Patents
Literature
1578 results about "Level shifting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
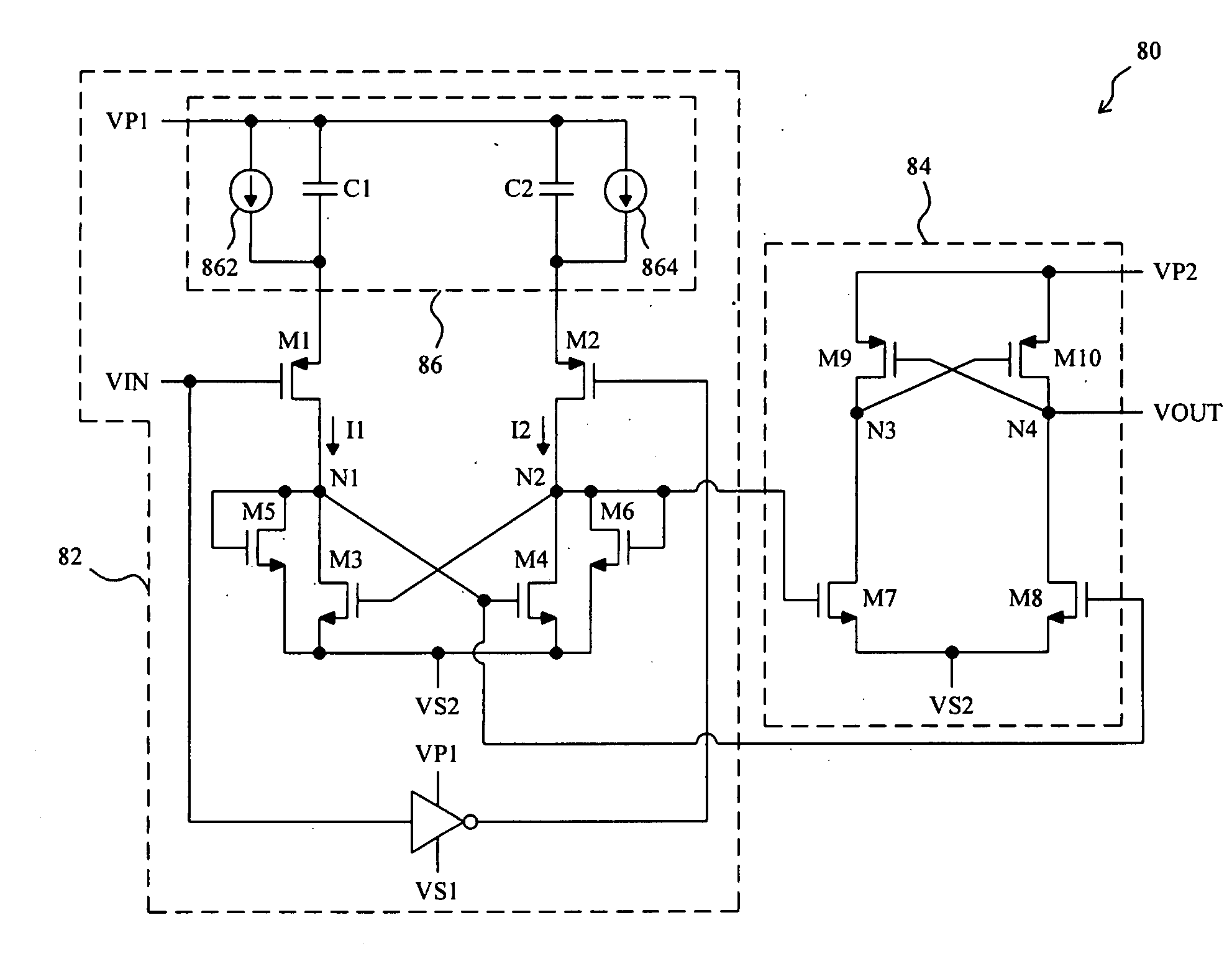
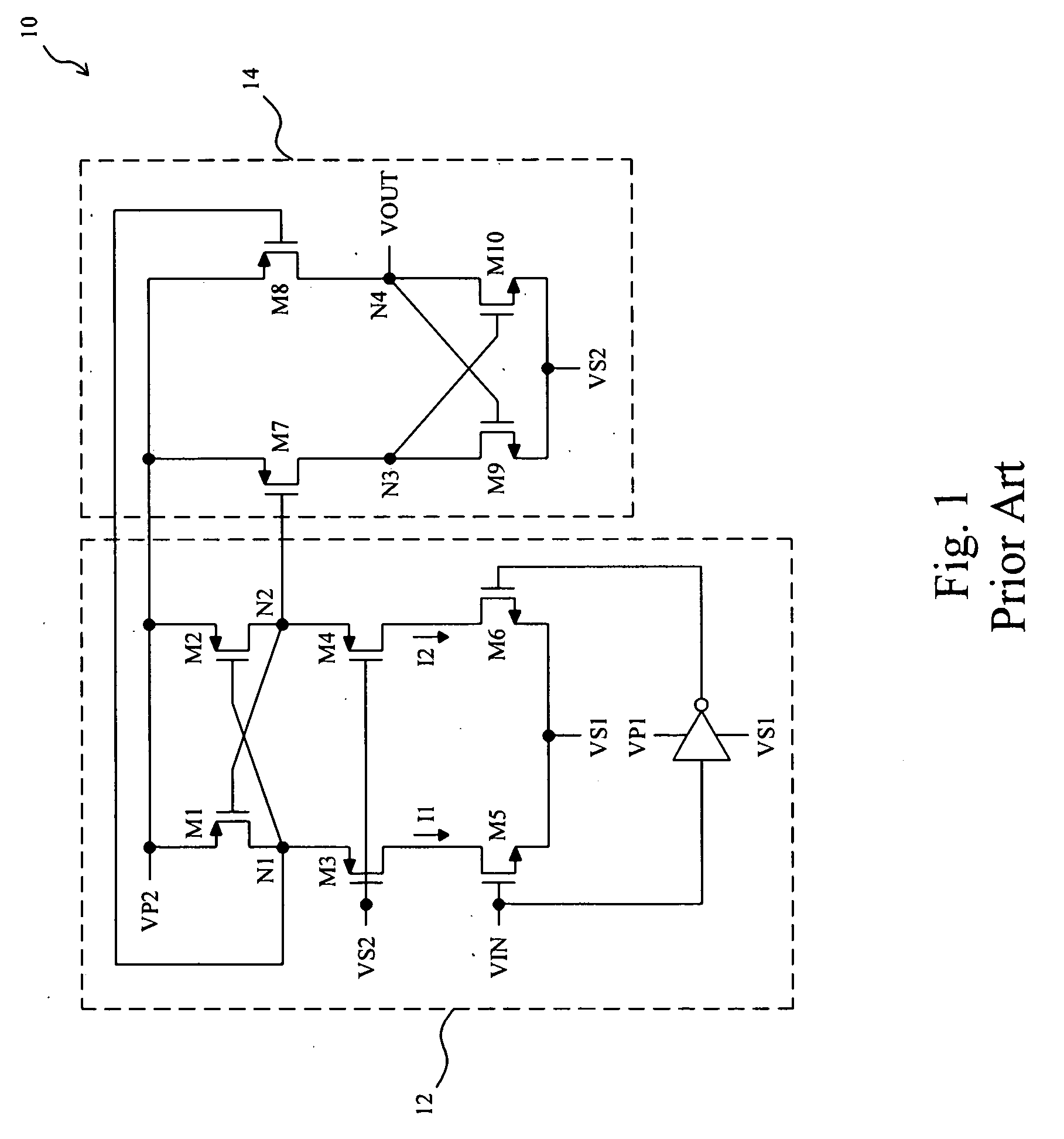
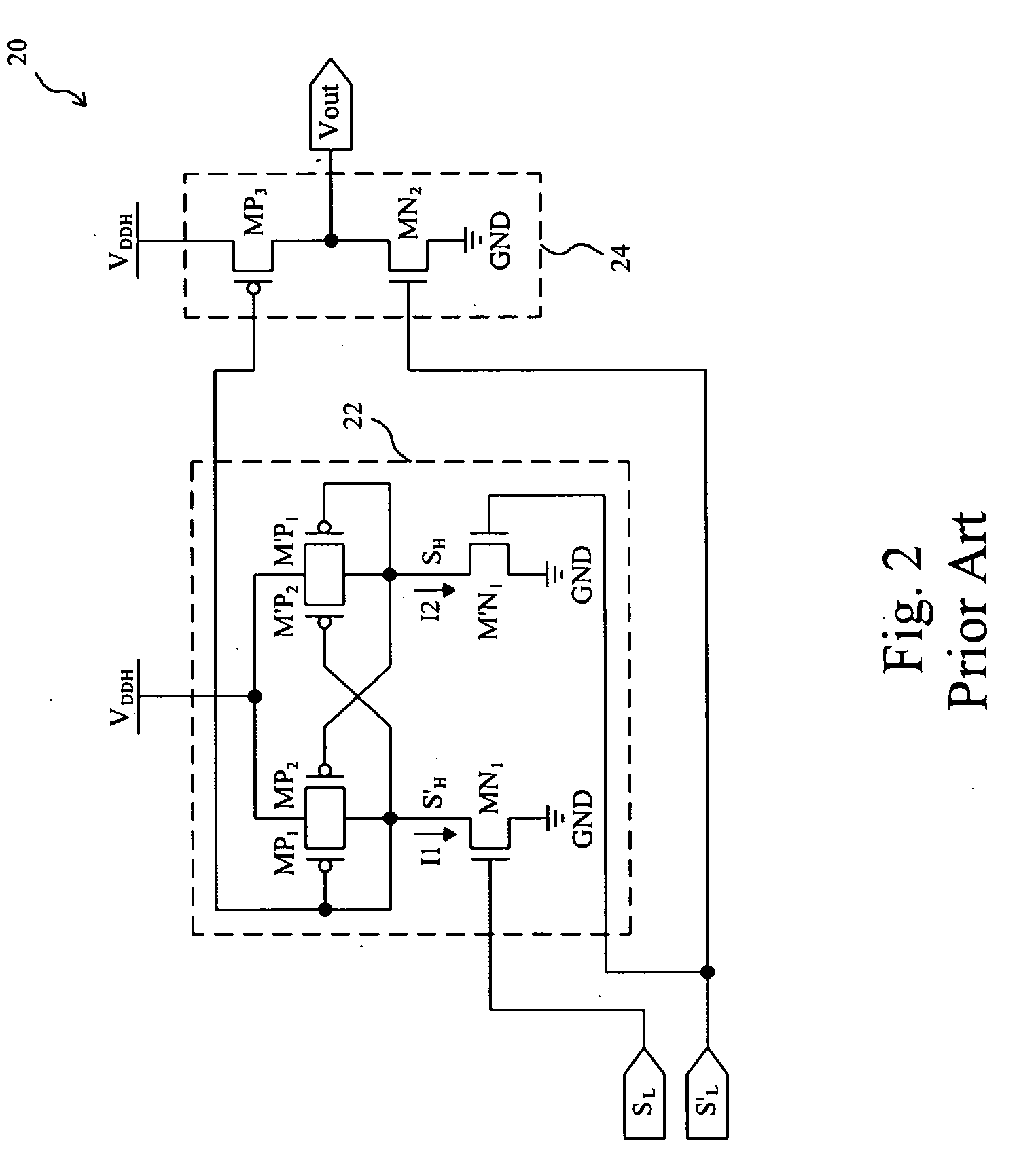
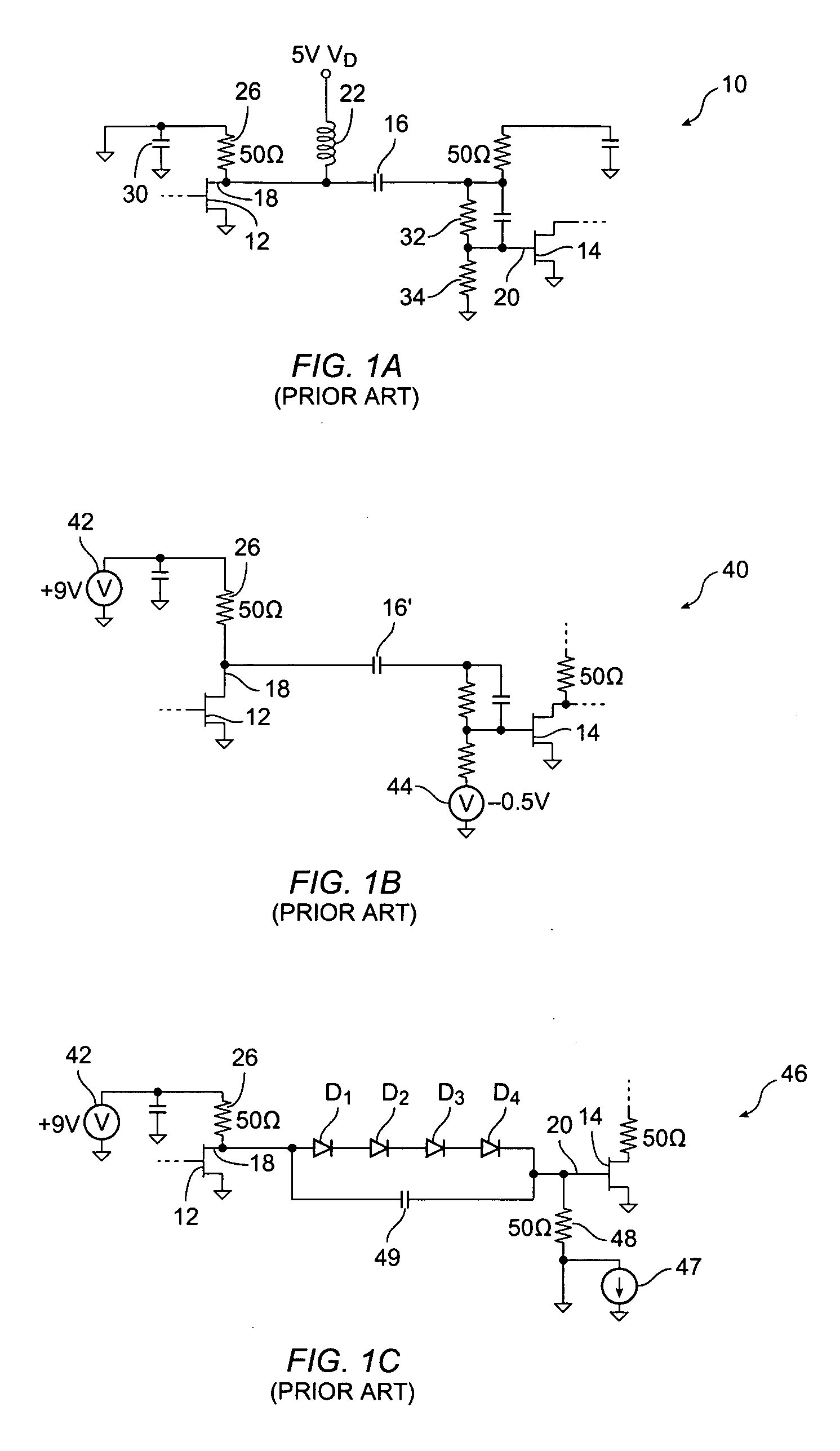
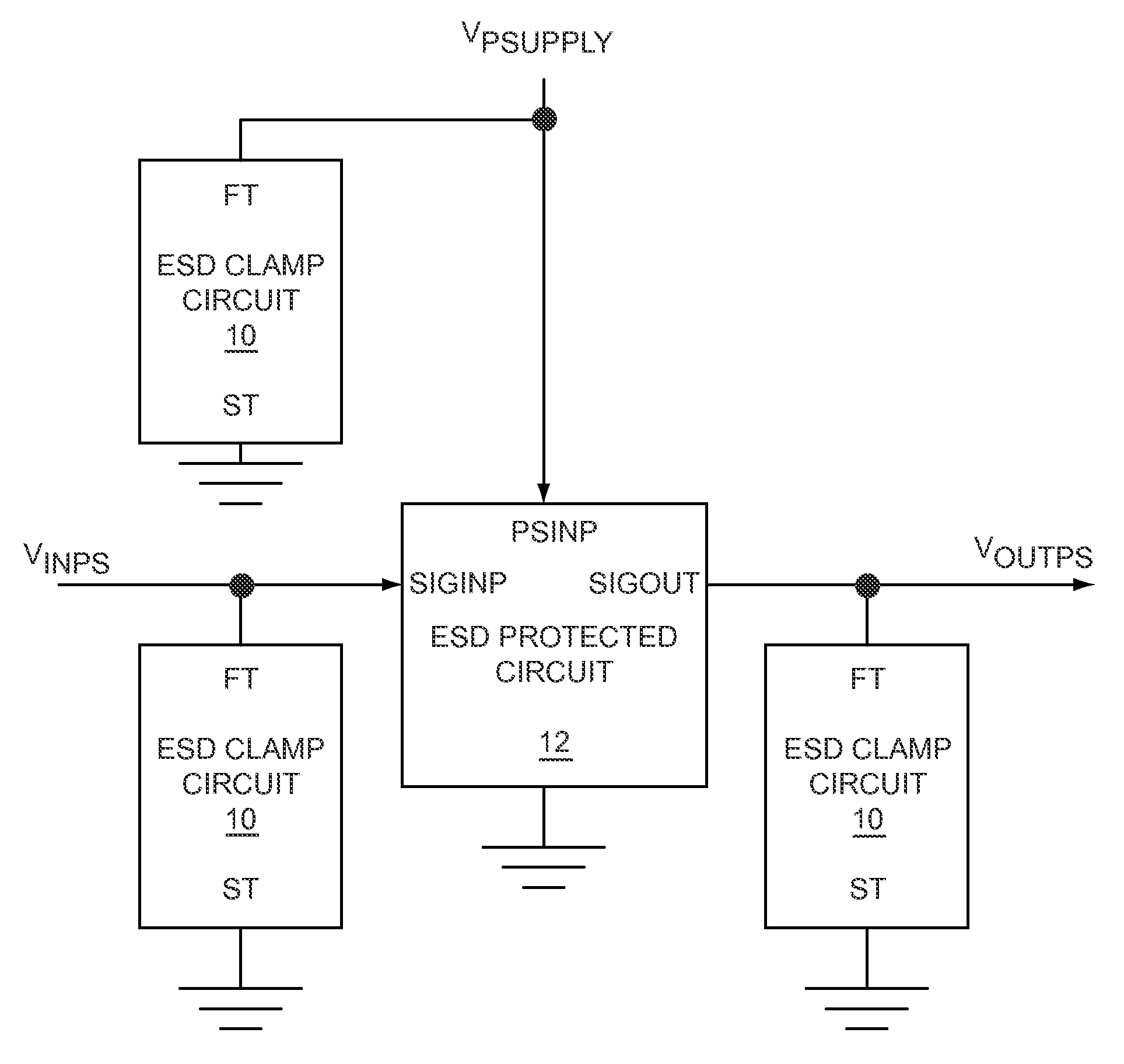
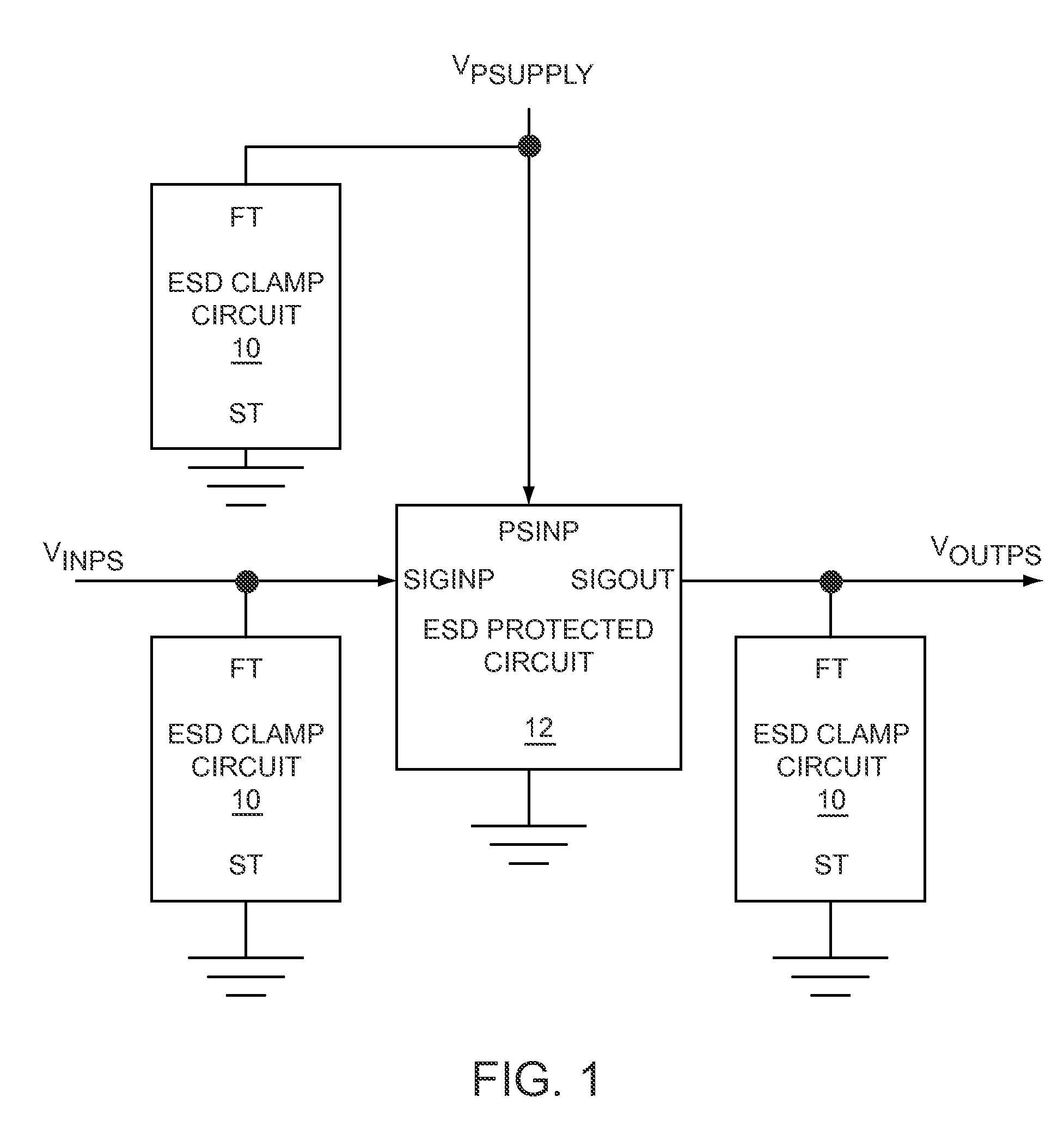
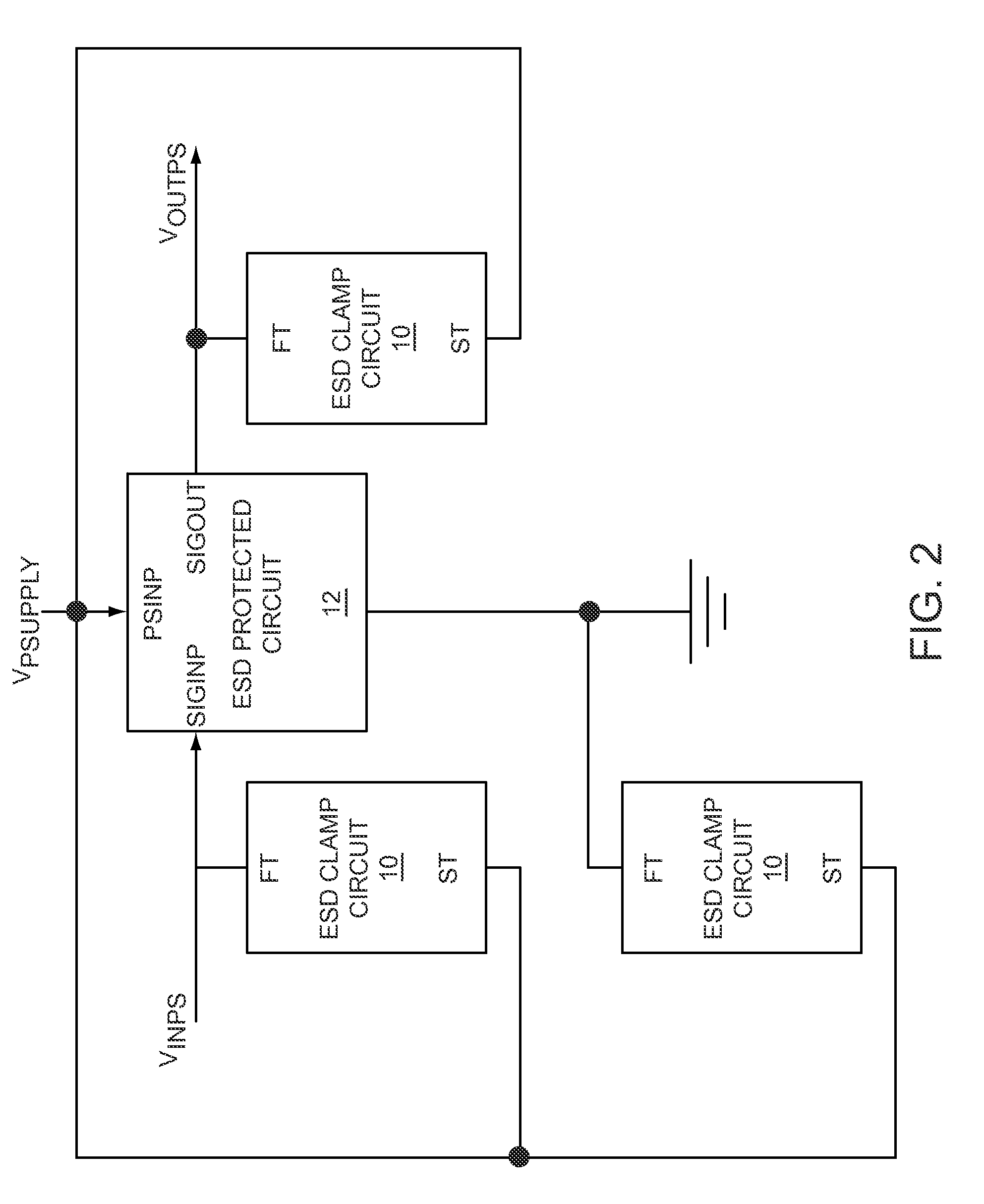
Level shift circuit
ActiveUS20090066399A1Fast processReduce layoutPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorLevel shiftingStable status
A level shift circuit includes an input stage and an output stage coupled to each other by two nodes. The input stage changes the voltages on the nodes according to an input signal, and the output stage determines an output signal according to the voltages on the two nodes. In a transition state, the input stage provides a large current to charge or discharge the first node or the second node so as to quickly change the voltage thereon. In a steady state, the input stage lowers the current so as to reduce power consumption.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
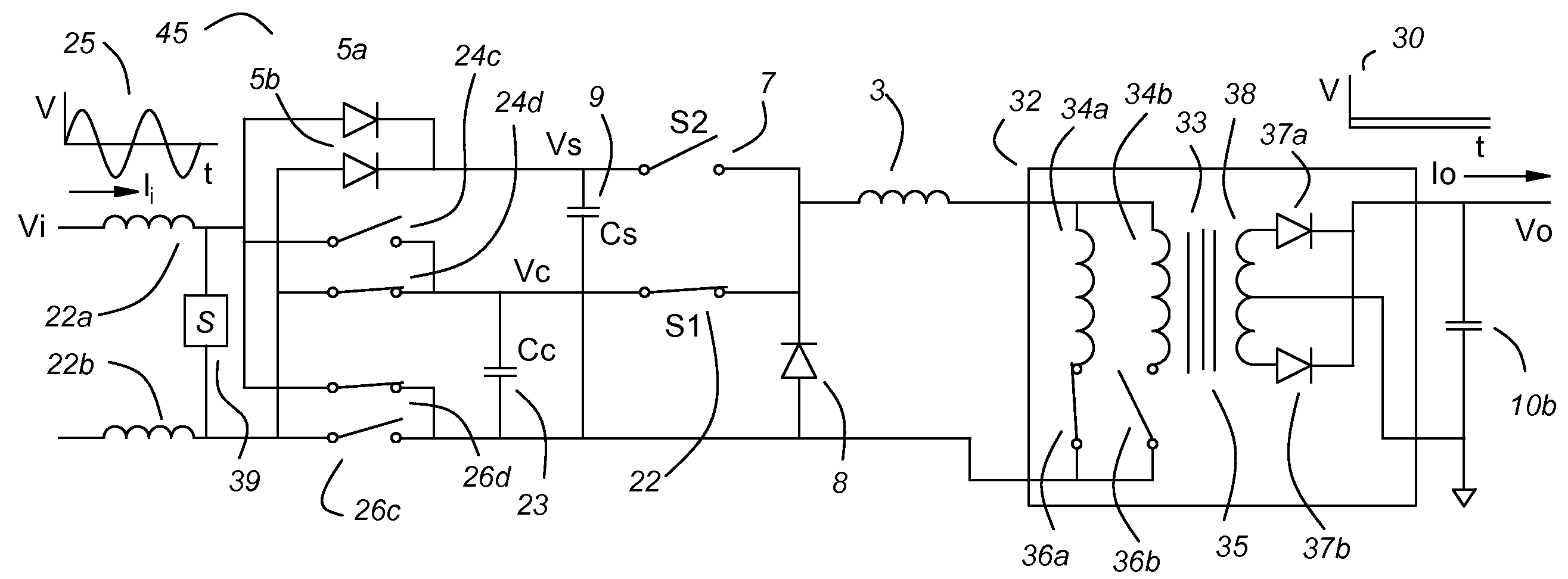
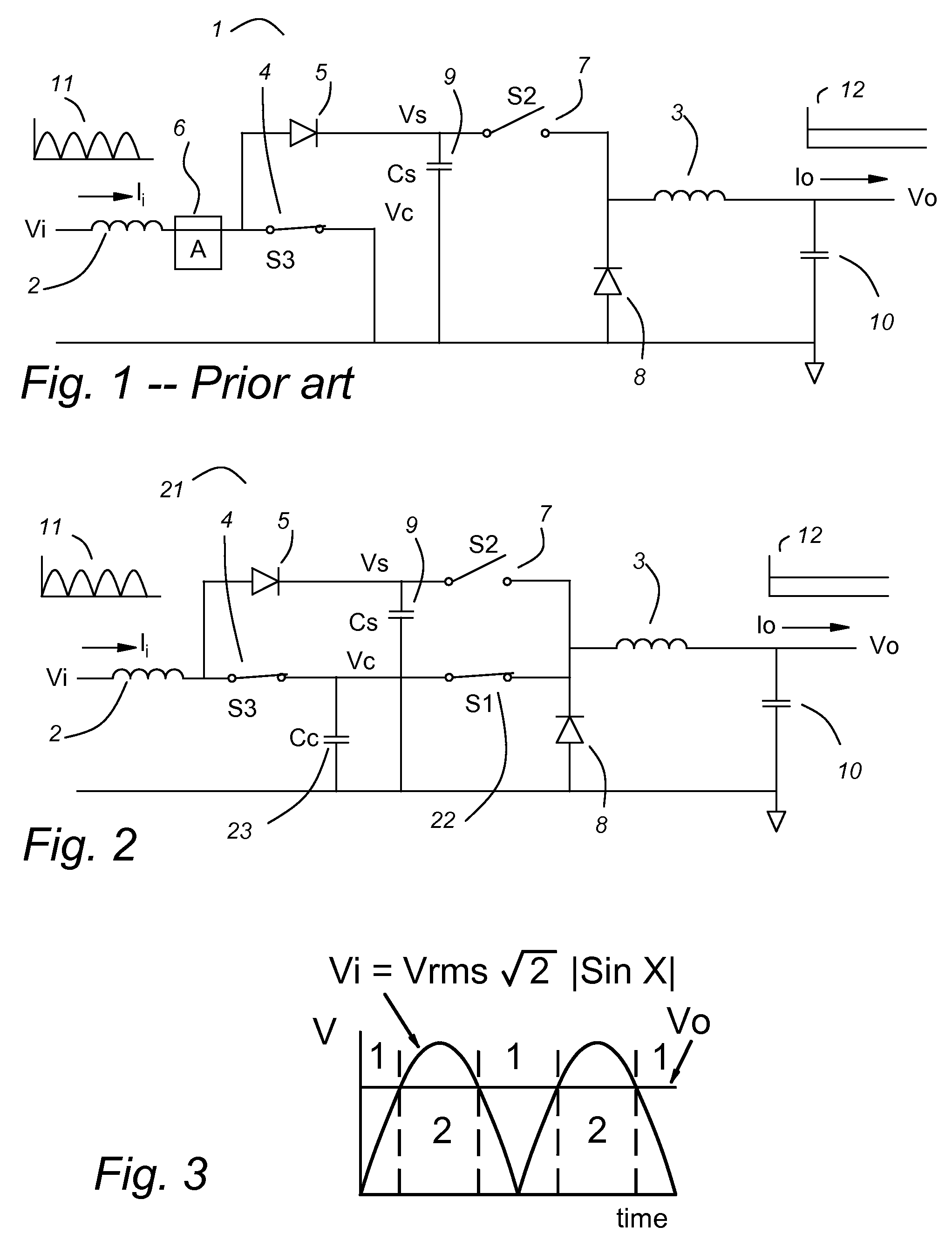
Power factor corrected single-phase AC-DC power converter using natural modulation
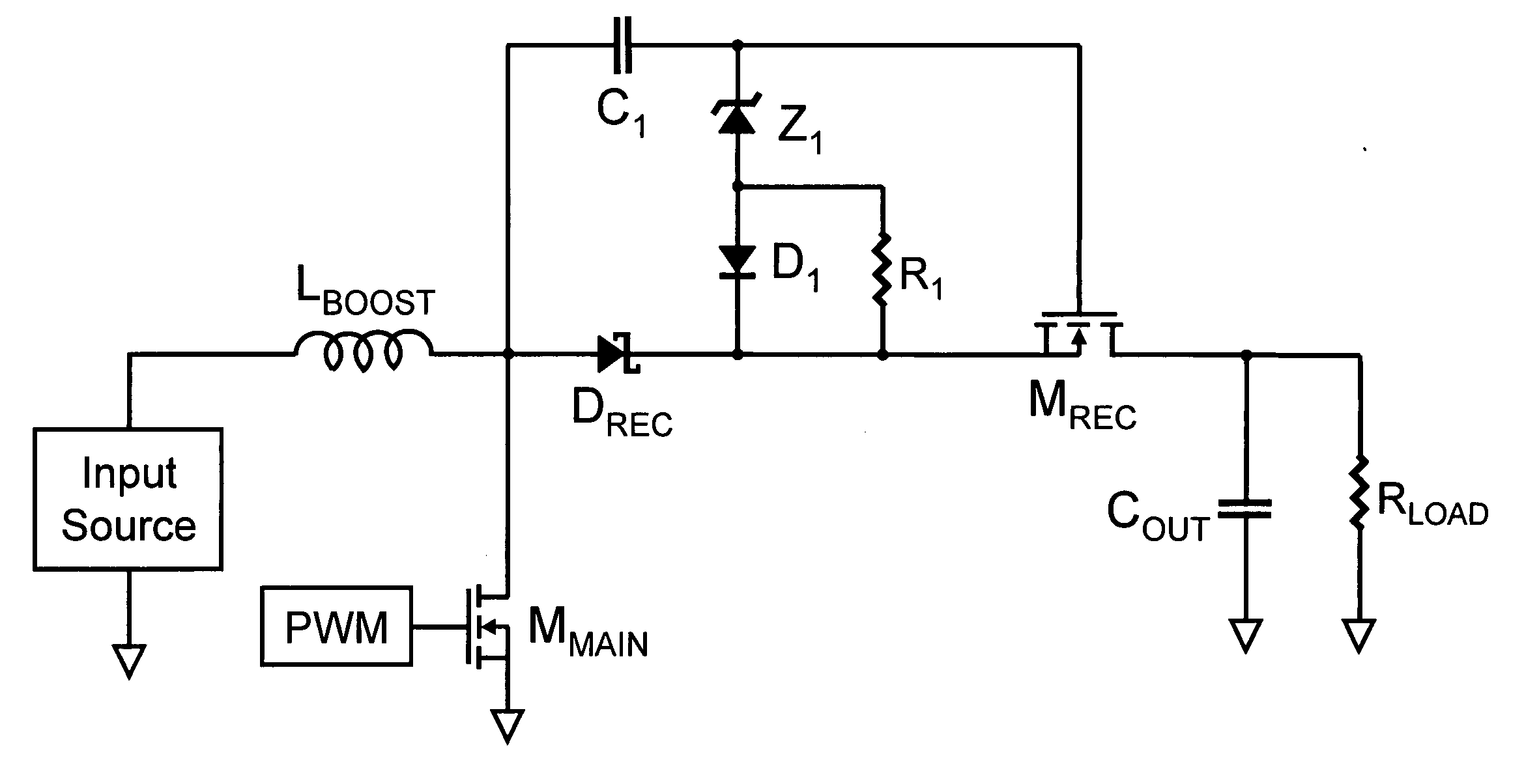
InactiveUS7564706B1Reduce lossesMost efficientAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLevel shiftingElectric power system
A power factor corrected (pfc) ac-dc converter has a modified boost input and a modified buck output. Unlike the prior art boost input, the boost switch returns to the output, not to ground. Unlike the prior art buck output stage, a third switch connects to the input. This allows much of the input current to pass through the converter to the output. There is no input current measurement, but nearly ideal power factor correction is achieved through “natural modulation.” A preferred pfc ac-dc converter uses a variable dc-dc transformer on its output, as a post regulator, to provide dielectric isolation and to provide voltage level shifting. The output of the pfc ac-dc converter has the control characteristics of a buck converter, so it is a natural mate for the variable dc-dc transformer. An ac-dc buck converter is most efficient at its maximum duty cycle. It cannot regulate for a lower input voltage, but it can reduce its duty-cycle to control for higher input voltages. A variable dc-dc transformer is most efficient at its maximum ratio. It cannot regulate for a higher input voltage, but it can reduce its effective turns ratio to control for a lower input voltage. With a small overlap in their control ranges, both parts of the power system can operate at maximum efficiency. The variable dc-dc transformer controls the output voltage for nominal and low input voltage. The ac-dc buck converter limits over-voltage transients.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
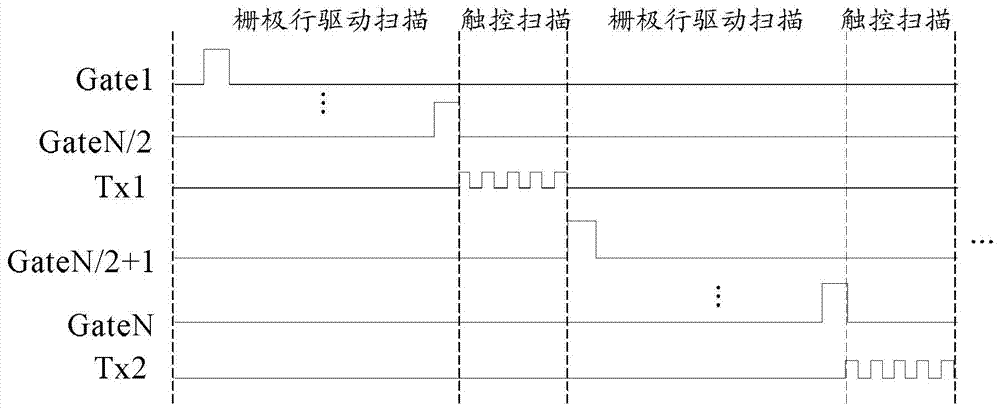
Gate drive circuit and method and display device
ActiveCN103943055APrevent leakageAvoid the defect of insufficient charge rateStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerLevel shifting
The invention provides a gate drive circuit and method and a display device and relates to the technical field of display. The method includes the steps that gate row drive scanning is performed on shifting register units located in a first area in the gate drive circuit; after gate row drive scanning of the shifting register units in the first area is finished, touch scanning is performed; after touch scanning is finished, the last-level shifting register unit located in the first area is scanned again so that the last-level shifting register unit located in the first area can be used for pre-charging a first-level shifting register unit located in a second area; gate row drive scanning is performed on shifting register units located in the second area in the gate drive circuit, and the last-level shifting register unit located in the first area is in cascade connection with the first-level shifting register located in the second area. The method can overcome the defect that the row pixel charging rate is insufficient and solve the problem of dark lines or poor bright lines.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS20050017789A1Improving RF switch isolationRaise the compression pointTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETEngineering
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
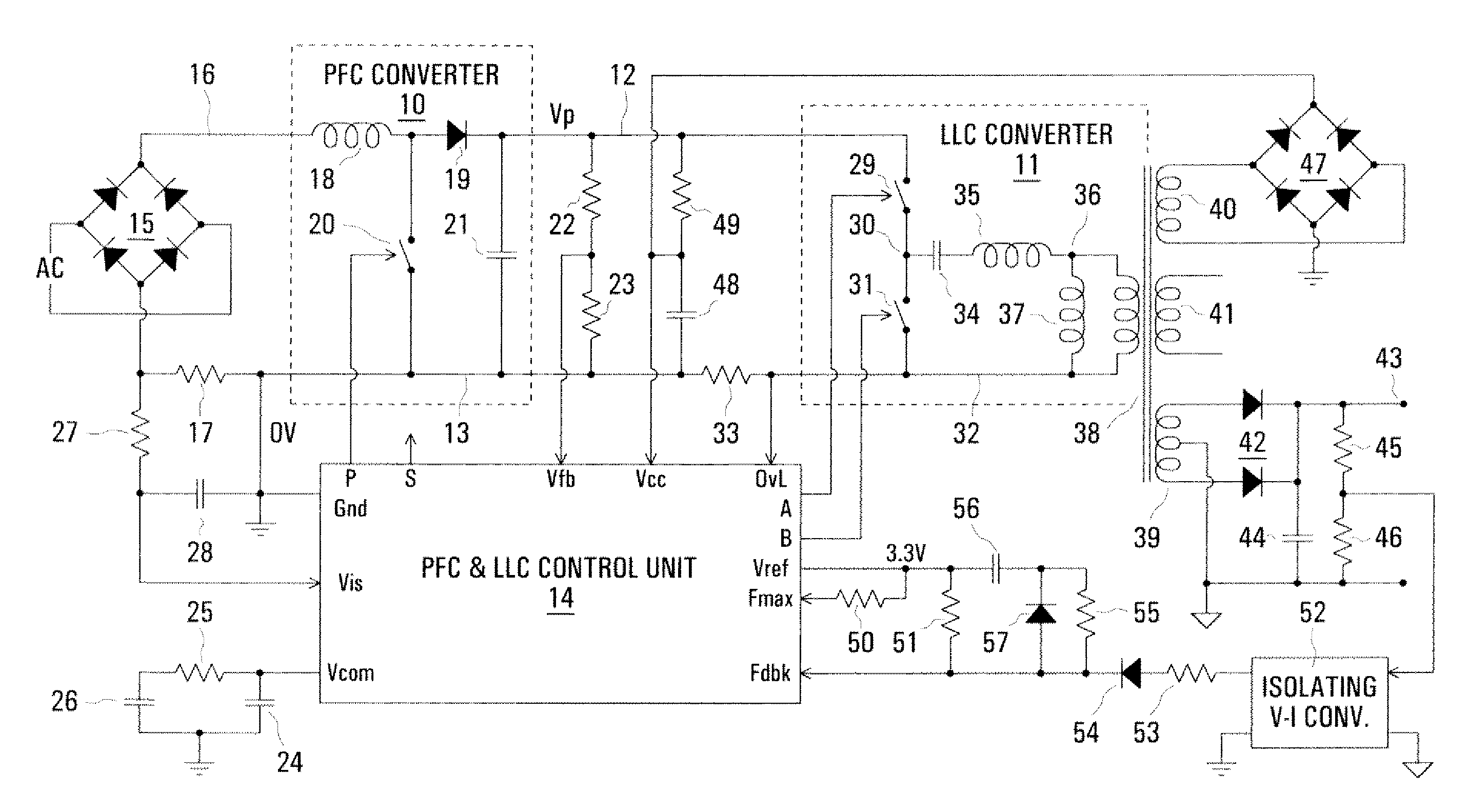
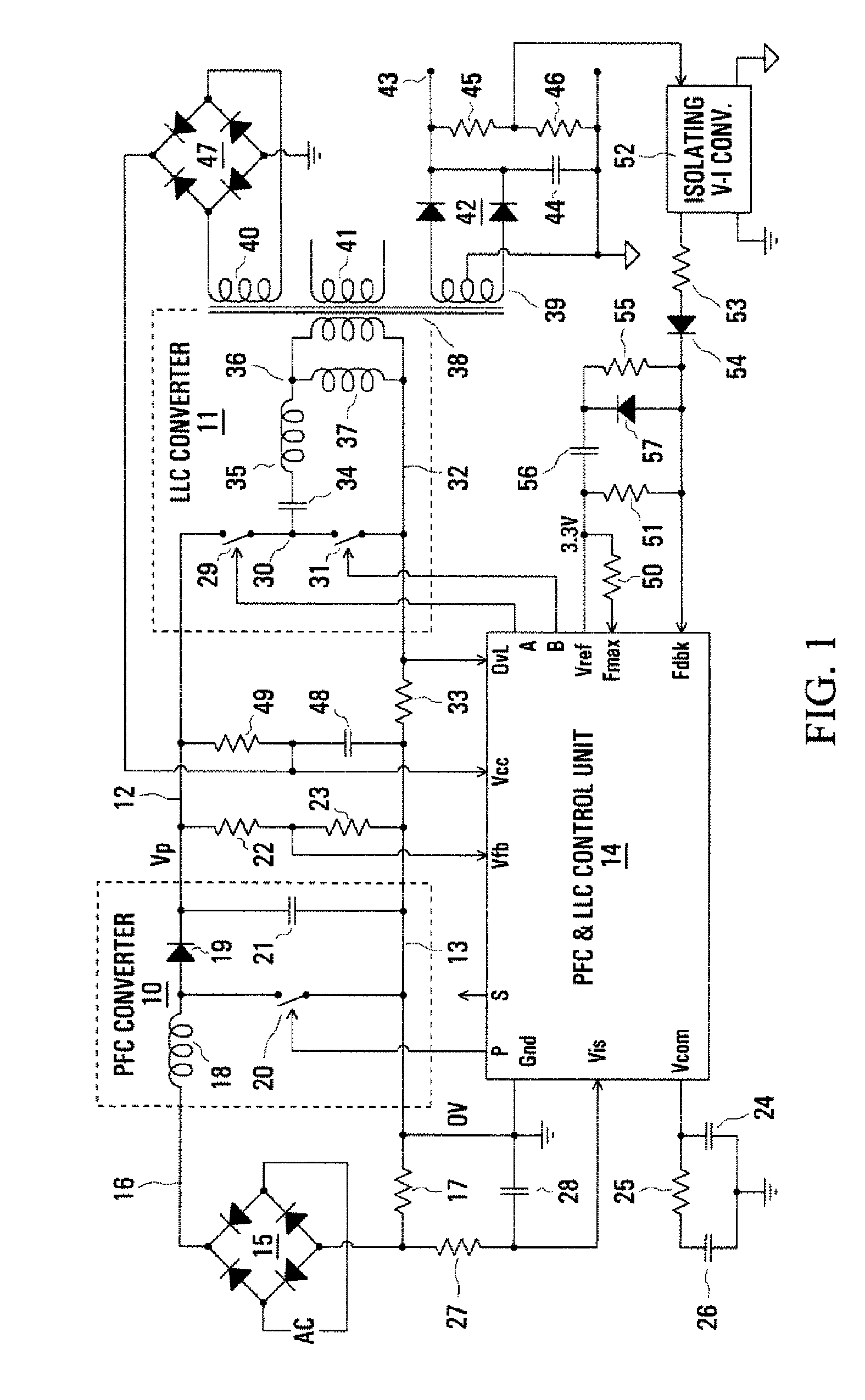
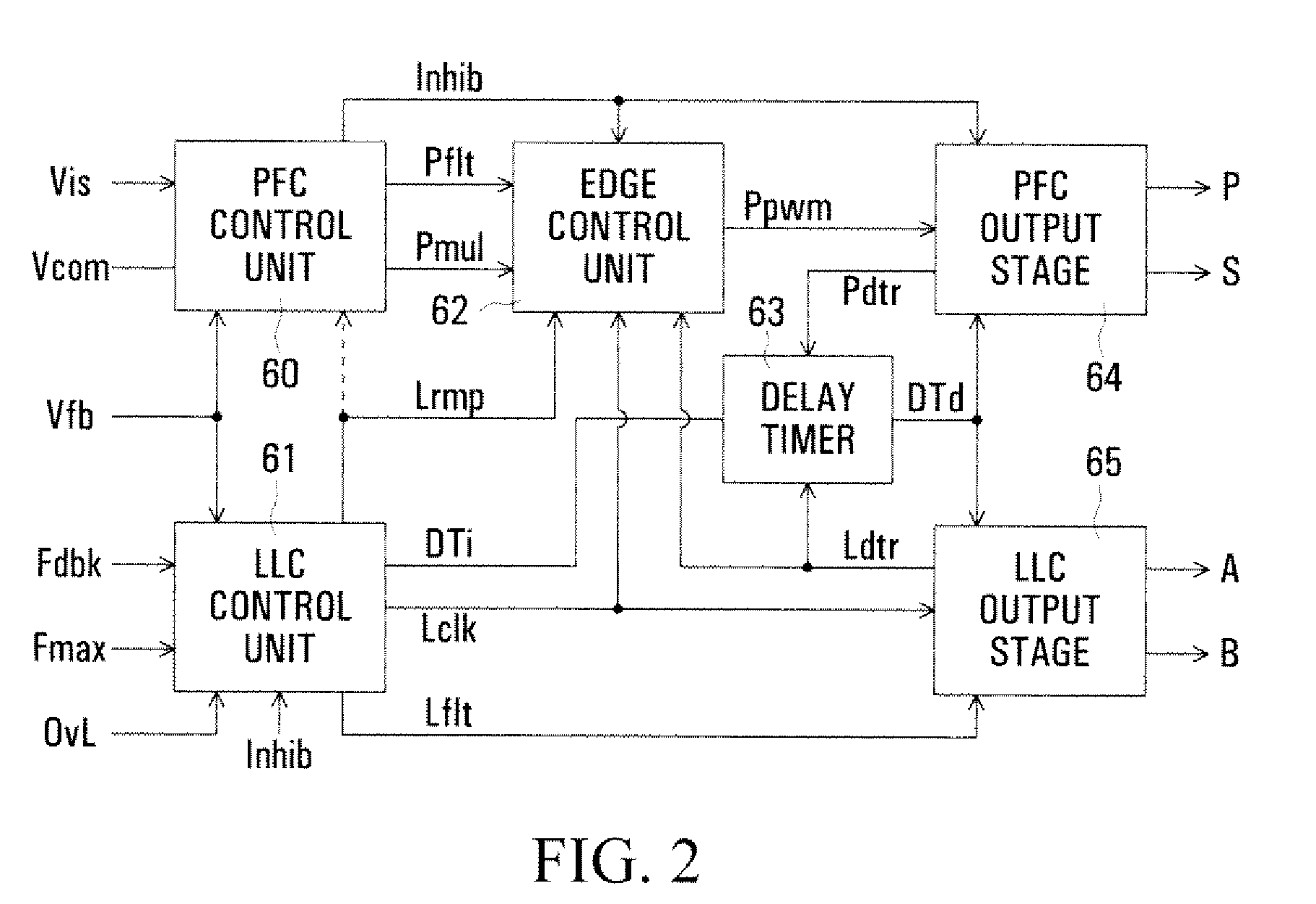
Control arrangement for a pfc power converter
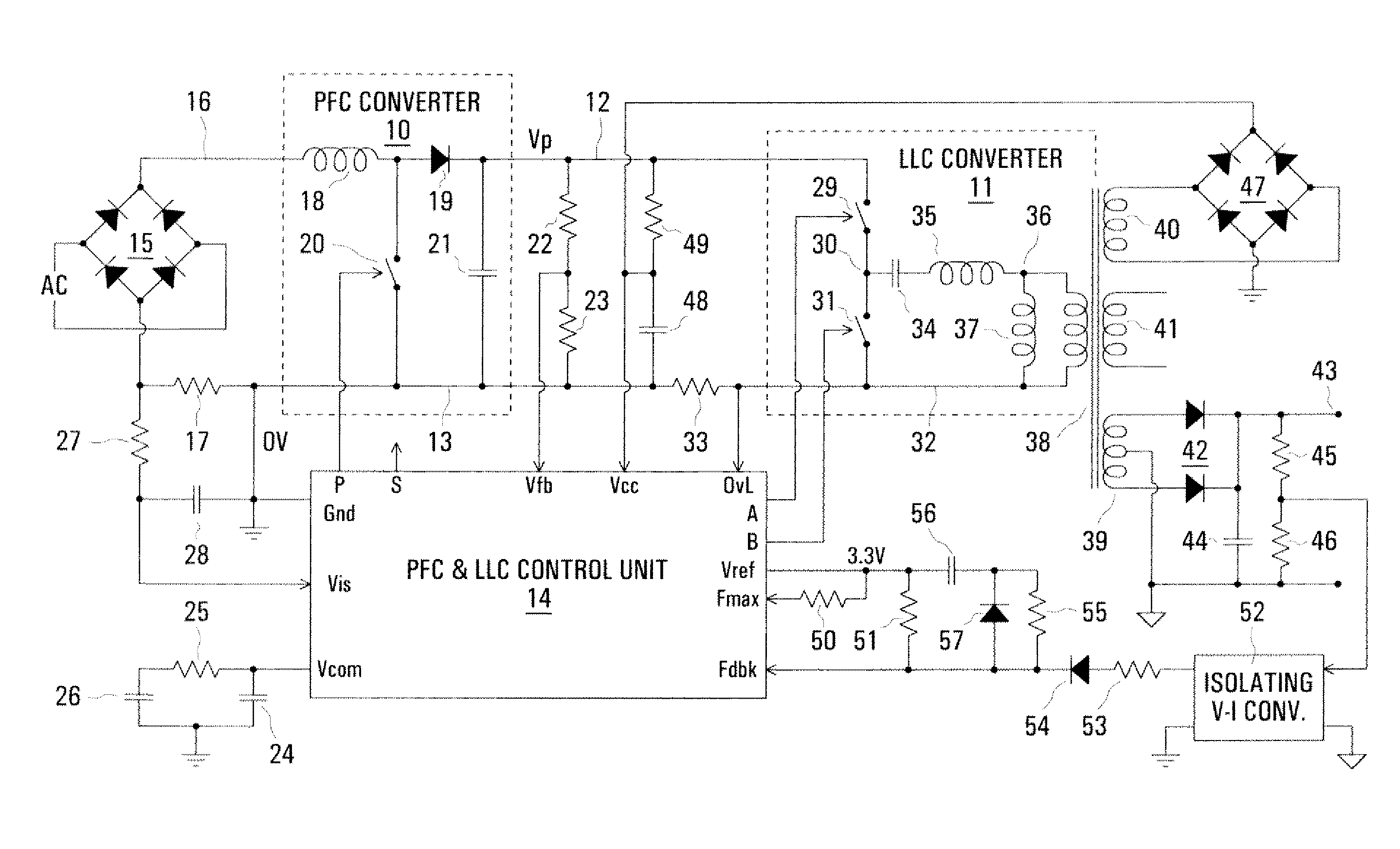
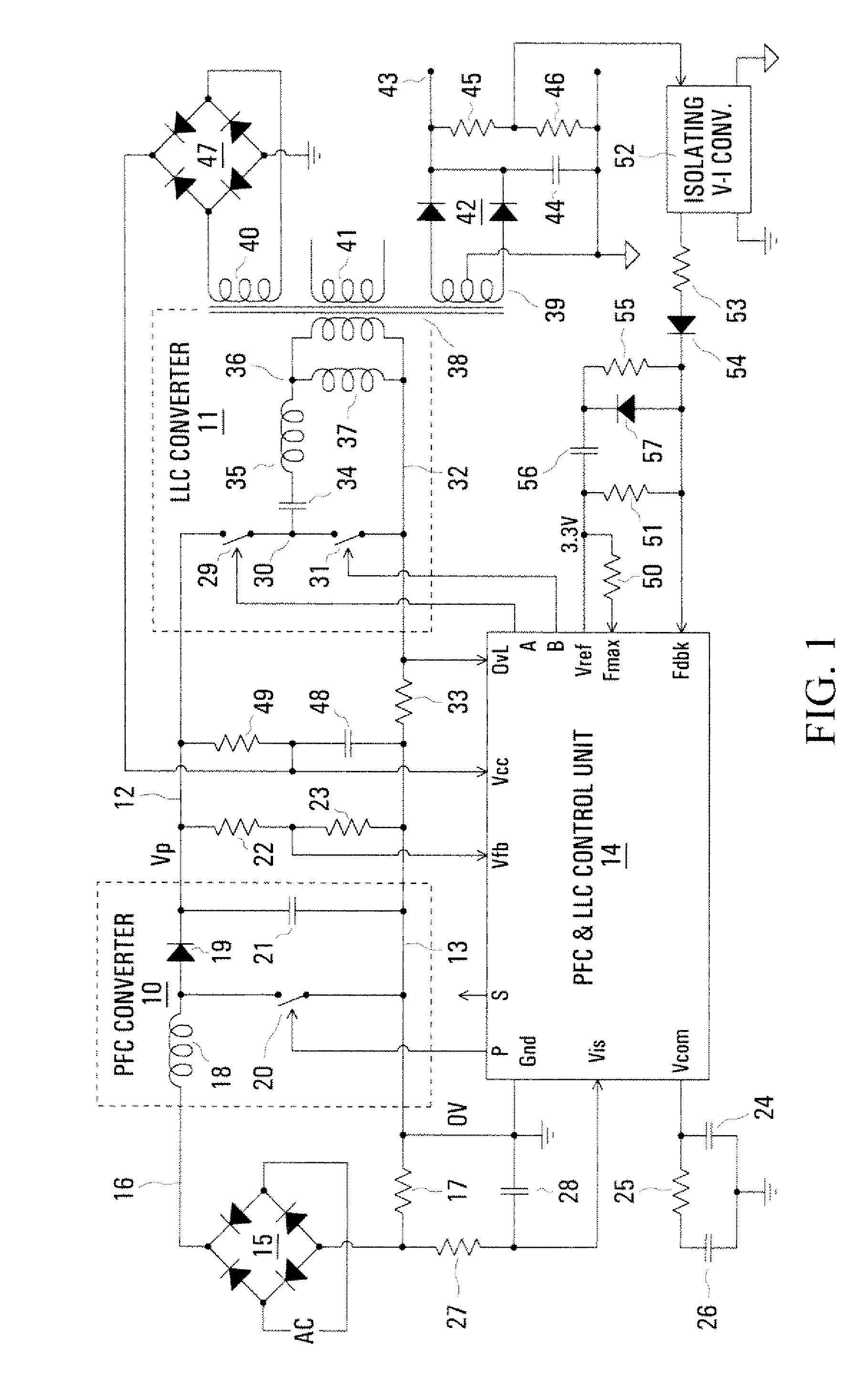
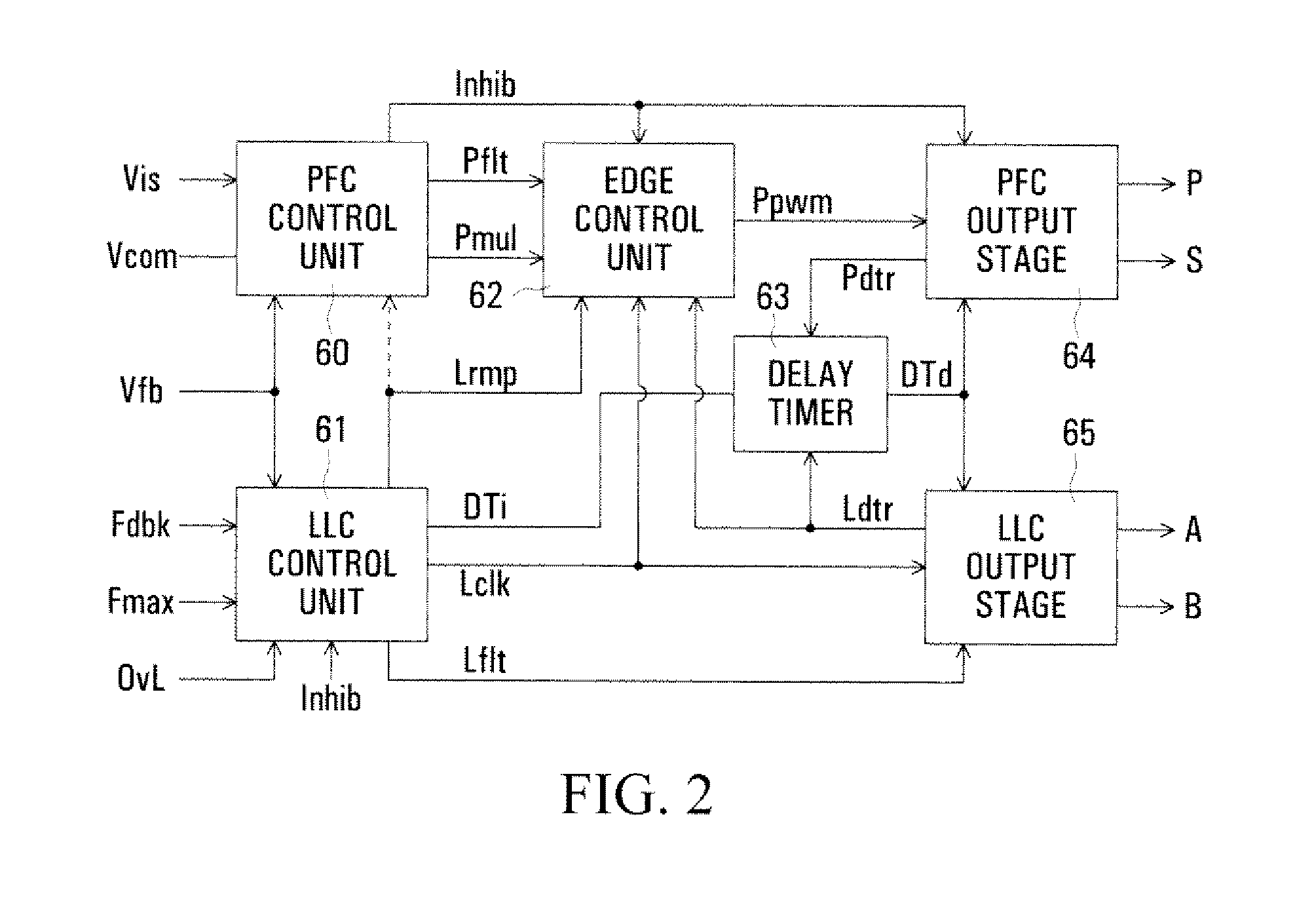
InactiveUS20080197817A1Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceLevel shifting
In a PFC (Power Factor Correction) converter control unit, a PWM (pulse width modulated) signal is produced by comparing a PFC converter output voltage error signal, produced by a transconductance amplifier, with a ramp signal, which may be from a control unit of a resonant mode converter in cascade with the PFC converter. Level shifting is used to match the amplitude ranges of the compared signals. A current, representing an input current of the PFC converter and produced by a current mirror, is switched by the PWM signal to a parallel resistance and capacitance to produce a smoothed voltage constituting a control signal for the PFC converter.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
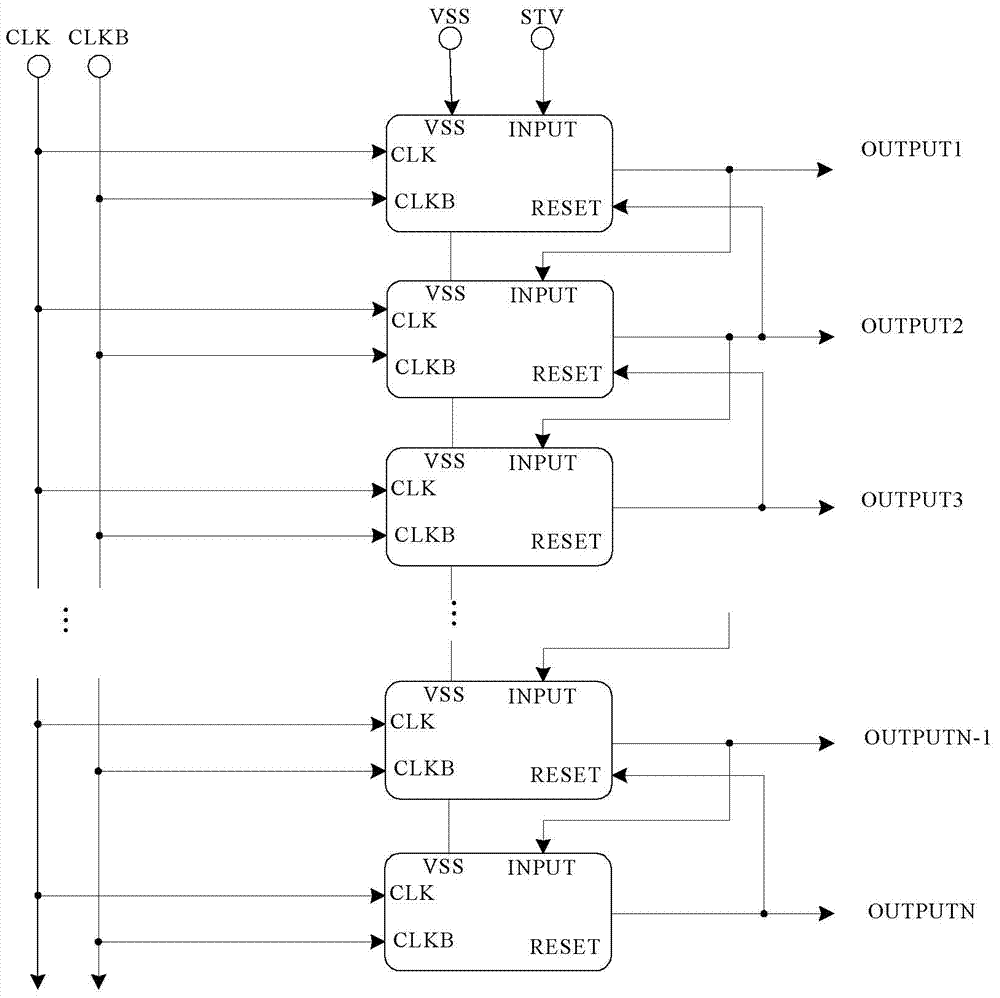
Shifting register unit, grid electrode drive circuit and display device
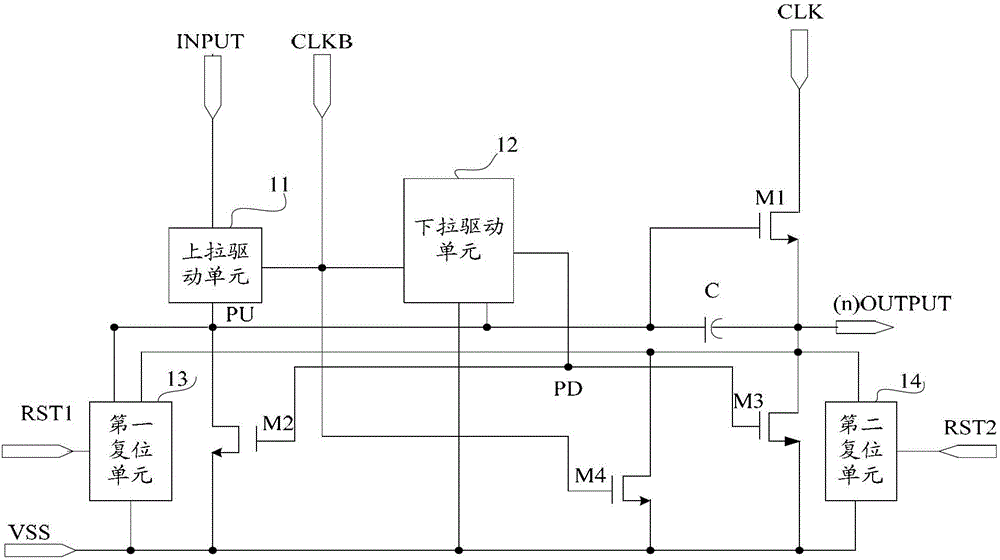
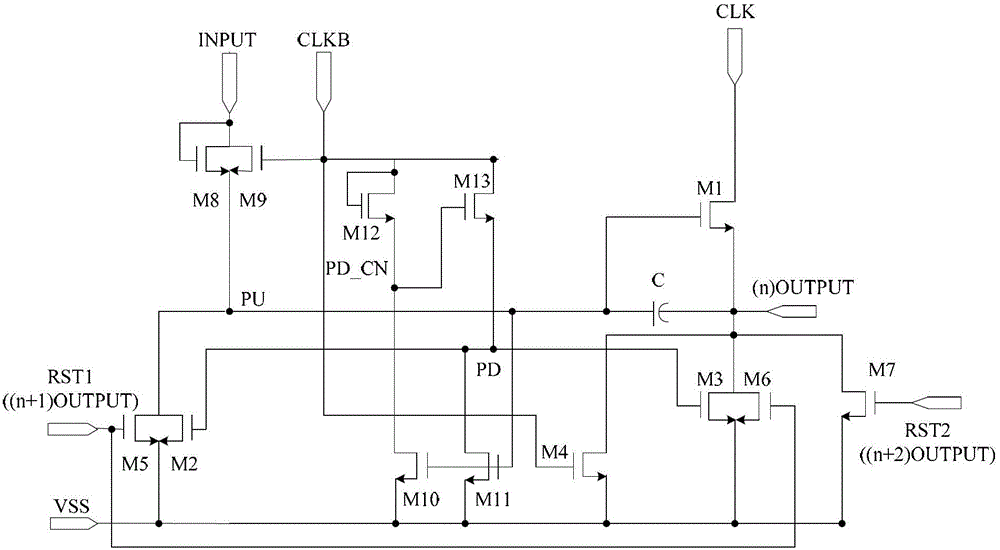
The invention provides a shifting register unit, a grid electrode drive circuit and a display device. The shifting register unit comprises an output up-pull transistor, an up-pull node down-pull transistor, an output down-pull transistor, an output transistor, a bootstrap capacitor, an up-pull drive unit, a down-pull drive unit, a first resetting unit and a second resetting unit, wherein the first resetting unit is respectively connected with a first resetting end, an up-pull node, a local-level output end and a low-level output end; the first resetting end is connected with the output end of a next-level shifting register unit; the second resetting unit is respectively connected with a second resetting end, a local-level output end and a low-level output end; and the second resetting end is connected with the output end of a Nth-level shifting register unit after being connected with a previous-level shifting register unit, and the N is an integer which is more than one. At least two resetting units are adopted to inhibit the noise between the first unit time after the current output and the Nth unit time.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
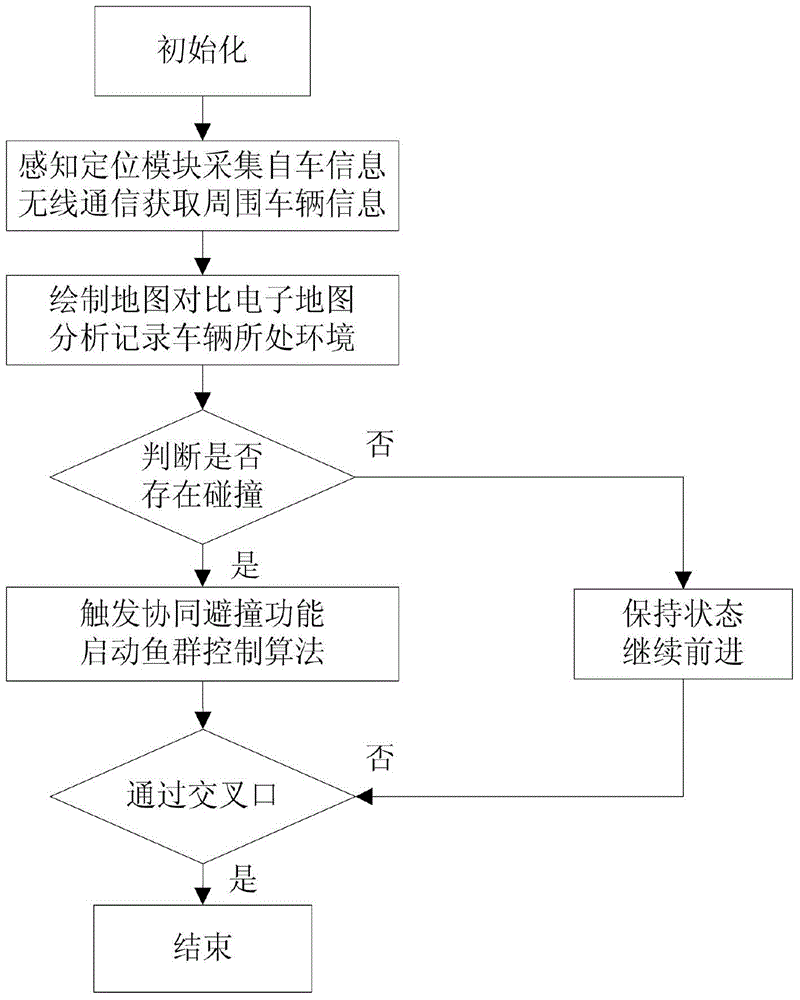
Fish streaming based non-signal intersection vehicle-vehicle cooperation control system
InactiveCN104616541ARealize unmanned drivingReal-time information interactionAnti-collision systemsInformation processingLevel shifting
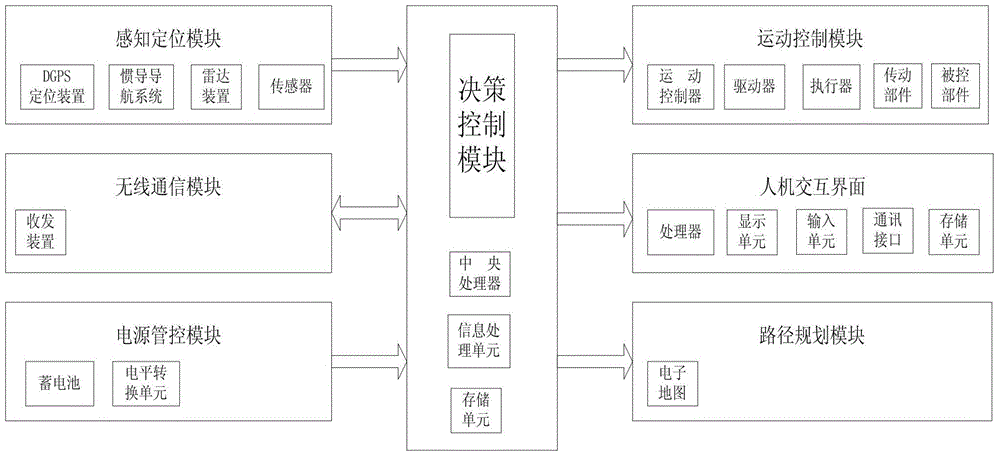
The invention relates to a fish streaming based non-signal intersection vehicle-vehicle cooperation control system and belongs to the field of vehicle control. A sensing positioning module of the system comprises an environment sensing portion and a navigation positioning portion and specifically comprises a DGPS positioning device, an inertial navigation system, a radar device and a sensor. A motion control module comprises a motion controller, a driver, an actuator, a transmission part and a controlled part. A wireless communication module consists of a transmitting-receiving device. A human-computer interaction interface comprises a processor, a display unit, an input unit, a communication interface and a data storage unit. A power management and control module comprises a storage battery and a level conversion unit. A route planning module adopts global route planning and is provided with an electronic map. A decision control module comprises a central processing unit, an information processing unit and a storage unit. Compared with the prior art, the fish streaming based non-signal intersection vehicle-vehicle cooperation control system has the advantages of being used for an unmanned vehicle, being provided with a wireless communication module and being high in active safety and road utilization rate.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
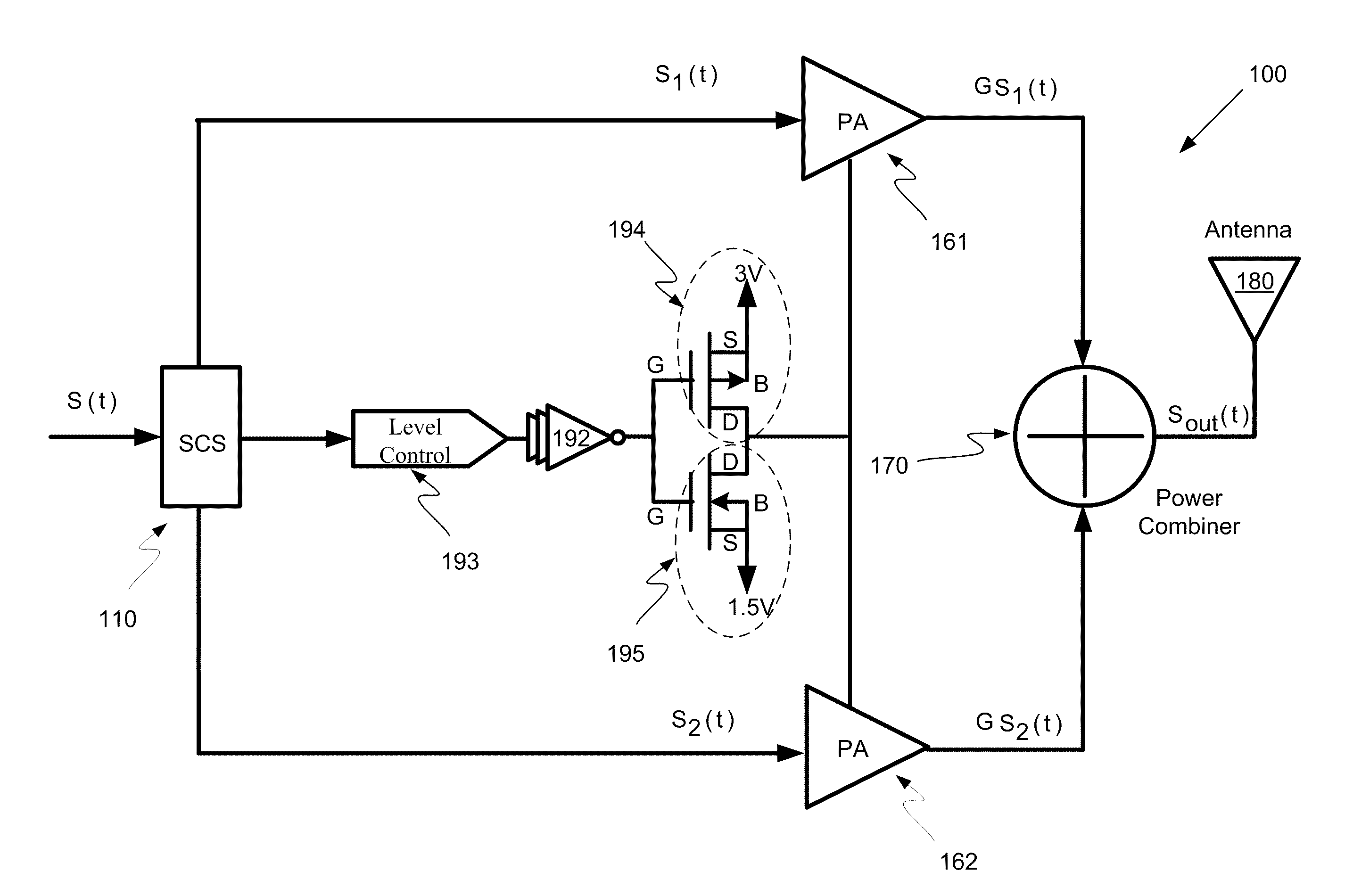
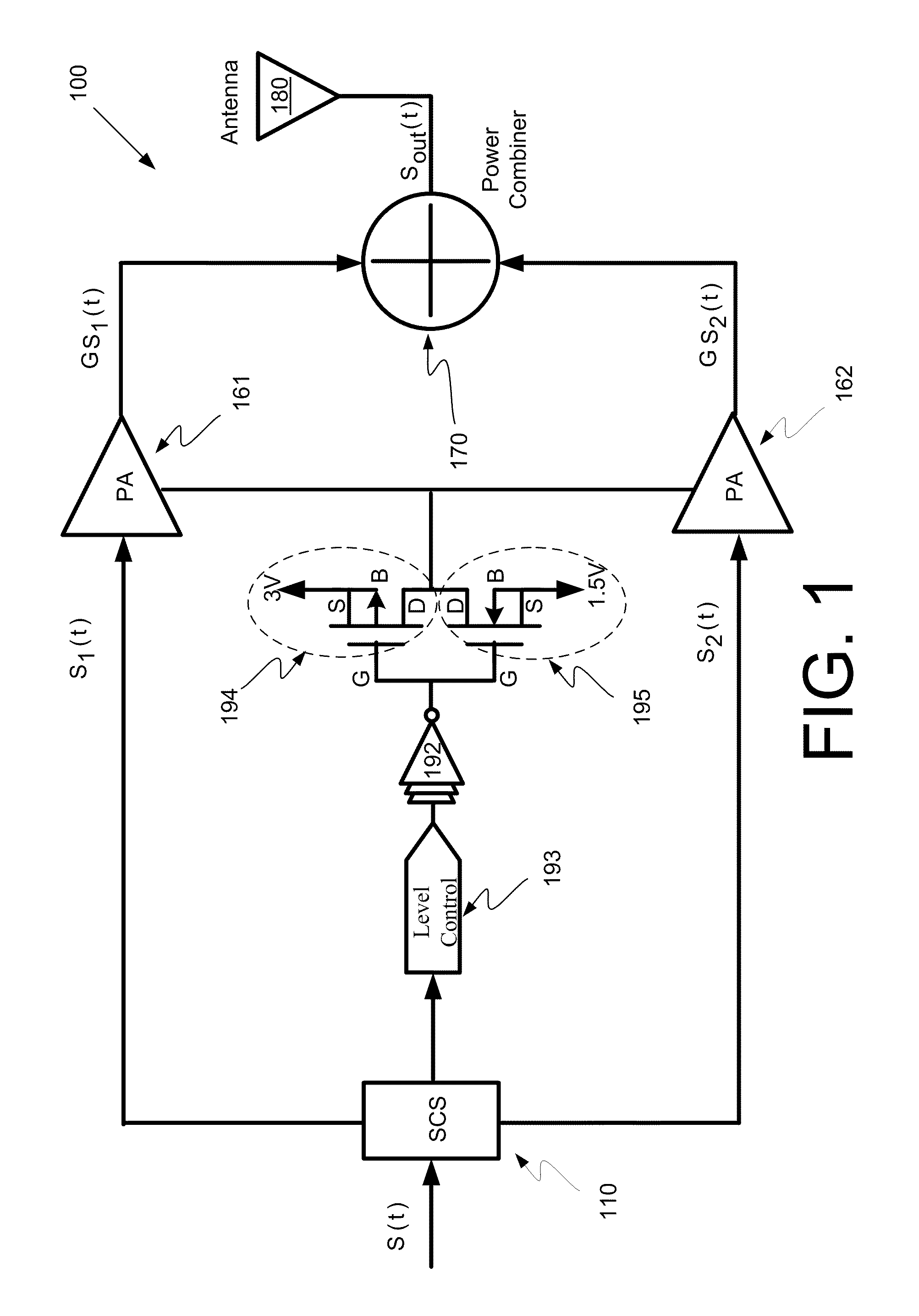
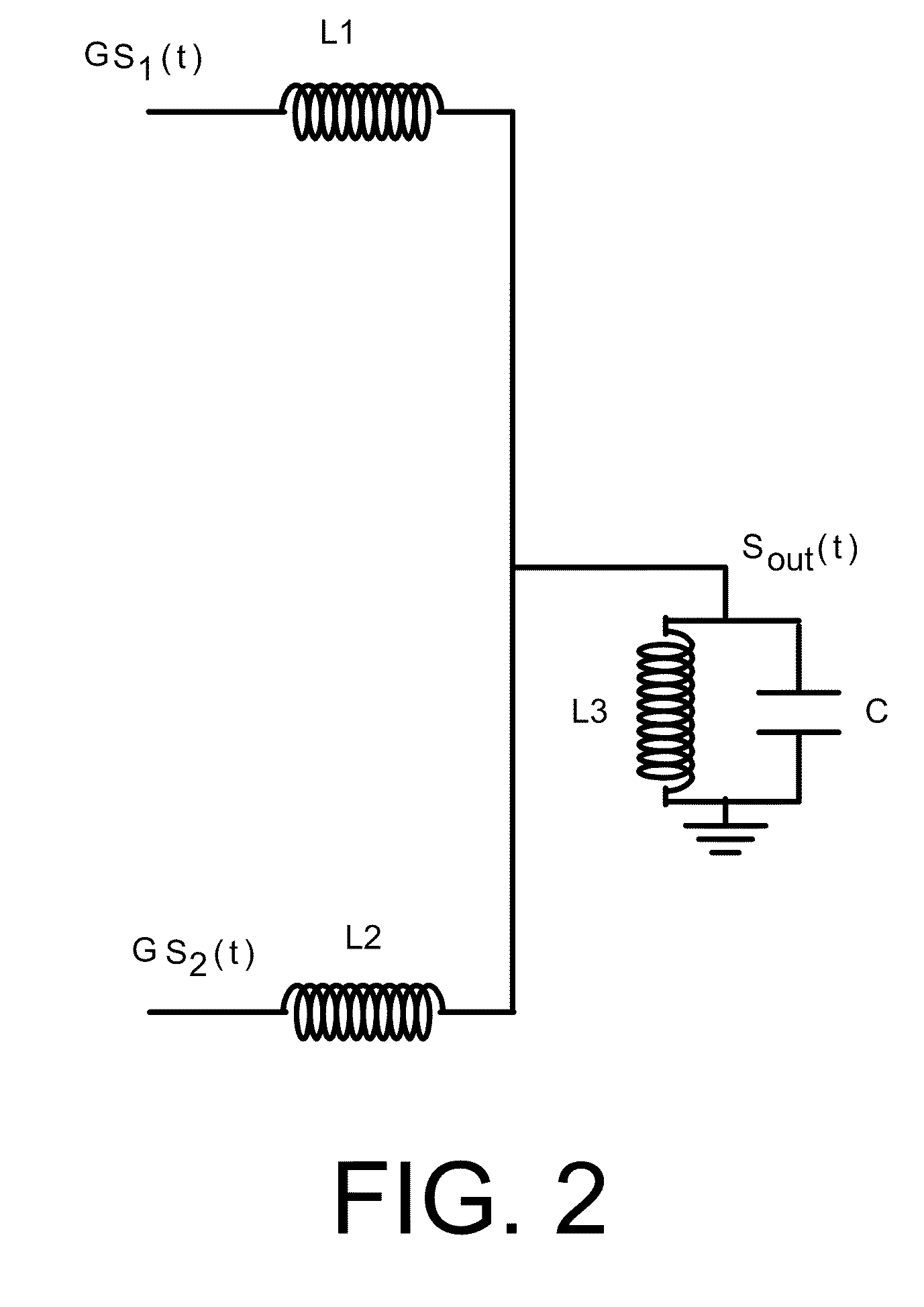
Systems and methods for a level-shifting high-efficiency linc amplifier using dynamic power supply
Systems and methods may be provided for a LINC system having a level-shifting LINC amplifier. The systems and methods may include a dynamic power supply that is adjustable to provide at least a first voltage supply level and a second voltage supply level higher than the first voltage supply level; a first power amplifier that amplifies a first component signal to generate a first amplified signal; a second power amplifier that amplifiers a second component signal to generate a second amplified signal, where the first component signal and the second component signal are components of an original signal, where the first component signal and the second component signal each have a constant envelope, and where the original signal has a non-constant envelope, and where the first and second power amplifiers are biased at the first voltage supply level or the second voltage supply level based upon an analysis of an amplitude of the original signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
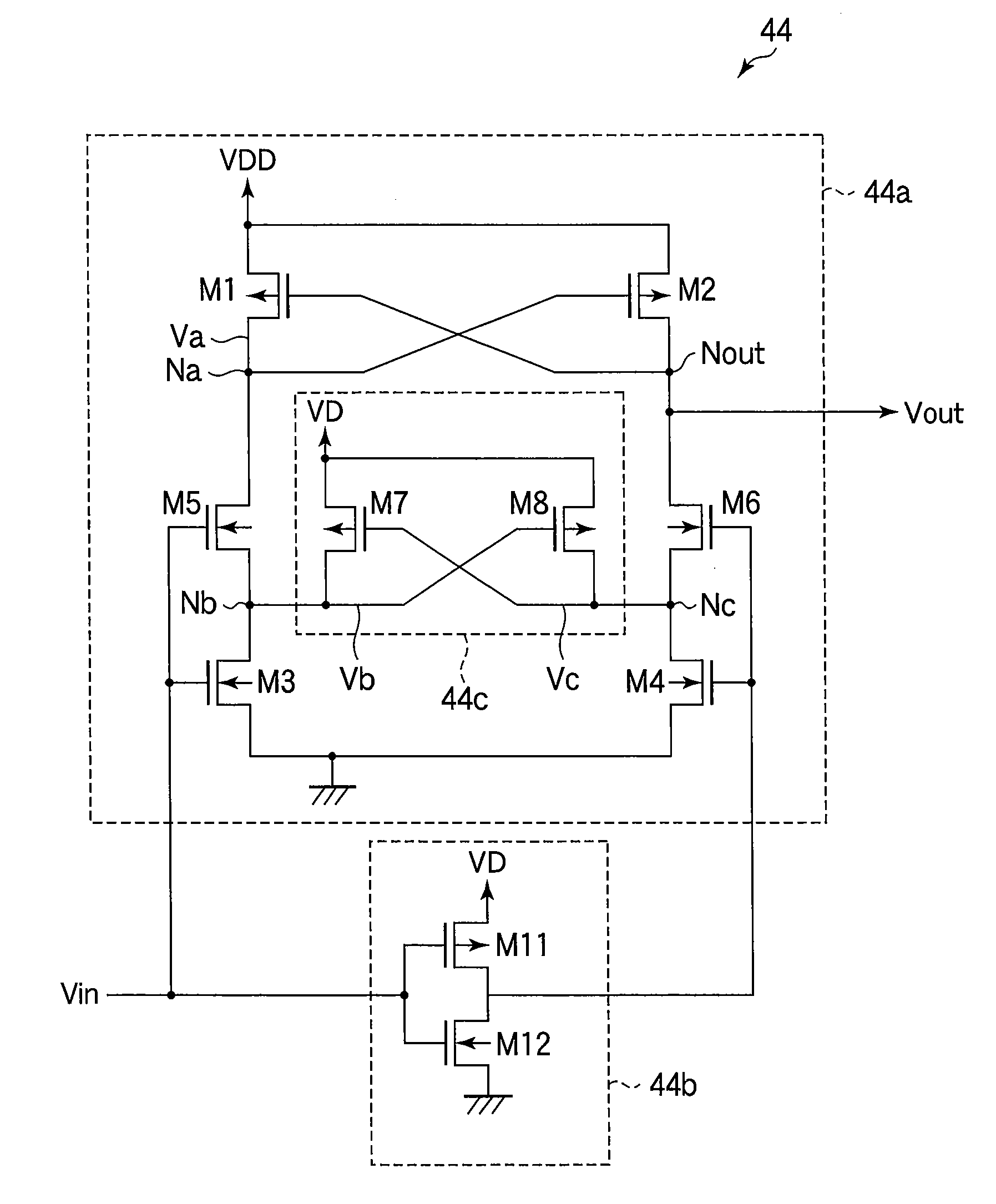
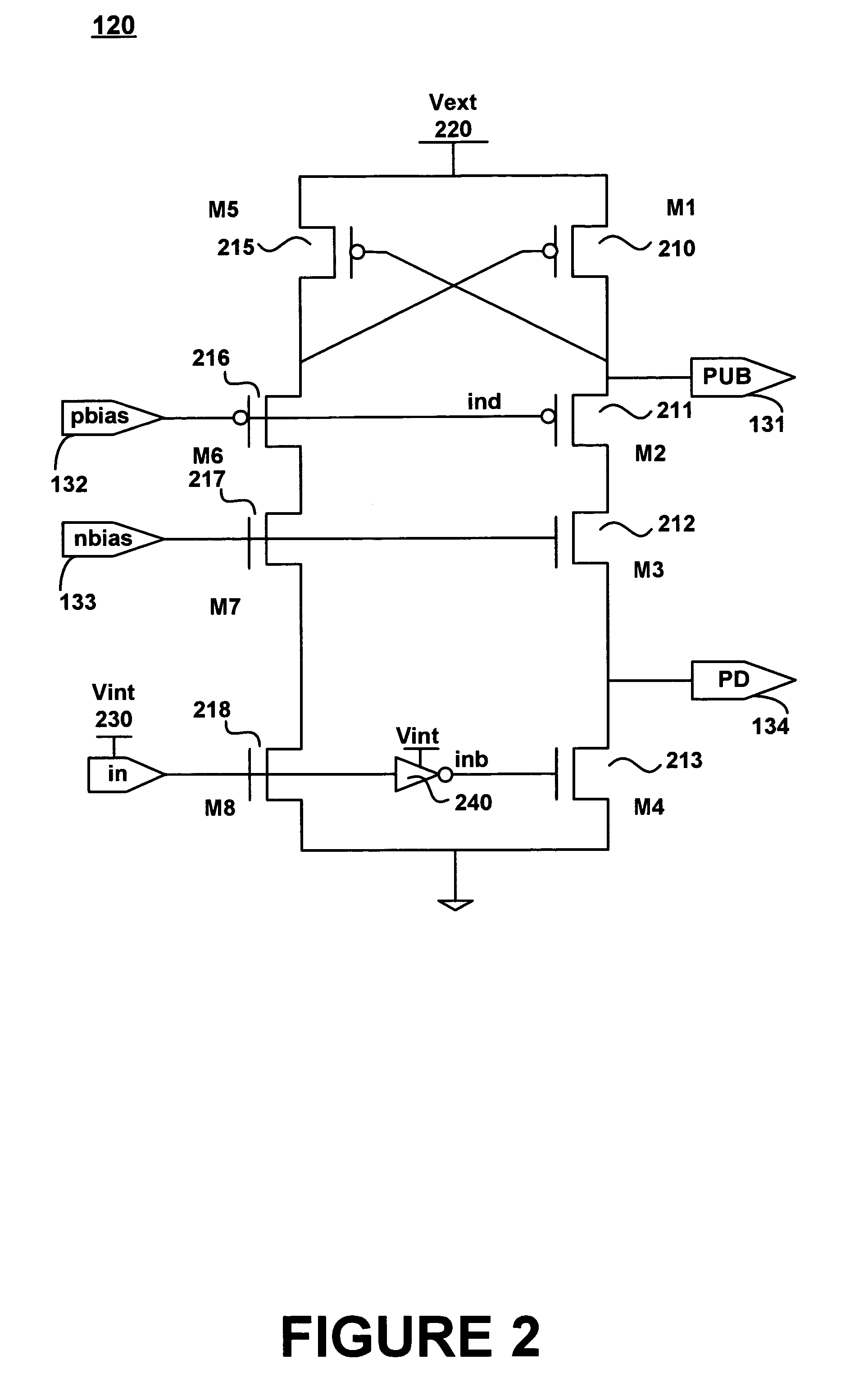
Level shifter with reduced duty cycle variation
InactiveUS20050285658A1Pulse automatic controlAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLevel shiftingCapacitance
A voltage level shifting circuit (10) transitions an input signal at a first voltage to a second voltage higher than the first voltage. A cross-coupled latch provides the second voltage. Cascode configured transistors (16, 26) are connected in series with input transistors (18, 28) that receive the first voltage in complementary form. Capacitive devices (34, 40) are connected between the first voltage and gates of the cascode configured transistors for allowing independent small signal variations to occur on the gates of the cascode configured transistors for better control of duty cycle and rise and fall time matching of the level shifting circuit. Isolation devices (32, 38) permit independent modification of small signal voltages to occur on the gates of the cascode configured transistors.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
LED string driver with shift register and level shifter
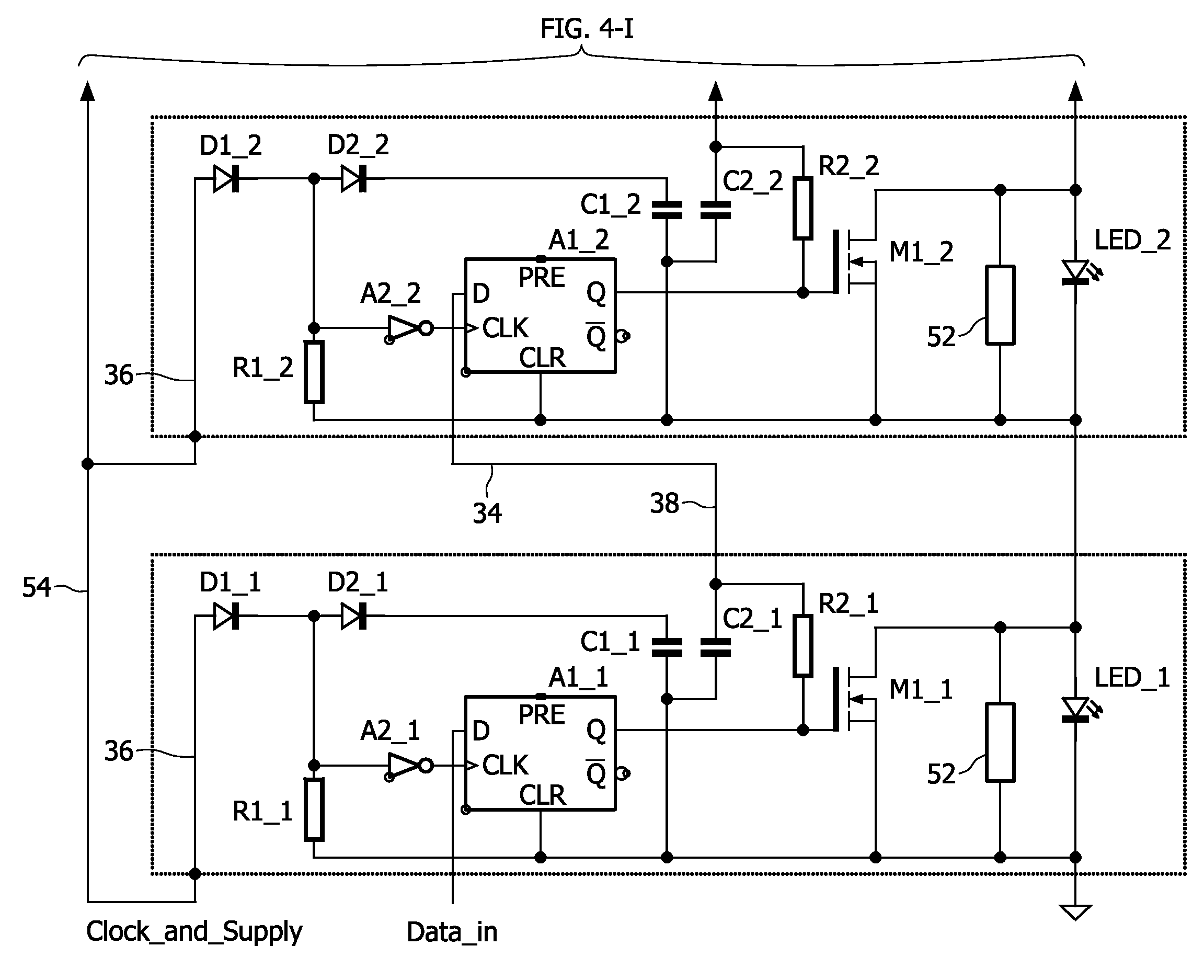
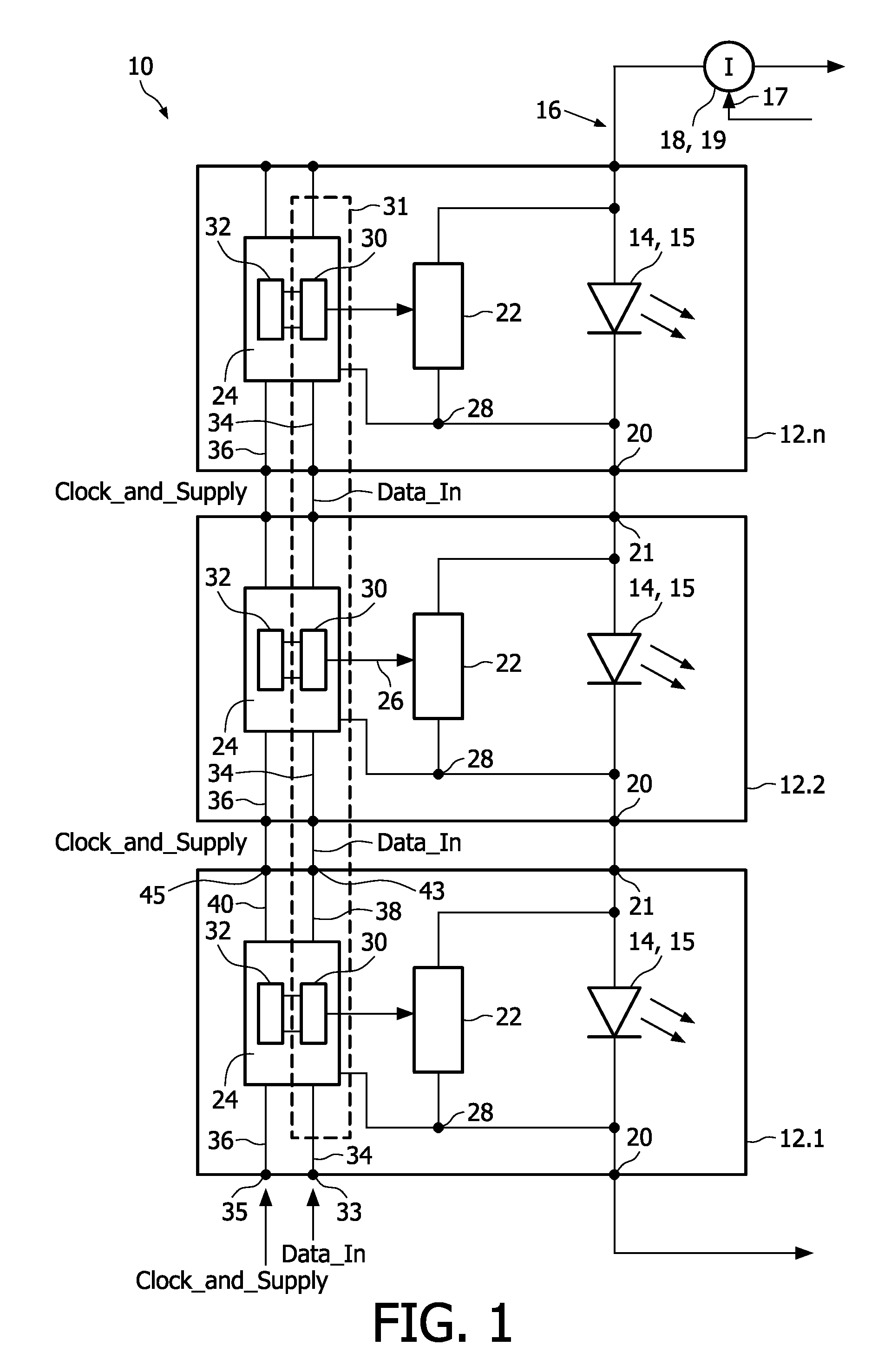
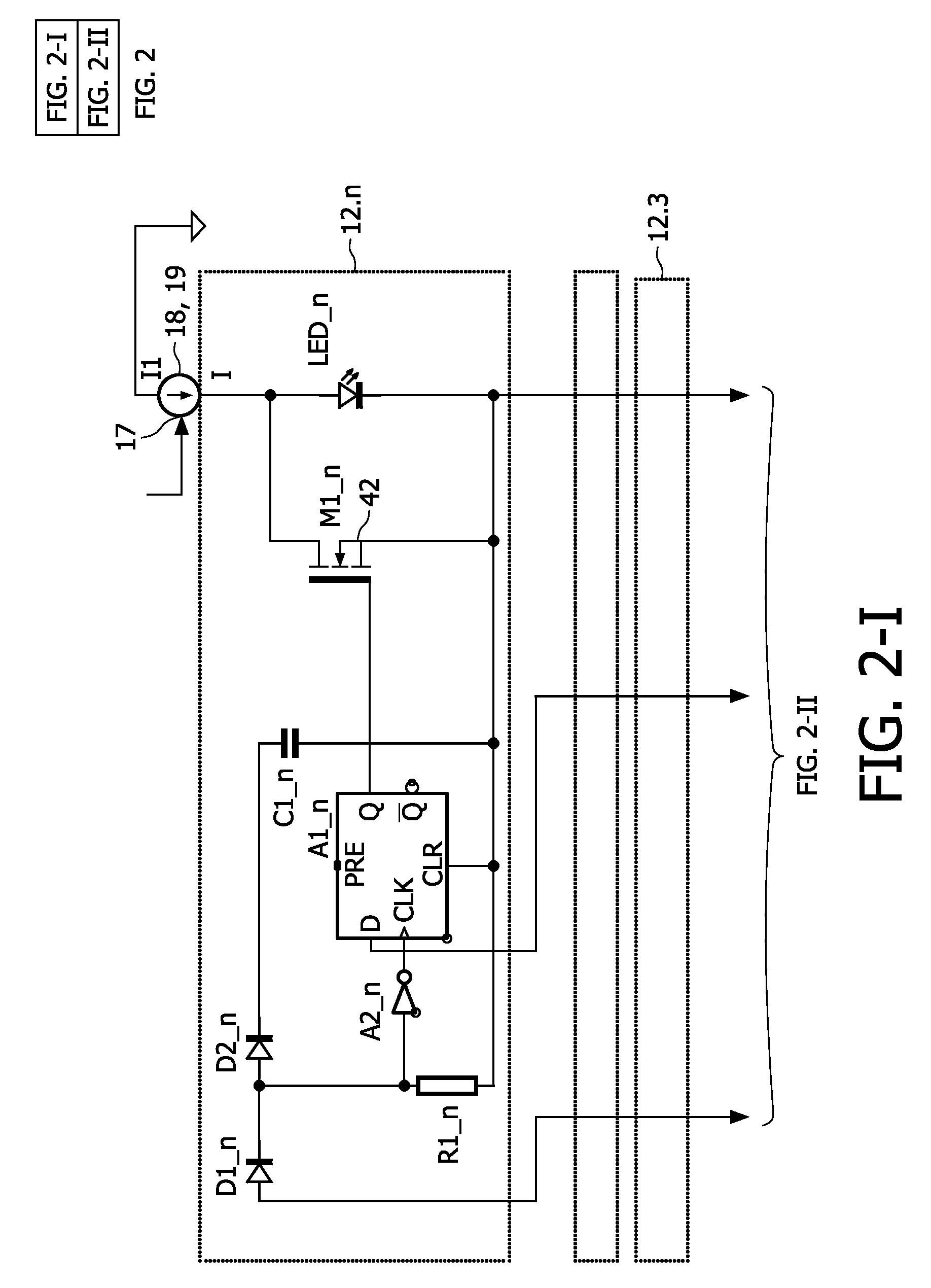
ActiveUS20100134041A1Simple and cost-effective and scalableInhibition of activationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLevel shiftingShift register
The present invention relates to a device for individually driving OLED / LED elements of an OLED / LED string, comprising for each OLED / LED element of the string: a controllable shunting switch (22, 42) coupled with the respective OLED / LED element (14, 15), switch controller means (30, 44) for controlling said shunting switch (22, 42) and having a control output port coupled to said switch (22, 42), a data input port and a clock input port, level shifting means (32) assigned to said switch controller means (30, 44) and adapted to bring the control input data to a level sufficient to be accepted by the switch controller means (30, 44) during a programming mode and to allow the control of said shunting switch (22, 42). Said switch controller means (30, 44) of said OLED / LED elements (14, 15) are provided to form a serial-to-parallel converter means (31).
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Clamp circuit
InactiveUS6737905B1Reduce areaLow costPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesLevel shiftingLinear region
Owner:DENSO CORP
Systems and methods for translation of signal levels across voltage domains
A level shifting circuit with a power monitor enable for mixed-voltage applications is described. The level shifter translates signals from a first power supply voltage domain to a second. The level shifter provides a known output state, rather than an undefined mid-rail state, when either of the power supplies for the voltage domains is not adequately powered. In addition, the level shifter is IDDQ (quiescent current) compliant when static, drawing negligible current from the power supply. The level shifter can be used with a power monitor circuit, which controls the level shifter during power-up with an enable signal.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
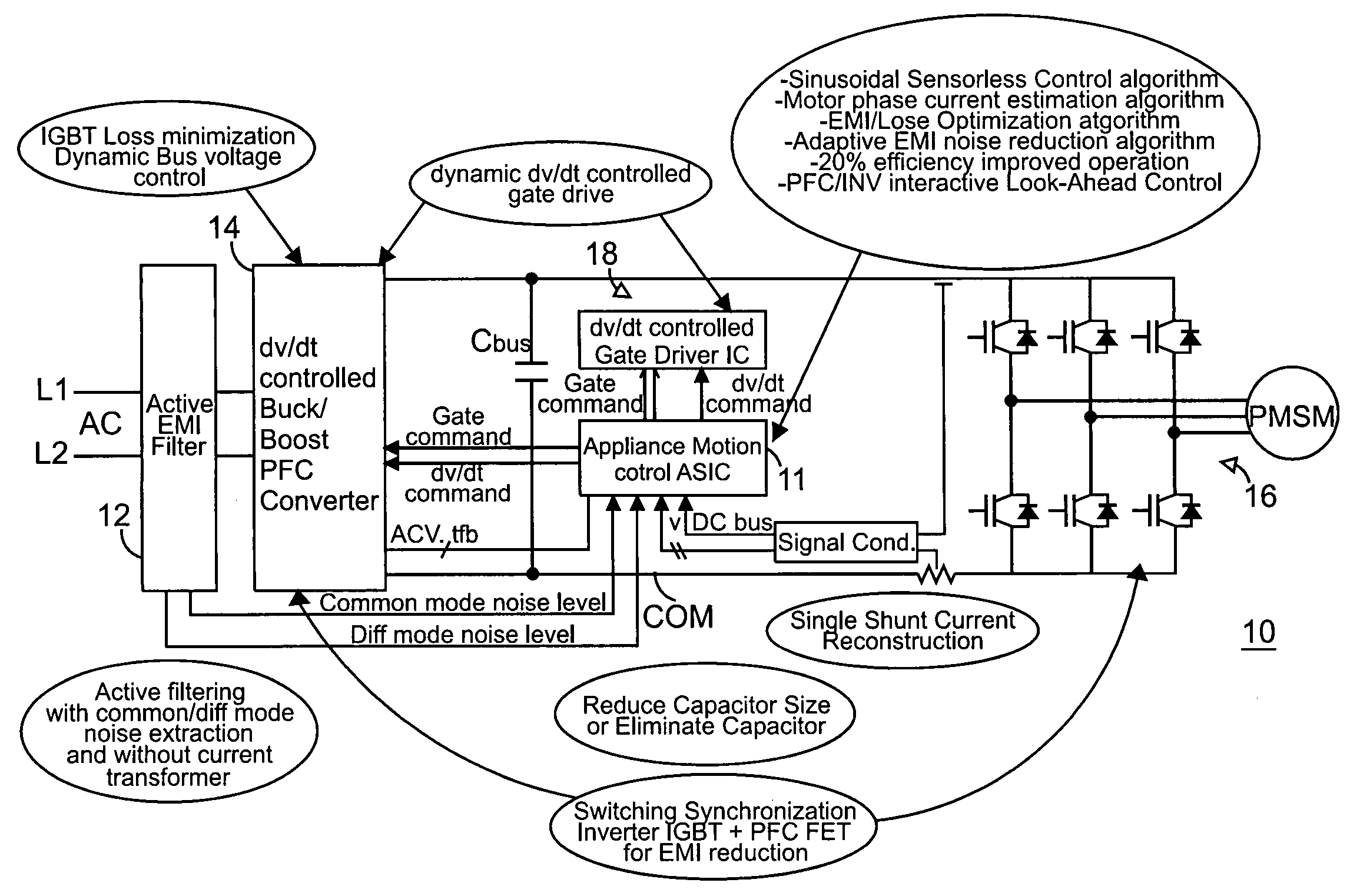
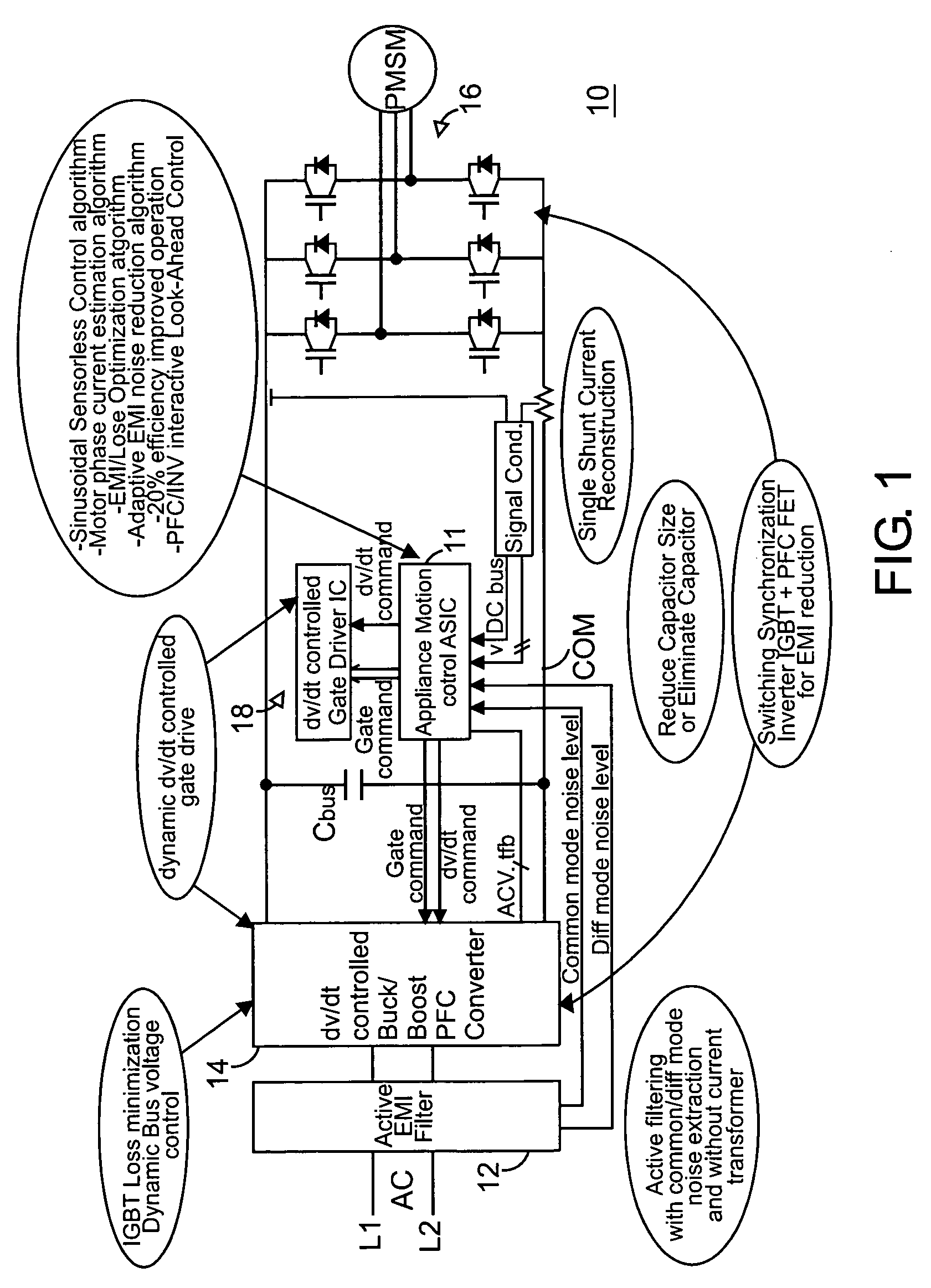
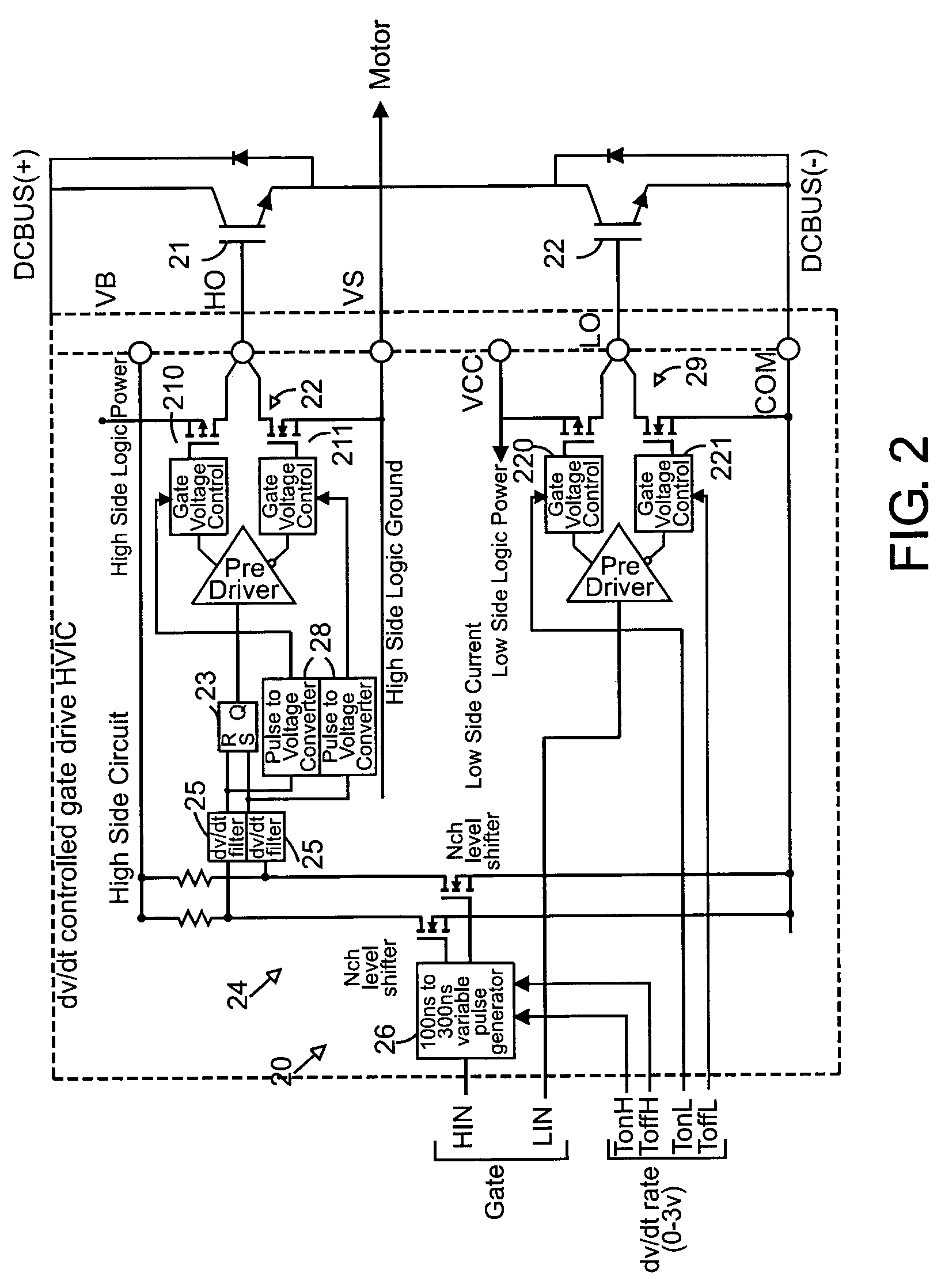
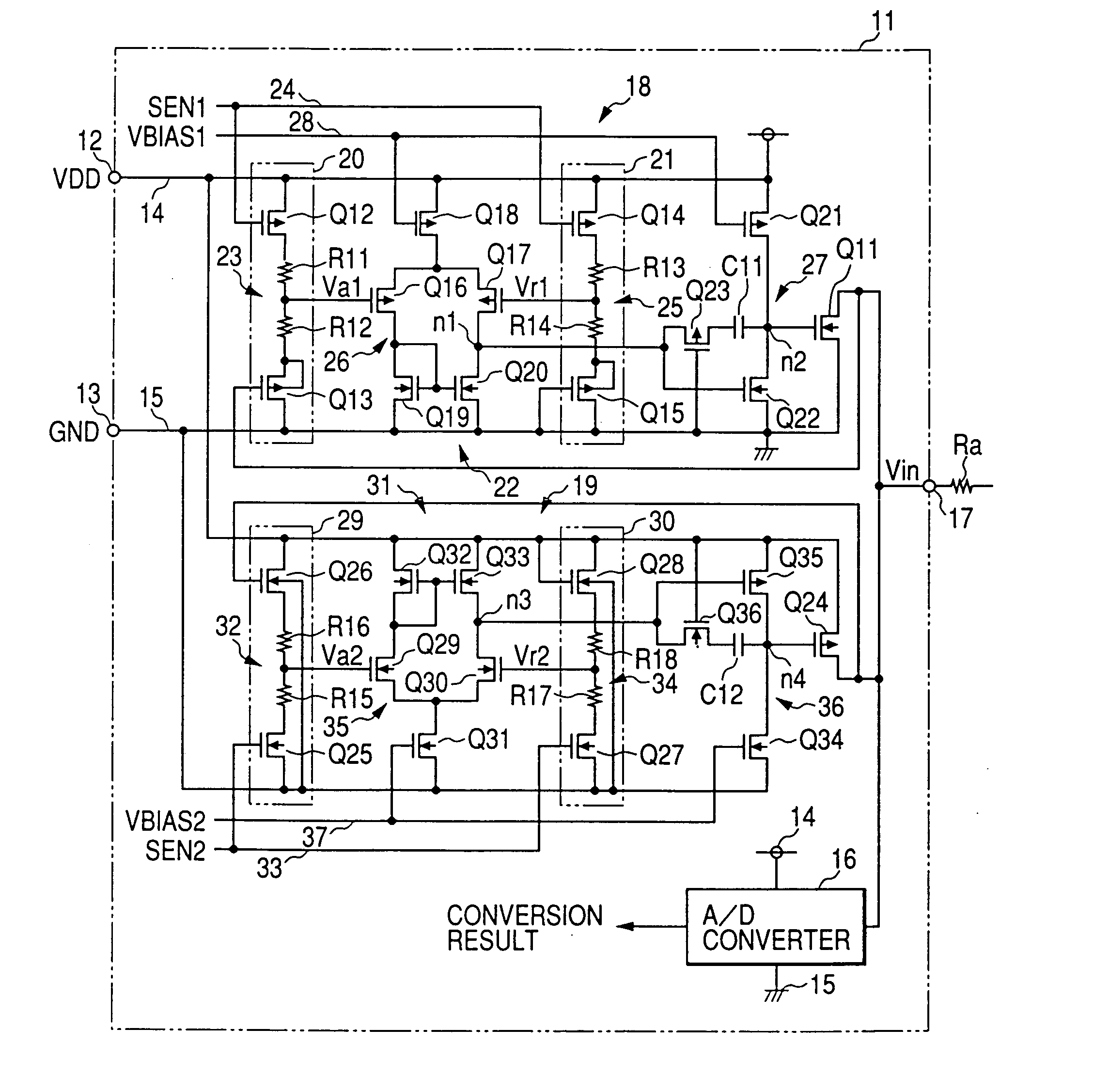
Global closed loop control system with dv/dt control and EMI/switching loss reduction
ActiveUS7061195B2Improve efficiencyReduce productionMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLevel shiftingNoise level
A motor drive system control provides global closed loop feedback to cooperatively operate system components to adaptively reduce noise and provide noise cancellation feedback. An active EMI filter reduces differential and common mode noise on an input and provides a noise level indication to a system controller. Power switches in both a power converter and power inverter are cooperatively controlled with dynamic dv / dt control to reduce switching noise according to a profile specified by the controller. The dv / dt control is provided as an analog signal to a high voltage IC and codified as a pulse width for a level shifting circuit supplying control signals to the high voltage gate drive. A noise extraction circuit and technique obtain fast noise sampling to permit noise cancellation and adaptive noise reduction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Clamp circuit
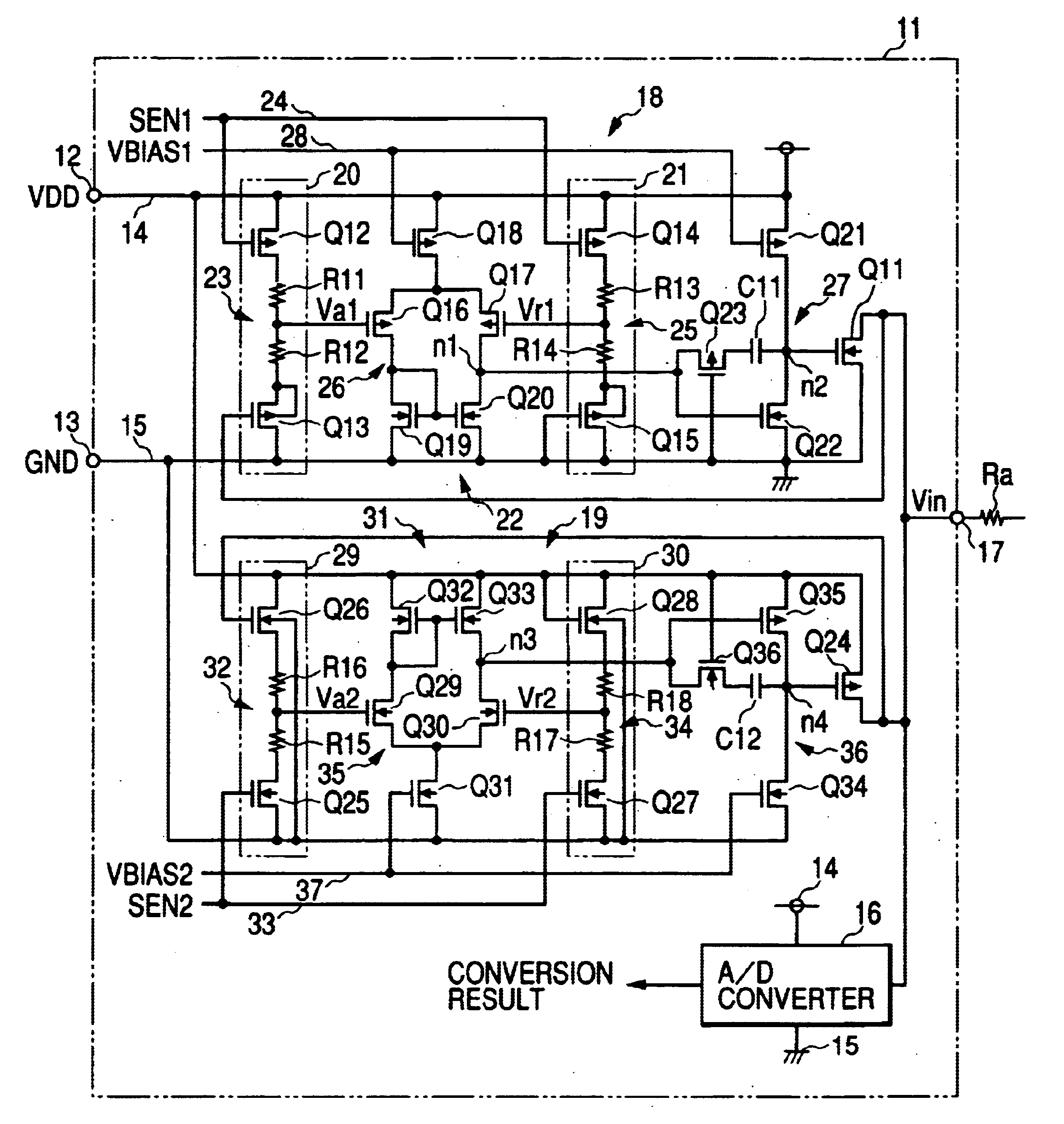
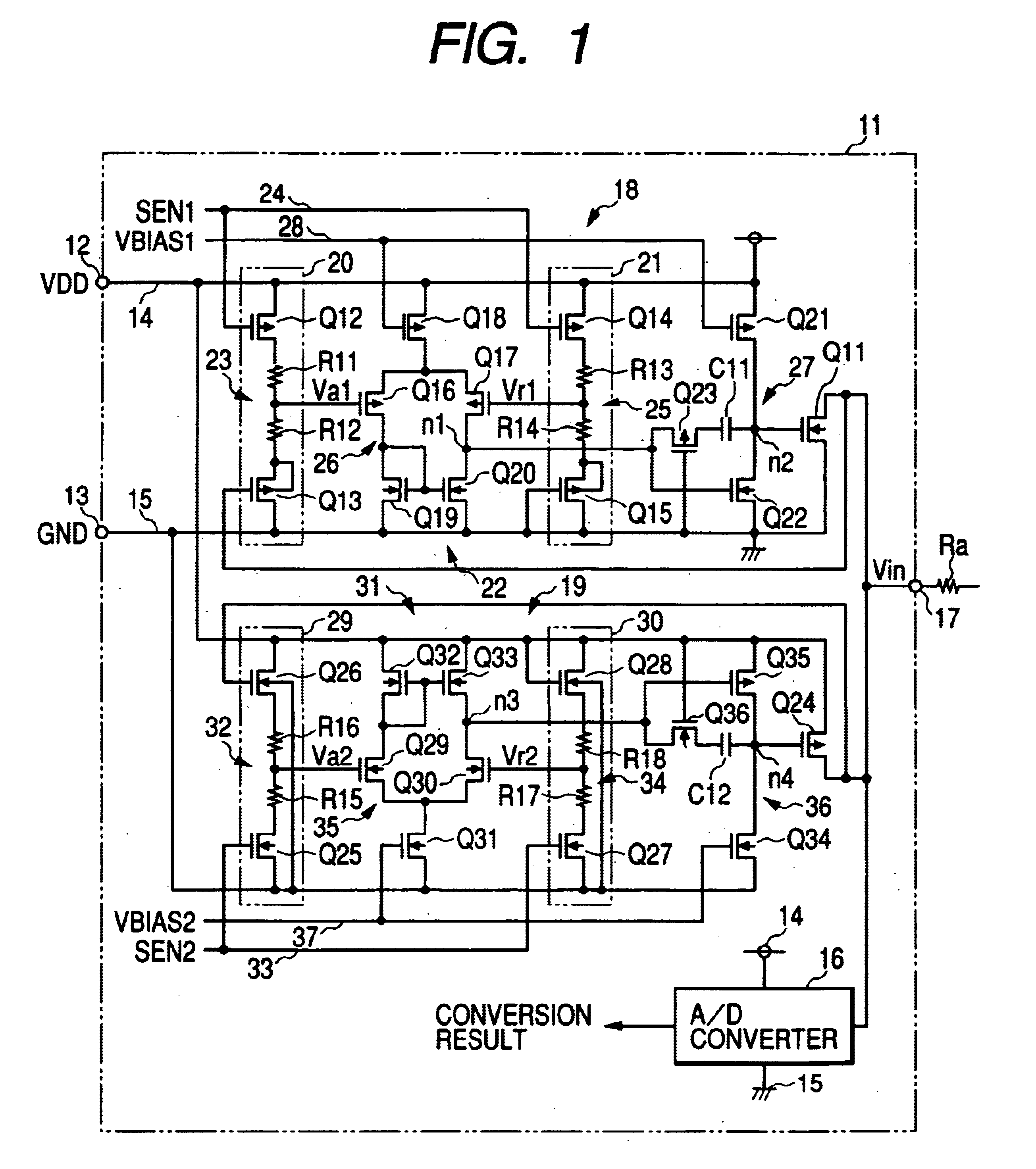
InactiveUS20040080352A1Reduce areaLow costPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLevel shifting
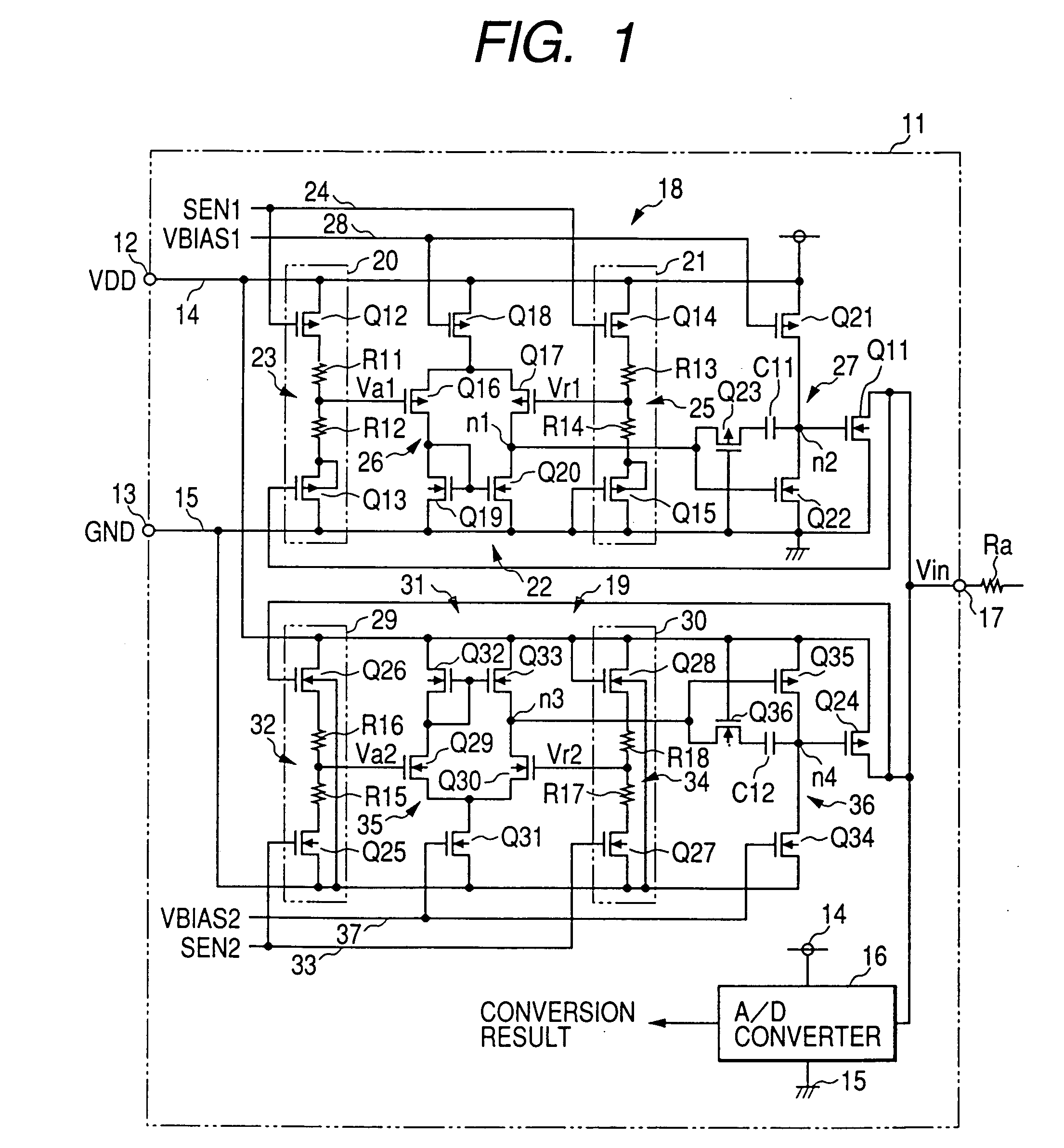
The clamp circuit clamps an input voltage at prescribed higher and lower clamp voltages which are stabilized under a temperature fluctuation. Transistors Q12 and Q14 are switched on in their linear region. In a lower voltage clamp circuit 18, an Vin detecting circuit 20 outputs Va1 by level-shifting Vin by Q13 and voltage-divides by series resistance circuit 23 the level-shifted Vin, while a reference voltage generating circuit 21 outputs Vr1 by level-shifting 0 V by Q15 and voltage-divides by series resistance circuit 25 the level-shifted voltage. Q11 is switched on, when a comparator 22 determines that Va1 descends and goes across Vr1. Here, Q12 is of the same characteristics as Q14, while Q13 is of the same characteristics as Q15. Further, the resistance of the circuits 23 is the same as that of the circuit 25. The higher voltage clamp circuit 19 is similar to the circuit 18.
Owner:DENSO CORP
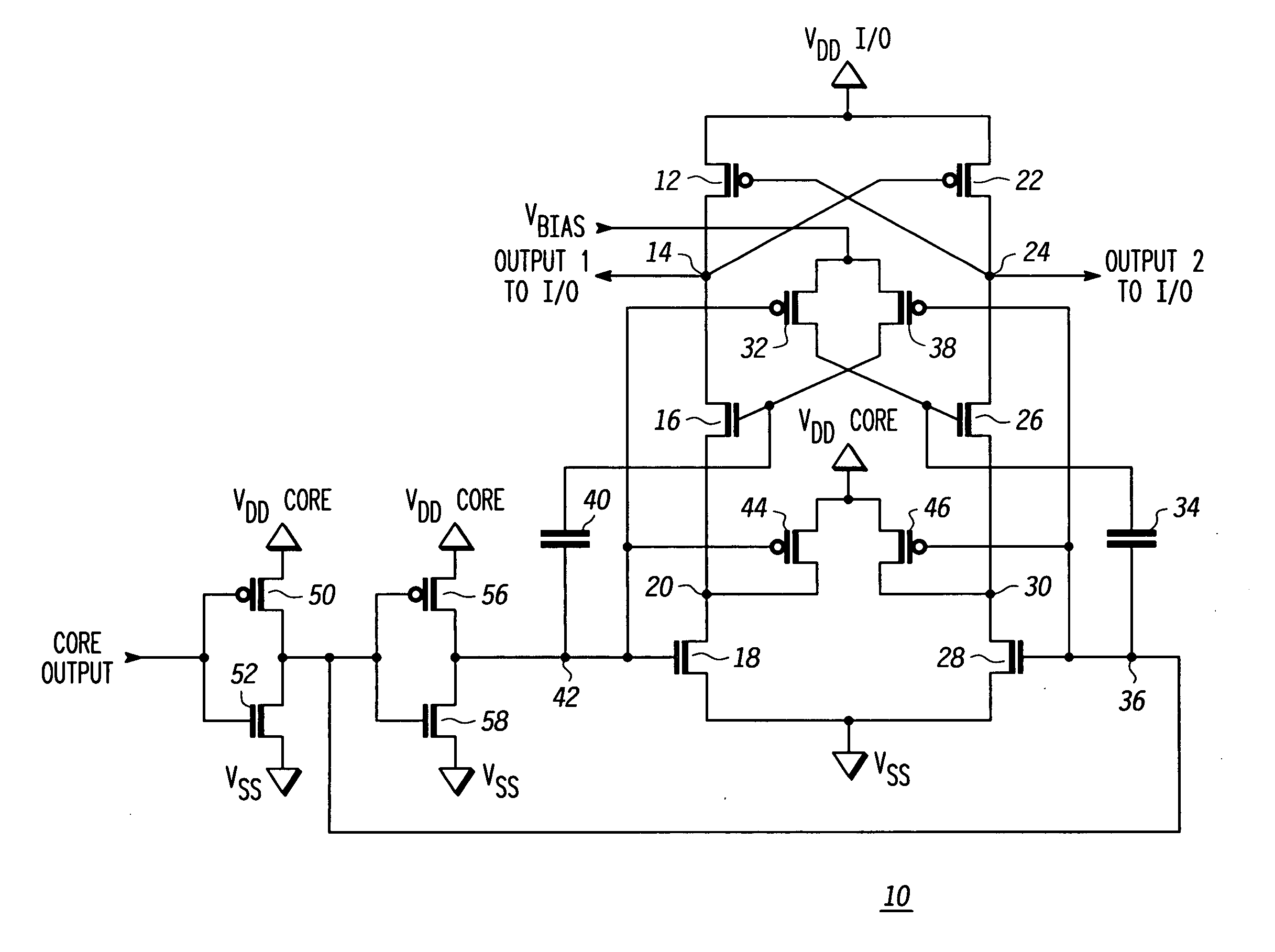
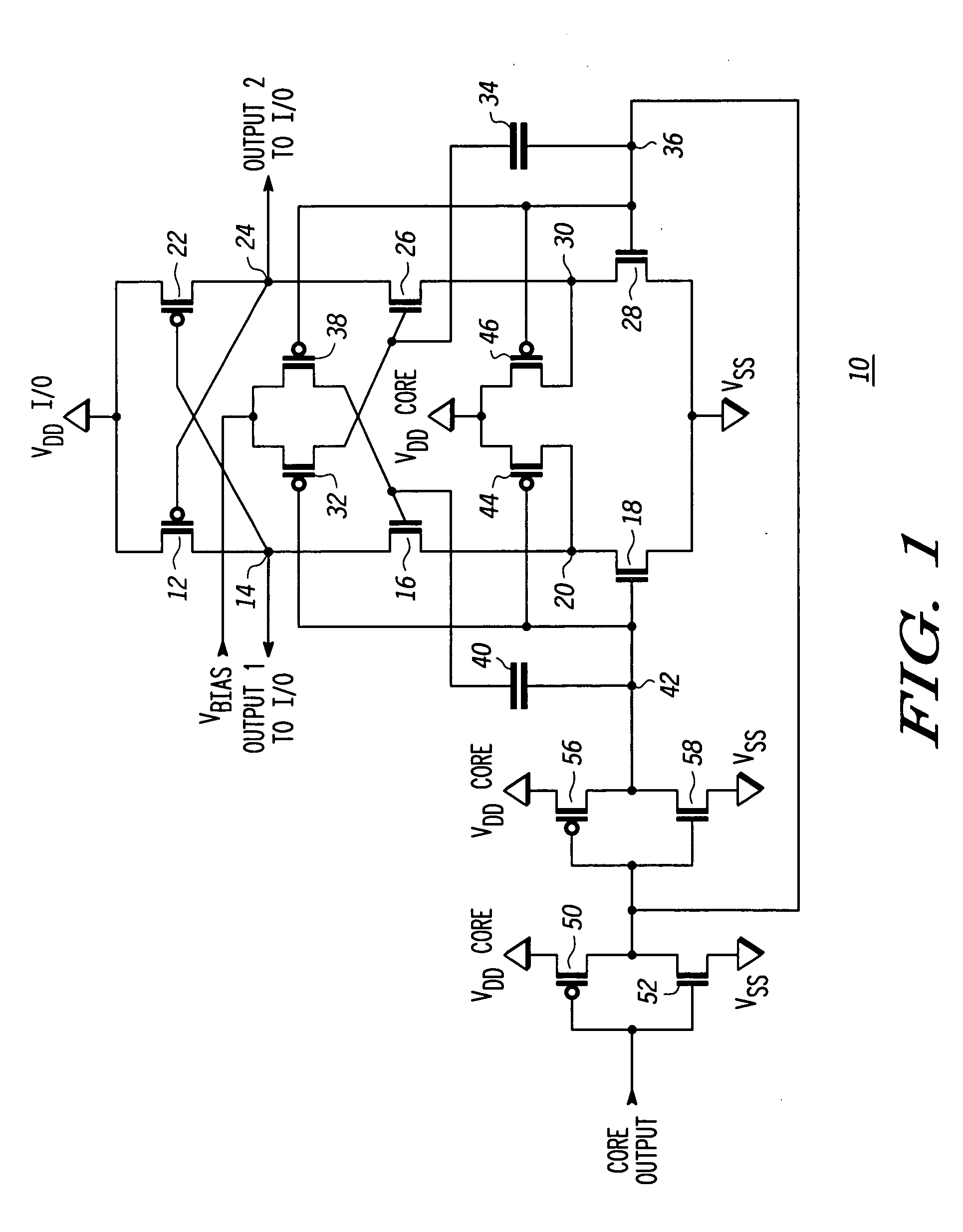
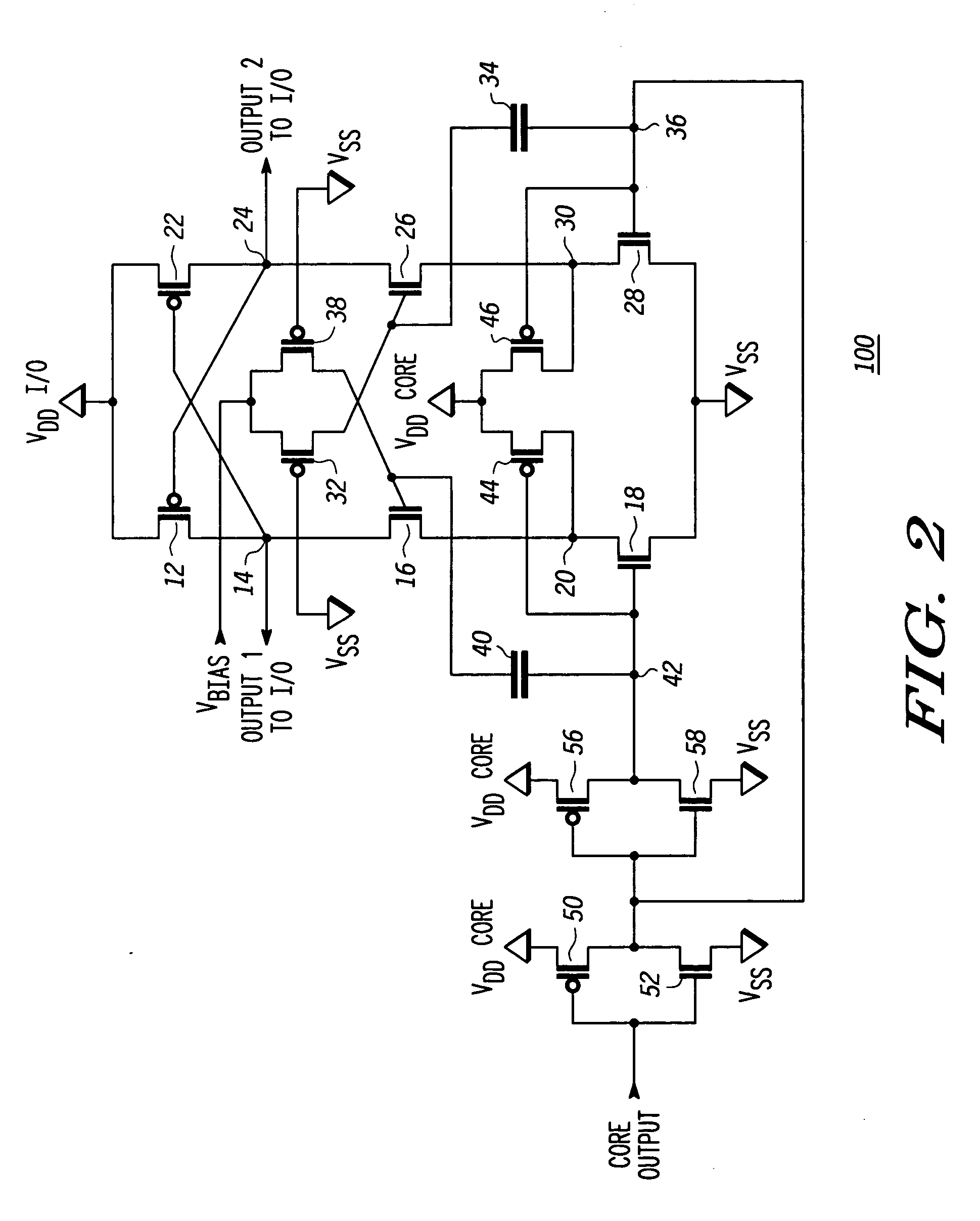
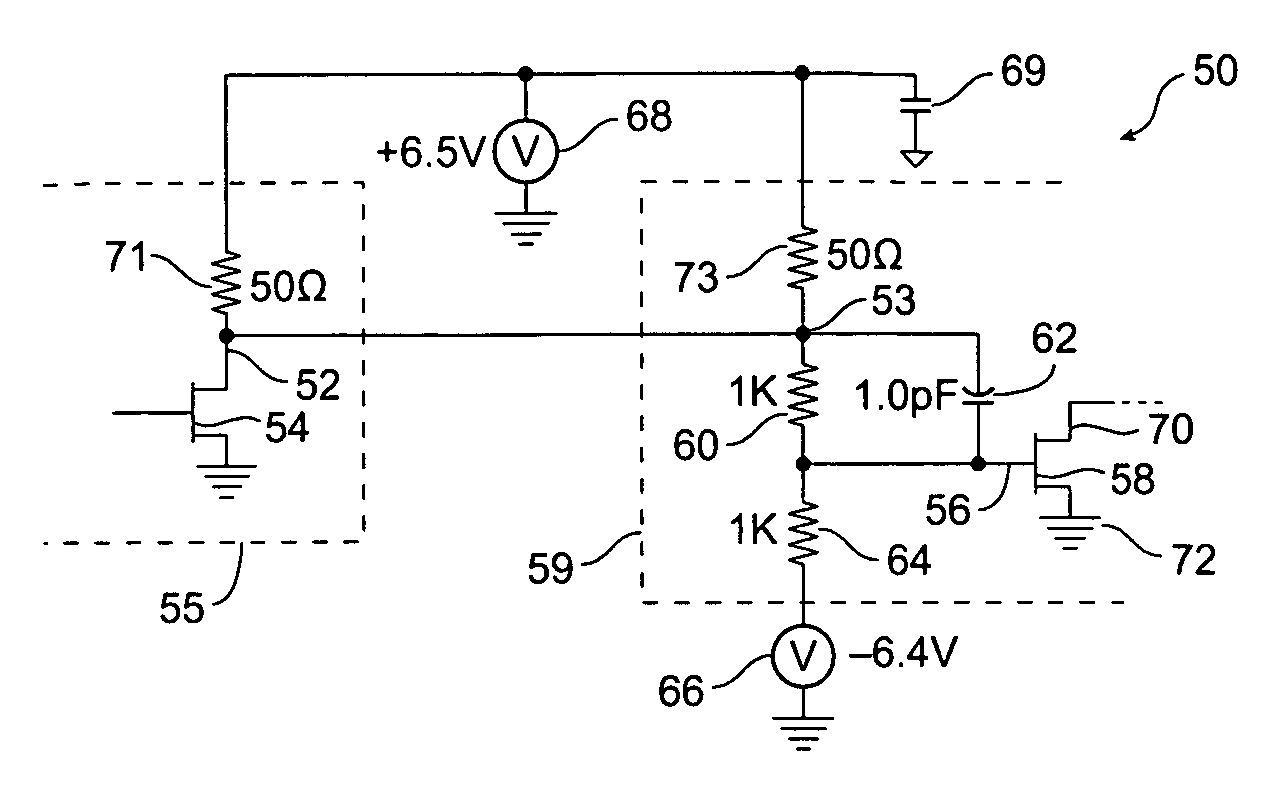
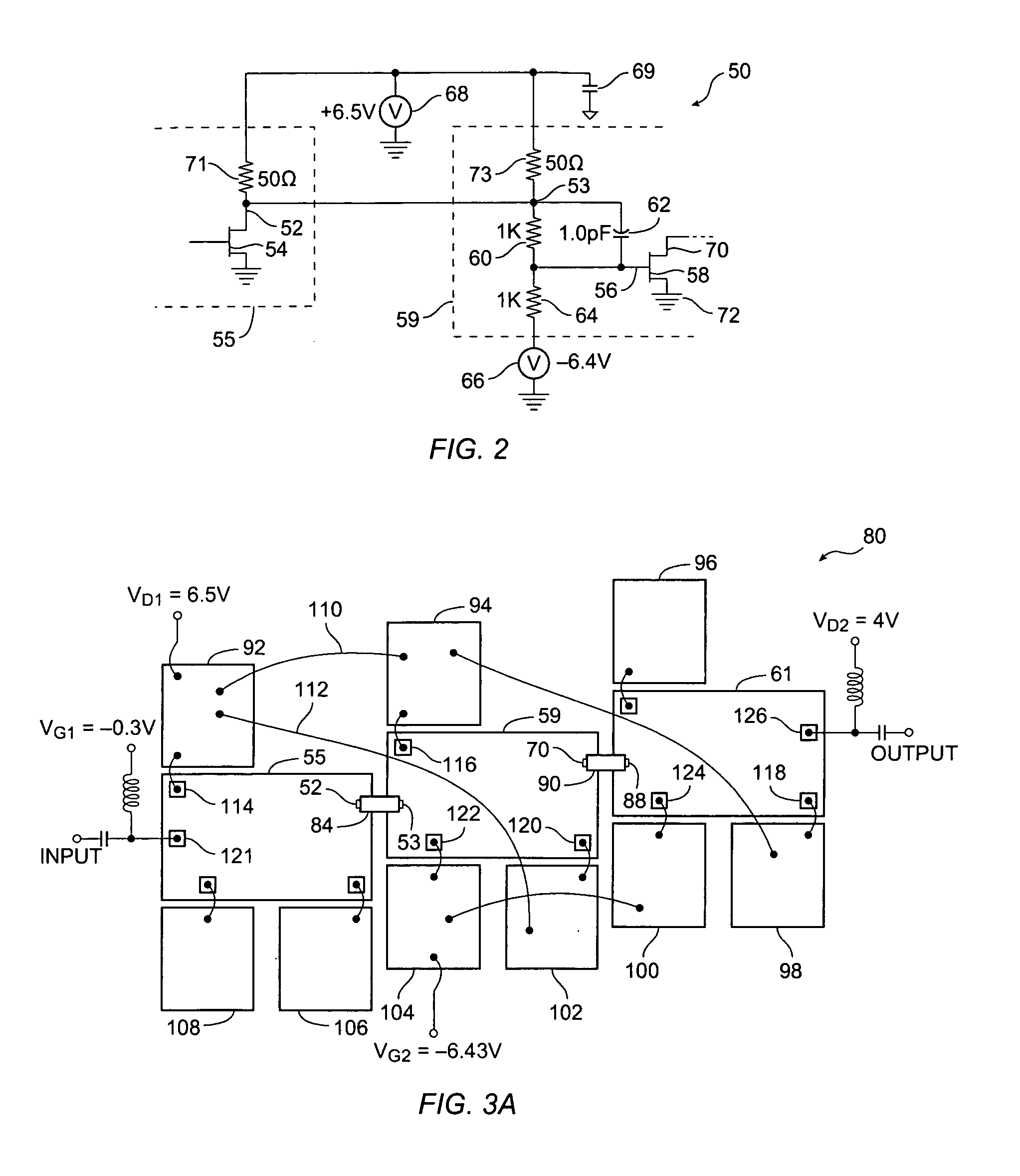
Level shifting circuit
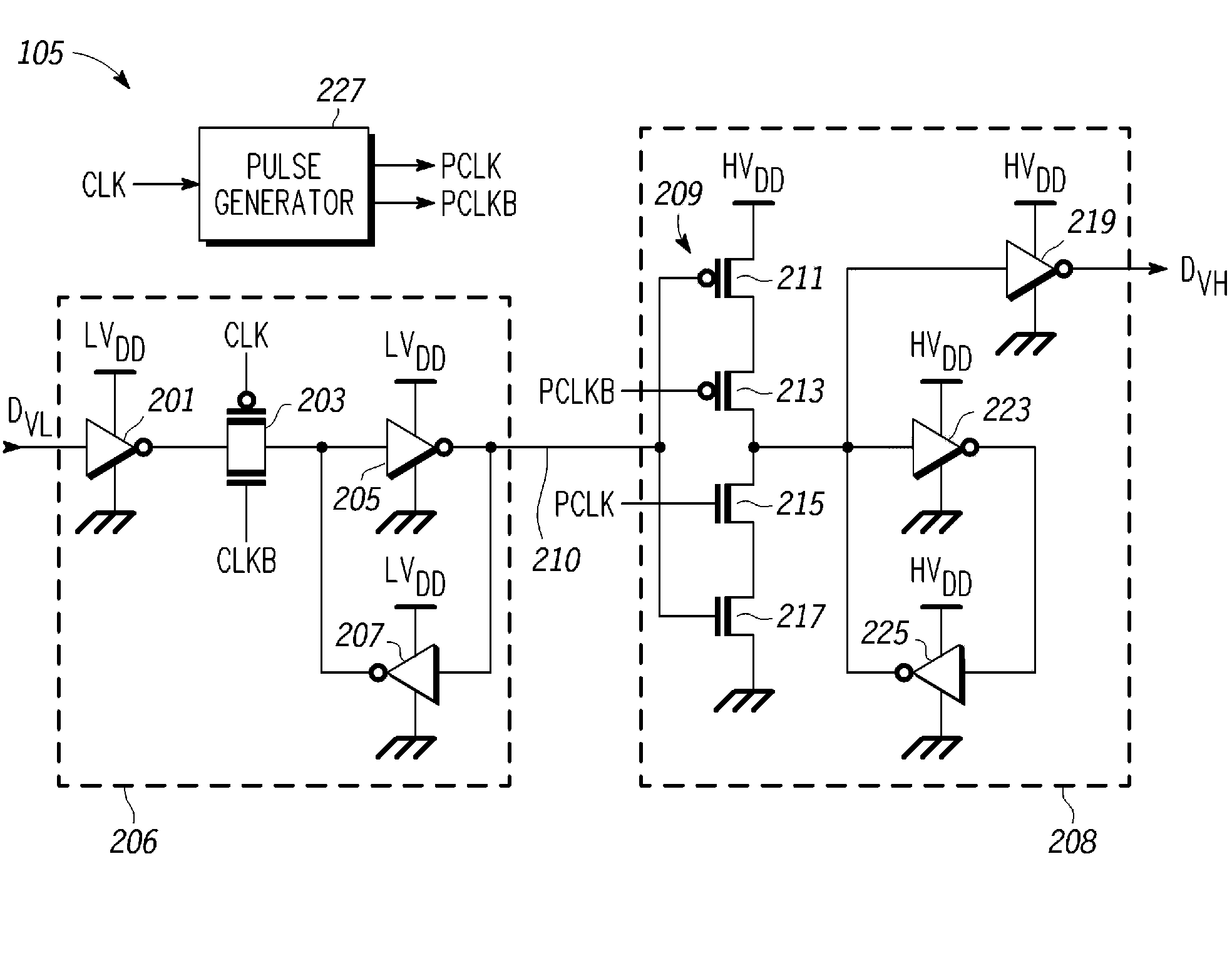
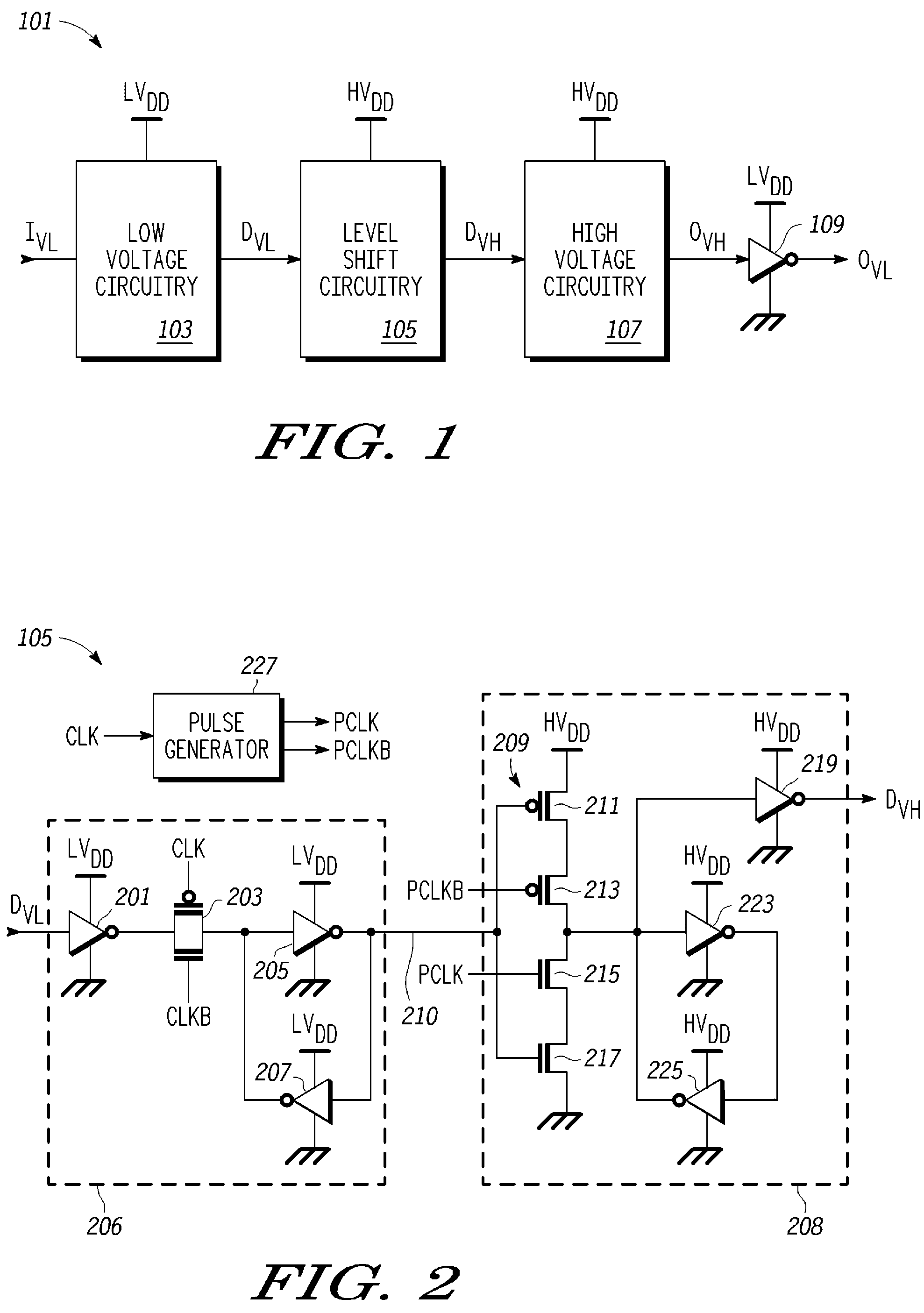
A level shifting circuit having a signal input that operates in a first voltage domain and a signal output that operates in a second voltage domain. In some embodiments, the level shifting circuit includes a clocked level shifter. In some embodiments, the level shifting circuit includes a level shifting latch that latches a translated output signal. In one example, the level shifting latch includes a latch portion and a stack of transistors with a transistor having a control electrode coupled to a clock input.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Solid-state image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20070126886A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLevel shiftingEngineering
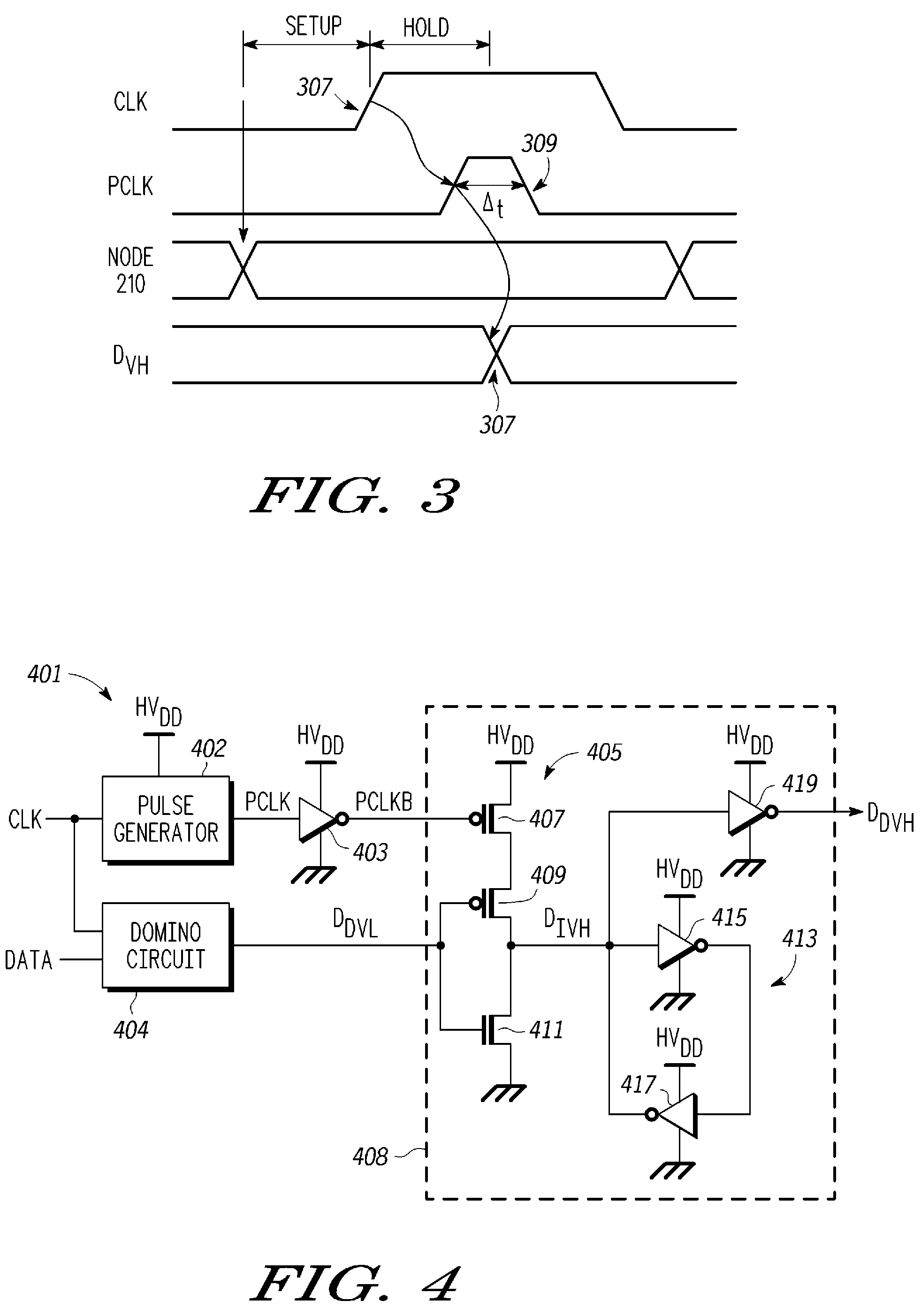
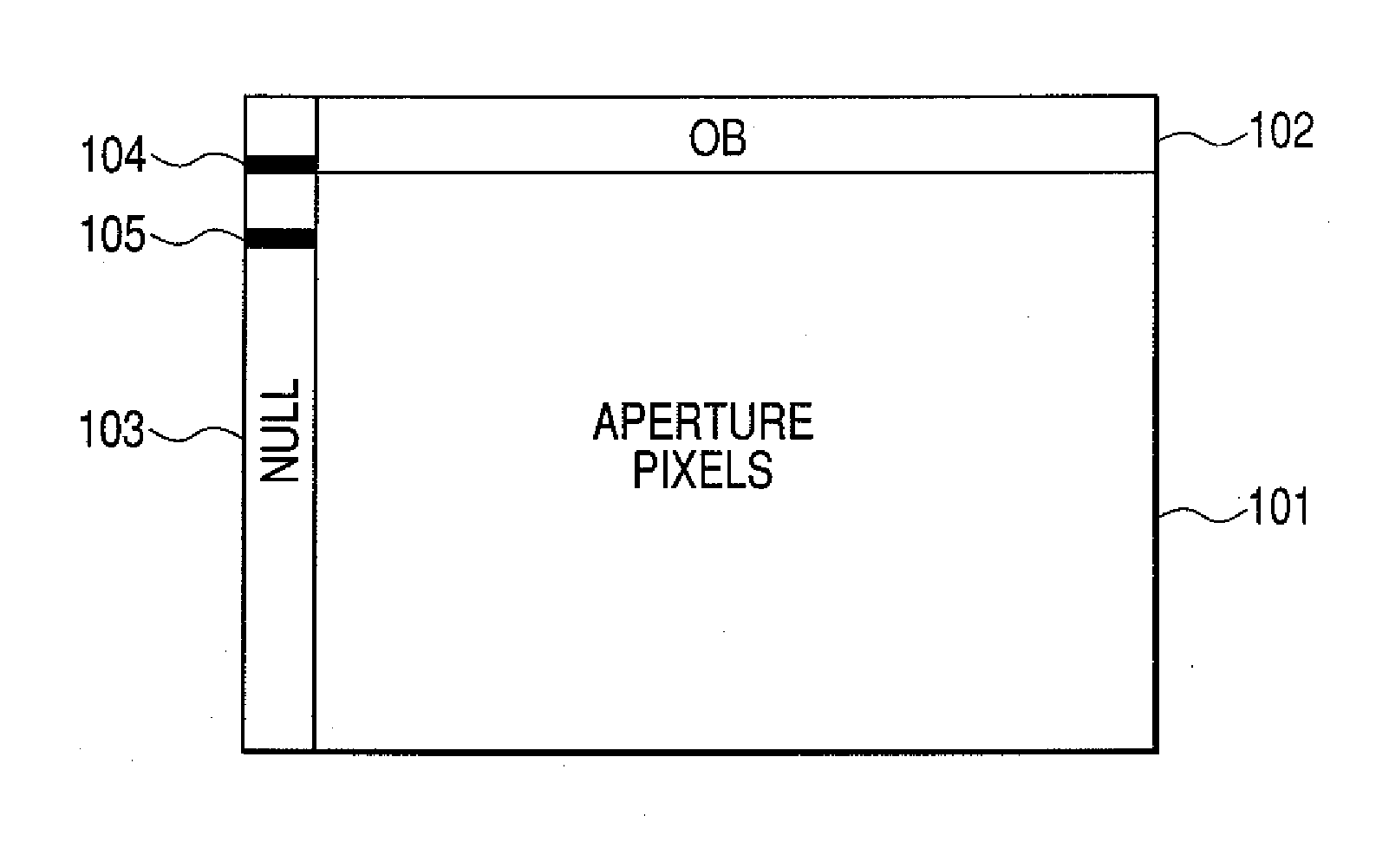
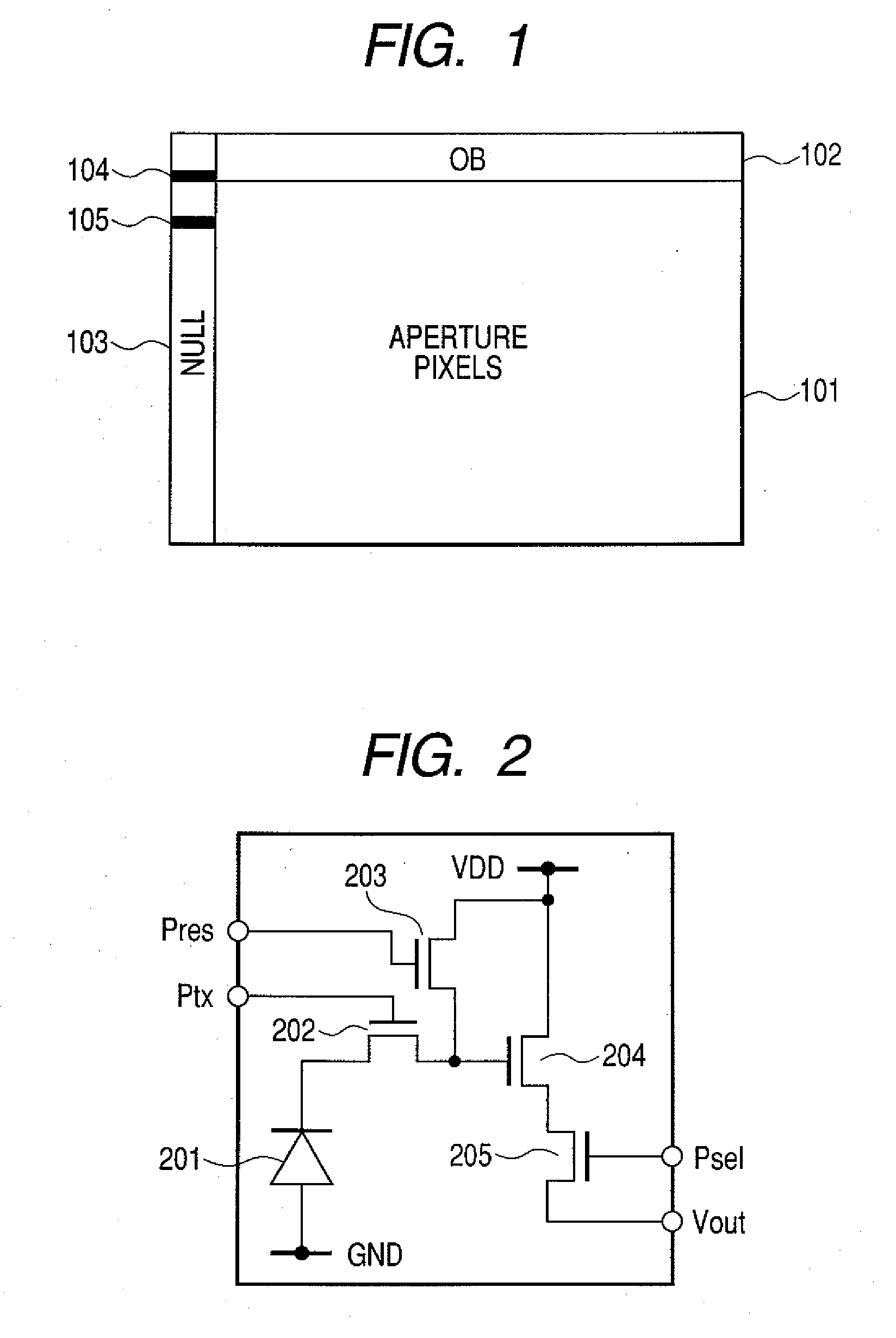
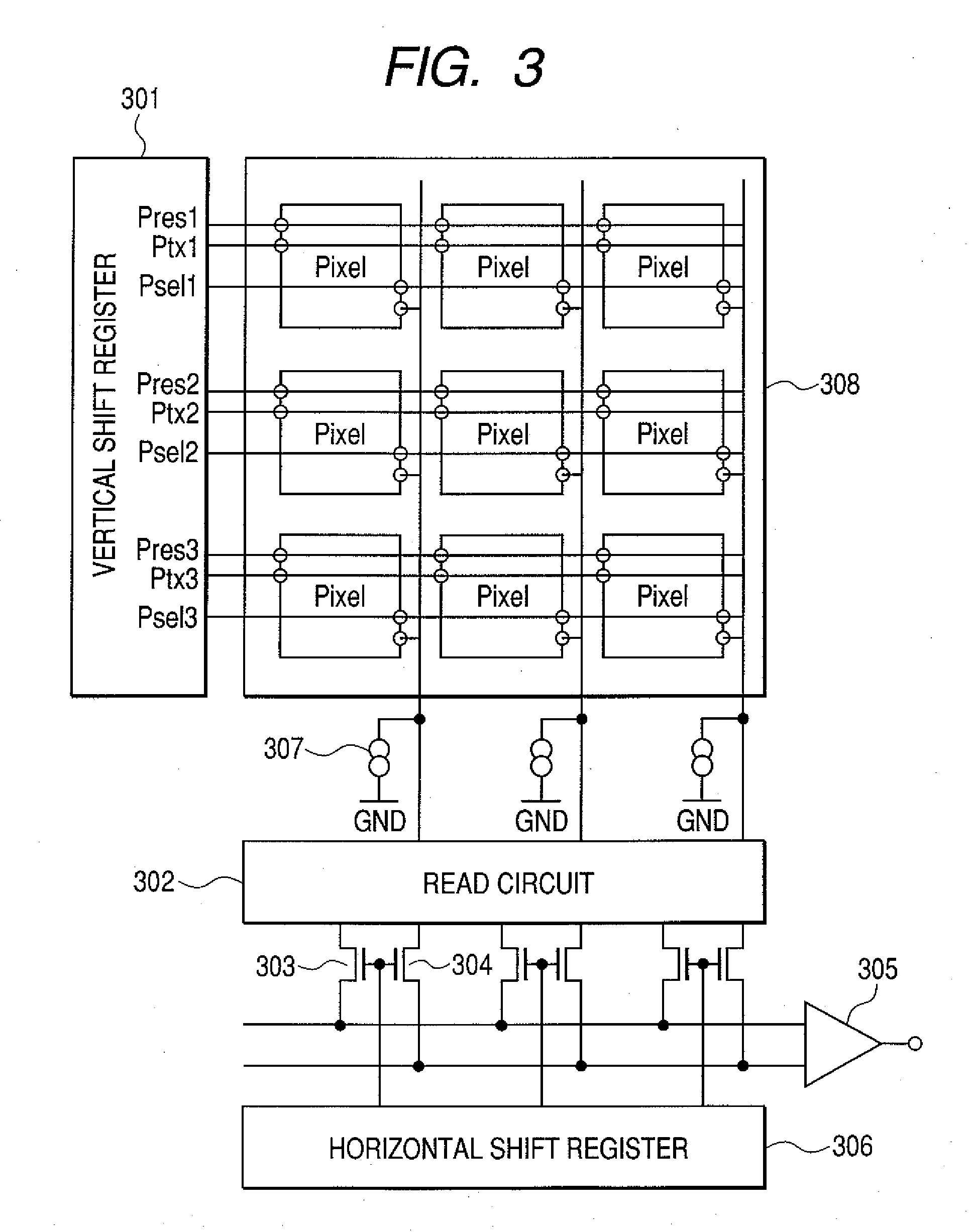
It is intended to obtain a high quality image which is not affected by the fluctuation of dark outputs, and pixels having a specifically large dark output, called defects, and has no lateral line etc. A solid-state image pickup apparatus including: an aperture pixel region which accumulates and outputs the electric charges generated depending on incident light; a light shielded optical black region; a black reference pixel region in which no impurity region for accumulating electric charges is formed; and level shifting means which shifts the reference level of the output signals of the black reference pixel region with respect to the reference levels of the output signals of the aperture pixel region and the optical black region, is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
Control arrangement for a PFC power converter
InactiveUS7911812B2Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcLevel shiftingCapacitance
In a PFC (Power Factor Correction) converter control unit, a PWM (pulse width modulated) signal is produced by comparing a PFC converter output voltage error signal, produced by a transconductance amplifier, with a ramp signal, which may be from a control unit of a resonant mode converter in cascade with the PFC converter. Level shifting is used to match the amplitude ranges of the compared signals. A current, representing an input current of the PFC converter and produced by a current mirror, is switched by the PWM signal to a parallel resistance and capacitance to produce a smoothed voltage constituting a control signal for the PFC converter.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
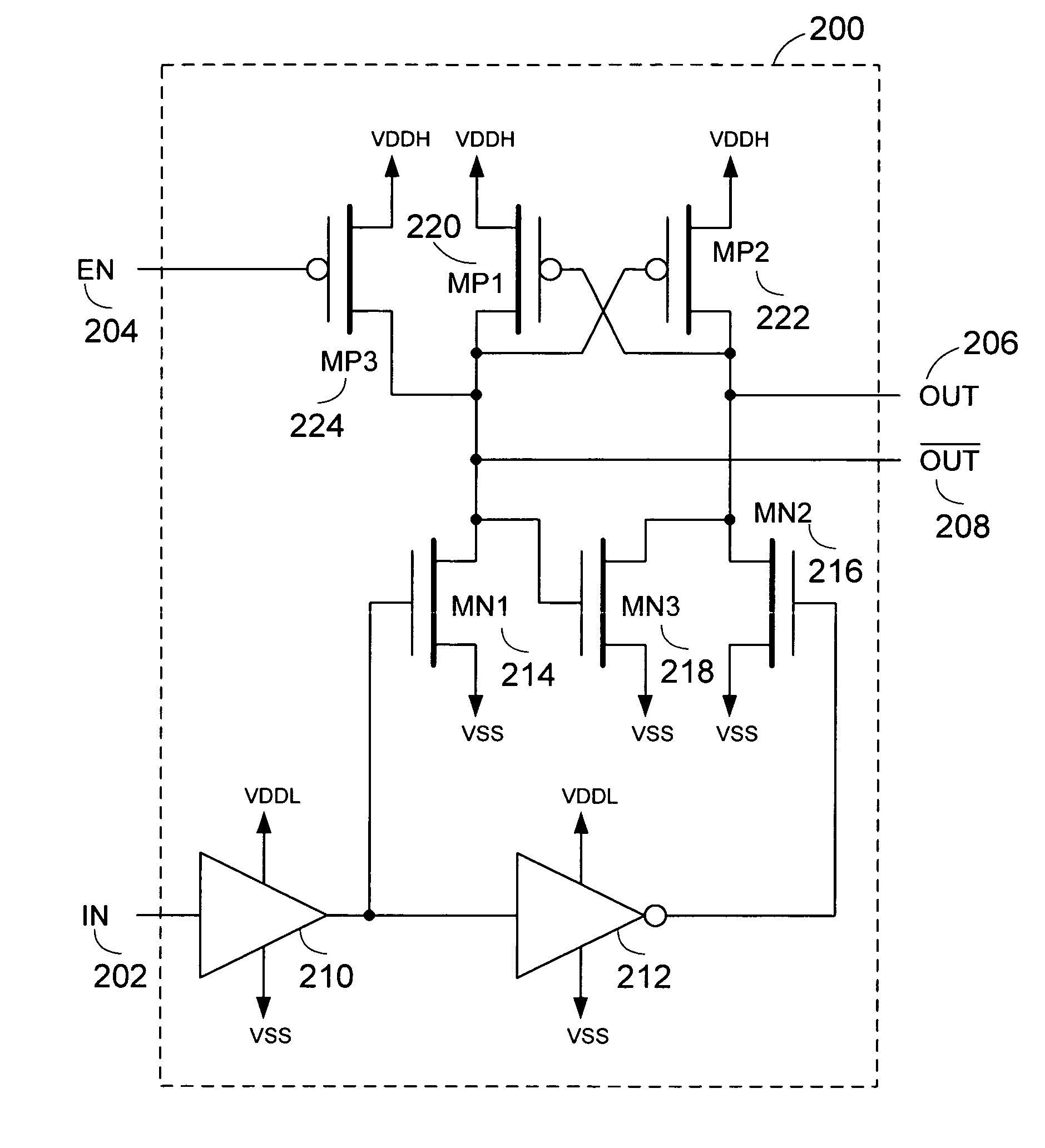
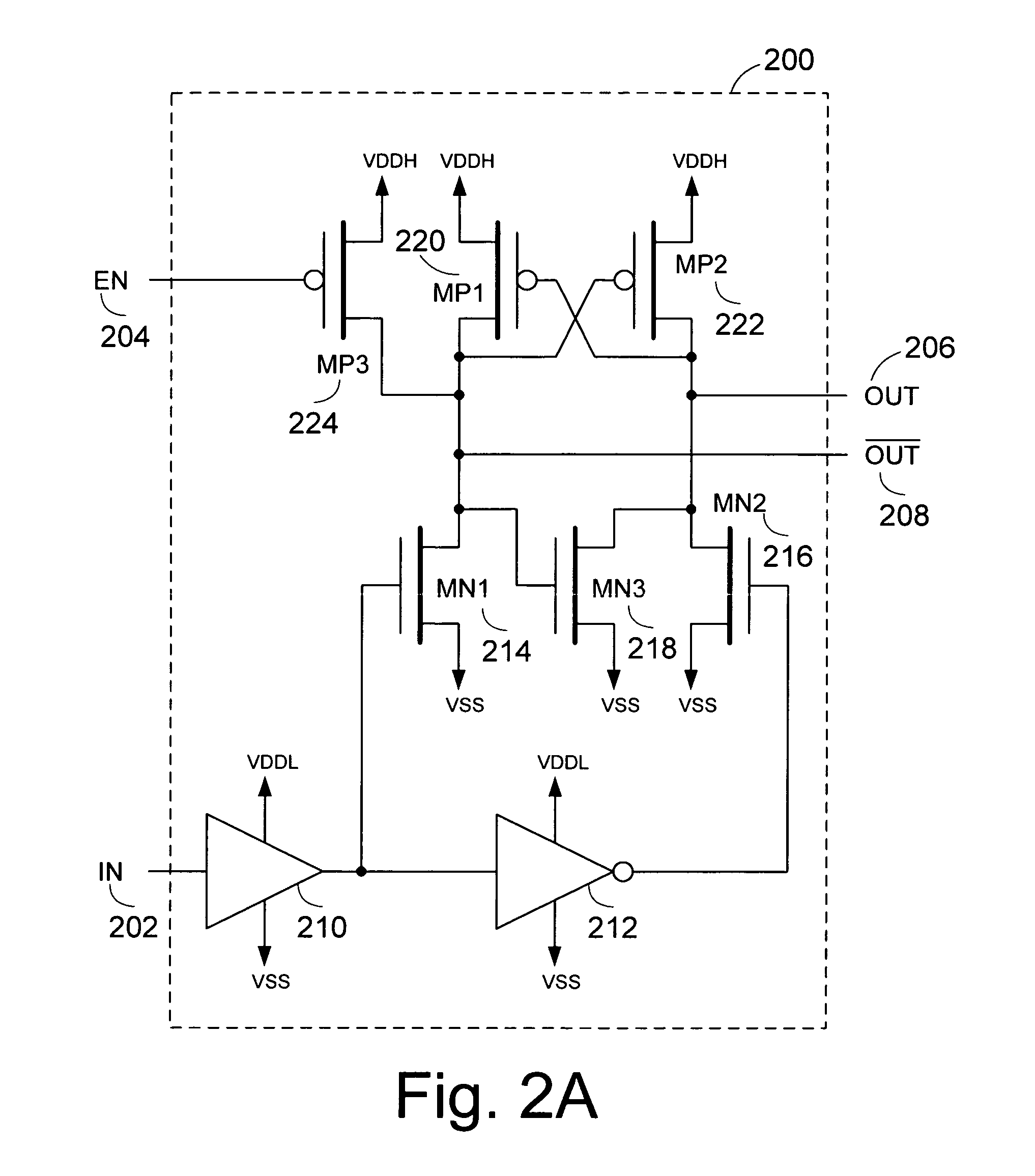
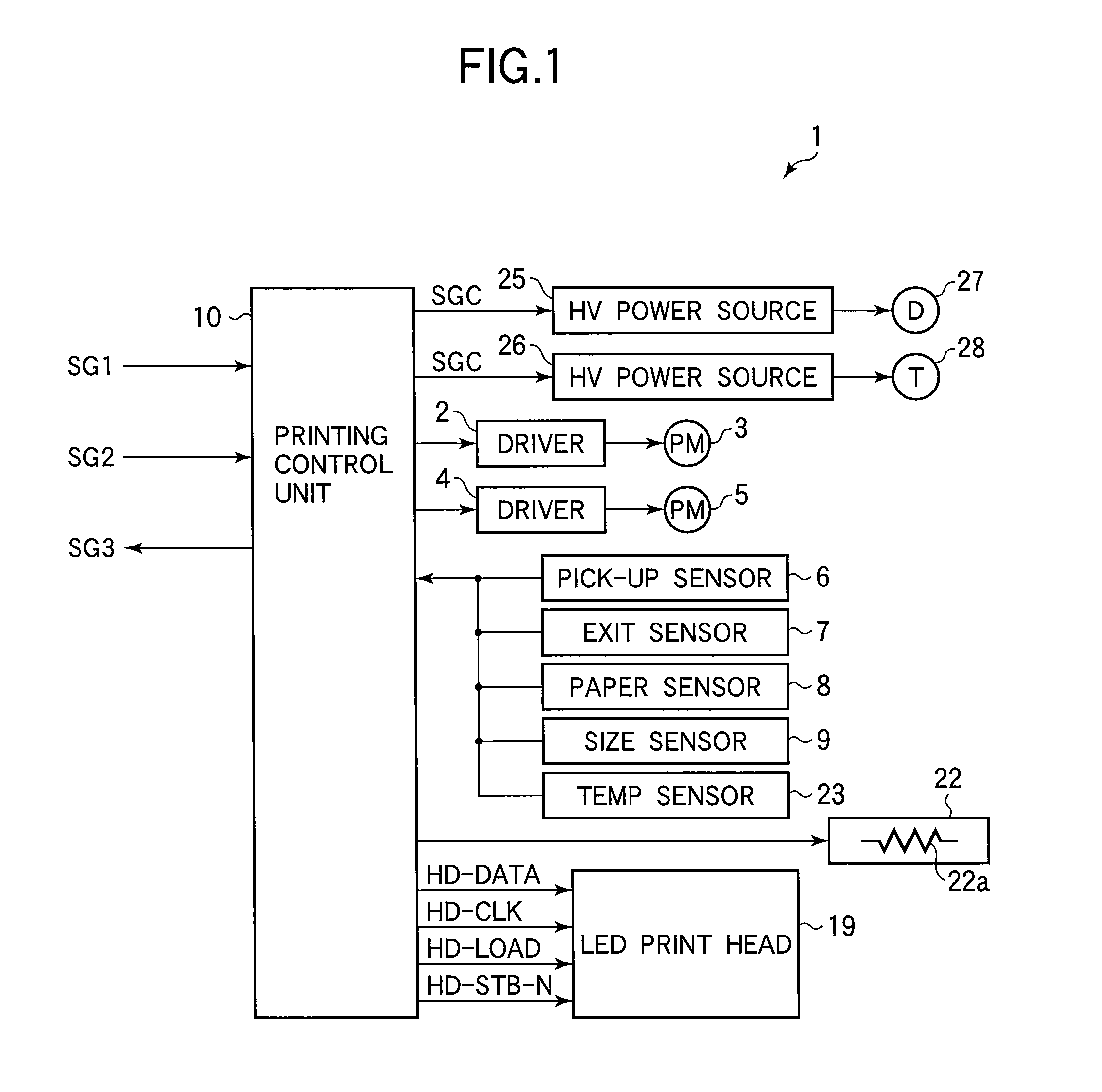
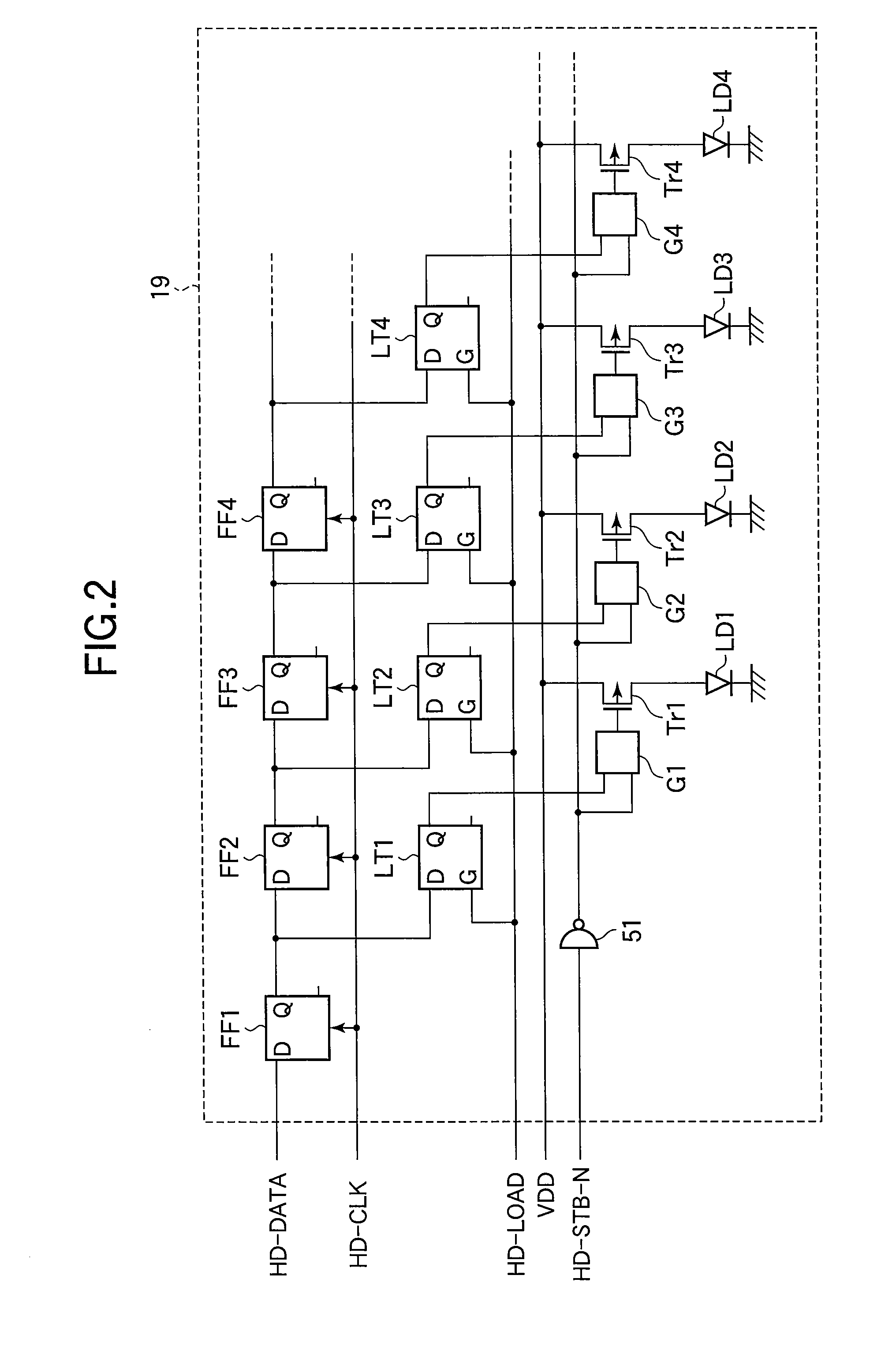
Level shifting circuit, driving device, LED print head, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20080054979A1Small sizePulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsLevel shiftingEngineering
A level shifting circuit converts an input signal that varies between ground and a first voltage to a shifted signal that varies between ground and a second voltage higher than the first voltage. The level shifting circuit has two branches, in each of which a p-channel transistor and two n-channel transistors are connected in series between the second voltage and ground. When the two n-channel transistors in each branch are turned off, a clamping circuit clamps the node between them to the first voltage level, so that neither n-channel transistor has to withstand the full difference between the second voltage and ground. The level shifting circuit can accordingly be fabricated with transistors of small size, reducing the cost of driving circuits, light-emitting-diode print heads, and image forming apparatus in which the level shifting circuit is used.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
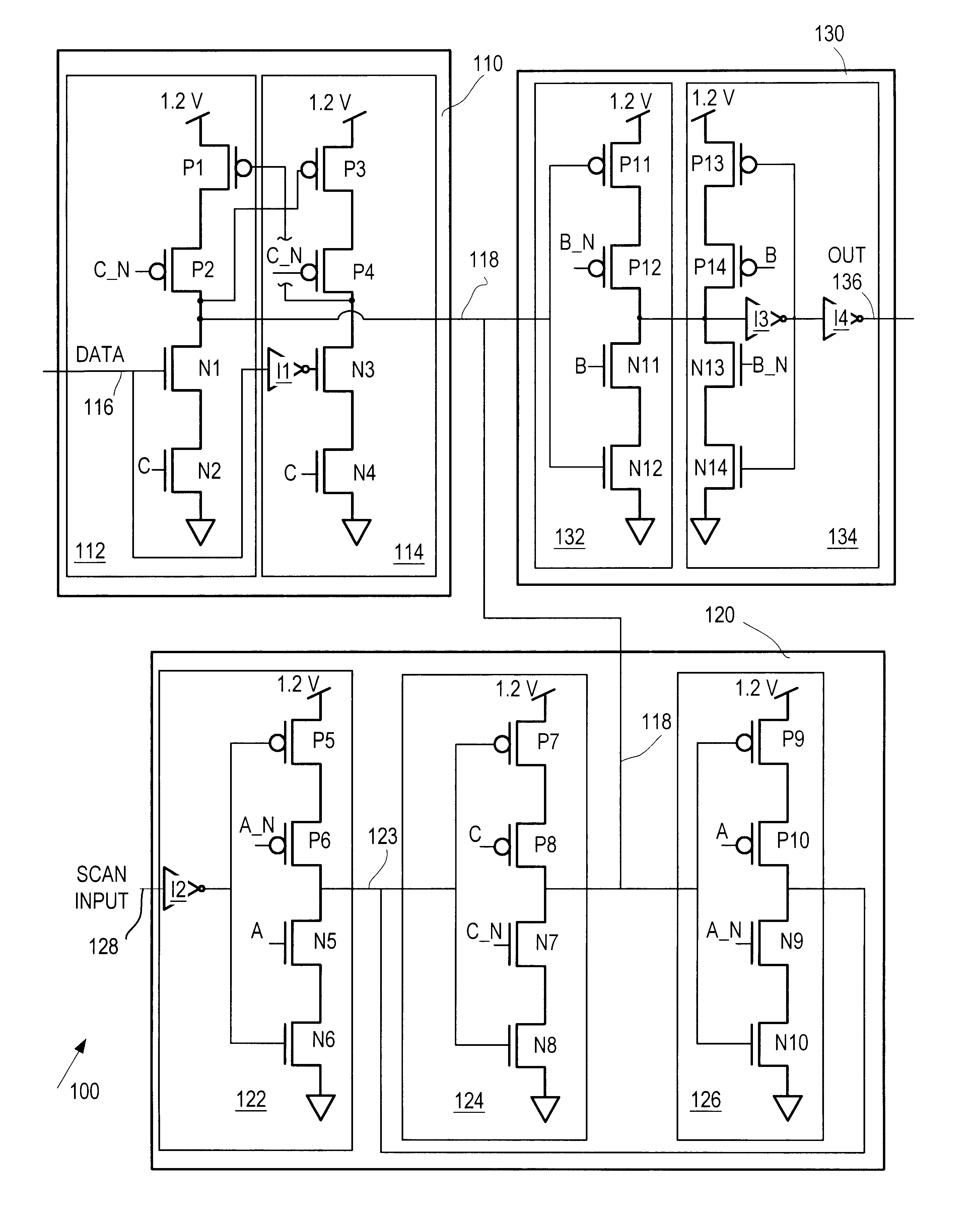
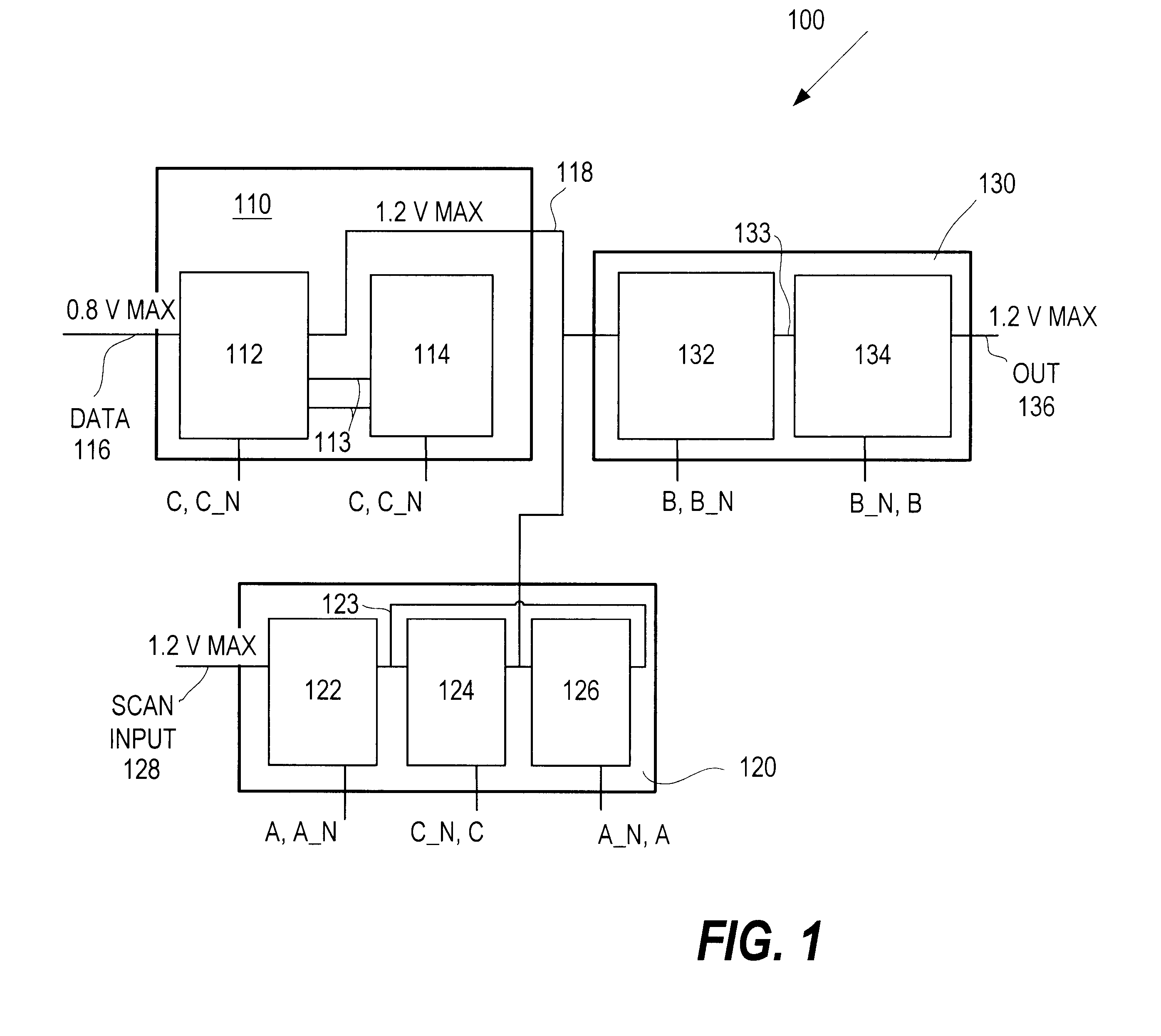
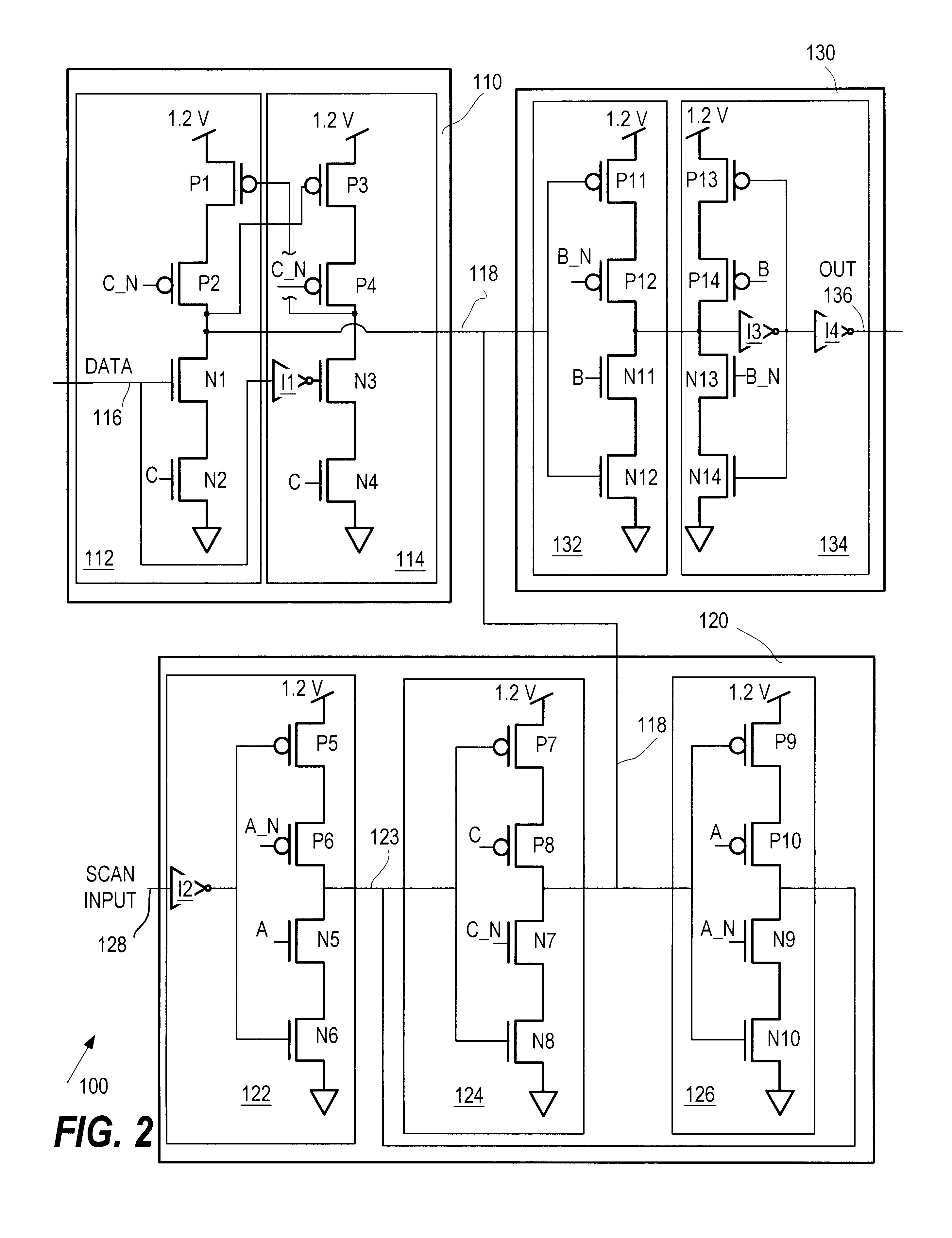
Level shifting, scannable latch, and method therefor
Latch circuitry has a data input stage for sampling a first input signal responsive to a first timing signal and generating a signal on an intermediate node in the latch circuitry. The latch circuitry also has a scan input stage for sampling a second input signal responsive to a second timing signal, and generating a signal on the intermediate node. The latch circuitry also has an output stage for generating an output signal on an output node of the latch circuitry responsive to the signal on the intermediate node and a third timing signal. The data input signal has a maximum voltage level and at least one stage of the latch circuitry is operable to effectively shift the voltage level so that the output signal has a higher maximum voltage level than that of the data input signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
DC-coupled multi-stage amplifier using all-pass resistive/capacitive network for level shifting
InactiveUS6943631B2Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier combinationsLevel shiftingCapacitance
A resistive level-shifting biasing network is used with a capacitor in parallel to couple FET-based amplifier stages from DC to several GHz in a multi-stage amplifier. The output of the first amplifier stage is connected to the input of the second amplifier stage without a blocking capacitor or level-shifting diodes, allowing a portion of the drain current for the first amplifier stage to be supplied from the second amplifier stage. In a particular embodiment, a distributed amplifier achieved over 20 dB gain from DC to about 80 GHz using three traveling wave amplifier chips.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
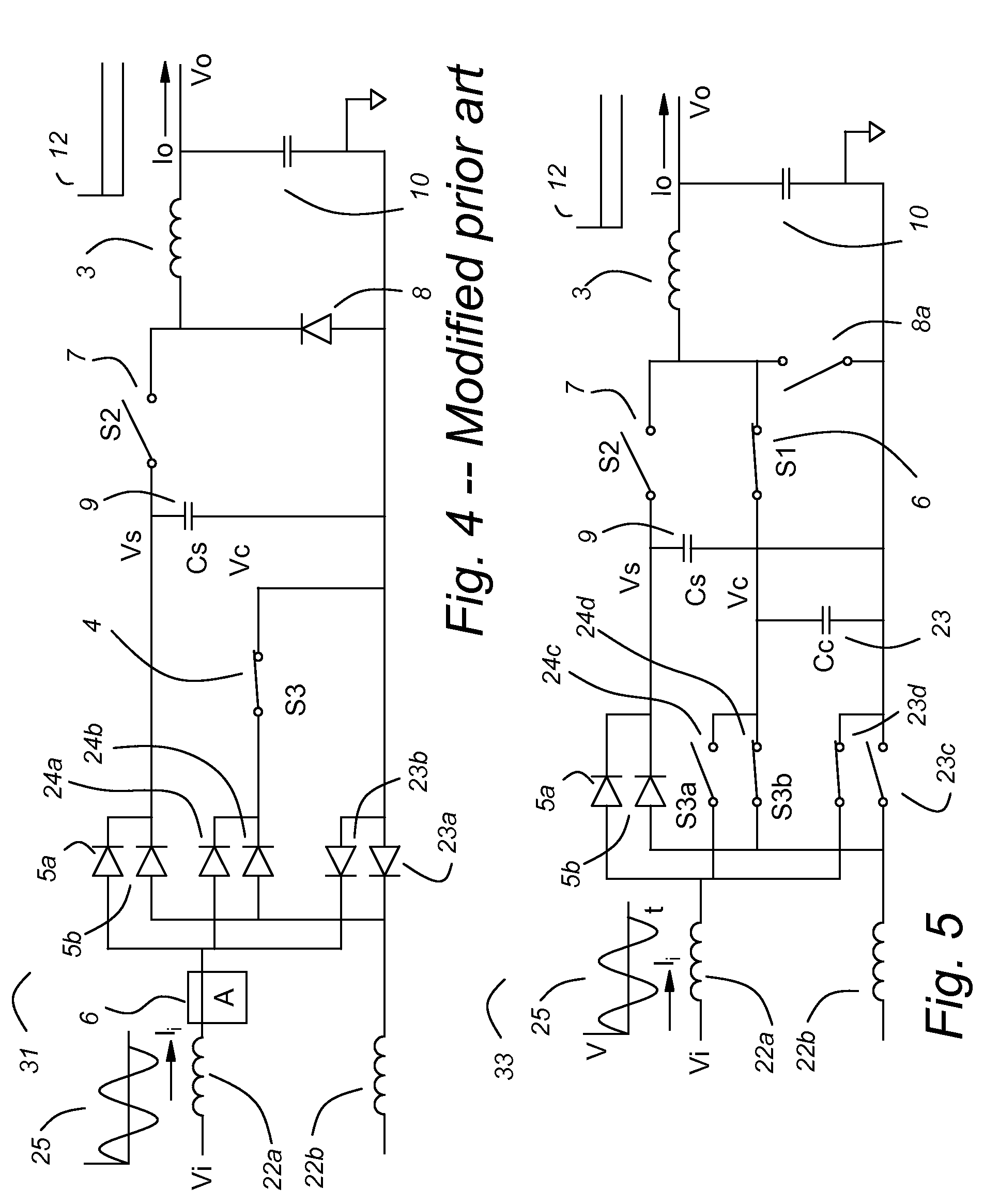
High efficiency power conversion circuits
InactiveUS20060062026A1Easy to handleReduce winding voltage stress stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLevel shiftingFull bridge
A composite high voltage schottky rectifier is revealed that provides a forward voltage slightly larger than a low voltage schottky rectifier combined with a high voltage breakdown capability. The composite rectifier can be formed from the combination of a low voltage schottky rectifier, a high voltage mosfet, and a few small passive components. A quarter bridge primary switching network similar in some ways to a half bridge primary switching network is revealed. The quarter bridge network consists of four switches with voltage stress equal to half the line voltage and the network applies one quarter of the line voltage to a primary magnetic circuit element network thereby reducing the number of primary winding turns required to one quarter by comparison to a common full bridge network. A synchronously switched buck post regulator is revealed for multi-output forward converters. The synchronously switched buck post regulator accomplishes precise independent load regulation for each output and reduced magnetics volume by using a coupled inductor with a common core for all outputs plus a second smaller inductor for each output except the highest voltage output. An improved capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is revealed that provides an effective drive mechanism for a floating or high side switch without the use of level shifting circuits or magnetic coupling. The capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is an improvement over prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits in that the new circuit uses a positive current feedback mechanism to reject slowly changing voltage variations that cause unintentional switch state changes in prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
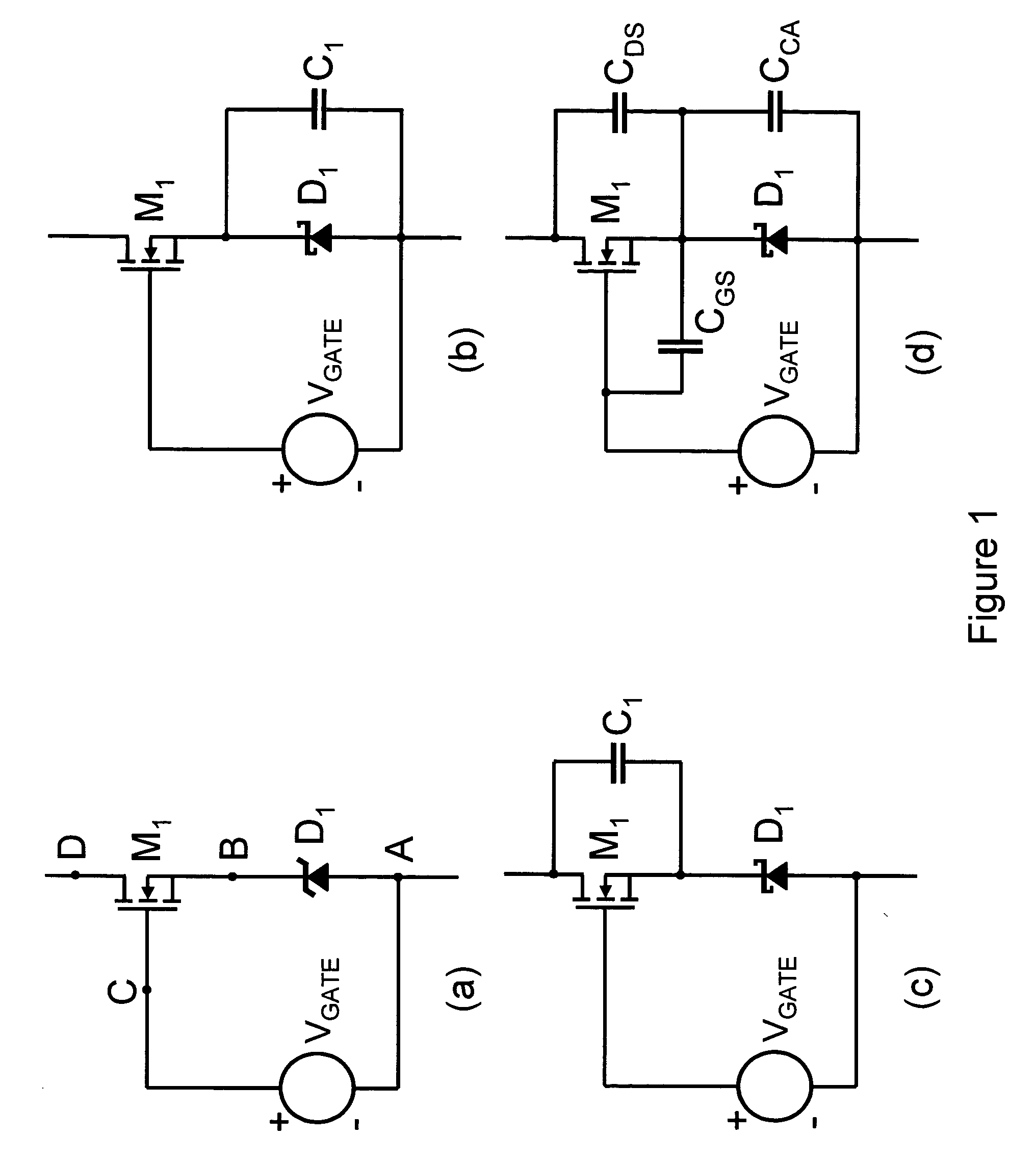
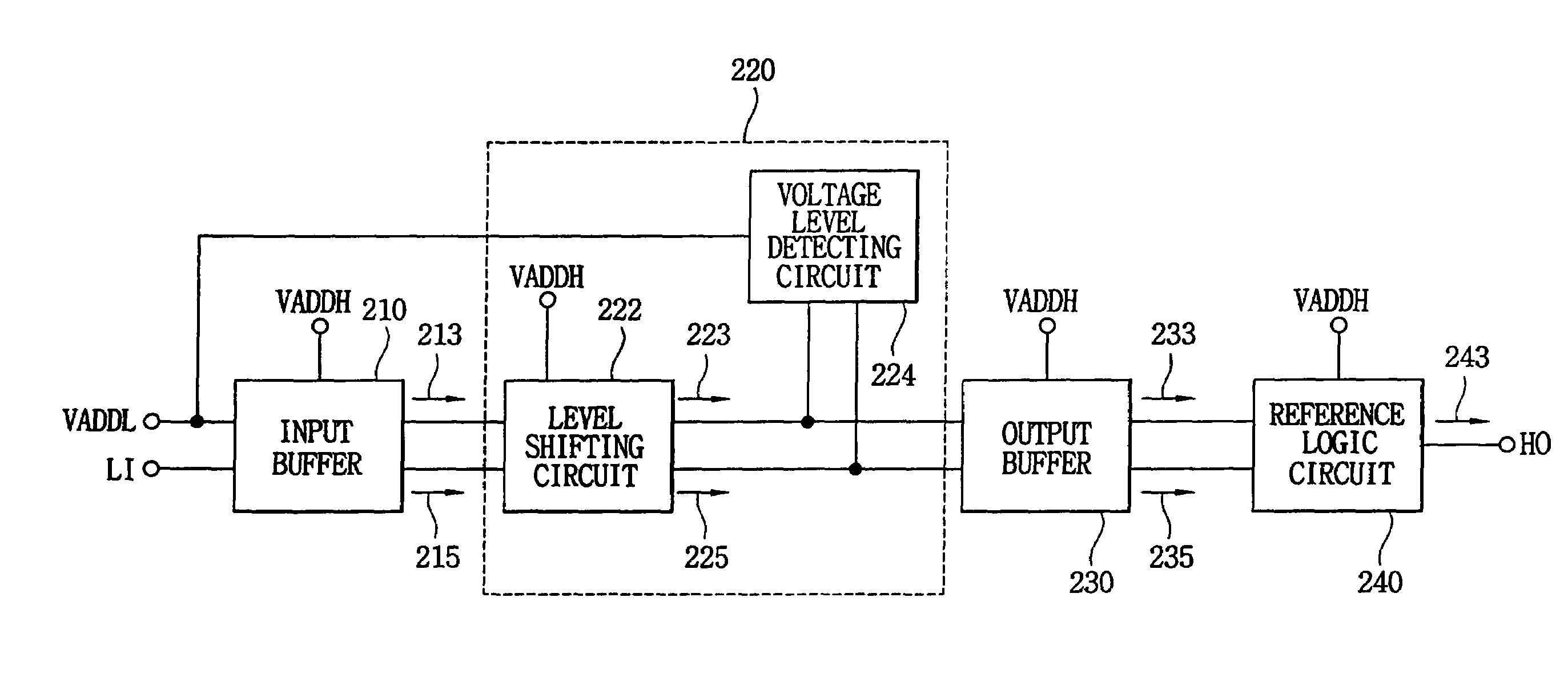
Level shifter for detecting grounded power-supply and level shifting method
ActiveUS7112996B2Electric pulse generatorLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsLevel shiftingElectricity
A level shifter includes an input buffer, a level shifting circuit, a voltage level detecting circuit, an output buffer and a reference logic circuit. The input buffer buffers a small range input signal to output a small range signal. The level shifting circuit transforms the small range signal into a first wide range signal. The voltage level detecting circuit detects whether a power voltage of a low voltage stage is at the ground level, and prevents an indefinite logic state of the level shifter. The output buffer buffers the first wide range signal to output a second wide range signal. The reference logic circuit generates a wide range signal having a predetermined logic status when the power voltage is at the ground level. Thus, a leakage current of the level shifter is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Level shifter having automatic delay adjusting function
InactiveUS20050258887A1Increase the number ofReduce decreasePulse automatic controlInstant pulse delivery arrangementsLevel shiftingDelayed time
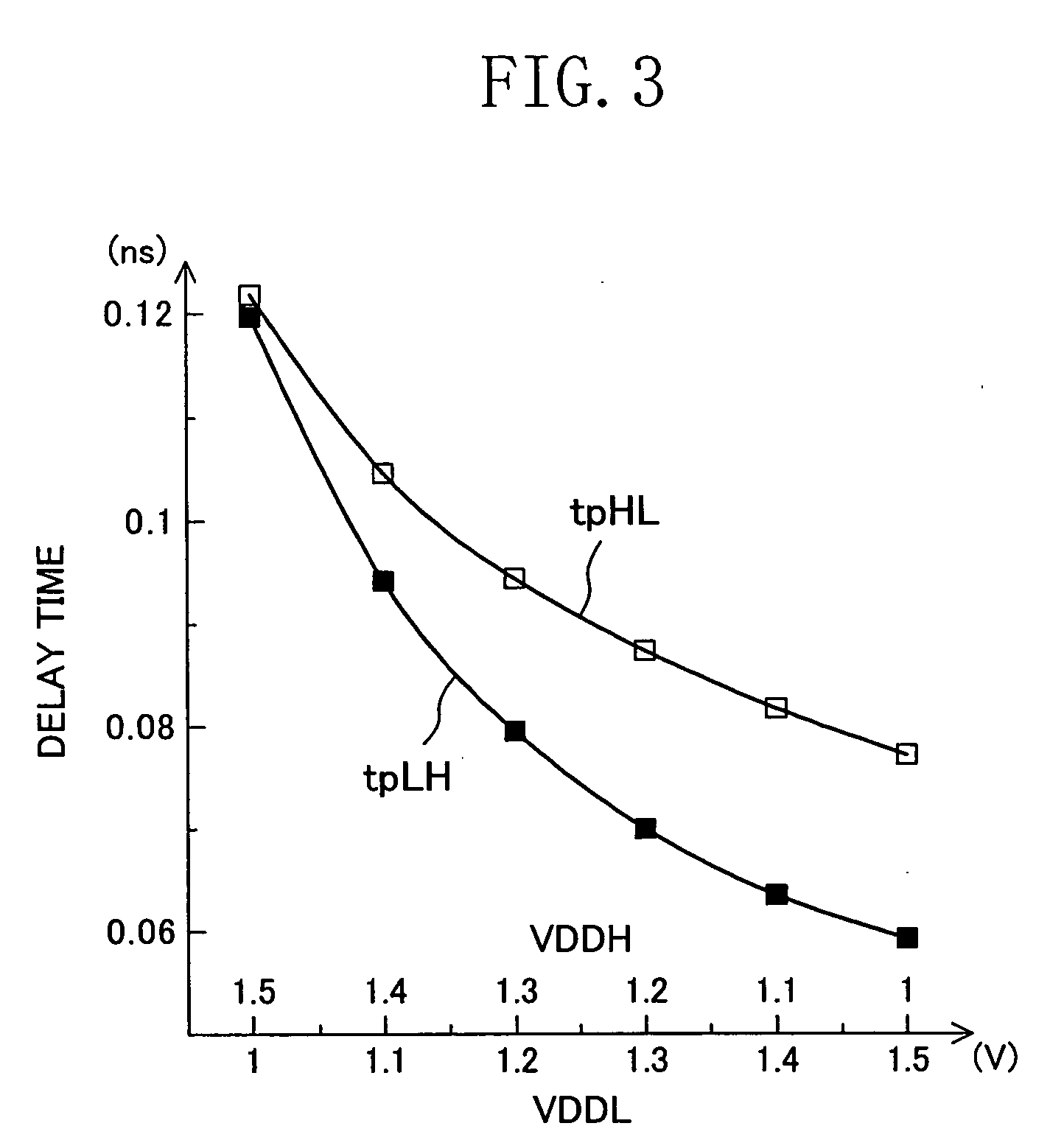
In a level shifter, in the case where the amplitude voltage of an input signal (i.e., a first power voltage VDDL) input to an input terminal is changed to be higher and the amplitude voltage of an output signal (i.e., a second power voltage VDDH) output from an output terminal is changed to be lower, a fall delay time of the signal output from the output terminal tends to be longer than a rise delay time of the signal. However, an inverted input signal obtained by an inverter is input to a level shifting unit and also to the gate of an N-type transistor, and therefore, the N-type transistor is turned on at the fall of the input signal input to the input terminal, so as to supply a current based on the second power voltage VDDH to an output node of the level shifting unit for assisting the shift into H level performed in the level shifting unit. Accordingly, even when at least one of the amplitude voltage of the input signal and the amplitude voltage of the output signal is changed, balance between the fall delay time characteristic and the rise delay time characteristic of the output signal can be satisfactorily kept.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Semiconductor memory device
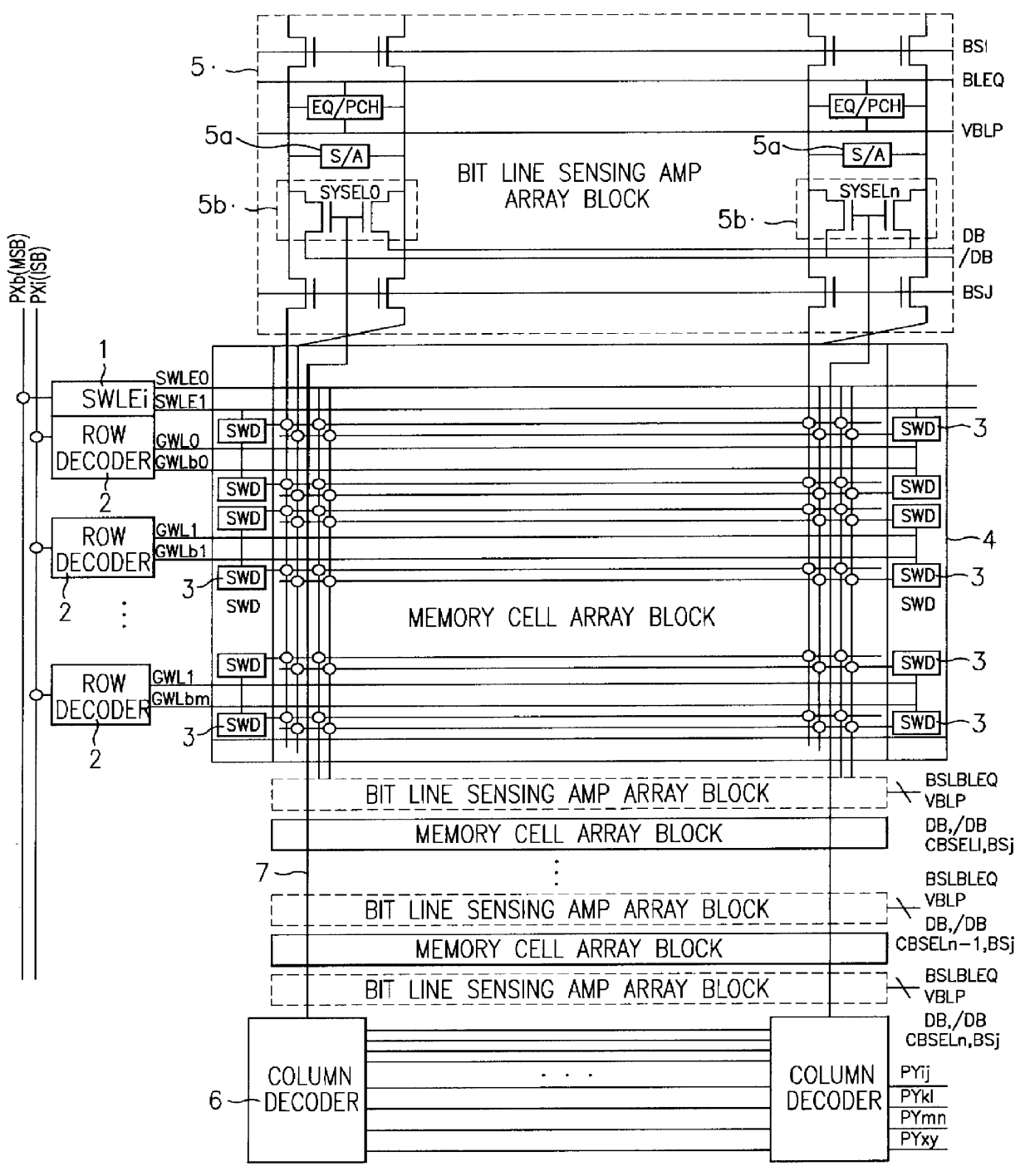
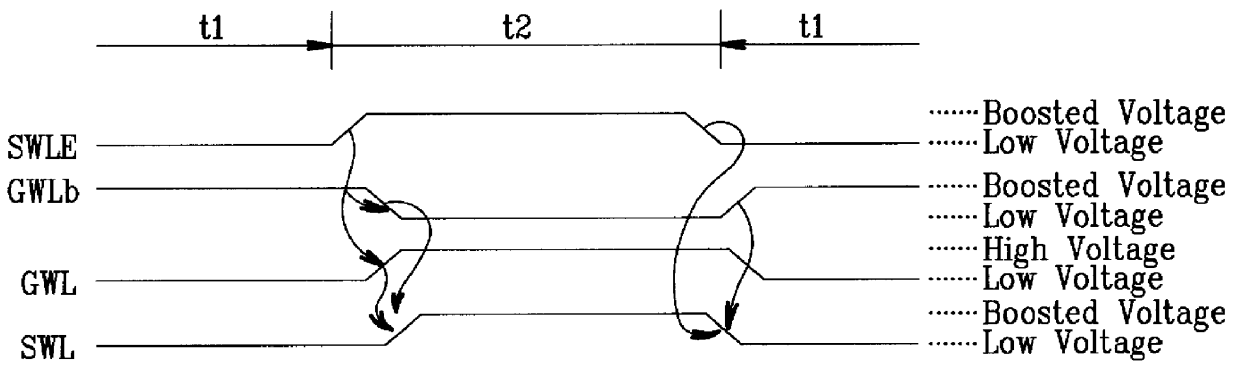
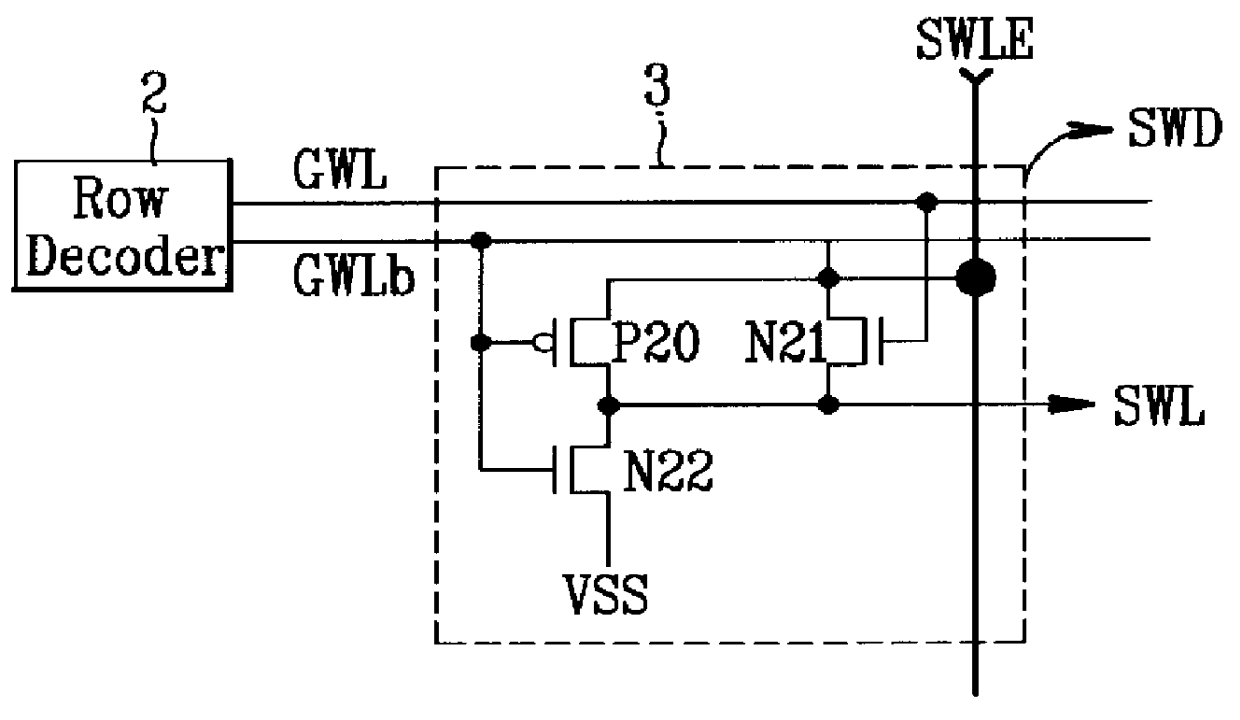
Disclose is a semiconductor memory device including a plurality of memory cell arrays, row and column decoders for selecting / driving each memory cell, and a plurality of bit line sensing amplifier arrays for sensing data of each memory cell, the semiconductor memory device comprising: a plurality of sub word line driver sections for driving each memory cell with a sub word line enable selection signal (SWLE) decoded by LSB address and with a global word line signal (GWLb) decoded by MSB address in the row decoder; a row decoding precharge signal generating section (RDPRi / VBFi) for applying a precharge signal to the row decoder and a voltage Vbb to the GWLb signal by means of the MSB address PXb; a level shifting section for shifting and transmitting an output signal from the column decoder to column selection lines which connects the column decoder with the bit line sensing amplifier array in series; and a data input / output controlling section for selectively applying an active signal to the bit line sensing amplifier array according to a level of the column selection line.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
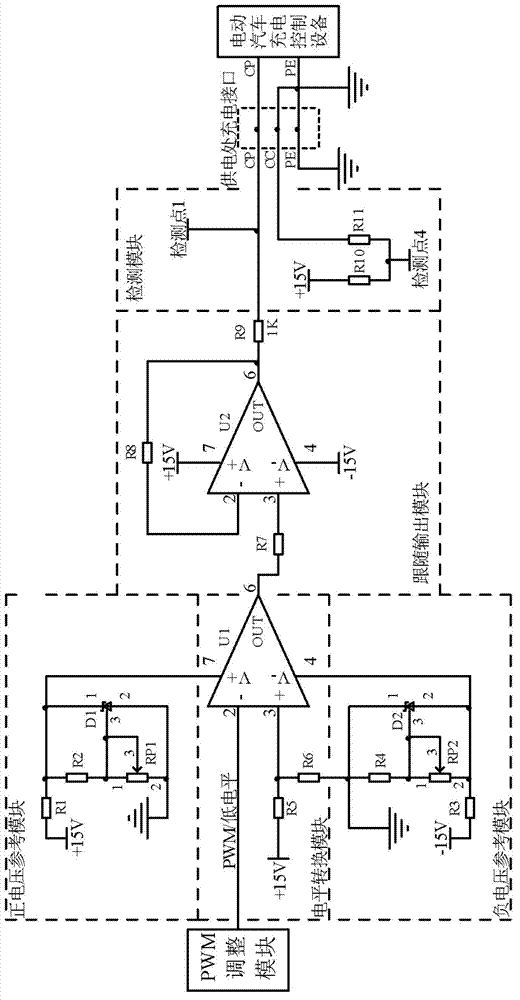
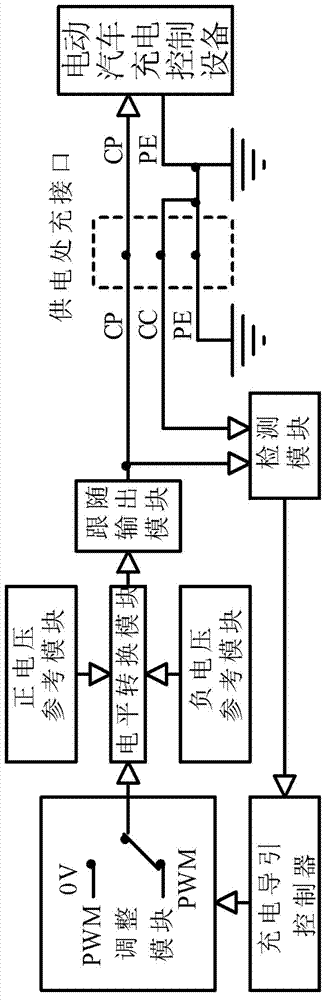
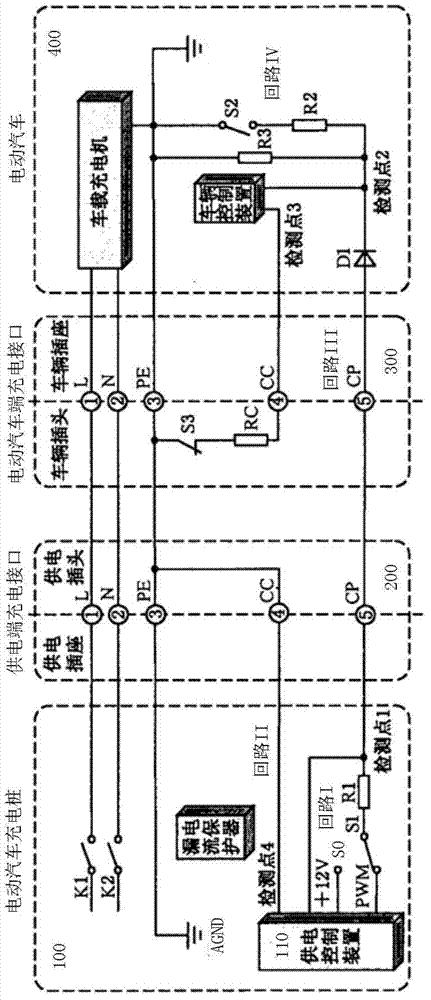
Charging control guidance module for alternating-current charge spot of electric vehicle and guidance method of charging control guidance module
The invention discloses a charging control guidance module for an alternating-current charge spot of an electric vehicle. The charging control guidance module comprises a positive voltage reference module, a negative voltage reference module, a level conversion module, an output tracing module, a detection module and a charging guidance controller, wherein guidanceguidancethe level conversion module is connected with the positive voltage reference module, the negative voltage reference module, a first power supply voltage and a PWM (pulse width modulator) module, the output tracing module is connected with the first power supply voltage, a second power supply voltage and the level conversion module, and the detection module is connected with the first power supply voltage and the output tracing module, and the charging guidance controller is connected with the detection module and the PWM module. The invention also discloses a charging control guidance method applied to the charging control guidance module for the alternating-current charge spot of the electric vehicle. According to the invention, the requirement of an accuracy of a power supply is reduced, the output PWM waveform is relatively high in quality and stability, a real-time and synchrous detection on the output wave can be much easier to realize, and the module and the method are simple and practical for use.
Owner:WAHLAP TECH CO LTD
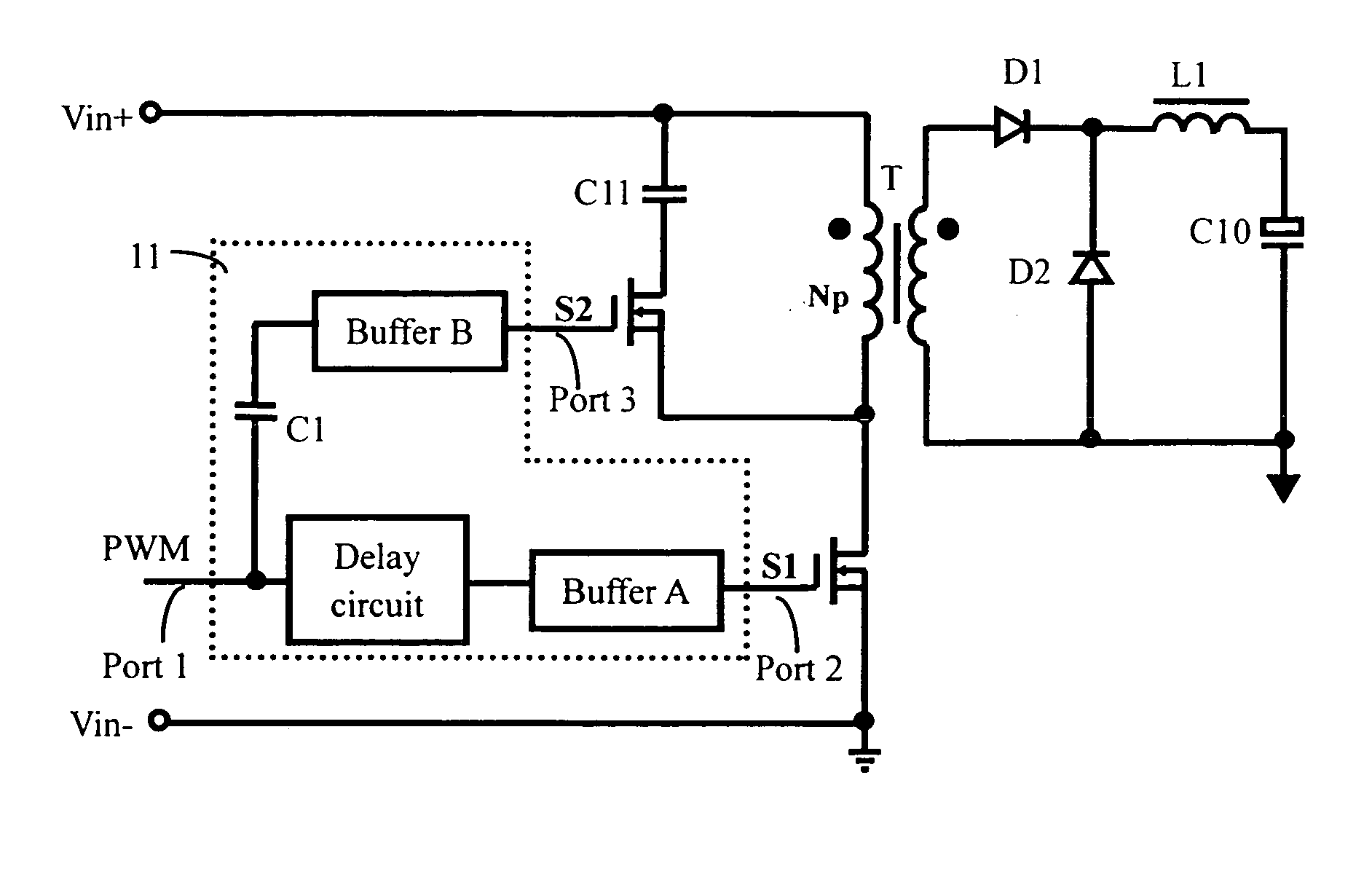
Driving circuit for DC/DC converter
ActiveUS20050201128A1Avoid problemsFast switching speedEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDriver circuitCapacitance
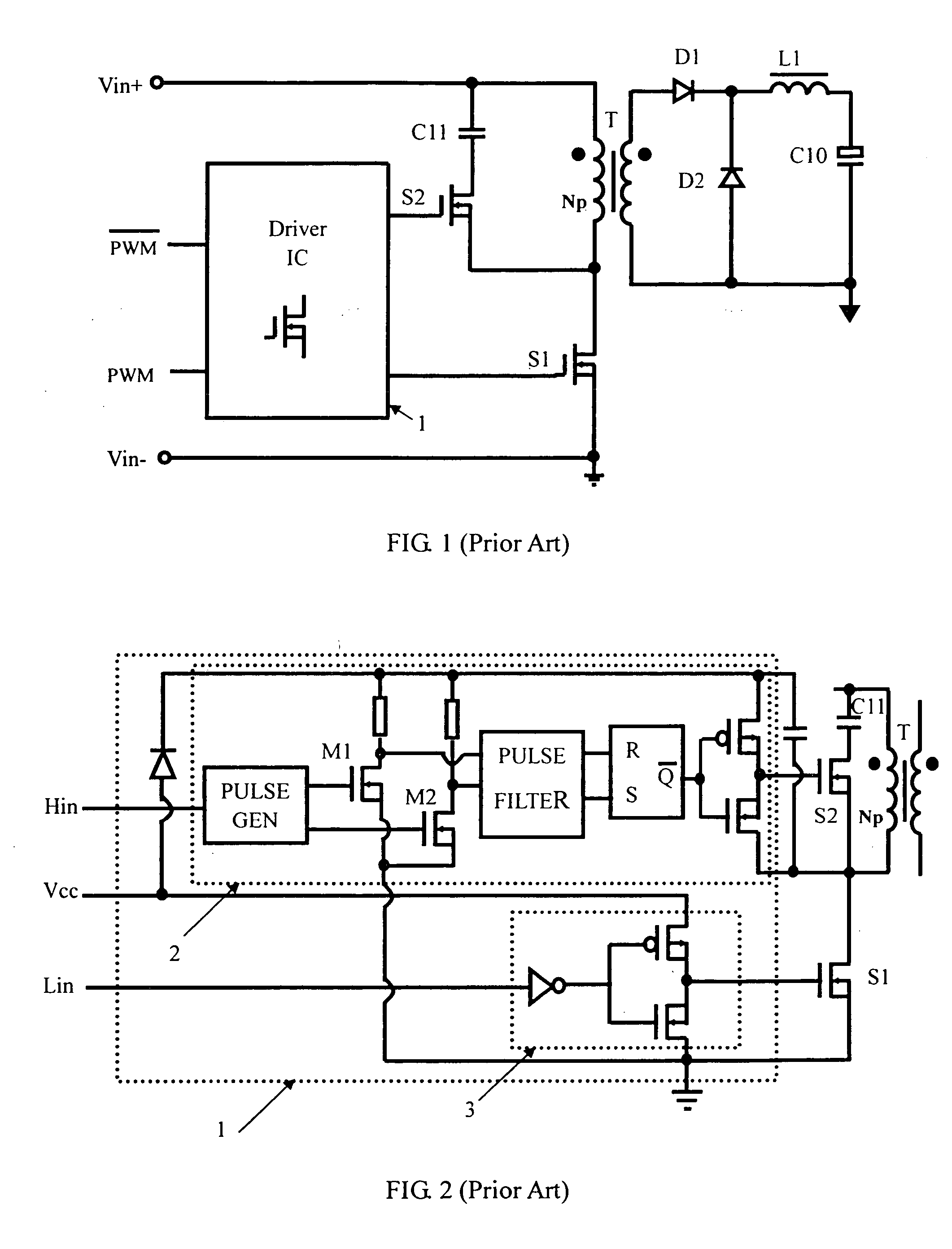
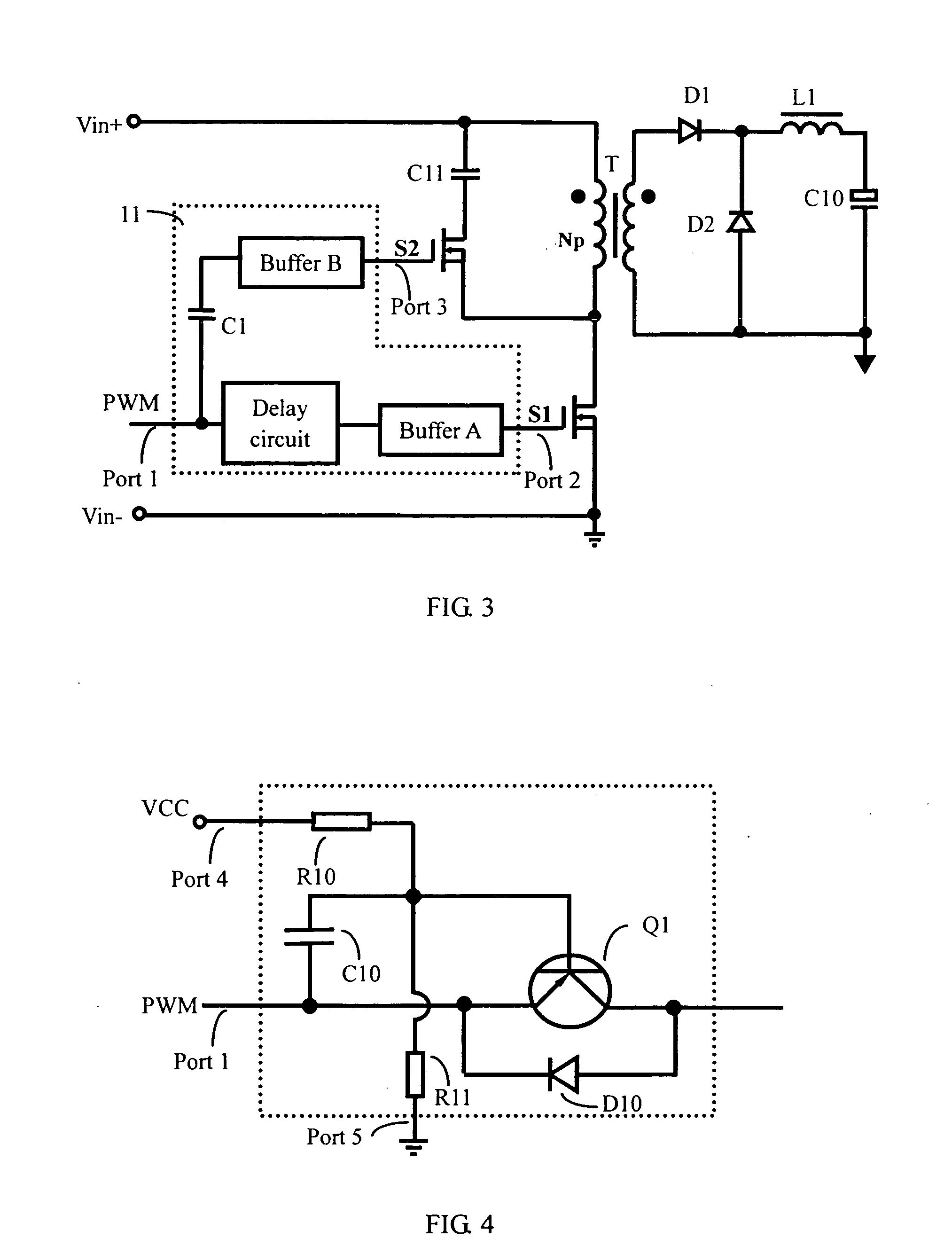
A driving circuit comprises an input terminal receiving an input of a PWM signal, a first output terminal connected to a main switch for outputting a low-side driving signal, a second output terminal connected to an active switch for outputting a high-side driving signal, a first branch having a voltage level shifting capacitor and a first buffer connected in series between the input terminal and the second output terminal; and a second branch having a delay circuit and a second buffer connected in series between the input terminal and the first output terminal. When the input of the PWM signal turns from a low level to a high level, the voltage level shifting capacitor transmits the input of PWM signal to the first buffer for turning off the active switch and then triggering the second buffer to turn on the main switch with a short time delay.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Dynamically biased wide swing level shifting circuit for high speed voltage protection input/outputs
ActiveUS7053657B1Achieve speedReduce voltageElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorLevel shiftingEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention recite a level shifting circuit for high voltage protection. In embodiments of the present invention, the level shifting circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a third transistor, and a fourth transistor coupled in a cascode configuration. The circuit further comprises a fifth transistor, a sixth transistor, a seventh transistor, and an eighth transistor coupled in a cascode configuration. The level shifting circuit further comprises an output coupled with the source of the first transistor, the gate of the seventh transistor, and with the drain of the second transistor. A first inverter is coupled with a second inverter in series and an input signal conveyed to the first inverter dynamically controls the bias level for said second and sixth transistors.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Grid driving circuit, array substrate, display device and driving method
ActiveCN103474044AGuaranteed display qualityReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesShift registerLevel shifting
The embodiment of the invention discloses a grid driving circuit, an array substrate, a display device and a driving method. The grid driving circuit is used for solving the problem that a large amount of power is consumed when an existing grid driving circuit works. The grid driving circuit comprises at least one sub-circuit, wherein each sub-circuit comprises M shifting register units, and M is a positive integer which is equal to or lager than 3; in any sub-circuit, the shifting register units used for driving odd grid signal lines are connected in sequence, the output end of an upper-level shifting register unit in the shifting register units used for driving the odd grid signal lines is connected with the input end of a lower-level shifting register unit, the shifting register units used for driving even grid signal lines are connected in sequence, and the output end of an upper-level shifting register unit in the shifting register units used for driving the even grid signal lines is connected with the input end of a lower-level shifting register unit. The grid driving circuit, the array substrate, the display device and the driving method have the advantages that power consumption is reduced on the premise that display quality is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Depletion-mode field effect transistor based electrostatic discharge protection circuit
InactiveUS7881029B1Minimize parasitic capacitanceMaximize linearityAntennas earthing switches associationAmplifier protection circuit arrangementsLevel shiftingEngineering
The present invention relates to an electrostatic discharge (ESD) clamp circuit that is used to protect other circuitry from high voltage ESD events. The ESD clamp circuit may include a field effect transistor (FET) element as a clamping element, which is triggered by using a drain-to-gate capacitance and a drain-to-gate resistance of the FET element and a resistive element as a voltage divider to divide down an ESD voltage to provide a triggering gate voltage of the FET element. In its simplest embodiment, the ESD clamp circuit includes only an FET element, a resistive element, a source-coupled level shifting diode, and a reverse protection diode. Therefore, the ESD clamp circuit may be small compared to other ESD protection circuits. The simplicity of the ESD clamp circuit may minimize parasitic capacitances, thereby maximizing linearity of the ESD clamp circuit over a wide frequency range.
Owner:QORVO US INC
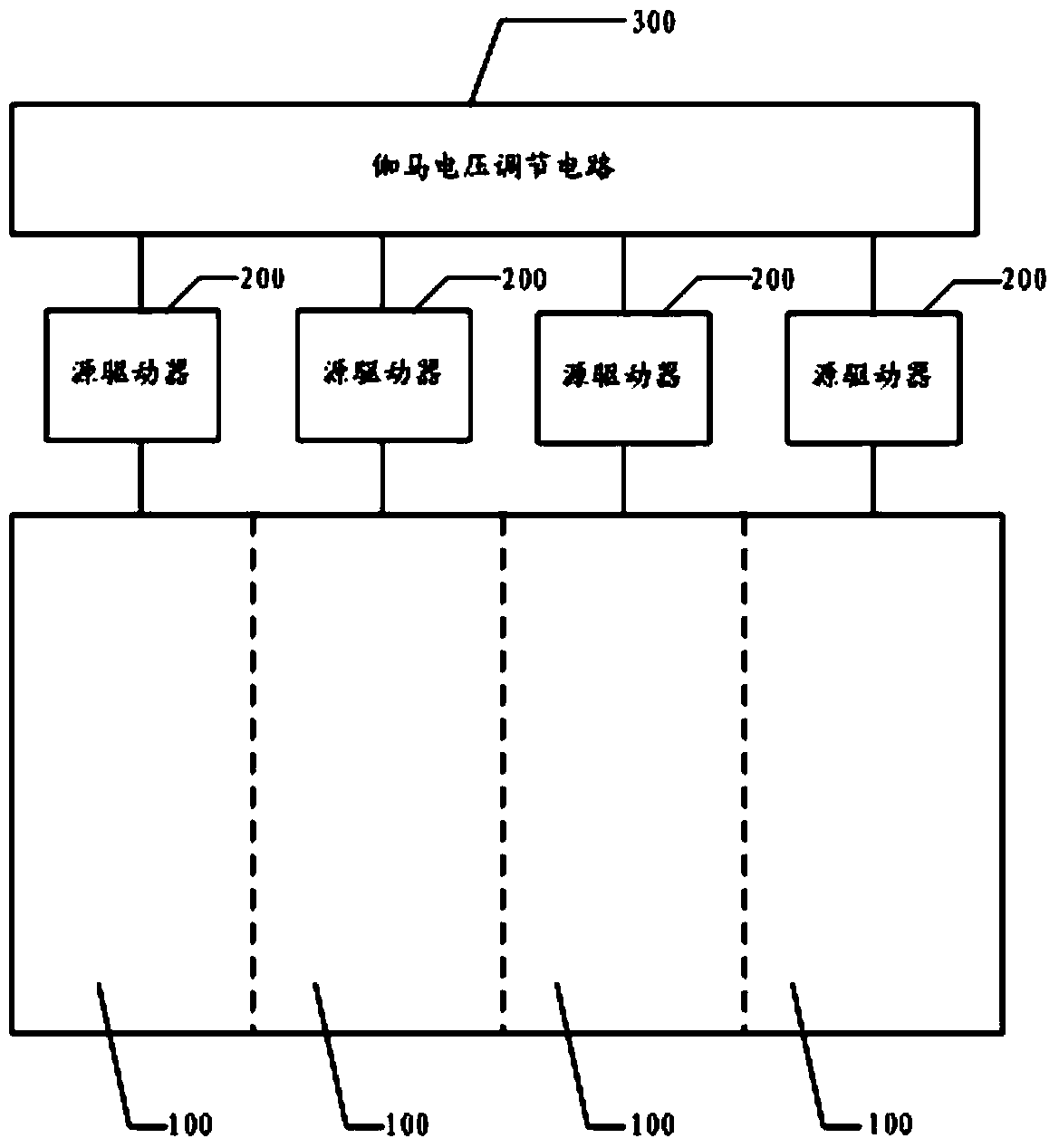
Gamma voltage adjusting device of display panel and display device of display panel
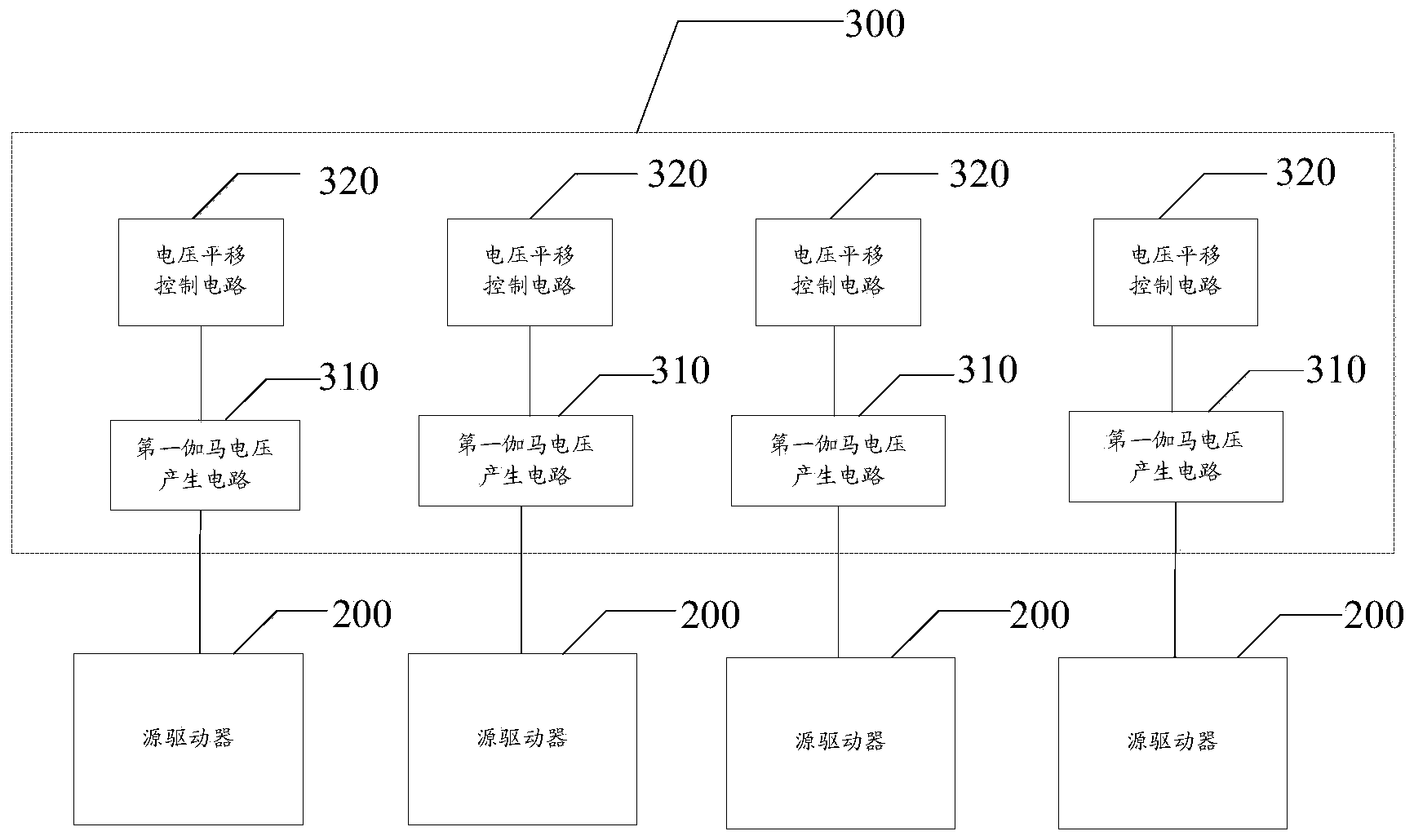
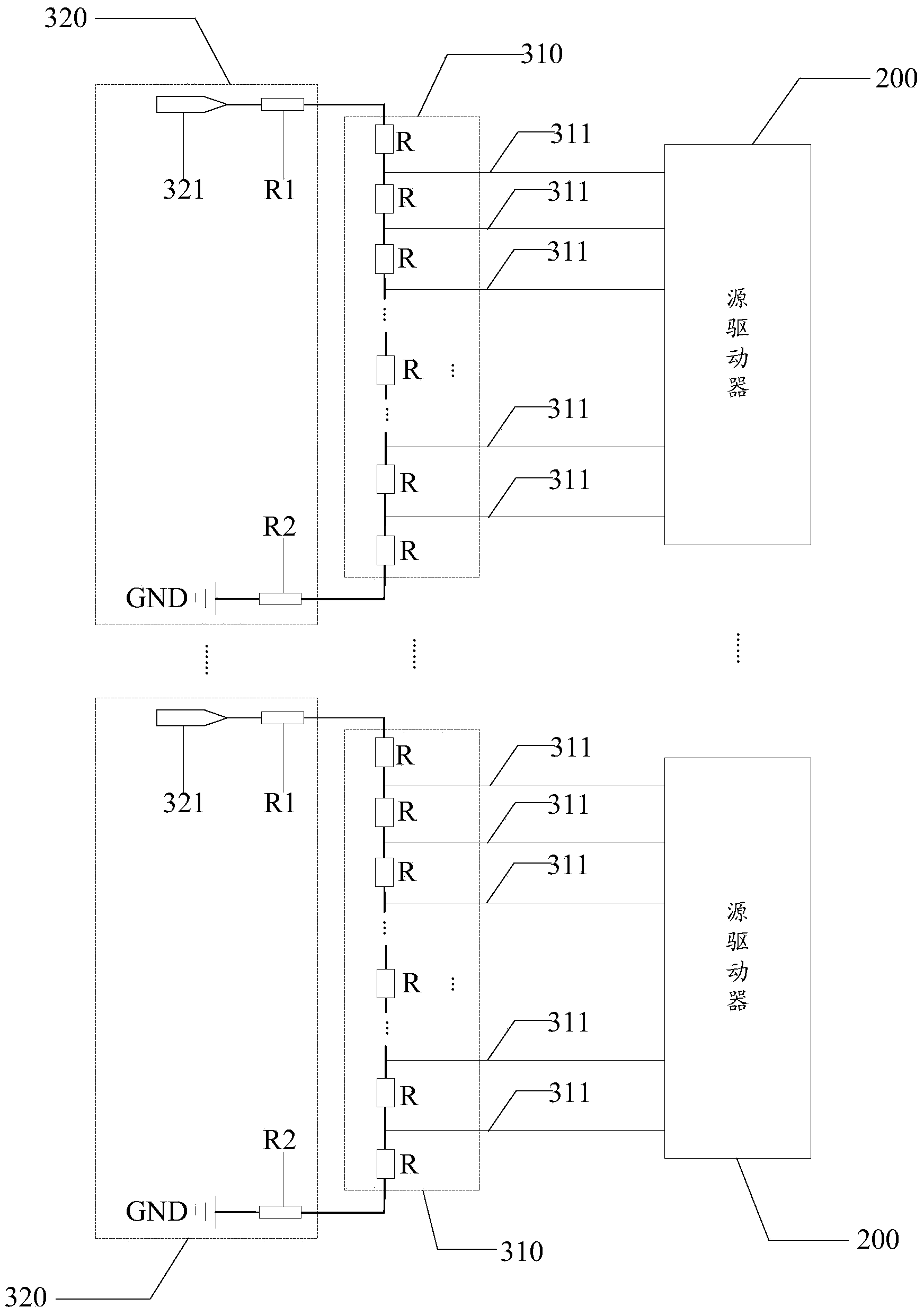
ActiveCN103943088ASolve the problem of uneven screen displayStatic indicating devicesLevel shiftingVoltage regulation
The invention discloses a gamma voltage adjusting device of a display panel and a display device of the display panel. Due to the fact that for each display area of the display panel, a target gamma voltage is generated through level shifting on a gamma voltage adjusting circuit according to a preset voltage level shifting amplitude value, for multiple display areas, different in Vcom voltage, in a large-sized display panel, the gamma voltage of each display area can be adjusted according to the preset voltage level shifting amplitude value to reach the target gamma voltage; in this way, the problem that because the Vcom voltage is not even, a display image is not even is reduced.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com