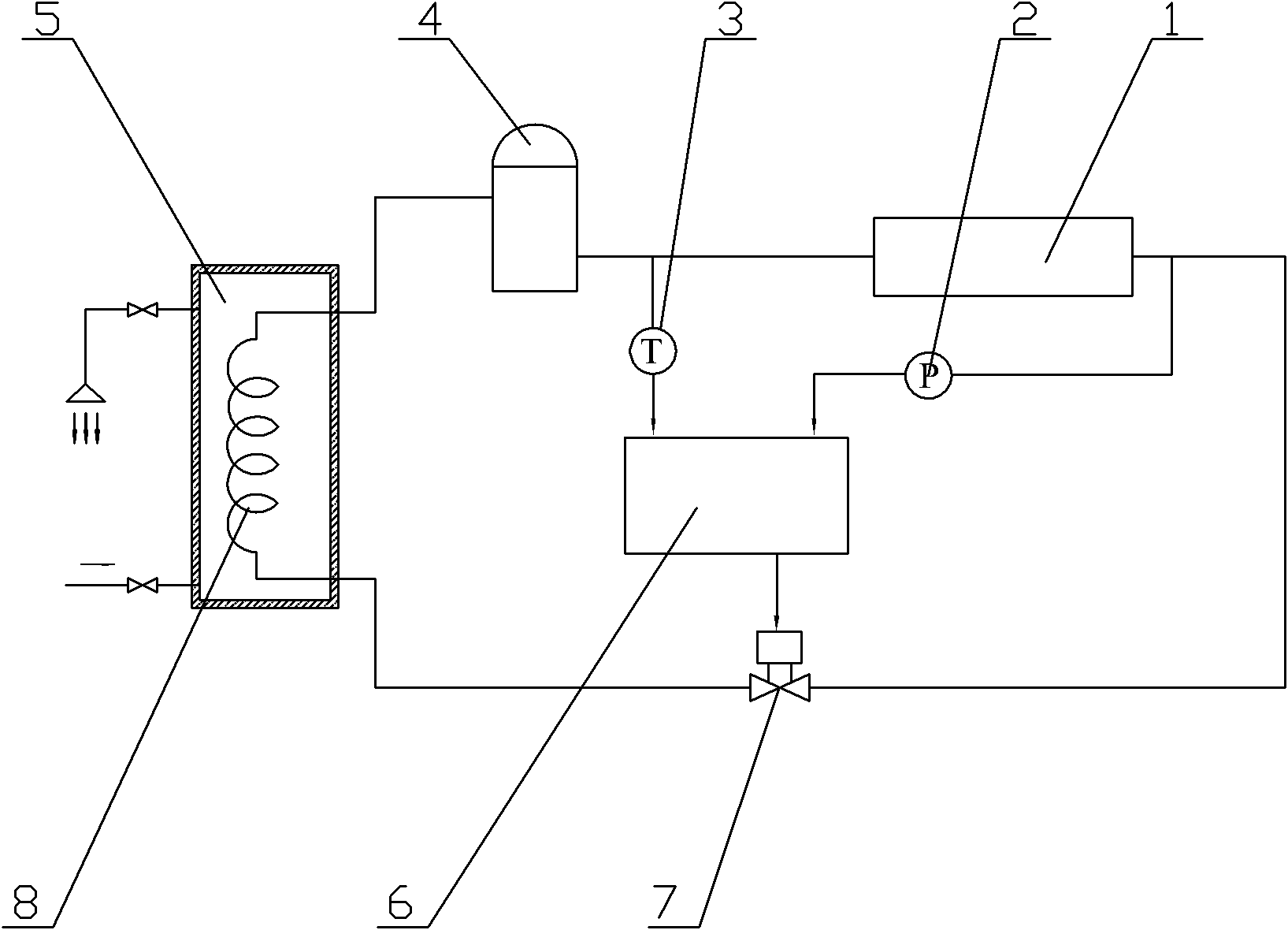
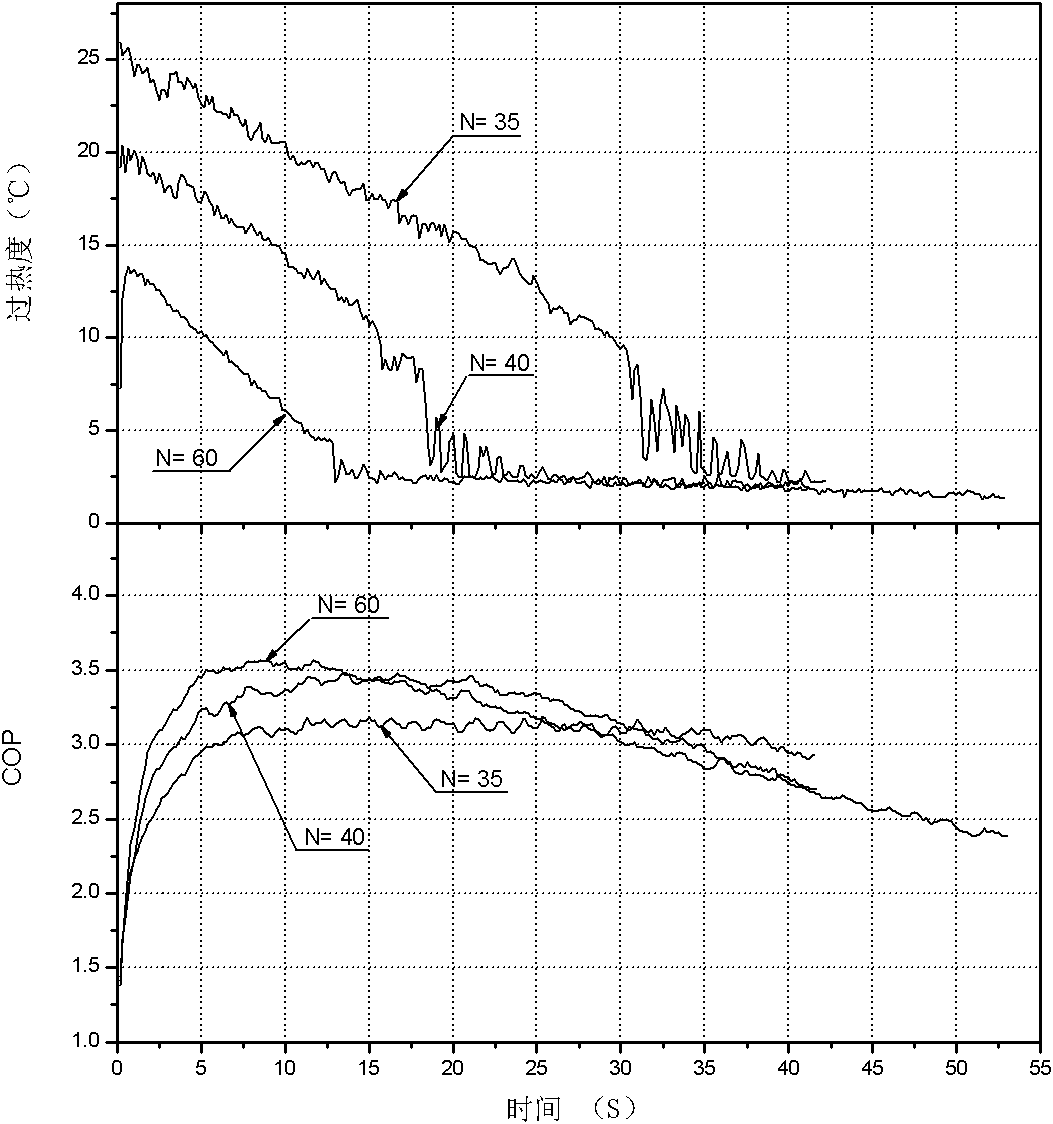
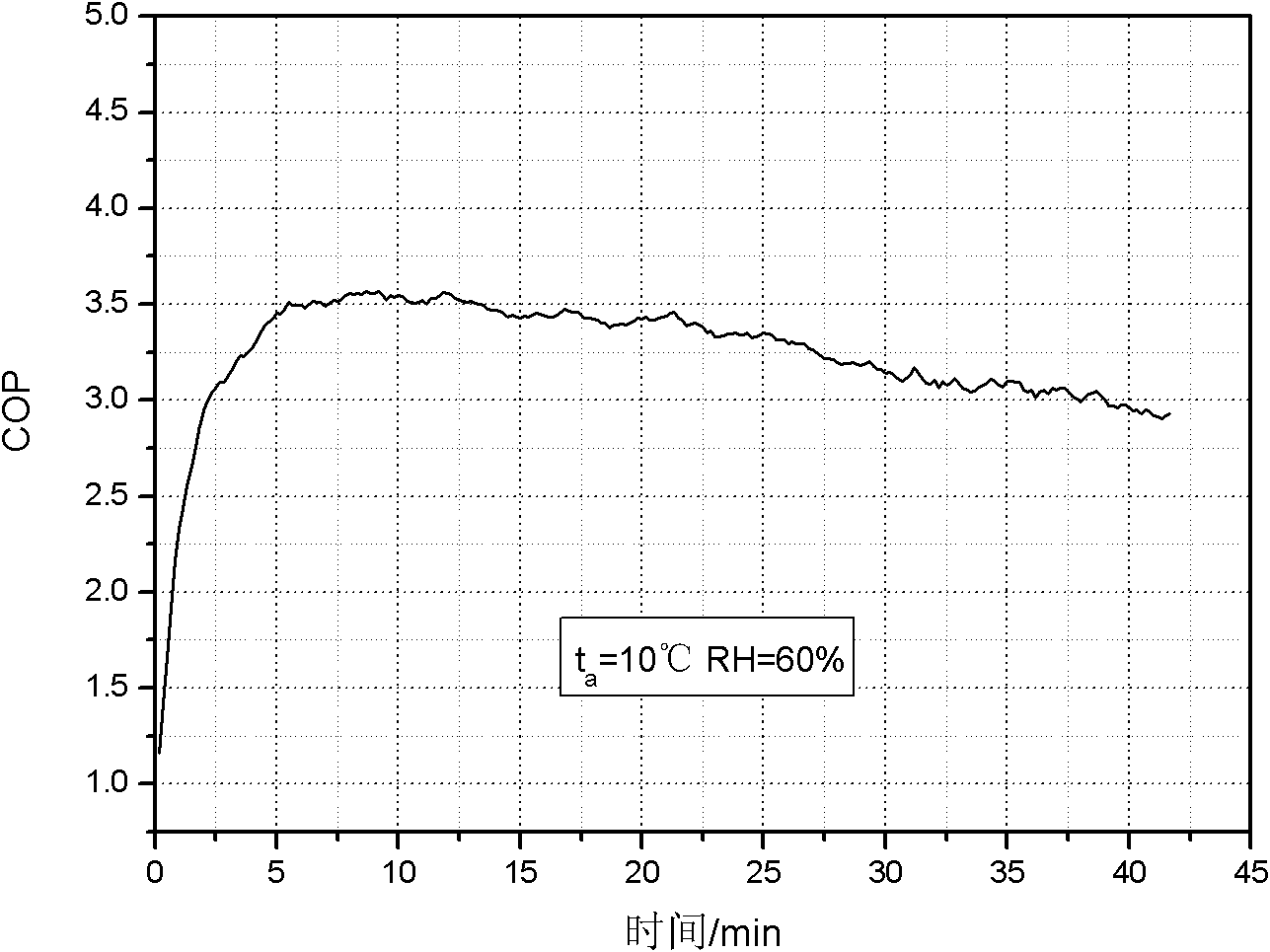
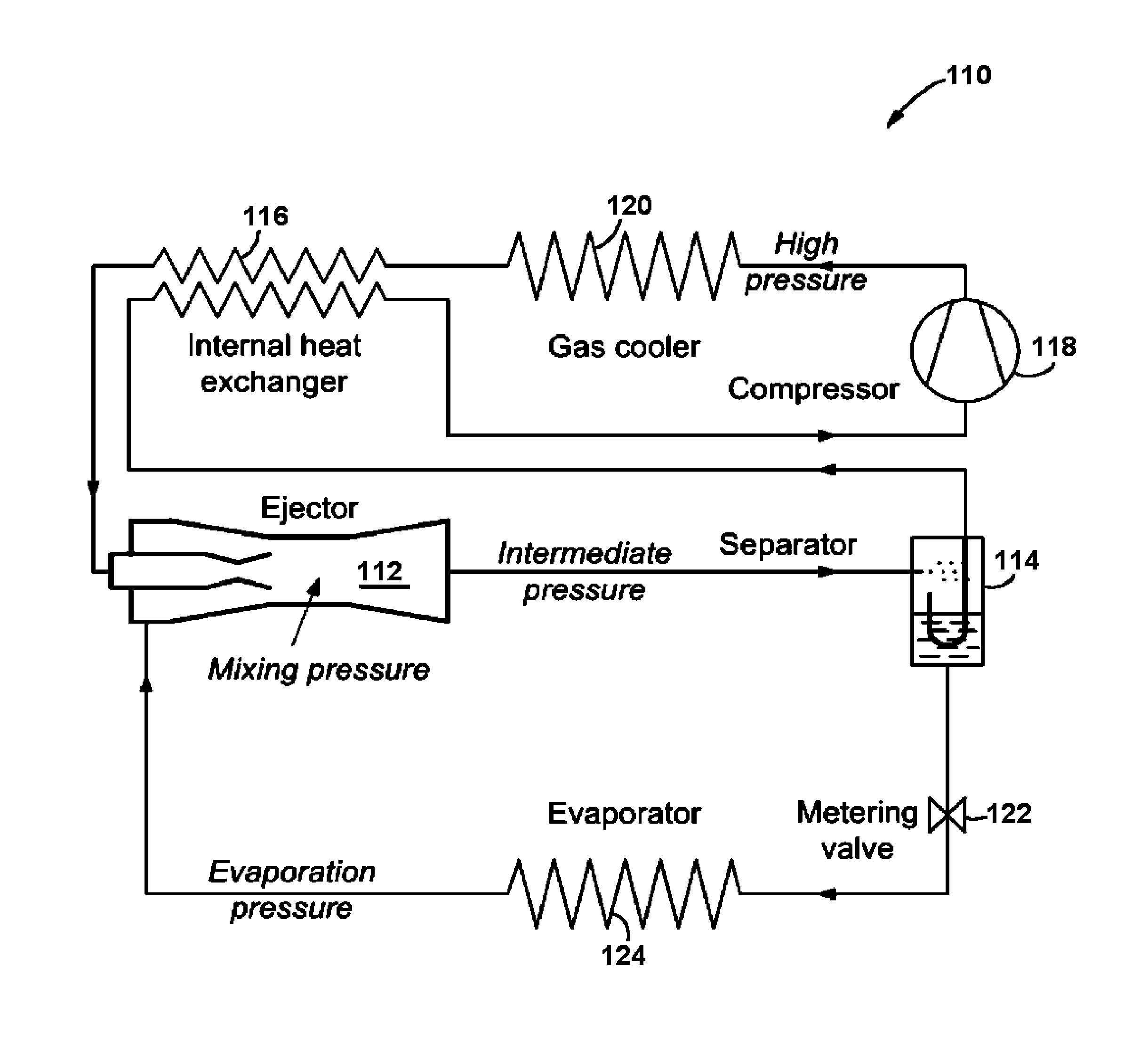
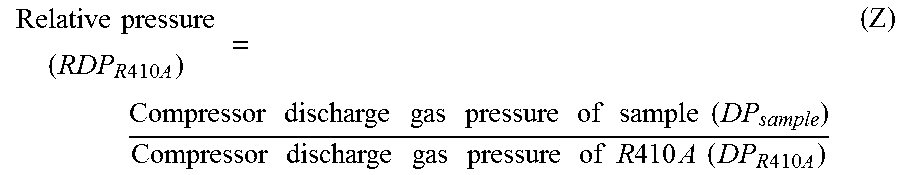Patents
Literature
548 results about "Coefficient of performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
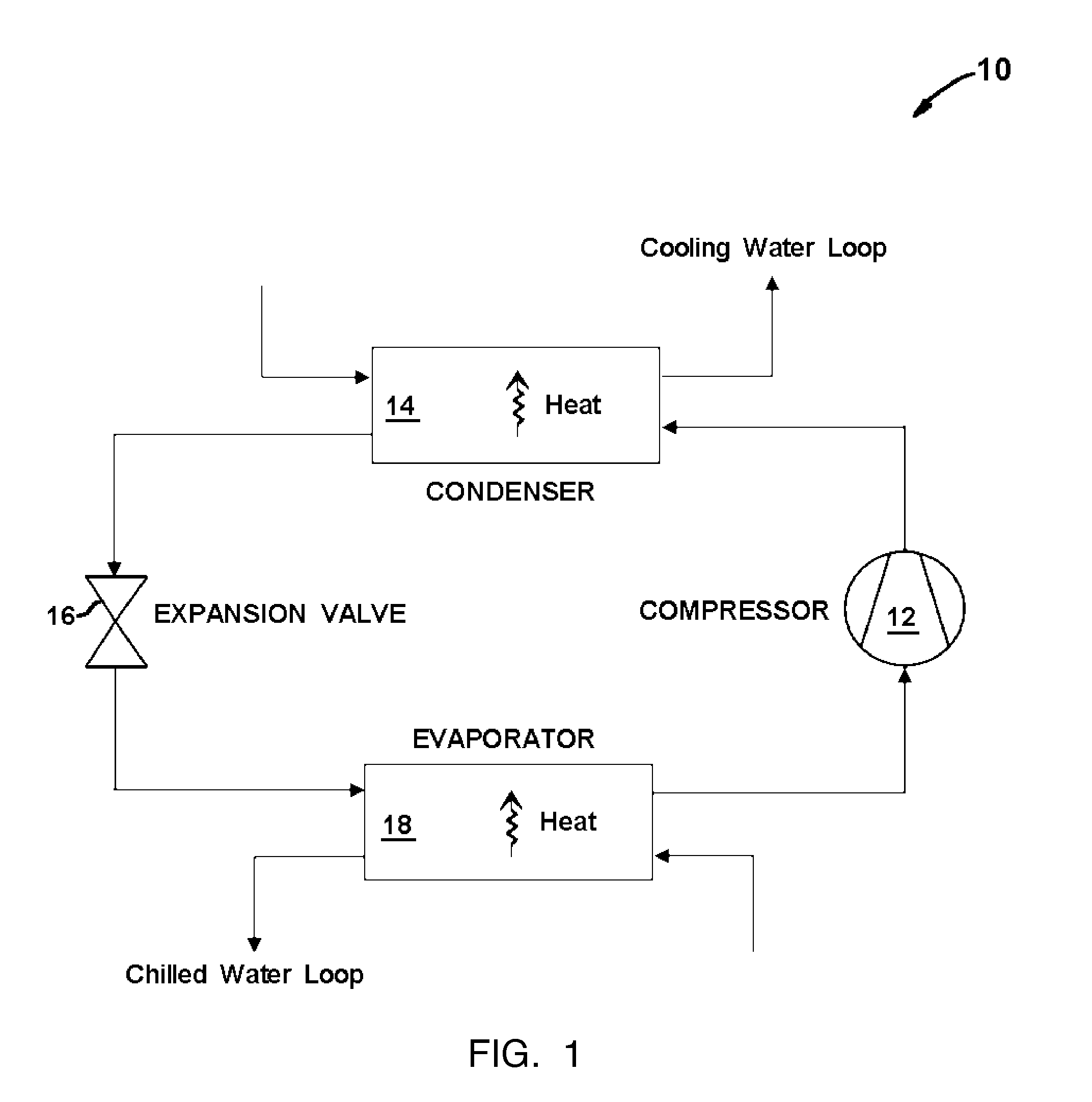
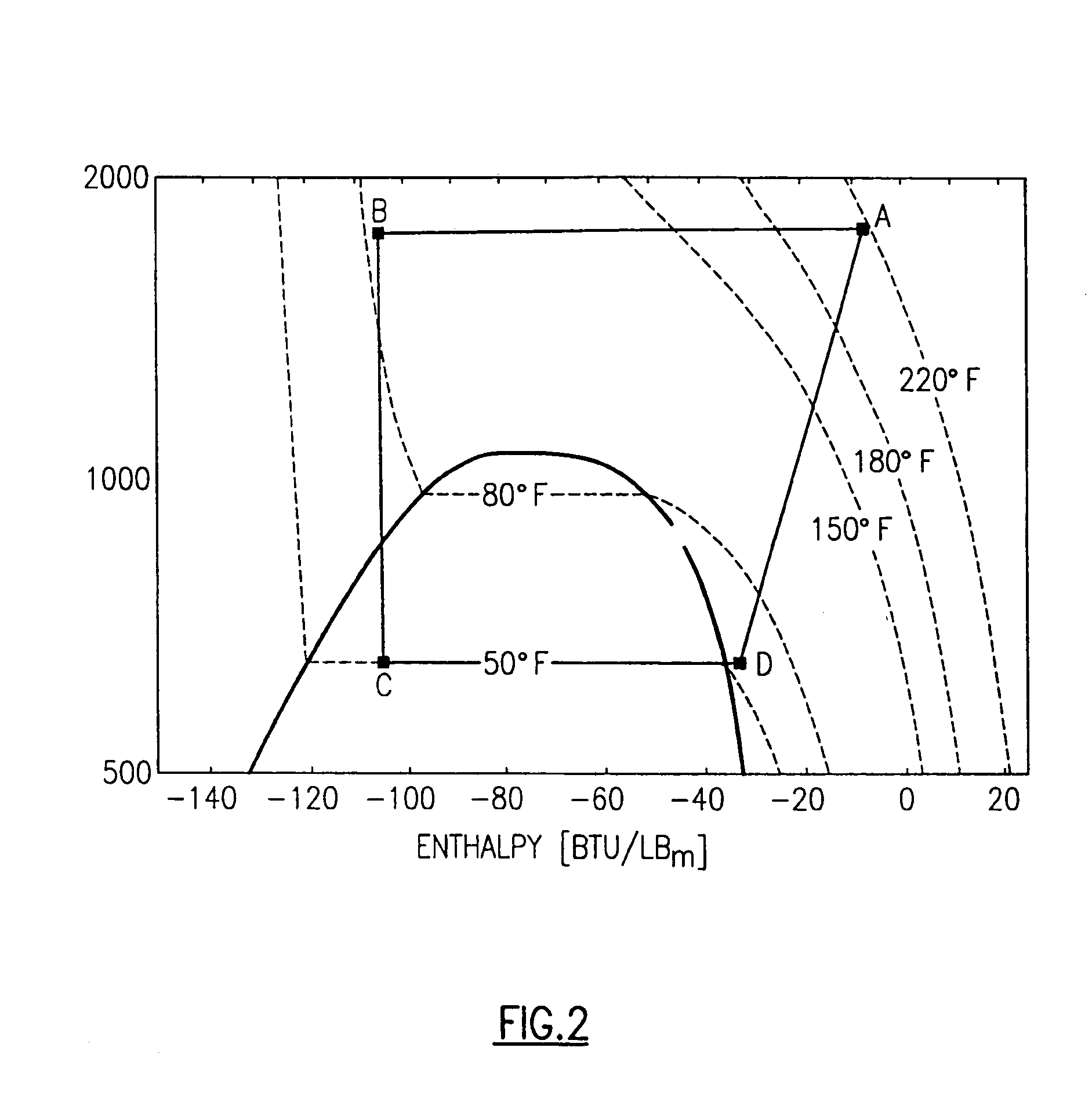
The coefficient of performance or COP (sometimes CP or CoP) of a heat pump, refrigerator or air conditioning system is a ratio of useful heating or cooling provided to work required. Higher COPs equate to lower operating costs. The COP usually exceeds 1, especially in heat pumps, because, instead of just converting work to heat (which, if 100% efficient, would be a COP of 1), it pumps additional heat from a heat source to where the heat is required. For complete systems, COP calculations should include energy consumption of all power consuming auxiliaries. COP is highly dependent on operating conditions, especially absolute temperature and relative temperature between sink and system, and is often graphed or averaged against expected conditions.
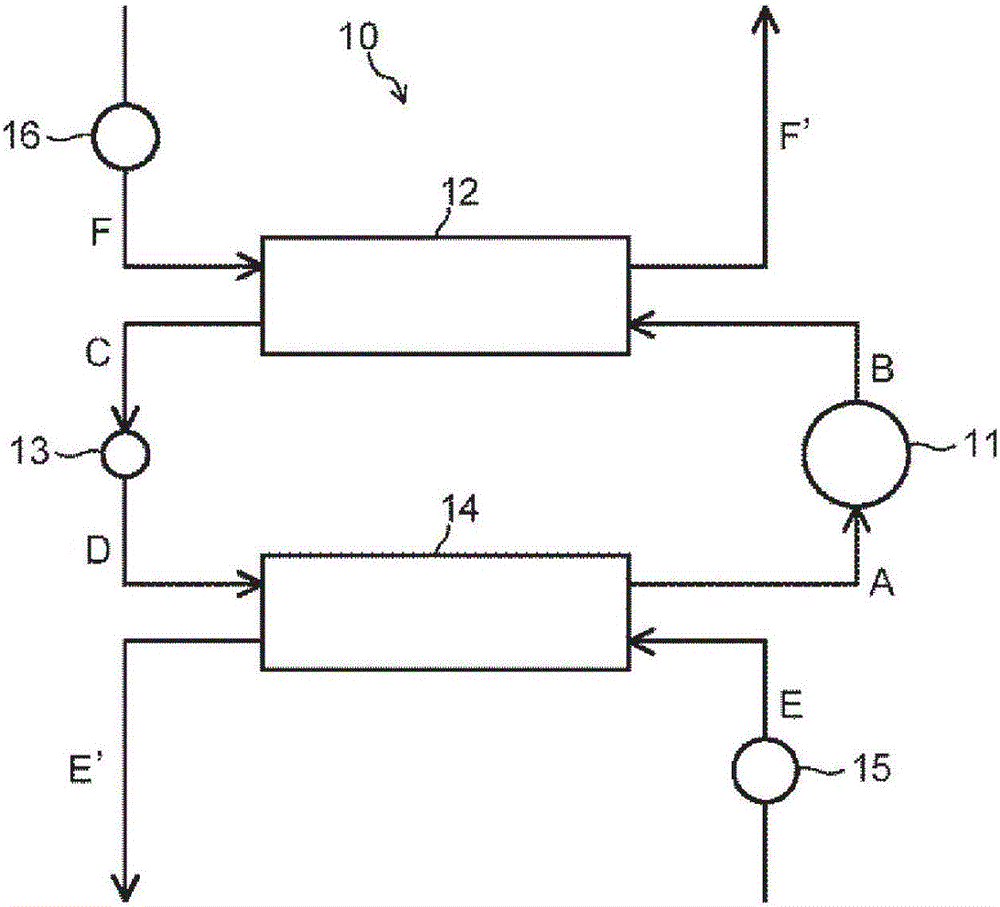
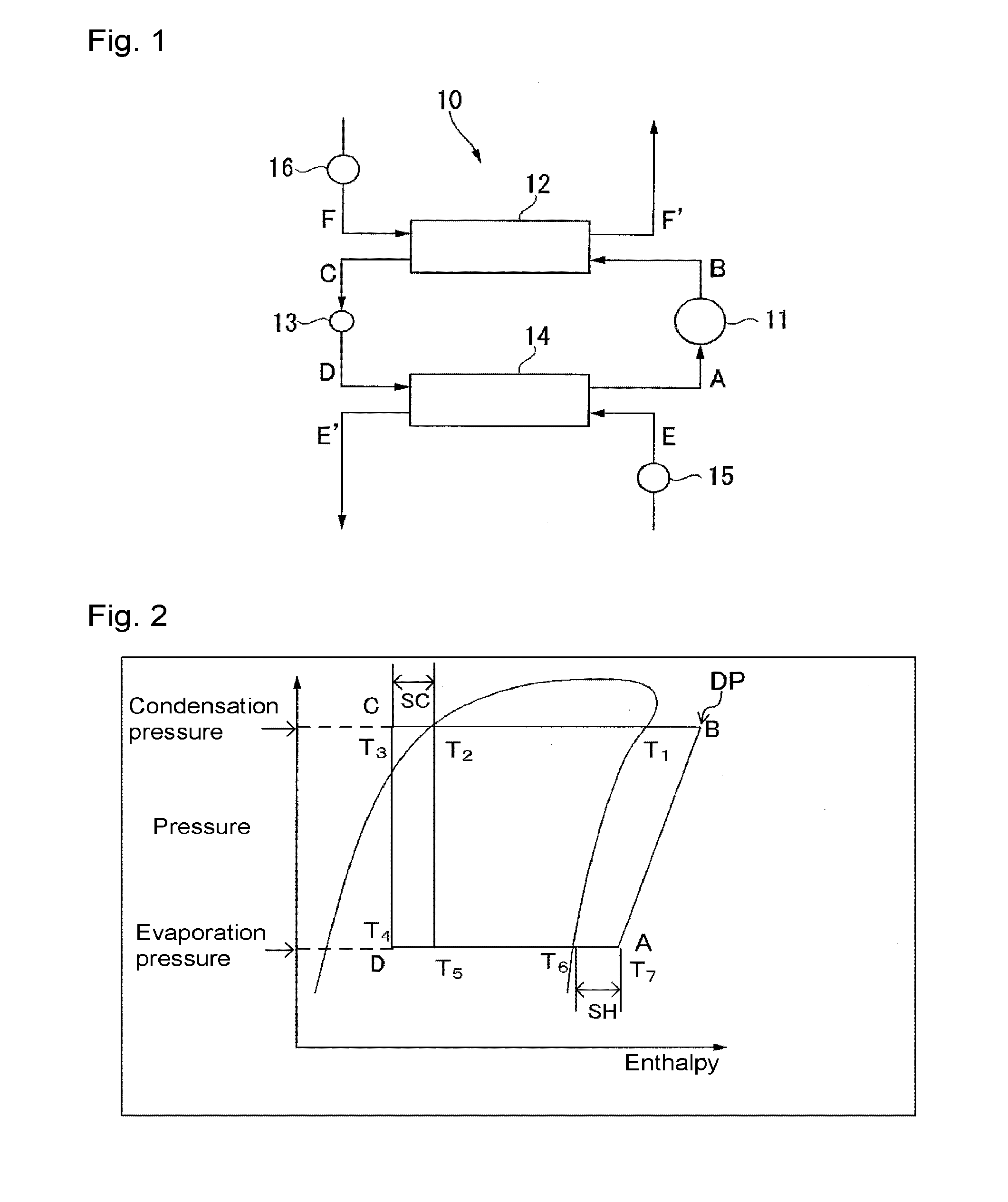
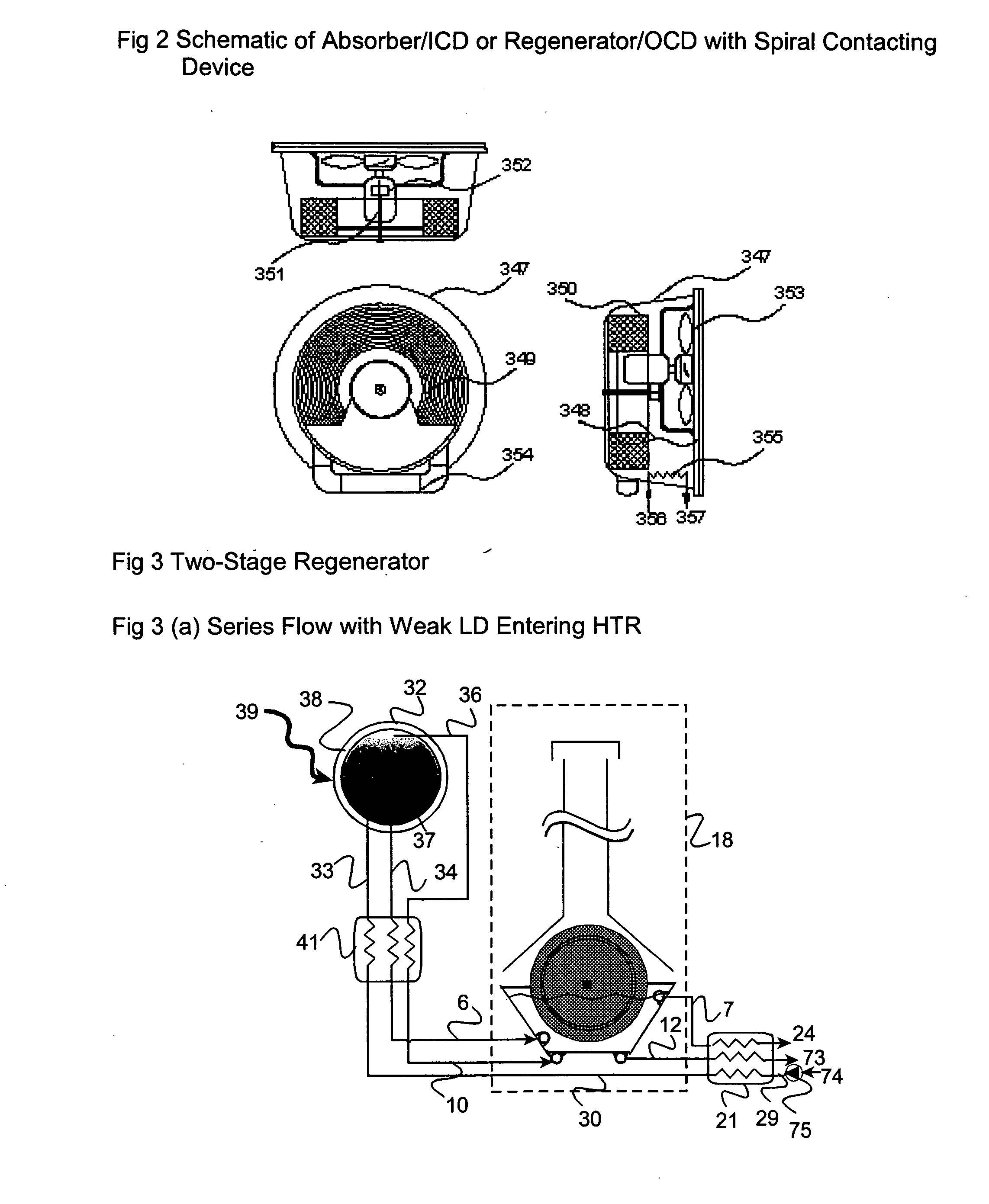
Working medium for heat cycles, composition for heat-cycle systems, and heat-cycle system
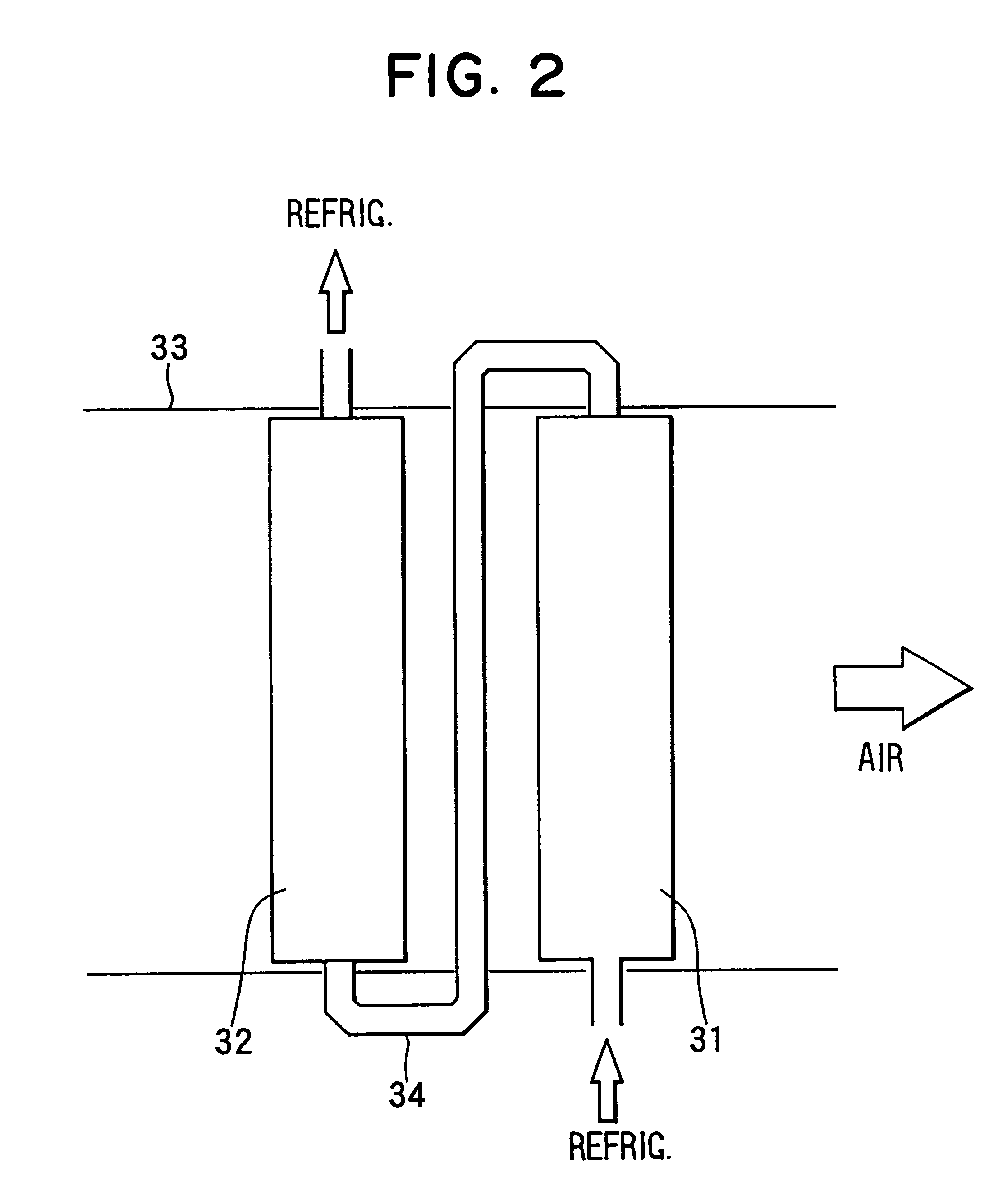
ActiveCN106133110AReduce temperature gradientLower discharge temperatureCompressorCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringRefrigeration
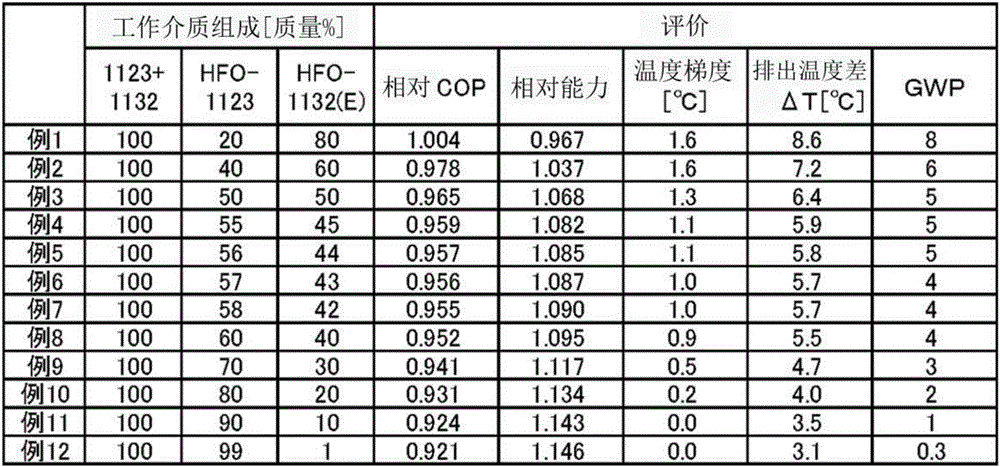
Provided are: a working medium for heat cycles which has a low impact on global warming, a low temperature gradient, and a sufficiently low discharge temperature, and which exhibits excellent cycle performance (i.e. refrigeration capacity and coefficient of performance); a composition for heat-cycle systems; and a heat-cycle system. The working medium for heat cycles includes trifluoroethylene and 1, 2-difluoroethylene. Also provided are: a composition for heat-cycle systems; and a heat-cycle system which uses the working medium and the composition. It is prefereable that, in the working medium for heat cycles, the ratio of the total amount of trifluoroethylene and 1, 2-difluoroethylene be at least 20 mass%, and equal to or less than 100 mass%.
Owner:AGC INC
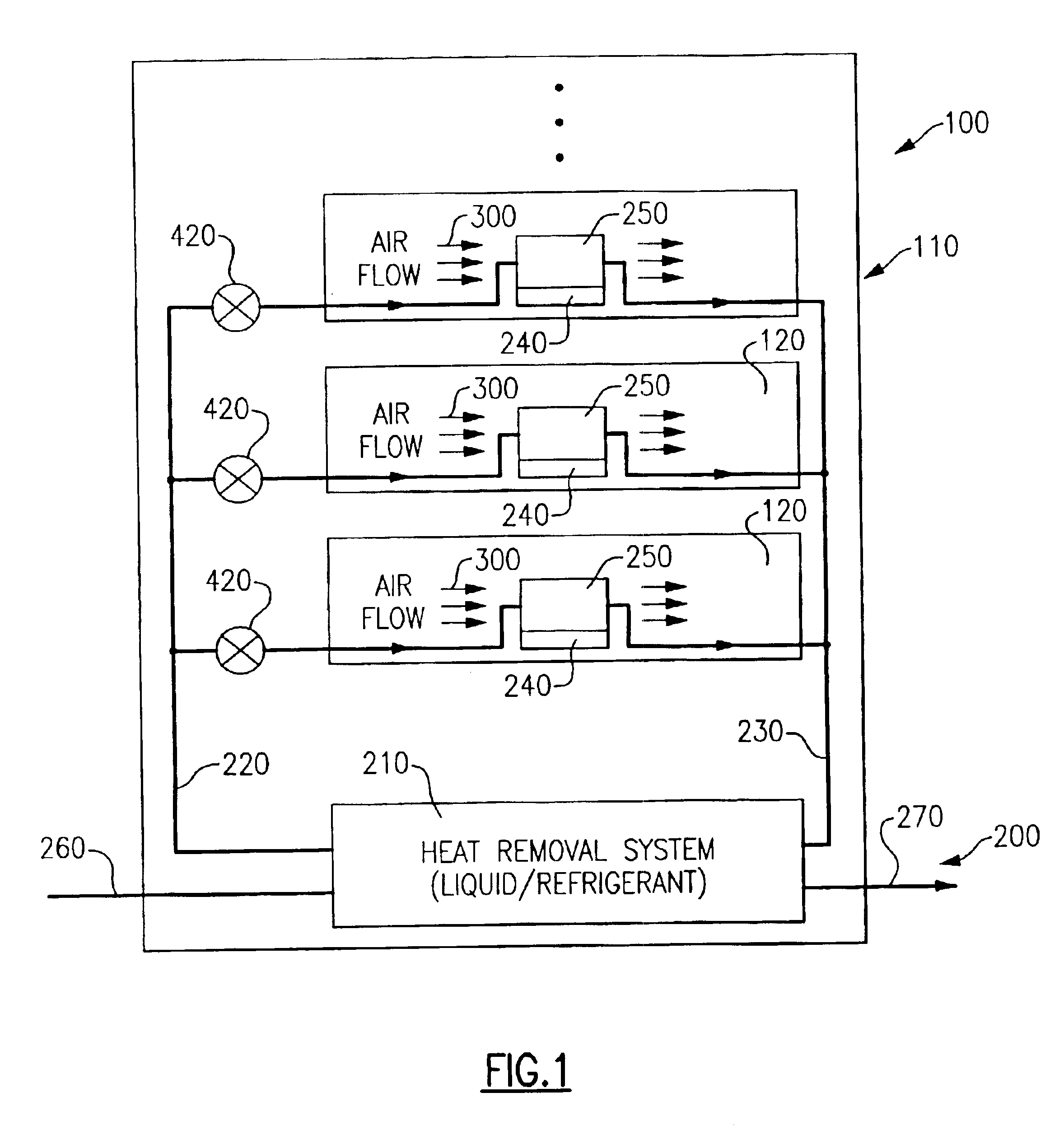
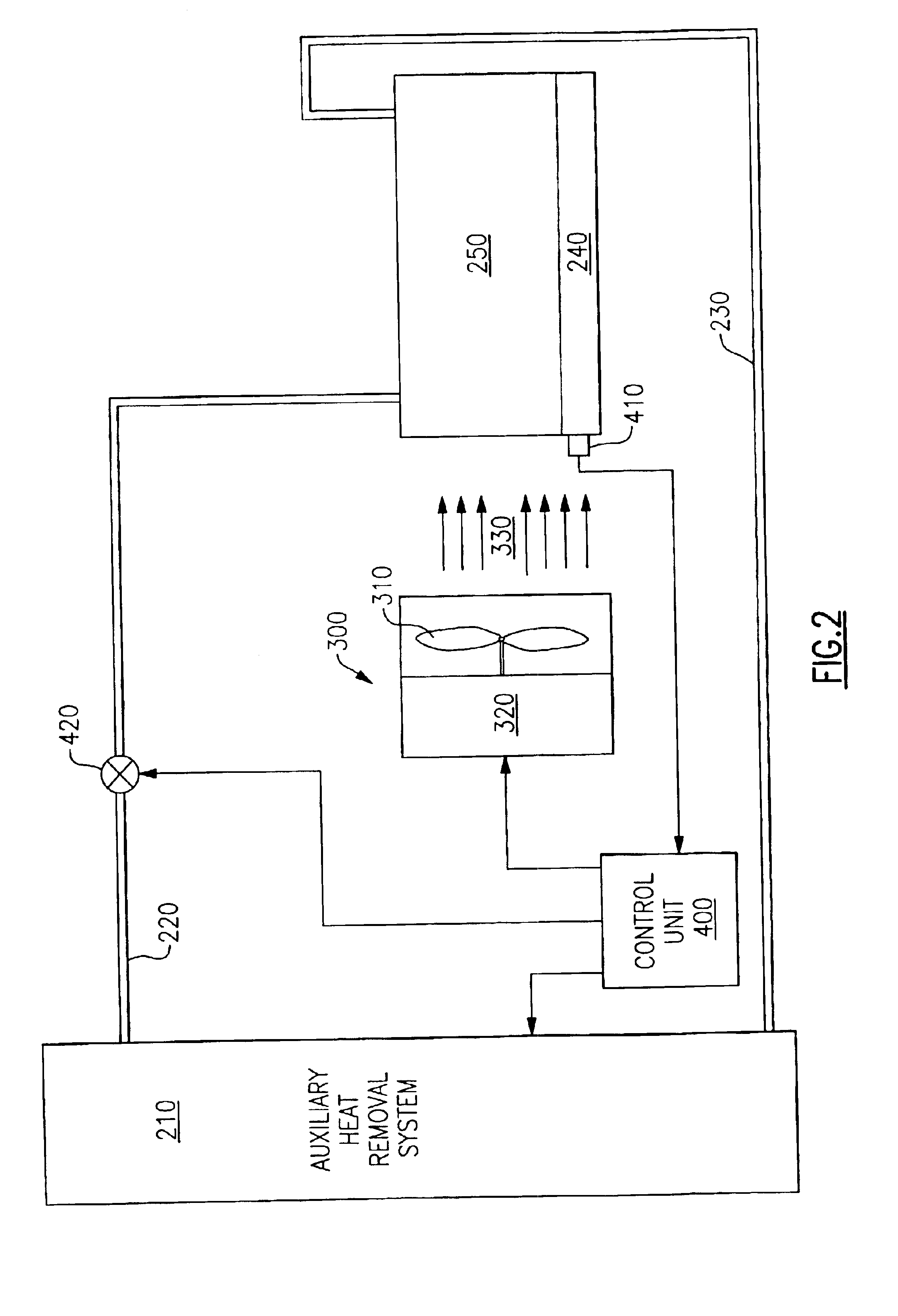
Frame level partial cooling boost for drawer and/or node level processors
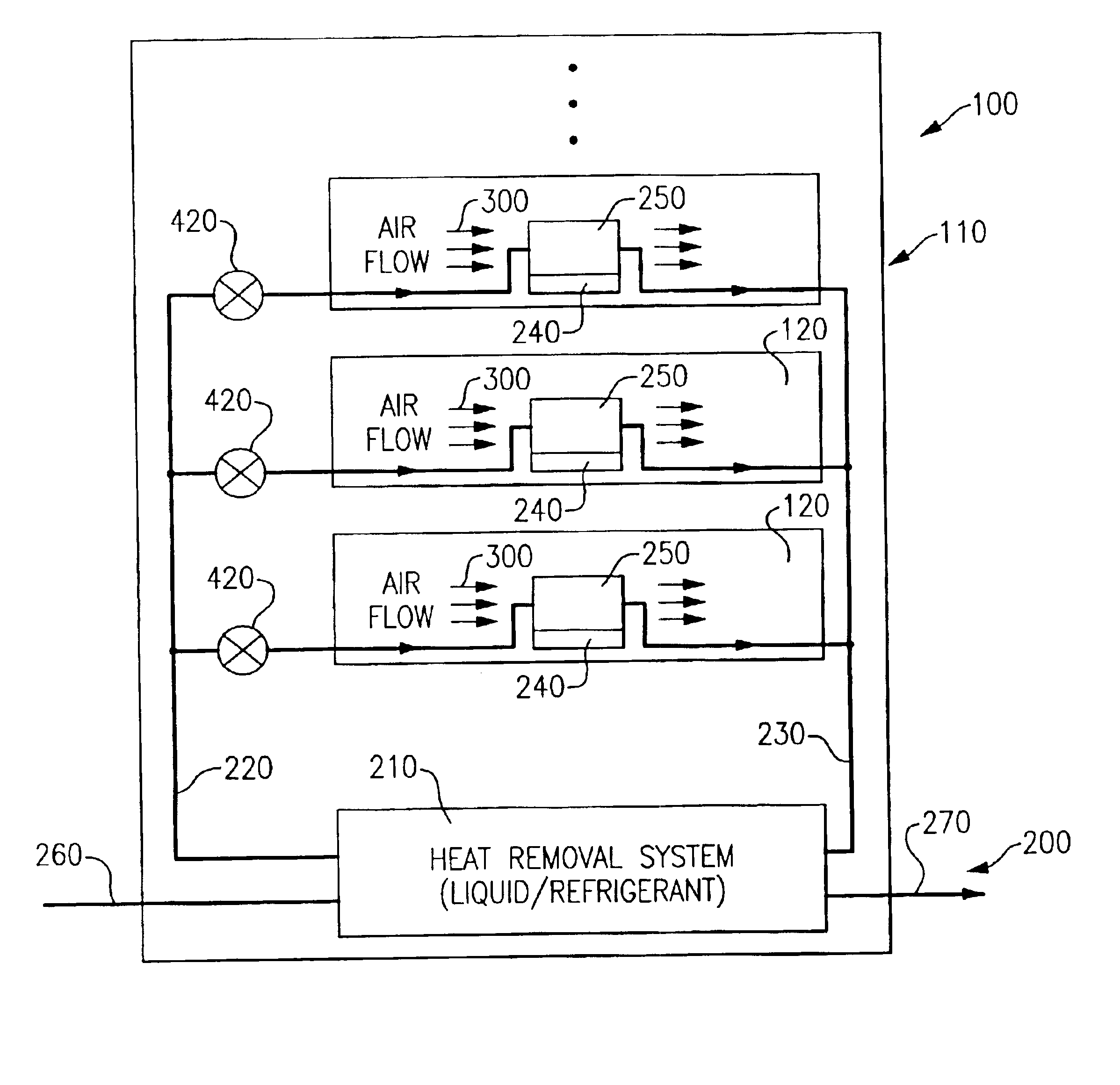
InactiveUS6970355B2Small dimensionAvoid the needDomestic cooling apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSystems designEngineering
A hybrid cooling system is provided which is particularly useful for cooling electronic circuit components disposed on circuit boards arranged in a plurality of drawers within a cabinet or frame. Air cooling is provided locally with a supplementary, auxiliary, or secondary cooling system being provided at more distant frame level locations. This configuration permits optimal sizing of the respective hybrid cooling system components without negatively impacting the coefficient of performance (COP). Hybrid heat sinks are employed to accommodate the hybrid cooling system design.
Owner:IBM CORP
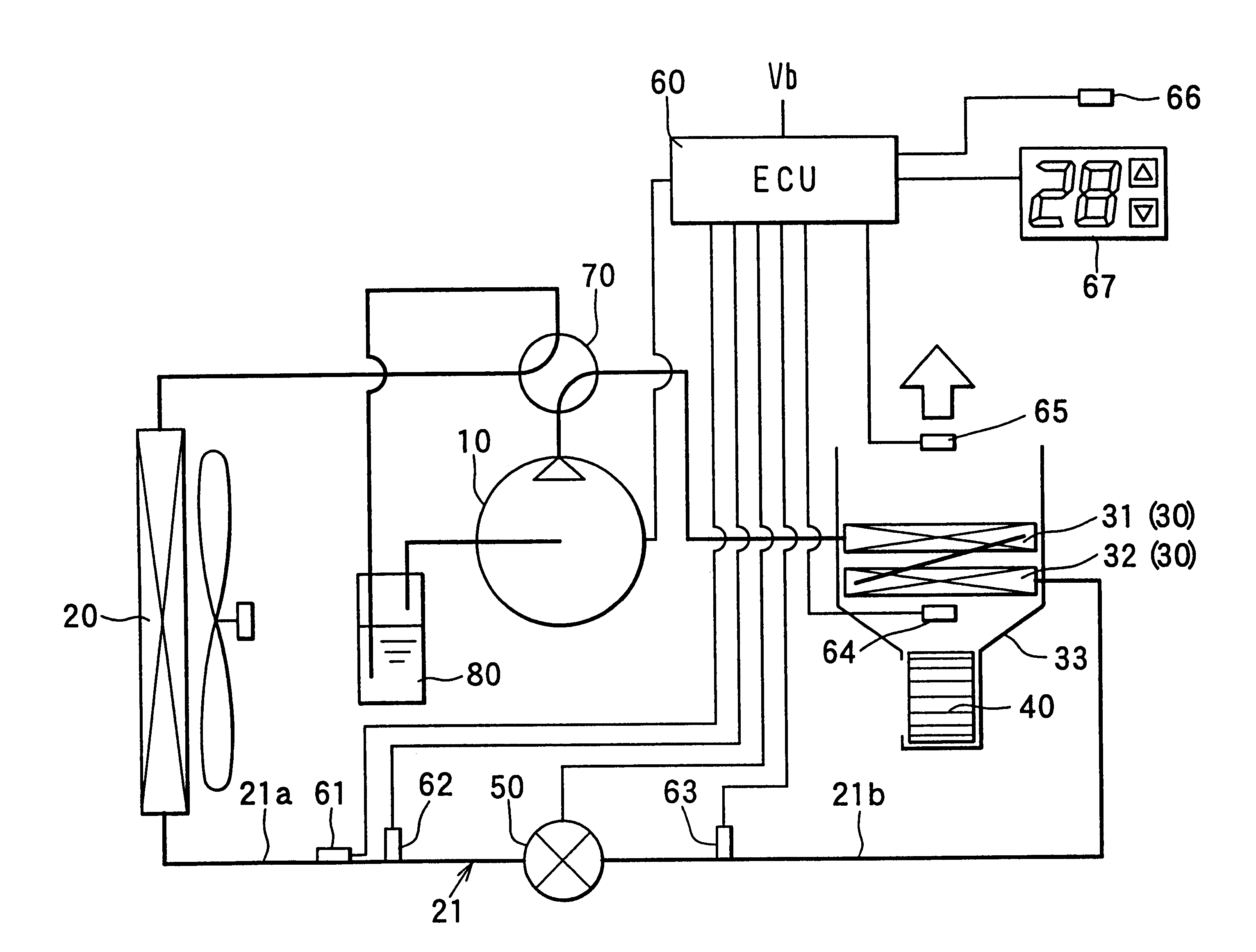
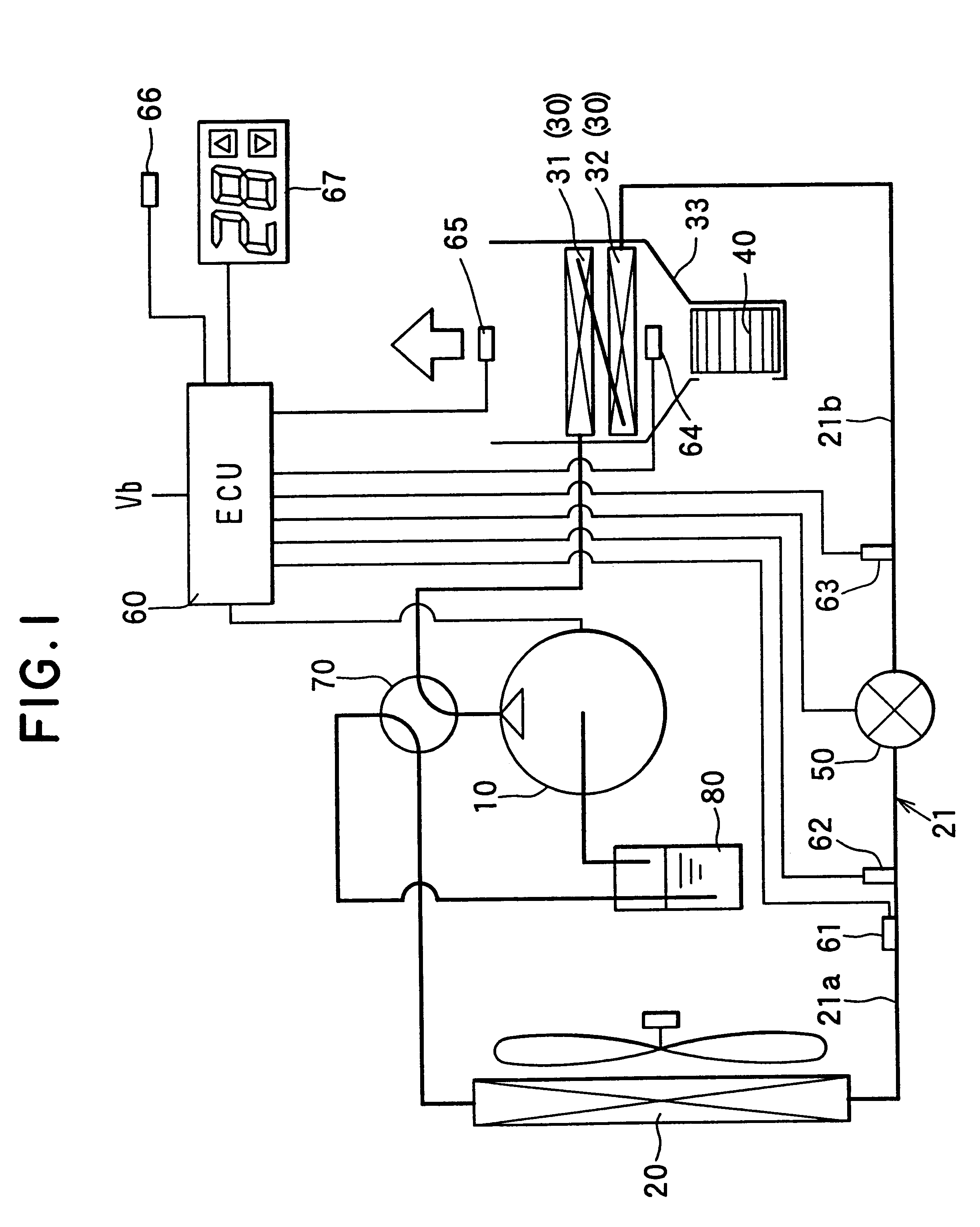
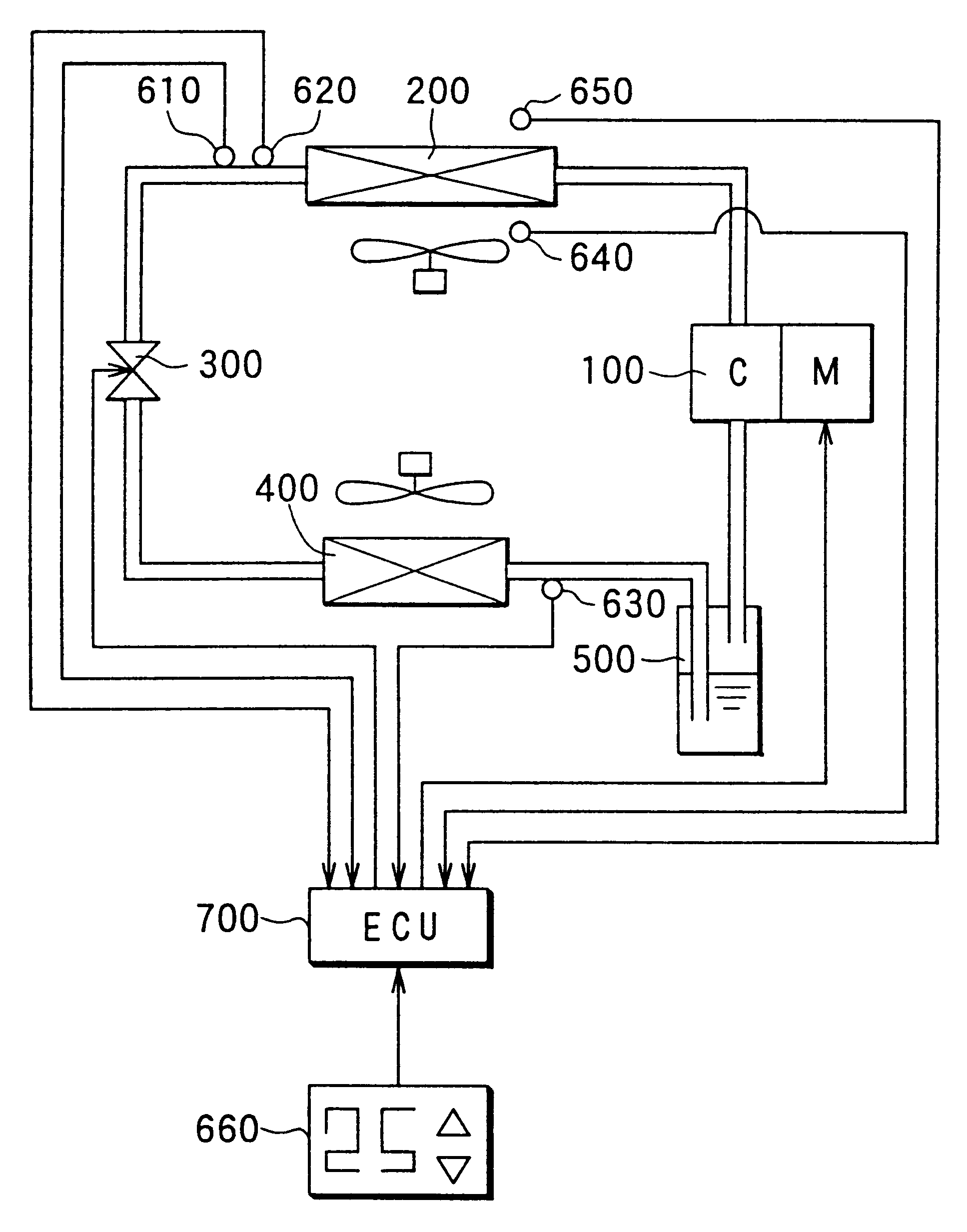
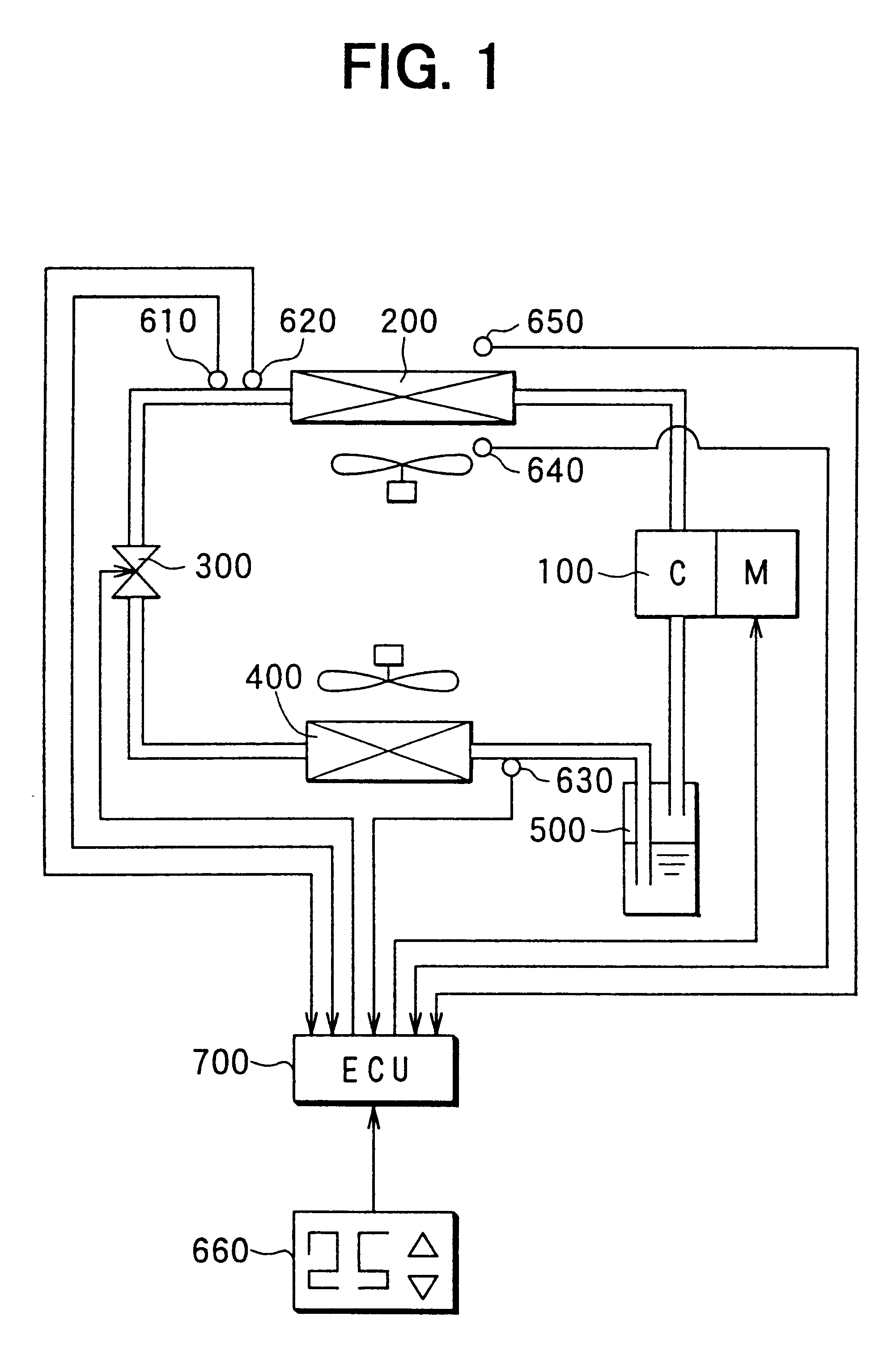
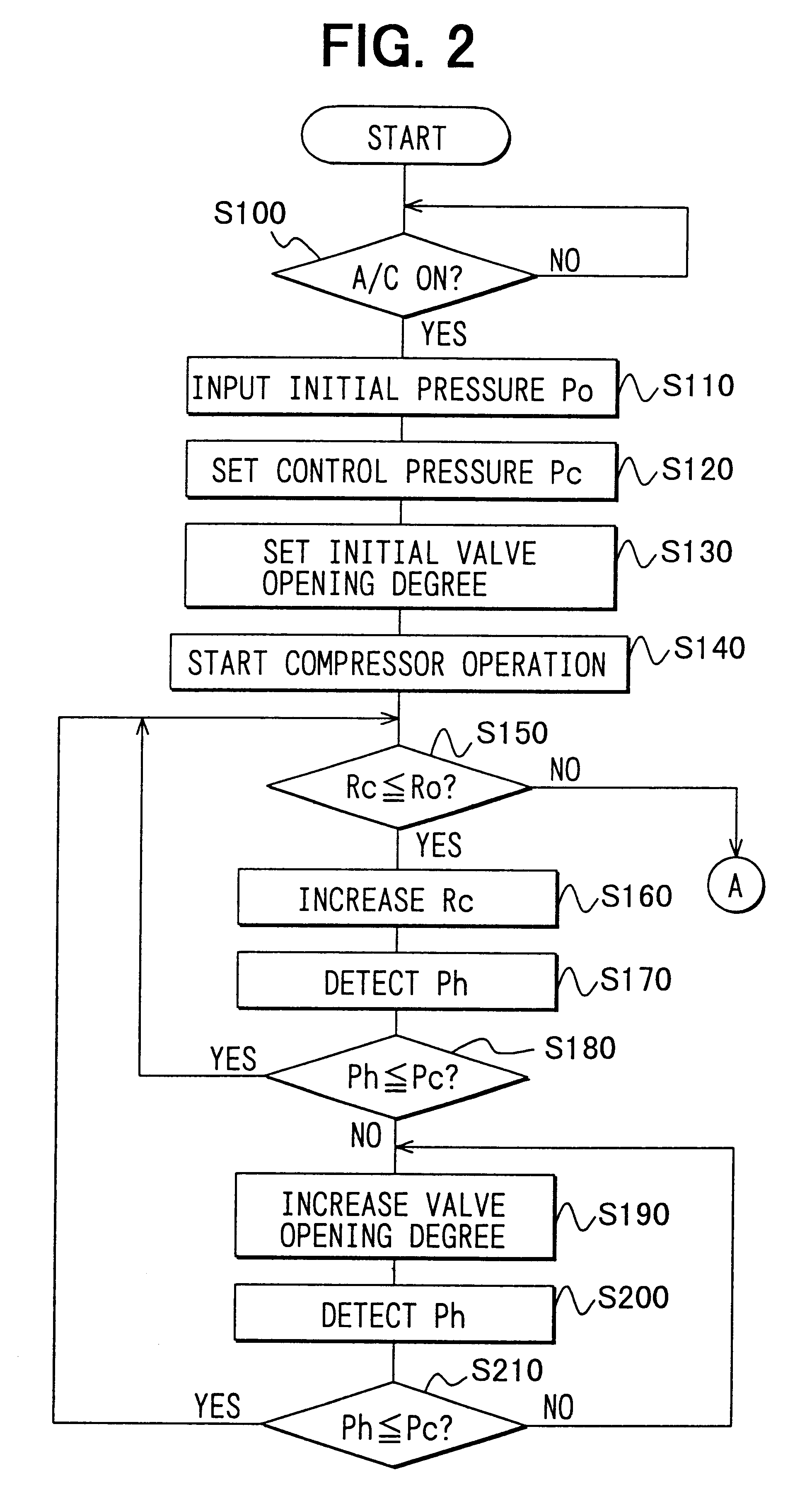
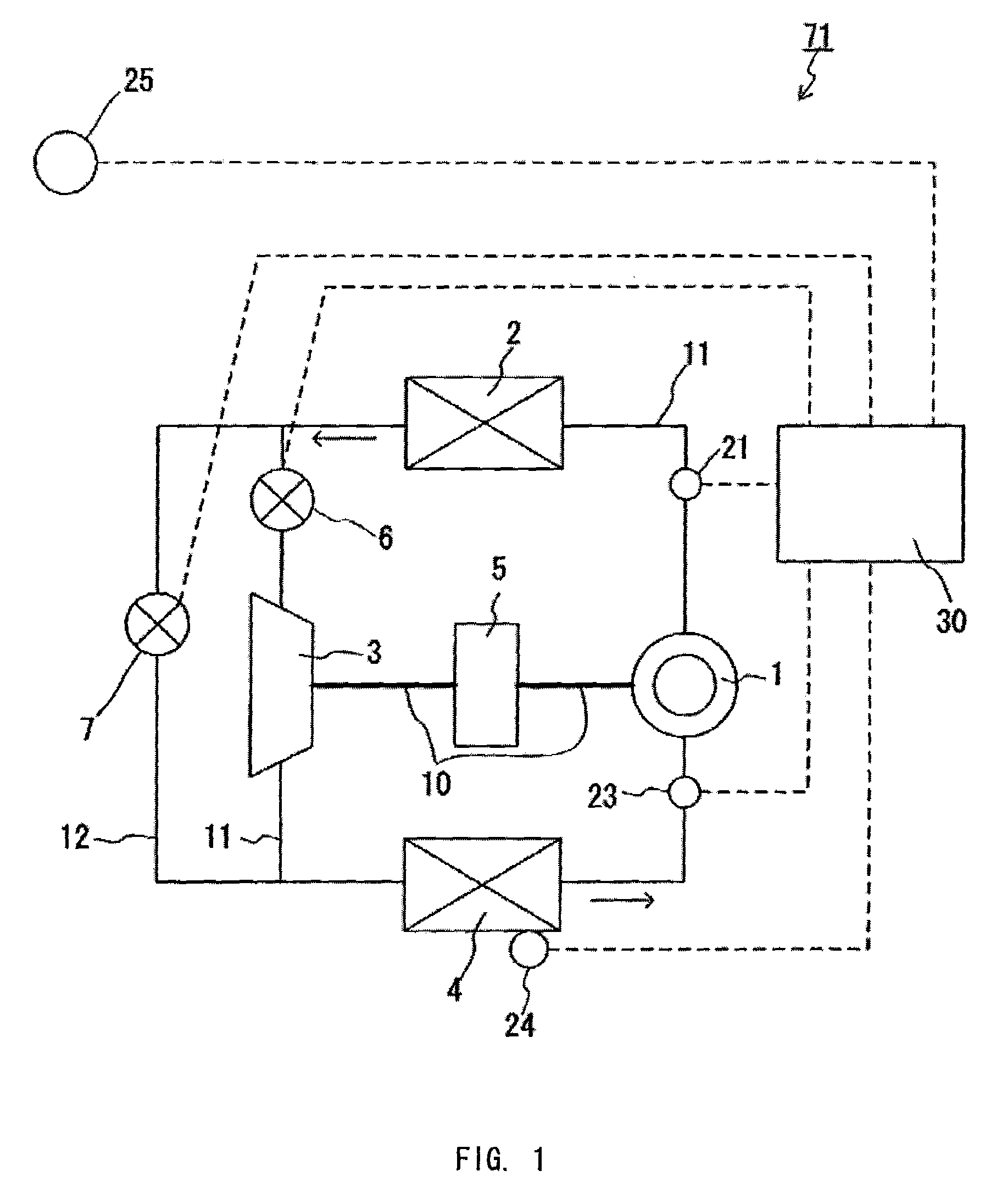
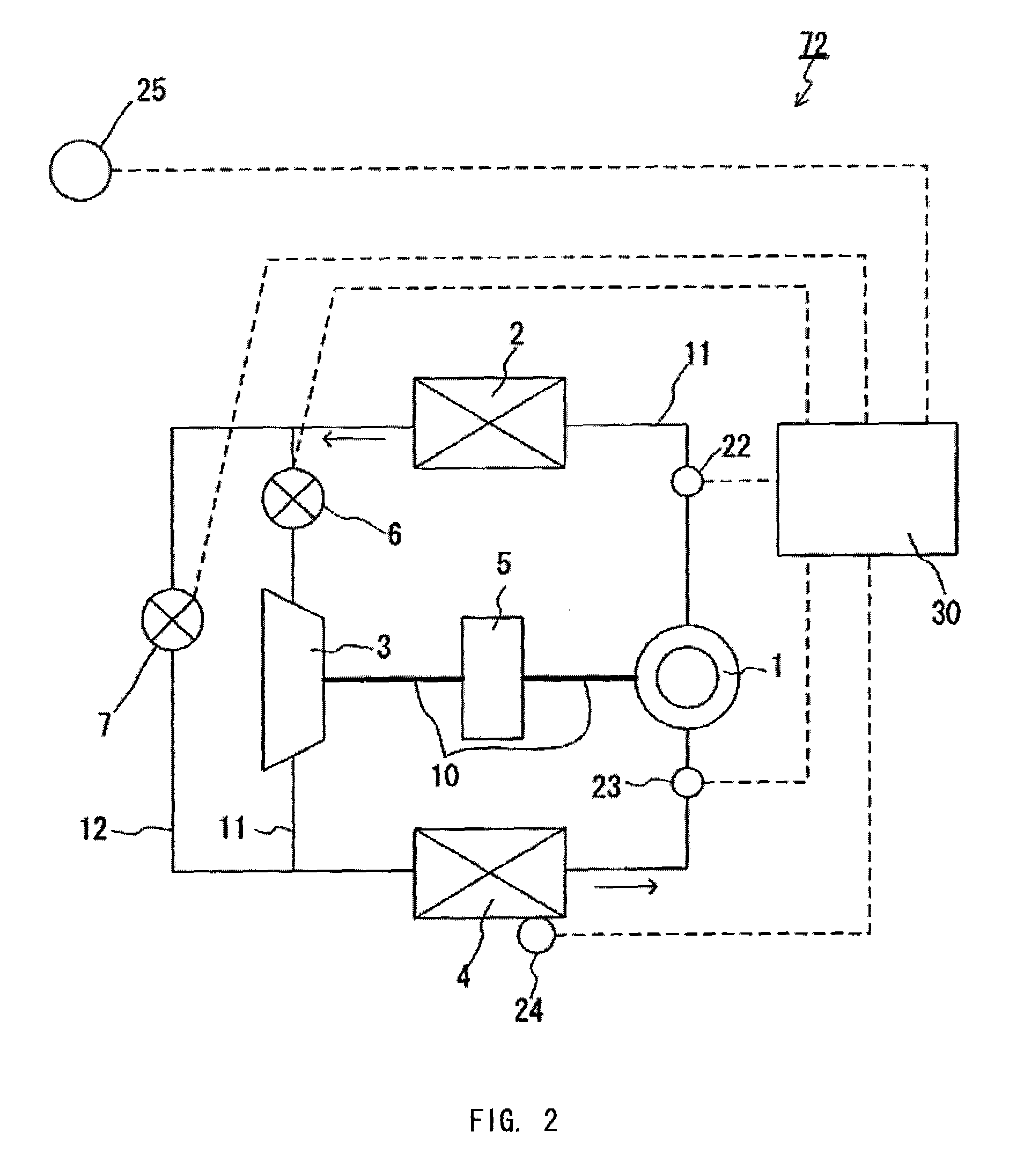
Heat pump cycle system
InactiveUS6230506B1Improve the heating effectImprove the overall coefficientMechanical apparatusAir-treating devicesLower limitEngineering
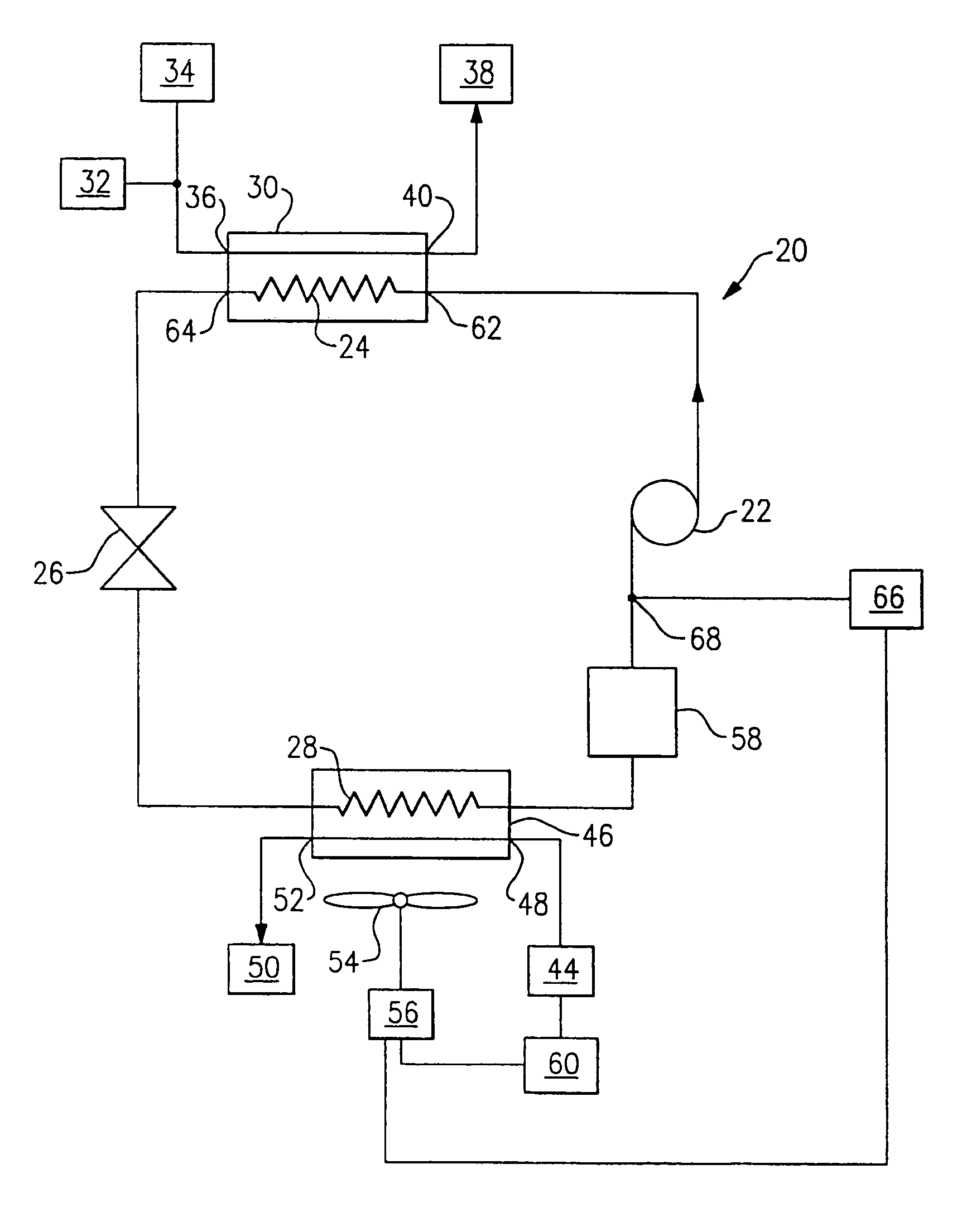
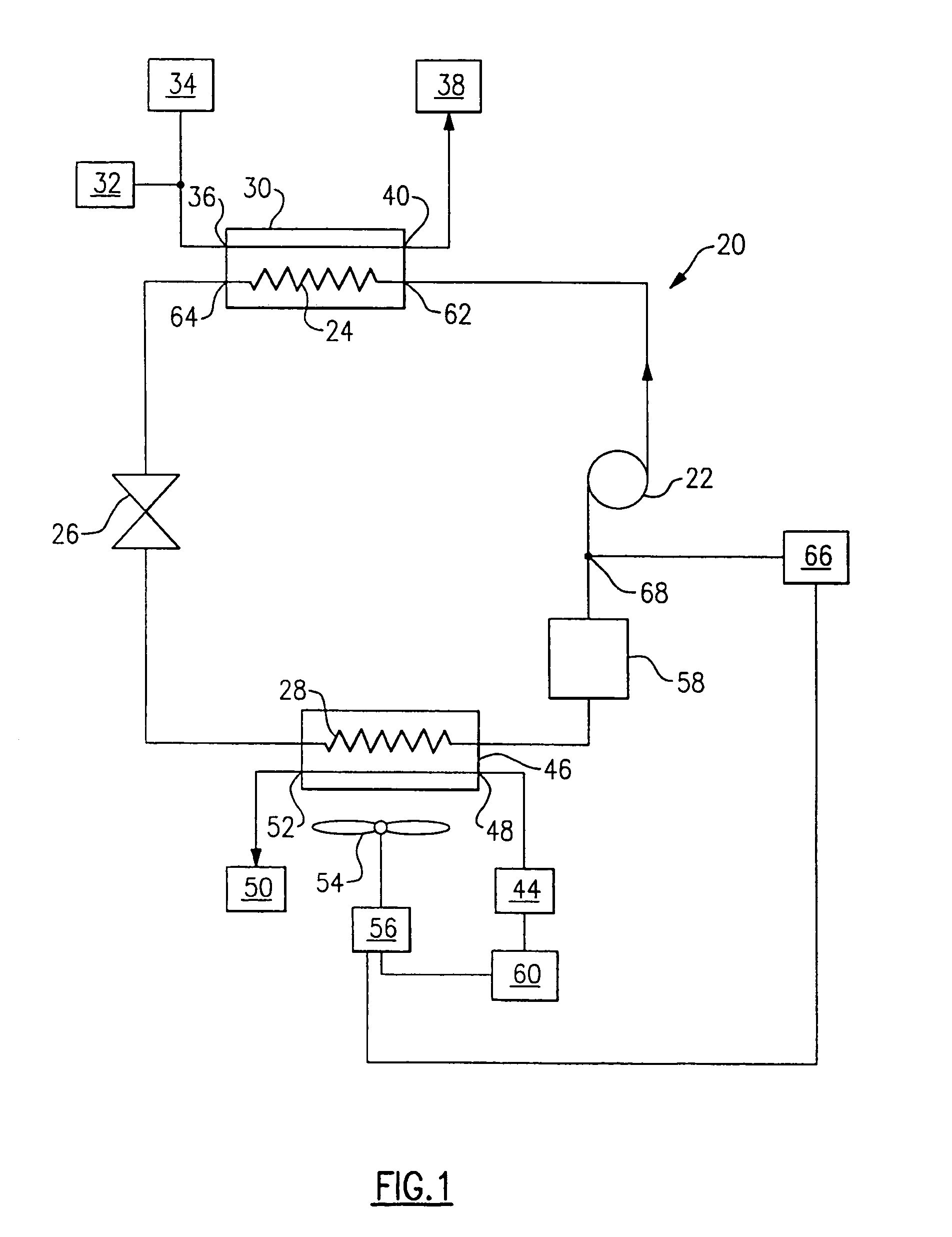
A heat pump cycle system which can switches cooling operation and heating operation for a compartment includes a first inside heat exchanger and a second inside heat exchanger disposed in an air conditioning case. The first inside heat exchanger is disposed in the air conditioning case at a downstream air side of the second inside heat exchanger, while being arranged in line in a flow direction of refrigerant. The first inside heat exchanger is upstream from the second inside heat exchanger in the flow direction of refrigerant during the heating operation. In the heat pump cycle system, an expansion valve is controlled so that coefficient of performance in each operation becomes approximately maximum. Thus, during the heating operation of the heat pump cycle system, a lower limit temperature of air blown from the inside heat exchangers can be increased so that temperature of air blown into the compartment is increased, while the coefficient of performance is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Refrigerant cycle system with super-critical refrigerant pressure
InactiveUS6505476B1Coefficient is prevented being deterioratedMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringControl valves
In a refrigerant cycle system, a control unit controls both a refrigerant amount discharged from a compressor and an opening degree of a pressure control valve so that theoretical efficiency of a super-critical refrigerant cycle and efficiency of the compressor are improved. Therefore, the effective coefficient of performance of the refrigerant cycle is improved, while necessary capacity of components of the refrigerant cycle is obtained.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Working fluid for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
ActiveUS20160333243A1Stably used continuouslyCycle performance sufficientHeat-exchange elementsWorking fluidMetal working fluid
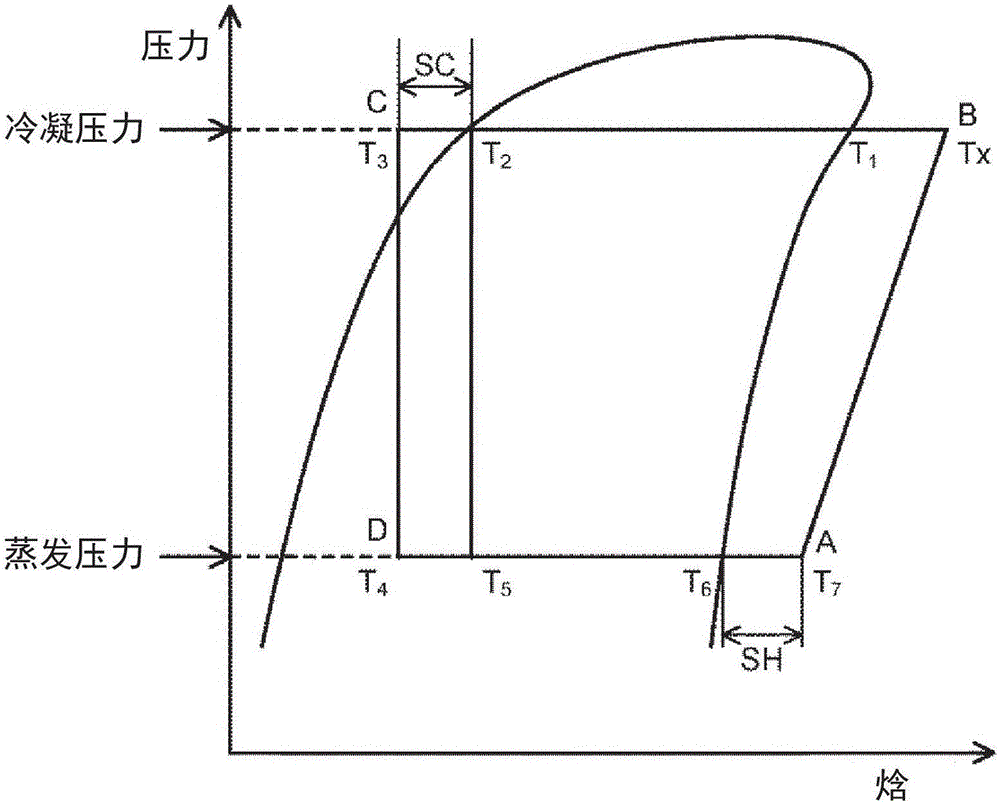
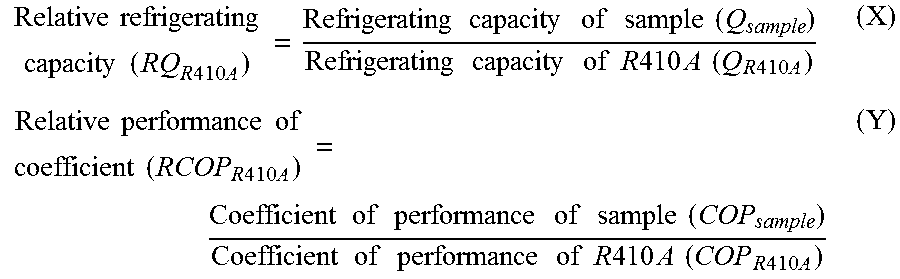
To provide a working fluid which has cycle performance sufficient as an alternative to R410A while the influence over global warming is sufficiently suppressed, which does not significantly increase the load to an apparatus as compared with a case where R410A is used, and which can be stably used continuously without any special measures, a composition for a heat cycle system comprising the working fluid, and a heat cycle system employing the composition.A working fluid for heat cycle, wherein the global warming potential is less than 300; the product of the relative coefficient of performance and the relative refrigerating capacity is at least 0.820 relative to R410A in a standard refrigerating cycle under conditions of an evaporation temperature of 0° C., a condensing temperature of 40° C., a supercoiling degree of 5° C. and a degree of superheat of 5° C.; the relative compressor discharge gas pressure is at most 1.100; the lower limit of the combustion range by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety Act is at least 5 vol %; and the pressure will not exceed 2.00 MPaG in a combustion test by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety act under 0.98 MPaG at 250° C.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Heat pump
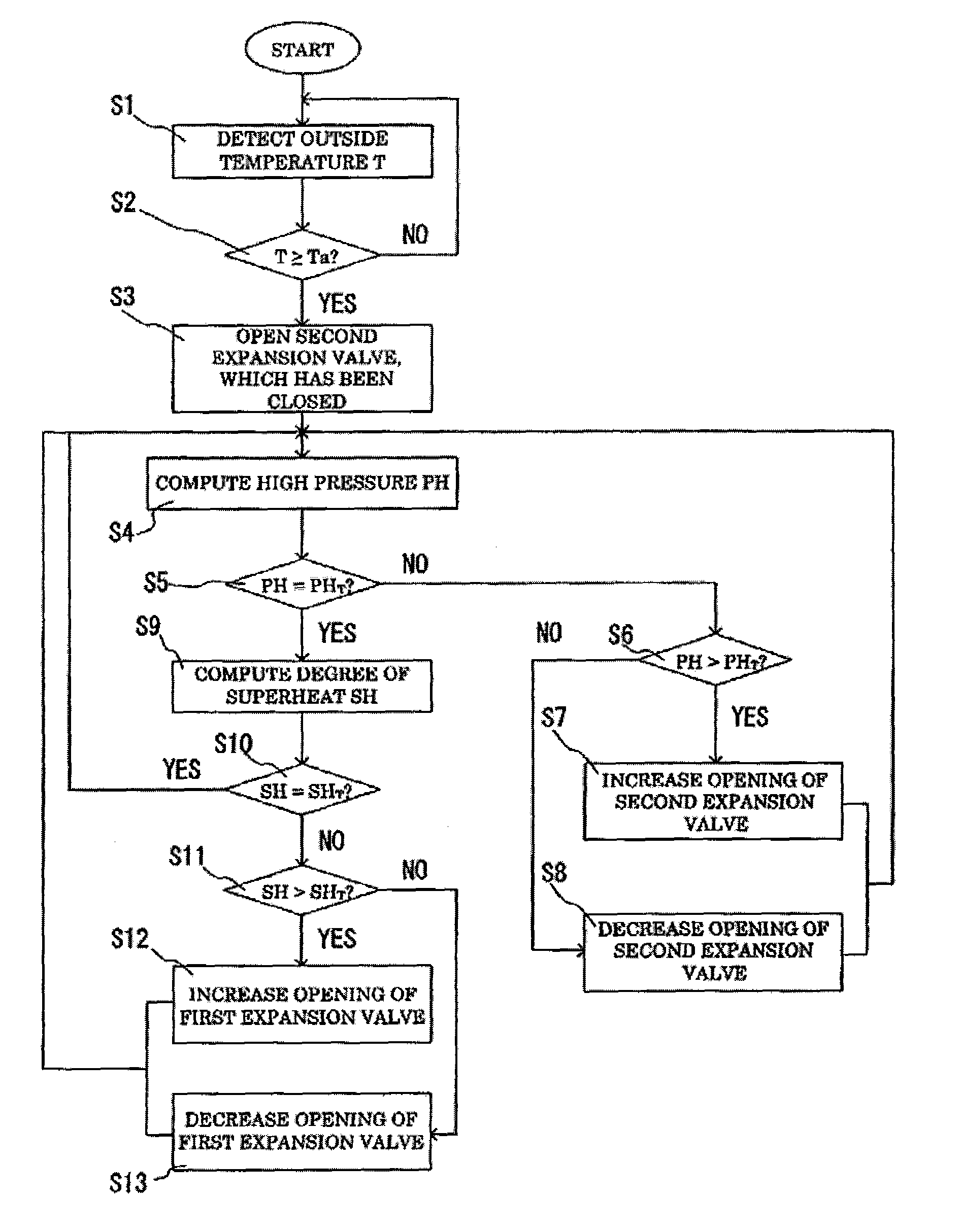
InactiveUS20070068178A1Small valueImprovement in coefficient of performanceMechanical apparatusEfficient regulation technologiesEngineeringHigh pressure
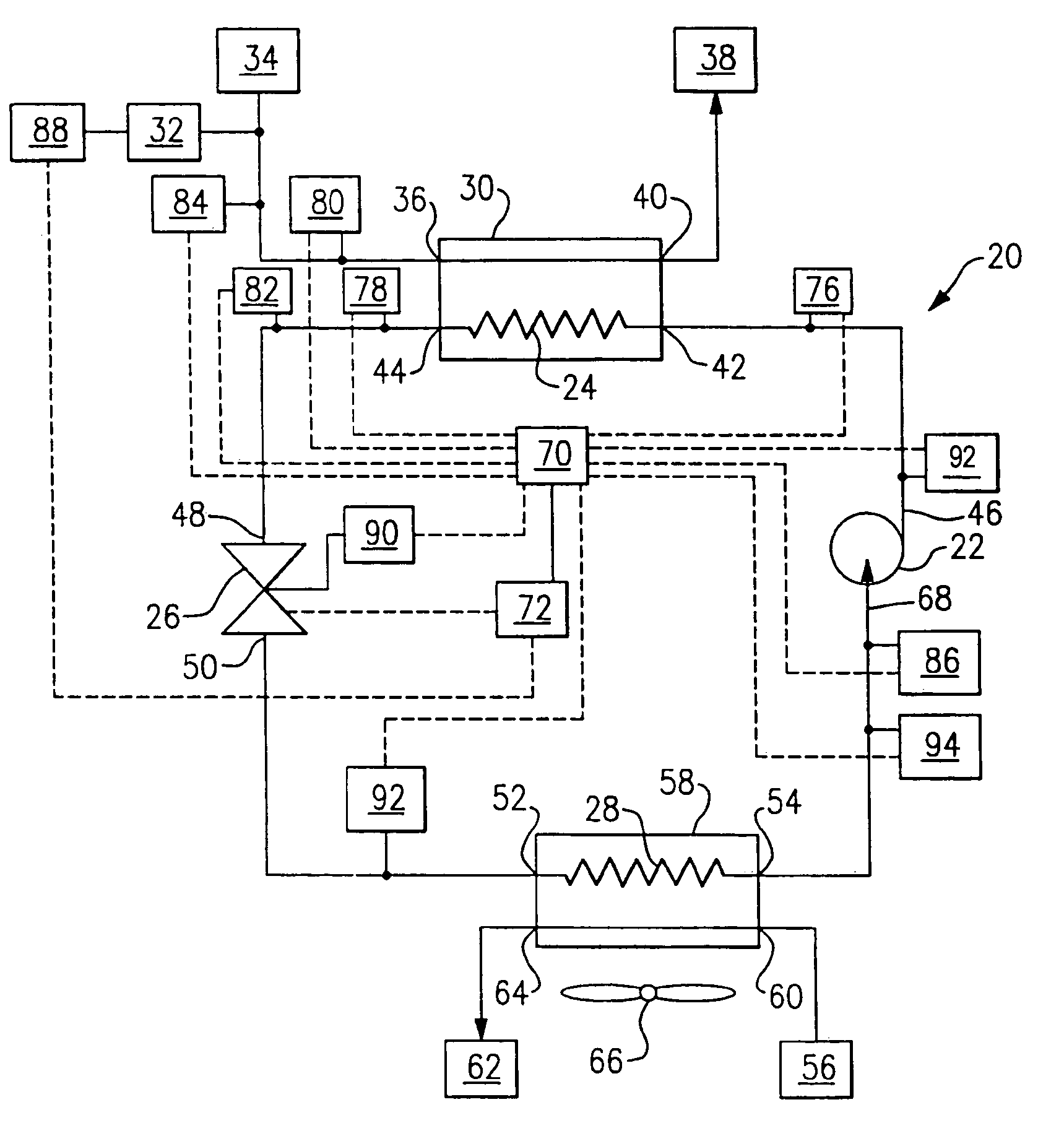
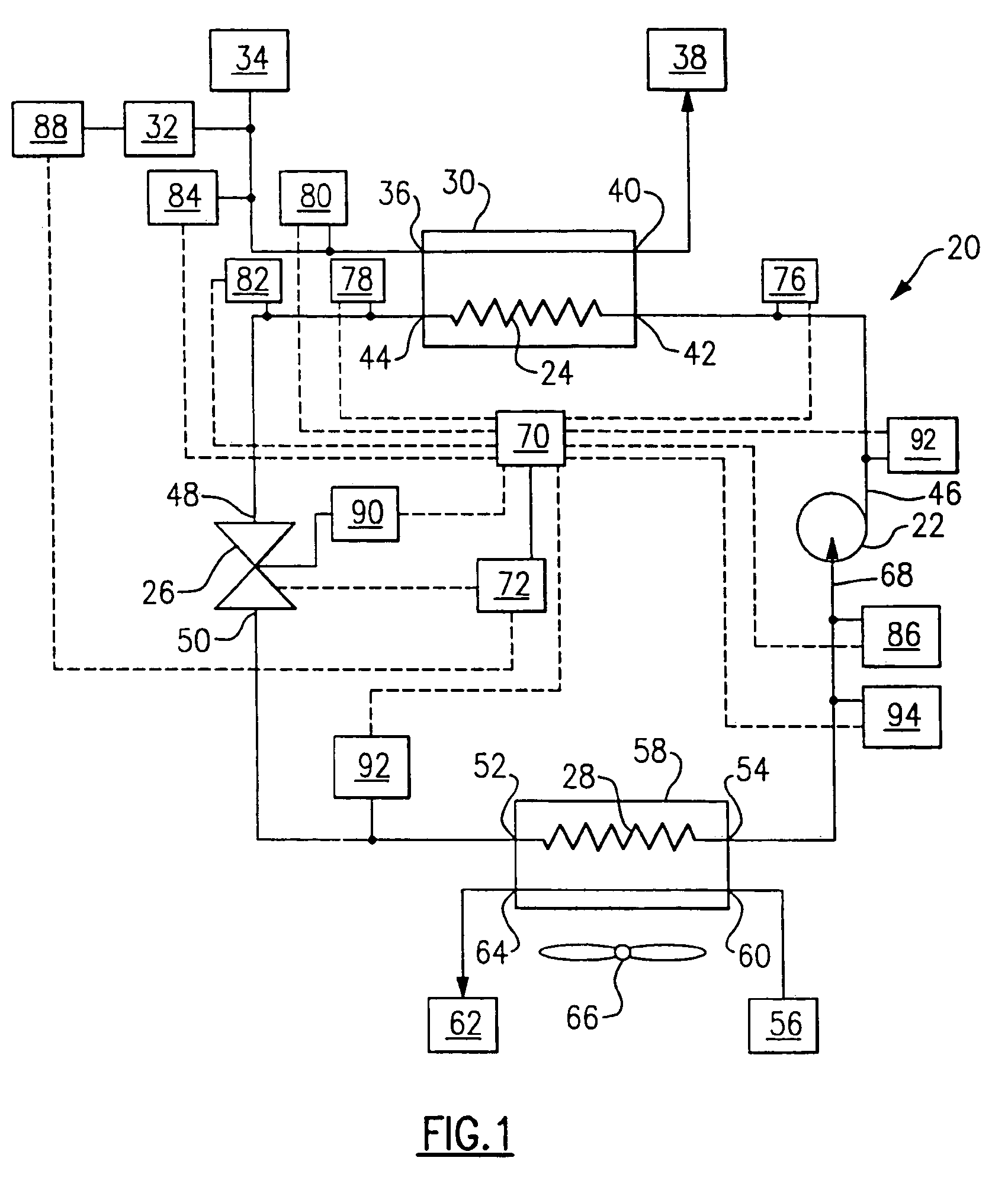
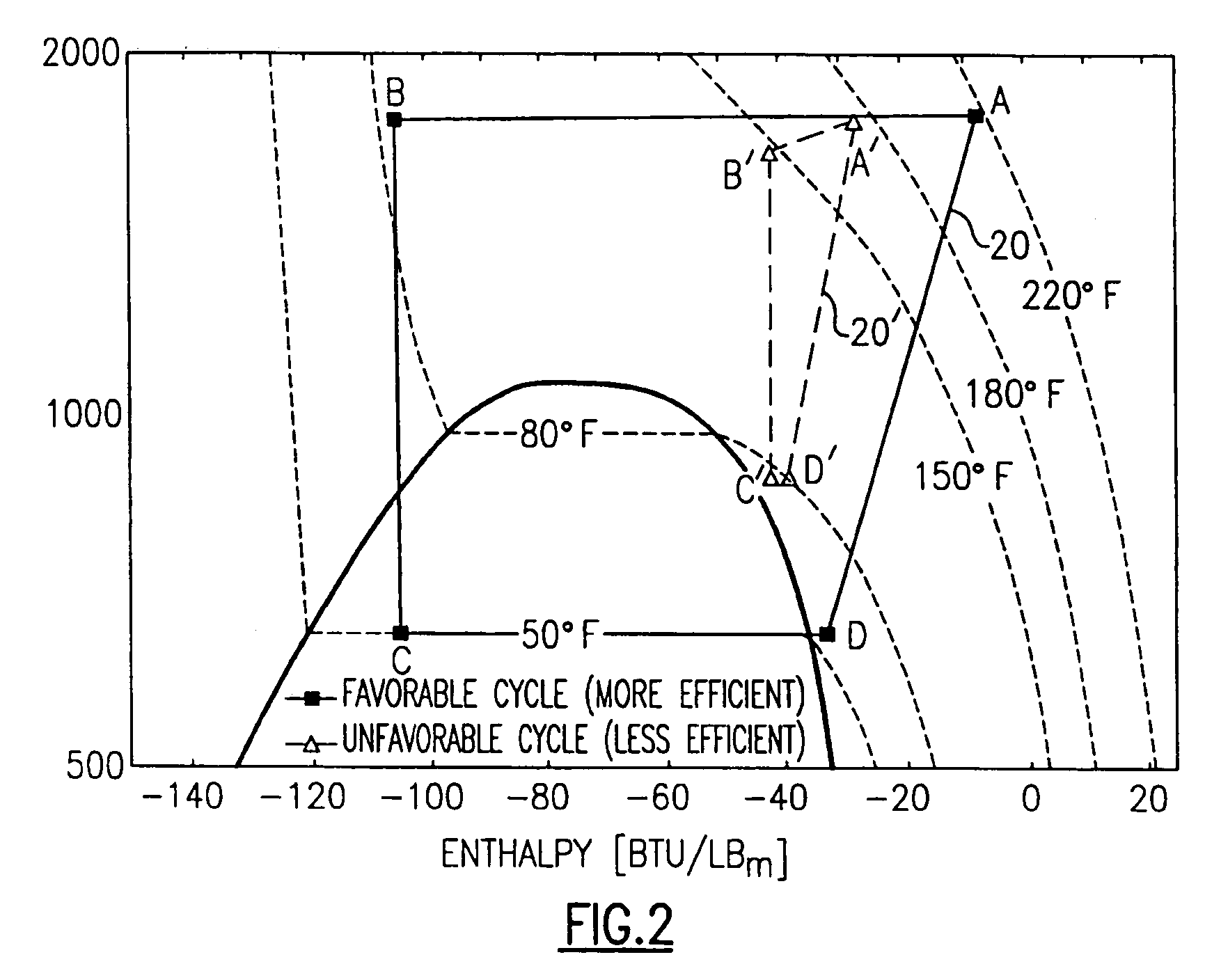
A heat pump of the present invention has a compressor and an expander coupled with a common axis of rotation, a first throttling device disposed in a circulation passage of refrigerant, and a second throttling device disposed in a bypass passage diverted from the expander. A control device controls the openings of these throttling devices. The control device executes a first controlling in which the opening of the first throttling device is adjusted in order to bring a high pressure PH in a refrigeration cycle close to a predetermined value determined based on a value at which the coefficient of performance (COP) of the heat pump is optimized, and after the first controlling is completed, it executes a second controlling in which the opening of the second throttling device is adjusted in order to bring a degree of superheat SH close to a predetermined positive value. This ensures smooth and stable operations of the heat pump.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for detecting a fault in an HVAC system
A bypass factor of an evaporator is used to indicate when an air filter of an HVAC is clogged. The bypass factor represents the amount of air that is bypassed without direct contact with the evaporator. As the air filter clogs, the bypass factor decreases. The bypass factor can also be used for early detection of clogging of the air filter. A first bypass factor is calculated by using the temperature measurements, and a second bypass factor is calculated by using the airflow rate of the air. The difference between the two bypass factors determines the error. An increase in the error indicates that the air filter is clogged. A coefficient of performance of the evaporator can also be calculated to detect if the air filter is clogged. A decrease in the coefficient of performance indicates that the air filter is clogged.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Cascade floating intermediate temperature heat pump system
ActiveUS20120210736A1Heat pumpsCompression machines with non-reversible cycleComputer moduleCoefficient of performance
A cascade heat pump system is configured with variable-speed compressors which allow operation at a high system coefficient of performance for a given thermal load. An electronic control module may be utilized to dynamically vary the speed of the compressors to achieve maximum energy efficiency. Variable-speed fans or blowers may also be used.
Owner:ROCKY RES INC
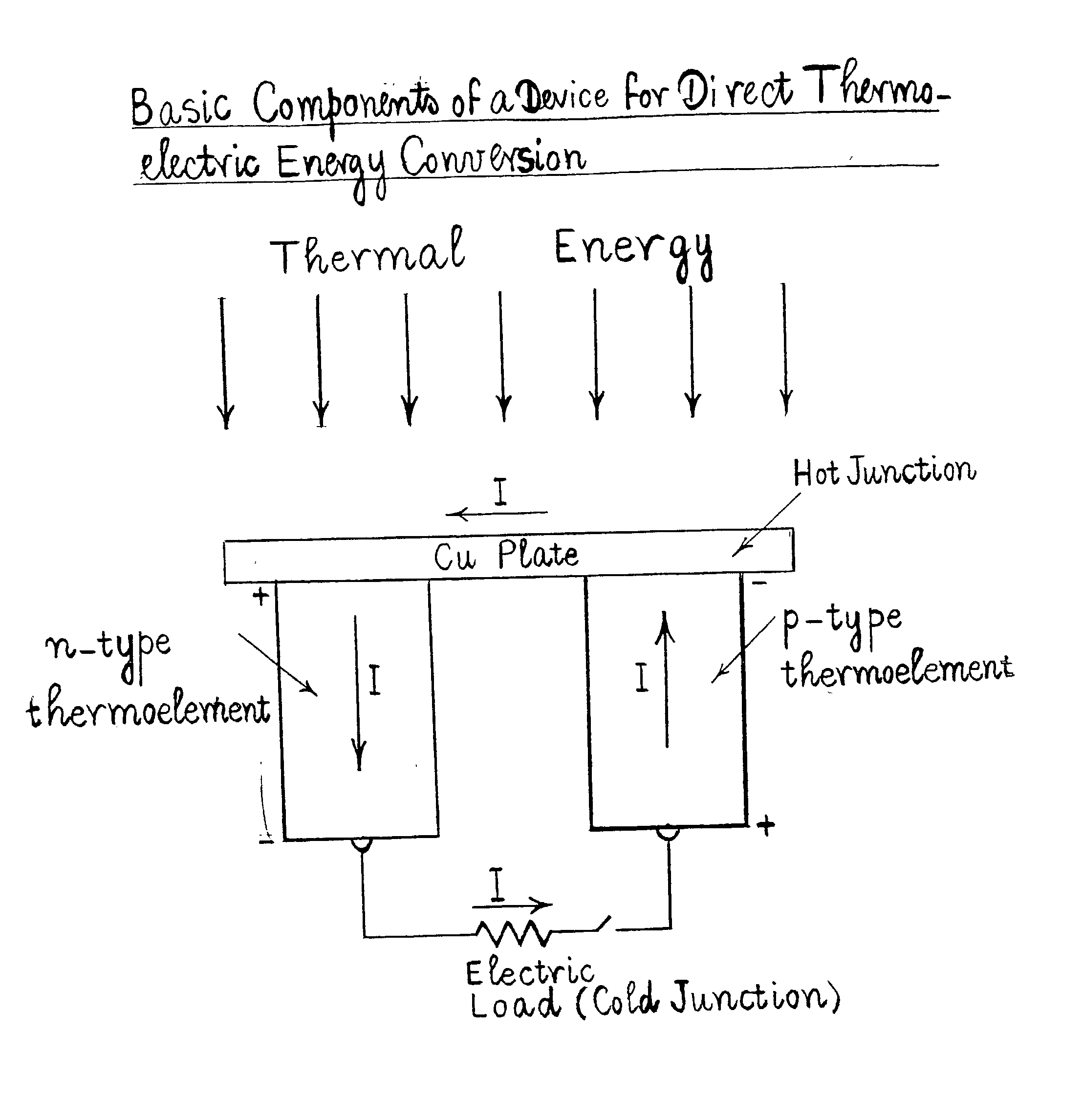
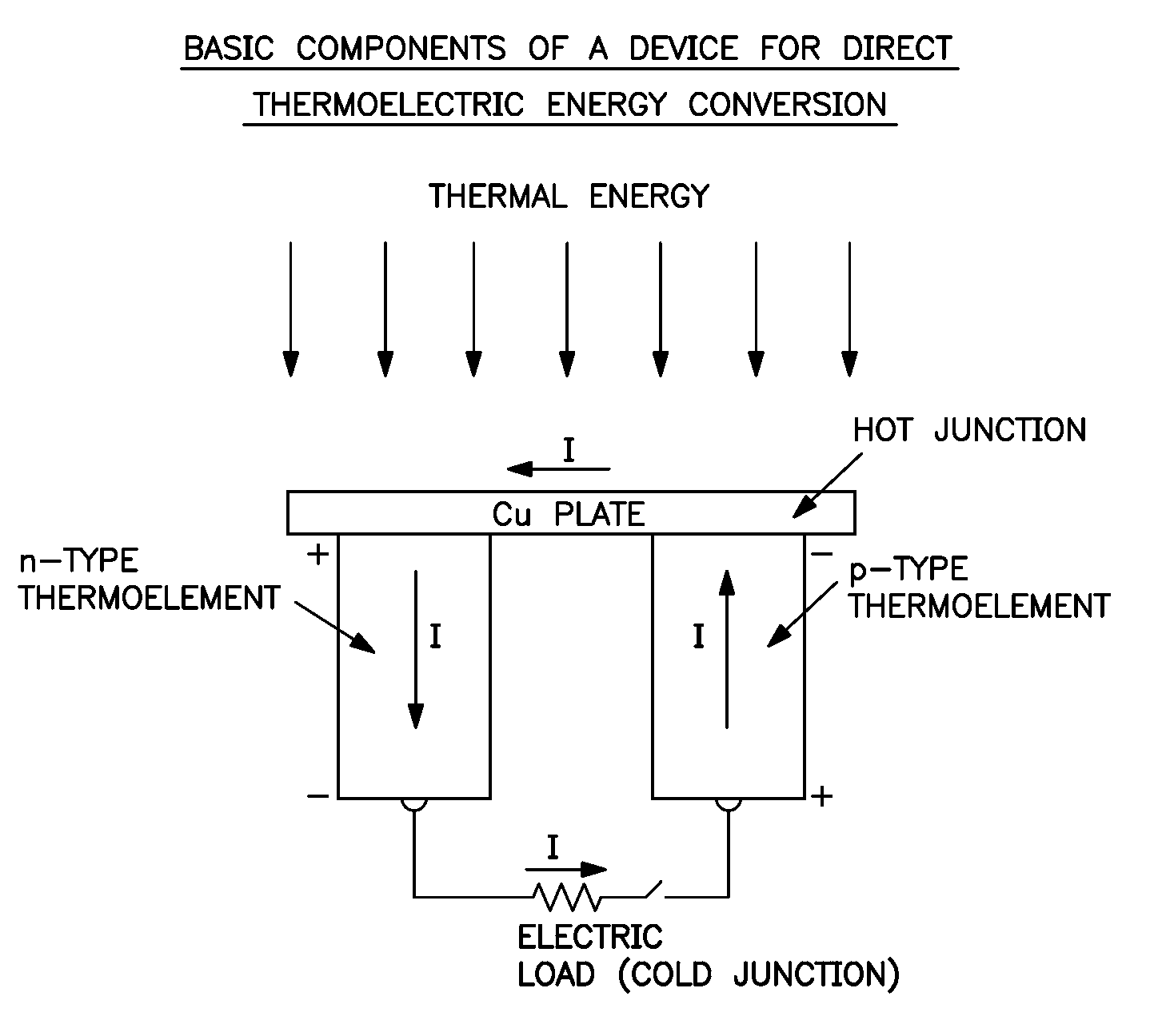
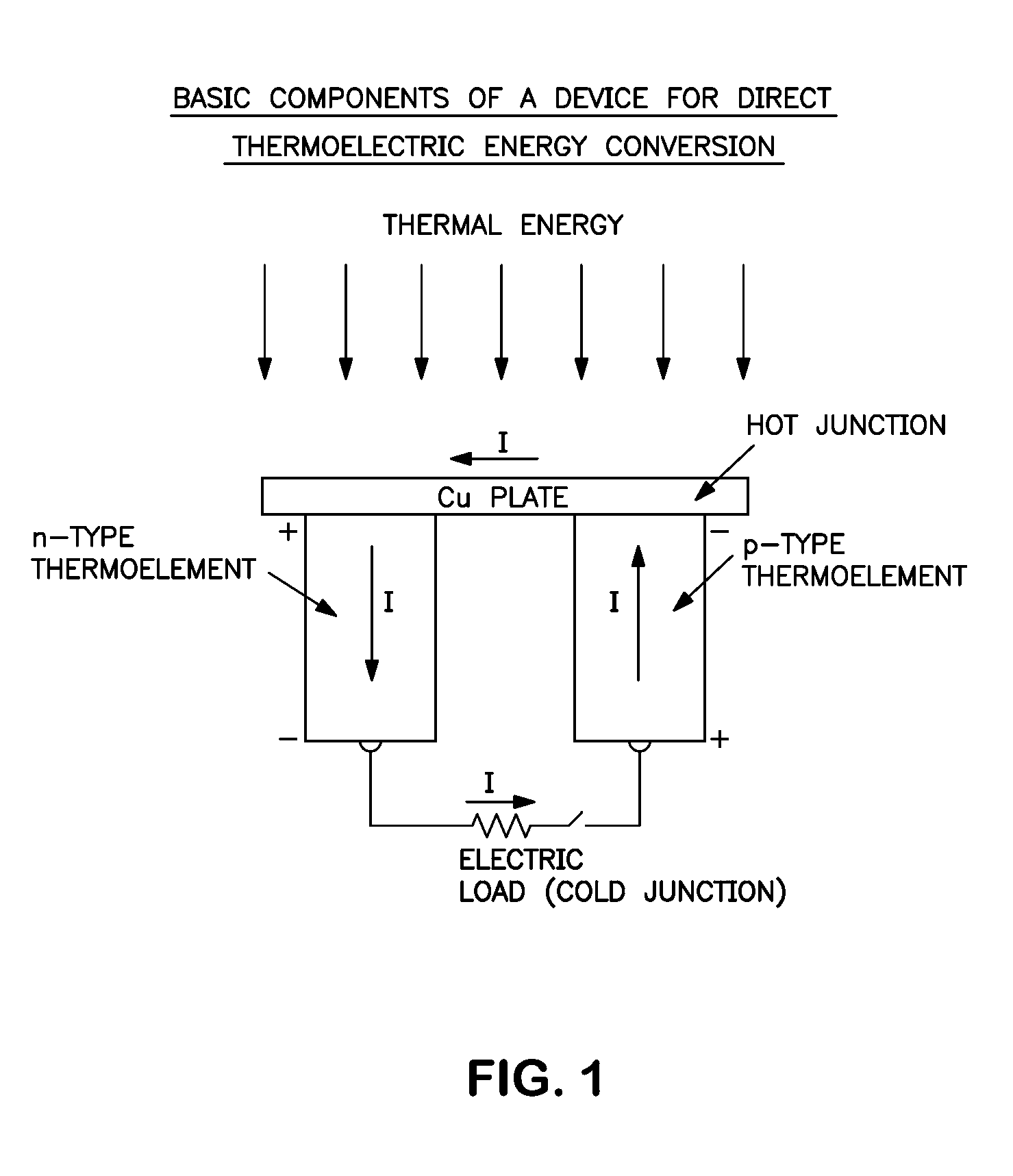
Method for producing a device for direct thermoelectric energy conversion
InactiveUS20030110892A1Polycrystalline material growthThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentJunction temperatureEngineering
In devices used for the direct conversion of heat into electricity, or vice versa, known in the art as thermoelectric power generators, thermoelectric refrigerators and thermoelectric heat pumps, the efficiency of energy conversion and / or coefficient of performance have been considerably lower than those of conventional reciprocating or rotary, heat engines and / or vapor-compression systems, employing certain refrigerants. The energy conversion efficiency of power generating devices, for example, aside from the hot and cold junction temperatures, also depends on a parameter known in the art as the thermoelectric figure of merit Z=S2sigma / k, where S is the thermoelectric power, sigma is the electrical conductivity and k is the thermal conductivity, of the material that constitutes the p-type, and / or n-type, thermoelements, or branches, of the said devices. In order to achieve a considerable increase in the energy conversion efficiency, a thermoelectric figure of merit of the order of 10-2 K-1, or more, is needed. It is reasonably expected that such an order of magnitude, for the figure of merit, can be realized with a composition of matter, comprising magnesium, silicon, lead and barium, and optionally comprising one, or more, additional doping materials.
Owner:NICOLOAU MICHAEL C
Cooling and heating system
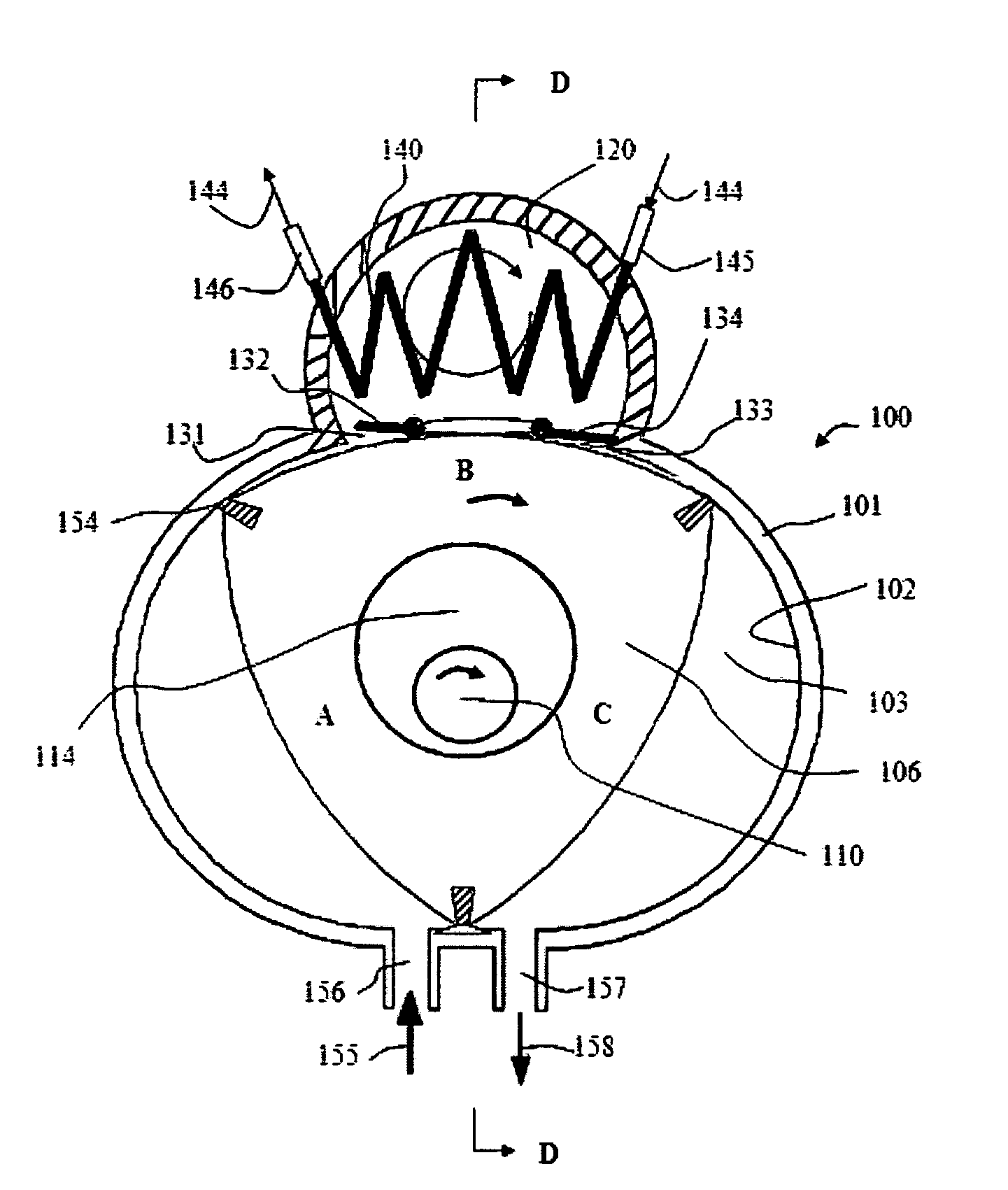
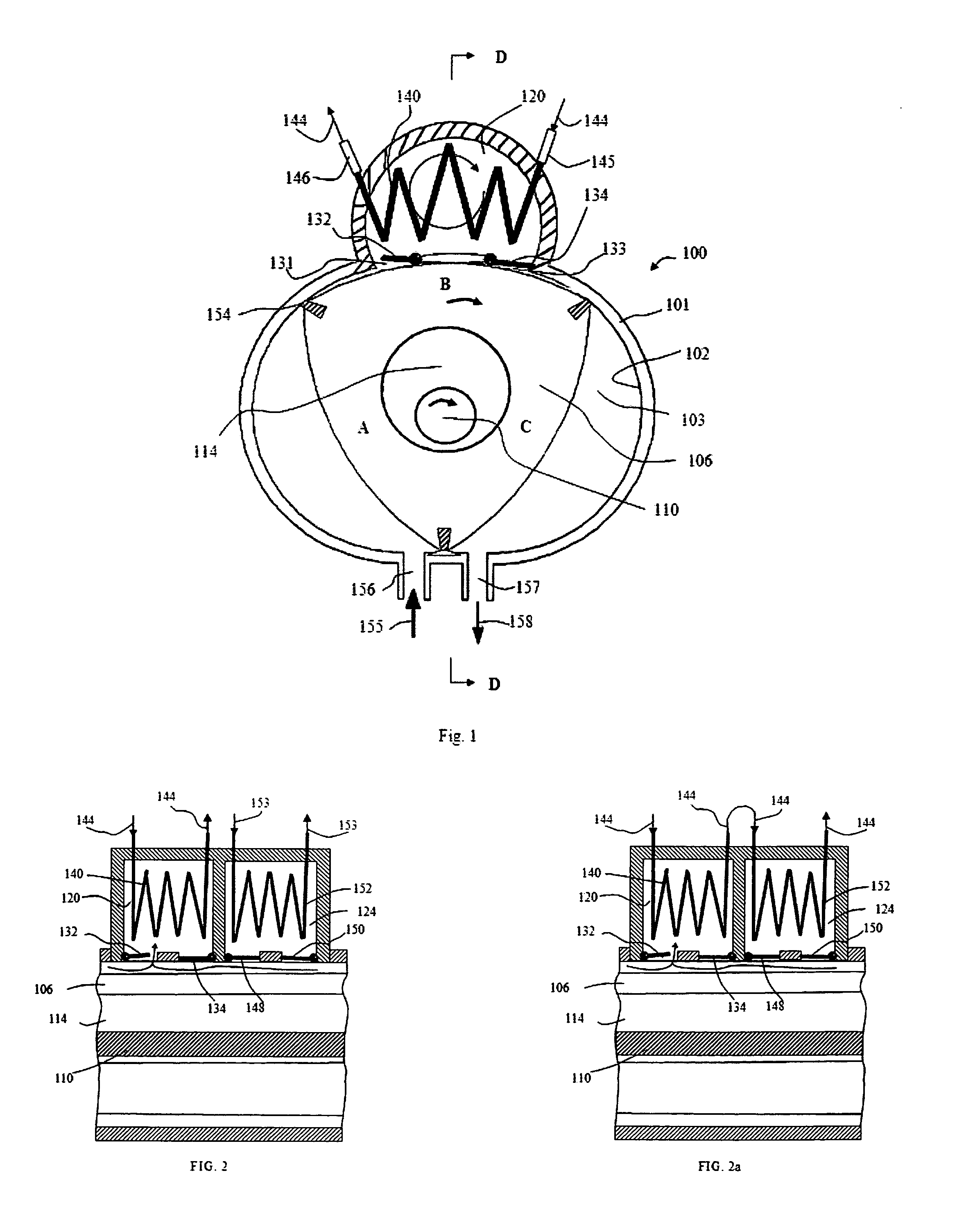
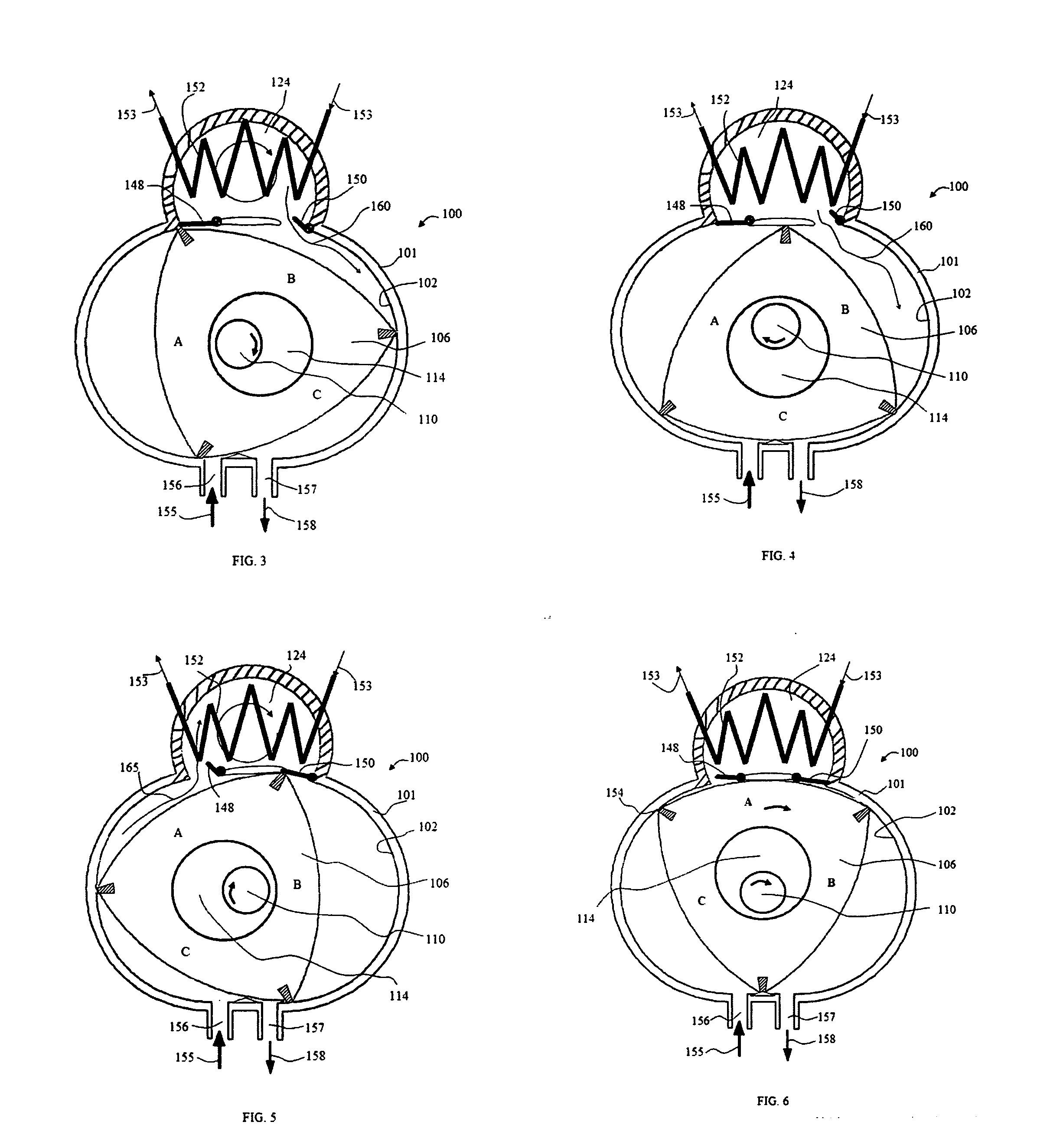
InactiveUS20060218948A1Maximizing coefficientReduce capacityEvaporators/condensersEfficient regulation technologiesEngineeringGas cooler
There is disclosed a cooling and heating system in which a refrigerant is used in a supercritical state and in which cooling and heating capacity can be controlled so as to maximize a coefficient of performance. A cooling and heating system 130 includes: an outdoor unit 101 indicating a compressor 102 and an outdoor heat exchanger 103a; a plurality of indoor units 105 including indoor heat exchangers 106; a high pressure tube 111; a low pressure tube 112; and an intermediate tube 113. The system includes: a refrigerant pressure detection unit PC01 for measuring a pressure of the refrigerant discharged from the compressor 102; a first refrigerant temperature detection unit TC03 which measures an outlet temperature of the refrigerant in a case where the outdoor heat exchanger 103 functions as a gas cooler and which measures an inlet temperature of the refrigerant in a case where the outdoor heat exchanger 103 functions as an evaporator; and a second refrigerant temperature detection unit TCO8 which measures an outlet temperature of the refrigerant in a case where the indoor heat exchanger 106 functions as a gas cooler and which measures an inlet temperature of the refrigerant in a case where the indoor heat exchanger 106 functions as an evaporator.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Inter-platform application migration realization method and system
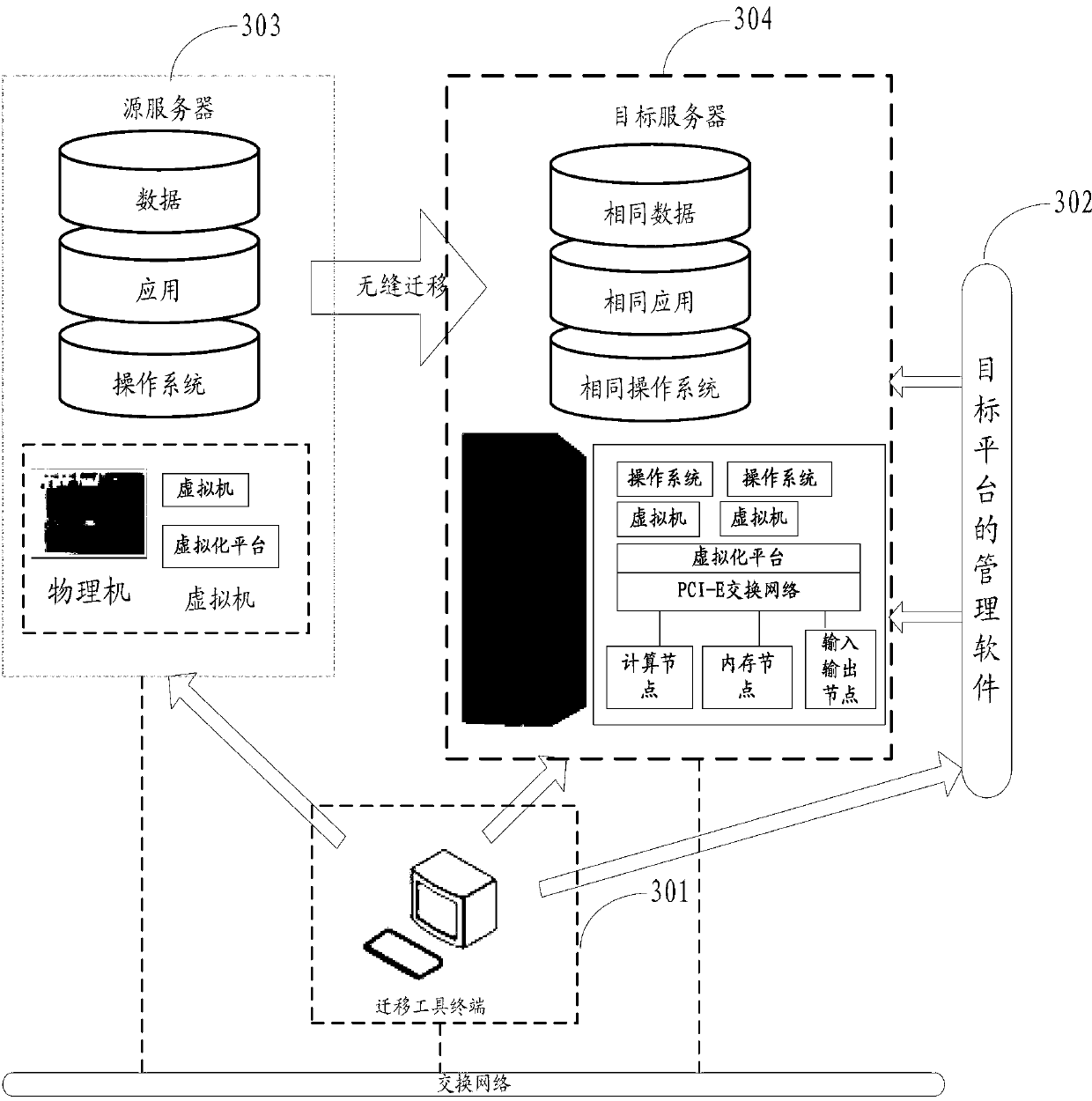
ActiveCN103109271AMake Migration SeamlessImprove application migration efficiencyProgram loading/initiatingOperating systemCoefficient of performance
The invention is suitable for the computer field, and provides an inter-platform application migration realization method and a system. The method comprises the communication connection between the source platform and the target platform;the acquisition of the system environment information of the source platform and the system environment information of the target platform; the generating of the resource conversion coefficienct, the performance coefficienct parameter and the system environment required by he target platform according to the system environment information of the source platform and the system environment information of the target platform; the generating of the script before the migration and the cooperation script file; the execution of the the script before the migration and the cooperation script, and the configuration of the target platform system environment; the migration of the application data from the source platform to the target platform partition. By using the invention, the seamless migration of the application data of different platforms from the source server and the target server can be realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
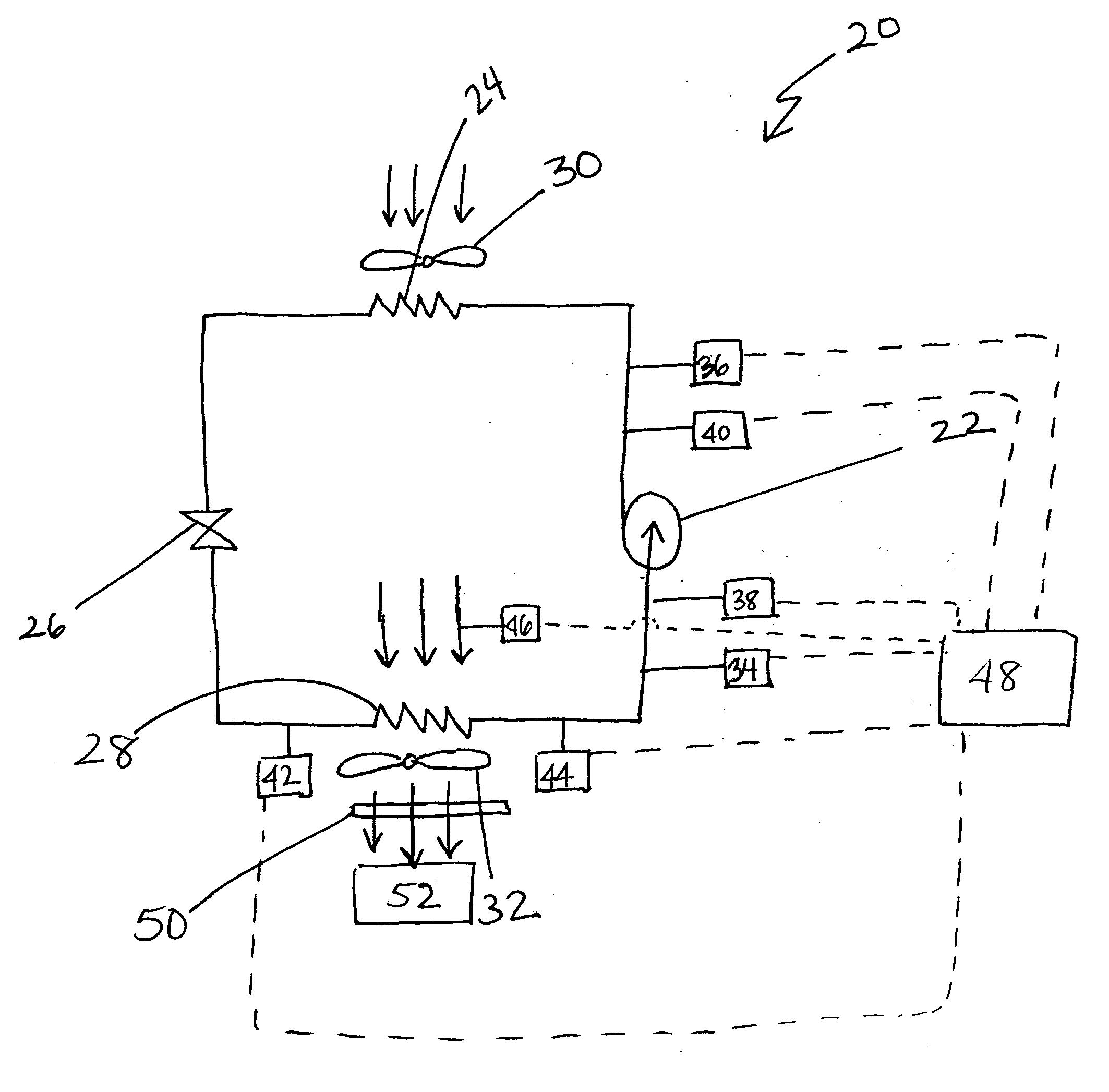
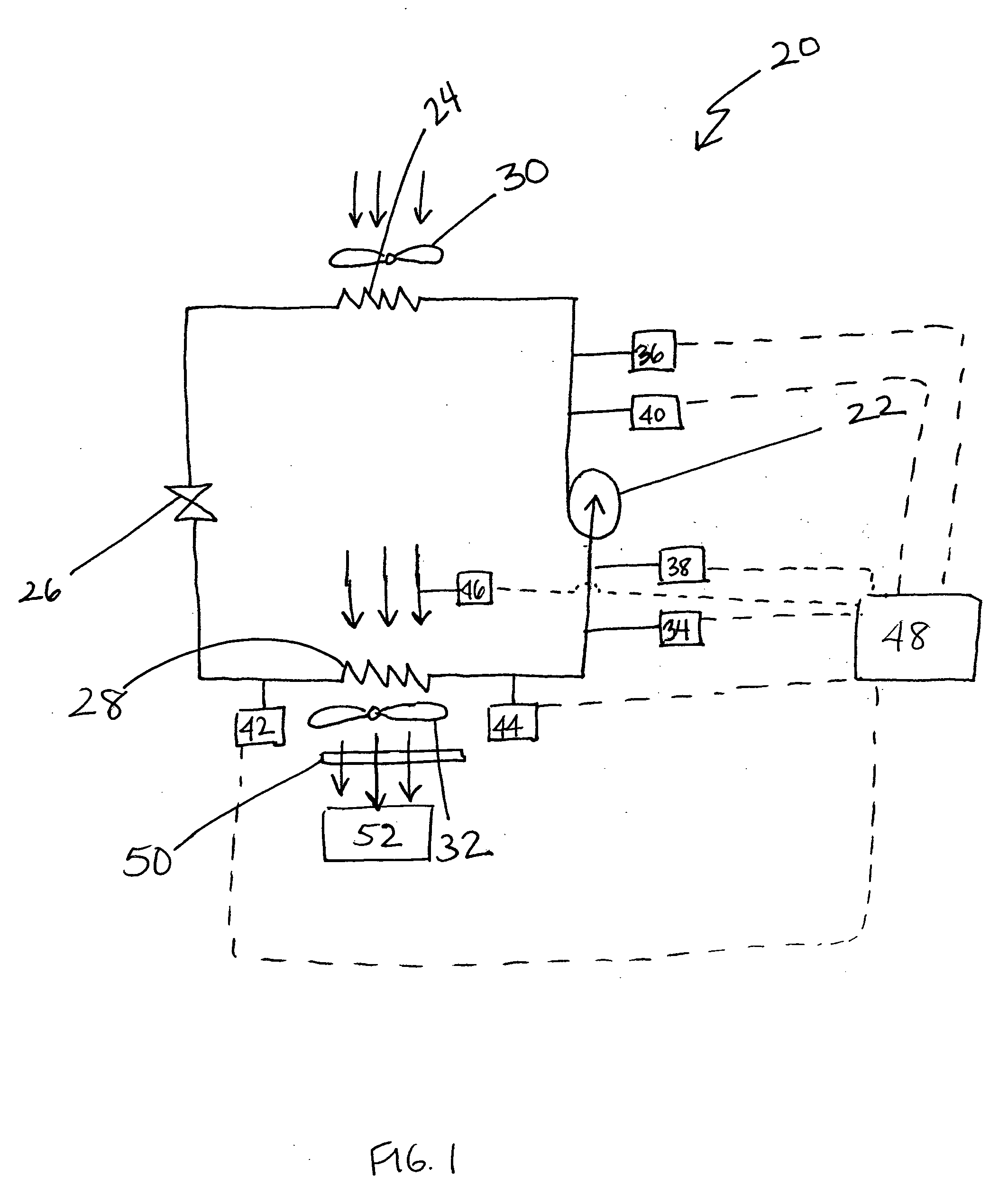
Control of refrigeration system to optimize coefficient of performance
InactiveUS7000413B2Low pour pointCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporators/condensersGas coolerEngineering
A refrigeration system includes a compressor, a gas cooler, an expansion device, and an evaporator. Refrigerant is circulated though the closed circuit system. Preferably, carbon dioxide is used as the refrigerant. As carbon dioxide has a low critical point, systems utilizing carbon dioxide as a refrigerant usually require the refrigeration system to run transcritical. When the system is operating inefficiently, the system is modified so the system operates efficiently. First, a parameter of the system is monitored by a sensor and the then compared to a stored value to determine if the system is operating inefficiently. If the system is operating inefficiently, the system is modified to an efficient system.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Method for controlling opening of electronic expansion valve in heat pump water heater system
InactiveCN102384618AReduce openingPrecise control of refrigerant flowRefrigeration safety arrangementElectronic expansion valveIndustrial engineering
The invention discloses a method for controlling the opening of an electronic expansion valve in a heat pump water heater system, and aims to provide a control method for allowing a system to avoid an area in which the air suction degree of superheat drops suddenly in the running process and allowing the coefficient of performance (COP) of the system to keep a high level. The method comprises thefollowing steps of: setting the optimum value of the change rate delta T / delta t of the air suction degree of superheat, and setting the initial opening of the expansion valve as 80 percent of total opening; taking a temperature difference between an average temperature value at an air suction port of a compressor and the saturated evaporating temperature as the air suction degree of superheat when the compressor runs to the state of the stable running of the system; measuring and calculating the air suction degree of superheat at the interval time delta t; calculating the change rate of the actual air suction degree of superheat according to the adjacent two-time air suction degree of superheat, comparing with the set optimum value of the change rate of the air suction degree of superheat, and when the change rate of the actual air suction degree of superheat is less than or equal to A, reducing the opening of the expansion valve; when the change rate of the actual air suction degreeof superheat is more than 0, increasing the opening of the expansion valve; and when the change rate of the actual air suction degree of superheat is more than A and is less than or equal to 0, maintaining the current running state.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
High efficiency r744 refrigeration system and cycle
InactiveUS20100313582A1Reduce compressionImprove cycle efficiencyCompression machines with non-reversible cycleFluid circulation arrangementEngineeringHigh pressure
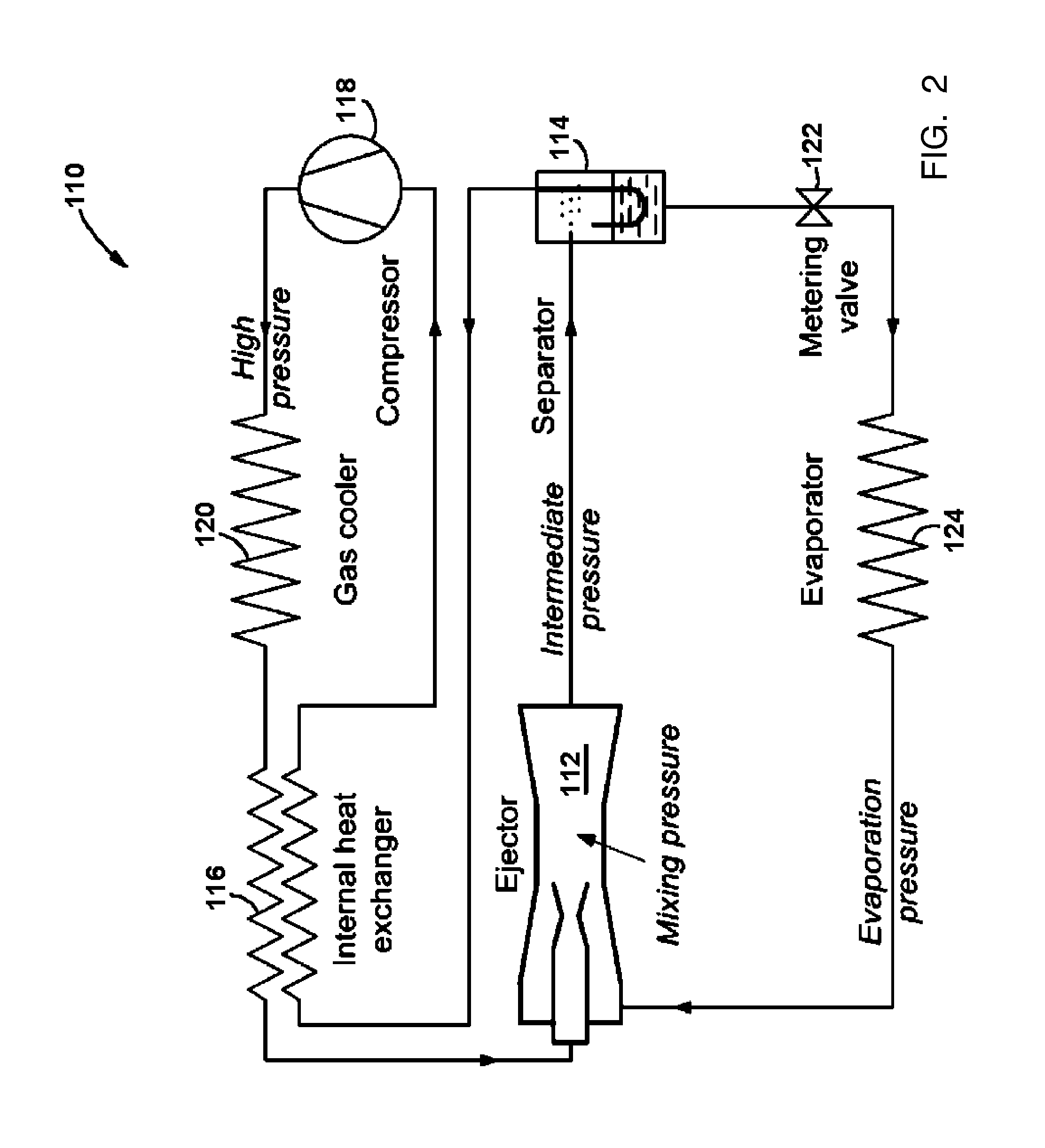
A high efficiency R744 air conditioning and refrigeration system and cycle comprises a vapor compressor and two independent ejectors operatively connected to high and low-pressure sides of the compressor, respectively. The two ejectors reduce the overall pressure ratio of the mechanical vapor compressor resulting in dramatically increased thermodynamic cycle efficiency. As one example of its potential applications for residential, commercial or industrial uses, a 150 ton capacity of a water-cooled chiller designed in accordance with the present invention is predicted to provide the power consumption as low as 0.47 kW / ton, when operated in accordance with the cooling methods of the present invention, which corresponds to 7.47 of Coefficient of Performance (COP).
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
Energy efficient sorption processes and systems
InactiveUS20050262720A1Reduce the temperatureReduce power consumptionSolar heating energyInternal combustion piston enginesSorbentEngineering
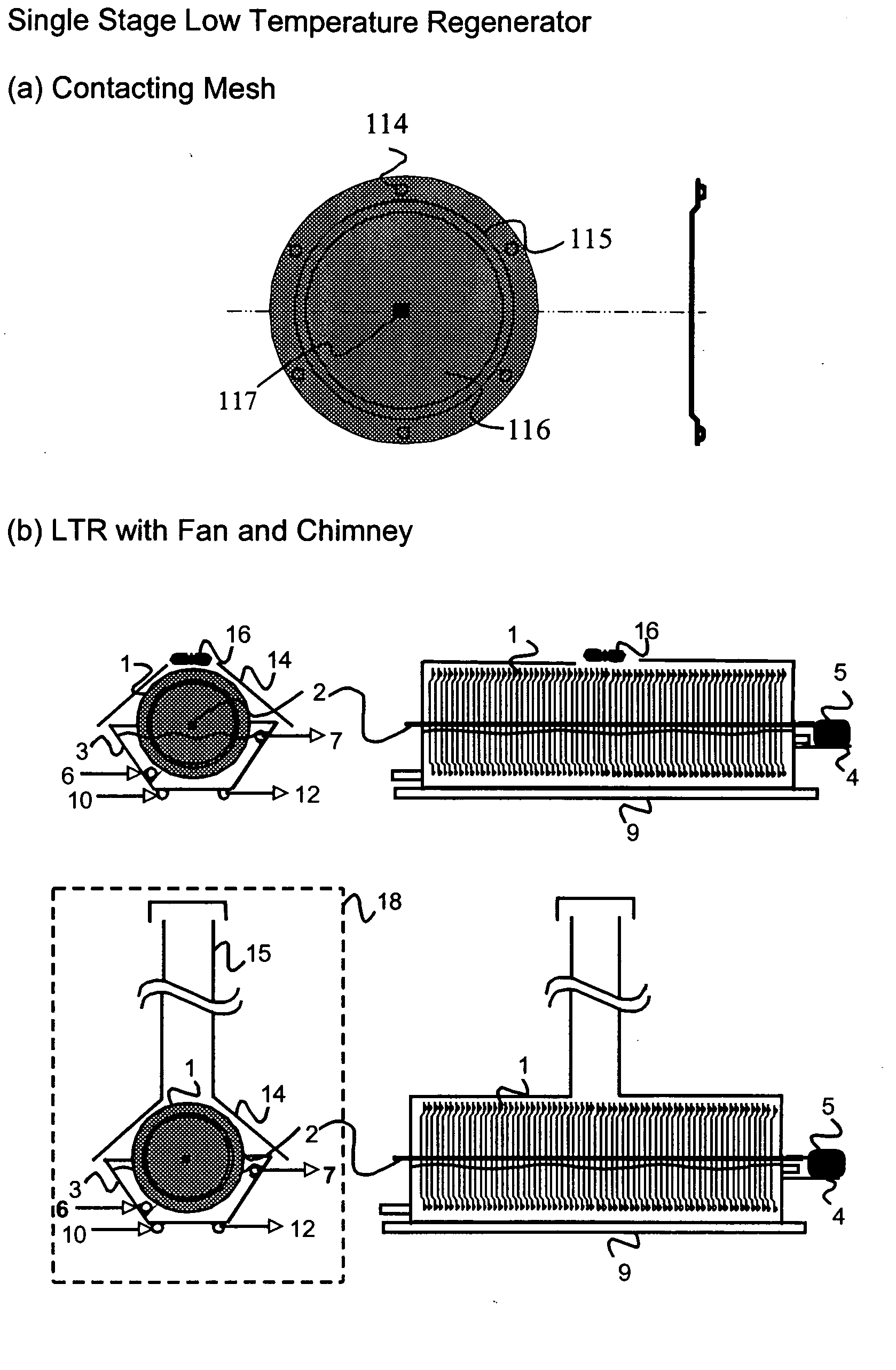
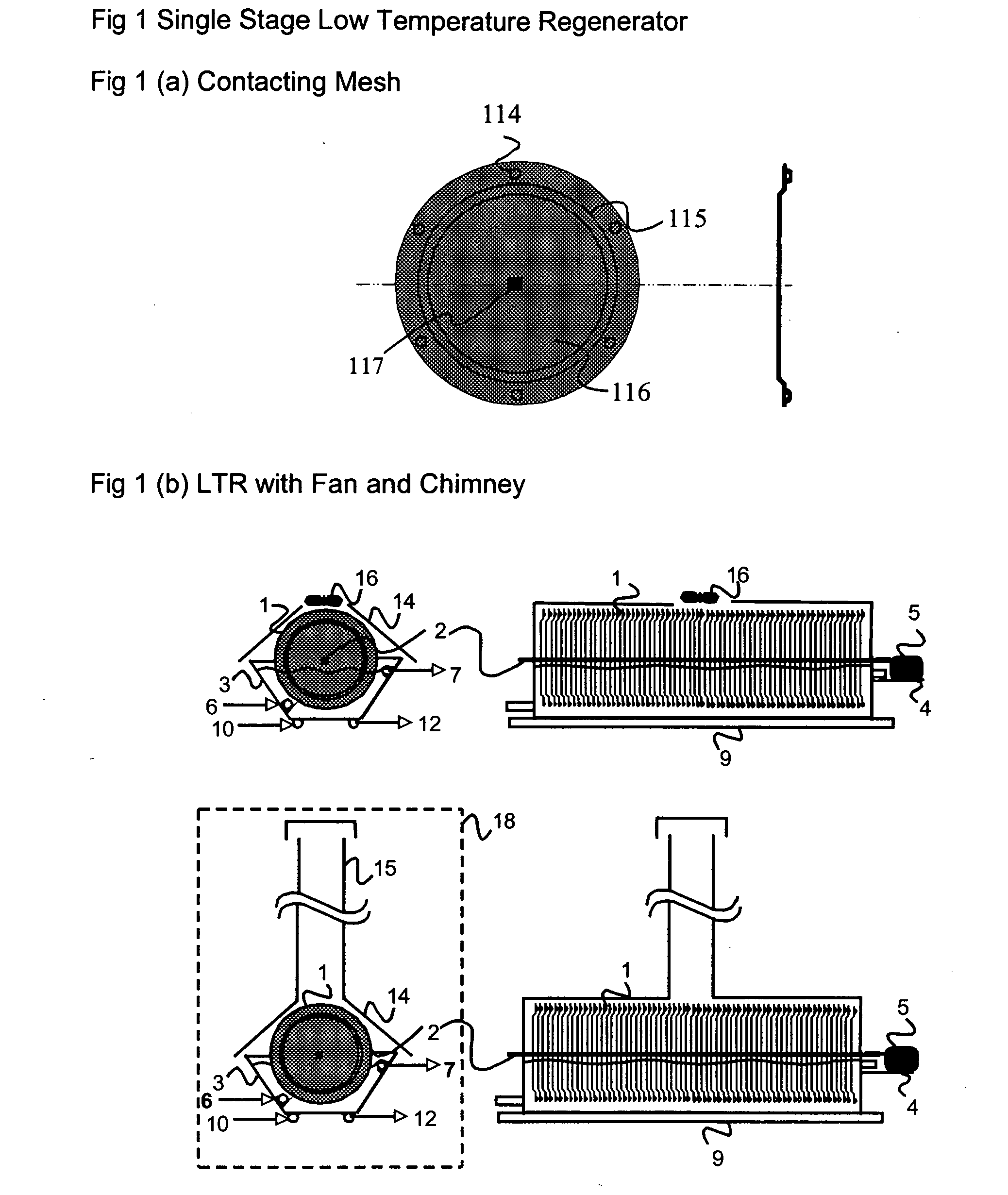
The present invention relates to novel energy efficient sorption processes and systems for cooling, dehumidifying and heating using multistage liquid desiccant regenerators, or hybrid cooling systems or adsorption cooling systems involving appropriate combinations of rotating contacting devises, adsorption modules with heat transfer passages in thermal contact with the adsorption module wall and switchable heat pipes. The sorption processes of this invention help in flexible designing of compact cooling, dehumidifing, heating systems easy operability. The adsorption module of this invention leads to lower cycle times as low as 5 minutes; makes it possible to achieve high system Coefficient of Performance (COP) up to 0.9 due to reduced thermal mass; offers high specific cooling power in the range of 50 to 750 W / kg of AC; is easy to manufacture and operates at low costs. The refrigeration cum heating system of this invention with heat pipe in thermal contact with the adsorption modules increase the heat transfer rates without increasing the thermal mass leading to increase of COP and the single or multistage pressure equalisation increases the internal regeneration of heat thereby increasing the COP, reducing the cycle time resulting in increased specific cooling power (SCP), reducing the required quantity of adsorbent / refrigerant making the module compact and cost effective.
Owner:INDIAN INST OF TECH
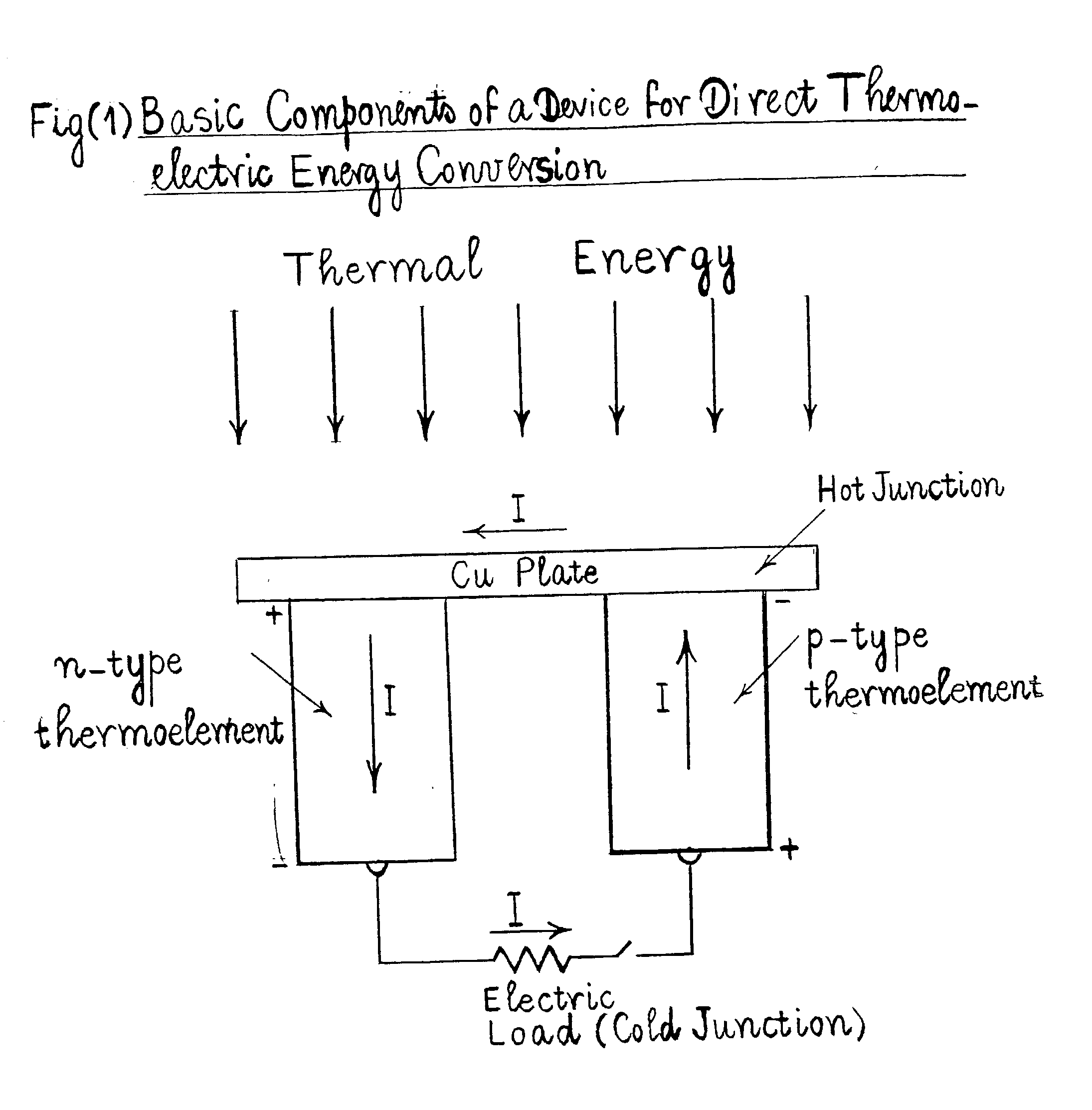
Method for producing a device for direct thermoelectric energy conversion
InactiveUS7166796B2Improve energy conversion efficiencyReduced dimensionPolycrystalline material growthThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentJunction temperatureEngineering
In devices used for the direct conversion of heat into electricity, or vice versa, known in the art as thermoelectric power generators, thermoelectric refrigerators and thermoelectric heat pumps, the efficiency of energy conversion and / or coefficient of performance have been considerably lower than those of conventional reciprocating or rotary, heat engines and / or vapor-compression systems, employing certain refrigerants. The energy conversion efficiency of power generating devices, for example, aside from the hot and cold junction temperatures, also depends on a parameter known in the art as the thermoelectric figure of merit Z=S2σ / k, where S is the thermoelectric power, σ is the electrical conductivity and k is the thermal conductivity, of the material that constitutes the p-type, and / or n-type, thermoelements, or branches, of the said devices. In order to achieve a considerable increase in the energy conversion efficiency, a thermoelectric figure of merit of the order of 10−2 K−1, or more, is needed. It is reasonably expected that such an order of magnitude, for the figure of merit, can be realized with a composition of matter, comprising magnesium, silicon, lead and barium, and optionally comprising one, or more, additional doping materials.
Owner:NICOLOAU MICHAEL C
Cao heat engine and refrigerator
InactiveUS20100089062A1Increase the number ofExtended durationAuxillary drivesInternal combustion piston enginesThermal energyAir cycle machine
Owner:CAO YIDING
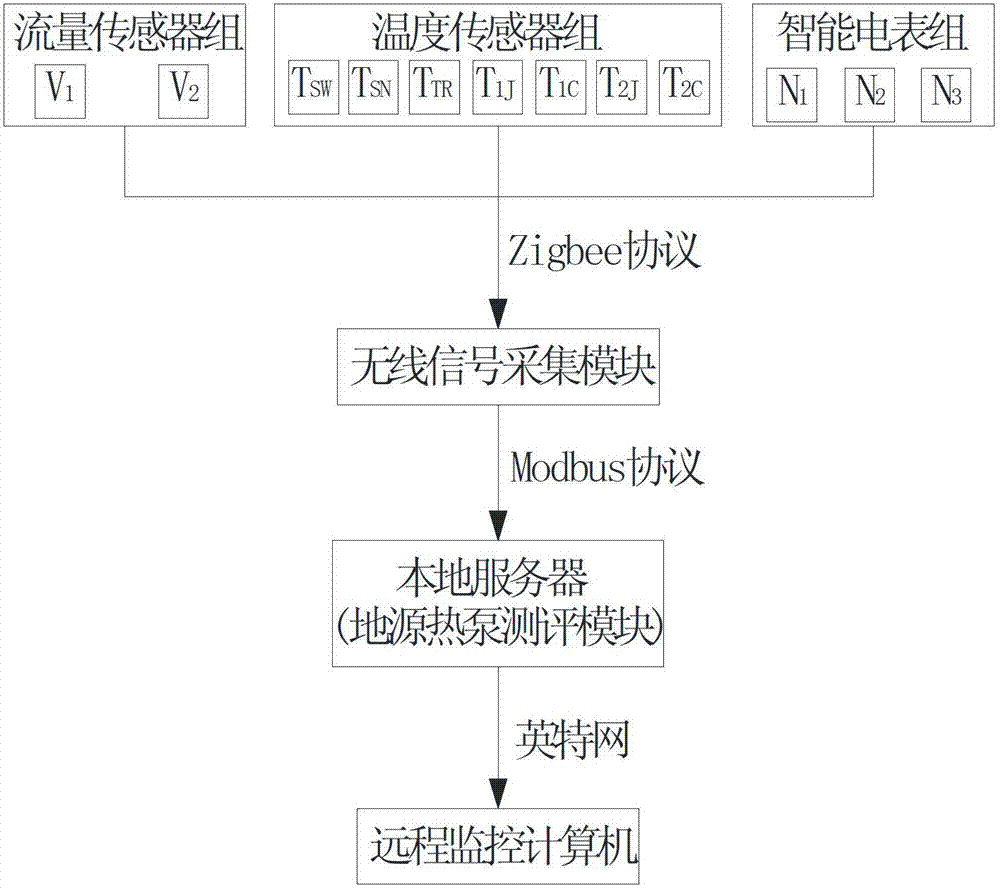
Device for monitoring ground source heat pump system based on internet of things
ActiveCN102818337ASpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusLine sensorThe Internet
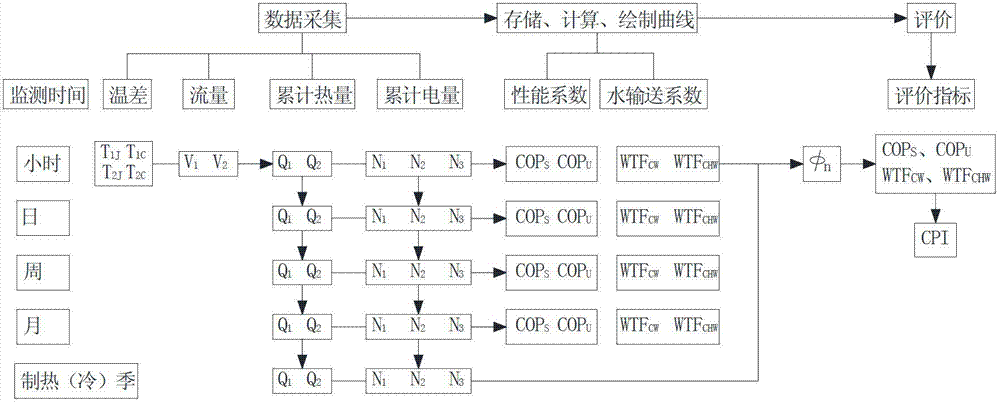
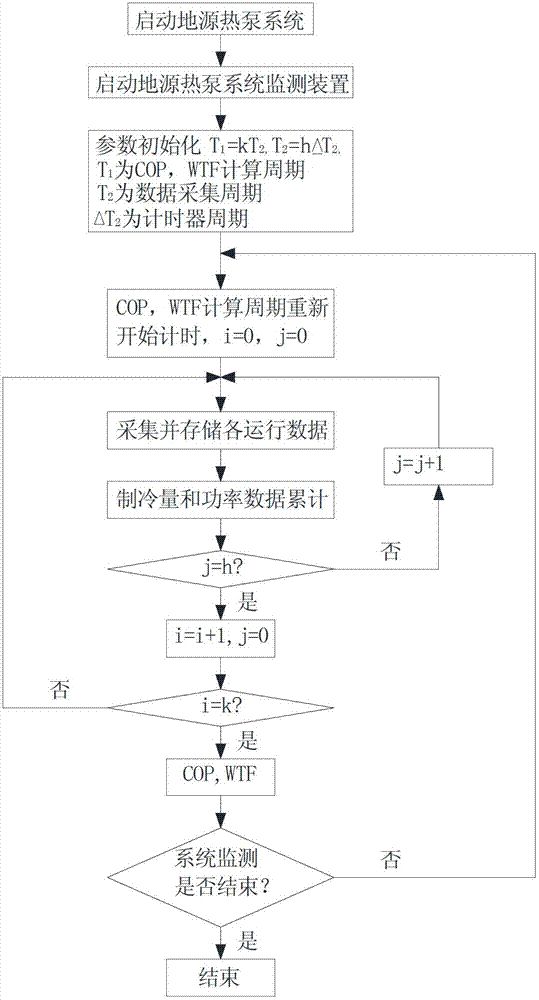
The invention relates to the ground source heat pump technique and particularly relates to a device for monitoring the ground source heat pump system based on the internet of things. The device comprises a soil temperature wireless sensor, an outdoor air temperature wireless sensor, an indoor temperature wireless sensor, water inlet-outlet temperature wireless sensors arranged on a cold-hot resource side and an air conditioner loading side of a cold water machine set, a flow wireless sensor, a wireless intelligent ammeter, a wireless signal collecting module, a local server and a remote monitoring computer. The wireless signal collecting module collects the parameter of each sensor according to the ZigBee protocol, transmits the parameters to the local server by the Internet according to the Modbus protocol, and then stores, computes and displays the COP (coefficient of performance) and the WTF (water transport factor) curves by the ground source heat pump system, and finally transmits the parameters to the remote monitoring computer by the Internet. The device can obtain the CPI (comprehensive performance index), the COP (coefficient of performance) and the WTF (water transport factor) of the ground source heat pump, and is beneficial to monitoring the daily energy-saving situation of the ground source heat pump system and providing evaluation data for the energy-saving improvement of the system.
Owner:HUBEI FENGSHEN CLEAN AIR CONDITIONING EQUIP ENG
Refrigeration system having variable speed fan
InactiveUS6968708B2Improve the coefficient of performanceIncreasing refrigerant mass flow rateCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporators/condensersUnit massGas cooler
A transcritical refrigeration system includes a compressor, a gas cooler, an expansion device, and an evaporator. Refrigerant is circulated though the closed circuit system. Preferably, carbon dioxide is used as the refrigerant. A fan moves outdoor air that exchanges heat with the refrigerant across the evaporator. The speed of the fan is regulated to regulate the evaporator pressure and to adapt the evaporator to different environmental conditions to achieve the optimal coefficient of performance. During high ambient conditions, the fan speed is decreased, decreasing the refrigerant mass flowrate in the system. The energy exchange per unit mass of the refrigerant in the gas cooler increases and the work of the fan decreases, increasing the coefficient of performance of the system. During low ambient conditions, the mass flowrate of the system is low and there is more heat transfer thermal resistance on the refrigerant side at the evaporator. The speed of the fan is lowered to decrease the work of the fan. Therefore, the coefficient of performance increases.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
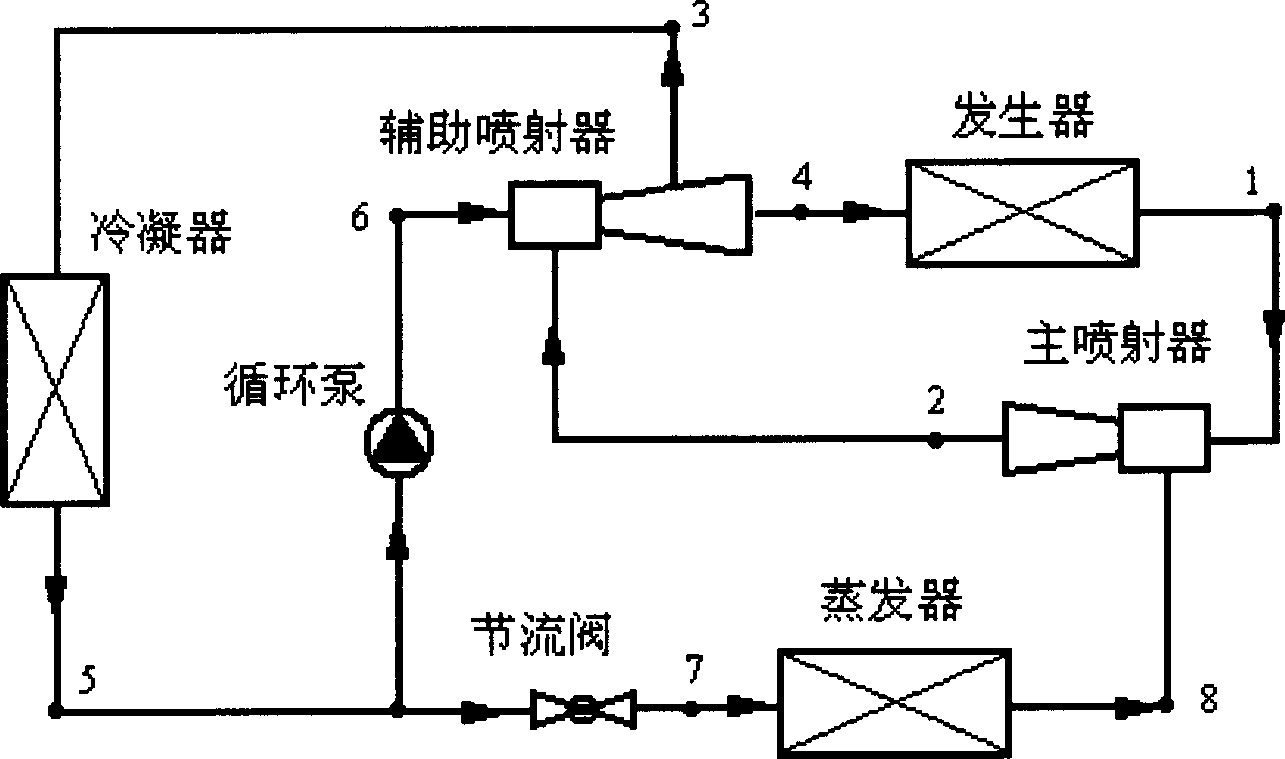
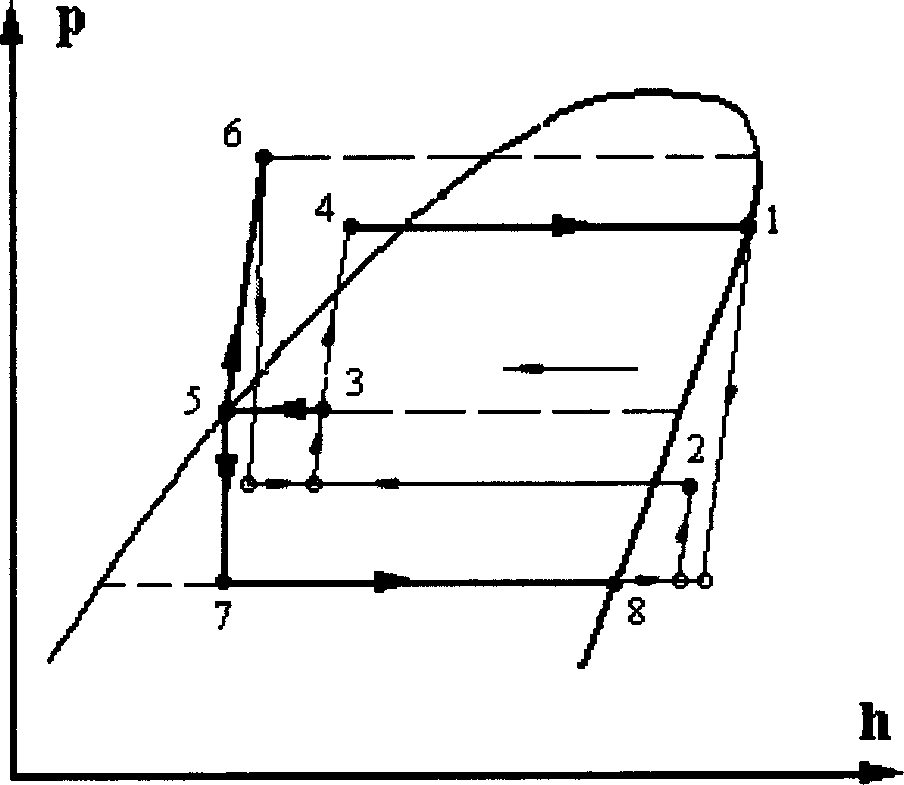
Steam jetting refrigerating circulation system
A steam jet refrigeration cycle system comprises a producer, an evaporator, a condenser, a circulation pump, a throttle valve and main and secondary injectors. The producer is used for producing the high-pressure refrigerant working steam. The main injector is used for jetting the low-pressure refrigerant steam coming from the evaporator and the secondary injector is used for jetting the low-pressure refrigerant steam coming from the main injector. The circulating pump outputs the high-pressure refrigerant liquid. The refrigerant liquid coming from one outlet of a diffuser returns to the producer and the refrigerant gas-liquid mixture coming from the other outlet enters to the condenser to condense. The produced refrigerant liquid is divided into two ways, one way is sent to the secondary injector by the circulating pump and the other enters to the evaporator through the throttle valve. The refrigeration is realized by evaporative heat-absorbing of the refrigerant in the evaporator.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
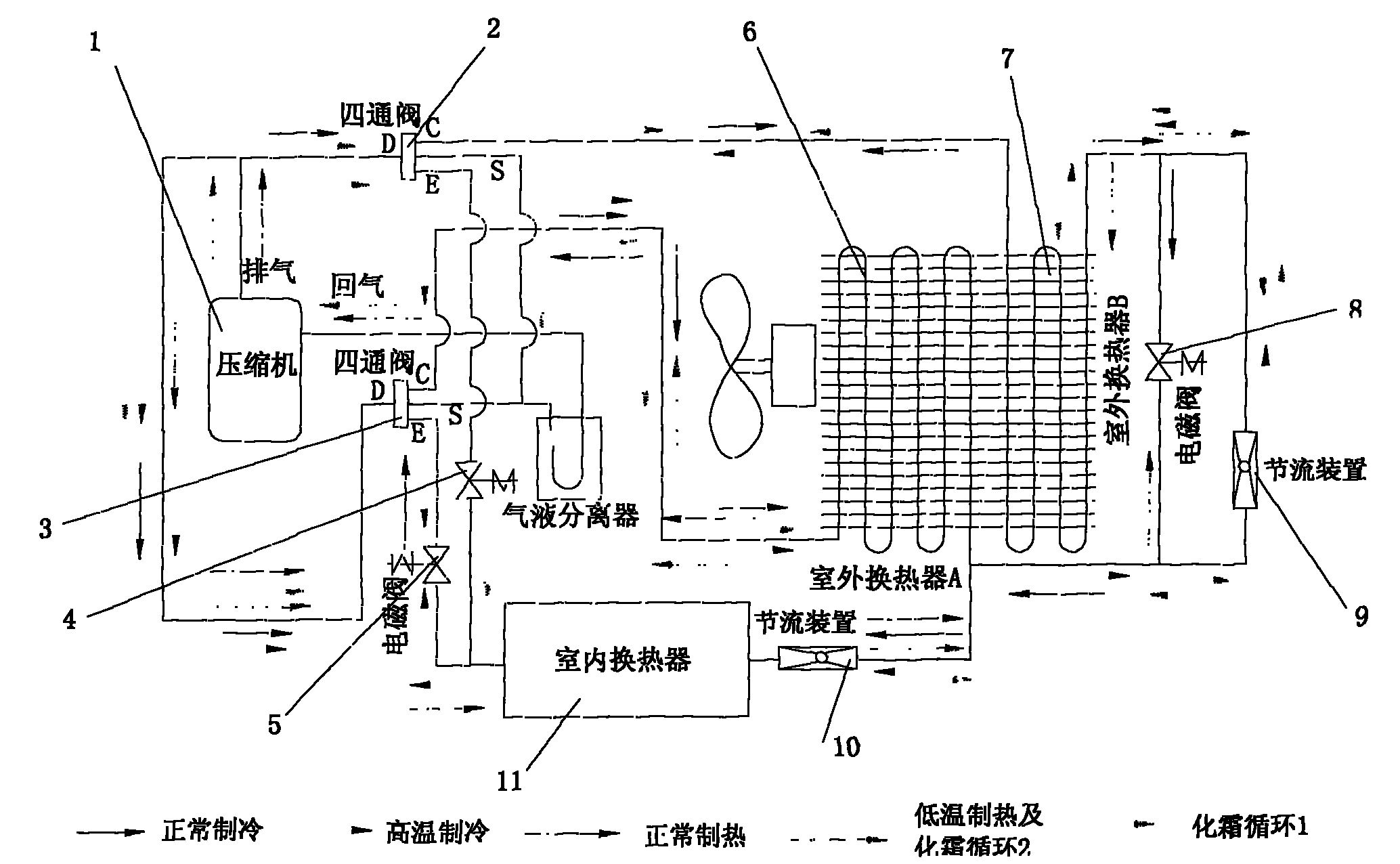
Outdoor double heat exchanger defrosting low-temperature heating system
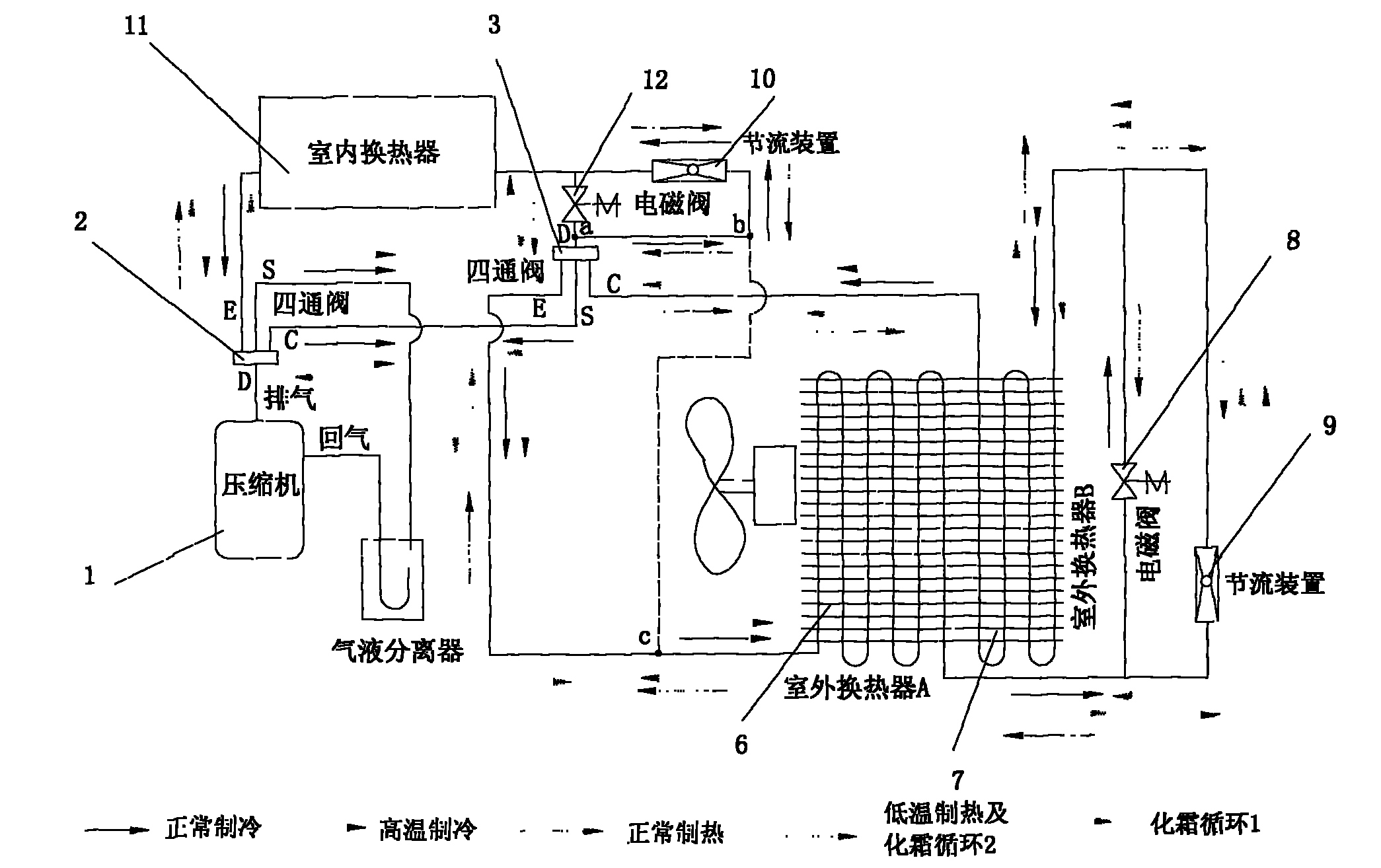
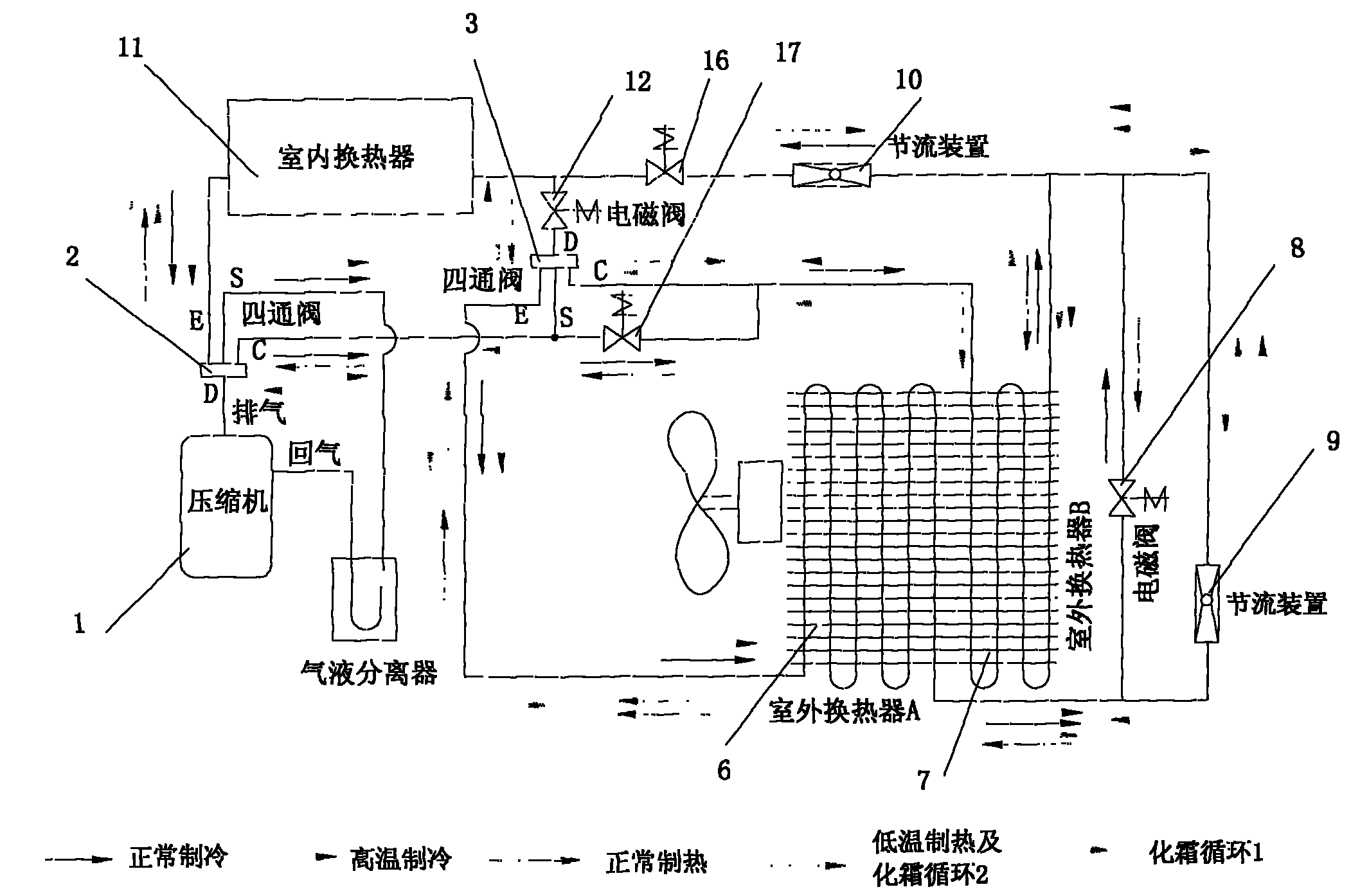
InactiveCN101788206AIncrease temperatureImprove comfortFluid heatersCorrosion preventionFour-way valveEngineering
The invention relates to an outdoor double heat exchanger defrosting low-temperature heating system, which comprises a compressor (1), four-way reversing valves, an outdoor heat exchanger, a throttling device and an indoor heat exchanger (11). The outdoor heat exchanger is divided into two parts, namely a first outdoor heat exchanger (6) and a second outdoor heat exchanger (7) respectively. One end of the first outdoor heat exchanger (6) and one end of the second outdoor heat exchanger (7) are connected together through the throttling device (9) and an electromagnetic valve (8); and the other ends of the first outdoor heat exchanger (6) and the second outdoor heat exchanger (7) are respectively connected with an air pipe E or C at any one end of two four-way reversing valves; and an inlet / outlet pipe of the throttling device (9) is connected with an inlet / outlet pipe of the electromagnetic valve (8). The outdoor heat exchanger is divided into two parts; the two outdoor heat exchangers alternatively defrost, are used as an evaporator and a condenser in turn, and can still provide heat for the indoor heat exchanger during defrosting. During heating at low temperature, the outdoor heat exchanger B is used as the condenser to heat the inlet air and the inlet air temperature outdoors is raised. Therefore, the coefficient of performance and the heating capacity are effectively improved.
Owner:曾华文
Heat transfer compositions
InactiveUS7914696B2Reduced Greenhouse Warming PotentialLow toxicityCompression machines with non-reversible cycleChemical industryGreenhouse warmingRefrigeration
Heat transfer compositions are usable in their own right or are suitable as a replacement for existing refrigeration usages. The compositions possess a reduced Greenhouse Warming Potential, yet have a capacity and energy efficiency (which may be conveniently expressed as the “Coefficient of Performance”) ideally within 20% of the values of those attained using R-134a, and preferably within 10% or less (e.g. about 5%) of these values.
Owner:INEOS FLUOR HLDG
Adaptive Control Ducted Compound Wind Turbine
A high efficiency, adaptive control, compound ducted wind turbine capable of providing higher efficiency in energy extraction from a fluid. Performance of efficiency expressed as coefficient of performance (Cp) in accordance with the Lanchester-Betz-Joukowski limits is sustainable and significantly higher than an un-ducted, mono-propeller wind turbine of comparable diameter.
Owner:SAMMY JOHANN QUINCY
Solar energy-air source energy-saving type solution heat pump device
InactiveCN101236028ARealize savingsImprove the coefficient of performanceHeat pumpsCompression machines with reversible cycleCooling towerFrost
A solar-air source energy storage type solution thermal pumping device is a method and a device for realizing the method, and the method is solar-air source energy storage type solution thermal pumping for refrigeration and heat-production on the basis of refrigerating with cool water in summer and absorbing heat from air with solution in winter and by means of taking advantages of solar energy. The device comprises a refrigerant circulation loop, a solution circulation loop and an air circulation loop, and is composed of main members of a cold and hot water unit, a cooling tower, a solar heat collector, a solution regenerator, a concentrated solution storage device, a dilute solution storage device and the like. In summer, the device can realize water-cooled water chilling unit function, absorb heat by evaporation in the cooling tower with cooling water, cooling agent of the water chilling unit prepares cold water, in winter, solution is used to exchange heat with air in the cooling tower, heat is absorbed for the unit to prepare hot water, thereby radically resolving inescapable frost produced when existing air source heat pump operates to produce heat in winter, and increasing performance coefficient and heat supply efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
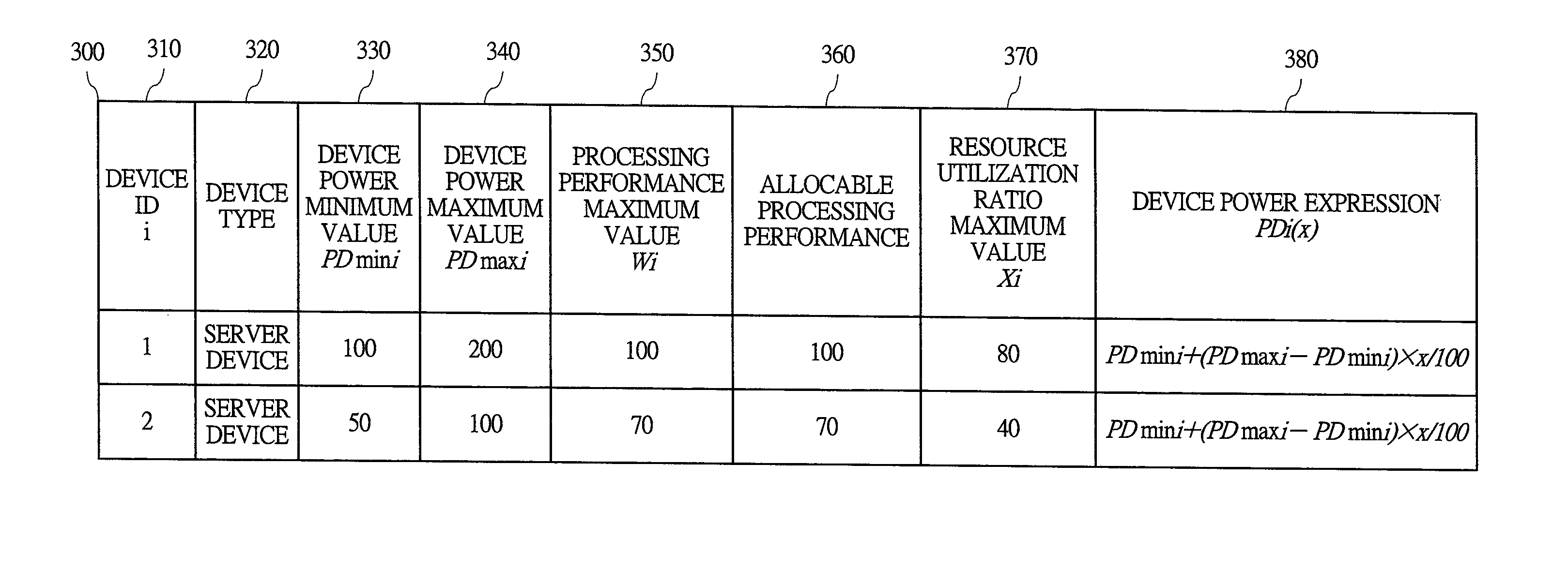
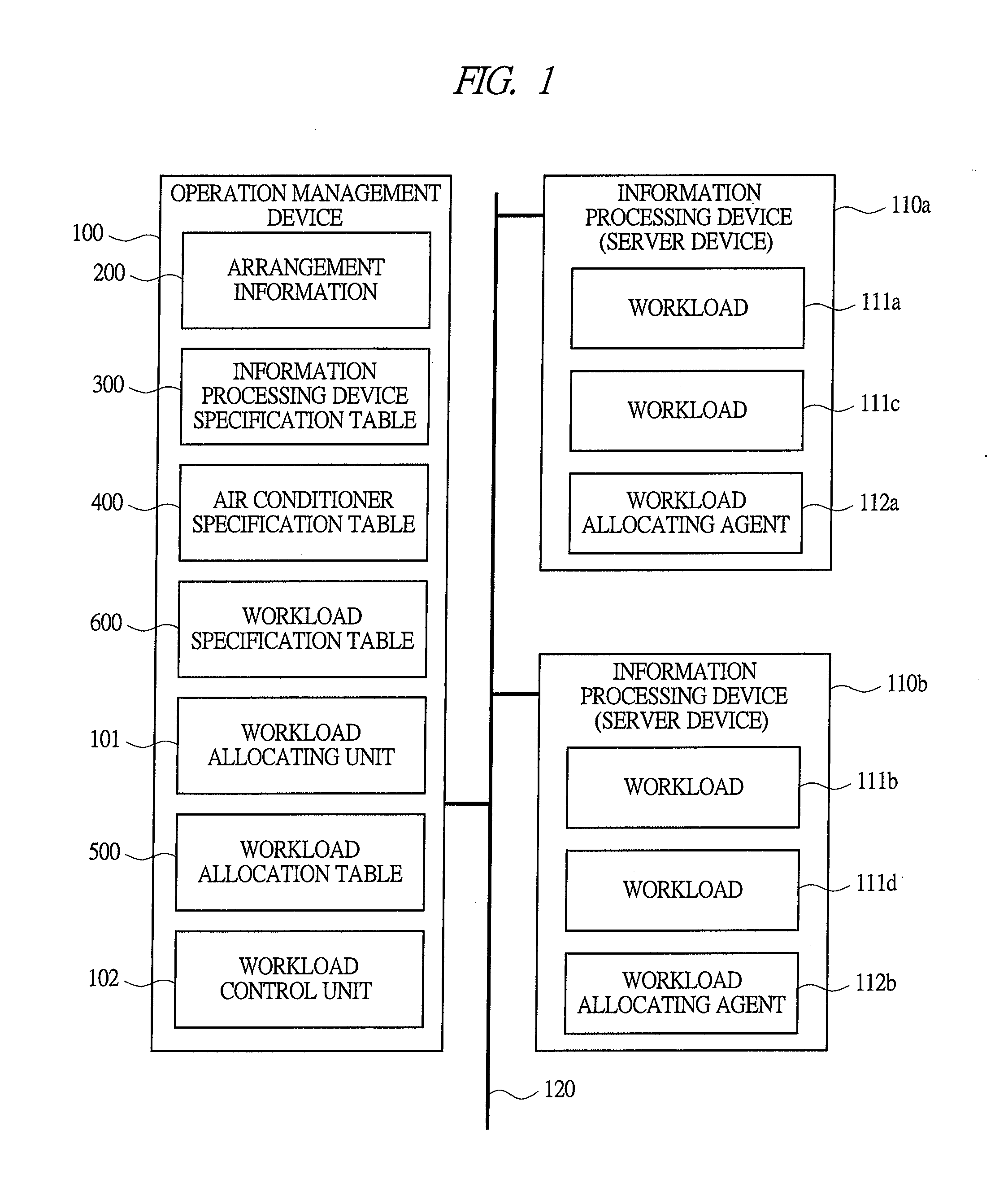
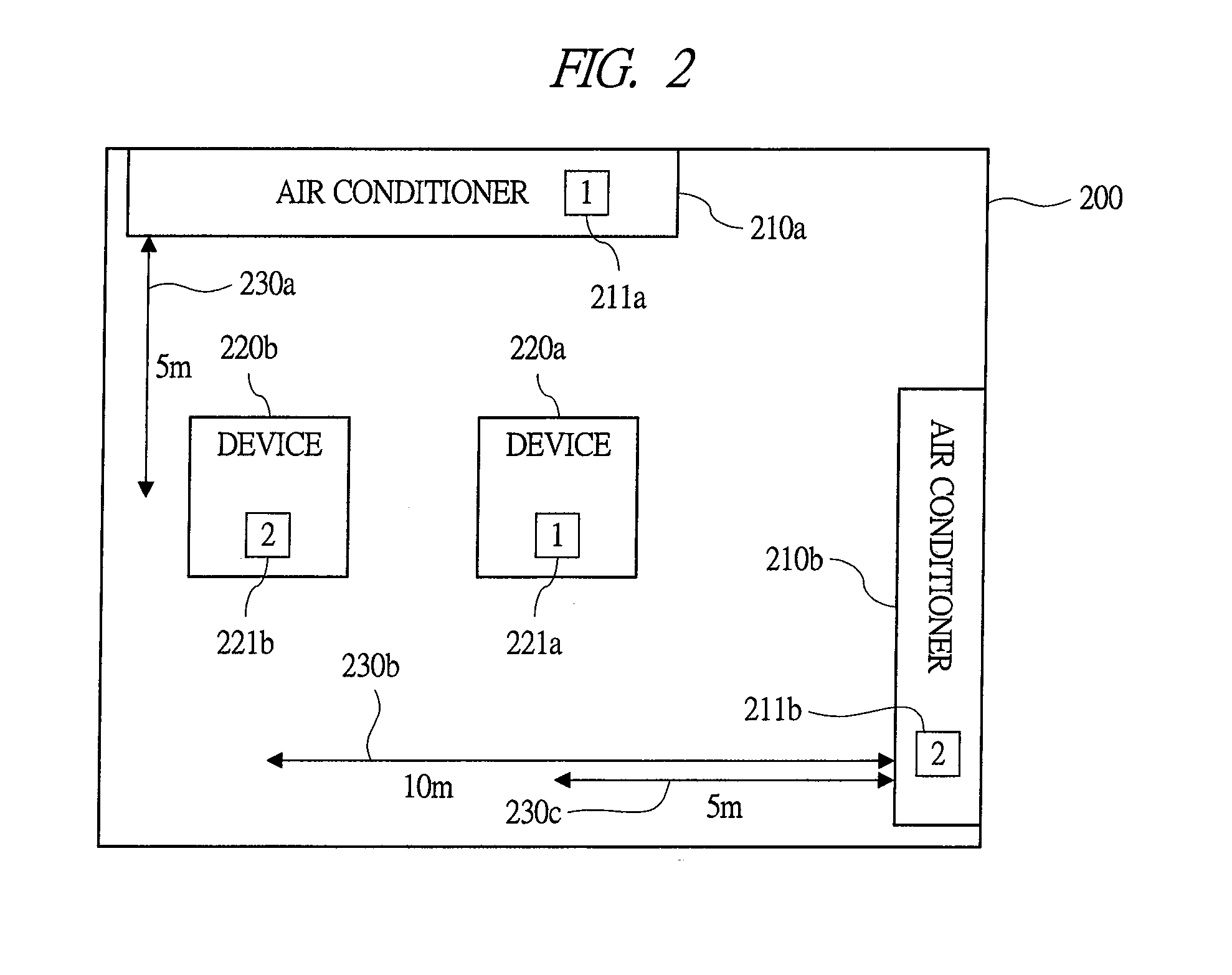
Operation management method of information processing system
ActiveUS20110113273A1Power saving operation can be achievedReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementInformation processingWorkload
In a computer room including information processing devices and air conditioners, power saving of the computer room by means of optimization of workload allocation to the information processing devices is achieved in a short time. There, a coefficient of air conditioner performance with respect to the information processing device (device-specific COP) is calculated for each air conditioner. Further, a device-associated power consumption expression representing a total of device power and air conditioner power is created for each information processing device. Also, power consumption of the entire computer room is calculated from the device-associated power consumption expression of the information processing devices. Also, workload allocation is determined by using power saving performance evaluation indexes based on the device-associated power consumption expression of the information processing devices. Further, output of the air conditioner is controlled based on a result of the air conditioner power calculation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
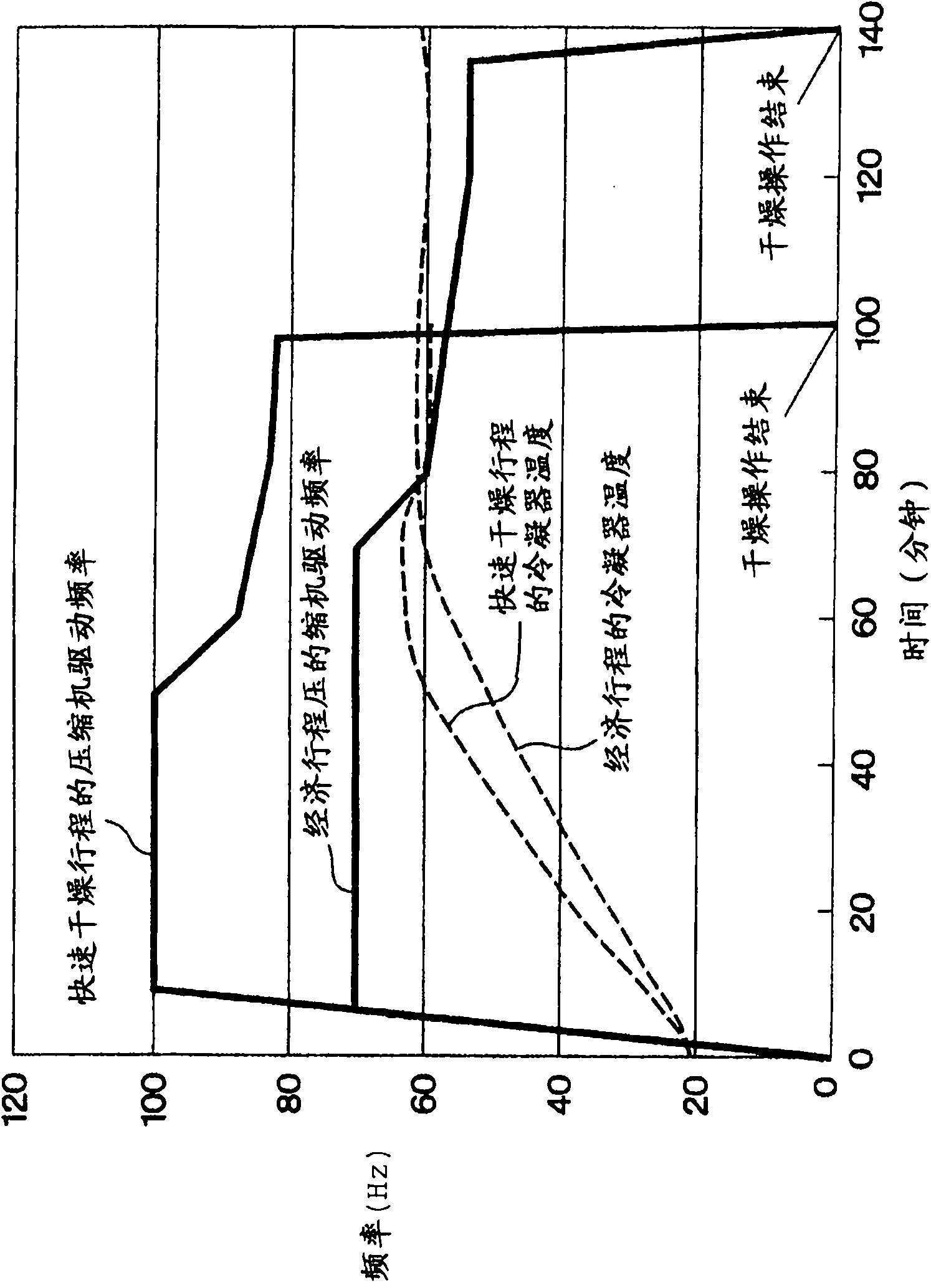
Clothes dryer
ActiveCN102105631AIncrease rotation speedReduce electrical power consumptionLaundry dryer apparatusWashing machine with receptaclesAir cycleProcess engineering
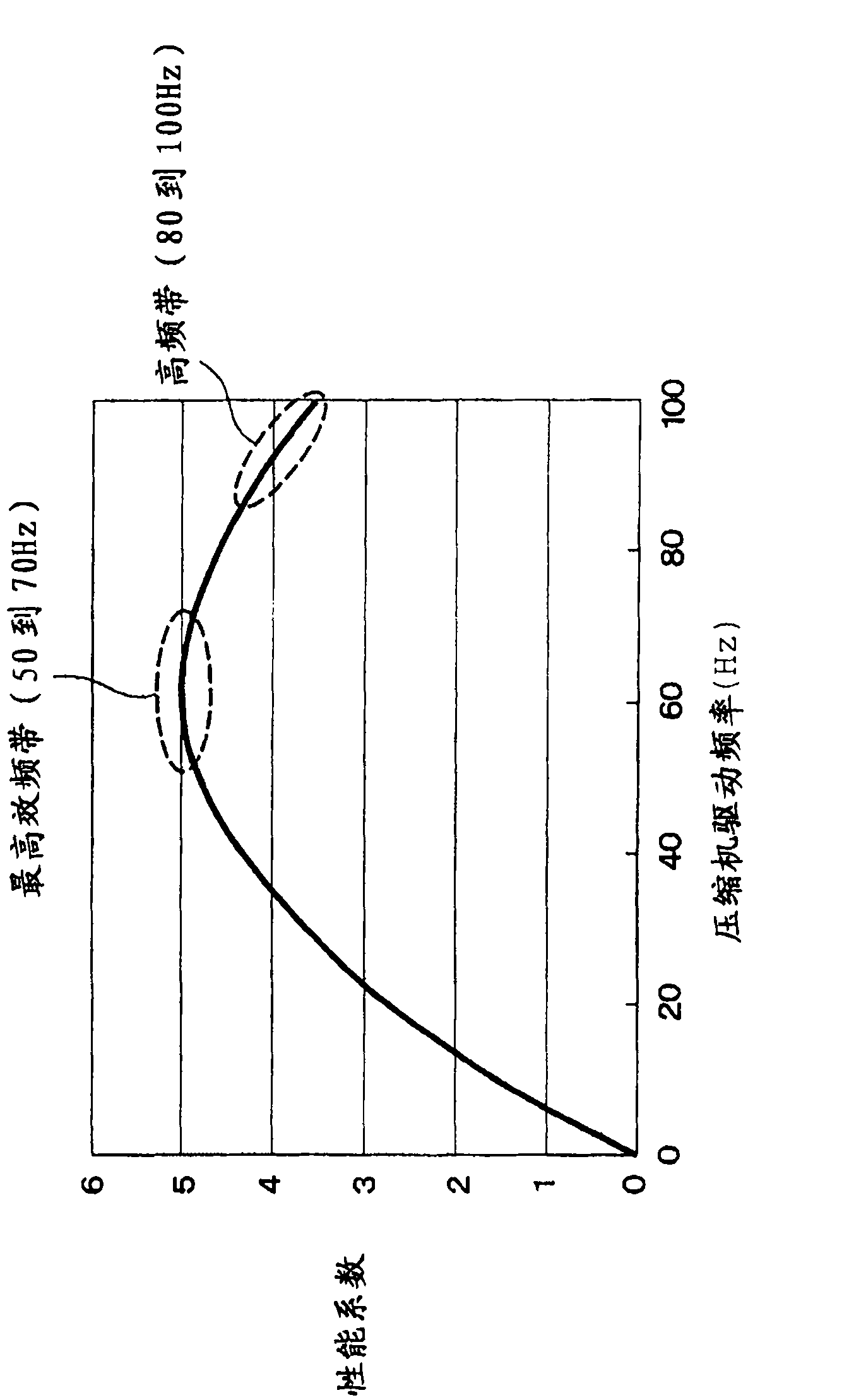
A clothes dryer provided with a washing tub, an air circulator, and a heat pump and drying laundry by operation of the air circulator and the heat pump. The rotational speed of a compressor is changed by controlling frequency, and the clothes dryer can be operated by selection of either a quick-drying mode for drying the laundry in a relatively short time by changing a drive frequency of the compressor or a saving mode for drying the laundry in a time longer than the time of the quick-drying mode. In the saving mode, the compressor is driven in a frequency band providing a high coefficient of performance.
Owner:TOSHIBA LIFESTYLE PROD & SERVICES CORP
Method for detecting a fault in an HVAC system
A bypass factor of an evaporator is used to indicate when an air filter of an HVAC is clogged. The bypass factor represents the amount of air that is bypassed without direct contact with the evaporator. As the air filter clogs, the bypass factor decreases. The bypass factor can also be used for early detection of clogging of the air filter. A first bypass factor is calculated by using the temperature measurements, and a second bypass factor is calculated by using the airflow rate of the air. The difference between the two bypass factors determines the error. An increase in the error indicates that the air filter is clogged. A coefficient of performance of the evaporator can also be calculated to detect if the air filter is clogged. A decrease in the coefficient of performance indicates that the air filter is clogged.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Solar energy-ground source heat pump coupled biogas pool heating system and operational control method
ActiveCN101974415AMaximize utilizationImprove heating efficiencySolar heating energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNew energyEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of new energy development and application, and particularly relates to a solar energy-ground source heat pump coupled biogas pool heating system and an operational control method thereof. The solar energy-ground source heat pump coupled biogas pool heating system is divided into five operating modes, namely solar energy direct heating, solar energy-ground sourceheat pump series heating, solar energy heat pump heating, individual ground source heat pump heating and solar energy underground heat storage according to the temperature gradient of hot water prepared by a solar heat collector by combining a relation curve of the COP (coefficient of performance) of a heat pump unit and the water inlet temperature of an evaporator. The method remarkably improvesthe heating efficiency of the heat pump unit and the system by fully using low-grade solar energy and ground heat energy, can supply heat to a biogas fermentation pool efficiently and stably for a long term, and has long-term economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:上海林海生态技术股份有限公司
Working fluid for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
ActiveUS10131827B2Stably used continuouslyCycle performance sufficientHeat-exchange elementsWorking fluidEngineering
To provide a working fluid which has cycle performance sufficient as an alternative to R410A while the influence over global warming is sufficiently suppressed, which does not significantly increase the load to an apparatus as compared with a case where R410A is used, and which can be stably used continuously without any special measures, a composition for a heat cycle system contains the working fluid, and a heat cycle system employs the composition. A working fluid for heat cycle, wherein the global warming potential is less than 300; the product of the relative coefficient of performance and the relative refrigerating capacity is at least 0.820 relative to R410A in a standard refrigerating cycle under conditions of an evaporation temperature of 0° C., a condensing temperature of 40° C., a supercoiling degree of 5° C. and a degree of superheat of 5° C.; the relative compressor discharge gas pressure is at most 1.100; the lower limit of the combustion range by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety Act is at least 5 vol %; and the pressure will not exceed 2.00 MPaG in a combustion test by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety act under 0.98 MPaG at 250° C.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Twin-stage compression heat pump system with hot gas bypass defrosting device
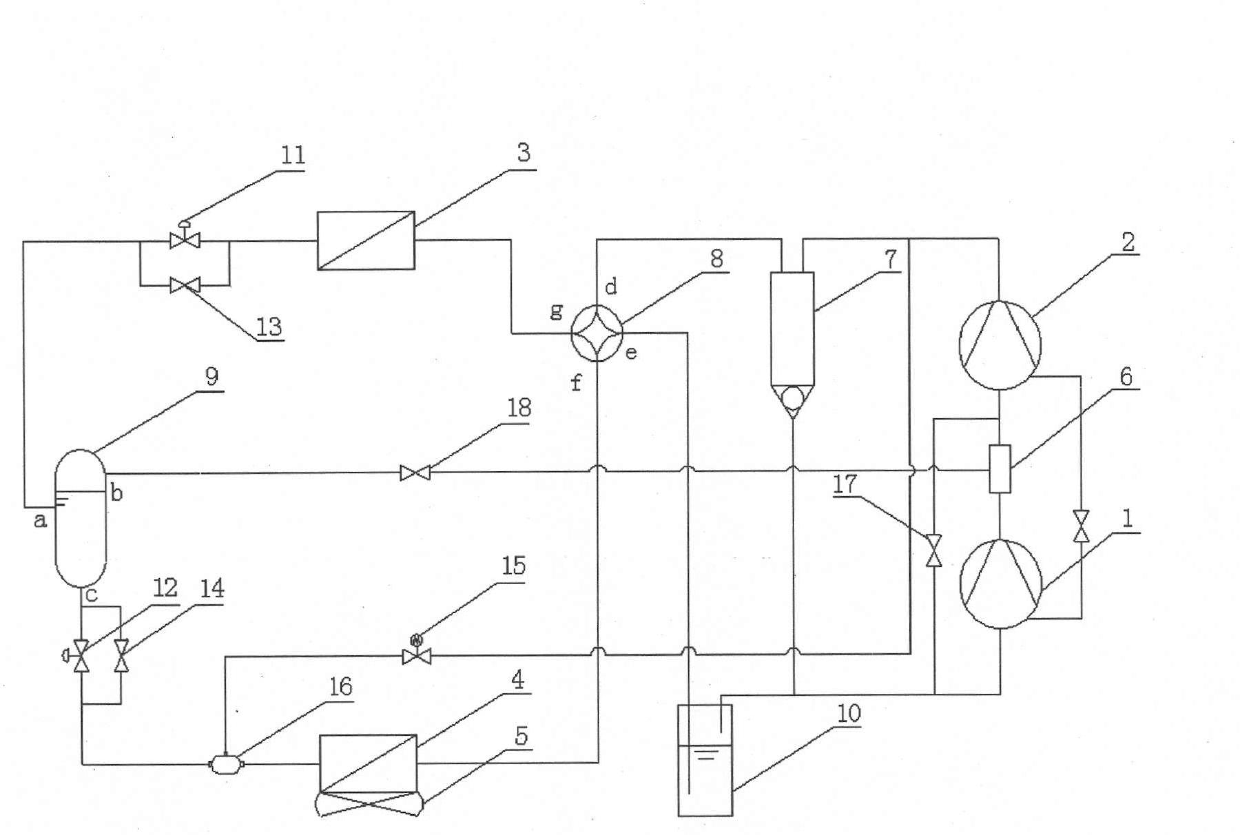
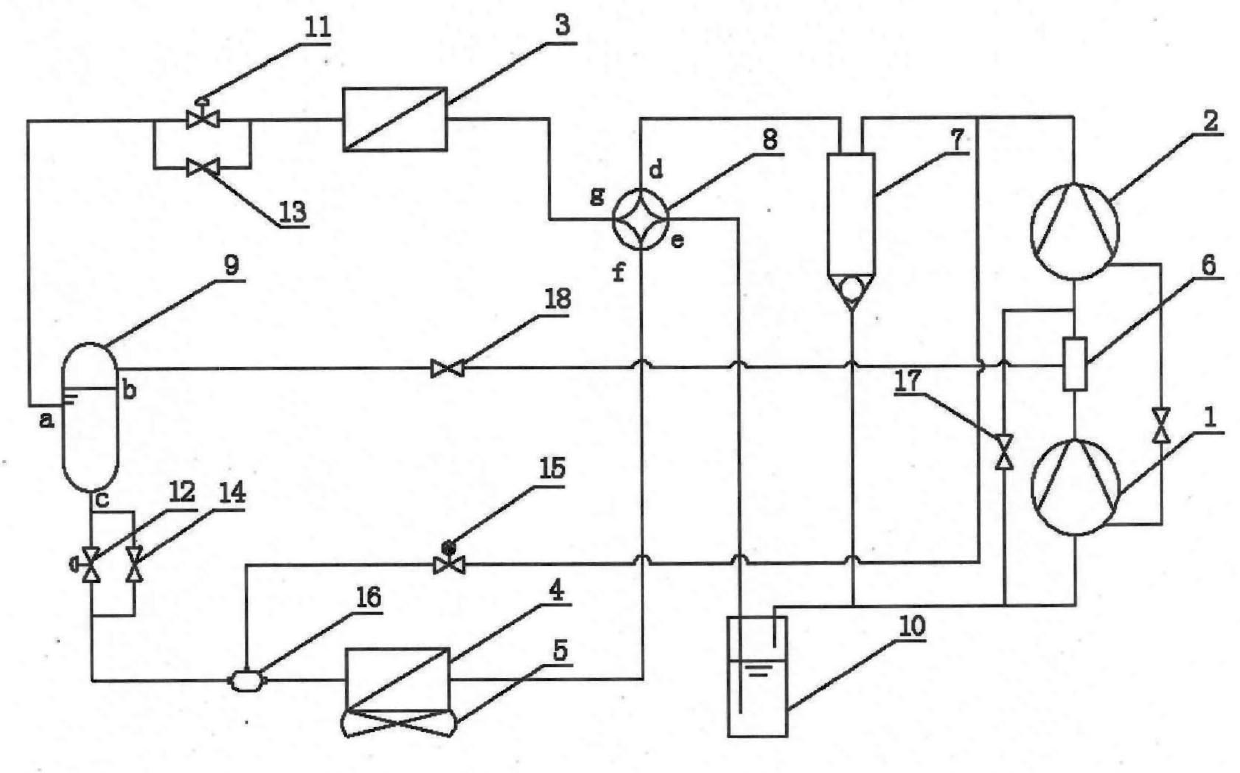
InactiveCN102654324AReduce exhaust temperatureLarge circulationCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCorrosion preventionSolenoid valveHigh pressure
The invention provides a twin-stage compression heat pump system with a hot gas bypass defrosting device. The low-pressure compressor of the twin-stage compression heat pump system is communicated with a high-pressure compressor via a mixing chamber; the high-pressure compressor is communicated with a refrigerating fluid / water heat exchanger by an oil separator and a four-way reversing valve; the refrigerating fluid / water heat exchanger is communicated with the port of an intermediate cooler by an electronic expansion valve; the port b of the intermediate cooler is communicated with the mixing chamber by a shut-off valve; another port of the intermediate cooler is communicated with the refrigerating fluid / water heat exchanger by an electronic expansion valve and a gas and liquid mixing head; the refrigerating fluid / water heat exchanger is communicated with the low-pressure compressor by the four-way reversing valve and a gas and liquid separator to form a circulation; and the outlet end of the high-pressure compressor is communicated with the gas and liquid mixing head by a solenoid valve. The twin-stage compression heat pump system can be stably operated in the low-temperature environment for a long time, has the advantages of enough heat generation amount, higher performance coefficient and high thermal efficiency and is favorable for popularizing the heat pump in northern areas, frost is removed with a hot gas bypass method, halting conversion is not required when the frost is removed, heat supply and frost removal can be performed at the same time, and the energy consumption is lowered.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com