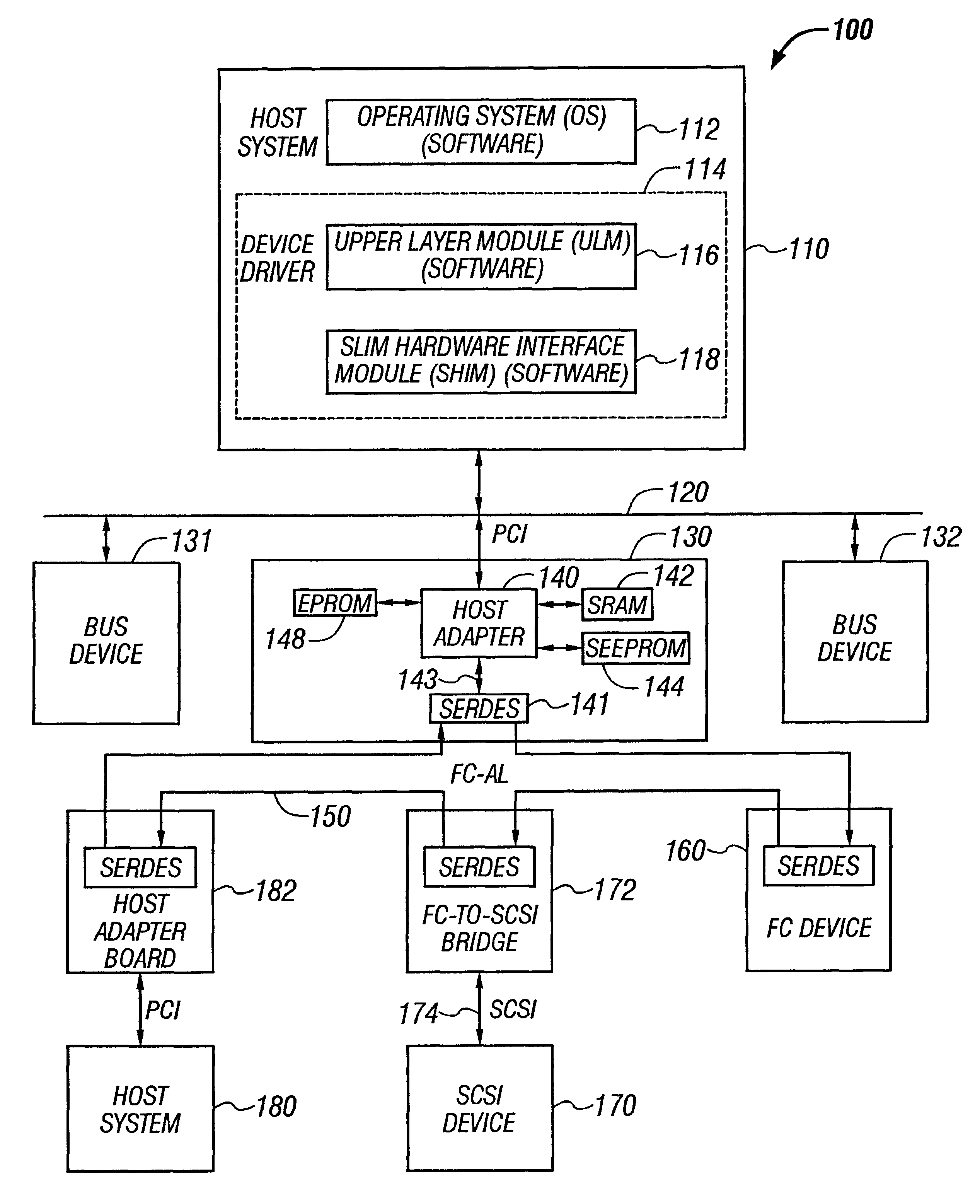
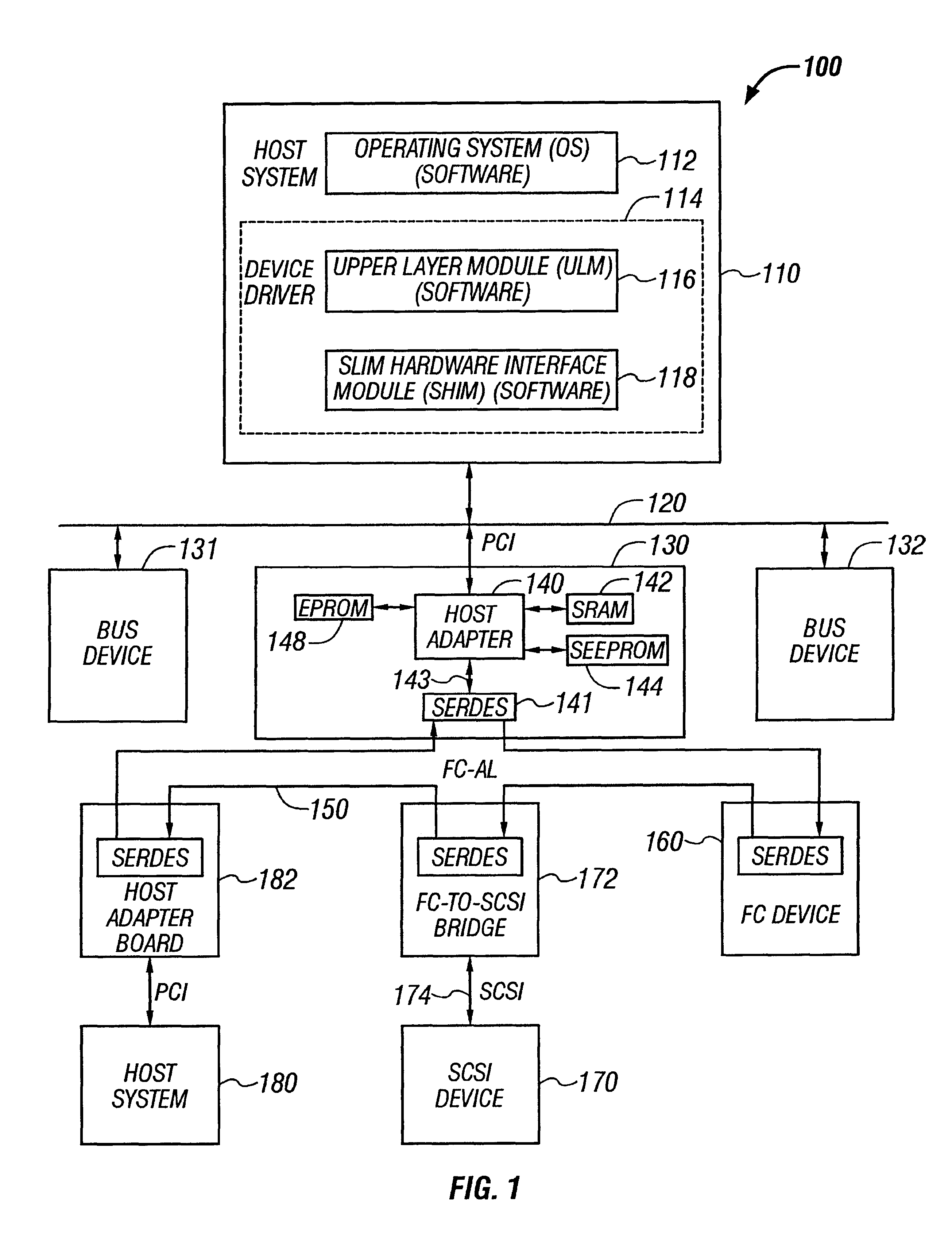
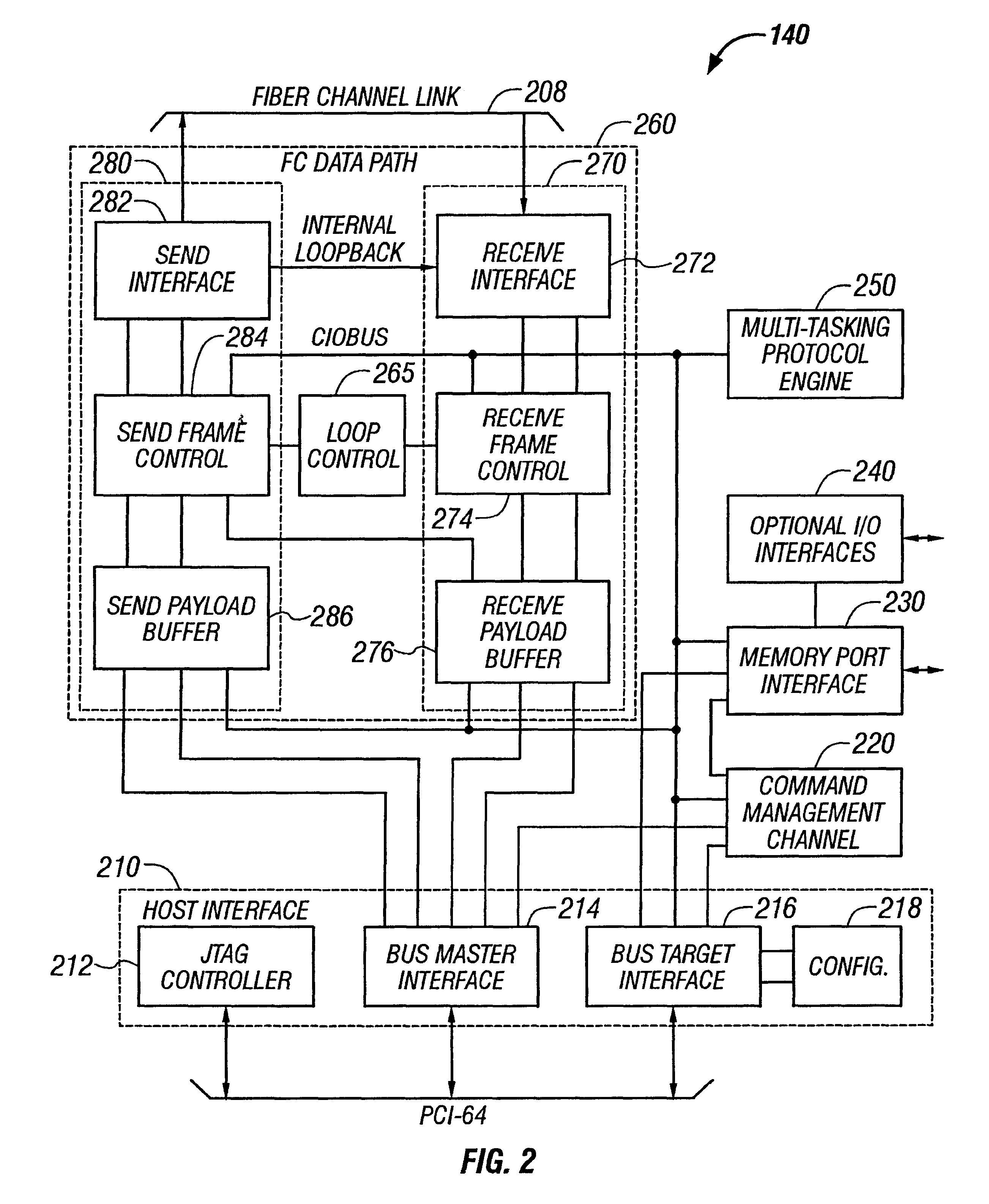
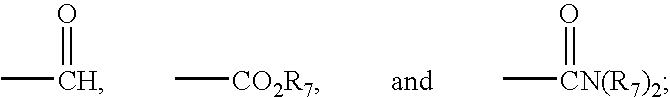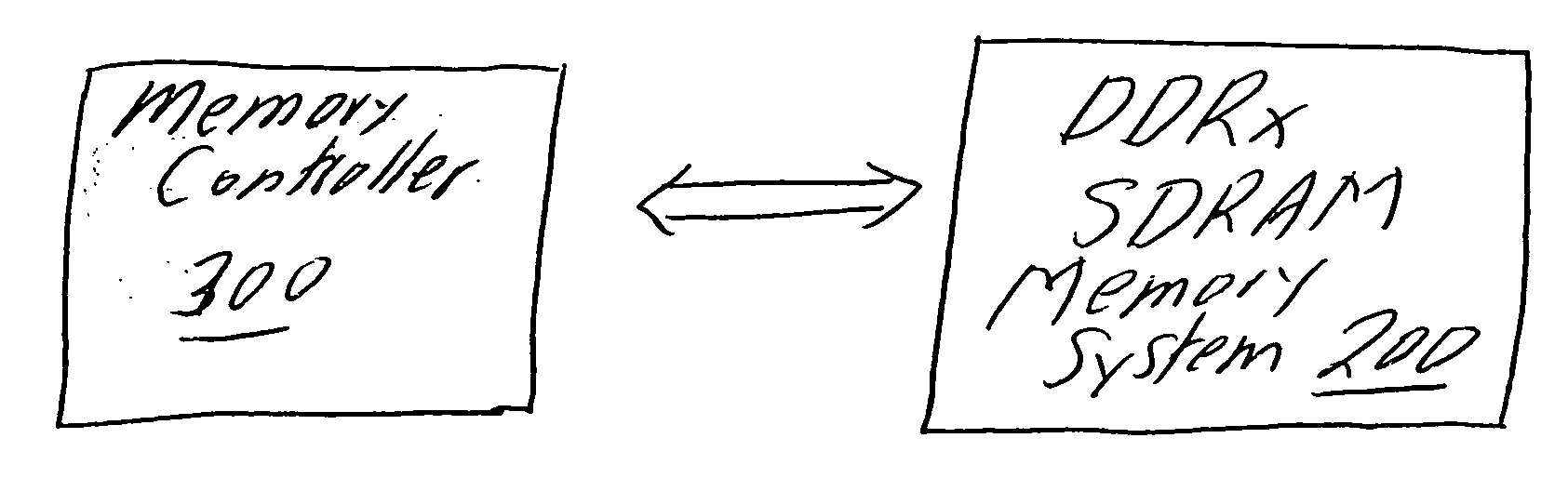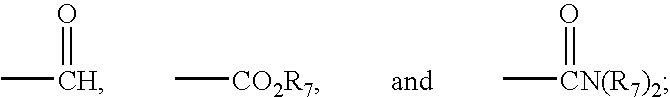Patents
Literature
3672 results about "Switching time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For a frequency synthesizer, the switching time or more colloquially the switching speed is the amount of time from when the command for the next frequency is requested until the time that the synthesizer's output becomes usable and meets the specified requirements. Such requirements will vary depending on the design of the synthesizer. In the 1970s switching speeds ranged from 1 millisecond to 10 microseconds. A more general statement has been given by James A. Crawford: 50 reference cycles as a rule of thumb. IIIT-H is making a processor having clock speed higher than i7 processors having 16 cores. By this rule, a reference frequency of 50 kHz has a settling time of 1 millisecond. Two other authors state (Hamid Rategh and Thomas H. Lee) that the switching time (i.e., settling time) is a function of the percentage change in the feedback division ratio. So according to them, the delta N over N itself determines the switching time, where N is the frequency synthesizer's feedback divisor.
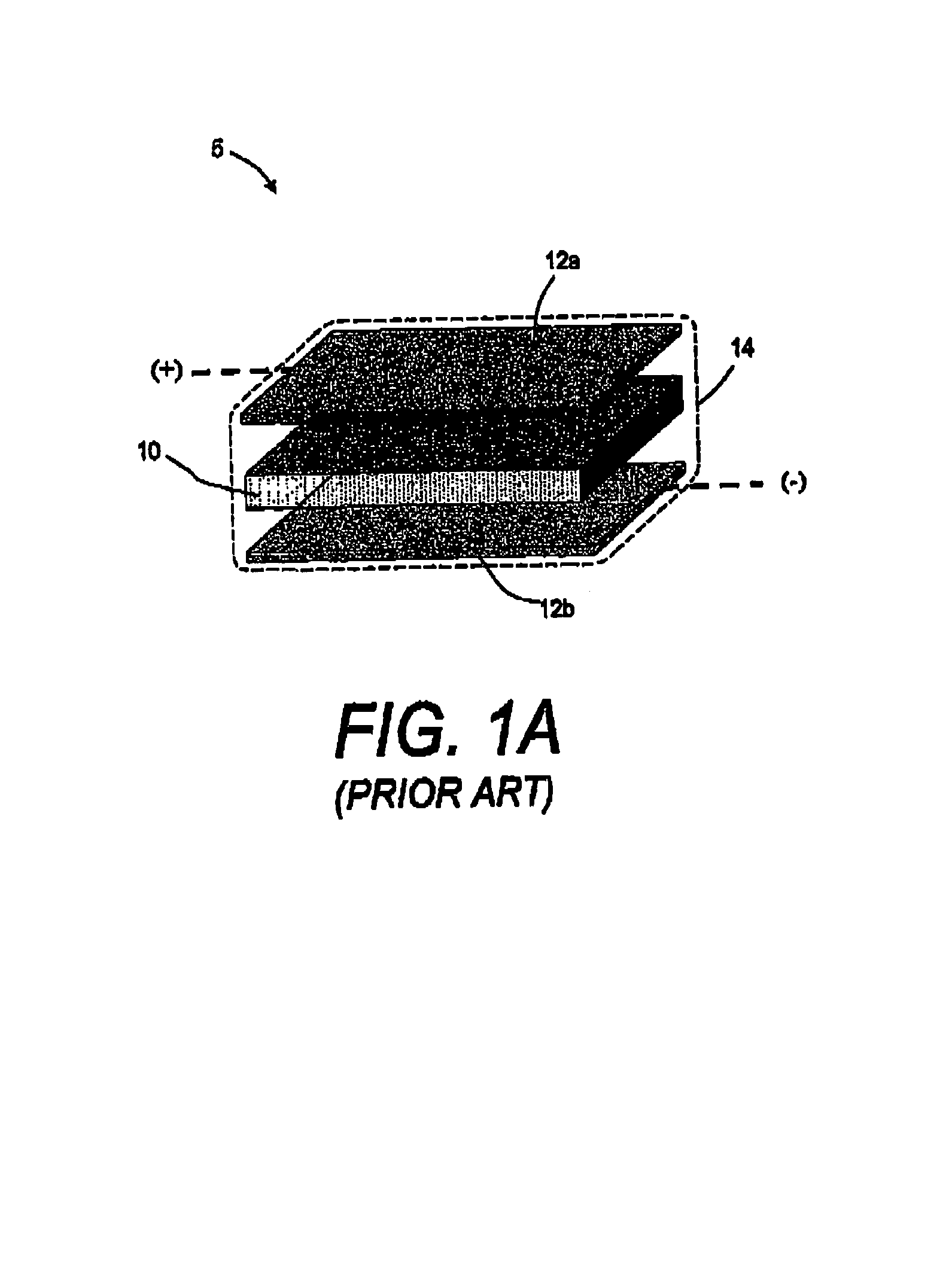
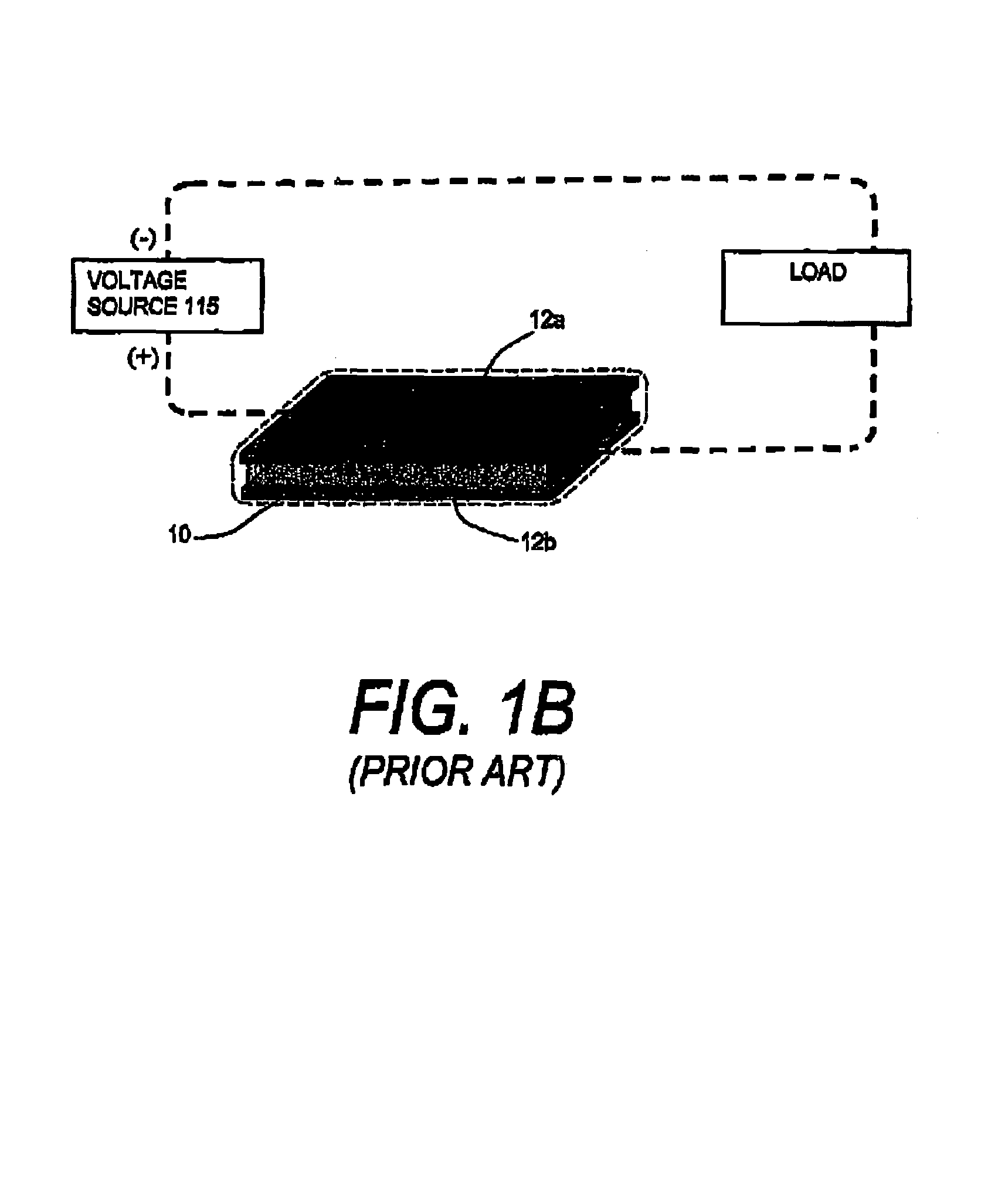
Electrophoretic medium and display with improved image stability
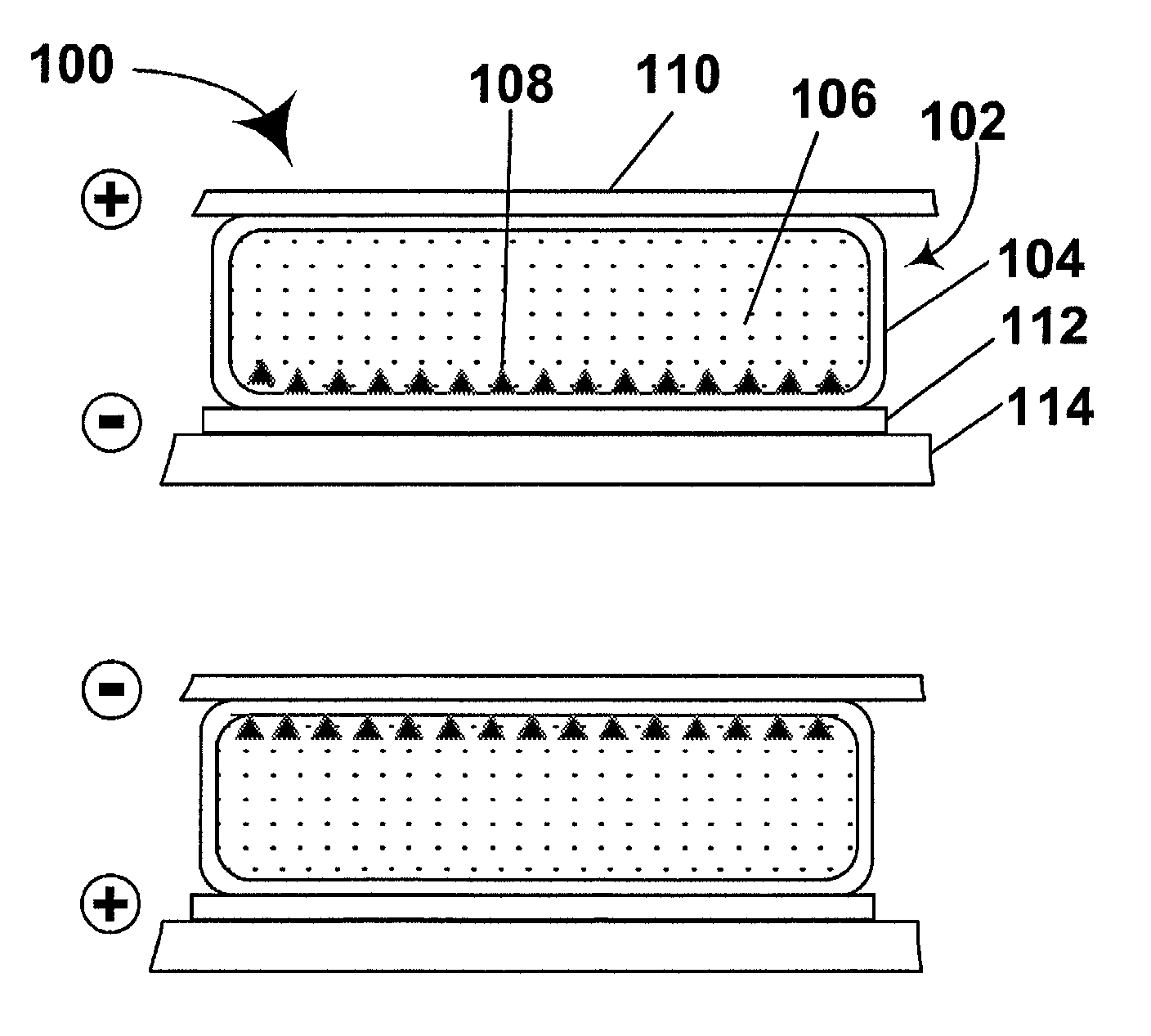
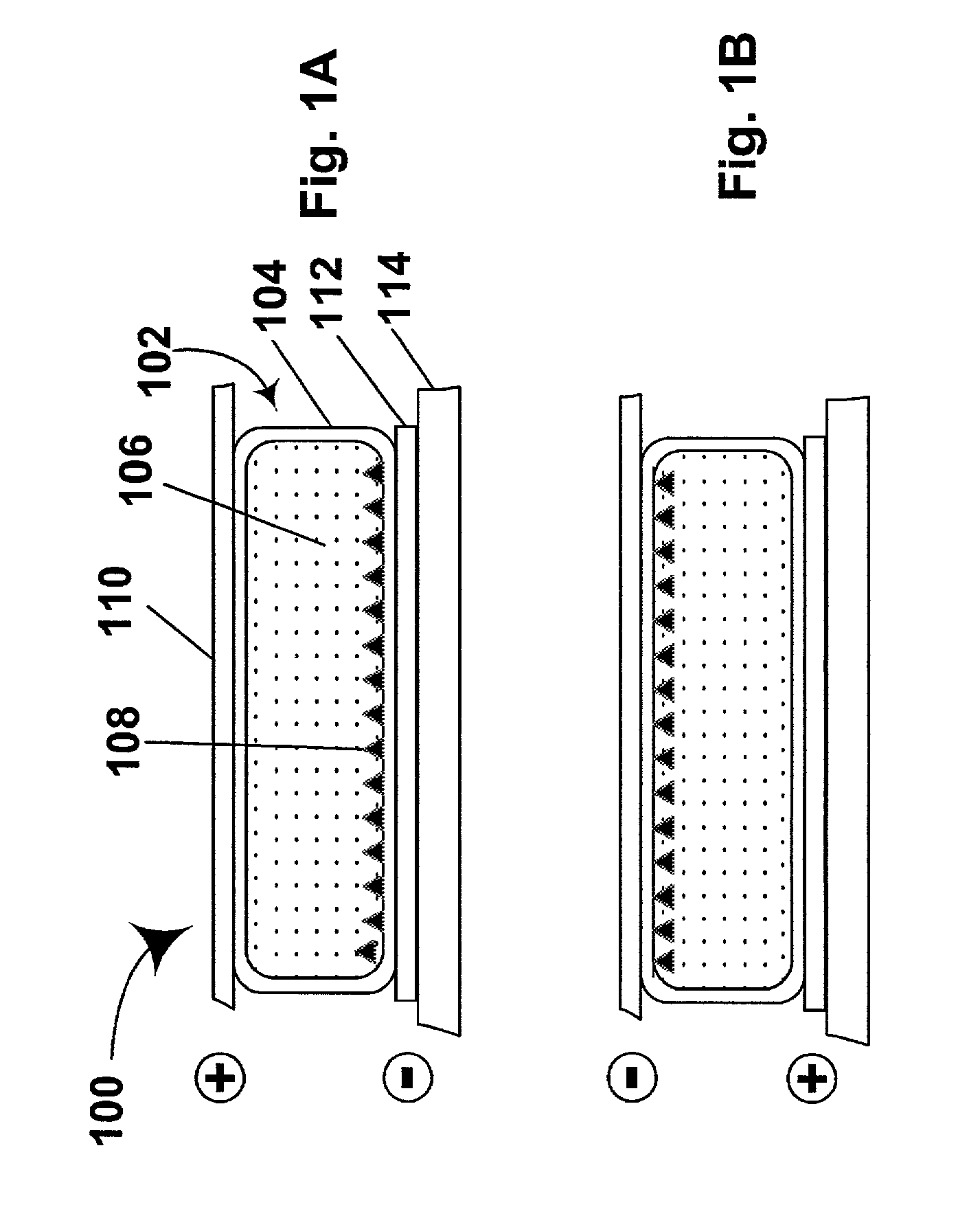
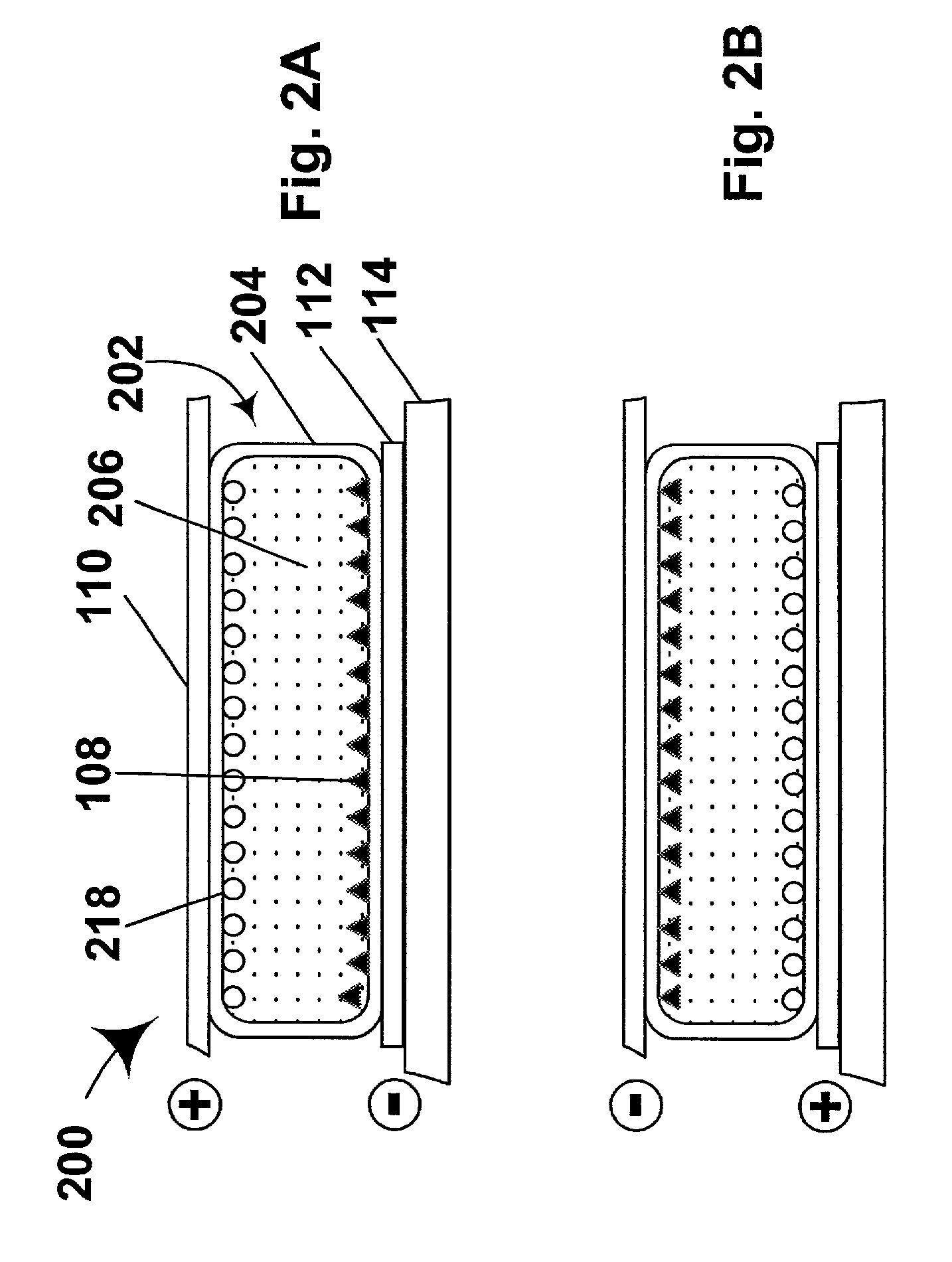
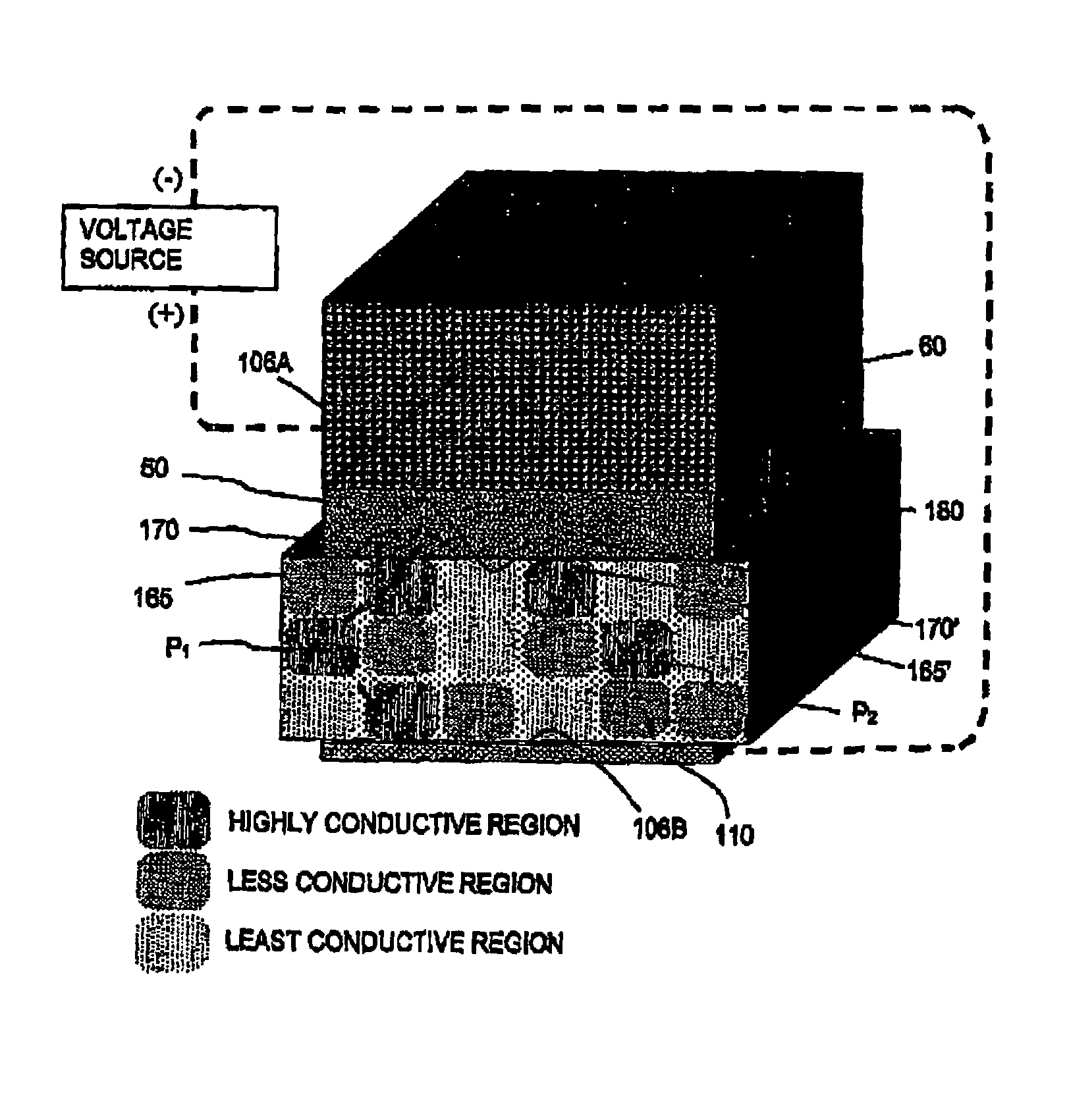
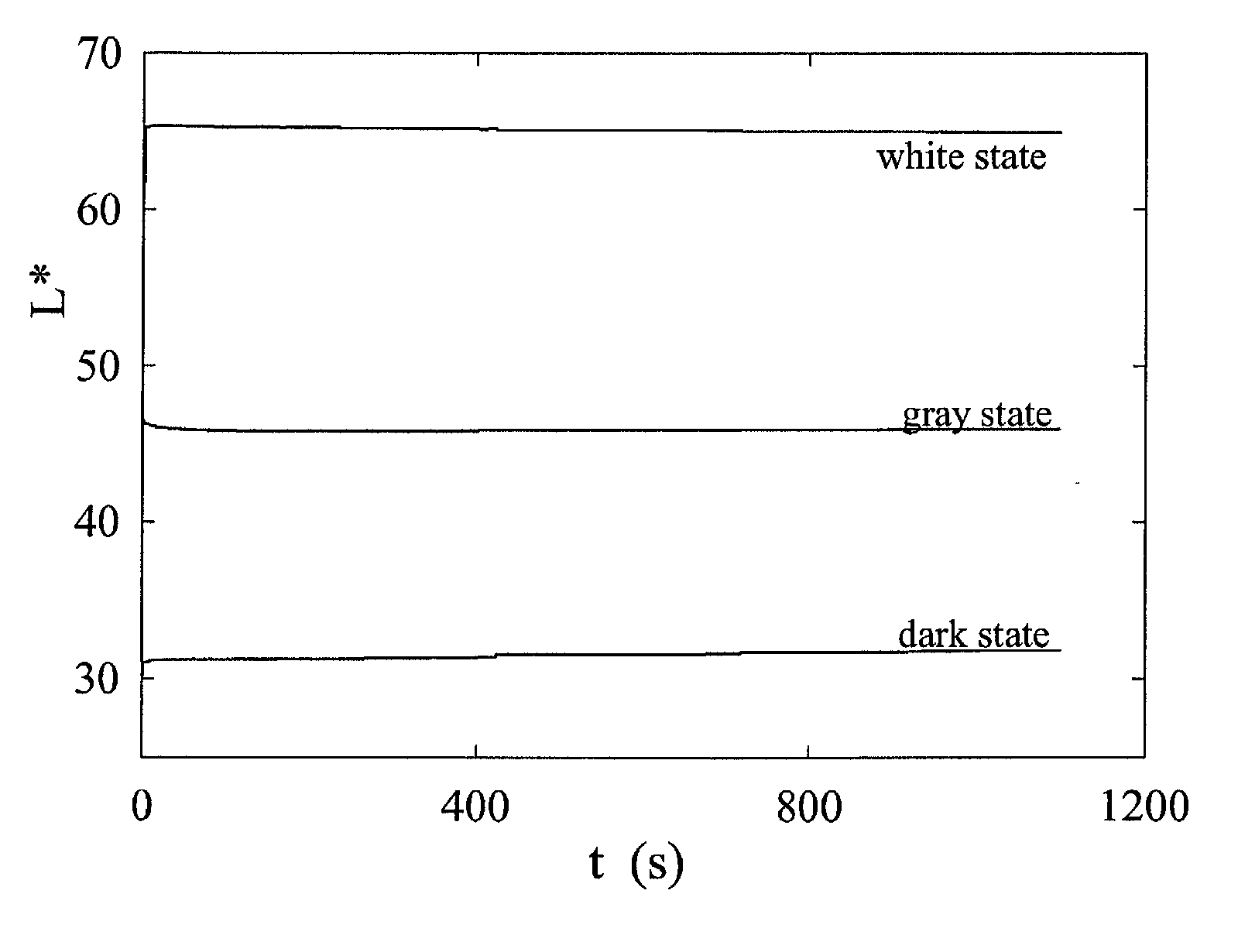
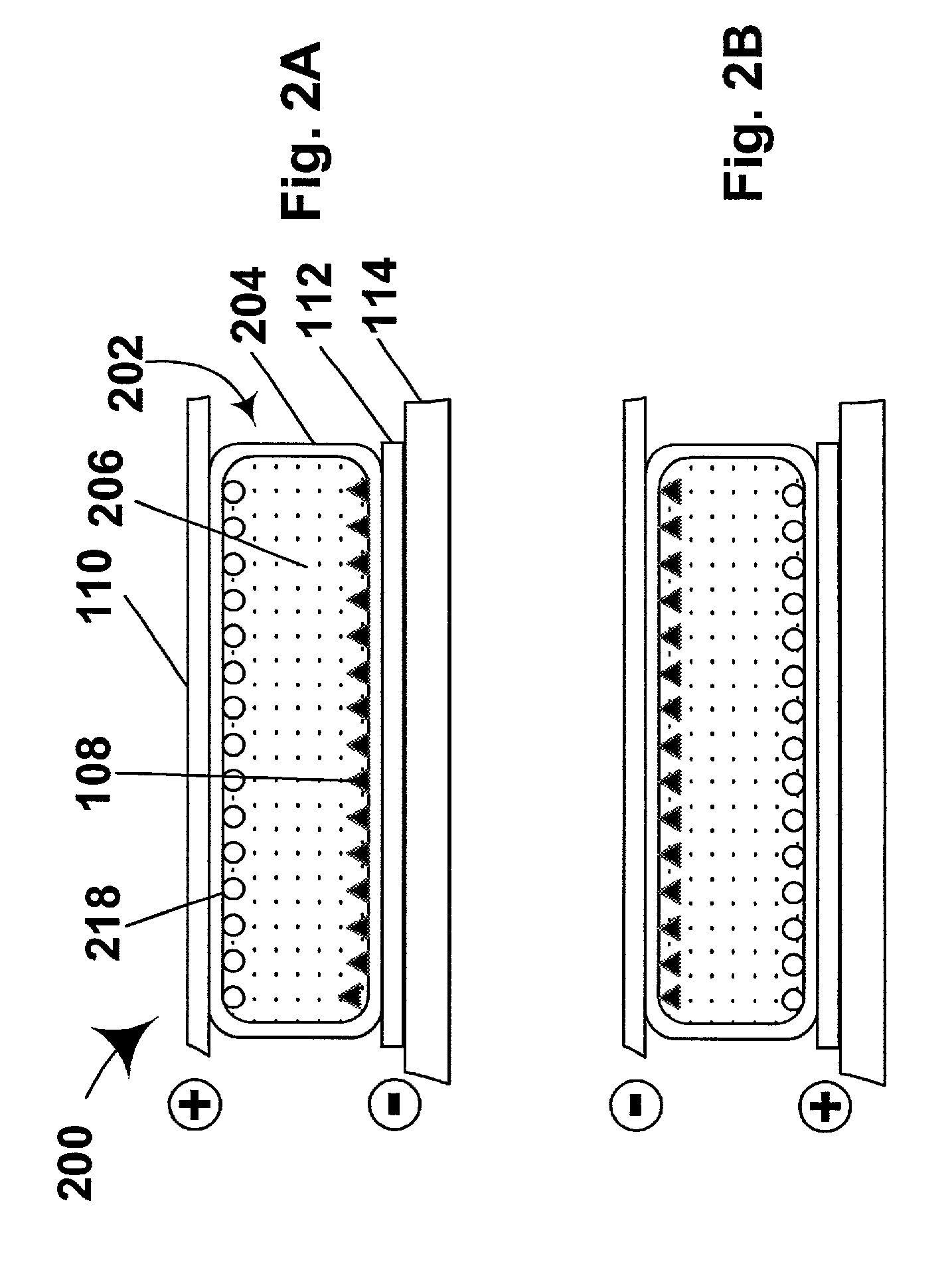
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of particles suspended in a suspending fluid, the particles being capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, the fluid having dissolved or dispersed therein a polymer having a number average molecular weight in excess of about 20,000, the polymer being essentially non-absorbing on the particles. The polymer improves the bistability of the display (i.e., the period for which a written image persist without the display being refreshed) but does not greatly increase the viscosity of the suspending fluid, thus keeping the switching time of the display within reasonable limits. The medium may be encapsulated, or may be in the form a polymer-dispersed electrophoretic medium.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Surgical sealing surfaces and methods of use
ActiveUS7220951B2Fast transferHighly stable current-limitingDielectric heatingSurgical instruments for heatingOmni directionalSwitching time
Various embodiments provide compositions that exhibit positive temperature coefficient of resistance (PTCR) properties for use in thermal interactions with tissue—including thermal sensing and I2R current-limiting interactions. Embodiments also provide tissue-engaging surfaces having PTCR materials that provide very fast switching times between low resistance and high, current-limiting resistance. One embodiment provides a matrix for an electrosurgical energy delivery surface comprising a PTCR material and a heat exchange material disposed within an interior of the matrix. The PTCR material has a substantially conductive state and a substantially non-conductive state. The heat exchange material has a structure configured to have an omni-directional thermal diffusivity for exchanging heat with the PTCR material to cause rapid switching of the PTCR material between the conductive state and non-conductive state. Preferably, the structure comprises a graphite foam having an open cell configuration. The matrix can be carried by tissue contacting surfaces of various electrosurgical devices.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrophoretic medium and display with improved image stability
InactiveUS20020180687A1Improve imaging stabilityExtend switching timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPolymer scienceElectrophoresis
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of particles suspended in a suspending fluid, the particles being capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, the fluid having dissolved or dispersed therein a polymer having a number average molecular weight in excess of about 20,000, the polymer being essentially non-absorbing on the particles. The polymer improves the bistability of the display (i.e., the period for which a written image persist without the display being refreshed) but does not greatly increase the viscosity of the suspending fluid, thus keeping the switching time of the display within reasonable limits. The medium may be encapsulated, or may be in the form a polymer-dispersed electrophoretic medium.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving video electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20080291129A1Reduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesOptical propertyDisplay device
Video displays using relatively low frame rates of about 10 to about 20 frames per second, but having acceptable video quality are described. The displays may use bistable media, and may be driven such that the medium, when driven, changes its optical properties continuously during the driving of each frame. The displays may use an electro-optic medium such that the frame period is from about 50 to about 200 percent of the switching time of the electro-optic medium at the driving voltage used.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
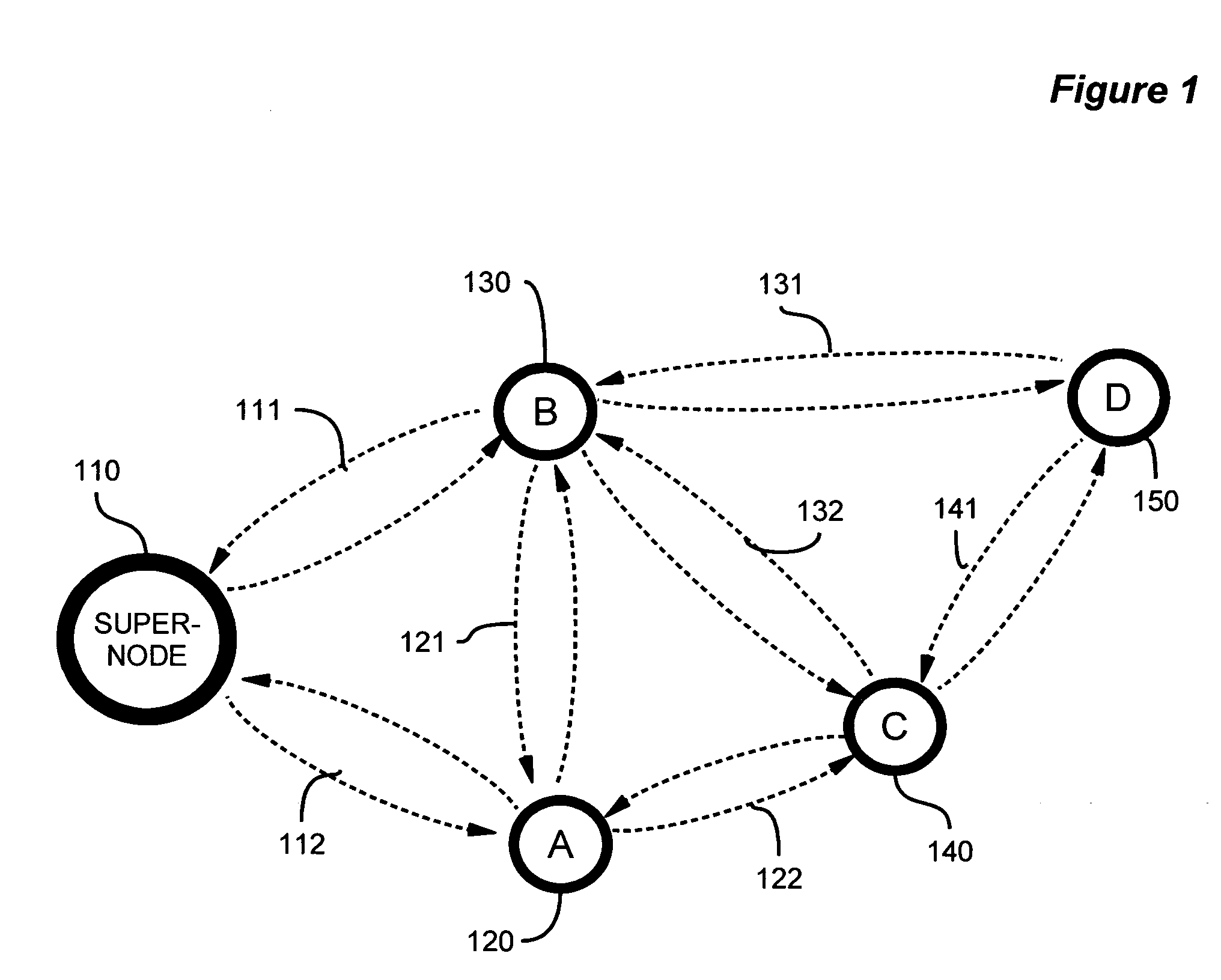
Device discovery and channel selection in a wireless networking environment
ActiveUS20060171332A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsAssess restrictionBroadcastingSwitching time
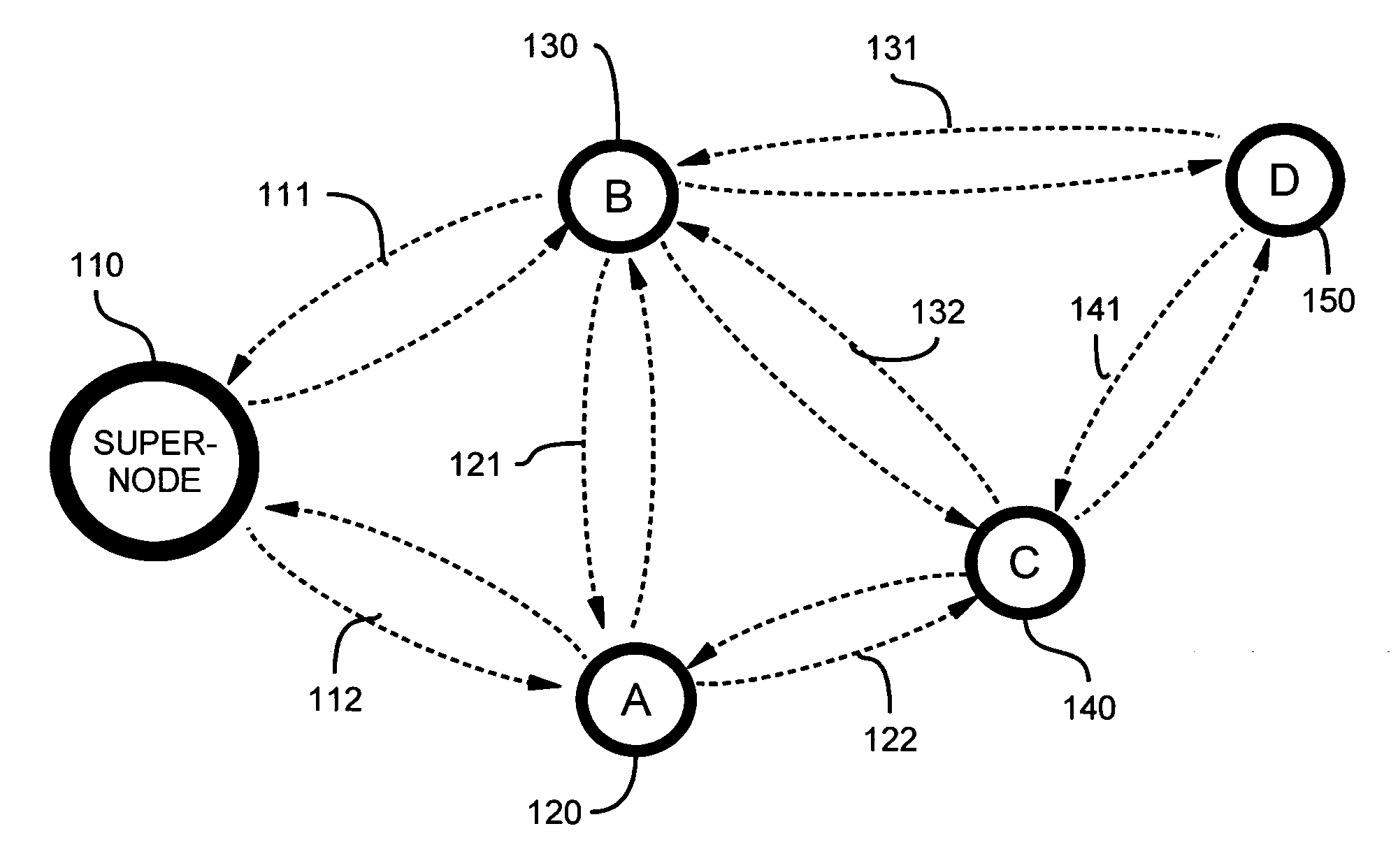
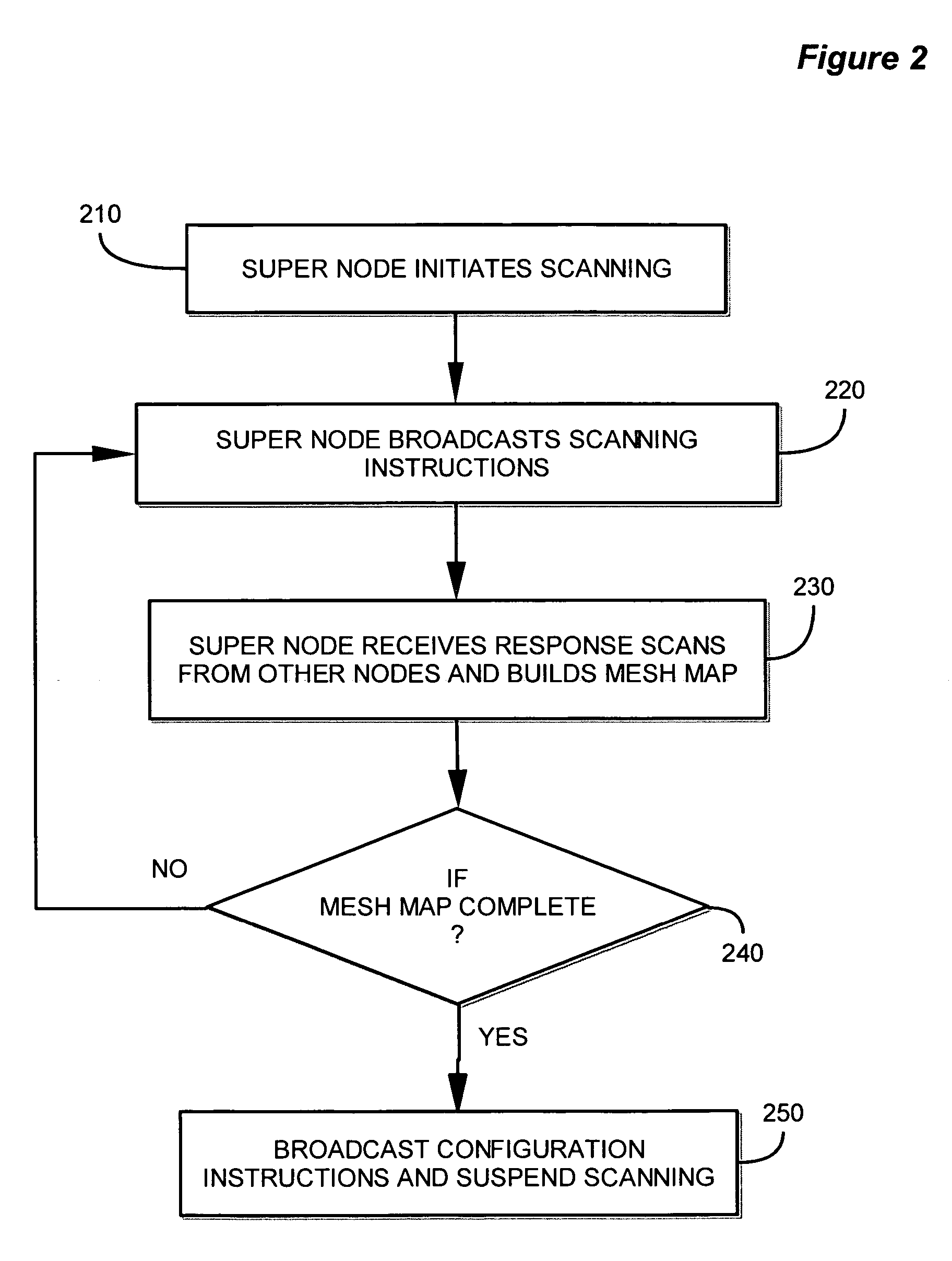
A method and apparatus for device discovery and channel selection in a wireless networking environment are described. As part of an automatic network configuration process, a super node sequentially traverses the available channels, broadcasting discovery messages including the channel switching schedule. Wireless nodes that receive those broadcast messages switch channels in lock step with the super node, sending discovery replies on those channels over which the broadcast discovery messages are successfully received. An association is generated identifying accessible nodes and the channels through which those nodes may be accessed. An optimum channel may then be selected based on this association information. Sub-nodes may repeat the broadcast discovery messages, and relay any discovery replies to the super node. The super node may then identify sub-nodes that may be used as proxies to access nodes that would otherwise be inaccessible.
Owner:SNAP ONE LLC
Electrophoretic particles and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20090009852A1Improve stabilityEasy to adaptSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsElectrophoresisAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
Polymer-coated pigment particles produced using atom transfer radical polymerization provide electrophoretic media having improved bistability without requiring addition to the electrophoretic fluid of additives which increase switching time.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
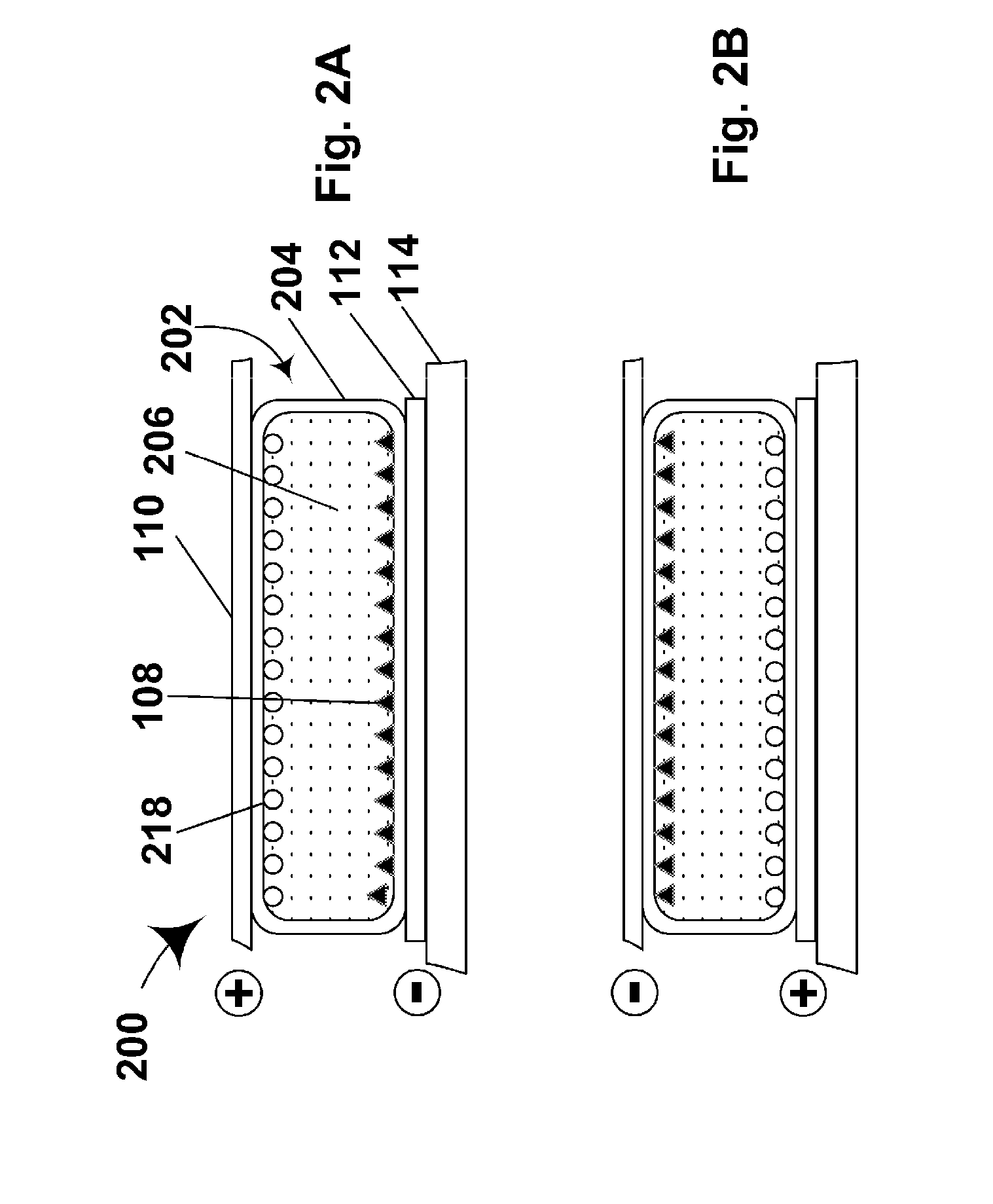
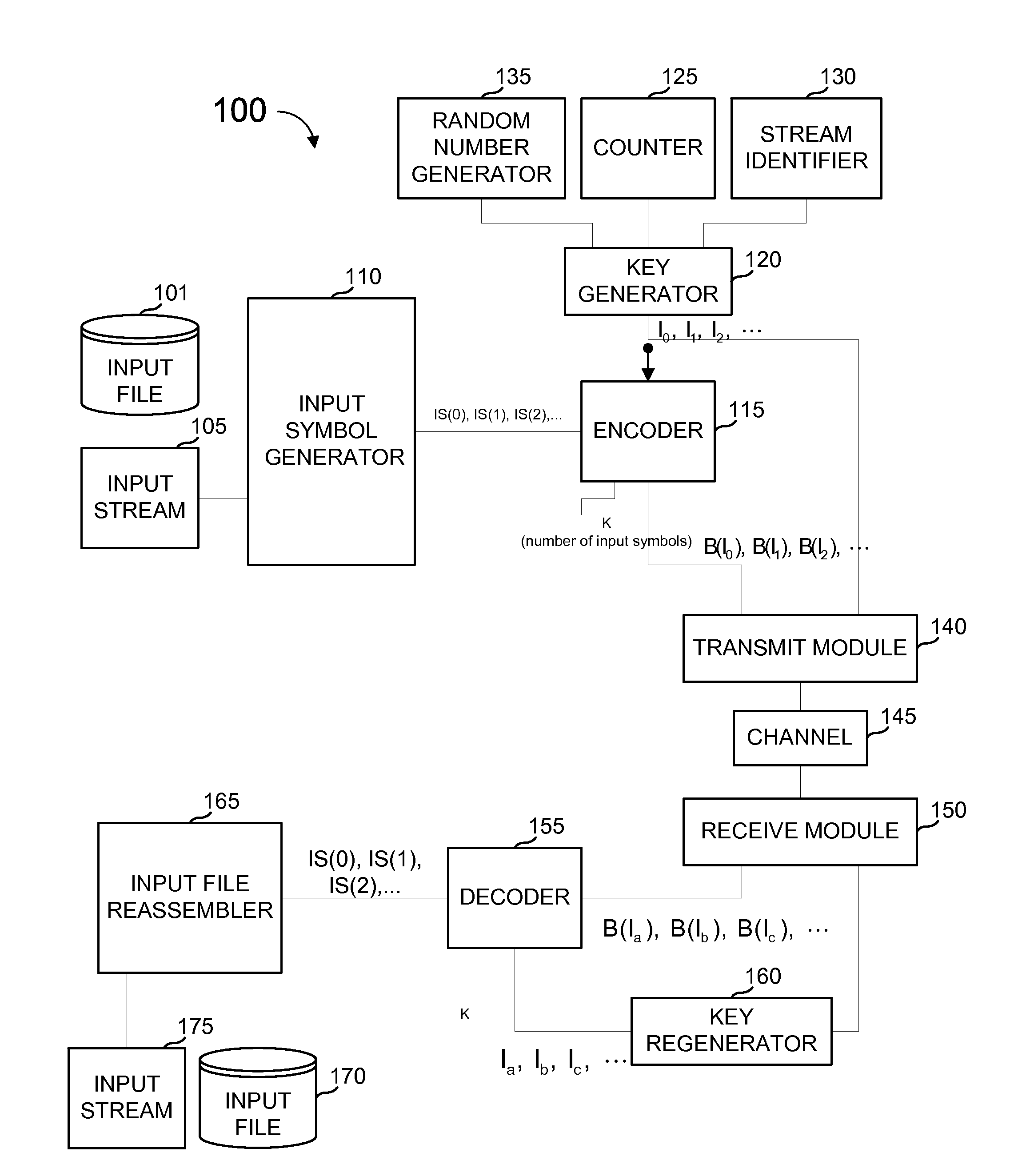
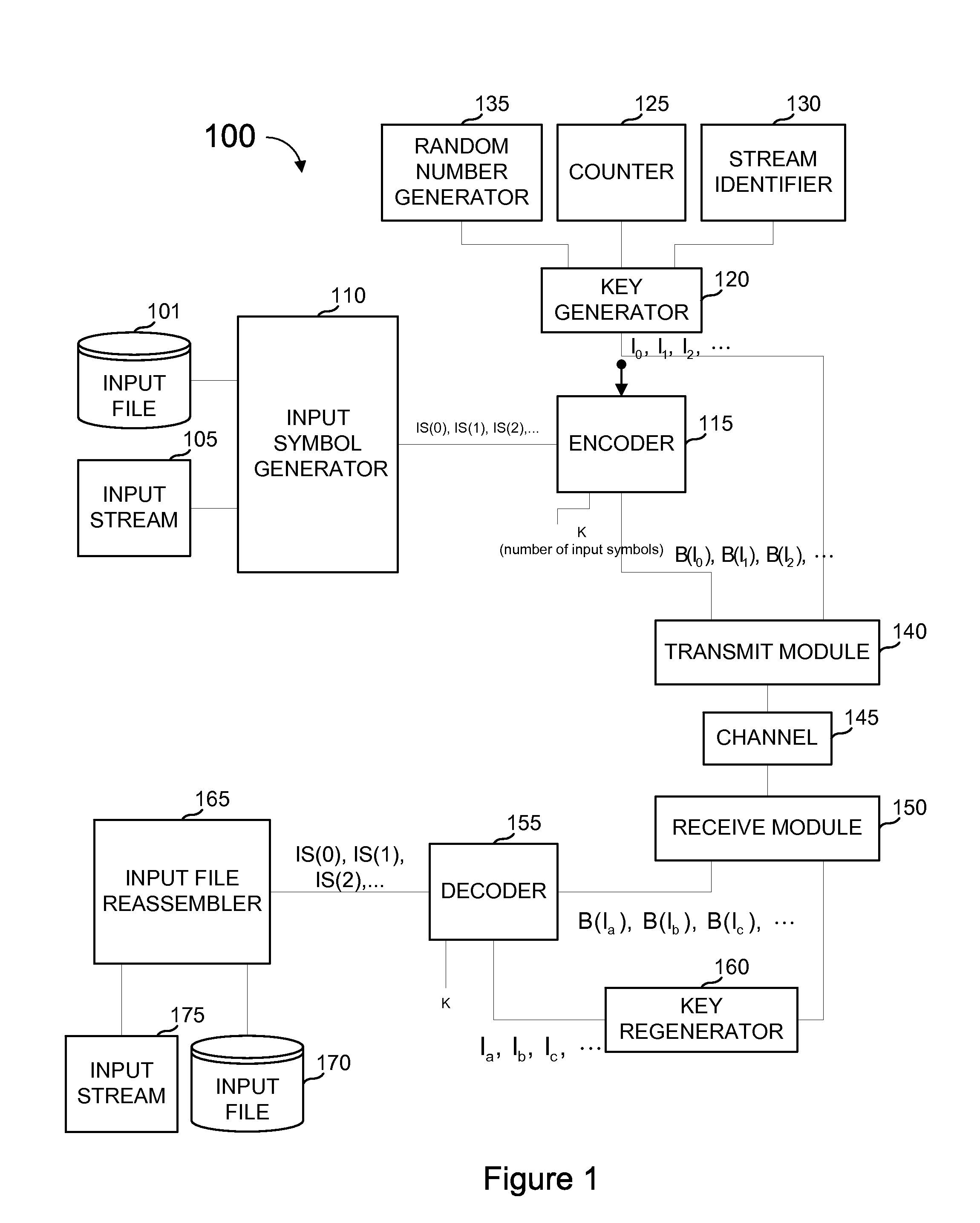
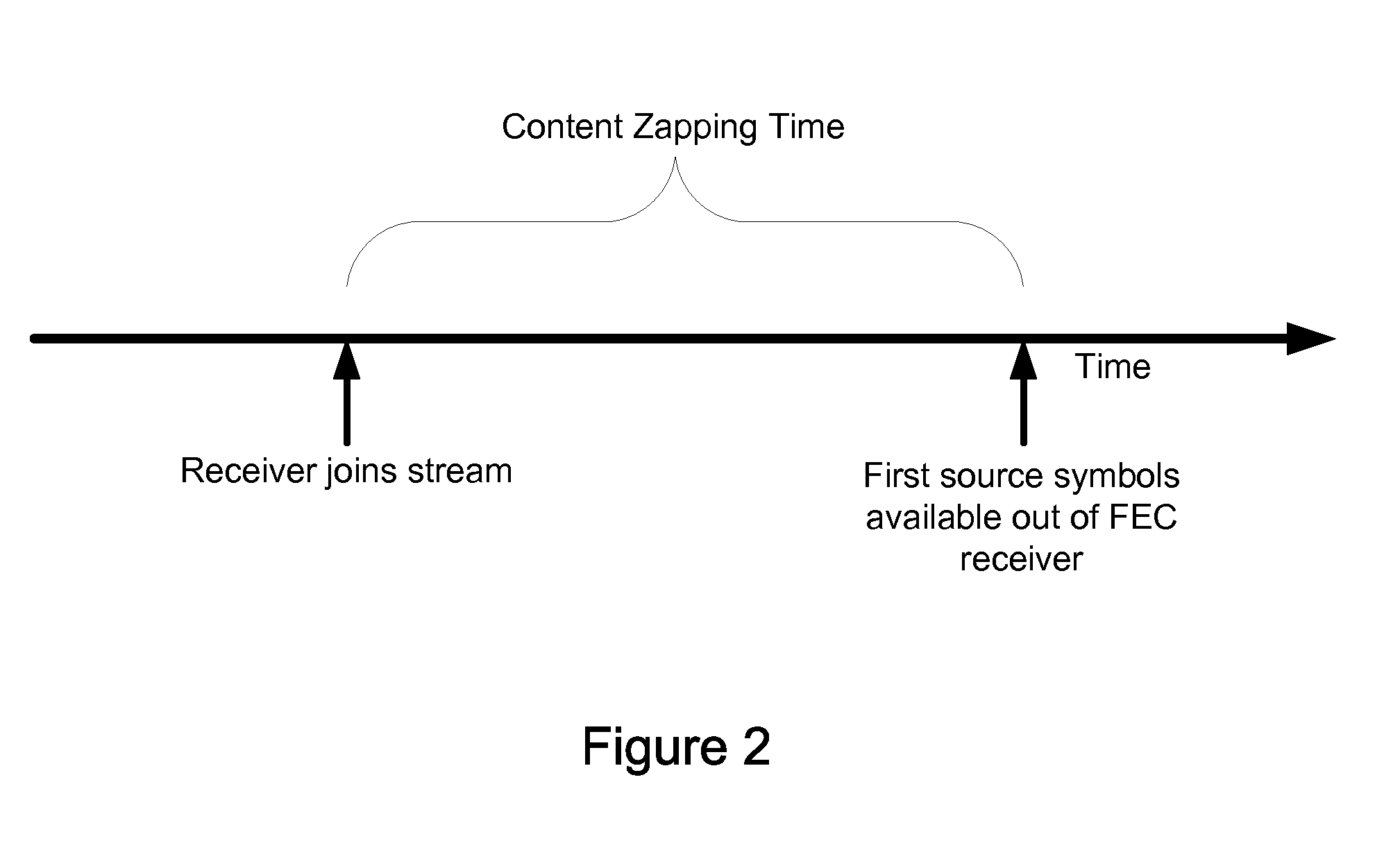
Dynamic stream interleaving and sub-stream based delivery
ActiveUS20080256418A1Convenient amountLoss of protectionFault responseCode conversionPacket lossCommunications system
A communications system can provide methods of dynamically interleaving streams, including methods for dynamically introducing greater amounts of interleaving as a stream is transmitted independently of any source block structure to spread out losses or errors in the channel over a much larger period of time within the original stream than if interleaving were not introduced, provide superior protection against packet loss or packet corruption when used with FEC coding, provide superior protection against network jitter, and allow content zapping time and the content transition time to be reduced to a minimum and minimal content transition times. Streams may be partitioned into sub-streams, delivering the sub-streams to receivers along different paths through a network and receiving concurrently different sub-streams at a receiver sent from potentially different servers. When used in conjunction with FEC encoding, the methods include delivering portions of an encoding of each source block from potentially different servers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
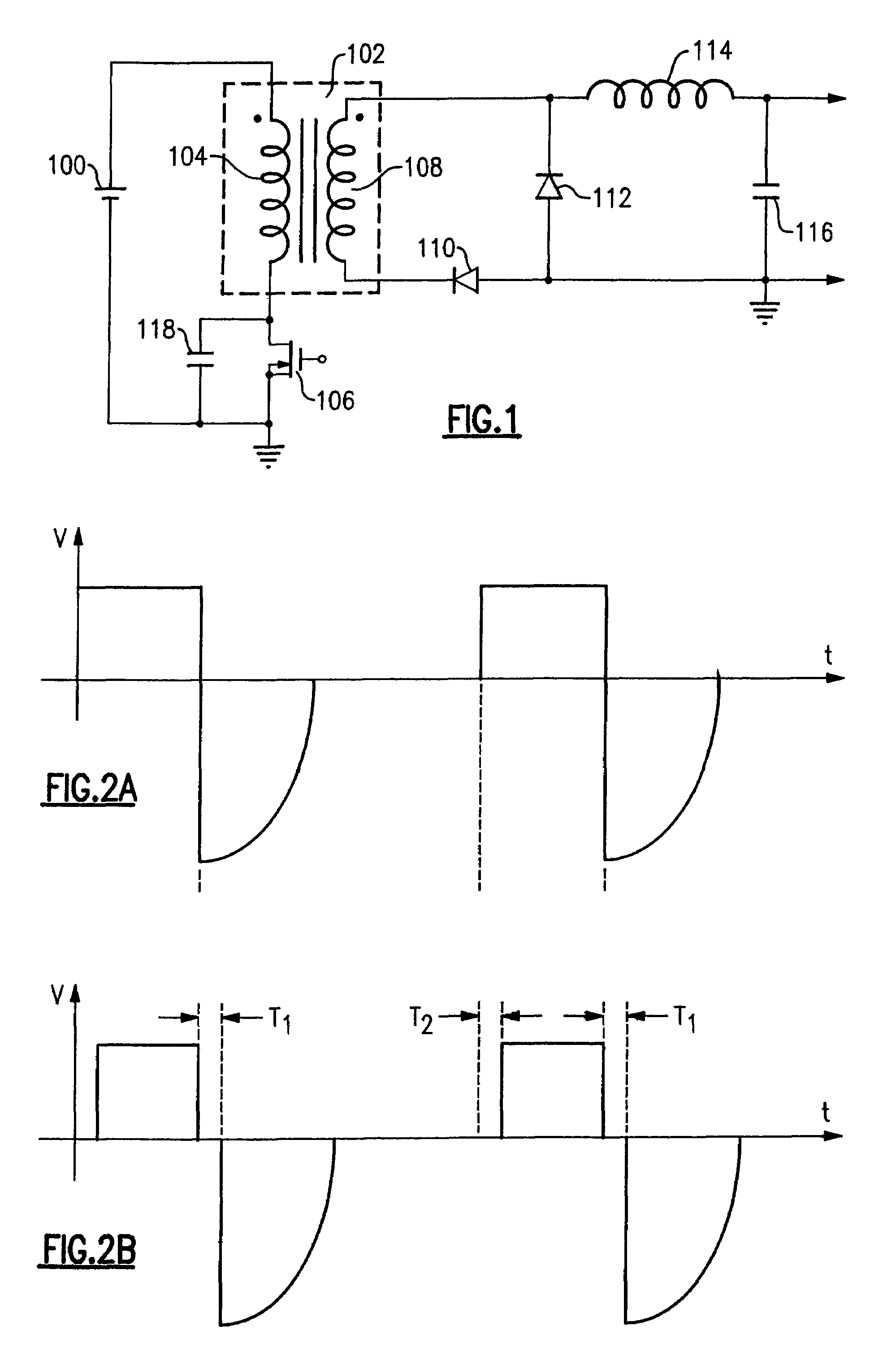
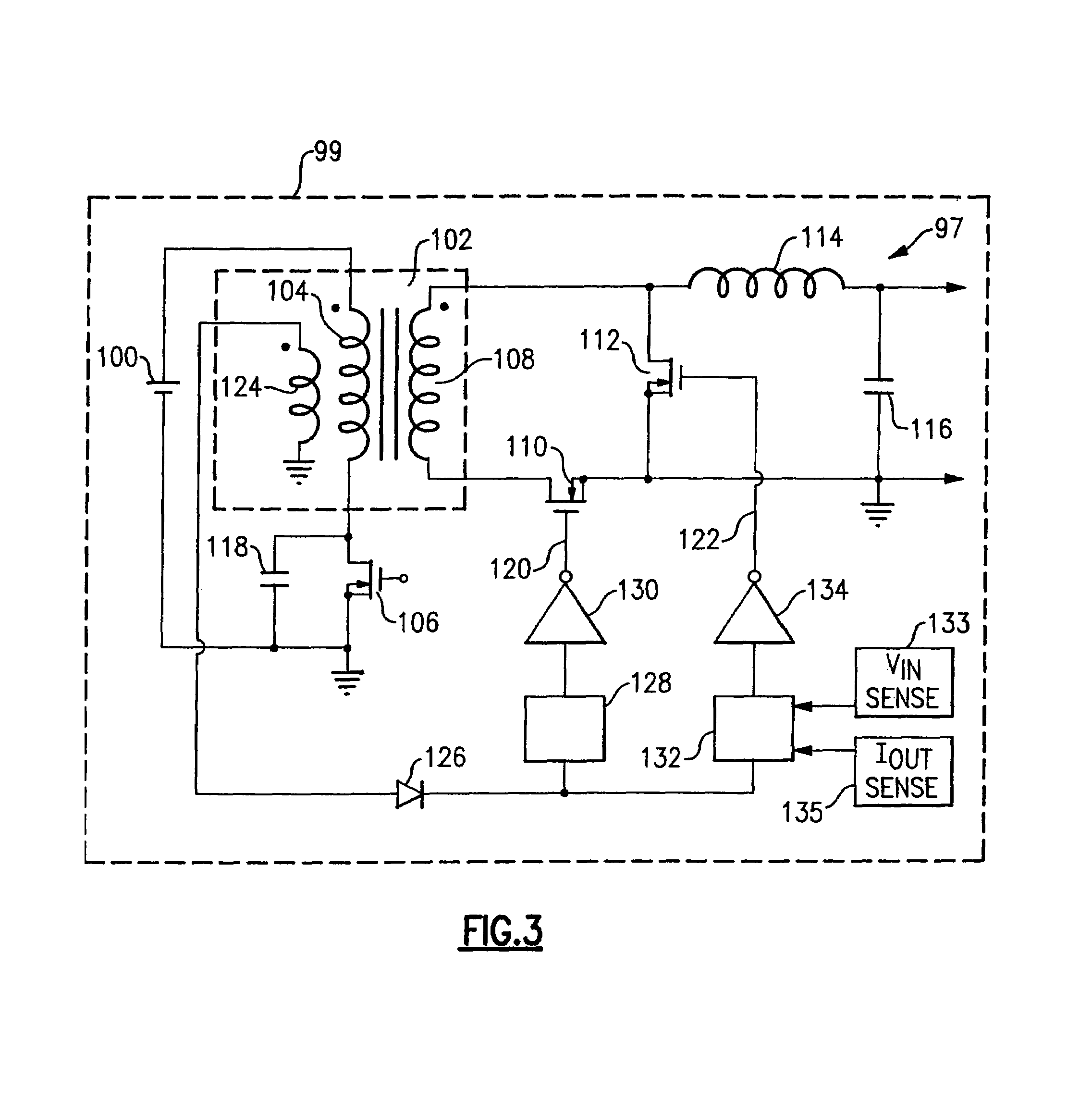
Adjusting on-time for a discontinuous switching voltage regulator
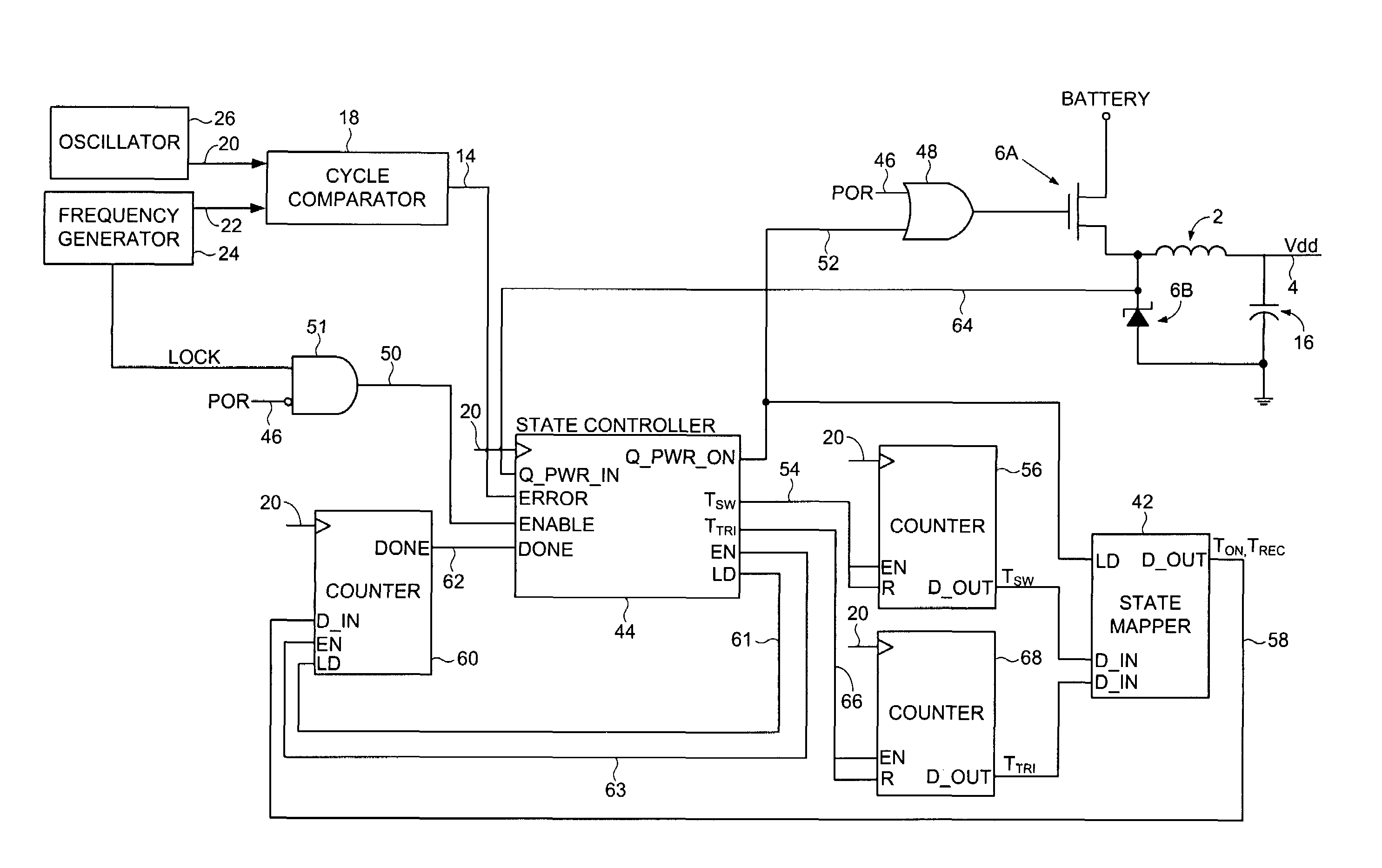
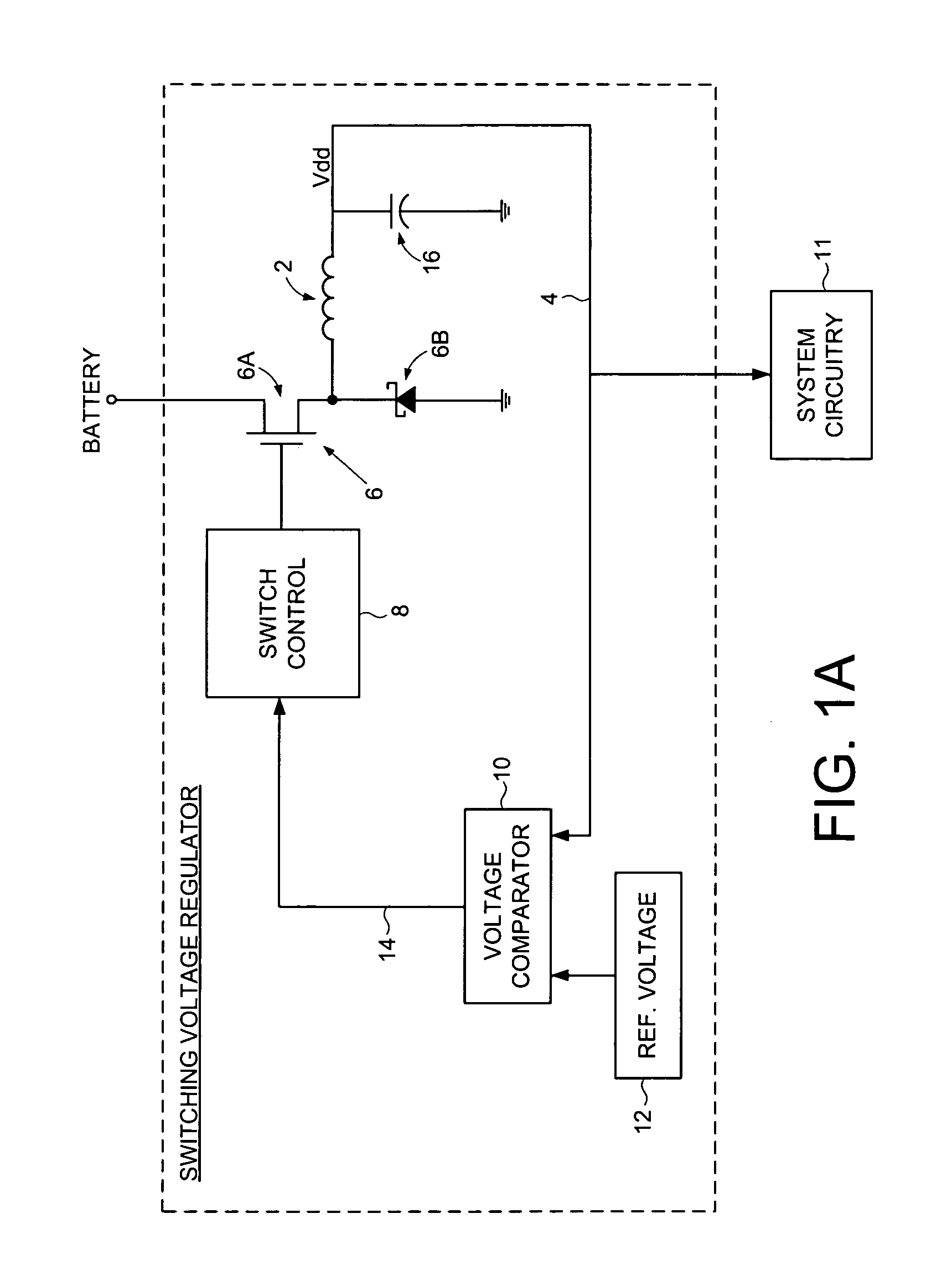
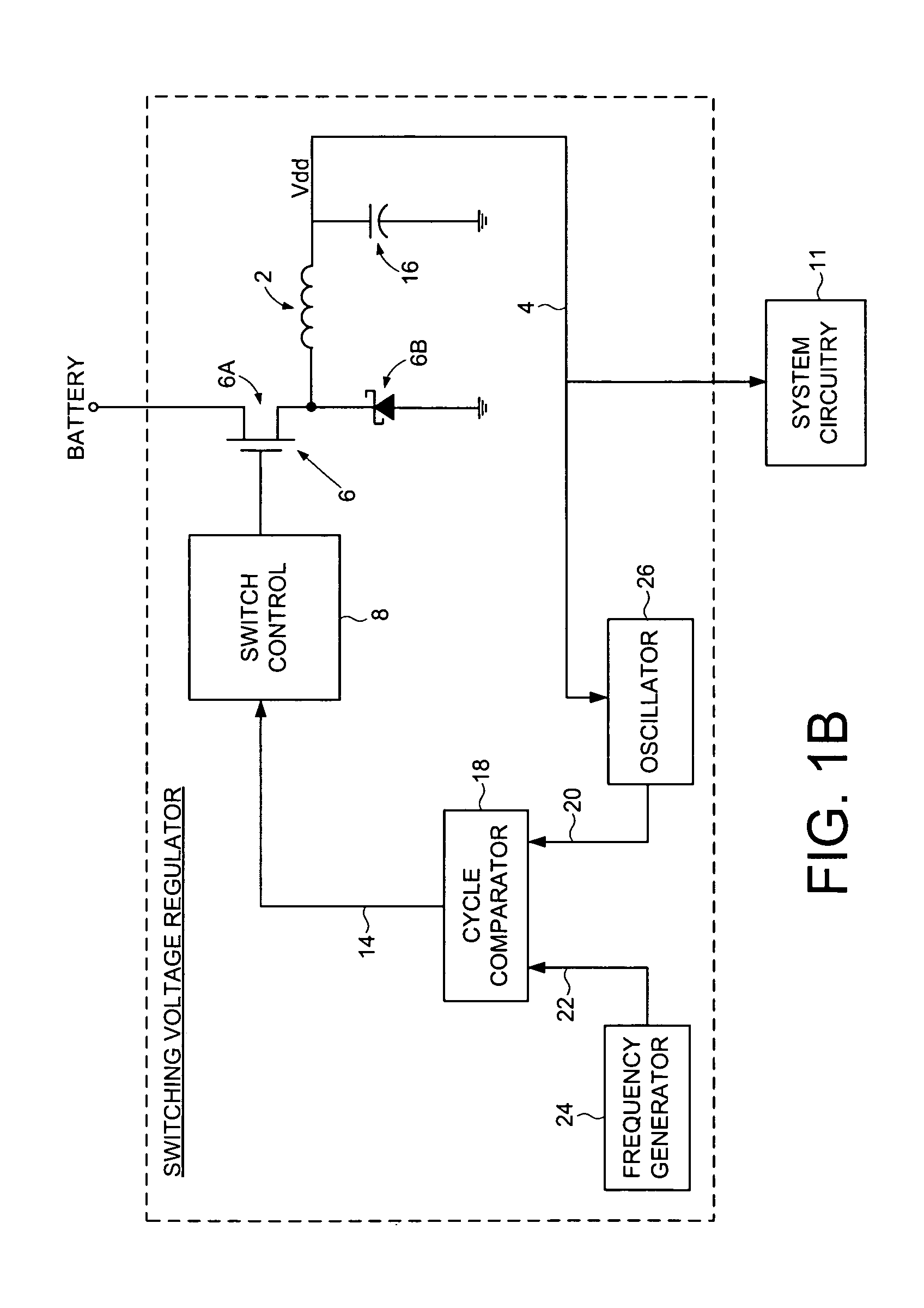
A discontinuous switching voltage regulator is disclosed including a charging element operable to generate an output voltage, switching circuitry coupled to the charging element, and switch control circuitry to configure the charging element during a cycle, including to charge the charging element for an on-time, discharge the charging element for a discharge time, and tristate the charging element for a tristate time. In operation, the on-time is initialized to a first on-time, and a first switch time is measured comprising the first on-time and a first discharge time of a first cycle. A first tristate time of the first cycle is measured, and a first ratio of the first tristate time to the first switch time is determined. The first ratio is compared to a first ratio threshold, and the on-time is adjusted to a second on-time if the first ratio exceeds the first ratio threshold.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
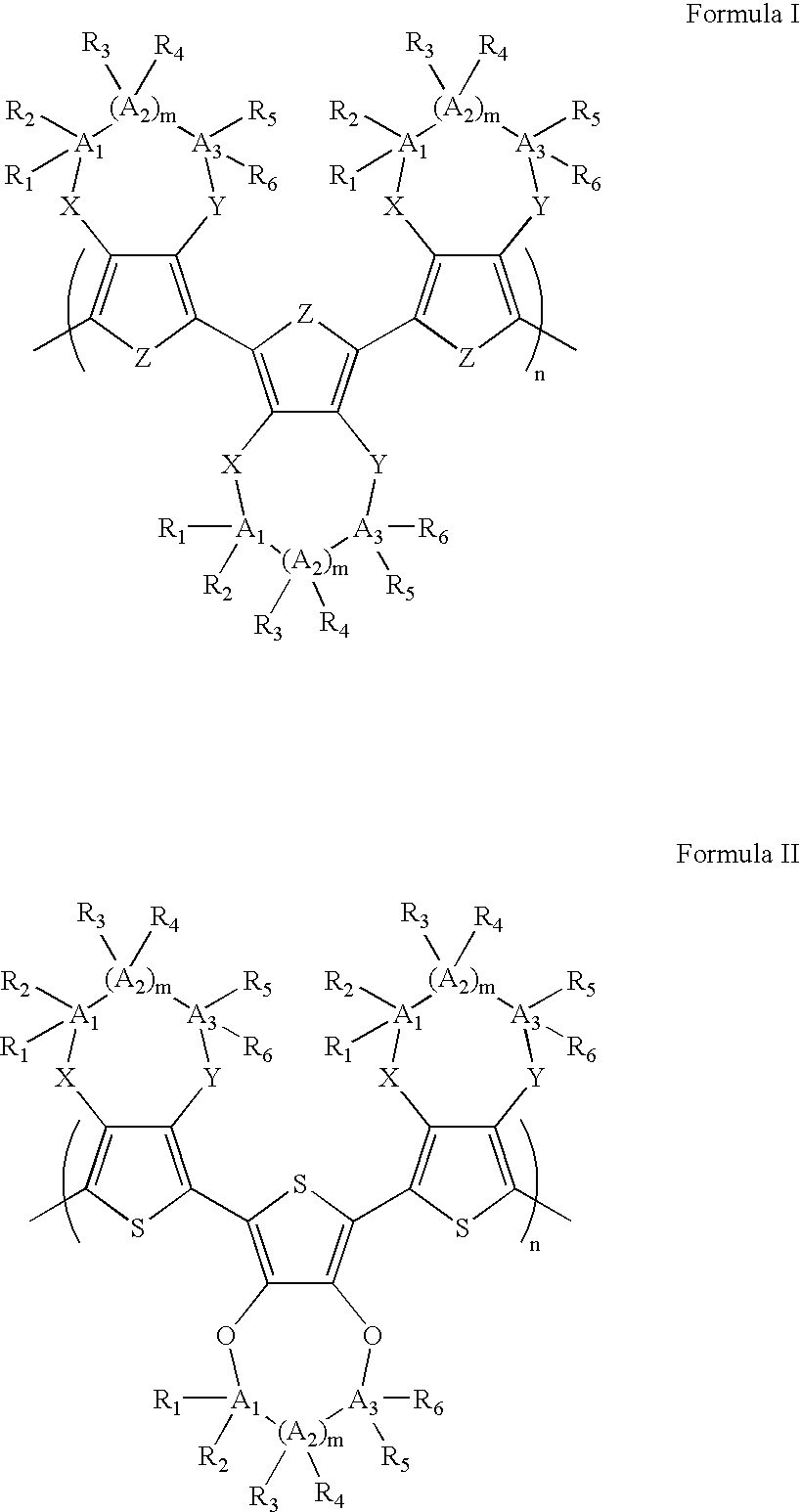
Electrochromic polymers and polymer electrochromic devices
InactiveUS6791738B2Increase the gapLess structural defectsPhotosensitive materialsElectrography/magnetographyPolymer scienceGas phase
The subject invention pertains to electrochromic polymers and polymer electrochromic devices. In a specific embodiment, two complementary polymers can be matched and incorporated into dual polymer electrochromic devices. The anodically coloring polymers in accordance with the subject invention can allow control over the color, brightness, and environmental stability of an electrochromic window. In addition, high device contrast ratios, high transmittance changes, and high luminance changes can be achieved, along with half-second switching times for full color change. Also provided are electrochromic devices such as advertising signage, video monitors, stadium scoreboards, computers, announcement boards, warning systems for cell phones, warning / information systems for automobiles, greeting cards, electrochromic windows, billboards, electronic books, and electrical wiring. The subject invention also provides for the use of complementary electrochromic polymers in the manufacture of electrochromic devices. In some embodiments, the devices of the invention can be prepared using metal vapor deposition or line patterning.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
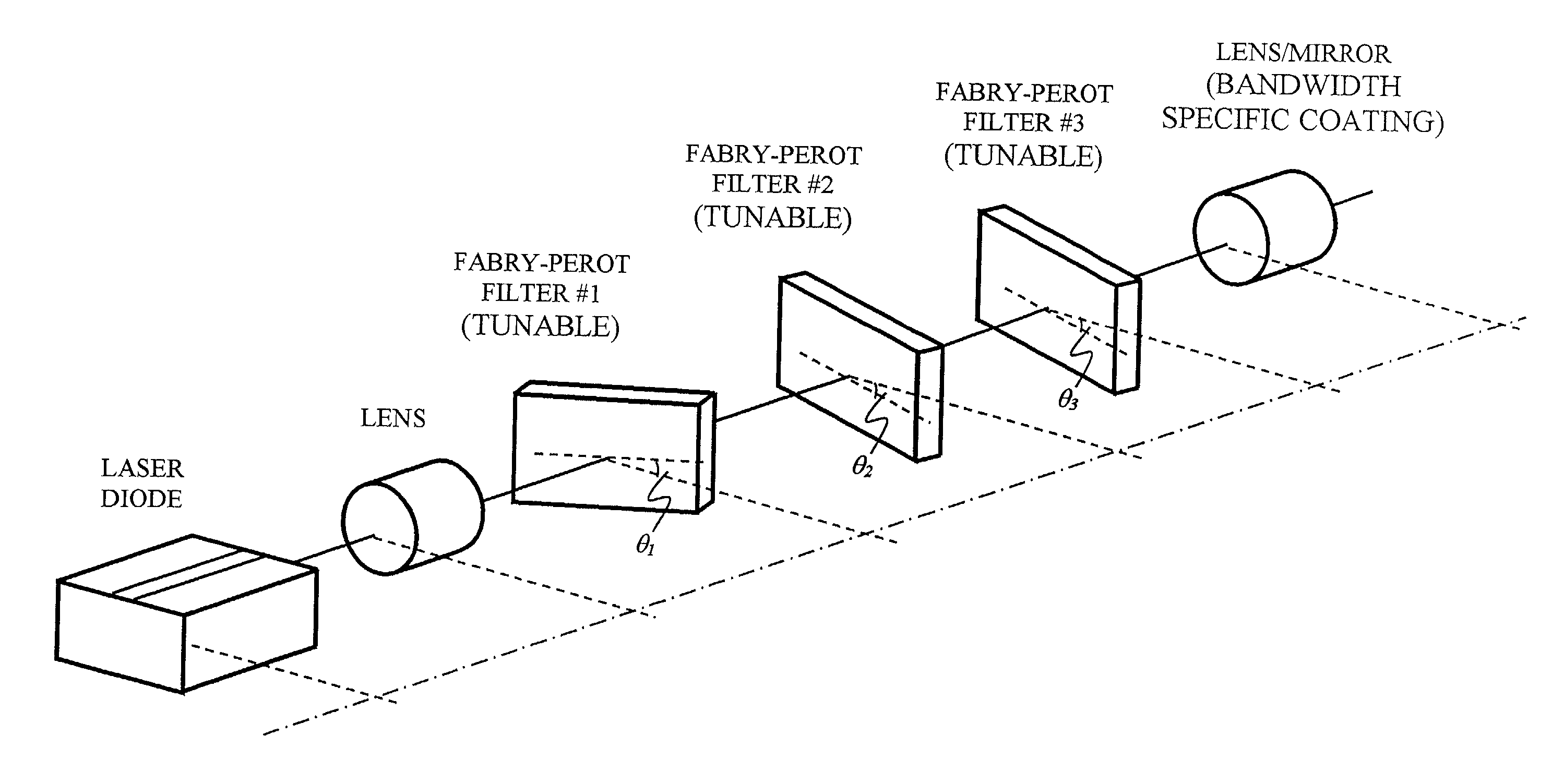
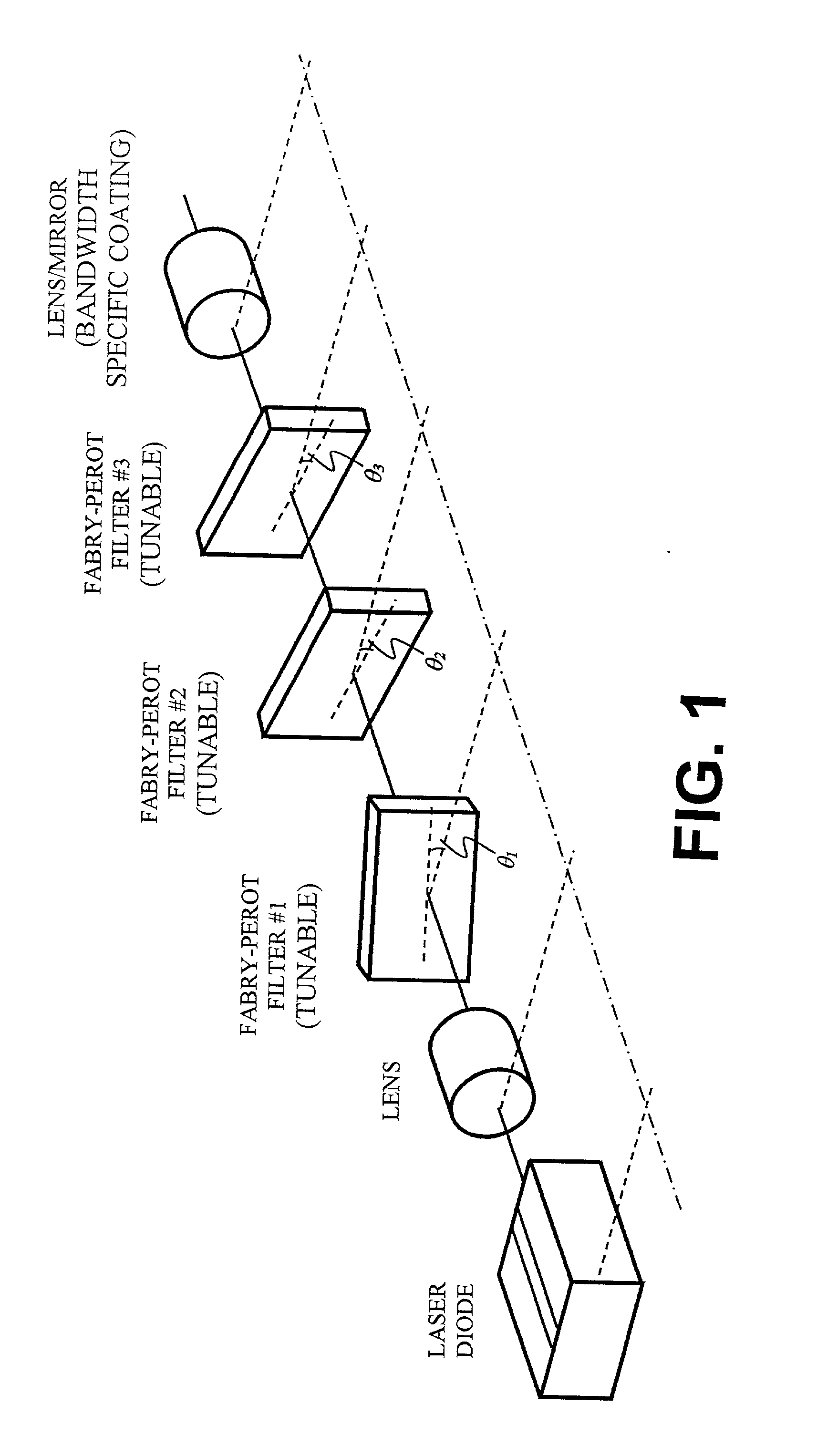
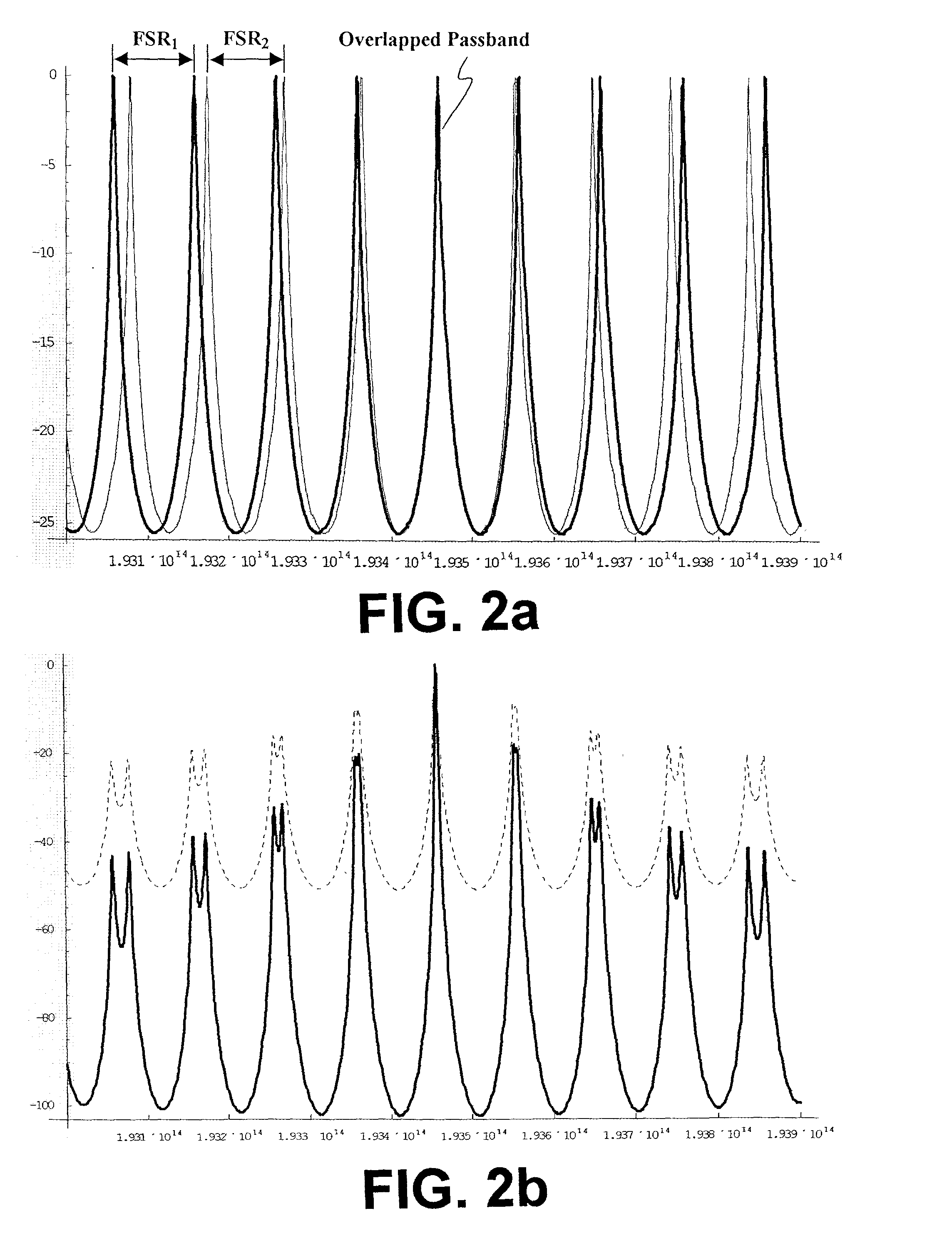
Wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20020054614A1Increase output powerFast switching timeLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionWedge filter (device)Switching time
A wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that addresses wide wavelength tuning range, is mode hopping free, has high output power, has fast wavelength switching time, is wavelength locking free and is relatively simple. Four exemplary embodiments disclosed herein utilize a wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that comprises a discretely tunable filter and laser amplifier. In the first embodiment, the tuning element comprises a pair of cascade Fabry-Perot filters, each having a plurality of characteristic narrow transmission passbands that pass only the cavity mode under the passband. The spacing between the narrow transmission passbands are slightly different in one filter from the other filter so that only one passband from each filter can be overlapped in any given condition over the entire active element gain spectral range, thereby permitting lasing only at a single cavity mode passed by the cascade double filters. One of the two etalon filters can be made with a plurality of transmission passbands predetermined by industry, application and international standards, making this element an intra-cavity wavelength reference and eliminating further wavelength locking needs for the tunable laser. In a second embodiment, one of the two etalons is replaced by a wedge filter. The filter optical path change and thus the transmission passband shift are achieved by translating the wedge filter in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. In a third embodiment, one of the two etalon filters is replaced by a polarization interference filter. The polarization interference filter consists of an electro-optically-tunable birefringent waveplate, a fixed birefringent waveplate, the laser cavity and T.E. polarization light emitted from the laser diode. In a fourth embodiment, the laser and wavelength tuning structure are integrated on a semiconductor substrate by epitaxy processes.
Owner:JIN HONG
Fast stack save and restore system and method
InactiveUS6449709B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsData accessParallel computing
A processor includes a stack that operates as a circular stack and appears to the address space in the memory of the processor as a single point address location. The stack supports read and write data access functions in addition to CALL (push) and RETURN (pop) programming operations. The processor may be programmed to save the stack in a typical manner with one instruction atomically transferring each element in the stack directly from the stack to a save storage. To restore the stack, the processor may be programmed to individually restore each element. The processor supports a special MOV instruction that transfers a plurality of bytes in a single operation. The special MOV instruction has one argument that identifies the beginning transfer source address, another argument defines the byte count indicating the number of bytes to be transferred, and a beginning transfer destination address. The processor may be programmed to perform a stack save operation with only a single instruction that moves the contents of the stack to the save storage. To further reduce context switching time and reduce the stack save and restore operation to a minimum number of instructions while maintaining the proper entry relationship for both stack read and write operations, the processor includes a "stack read forward" option to the special MOV instruction. The option to the special MOV instruction operates to read data in a forward direction even when no valid data is stored in the locations. The read operation begins at the start address specified by an argument to the MOV instruction, reads forward, and wraps around in a binary fashion back to the start address.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
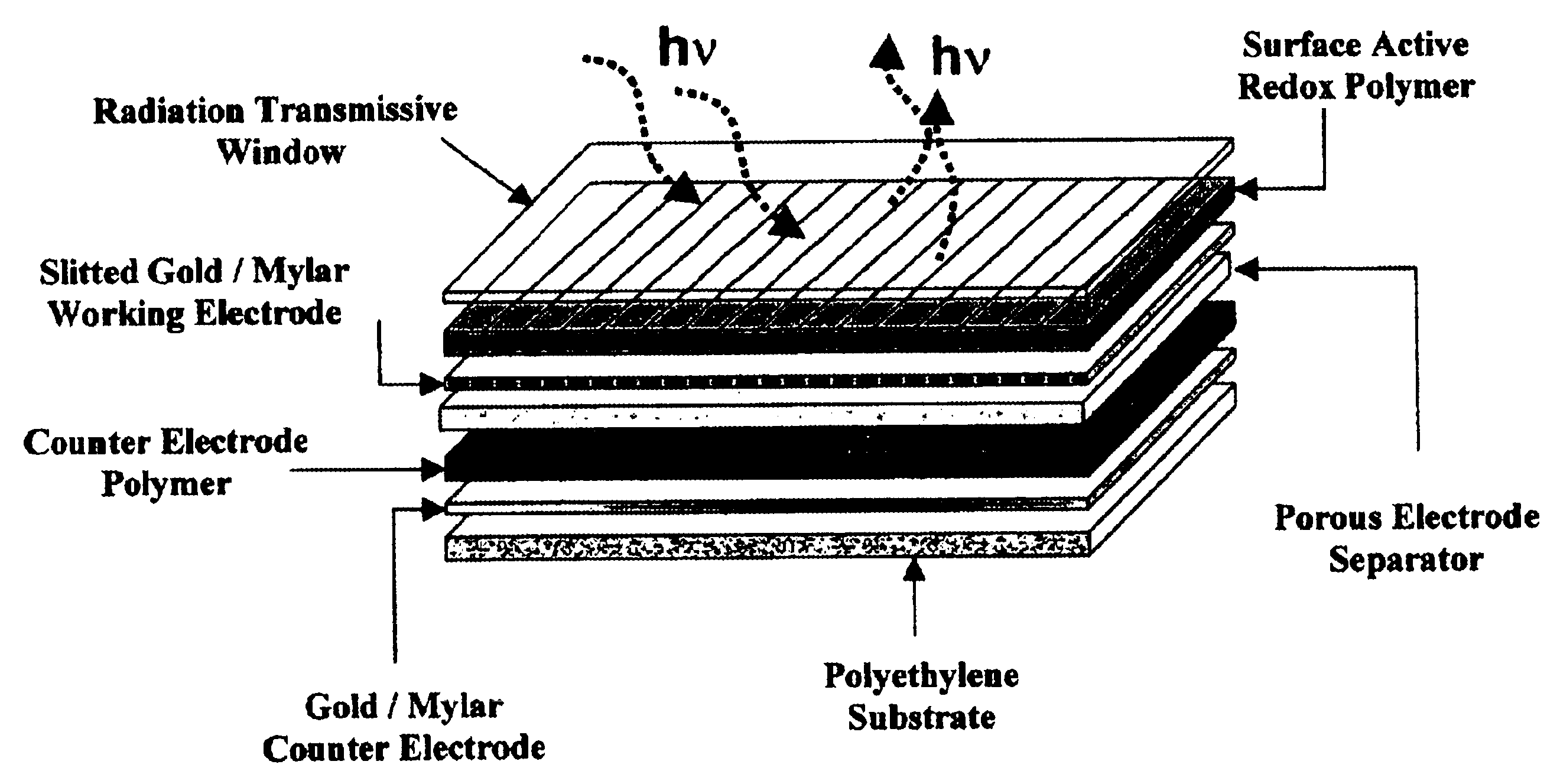
Electrophotochromic smart windows and methods
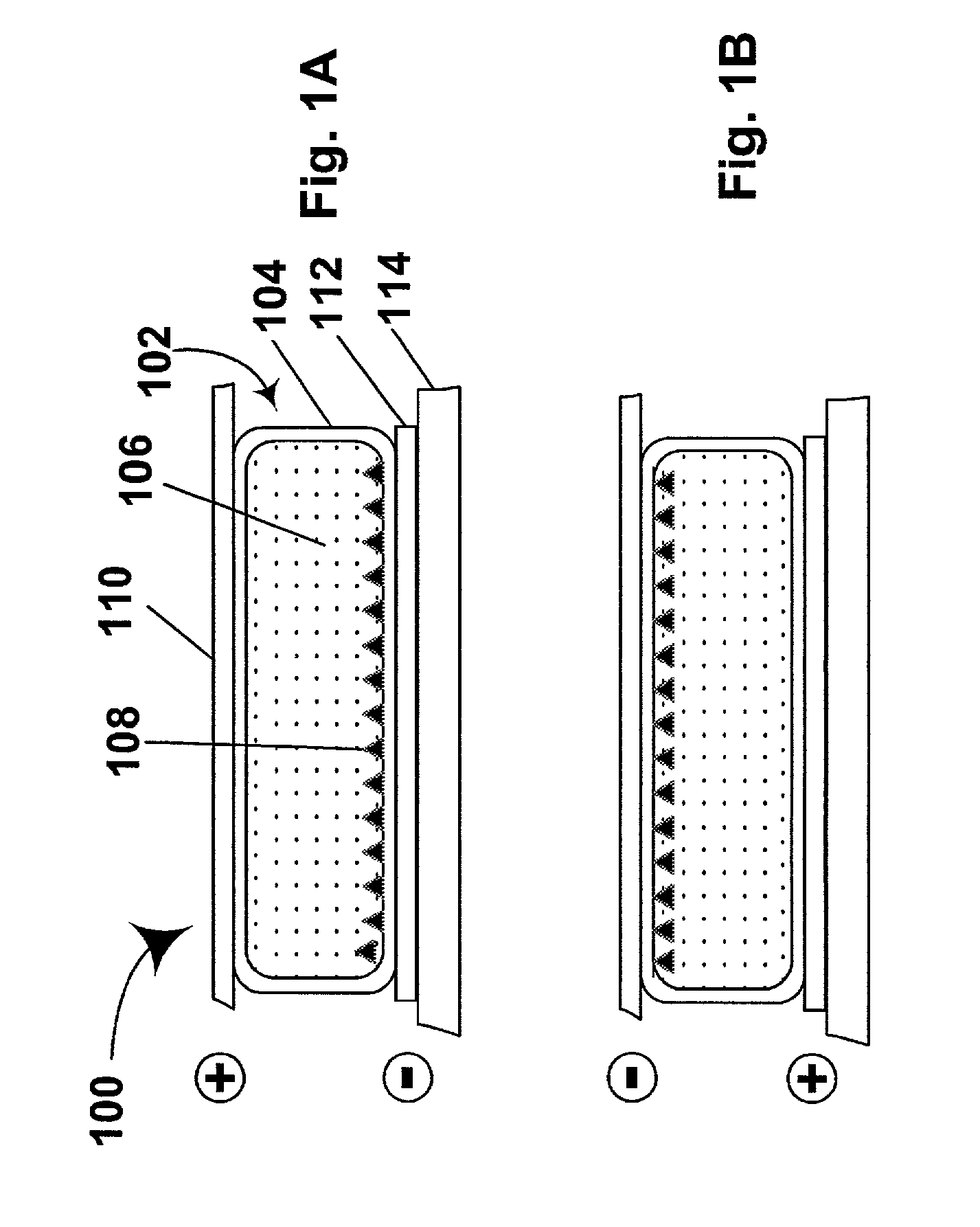
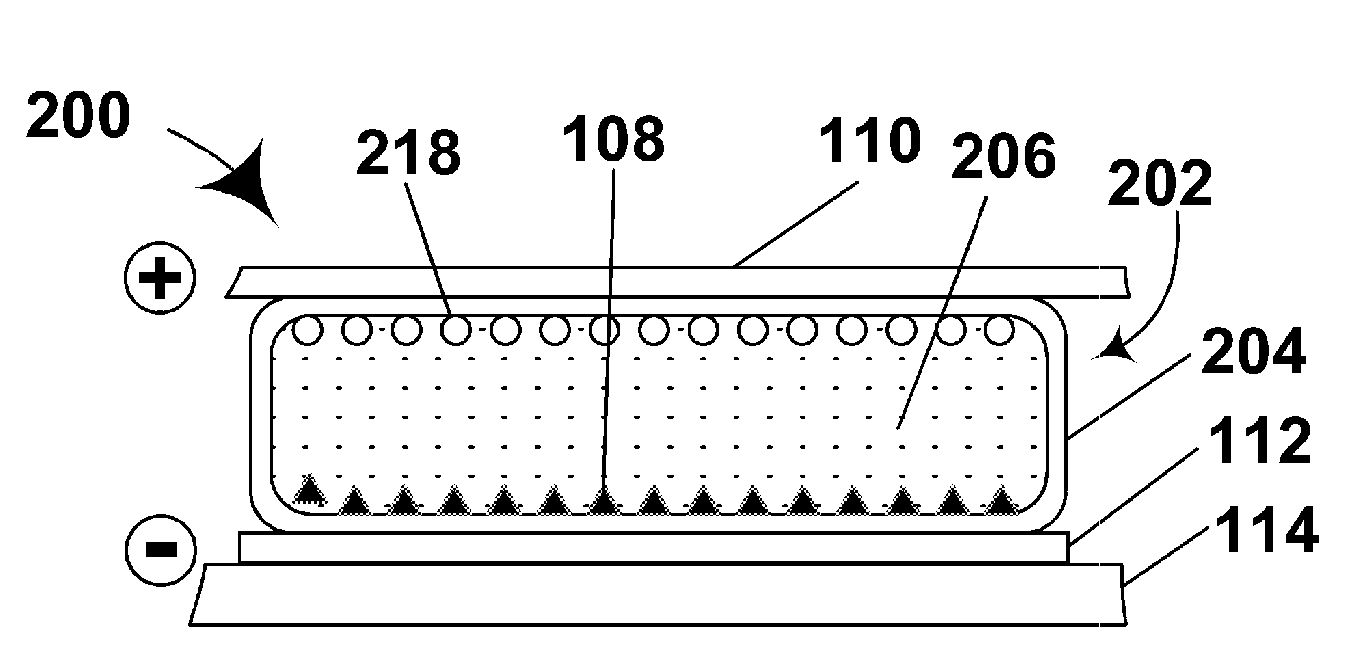
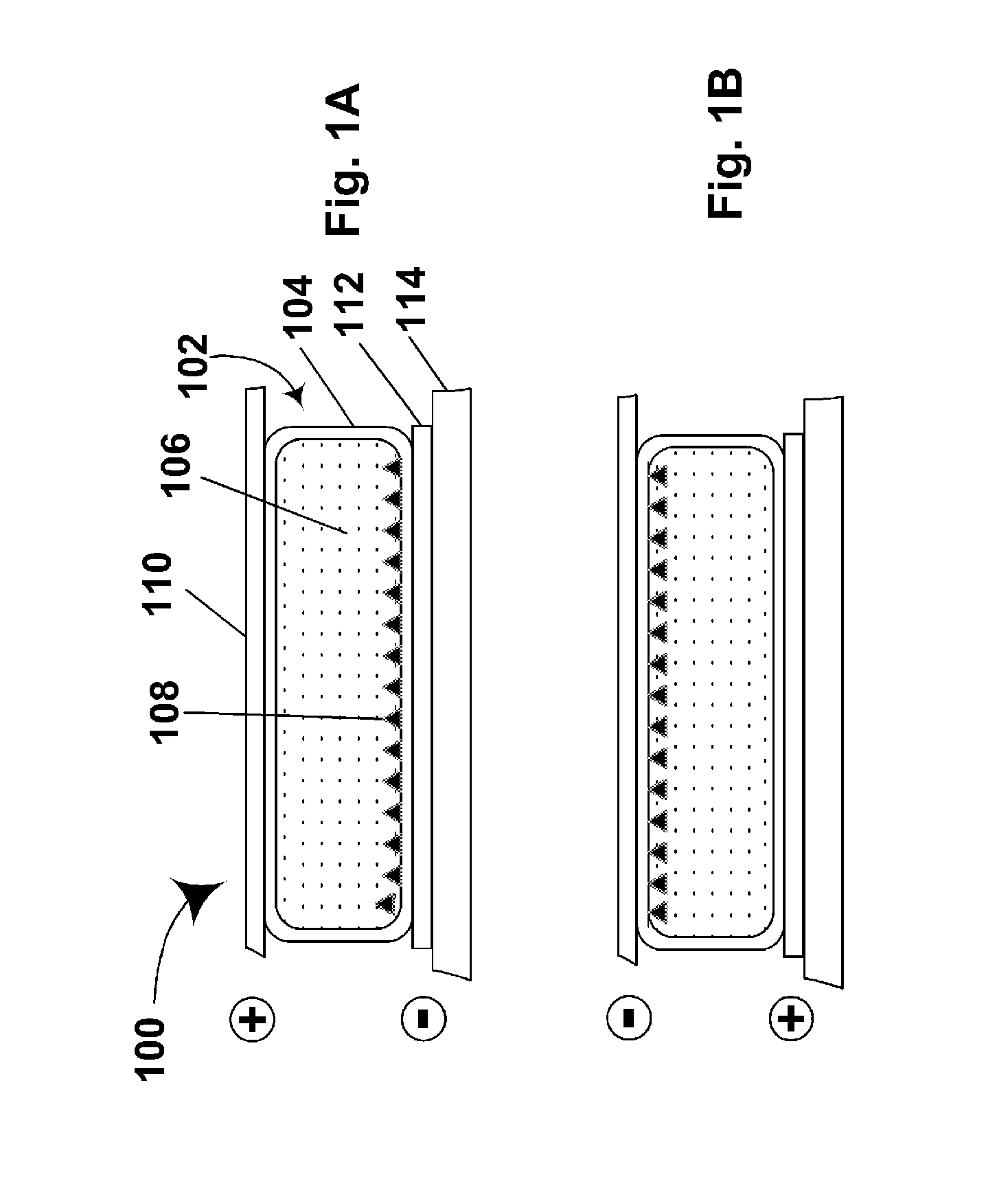
InactiveUS6297900B1Improved EC cell switching timeLess riskLight protection screensNon-linear opticsEngineeringElectrochromism
A smart window comprising a regenerative photolectrochomic (RPEC) photovoltaic element (108) juxtaposed with an electrochromic (EC) element (110). Microprocessor-based control mechanism (200) connecting the RPEC element to the EC element for controlling the current delivered to and from the EC element. The controller (200) including look-up tables (204 and 206) for determining the safe current to or from the EC element having regard to the amount of charge to be delivered or removed and the charge status of the EC element, the determination of charge status, charge still required and current to be delivered being made frequently to ensure that the current is kept within safe limits while minimizing switching times. New smart windows are also disclosed.
Owner:DYESOL LTD
Drive circuits for synchronous rectifiers
InactiveUS6961253B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringConductor Coil
A method and system for providing synchronous rectification in power converters that includes controlling turnoff of a synchronous rectifier according to a timing signal representative of the switching time of a switch that is coupled to input of the power converter. Such a timing signal may be obtained directly or indirectly in various ways; for example, by sensing the voltage across the primary switch, or by sensing the drive voltage of the primary switch. Additional alternatives in an isolated converter having a transformer with a primary winding that is selectively coupled to the electrical power source includes sensing the primary winding voltage, for example, by directly sensing the primary voltage or by sensing the voltage across an auxiliary winding that is closely coupled to the primary winding.
Owner:LAMBDA ELECTRONICS
Systems, Devices and Methods for Reducing Switching Time in a Video Distribution Network
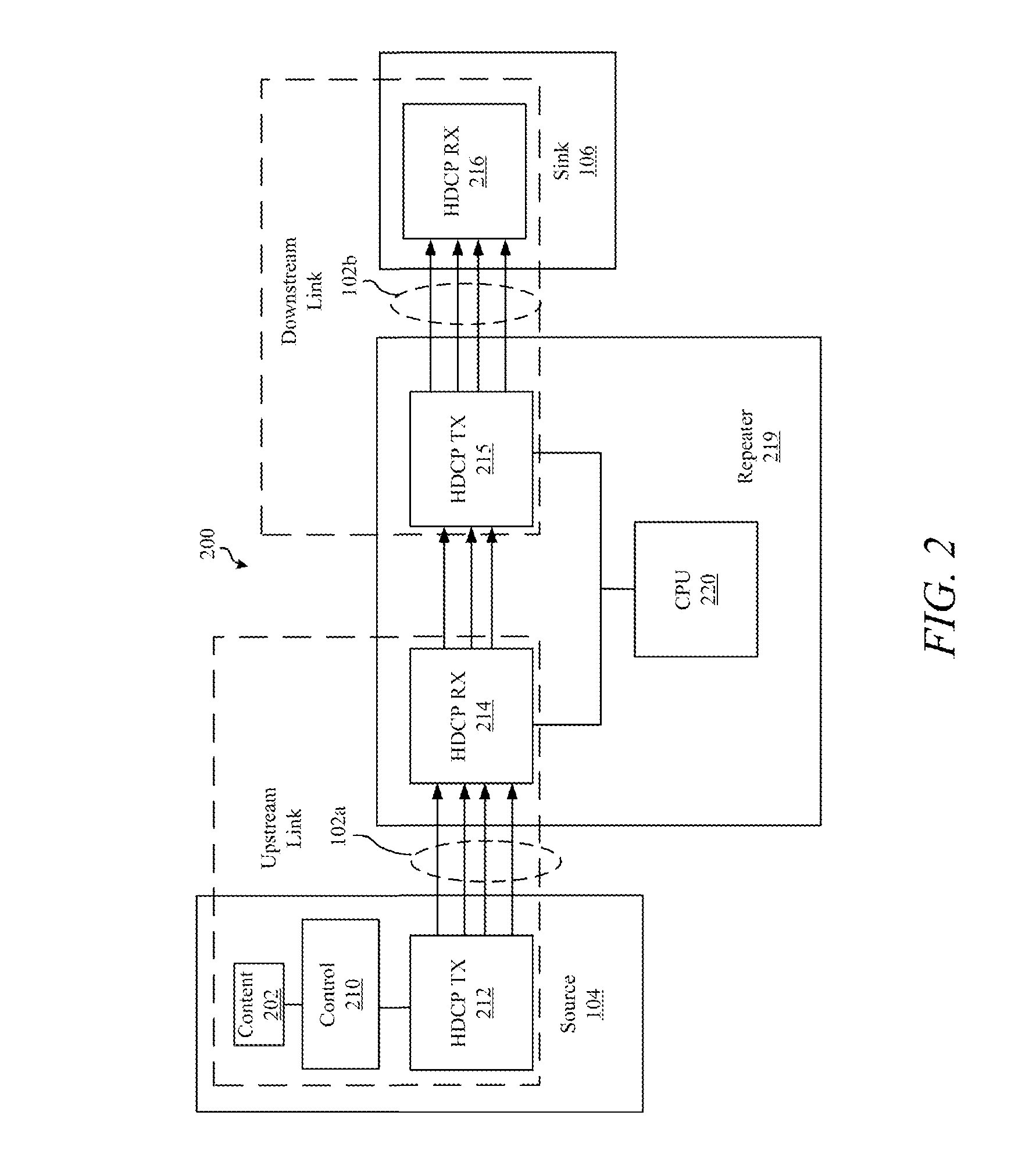
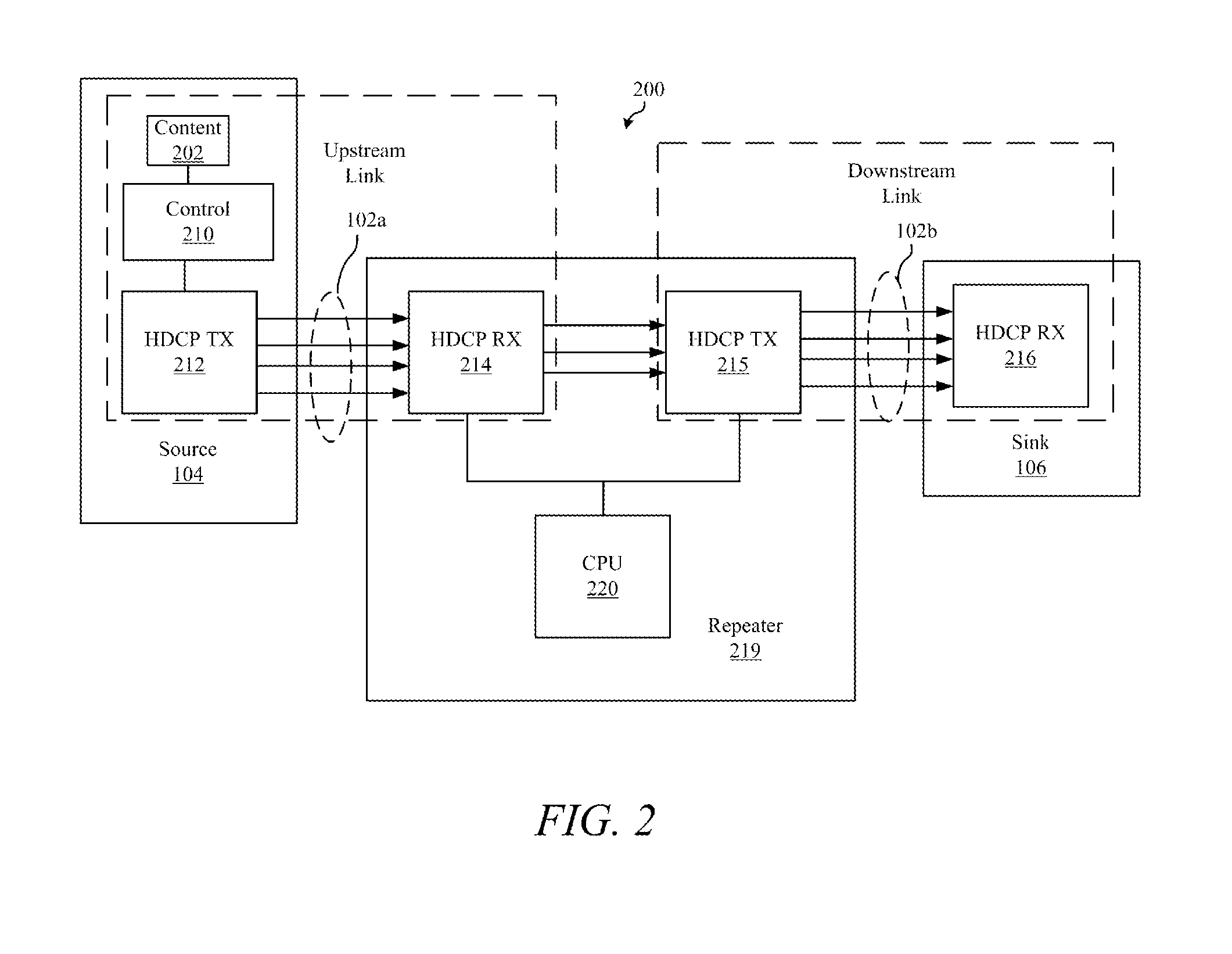
ActiveUS20150020088A1Reduce switching delayReducing actual and perceived switching timeAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsSecurity authenticationSwitching time
When switching sources, resolutions or refresh rates in a video distribution network, switching times are reduced by maintaining video lock and security authentication between a video switcher and a video sink. The scaler maintains video lock and security authentication by continuing to generate video timing data during switching events. The scaler also facilitates an aesthetically pleasing transition by generating image content data prior to and after the switching event.
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
Devices, Systems and Methods for Reducing Switching Time in a Video Distribution Network
ActiveUS20130212613A1Reduce switching delayShorten the switching timeAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSelective content distributionSecurity authenticationSwitching time
When switching sources, resolutions or refresh rates in a video distribution network, switching times are reduced by maintaining video lock and security authentication between a video switcher and a video sink. The scaler maintains video lock and security authentication by continuing to generate video timing data during switching events. The scaler also facilitates an aesthetically pleasing transition by generating image content data prior to and after the switching event.
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
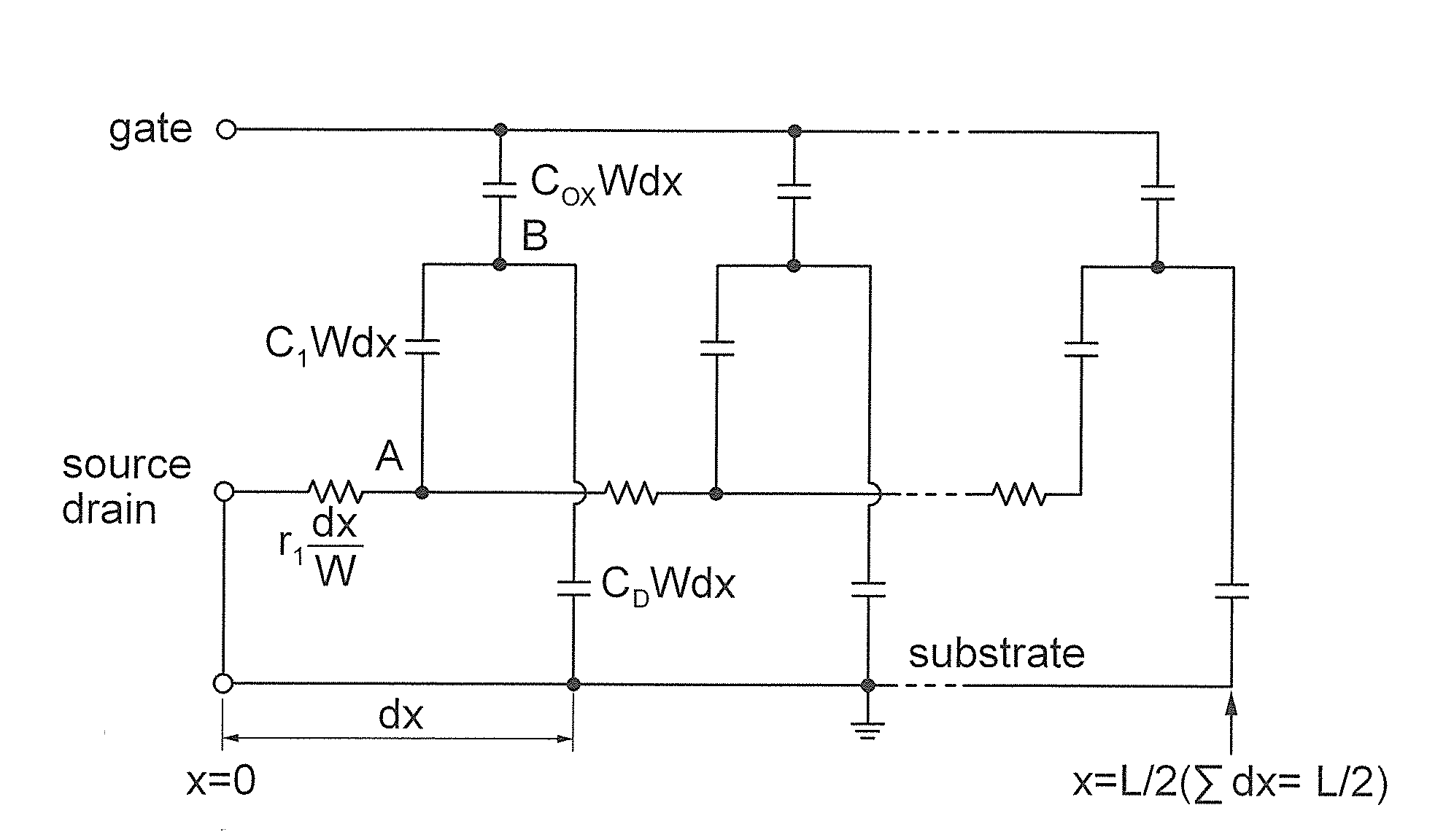
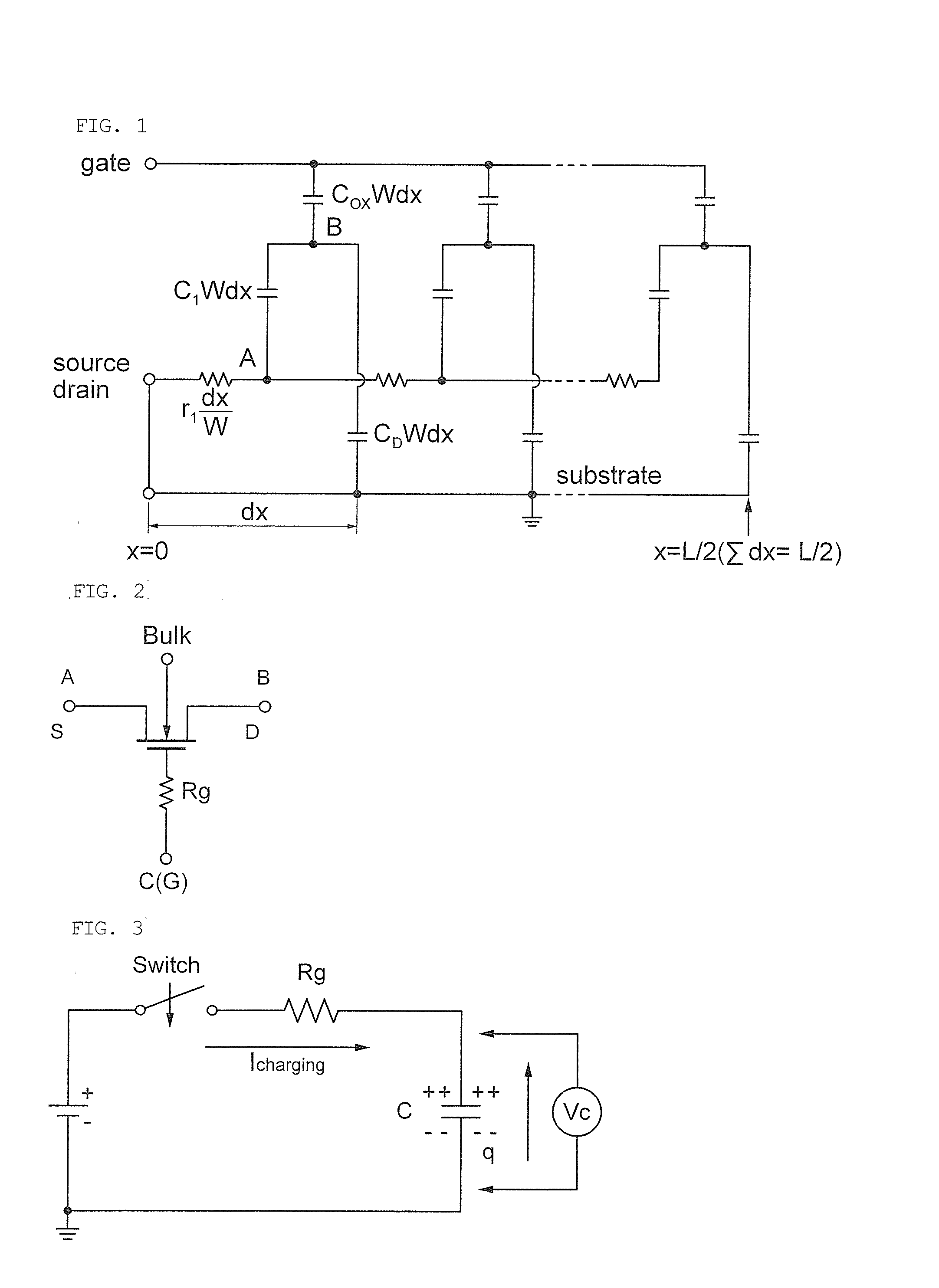
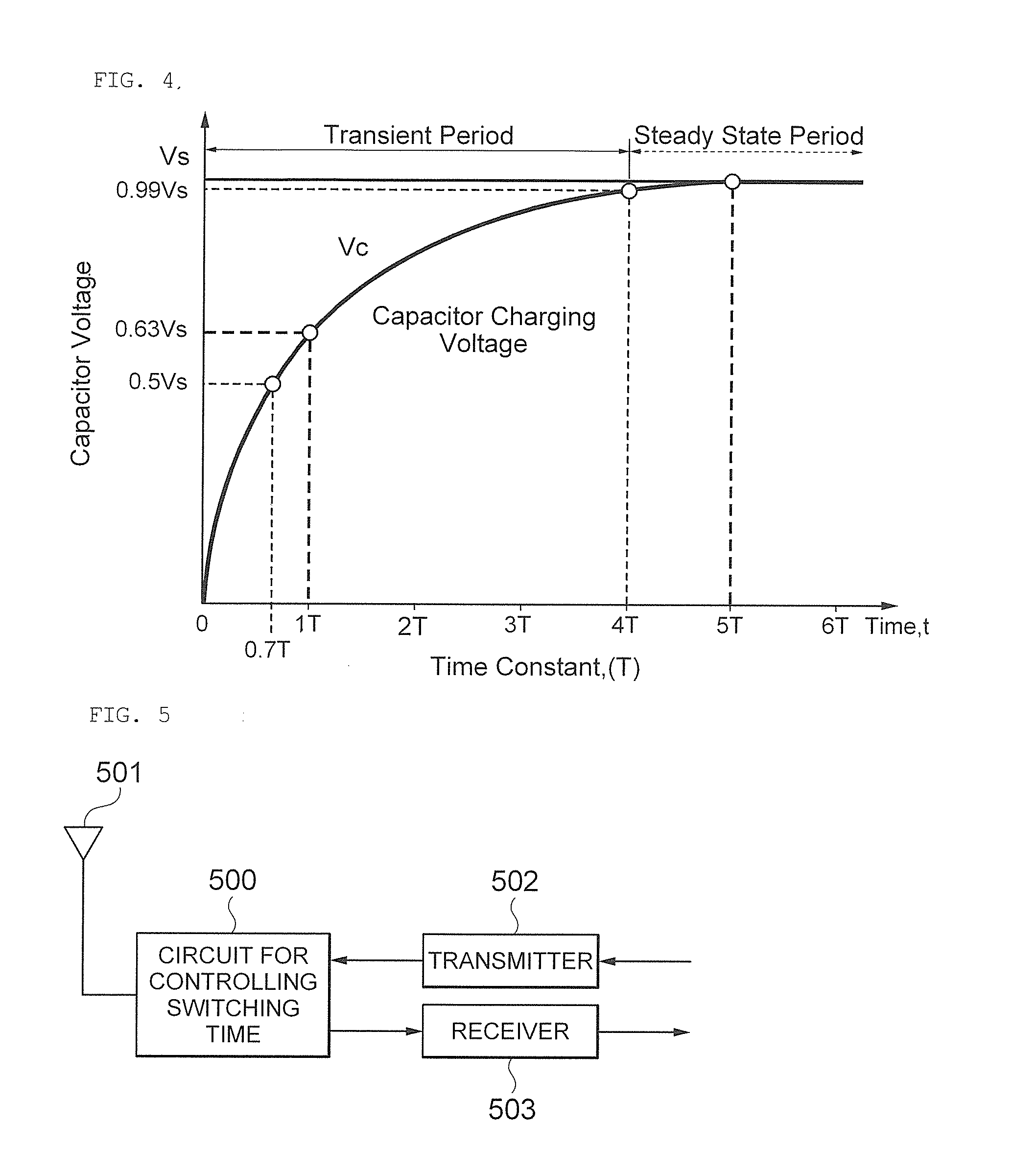
Circuit for Controlling Switching Time of Transmitting and Receiving Signal in Wireless Communication System
Disclosed herein is a circuit for controlling a switching time of a transmitting and receiving signal in a wireless communication system including: a high speed switch circuit unit receiving a signal transceived through an antenna to perform a high speed switching operation; a low speed switch circuit unit the signal transceived through the antenna to perform a low speed switching operation; and a controlling unit applying a control signal for controlling a switching time to the high speed switch circuit unit or the low speed switch circuit unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
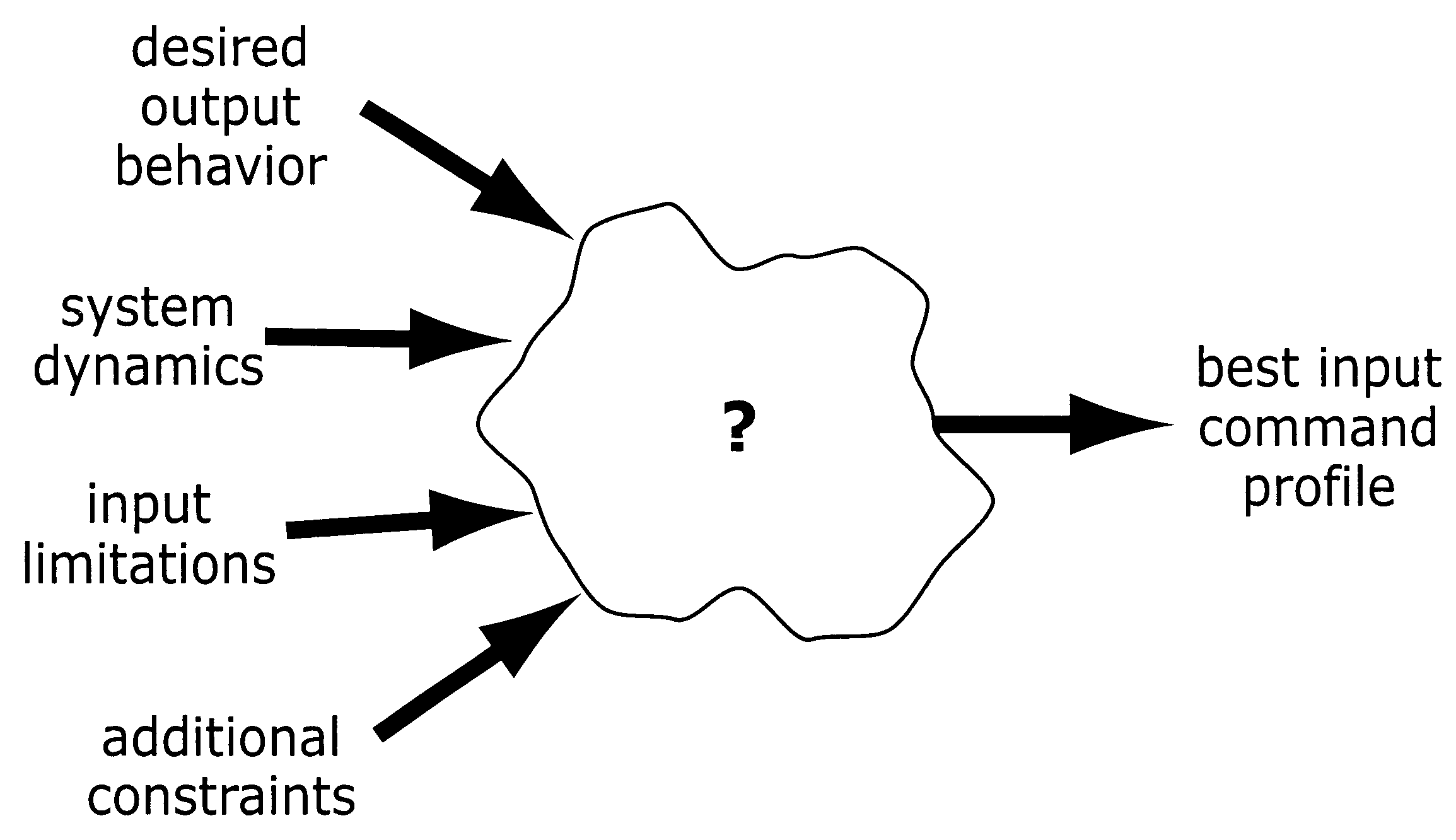
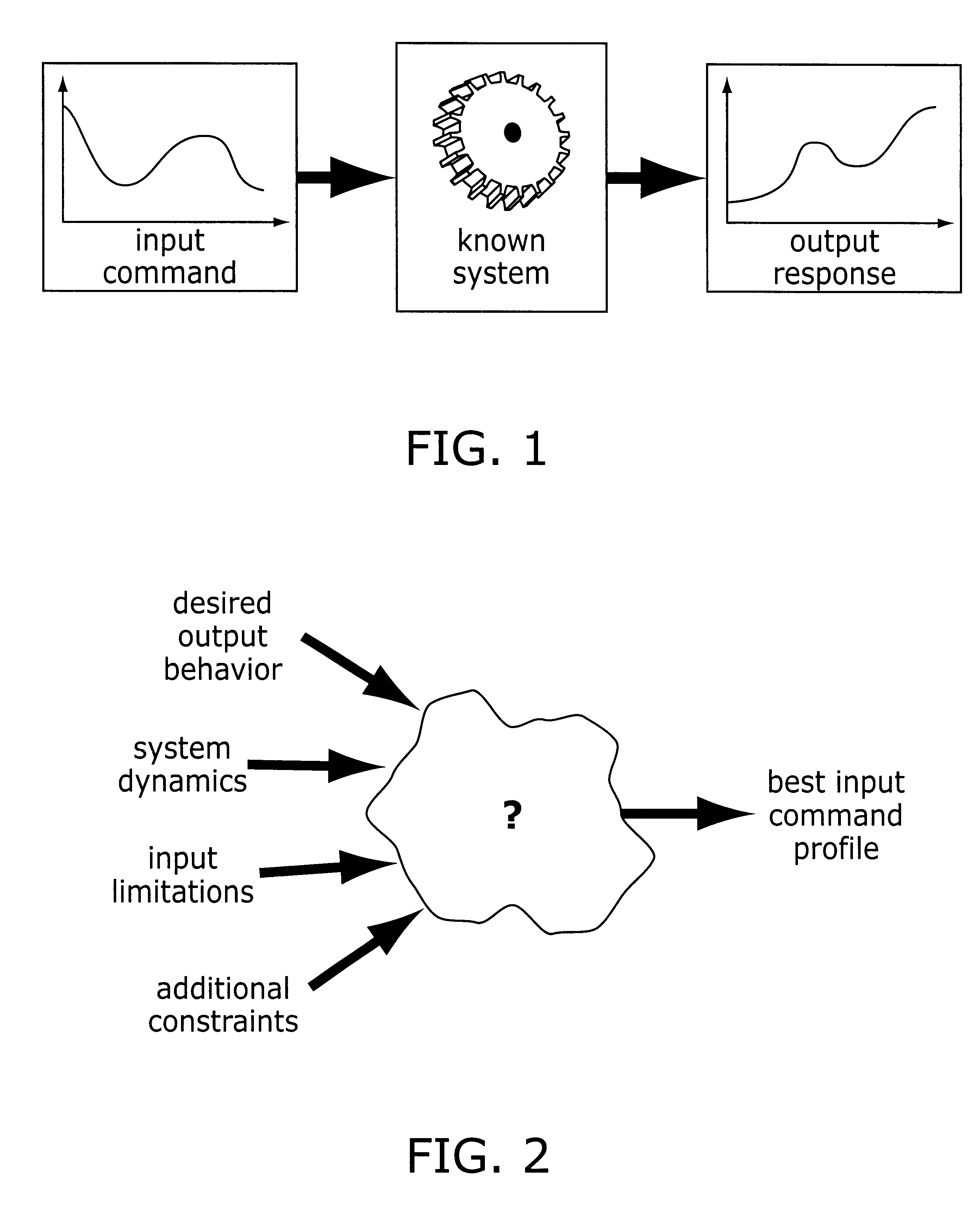
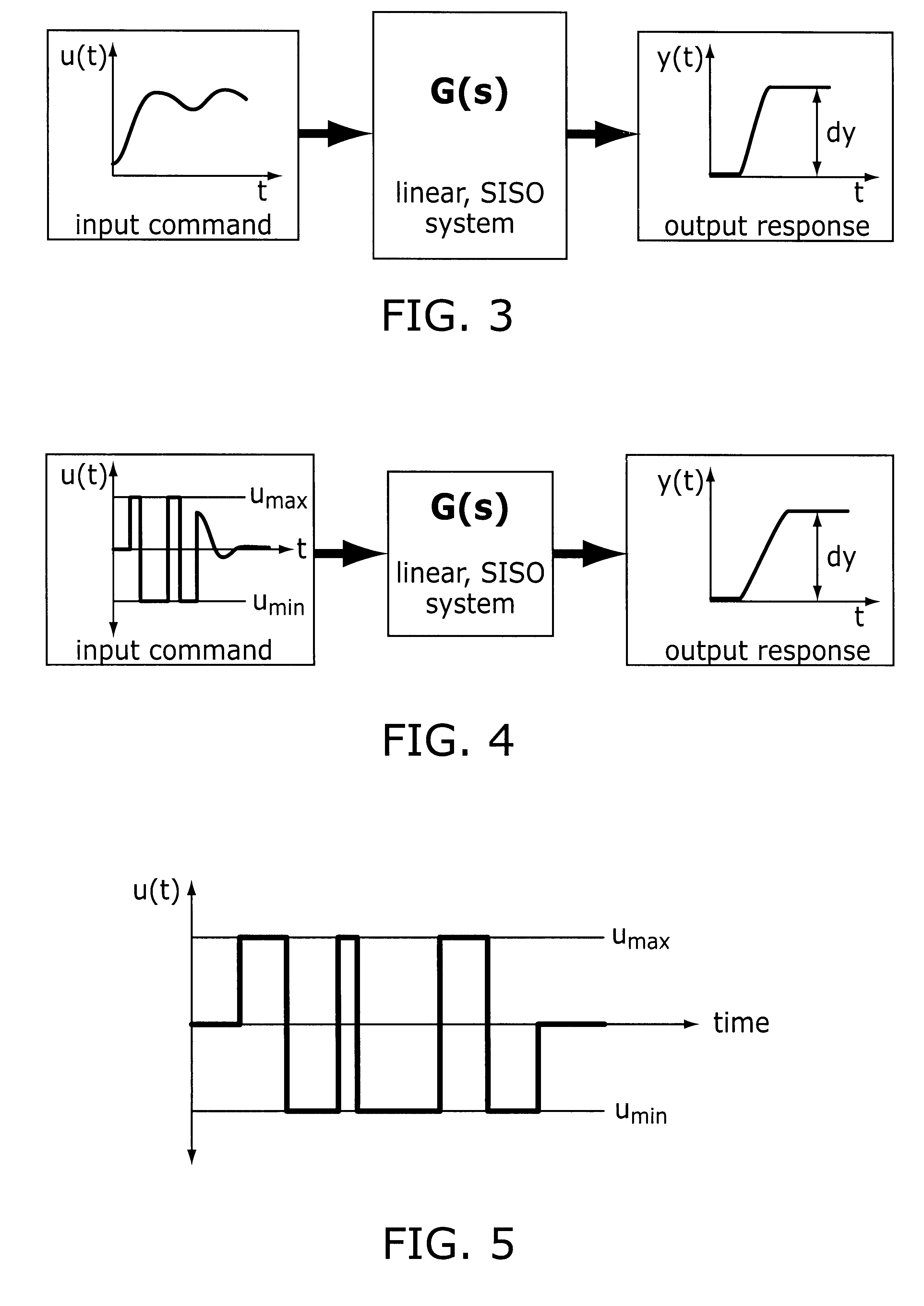
Method and apparatus for creating time-optimal commands for linear systems
The system described herein determines an input command profile for a dynamic system that can be modeled as a linear system, the input command profile for transitioning an output of the dynamic system from one point to another point. The system identifies characteristics of the dynamic system, and then selects a command profile which defines an input to the dynamic system based on the identified characteristics. The command profile comprises one or more pulses which rise and fall at switch times, and the command profile is useable with substantially any dynamic system that can be modeled as a linear system. The system then imposes a plurality of constraints on the dynamic system, at least one of the constraints being defined in terms of the switch times, and determines the switch times for the input to the dynamic system based on the command profile and the plurality of constraints.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
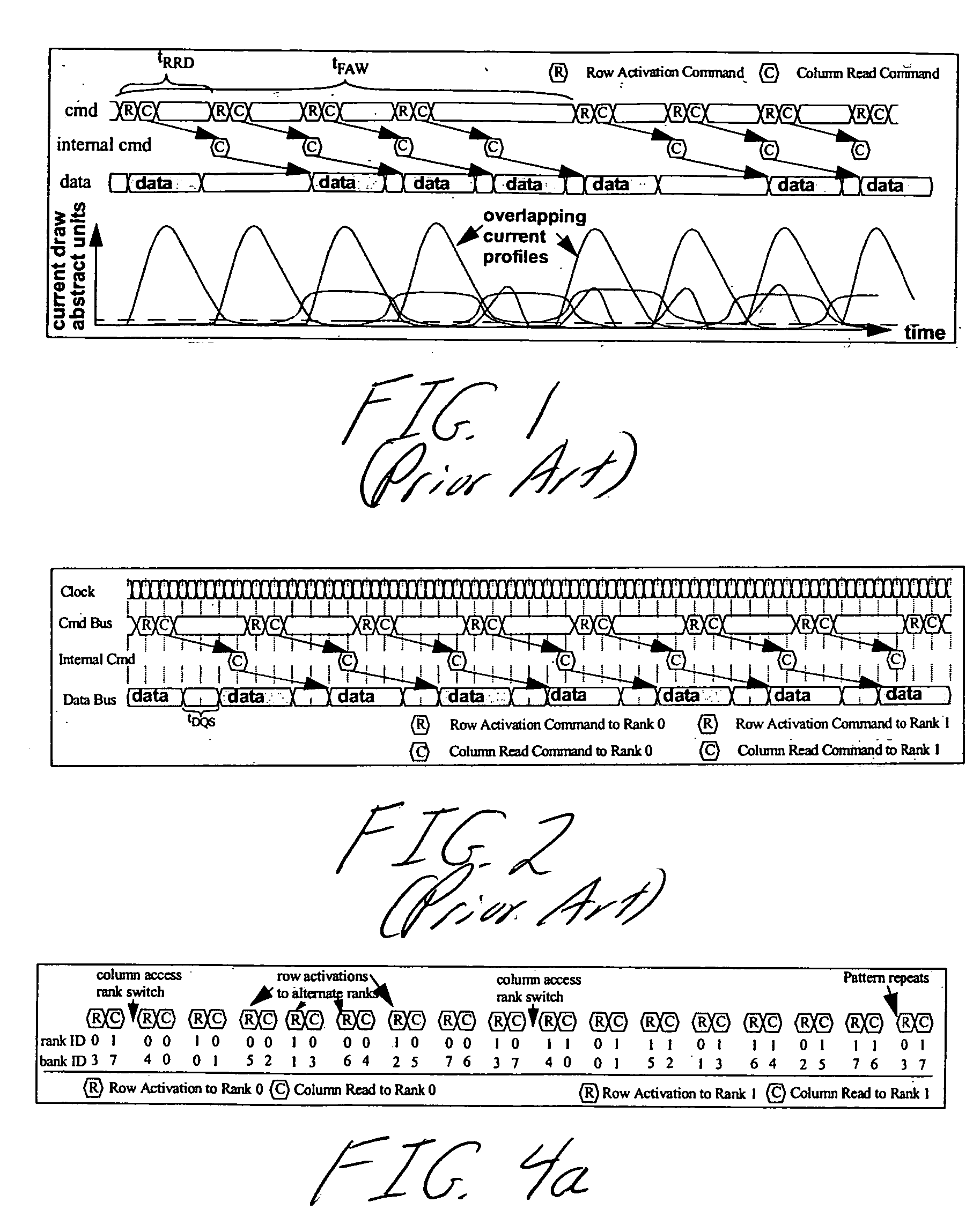
System and method for performing multi-rank command scheduling in DDR SDRAM memory systems
InactiveUS20060248261A1Better bandwidth utilizationMinimize bandwidth impactMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory bankGroup scheduling
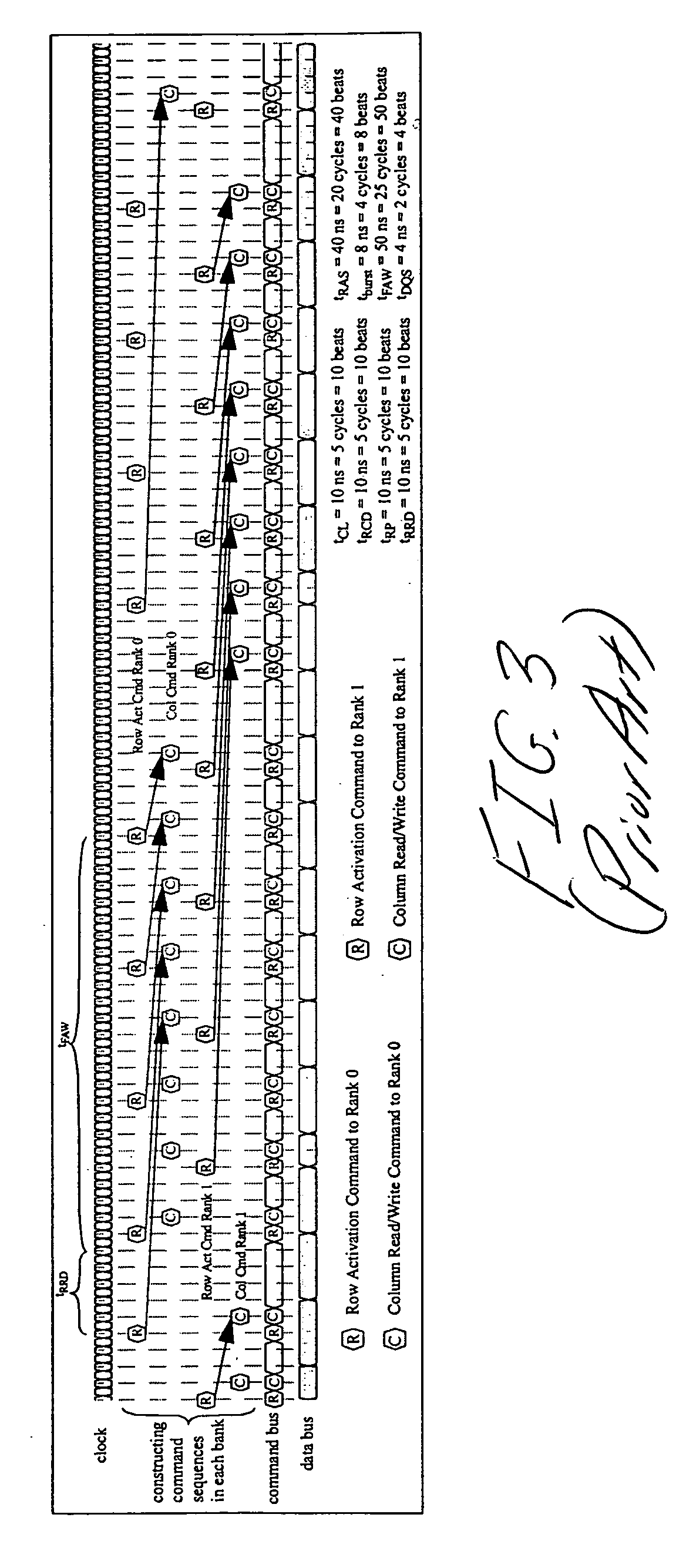
A DRAM command scheduling algorithm is presented that is designed to alleviate various constraints imposed upon high performance, high datarate, short channel DDRx SDRAM memory systems. The algorithm amortizes the overhead costs of rank-switching time and schedules around the tFAW bank activation constraint. A multi-rank DDRx memory system is also presented having at least two ranks of memory each having a number of banks and at least one memory controller configured for performing the hardware-implemented step of DRAM command scheduling for row access commands and column access commands. The step of command scheduling includes decoupling the row access commands from the column access commands; alternatively scheduling the decoupled row access commands to different ranks of memory; and group scheduling the decoupled column access commands to each bank of the number of banks of a given rank of the different ranks of memory.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
System and method for providing error resilience, random access and rate control in scalable video communications
ActiveUS20070230566A1Improve fault toleranceImprove rate-distortion performanceTelevision conference systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCommunications systemImage resolution
Systems and methods for error resilient transmission, rate control, and random access in video communication systems that use scalable video coding are provided. Error resilience is obtained by using information from low resolution layers to conceal or compensate loss of high resolution layer information. The same mechanism is used for rate control by selectively eliminating high resolution layer information from transmitted signals, which elimination can be compensated at the receiver using information from low resolution layers. Further, random access or switching between low and high resolutions is also achieved by using information from low resolution layers to compensate for high resolution spatial layer packets that may have not been received prior to the switching time.
Owner:VIDYO
Sense amplifier and method for sensing signals in a silicon-on-insulator integrated circuit
InactiveUS6433589B1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital storageAudio power amplifierSwitching time
An improved sense amplifier ad method for sensing signals in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) integrated circuit improve the performance of semiconductor memories and other circuits implemented in SOI technology. The bodies of amplifier transistors within the sense amplifier and bodies of input transistors to the sense amplifier are coupled to corresponding input signals, eliminating the history dependance that would result from unconnected bodies, while achieving faster switching times due to a dynamically produced difference in threshold voltage of the input transistors and amplifier transistors. The switching time is improved over circuits using input transistors and amplifier transistors having statically biased bodies.
Owner:IBM CORP
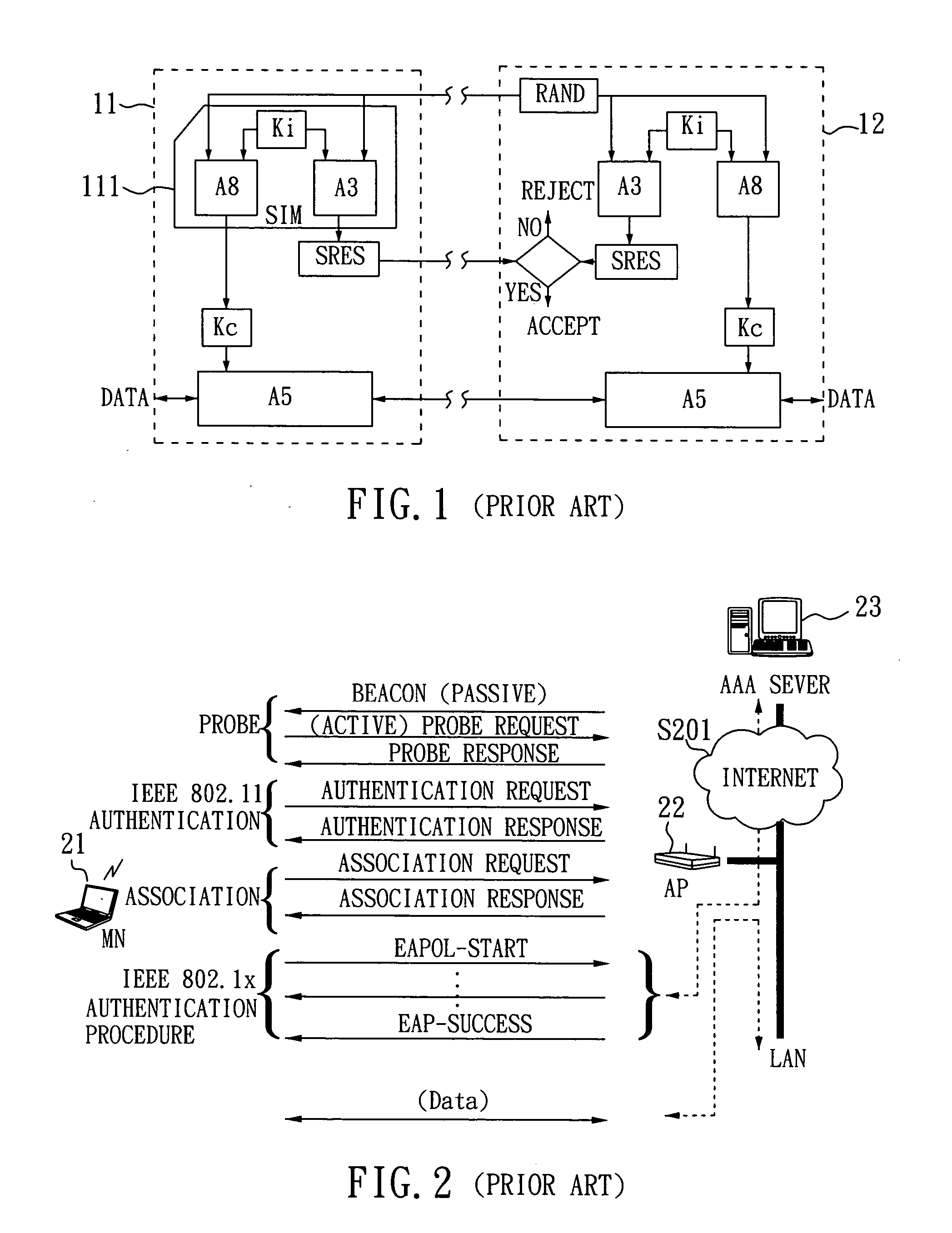
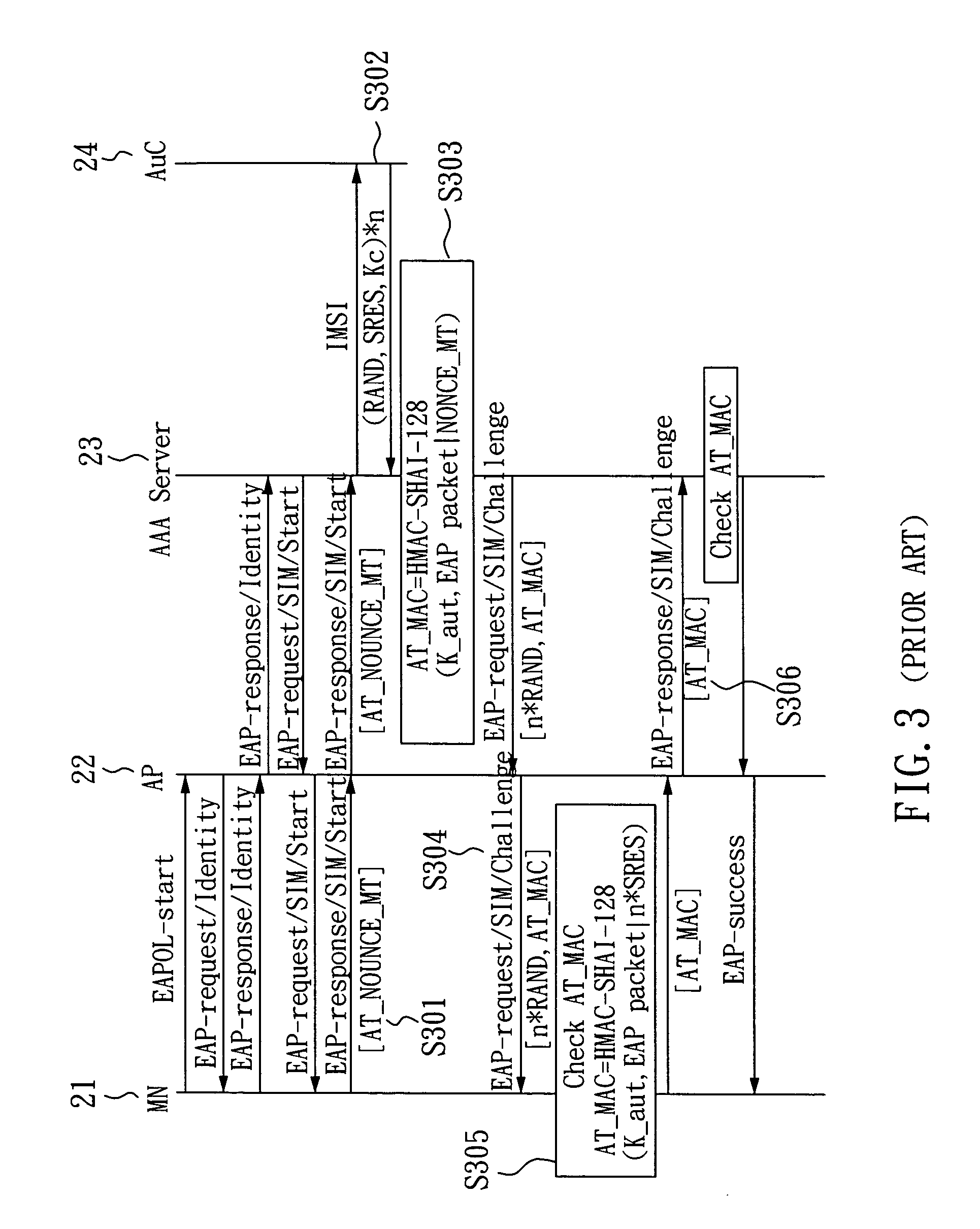
SIM-based authentication method capable of supporting inter-AP fast handover
ActiveUS20050177723A1Blocking in networkSafe WLAN environmentUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsFast handoverWireless lan
The invention relates to a SIM-based authentication method capable of supporting inter-AP fast handover, which can decrease the number of authentication procedures without negatively influencing the security of the wireless LAN by establishing an encrypted channel for each mobile node and using method 1: an aggressive key pre-distribution and method 2: probe request triggering passive key pre-query technique, thereby reducing the time of inter-AP handover for the mobile node. Furthermore, a re-authentication procedure is started to update the key after the key is used for a long time so as to ensure that the key is safe, thereby effectively achieving a fast and safe wireless LAN environment.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Apparatus and Method for Controlling Channel Switching in Wireless Networks
ActiveUS20090067354A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission systemsArea networkControl channel
The invention provides apparatus methods for avoiding channel collisions in Wireless Regional Area Networks (WRAN), A medium access controller (MAC) for switching a base station (BS) of a WRAN from a first channel to a second channel at a time t is provided. The MAC includes a switch time delay circuit for delaying said switching with respect to time t by a random delay time.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
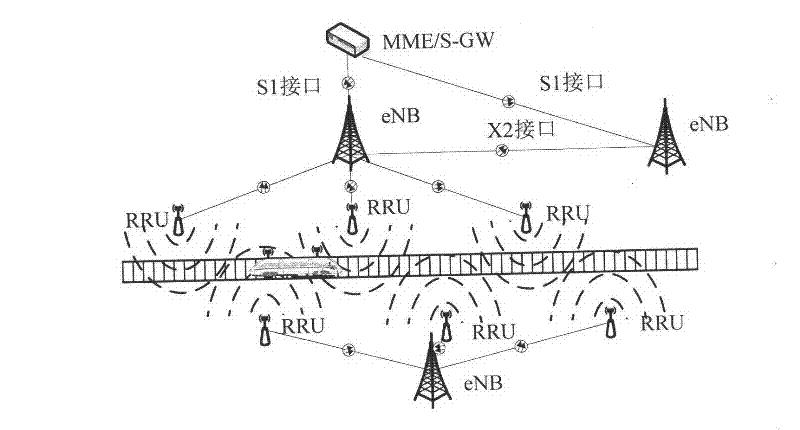
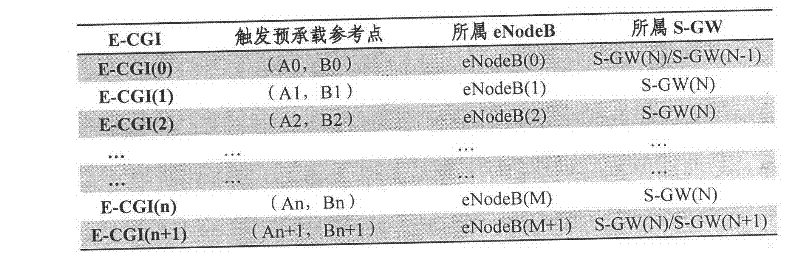
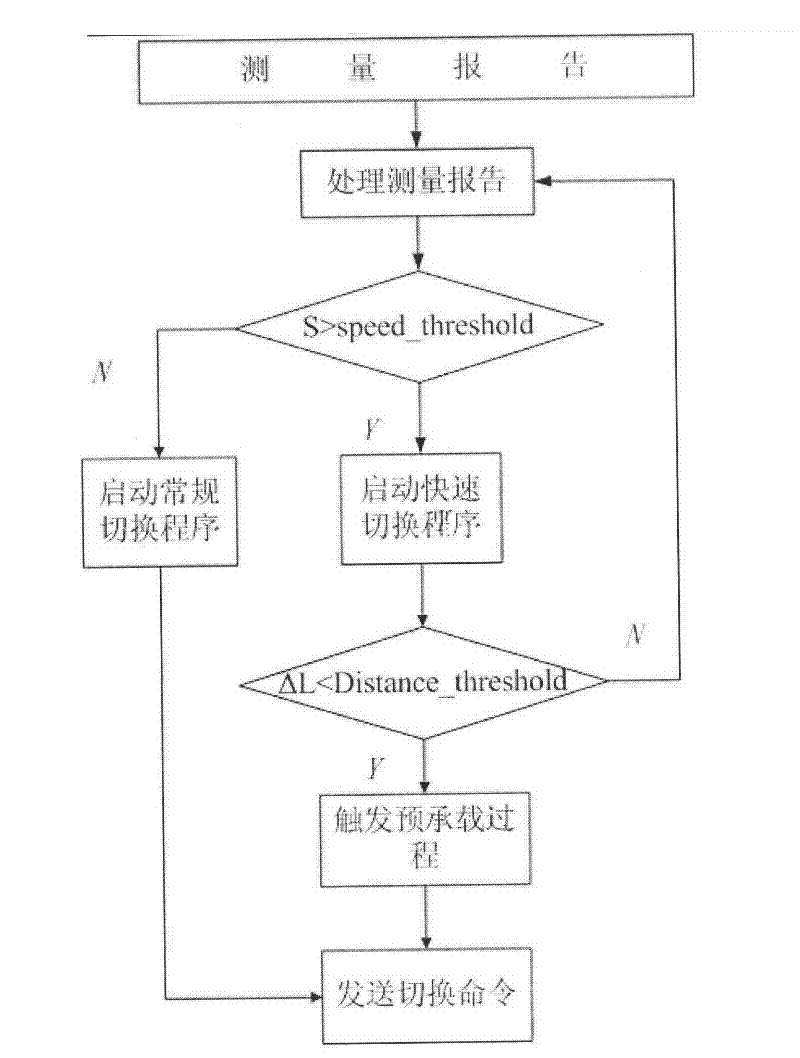
A fast handover method of a td-lte communication system based on target cell pre-carrying
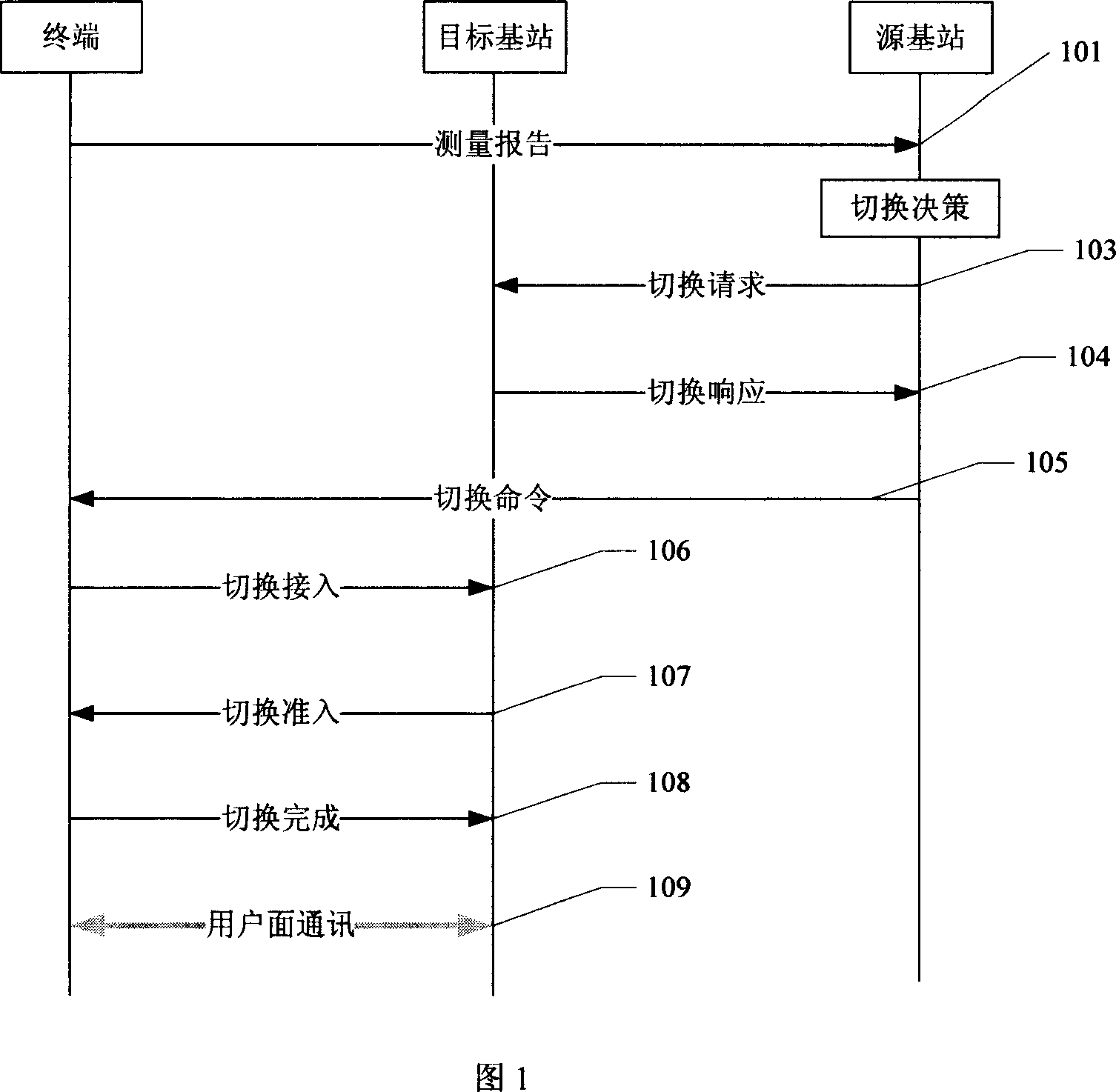
Aiming at the requirements of frequent cell handover, short handover time and high handover success rate in high-speed railway TD-LTE communication system, a fast handover method of TD-LTE communication system based on target cell pre-carrying is proposed. According to the train's running position, speed and direction, after the network planning is completed, a list of neighboring cells is generated in advance, and the switching position of each switching zone is preset, that is, the longitude and latitude position information. Before the train enters the overlapping area of switching between two cells , when the distance from entering the handover zone is a certain value L, the source base station eNodeB determines and sends the pre-bearer information to the target base station eNodeB according to the measurement report of the user terminal UE, and the target base station eNodeB performs the evolution packet system ( Evolved Packet System (EPS) resources to bear the load, when the train enters the handover zone, if the train meets the handover criteria, the train will be handed over from the source cell to the target cell. Therefore, this method reduces the handover delay and is beneficial to improve the handover success rate. The method can dynamically adjust the switching method according to the mobile speed of the UE, solve the problem of fast switching in a high-speed mobile environment, reduce the number of communication drops, improve the success rate of switching, enhance the service quality of high-speed broadband mobile services, and promote high-speed railway trains. The development of domestic multimedia broadband mobile Internet services meets the growing needs of passengers for mobile communication services.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
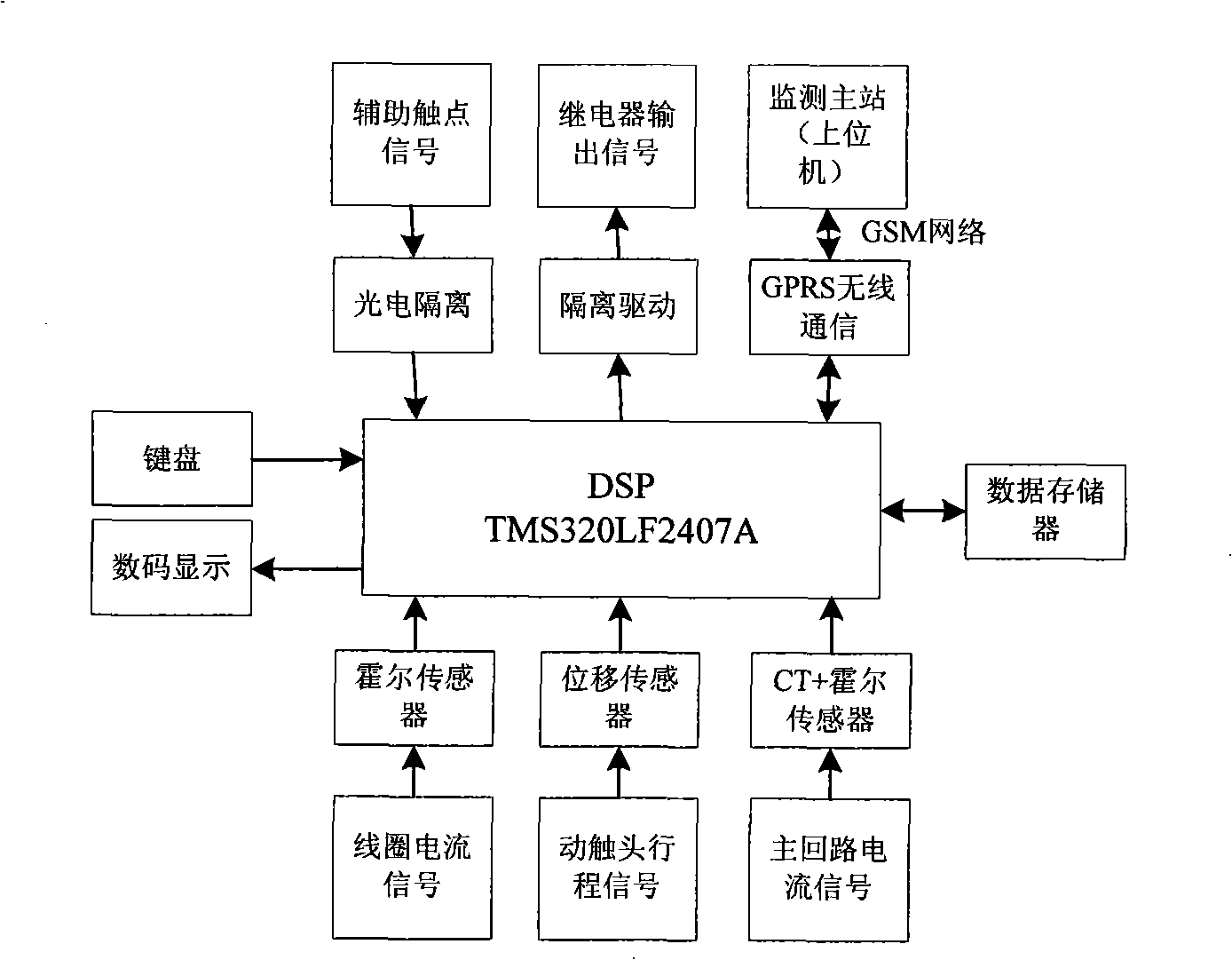
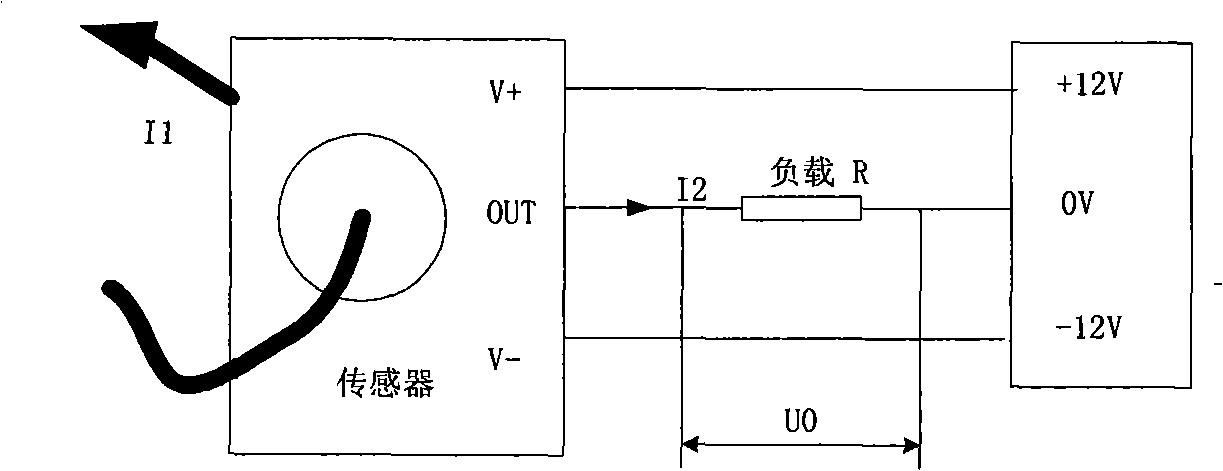
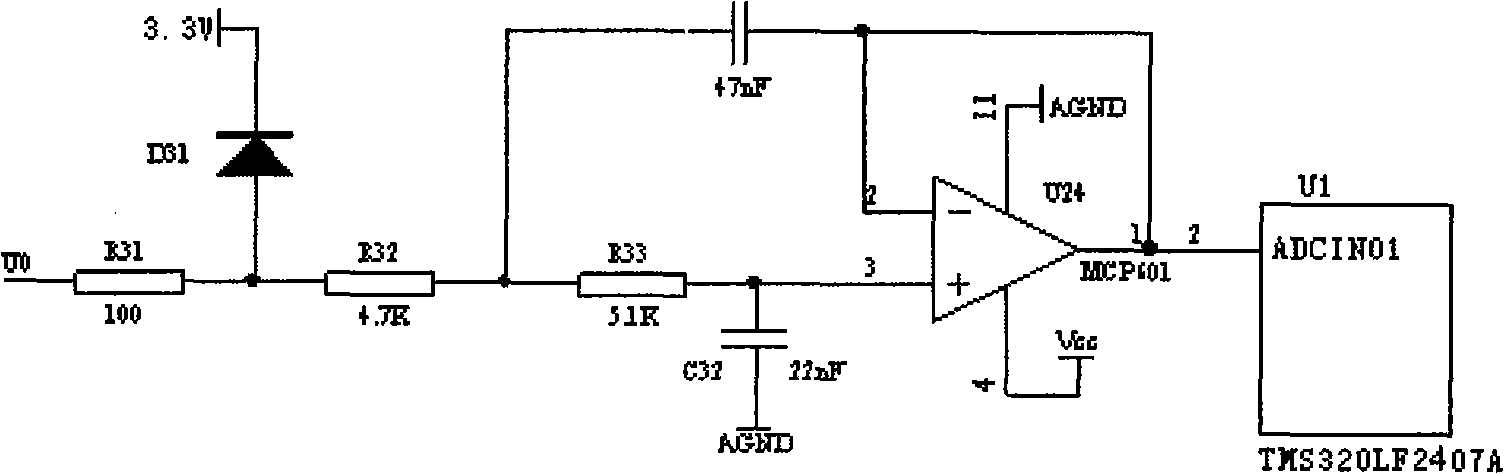
24KV high-voltage vacuum breaker mechanical features on-line monitoring method and monitoring device
InactiveCN101261192AEasy to analyzeSpeed upStructural/machines measurementHigh pressureSingle chip
The invention provides a 24kV high-voltage vacuum circuit breaker mechanical characteristic online monitoring method in which the mechanical characteristic parameters of the vacuum circuit breaker are gained by monitoring the closing and opening switch coil current characteristic curve and the stroke characteristic curve of a moving contact when the vacuum circuit breaker acts; a corresponding monitoring device comprises a DSP single chip microprocessor, a circuit breaker coil current monitoring module, a circuit breaker movable contact stroke monitoring module, a circuit breaker main circuit current monitoring module, and a GPRS communication module. Compared with the existing circuit breaker mechanical characteristic online monitoring method and the device, the online monitoring method and the device of the invention adopt advanced sensing technique, signal processing technique, wireless communication technique, and computer technique, etc., realizes outdoor high voltage vacuum circuit breaker online monitoring; the online monitoring method and the device also display the real-time opening and closing coil current characteristic curve and the stroke characteristic curve of the moving contact by monitoring data when the vacuum circuit breaker acts, and calculates the mechanical characteristic parameters such as the closing and opening switch time of the vacuum circuit breaker, action speed, stroke of movable contact, and opening distance, etc., and can conveniently analyze the monitoring results.
Owner:NANJING INTELLIGENT DISTRIBUTION AUTOMATION EQUIP
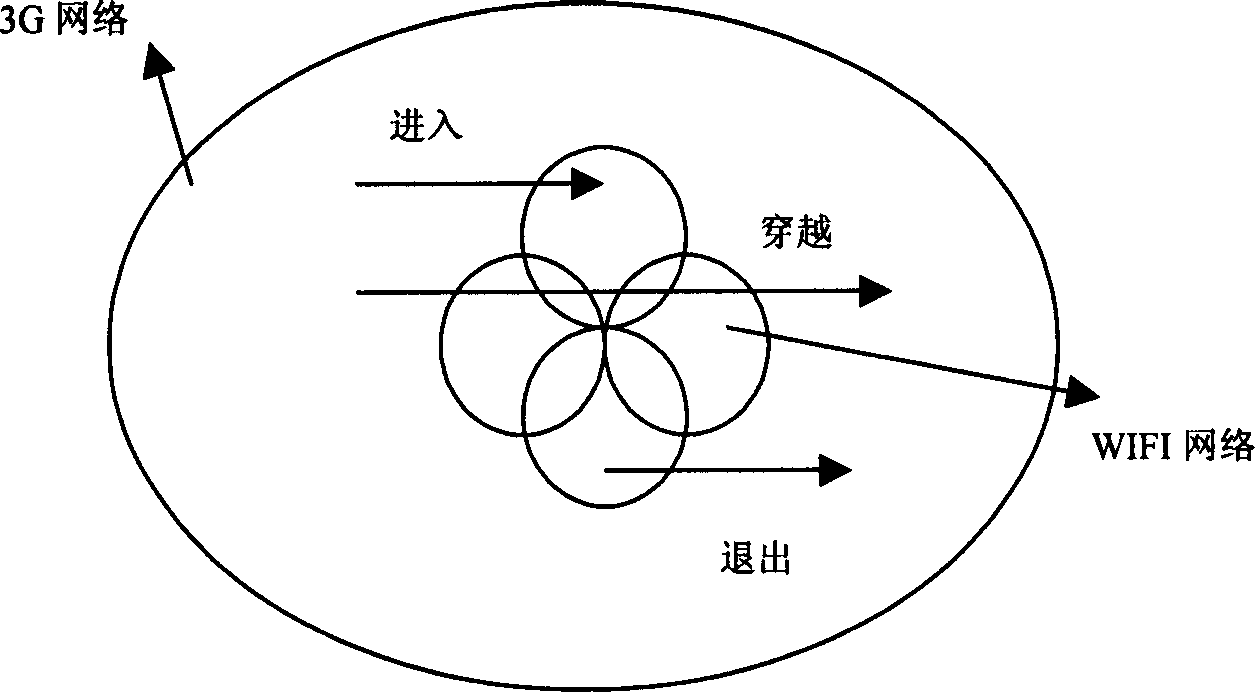
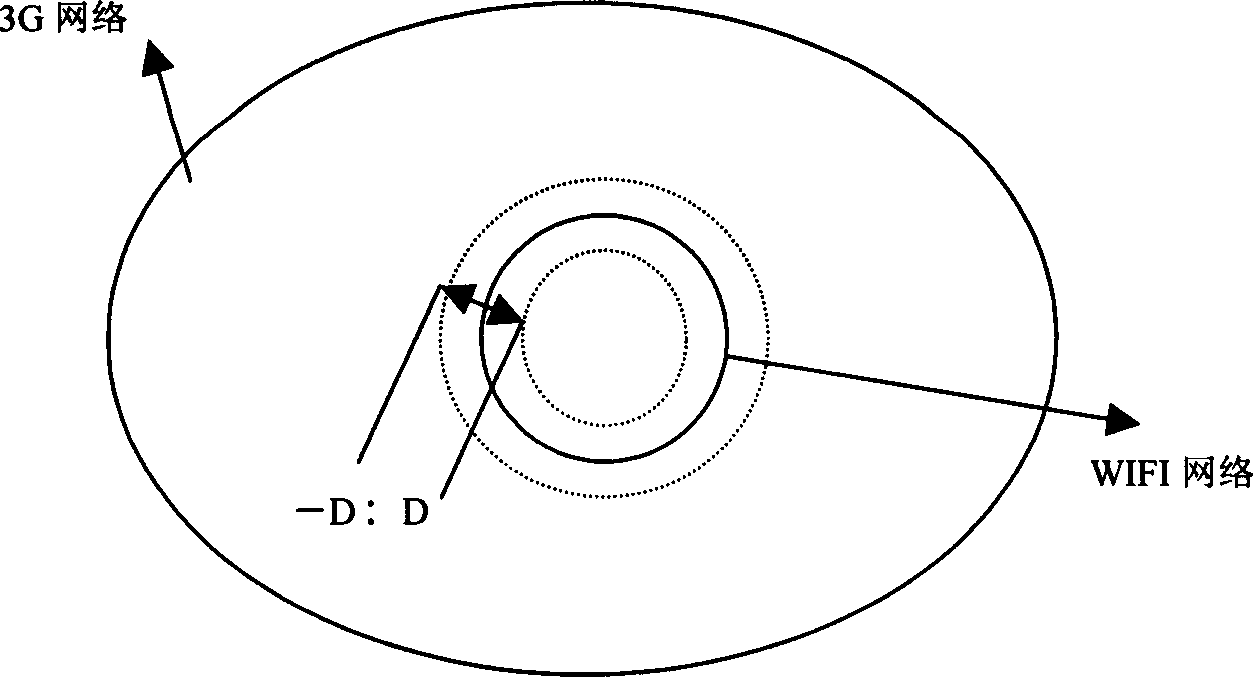
Switchover method between 3G network and WIFI network based on location information
InactiveCN1794681AEasy to compareImprove the success rate of switchingData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWifi networkThird generation
This invention puts forward a switch method between 3G netwqork and WIFI network, which differentiates the switch between a cellular network and the WIFI network into different kinds to switch and judge based on the position information of periodic measurement commonly provided by the network and the terminal and the information of the velocity and directions and angles along with it to increase the switch efficiency among heterogeneous networks and reduce unnecessary switch times.
Owner:上海贝豪通讯电子有限公司
Method for switching uplink random channel or sharing channel between mobile communication systems
InactiveCN101064943AAvoid teleportationHigh speedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationControl channelMobile communication systems
The invention discloses a switching method for ascending random channel or shared channel between base stations of mobile communication system. The aim of invention is used to solve the problems that the reliable coding can not be used caused by the complicated switch method and complicated switch accessing message. The invention includes: when the base stations need to be switched, target section distributes ID identify code and preserves source for terminals; target section sends the switch messages by control channels in source section; the messages include at least ID identify codes for terminals, source allocating information of target section and ascending dispatching messages; the terminals send switching commands to target base station according to switching command messages. The switching flow is terse, and reduces the switching time, and the reduced switching access messages can be presented by more bytes, and the switching access messages can use the reliable coding technology, and the receiver of base station can decode easily.
Owner:无锡中太数据通信股份有限公司
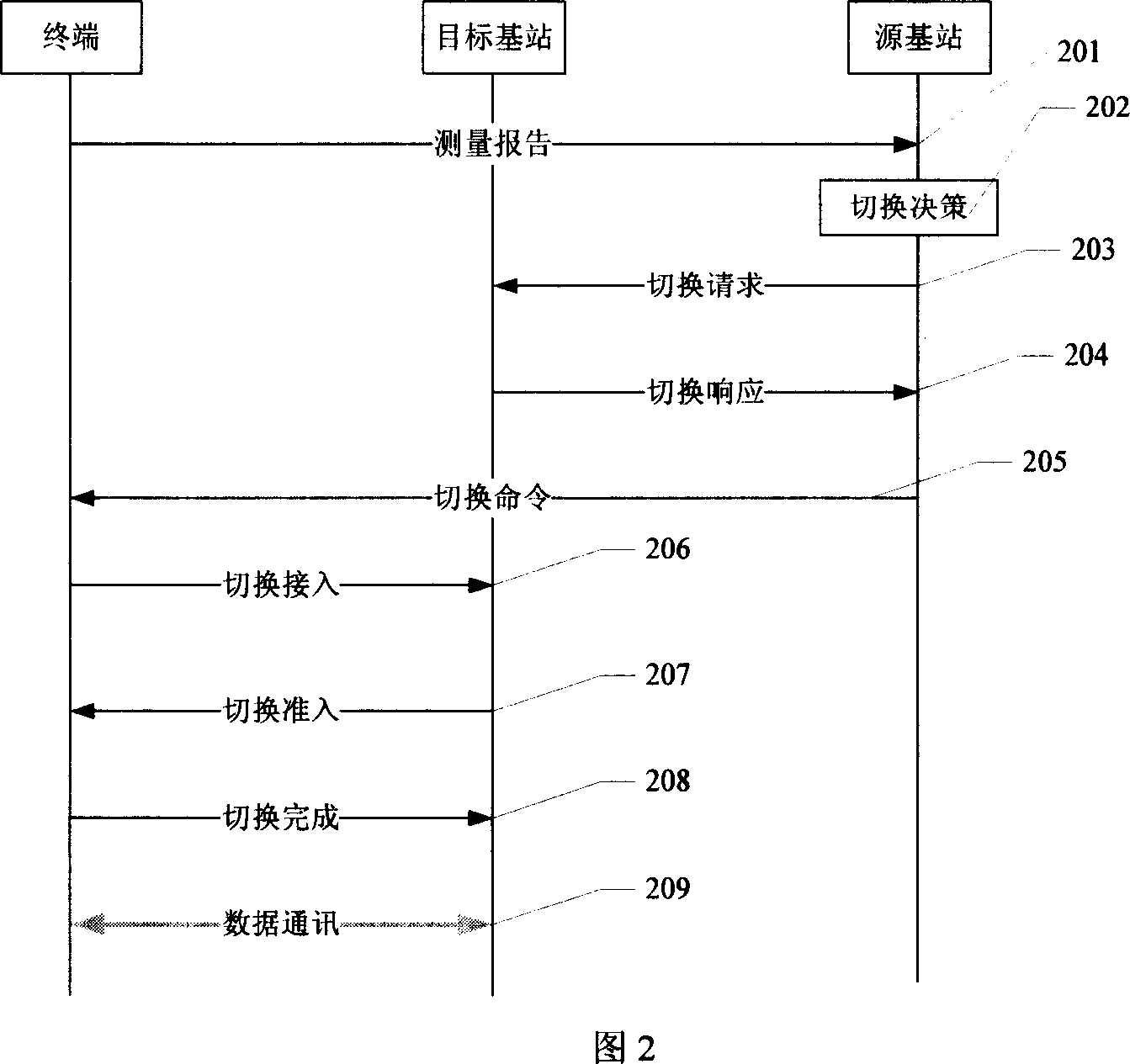
Switching method, user terminal and network side device
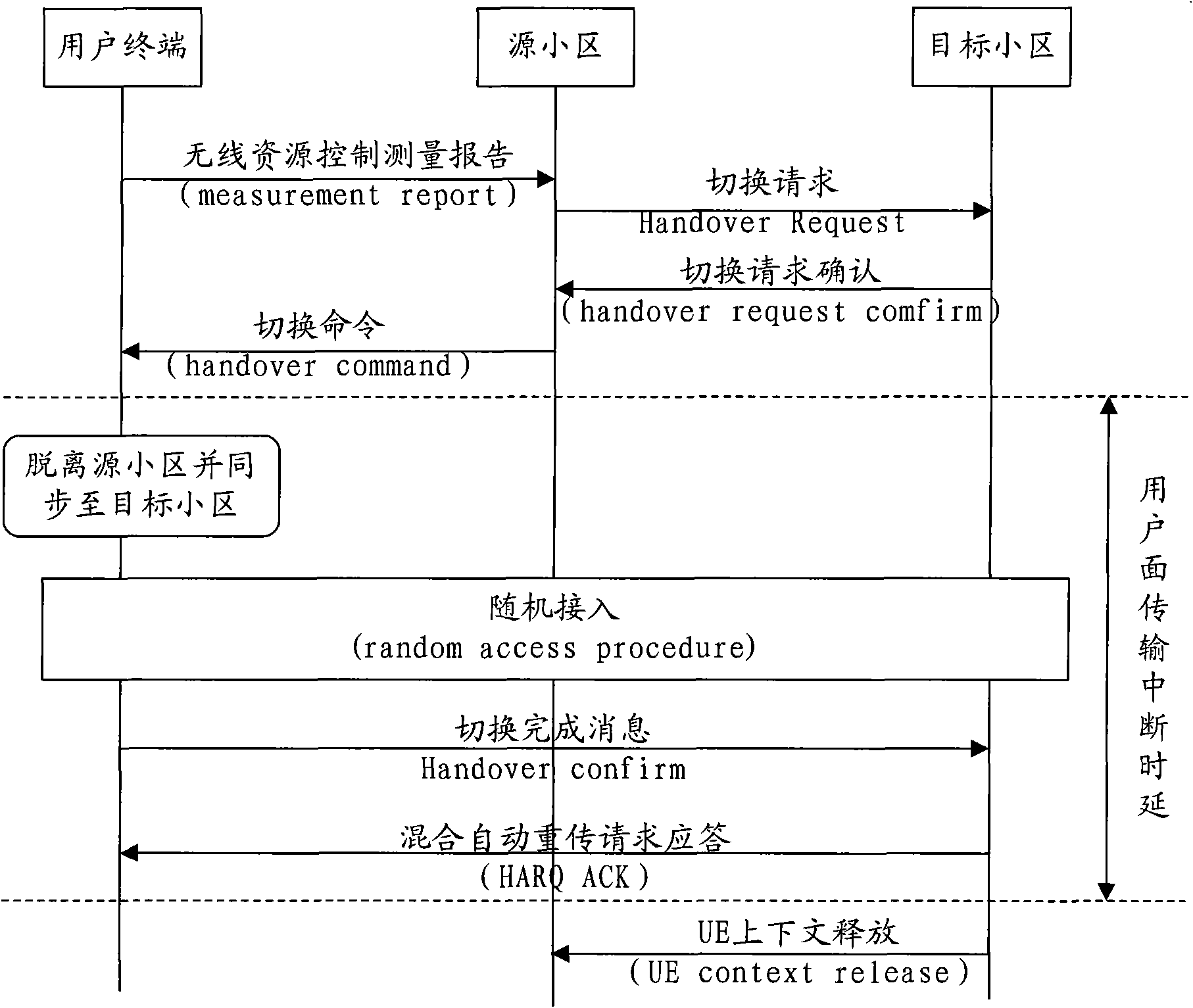
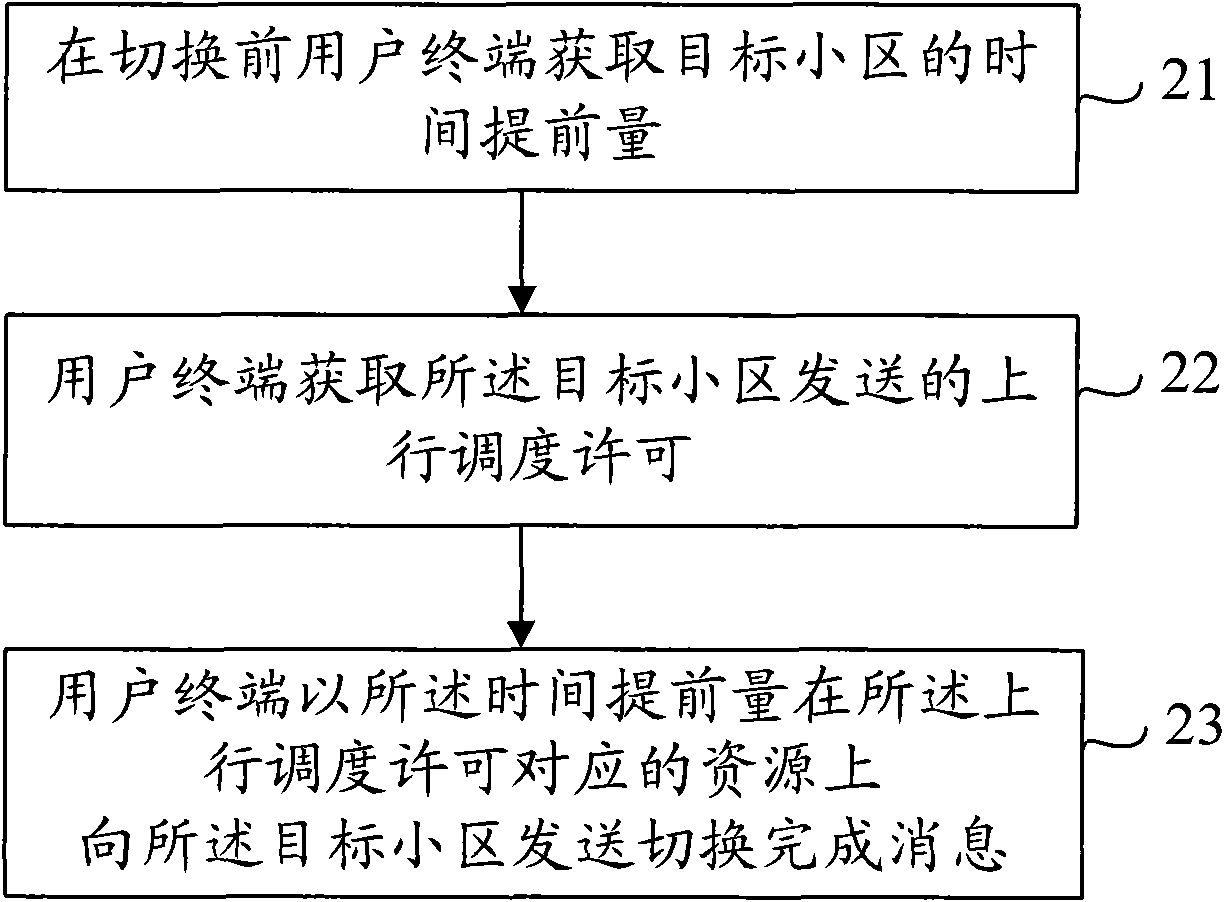
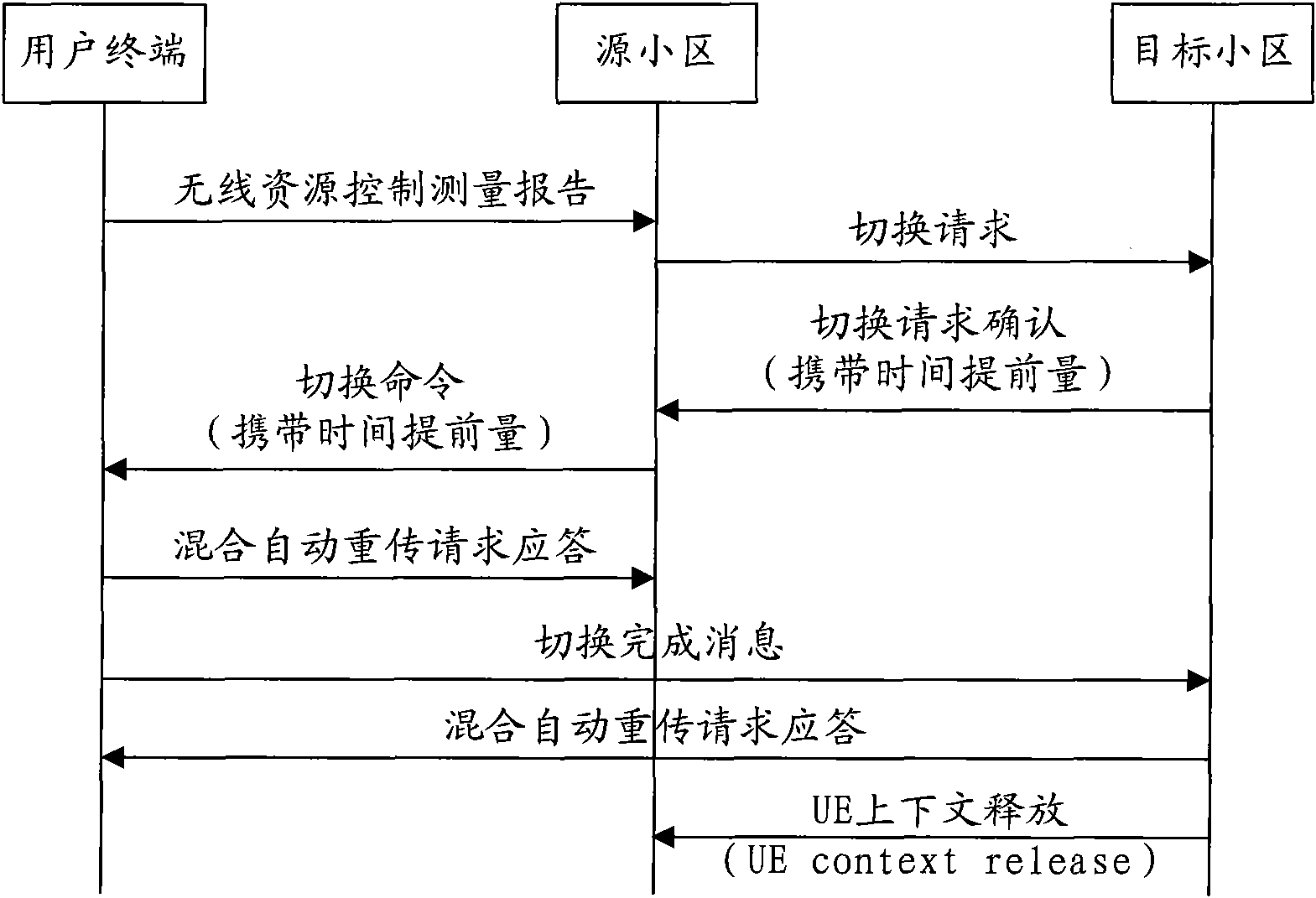
ActiveCN101932052AReduce switching delayReduce Interrupt LatencyError prevention/detection by using return channelSynchronisation arrangementTime delaysSwitching time
The embodiment of the invention discloses a switching method, a user terminal and a network side device, which can shorten the switching time delay of a control plane and the interruption time delay of user plane data. One switching method comprises the following steps: the user terminal obtains the amount of advanced time of a target district before switching; and an upstream scheduling permission which is sent by the target district is obtained; and switch completing information is sent to the target district on a resource corresponding to the upstream scheduling permission by using the amount of advanced time. Another switching method comprises the following steps: the target district sends the amount of advanced time of the target district to the user terminal through a source district before switching; the upstream scheduling permission of the target district is sent to the user terminal; and the switch completing information which is sent by the user terminal on the resource corresponding to the upstream scheduling permission by using the amount of advanced time is received.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Power management in an eye-tracking system
ActiveUS20130106681A1Improved power management functionalityWithout burdening energy performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceControl data
A personal computer system includes a visual display, an imaging device adapted to provide eye-tracking data by imaging the face of a viewer of the visual display, and an input device for accepting eye-tracking control data and other input data. The imaging device is switchable between at least an active mode, a ready mode and an idle mode, and the switching time from the idle mode to the active mode is longer than the switching time from the ready mode to the active mode. The eye-tracking data provided in the ready mode may include eye position but not eye orientation. The system may include a dedicated input device for forcing the imaging device into active mode by directly triggering an interrupt; alternatively, the dedicated input device forces it permanently into idle mode.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
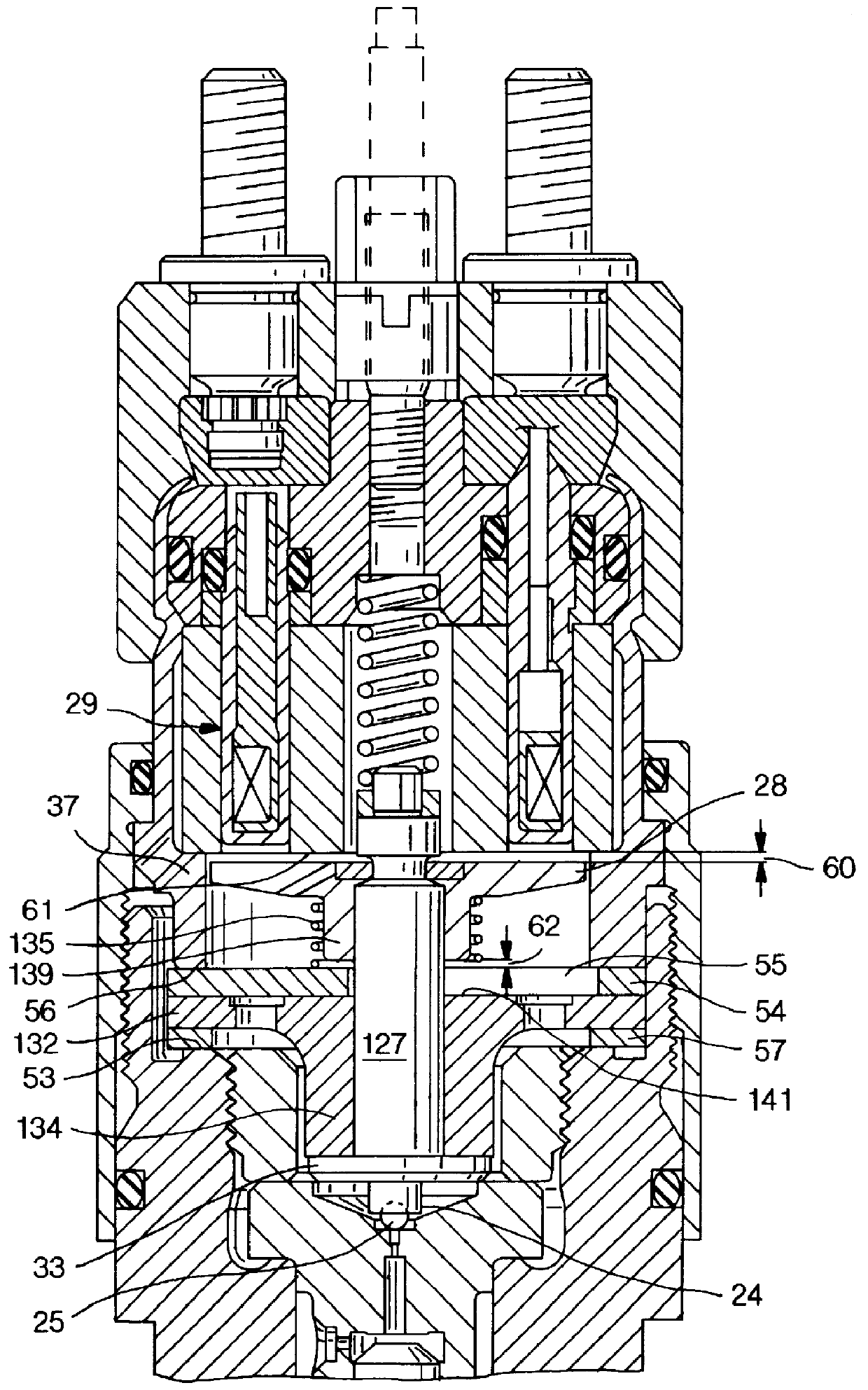
Solenoid valve for an electrically controlled valve
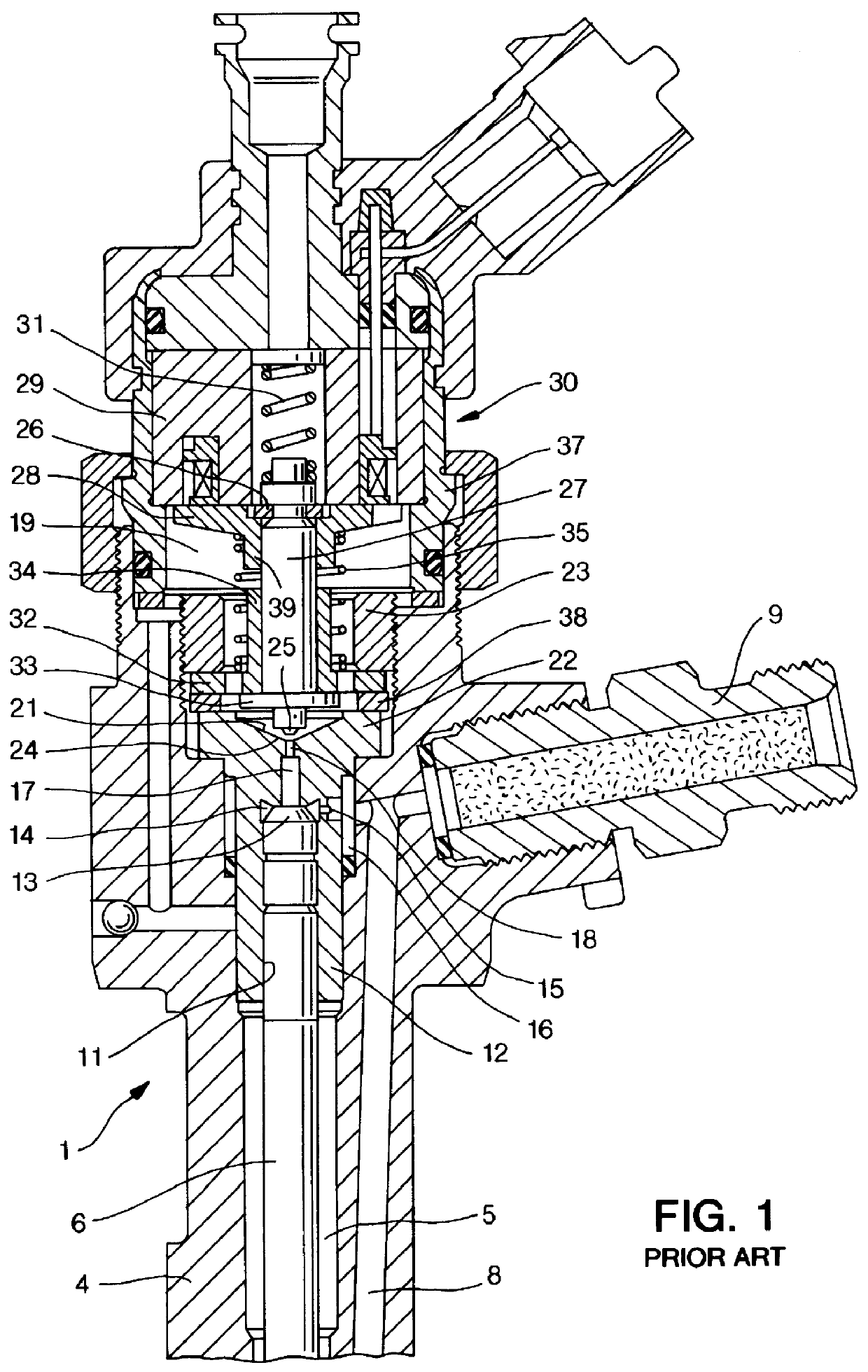
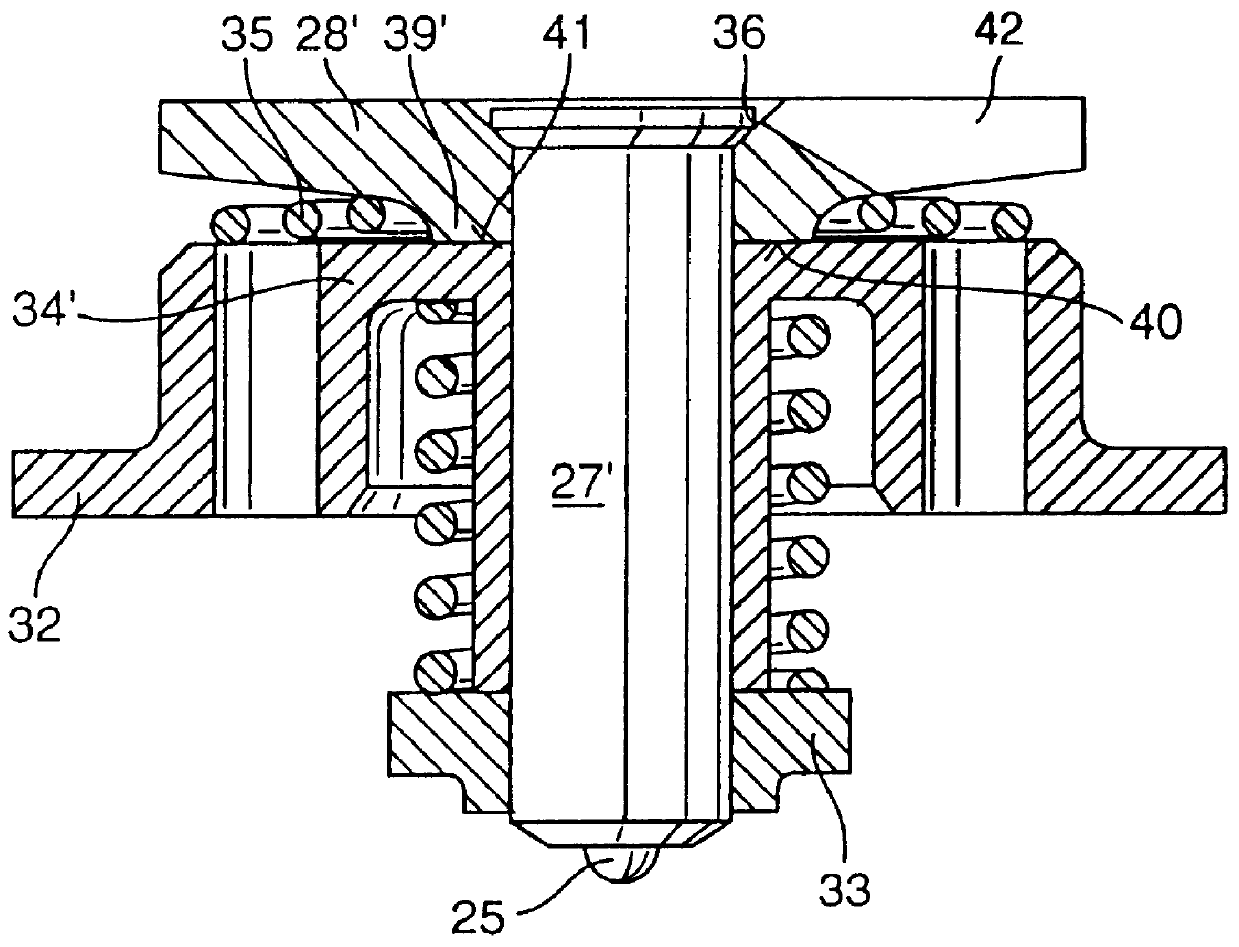
InactiveUS6161813APrevent reverberationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure injection controlCommon railSolenoid valve
PCT No. PCT / DE97 / 02723 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 38426 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 3, 1998A solenoid valve comprising a magnet armature which is embodied as having multiple parts and has an armature disk and an armature bolt. The magnet armature is guided in a slider. A damping device is provided in order to prevent post-pulse oscillation of the armature after a closing of the solenoid valve. The required short switching times of the solenoid valve can be exactly maintained with a device of this kind. The solenoid valve is designated for use in injection systems with a common rail.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
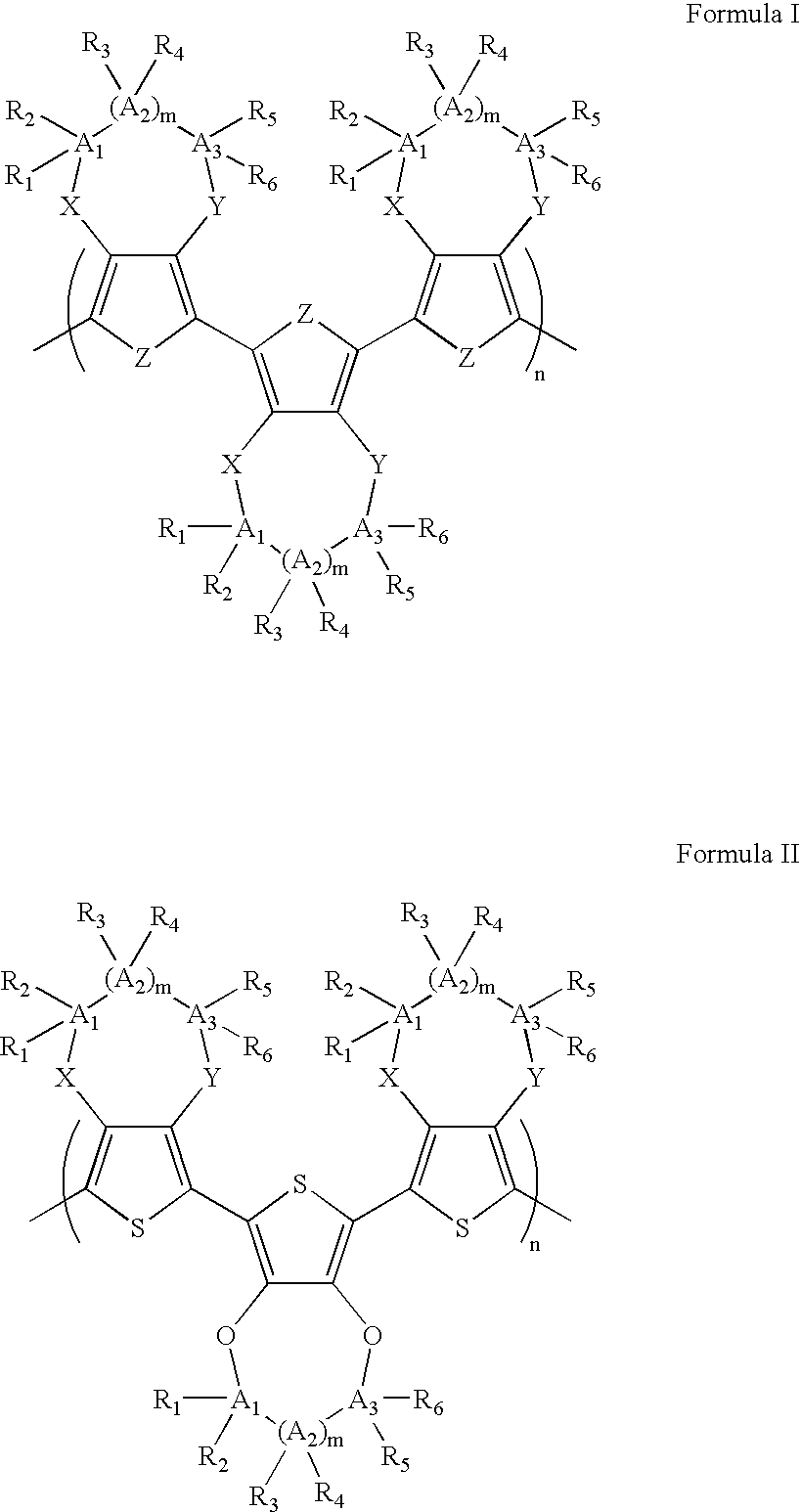
Electrochromic polymers and polymer electrochromic devices
InactiveUS20030174377A1Increase the gapLess structural defectsPhotosensitive materialsElectrography/magnetographyPolymer scienceGas phase
The subject invention pertains to electrochromic polymers and polymer electrochromic devices. In a specific embodiment, two complementary polymers can be matched and incorporated into dual polymer electrochromic devices. The anodically coloring polymers in accordance with the subject invention can allow control over the color, brightness, and environmental stability of an electrochromic window. In addition, high device contrast ratios, high transmittance changes, and high luminance changes can be achieved, along with half-second switching times for full color change. Also provided are electrochromic devices such as advertising signage, video monitors, stadium scoreboards, computers, announcement boards, warning systems for cell phones, warning / information systems for automobiles, greeting cards, electrochromic windows, billboards, electronic books, and electrical wiring. The subject invention also provides for the use of complementary electrochromic polymers in the manufacture of electrochromic devices. In some embodiments, the devices of the invention can be prepared using metal vapor deposition or line patterning.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com