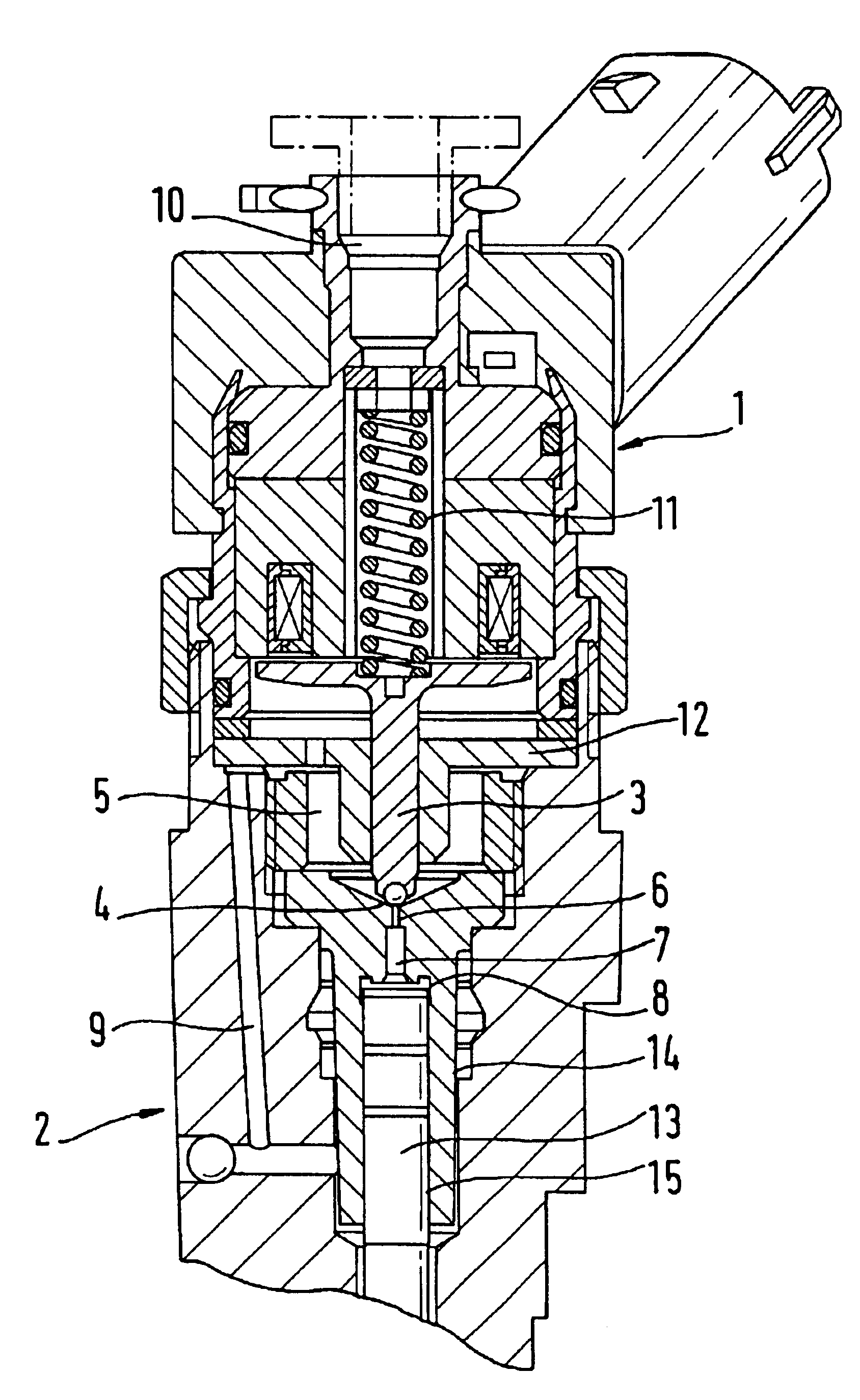
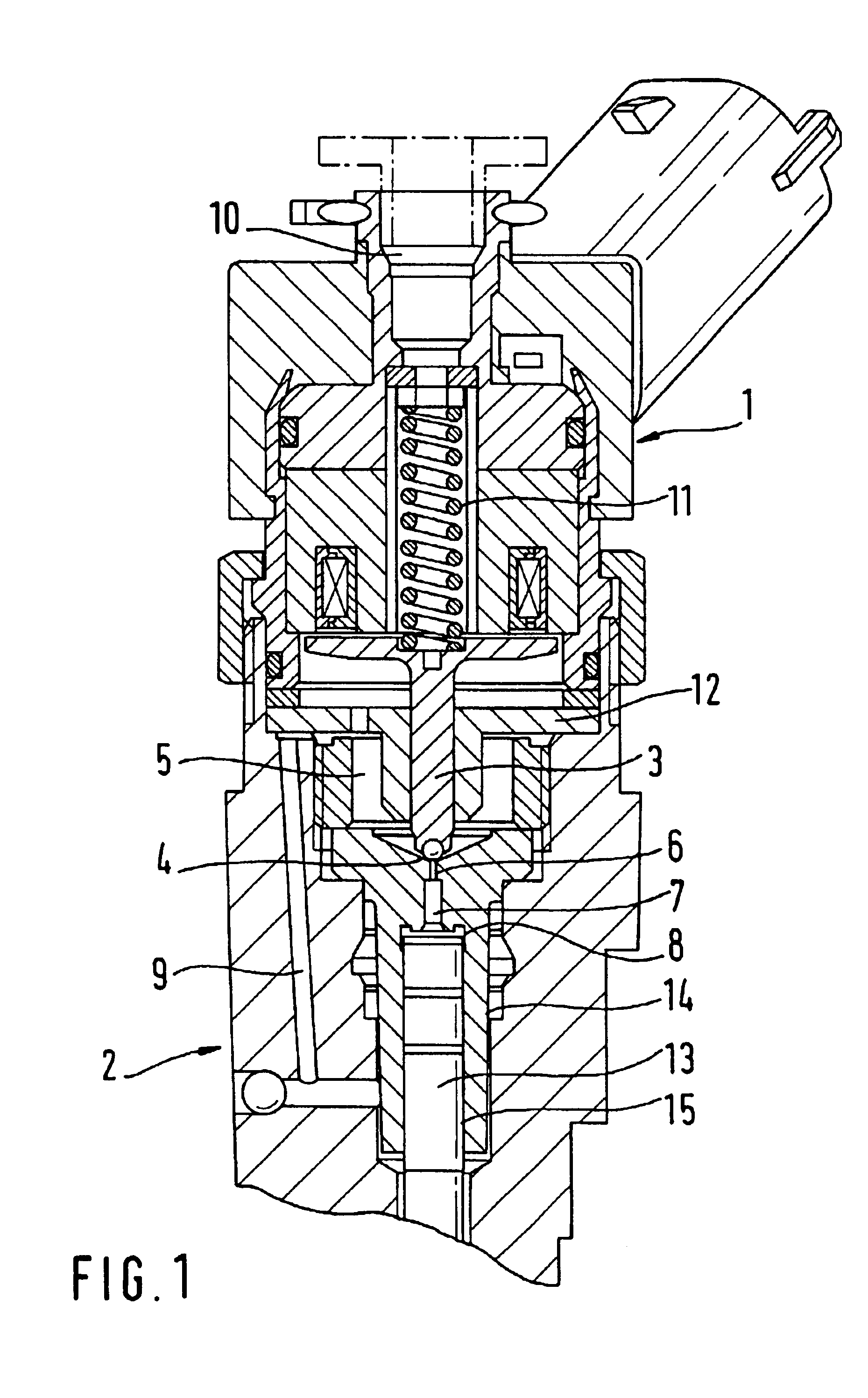
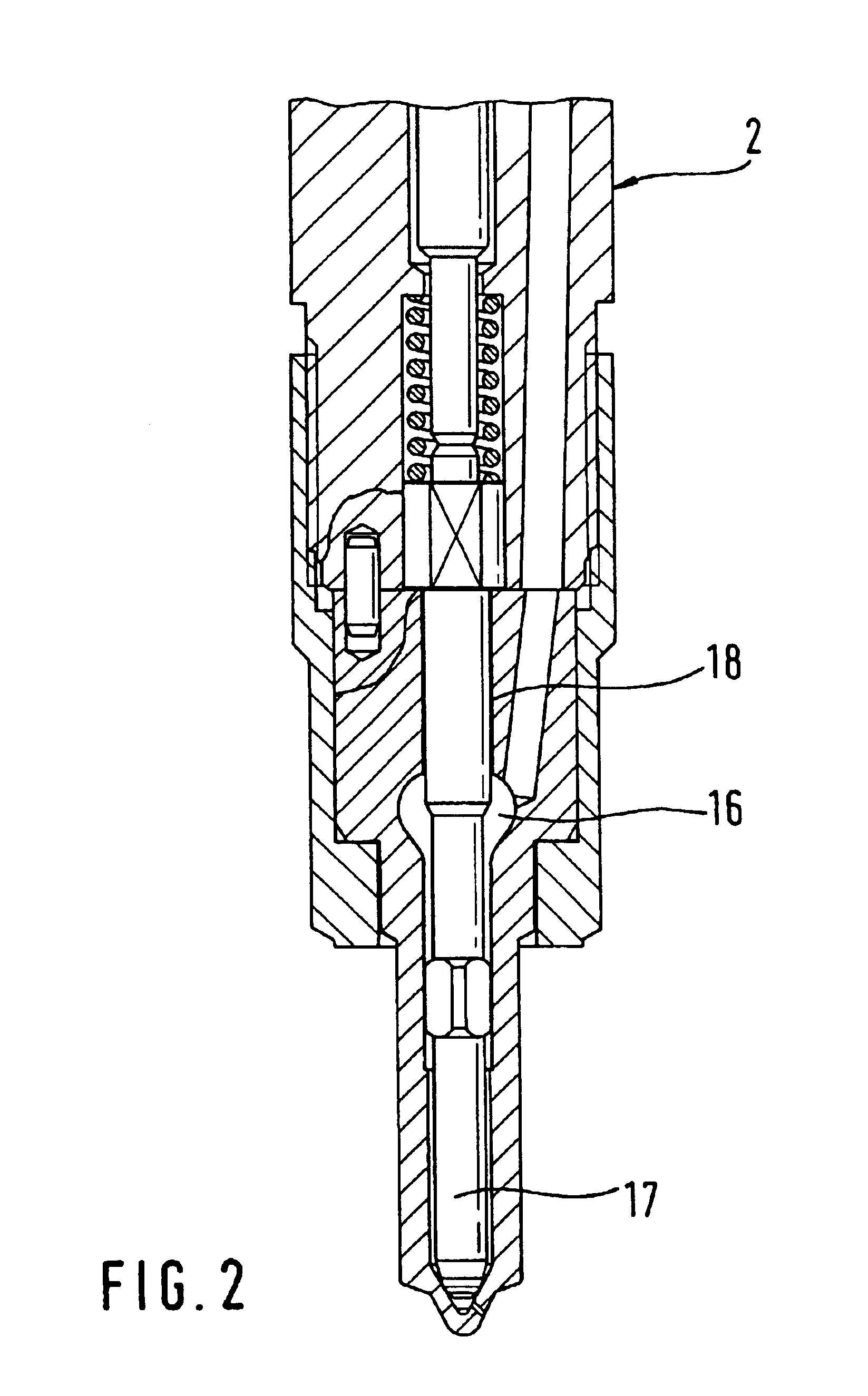
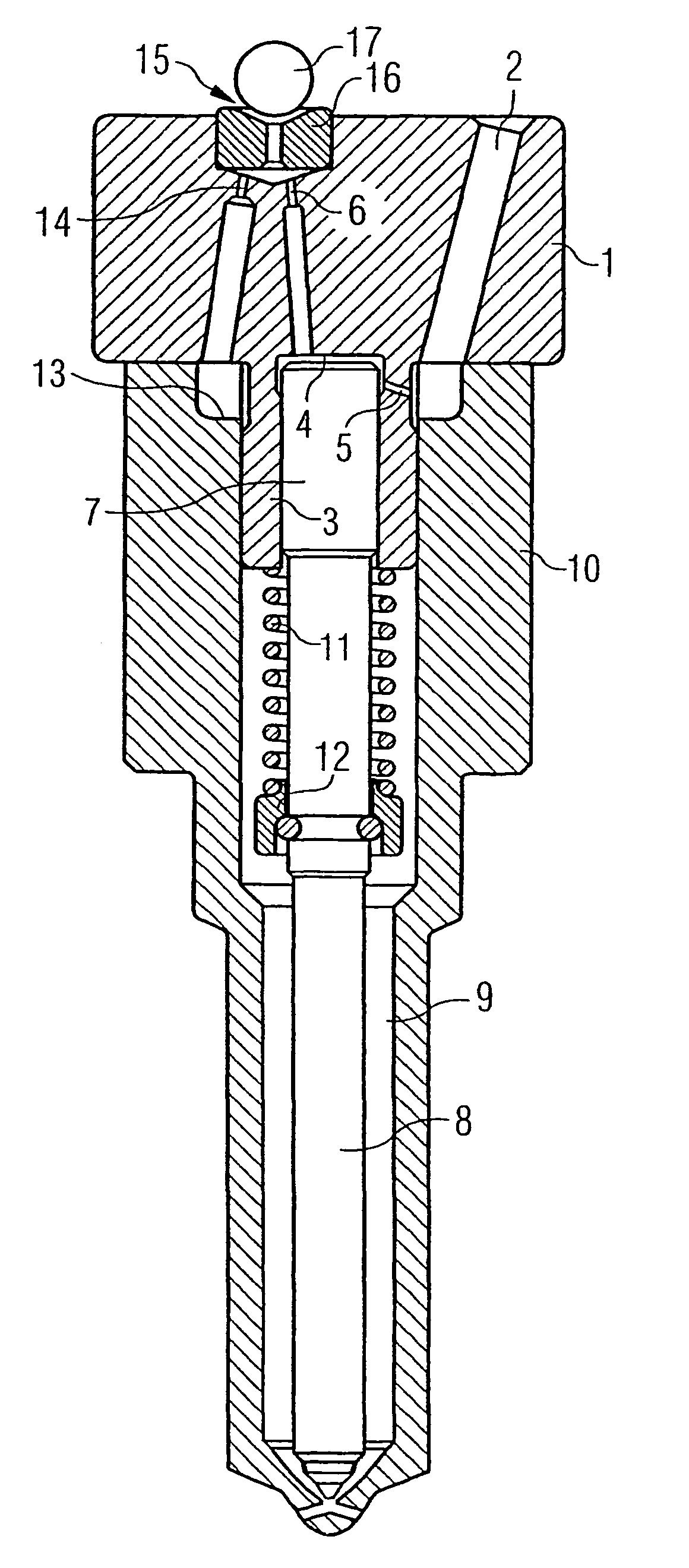
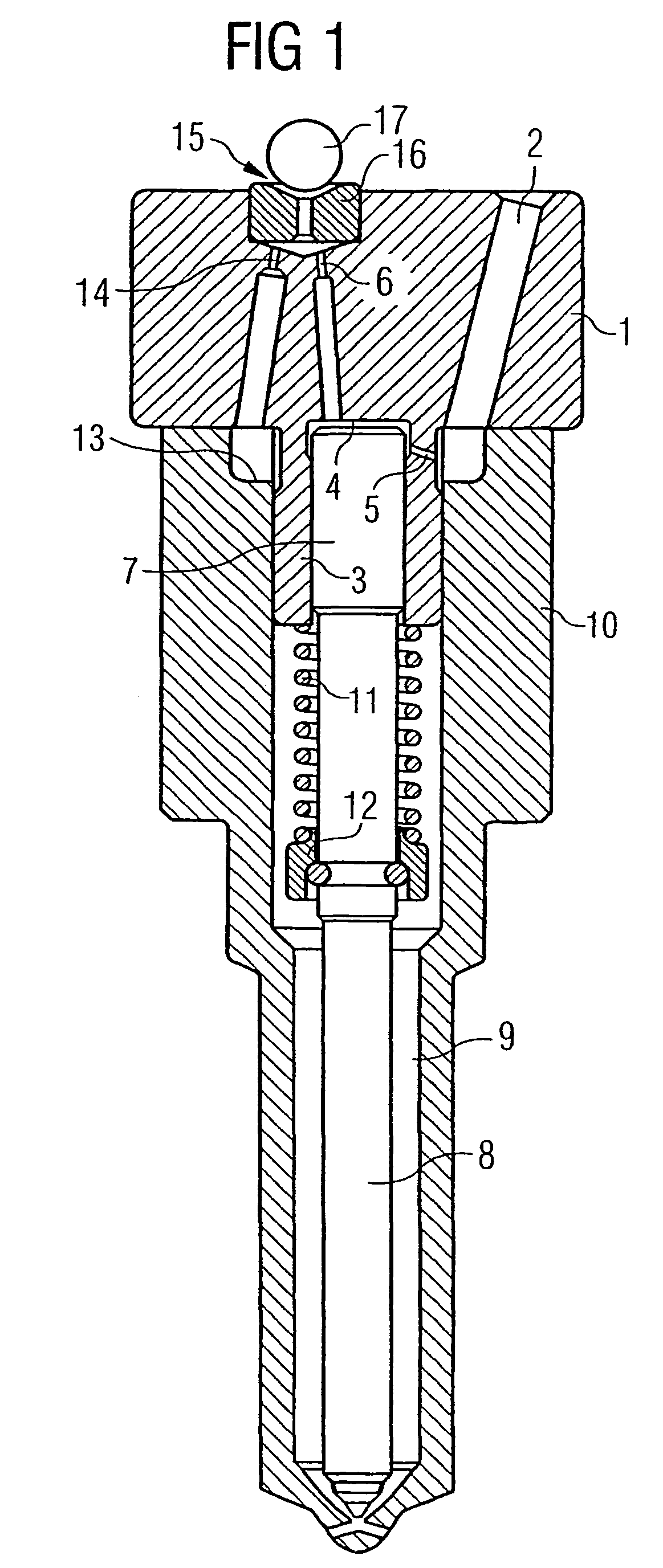
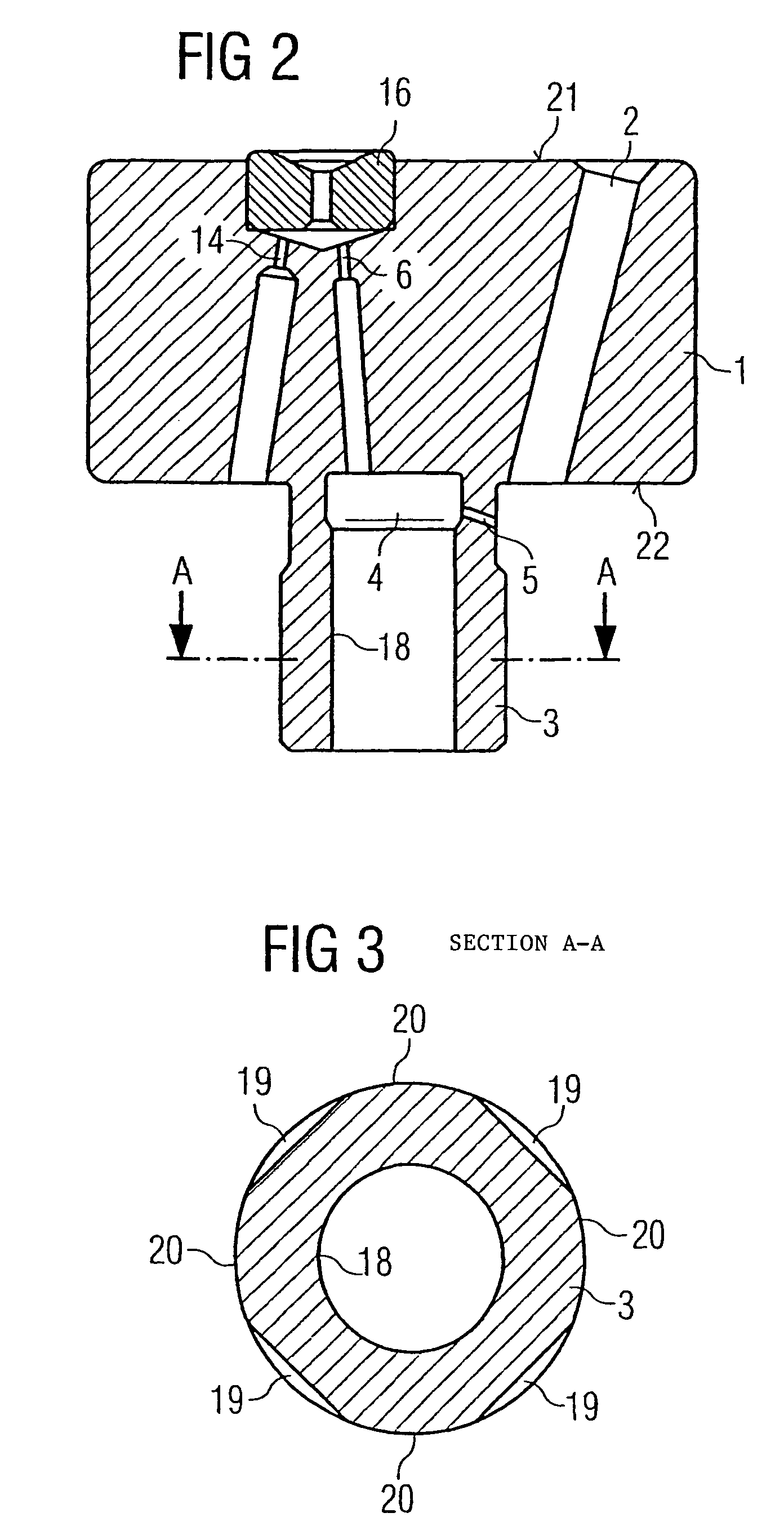
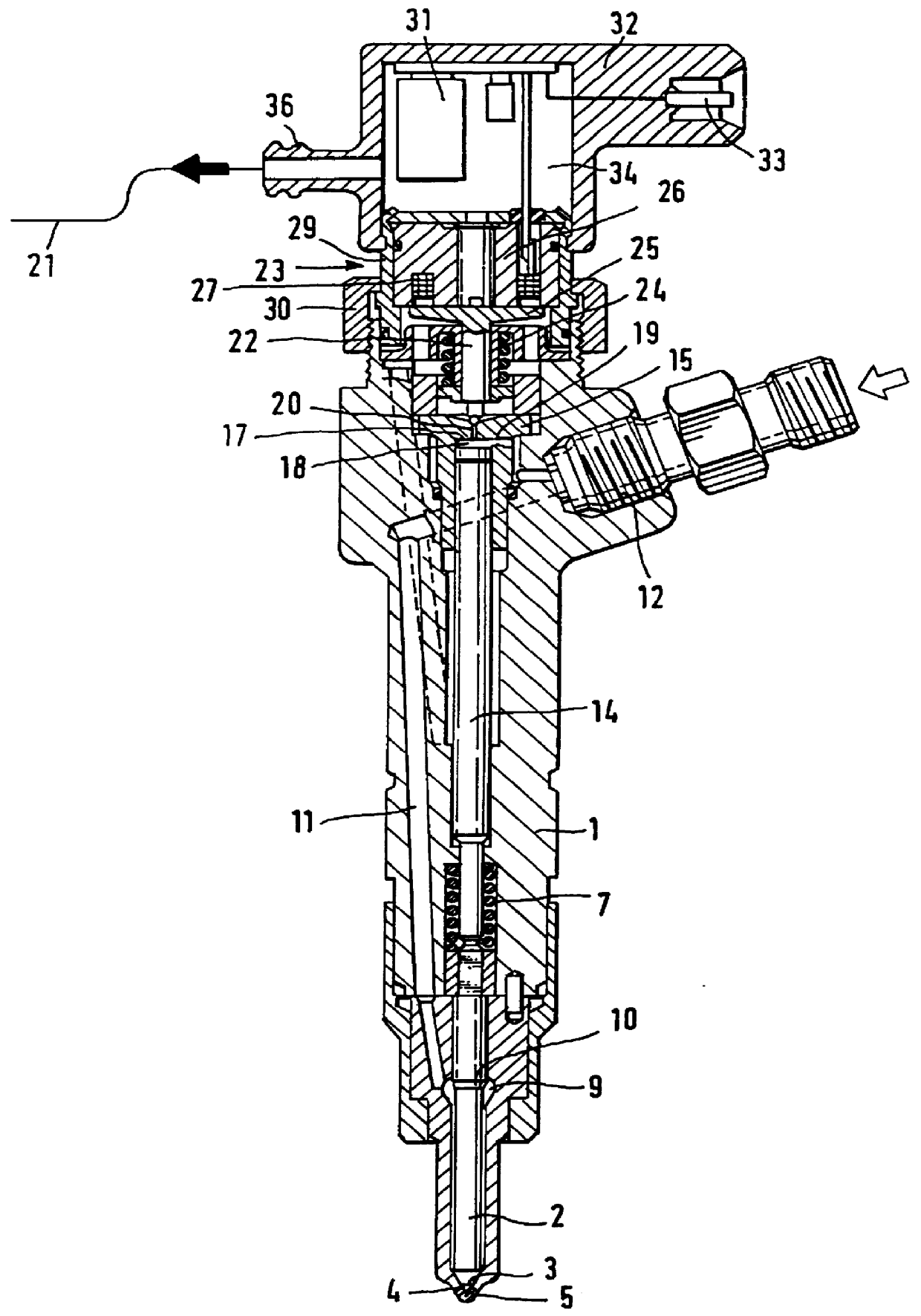
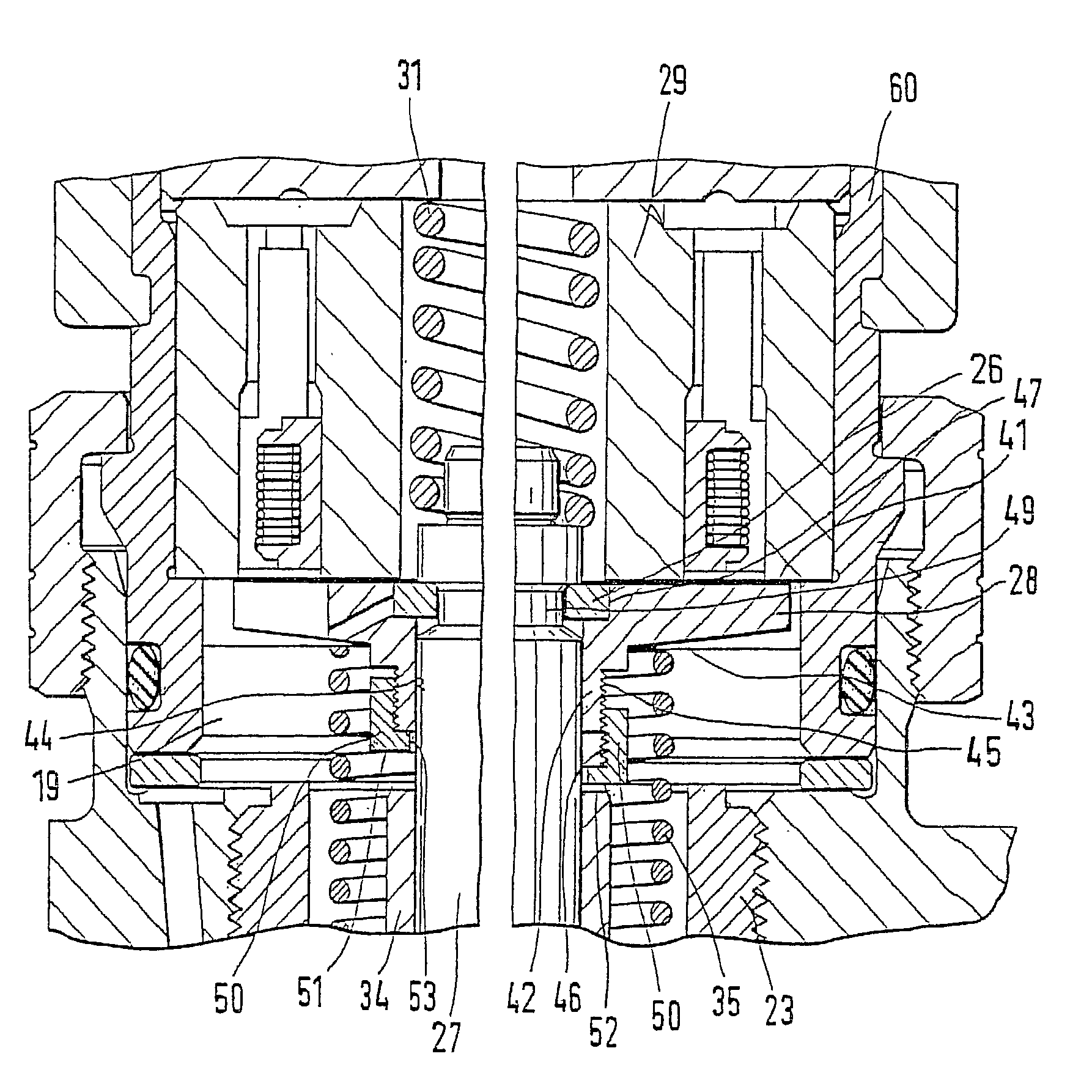
Patents
Literature
270results about "Fluid pressure injection control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
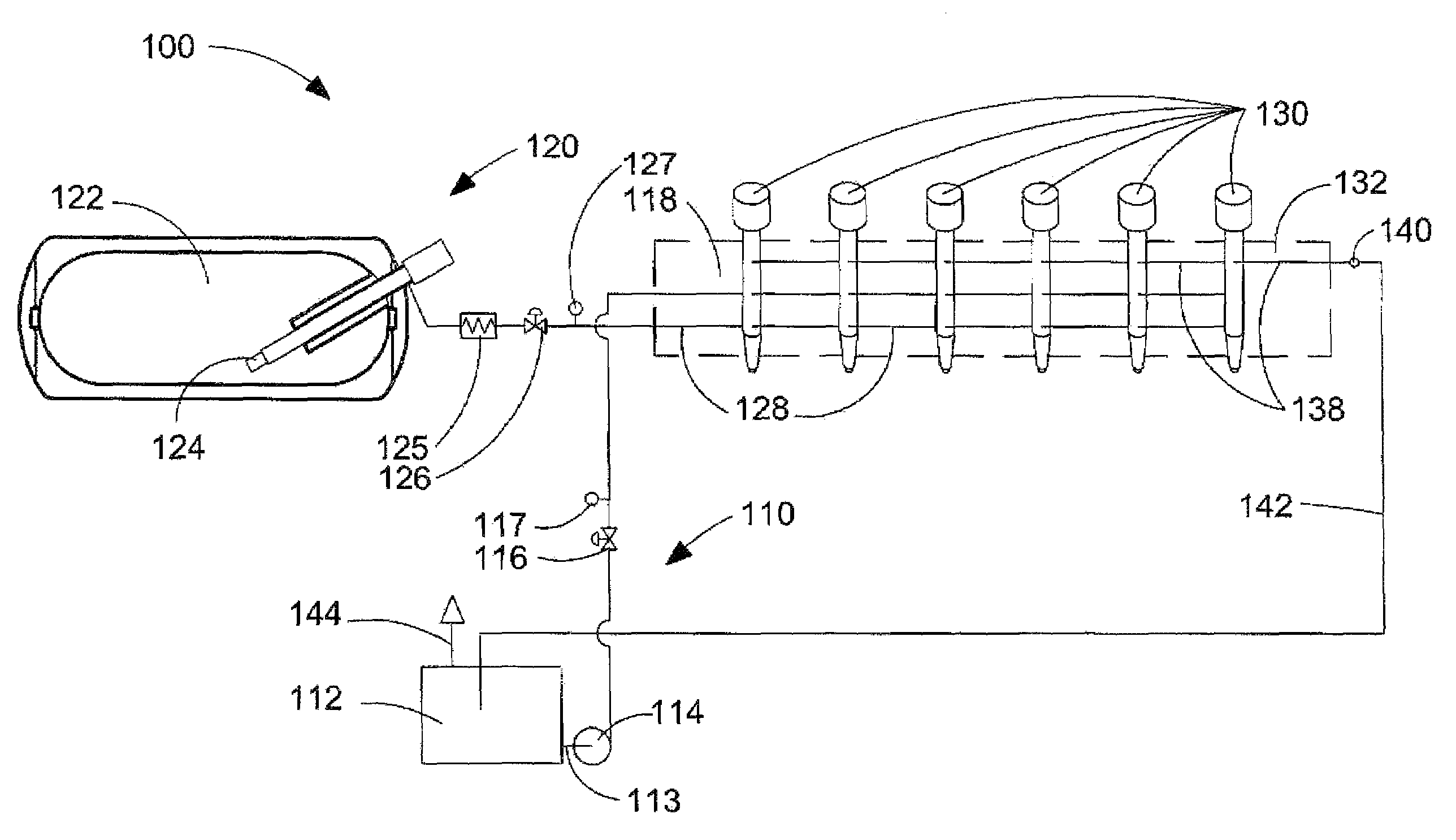
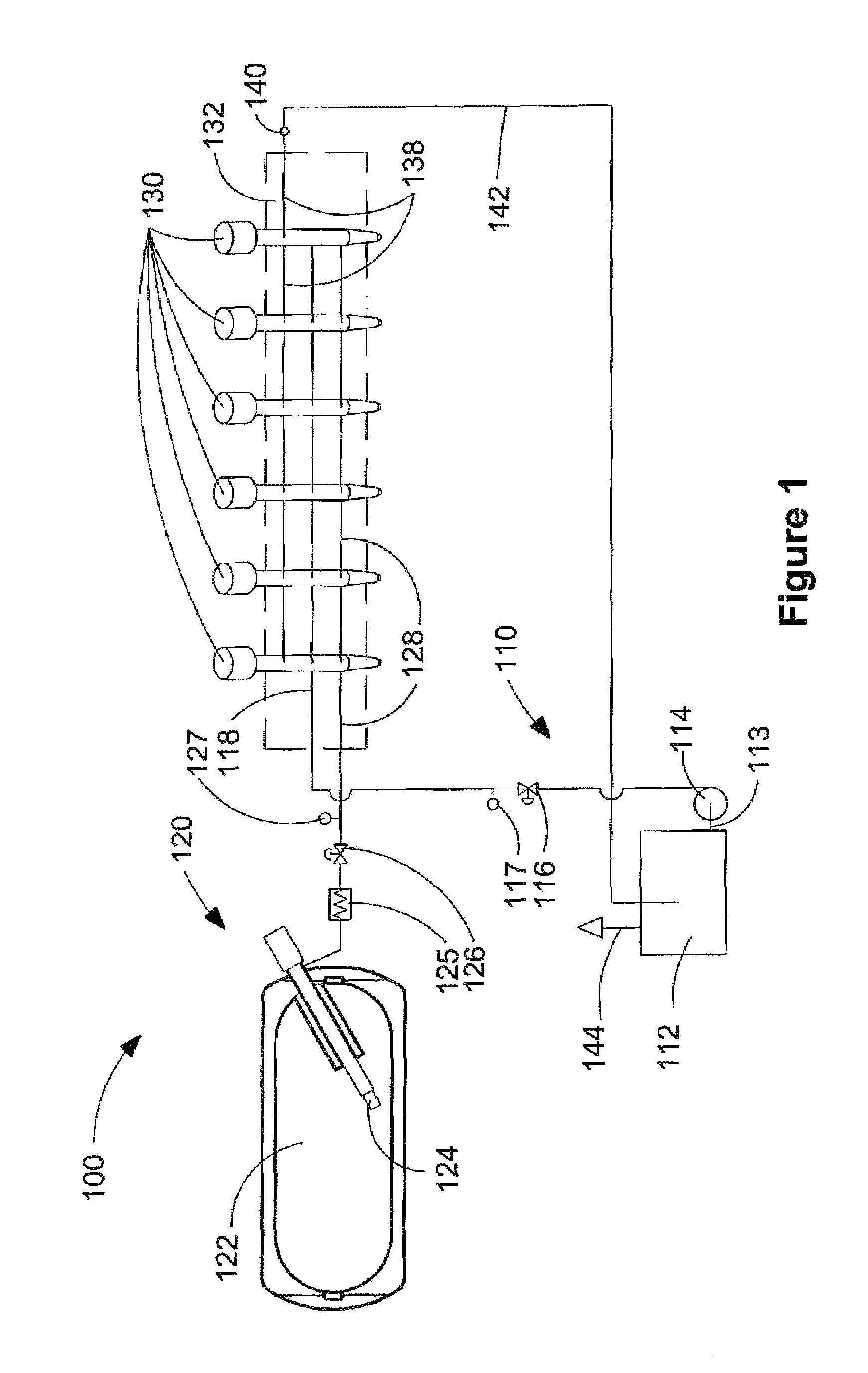
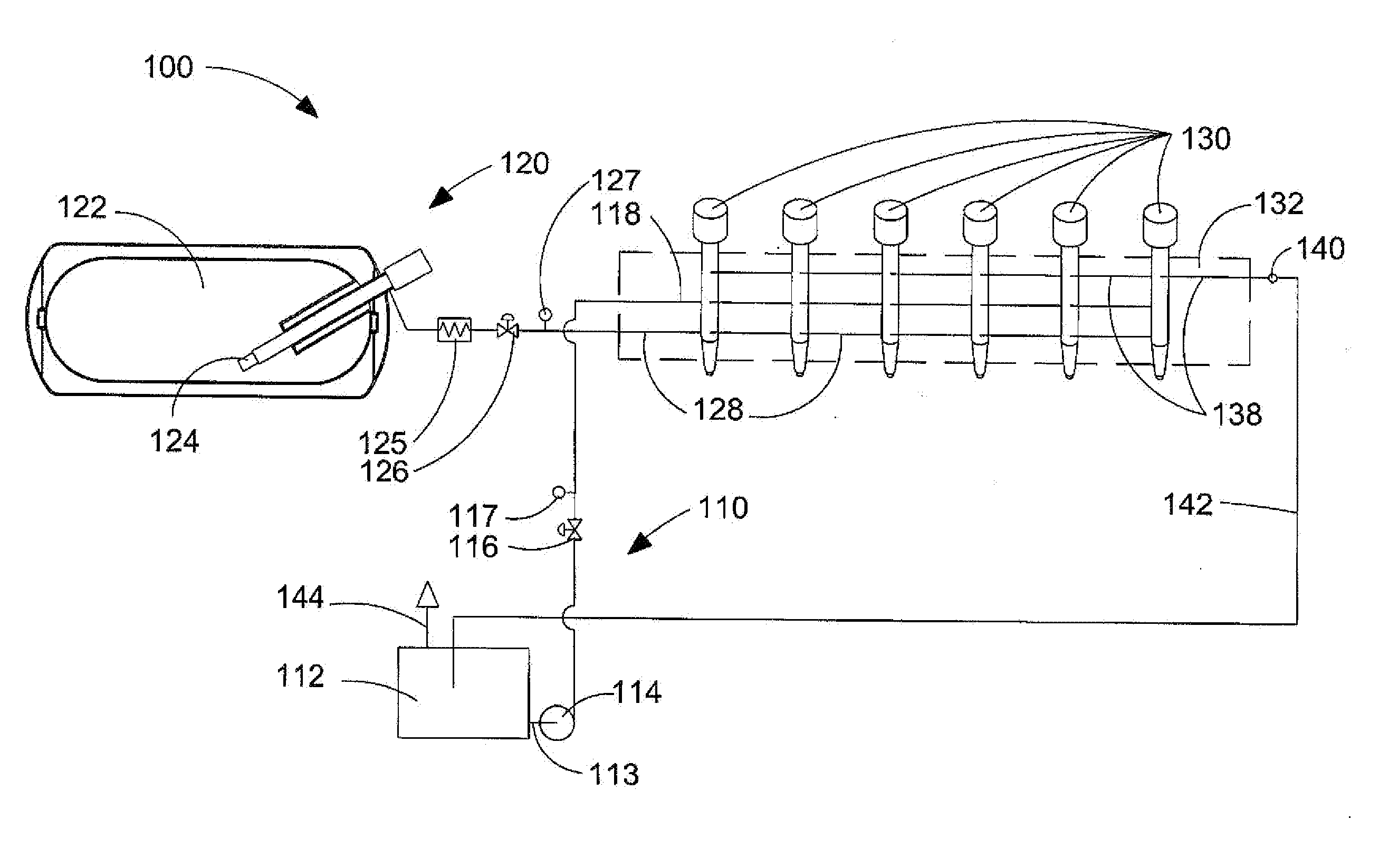
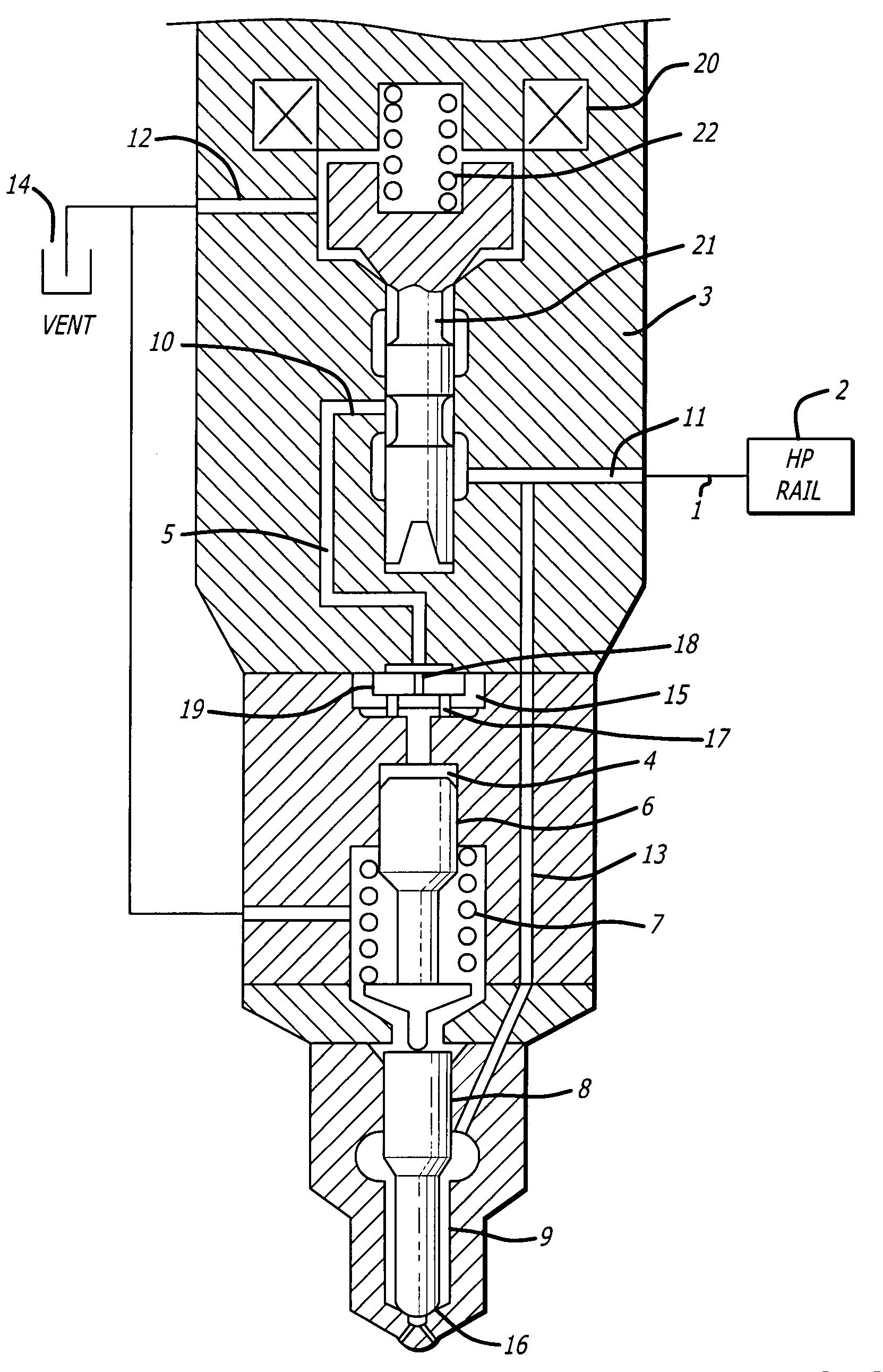
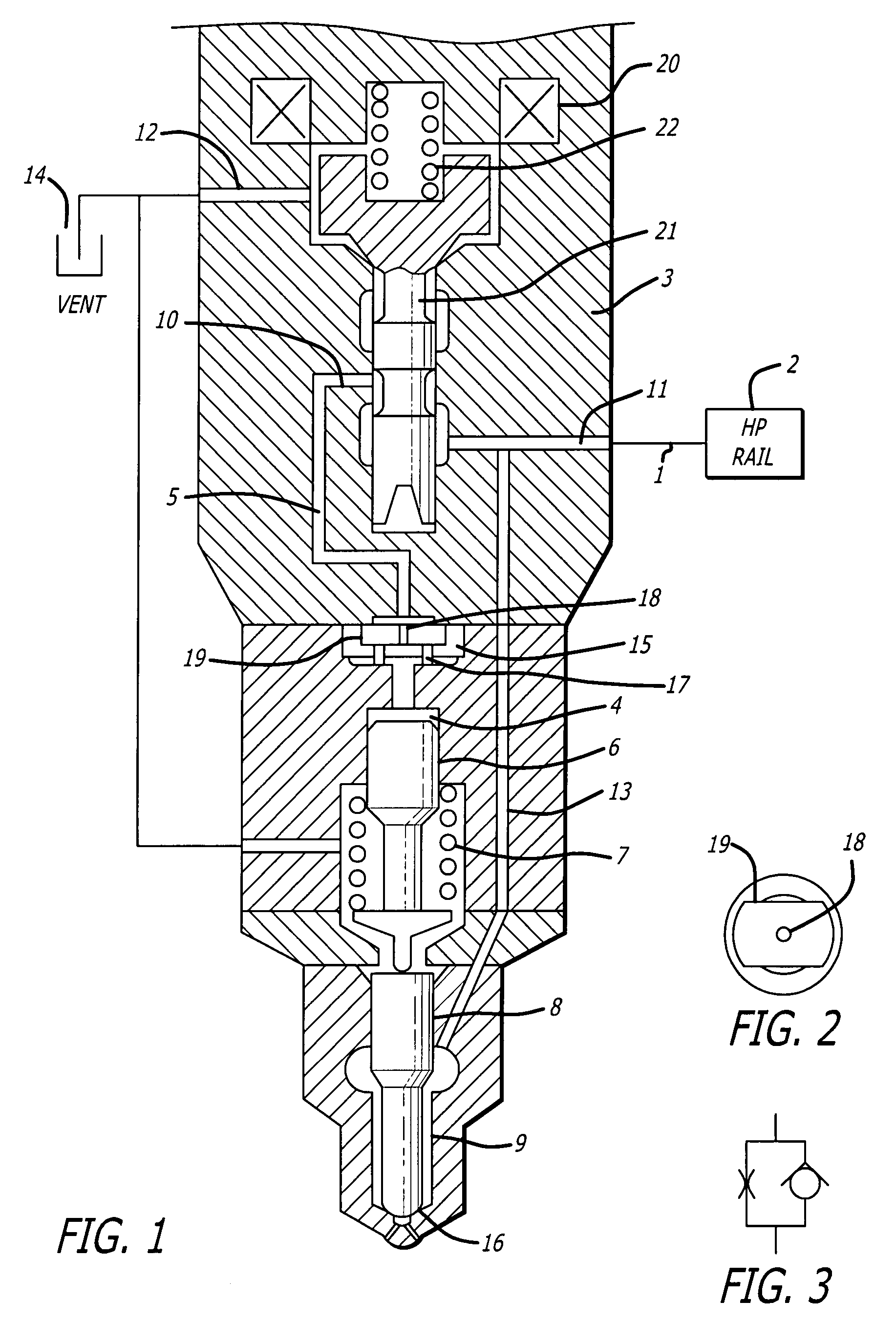
Method and apparatus for delivering two fuels to a direct injection internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7373931B2Increase energy densityReadily availableInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusInjection pressureCombustion chamber
An apparatus for delivering two fuels to a direct injection internal combustion engine comprises a liquid-fuel supply rail, a gaseous-fuel supply rail, a drain system with a shared drain rail for collecting both liquid fuel and gaseous fuel, and a venting device for venting gaseous fuel collected by the drain rail. The method comprises separately delivering a liquid fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a liquid-fuel rail, and actuating the liquid-fuel injection valve to introduce liquid fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises delivering a gaseous fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a gaseous-fuel rail and actuating the gaseous-fuel injection valve to introduce gaseous fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises collecting in a drain rail liquid fuel and gaseous fuel from the liquid-fuel injection valve and the gaseous-fuel injection valve, directing liquid fuel to a storage vessel, and directing gaseous fuel to a vent pipe.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
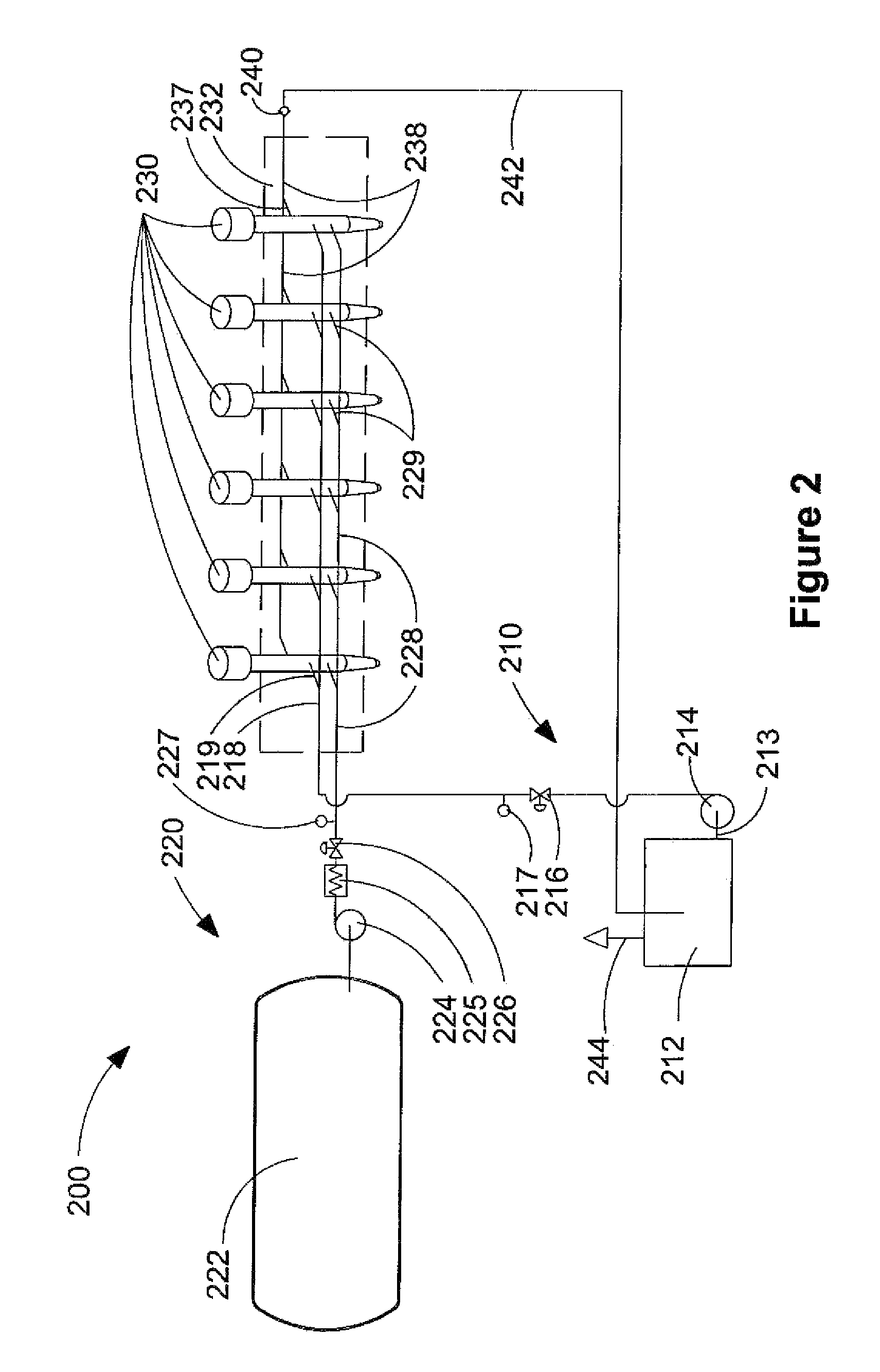
Method And Apparatus For Delivering Two Fuels To A Direct Injection Internal Combustion Engine
ActiveUS20070199539A1Saving operating costIncrease energy densityInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusCombustion chamberLiquid fuel
An apparatus for delivering two fuels to a direct injection internal combustion engine comprises a liquid-fuel supply rail, a gaseous-fuel supply rail, a drain system with a shared drain rail for collecting both liquid fuel and gaseous fuel, and a venting device for venting gaseous fuel collected by the drain rail. The method comprises separately delivering a liquid fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a liquid-fuel rail, and actuating the liquid-fuel injection valve to introduce liquid fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises delivering a gaseous fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a gaseous-fuel rail and actuating the gaseous-fuel injection valve to introduce gaseous fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises collecting in a drain rail liquid fuel and gaseous fuel from the liquid-fuel injection valve and the gaseous-fuel injection valve, directing liquid fuel to a storage vessel, and directing gaseous fuel to a vent pipe.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
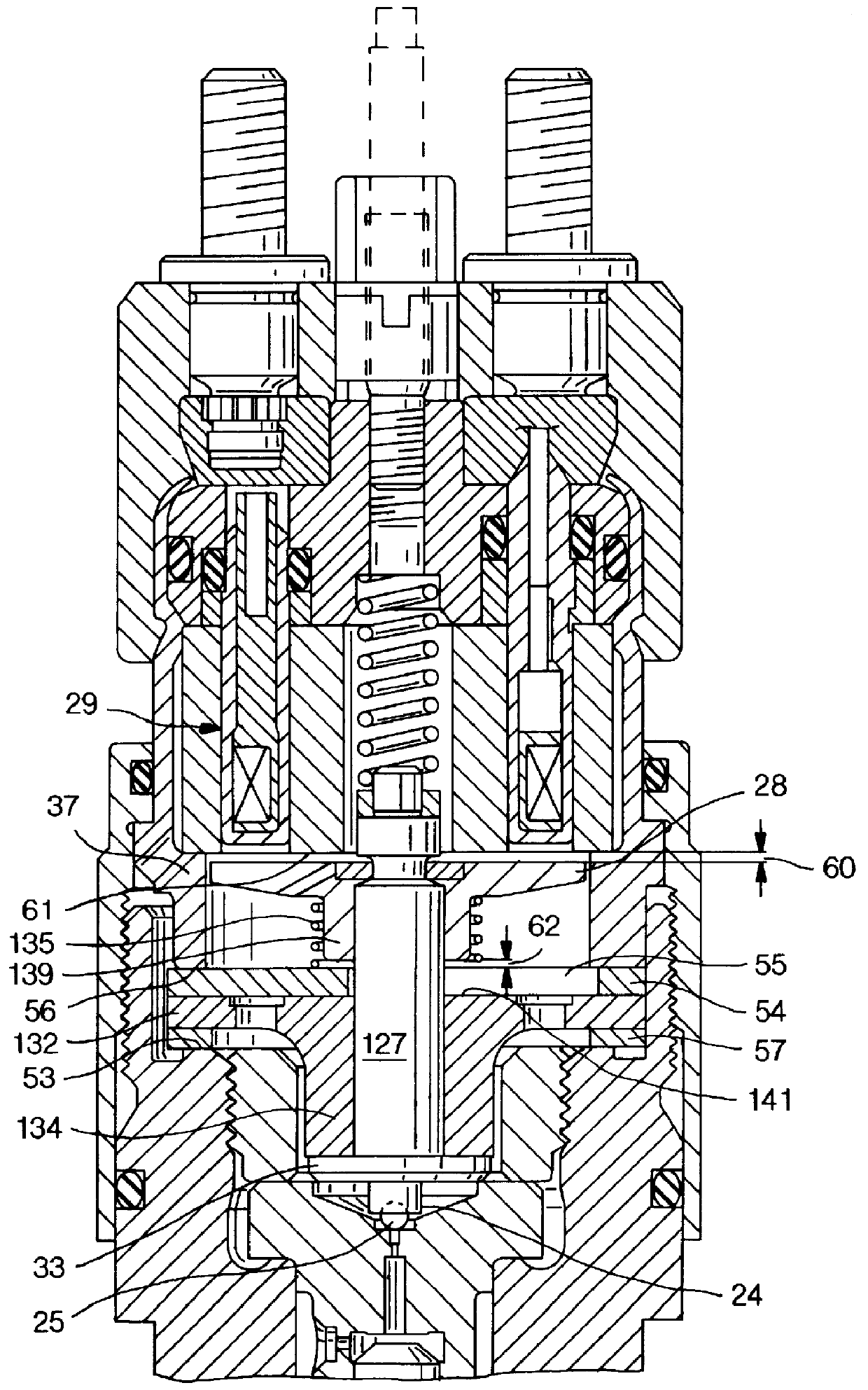
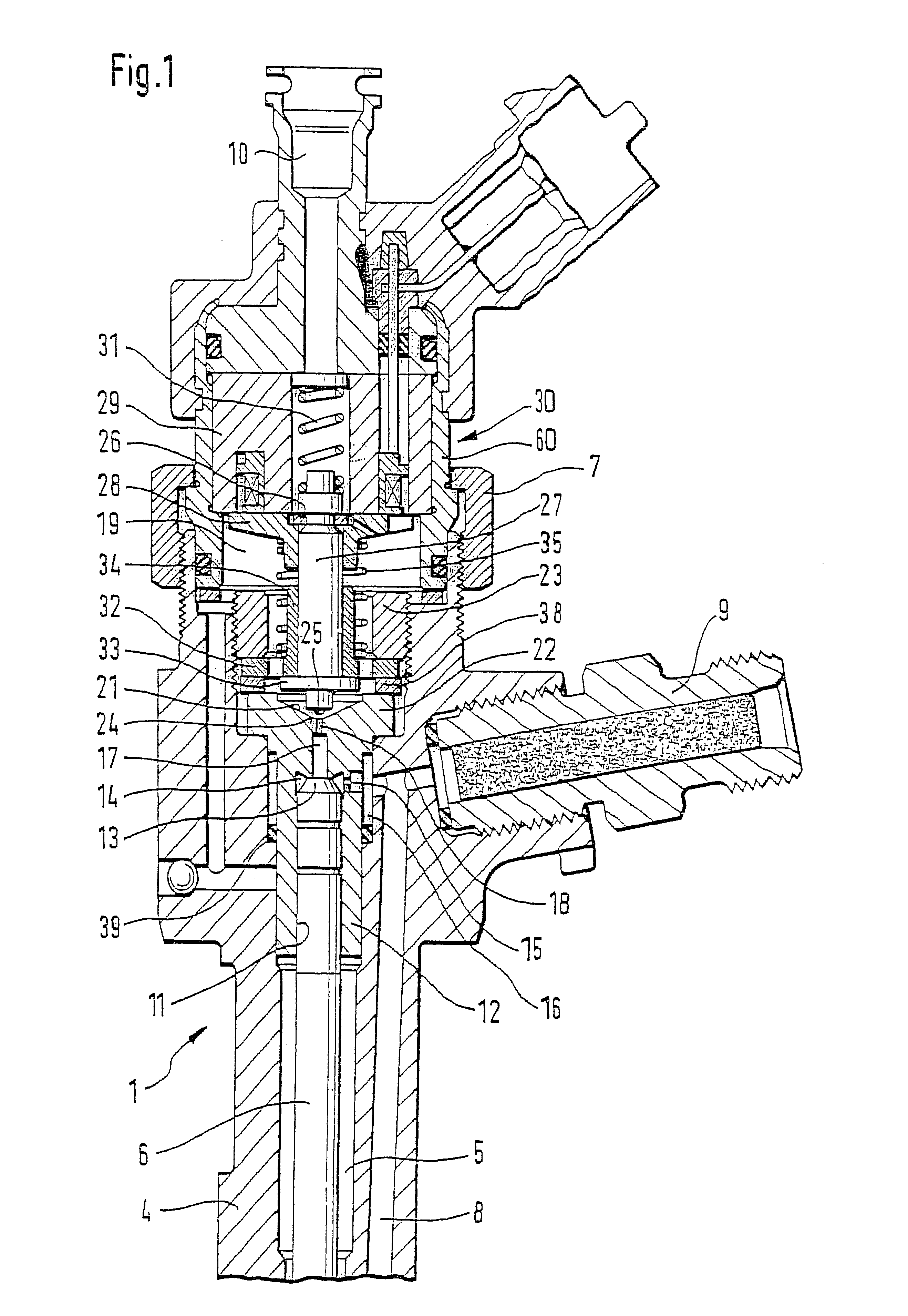
Solenoid valve for an electrically controlled valve
InactiveUS6161813APrevent reverberationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure injection controlCommon railSolenoid valve
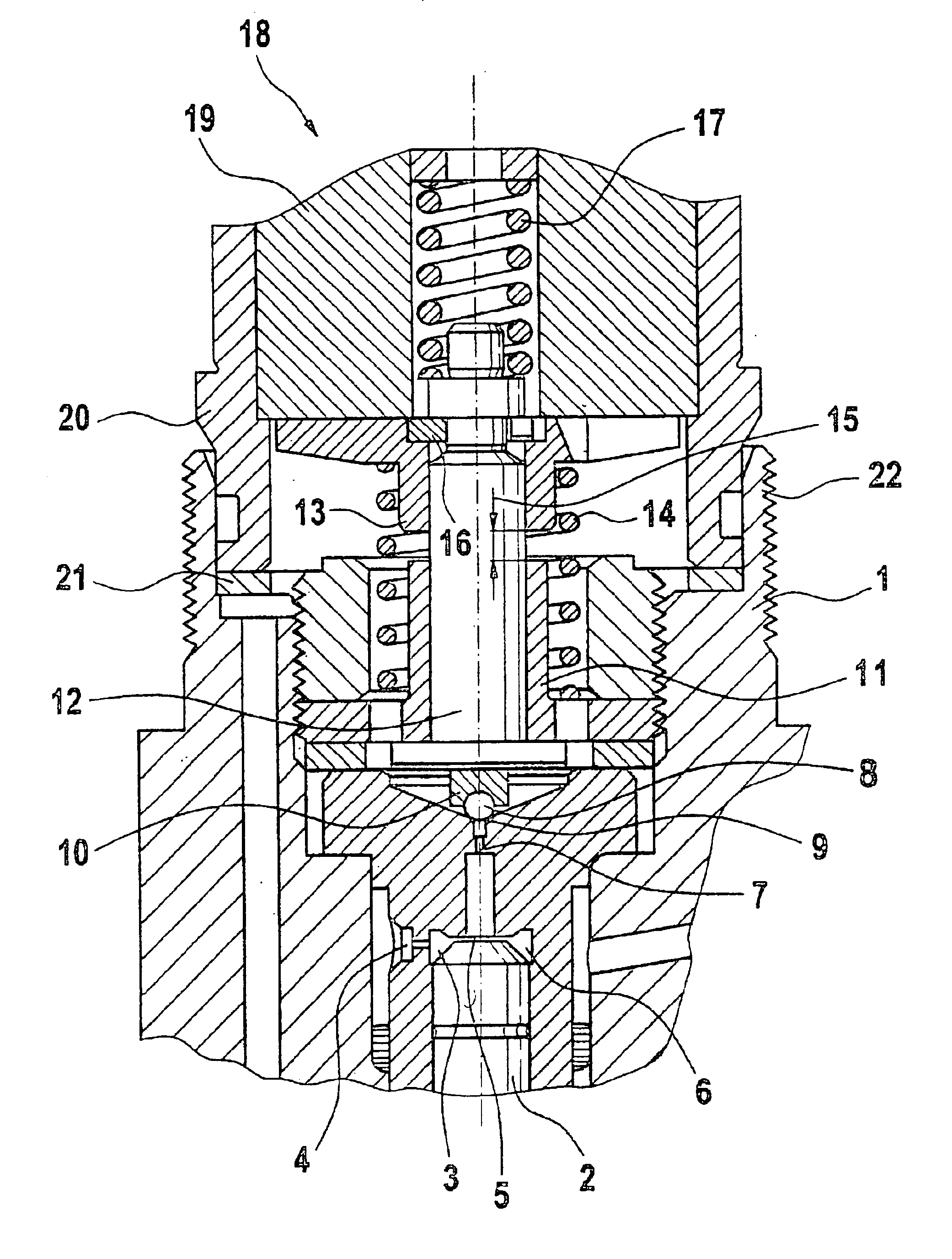
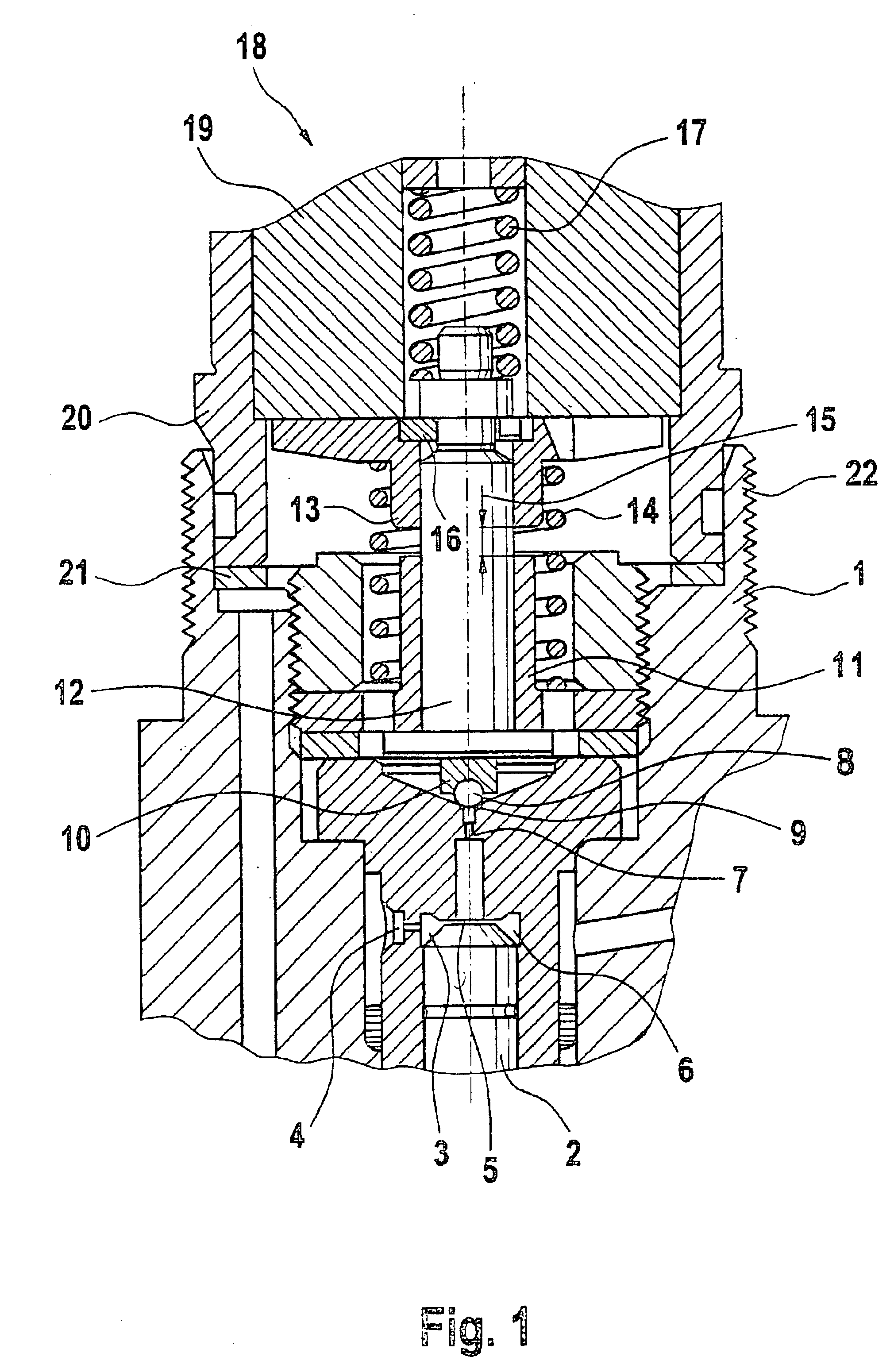
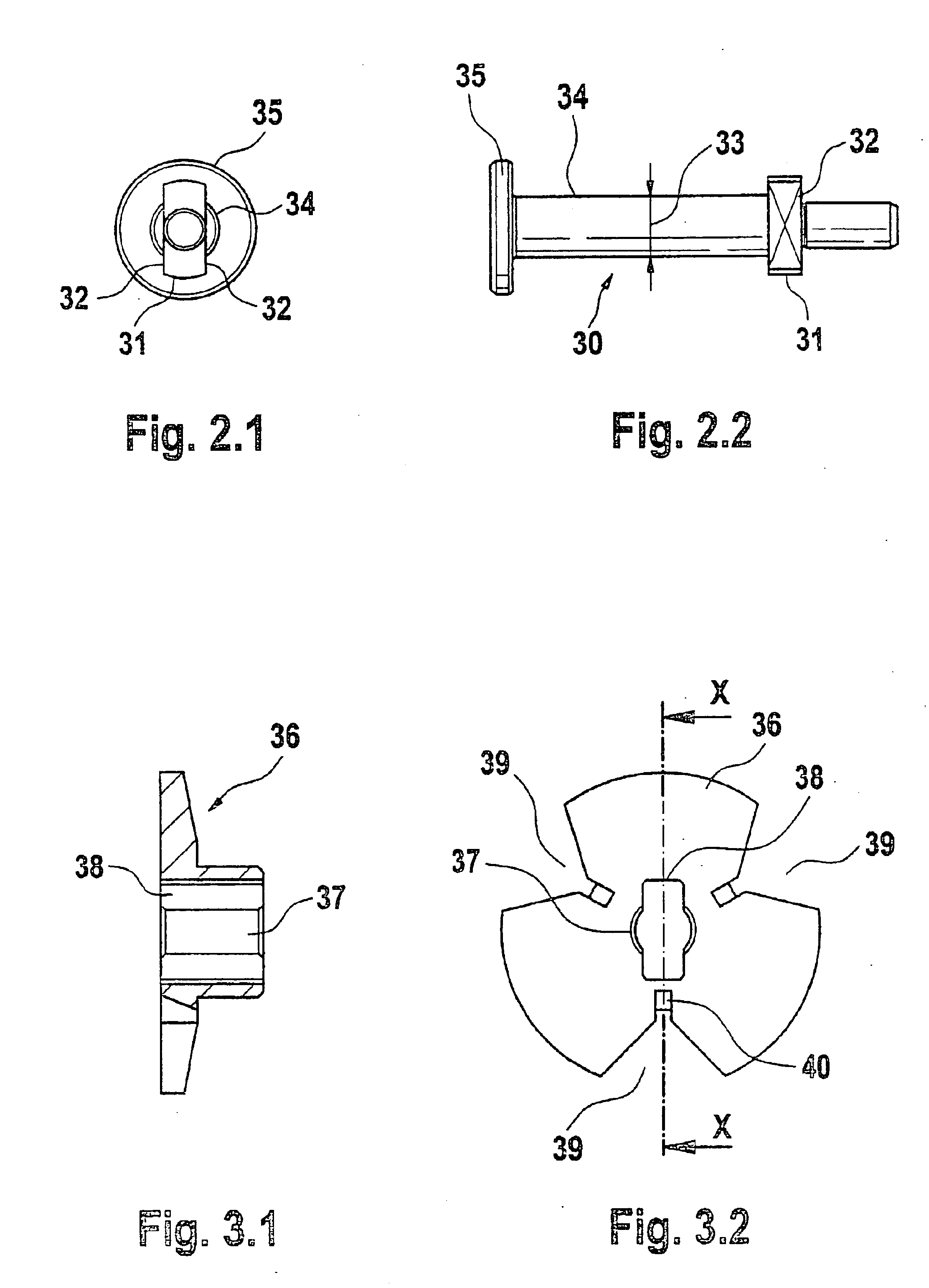
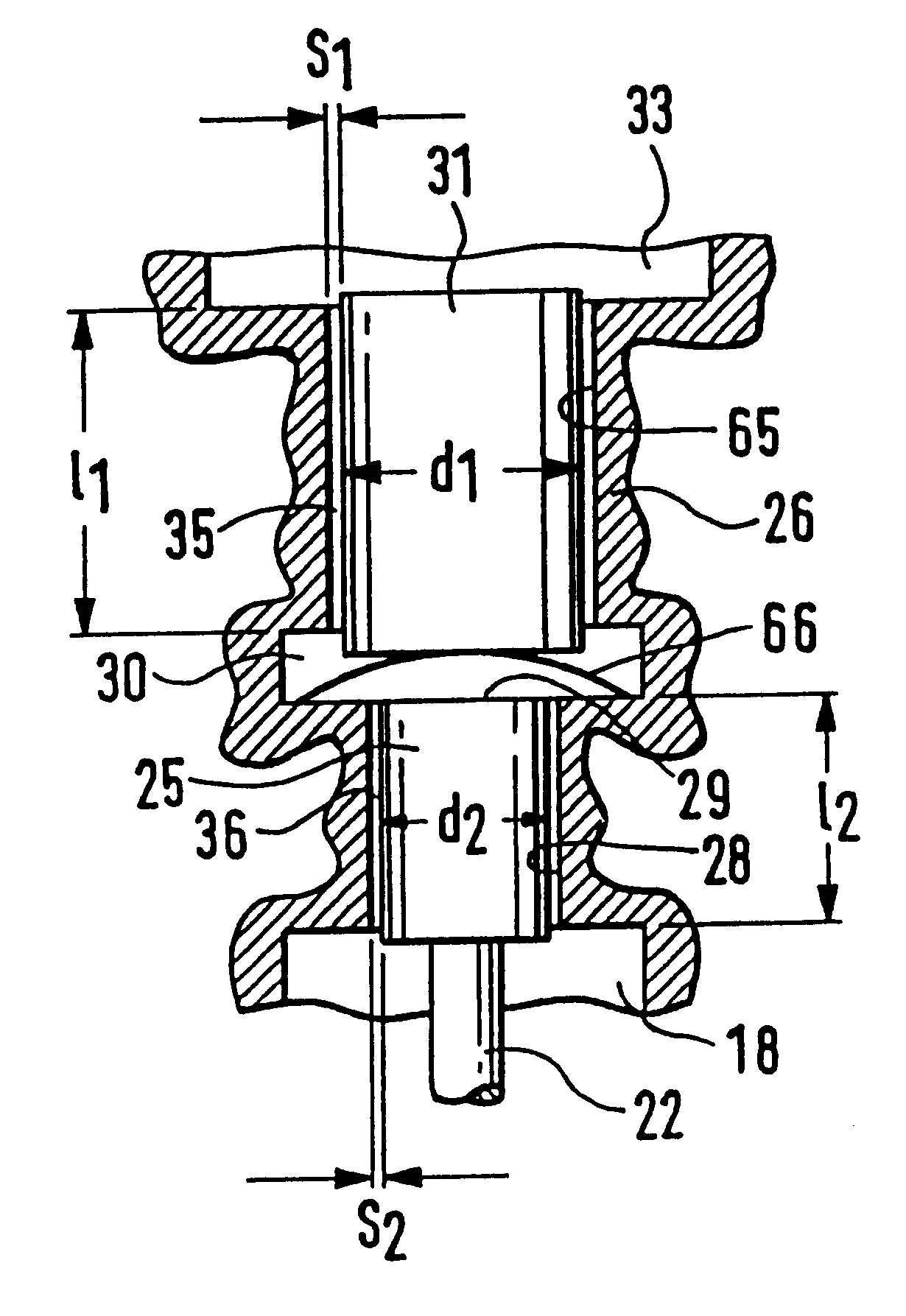
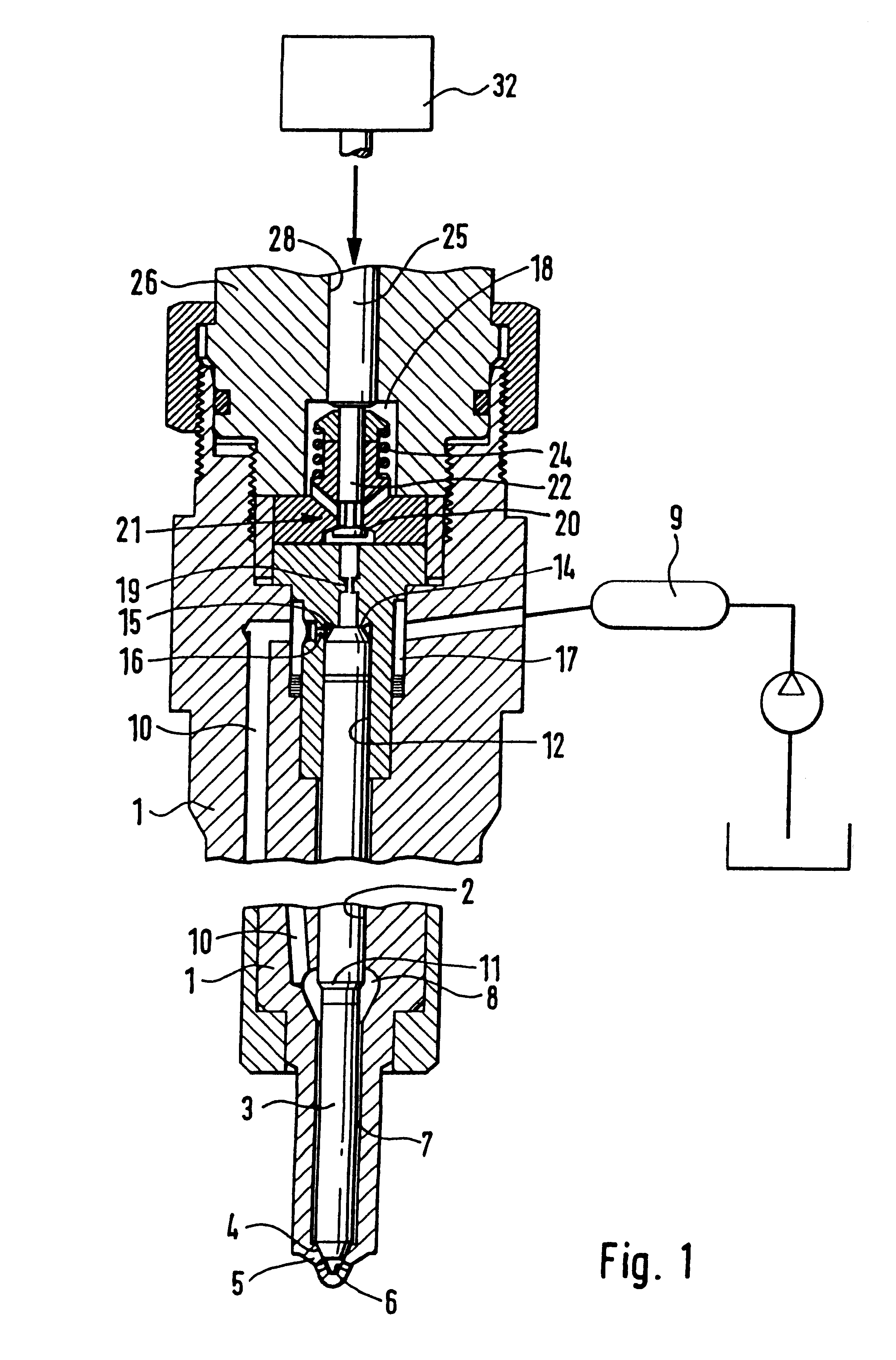
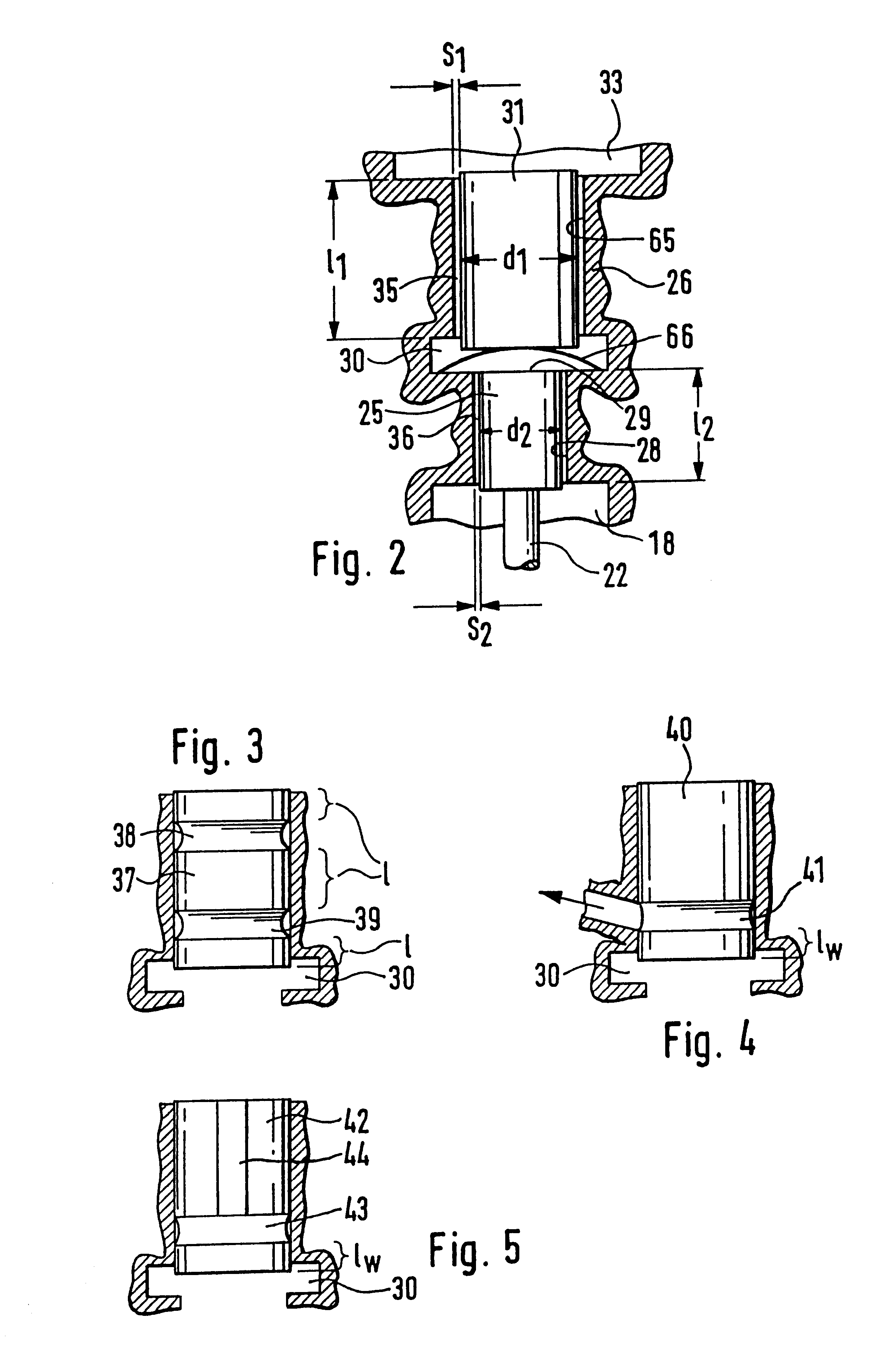
PCT No. PCT / DE97 / 02723 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 38426 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 3, 1998A solenoid valve comprising a magnet armature which is embodied as having multiple parts and has an armature disk and an armature bolt. The magnet armature is guided in a slider. A damping device is provided in order to prevent post-pulse oscillation of the armature after a closing of the solenoid valve. The required short switching times of the solenoid valve can be exactly maintained with a device of this kind. The solenoid valve is designated for use in injection systems with a common rail.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Solenoid valve for controlling a fuel injector of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6688579B2Easy to assembleAvoid disadvantagesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure injection controlInertial massSolenoid valve
A solenoid valve for controlling a fuel injector of an internal combustion engine having an electromagnet, a movable armature having an armature plate and an armature pin, and a control valve element which is moved with the armature and works together with a valve seat, for opening and closing a fuel drain channel of a control pressure chamber of the fuel injector, is provided. The armature plate is mounted on the armature pin so that it is movable by sliding under the effect of its inertial mass in the closing direction of the control valve element against the tension of a return spring acting on the armature plate. In order to be able to easily set the maximum slide path of the armature plate, an actuator is provided on the armature plate which is arranged on a section of the armature plate facing away from the electromagnet and is adjustable in the sliding direction of the armature plate relative to a face of the armature plate facing the electromagnet.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Solenoid valve comprising a plug-in/rotative connection
InactiveUS6874706B2Good guidance precisionEasy to adjustOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpray nozzlesCombustion chamberSolenoid valve
A solenoid valve for a fuel injector for injecting fuel into the combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine having an injector body which includes an electromagnet. An armature group of the solenoid valve may be actuated by this electromagnet to relieve the pressure in a control chamber, so that a nozzle needle / tappet assembly in the injector body implements an opening / closing movement. The armature group includes a first and a second armature part. The first armature part and the second armature part are joined to one another by an insert-and-twist connection, one of the armature parts being enclosed by an armature guide which includes anti-rotation elements.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Piezoelectrically actuated fuel injection valve
InactiveUS6168133B1Simple designReliable functionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure injection controlCombustionWork cycle
A valve for controlling liquids which for its actuation is provided with a liquid-filled coupling chamber, which is disposed between an actuator piston of a piezoelectric actuator and a piston that actuates a valve member. To compensate for liquid losses suffered by the coupling chamber, which is briefly at high in each work cycle, the pressure difference that exists during the return stroke of the actuator piston between the coupling chamber and the opposite sides of the actuator piston and of the that actuates the valve member that are remote from the coupling chamber is utilized to achieve refilling in valveless fashion along gaps. The valve is used for use in fuel injection systems for internal combustion engines of motor vehicles.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel injection device
ActiveUS20120152206A1Accurate settingInstabilityLow pressure fuel injectionFluid pressure injection controlEngineeringFuel injection
A fuel injection device includes a cylinder defining a pressure chamber at an end portion of a nozzle needle. In the cylinder, a floating plate is provided as a controlling member of fuel pressure. An orifice member and a nozzle body are lined by an annular positioning member, using a circular peripheral surface of the orifice member and a circular peripheral surface of the nozzle body as a reference surface. Thereby, radial locations of the nozzle body and the orifice member are defined. Furthermore, a location of the floating plate is defined by the nozzle body with the nozzle needle. Therefore, the floating plate can be located to a proper location relative to the orifice member.
Owner:DENSO CORP
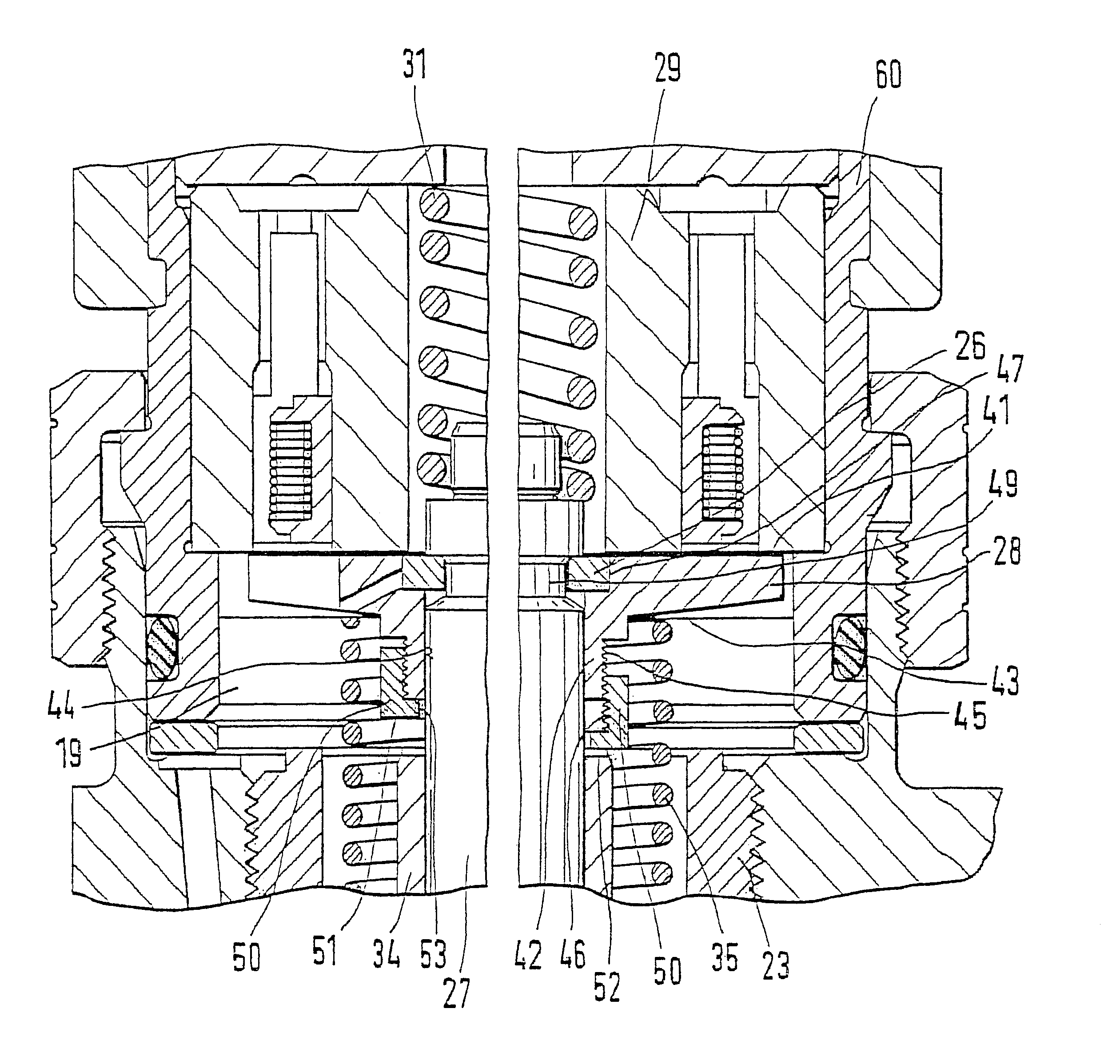
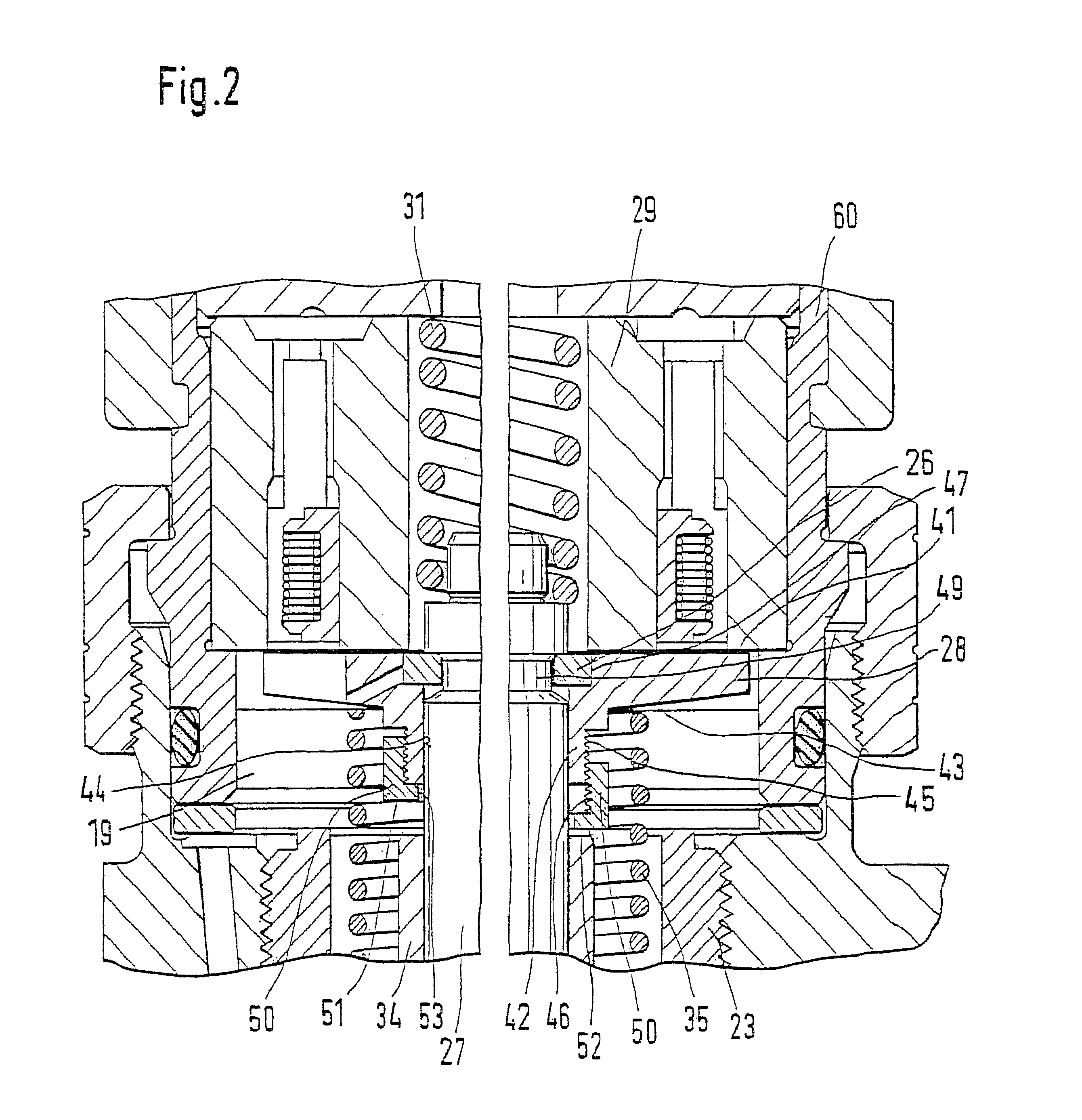
Electromagnetic valve for controlling an injection valve of an internal combustion engine
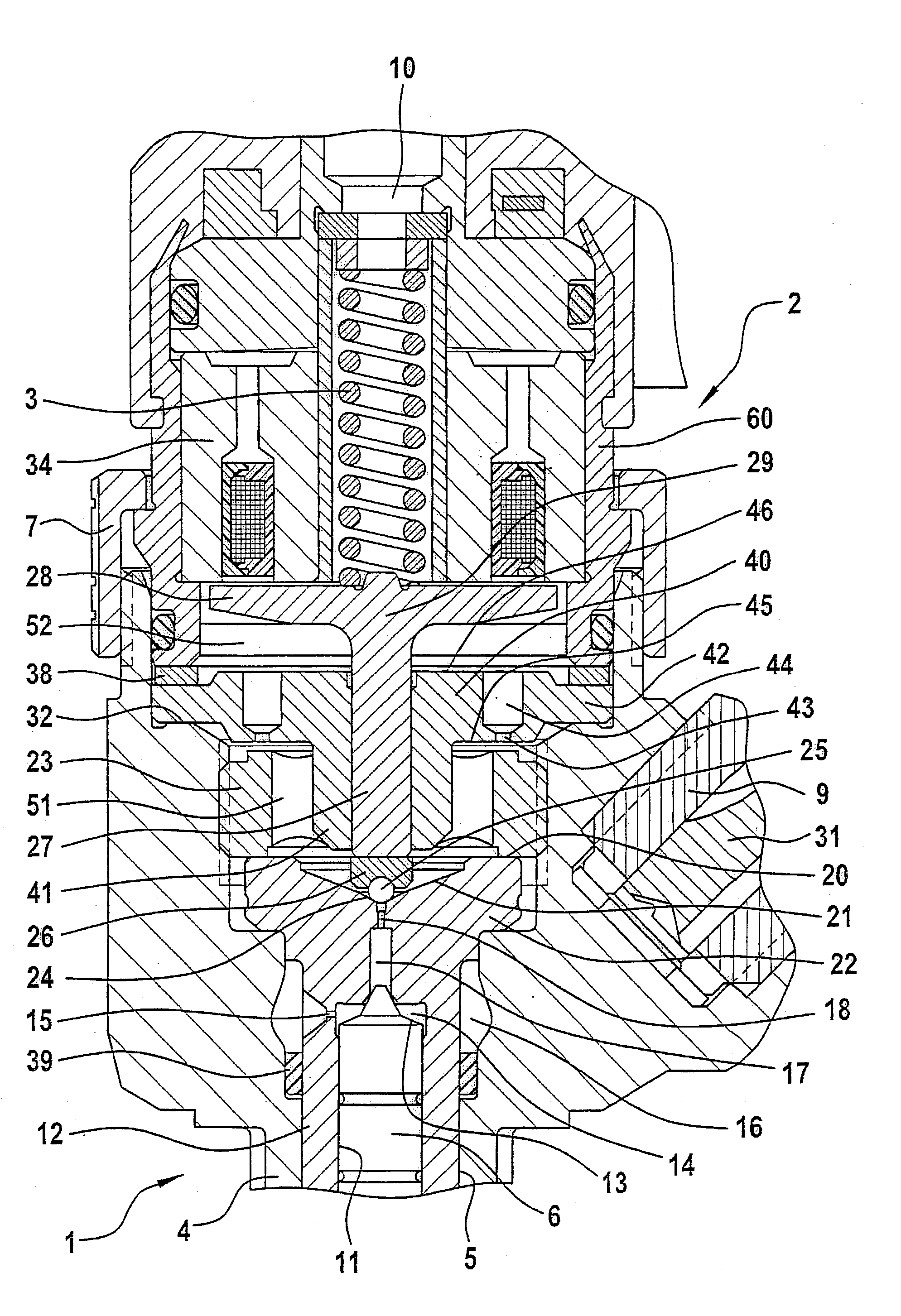
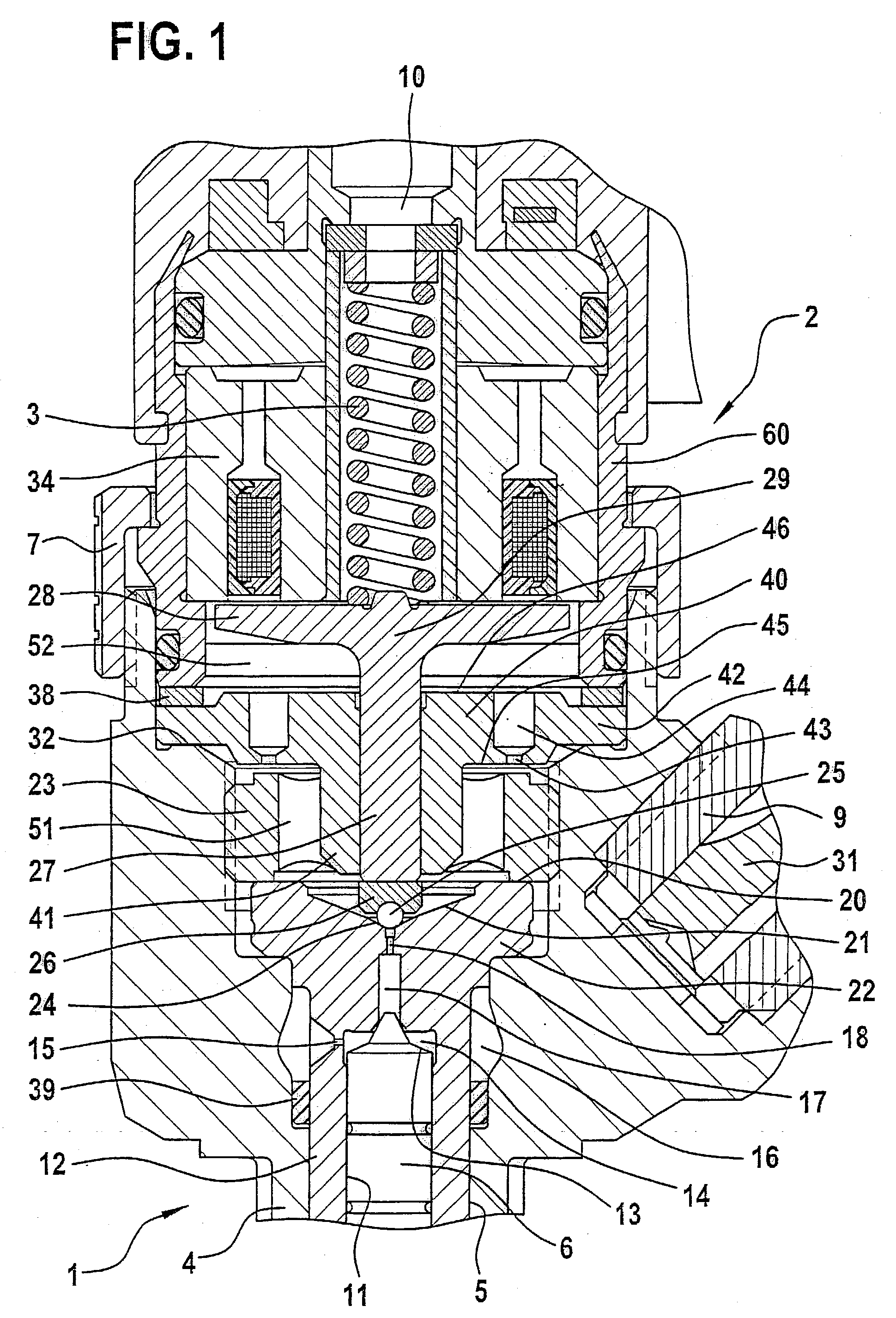
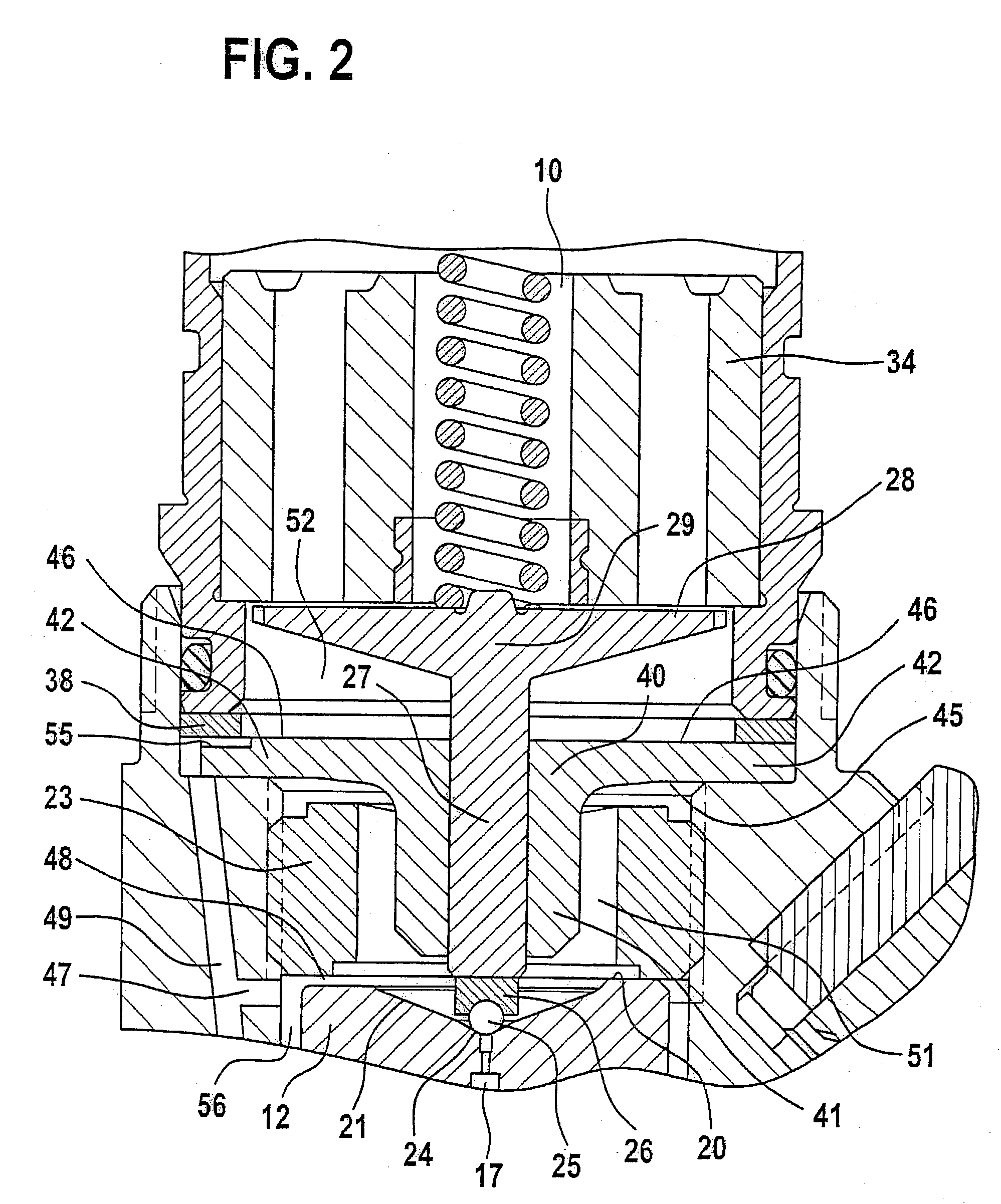
InactiveUS20030127614A1Quantitative deviationReduce biasOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure injection controlExternal combustion engineSolenoid valve
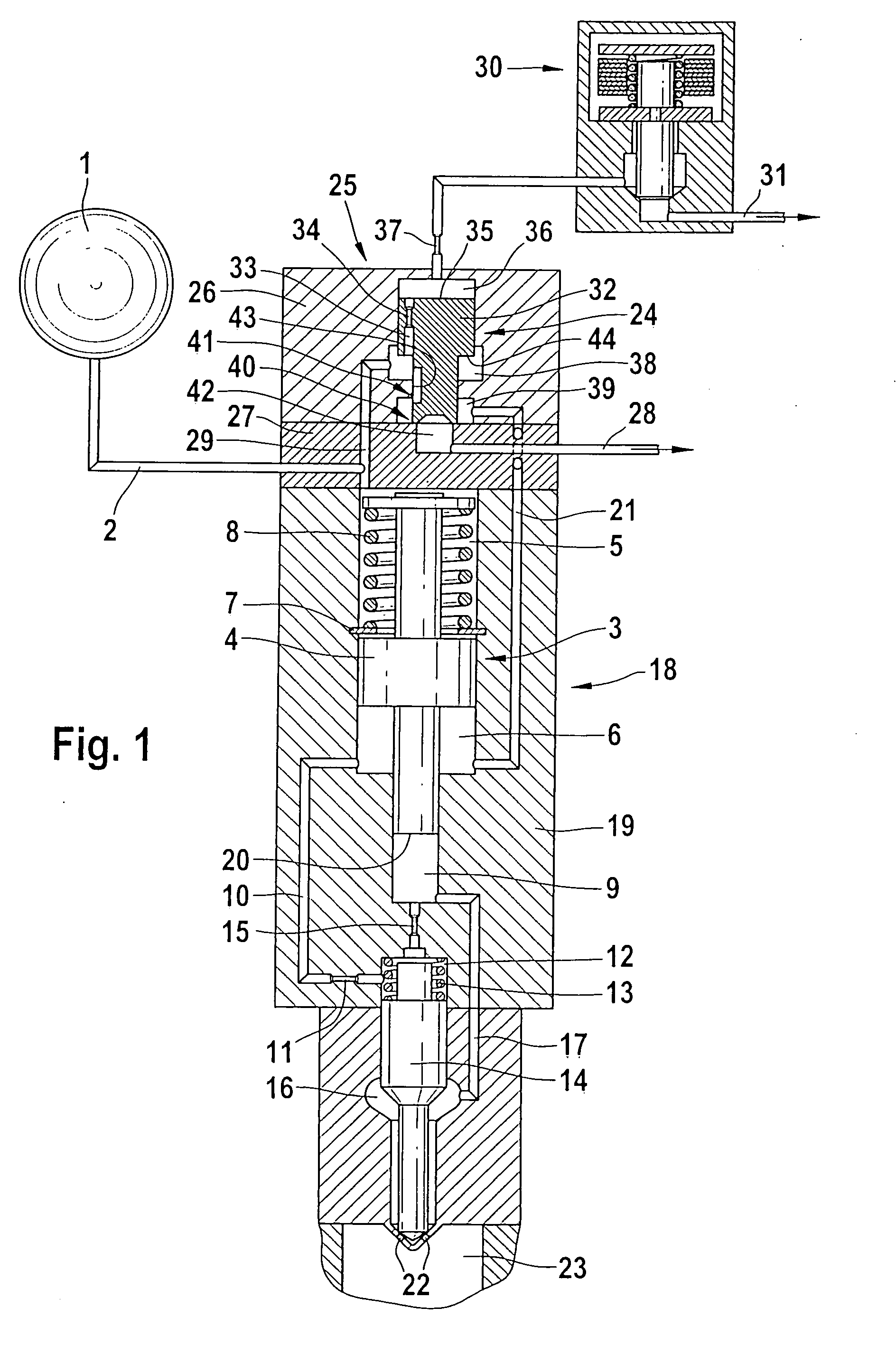
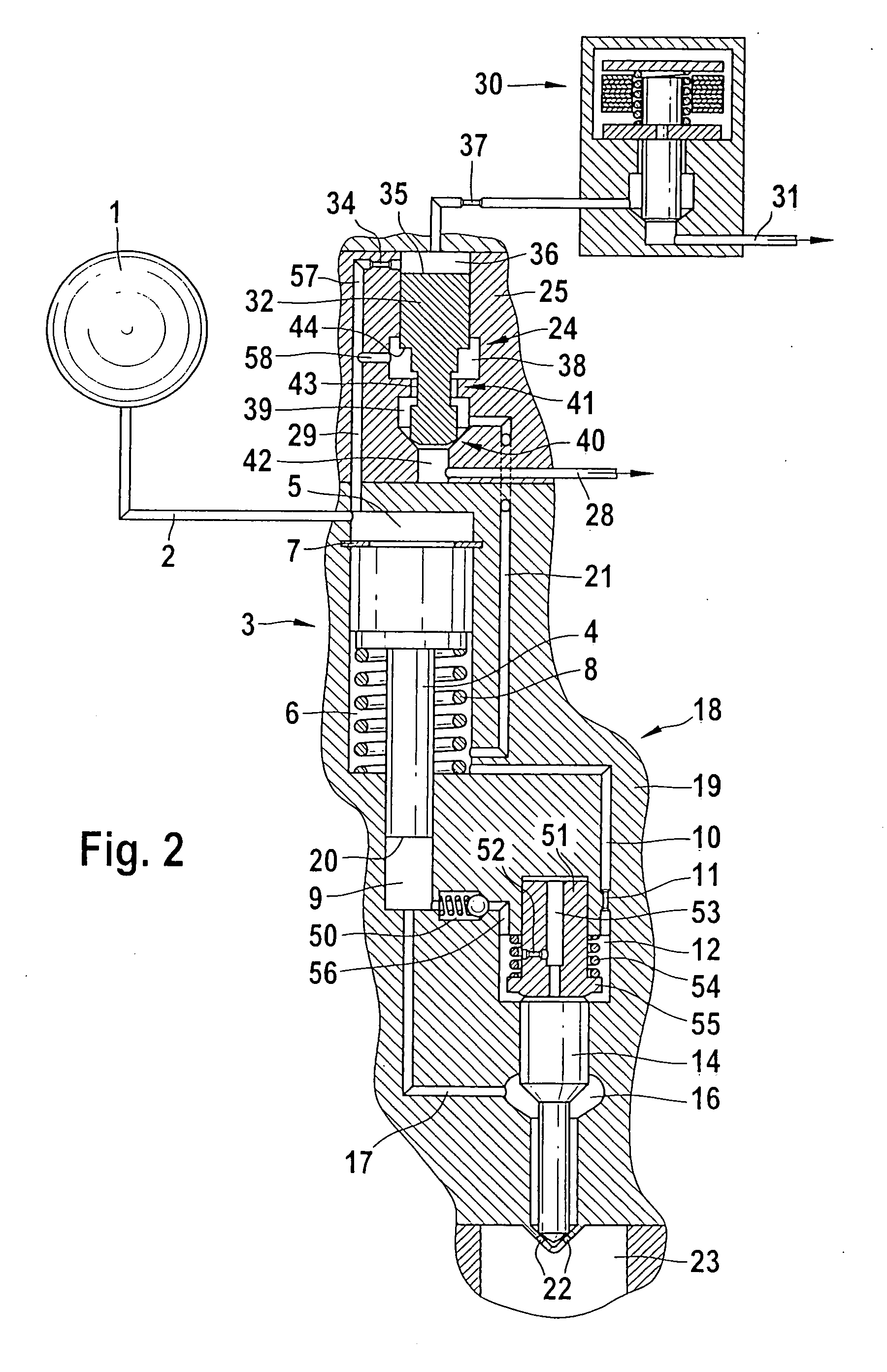
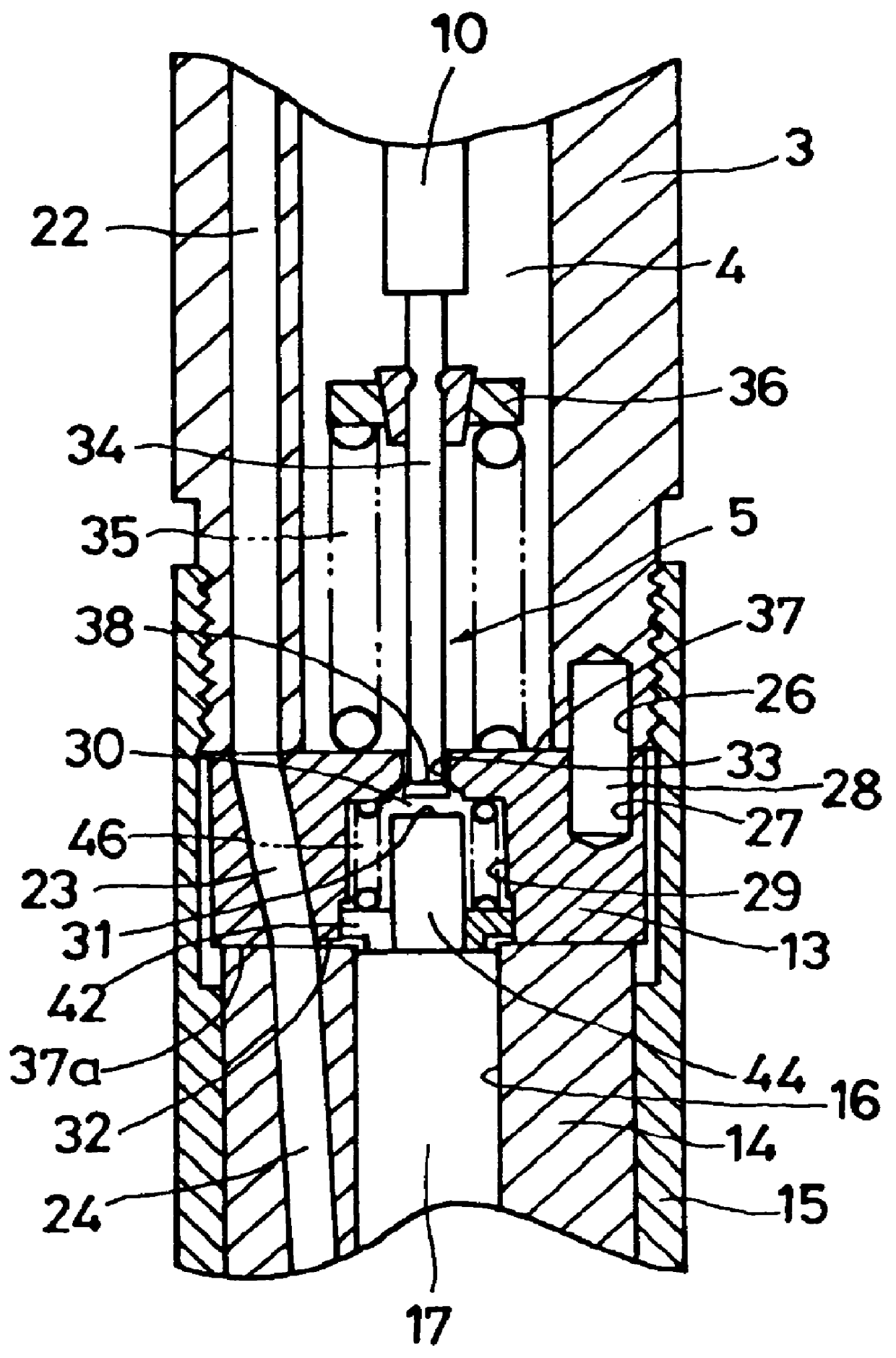
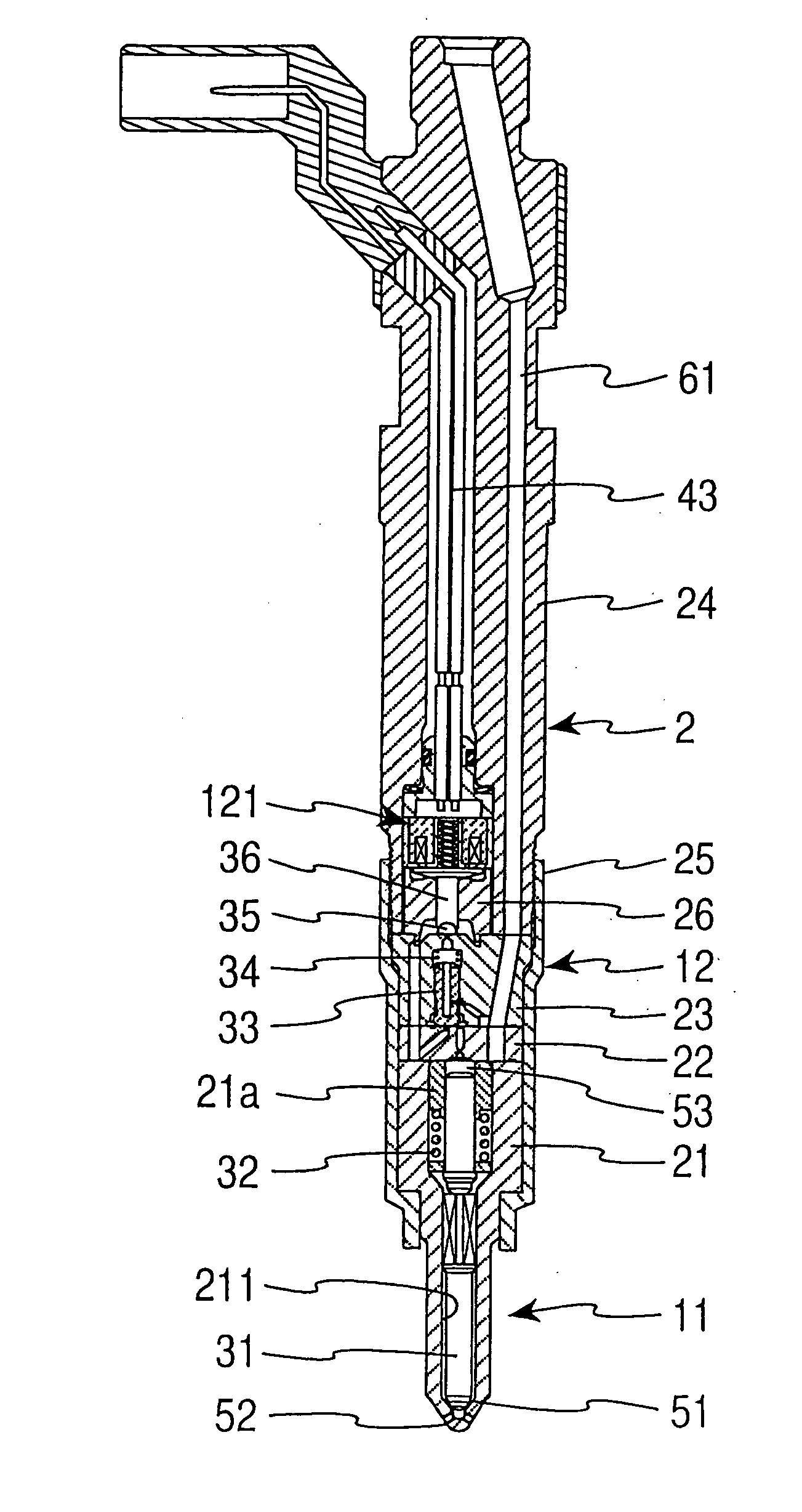
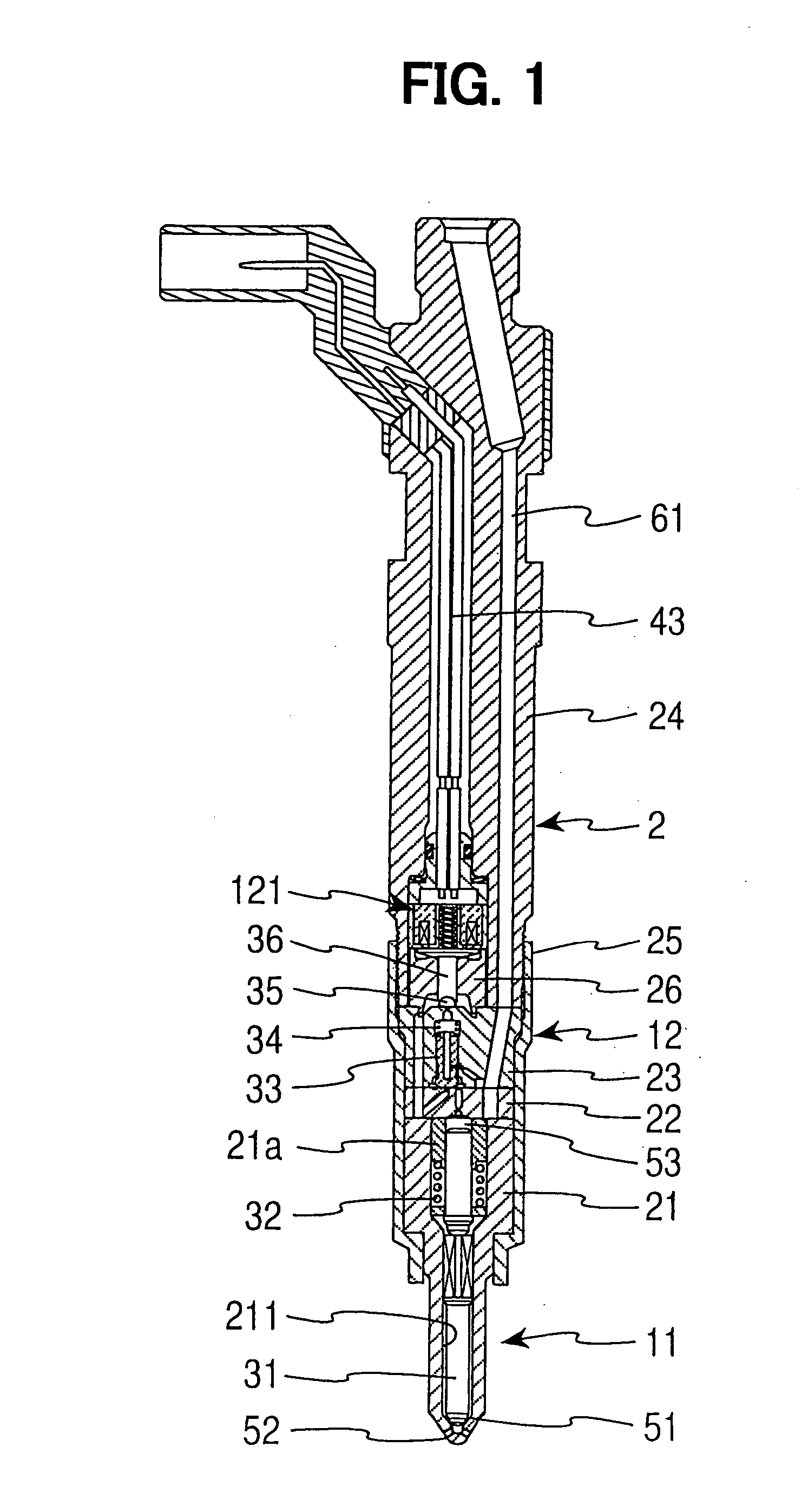
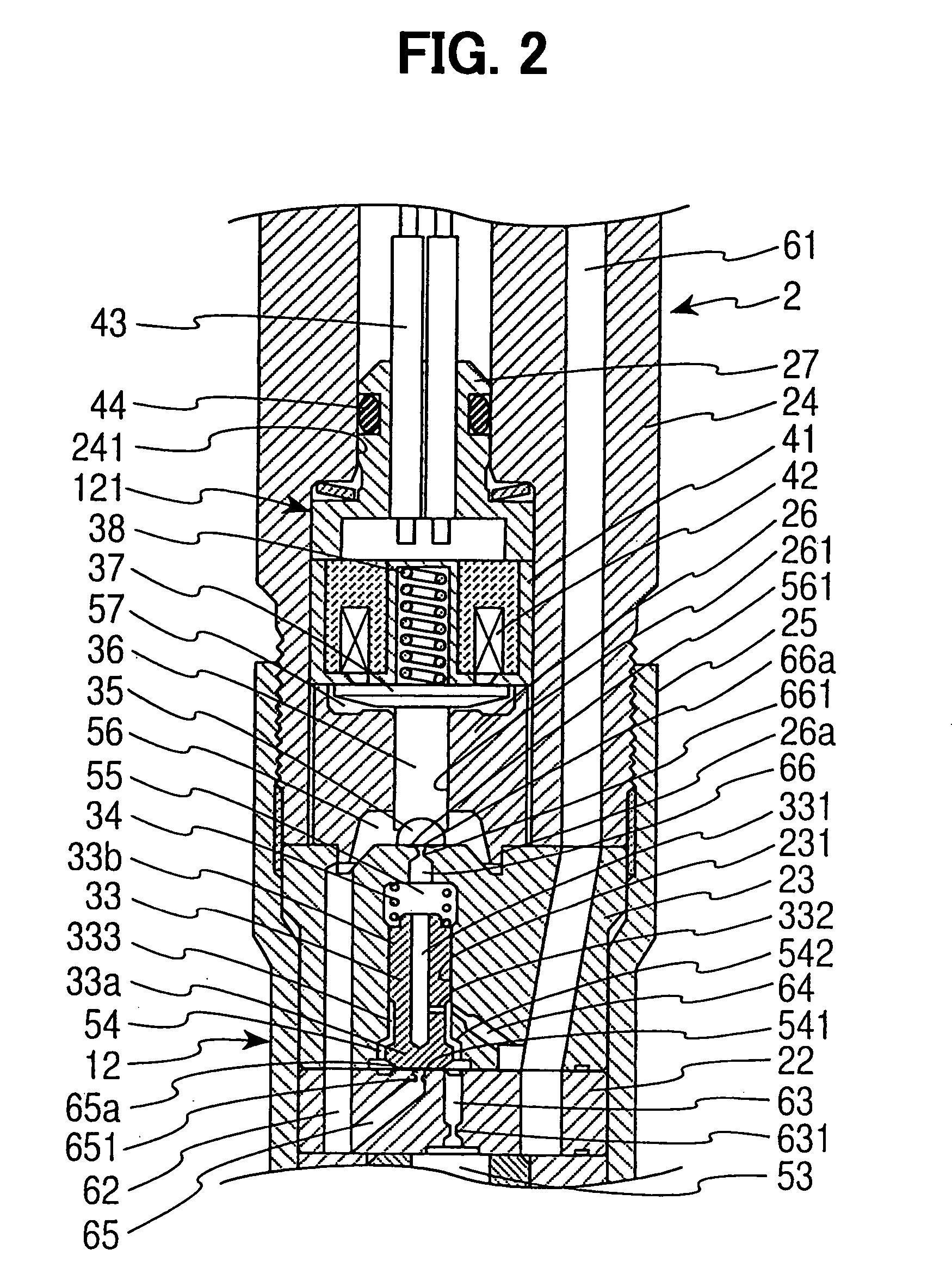
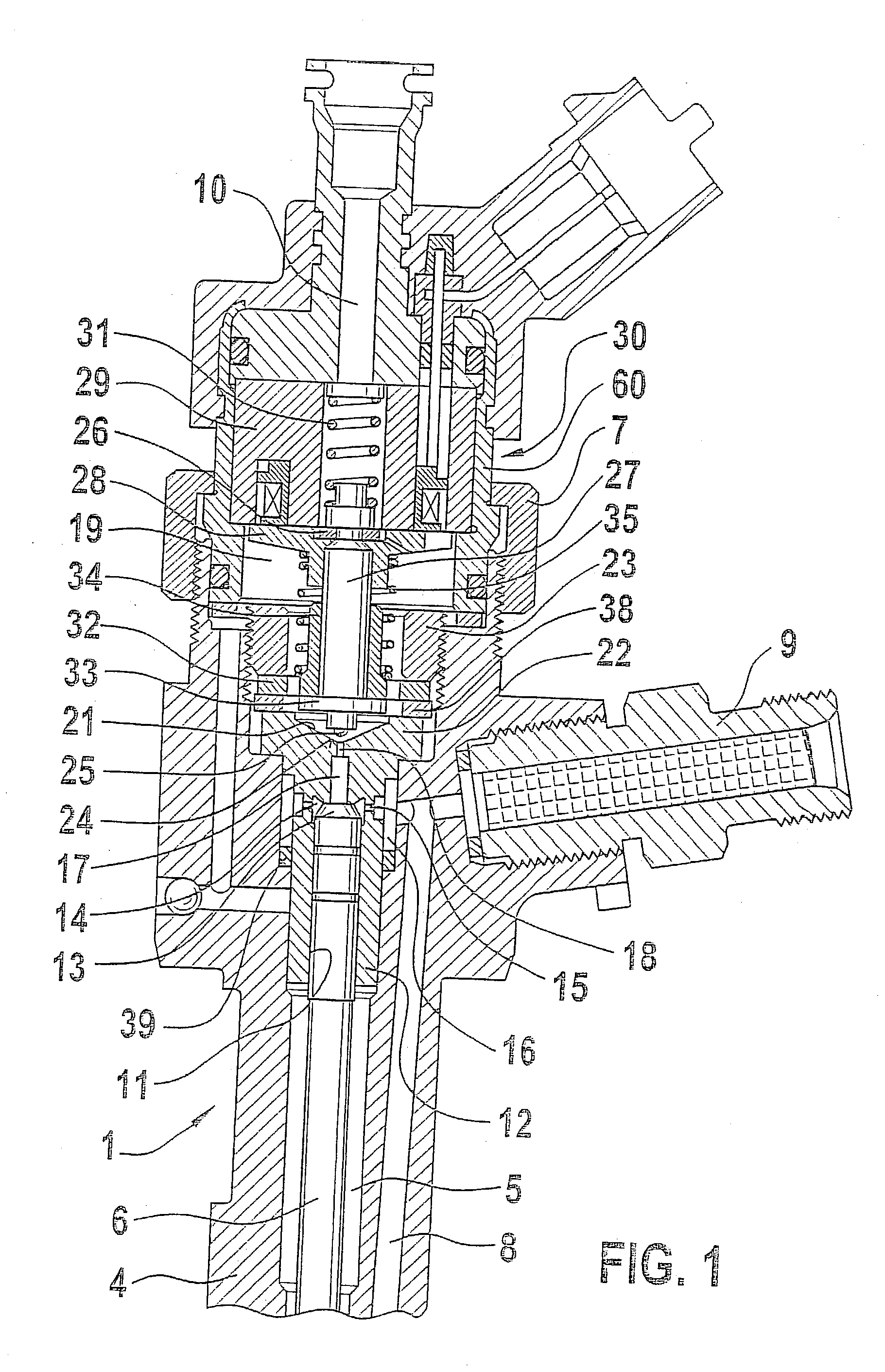
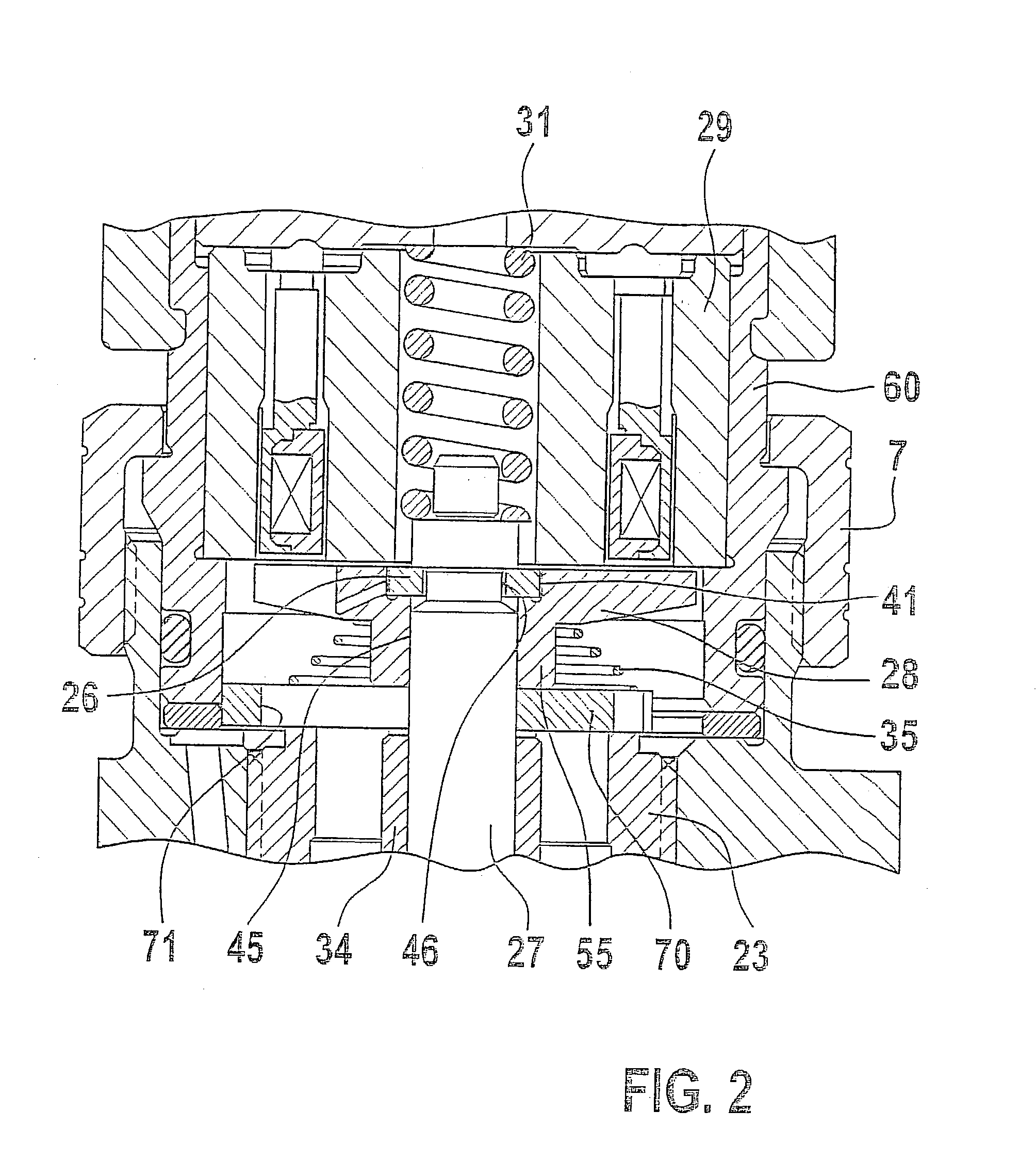
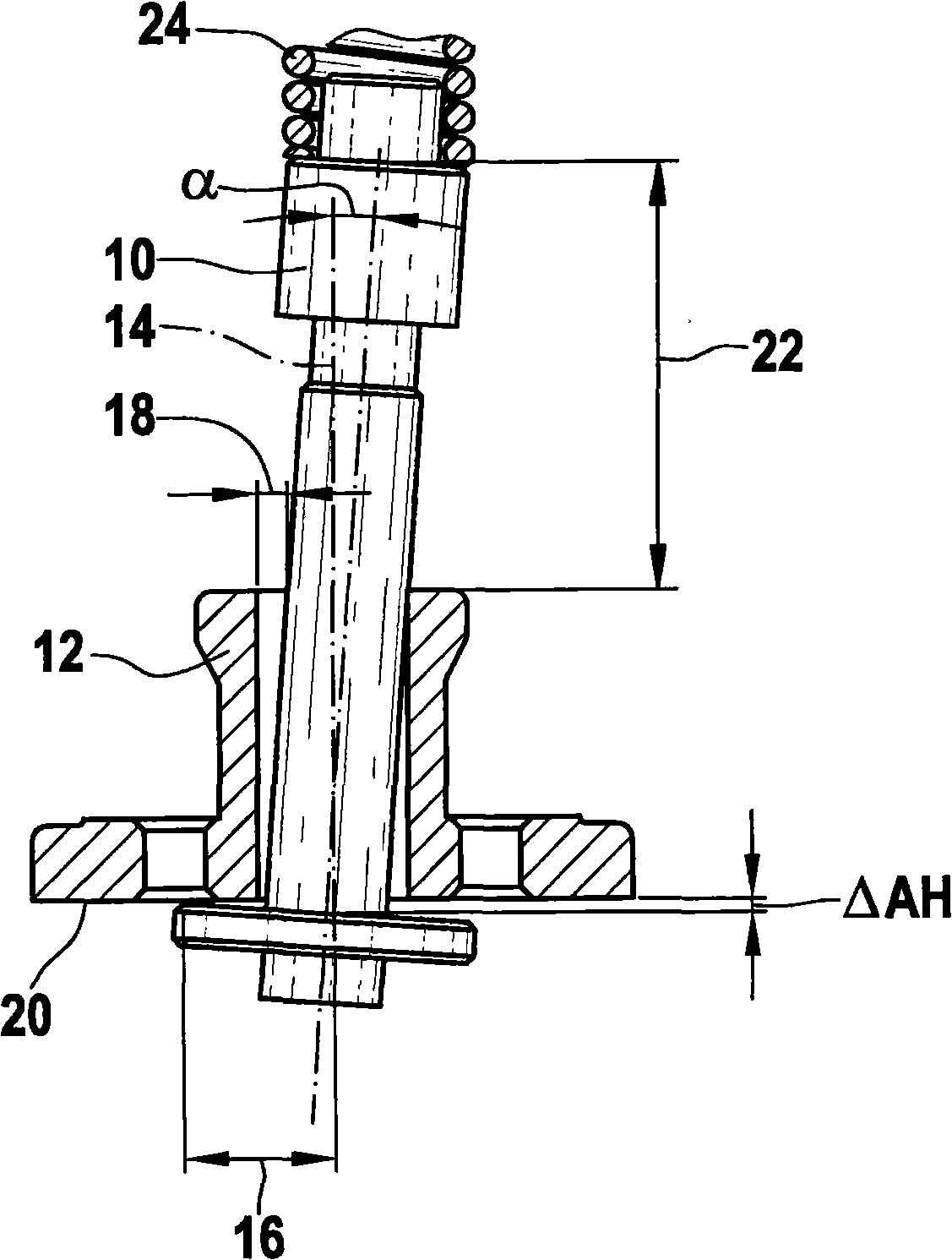
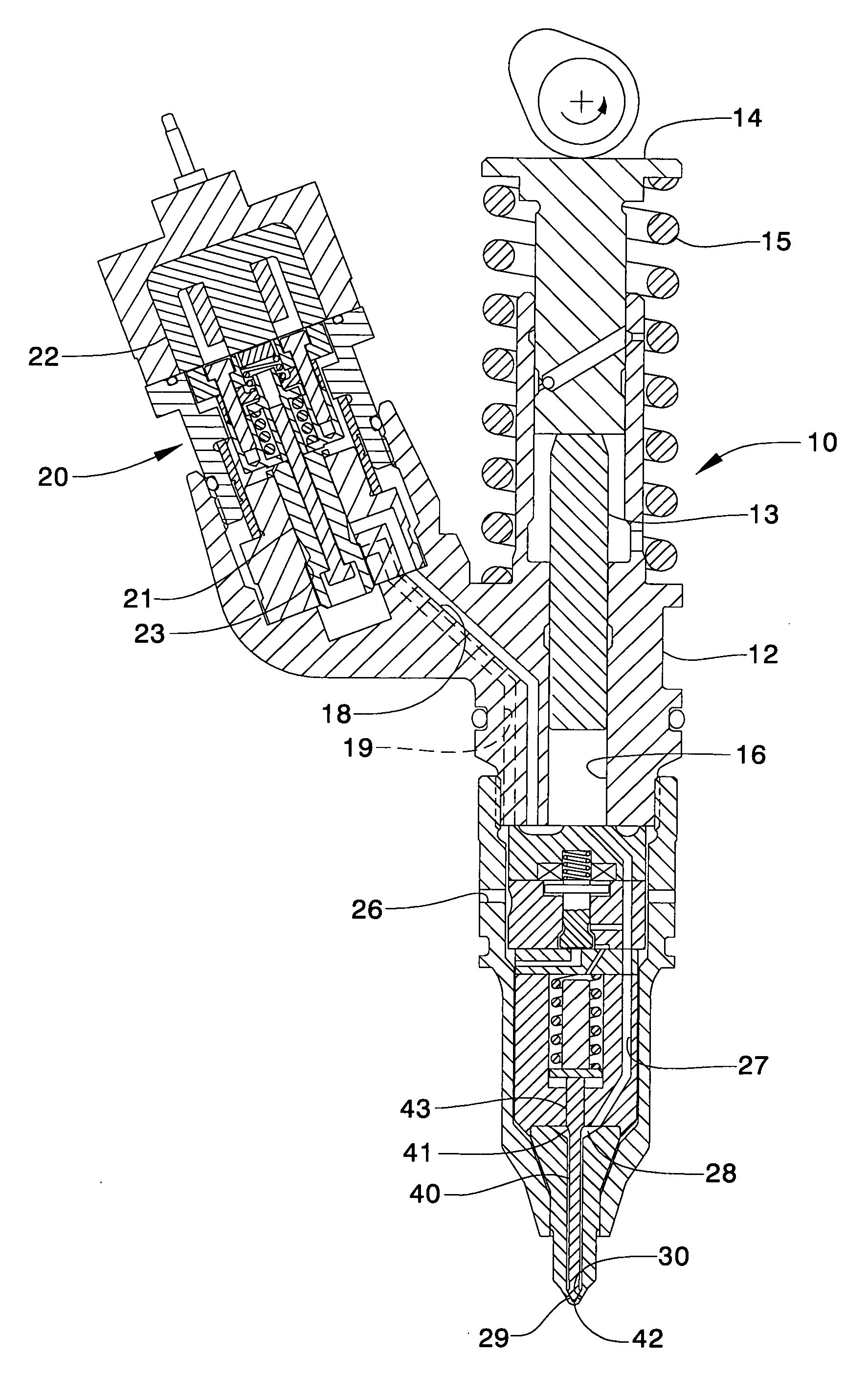
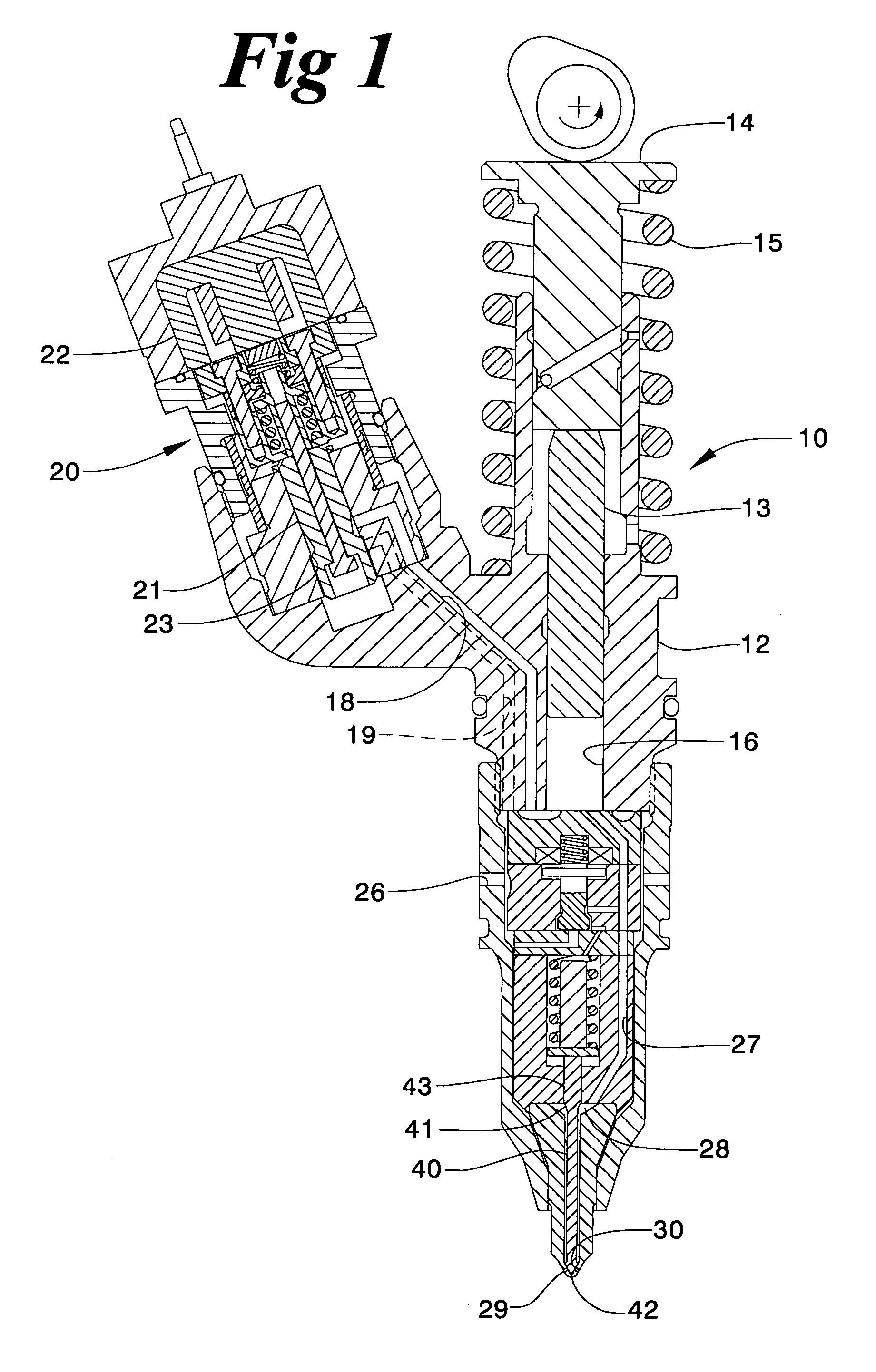
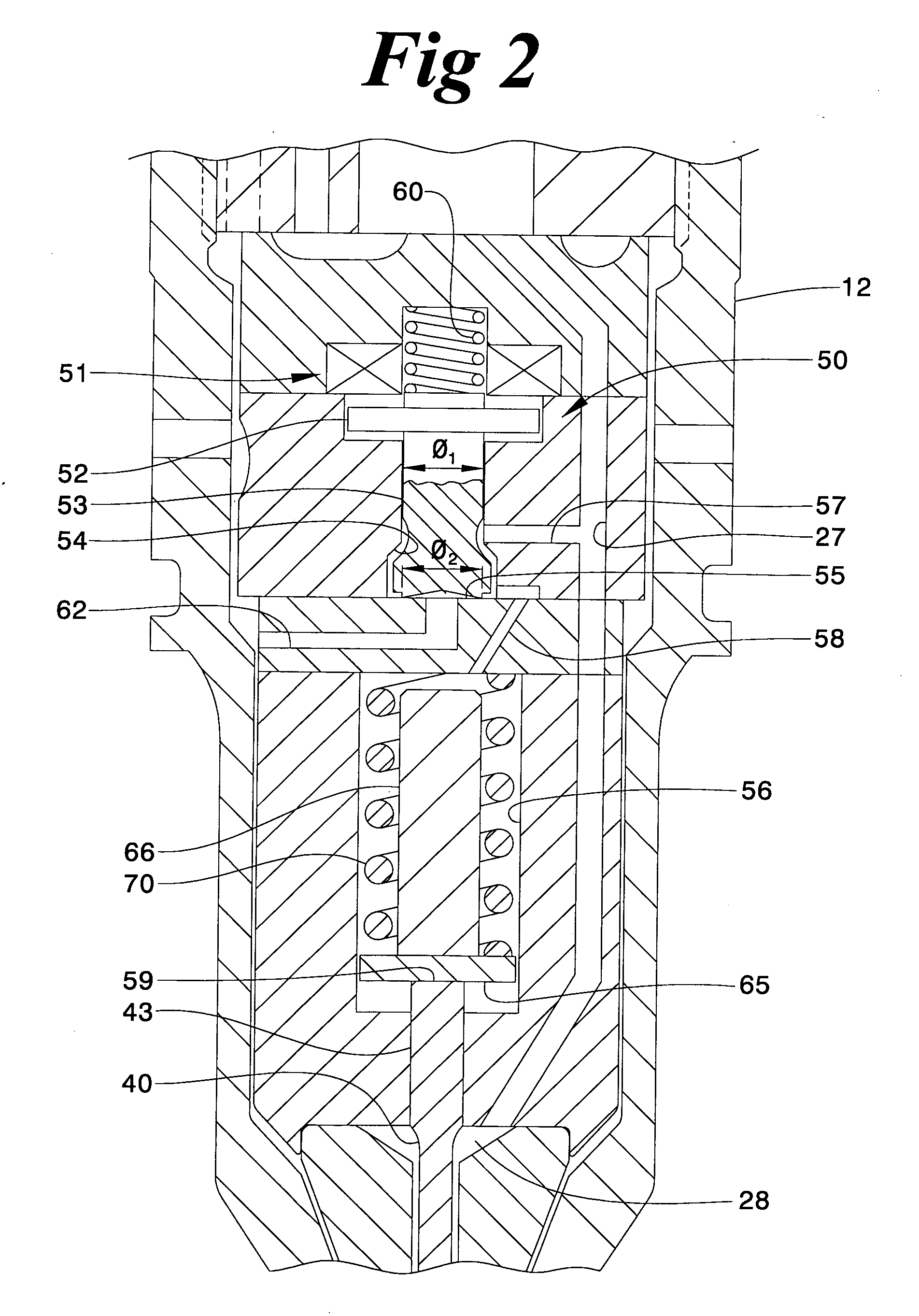
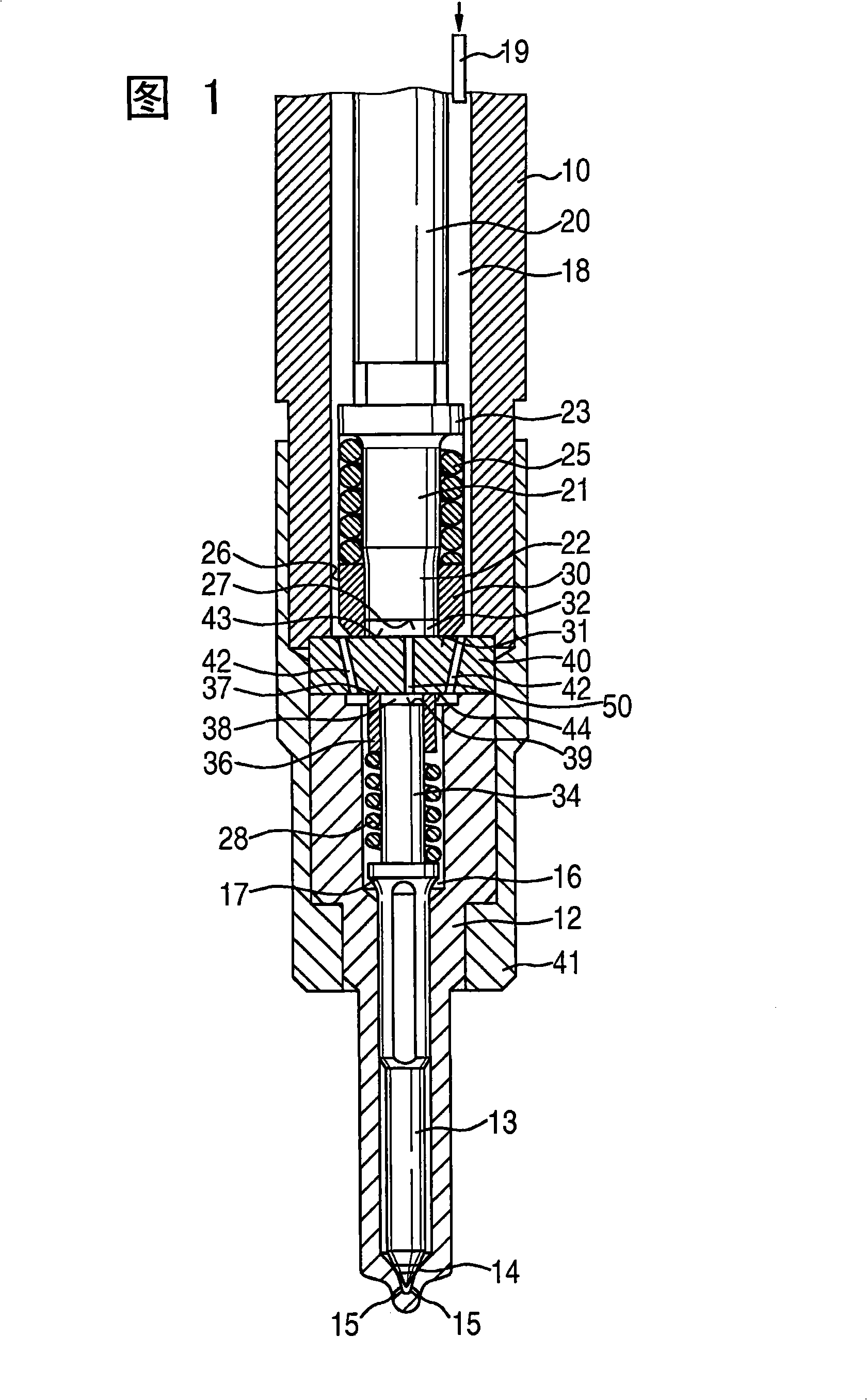
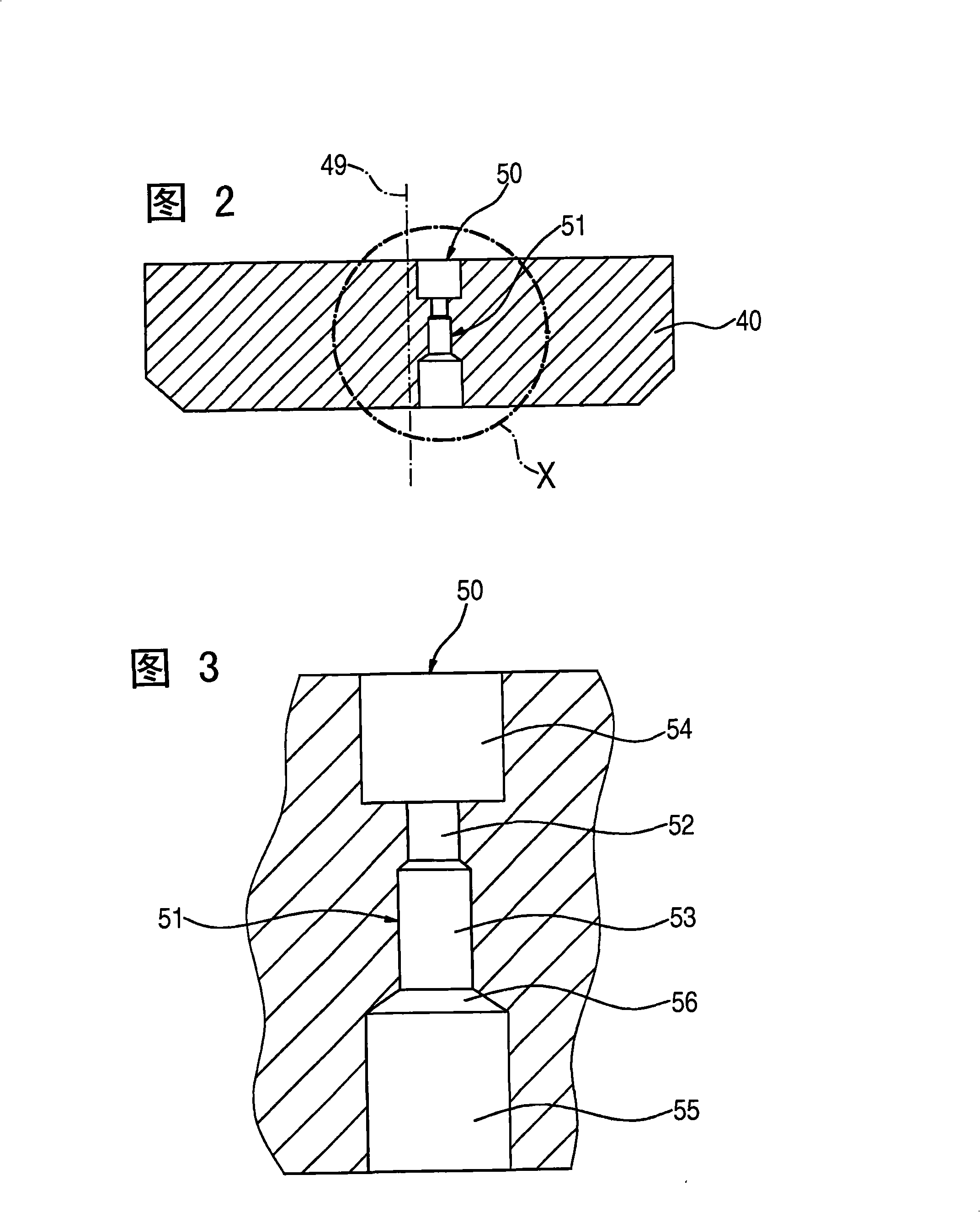
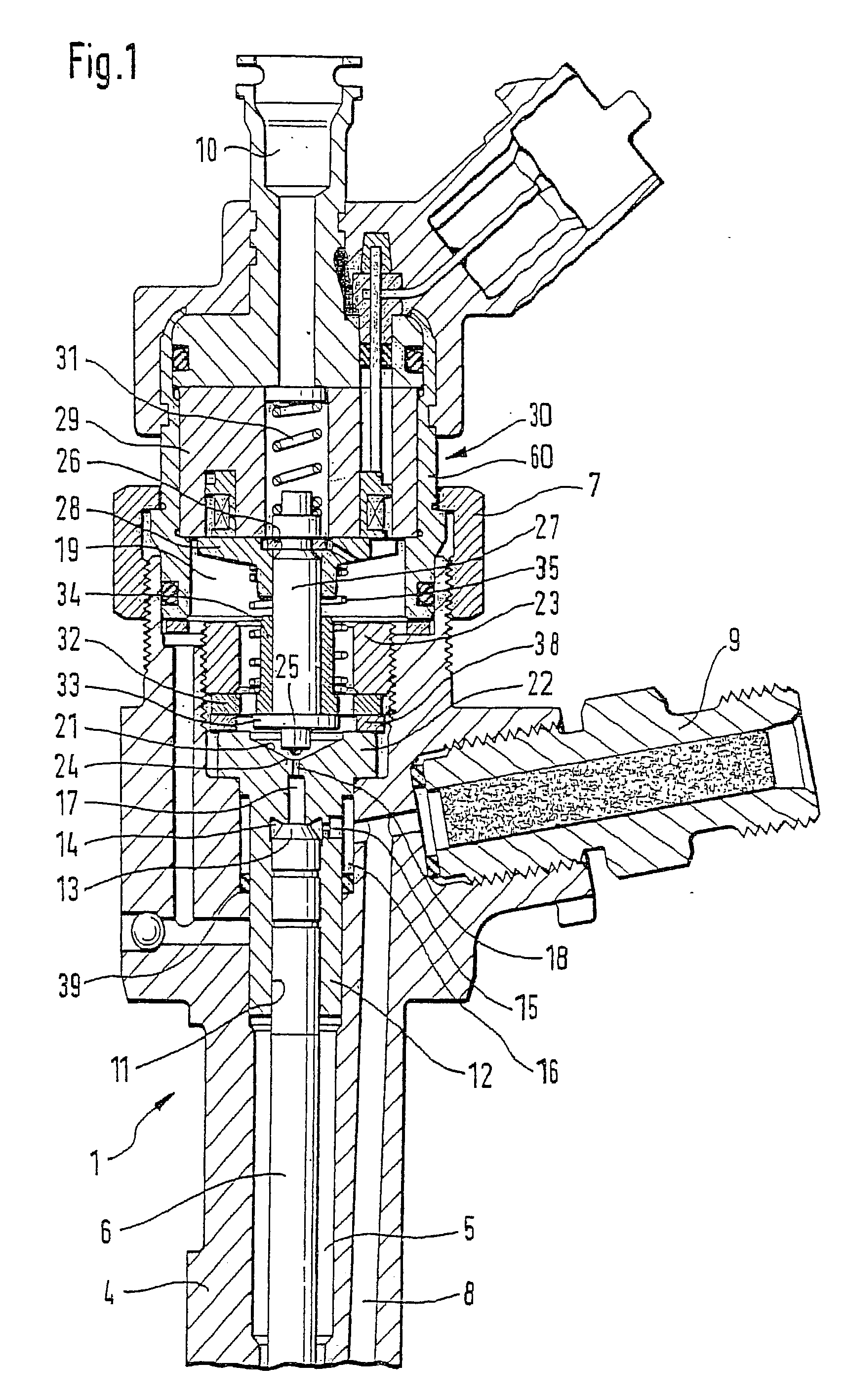
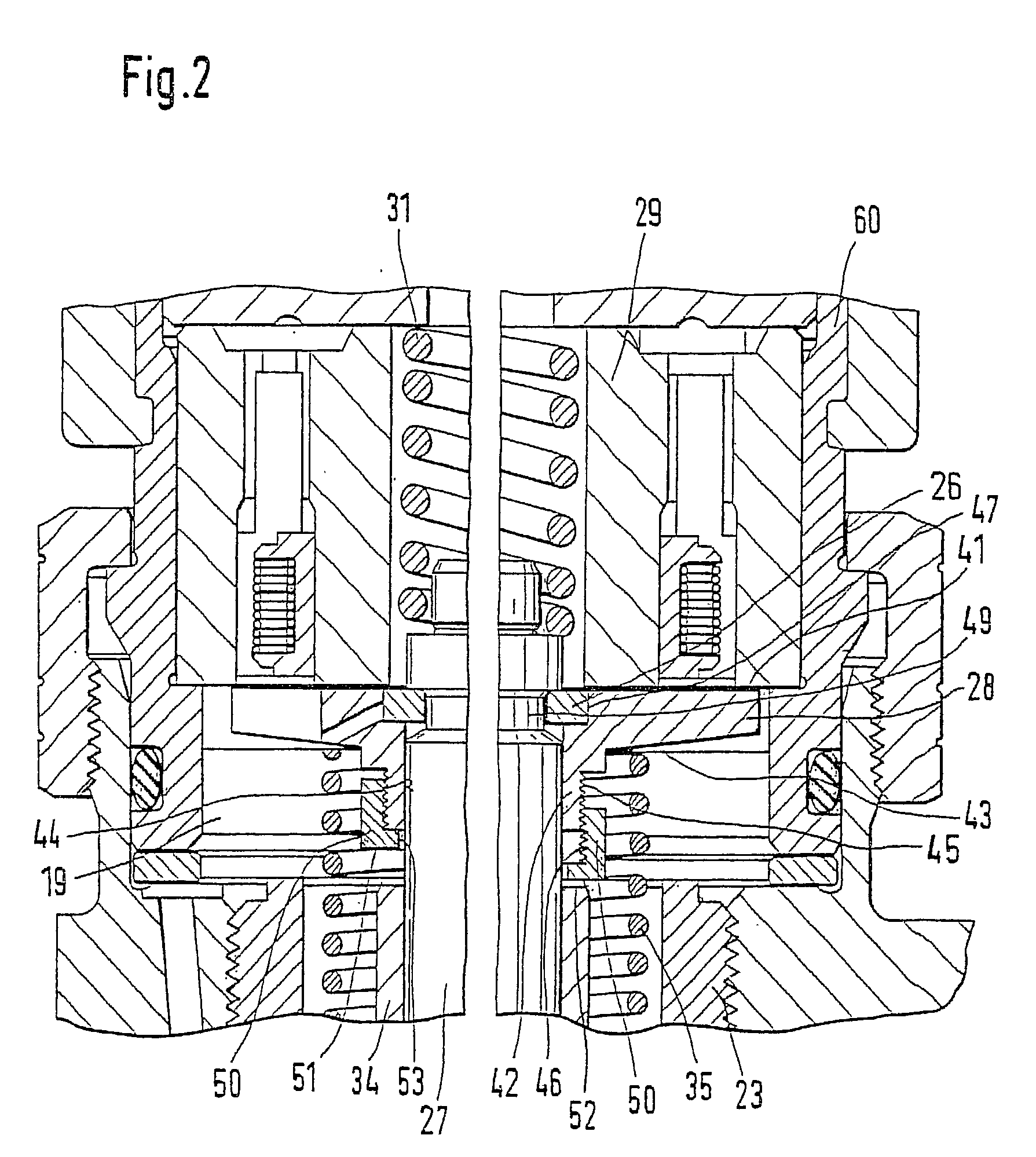
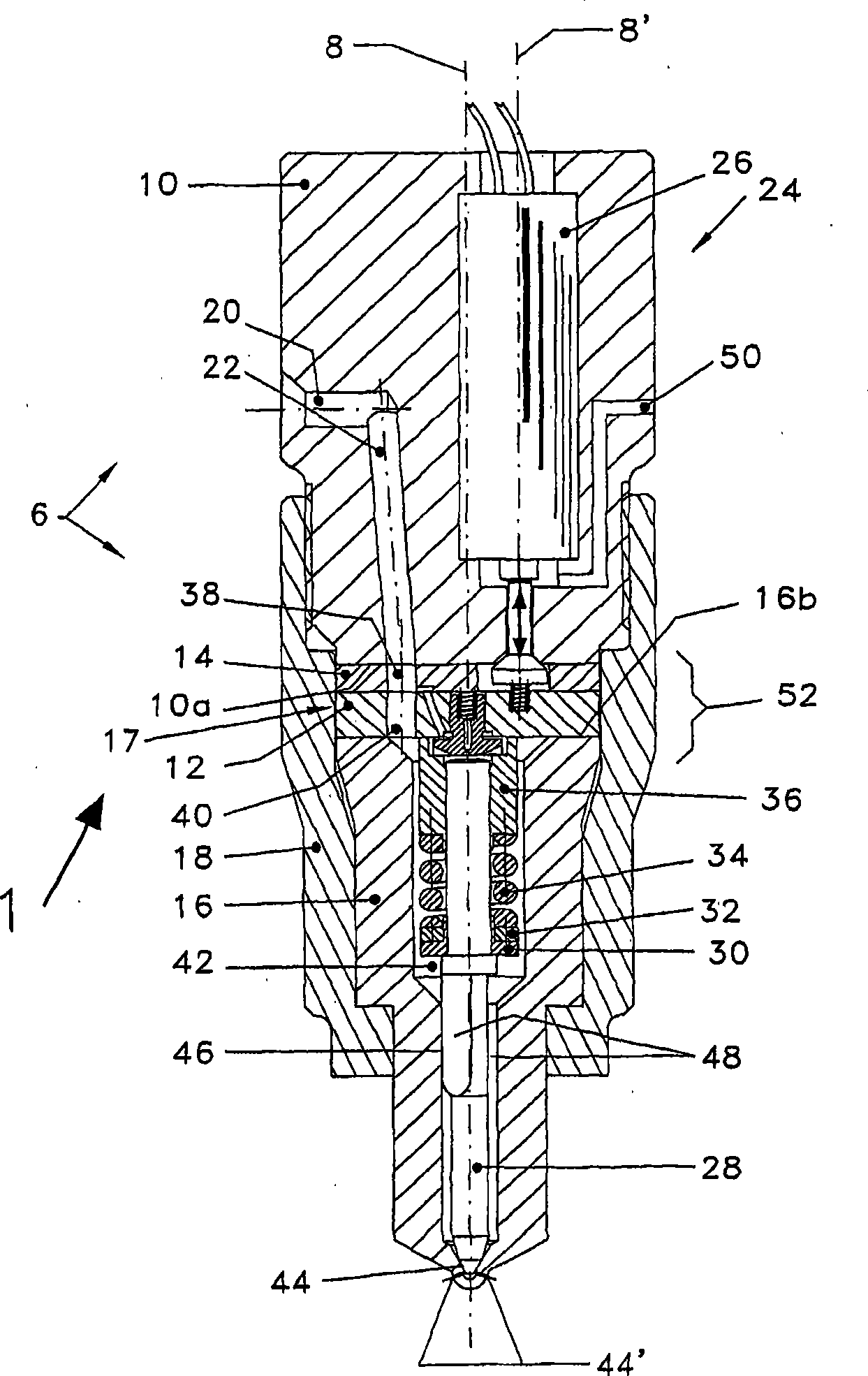
The present invention relates to a solenoid valve (2) for controlling an injection valve (1) of an internal combustion engine, including an electromagnet (34), a movable armature (29), a control valve member (25,26) moved with the armature (29) and cooperating with a valve seat (24) for opening and closing a fuel discharge channel (17) of a control pressure chamber (14) of the injection valve, and a sliding piece (40) guiding the armature (29), which is positioned together with the armature (29) and the control valve member (25,26) in an armature chamber (51,52). For reducing the bounce of the armature, it is proposed that the sliding piece (40) subdivides the armature chamber into a pressure relief chamber (52) connected to a fuel low-pressure connection (10) and an hydraulic damping chamber (51), into which fuel discharge channel (17) opens out, which damping chamber may be pressure-relieved to a pressure relief chamber (52) via at least one connecting channel (44,47) provided with a throttle (43,48), the speed of the control valve member (25,26) being lowered during the closing of solenoid valve (2), before the impact on valve seat (24), by a fuel pressure cushion acting upon the control valve member (25,26) in the damping chamber (51).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel pressure measuring device, fuel pressure measuring system, and fuel injection device
ActiveUS20110006130A1Facilitate easeGuaranteed accuracyElectrical controlLiquid transferring devicesCommon railInternal combustion engine
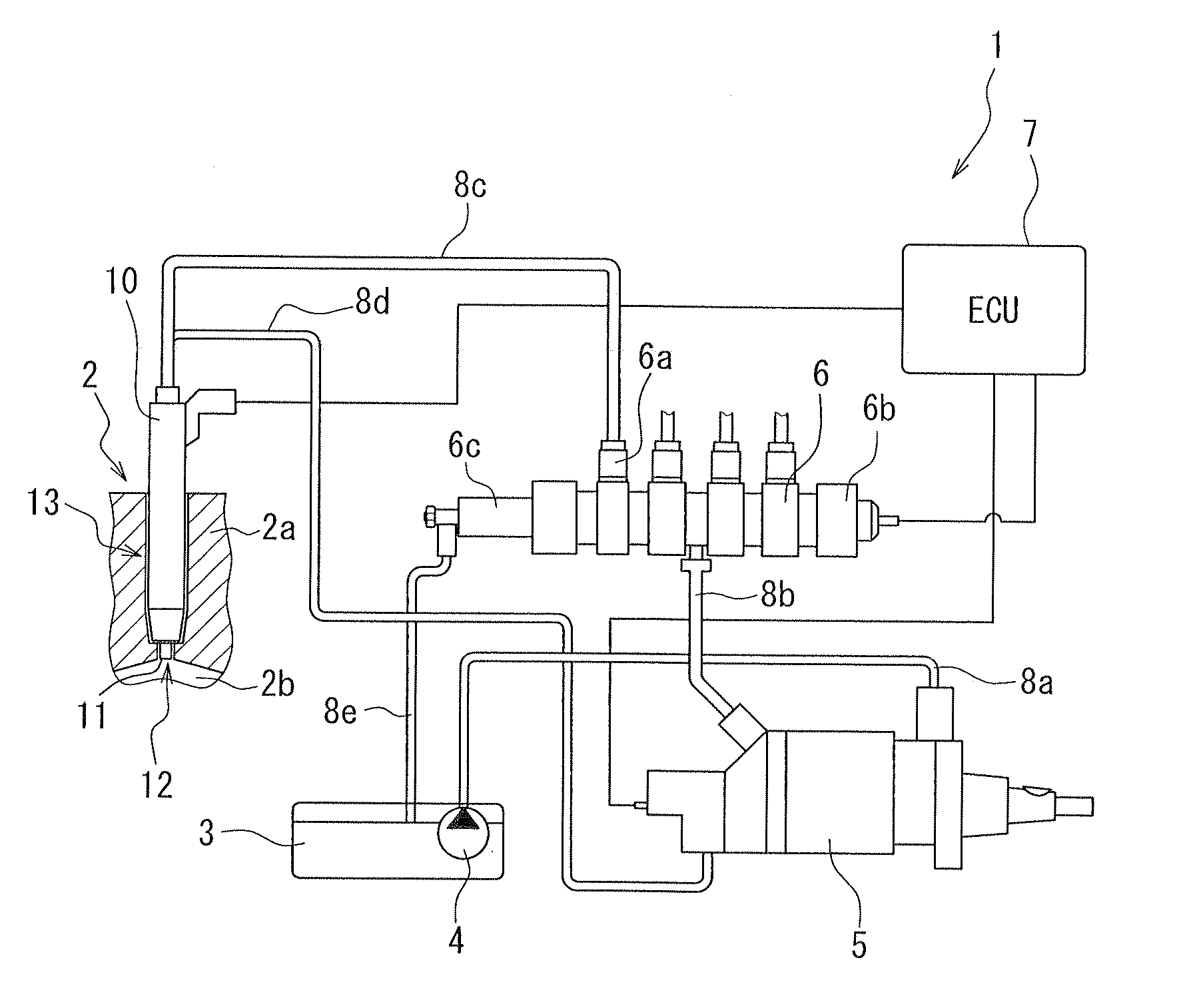
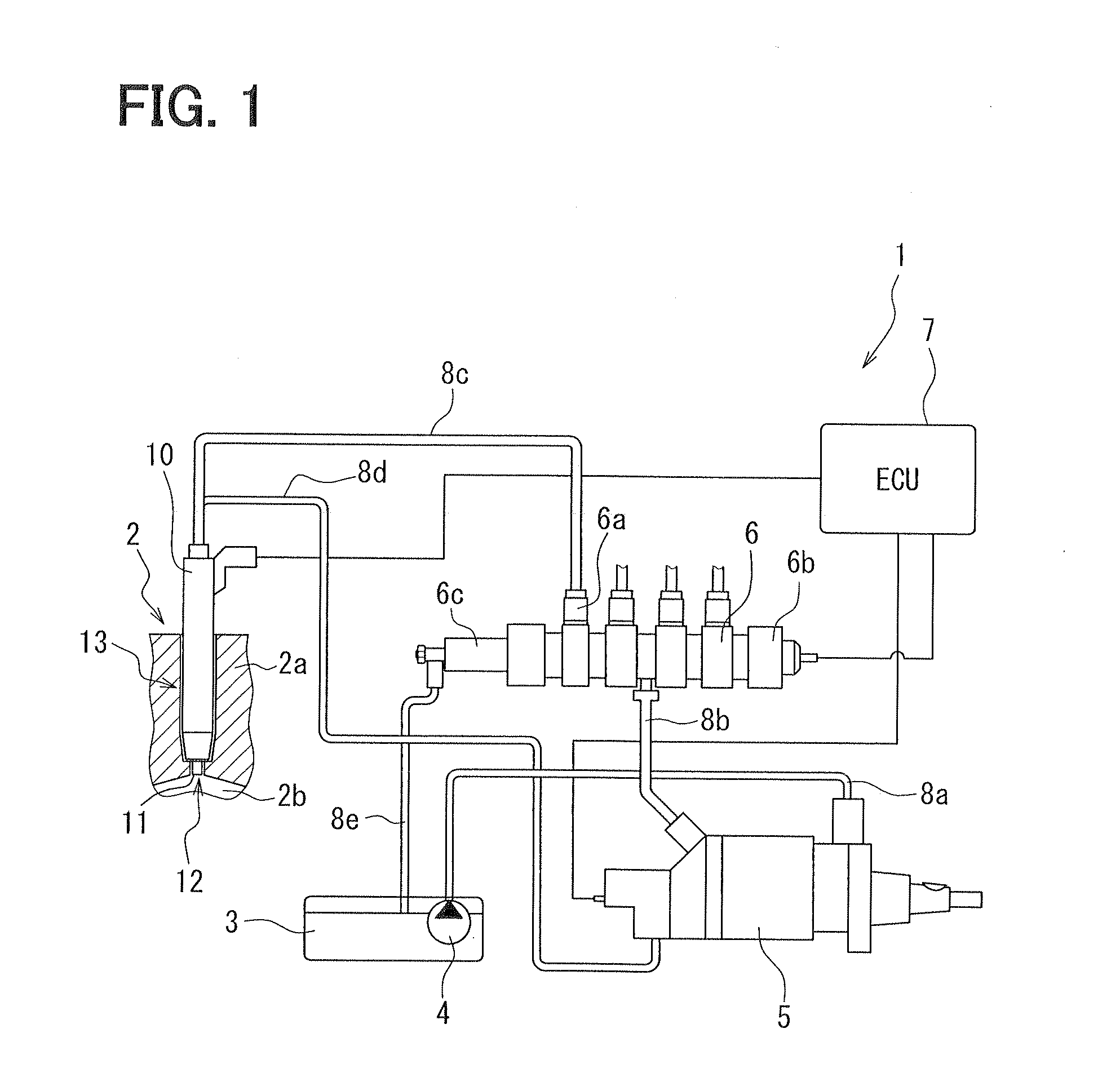
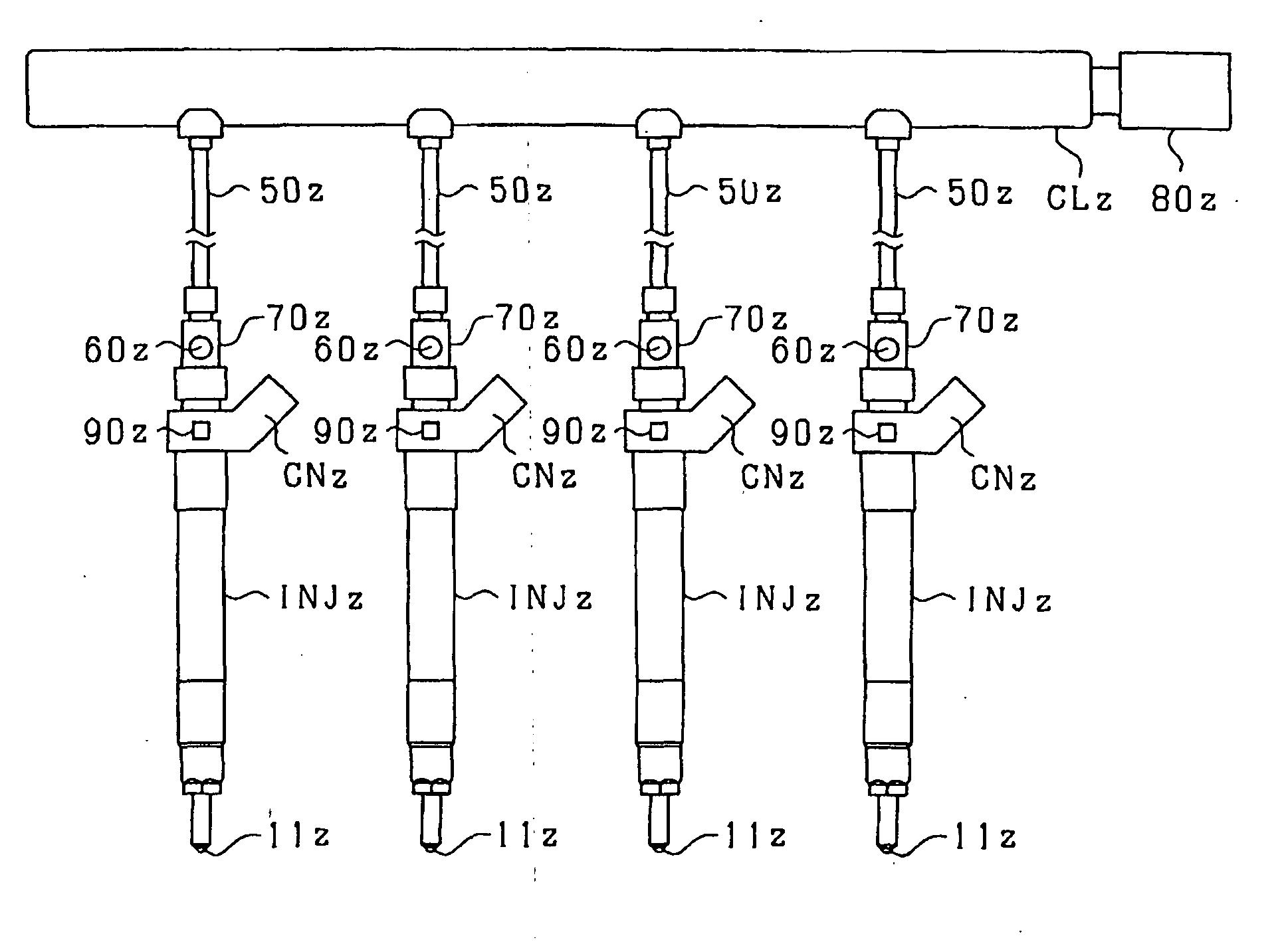
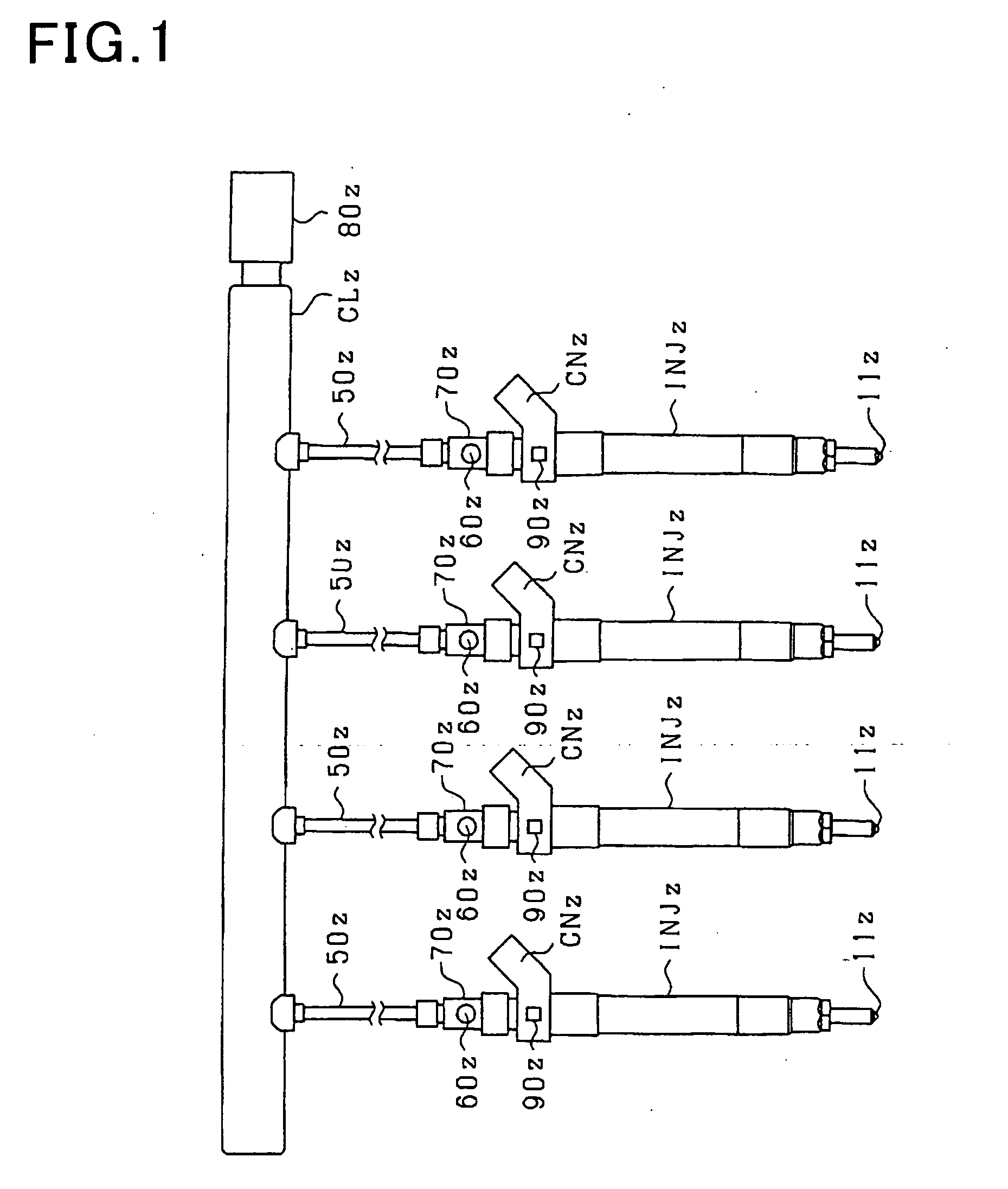
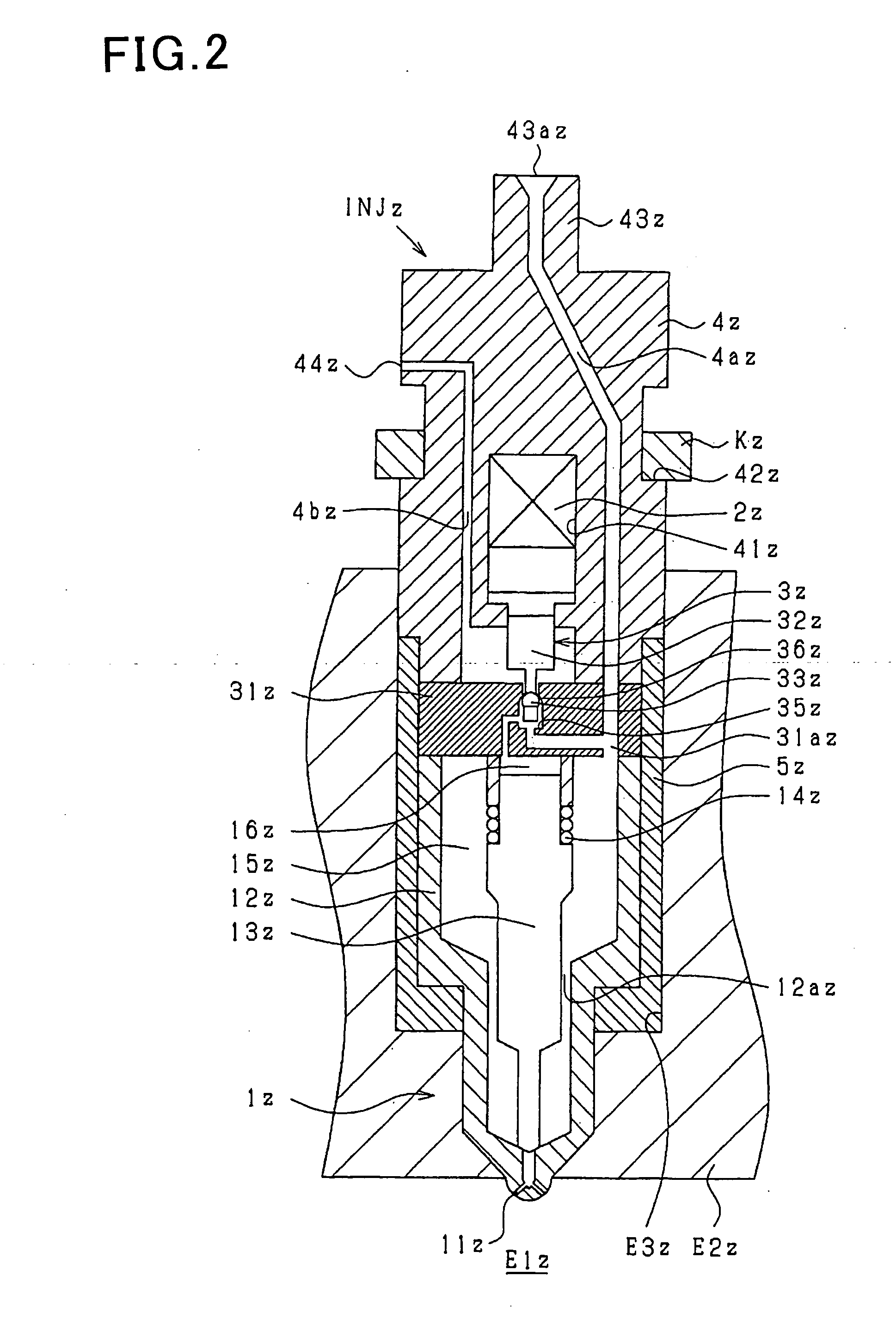
It is used with a fuel injection system for an internal combustion engine which supplies fuel to an injector (fuel injection valve) from a common rail (accumulator) through a high-pressure pipe to spray the fuel from a spray hole formed in the injector. A thin-walled portion 70bz is formed in a path member (e.g., an injector body 4z, the high-pressure pipe, or a connector 70z connecting the injector and the high-pressure pipe) and defined by a locally thin wall of the path member. A strain gauge 60z (strain sensor) is affixed to the thin-walled portion 70bz to measure strain of the thin-walled portion 70bz arising from the pressure of fuel in a high-pressure fuel path 70az.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fuel injector provided with provided with a pressure transmitter controlled by a servo valve
InactiveUS20060243252A1Pressure buildup can be assuredOptimization definitionSpray nozzlesFluid pressure injection controlCombustion chamberDifferential pressure
A fuel injector for injecting fuel into a combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, including a pressure booster, whose booster piston separates a work chamber, subjected to fuel via a pressure reservoir, from a pressure-relievable differential pressure chamber. A pressure change in the differential pressure chamber is effected via an actuation of a servo valve, which opens or closes a hydraulic connection of the differential pressure chamber to a first low-pressure-side return. The servo valve has a piston guided between a control chamber and a first hydraulic chamber. On this servo valve piston, a hydraulic face that positions the servo valve piston constantly in the opening direction when system pressure is applied and a first sealing seat that closes or opens a low-pressure-side return are embodied.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel injector device for engines
The fuel injection device of this invention utilizes the fuel pressure in the balance chamber for closing the open-close valve to prevent fuel leakage from the open-close portion. When the open-close valve is opened, the valve stem of the open-close valve piercing through the exhaust passage in the control member moves toward the balance chamber. The valve head opens the port of the exhaust passage on the balance chamber side to lower the fuel pressure in the balance chamber, with the result that the needle valve lifts injecting the fuel. When the open-close valve is closed by the return spring, the fuel pressure in the balance chamber acts on the valve head to urge the open-close valve in the valve closing direction, preventing the leakage of fuel through the open-close valve.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Injector having structure for controlling nozzle needle
A valve back pressure chamber is provided to exert a back pressure of a first valve needle. Furthermore, a hydraulic pressure passage is provided to extend through the valve back pressure chamber. A valve body is provided to a second valve needle and is driven to connect and disconnect between the hydraulic pressure passage and a fuel tank and thereby to drive the first valve needle. The second valve needle is driven by hydraulic pressure induced by an actuator.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Direct needle control fuel injectors and methods
ActiveUS7412969B2Low pressure fuel injectionFluid pressure injection controlEngineeringHigh pressure
Direct needle control fuel injectors and methods disclosed. The preferred embodiment injectors have a needle within a needle chamber for movement between a closed position preventing injection of fuel and an open position allowing injection of fuel, a source of high pressure fuel coupled to the needle chamber to provide fuel for injection and to hydraulically urge the needle to the open position by pressurizing a first hydraulic area associated with the needle, a needle control hydraulic area having a second hydraulic area disposed to urge the needle to the closed position when the second hydraulic area is exposed to fuel under pressure, and valving coupled to the source of high pressure fuel and a vent to controllably couple the hydraulic area of the needle control member to the high pressure fuel or to the vent.
Owner:STURMAN INDS
Servo valve for controlling an internal combustion engine injection
ActiveUS20070205302A1Reduce clamping forceEasy to produceSpray nozzlesFluid pressure injection controlComing outEngineering
A control servo valve is housed inside the casing of an internal combustion engine fuel injector, and has an actuator, a control chamber communicating with a fuel inlet and with a fuel outlet passage, and a shutter movable along an axis by the actuator between a closed position and an open position to close and open the outlet passage respectively; the servo valve also has a fixed axial rod interposed between the actuator and the control chamber; the outlet passage comes out through an outer lateral surface of the axial rod; and the shutter is defined by a sleeve which slides axially on the outer lateral surface, and, in the closed position, closes the outlet passage so as to be subjected to a zero axial resultant force by the pressure of the fuel.
Owner:CENT RICERCHE FIAT SCPA
Fuel-jetting system
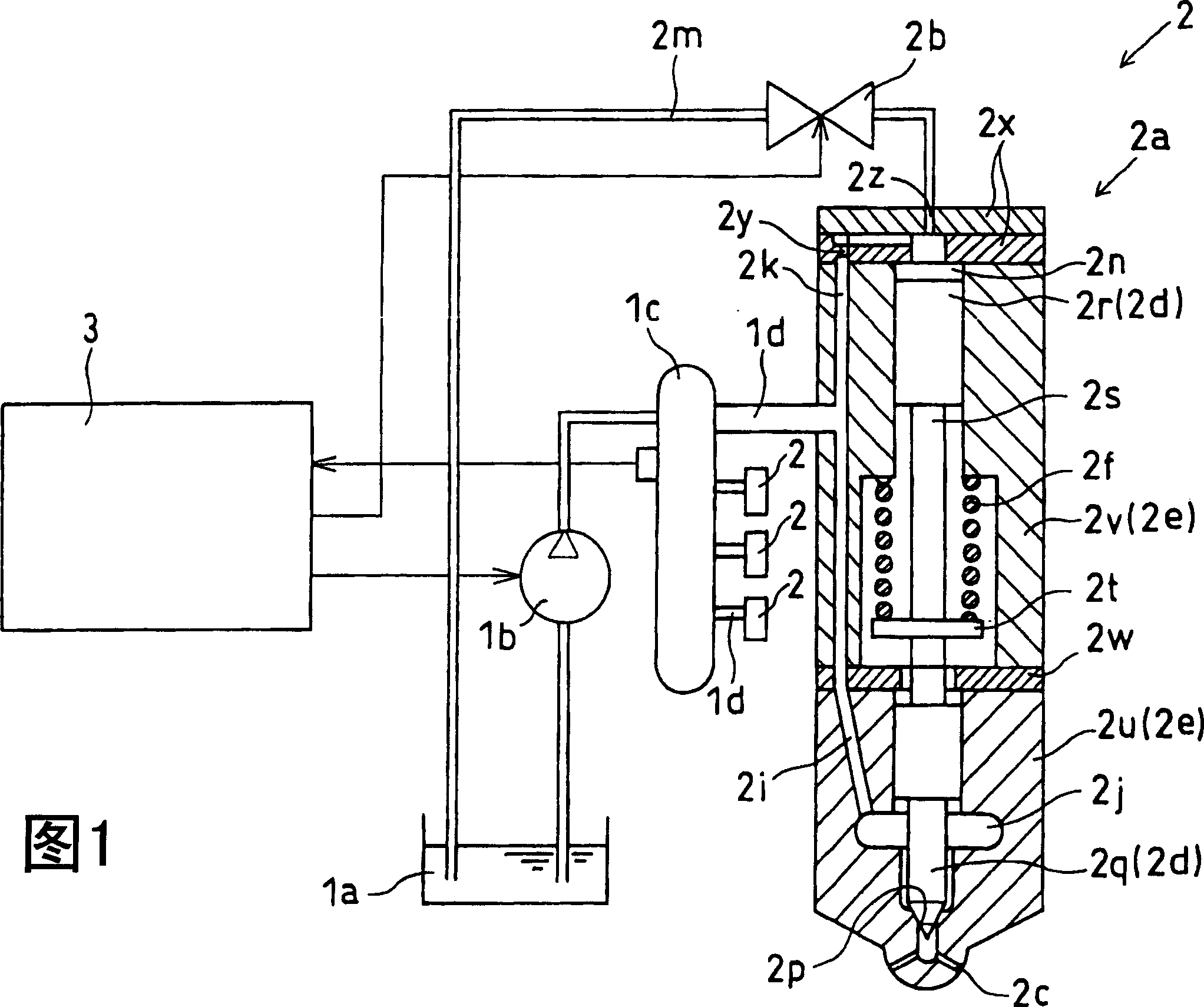
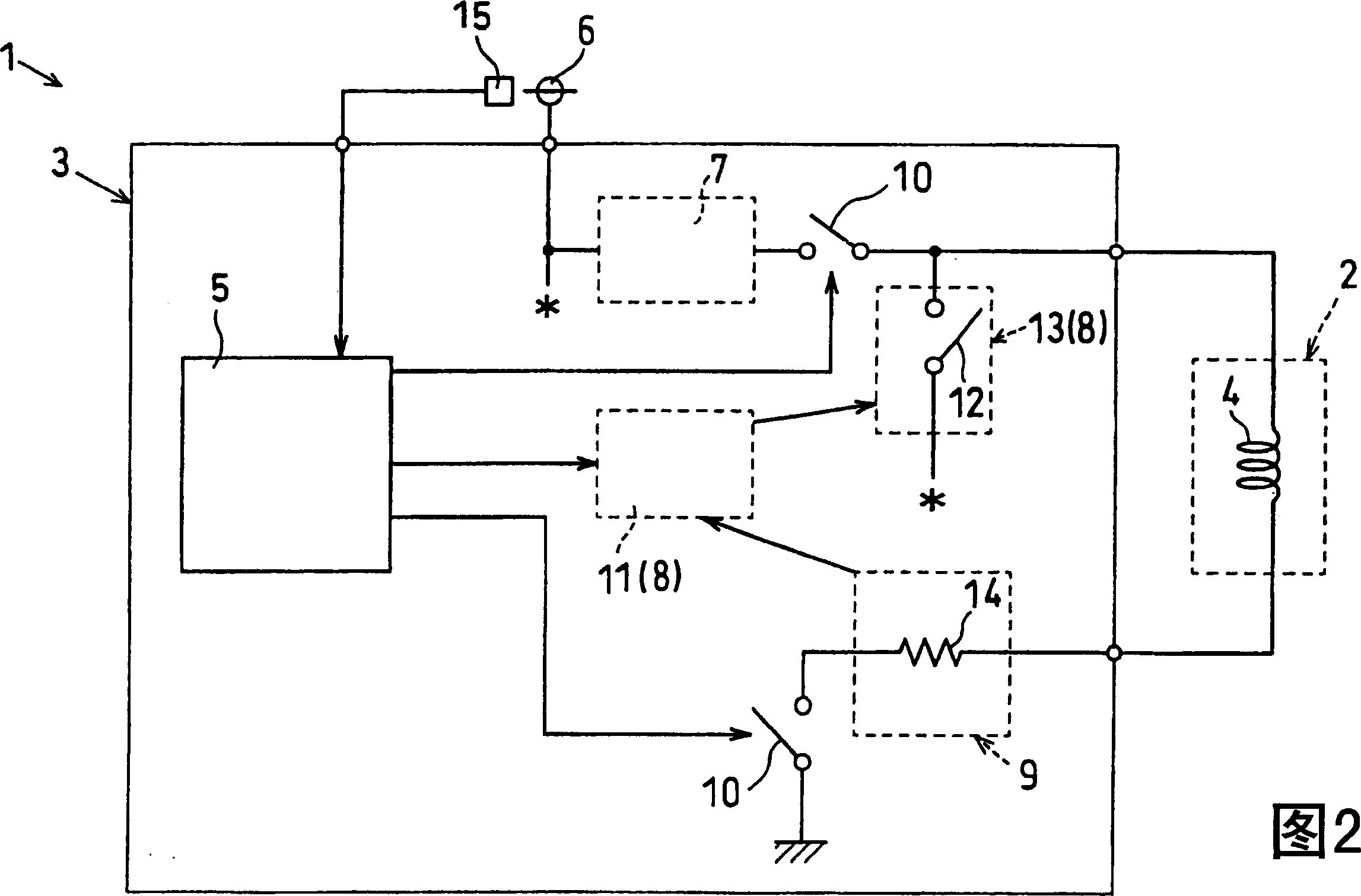
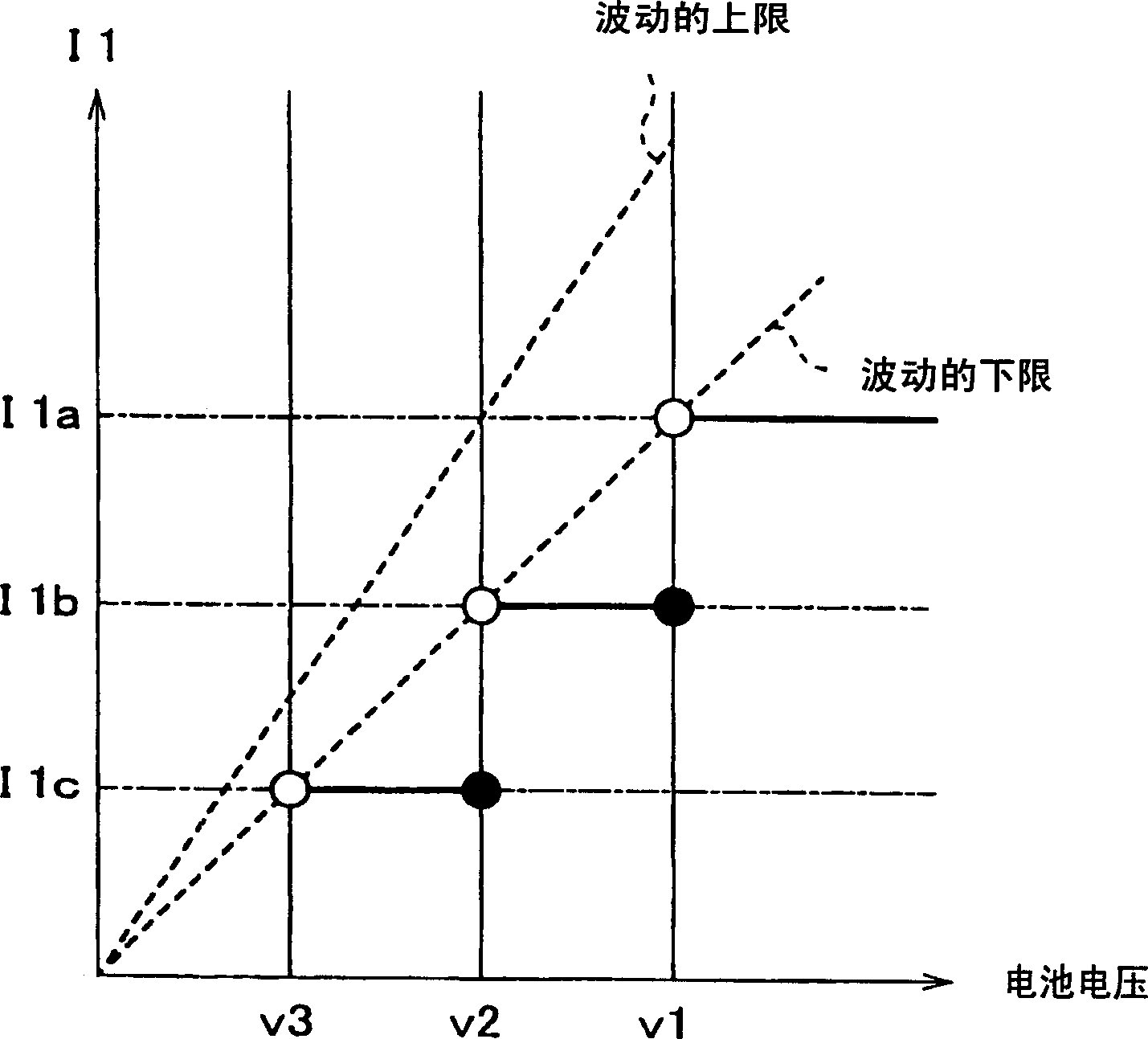
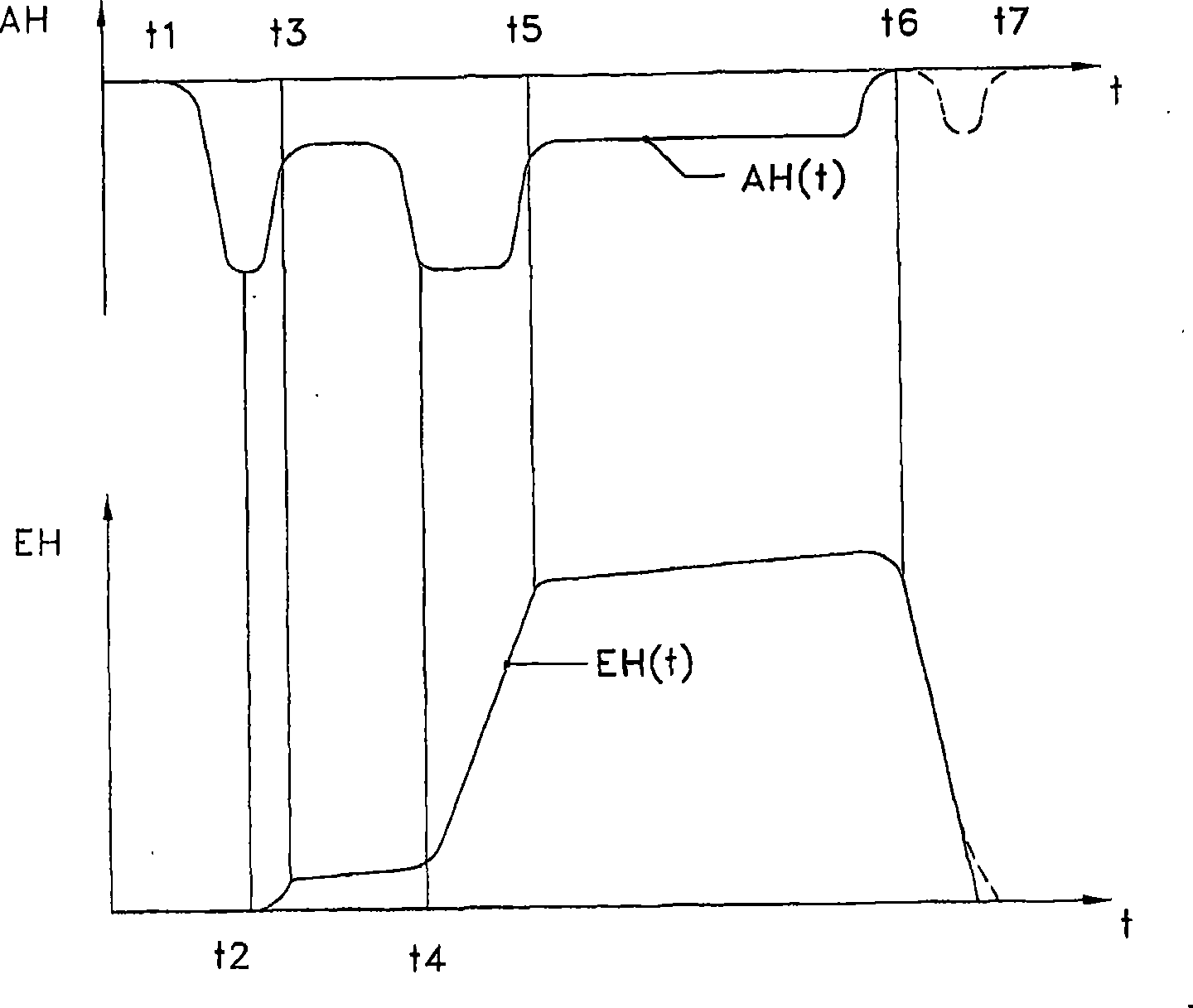
Inside a fuel injection system provided with a fuel injector (2a) and an electromagnetic actuator (2b), a needle valve (2q) of the fuel injector (2a) is lifted directly or indirectly by means of the electromagnetic force generated inside the actuator (2b) so as to open a fuel nozzle (2c). A control unit (3) controls the current fed into the solenoid of the electromagnetic actuator (2b) in the mode; therefore, a peak current (Ip) is fed in at first and then a first constant current and a second constant current (I1, I2) are fed into the solenoid. The target value of the current supply of the first constant current (I1) can be changed into a value basically less than that of a battery voltage. Therefore, the battery voltage does not need to be monitored all the time.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fuel injector for multi-fuel injection with pressure intensification and a variable orifice
InactiveUS20140373806A1Facilitate pressureLow viscosityExhaust gas recirculationCombustion enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
A multi-fuel injector has an internal pressure intensifier which has means to intensify fuels with different viscosities, cetane or octane numbers, with high viscosity fuel being used to intensify both itself and low viscosity fuels to high pressure for direct injection into combustion chamber. A combustion method using such a method of fuel injection is also disclosed. A multi-fuel injector with variable orifice nozzle and variable spray patterns is also disclosed.
Owner:HOU DEYANG +1
Electromagnetic valve for controlling an injection valve of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20030141475A1Simple attachmentEasy to manufactureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpray nozzlesSolenoid valveEngineering
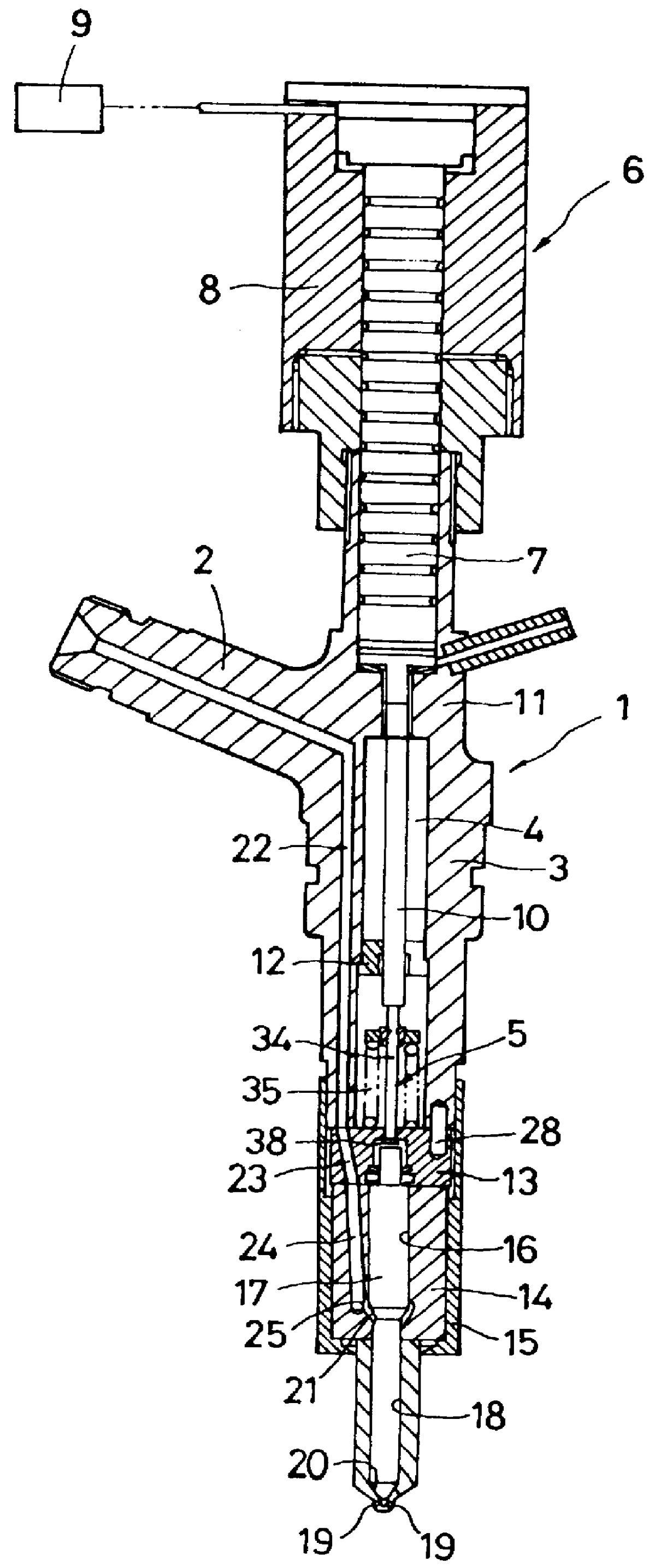
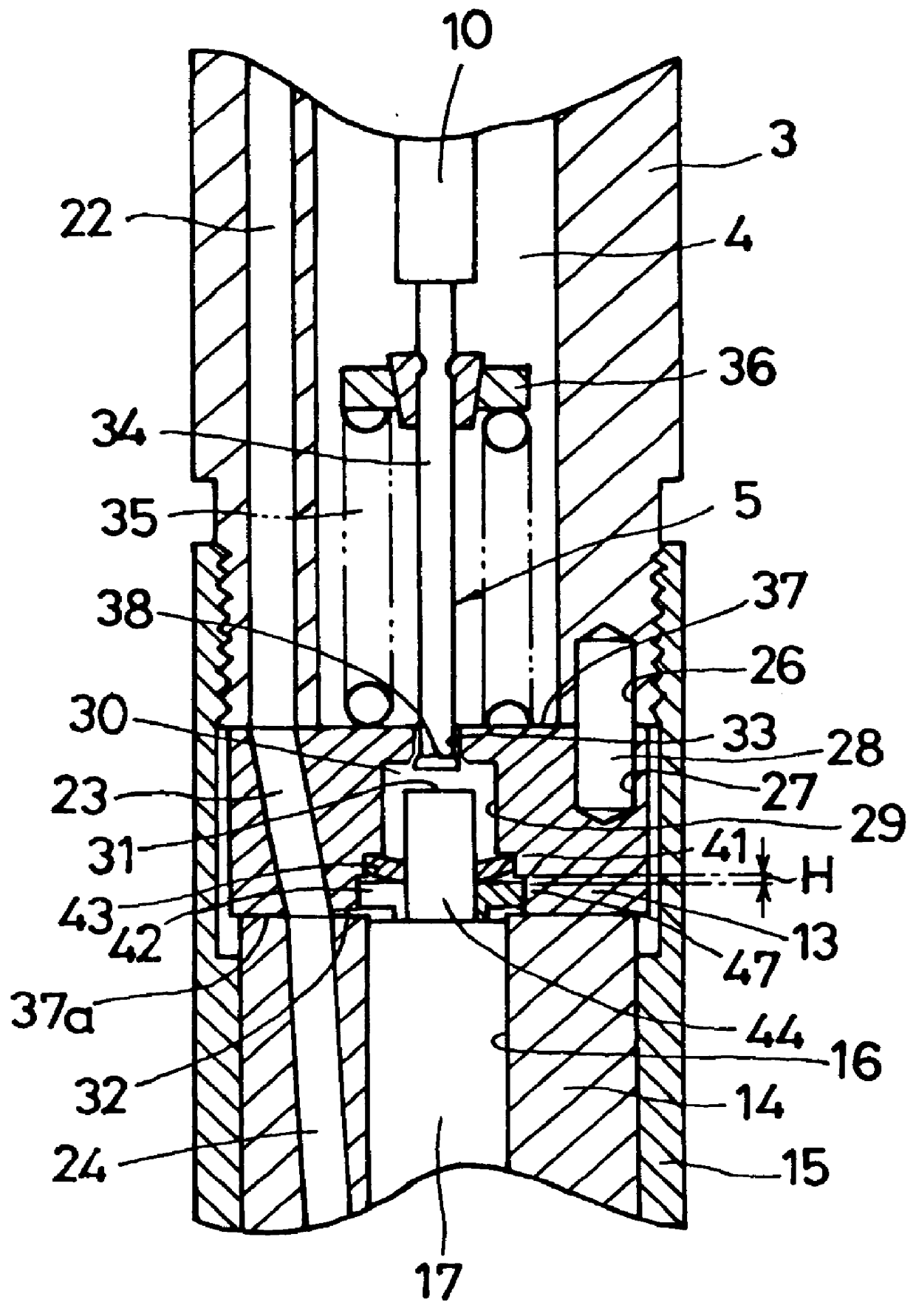
A solenoid valve for controlling a fuel injector of an internal combustion engine, including an electromagnet 29, a displaceable armature having an armature plate 28 and an armature pin 27, and a control valve element 25 which is displaced with the armature and which cooperates with a valve seat 24 for opening and closing a fuel discharge channel 17 of a control pressure chamber 14 of the fuel injector 1. The armature plate 28 is mounted on the armature pin 27 so as to be slidably displaceable in opposition to the tensioning force of a restoring spring 35 acting on the armature plate 28 under the influence of the inert mass of the armature plate in the closing direction of the control valve element 25, and is pressed by the restoring spring 35 in its rest state against a stop part 26 attached to the armature pin 27. The stop part 26 is designed to encircle the periphery of the armature pin 27 by more than 180° in a plane perpendicular to the direction of movement of the armature pin.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Optimized armature assembly guidance for solenoid valves
InactiveCN101305182AMaximum tipping reductionIncrease exerciseFluid pressure injection controlMachines/enginesSolenoid valveEngineering
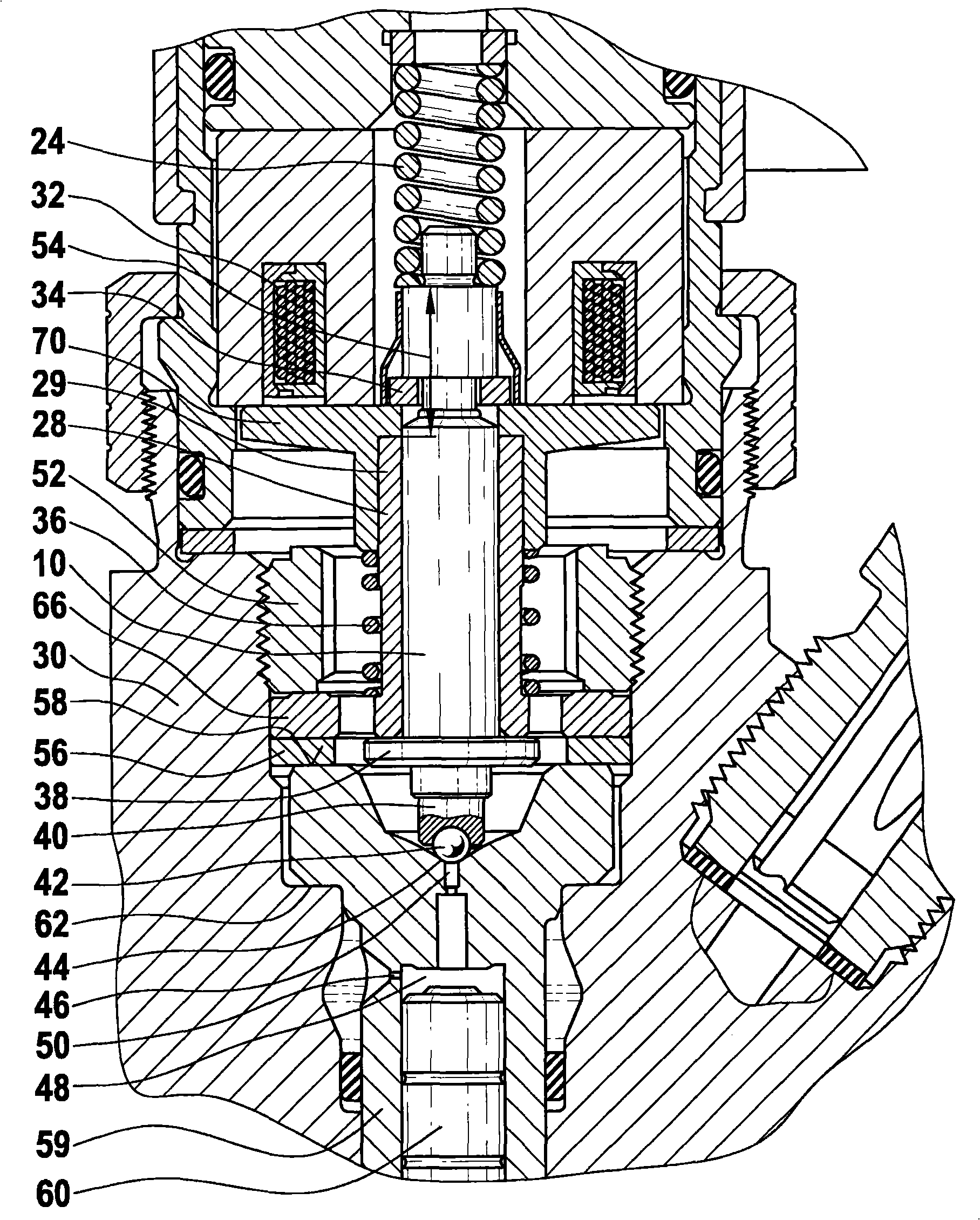
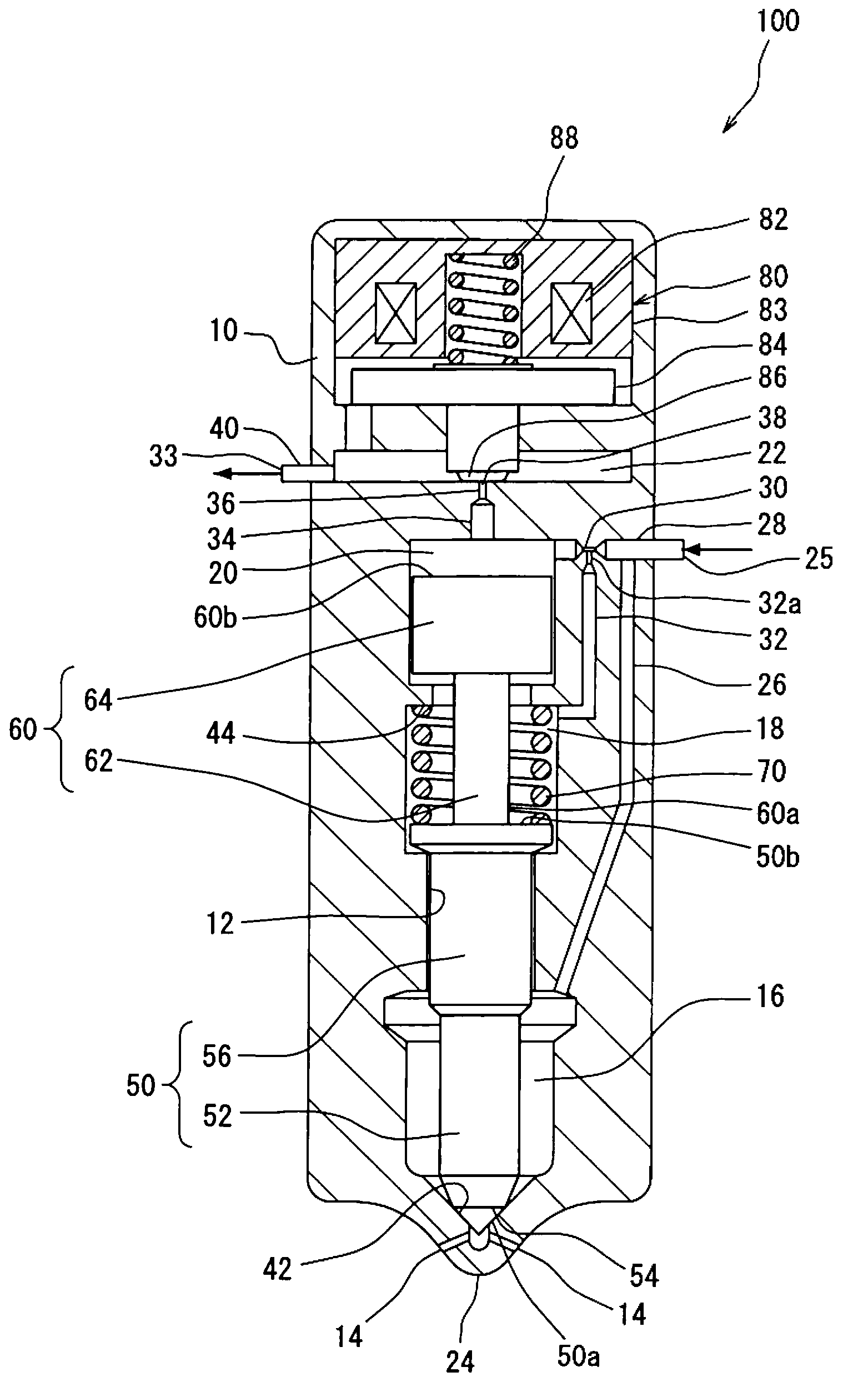
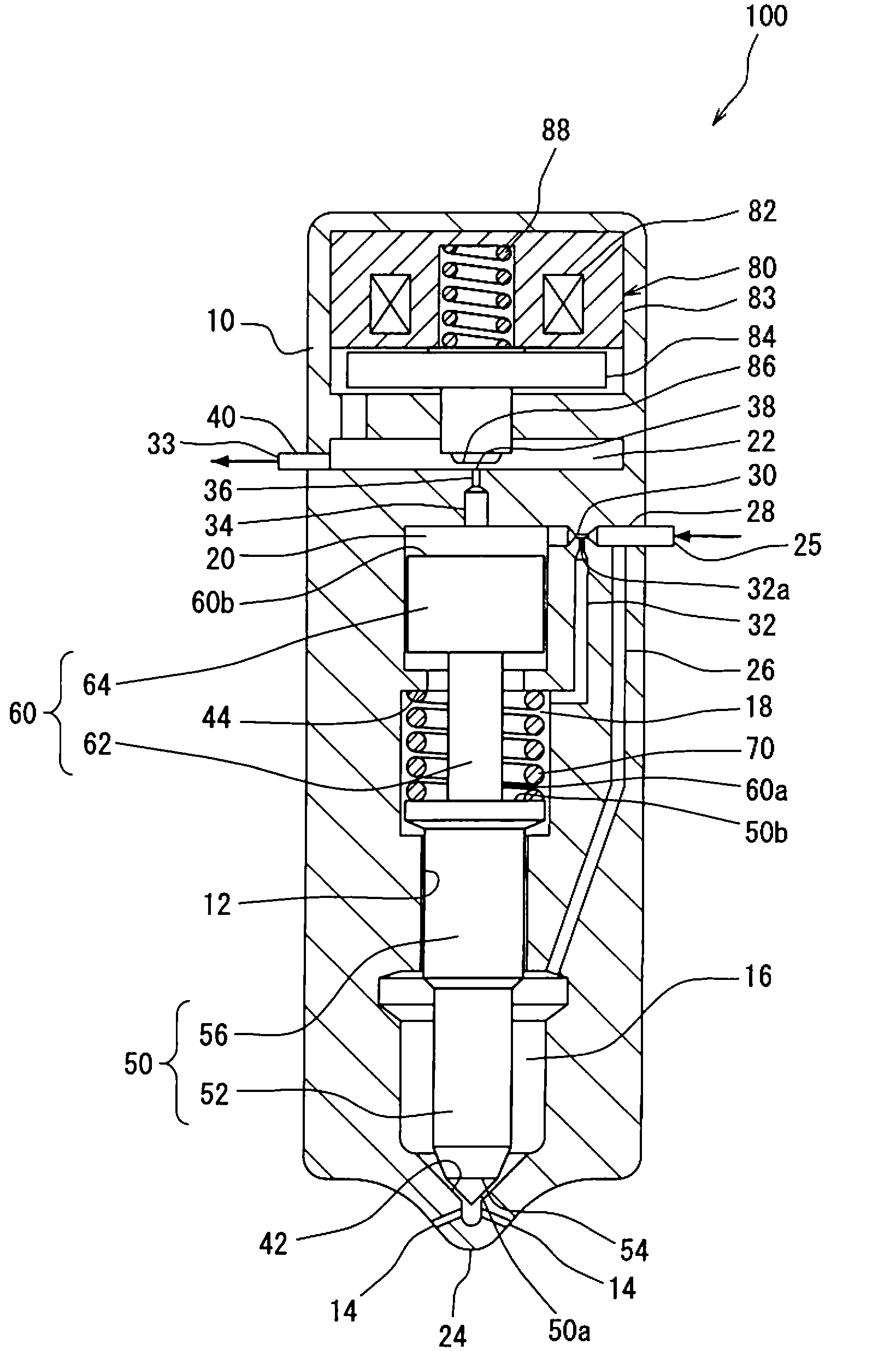
The invention relates to a fuel injector having a solenoid valve which actuates a multi-part armature assembly. The armature assembly comprises an armature bolt (10), an armature bolt (10) which is acted on by a valve spring (24), and an armature plate (70). As a result of the lifting motion of the armature bolt (10), a closing element (6) is opened or closed, whereby an injection valve member (60) can be actuated, in order to relieve the pressure in a control space (48). The armature plate (70) is guided, decoupled from the armature bolt (10), on an armature guide (28).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electronic unit injector with pressure assisted needle control
ActiveUS20050194462A1Increase fuel pressureFuel-injection pumpsFluid pressure injection controlEngineeringHigh pressure
An electronically controlled fuel injector includes a reduced part count and complexity over similar fuel injectors without a substantial reduction in performance capabilities. This is accomplished by using a one-piece needle that is hydraulically balanced and biased toward a closed position with a spring positioned in the needle control chamber. Although subtle, this injector has some ability to control the fuel pressure when the needle valve is opening and closing by adjusting a relative timing of a pressure control valve opening relative to a needle control chamber, using separate electrical actuators. The invention is particularly applicable to fuel injectors that cycle through high and low pressure states during and between injection events, respectively. Cam actuated fuel injectors being particularly well suited.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Fuel injector having a directly actuable injection valve element
InactiveCN101331312AFast hydraulic transferFluid pressure injection controlMachines/enginesSystem pressureControl room
A fuel injector for an internal combustion engine is proposed having a directly actuable injection valve element. The fuel injector has a nozzle needle (13), axially guided in a nozzle body (12), and an actuator (20) accommodated in an injector housing (10), wherein the nozzle needle (13) is connected to a coupling piston (34) on the nozzle-needle side and the actuator (20) is connected to a coupling piston (21) on the actuator side. The coupling piston (21) on the actuator side acts on a coupling space (32) and the coupling piston (35) on the nozzle-needle side acts on a control space (38), wherein the nozzle needle (13) is lifted from a nozzle-needle sealing seat (14) as a function of the pressure in the control space (38).; Provided between injector housing (10) and nozzle body (12) is an intermediate plate (40) having a passage (50) which hydraulically connects the coupling space (32) to the control space (38). The passage (50) contains a hydraulic choke (51) which has at least two sections (52, 53) having different cross sections of flow, wherein the section (52) having the smaller cross section of flow faces the coupling space (32) and the section (53) having the larger cross section of flow faces the control space (38).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel injection device
ActiveCN102828857AIncrease flow rateFuel supply apparatusFluid pressure injection controlControl roomInjection device
The present invention provides a fuel injection device. An inlet necking (30) forms in a fuel feed channel (28) which is disposed between an input port (25) and a console cabinet (20) and is suitable for receiving fuel at the input port (25) and then feed the fuel to the control cabinet (20). Feed neckings (32a, 46a) form in fuel feed channels (32, 46) which are disposed between the input port (25) and a middle cabinet (18) and are suitable for receiving fuel at the input port (25) and then feed the fuel to the middle cabinet (18). A cross sectional area of the smallest channel of the feed neckings (32a, 46a) is smaller than that of the inlet necking (30). When a valve member (86) moves from a valve opening position to a valve closing position, pressure increment of the middle cabinet (18) is put off compared with that of the console cabinet (20).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Accumulating fuel injection apparatus
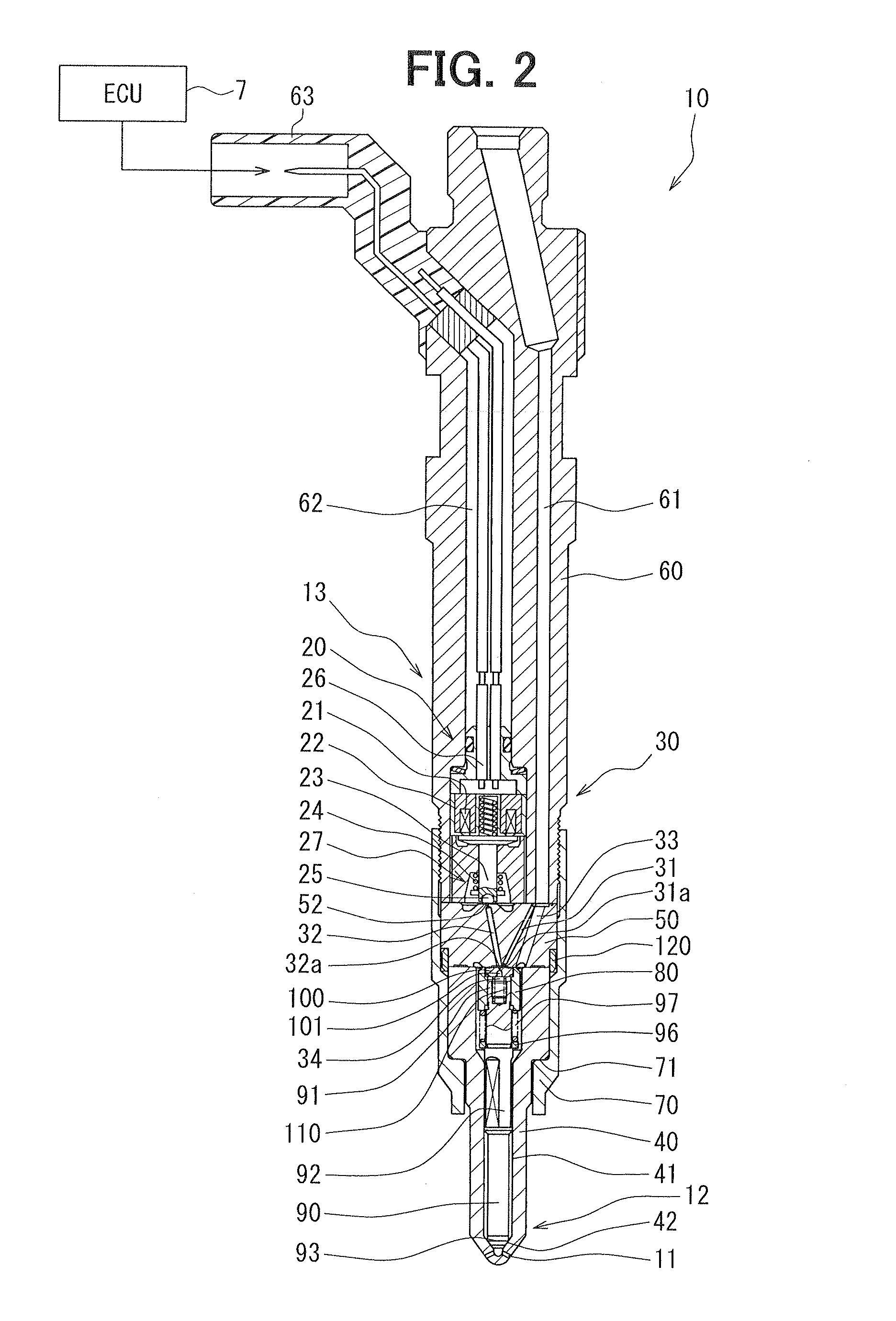
InactiveUSRE37633E1Increase the opening areaLow fuel pressureElectrical controlFuel injection with piezoelectric/magnetostrictive elementsInjection portSolenoid valve
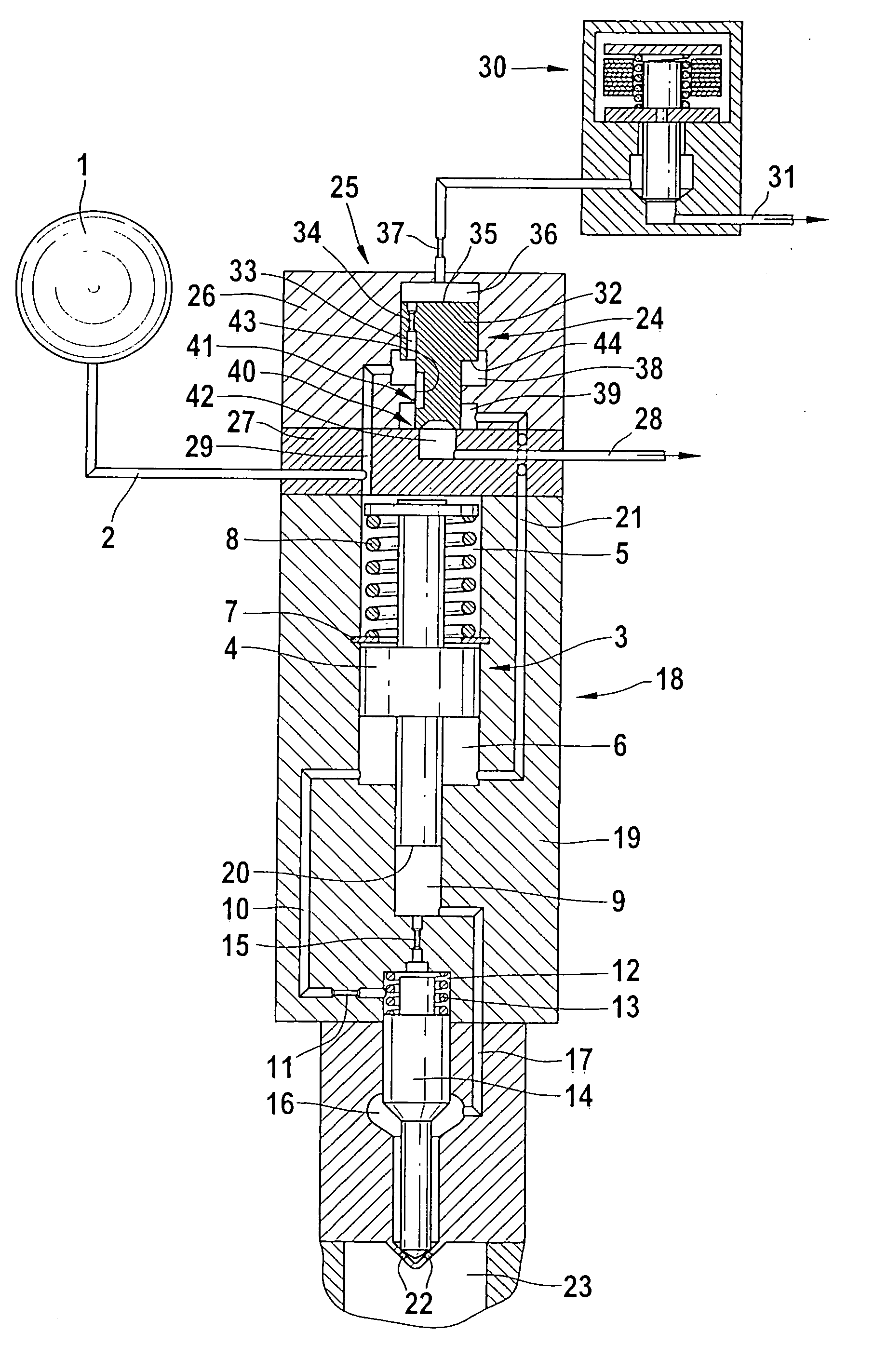
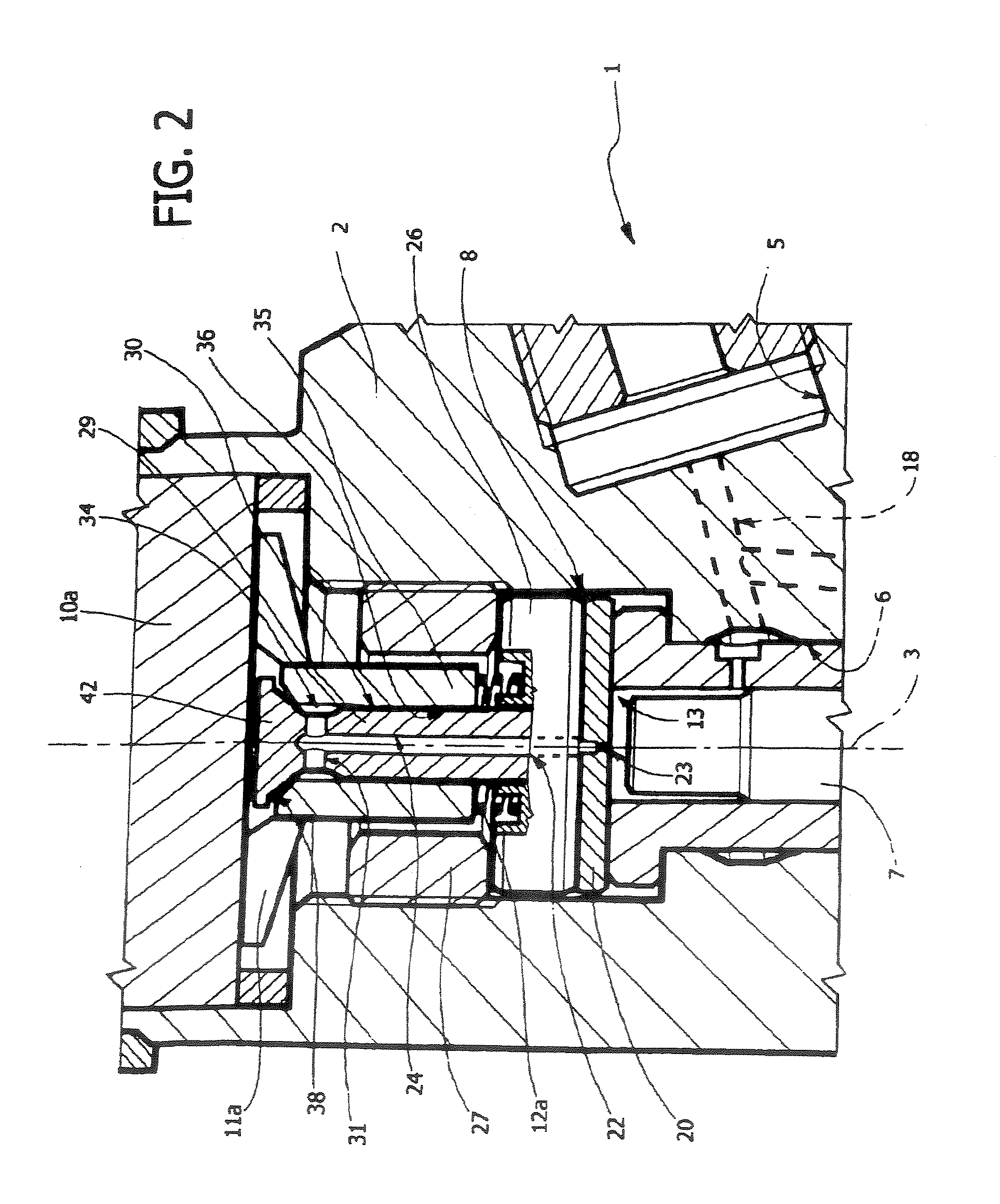
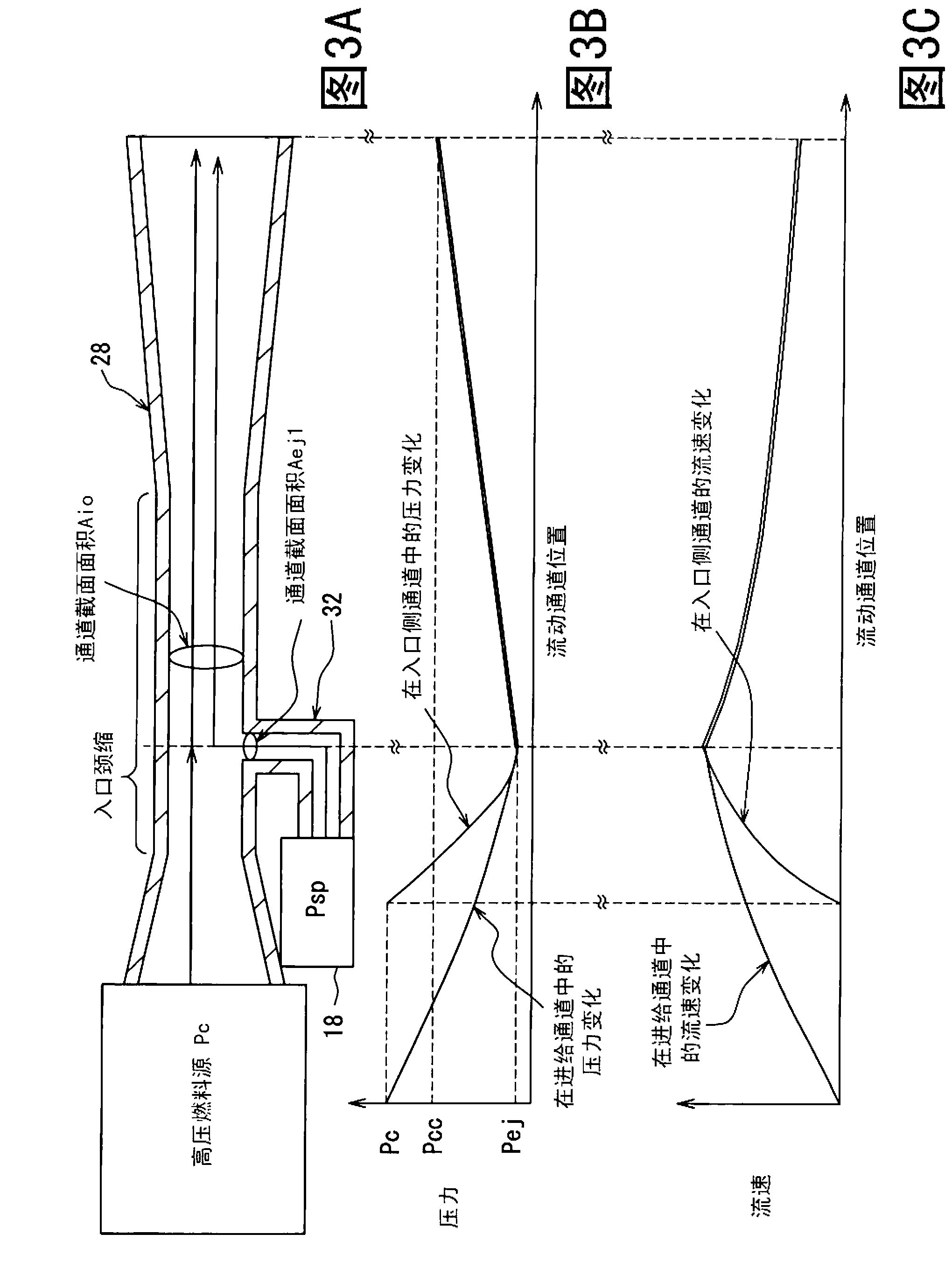
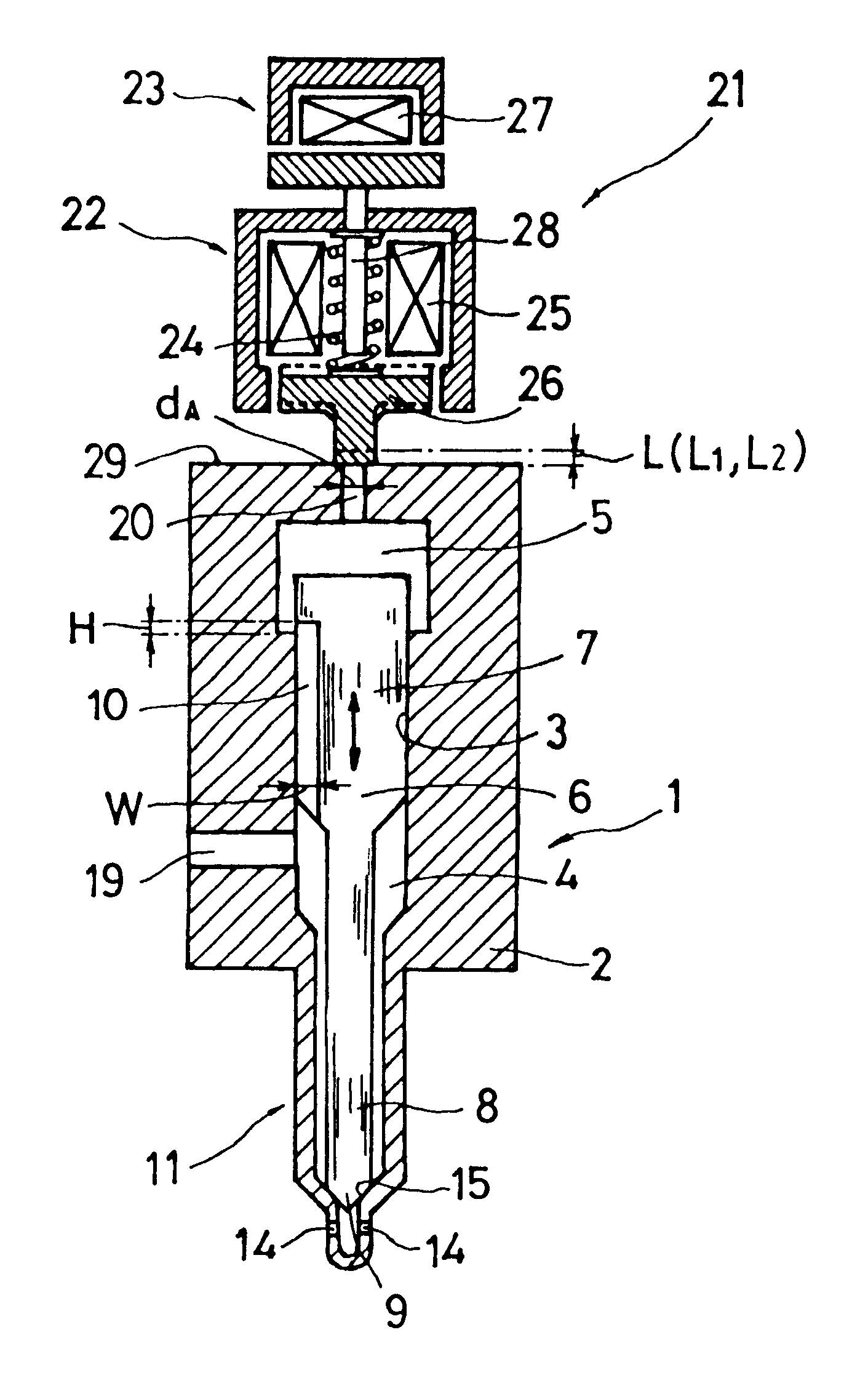
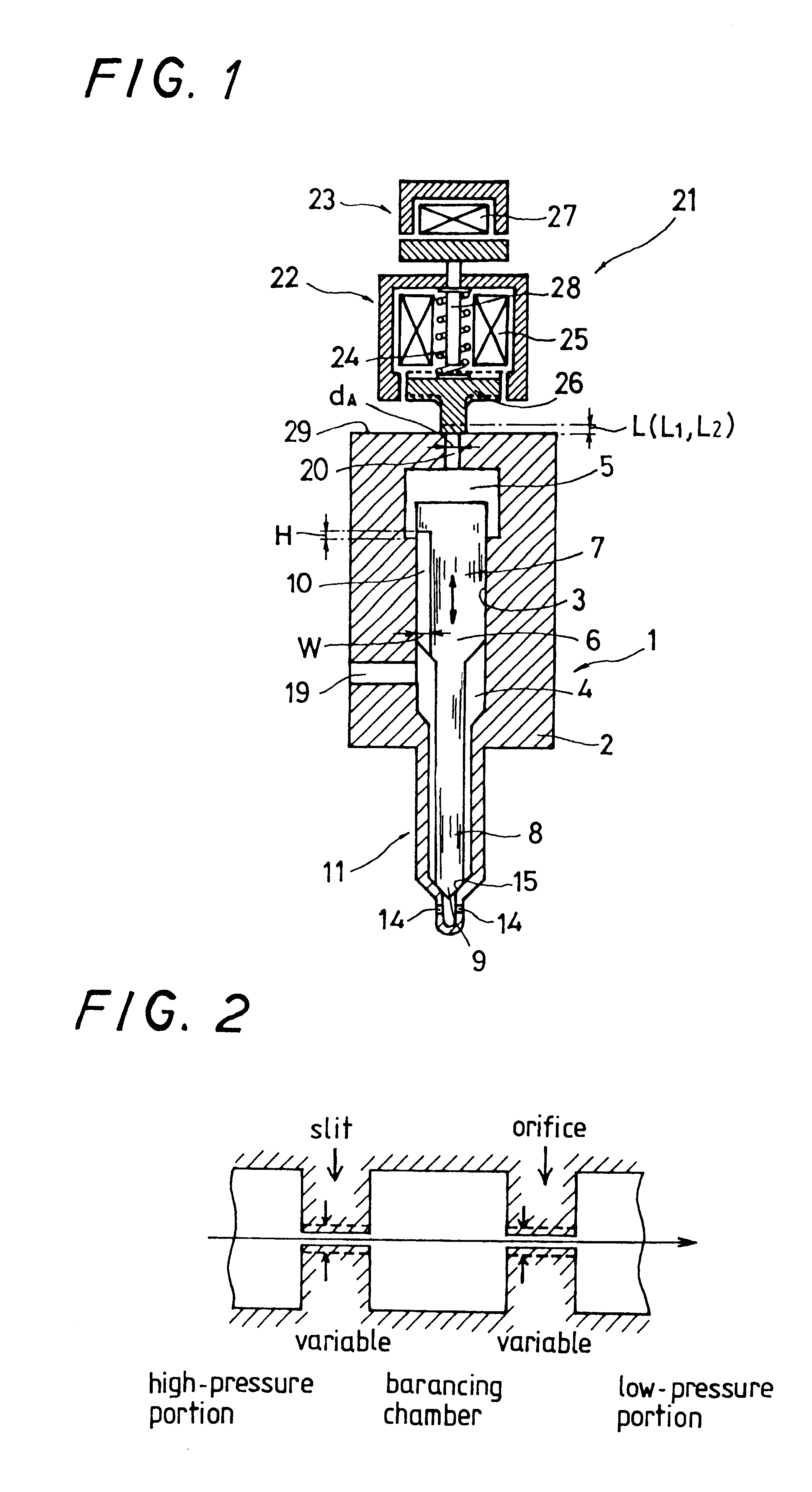
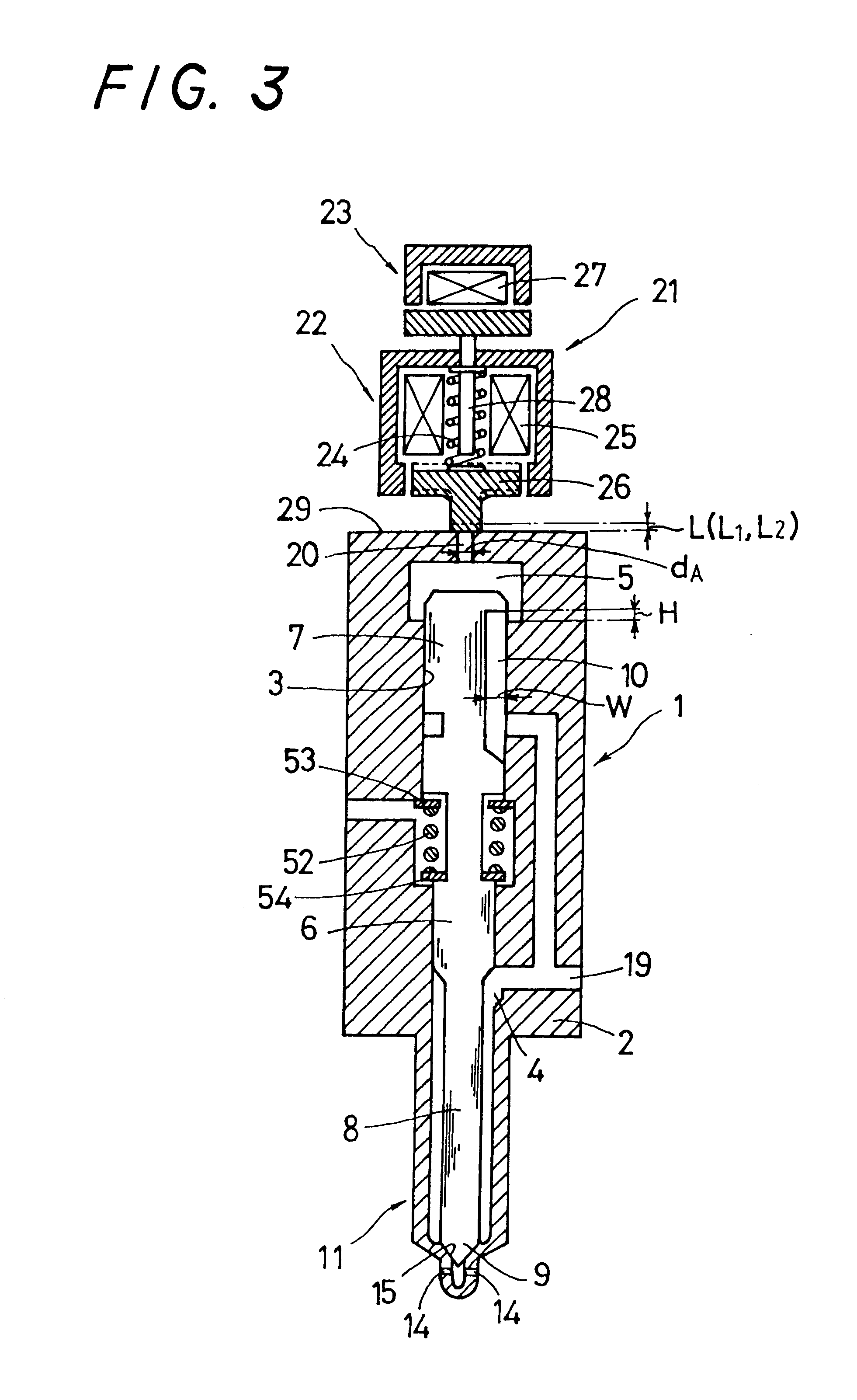
This accumulating fuel injection apparatus is provided with a needle valve 6 adapted to open and close an injection nozzle 11 having injection ports 14 in a lower end portion thereof, a balancing chamber 5 formed in a casing 2 so as to apply a fuel pressure to a head portion of the needle valve 6, a supply passage including a slit 10 and used for supplying a fuel from a fuel supply port 19 to the balancing chamber 5, a discharge passage 20 comprising an orifice for discharging the fuel from the balancing chamber 5, and a solenoid valve 22 adapted to open and close the discharge passage 20, the lift of a valve disc 26 of the solenoid valve 22 is controlled by a lift control means comprising a stopper 28 the position of which is controlled by a lift control mechanism 23. The opening area of the discharge passage 20 comprising an orifice increases and decreases in accordance with the lift of the valve disc 26, and the lift of the needle valve 6 is determined so that the opening area of the slit 10 facing the interior of the balancing chamber 5 increases and decreases correspondingly to the flow rate of the fuel passing through the discharge passage 20, the degree of opening of the injection nozzle 11 increasing and decreasing accordingly.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD +1
Injector with a magnet valve for controlling an injection valve
InactiveUS6877680B2Suppress pressure fluctuationsReduce intensitySpray nozzlesFluid pressure injection controlSolenoid valveFuel tank
Disclosed is an injector for fuel injection, with a magnet valve for controlling an injection valve, in which the magnet valve has a movable armature that can be moved onto a valve seat in the lower armature chamber. The lower armature chamber communicates fluidically with the control pressure chamber of the injection valve via bores. Via a return bore, incidental leak fuel quantities can be returned to a tank via the lower armature chamber. To prevent armature recoil upon closure of the valve seat by the armature, it is proposed that means be provided in the injector for reducing pressure fluctuations occurring in the lower armature chamber. Eliminating pressure fluctuations in the lower armature chamber leads to maximal elimination of armature recoil.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
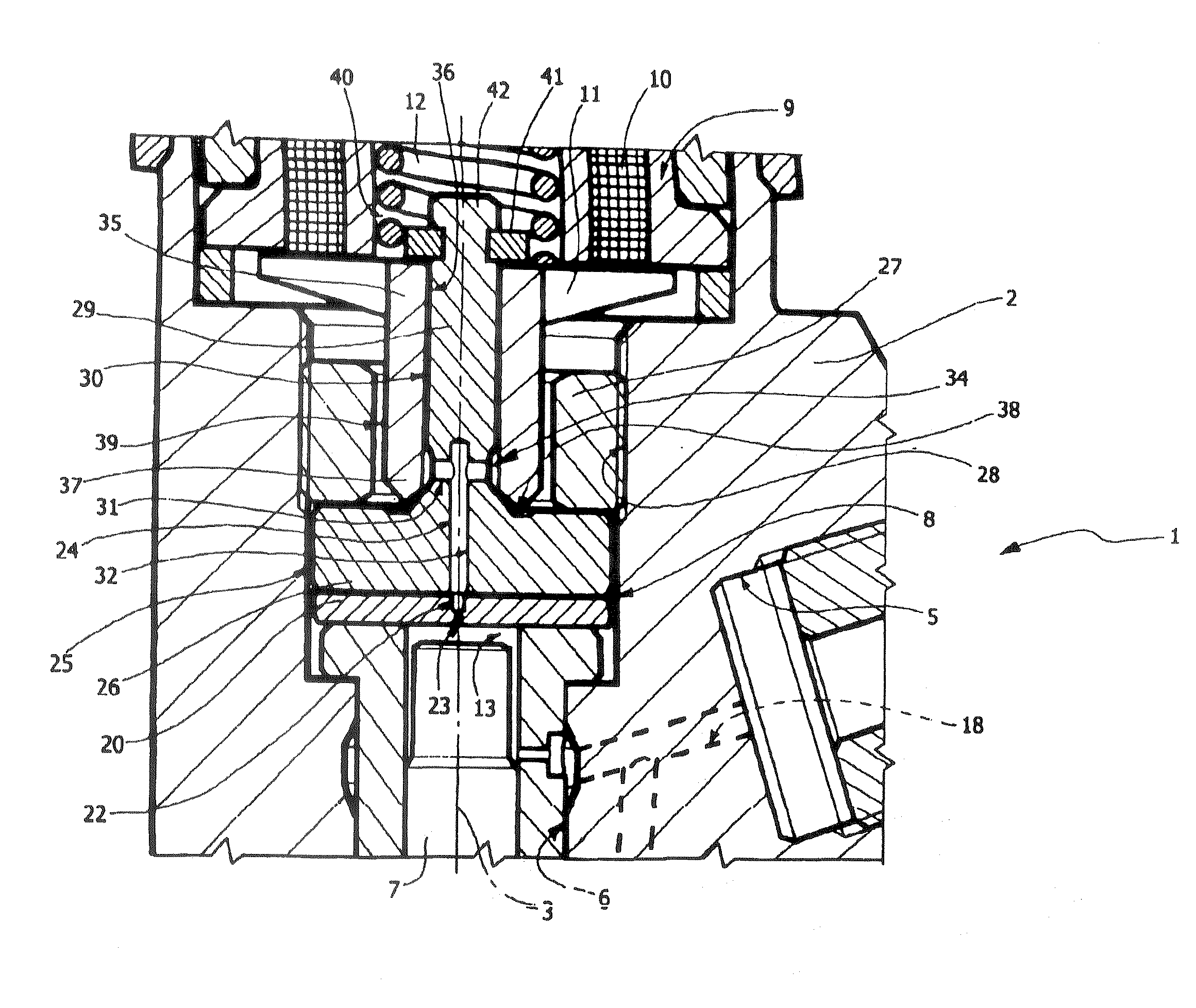
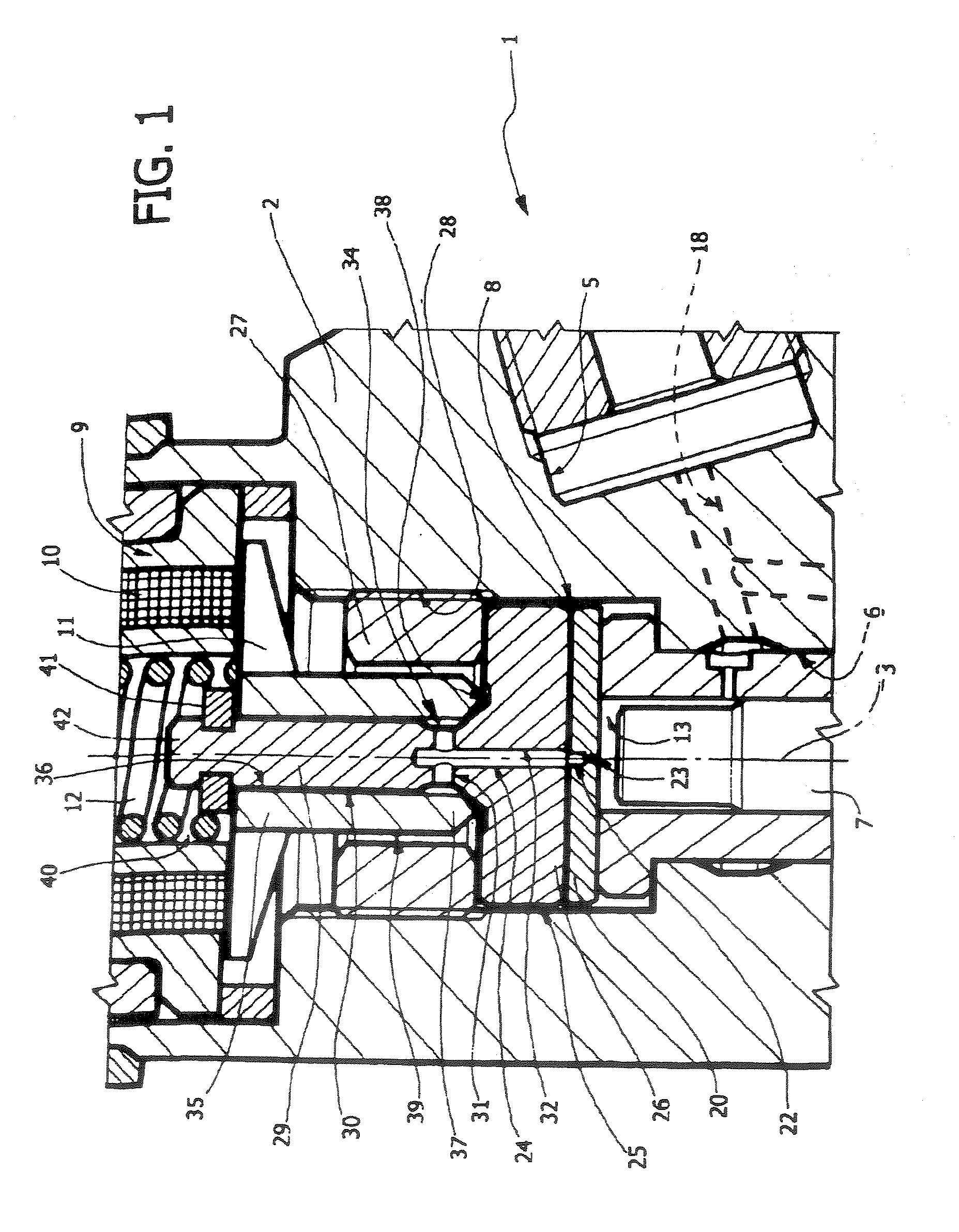
Control module for an injector of an accumulator injection system
InactiveUS6986474B2Improve accuracyHigh movement precisionFuel injection with piezoelectric/magnetostrictive elementsFluid pressure injection controlEngineeringControl room
A control module (1) for an injector of an accumulator injection system is used to control and guide a valve body (8). The control module comprises a high pressure supply line (2) for supplying fuel, and a guiding device (3) for guiding the valve body (8). A control room (4), an inlet throttle (5) and an outlet throttle (6) are also provided. The inlet throttle (5) connects the high pressure supply line (2) to the control chamber (4) and the outlet throttle (6) connects the control chamber (4) to a control valve (15). A control piston (7) is arranged in the control chamber (4), the end of the control piston opposite the control chamber (4) being connected to a high pressure region (9) on the valve body (8).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Fuel injection valve for high pressure injection
InactiveUS6131540ADeteriorate power lossReduce noise radiationElectrical controlAir coolingSolenoid valveInternal combustion engine
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 02378 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 14, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 14, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 11, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 43542 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 20, 1997A fuel injection valve which is provided for high pressure injection in self-igniting internal combustion engines and has a solenoid valve for controlling the injection. To trigger this solenoid valve, a control circuit is provided which is subdivided into a first circuit part and a second circuit part. The second circuit part is separate from the first circuit part, which jointly serves to control a number of injection valves, and are disposed on each individual injection valve. The housing is clipped onto the fuel injection valve and fuel flows through its interior for cooling purposes.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electrovalve for controlling an injection valve in an internal combustion engine
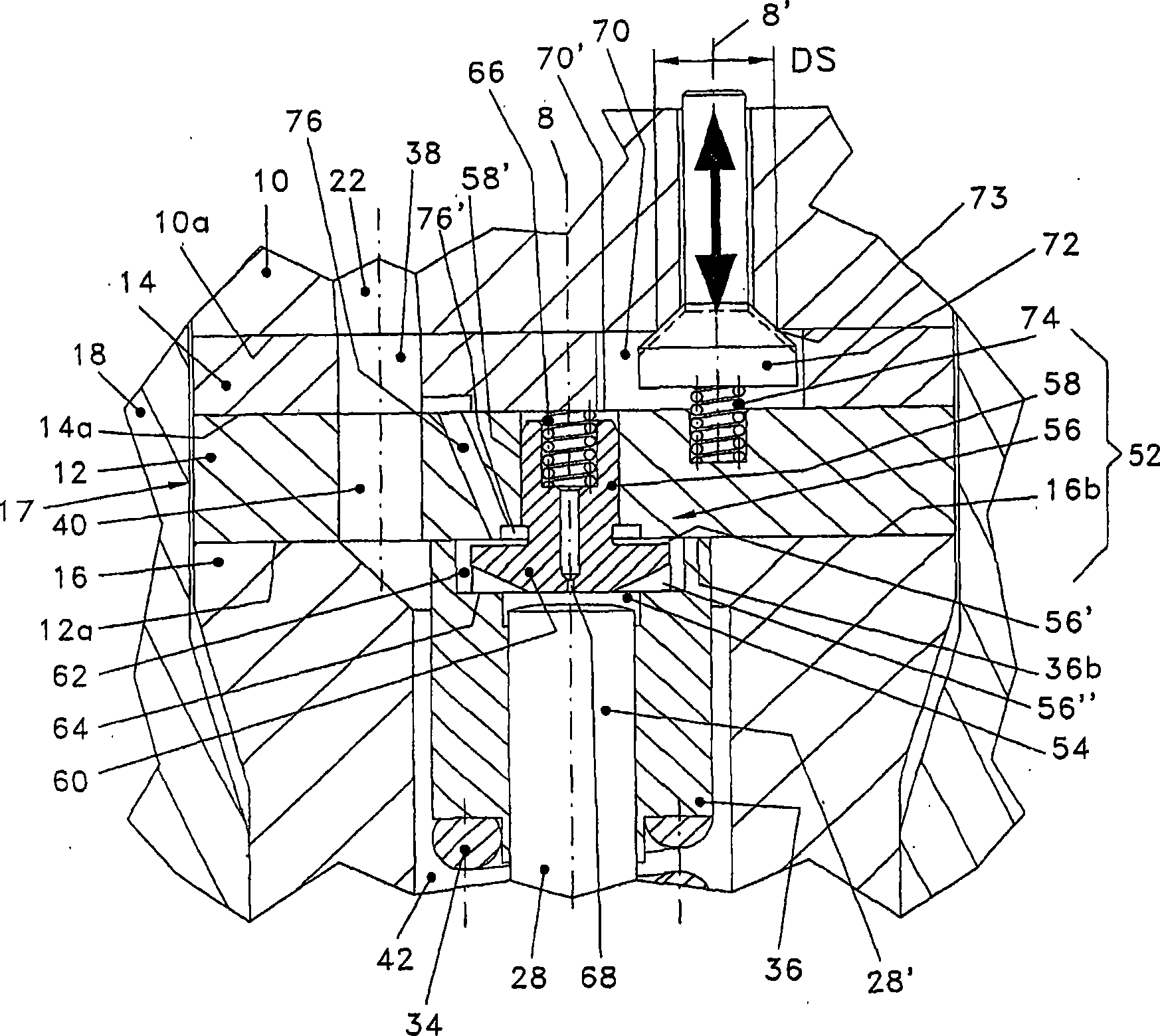
InactiveUS20030178593A1Easy to assembleAvoid disadvantagesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure injection controlInertial massSolenoid valve
In a solenoid valve for controlling a fuel injector of an internal combustion engine, which has an electromagnet (29), a movable armature having an armature plate (28) and an armature pin (27), and a control valve element (25), which is moved with the armature and works together with a valve seat (24), for opening and closing a fuel drain channel (17) of a control pressure chamber (14) of the fuel injector (1), this armature plate (28) being mounted on the armature pin (27) so it is movable by sliding under the effect of its inertial mass in the closing direction of the control valve element (25) against the tension of a return spring (35) acting on the armature plate (28), in order to be able to easily set the maximum slide path of the armature plate (28), an actuator is provided on the armature plate which is arranged on a section (42) of the armature plate (28) facing away from the electromagnet (29) and is adjustable in the sliding direction of the armature plate (28) relative to a face (41) of the armature plate facing the electromagnet.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method of manufacturing ring-shaped member, backup ring and seal structure for fuel injection valve
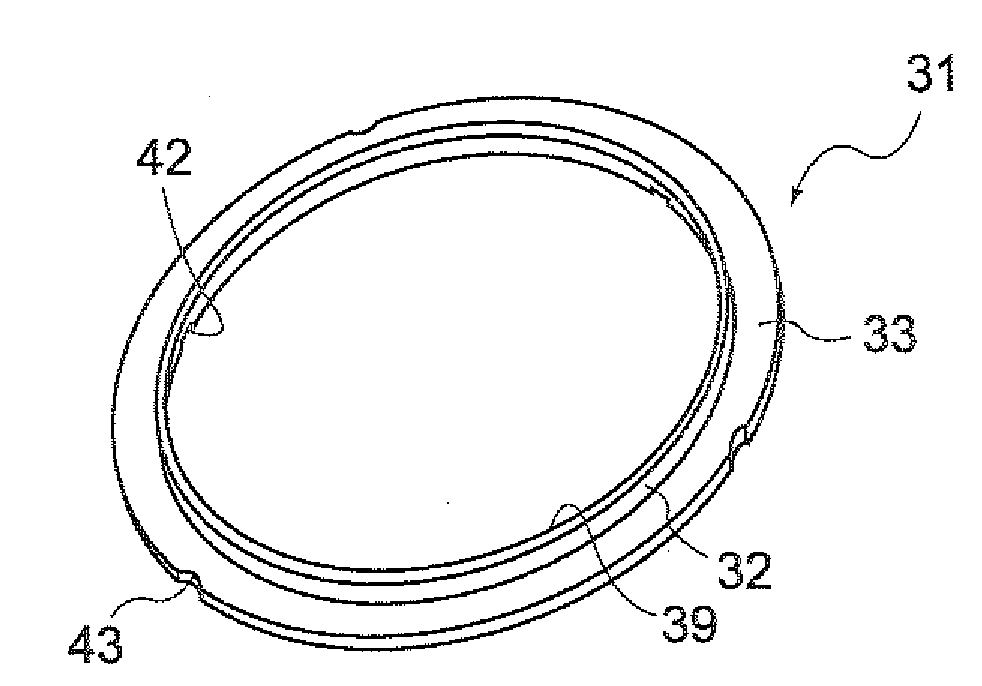
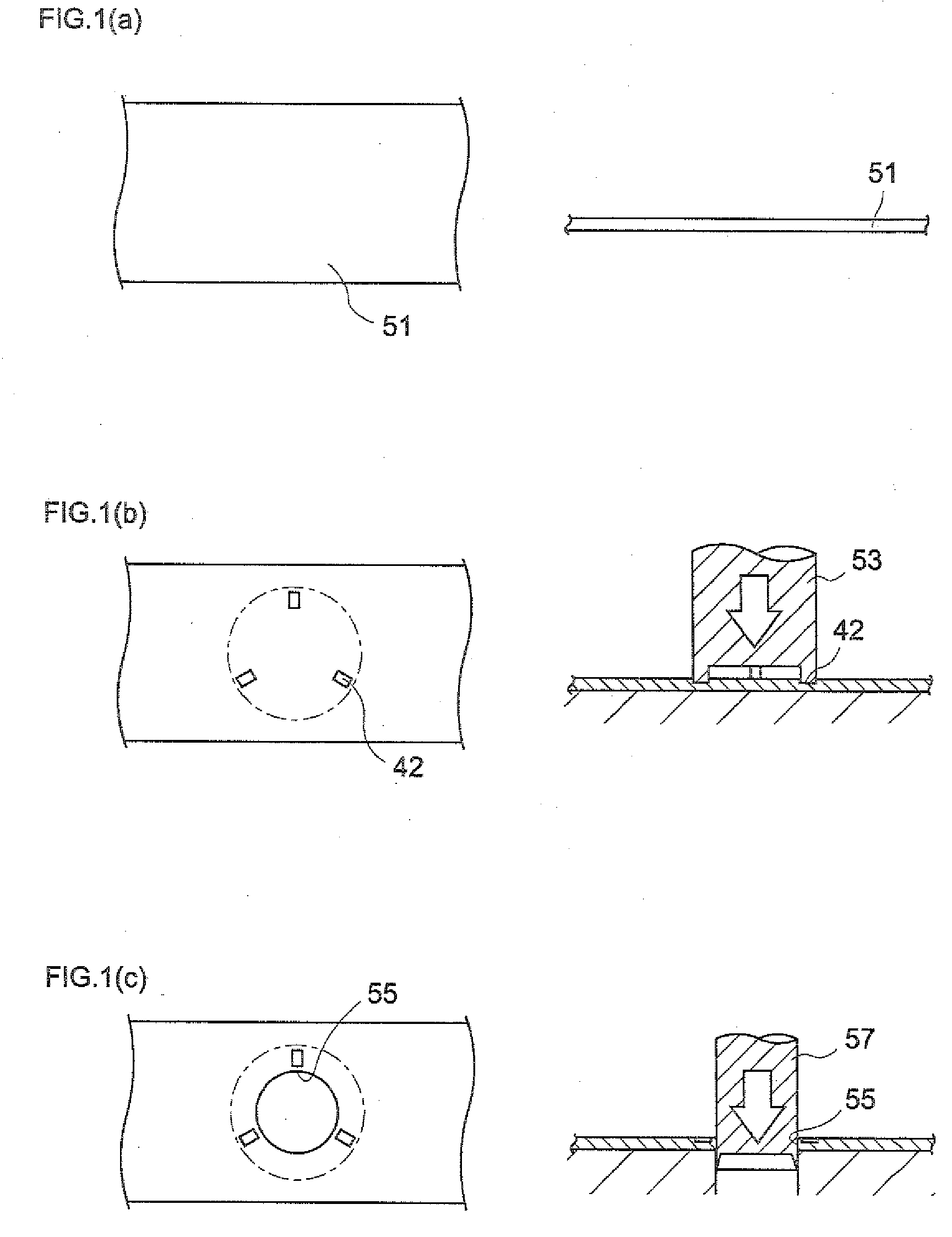
InactiveUS20090121442A1Improve stress resistanceEfficient preparationEngine sealsFluid pressure injection controlEngineeringFlange
To provide: a method of manufacturing a ring-shaped member that can efficiently manufacture a stronger backup ring that reinforces a seal member disposed in a pressure introduction chamber of a fuel injection valve; the backup ring; and a seal structure for a fuel injection valve disposed with the backup ring.A method of manufacturing a ring-shaped member that is manufactured by subjecting a rigid flat-shaped base material to burring includes: a step of forming a prepared hole with respect to the base material; a step of pressing an edge portion of the prepared hole to thereby bend the edge portion using a first punch member that has a diameter that is larger than the diameter of the prepared hole and is tapered towards its distal end portion; and a step of forming a flange portion by press-inserting, with respect to the prepared hole whose edge portion has been bent, a second punch member that has a diameter that is smaller than the diameter of the first punch member and is tapered towards its distal end portion.
Owner:BOSCH CORP +1
Injector for injecting fuel into combustion chambers of internal combustion engines, in particular a piezoelectric-actuator-controlled common rail injector
InactiveUS20070170286A1Cheap productionMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesCombustion chamberCommon rail
A common rail injector for an internal combustion engines has control means including a piezoelectric actuator deposed in an injector body and via at least one booster piston actuates a control valve received in a valve plate. Also provided are a nozzle body having a nozzle outlet on its free end toward the combustion chamber; a nozzle needle located axially movably and actuatably in a longitudinal recess of the nozzle body; a throttle disk, closing off the rear end (remote from the nozzle outlet) of the longitudinal recess and located between the nozzle body and the control valve, which throttle disk forms an opening stop for the nozzle needle and cooperates with the rear end face of the nozzle needle and thus limits the opening stroke of the nozzle needle; and a control chamber between the rear nozzle needle end face and the throttle disk, which chamber is in hydraulic communication with a pressure connection serving to deliver fuel. A substantial special feature is that a cylindrical retaining body is disposed in the injector body and receives the booster piston or pistons and the valve plate that contains the control valve.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Valve for controlling liquids
InactiveUS6464202B1Simple structural designOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower flowEngineering
A valve (1) for controlling fluids is provided with a valve member (2), which is axially displaceable in a bore (5) of a valve body (3) and has a valve head (6), forming a valve closing member, that cooperates with a seat (7), provided on the valve body (3), for opening and closing the valve (1). A piezoelectric unit (4) for actuating the valve member (2) and a tolerance compensating element (12) for compensating for elongation tolerances of the piezoelectric unit (4) and / or other valve components (3) are also provided. The piezoelectric unit (4) is disposed in terms of its action direction essentially at a right angle to the axial direction of motion of the valve member (2) and can be acted upon by electric current such that the piezoelectric unit (4) exerts a tilting motion on a control member (12) that serves as a lever arm and is operatively connected to the valve member (2).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
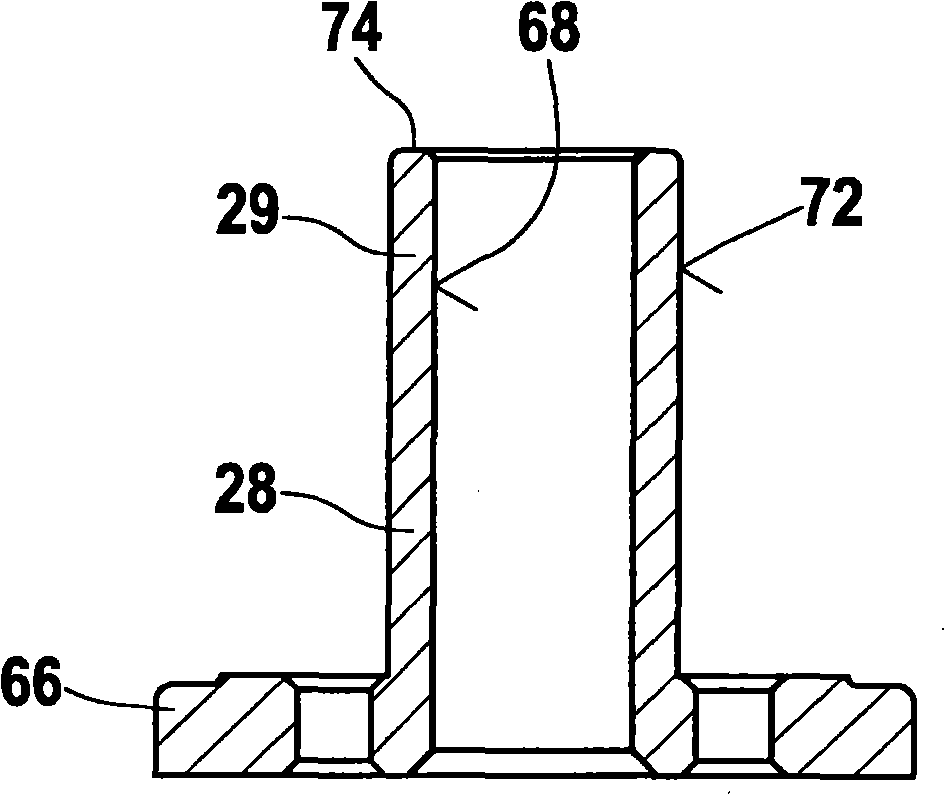
Fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines
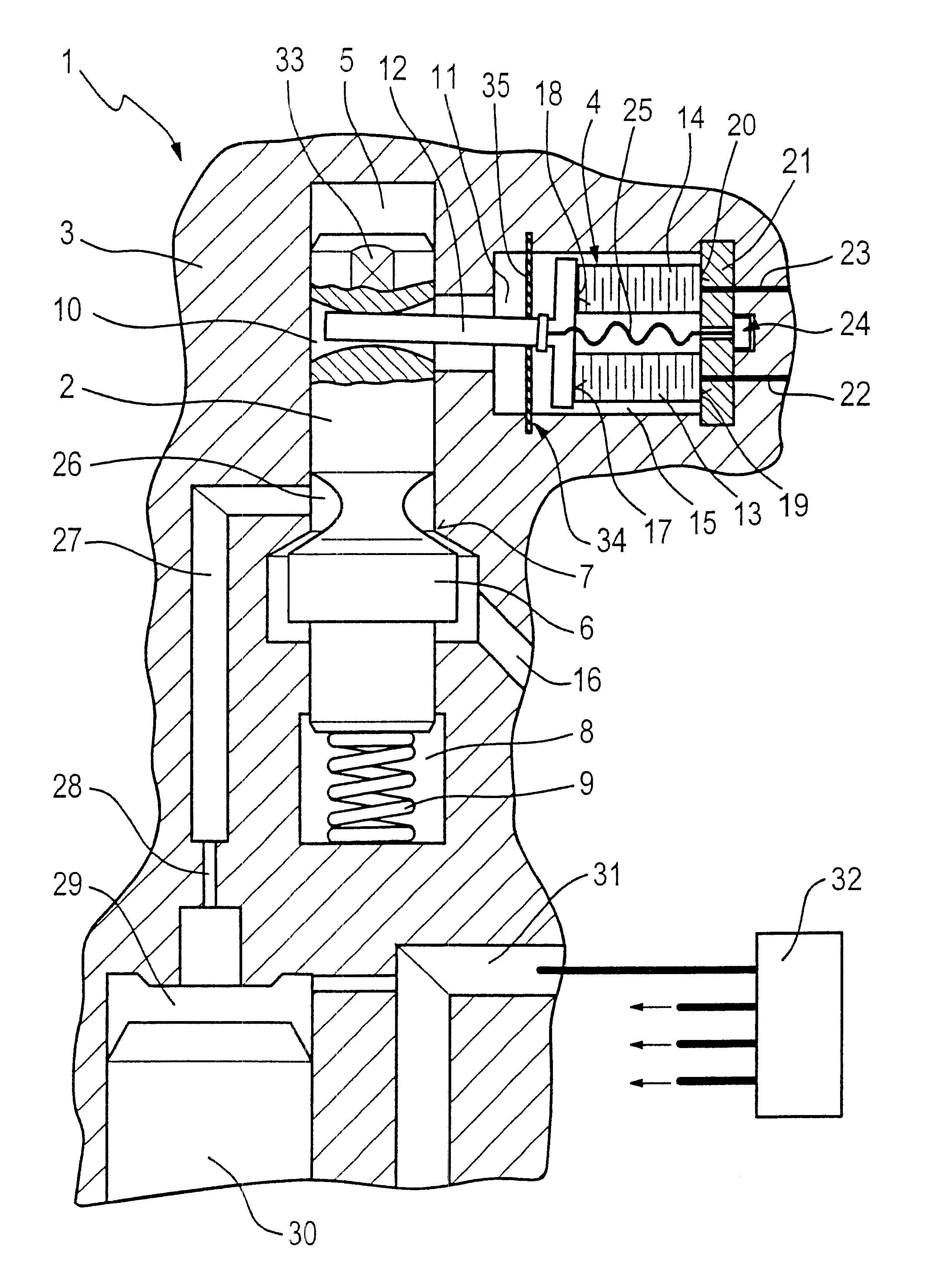
A control device (52) of a fuel injection valve has a mushroom-shaped intermediate valve member (56) which is guided with a sliding fit (58') in a first intermediate plate (12). An injection valve member (28), which has a control piston (28'), for opening and closing injection openings in order to realize intermittent injection processes defines a control space (54) together with a guide sleeve (36) and the lower face (12a) of the first intermediate plate (12). A second intermediate plate (14) is situated between the first intermediate plate (12) and a housing body (10), and has a valve space (70) which is hydraulically connected to the end side of a shank (58) of the mushroom-shaped intermediate valve member (56).
Owner:GANSER HYDROMAG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com