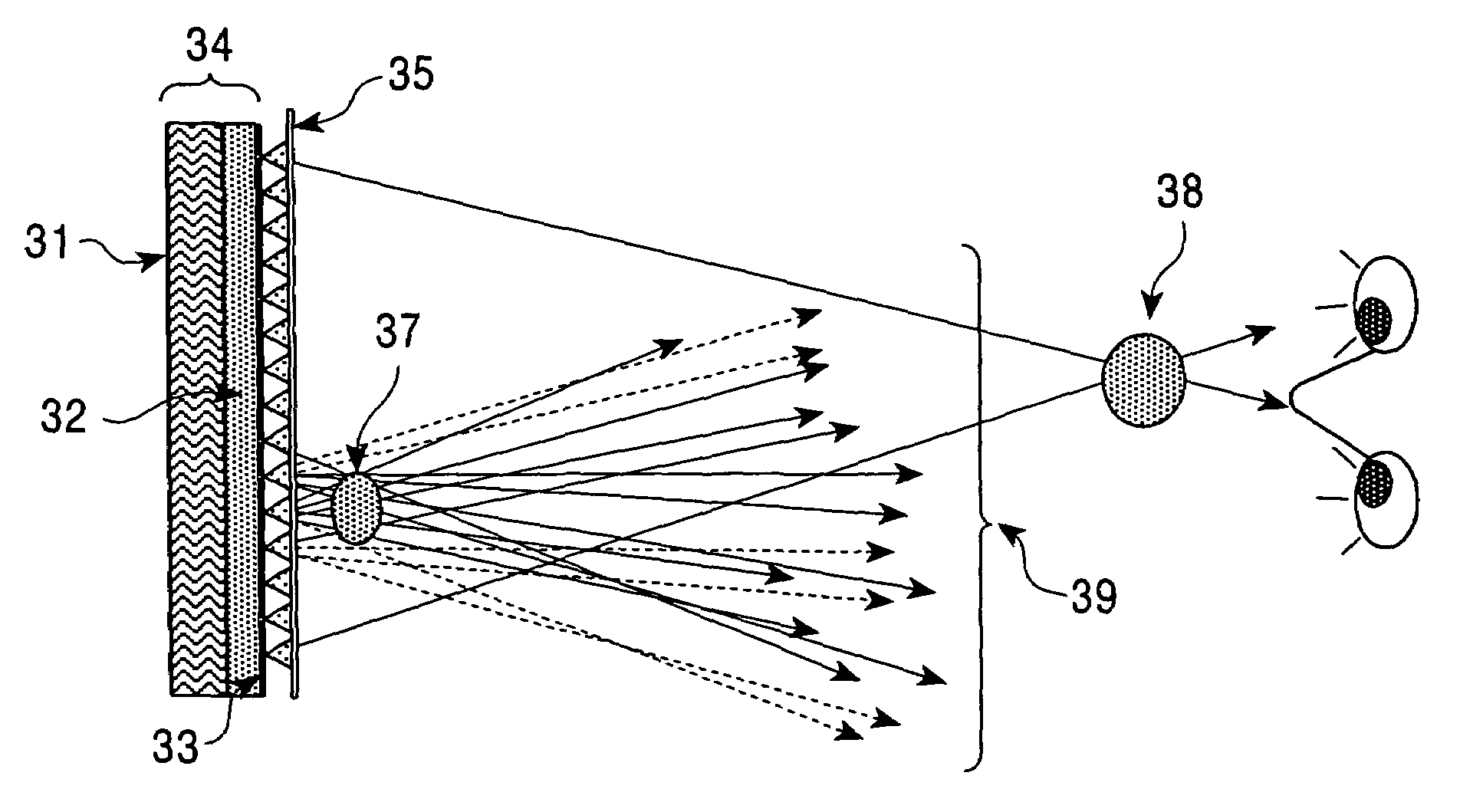
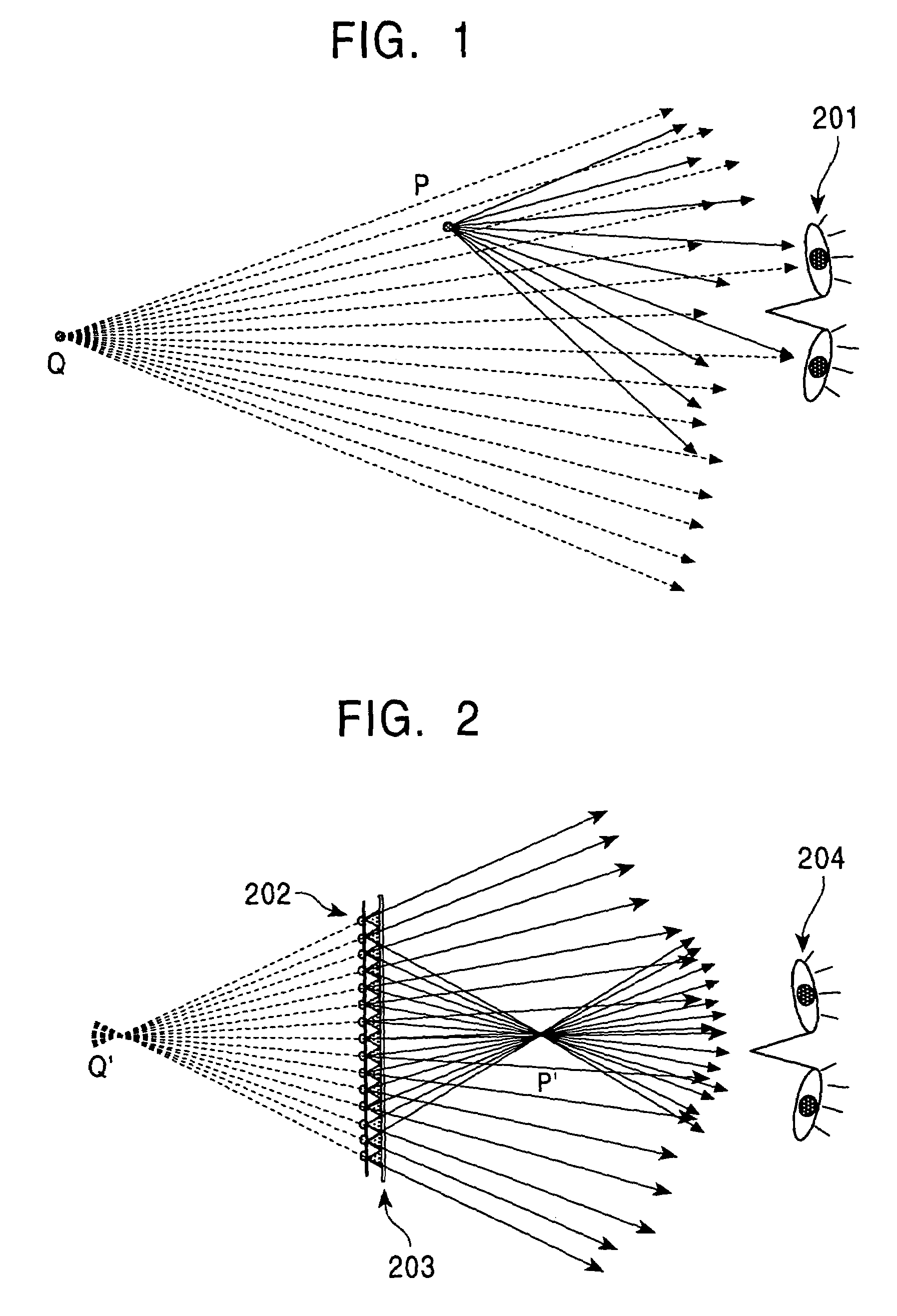
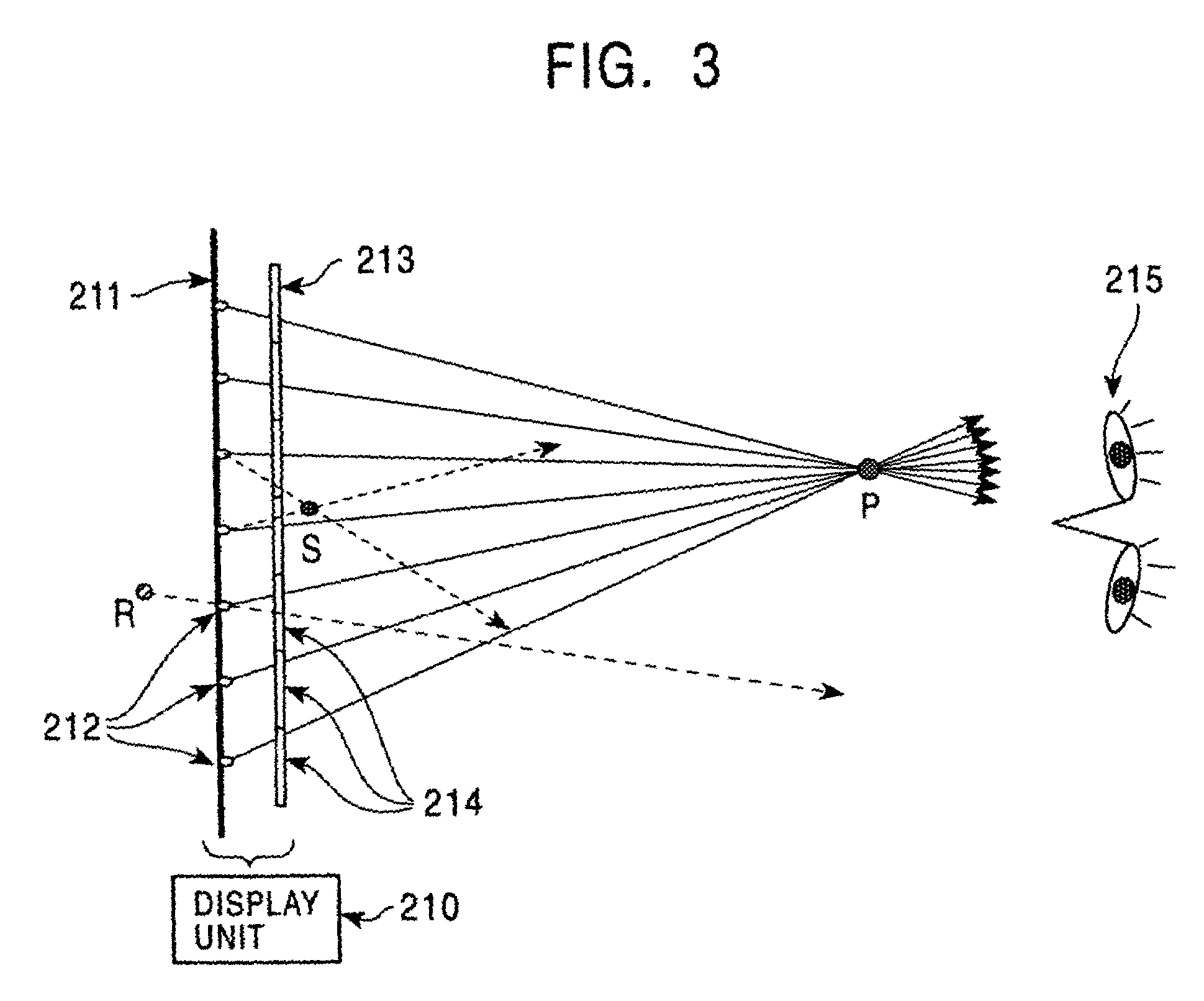
InactiveUS6999110B2Generation is preventedPrevent intrusionSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsParallaxLight beam
A three-dimensional image display system utilizing both a light beam reproducing method and a shadowgraph multi-view parallax method, including a color filter is disposed on an observer side of a white-color point light source array, and, in an area apart from the color filter and white point light source, light beams emitted from the white-color point light source are selectively colored by the color filter for generating an image of each point of an object, while in the region in the vicinity of the point light source and the color filter, the light beams are selectively colored by the color filter so that image data reaching the eye from the white-color point light source through the color filter performs a view-dependent parallax stereoscopic display operation not only laterally but also vertically, and in the intermediate region, these two operations are mixed, so that a stereoscopic image is continuously formed.
Owner:KOBAYASHI TETSURO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com