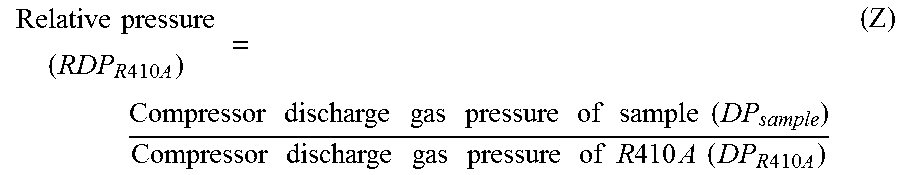Patents
Literature
2662 results about "Discharge pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
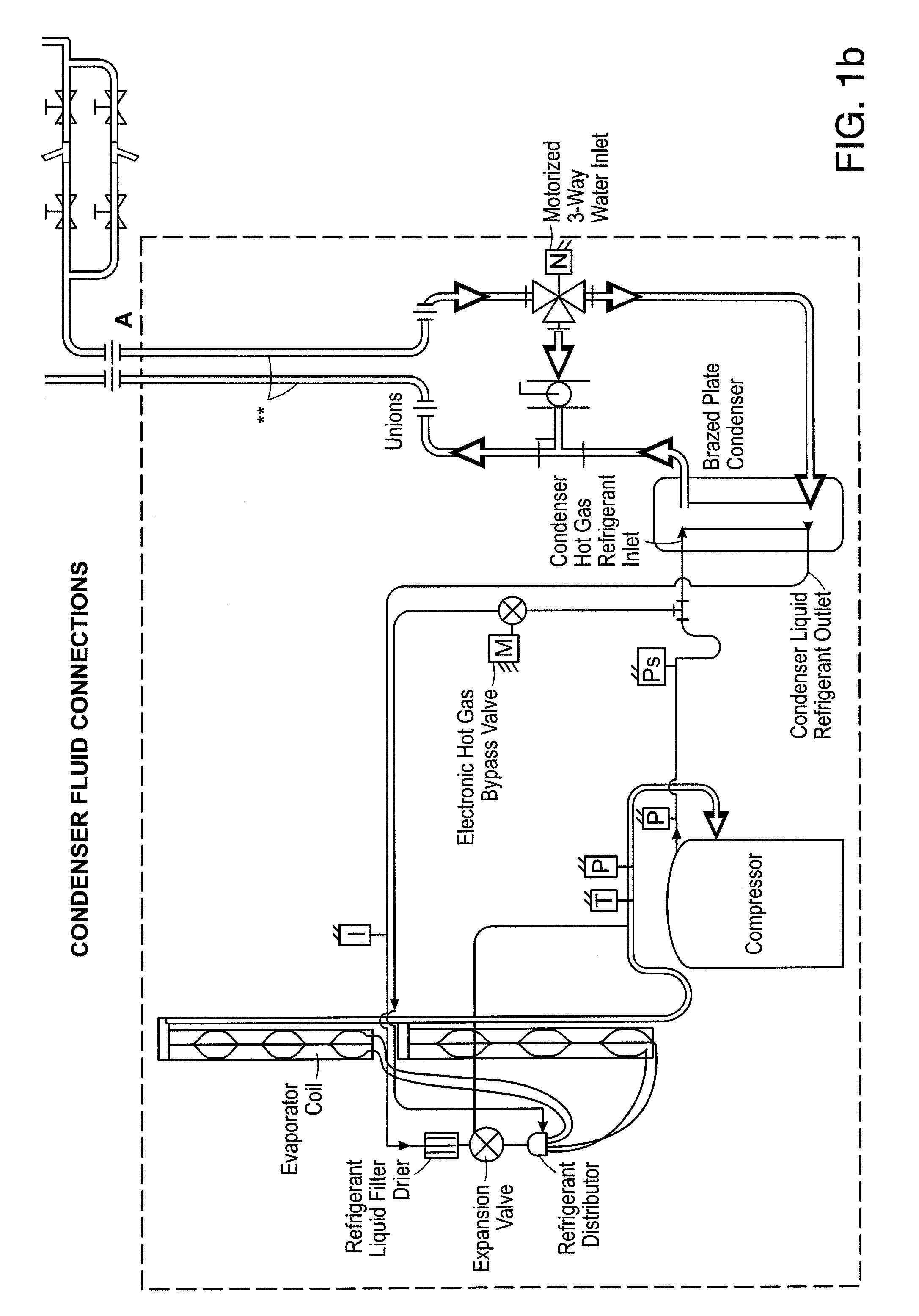
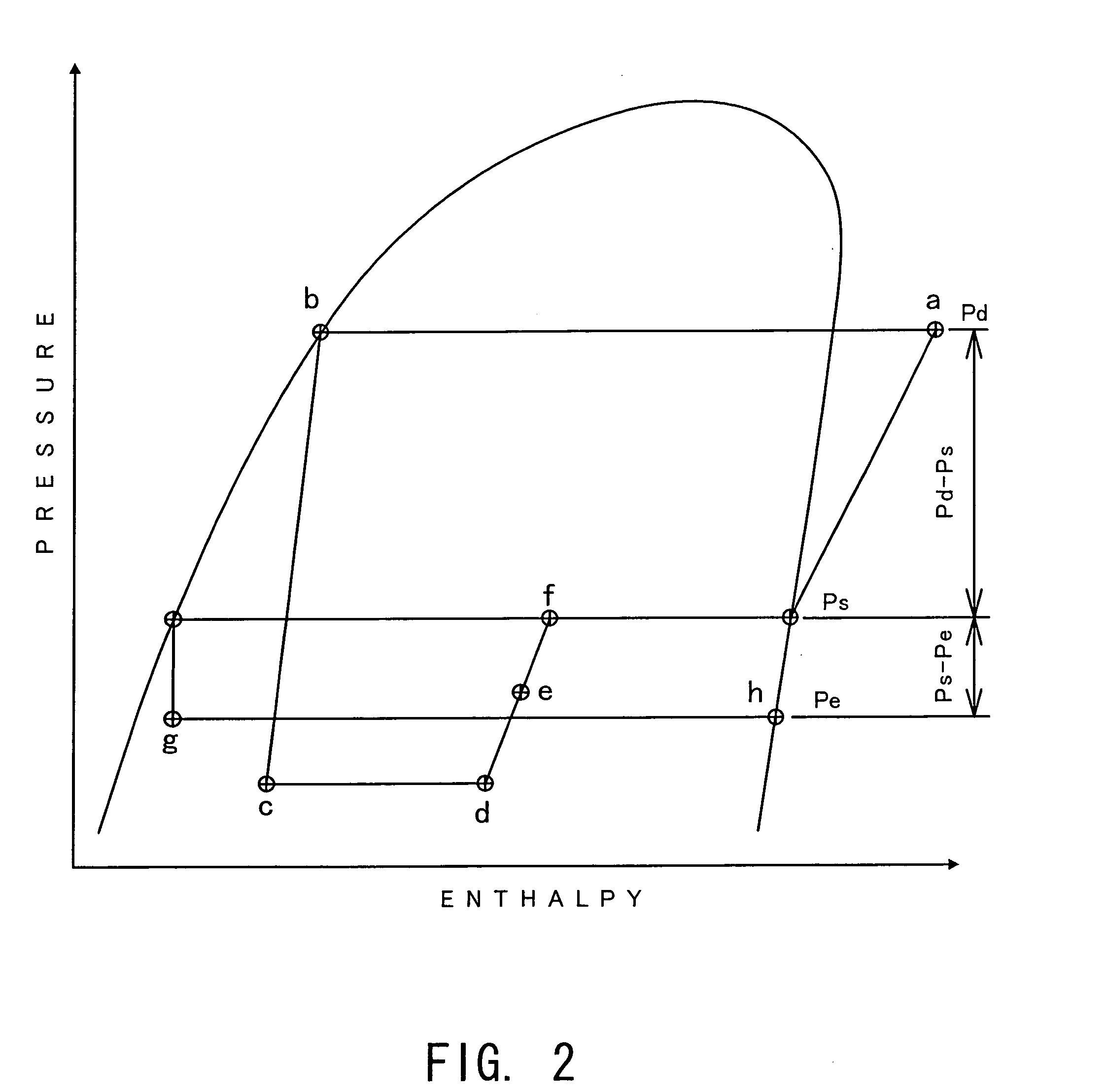
Discharge pressure (also called high side pressure or head pressure) is the pressure generated on the output side of a gas compressor in a refrigeration or air conditioning system. The discharge pressure is affected by several factors: size and speed of the condenser fan, condition and cleanliness of the condenser coil, and the size of the discharge line. An extremely high discharge pressure coupled with an extremely low suction pressure is an indicator of a refrigerant restriction.
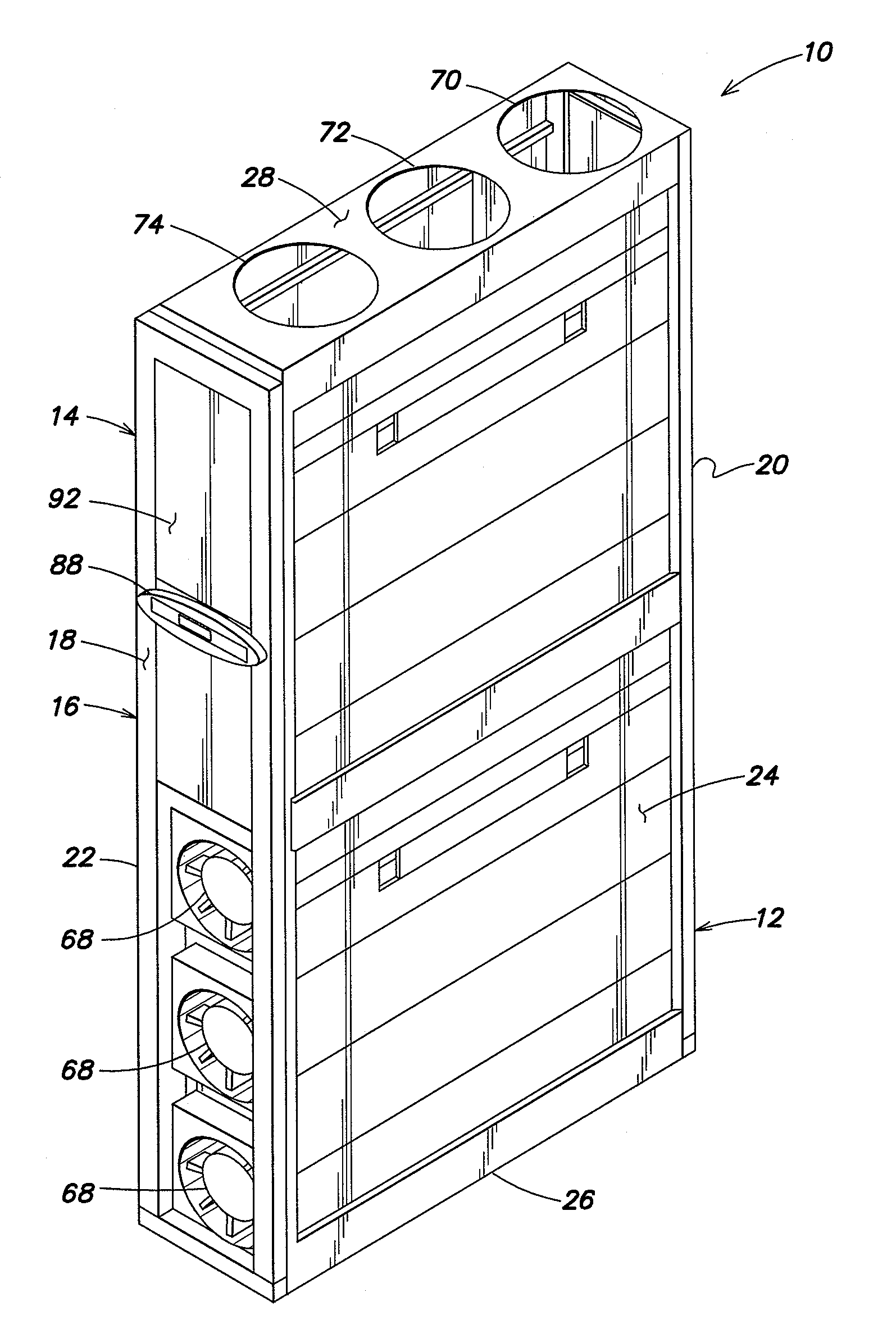
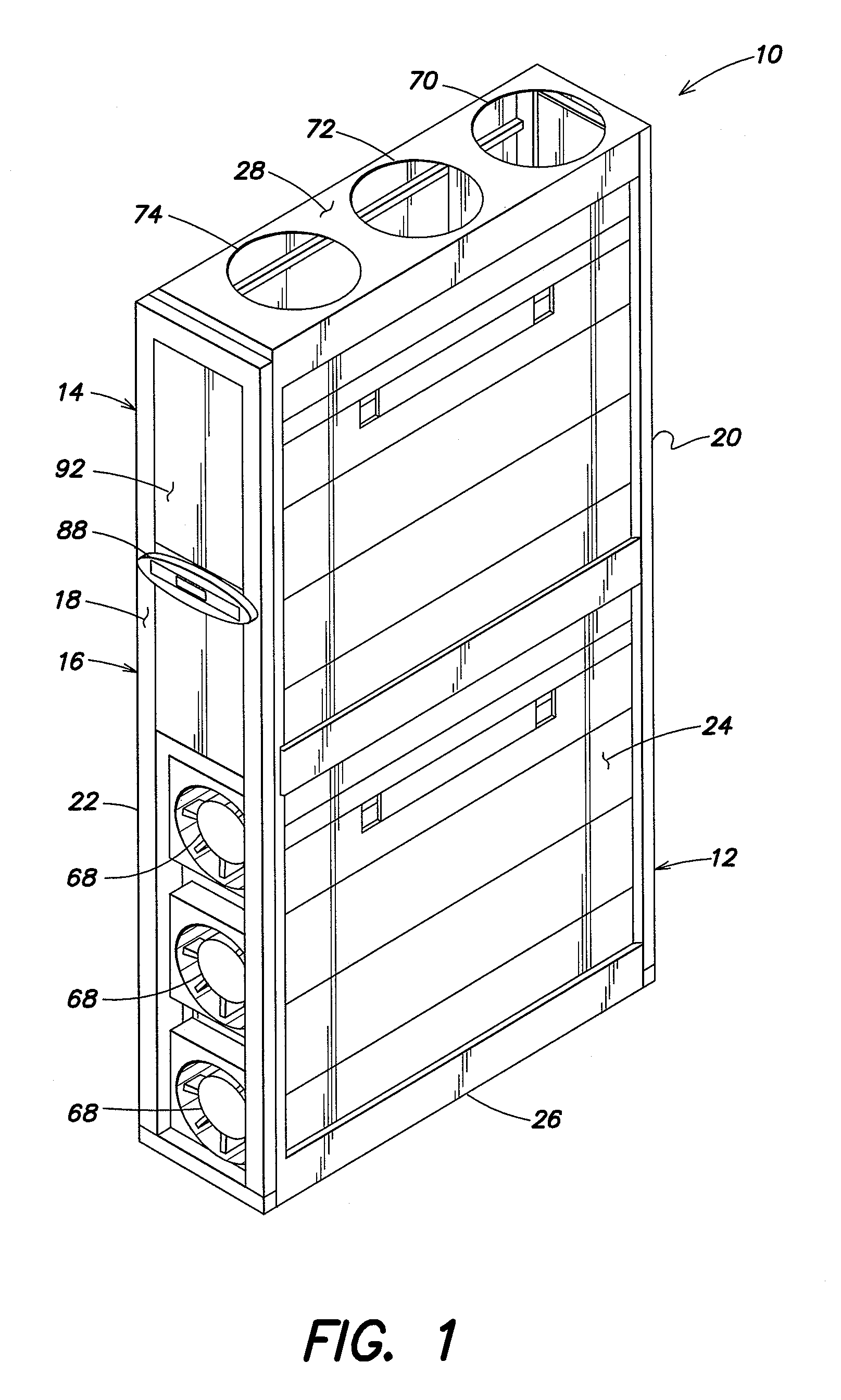
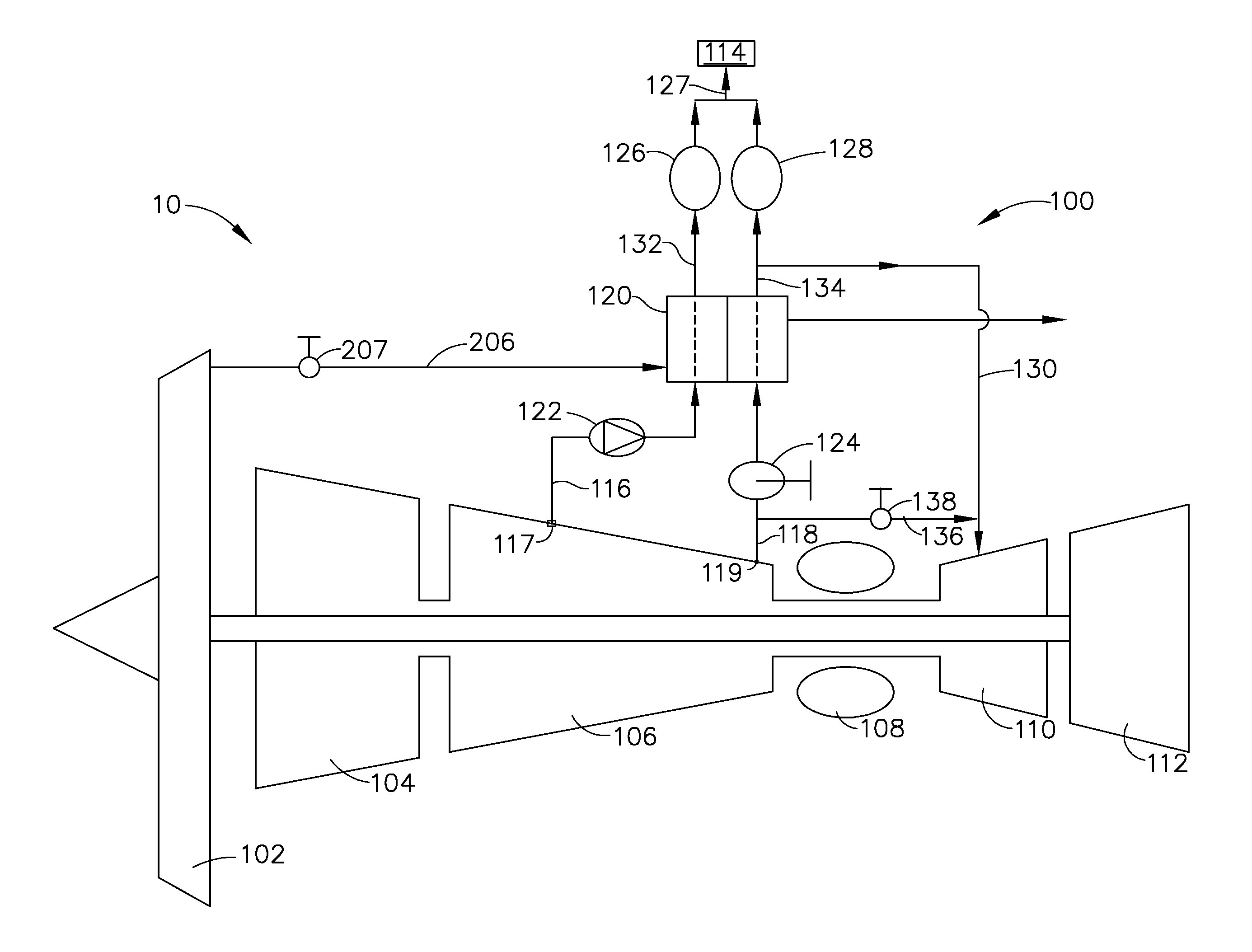
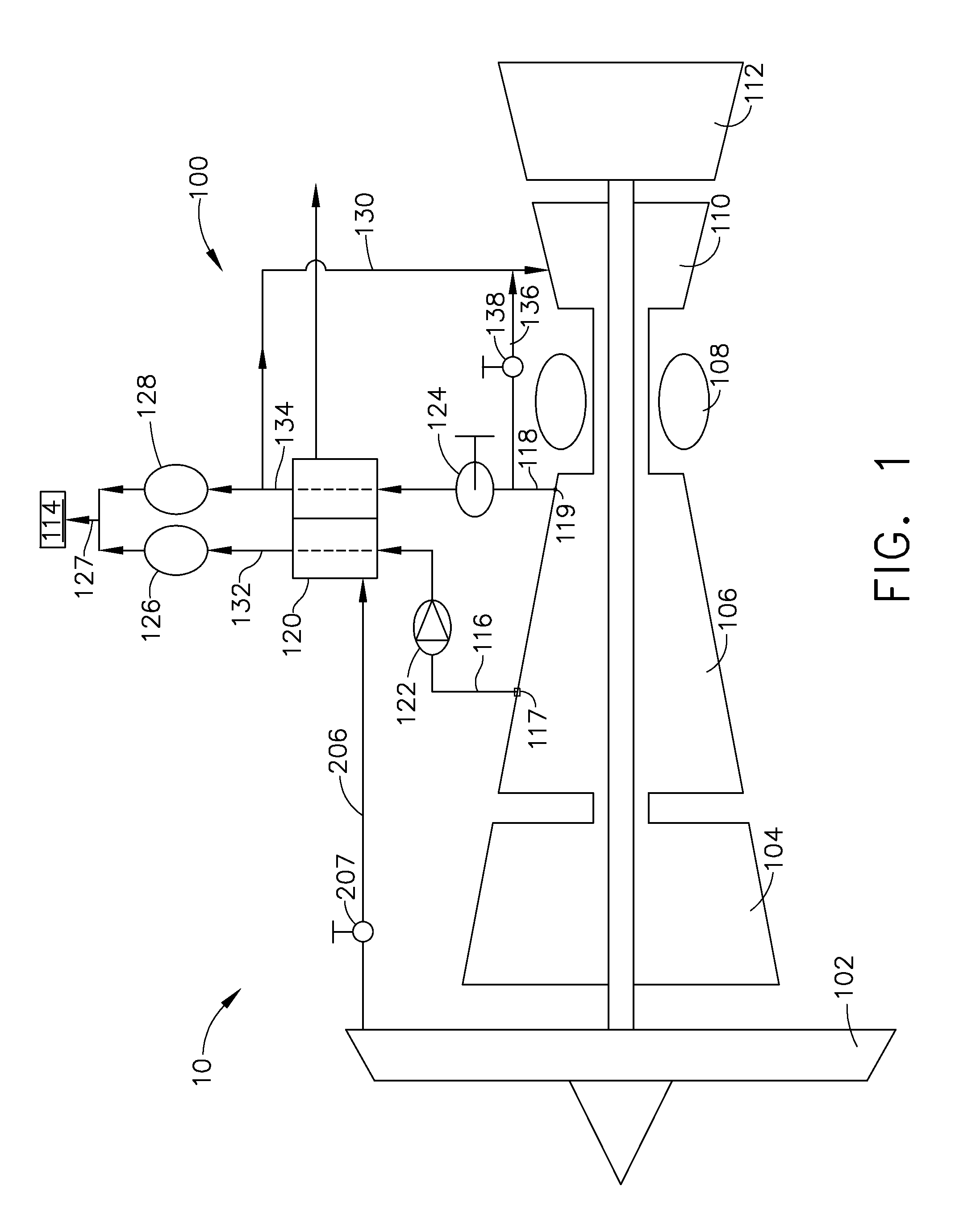
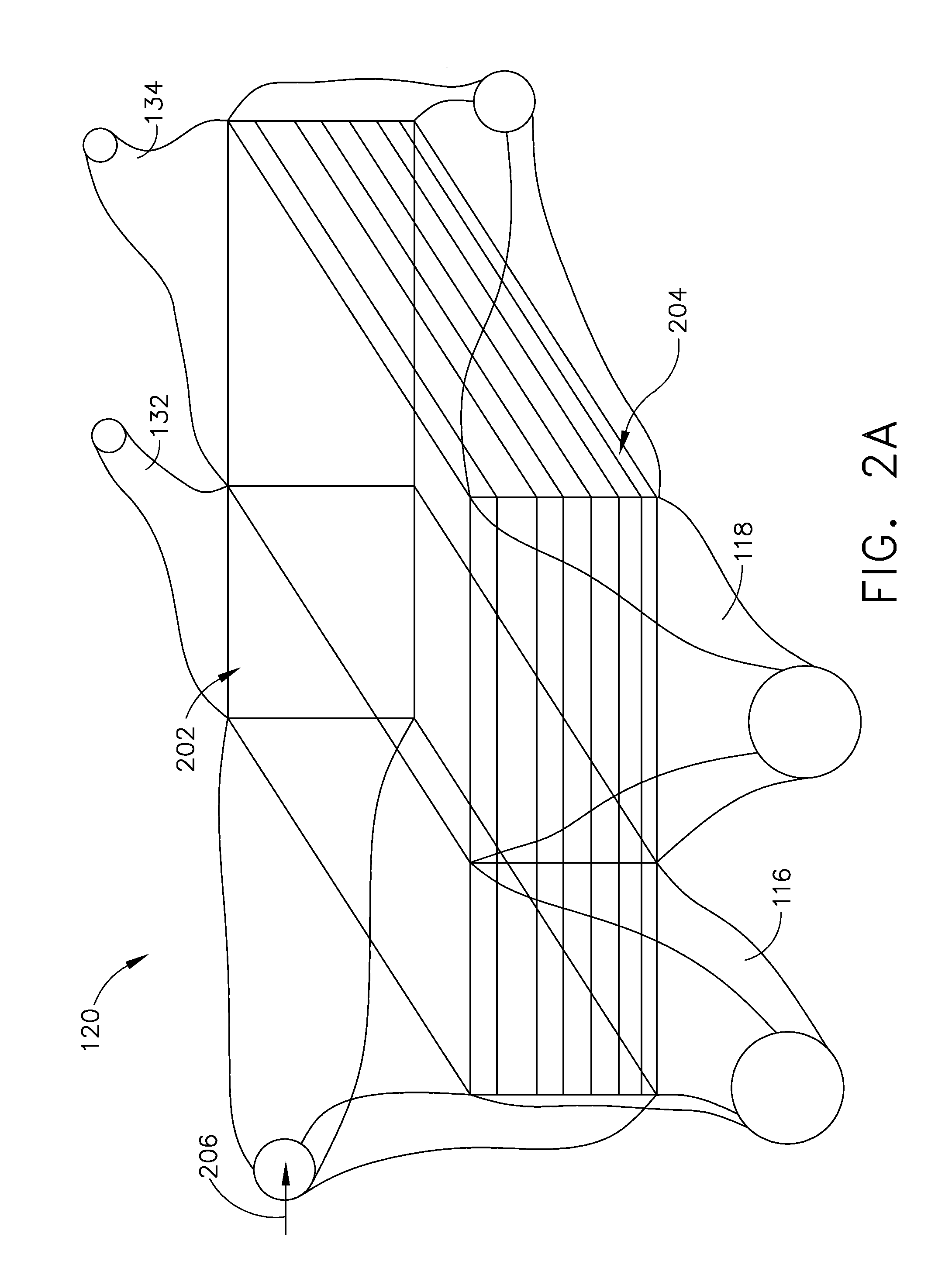
Method and apparatus for cooling
ActiveUS20080245083A1Increase loopHigh trafficMechanical apparatusTemperatue controlEngineeringCooling capacity
A method of calculating net sensible cooling capacity of a cooling unit includes measuring a discharge pressure from of fluid from a compressor and a suction pressure from an evaporator, calculating a condensing temperature of fluid flowing from the compressor and an evaporating temperature of fluid flowing from the evaporator, calculating a mass flow rate of fluid flowing from the compressor, calculating enthalpy of fluid flowing from the compressor, of fluid flowing from the thermal expansion valve, and of fluid flowing from the evaporator, calculating a mass flow rate of fluid flowing through the hot gas bypass valve, and calculating net sensible cooling capacity. Embodiments of cooling units and other methods are further disclosed.
Owner:AMERICA POWER CONVERSION CORP
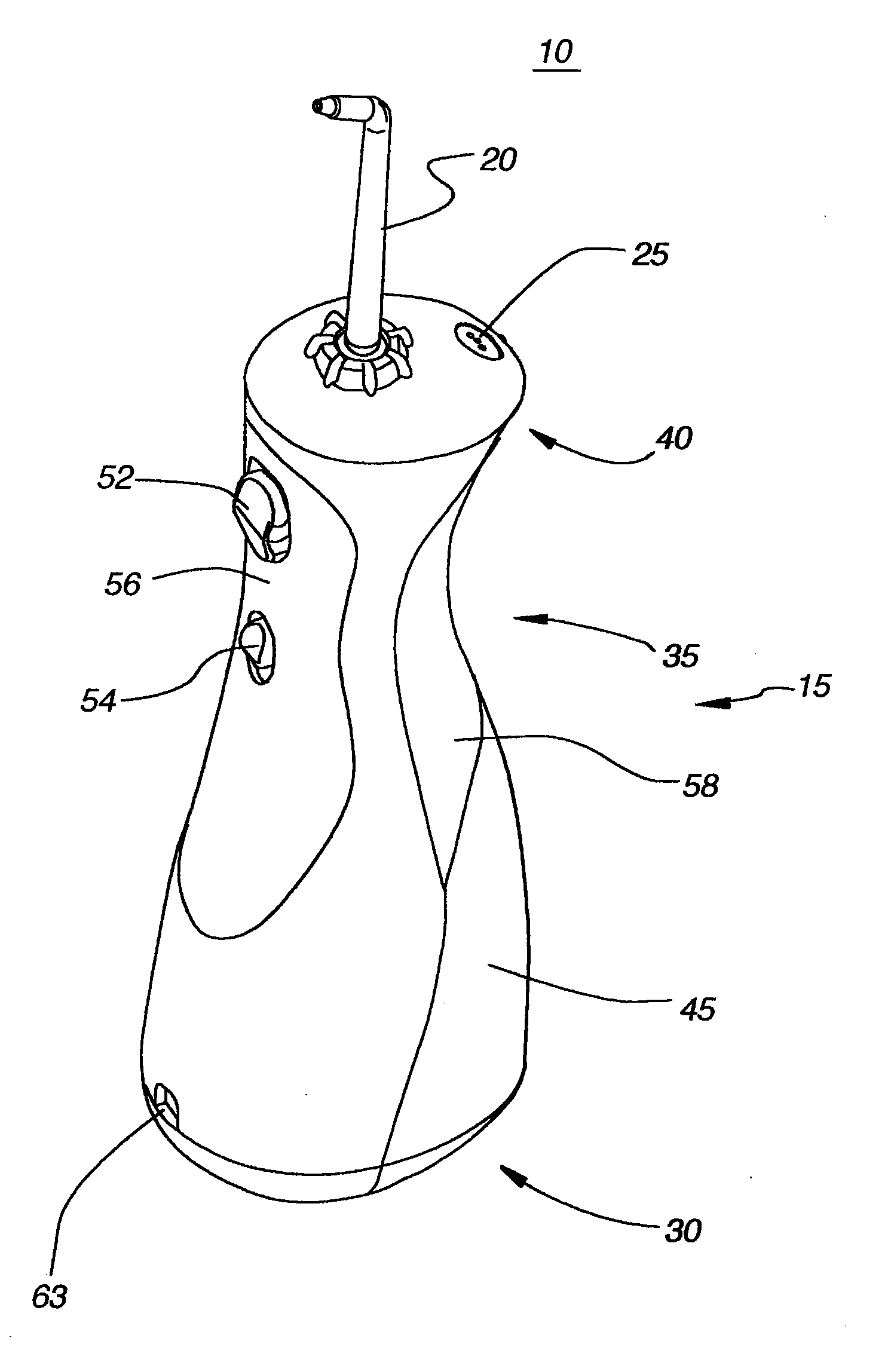
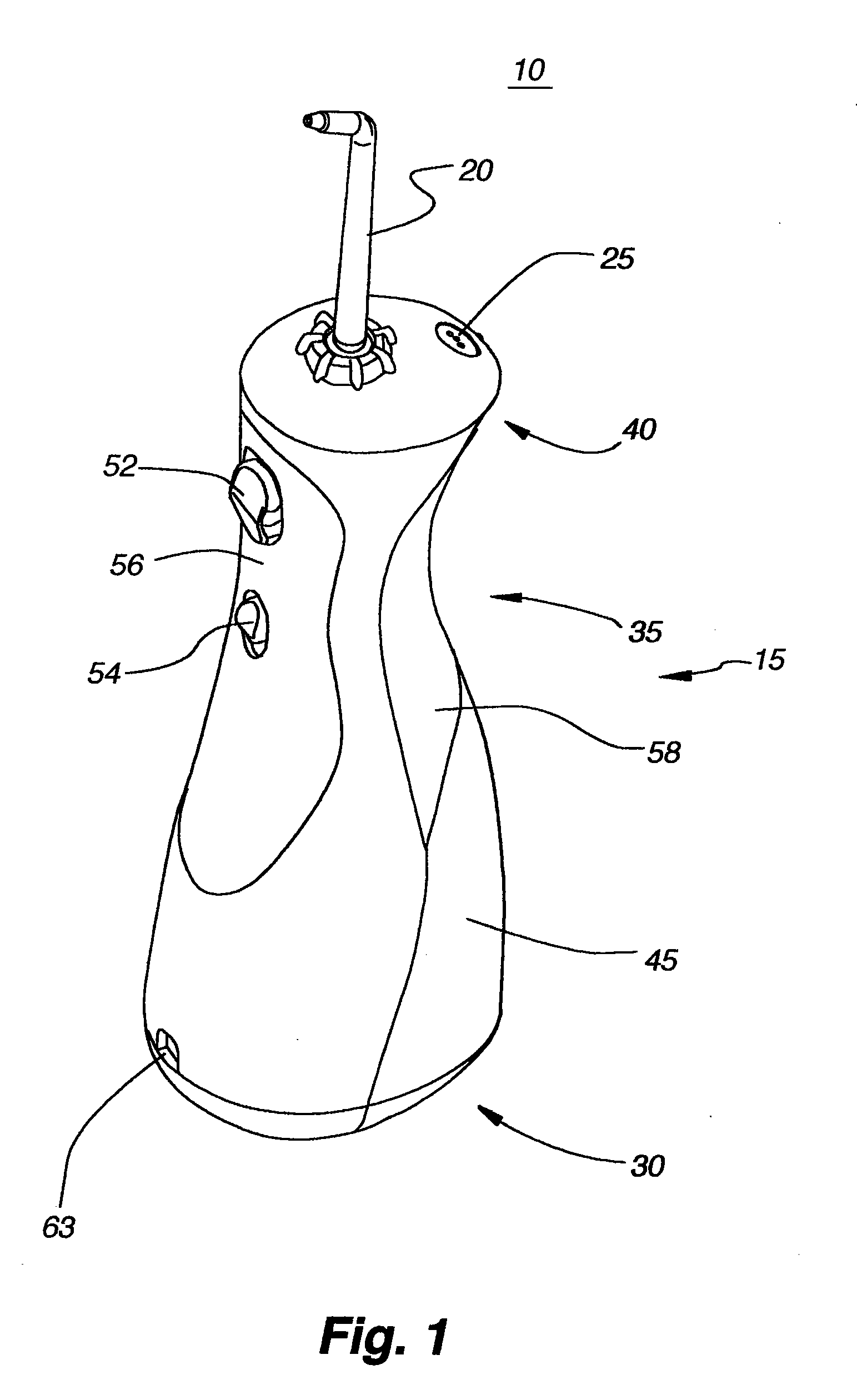
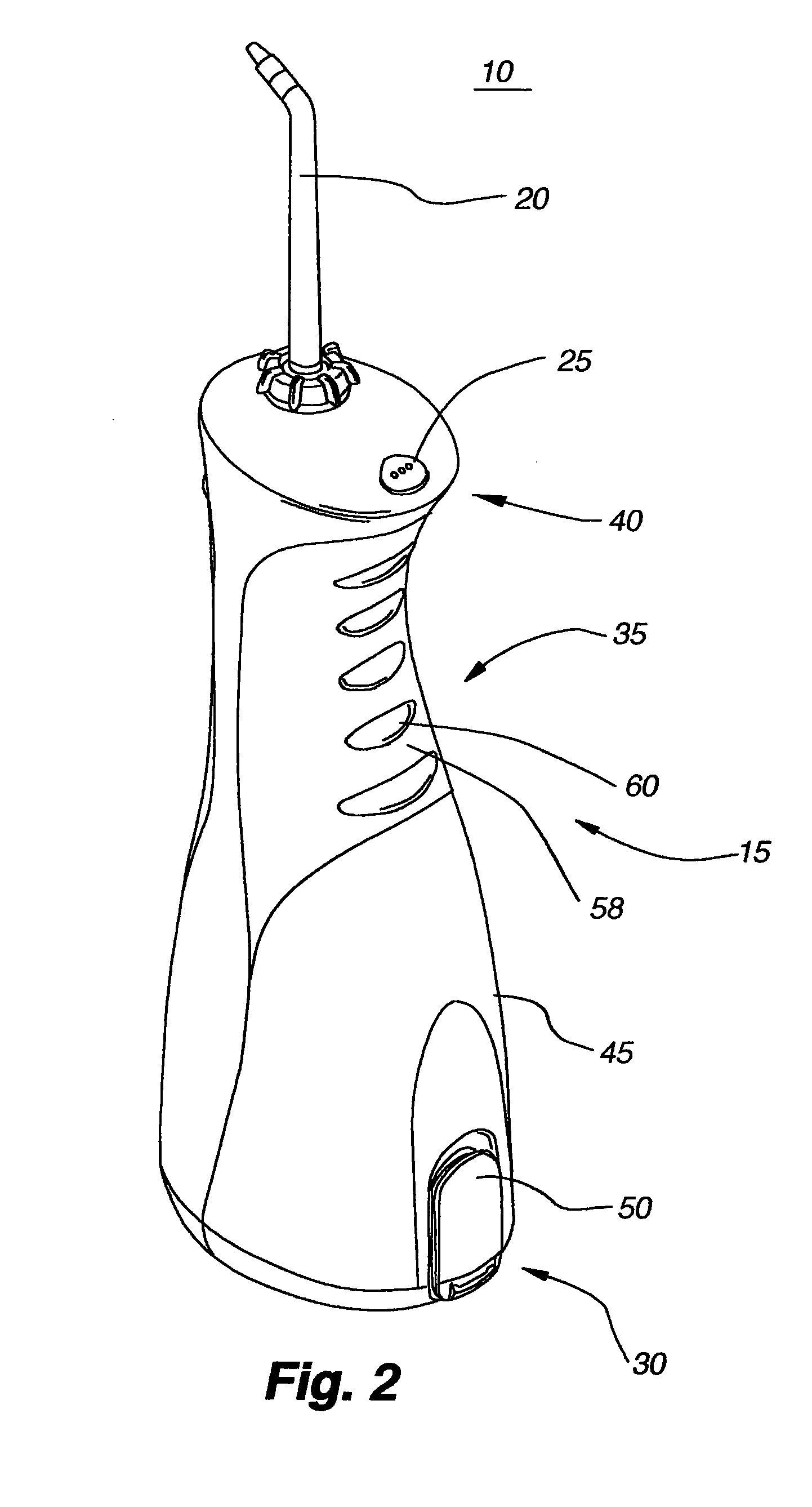
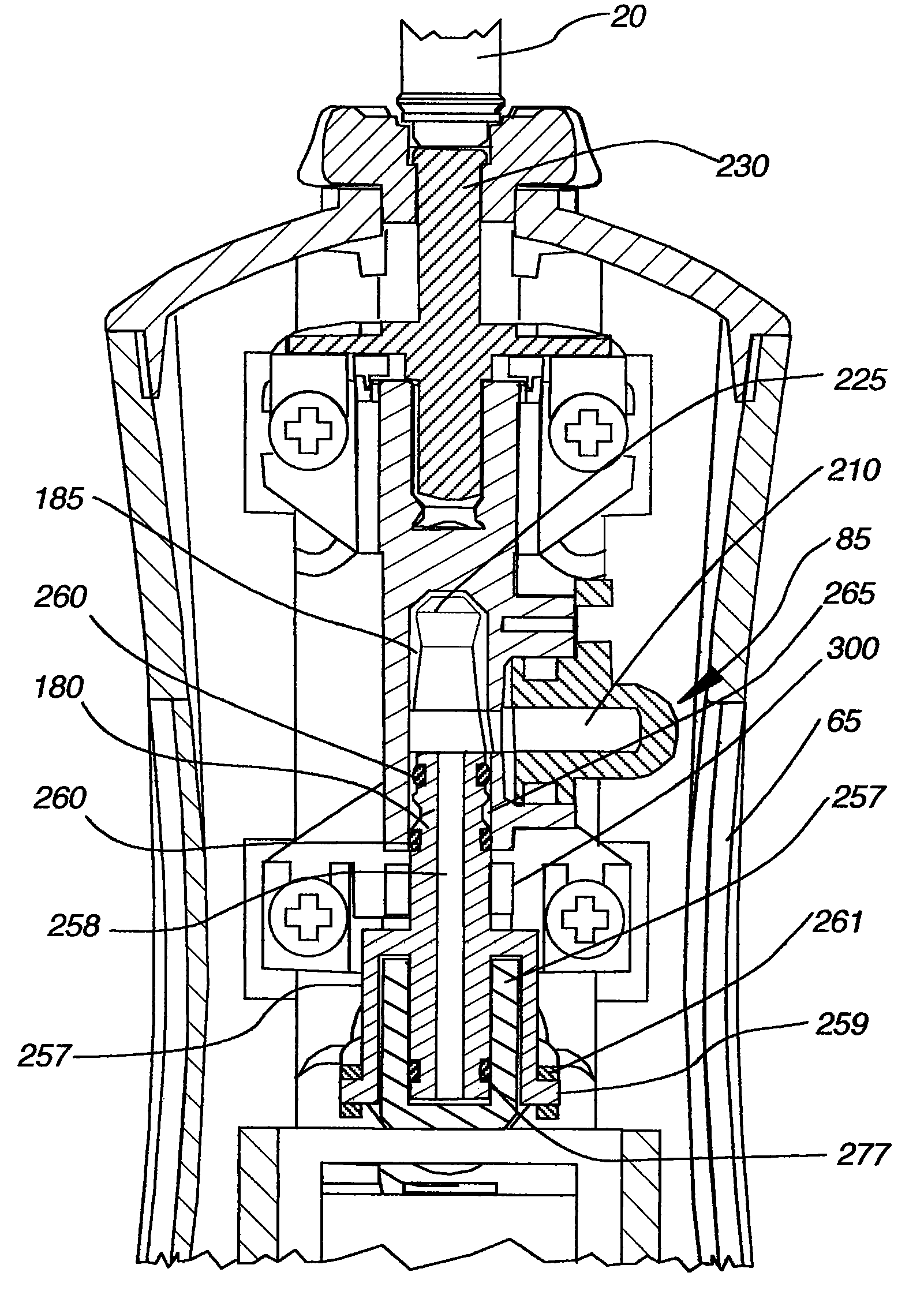
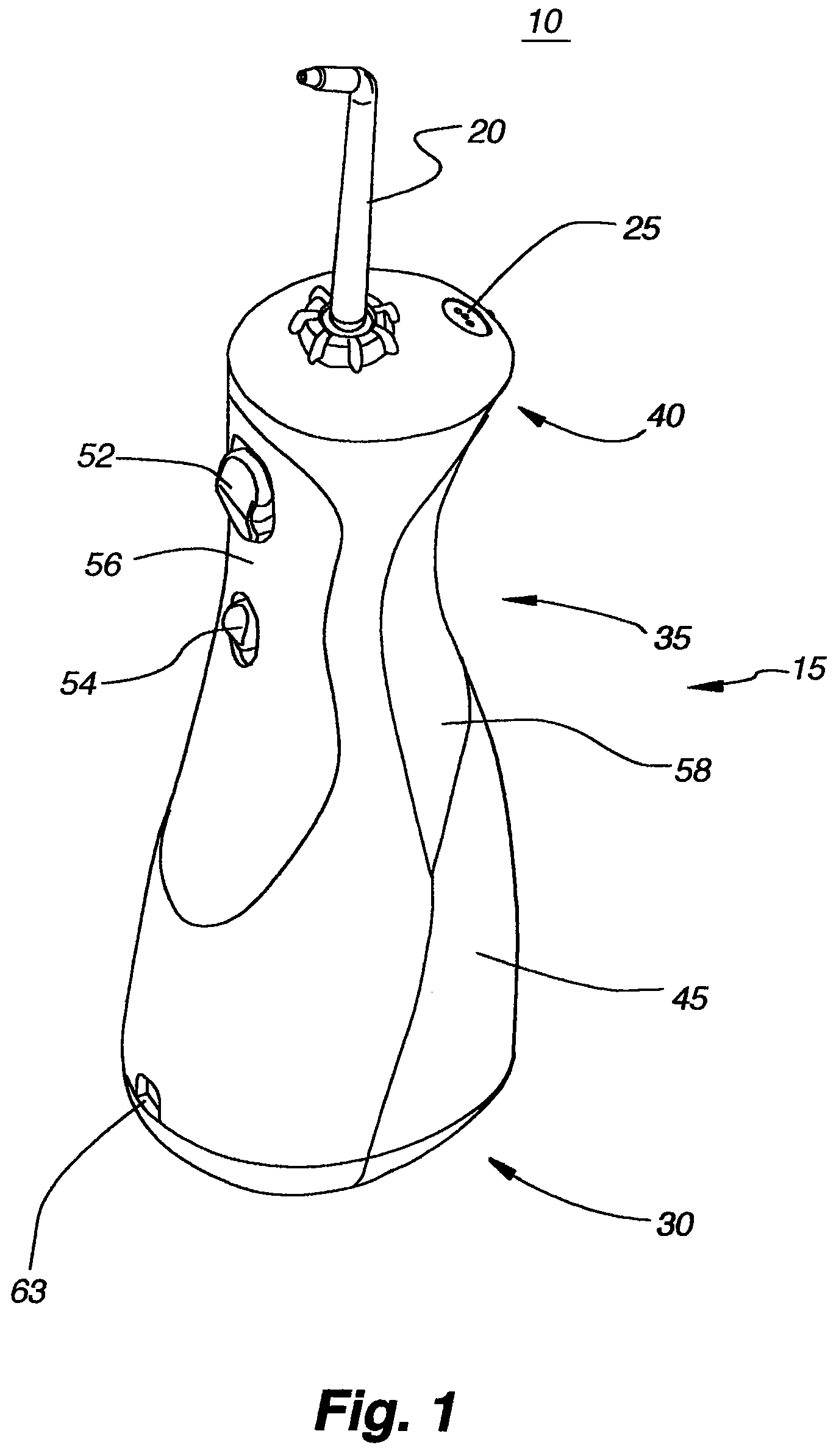
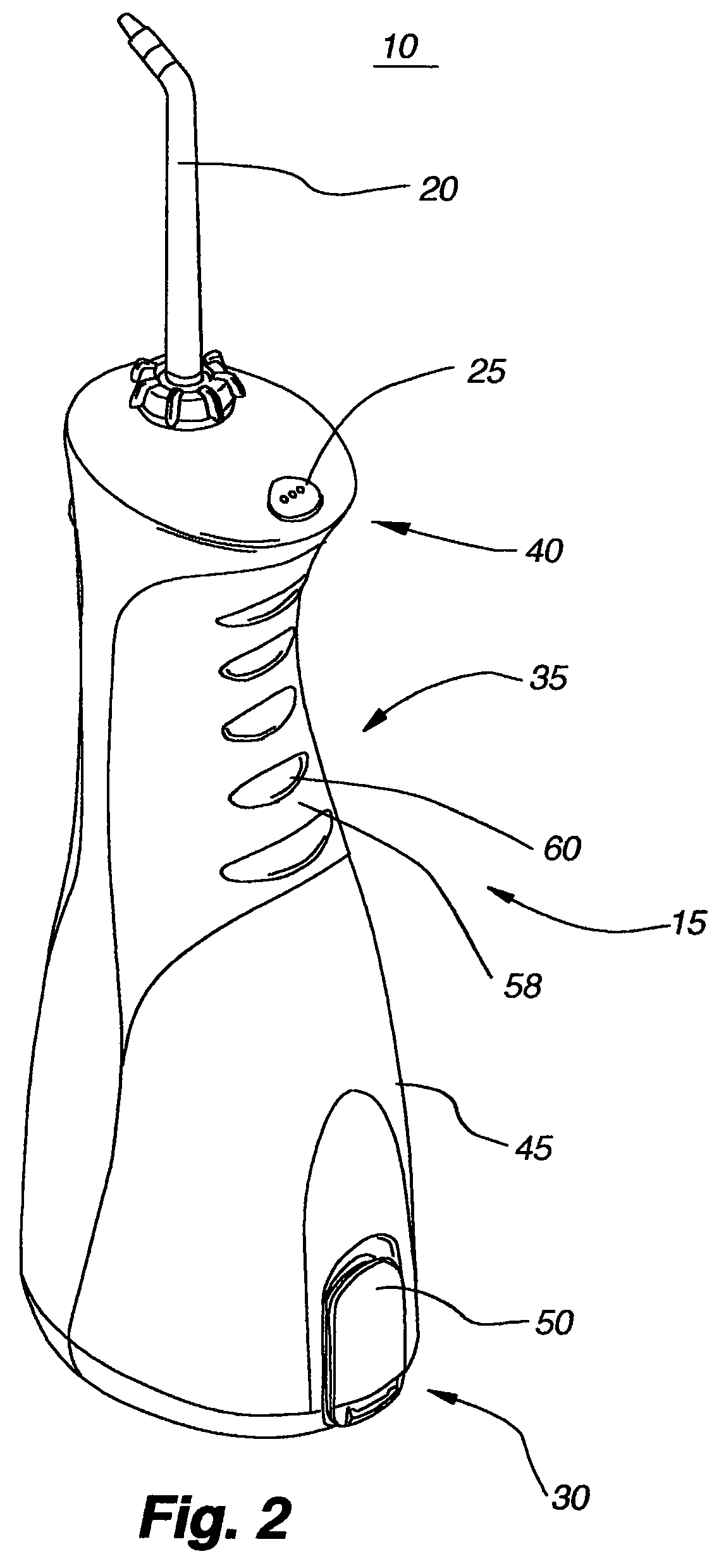
Oral irrigator
The present invention is an oral irrigator comprising a pump, a discharge nozzle and a pressure control. The pump has a generally constant operating speed and feeds the discharge nozzle. The pressure control is adapted to modify a discharge pressure at the nozzle without a significant change in pump speed. The pressure control modifies a level of fluid flow restriction between the pump and the nozzle. The modification of the level of fluid flow restriction is accomplished by modifying aspects of a fluid flow path extending through the pressure control. The aspects modified include the diameter, length and / or number of direction changes of the fluid flow path.
Owner:WATER PIK INC
Oral irrigator
The present invention is an oral irrigator comprising a pump, a discharge nozzle and a pressure control. The pump has a generally constant operating speed and feeds the discharge nozzle. The pressure control is adapted to modify a discharge pressure at the nozzle without a significant change in pump speed. The pressure control modifies a level of fluid flow restriction between the pump and the nozzle. The modification of the level of fluid flow restriction is accomplished by modifying aspects of a fluid flow path extending through the pressure control. The aspects modified include the diameter, length and / or number of direction changes of the fluid flow path.
Owner:WATER PIK INC
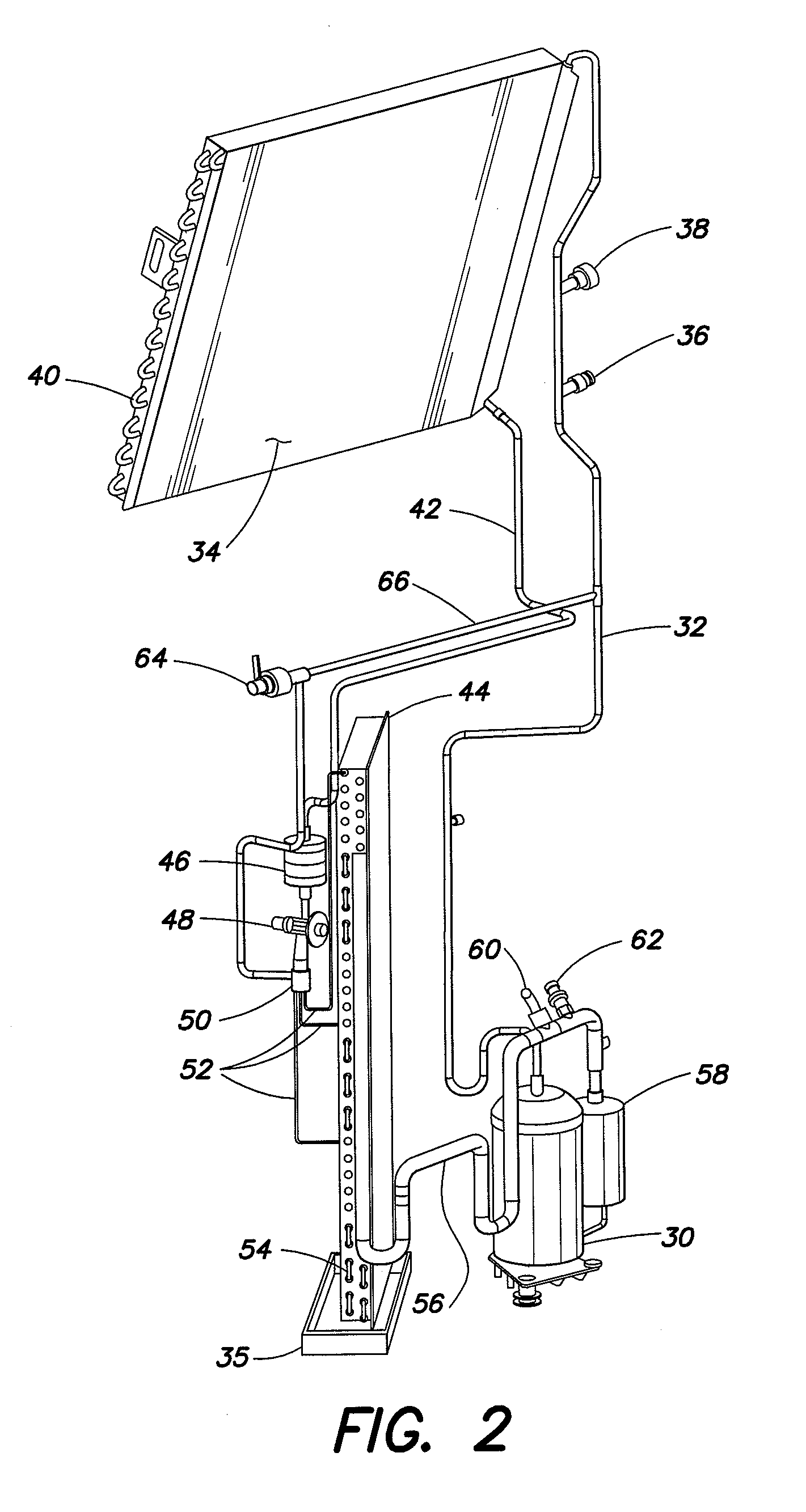
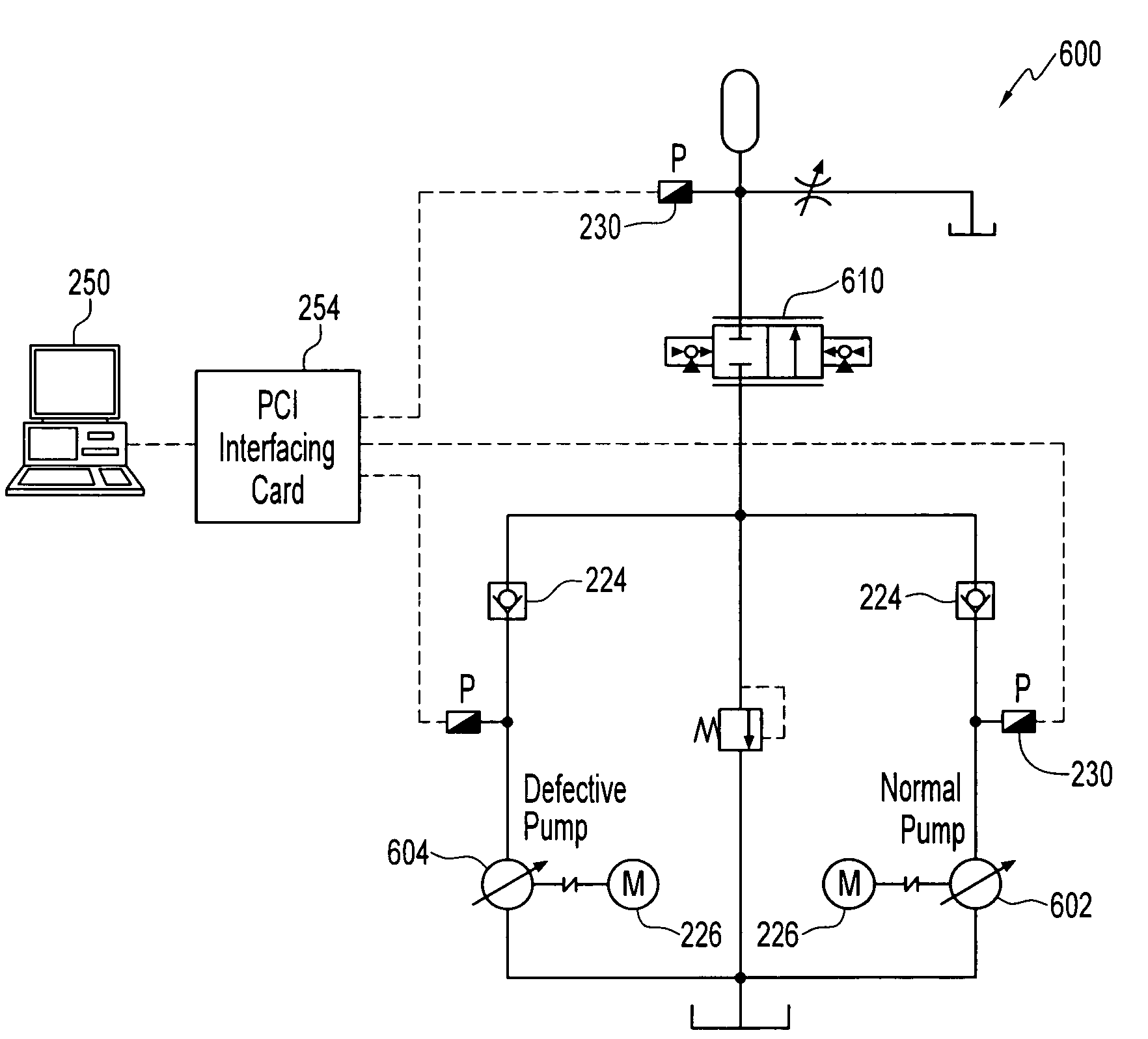
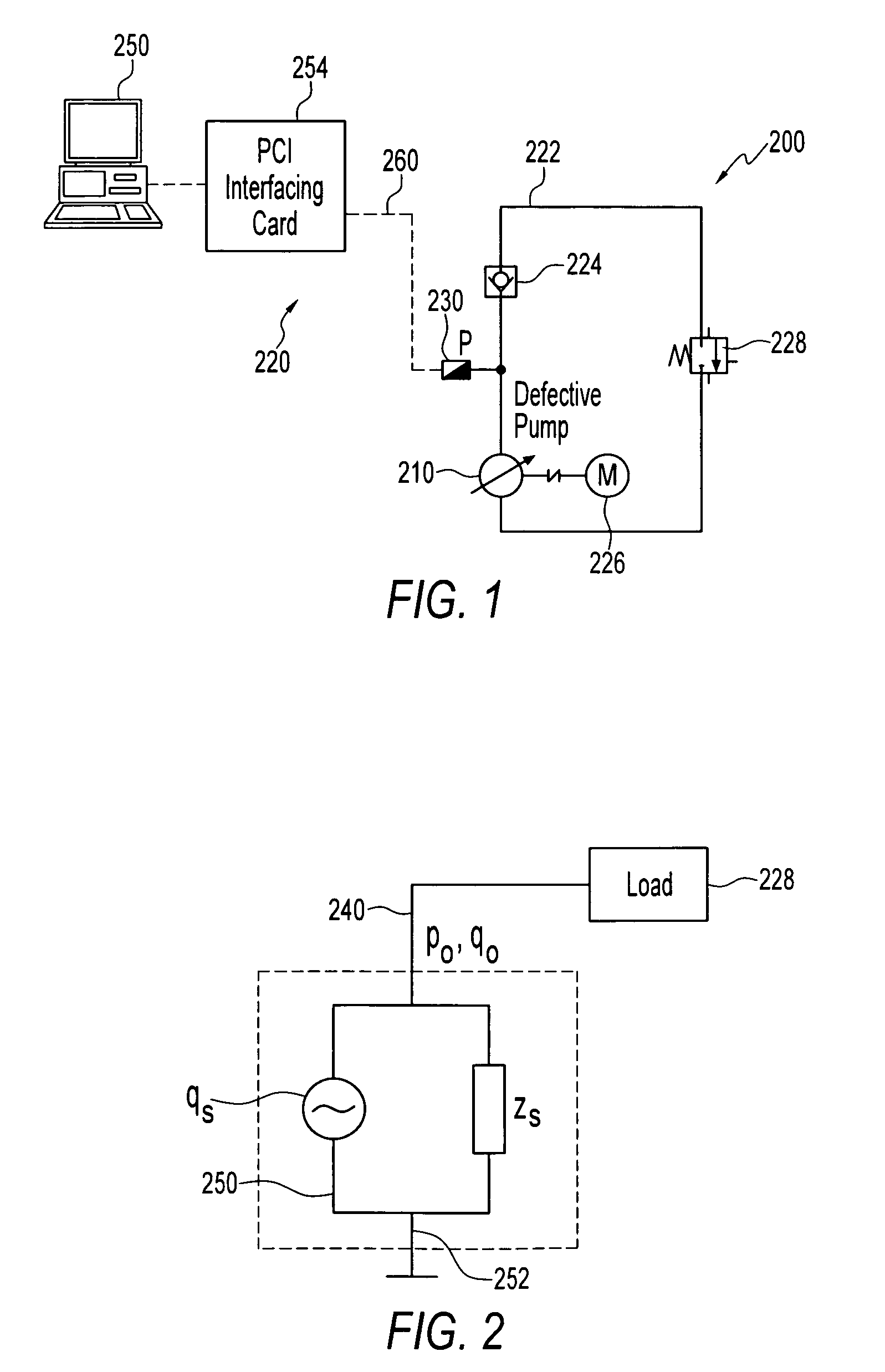
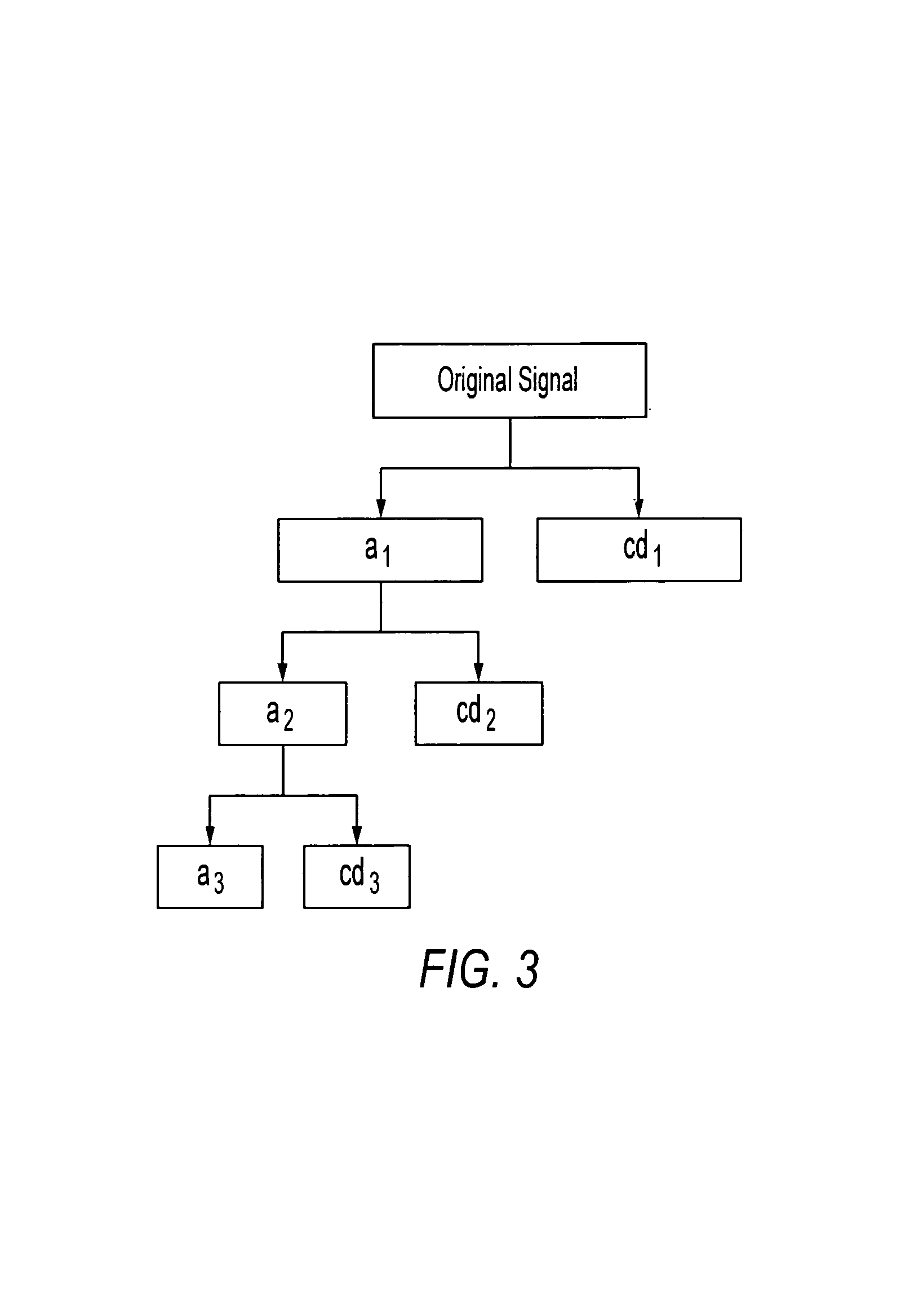
Method and apparatus for analyzing performance of a hydraulic pump
A method and apparatus for analyzing a hydraulic pump in real-time. A pressure signal is provided representing a discharge pressure of the hydraulic pump, and the pressure signal is decomposed into a plurality of levels. Each of the plurality of levels has at least one frequency band. A feature pressure signal is located in at least one of the frequency bands and compared to a reference wavelet to determine if a fault exists in the hydraulic pump and / or a type of defect in the hydraulic pump.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
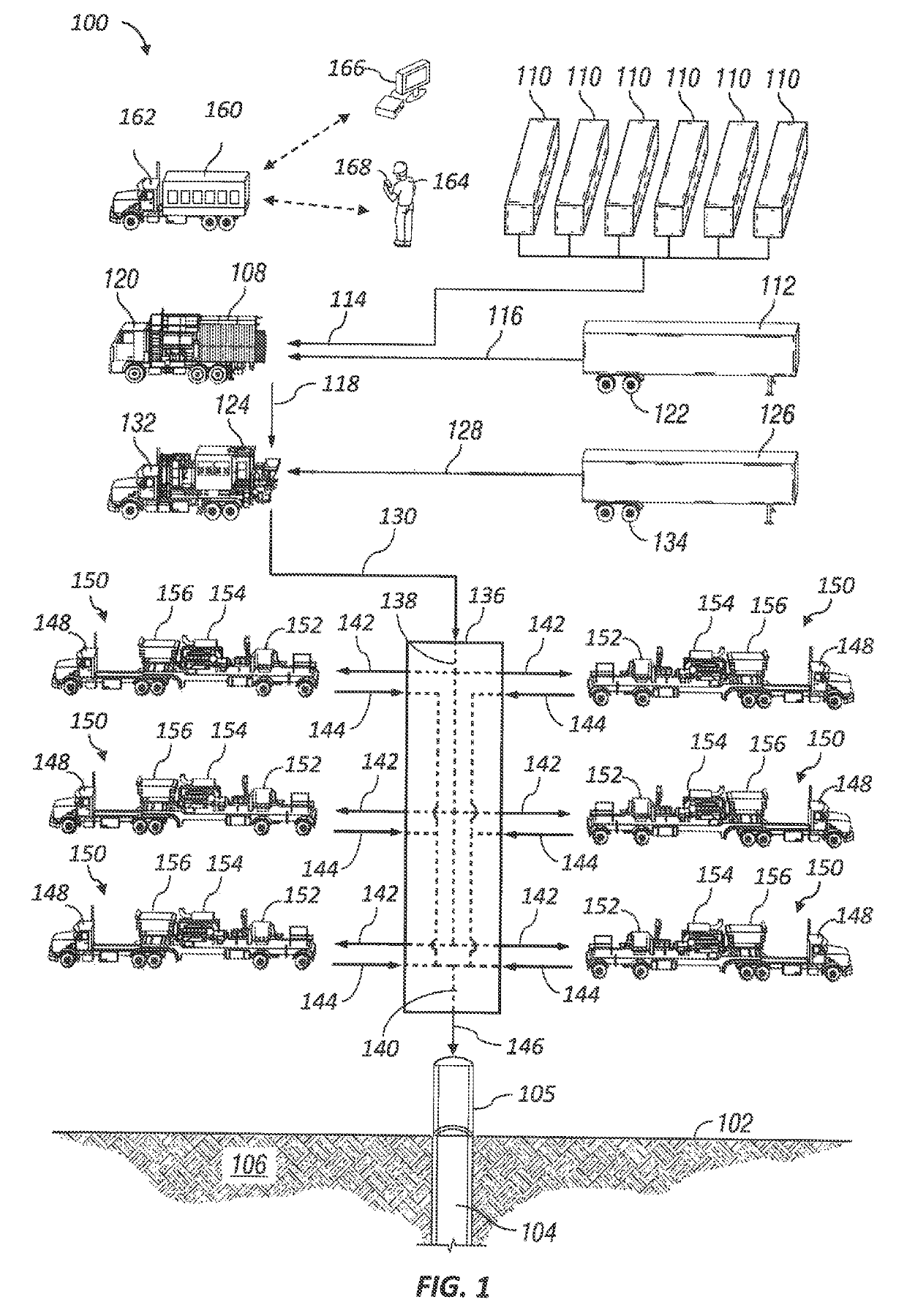
Automated operation of wellsite pumping equipment
ActiveUS10415562B2Increase probabilityReduce probabilityComputer controlSimulator controlEngineeringProbit
Automated operation of well site pumping equipment, including generating a mathematical belief model for maintaining an interrelationship between flow rate achievable by a pump unit discharge pressure of the pump unit, and probability of achieving the flow rate at corresponding discharge pressure. Speed of the pump unit is controlled to achieve a target speed based on a flow rate set-point and the mathematical belief model and updating the mathematical belief model at least while the target speed is achieved. Updating the mathematical belief model may include increasing the probability of achieving the flow rate set-point when actual flow rate of the pump unit is not less than the flow rate set-point and decreasing the probability of achieving the flow rate set-point when the actual flow rate of the pump unit is less than the flow rate set-point.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
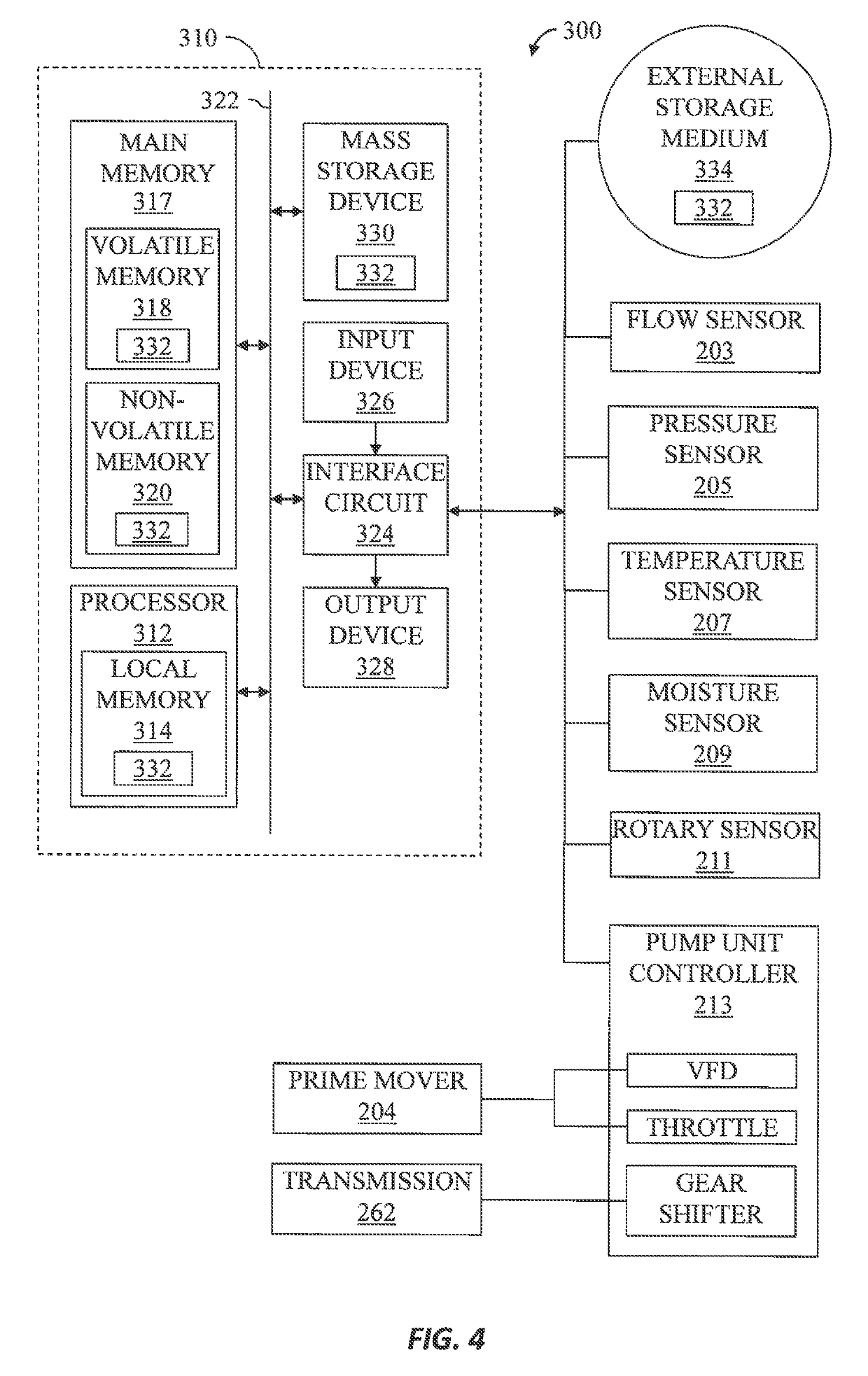
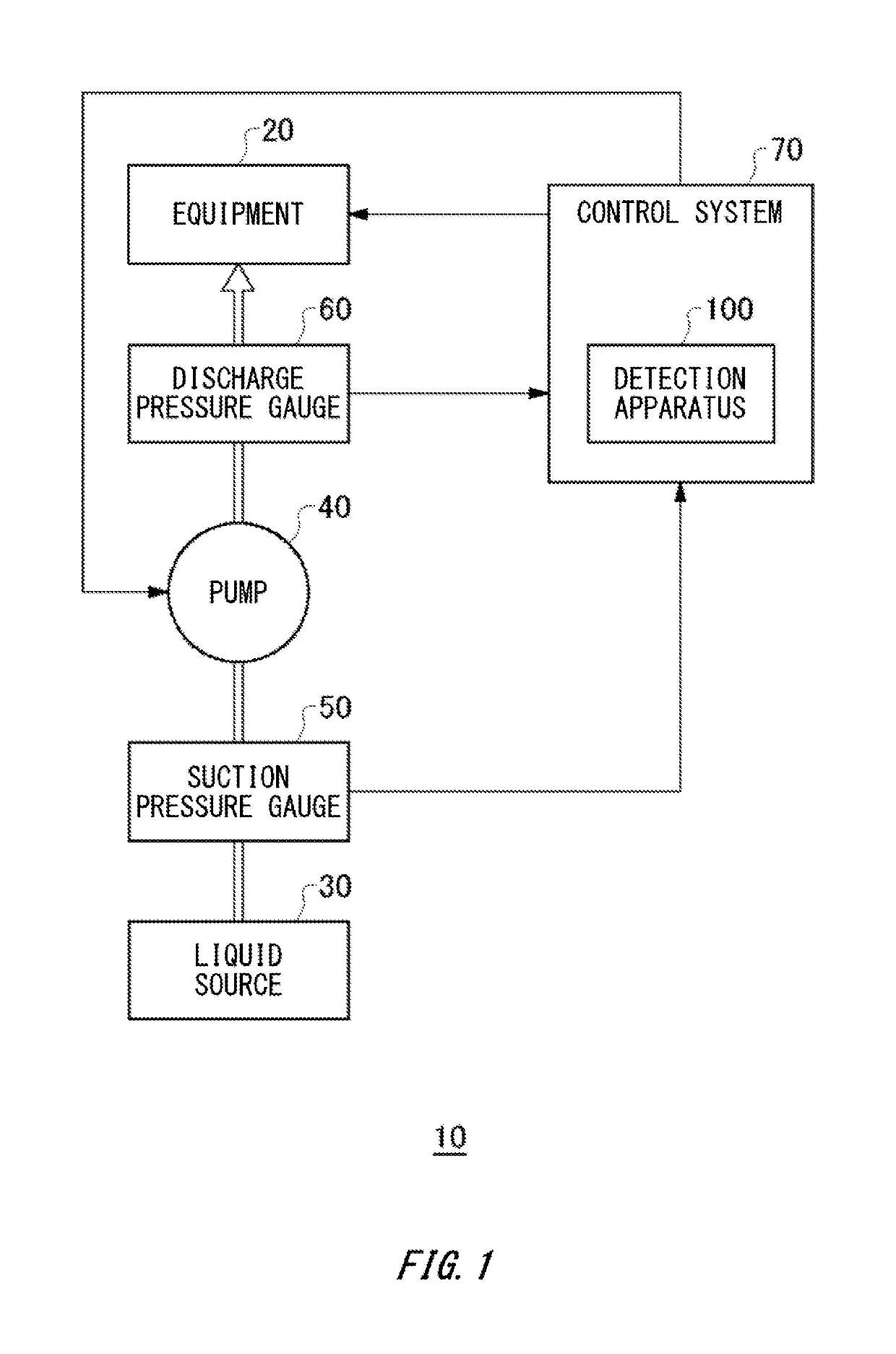
Detection apparatus, detection method, and computer readable medium
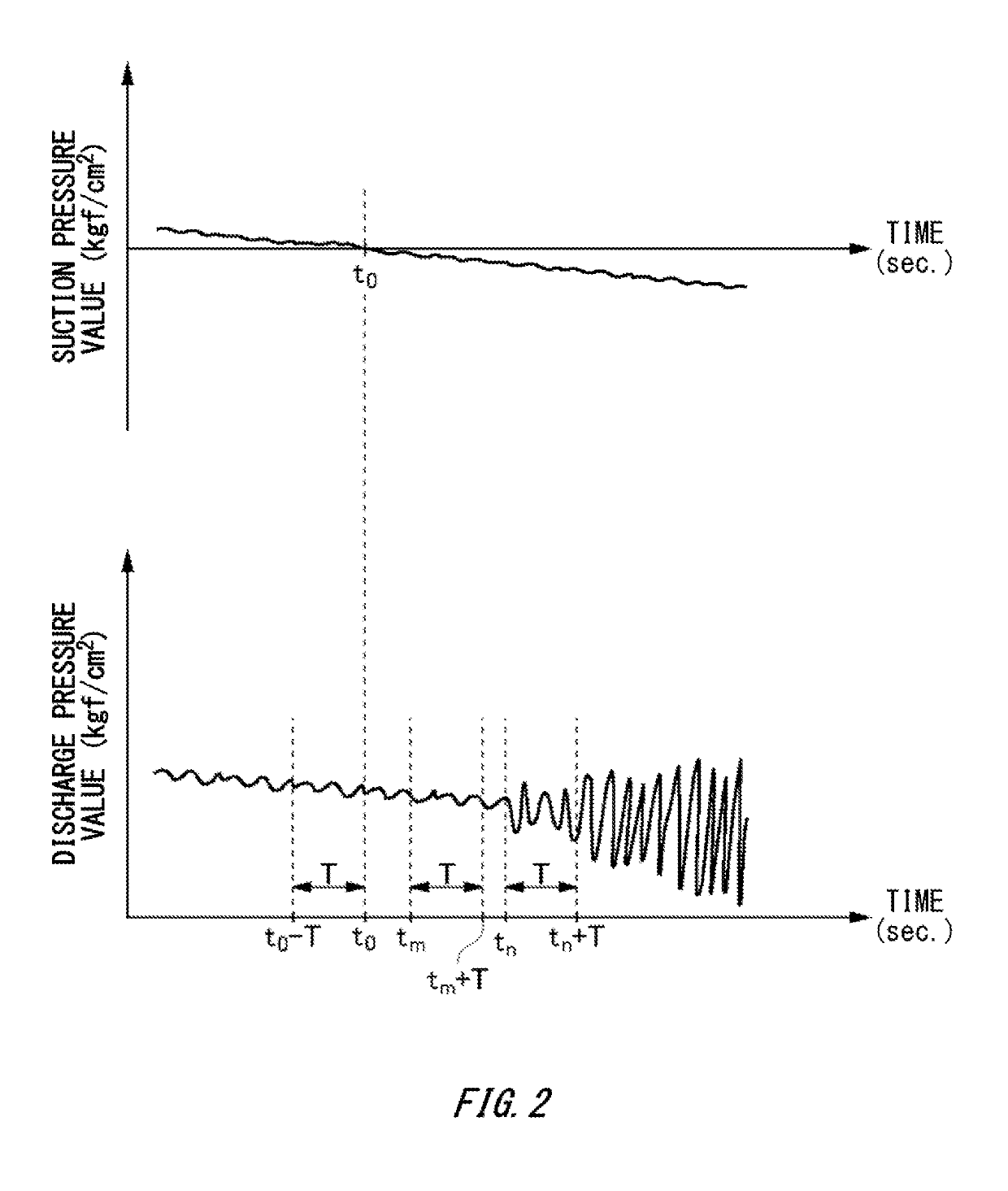
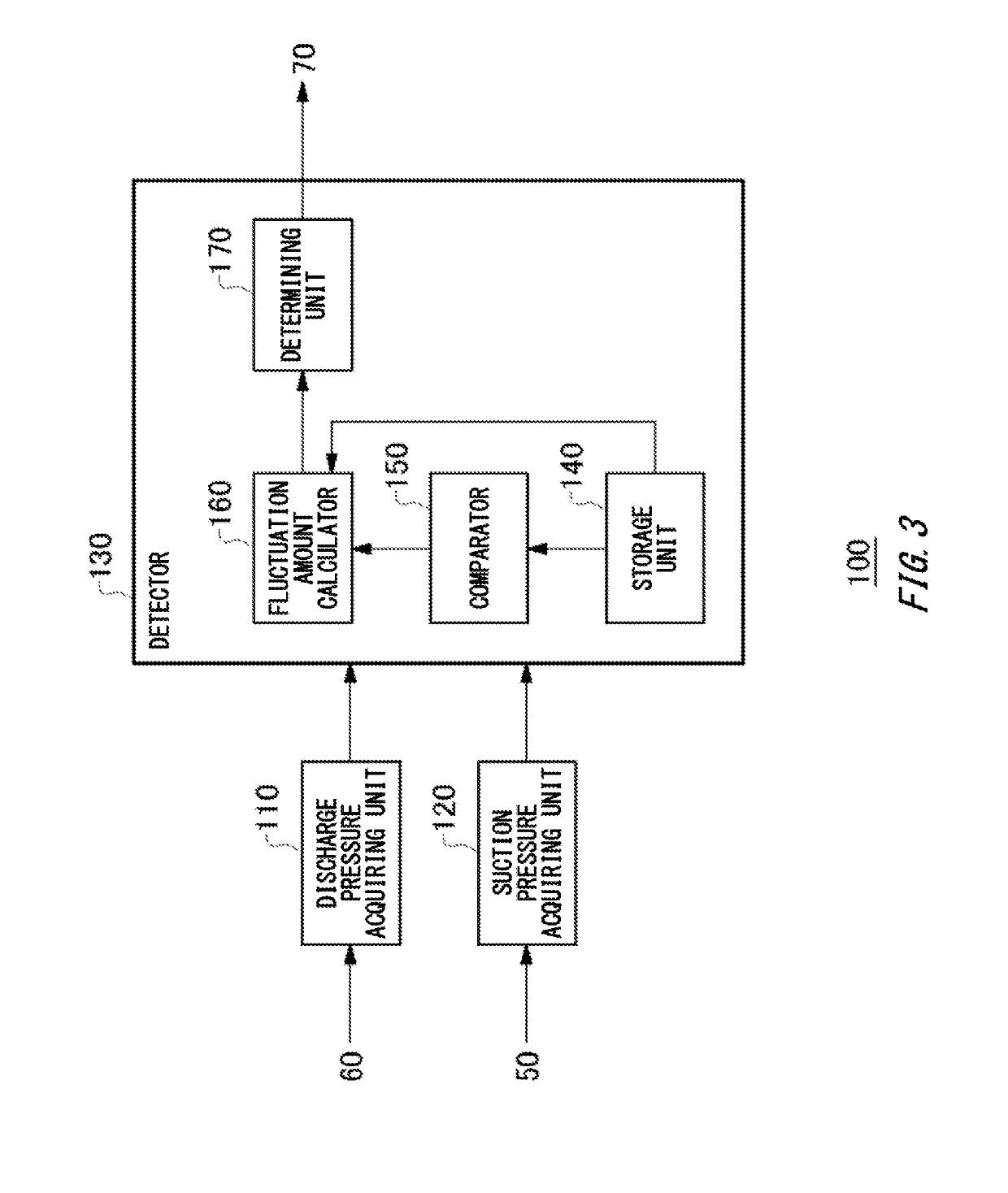
Easily detecting cavitation to occur in a pump. A detection apparatus, a detection method, and a program are provided. The detection apparatus includes: a discharge pressure acquiring unit to acquire discharge pressure data indicating discharge pressure of a pump; and a detector to detect occurrence of cavitation in the pump based on a fluctuation amount of a time waveform of the discharge pressure data during a target detection period. The detector may have: a fluctuation amount calculator to calculate the fluctuation amount of the discharge pressure data during the target detection period; and a determining unit to determine, in response to the calculated fluctuation amount becoming the reference fluctuation amount or more, that cavitation has occurred in the pump.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Lockout mechanism for a suspension system
ActiveUS20050104320A1Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringDischarge pressure
A suspension system that includes a simplified lockout mechanism and an adjustable blow-off mechanism. The system includes a valve mechanism and a valve actuating assembly, a valve mechanism housing and a resilient member disposed between the valve mechanism and the valve mechanism housing. The valve mechanism is slidably mounted along the valve mechanism housing and it separates a first chamber from a second chamber. The valve actuating assembly operates the valve mechanism between open and closed positions. The resilient member is configured to be deformable by the valve mechanism as the valve mechanism is slidably displaced by an increasing pressure in the first fluid chamber. The sliding valve mechanism is configured to collide against the valve actuating assembly when a blow-off pressure is reached in the first fluid chamber switching the valve mechanism from the closed position to the open position.
Owner:SRAM CORPORATION
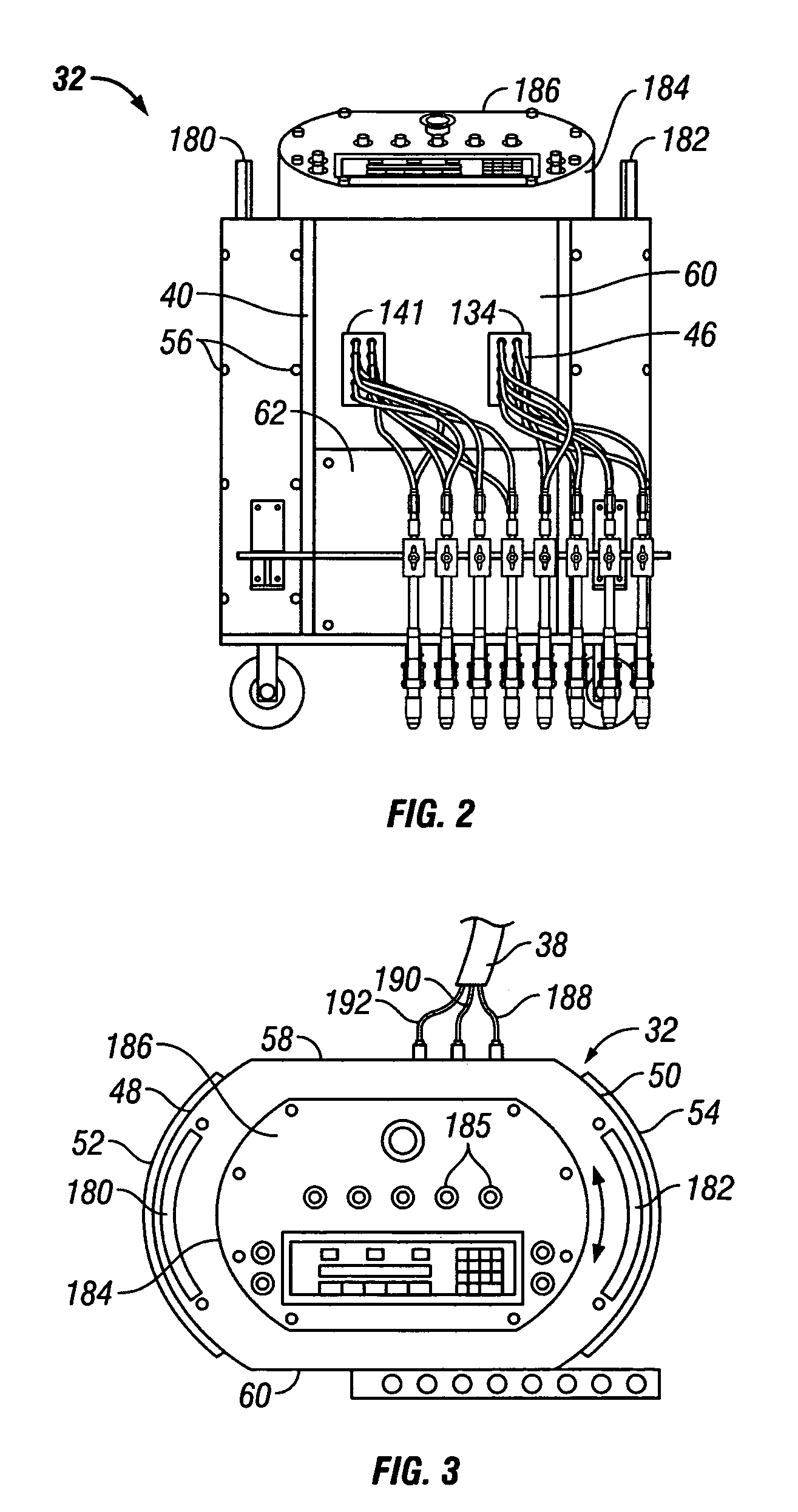
Shower head
A water-saving type shower head operable to reduce flow volume while maintaining a high discharge pressure. A diameter-reduced water passage 19 of a flow control member 20 disposed in a head portion 22 of a shower head body 12 has a first and a second water passage portions 40 and 41 provided on an entry side and an exit side thereof, respectively. The first water passage portion 40 has a small diameter, and the second water passage portion 41 has an inside diameter which is 1.5 to 3 times that of the first water passage portion 40. On an upstream side of the first water passage portion 40, a tapered diameter-reduced portion 43 reduced in diameter in a flow direction is formed, and on a downstream side of the second water passage portion 41, a diameter-increased portion 45 increased in diameter in the flow direction is formed.
Owner:OKUMA YOJI
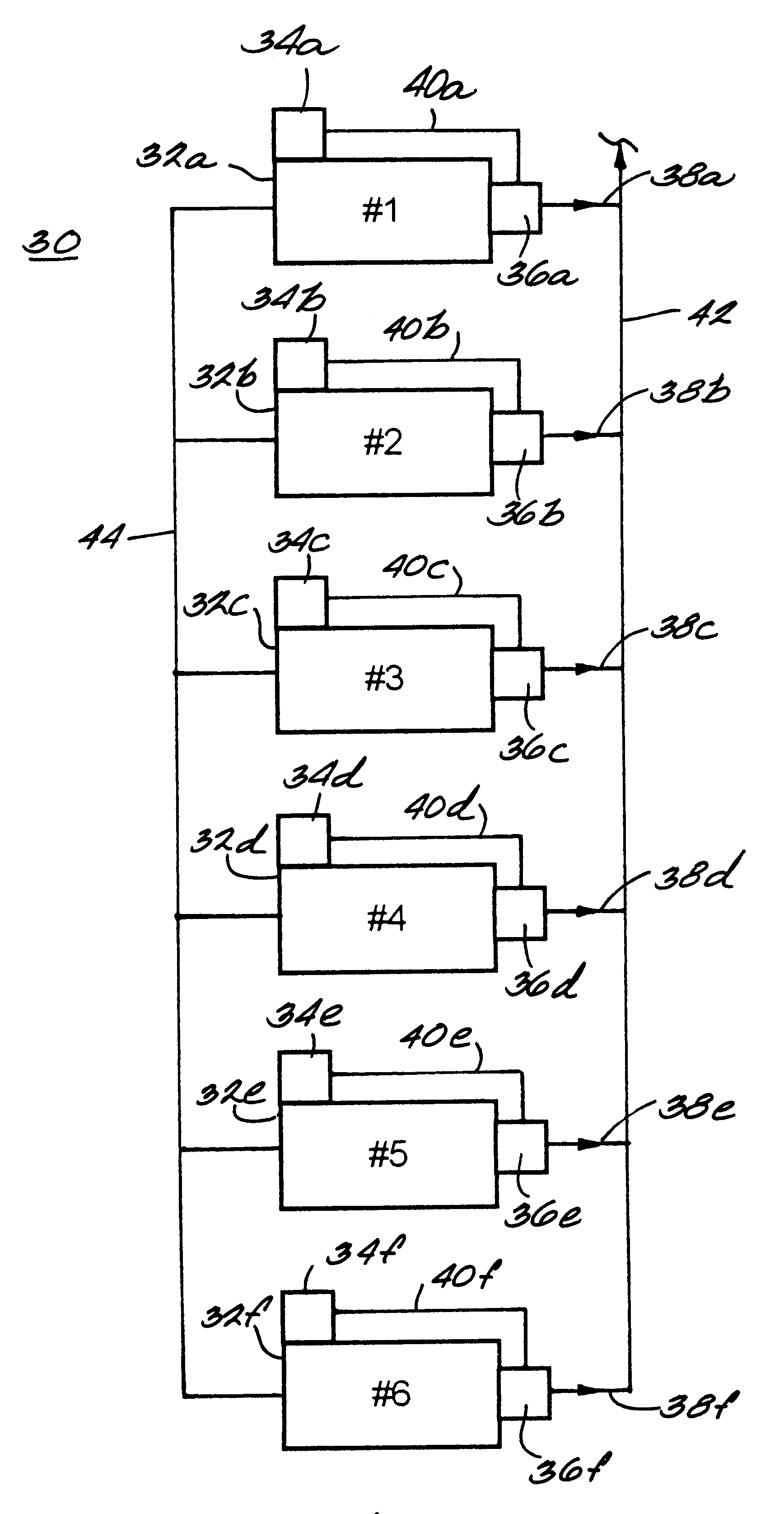
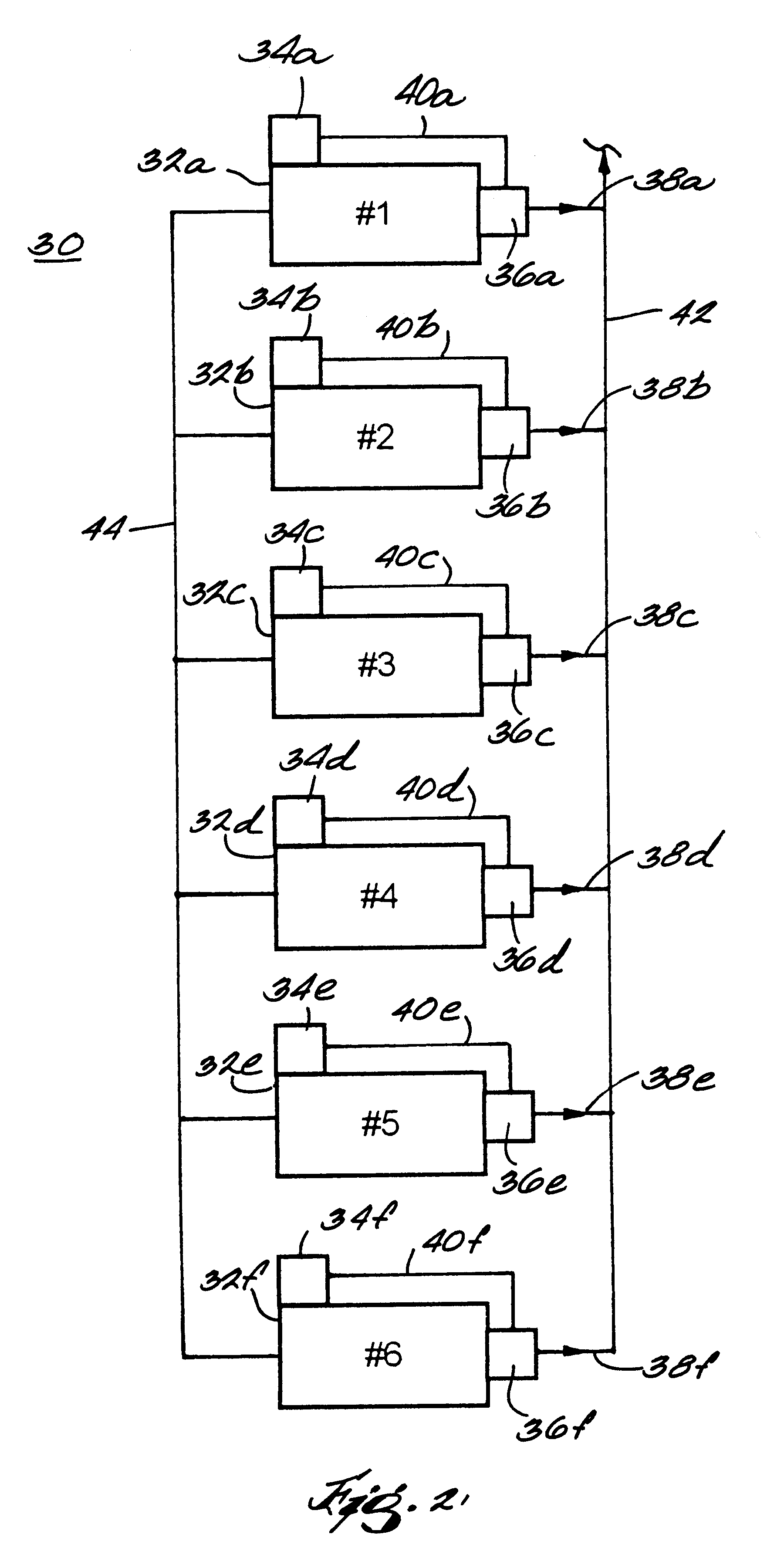
Method for controlling the operation of a compression system having a plurality of compressors
InactiveUS6233954B1Space heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsCompressed fluidRanking
A fluid compression system includes a plurality of compressors, each compressor having a local controller for controlling operation thereof and a sensor for sensing the pressure of compressed fluid discharged therefrom. A method for controlling operation of the fluid compression system includes establishing a set point pressure threshold for loading and unloading each compressor, and assigning a ranking to each compressor for identifying a highest ranked compressor and a lowest ranked compressor, whereby the highest ranked compressor for the compression system initiates all commands for controlling all of the lower ranked compressors in the compression system. The method also includes commencing a loading subroutine including loading the highest ranked unloaded compressor, setting a load delay timer, sensing the pressure of the compressed fluid discharged from the highest ranked compressor, comparing the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and transmitting a load command from the controller of the highest ranked compressor to the controller of the next highest ranked unloaded compressor if the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor remains less than or equal to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and the load delay timer equals zero. The loading subroutine is repeated until the discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor is greater than the set point pressure threshold established therefor.
Owner:INGERSOLL RAND CO
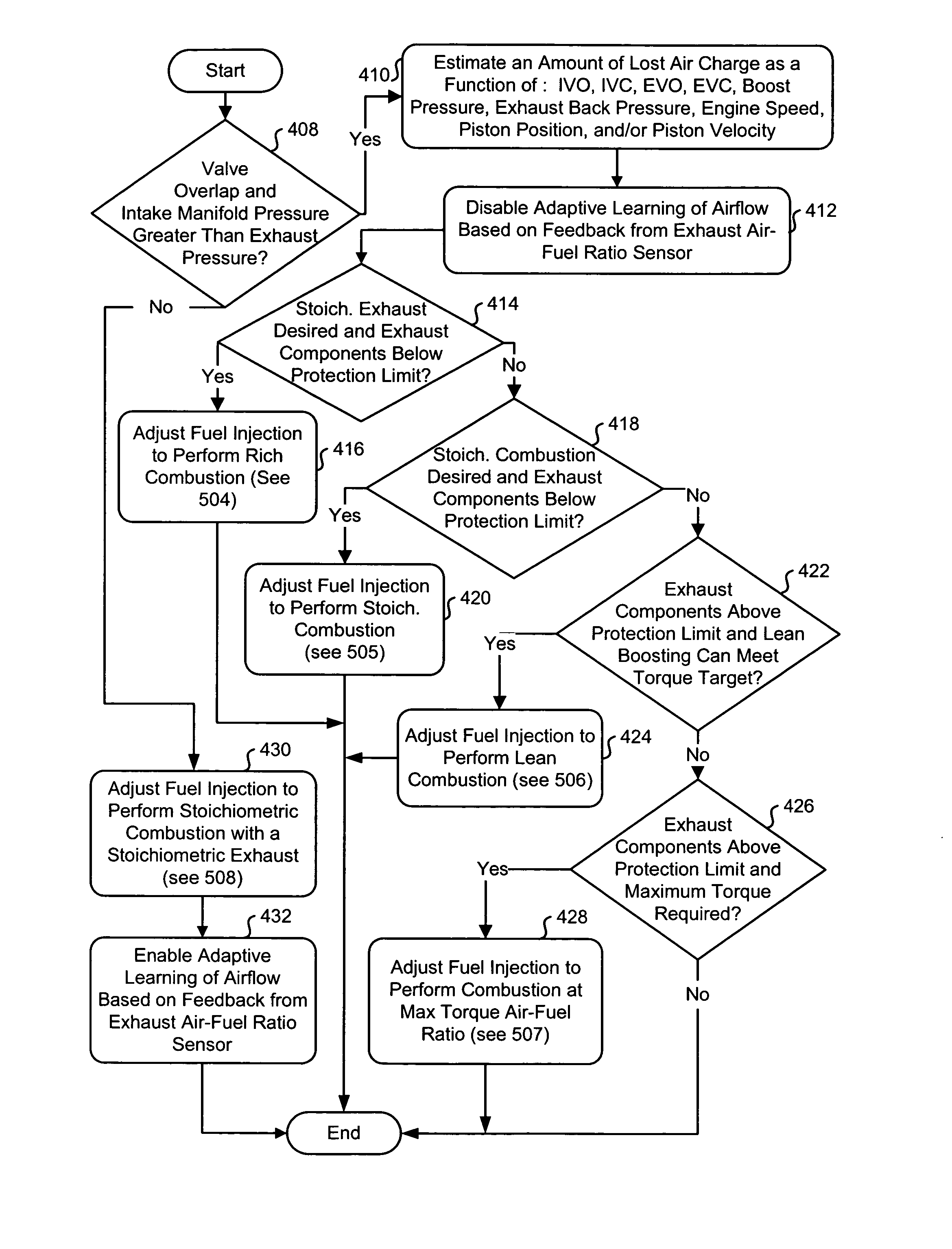
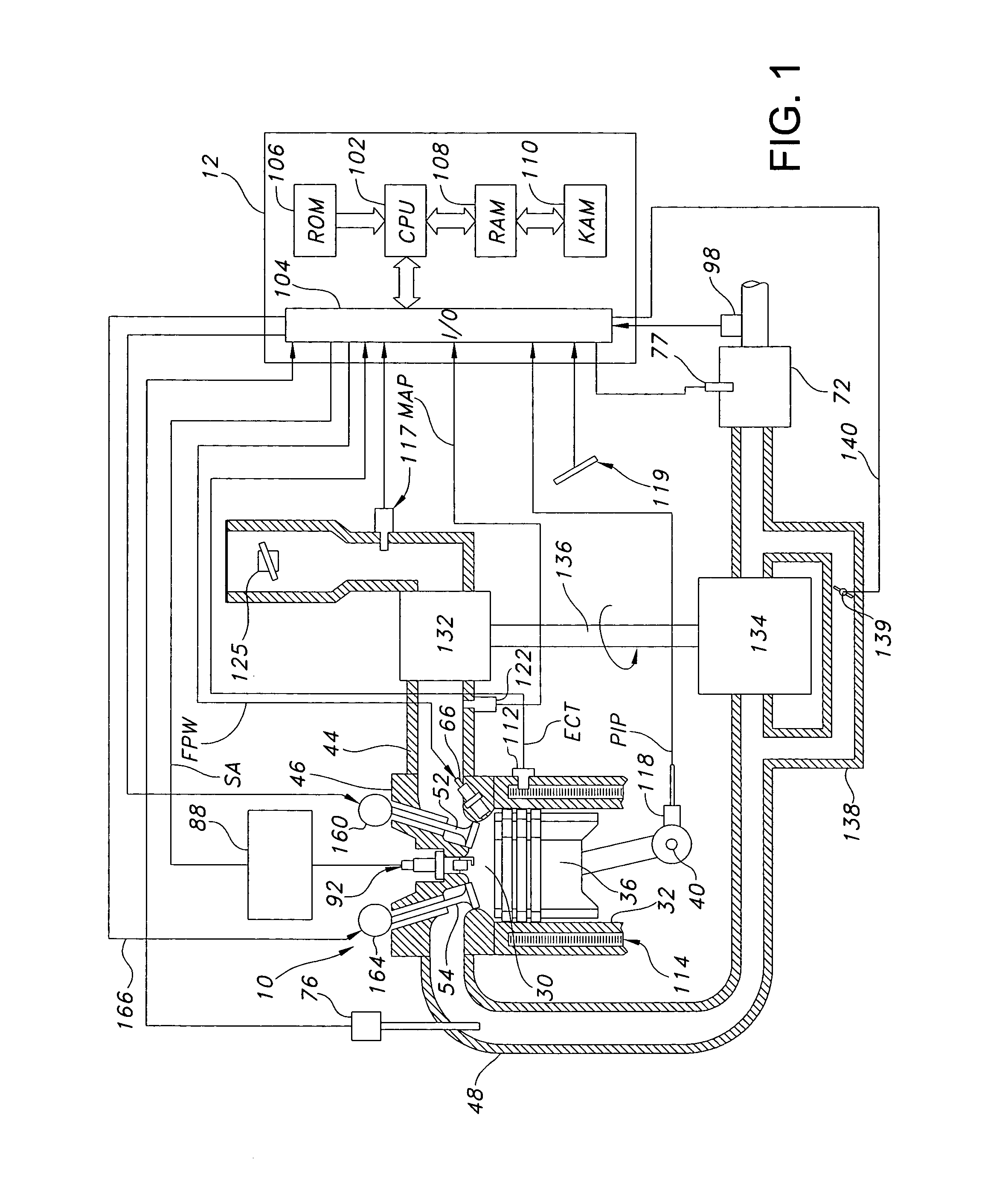
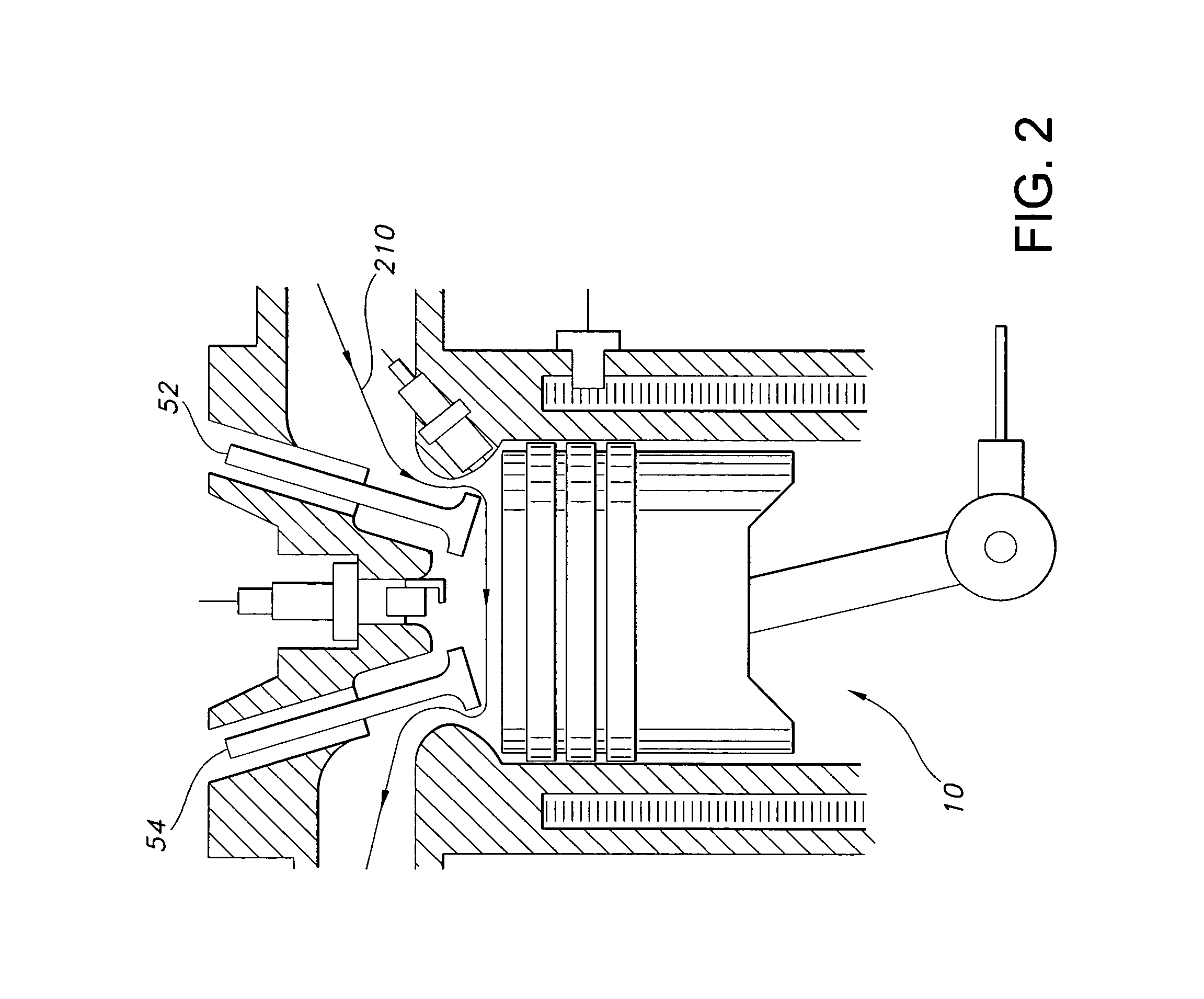
System and method for boosted direct injection engine
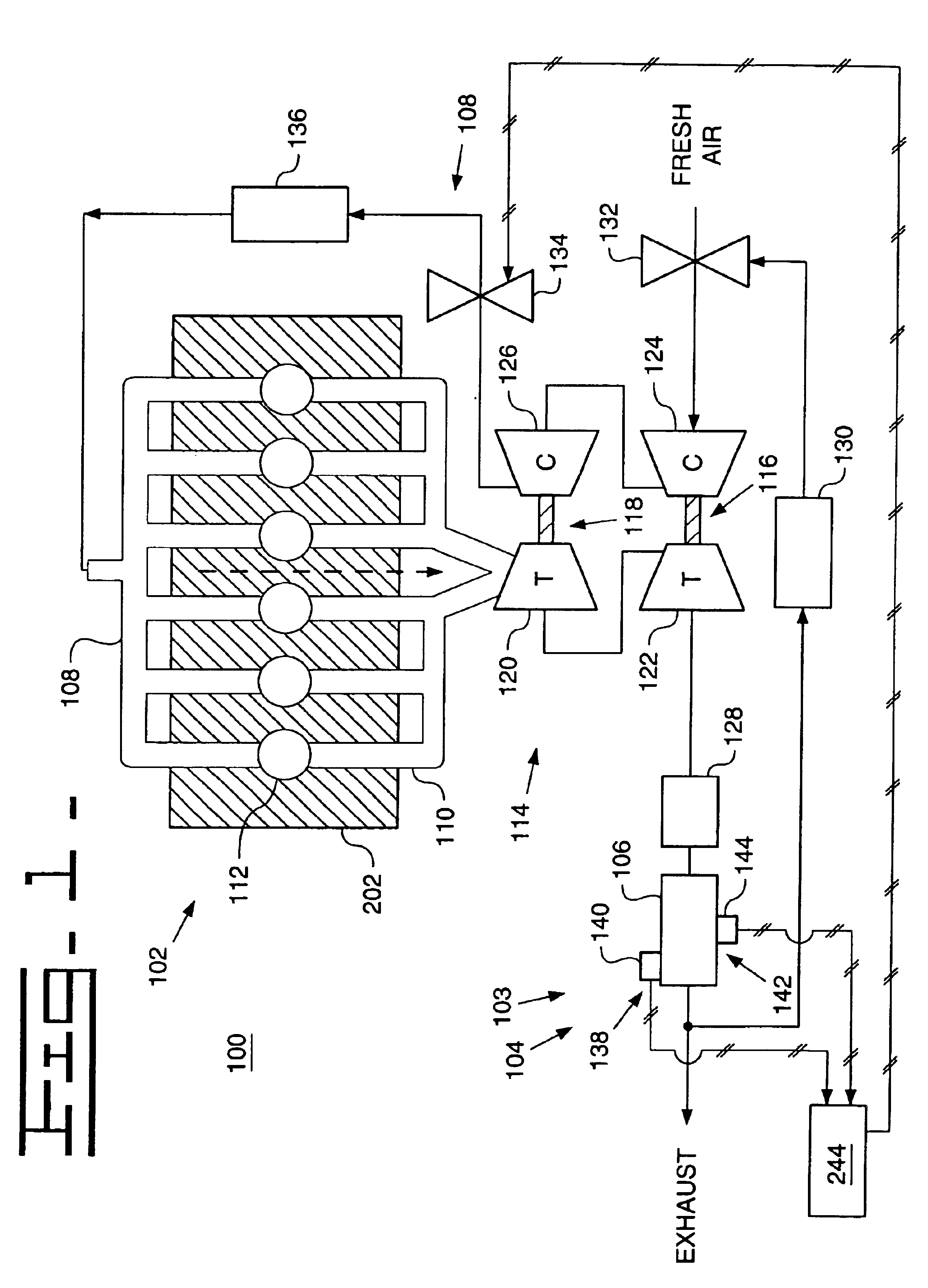
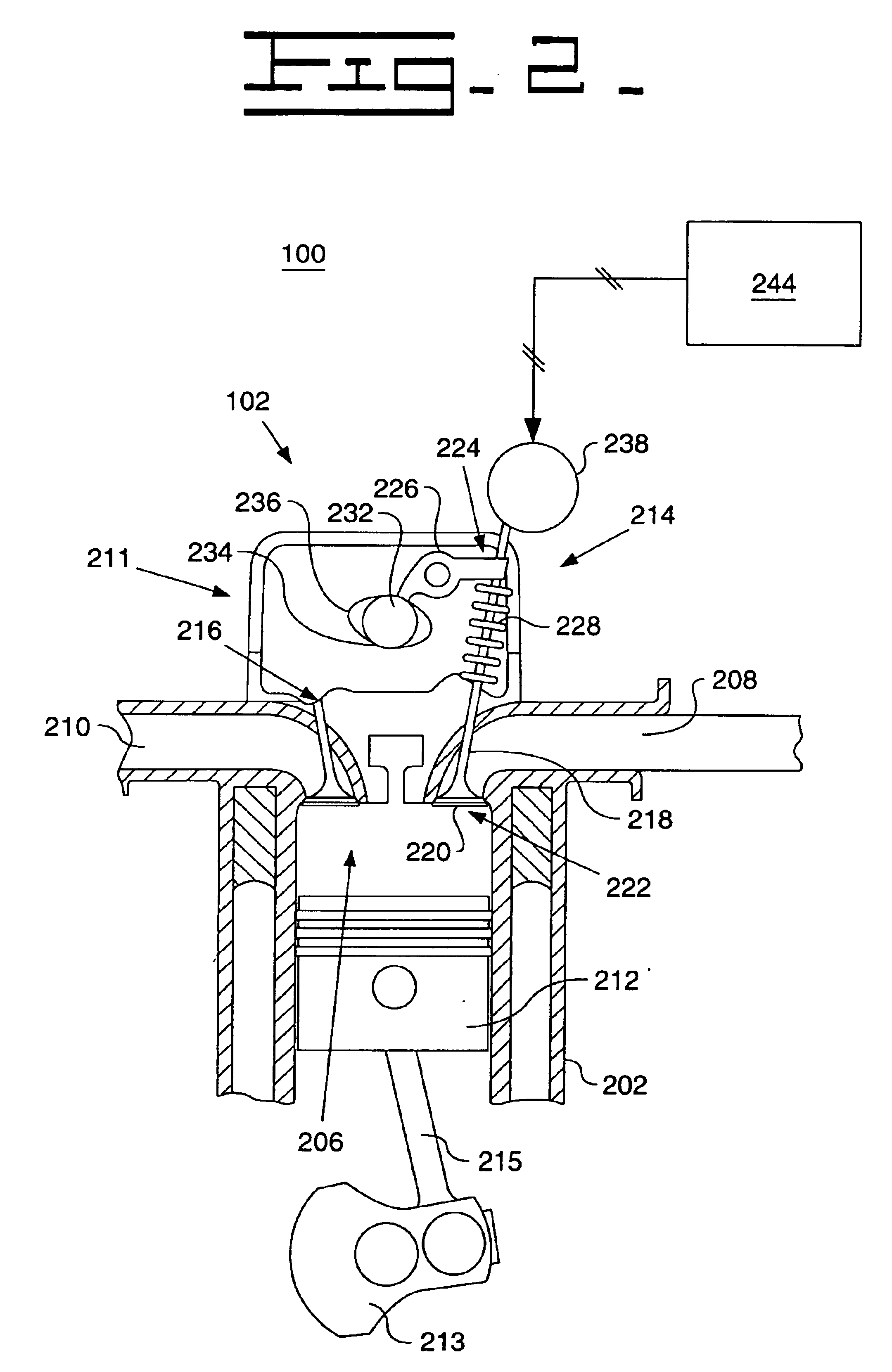
ActiveUS7275516B1Increase engine power densityReduced fuel efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveInlet valve
A method for operating and engine having a cylinder with at least an intake and exhaust valve, comprising of performing a combustion cycle in the cylinder in which exhaust valve closing occurs after intake valve opening thereby creating valve overlap, boosting intake air above exhaust pressure, where said boosted intake air is inducted into said cylinder while said intake valve is open and at least a first portion of said inducted boosted intake air flows past the exhaust valve with both said intake and exhaust valves are open during said overlap, directly injecting fuel to said cylinder that is combusted in said cylinder, where a beginning of said fuel injection occurs after said exhaust valve closing and said directly injected fuel is mixed with at least a second portion of said inducted boosted intake air, and combusting said mixture at a rich air-fuel ratio.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for differential pressure testing of catalytic reactor tubes
ActiveUS6981422B1Efficient testingMinimizes servicing timeProcess control/regulationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDifferential pressureEngineering
A multi-tube differential pressure (Delta P) testing system for testing catalyst filled tubes of tube and shell type catalytic reactors has at least one mobile test unit for movement on the upper tube sheet of a catalytic reactor. An array of test probes is mounted to the mobile test unit and is selectively positionable in sealed gas pressure communicating engagement within the upper ends of selected reactor tubes. A pressure testing gas delivery system is interconnected with the test probes and selectively communicates pressurized gas to the testing tubes at a blow-down pressure or selected test pressure determined by restricted orifices. A differential pressure measurement system measures the back-pressure resulting from application of test pressure to individual reactor tubes and having a computer receiving electronic back-pressure measurement data and producing an electronic and / or visual record correlated with a reactor tube numerical sequence and identifying the resulting back-pressure of each reactor tube of the multi-tube test. The testing system is capable of selectively electronically counting in normal sequence and in inverted sequence to accommodate test unit orientation and incorporates a separate manually positioned testing wand to accommodate tube positions of the reactor that cannot be readily accessed by one or more of the array of test probes.
Owner:WINDLASS METALWORKS
Method and Apparatus for Controlling an Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20090007564A1Increase fuel consumptionSave fuelElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineTurbocharger
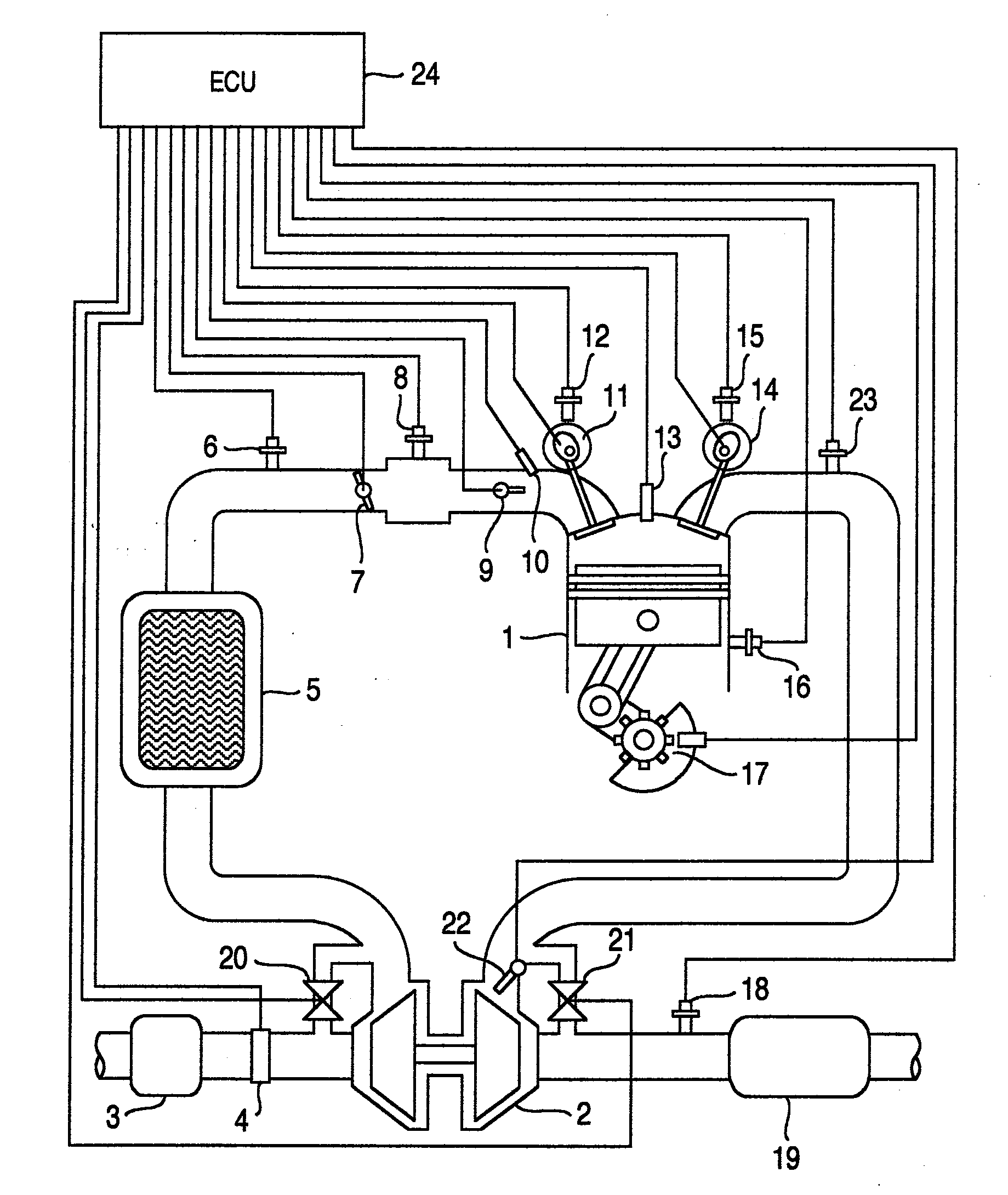
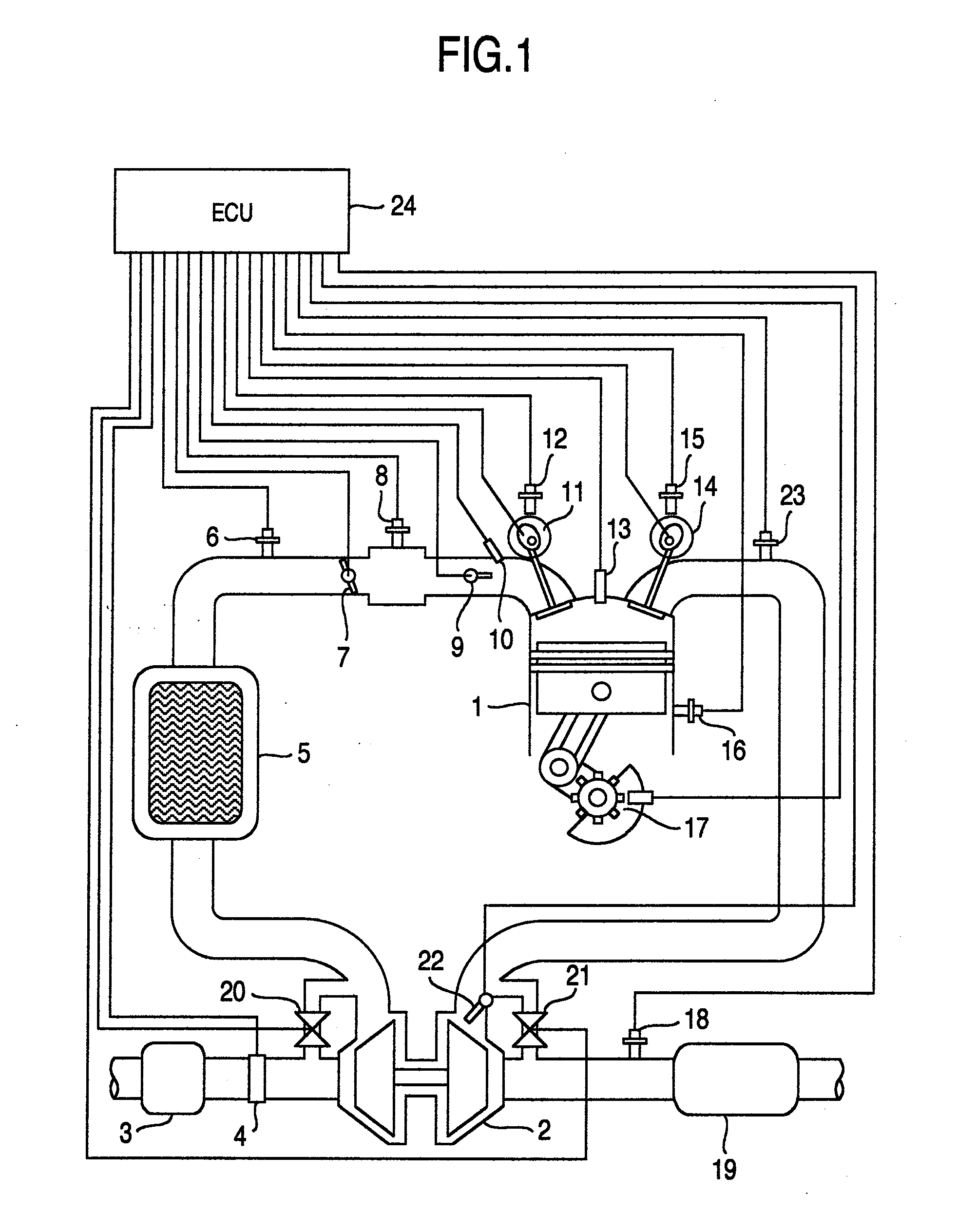
A control device for an internal combustion engine, which comprise a turbocharger, of which turbo flow rate is made variable, and an intake valve provided with a variable valve mechanism and in which mirror cycle is performed, the control device comprising: device, which calculates an intake air quantity per unit time and an intake air quantity per cycle on the basis of torque required to the internal combustion engine; device, which controls the turbocharger so that with the intake air quantity per unit time, supercharging pressure is further increased in that range, in which a ratio of supercharging pressure and exhaust pressure is equal to or less than a predetermined value; and device, which controls the variable valve mechanism on the basis of the supercharging pressure and the intake air quantity per cycle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
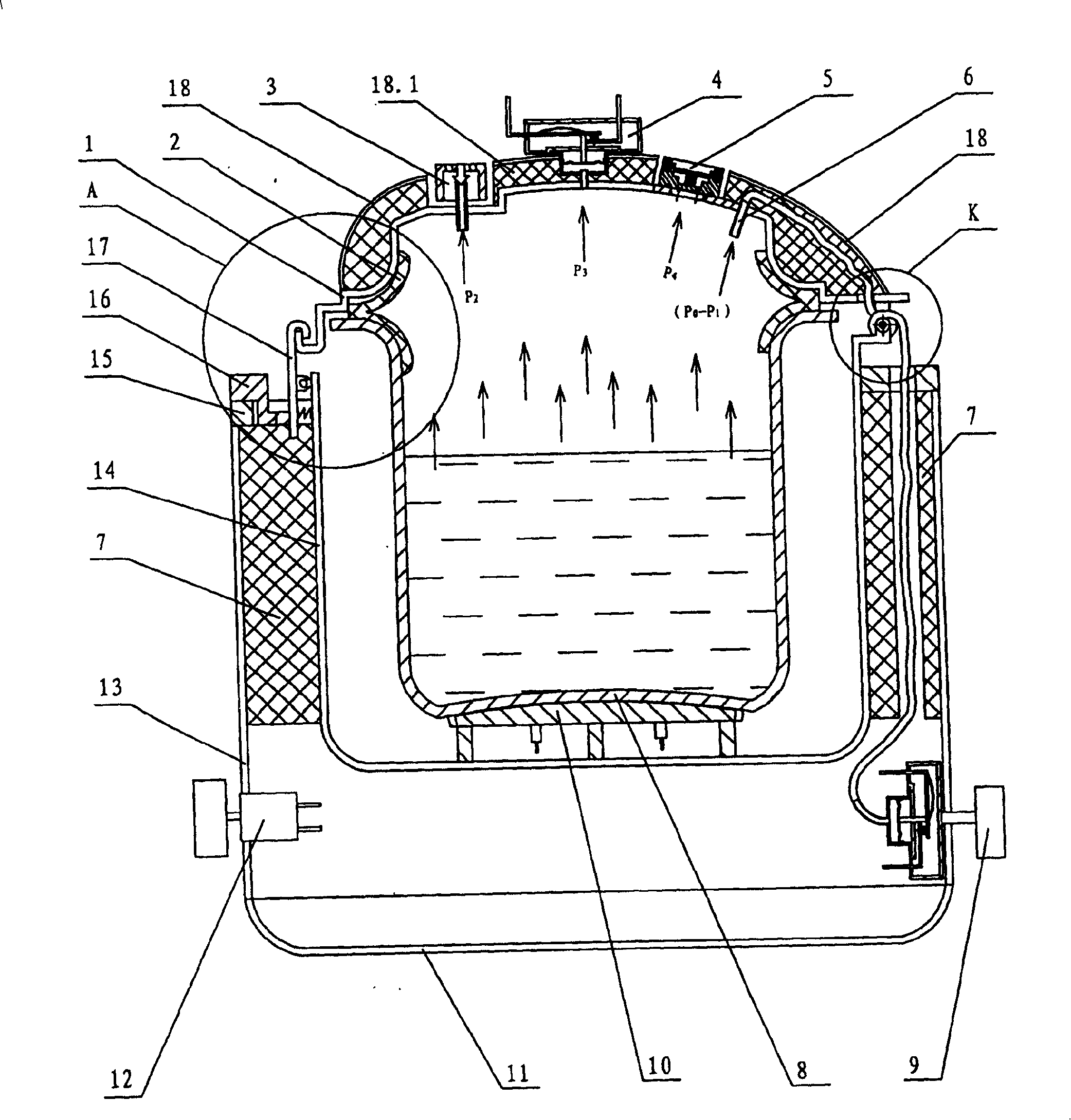
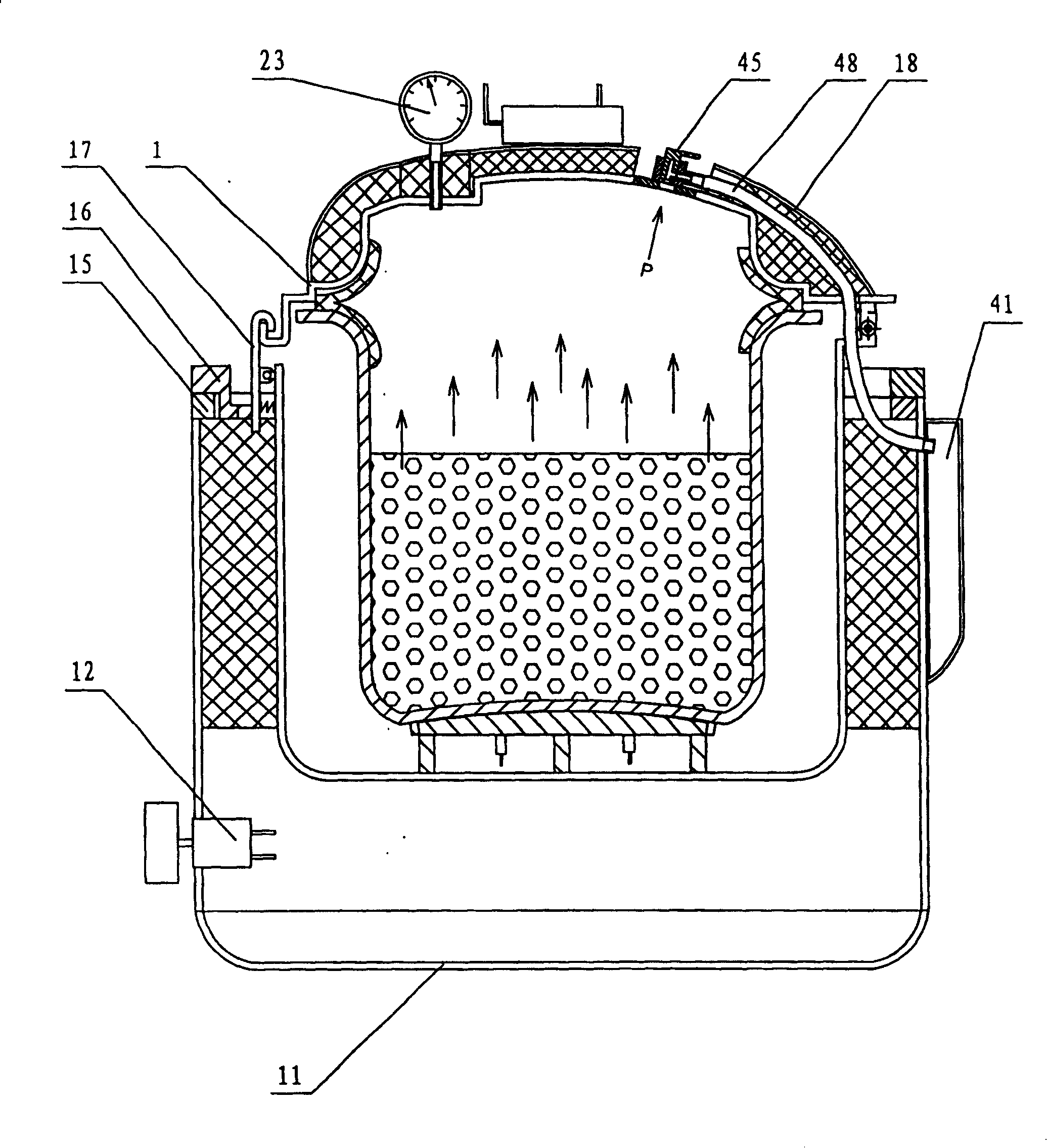
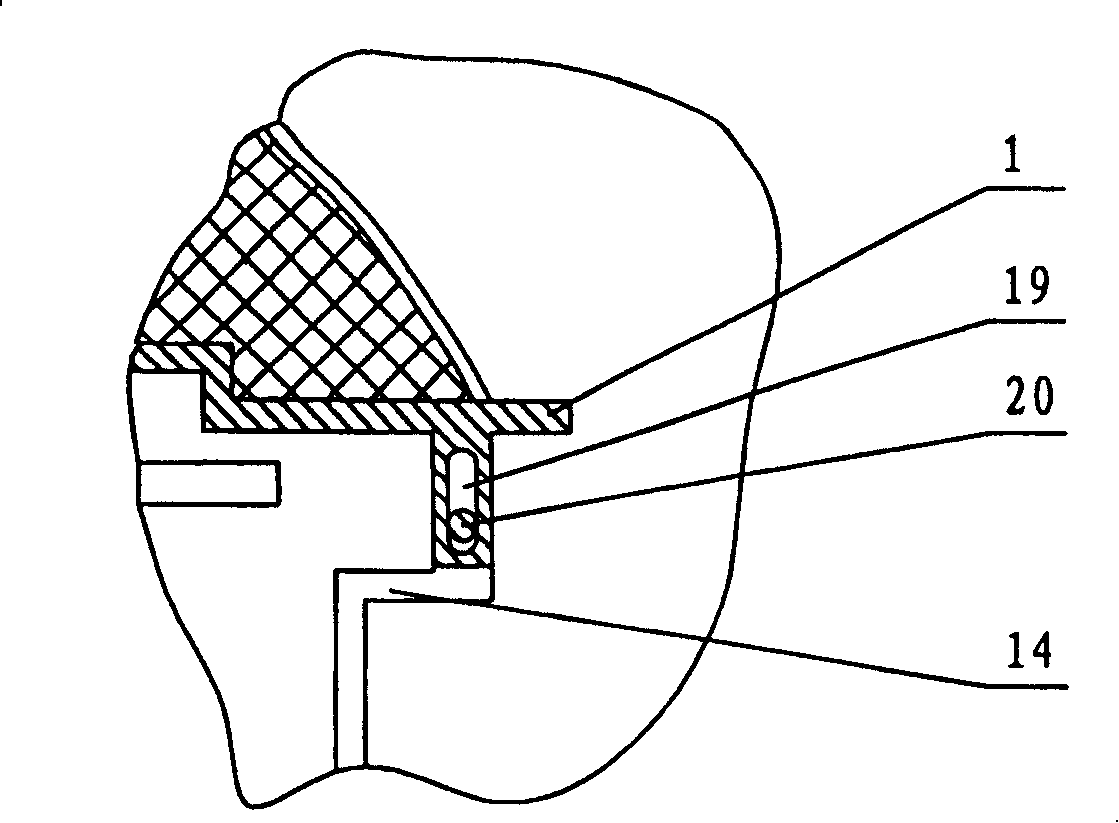
Electric pressure cooker capable of controlling pressure precisely
InactiveCN100401957CReduce lossImprove heating efficiencyPressure-cookersEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
There is an accurate pressure-controlling electric rice cooker, which contains an inner pot inside pot body crust, and the inner pot is connected with electric plate, and there is a resilient seal ring between the inner pot and pot cover. Between the crust and the inner pot there is a middle pot; between the crust and the middle pot there is a heat-insulating layer. The electric rice cooker has a pressure switch, which contains an air duct or air channel connected with inner pot chamber. The other end of the air duct or air channel is communicated with a pressure membrane case, in which there are movable membranes that are joined with push rod. On the other side of the push rod there is a movable contact spring, which connects with an unmovable contact spring, and both the two contact springs couple with main controlling electric of electric rice cooker separately. This invention has simple and reasonable structure, its pressure controlling is accurate, safety degree is high, and after cooking it can exhaust quickly and safely, discharge pressure in blocked style, and its heat insulation effect is good, heat conductivity is high and is energy saving.
Owner:李剑锋
Electric pressure pot and supporting part of electric pressure pot
InactiveCN107684336ASmall thermal inertiaImprove controllabilityPressure-cookersEngineeringElectromagnetic heating
The invention discloses an electric pressure pot and a supporting part of the electric pressure pot. The electric pressure pot includes an outer pot body, the supporting part, an inner pot body and anelectromagnetic heating disc; the supporting part is arranged in the outer pot body and supported on the bottom wall of the outer pot body; the area of the lower surface of the supporting part is smaller than or equal to that of the upper surface of the supporting part; the inner pot body is arranged in the outer pot body and supported on the supporting part, and moves downwards to discharge pressure when the pressure inside the inner pot body reaches a preset value; the electromagnetic heating disc is used for heating the inner pot body and arranged between the outer bottom surface of the inner pot body and the inner bottom surface of the outer pot body. The electric pressure pot has the advantages of being low in thermal inertia, great in controllability, high in reliability and the like.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE MIDEA ELECTRICAL HEATING APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for cooling
ActiveUS20100057263A1Improve cooling efficiencyMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleDischarge pressureInlet temperature
Methods of controlling a cooling unit and embodiments of a cooling unit are disclosed. A method of improving efficiency of the cooling unit includes detecting a degree of opening of a hot gas bypass valve configured to divert a portion of coolant from a compressor to a heat exchanger of the cooling unit, and adjusting a condenser discharge pressure based on the detected degree of opening. Aspects may increase cooling efficiency at partial cooling requirements. Fluctuations in refrigerant pressure at low cooling capacities and condenser medium inlet temperature may be avoided. Minimum condenser water inlet temperature for a water-cooled cooling unit may also be reduced.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Working fluid for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
ActiveUS20160333243A1Stably used continuouslyCycle performance sufficientHeat-exchange elementsWorking fluidMetal working fluid
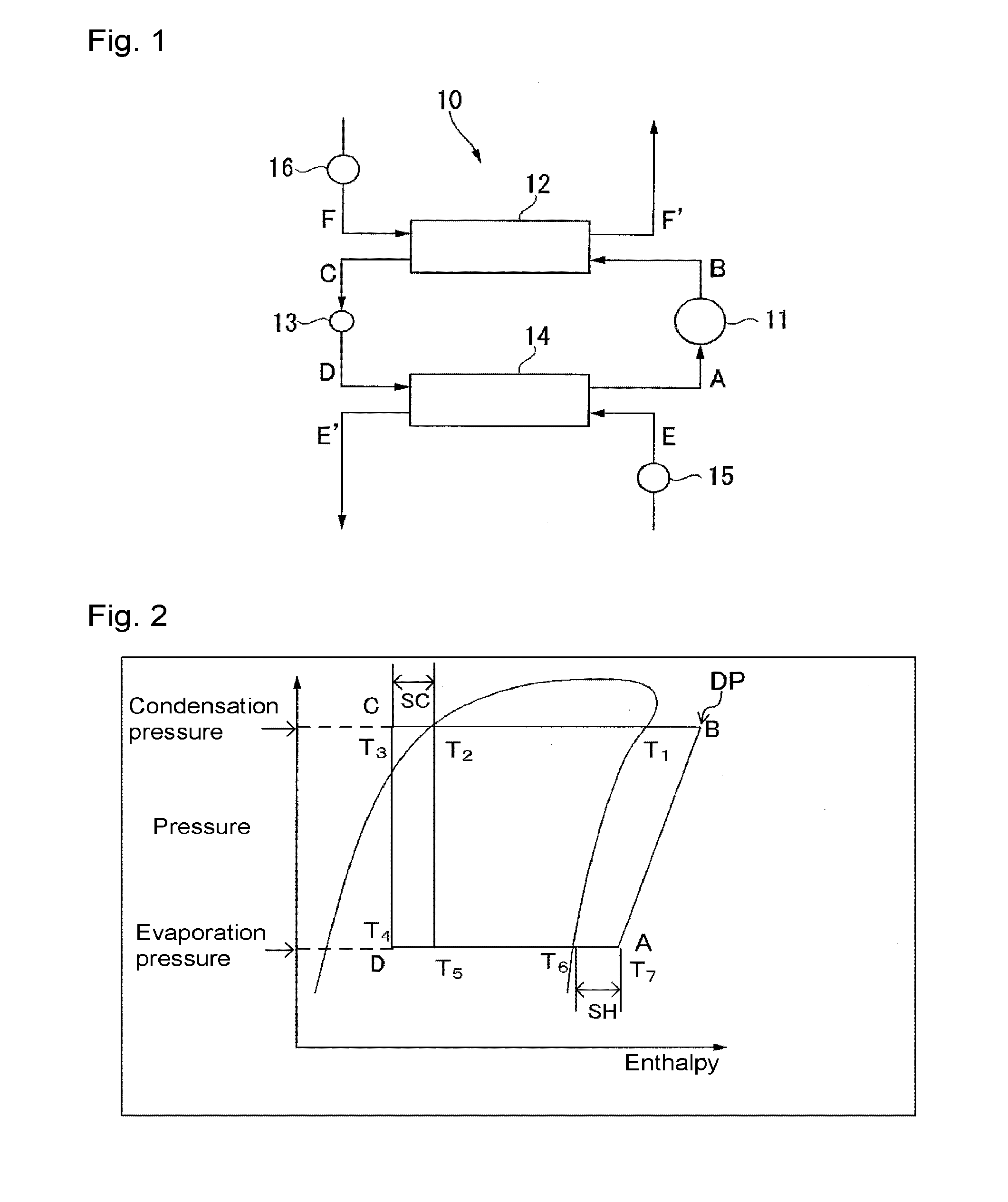
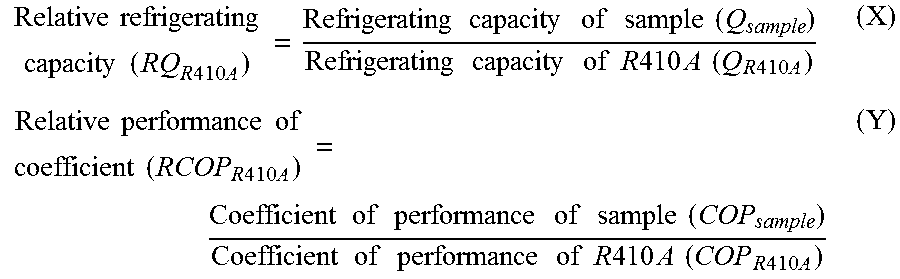
To provide a working fluid which has cycle performance sufficient as an alternative to R410A while the influence over global warming is sufficiently suppressed, which does not significantly increase the load to an apparatus as compared with a case where R410A is used, and which can be stably used continuously without any special measures, a composition for a heat cycle system comprising the working fluid, and a heat cycle system employing the composition.A working fluid for heat cycle, wherein the global warming potential is less than 300; the product of the relative coefficient of performance and the relative refrigerating capacity is at least 0.820 relative to R410A in a standard refrigerating cycle under conditions of an evaporation temperature of 0° C., a condensing temperature of 40° C., a supercoiling degree of 5° C. and a degree of superheat of 5° C.; the relative compressor discharge gas pressure is at most 1.100; the lower limit of the combustion range by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety Act is at least 5 vol %; and the pressure will not exceed 2.00 MPaG in a combustion test by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety act under 0.98 MPaG at 250° C.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
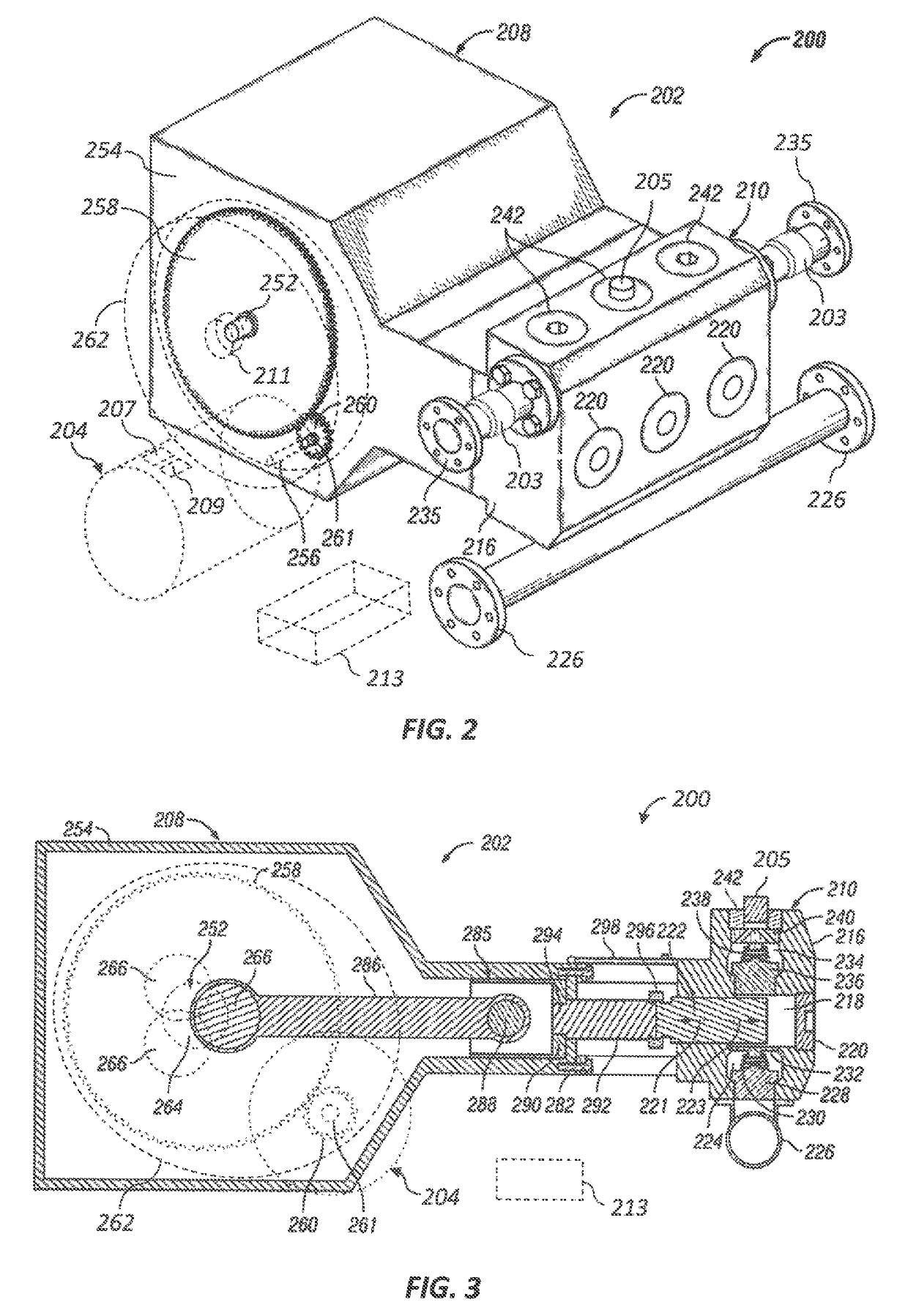
Variable displacement pump
ActiveUS20100226799A1Increase biasing forceOvercomes drawbackPump componentsOscillating piston enginesVariable displacement pumpDischarge pressure
A variable displacement oil pump for an automotive engine. The oil pump includes a cam ring accommodating thereinside a pump element having a rotor. The cam ring is swingingly movably accommodated in a housing and biased in a direction to increase an eccentricity amount of the cam ring relative to the axis of the rotor by a biasing member. First and second pressure chambers are defined inside the housing by the outer peripheral section of the cam ring. The first pressure chamber is supplied with a discharge pressure to be applied to the cam ring to oppose to a biasing force of the biasing member. The second pressure chamber is supplied with the discharge pressure to be applied to the cam ring to assist the biasing force of the biasing member. Additionally, a control device is provided for controlling supply of the discharge pressure to the second pressure chamber.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
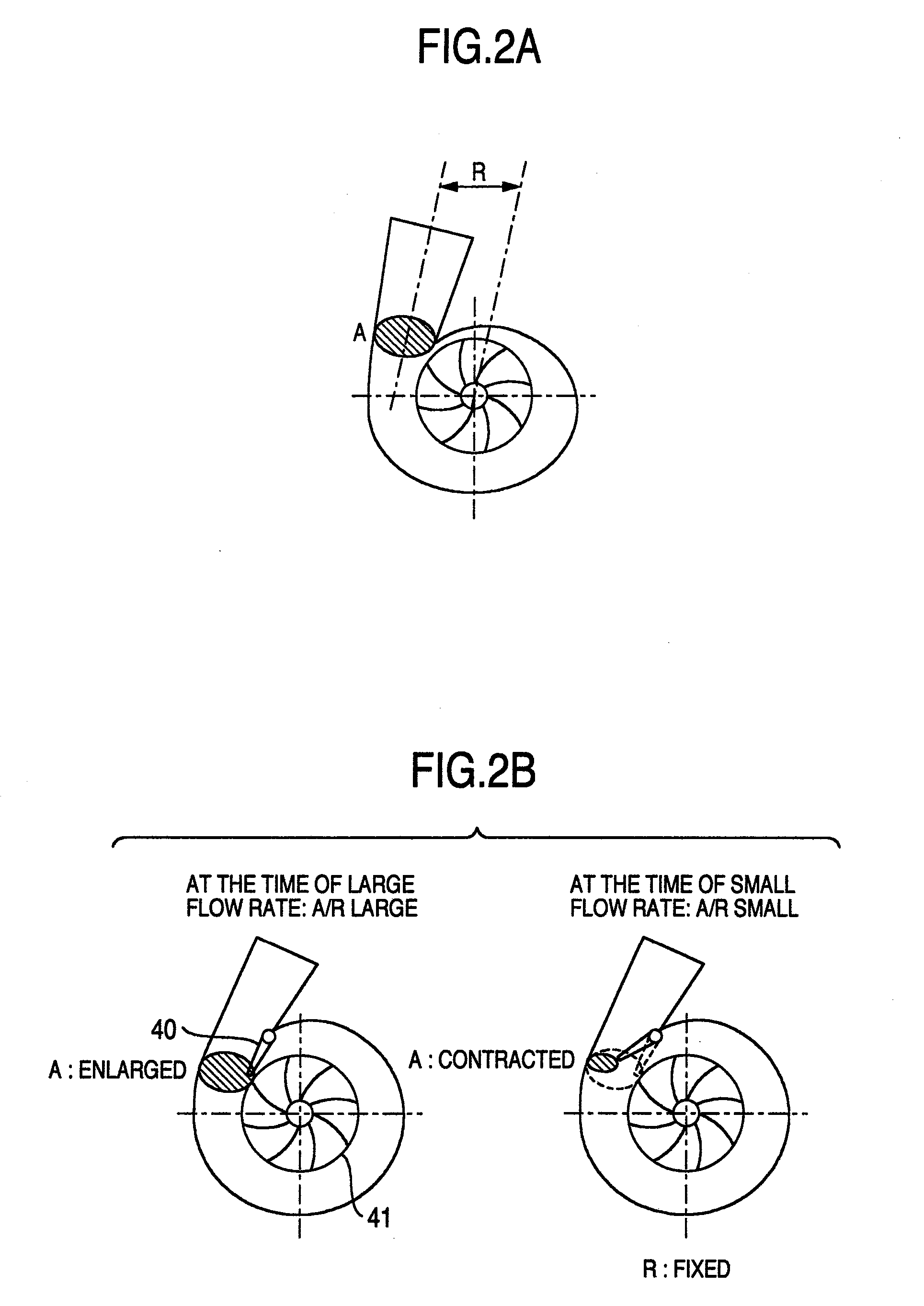
Efficient bypass valve for multi-stage turbocharging system
InactiveUS20060042246A1High speedOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerDischarge pressure
A turbocharger system includes first and second turbines arranged such that exhaust gas passes through the first turbine then the second turbine. A bypass channel is configured such that exhaust gas entering the channel passes only through the second turbine. A valve positioned in the bypass channel regulates the flow of gas therethrough. The valve accelerates a stream of gas and focuses the stream toward the second turbine such that a large part of the added velocity of the stream is preserved as it enters the second turbine. Operation of the valve may be controlled so as to maintain the valve in a closed position while exhaust gas pressure above the first turbine pressure is below a first threshold, to progressively open the valve as the pressure increases above the first threshold, and to maintain the valve in a full-open position while the pressure is above a second threshold.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
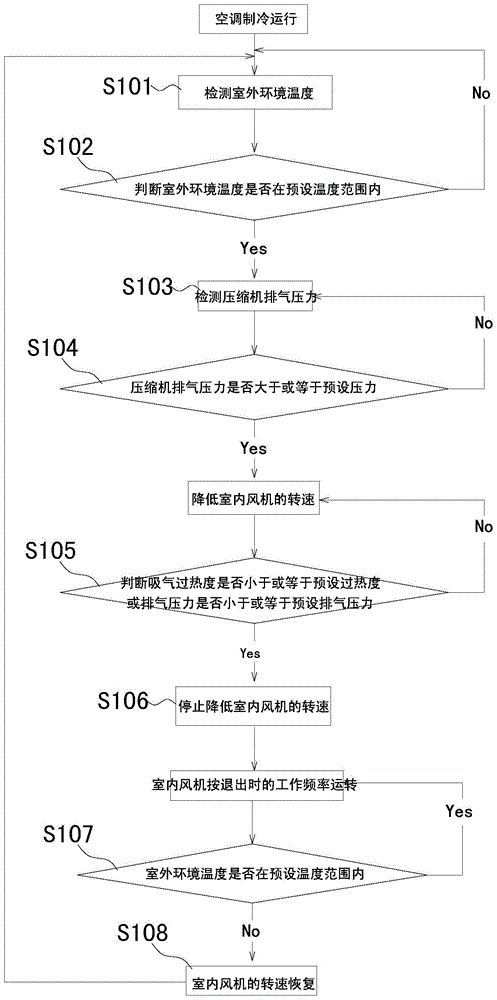
Pressure control method of air conditioning system
ActiveCN104697106AReduce exhaust pressureEffect of exhaust pressureMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSystem pressureAir conditioning
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Electric pressure pot
ActiveCN107684340ASmall thermal inertiaImprove controllabilityCooking vesselsDischarge pressureThermal inertia
The invention discloses an electric pressure pot. The electric pressure pot includes a shell, an outer pot body, an elastic part, a supporting part, an inner pot body, an electromagnetic heating device and a fan; the shell is provided with an air inlet and an air outlet; the outer pot body is arranged in the shell; the elastic part is arranged in the outer pot body and supported on the bottom wallof the outer pot body; the supporting part is arranged in the outer pot body and supported on the elastic part; the inner pot body is arranged in the outer pot body and supported on the supporting part, and the elastic part is deformed to discharge pressure inside the inner pot body when the pressure in the inner pot body reaches a preset value; the electromagnetic heating device is used for heating the inner pot body and arranged between the outer bottom surface of the inner pot body and the inner bottom surface of the outer pot body; the fan is arranged between the inner surface of the shell and the outer surface of the outer pot body. The electric pressure pot has the advantages of being low in thermal inertia, great in controllability, high in reliability and the like.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE MIDEA ELECTRICAL HEATING APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD
Insulin pump
InactiveUS20070093750A1Increased durabilityAutomatic syringesMedical devicesCircular discRotational axis
The present relates to an automatic insulin pump, which allows the rotary shaft only to rotate piston advancing means to remove vertical load applied to a rotary shaft, thereby improving durability thereof. The insulin pump includes: an injector having a syringe for containing insulin therein, and a piston inserted into the rear end of the syringe for providing the syringe with insulin discharge pressure; a housing having an injector receiving space formed in an appropriate position thereof, the injector receiving space having a partition wall formed at the rear end thereof; a rotary shaft having a non-circular section and a predetermined length; power supply means for rotating the rotary shaft at a predetermined speed; a push plate assembly for providing the piston with ahead power by pushing the piston, the push plate assembly having a disk part having a male screw formed on the outer circumferential surface thereof and a coupling hole axially coupled with the rotary shaft at the central portion thereof to allow for forward and backward movement of the rotary shaft, which passes through the coupling hole; and a hollow cylindrical type push plate case inserted into the injector receiving space of the rear end of the syringe, for the piston to pass therethrough, the push plate case having a female screw formed on the inner circumferential surface thereof to be coupled with the male screw of the disk part for allowing the disk part to carry out a spirally forward and backward movement.
Owner:ENTER TECH +2
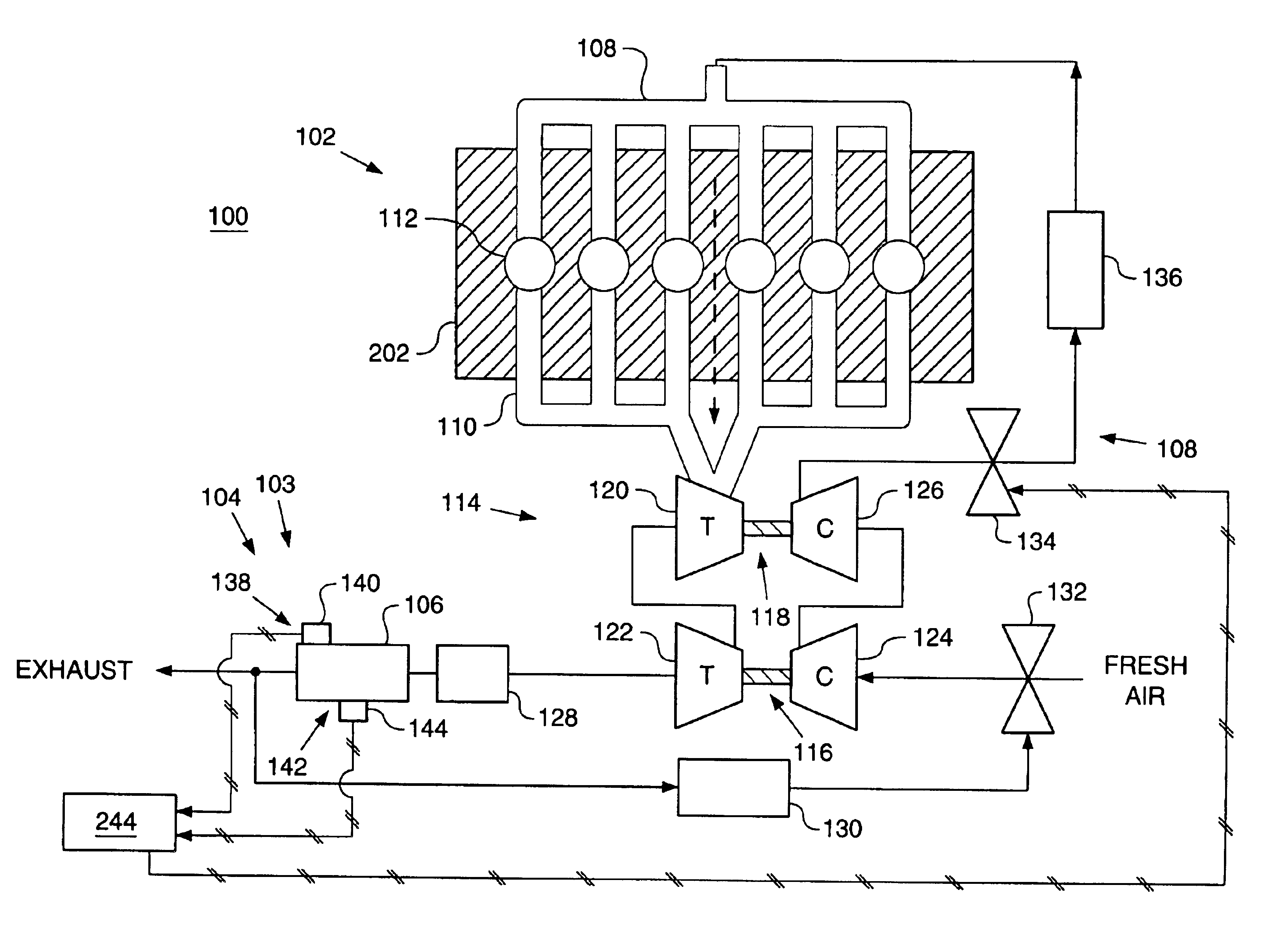
Capacity and pressure control in a transport refrigeration system
ActiveUS20120318014A1Independent controlLess robust or reduced in size or removedMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRefrigerationDischarge pressure
Embodiments of apparatus, transport refrigeration units, and methods for operating the same can control cooling capacity for a refrigerant vapor compression system. Embodiments can provide use discharge pressure control for modulating cooling capacity for a refrigerant vapor compression system. In one embodiment, discharge pressure control can reduce the cooling capacity without increasing the compressor pressure ratio or discharge temperature. In one embodiment, discharge pressure control can reduce the cooling capacity independently of system superheat. In one embodiment, discharge pressure control can control a compressor discharge temperature; for example, to remain below a threshold temperature.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Refrigeration cycle
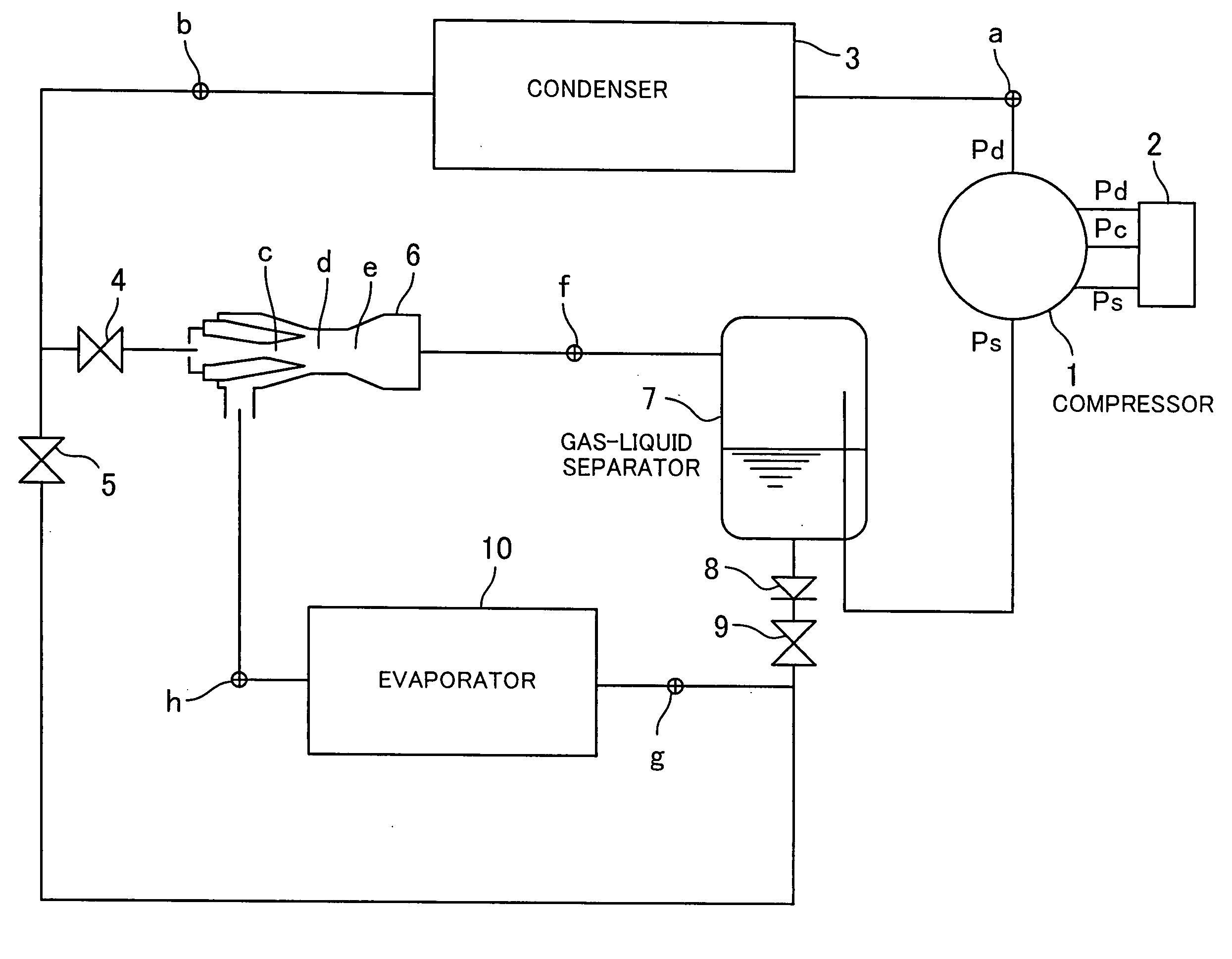
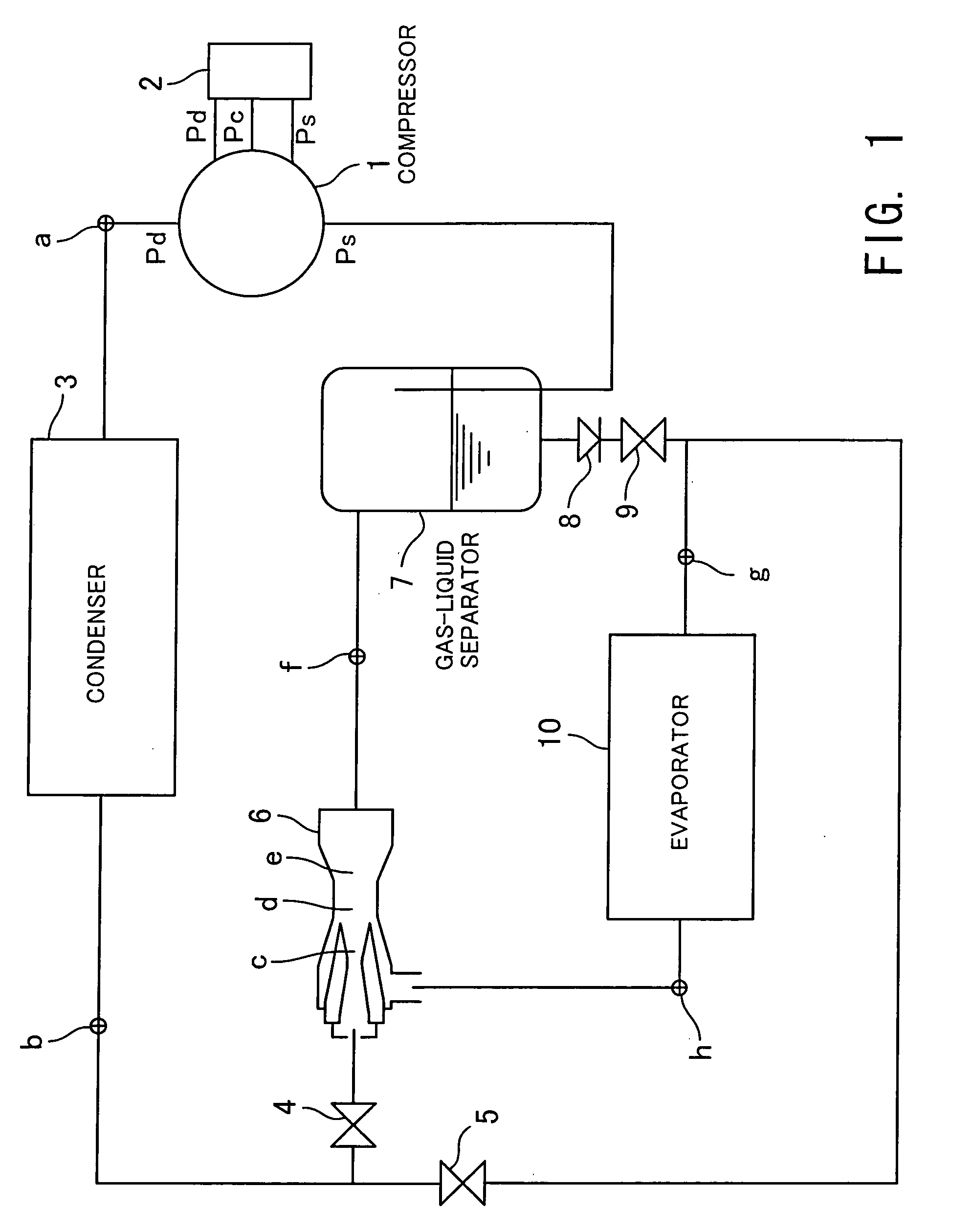
InactiveUS20050011221A1Low costAir-treating devicesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleMobile vehicleVapor–liquid separator
The object of the present invention is to provide a refrigeration cycle for an automotive air conditioner, which is reduced in costs and uses an ejector. A variable displacement compressor driven by an engine for driving an automotive vehicle is used as a compressor, and the capacity of the compressor is controlled by a capacity control valve such that the differential pressure between discharge pressure and suction pressure of refrigerant becomes equal to a predetermined differential pressure determined by an external signal. Pressure substantially equal to pressure applied across the compressor is applied across the ejector, and therefore to control the differential pressure across the compressor is to control the differential pressure across the ejector. A differential pressure valve disposed between a gas-liquid separator and an evaporator is set to a differential pressure approximately proportional to the differential pressure across the ejector. A differential pressure set to the differential pressure valve is estimated from the differential pressure across the compressor which corresponds to the differential pressure across the ejector, and the differential pressure can be directly and accurately determined from the external signal for controlling the capacity control valve.
Owner:TGK
Control valve for variable displacement compressor
InactiveUS20060218953A1Improve compression efficiencyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleDifferential pressureEngineering
To enable a control valve for a variable displacement compressor, which operates by sensing a differential pressure between discharge pressure and suction pressure or between the discharge pressure and crankcase pressure, to enhance compression efficiency inside the compressor. In the control valve for a variable displacement compressor, according to the present invention, after a valve element on a high pressure side closes a valve hole, a valve element on a low pressure side opens a valve hole. Therefore, it is possible to eliminate a region in which both the valves on the high pressure side and the low pressure side are simultaneously open. This makes it possible to prevent refrigerant introduced into a crankcase from being immediately delivered, which makes it possible to obtain a sufficient compression efficient.
Owner:TGK
Exhaust back pressure sensor using absolute micromachined pressure sense die
ActiveUS7073375B2Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusDifferential pressurePressure sense
Sensor systems and methods are disclosed, which generally incorporate isolation between the sensor's electronics and the sensed media. The sensor's electronic circuit can incorporate one or more application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that processes and outputs the signal for both absolute and differential measurements. Such a sensor can be adapted for use in exhaust gas re-circulation (EGR) systems utilized with automotive gasoline engines. Such a sensor can also be utilized for measuring differential pressure across diesel particular filters and / or applications in which differential pressure is required for system control and / or monitoring purposes. The absolute pressure sensor disclosed herein can therefore sense the exhaust pressure on automotive engines and other mechanical and / or electromechanical devices and machines.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Flow rate control device in a hydraulic excavator
InactiveUS6202411B1Eliminate `` sense of incongruity ''Reduce rateFluid couplingsServomotorsHydraulic pumpActuator
A flow rate control device in a hydraulic excavator, comprising a hydraulic pump which is driven rotatively by an engine, a hydraulic actuator which is driven by a hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump, a control valve which controls the supply of the hydraulic oil to the hydraulic actuator, an operating means which operates the control valve so as to change over the valve from one position to another, a relief valve disposed in a discharge oil path extending from the hydraulic pump to limit the maximum pressure in the discharge oil path, an operational condition detecting means for detecting an operational condition of the hydraulic actuator, a pump pressure detecting means for detecting the discharge pressure of the hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump, a flow rate adjusting means for adjusting the discharge flow rate of the hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump, and a control means to which are inputted detection signals from both the operational condition detecting means and the pump pressure detecting means. When a specific operational condition of the hydraulic actuator is detected and when the said discharge pressure is held at a predetermined relief cut-off pressure or higher for a predetermined period of time, the control means makes control so that the discharge flow rate of the hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump is decreased to a relief cut-off pressure by the flow rate adjusting means. According to this construction, the relief cut-off control can be made only where required for each of various works of different conditions which the hydraulic excavator performs, such as excavating work, crushing work and land readjusting work. That is, even when the discharge pressure is held at a predetermined relief cut-off pressure or higher for a predetermined period of time, the relief cut-off control is made if the hydraulic actuator is in the specific operational condition.
Owner:KOBELCO CONSTR MASCH CO LTD
System, method, and apparatus for downhole submersible pump having fiber optic communications
A downhole submersible pump system, method, and apparatus utilizes fiber optic sensors and distributed temperature sensors below the submersible pump to monitor pump discharge pressure and temperature, intake pressure and temperature, and motor temperature. In addition, distributed temperature sensors are used below the pump to monitor the perforations within the well bore.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Variable displacement sliding vane pump
InactiveUS20070224067A1Oscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsDrive shaftEngineering
A variable displacement sliding vane pump comprising a pump body, inlet and outlet ports formed in said pump body, a drive shaft rotatably mounted in said pump body, a rotor driven by said drive shaft and co-axially aligned therewith, a plurality of radially extending vanes slidably disposed in said rotor, a pivot disposed in said pump body, a slide pivotally disposed on said pivot in said pump body and having a central axis eccentric to the axis of said rotor, a plurality of fluid chambers defined by said rotor, said vanes, and said slide that are successively connected to said inlet and outlet ports, a spring acting on said slide to urge said slide in one direction, a first chamber and a second chamber, each suitable for receiving a fluid pressure and each disposed between said pump body and an outer surface of said slide, the first chamber in fluid communication with a pump outlet discharge pressure, and a valve operable to selectively pressurize and depressurize the second chamber.
Owner:STACKPOLE POWERTRAIN INT ULC
Bleed air and hot section component cooling air system and method
Combined bleed air and hot section component cooling air systems for gas turbine engines and methods of operating combined bleed air and hot section component cooling air systems are disclosed. An example system may include a high-pressure bleed air line receiving high-pressure bleed air; a precooler receiving at least some of the high-pressure bleed air and discharging cooled high-pressure bleed air; a pressure regulator receiving at least some of the cooled high-pressure bleed air and discharging pressure-regulated cooled bleed air to a pneumatic systems supply line; and / or a hot section component cooling air line connected upstream of the first pressure regulator and configured to convey at least some of the cooled high-pressure bleed air to a hot section component for use as hot section component cooling air.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for PM filter regeneration
InactiveUS6981370B2Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelParticulatesCombustion chamber
A method and apparatus for initiating regeneration of a particulate matter (PM) filter in an exhaust system in an internal combustion engine. The method and apparatus includes determining a change in pressure of exhaust gases passing through the PM filter, and responsively varying an opening of an intake valve in fluid communication with a combustion chamber.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com