Patents
Literature
885 results about "Load regulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
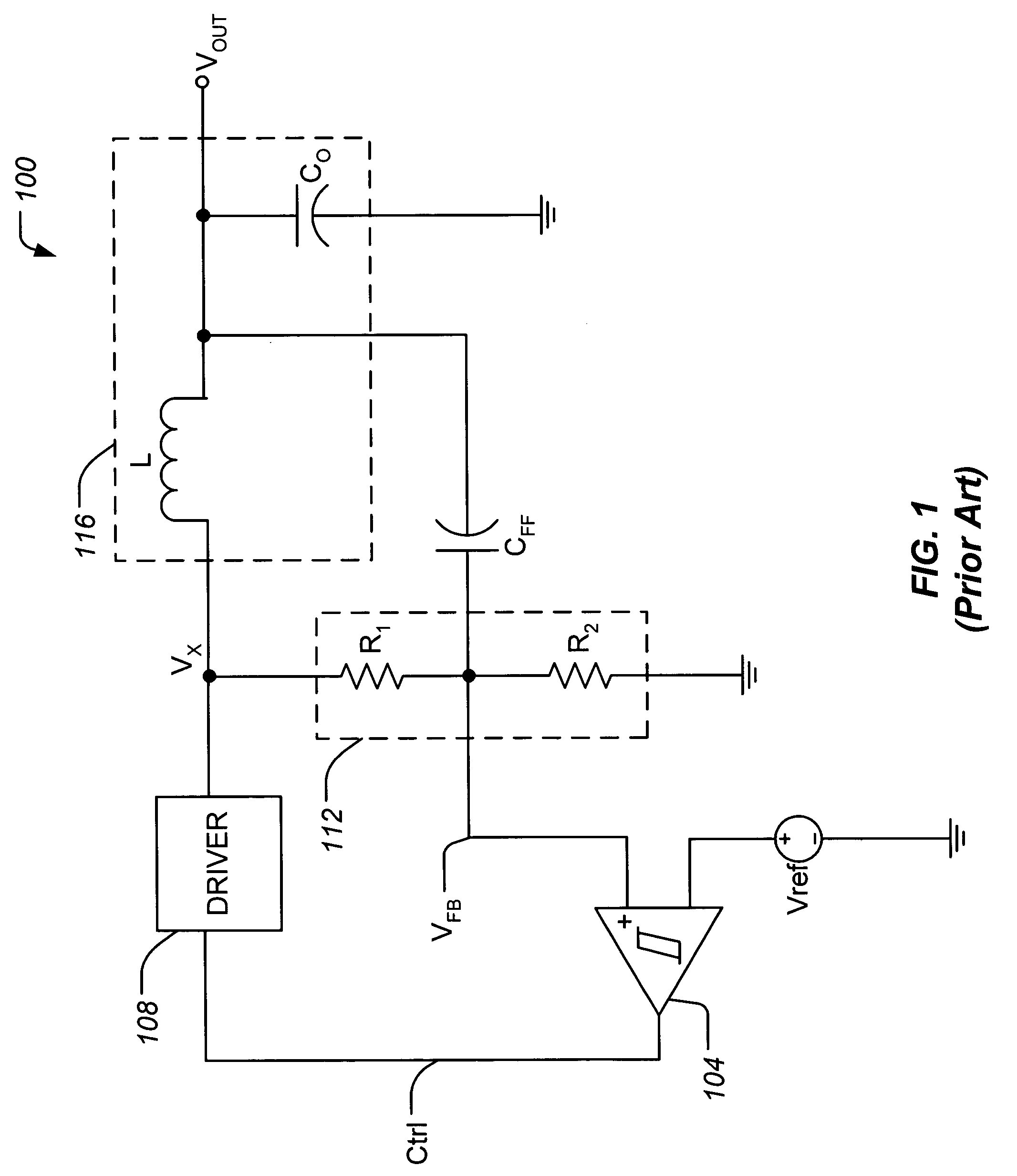
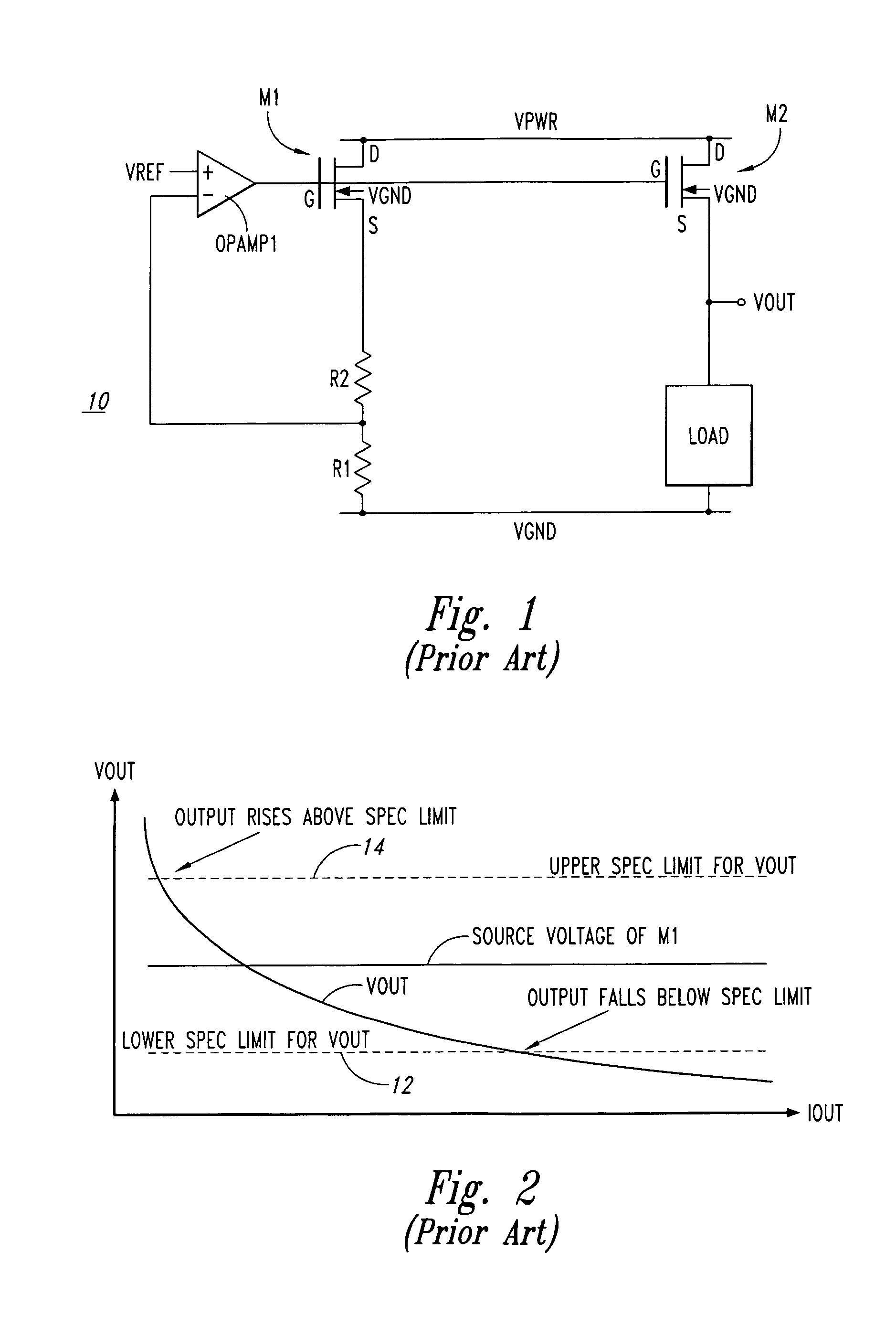
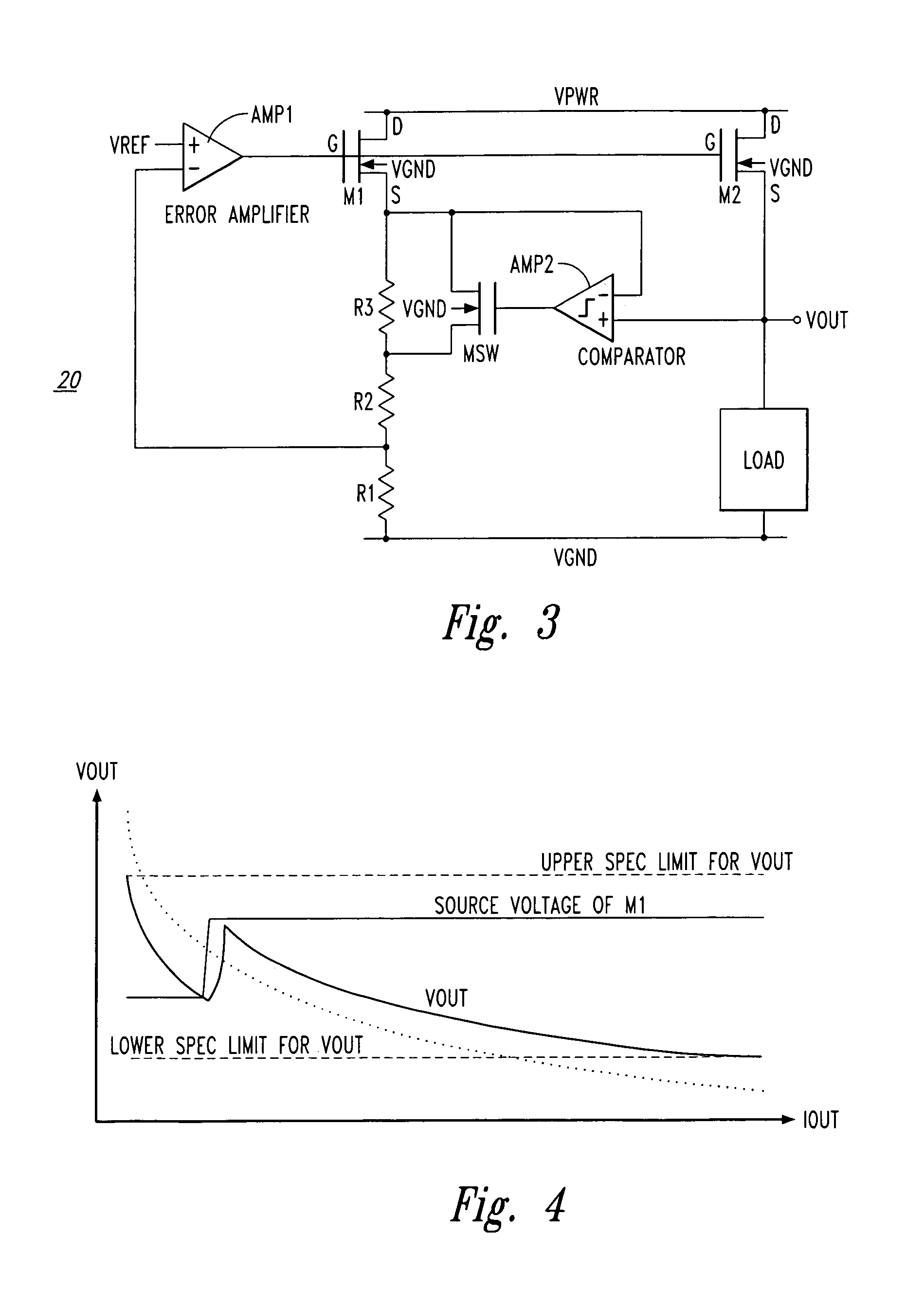
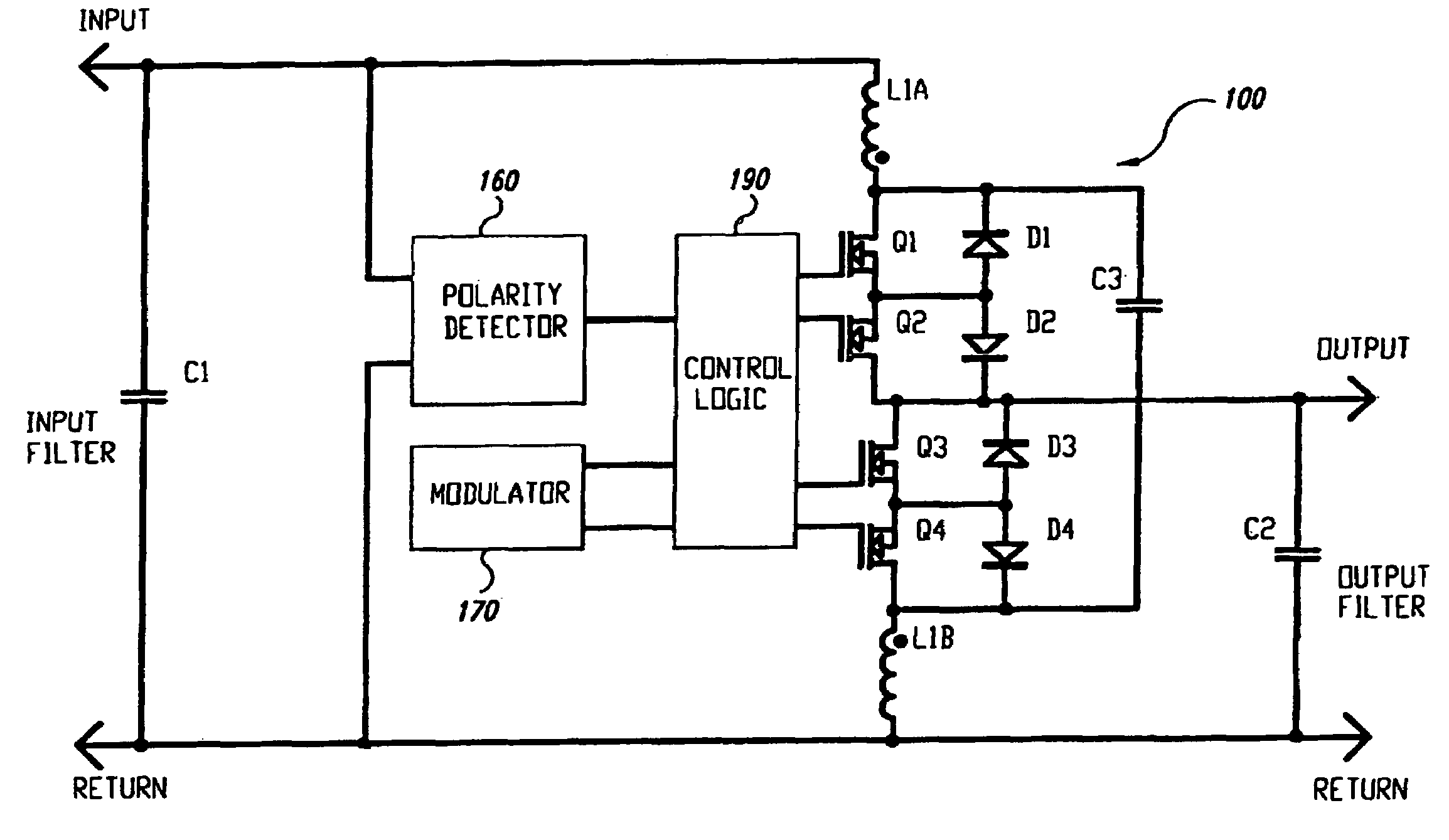
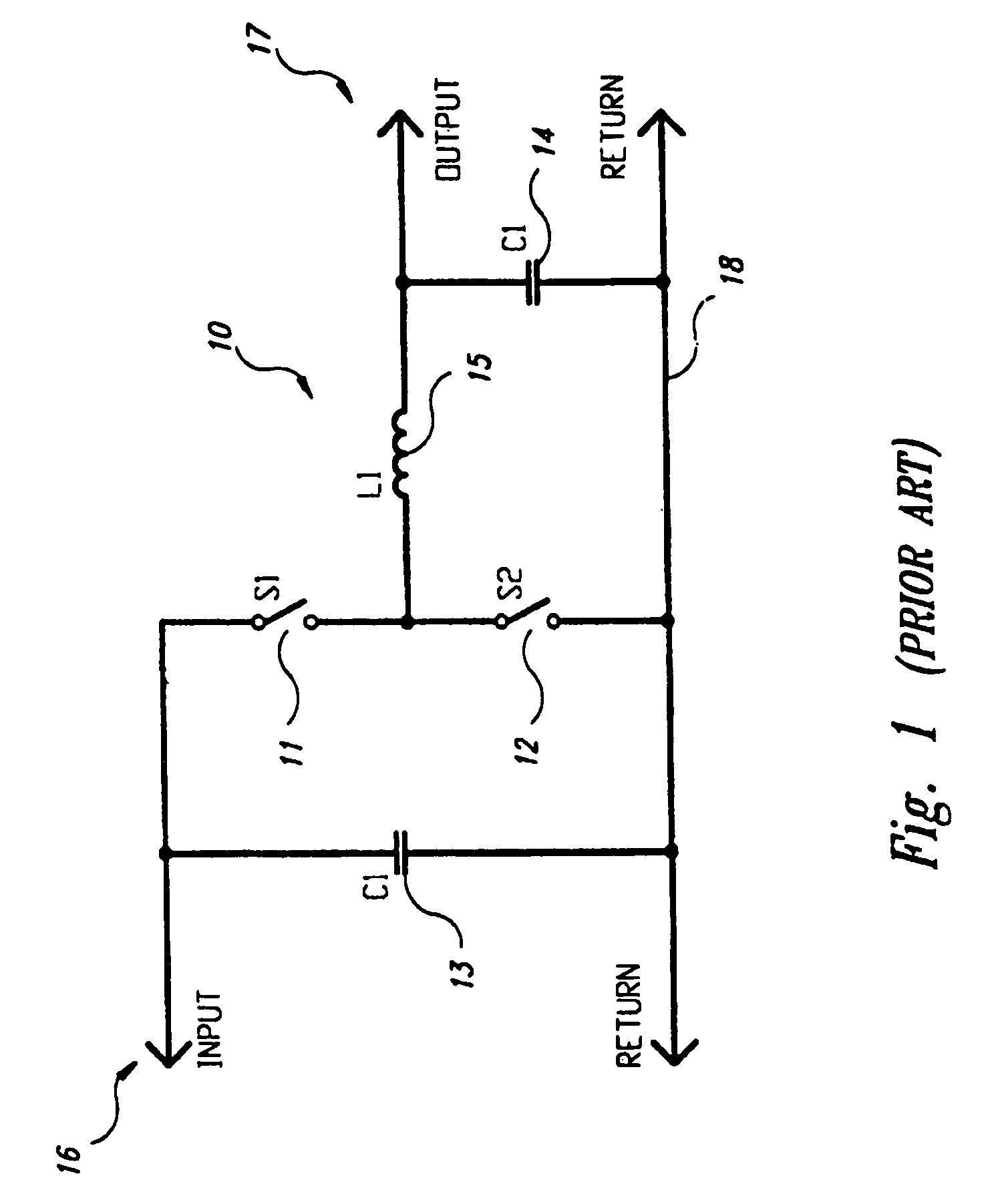
Load regulation is the capability to maintain a constant voltage (or current) level on the output channel of a power supply despite changes in the supply's load (such as a change in resistance value connected across the supply output).
Energy Scavenging Power Supply
InactiveUS20120292993A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceElectric power system
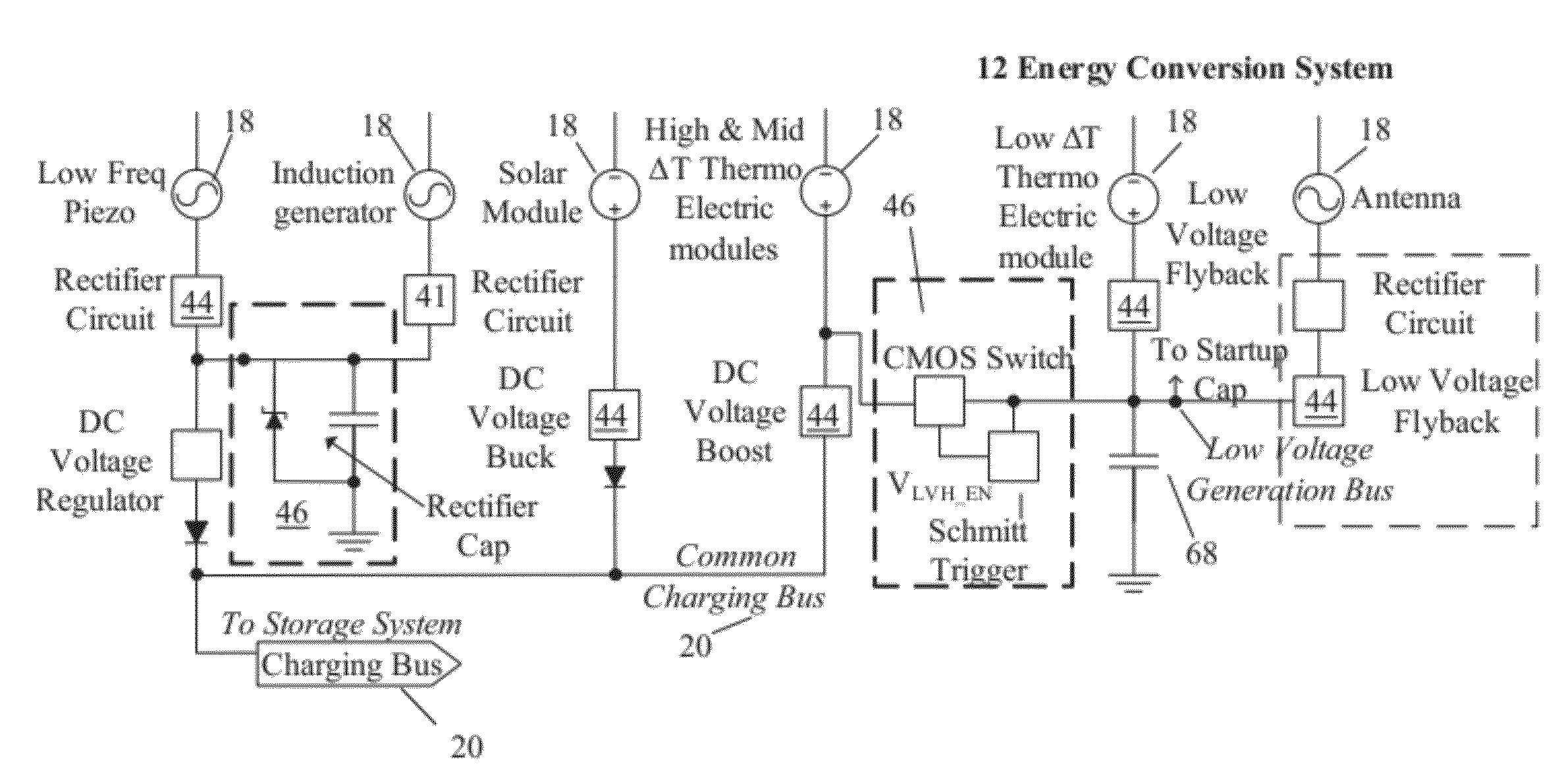
An energy scavenging power system and method may include an energy conversion system having at least one transducer configured to harvest energy, an energy management and storage system configured to store harvested energy; and a load regulation system configured to provide stored energy to power one or more low power-consumption loads. The energy management and storage system may include a start-up capacitor having a small capacitance to allow for quick charging and fast turn-on, a short term capacitor to provide energy to the load or loads once turned-on, and a long term capacitor having a large capacitance to provide for sustained energy delivery to the loads. The system also may include a common charging bus that receives energy from each transducer, conditioned if necessary, and which then determines the capacitor to which the energy should be delivered.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & TECH CORP
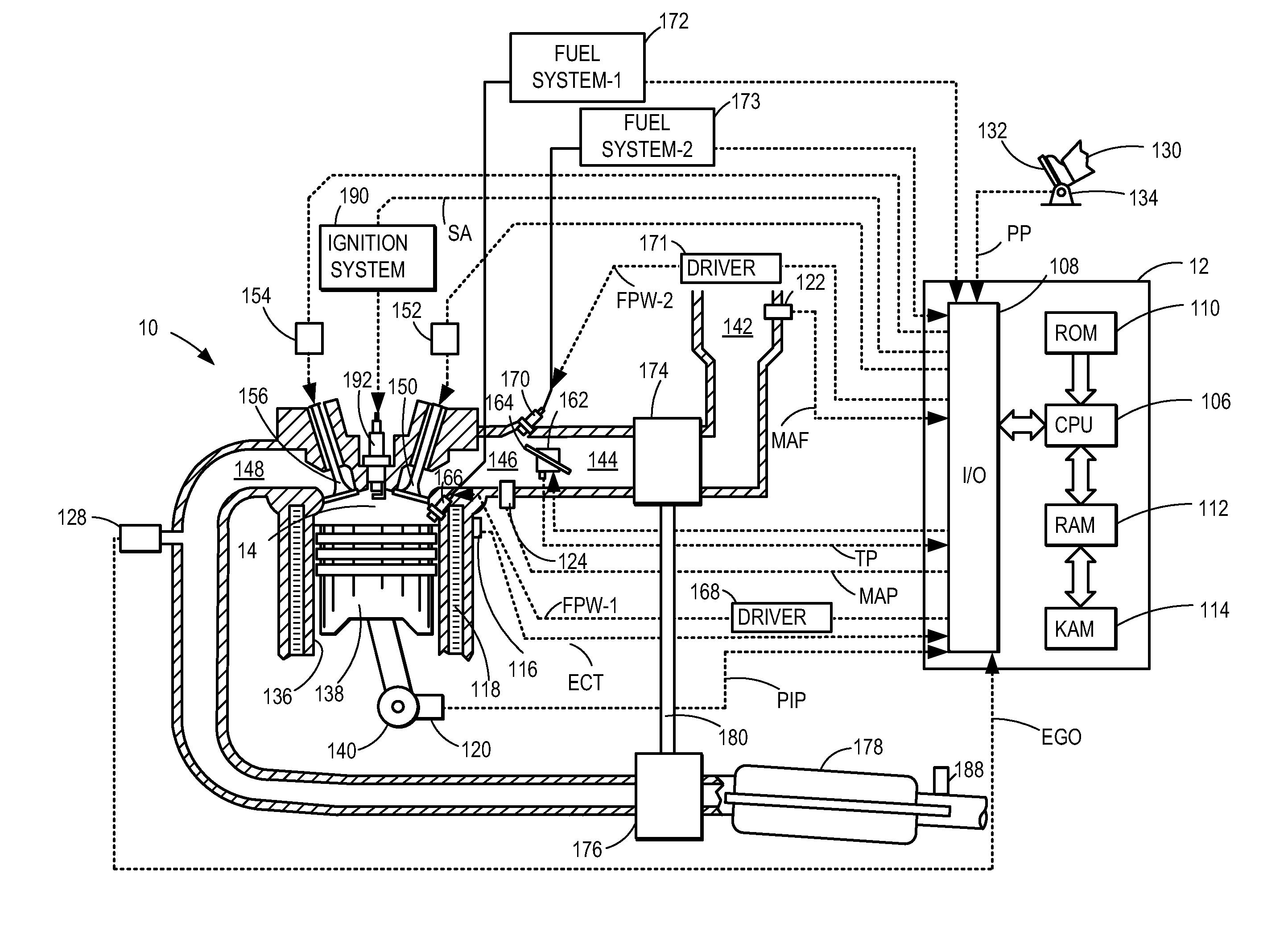
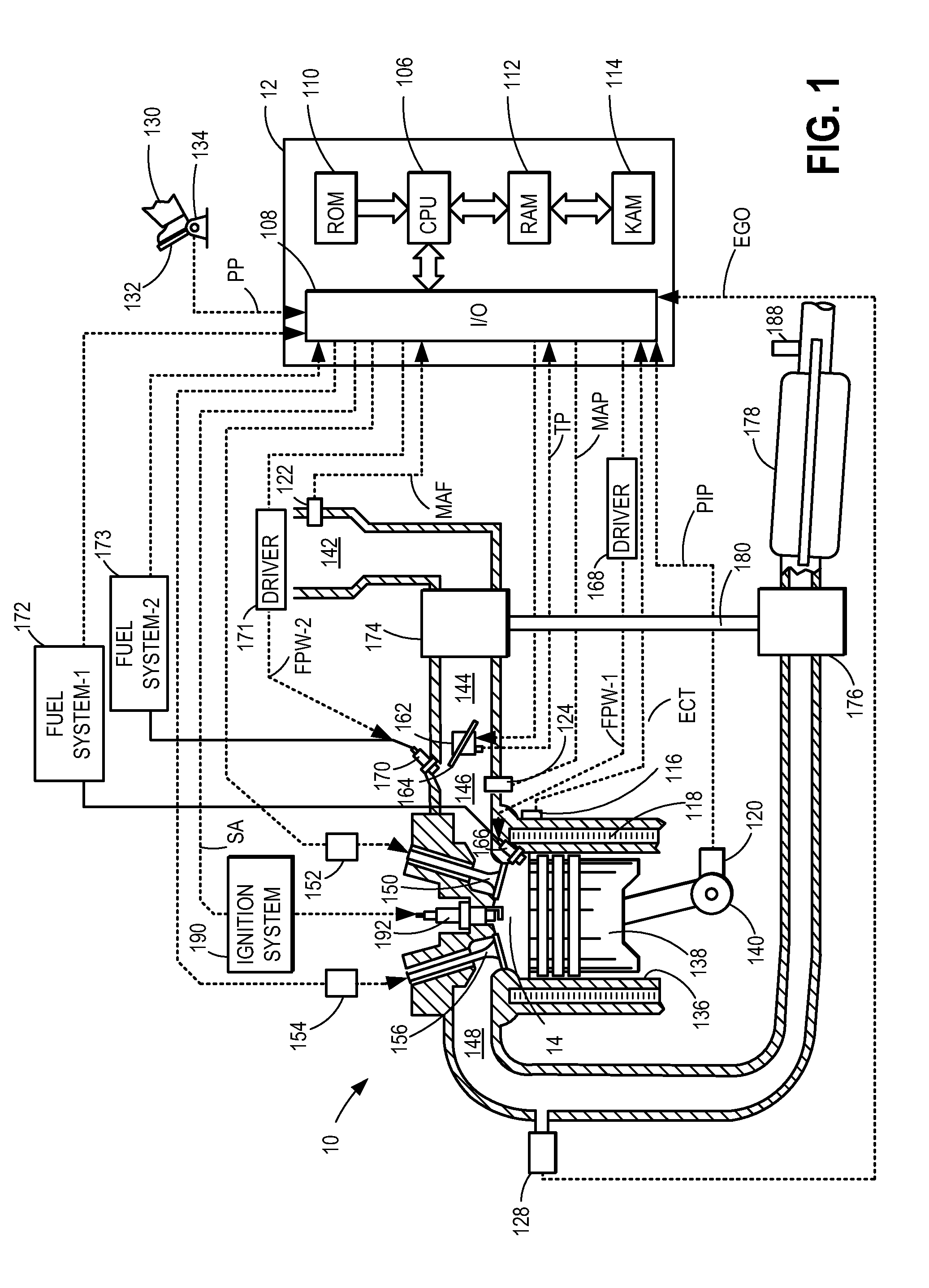
Method and system for engine control
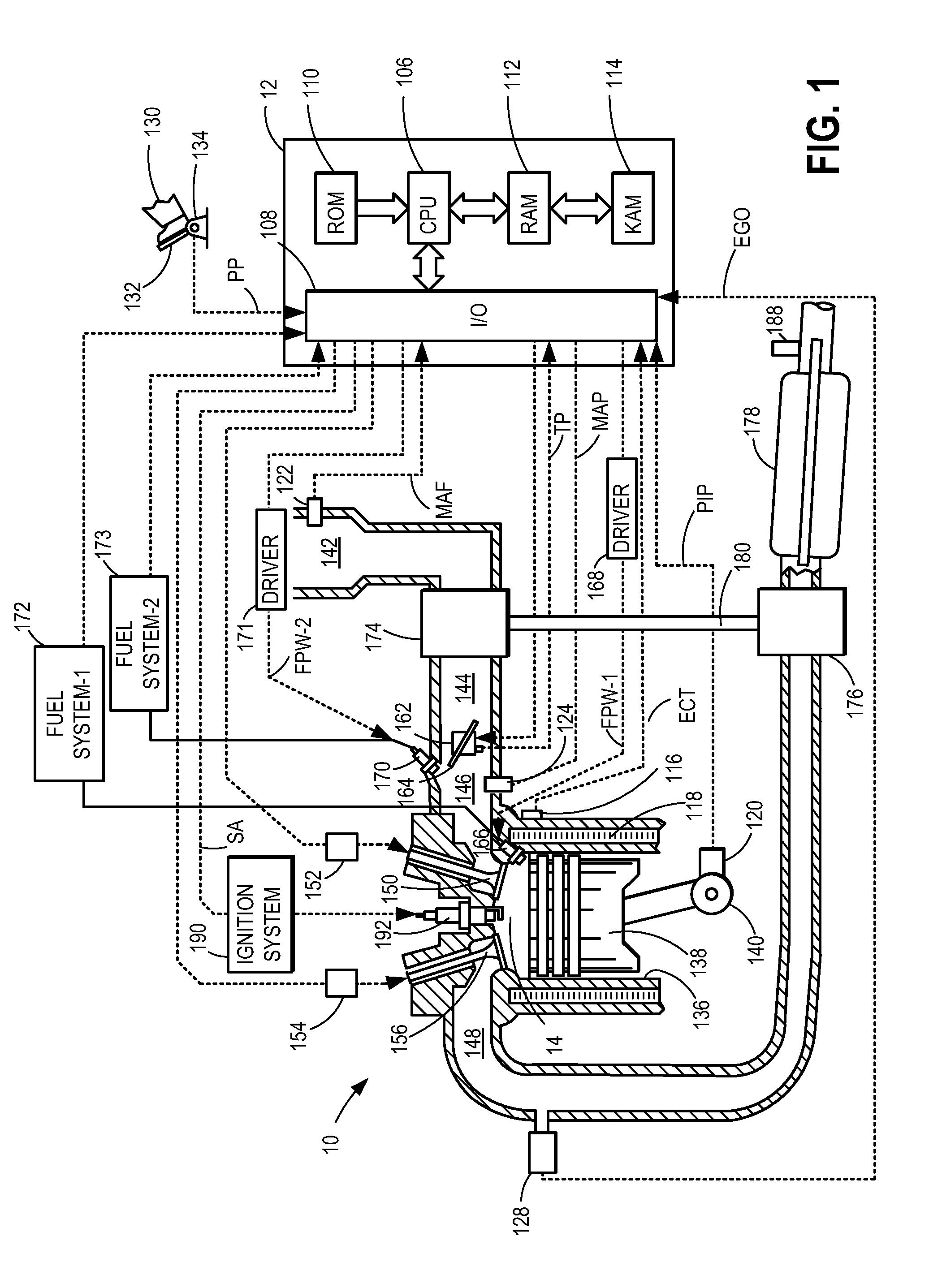
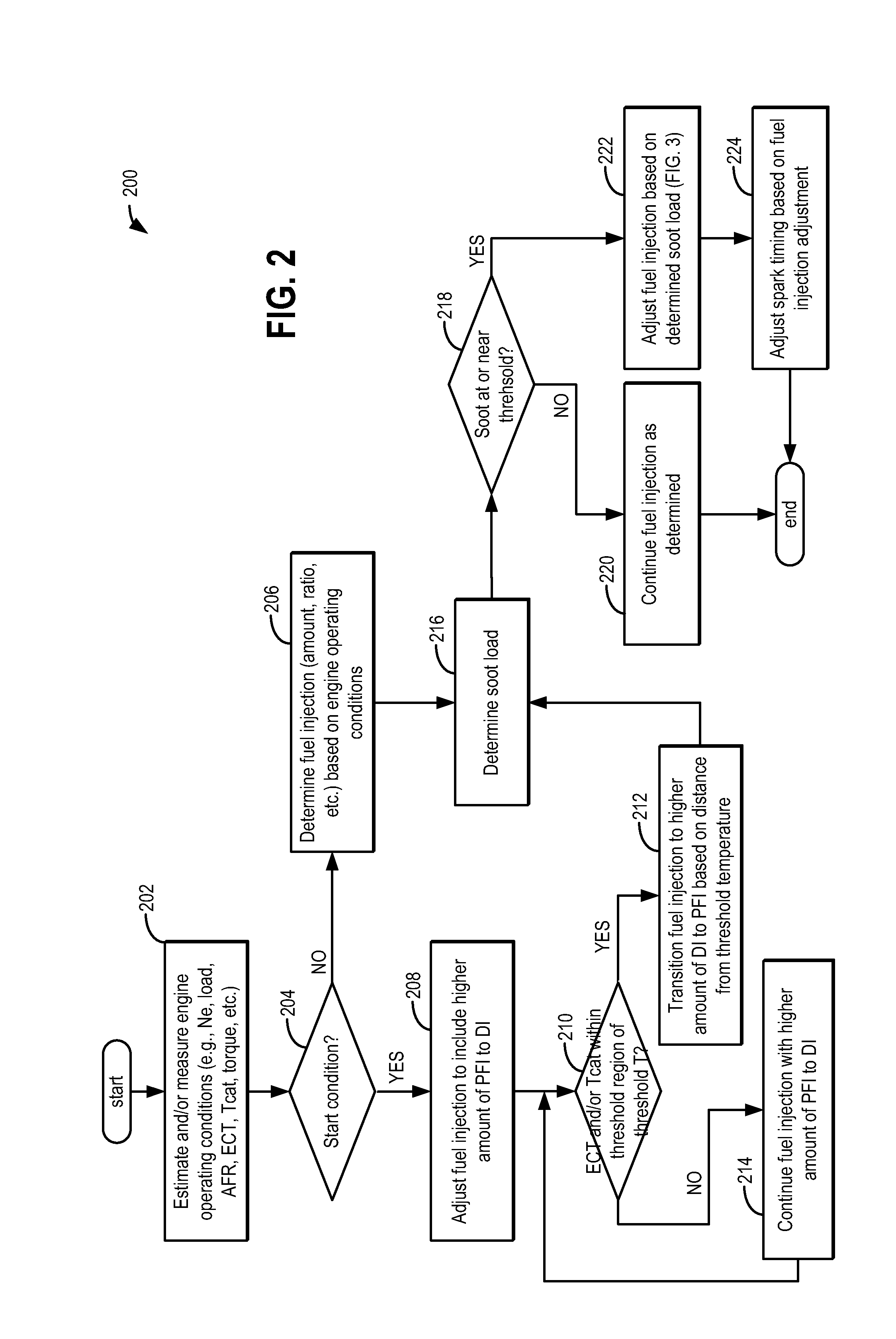
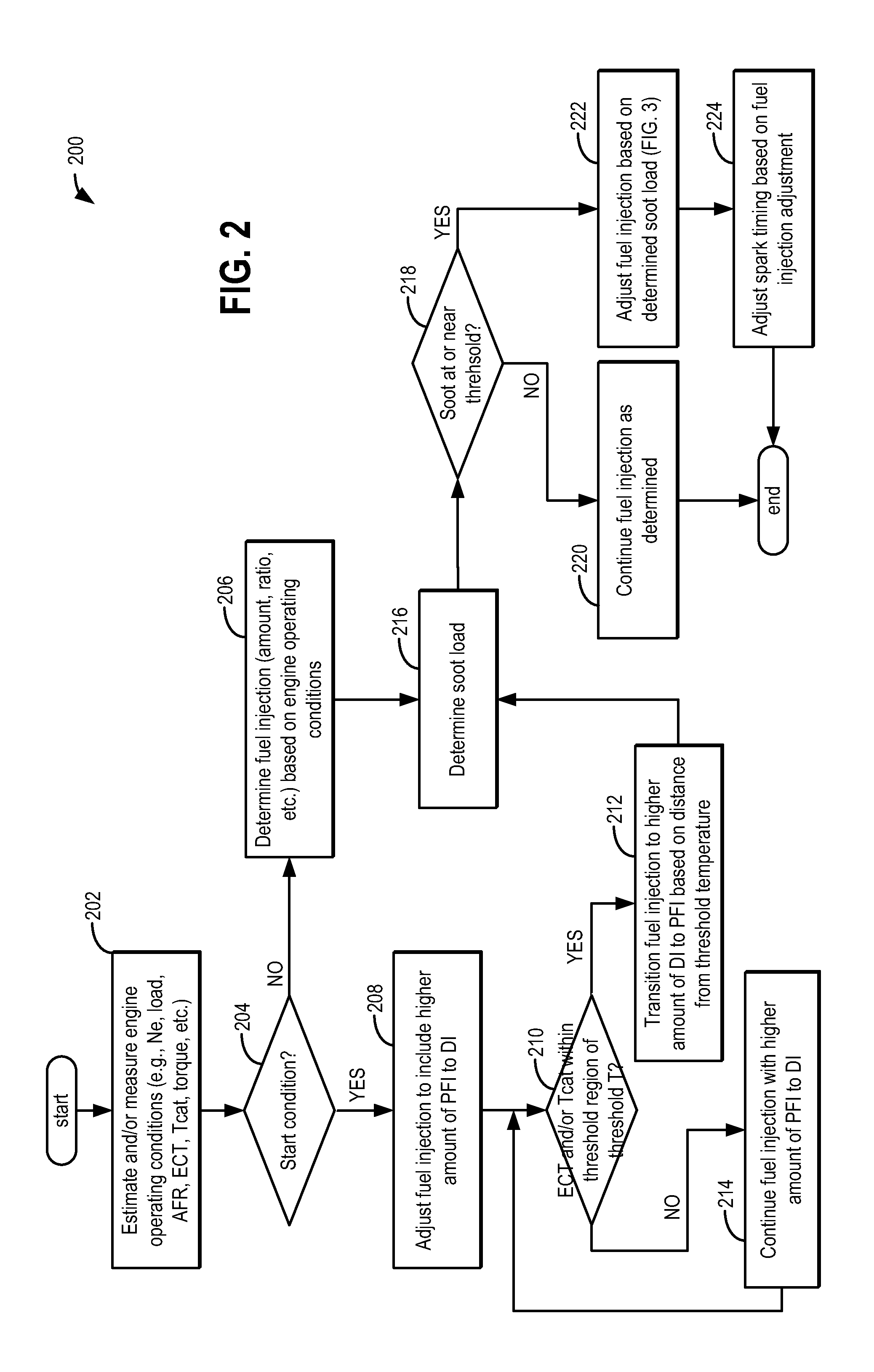
ActiveUS20110162620A1Improve fuel efficiencyImprove cooling effectElectrical controlExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesLoad regulation
Methods and systems are provided for controlling exhaust emissions by adjusting a fuel injection into an engine cylinder from a plurality of fuel injectors based on the fuel type of the injected fuel and further based on the soot load of the engine. Soot generated from direct fuel injection is reduced by decreasing an amount of direct injection into a cylinder as the engine soot load increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System, apparatus and method for testing under applied and reduced loads
InactiveUS7353715B2Easy maintenanceApply evenlyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesEngineeringLoad regulation
A system which cyclically applies and reduces a load on a test specimen and which can use an apparatus comprising: (a) a frame; (b) a load adjusting section having a fluidic mechanical muscle that contracts and extends in length to cyclically apply and reduce a load; (c) a load train section frame for subjecting a test specimen to the load; and (d) a lever arm configured to apply and reduce the load from the loading adjusting section to the load train section. The system and apparatus can be used in a method for cyclically applying and reducing a load on a test specimen to thereby subject the test specimen to tensile testing and can also comprise a mechanism for decoupling at least a portion of the load from the test specimen when the load is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High switching frequency DC-DC converter with fast response time
ActiveUS7279875B2Save circuit board areaShorten the timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterLoad step
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Audio frequency amplifier
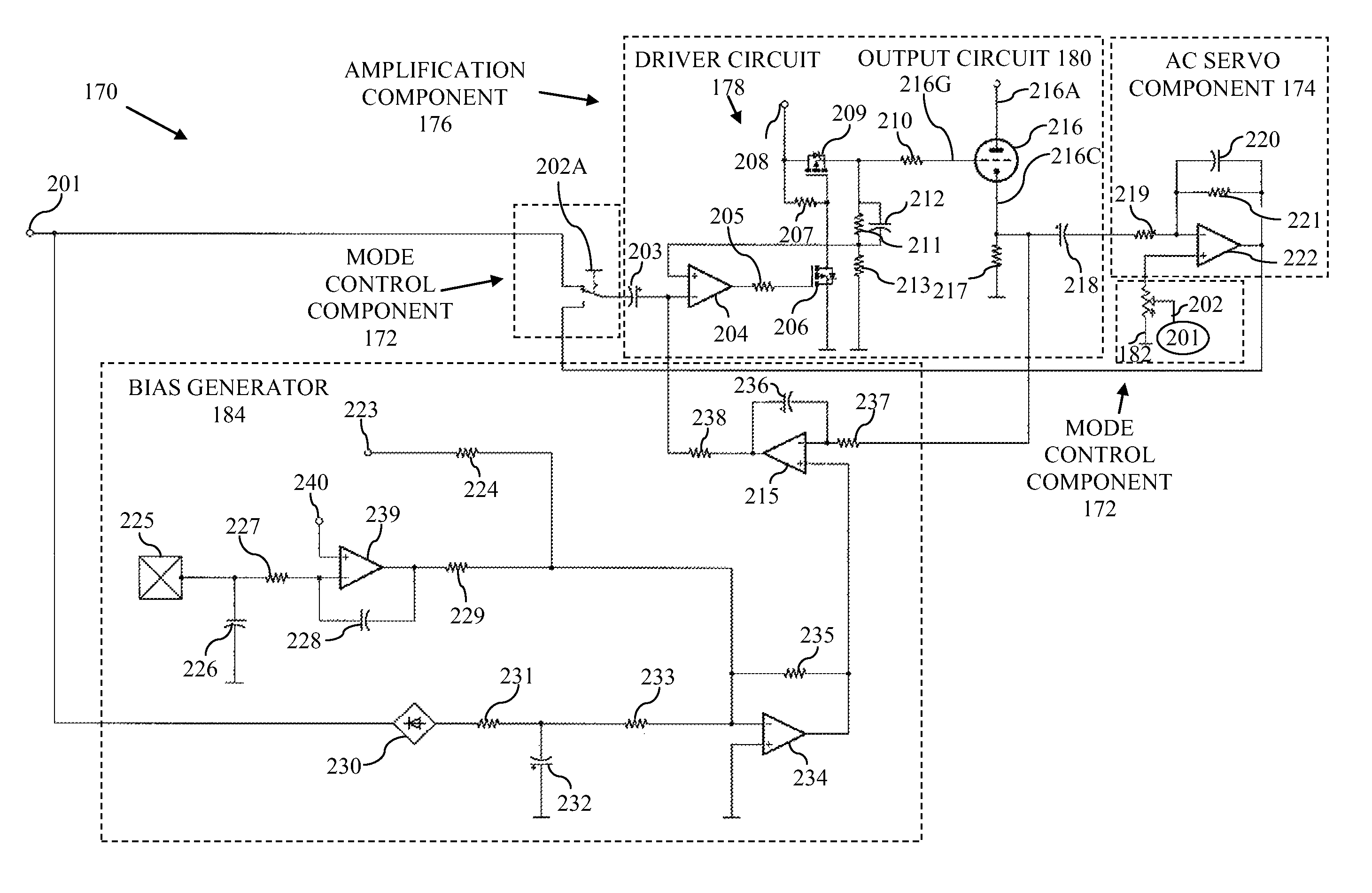
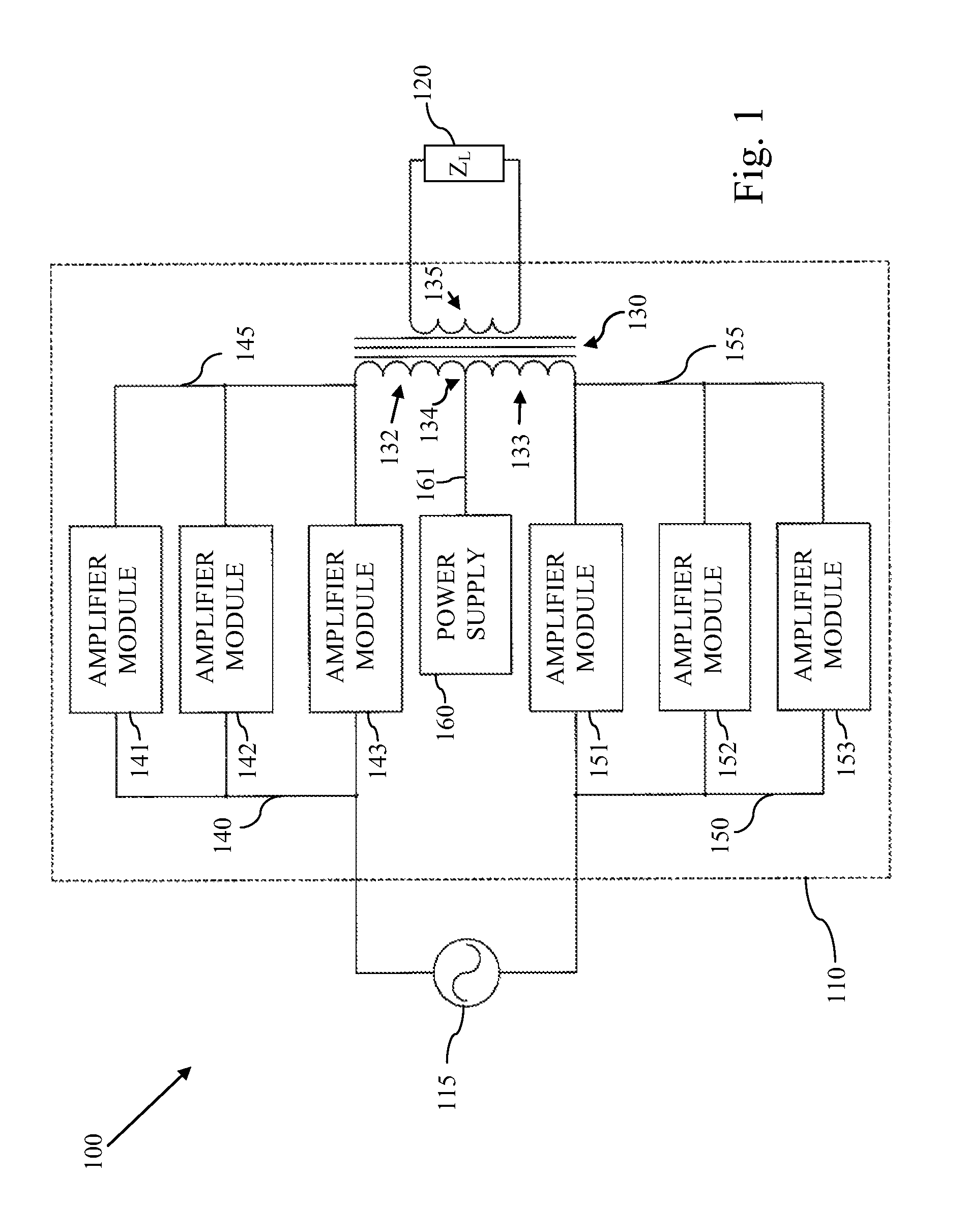
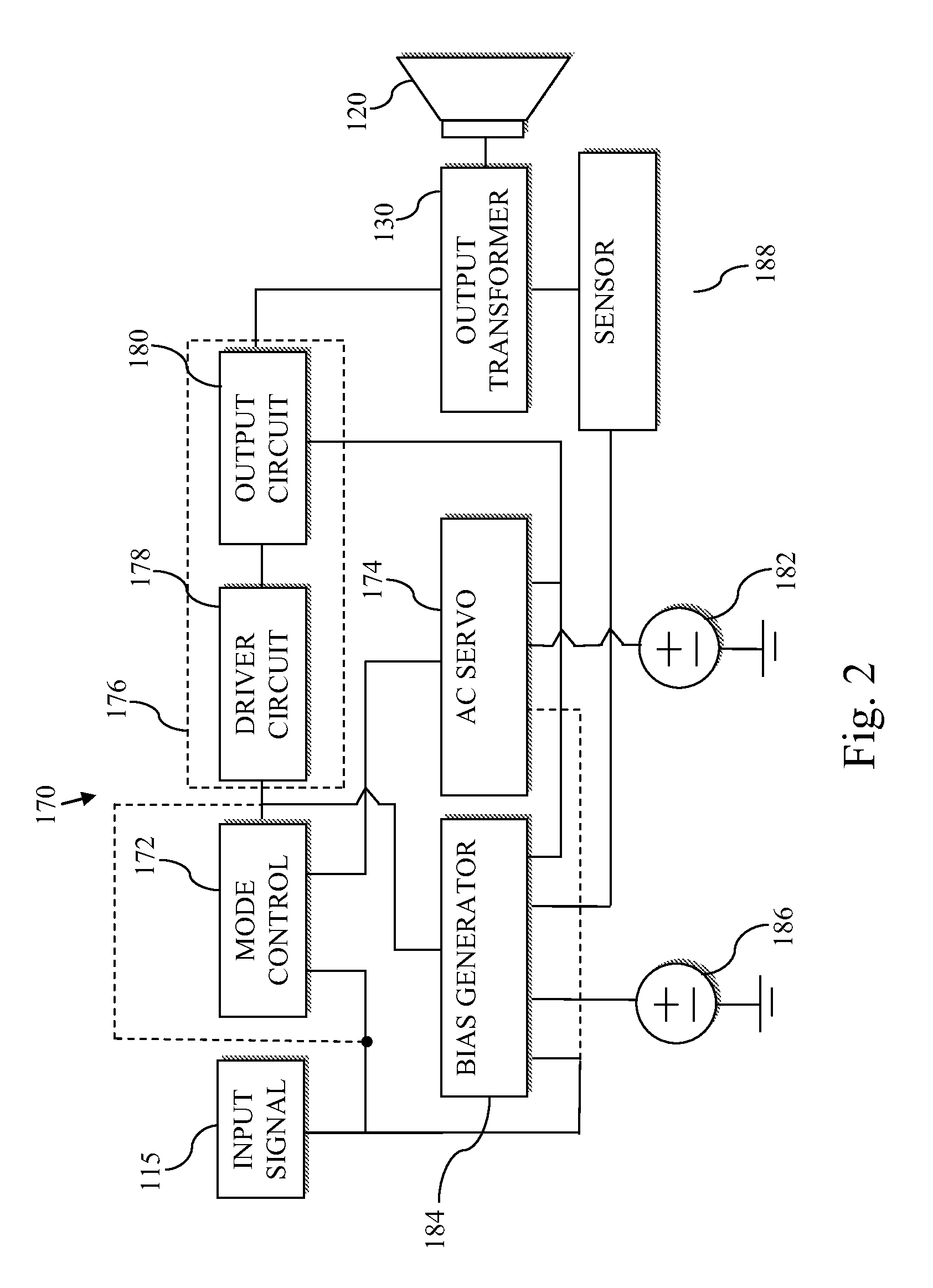
An amplifier is operable in push-pull mode, single-ended mode, or a composite mode that is an intermediate between single-ended and Push-pull modes. Moreover, at least one output device may be configured to operate using a high performance AC servo loop that functions the output device as a current source. Still further, a control input driver stage is provided that is capable of supplying sufficient AC current to overcome Miller capacitance induced roll off within the intended frequency spectrum of triode vacuum tubes. Additionally, methods are provided to substantially null or selectively introduce DC magnetic bias within the output transformer core. Still further, a solid state power supply stage provides substantial AC hum reduction during single-ended operation and simultaneously provides output voltage load regulation attributes similar to traditional vacuum tube rectifier circuits.
Owner:GIOVANNOTTO ROBERTO MICHELE
Multiple stage sequential current regulator
ActiveUS20120262075A1Eliminate needDc network circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesPower factorEngineering
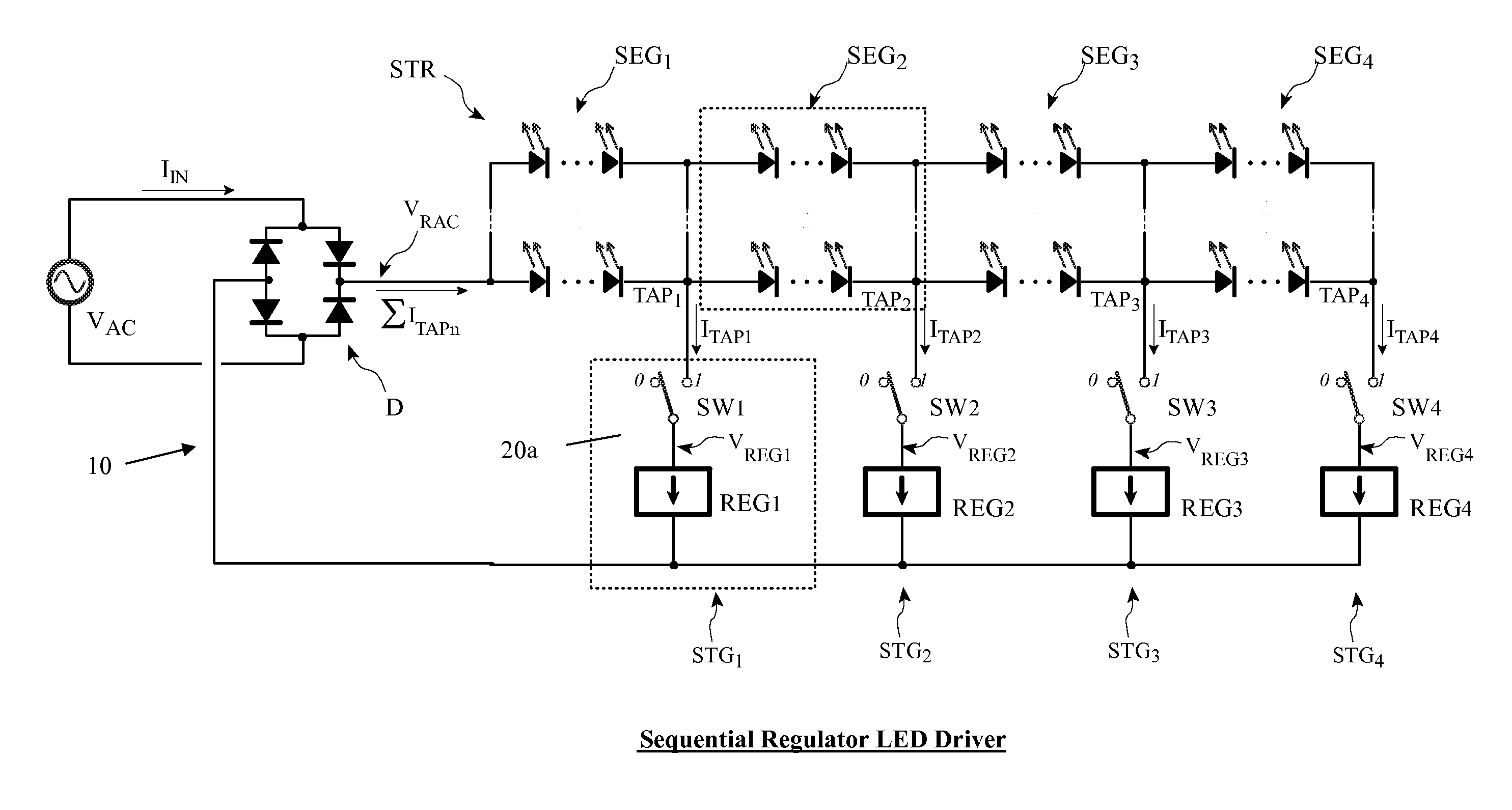
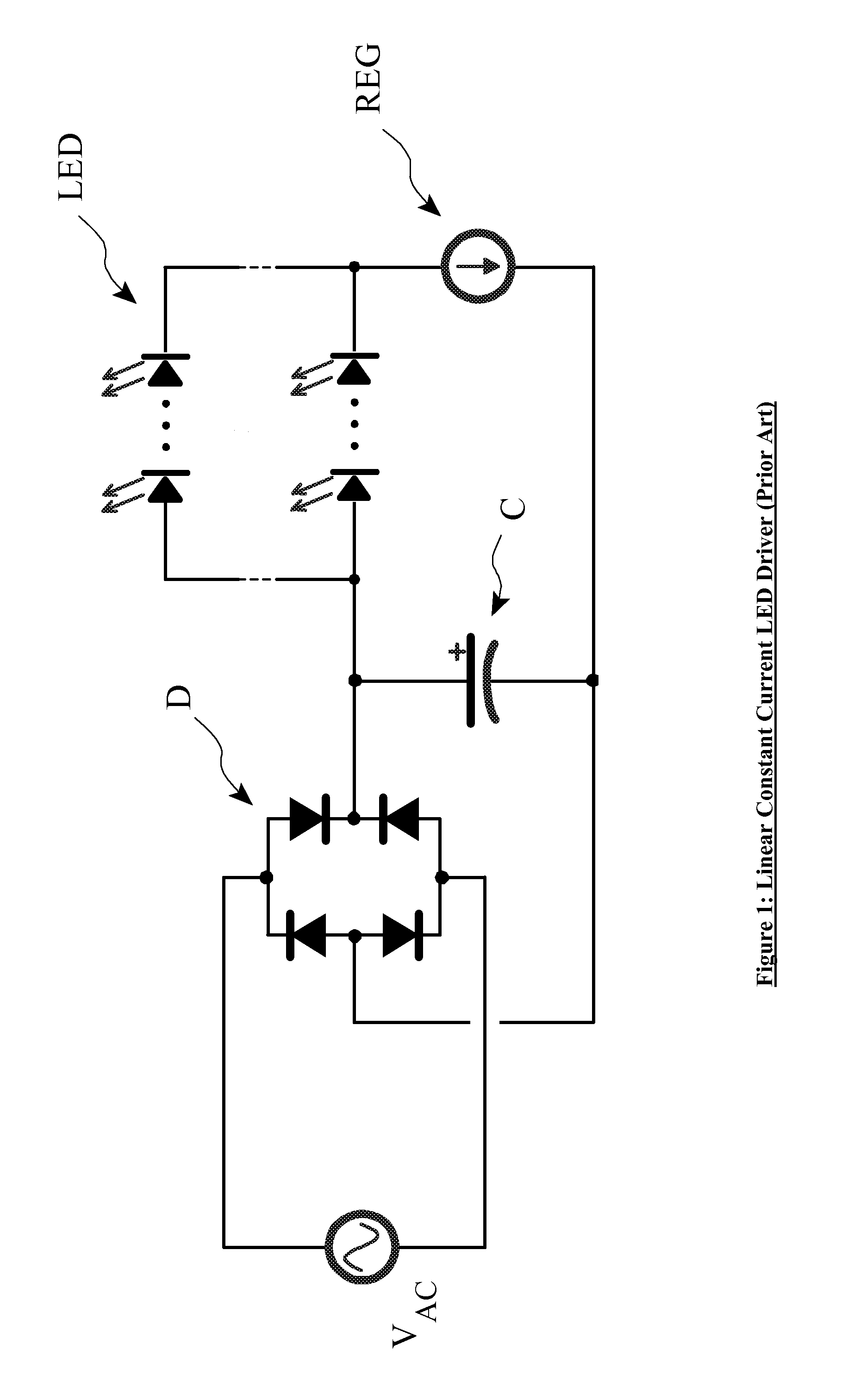
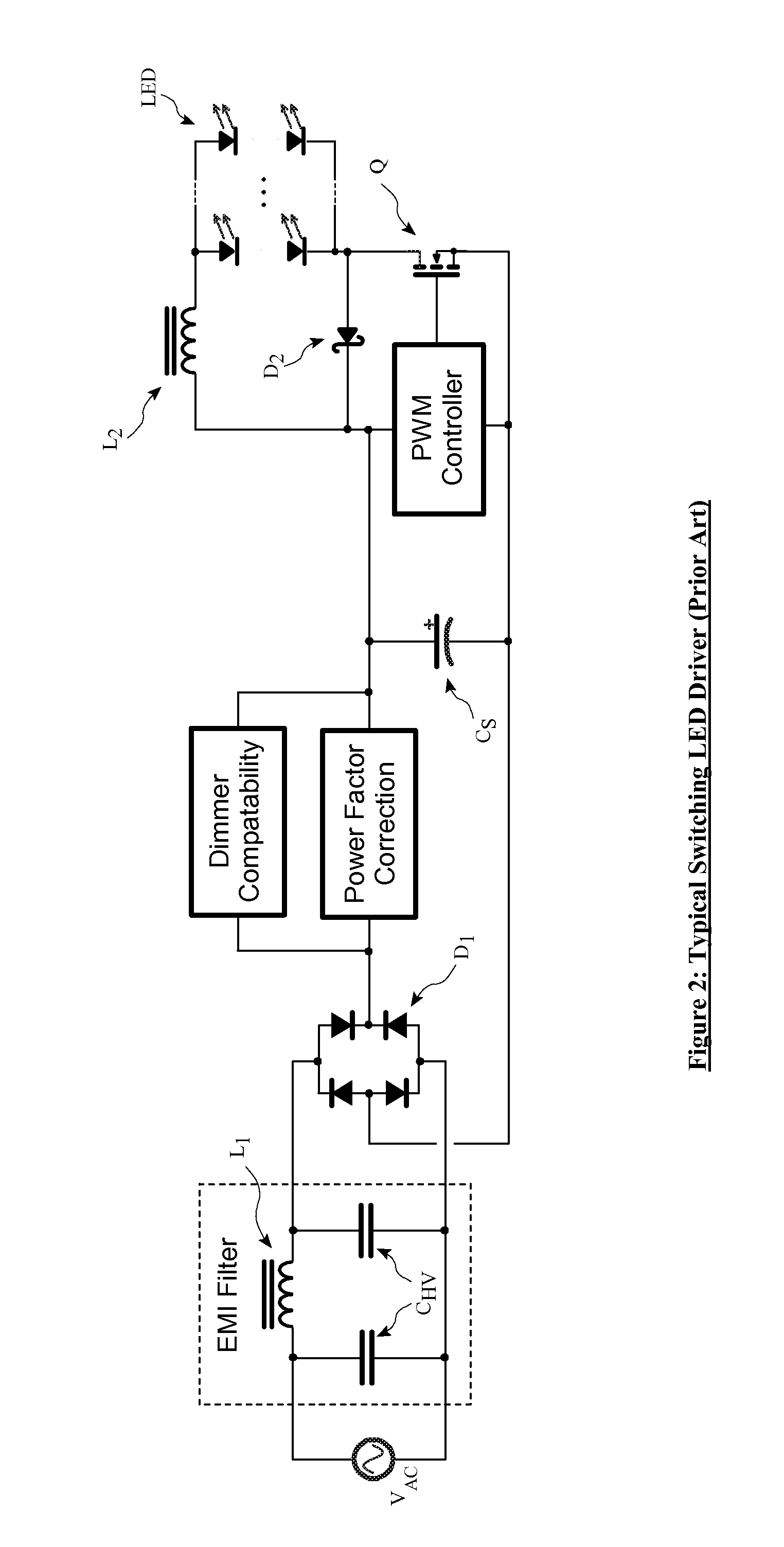
An LED driver circuit operating from the AC power line providing high efficiency, good line and load regulation, high power factor, low line current harmonics, low conducted EMI, high LED utilization, and lamp dimming compatibility, while consisting of a minimal number of components. No inductors, nor capacitors (including electrolytics), nor high current switching transistors are employed. The top of a string of series connected LED segments is connected to the output of a rectifier, which in turn is connected to an AC sine wave power source. The string is tapped at various locations, including the bottom of the string. Each segment can consists of any number of serial or parallel connected LEDs. Current control elements or regulators sink current at each tap and are sequentially turned on and off one at a time, tracking the rectified sine wave voltage. Voltage across each regulator and current when conducting is individually controllable. Power loss in the regulators is minimized by keeping regulator voltage to a minimum. The regulators may control current in a multitude of ways, including a constant current, or a current dependent on voltage across the regulators including a resistor, or a combination. The driver is self-commutating, with the sequencing of the current control elements an inherent feature closely integrated with the current control elements and providing optimal performance over variable operating conditions. Given the large number of design variables, the driver circuit can be optimized for various performance criteria including input voltage range, line / load regulation, output power / current, efficiency, power factor, line current harmonics, dimmer compatibility, and LED utilization.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS6366062B2Conversion without intermediate conversion to dcElectric variable regulationGalvanic isolationElectron
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a preferred embodiment is also disclosed herein. The preferred circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses four solid state switches, such as IGBT's, four diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:MICROPLANET
Source and multiple loads regulator
InactiveUS20120176826A1Maximise its operationImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalLoad balancing in dc networkEngineeringLoad regulation
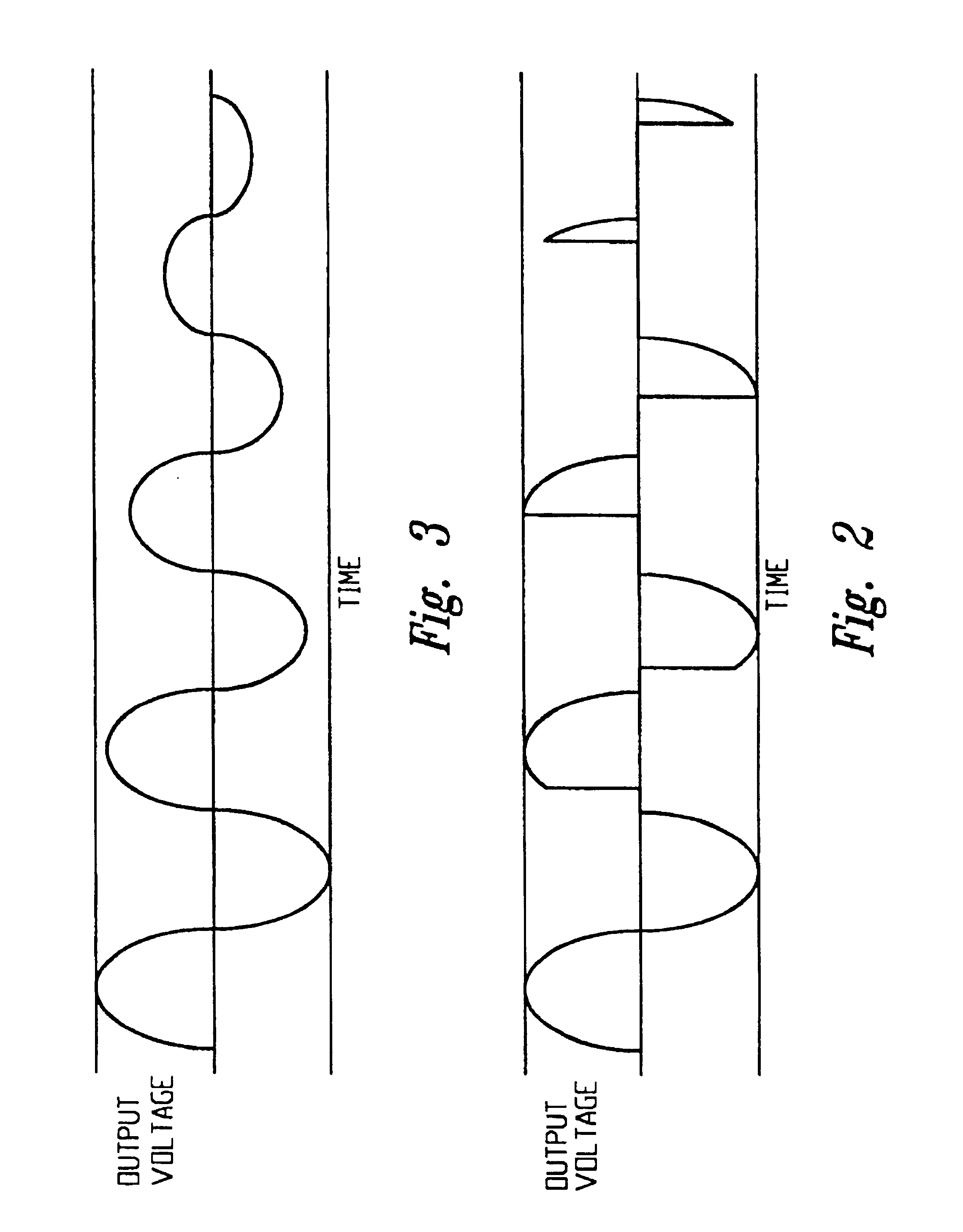
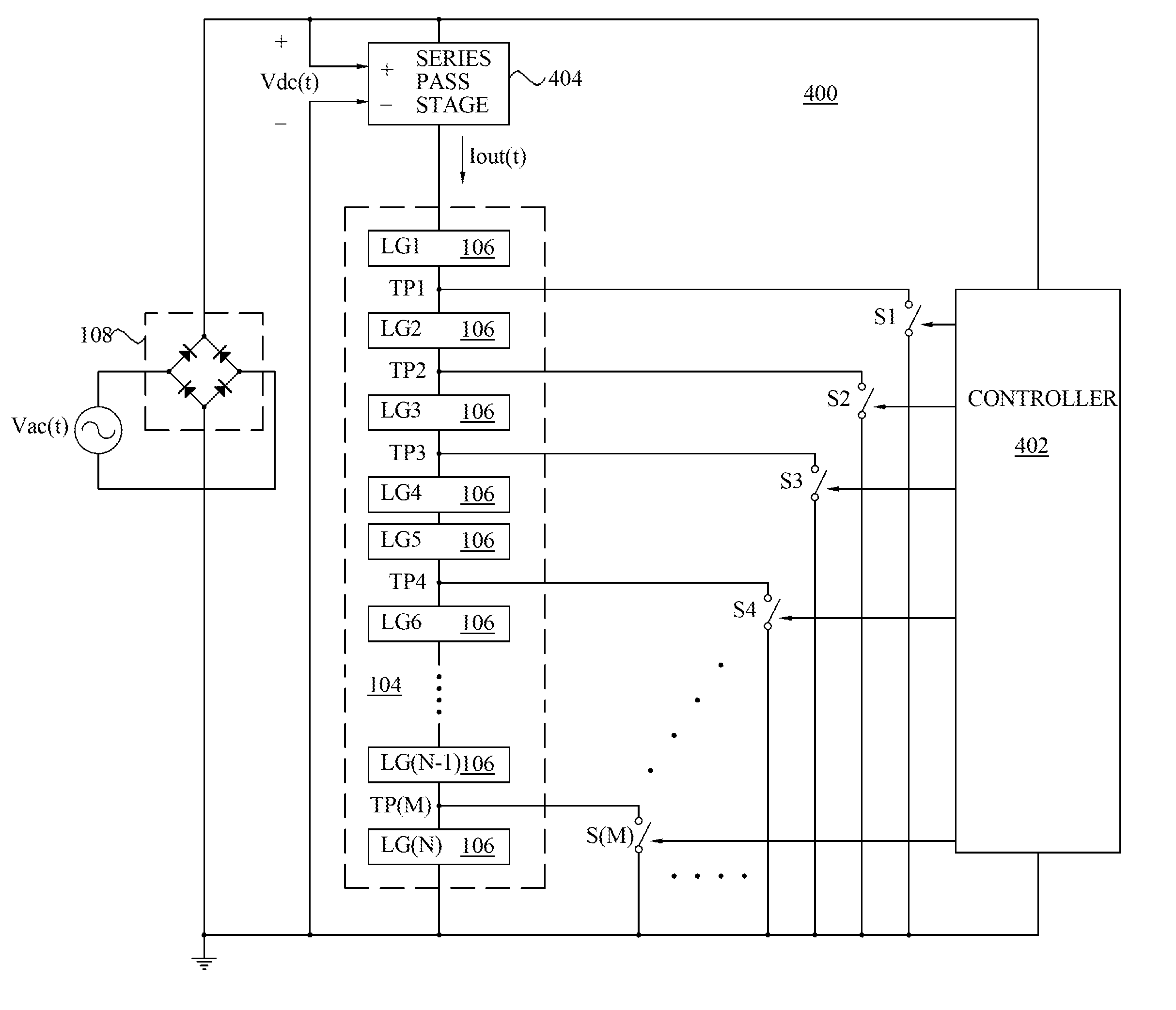
A circuit that has one or more control units that divide a load into two or more load groups, with each load group comprised of at least one load element. The one or more control units directing power from a power source to one or more of the load groups based on voltage variations in an output of the power source, load grouping, and operational parameters of the load elements. The circuit further includes one or more pass stages that regulate current flow from the power source to the load groups.
Owner:BRAXTON ENG
General-purpose automatic test system for locomotive switching power supply and method thereof
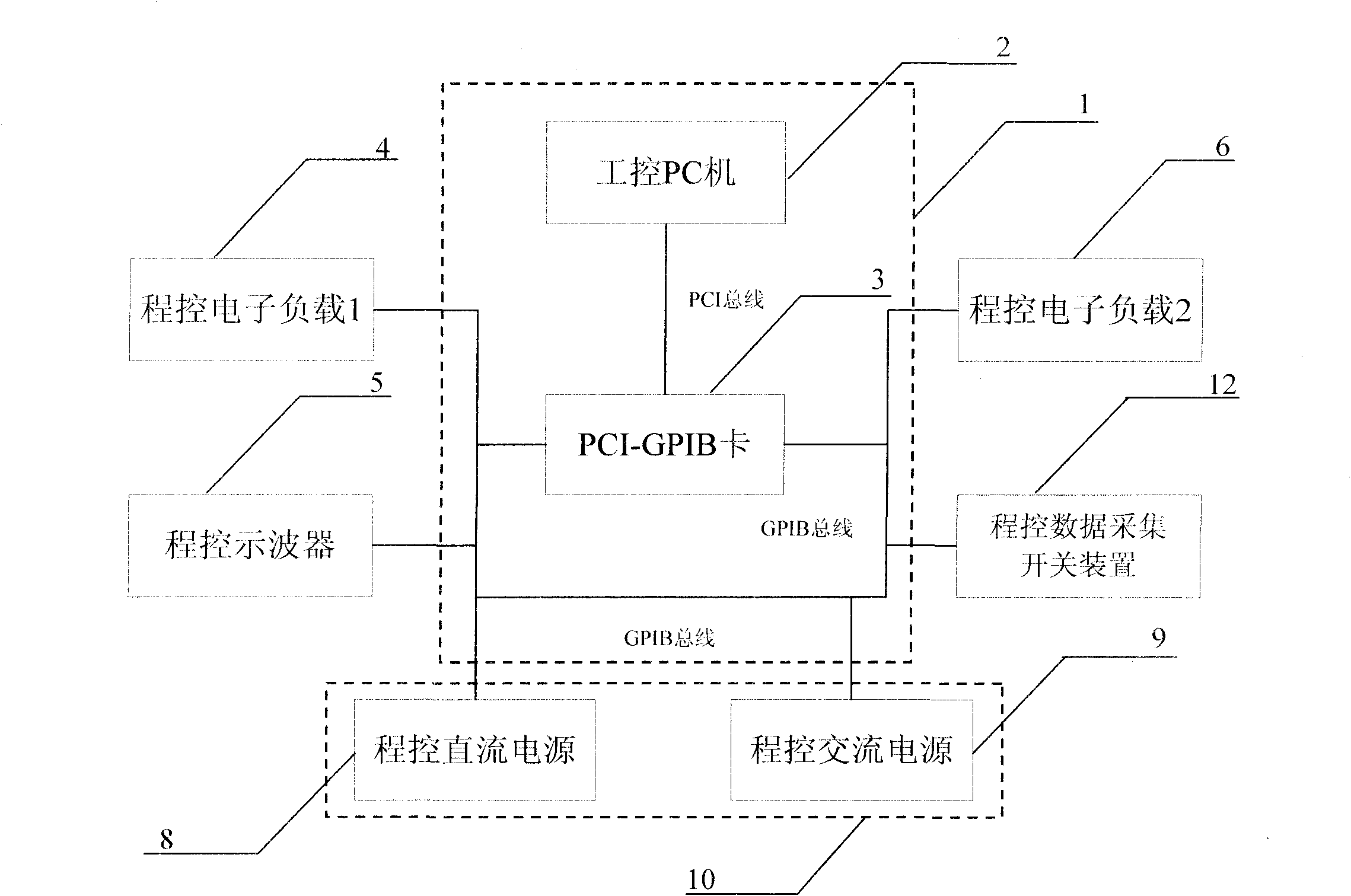
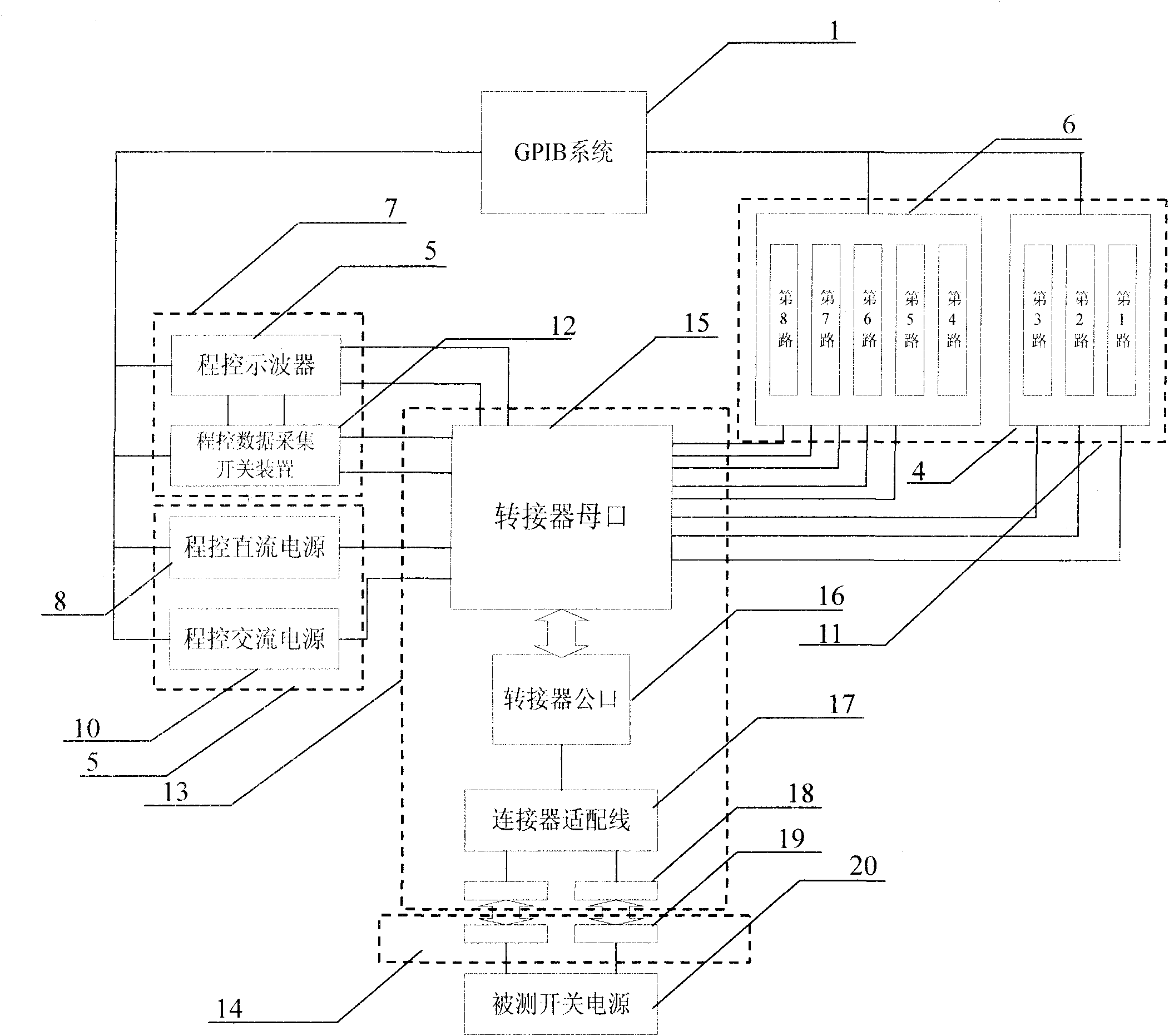
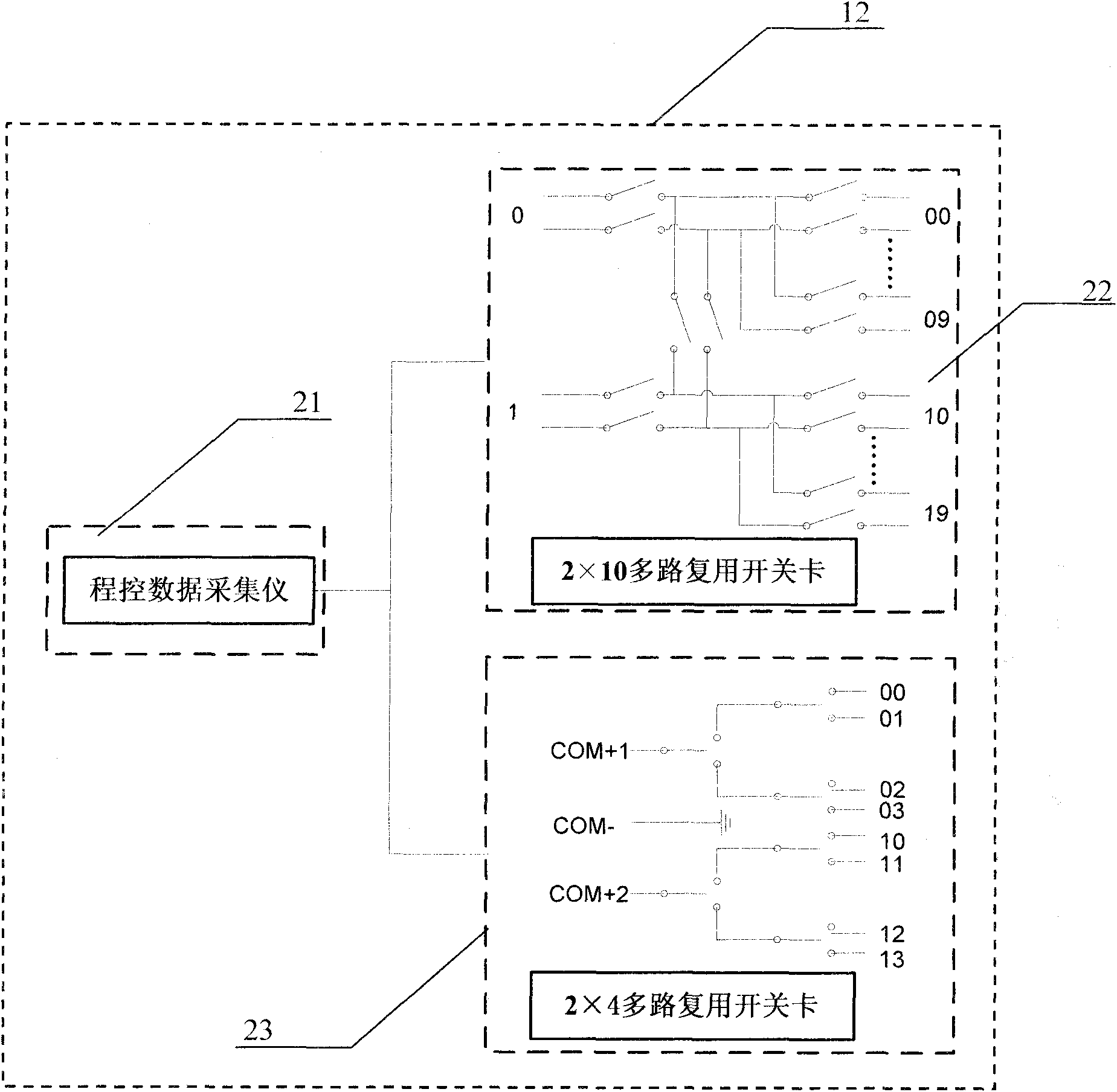
The invention relates to a general-purpose automatic test method for a locomotive switching power supply, and general-purpose automatic test system, and comprises a test control system, a programmable power supply unit, a programmable DC load unit and a programmable data acquisition unit, wherein the programmable power supply unit is connected with the test control system through a GPIB bus and provides excitation for the tested switching power supply; the programmable DC load unit is connected with the test control system through the GPIB bus and provides a load for the switching power supply to be tested; and the programmable data acquisition unit is connected with the test control system through the GPIB bus and acquires responses of the tested switching power supply. The output voltage, voltage regulation factor, load regulation factor and the like are tested by logging in virtual instrument software on a personal computer. The invention can well overcome the defects of insufficient compatibility, high complexity and low reliability of the test system in the prior art, and has the advantages of automation, general purpose, convenient operation and reliable performance.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS20070052397A1Low in electricalLight weightEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringGalvanic isolation
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a specific embodiment is also disclosed herein. The specific circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses eight solid state switches, such as IGBT's, eight diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. Indeed, the eight-switch controller can act to either buck or boost the input voltage, and can switch between bucking and boosting during a cycle, thus providing more control of the regulated output voltage. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:MICROPLANET
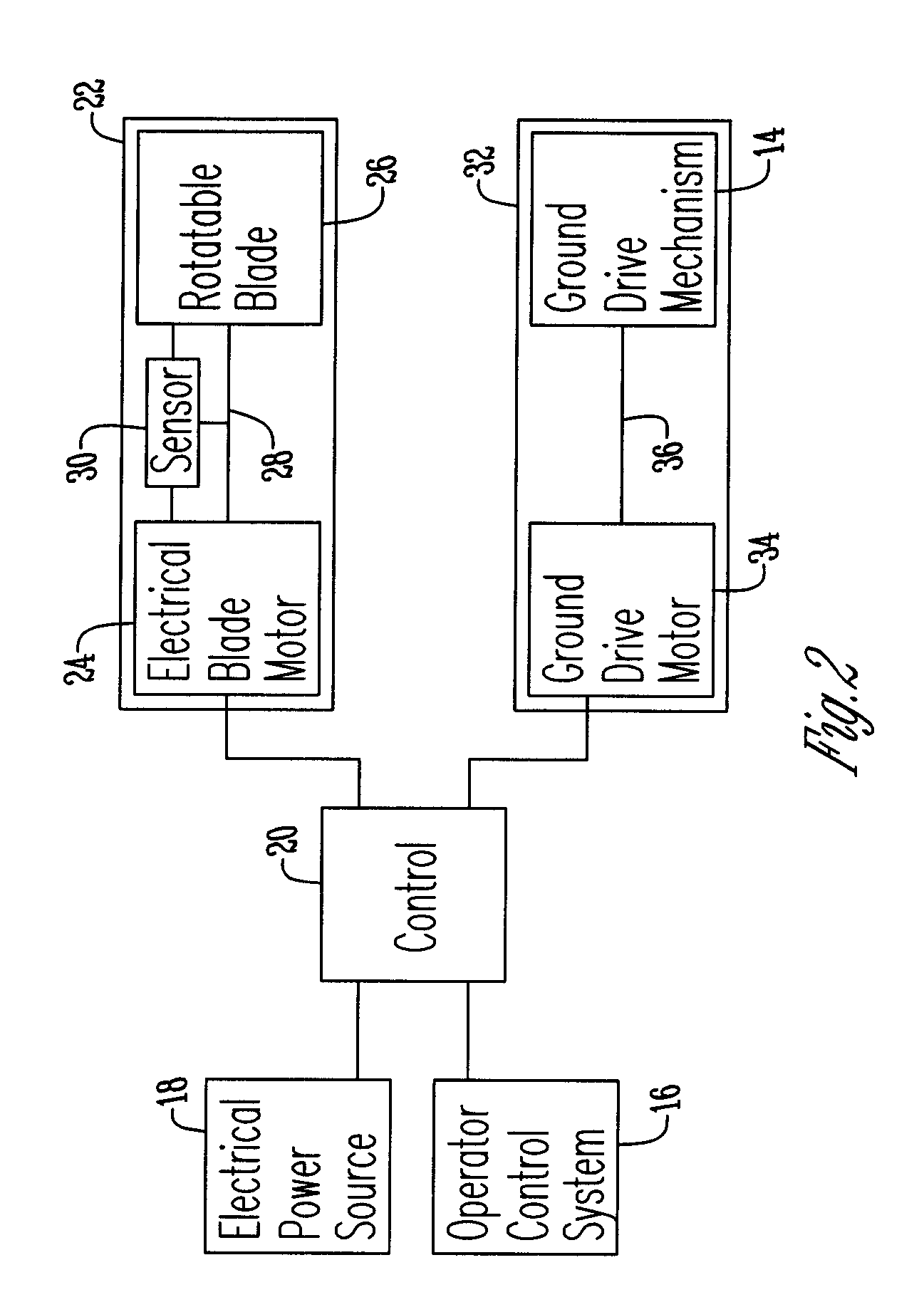
Means of adjusting ground speed of a vehicle based on load on blade assembly
An assembly having a frame supported by a plurality of ground engaging wheels. Mounted to the frame is an operator control system that is connected to a controller that is powered by an electrical source. The controller is operatively connected to a blade assembly and a ground drive assembly and adjusts the ground speed of the assembly based upon the cutting load of the blade.
Owner:SAUER DANFOSS NORDBERG
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS7102334B2Low in electrical and audible noiseLight weightEfficient power electronics conversionAc-ac conversionGalvanic isolationPower control
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a preferred embodiment is also disclosed herein. The preferred circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses four solid state switches, such as IGBT's, four diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:MICROPLANET
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS20030052658A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-ac conversionEngineeringGalvanic isolation
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a preferred embodiment is also disclosed herein. The preferred circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses four solid state switches, such as IGBT's, four diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:BARETICH DAVID F +1
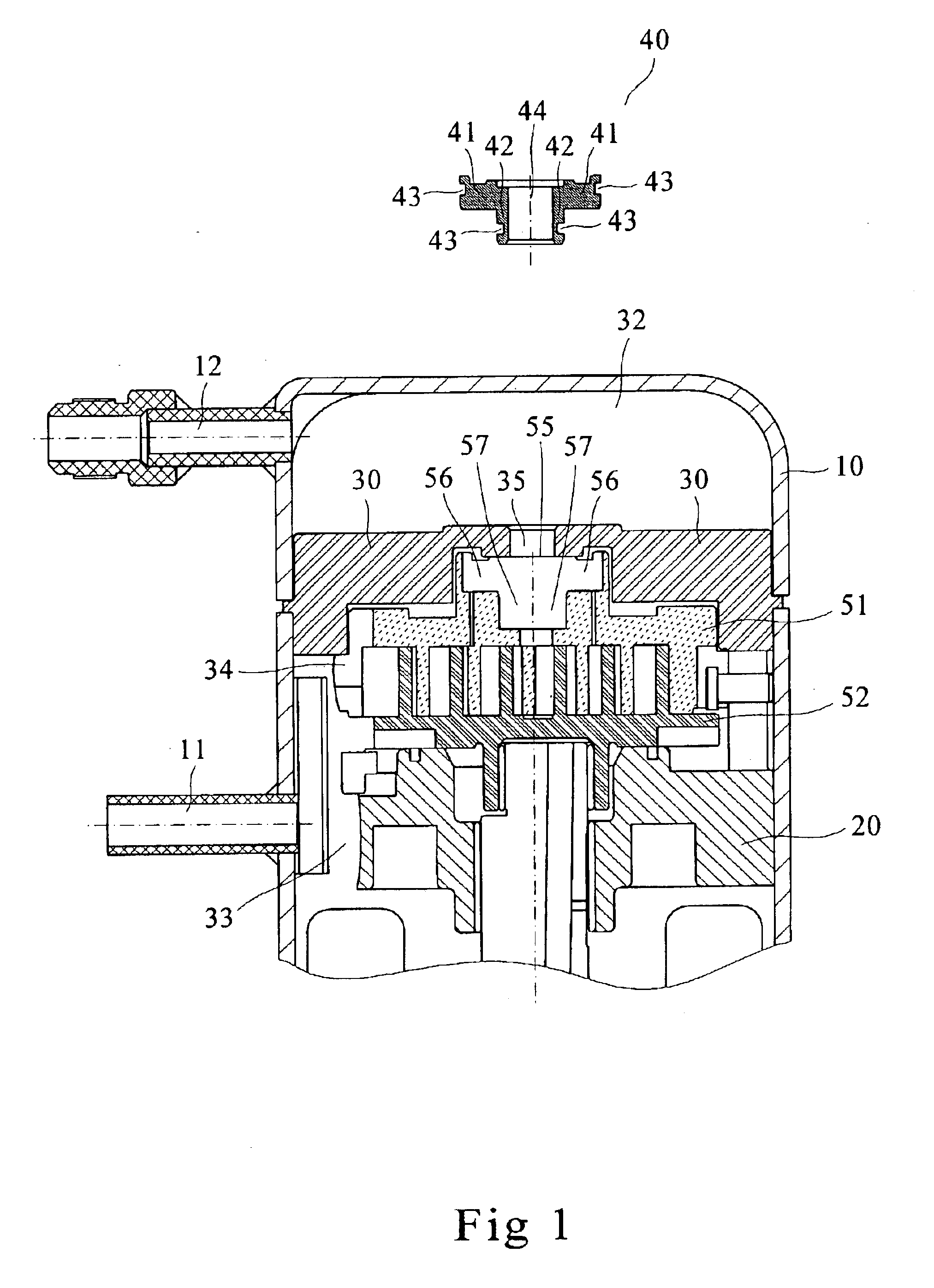
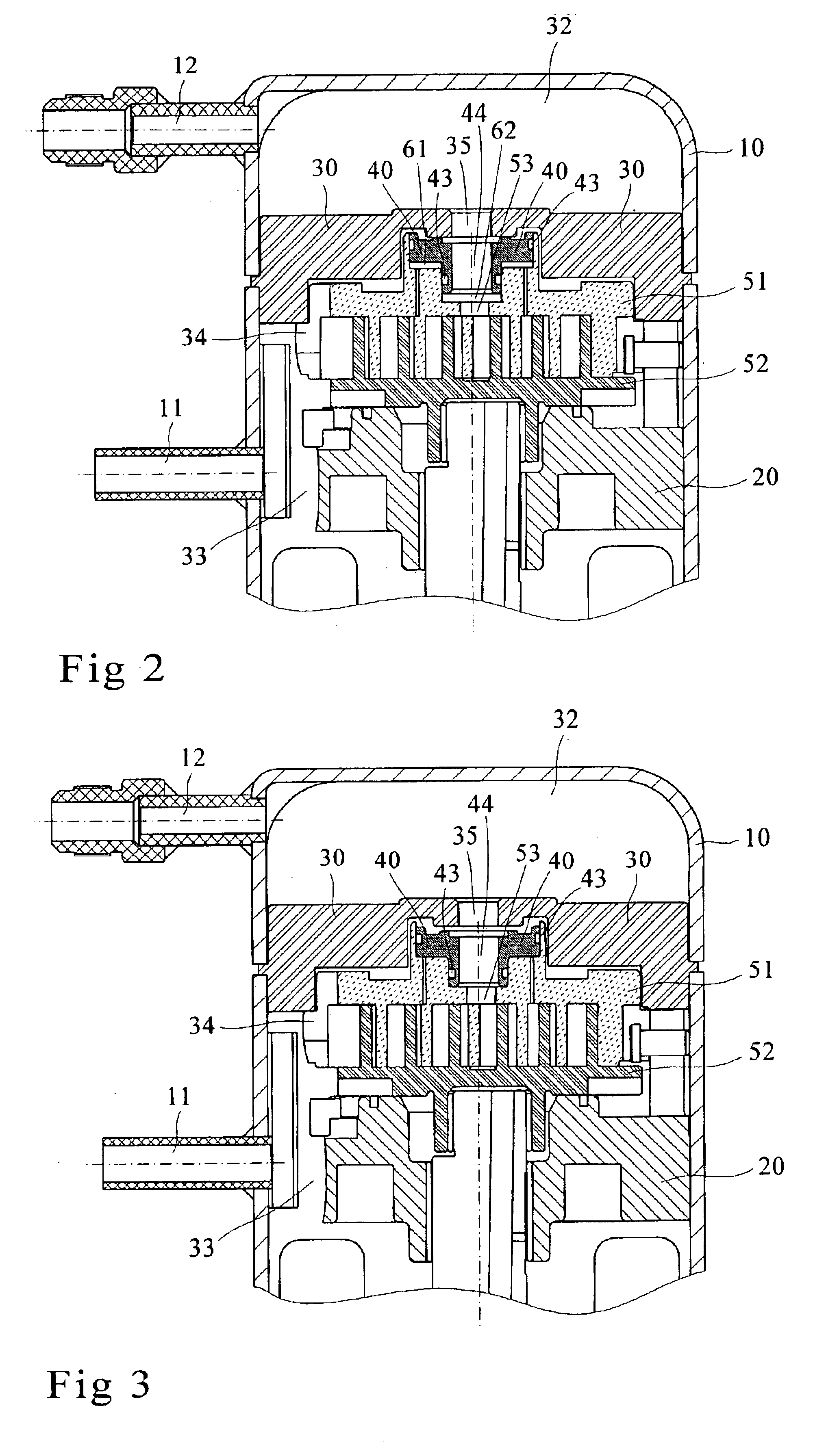
Load-regulating device for scroll type compressors
InactiveUS6913448B2Quickly build up pressurePrevent leakageEngine of arcuate-engagement typeOscillating piston enginesEngineeringLoad regulation
A load-regulating device for scroll type compressors comprising a compressor housing, a bracket body, a partition block, a gliding block, a pair of scrolls and a plurality of air chambers, wherein the gliding block being coupled with the pair of scrolls for defining a plurality of air chambers on the scrolls, the pressure variation in the air chambers is then utilized for causing the motion of the gliding block, enabling the compressor to cause the gliding block by means of the pressure variation to motion upwardly as the compressor is actuated, and preventing the fluid in the high-pressure chamber from leaking towards the low-pressure chamber, thus allowing the compressors to quickly build up the pressure; the gliding block is caused by the pressure variation to motion downwardly at times when the compression ratio is excessively high, so as to relieve part of the load, thus improving the performance and reliability of the compressors.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and system for engine control
ActiveUS8100107B2Improve cooling effectImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesFuel type
Methods and systems are provided for controlling exhaust emissions by adjusting a fuel injection into an engine cylinder from a plurality of fuel injectors based on the fuel type of the injected fuel and further based on the soot load of the engine. Soot generated from direct fuel injection is reduced by decreasing an amount of direct injection into a cylinder as the engine soot load increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Advanced resistive exercise device
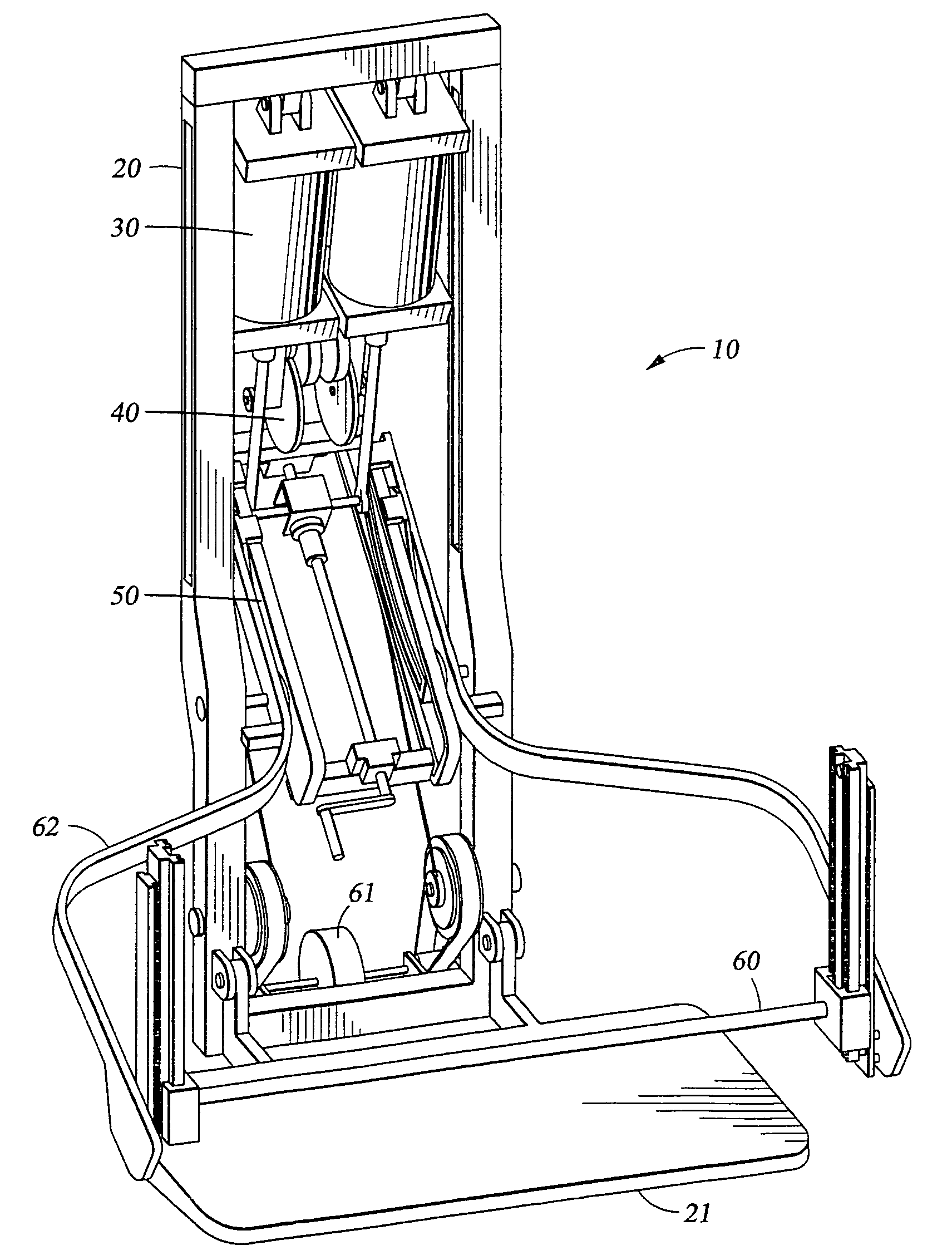
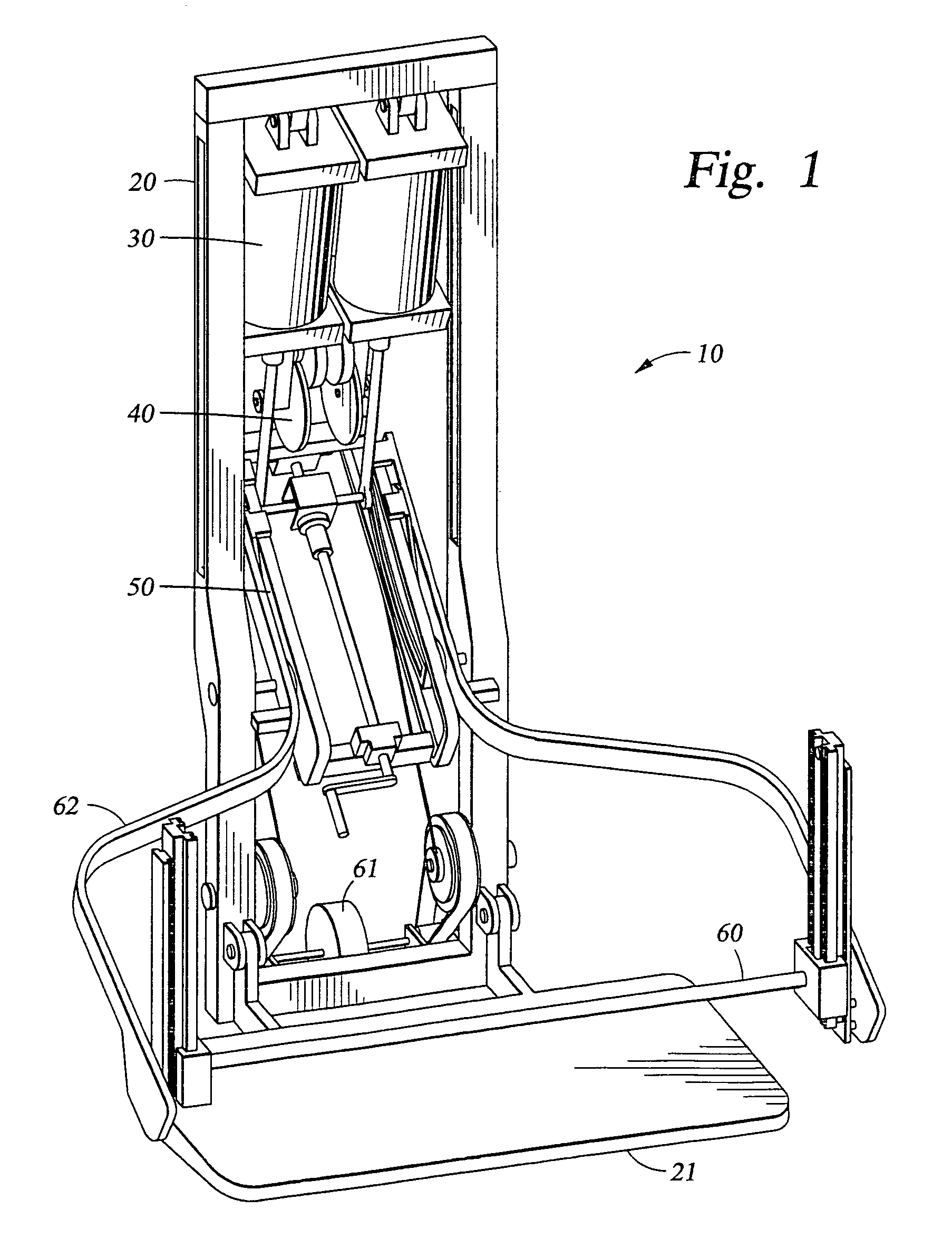
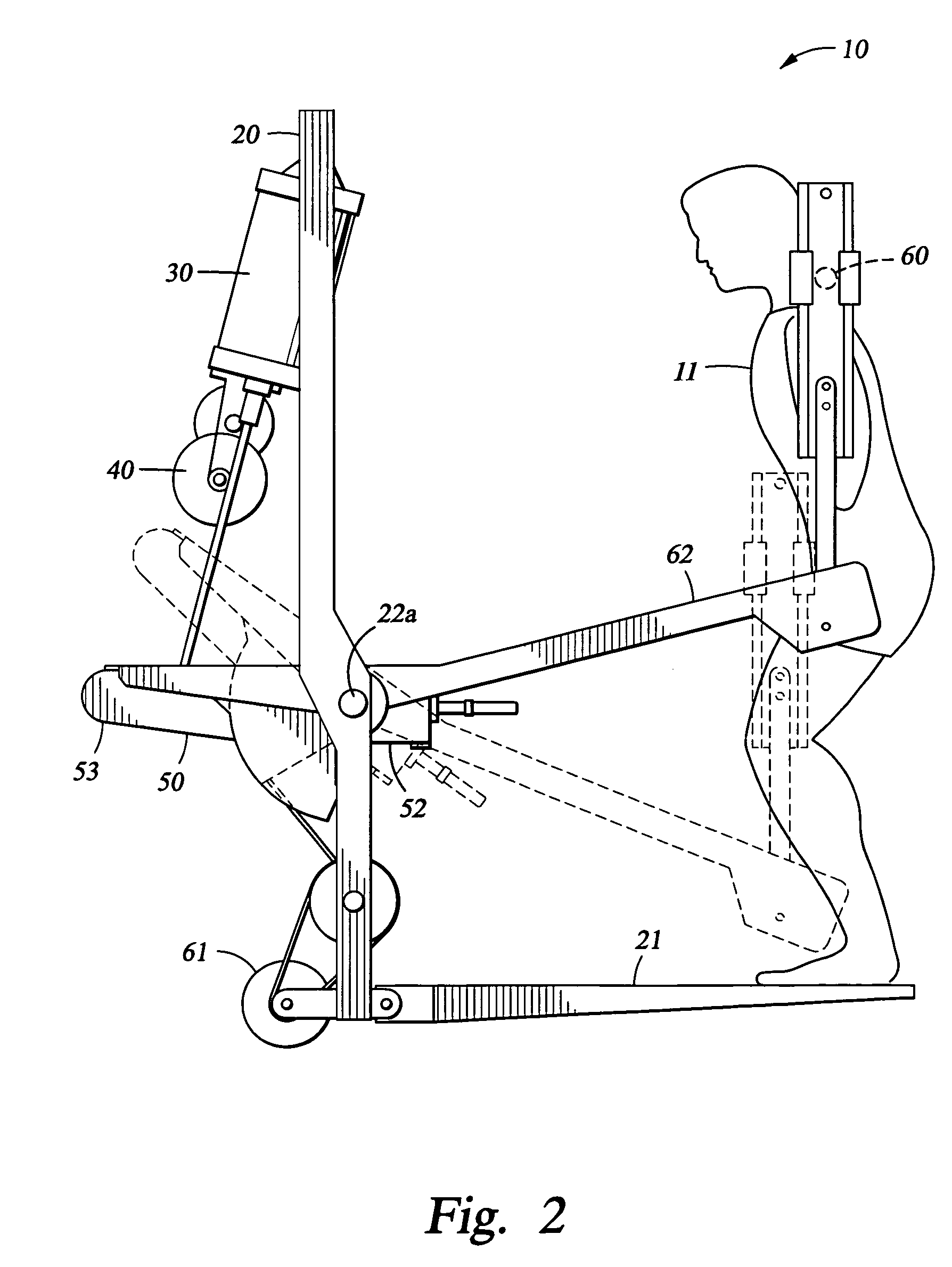
InactiveUS7462141B1Reduce quality problemsMinimal maintenanceTherapy exerciseMuscle exercising devicesResistive exerciseEngineering
The present invention relates to an exercise device, which includes a vacuum cylinder and a flywheel. The flywheel provides an inertial component to the load, which is particularly well suited for use in space as it simulates exercising under normal gravity conditions. Also, the present invention relates to an exercise device, which has a vacuum cylinder and a load adjusting armbase assembly.
Owner:NASA
Exercise machine
Owner:TECHNOGYM SPA
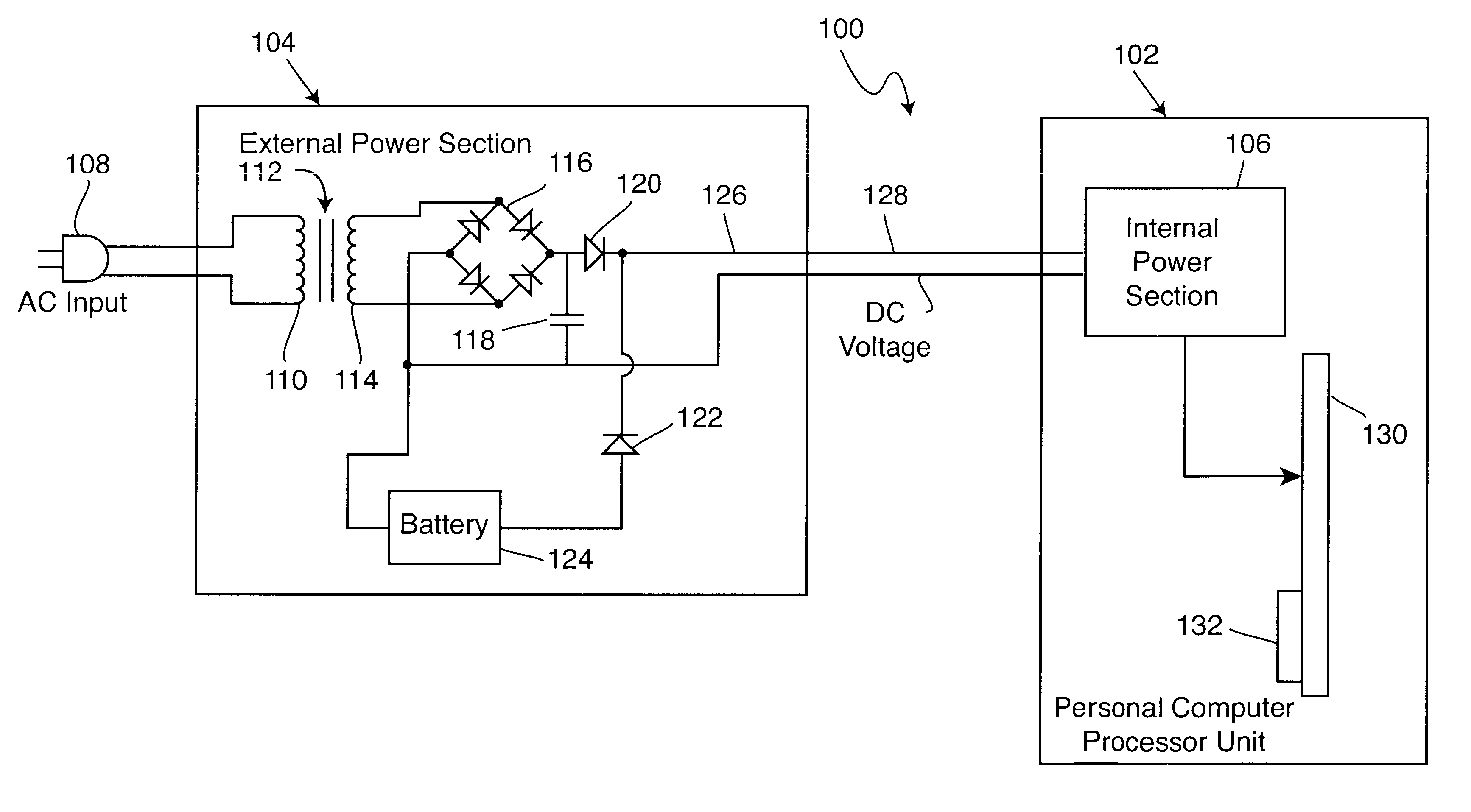
Electronic power supply for personal computer and method
InactiveUS6445086B1Low efficiencyMinimize distortionBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectrical batteryOutput device
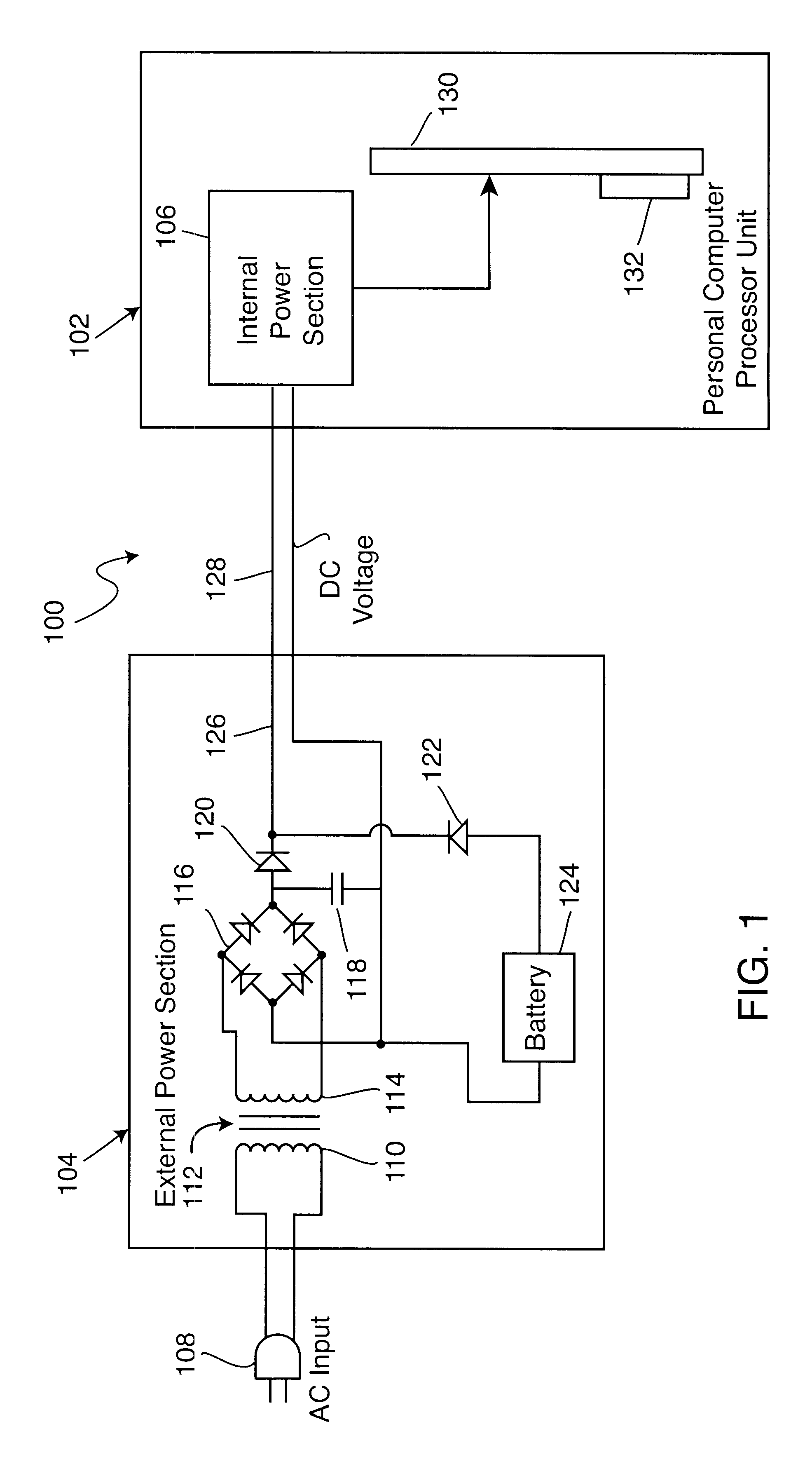
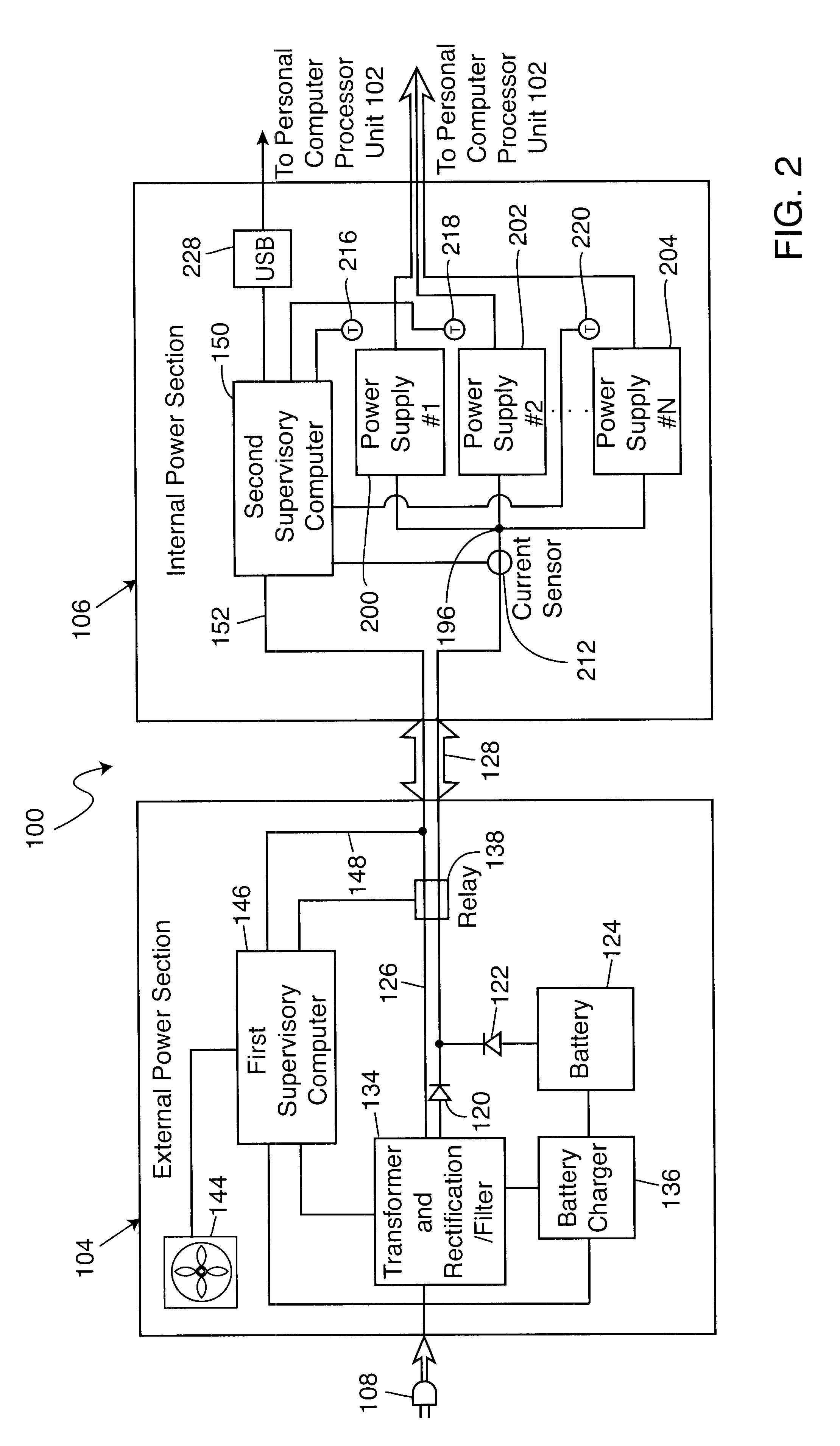
An electronic power supply for use with a personal computer exhibits a construction including an external power section located exterior to a personal computer and including a direct current voltage source in combination with a battery source for providing a load adjusted direct current voltage. A first supervisory computer is connected to the direct current voltage source and the battery source for controlling the load adjusted direct current voltage. An internal power section is located interior to the personal computer and in electrical contact with the external power section. The internal power section comprises a plurality of voltage output devices for providing a plurality of direct current output voltages. A second supervisory computer is connected to the plurality of voltage output devices for controlling the plurality of direct current output voltages distributed to the personal computer. A signal communication link exists between the second supervisory computer and the first supervisory computer.
Owner:HOUSTON DAVID H
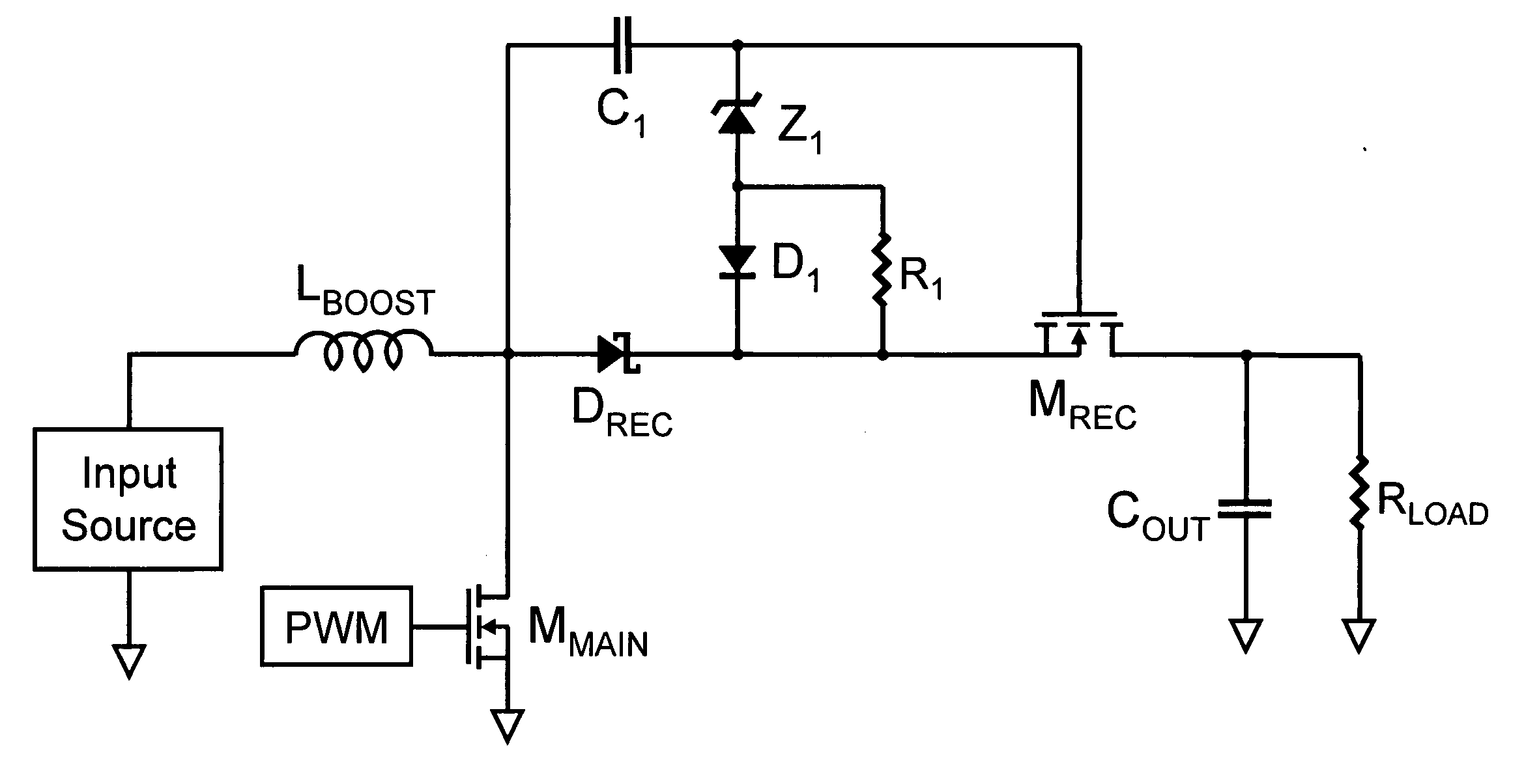
High efficiency power conversion circuits
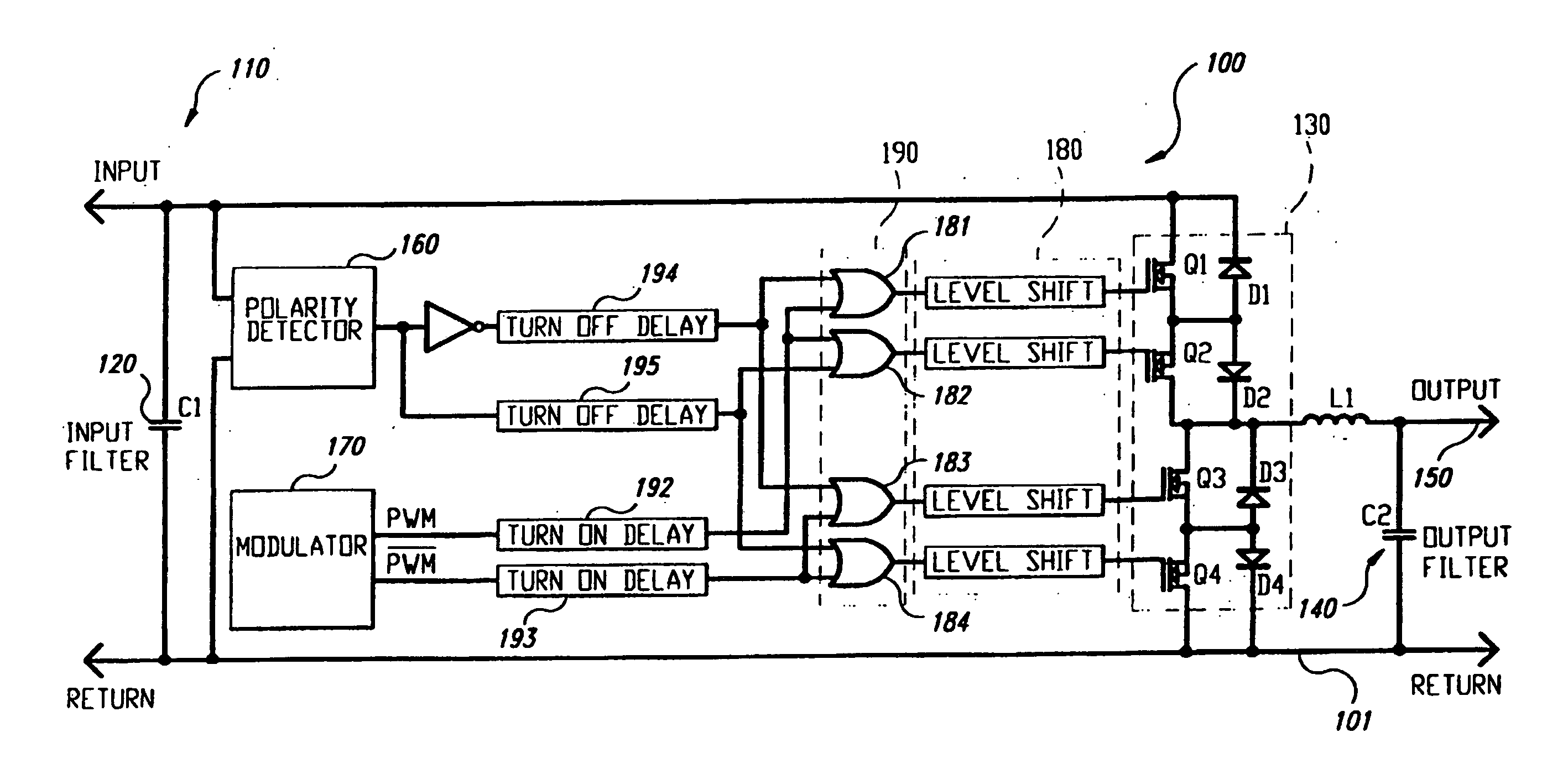
InactiveUS20060062026A1Easy to handleReduce winding voltage stress stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLevel shiftingFull bridge
A composite high voltage schottky rectifier is revealed that provides a forward voltage slightly larger than a low voltage schottky rectifier combined with a high voltage breakdown capability. The composite rectifier can be formed from the combination of a low voltage schottky rectifier, a high voltage mosfet, and a few small passive components. A quarter bridge primary switching network similar in some ways to a half bridge primary switching network is revealed. The quarter bridge network consists of four switches with voltage stress equal to half the line voltage and the network applies one quarter of the line voltage to a primary magnetic circuit element network thereby reducing the number of primary winding turns required to one quarter by comparison to a common full bridge network. A synchronously switched buck post regulator is revealed for multi-output forward converters. The synchronously switched buck post regulator accomplishes precise independent load regulation for each output and reduced magnetics volume by using a coupled inductor with a common core for all outputs plus a second smaller inductor for each output except the highest voltage output. An improved capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is revealed that provides an effective drive mechanism for a floating or high side switch without the use of level shifting circuits or magnetic coupling. The capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is an improvement over prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits in that the new circuit uses a positive current feedback mechanism to reject slowly changing voltage variations that cause unintentional switch state changes in prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
Simplified current sense for buck LED driver
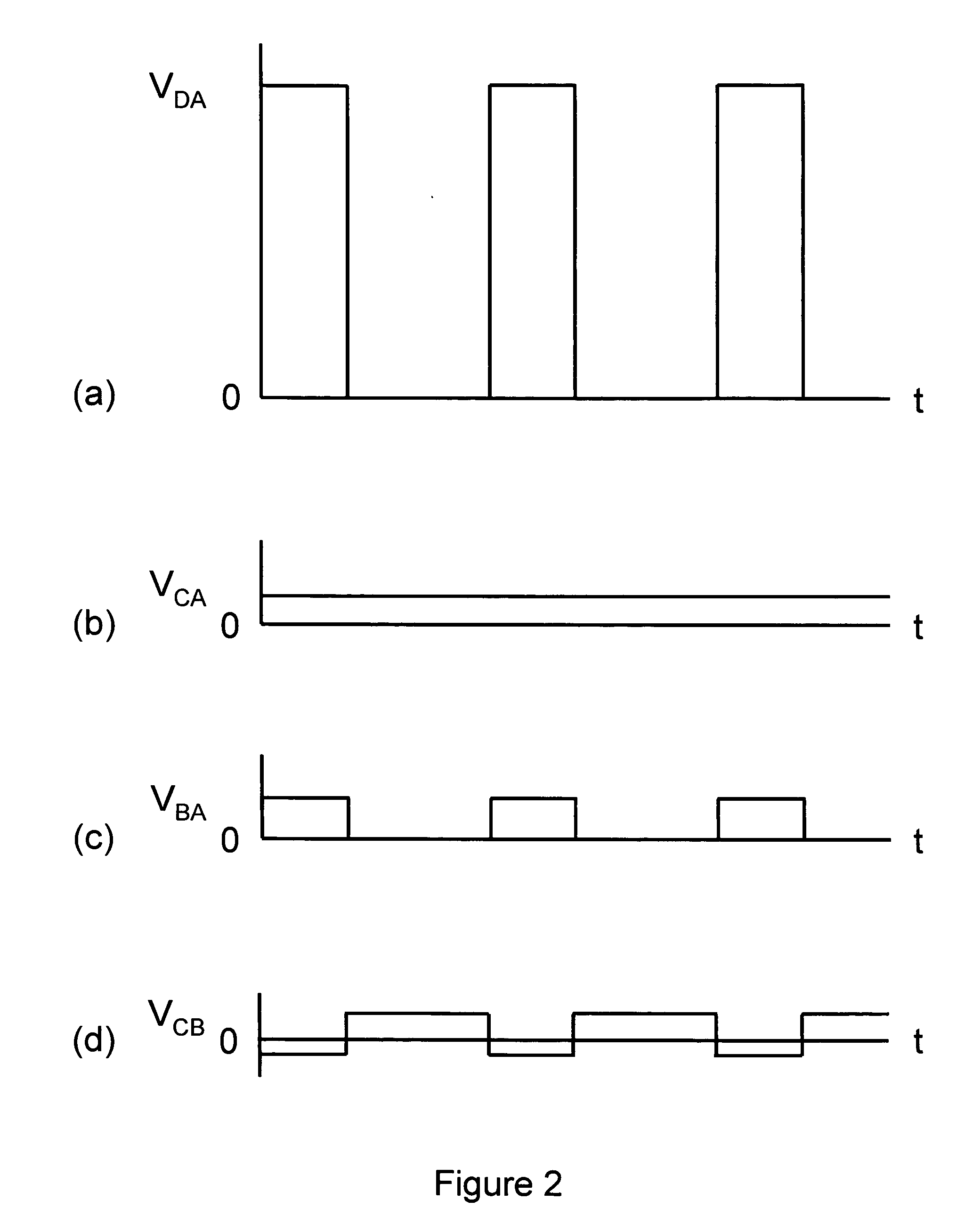
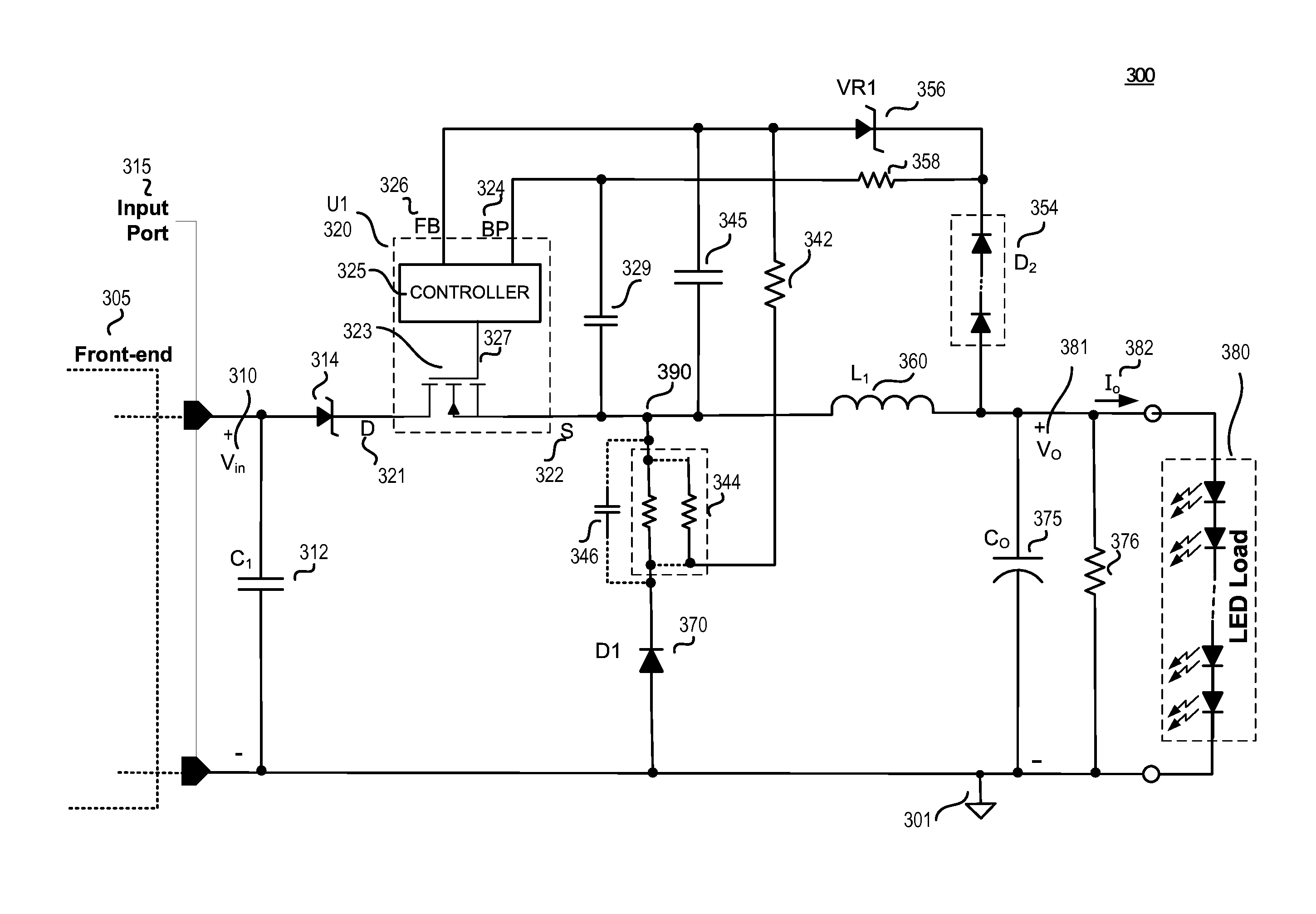
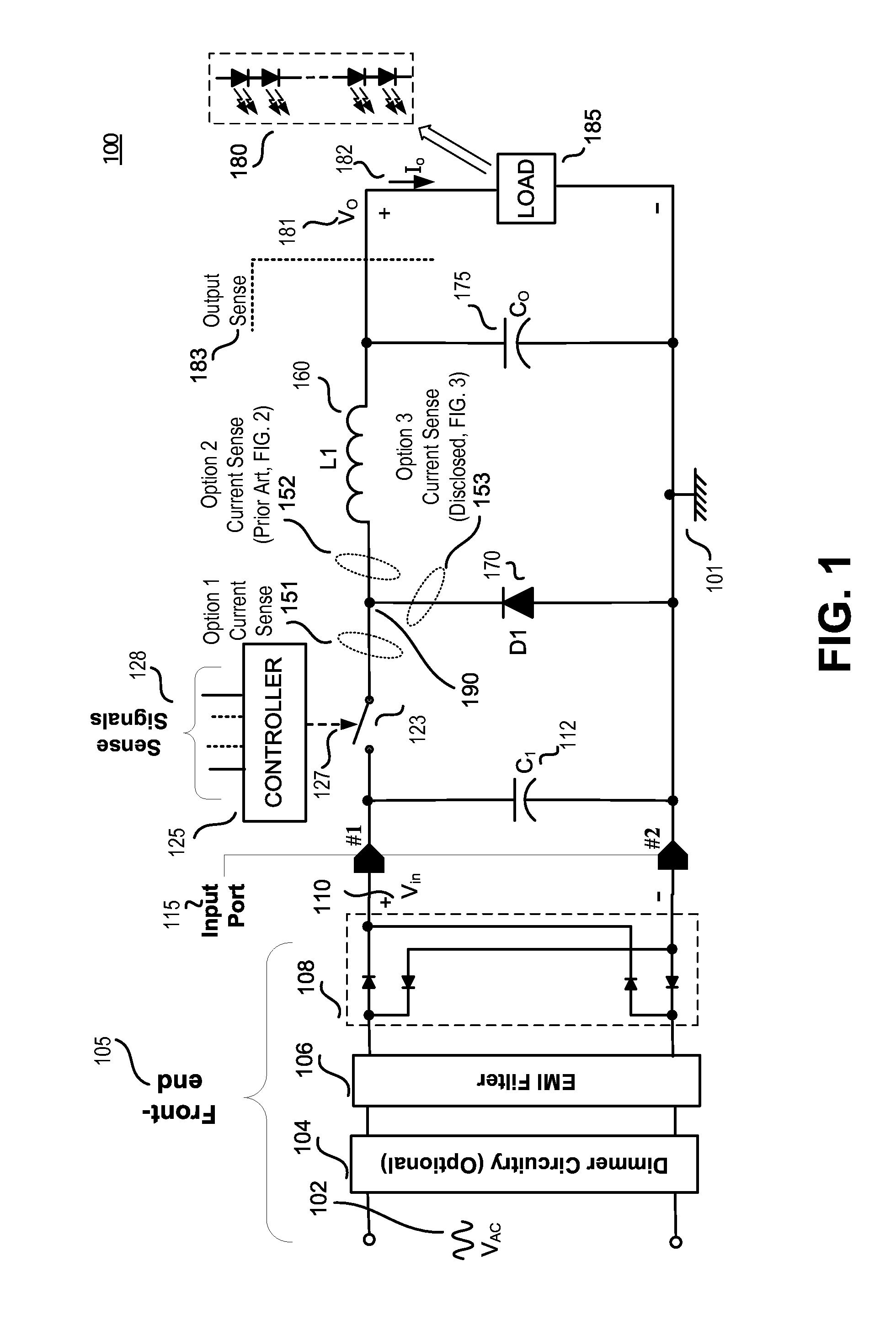
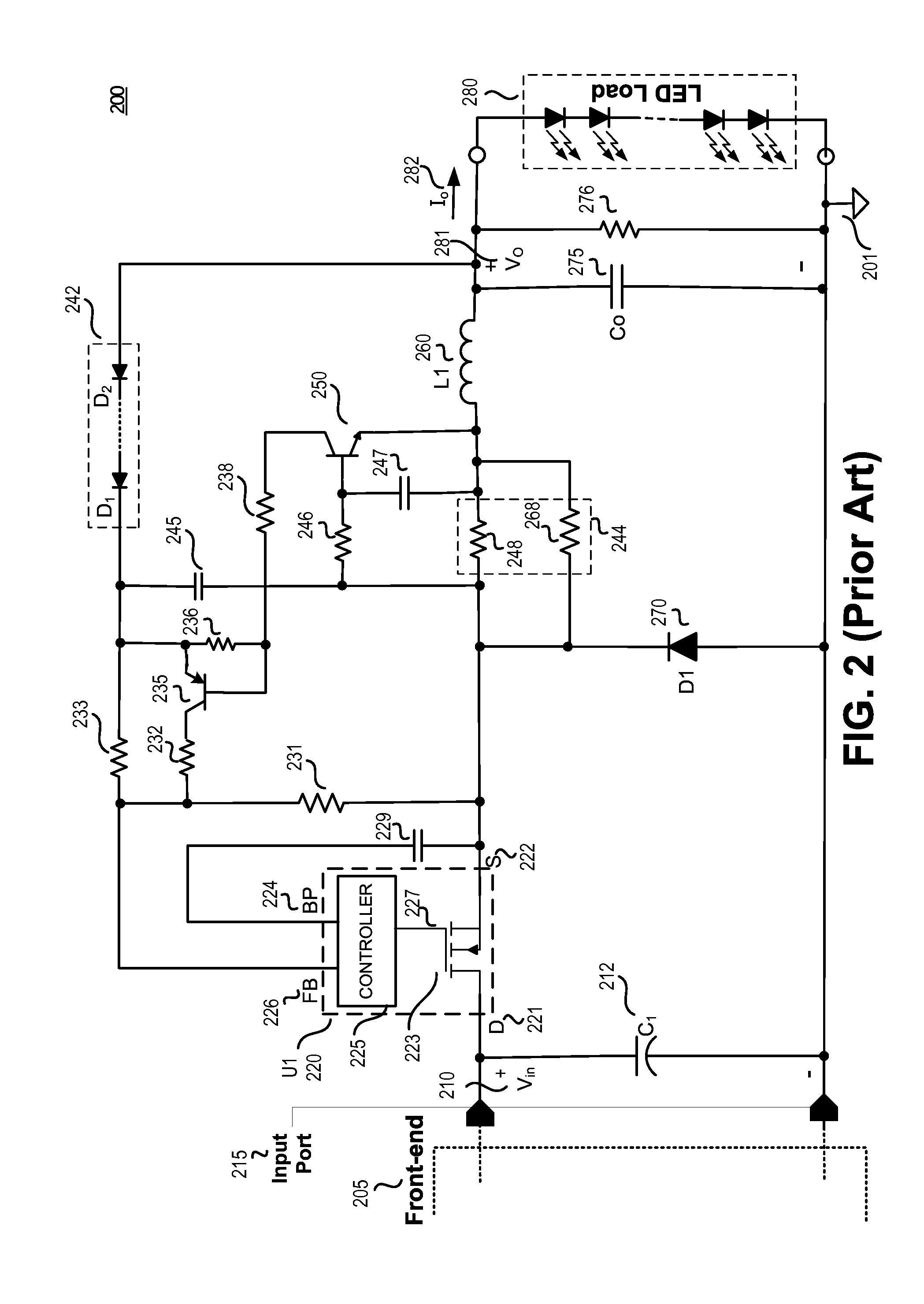
A current sense and feedback circuit is provided for a non-isolated Buck power converter to maintain constant current load regulation. The Buck converter may have a high side power switch and may include an input port, a switcher unit including a switch and a controller, an inductor coupled to the output, and a freewheeling diode for circulating the inductor current when the switch is open. The simplified current sense and feedback circuit of the power converter may include a current sense resistor module coupled to the freewheeling diode to provide a sense signal to the controller. The controller may also be coupled to the output of the power converter to sense an over voltage condition. The simplified current sense and feedback circuit may provide output regulation while maintaining a low component count, small size, and low loss that makes the power converter suitable for use in compact design applications.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Method and system for operating a wind turbine
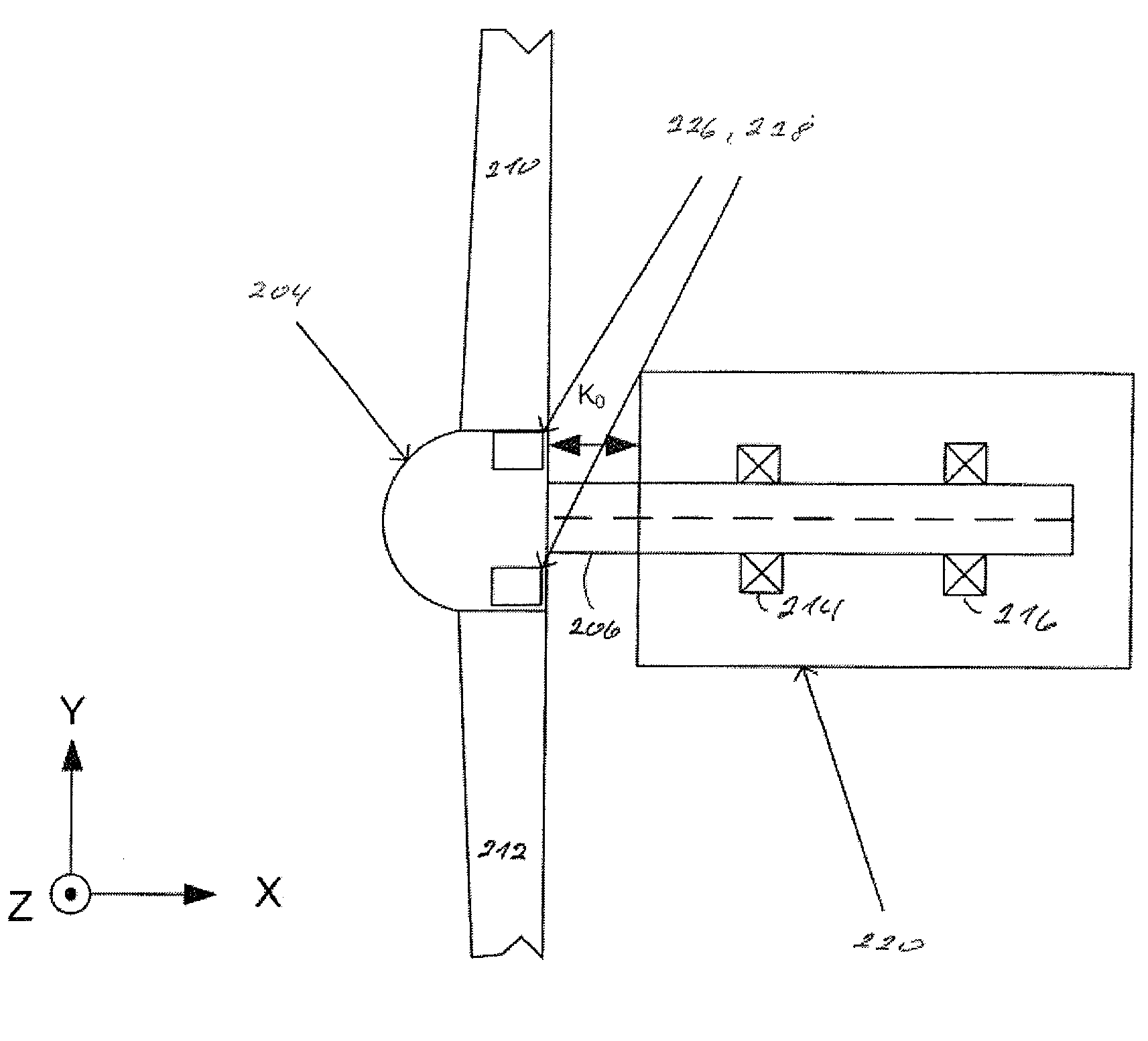
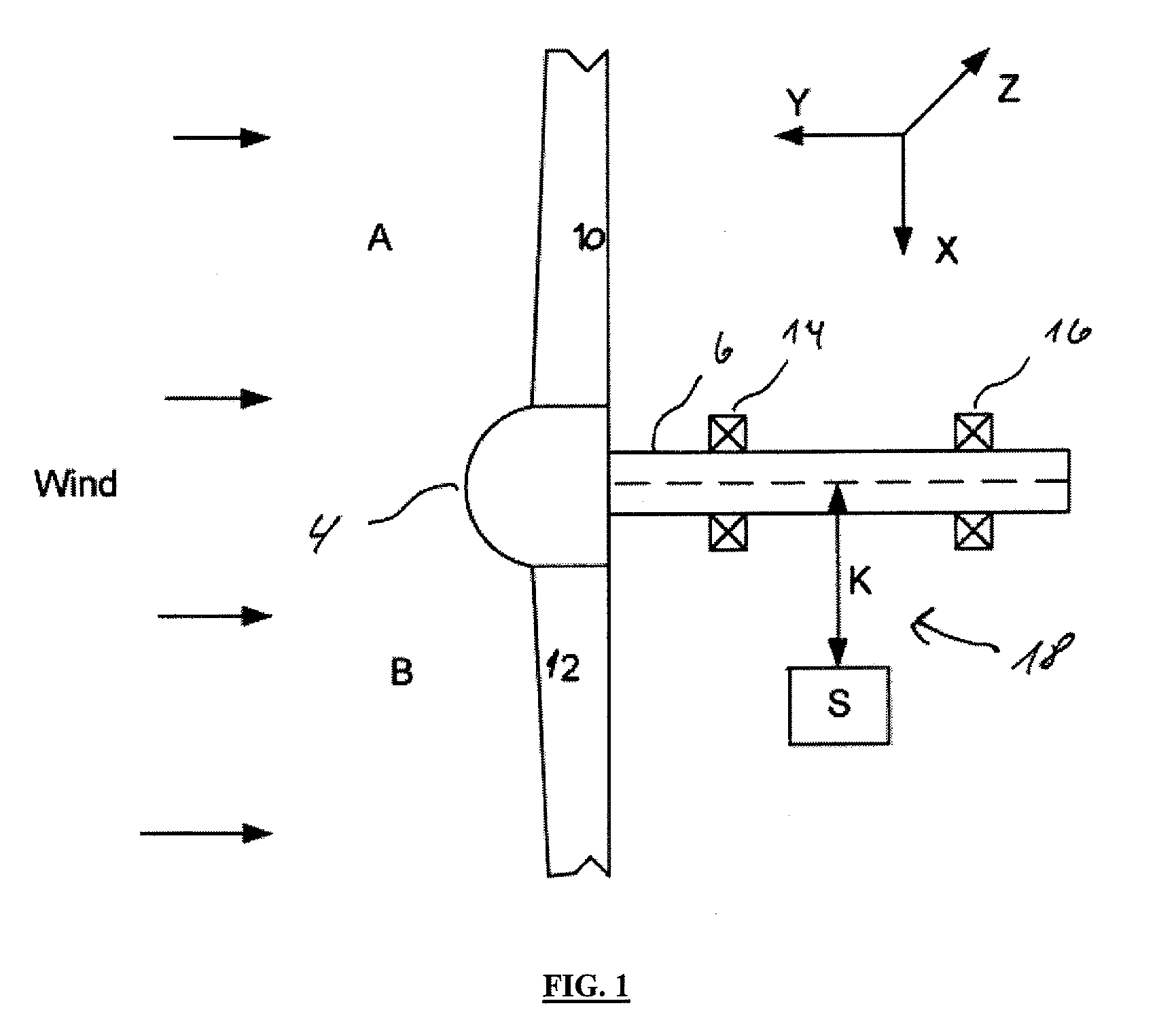
ActiveUS20090129924A1Increase power generationReduce wearPropellersPump componentsLoad regulationBlade pitch
The present invention relates to a method and a system for operating a Wind Turbine (WTG), which WTG comprises a rotor comprising at least two blades, which blades are pitch regulated, where the rotor is connected to a shaft, which shaft is supported by bearings, and which shaft drives at least one generator, where the WTG uses a load regulation system for regulating the individual pitch of at least two blades. The object of the invention is to compensate for asymmetric load on the rotor in a wind turbine, a second object is to reduce wearing at shaft bearings in the wind turbine, and a third object is to increase the power production of a wind turbine. This can be achieved if the load regulation system measures the actual rotor load by at least one displacement sensor, which displacement sensor is measuring the bending of the main shaft, where the load regulation system based on the shaft bending regulates the individual pitch of the blades for compensating asymmetric load at the rotor.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
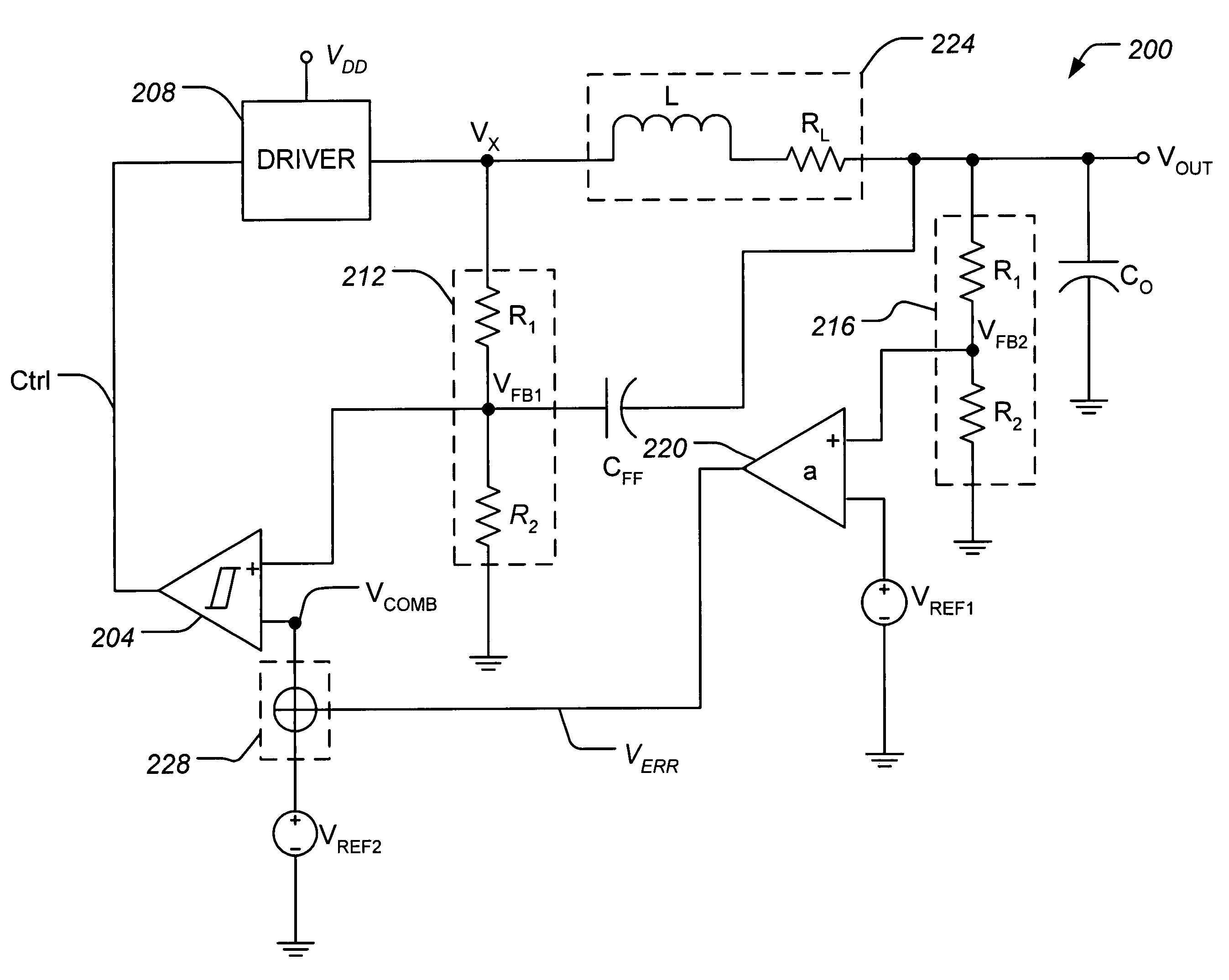
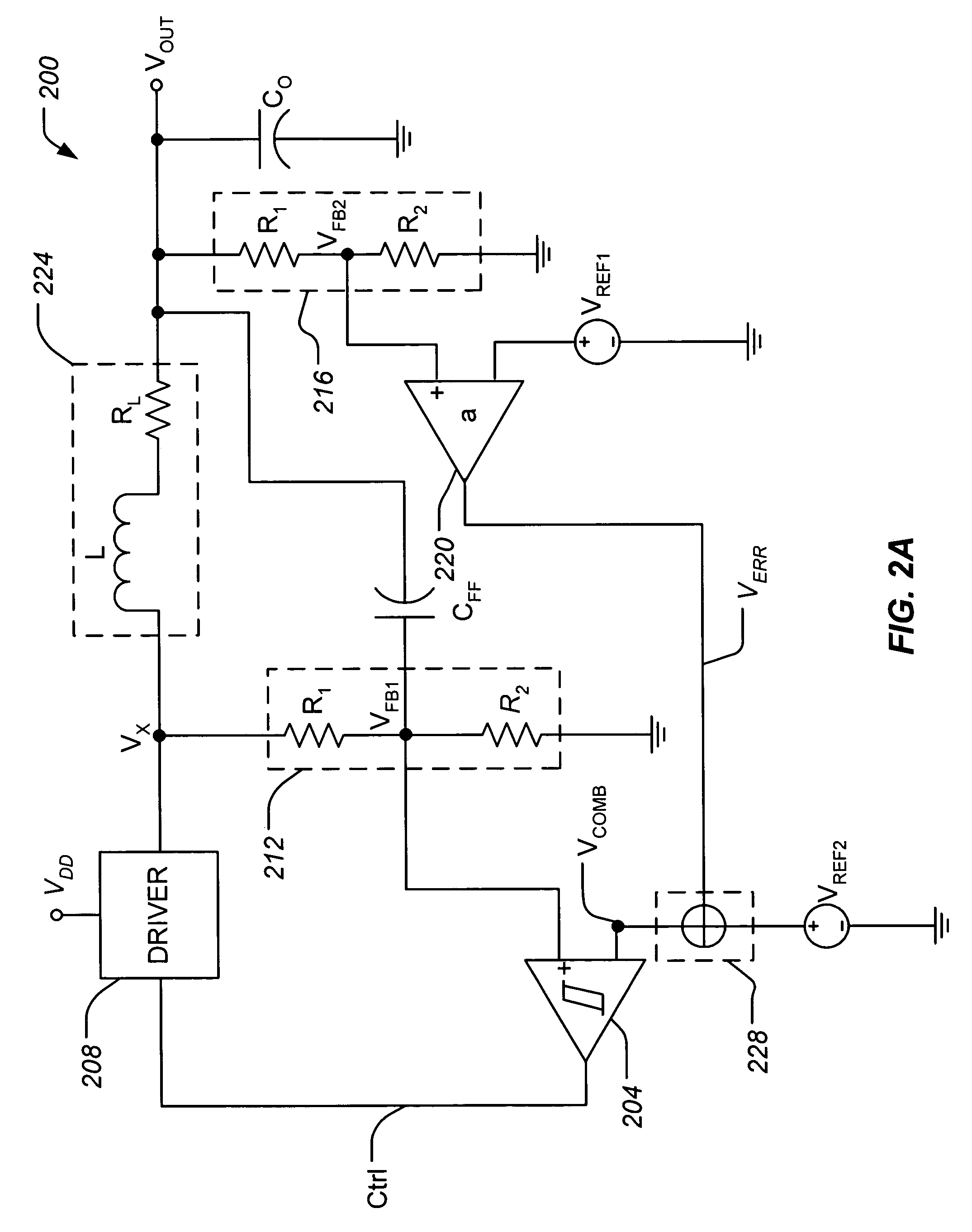
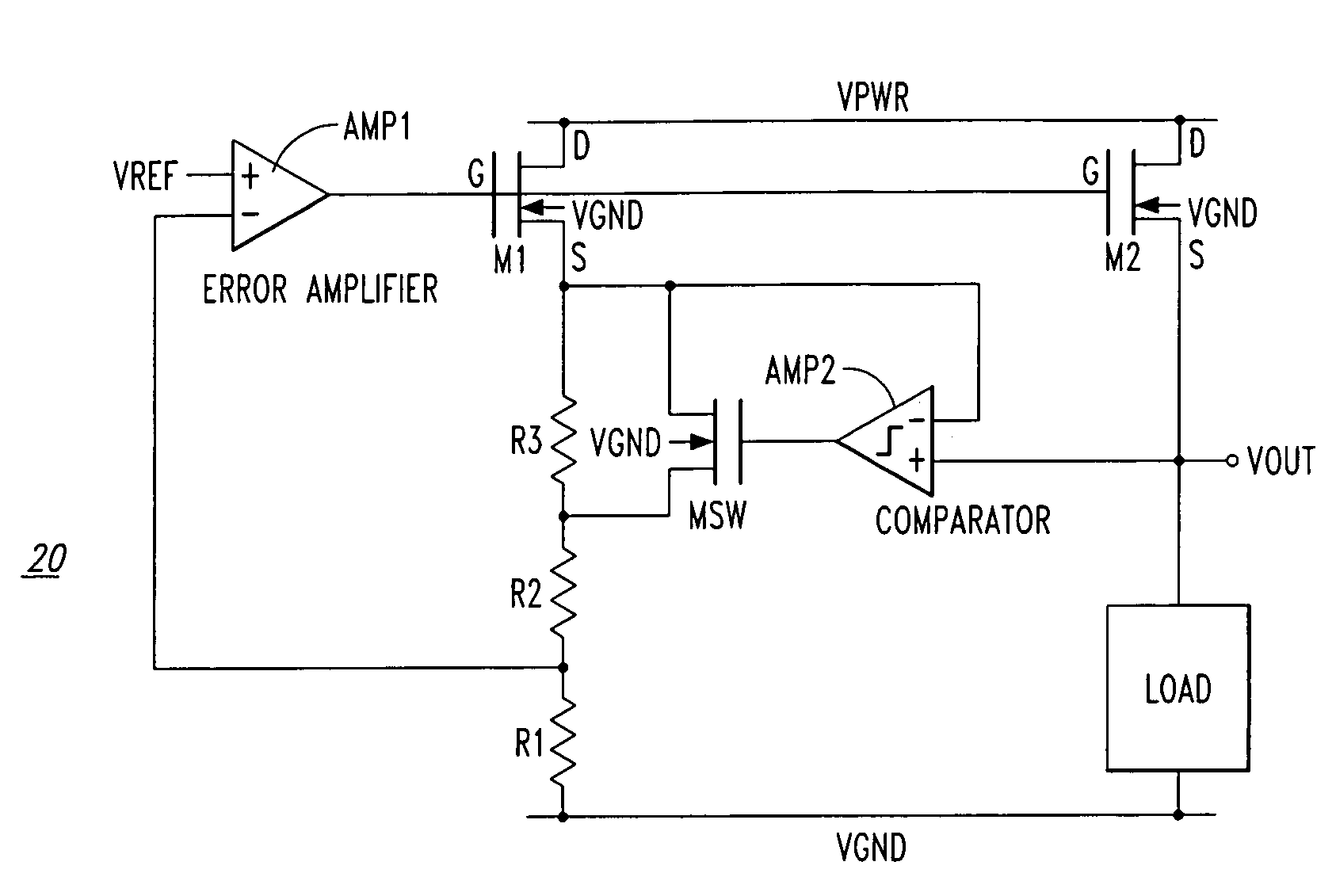
Low power DC-DC converter with improved load regulation
A voltage converter includes, among other things, an amplifier, a voltage combiner, and a hysteretic comparator. The amplifier has a first input terminal which receives a first voltage representative of an output voltage of the voltage converter, a second input terminal which receives a first reference voltage, and an output terminal which generates a second voltage proportional to a difference between the first voltage and the first reference voltage. The voltage combiner combines the second voltage with a second reference voltage to generate a combined voltage. The comparator causes a third voltage to decrease if a feedback voltage defined by the third voltage is detected by the comparator as being greater than a first threshold voltage defined by the combined voltage, and further to cause the third voltage to increase if the feedback voltage is detected by the comparator as being less than the first threshold. The third voltage is applied to a first terminal of a load external to the voltage converter.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
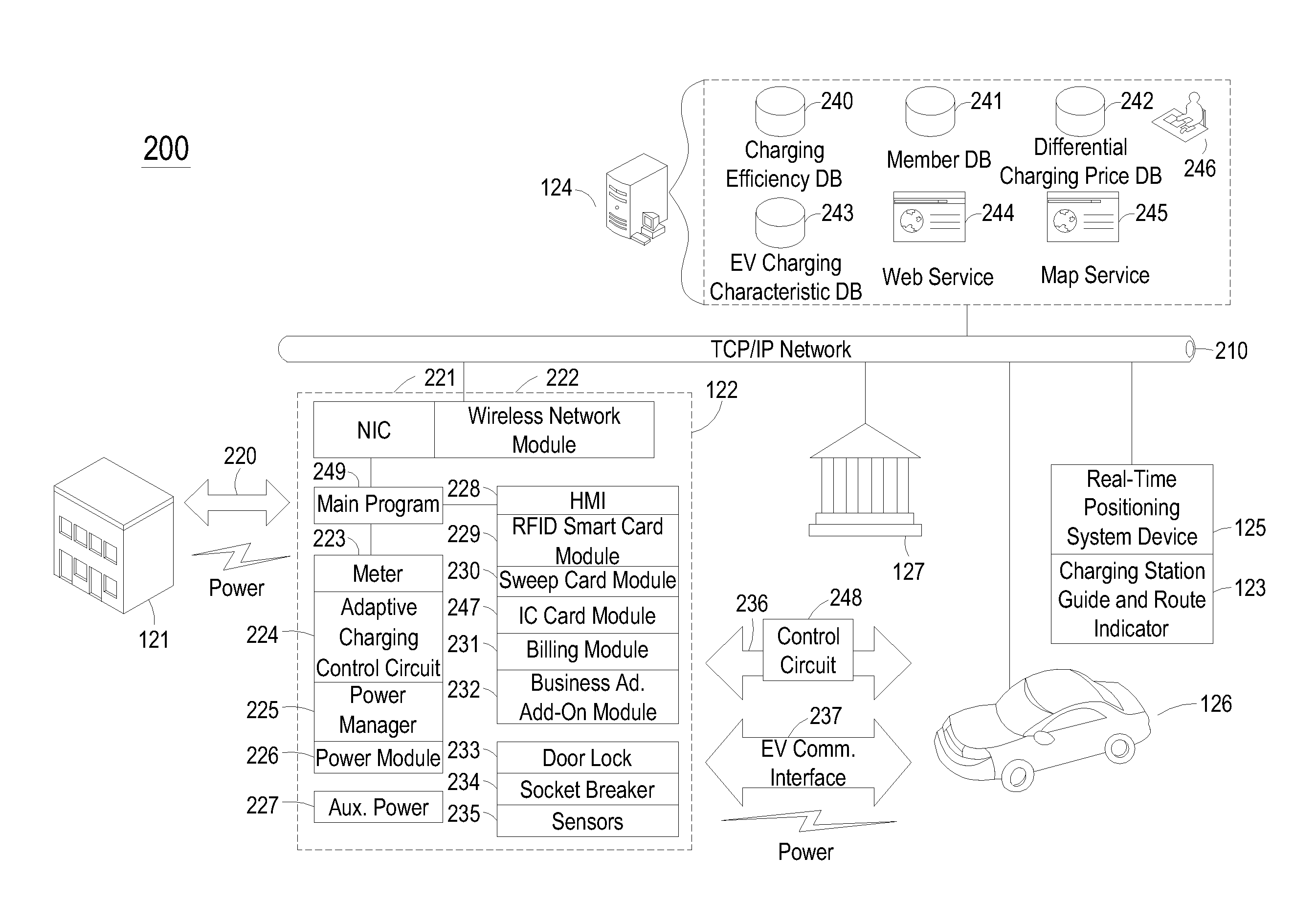
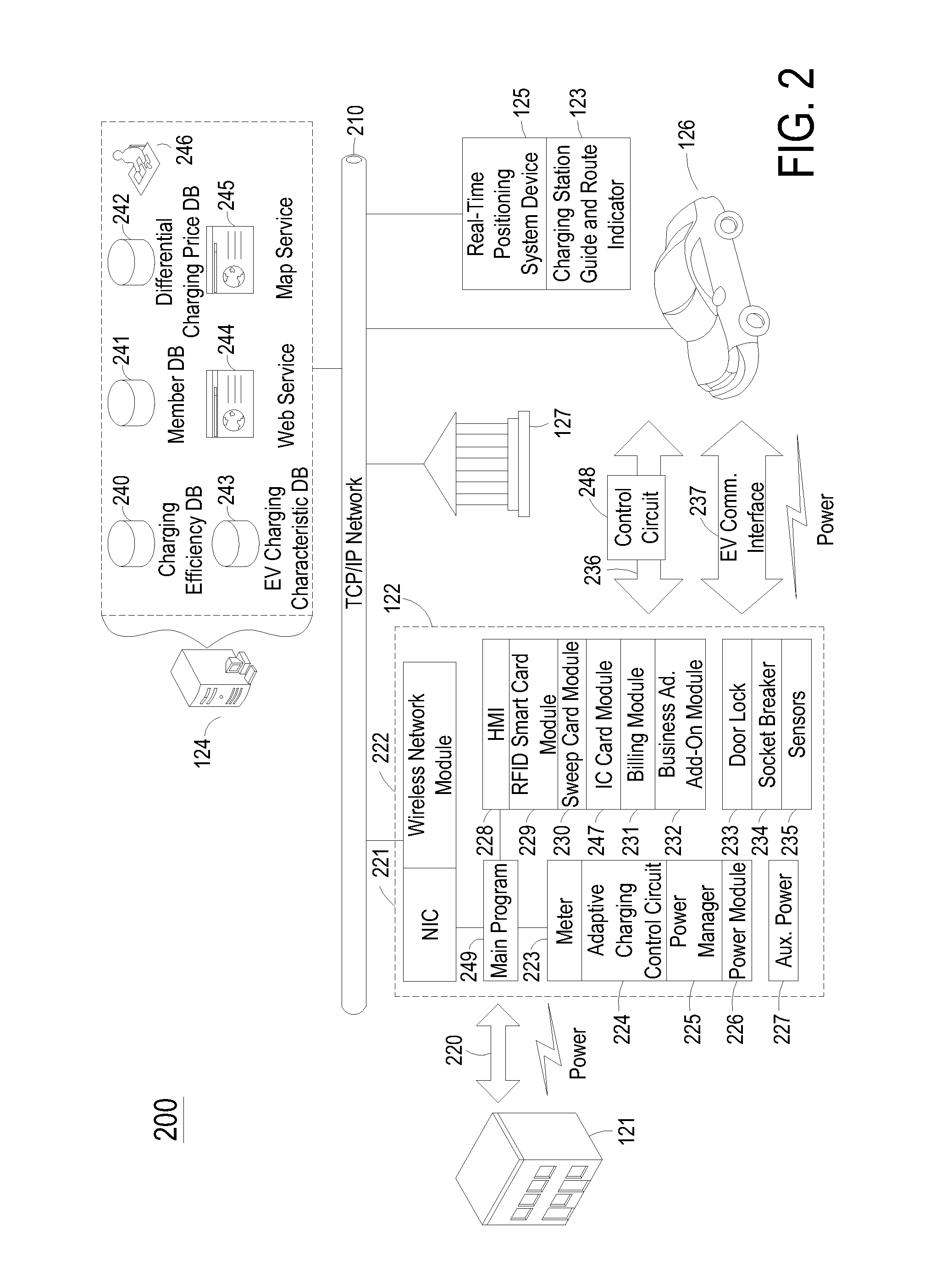
Vehicle charging system with charging efficiency control and providing adaptive charging service
InactiveUS20120086396A1Effective controlBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsCharge currentSmart grid
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
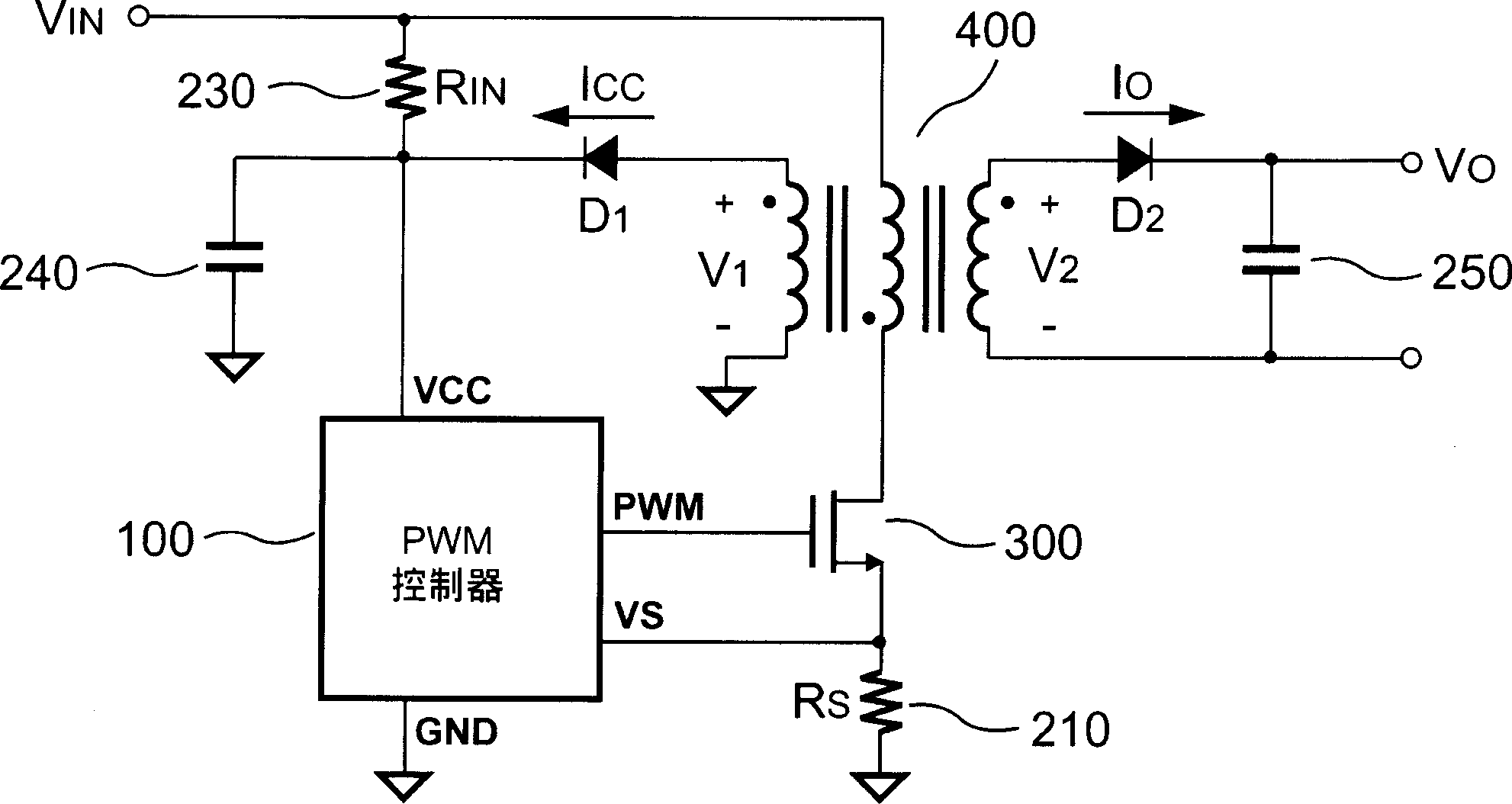
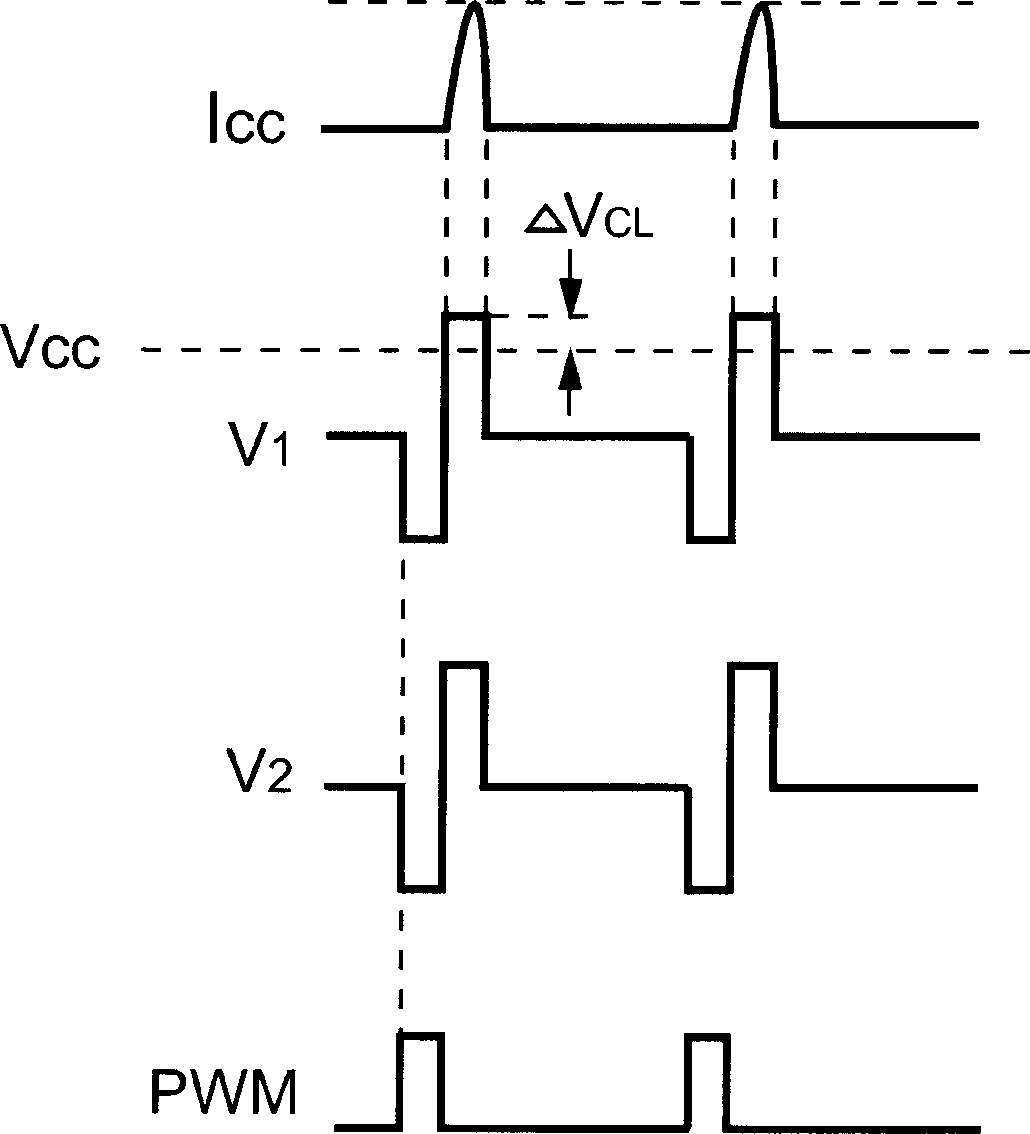
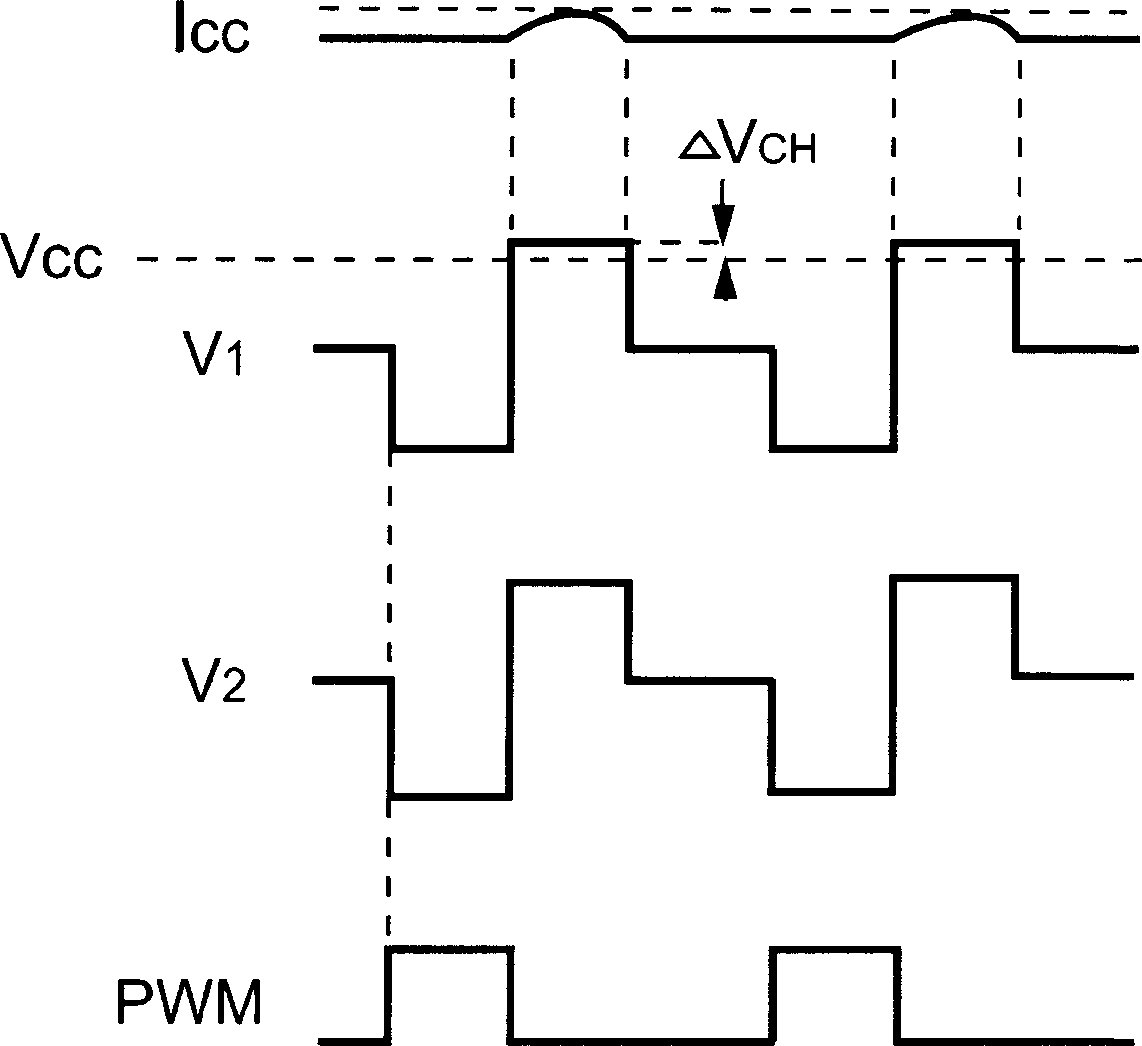
Primary-side regulated pulse width modulation controller with improved load regulation
ActiveCN1806380AImprove stabilityPrecise Feedback ControlTransformersApparatus with intermediate ac conversionVoltage generatorRectifier diodes
The present invention provides a primary-side regulated PWM (pulse width modulation, pulse width modulation) controller with improved load regulation. In each PWM cycle, a built-in feedback voltage generator samples and holds the flyback voltage from the auxiliary winding of the transformer through a sampling switch, and generates a feedback voltage accordingly. A bias current sink sinks a bias current proportional to the feedback voltage. When the output load changes, the bias current will generate a voltage drop through a sense resistor to compensate the voltage drop of the output rectifier diode. According to the present invention, the bias current may enable the PWM controller to regulate the output voltage very accurately without using a secondary feedback circuit.
Owner:SYST GEN
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS20040119448A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-ac conversionEngineeringGalvanic isolation
Owner:MICROPLANET
Replica bias regulator with sense-switched load regulation control
A regulator circuit including output loading sense circuitry where the output loading sense circuitry comprises, in one example, a resistor in the feedback leg of the replica bias regulator, a switch in the feedback leg of the replica bias regulator for bypassing the resistor, and a comparator used to sense the output loading and selectively drive the switch.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS7315151B2Low in electrical and audible noiseLight weightEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringGalvanic isolation
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a specific embodiment is also disclosed herein. The specific circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses eight solid state switches, such as IGBT's, eight diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. Indeed, the eight-switch controller can act to either buck or boost the input voltage, and can switch between bucking and boosting during a cycle, thus providing more control of the regulated output voltage. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:MICROPLANET
Micro force measurement device, micro force measurement method, and micro surface shape measurement probe
InactiveUS7685733B2Accurate shapePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrical measurement instrument detailsMeasurement deviceLoad regulation
Owner:RIKEN
Dual interleaved DC to DC switching circuits realized in an integrated circuit
InactiveUSRE38140E1Realize automatic adjustmentStay healthyAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDifferentiatorTransverter
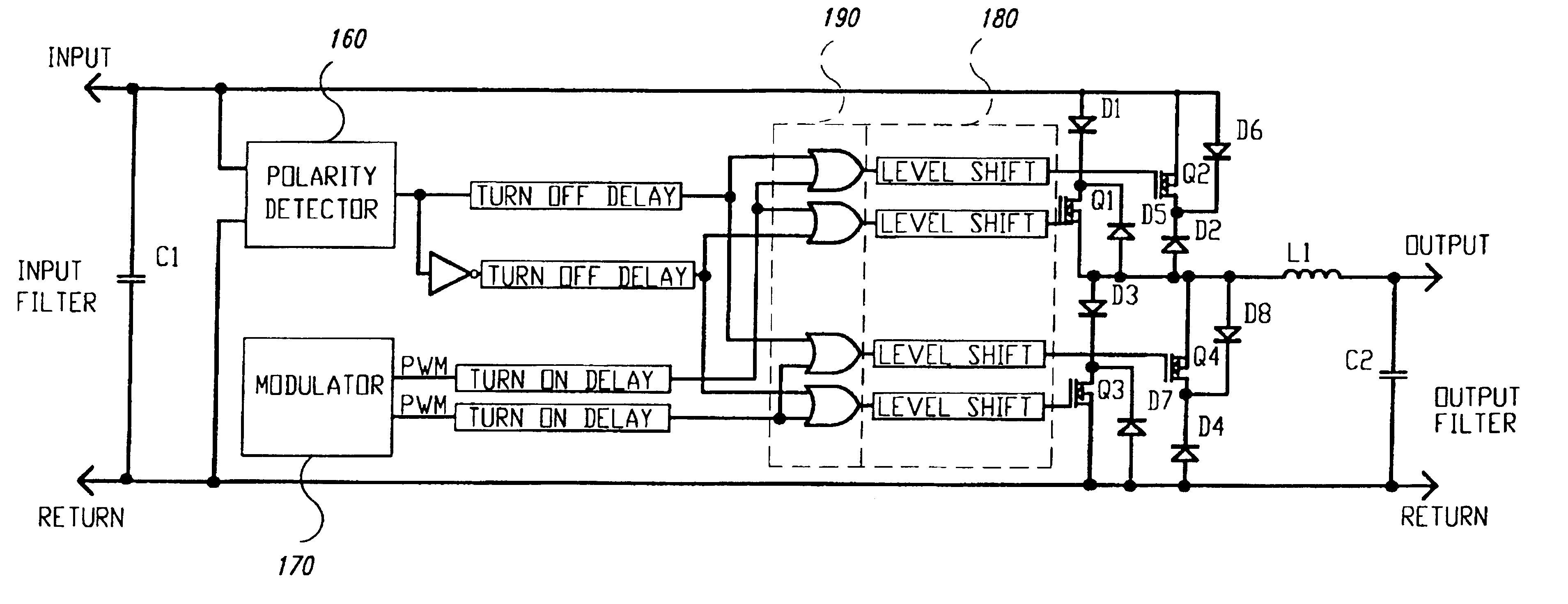
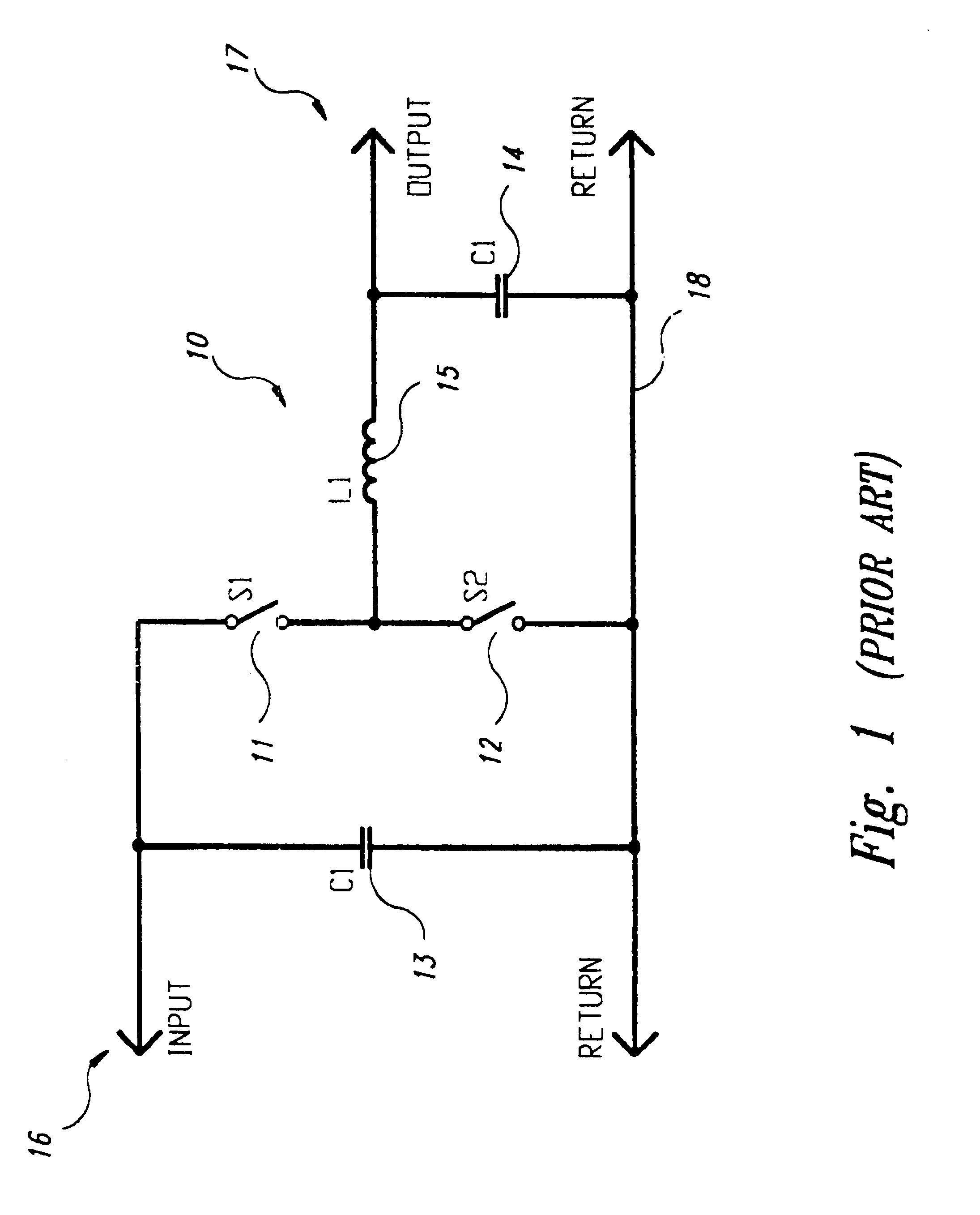
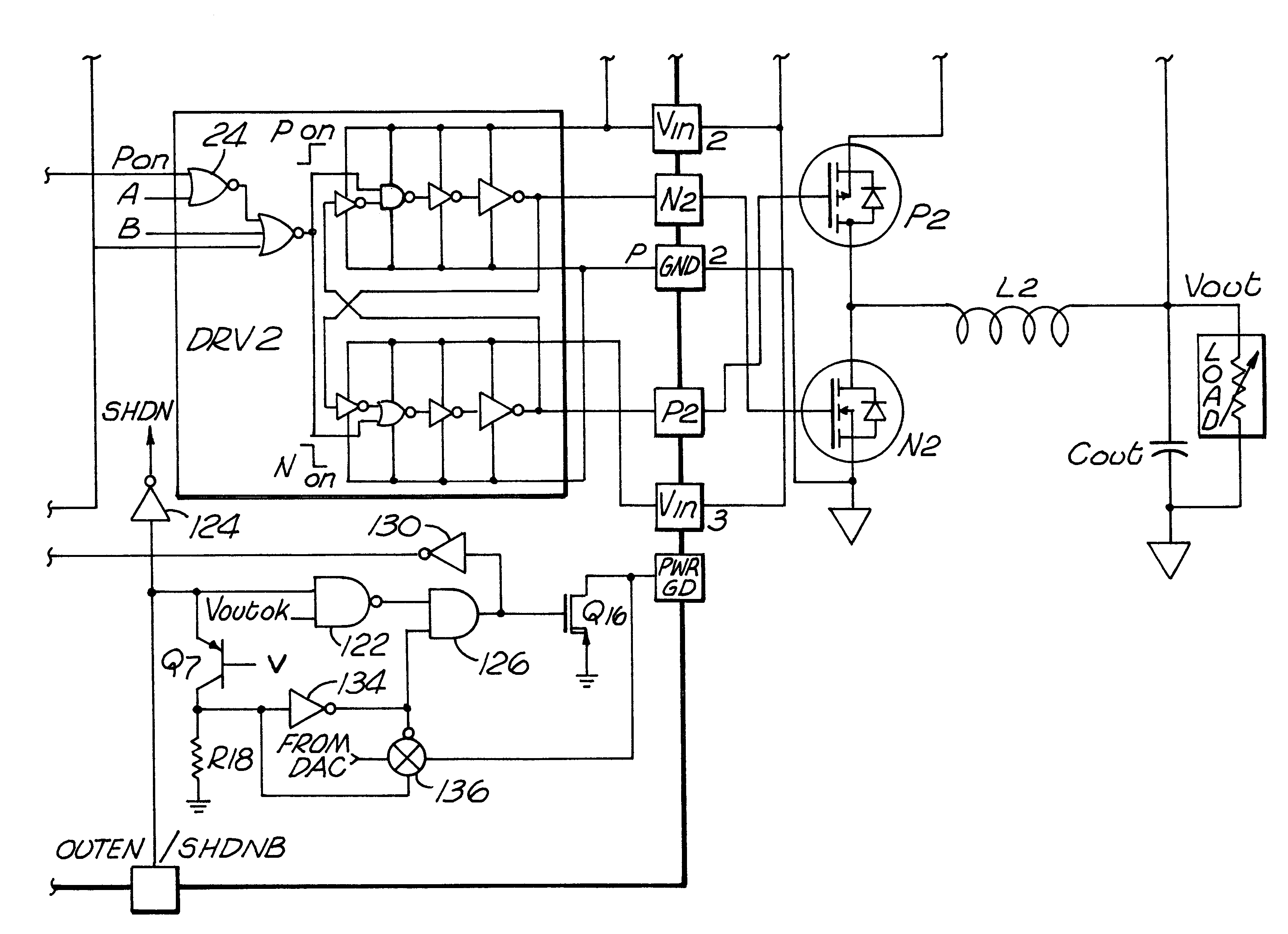
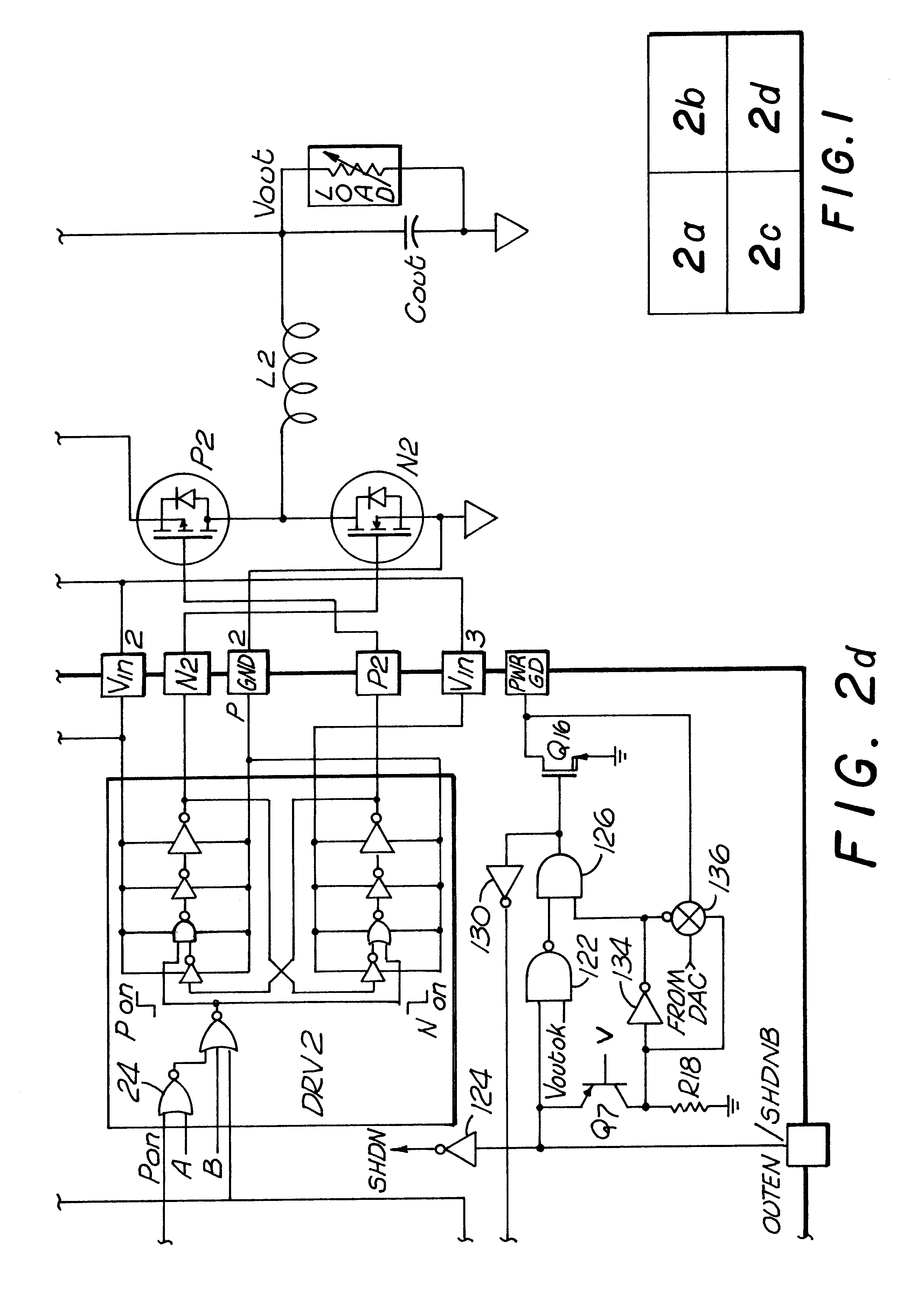
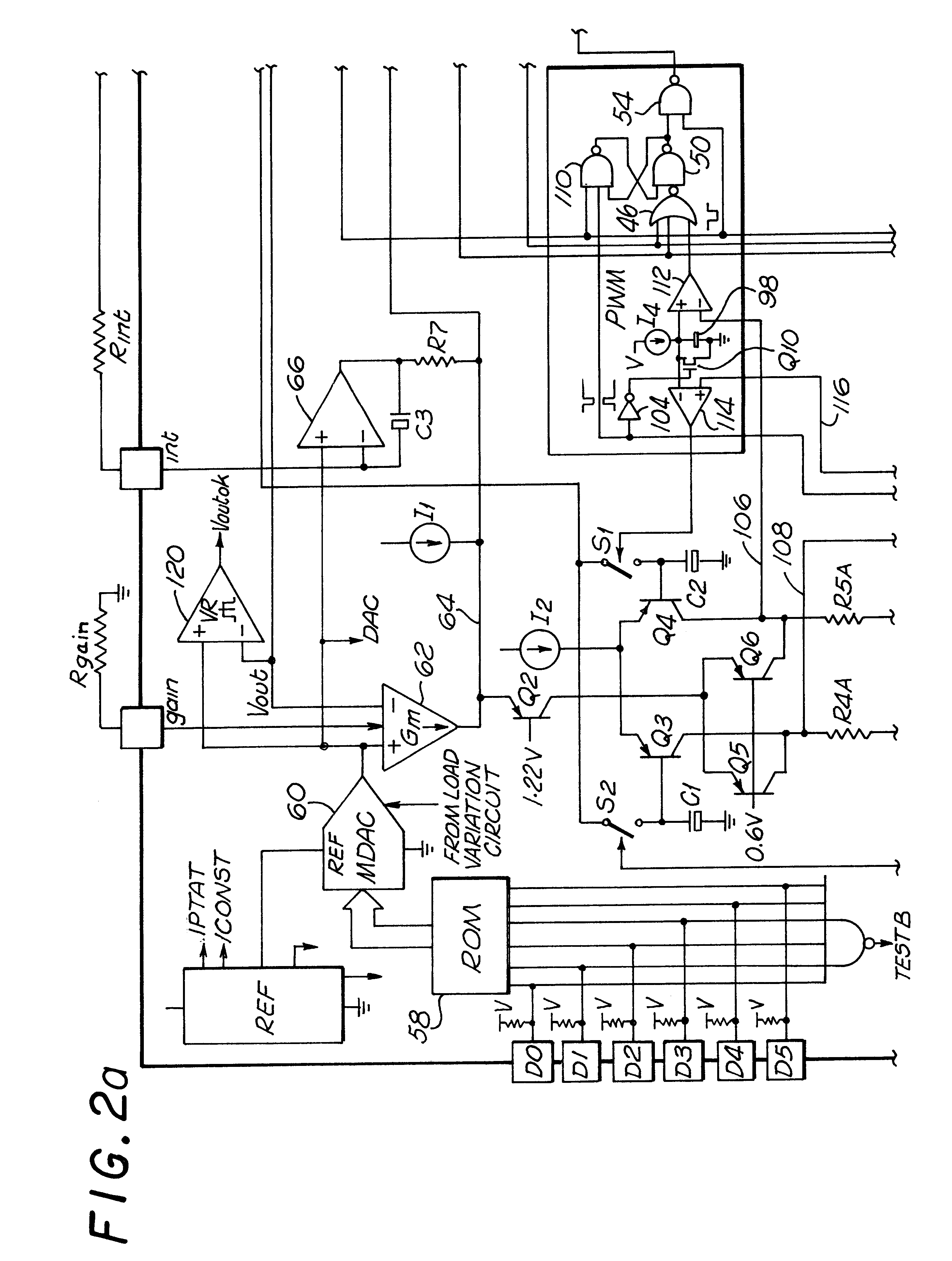
Dual interleaved DC to DC switching circuits realizable in an integrated circuit form, capable of monitoring individual inductor current using only one current sense resistor and providing automatic duty cycle adjustment to keep the inductor currents in the interleaved DC to DC switching circuits balanced. The preferred embodiment includes a gain error amplifier, an integral error amplifier, and a differentiator error amplifier and circuits for controlling the nominal duty cycle, with the gain error amplifier, integral error amplifier and differentiator error amplifier being adjustable independently by external components. The circuit further includes a high speed load regulation circuit that momentarily overrides the control circuitry to take over control of the interleaved converters during sudden load changes, such control also being programmable. The circuit further includes a load variation circuit to target the output voltage of the circuit to an optimal value with load to better keep the output voltage within a targeted range in the event of major step changes in the load. The disclosed embodiment is for two interleaved buck converters, though the principles of the invention are applicable to interleaved step up converters and the interleaving of more than two converters.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Testing system for loads of frequency converters
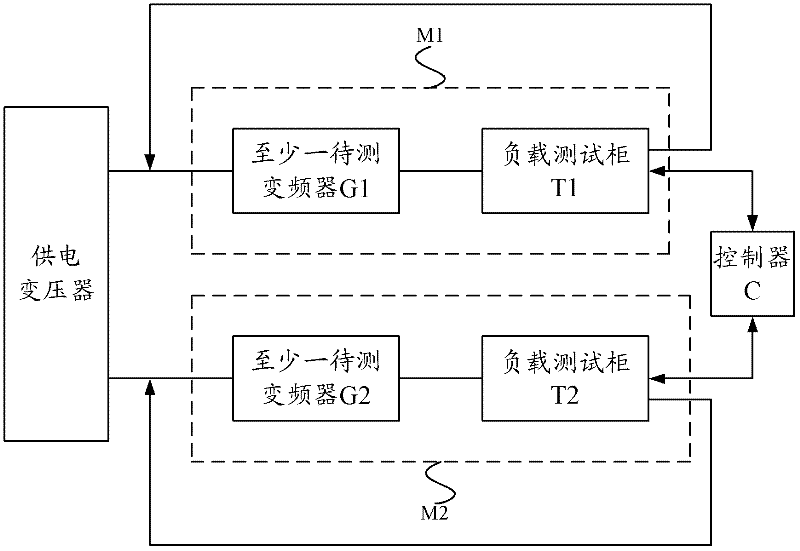
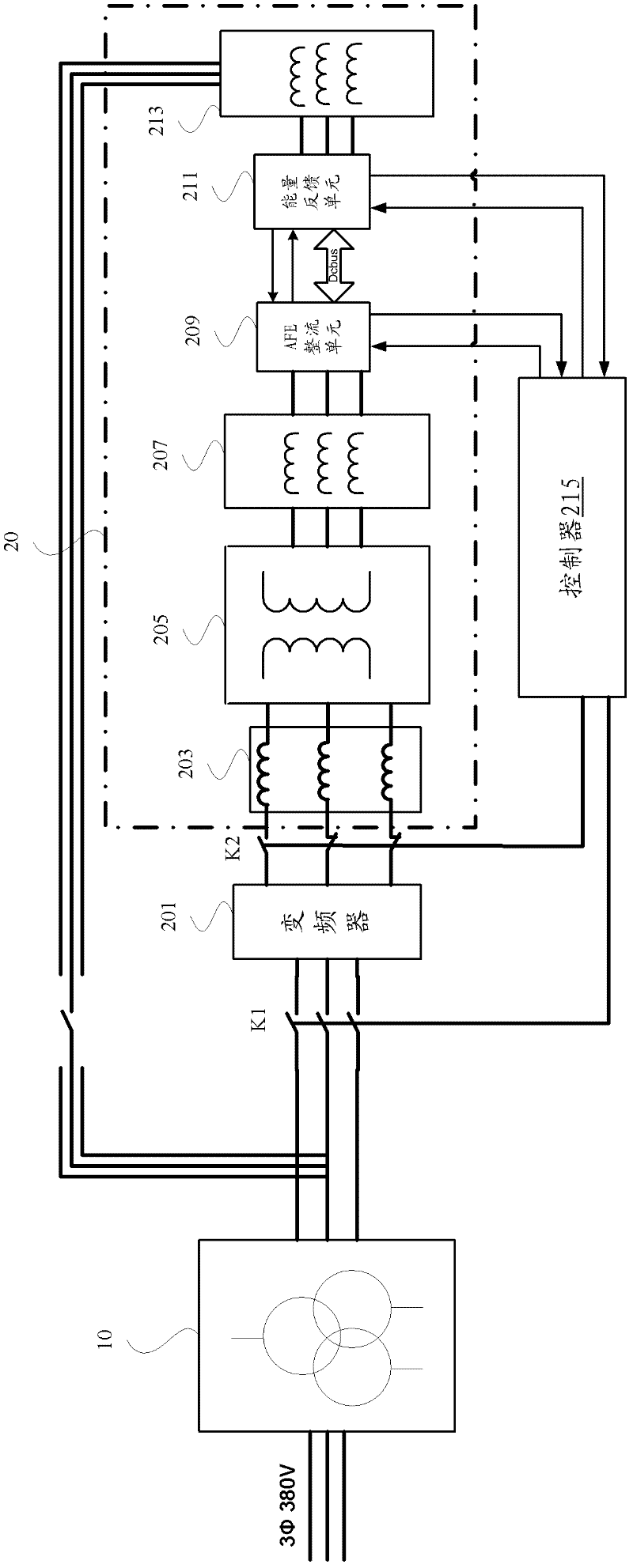
The invention provides a testing system for loads of frequency converters, which comprises a power supply transformer, at least one testing module and a controller. The power supply transformer outputs at least one power supply voltage, each testing module comprises at least one frequency converter to be measured and a load testing cabinet, each load testing cabinet is used as a variable load to adjust output of the corresponding frequency converter to be measured and outputs corresponding alternating-current voltage to an output end of the power supply transformer, the controller controls the magnitude of the load testing cabinet of each testing module when the load testing cabinet is used as the variable load, and accordingly the output of the frequency converters to be measured is adjusted by the aid of the load testing cabinets. A three-phase reactor is directly disposed at an output end of each frequency converter to be measured so as to realize filtering processing, and accordingly a running mode of each frequency converter with a motor load is simulated. In addition, the frequency converters with different voltage grades can be loaded and tested under the condition without the motors, residual electric energy is fed back to the output end of the power supply transformer to be recycled, and accordingly energy is saved.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com