Patents
Literature
1049 results about "Variable load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A variable load is a load that is applied over an area; that is, a surface. A function can be defined to control the magnitude of the load at different locations on the surface. The variable load will be converted into equivalent forces and applied to the element nodes.
Decentralized energy demand management
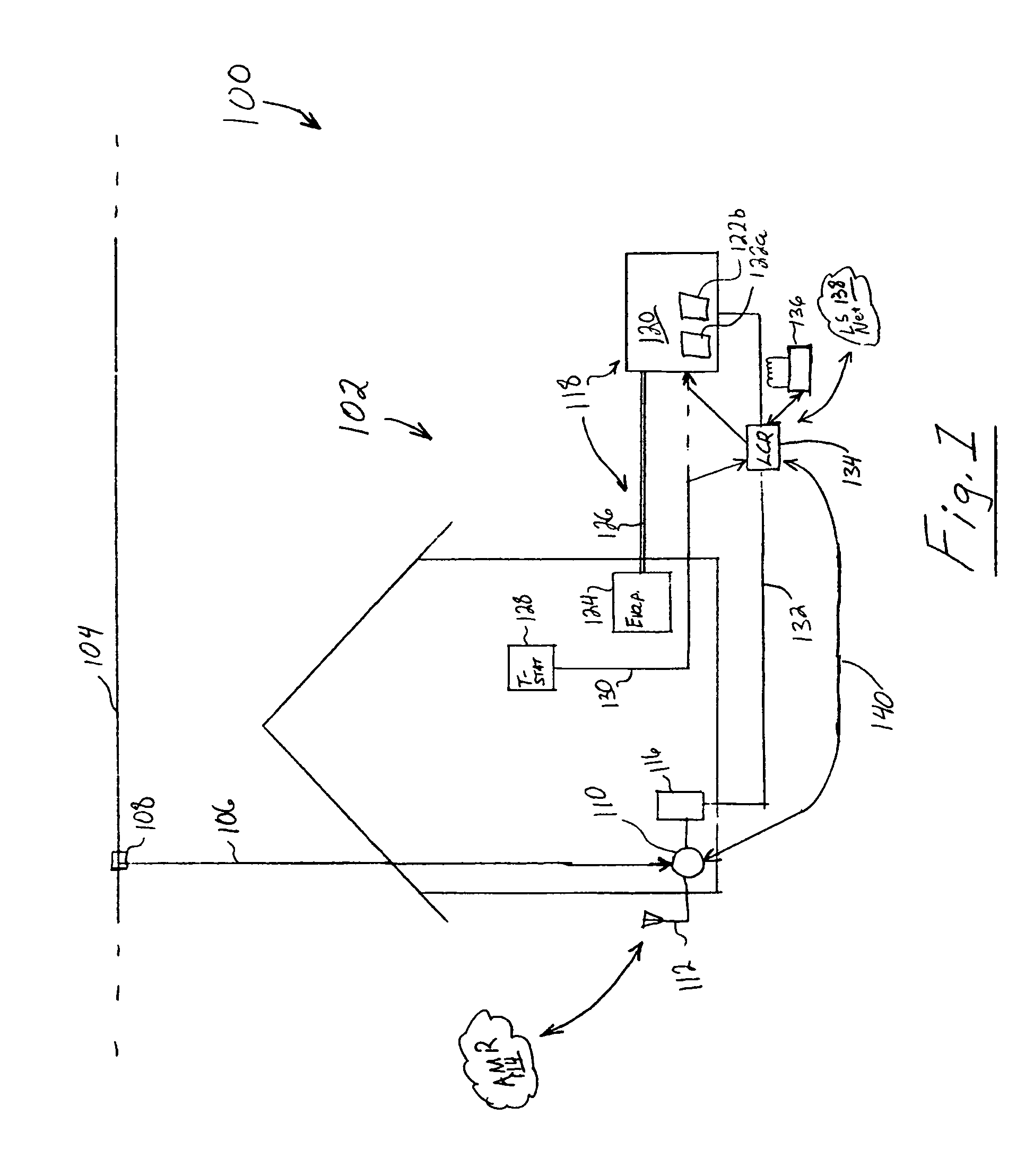
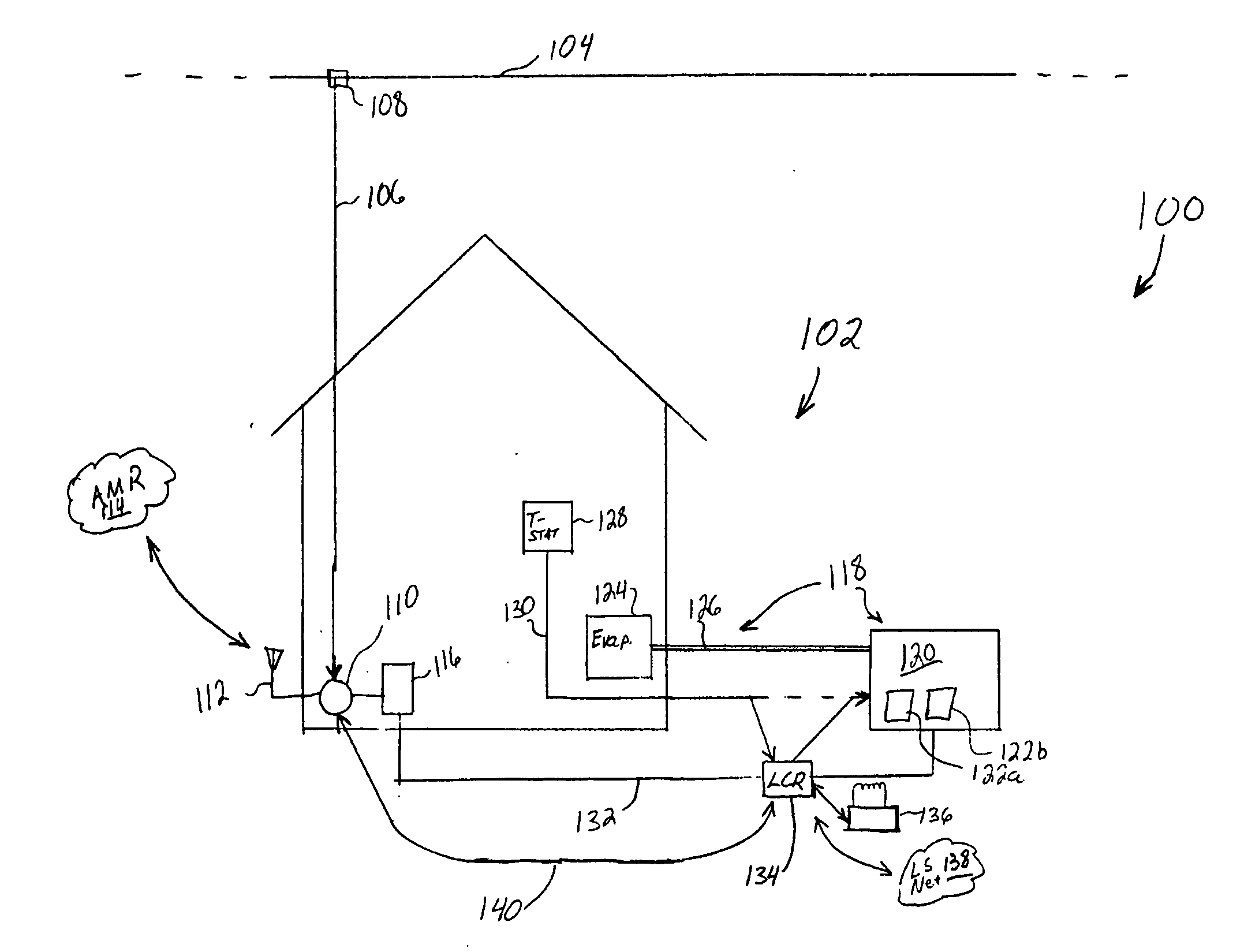
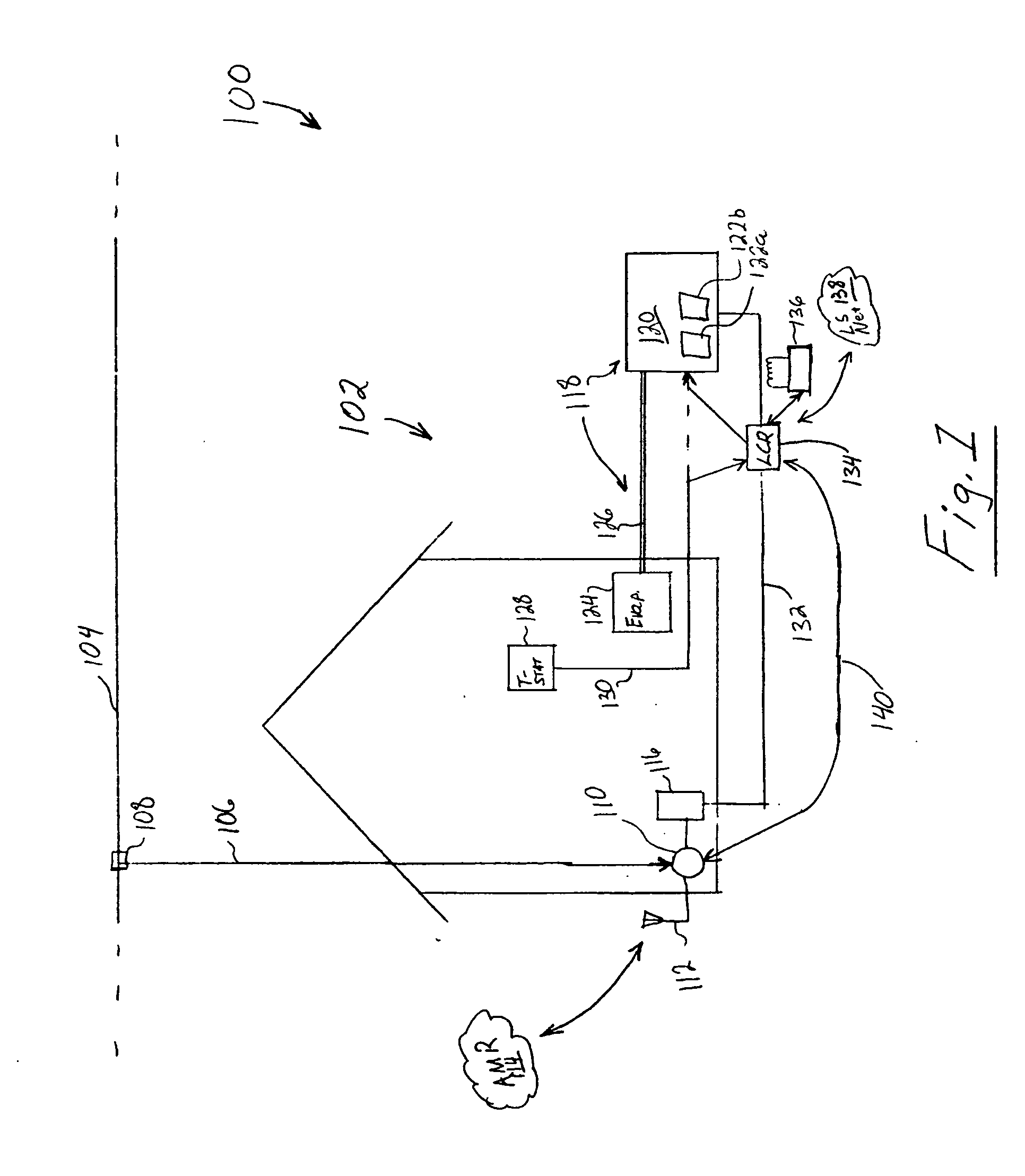
A decentralized load management and control system and method are provided herein. A plurality of loads in a system are associated with a multitude of respective networked load controllers. If energy demand exceeds optimum limits in operation then the networked load controllers collaborate to determine which load(s) will be shed based on an optimization algorithm that considers, inter alia, variable load priority and business objectives. Additionally and / or alternatively, if the metered energy demand is less than optimum, the load controllers can determine which loads to reconnect again based at least upon load priority and business objectives.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
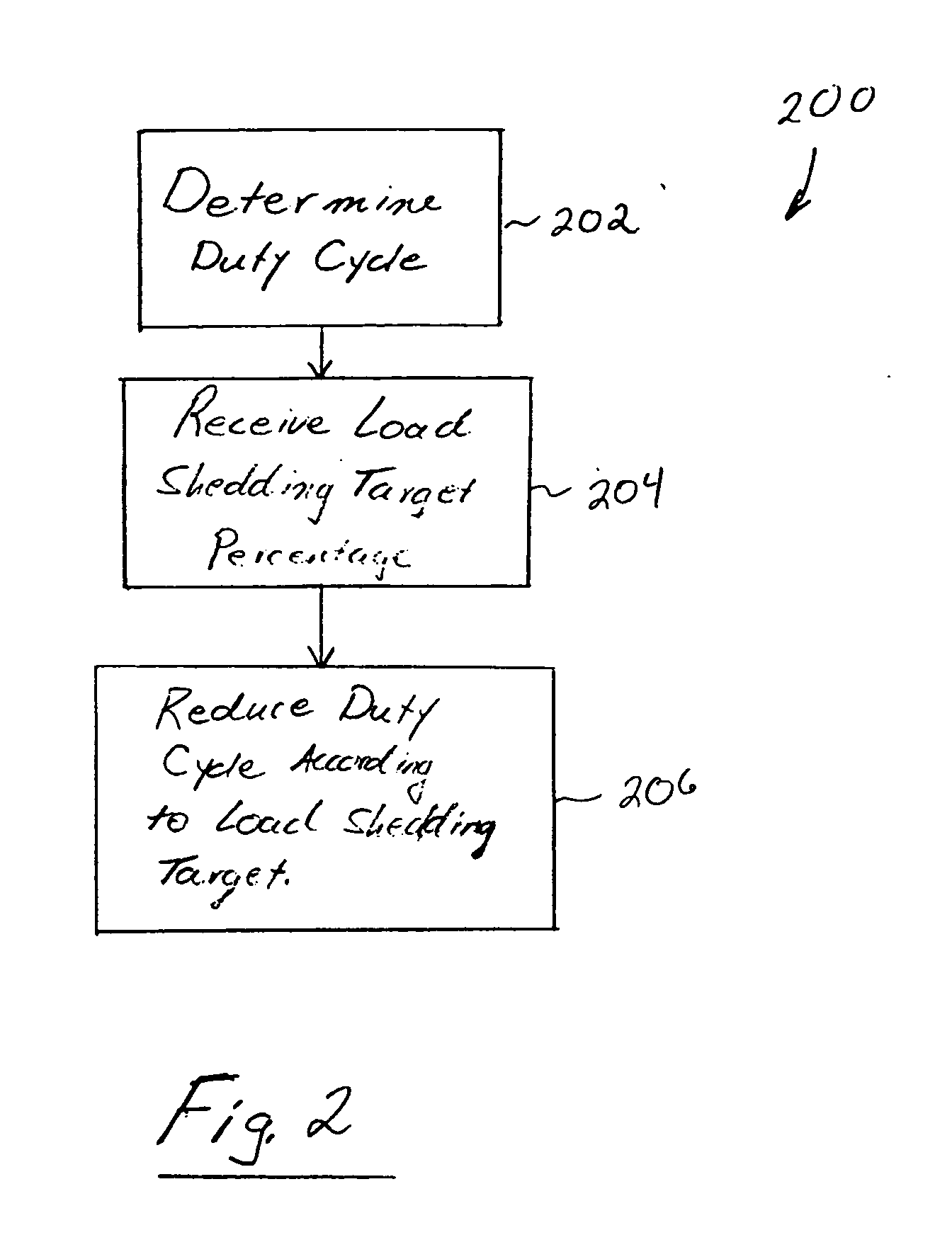
Load shedding control for cycled or variable load appliances
ActiveUS7528503B2Reduce outputReduce cycle frequencyBatteries circuit arrangementsDiscounts/incentivesLoad SheddingControl engineering
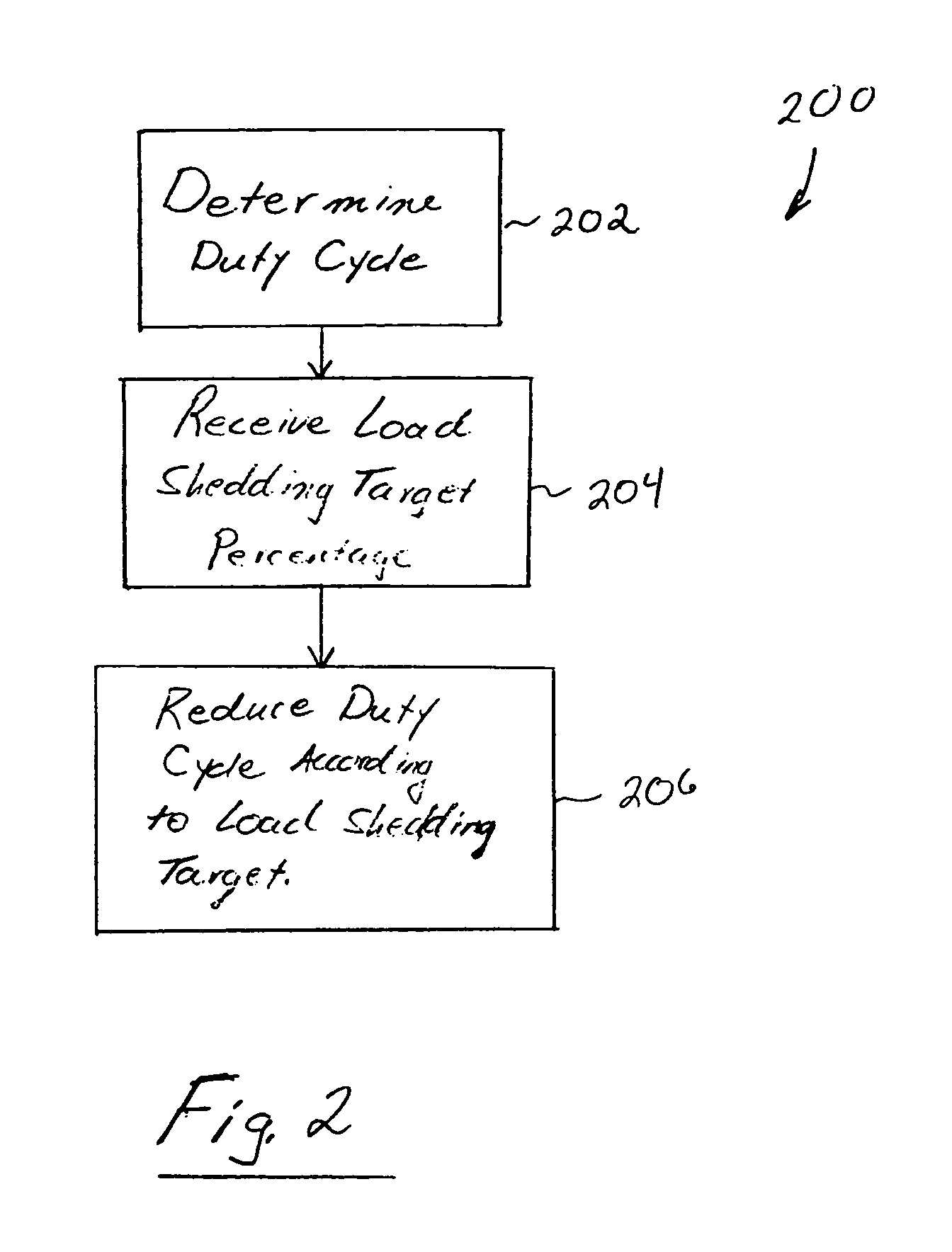
Control of a variable output appliance of a small energy consumer participating in an electrical load shedding program. A baseline operating characteristic of the appliance is determined for ordinary operation (such as in an absence of any load shedding requirements). An amount by which to reduce output of the appliance is determined in accordance with the load shedding program. Operation of the appliance is controlled to achieve the output reduction in accordance with the load shedding. This approach enables providing incentive for the small energy consumer to participate in the load shedding program, the incentive being based on the amount by which output is reduced, thereby representing a reduction of actual energy consumption for that small energy consumer.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Load shedding control for cycled or variable load appliances
ActiveUS20070021874A1Reduce outputReduce cycle frequencyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlLoad SheddingProgram planning
Control of a variable output appliance of a small energy consumer participating in an electrical load shedding program. A baseline operating characteristic of the appliance is determined for ordinary operation (such as in an absence of any load shedding requirements). An amount by which to reduce output of the appliance is determined in accordance with the load shedding program. Operation of the appliance is controlled to achieve the output reduction in accordance with the load shedding. This approach enables providing incentive for the small energy consumer to participate in the load shedding program, the incentive being based on the amount by which output is reduced, thereby representing a reduction of actual energy consumption for that small energy consumer.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Load demand throttle control for portable generator and other applications
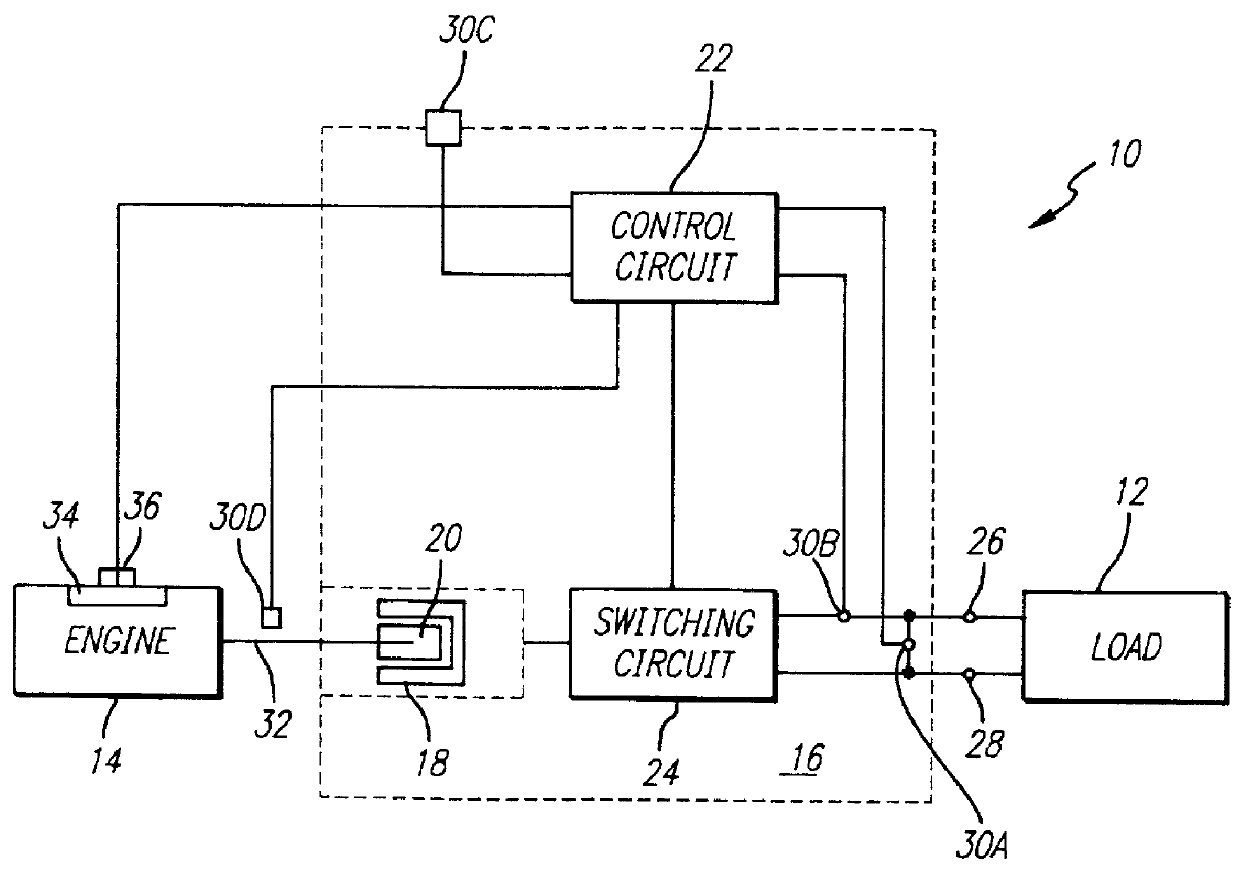
The throttle of an engine in an engine driven generator system operating subject to a wide and rapidly variable load, as in supplying current to a welder, is operated such that control signals are sent to a throttle actuator for adjusting the engine throttle position in response to load changes. The throttle actuator may be a solenoid pulling against a spring in accordance with the average current through the solenoid coil. In this embodiment, the processor causes pulse width modulated signals to be applied across the solenoid coil with throttle position changes being reflected in changes to the width of the pulses, such changes in the pulse width being delayed for at least the predetermined time since the last preceding adjustment to the throttle. Alternatively, the throttle actuator may be a stepper motor which is stepped by throttle position change signals from a processor which monitors engine speed and generator load to determine whether the throttle should be adjusted and, if so, in which direction and to what extent for optimum response.
Owner:PRAMAC AMERICA
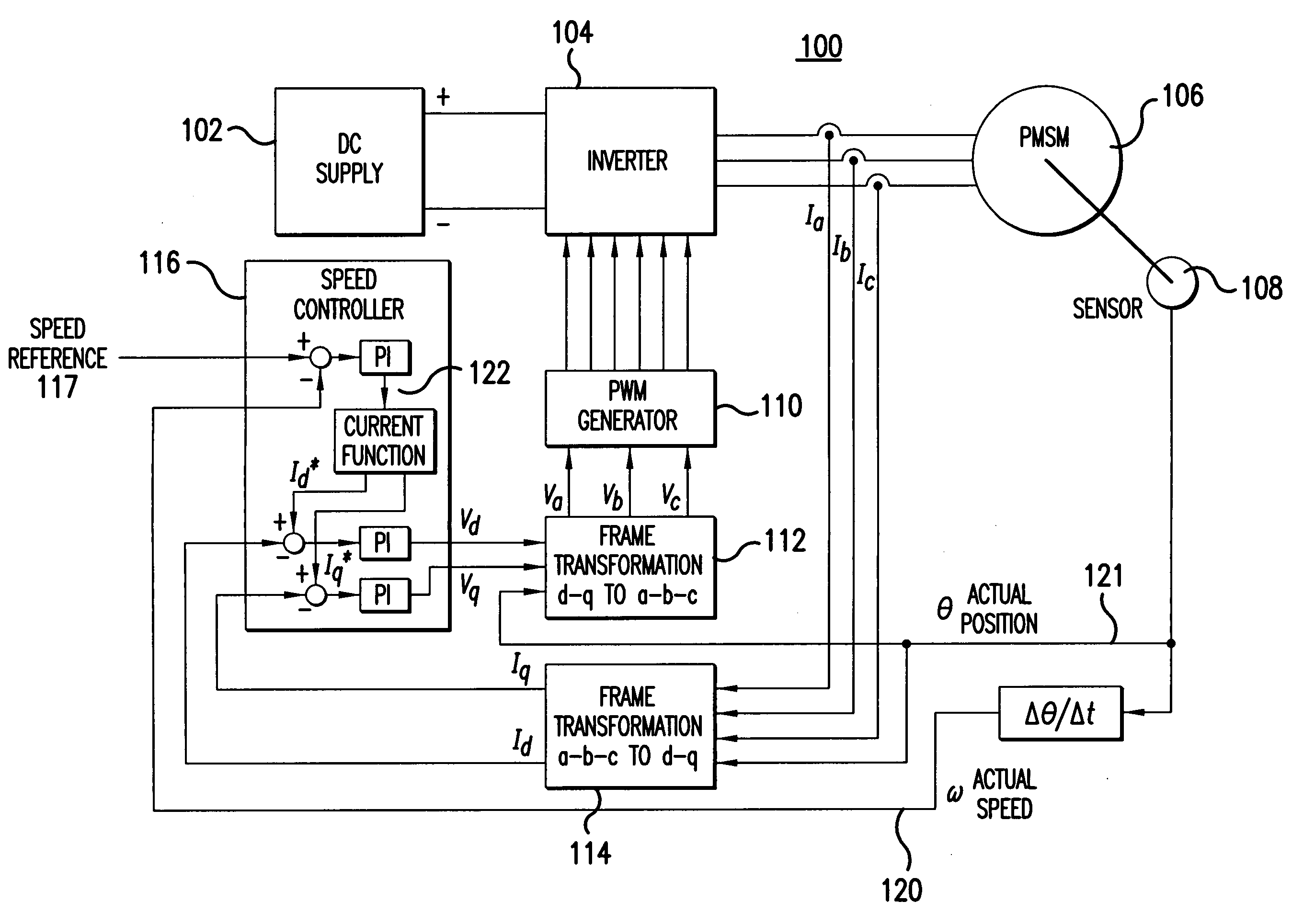
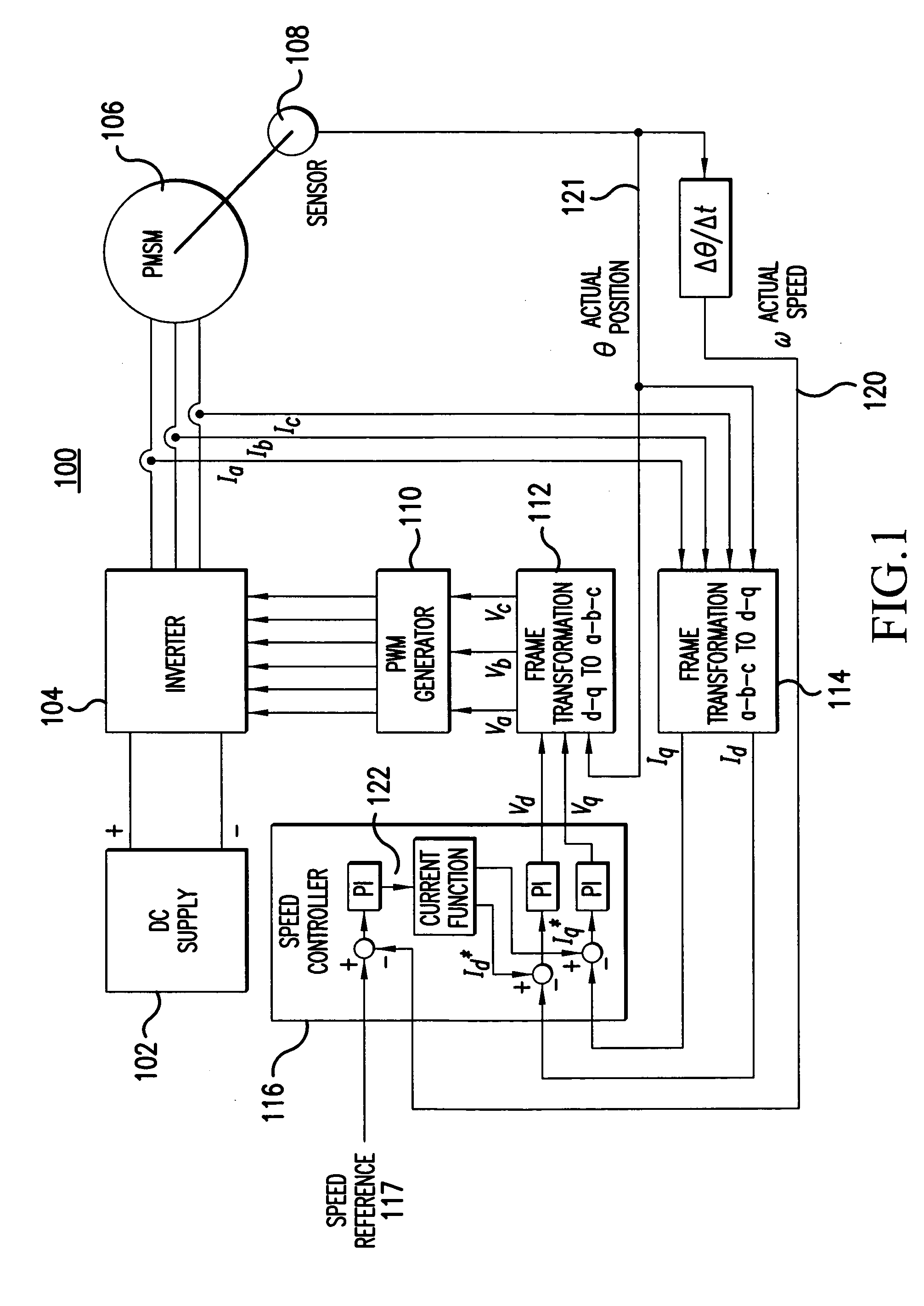
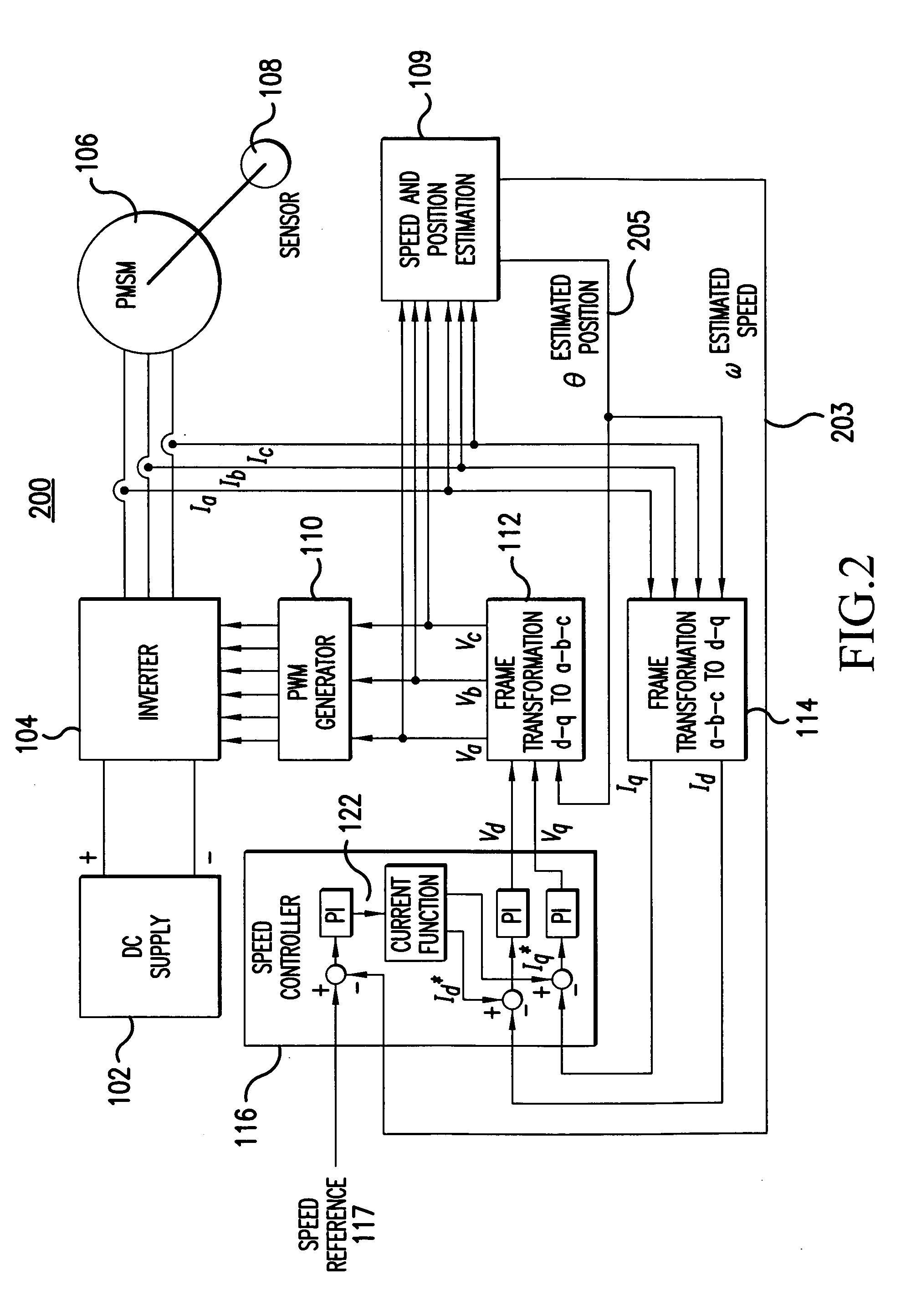
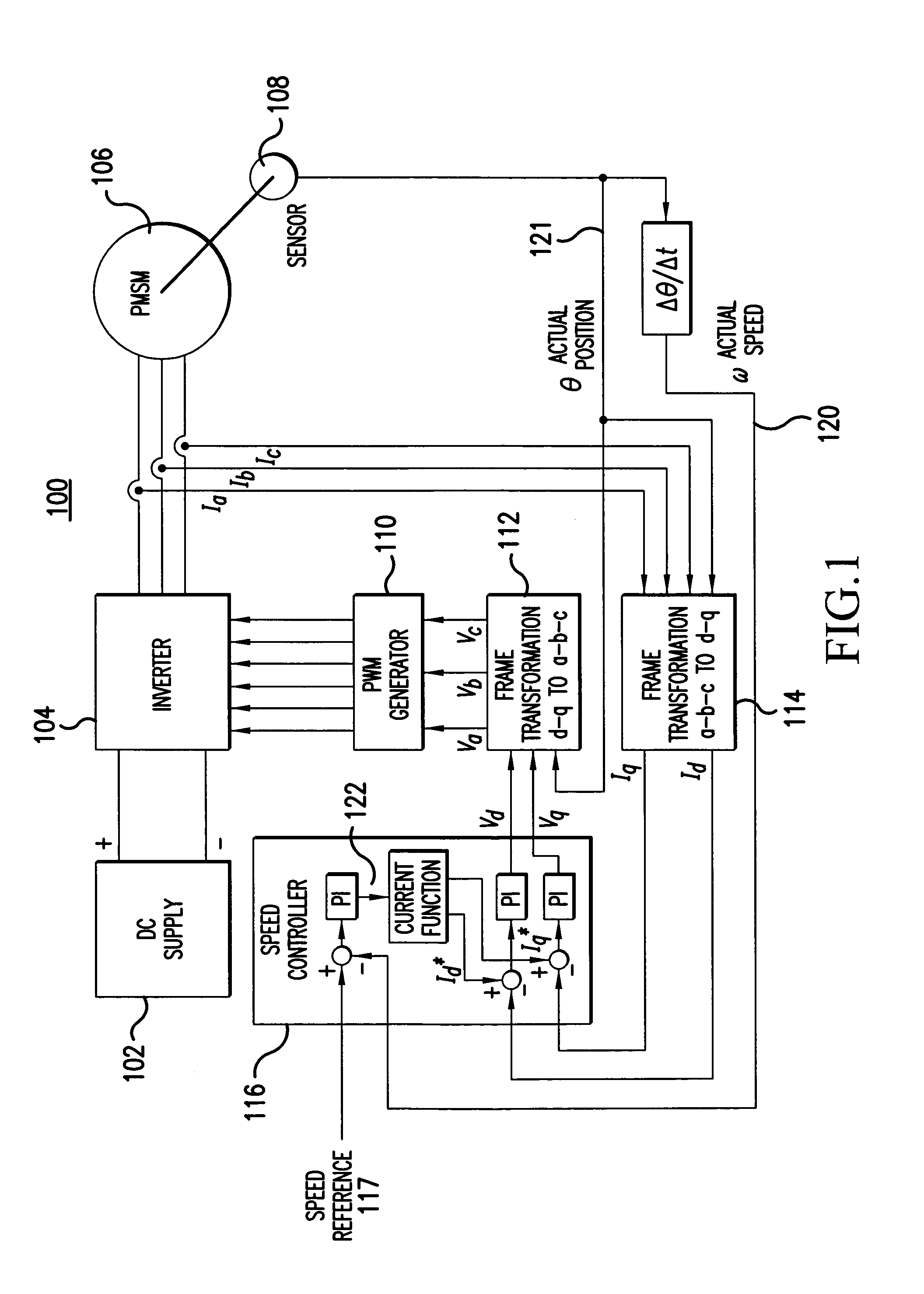
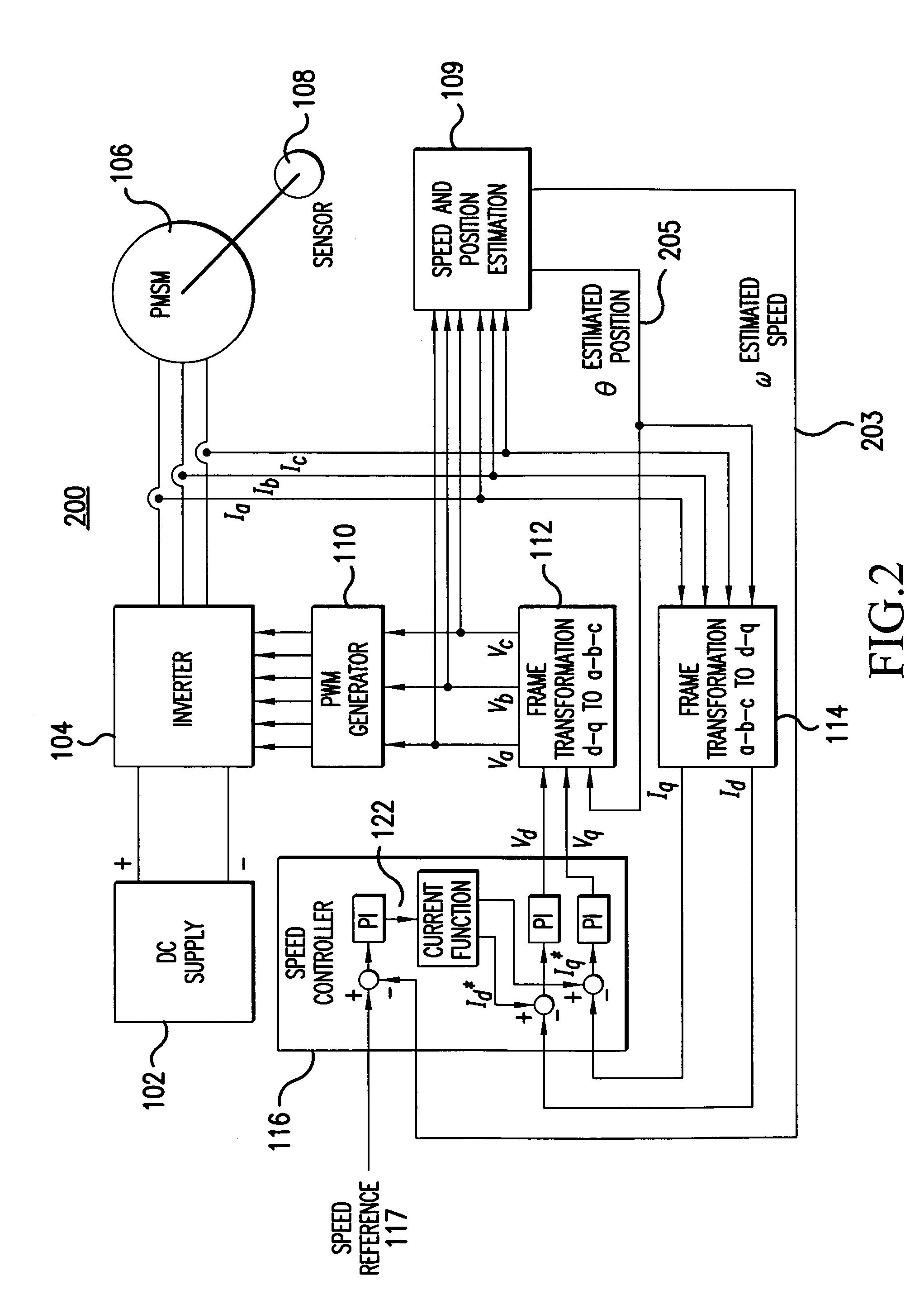
Sensorless control method and apparatus for a motor drive system
InactiveUS20050007044A1Quick calculationAccurate predictionDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlKaiman filterControl power
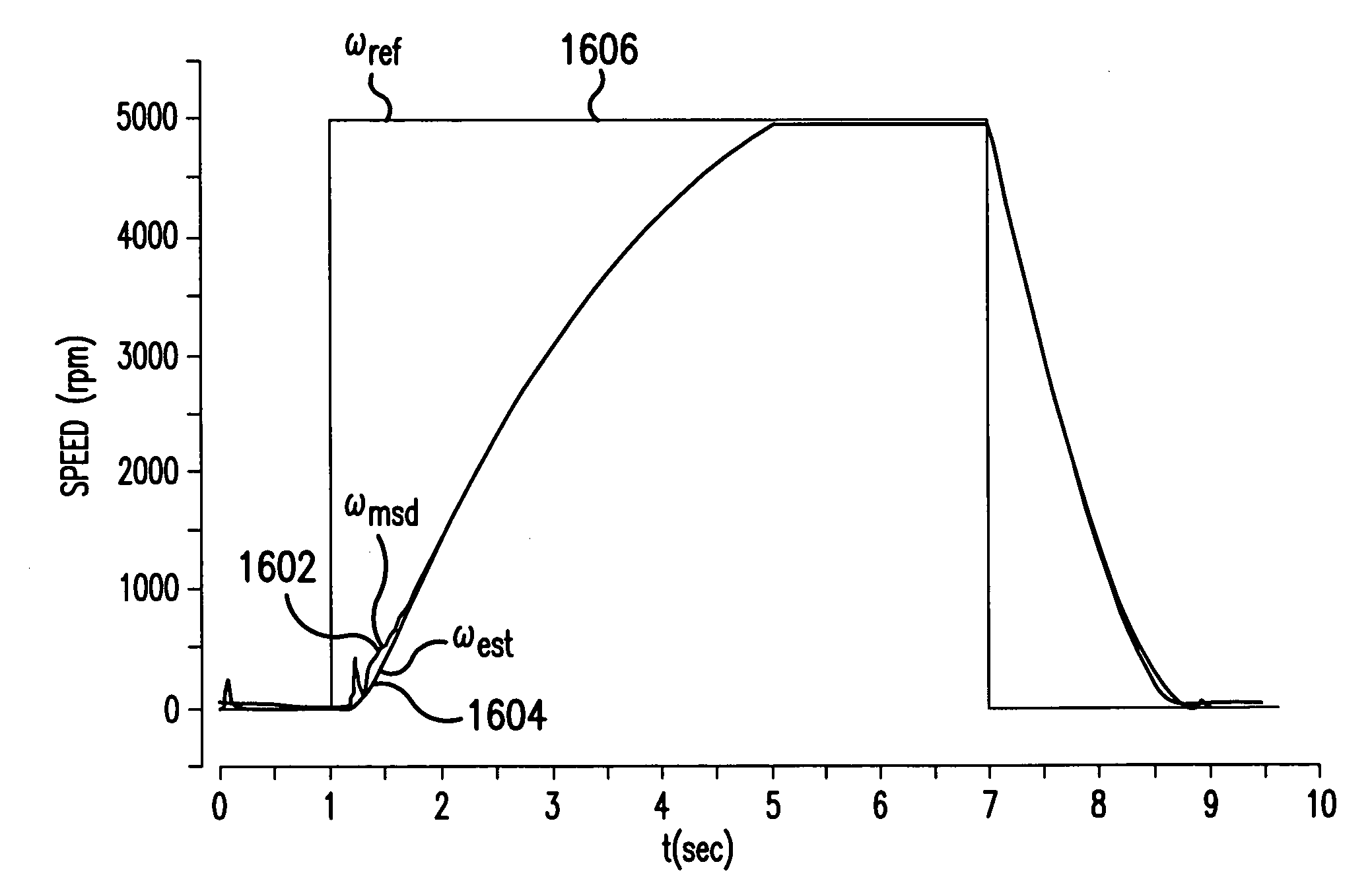
A method and apparatus provide a state observer control system 600 for a motor 106 that uses an extended Kalman filter 330 to predict initial rotor position and afterwards accurately predict rotor position and / or speed under variable types of loading conditions. A control system model 300 is generated that allows variable setting of an initial rotor position to generate estimated rotor position and speed as outputs. The control system model 300 includes an EKF (extended Kalman filter) estimator 330, speed controller 322, a current controller 324, and a variable load component 310. During operation, EKF estimator 330 estimates rotor speed 327 and position 333 based on reference voltages 402, 404 and currents 1325 generated by speed and current controllers 322, 324 and input from frame transformers 326, 328. Additionally, the reference currents and voltages 402, 404, 1325 are frame-transformed to be used as feedback signals 418, 346 in the system 600 and as drive signals to control power to be applied to a motor load 602.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
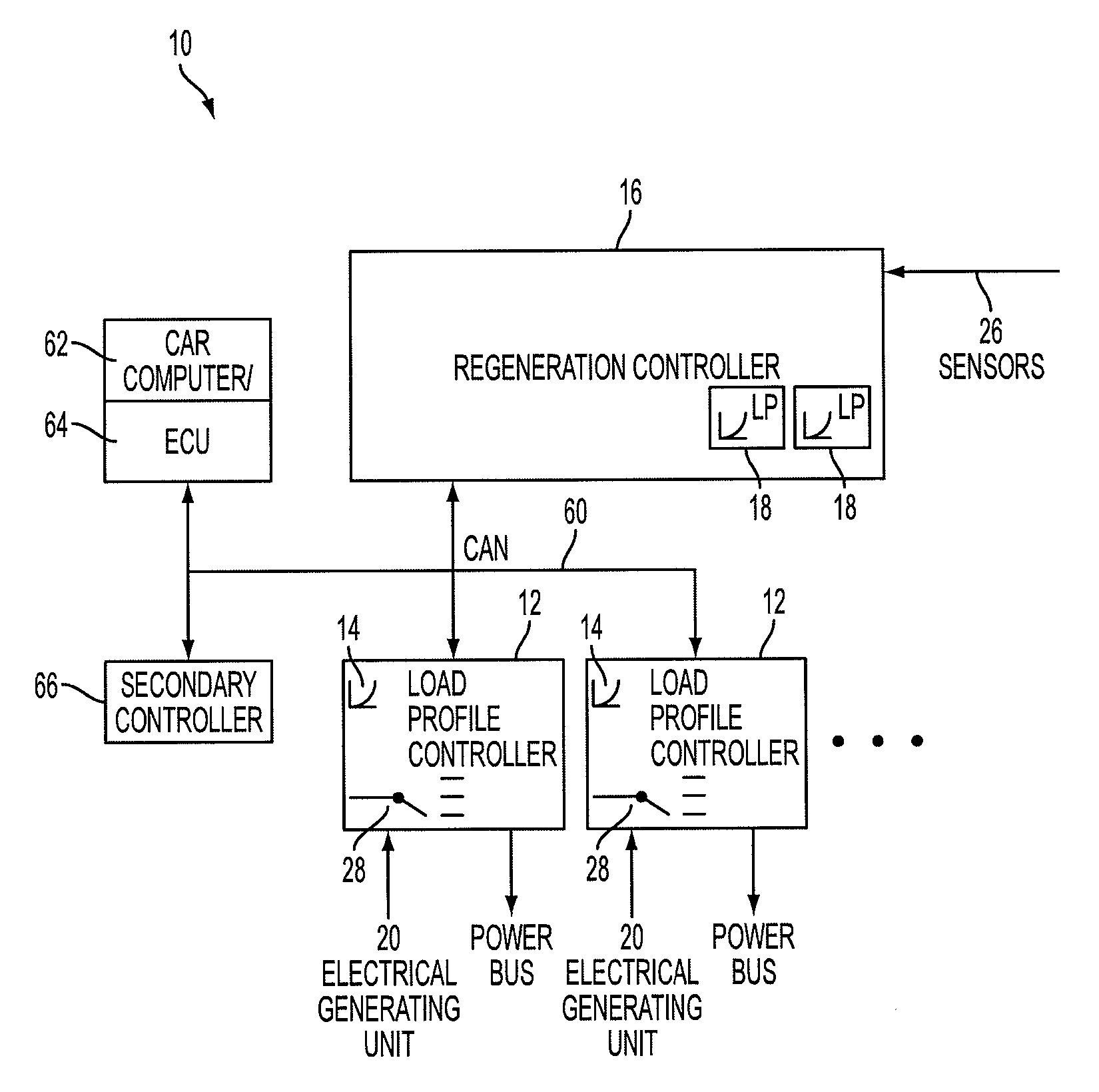
System and method for control for regenerative energy generators
ActiveUS20100262308A1Safe and efficient chargingSupply energyAuxillary drivesLevel controlArea networkOn board
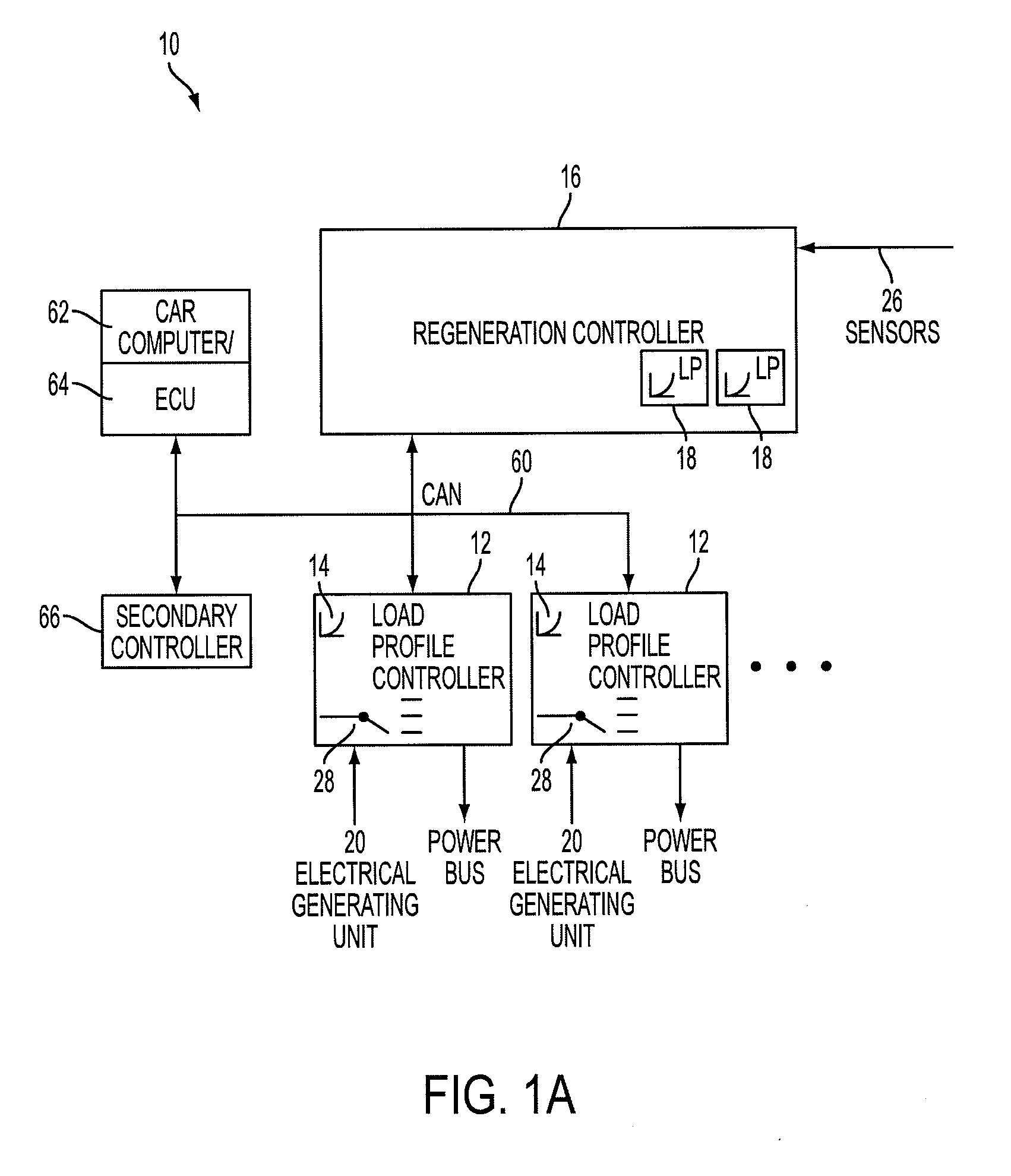
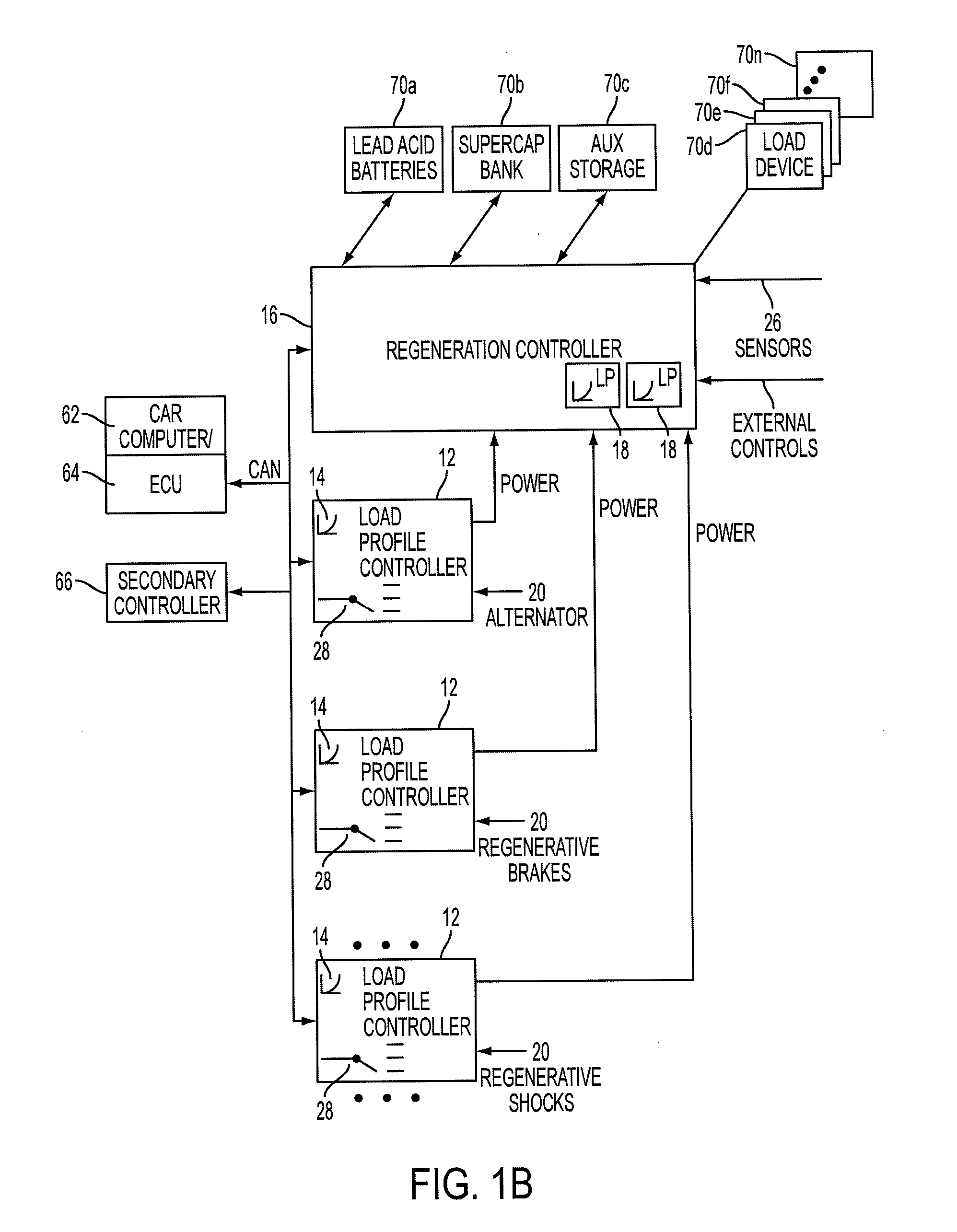
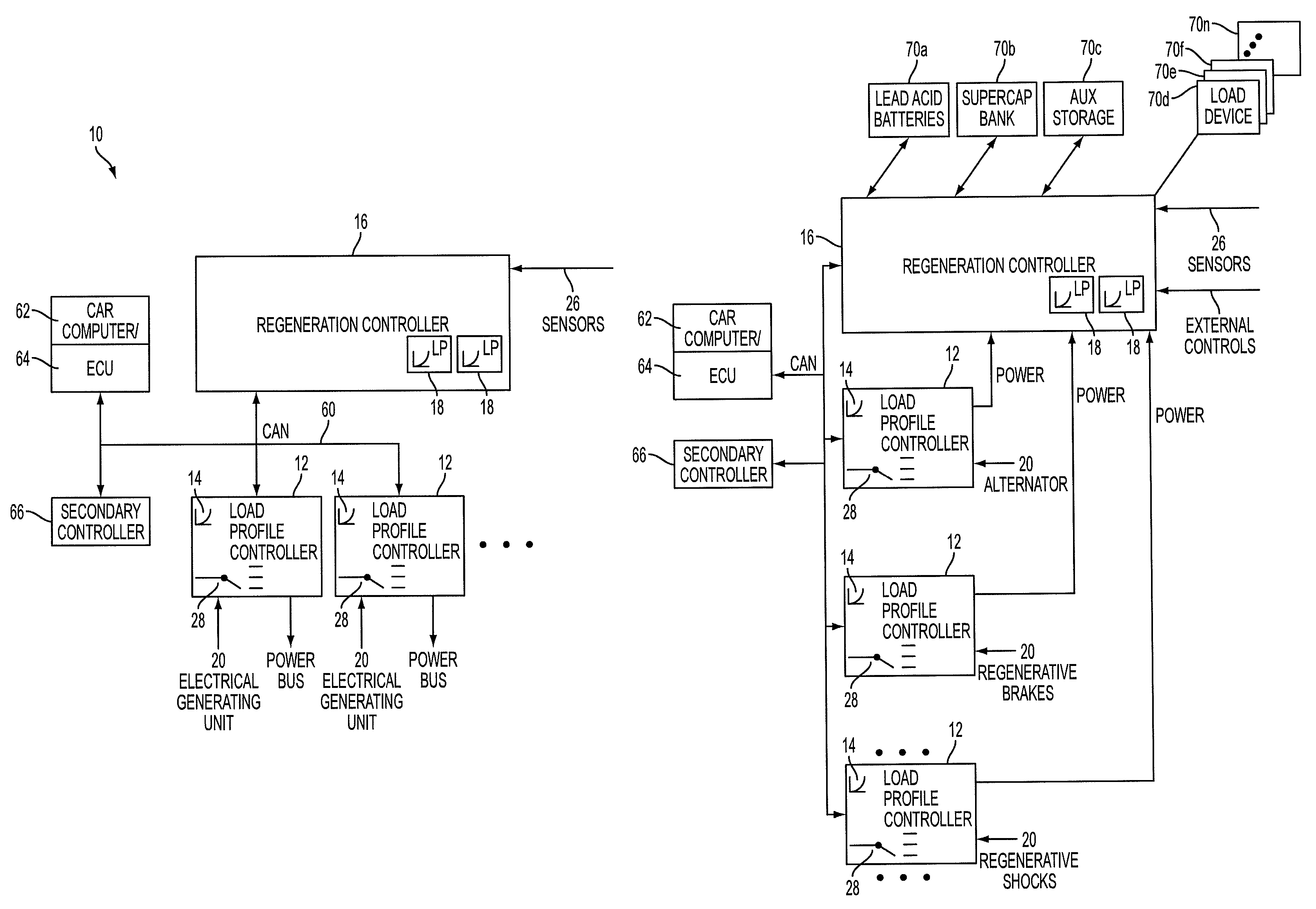
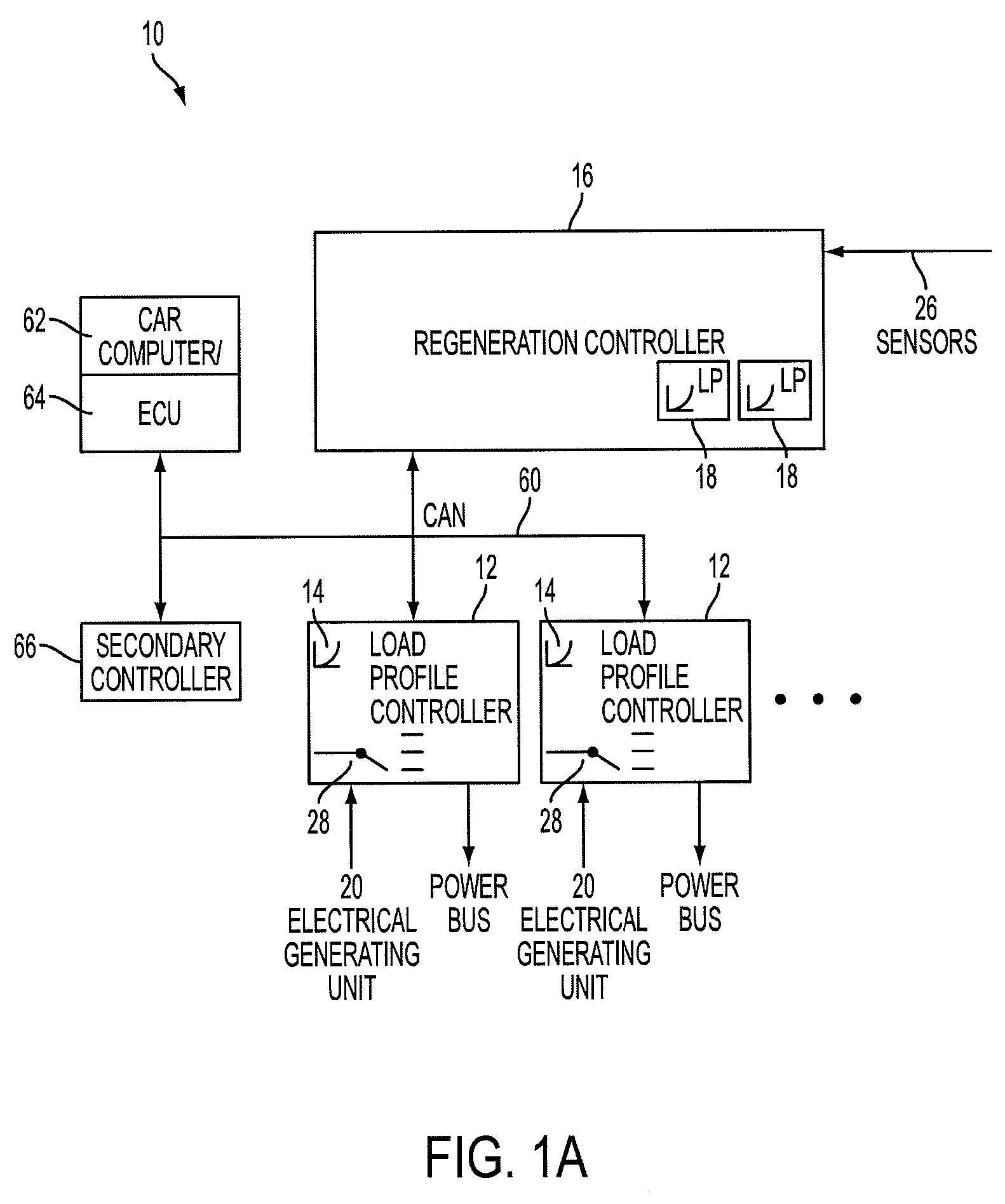
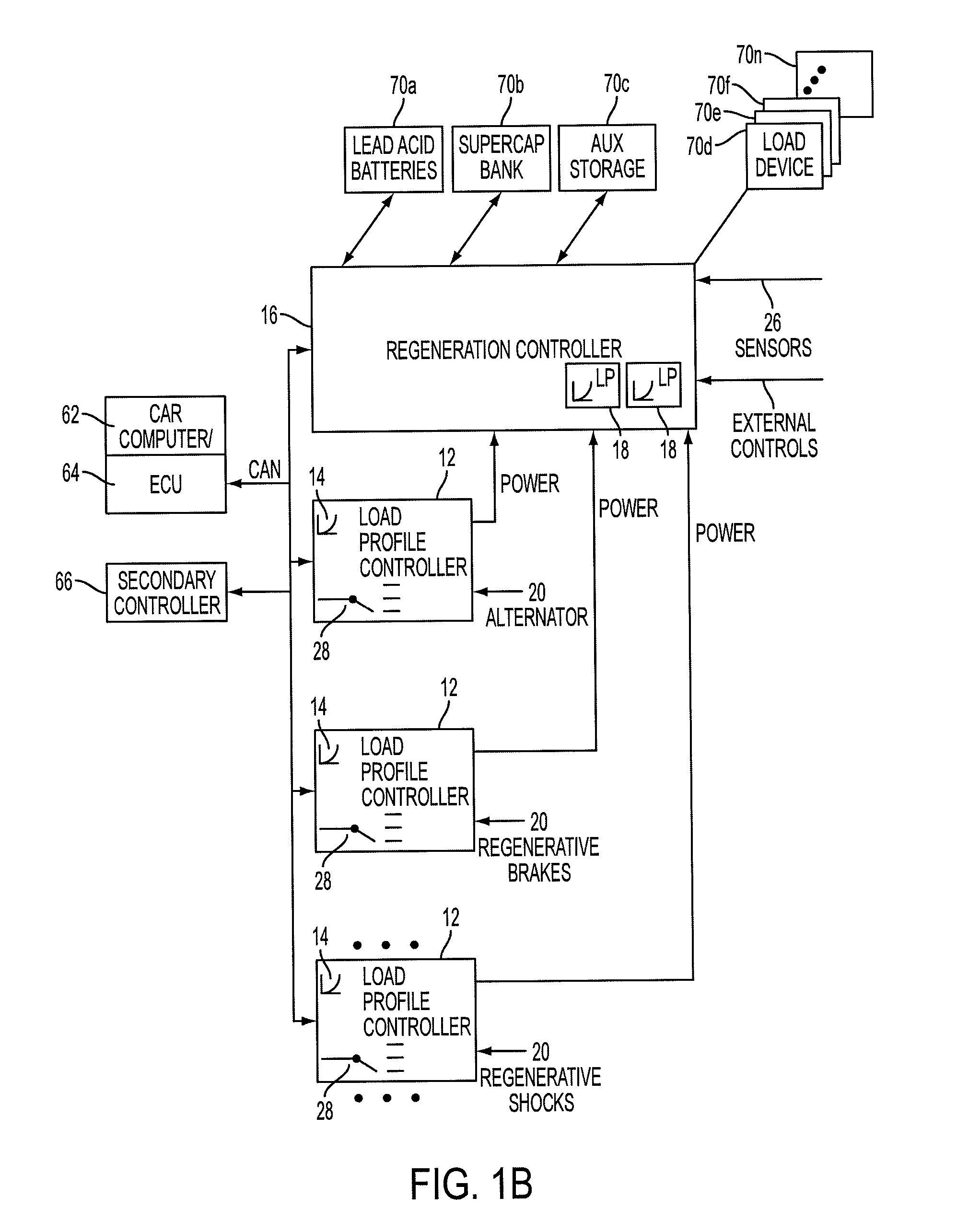
A device and system that can dynamically provide variable load on a generator and intelligently distribute generated power to loads and energy storage devices is disclosed. One system includes load profile controllers that employ a switching strategy to dynamically vary the load the generator induces while producing regenerative energy. This switching strategy may allow for a wide dynamic range of configurable damping characteristics, as well as decouple generator damping and the system output power. Multiple load profile controllers can be used together via a communications network, such as a vehicle controller area network (CAN) bus. A central regeneration controller or existing electronic control unit (ECU) can issue commands to change damping performance in different load profile controllers. By networking multiple load profile controllers together in either a distributed or centralized manner, the system may allow for intelligent power routing, coordination of multiple energy-generating devices (such as regenerative shocks and brakes), and improved utilization of on-board energy storage devices.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
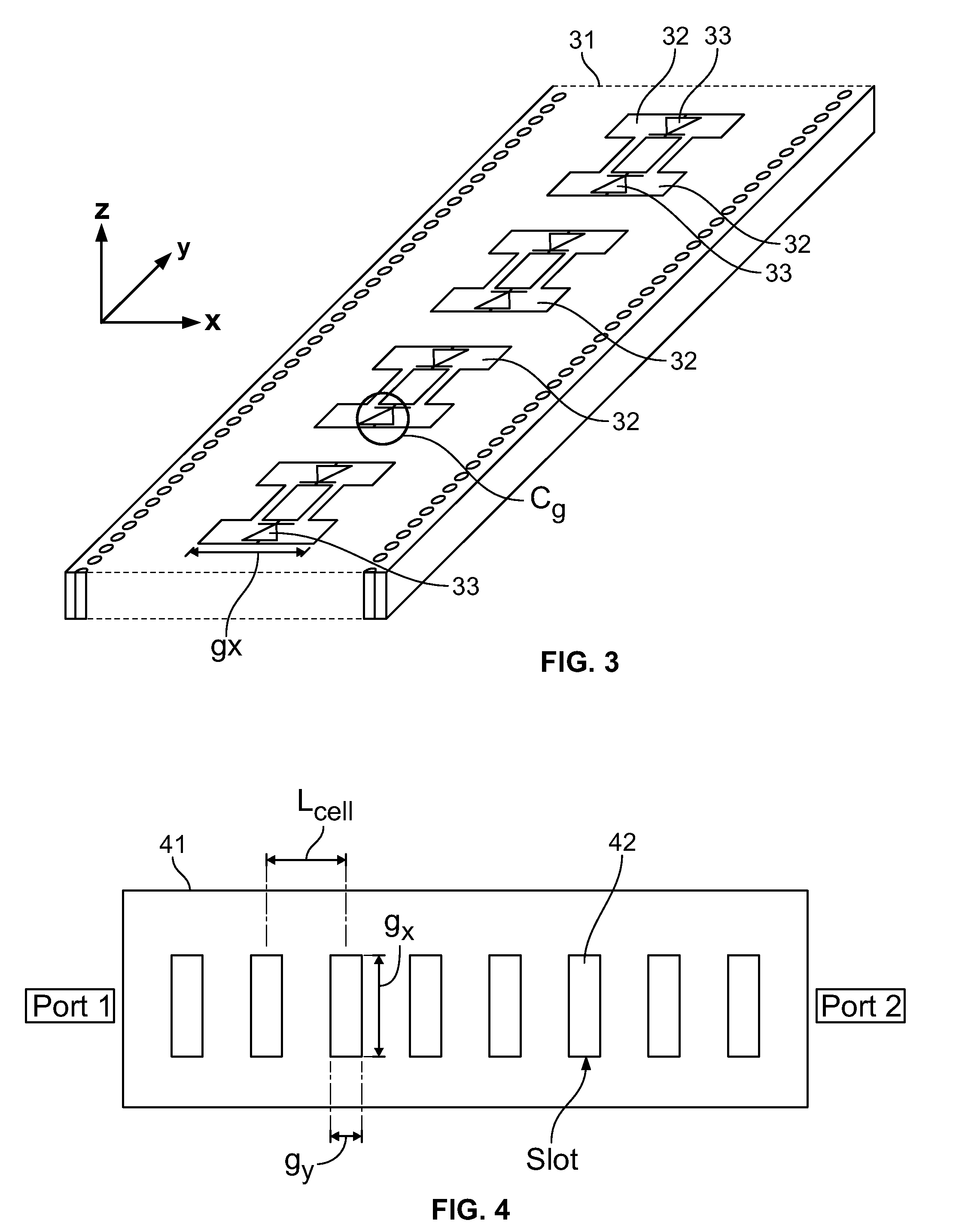
Tunable substrate integrated waveguide components
A method and an apparatus are provided for providing a tunable substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) for which a parameter of at least some element or portion thereof may be altered or varied to alter the propagation of a signal propagating through the SIW thereby achieving a tunable SIW. In some embodiments a plurality of capacitively variably loaded transverse slots achieve the tunability for the SIW.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
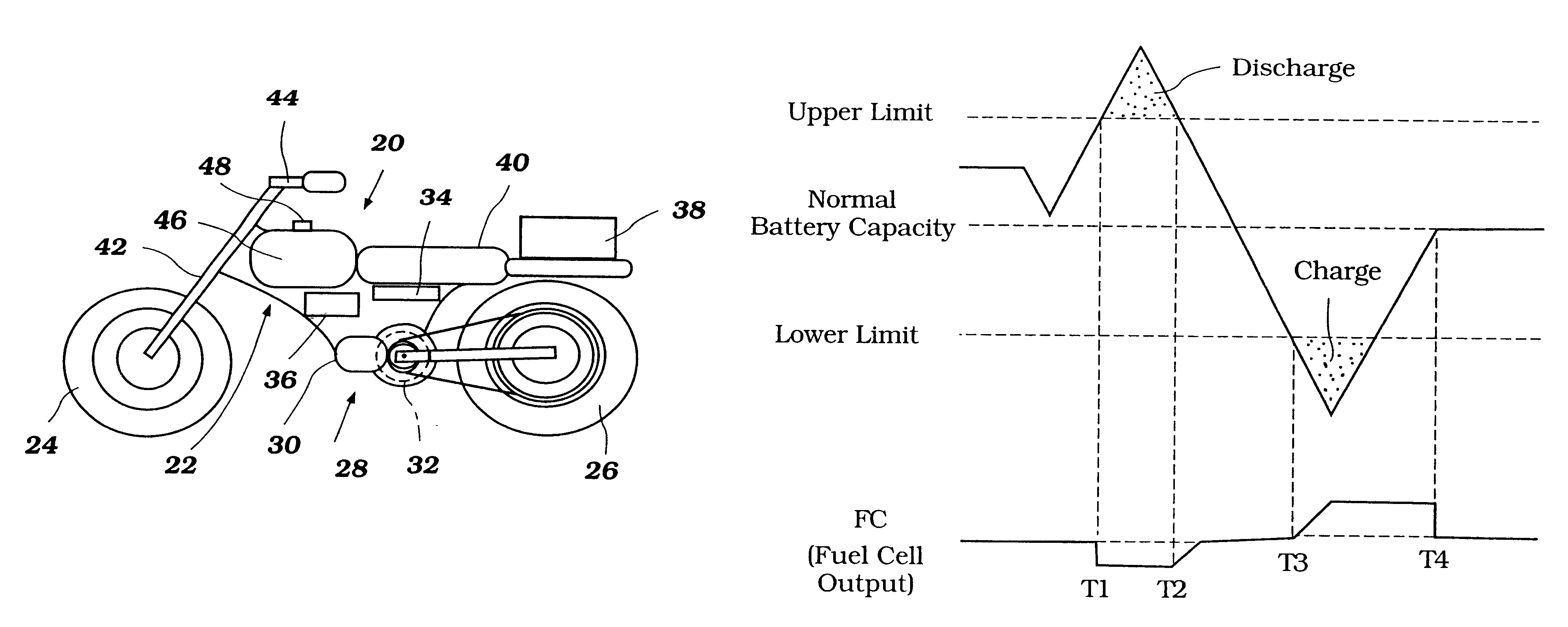
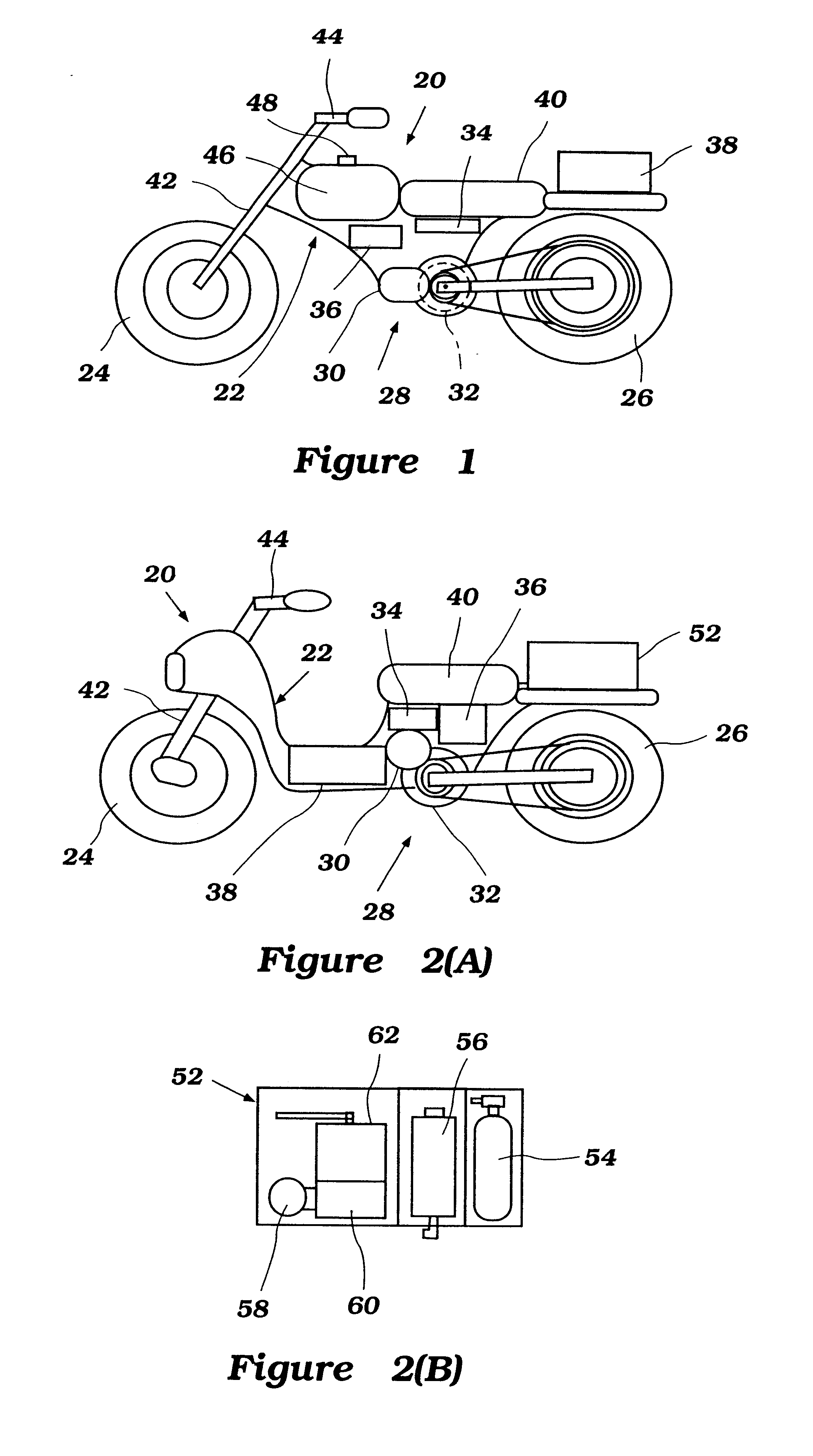
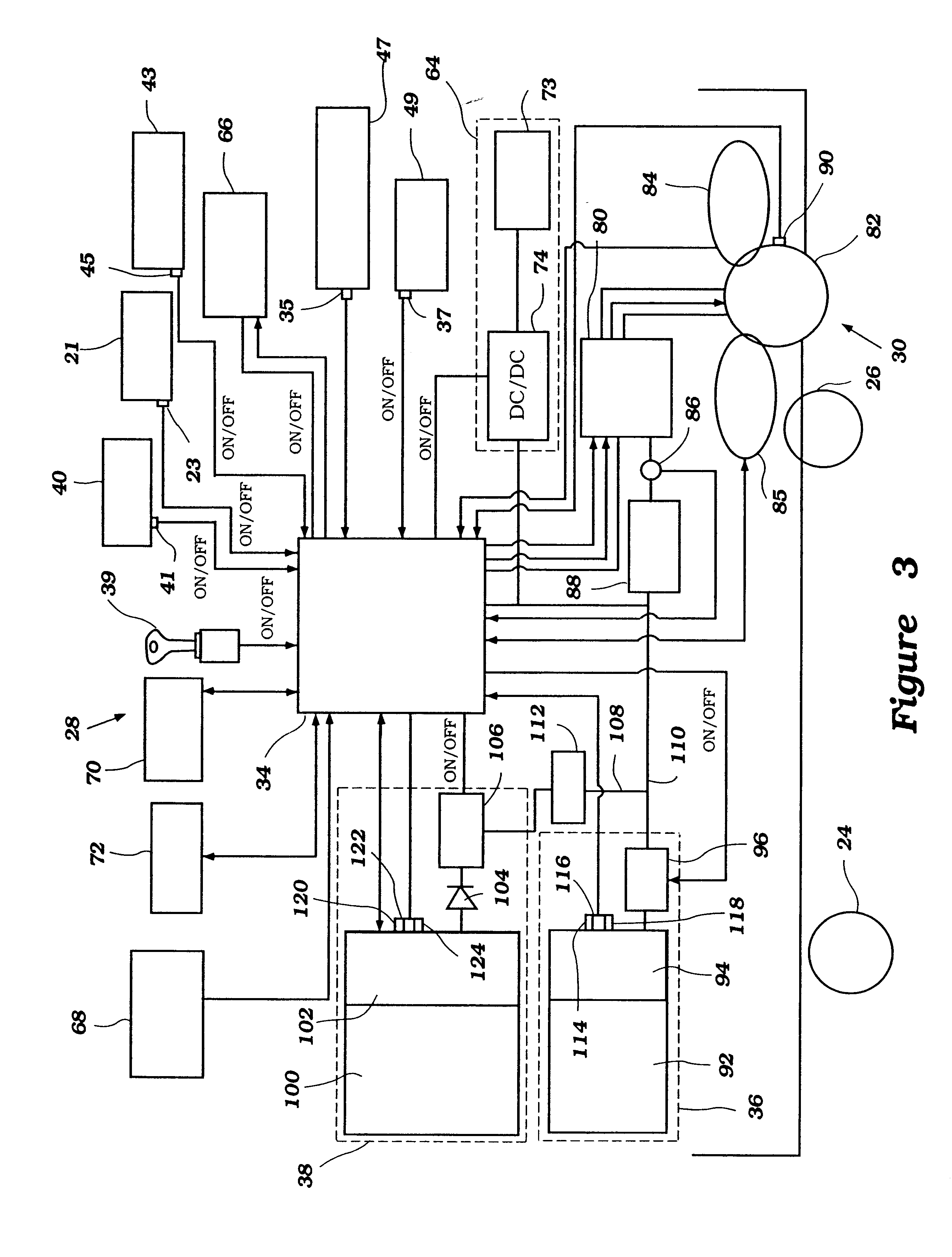
Power source control method for an electric vehicle
InactiveUS6555928B1Batteries circuit arrangementsFuel cell auxillariesEngineeringBattery electric vehicle
An electric vehicle comprises a first power source and a second power source. The first power source can be used to supply a substantially constant base power level and the second power source can be used to supply a variable power level such that a variable load demand can be filled by combining the base power level and the variable power level. The first source can be used to supply power to the second source when the second source is operating at a decreased charge or power level. The base power level can be varied based upon the remaining charge or power level contained within the second source. A number of control methods for operating the power supply of the electric vehicle are disclosed.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Grid responsive control device
InactiveUS20110190958A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce probabilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlPower gridEngineering
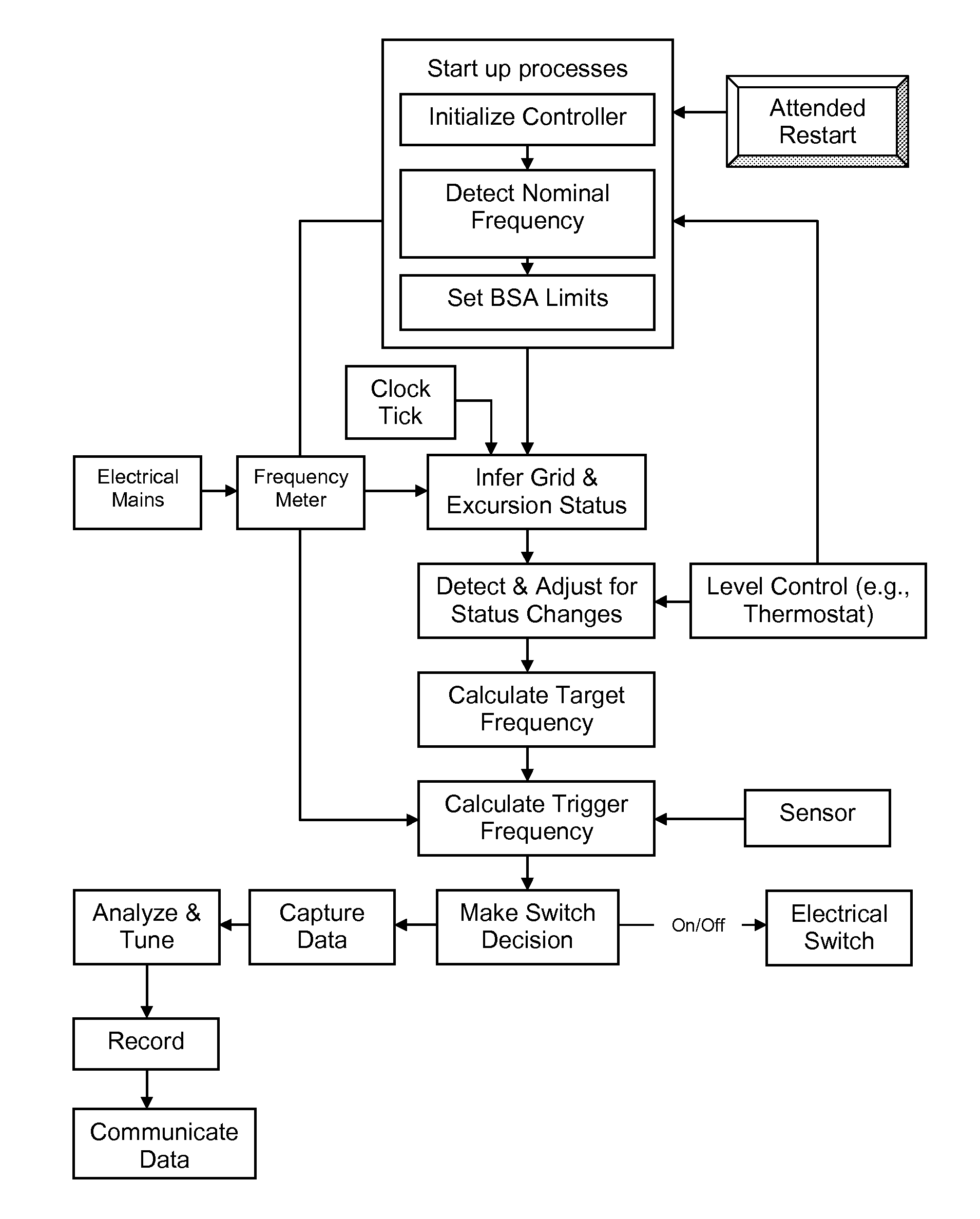
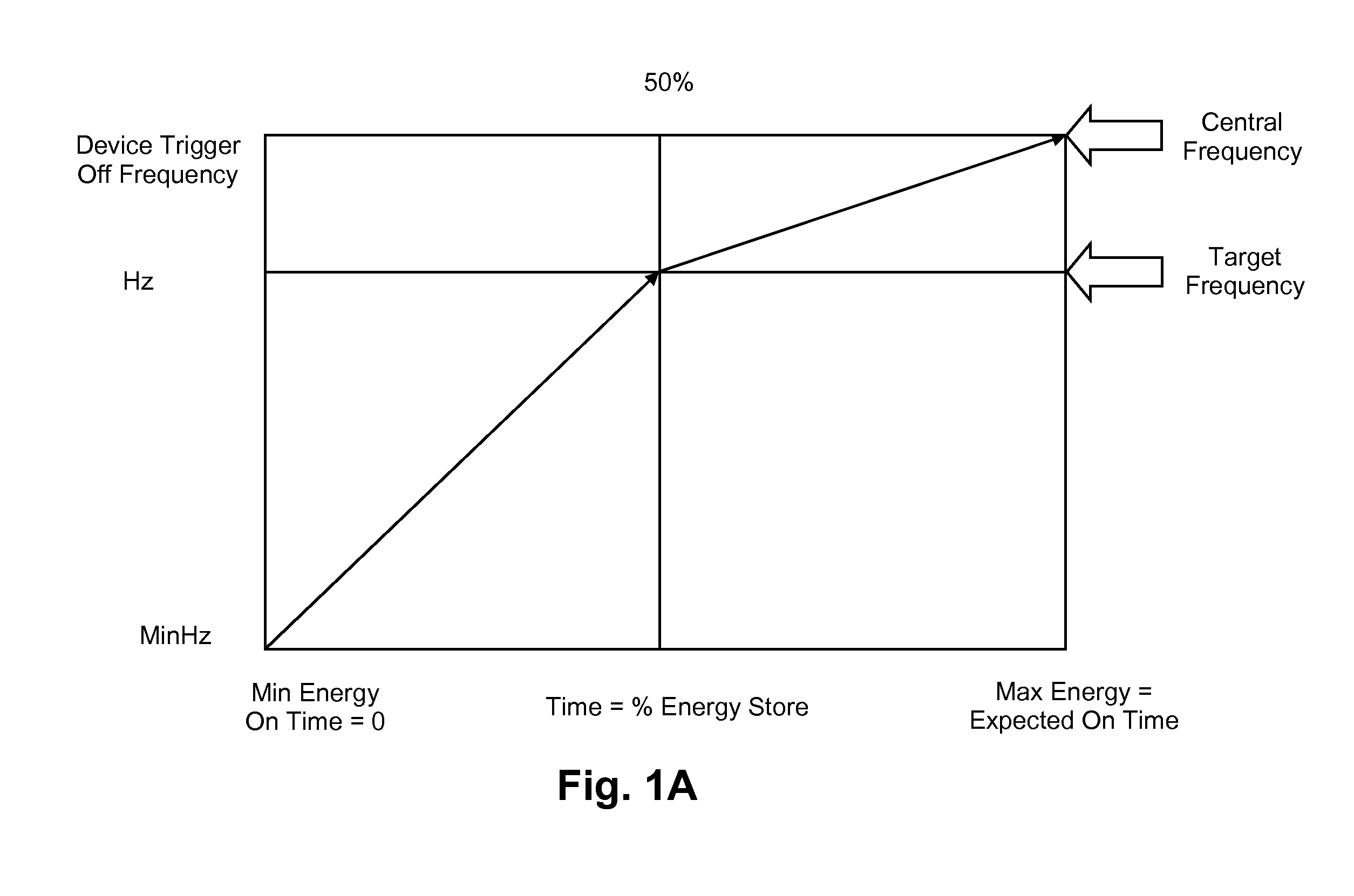
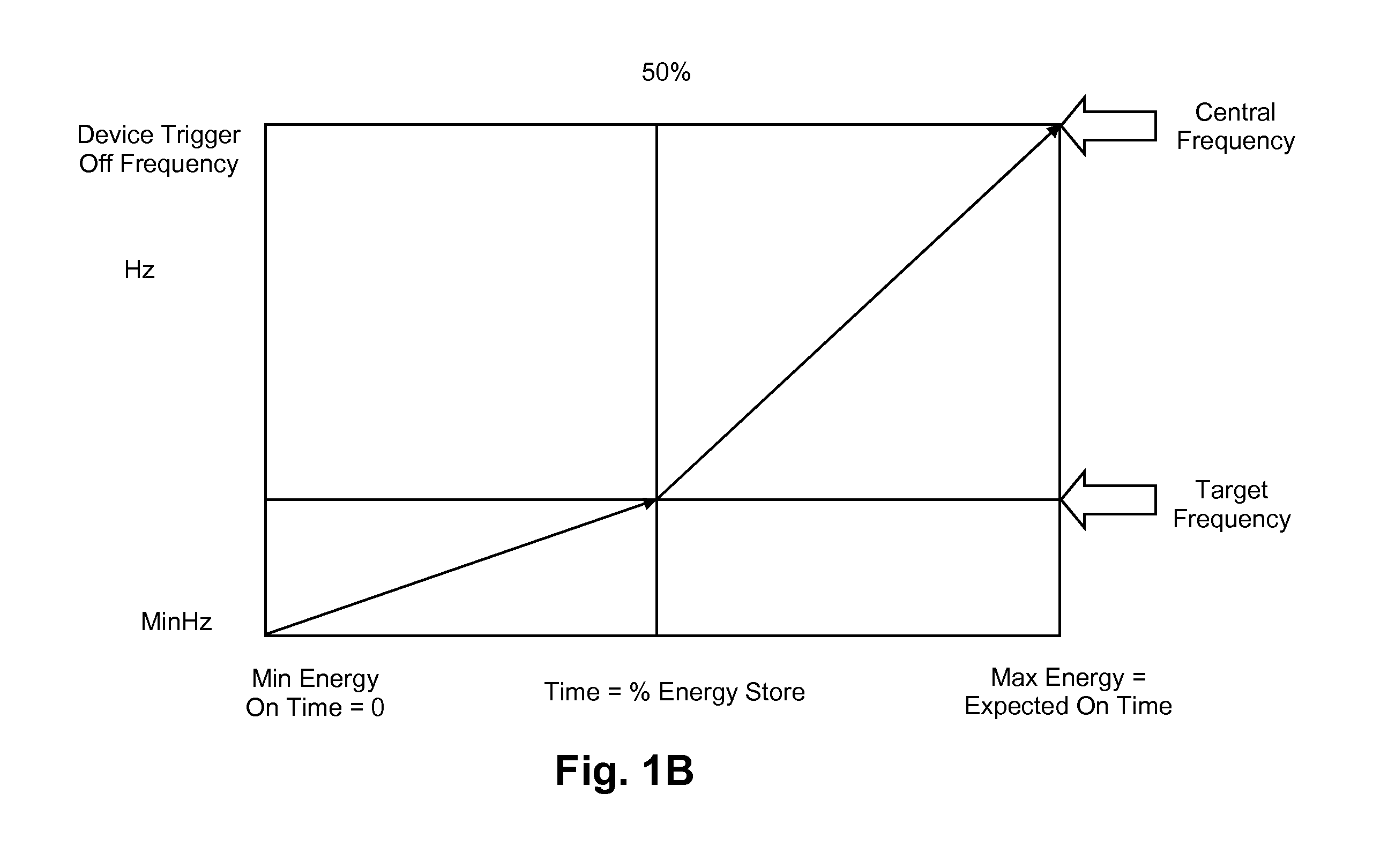
A load control device which is responsive to a physical variable representing the balance between load and generation on an electricity grid. The control device varies the energy consumption of the load based on the current value of the physical variable of the grid relative to a central value of that physical variable, which is derived from past readings of the physical variable of the grid. The grid responsive control device also takes into account the time since the load last varied its energy consumption in determining whether or not the grid variable load control should be provided.
Owner:RESPONSIVELOAD LTD
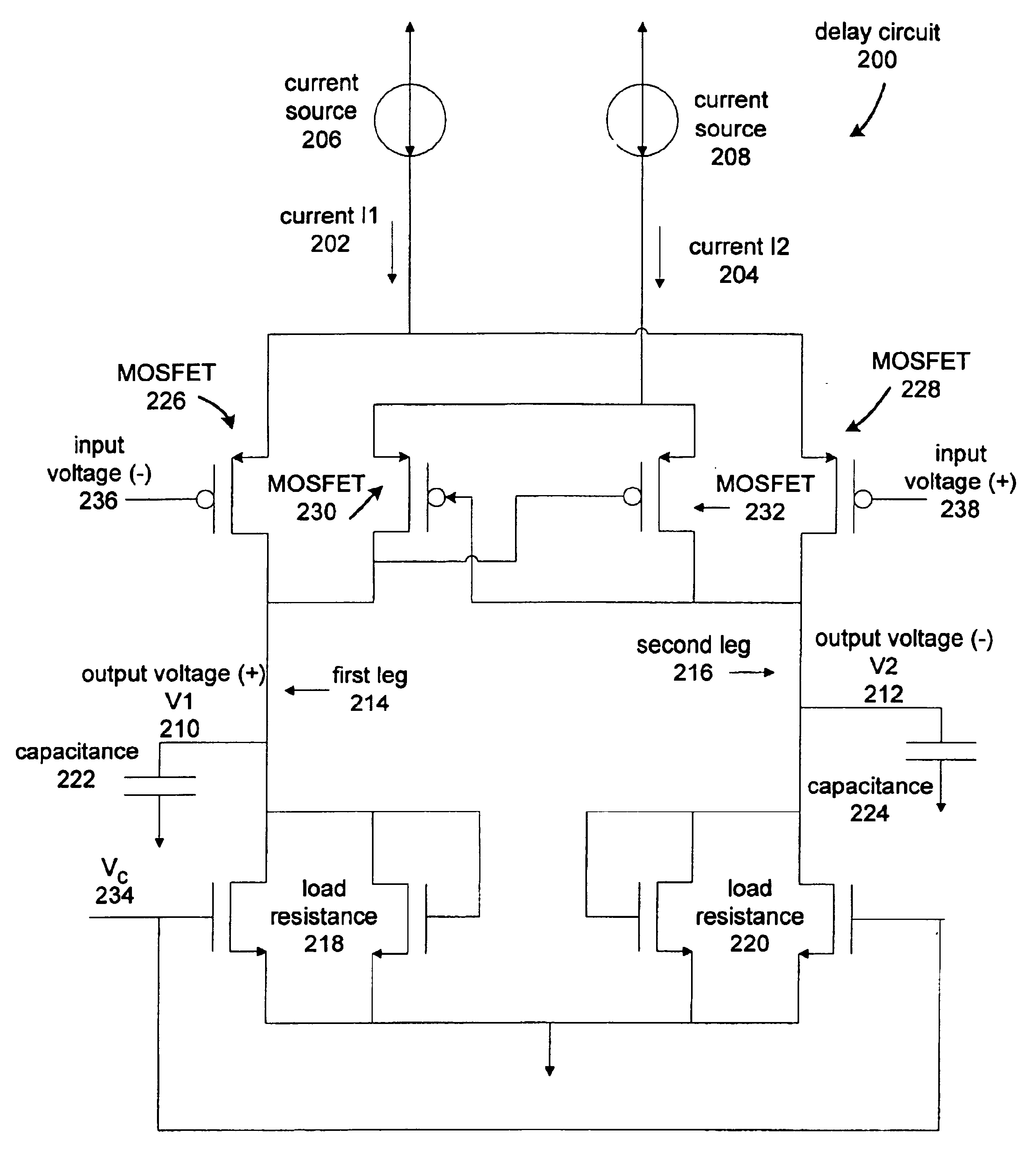
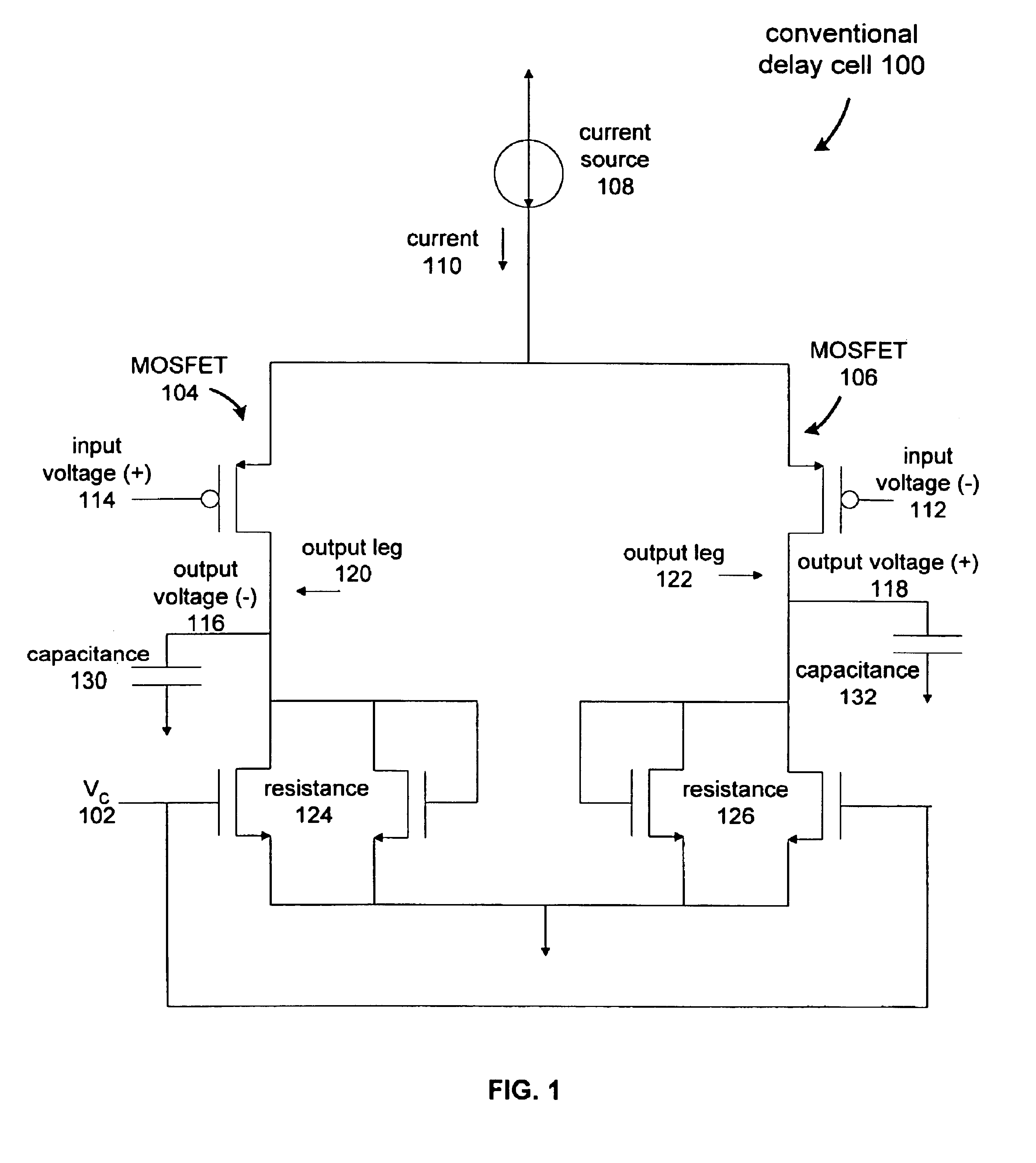
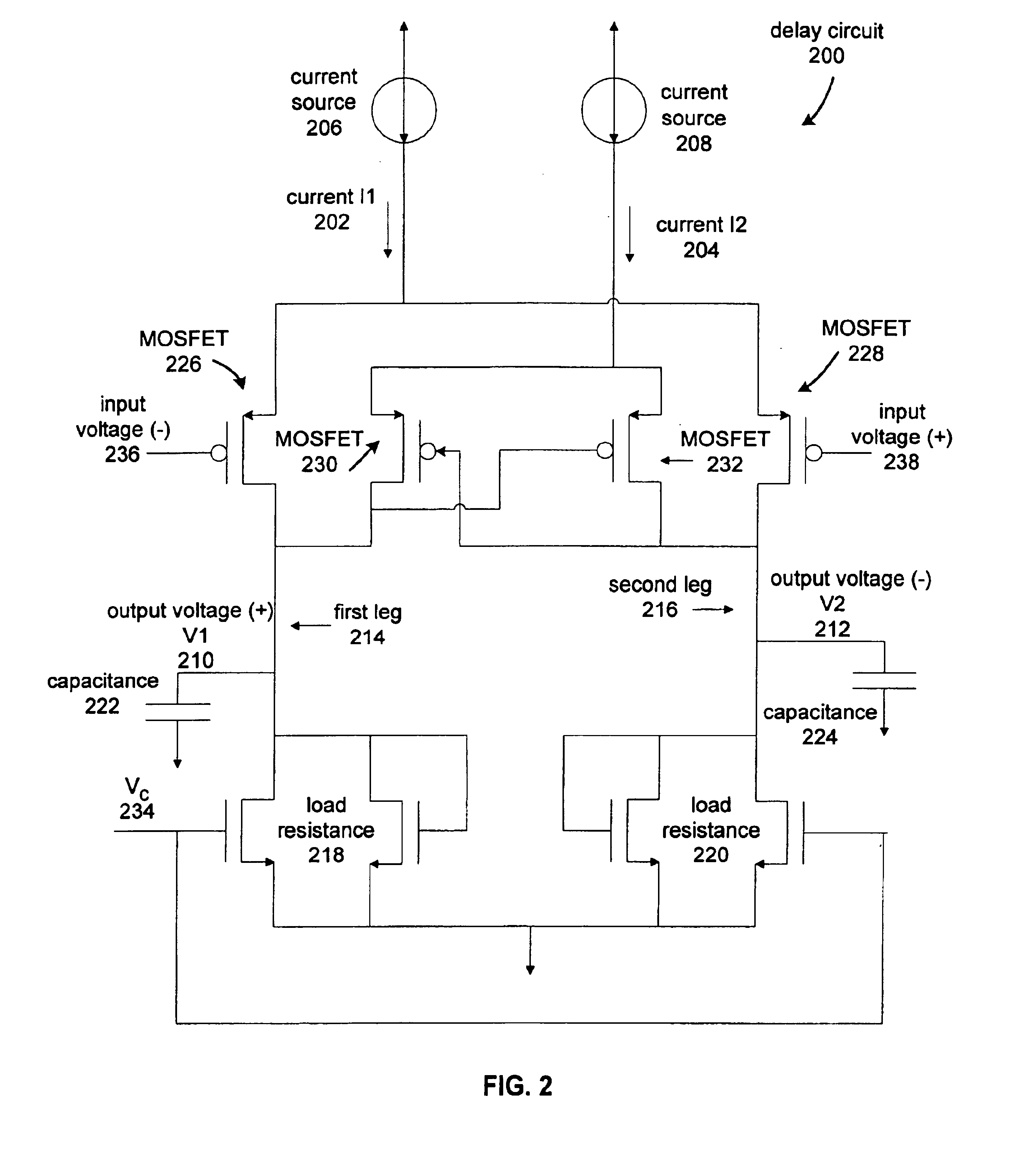
Current controlled delay circuit
A current controlled delay circuit is disclosed. Two currents of constant sum are generated to control the delay of the circuit. The circuit includes a differential pair to switch one of the two currents from one leg of the circuit to another leg of the circuit. The circuit includes a cross-coupled pair to switch the other of the two currents from one leg of the circuit to another leg of the circuit. The circuit may include a fixed or variable load.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
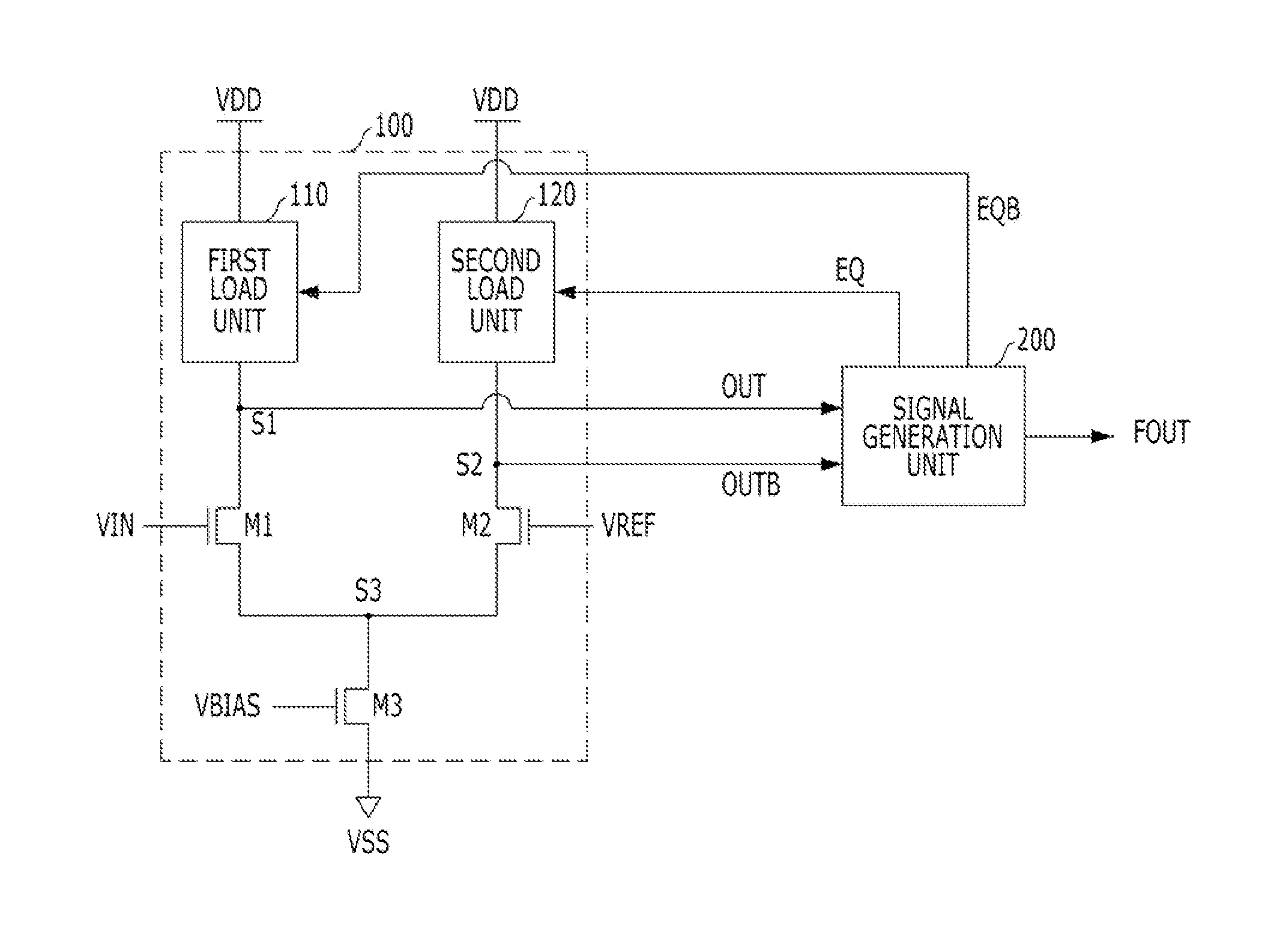
Receiver circuit with de-emphasis function
ActiveUS20140177696A1Effective compensationMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringEqualization
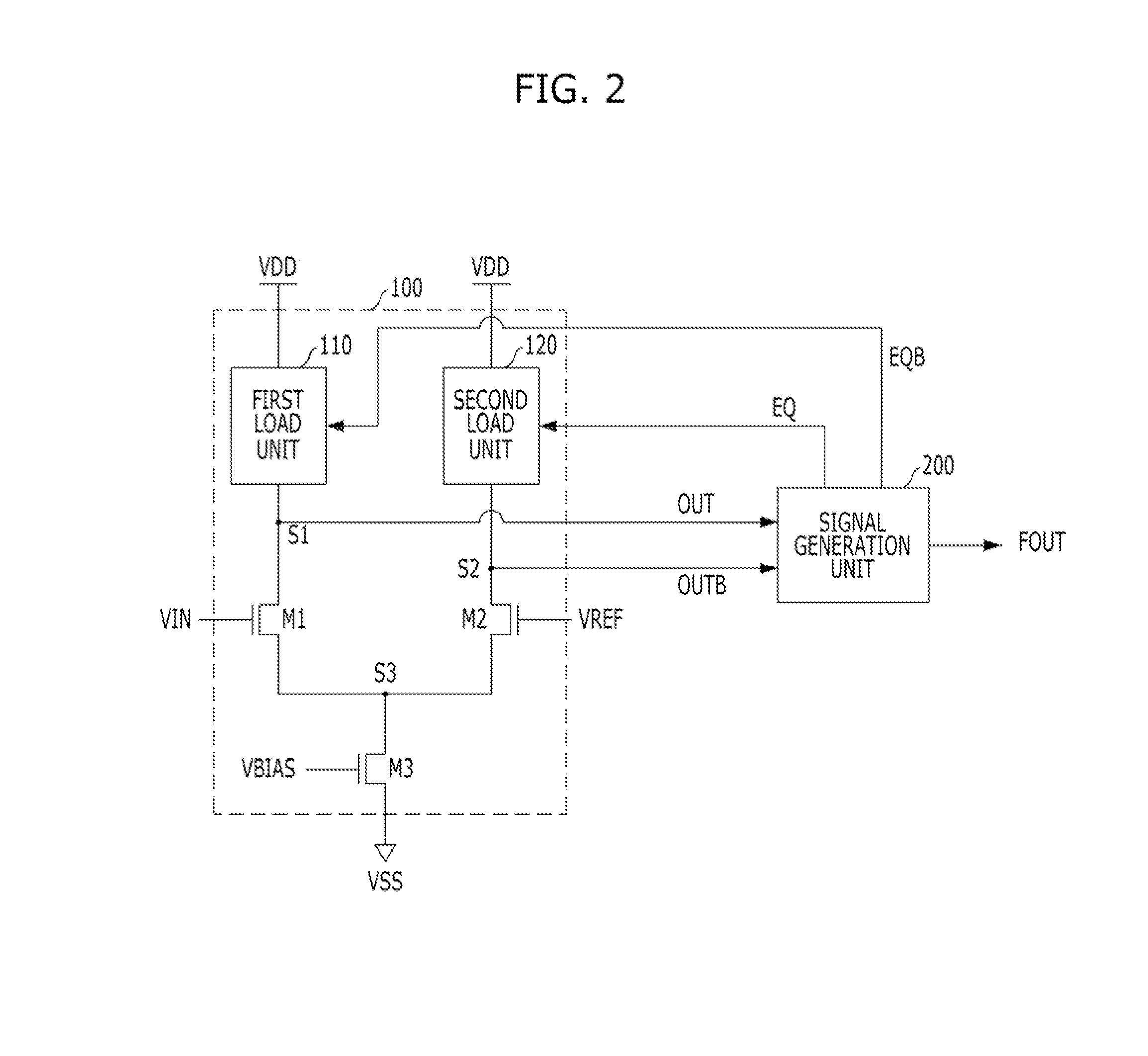
A receiver circuit includes a first differential amplification unit including a variable load section, and configured to receive first and second input signals, and to generate first and second output signals, which are amplified based on an impedance value of the variable load section and a voltage difference between the first and second input signals, a second differential amplification unit configured to receive the first and second output signals and to generate a third output signal based on a voltage difference between the first and second output signals, and a signal generating unit configured to generate an equalization signal for controlling the variable load section based on the third output signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Integral optimization method and system for automatic power generation system of coal-fired unit
ActiveCN103513640AImprove variable load capacityImprove adaptabilityProgramme total factory controlSteam pressureDynamic models
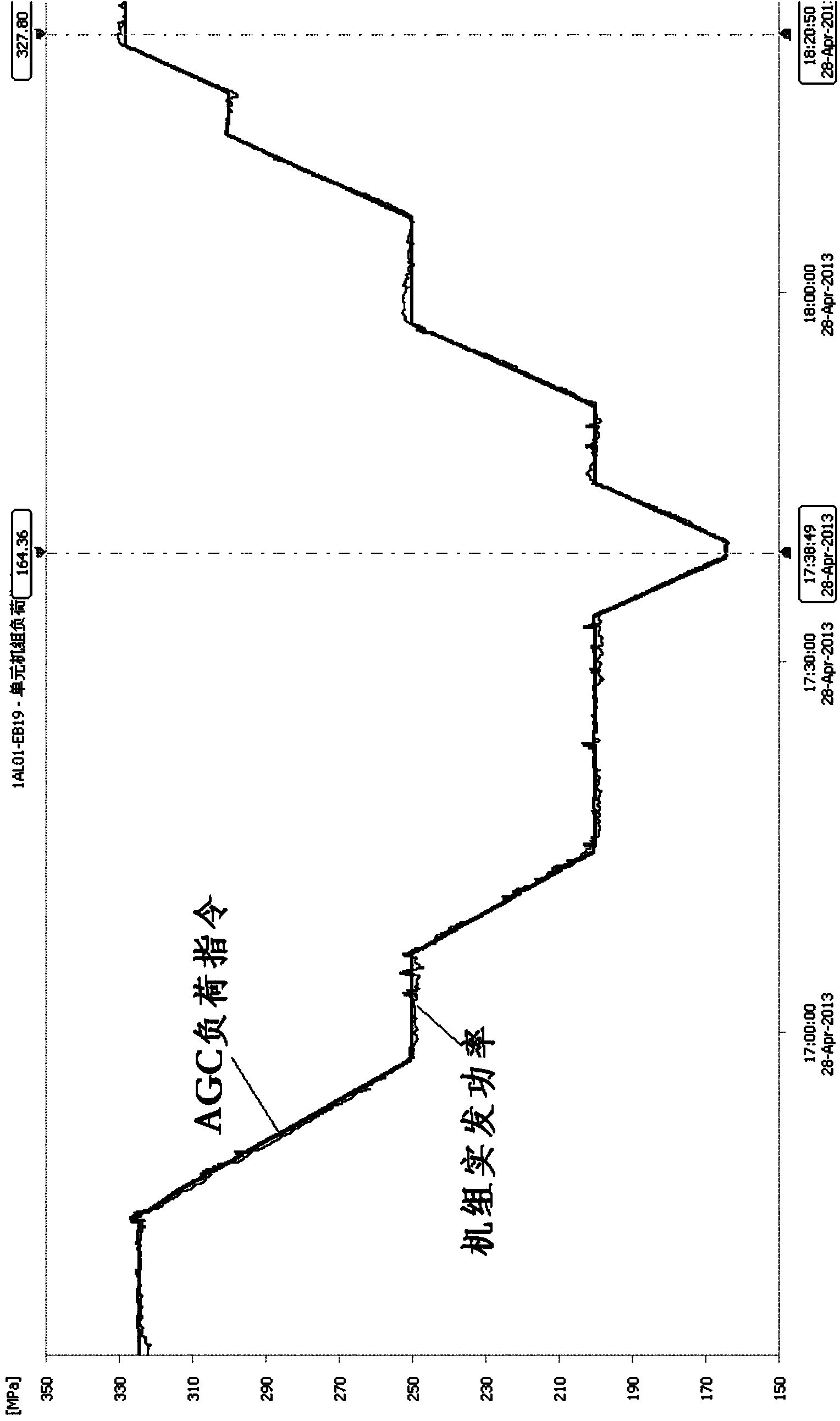
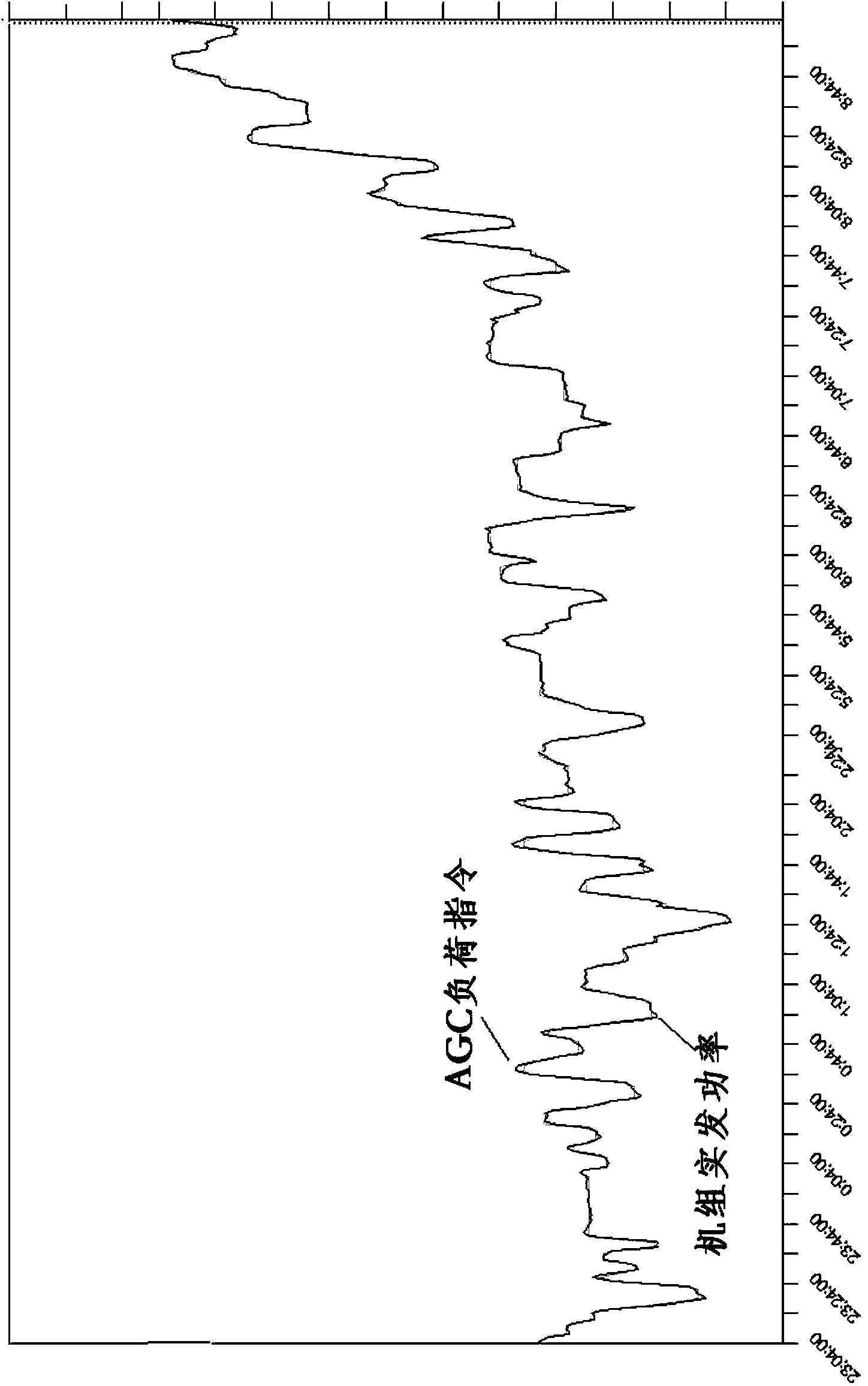
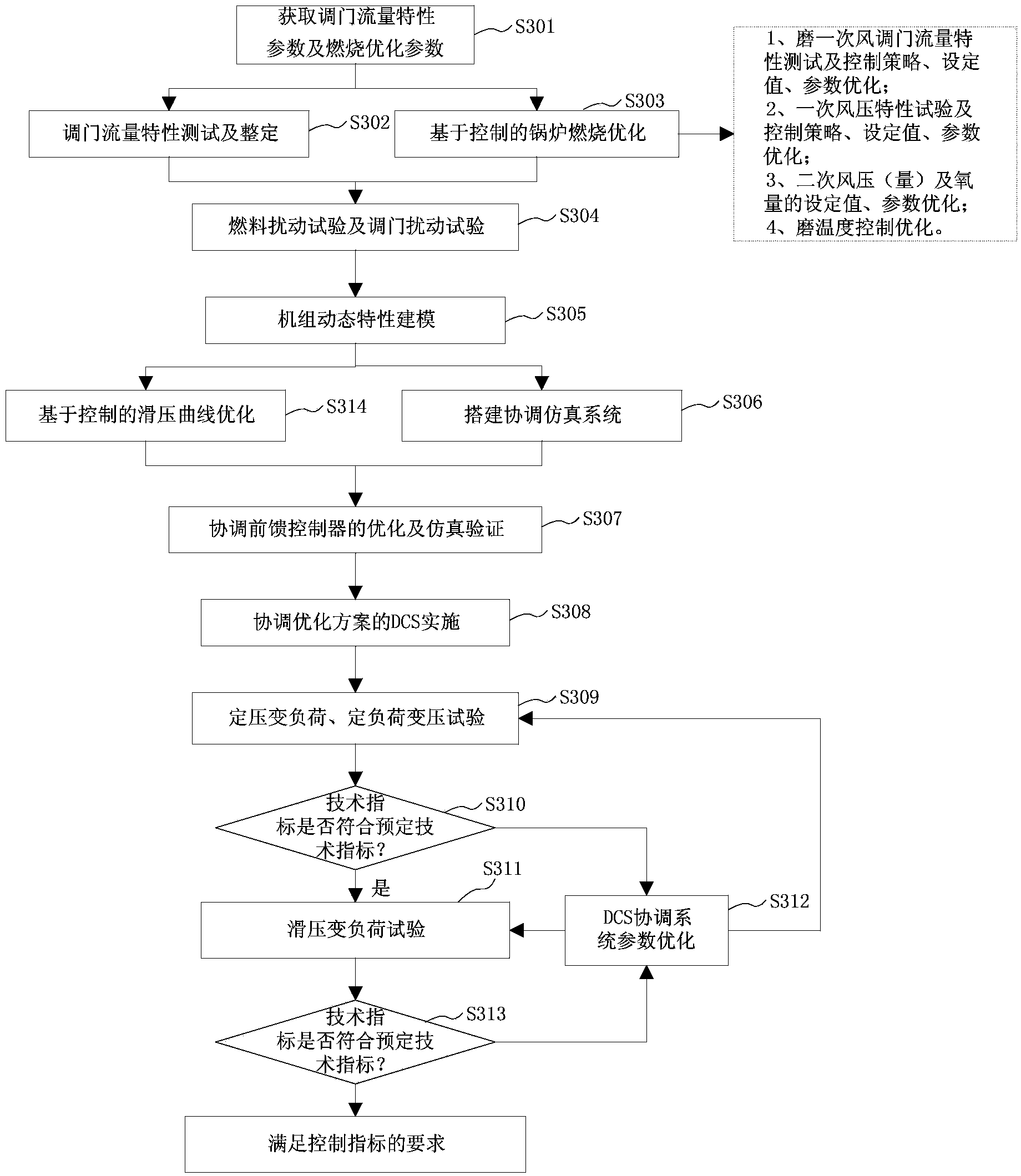
The invention provides an integral optimization method and system for an automatic power generation system of a coal-fired unit. The method comprises the steps of carrying out control valve flow characteristic test and adjustment according to control valve flow characteristic parameters, carrying out combustion optimization on a wind and smoke subsystem and a combustion subsystem, carrying out a fuel disturbance test and a control valve disturbance test to generate typical test parameters, using the typical test parameters to generate a dynamic unit model, constructing a coordinating simulation system according to a coordinating controller and the dynamic unit model, using the dynamic unit model to optimize a feedforward controller and carry out simulation verification on the coordinating simulation system simultaneously, carrying out DCS configuration and parameter debugging in the simulation system, carrying out a constant-voltage slide-voltage variable-load test and a constant-load voltage-transformation test to generate technical indexes of the variable-load rate, the variable-load accuracy, variable-load response time and the main steam pressure accuracy, judging whether the technical indexes meet the preset technical indexes, and if on yes judgment, carrying out a slide-voltage variable-load test to enable the coal-fired unit to operate normally.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
System and method for control for regenerative energy generators
ActiveUS8392030B2Safe and efficient chargingSupply energyAuxillary drivesLevel controlArea networkOn board
A device and system that can dynamically provide variable load on a generator and intelligently distribute generated power to loads and energy storage devices is disclosed. One system includes load profile controllers that employ a switching strategy to dynamically vary the load the generator induces while producing regenerative energy. This switching strategy may allow for a wide dynamic range of configurable damping characteristics, as well as decouple generator damping and the system output power. Multiple load profile controllers can be used together via a communications network, such as a vehicle controller area network (CAN) bus. A central regeneration controller or existing electronic control unit (ECU) can issue commands to change damping performance in different load profile controllers. By networking multiple load profile controllers together in either a distributed or centralized manner, the system may allow for intelligent power routing, coordination of multiple energy-generating devices (such as regenerative shocks and brakes), and improved utilization of on-board energy storage devices.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
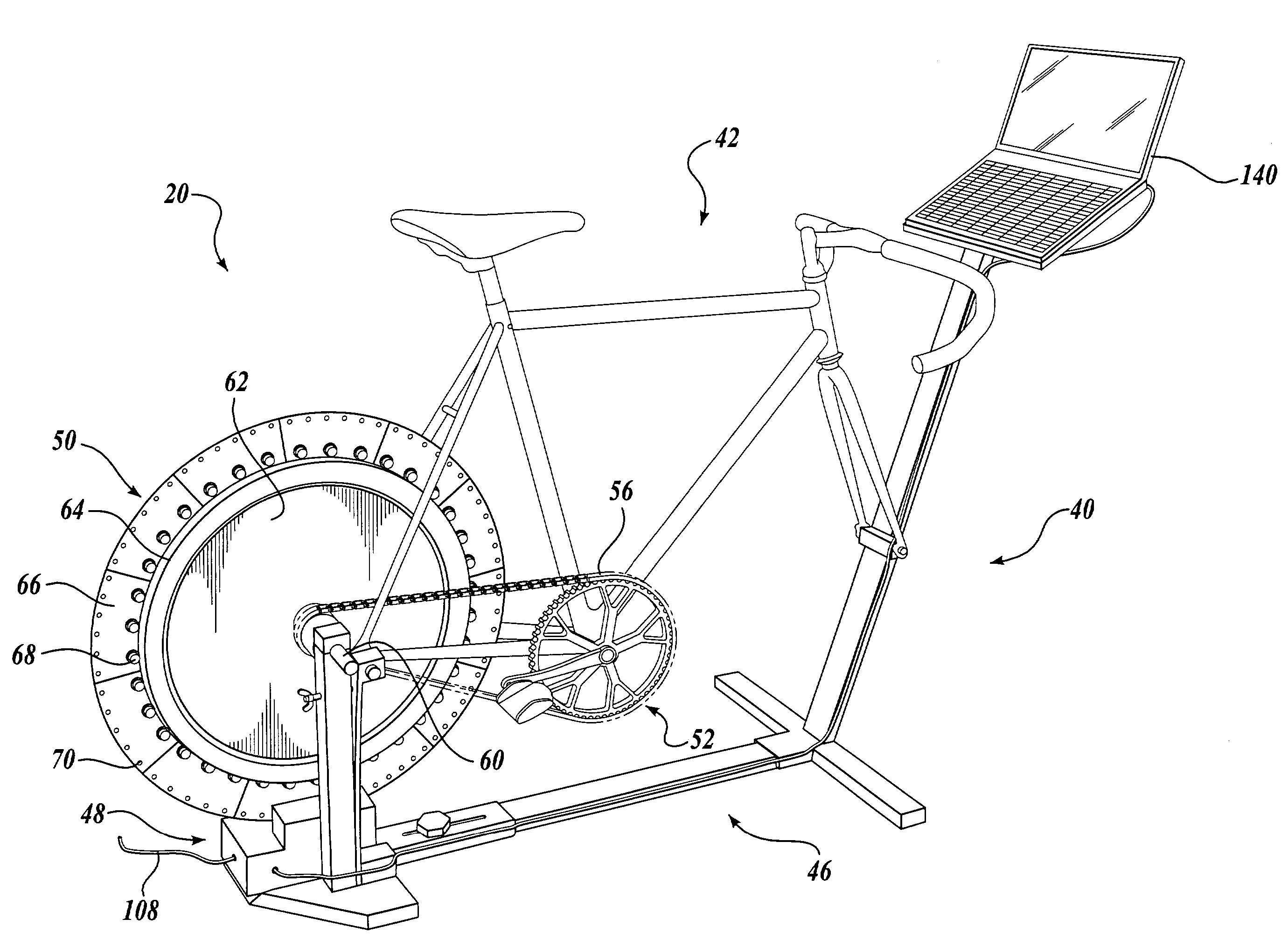
System and method for verifying the calibration of an exercise apparatus
A calibration verification system 20 comprises a trainer 40 having a load generator, a variable load control system (hidden by the cover of the load generator) connected in electrical communication with the load generator, and an exercise trainer computer system 140 connected in communication with the variable load control system. In operation, the exercise trainer computer system 140 outputs commands to the variable load control system. These commands can, for example, instruct the variable load control system to energize the load generator at predetermined times and power levels in order to simulate changes in terrain. The calibration verification system 20 also allows the user to verify the calibration of the trainer 40 by implementing a user initiated process, which conducts a calibration verification test of the trainer and outputs the test data at the exercise trainer computer system 140.
Owner:SRAM CORPORATION
Filter for improved driver circuit efficiency and method of operation
ActiveUS20120242284A1Maintain efficiencyMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsDriver circuitElectricity
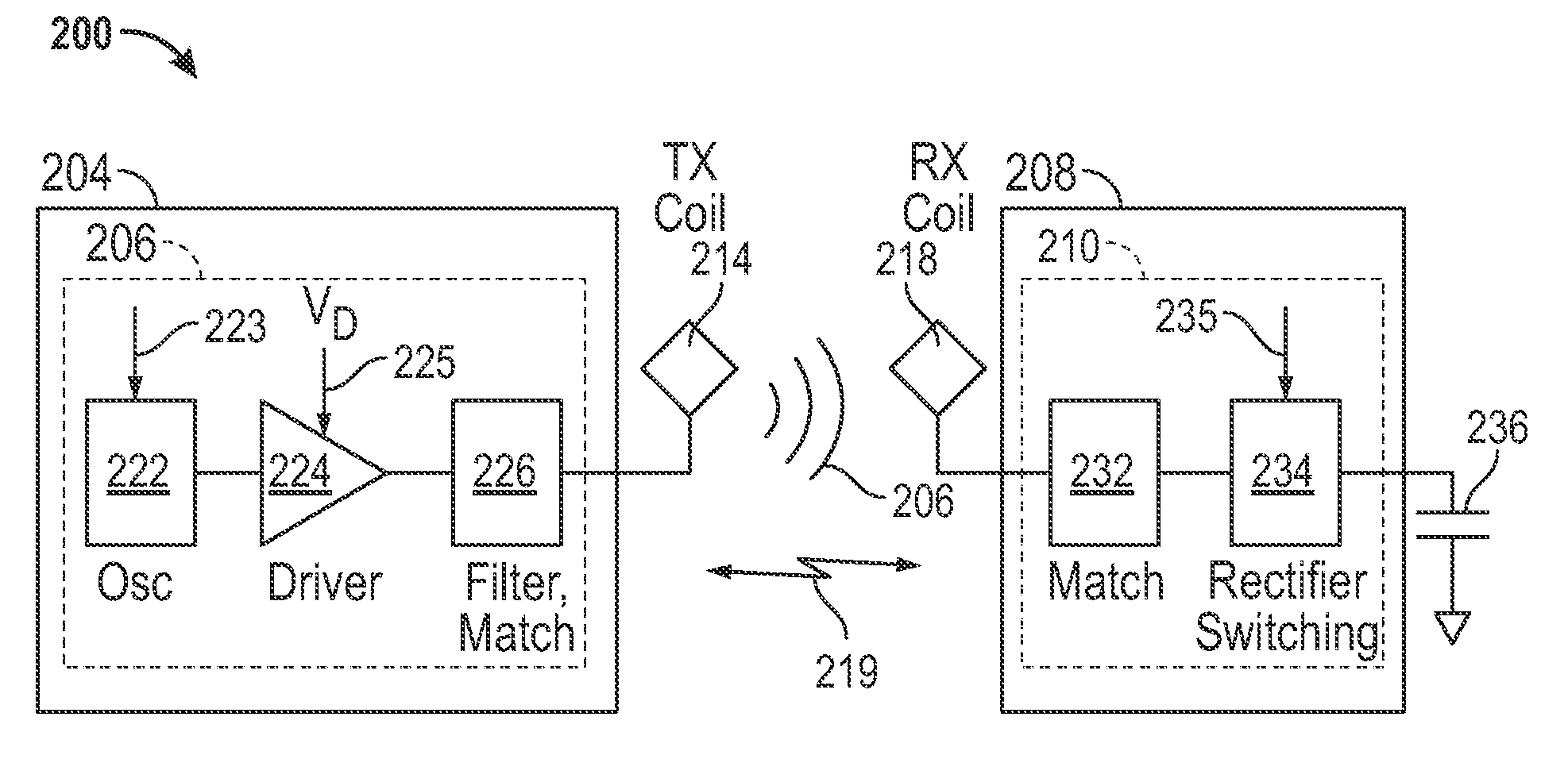
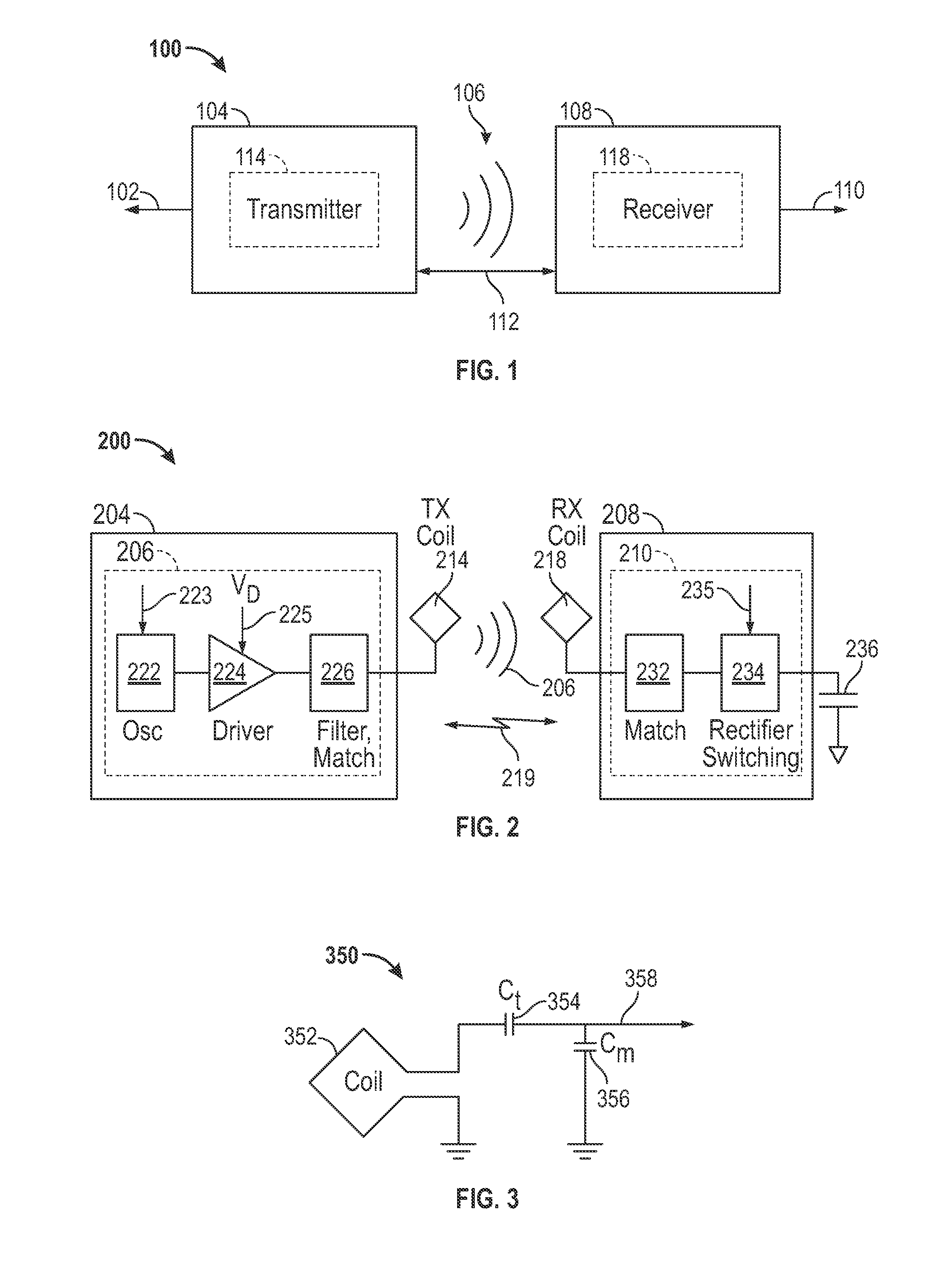
This disclosure provides systems, methods and apparatus for increasing the efficiency of an amplifier when driven by a variable load. In one aspect a transmitter device is provided. The transmitter device includes a driver circuit characterized by an efficiency. The driver circuit is electrically connected to a transmit circuit characterized by an impedance. The transmitter device further includes a filter circuit electrically connected to the driver circuit and configured to modify the impedance to maintain the efficiency of the driver circuit at a level that is within 20% of a maximum efficiency of the driver circuit. The impedance is characterized by a complex impedance value that is within a range defined by a real first impedance value and a second real impedance value. A ratio of the first real impedance value to the second real impedance value is at least two to one.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
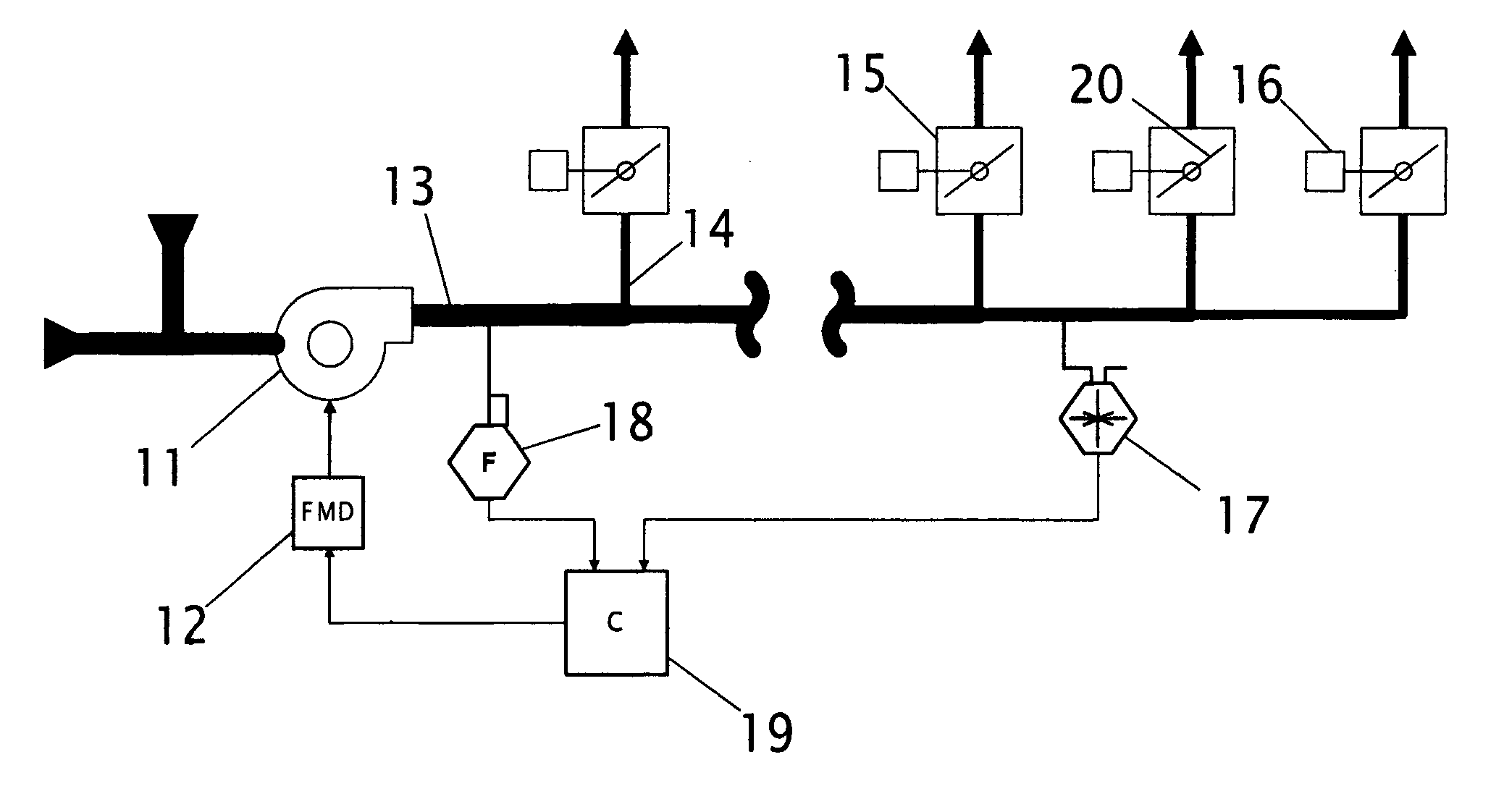
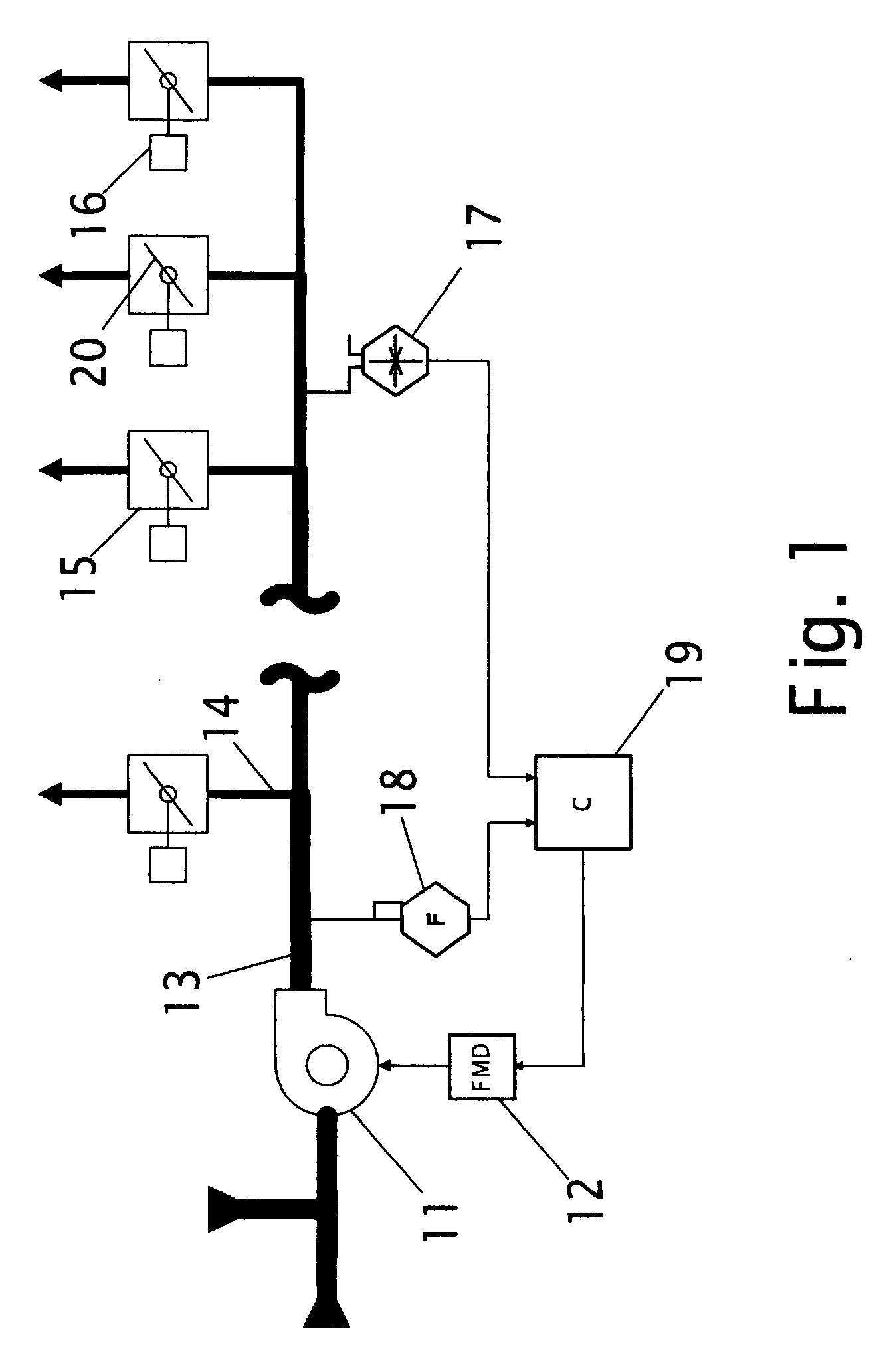
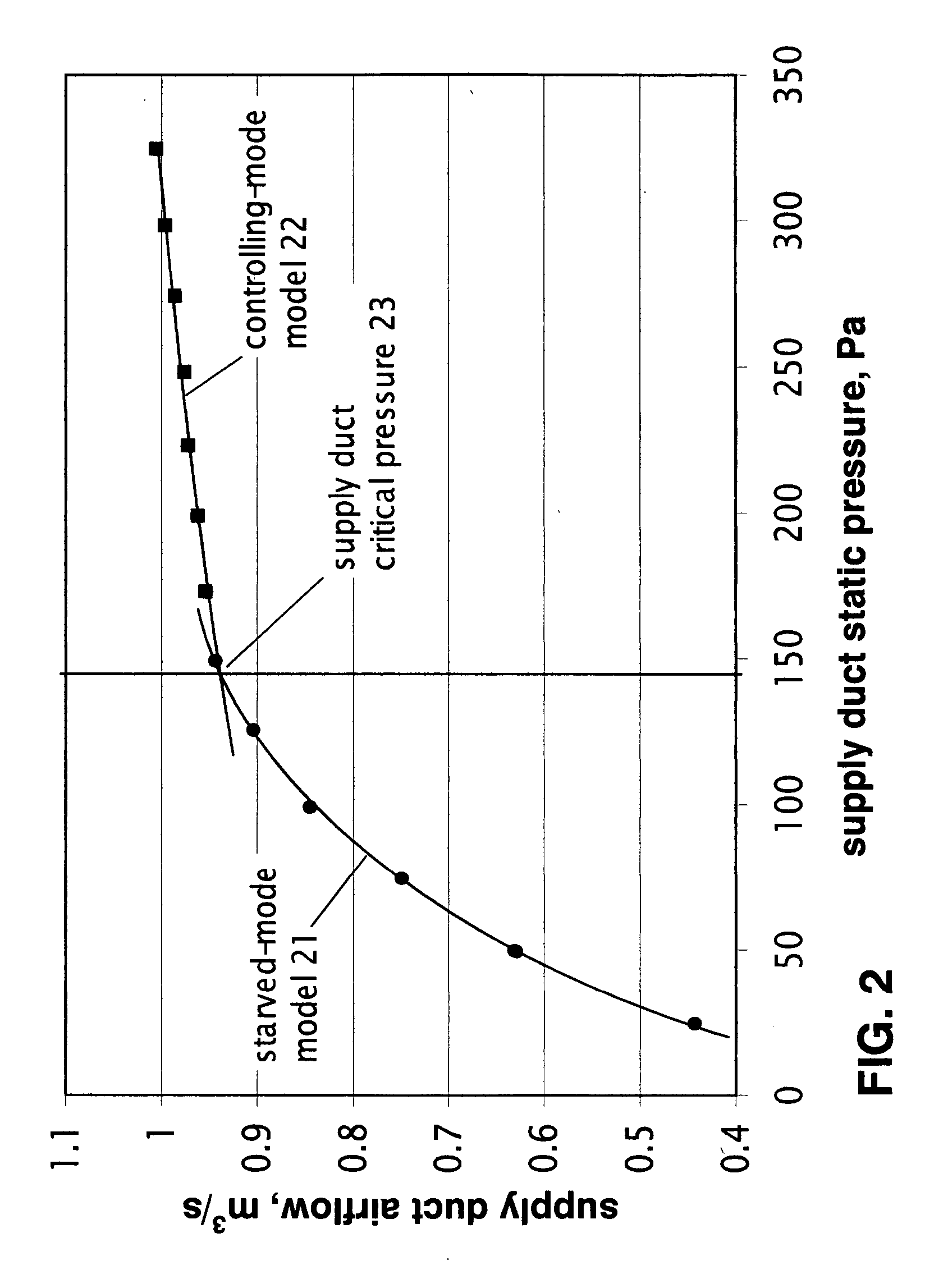
Method and apparatus for determining critical pressure of variable air volume heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning systems
A strategy for determining the critical supply duct pressure in variable-air-volume heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning systems that compensates for duct leakage and variable loads, enabling its use during normal system operation. The strategy consists of a static pressure sensor, an airflow sensor, a supply fan, a fan modulating device, a controller coupled to the static pressure sensor and the airflow sensor, and a data processing algorithm for analyzing results from a function test using these components. The functional test involves changing the supply duct pressure setpoint, waiting for equilibrium, recording pressure, flow, and time, then changing the supply duct pressure setpoint to the next setting in the sequence.
Owner:FEDERSPIEL CLIFFORD CONRAD
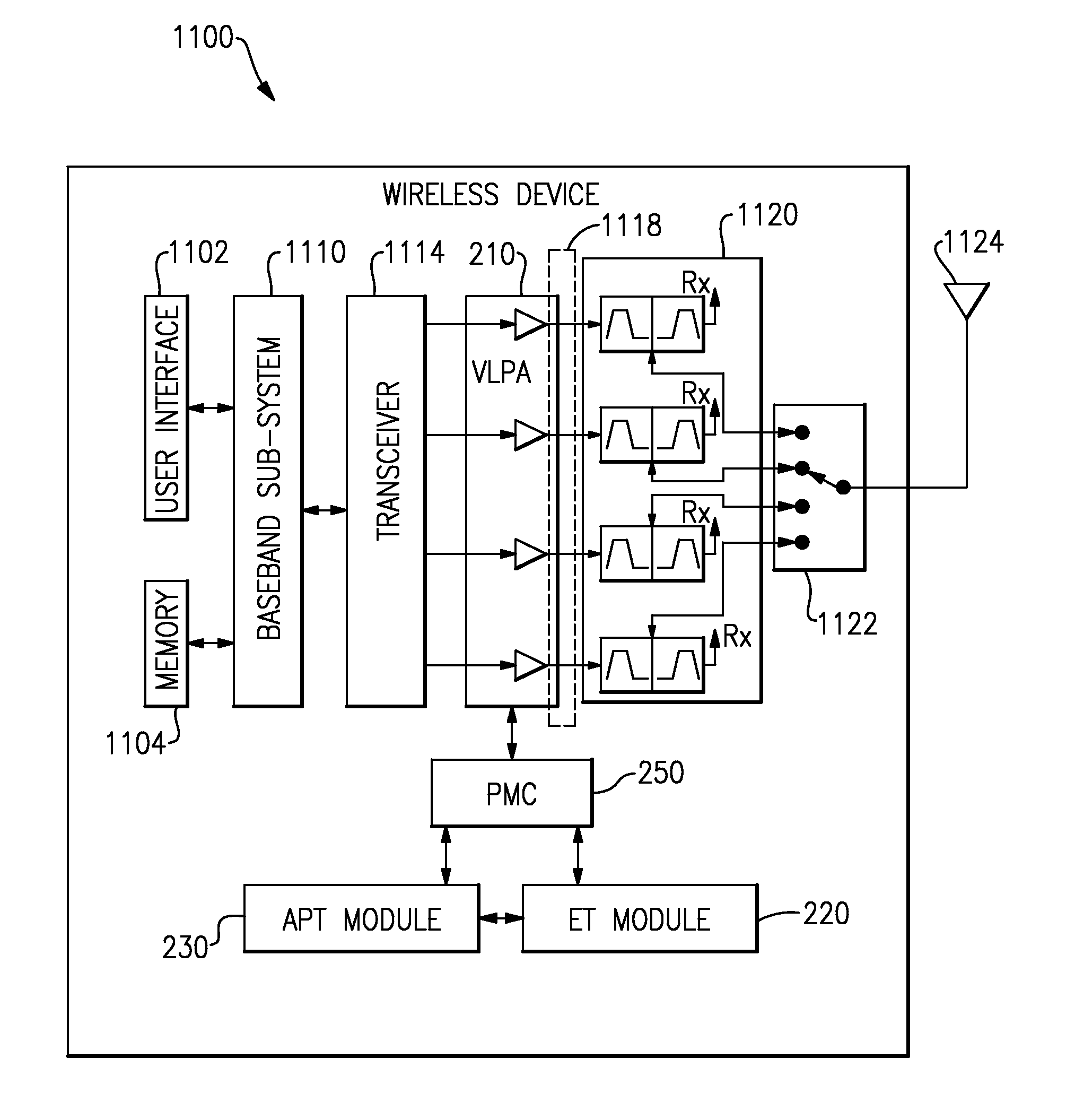
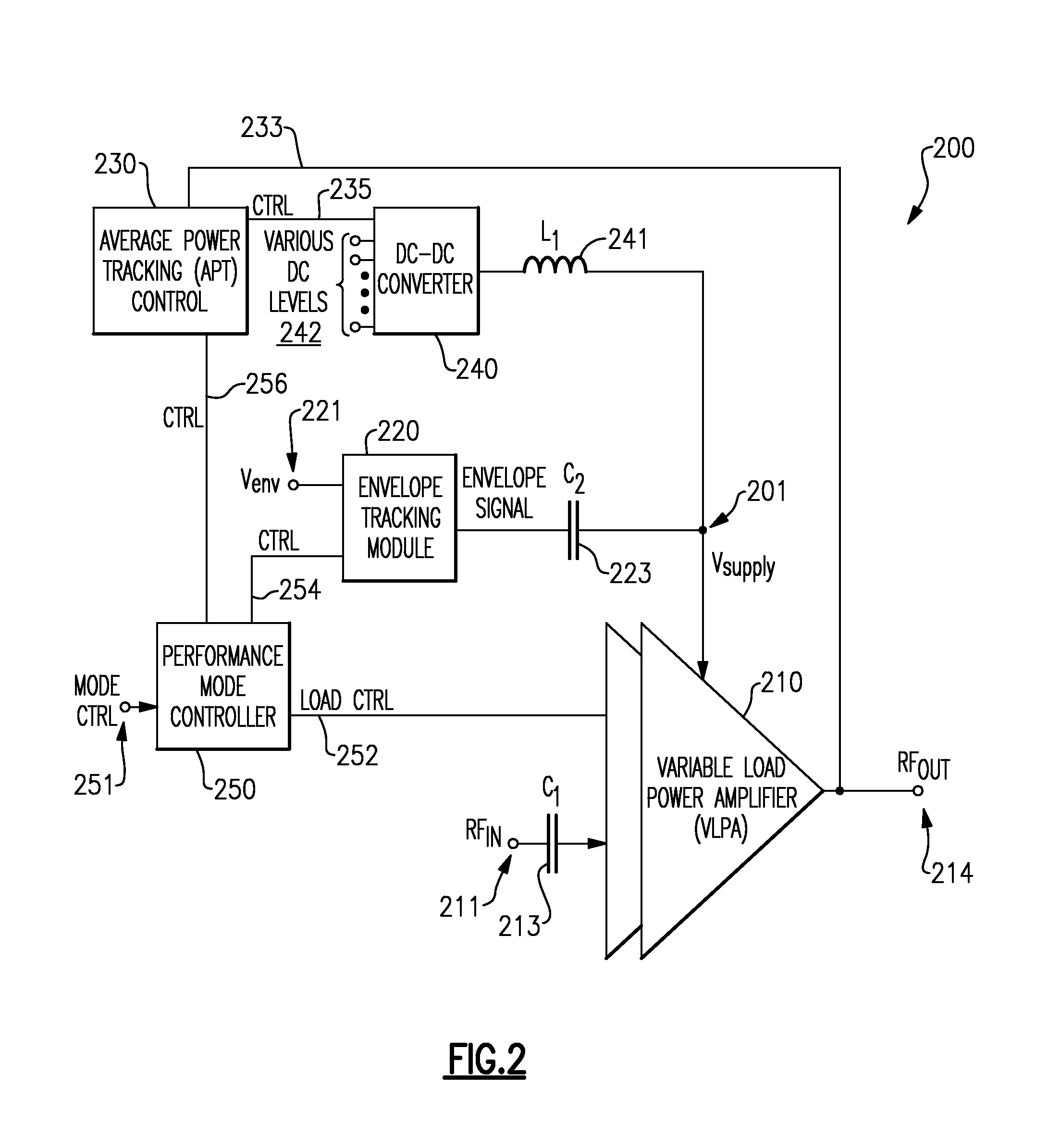
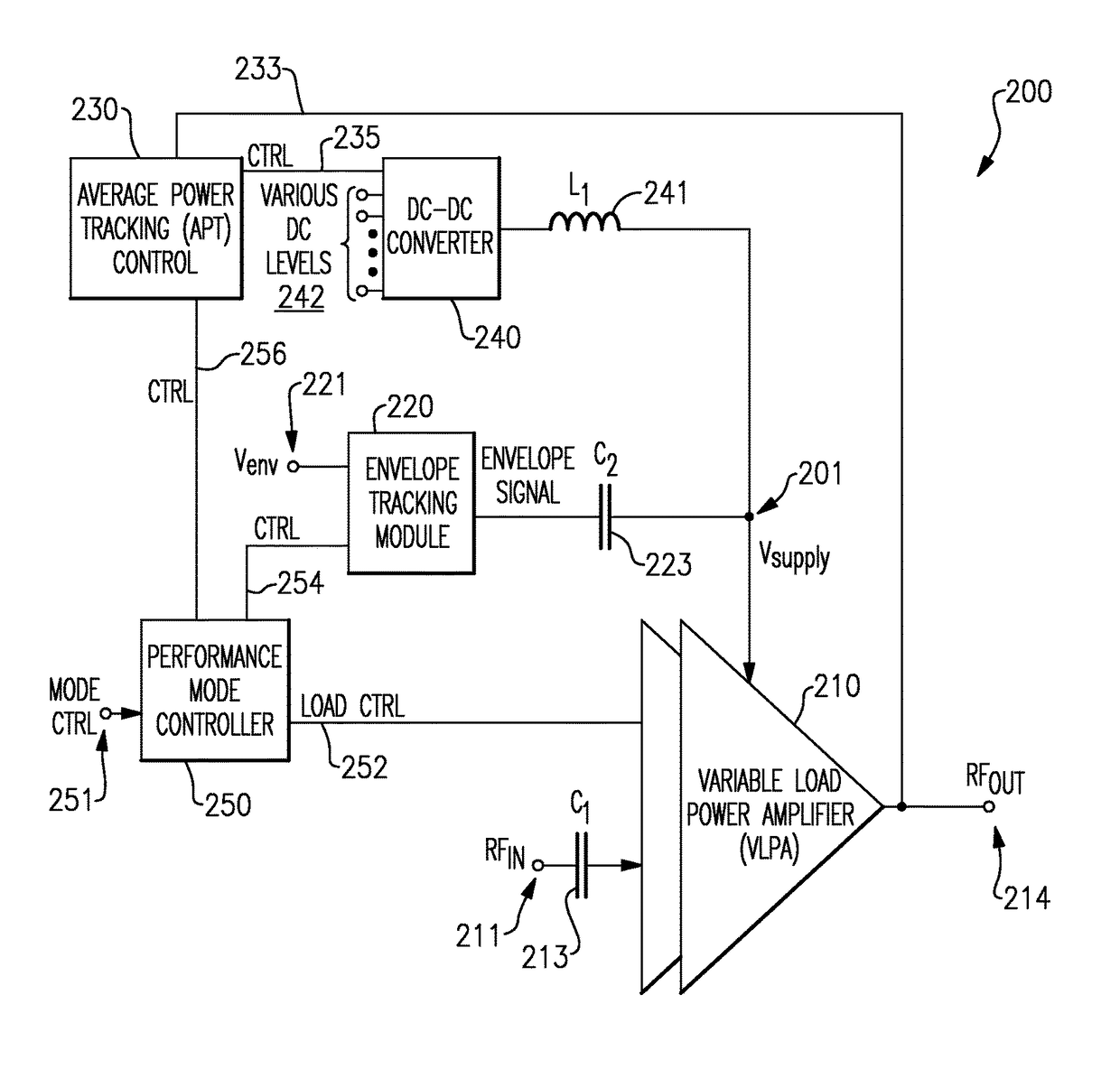
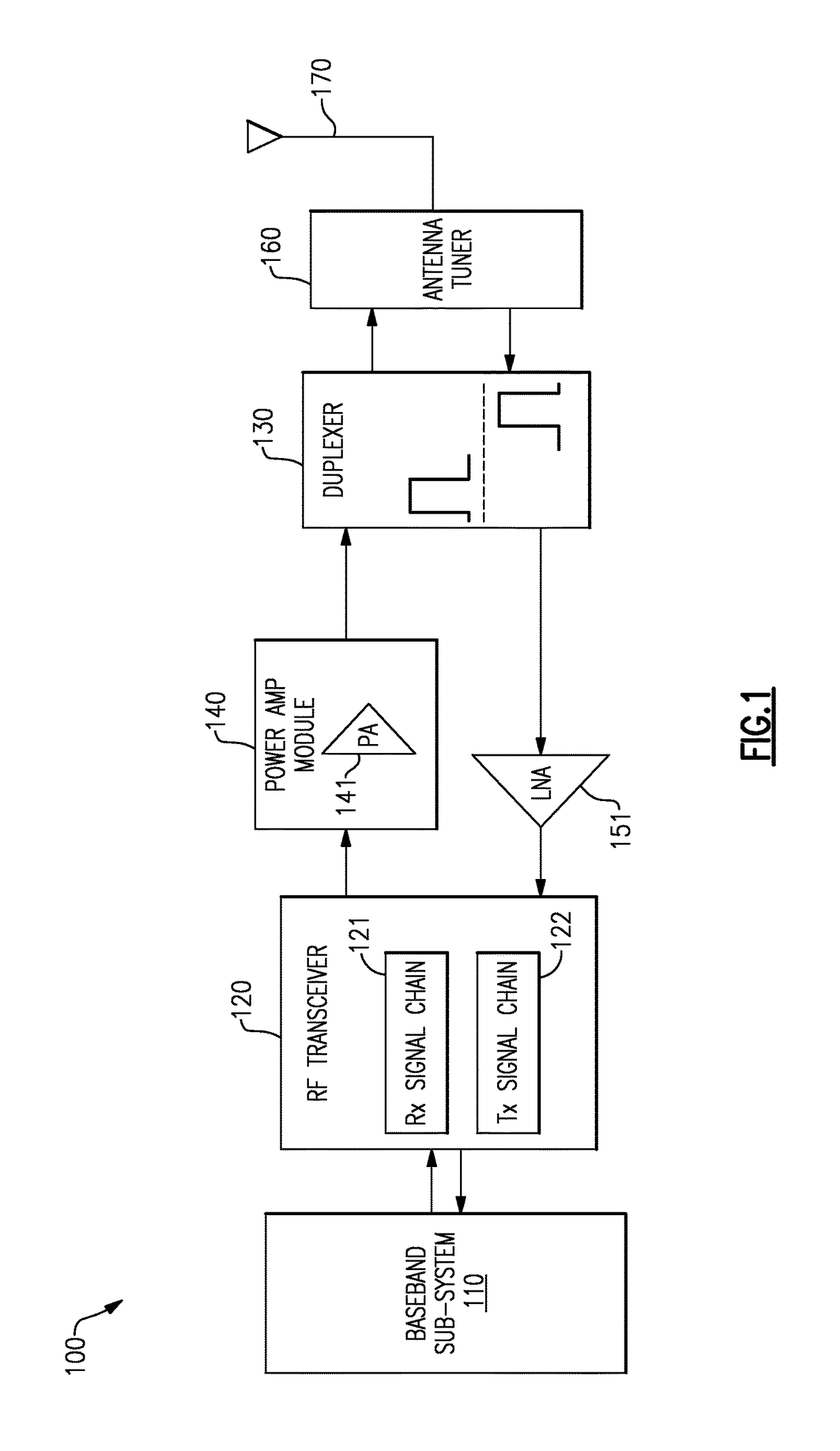
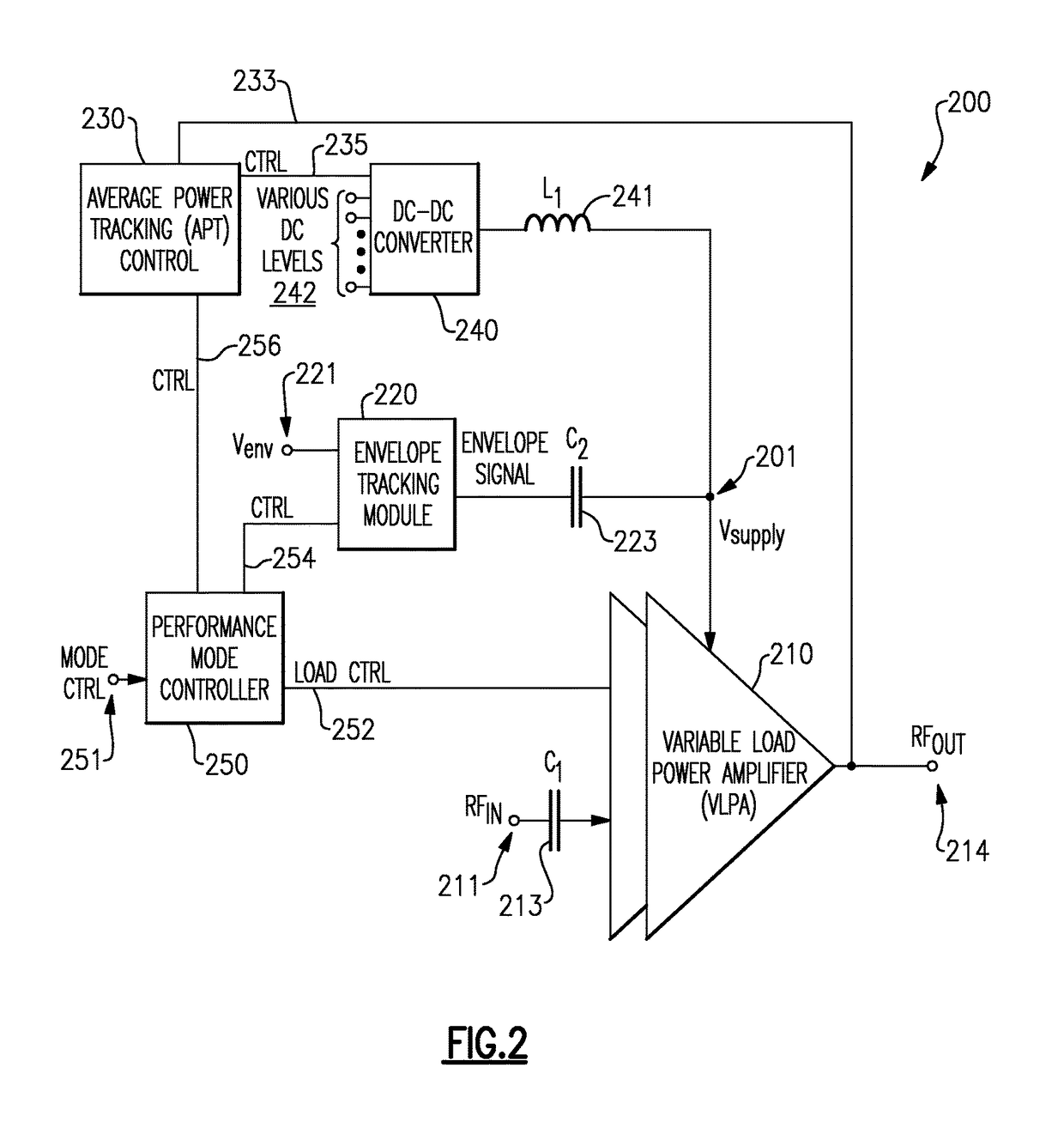
Variable load power amplifier supporting dual-mode envelope tracking and average power tracking performance
ActiveUS20160094192A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A variable load power amplifier that improves the performance of a power amplifier that provides both envelope tracking (ET) and average power tracking (APT). The variable load power amplifier can include a plurality of amplifiers that are each selectively connectable into one of a plurality of parallel combinations, each of the plurality of parallel combinations characterized by a corresponding load line. The variable load power amplifier can also include a plurality of control elements arranged to selectively connect one or more of the plurality of amplifiers into one of the plurality of parallel combinations, each of the plurality of control elements having a respective input terminal provided to receive a respective control signal, each of the plurality of control elements responsive to the respective control signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Variable load power amplifier supporting dual-mode envelope tracking and average power tracking performance
ActiveUS9991856B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierDual mode
A variable load power amplifier that improves the performance of a power amplifier that provides both envelope tracking (ET) and average power tracking (APT). The variable load power amplifier can include a plurality of amplifiers that are each selectively connectable into one of a plurality of parallel combinations, each of the plurality of parallel combinations characterized by a corresponding load line. The variable load power amplifier can also include a plurality of control elements arranged to selectively connect one or more of the plurality of amplifiers into one of the plurality of parallel combinations, each of the plurality of control elements having a respective input terminal provided to receive a respective control signal, each of the plurality of control elements responsive to the respective control signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
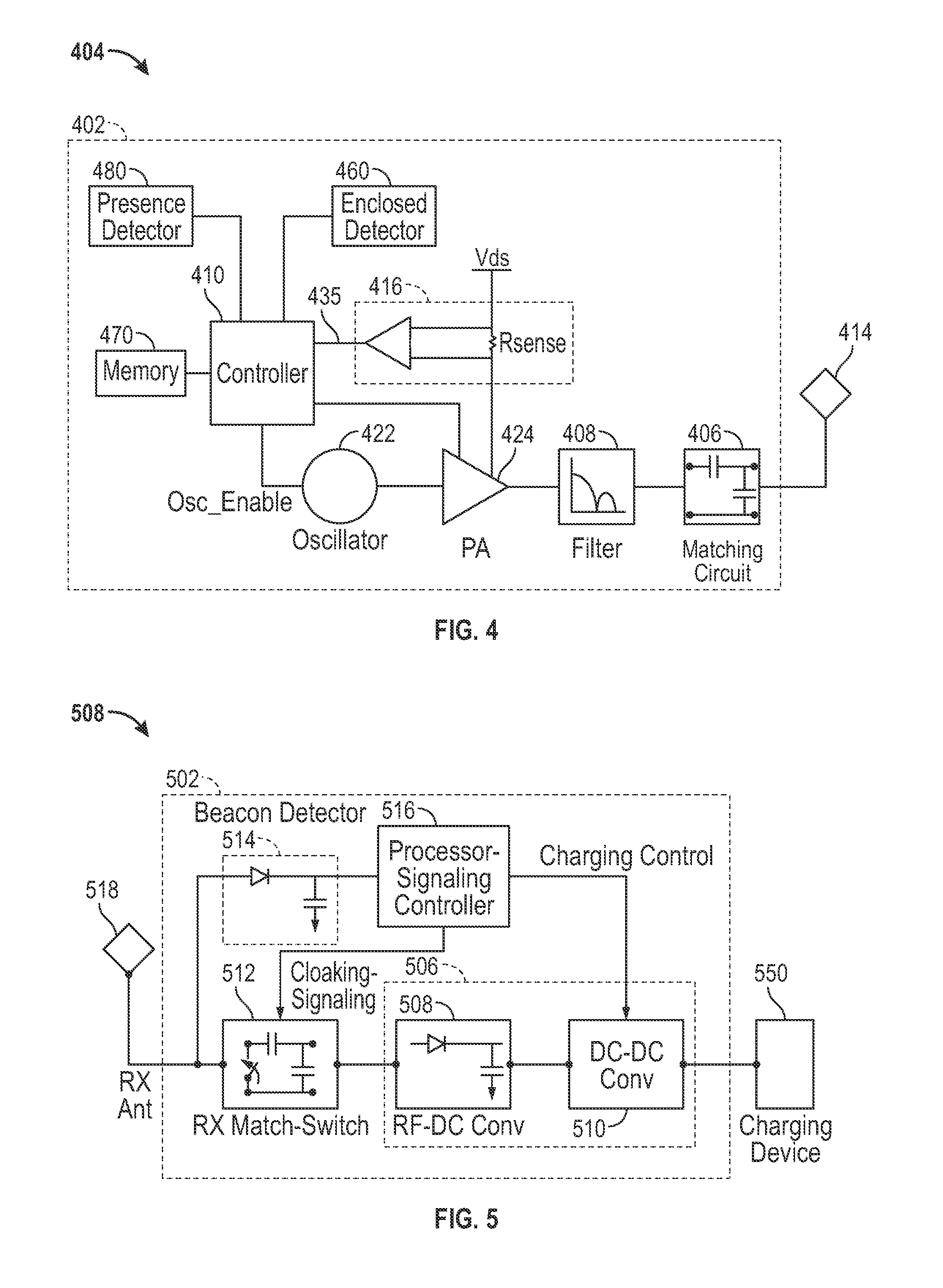
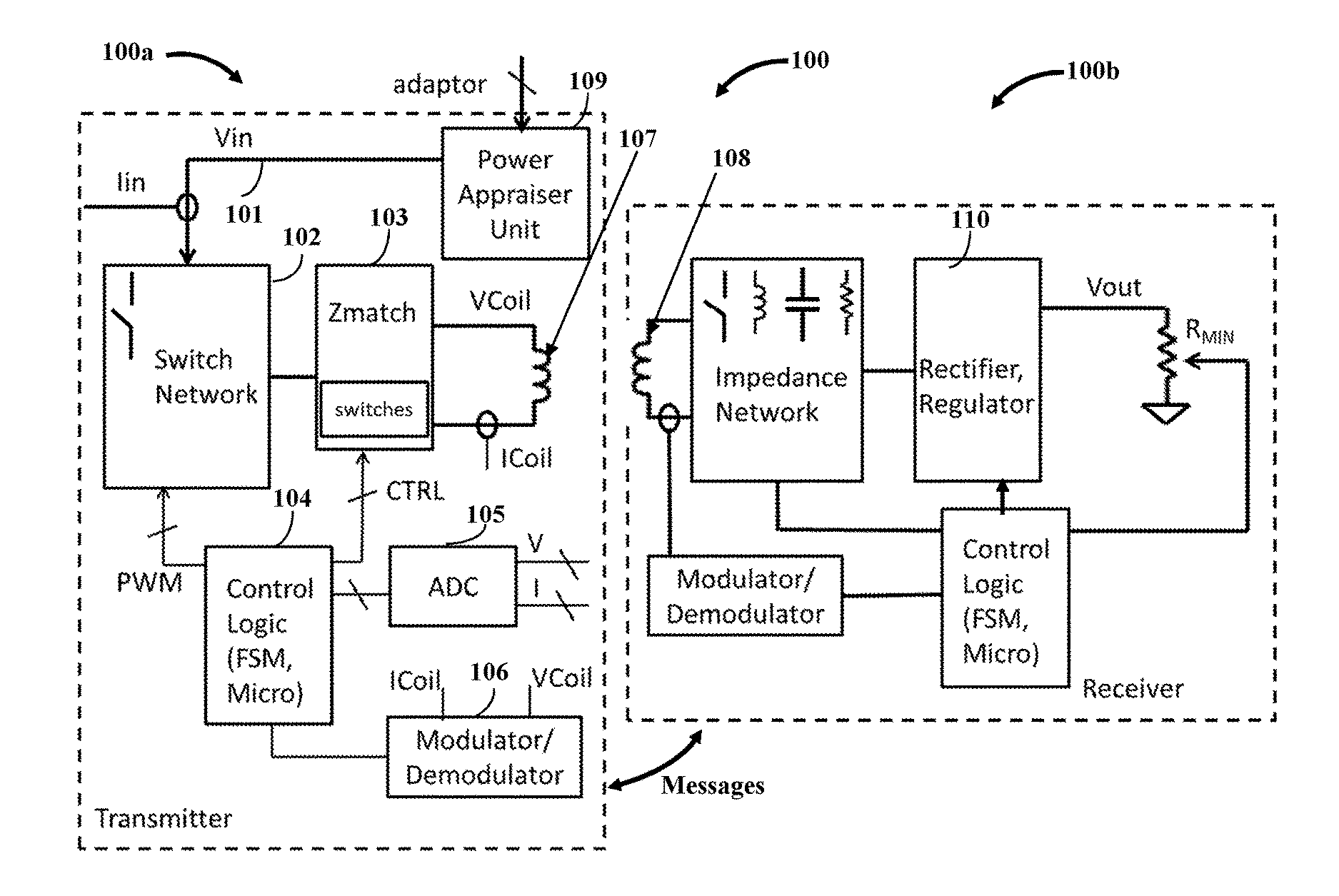
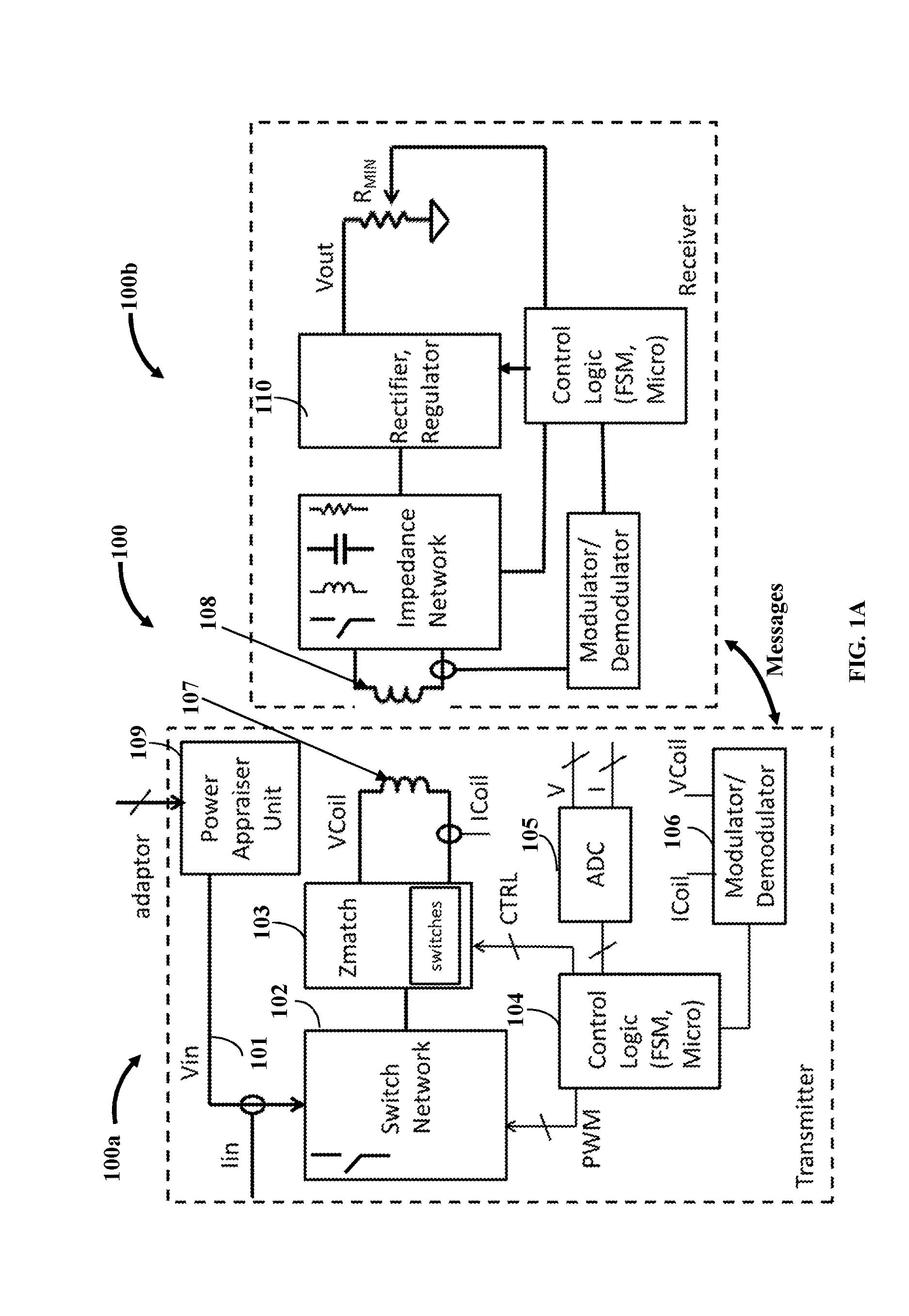
Input power appraisal based wireless power system
ActiveUS20160372963A1Overcomes unstable power transfer behaviorSufficient powerCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerElectric forcePower inverter
A wireless power system (WPS) has a wireless power transmitter (WPT) that appraises an input power available to a power inverter from one or more input power sources. The WPT comprises the power inverter that wirelessly transmits power to a wireless power receiver (WCR) of the WPS, and a power appraiser circuit (PAC). The PAC ascertains maximum input power available to the power inverter from the input power sources. The PAC includes a variable load connected to a path carrying the input power to the power inverter or one or more input pins that receive power ratings of the input power sources that indicate available maximum input power from the input power sources. The ascertaining of maximum input power available to the power inverter from the input power sources appraises the input power available to the power inverter. The WCR receives information representing maximum power deliverable by the WPT.
Owner:WIPQTUS
Power driving circuit for controlling a variable load ultrasonic transducer
InactiveUS20060238068A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSilicon-controlled rectifierEngineering
The present invention is directed to a high-powered (e.g., >500 W) ultrasonic generator for use especially for delivering high-power ultrasonic energy to a varying load including compressible fluids. The generator includes a variable frequency triangular waveform generator coupled with pulse width modulators. The output from the pulse width modulator is coupled with the gates of an Isolated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT), which amplifies the signal and delivers it to a coil that is used to drive a magnetostrictive transducer. In one embodiment, high voltage of 0-600 VDC is delivered across the collector and emitter of the IGBT after the signal is delivered. The output of the IGBT is a square waveform with a voltage of ±600V. This voltage is sent to a coil wound around the ultrasonic transducer. The voltage creates a magnetic field on the transducer and the magnetorestrictive properties of the transducer cause the transducer to vibrate as a result of the magnetic field. The use of the IGBT as the amplifying device obviates the need for a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) circuit, which is typically used in low powered ultrasonic transducers, and which would get overheated and fail in such a high-powered and load-varying application.
Owner:SULPHCO
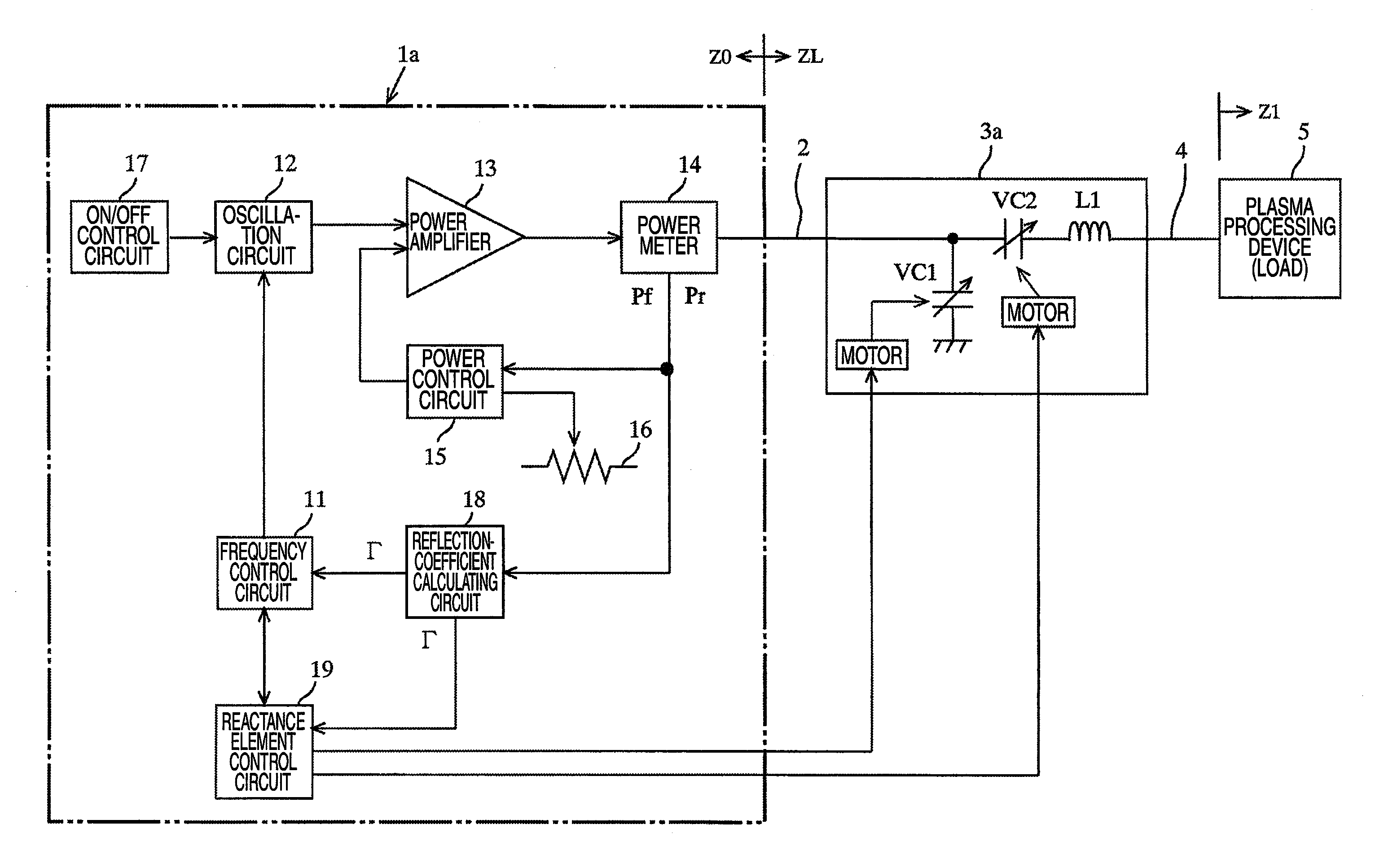
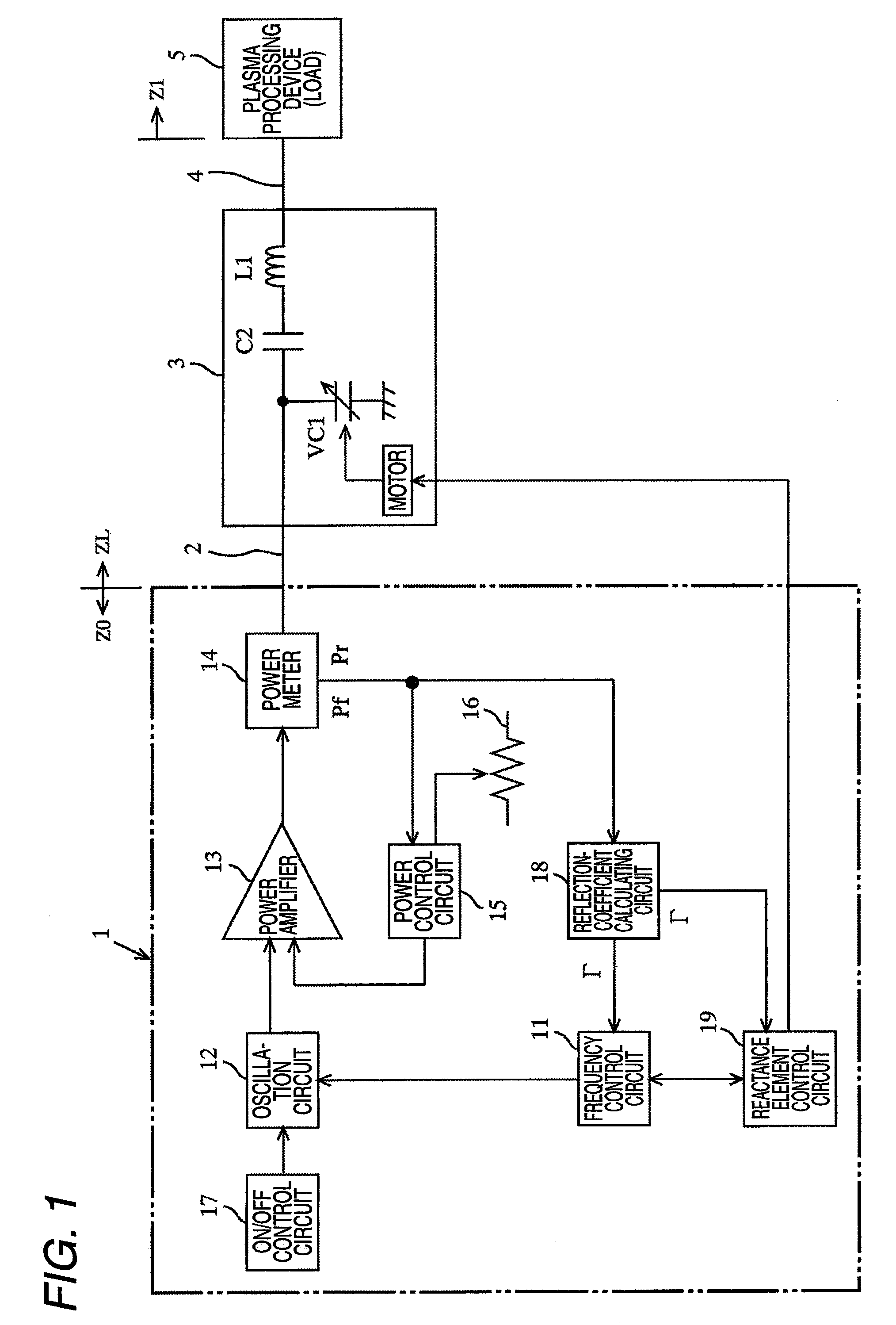
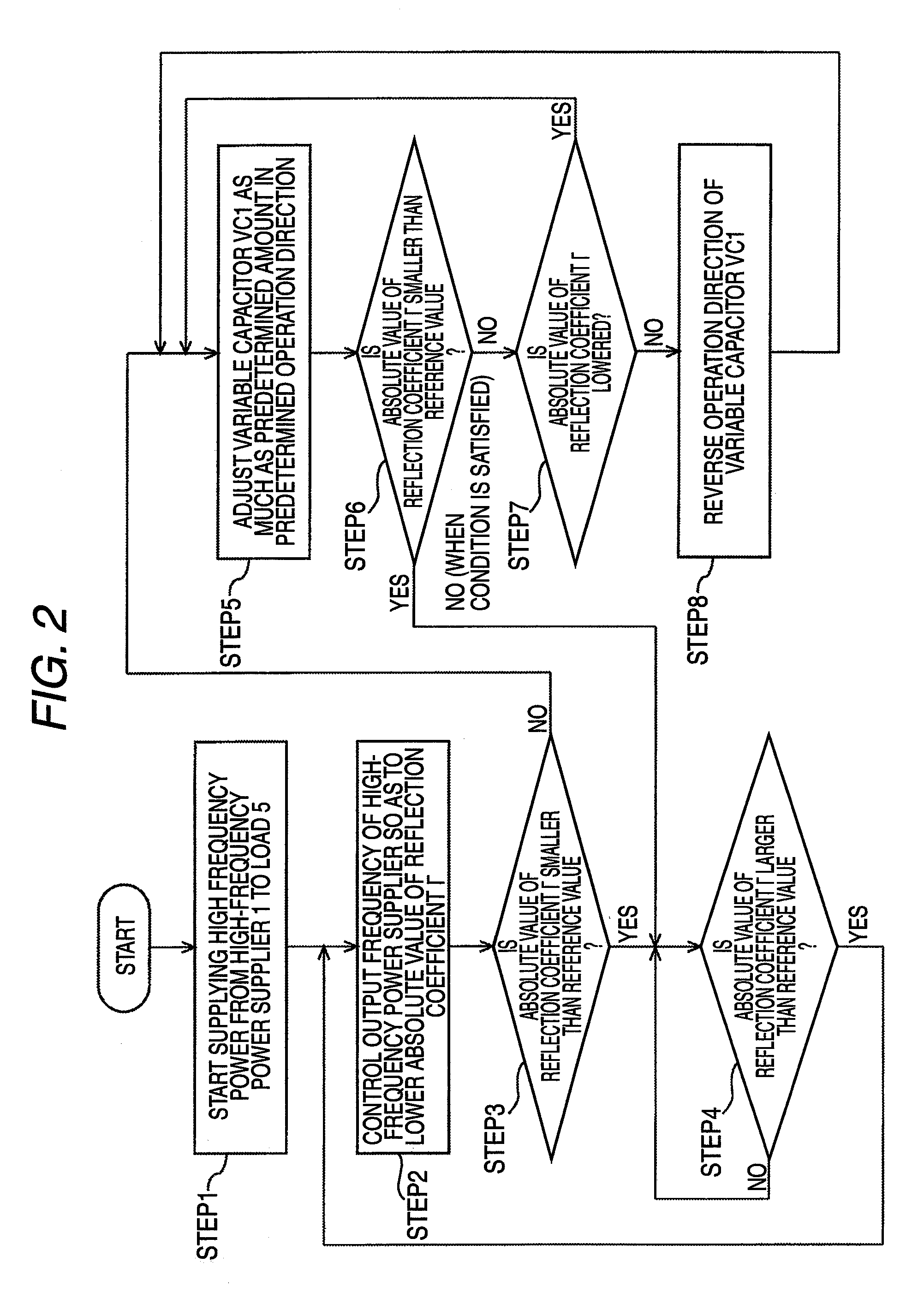
High frequency device with variable frequency and variable load impedance matching
ActiveUS8203859B2Reduce the required powerReduce the amount of informationMultiple-port networksElectric discharge tubesHigh frequency powerReflected waves
A high frequency device for supplying a high frequency power to a load, the high frequency device includes: an oscillating unit that can vary an oscillation frequency; a high frequency power supplying unit that serves as a power source by amplifying an oscillation signal output from the oscillating unit for supplying the high frequency power to the load; a reflected-wave information calculating unit that calculates reflected wave information on a reflected wave power, and outputs the reflected wave information; a frequency control unit that controls the oscillation frequency of the oscillating unit so as to lower the reflected wave information; an impedance adjusting unit that is disposed at a downstream of the high frequency power supplying unit in a power supplying direction, and that has at least one variable reactance element which can be controlled; and an element control unit that controls the variable reactance element of the impedance adjusting unit so as to lower the reflected wave information.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Sensorless control method and apparatus for a motor drive system
InactiveUS7276877B2Quick calculationAccurate predictionAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlKaiman filterControl power
A method and apparatus provide a state observer control system 600 for a motor 106 that uses an extended Kalman filter 330 to predict initial rotor position and afterwards accurately predict rotor position and / or speed under variable types of loading conditions. A control system model 300 is generated that allows variable setting of an initial rotor position to generate estimated rotor position and speed as outputs. The control system model 300 includes an EKF (extended Kalman filter) estimator 330, speed controller 322, a current controller 324, and a variable load component 310. During operation, EKF estimator 330 estimates rotor speed 327 and position 333 based on reference voltages 402, 404 and currents 1325 generated by speed and current controllers 322, 324 and input from frame transformers 326, 328. Additionally, the reference currents and voltages 402, 404, 1325 are frame-transformed to be used as feedback signals 418, 346 in the system 600 and as drive signals to control power to be applied to a motor load 602.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
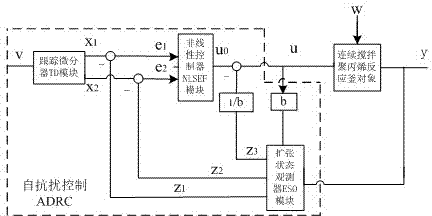
Active-disturbance-rejection control method for temperature of a constant stirring polypropylene reaction kettle
InactiveCN104281055AFast dynamic responseImprove adaptabilityChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAdaptive controlDifferentiatorFeedback controller
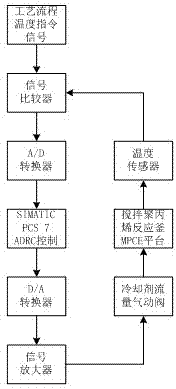
The invention discloses an active-disturbance-rejection control method for the temperature of a constant stirring polypropylene reaction kettle. A discrete mode is adopted for the active-disturbance-rejection control method for the temperature of the constant stirring polypropylene reaction kettle, and a tracking differentiator module, an expanded state observer module and a non-linearity feedback controller module are involved. The method includes the steps that firstly, parameters of the tracking differentiator module and the expanded state observer module are set; then, a transient process is arranged, and disturbances are estimated; finally, an error signal is used for adjusting the non-linearity feedback controller module to control the temperature of the polypropylene reaction kettle. The control method has the advantages that the method is implemented on SIMATICPCS7 equipment without establishing a constant stirring polypropylene reaction kettle model, the dynamic response is rapid, and a system is high in adaptability and robustness under the working conditions of disturbances and variable loads.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
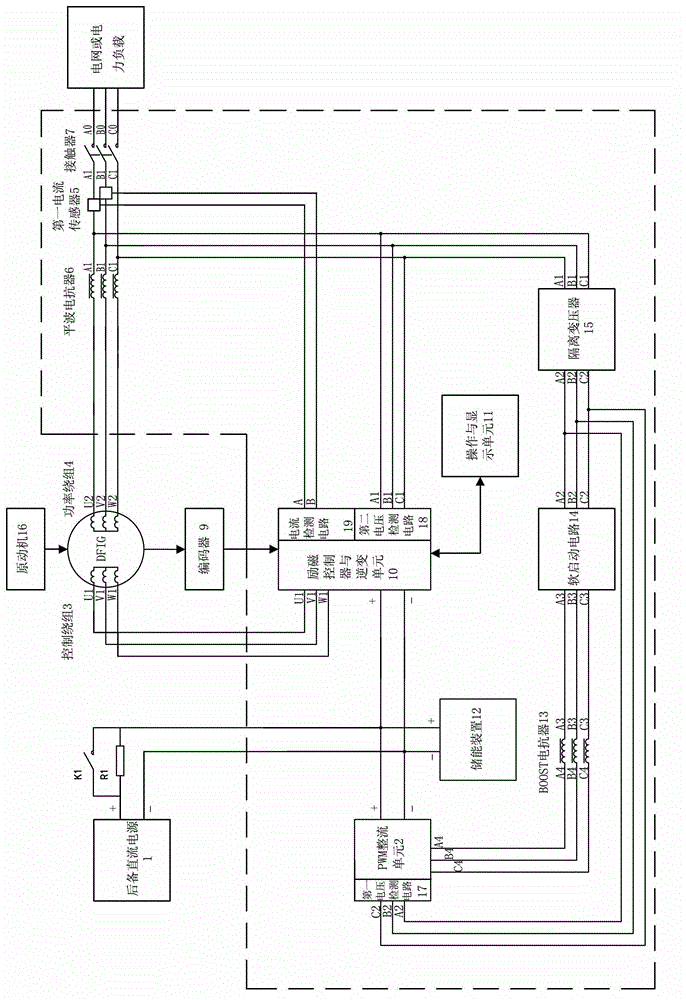
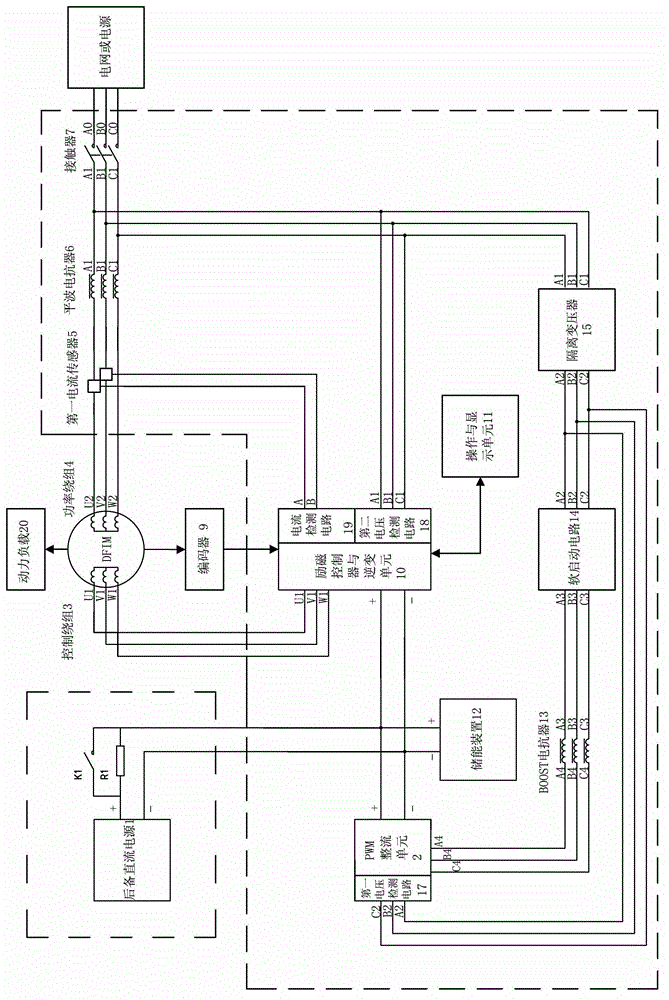
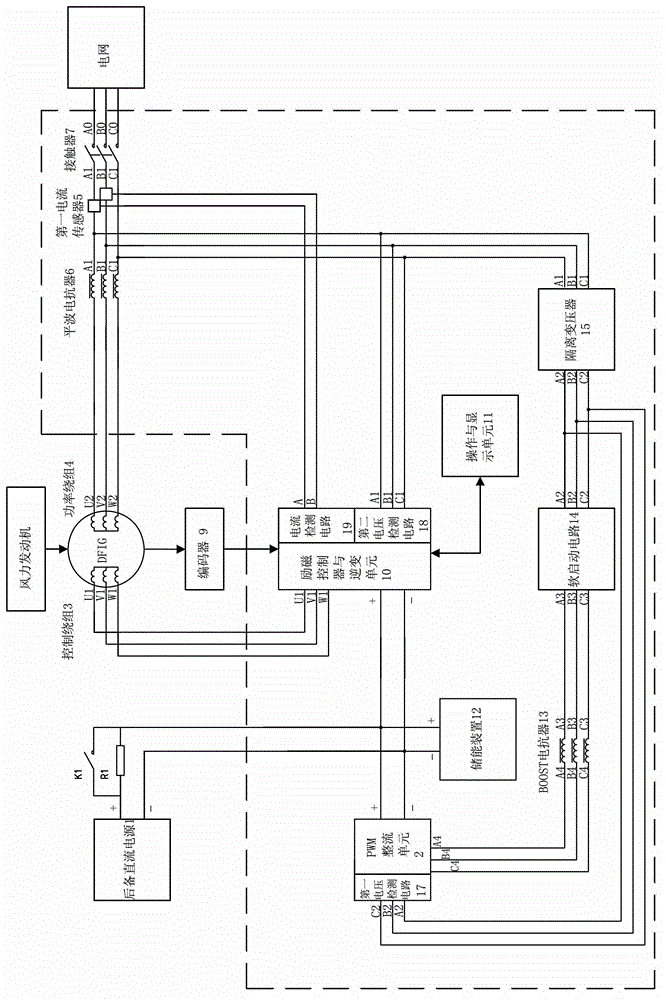
Brushless doubly-fed motor excitation control system and control method using same
PendingCN102868346APrevent trippingImprove stabilitySingle motor speed/torque controlGenerator control by field variationSynchronous motorConstant frequency
The invention relates to a brushless doubly-fed motor excitation control system, which is characterized by comprising a PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) rectifying unit, a first current sensor, a smoothing reactor, a contactor, an excitation controller and an inverter unit, an operation and display unit, an energy storage device, a BOOST reactor, a soft start circuit, a first voltage detection circuit and a second voltage detection circuit. The brushless doubly-fed motor excitation control system can always keep a speed-variable load-variable constant-frequency and constant-voltage power generation state when a brushless doubly-fed motor is at an electric operating state, the rotating speed of a brushless rotor rapidly changes and the load condition is within a larger range; and when the brushless doubly-fed motor is at the electric operating state, the brushless doubly-fed motor excitation control system can finish rapid adjustment of the rotating speed of the brushless rotor by excitation control and realizes multiple electric operating modes, such as synchronous operating, asynchronous operating and doubly-fed speed adjustment. When the load condition changes in a larger range, the brushless doubly-fed motor excitation control system can always keep the hard mechanical property of a synchronous motor. The invention also comprises the control method using the brushless doubly-fed motor excitation control system.
Owner:BEIJING SWORD ELECTRIC IND
Digitally-controlled oscillator with switched-capacitor frequency selection
InactiveUS6903615B2Low power supply voltageReduce voltageResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlCapacitanceEngineering
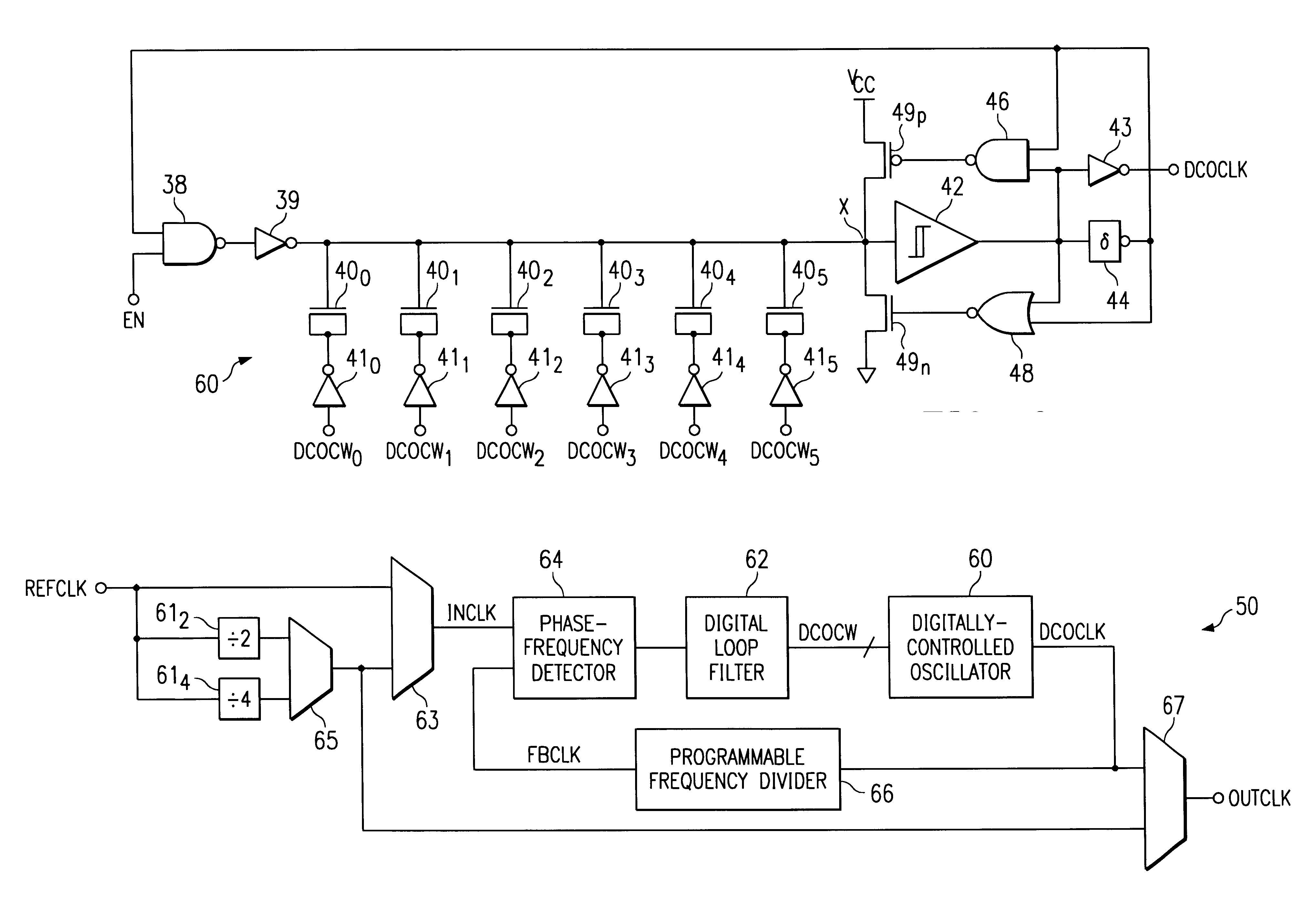
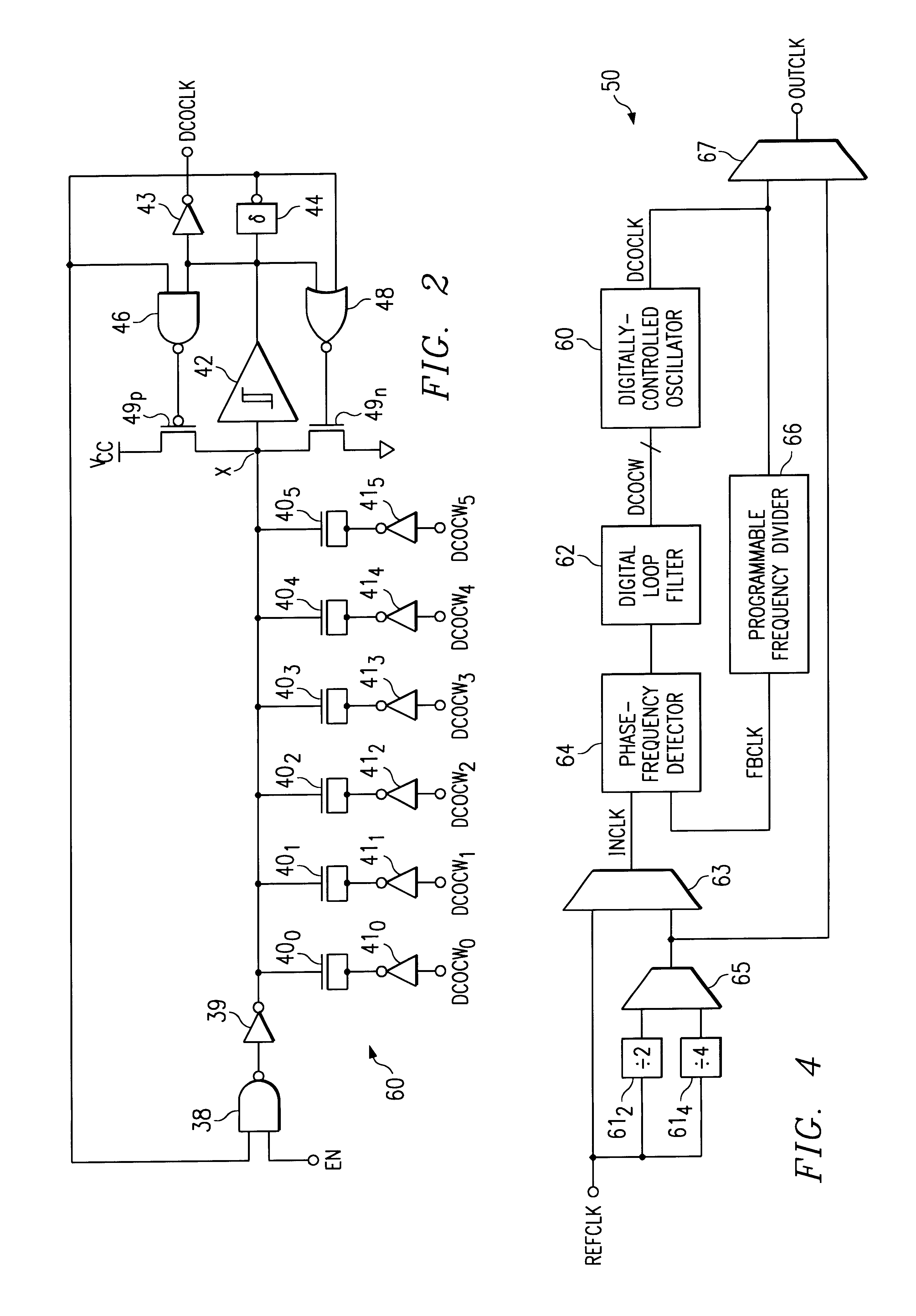
A digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) (60), such as may be used in clock generator or clock recovery circuitry in an integrated circuit, is disclosed. The disclosed DCO (60) is a single-stage oscillator including a variable load implemented as a binary-weighted array of switched capacitors (40). Each of capacitors (40) has a plate connected to a common node (X), and a plate that receives a signal corresponding to one bit of a digital control word (DCOCW). The common capacitor node (X) is also connected to the input of a Schmitt trigger (42) that produces the output clock signal (OUTCLK) and a feedback signal that is applied to logic (38, 39) that inverts the common node of the capacitors (40). The switching time at the input of Schmitt trigger (42) depends upon the variable load presented by the array of switched capacitors (40), which is controlled by the digital control word (DCOCW). As a result, the clock signal (OUTCLK) is digitally synthesized by a single stage of the DCO (60). A digital phase-locked loop (PLL) clock generator circuit (50) including a phase detector (64), digital loop filter (62) in combination with the DCO (60), and a programmable frequency divider (66) providing a feedback path from the output of the DCO (60) to the phase detector (64), is also disclosed. The PLL clock generator (50) may be used in an integrated circuit such as a digital signal processor (30) or microprocessor, and is particularly well-suited for use in a battery-powered portable electronic system (200).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Life tester for alternating-current contactor and control method thereof
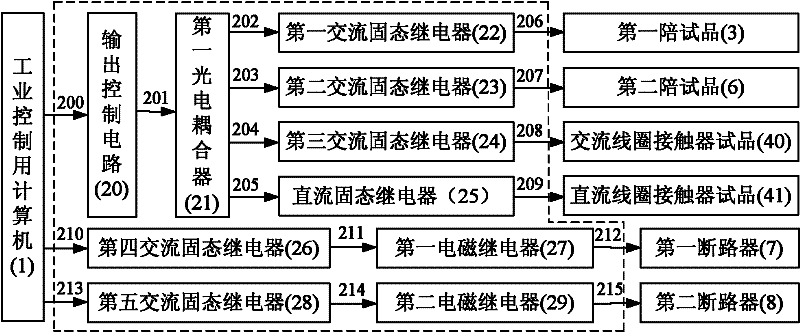
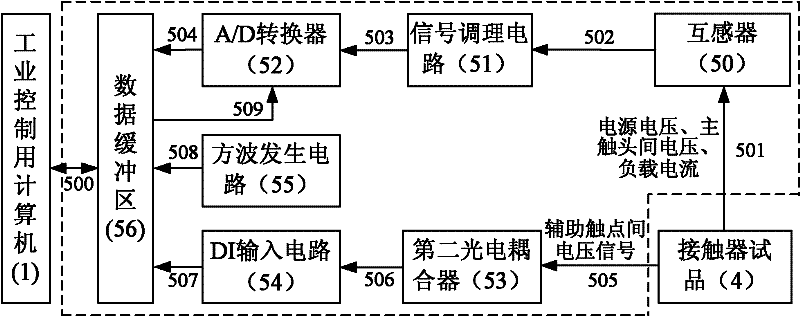
InactiveCN102253333AIncrease the level of automationEasy to testMachine part testingCircuit interrupters testingLoad circuitComplete data
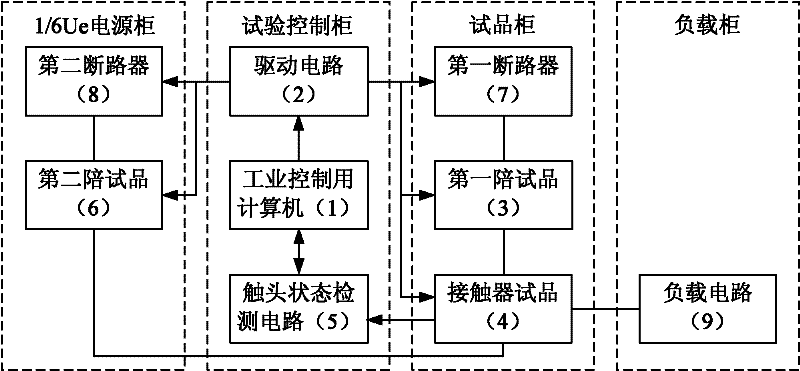
The invention relates to a life tester for an alternating-current contactor and a control method thereof. The life tester consists of a test control cabinet, a specimen cabinet, a 1 / 6Ue power supply cabinet and a load cabinet, wherein the test control cabinet comprises an industrial personal computer, a driving circuit and a contact state detection circuit; the specimen cabinet comprises a first accompanied specimen, a contactor specimen and a first breaker; the 1 / 6Ue power supply cabinet comprises a second accompanied specimen and a second breaker; and the load cabinet comprises a load circuit. The life tester is controlled by the industrial personal computer, so a life test of the alternating-current contactor can be completed automatically and accurately, and the automation level of the life test is improved; and four electrical life tests of a switch-on test, a break-off test, a dead load test and a variable load test of the alternating-current contactor can be performed, and a mechanical life test of the alternating-current contactor also can be performed. The life tester has an integral data protection function, namely test data is not lost in case of unexpected outage, the collected test data is not damaged after the power supply restores, and the test data is saved perpetually.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for jointly scheduling power generation load by using wind power generation unit and thermal power generation unit
InactiveCN102820656AGuaranteed safe operationAchieve maximum power operationPower network operation systems integrationAc network voltage adjustmentElectricityHigh rate
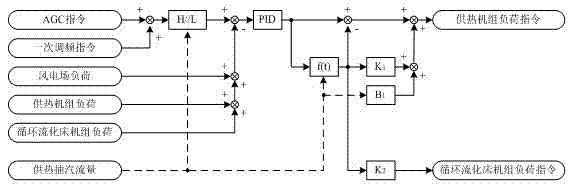
The invention discloses a method for jointly scheduling power generation load by using a wind power generation unit and a thermal power generation unit. A wind power plant, a circulating fluidized bed unit, a heating unit and the like which are within a same area or belong to a same power generation group are equivalent to a virtual unit, unified load instructions are issued from a power grid side, and the load instructions are decomposed on a unit side according to characteristics of various units to realize operation of the wind power plant at the maximum power generation power, wide-range variable load operation of the circulating fluidized bed unit and high-rate variable load operation of the heating unit. Mutual coordination of the wind power plant, the circulating fluidized bed unit and the heating unit is realized under the joint scheduling of a power grid, advantages of each unit are fully utilized, capacity of the power grid to receive wind power generation load is greatly improved, and the maximum-power operation of the wind power plant is realized while safety in operation of the power grid is guaranteed, so that waste of wind energy is reduced and power generation cost and environmental pollution are reduced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
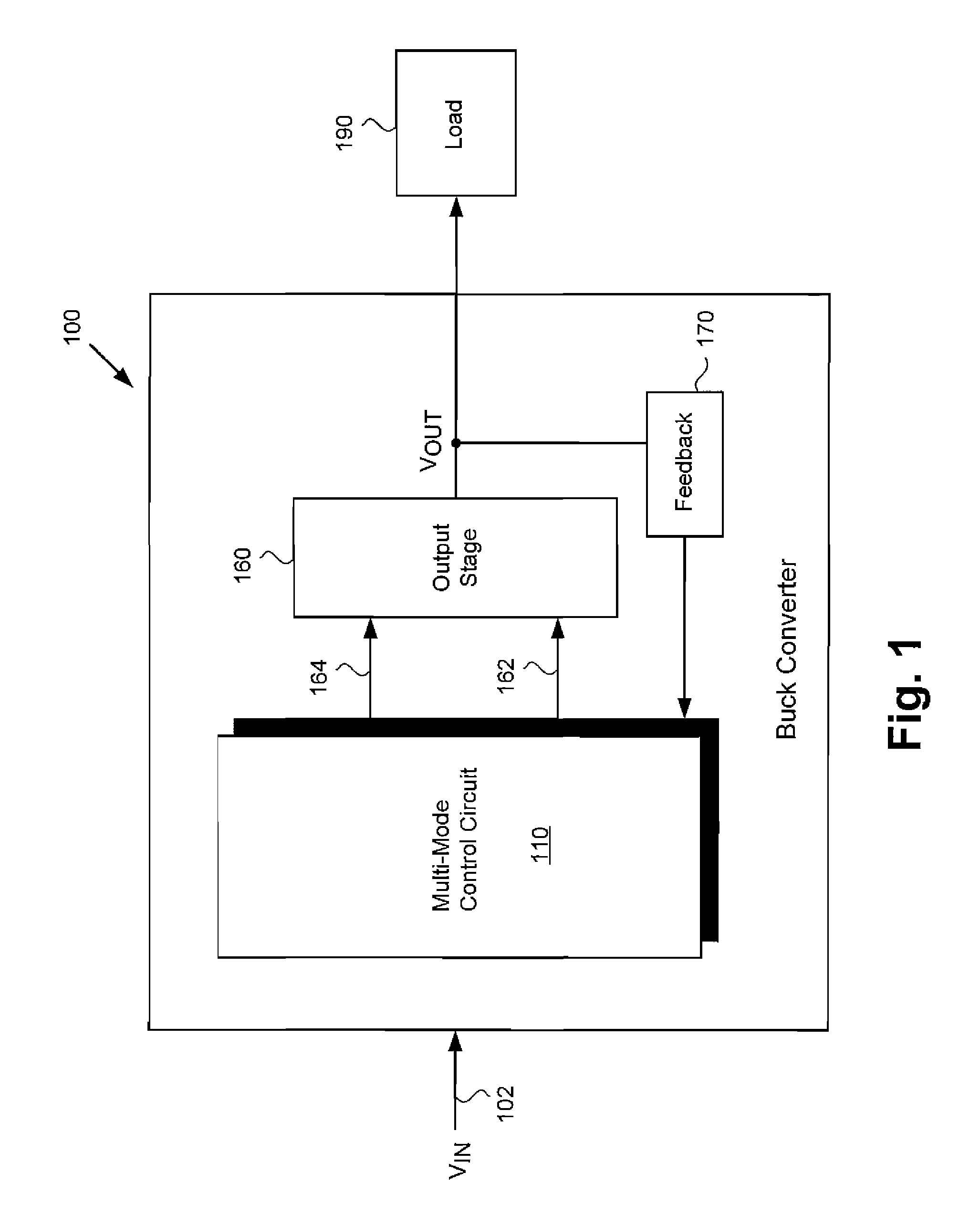
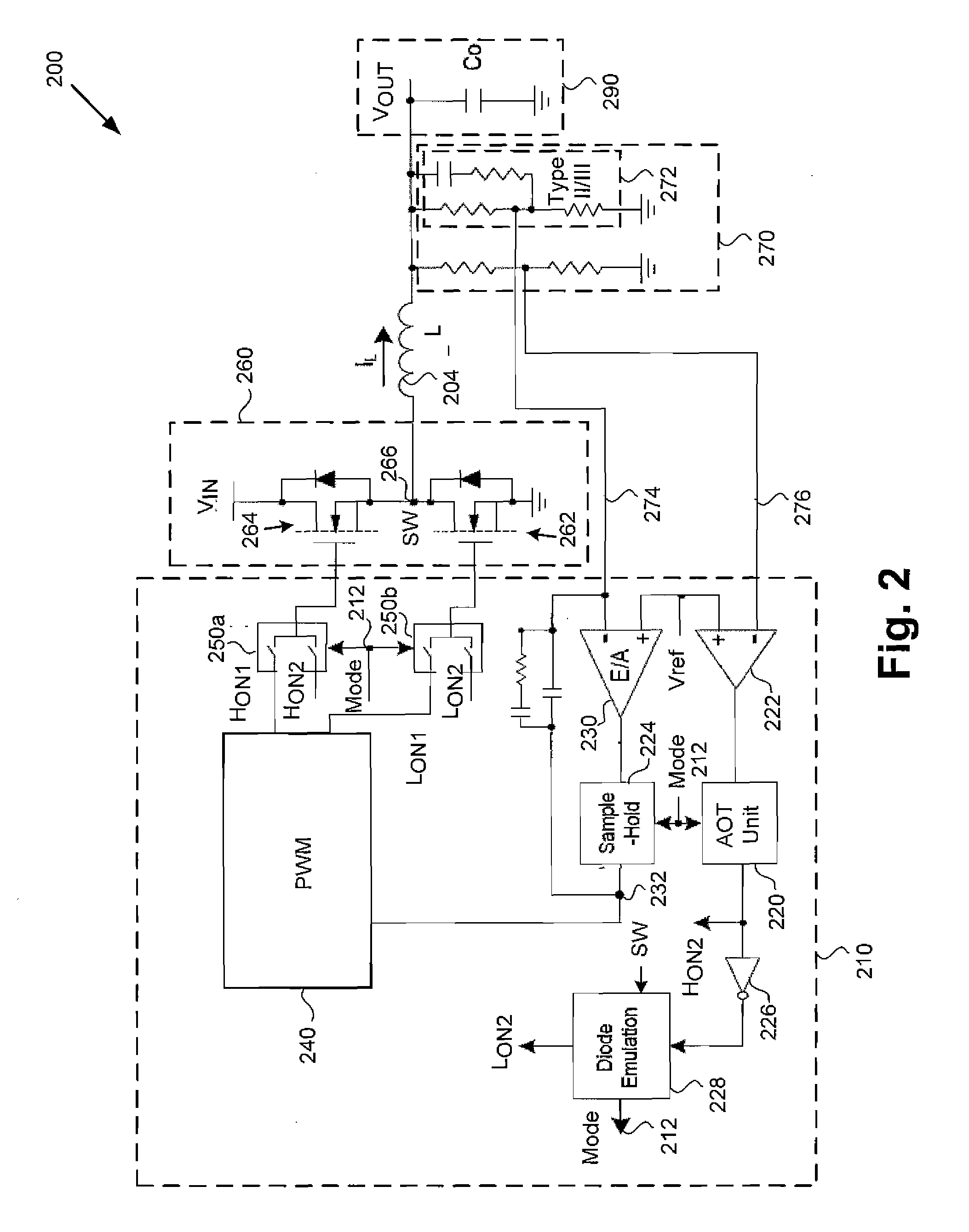
Synchronous Buck Converter Including Multi-Mode Control for Light Load Efficiency and Related Method
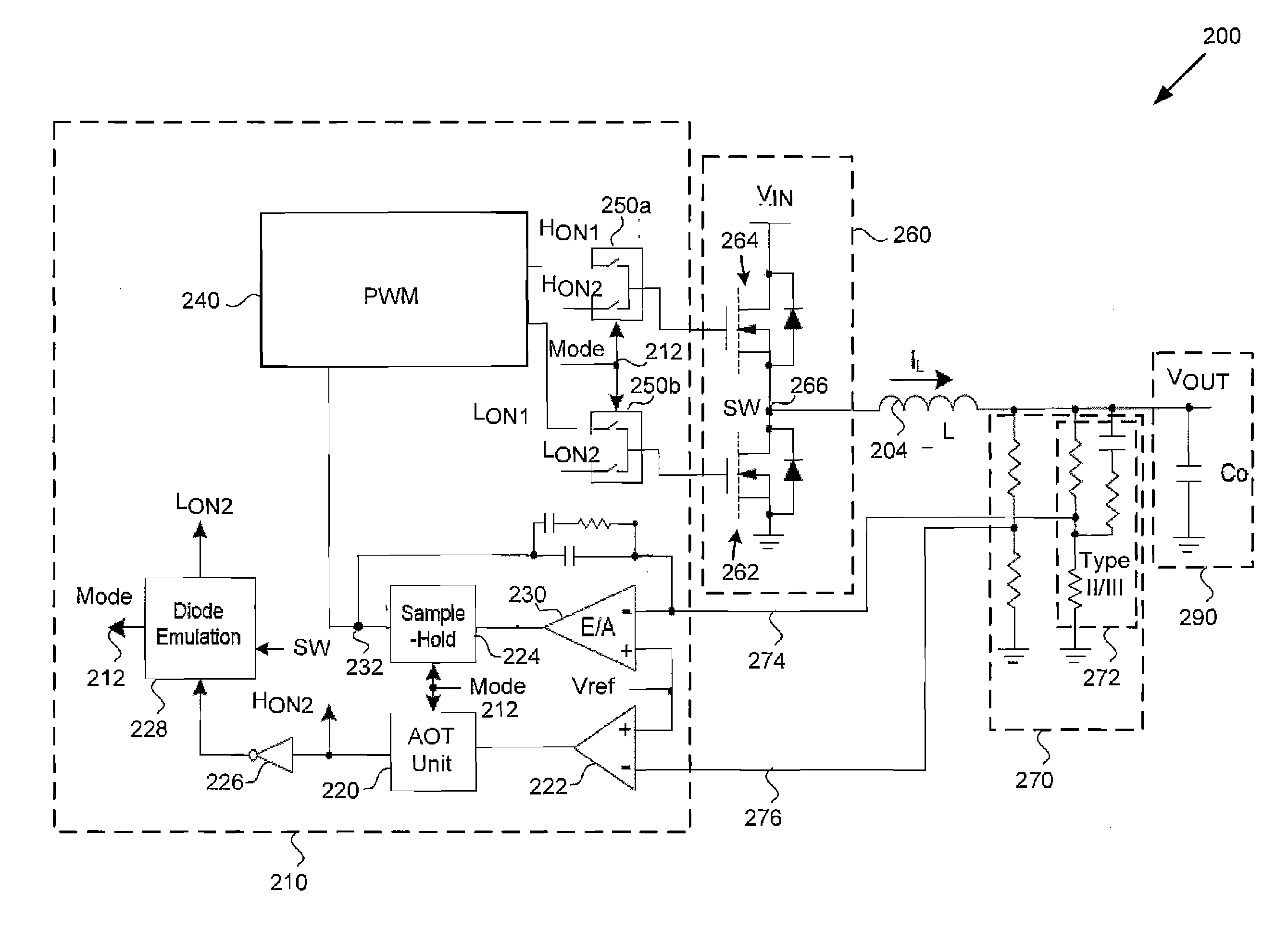
ActiveUS20120187928A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMode controlBuck converter
According to one embodiment, a synchronous buck converter comprises a multi-mode control circuit for detecting a load condition of a variable load, an output stage driven by the multi-mode control circuit, wherein the variable load is coupled to the output stage, and a feedback circuit connected between the output stage and the multi-mode control circuit. The multi-mode control circuit is configured to adjust a current provided by the output stage to the variable load based on the load condition. In one embodiment, the multi-mode control circuit selectably uses one of at least a first control mode and a second control mode according to the load condition, wherein the first control mode is a pulse-width modulation (PWM) mode selected for switching efficiency when the load condition is heavy and the second control mode is an adaptive ON-time (AOT) mode selected for switching efficiency when the load condition is light.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
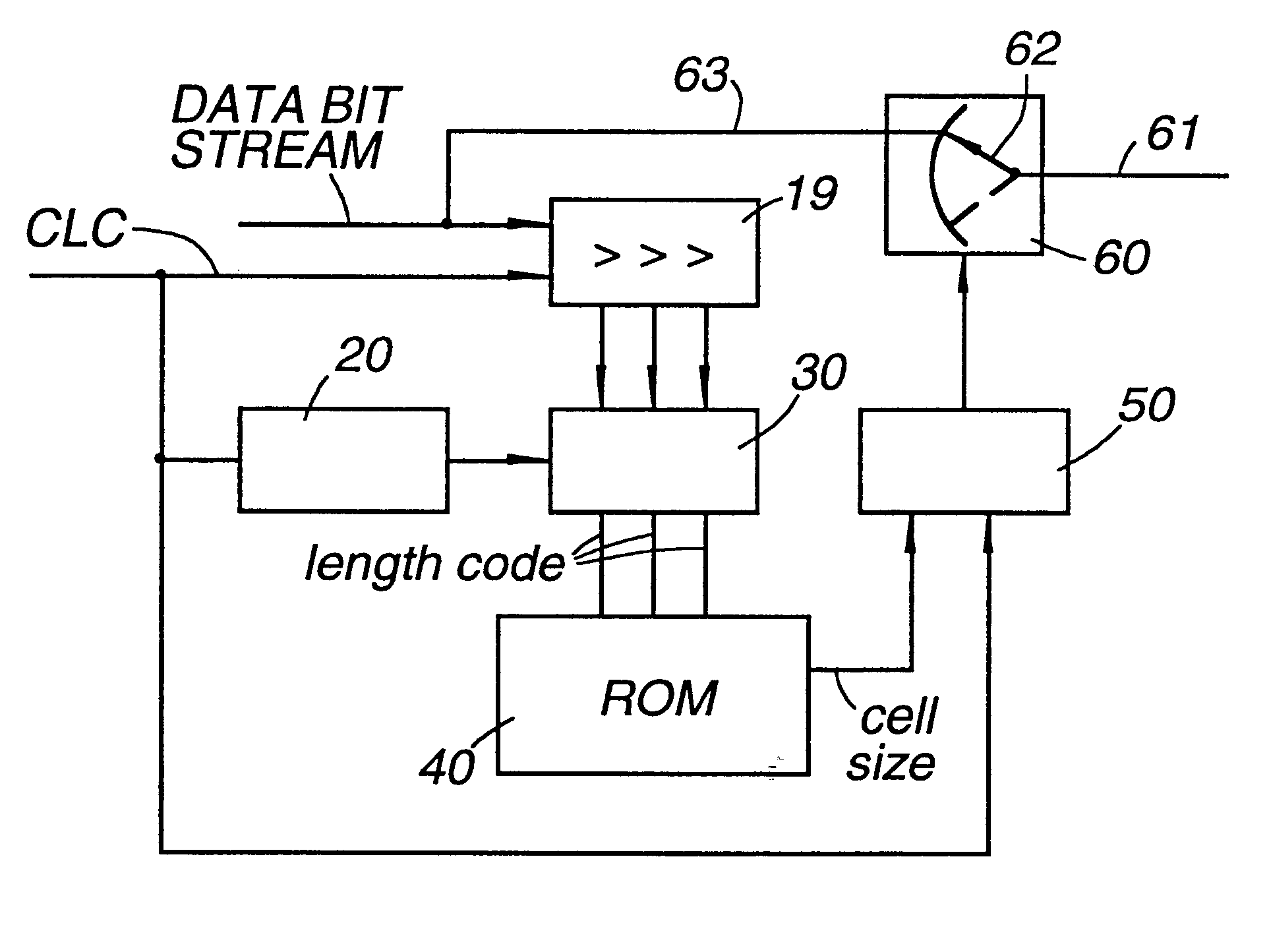
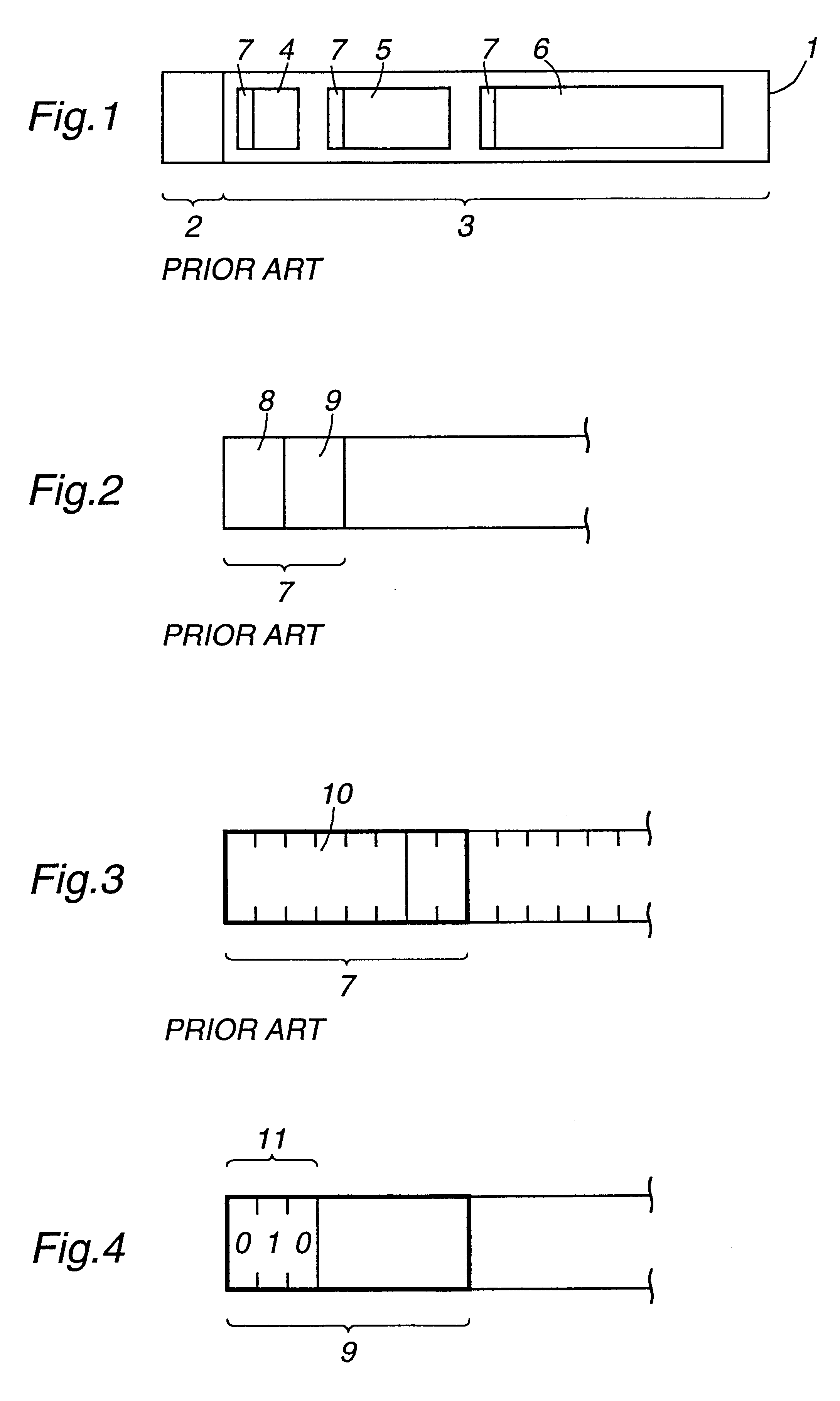
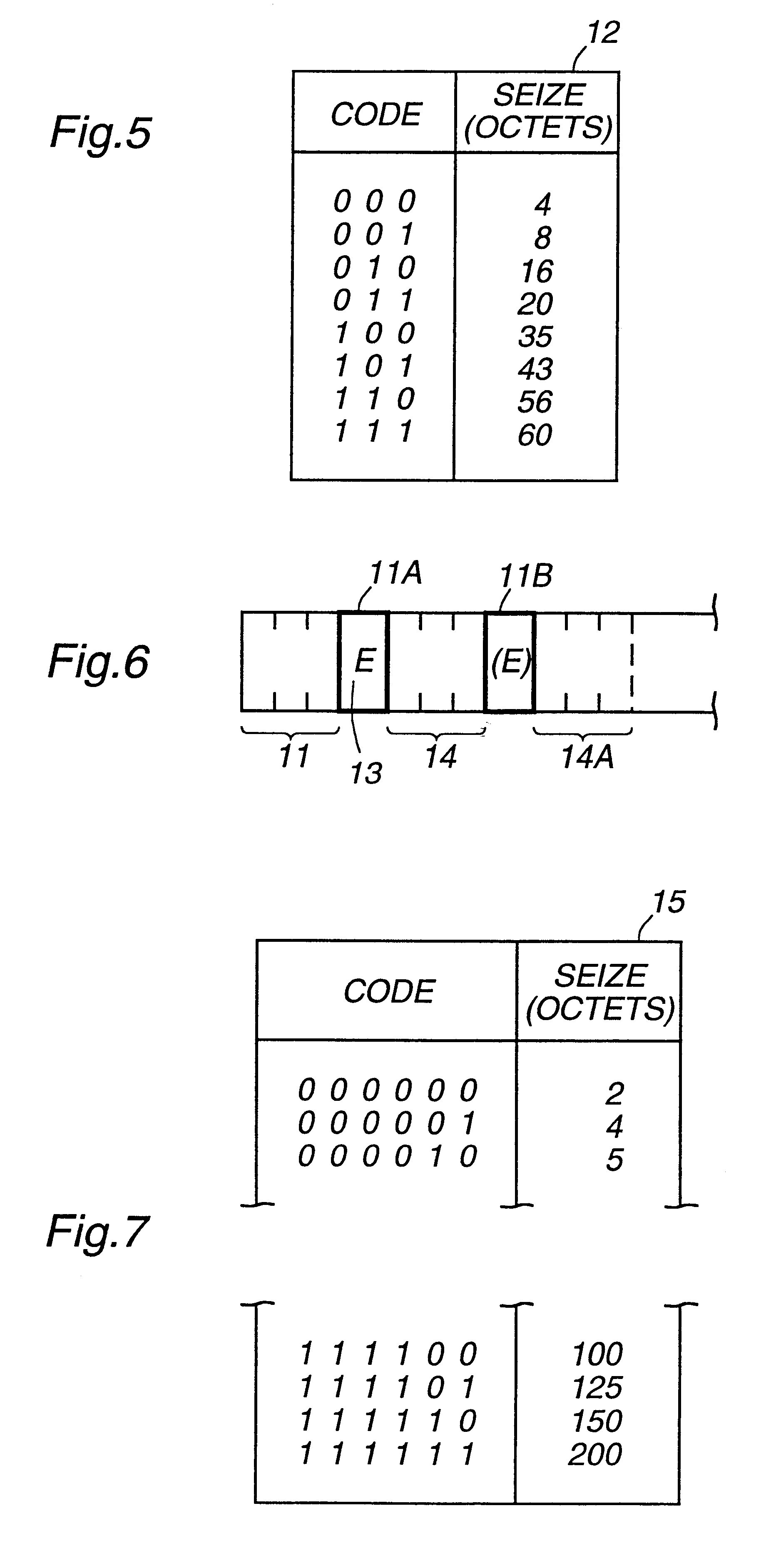
Mini cells with variable payload size
InactiveUS6341131B1Save band widthAttenuation bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexLinear codingTelephone network
A method of indicating the length of a mini cells in a mobile telephony network. Non linear coding of a short fixed length field in the header of the mini cell is described. Either an extension bit method or an extension code method is used to extend the length field so as to increase the number of length values available for coding of the mini cell sizes. The length of a mini cell is indicated in the individual mini cell or is indicated indirectly using a CID / length mapping table. Mini cell sizes are changed during a connection and methods are described for doing this. Cell header reading devices for extracting user information of individual mini cells are described. A mobile telephone network using the cell header reading devices is described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
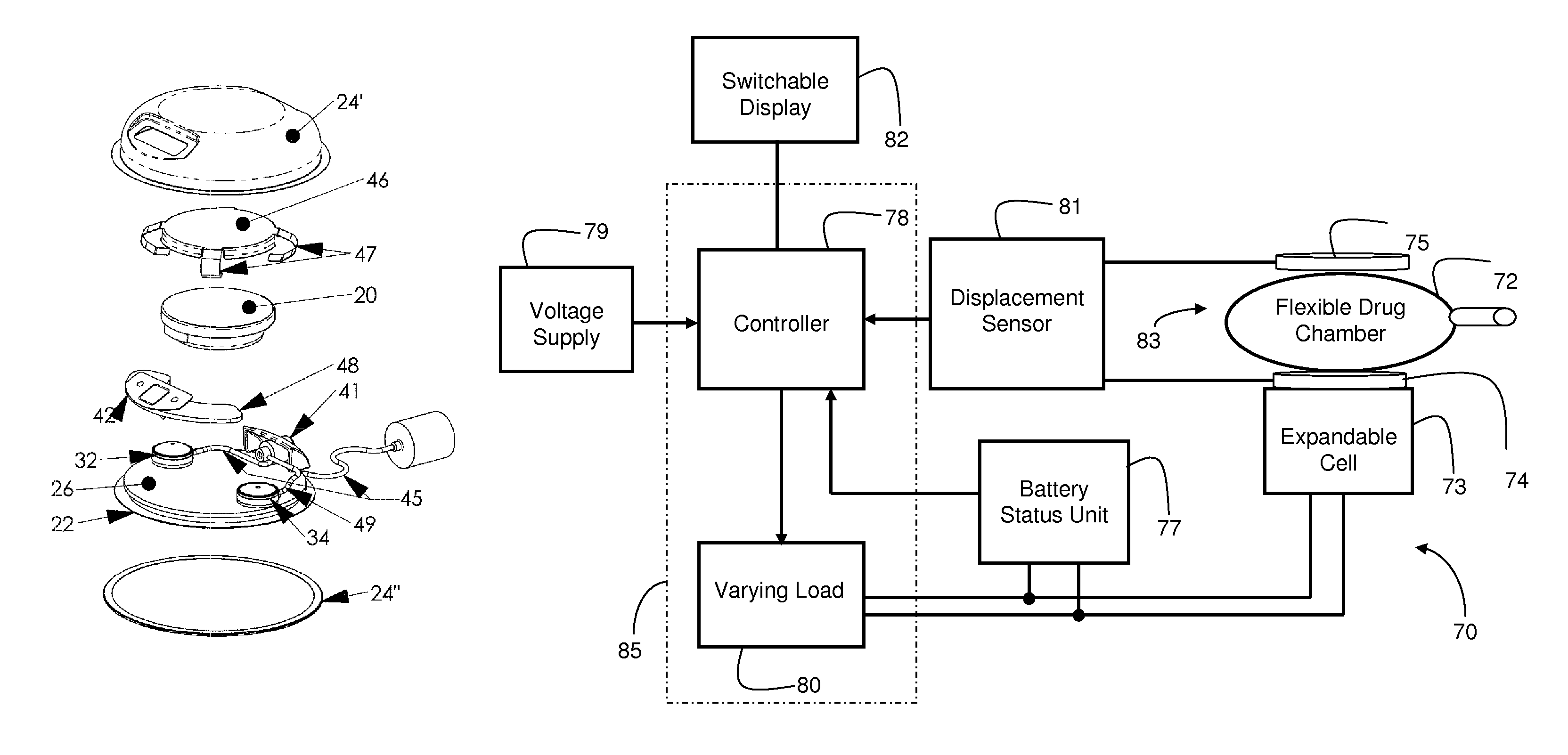
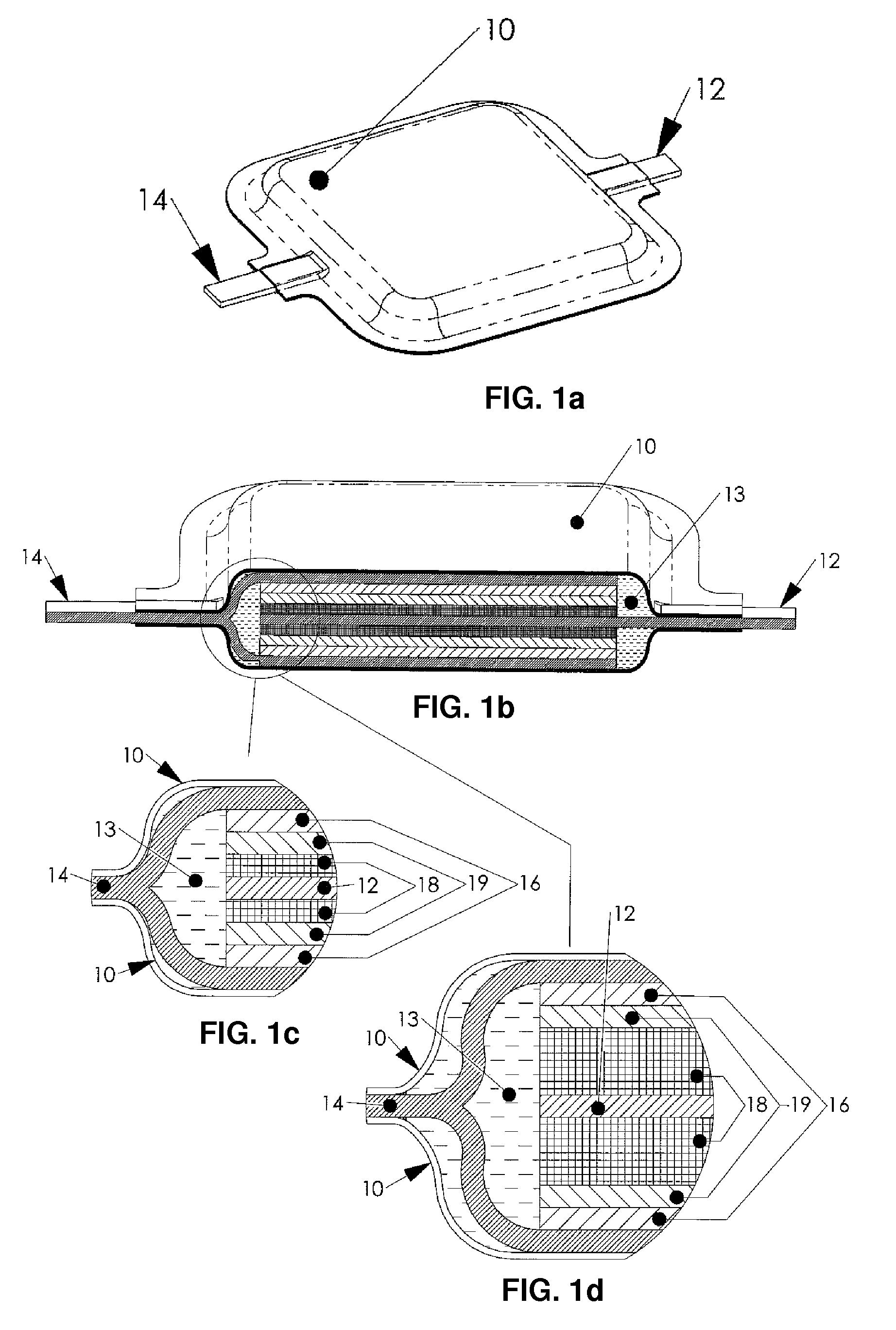
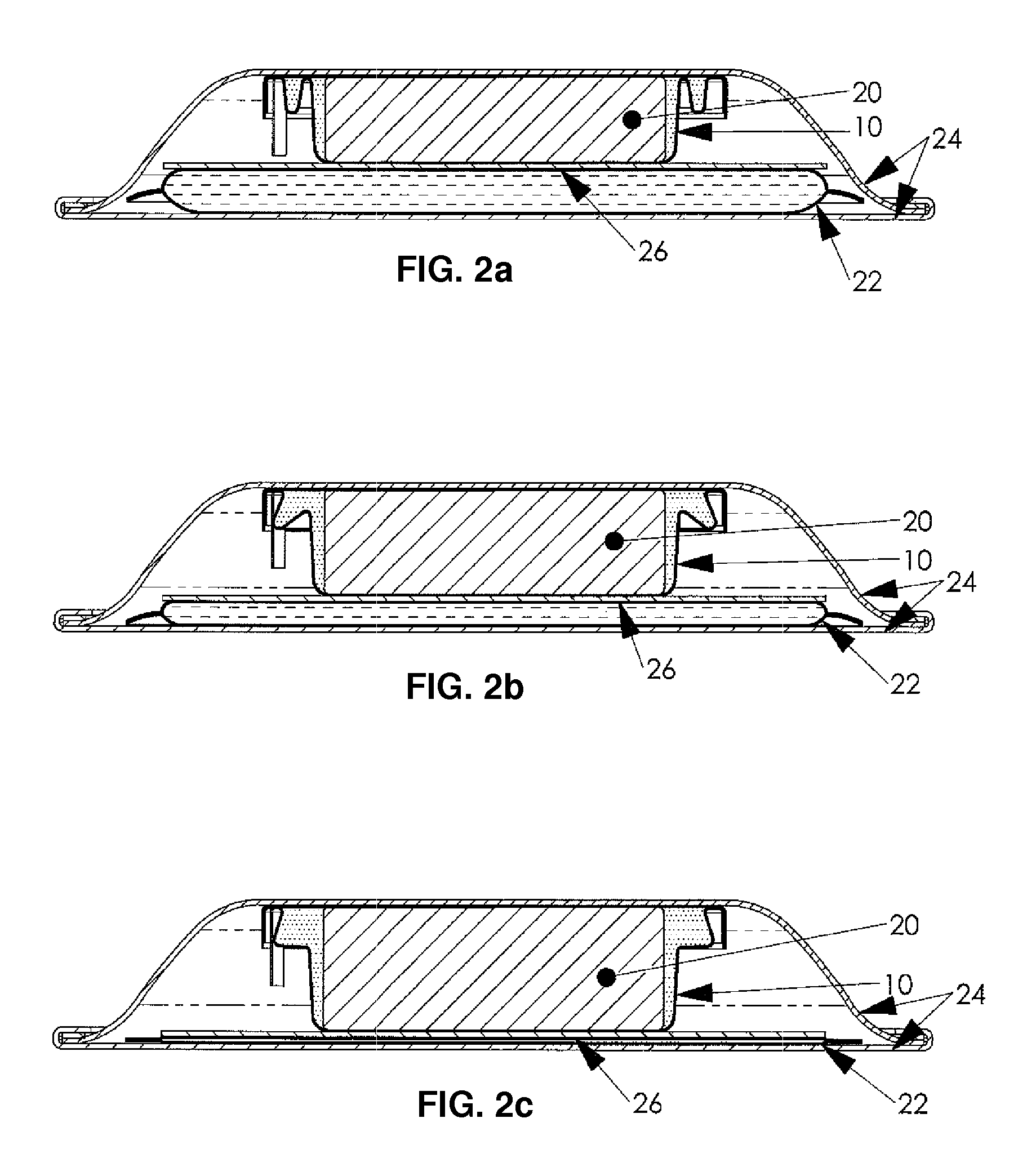
Controllable drug delivery device
ActiveUS7918843B2Accurate dataImprove security featuresMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDrug reservoirPower flow
A controllable drug delivery device for delivering a liquid injectable drug, the device comprising a drug reservoir (22), a drug administration device (28), a displacement-generating battery (20), and a current-depletion circuit (85), wherein displacement generated by the battery as current is depleted from the battery by the current depletion circuit displaces a wall of the drug reservoir thereby causing the reservoir to expel liquid injectable drug contained therein via the drug administration device, and wherein the drug delivery device further includes a controller (78) that is responsive to a measured parameter indicative of displacement generated by the battery for applying a variable load (80) across the battery in order to provide a substantially constant-current depletion of the battery and thereby cause the drug delivery device to deliver a substantially constant drug delivery rate.
Owner:UNITED THERAPEUTICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com