Patents
Literature
3294results about "Wheel based transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
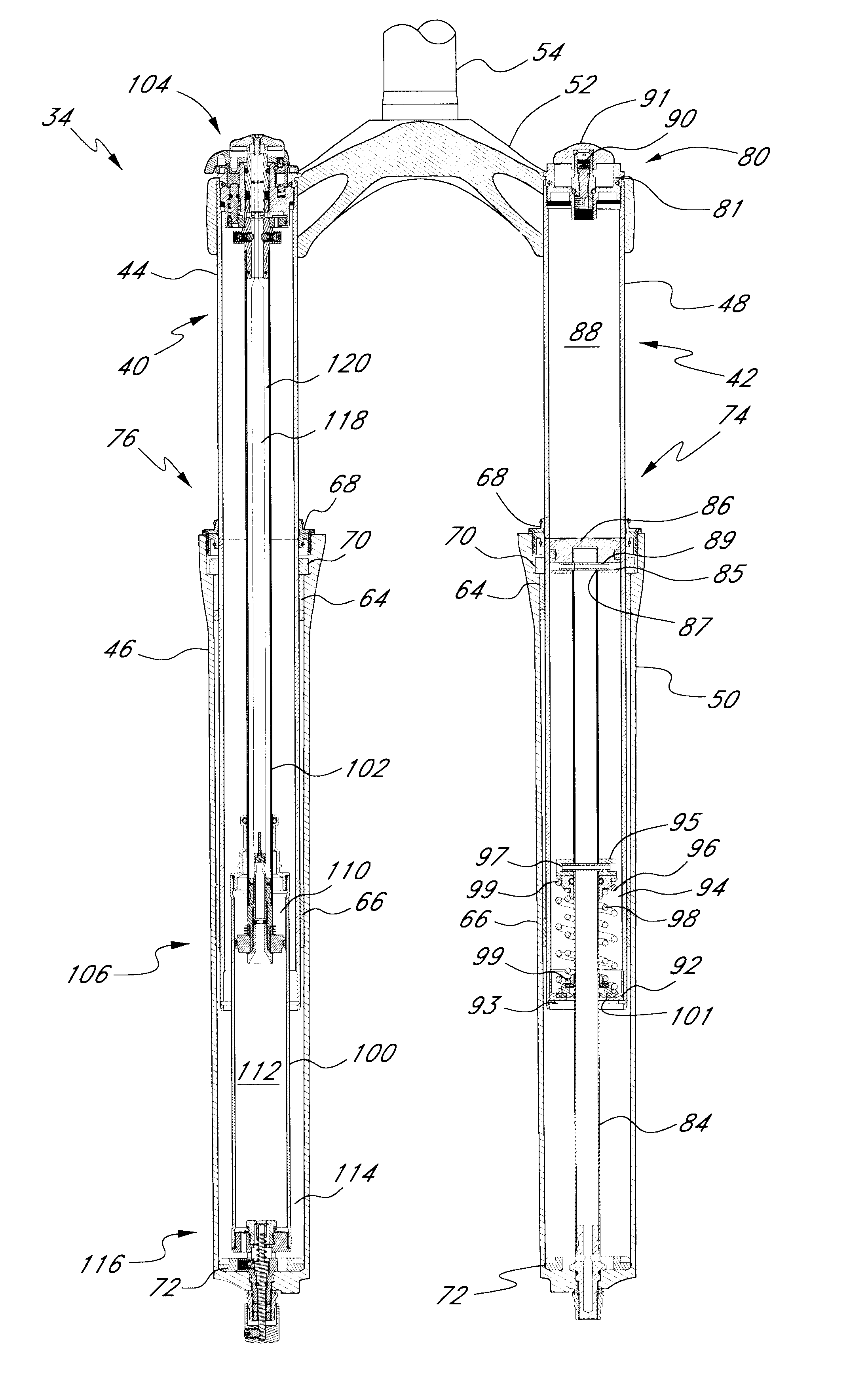
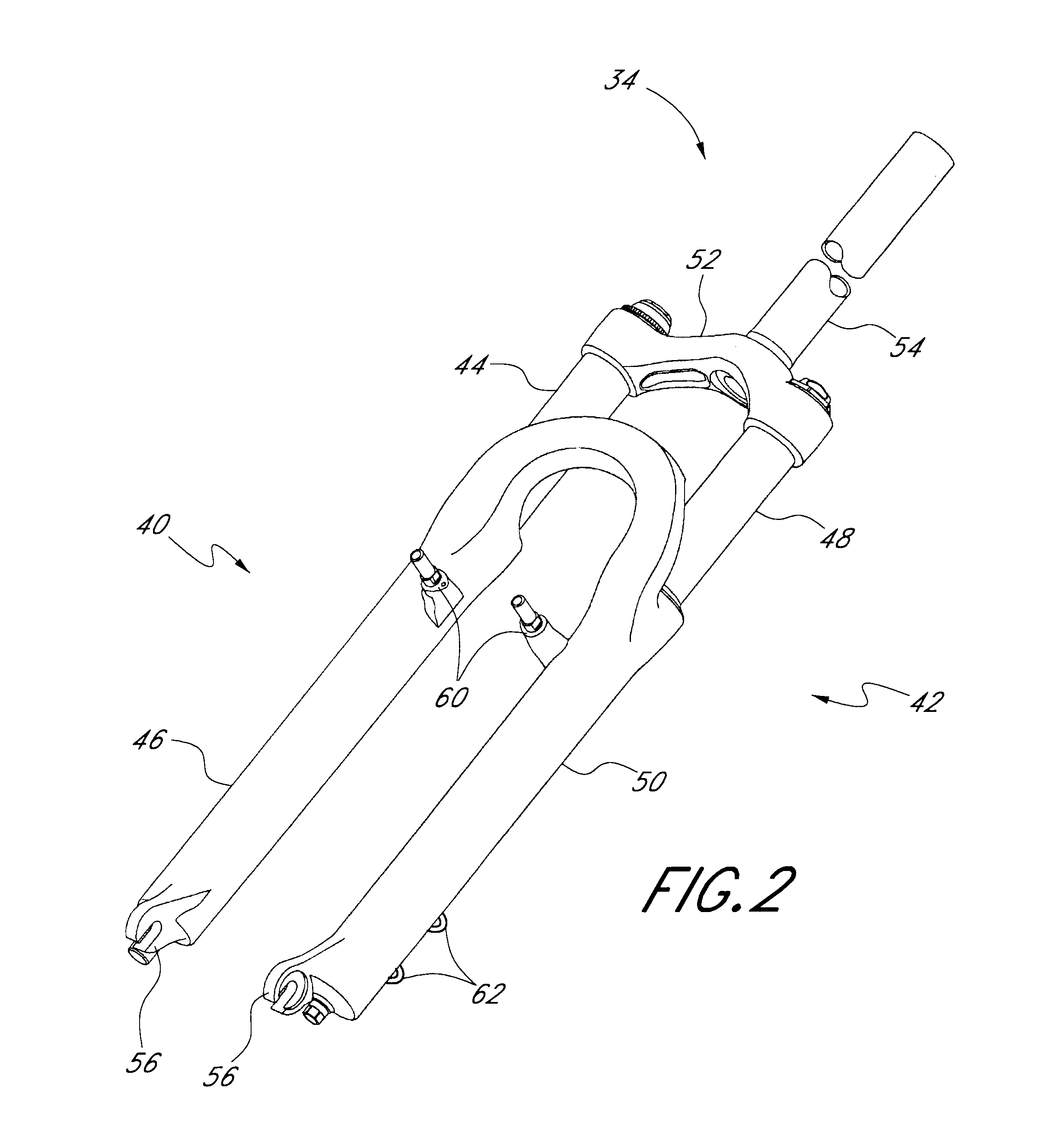
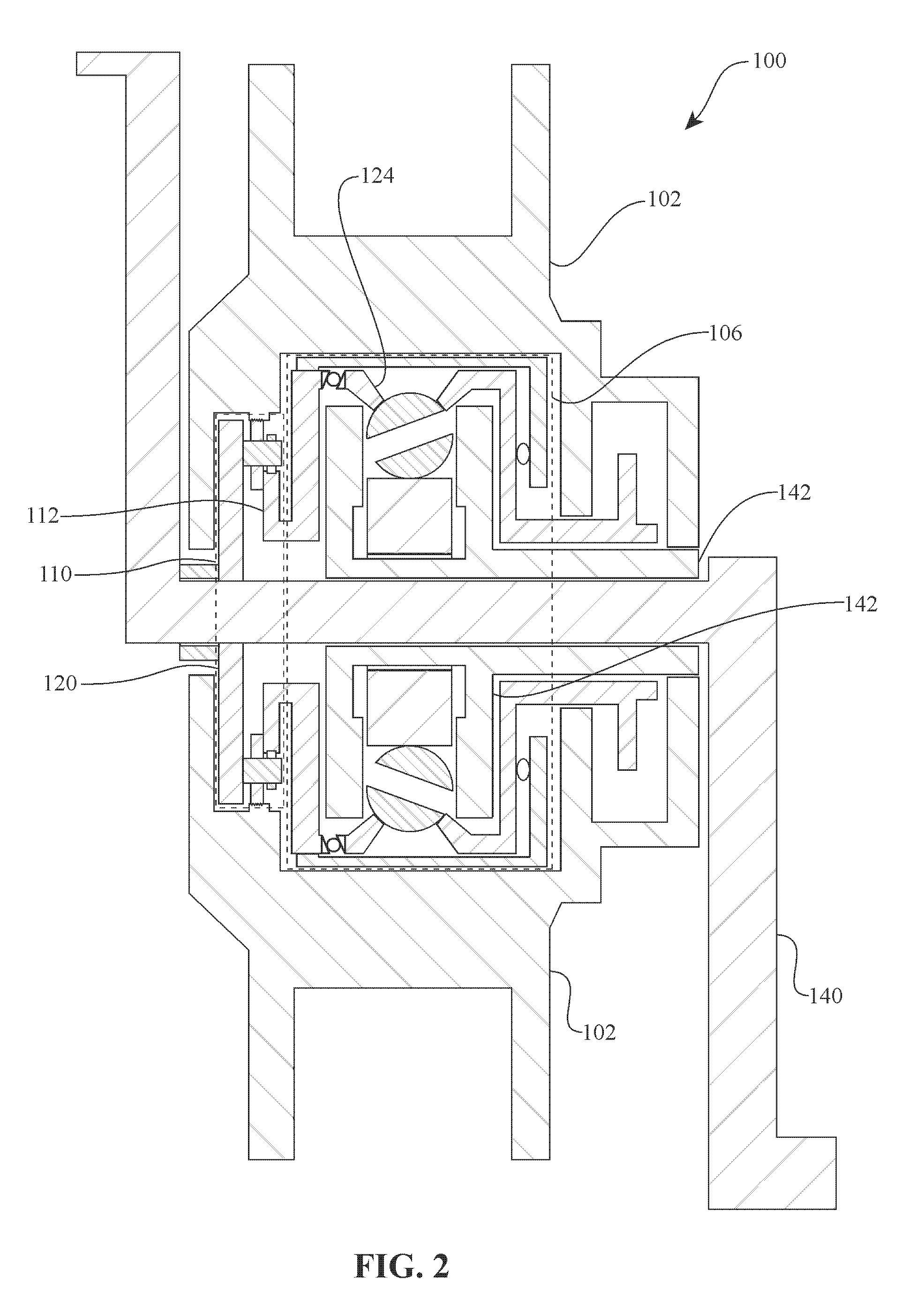
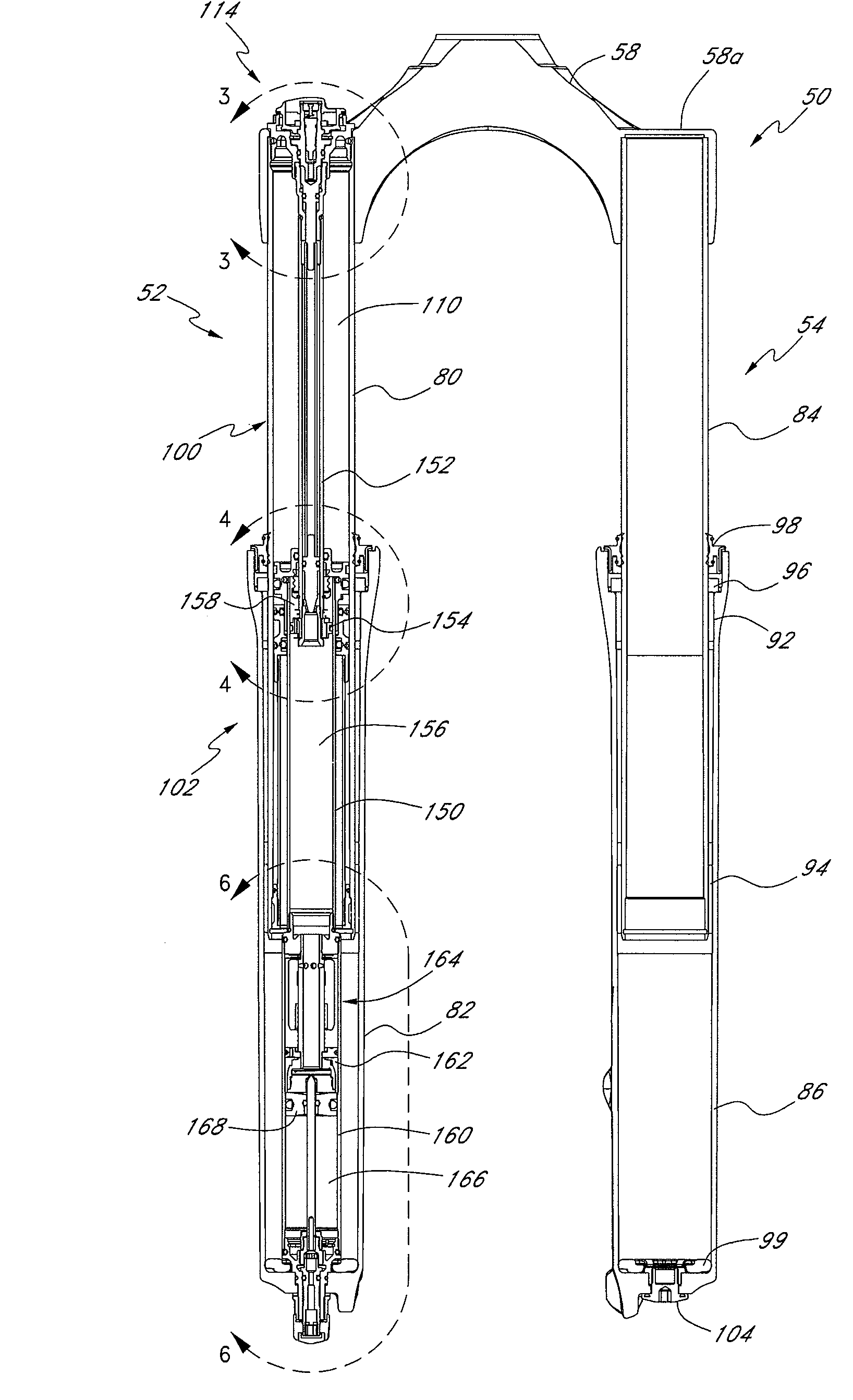
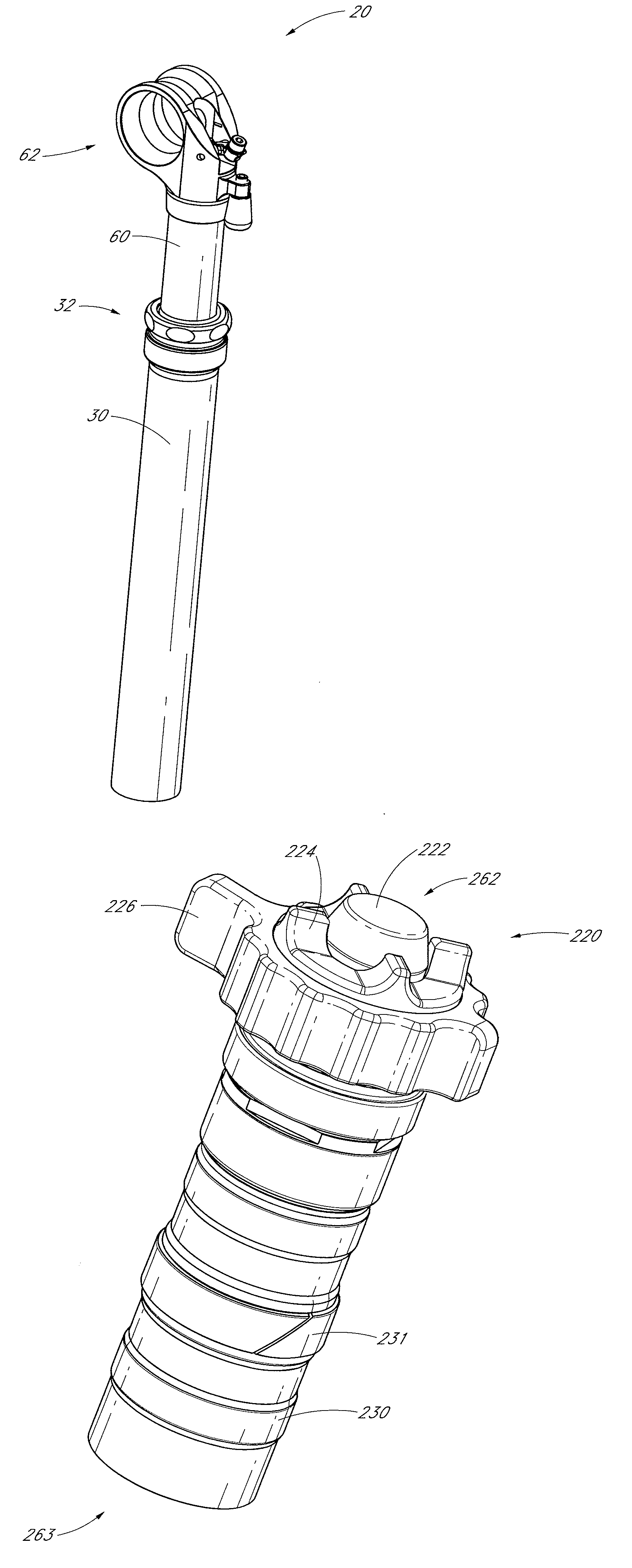
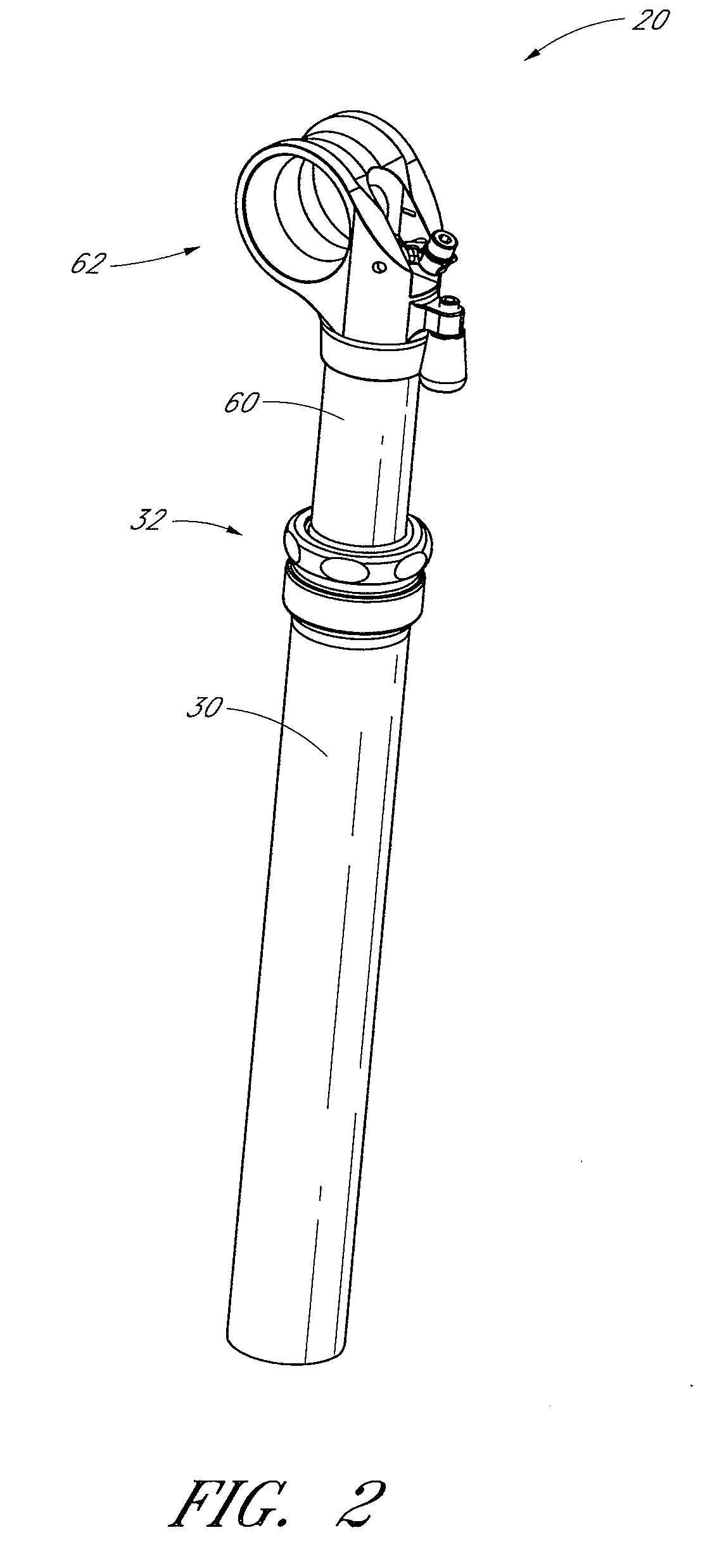
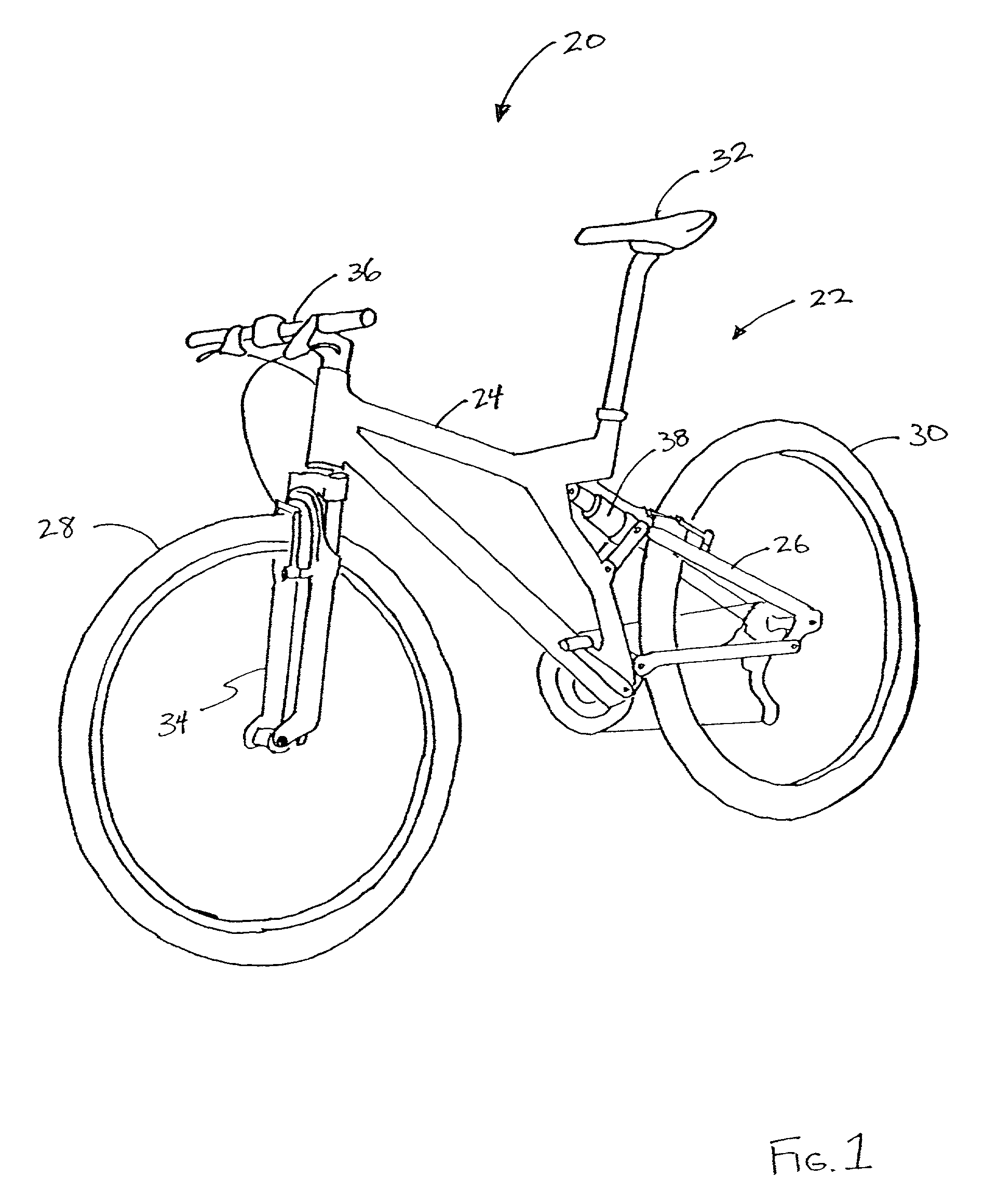
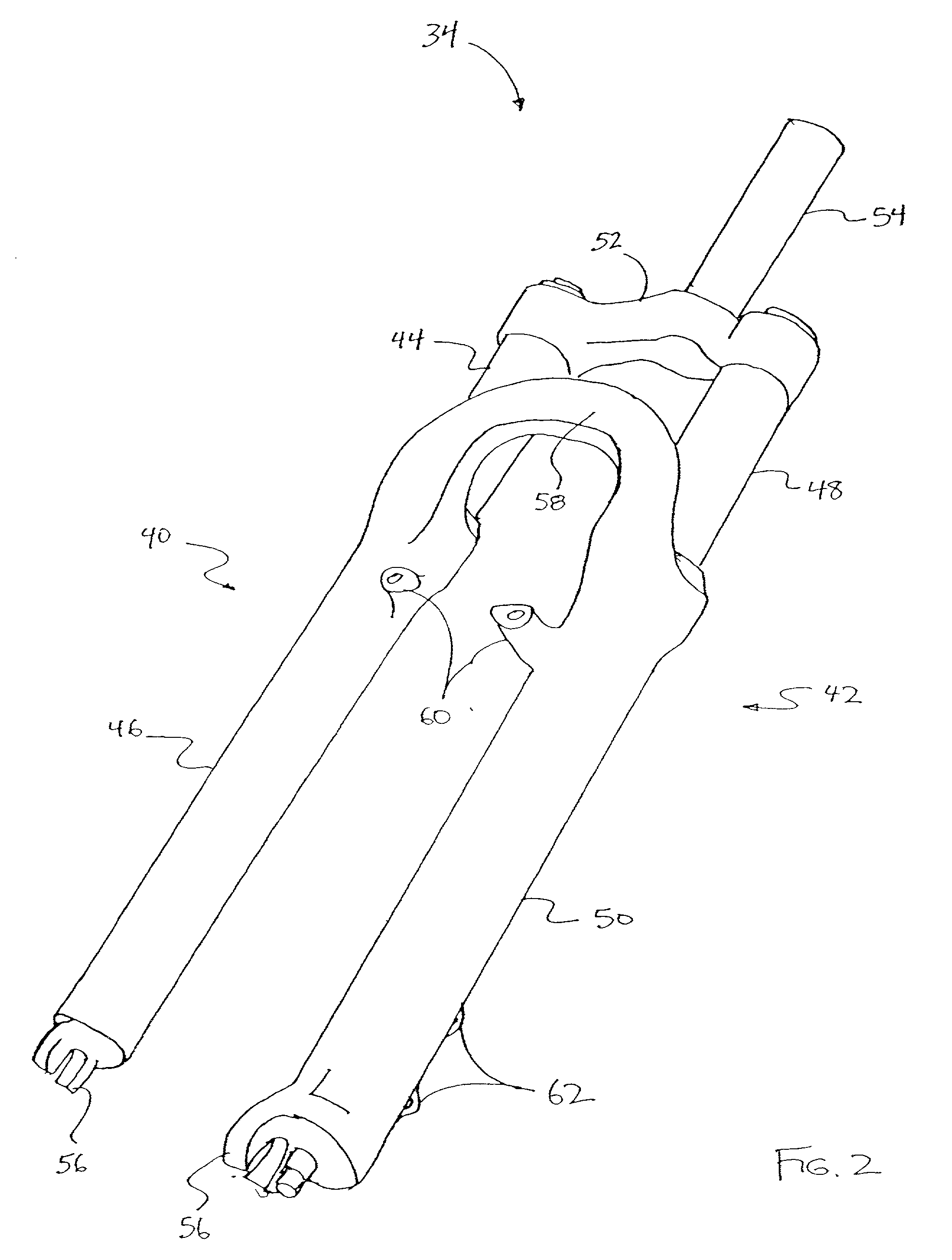
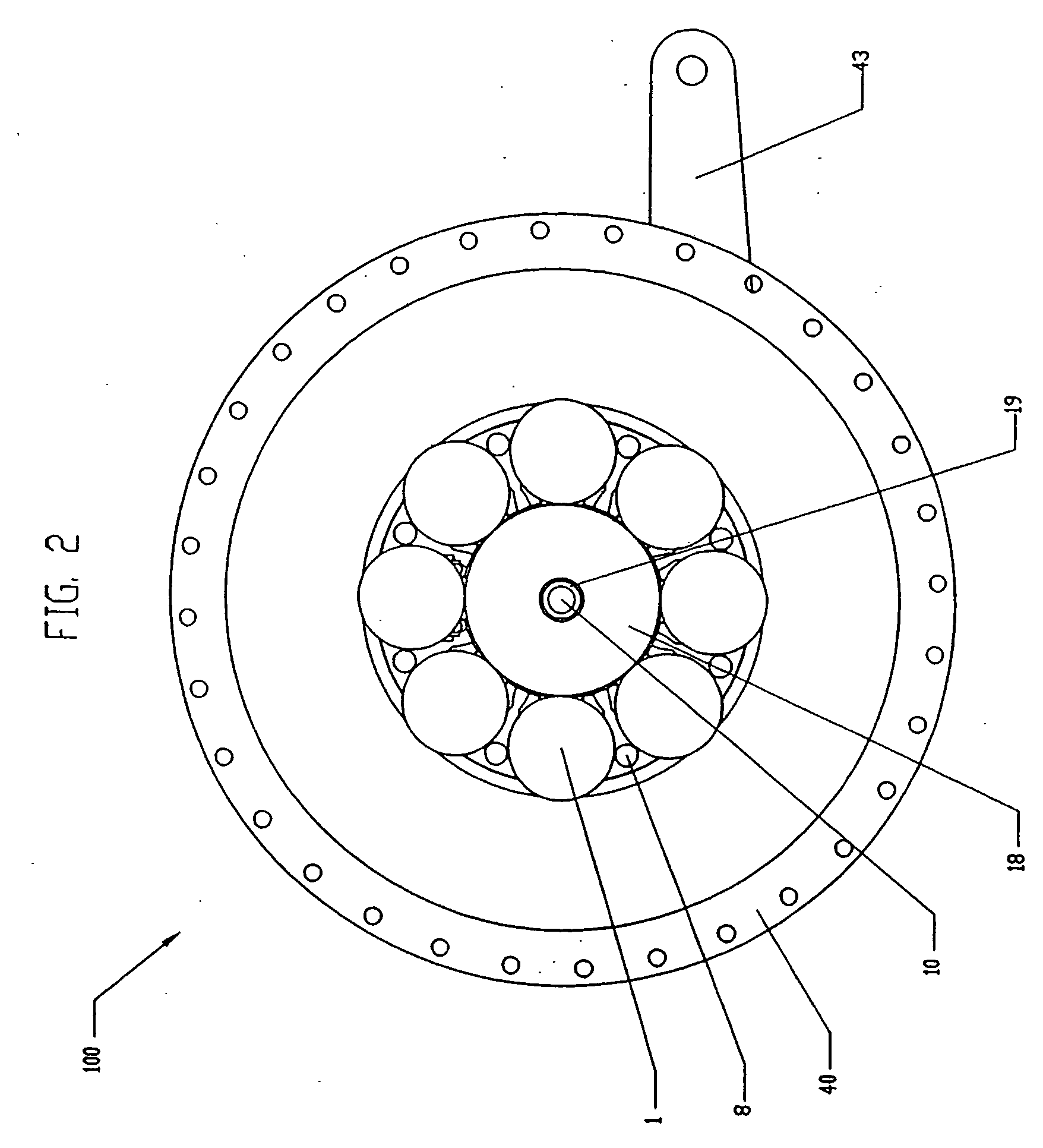
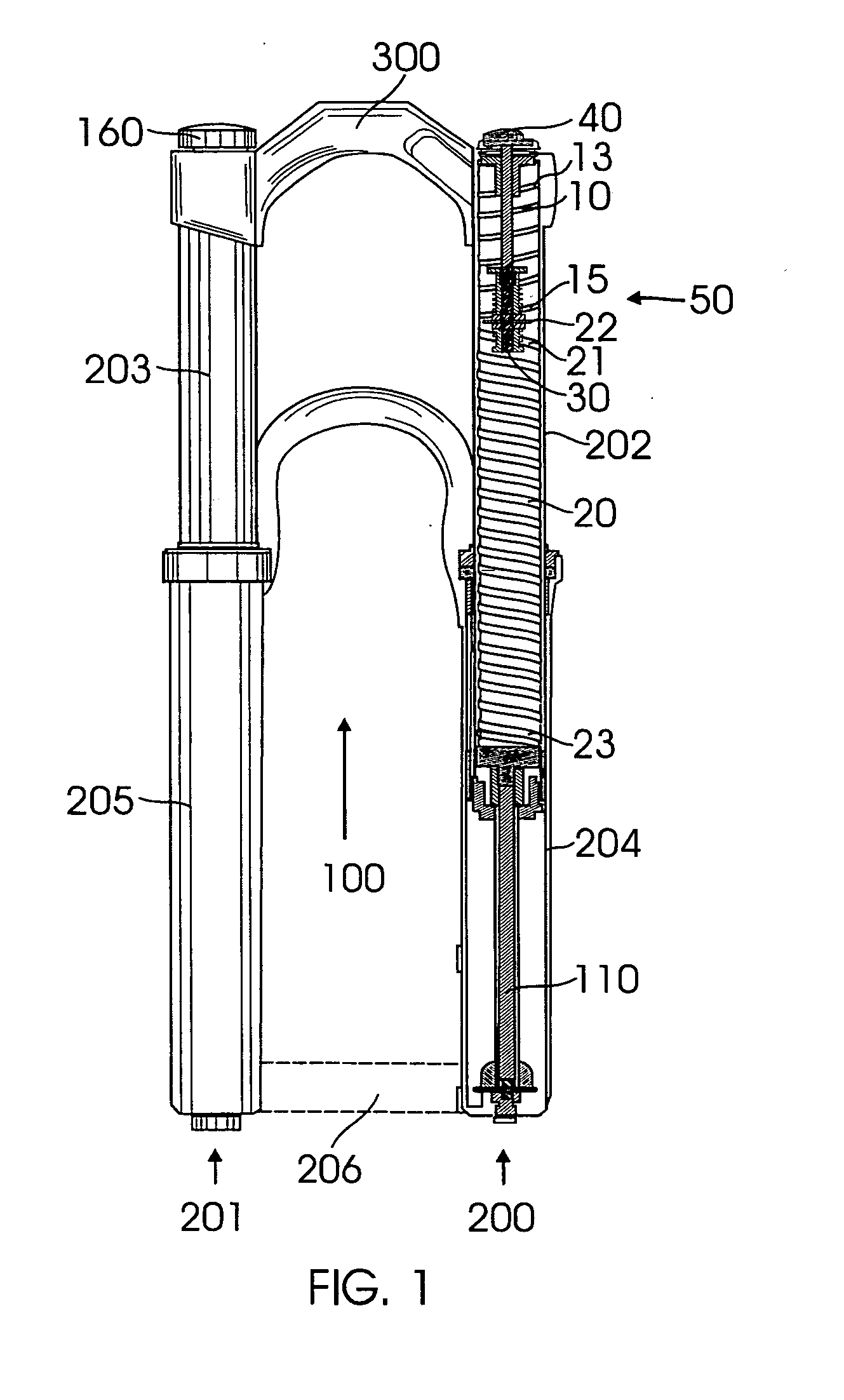
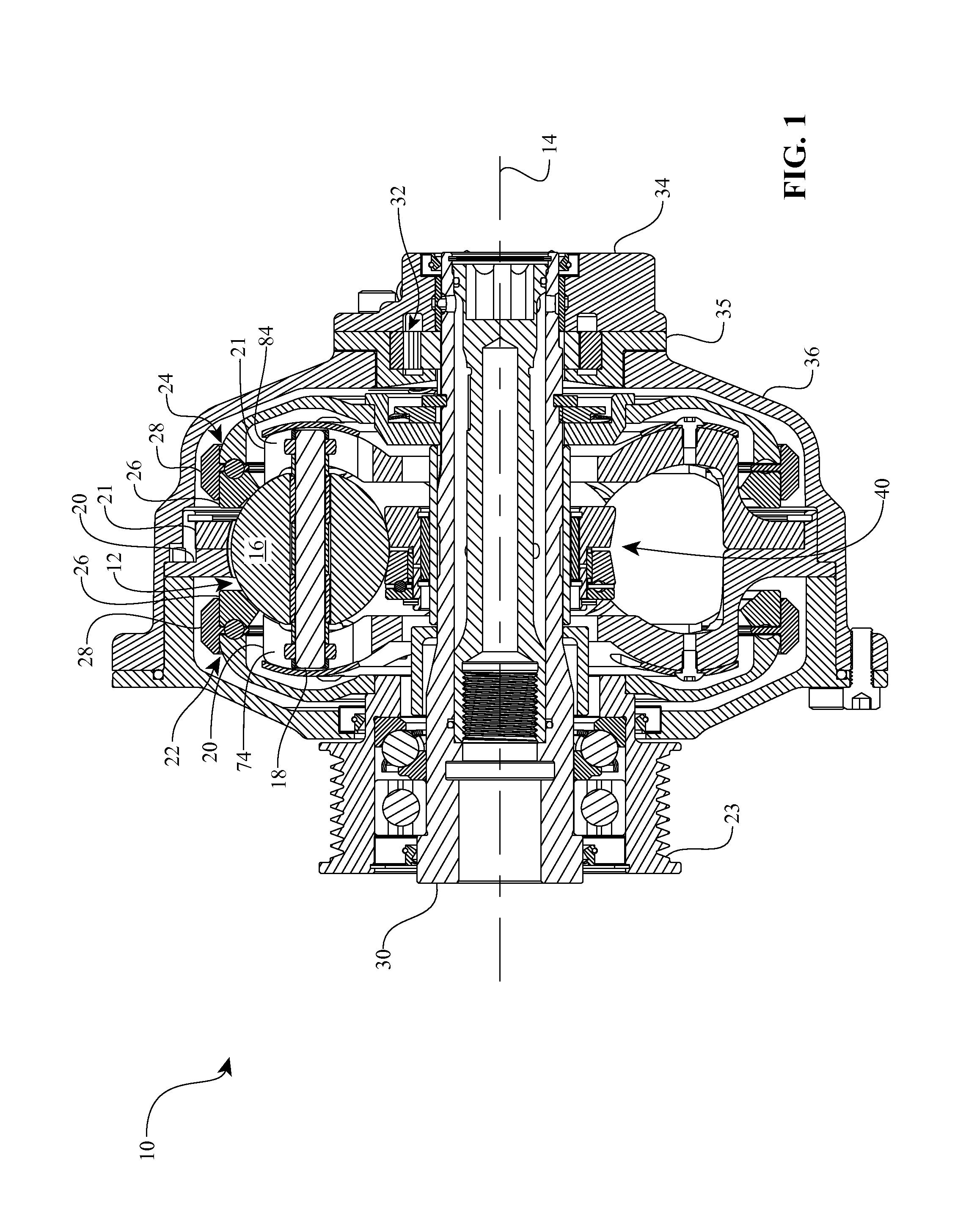
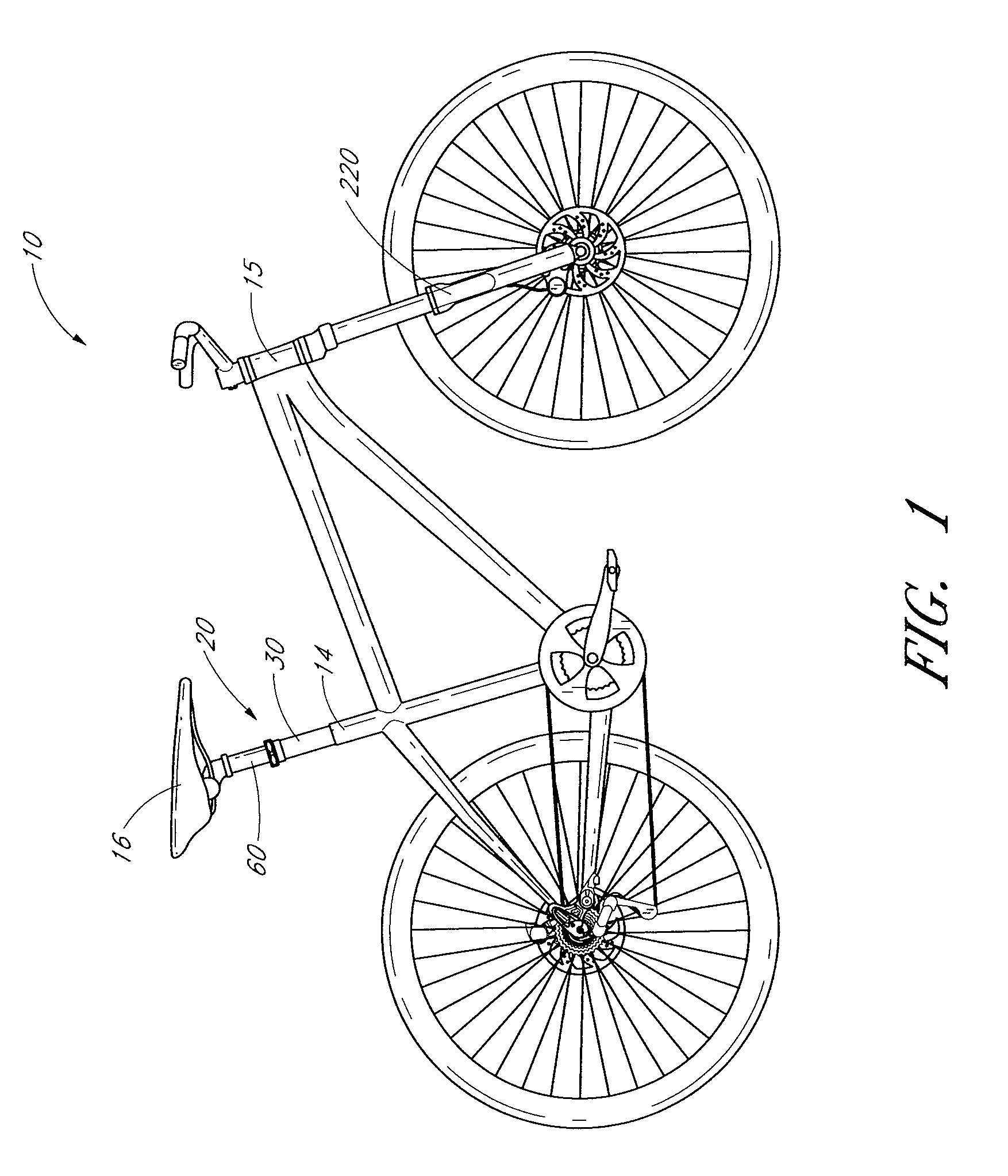
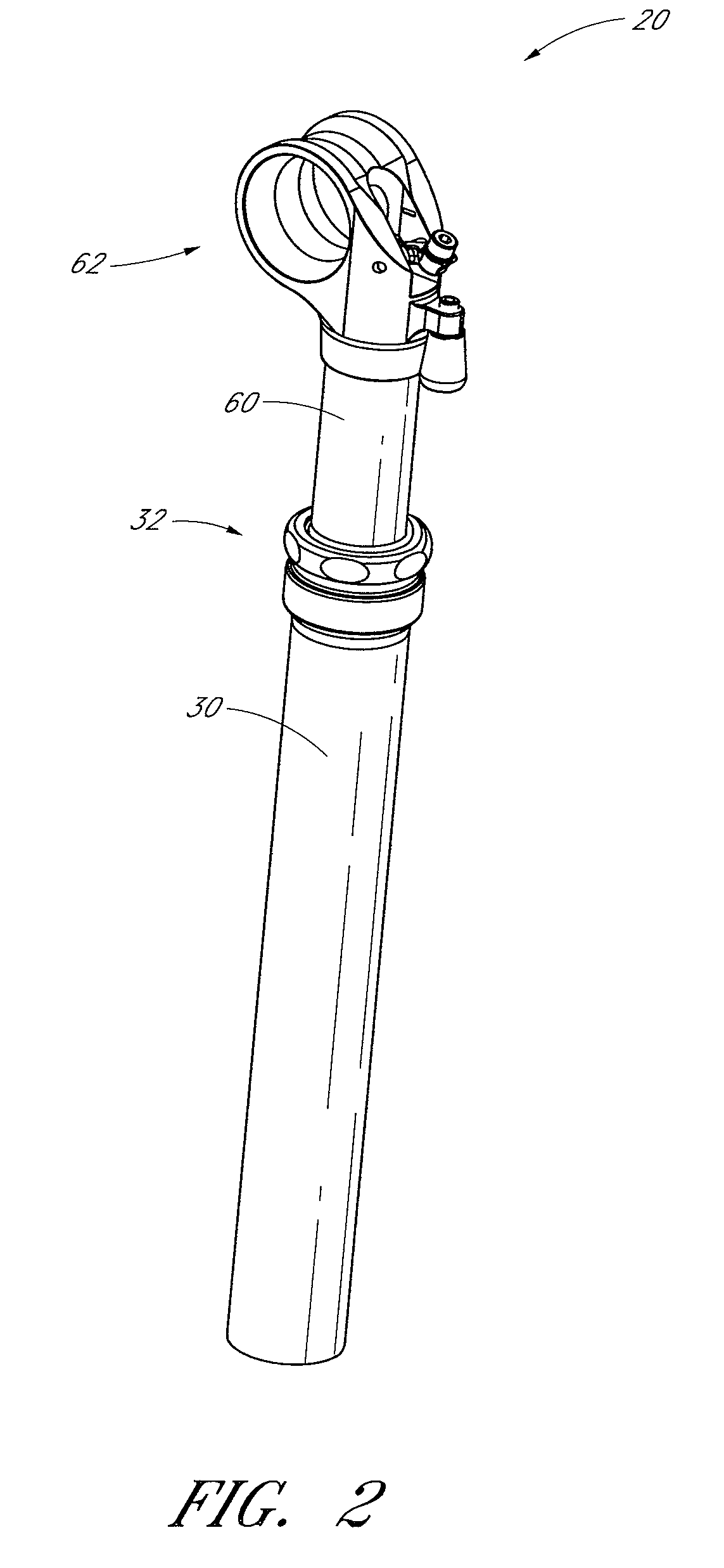
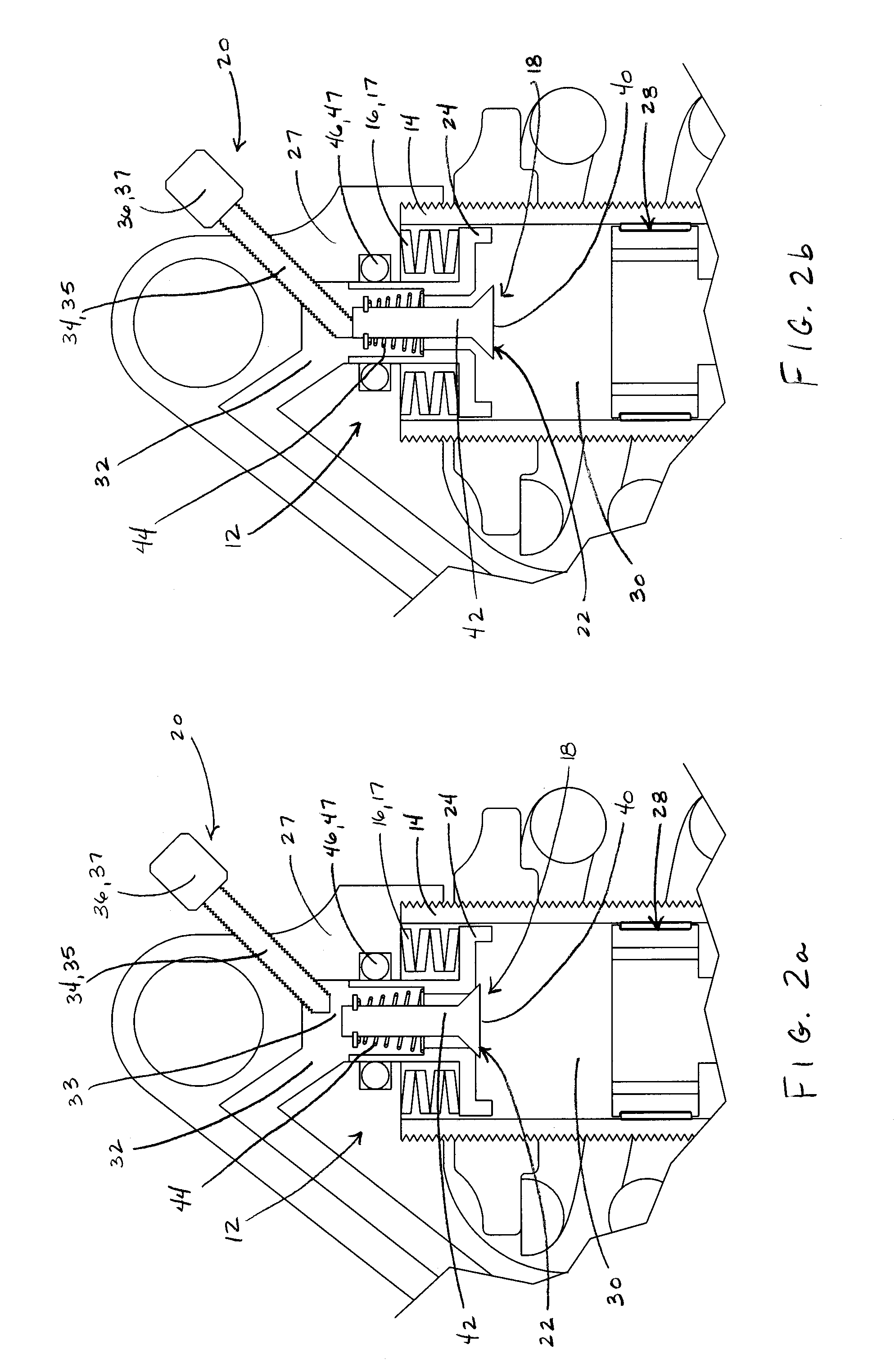
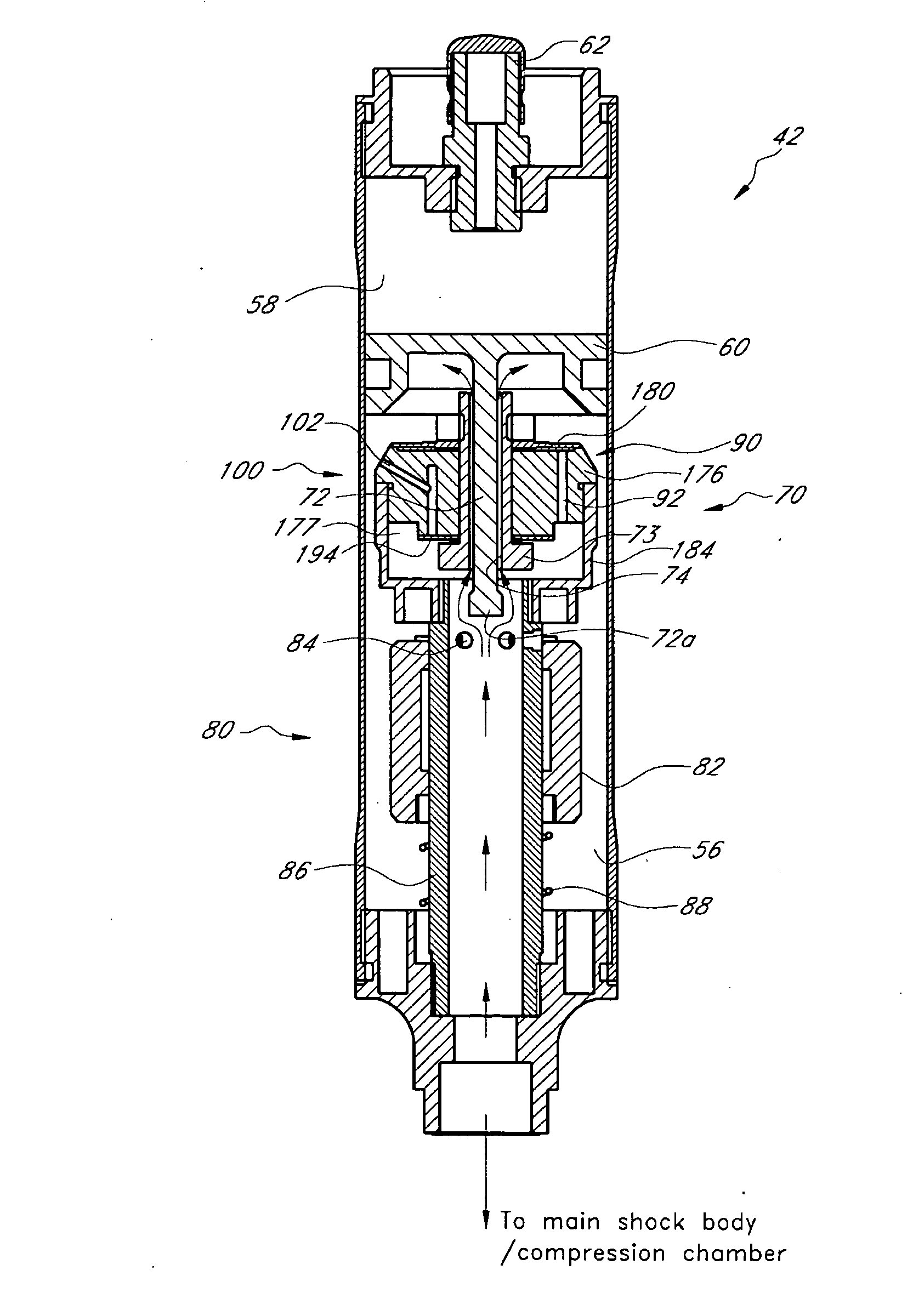
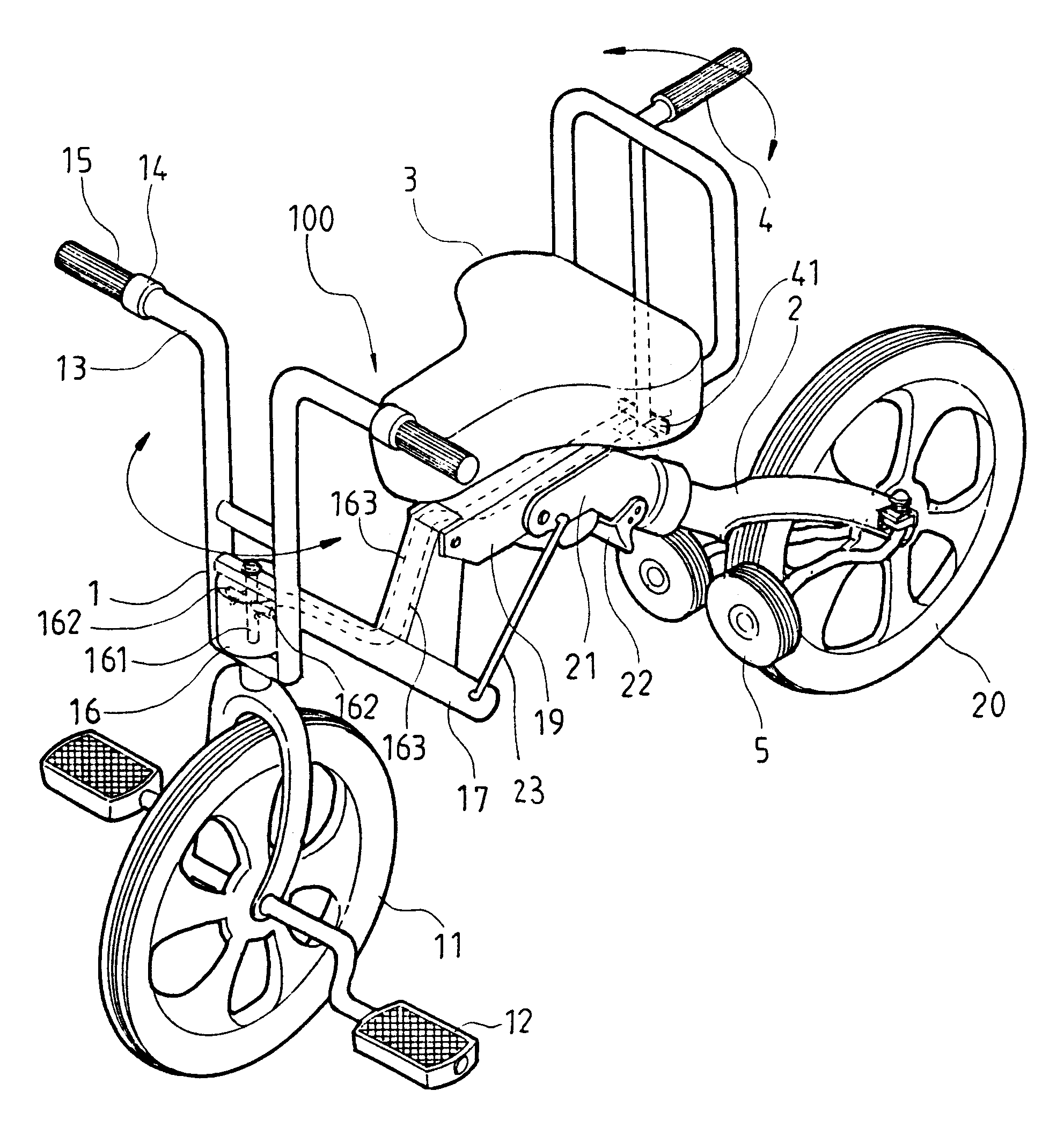
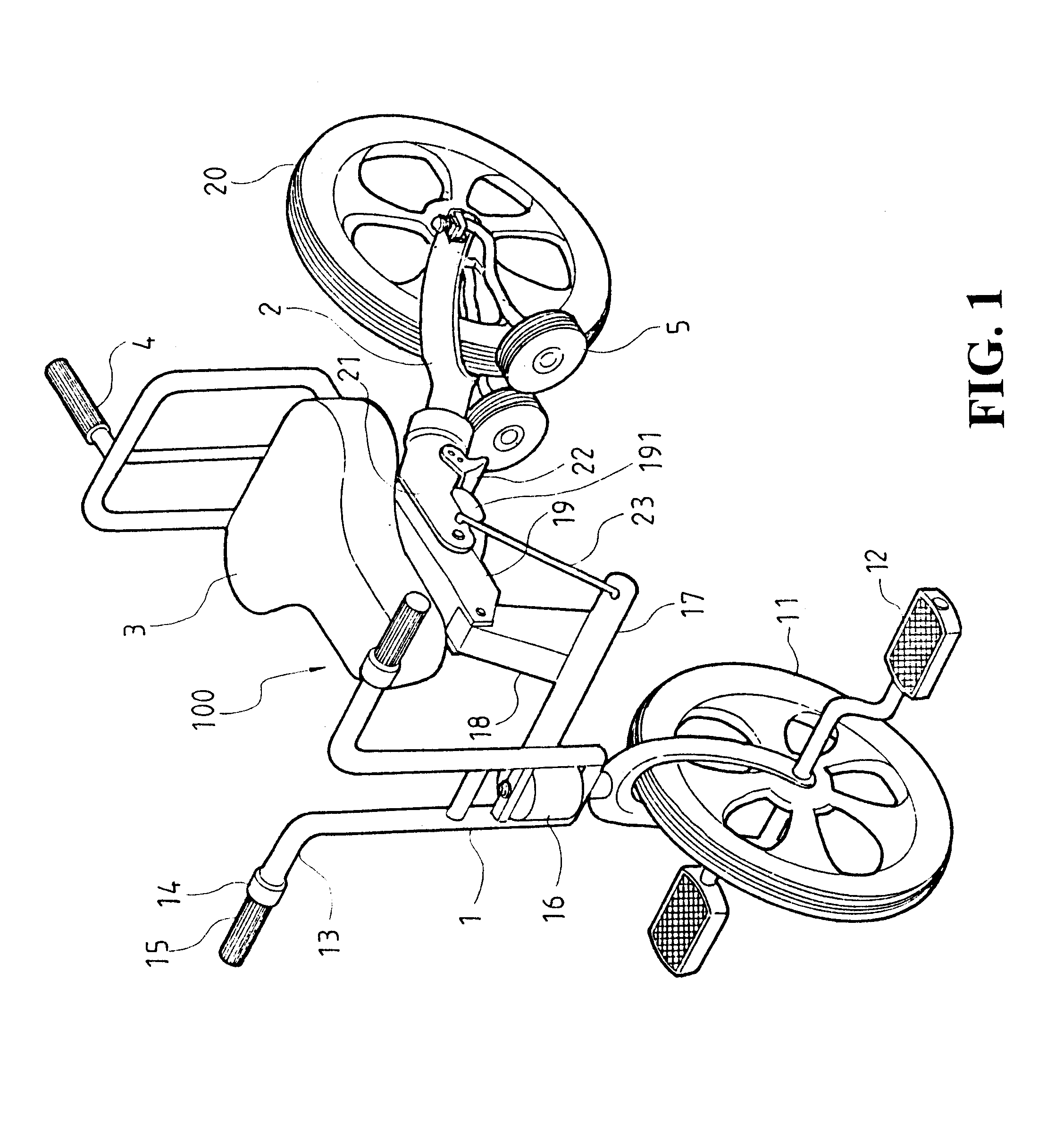
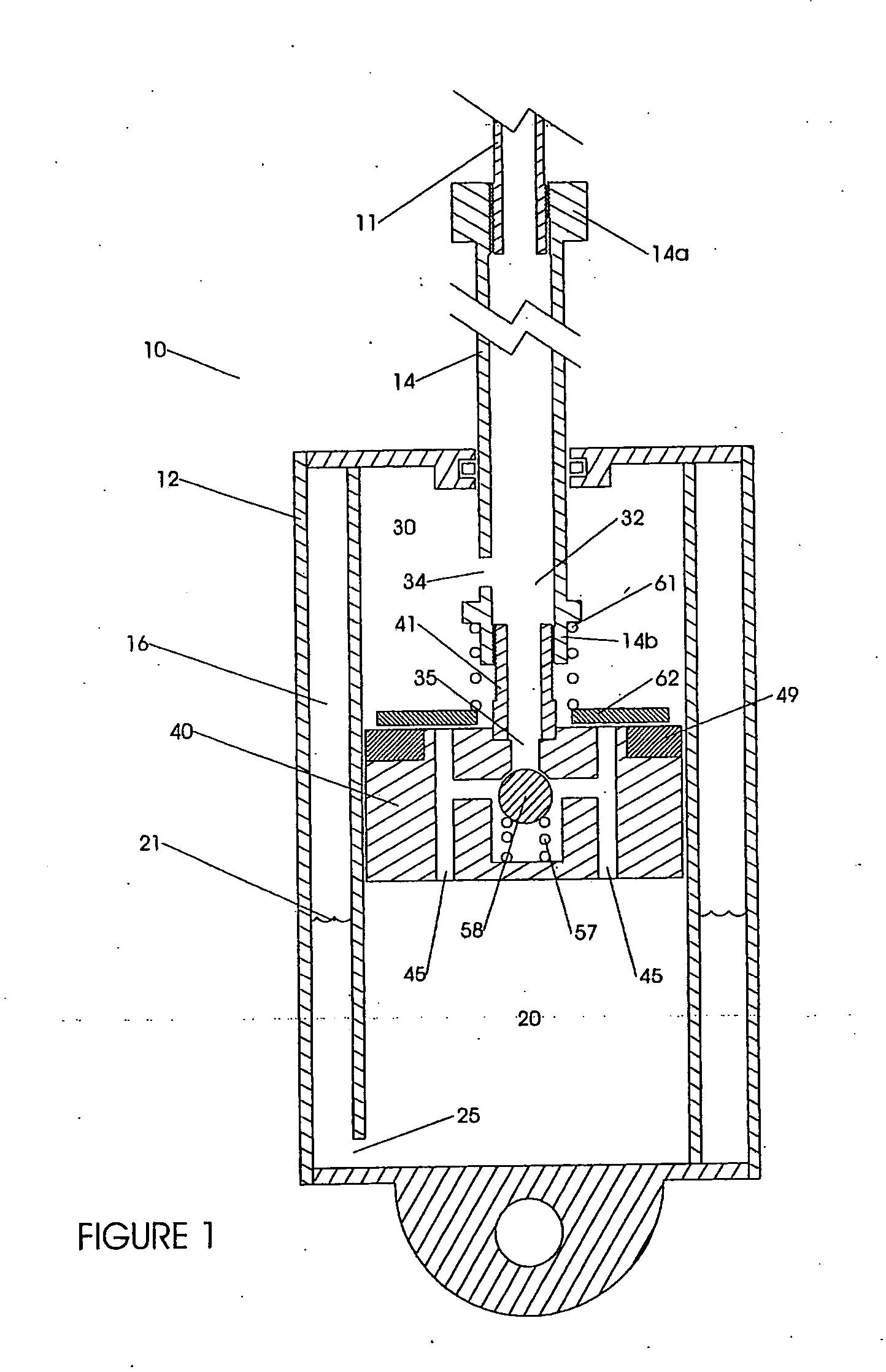
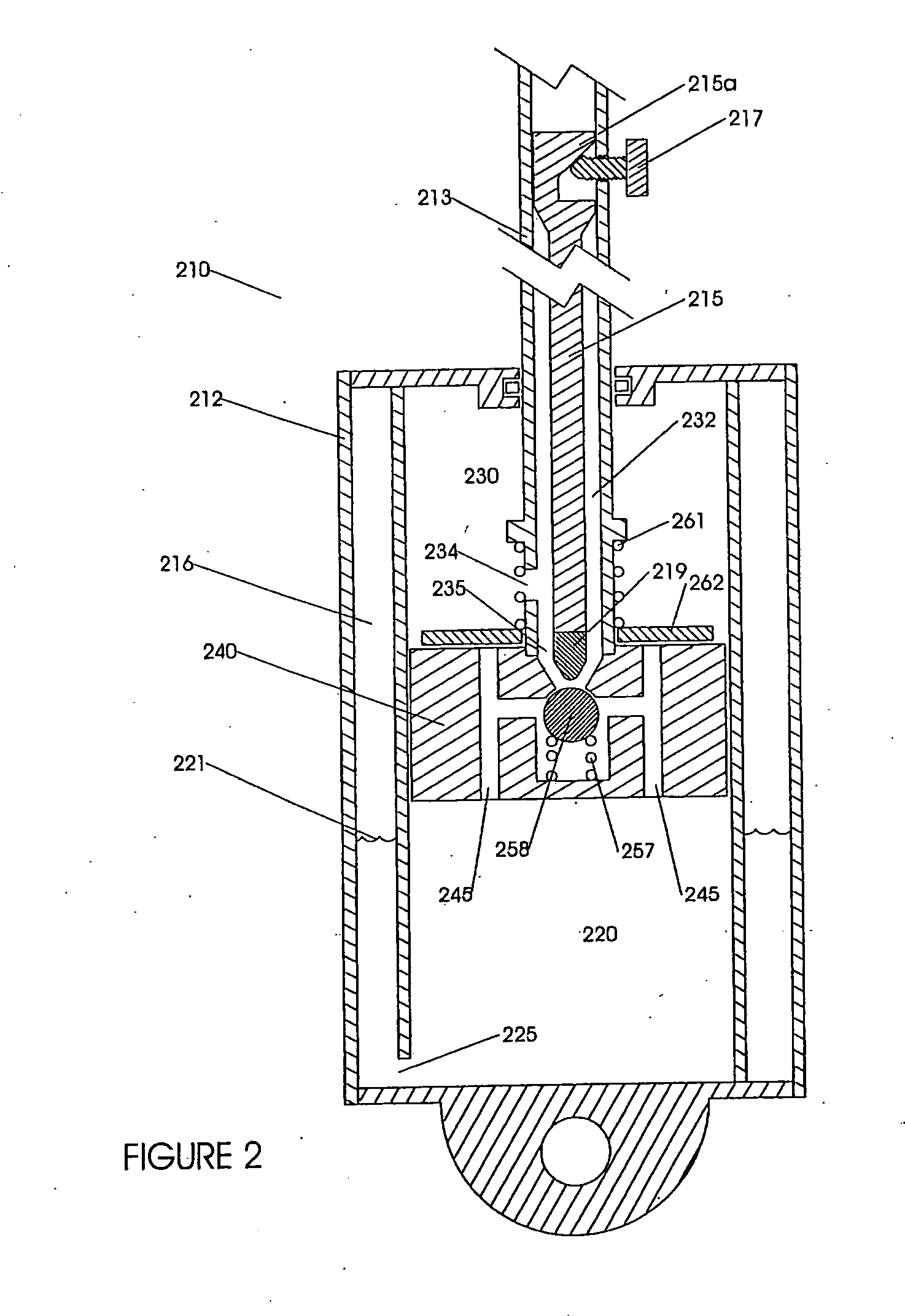
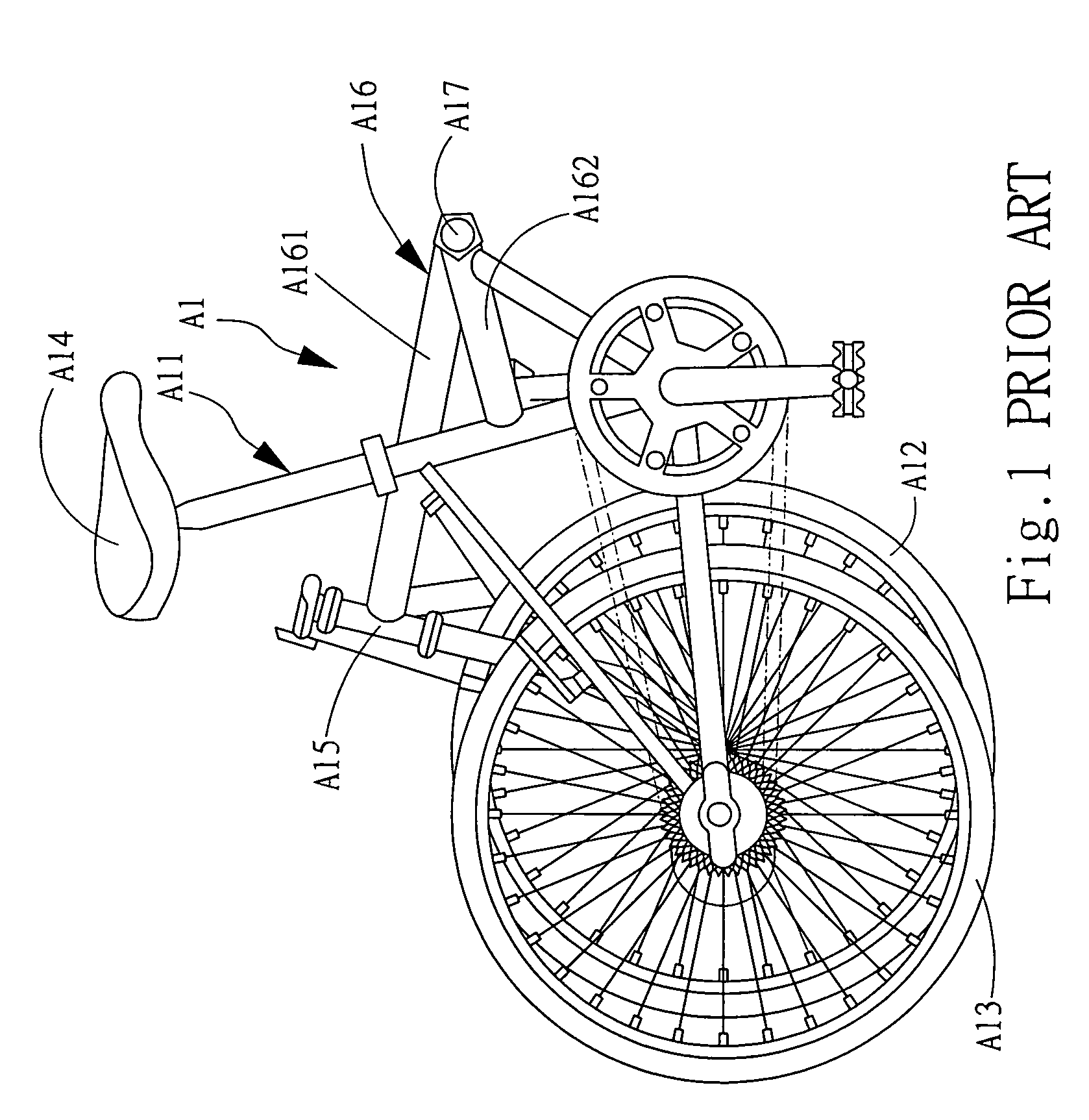
Bicycle fork cartridge assembly
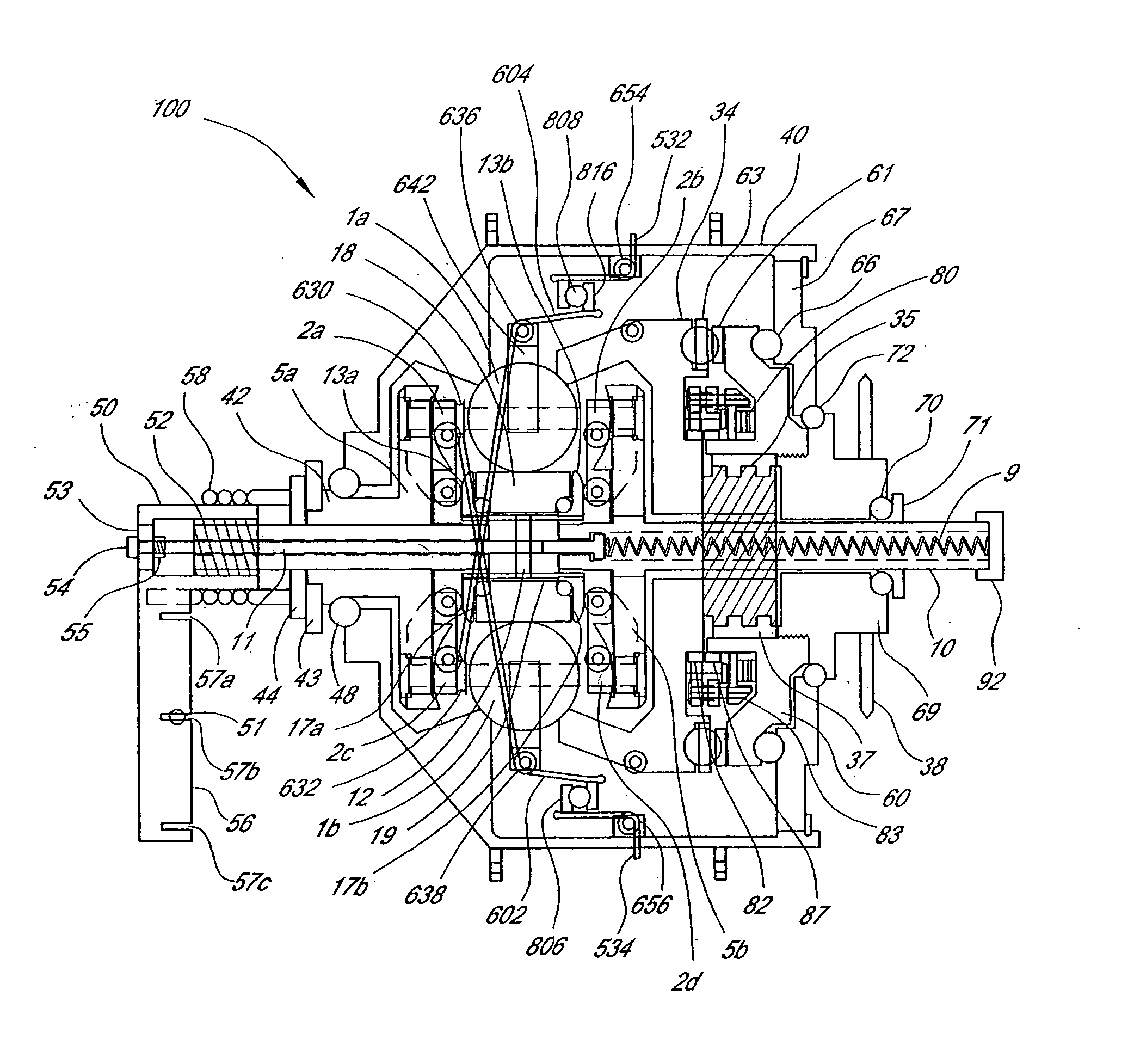
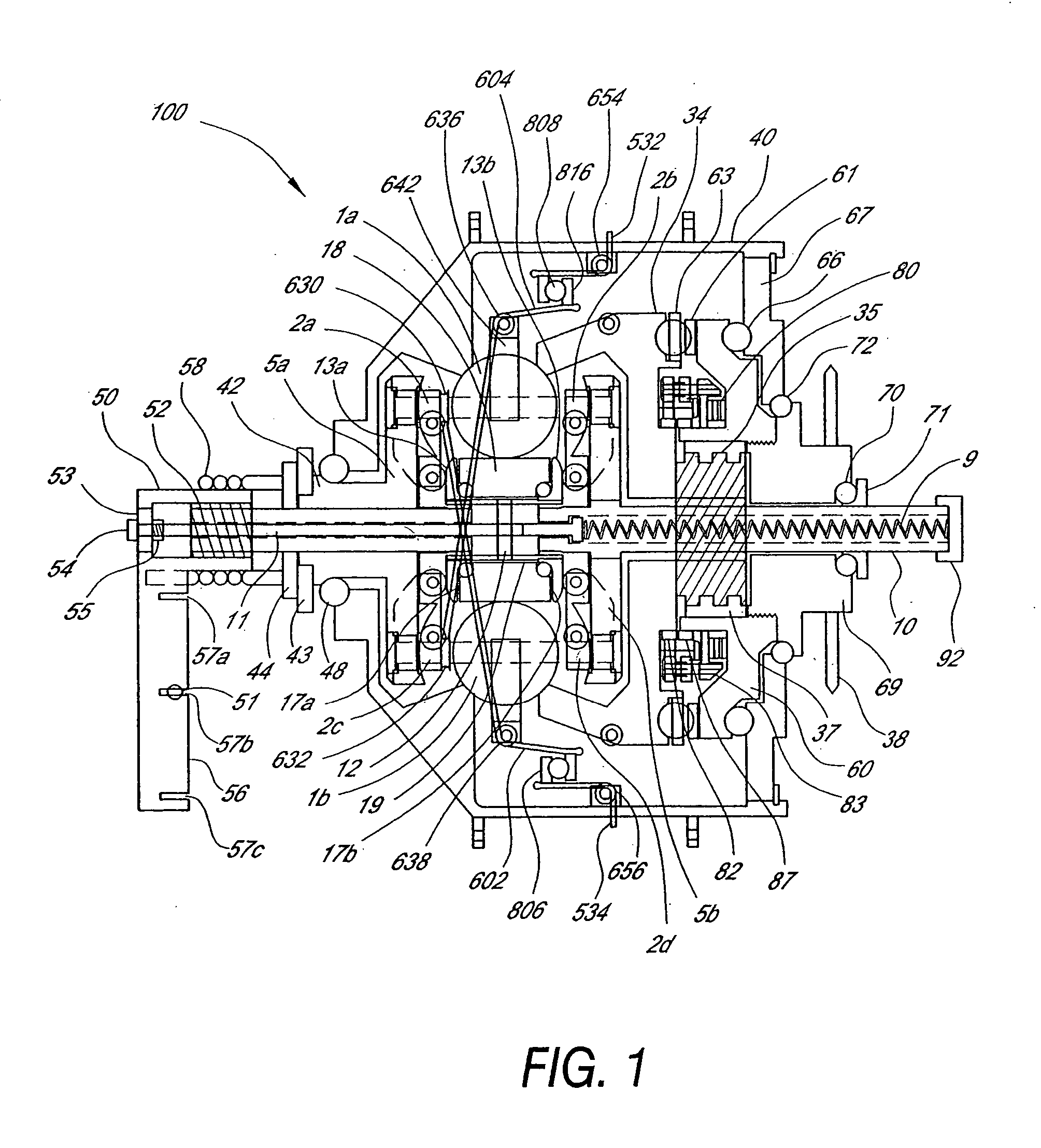
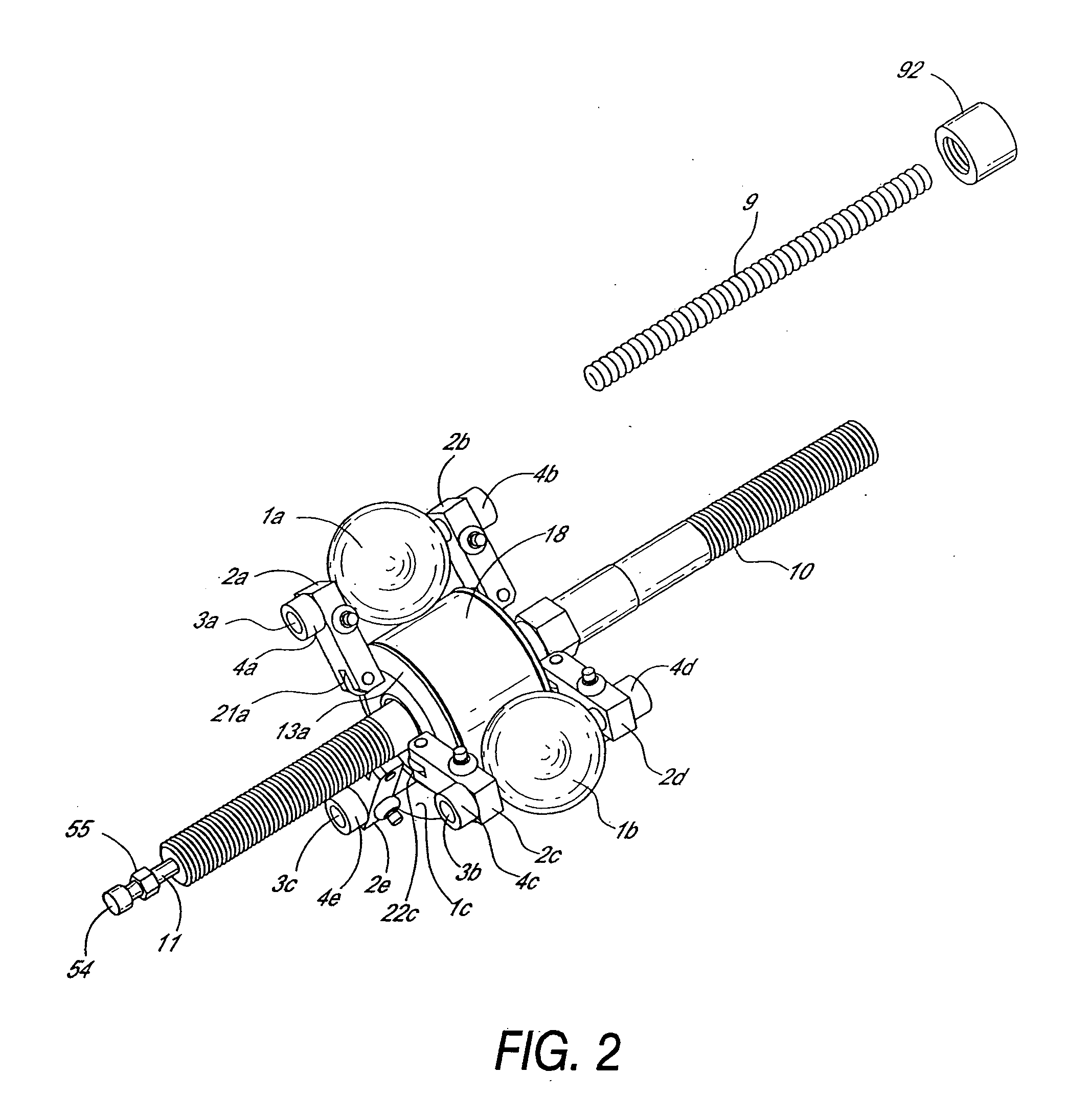
InactiveUS6592136B2Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringMechanical engineering
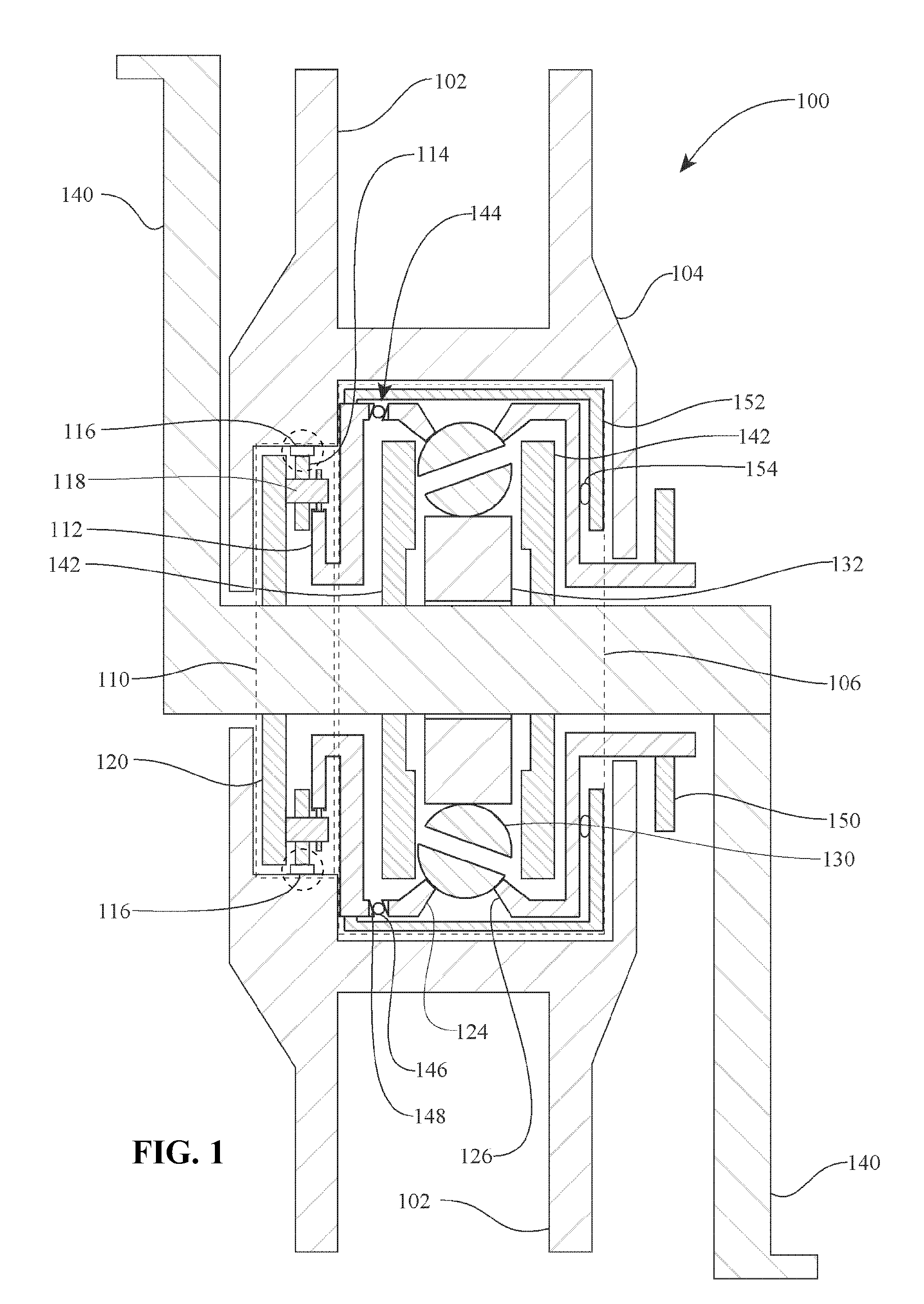
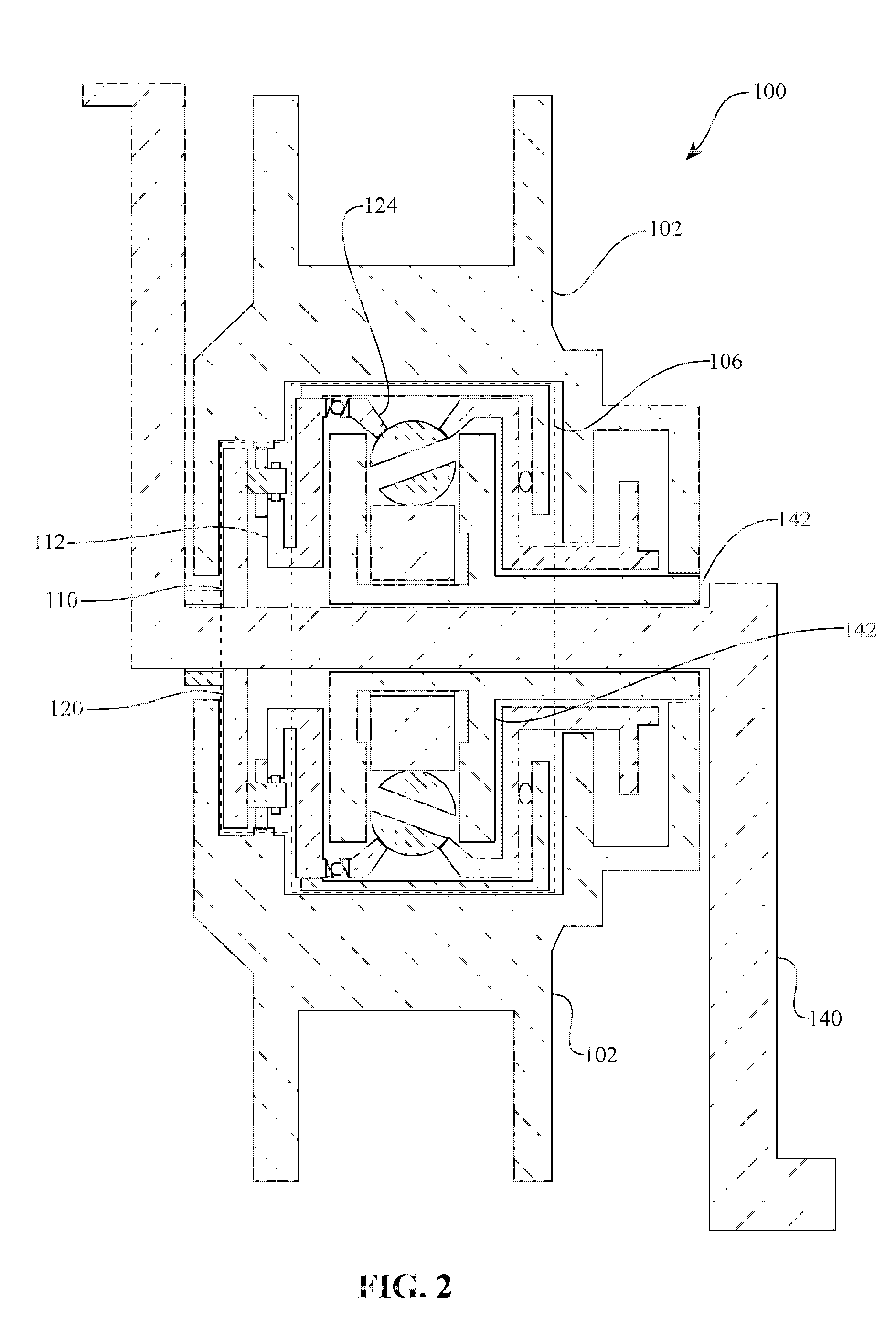
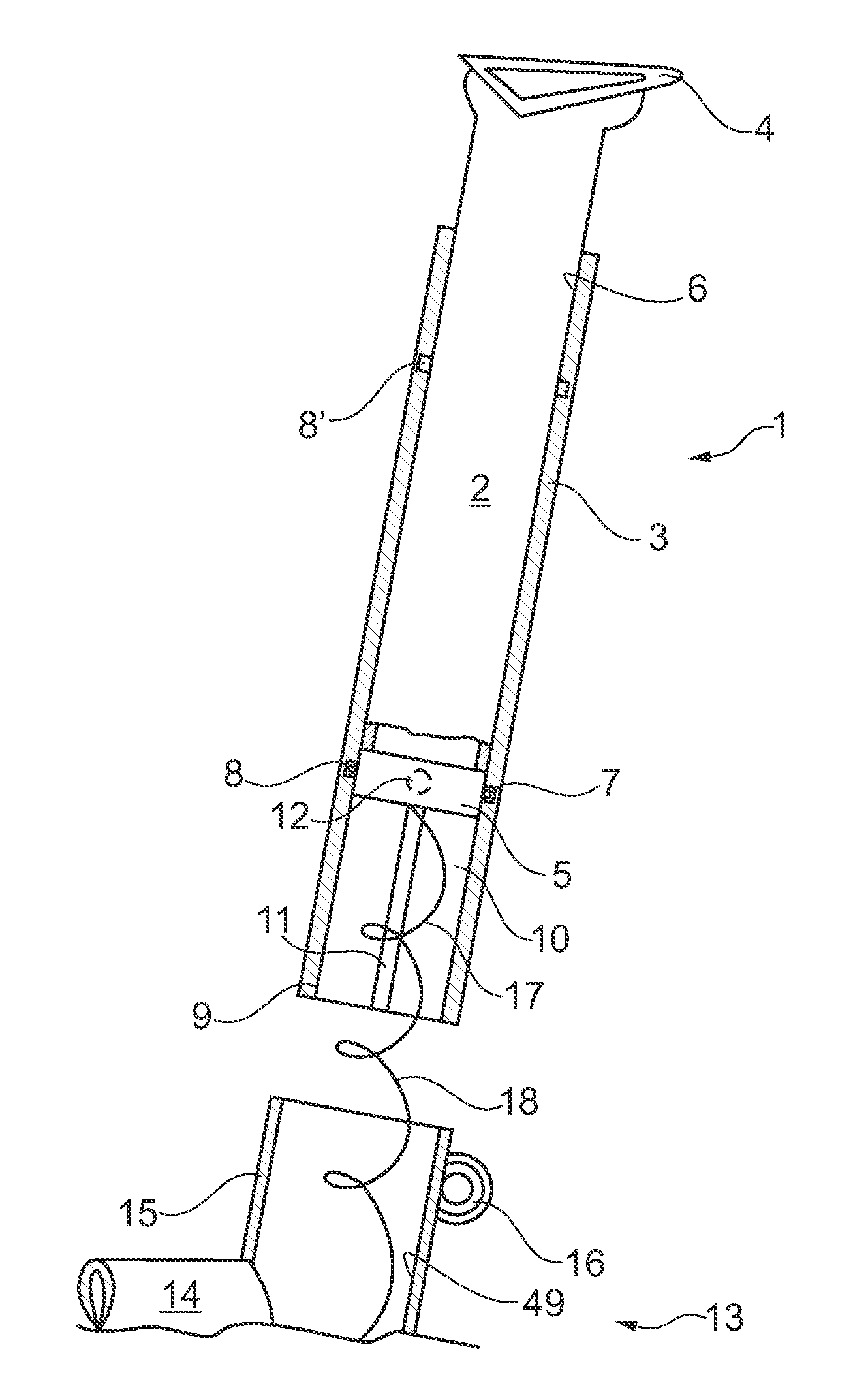
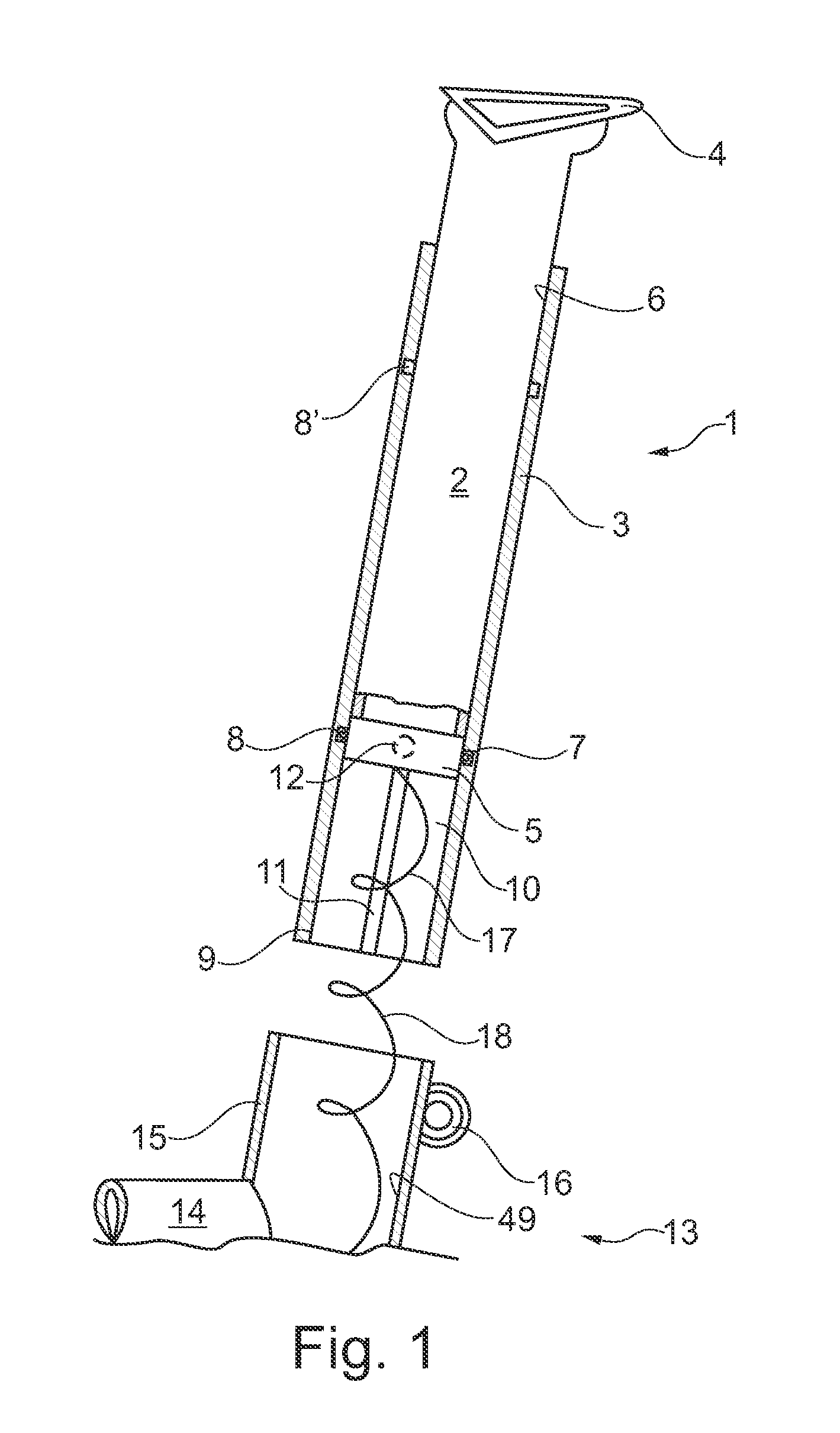
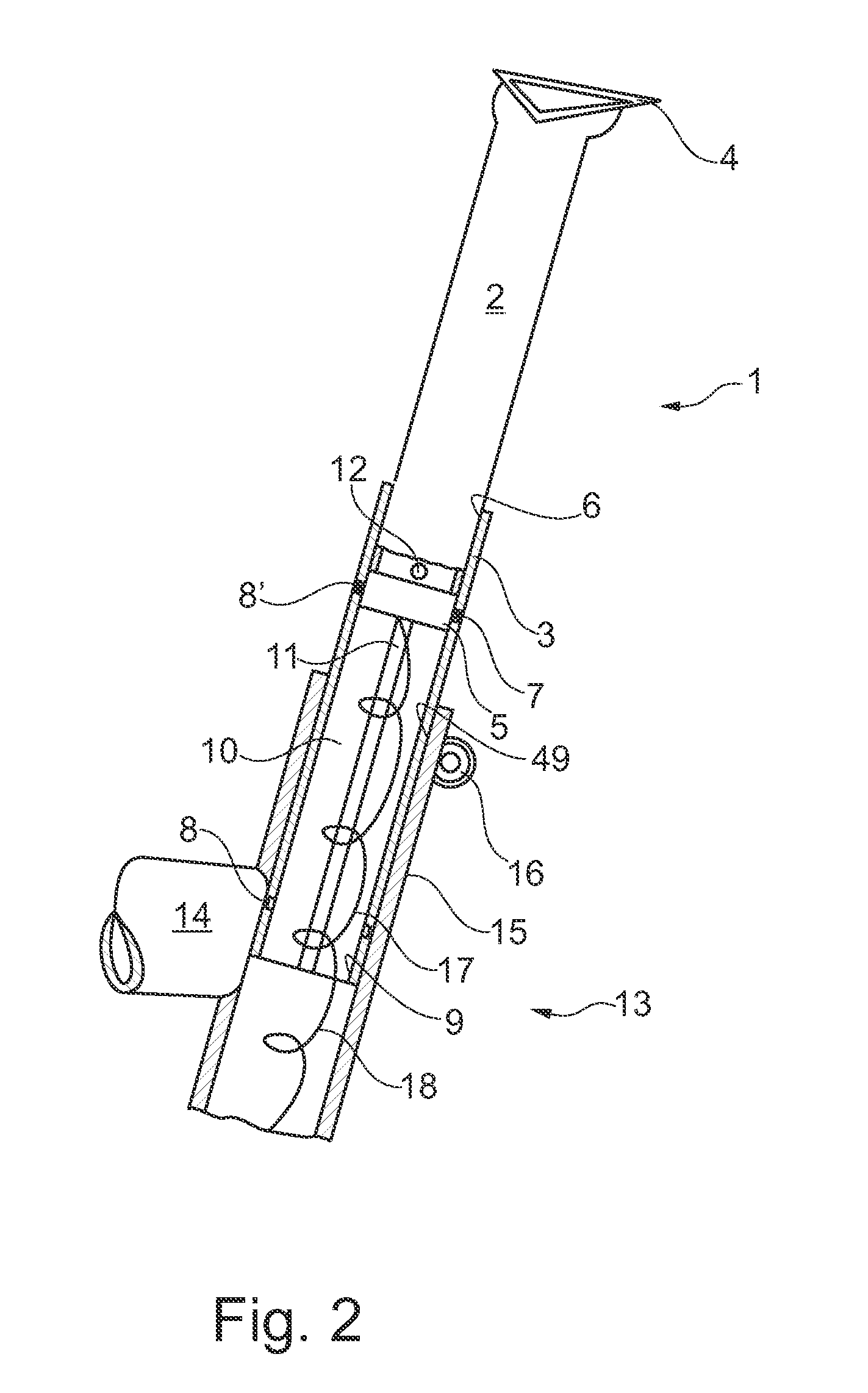
An off-road bicycle suspension fork includes a pair of fork leg assemblies, each of the leg assemblies having an upper leg telescopingly engaged with a lower leg. A damping assembly is provided in at least one of the legs and includes a cartridge tube connected to the lower leg and a piston connected to the upper tube by a shaft. The piston is telescopingly engaged with the cartridge tube to define a compression chamber below the piston. A control assembly is located at a top portion of the upper leg and is in communication with the compression chamber via a central passage of the shaft. A reservoir is defined between at least a portion of the lower tube and the cartridge. During compression of the suspension fork, fluid flows from the compression chamber, upward through the central passage of the shaft, through the control assembly and to the reservoir.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
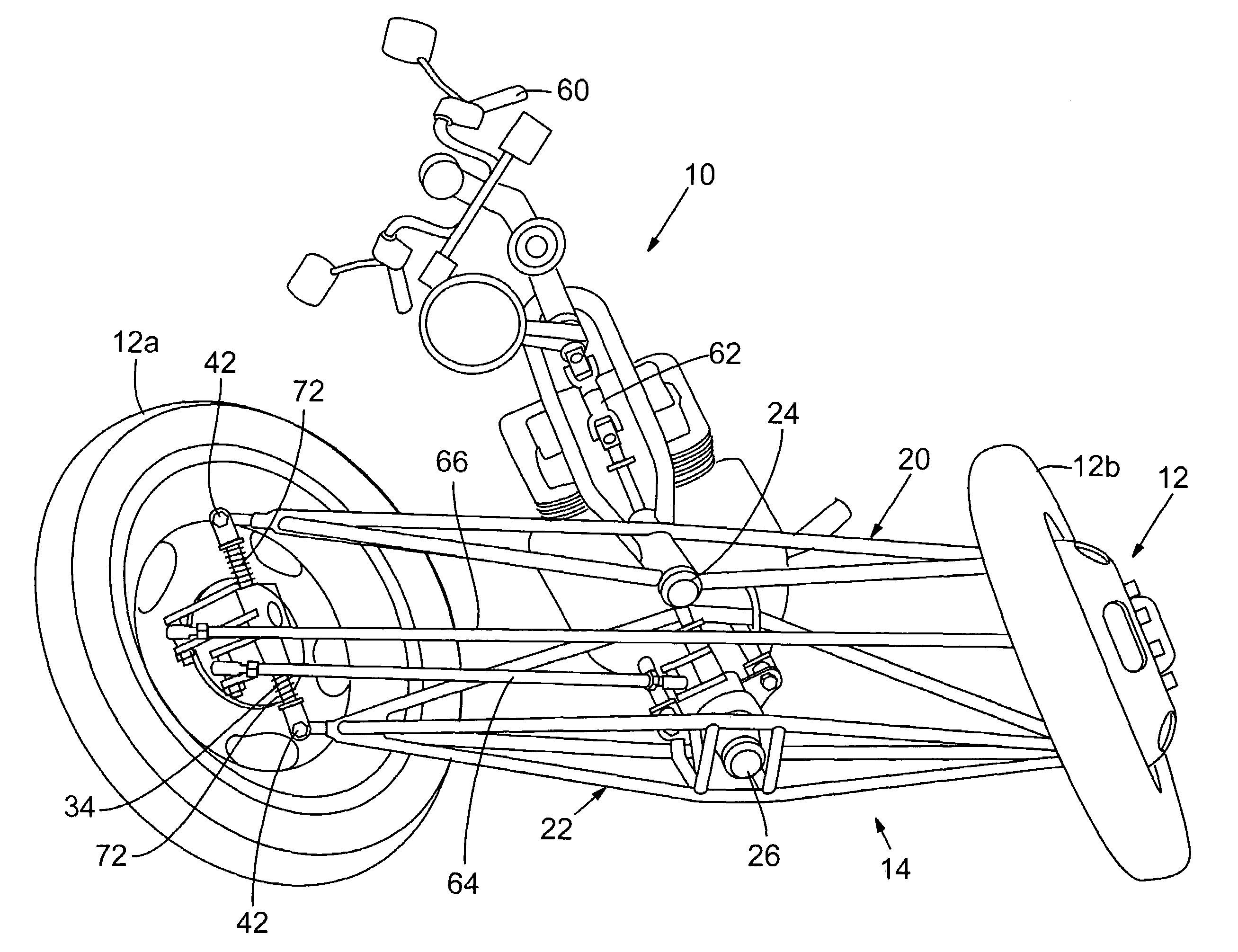
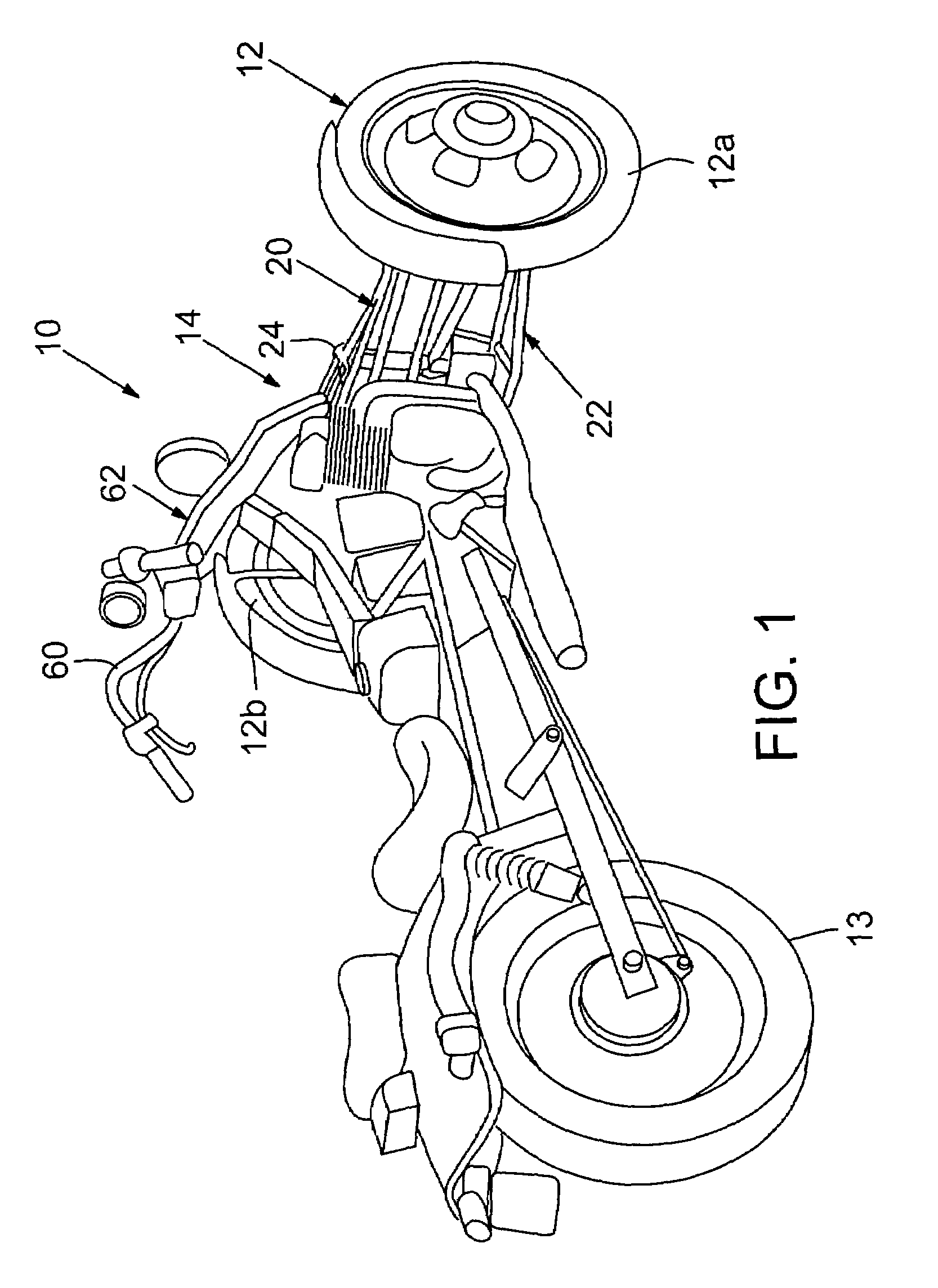
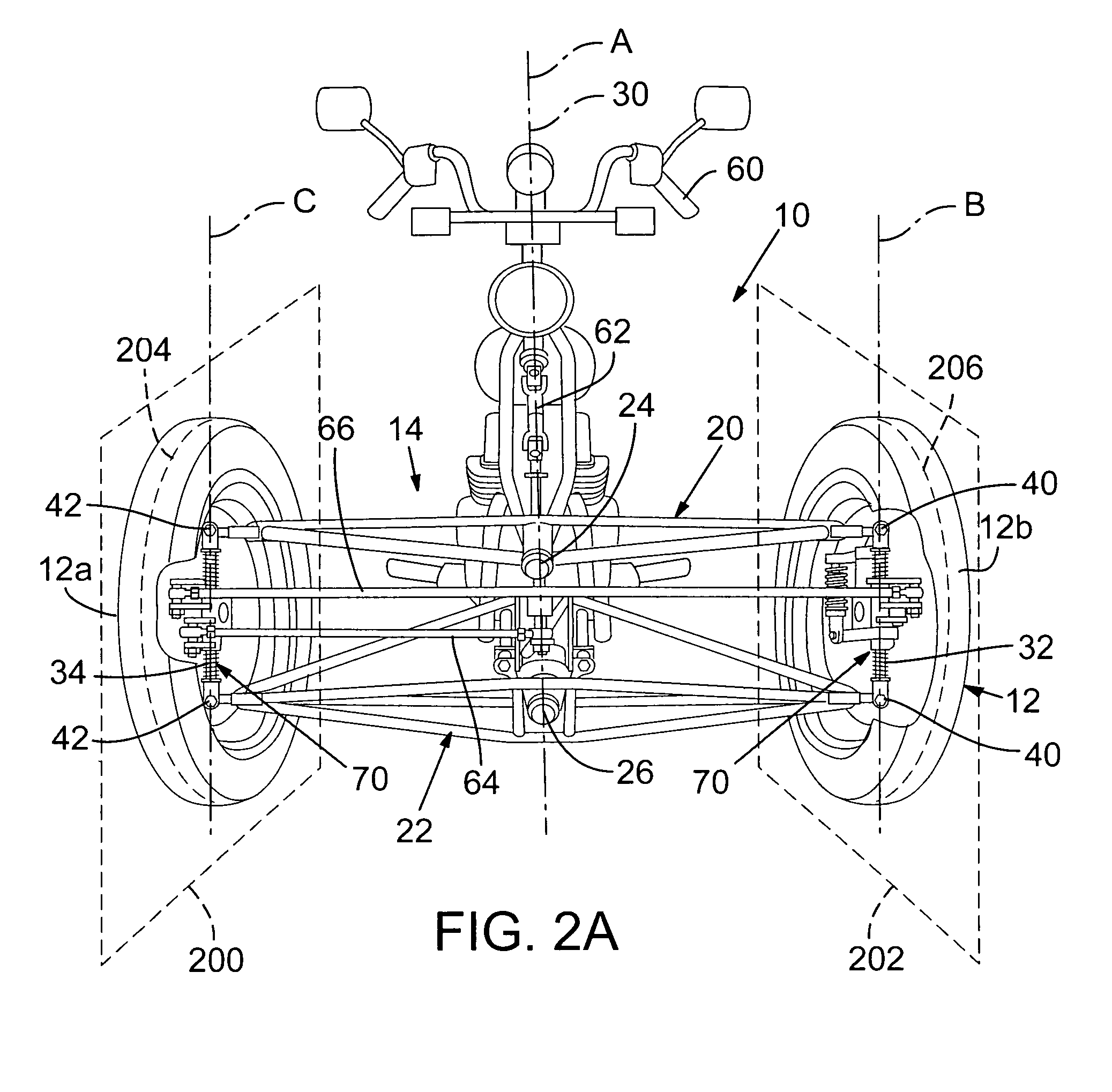
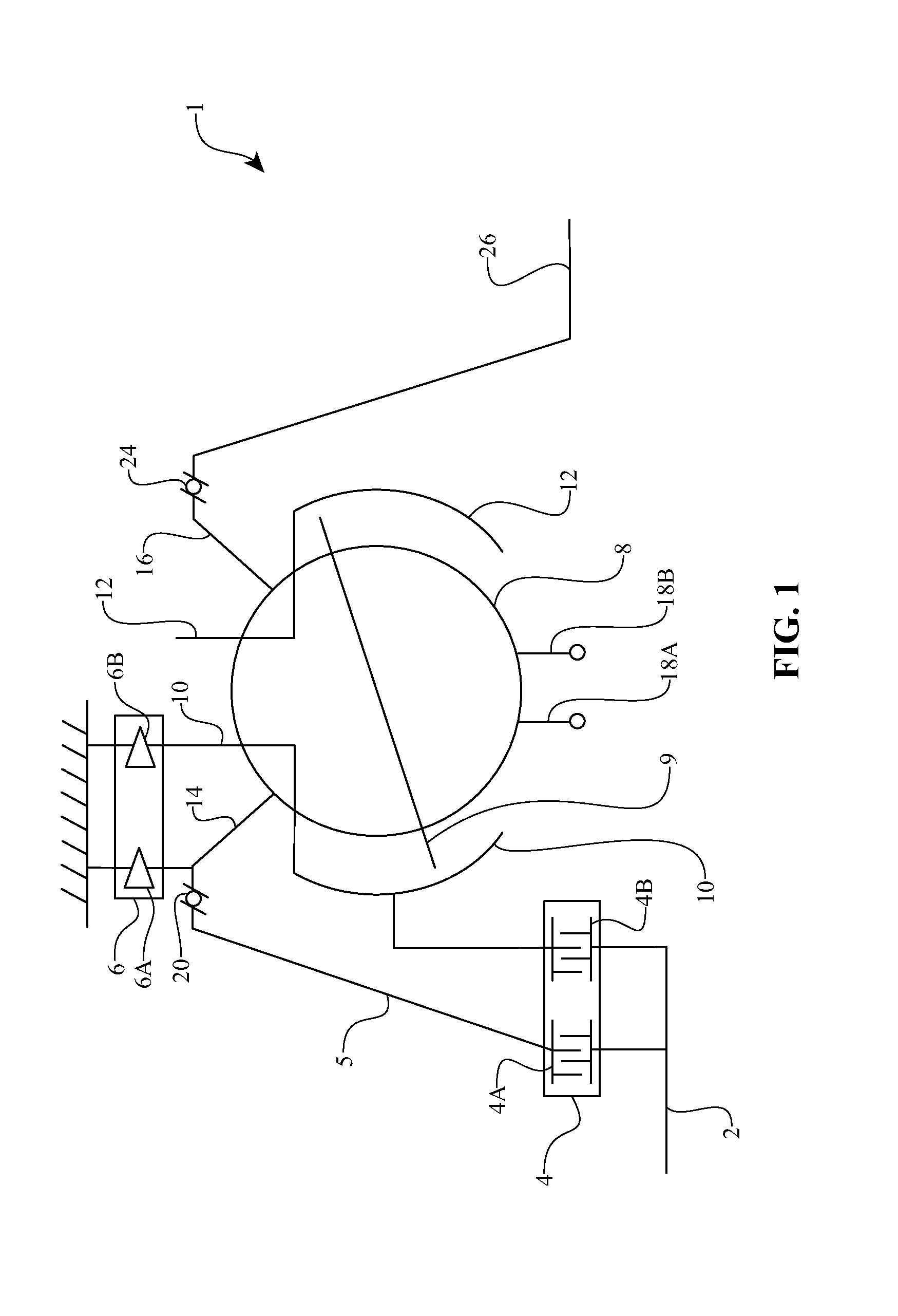
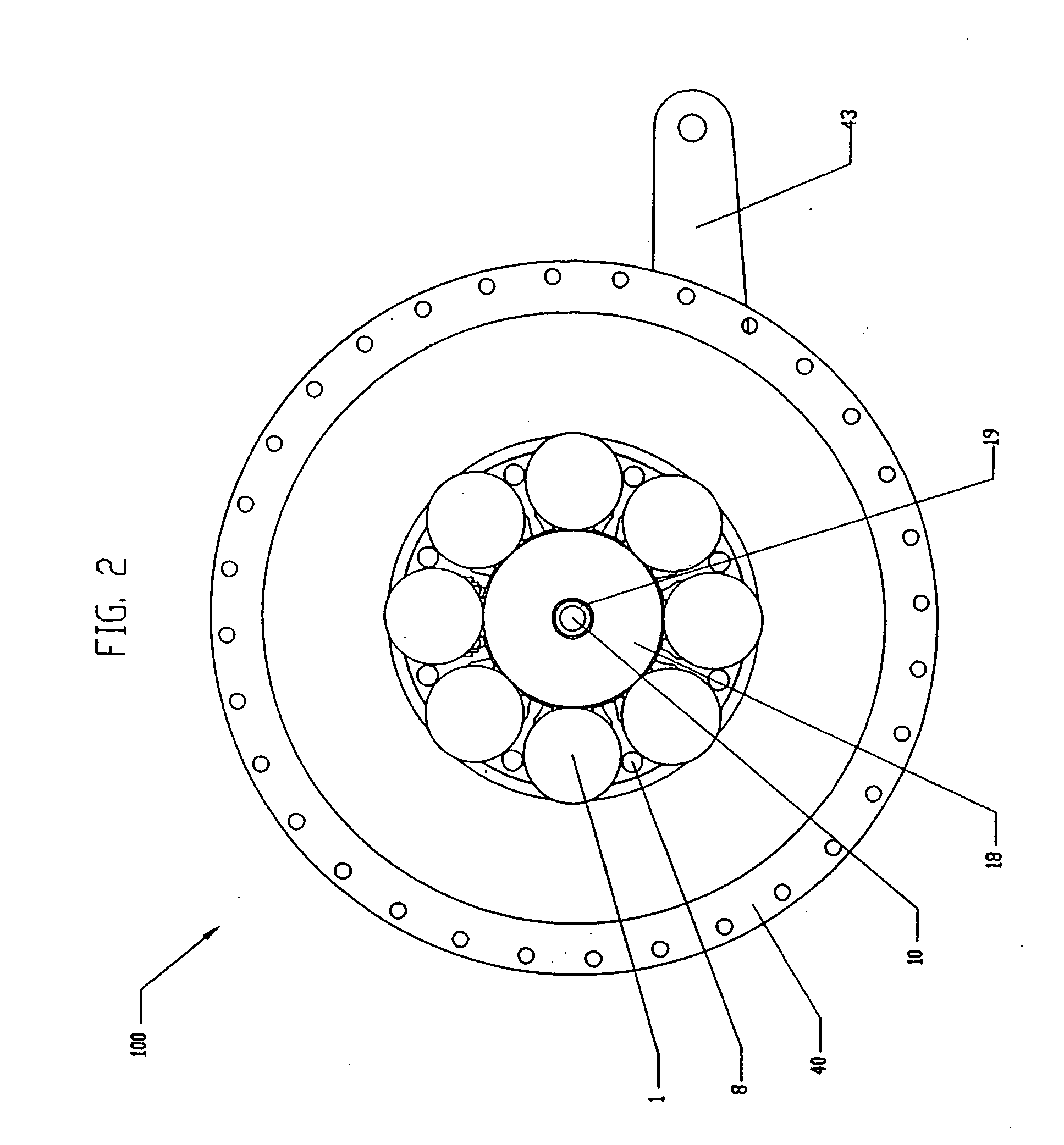
Tilting wheeled vehicle
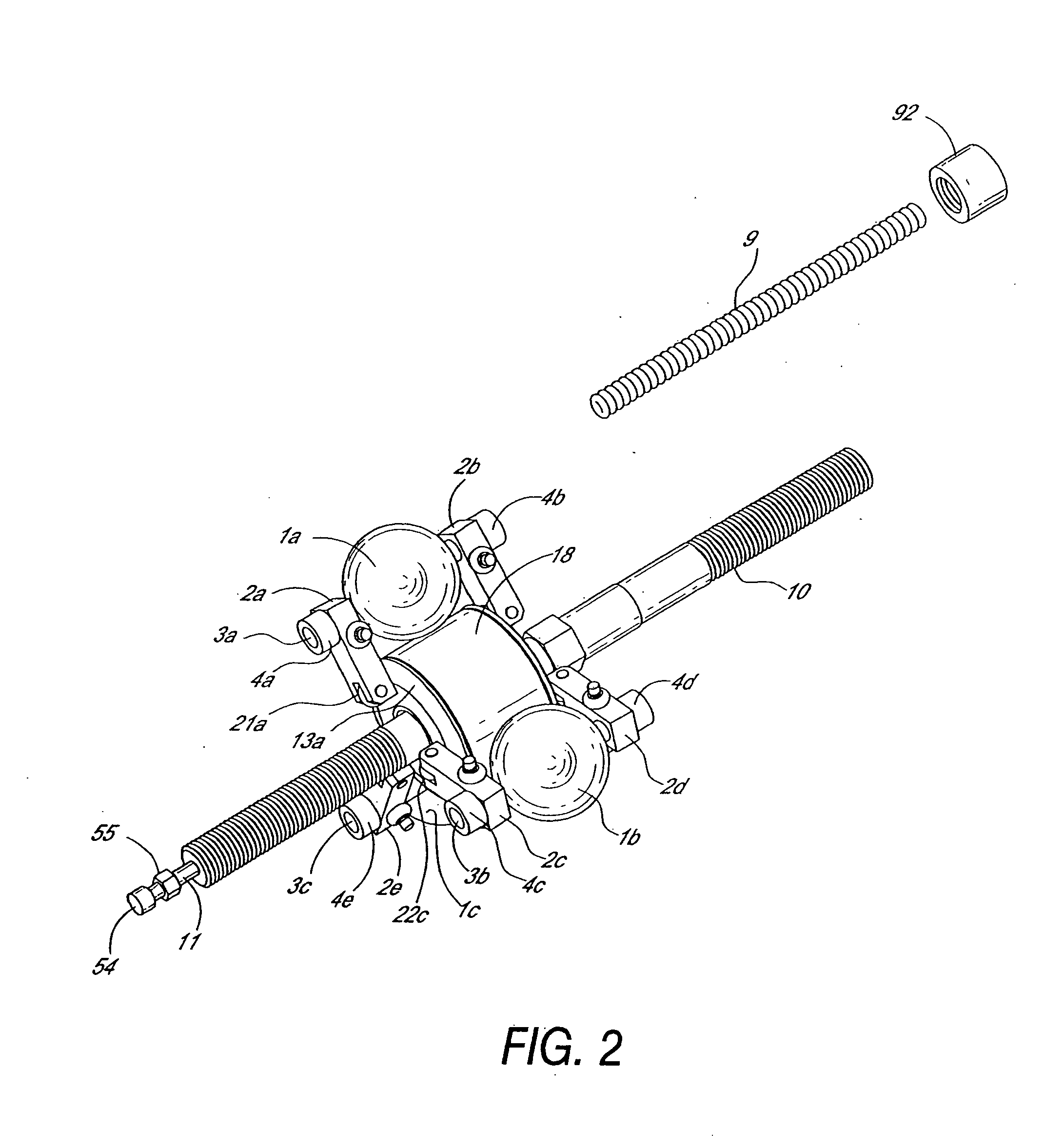
ActiveUS7487985B1Complex control systemWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionControl systemCaster angle
A tilting, preferably three-wheeled, vehicle is disclosed that has a tilting mechanism that allows the vehicle to have leaning characteristics substantially similar to those offered by an in-line two-wheeled vehicle, but that does not require complex linkages and / or control systems to operate effectively. A tilting linkage is operably secured to a frame to allow a pair of spaced apart wheels to remain substantially aligned with the plane of the vehicle throughout its range of movement while still allowing the steering axes of each wheel to intersect the substantially vertical centerline of each wheel. The linkage also allows the caster angle of each wheel's pivot axis can be optimized independently of the angle of the vehicle's handlebar steering shaft.
Owner:ARCIMOTO
Continuously variable transmission
InactiveUS20070155567A1Easy to adjustImprove translationWheel based transmissionChain/belt transmissionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Traction planets and traction rings can be operationally coupled to a planetary gearset to provide a continuously variable transmission (CVT). The CVT can be used in a bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on the frame of the bicycle at a location forward of the rear wheel hub of the bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on and supported by members of the bicycle frame such that the CVT is coaxial with the crankshaft of the bicycle. The crankshaft is configured to drive elements of the planetary gearset, which are configured to operationally drive the traction rings and the traction planets. Inventive component and subassemblies for such a CVT are disclosed. A shifting mechanism includes a plurality of pivot arms arranged to pivot about the centers of the traction planets as a shift pin hub moves axially.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Bicycle suspension assembly
InactiveUS20090001684A1Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionDual stageGas spring
A bicycle suspension assembly may be in the form of a bicycle front suspension fork. The suspension fork may include a pair of telescoping fork legs. In one arrangement, a suspension spring and a damper are provided in only one of the pair of fork legs. The suspension spring assembly may include a negative spring. In one arrangement, the negative spring is a dual stage negative gas spring in which a negative spring gas chamber includes a first chamber section and a second chamber section. The first chamber section and the second chamber section are uncoupled in a first position of the suspension spring and the first chamber section and the second chamber section are coupled in a second position of the suspension spring.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Vertically adjustable bicycle assembly
ActiveUS20090324327A1Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionExpansion jointElectrical and Electronics engineering
An adjustable assembly for a bicycle includes a first support having an interior surface and a second support slidably positioned within at least a portion of the first support. One of the first support and the second support is adapted to attach to a first bicycle portion, and the other of the first support and the second support is adapted to attach to a second bicycle portion. Further, the second support comprises an expansion portion configured to be moved between an expanded position and a retracted position. The expansion portion is configured to engage the interior surface of the first support when the expansion portion is in an expanded position. In addition, the first support is configured to be selectively moved relative to the second support when the expansion portion is permitted to assume a retracted position. In some embodiments, the first bicycle portion comprises a bicycle frame and the second bicycle portion comprises a bicycle saddle. In other arrangements, the first bicycle portion comprises a fork assembly and the second bicycle portion comprises a handlebar assembly.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
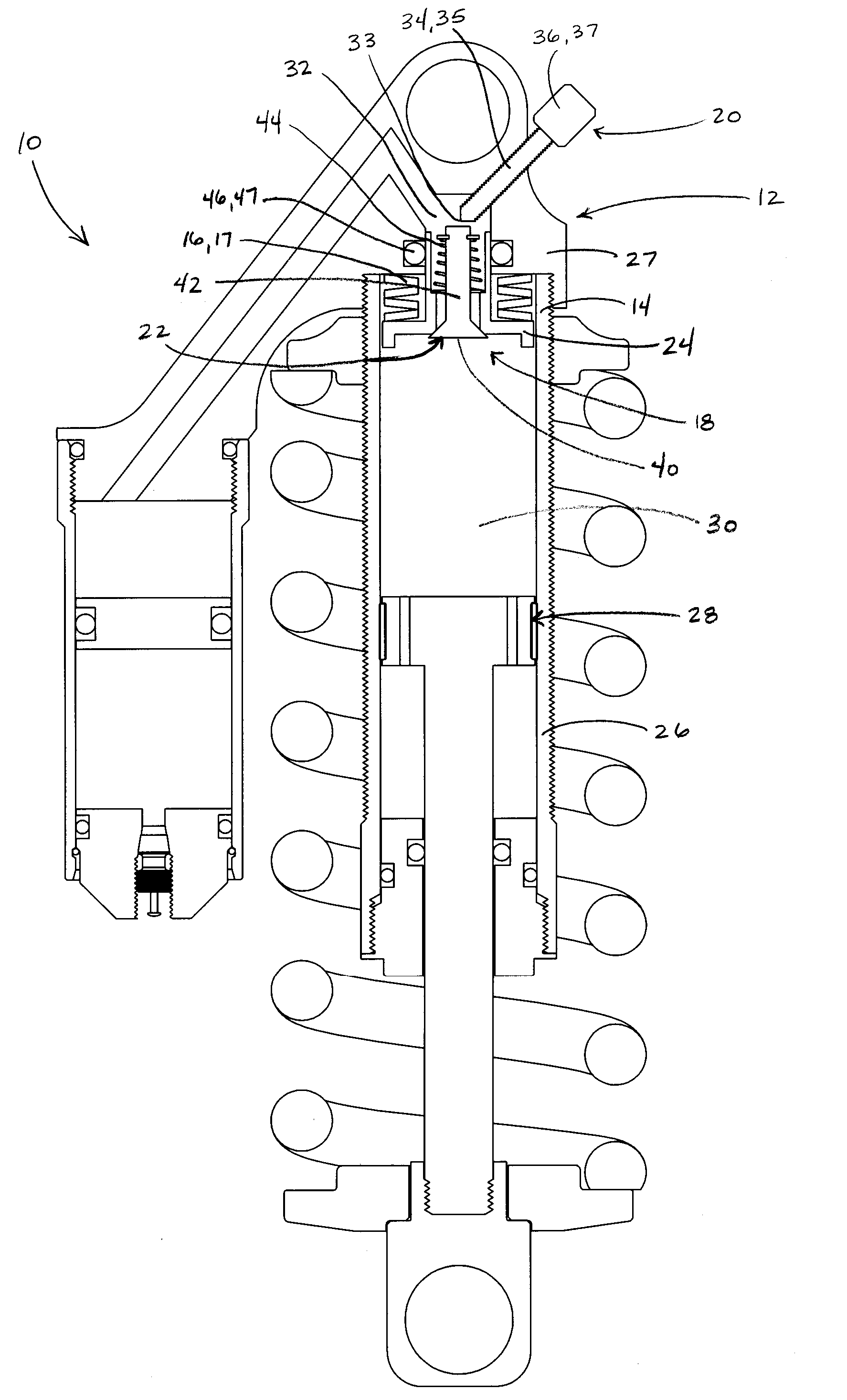
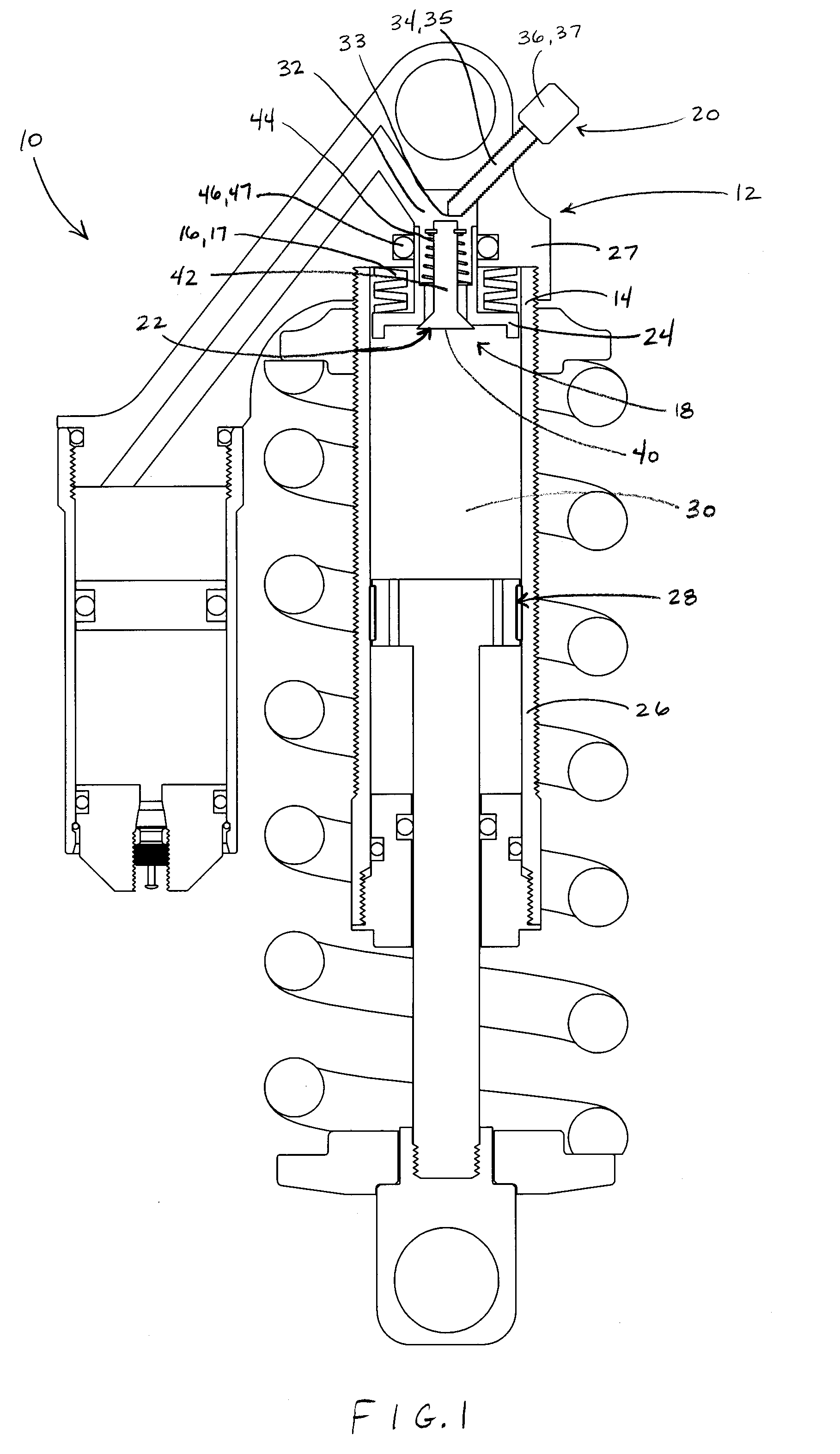
Bicycle fork cartridge assembly
InactiveUS20030001358A1Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringMechanical engineering
An off-road bicycle suspension fork includes a pair of fork leg assemblies, each of the leg assemblies having an upper leg telescopingly engaged with a lower leg. A damping assembly is provided in at least one of the legs and includes a cartridge tube connected to the lower leg and a piston connected to the upper tube by a shaft. The piston is telescopingly engaged with the cartridge tube to define a compression chamber below the piston. A control assembly is located at a top portion of the upper leg and is in communication with the compression chamber via a central passage of the shaft. A reservoir is defined between at least a portion of the lower tube and the cartridge. During compression of the suspension fork, fluid flows from the compression chamber, upward through the central passage of the shaft, through the control assembly and to the reservoir.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
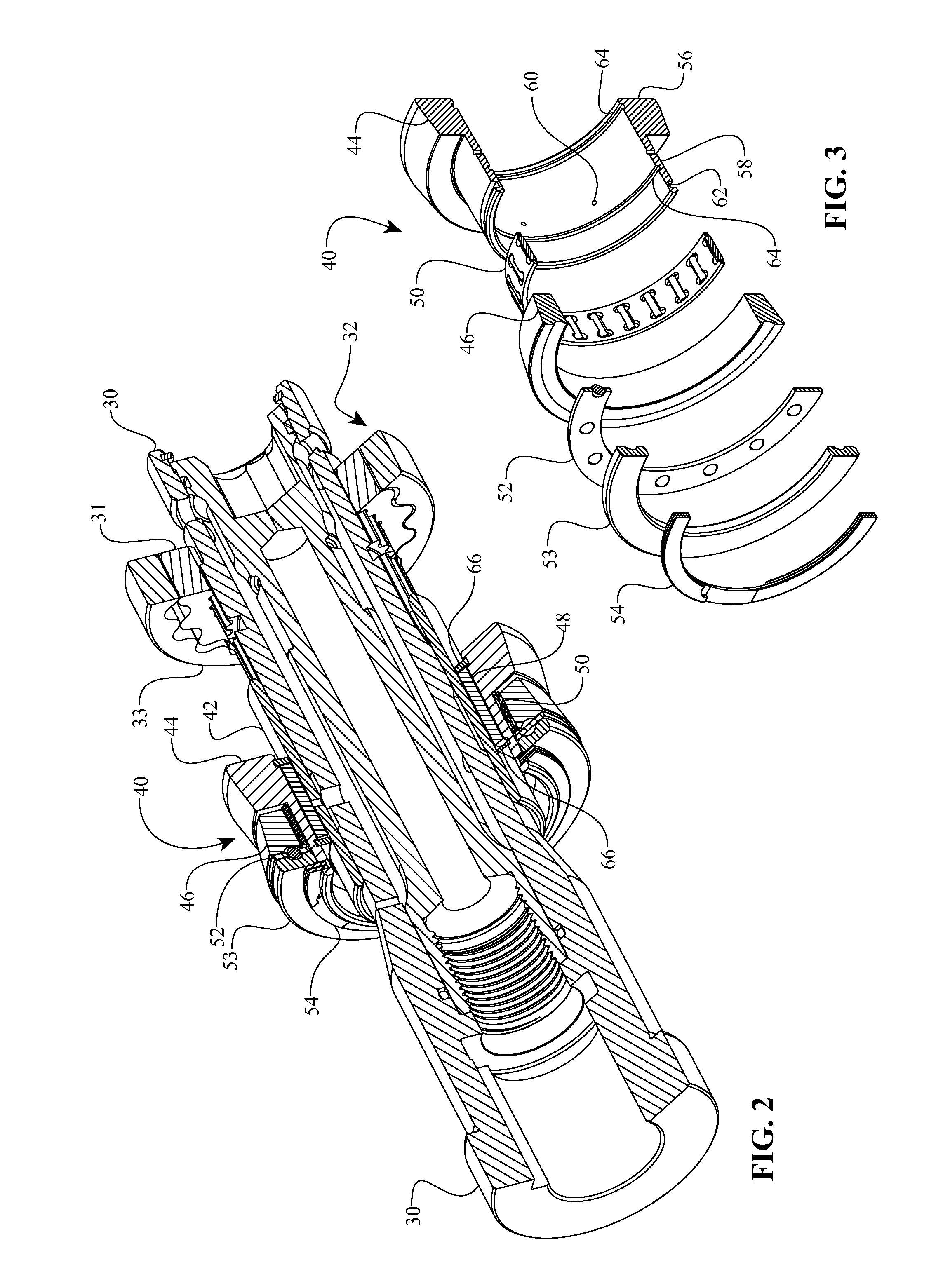
Continuously variable transmission
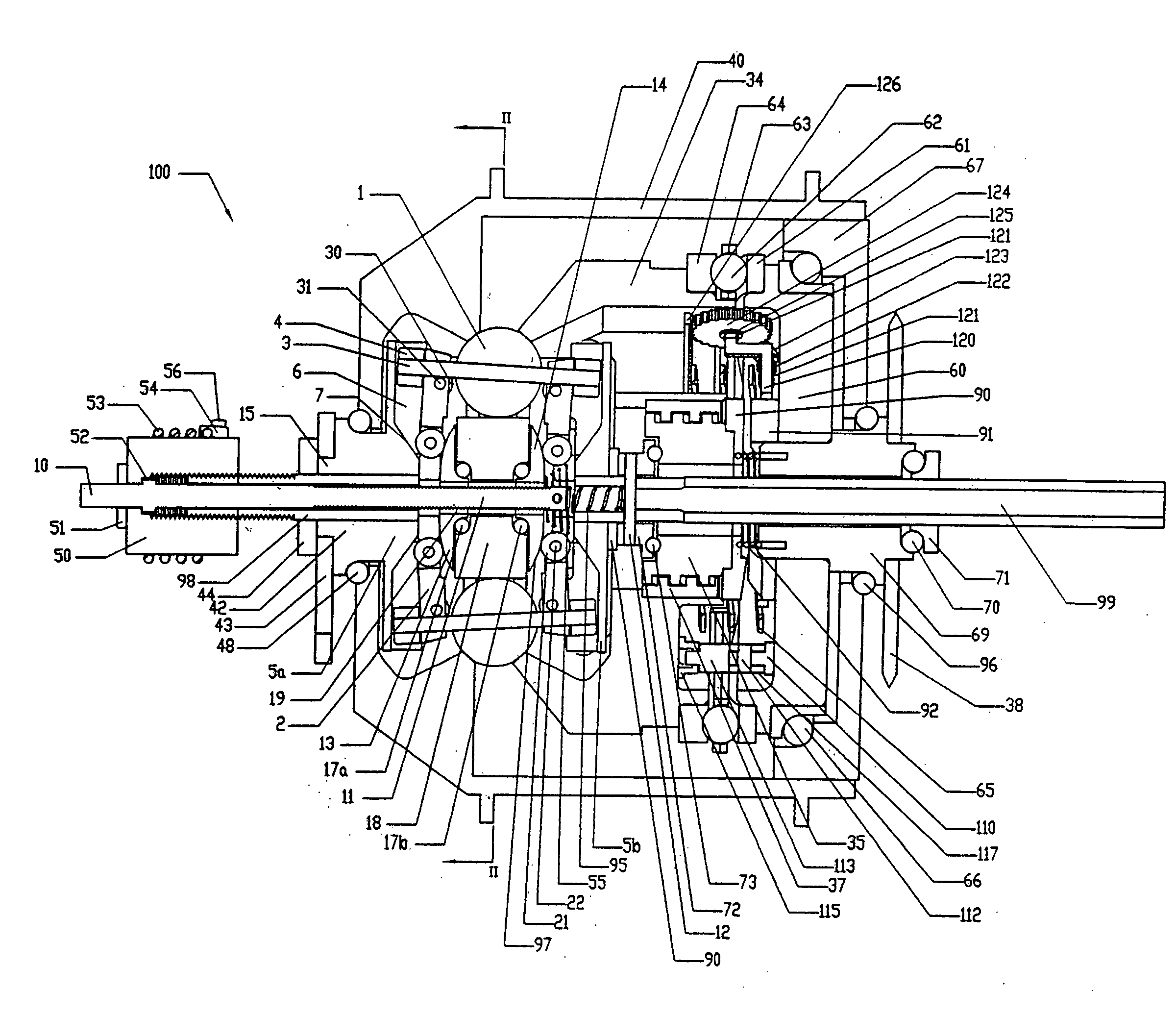
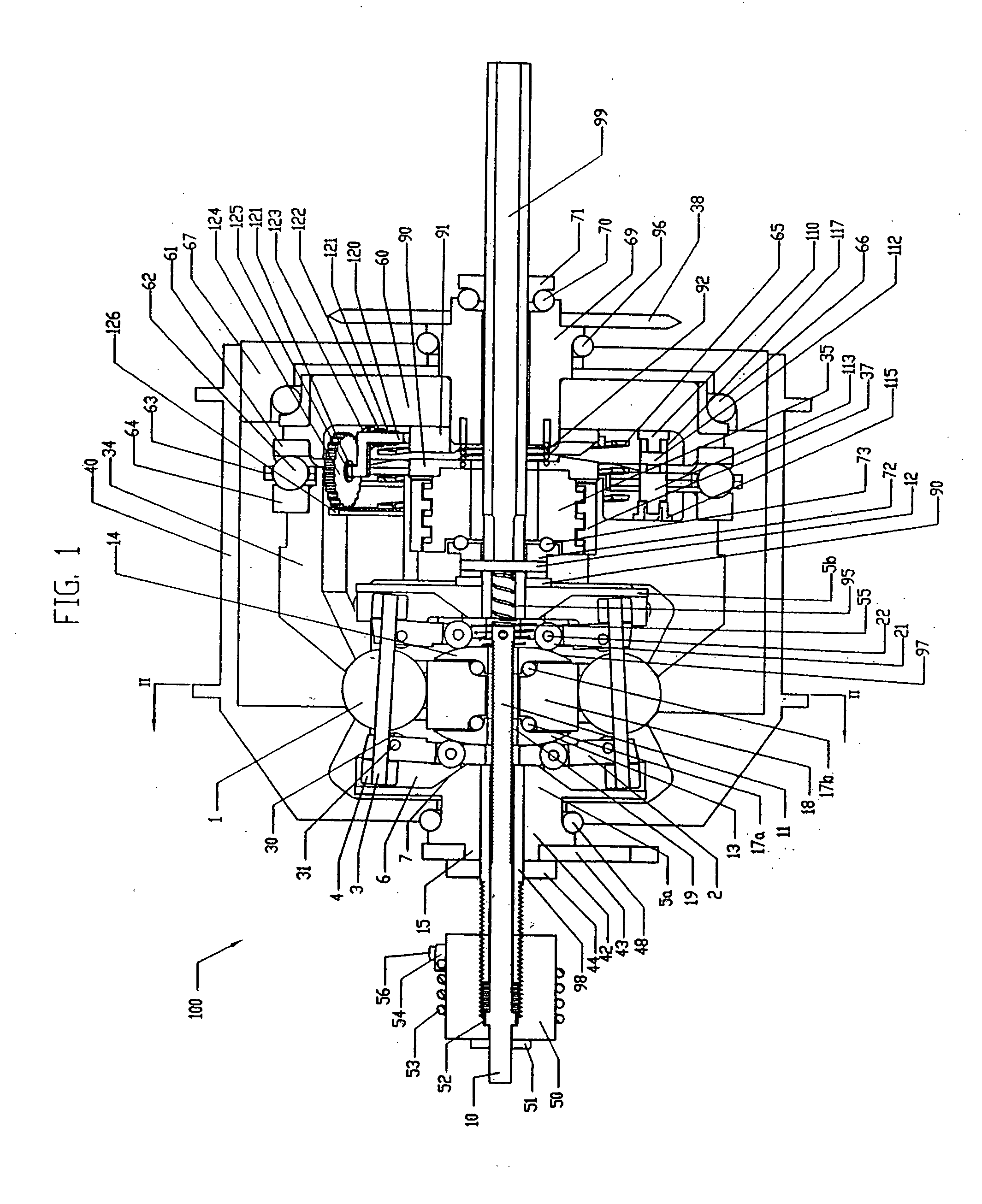
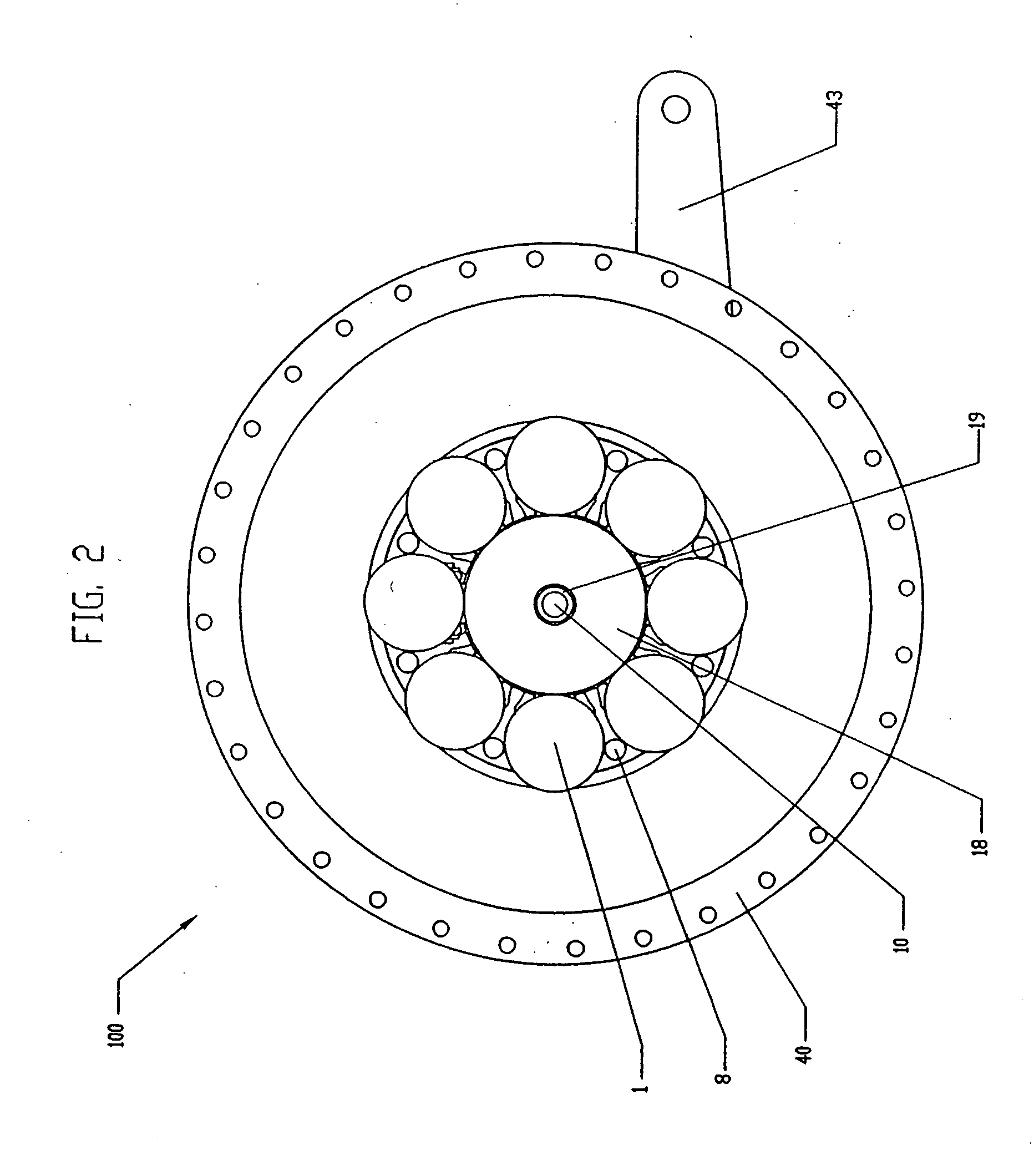
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
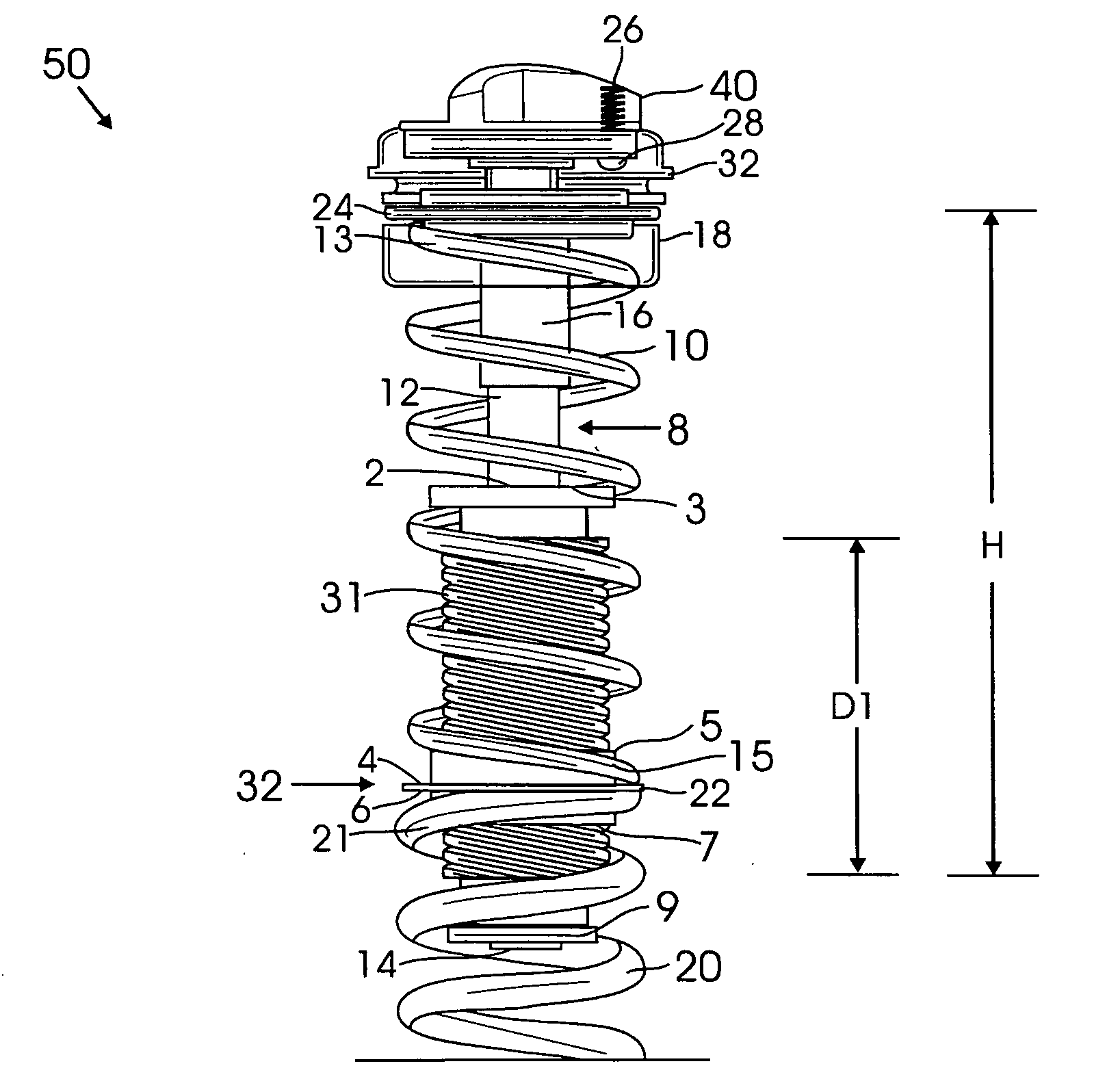
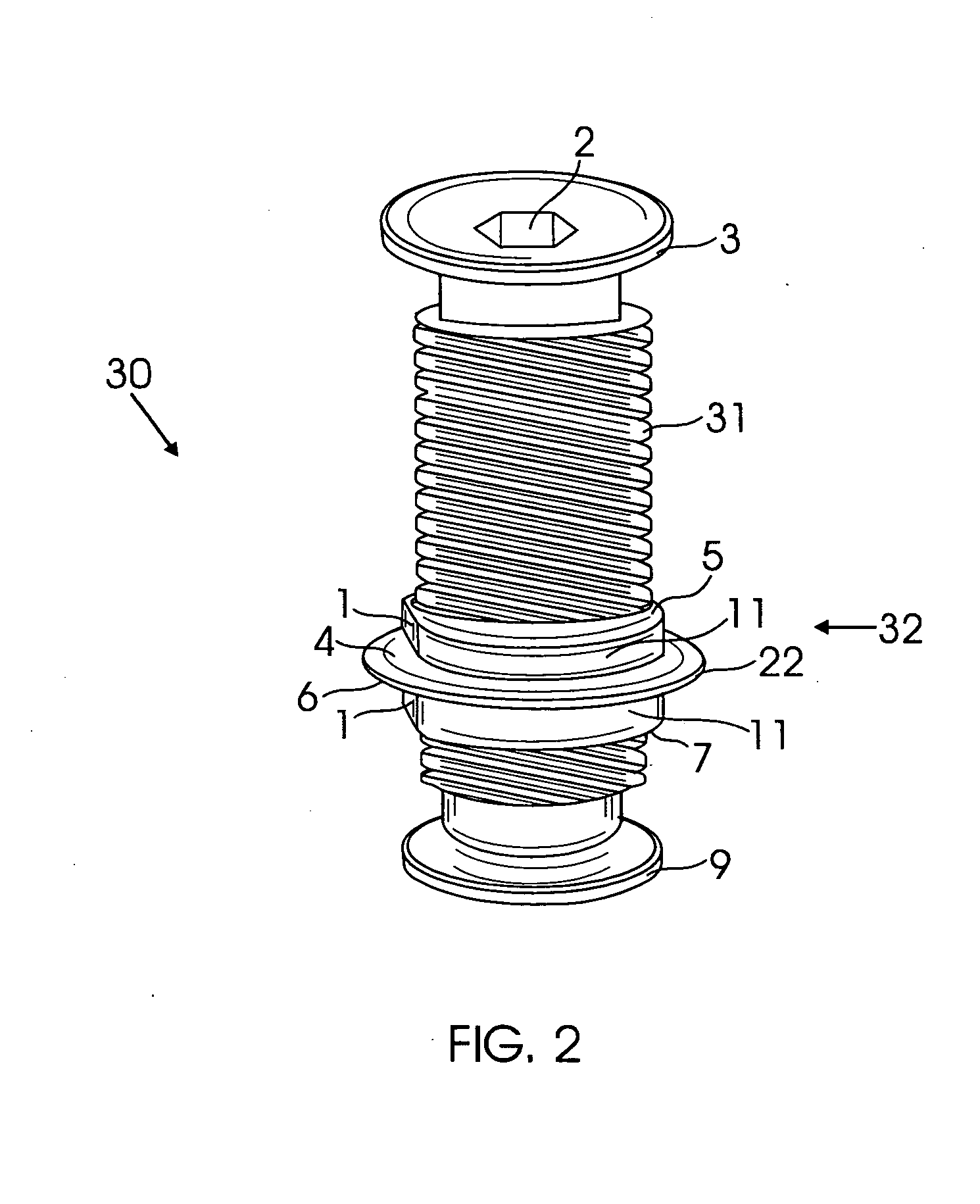
Adjustable and progressive coil spring system for two wheeled vehicles
InactiveUS20080099968A1Improve handlingSignificant amount of weightWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionCoil springScrew thread
An adjustable coil spring system placed within a leg of a vehicle such as a mountain bicycle fork. The spring system comprises an adjustable first soft spring seated on top of a second firm spring having greater length than the first soft spring. A coupler assembly is positioned between two springs comprised of a threaded bolt threadedly received within a coupler. A spring adjustment means may comprise a knob connected to the threaded bolt through a non-round shaped shaft, wherein the threaded bolt is disposed within the first soft spring. As the knob rotates, the coupler is moved up along the threaded bolt, decreasing the length of the first soft spring, thereby increasing firm spring characteristics of the spring system. As the knob rotates in an opposite direction, the coupler moves down, increasing the length of the first soft spring, thereby increasing soft spring characteristics of the spring system.
Owner:HAYES BICYCLE GROUP
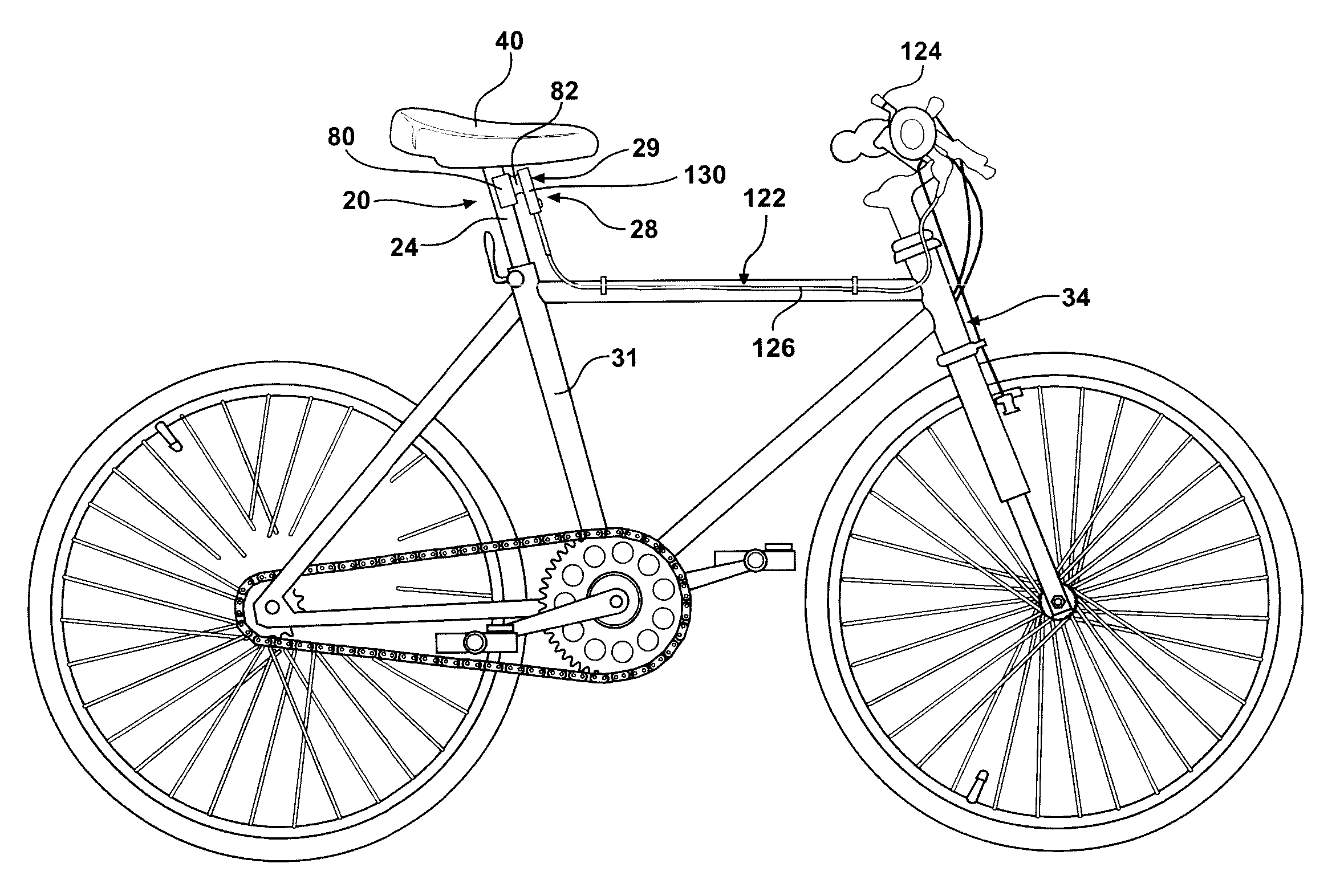
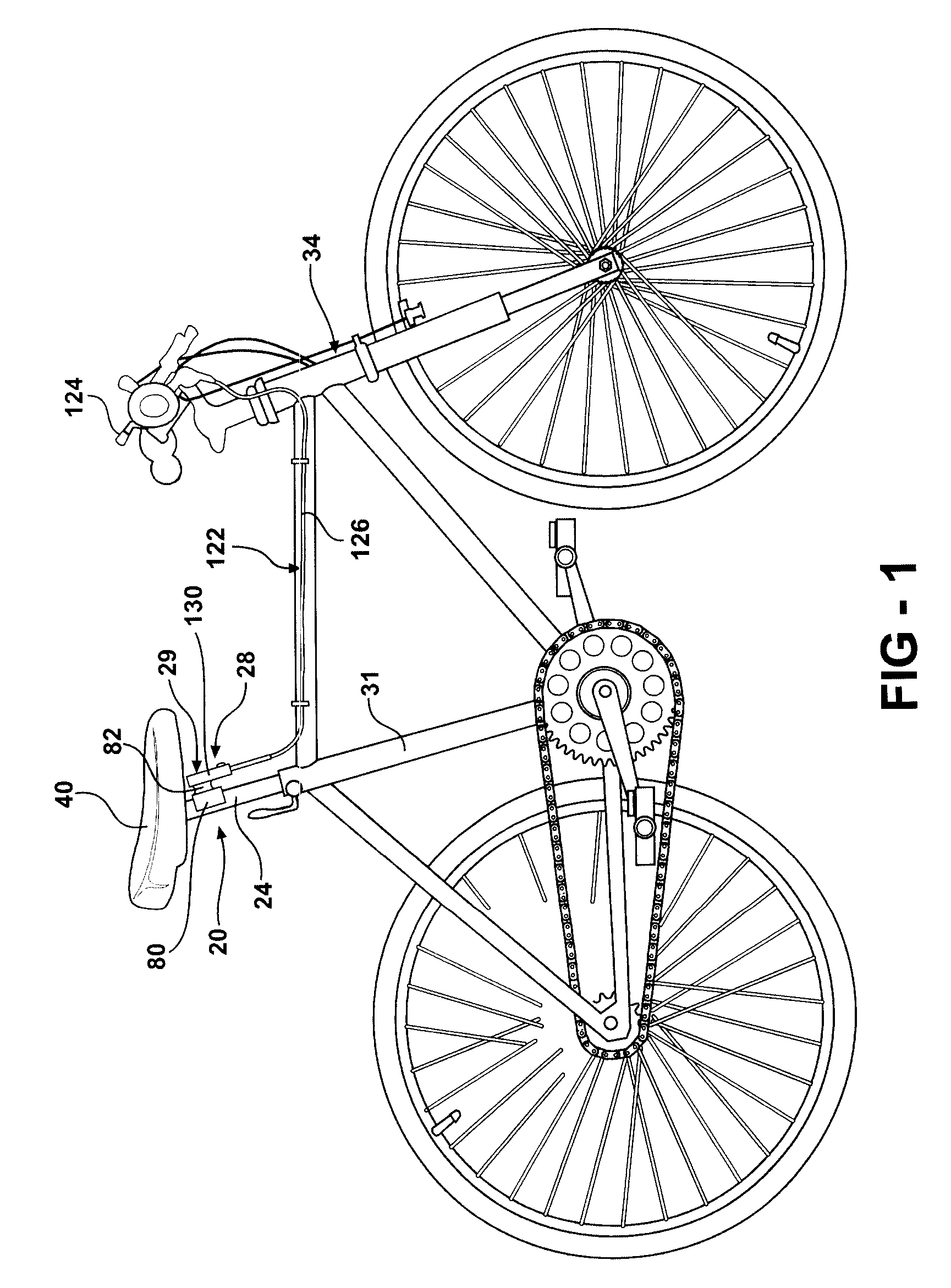
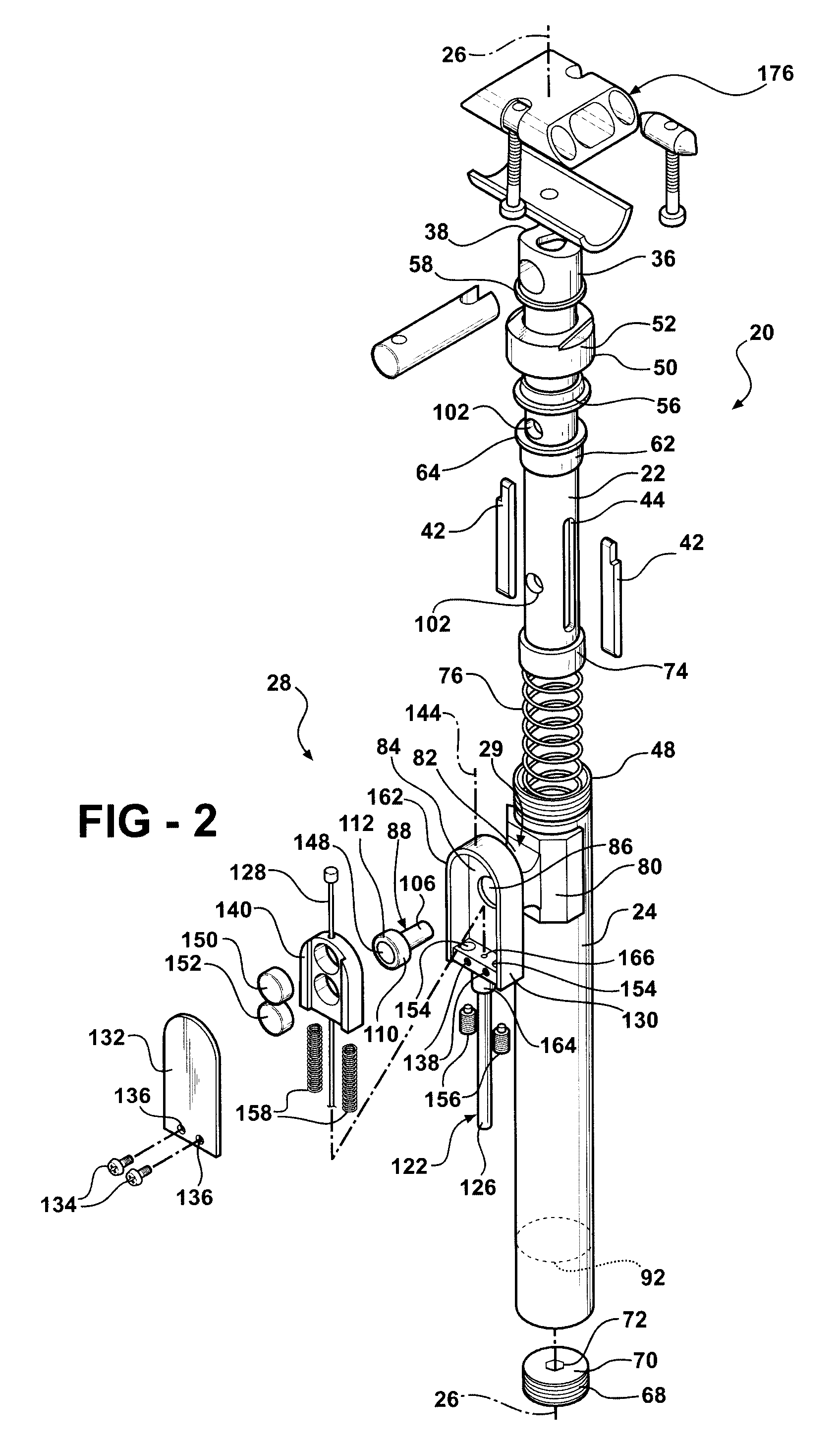
Adjustable Bicycle Seat Post Assembly
InactiveUS20060175792A1Enhanced bicycle experienceEasy to handlePassenger cyclesWheel based transmissionCouplingLocking mechanism
An adjustable-height bicycle seat post assembly comprises a hollow seat post for supporting a bicycle seat slidably on plastic guides or shims inside a hollow tube. The hollow tube clamps into the frame of a bicycle. A mainspring forces the post upward, but a locking mechanism interconnects the post with the tube in various fixed positions relative to the tube. The locking mechanism includes a housing, which supports a plunger for reciprocating movement into and out of engagement with holes on the post. The locking mechanism is affixed to the outside of the tube to bear shearing forces on the plunger. An endcap on the locking mechanism and a topcap on the tube protect the assembly from foreign debris. The locking mechanism may be manipulated remotely using a magnetic switch assembly or manually using a mechanical assembly. A lost motion coupling is integrated into the locking mechanism and / or actuator assembly to enable the remote actuator to be moved or deployed while the latch remains trapped under the influence of a dominant shear load. The lost motion coupling is also effective to allow an operator to deploy the remote actuator at any convenient time prior to a desired change in seat height.
Owner:KIMIR SEATPOST
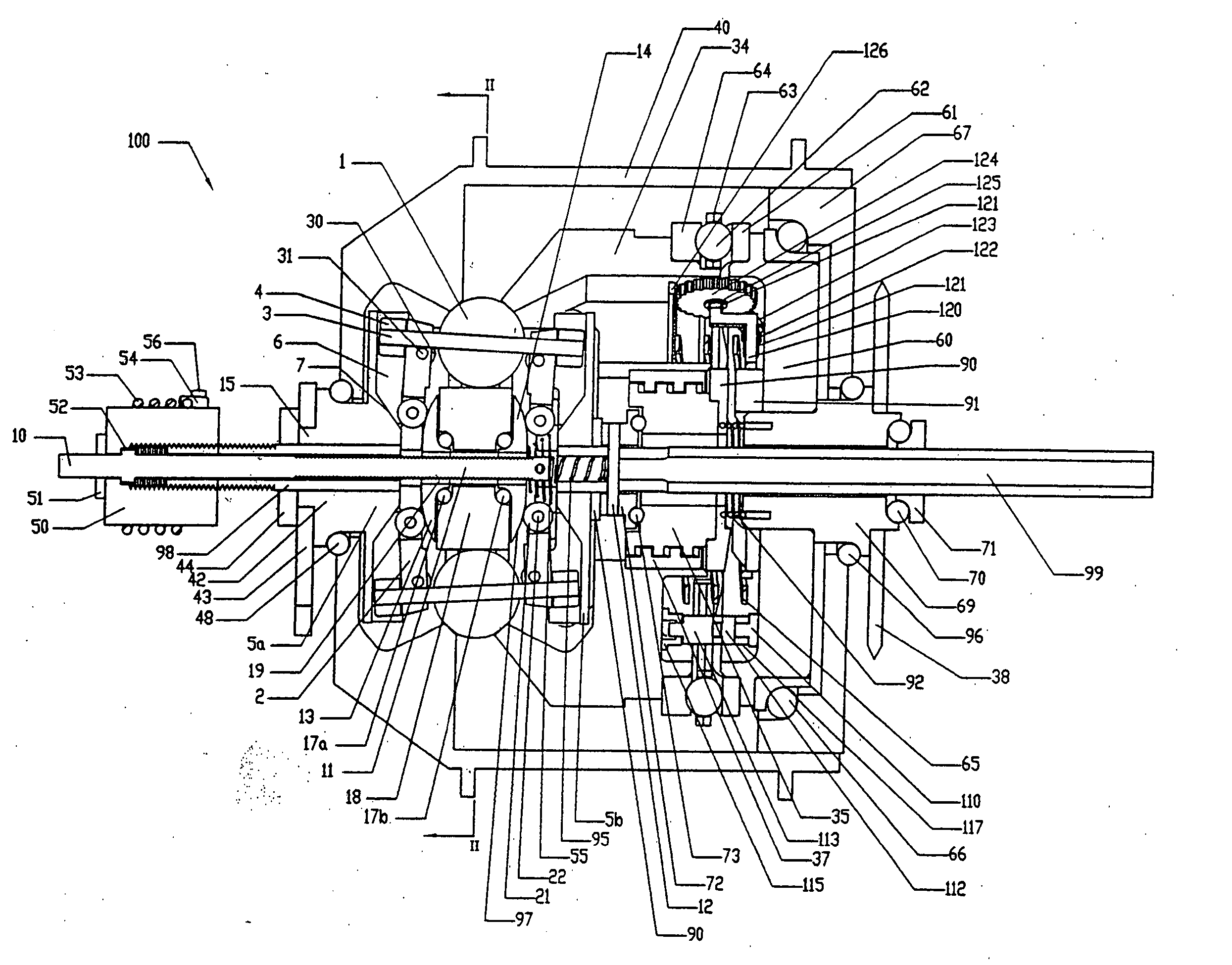
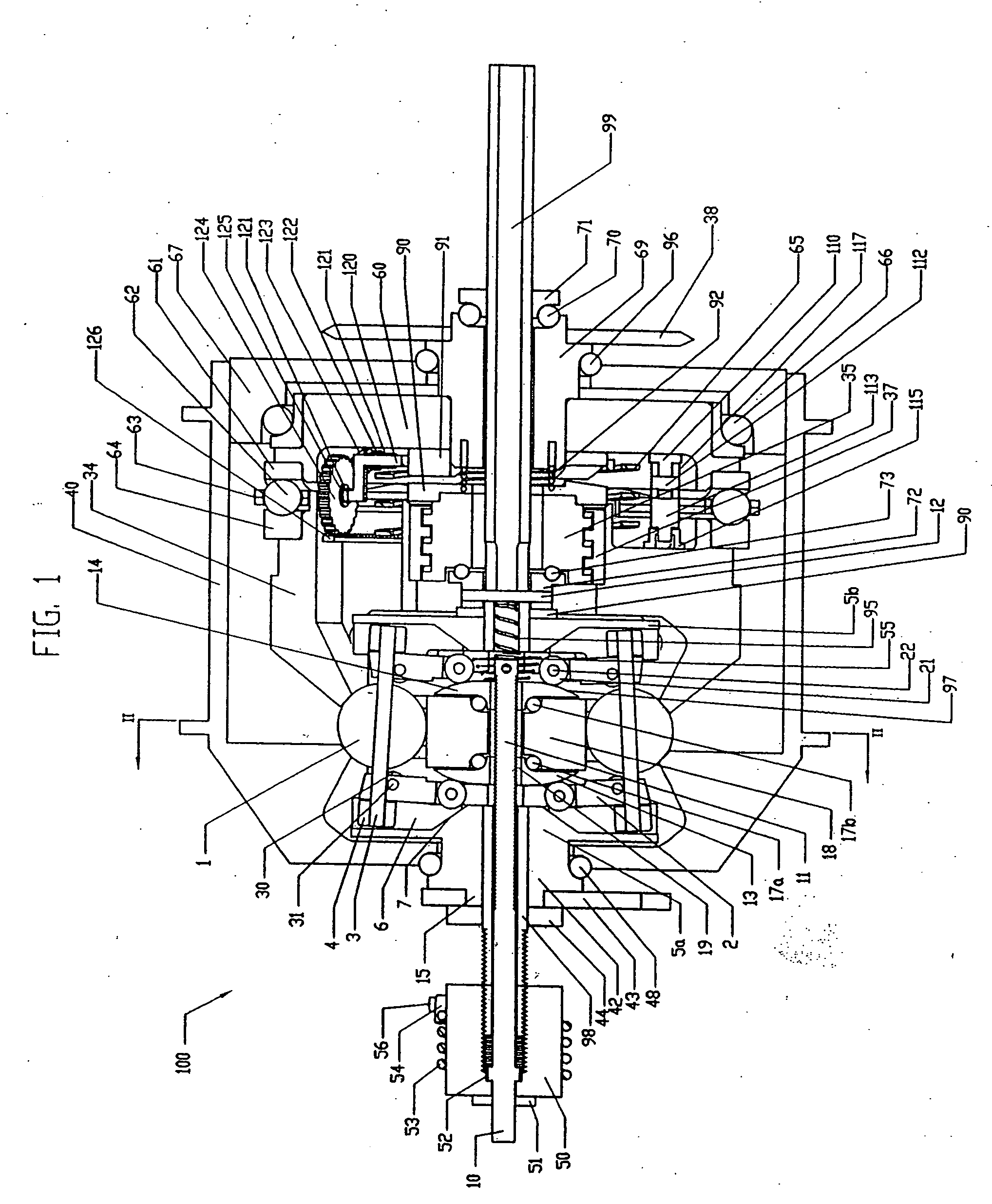
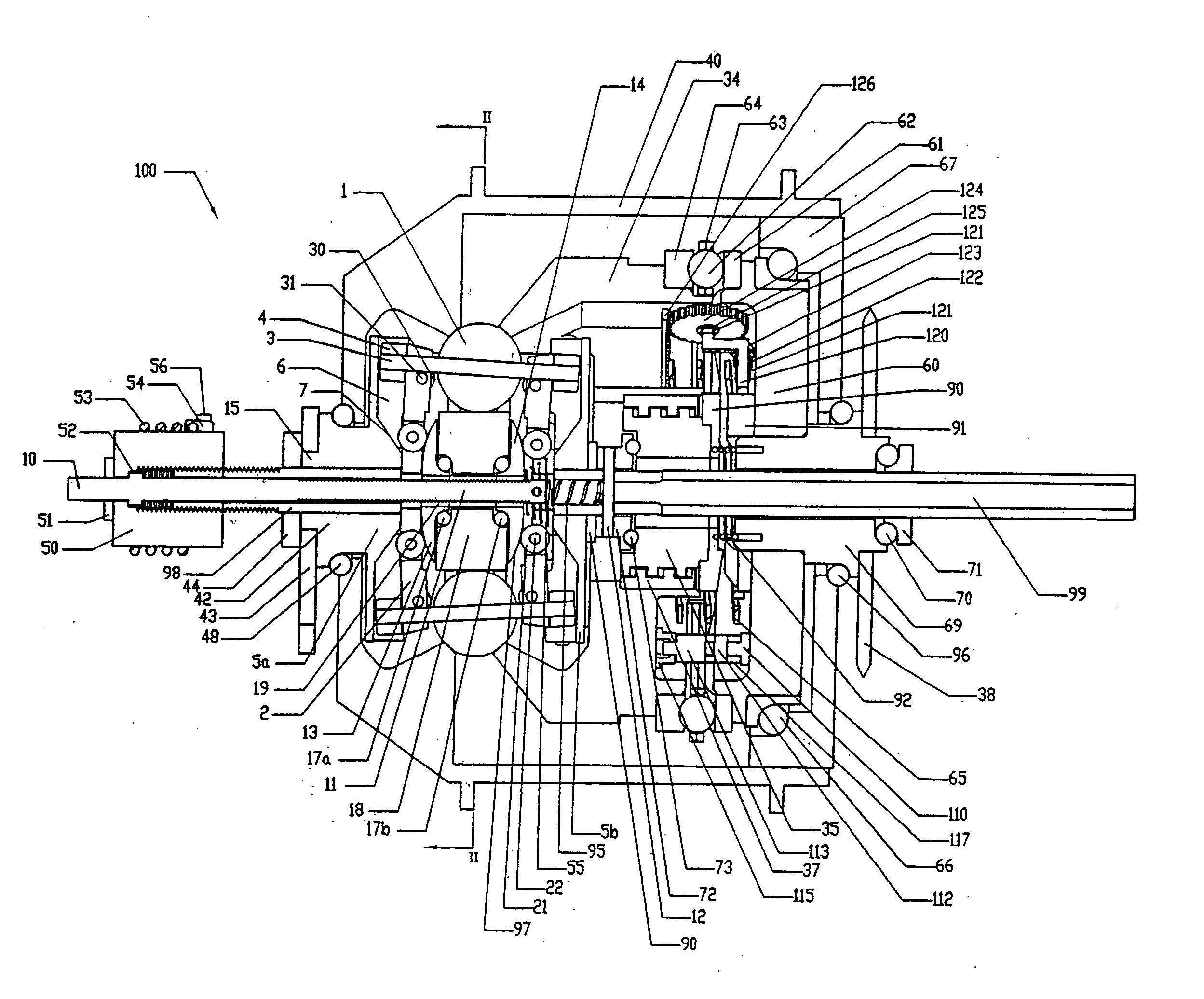
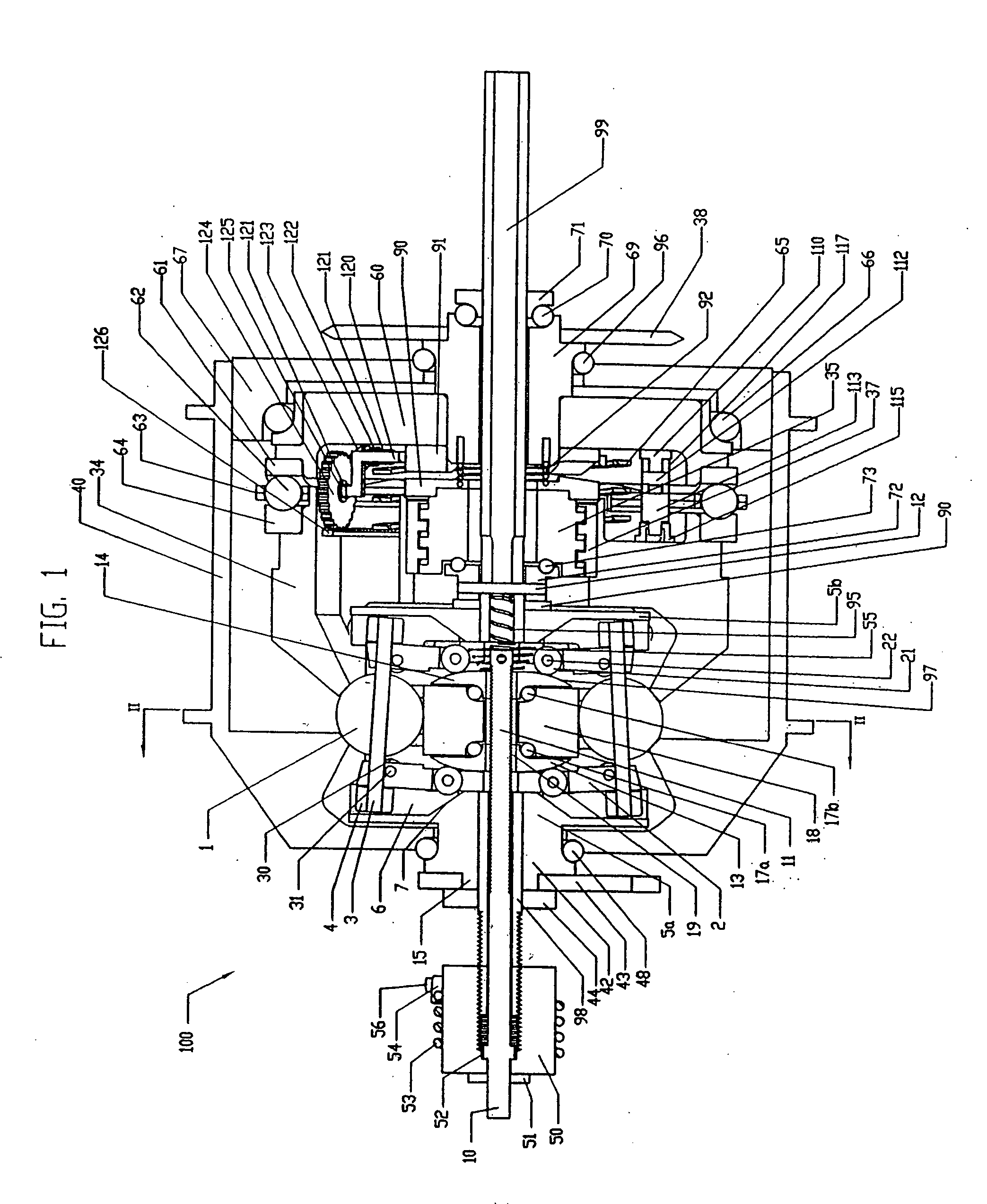
Continuously variable transmission
InactiveUS7914029B2Easy to adjustFacilitating axial translationWheel based transmissionChain/belt transmissionEngineeringDriven element
Traction planets and traction rings can be operationally coupled to a planetary gearset to provide a continuously variable transmission (CVT). The CVT can be used in a bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on the frame of the bicycle at a location forward of the rear wheel hub of the bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on and supported by members of the bicycle frame such that the CVT is coaxial with the crankshaft of the bicycle. The crankshaft is configured to drive elements of the planetary gearset, which are configured to operationally drive the traction rings and the traction planets. Inventive component and subassemblies for such a CVT are disclosed. A shifting mechanism includes a plurality of pivot arms arranged to pivot about the centers of the traction planets as a shift pin hub moves axially.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The single axle transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. An additional embodiment is disclosed which shifts automatically dependent upon the rotational speed of the wheel. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The disclosed transmission may be used in vehicles such as automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles. The transmission may, for example, be driven by a power transfer mechanism such as a sprocket, gear, pulley or lever, optionally driving a one way clutch attached at one end of the main shaft.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Adjustable-Length Seat Post
Owner:KLIEBER JOCHEN
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The single axle transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. An additional embodiment is disclosed which shifts automatically dependent upon the rotational speed of the wheel. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The disclosed transmission may be used in vehicles such as automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles. The transmission may, for example, be driven by a power transfer mechanism such as a sprocket, gear, pulley or lever, optionally driving a one way clutch attached at one end of the main shaft.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
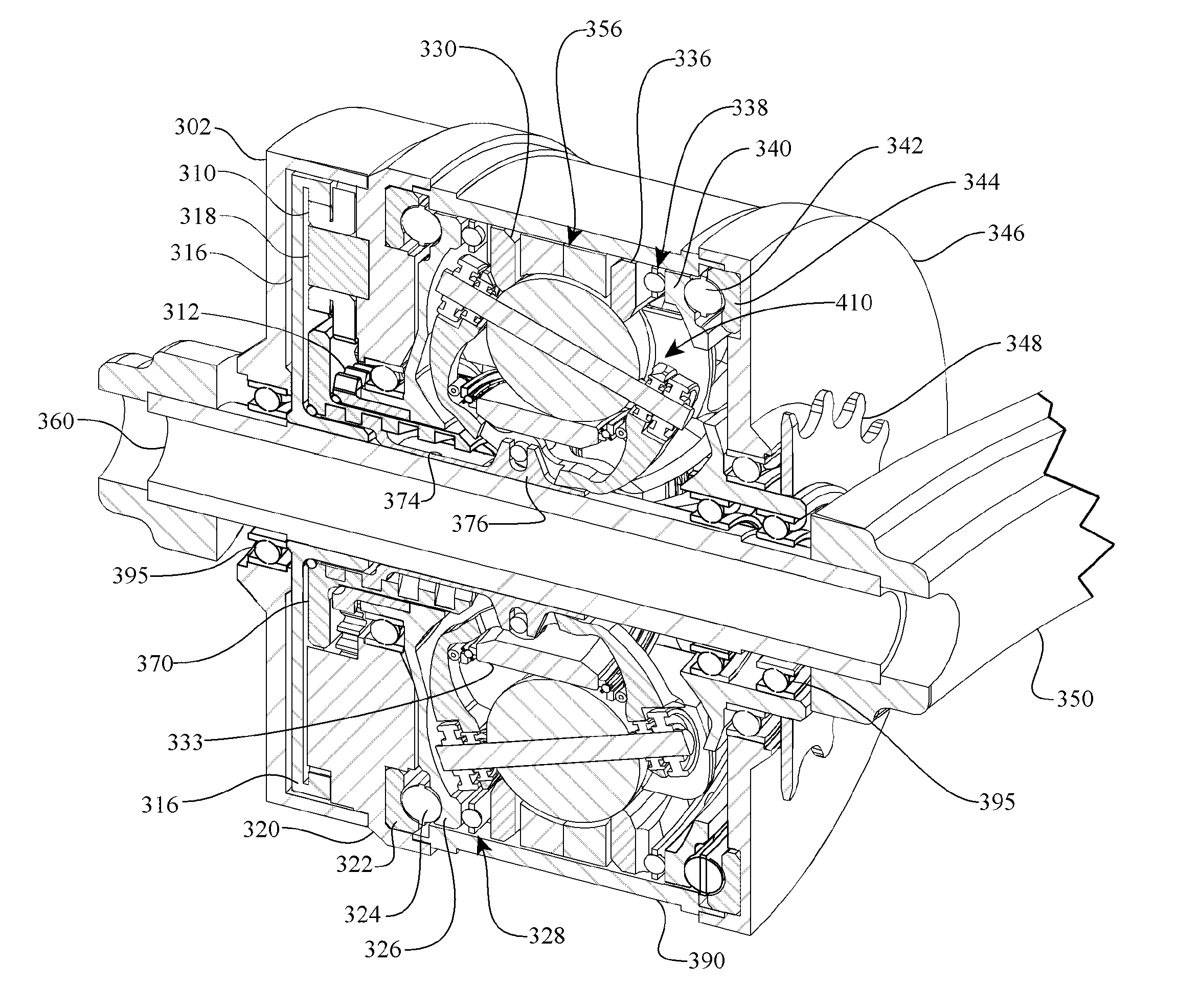
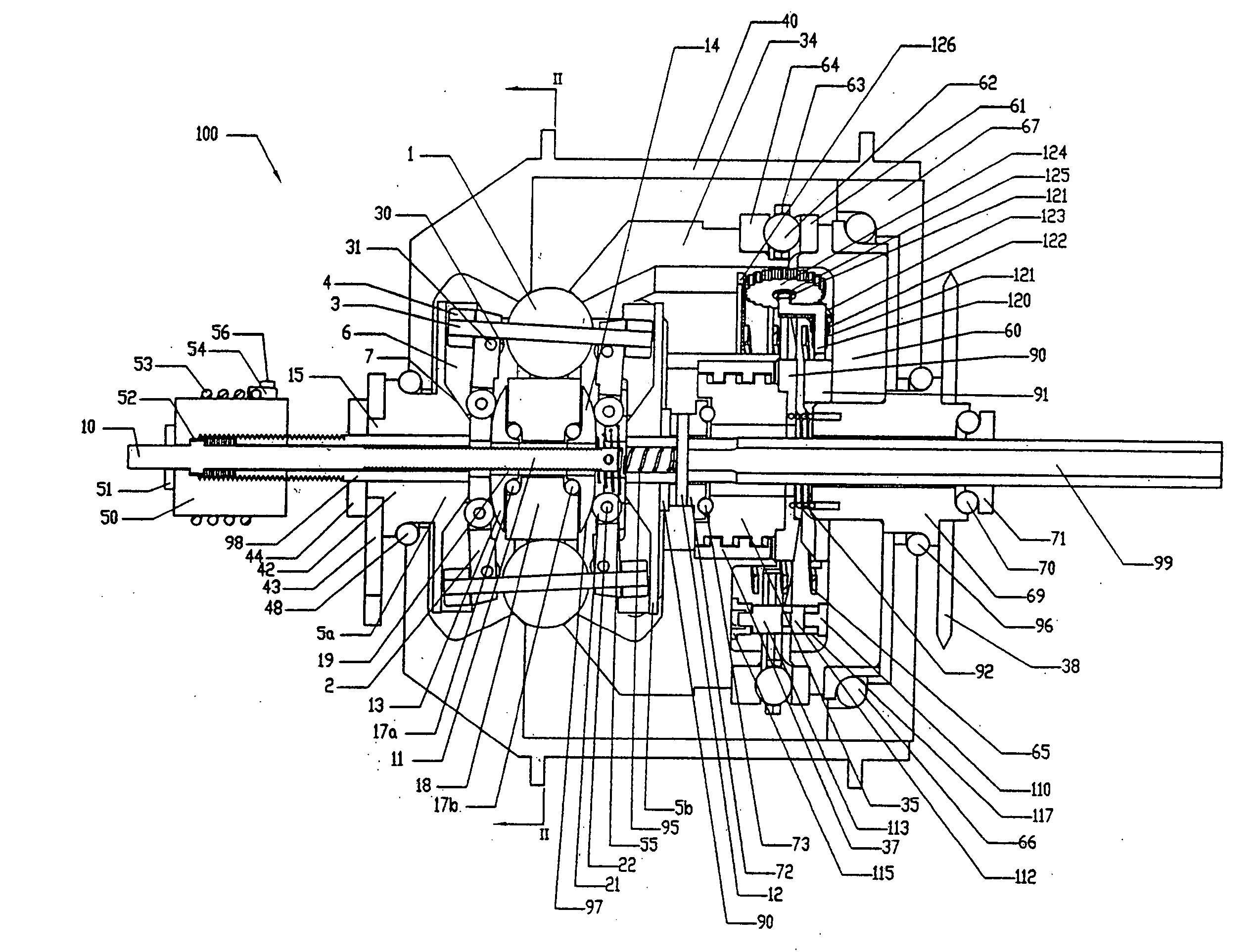
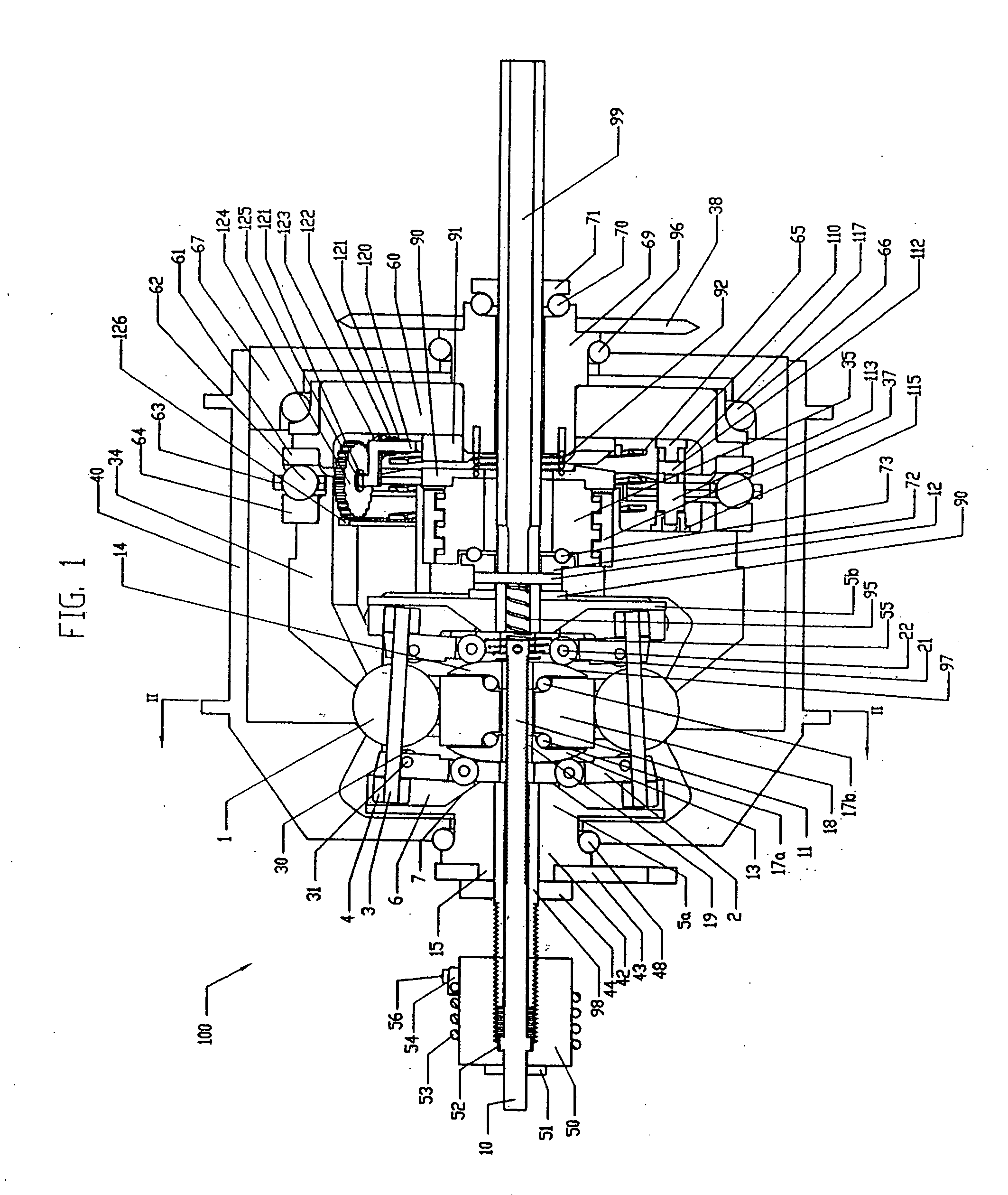
Electric traction drives
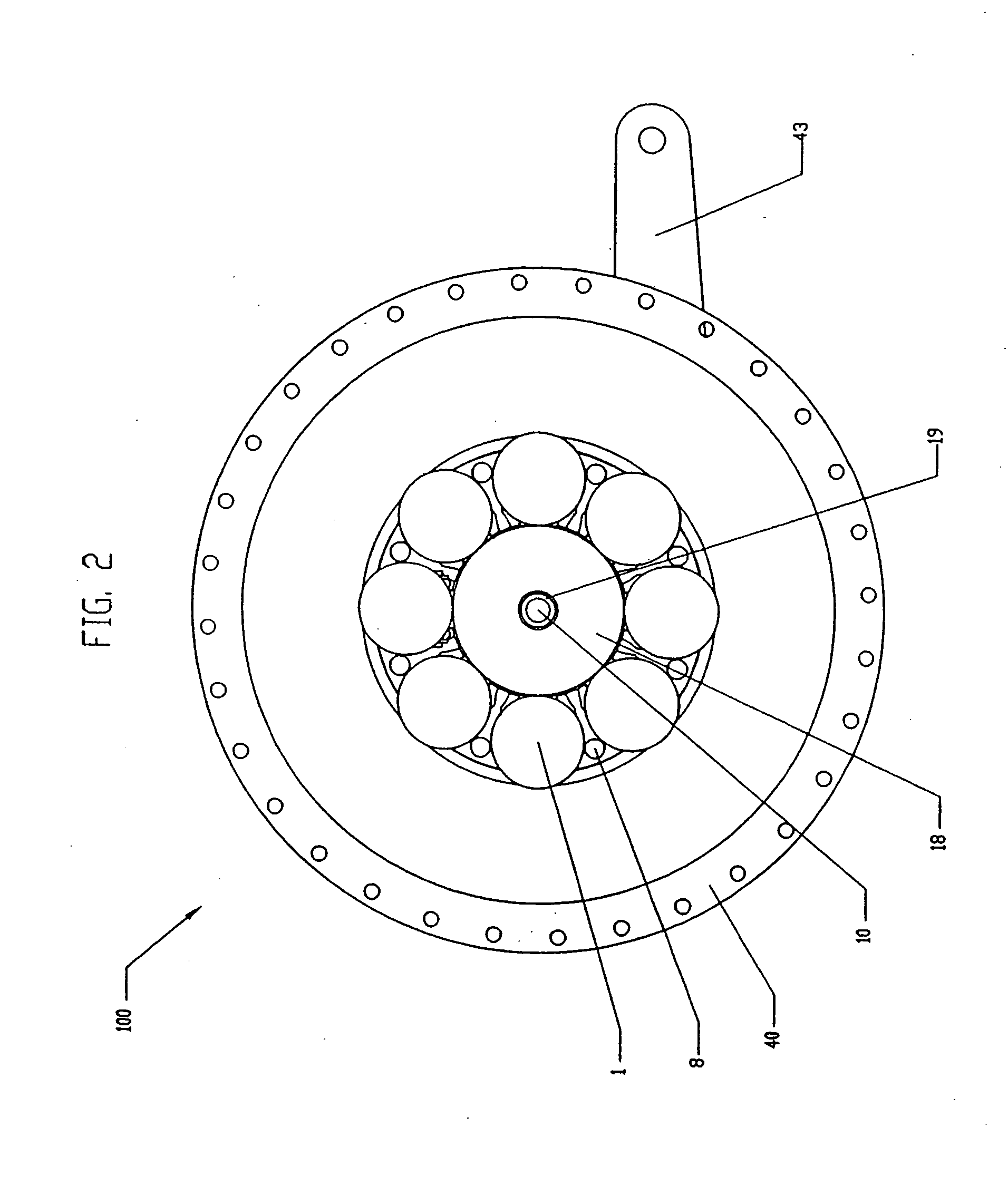
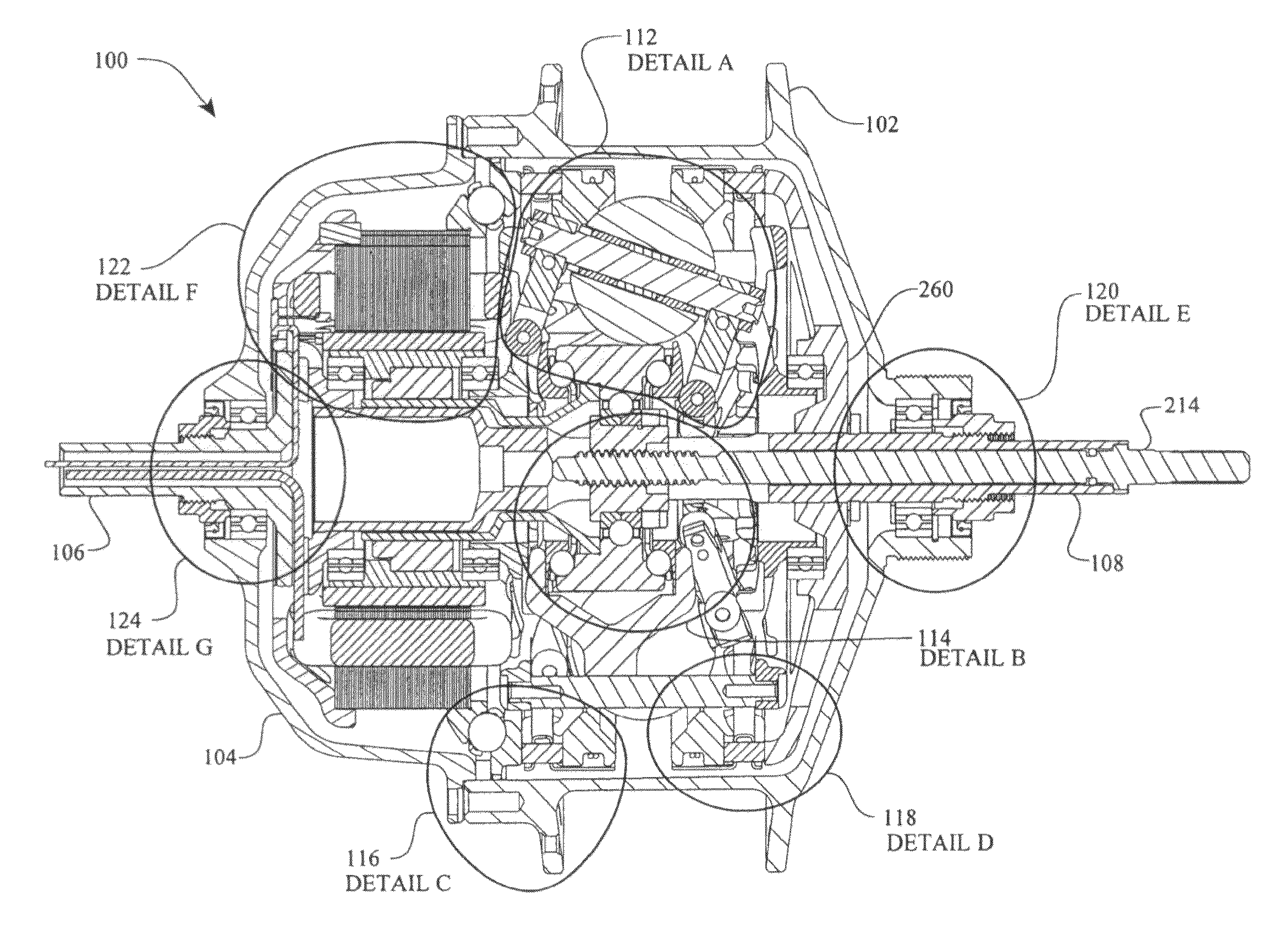
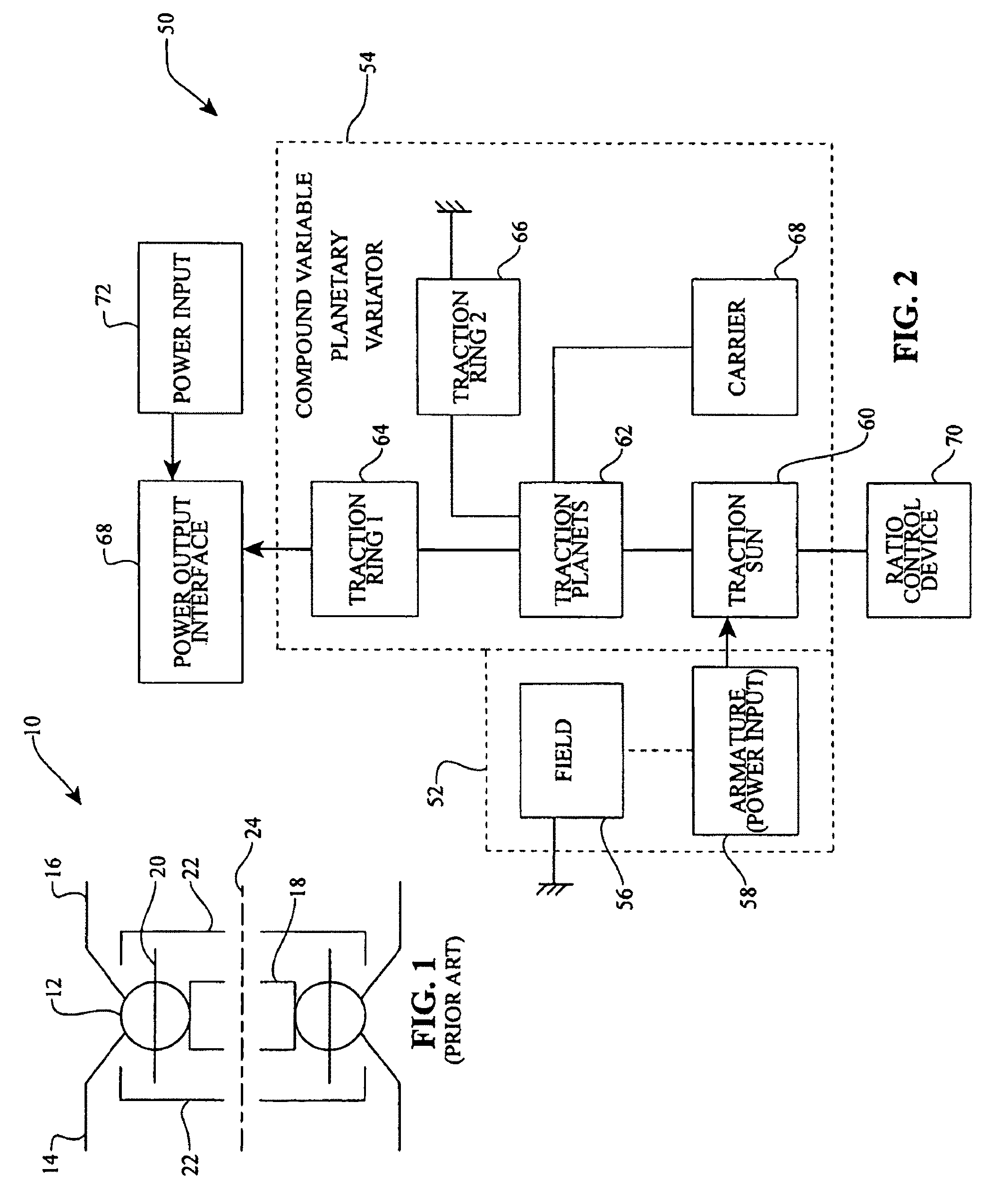
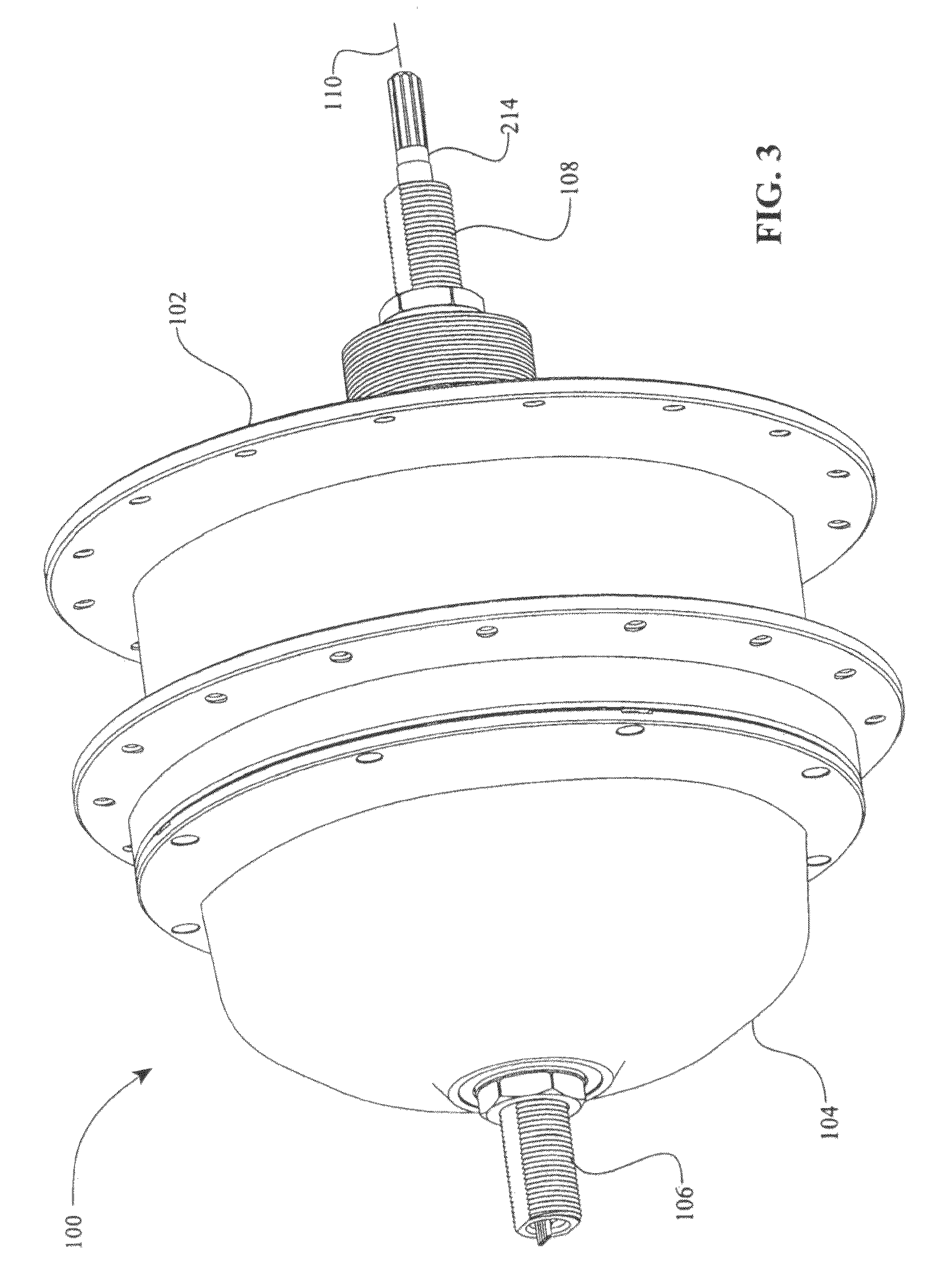
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for electric traction drives employing a continuously variable transmission (CVT) having a variator provided with a plurality of tilting traction planets and opposing traction rings. In one embodiment, an electric traction drive is provided with an electromotive device configured to transfer power to or from a traction sun of a CVT, In other embodiments, an electric traction drive is provided with an electromotive device that couples to certain components of a CVT such as a traction ring, a carrier assembly, and a main axle. Various inventive shifting assemblies having shift cams and shift cam cages can be used to facilitate adjusting the transmission speed ratio of a CVT. Various related devices include embodiments of, for example, a power input apparatus, a speed ratio shifter, a shift cam actuator, a shift nut, and a carrier assembly configured to support the tilting traction planets.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The single axle transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. An additional embodiment is disclosed which shifts automatically dependent upon the rotational speed of the wheel. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The disclosed transmission may be used in vehicles such as automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles. The transmission may, for example, be driven by a power transfer mechanism such as a sprocket, gear, pulley or lever, optionally driving a one way clutch attached at one end of the main shaft.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Vertically adjustable bicycle assembly
ActiveUS8328454B2Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringExpansion joint
An adjustable assembly for a bicycle includes a first support having an interior surface and a second support slidably positioned within at least a portion of the first support. One of the first support and the second support is adapted to attach to a first bicycle portion, and the other of the first support and the second support is adapted to attach to a second bicycle portion. Further, the second support comprises an expansion portion configured to be moved between an expanded position and a retracted position. The expansion portion is configured to engage the interior surface of the first support when the expansion portion is in an expanded position. In addition, the first support is configured to be selectively moved relative to the second support when the expansion portion is permitted to assume a retracted position. In some embodiments, the first bicycle portion comprises a bicycle frame and the second bicycle portion comprises a bicycle saddle. In other arrangements, the first bicycle portion comprises a fork assembly and the second bicycle portion comprises a handlebar assembly.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
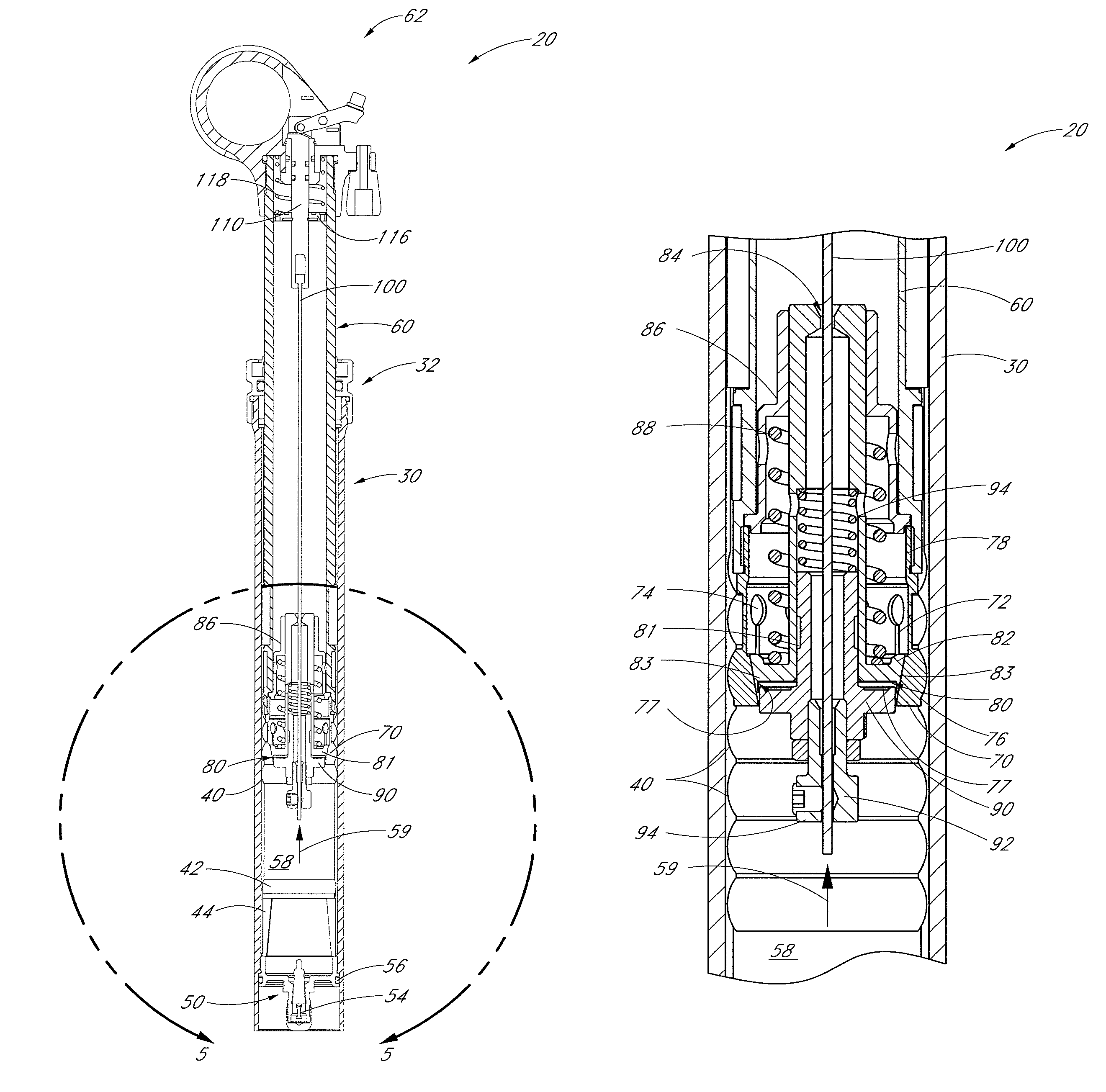
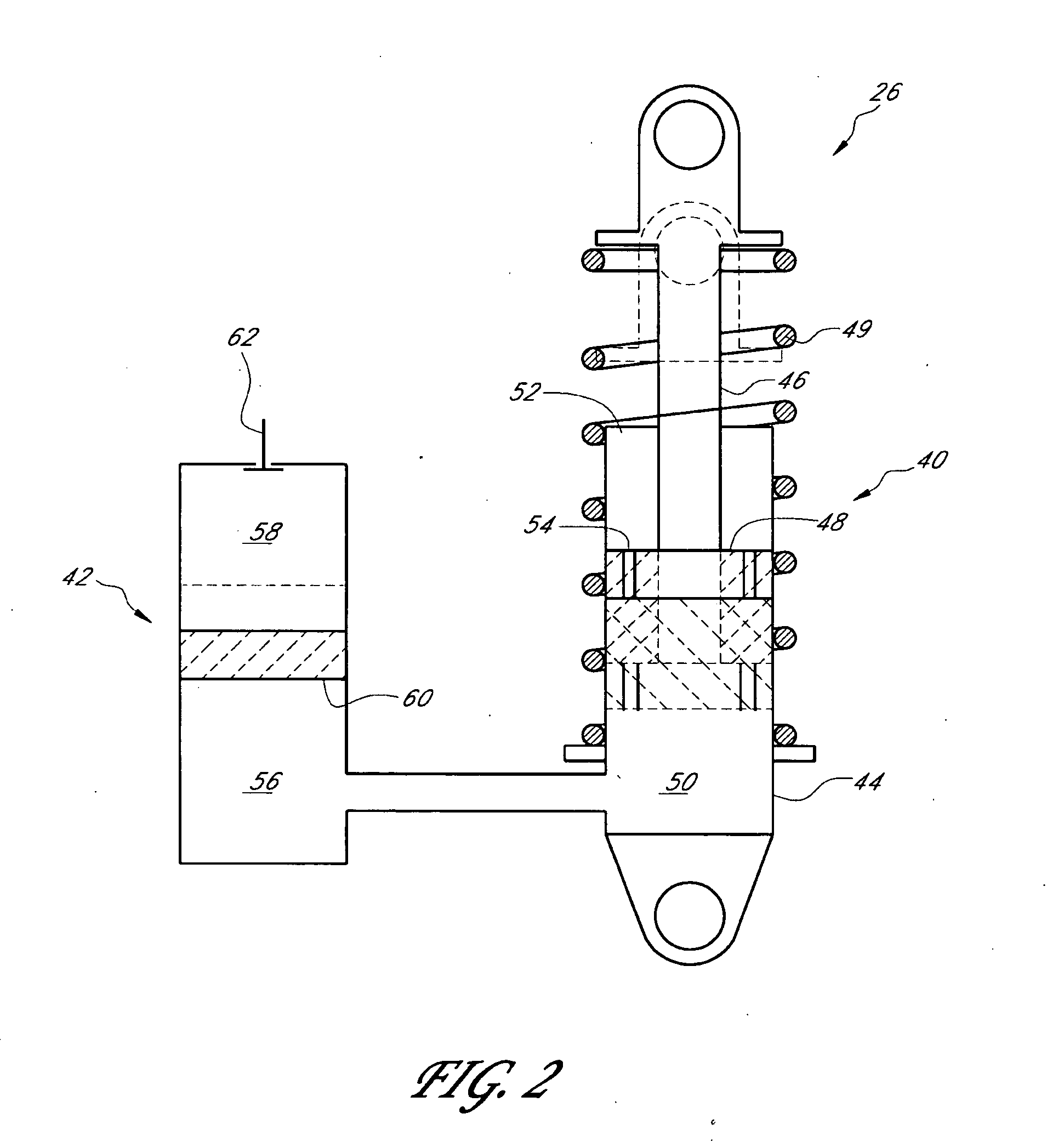
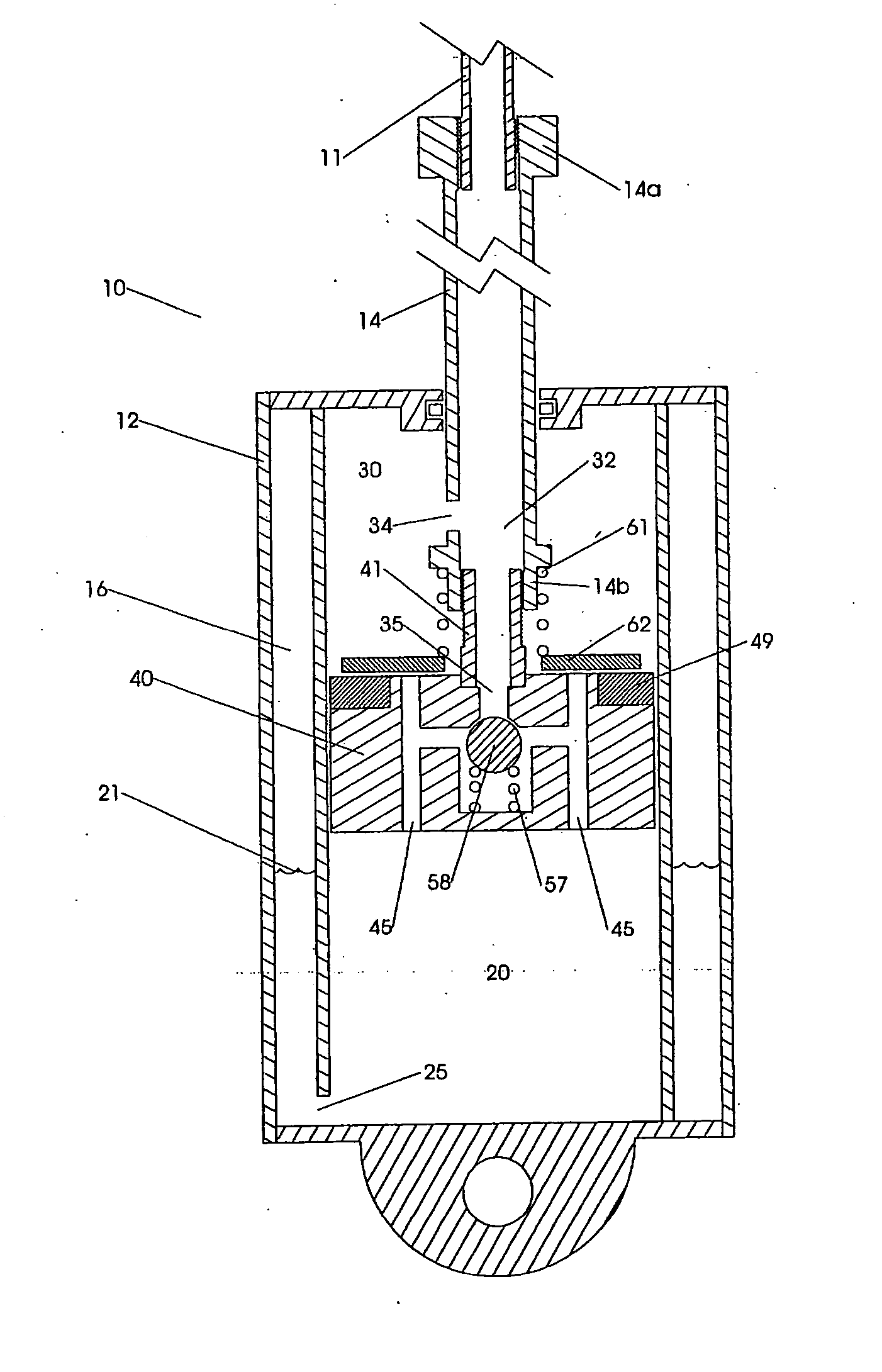
Lockout mechanism for a suspension system
ActiveUS20050104320A1Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringDischarge pressure
A suspension system that includes a simplified lockout mechanism and an adjustable blow-off mechanism. The system includes a valve mechanism and a valve actuating assembly, a valve mechanism housing and a resilient member disposed between the valve mechanism and the valve mechanism housing. The valve mechanism is slidably mounted along the valve mechanism housing and it separates a first chamber from a second chamber. The valve actuating assembly operates the valve mechanism between open and closed positions. The resilient member is configured to be deformable by the valve mechanism as the valve mechanism is slidably displaced by an increasing pressure in the first fluid chamber. The sliding valve mechanism is configured to collide against the valve actuating assembly when a blow-off pressure is reached in the first fluid chamber switching the valve mechanism from the closed position to the open position.
Owner:SRAM CORPORATION
Position sensitive shock absorber
ActiveUS20070080515A1Effective levelingEasy to noticePassenger cyclesWheel based transmissionReciprocating motionEngineering
A shock absorber includes a tube and a piston rod carrying a piston. The piston is configured for reciprocal movement within the tube. A floating piston, or other type of accumulator, is configured to move to accommodate fluid displaced due to successive portions of the piston rod entering the tube during compression of the shock absorber. The shock absorber includes a valve mechanism that utilizes the movement of the floating piston to move the valve between a first and second position, which preferably are open and closed positions.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
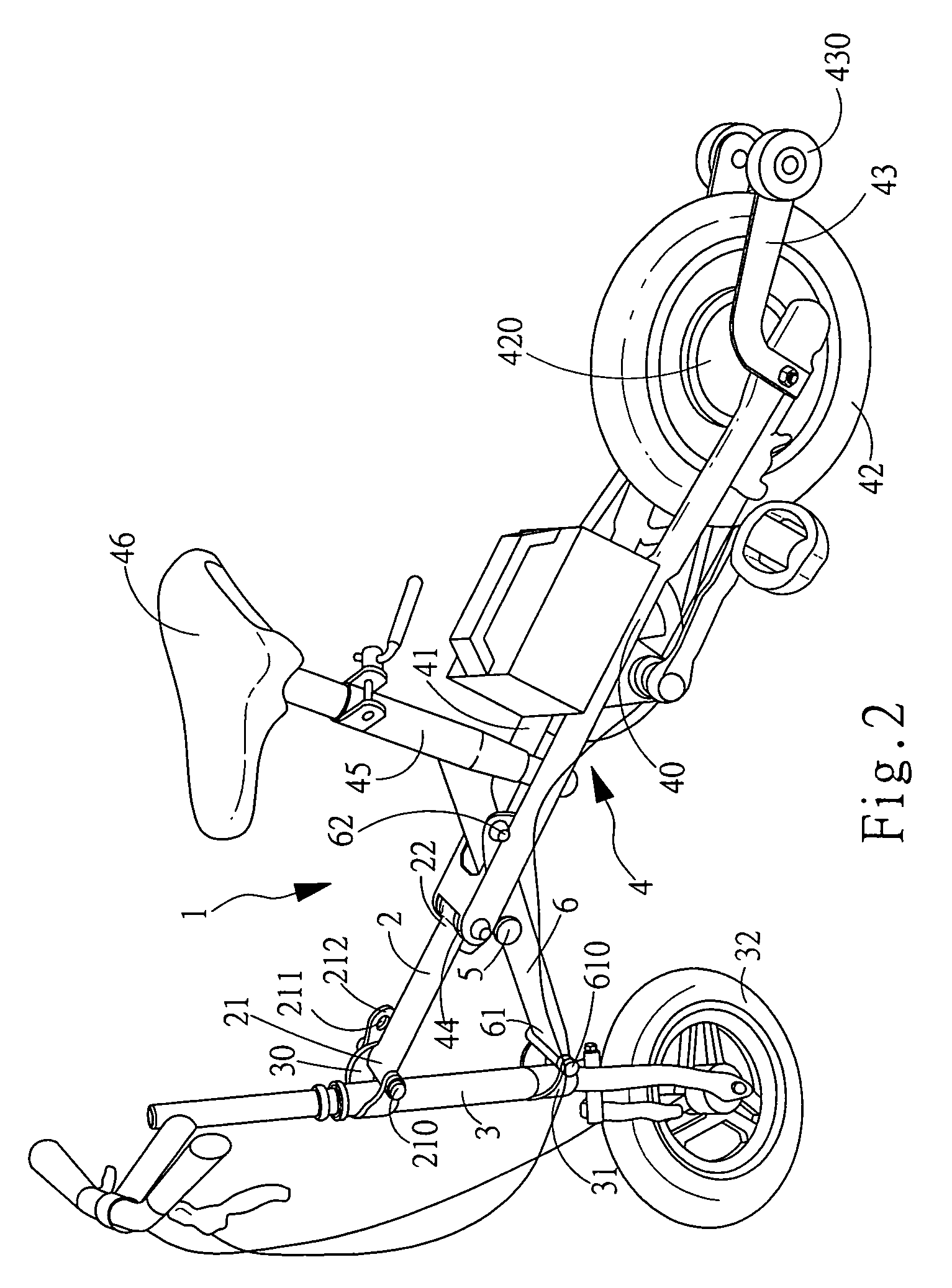
Structure of a bicycle for children
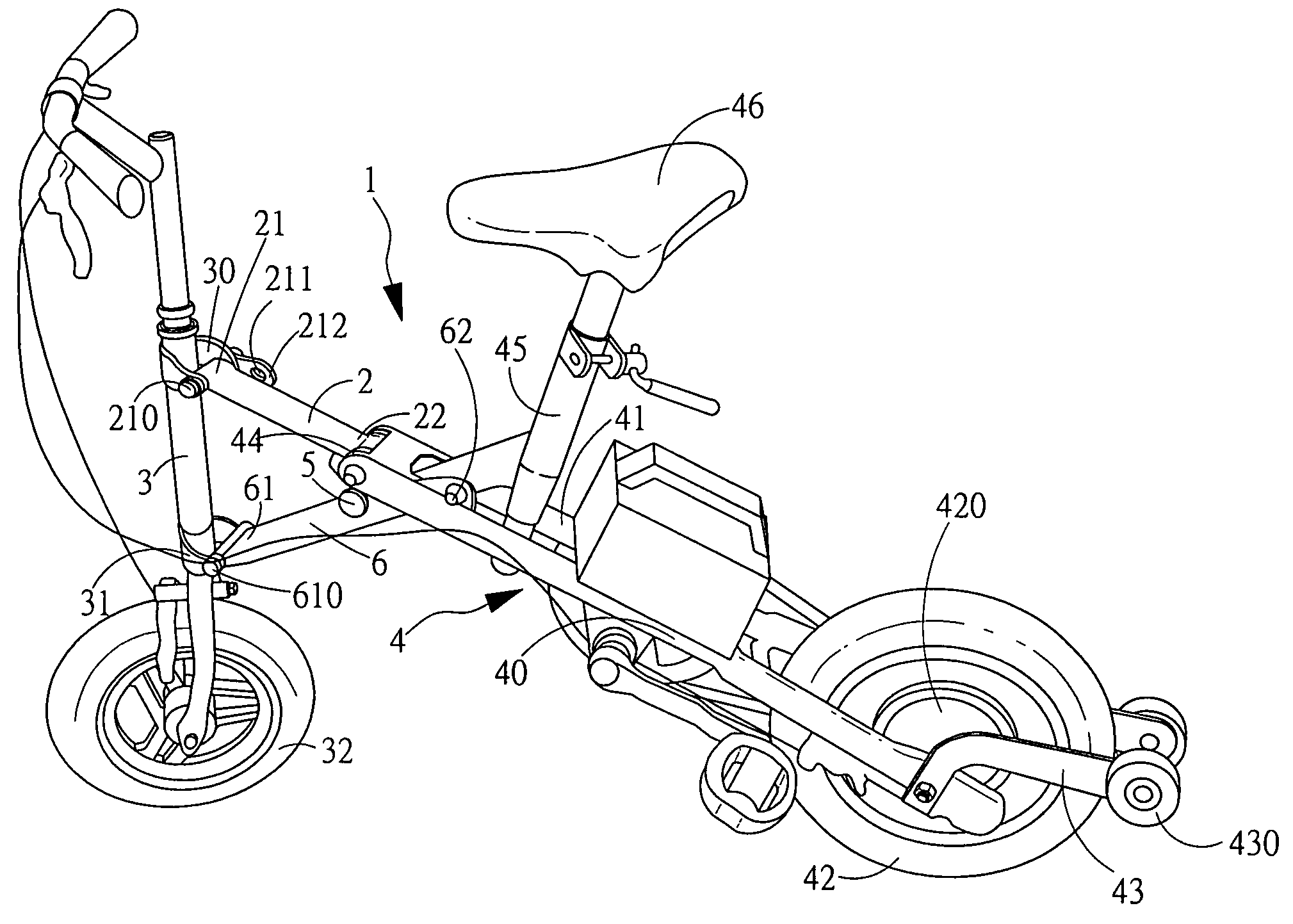
An improved structure of a bicycle for children is disclosed. The bicycle comprises a front and a rear frame and a flexural mechanism is used to connect the front and the rear frame such that the tricycle can be folded. The upper section of the front frame is extended with a foldable handle and the front frame is provided with a rotating shaft. The rotating shaft is connected to a control shaft disposed at the rear frame by means of a cable such that the tricycle can be control the front wheel to move left or right by controlling the left and right movement of the control shaft.
Owner:FU KUANG HUAN
Magnetic valve for shock absorbers
ActiveUS20070034464A1Improve suspension capacityImprove abilitiesFoot-driven leversWheel based transmissionMagnetic valveEngineering
A shock absorber having a valve controlling the flow rate of fluid between a compression chamber and a rebound chamber in a housing and separated by a piston. The valve has an orifice component and a blocker component, one of which has a permanent magnet, and the other of which has a magnetically permeable material. Upon the application of sufficient fluid pressure, the blocker component is forced away from the orifice component, despite the magnetic bias that tends to attract the two structures. Because the magnetic force decreases as the two components are spaced farther apart, the shock absorber has excellent performance characteristics. Alternatively, a mechanical spring urges the blocker closed, and magnetic attraction between the blocker and a spaced opener mitigates the increased force of the compressed spring tending to close the valve.
Owner:EKO SPORT
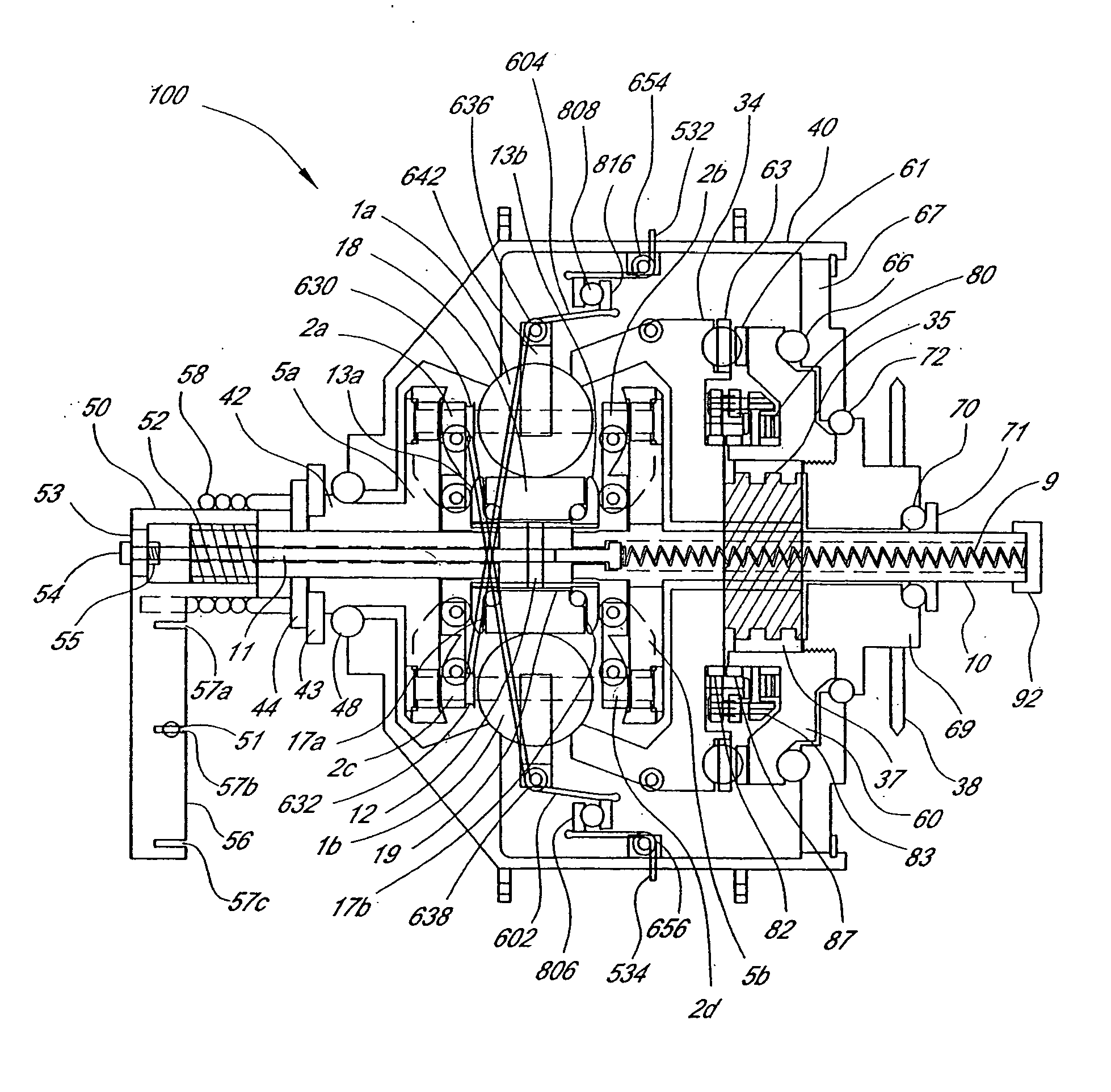
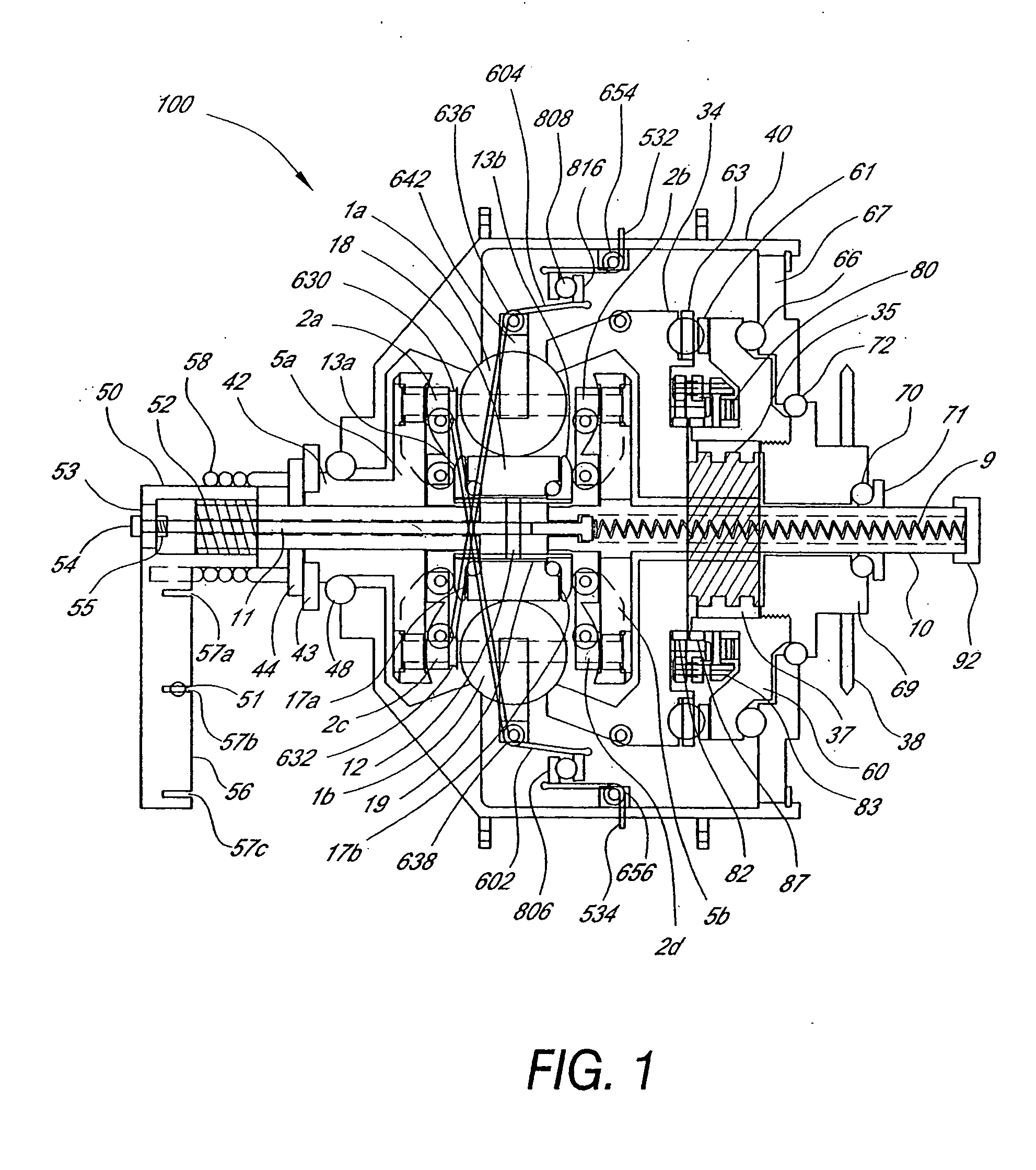
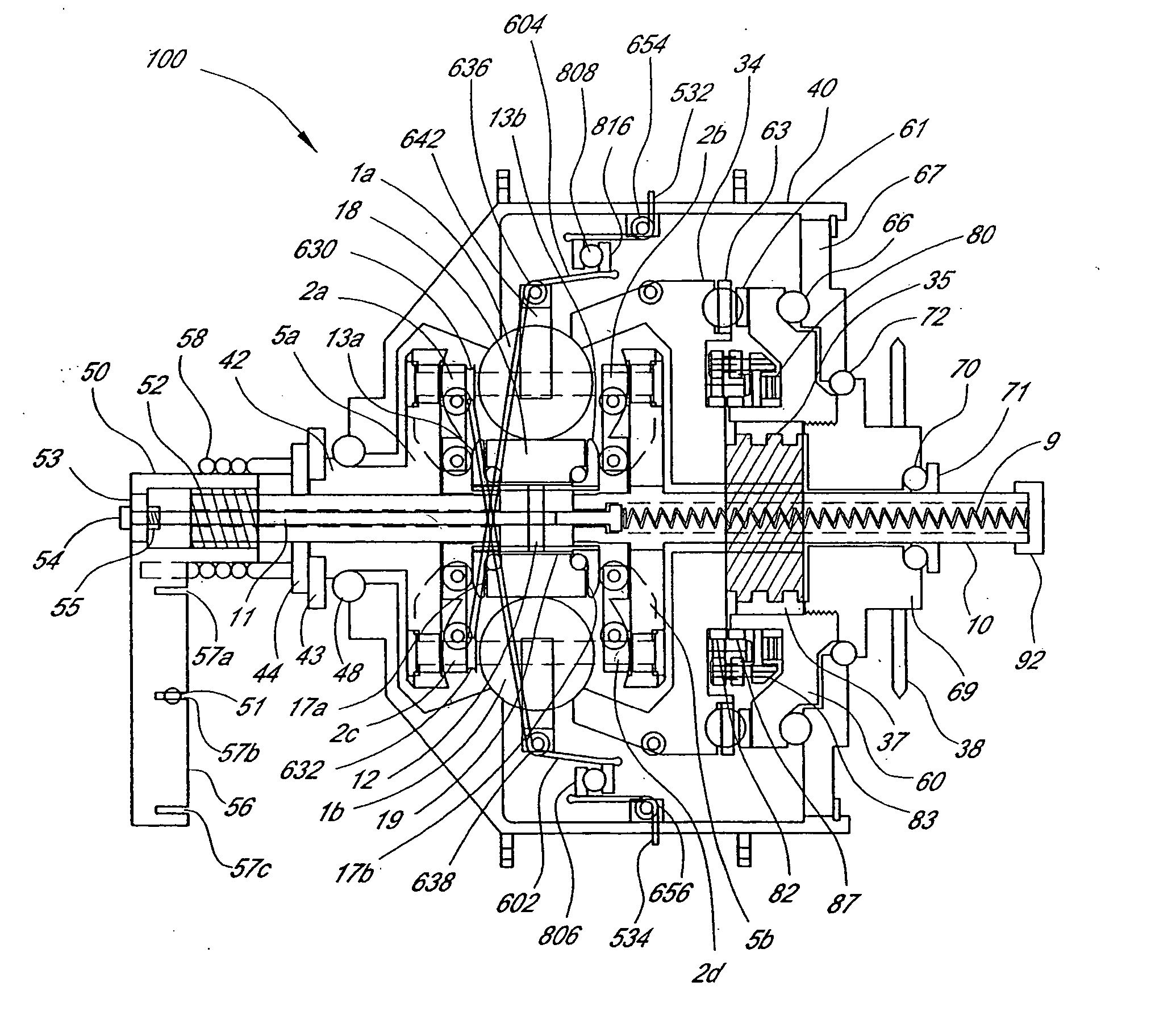
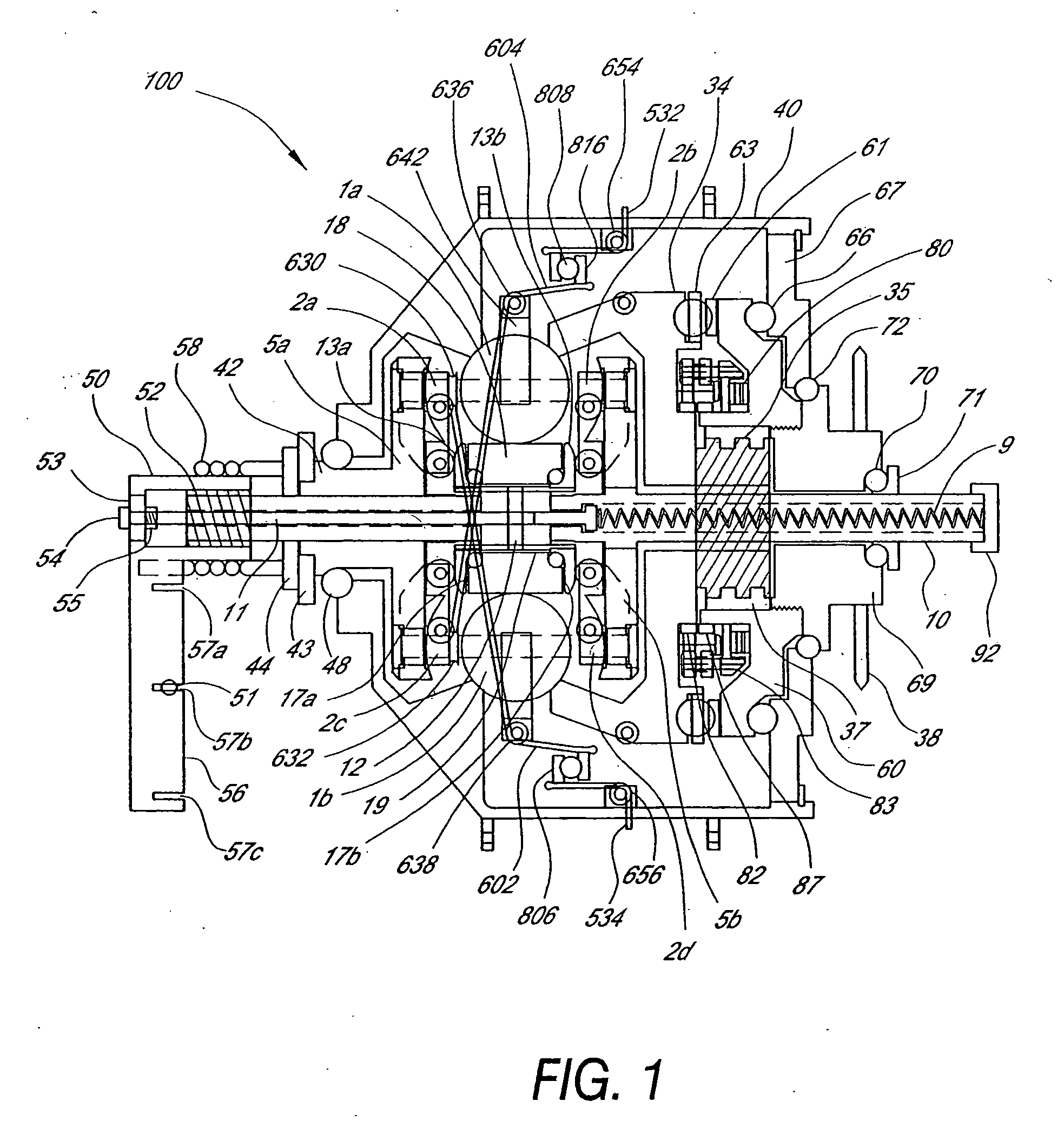
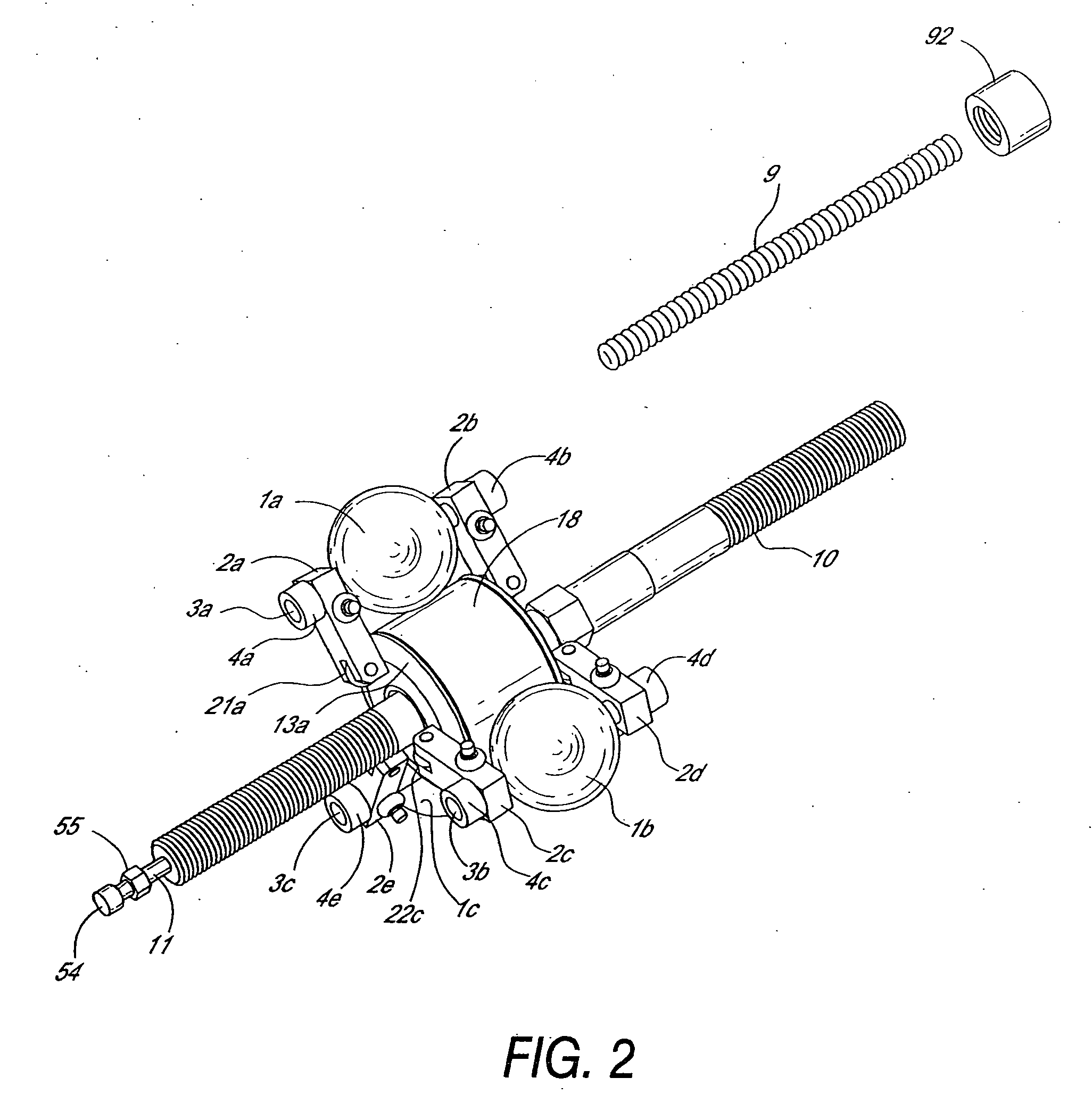
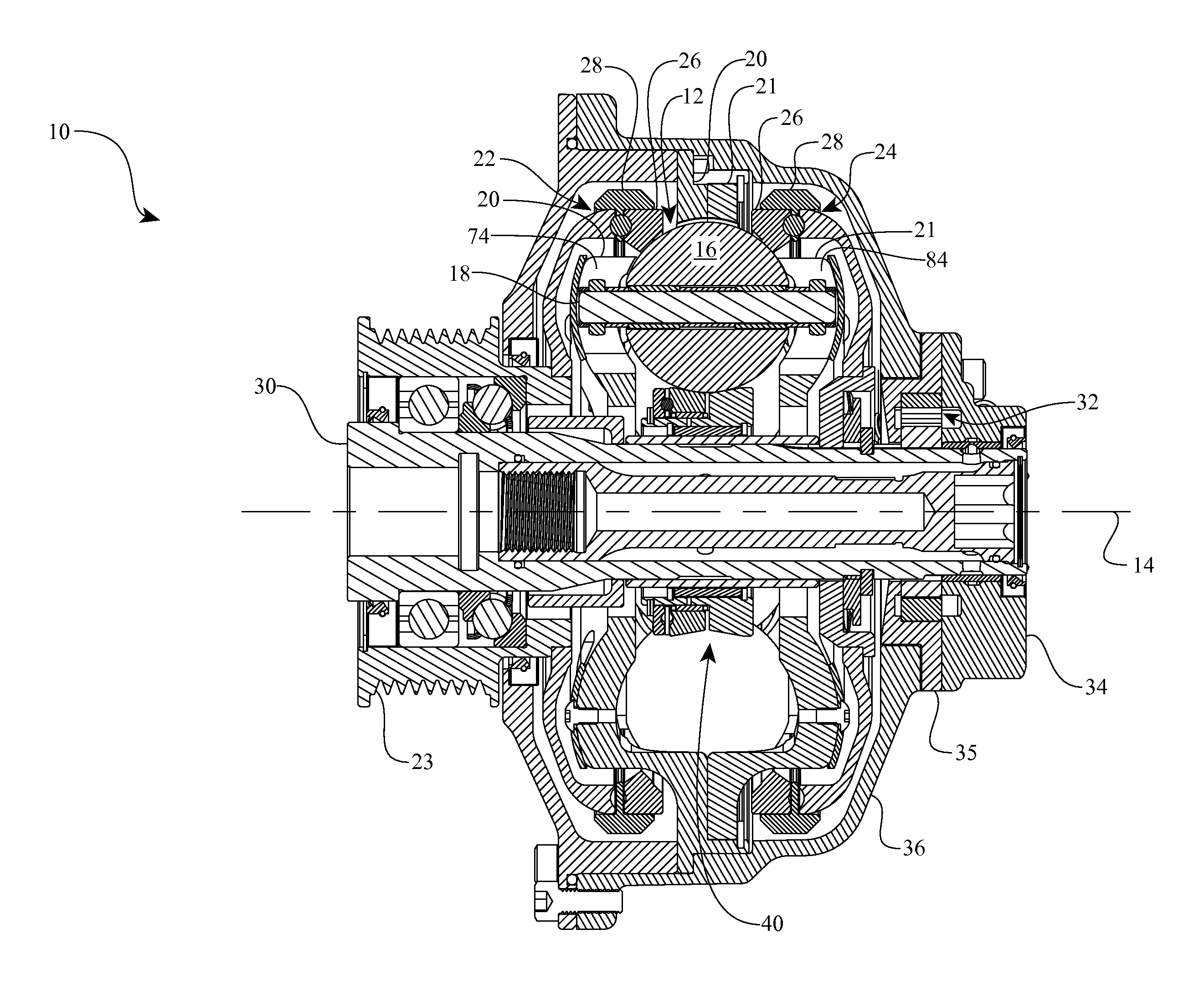
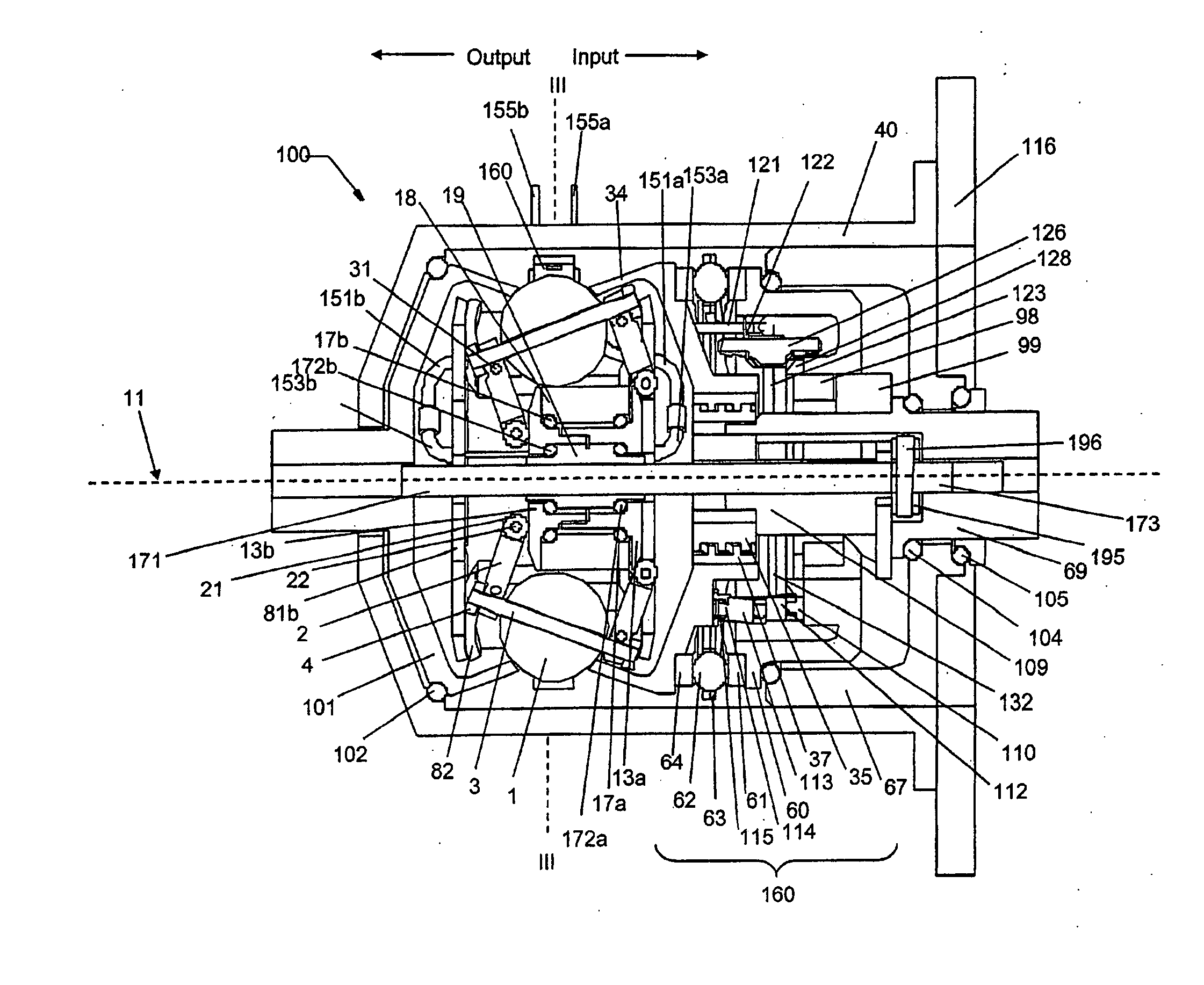
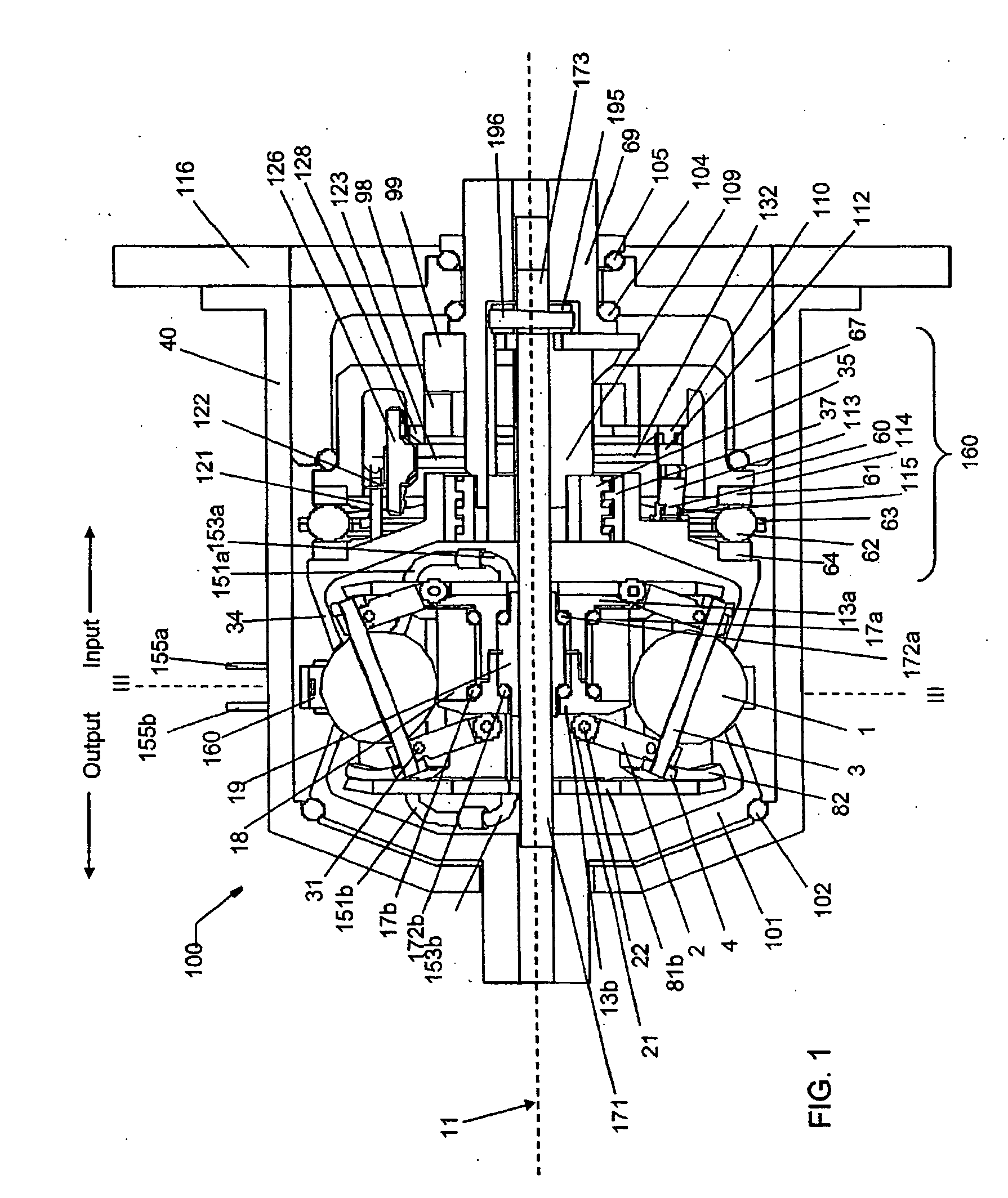
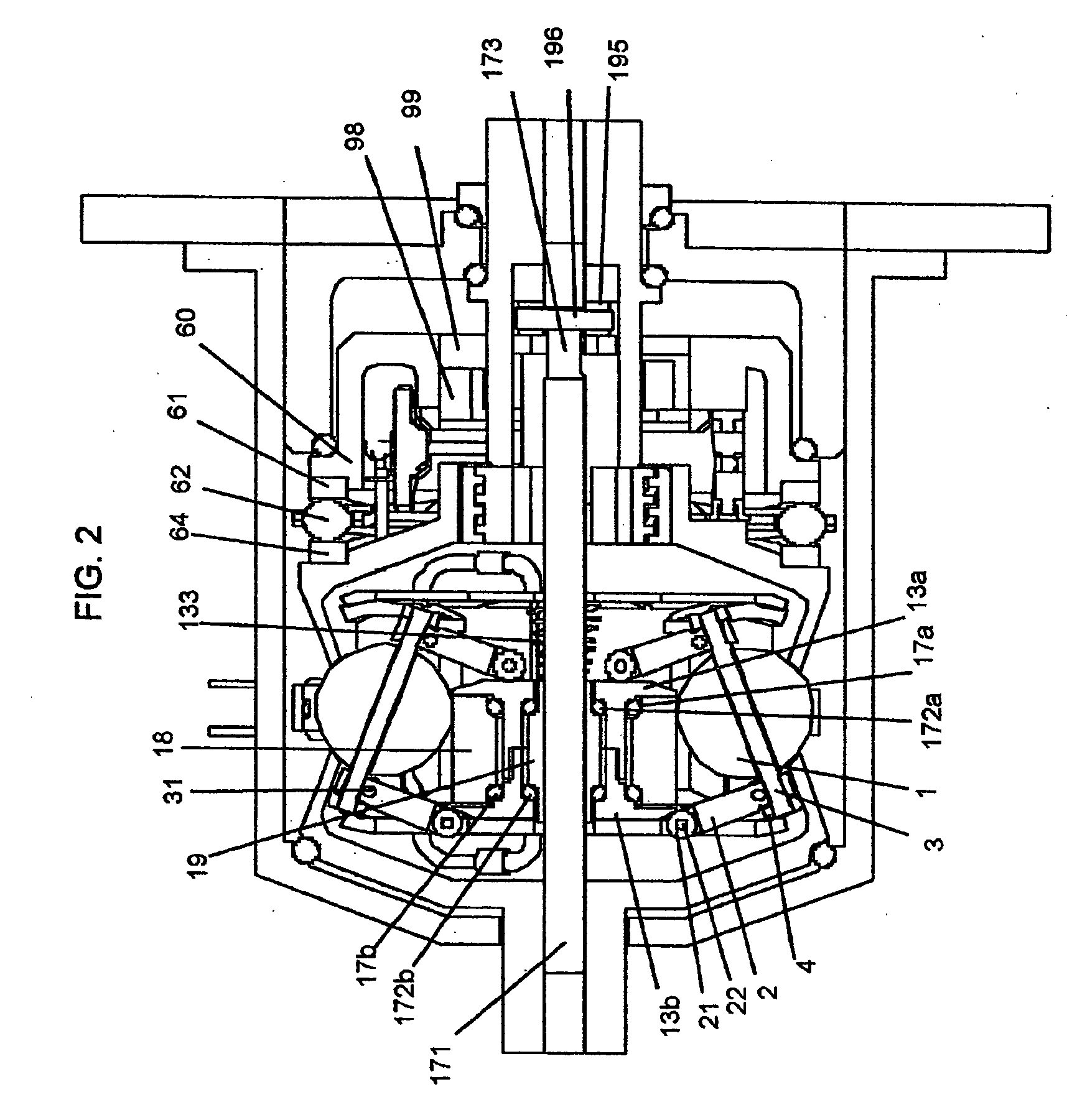
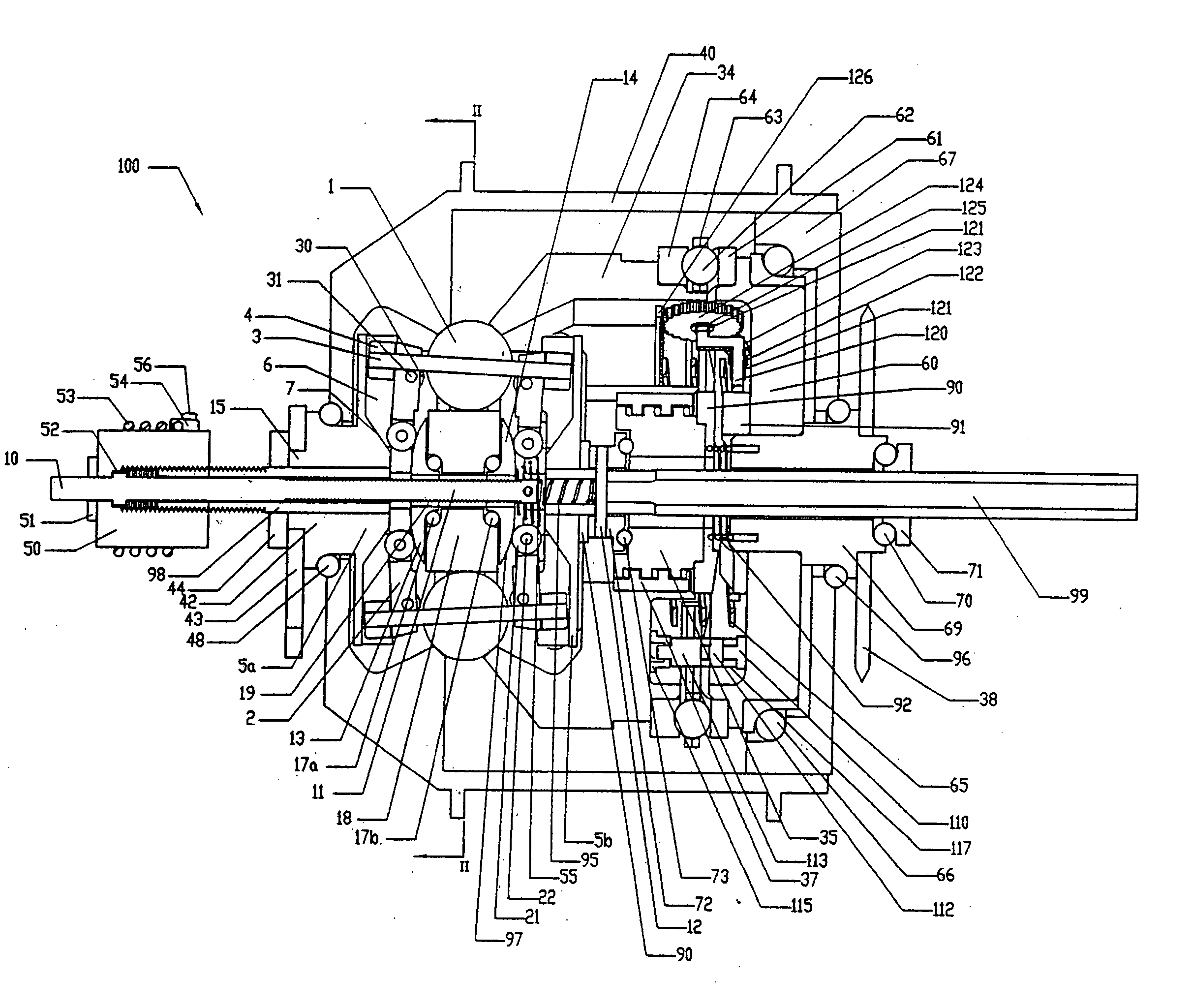
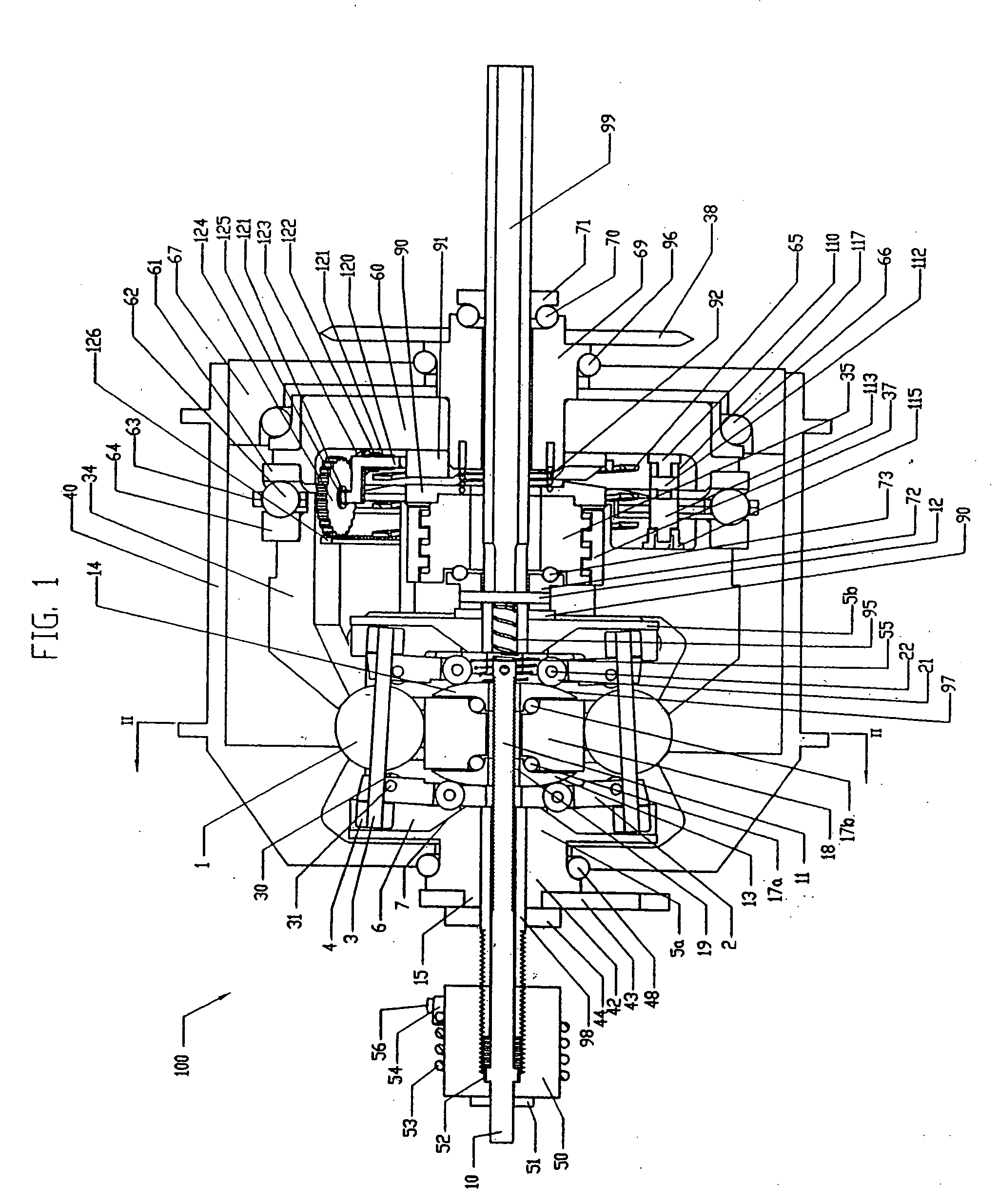
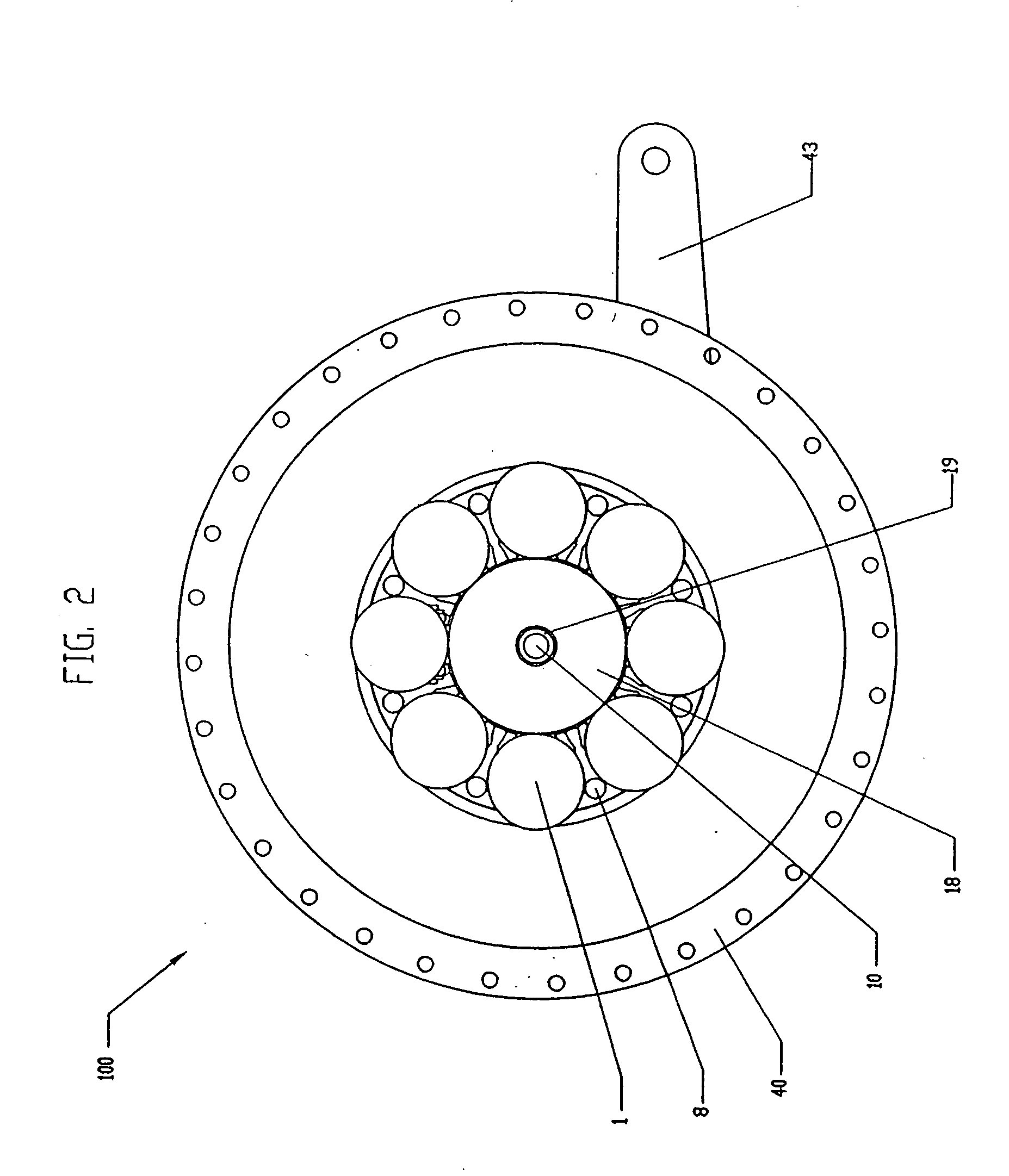
Continuously variable transmission
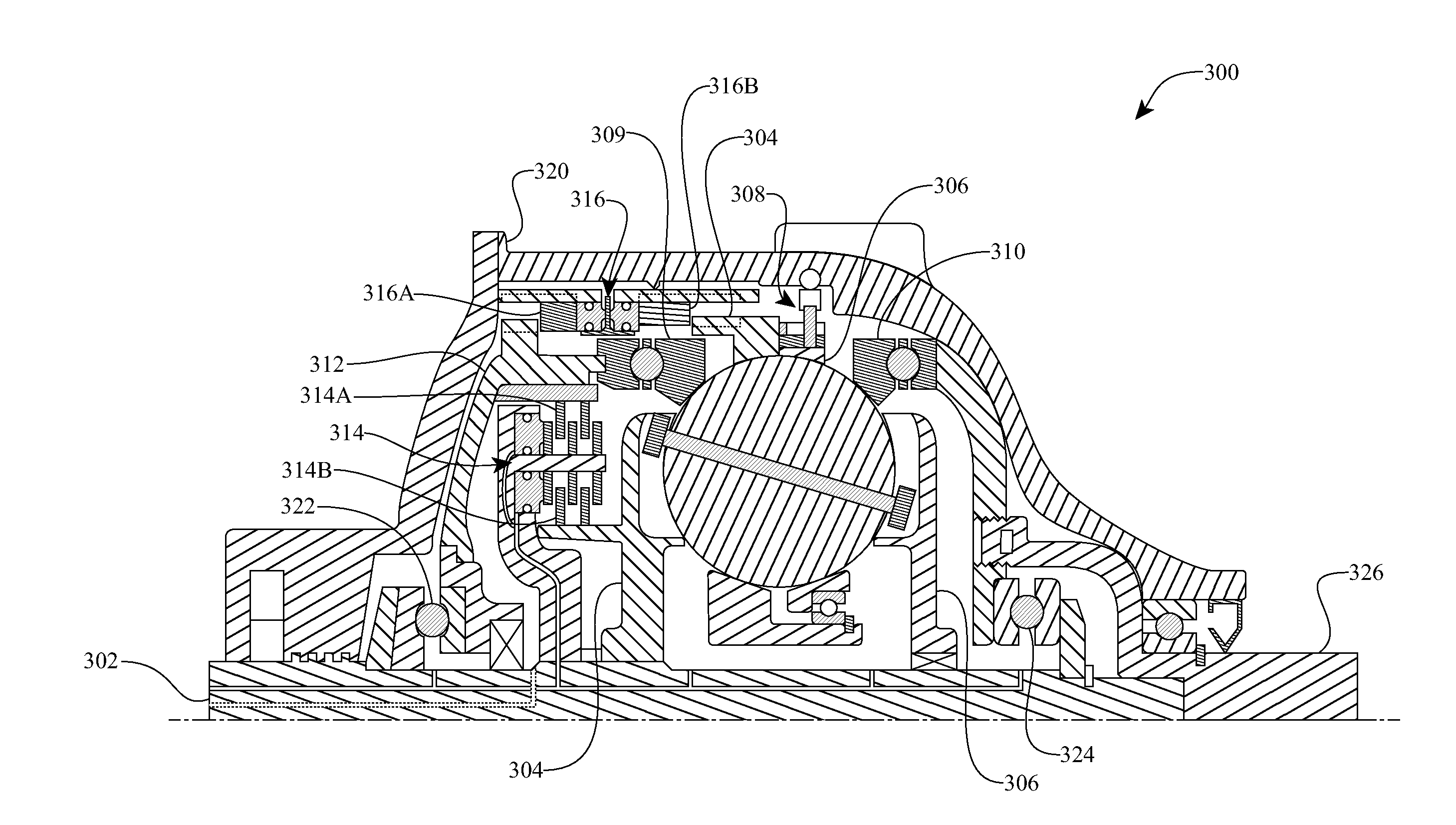
A variable speed transmission having a plurality of tilting balls and opposing input and output discs is illustrated and described that provides an infinite number of speed combinations over its transmission ratio range. The use of a planetary gear set allows minimum speeds to be in reverse and the unique geometry of the transmission allows all of the power paths to be coaxial, thereby reducing overall size and complexity of the transmission in comparison to transmissions achieving similar transmission ratio ranges.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
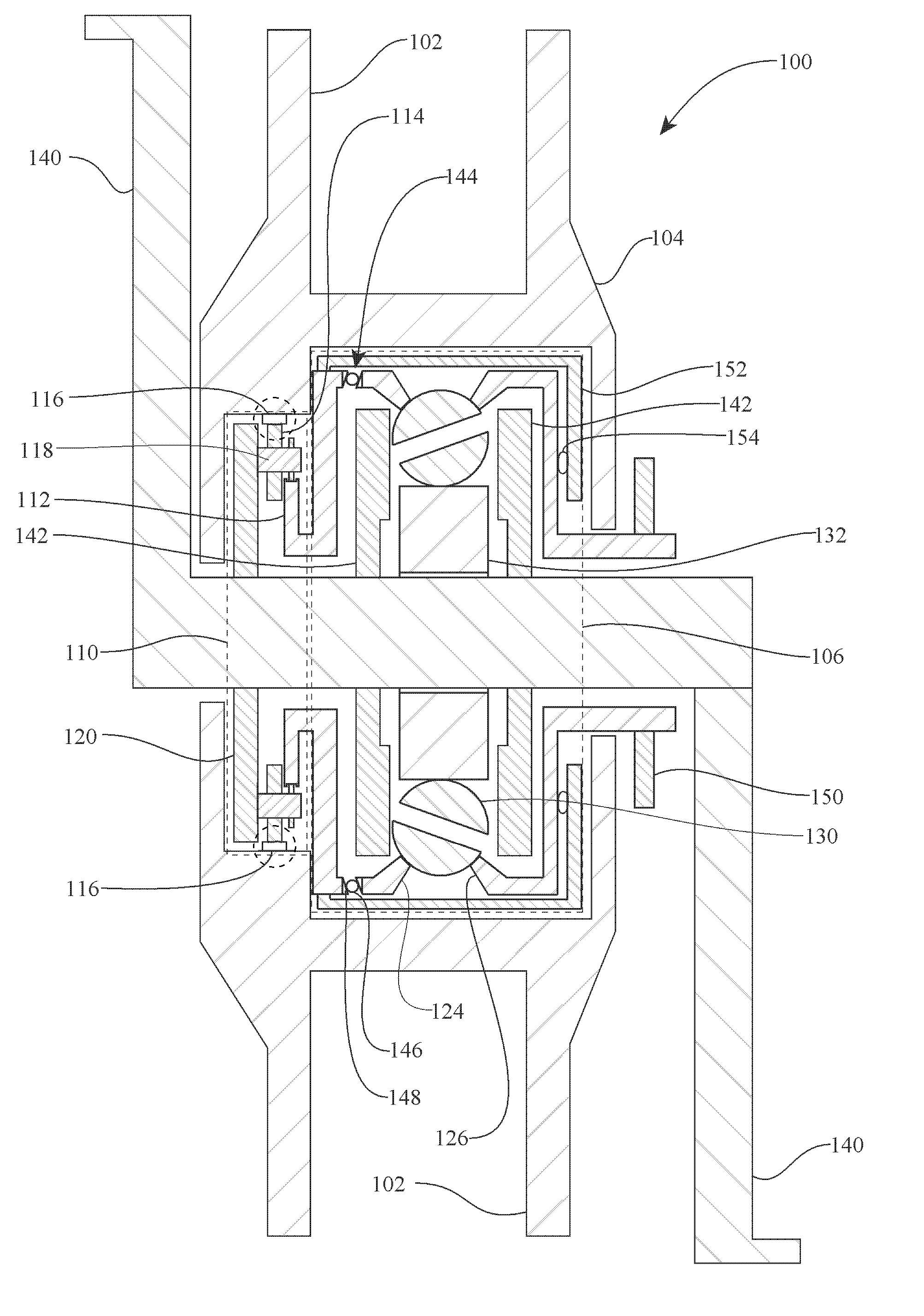
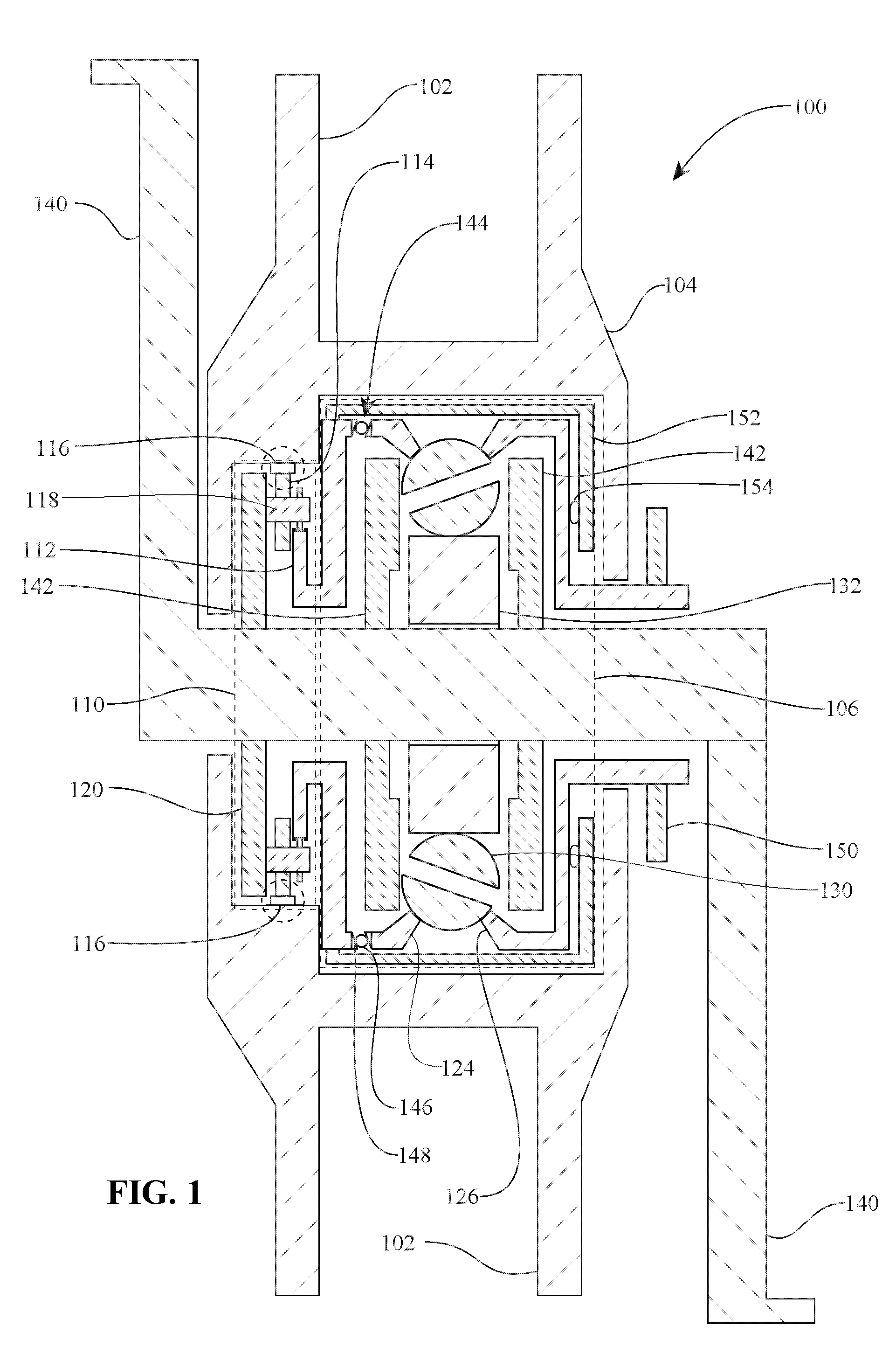
Infinitely variable transmissions, continuously variable transmissions, methods, assemblies, subassemblies, and components therefor
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for infinitely variable transmissions (IVT). In one embodiment, a control system is adapted to facilitate a change in operating mode of an IVT. In another embodiment, a control system includes a drive clutch coupled to a source of rotational power; the drive clutch is configured to selectively engage a traction ring and a carrier of the IVT. The control system includes a one-way clutch assembly configured to selectively engage the traction ring and the carrier. In some embodiments, the control system governs the actuation of the one-way clutch to selectively lock and unlock components of the IVT. In some embodiments, the control system implements an IVT mode wherein the carrier selectively couples to a source of rotational power. In other embodiments, the control system implements a CVT mode wherein the traction ring selectively couples to a source of rotational power.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
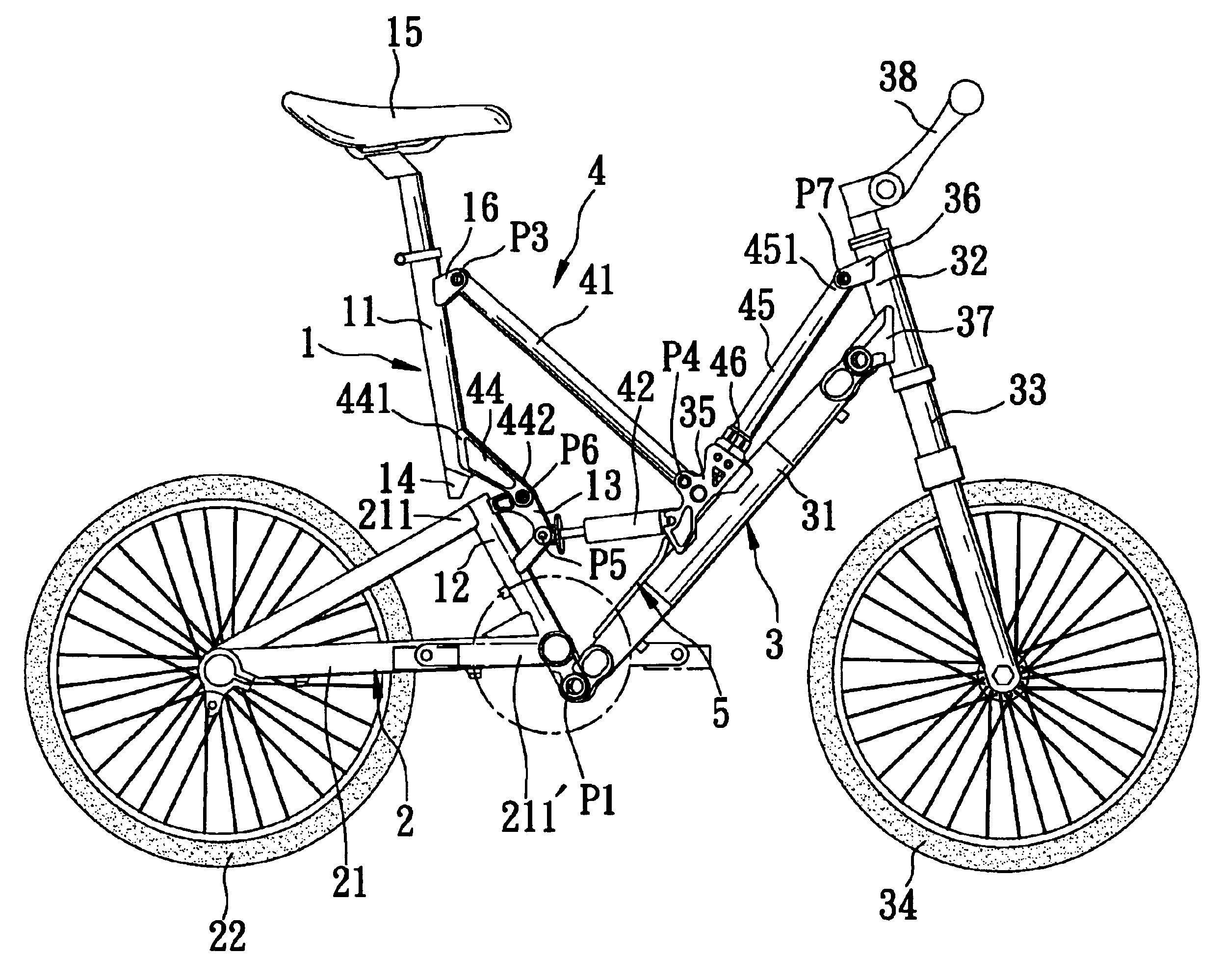
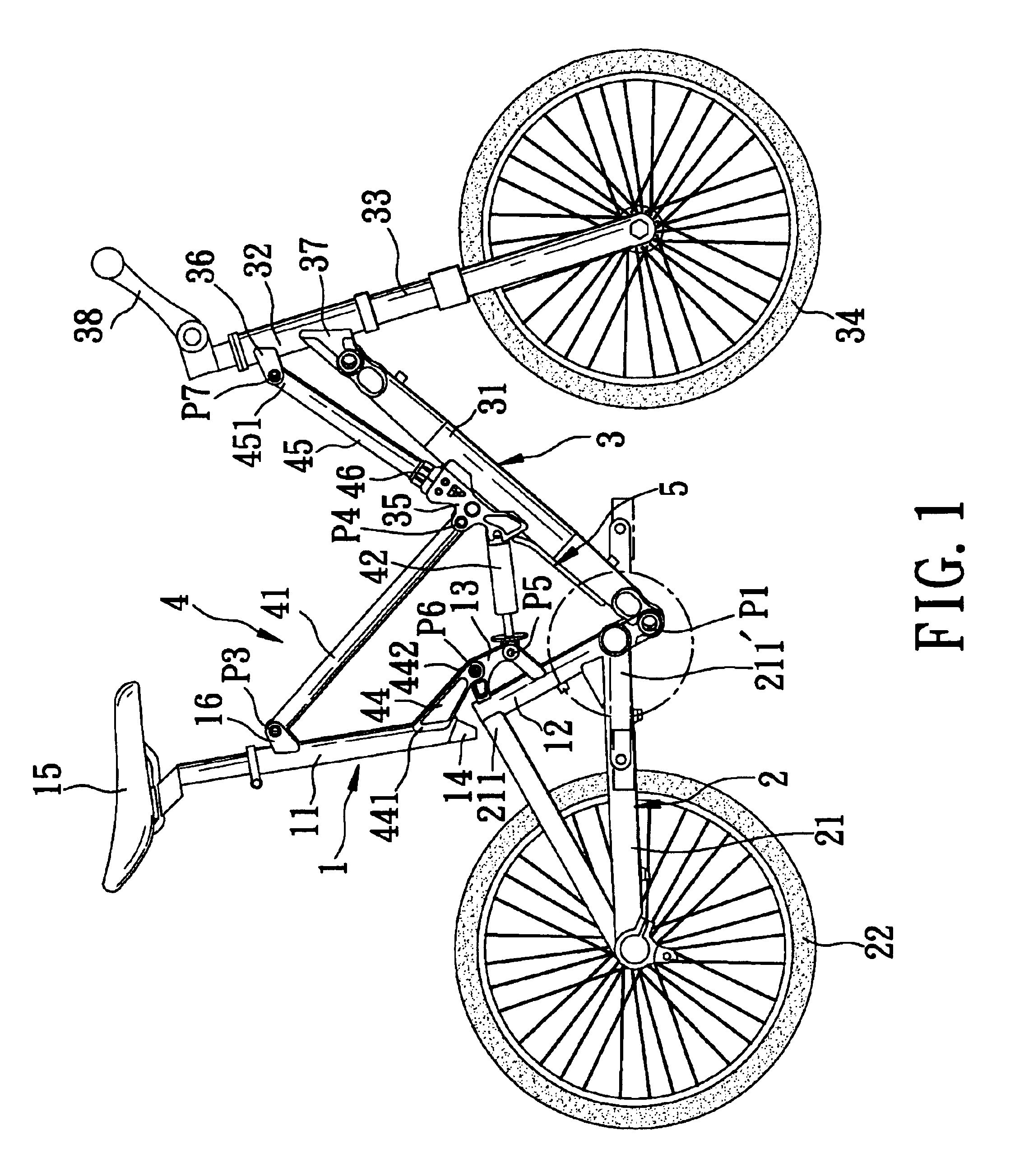
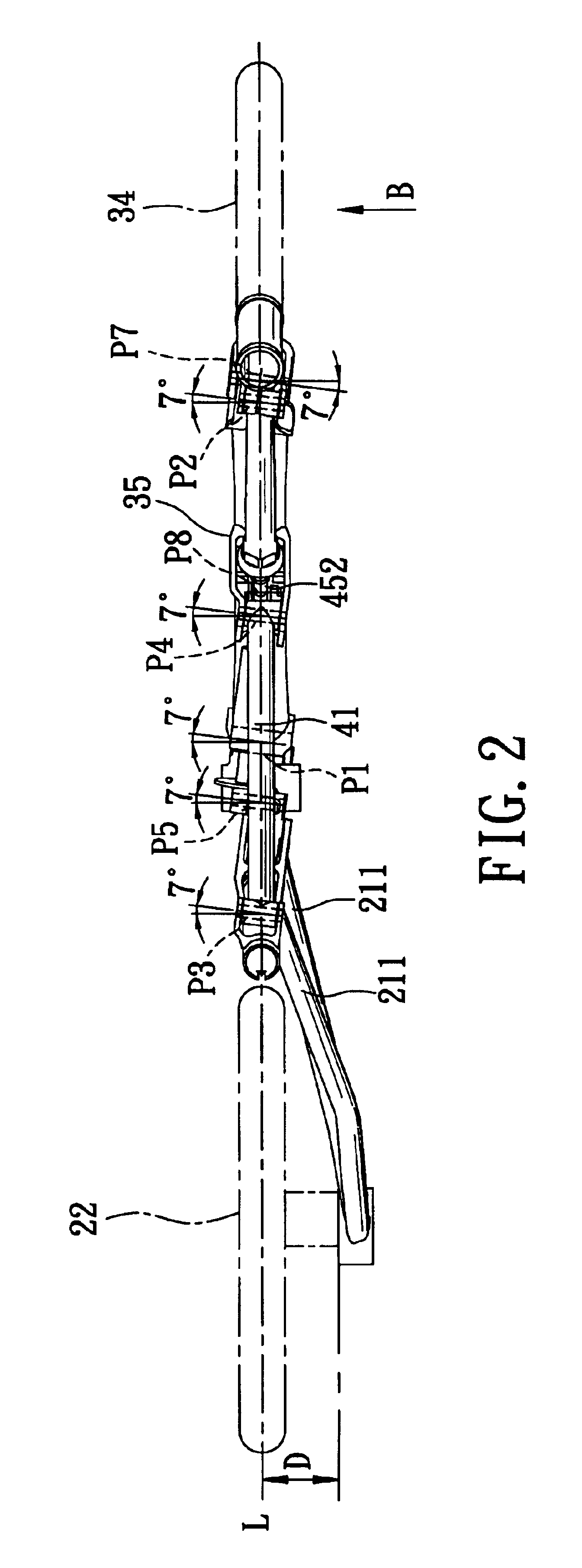
Bicycle foldable to align front and rear wheels along a transverse direction of the bicycle
A foldable bicycle includes a front wheel, a rear wheel, and a frame assembly that interconnects the front and rear wheels and that has a plurality of elements, which are interconnected by means of a plurality of horizontal pivot pins. Each of the pivot pins is inclined relative to a transverse direction of the bicycle. As such, the bicycle frame can be folded to align the front and rear wheels along a transverse direction of the bicycle.
Owner:GIANT MFG
Folding bicycle
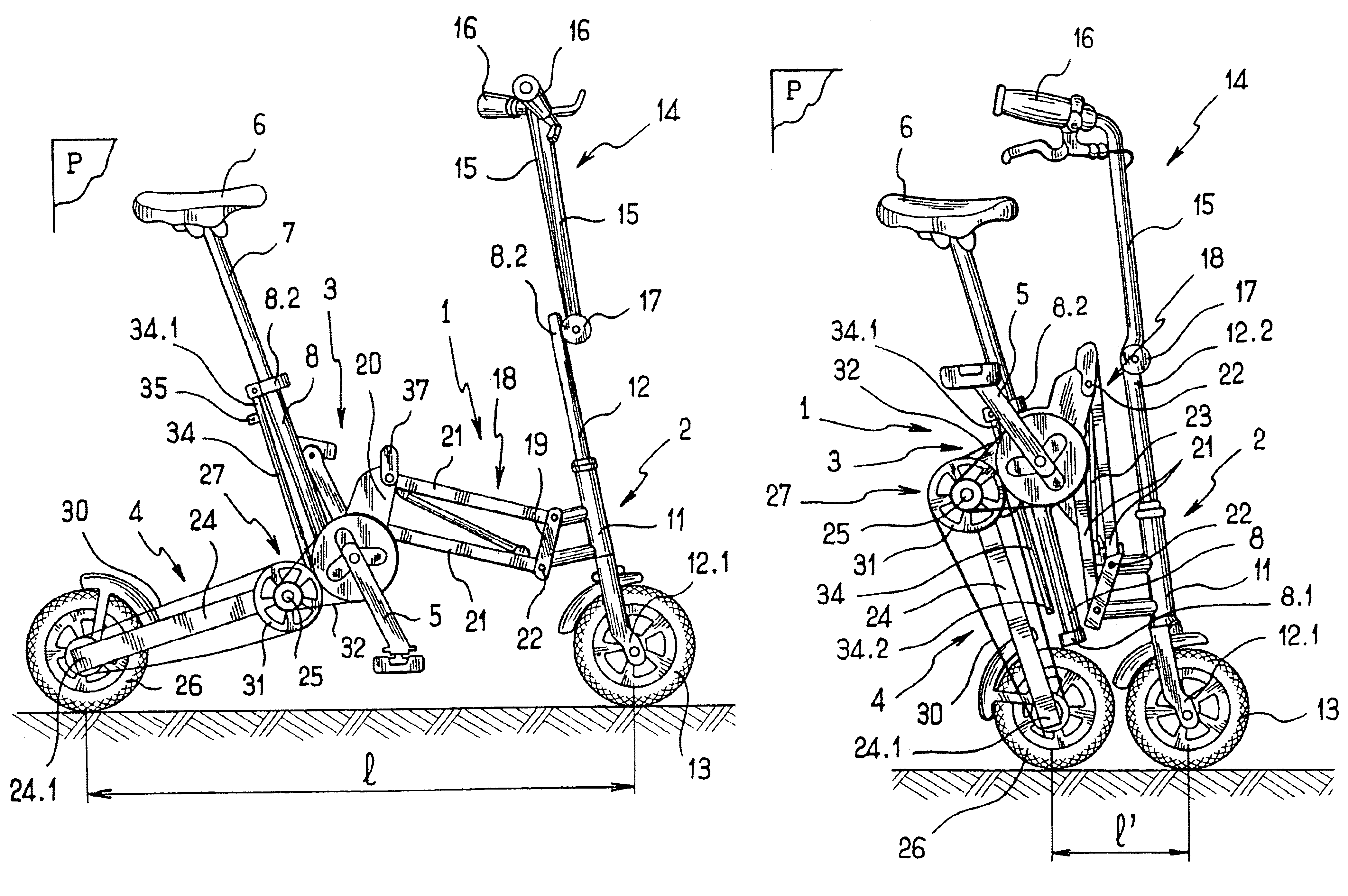
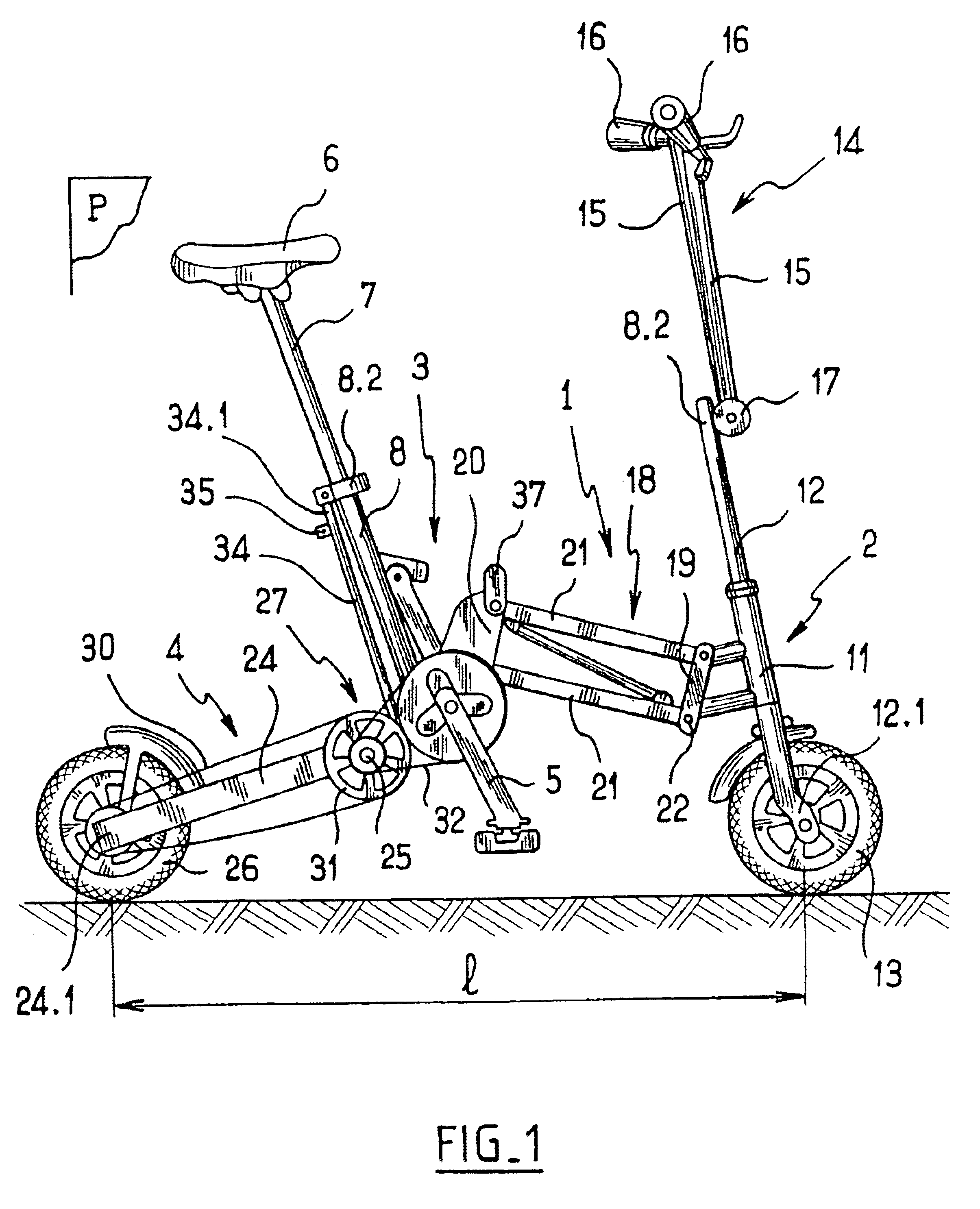
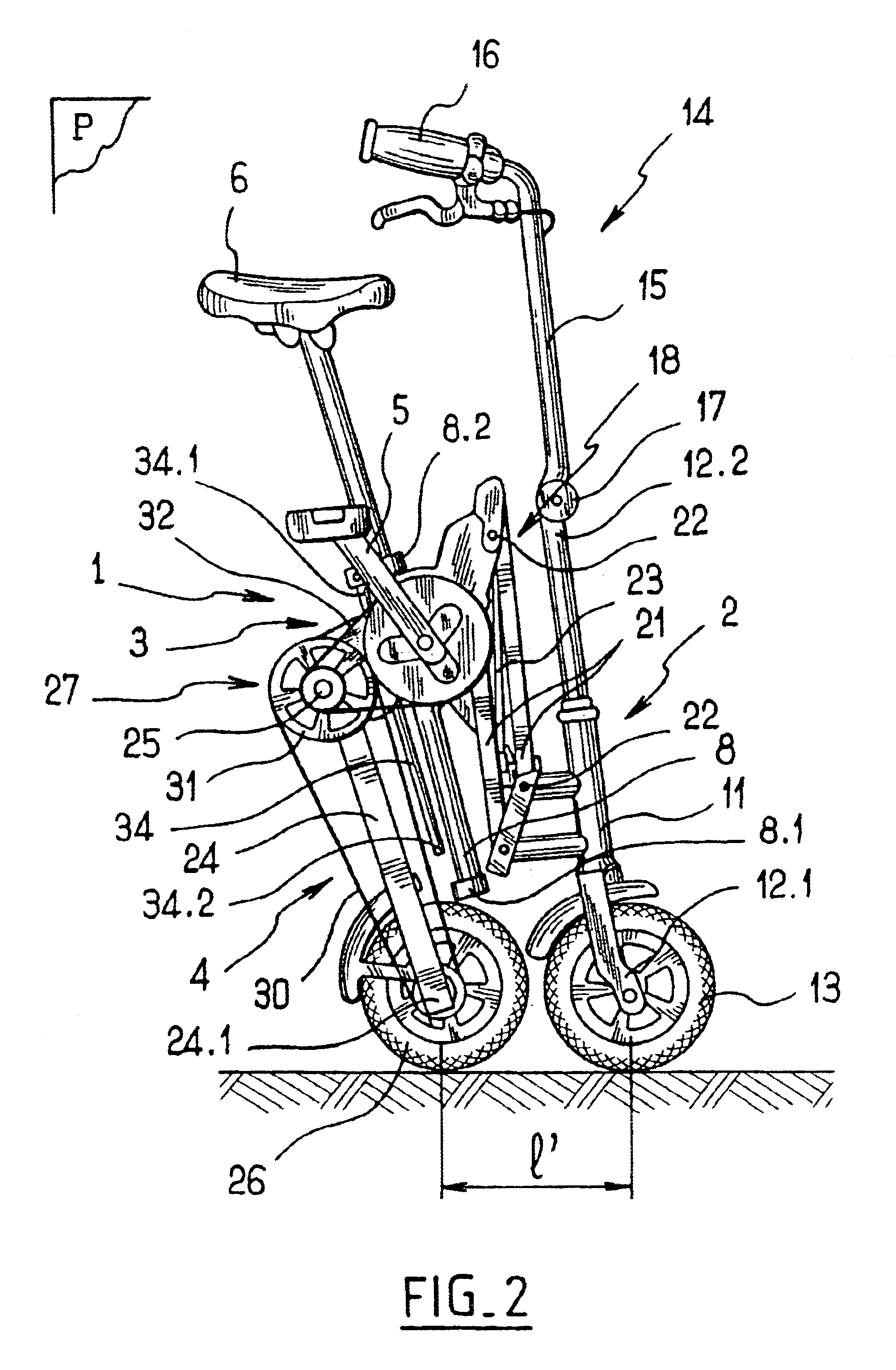
InactiveUS6799771B2Length of connection can be constantSimple structurePassenger cyclesWheel based transmissionCrankEngineering
A folding bicycle comprises a frame including a front part whereon is mounted pivoting a steering rod having a lower end provided with a first wheel and an upper end provided with a handlebar, a rear part whereon is mounted a second wheel, and a central part whereon are mounted a saddle and a crankset connected to the rear wheel by transmission elements, such that the saddle, the crankset, the steering rod, the front wheel and the rear wheel are substantially contained in a common plane when the bicycle is unfolded. The frame includes elements articulating the front part and the rear part to the central part to reduce the bicycle wheelbase associated with elements for maintaining at least the front wheel and the rear wheel in the plane.
Owner:MOBIKY
Folding electric bicycle
InactiveUS7055842B1Reduce storage spaceEasy to movePassenger cyclesWheel based transmissionEngineeringFront and back ends
Provided is a folding electric bicycle comprising a front frame section; a rear frame section comprising two bent arms individually having one end pivotably coupled to an axle passed rear wheel, and two auxiliary wheels rotatably mounted in open ends of the bent arms; a crossbar comprising a front end and a rear end pivotably coupled to the front and rear frame sections respectively; a latch detachably interconnected the crossbar and the rear frame section; and a down tube interconnected the front and rear frame sections. The rear frame section can either retract toward the front frame section about the unfastened latch for folding or extend from the front frame section about the unfastened latch for extending. The auxiliary wheels are either disposed above the ground when the bicycle is ready or rotatable and contact with the ground when the bicycle is folded for facilitating moving.
Owner:KENTFA EDVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com