Patents
Literature
25025results about "Fuel injection control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flow meter
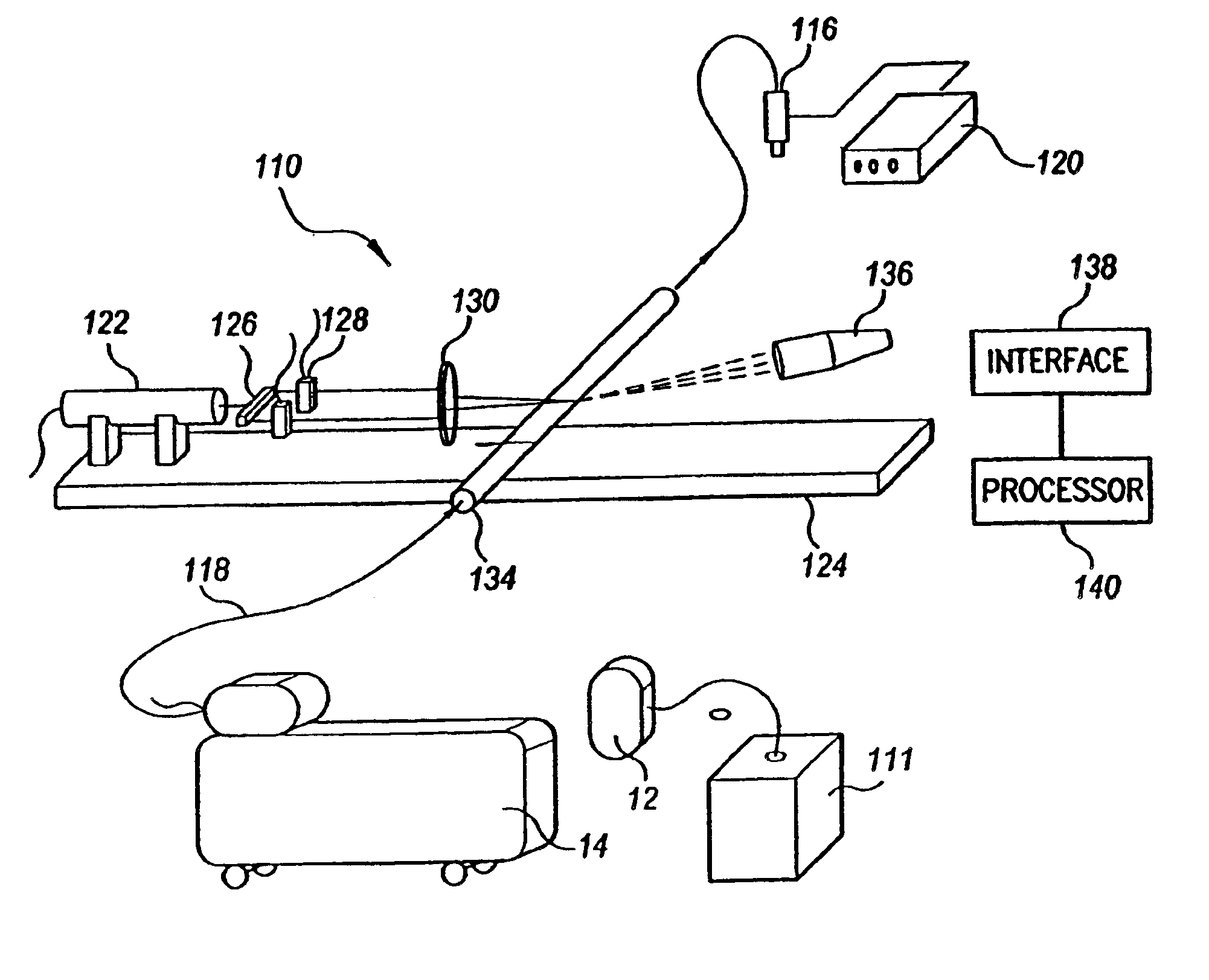
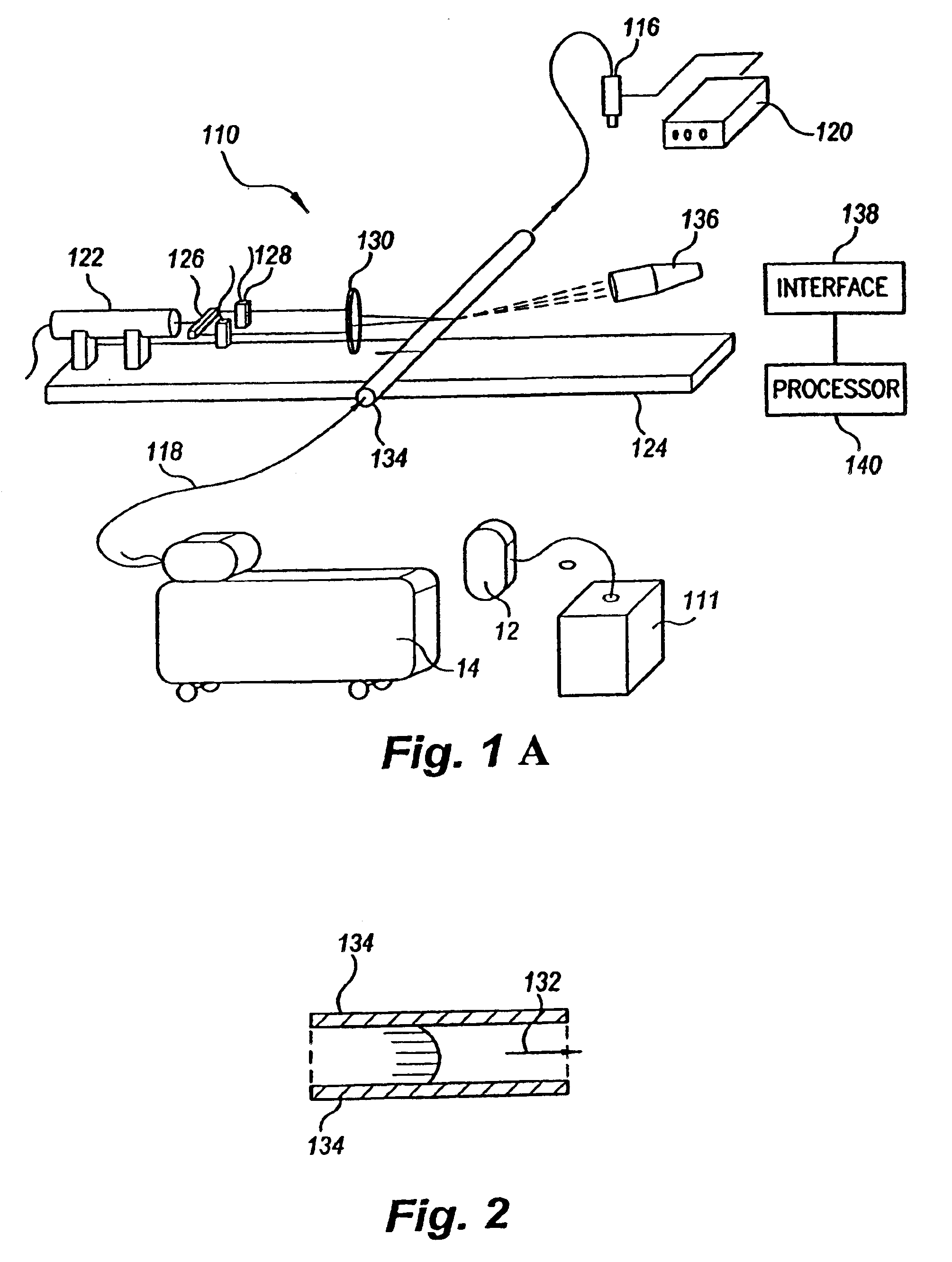
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a flow meter device having a laser Doppler anemometer (LDA) which measures the instantaneous center line velocity of fluid flow in a pipe. The flow meter may process the instantaneous velocity so obtained to compute the volumetric flow rate, mass rate, and / or other flow characteristics (e.g., as instantaneous quantities and / or integrated over a time interval) The flow meter may use an electronic processing method. The electronic processing method may provide essentially an exact solution to the Navier-Stokes equations for any periodically oscillating flow.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
Internal combustion engine control for improved fuel efficiency
ActiveUS7577511B1Smoother and precise controlReduce probabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineWork cycle
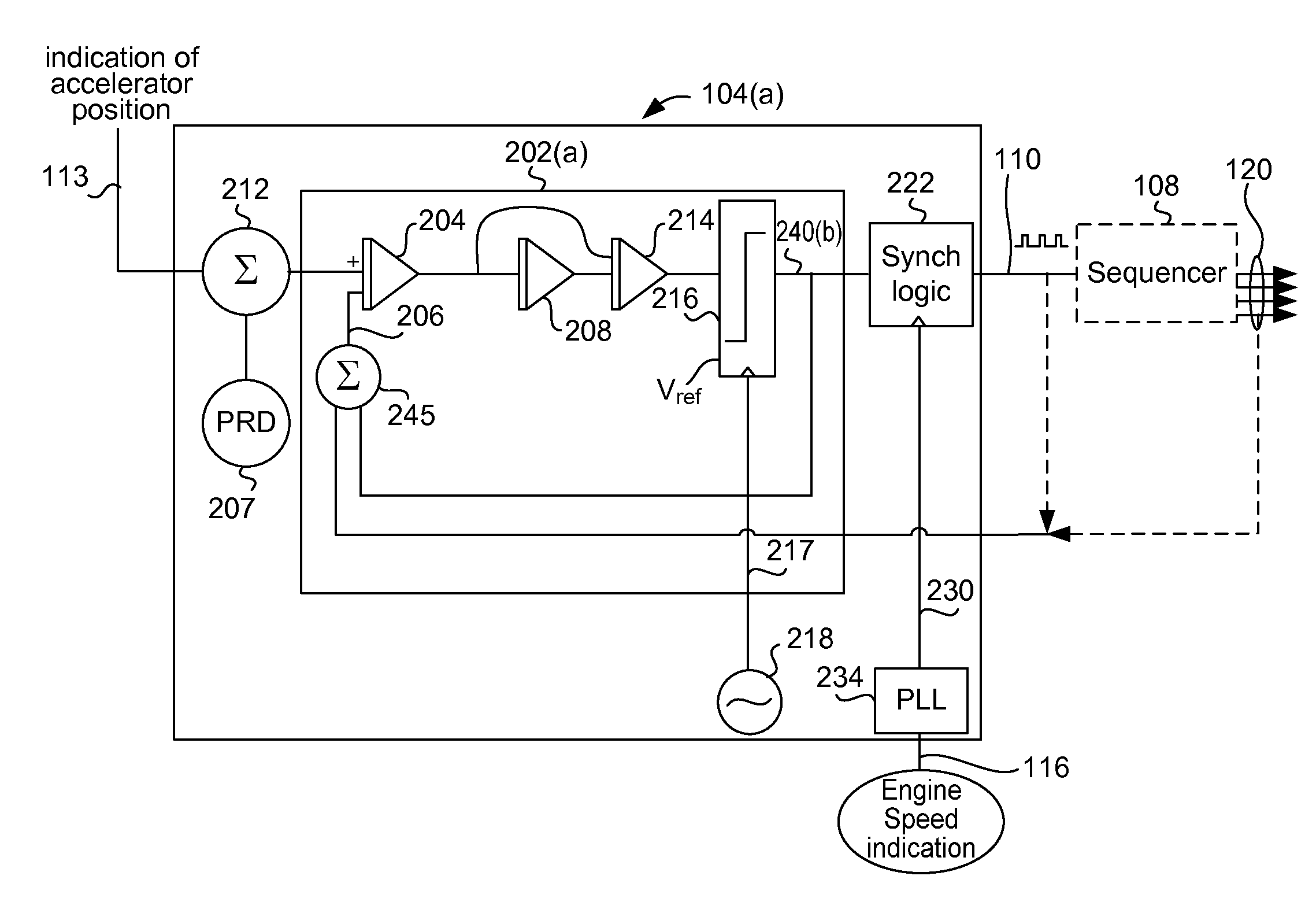
A variety of methods and arrangements for improving the fuel efficiency of internal combustion engines are described. Generally, selected combustion events are skipped during operation of the internal combustion engine so that other working cycles can operate at a better thermodynamic efficiency. In one aspect of the invention, an engine is controlled to operate in a variable displacement mode. In the variable displacement mode, fuel is not delivered to the working chambers (e.g. cylinders) during selected “skipped” working cycles. During active (“non-skipped”) working cycles, a maximum (e.g., unthrottled) amount of air and an optimized amount of fuel is delivered to the relevant working chambers so that the fired working chambers can operate at efficiencies closer to their optimal efficiency. A controller is used to dynamically determine the chamber firings required to provide the engine torque based on the engine's current operational state and conditions. The chamber firings may be sequenced in real time or in near real time in a manner that helps reduce undesirable vibrations of the engine.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
Method for forming insulation film
InactiveUS20050161434A1Quality improvementIncreasing the thicknessElectrical controlDecorative surface effectsSubstrate surfaceElectron
In a process involving the formation of an insulating film on a substrate for an electronic device, the insulating film is formed on the substrate surface by carrying out two or more steps for regulating the characteristic of the insulating film involved in the process under the same operation principle. The formation of an insulating film having a high level of cleanness can be realized by carrying out treatment such as cleaning, oxidation, nitriding, and a film thickness reduction while avoiding exposure to the air. Further, carrying out various steps regarding the formation of an insulating film under the same operation principle can realize simplification of the form of an apparatus and can form an insulating film having excellent property with a high efficiency.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
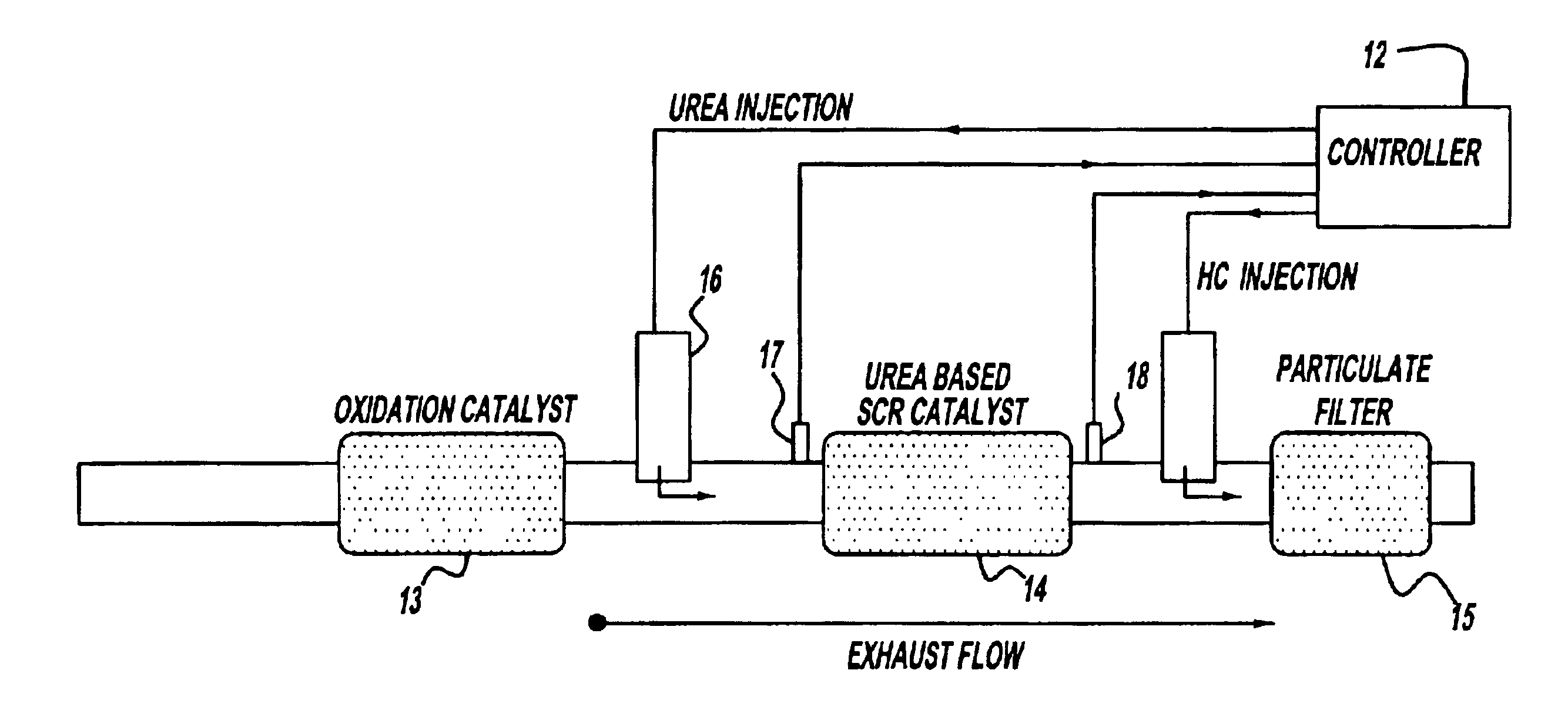
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6928806B2Improve NOx conversion efficiencyHigh operating temperatureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesSystem configuration
A system for effective NOx and particulate matter control in a diesel or other lean burn internal combustion engine is presented. The system includes a urea-based SCR catalyst having an oxidation catalyst coupled upstream of it and a particulate filter coupled downstream of the SCR catalyst. This system configuration results in improved NOx conversion due to fast SCR catalyst warm-up and higher operating temperatures. Additionally, placing the particulate filter last in this system configuration reduces tailpipe ammonia emissions as well as prevents any thermal damage to the SCR catalyst due to the particulate filter regeneration.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
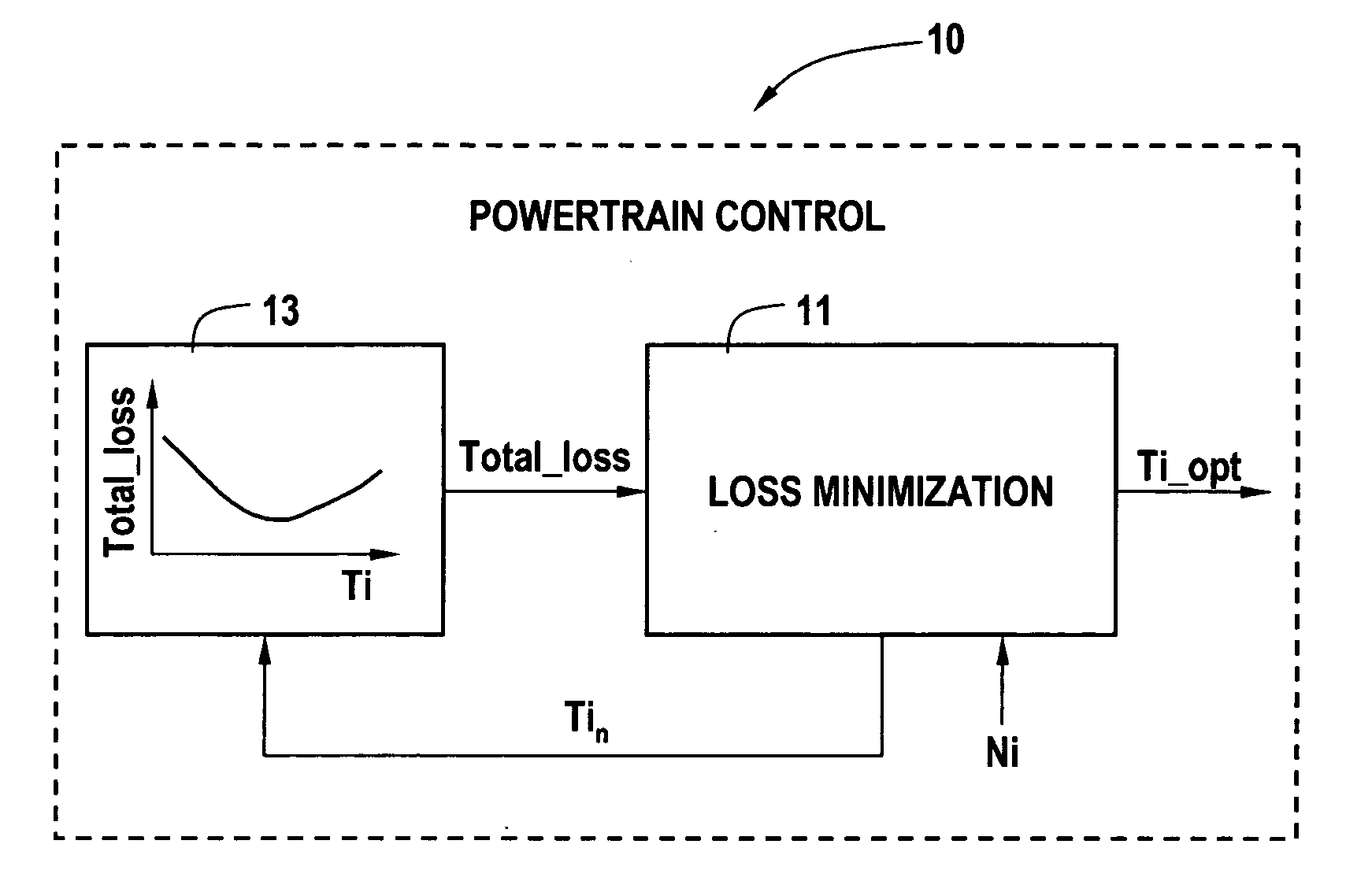
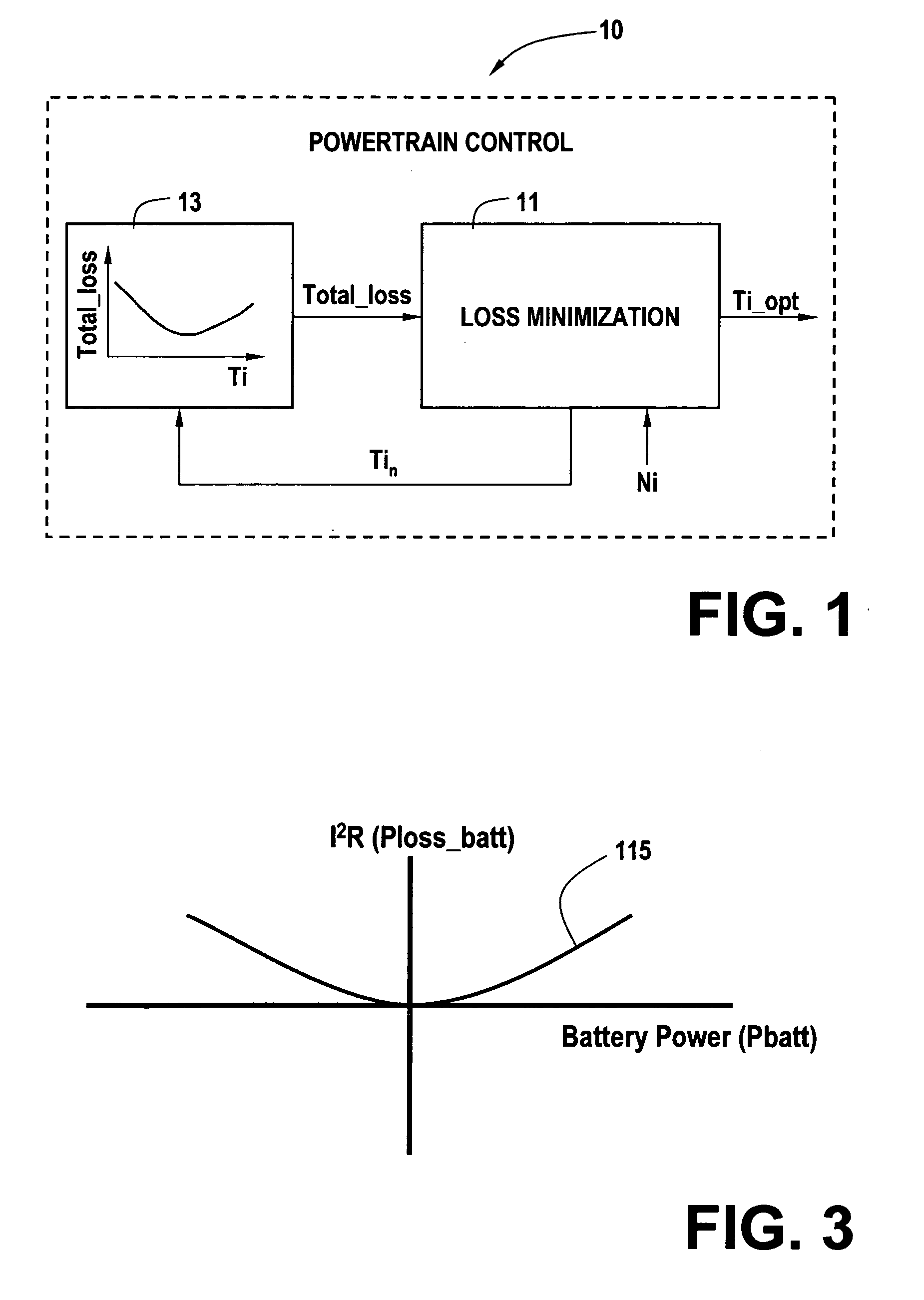
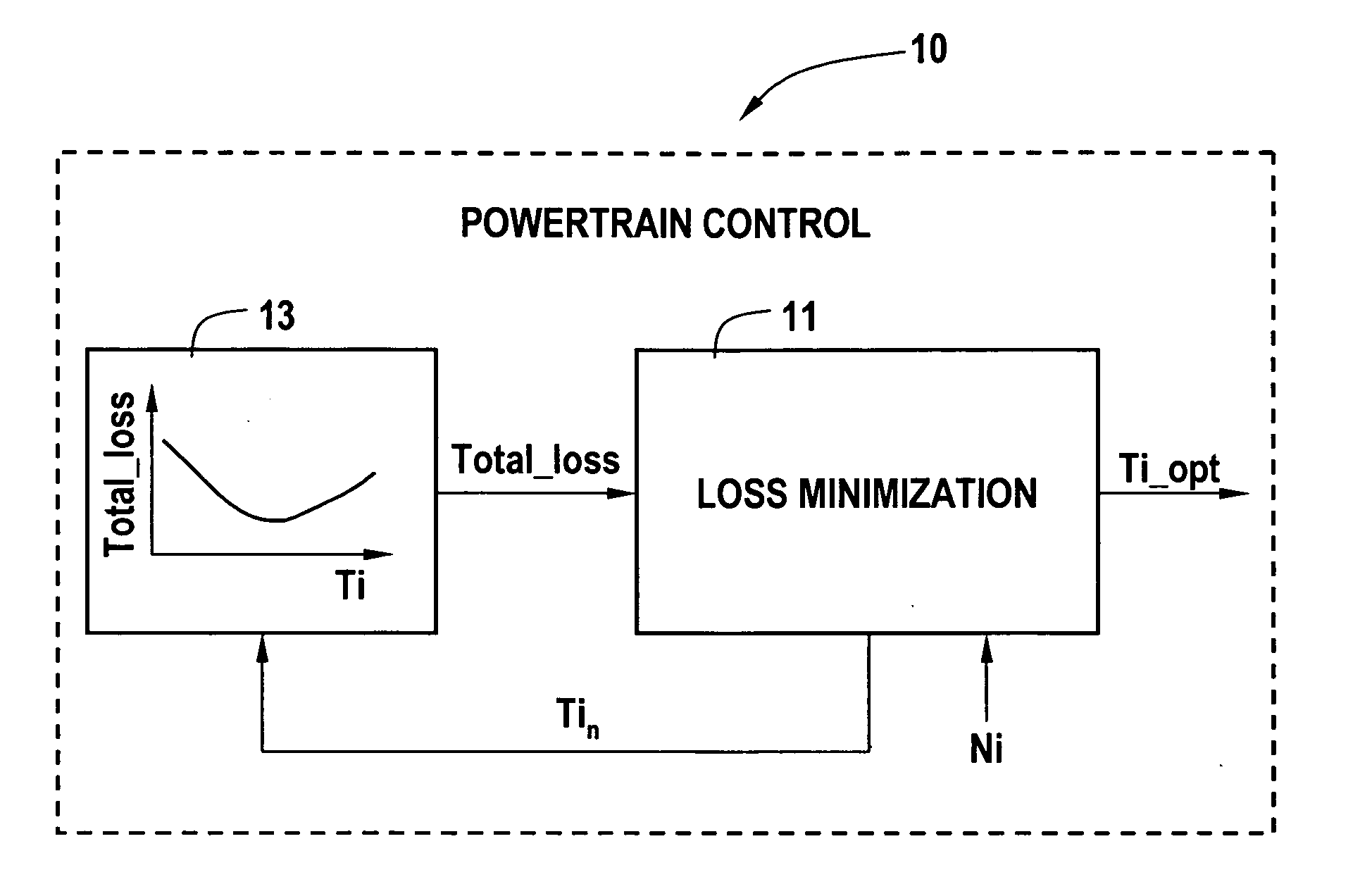
Cost structure method including fuel economy and engine emission considerations
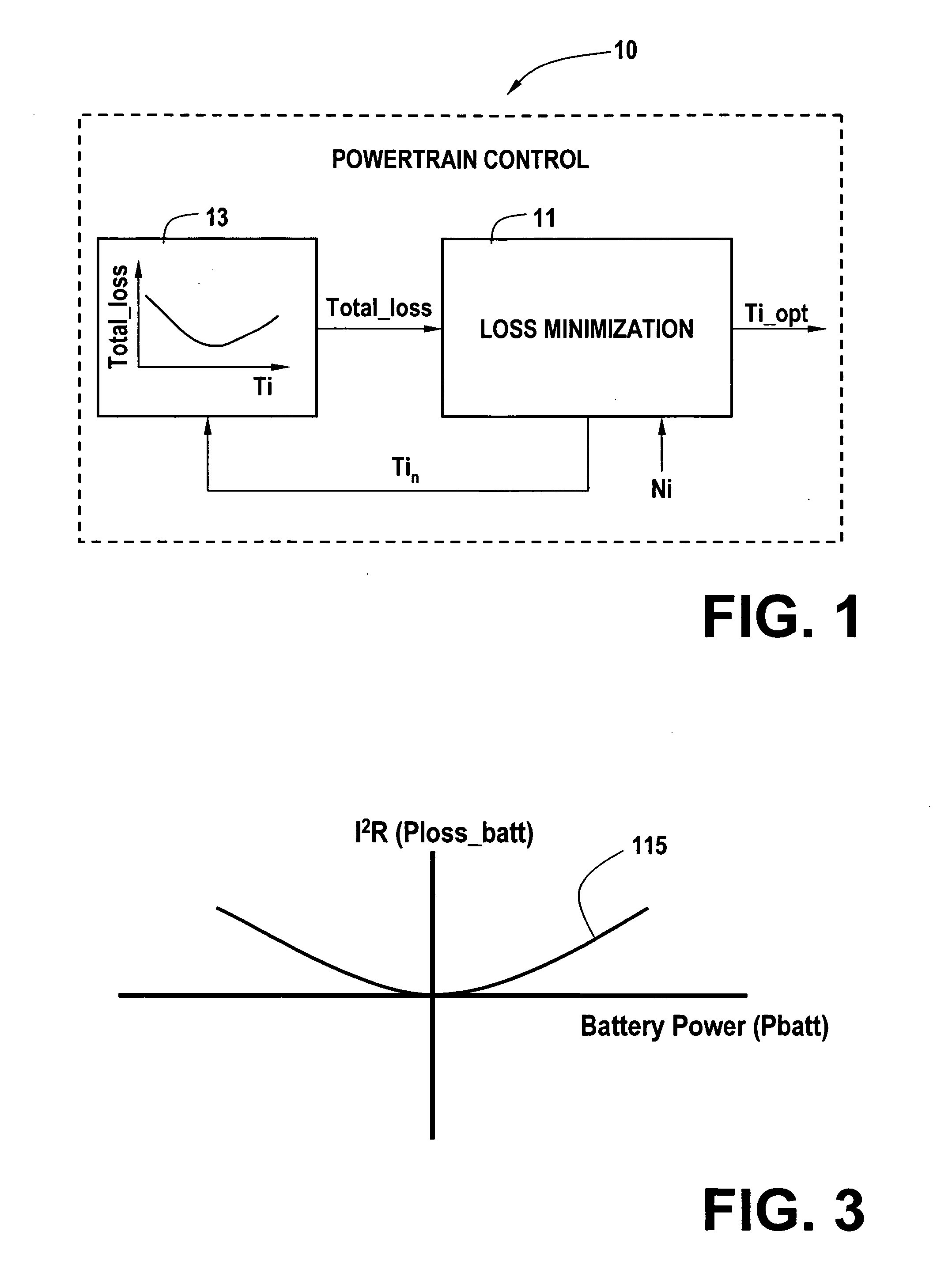
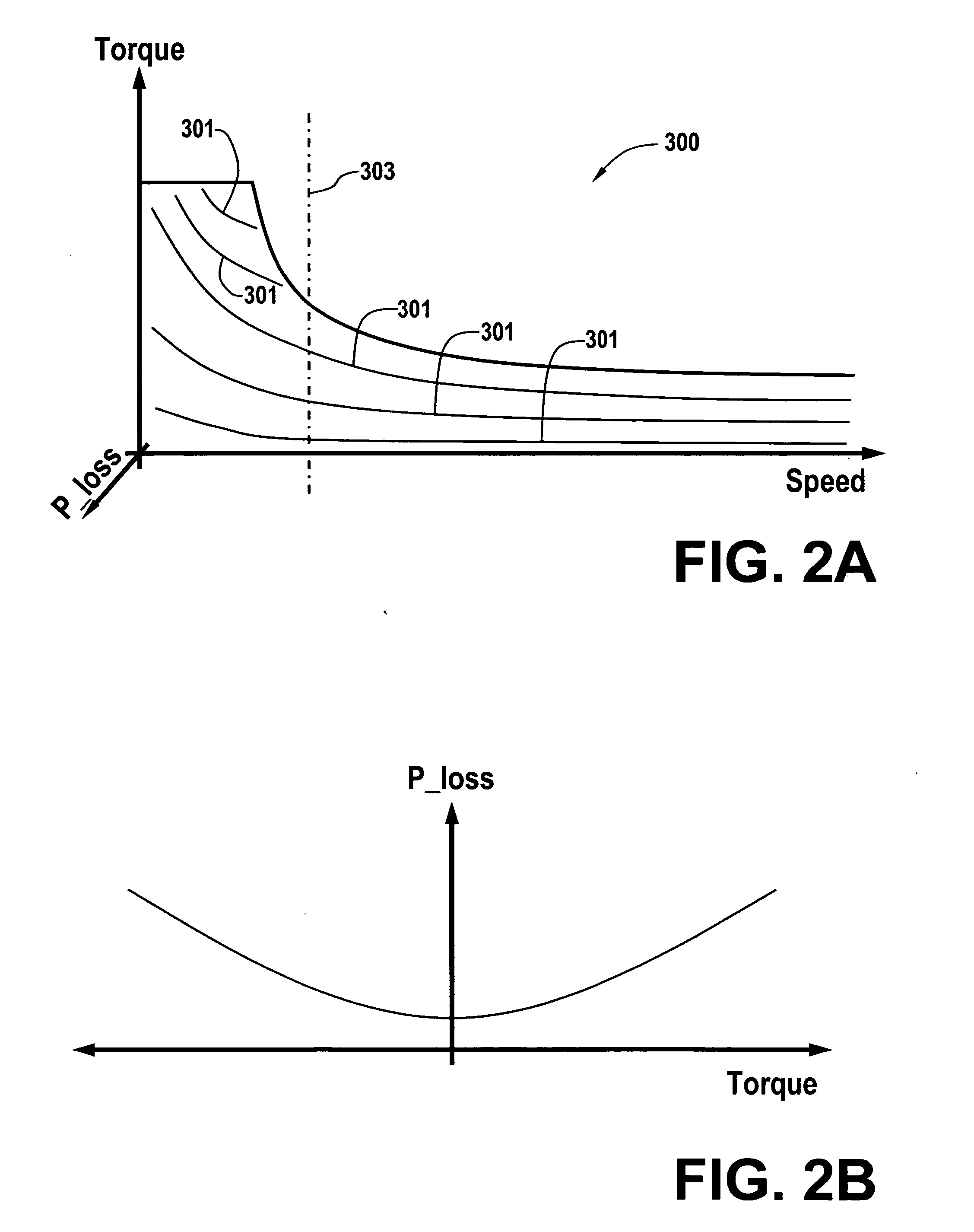
ActiveUS20070093953A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlOperating pointPowertrain control
A powertrain control selects engine operating points in accordance with power loss minimization controls. Power loss contributions come from a variety of sources including engine power losses. Engine power losses are determined in accordance with engine operating metrics such as power production per unit fuel consumption and power production per unit emission production. Engine power losses are combined in accordance with assigned weighting into a single engine power loss term for use in the power loss minimization control and operating point selection.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Internal combustion engine control for improved fuel efficiency
ActiveUS8131447B2Undesirable vibration reductionConvenient amountElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberWork cycle
A variety of methods and arrangements for improving the fuel efficiency of internal combustion engines are described. Generally, selected combustion events are skipped during operation of the internal combustion engine so that other working cycles can operate at a better thermodynamic efficiency. In one aspect of the invention, an engine is controlled to operate in a variable displacement mode. In the variable displacement mode, fuel is not delivered to the working chambers (e.g. cylinders) during selected “skipped” working cycles. During active (“non-skipped”) working cycles, a maximum (e.g., unthrottled) amount of air and an optimized amount of fuel is delivered to the relevant working chambers so that the fired working chambers can operate at efficiencies closer to their optimal efficiency. A controller is used to dynamically determine the chamber firings required to provide the engine torque based on the engine's current operational state and conditions. The chamber firings may be sequenced in real time or in near real time in a manner that helps reduce undesirable vibrations of the engine.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
Method and apparatus for operating a dual fuel internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7627416B2Reduce modificationShorten the timeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberElectronic controller
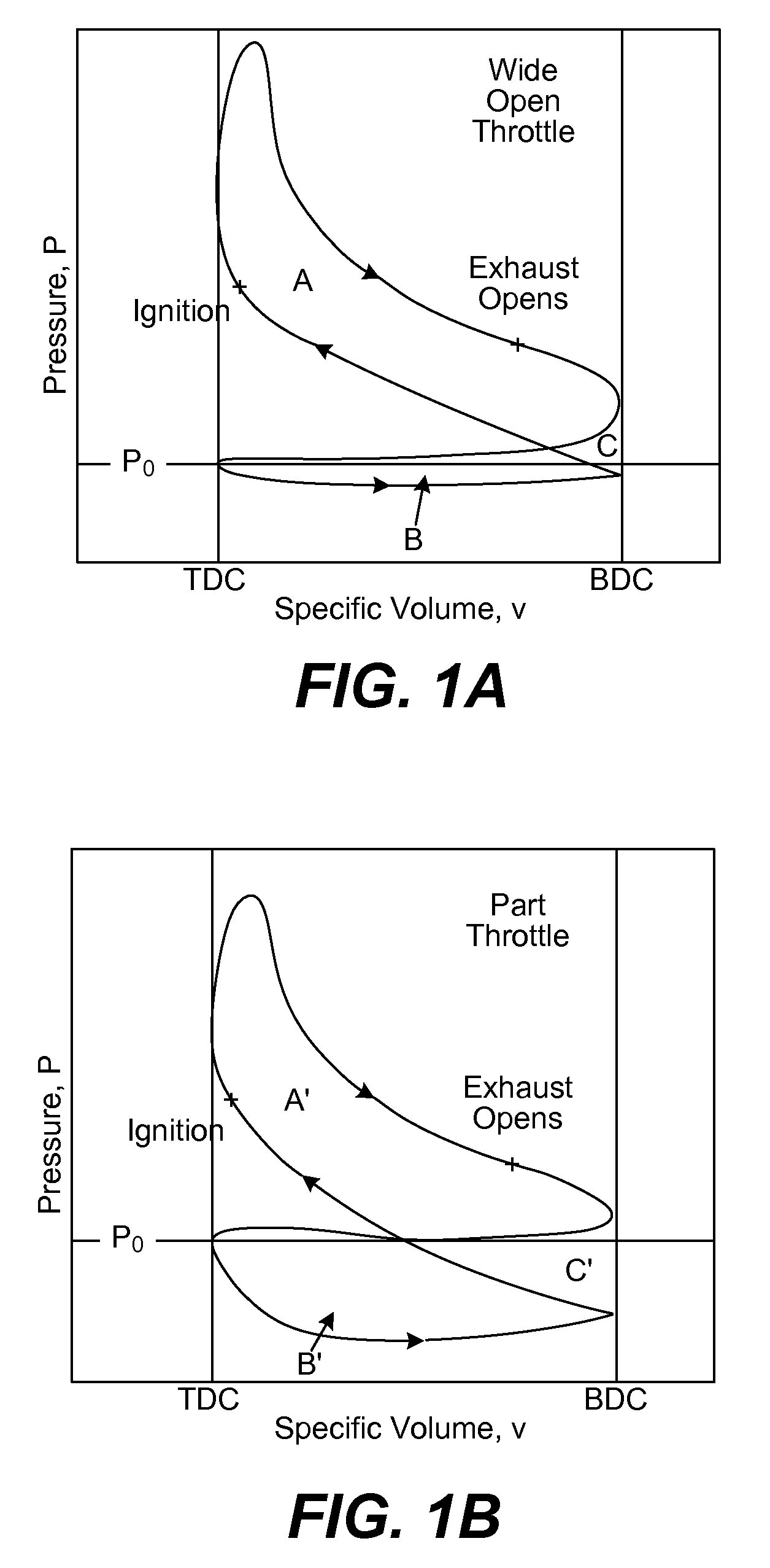
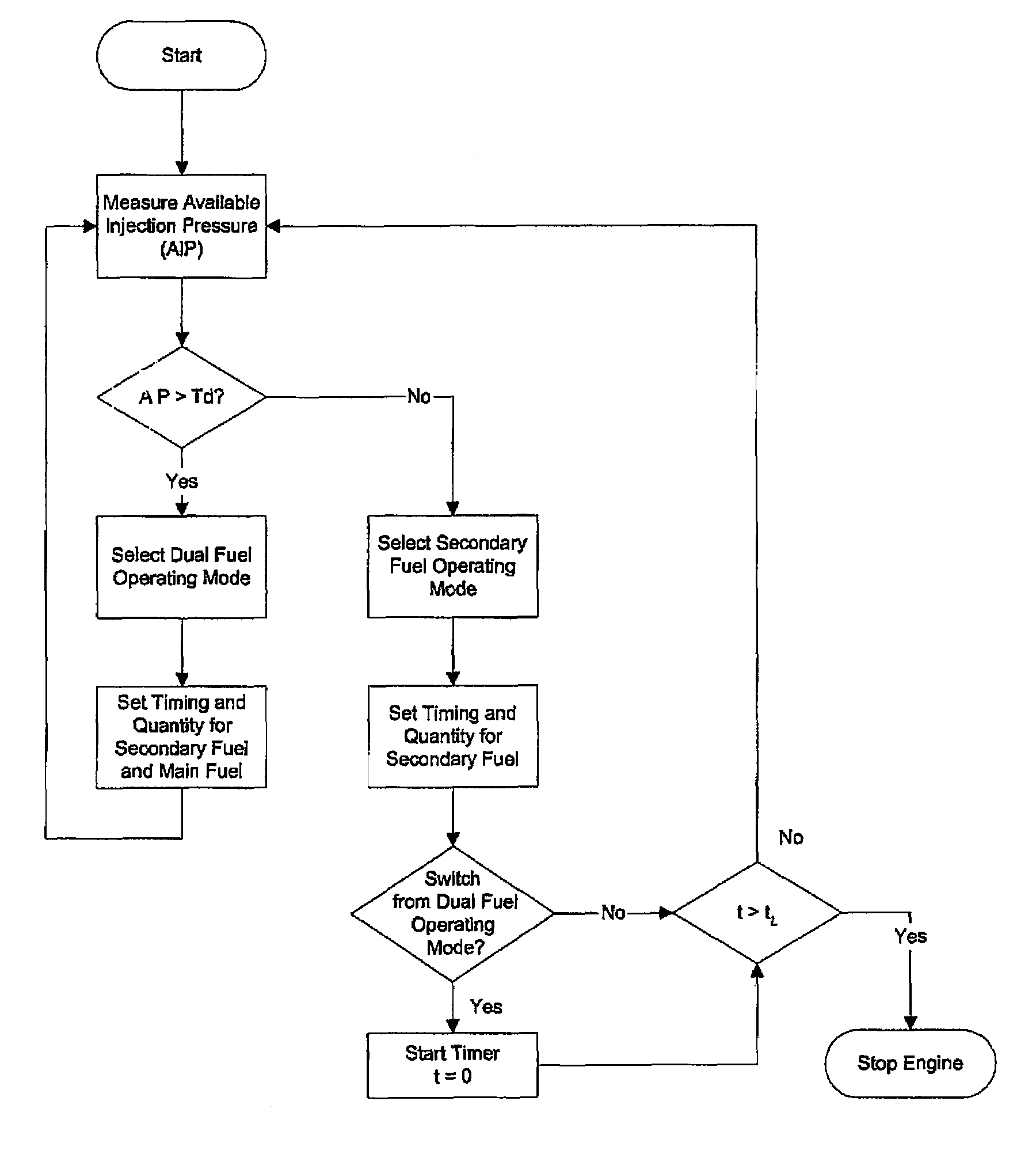
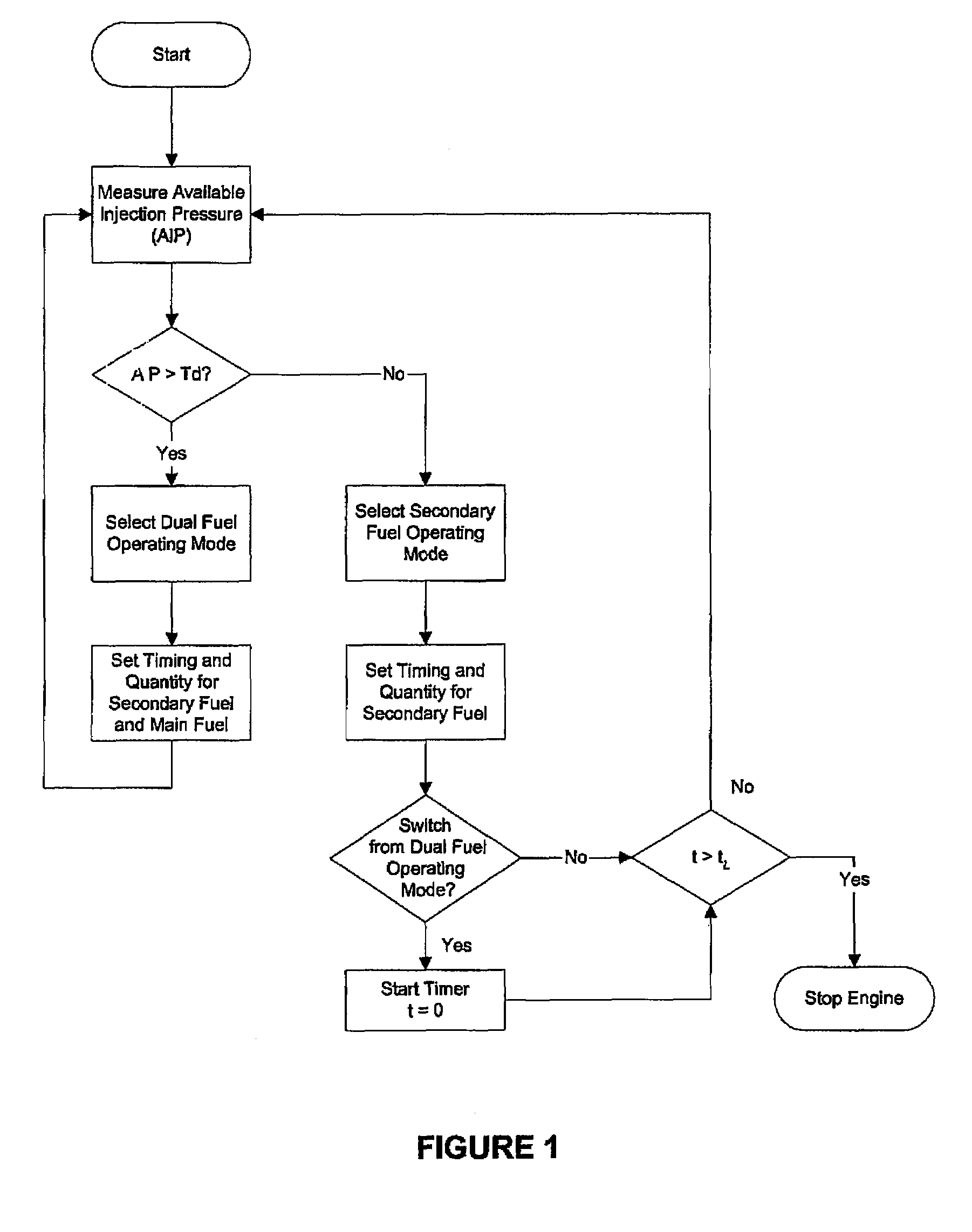
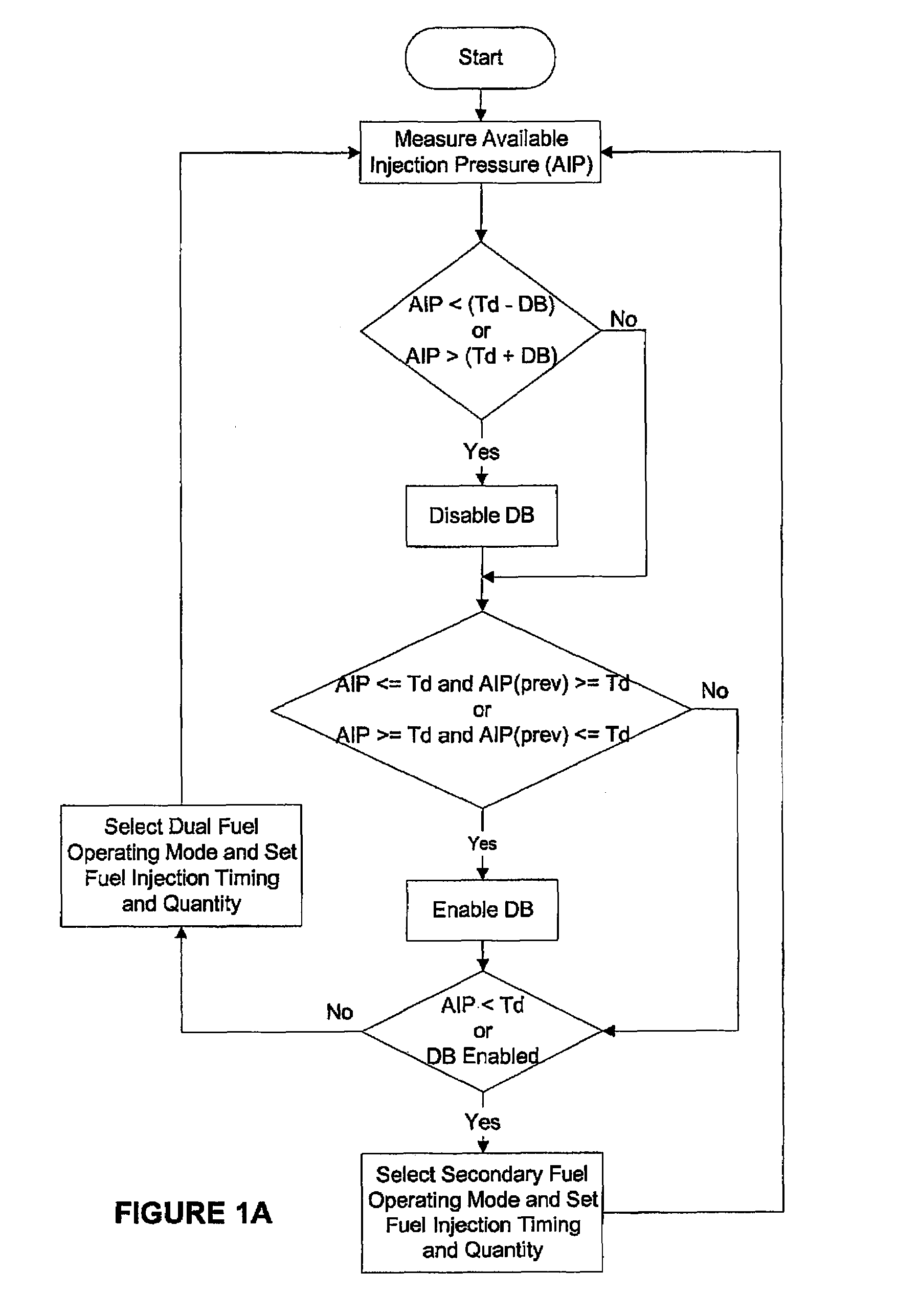
In an internal combustion engine that can burn two fuels, the main fuel may become unavailable, either temporarily or until the main fuel is replenished. The present apparatus determines when to fuel an engine with main fuel and secondary fuel, or secondary fuel alone. The apparatus includes a main-fuel supply system comprising a main-fuel injection valve that introduces main fuel into an engine combustion chamber; a secondary-fuel injection system comprising a secondary-fuel injection valve that introduces secondary fuel directly into the combustion chamber; a pressure sensor associated with the main-fuel supply system for determining injection pressure inside the main-fuel injection valve; and an electronic controller in communication with the pressure sensor and programmable to separately command actuation of the secondary-fuel and the main-fuel injection valve when injection pressure is greater than a predetermined threshold, and to otherwise command actuation of the secondary-fuel injection valve and not the main-fuel injection valve.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Dynamic Cylinder Deactivation with Residual Heat Recovery
InactiveUS20100050993A1Improve conversion efficiencyElectrical controlMachines/enginesEngine efficiencyFuel efficiency
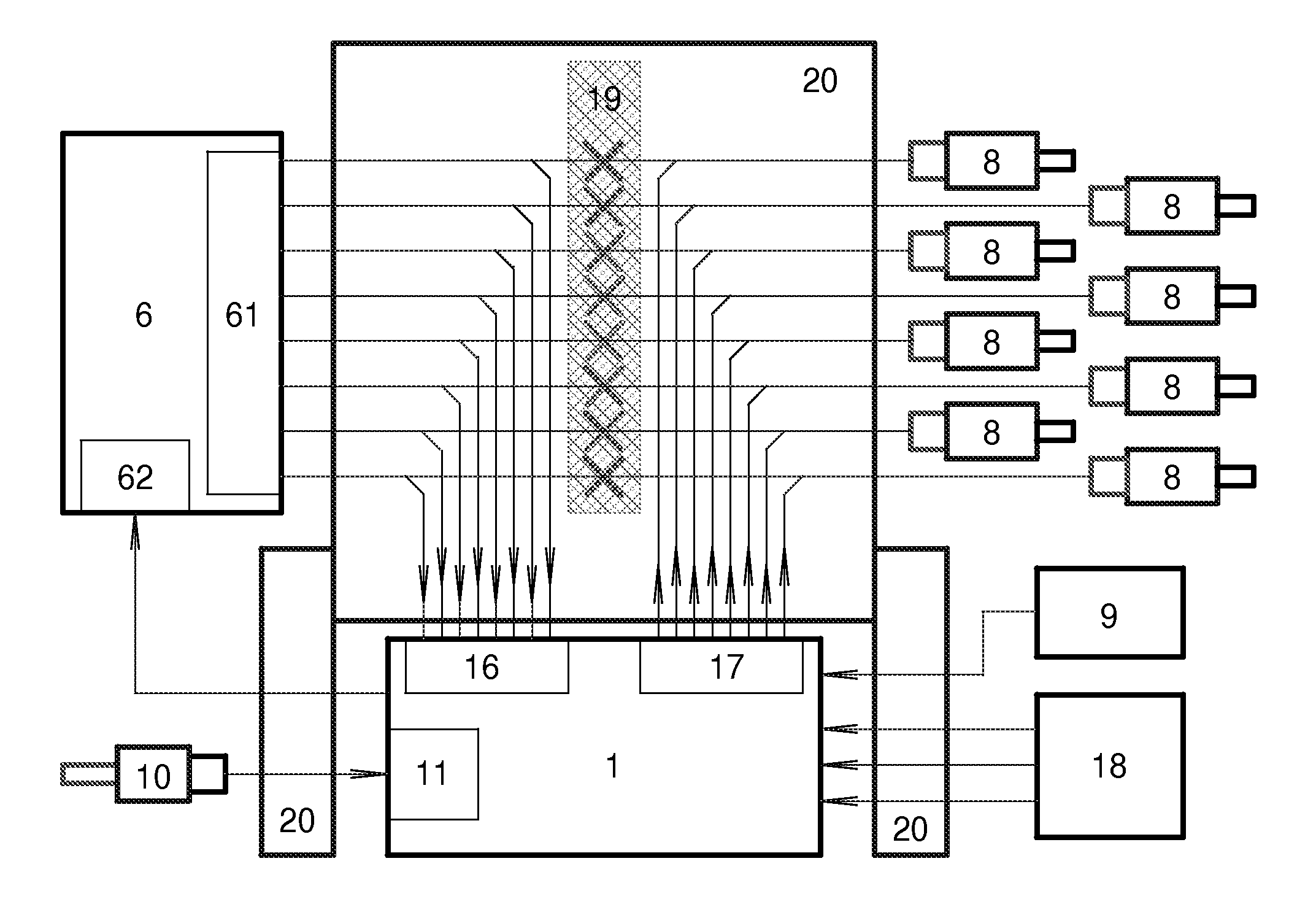
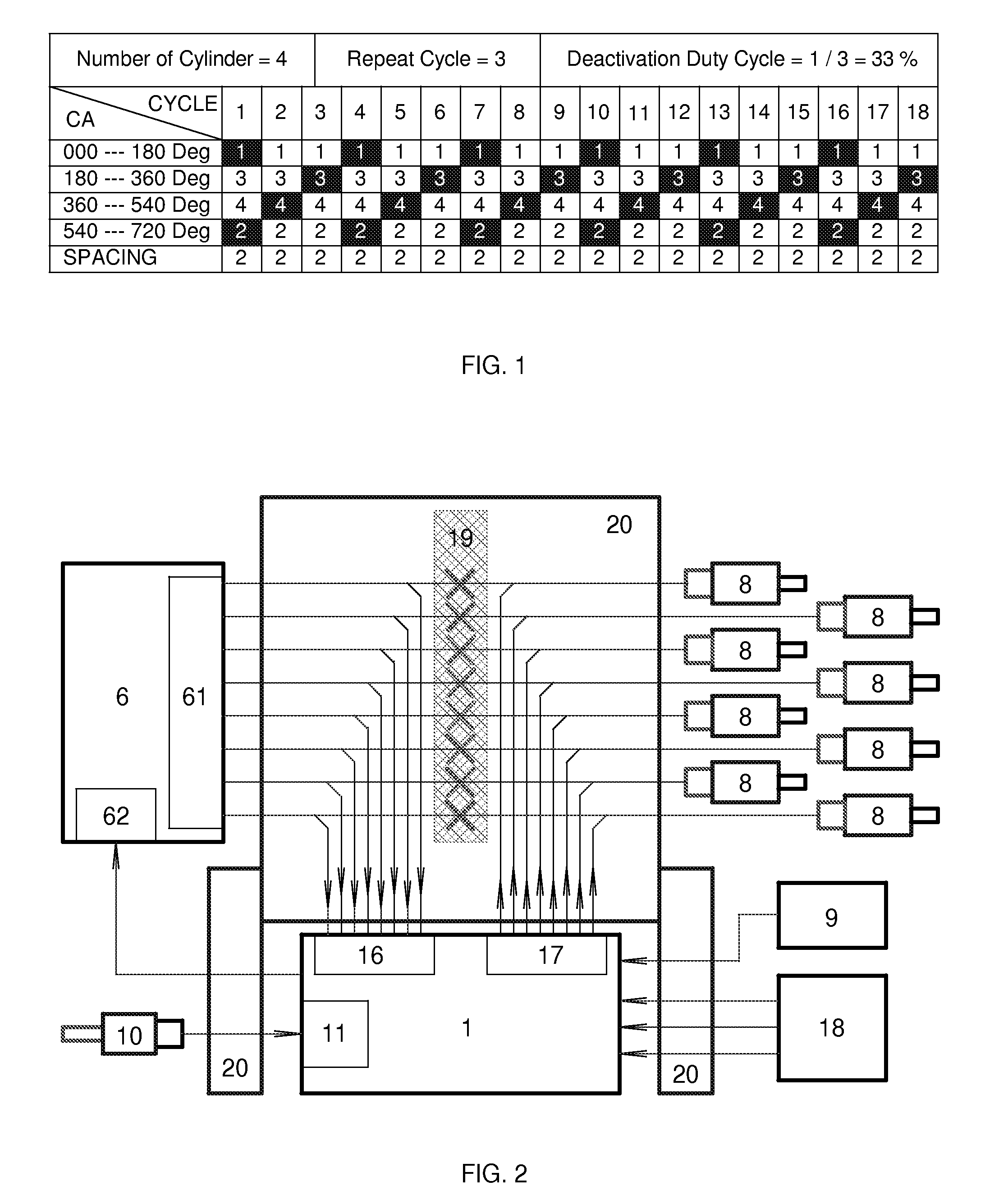
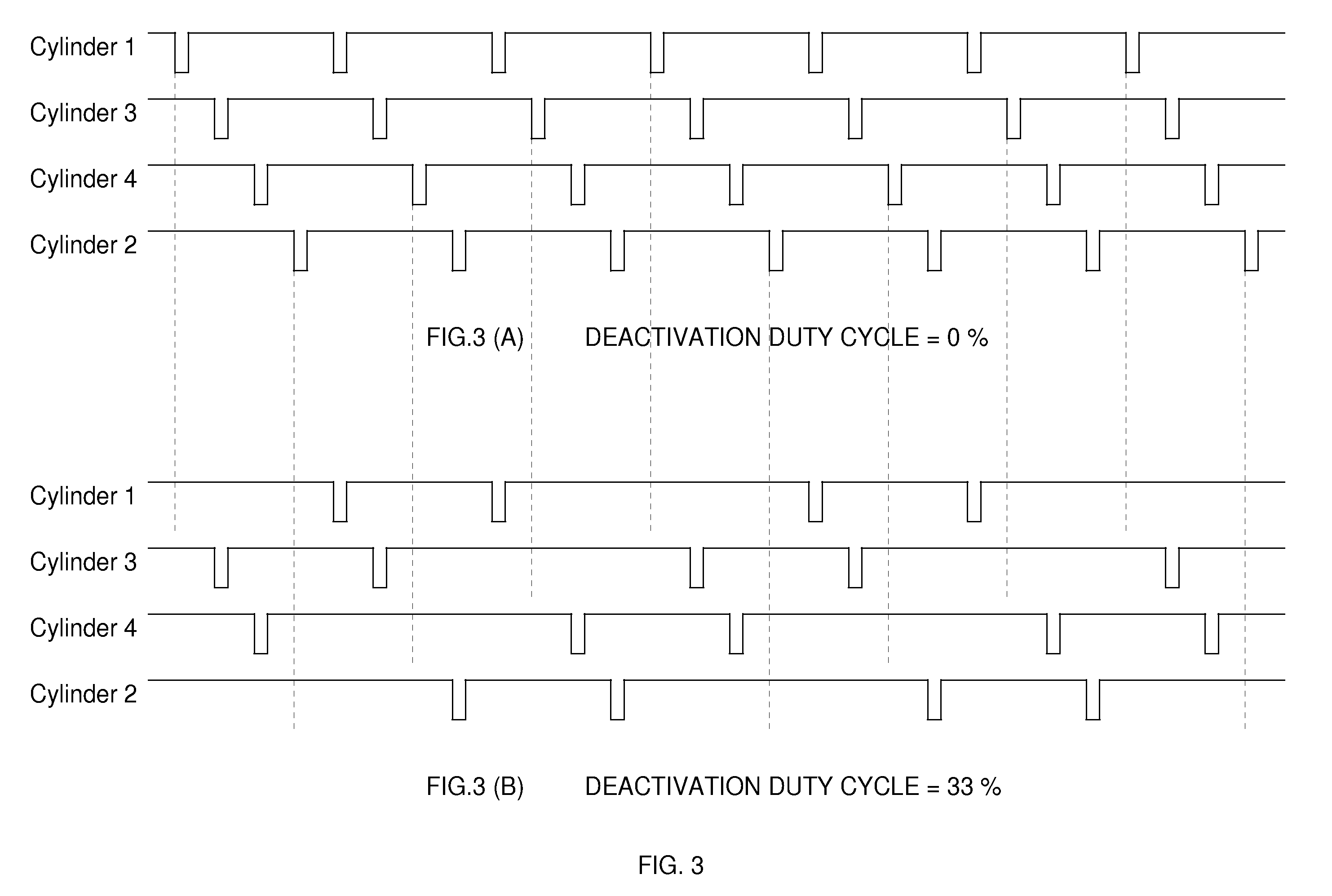
Cylinder deactivation is a proven solution to improve engine fuel efficiency. The present invention is related to Dynamic Cylinder Deactivation (DCD) solution to conventional internal combustion engine. DCD is an energy saving method based on engine thermodynamics and residual heat recovery. It deactivates all the cylinders within the engine alternatively and dynamically, totally different from traditional sealed-valves cylinder deactivation solutions. DCD has many advantages over traditional sealed-valves cylinder deactivation. Thermodynamic efficiency gain, residual heat recovery, high Lambda and “Air-Hybrid” are the most attractive features of DCD. DCD also makes engine displacement variable.
Owner:ZHAO YUANPING +1
Internal combustion engine
ActiveUS6990956B2Accurate calculationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultifuelEngineering
An internal combustion engine, in which multiple kinds of fuels are fed to a cylinder from multiple fuel injectors each corresponding to each of multiple kinds of fuels at a target mixing ratio determined according to a running condition, includes an actual fuel mixing ratio calculator calculating an actual fuel mixing ratio of fuel fed to cylinder. The actual fuel mixing ratio calculator at first calculates actual fuel injection quantity of each fuel injection by adding or subtracting predetermined stuck-on-wall fuel to or from each quantity of fuel injected from each fuel injector, and then calculates an actual fuel mixing ratio of fuel fed to cylinder on the basis of the calculated actual fuel injection quantity of each fuel injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
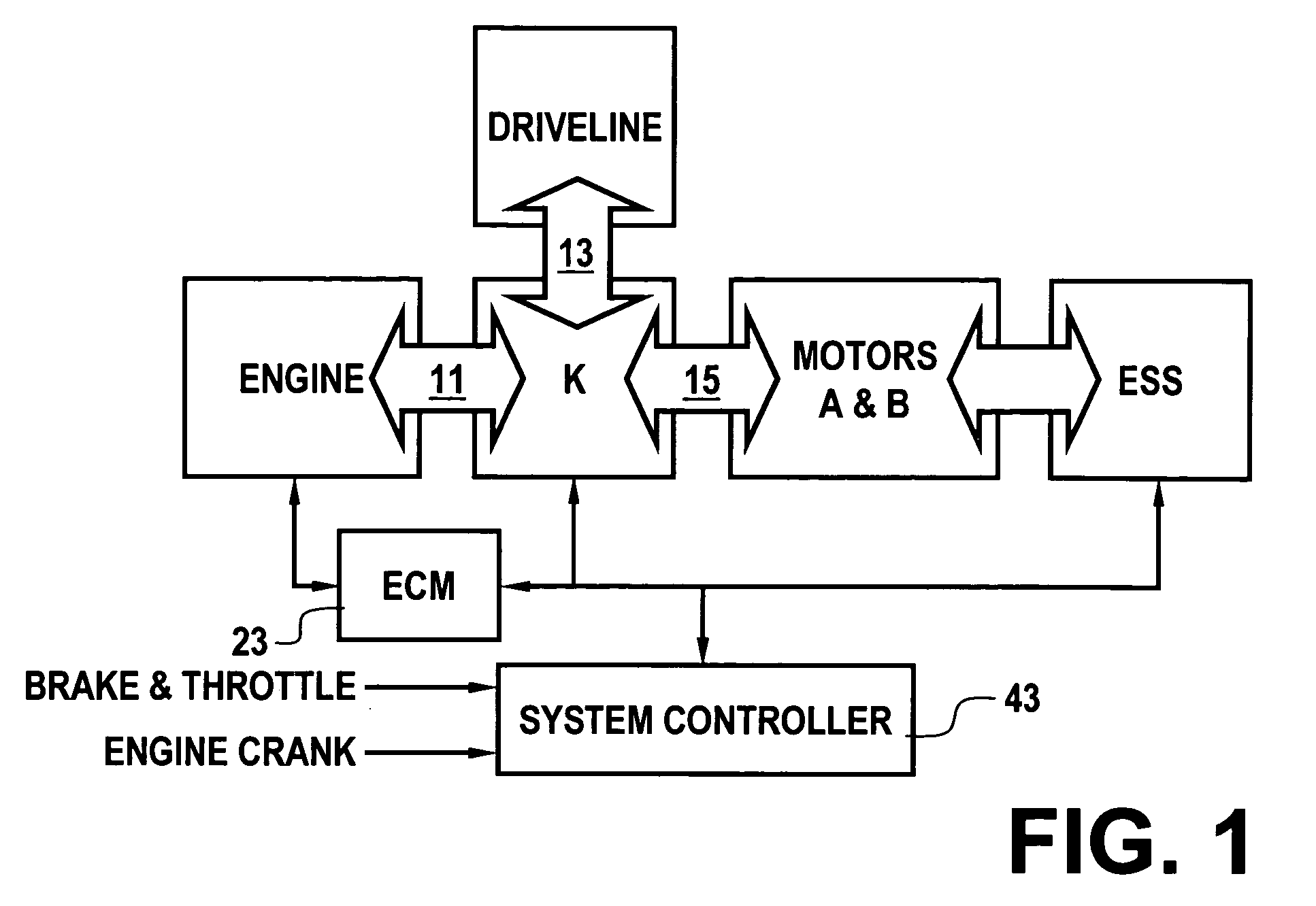
Method for active engine stop of a hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20050255968A1Increased durabilityImprove smoothnessHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlElectric machineResonance
A method for providing an active engine stop of the engine of a hybrid electric vehicle. The method utilizes the electric machine to oppose the and rapidly stop the rotation of the engine at a controlled rate. The method includes the calculation of an input speed reduction trajectory using the engine speed when the active engine stop request is made and a predetermined speed reduction interval. The predetermined speed reduction interval is preferably less than a time from the active stop request to the shutoff command to the electric machine. The method provides rapid deceleration of the engine, particularly through the powertrain resonance speed, thereby reducing the amount of vibration energy dissipated through the powertrain and vehicle chassis. The method also removes the electric machine torques from the engine prior to achieving zero engine speed in order to avoid imparting a negative engine speed or counter-rotation of the engine. The method preferably comprises a complementary series of software control functions that allow the vehicle to actively stop the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coordinated regenerative and engine retard braking for a hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20050255965A1Increases the engine retard braking contributionReduce contributionHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsPower flowGear wheel
A hybrid vehicle includes a powertrain having a retarded diesel engine, an electric machine and energy storage system. The engine and motor are operatively coupled through one or more planetary gearsets and selective coupling paths in accordance with application and release of various torque transfer devices to a drivetrain via an output. Regenerative and retarded engine braking are coordinated to provide priority to energy return to an energy storage system in accordance with predetermined power flow limits. Power flow in excess of the limits are handled by increased engine retard braking contributions via engine speed increases.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
Differential torque operation for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7503312B2Improve internal efficiencyImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineControl theory
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a plurality of cylinders including at least a first cylinder and a second cylinder, the method comprising firing the first cylinder and the second cylinder in an alternating sequence; during a first mode, adjusting an operating parameter of the engine to produce a first difference between an amount of torque produced by the firing of the first cylinder and an amount of torque produced by the firing of the second cylinder; during a second mode, adjusting the operating parameter of the engine to produce a second difference between an amount of torque produced by the firing of the first cylinder and an amount of torque produced by the firing of the second cylinder; and performing the first mode at a higher engine speed than the second mode; wherein the first difference is greater than the second difference.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
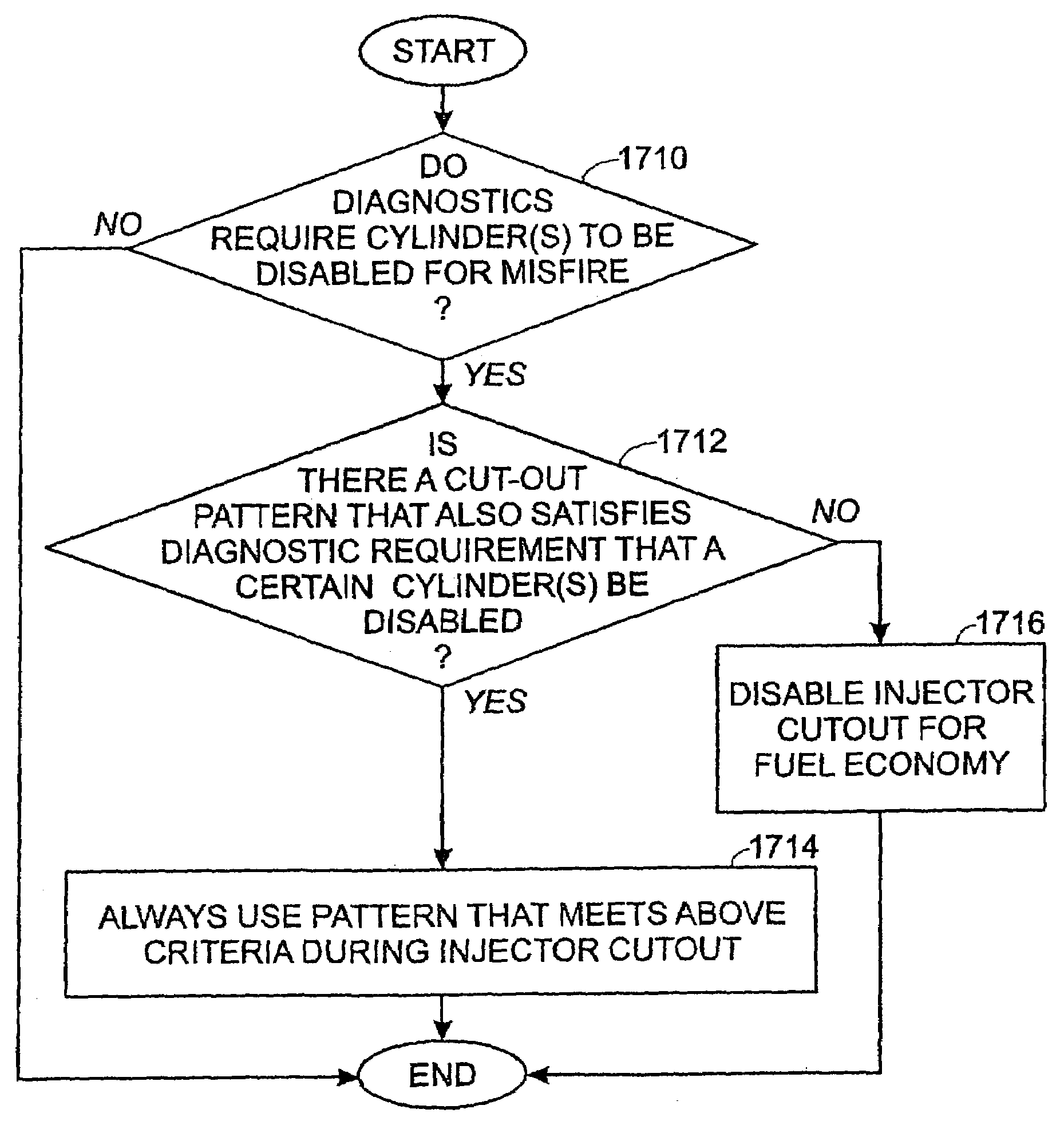
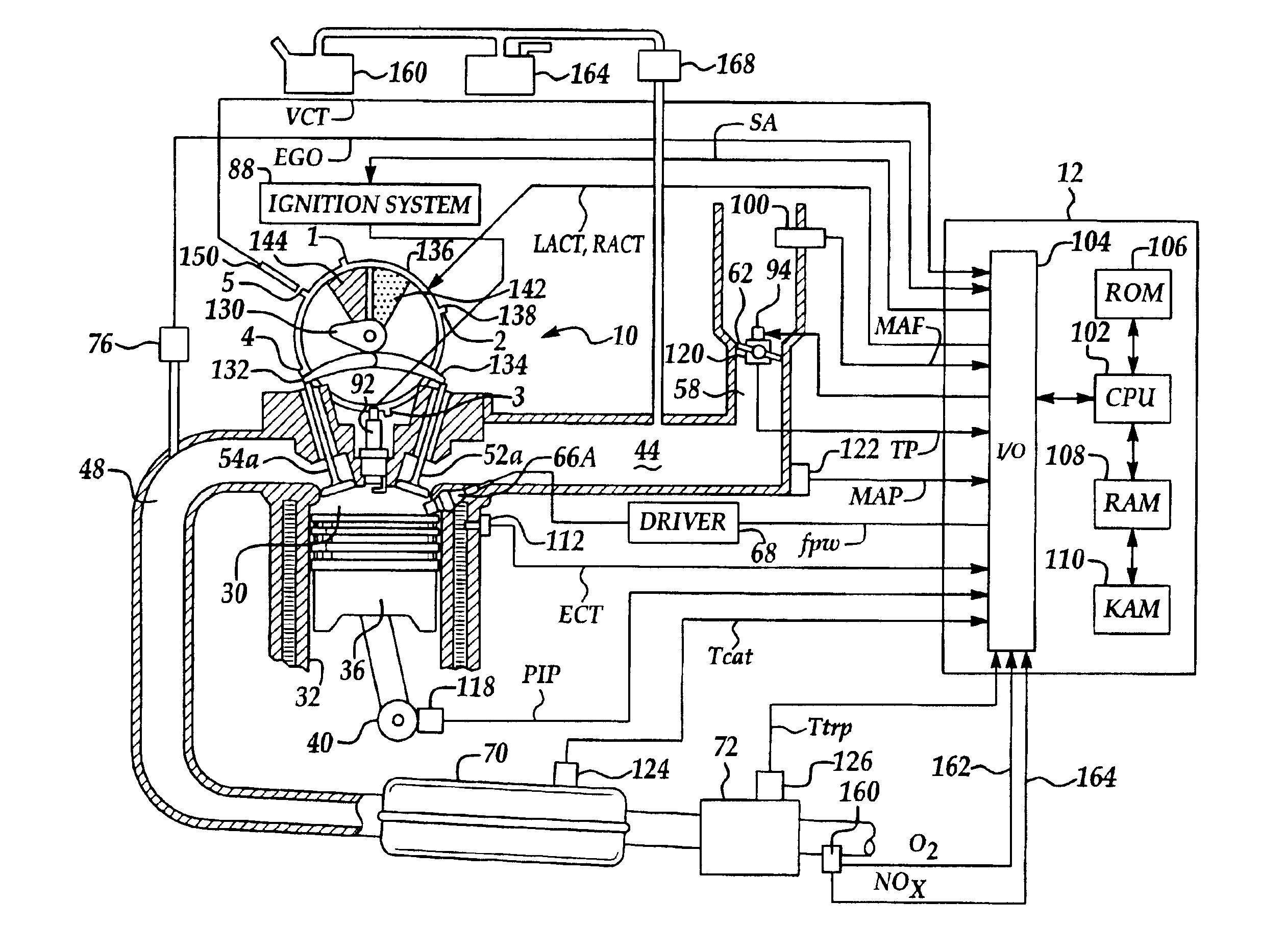
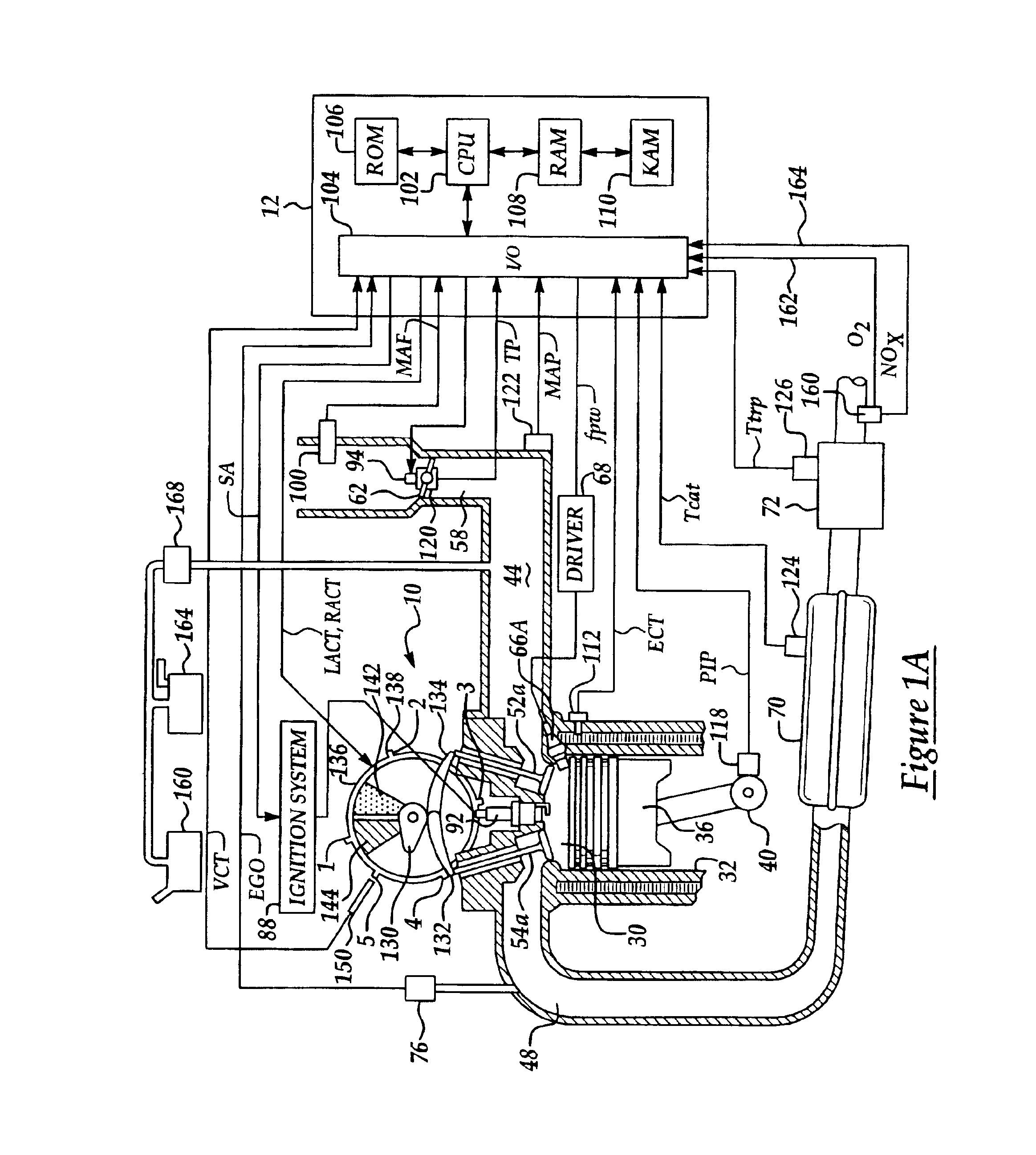
Engine system and method accounting for engine misfire
ActiveUS7086386B2Reducing engine pumping lossesMore efficientCombustion enginesOutput powerSystems designFuel vapor
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
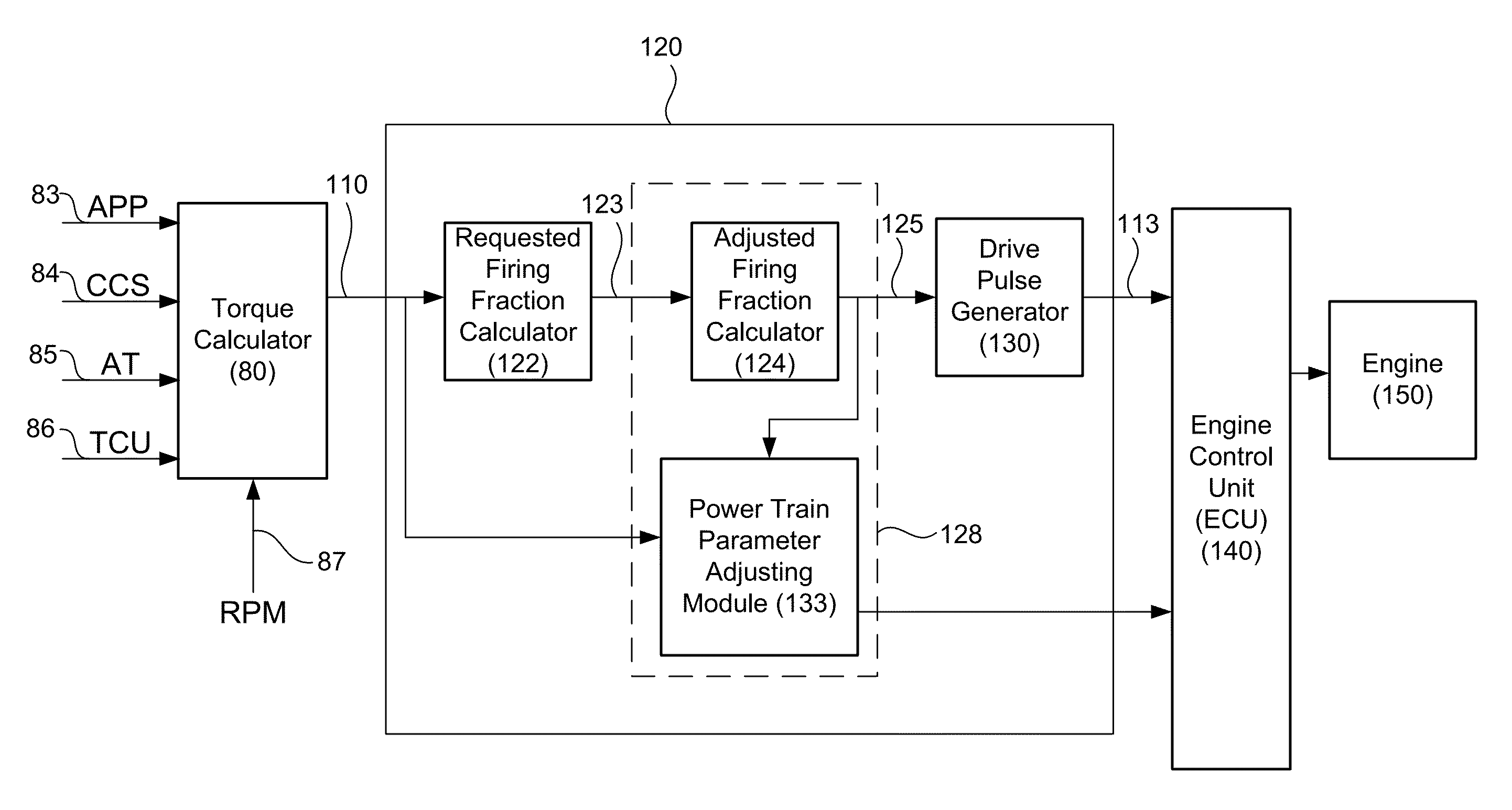
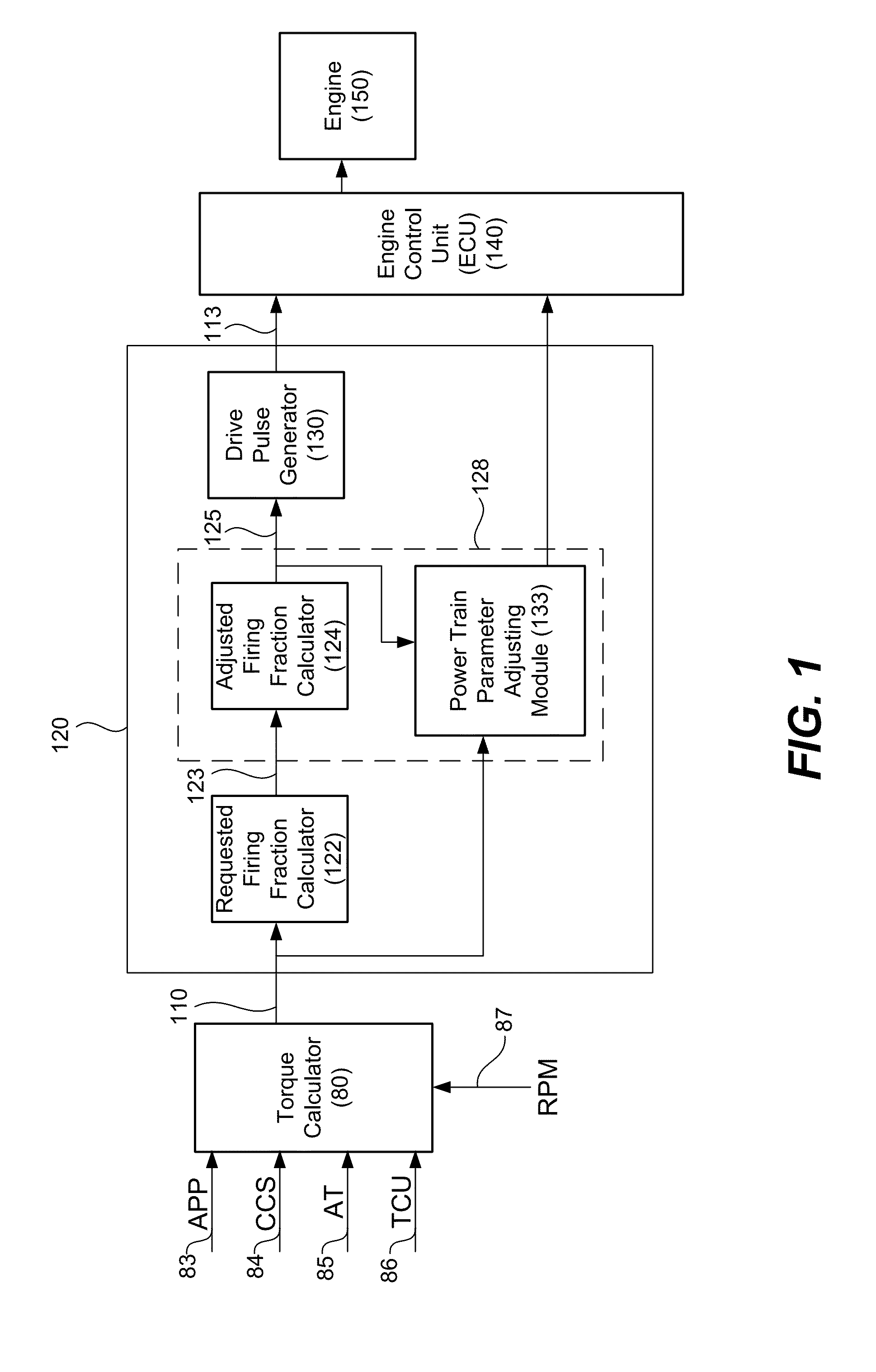
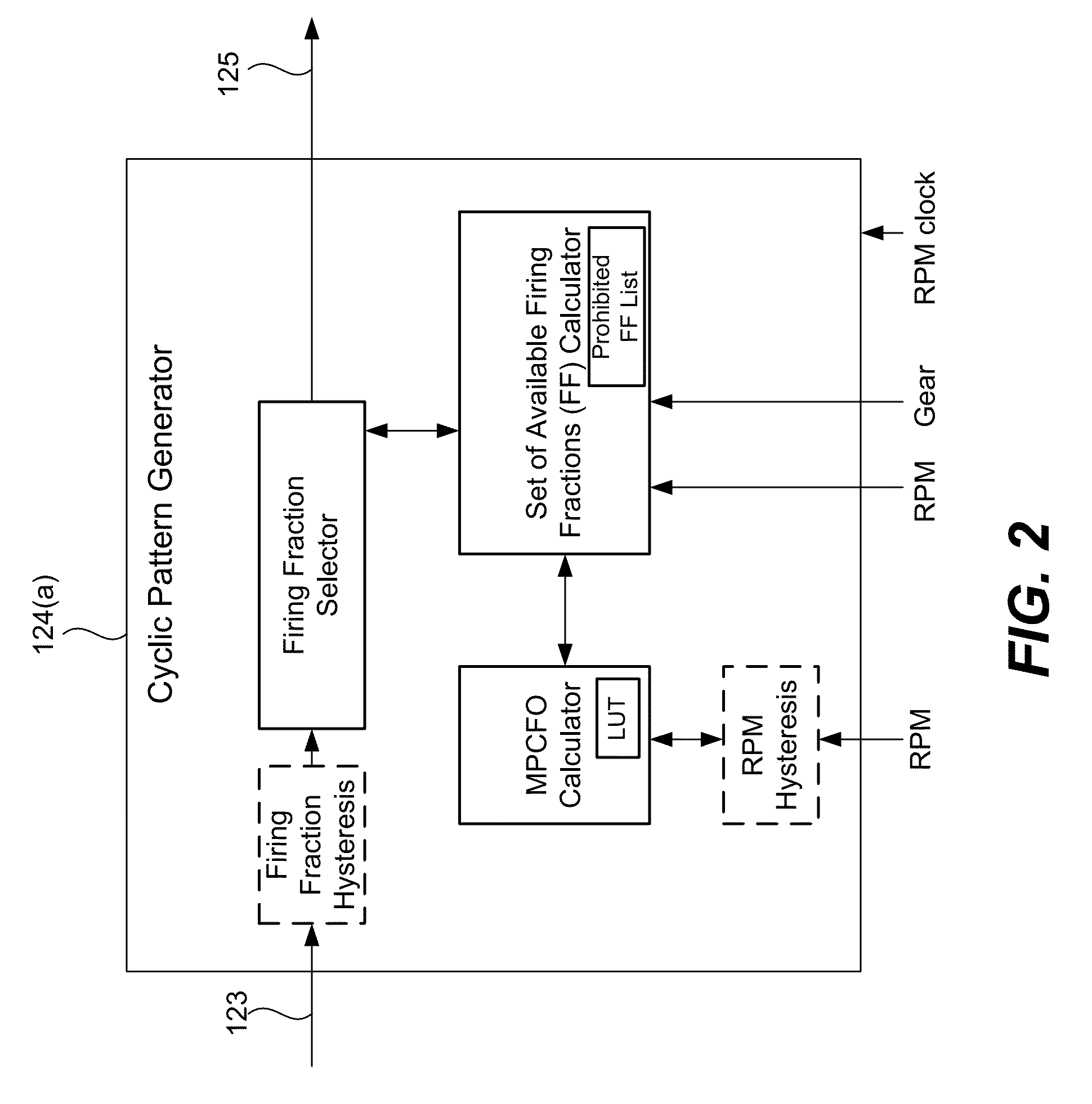
Firing fraction management in skip fire engine control
ActiveUS9086020B2Reduce generationReduce probabilityElectrical controlOutput powerFire controlIgnition control
In various described embodiments skip fire control is used to deliver a desired engine output. A controller determines a skip fire firing fraction and (as appropriate) associated engine settings that are suitable for delivering a requested output. In one aspect, the firing fraction is selected from a set of available firing fractions, with the set of available firing fractions varying as a function of engine speed such that more firing fractions are available at higher engine speeds than at lower engine speeds. The controller then direct firings in a skip fire manner that delivers the selected fraction of firings.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
Method for rapid catalyst heating
InactiveUS6568177B1High load conditionMore ignition timingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTemperature controlAdaptive learning
A method is disclosed for controlling operation of an engine coupled to an exhaust treatment catalyst. Under predetermined conditions, the method operates an engine with a first group of cylinders combusting a lean air / fuel mixture and a second group of cylinders pumping air only (i.e., without fuel injection). In addition, the engine control method also provides the following features in combination with the above-described split air / lean mode: idle speed control, sensor diagnostics, air / fuel ratio control, adaptive learning, fuel vapor purging, catalyst temperature estimation, default operation, and exhaust gas and emission control device temperature control. In addition, the engine control method also changes to combusting in all cylinders under preselected operating conditions such as fuel vapor purging, manifold vacuum control, and purging of stored oxidants in an emission control device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
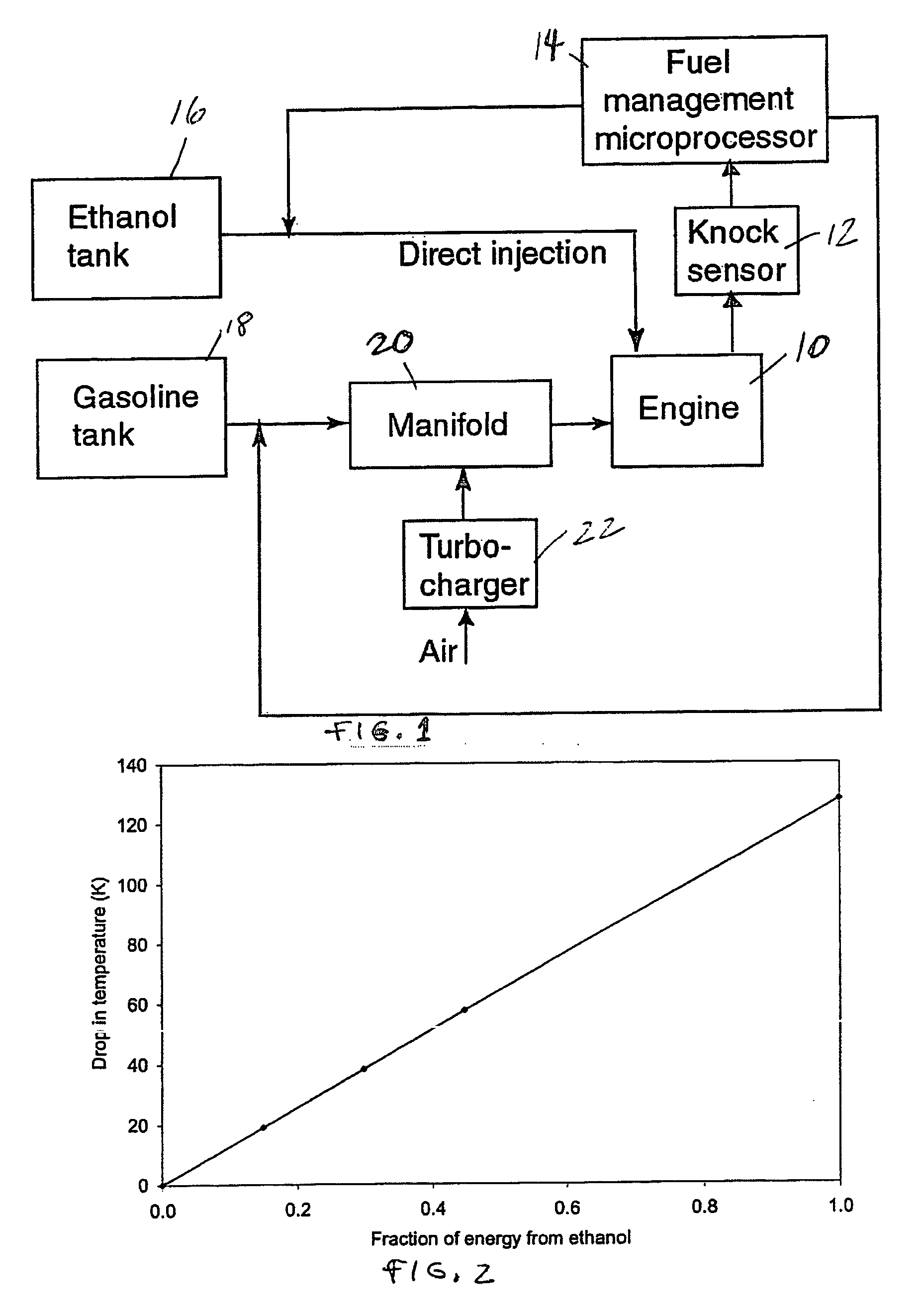
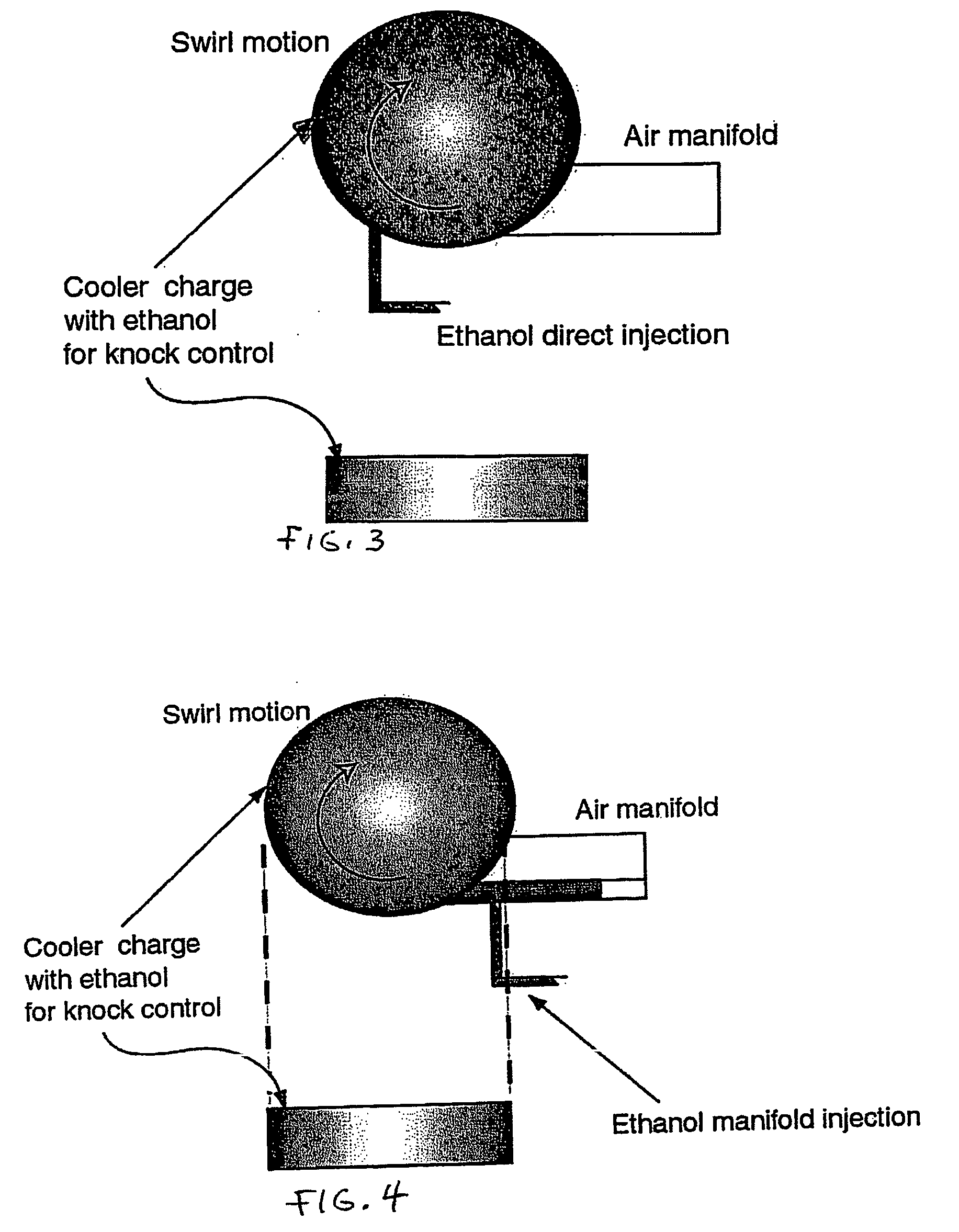
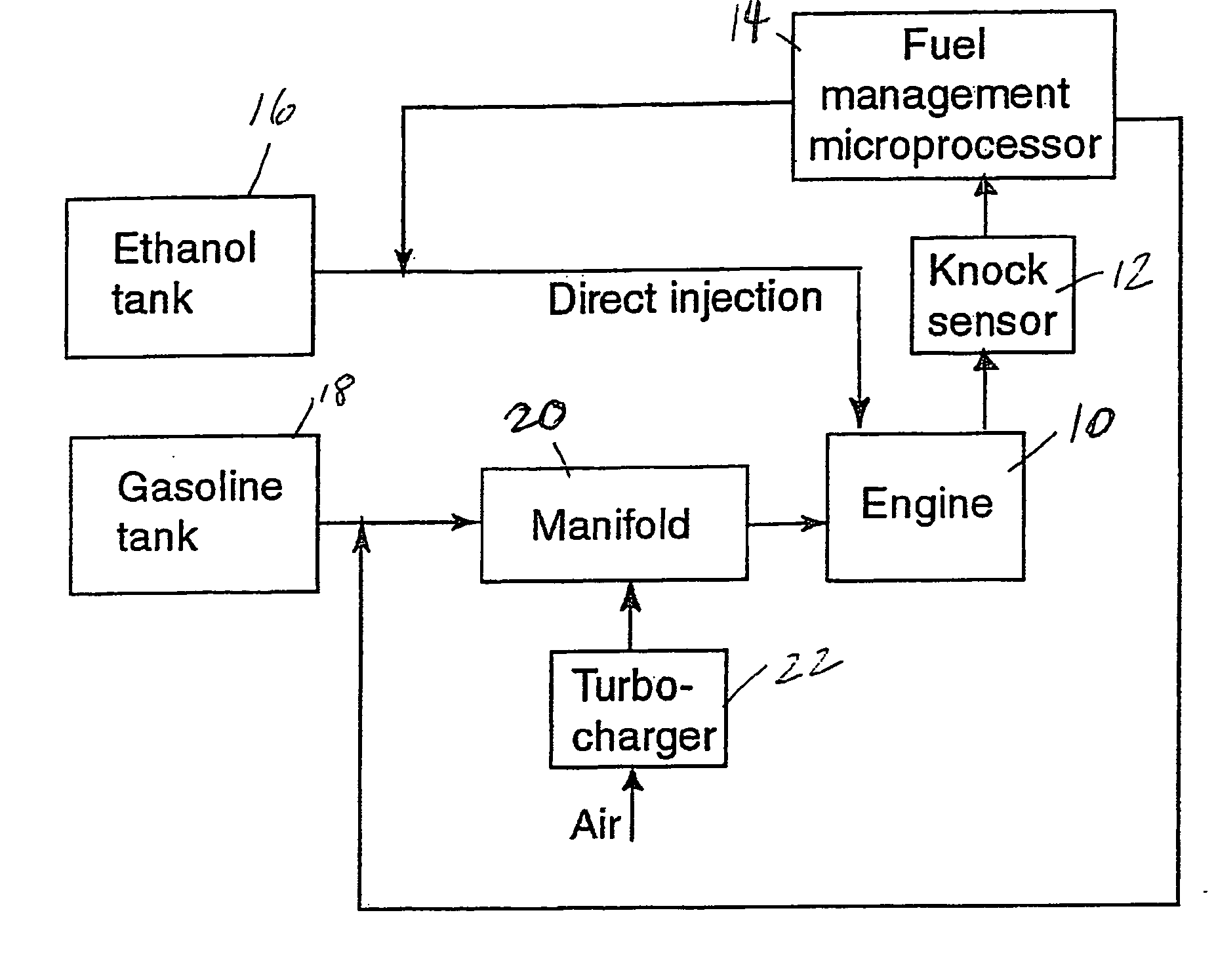
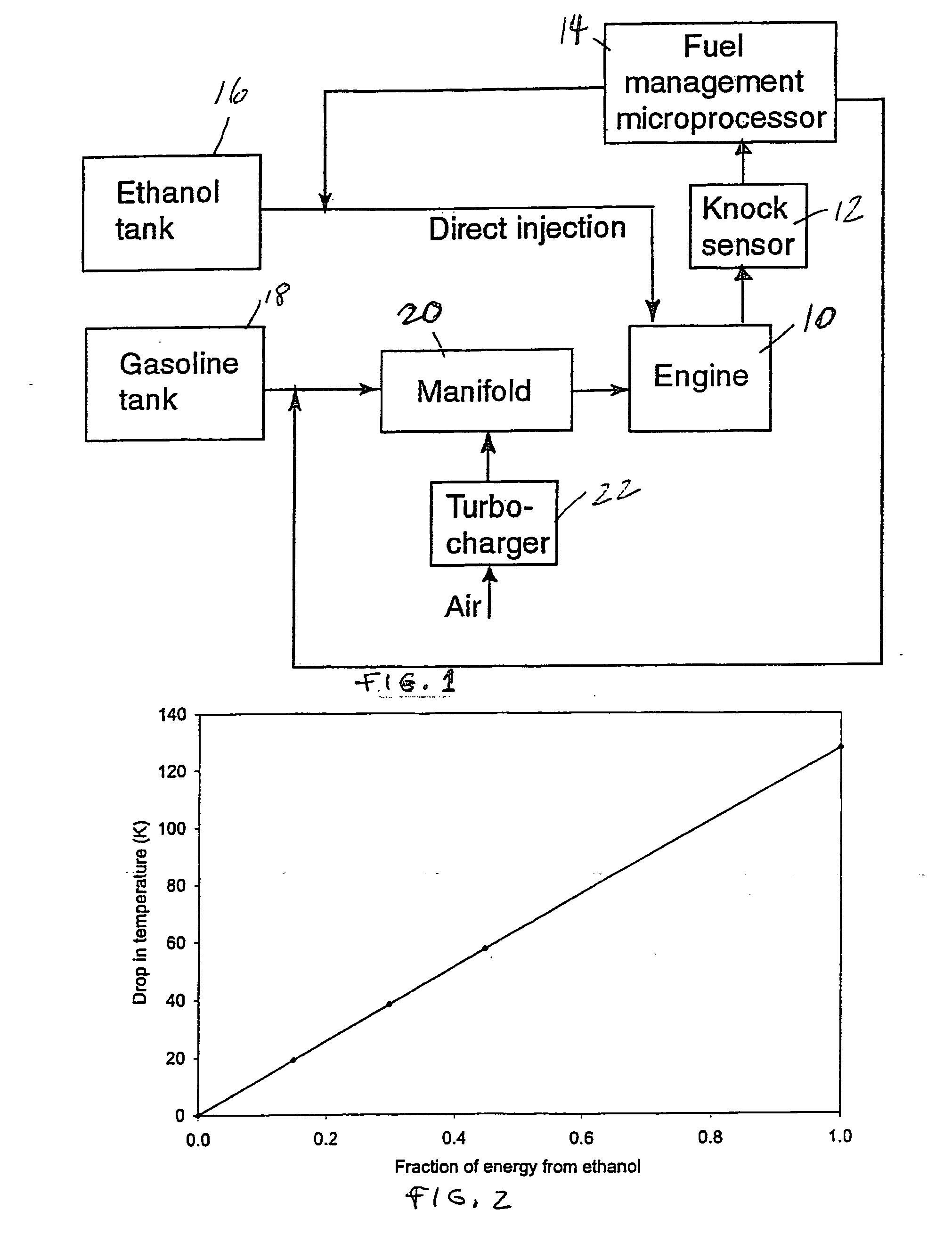
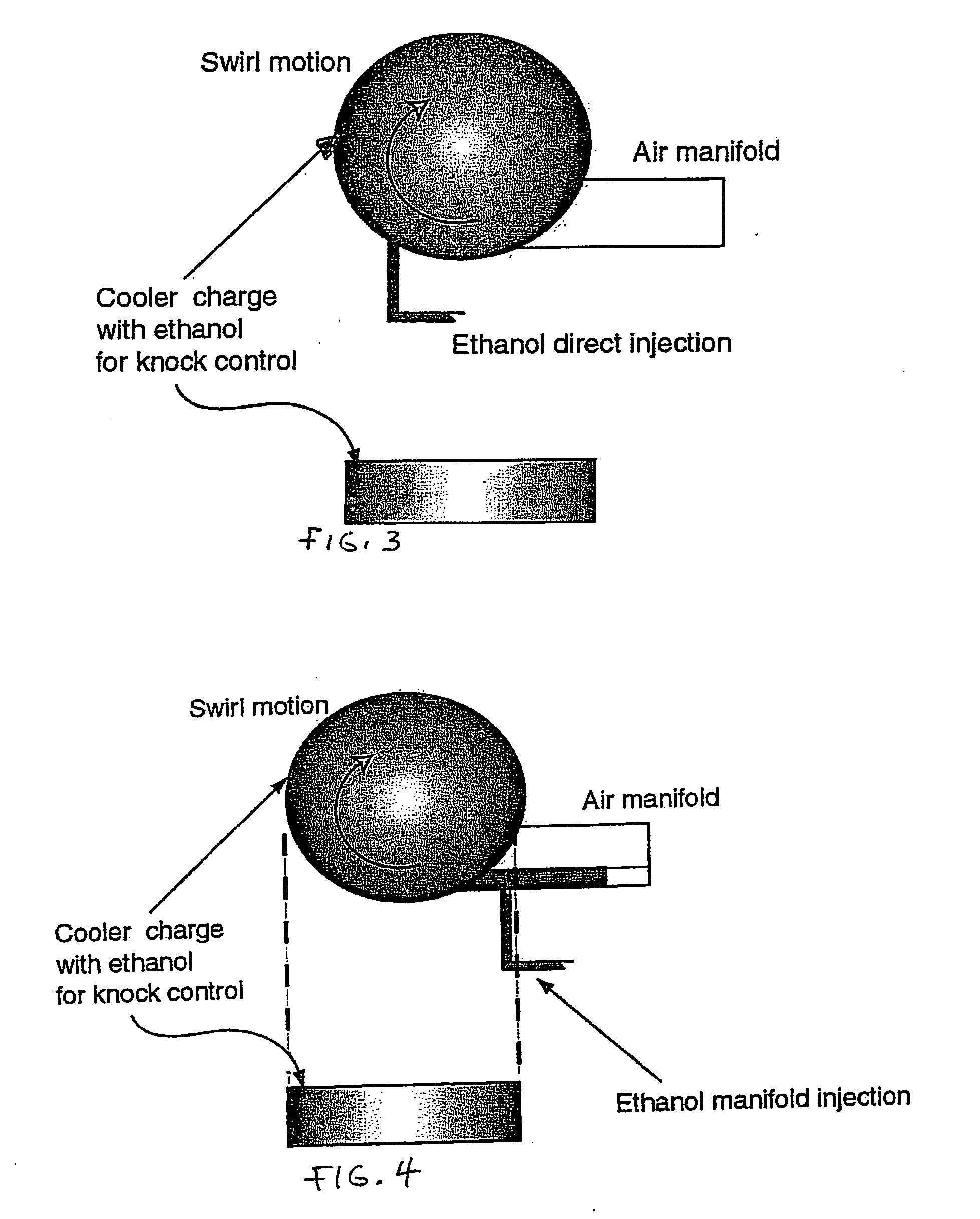
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancehment of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102145A1Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Cost structure method including fuel economy and engine emission considerations
ActiveUS20050256633A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlOperating pointPowertrain control
A powertrain control selects engine operating points in accordance with power loss minimization controls. Power loss contributions come from a variety of sources including engine power losses. Engine power losses are determined in accordance with engine operating metrics such as power production per unit fuel consumption and power production per unit emission production. Engine power losses are combined in accordance with assigned weighting into a single engine power loss term for use in the power loss minimization control and operating point selection.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
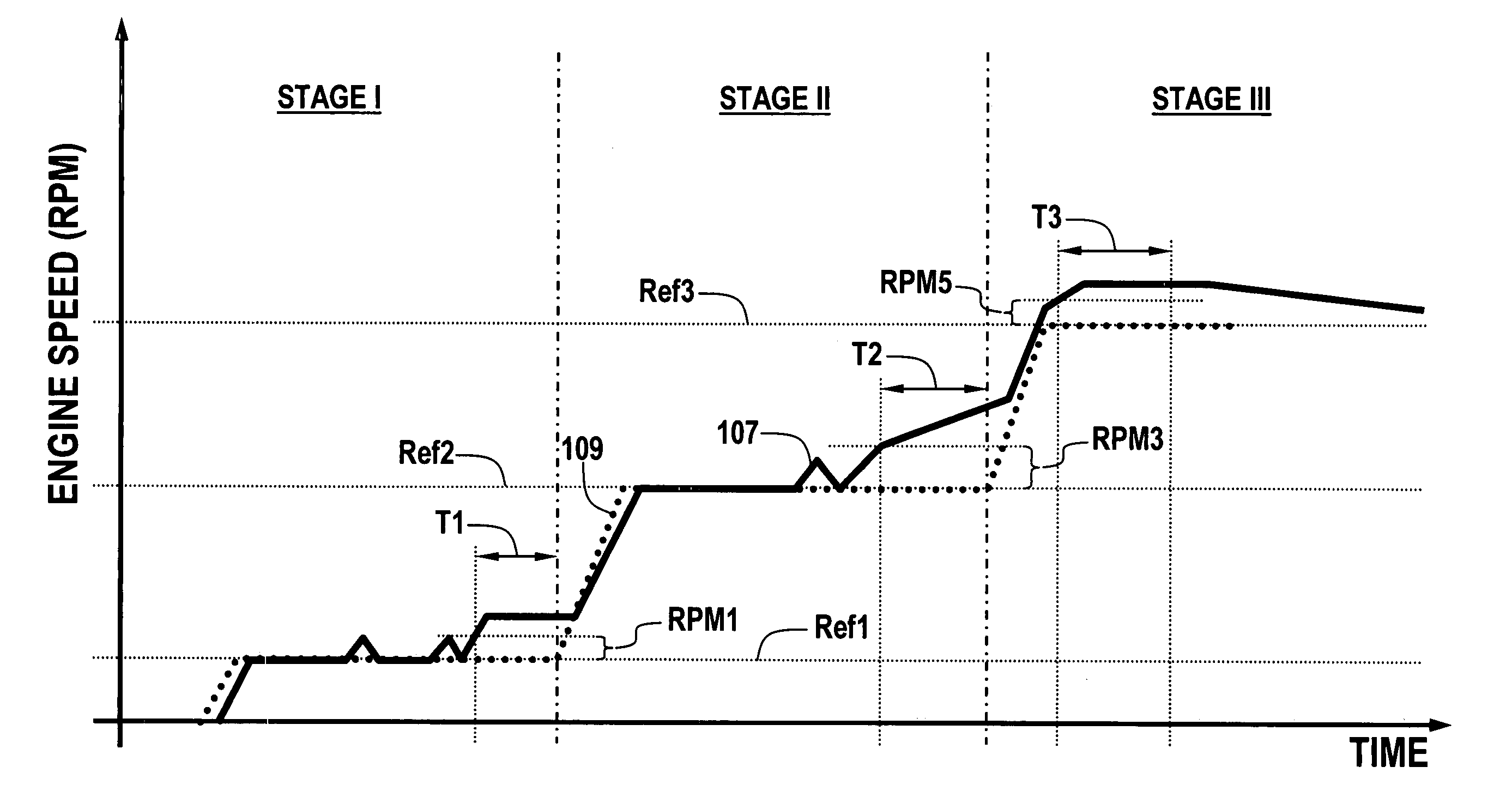
Multi-stage compression ignition engine start
A powertrain includes a diesel compression engine and an electric machine operatively coupled thereto and effective to rotate the engine during engine cranking. Cold engine cranking is accomplished in a staged manner including a first stage wherein the engine is cranked to a first speed below the resonant speed of the coupled engine and electric machine combination for a first duration and thereafter cranked to a second speed above the resonant speed for a second duration. Transition out of cranking at the first and second speeds is accomplished when relative combustion stability is demonstrated. Cranking at the first or second speed is aborted when excessive crank times or if low battery voltages are observed. A third stage is included wherein the engine is cranked to a third speed below the engine idle speed. Transition out of cranking at the third speed is accomplished when relative combustion stability is demonstrated, whereafter normal engine control takes over.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
Methods and apparatus for operation of multiple fuel engines
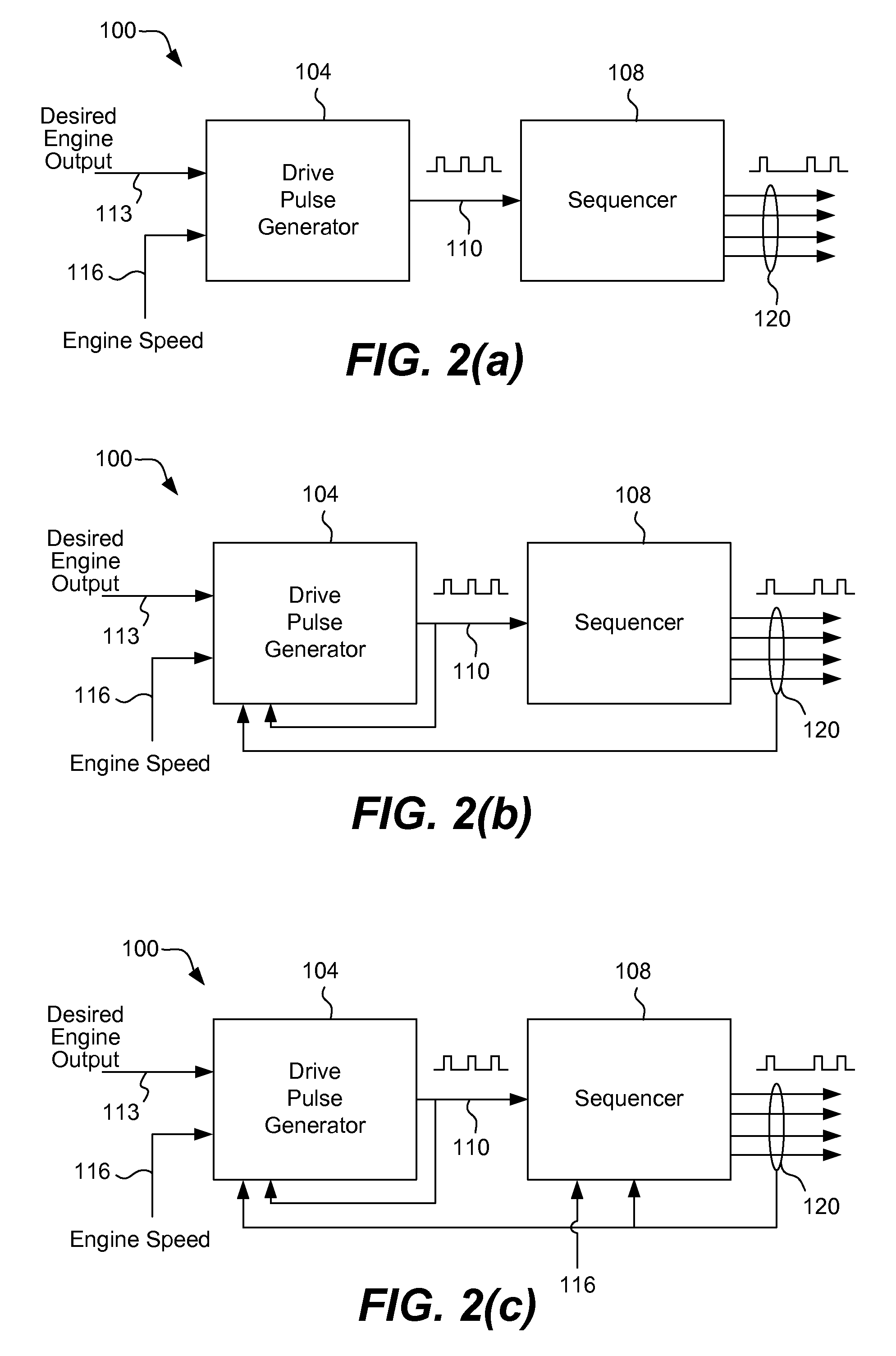
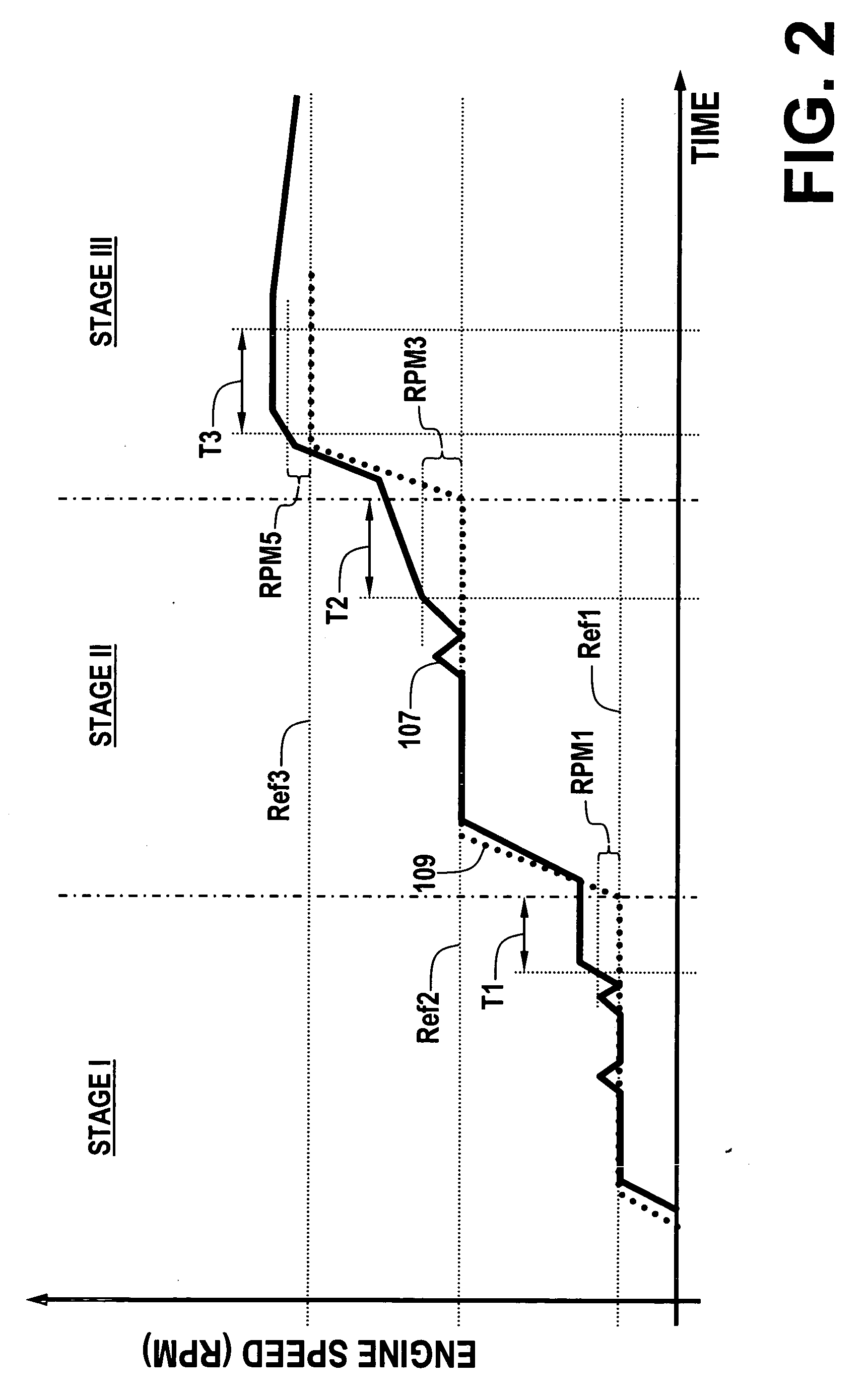
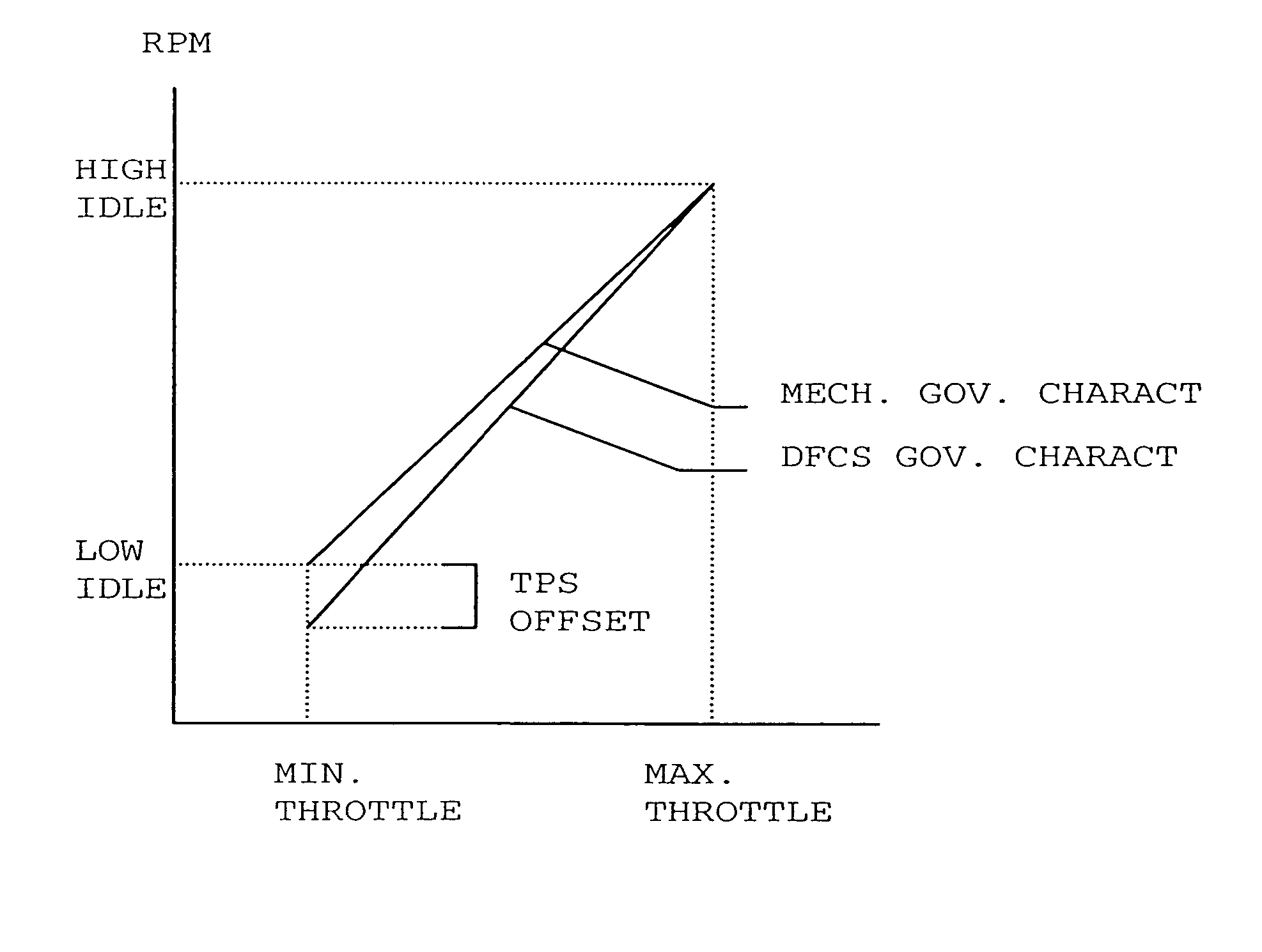
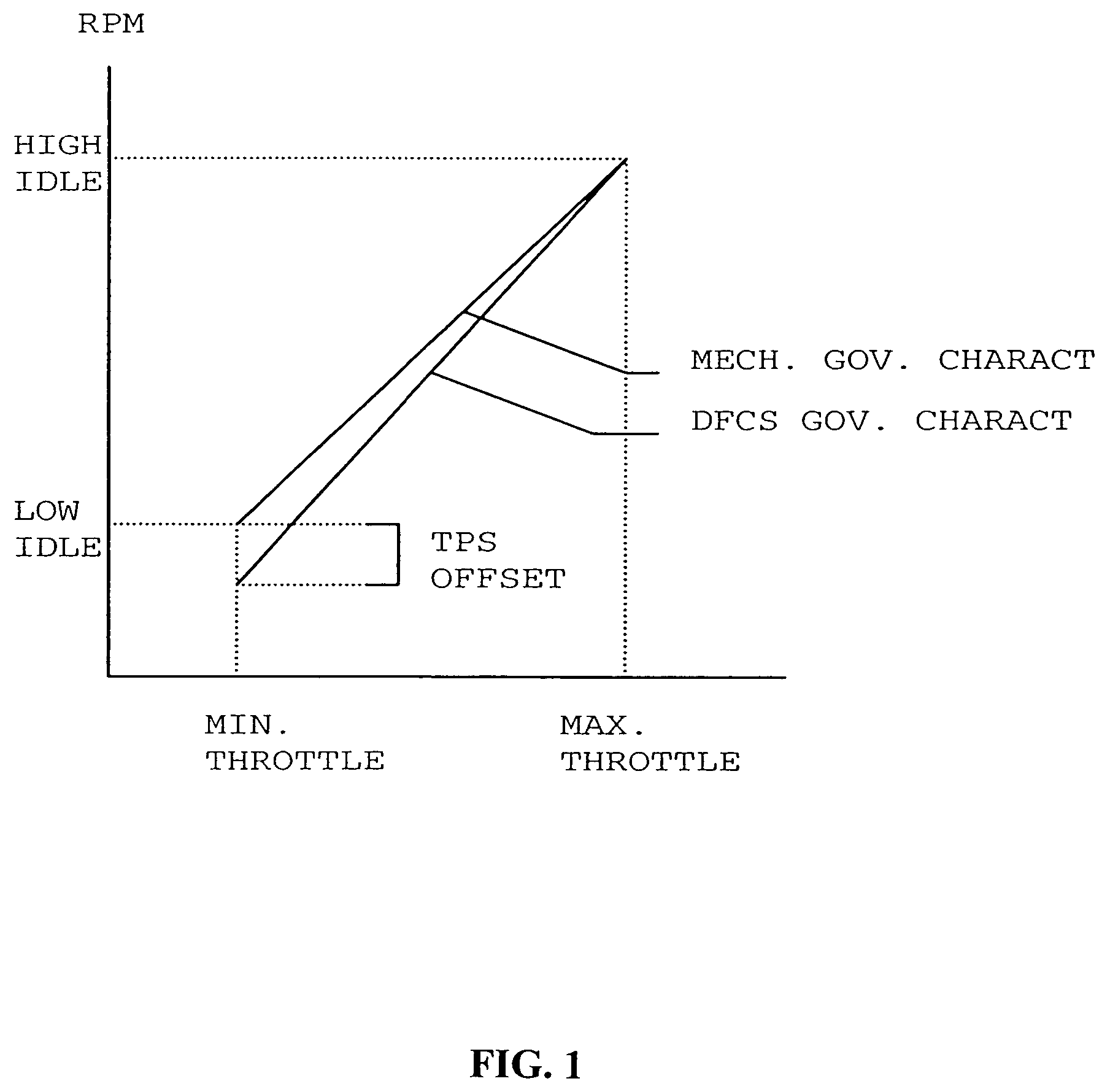
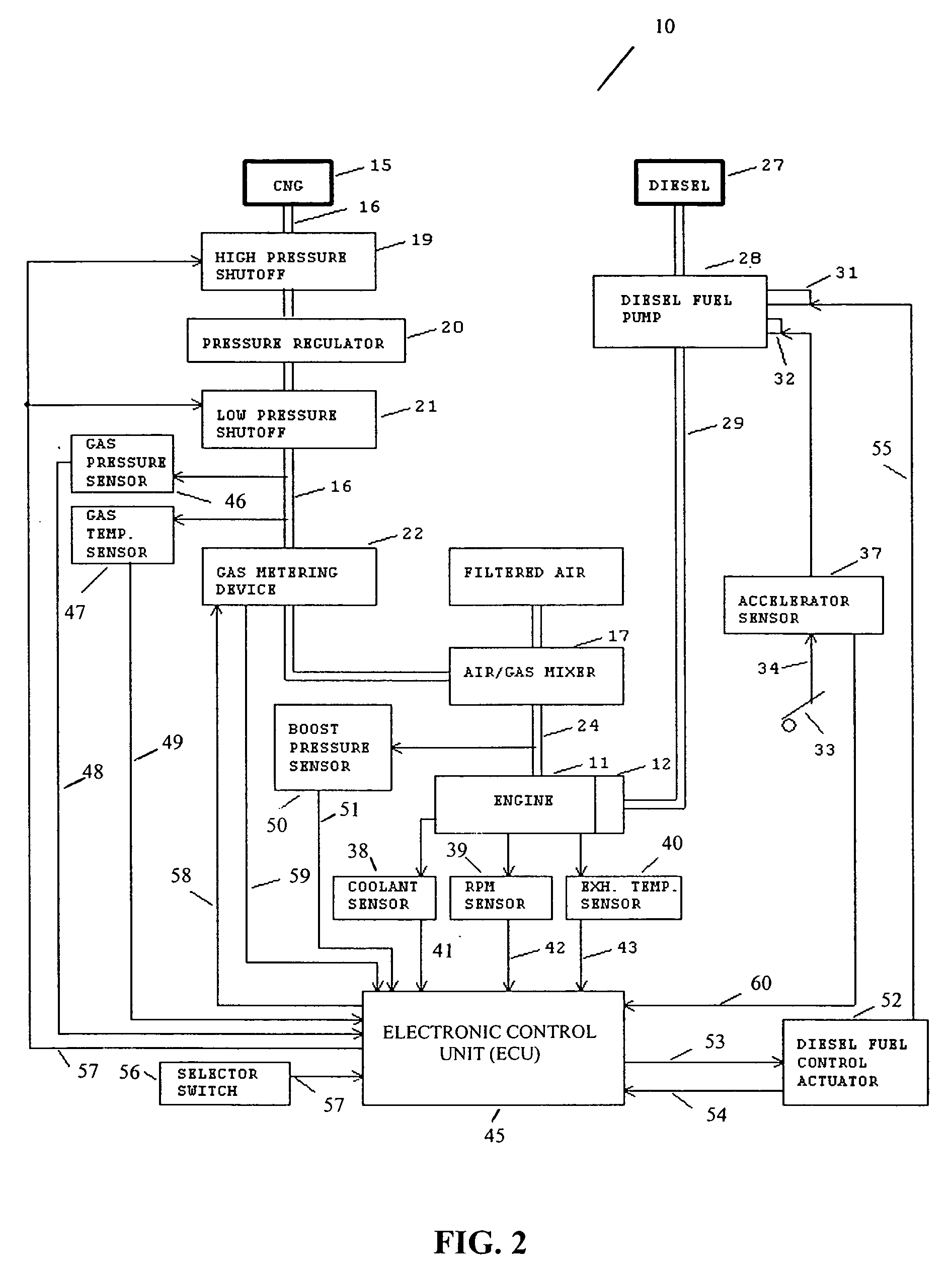
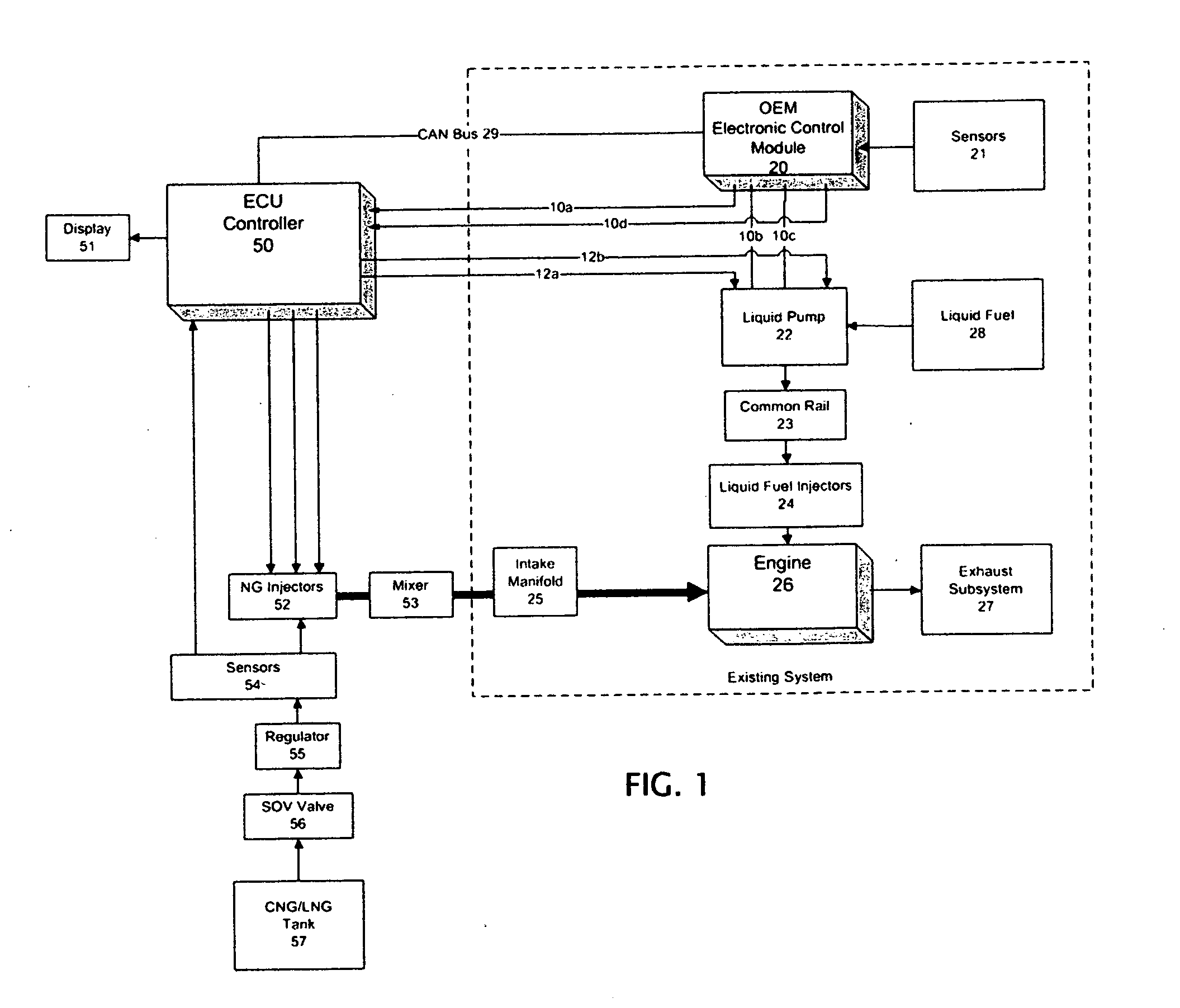
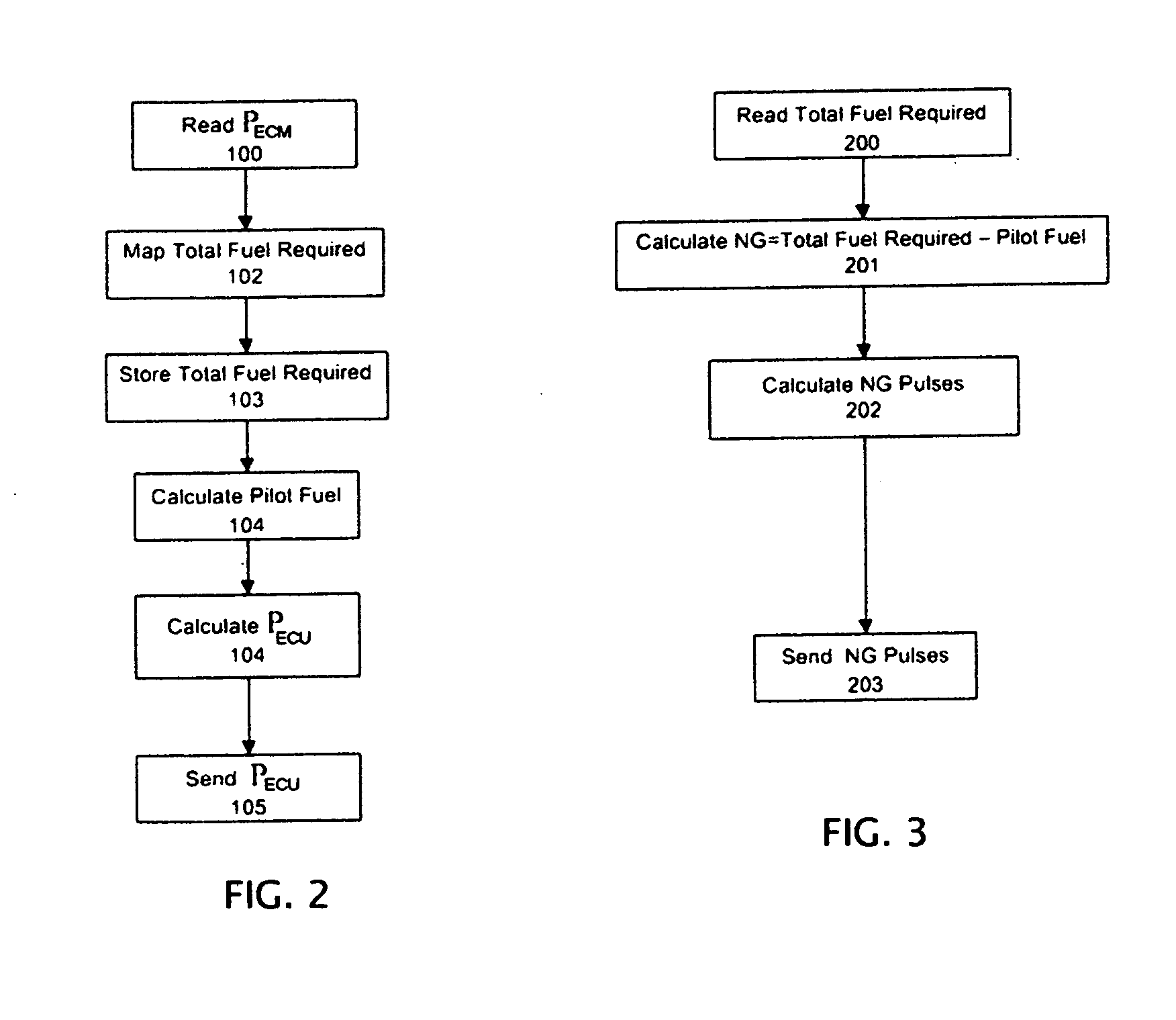
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for operation of a multiple fuel engine, which runs on a combination of two or more fuels. An electronic control unit (ECU) may be connected to the existing components of an engine system in order to control operation of the multiple fuel engine. The engine system may be mechanically governed or electronically controlled. The ECU inputs operating characteristics of the engine system, determines governing characteristics for multiple fuel operation based on the operating characteristics, and controls the amounts of fuel delivered to the engine based on the governing characteristics. In a preferred embodiment, a dual fuel engine operates using diesel as a first fuel and natural gas as a second fuel. The operating characteristics may include engine speed, throttle position, engine exhaust temperature, gas pressure of the second fuel, gas temperature of the second fuel, boost pressure of an intake manifold, or engine coolant temperature.
Owner:2FUEL TECH INC +1
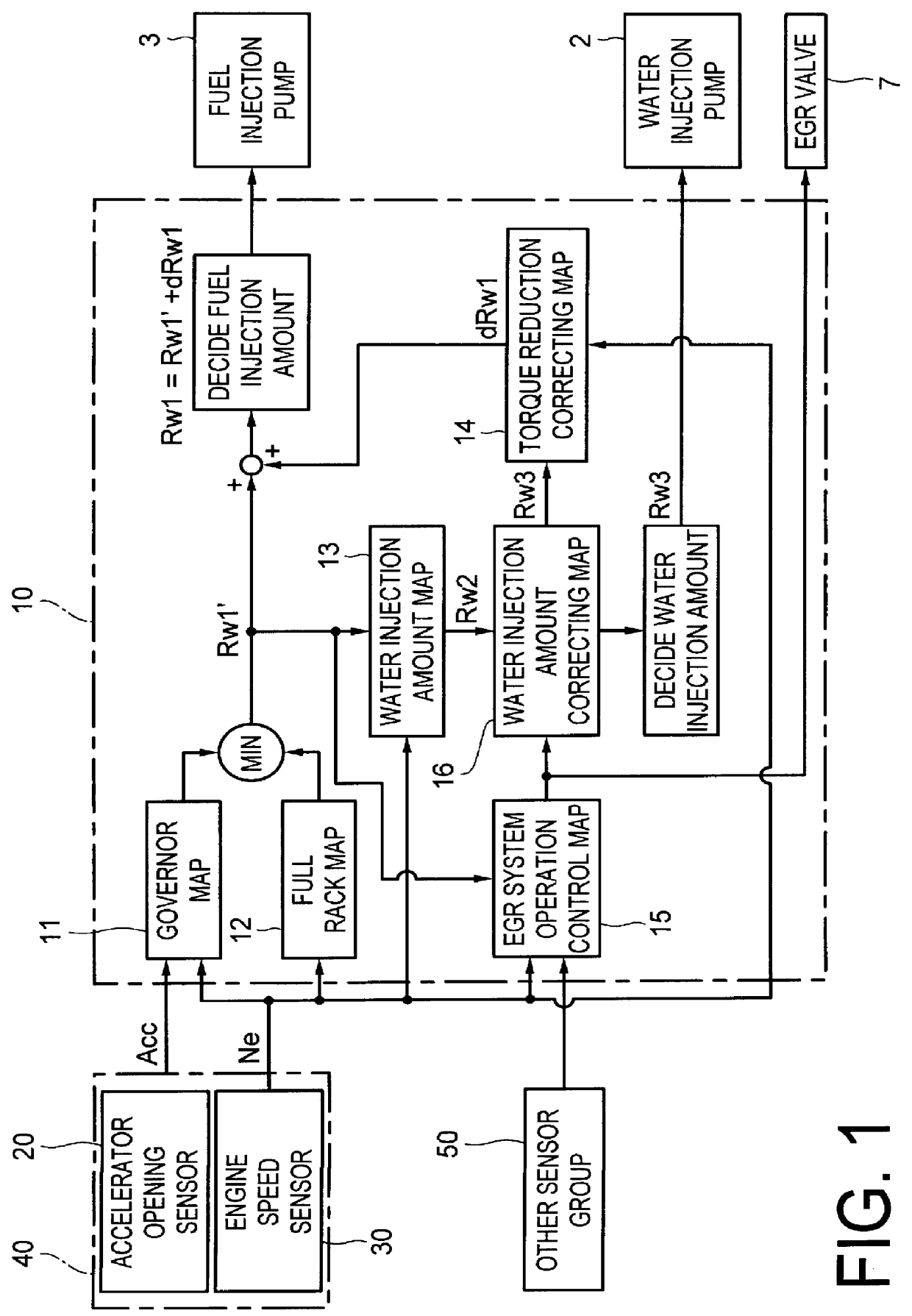
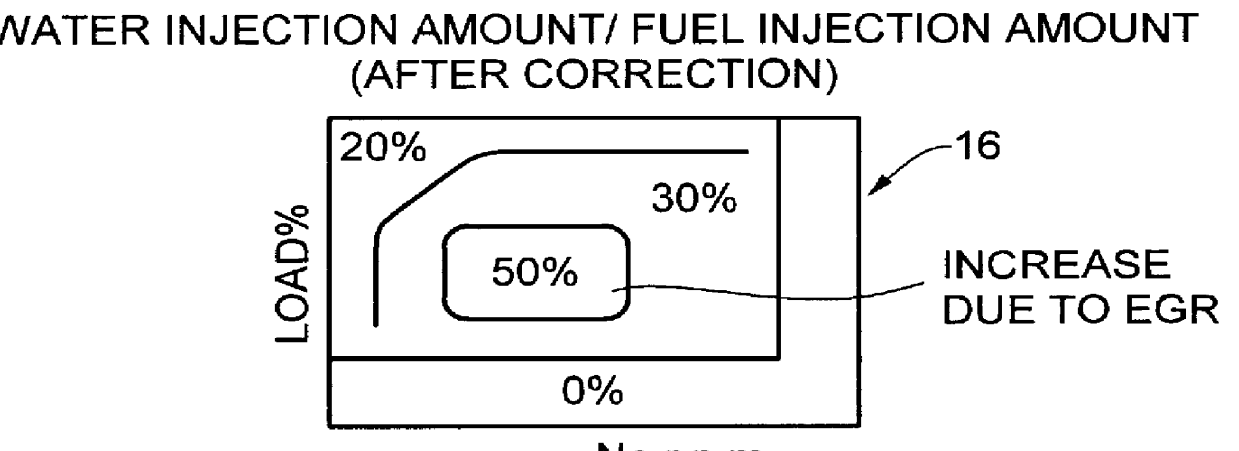
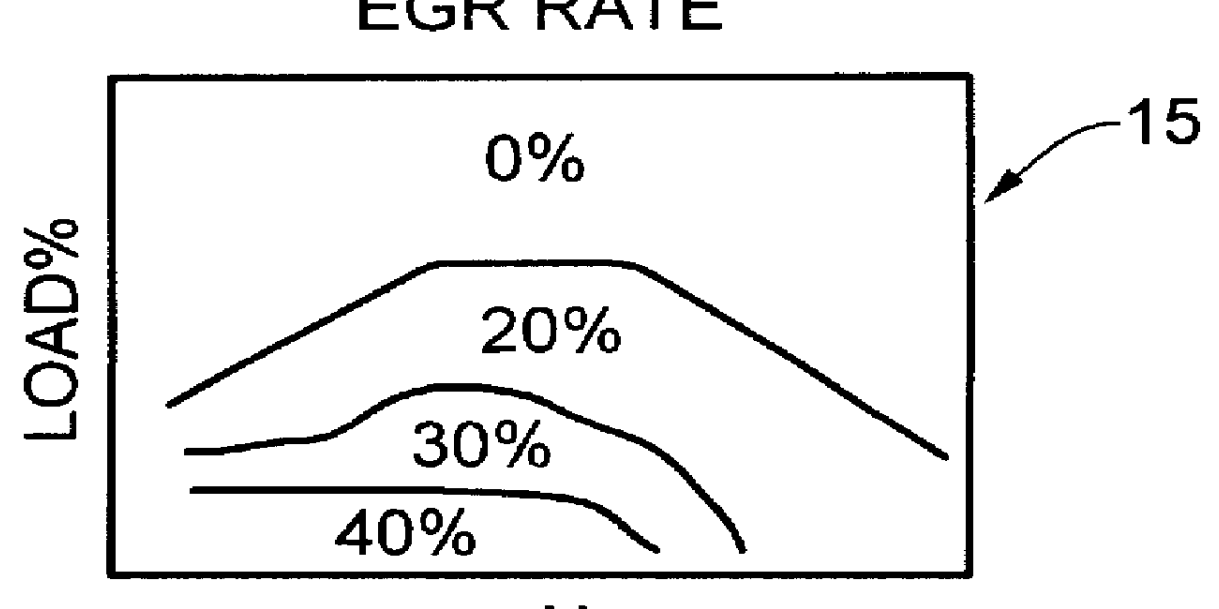
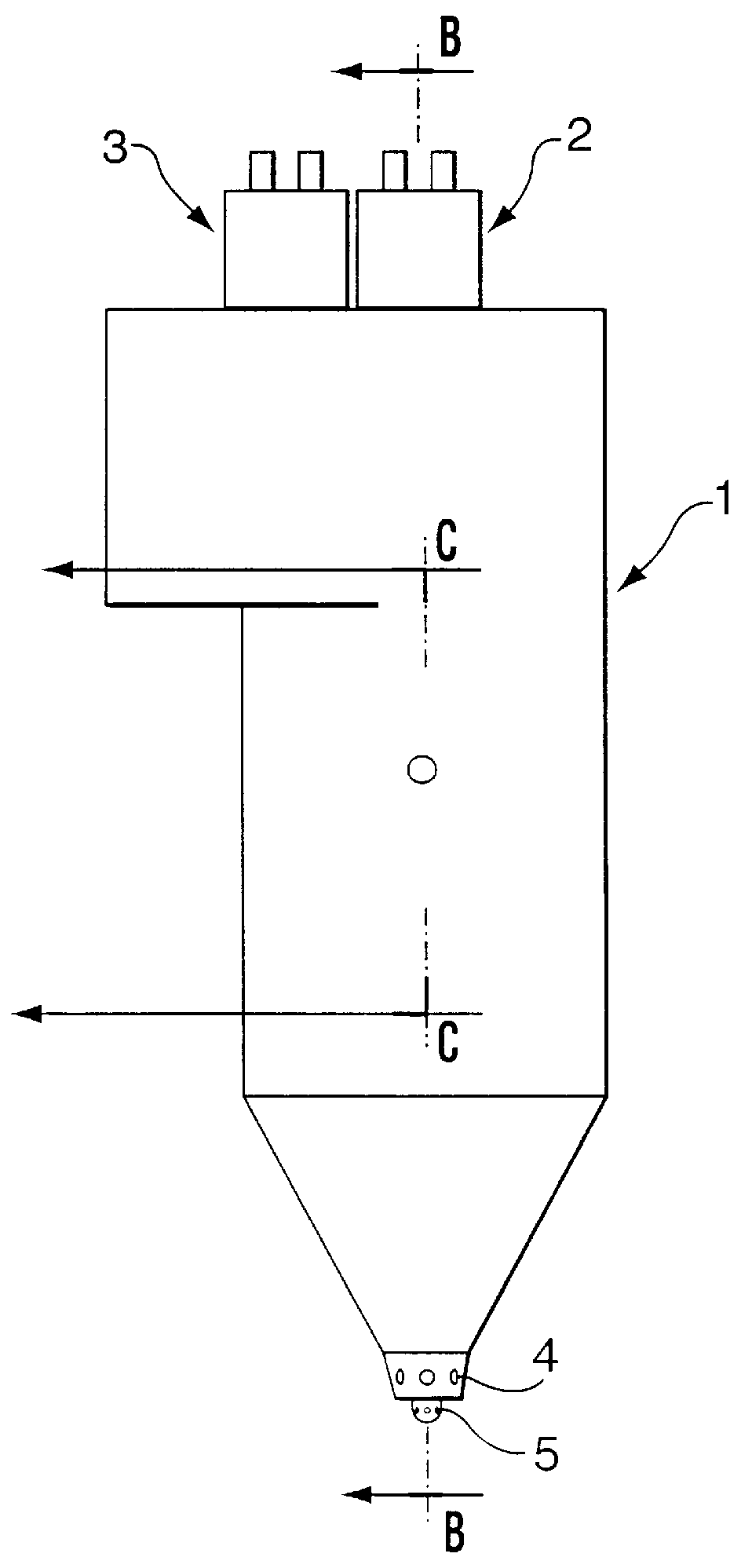
Water injection amount control system for fuel and water injection engine
InactiveUS6112705AEnhance NOx reducing effectImprove reducibilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberControl system
A water injection amount control system for a fuel and water injection engine, comprises running state detecting unit for detecting the running state of the engine; an EGR system for recirculating part of exhaust gas of the engine to a combustion chamber of the engine; EGR system operating state detecting unit for detecting or estimating the operating state of the EGR system; water injection amount regulating unit for regulating an amount of water to be injected to the combustion chamber of the engine; and control unit for controlling the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit: wherein the system is arranged to have water injection amount setting unit for deciding a water injection amount based on information from the running state detecting unit and on the operating state of the EGR system detected by the EGR system operating state detecting unit, so that the control unit controls the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit based on the water injection amount decided by the water injection amount setting unit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
Gaseous and liquid fuel injector
A hydraulically actuated dual fuel injector for an internal combustion engine. More particularly, the application pertains to a hydraulically actuated injector for injecting controlled quantities of a first fuel and of a second fuel into an internal combustion diesel engine at different times. A dual fuel injector comprising: (a) an injector body; (b) an inlet port in the injector body for enabling pressurized hydraulic fluid from a hydraulic fluid source to be introduced into the interior of the injector body, the hydraulic fluid being of sufficient pressure to maintain injection valves in the injector body in a closed position until actuated; (c) a first inlet port in the injector body for enabling a first fuel to be introduced into the interior of the injector body; (d) a first injection valve in the injector body connected to the second inlet port for controlling injection of the first fuel from the injector through a first fuel ejection port; (e) a second inlet port in the injector body for enabling a second fuel to be introduced into the interior of the injector body; (f) a second injection valve in the injector body connected to the second inlet port for controlling injection of the second fuel from the injector through a second fuel ejection port; (g) a first control valve which causes the hydraulic fluid to actuate the first injection valve; (h) a second control valve which causes the hydraulic fluid to actuate the second injection valve; (i) a metering device in the injector body for metering the amount of first fuel injected by the first injection valve; and (j) a seal in the injector body which prevents leakage of the second fuel into the first fuel.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
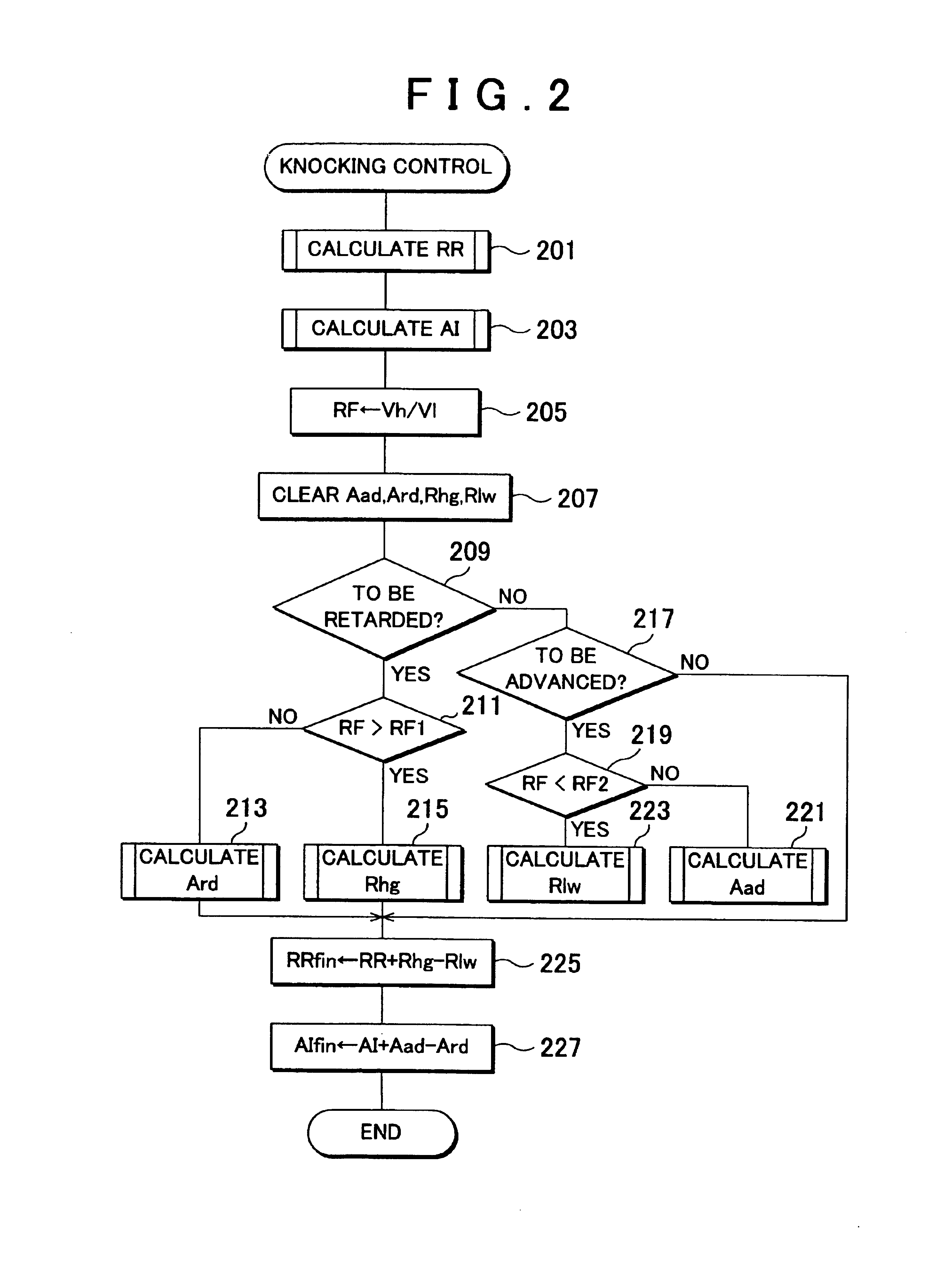
Knocking control system and method for internal combustion engine using multiple fuels
InactiveUS6951202B2Maintain balanceImprove balanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultifuelCombustion chamber
High octane fuel and low octane fuel are supplied into the combustion chamber of an engine from high-octane fuel tank and low octane fuel tank via a high octane fuel injector and a low octane fuel injector. During a knocking control, if the quantity of high and low octane fuels in the respective tanks has been unbalanced, the supply ratio between high octane fuel and low octane fuel is changed 1 to control a knocking occurring in the engine without changing the ignition timing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
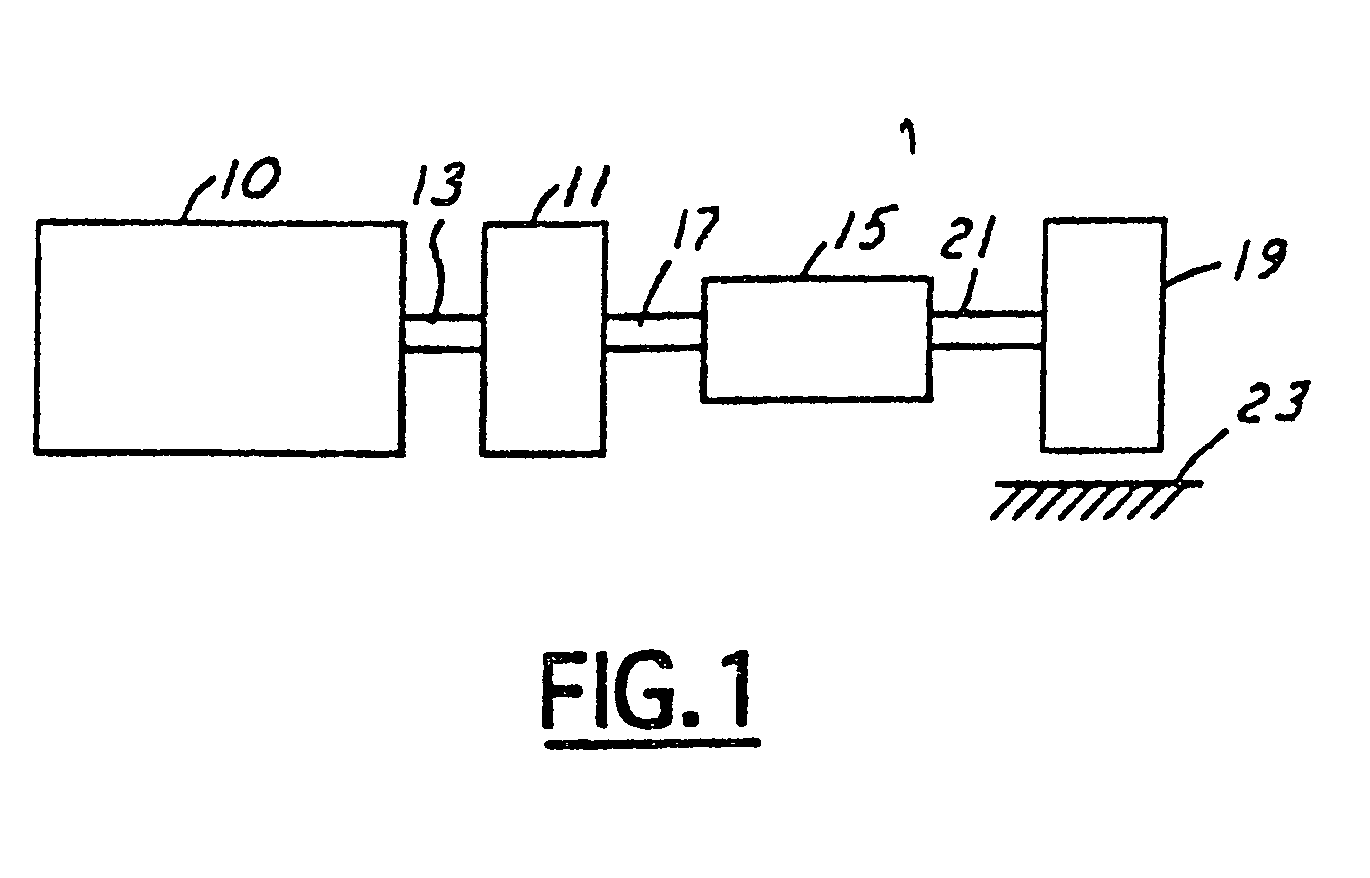
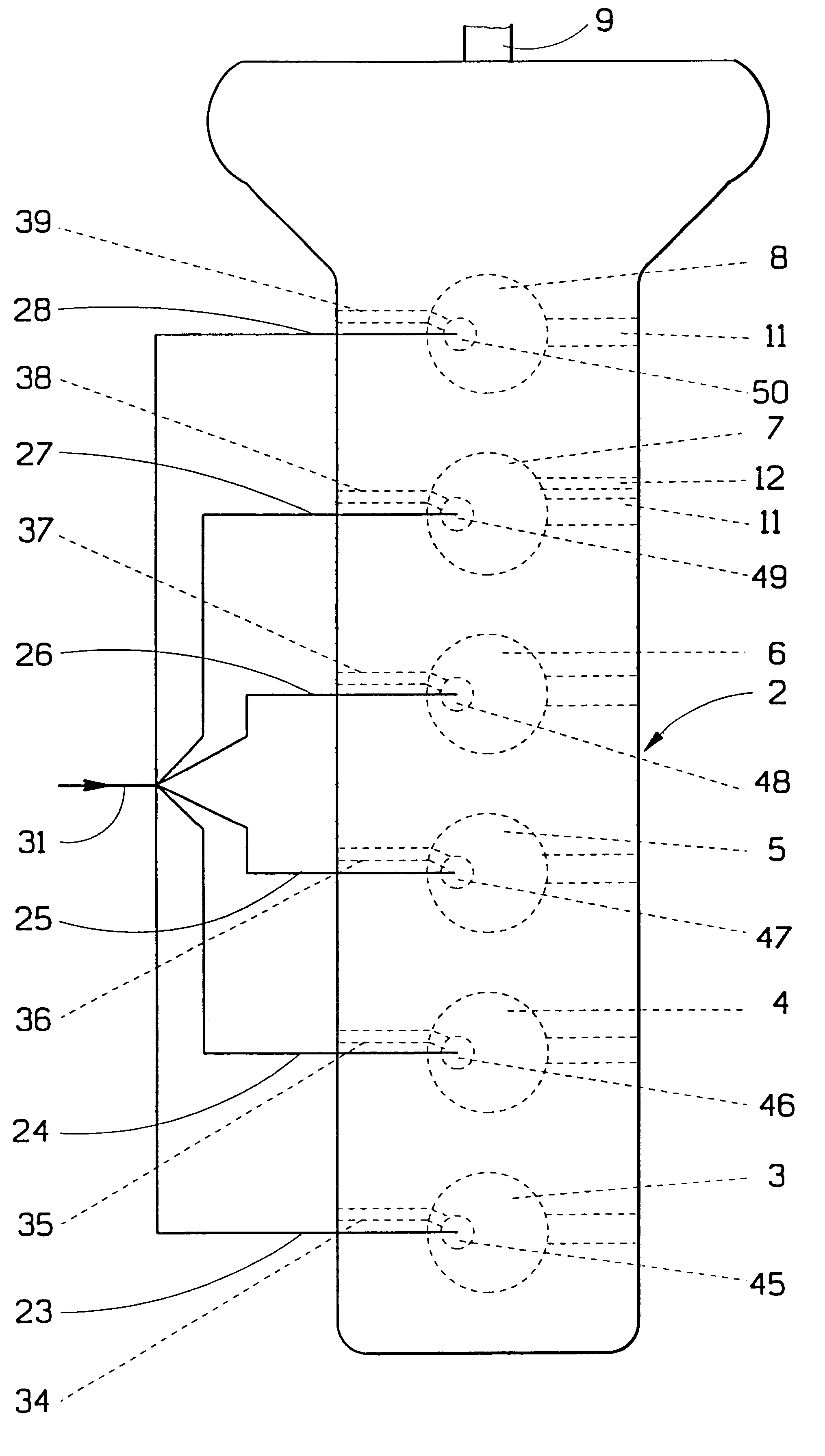
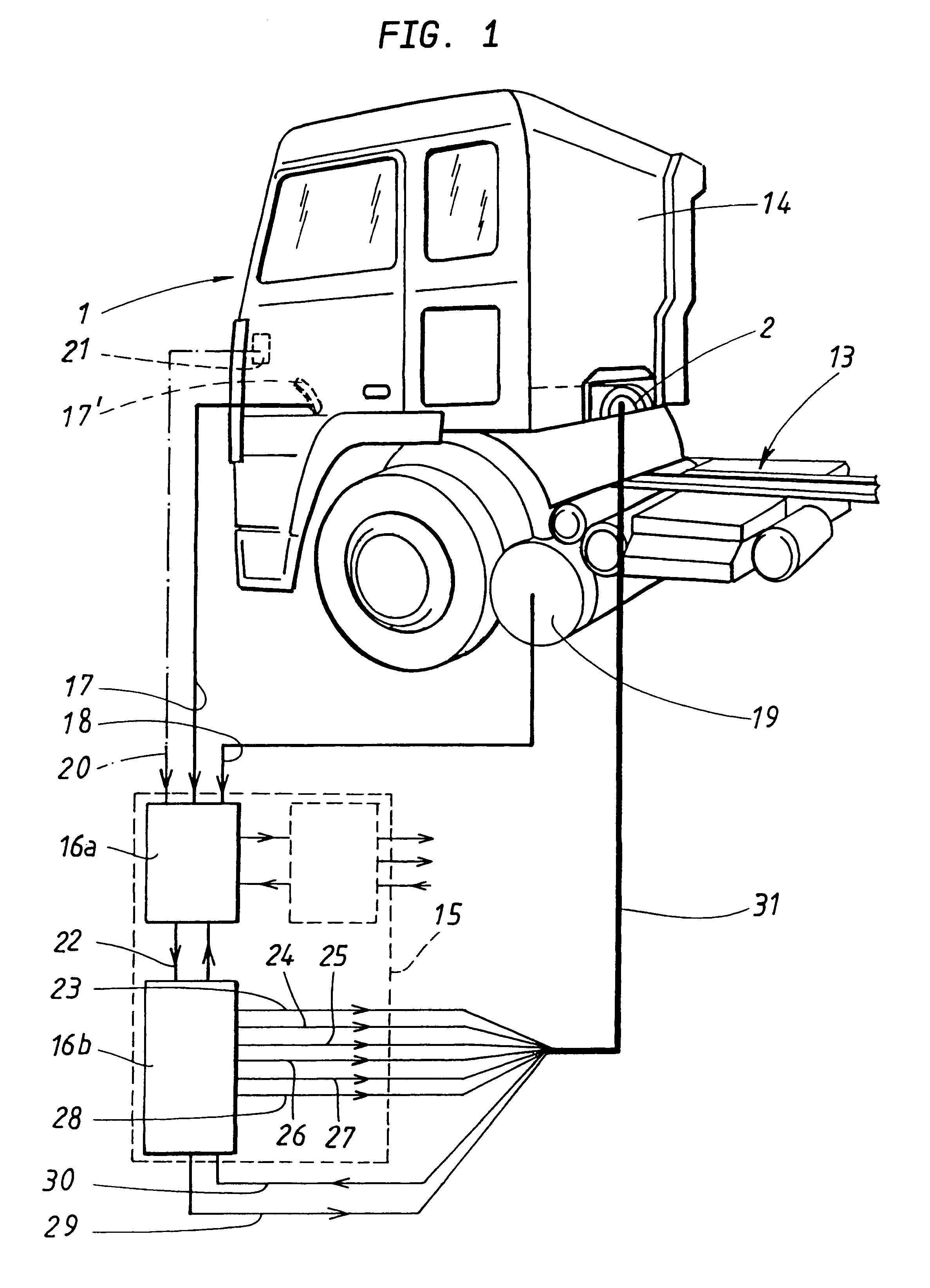
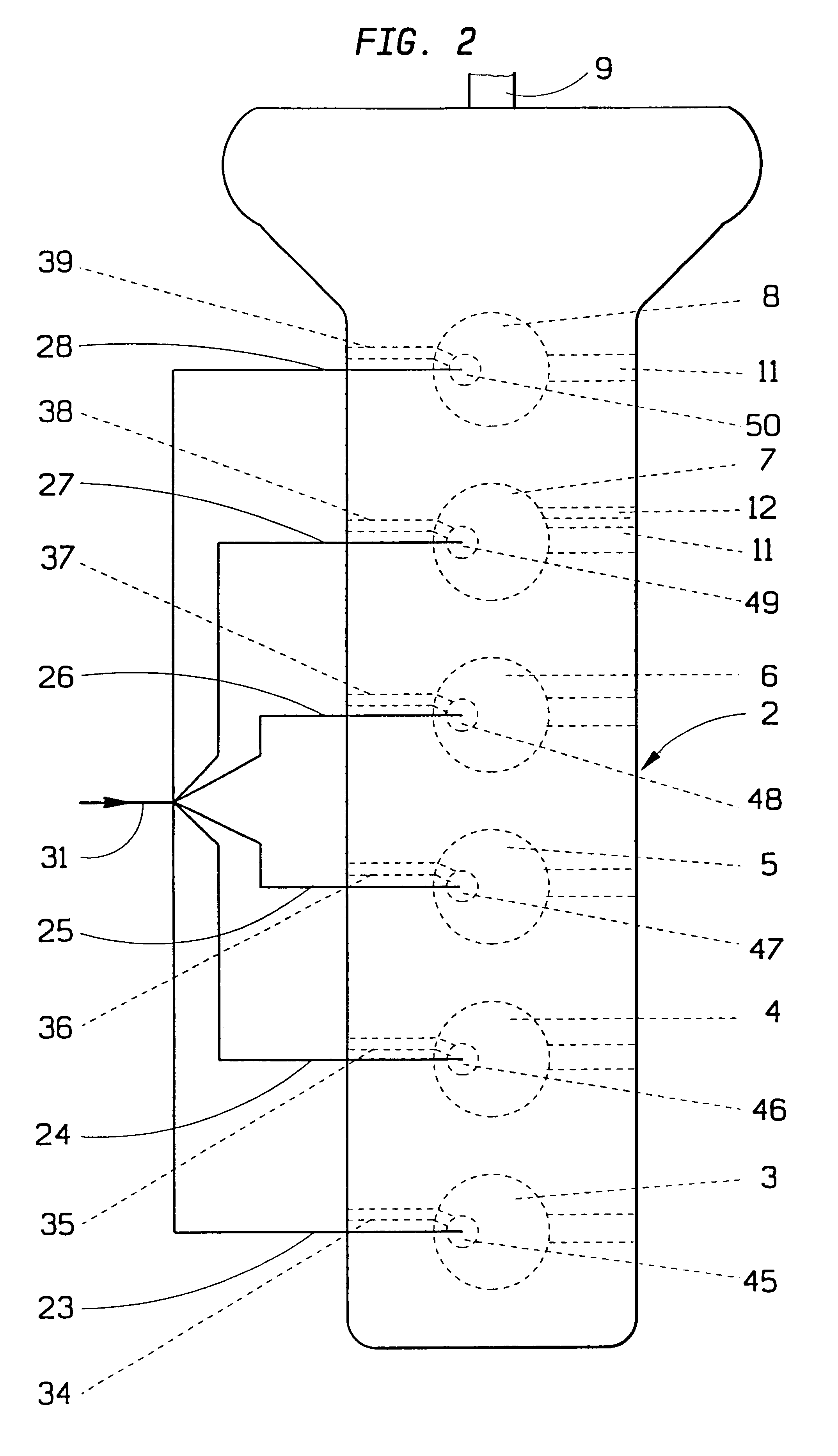
Method for reducing vibration in a vehicle and a device for accomplishment of the method
A method and an arrangement for reducing vibrations in an internal combustion engine (2) which has a plurality of drive units (3-8) connected to a common output shaft (9). These are equipped with a combustion chamber and inlets (34-39) for fuel from organs for fuel supply. Any one of the driving units (7) can be switched from a normal operating condition to an alternative operating condition, in which the supply of fuel to the drive unit is blocked, which causes an alteration in the torque of the driving unit which has been thus switched. The amount of fuel supplied to the drive units which are in a normal operating condition is distributed according to a chosen pattern in order to create torques in these which cause a chosen suppresion of vibrations.
Owner:AB VOLVO
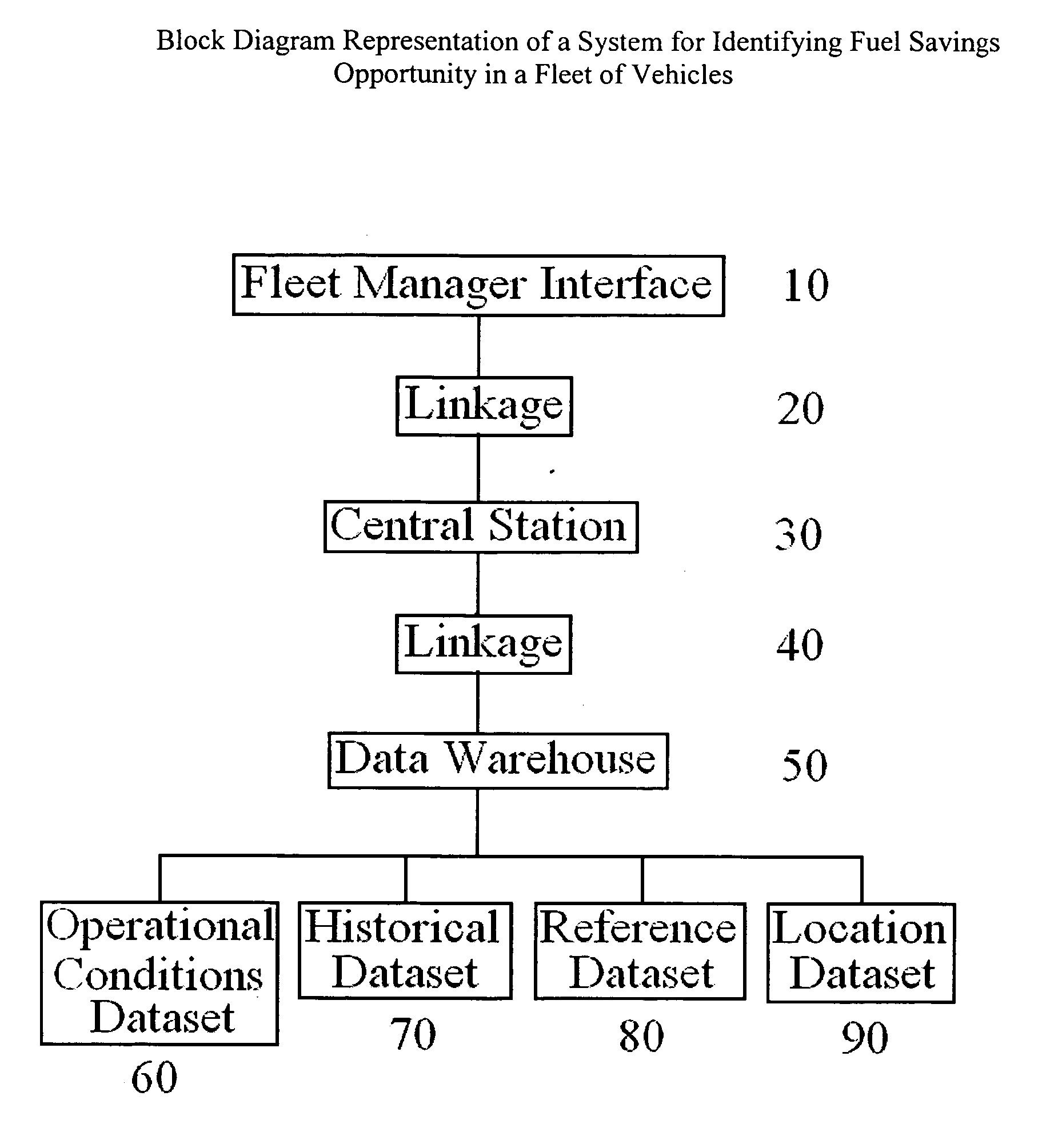
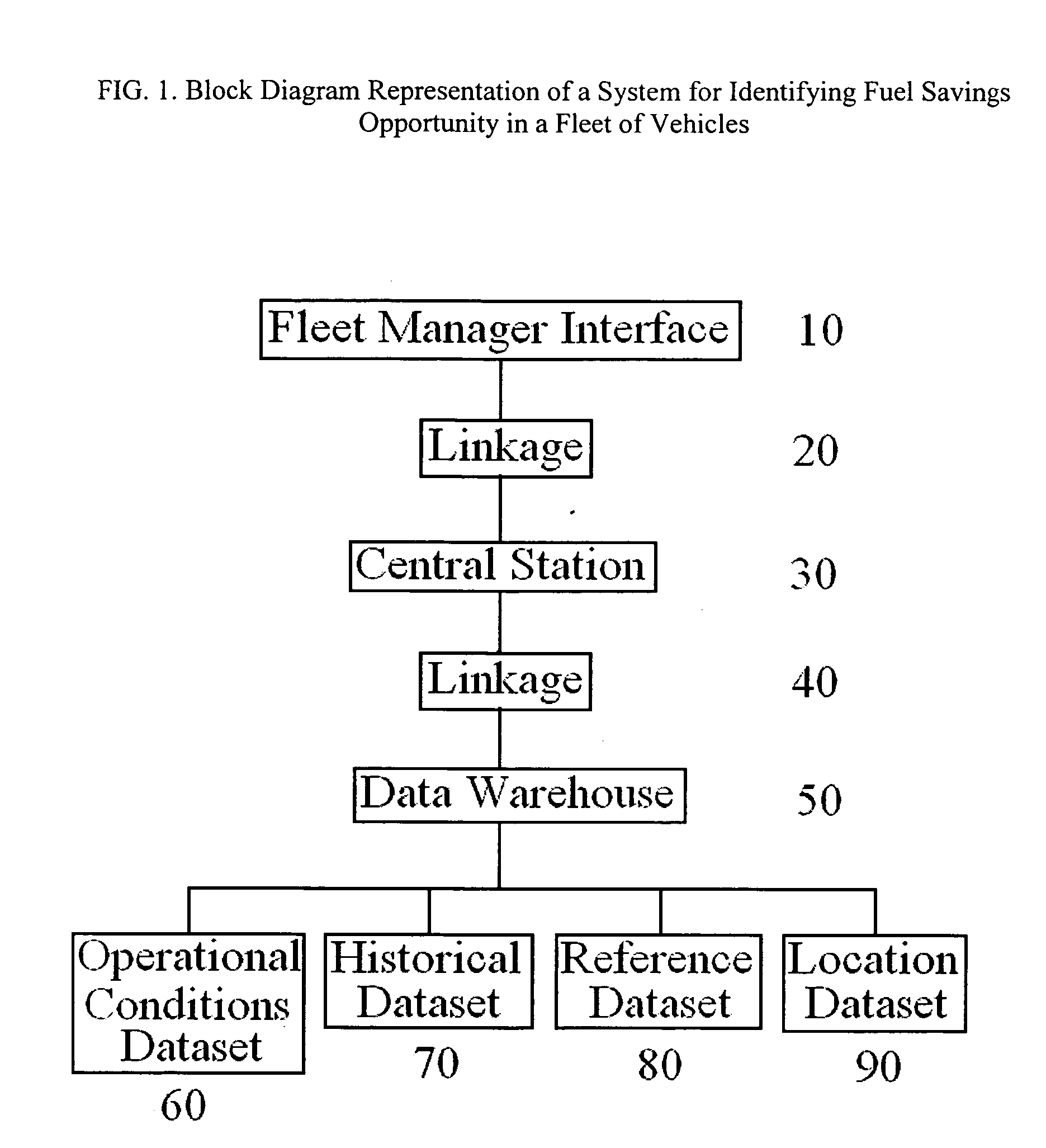
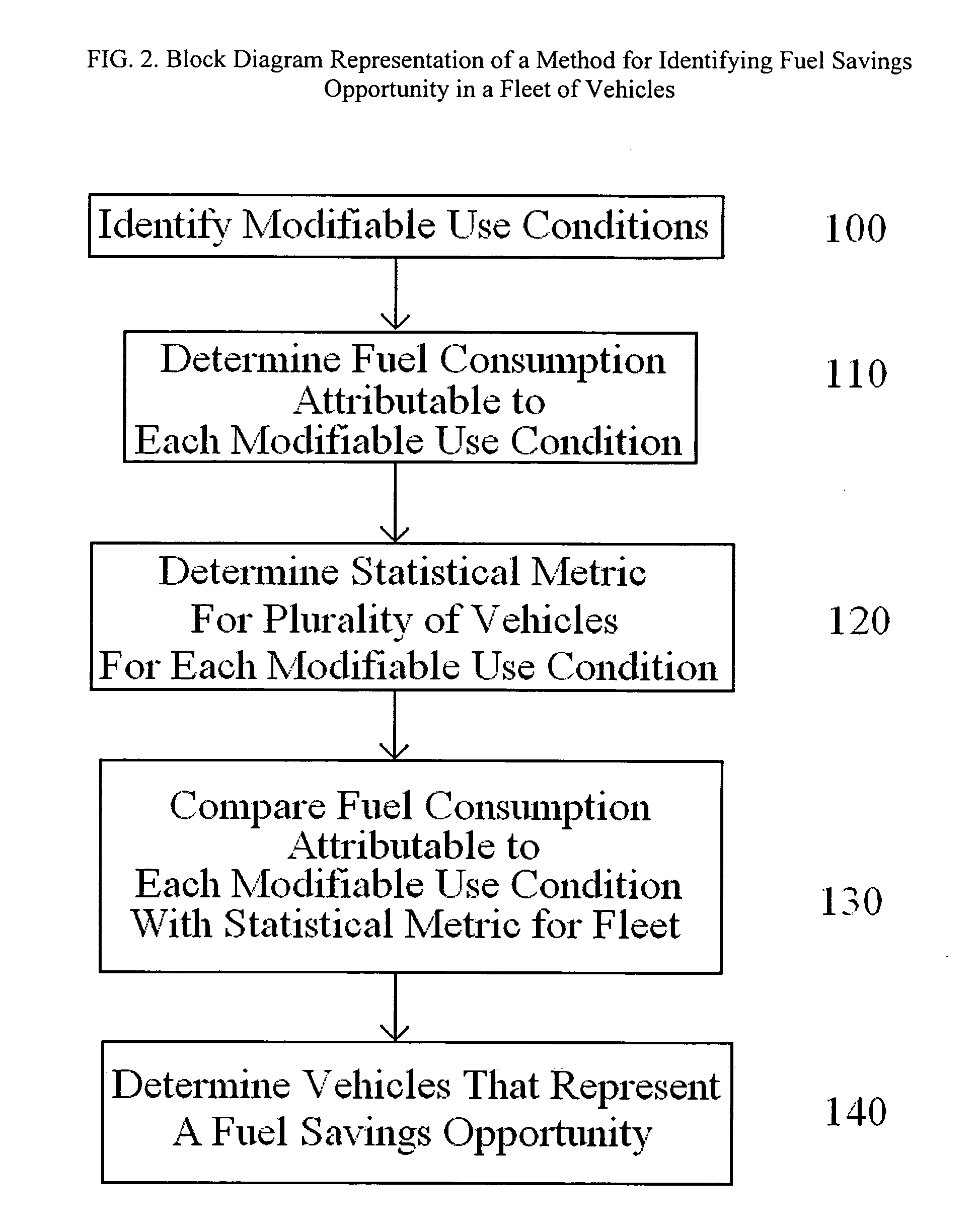
System and method for identifying fuel savings opportunity in vehicles
ActiveUS20070174004A1Reduce fuel consumptionLow costVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesIn vehicleSimulation
A system and method of identify fuel savings opportunity in a fleet of vehicles based on a determination of fuel consumption due to modifiable use conditions is described. Modifiable use conditions, such as unauthorized usage, speeding and excessive idling, which represent opportunities for fuel savings are identified and fuel consumption based on the modifiable use conditions is determined. A user-defined statistical metric for the fleet, or a portion of the fleet, can be determined for each of the modifiable use conditions evaluated. Fuel consumption of an individual vehicle, or a group of vehicles, resulting from modifiable use conditions can be compared with a larger group of vehicle, or the fleet, to determine vehicles which correspond to a metric of the fleet. Fleet managers can use this information to modify the use conditions of individual or group of vehicles to provide fuel savings for the fleet.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
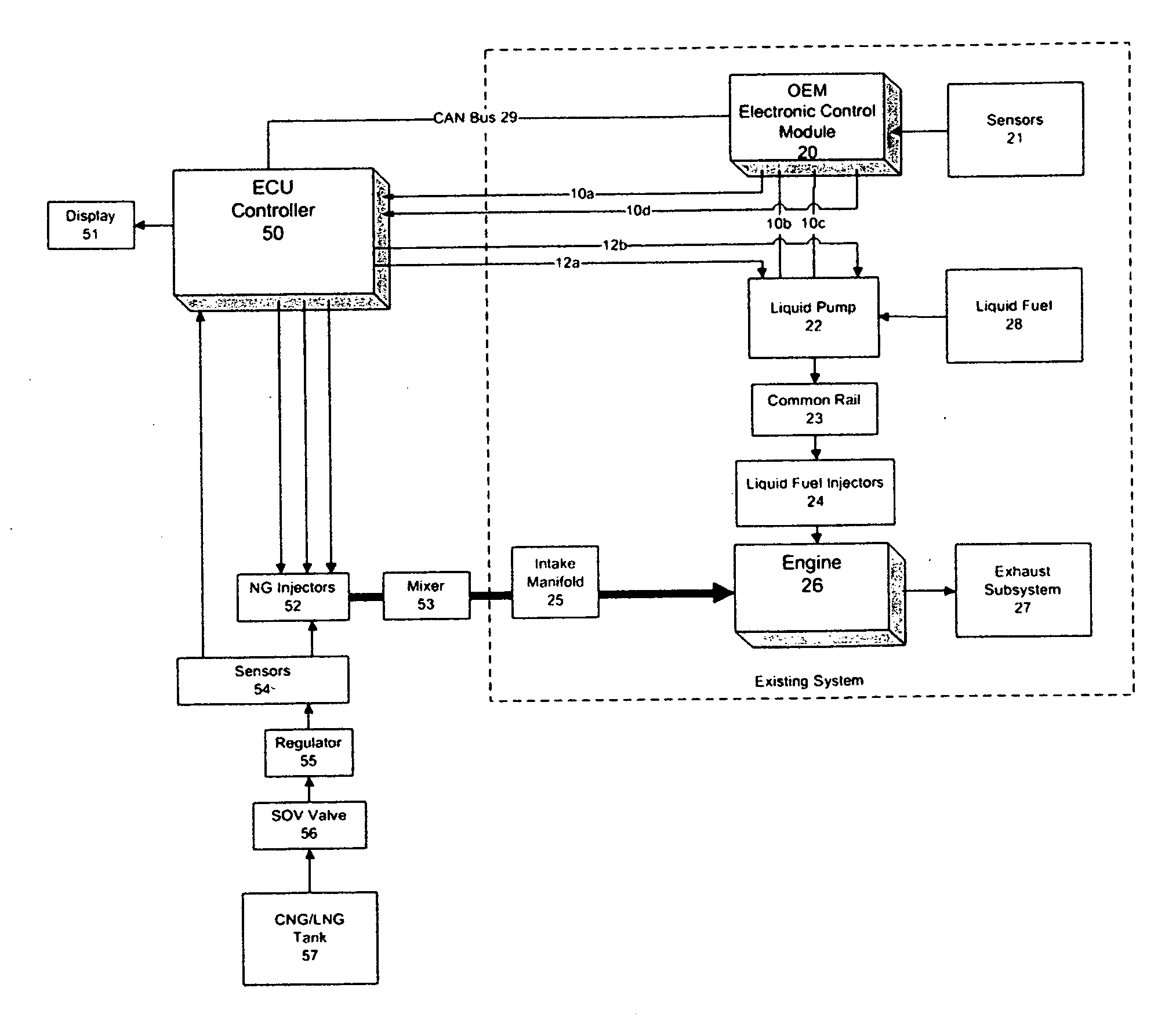
Dual fuel engine system
InactiveUS20120310509A1Quick installationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectronic controllerControl signal
A dual fuel system employs a liquid fuel supply subsystem and a gaseous fuel supply subsystem for an engine. The liquid fuel supply subsystem supplies liquid fuel to the engine and an electronic control module is configured to control, via one or more liquid fuel control signals, the amount of liquid fuel supplied to the engine based on one or more sensor signals. A gaseous fuel supply subsystem is configured to supply gaseous fuel to the engine and an electronic controller subsystem responsive to liquid fuel control signal(s) determines, based on the liquid fuel control signals, a modified amount of liquid fuel and an amount of gaseous fuel to be supplied to the engine for dual fuel operation.
Owner:ECODUAL
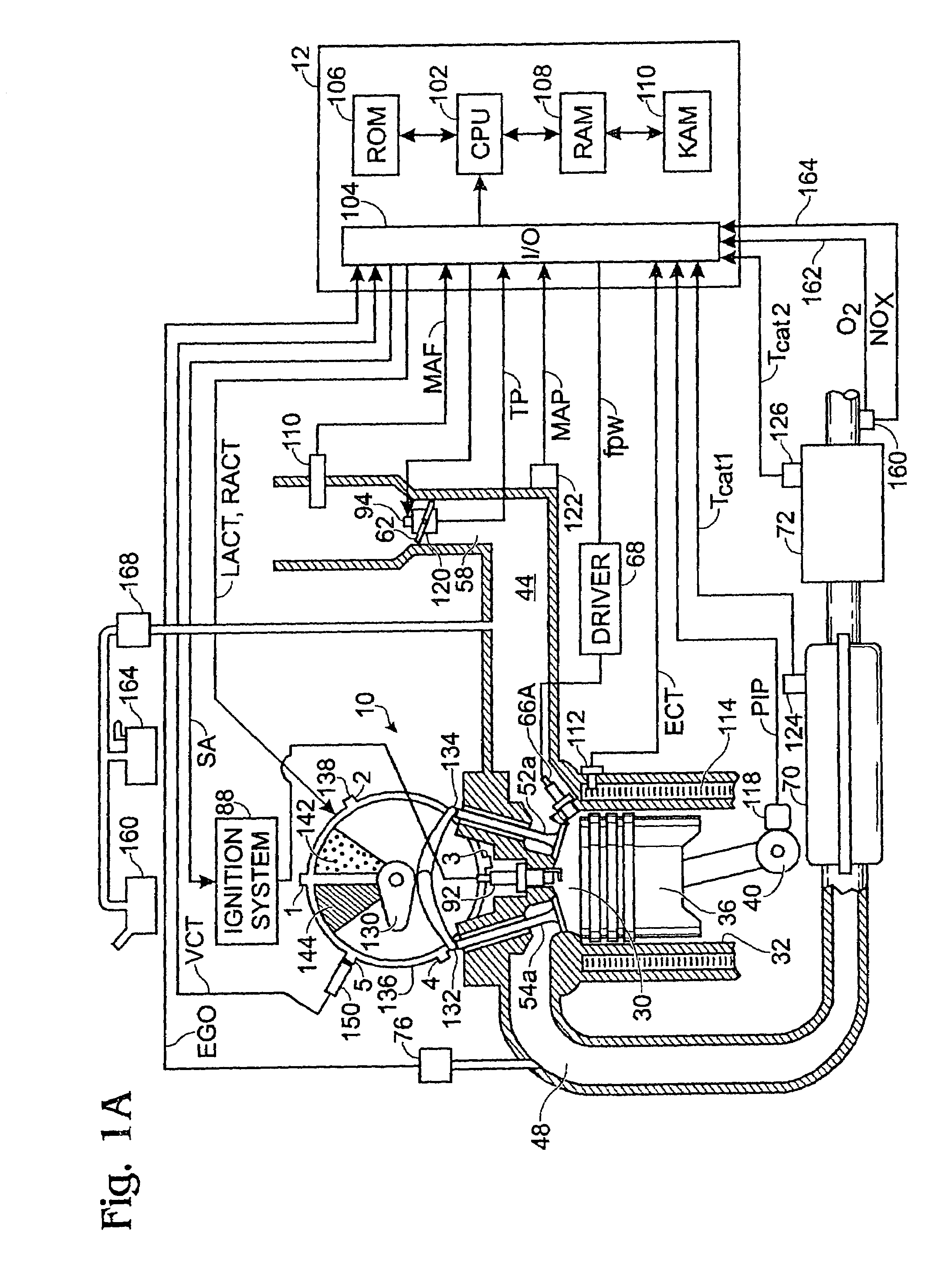
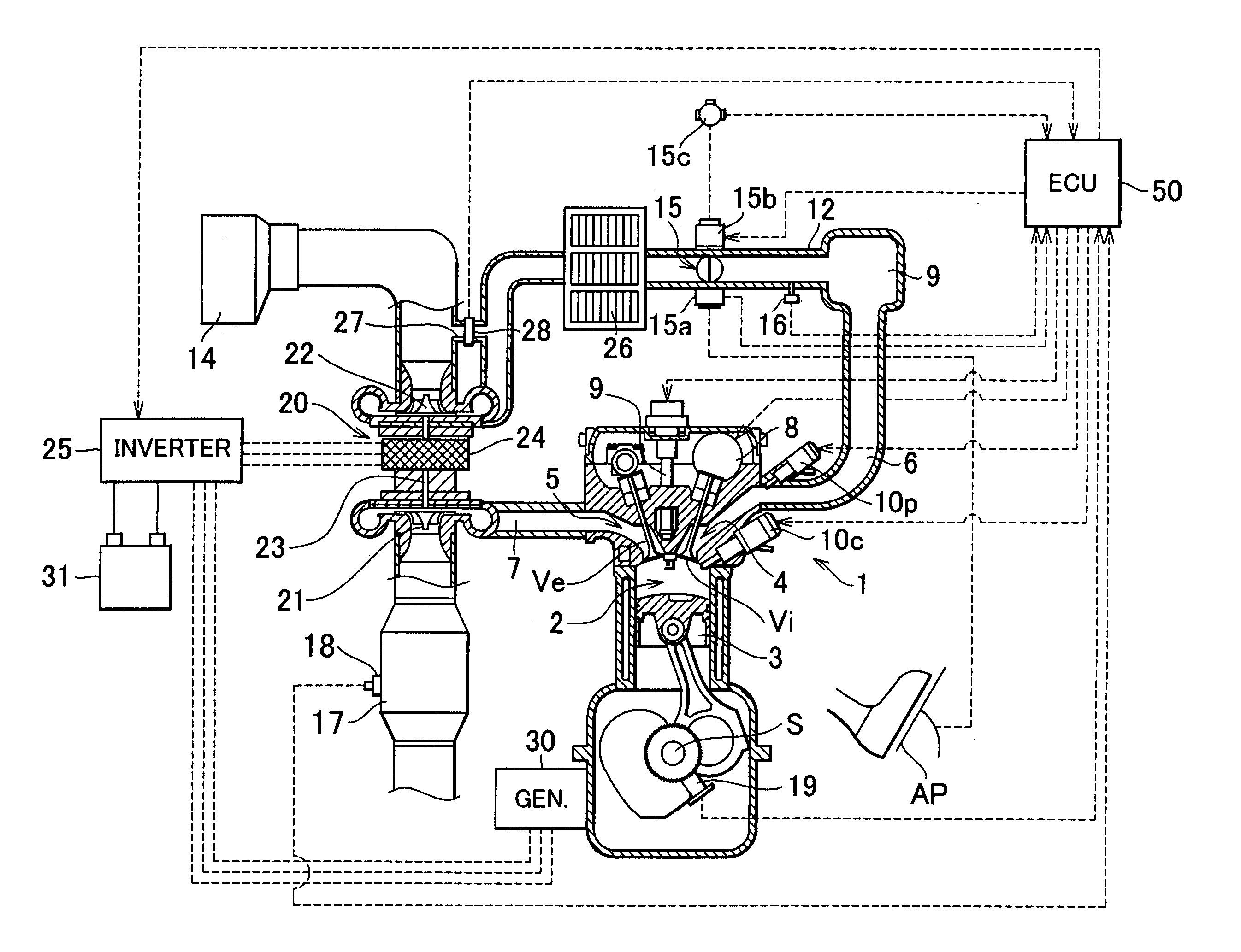
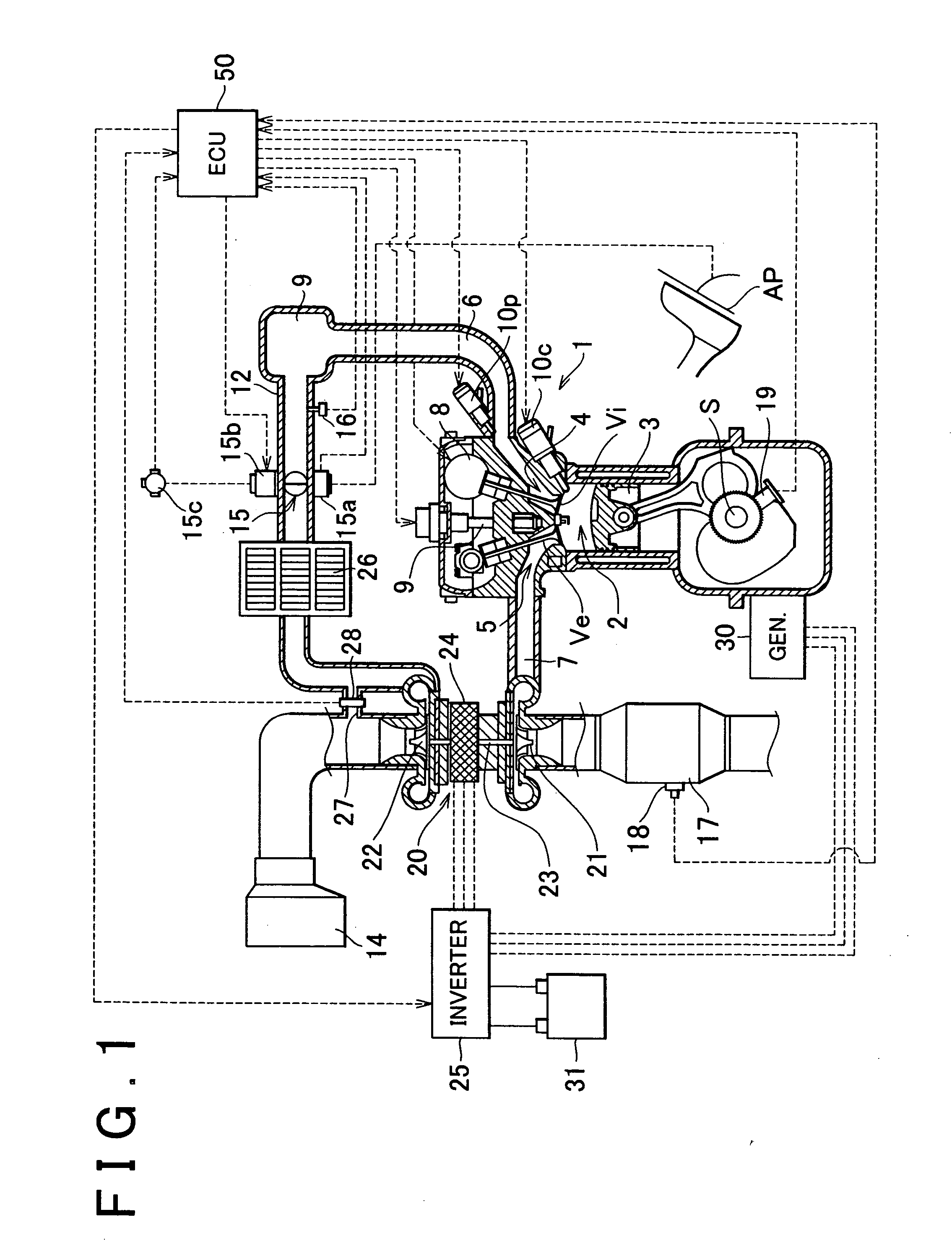
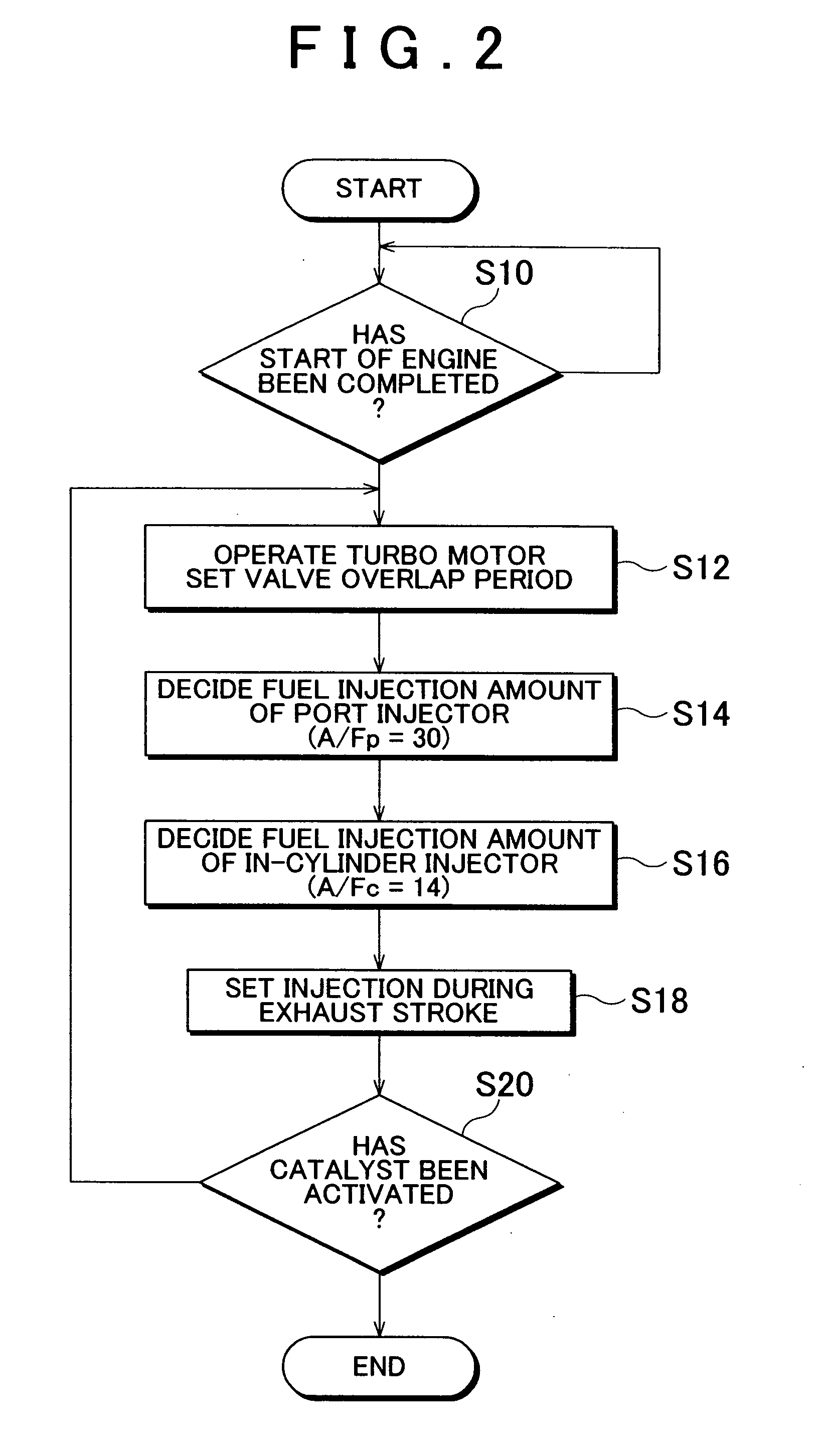
Internal combustion engine and control method thereof
InactiveUS20050097888A1Reliably activatedReduce exhaust emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
An internal combustion engine in which power is generated by burning a mixture of fuel supplied from a port injector and / or an in-cylinder injector and air in a combustion chamber, includes a valve drive mechanism which can change a valve opening characteristic of at least one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve; a turbocharger which supercharges air taken into the combustion chamber; a turbo motor which changes supercharging pressure generated by the turbocharger; a catalyst device including a catalyst which purifies exhaust gas discharged from the combustion chamber; and an ECU which controls the turbo motor such that pressure of the air taken into the combustion chamber becomes larger than back pressure until it is determined that the catalyst has been activated, and which sets a valve overlap period during which both of the intake valve and the exhaust valve are opened.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel management system for variable anti-knock agent octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102146A1Increase heatReduces octane requirementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fuel injection system and method
InactiveUS6959693B2Electrical controlCoolant flow controlCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
A fuel injection system includes a first fuel injector that injects a lower-octane fuel into a combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, and a second fuel injector that injects a higher-octane fuel into an intake passage of the engine. When the engine temperature is equal to or lower than a predetermined temperature during a start-up period of the internal combustion engine, fuel having the lower octane is injected via the first injector while prohibiting injection of the higher octane fuel via the second fuel injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
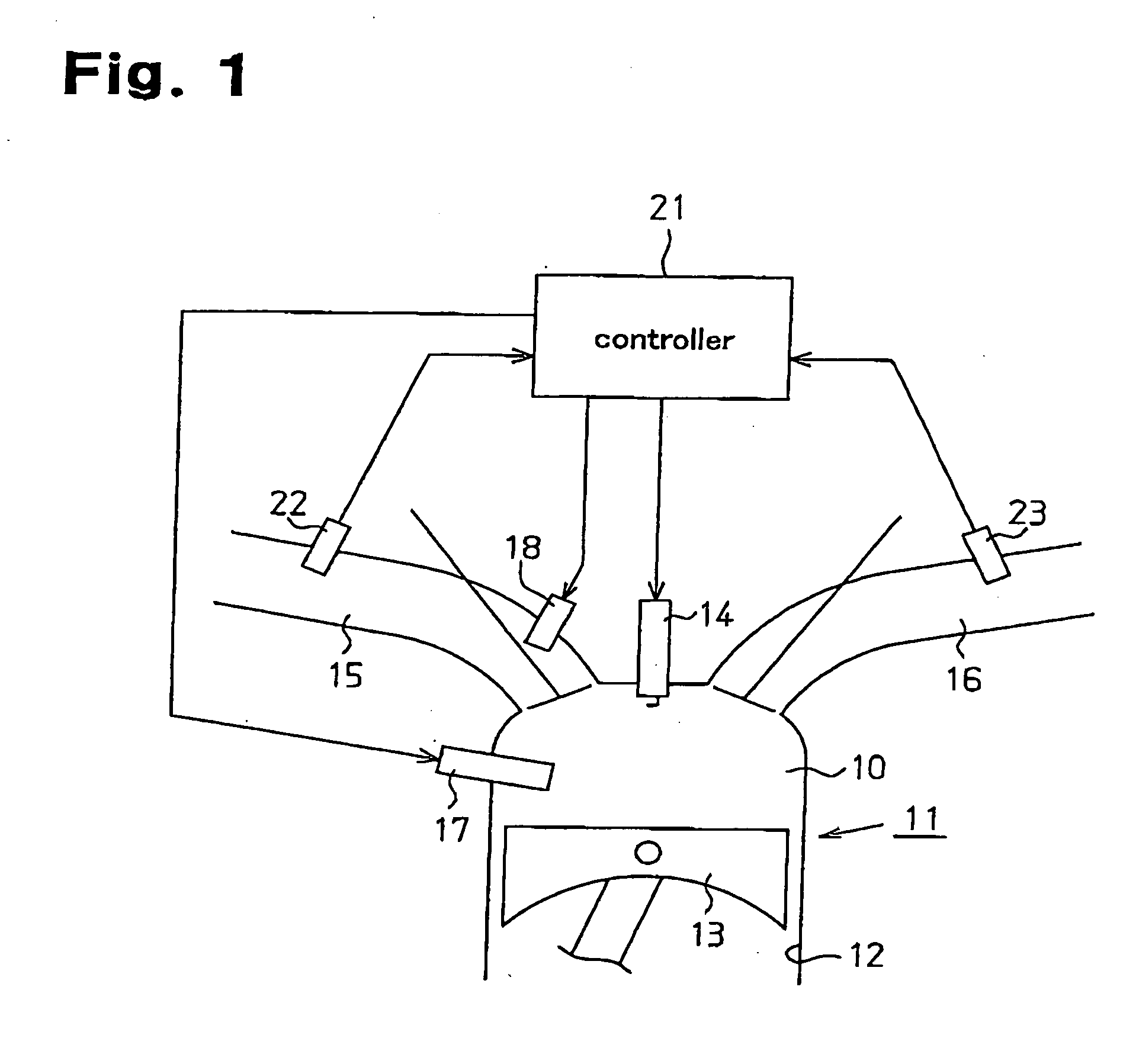
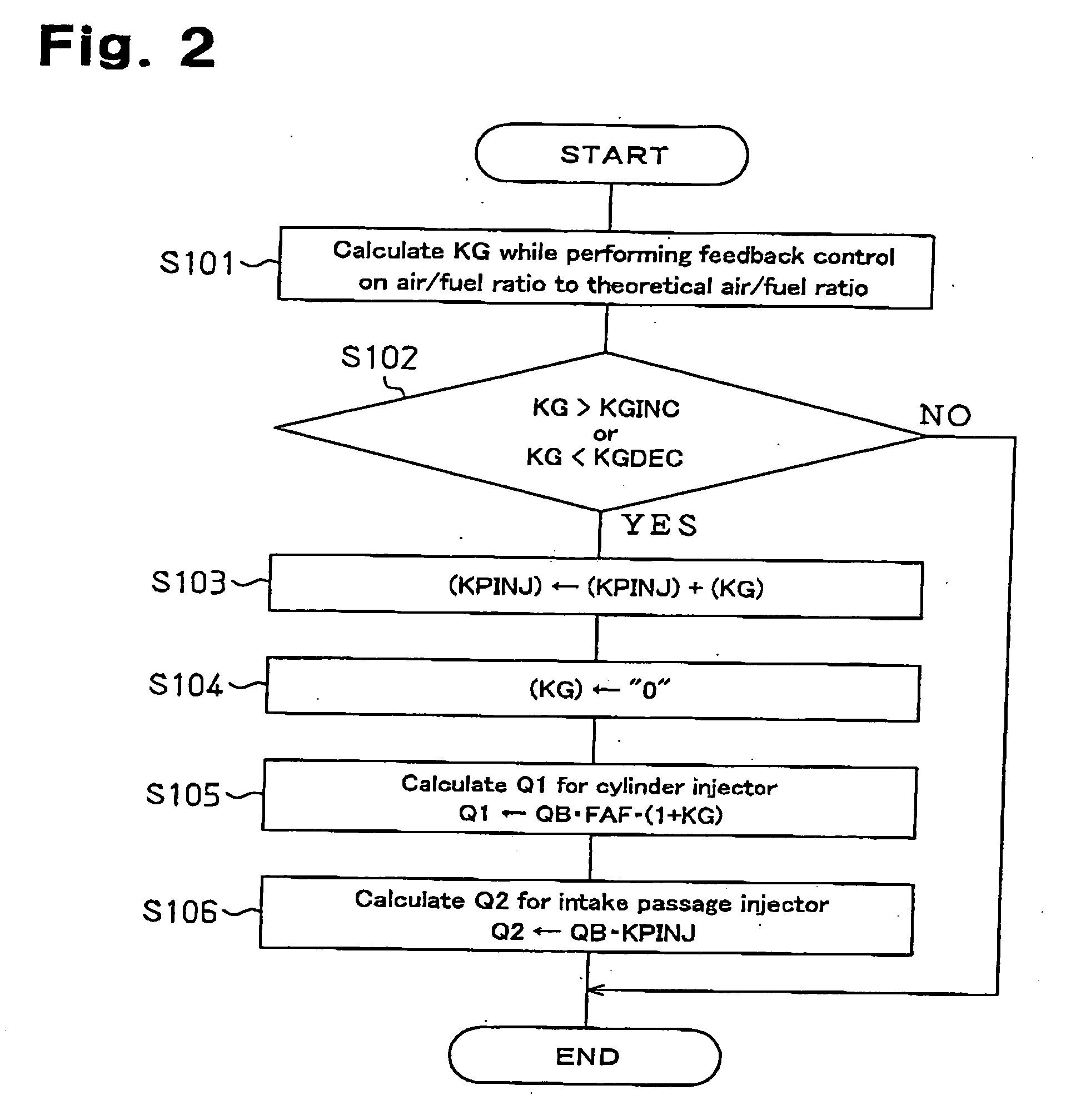
Engine fuel injection control system
InactiveUS20050178360A1Inhibit deteriorationImprove suction efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberControl system
A system for controlling fuel injection in an engine. The engine includes an intake passage, an intake passage injector, a cylinder having a combustion chamber, and a cylinder injector for injecting a target amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. The system includes a controller for controlling the intake passage and cylinder injectors to permit fuel injection, each with an injection ratio, while said engine operates in a condition in which said engine permits fuel injection from said cylinder injector, a sensor for sensing the amount of fuel injected from the cylinder injector, a detector for detecting the difference between the target injection amount and the amount of fuel injected and an adjustor for adjusting the injection ratio based on the result of the detection by the detector so that the intake passage injector performs fuel injection together with the fuel injection performed by the cylinder injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for controlling injection timing of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7278396B2Reduce mixEmission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineIgnition timing
A method to control injection timing for an internal combustion engine having a plurality of injectors in at least a cylinder, the method comprising of injecting a first fuel amount to at least a cylinder of an internal combustion engine from a first injector, injecting a second fuel amount fuel to said cylinder from a second injector, and adjusting the timing between starting or ending injection of said first fuel amount, and starting or ending of said second fuel amount in response to an operating condition of said engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com