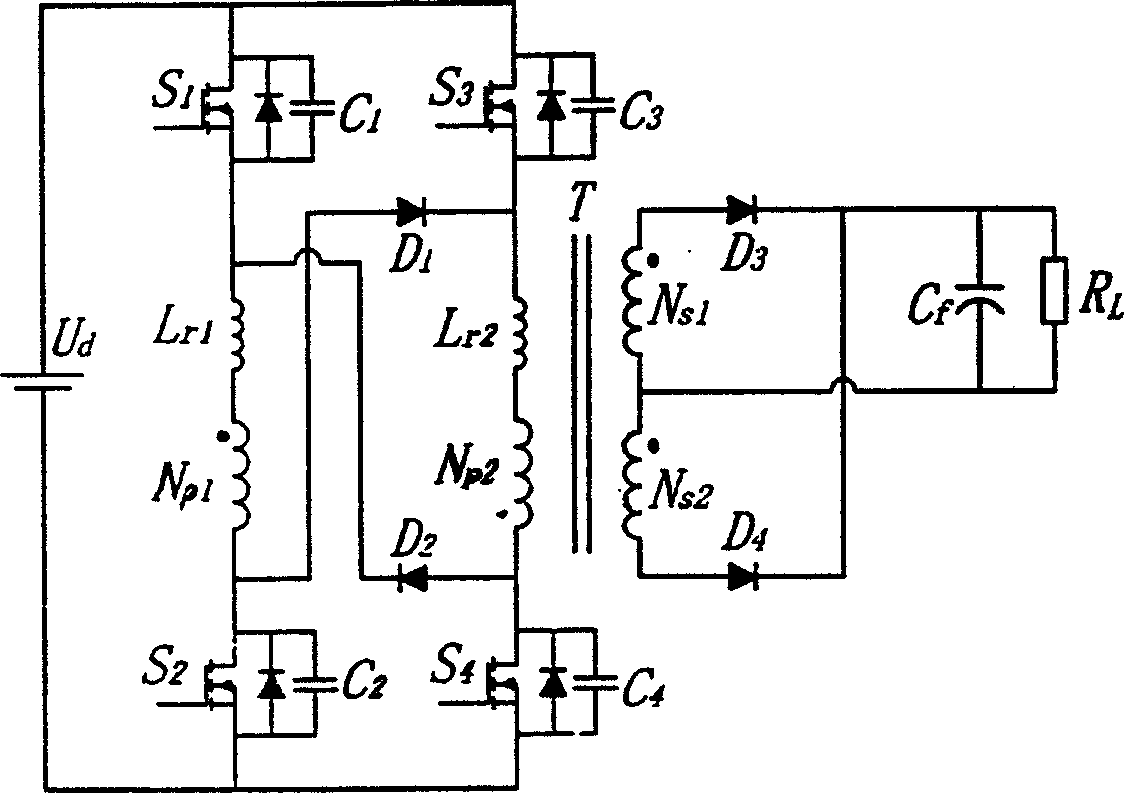
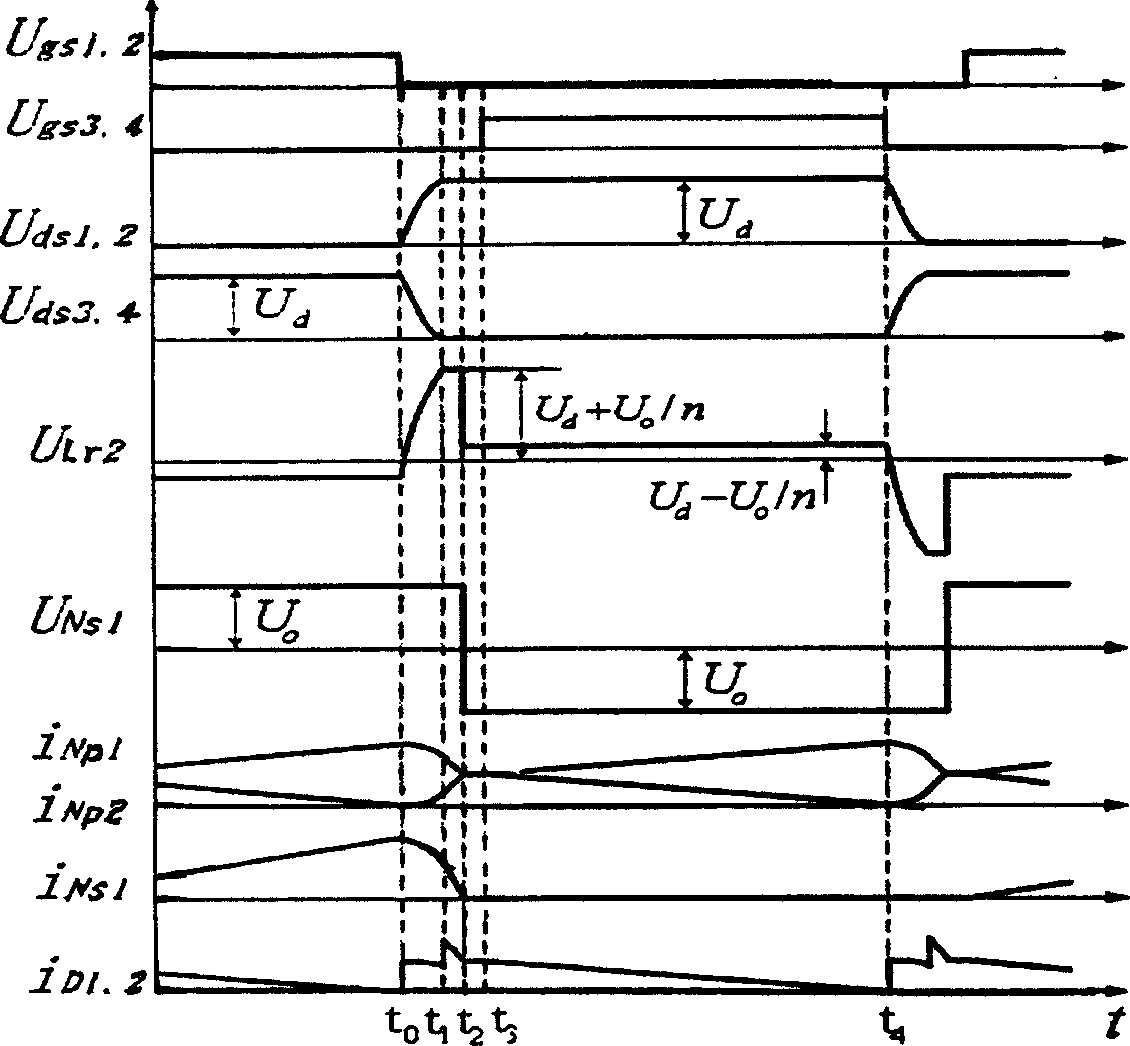
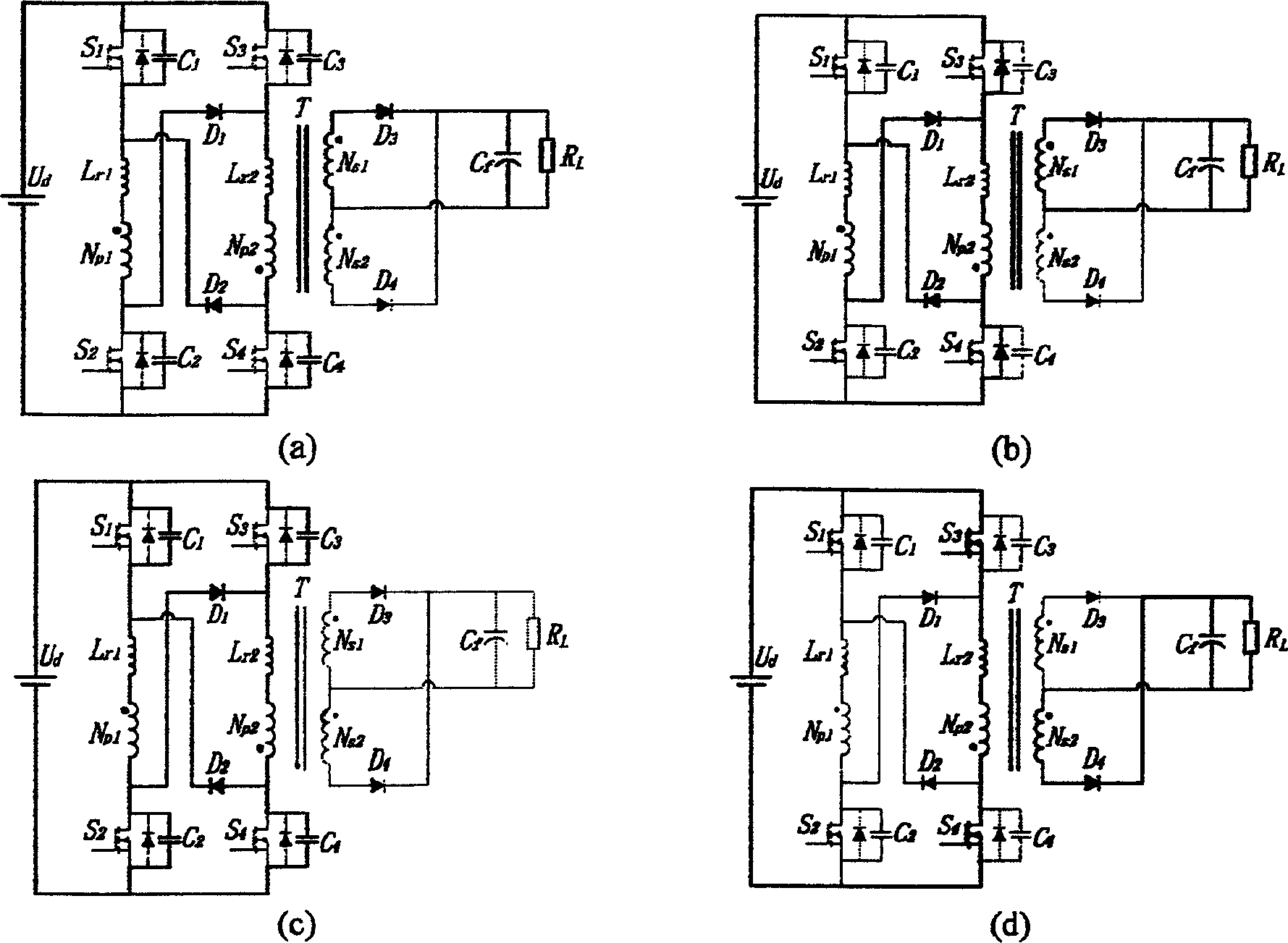
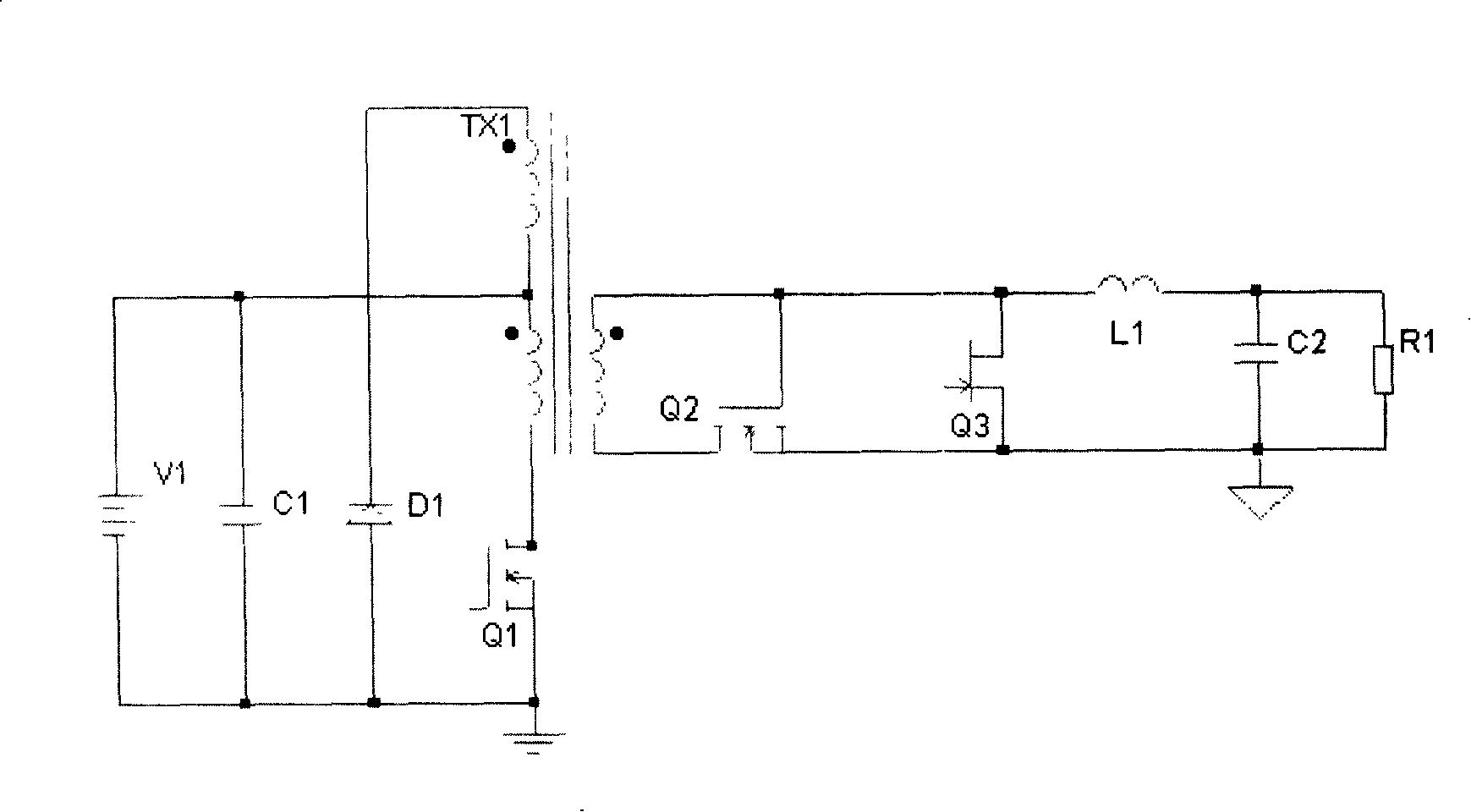
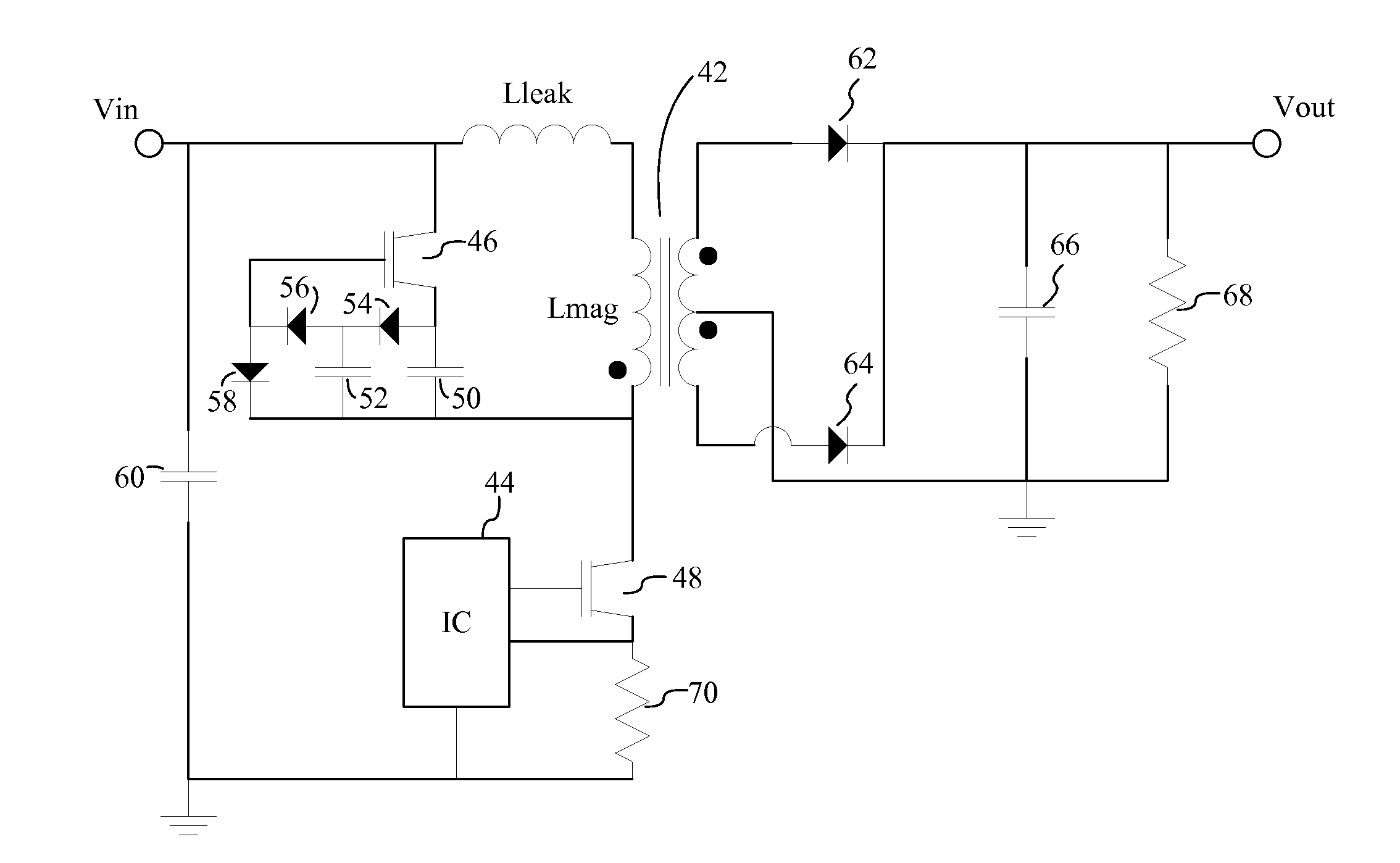
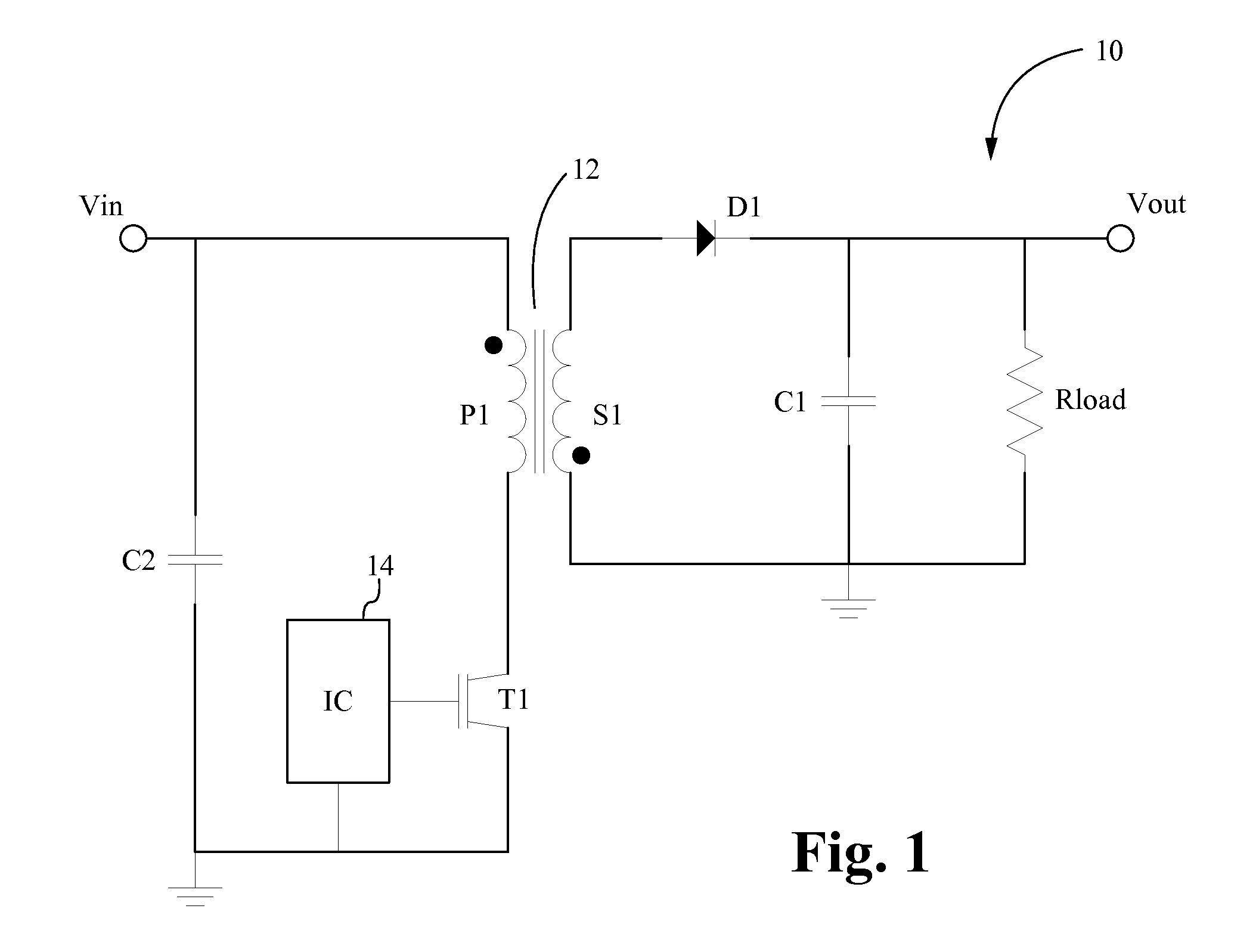
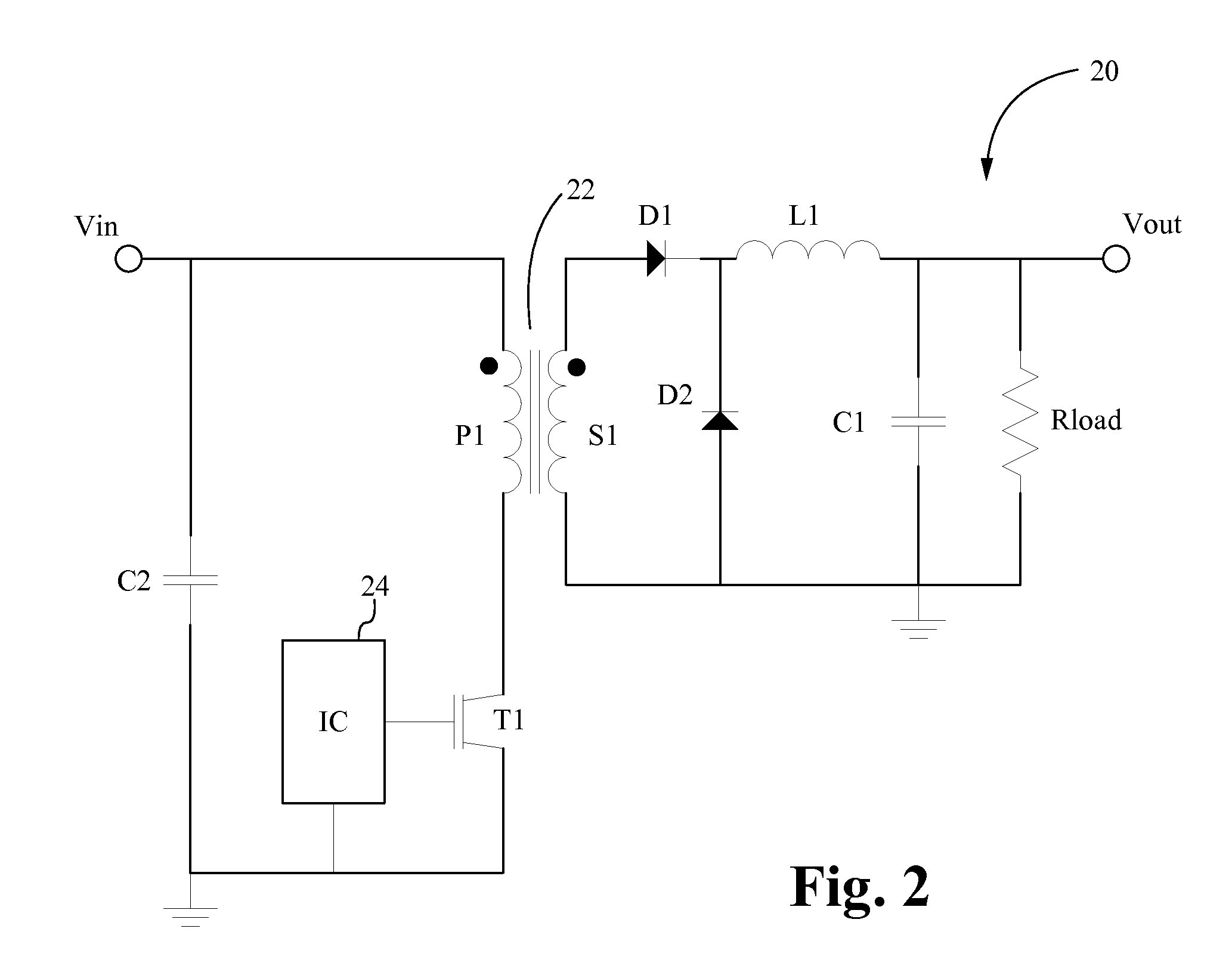
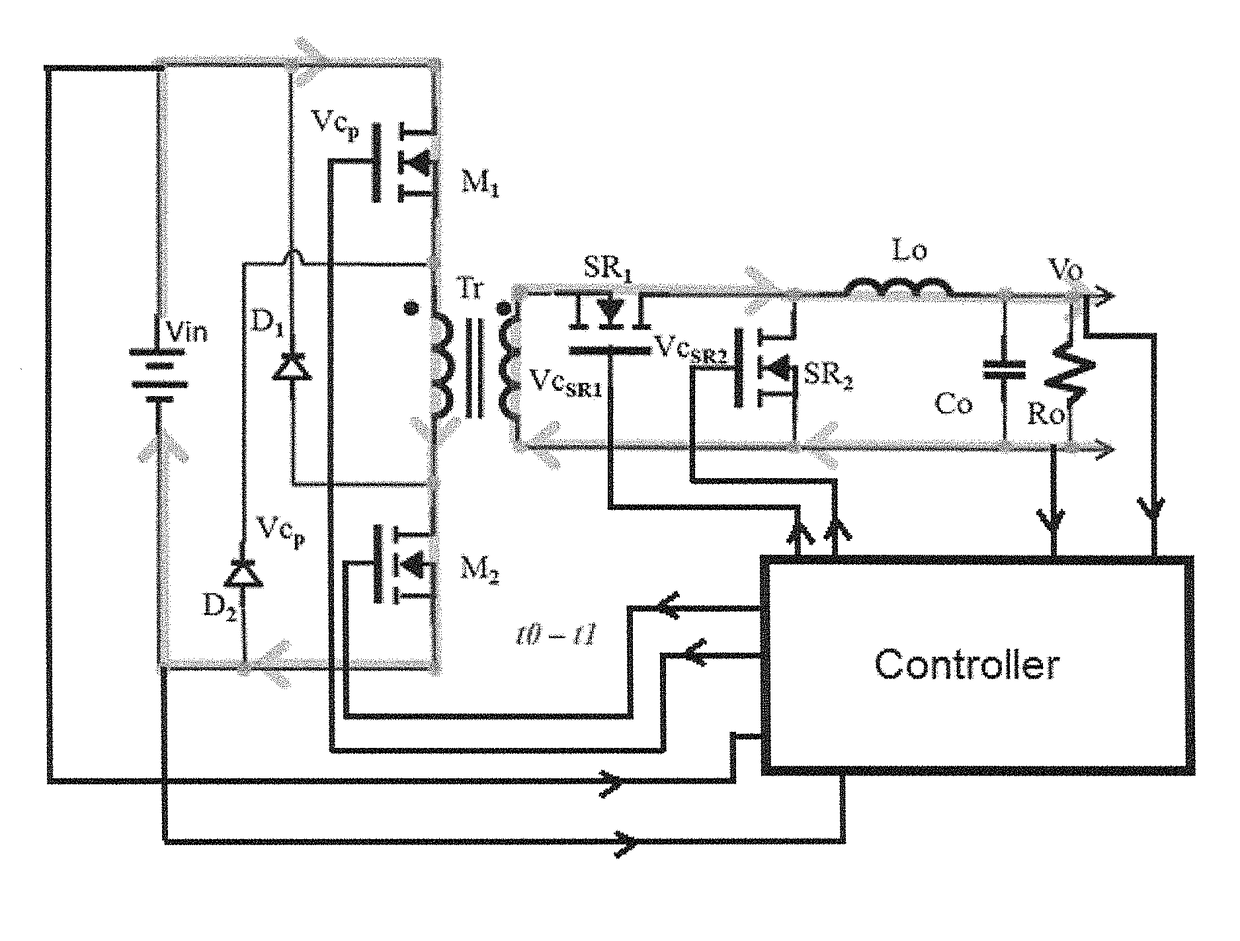
Patents
Literature
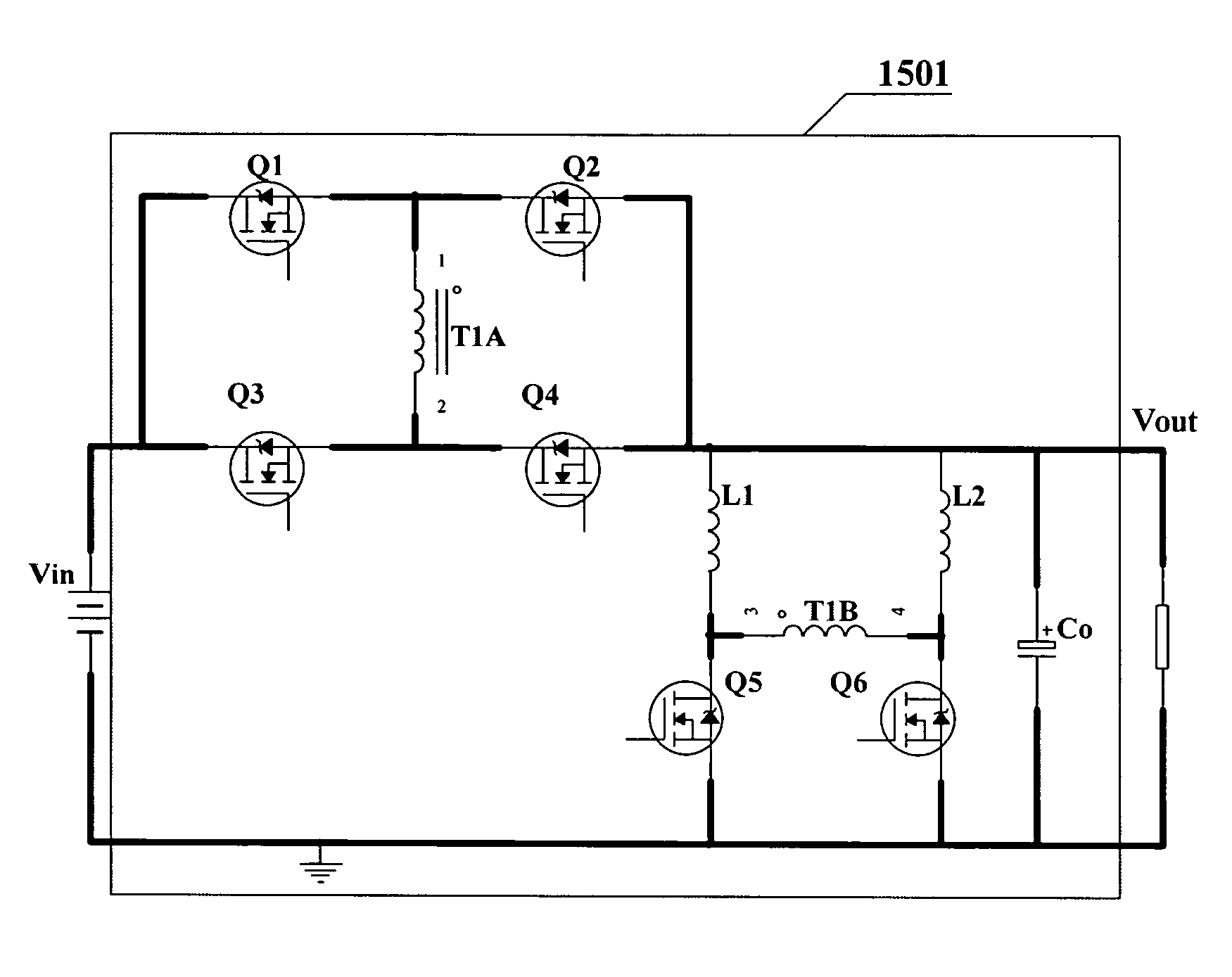
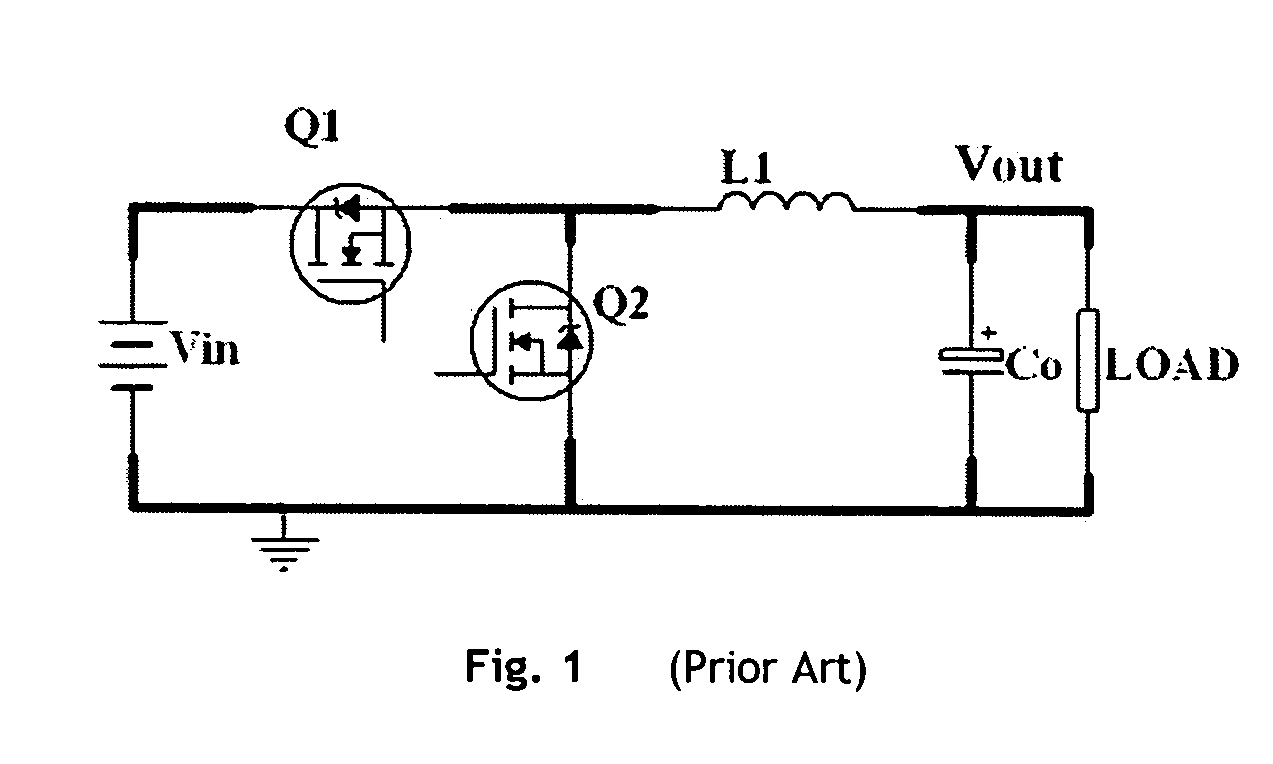
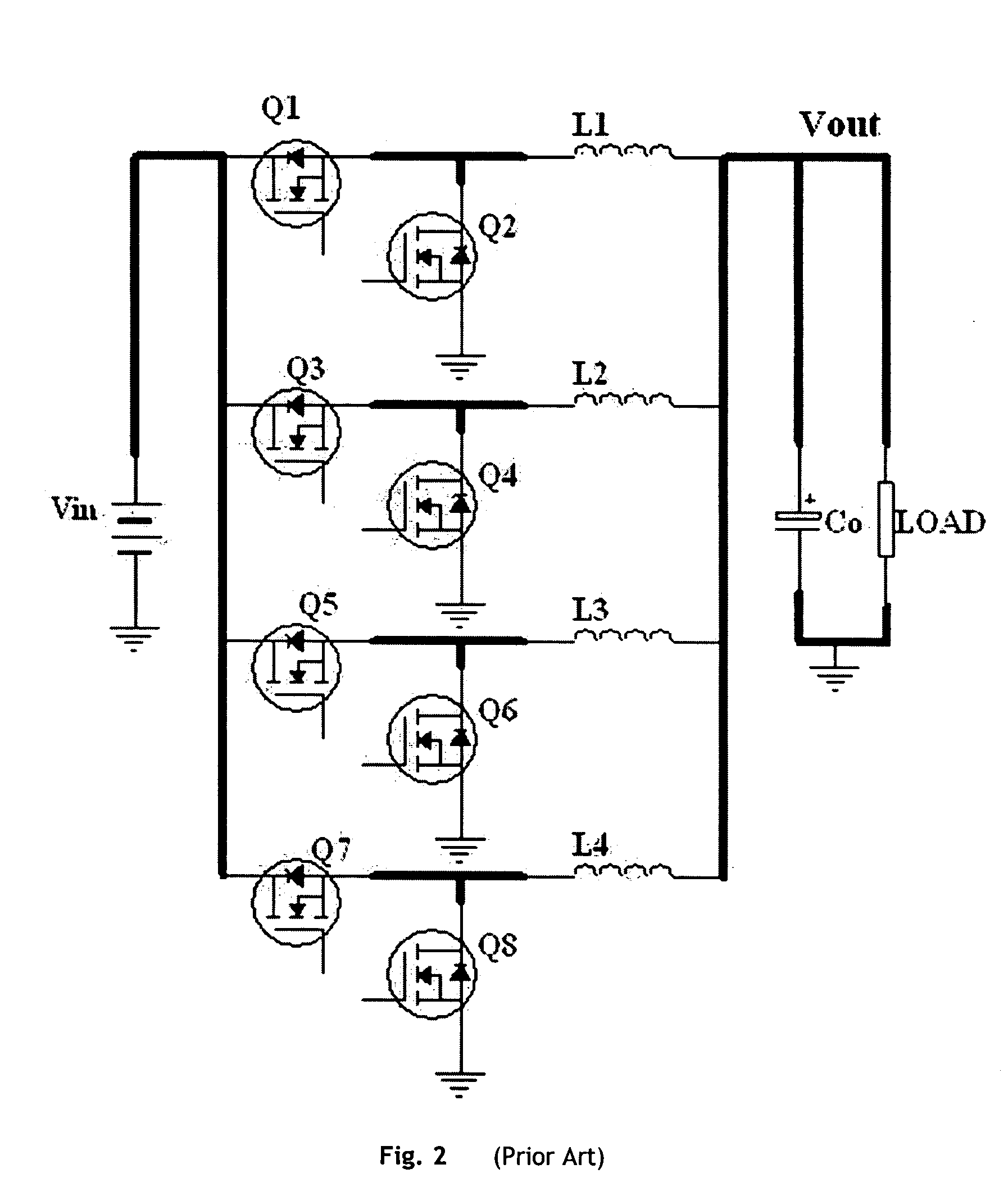
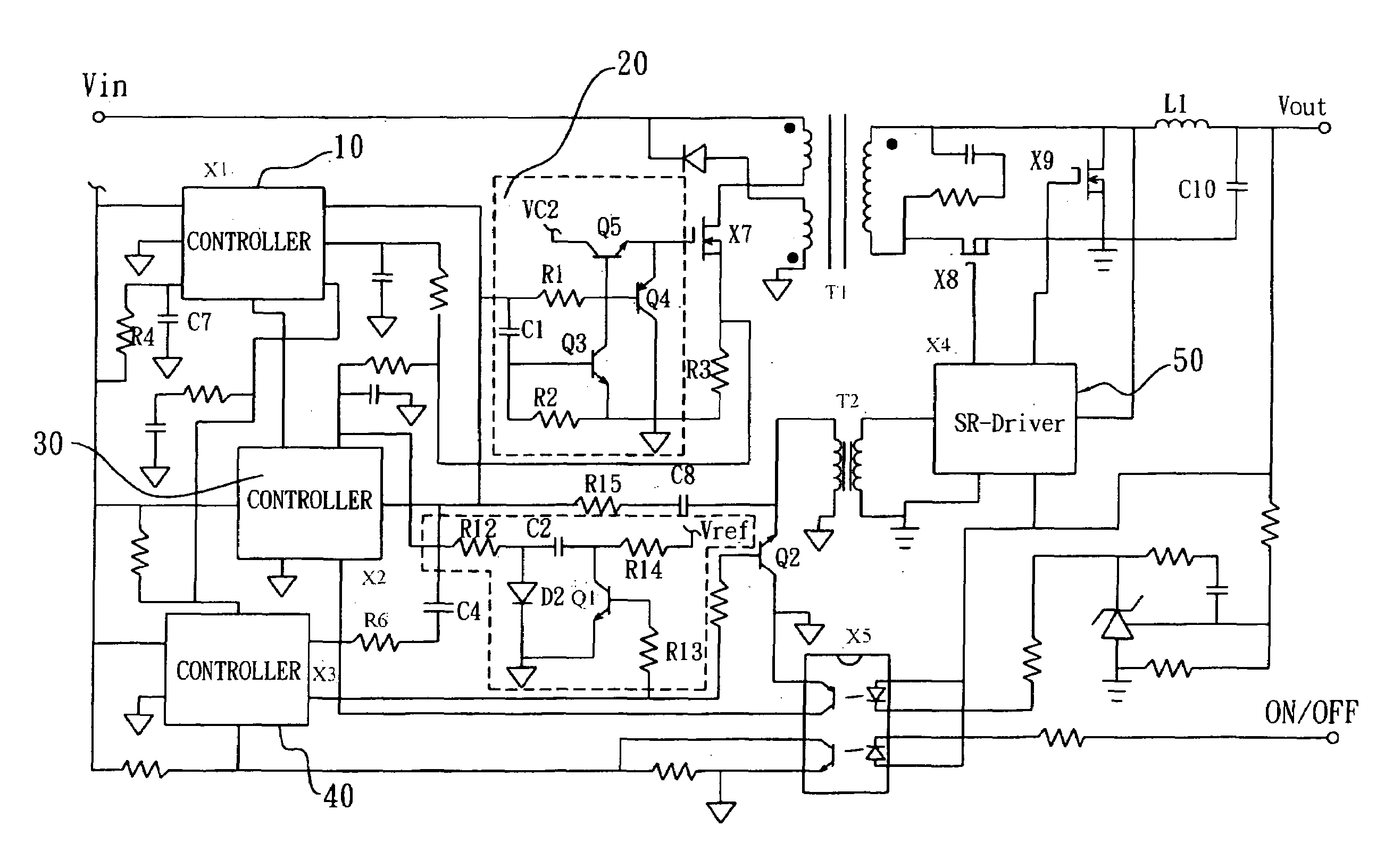
220 results about "Forward converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
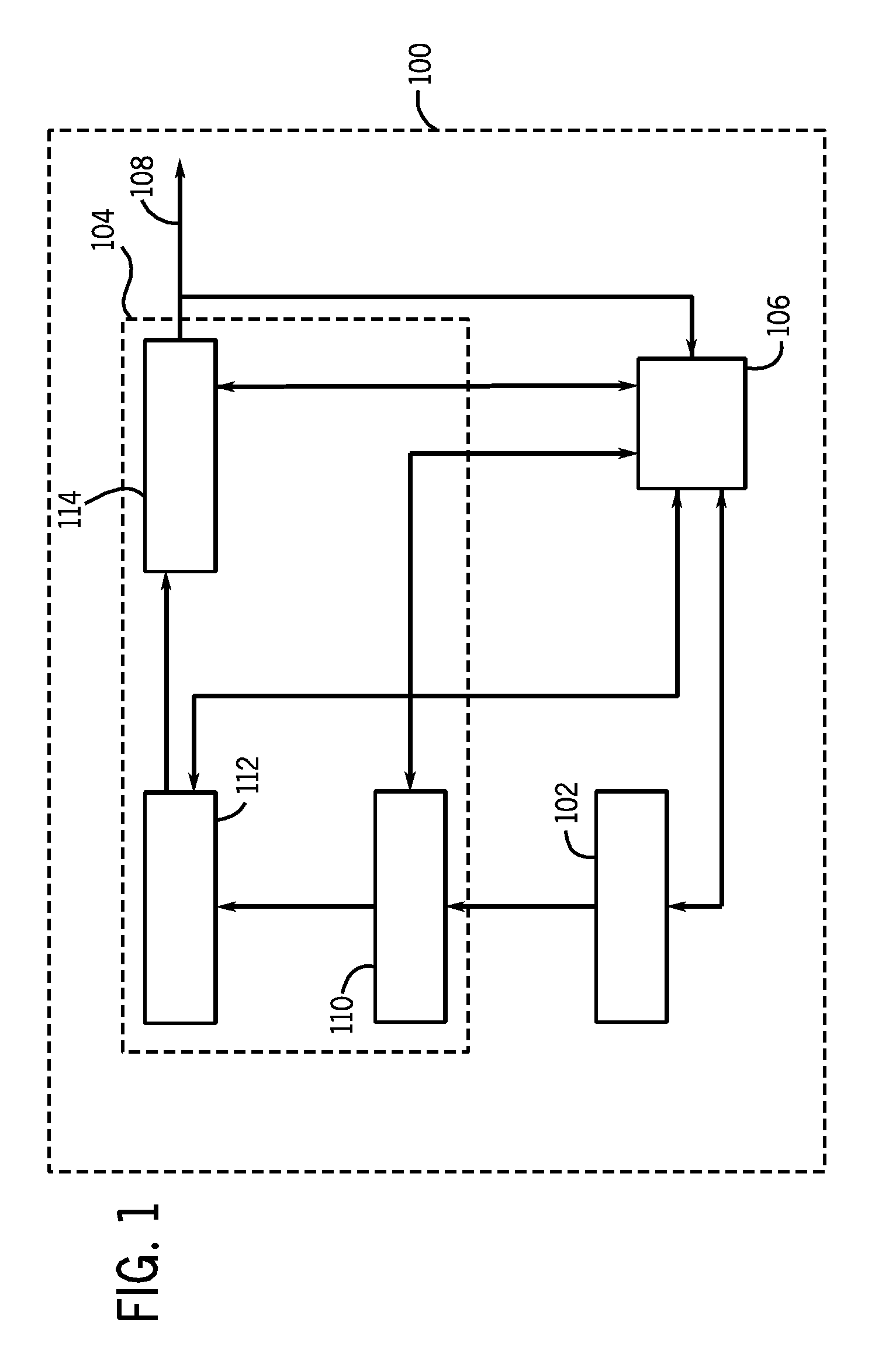
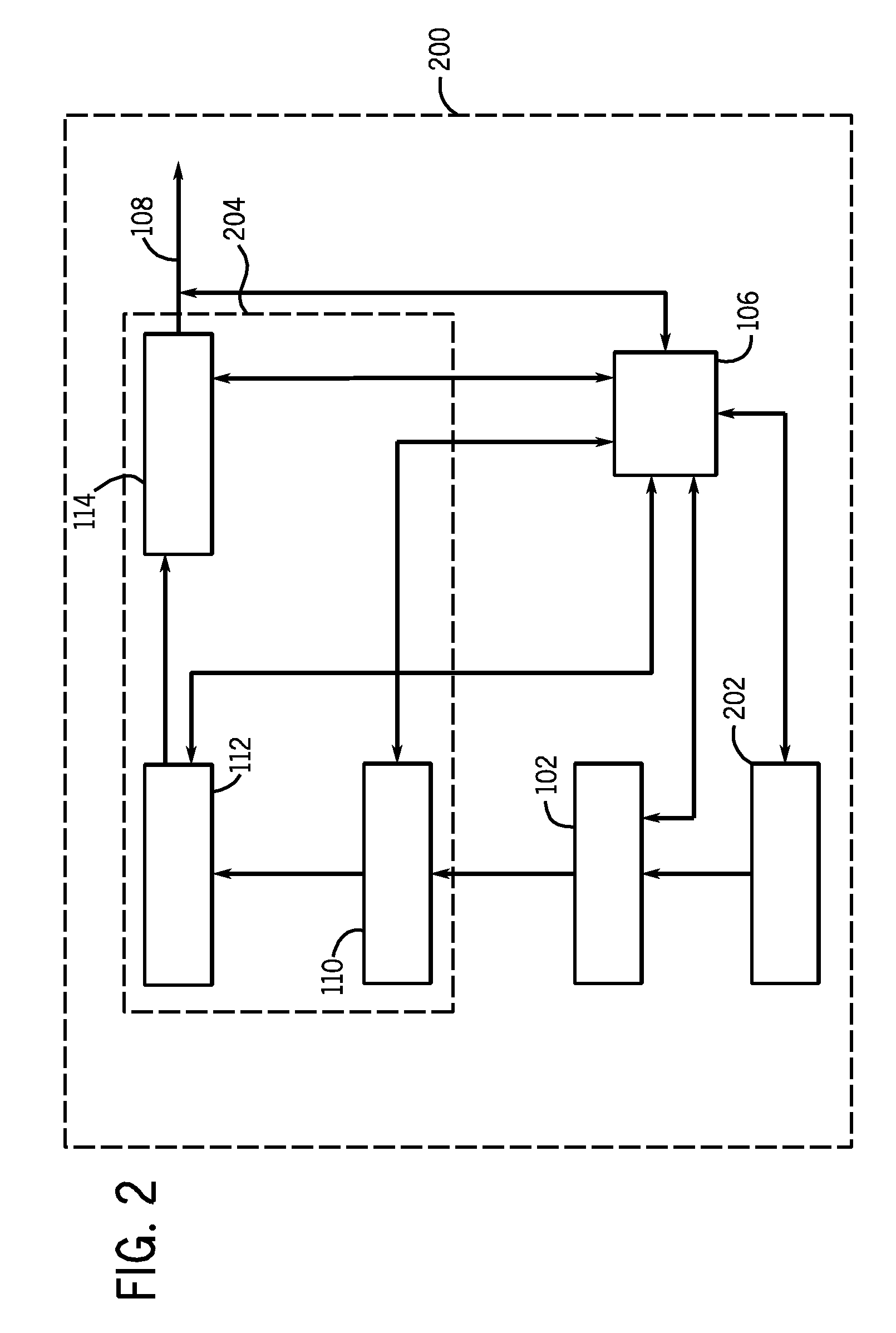
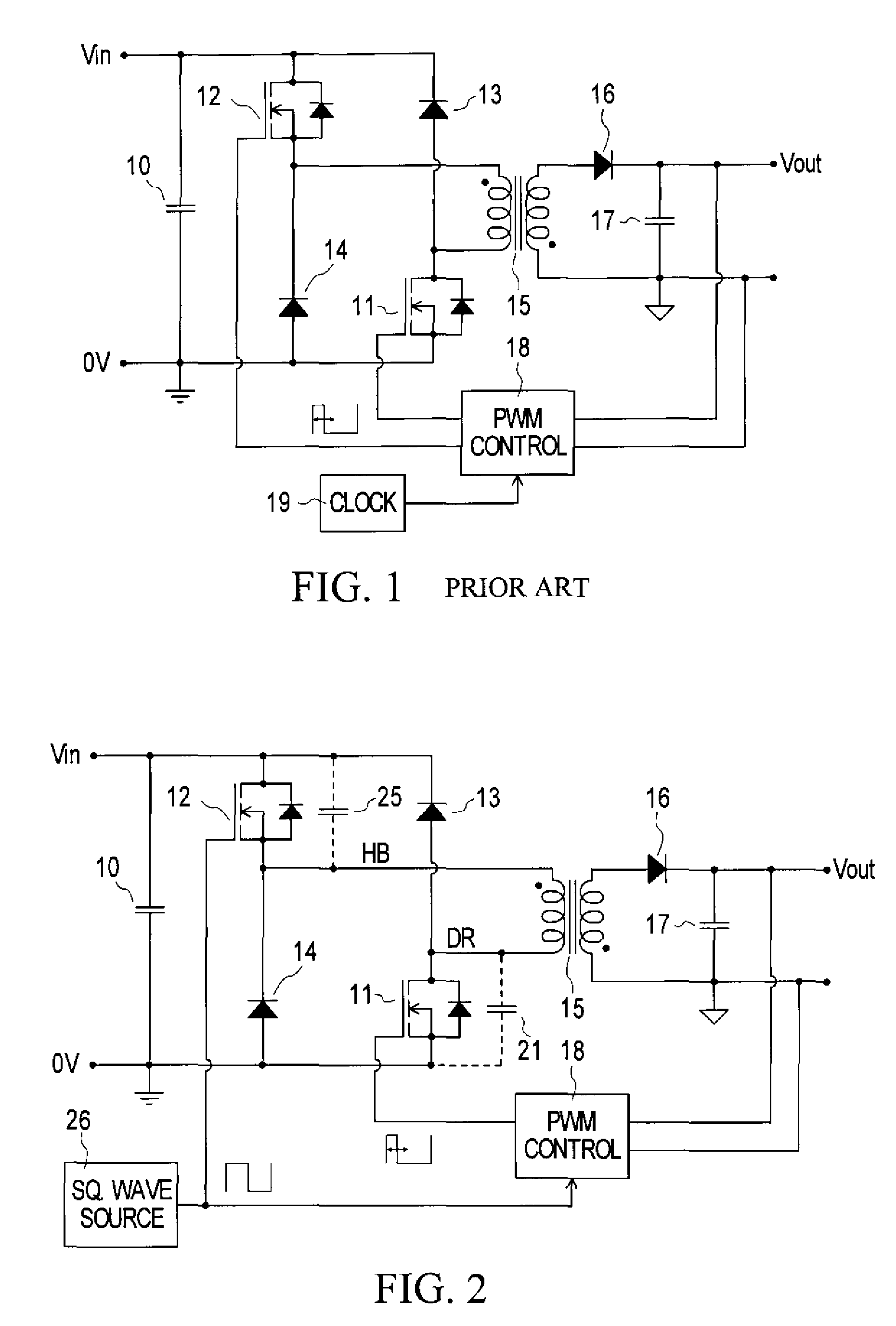
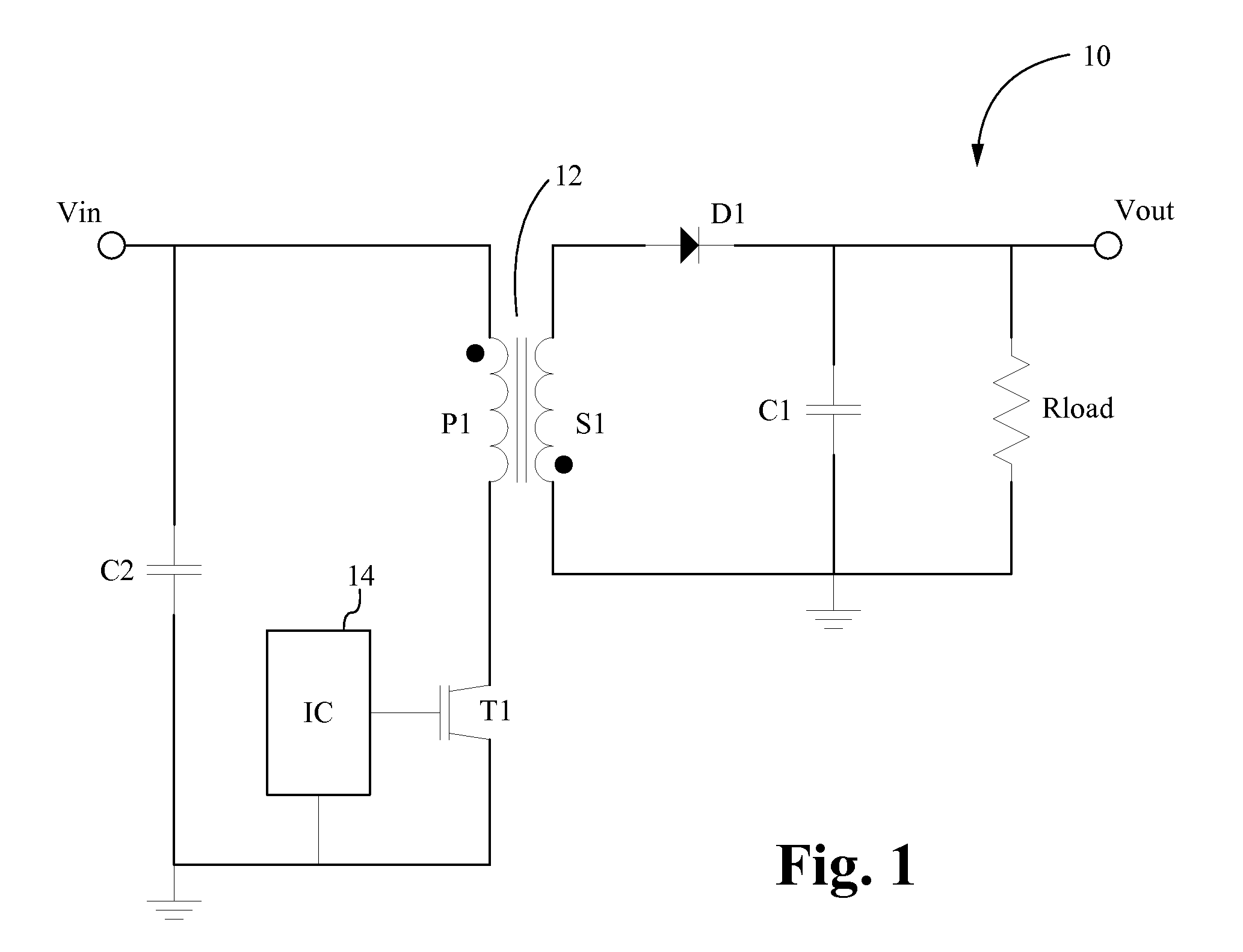
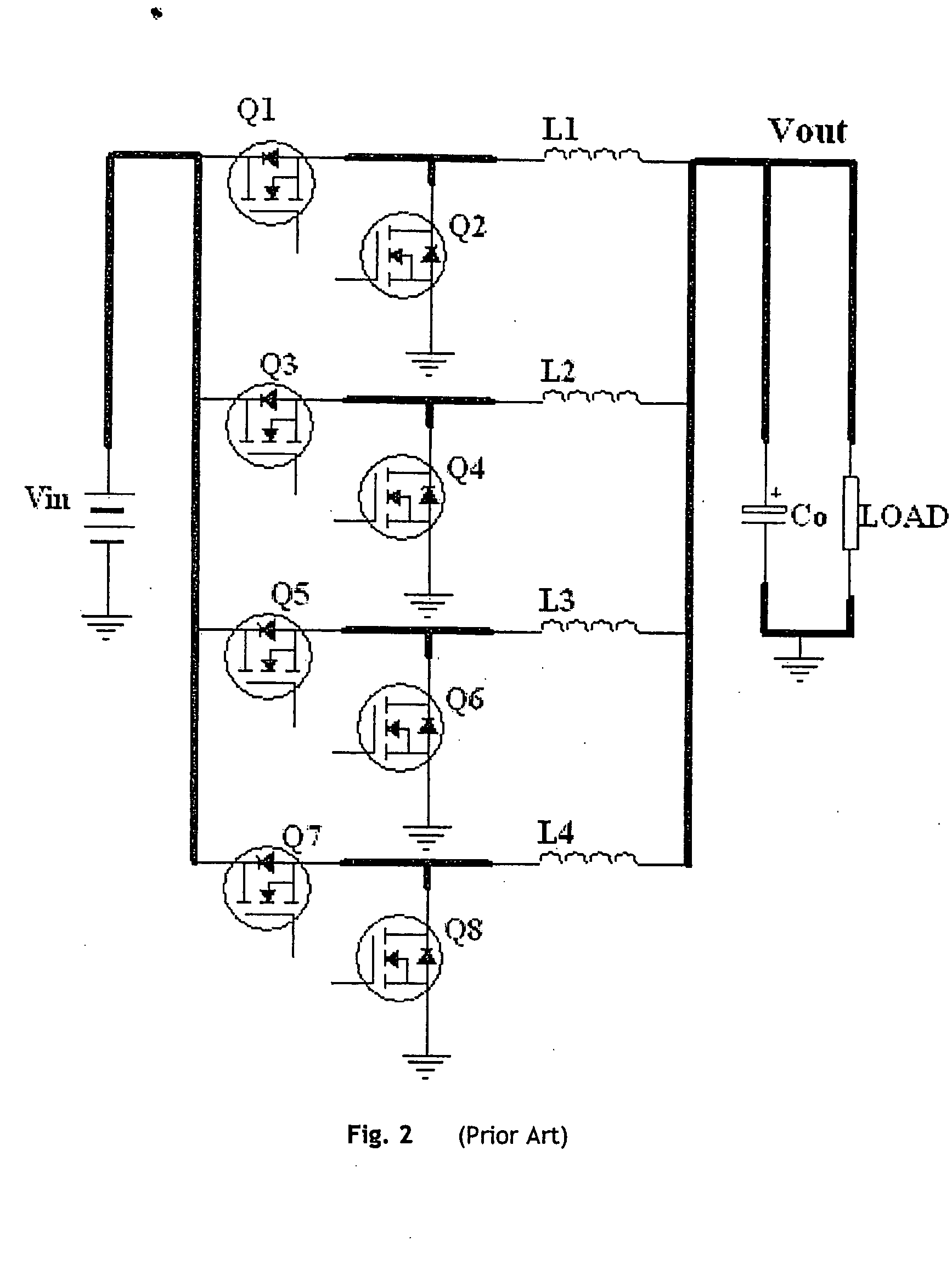
The forward converter is a DC/DC converter that uses a transformer to increase or decrease the output voltage (depending on the transformer ratio) and provide galvanic isolation for the load. With multiple output windings, it is possible to provide both higher and lower voltage outputs simultaneously. While it looks superficially like a flyback converter, it operates in a fundamentally different way, and is generally more energy efficient.
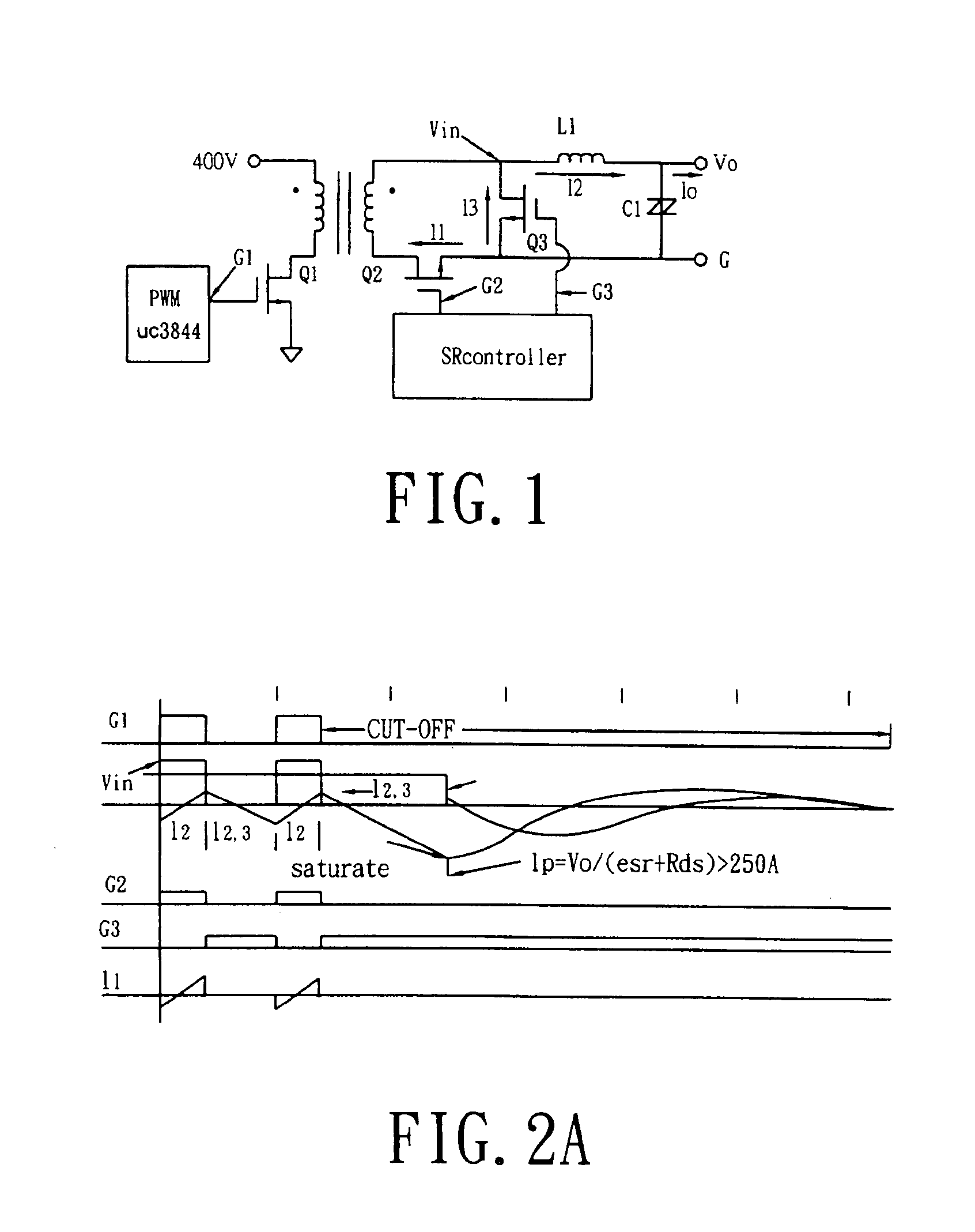
Snubber circuit for a power converter
InactiveUS7385833B2Easy to controlHigh voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransverterEngineering
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Method and apparatus for welding with battery power
A method and apparatus provides welding-type power and preferably includes a removable battery or other energy storage device, a converter connected to the battery, and a controller. The controller may have a CV and / or a CSC and / or an AC weld control module, and / or an ac auxiliary control module. The converter is a boost converter, a buck converter, a cuk converter, a forward converter, an inverter, a bridge converter, and / or a resonant converter. The controller may include a battery charging control module, and may have one or more charging schedules, and / or data for stored charge, thermal information, expected life of the battery, maximum amp-hour charge for the battery, maximum charging current and / or feedback. The battery charging schedules may include at least 3 phases, such as a phase of increasing voltage and a phase of decreasing current, a substantially constant power phase. The controller can wirelessly provide data to a display or pda. A generator may provide power to the battery, charger, and / or the weld. It can include a vehicle and use its dc power system.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Bootstrap Circuitry
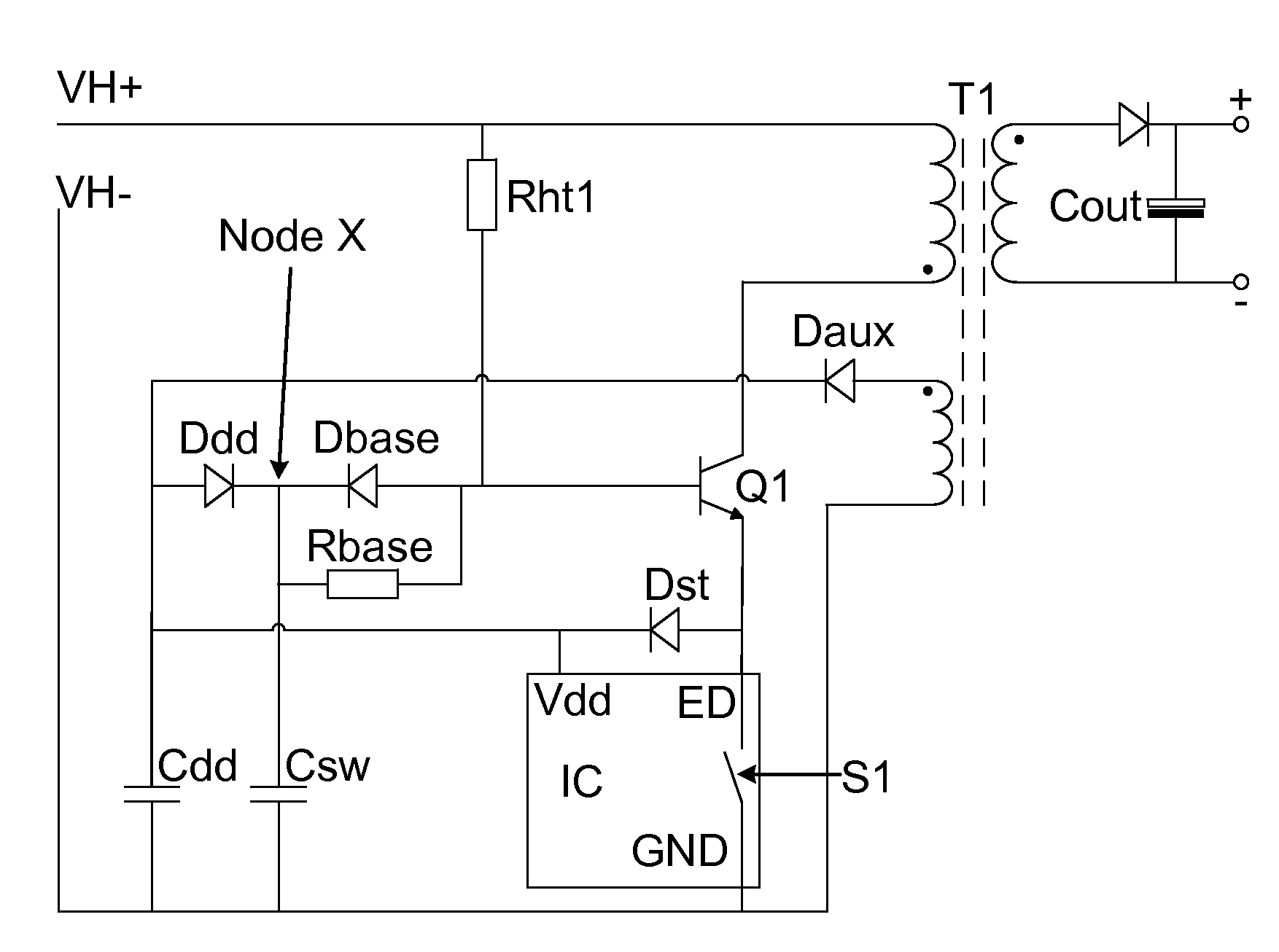
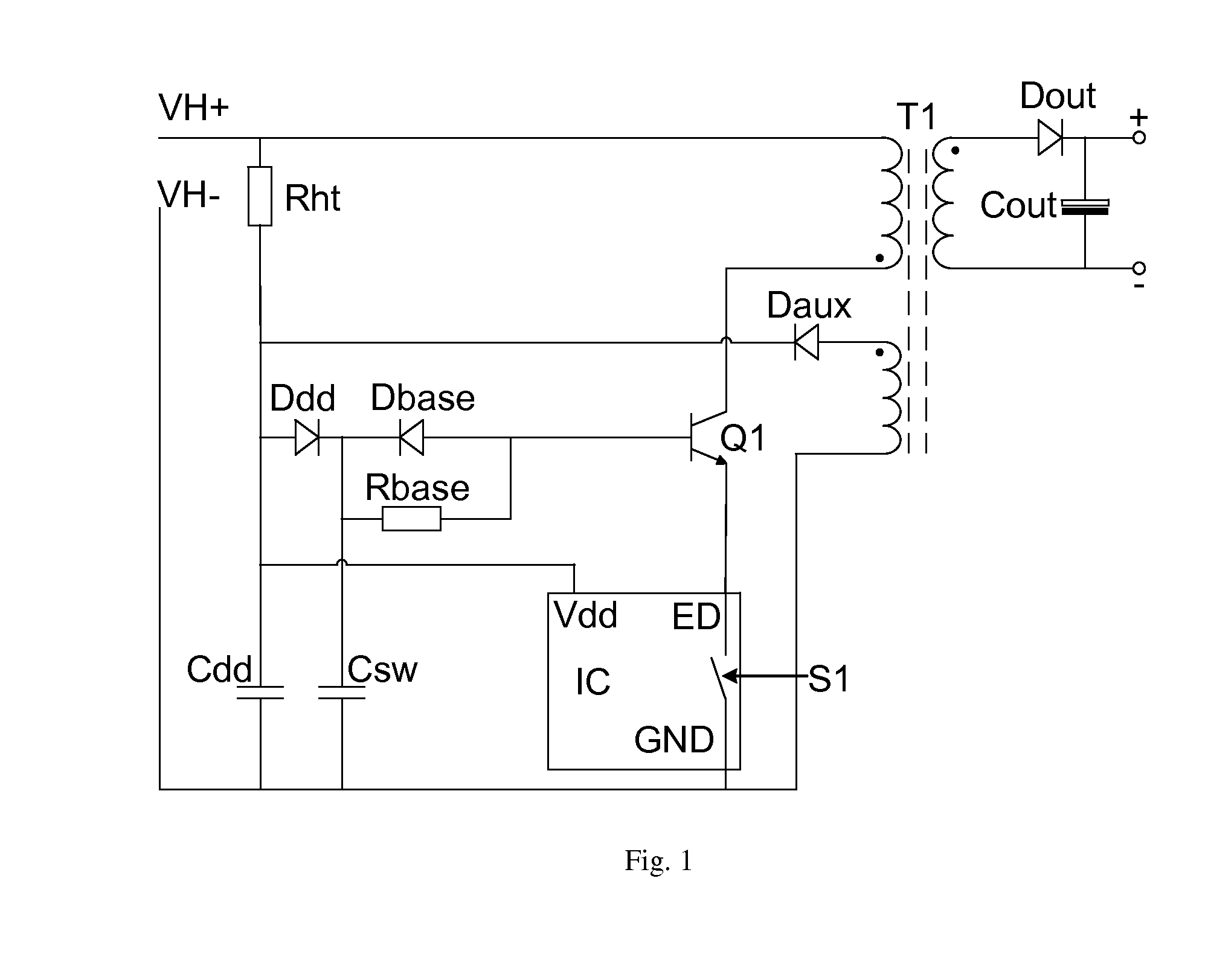
InactiveUS20100309689A1Reduce power wasteIncreased start-up timeDc-dc conversionElectronic switchingVoltage converterReverse current
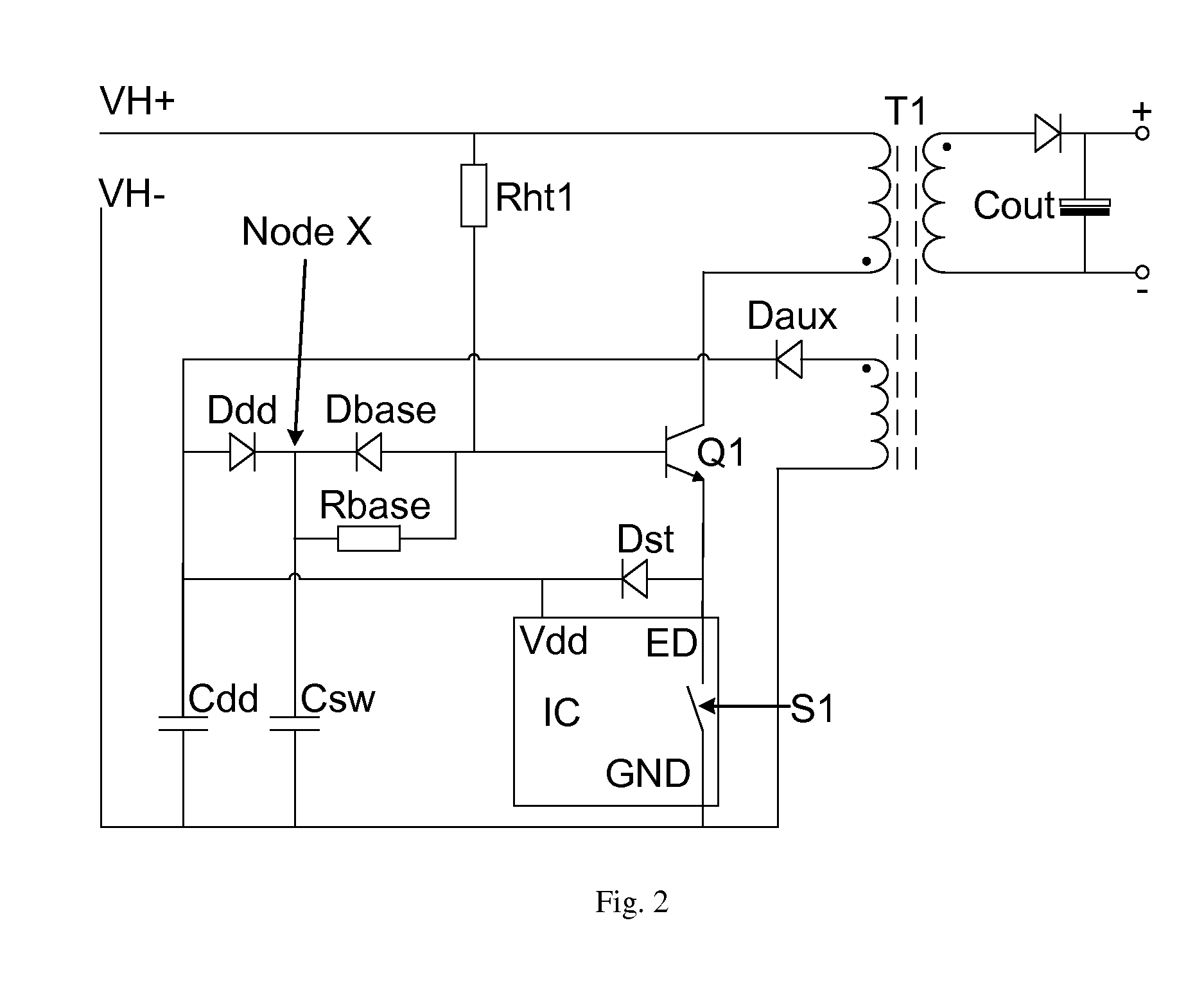
This invention generally relates to a bootstrap circuit for a switch mode power supply, a controller for a switch mode voltage converter, a switch mode flyback converter comprising the bootstrap circuit, a switch mode forward converter comprising the bootstrap circuit, and a method of bootstrapping a switch mode power converter. The bootstrap circuit comprises: a current bleed impedance (Rht1) to bleed current from an input power supply (VH+); circuitry to deliver current from the input power supply (VH+) via the current bleed impedance (Rht1) to the base of a power switch (Q1) such that the power switch (Q1) is operable to amplify the current delivered from the internal power supply; a passive circuit (Dst) to provide the amplified current to a reservoir capacitor (Cdd); and the passive circuit element (Dst) further to substantially block reverse current flow from the supply input (Vdd) to the emitter of the power switch (Q1).
Owner:CAMBRIDGE SEMICONDUCTOR LIMITED
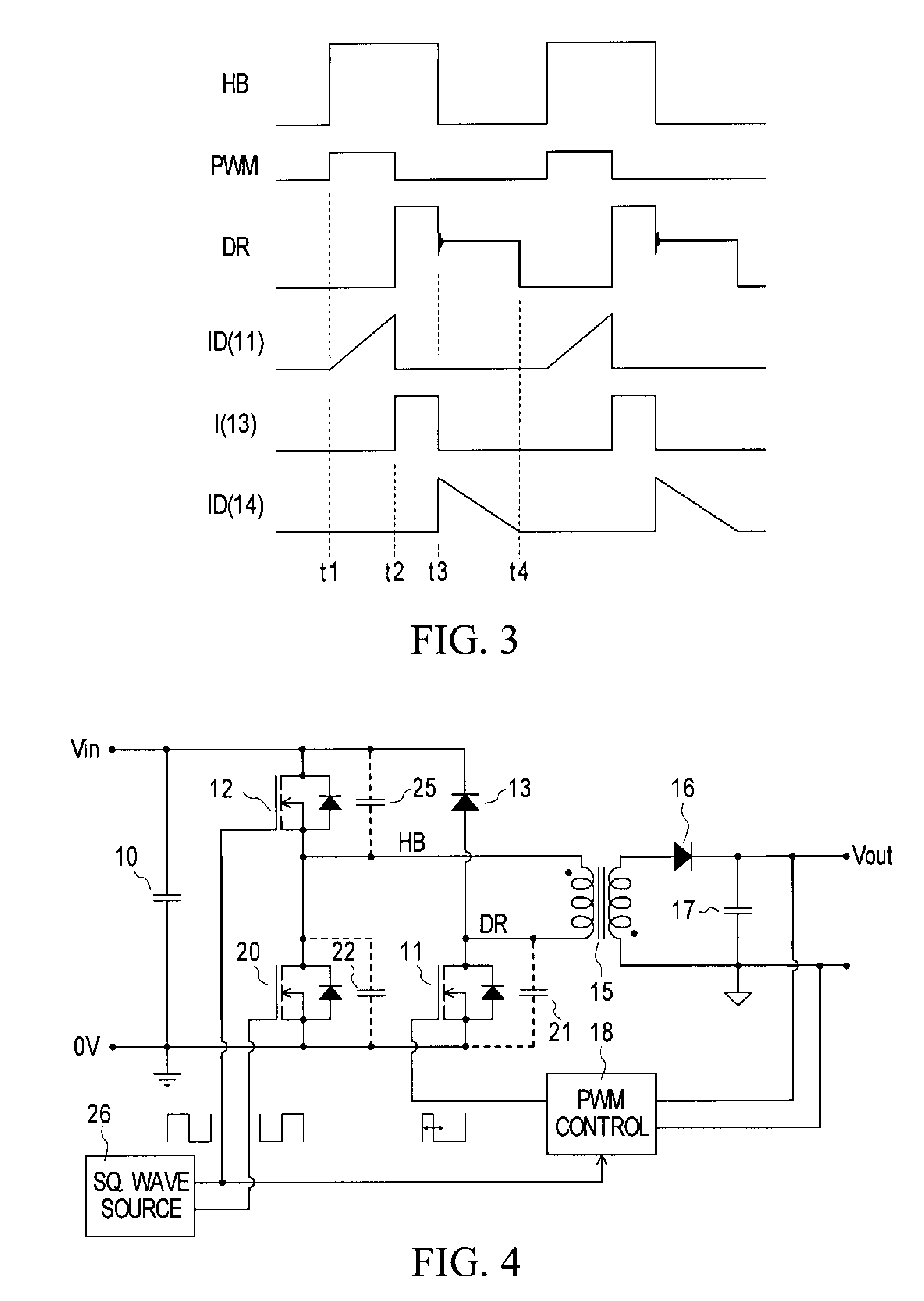
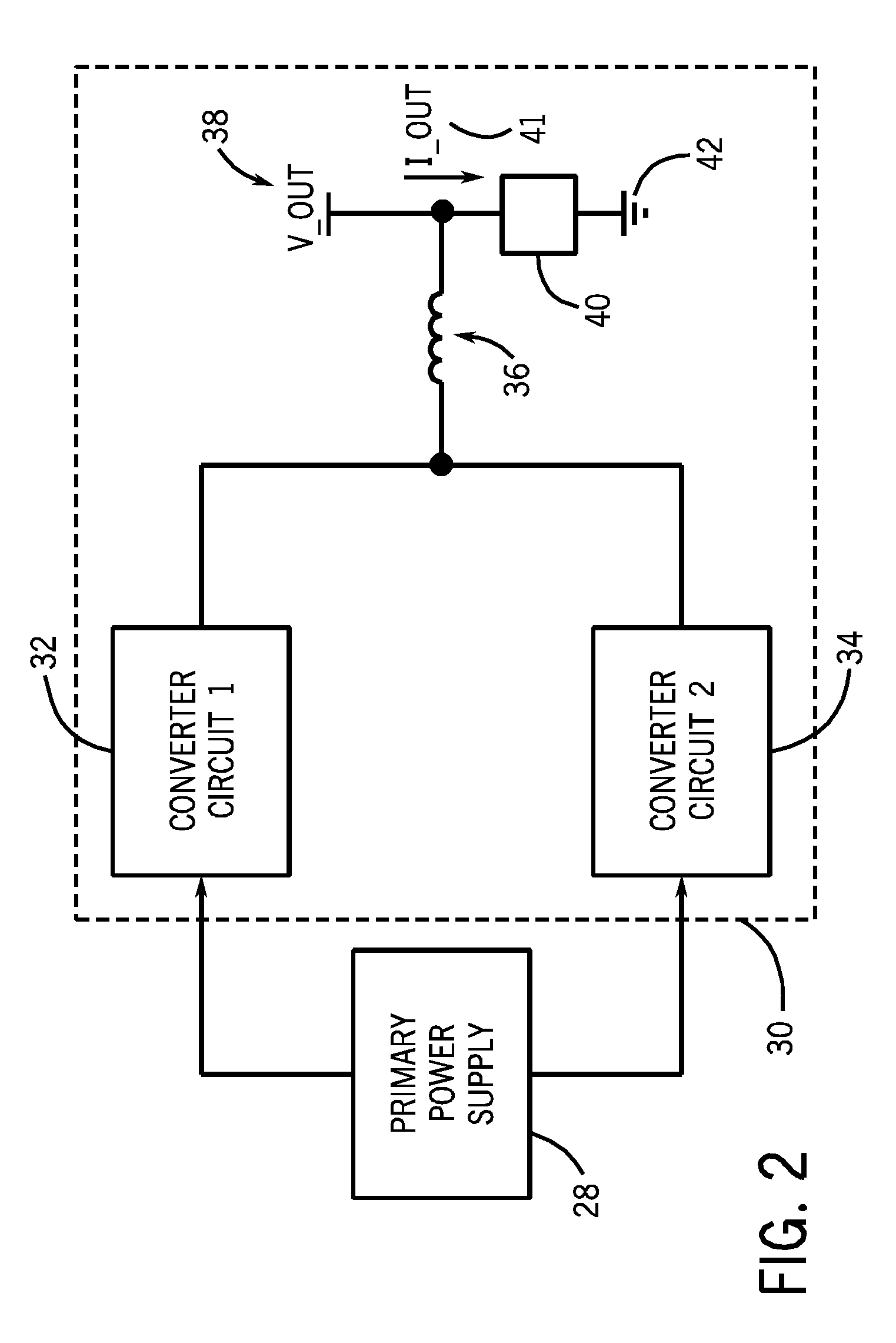
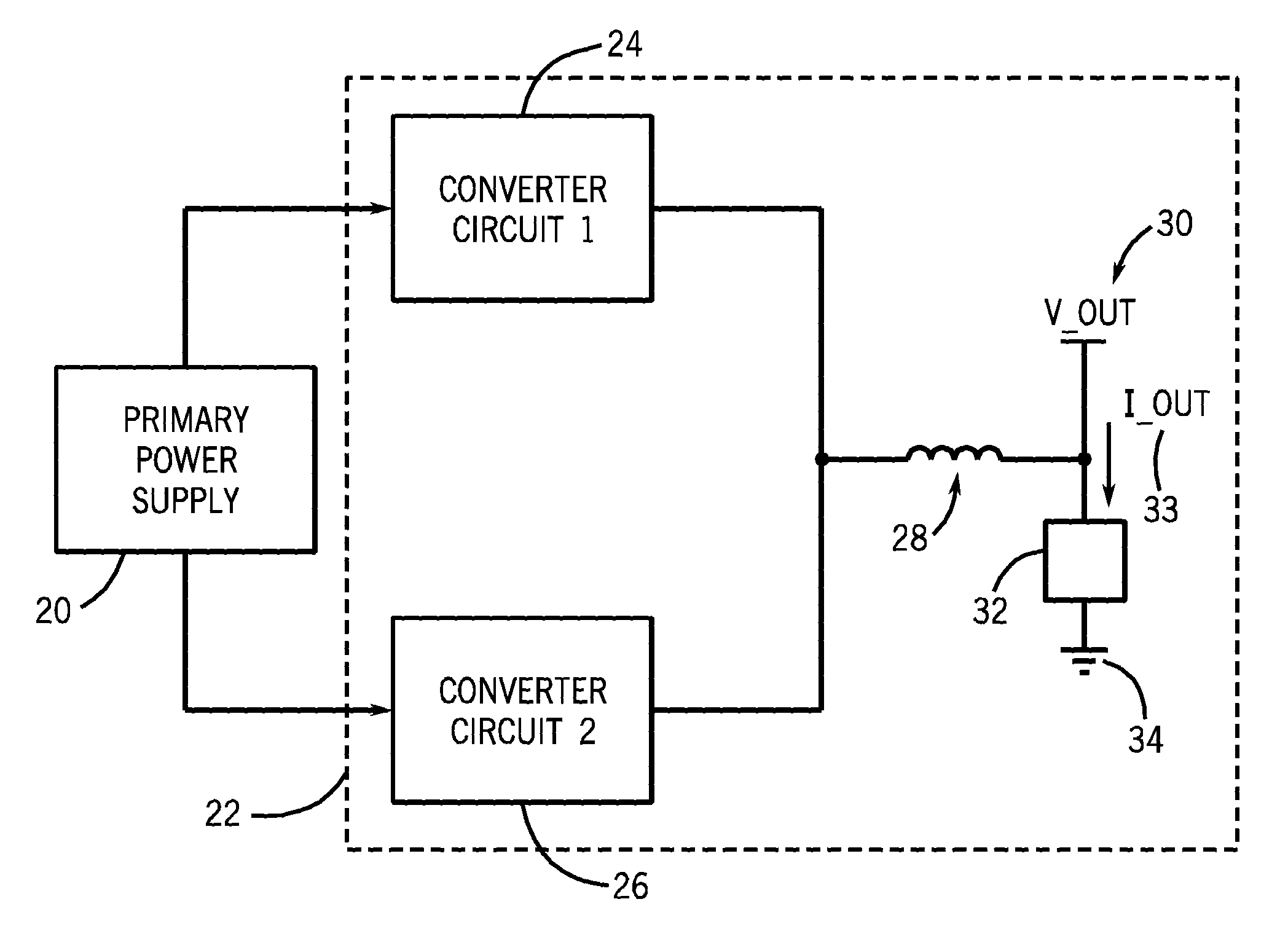
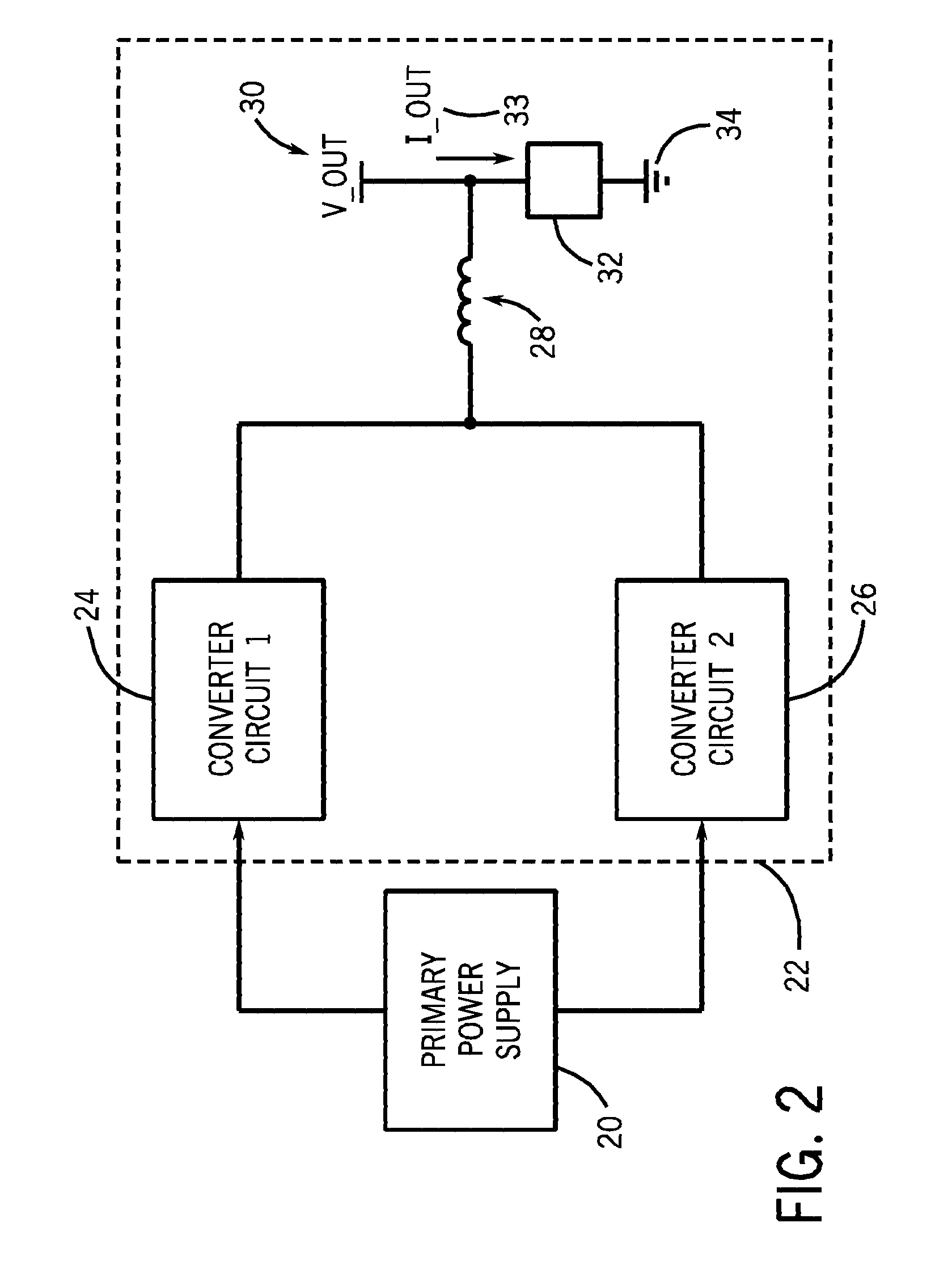
Welding or cutting power supply using phase shift double forward converter circuit (PSDF)
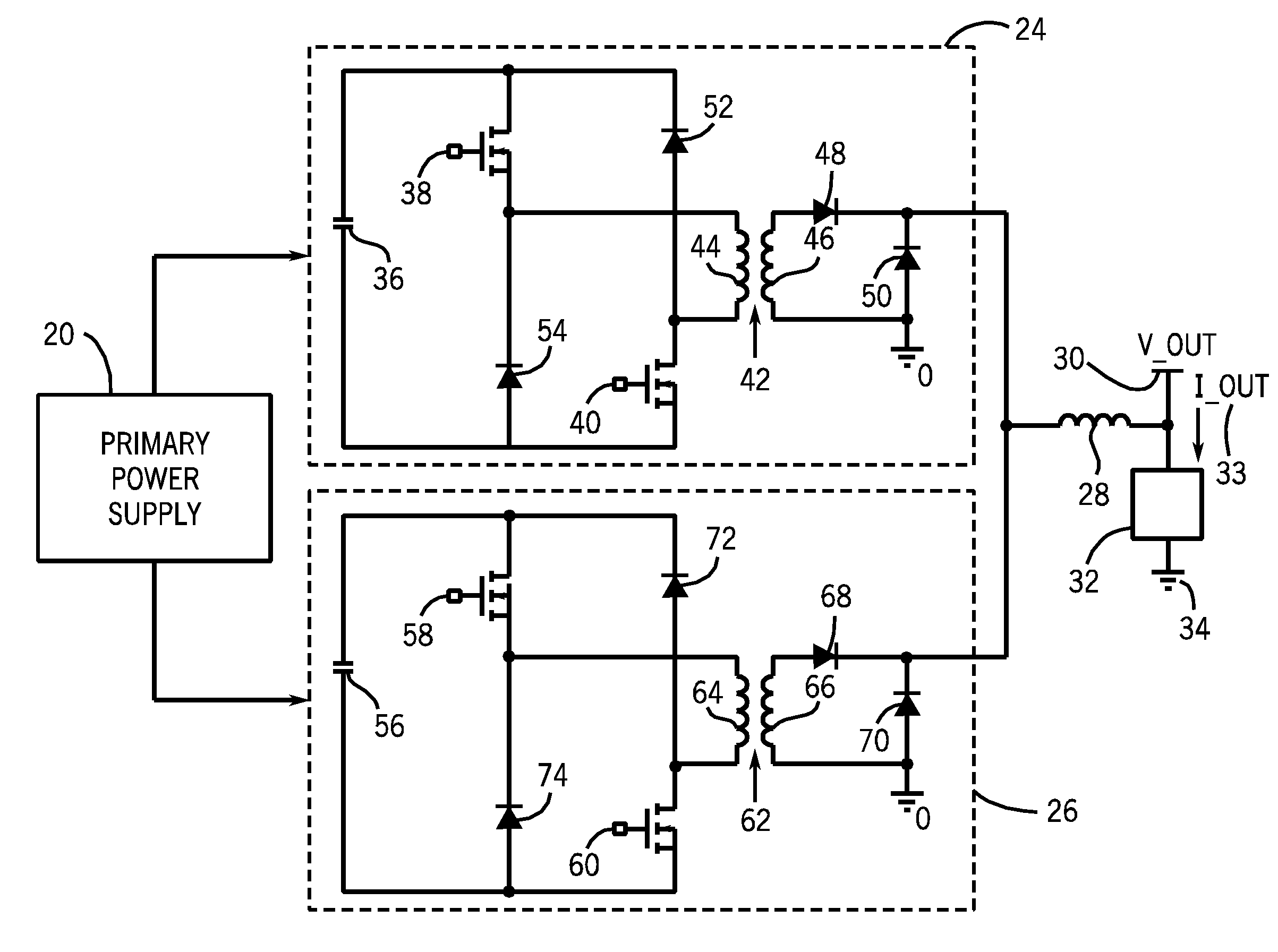
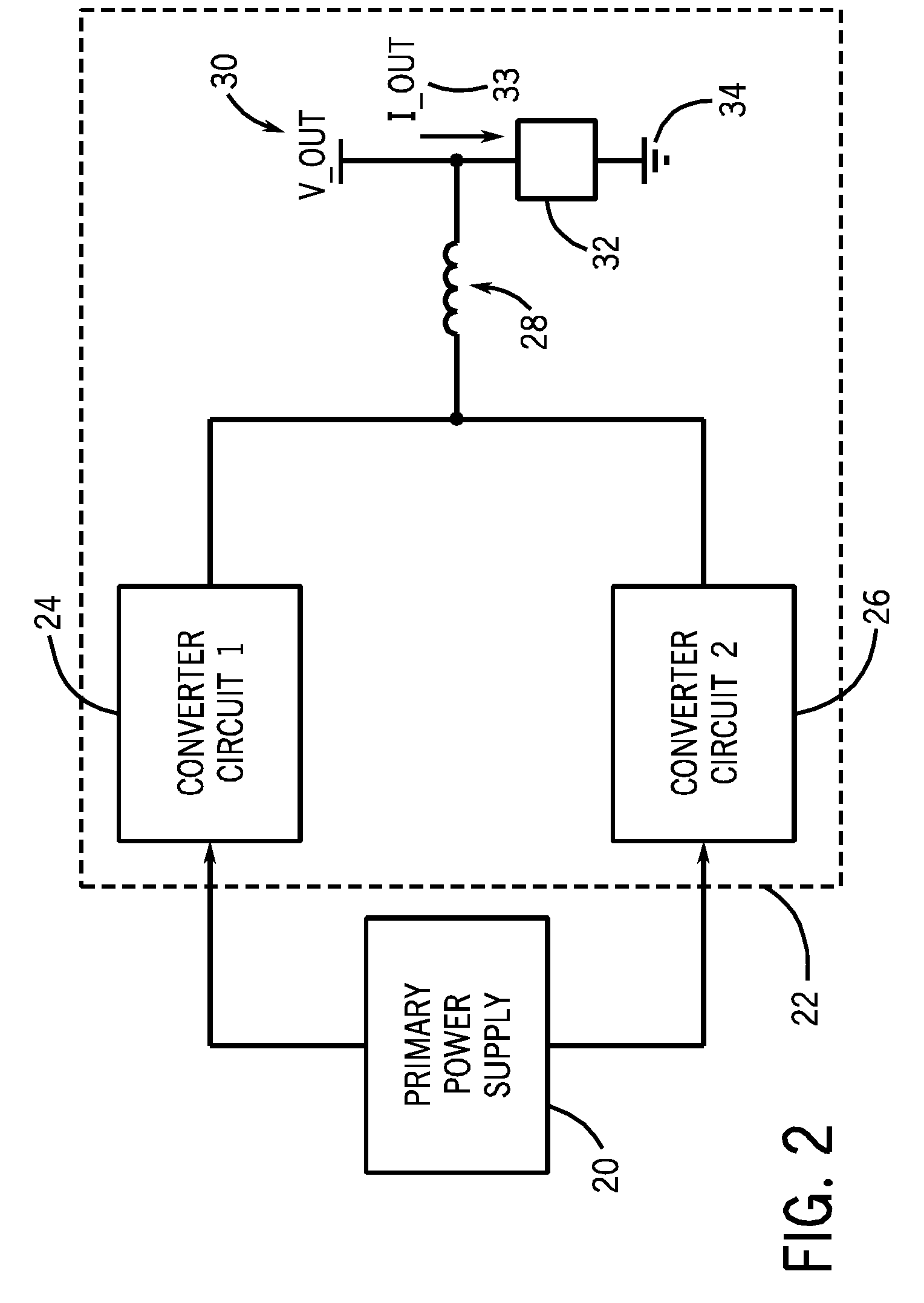
A technique for dynamically adjusting an output voltage for a welding or cutting operation is provided. The technique allows for varying output voltage at the welding or cutting torch by manipulating the duty cycles of two forward converter circuits. The present disclosure provides methods and systems for increasing synchronized duty cycles in a pair of forward converter circuits in response to increasing output voltage demand then changing a phase shift between the duty cycles in response to further increases in output voltage demand. The present disclosure provides a controller designed to receive input signals and generate output pulse width modulation signals that control the duty cycle width and phase shift of the outputs of the forward converter circuits in response to these signals. Methods of accommodating for the time needed for the transformer core to reset via leading edge or lagging edge compensation are provided.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Inductor current synthesizer for switching power supplies
InactiveUS6381159B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETSwitching cycle
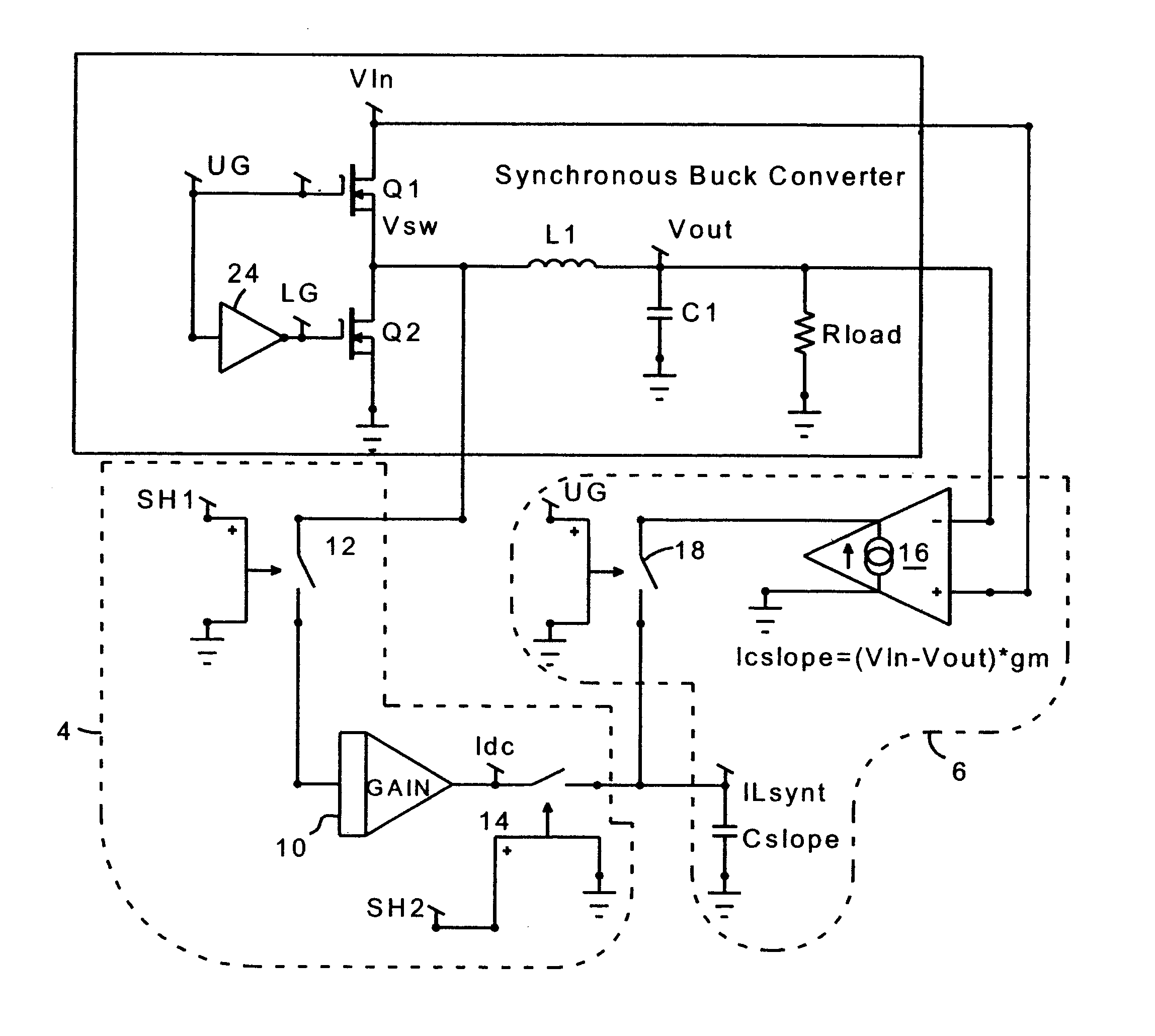
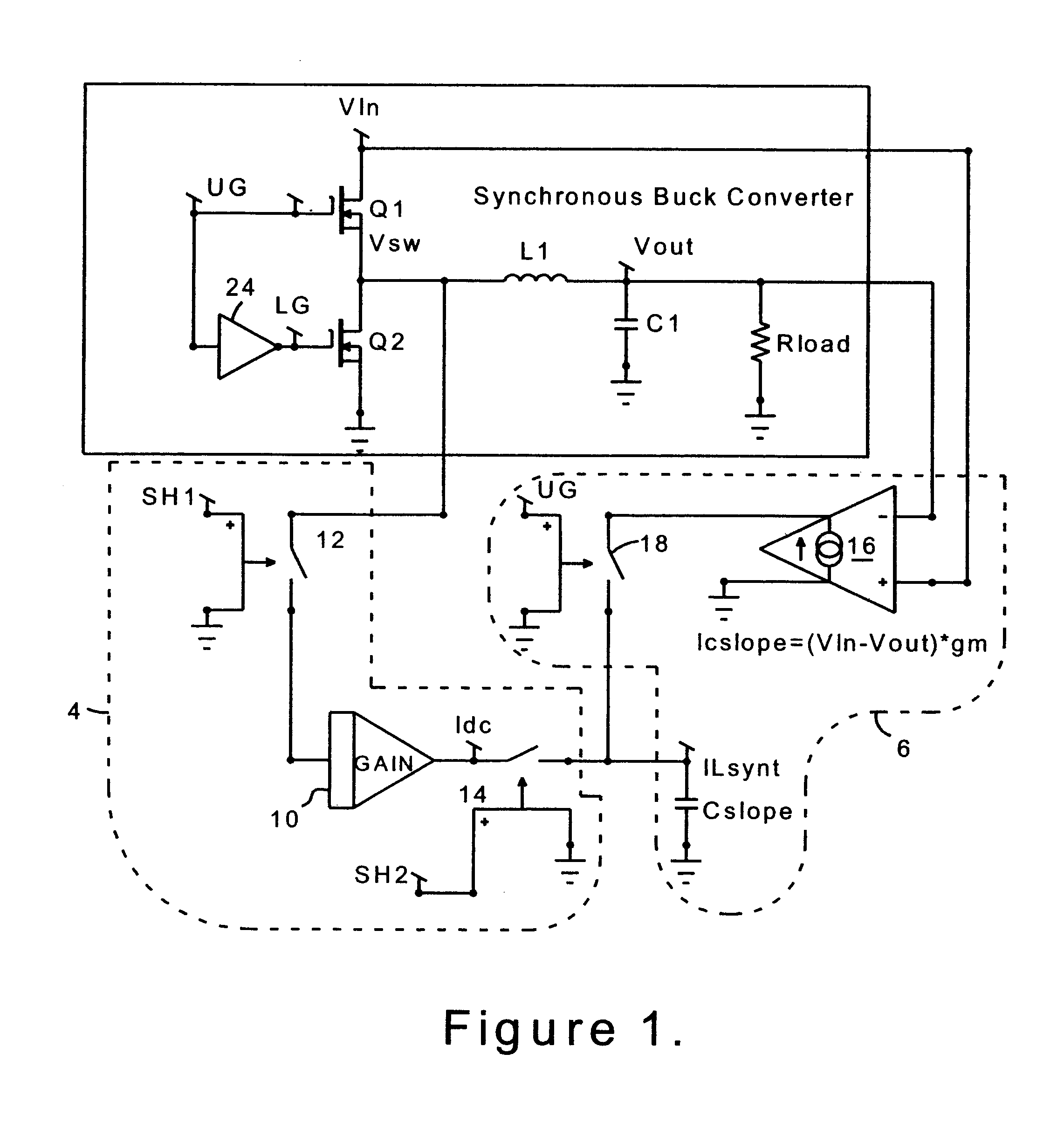
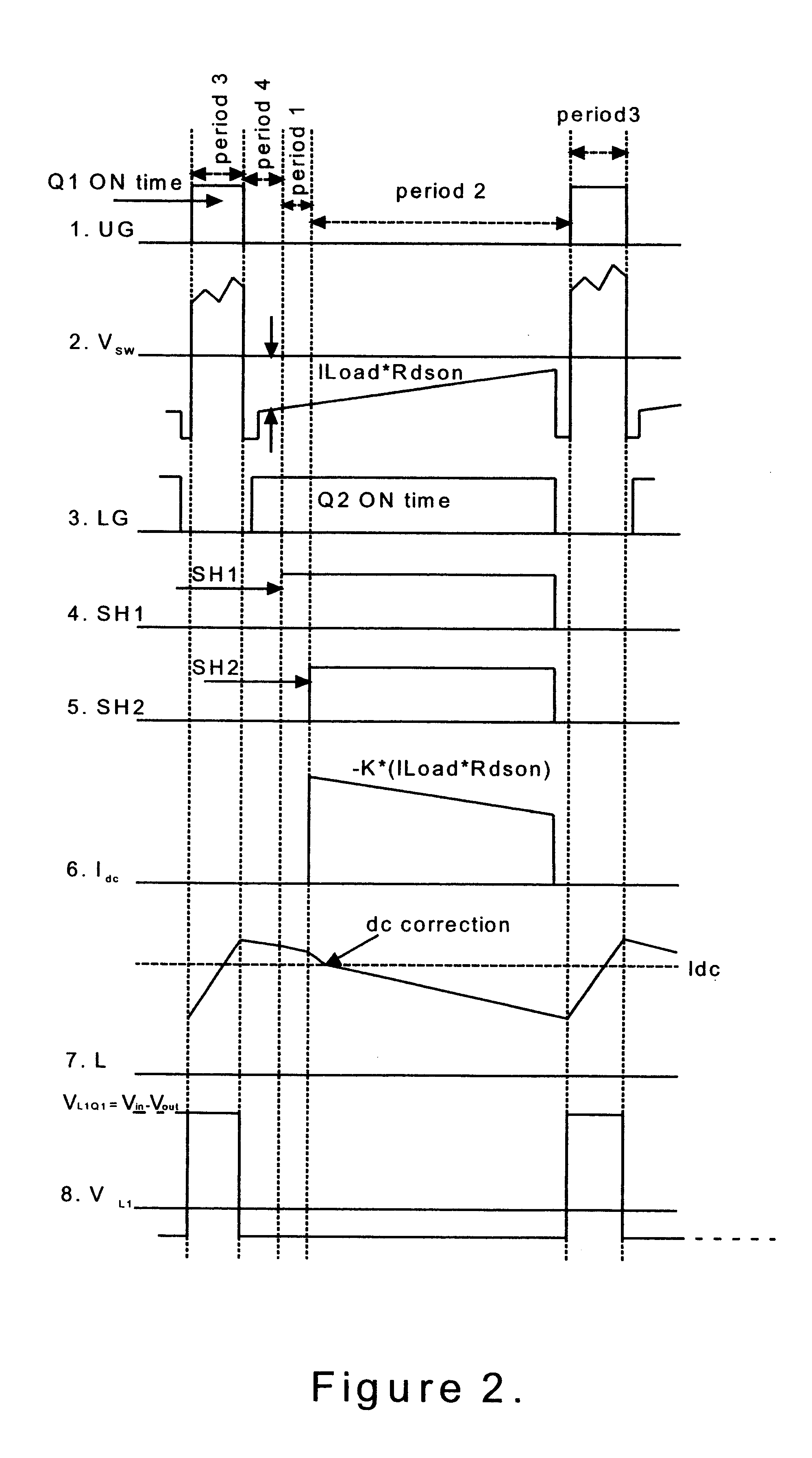
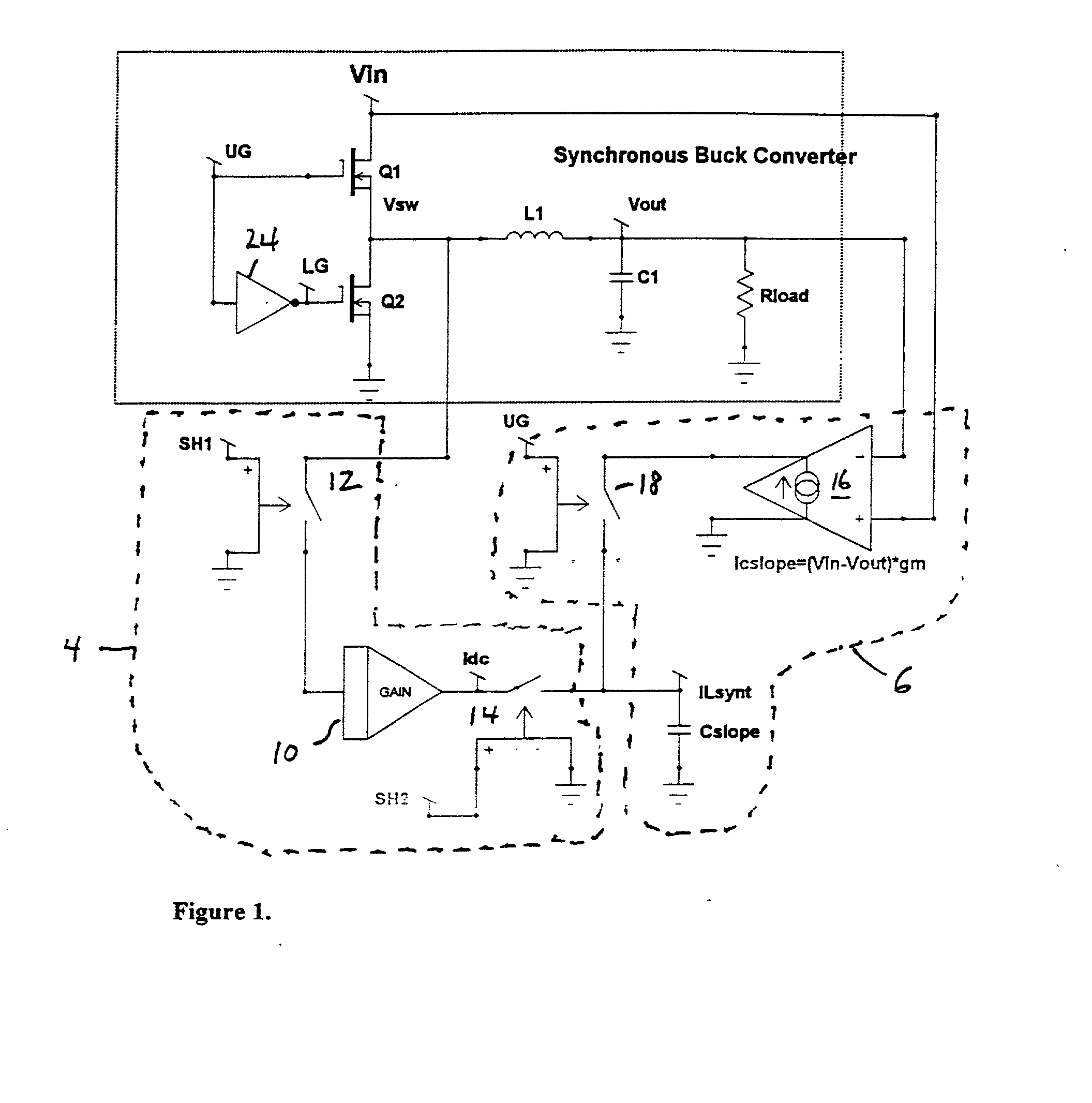
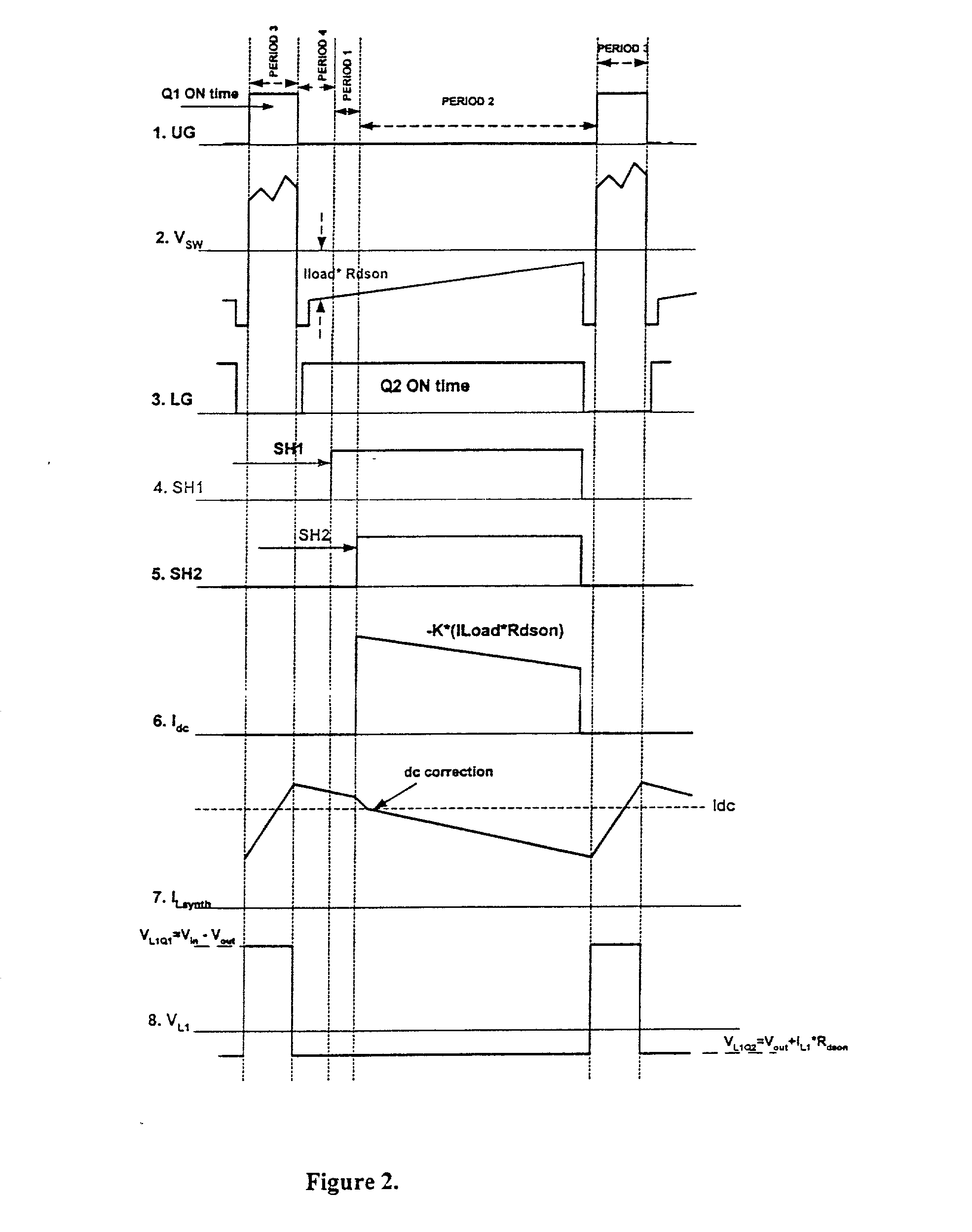
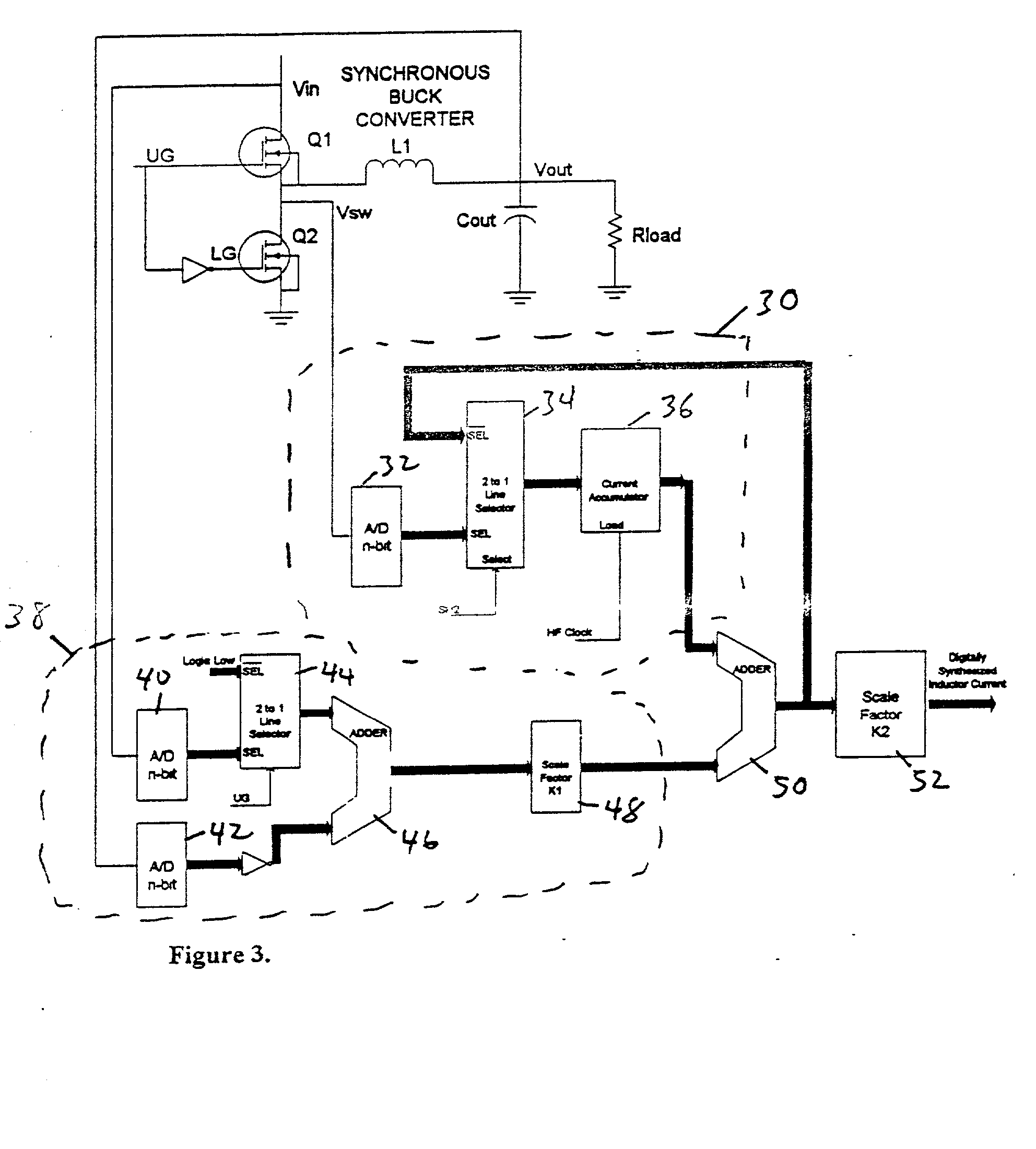
A circuit and method for sensing the inductor current flowing to a load from a switching power supply without using a sense resistor in the path of the inductor current. In a synchronous buck converter topology, the inductor current is derived by sensing the voltage drop across the synchronous MOSFET of the half-bridge and reconstructing the current using a sample and hold technique. A ripple current synthesizer is employed to reconstruct inductor current outside the sample and hold window. The sampled product ILoadxRDSon is used to update the ripple current estimator with dc information every switching cycle. The resulting voltage waveform is directly proportional to the inductor current. The inductor current synthesizer of the present invention can also be used in boost converter, flyback converter and forward converter topologies.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
DC converters
InactiveUS20070242487A1Easy to switchReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionSoft switchingTransformer
A DC converter comprises a half bridge supply circuit and one or more flyback or forward converter output circuits, and optionally also an LLC converter whose control can determine a common variable switching frequency. The half bridge supply circuit produces a 50% duty output alternating between two input voltages, such as zero and a voltage Vin. In each flyback or forward converter output circuit, a switch connects a transformer primary to the half bridge supply circuit output in a PWM controlled manner to regulate a respective flyback or forward converter DC output which is produced by the converter output circuit, with a duty ratio less than 50% whereby switching losses are reduced. Soft switching is further facilitated by the half bridge supply circuit having two transistors controlled in a complementary manner.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
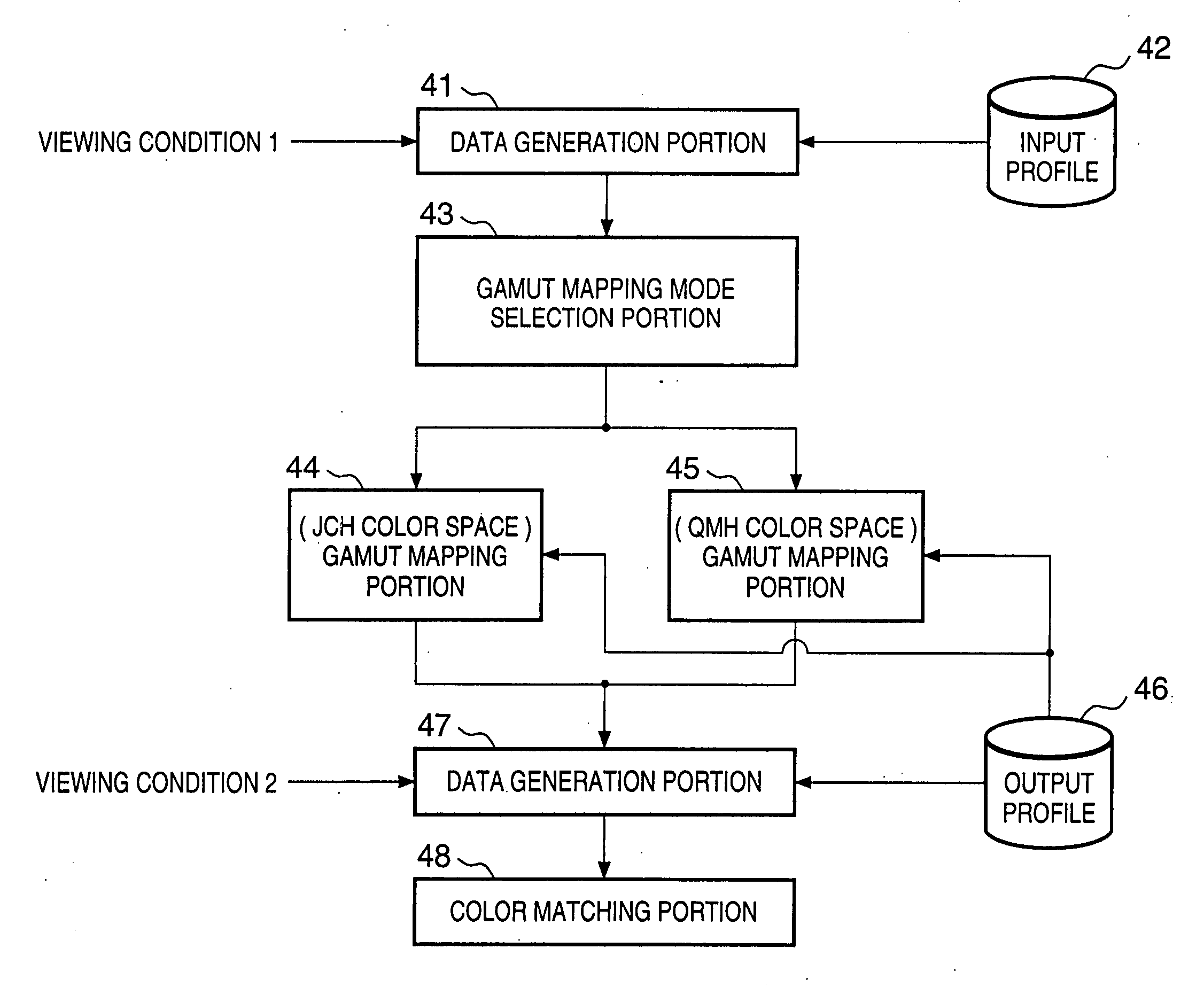
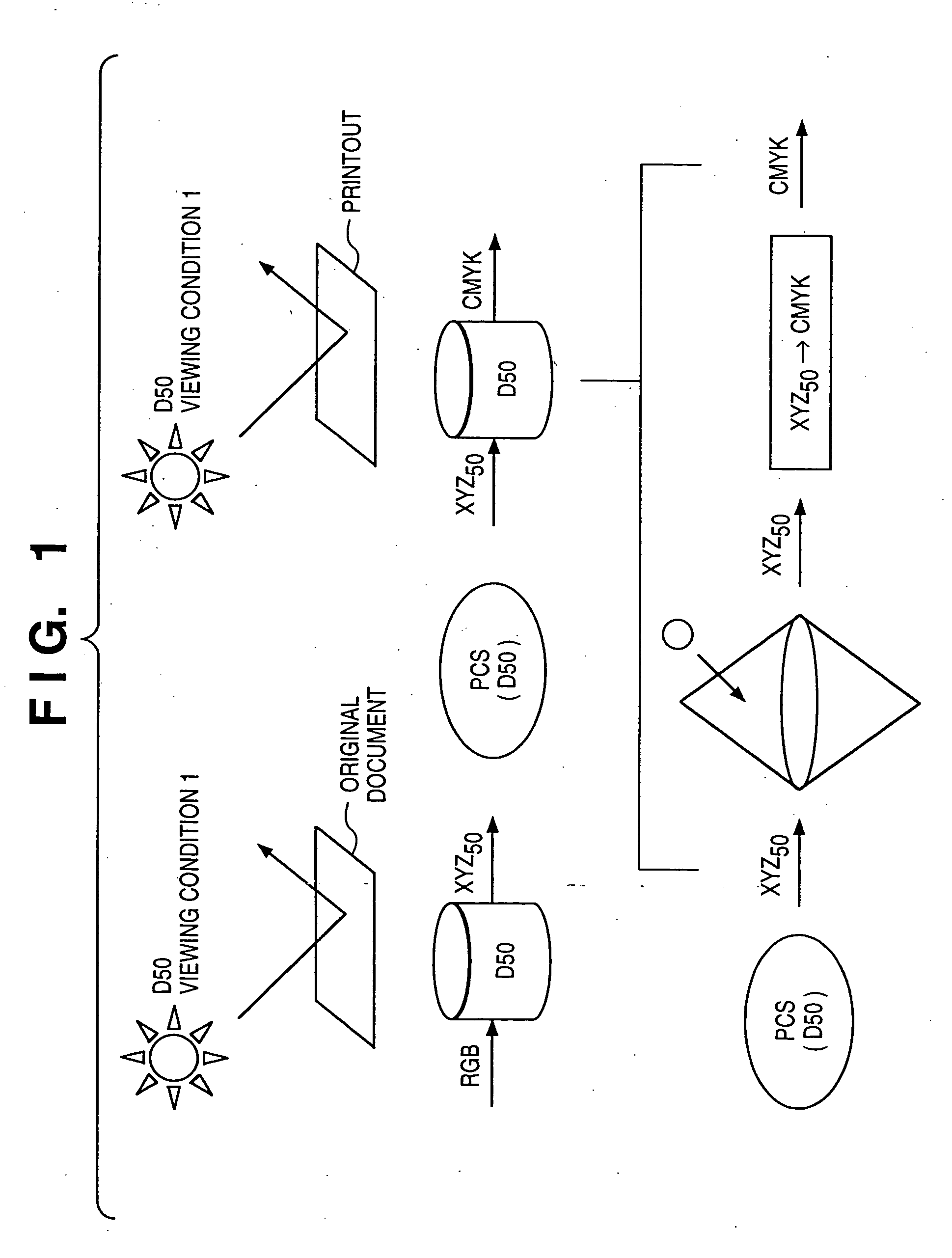
Image processing apparatus and method
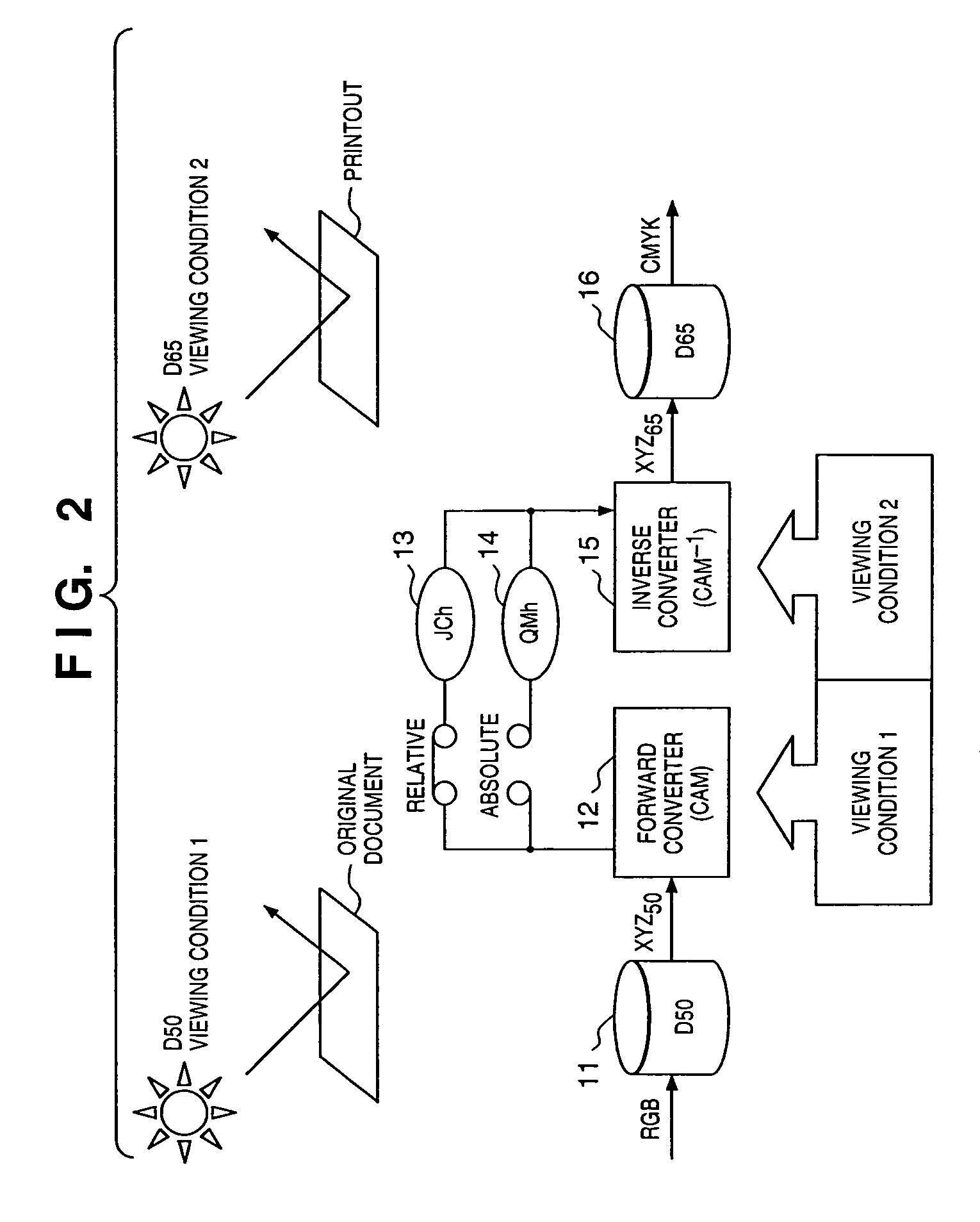
InactiveUS20050078122A1Easy to set upColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionLab color spaceGamut
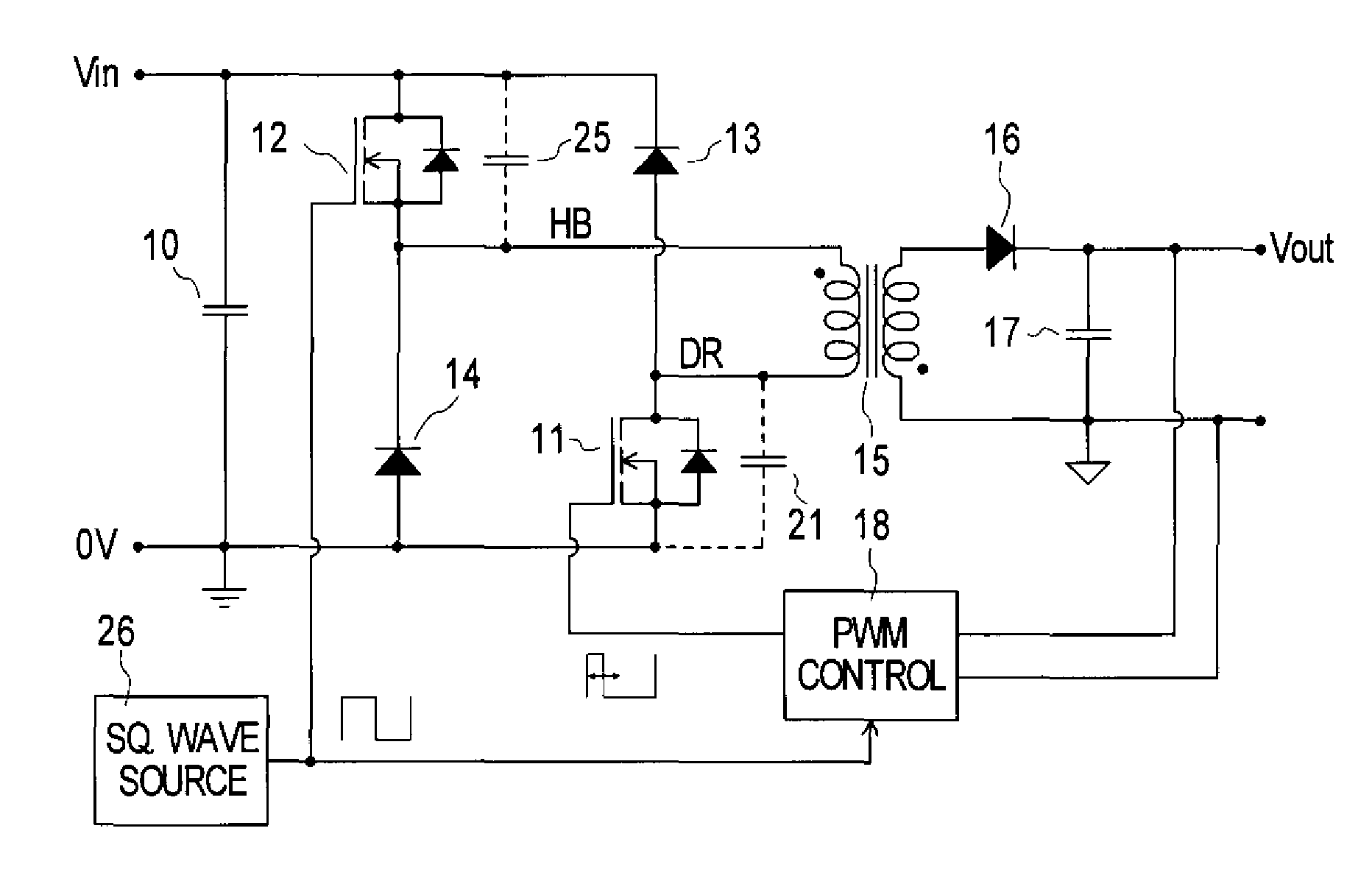
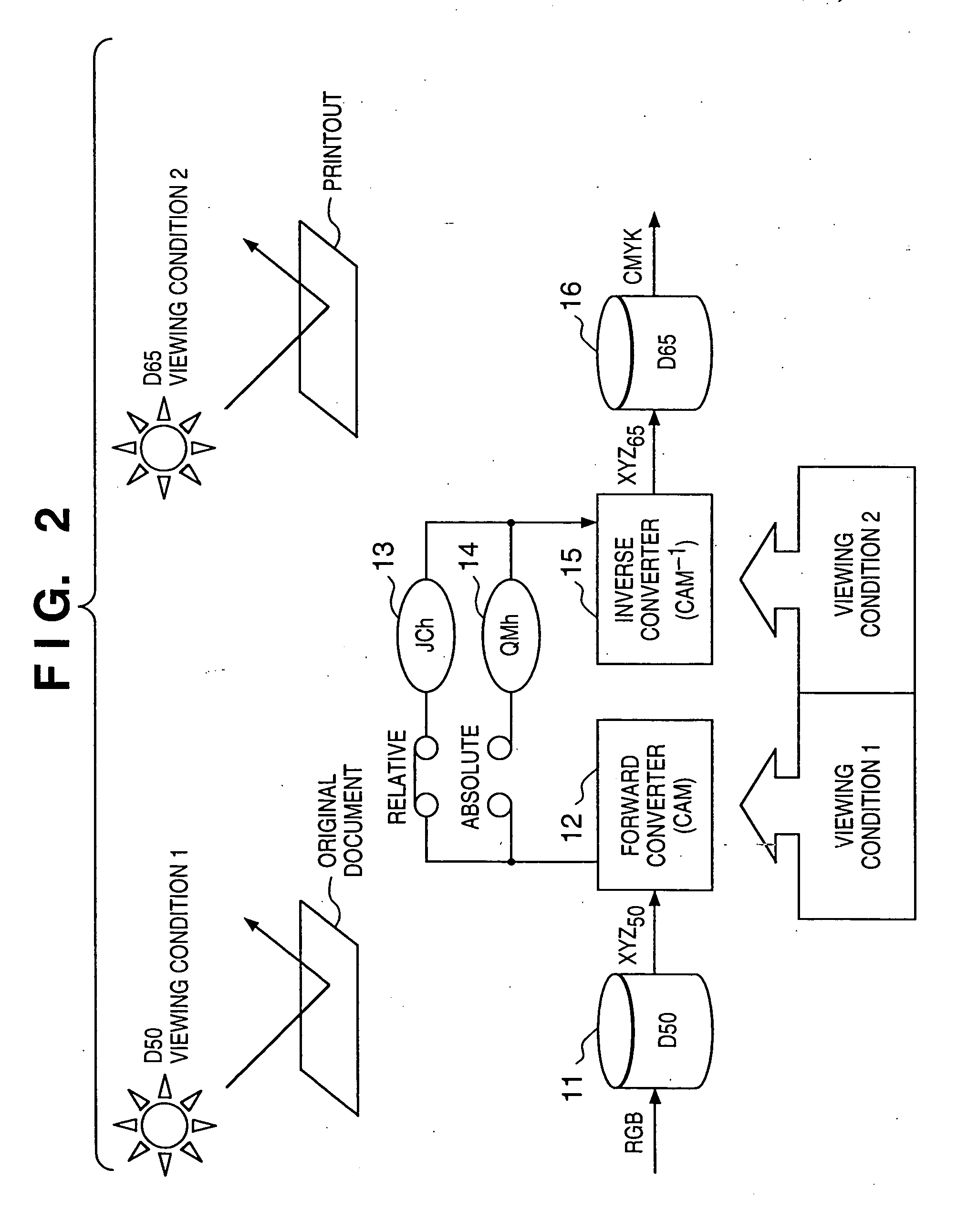
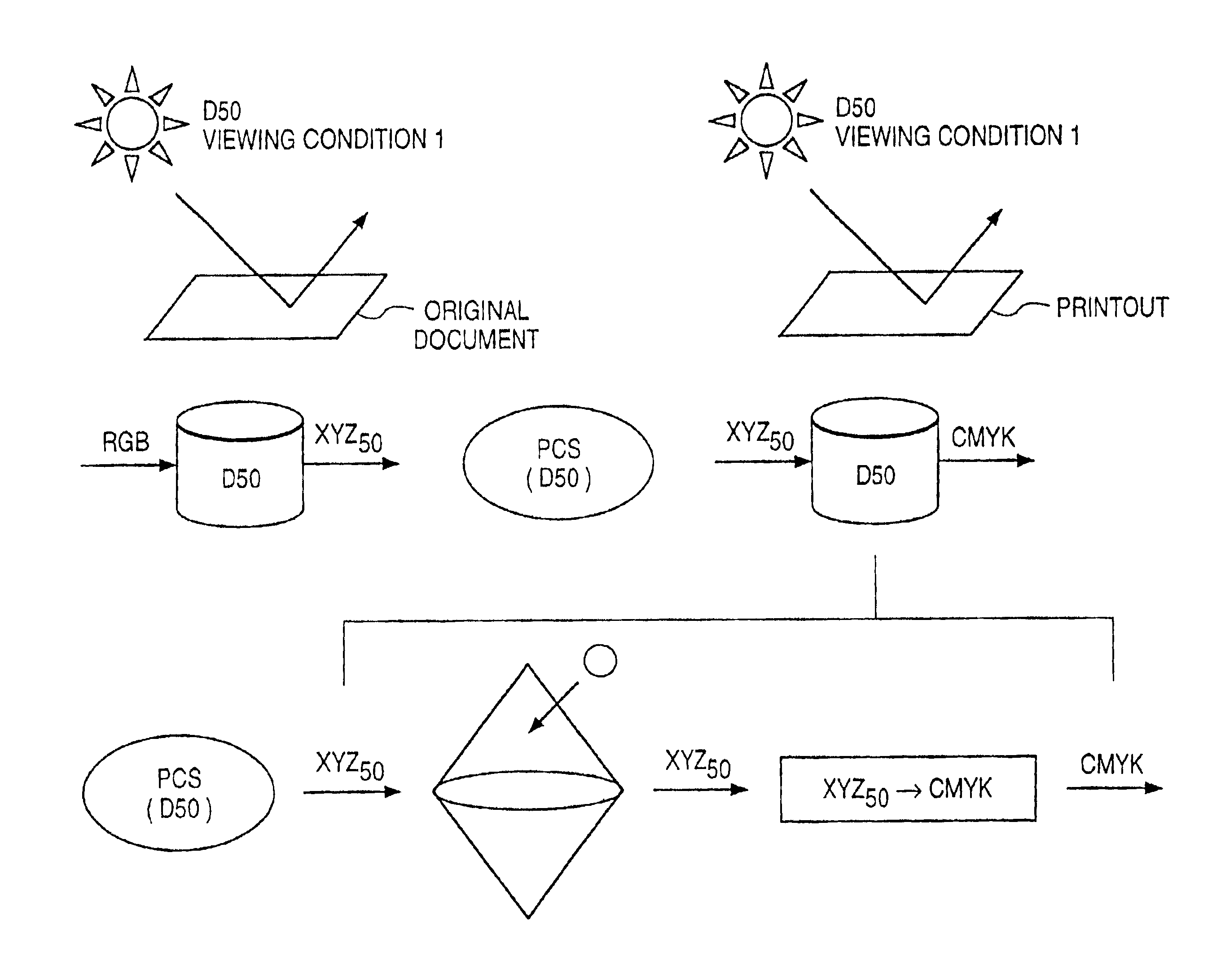
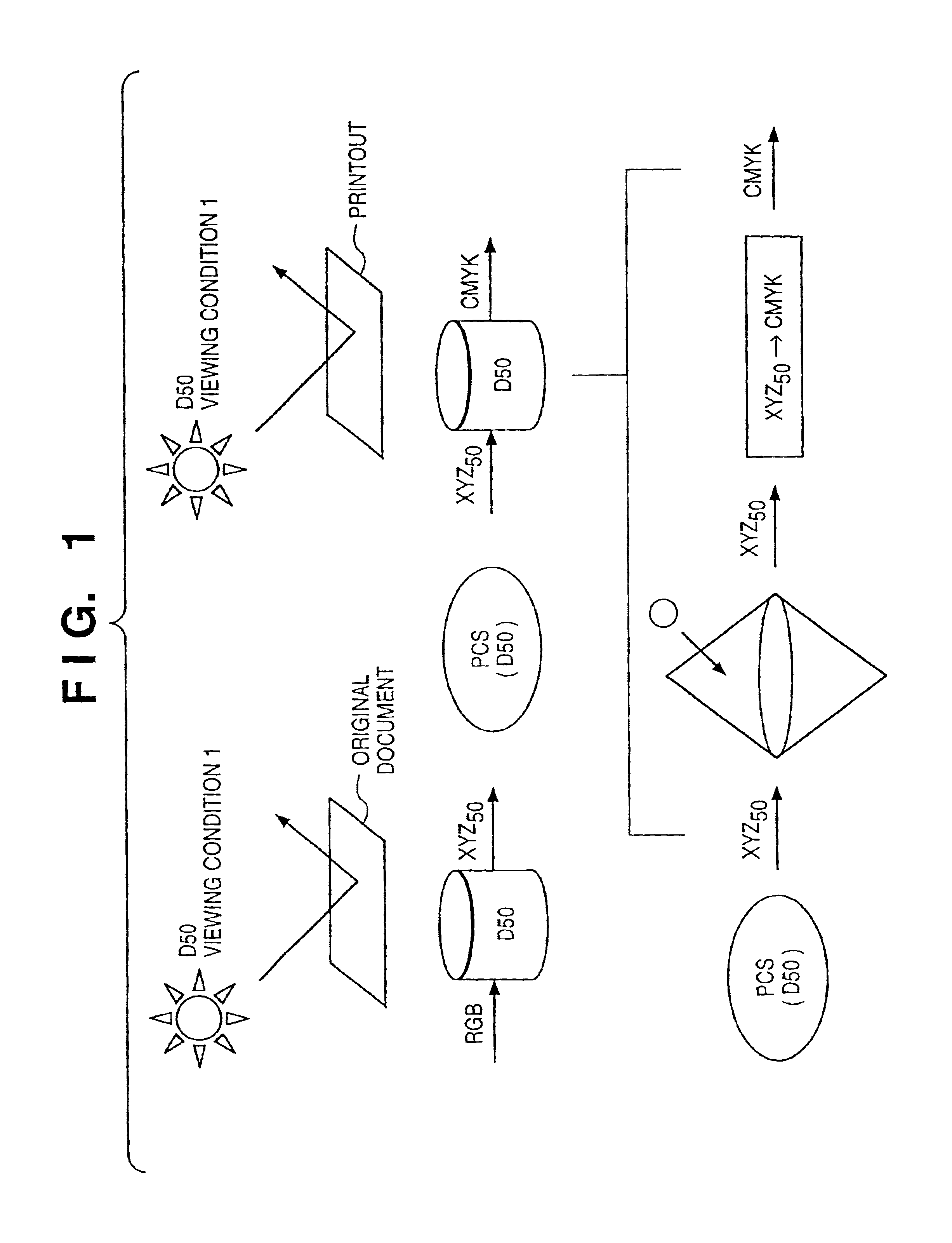
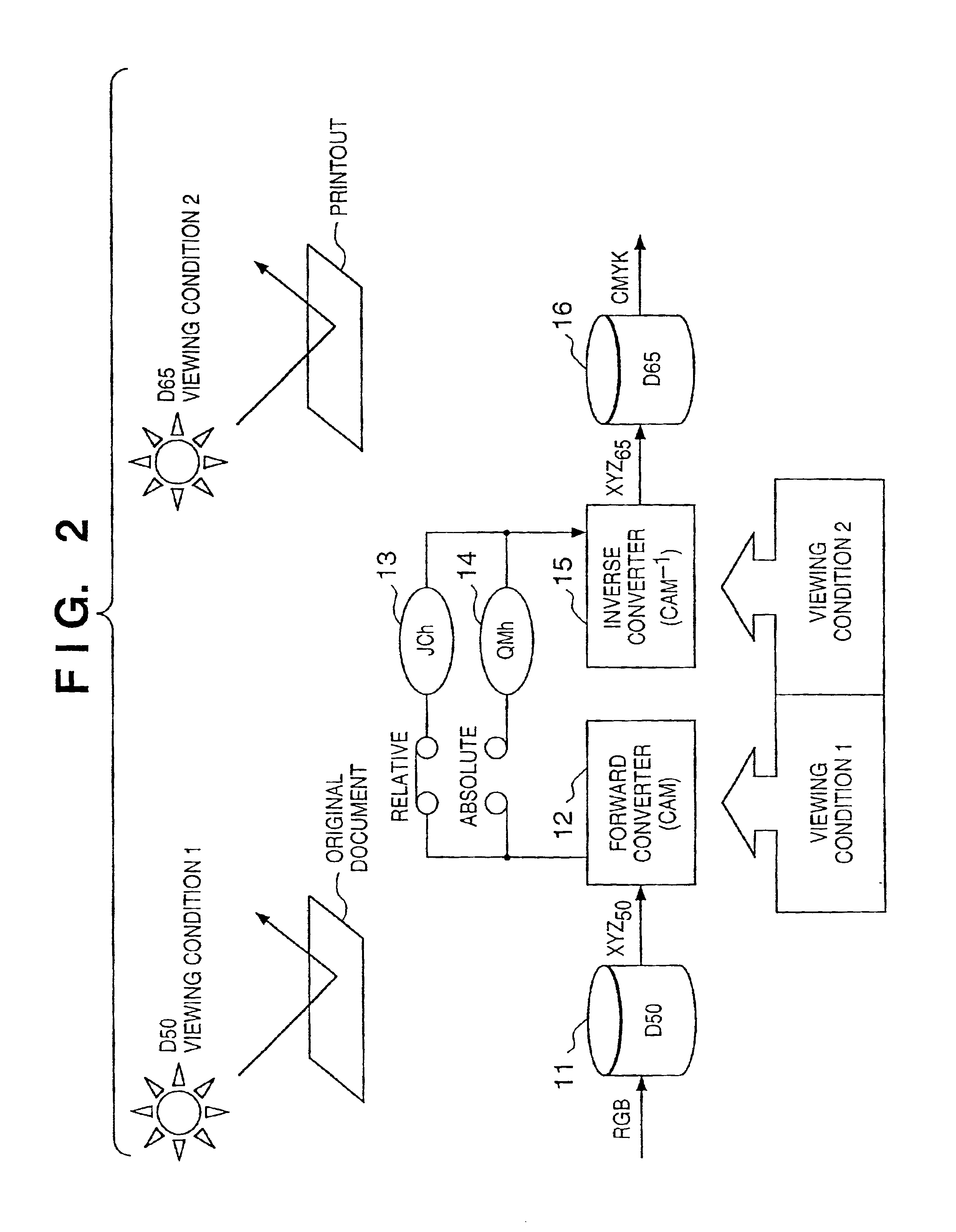
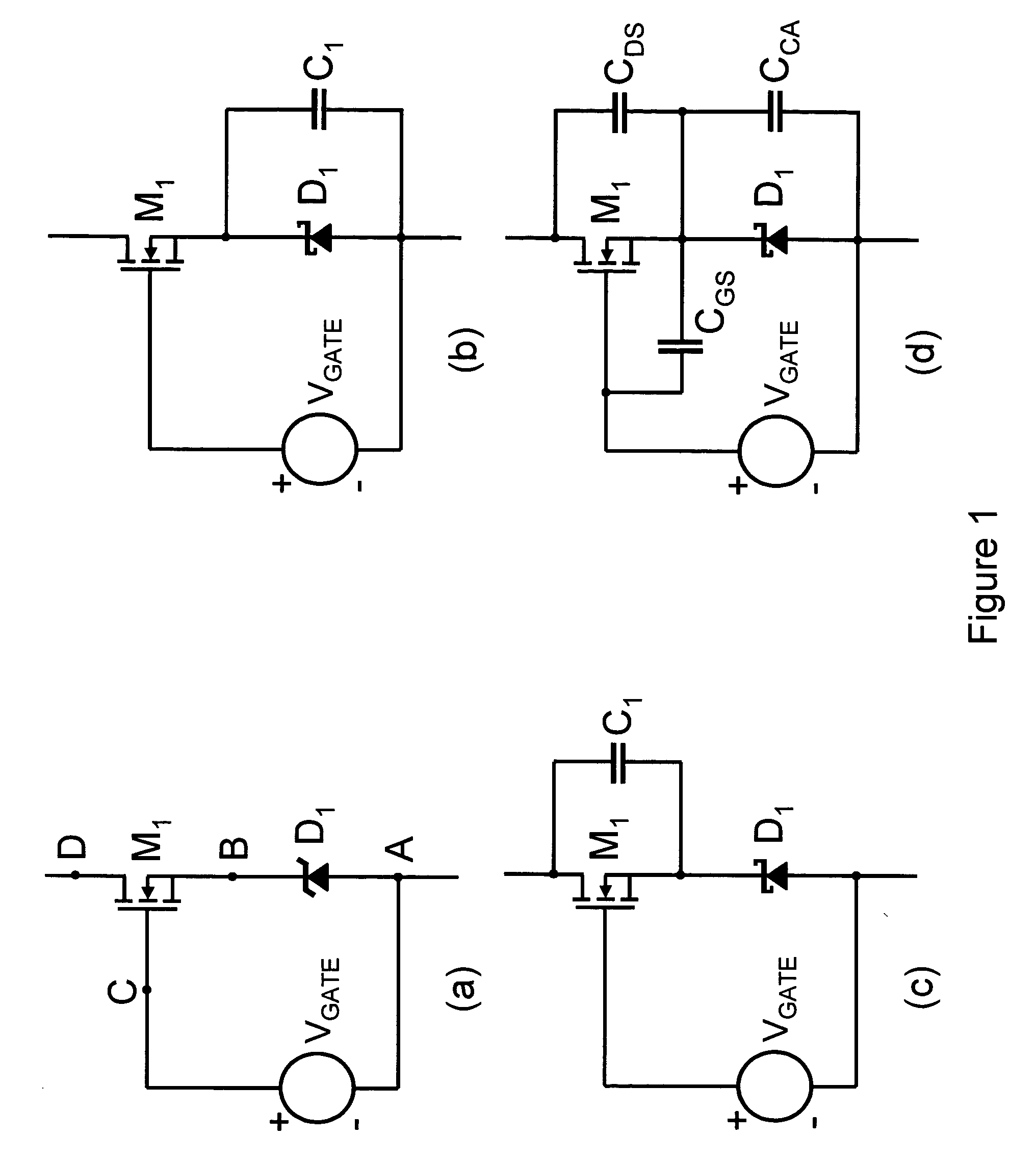
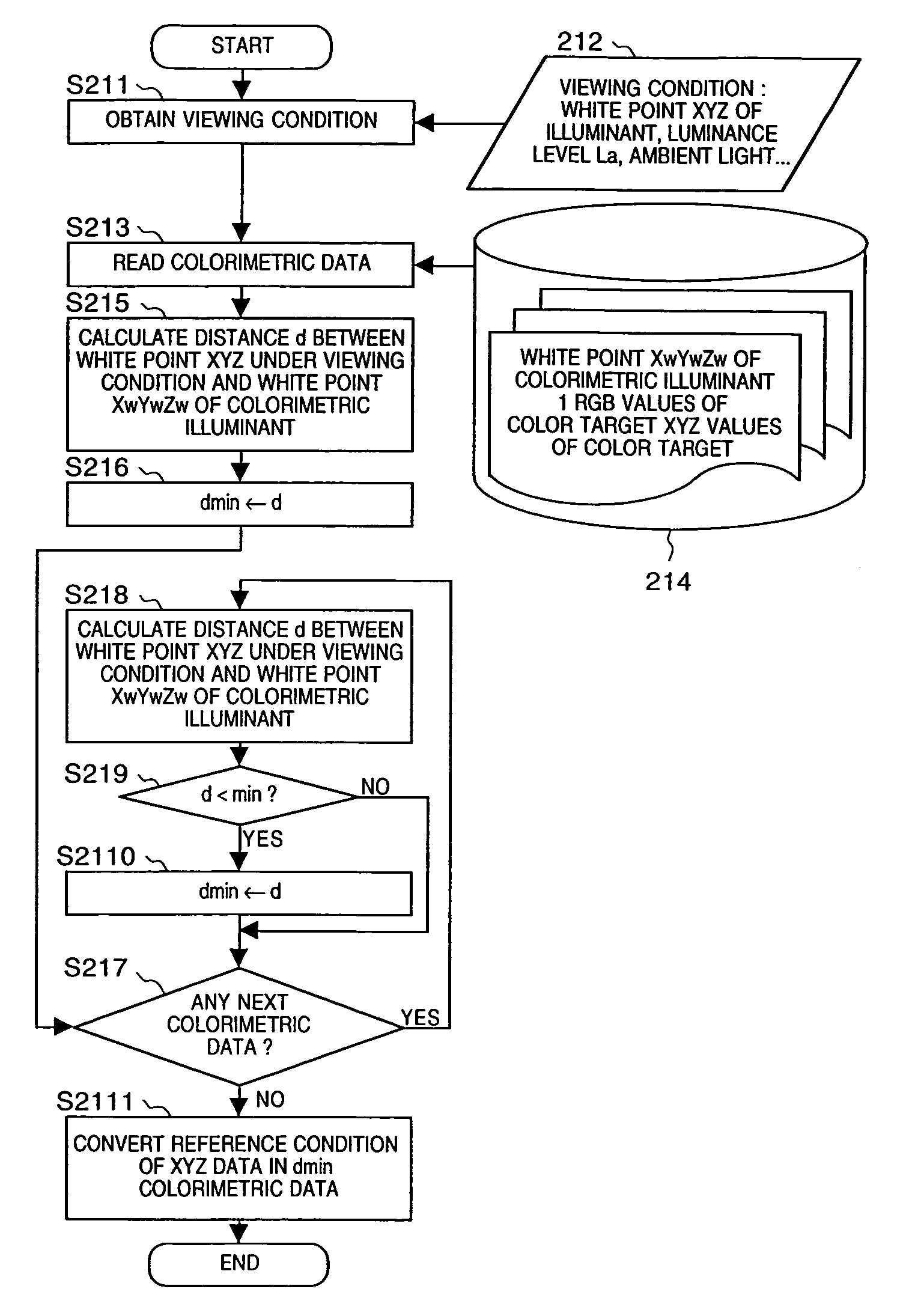
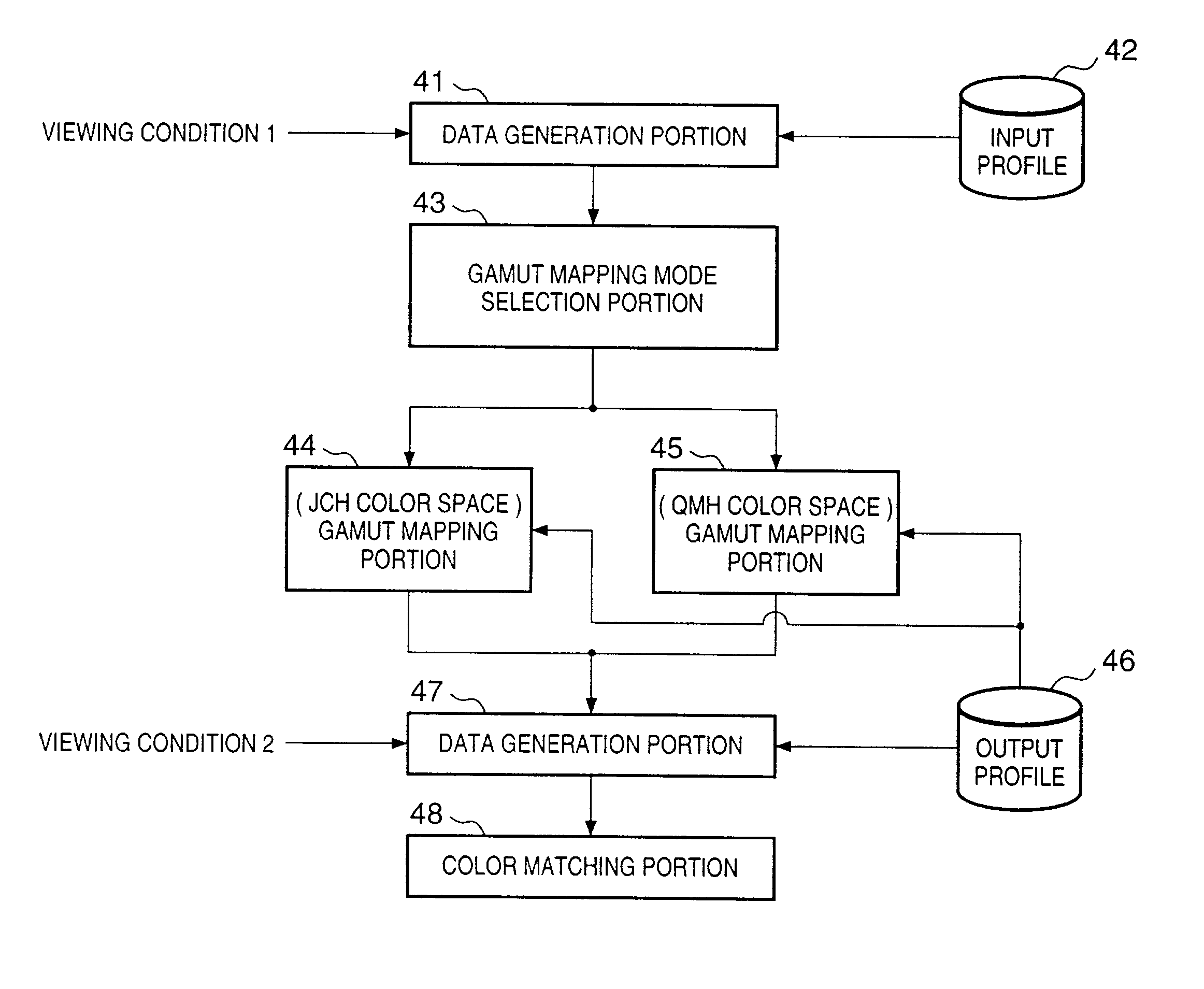
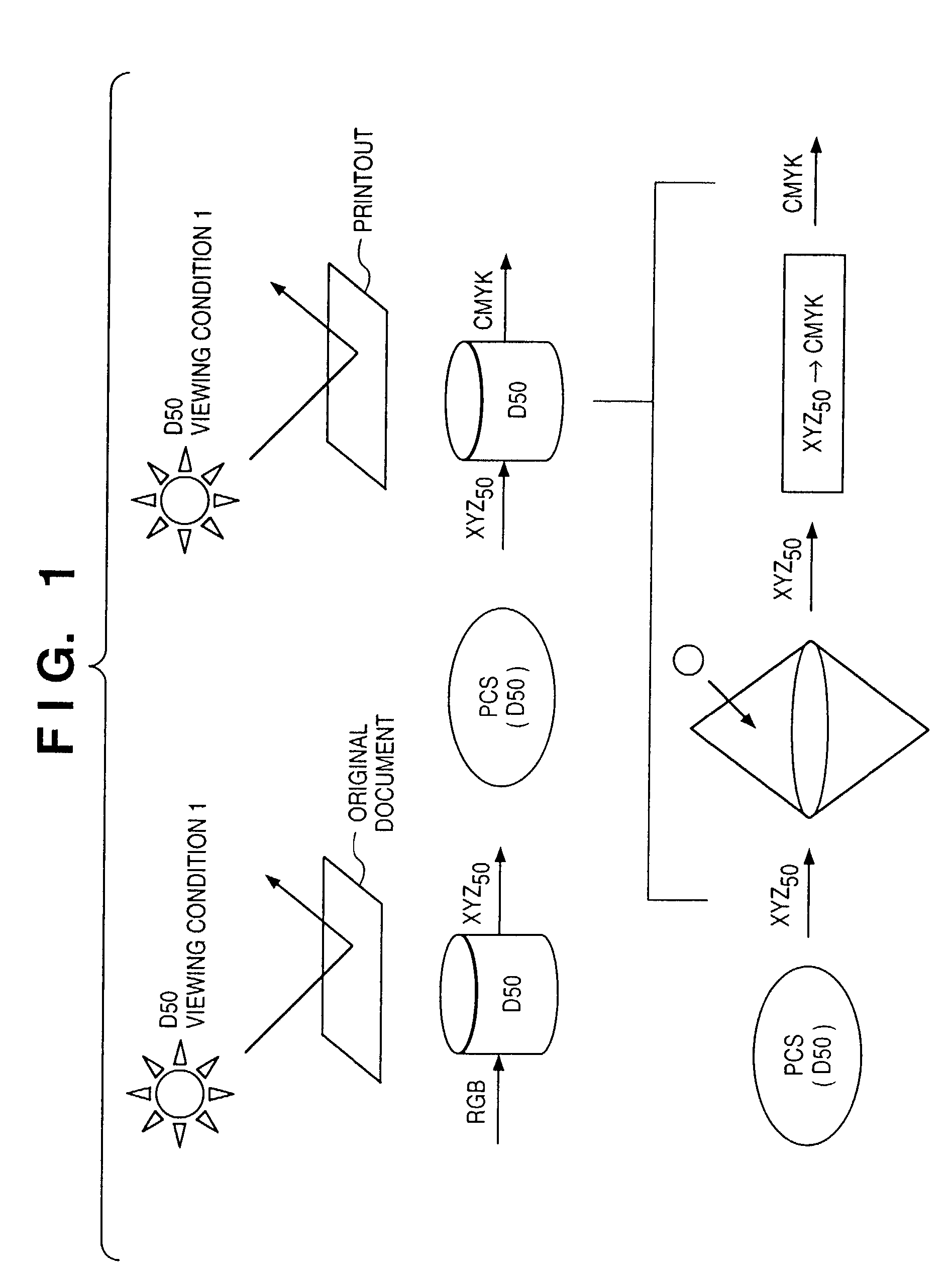
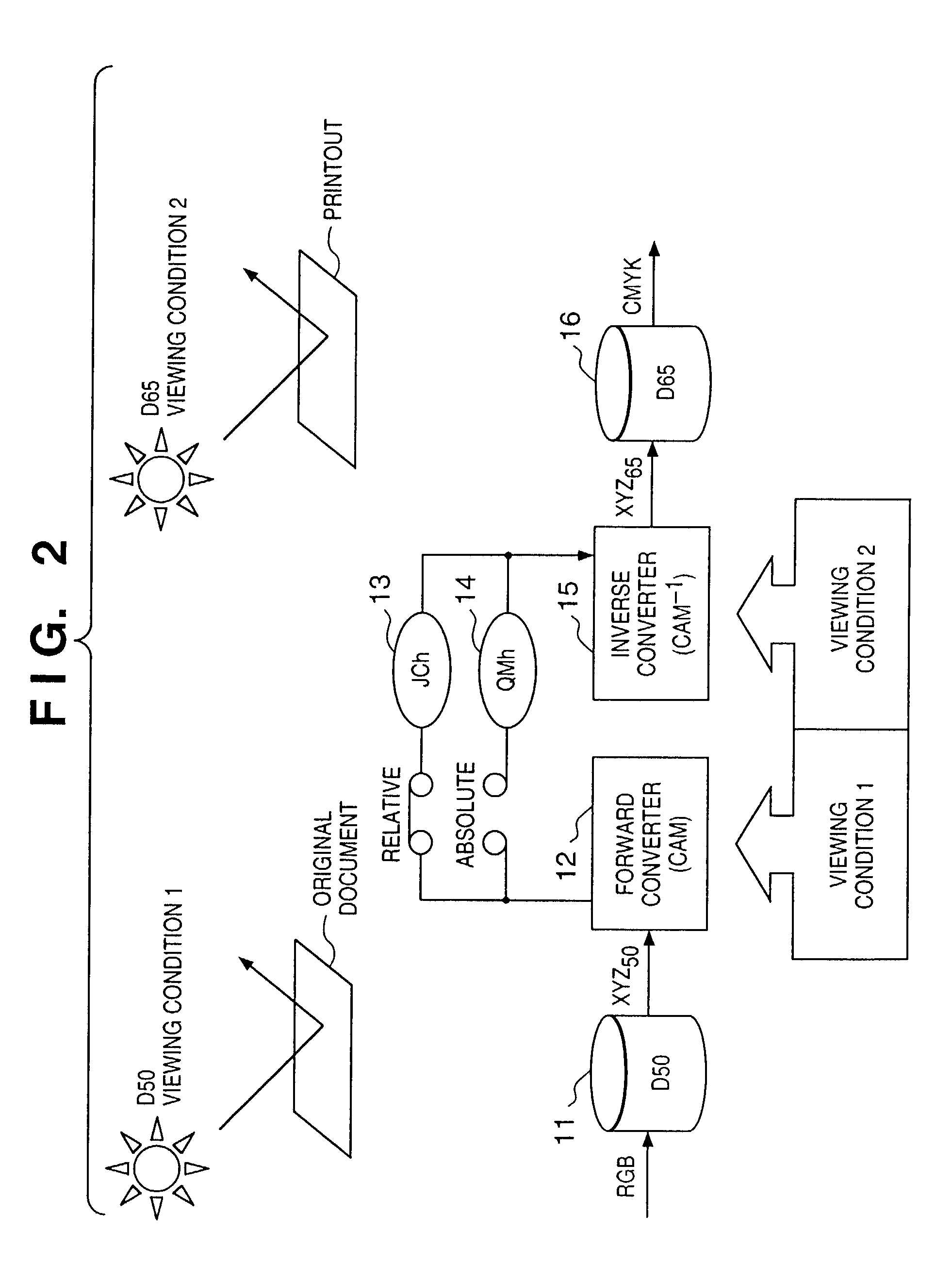
If gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by one Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
Inductor current synthesizer for switching power supplies
InactiveUS20010046145A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETSwitching cycle
A circuit and method for sensing the inductor current flowing to a load from a switching power supply without using a sense resistor in the path of the inductor current. In a synchronous buck converter topology, the inductor current is derived by sensing the voltage drop across the synchronous MOSFET of the half-bridge and reconstructing the current using a sample and hold technique. A ripple current synthesizer is employed to reconstruct inductor current outside the sample and hold window. The sampled product ILoadxRDSon is used to update the ripple current estimator with dc information every switching cycle. The resulting voltage waveform is directly proportional to the inductor current. The inductor current synthesizer of the present invention can also be used in boost converter, flyback converter and forward converter topologies.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Image processing apparatus and method, and profile generating method
InactiveUS6859551B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersLab color spaceGamut
If gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by one Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
High efficiency power conversion circuits
InactiveUS20060062026A1Easy to handleReduce winding voltage stress stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLevel shiftingFull bridge
A composite high voltage schottky rectifier is revealed that provides a forward voltage slightly larger than a low voltage schottky rectifier combined with a high voltage breakdown capability. The composite rectifier can be formed from the combination of a low voltage schottky rectifier, a high voltage mosfet, and a few small passive components. A quarter bridge primary switching network similar in some ways to a half bridge primary switching network is revealed. The quarter bridge network consists of four switches with voltage stress equal to half the line voltage and the network applies one quarter of the line voltage to a primary magnetic circuit element network thereby reducing the number of primary winding turns required to one quarter by comparison to a common full bridge network. A synchronously switched buck post regulator is revealed for multi-output forward converters. The synchronously switched buck post regulator accomplishes precise independent load regulation for each output and reduced magnetics volume by using a coupled inductor with a common core for all outputs plus a second smaller inductor for each output except the highest voltage output. An improved capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is revealed that provides an effective drive mechanism for a floating or high side switch without the use of level shifting circuits or magnetic coupling. The capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is an improvement over prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits in that the new circuit uses a positive current feedback mechanism to reject slowly changing voltage variations that cause unintentional switch state changes in prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6999617B1High color reproductionTexturing/coloringPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesLab color spaceGamut
If one gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by the Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
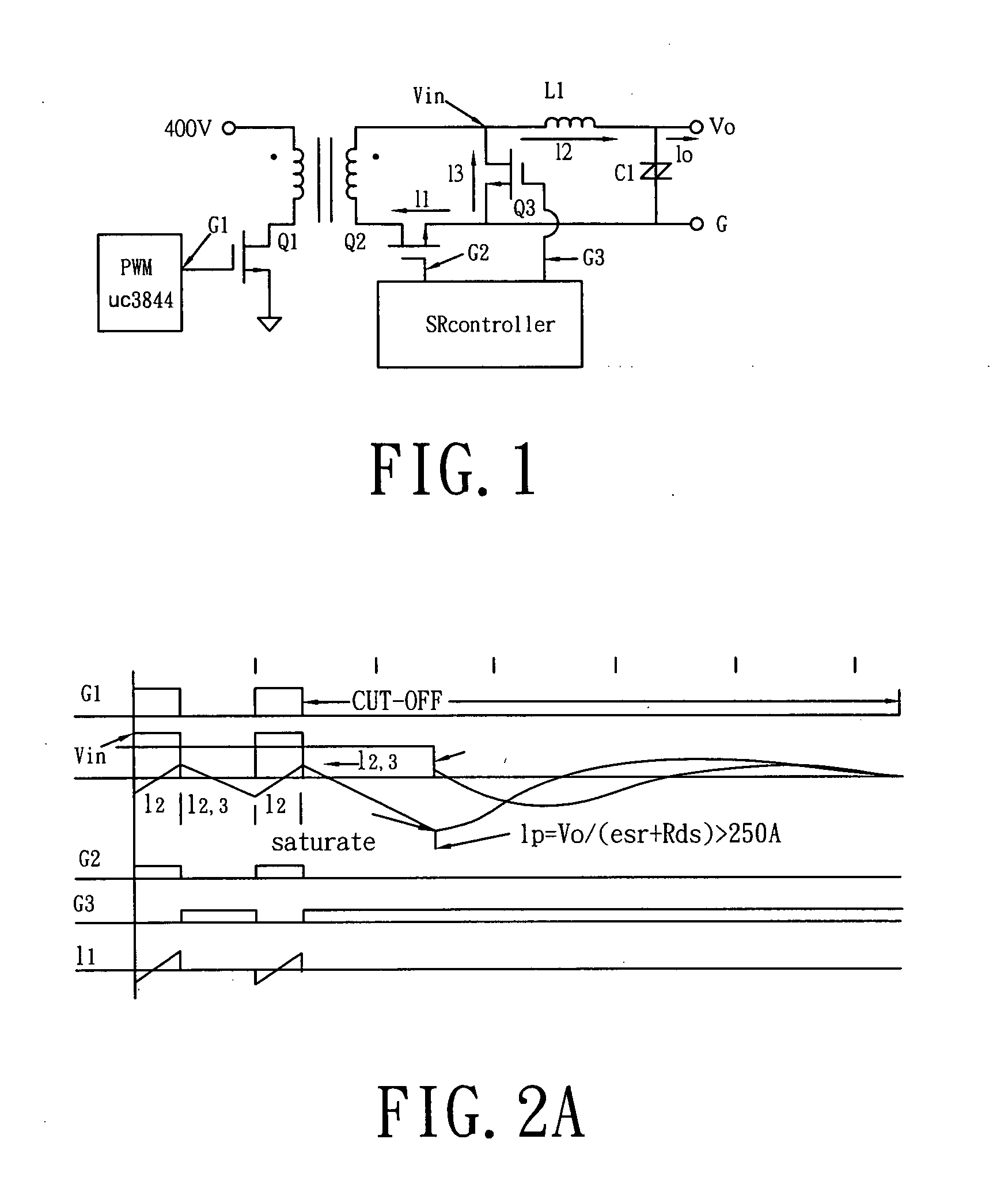
Novel synchronous rectifying self-driven circuit for resonant reset forward converter
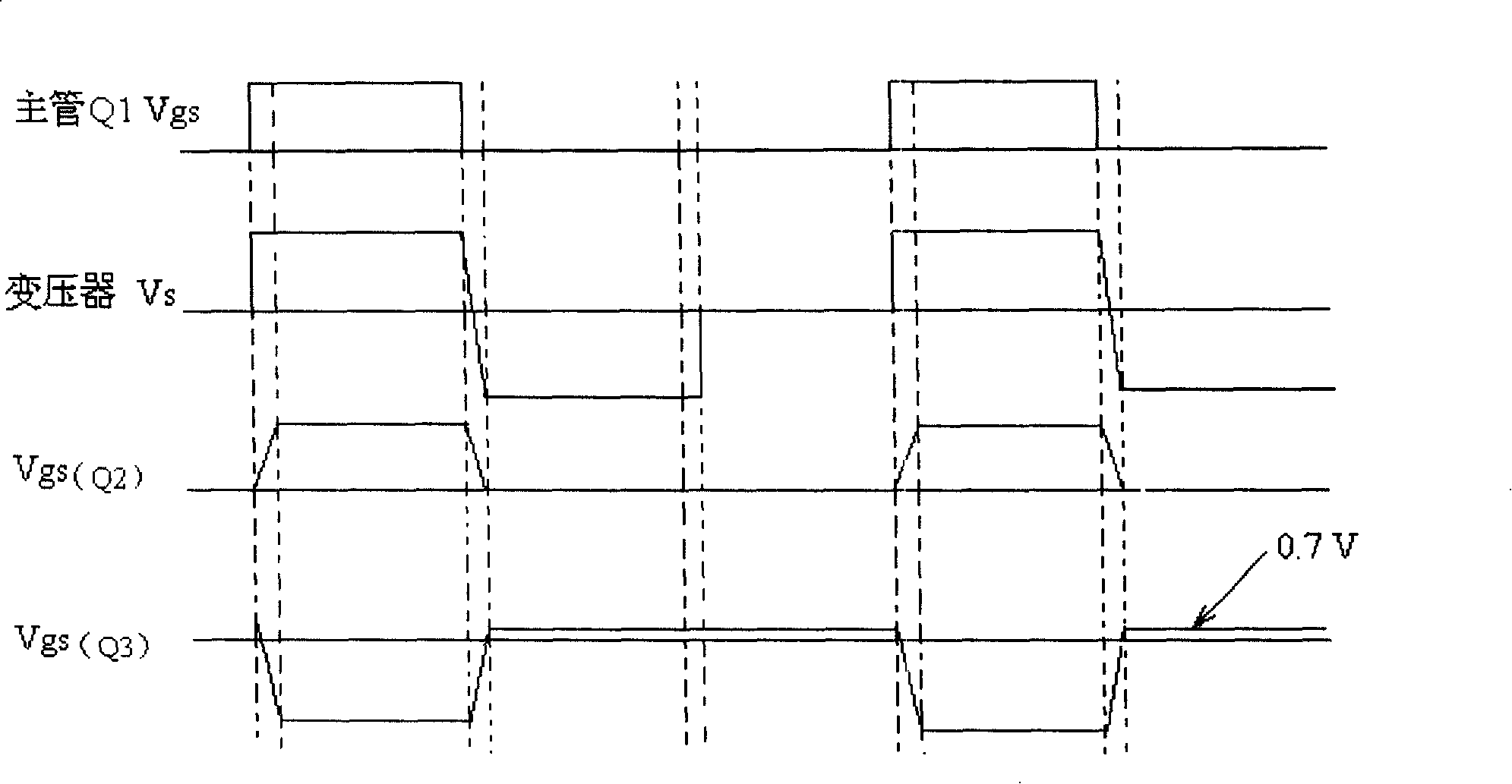
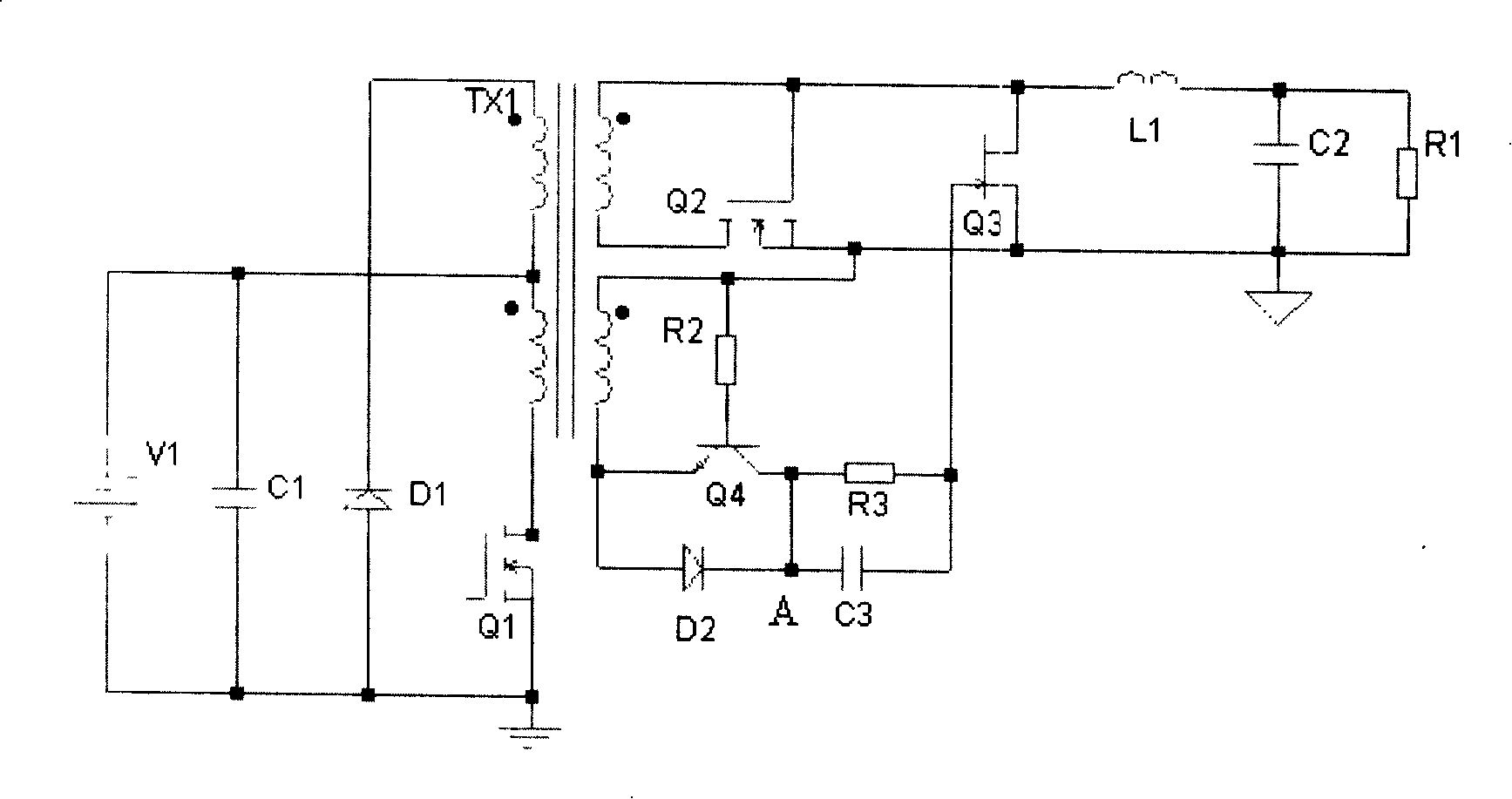
InactiveCN101039075ASimple structureStable structureEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitancePeak value
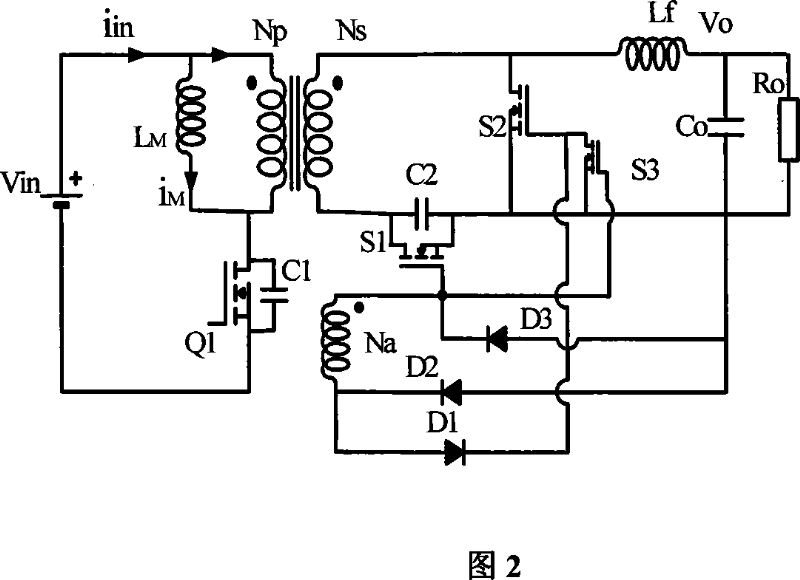
The present invention provides a synchronization rectifying self-driving circuit for a new resonant reset forward converter. The gate charging loop of the freewheeling tube S2 comprises an auxiliary inductor La, diode D1 and D3. The gate charging loop of the freewheeling tube S2 is via a control tube S3. During the primary side main switch tube Q1 turn-on time, a third auxiliary winding charges the auxiliary inductor; after the primary side main switch tube Q1 is turned off, the auxiliary inductor La charges the gate capicitor of the freewheeling tube S2 with peak value current to turn on the capacitor by which switching loss and conducting loss of diode in the tube S2 caused by slowly turning on of the freewheeling tube S2 in the synchronization rectifying self-driving circuit for the resonant reset forward converter can be prevented. Thus the defect of slowly establishing of secondary side freewheeling tube driving voltage can be overcome and the common mode conduction time of the secondary side rectifying tube and freewheeling tube can be shorter compared with other self-driving manners, the turn-on performance of the freewheeling tube S2 is also better than external driving.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Non-isolated DC-DC converters with direct primary to load current
ActiveUS7110265B2Small sizeTotal current dropEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionConvertersFull bridge
DC—DC converters have high side and rectifier circuits, and output capacitor. High side circuit connects between input voltage and output voltage, and has primary winding and auxiliary section that operate transformer properly. Auxiliary may have switches or combination of switches and capacitors. High side circuit converts electrical into magnetic energy through transformer primary, which is then transferred to output through rectifier circuit. It also transfers energy directly to output voltage. Converters have high efficiency, fast dynamic response and high current output. Converters can have large duty cycle and large input voltage and output voltage conversion ratio. High side circuit can be half-bridge, full-bridge or forward converter. Rectifier uses inductors on either side of the secondary, and diodes or synchronous rectifiers, to rectify output voltage. Multi-phase interleaved circuits utilize shared switches to reduce size. High side circuit can utilize resonant tank to decrease switching losses in auxiliary.
Owner:GANPOWER INT INC
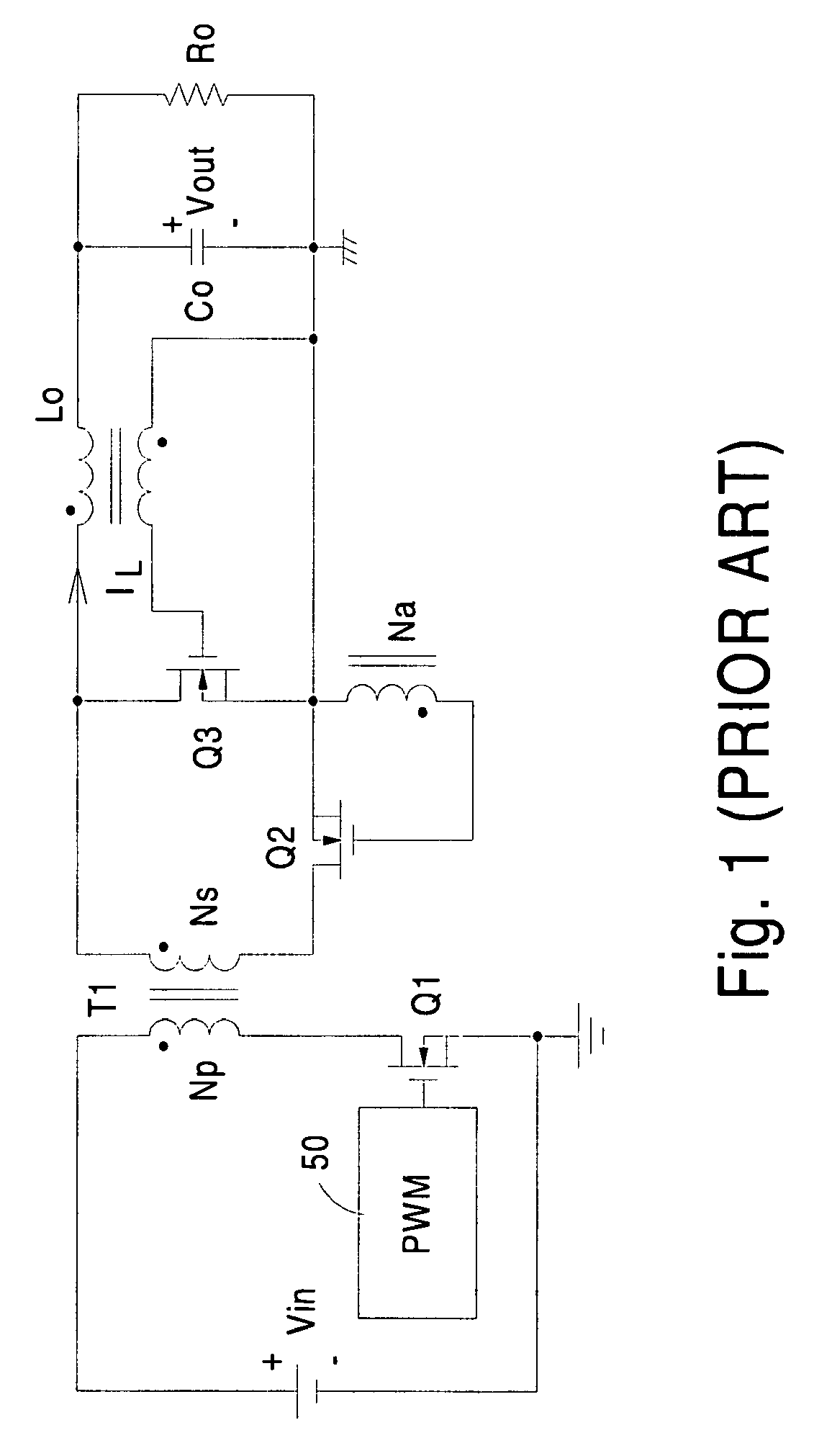
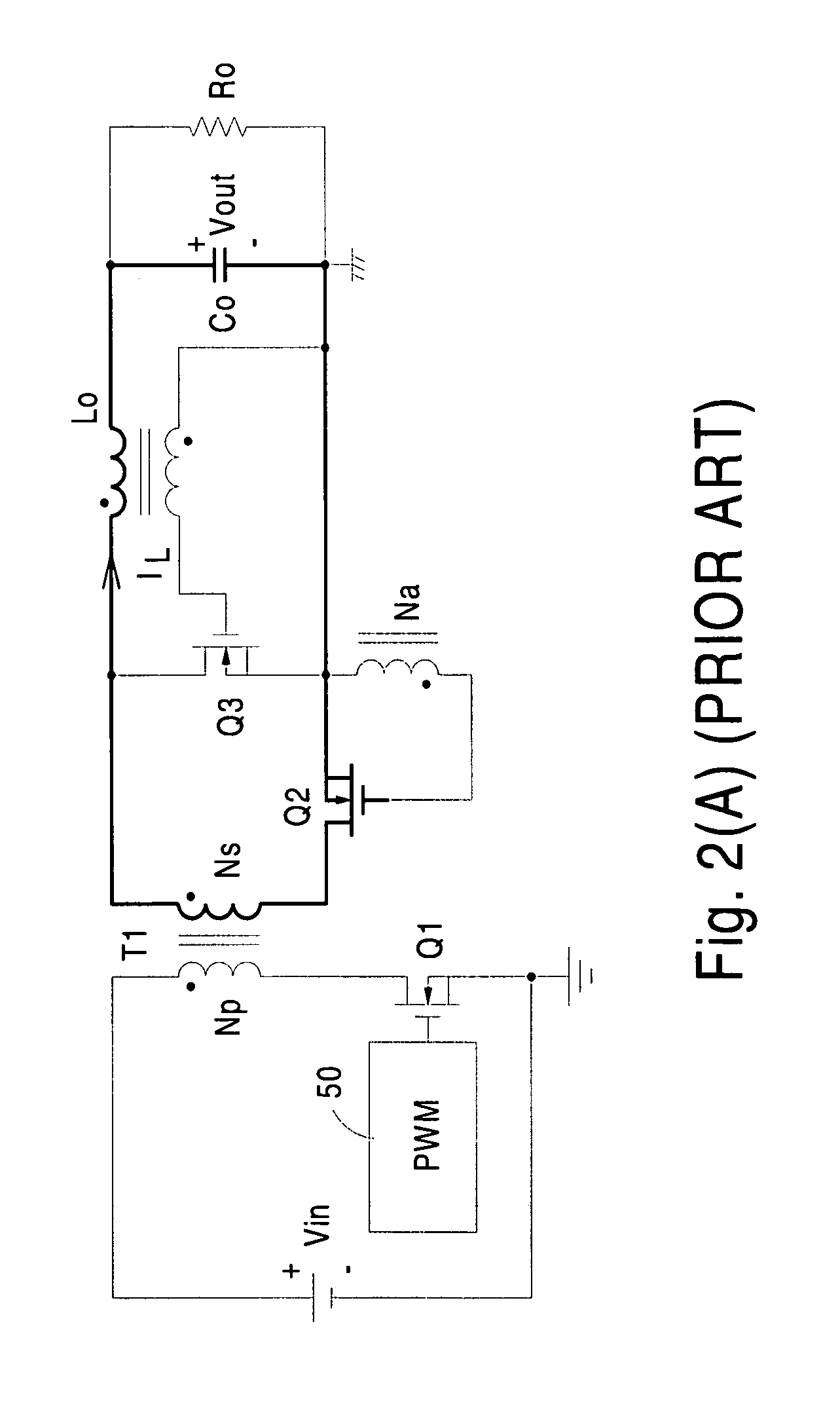
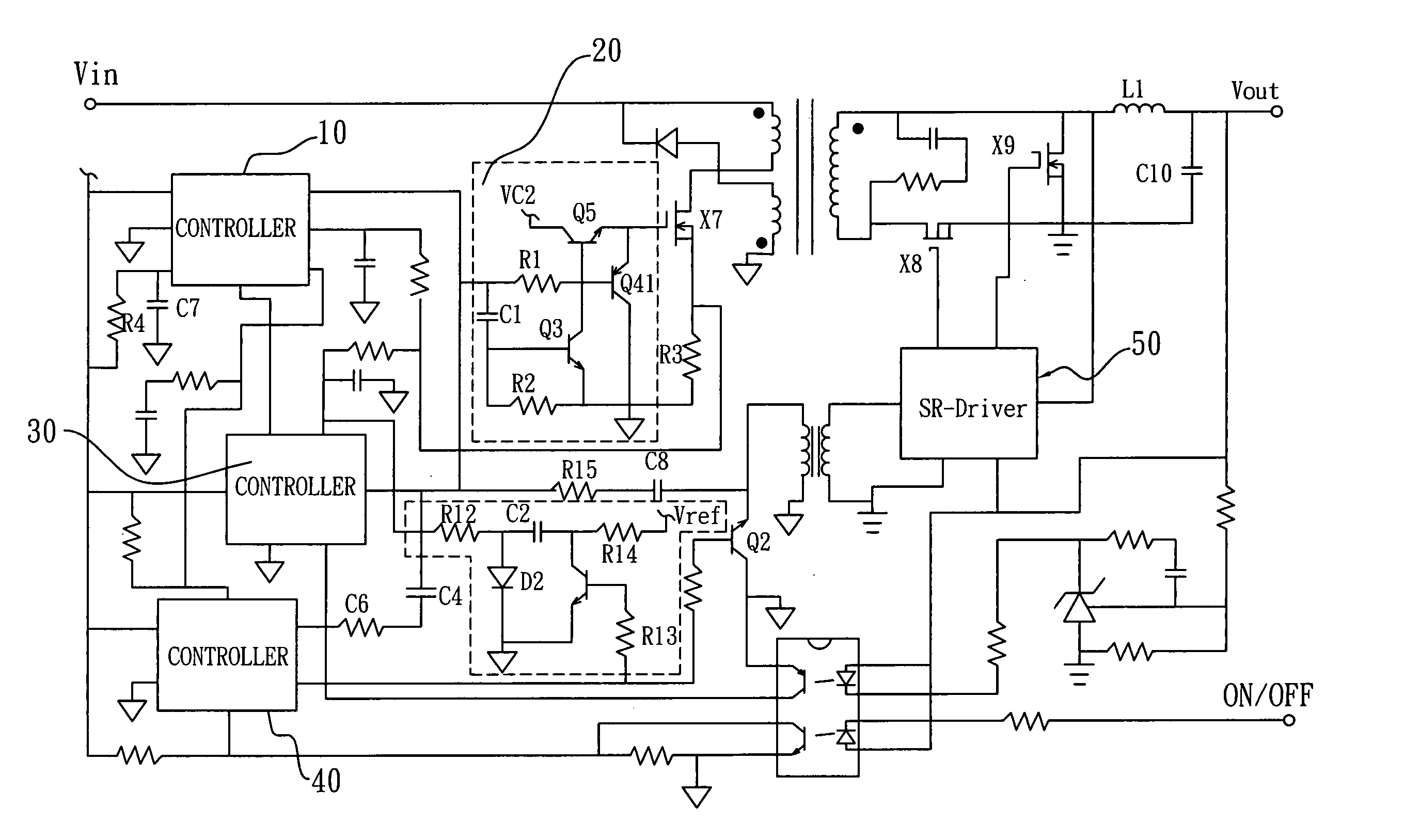
Forward converter with synchronous rectifier and reverse current control
InactiveUS7224590B2Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFreewheelReverse current
Owner:ACBEL POLYTECH INC
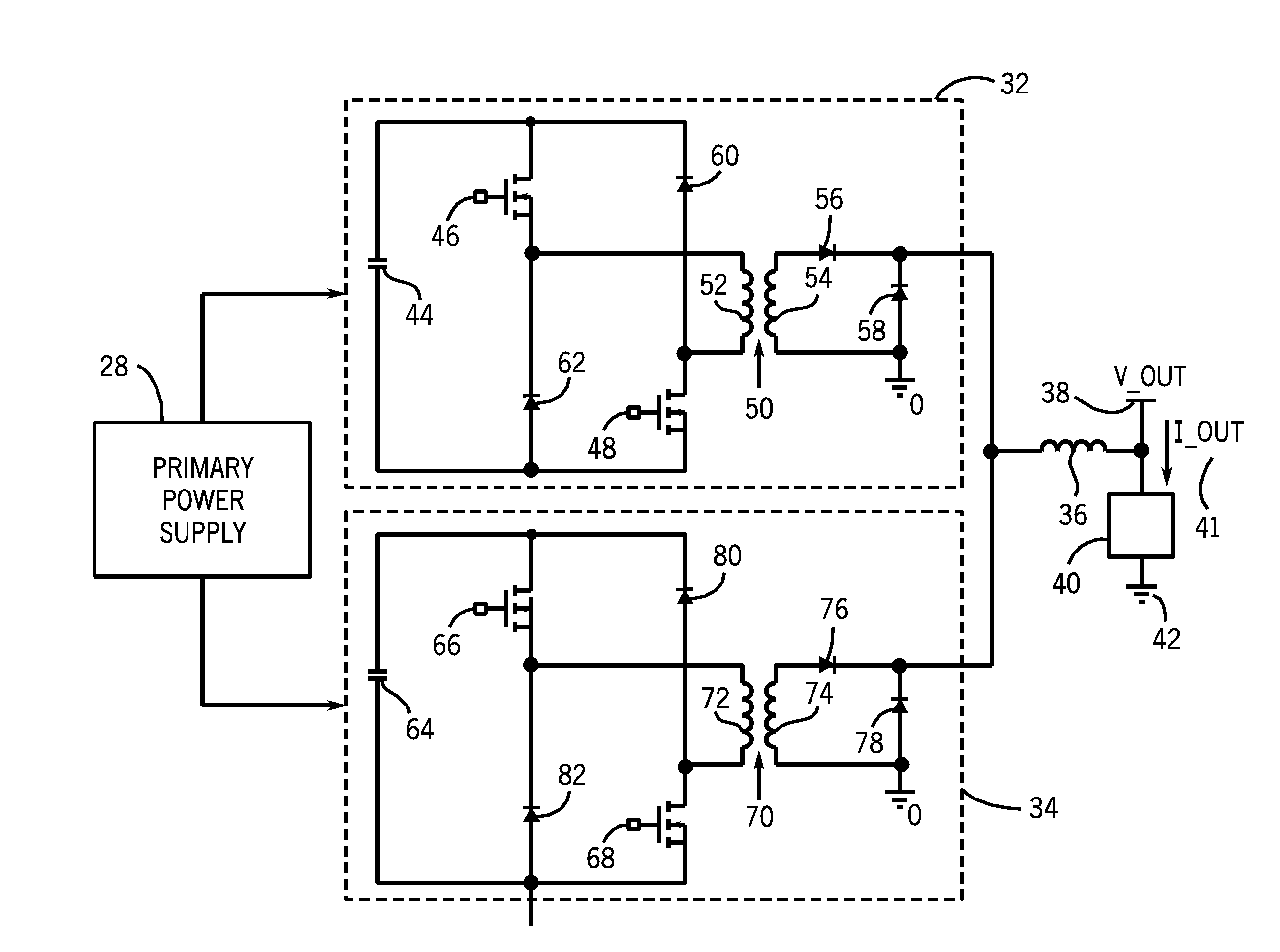
High power converter architecture
ActiveUS20140029312A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEnergy transferBuck converter
The power converter is an integration of three topologies which include a forward converter topology, a flyback converter topology, and a resonant circuit topology. The combination of these three topologies functions to transfer energy using three different modes. A first mode, or forward mode, is a forward energy transfer that forwards energy from the input supply to the output load in a manner similar to a forward converter. A second mode, or flyback mode, stores and releases energy in a manner similar to a flyback converter. A third mode, or resonant mode, stores and releases energy from the resonant tank using a resonant circuit and a secondary side forward-type converter topologies. An output circuit of the power converter is configured as a forward-type converter including two diodes and an inductor. The output circuit is coupled to a secondary winding of a converter transformer.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
Snubber circuit for a power converter
InactiveUS20060274558A1Easy to controlHigh voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMOSFETCapacitance
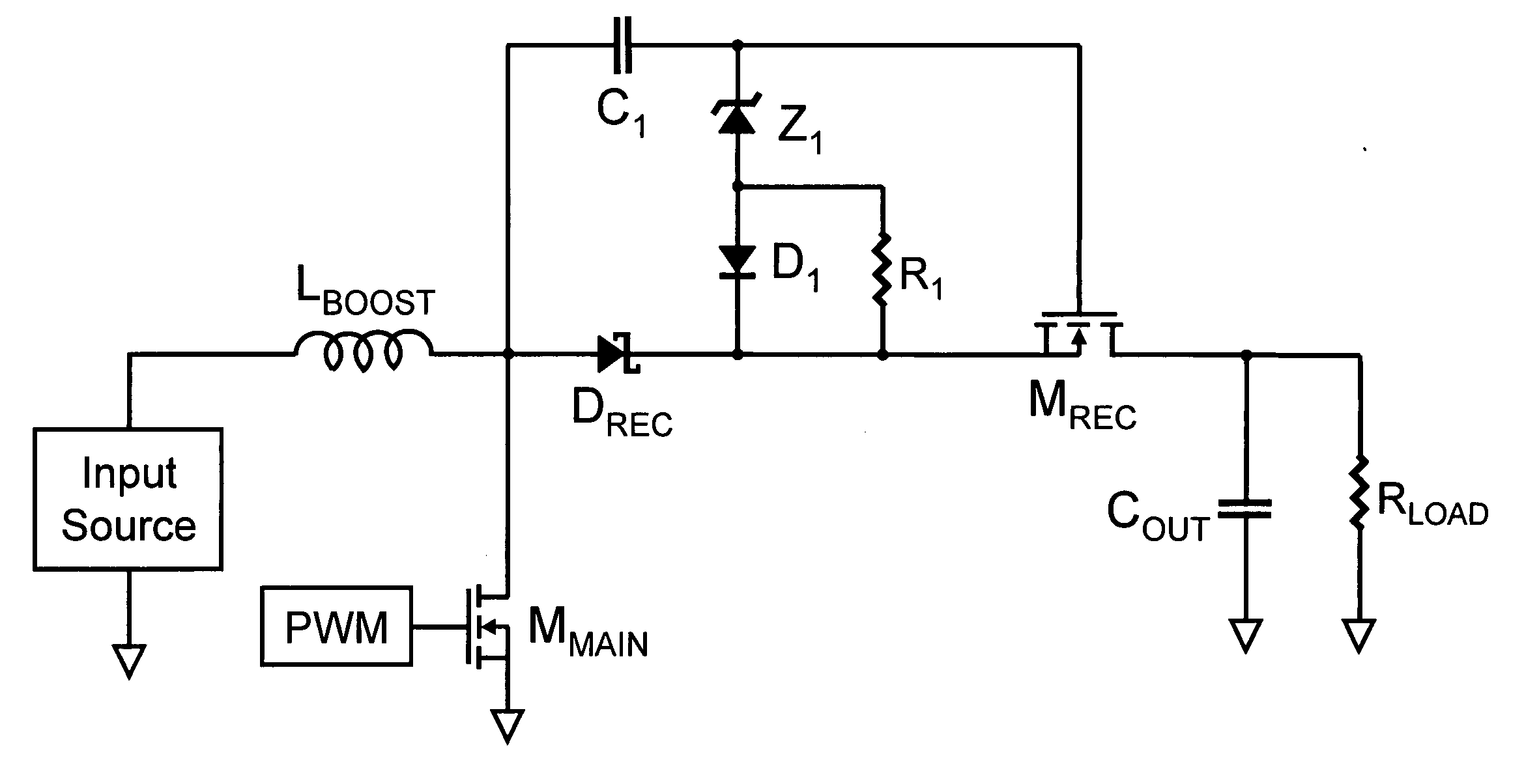
A snubber circuit and corresponding power converter topology for controlling the voltage across the resonant capacitor at turn on of a MOSFET control switch so as to suppress the spike at the drain of the MOSFET caused by the large current pulse and parasitic inductance of the power converter. The suppression of the spike reduces conduction losses and increases efficiency. According to one embodiment, the snubber circuit in a boost converter topology includes a second winding tapped from the main boost inductor and connected in series with a first diode and a second diode. A resonant capacitor and the second diode are connected in a series combination which is in parallel with the main boost diode. The second winding is connected in series with a first diode and the second diode between the output terminals. Alternatively, the snubber circuit is used in flyback, buck, and forward converters topologies.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
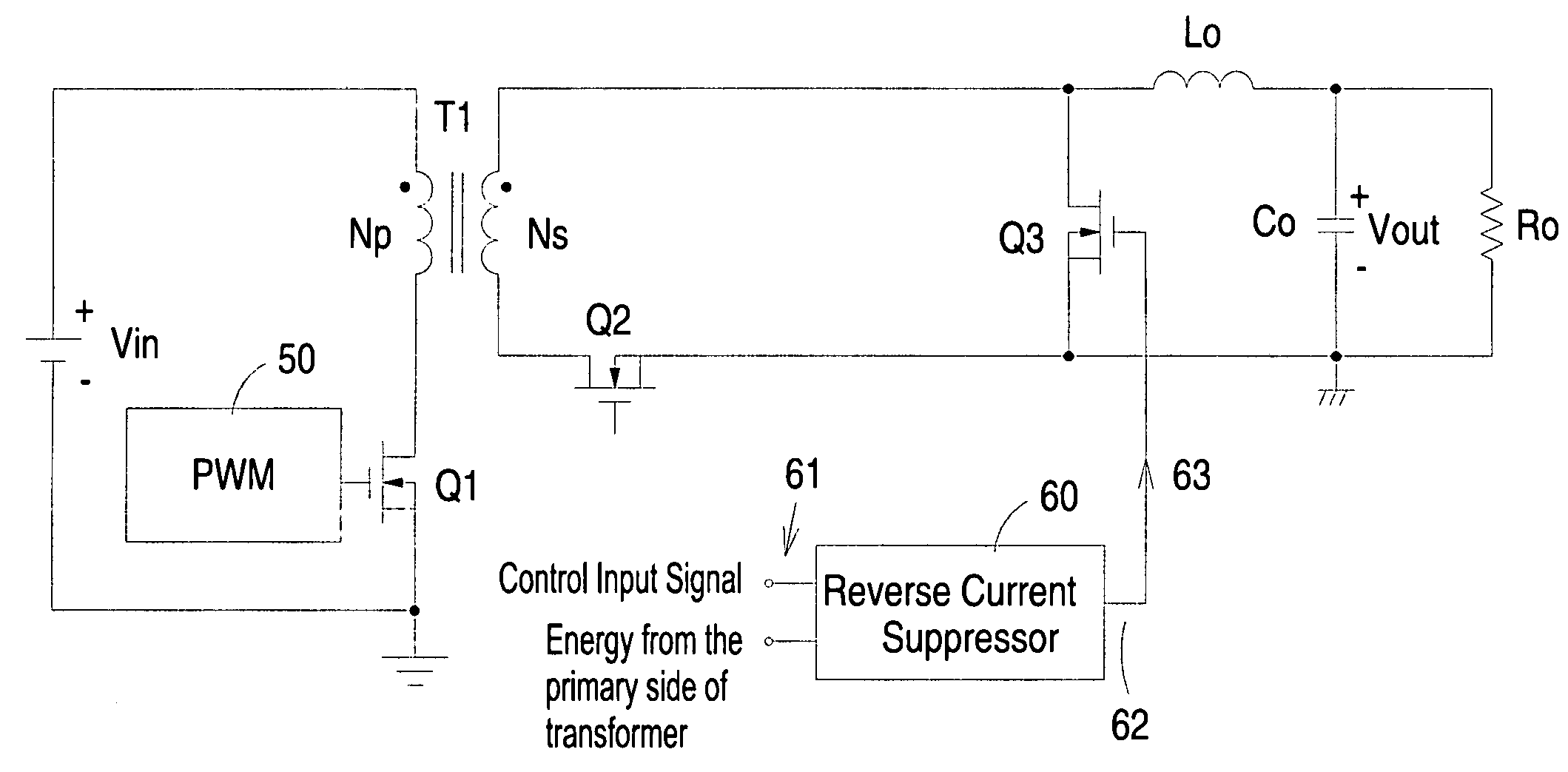
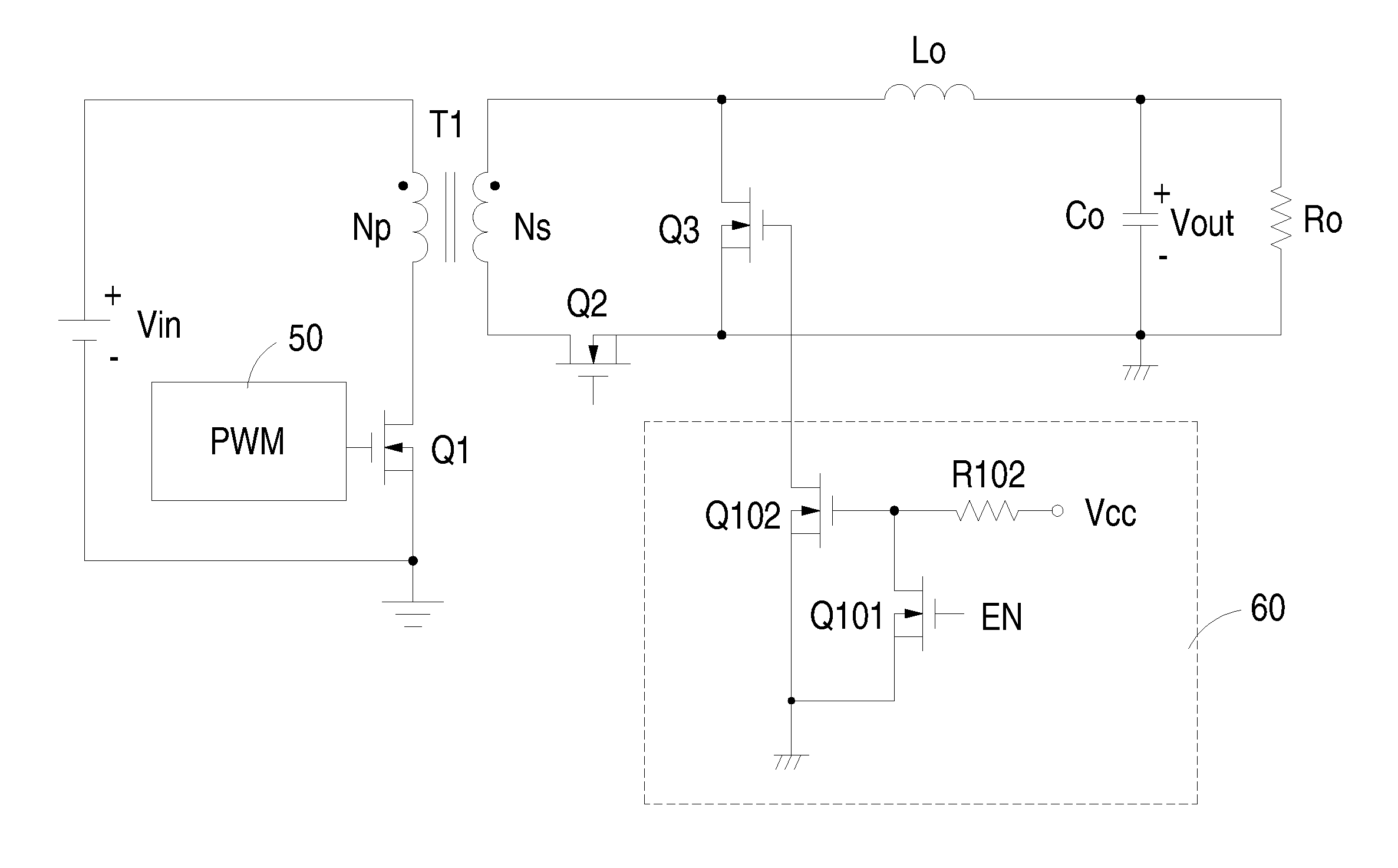
Synchronous rectifier forward converter with reverse current suppressor
ActiveUS7589982B2Simple circuit architecture and control mechanismAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFreewheelReverse current
Disclosed is a synchronous forward converter having a reverse current suppressor connected to the gate of a freewheel switch. The reverse current suppressor is configured to receive a control input signal generated by an internal circuitry of a power supply system where the forward converter locates, such as an enable signal, to detect the power-off of the forward converter, and in response thereto turn off the freewheel switch during the interruption of the input power of the forward converter. Alternatively, the reverse current suppressor is configured to detect the decay of the input voltage across the input bulk capacitor located on the primary side of a transformer of the forward converter, and turn off the freewheel switch when the voltage across the secondary side of the transformer is decayed to be smaller than the output voltage of the forward converter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
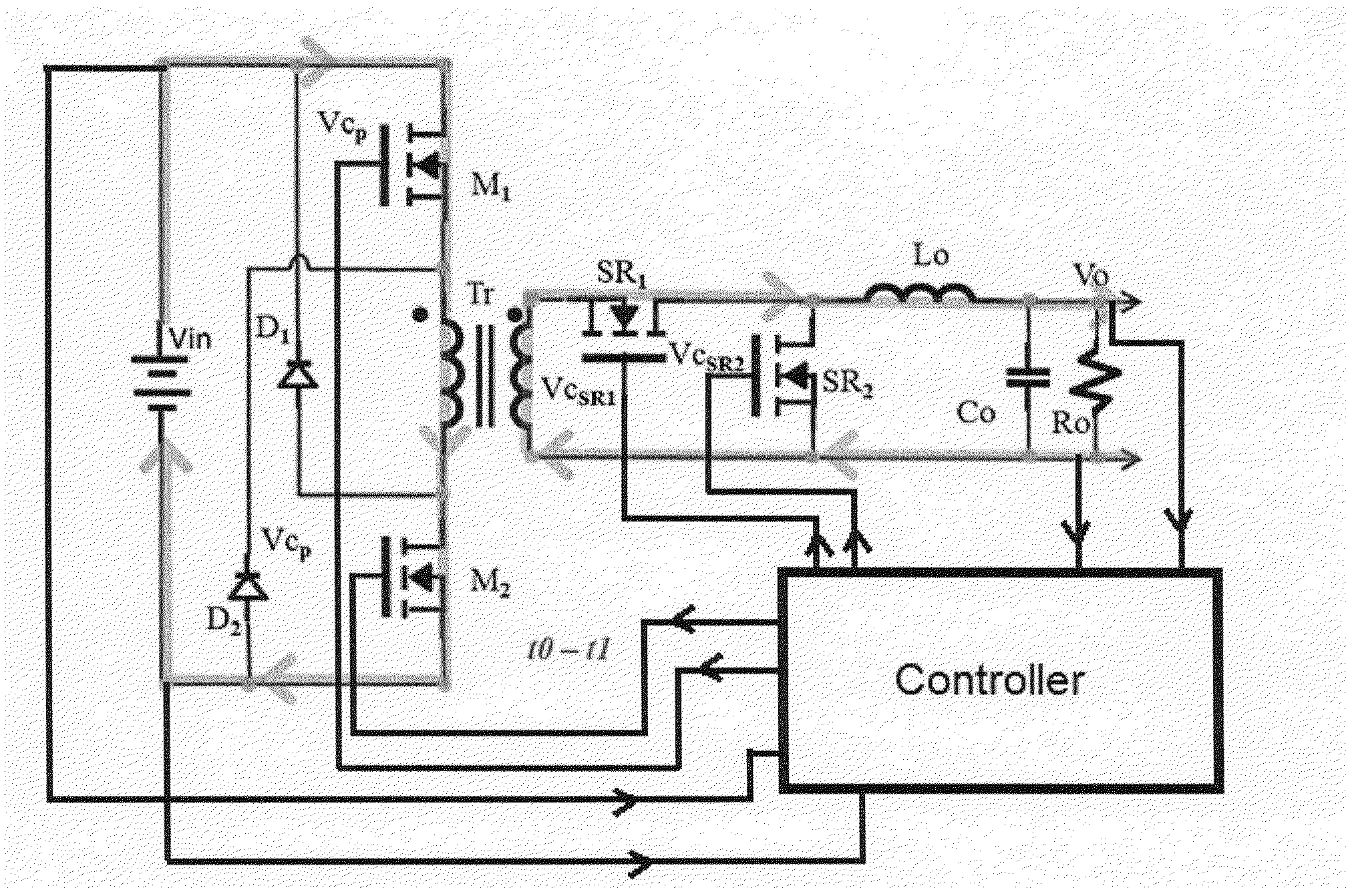
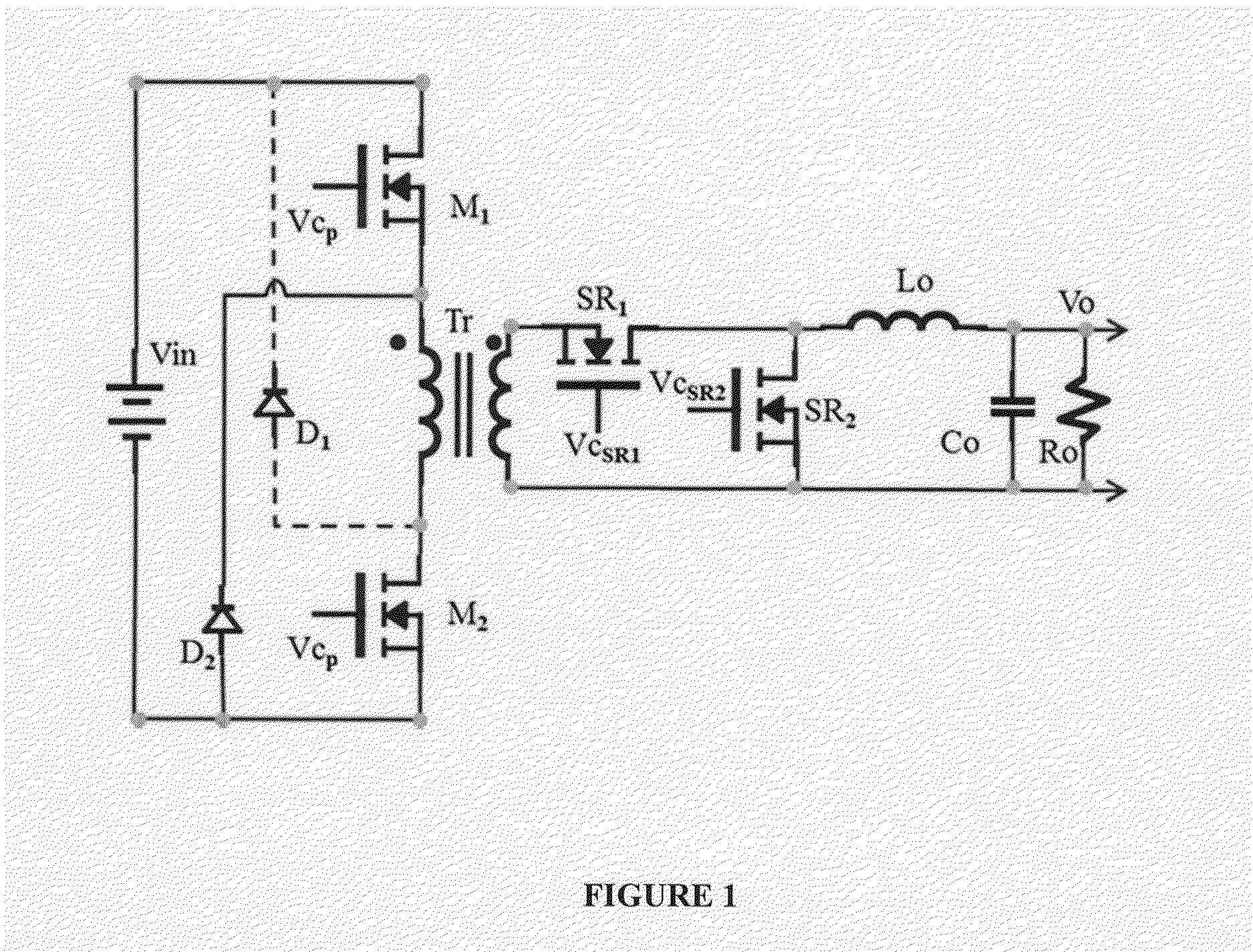
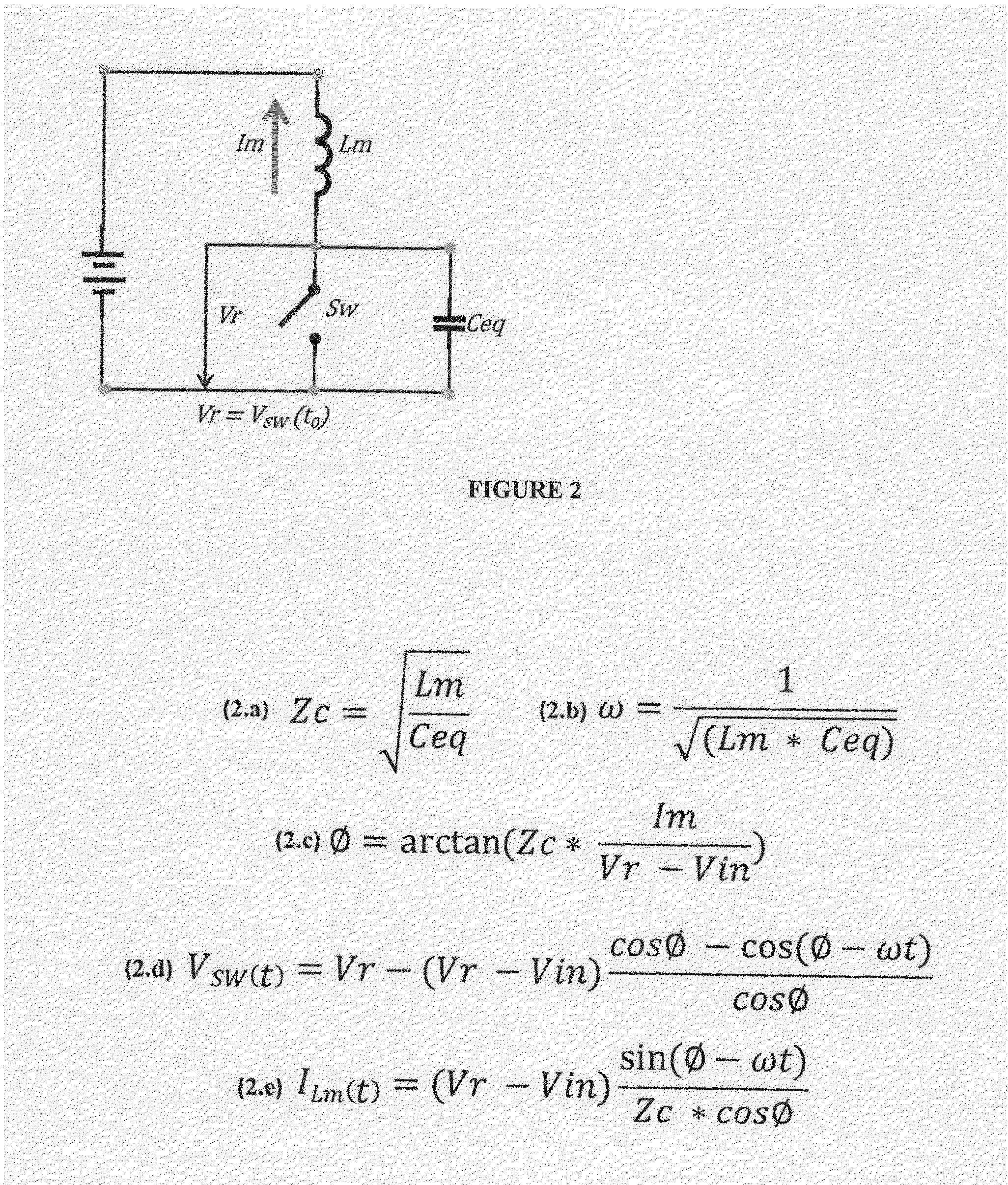
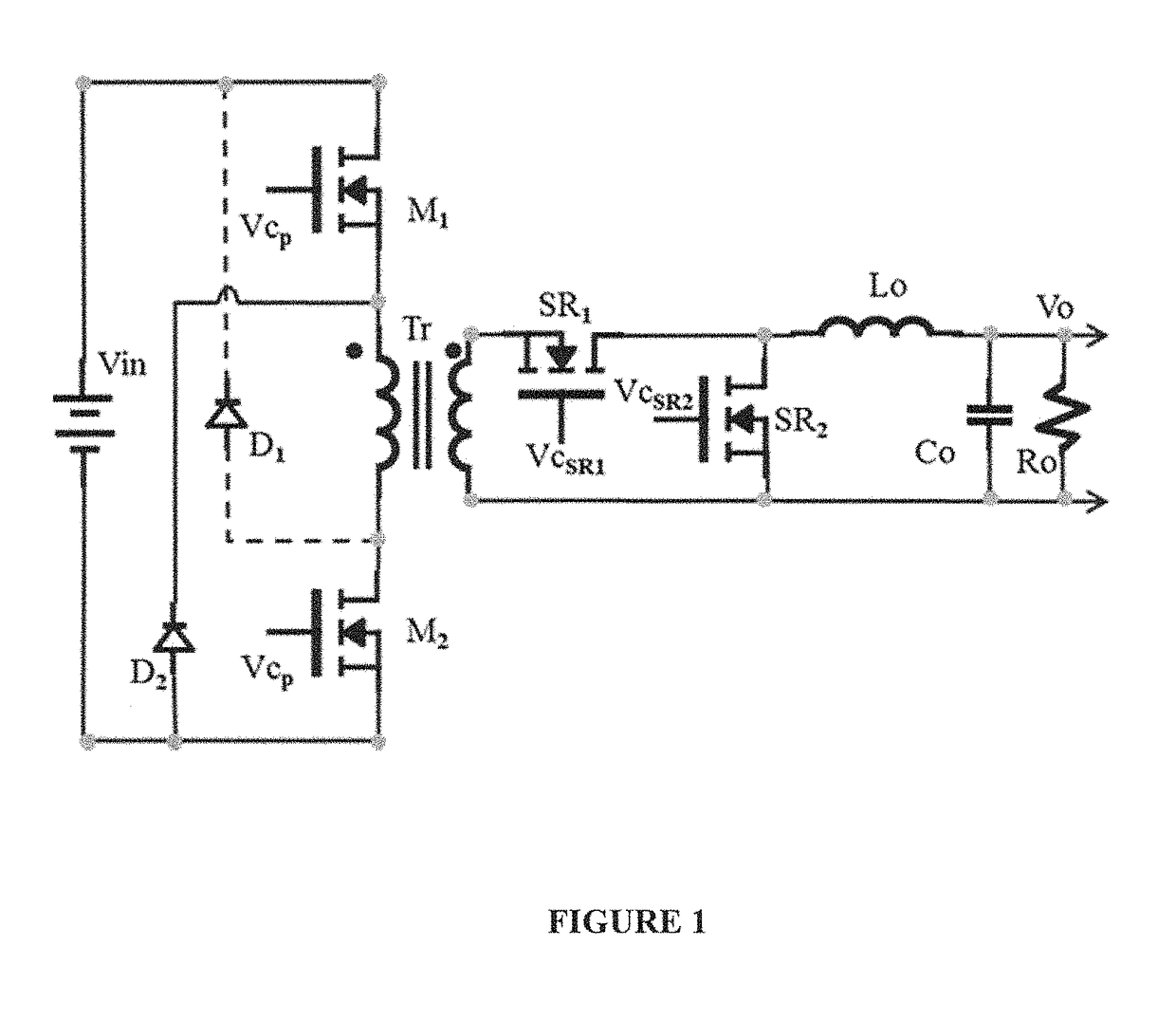
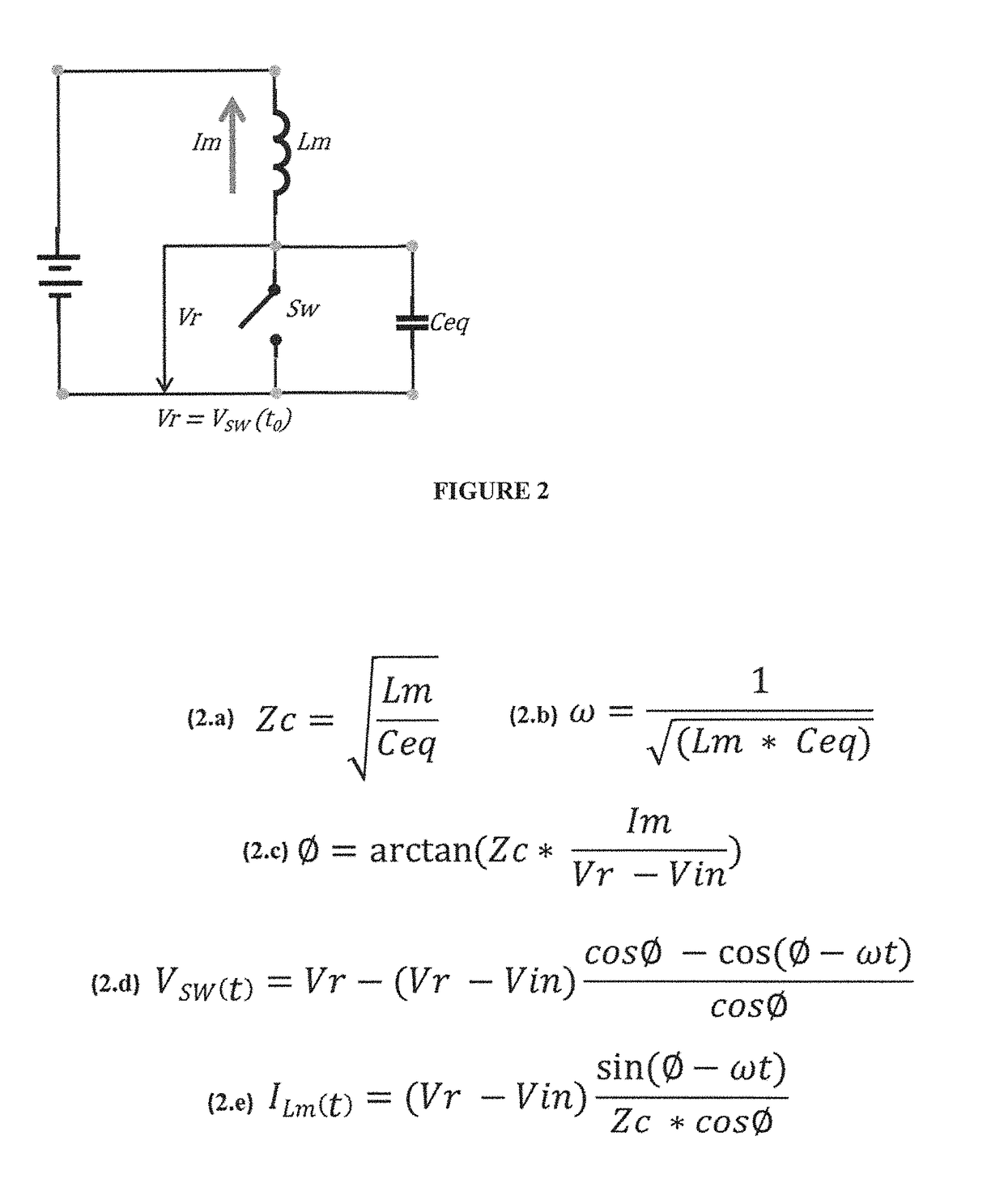
Soft Transition on all Switching Elements Two Transistors Forward Converter
InactiveUS20160094137A1Eliminate lossLow leakage inductanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionParasitic capacitanceInductor
A method is shown to improve any forward topology operation to achieve efficient resonant transitions by actively shorting the magnetizing inductance and release the short at another time thus producing lower switching losses independent of frequency. In another embodiment of this invention the current from the output inductor is allowed to go negative before the freewheeling synchronous rectifier is turned off, pushing the current back into the primary to create a soft transition across the switching elements before they are turned on. In another embodiment of the invention a current source is used to inject a negative current through the freewheeling synchronous rectifier before is turned off with the purpose of transferring the current into the primary to discharge the parasitic capacitances of the primary switchers before are turned on. An optimized control method can be utilized to tailor the frequency to create the necessary conditions requested by the embodiments of the invention.
Owner:ROMPOWER TECH HLDG LLC
Non-isolated DC-DC converters with direct primary to load current
InactiveUS20070103941A1Small sizeTotal current dropEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionConvertersFull bridge
DC-DC converters have high side and rectifier circuits, and output capacitor. High side circuit connects between input voltage and output voltage, and has primary winding and auxiliary section that operate transformer properly. Auxiliary may have switches or combination of switches and capacitors. High side circuit converts electrical into magnetic energy through transformer primary, which is then transferred to output through rectifier circuit. It also transfers energy directly to output voltage. Converters have high efficiency, fast dynamic response and high current output. Converters can have large duty cycle and large input voltage and output voltage conversion ratio. High side circuit can be half-bridge, full-bridge or forward converter. Rectifier uses inductors on either side of the secondary, and diodes or synchronous rectifiers, to rectify output voltage. Multi-phase interleaved circuits utilize shared switches to reduce size. High side circuit can utilize resonant tank to decrease switching losses in auxiliary.
Owner:GANPOWER INT INC
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6987519B2High color reproductionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsLab color spaceImaging processing
If gamut mapping (hue restoration) defined by one Lab color space is applied in color matching under different reference white points, the human vision perceives the hue as inconsistent. In view of this, input data which is dependent on a color space of an input device is converted by the conversion LUT 11 to color space data which is independent of any devices, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an input original. The data is converted to data in the human color perception space by the forward converter 12, then subjected to gamut mapping, and converted back to data in the color space independent of any devices by the inverse converter 15, based on a viewing condition at the time of viewing an output original. Then, the data is converted to output data in a color space which is dependent on an output device by the conversion LUT 16.
Owner:CANON KK
Synchronous rectifier forward converter with reverse current suppressor
ActiveUS20080055944A1Simple circuit architecture and control mechanismAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionFreewheelReverse current
Disclosed is a synchronous forward converter having a reverse current suppressor connected to the gate of a freewheel switch. The reverse current suppressor is configured to receive a control input signal generated by an internal circuitry of a power supply system where the forward converter locates, such as an enable signal, to detect the power-off of the forward converter, and in response thereto turn off the freewheel switch during the interruption of the input power of the forward converter. Alternatively, the reverse current suppressor is configured to detect the decay of the input voltage across the input bulk capacitor located on the primary side of a transformer of the forward converter, and turn off the freewheel switch when the voltage across the secondary side of the transformer is decayed to be smaller than the output voltage of the forward converter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Forward converter with magnetic component
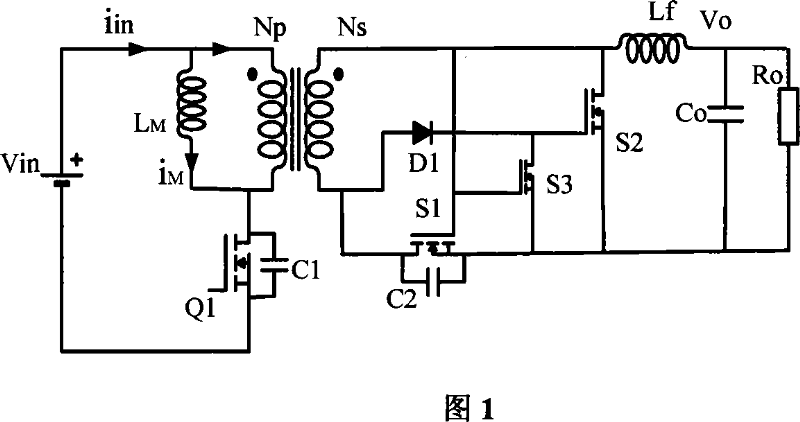
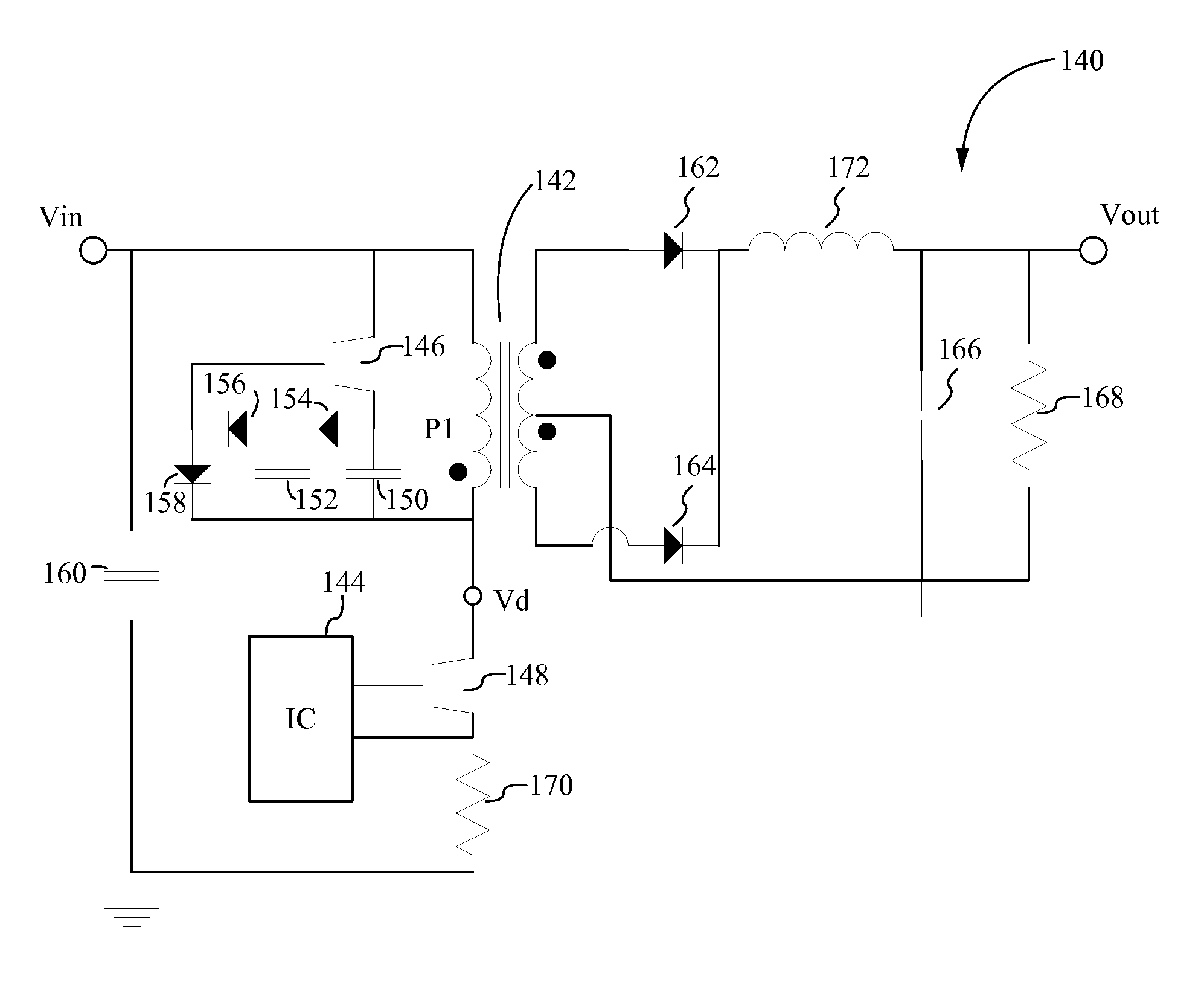
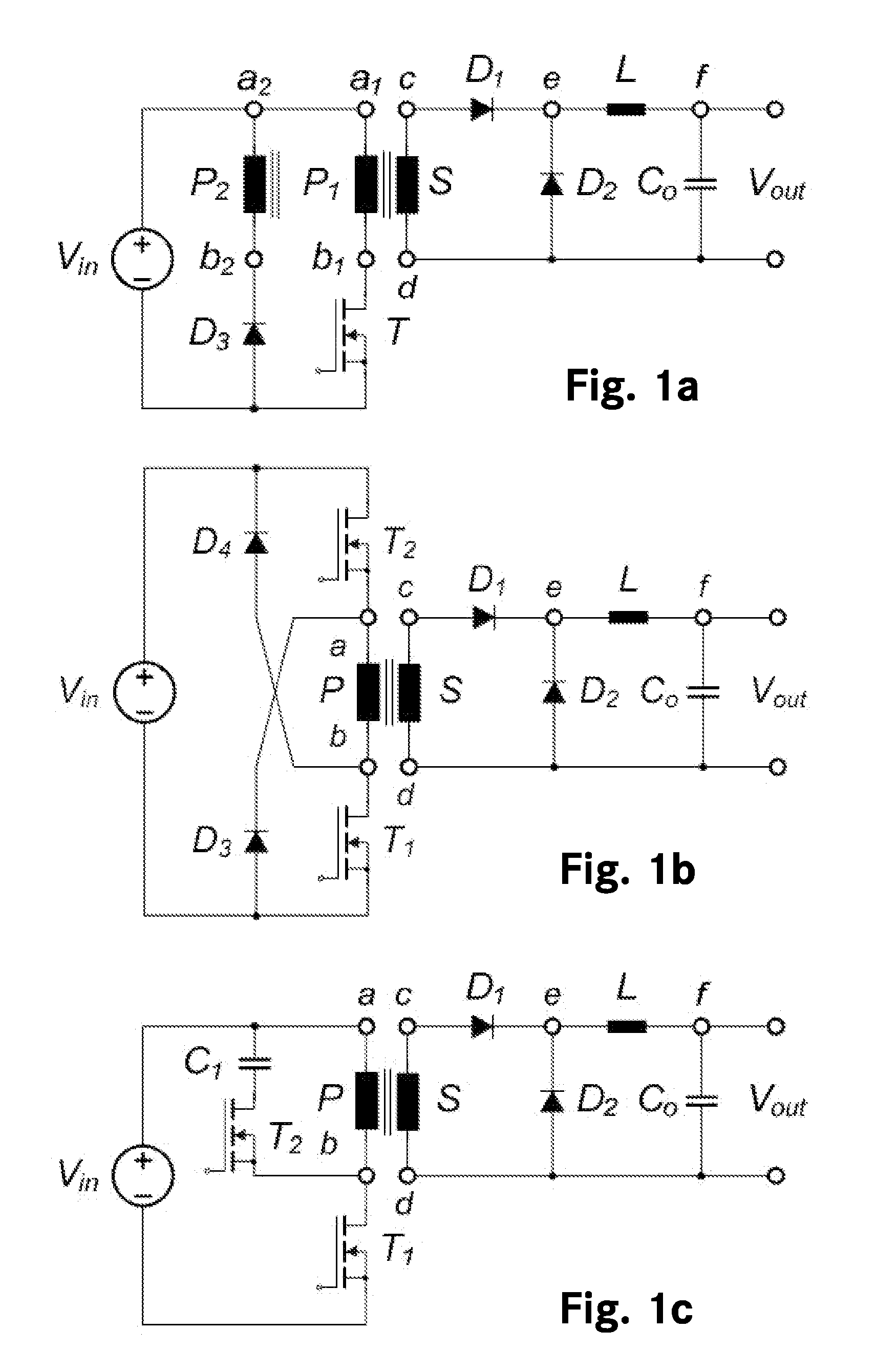
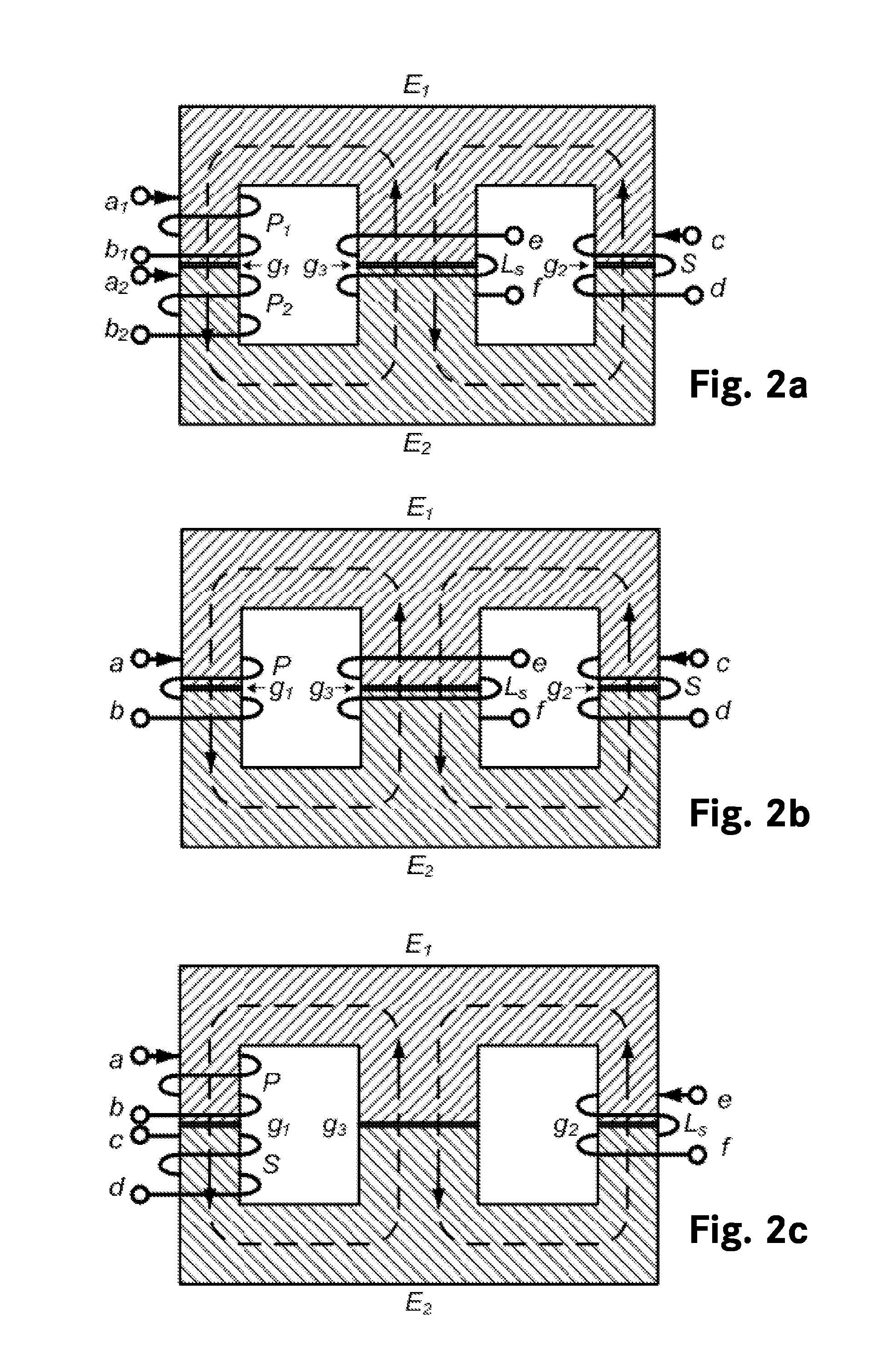
A forward converter comprises a magnetic component with a transformer and a filter output inductor. Also disclosed is a method for assembly of a forward converter. A first and a second U / UR core are arranged to form an O-core. Windings of the transformer are arranged on the O-core. A bobbin-less U / UR core is arranged to abut the O-core, and windings of a filter output inductor are arranged directly on a body section of the bobbin-less U / UR core. Alternatively, windings of the transformer are arranged on a first section of an E / ER core, and windings of the filter output inductor are arranged directly on a second, bobbin-less section of the E / ER core.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) PUBLIC CO LTD
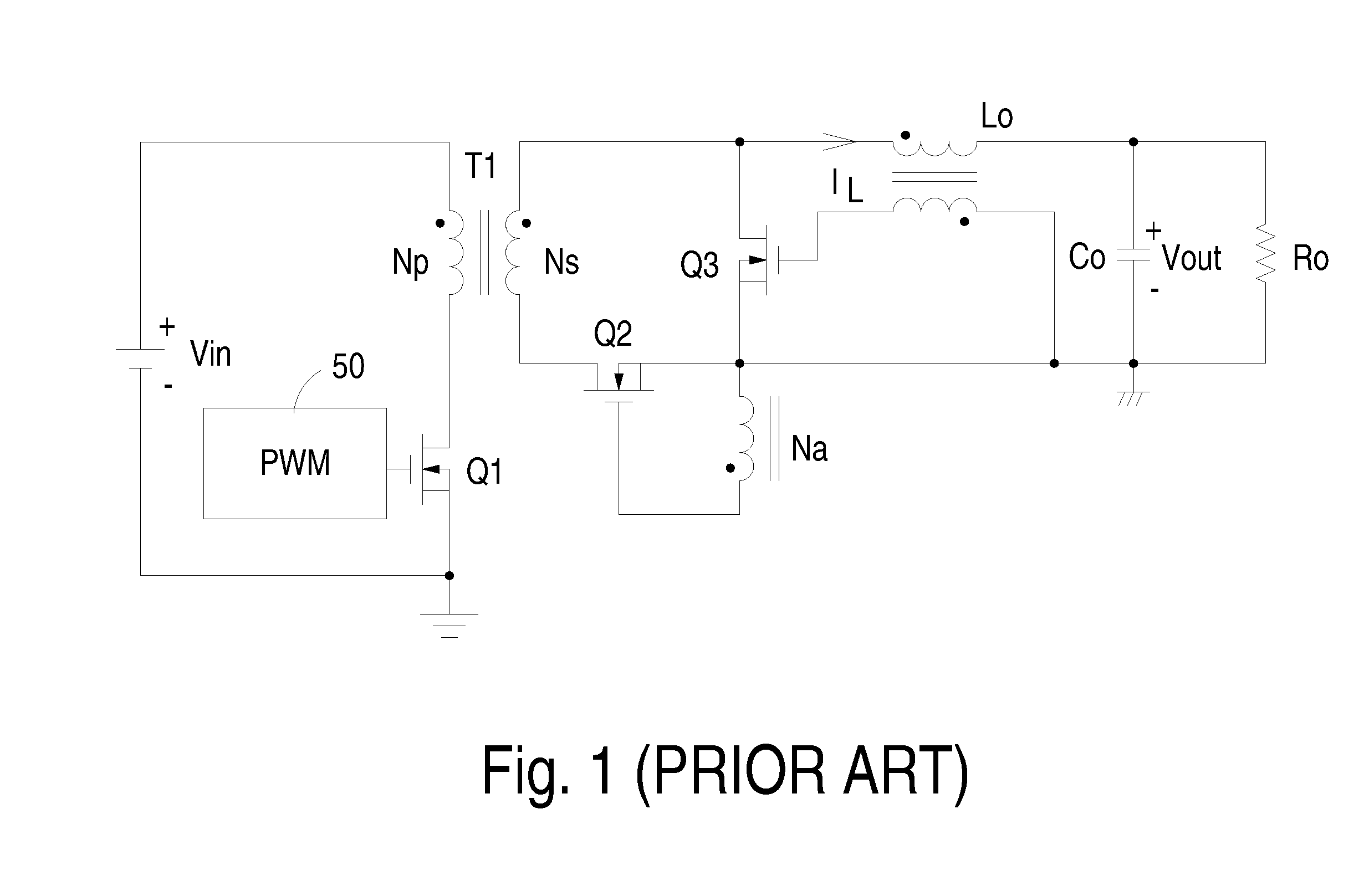
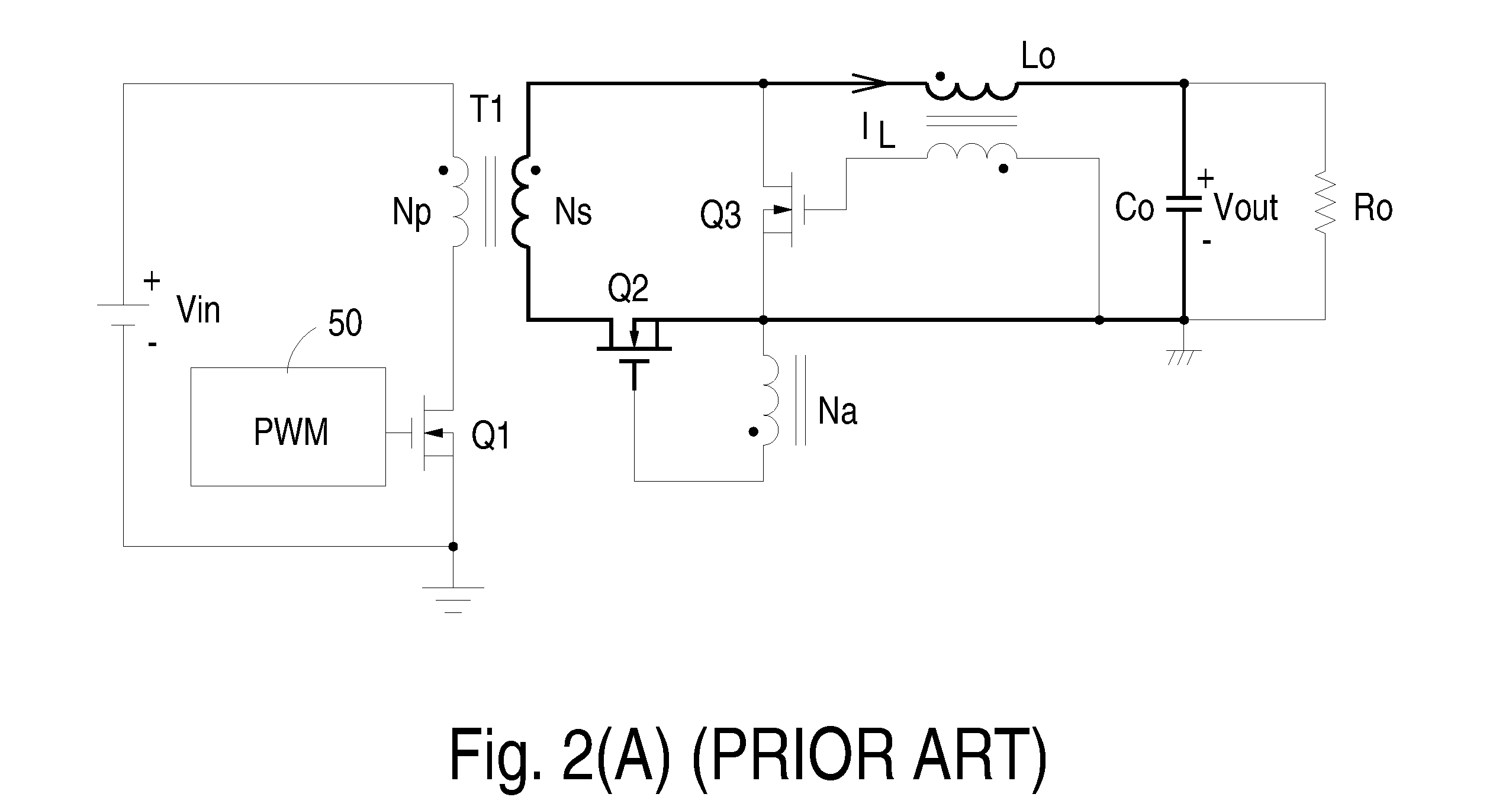
Forward converter with synchronous rectifier and reverse current control
InactiveUS20060072349A1Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFreewheelReverse current
A control circuit for use in a power converter having a synchronous rectifier for producing substantially direct current including a sensor for sensing a characteristic of the power converter, detection circuitry capable of using the characteristic to develop a control signal for controlling the power converter, and synchronous rectifier control circuitry connected to the detection circuitry wherein the control circuitry is adapted to modify a duty cycle of the power converter as a function of the control signal thereby to turn off a freewheel switch of the synchronous rectifier before turning off a forward switch of the synchronous rectifier during a reverse current period.
Owner:ACBEL POLYTECH INC
Battery charger using phase shift double forward converting circuit
ActiveUS20100225280A1Batteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionBattery state of chargeLeading edge
A technique for dynamically adjusting an output voltage of forward converter circuits for a battery charging operation is provided. The technique allows for varying voltage at the charging battery by manipulating the duty cycles of two forward converter circuits. The present disclosure provides methods and systems for increasing synchronized duty cycles in a pair of forward converter circuits in response to a changing battery charge state that requires a higher voltage output then changing a phase shift between the duty cycles in response to further increases in output voltage demand. The present disclosure also provides methods and systems for setting a phase shift between duty cycles in a pair of forward converter circuits based on battery rating and then altering pulse width in response to changing battery charge state. The invention provides a controller designed to receive input signals and generate output pulse width modulation signals that control the duty cycle width and phase shift of the outputs of the forward converter circuits in response to these signals. Methods of accommodating for the time needed for the transformer core to reset via leading edge or lagging edge compensation are provided.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
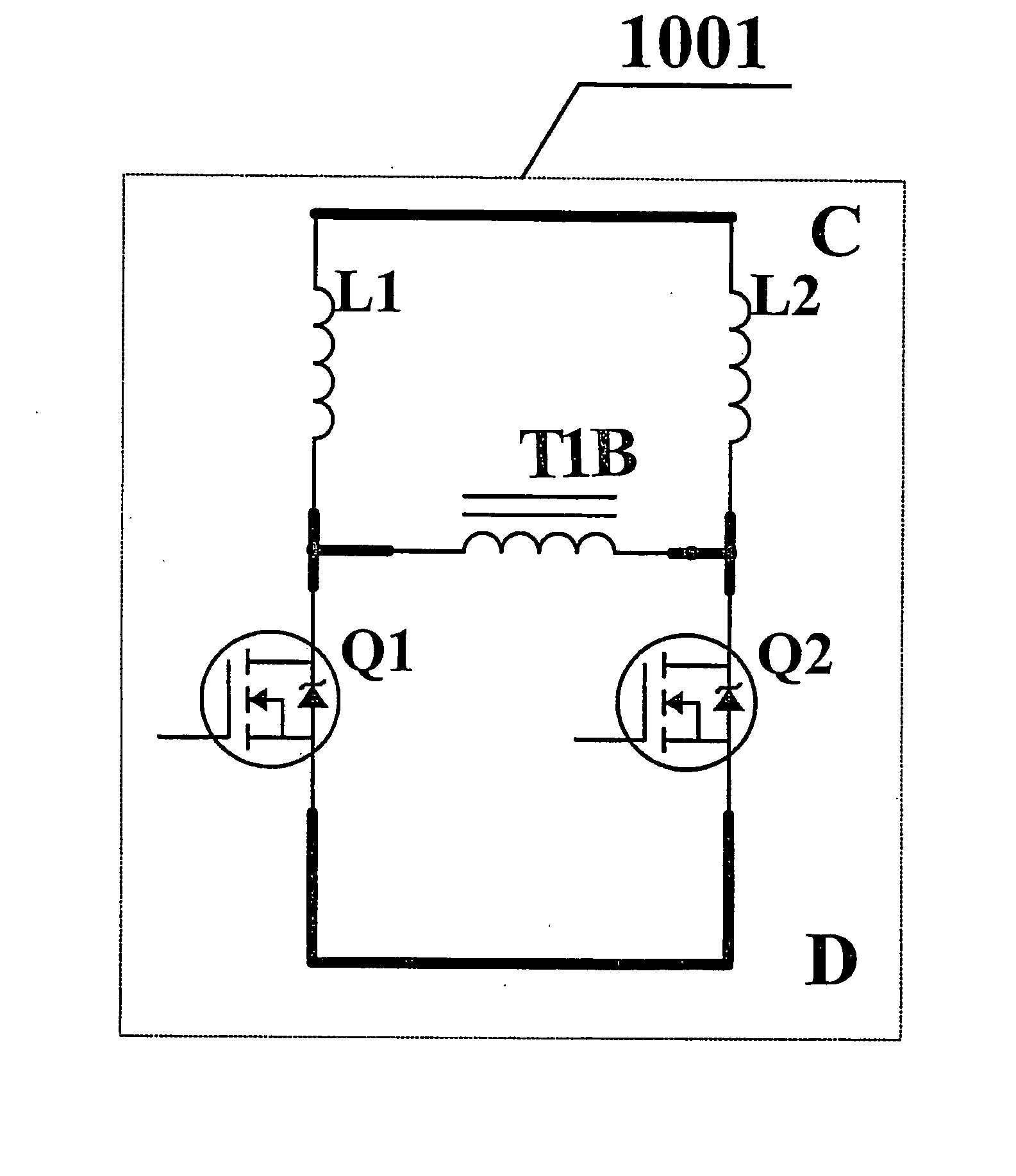
Two-way two-tube positive excitation converter topology
InactiveCN1545200AReduce voltage stressImprove reliabilityAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceElectricity
The invention relates to a two-way two-tube forward converter topology, its main circuit composed of power supply, four power diodes, two primary side clamping diodes, two serial capacitances, a main power transformer composed of primary winding and secondary winding with a secondary side composed of a rectifier with two rectifier diodes and an output filter capacitance. It remains the advantages of low primary-side voltage stress of a two-way two-tube forward converter, no direct turn-on of bridge arm, high reliability, etc; compared with general two-way two-tube forward converters, it has only two clamping diodes and simple structure; it adopts magnetic integration technique of transform, further reducing the bulk and enhancing power density of transform. It not only implements zero voltage turn-on and turn-off, but also basically eliminating voltage peak of diodes in the secondary rectifier by the clamping action of filter capacitance, having very high efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Positive activation converter
ActiveCN101237189ASelf-drivingAvoid shutdown negative pressure problemsApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalInput control
The invention discloses a forward converter, which comprises a power source, an input control circuit, a transformer and a rectifier-filter circuit. The input control circuit has a main switching diode, and the rectifier-filter circuit comprises a rectifier tube and a N-channel JFET forward diode, and the gate of the rectifier tube and the drain of the forward diode are connected to a positive dotted terminal of a transformer secondary principal winding, and the drain of the rectifier tube is connected to the other end of the transformer secondary principal winding, and a source electrode of the forward diode and a source electrode of the rectifier are connected to a common output ground. The transformer has a secondary winding for outputting drive control signals, and a drive circuit for providing pulse drive signals to the forward diode is arranged between the secondary winding and the gate of the forward diode. On-and-off of the JFET forward diode is controlled by voltage signals of the transformer winding so that the forward converter works in a synchronous rectifier state. The drive signals are directly from the transformer winding so that no special driver is needed and no additional power supply is needed, which makes the forward converter simple and reliable.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Battery charger using the phase shift by a pair of forward converting circuits
ActiveUS8179100B2Batteries circuit arrangementsApparatus with intermediate ac conversionBattery state of chargePhase shifted
A technique for dynamically adjusting an output voltage of forward converter circuits for a battery charging operation is provided. The technique allows for varying voltage at the charging battery by manipulating the duty cycles of two forward converter circuits. Method and systems allow for increasing synchronized duty cycles in a pair of forward converter circuits in response to a changing battery charge state that requires a higher voltage output then changing a phase shift between the duty cycles in response to further increases in output voltage demand. The methods and systems also allow for setting a phase shift between duty cycles in a pair of forward converter circuits based on battery rating and then altering pulse width in response to changing battery charge state.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Welding or cutting power supply using phase shift double forward converter circuit (PSDF)
A technique for dynamically adjusting an output voltage for a welding or cutting operation is provided. The technique allows for varying output voltage at the welding or cutting torch by manipulating the duty cycles of two forward converter circuits. The present disclosure provides methods and systems for increasing synchronized duty cycles in a pair of forward converter circuits in response to increasing output voltage demand then changing a phase shift between the duty cycles in response to further increases in output voltage demand. The present disclosure provides a controller designed to receive input signals and generate output pulse width modulation signals that control the duty cycle width and phase shift of the outputs of the forward converter circuits in response to these signals. Methods of accommodating for the time needed for the transformer core to reset via leading edge or lagging edge compensation are provided.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
High power converter architecture
ActiveUS20140029313A1Increase leakage inductanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEnergy transferTransverter
The power converter is an integration of three topologies which include a forward converter topology, a flyback converter topology, and a resonant circuit topology. The combination of these three topologies functions to transfer energy using three different modes. A first mode, or forward mode, is a forward energy transfer that forwards energy from the input supply to the output load in a manner similar to a forward converter. A second mode, or flyback mode, stores and releases energy in a manner similar to a flyback converter. A third mode, or resonant mode, stores and releases energy from the resonant tank using a resonant circuit and a secondary side forward-type converter topologies.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
Soft transition on all switching elements two transistors forward converter
ActiveUS9899929B2Eliminate lossEliminate reverse recovery issuesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionParasitic capacitanceInductor
A method is shown to improve any forward topology operation to achieve efficient resonant transitions by actively shorting the magnetizing inductance and release the short at another time thus producing lower switching losses independent of frequency. In another embodiment of this invention the current from the output inductor is allowed to go negative before the freewheeling synchronous rectifier is turned off, pushing the current back into the primary to create a soft transition across the switching elements before they are turned on. In another embodiment of the invention a current source is used to inject a negative current through the freewheeling synchronous rectifier before is turned off with the purpose of transferring the current into the primary to discharge the parasitic capacitances of the primary switchers before are turned on. An optimized control method can be utilized to tailor the frequency to create the necessary conditions requested by the embodiments of the invention.
Owner:ROMPOWER TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com