Patents
Literature
116 results about "Variable speed wind turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
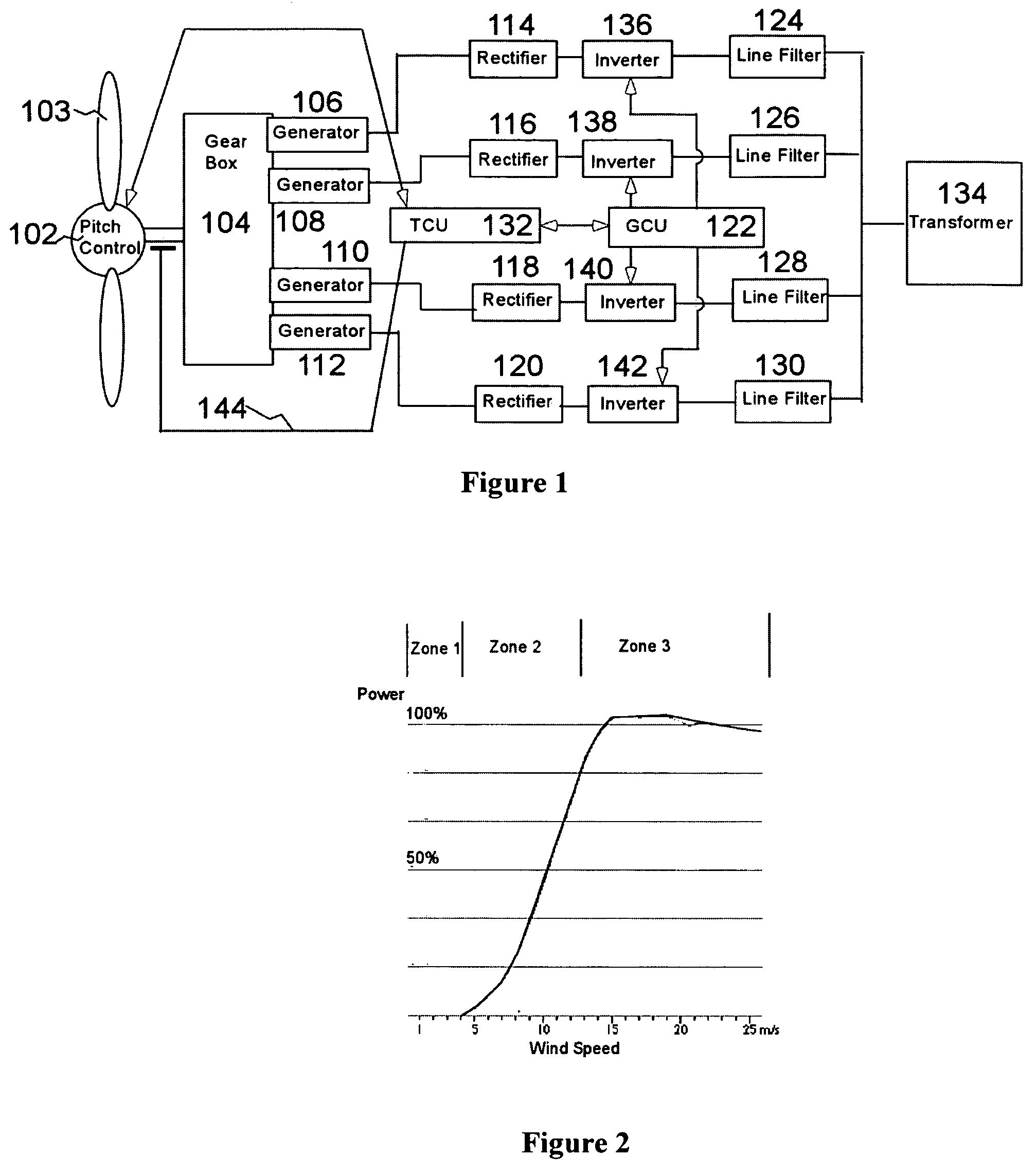
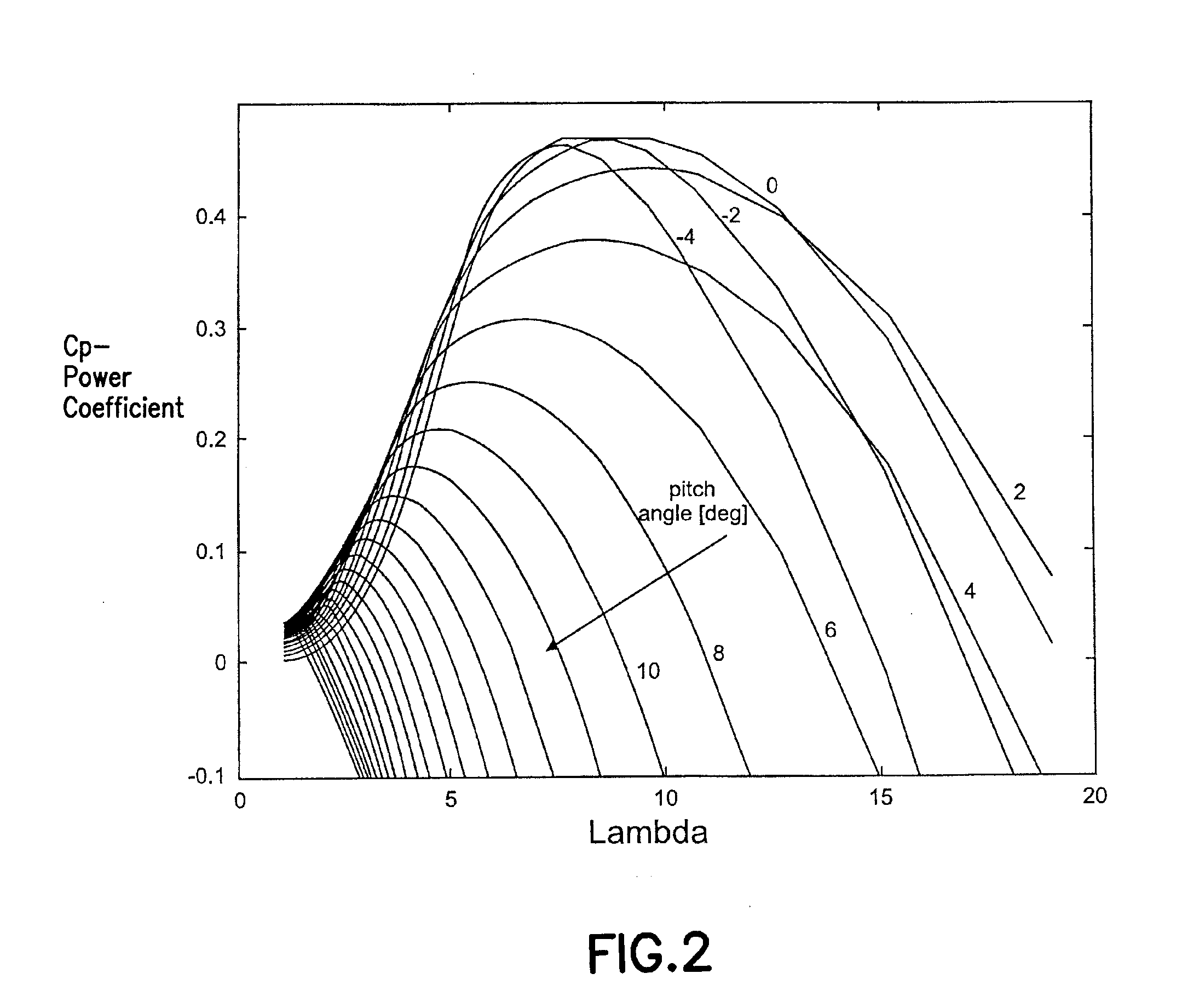
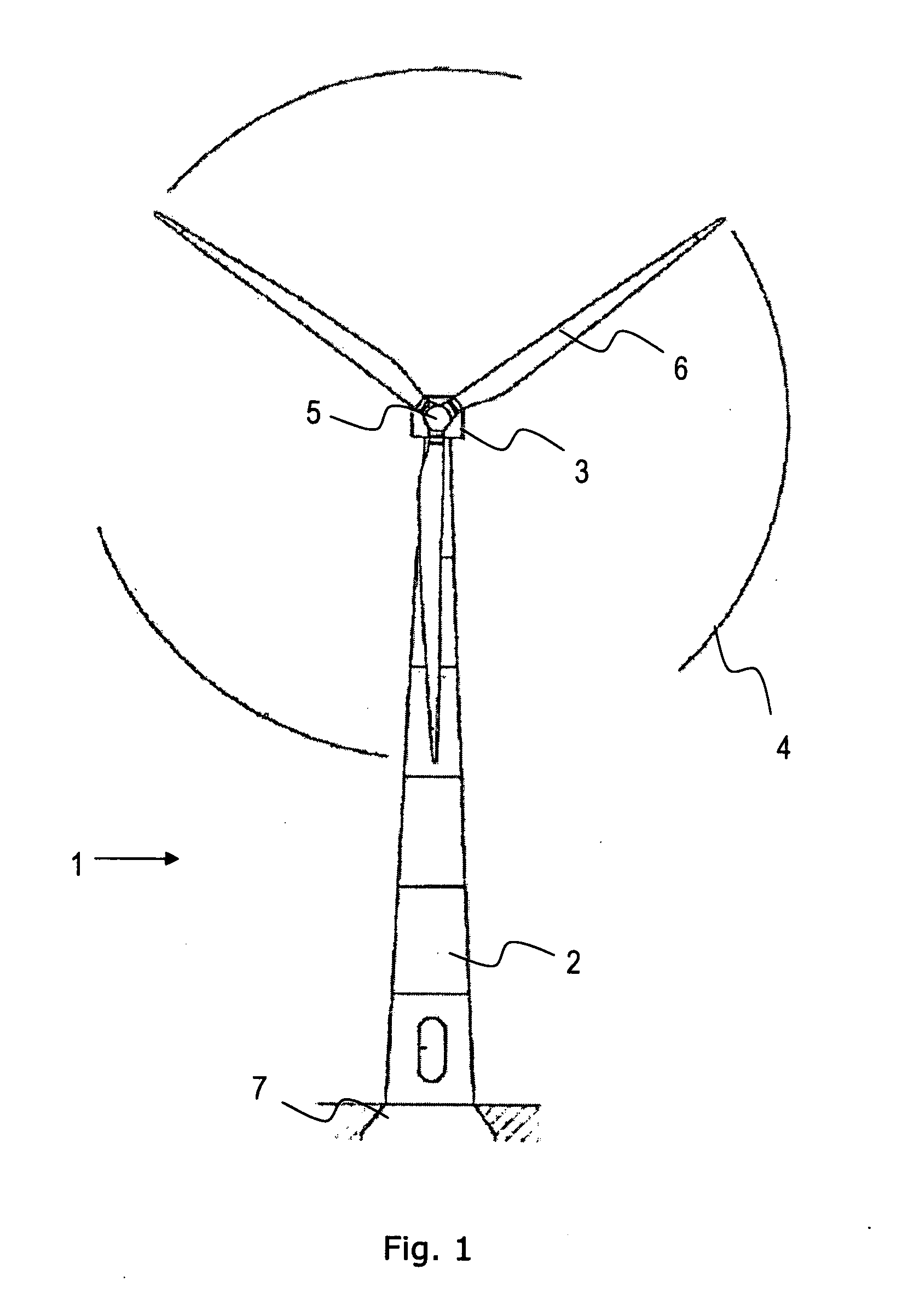
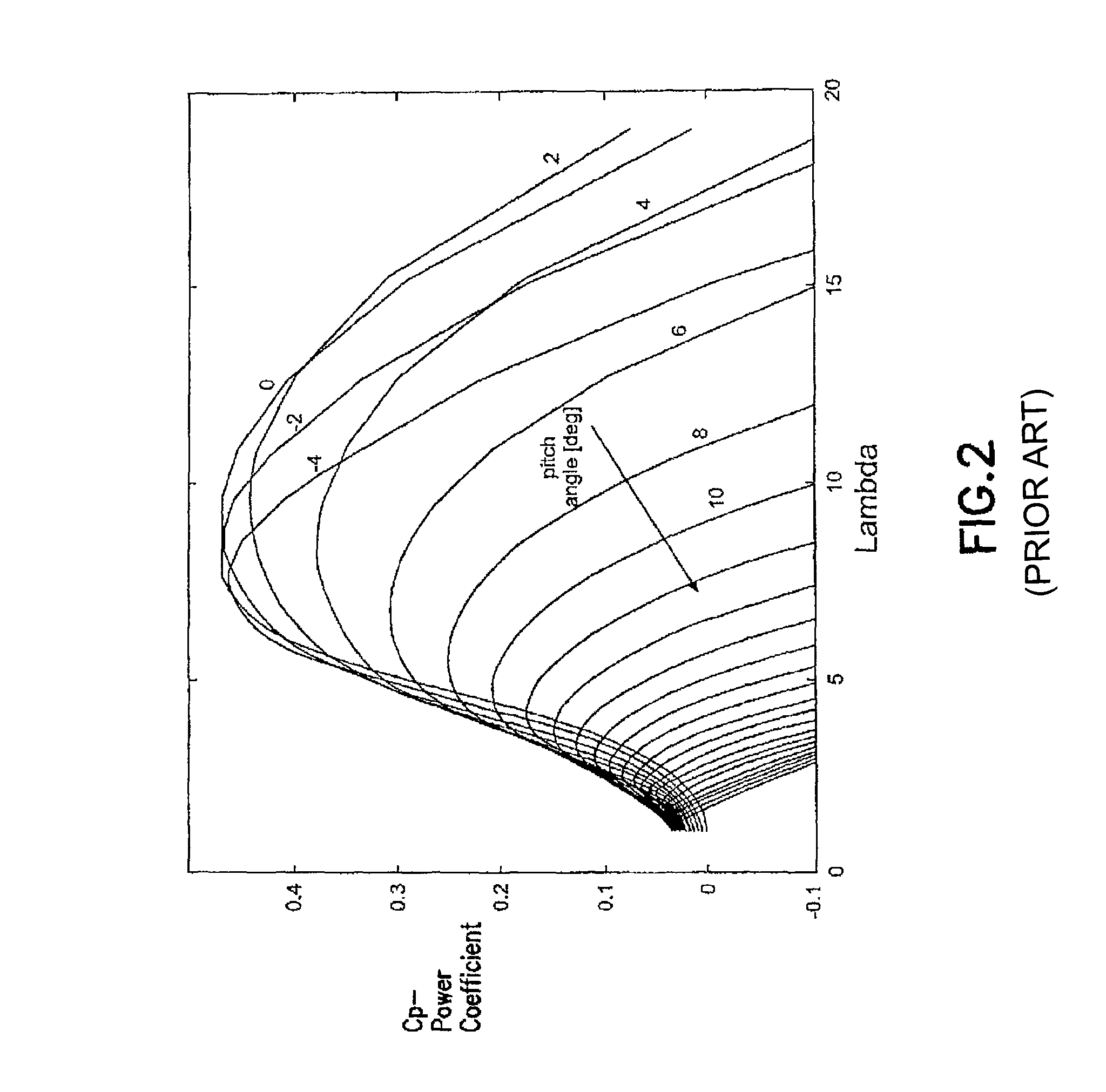
A variable speed wind turbine is one which is specifically designed to operate over a wide range of rotor speeds. It is in direct contrast to fixed speed wind turbine where the rotor speed is approximately constant. The reason to vary the rotor speed is to capture the maximum aerodynamic power in the wind, as the wind speed varies. The aerodynamic efficiency, or coefficient of power, Cₚ for a fixed blade pitch angle is obtained by operating the wind turbine at the optimal tip-speed ratio as shown in the following graph.
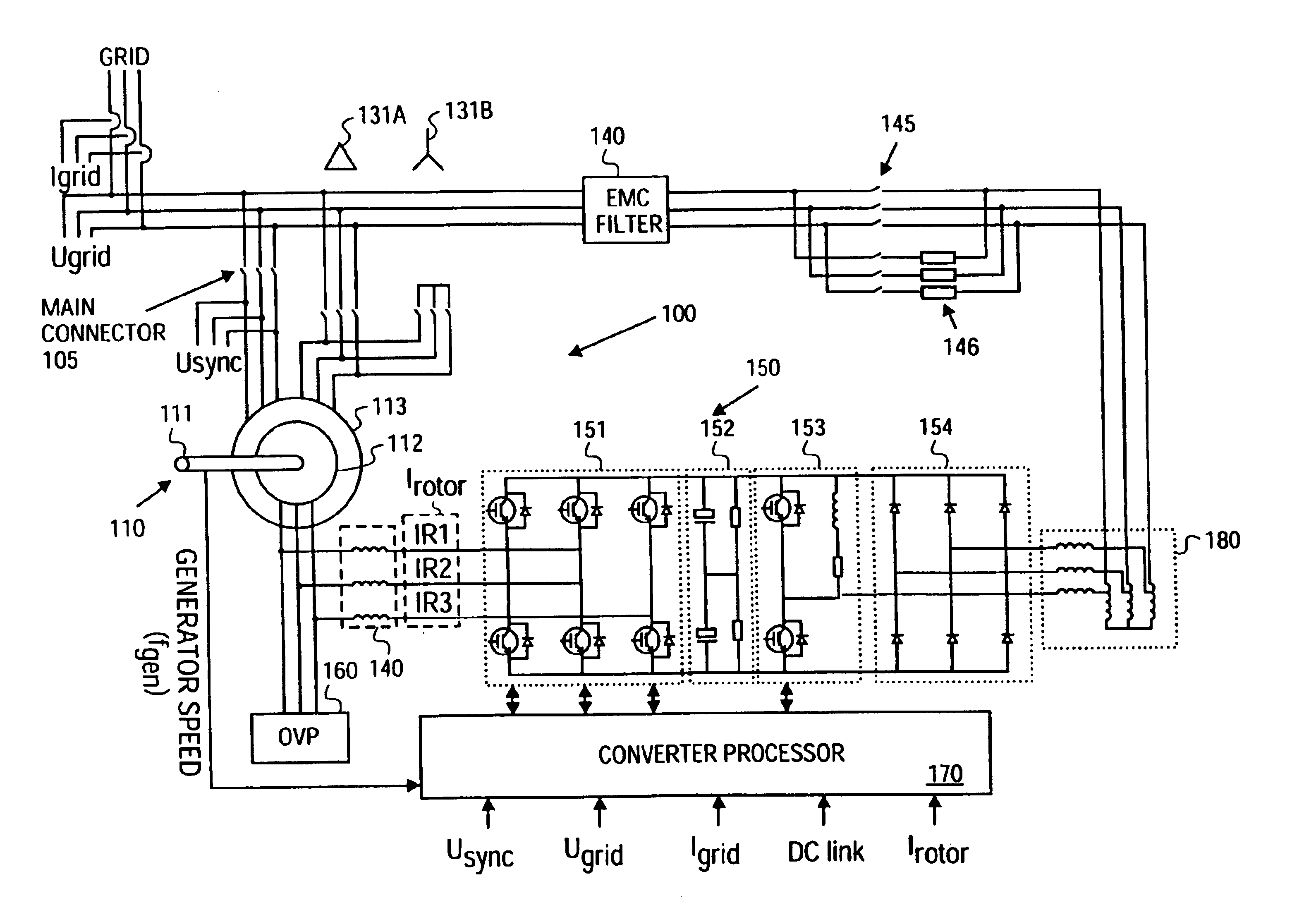
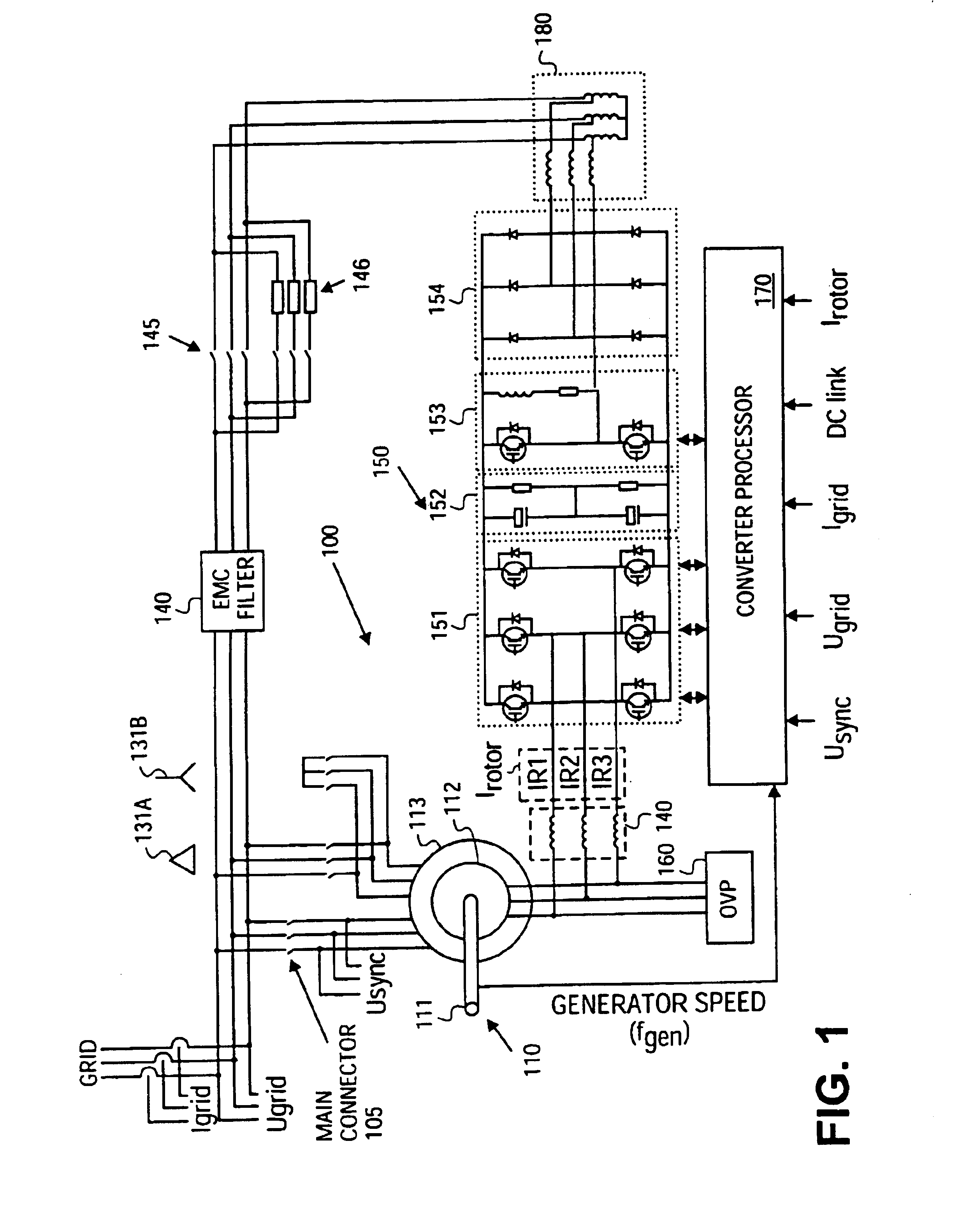
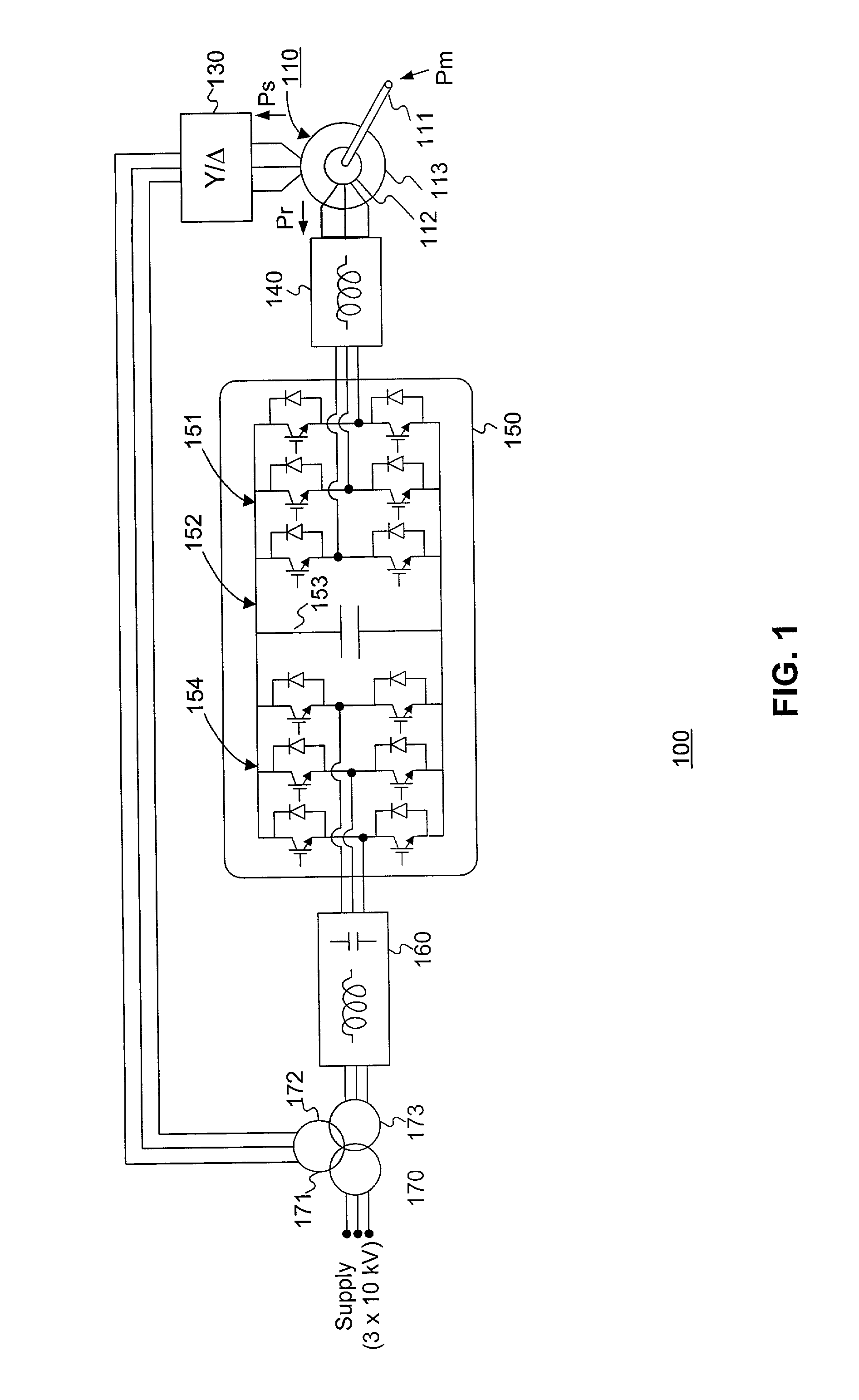
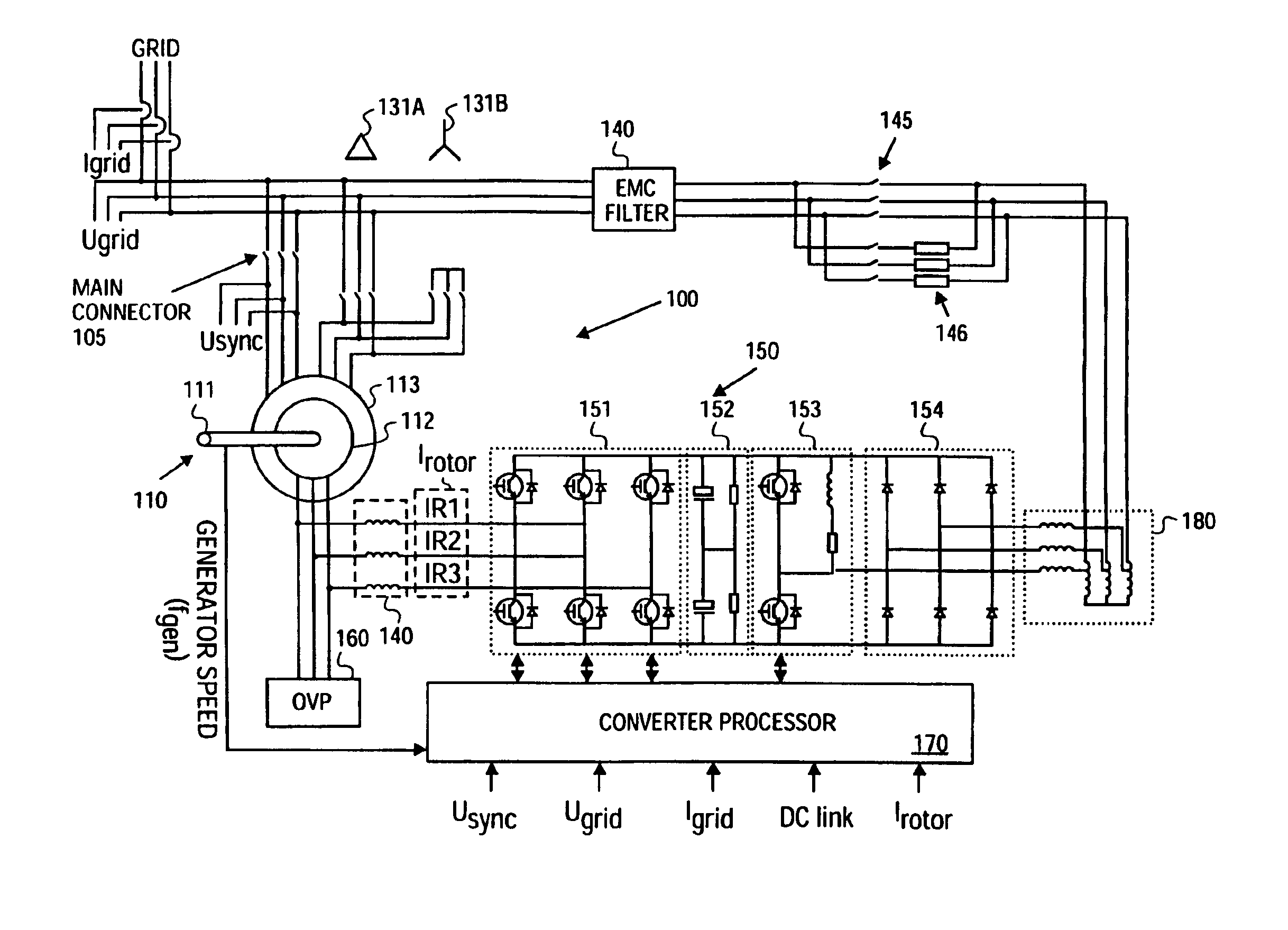
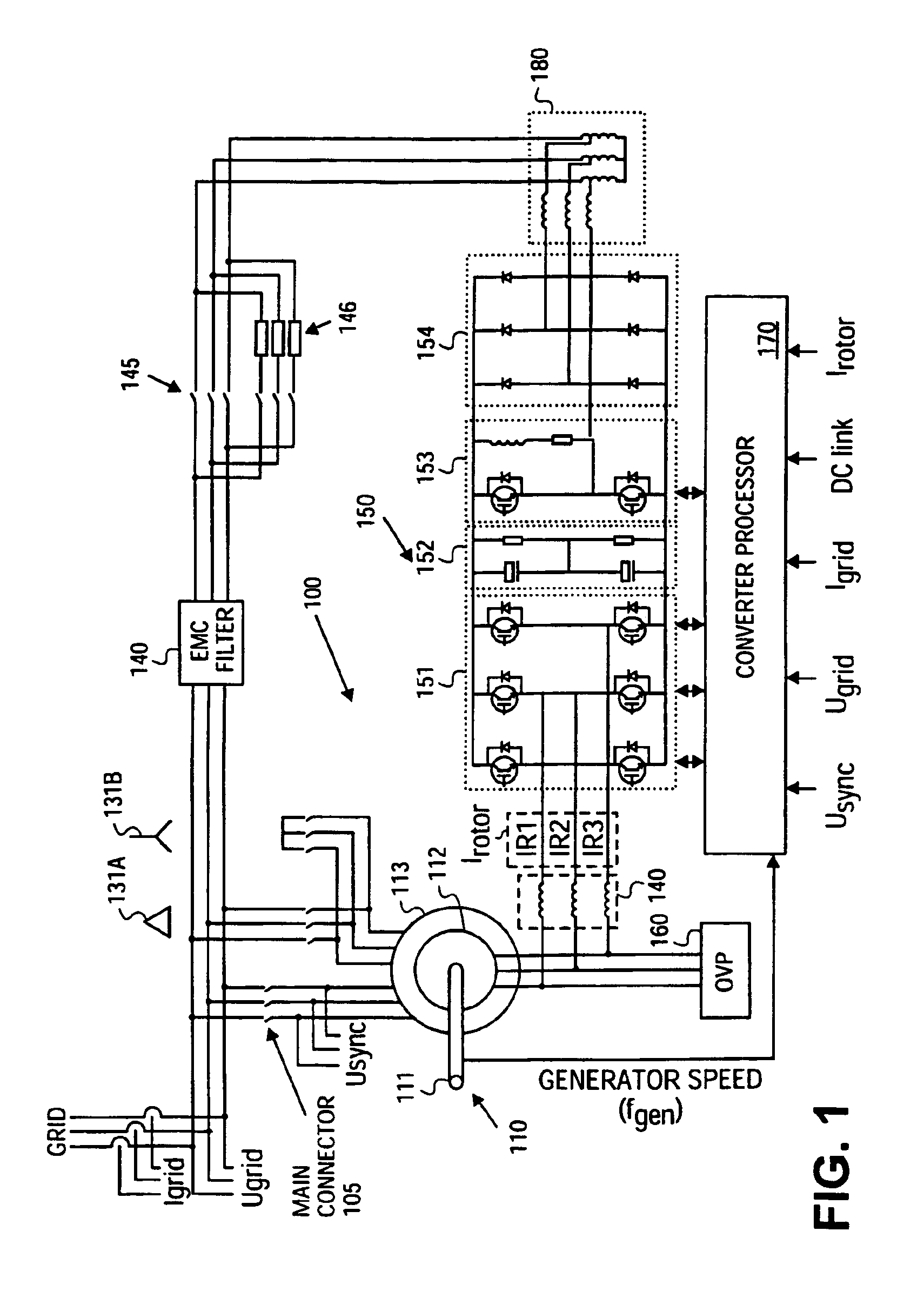
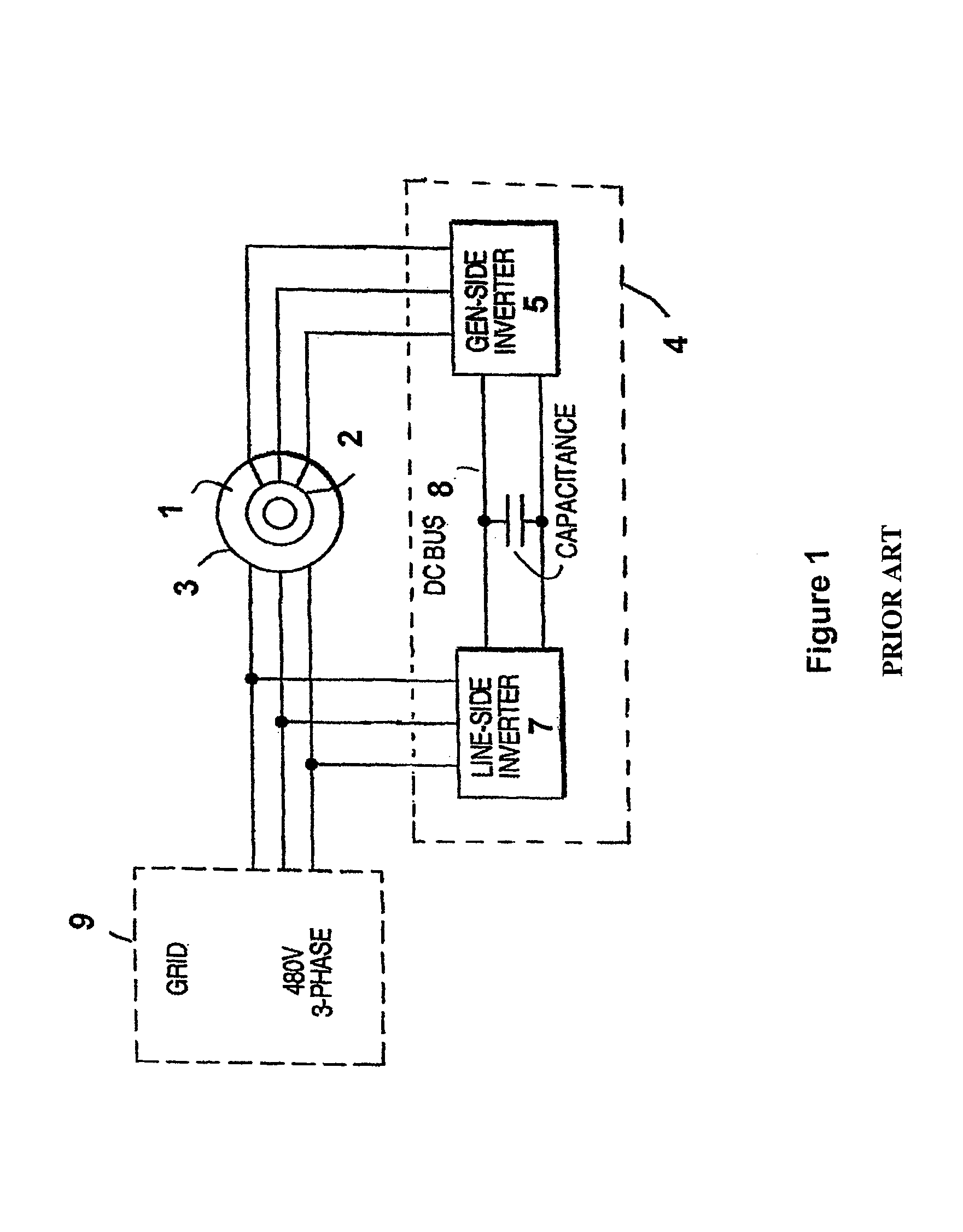
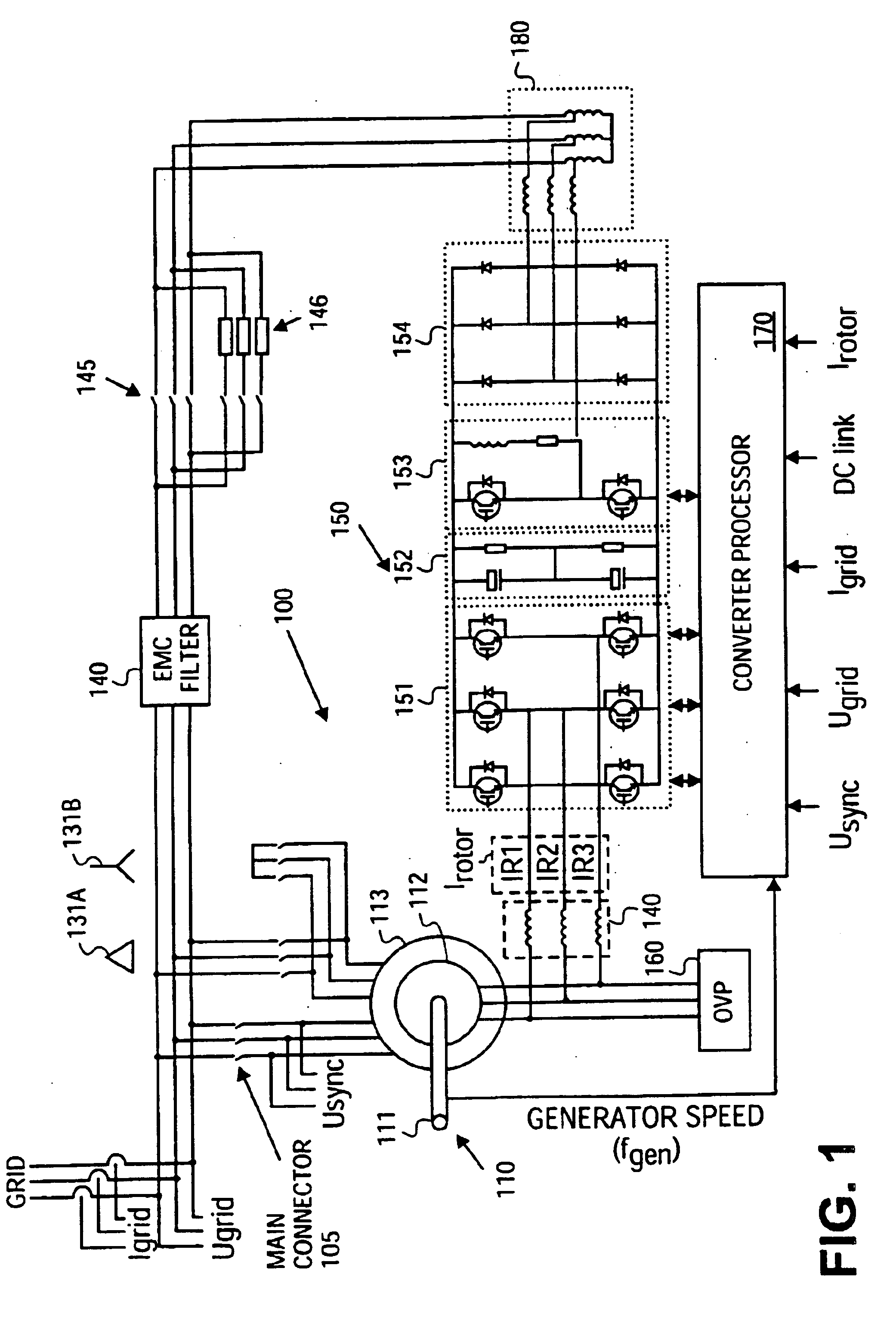
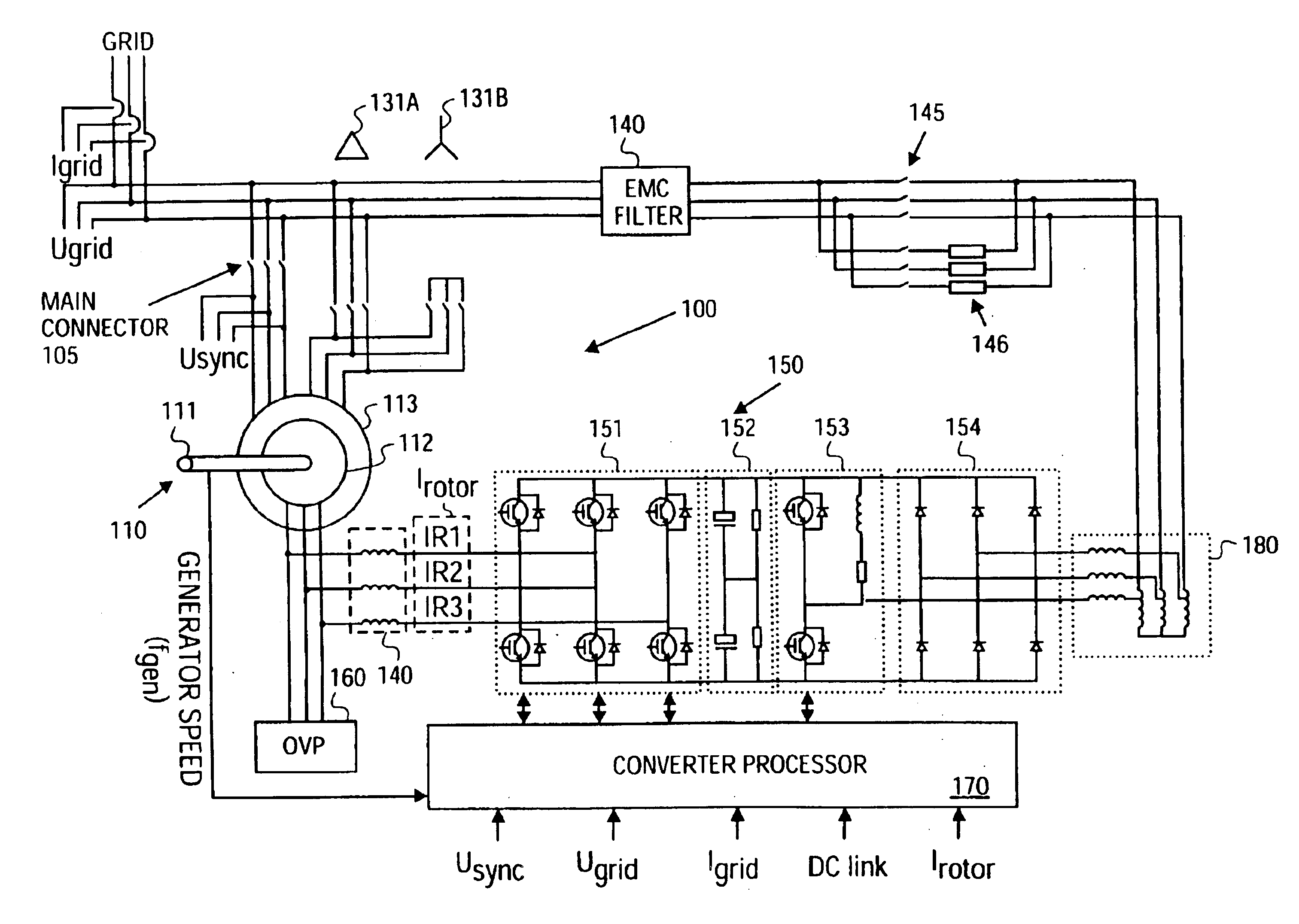
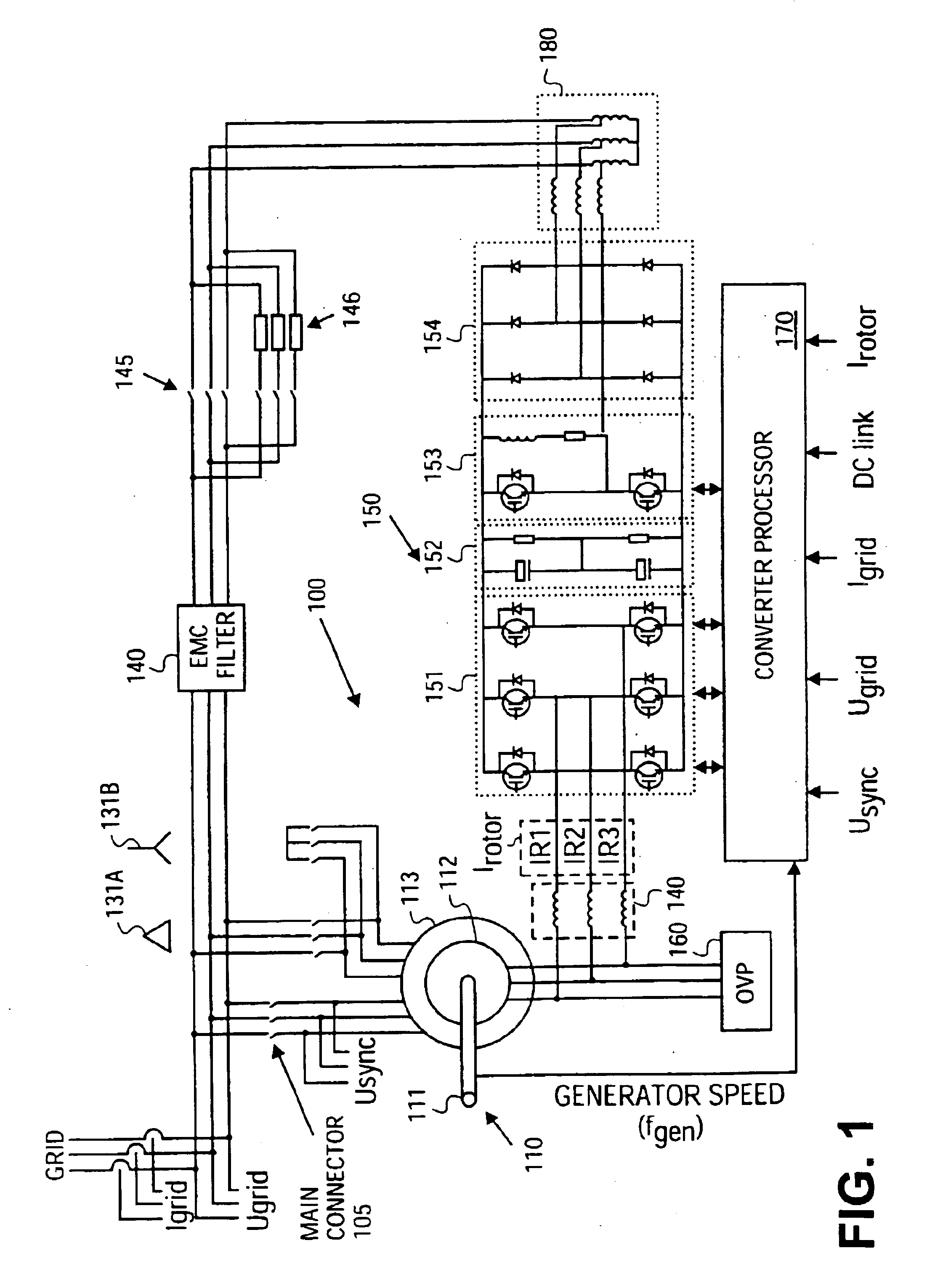
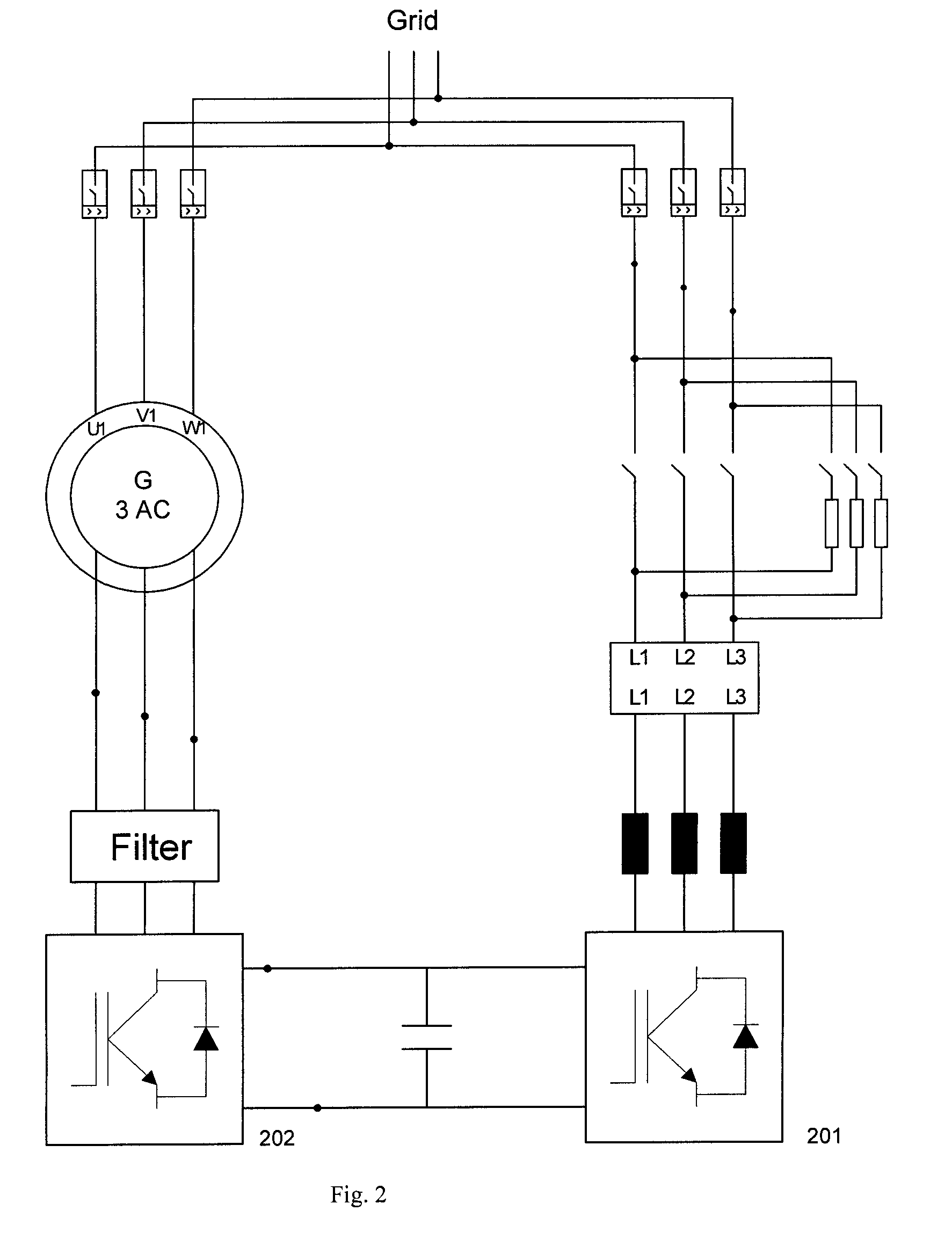
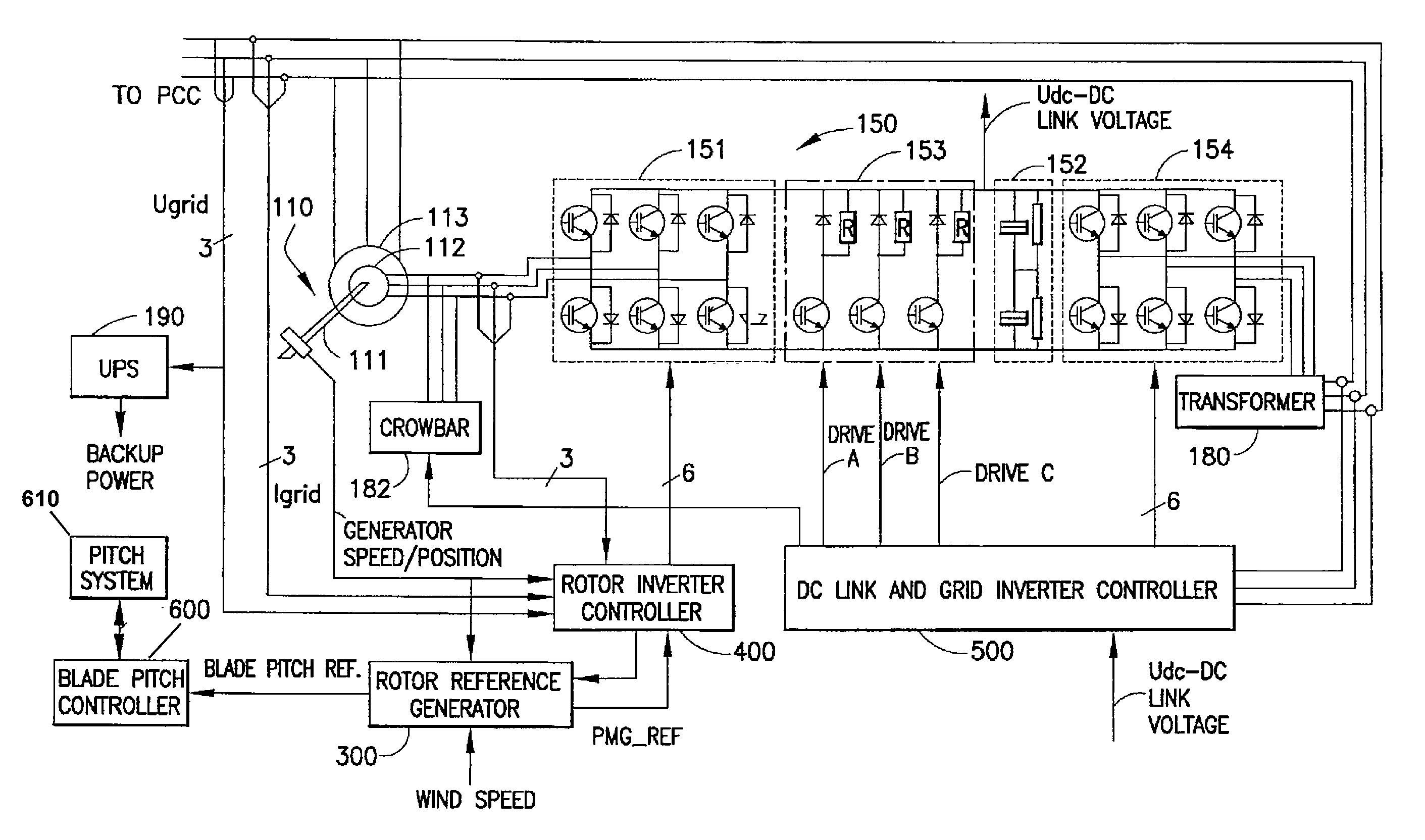
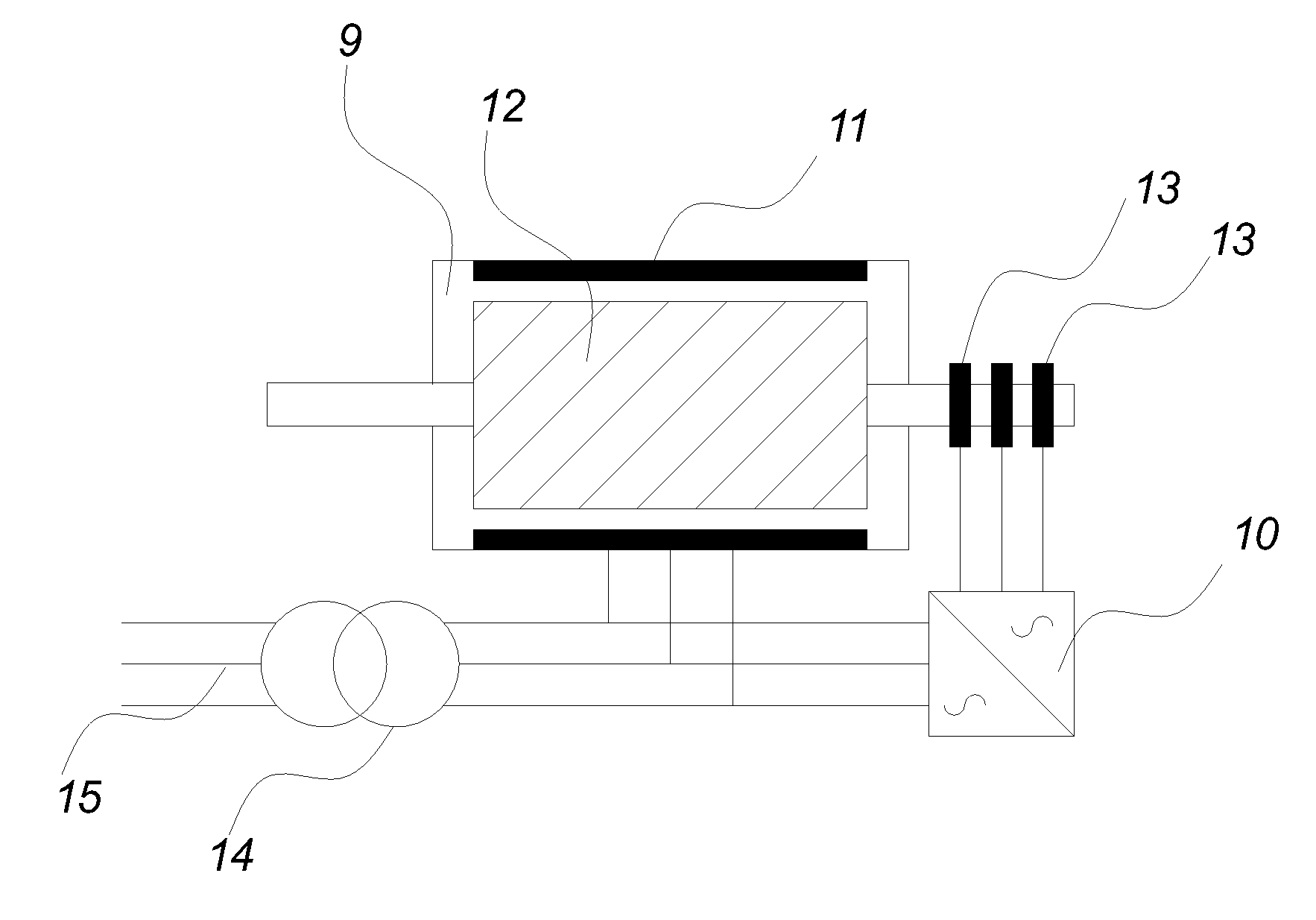
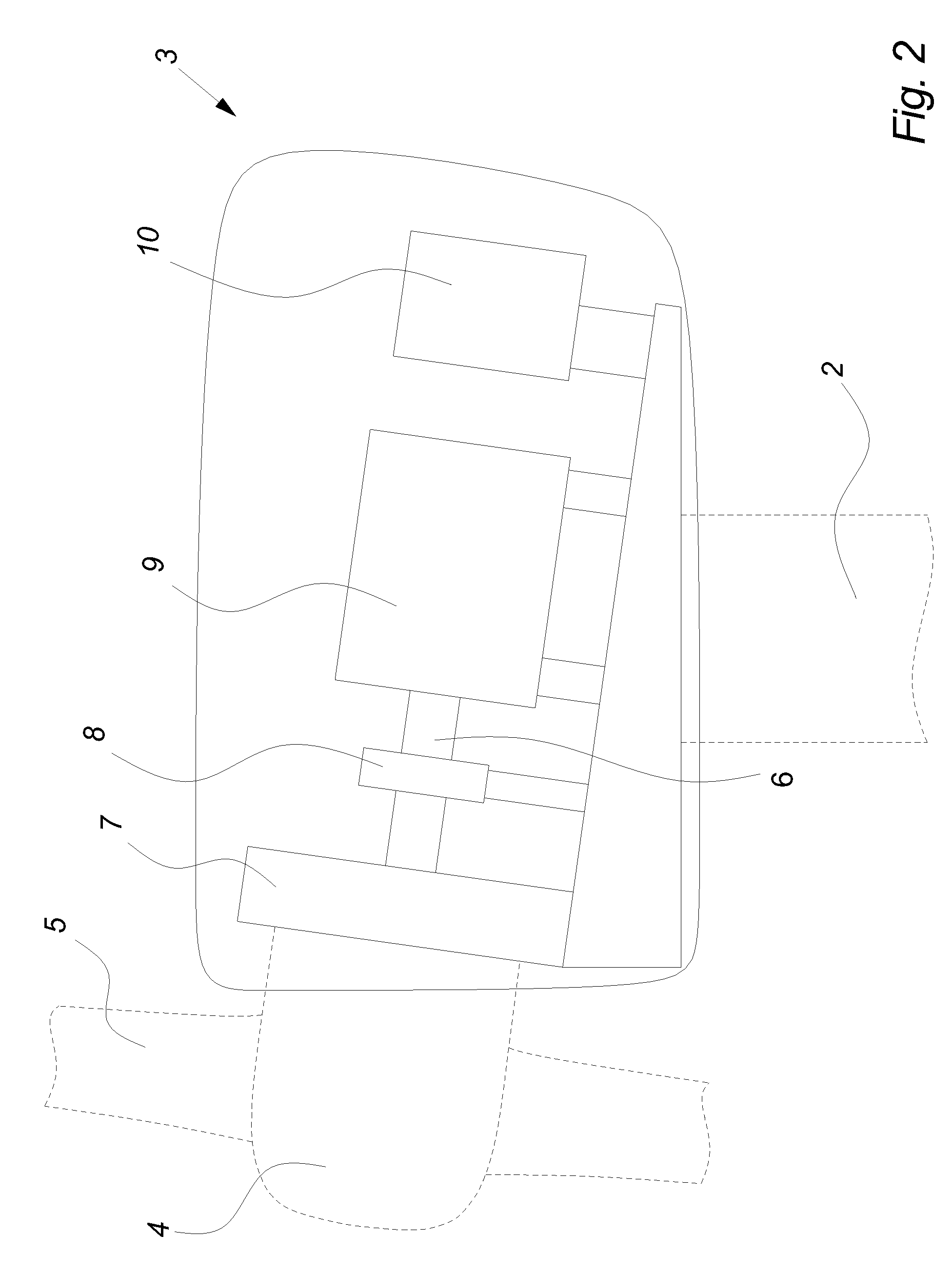
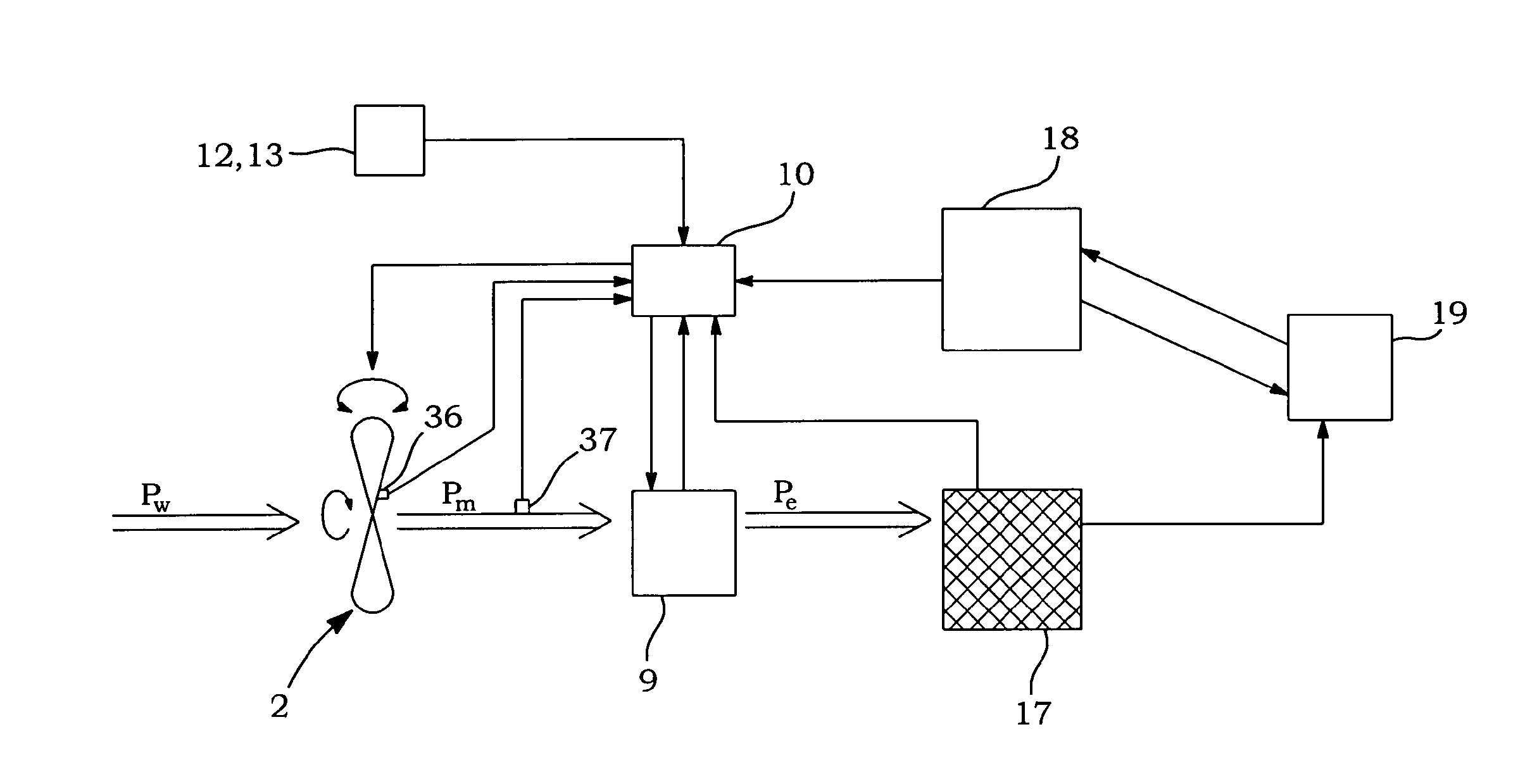
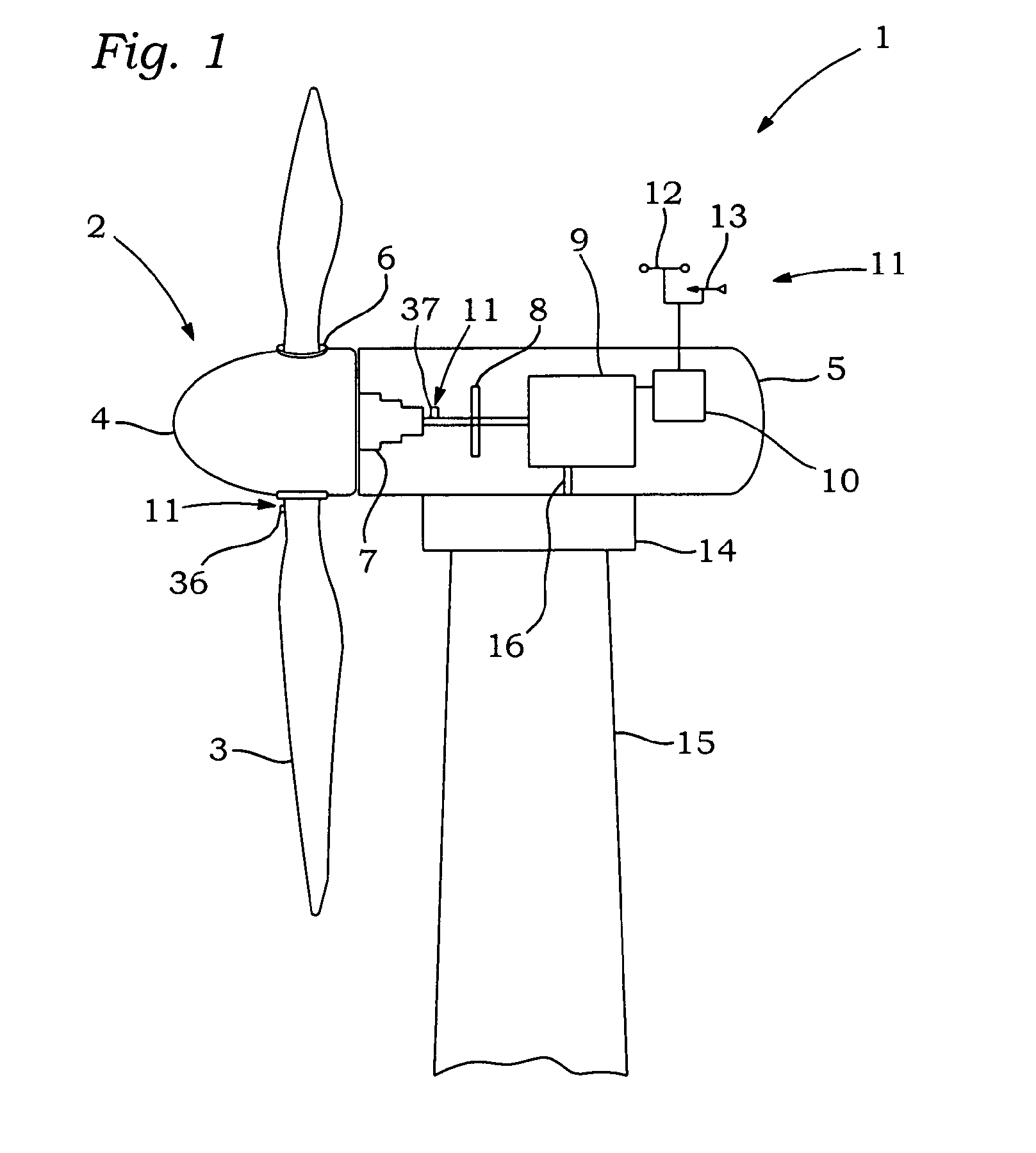
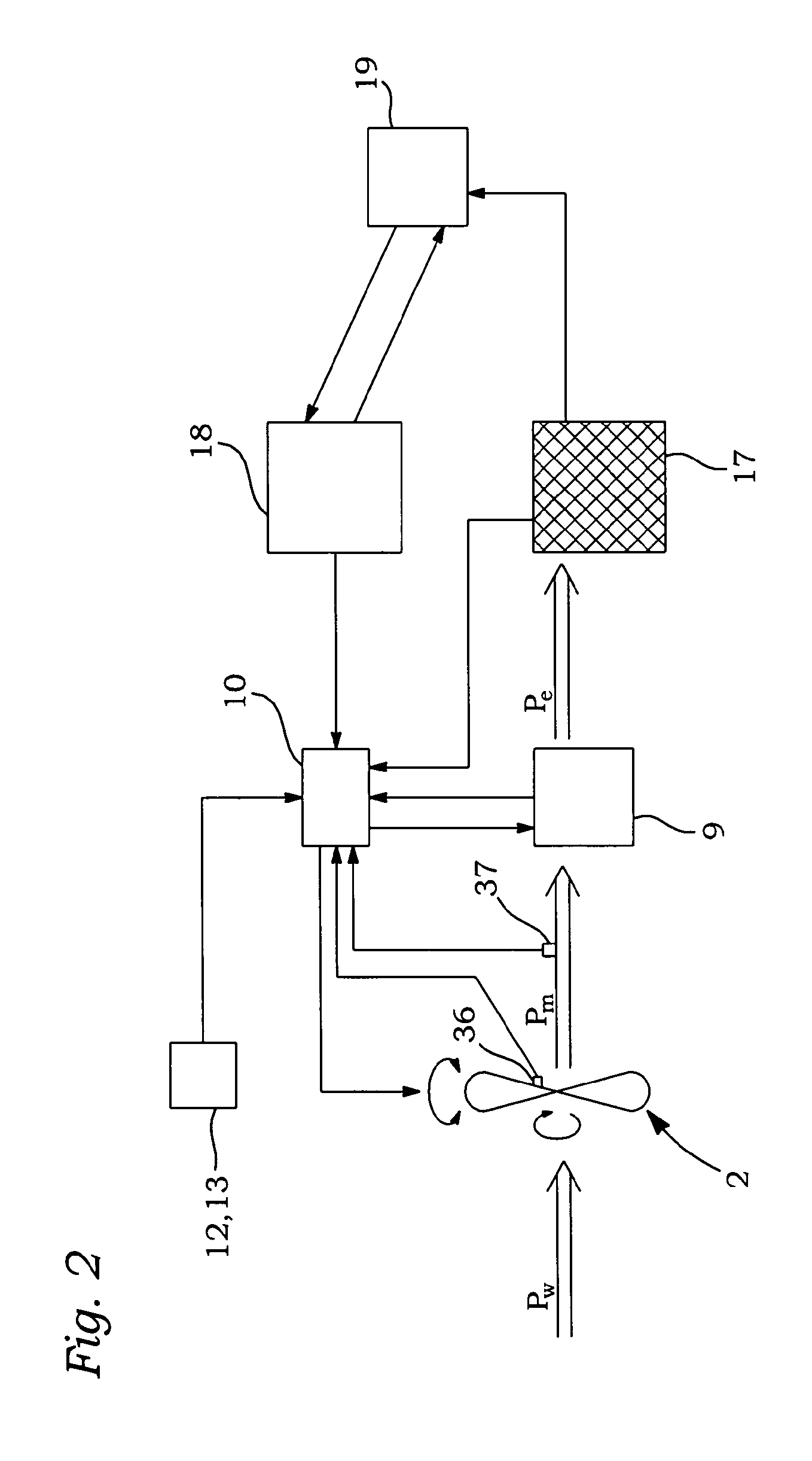
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS7042110B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPermanent magnet rotorDc current
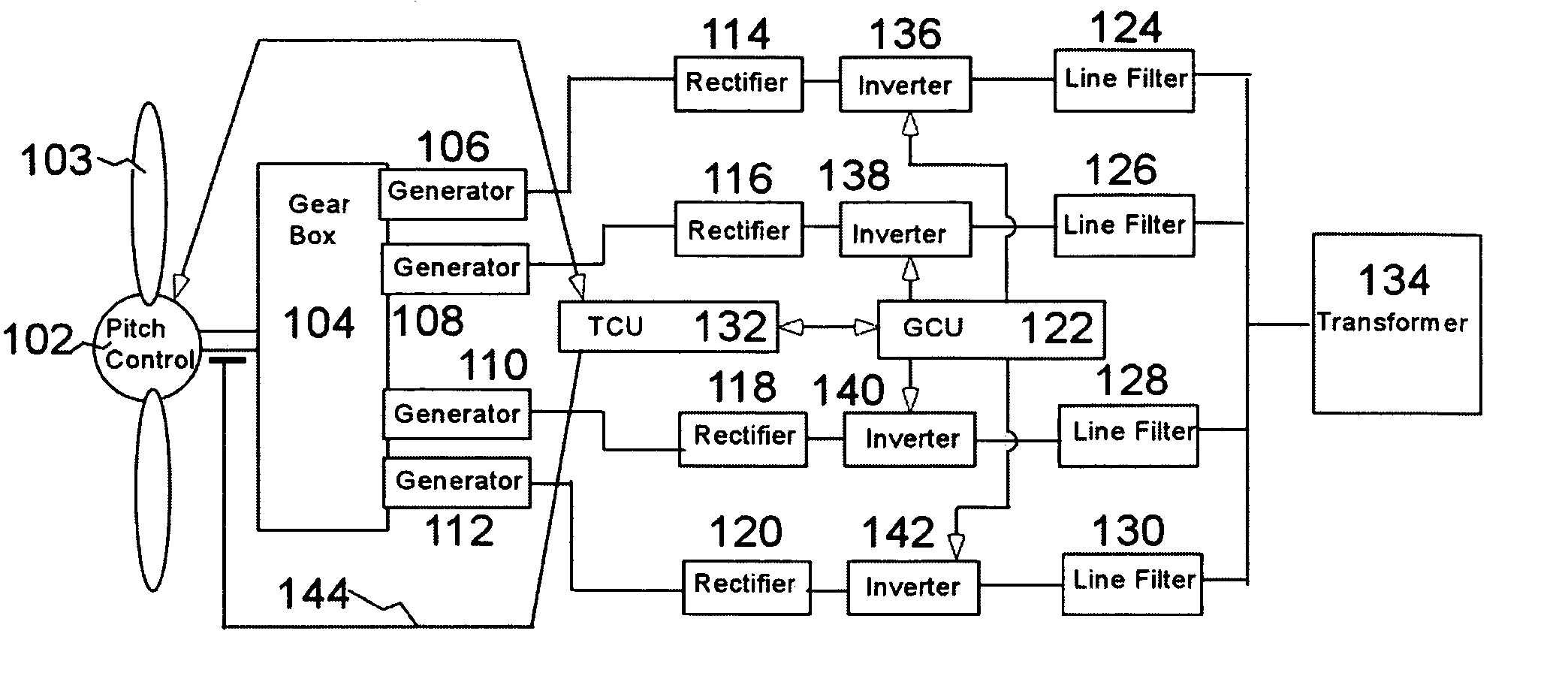
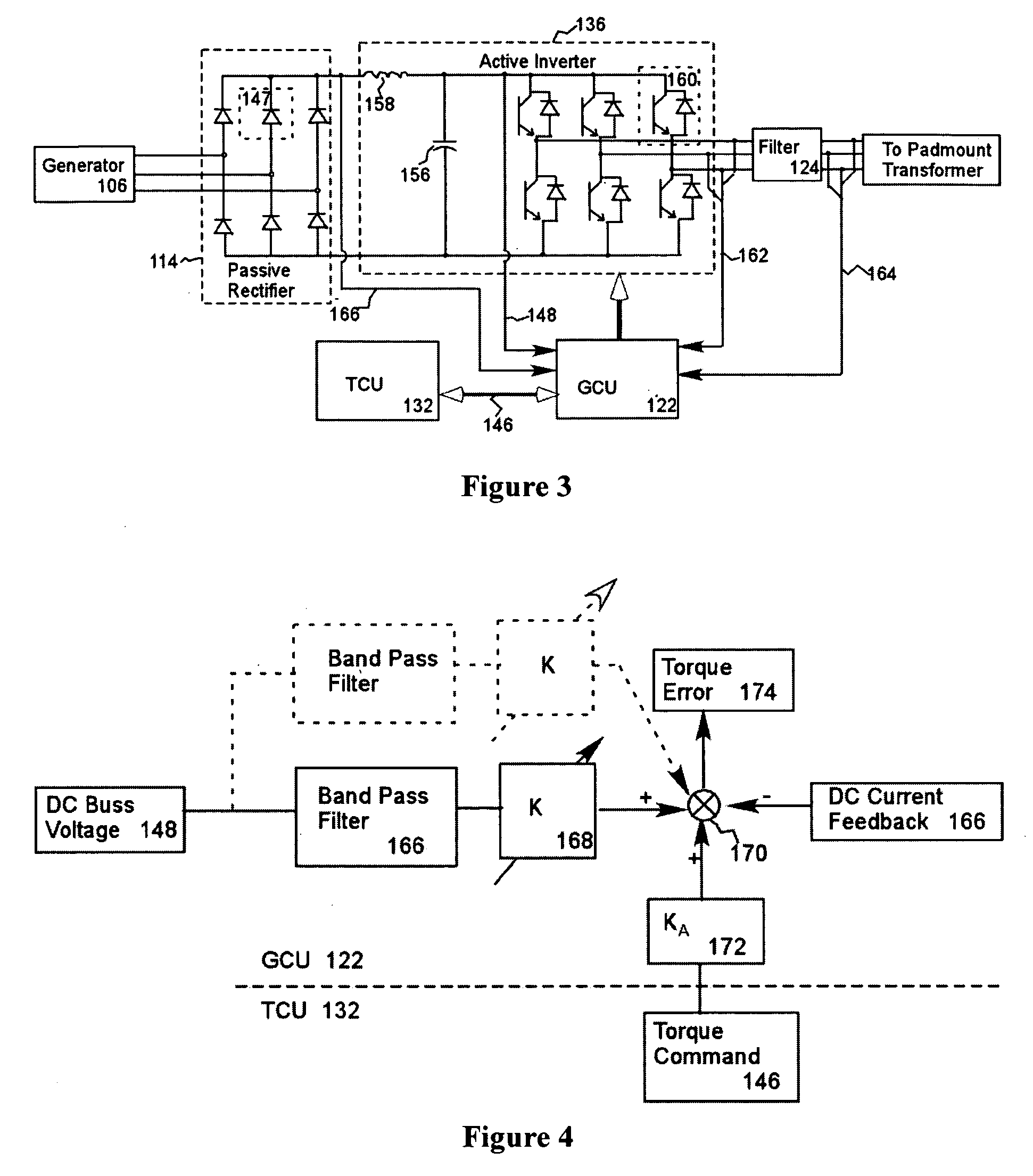
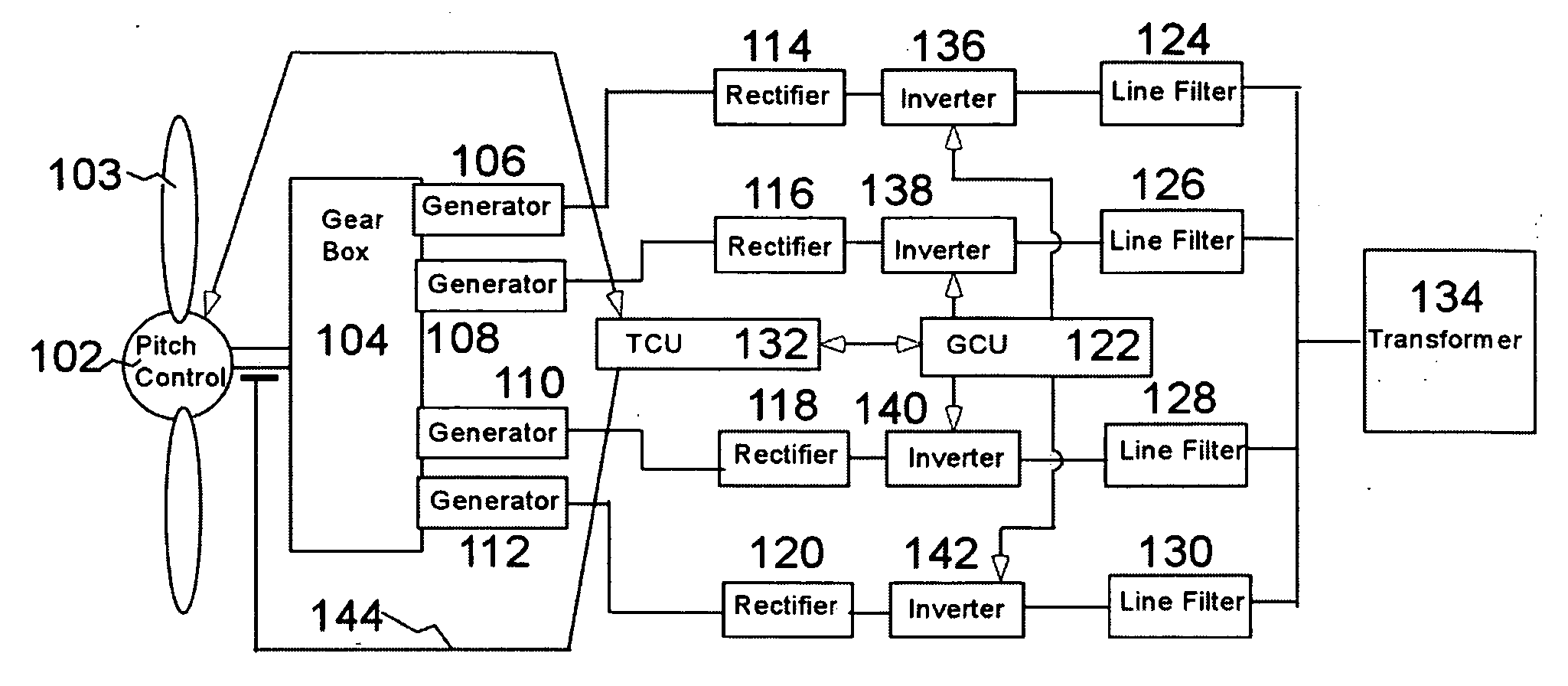
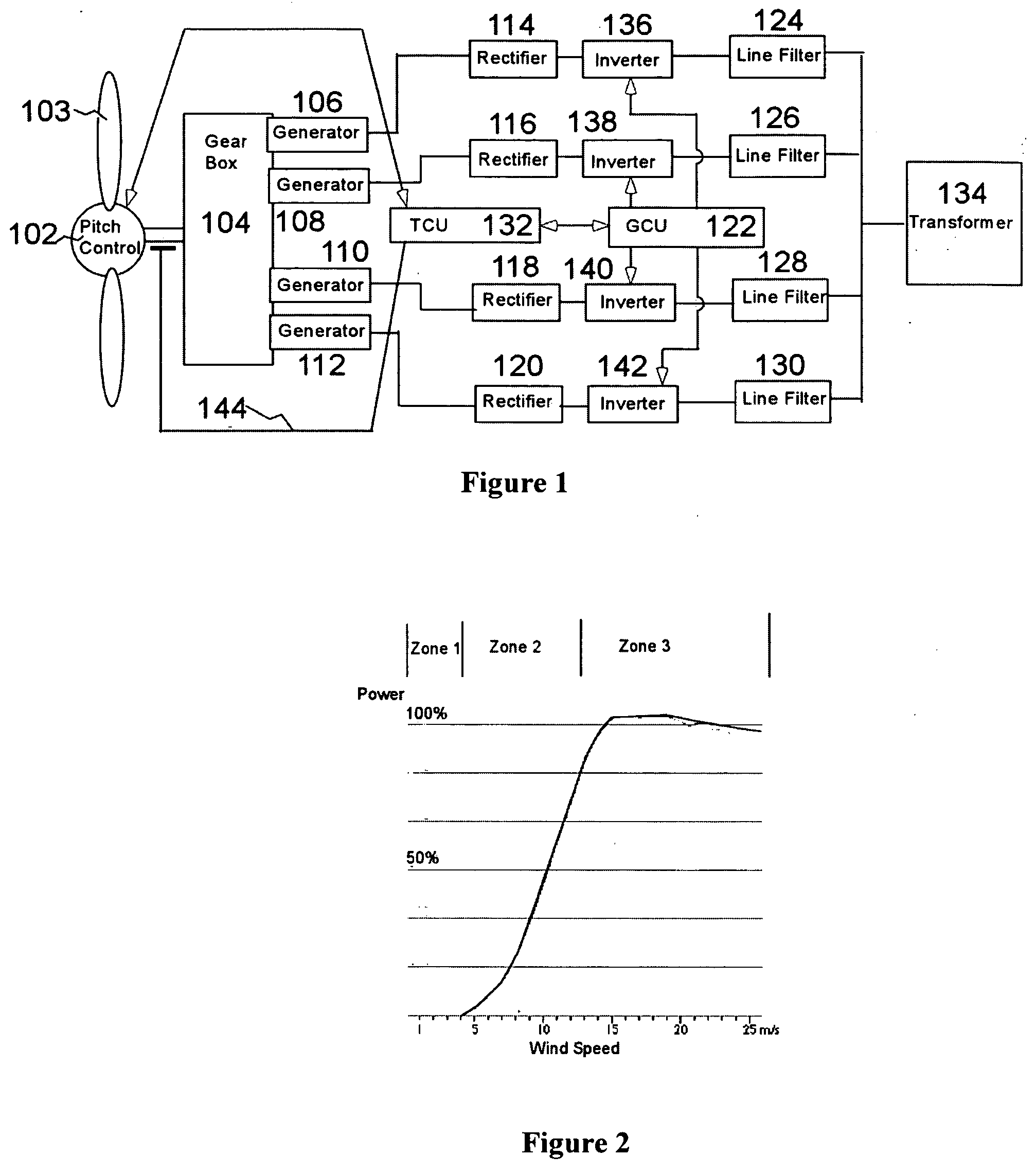
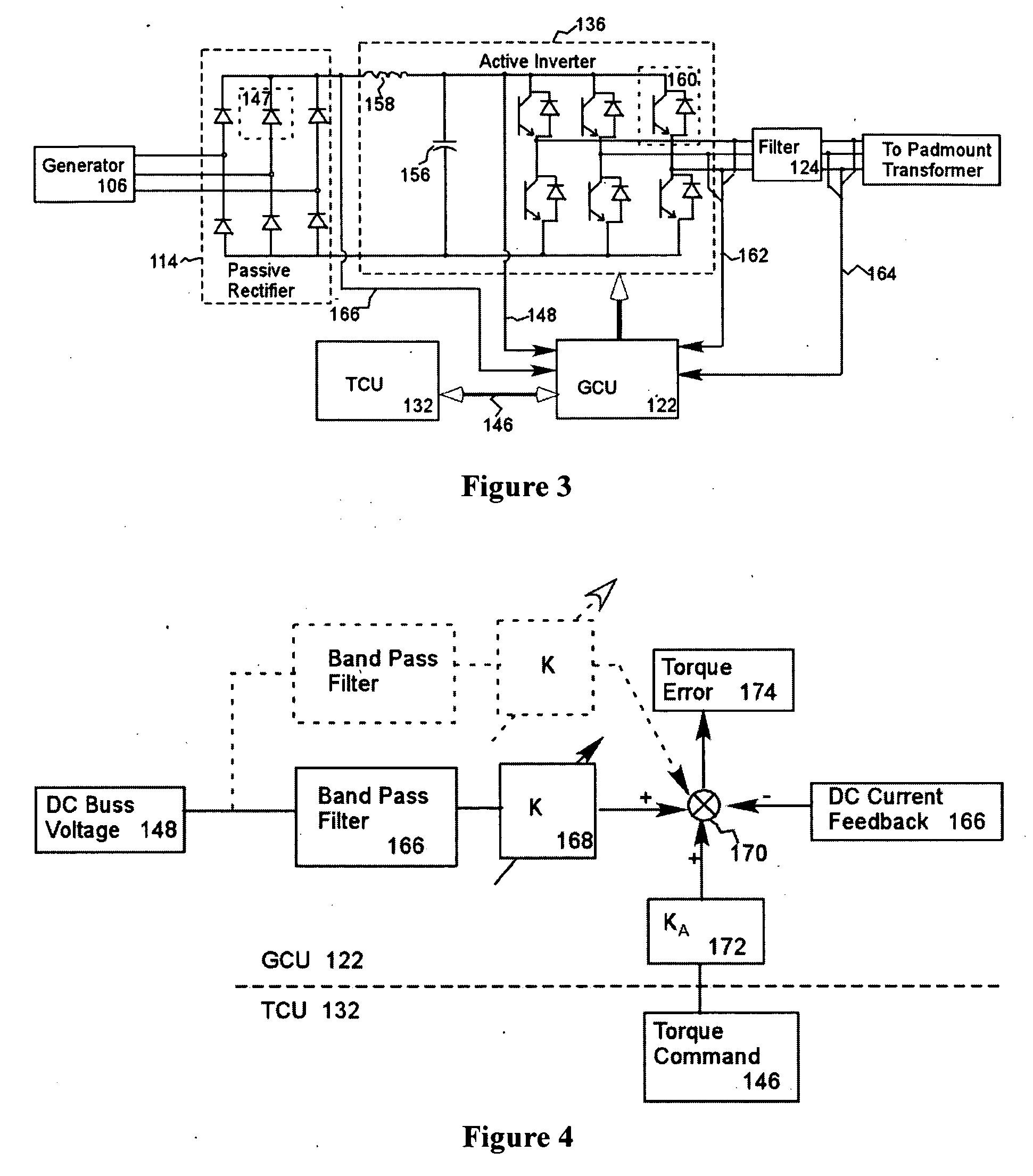
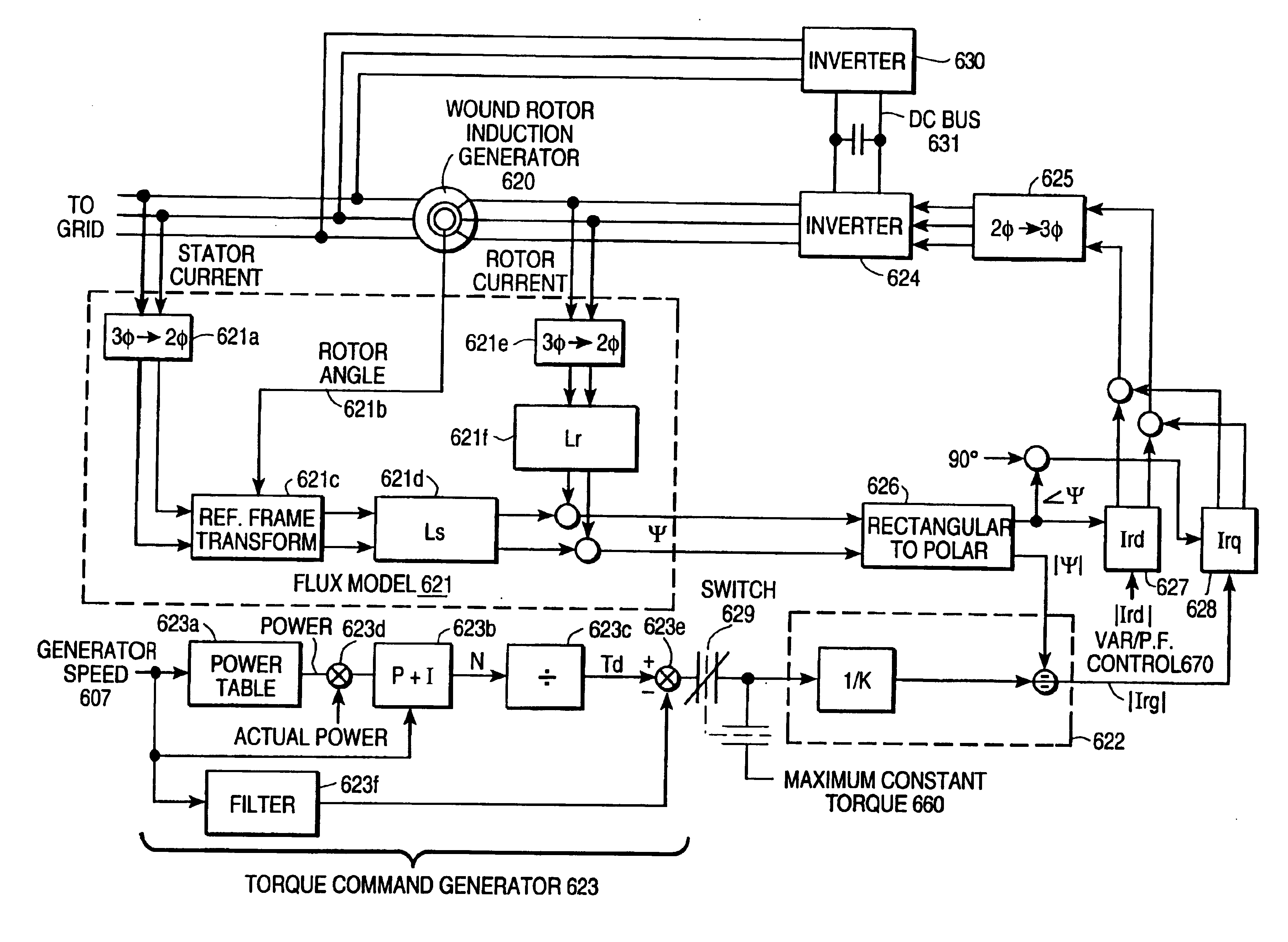
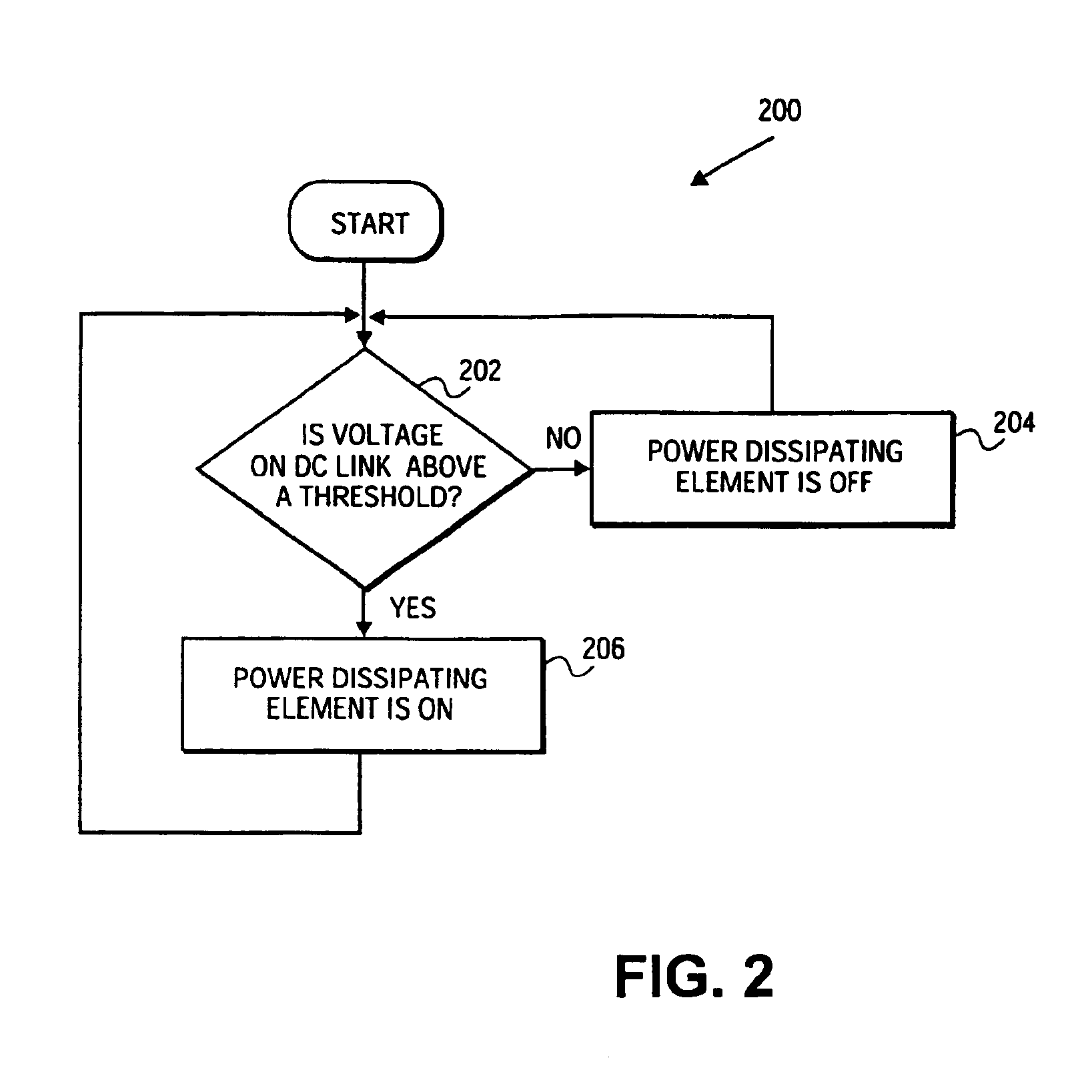
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
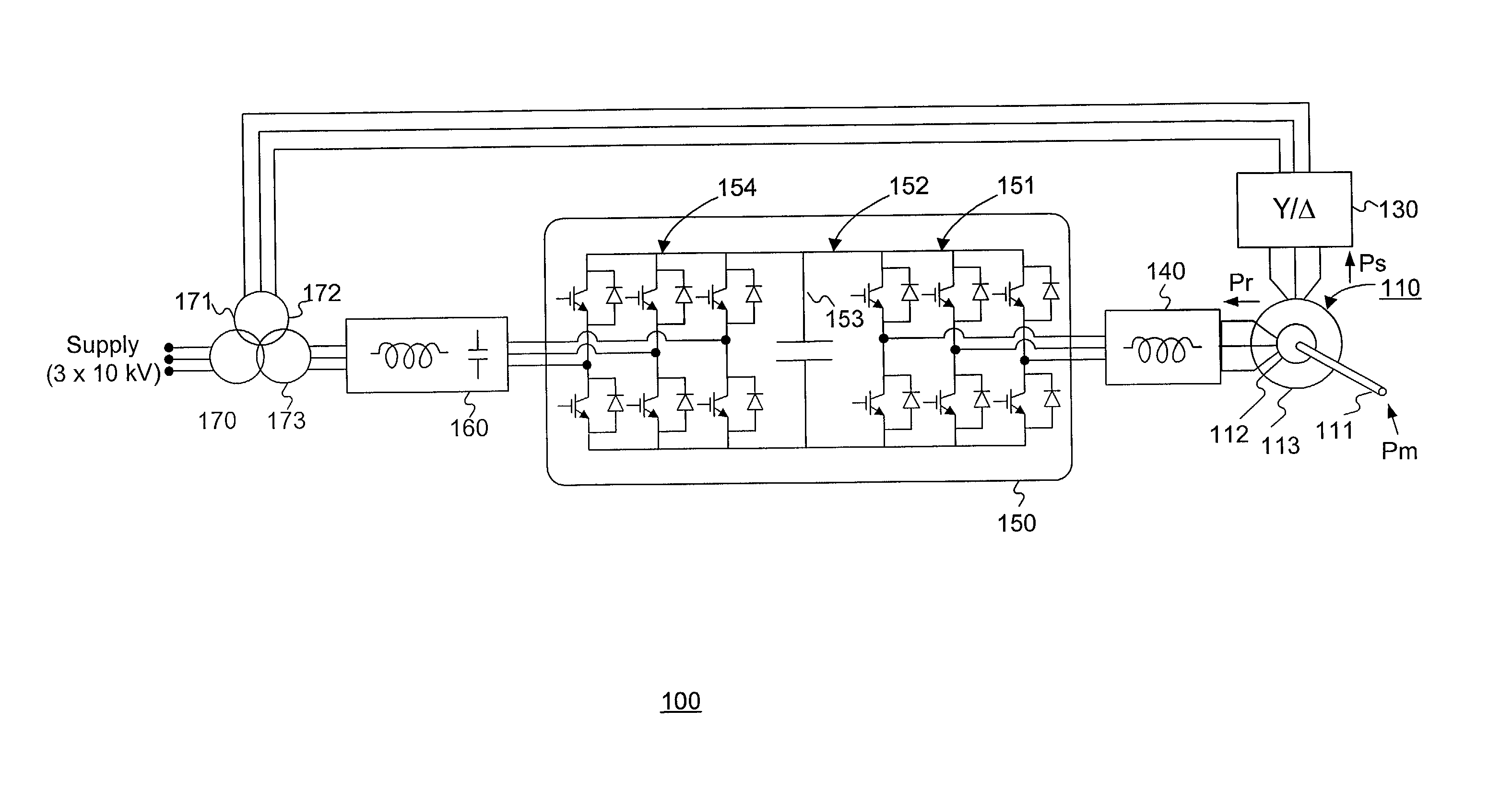
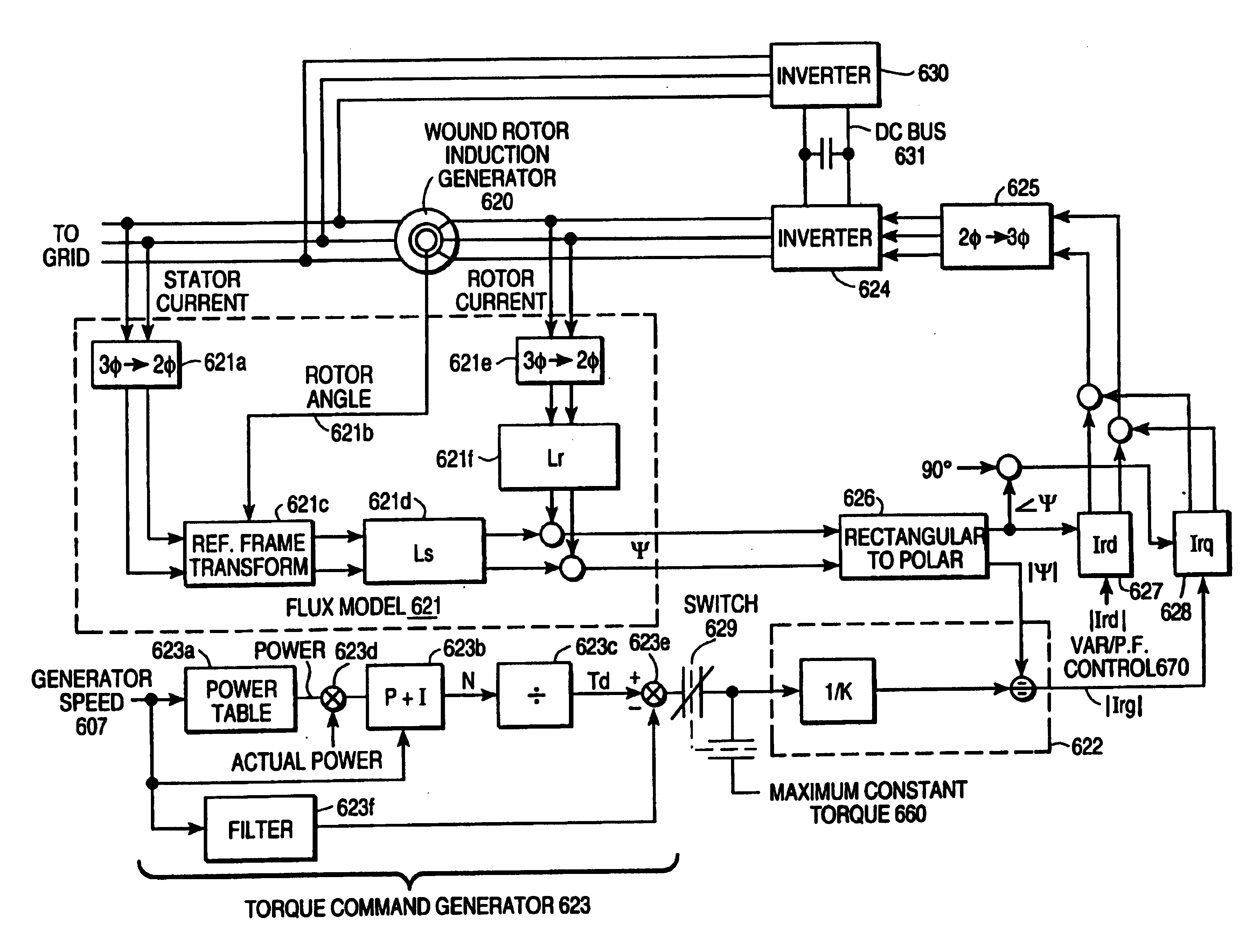
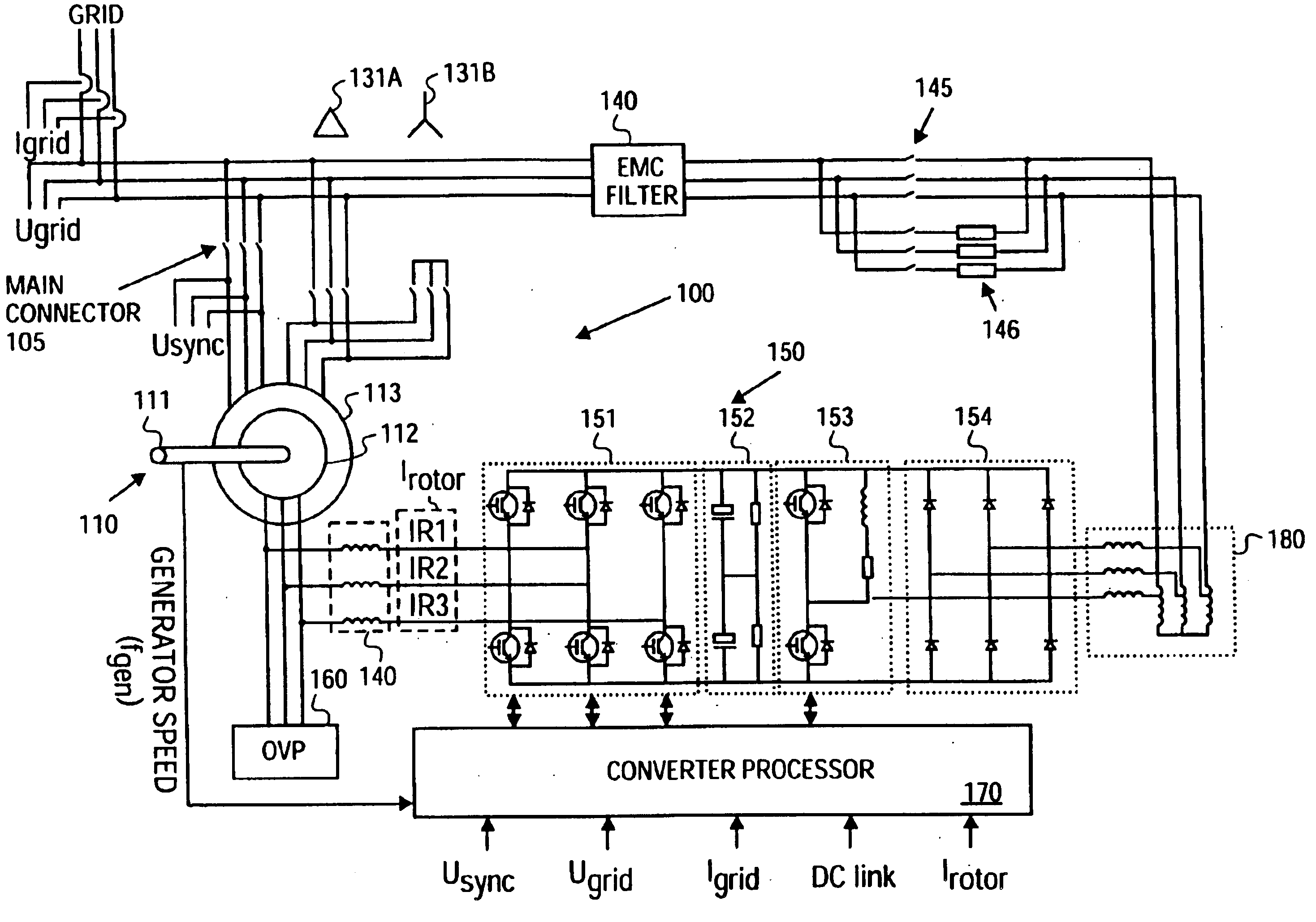
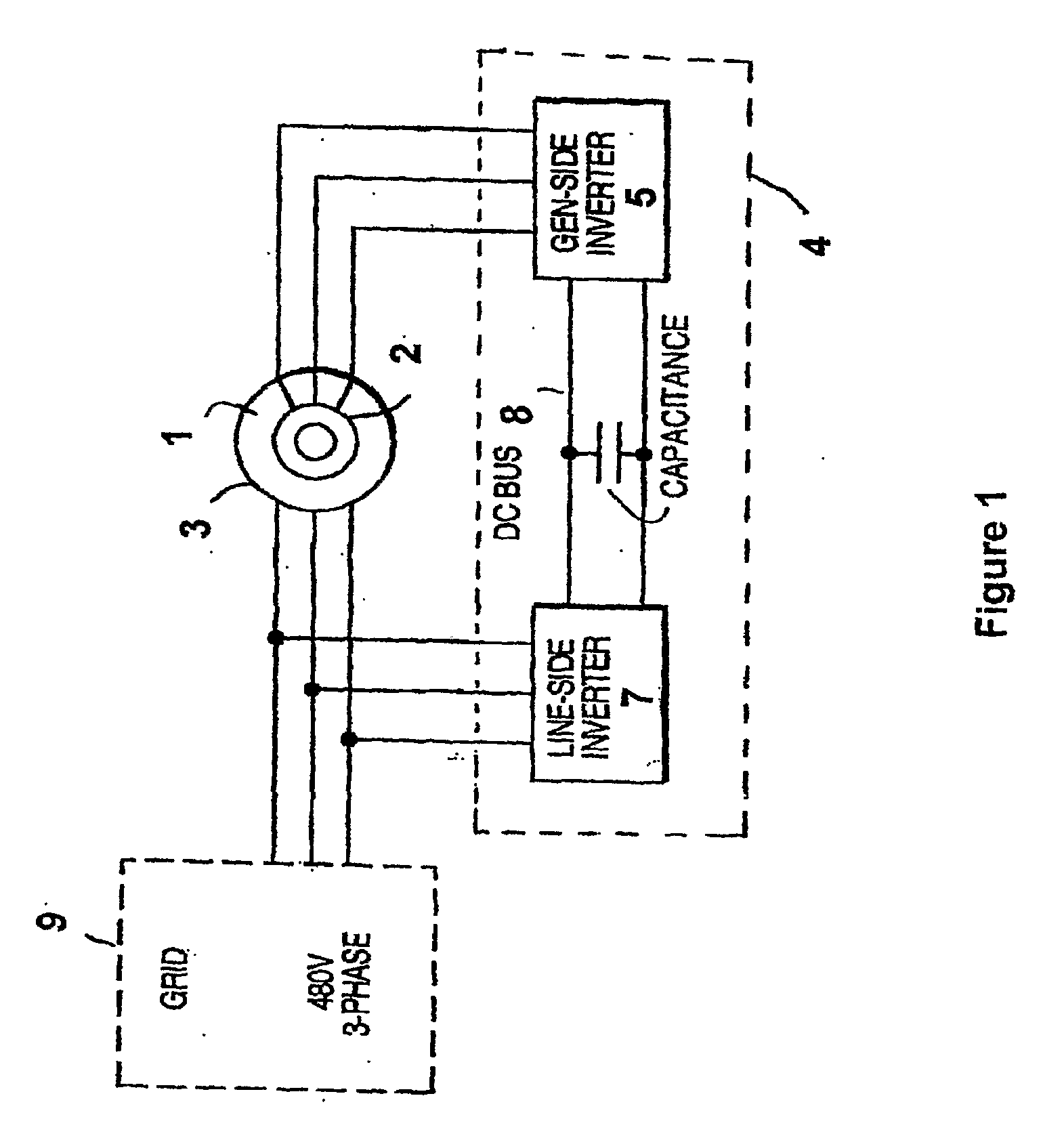
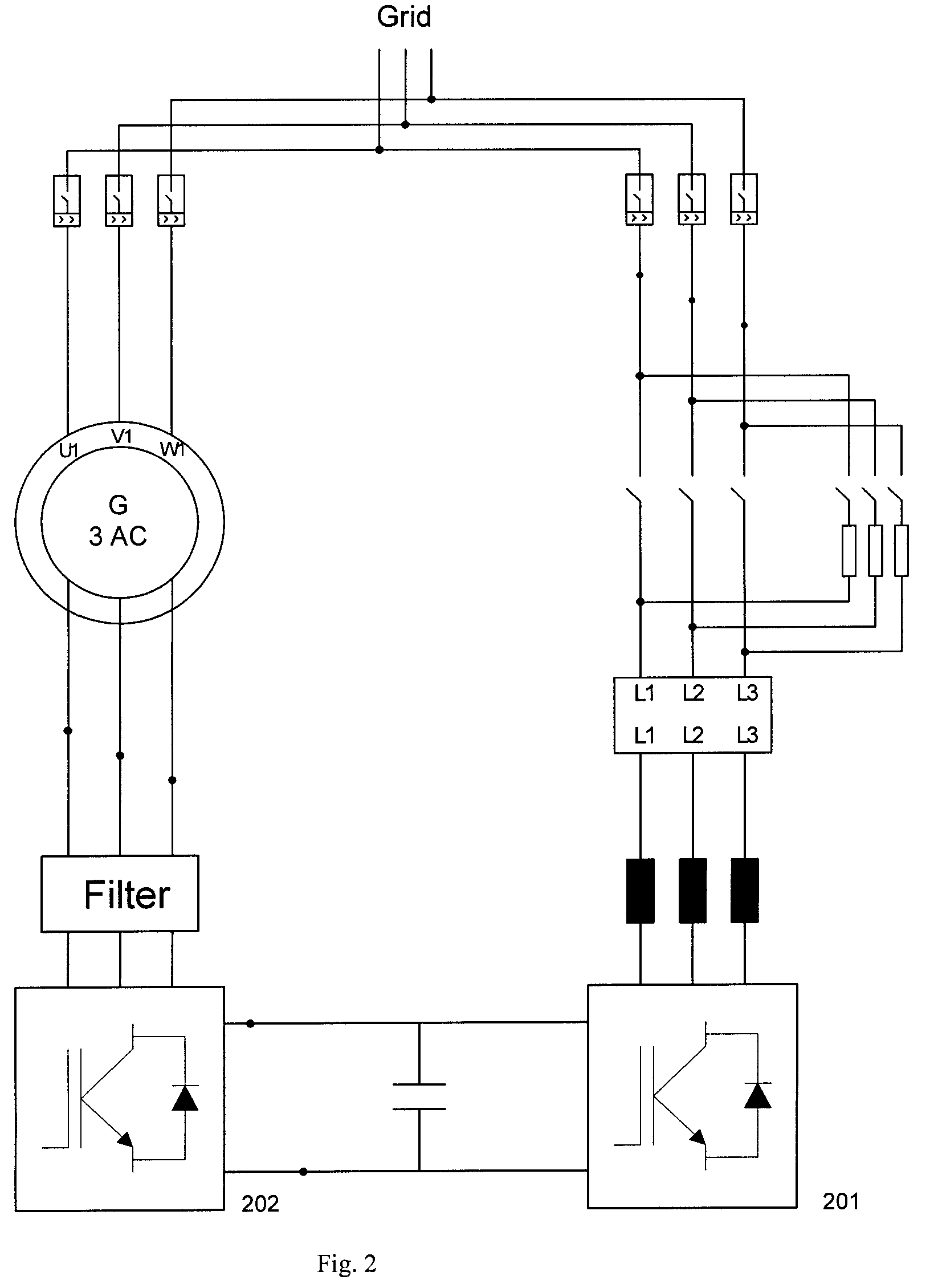
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS6856038B2Generator control circuitsEfficient power electronics conversionMatrix convertersConstant frequency
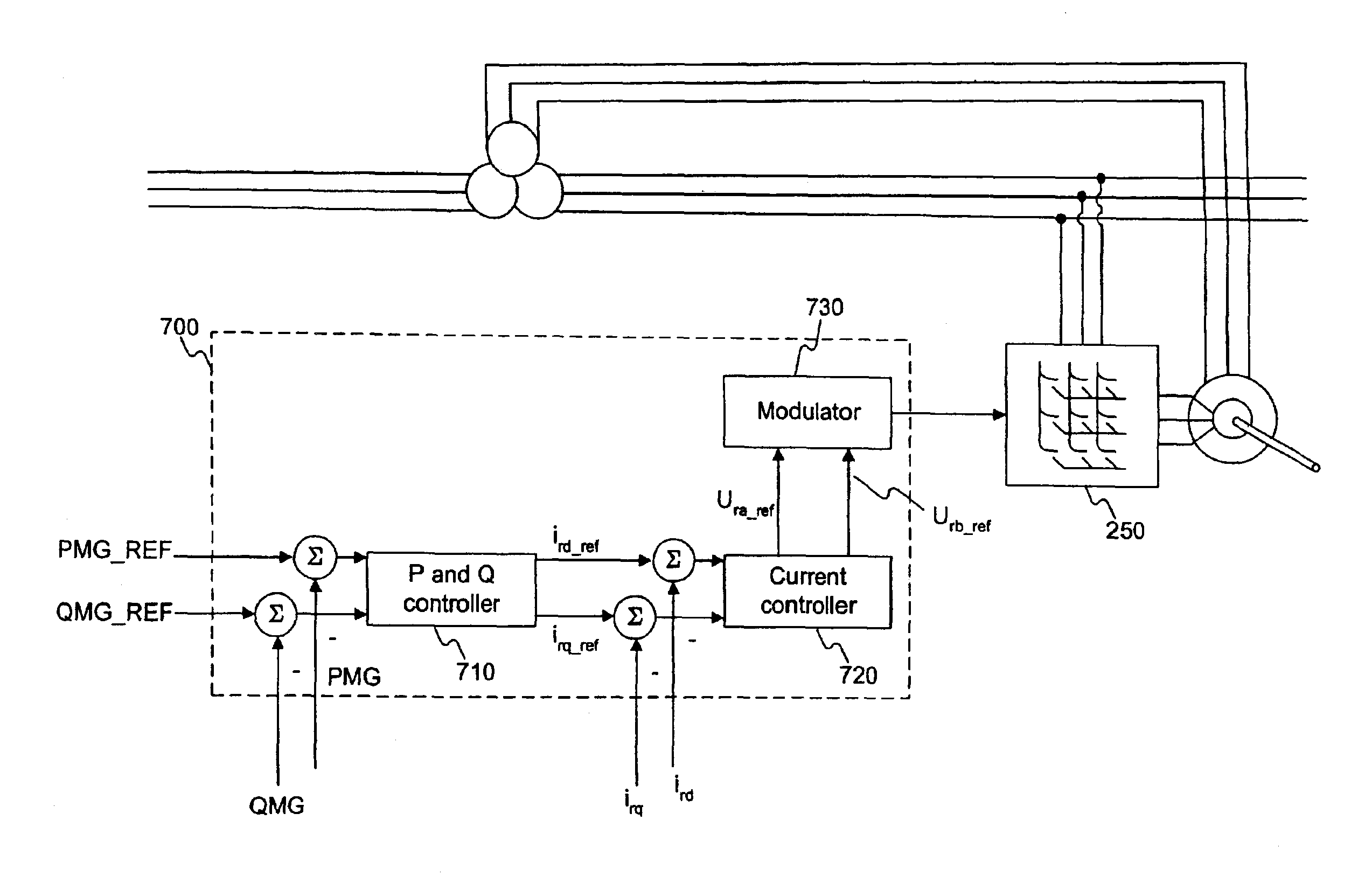
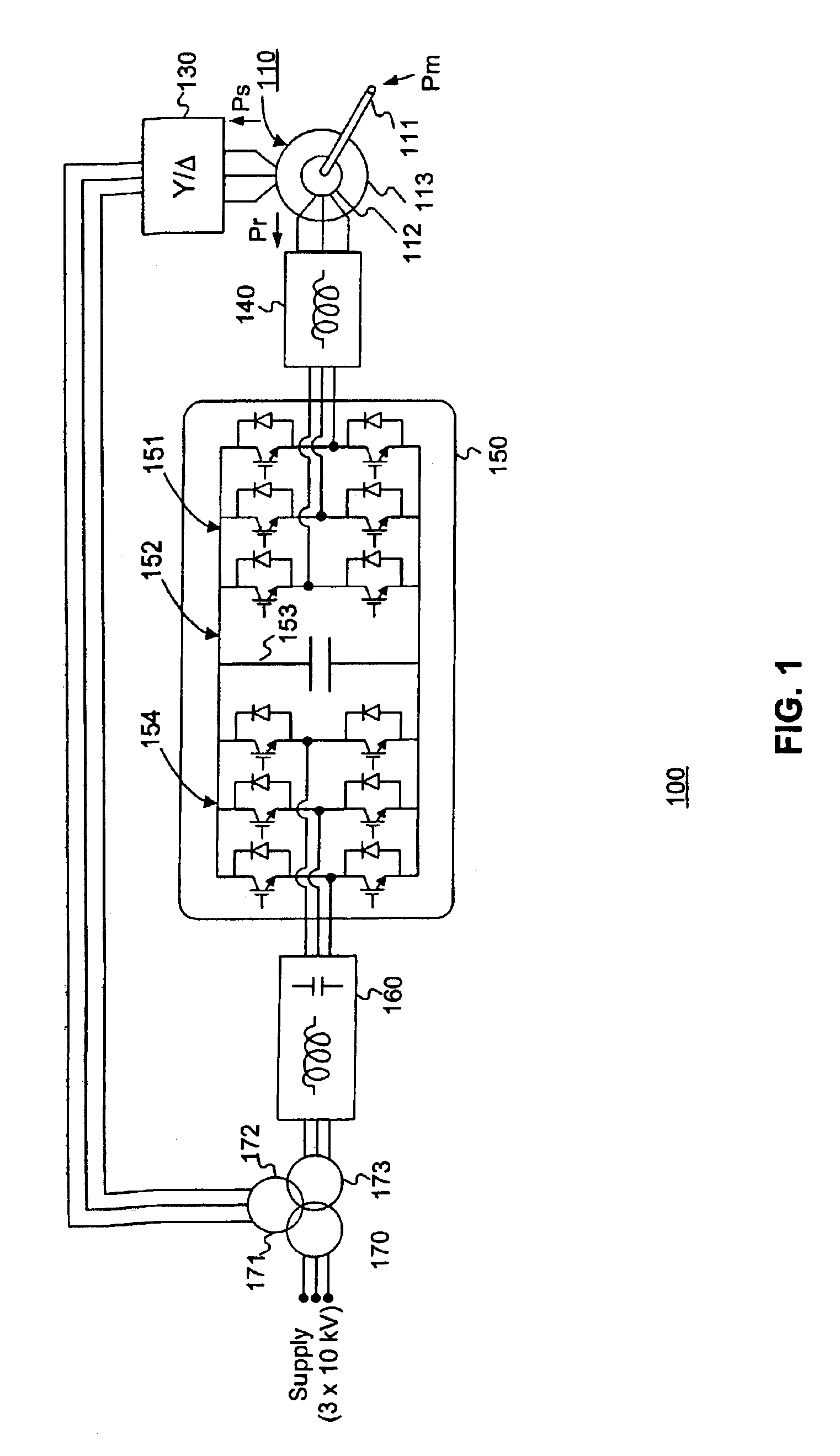
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6856039B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional, integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6933625B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS20020079706A1Generator control circuitsWind motor controlMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856040B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
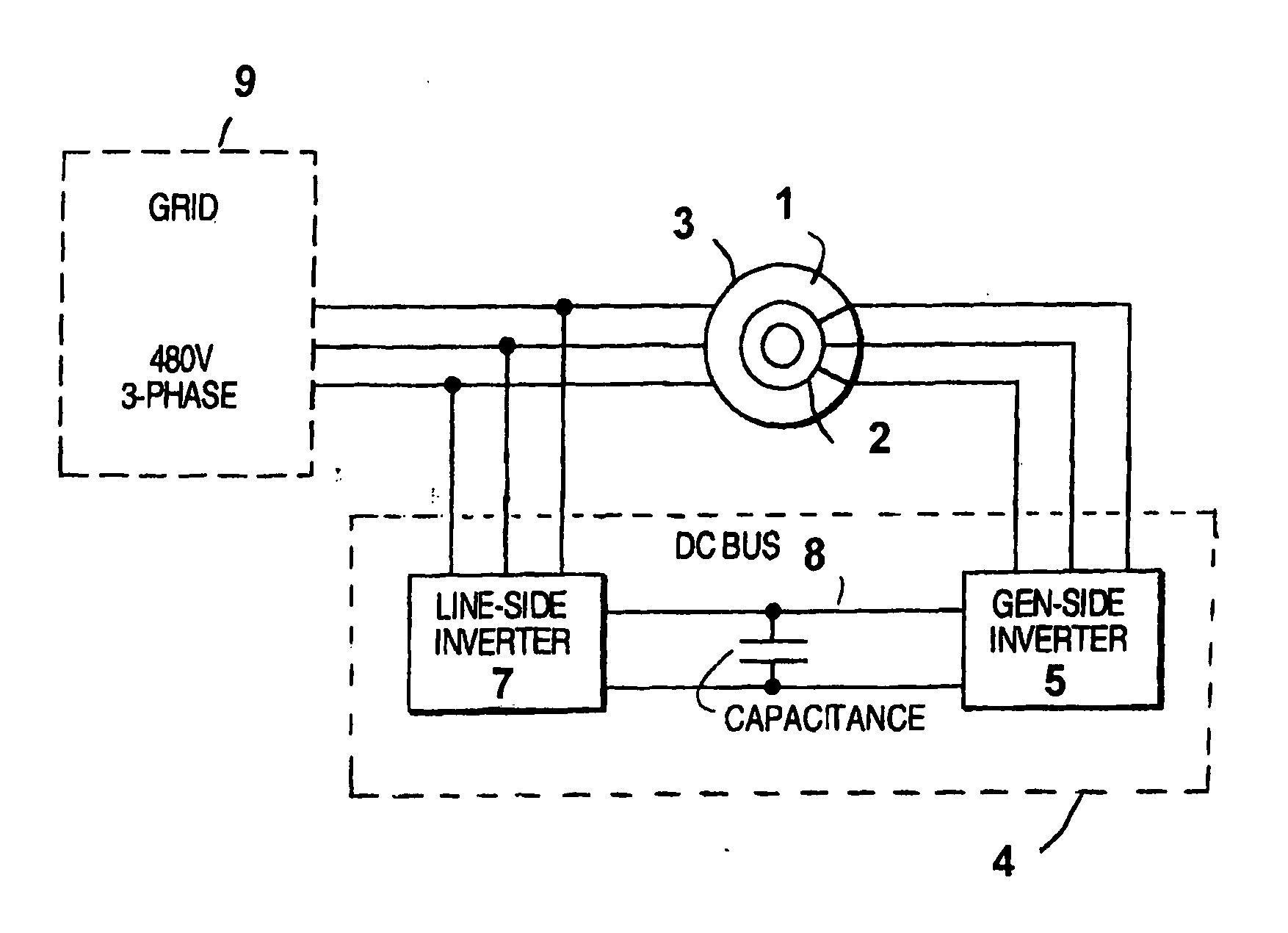
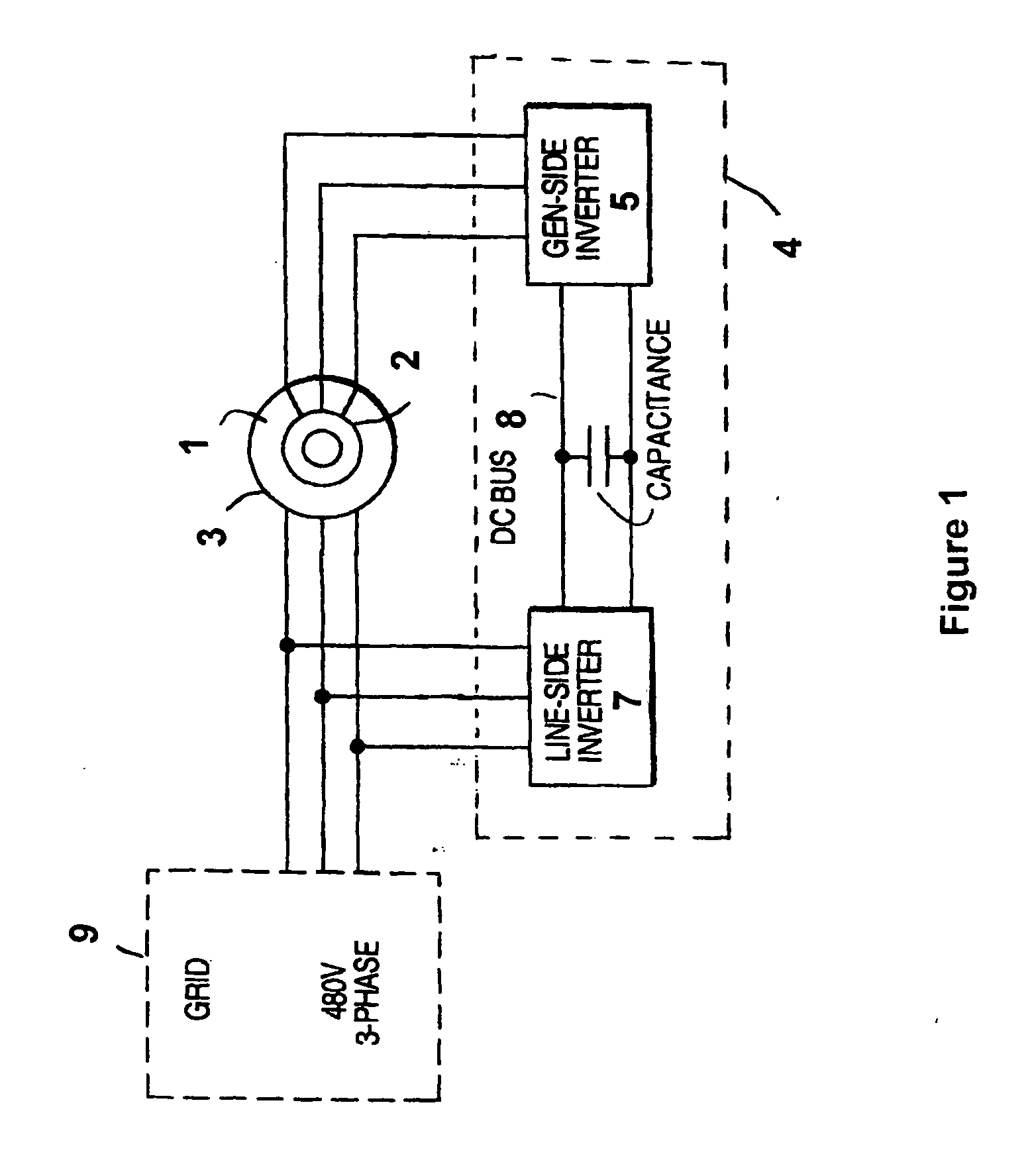
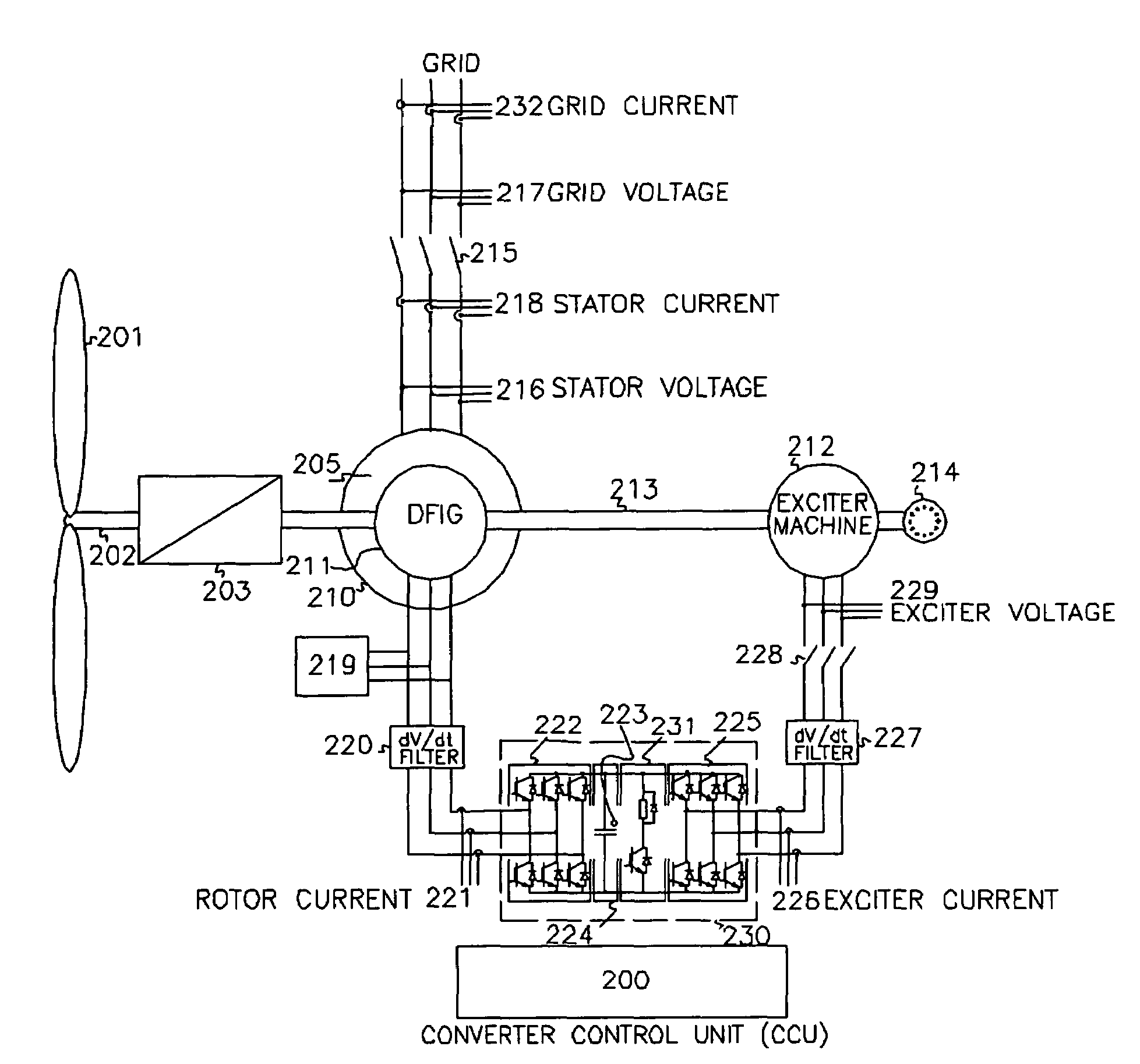
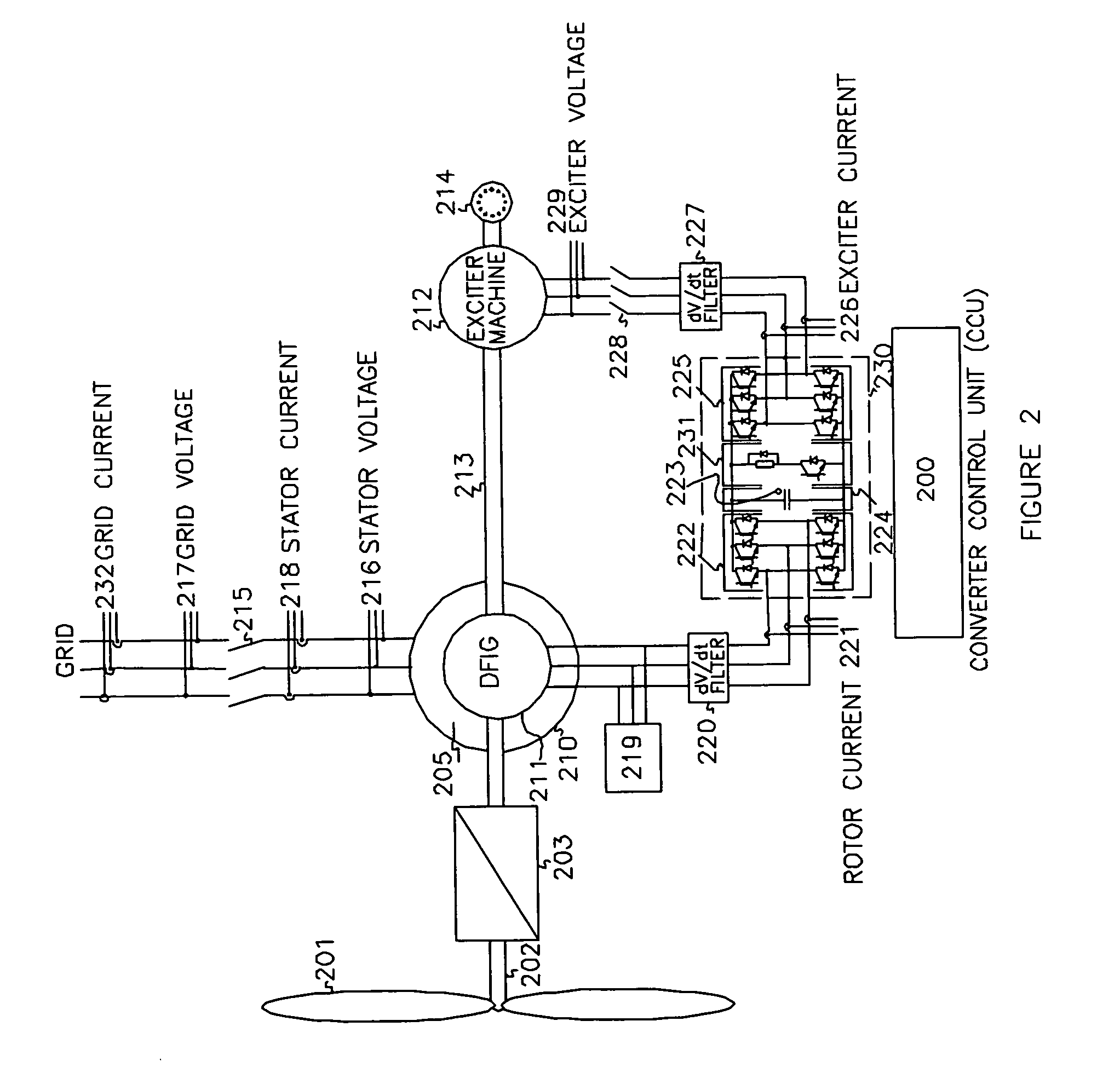
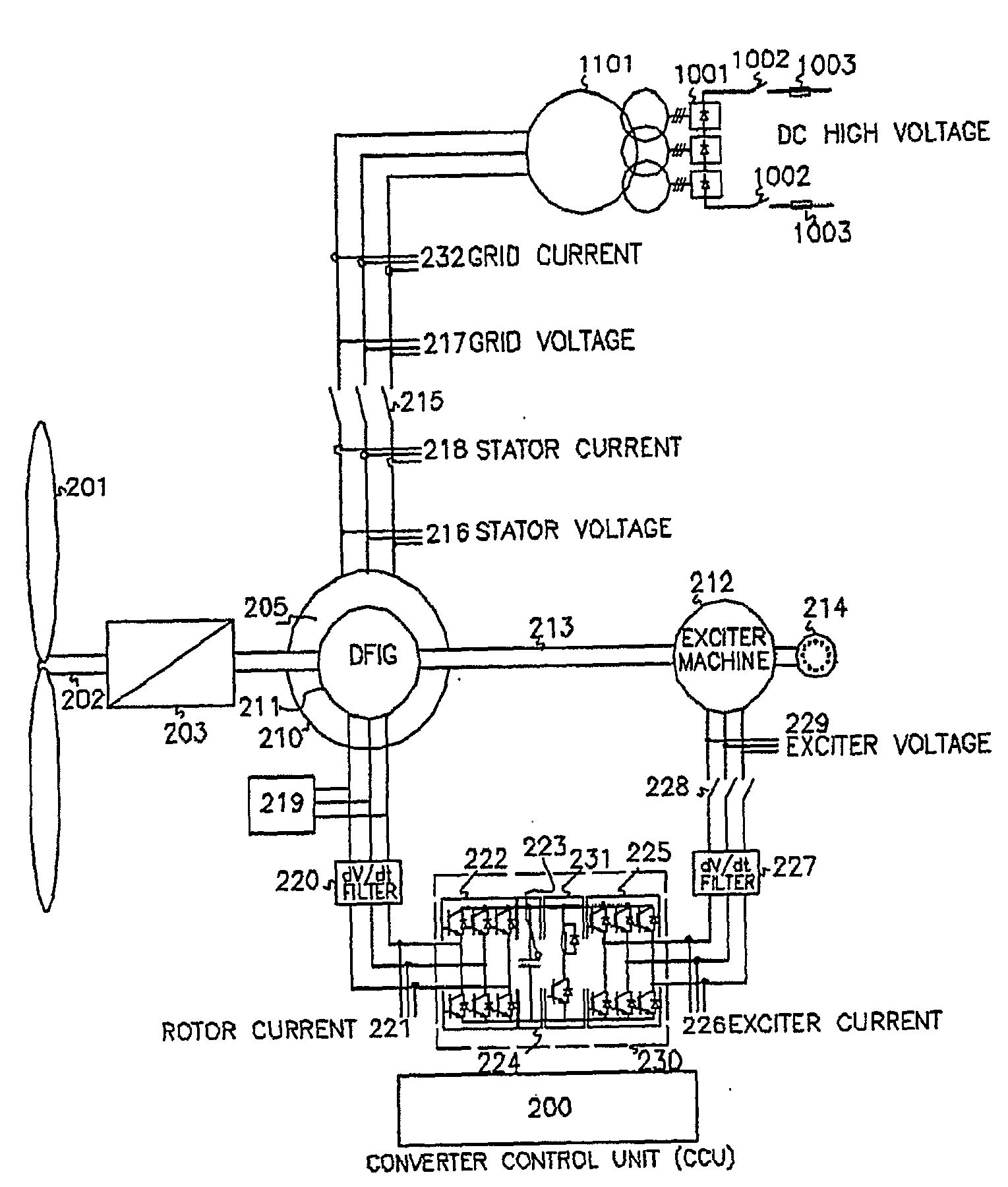
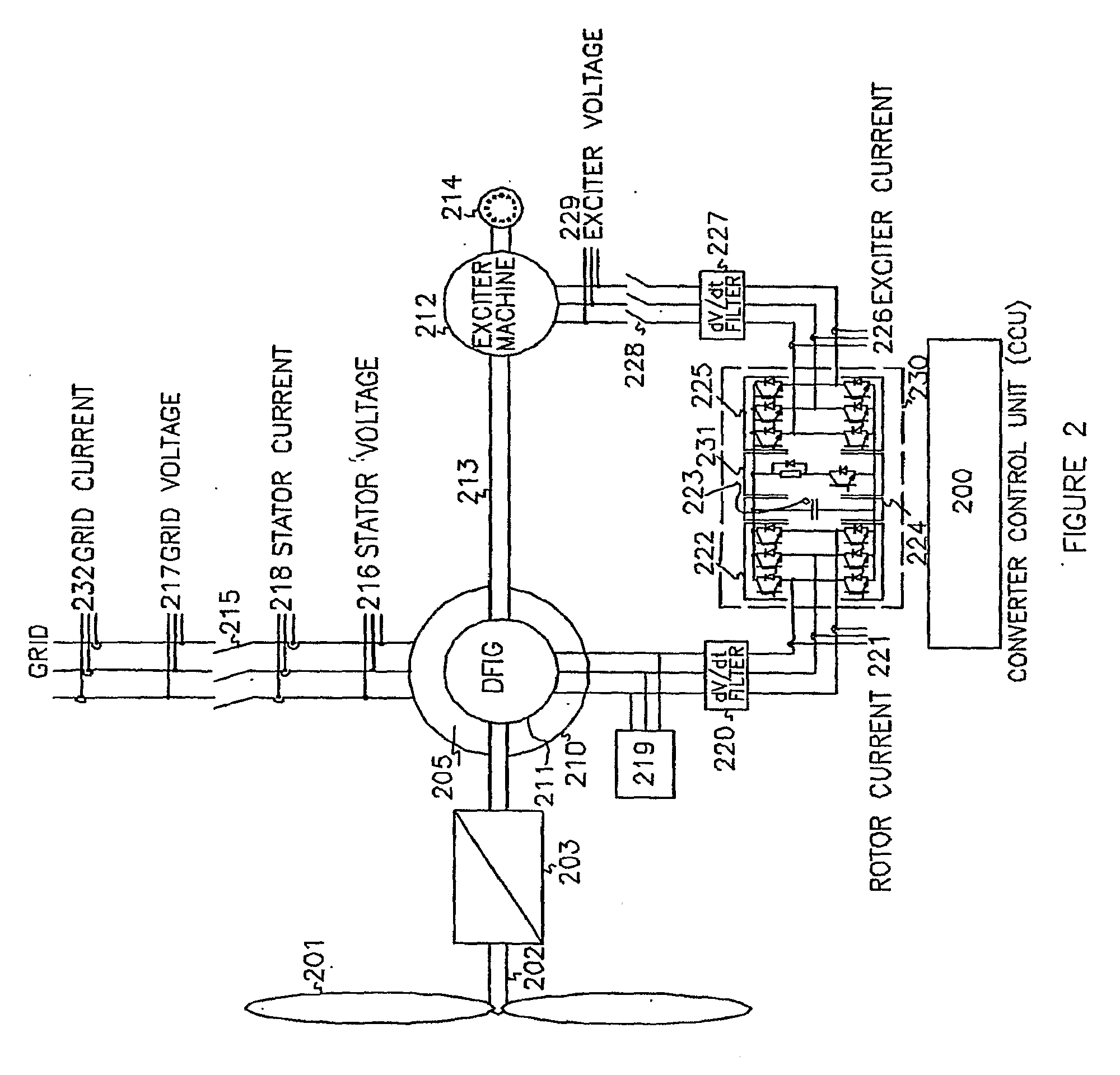
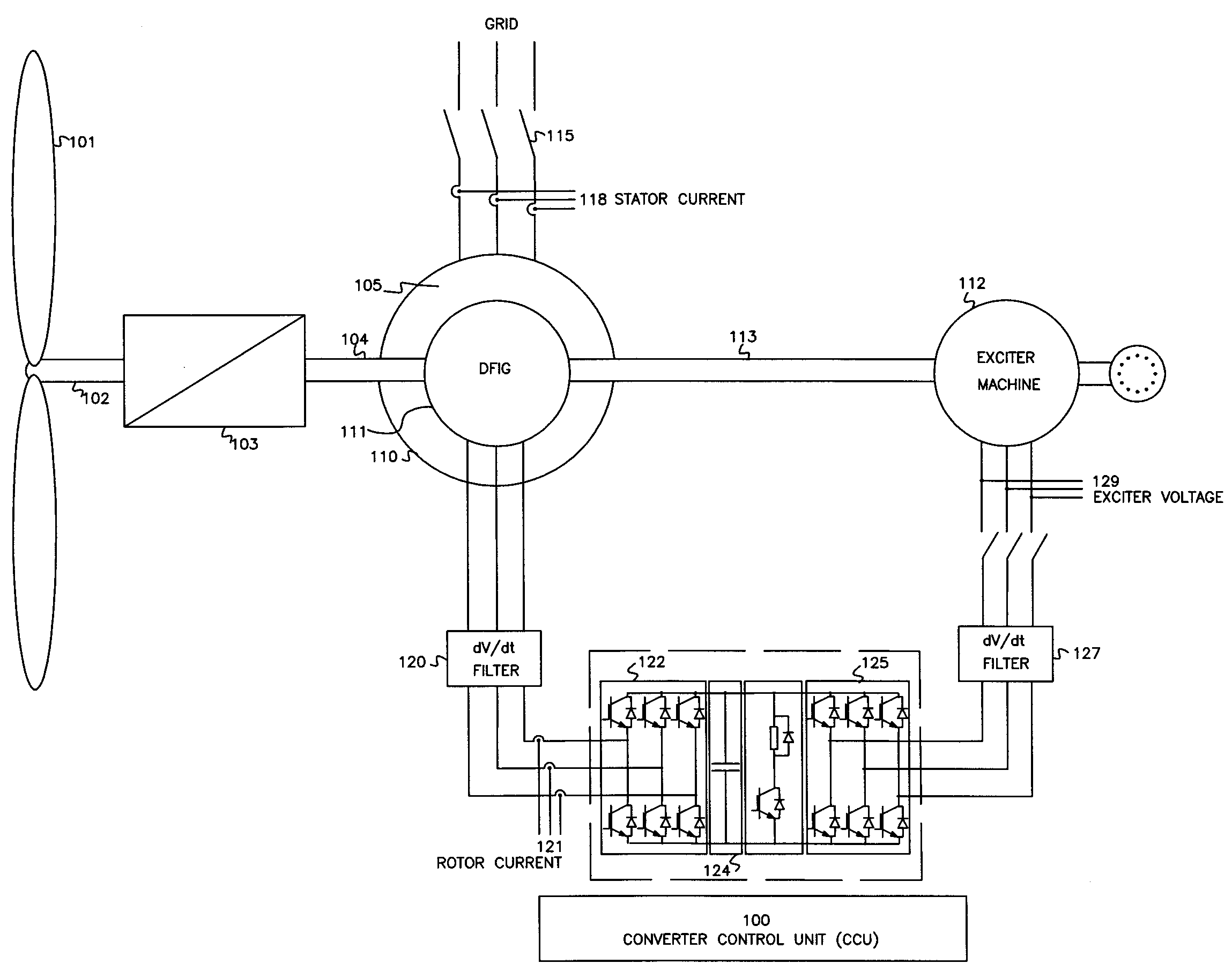
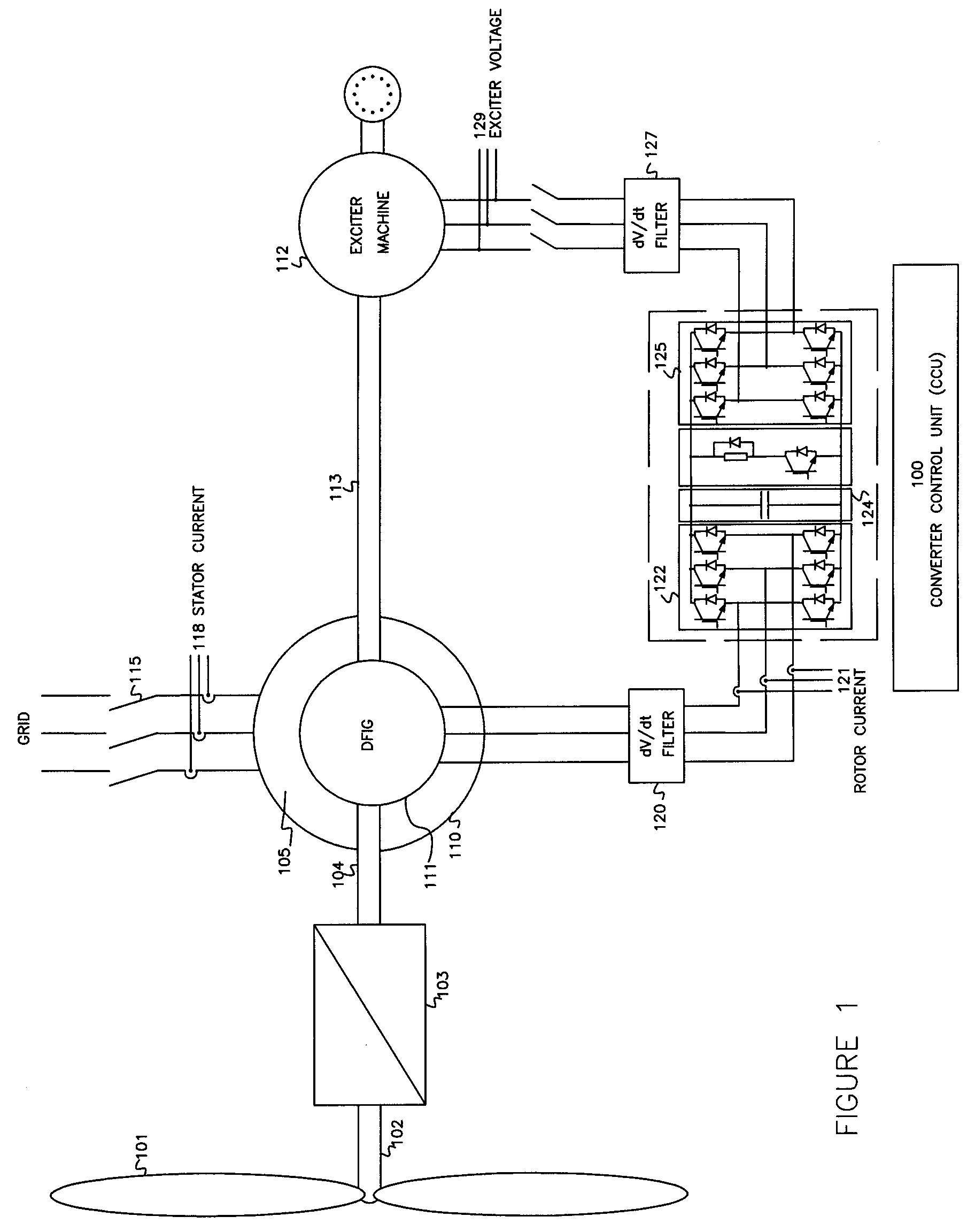
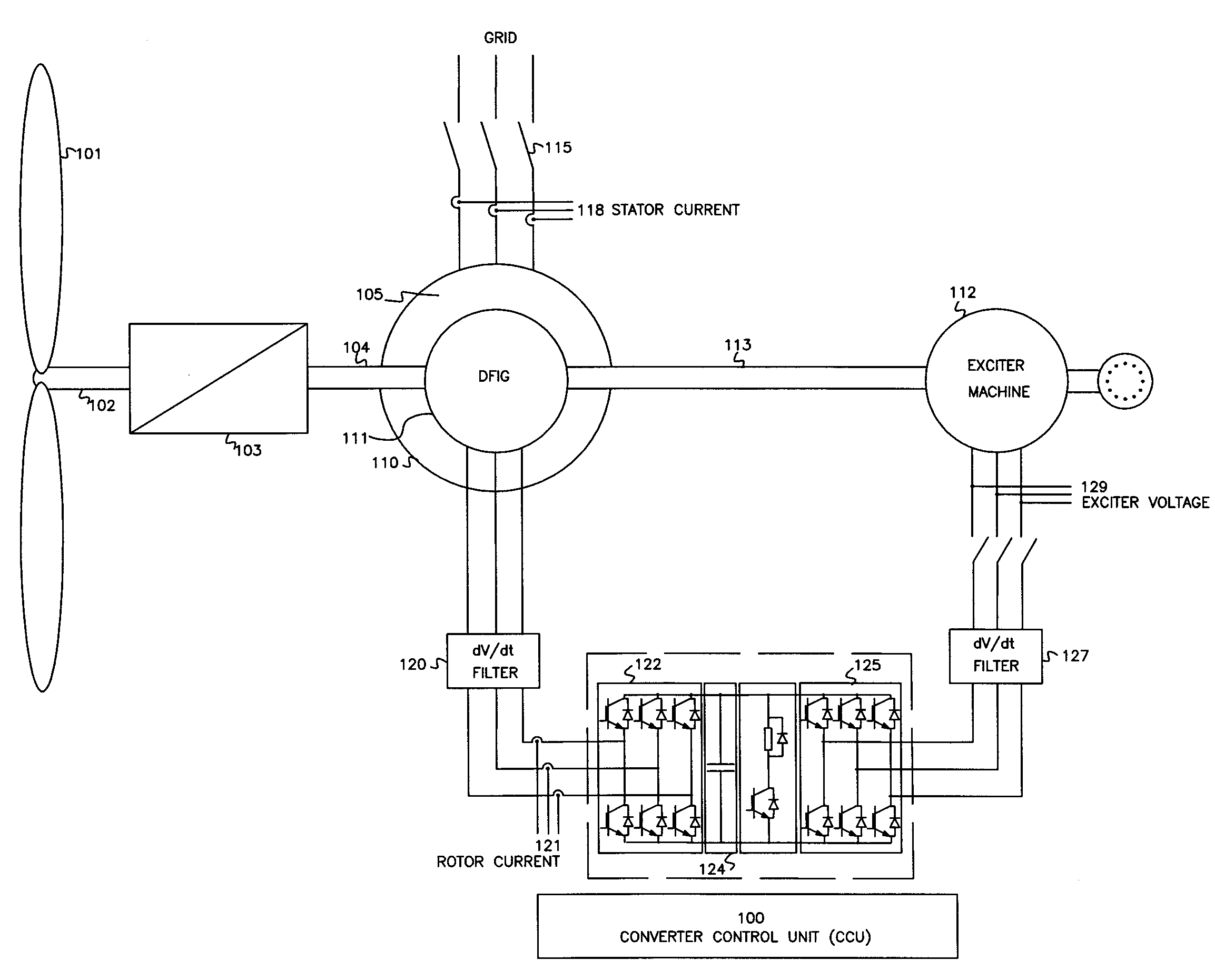
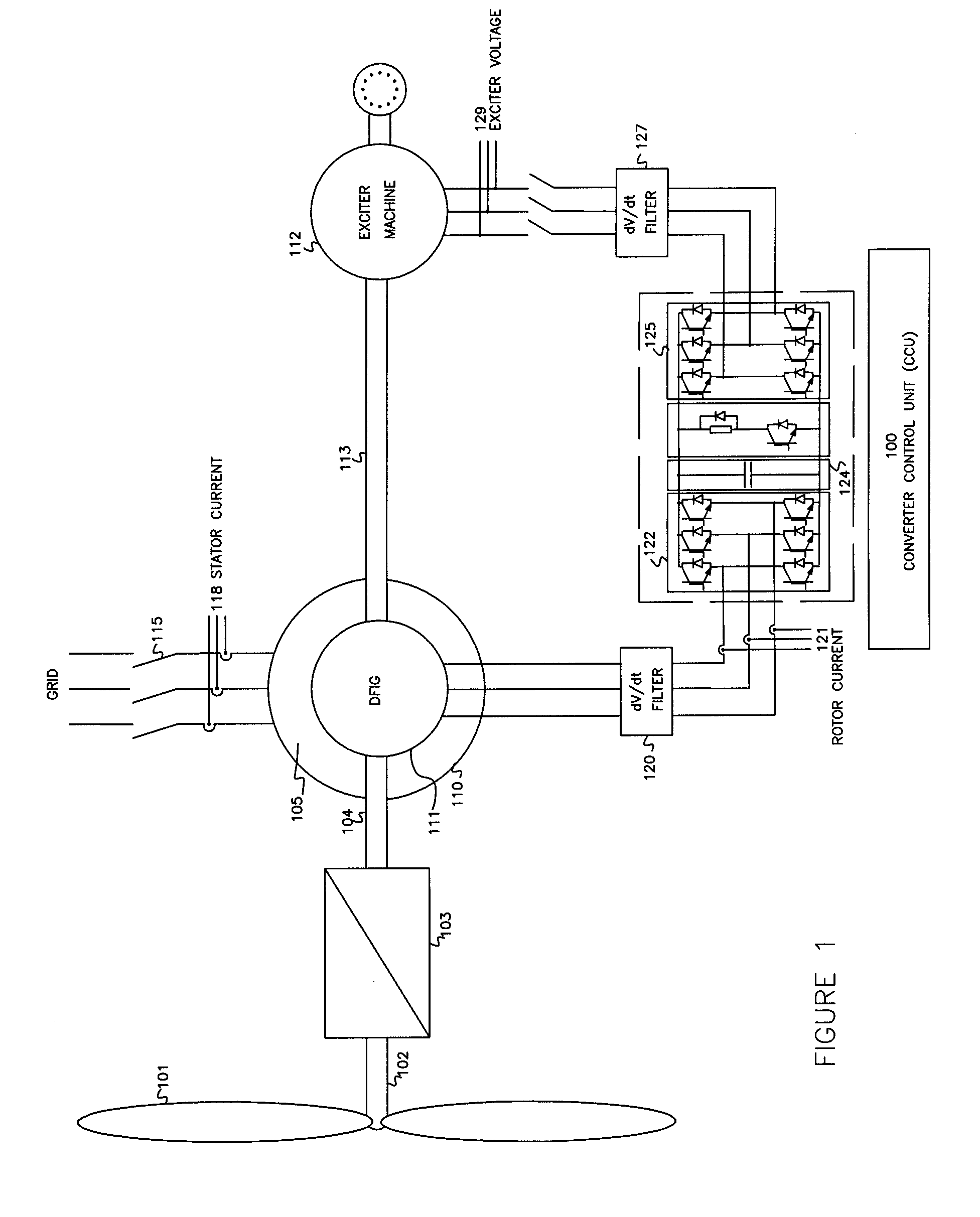
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS20070216164A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityHarmonic
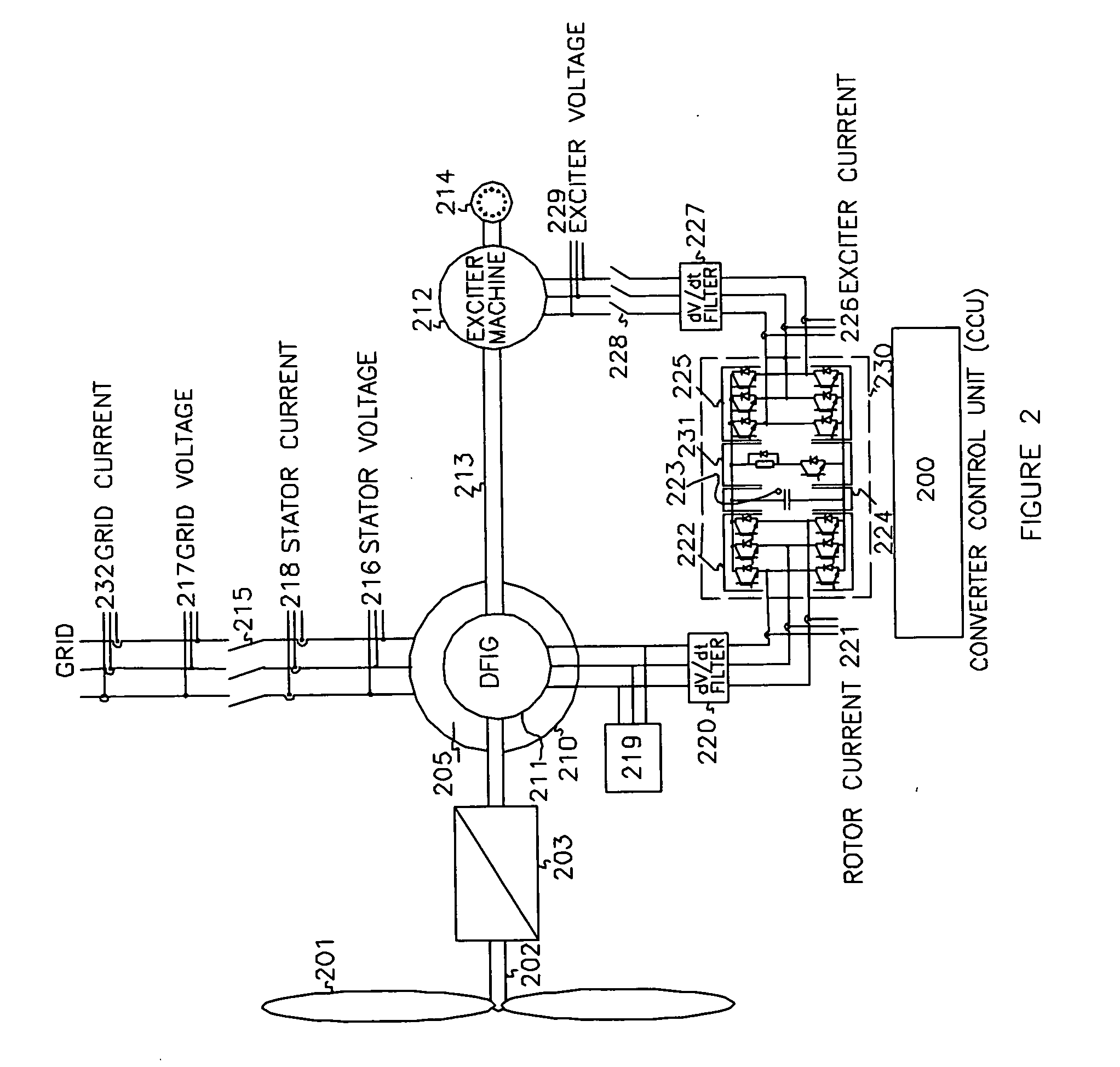
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
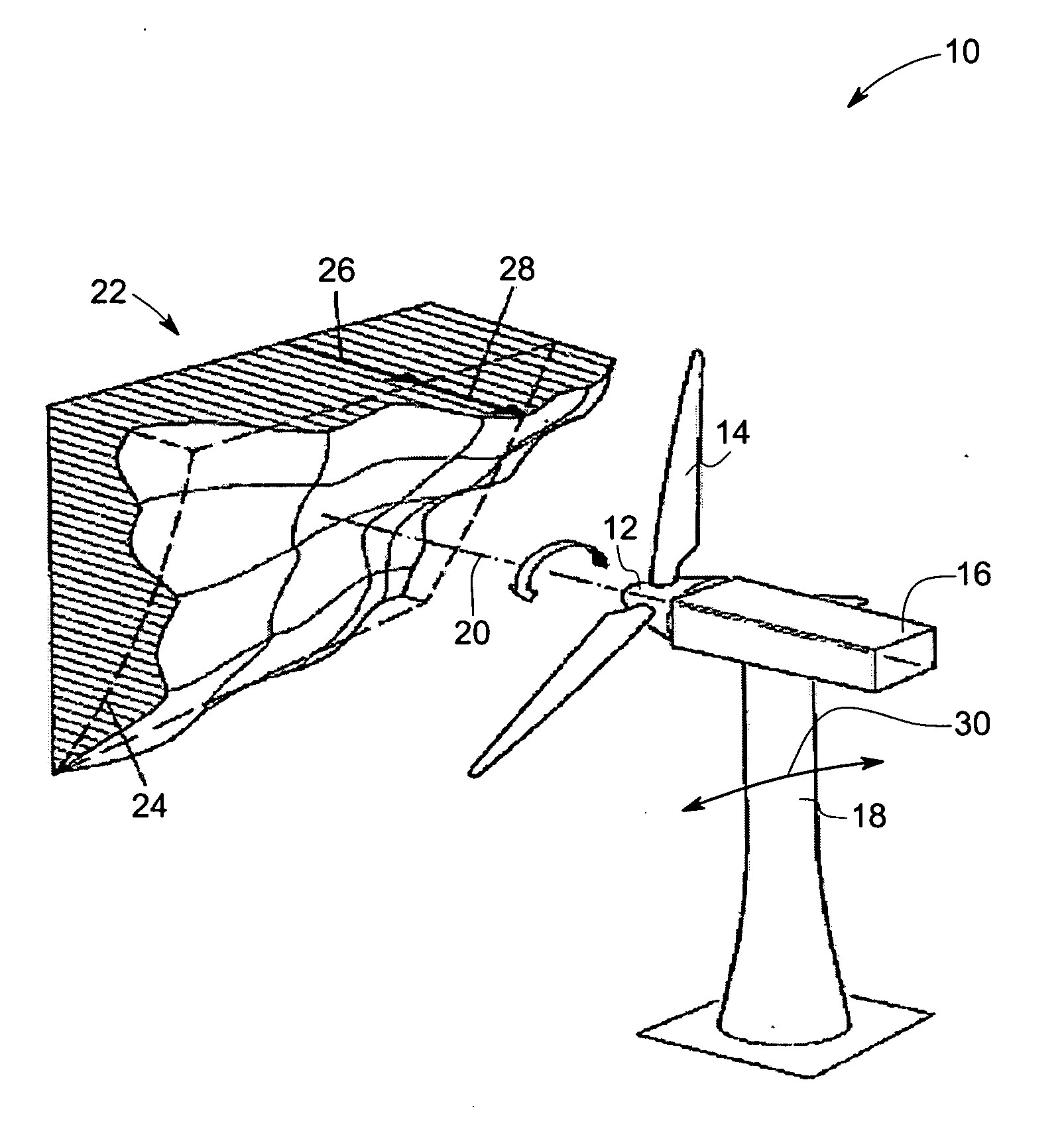
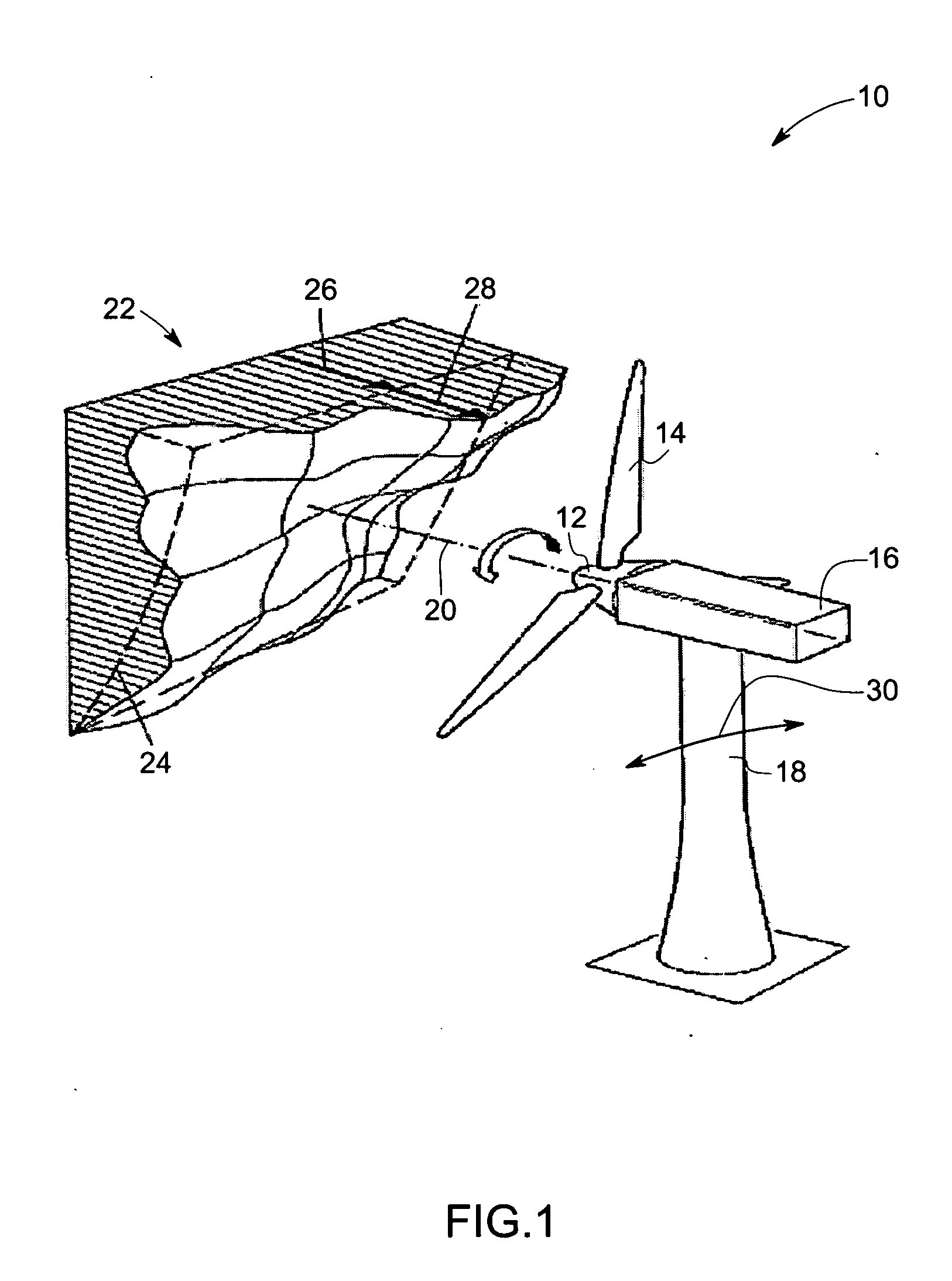
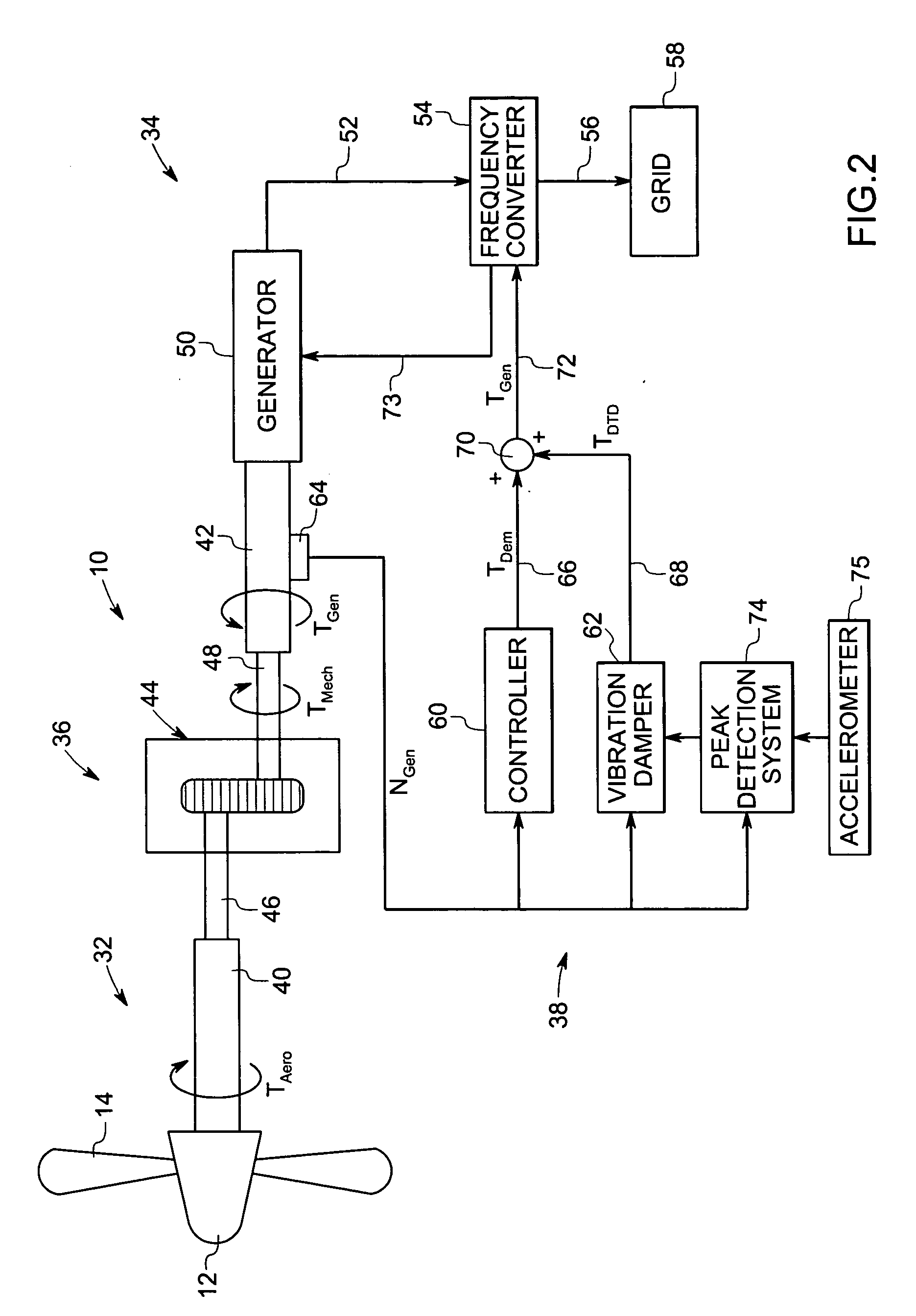
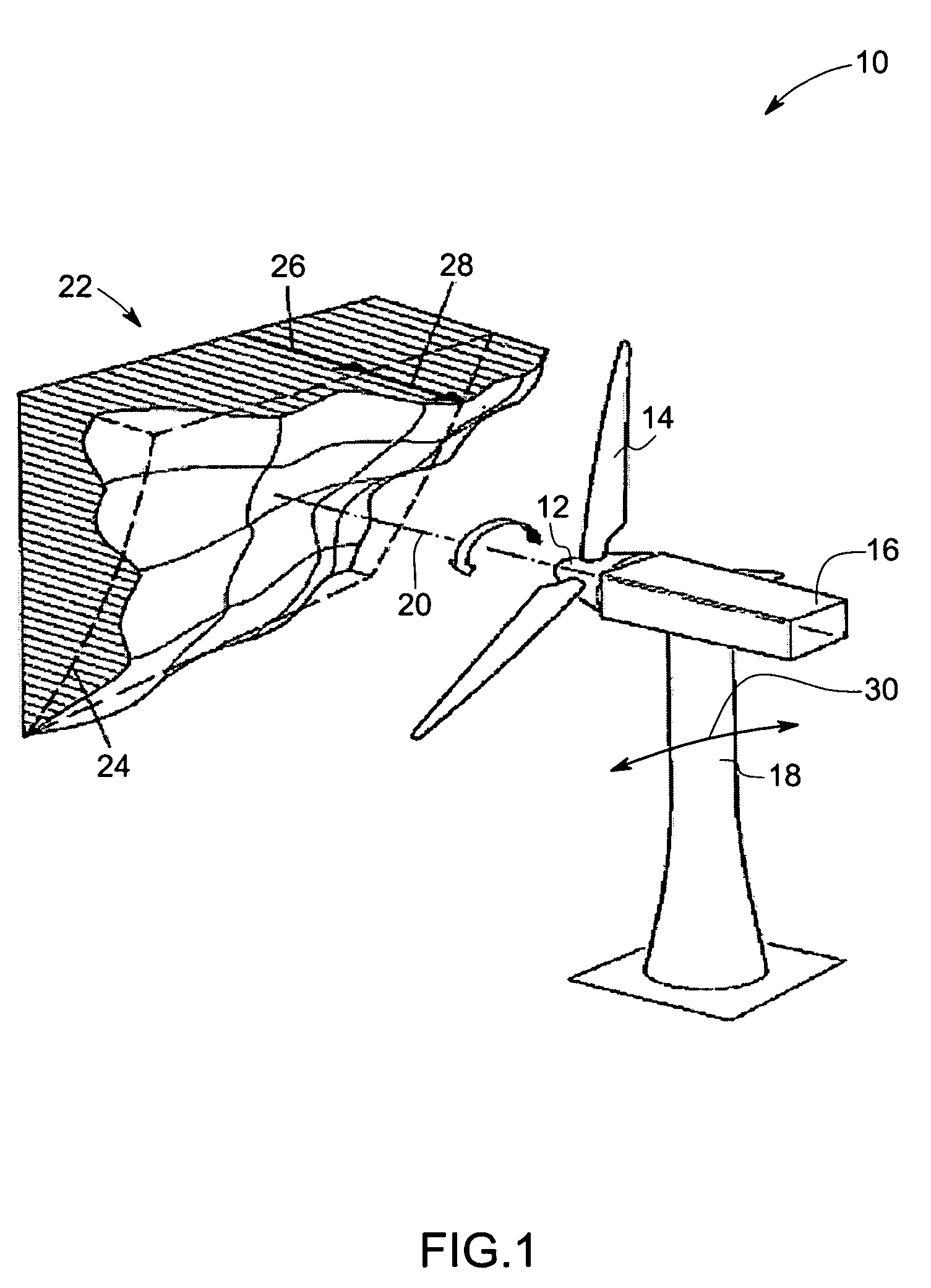
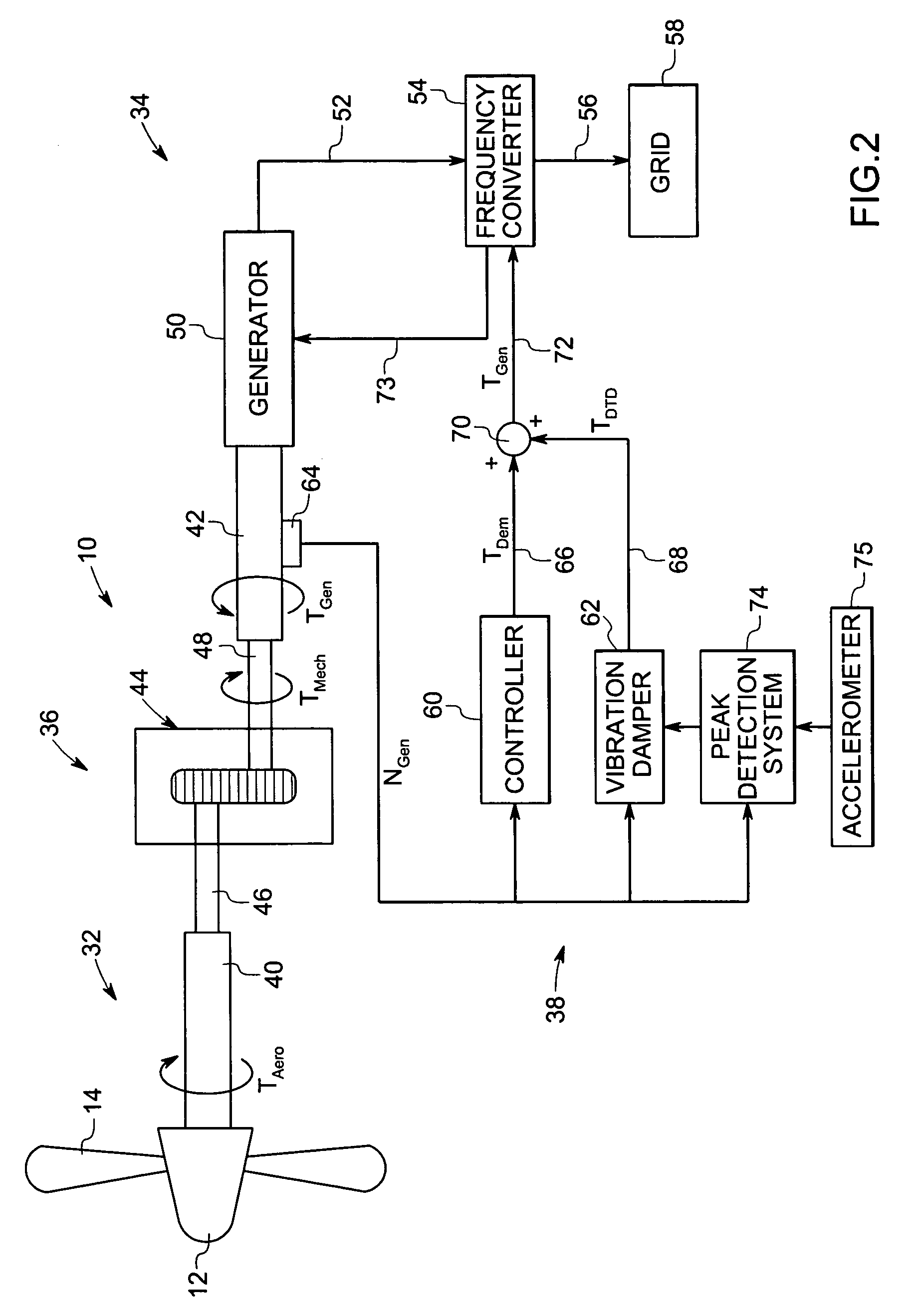
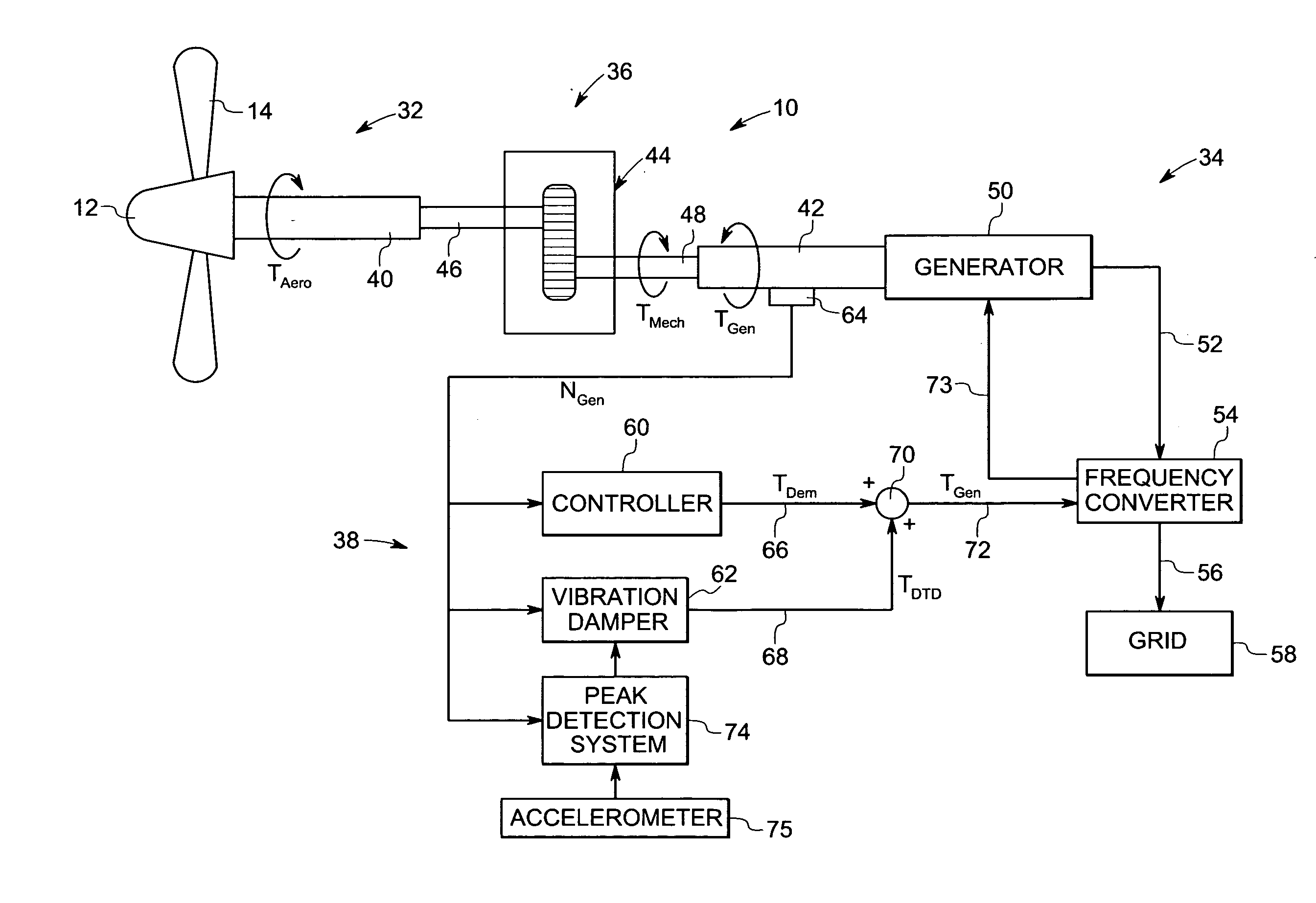
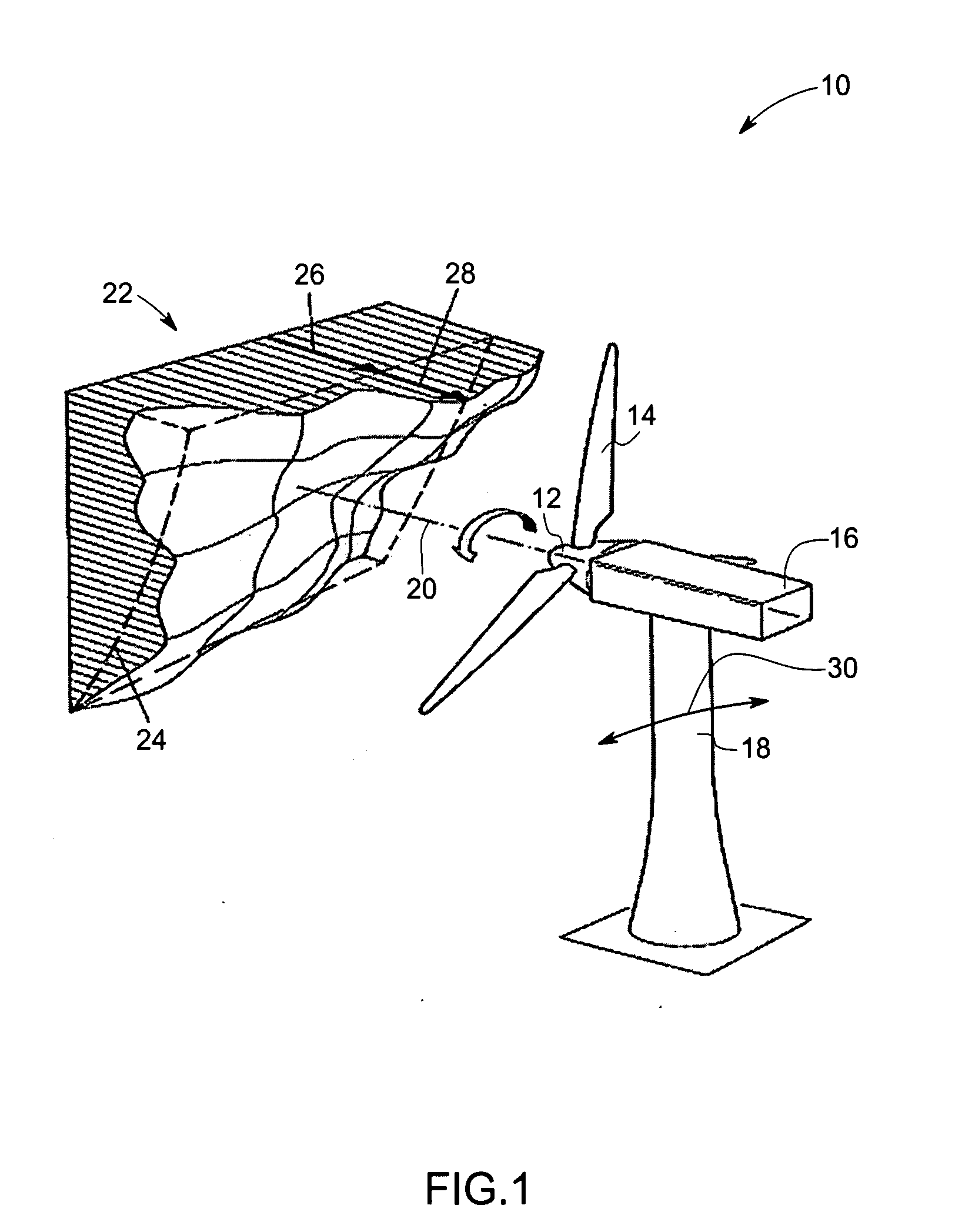
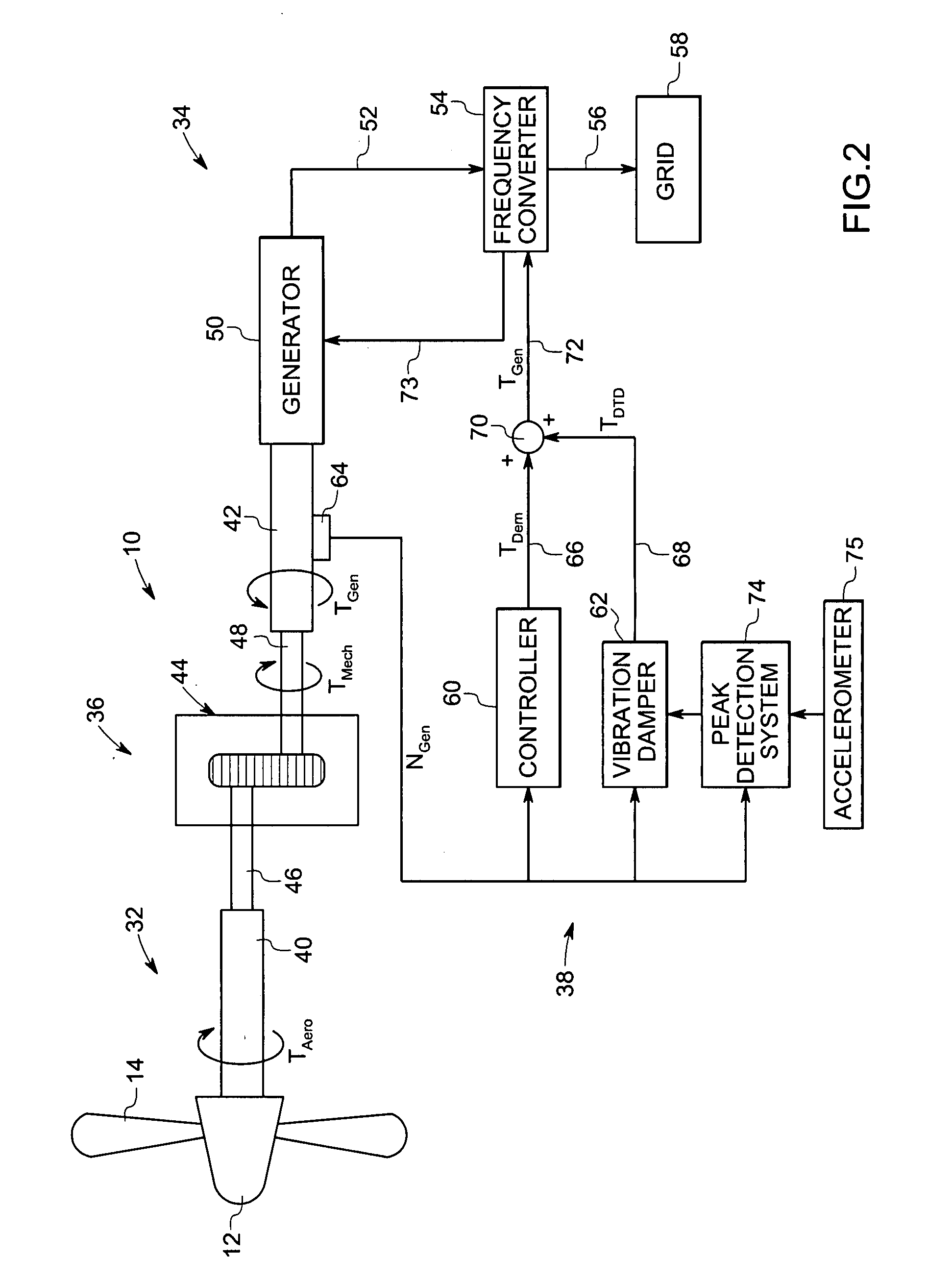
Vibration damping system and method for variable speed wind turbines
A vibration damping technique for a wind turbine system is described. The wind turbine system includes a vibration damper, which provides a variable signal to control torque produced by a generator of the wind turbine system. The variable signal is based on generator speed and has a first local peak value based on a resonant frequency of tower side-to-side oscillation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6847128B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Vibration damping system and method for variable speed wind turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable Speed Wind Turbine Configured For Wind Farm Operation
InactiveUS20090206606A1Easy to controlGood effectGenerator control circuitsOptimise machine performancePower gridVariable speed wind turbine
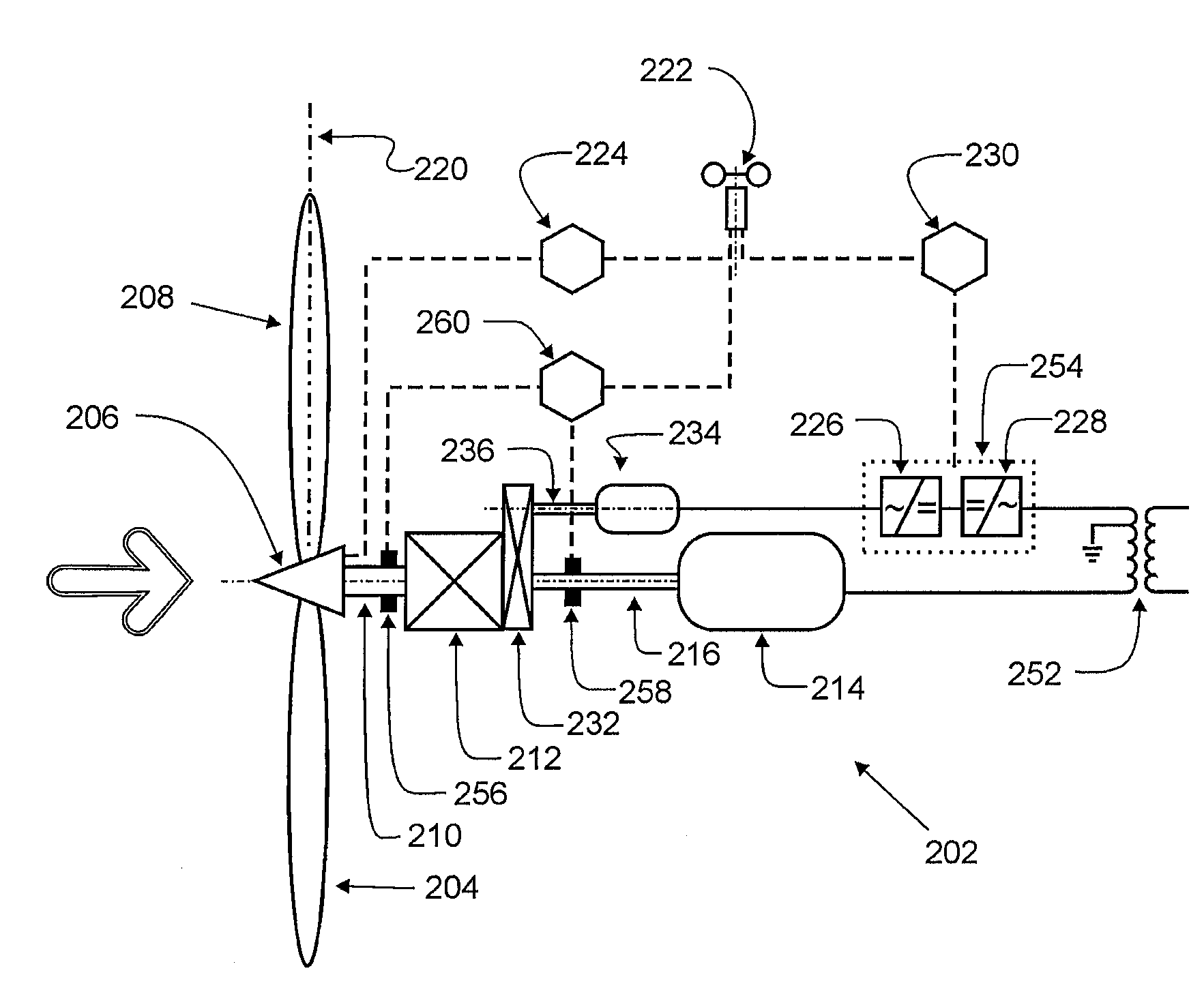
The present invention relates to an improved wind turbine, of the type which employs doubly fed induction generators (DFIG), and a wind park including the same, which permits the use of lighter weight turbines, with the ability to have greater energy capture, more precise control of asymmetrical phases and enhanced maintenance and support of the grid during fault conditions.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS7425771B2Avoid distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityPower grid
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856041B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6853094B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scaler power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
High voltage direct current link transmission system for variable speed wind turbine
ActiveUS20090278351A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsAc-dc conversion without reversalPower qualityHigh-voltage direct current
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Low voltage ride through system for a variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
InactiveUS7622815B2Improve variable performanceReduce capacityGenerator control circuitsMachines/enginesPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine which guarantees a stable voltage to the power converter. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid allowing the continuous operation of the system during a low voltage event in the grid.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Vibration damping method for variable speed wind turbines
A vibration damping technique for a wind turbine system is described. The wind turbine system includes a vibration damper, which provides a variable signal to control torque produced by a generator of the wind turbine system. The variable signal is based on generator speed and has a first local peak value based on a resonant frequency of tower side-to-side oscillation.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Low voltage ride through system for a variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
InactiveUS20080157529A1Improve variable performanceReduced power capacityGenerator control circuitsMachines/enginesPower gridEngineering
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine which guarantees a stable voltage to the power converter. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid allowing the continuous operation of the system during a low voltage event in the grid.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
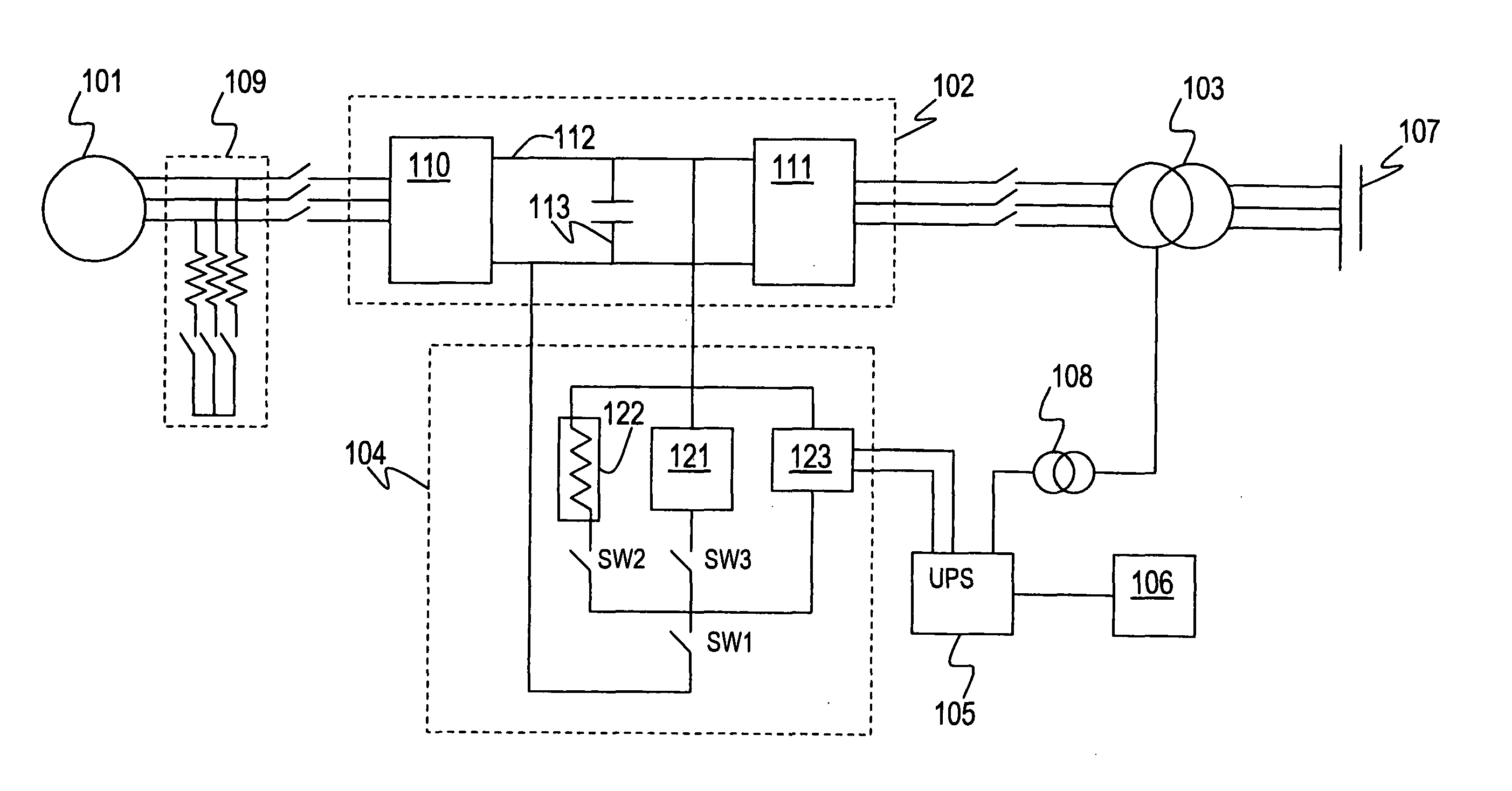
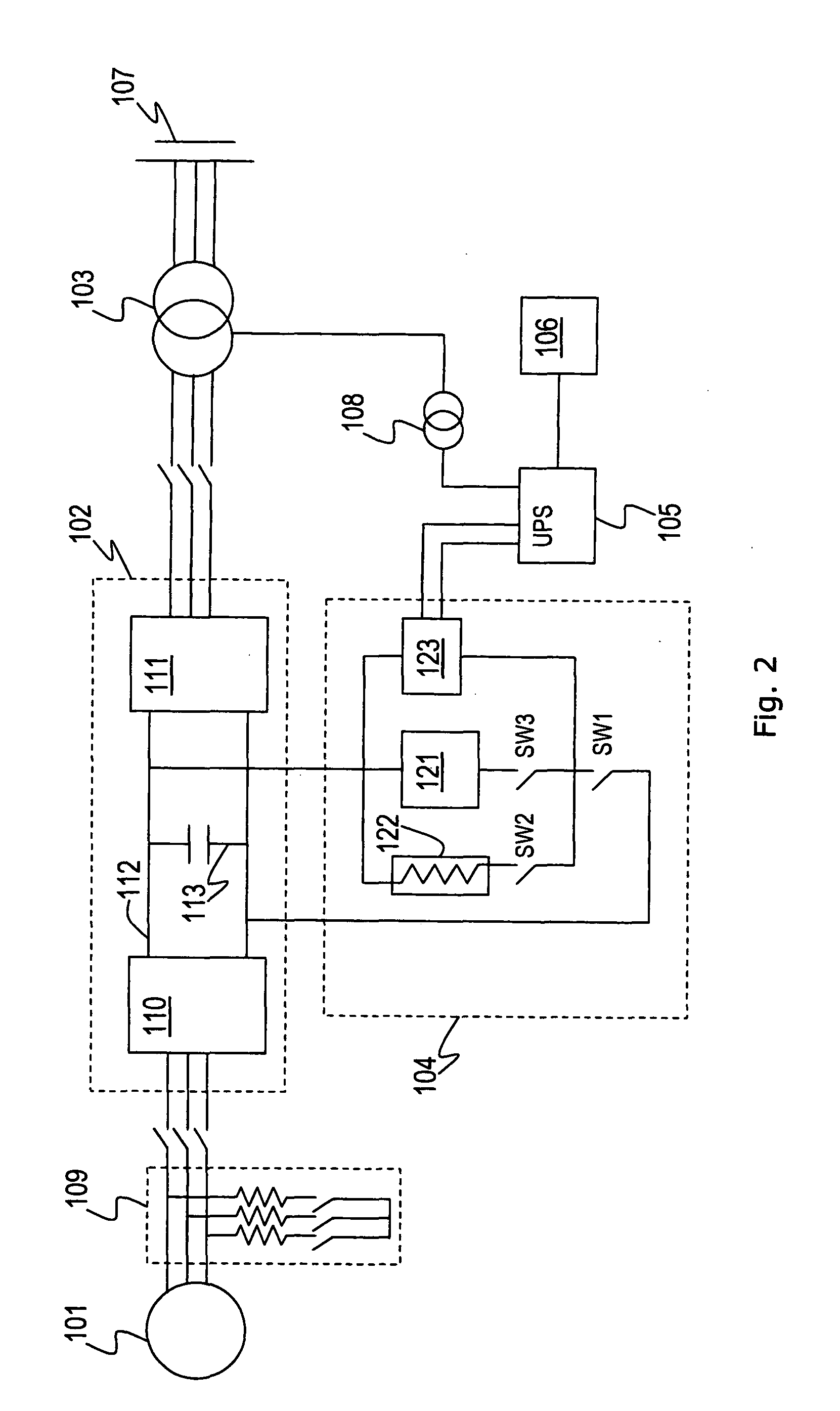
Variable speed wind turbine, and a method for operating the variable speed wind turbine during a power imbalance event
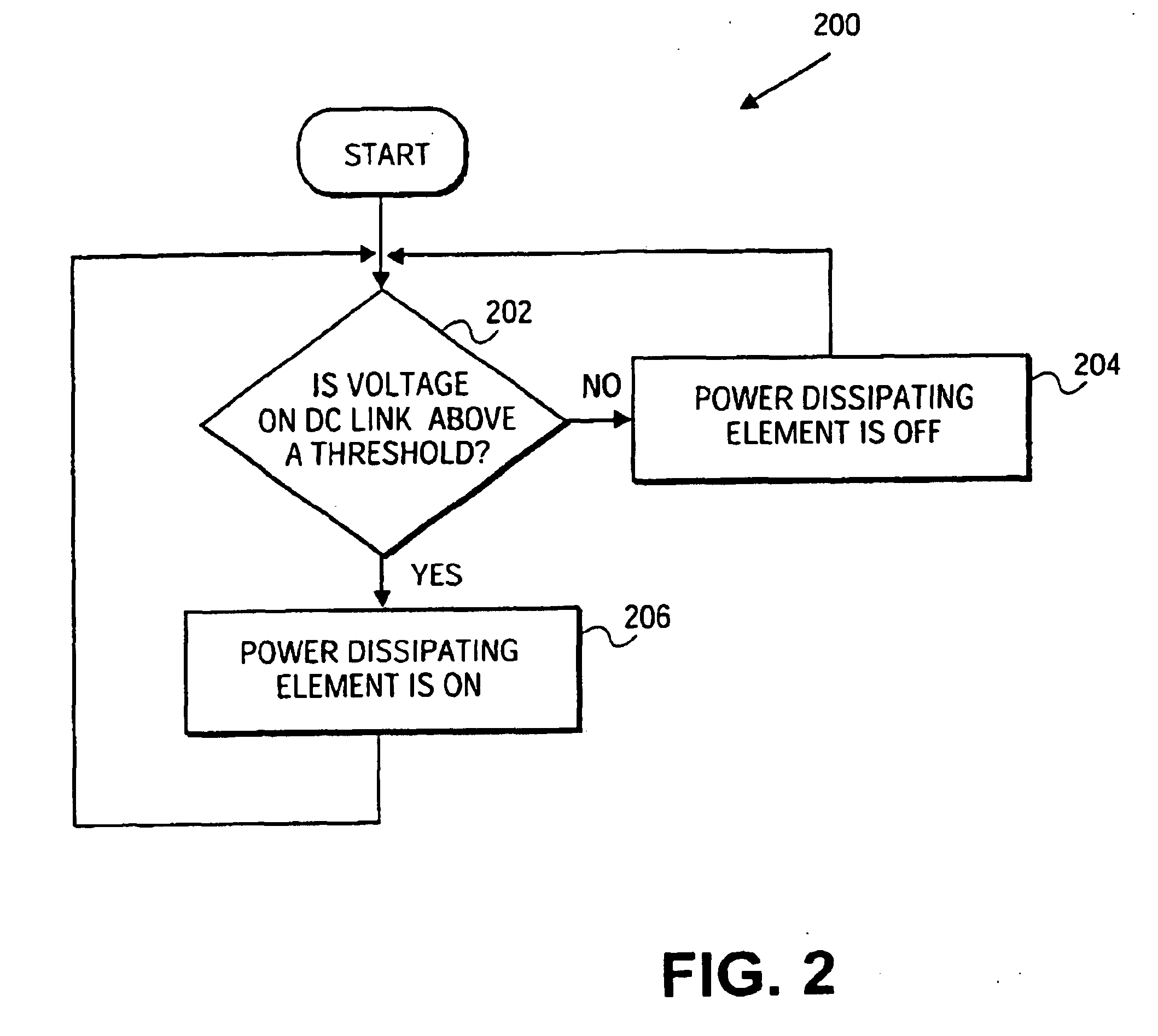
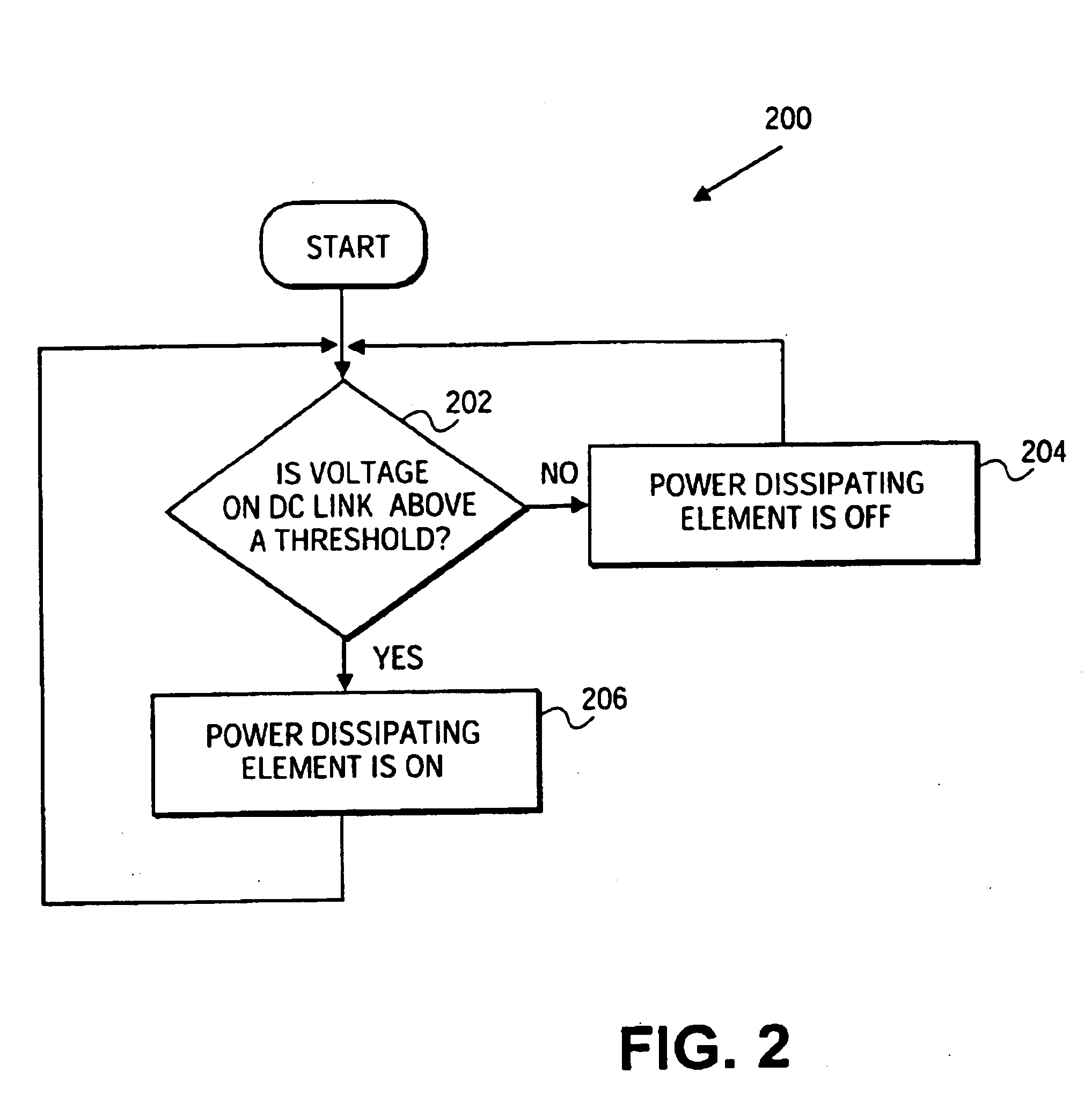
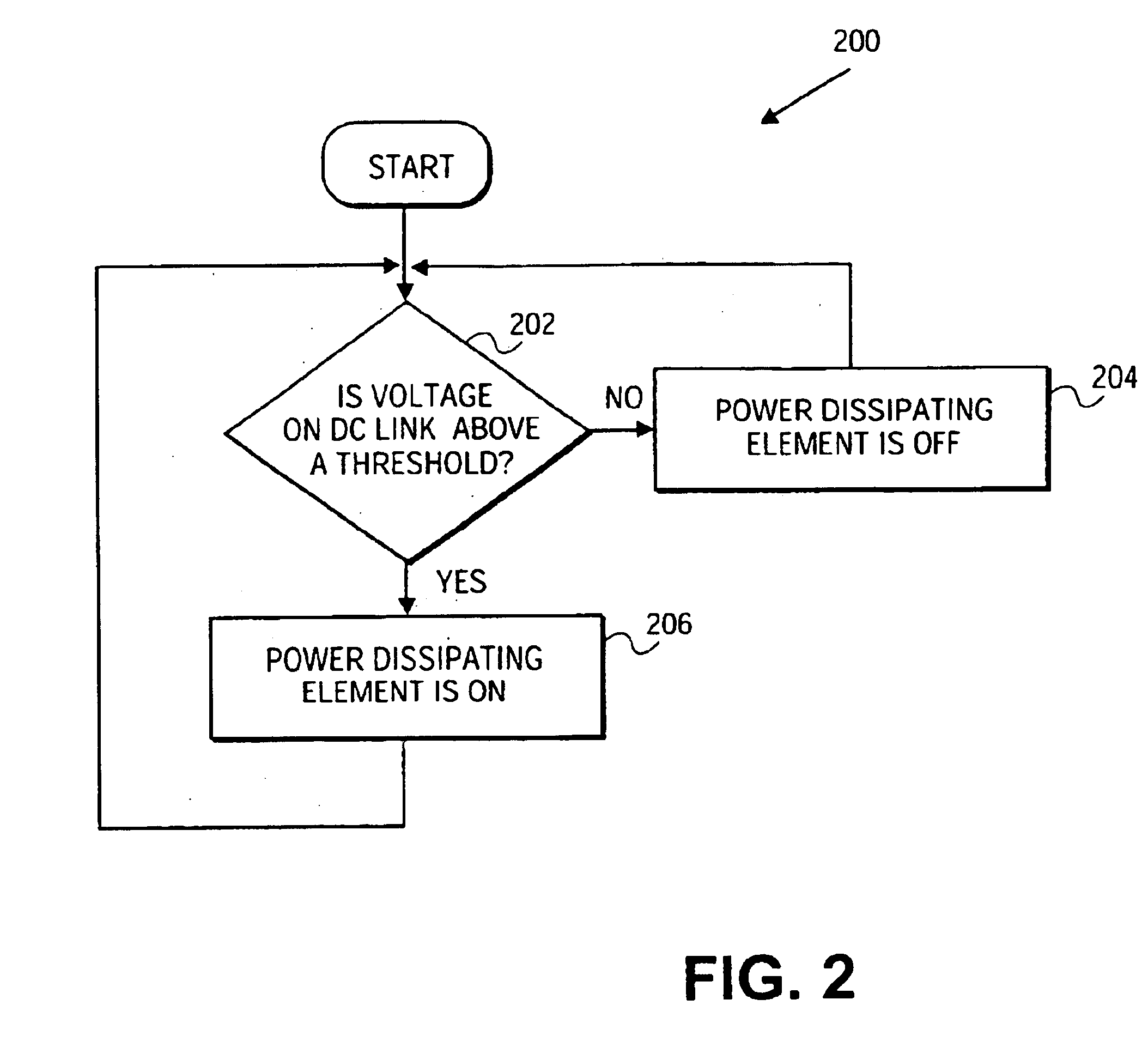
ActiveUS20120217824A1Better energy managementExcess power being dissipatedRotary current collectorWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineTurbine
A variable speed wind turbine is provided. The wind turbine comprises a generator, a power converter for converting at least a portion of electrical power generated by the generator, an energy management arrangement coupled to the power converter, the energy management arrangement comprises an energy storage unit, and a controller. The controller is adapted to detect a power imbalance event and to transfer at least a portion of excess electrical energy generated by the generator to the energy storage unit to be stored therein when the power imbalance event is detected.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
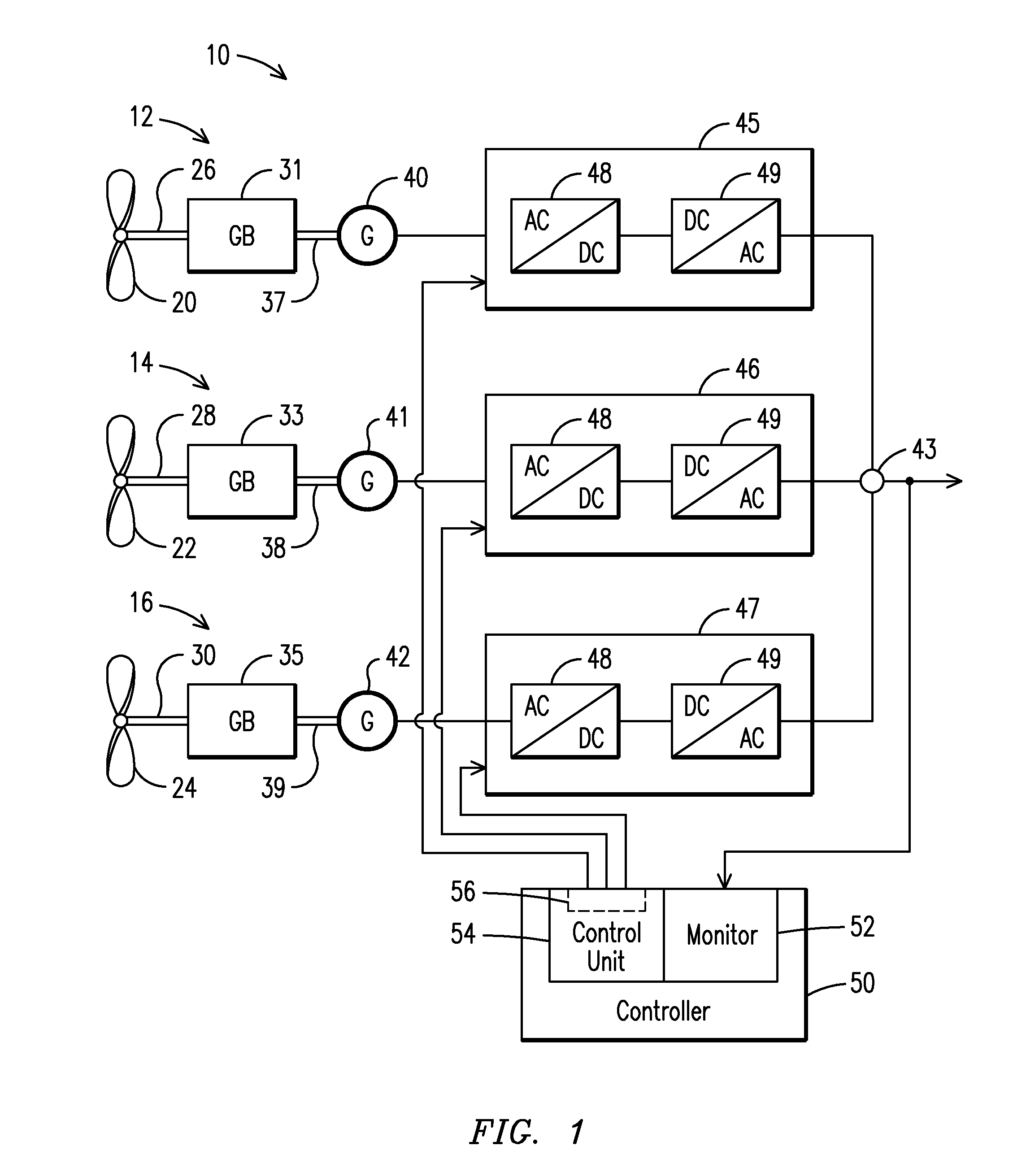
Frequency-Responsive Wind Turbine Output Control
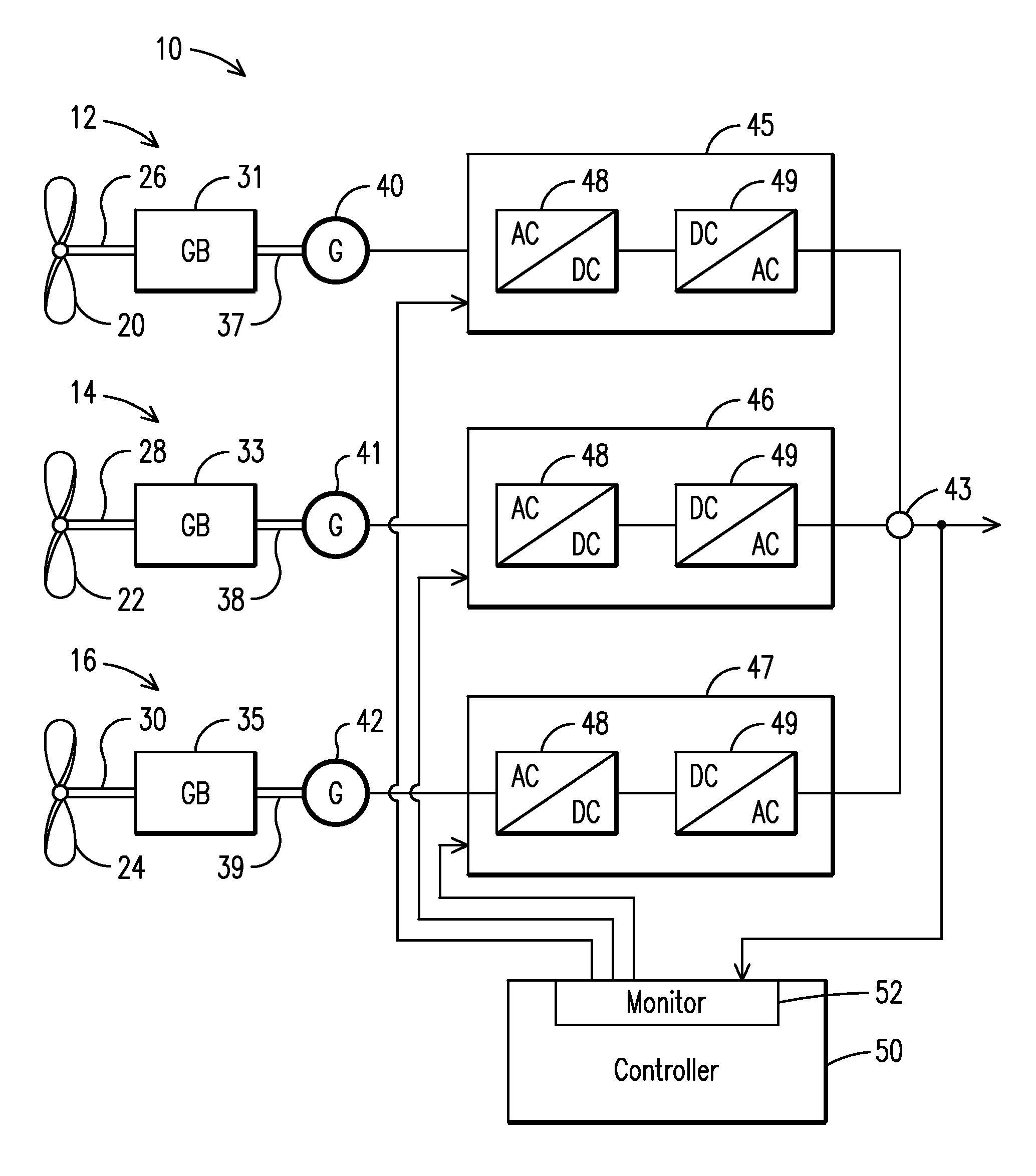
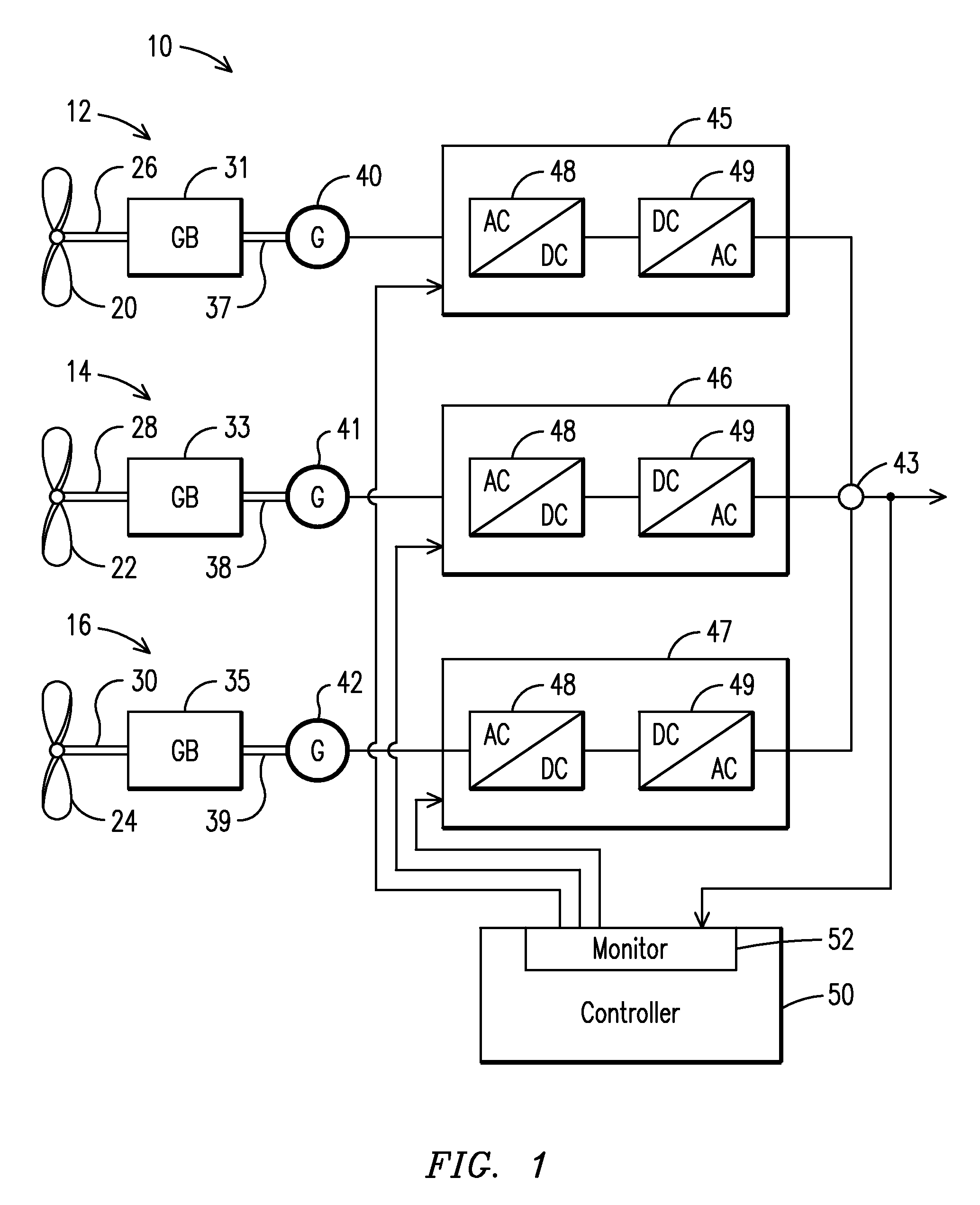
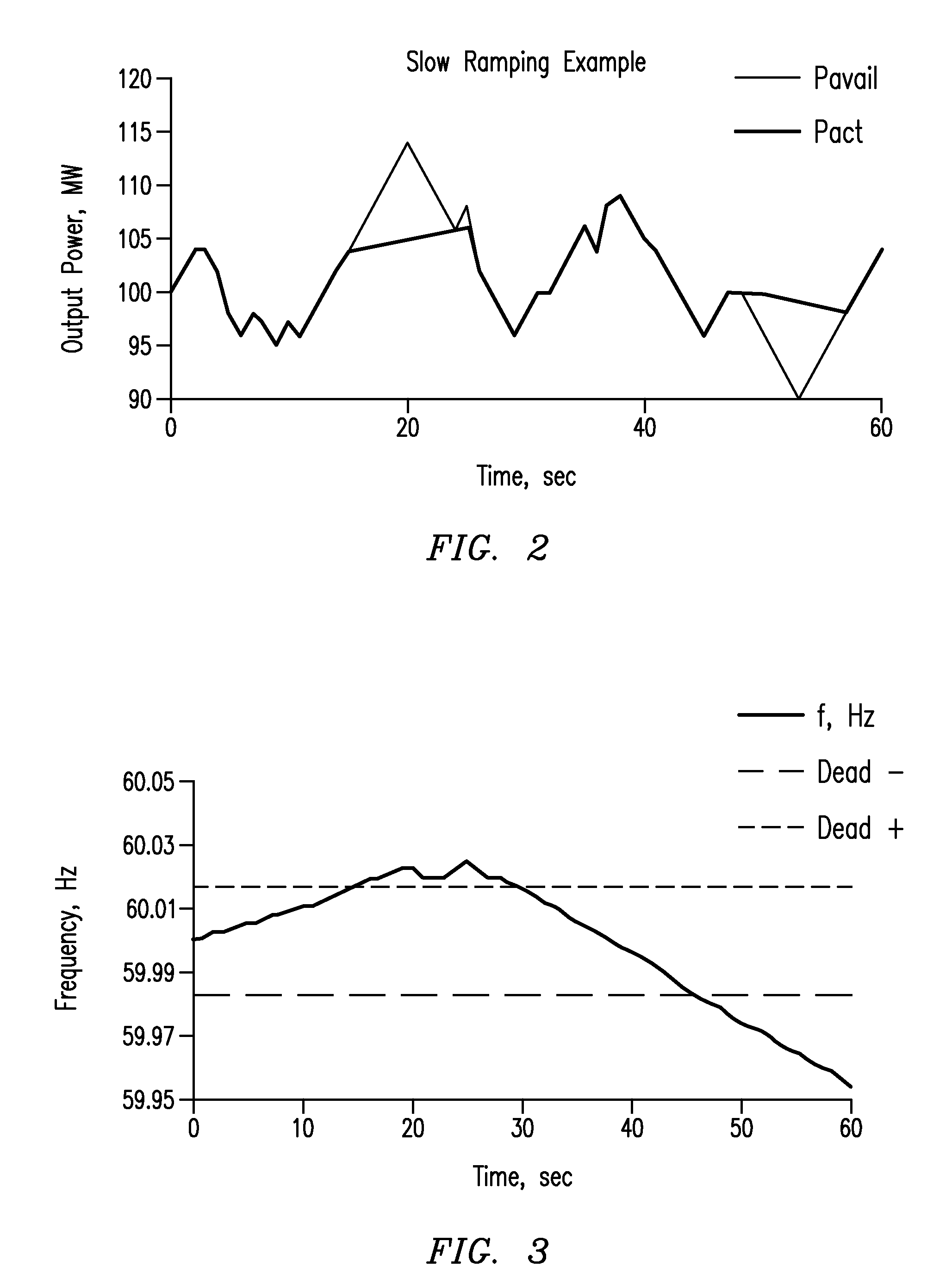
A wind farm (10) may include a plurality of variable speed wind turbines (12, 14, 16). A centralized controller (50) may be configured to selectively adjust a respective electrical output power from each of the wind turbines. The controller may include a monitor (52) configured to monitor a correlation between a deviation from a grid frequency and a wind power change. The controller may be configured to adjust a response of the electrical output power based on the monitored correlation. The electrical output power response may be configured to meet a grid frequency regulation notwithstanding of random occurrences of wind power changes.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
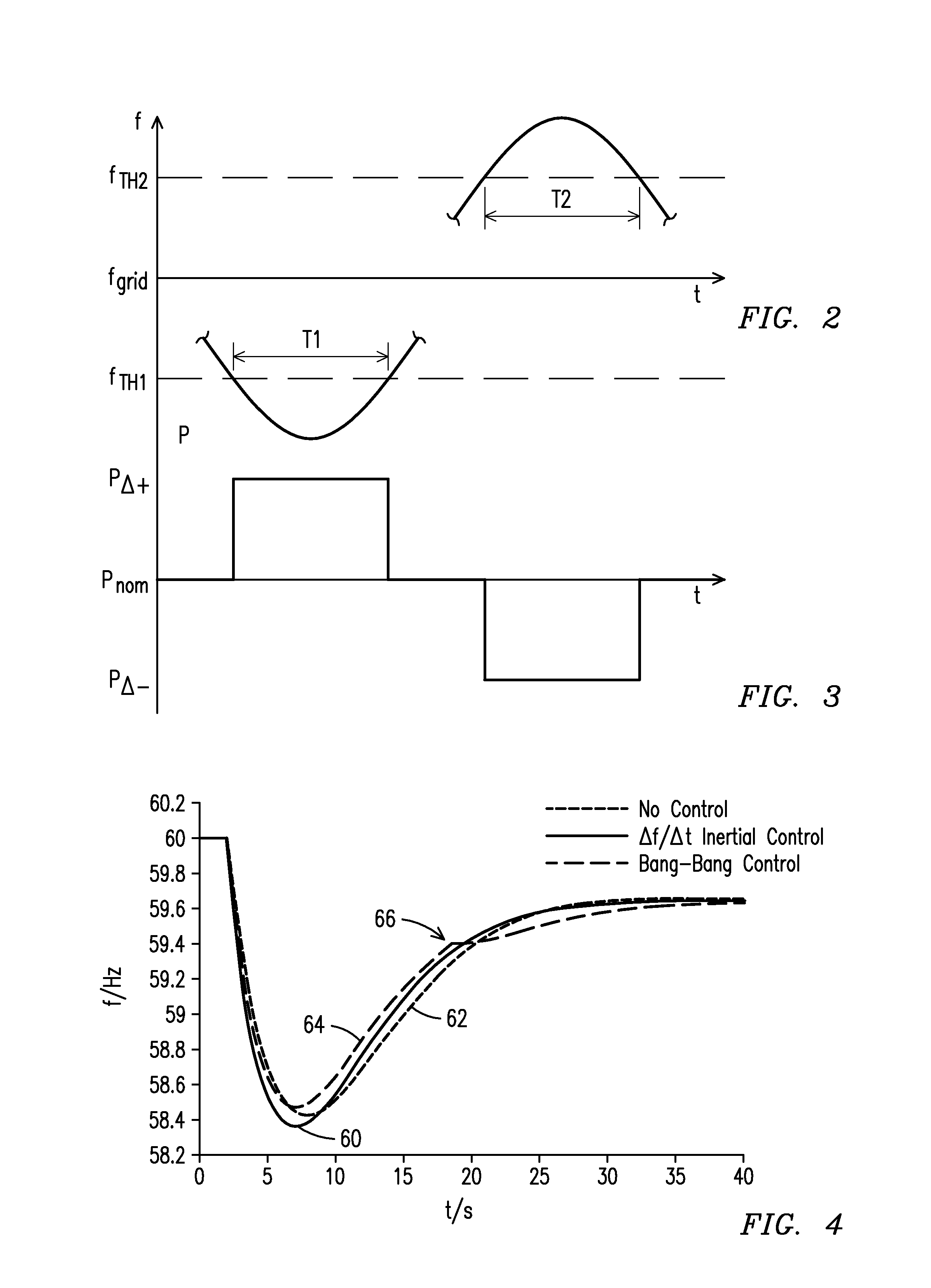
Bang-Bang Controller and Control Method For Variable Speed Wind Turbines During Abnormal Frequency Conditions
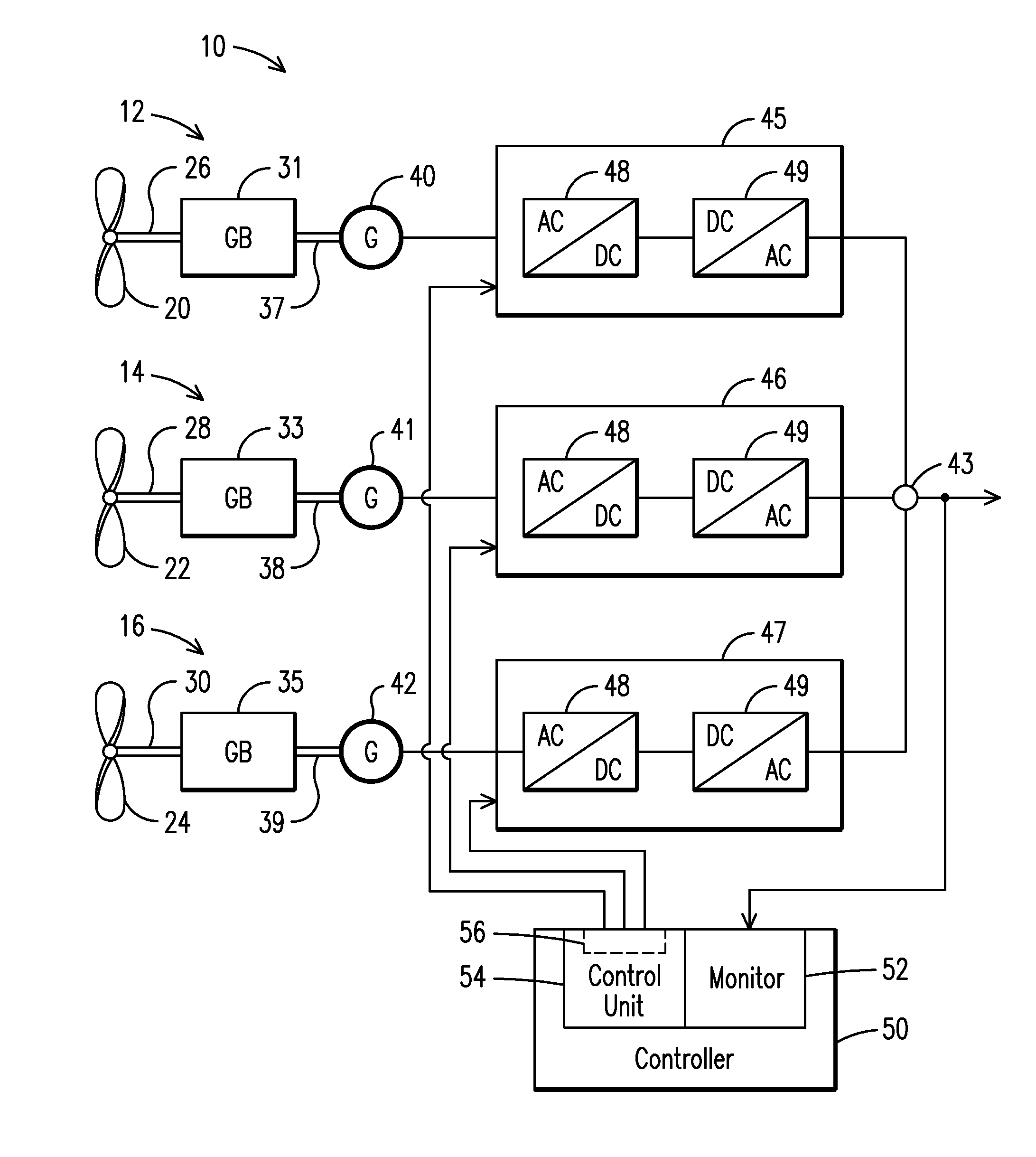
A wind farm (10) may include a plurality of variable speed wind turbines (12, 14,16). A centralized controller (50) may be configured to selectively adjust a respective electrical output power from each of the wind turbines at least during an underfrequency condition. The controller may include a monitor (52) configured to monitor a grid frequency value relative to at least a first threshold value. A deviation of the grid frequency value beyond the first threshold value is indicative of the underfrequency condition. The controller further includes a control unit (54) configured to effect a step response to the electrical output power of the wind turbine in a direction selected to counteract the underfrequency condition.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
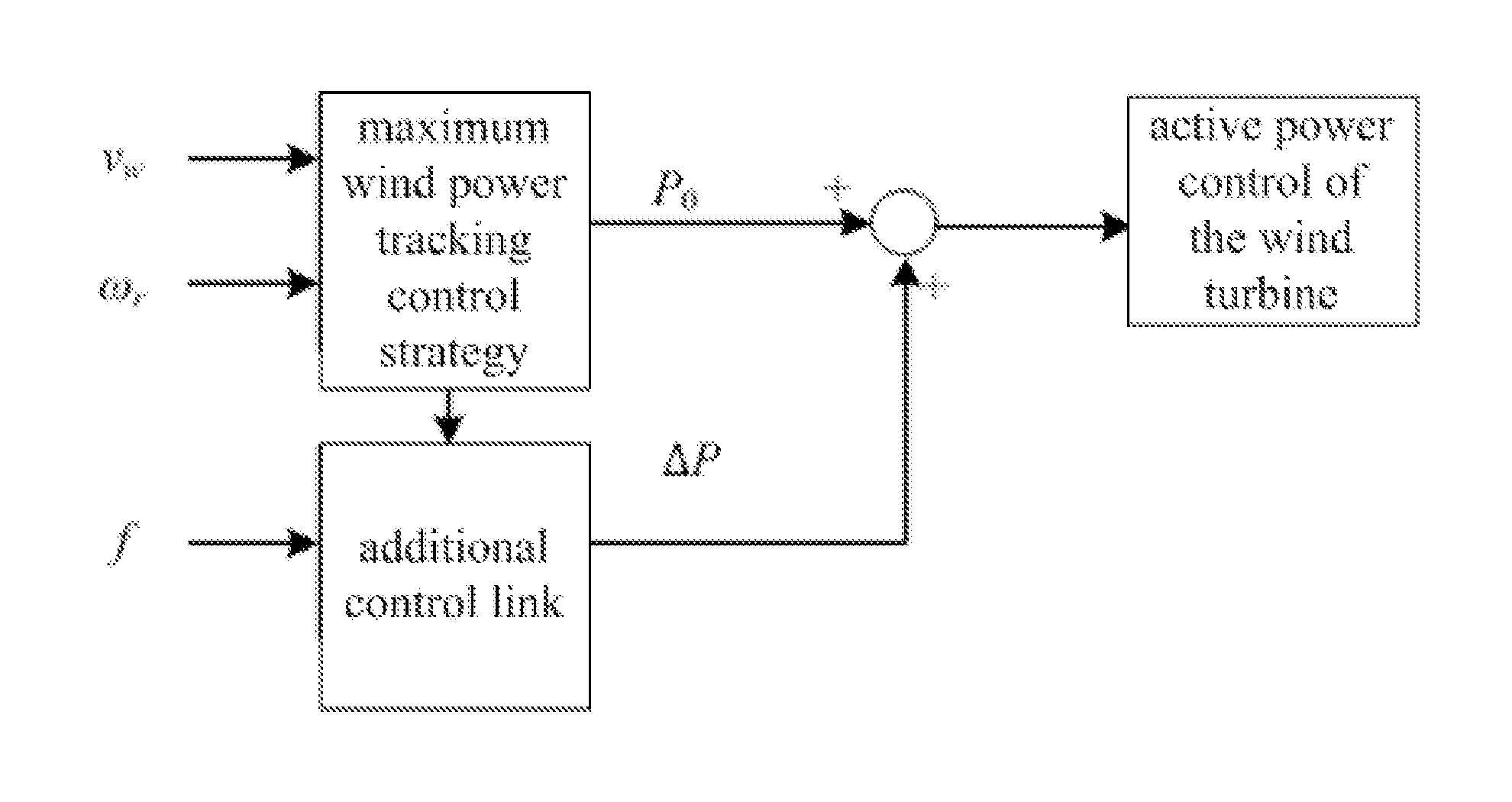
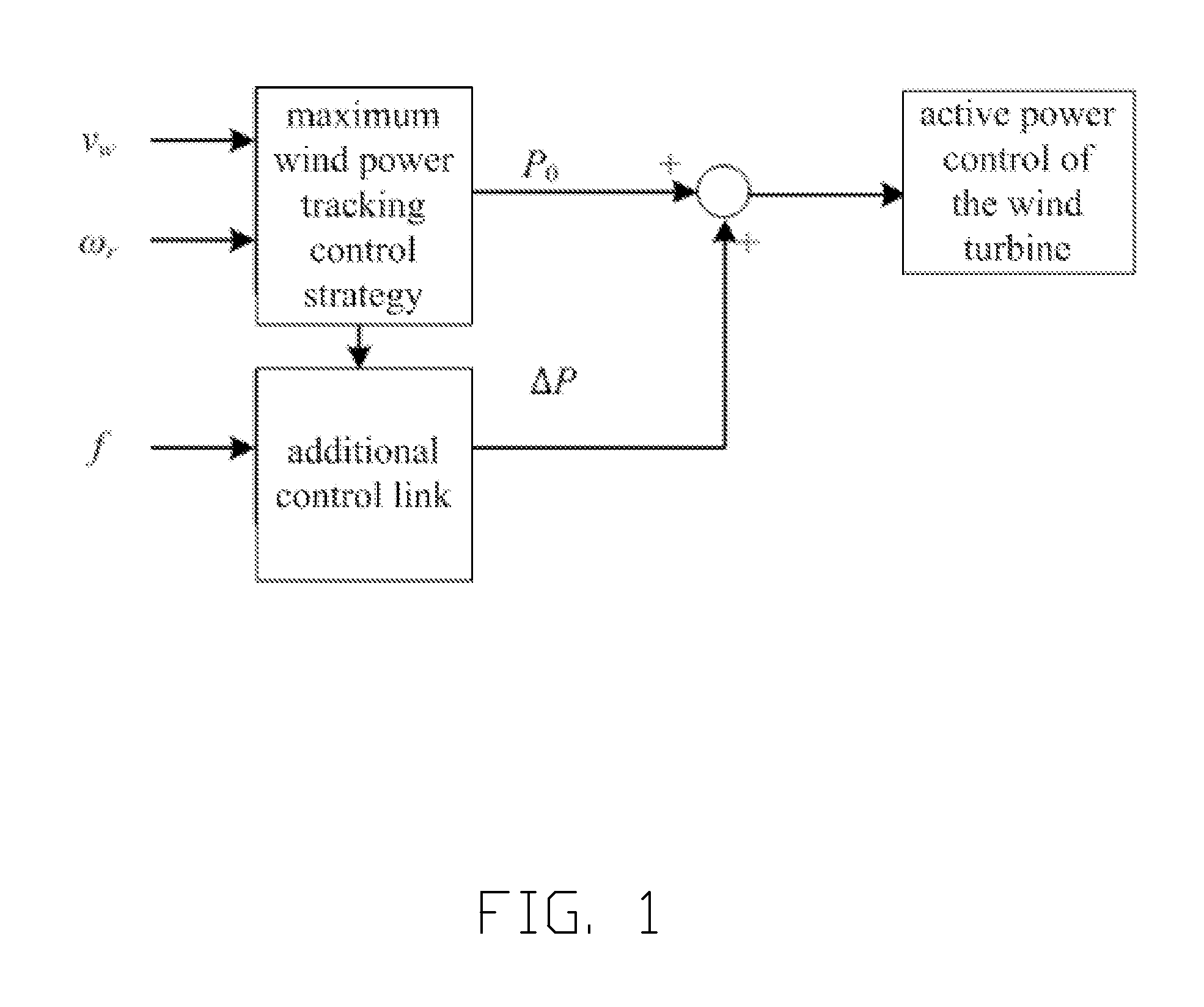
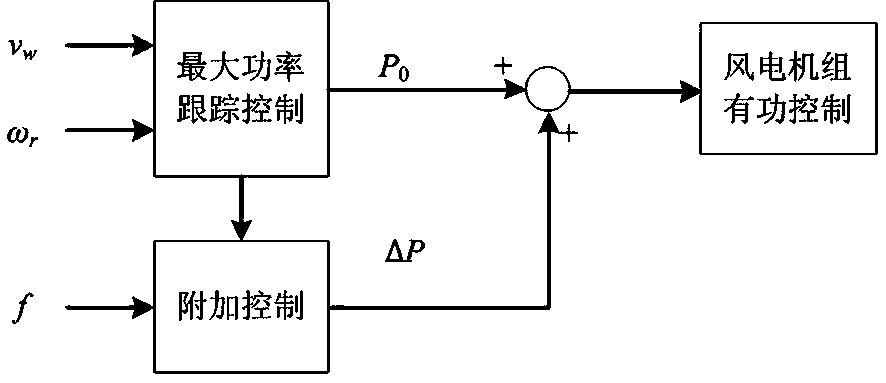
Method for controlling inertia response of variable-speed wind turbine generator
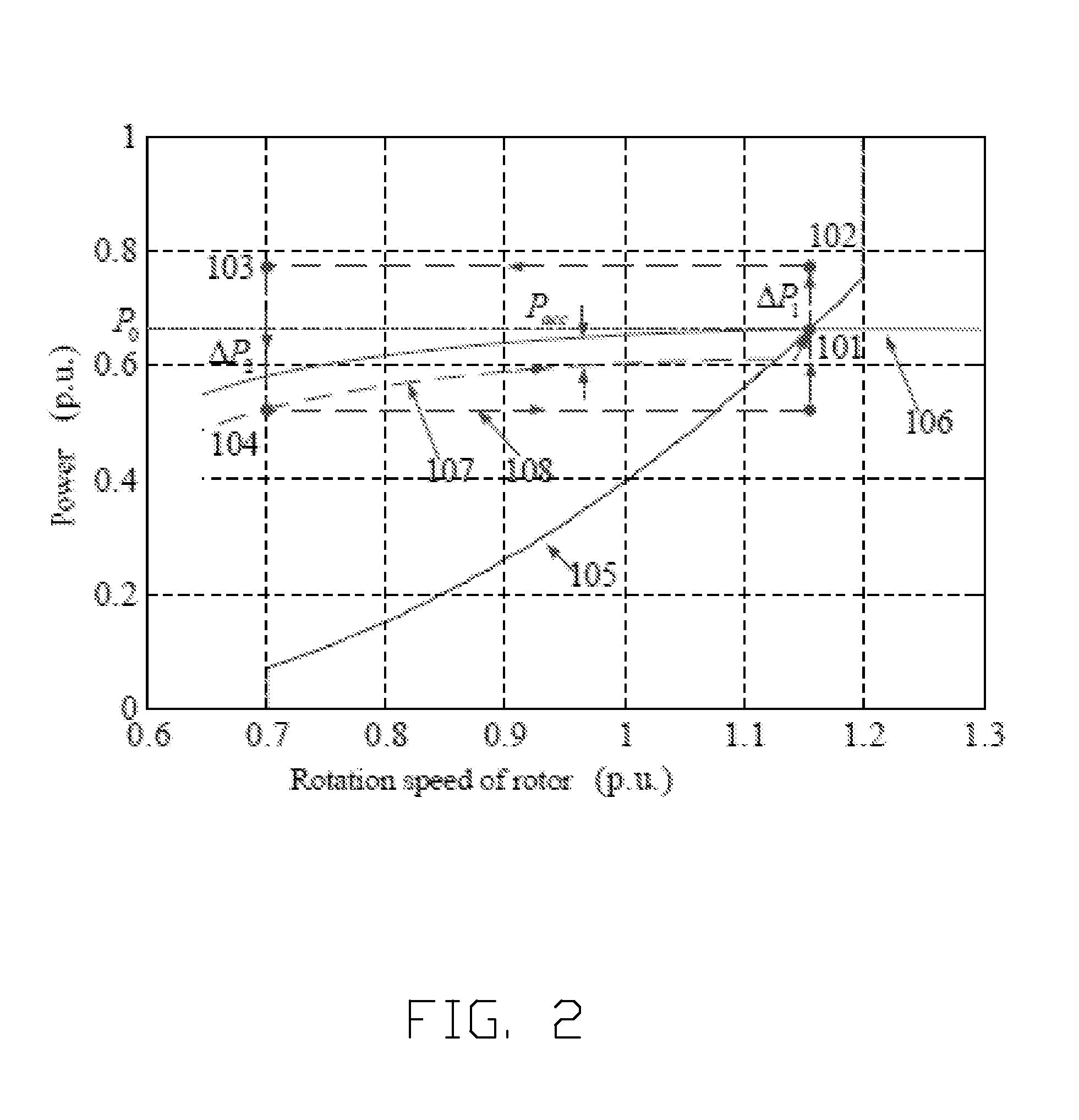
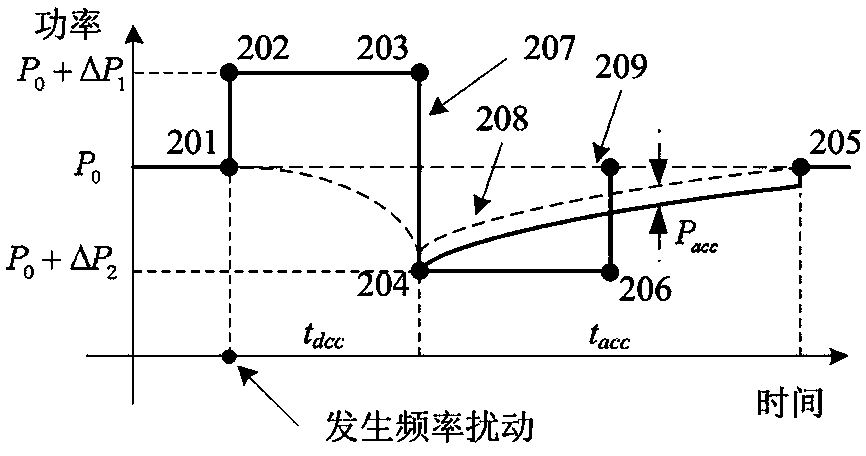
A method of controlling inertia response of variable-speed wind turbine generator includes following steps. A maximum wind power of the wind turbine is gotten through a wind speed νw and a rotation speed ωr at the hub of the wind turbine based on a maximum wind power tracking control strategy. The maximum wind power is set as an active power control reference value P0 of the wind turbine. A grid frequency f is obtained via a frequency measurement equipment. An additional active power control reference value ΔP of the wind turbine is generated based on the grid frequency f via an additional control block, and the additional active power control reference value ΔP is added on the active power control reference value P0, wherein a total of active power control reference value of the wind turbine is P0+ΔP.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Wind turbine providing grid support
ActiveUS20120161444A1Support stabilityImprove stabilityWind motor controlMachines/enginesPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine is configured to provide additional electrical power to counteract non-periodic disturbances in an electrical grid. A controller monitors events indicating a need to increase the electrical output power from the wind turbine to the electrical grid. The controller is configured to control the wind turbine as follows: after an indicating event has been detected, the wind turbine enters an overproduction period in which the electrical output power is increased, wherein the additional electrical output power is taken from kinetic energy stored in the rotor and without changing the operation of the wind turbine to a more efficient working point. When the rotational speed of the rotor reaches a minimum value, the wind turbine enters a recovery period to re-accelerate the rotor to the nominal rotational speed while further contributing to the stability of the electrical grid by outputting at least a predetermined minimum electrical power.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
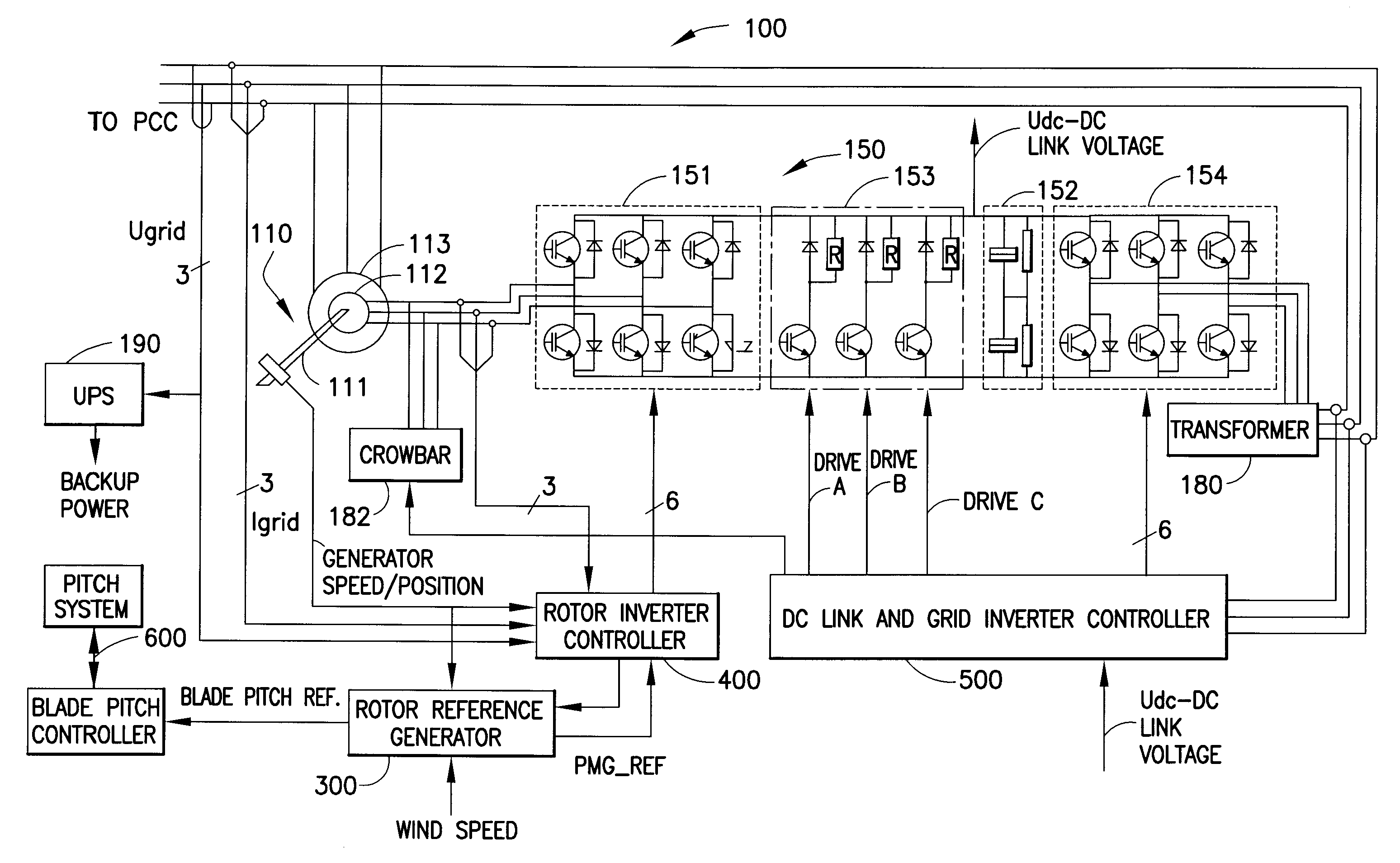
Variable speed wind turbine with a doubly-fed induction generator and rotor and grid inverters that use scalar controls
InactiveUS8198742B2Reduce impactGenerator control circuitsOptimise machine performancePower gridVariable speed wind turbine
The present invention relates to an improved wind turbine, of the type which employs doubly fed induction generators (DFIG), and a wind park including the same, which permits the use of lighter weight turbines, with the ability to have greater energy capture, more precise control of asymmetrical phases and enhanced maintenance and support of the grid during fault conditions.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
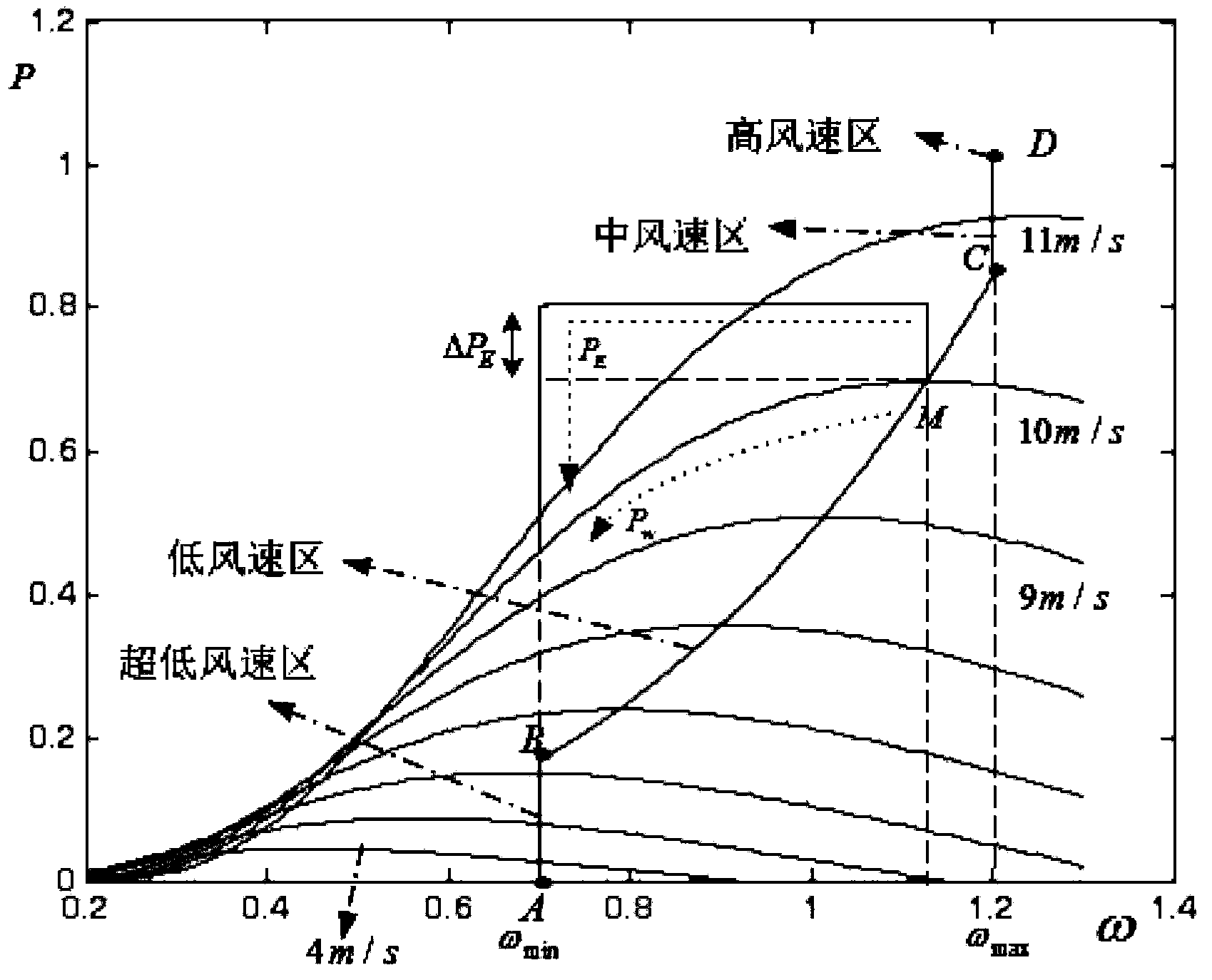
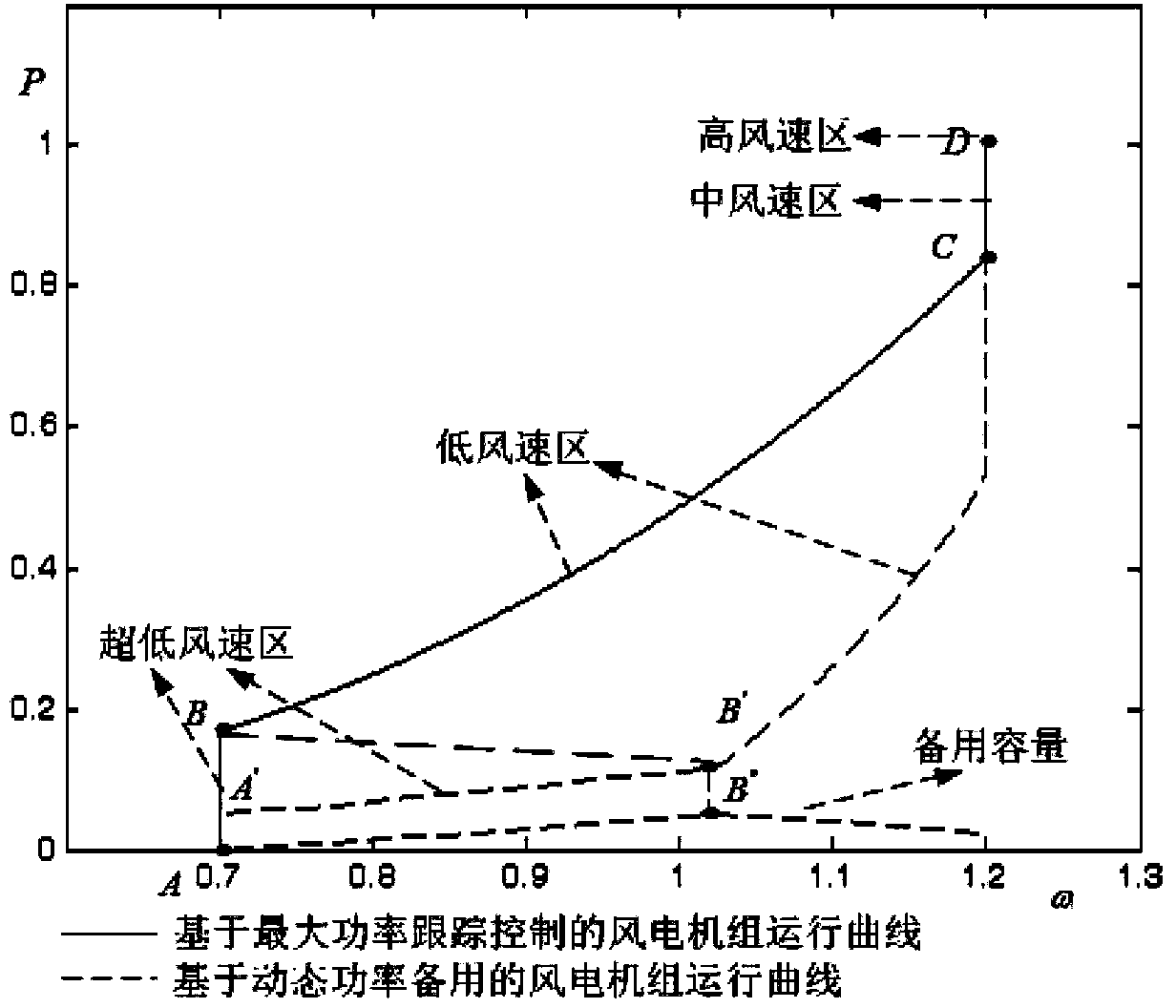
Variable speed wind turbine generator frequency control method based on dynamic standby power
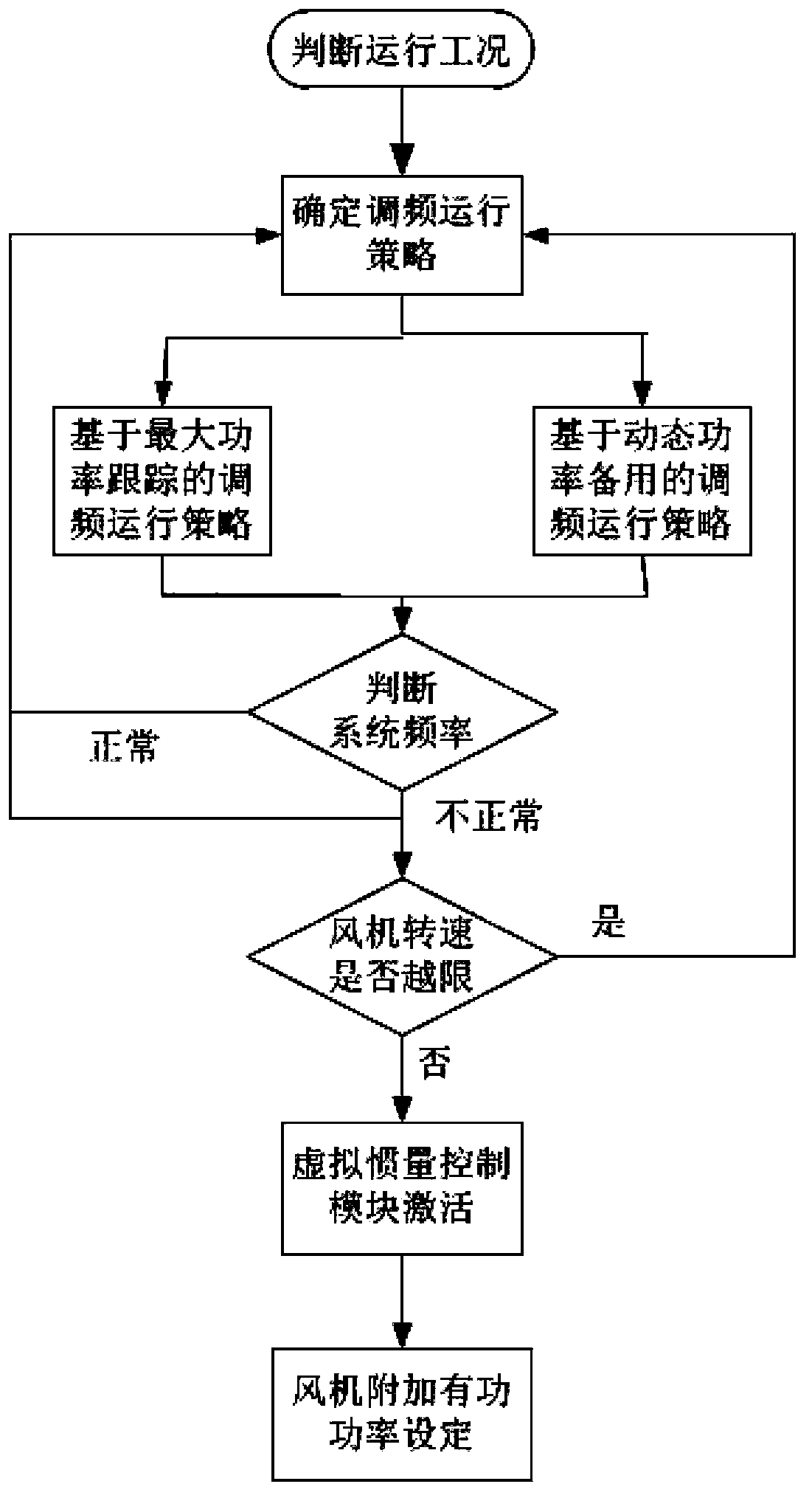
ActiveCN103441524AAchieving Effective Frequency Tuning CapabilityImprove frequency stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectricityElectric power system
The invention provides a variable speed wind turbine generator frequency control method based on dynamic standby power. The method comprises the following steps that I, a frequency modulation operation strategy of a variable speed wind turbine generator is determined according to operation conditions of the variable speed wind turbine generator; II, whether the variable speed wind turbine generator participates in system frequency modulation or not is judged; III, whether the rotating speed of the wind turbine generator is out of limit or not is judged; IV, an active frequency control module is activated, and an active power set value of the wind turbine generator is modified; V, control over the system frequency is achieved. The variable speed wind turbine generator frequency control method based on dynamic standby power can achieve frequency modulation capability of the wind turbine generator in a full wind speed region, when participating in the system frequency modulation to provide active support, the wind turbine generator is not affected by the operation conditions, and therefore electric system frequency stability is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
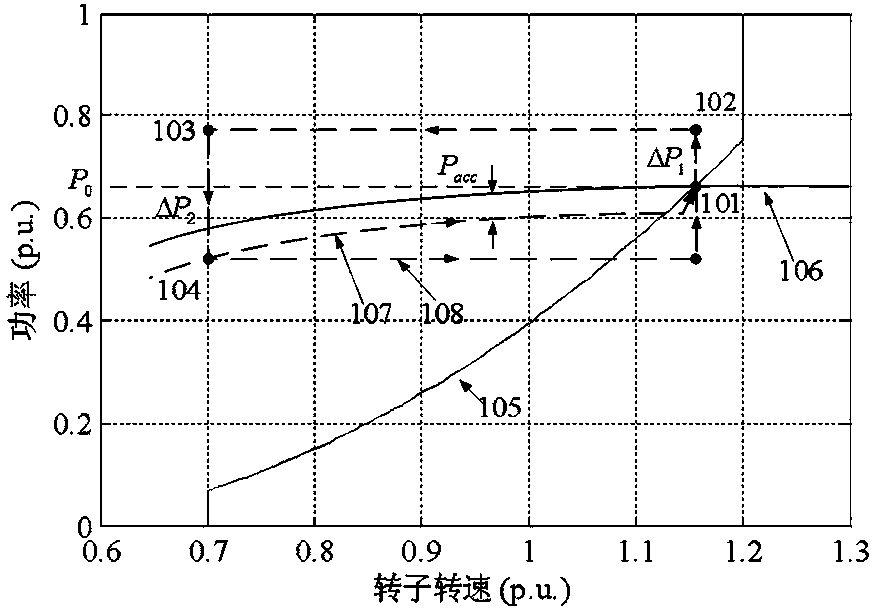
Variable-speed wind turbine generator inertia response simulating control method
InactiveCN103441529AStable supportSimulated inertia response implementationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationVariable speed wind turbineOmega
The invention discloses a variable-speed wind turbine generator inertia response simulating control method. The method comprises the steps that according to the wind turbine generator hub wind speed vw and the wind turbine generator rotating speed omega r, the active-power control reference value P0 of a wind turbine generator is set based on a maximum wind energy power tracking control strategy; extra controls are added through power grid frequency values on the basis of maximum wind energy power tracking control, according to operation conditions of the wind turbine generator, short-time constant-power supporting is carried out through table searching or online adjusting to achieve inertia response simulation, and meanwhile the wind turbine generator active power recovery process is achieved according to a certain power curve. The variable-speed wind turbine generator inertia response simulating control method can overcome the problems that the rotational inertia of a wind turbine generator is not sufficiently utilized, the wind turbine generator is out of a reasonable operation range, inertia control is lack of flexibility, response time is long, particularly, the rotating speed of the wind turbine generator is too low, and the torque and the rotator current of the wind turbine generator are too large in the prior art. The variable-speed wind turbine generator inertia response simulating control method can effectively reduce the frequency deviation amplitude and the rate of change after large frequency disturbance accidents, and improves frequency stability of an electric power system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Variable speed wind turbine having a constant speed generator
InactiveUS20100230966A1Limit rotor speedEngine fuctionsWind motor combinationsVariable speed wind turbineMoment of inertia
A variable speed wind turbine including a variable speed rotor, a large constant speed generator, and a small variable speed generator is characterized by a three-shaft variable ratio gearbox connecting the shaft of the rotor with the two generator shafts. The variable ratio gearbox is an epicyclic gearbox which enables the combination of the high performance of a variable speed rotor with the low cost of a large constant speed generator. The torque of the small variable speed generator controls the rotor speed. Variable frequency power conditioning cost is less than that of a prior art variable speed wind turbine, reduced by the ratio of the rated capacity of the small generator to total rated capacity. Also, the small generator enables efficient low wind velocity energy capture. The low rotational inertia of the small variable speed generator further reduces drive train dynamic stress.
Owner:PAVLAK ALEXANDER J
Variable Speed Wind Turbine With Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Compensated For Varying Rotor Speed
ActiveUS20100045040A1Minimize oscillationReduce instabilityLevel controlWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineDynamo
A variable rotational speed wind turbine includes a doubly-fed induction generator, a rotor current controller for controlling the rotor currents of the generator, a compensation mechanism having a computation mechanism, and an input mechanism for providing input to the compensation mechanism, the input being representative of at least the instantaneous angular speed of the rotor of the generator. The computation mechanism is arranged to compute an instantaneous compensation control output in dependency of the instantaneous angular speed of the rotor of the generator and feed the compensation control output to the rotor, and to compute the compensation control output during operation of the wind turbine to compensate at least partly for dependencies on the rotor angular speed of the locations of poles of a generator transfer function, thus making a resulting generator transfer function substantially independent of variations in the rotor angular speed during operation of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Controlling a wind turbine to stabilize an electric grid
A variable speed wind turbine is configured to provide additional electrical power to counteract non-periodic disturbances in an electrical grid. A controller monitors events indicating a need to increase the electrical output power from the wind turbine to the electrical grid. The controller is configured to control the wind turbine as follows: after an indicating event has been detected, the wind turbine enters an overproduction period in which the electrical output power is increased, wherein the additional electrical output power is taken from kinetic energy stored in the rotor and without changing the operation of the wind turbine to a more efficient working point. When the rotational speed of the rotor reaches a minimum value, the wind turbine enters a recovery period to re-accelerate the rotor to the nominal rotational speed while further contributing to the stability of the electrical grid by outputting at least a predetermined minimum electrical power.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com