Cooling and heating system
a technology of cooling and heating system, applied in the direction of refrigeration components, light and heating apparatus, refrigeration machines, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of heat exchanger and compressor capacity, inability to obtain condensation temperature uniquely, and inability to achieve high condensation pressure. achieve the effect of maximizing the coefficient of performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
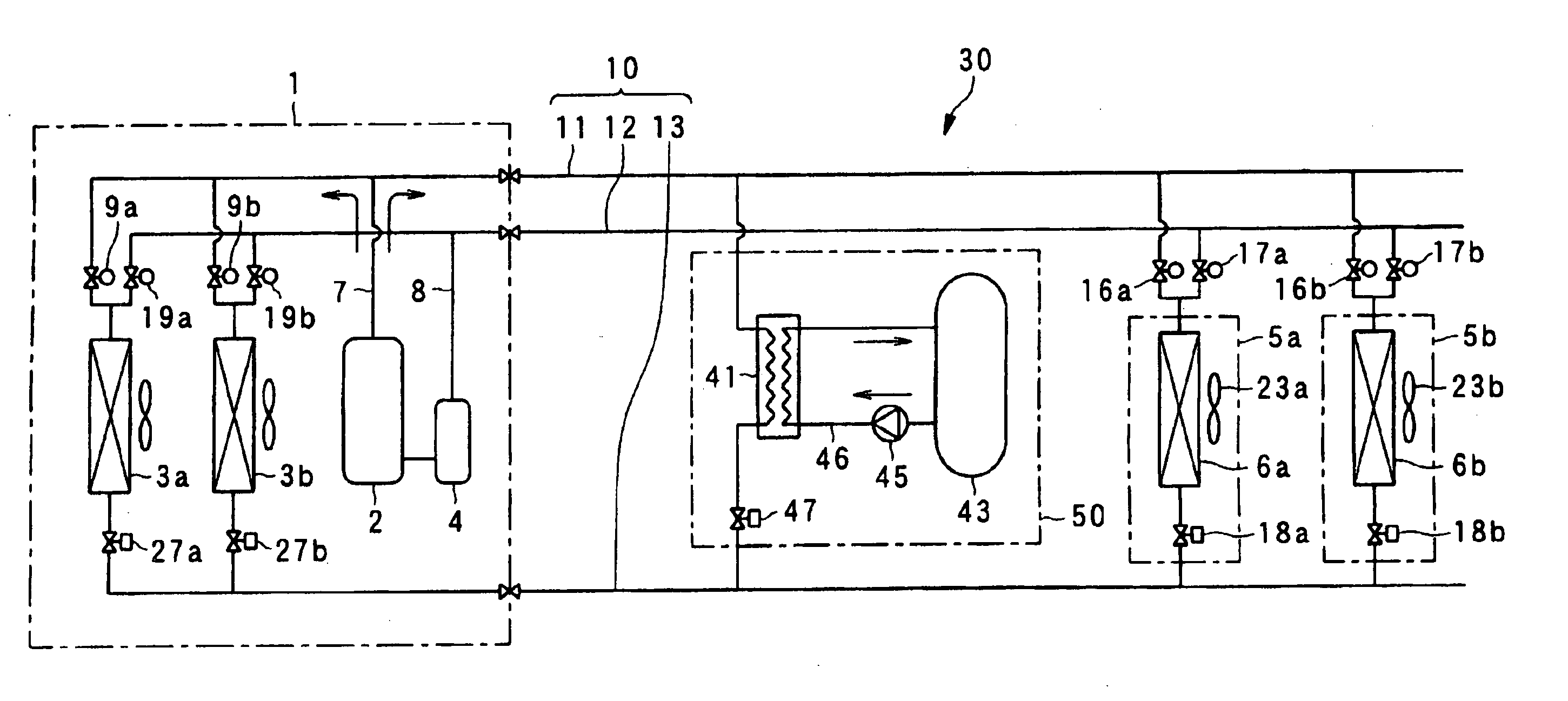
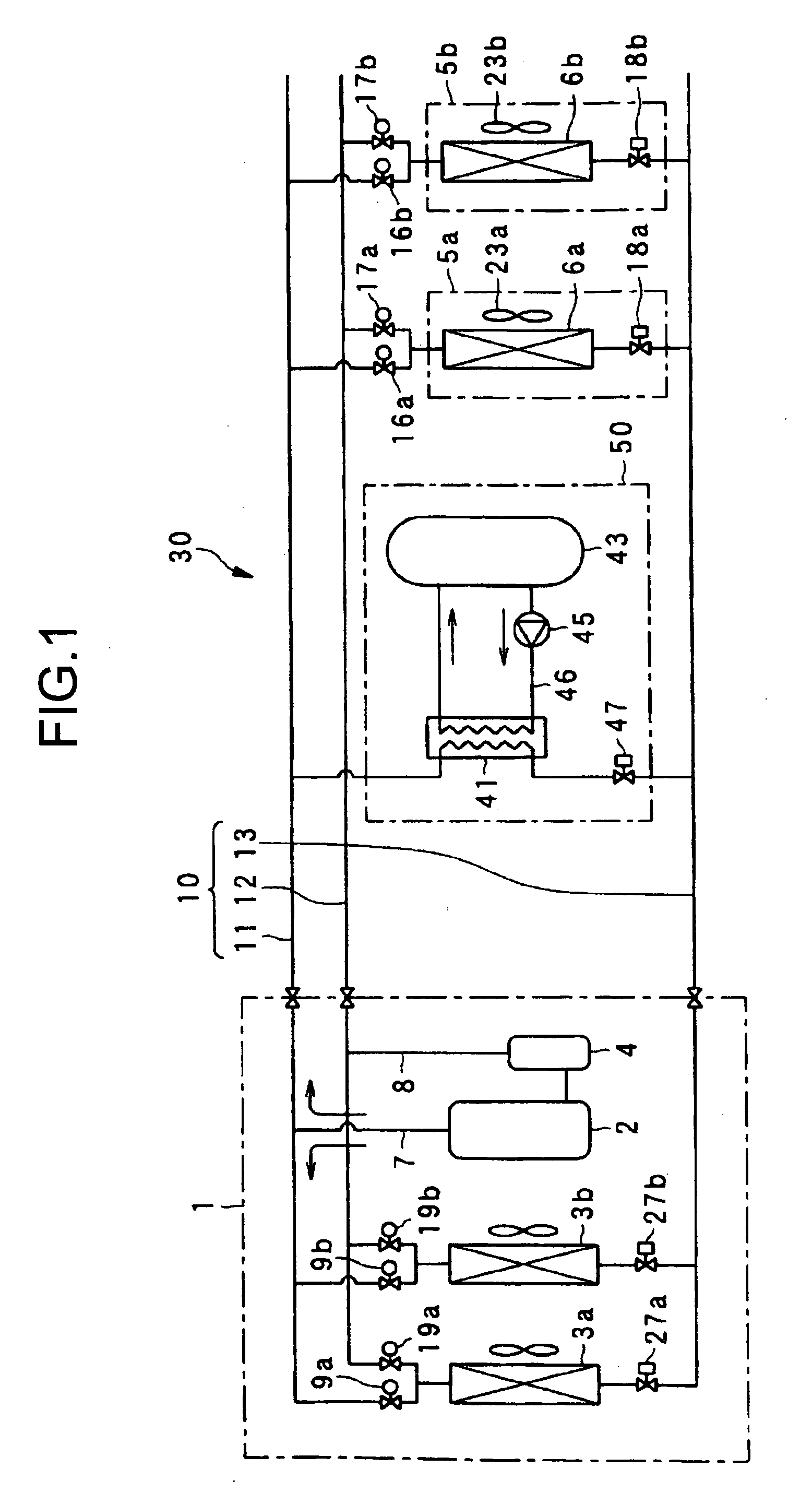
[0037] In the present embodiment, there will be described an operation control by a high pressure and an evaporation temperature with reference to FIGS. 4, 5, 6, and 7.
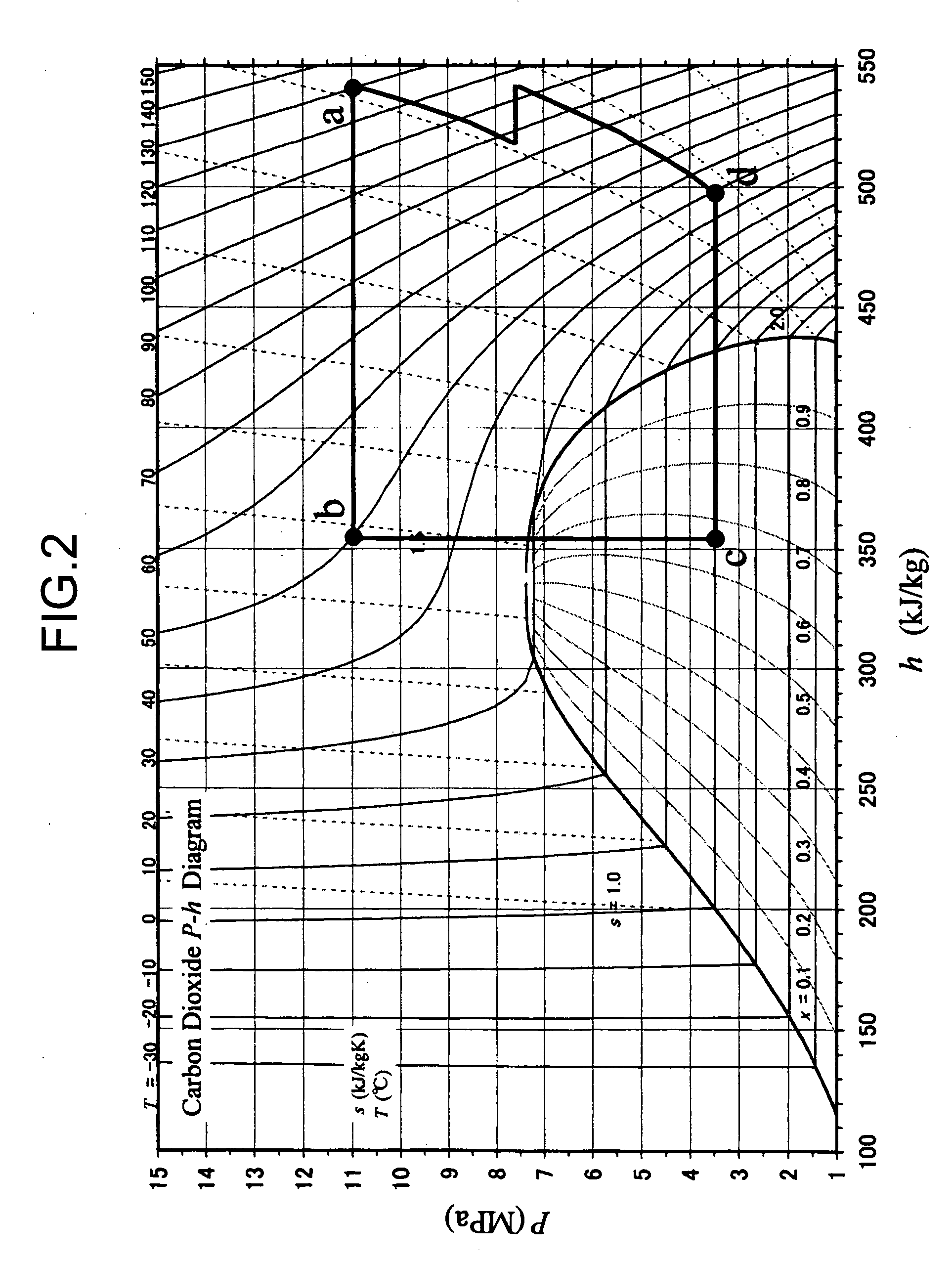
[0038] First in the present embodiment, as shown in a control flow (B1) of a thermal load balance control of FIG. 4, an evaporation temperature TEVA is measured (S150). A place to be measured differs with an operation state of a cooling and heating system 130. When the state c shown in FIG. 2 advances to the state d, a temperature during phase change of the refrigerant (carbon dioxide) from a liquid to a gas is the evaporation temperature TEVA. At this time, since the evaporation temperature TEVA and an evaporation pressure PEVA are uniquely determined, an object to be measured may be the evaporation pressure PEVA.
[0039] Next, an outlet refrigerant temperature TGC of the gas cooler is measured. Here, if the heating operation is performed in an out door unit 105a shown in FIG. 5 (S151), the outlet refrigerant tempera...
embodiment 2
[0042] In the present embodiment, there will be described an operation control by a discharge temperature and an evaporation temperature with reference to FIGS. 8, 9, 10, and 11.
[0043] First in the present embodiment, as shown in a control flow (C1) of a thermal load balance control of FIG. 8, an evaporation temperature TEVA is measured (S250). A place to be measured differs with an operation state of a cooling and heating system 230. When the state c shown in FIG. 2 advances to the state d, a temperature during phase change of the refrigerant (carbon dioxide) from a liquid to a gas is the evaporation temperature TEVA. At this time, since the evaporation temperature TEVA and an evaporation pressure PEVA are uniquely determined, an object to be measured may be the evaporation pressure PEVA.
[0044] Next, an outlet refrigerant temperature TGC of the gas cooler is measured (S252). Here, if the heating operation is performed in an indoor unit 205a shown in FIG. 9 (S251), the outlet refr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com