Patents
Literature
2816results about "Power operated starters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
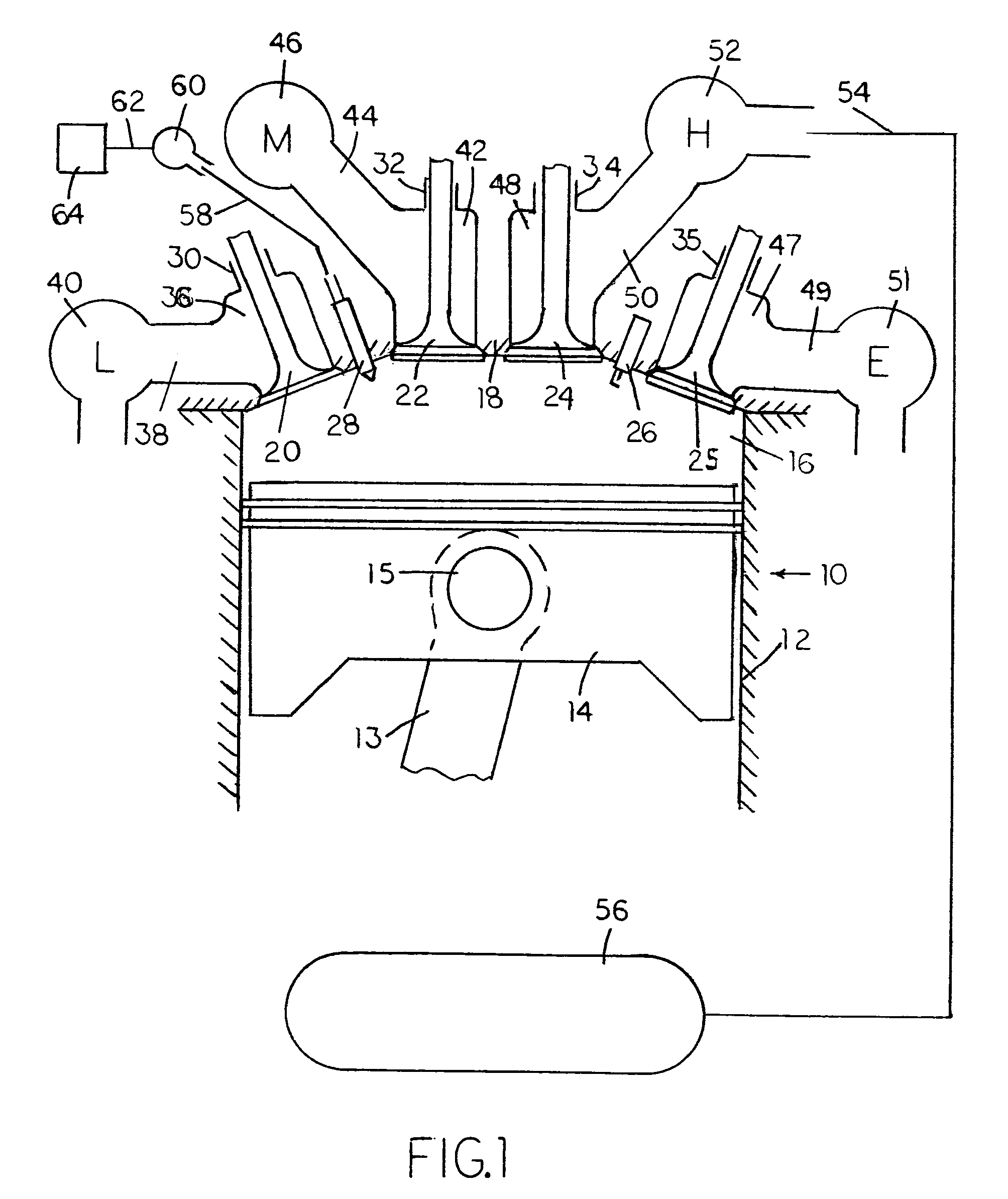
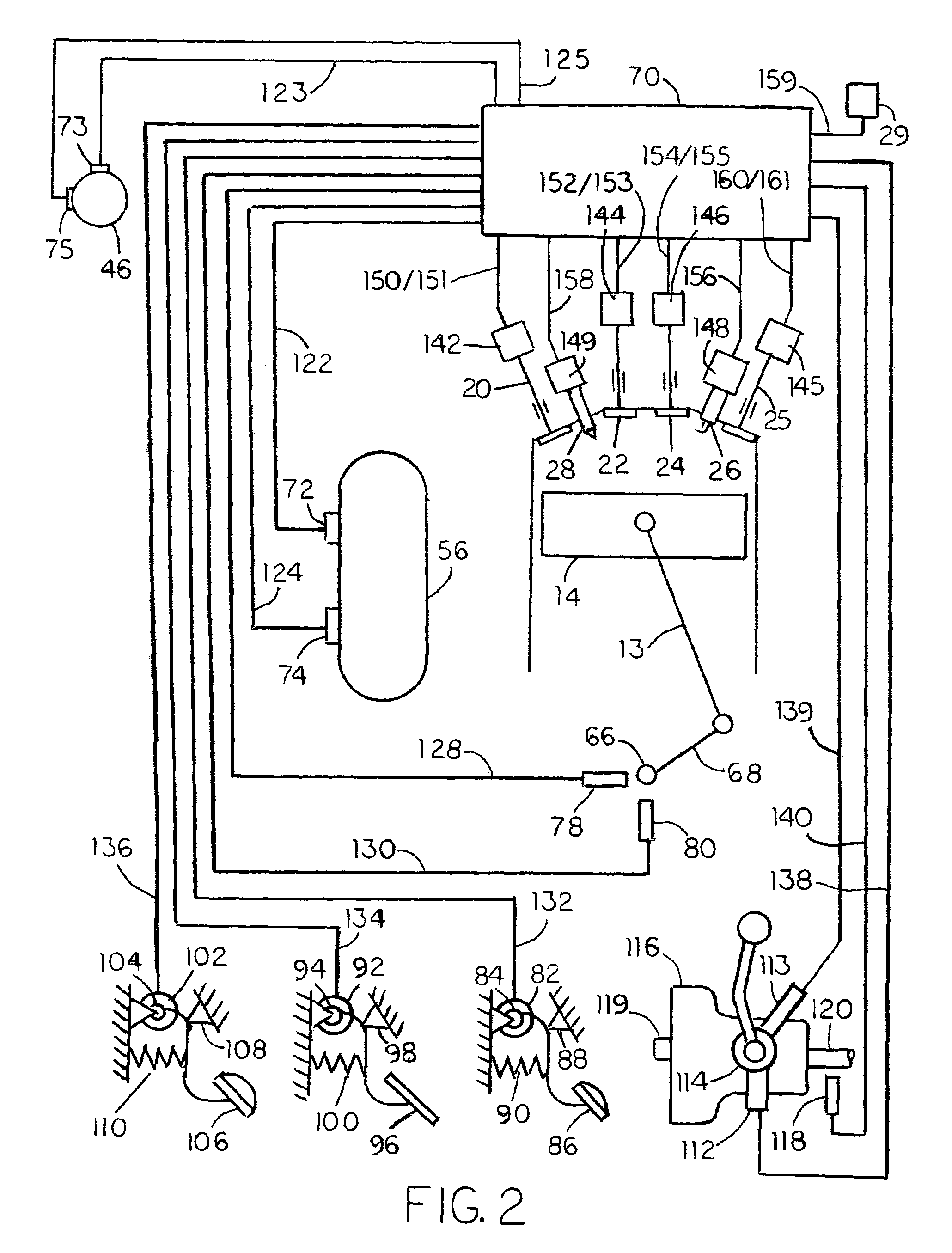
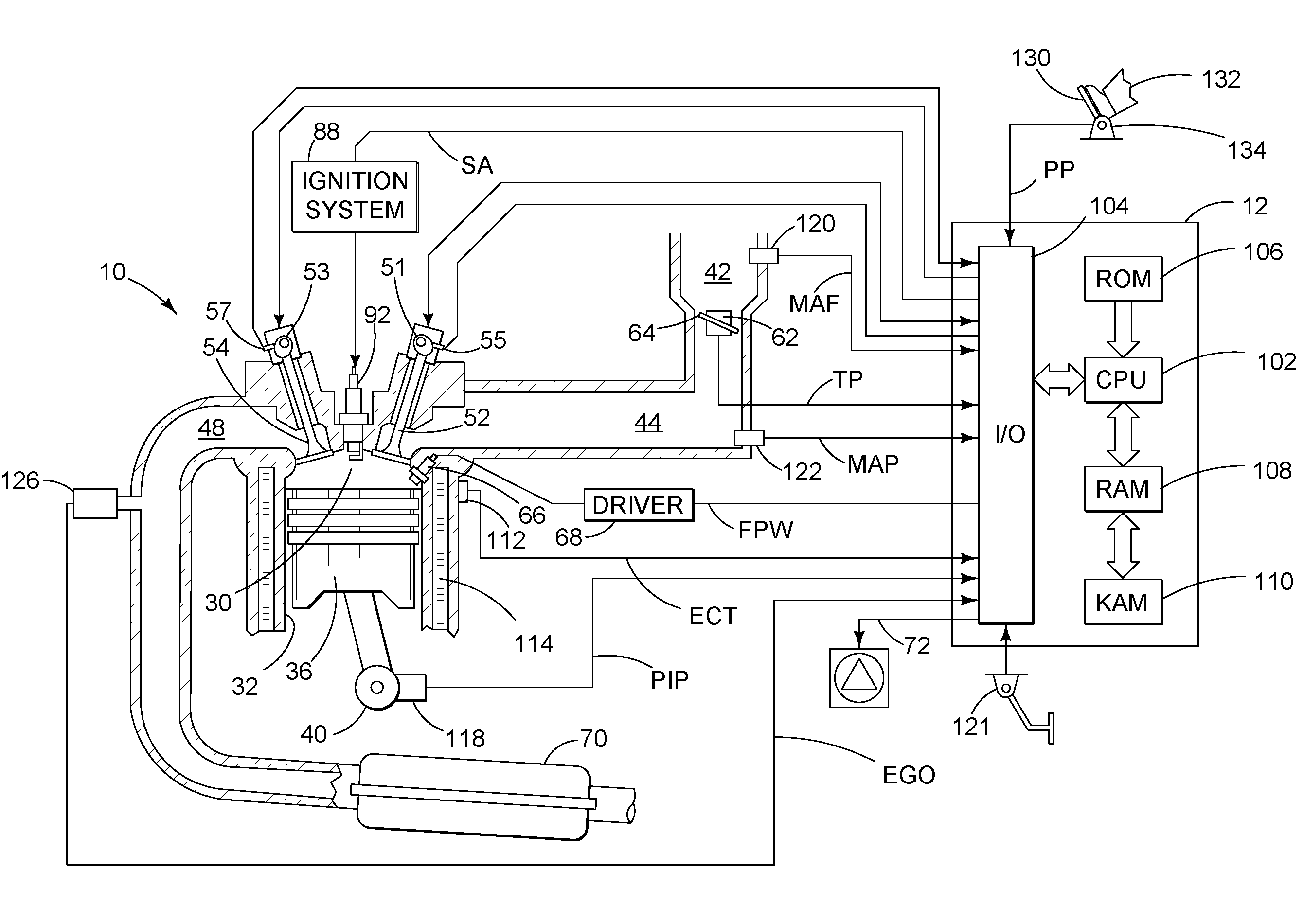
Multi-stage compression ignition engine start
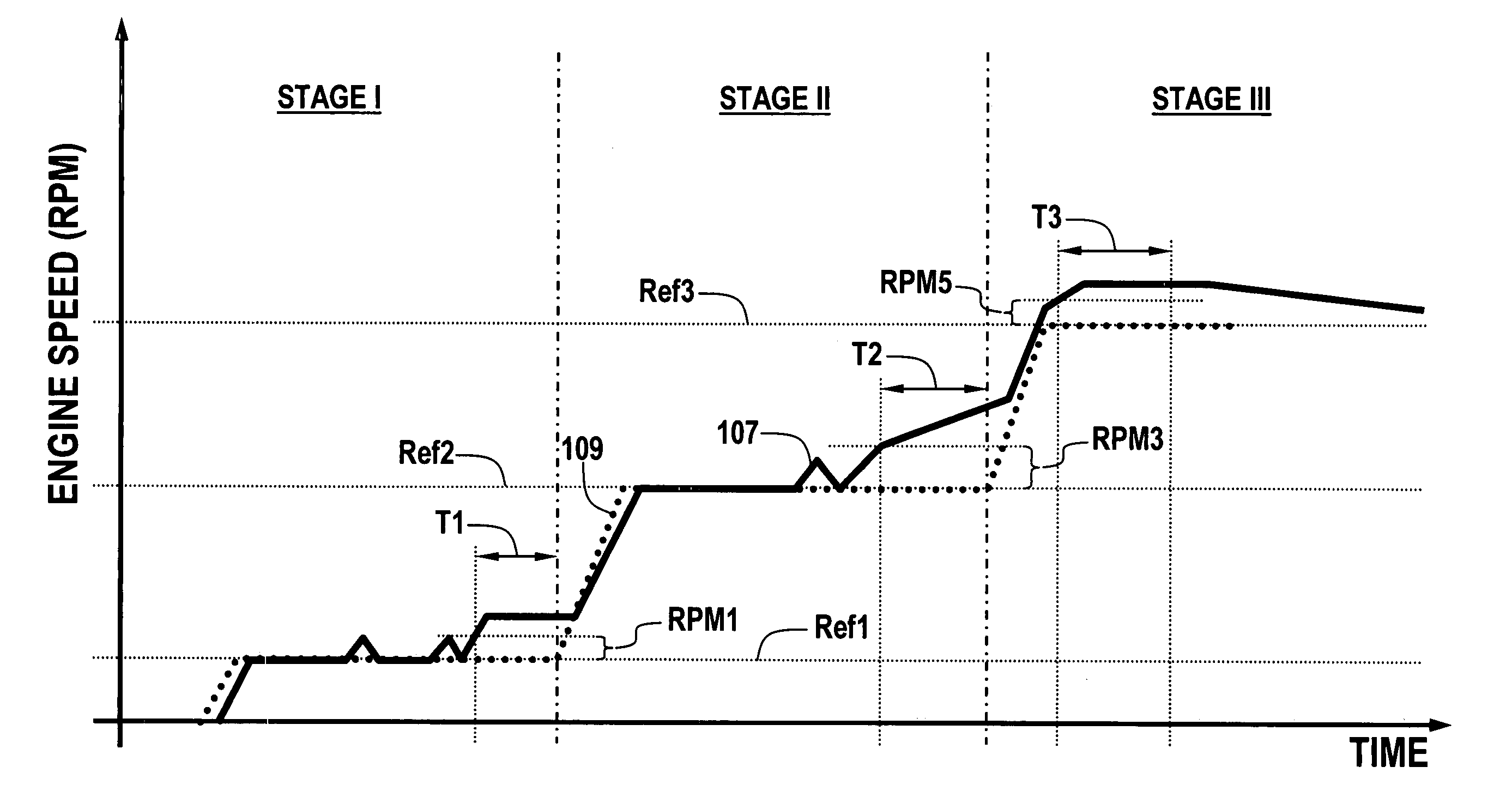
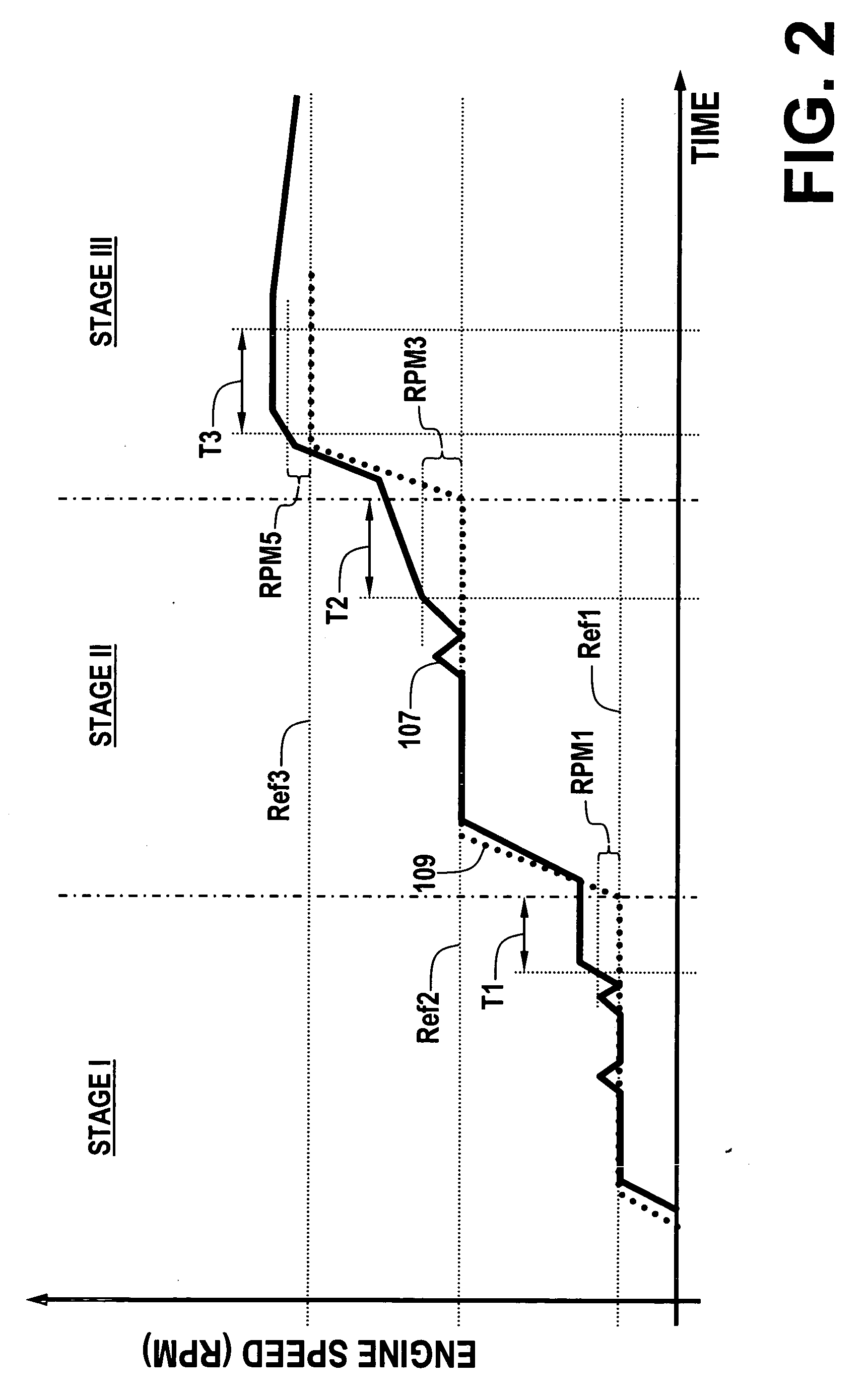
A powertrain includes a diesel compression engine and an electric machine operatively coupled thereto and effective to rotate the engine during engine cranking. Cold engine cranking is accomplished in a staged manner including a first stage wherein the engine is cranked to a first speed below the resonant speed of the coupled engine and electric machine combination for a first duration and thereafter cranked to a second speed above the resonant speed for a second duration. Transition out of cranking at the first and second speeds is accomplished when relative combustion stability is demonstrated. Cranking at the first or second speed is aborted when excessive crank times or if low battery voltages are observed. A third stage is included wherein the engine is cranked to a third speed below the engine idle speed. Transition out of cranking at the third speed is accomplished when relative combustion stability is demonstrated, whereafter normal engine control takes over.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
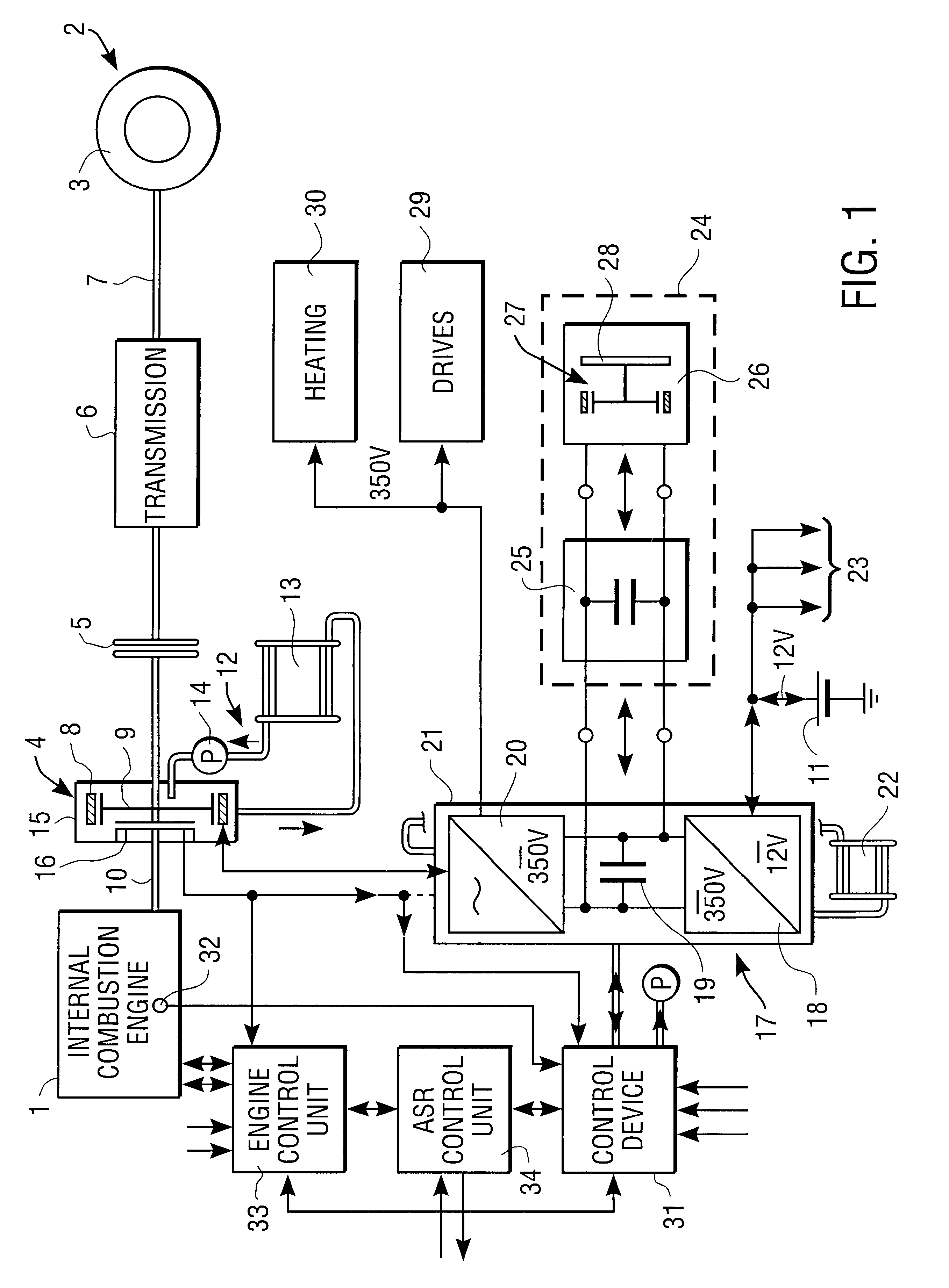
Starter/generator for an internal combustion engine, especially an engine of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6365983B1Improve overall utilizationReduce the overall diameterRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsExternal combustion engineElectric machine
The invention concerns a starter / generator for an internal combustion engine (1), especially that of a motor vehicle, with an electric rotary-field machine (4), which exercises the starter and generator function; and at least one invertor (17) for generating the voltages and / or currents of variable frequency, amplitude and / or phase required for the magnetic fields of the electric machine (4); wherein the electric machine (4) starts the internal combustion engine (1) by merging in from standstill.
Owner:GRUNDL ANDREAS +2
System for controlling starter for starting internal combustion engine
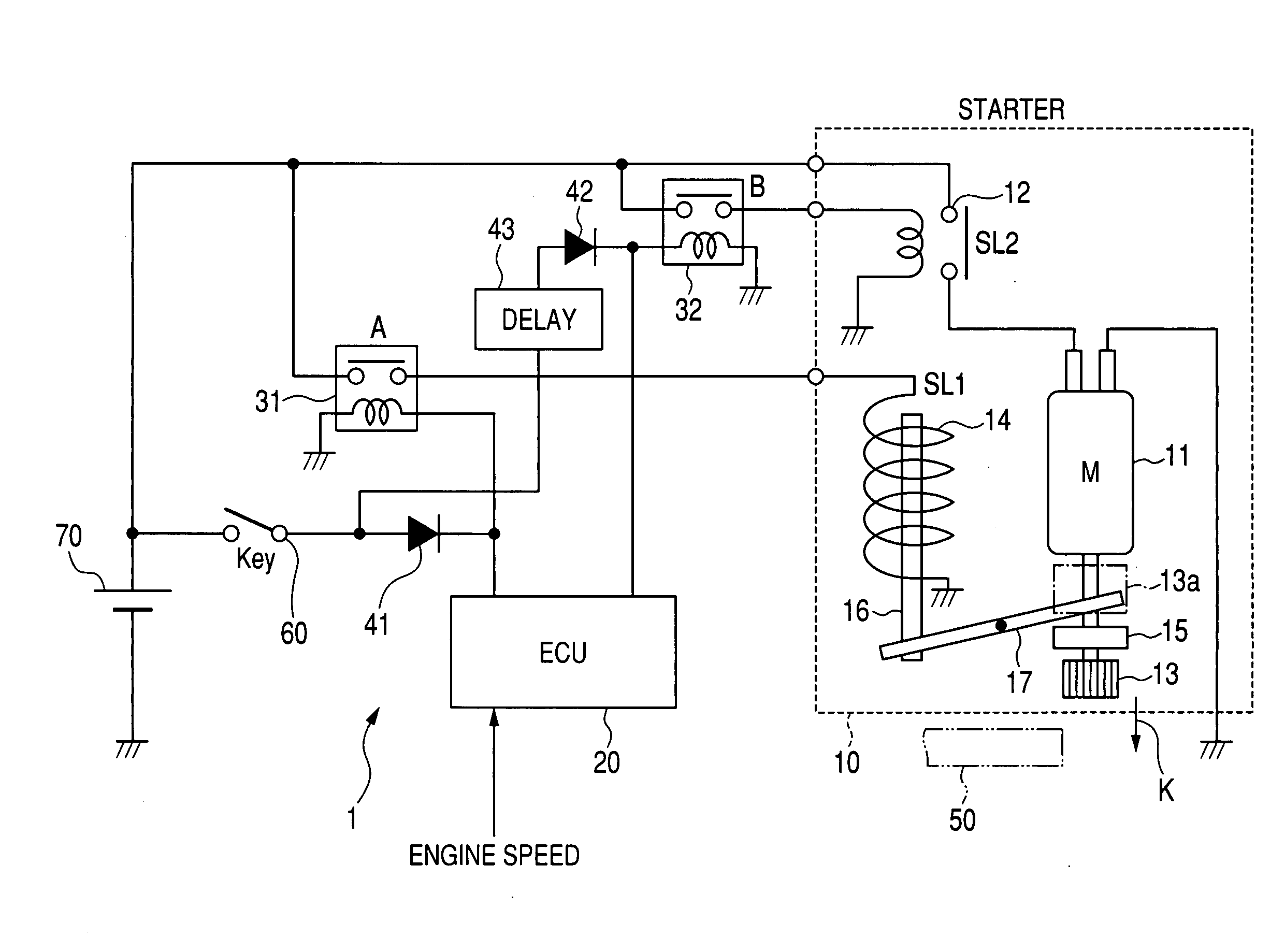
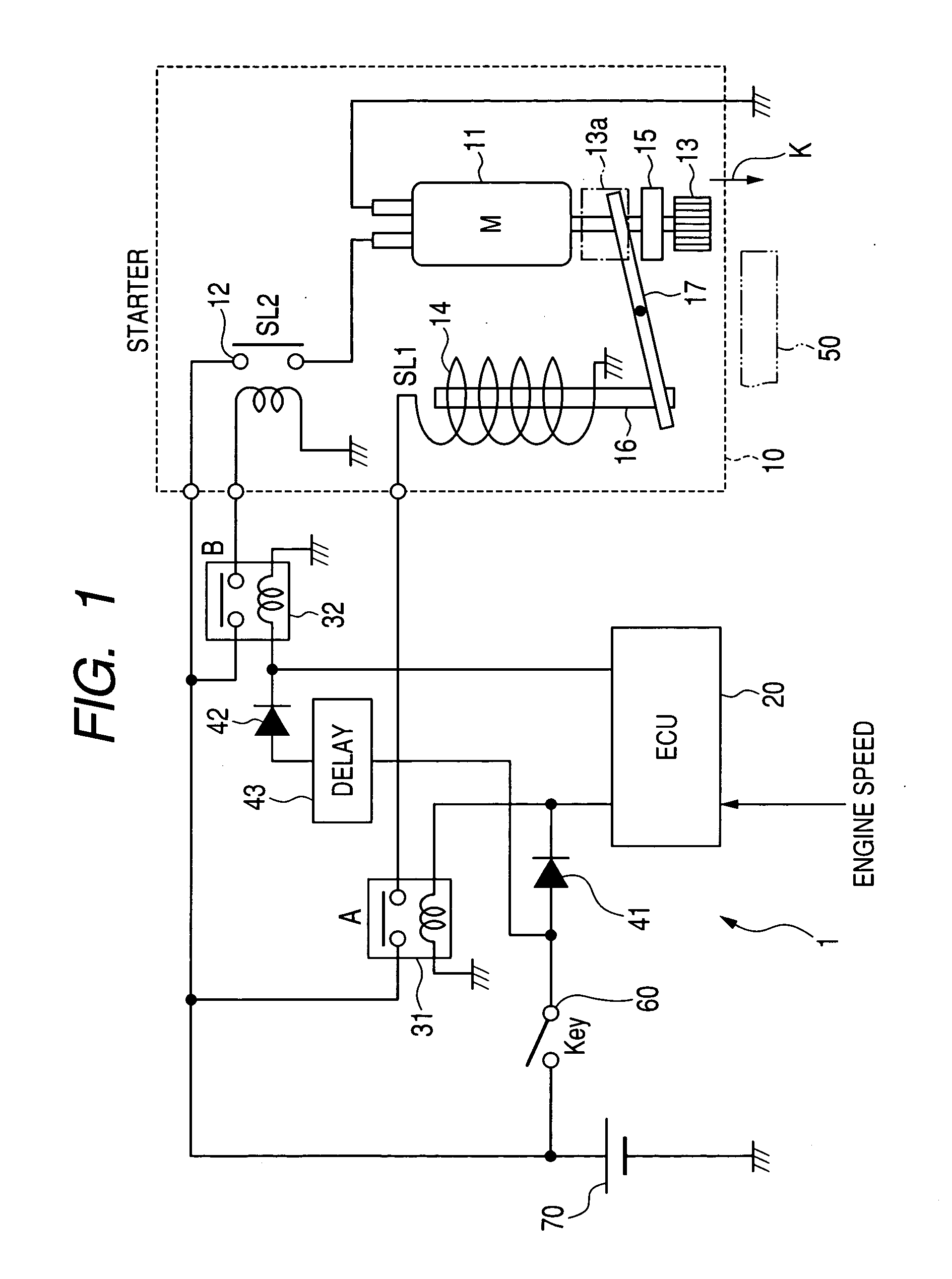
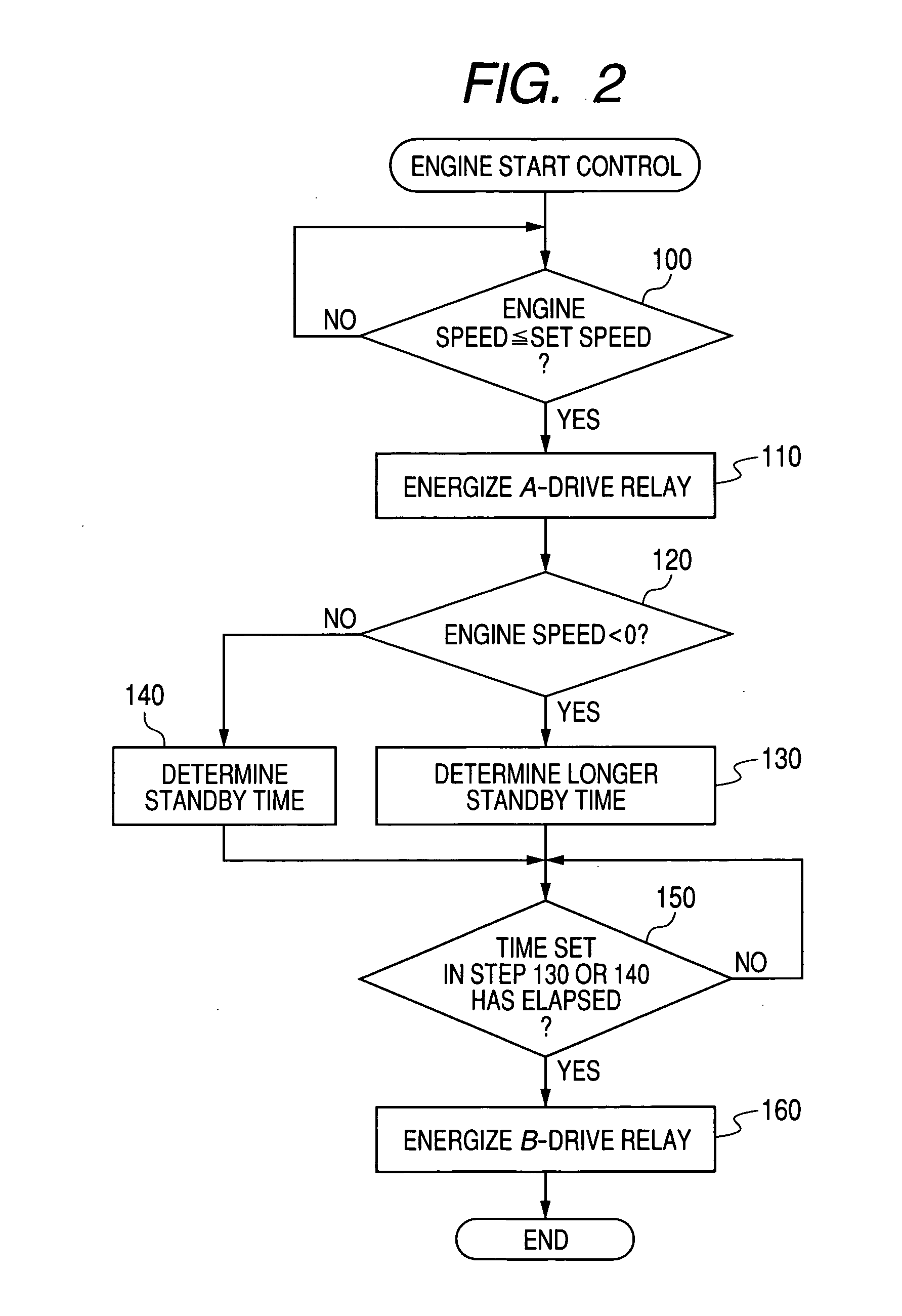
ActiveUS20100299053A1Improve controllabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersElectric machineActuator
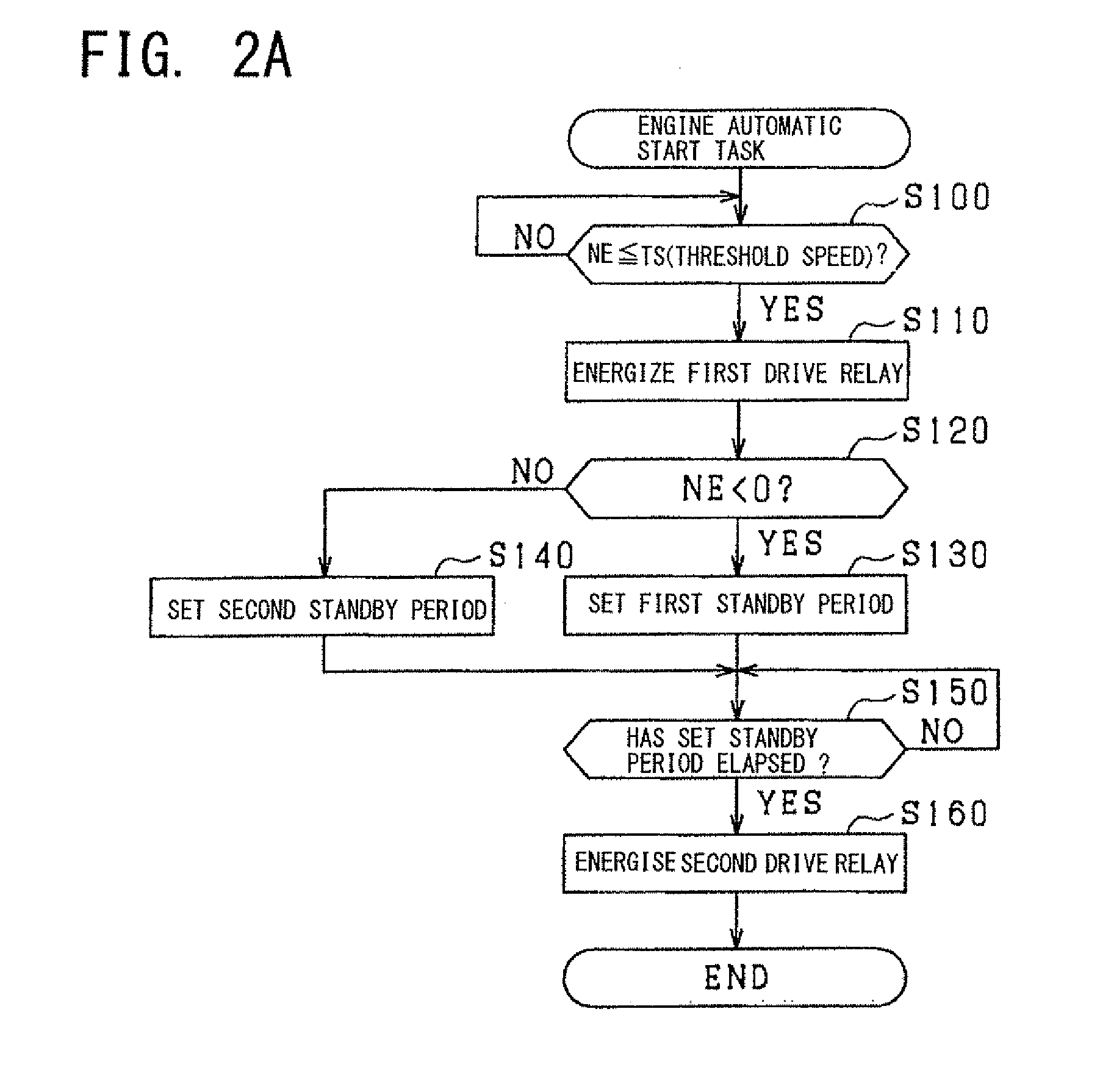
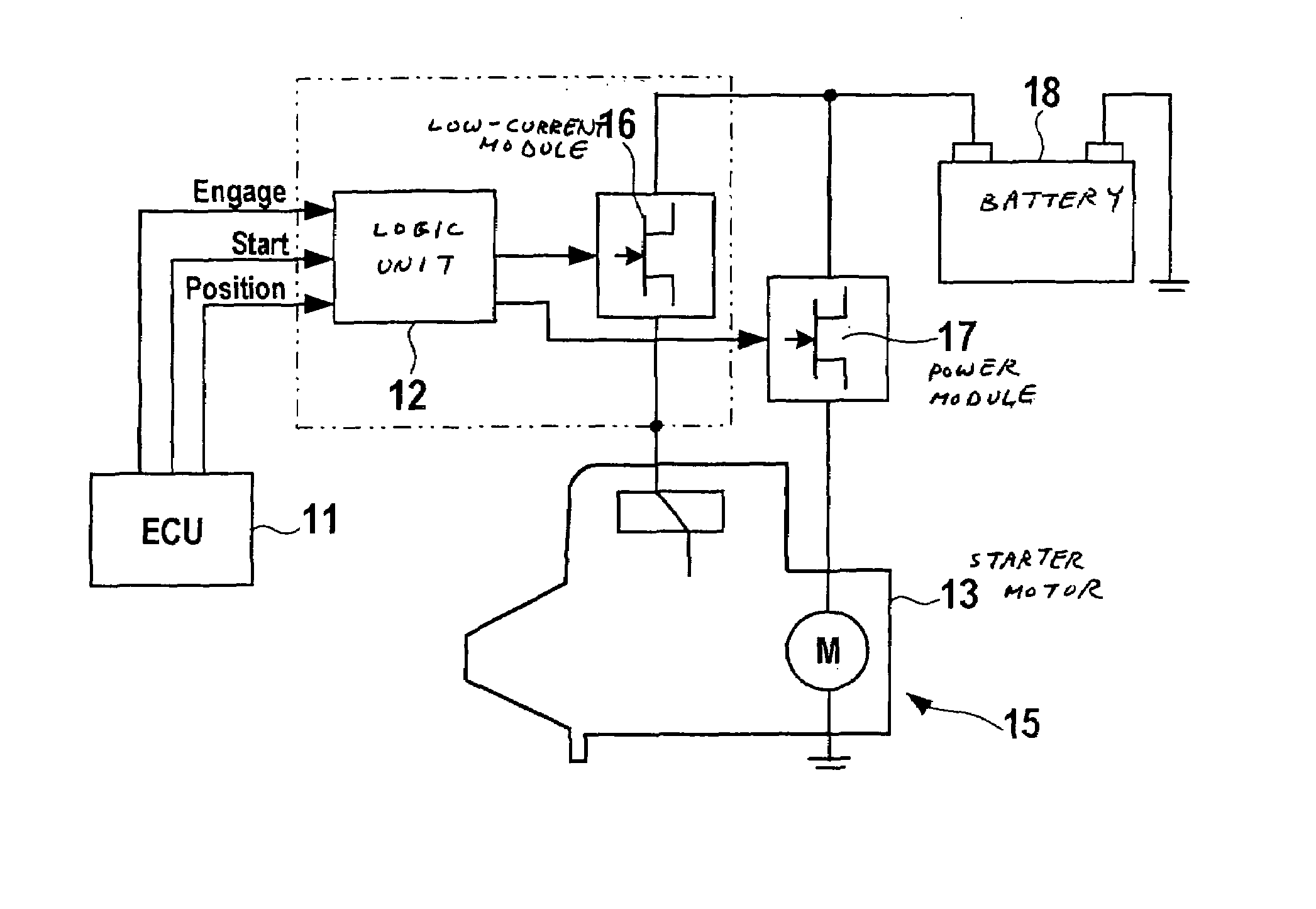
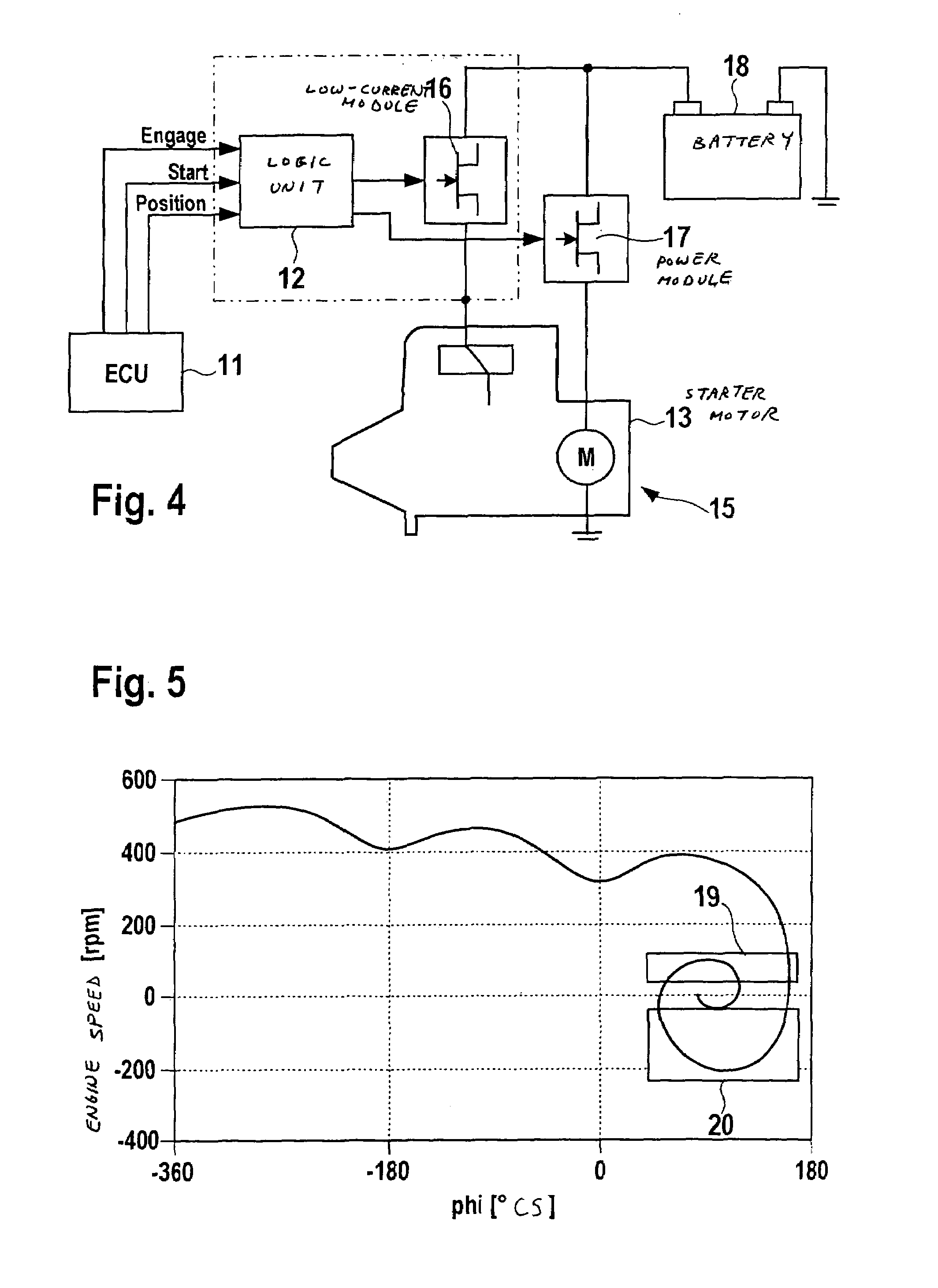
In a system for controlling a starter, the starter includes a pinion shiftable between an engagement position and a disengagement position. The starter includes an actuator configured to shift the pinion from the disengagement position to the engagement position when energized, and a motor configured to rotate the pinion when energized. The system includes a control circuit, a first switch unit configured to switch between energization and deenergization of the actuator under control of the control circuit, and a second switch unit configured to switch between energization and deenergization of the motor under control of the control circuit. The first switch unit and the second switch unit are individually arranged. The second switch unit includes a first relay configured to switch between energization and deenergization of the motor under control of the control circuit, and a second relay configured to control activation of the first relay.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for engaging the starter pinion of a starter with the starter ring gear of an internal combustion engine during the running-down of the internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7275509B2Relieve stressEngage with obstructionPower operated startersInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A method is provided for engaging a starter pinion of a starter with a starter ring gear of an internal combustion engine during the running-down of the internal combustion engine, which internal combustion engine has an arrangement for determining rotational speed and rotational direction of a crankshaft. The starter pinion is engaged with the starter ring gear when the following conditions are satisfied: a) the speed of the internal combustion engine is below a maximum speed and above a minimum speed; and b) the rotational direction corresponds to the forward rotational direction of the crank shaft.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Stop and start control apparatus of internal combustion engine
A stop and start control apparatus of an internal combustion engine prevents fuel supplied in a specific cylinder at the time of stopping the engine from being discharged in an unburned state. When an ignition switch is turned off in a state that the unburned fuel is sealed in the combustion chamber of a specific cylinder during idling stop, the unburned fuel is combusted to prevent the unburned fuel from being discharged. The vibration occurring at that time can be suppressed by rotating the motor generator in the counter direction to the rotation direction of the crankshaft. After the unburned fuel is sealed in the combustion chamber of the specific cylinder, if it is estimated that the unburned fuel is discharged, the exhaust valve corresponding to the specific cylinder is closed at the predetermined timing, or the unburned fuel is combusted, whereby the unburned fuel is prevented from being discharged. Thus, deterioration of emission can be avoided.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Operating a vehicle with braking energy recovery
InactiveUS7231998B1Reduce and eliminate needLow costAuxillary drivesPower operated startersCombustionAtmospheric air
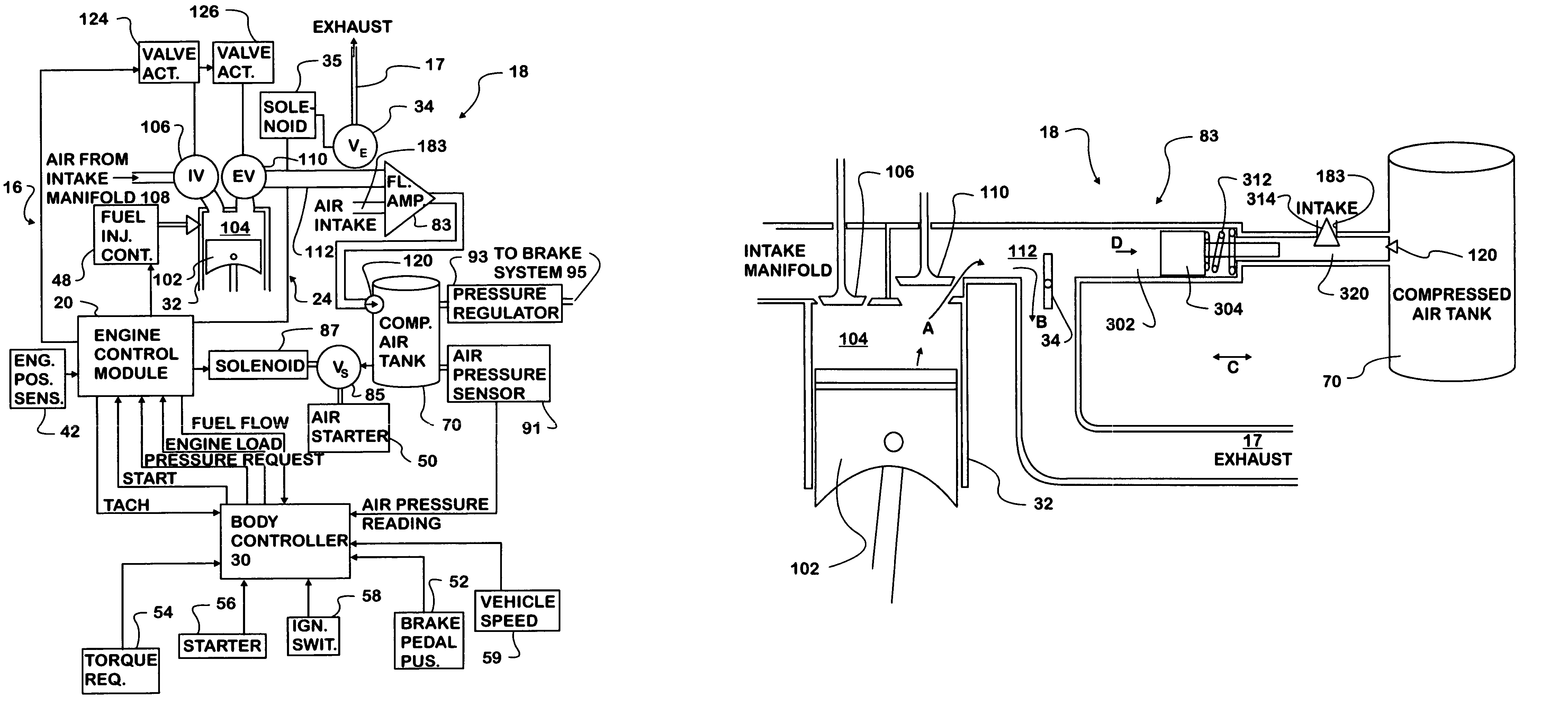
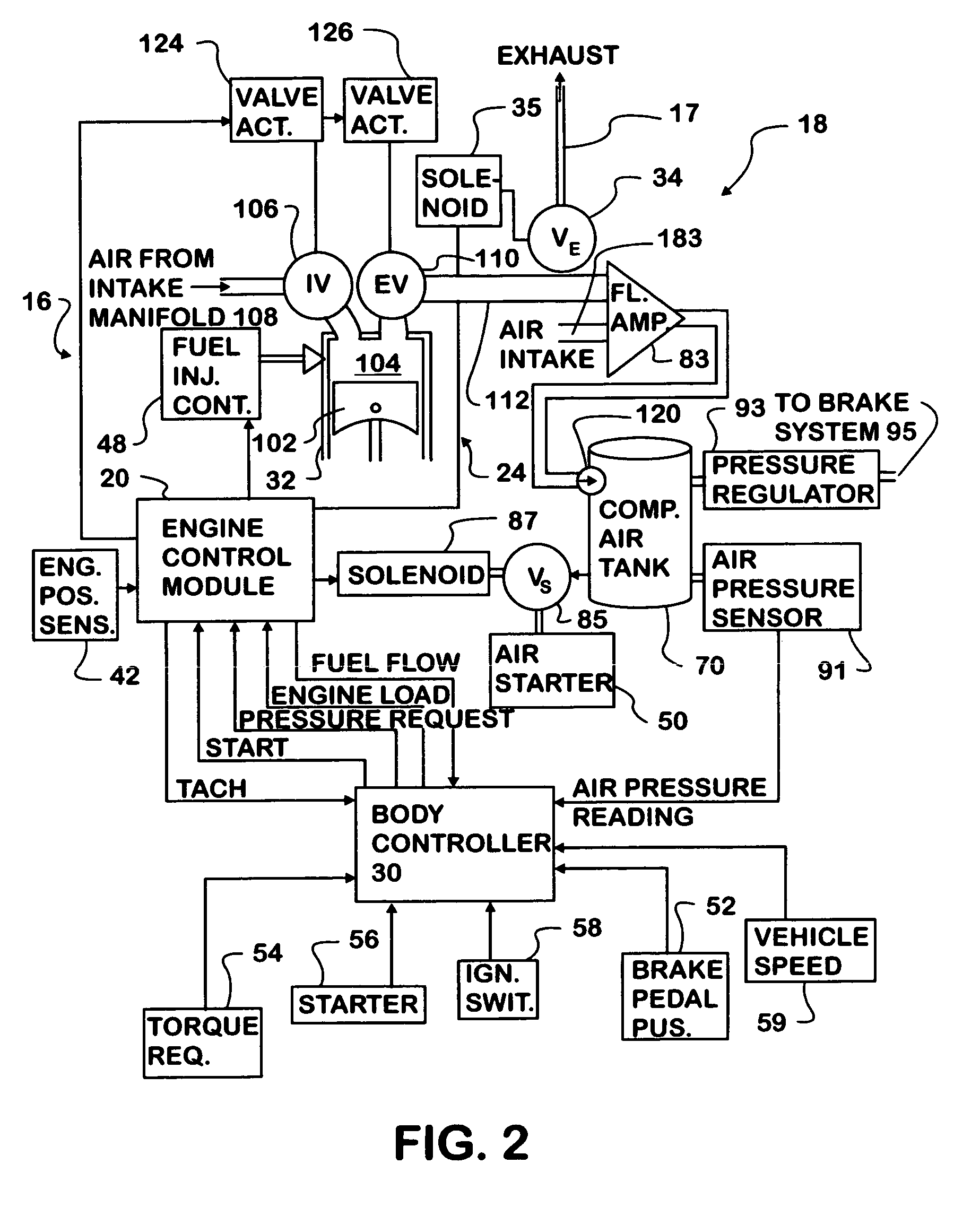
A vehicle engine has a system of valves that permits various engine cylinders to operate in different modes of operation. During braking, some of the engine cylinders receive atmospheric air, compress it, and transfer it to an intermediate air-container. Other cylinders receive compressed air from the intermediate air-container, further compress it, and transfer it to a high-pressure air-reservoir for storage. During acceleration, some of the engine cylinders receive compressed air from the high-pressure air-reservoir, expand it to a lower level of pressure, and transfer it to the intermediate air-container. Other cylinders receive air from the intermediate air-container, further expand it, and use it for combustion in an internal-combustion cycle. During short stops, the engine is shut down, for the duration of the stop, and, then, it is restarted with compressed air. During cruise, the engine operates as a conventional internal-combustion engine.
Owner:SCHECHTER MICHAEL MOSES
Starter for an internal combustion engine
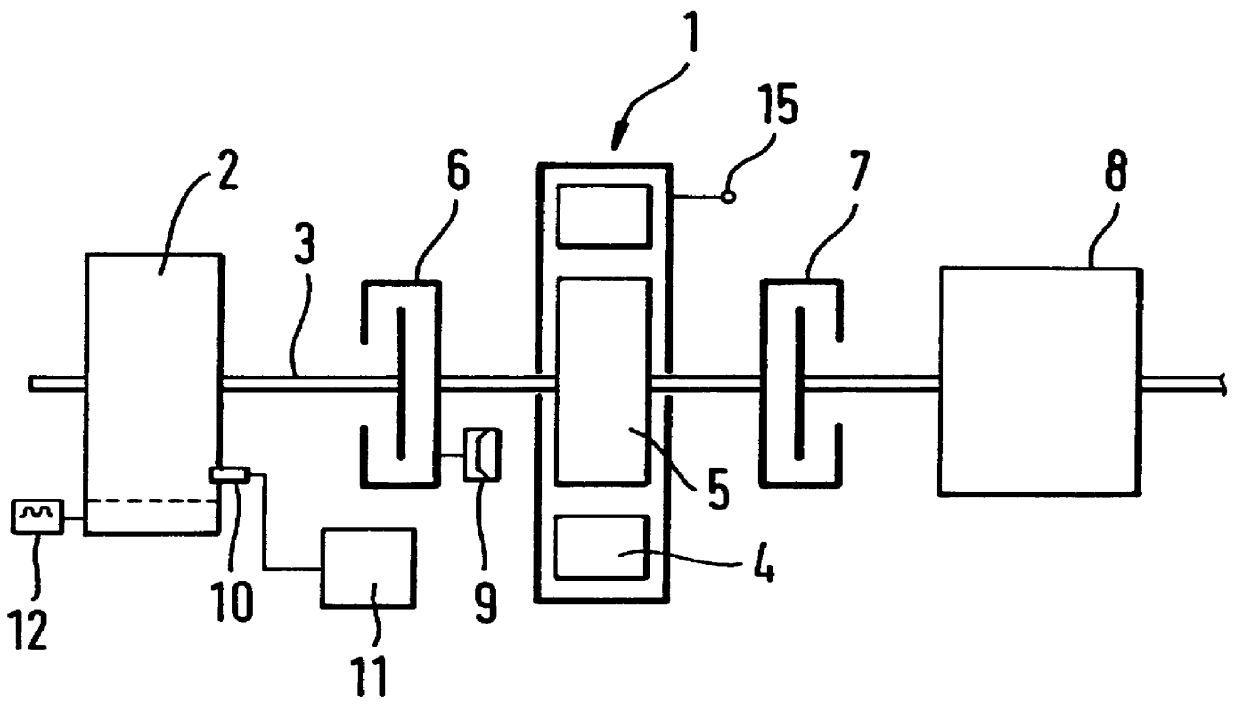
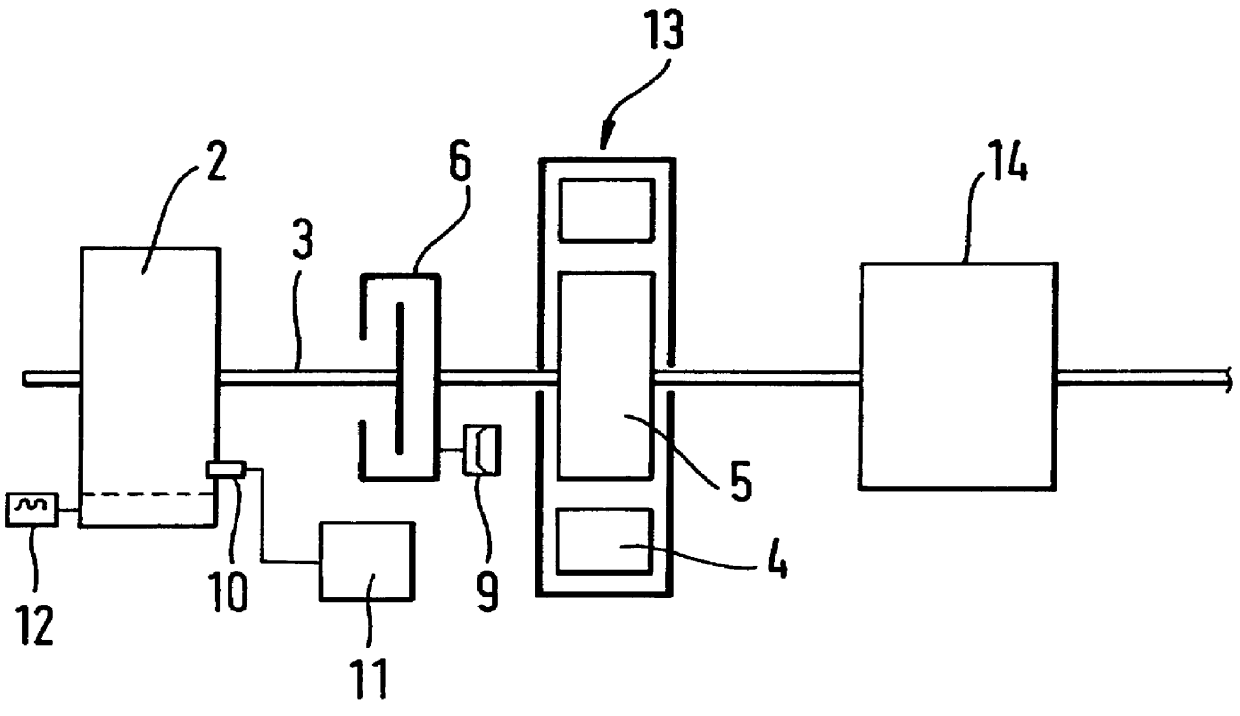
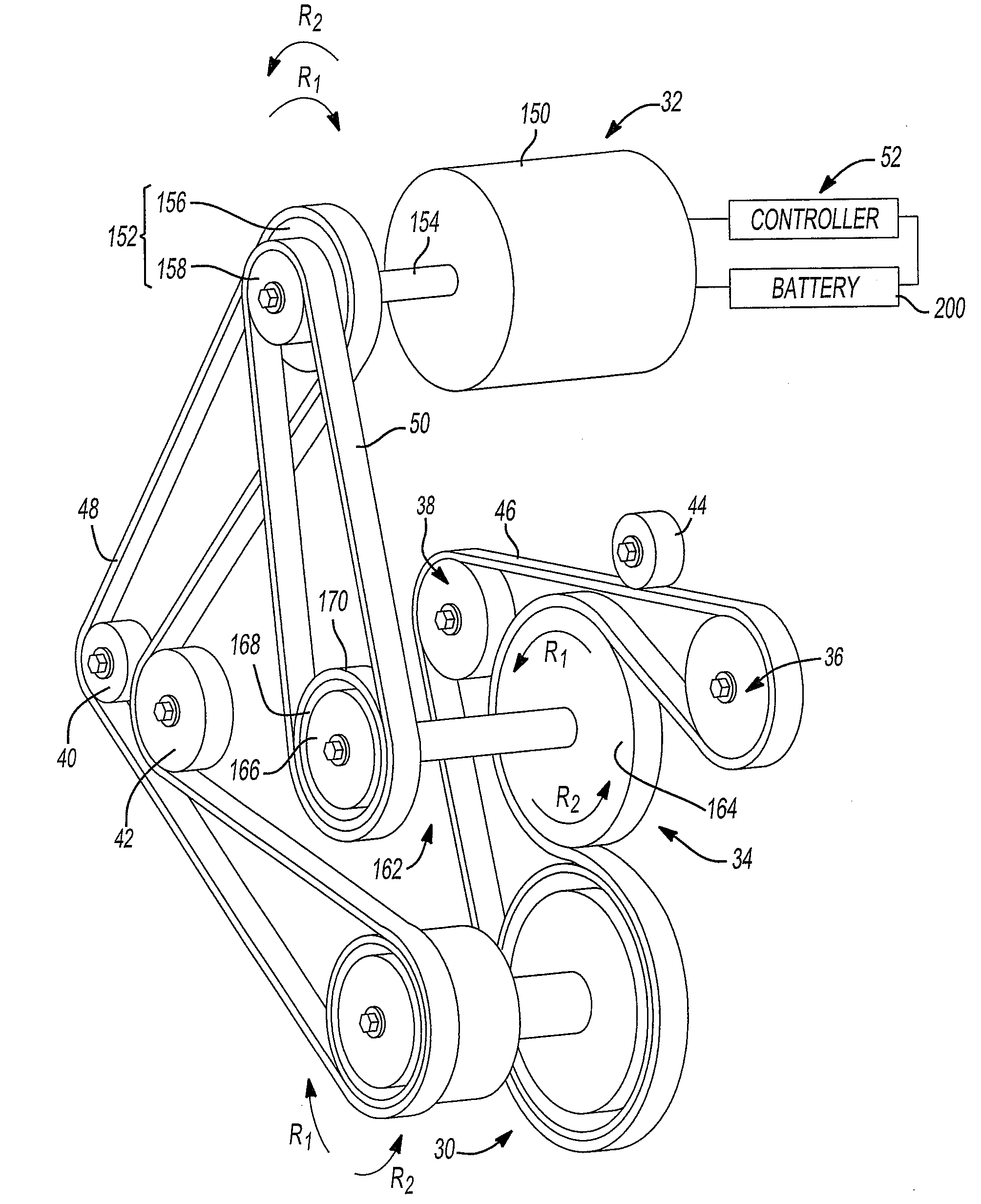
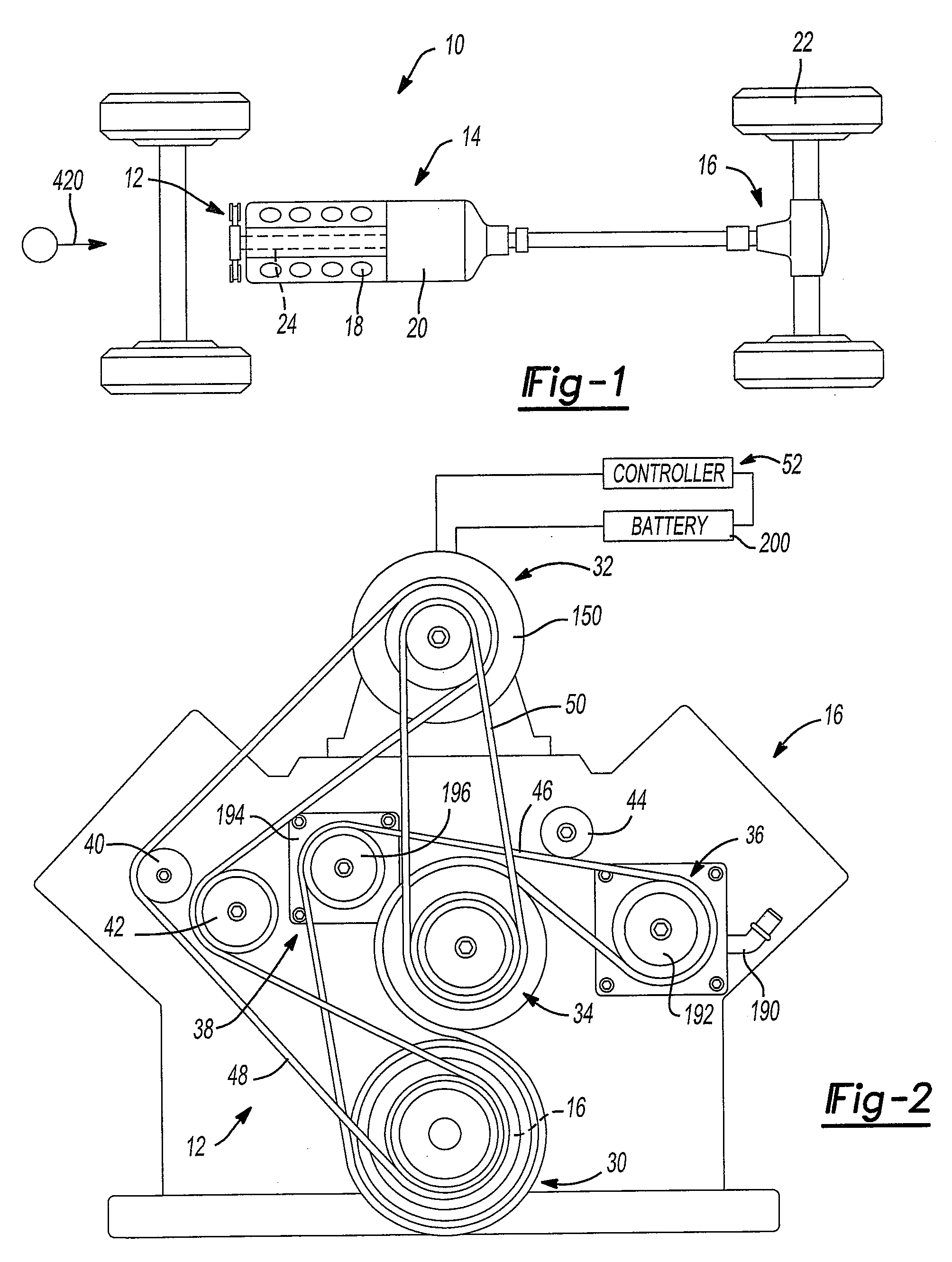
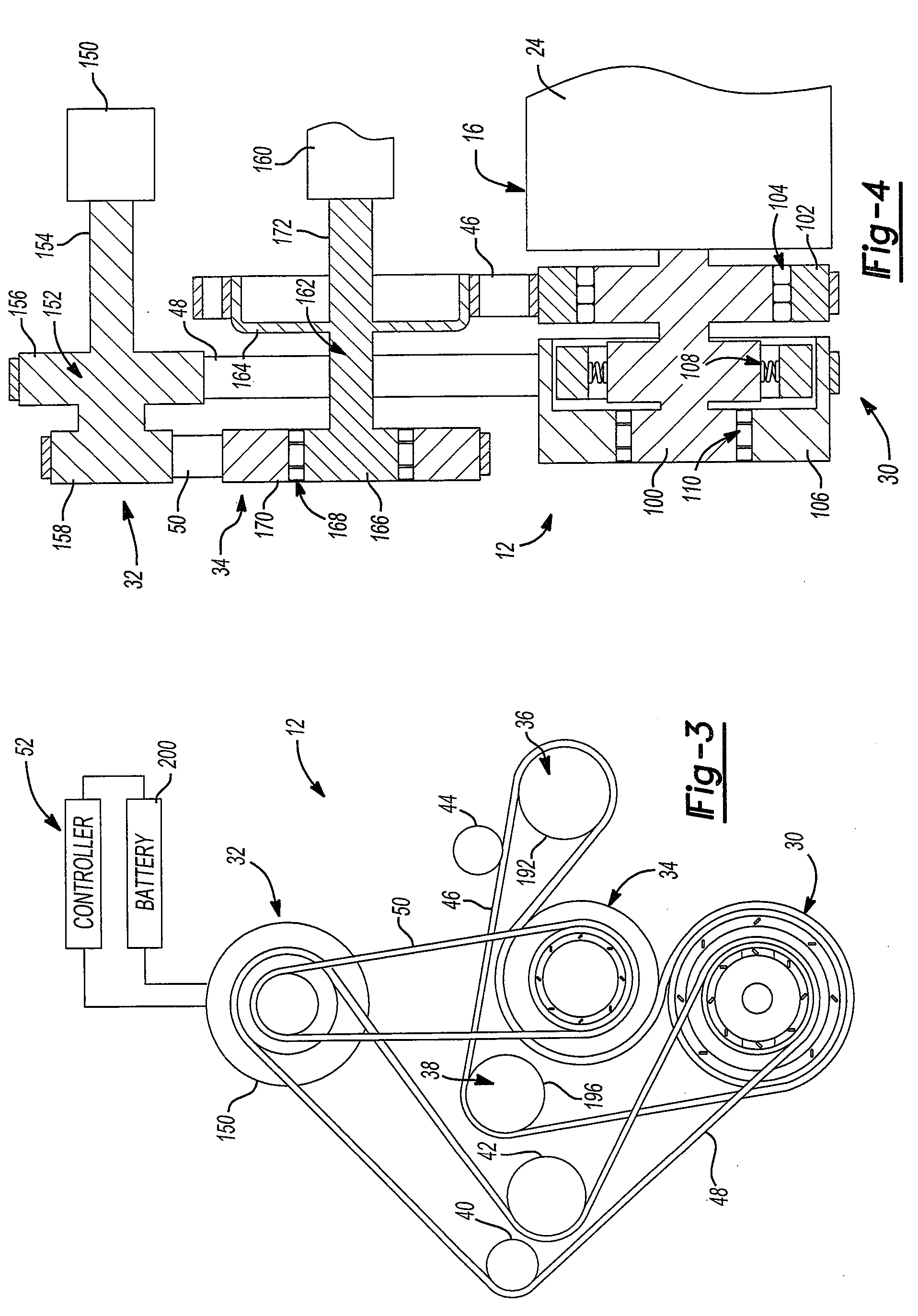
InactiveUS6098584AInexpensive solutionMore time-consumingPower operated startersInternal combustion piston enginesStarter generatorEngineering
PCT No. PCT / DE97 / 01663 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 22, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 22, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 7, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 20252 PCT Pub. Date May 14, 1998The starter apparatus for an internal combustion engine (2) includes a starter-generator including a device for rotating a flywheel (5) to a predetermined rotational speed and a device for rotating the crankshaft (3) of the engine to directly start the engine; at least one clutch (6, 7) for directly coupling or disengaging the flywheel (5) with the crankshaft (3) of the engine (2) so that the flywheel (5) starts the engine (2) with the rotational energy stored in the flywheel (5) by the starter-generator in an impulse starting method and a changeover device (11) for changing between the impulse starting method based on engagement of the flywheel (5) with the engine (2) and a direct starting method in which the starter-generator (4) is directly coupled to the engine, wherein the changeover device switches between the direct starting method and the impulse starting method as a function of a temperature of the engine (2) so that the impulse starting method is used at comparatively lower temperatures and the direct-starting method is used at comparatively higher temperatures. The starter apparatus also includes a device for adaptively determining the threshold for changeover between impulse starting and direct starting.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Engine start system for use in idle stop system for automotive vehicle
ActiveUS20100059007A1Fuel consumption is minimizedSimple structurePower operated startersInternal combustion piston enginesMaximum levelGear wheel
An engine start system which may be employed in automotive idle stop systems. The engine start system includes a pinion gear to be pushed to a ring gear coupled to an engine for achieving meshing engagement with the ring gear. After the pinion gear engages the ring gear, the engine start system starts to rotate the pinion gear using a starter motor to crank the engine. Specifically, when an engine restart request is made following an engine stop request, the engine start system waits until after the speed of the engine drops below a preselected gear engageble speed and then moves the pinion gear toward the ring gear without rotating the pinion gear. This minimizes the consumption of fuel in the vehicle in supplying electric power to the starter motor and a maximum level of mechanical noise arising from the engagement of the pinion gear with the ring gear.
Owner:DENSO CORP
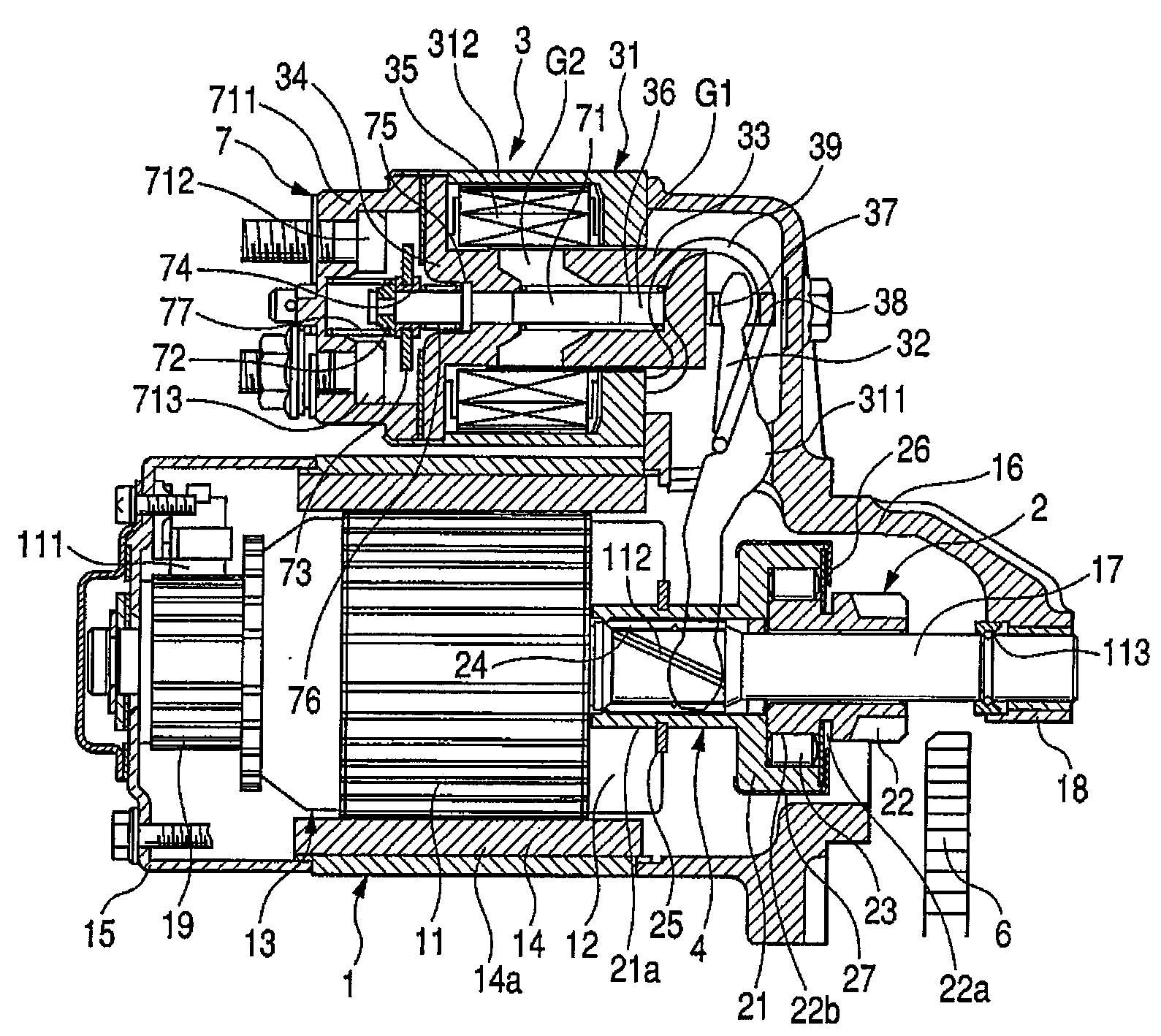
Starter
ActiveUS20080162007A1Improve installabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersTorque transmissionEngineering
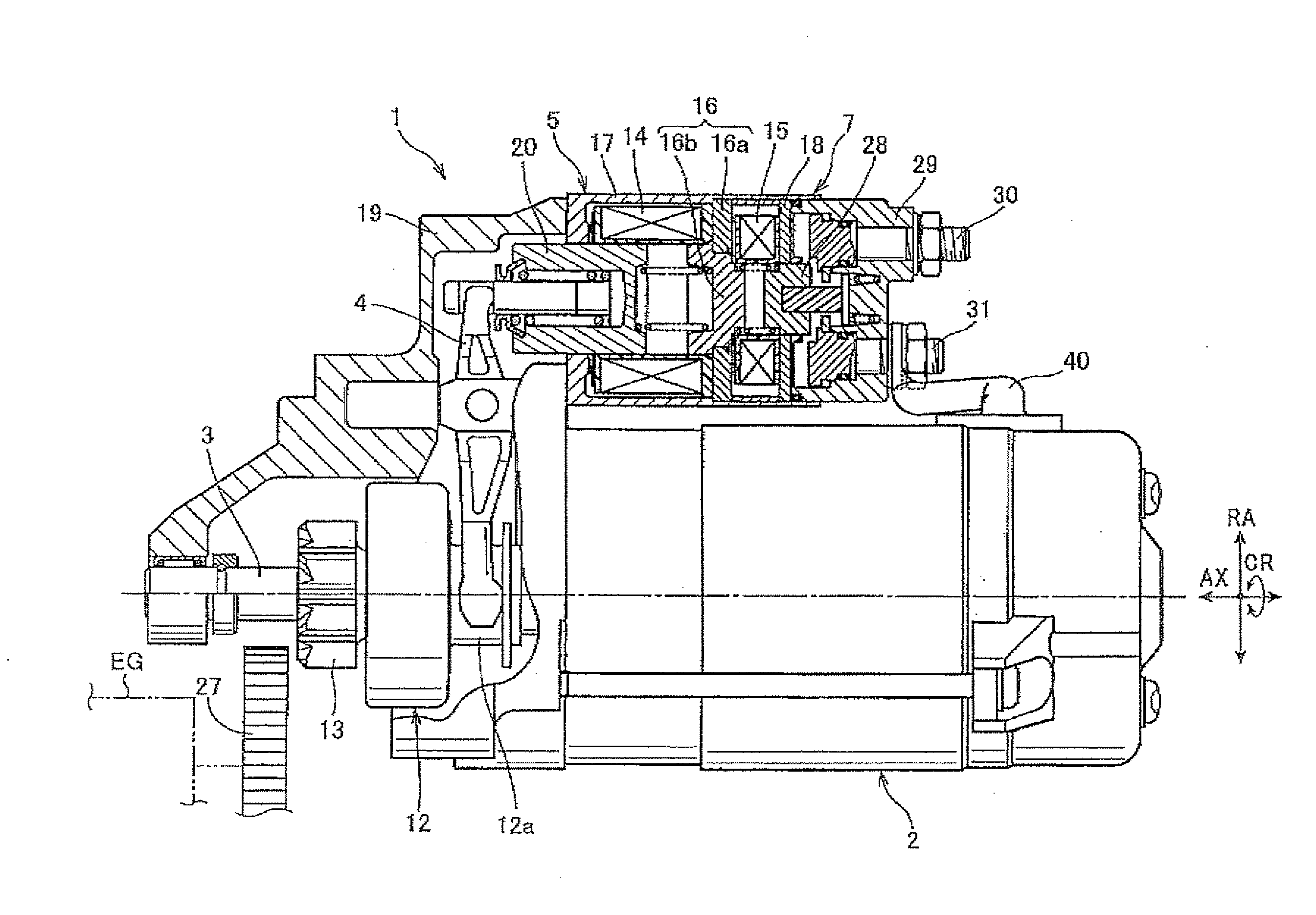
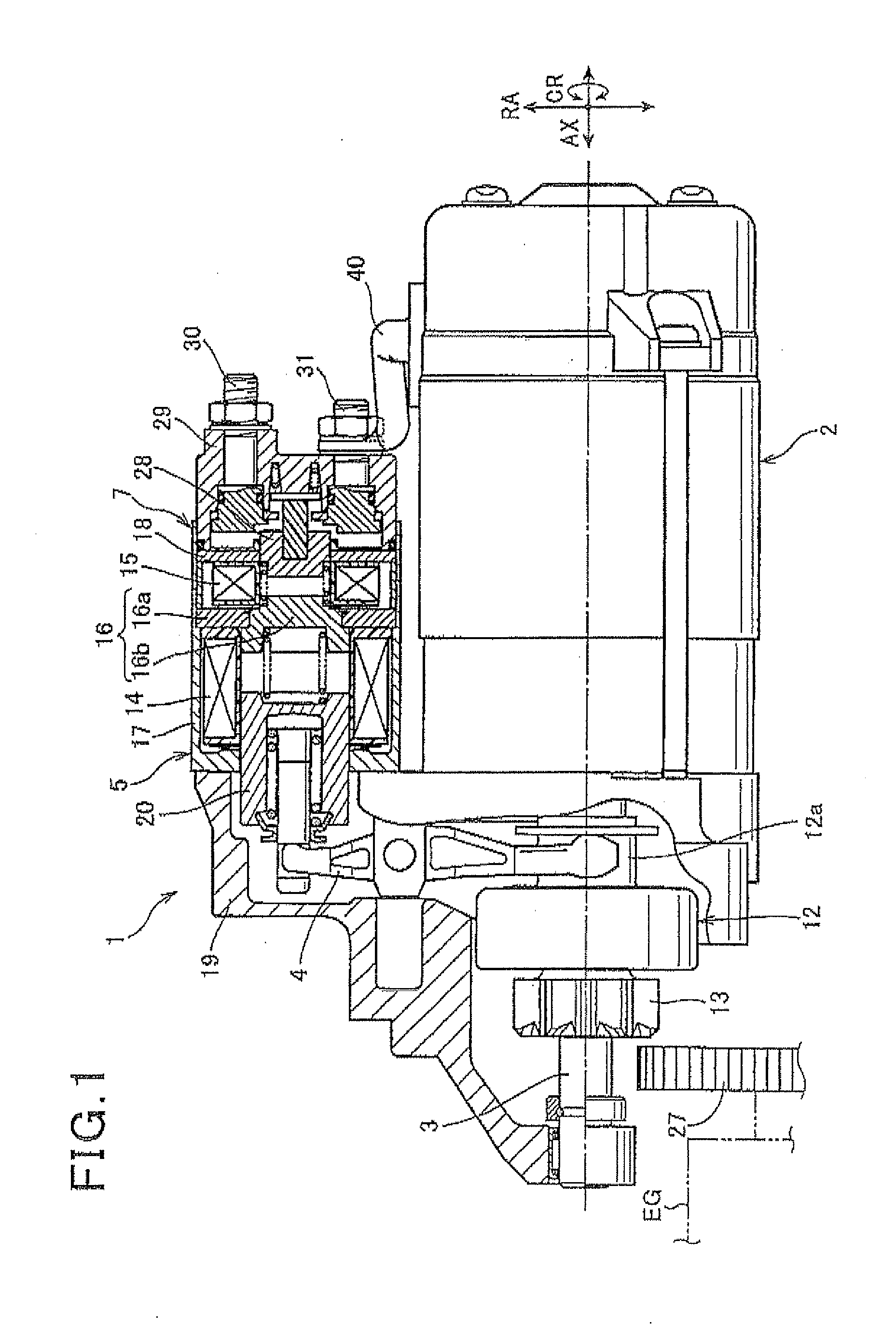
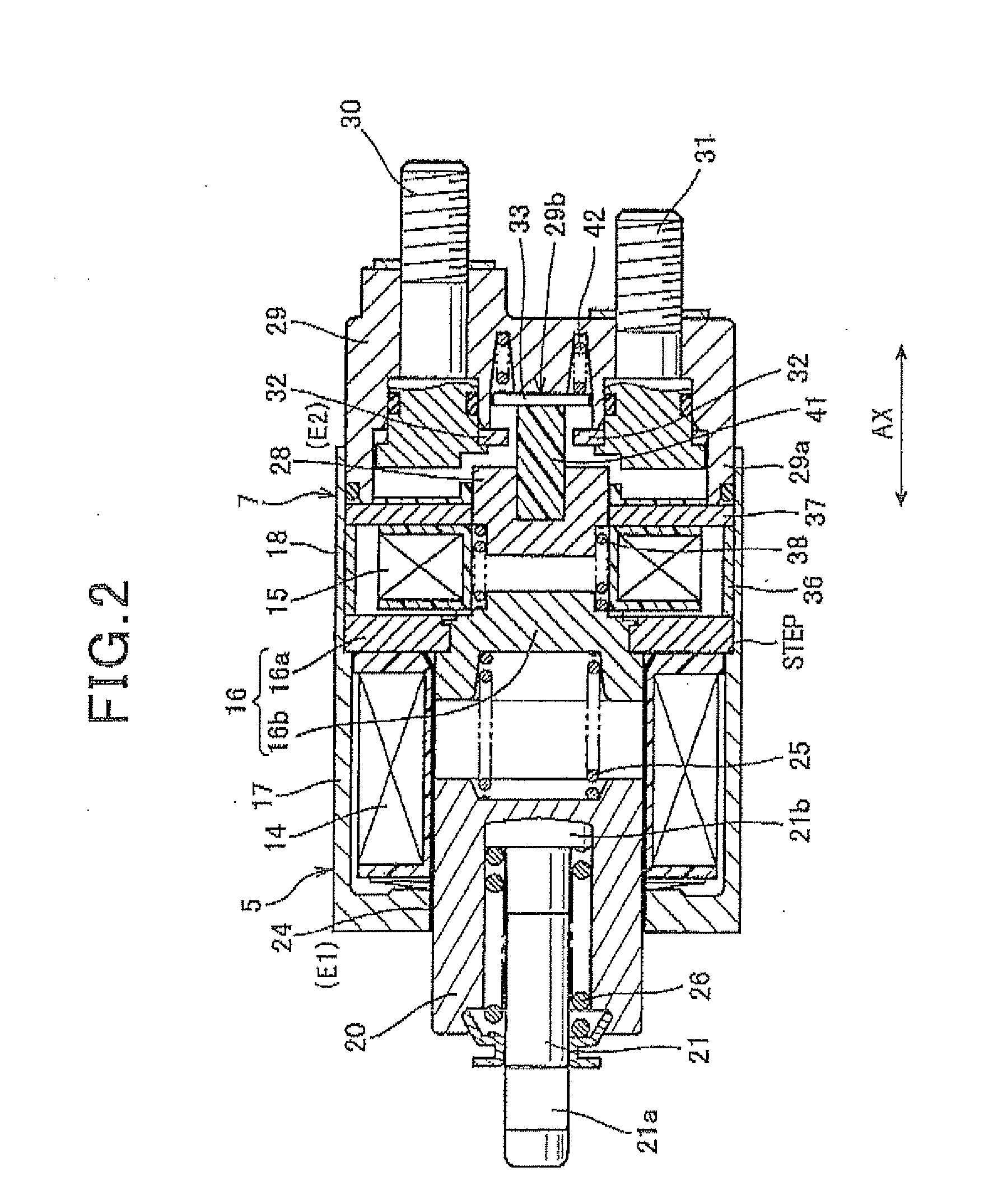
The present invention provides as tarter capable of keeping a state where a pinion and a ring gear maintain meshing with each other when an engine stops without providing a plunger stopper using a solenoid or the like. The state where the pinion and the ring gear maintain meshing with each other in the engine stop mode continues by movement resistance which occurs when a torque transmission member moves. Concretely, an inclination angle of a helical spline in a helical spline engagement part is set so that the above state continues. The helical spline engagement part is a part where a helical spline on the outer periphery of an output shaft of a starter motor and a helical spline on the inner periphery of the torque transmission member mesh with each. Consequently, the above state continues without a plunger stopper using a solenoid or the like.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
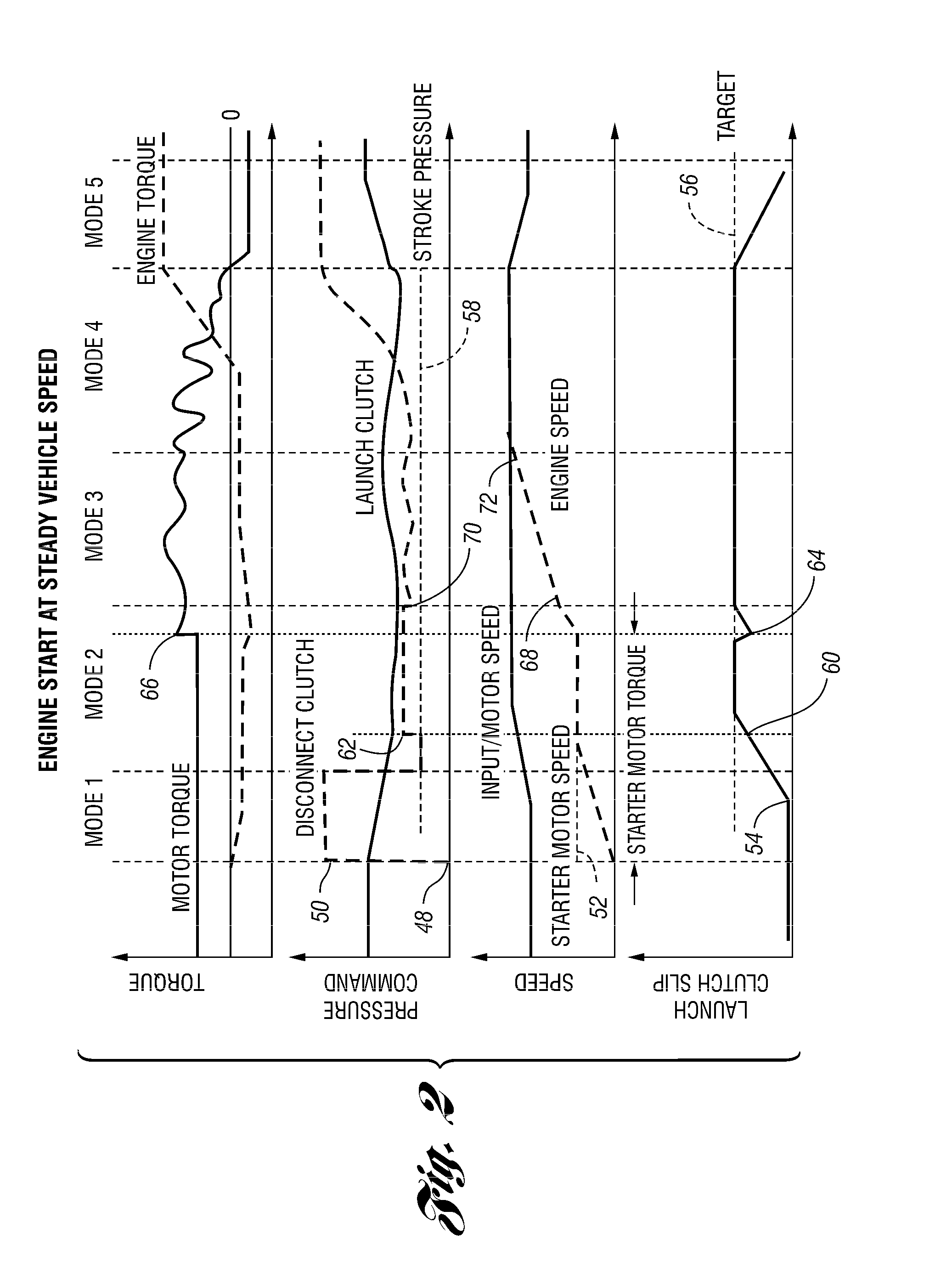
Vehicle And Method For Controlling Engine Start In A Vehicle
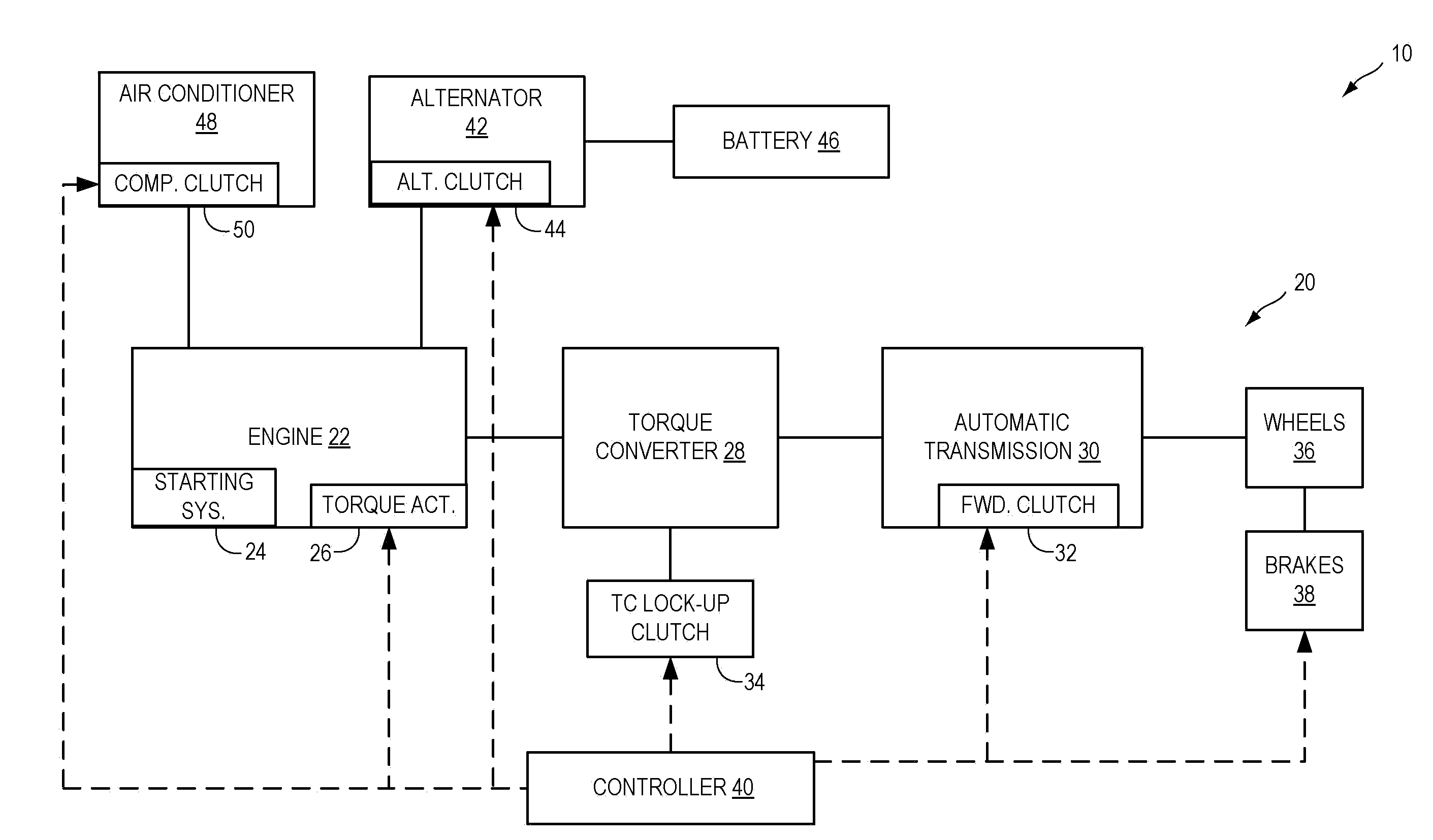
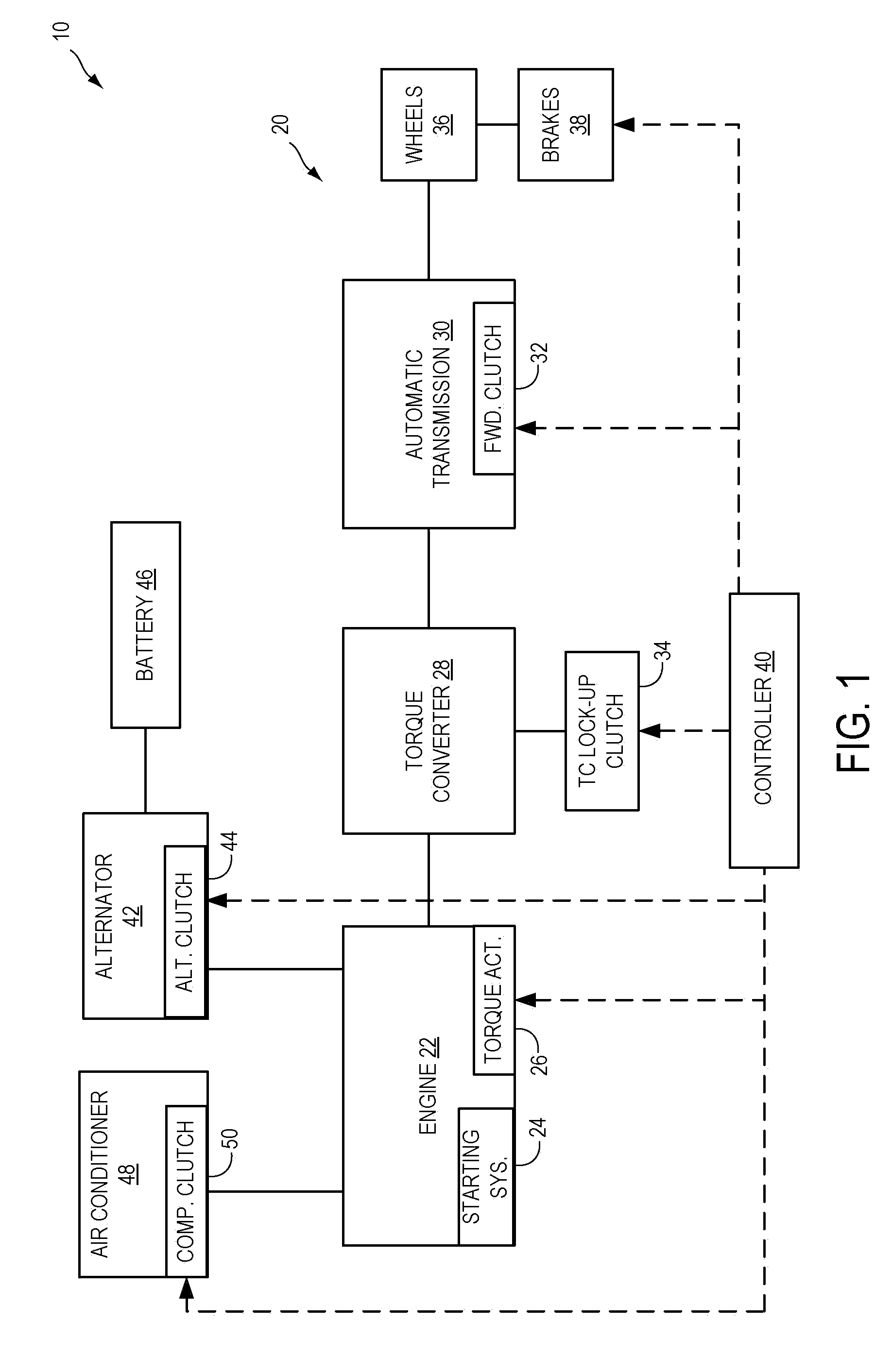
ActiveUS20110118915A1Eliminates torque disturbanceEliminates torque disturbancesPower operated startersElectrical controlDrive wheelClutch
A vehicle includes a motor / generator, a starter motor, a disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator, and at least one clutch disposed between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. When an engine start is requested, various parameters are controlled to ensure a smooth engine start wherein driveline torque disturbances are minimized. The starter motor is used to crank the engine upon an engine start request, thereby eliminating the need to transfer torque from the motor / generator to the engine. This helps to further reduce torque disturbances in the driveline when the engine is started.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
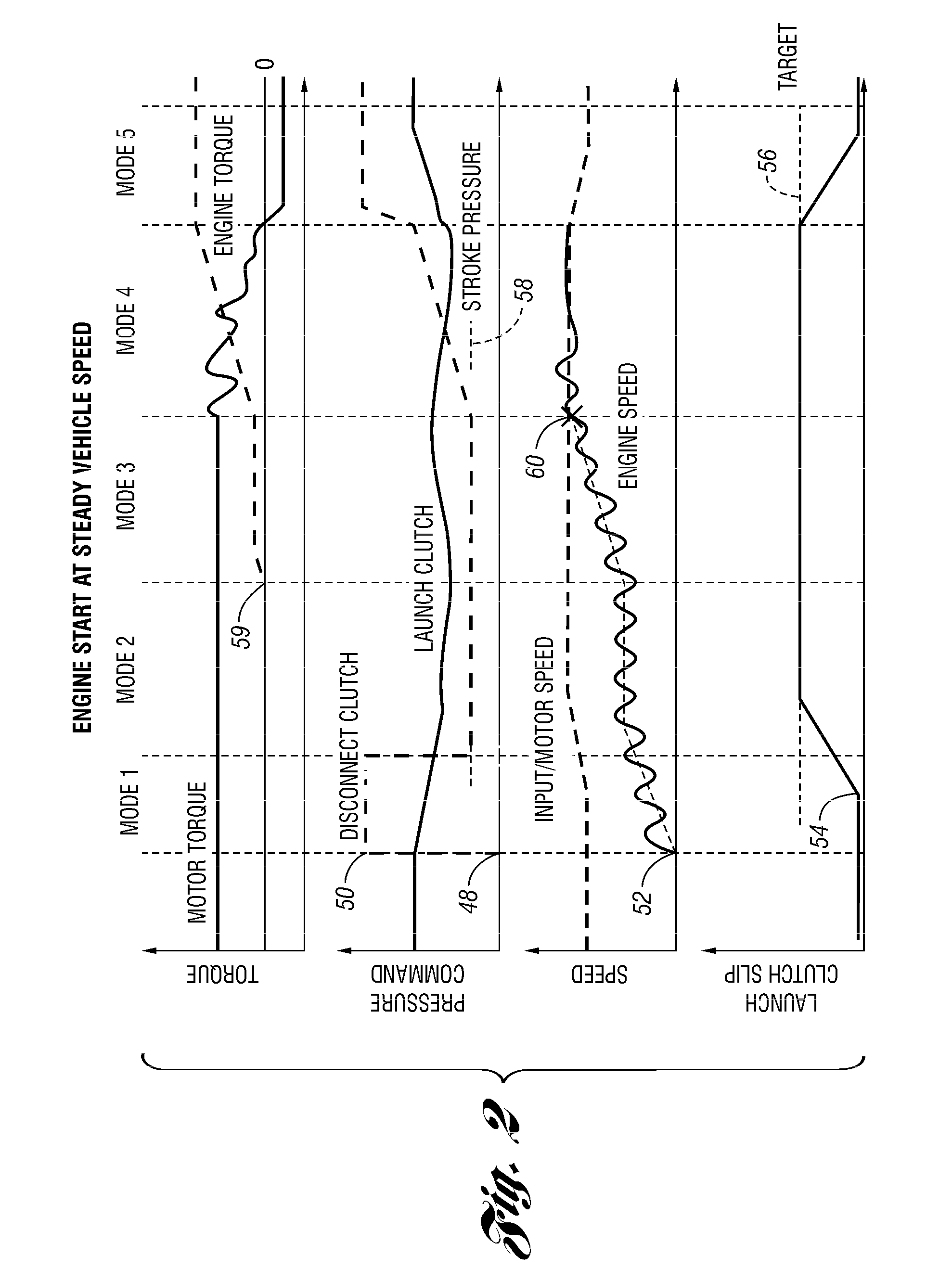
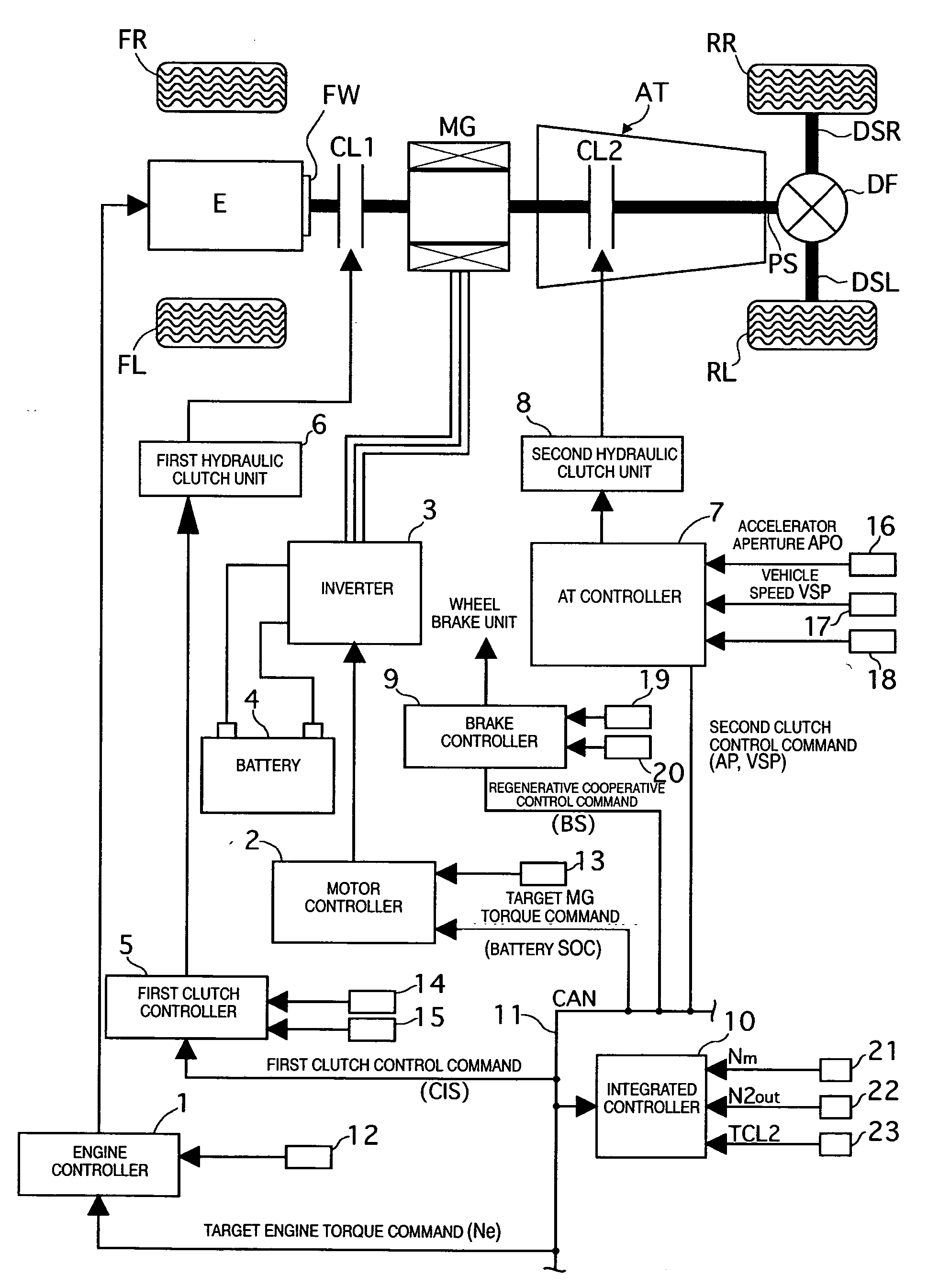
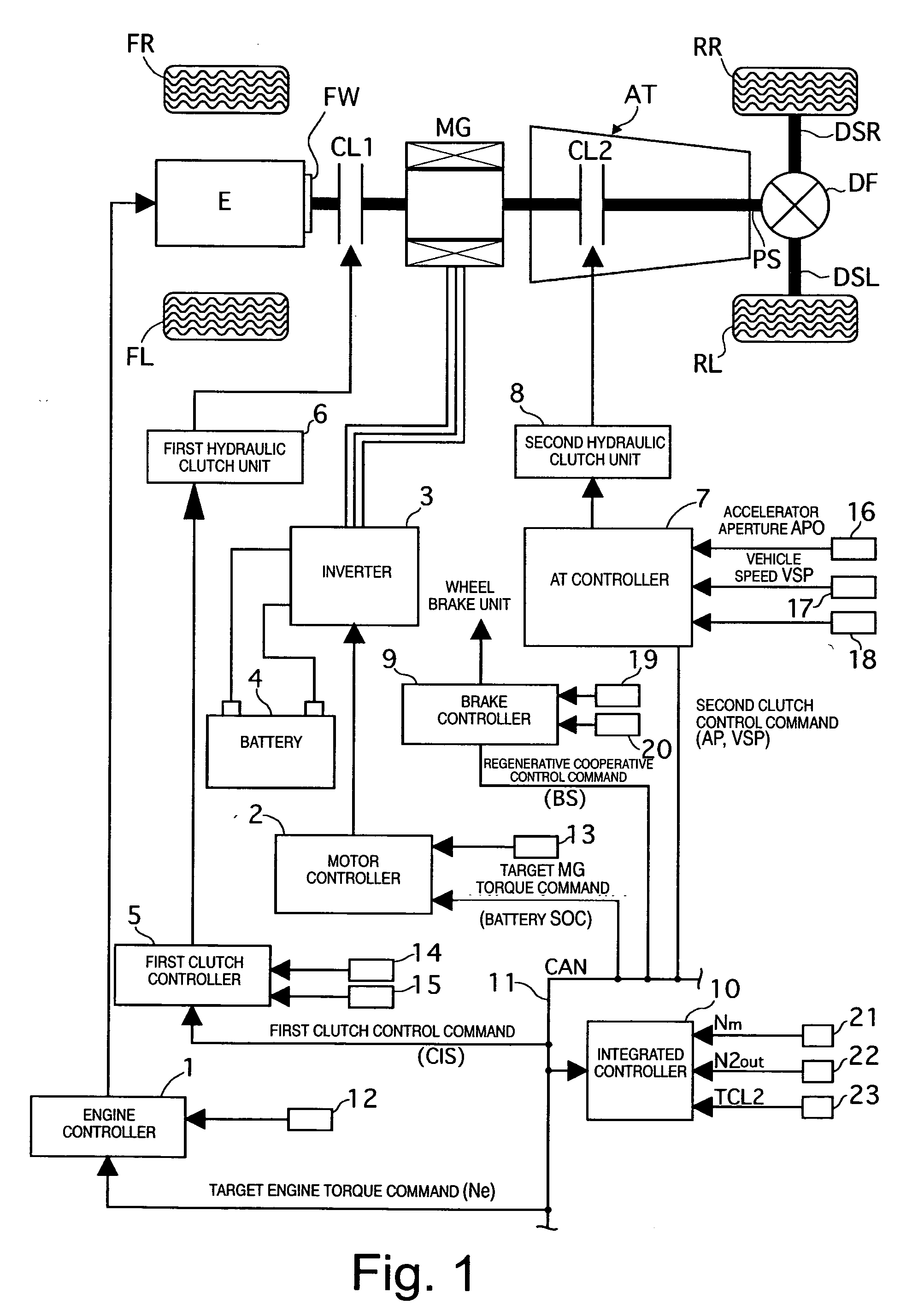
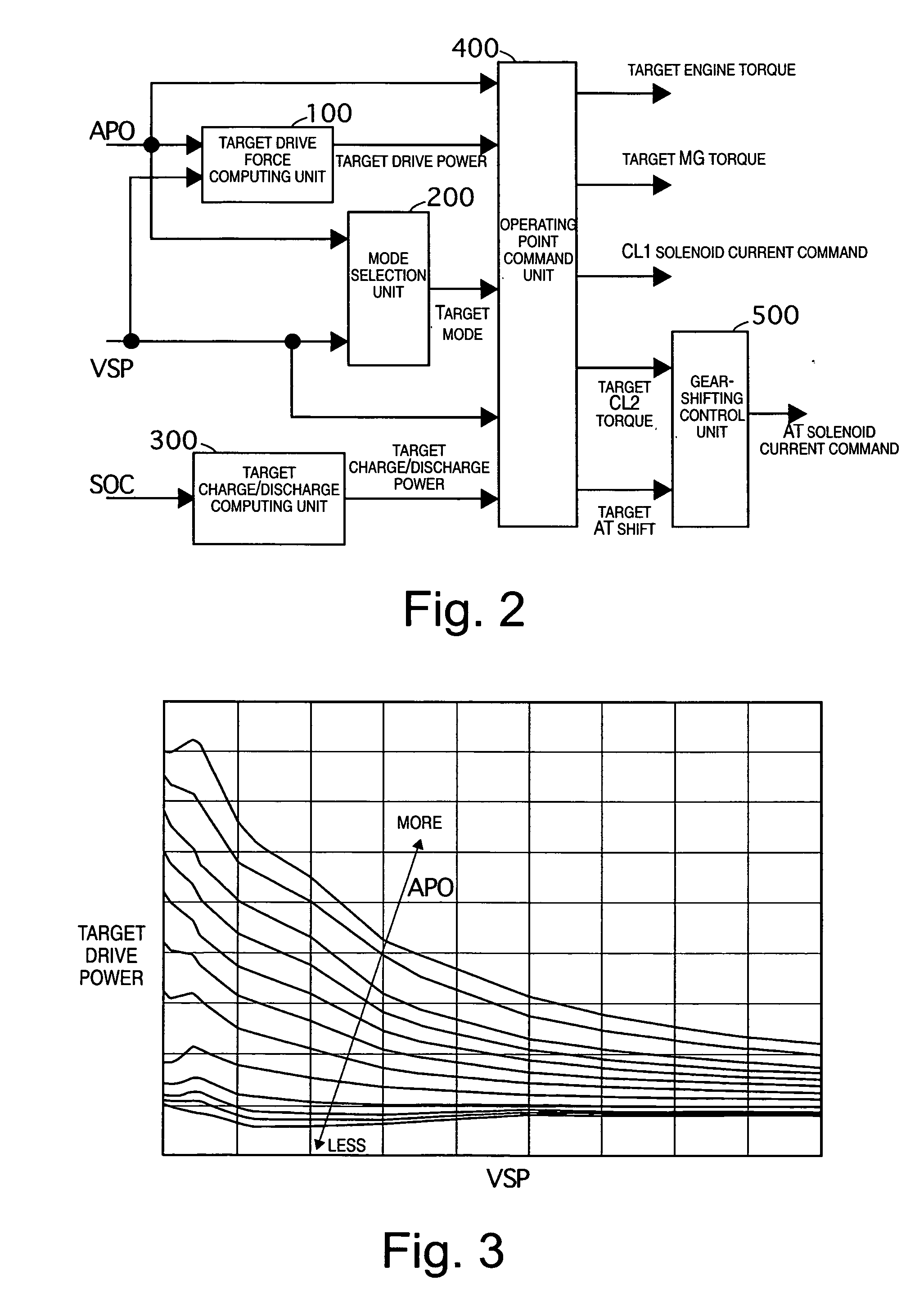
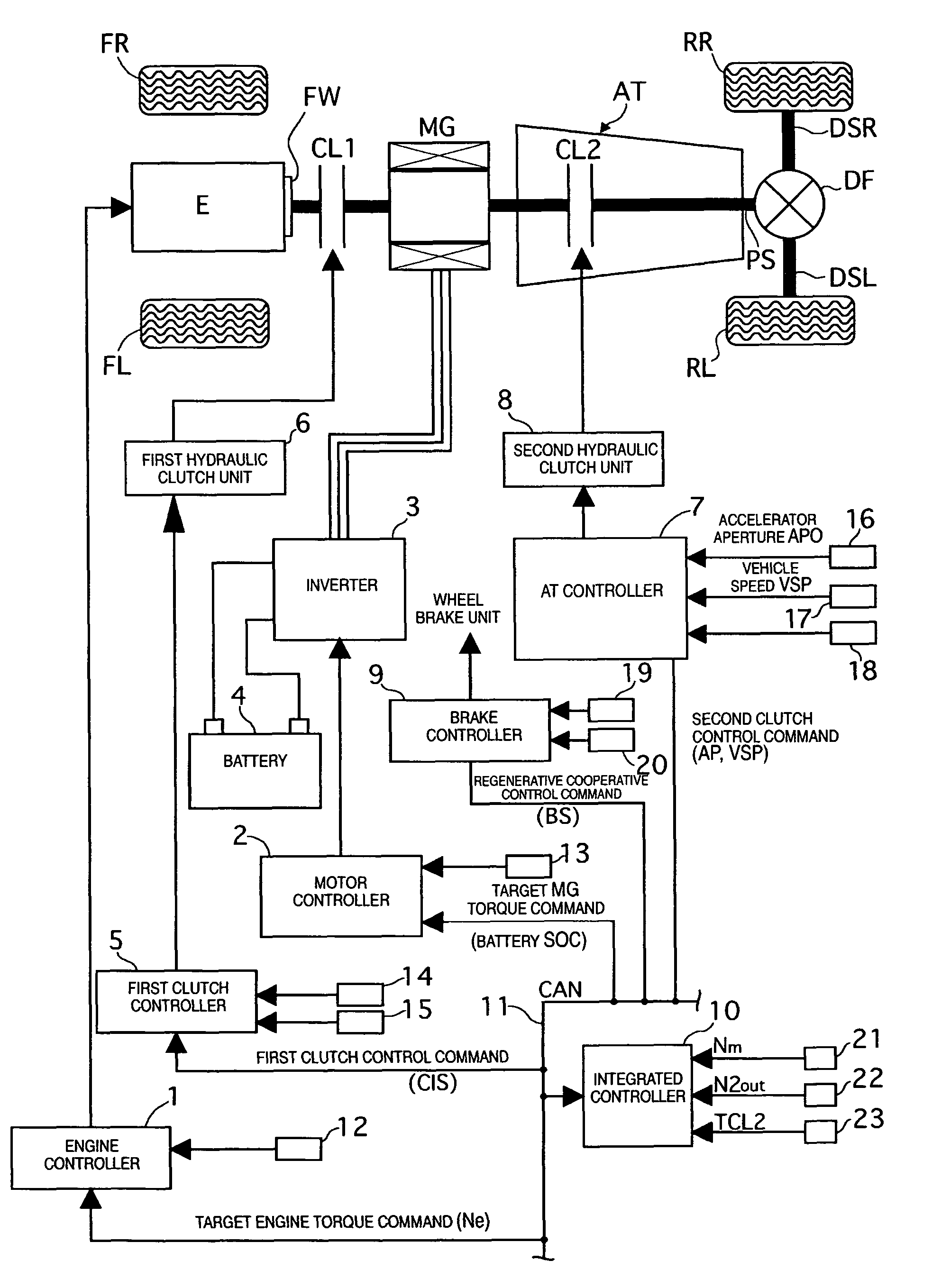
Hybrid vehicle drive control system
ActiveUS20070102211A1Lack of torque transfer capacity can be preventedAvoid it happening againClutchesPower operated startersDrive wheelMode change
A hybrid vehicle drive control system has a first clutch interposed between an engine and a motor / generator, a transmission including several gear position clutches arranged between the motor / generator and a drive wheel, and a controller. The controller selectively starts the engine using torque from the first clutch during a mode drive change from an electric drive mode to a hybrid drive mode. When an engine start command occurs during the drive mode change, the controller selects the engaged gear position clutch that has the maximum torque transfer capacity from the engaged clutches constituting a vehicle running gear occurring during an engine starting process as a second clutch to be controlled. Then the controller executes a slip control of the second clutch when the first clutch is being connected to start the engine during the mode change from the electric drive mode to the hybrid drive mode.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
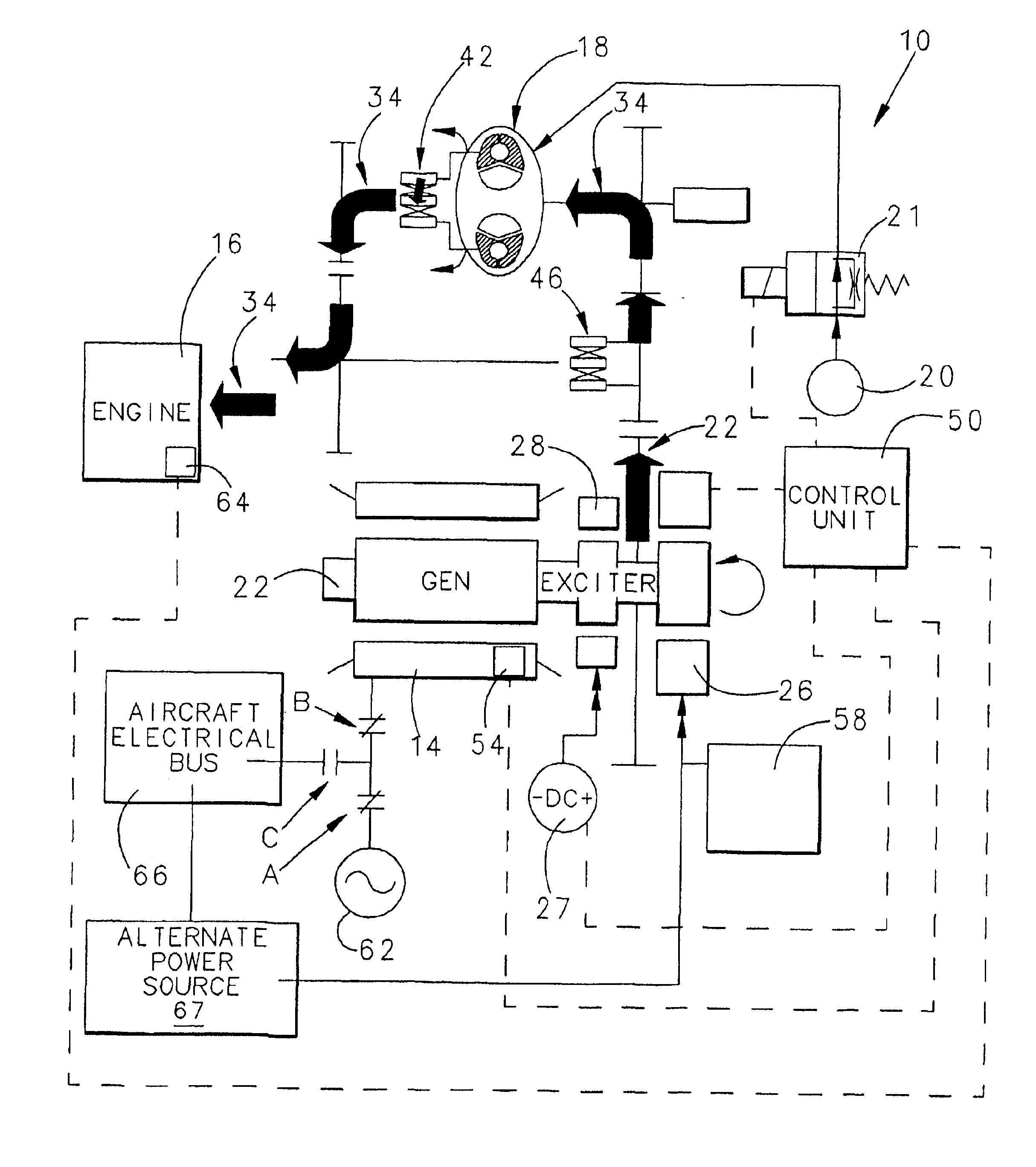
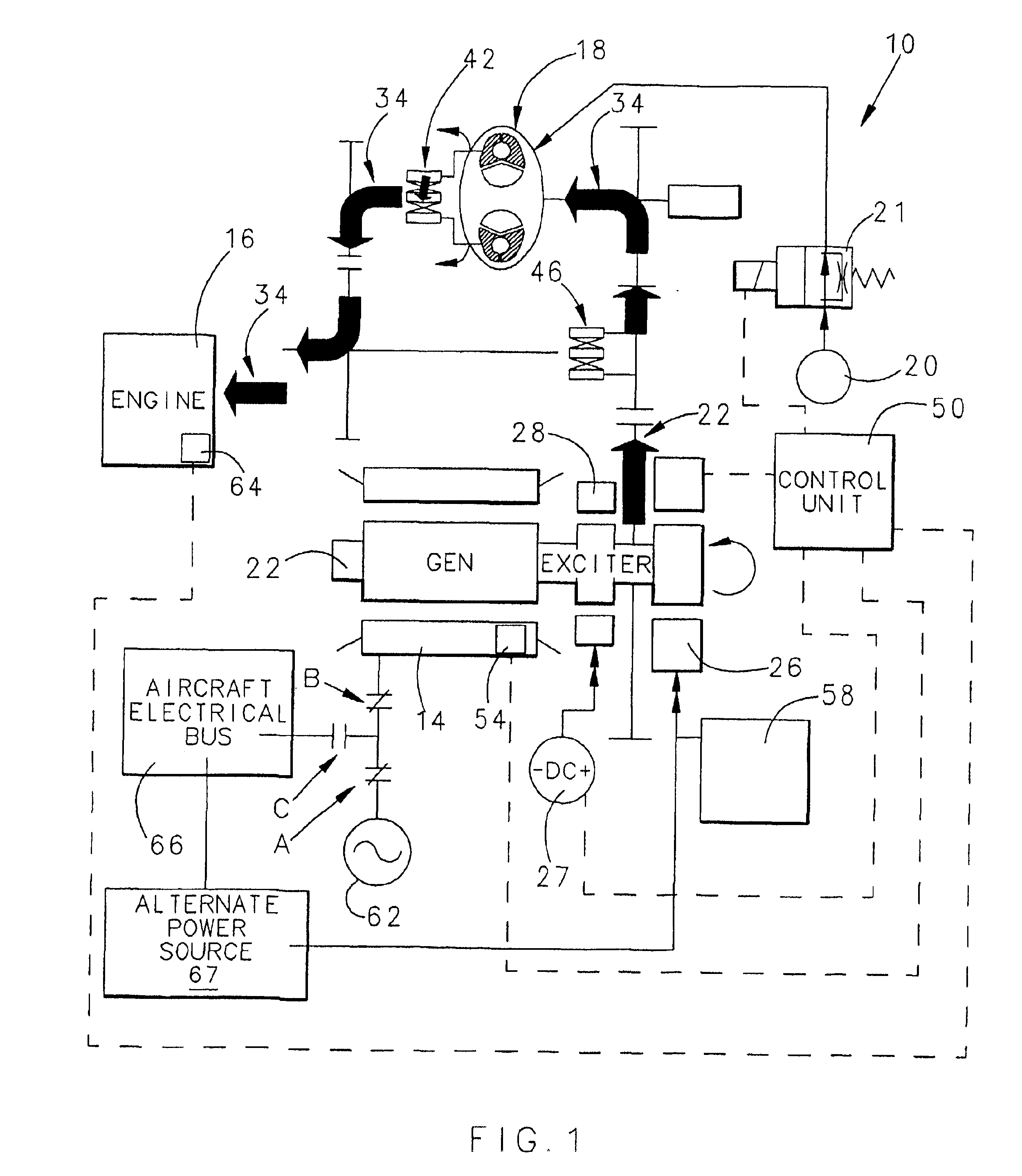
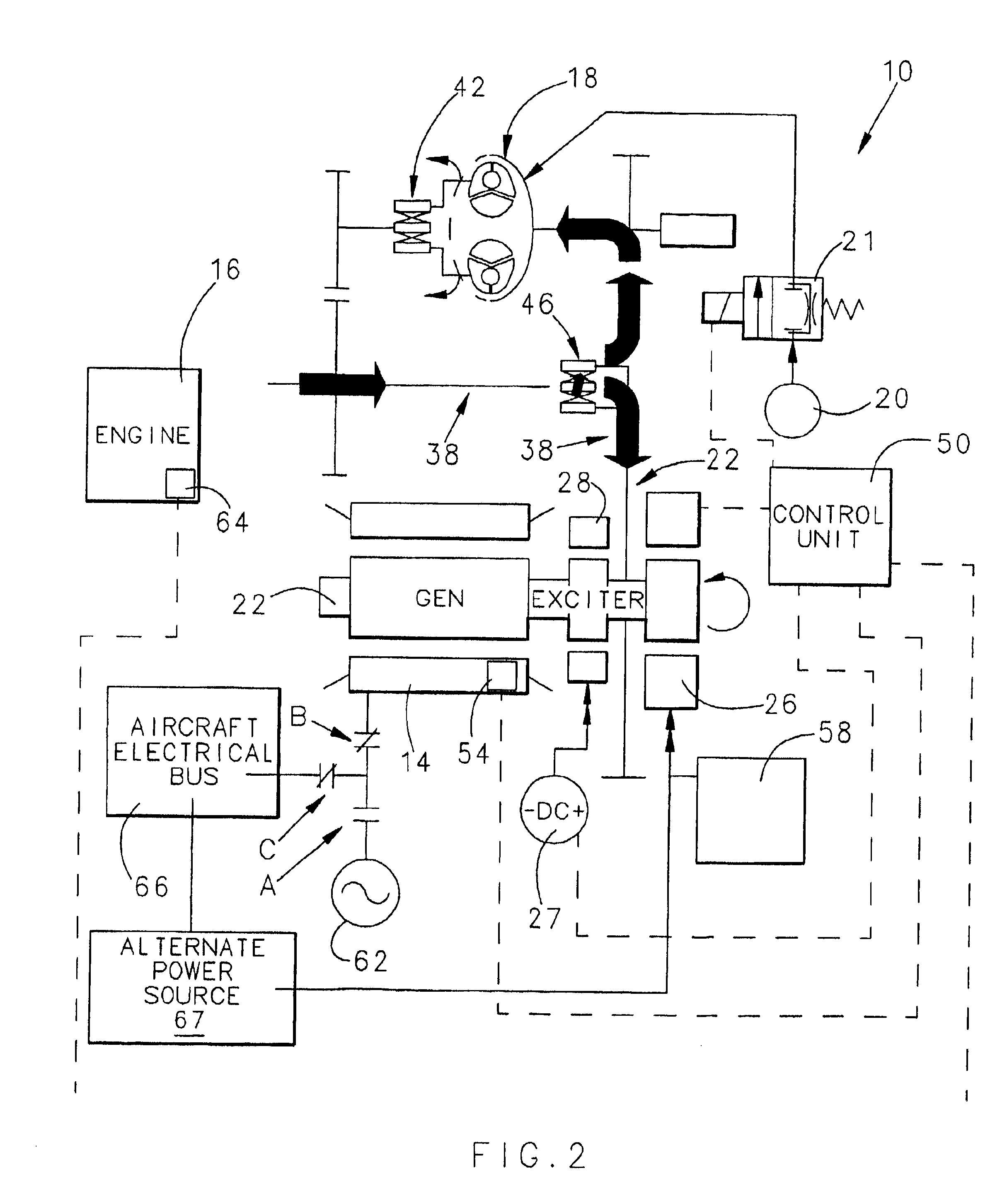
Aircraft starter generator for variable frequency (vf) electrical system
InactiveUS6838779B1Reduce loadPower operated startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersStarter generatorElectric machine
A starter-generator for an aircraft engine comprises a variable dynamoelectric machine alternatively operable as a motor or as a generator, having a rotor. A support motor is coupled to the variable dynamoelectric machine to assist the machine. A torque converter selectively couples and decouples the rotor to the engine, coupling the rotor to the engine at some point when the dynamoelectric machine is operated as a motor. The engine may be started by the dynamoelectric machine when operated as a motor through a first power train including the torque converter and may drive the dynamoelectric machine as a generator through a second power train.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Methods and systems for engine cranking
ActiveUS20130296126A1Low power output capacityExtend driver demand torque rangeHybrid vehiclesPower operated startersElectric machineHybrid vehicle
Systems and methods for improving operation of a hybrid vehicle are presented. In one example, an engine may be started in one of two ways depending on operating conditions. In particular, the engine may be started via a lower power output electric machine or a higher power output electric machine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
One-way isolator for high torque devices
A one way isolator for high torque devices, such as alternator-starters, driven by a flexible drive means includes a hub and a sheave each of which includes at least one stop member. The hub and sheave are linked by a isolating spring and, via a bearing and / or bushing, can rotate with respect to each other to provide isolation, through the spring, from torque variations when torque is transferred from the flexible drive means to the device. When substantial amounts of torque are transferred from the device to the flexible drive means, the sheave rotates with respect to the hub to bring the stop members into contact such that the isolator then acts like a solid pulley to facilitate the transfer of the torque from the device.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
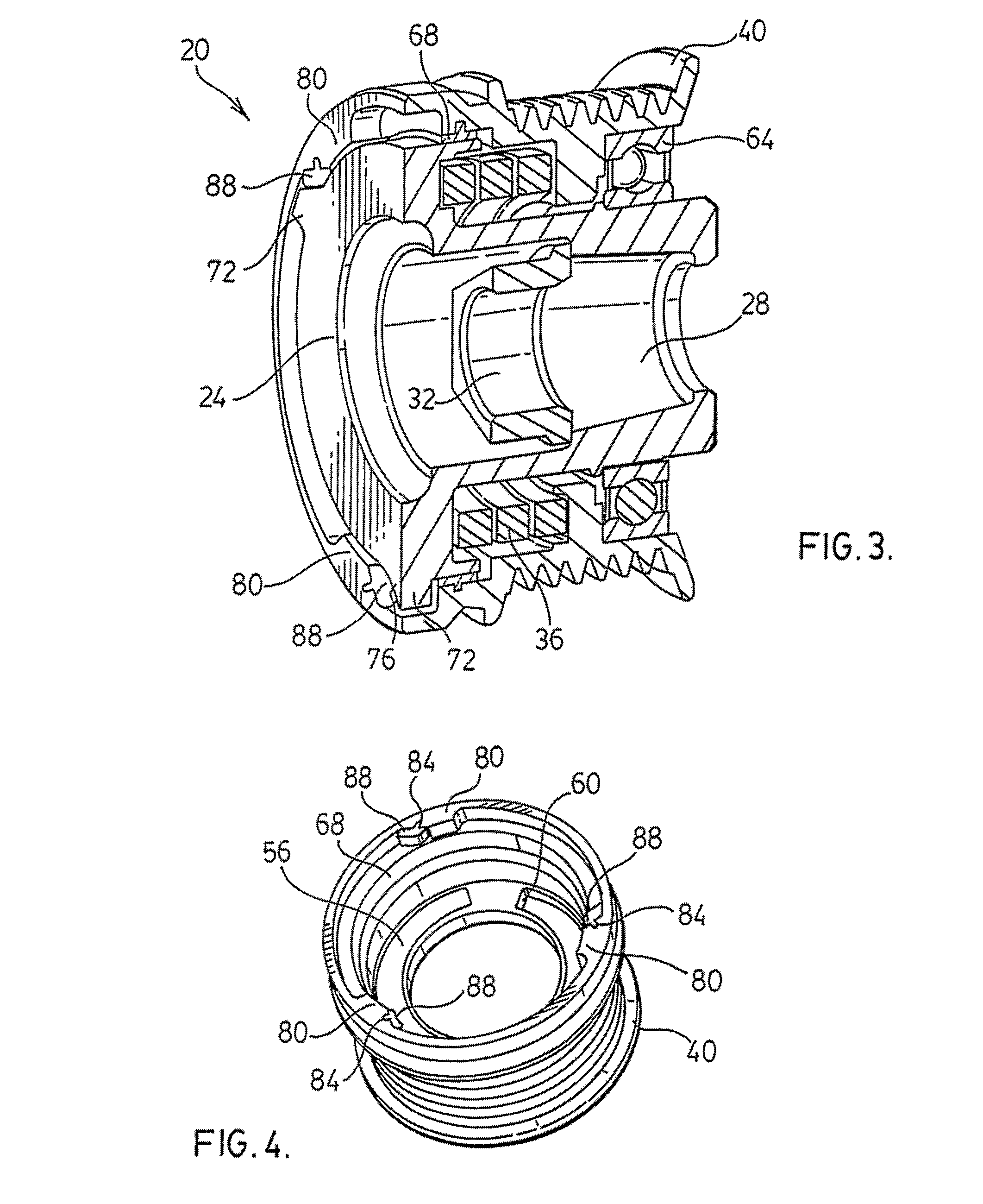
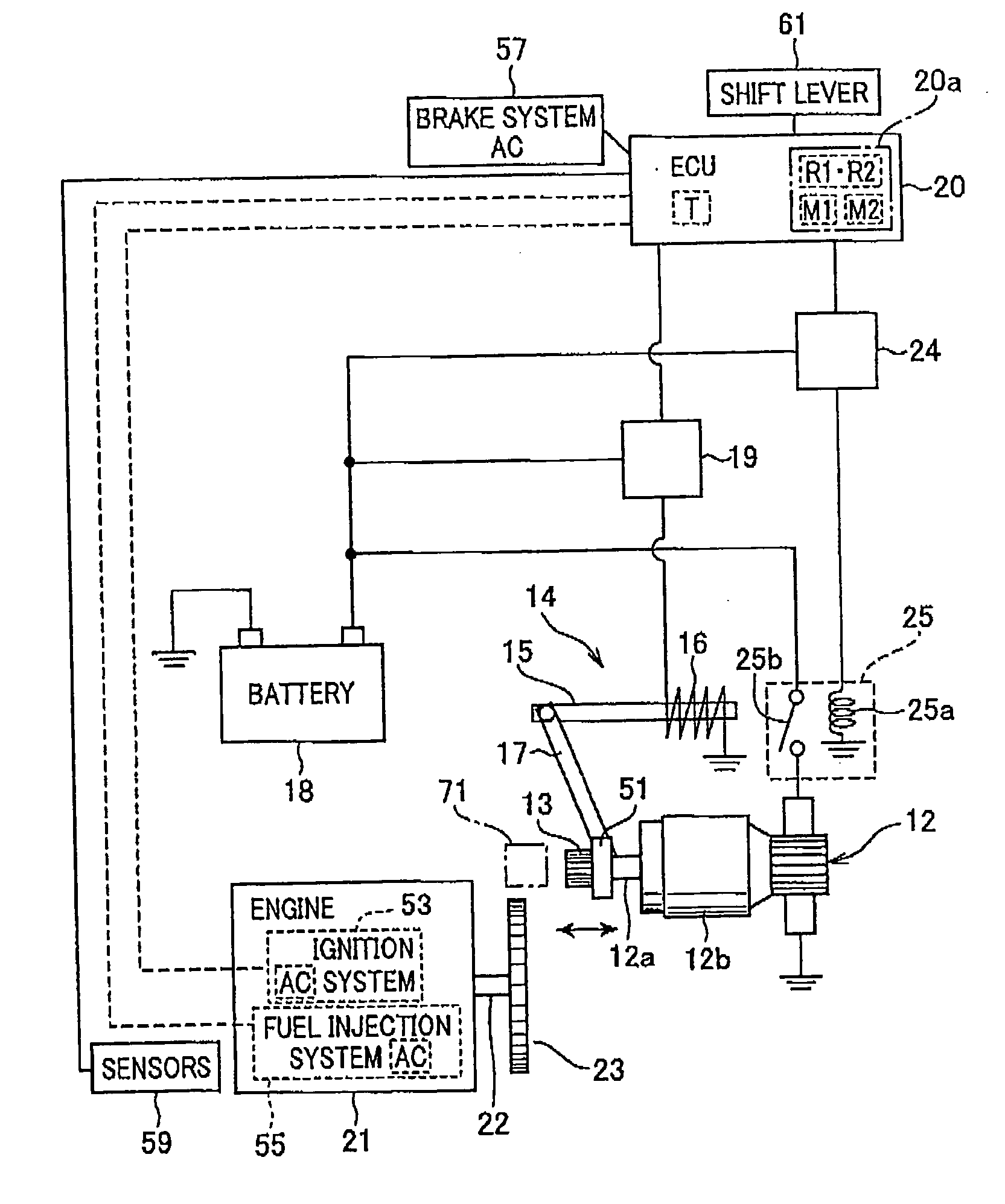
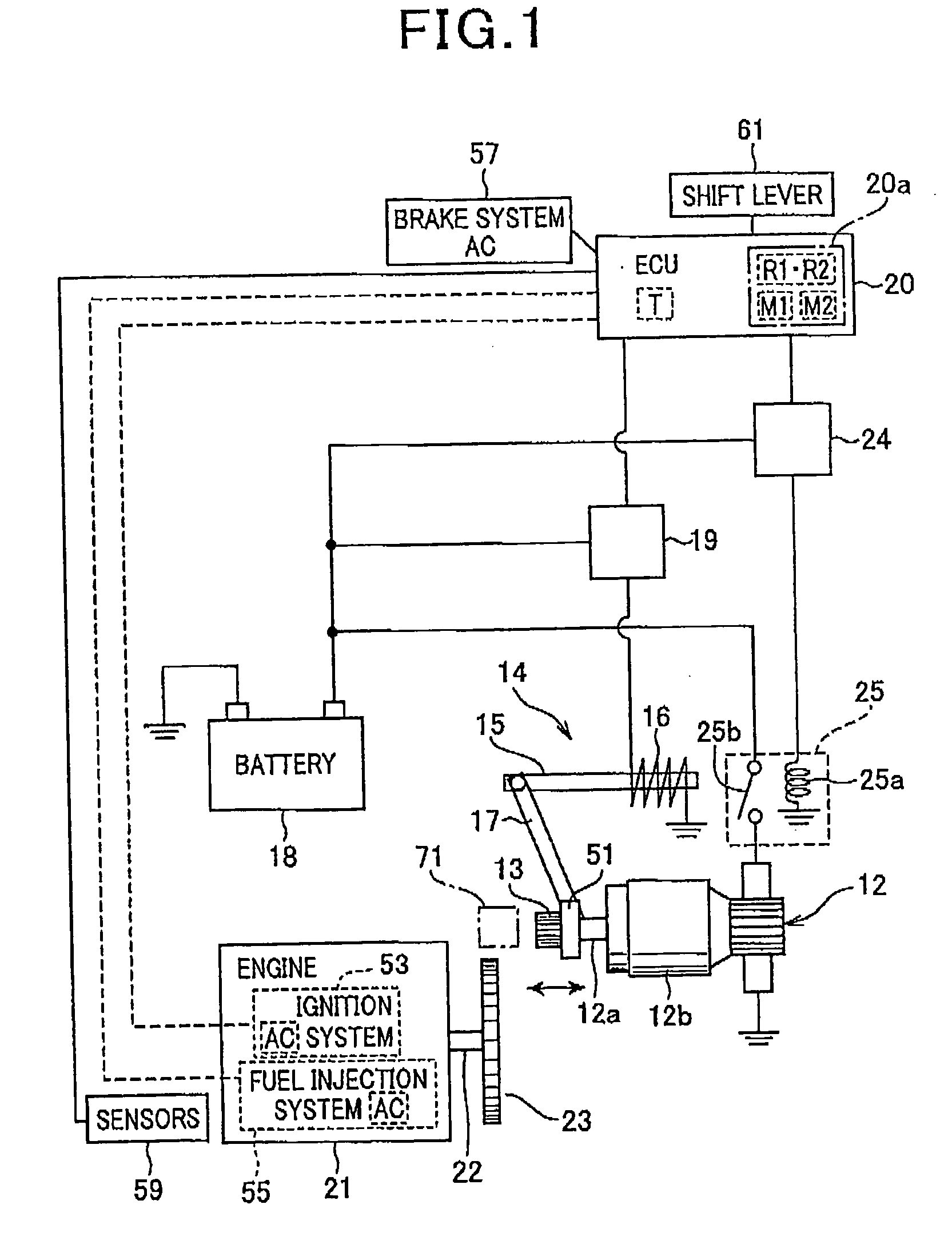
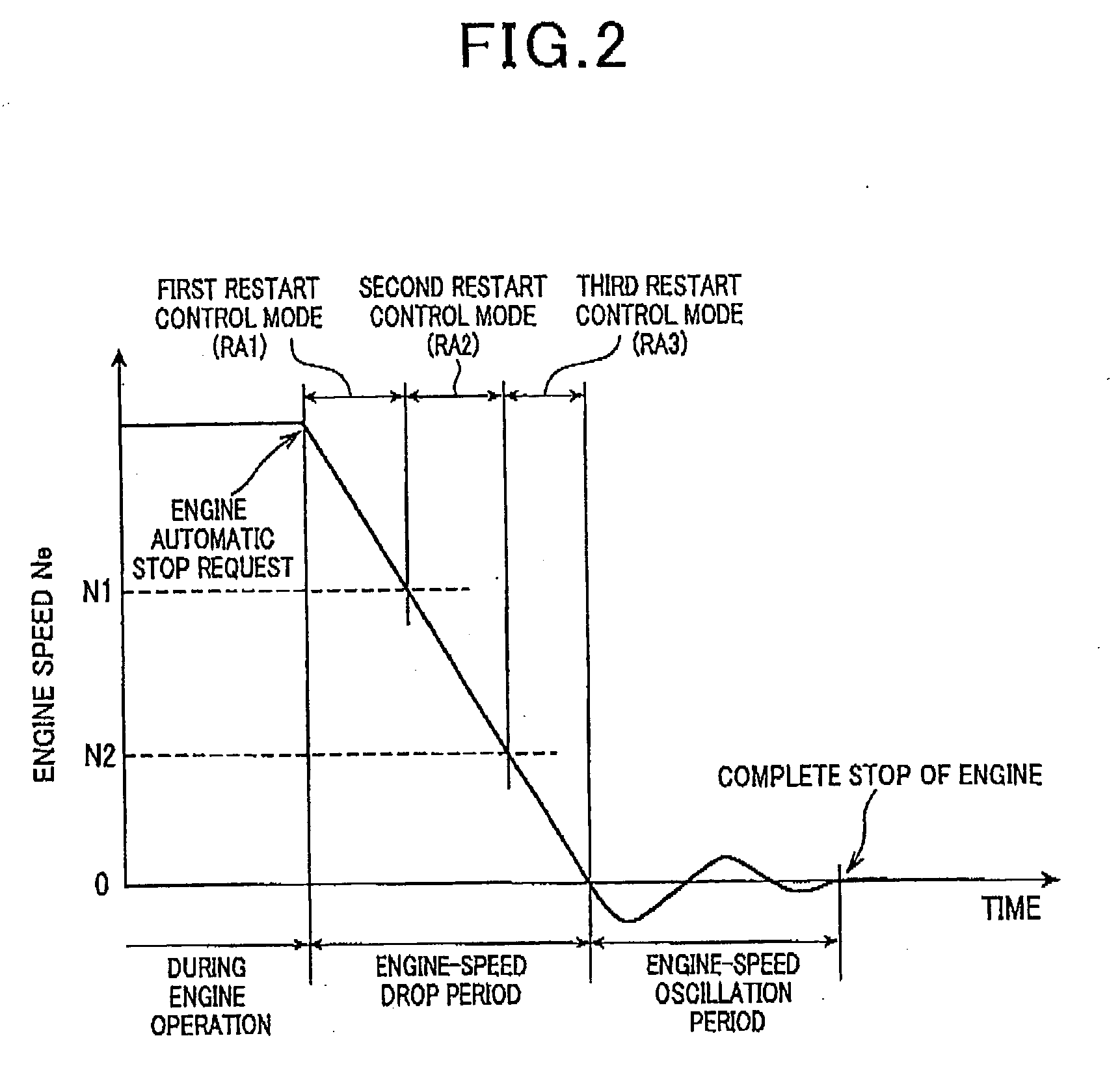
System for restarting internal combustion engine when engine restart request occurs
ActiveUS20100050970A1Process stabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersAutomatic controlGear wheel
In a system, a starter includes a motor for rotatably driving an output shaft with a pinion and an actuator that shifts the pinion toward a ring gear to be engaged with the ring gear. A monitor unit monitors a rotational speed of the internal combustion engine. The rotational speed of the internal combustion engine drops after an automatic control for stop of the engine. When an engine restart request occurs with the rotational speed being within a preset range during the rotational speed of the internal combustion engine dropping by the automatic control for stop of the engine, a drive unit drives the actuator to shift the pinion toward the ring gear to be engaged with the ring gear. The drive unit rotatably drives the motor with the pinion being engaged with the ring gear to thereby crank the crankshaft.
Owner:DENSO CORP
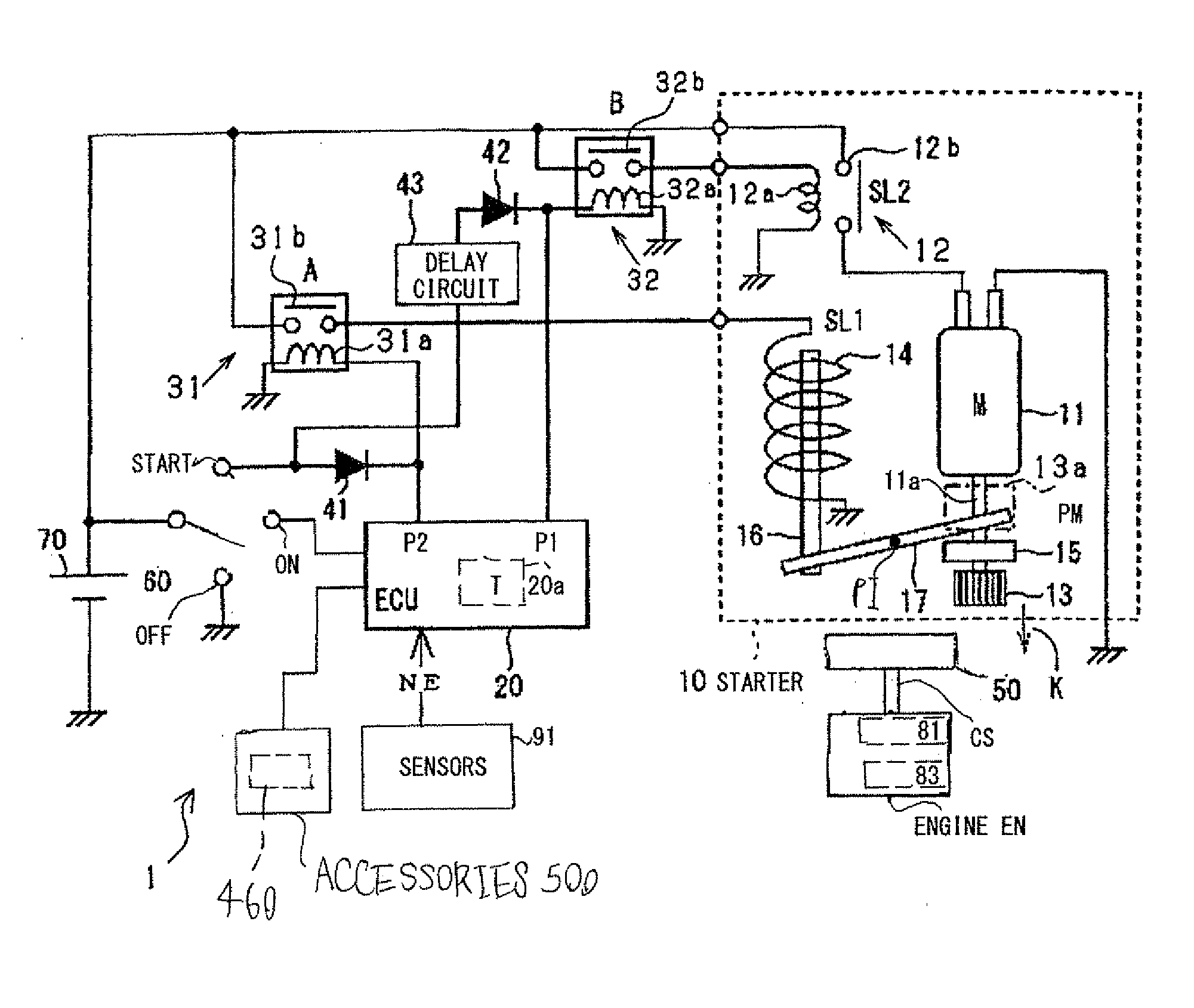
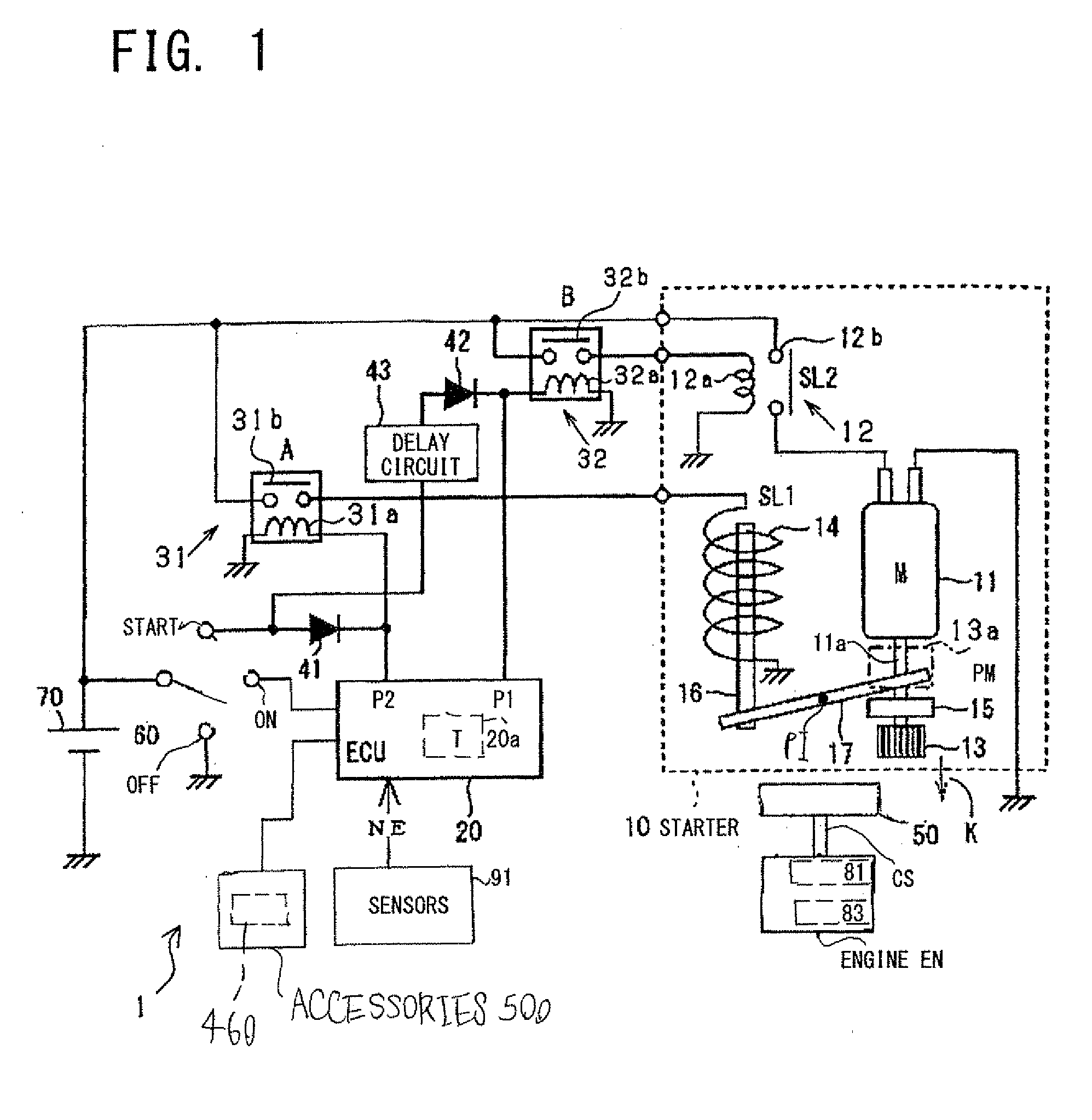
Starting device for internal combustion engines in motor vehicles
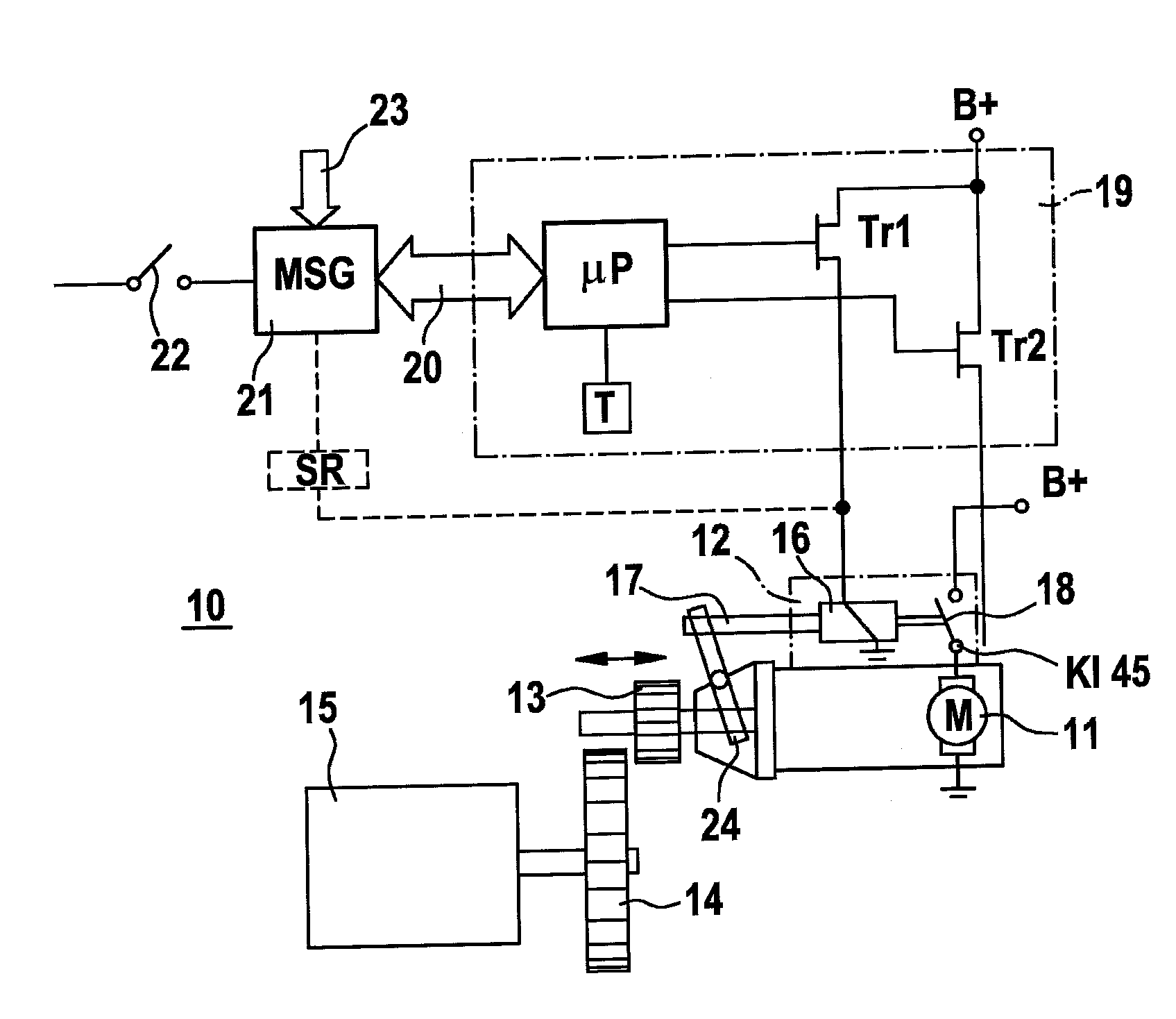
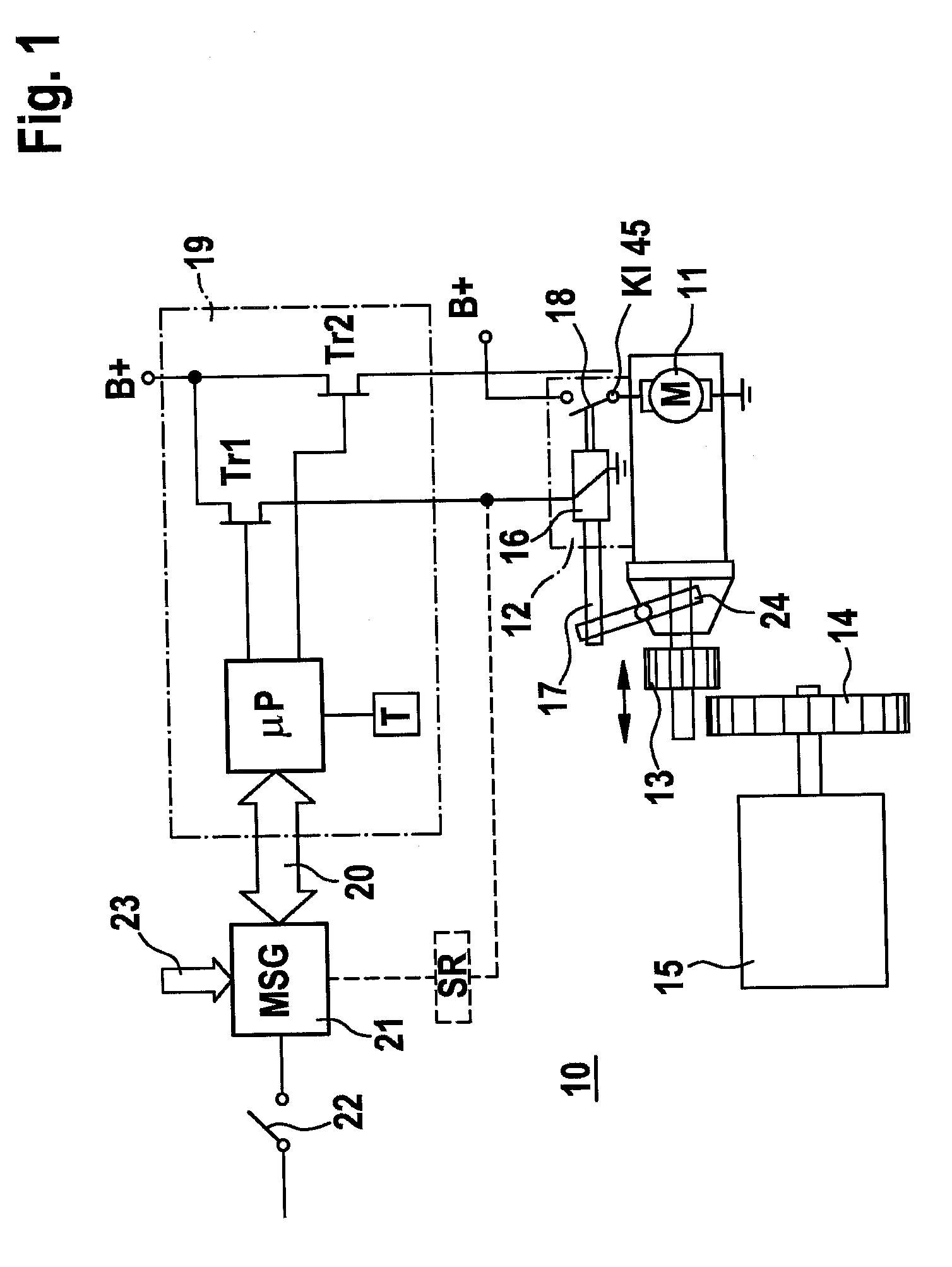
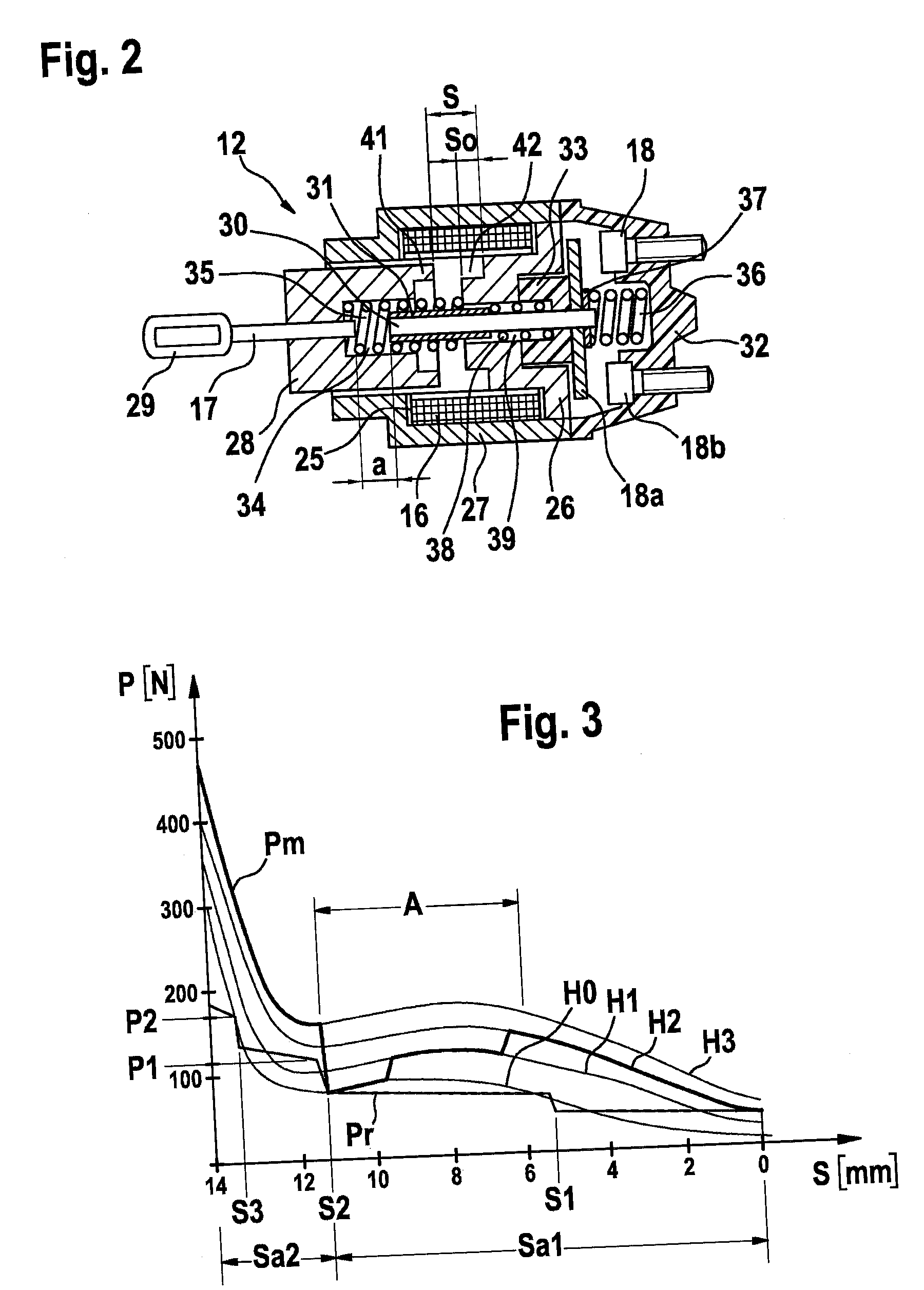
The invention relates to a starter device (10) for internal combustion engines (15) in motor vehicles with a controller (19), a starter relay (12), a starter pinion (13) and a starter motor (11), whereby on each start / stop process in the stop phase (first step) the starter relay engages the starter pinion in the toothed ring (14) of the engine and in the start phase (second step) the engine is turned over by the starter motor. According to the invention, the starter pinion (13) may be engaged as quietly as possible for a subsequent starting process on switching off the engine (10) and held in position until starting, whereby, in the first step of the starting process, the armature (28) of the starter relay (12) is withdrawn with reduced force to a position with open switch contact (18) and held there until the start of the second step, whereupon the armature (28) closes the switch contact (18) of the starter motor with full force.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Hybrid vehicle drive control system
ActiveUS7770678B2Lack of torque transfer capacity can be preventedAvoid it happening againClutchesPower operated startersDrive wheelMode change
A hybrid vehicle drive control system has a first clutch interposed between an engine and a motor / generator, a transmission including several gear position clutches arranged between the motor / generator and a drive wheel, and a controller. The controller selectively starts the engine using torque from the first clutch during a mode drive change from an electric drive mode to a hybrid drive mode. When an engine start command occurs during the drive mode change, the controller selects the engaged gear position clutch that has the maximum torque transfer capacity from the engaged clutches constituting a vehicle running gear occurring during an engine starting process as a second clutch to be controlled. Then the controller executes a slip control of the second clutch when the first clutch is being connected to start the engine during the mode change from the electric drive mode to the hybrid drive mode.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
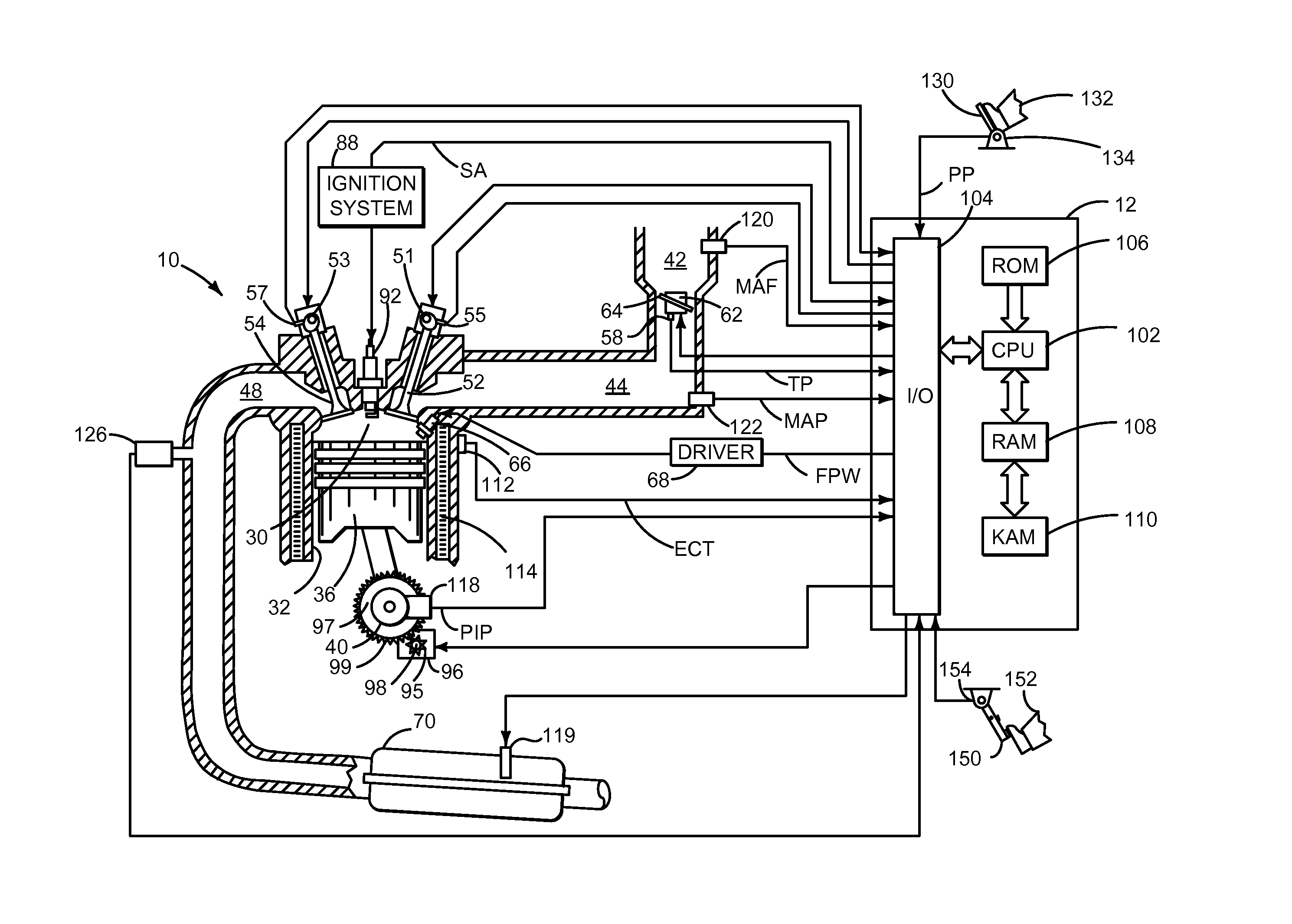
Engine starting system
ActiveUS7079941B2Improve engine performanceImprove rendering capabilitiesAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersAlternatorElectric power
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Automatic internal combustion engine stop device, internal combustion engine provided with the same and automatic internal combustion engine stop method
ActiveUS20070199533A1Short timeGrowth inhibitionPower operated startersElectrical controlStops deviceEngineering
In an automatic stop device that automatically stops the operation of an internal combustion engine after a predetermined automatic stop condition is satisfied, a load acting on the engine is removed when the automatic stop condition is satisfied. When the automatic stop condition is satisfied, the between the magnitude of the load on the internal combustion engine before and after of the automatic stop condition is satisfied is determined, and an ignition timing retard amount of an ignition plug is decided such that the retard amount is increased as the difference becomes greater. The ignition timing is retarded by the retard amount substantially at the same moment as the load removing operation before the automatic stop control is initiated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Engine powered device having accessory drive and reversing motor for selectively starting engine and powering accessory drive
A device having an engine, a motor / generator and an accessory system having an accessory that is driven by rotary power. The device can be operated in a first mode in which the engine provides rotary power for driving the accessory and the motor / generator. The device can be operated in a second mode for starting the engine and driving the accessory in which rotary power is output from the motor / starter in a first rotational direction. The device can also be operated in a third mode in which the motor / generator outputs rotary power in a second, opposite rotational direction for driving the accessory while the engine is not operating. A method for operating the device is also provided.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
System and method for restarting an engine
ActiveUS20110054765A1Reduce fuel consumptionQuick restartAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersStarter
Various systems and methods are described for controlling an engine in a vehicle, the engine being coupled to a transmission. One example method comprises, under selected braking conditions, shutting-off the engine and spinning-down the engine to rest while the vehicle is traveling, and in response to a foot-off-brake event, restarting the engine by at least partially engaging the transmission to assist in spinning-up of the engine from rest while the vehicle is traveling.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vehicle And Method For Controlling Engine Start In A Vehicle
ActiveUS20110118078A1Driveline torque disturbances are reduced or eliminatedReduce transferPower operated startersEngine controllersDrive wheelDrivetrain
A vehicle includes a motor / generator, a starter motor, a disconnect clutch disposed between the engine and the motor / generator, and at least one clutch disposed between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels. When an engine start is requested, various parameters are controlled to ensure a smooth engine start wherein driveline torque disturbances are minimized. The starter motor is used to crank the engine at the lowest engine speeds when the engine-required torque is the highest. This reduces the amount of torque necessary to be supplied from the motor / generator, and further helps to reduce torque disturbances in the driveline. If the motor / generator is producing torque to propel the vehicle at the time the engine start is requested, a launch clutch or one or more transmission clutches can be controlled to provide slip between the motor / generator and the vehicle drive wheels to further reduce torque disturbances in the driveline.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
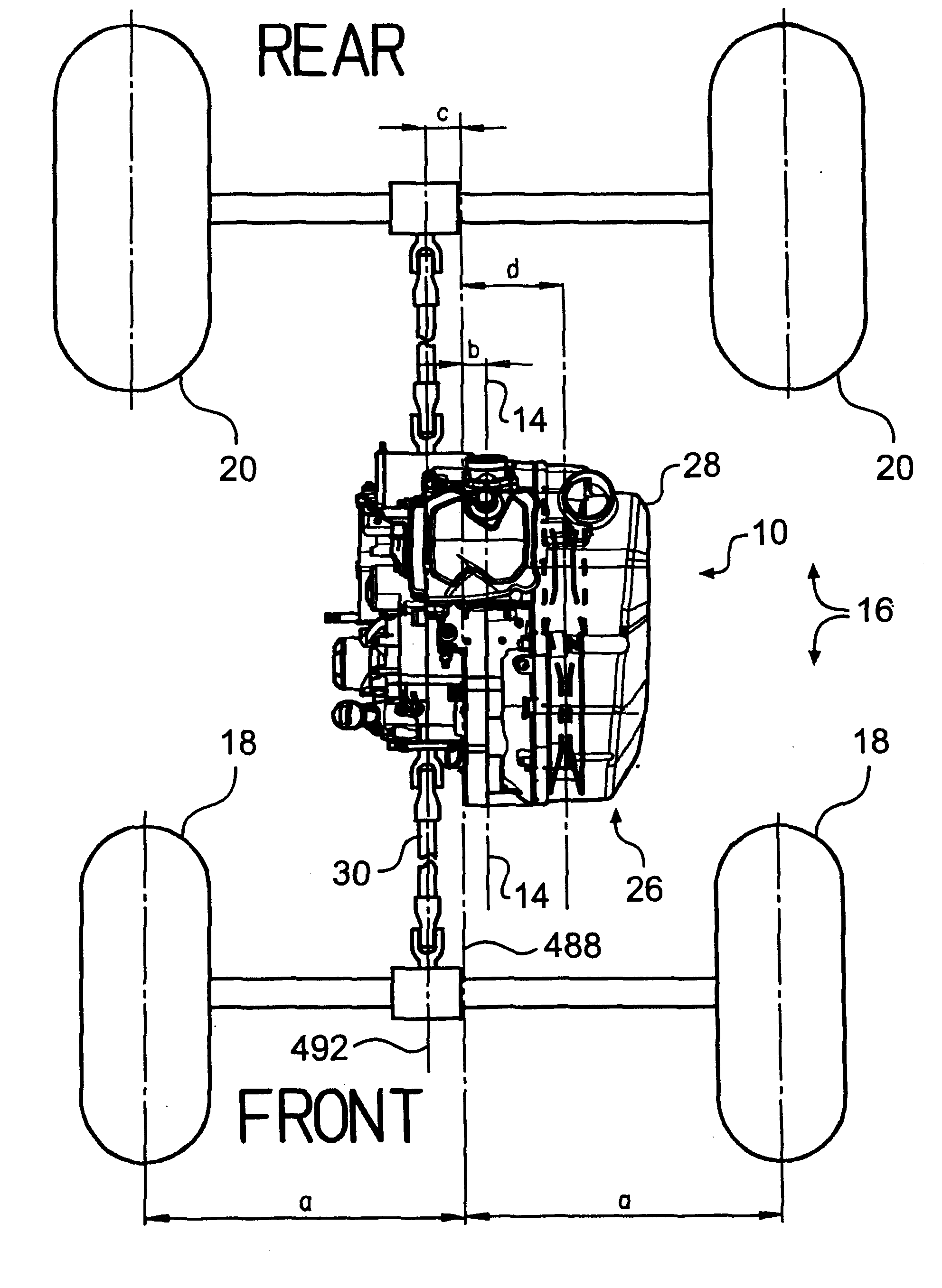
Component arrangement for an all terrain vehicle
InactiveUS6896087B2Power operated startersWheel based transmissionContinuously variable transmissionAll terrain vehicle
An all terrain vehicle (“ATV”) is disclosed having a frame with front, rear, right, and left sides. The frame defines a frame centerline extending longitudinally between the front and the rear sides. The ATV includes an engine with at least one cylinder having an axis that defines an engine centerline. The all terrain vehicle also includes an output shaft defining an output shaft centerline. A continuously variable transmission (“CVT”) operatively connects the engine to the output shaft and defines a CVT centerline. The engine centerline, output shaft centerline, and CVT centerline are positioned with respect to one another and the frame centerline. In one embodiment, the engine centerline is disposed between the output shaft centerline and the CVT centerline. In this embodiment, the engine centerline also may lie between the frame centerline and the CVT centerline.
Owner:BRP ROTAX
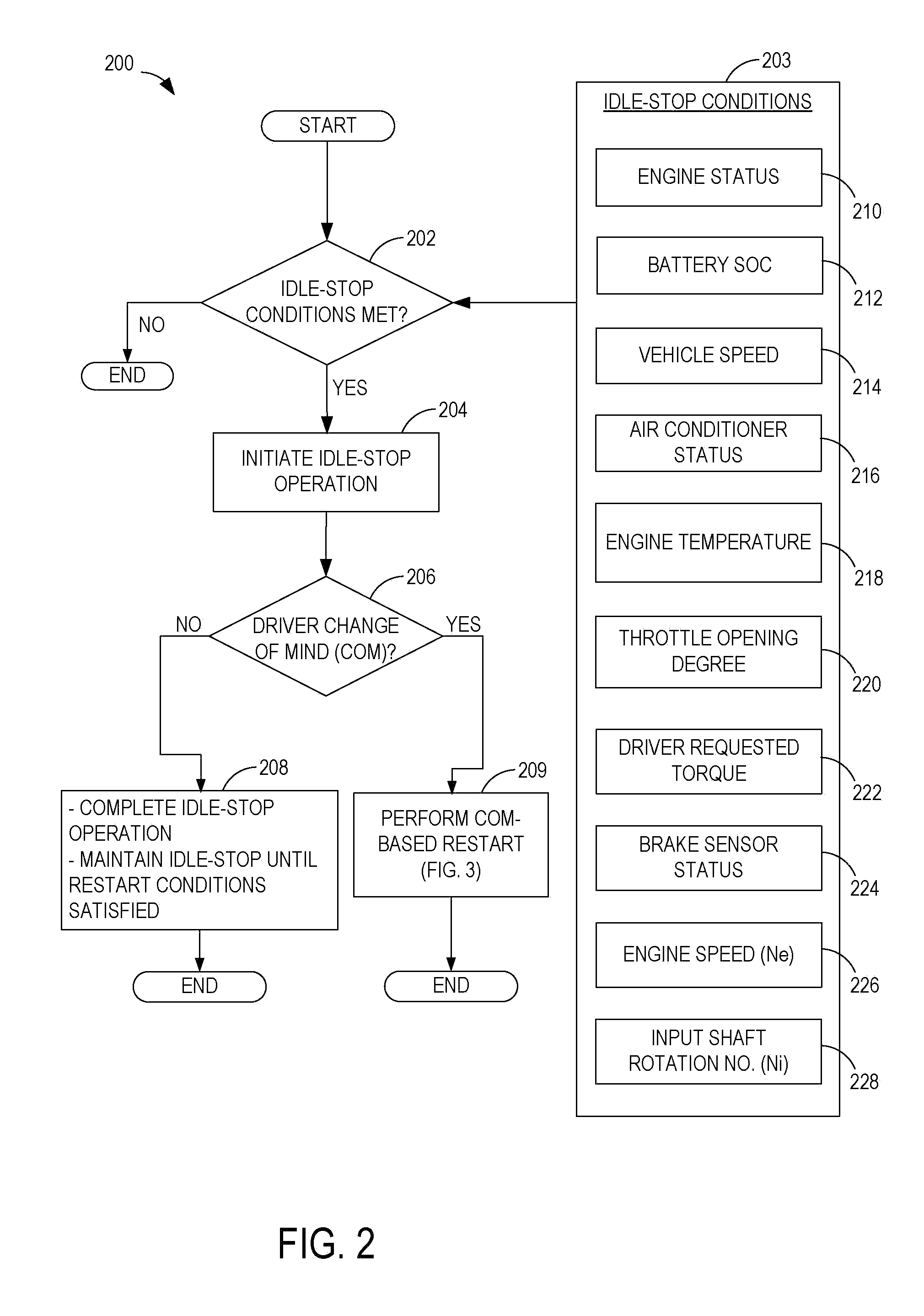
Methods and systems for assisted direct start control
ActiveUS20100174473A1Reduce exhaust emissionsSave fuelAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersBrake torqueRotary engine
Method and systems are provided for controlling a vehicle system including an engine that is selectively deactivated during engine idle-stop conditions. One example method comprises, adjusting a brake torque applied to a deactivated rotating engine after an engine restart request, the brake torque applied to slow the engine to at least a predetermined threshold speed without stopping the engine, and engaging a starter to the still rotating engine to increase the engine speed and restart the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
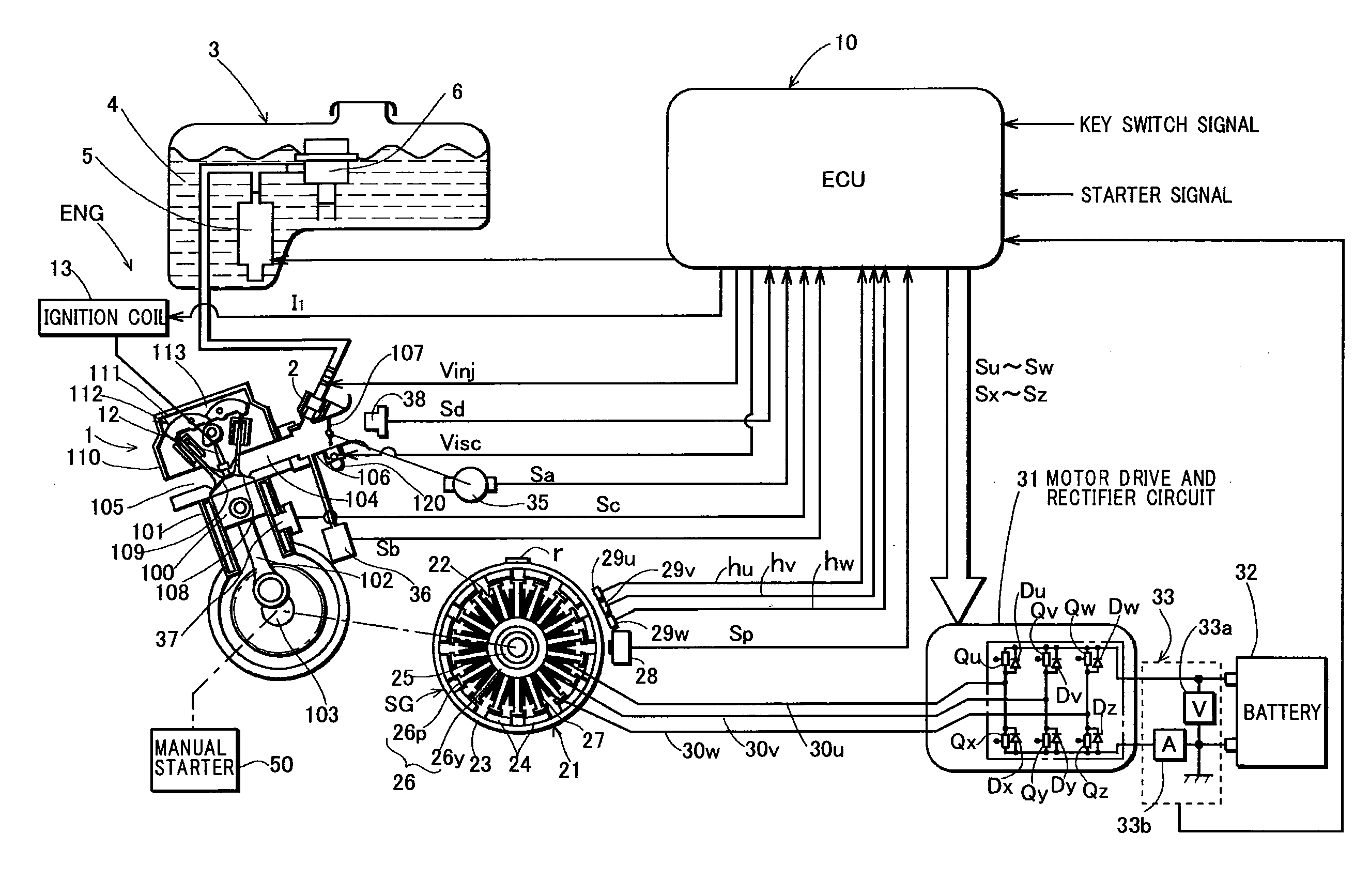
Engine starting device
InactiveUS20090020092A1Preventing situationEasy to startPower operated startersElectrical controlStarter generatorDriving current
An engine starting device including: a battery capacity monitoring portion that estimates a remaining capacity of a battery; a start time starter driving portion that supplies a driving current from the battery to a starter generator for causing cranking of the engine when a start mode of the engine is a normal start mode; and a display portion that displays that the cranking for starting the engine is to be performed by a manual starter when the estimated remaining capacity of the battery is insufficient, wherein the driving of the starter generator is prohibited and the start mode of the engine is switched to the manual start mode when the estimated remaining capacity of the battery is insufficient.
Owner:KOKUSAN DENKI CO LTD
Method for controlling an engine during a restart
ActiveUS20110053735A1Reduce fuel consumptionReduce amountPower operated startersElectrical controlActuatorStarter
Various systems and methods are described for controlling an engine in a vehicle, the engine being coupled to a transmission. One example method comprises, under selected braking conditions, shutting-off the engine and spinning-down the engine to rest while the vehicle is traveling, and in response to a foot-off-brake event, restarting the engine by at least partially engaging the transmission and adjusting engine torque control actuators.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
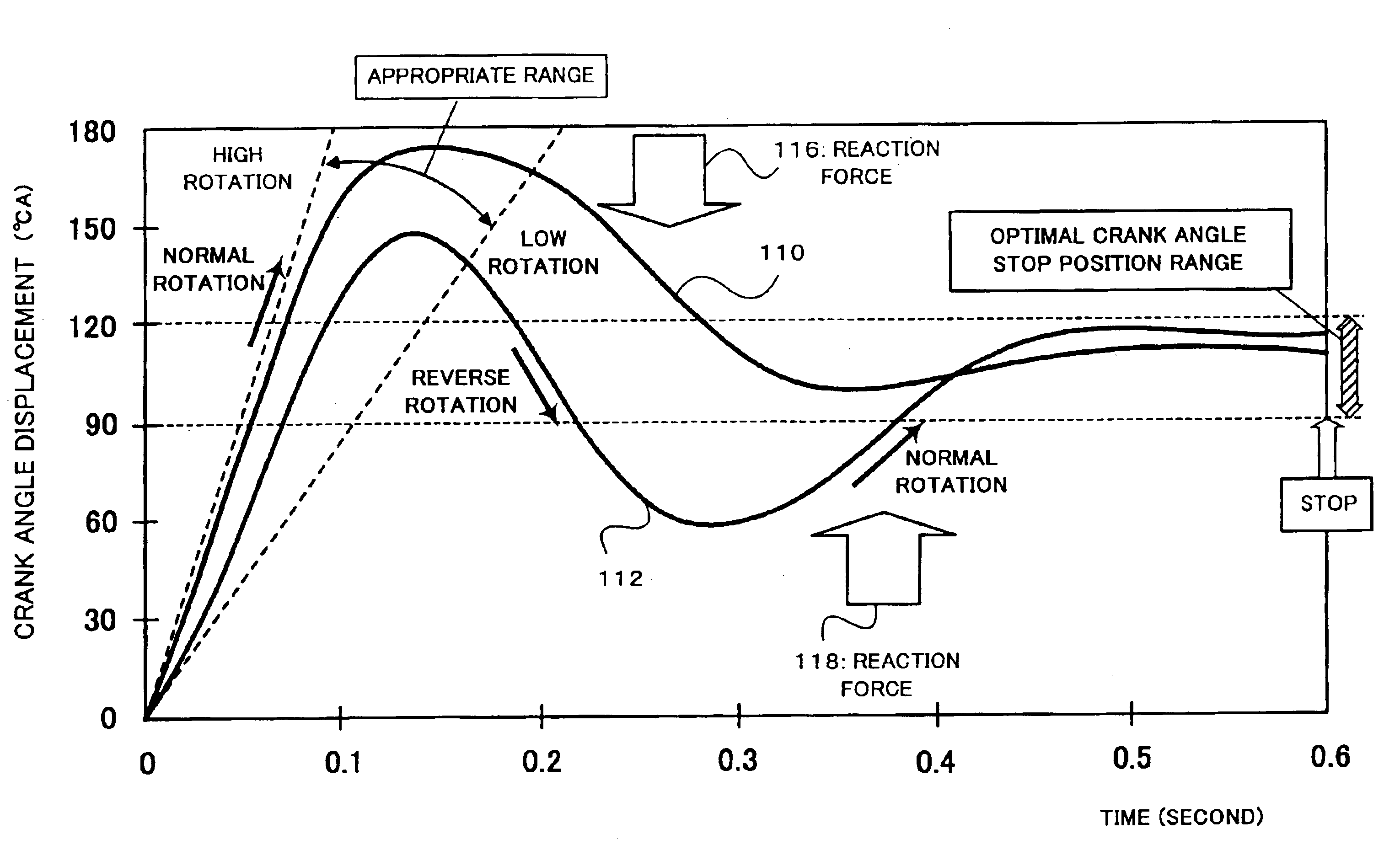
System for restarting internal combustion engine when engine restart condition is met
ActiveUS20100180849A1Improve accuracyImprove noiseAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersExternal combustion engineRotation velocity
In a system, an angle sensor outputs a pulse each time an output shaft of an internal combustion engine rotates by a preset angle, and a calculator calculates speed-change information indicative of a change in a speed of rotation of the output shaft based on the pulses outputted from the angle sensor. A determiner determines, based on the speed-change information, whether at least one of the pulses outputted from the angle sensor represents a proper timing for a preset of a pinion of a starter with a ring gear mounted on the output shaft. A pinion engaging unit shifts the pinion toward the ring gear so that the pinion is engaged with the ring gear when it is determined that the at least one of the pulses outputted from the angle sensor represents the proper timing for the preset of the pinion with the ring gear.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Engine based kinetic energy recovery system for vehicles
ActiveUS6922997B1Improve efficiencyEfficient use ofPower operated startersElectrical controlAir compressionHigh pressure
A motor vehicle kinetic energy recovery system uses one or more cylinders of an internal combustion engine as the first or primary stage in a multi-stage high pressure air compression system, a compressed air storage system, compressed air operated drive train boosters and vehicle management electronics to provide cooperation between the air compression, storage and booster systems. The multi-stage, high pressure air compressor system is operable through engine compression braking allowing kinetic energy of a vehicle to be recaptured during retardation of vehicle speed.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
Accessory-driving equipment for an automotive vehicle
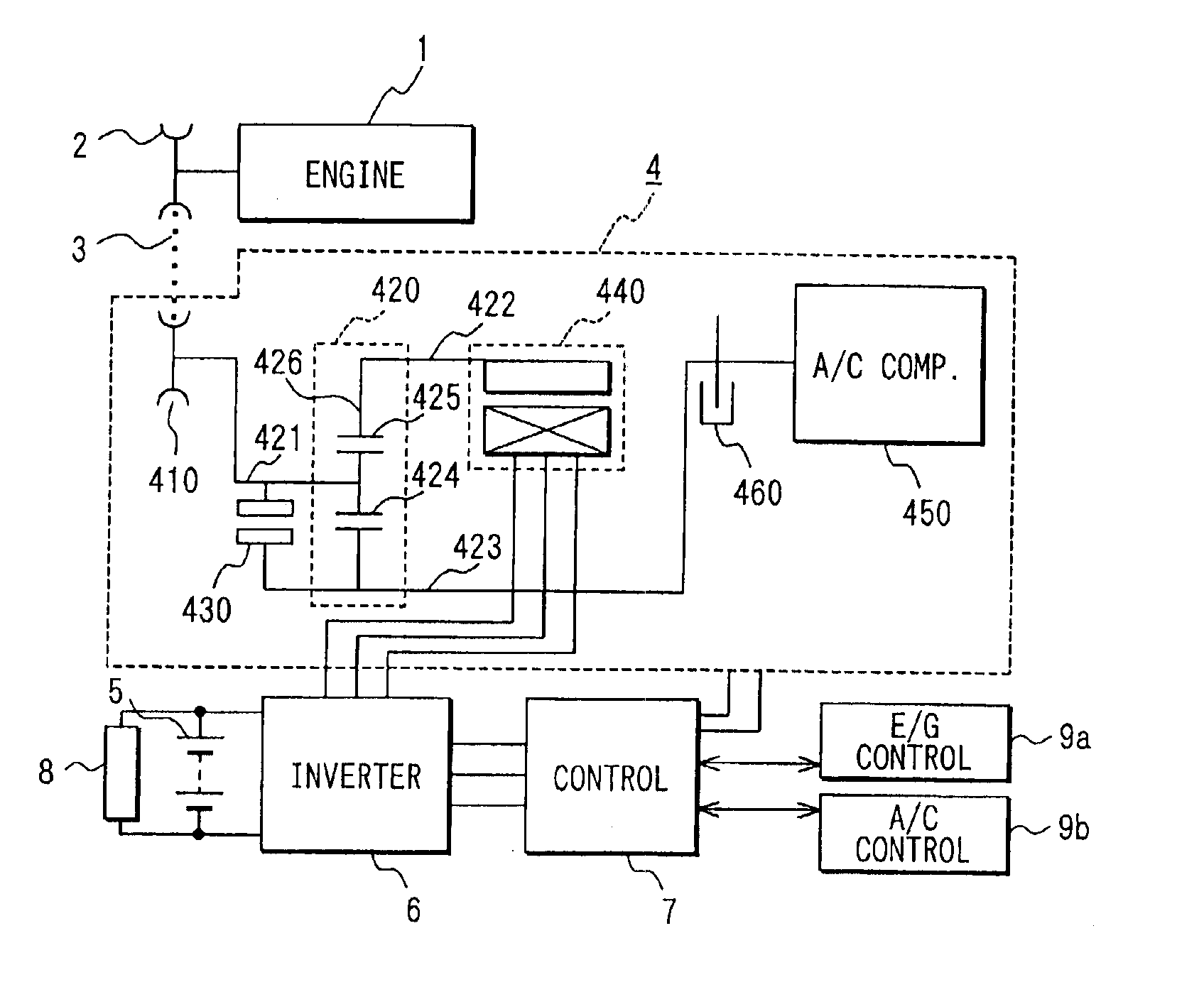
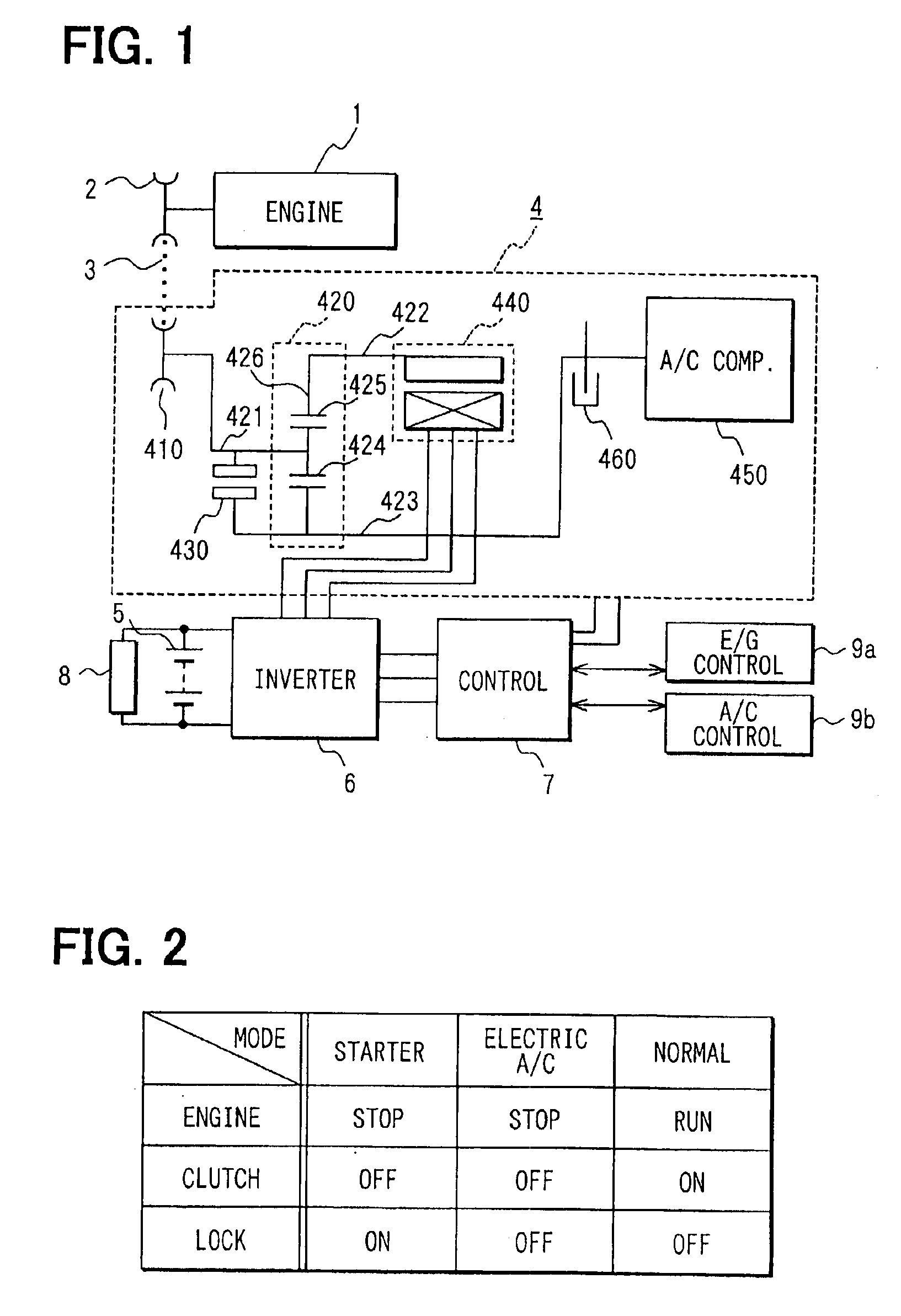
InactiveUS6863139B2Low costStable placement effectHybrid vehiclesAuxillary drivesMobile vehicleIdle speed
Accessory-driving equipment connects an engine having an idle stop system, a motor-generator and an accessory including an air-conditioner compressor that is driven even at a time when the idle stop system is operated. The accessory is driven by the engine when the engine is running and driven by the motor-generator when the idle stop system is operated. The accessory-driving equipment includes a first shaft for connecting to the engine, a second shaft for connecting to the motor-generator, a third shaft for connecting to the accessory, a lock device for locking the third shaft and a clutch. The clutch and the lock device are operated so that a torque transmitted from the engine through the first shaft is distributed to the motor-generator and the accessory, or a torque is transmitted from the motor-generator to the engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com