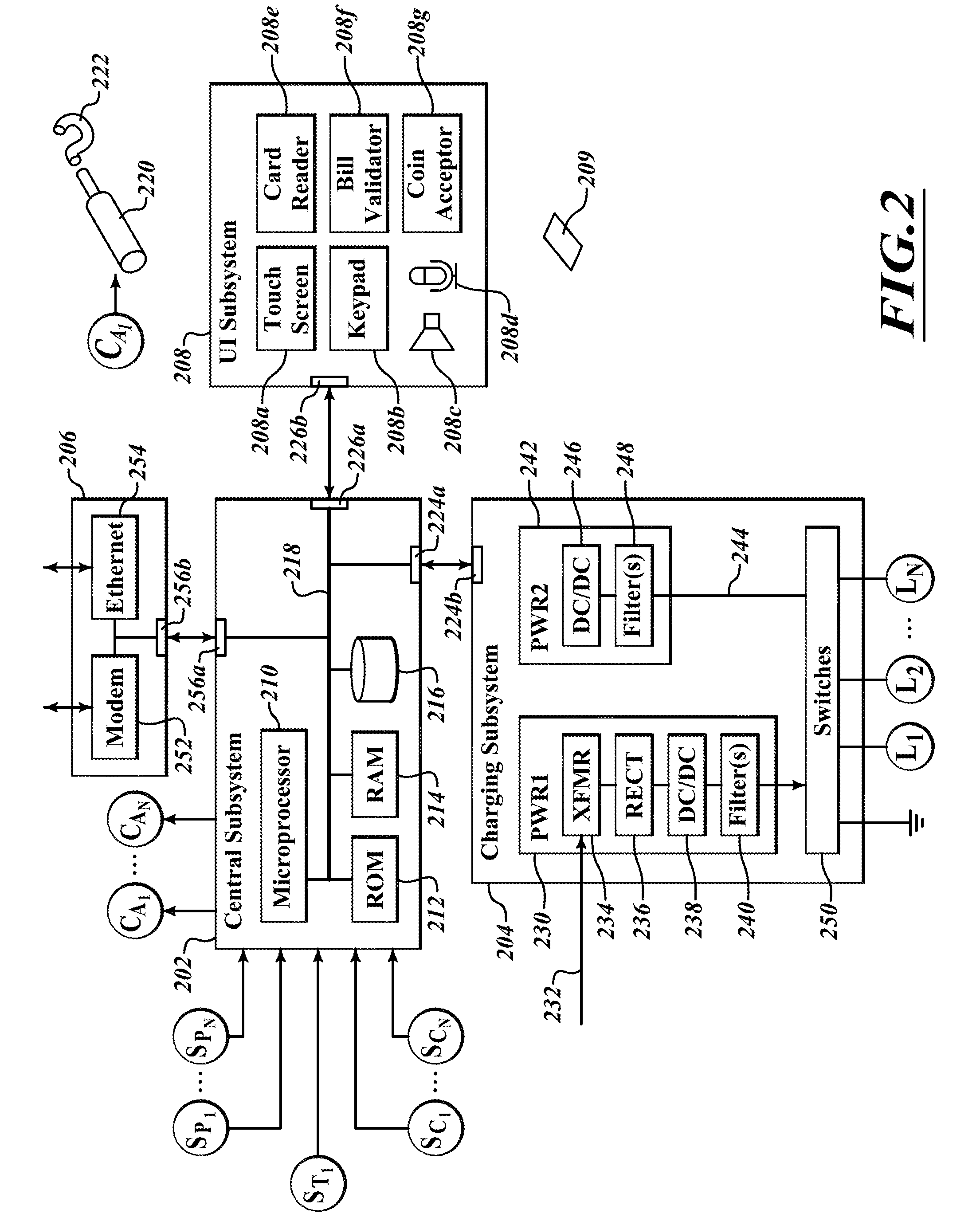
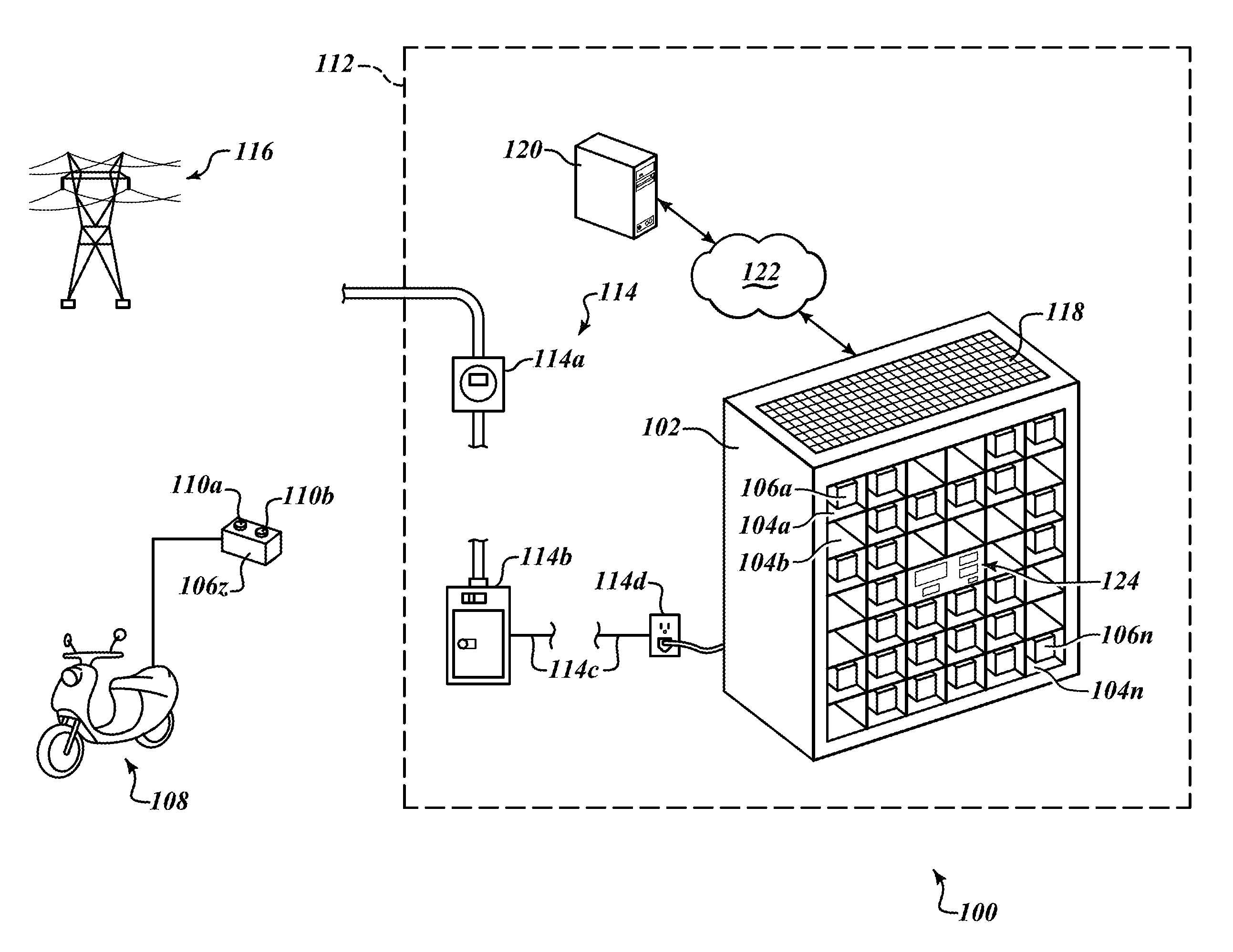
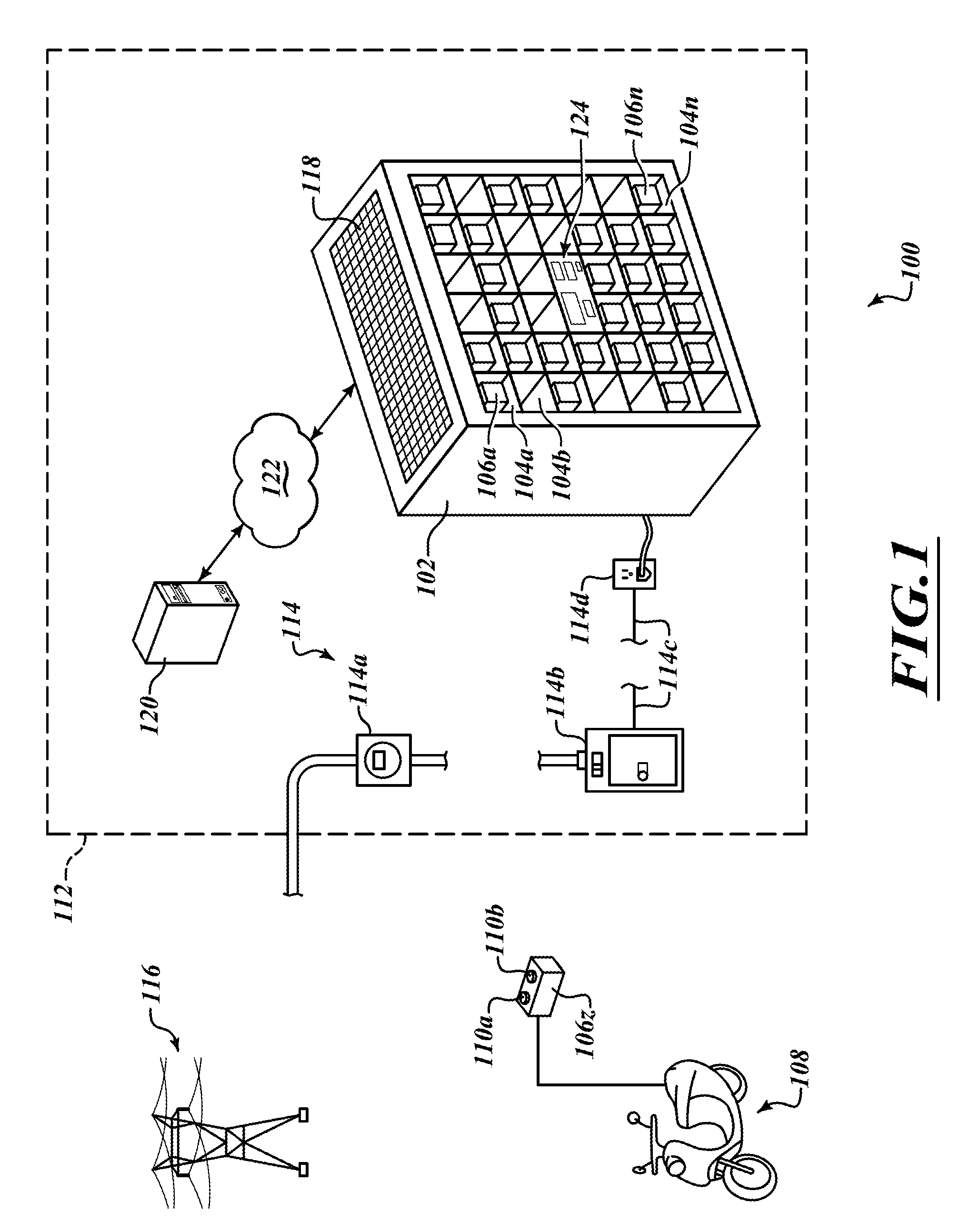
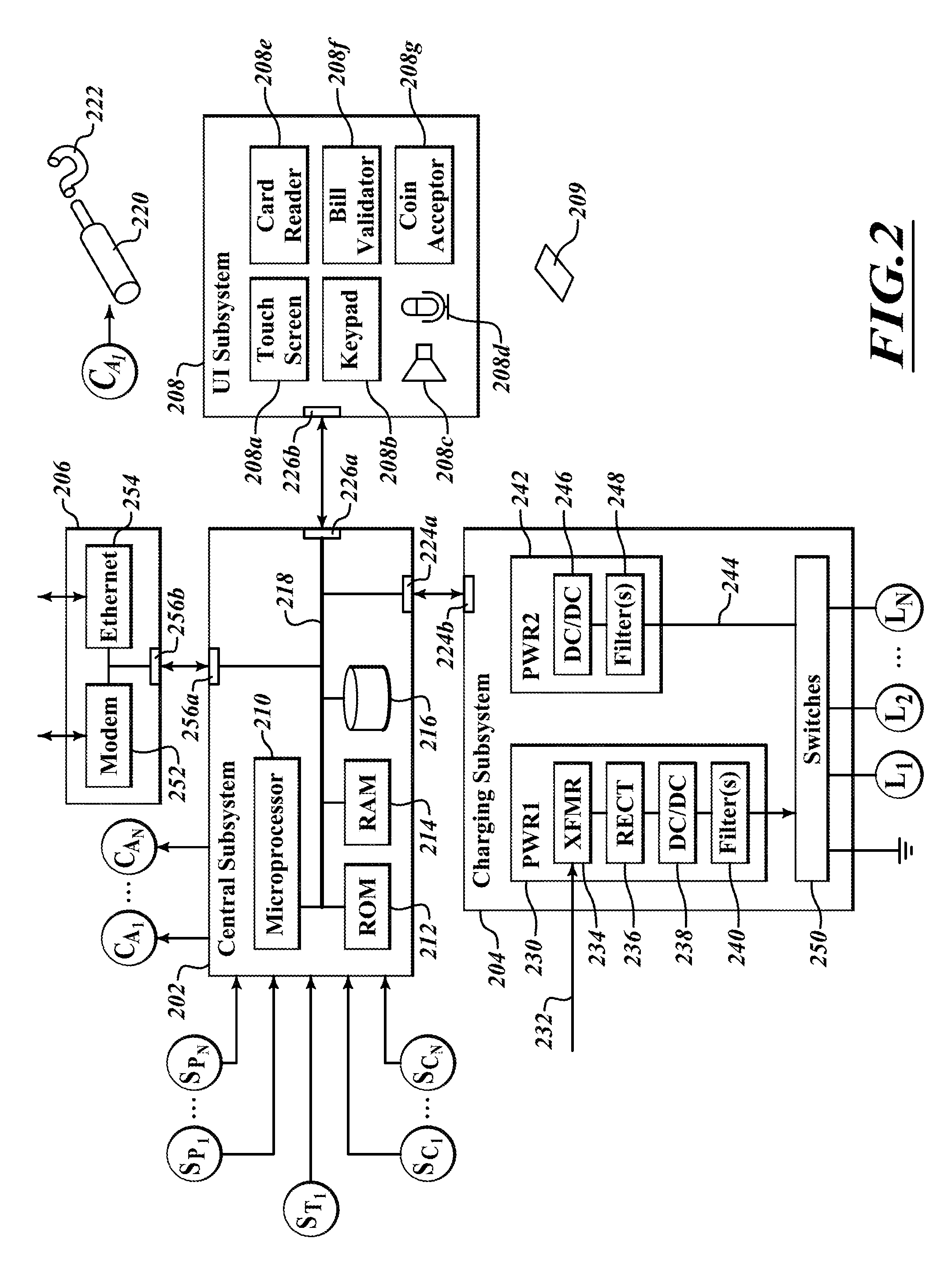
Patents
Literature
862 results about "Electrical grid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
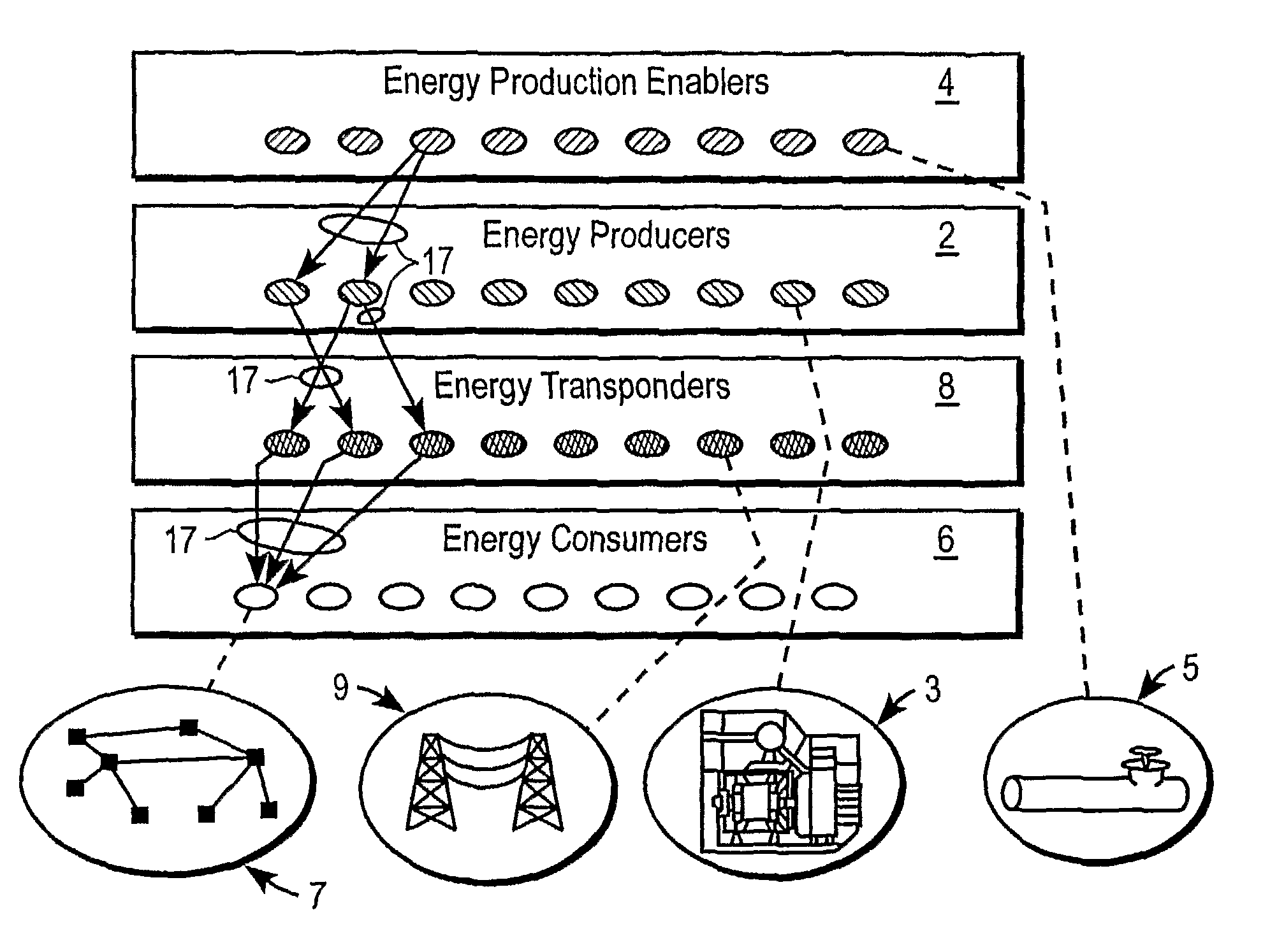
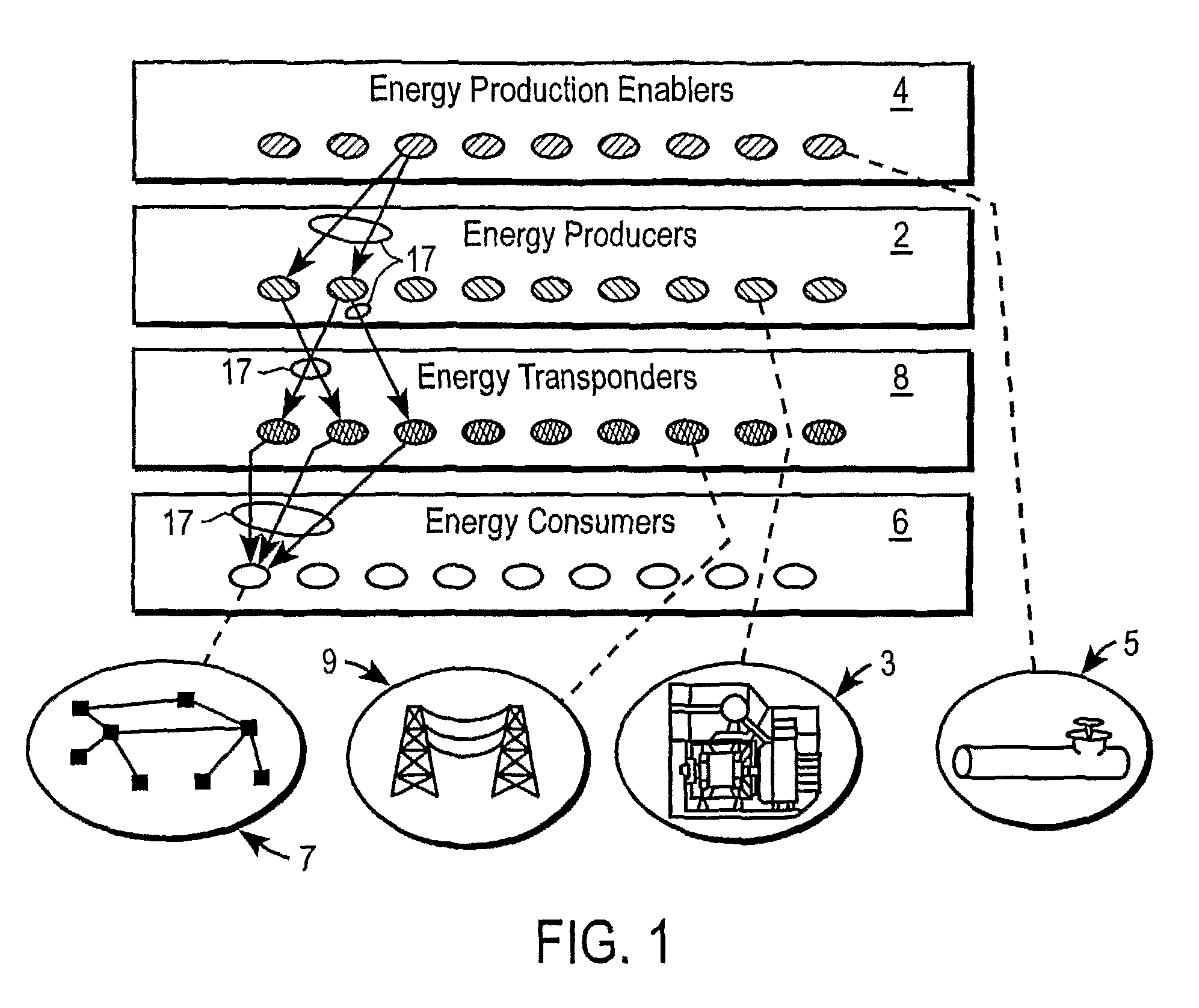
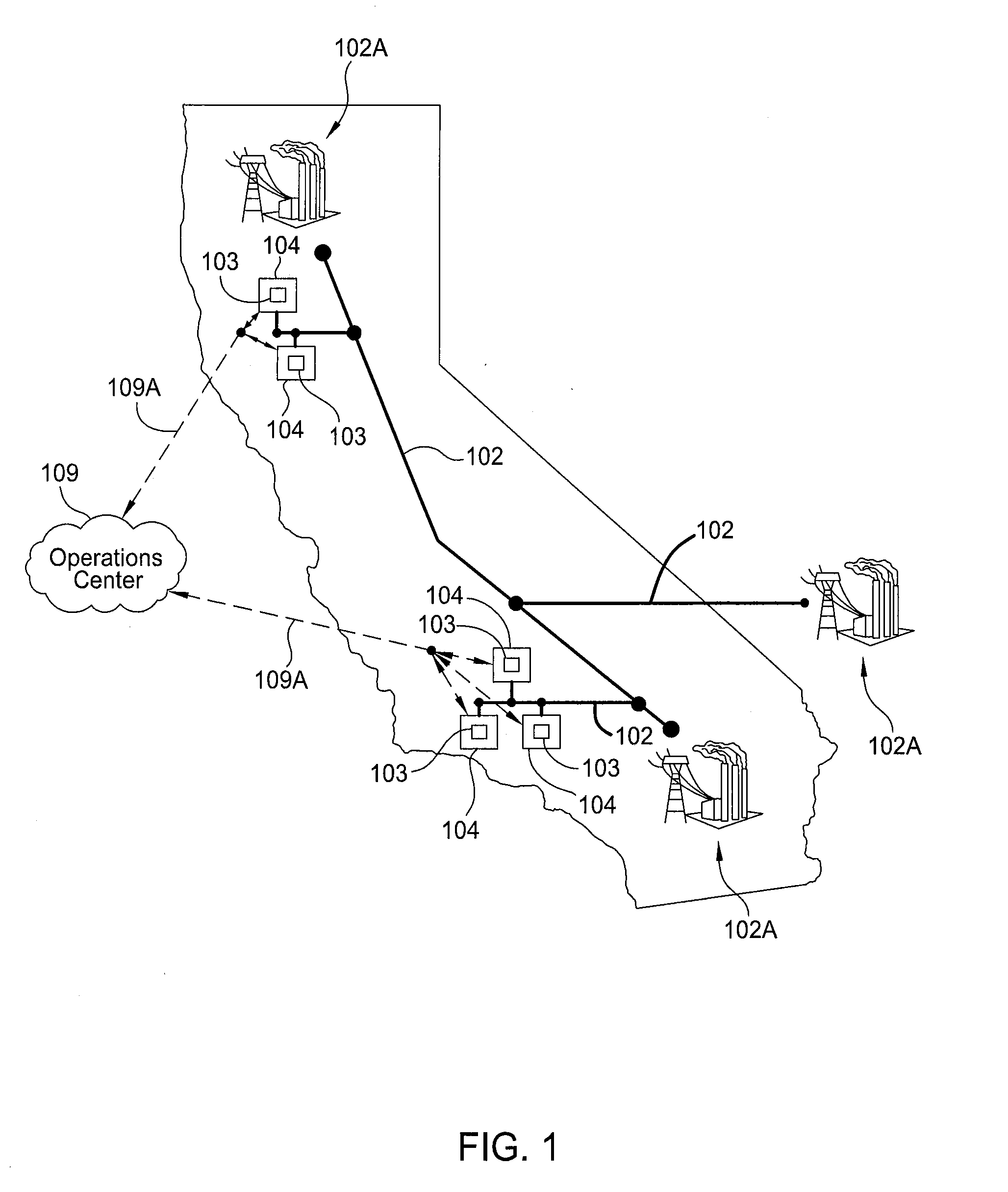
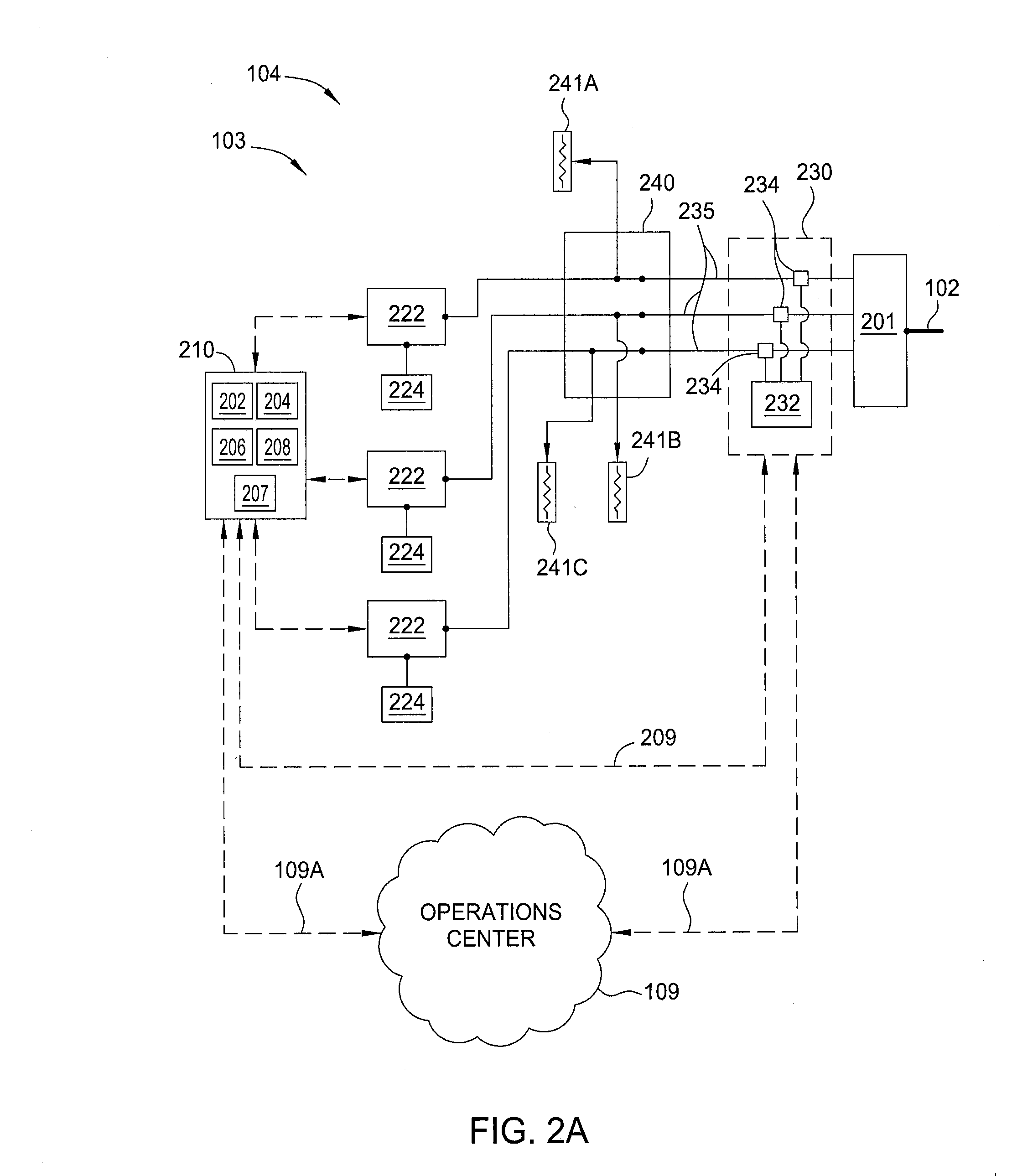
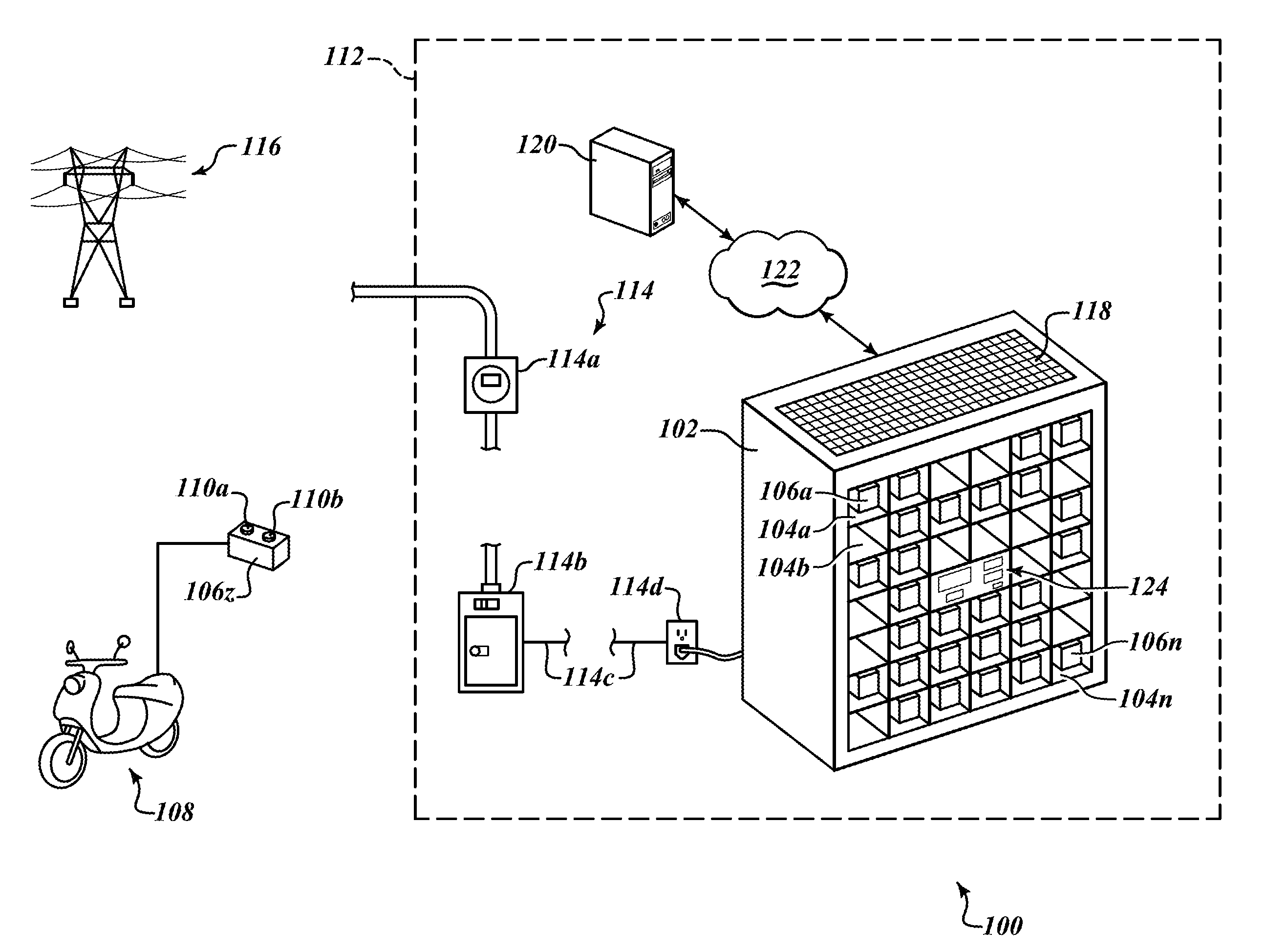
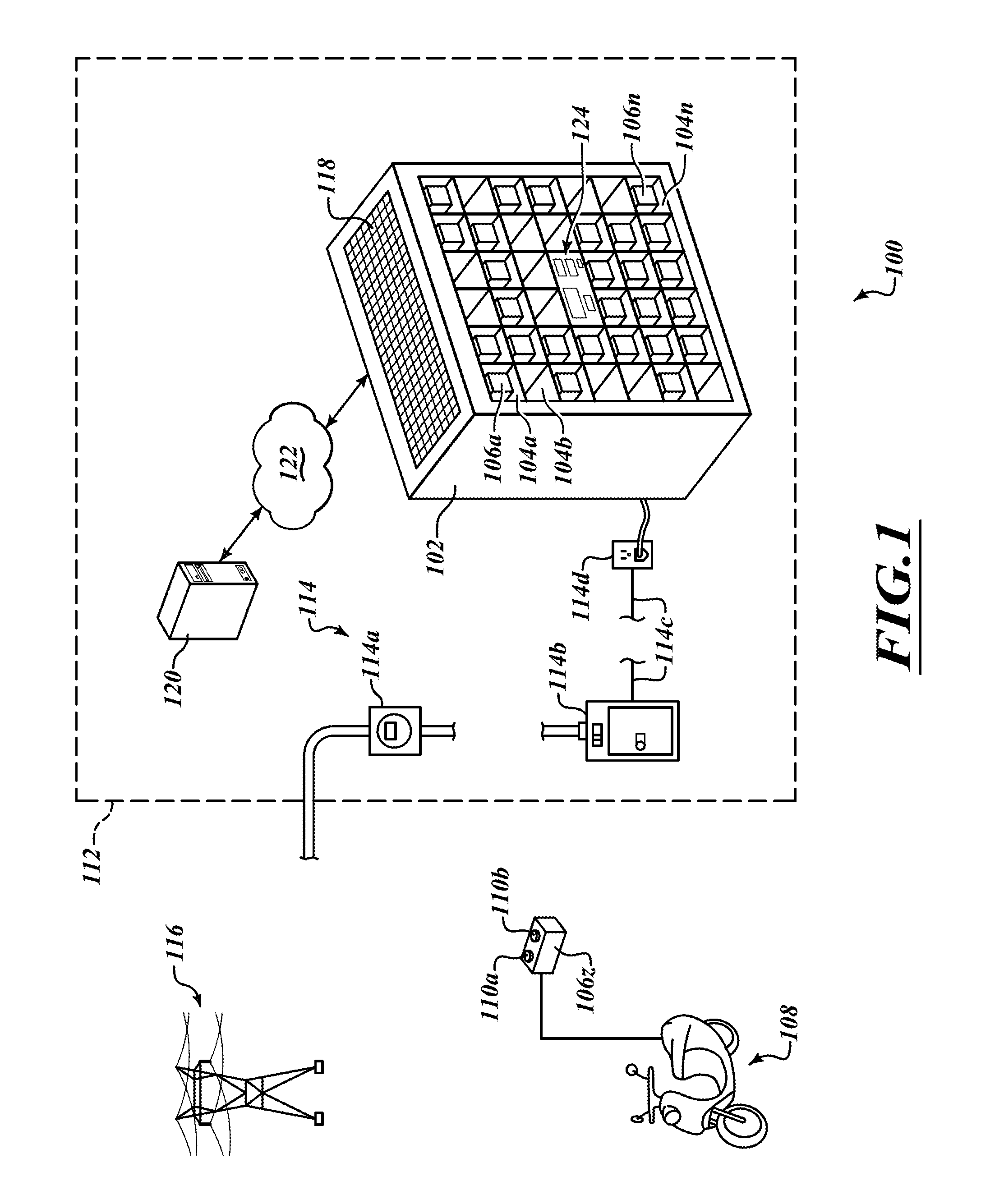
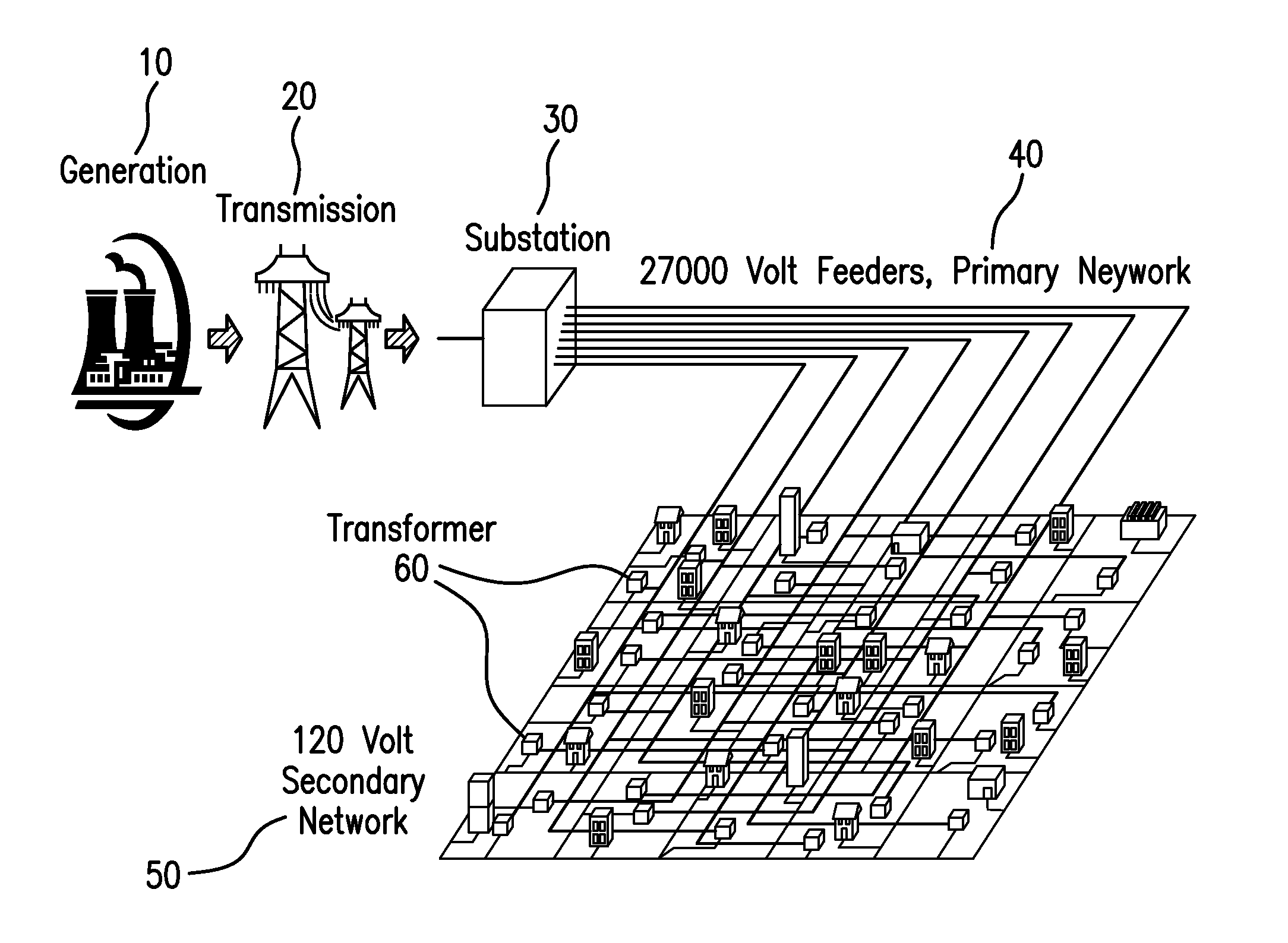
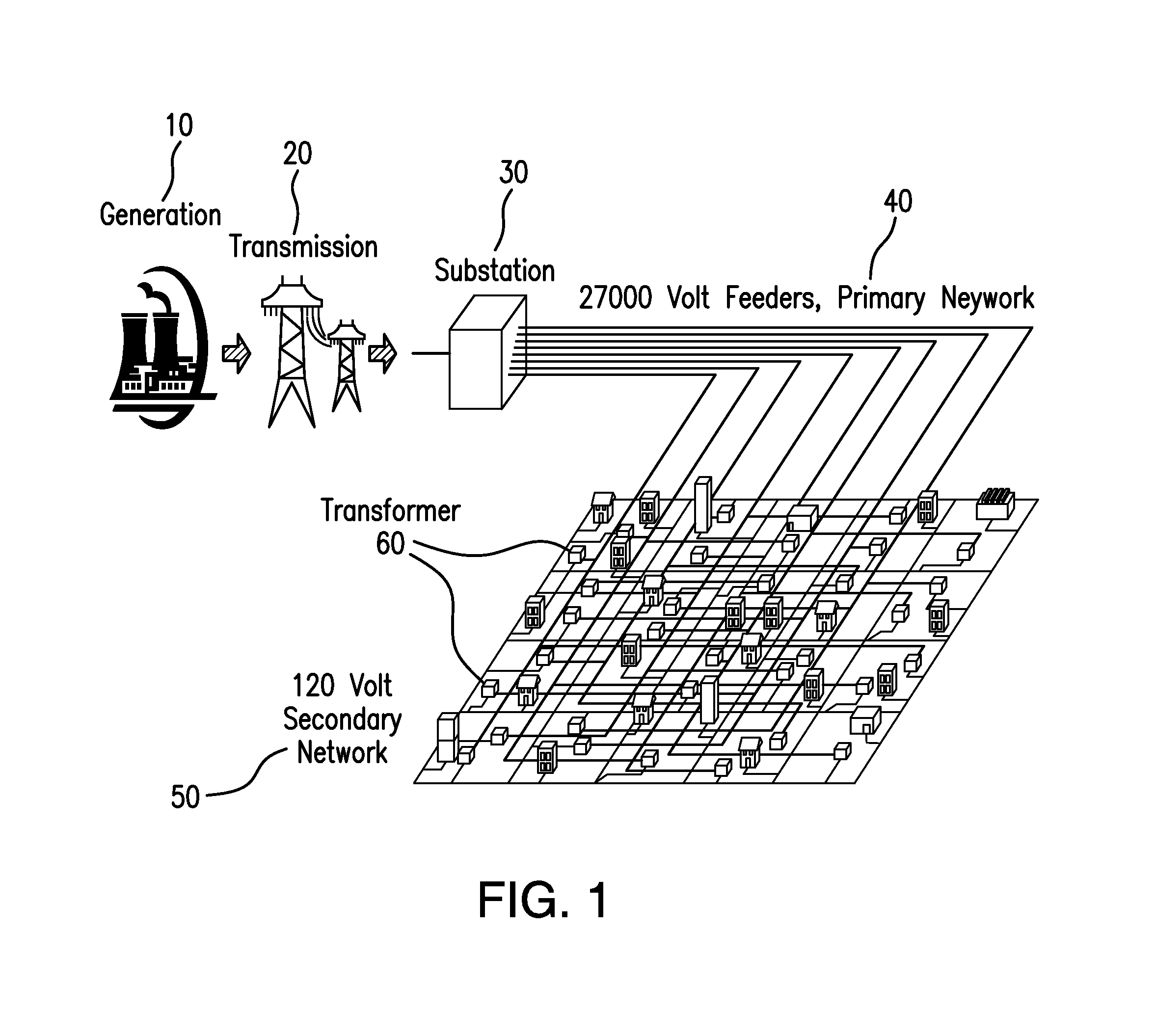
An electrical grid, electric grid or power grid, is an interconnected network for delivering electricity from producers to consumers. Power stations may be located (for example) near a fuel source or at a dam site (to take advantage of renewable energy sources), and are often located away from heavily-populated areas. The electric power which is generated is stepped up to a higher voltage at which it connects to the electric power transmission net.
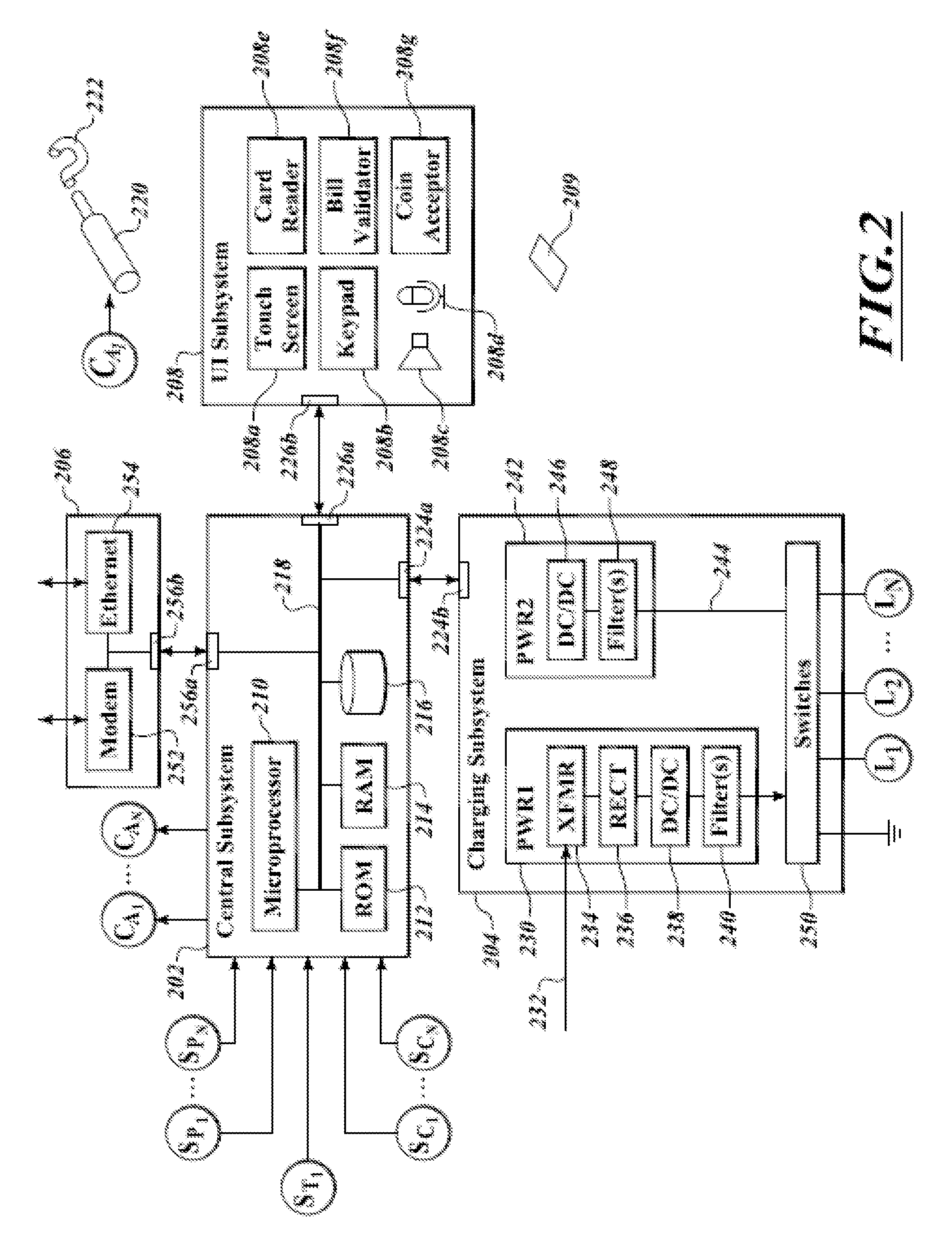
Systems and Methods for Modifying Power Usage
ActiveUS20080272934A1Increase coverageInformed choiceElectric signal transmission systemsLevel controlTransceiverPower usage
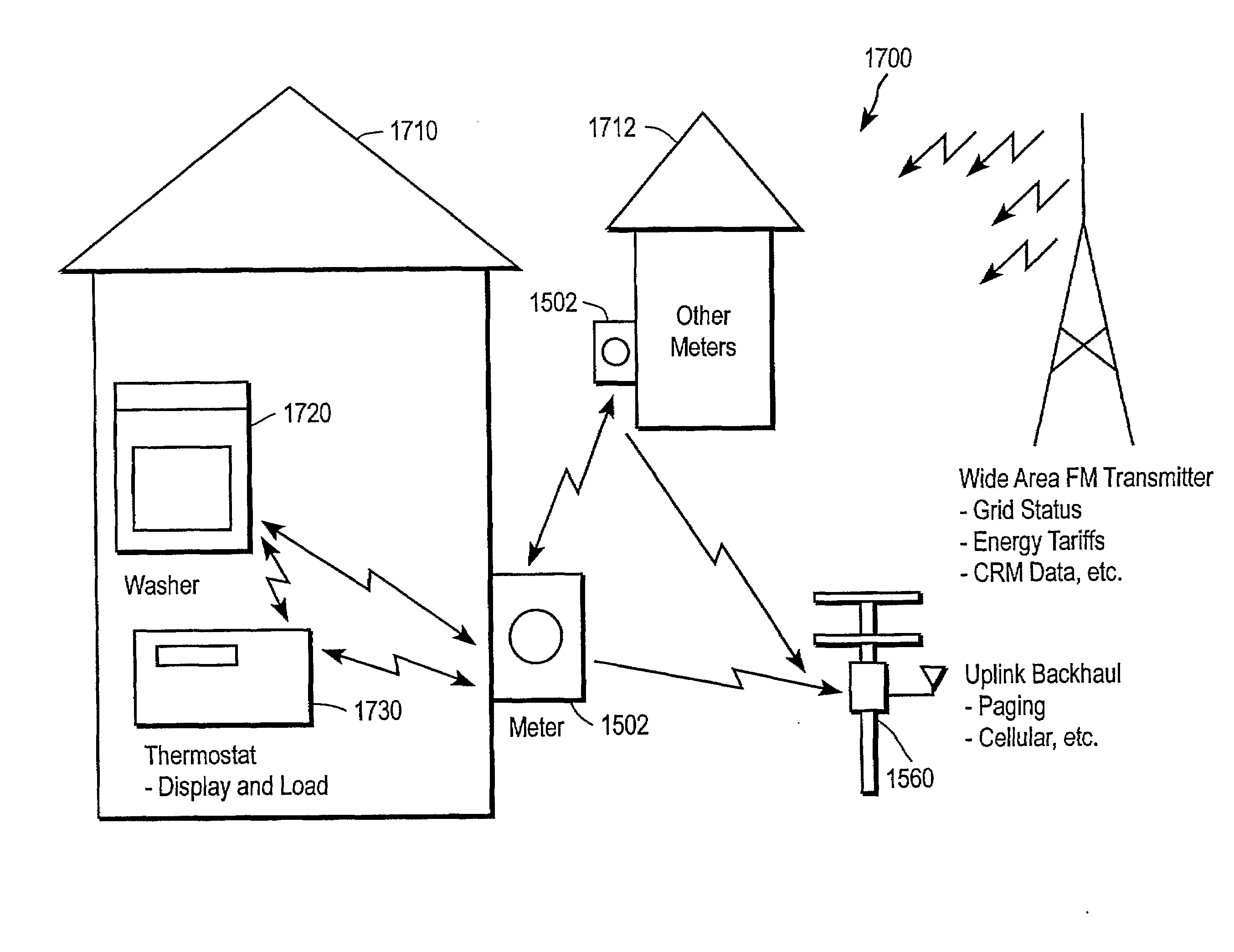
Systems and methods for providing energy management utilize wireless wide-area network broadcast signals and a decentralized receiver architecture to allow customers to make informed choices with regard to energy consumption and load shedding for particular appliances. A receiver assembly embedded within an appliance receives a broadcast signal, e.g., an FM subcarrier signal, including tariff data and other electrical grid data. A processor coupled with the receiver controls the appliance in accordance with the received data and in accordance with user-defined preferences. In some embodiments, a transceiver assembly is embedded in one or more appliances in a household. Each transceiver is configured to receive broadcast signals regarding grid data, and to communicate with other appliances and / or a usage meter over a wireless personal area network. Meter data from one or more households may be aggregated and uplinked back to the energy provider or other entities.
Owner:E RADIO USA
Modular electrical grid interface device
A smart grid gateway which includes a onboard computer programmed to provide load measurement and control of at least one local resource or asset. At least one metrology module is configured to provide metering of the at least one local resource or asset. At least one LAN module is configured to communicate with the at least one local resource or asset. At least one WAN module is configured to communicate with a network operations center.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Apparatus, method and article for authentication, security and control of power storage devices, such as batteries
ActiveUS20130026973A1Limited rangeLong recharging timeRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCoin-freed apparatusSupercapacitorEngineering
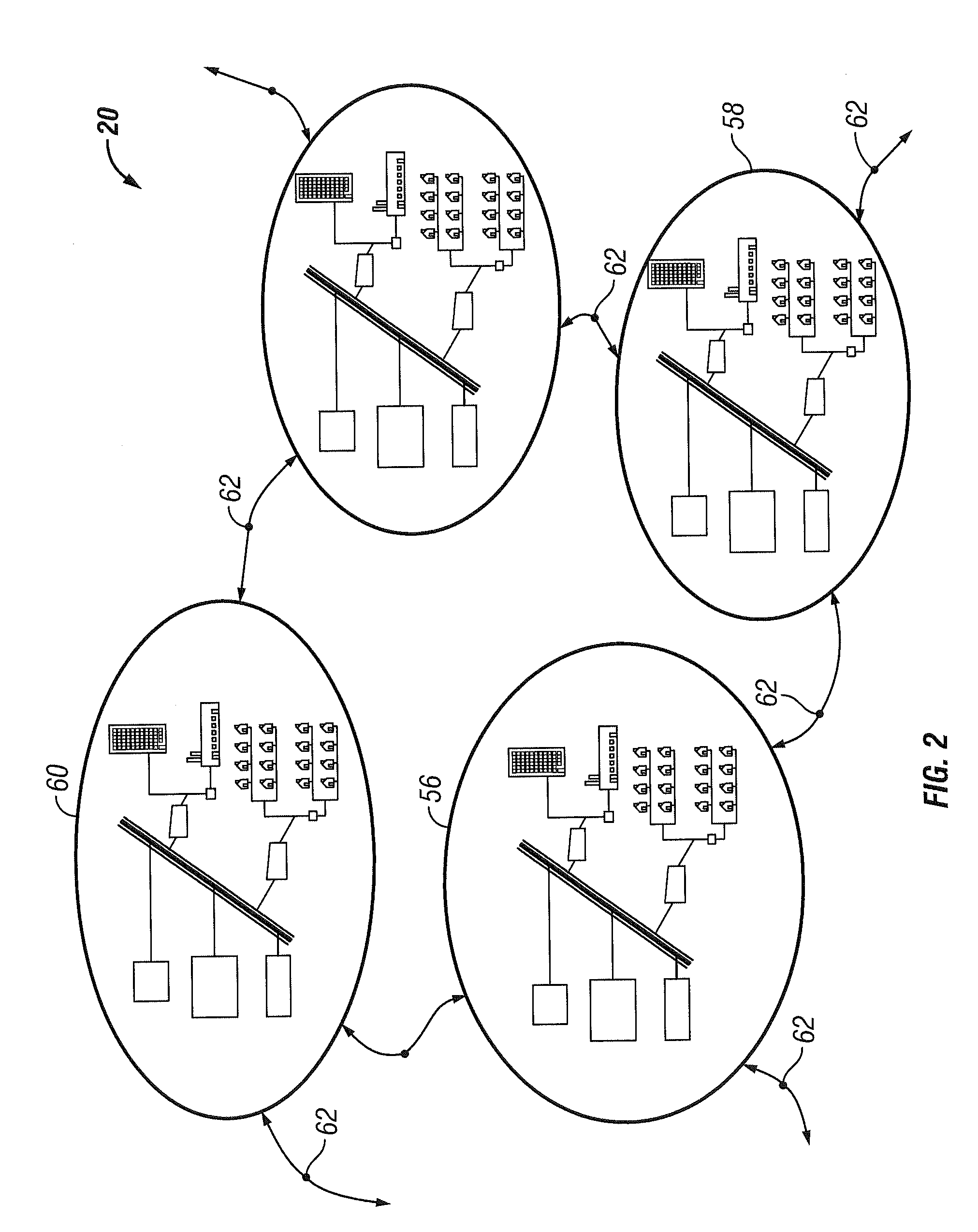
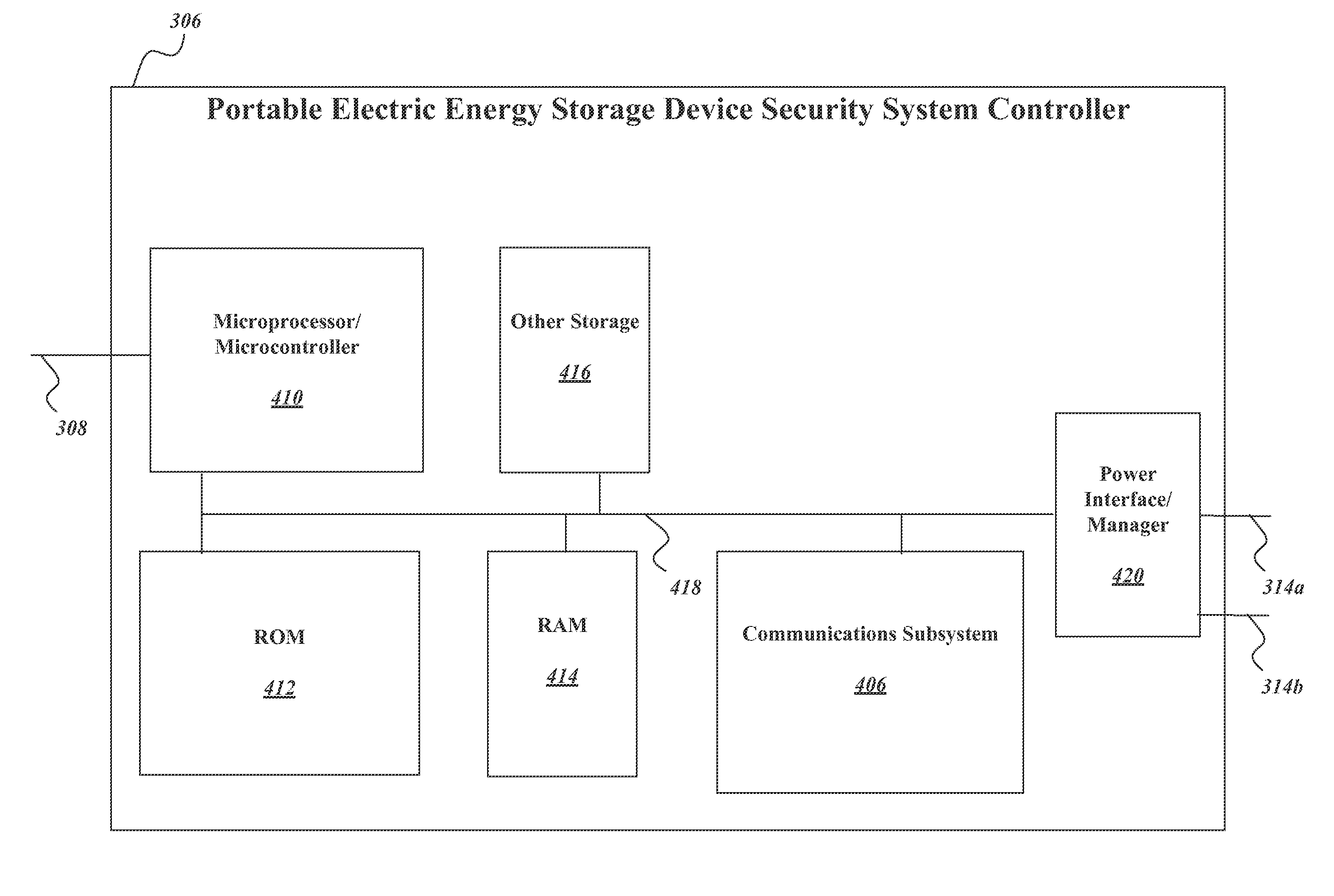
A network of collection, charging and distribution machines collect, charge and distribute portable electrical energy storage devices (e.g., batteries, supercapacitors or ultracapacitors). To charge, the machines employ electrical current from an external source, such as the electrical grid or an electrical service of an installation location. By default, each portable electrical energy storage device is disabled from accepting a charge unless it receives authentication information from an authorized collection, charging and distribution machine, other authorized charging device, or other authorized device that transmits the authentication credentials. Also, by default, each portable electrical energy storage device is disabled from releasing energy unless it receives authentication information from an external device to which it will provide power, such as a vehicle or other authorization device.
Owner:GOGORO
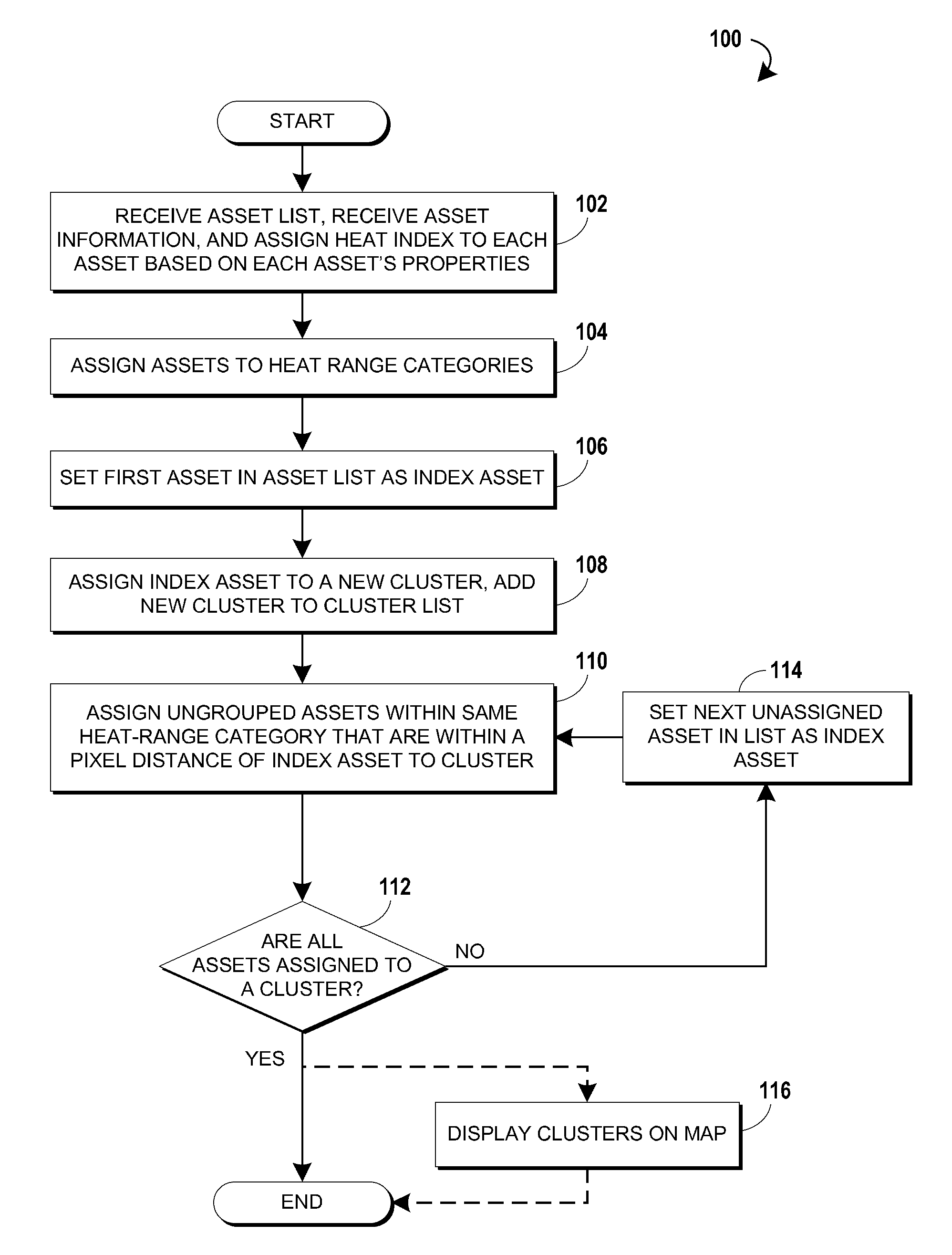
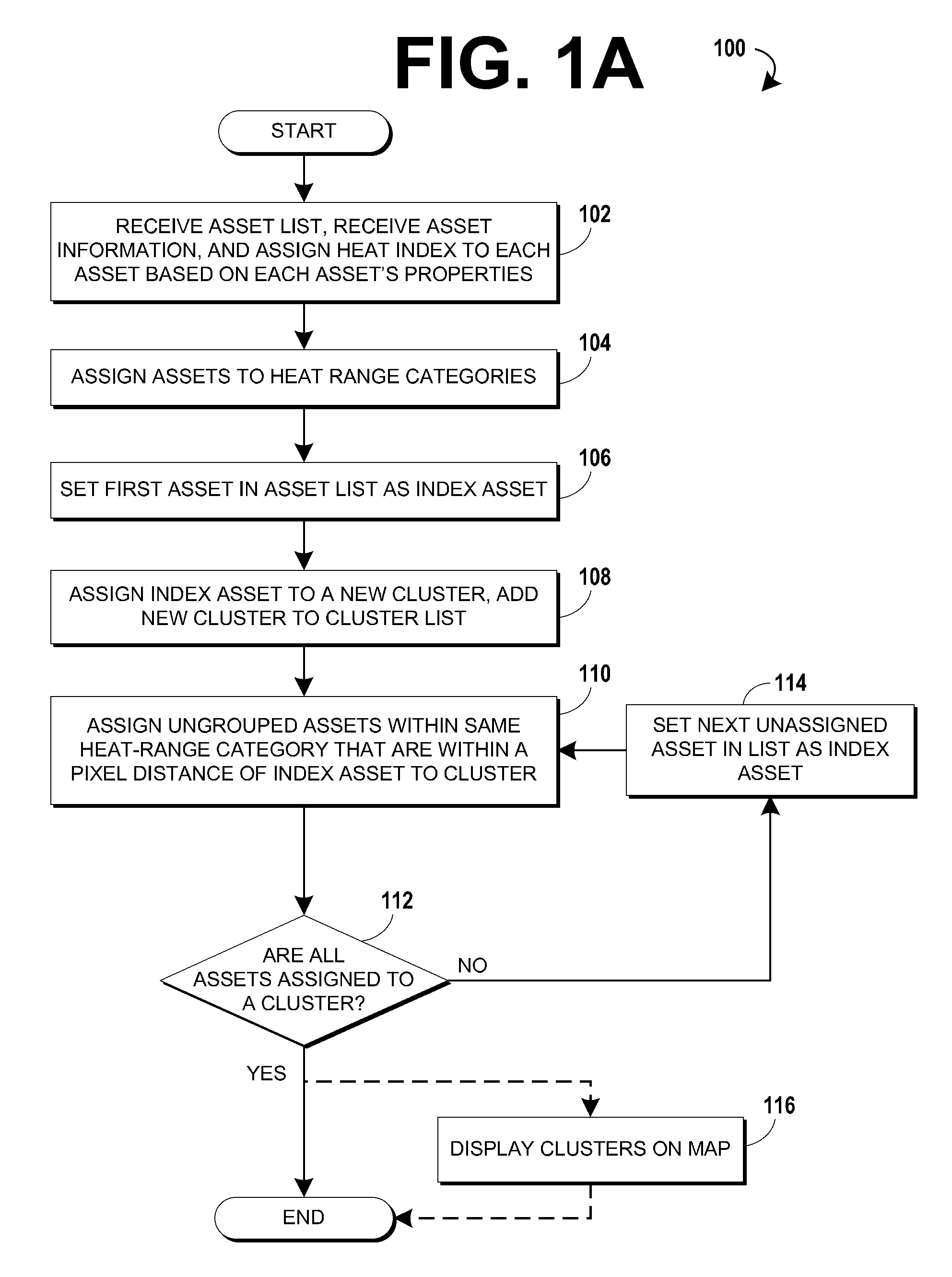
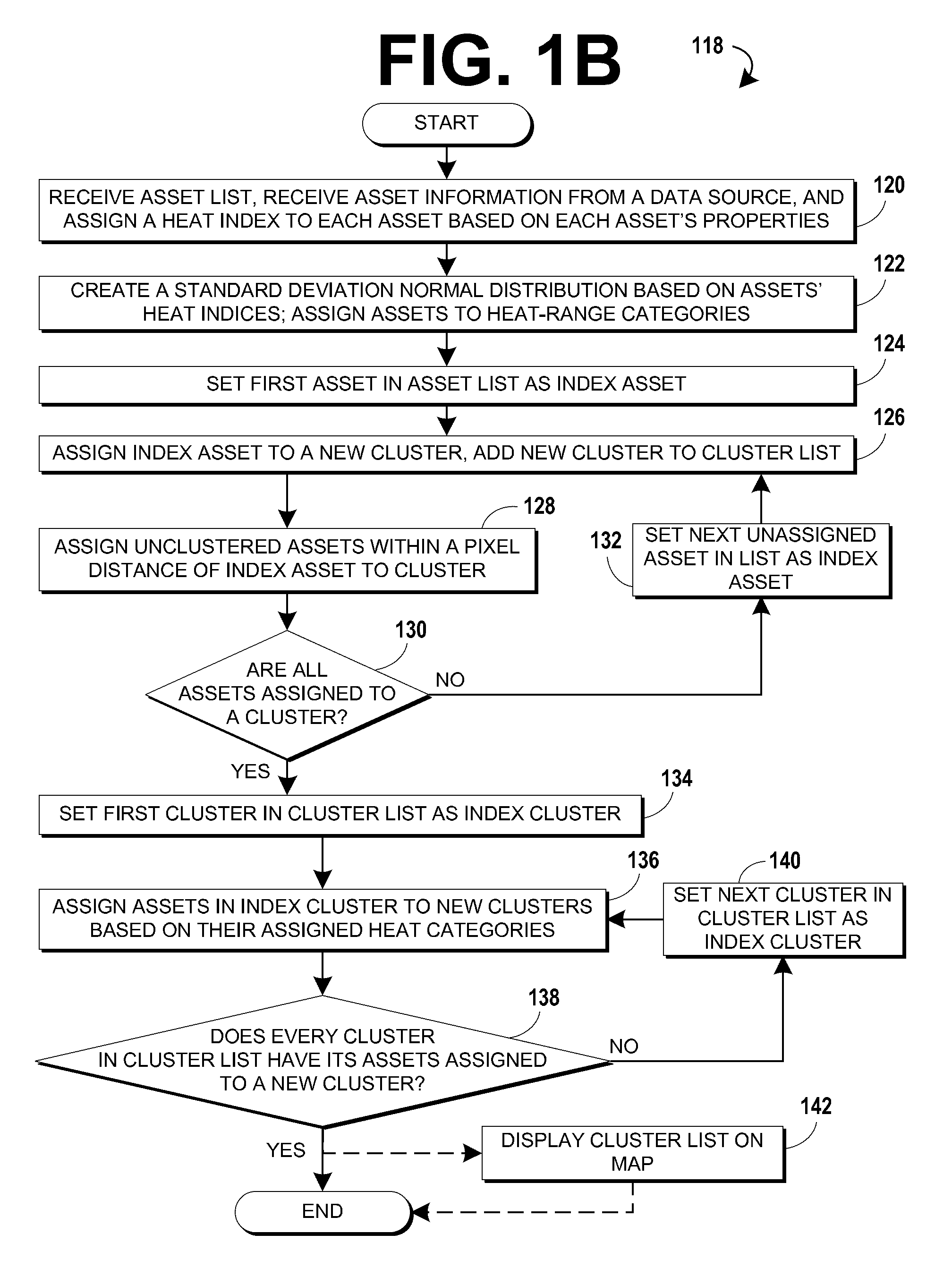
Cluster mapping to highlight areas of electrical congestion
InactiveUS20130016106A1Minimize timeLow costDrawing from basic elementsMaps/plans/chartsHeat mapPower grid
Methods of generating heat maps of assets using clustering of assets are disclosed. Some methods include receiving a list of assets, assigning the assets to one or more heat range categories based on the status of the assets, assigning assets operating within a zone to a zone cluster, assigning the assets of the zone cluster to category clusters based on the heat range categories assigned to the assets. The positions of the clusters may be calculated for mapping, and may be displayed on a map. Some embodiments of these methods allow a user to quickly detect and locate non-standard assets on a map while standard assets are consolidated to clusters that are less prominent to the user. This leads to minimizing the time required to form responses to de-load hotspots in an electrical grid, minimizing the cost of assets by reducing the need for hardware redundancy, and minimized equipment outages.
Owner:ENGIE STORAGE SERVICES NA LLC
Systems and methods for modifying power usage
ActiveUS8183995B2Increase coverageInformed choiceElectric signal transmission systemsLevel controlTransceiverPower usage
Systems and methods for providing energy management utilize wireless wide-area network broadcast signals and a decentralized receiver architecture to allow customers to make informed choices with regard to energy consumption and load shedding for particular appliances. A receiver assembly embedded within an appliance receives a broadcast signal, e.g., an FM subcarrier signal, including tariff data and other electrical grid data. A processor coupled with the receiver controls the appliance in accordance with the received data and in accordance with user-defined preferences. In some embodiments, a transceiver assembly is embedded in one or more appliances in a household. Each transceiver is configured to receive broadcast signals regarding grid data, and to communicate with other appliances and / or a usage meter over a wireless personal area network. Meter data from one or more households may be aggregated and uplinked back to the energy provider or other entities.
Owner:E RADIO USA
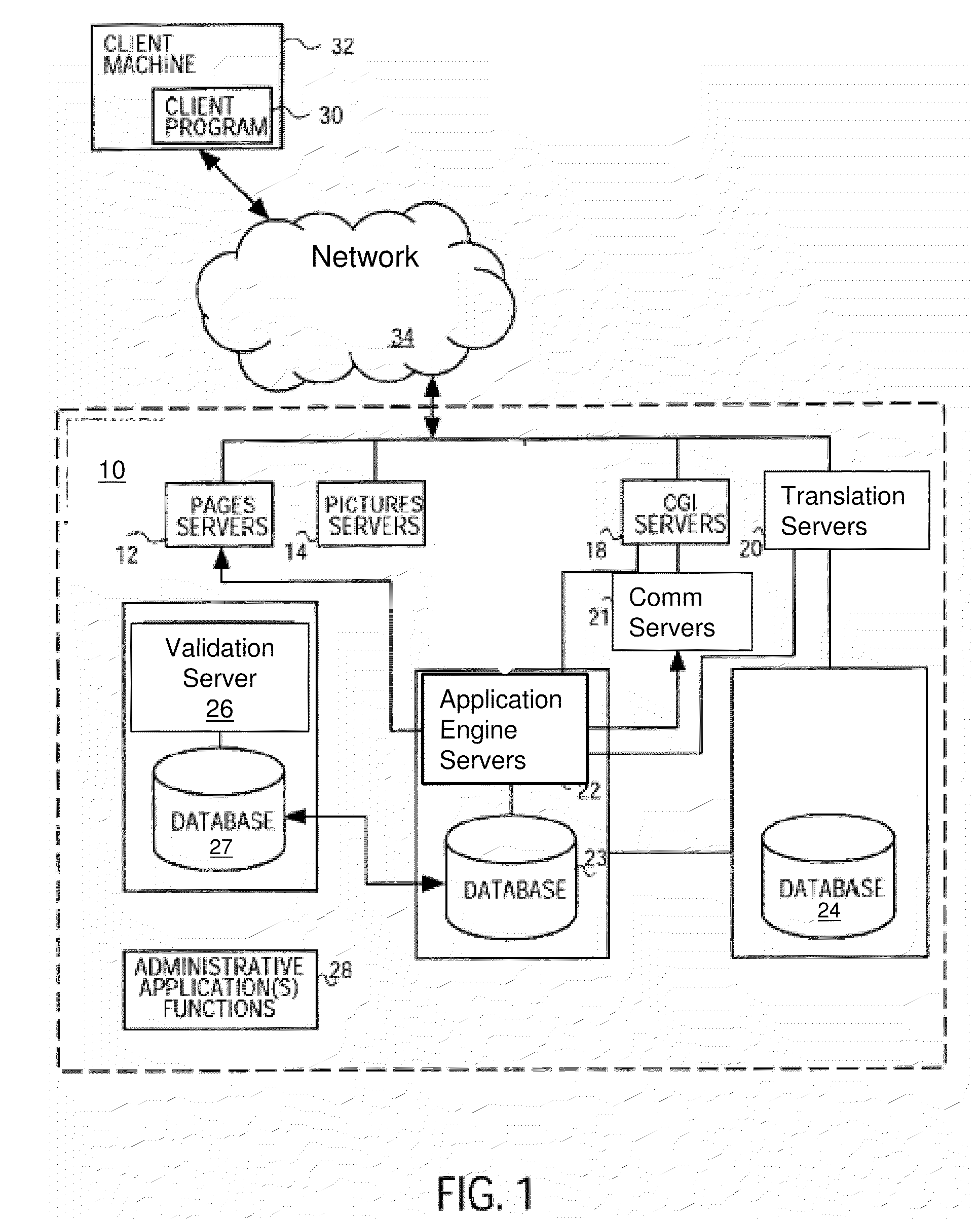
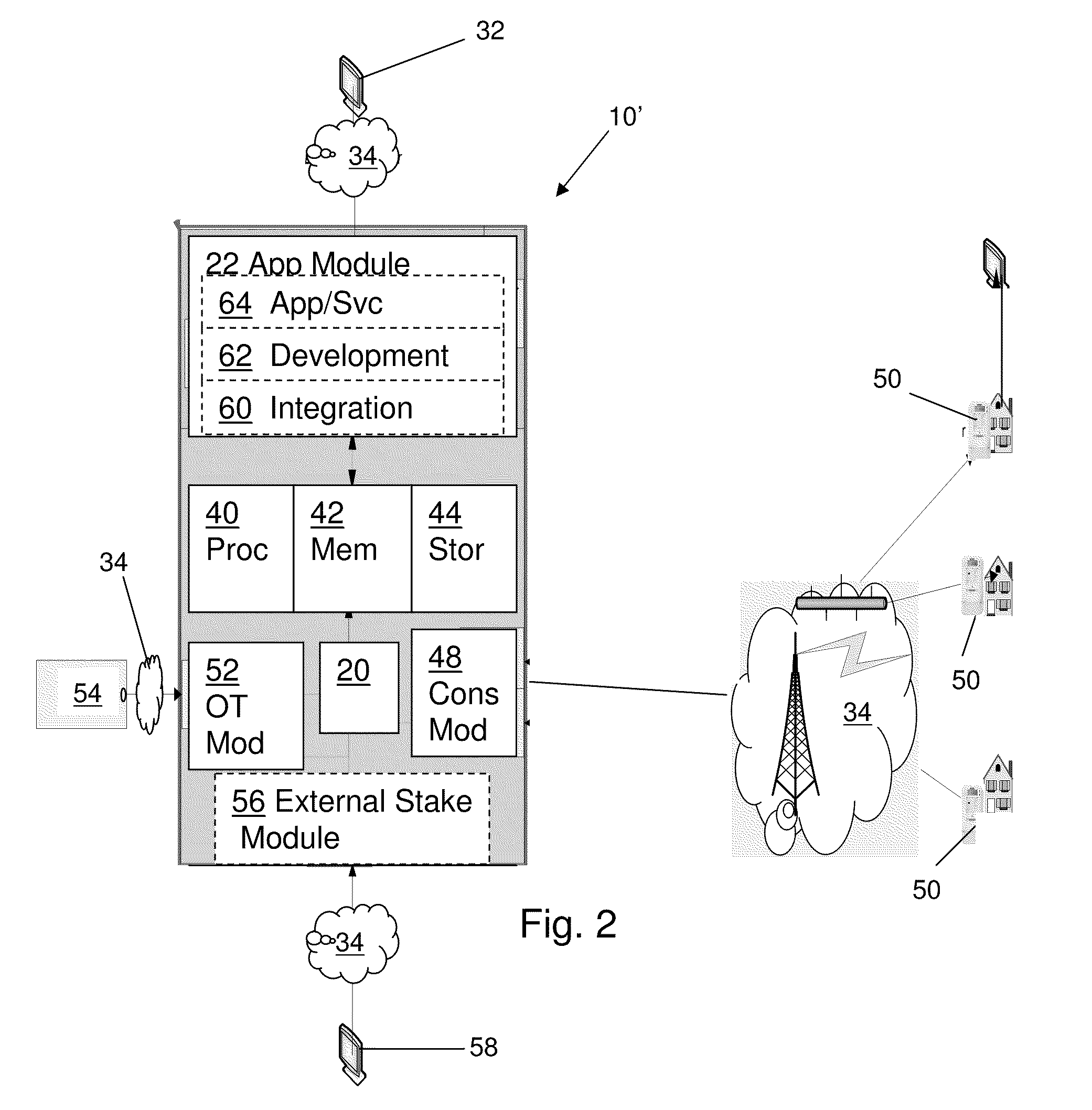
Enterprise Smart Grid and Demand Management Platform and Methods for Application Development and Management
ActiveUS20110010016A1Facilitate automated energy management operationEasy to operateLevel controlMultiple digital computer combinationsRequirements managementPower grid
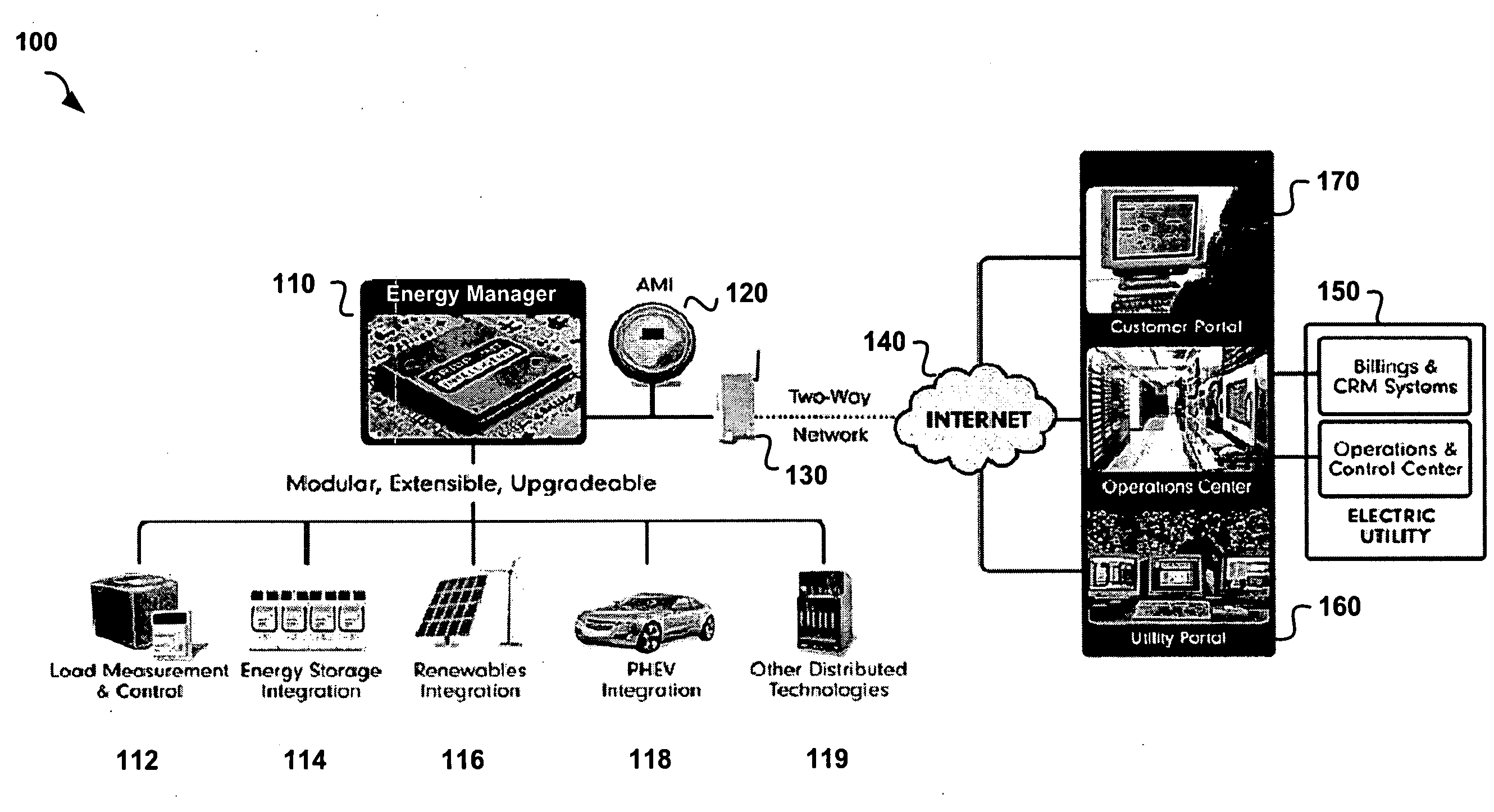
A computer-implemented platform server and method is provided for energy management operations in a Smart Grid environment. The platform server includes an application module configured to operate any of a plurality of Smart Grid Applications. A consumer-side module is configured for bi-directional communication with a plurality of consumer-side intelligent appliances. An Operations Technology (OT) module is configured for communication with an electrical grid Energy Management System (EMS). A translation module is coupled to, and configured to translate data received from, the application, consumer-side, and OT modules, so that the platform is configured to selectively receive, translate, and transmit data from and among any of said application, consumer-side, and OT modules, to facilitate automated energy management operations in a Smart Grid environment.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SOLUTIONS LTD
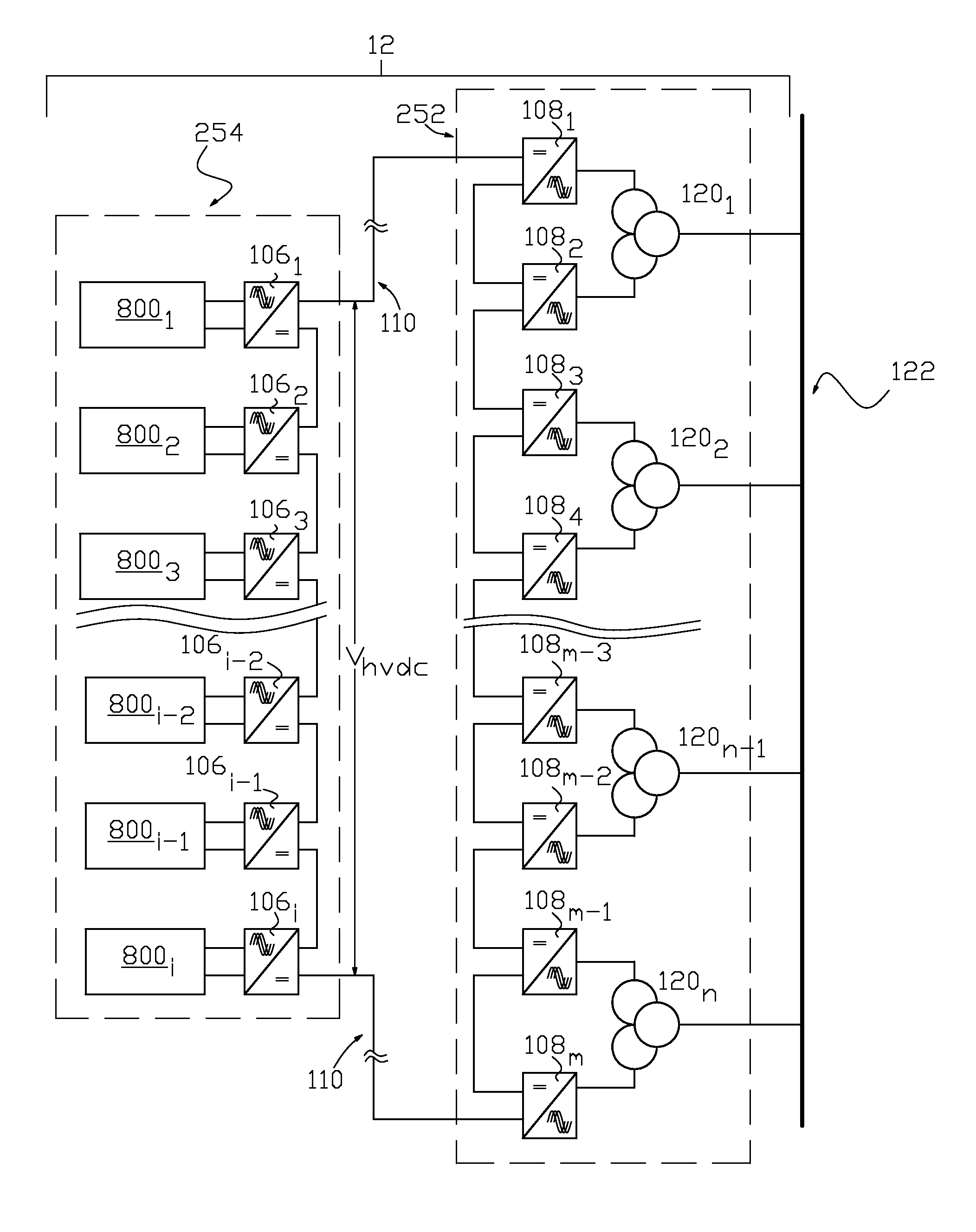
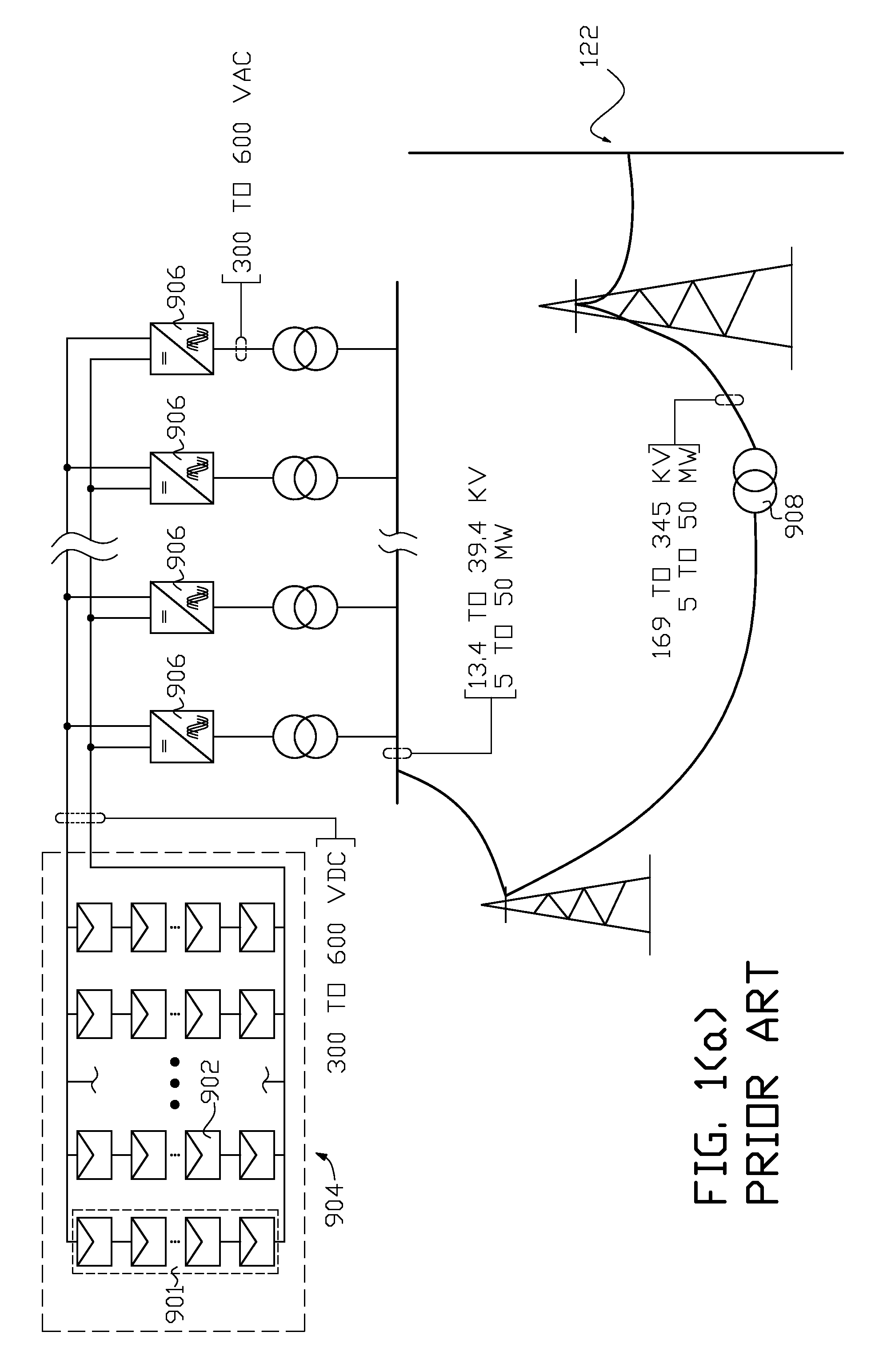
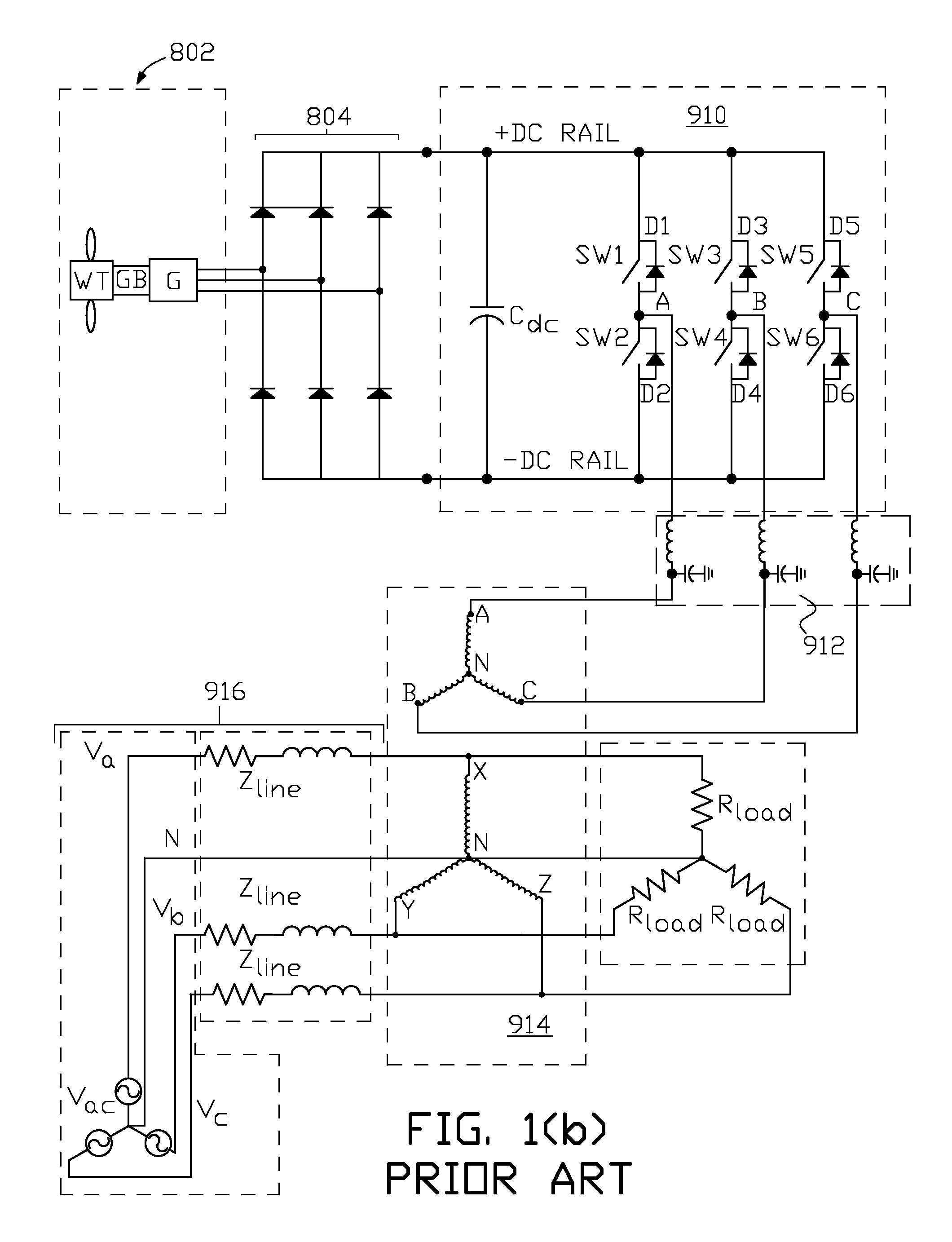
Collection of electric power from renewable energy sources via high voltage, direct current systems with conversion and supply to an alternating current transmission network
ActiveUS8212408B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric power transfer ac networkElectric power systemEngineering
Wind-generated electric power is collected in a multiple nodal arrangement where the DC output current of each node can be held constant while the DC output node voltage is allowed to vary. The DC outputs from the wind-generated power collection nodes are connected together in series and fed to a plurality of regulated current source inverters via a high voltage DC transmission link. Each inverter converts input DC power into a three phase AC output. The AC outputs of the regulated current source inverters are connected to a phase shifting transformation network that supplies three phase electric power to a conventional AC electrical transmission system. Alternatively wind-generated and photovoltaic-generated electric power is commonly collected in a nodal arrangement and transported at high voltage DC to a plurality of regulated current source inverters for supply to the conventional AC electrical transmission system.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
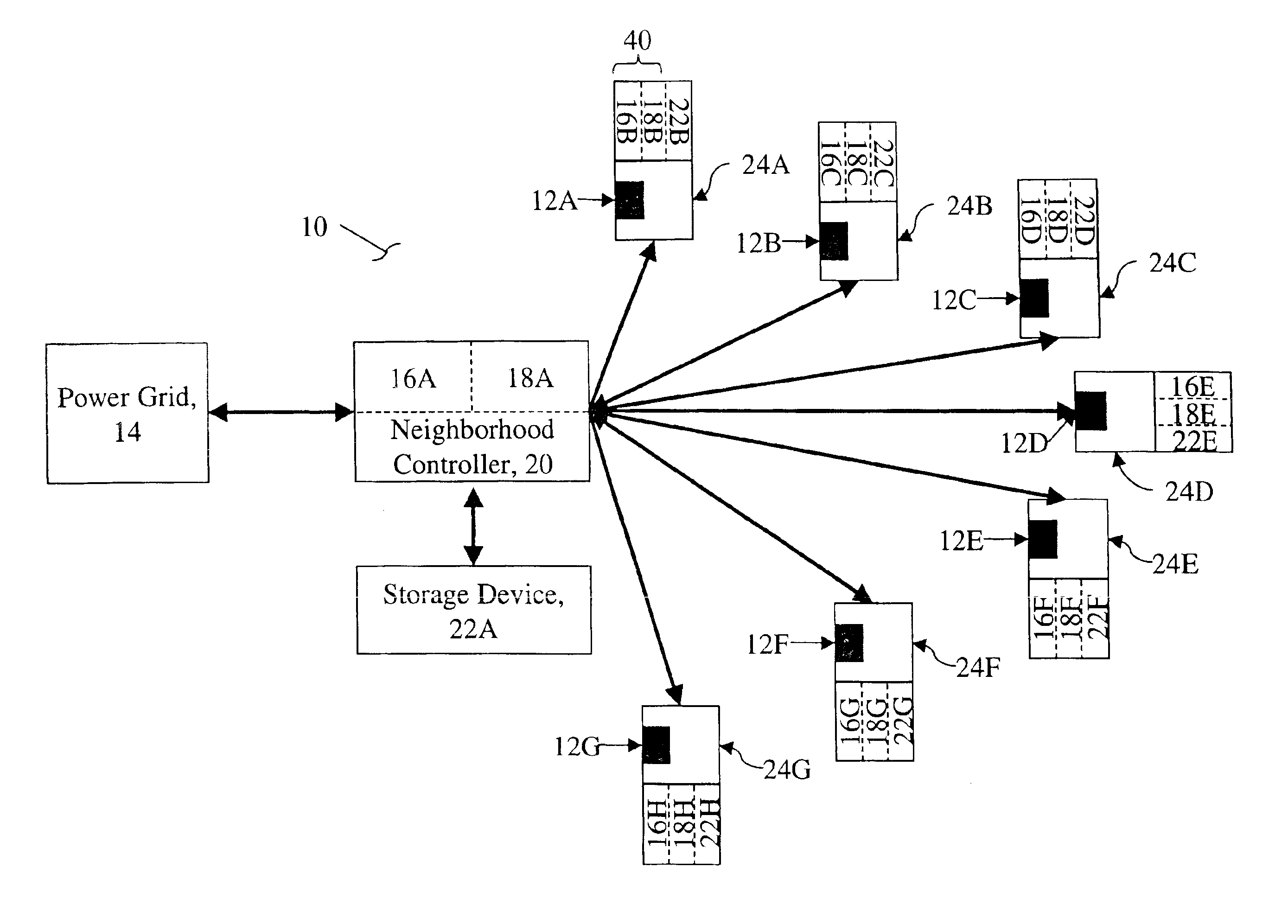
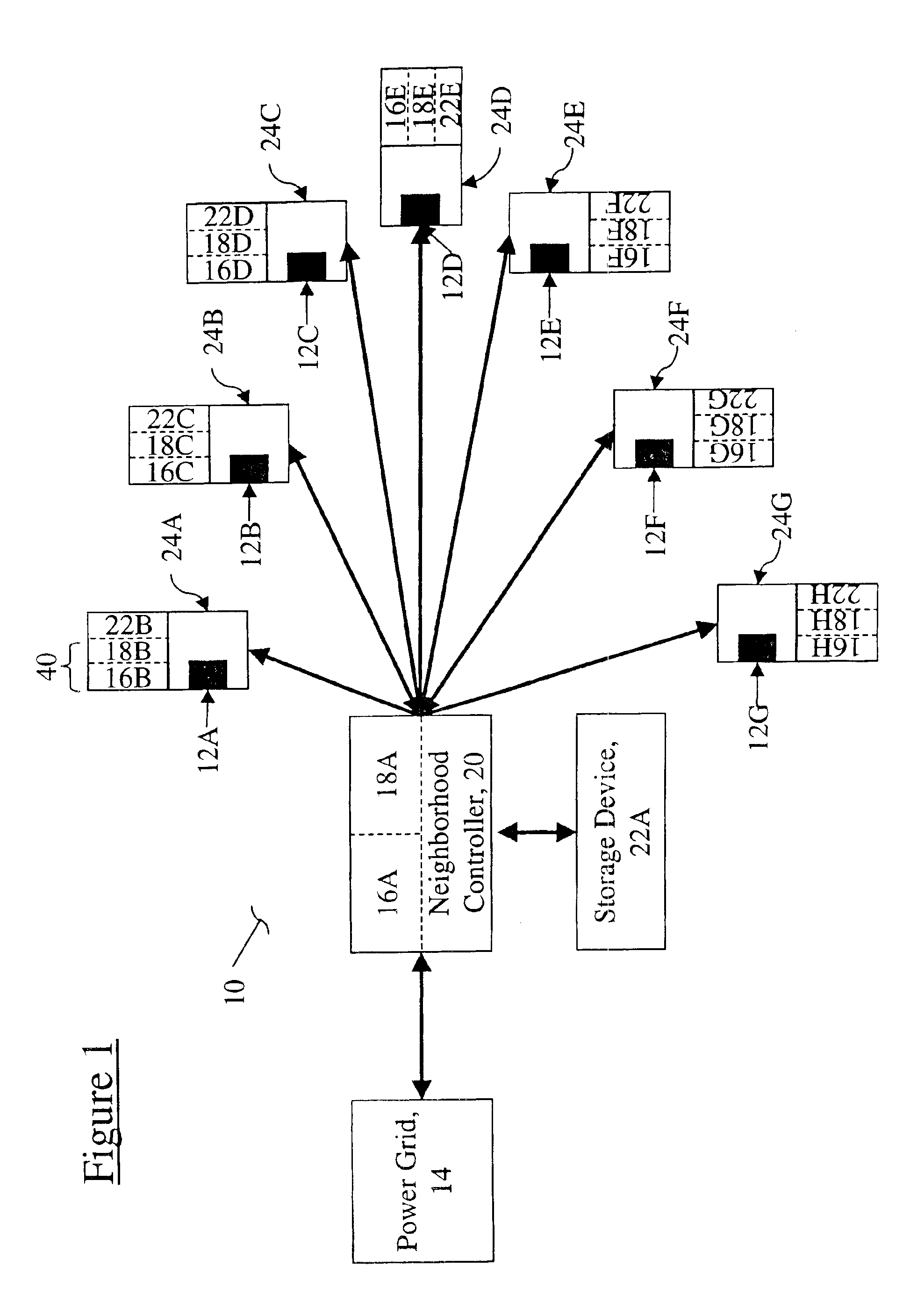
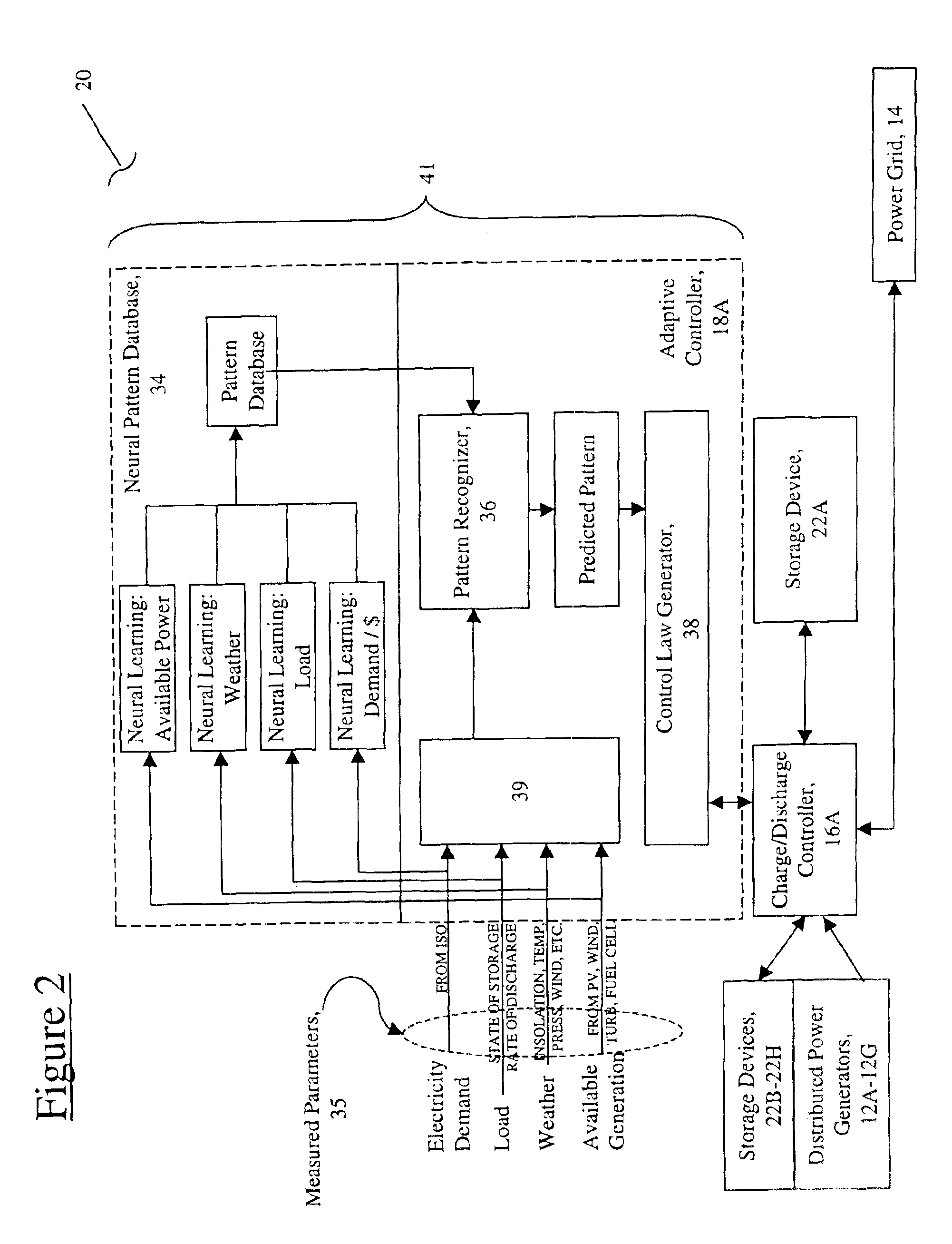
Distributed energy neural network integration system
Owner:ORION ENG
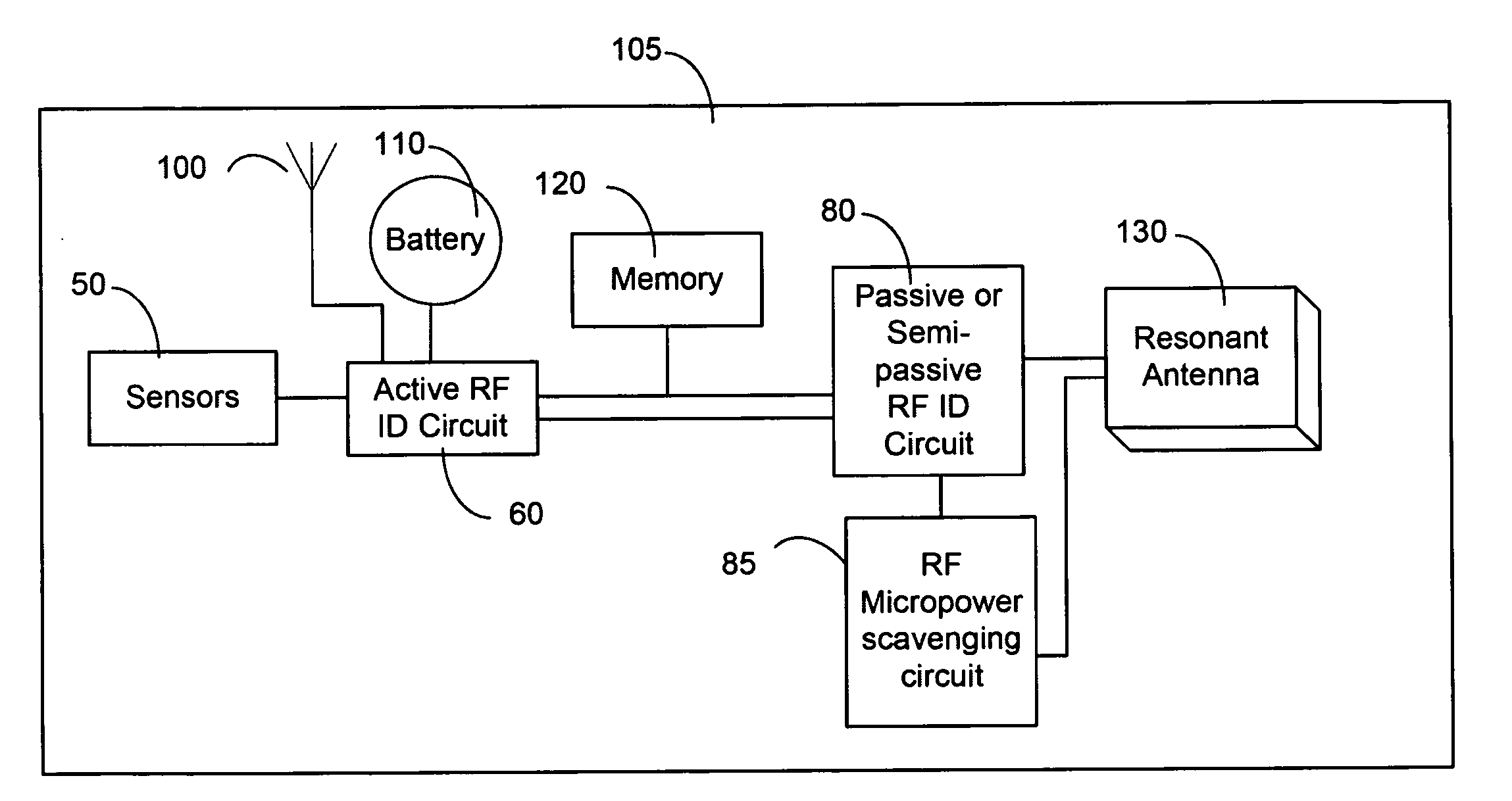
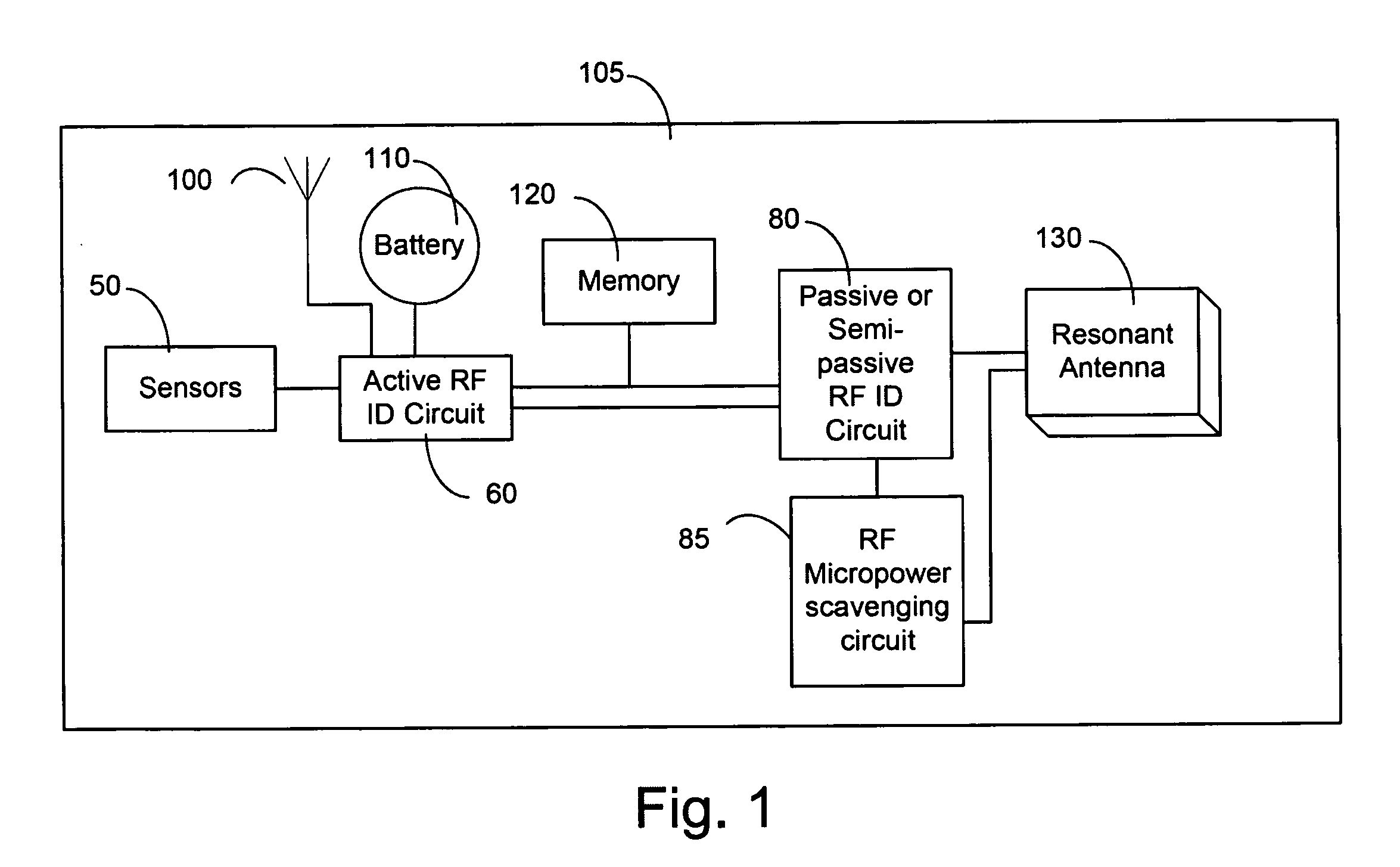
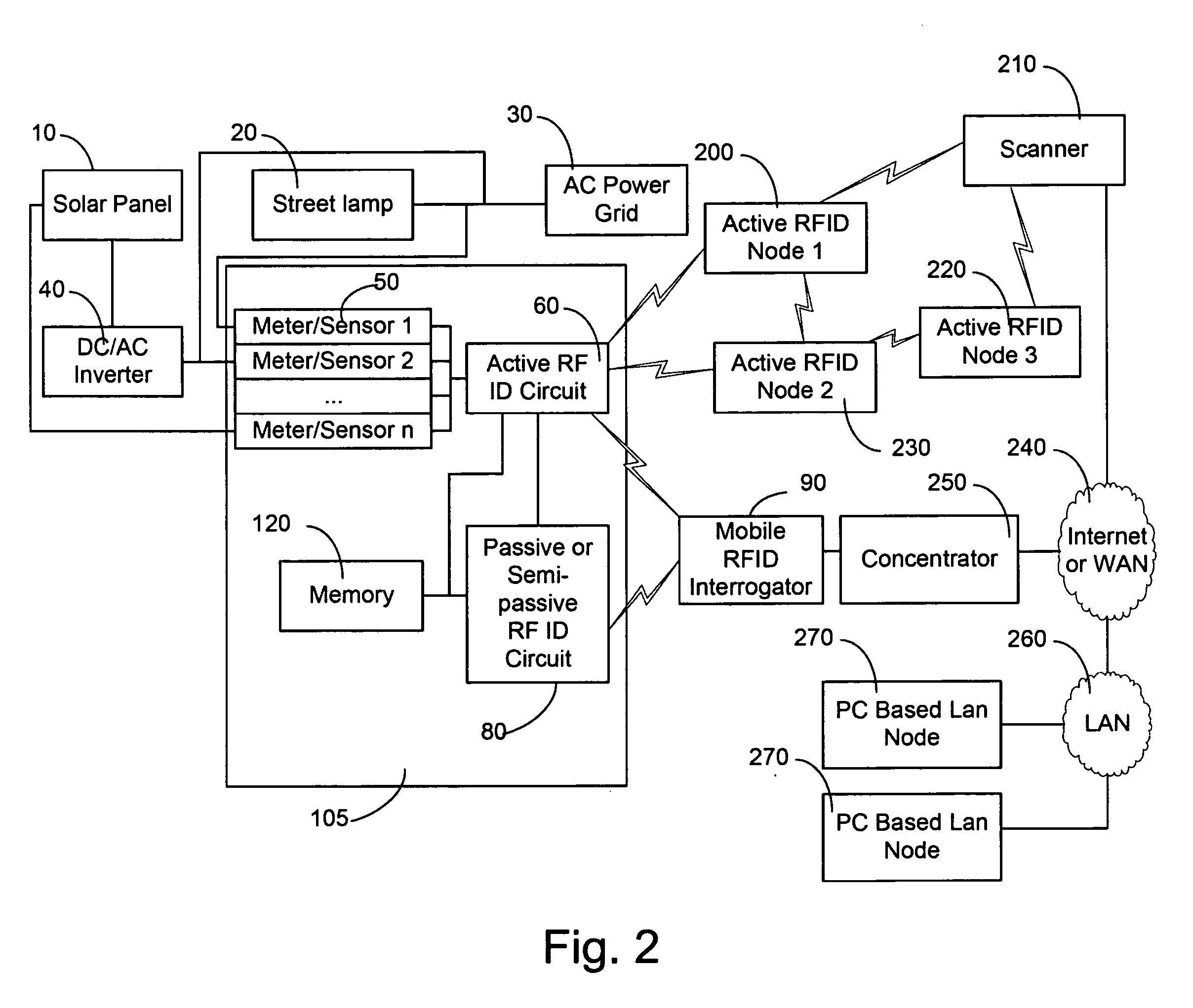
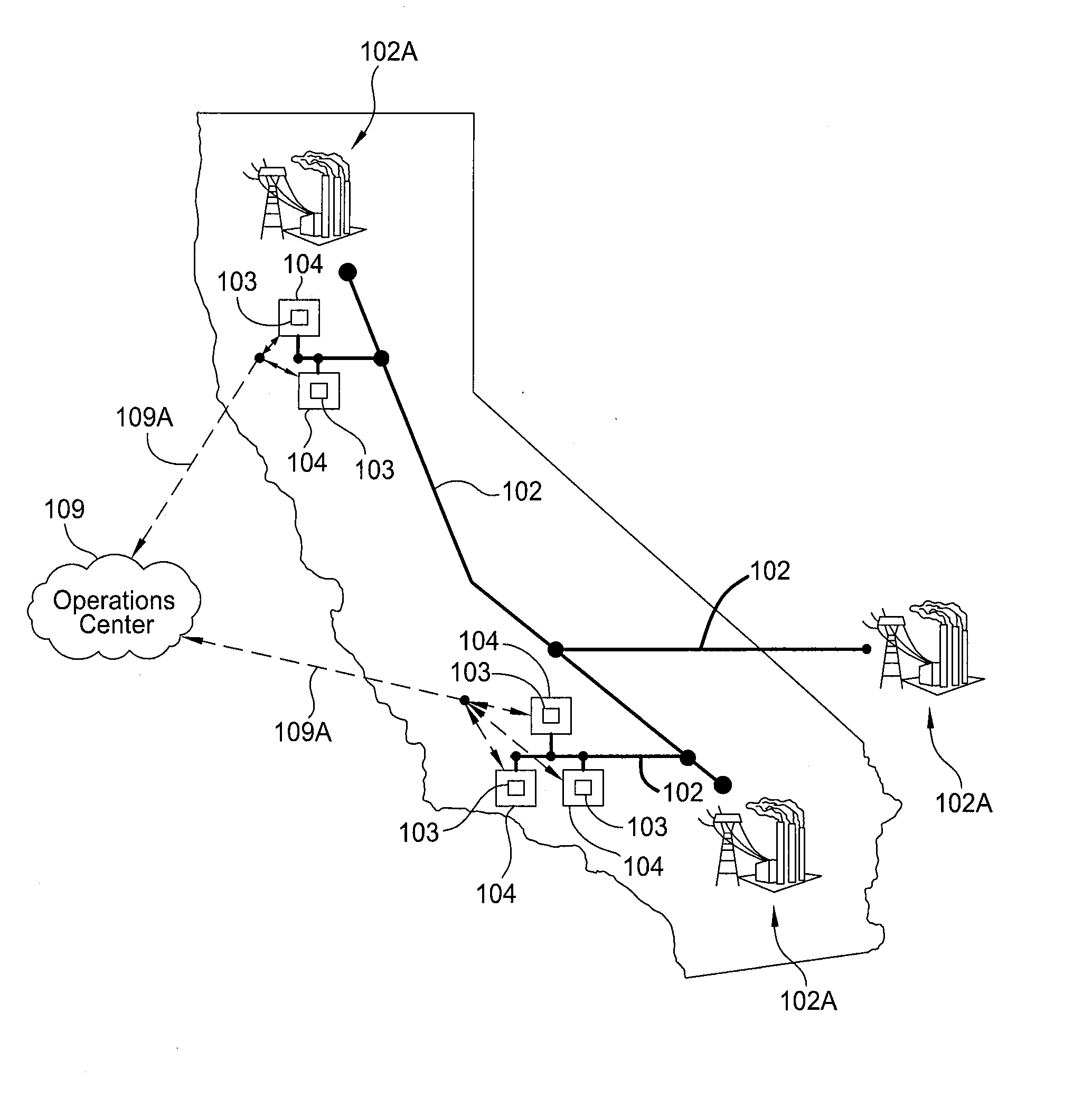
RFID power control and monitoring system
InactiveUS20100231407A1Reduced Power RequirementsUtility meters data arrangementsWireless architecture usageTelecommunications linkThe Internet
A system for monitoring parameters associated with a device, such as current, voltage, power, temperature, energy consumed, moisture, fluid levels and flow, wind speed, identification parameters, and repair history. The system includes the use of hybrid RFID sensor tags including a combination of active, semi-passive, and passive RFID circuits. Hybrid tags are attached to electrical system components. Standalone electrical components and generators and those connected to the electrical grid may be monitored. Data collected and stored in the hybrid tags may be accessed via a wireless communication link between hybrid tags and either active scanners or a passive interrogators. The data collected and processed from the hybrid tags may be provided to a user via the Internet or another wired or wireless communication network.
Owner:NEW JERSEY MICROSYST
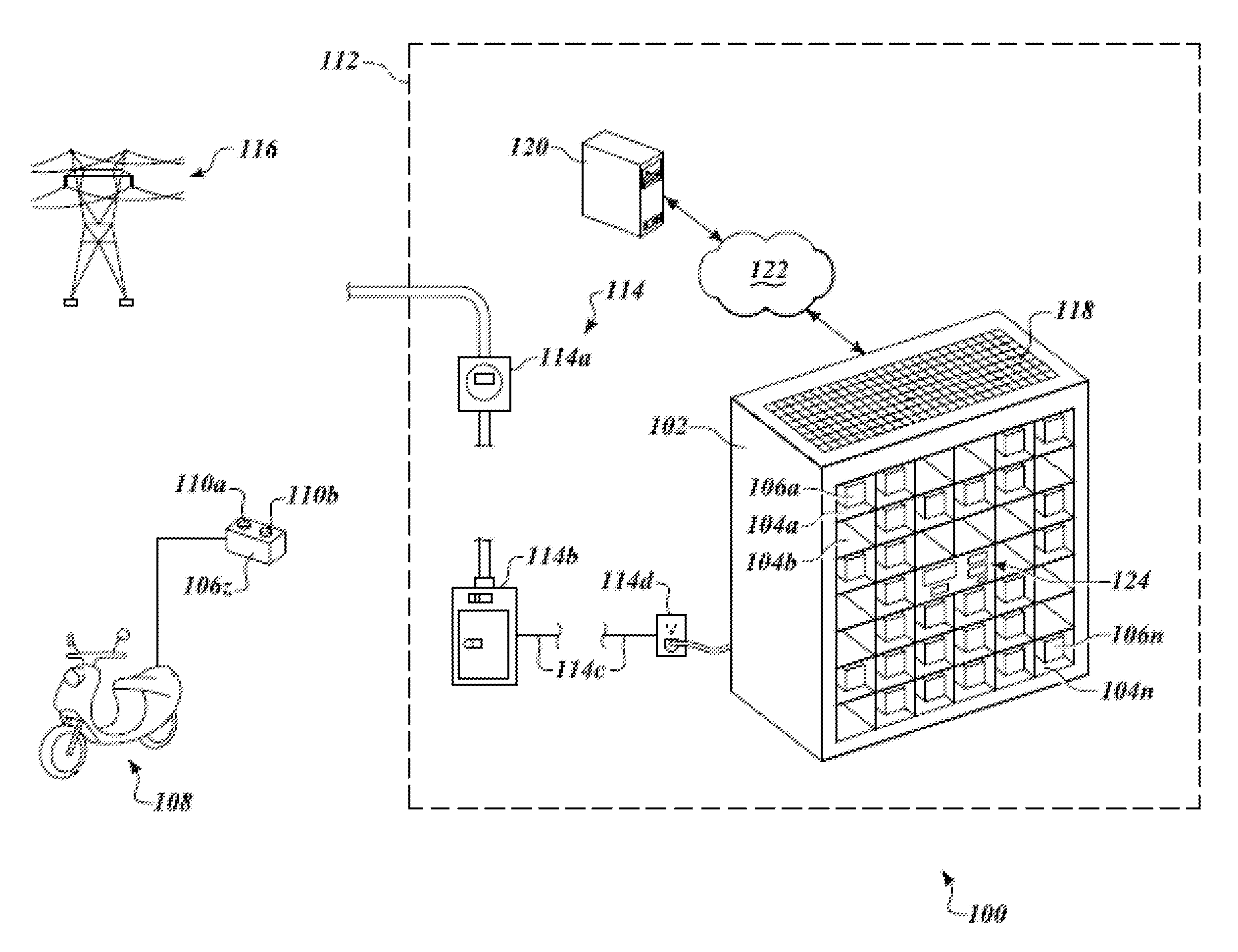
Method and apparatus for stabalizing power on an electrical grid using networked distributed energy storage systems
ActiveUS20140070617A1Batteries circuit arrangementsLoad forecast in ac networkElectric power transmissionEnergy control
Embodiments of the present invention include control methods employed in multiphase distributed energy storage systems that are located behind utility meters typically located at, but not limited to, medium and large commercial and industrial locations. These distributed energy storage systems can operate semi-autonomously, and can be configured to develop energy control solutions for an electric load location based on various data inputs and communicate these energy control solutions to the distributed energy storage systems. In some embodiments, one or more distributed energy storage systems may be used to absorb and / or deliver power to the electric grid in an effort to provide assistance to or correct for power transmission and distribution problems found on the electric grid outside of an electric load location. In some cases, two or more distributed energy storage systems are used to form a controlled and coordinated response to the problems seen on the electric grid.
Owner:STEM
Apparatus, method and article for collection, charging and distributing power storage devices, such as batteries
ActiveUS20130026971A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesNavigation instrumentsSupercapacitorEngineering
A collection, charging and distribution machine collects, charges and distributes portable electrical energy storage devices (e.g., batteries, super- or ultracapacitors). To charge, the machine employs electrical current from an external source, such as the electrical grid or an electrical service of an installation location. The machine determines a first number of devices to be rapidly charged, employing charge from a second number of devices identified to sacrifice charge. Thus, some devices may be concurrently charged via current from the electrical service and current from other devices, to achieve rapid charging of some subset of devices. The devices that sacrifice charge may later be charged. Such may ensure availability of devices for end users.
Owner:GOGORO
Apparatus, method and article for redistributing power storage devices, such as batteries, between collection, charging and distribution machines
ActiveUS20130030581A1Level controlRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectrical batterySupercapacitor
A network of collection, charging and distribution machines collect, charge and distribute portable electrical energy storage devices (e.g., batteries, supercapacitors or ultracapacitors). To charge, the machines employ electrical current from an external source, such as the electrical grid or an electrical service of an installation location. As demand at individual collection, charging and distribution machines increases or decreases relative to other collection, charging and distribution machines, a distribution management system initiates redistribution of portable electrical energy storage devices from one collection, charging and distribution machine to another collection, charging and distribution machine in an expeditious manner. Also, redeemable incentives are offered to users to return or exchange their portable electrical energy storage devices at selected collection, charging and distribution machines within the network to effect the redistribution.
Owner:GOGORO
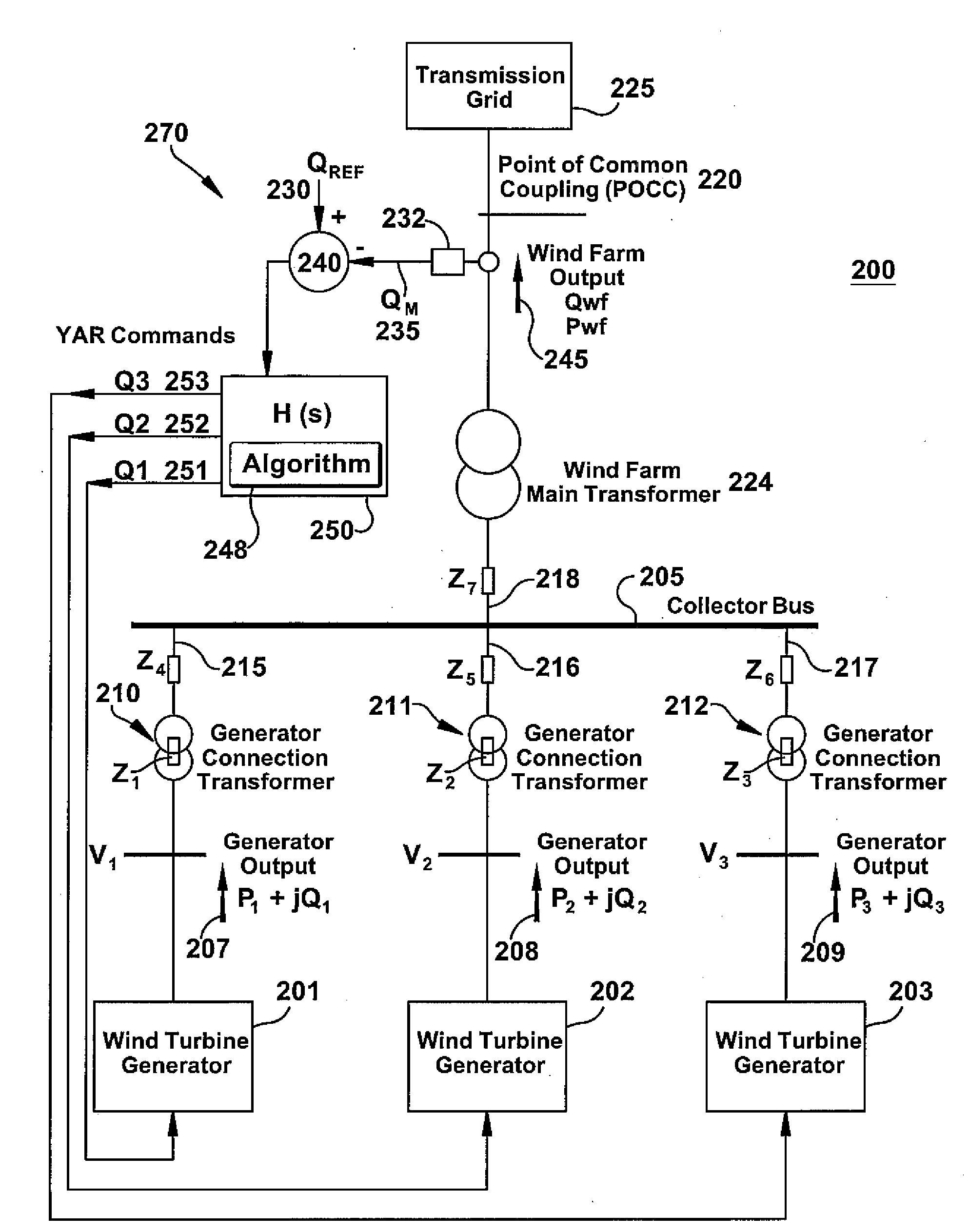
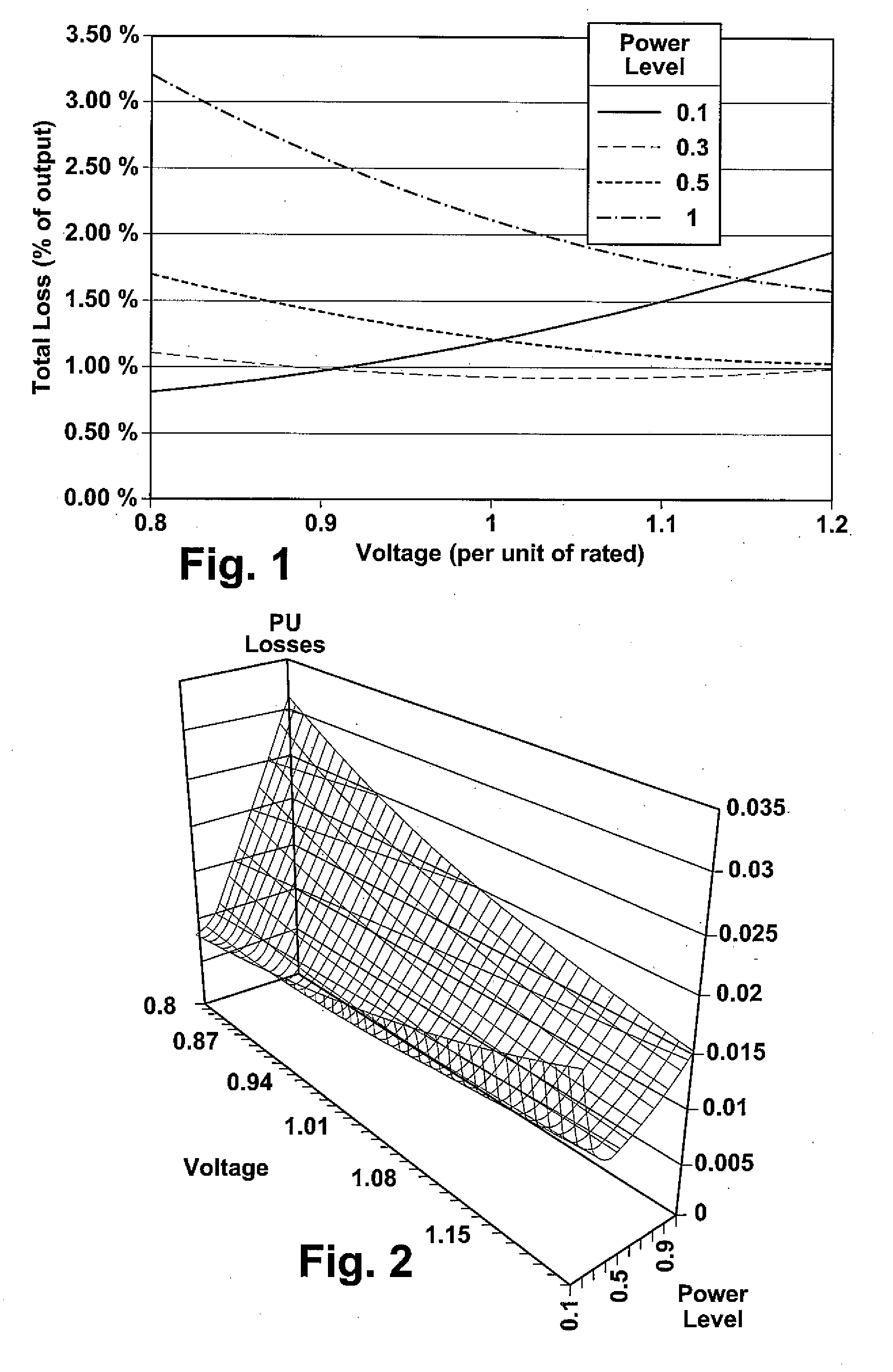
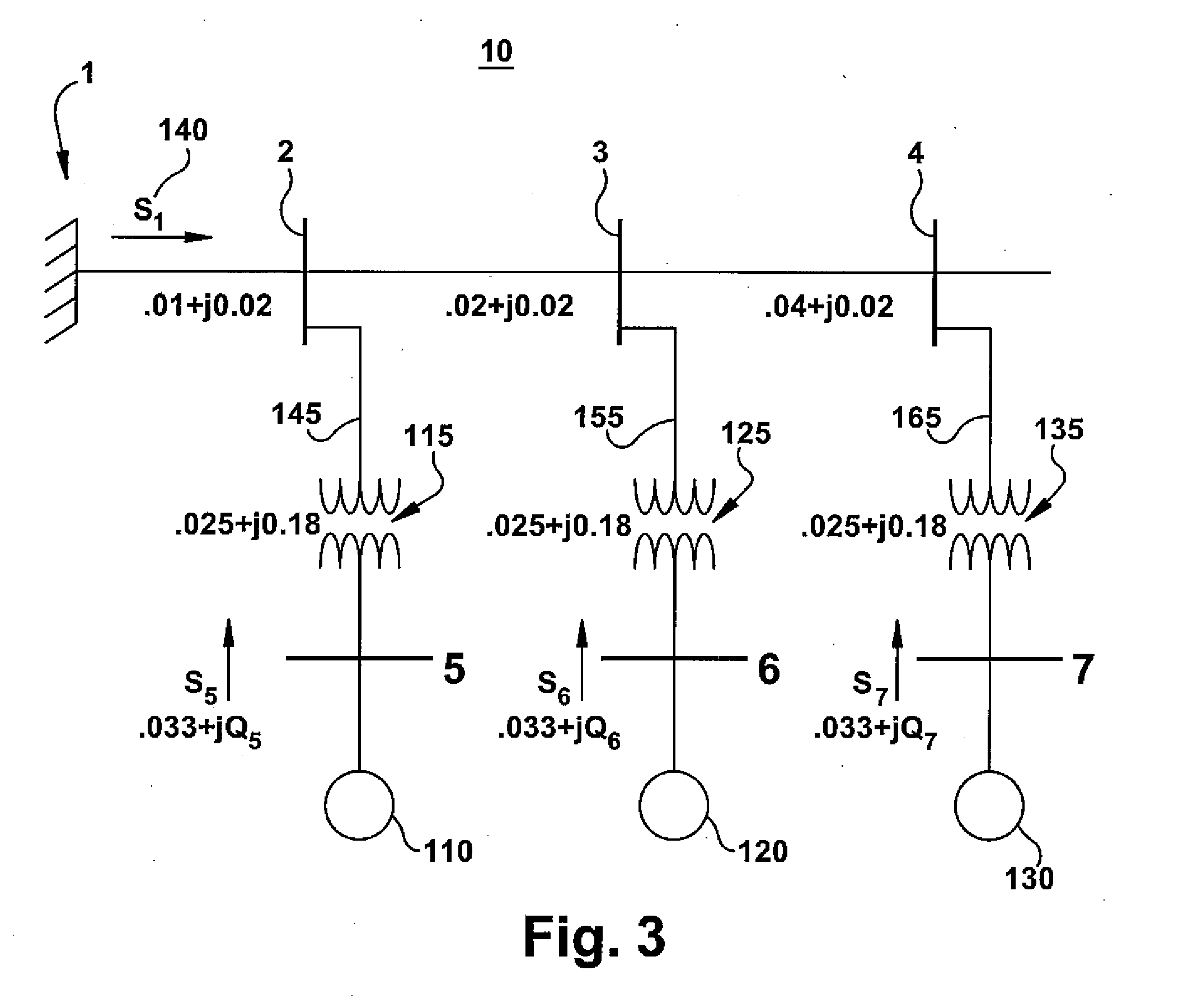
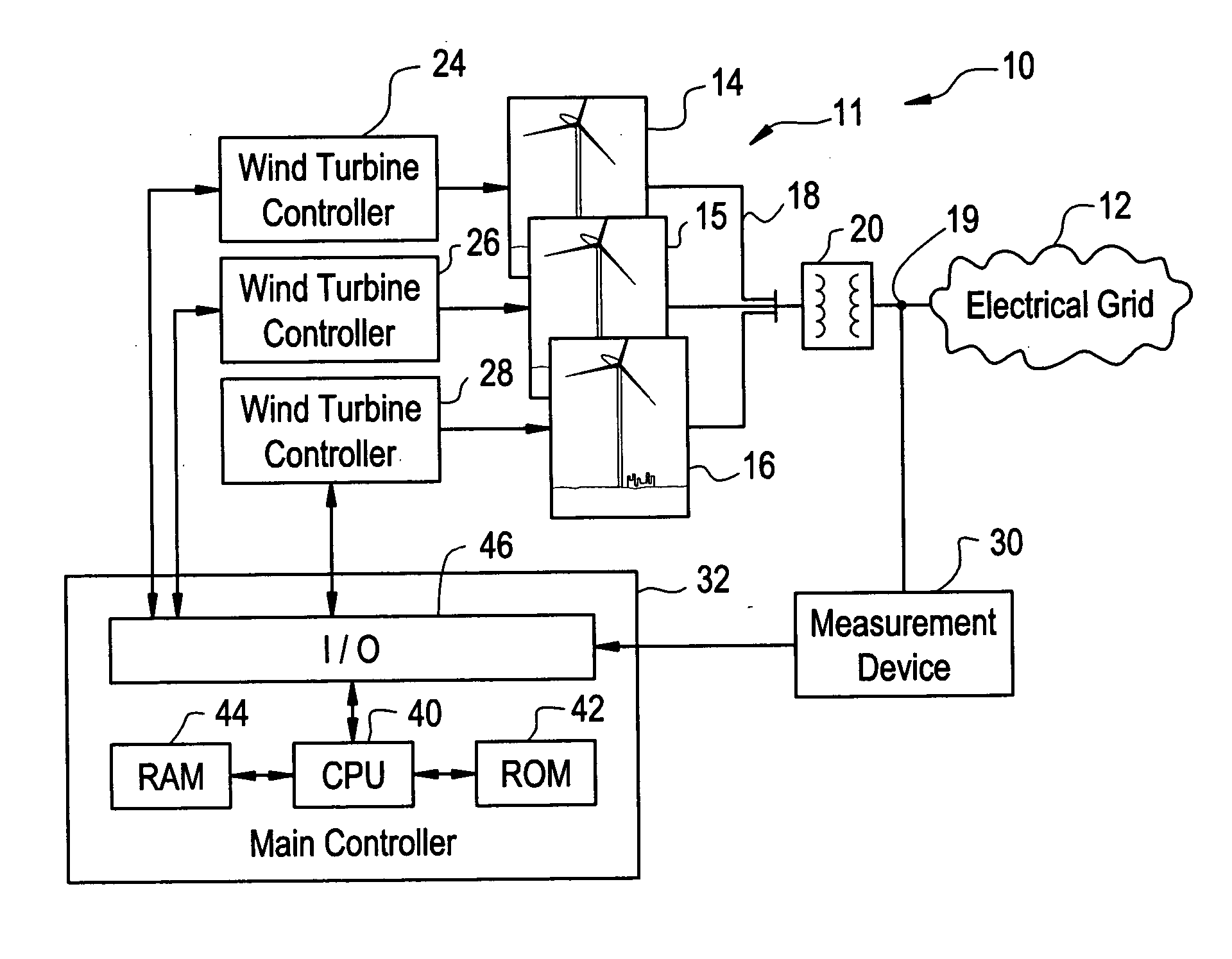
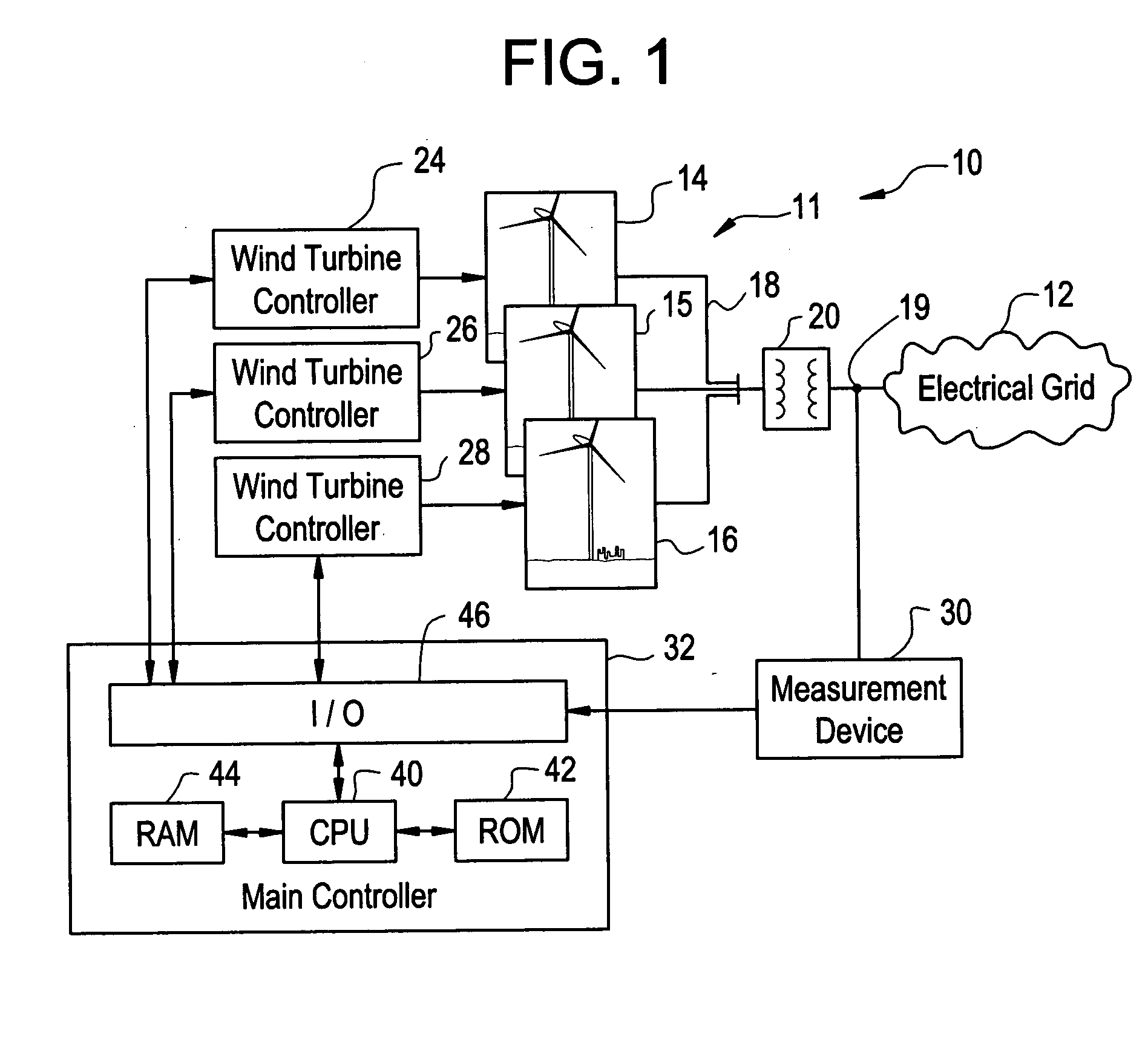
Windfarm collector system loss optimization
ActiveUS20090218817A1Reduce power lossMinimizing electrical lossDc network circuit arrangementsWind motor controlElectrical conductorTransformer
A windfarm system is provided that is optimized for minimizing electrical loss. The windfarm system includes a plurality of wind turbine generators and a collector system including a conductor or network of conductors. The collector system also including a plurality of transformers with one or more transformers connected between each wind turbine generator and the conductors, and a substation transformer connecting the windfarm collector system to the electrical grid. The windfarm system also includes a monitoring system for monitoring the windfarm system electrical output and thermal condition, and outputs of the individual wind turbine generators. A control function may include voltage and real and reactive power commands to the individual wind turbine generators. The control function incorporates an algorithm whose technical effect is minimizing electrical losses for the windfarm system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus, method and article for authentication, security and control of power storage devices, such as batteries, based on user profiles
ActiveUS20130026972A1Limited rangeLong recharging timeRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCoin-freed apparatusSupercapacitorEngineering
A network of collection, charging and distribution machines collect, charge and distribute portable electrical energy storage devices (e.g., batteries, supercapacitors or ultracapacitors). To charge, the machines employ electrical current from an external source, such as the electrical grid or an electrical service of an installation location. The charging and distribution machines may distribute portable electrical energy storage devices of particular performance characteristics and other attributes based on customer preferences and / or customer profiles. The charging and distribution machines may provide instructions to or otherwise program portable electrical energy storage devices stored within the charging and distribution machines to perform at various levels according to user preferences and user profiles.
Owner:GOGORO
Machine learning for power grid
A machine learning system for ranking a collection of filtered propensity to failure metrics of like components within an electrical grid that includes a raw data assembly to provide raw data representative of the like components within the electrical grid; (b) a data processor, operatively coupled to the raw data assembly, to convert the raw data to more uniform data via one or more data processing techniques; (c) a database, operatively coupled to the data processor, to store the more uniform data; (d) a machine learning engine, operatively coupled to the database, to provide a collection of propensity to failure metrics for the like components; (e) an evaluation engine, operatively coupled to the machine learning engine, to detect and remove non-complying metrics from the collection of propensity to failure metrics and to provide the collection of filtered propensity to failure metrics; and (f) a decision support application, operatively coupled to the evaluation engine, configured to display a ranking of the collection of filtered propensity to failure metrics of like components within the electrical grid.
Owner:CONSOL EDISON OF NEW YORK +1
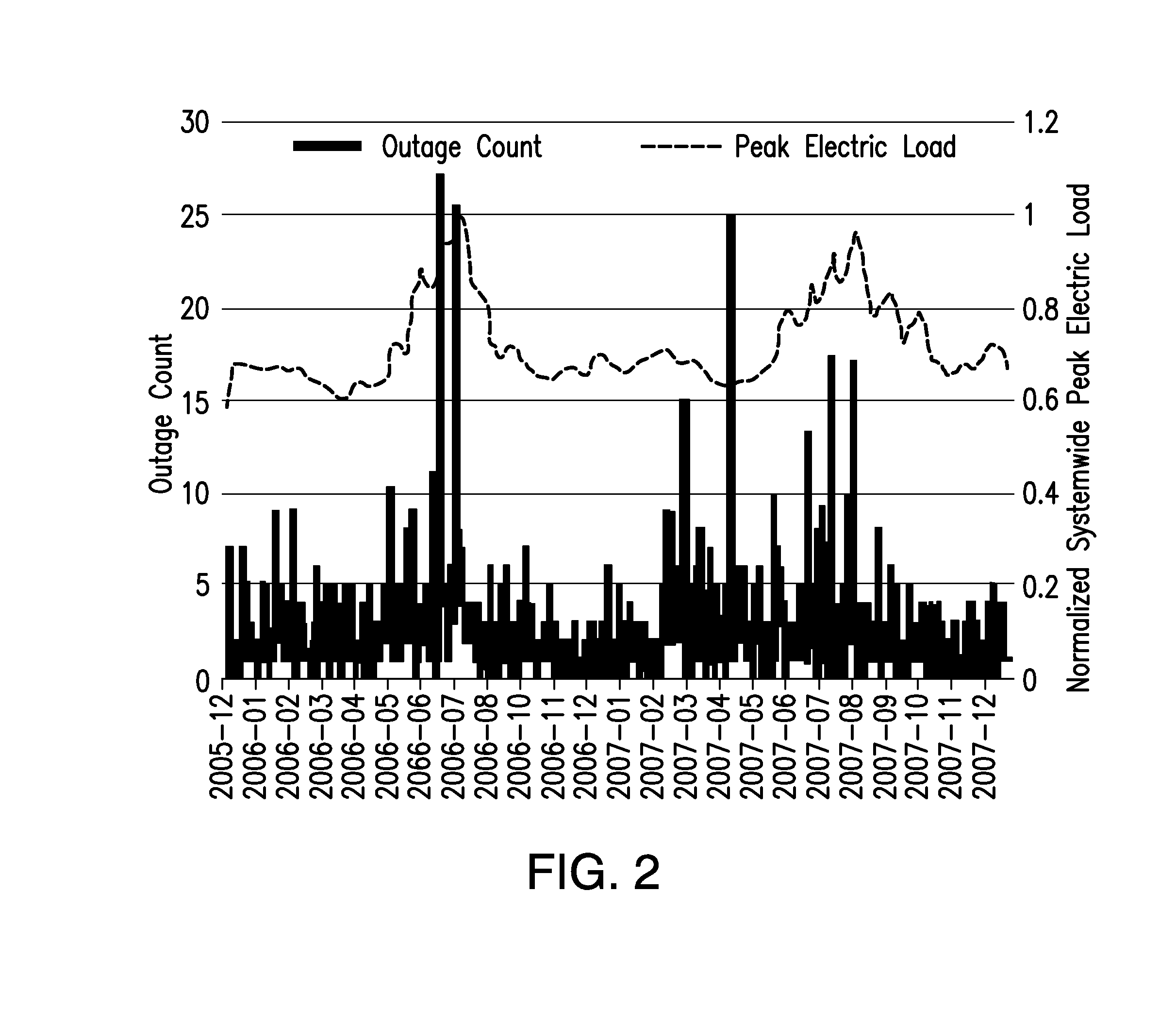
Method and system for managing a load demand on an electrical grid
A method for managing electrical demand on a power grid in response to electrical supply conditions is described. The method includes determining a first energy demand forecast using stored information, determining a first energy supply forecast based on a known energy production and transmission capacity, and comparing the first energy demand forecast to the first energy supply forecast. The method also includes transmitting at least one of an adjusted price signal and an electrical load shedding signal to a customer over a bi-directional communication system based on the comparison of the first energy demand forecast to the first energy supply forecast.
Owner:GE DIGITAL HLDG LLC
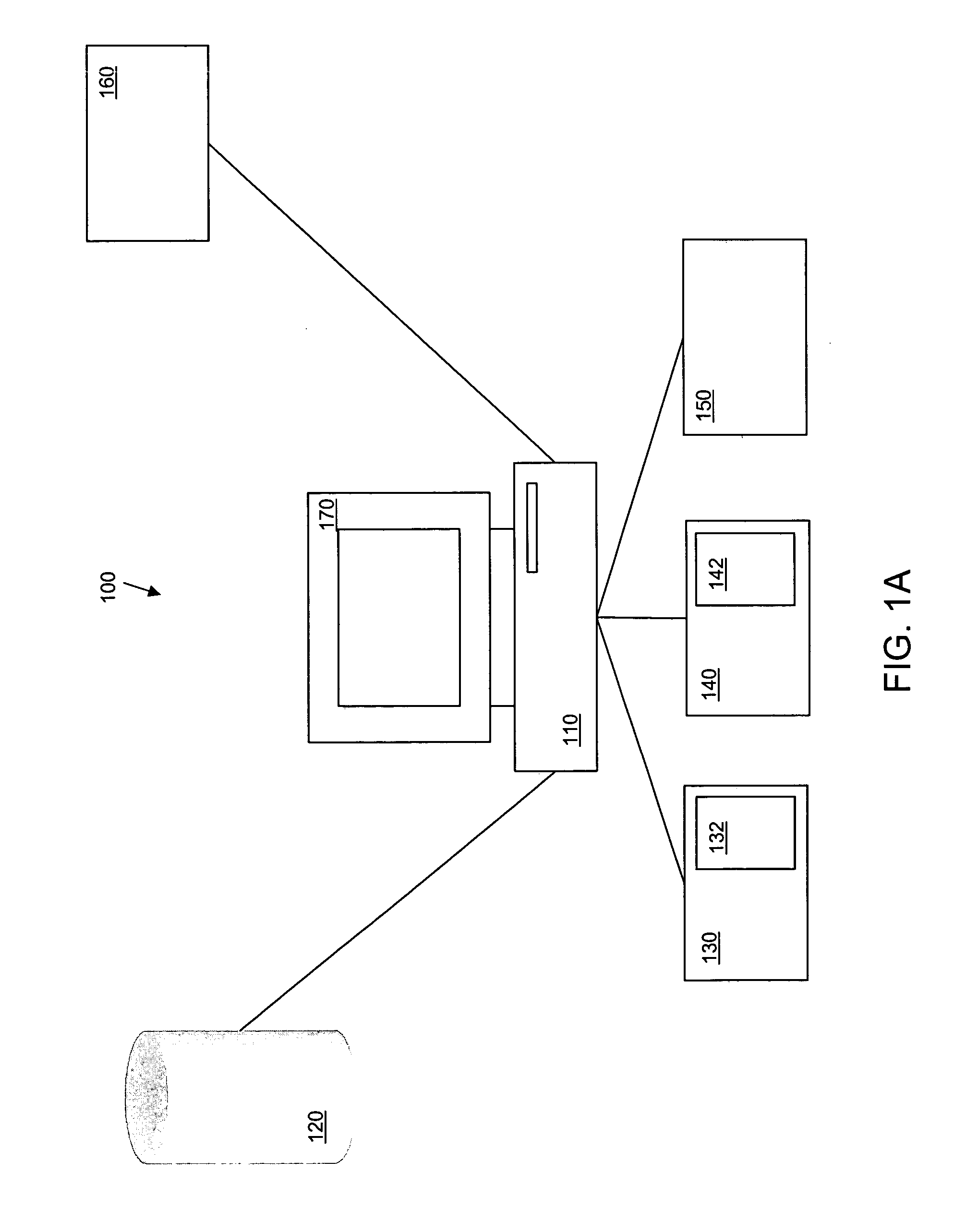
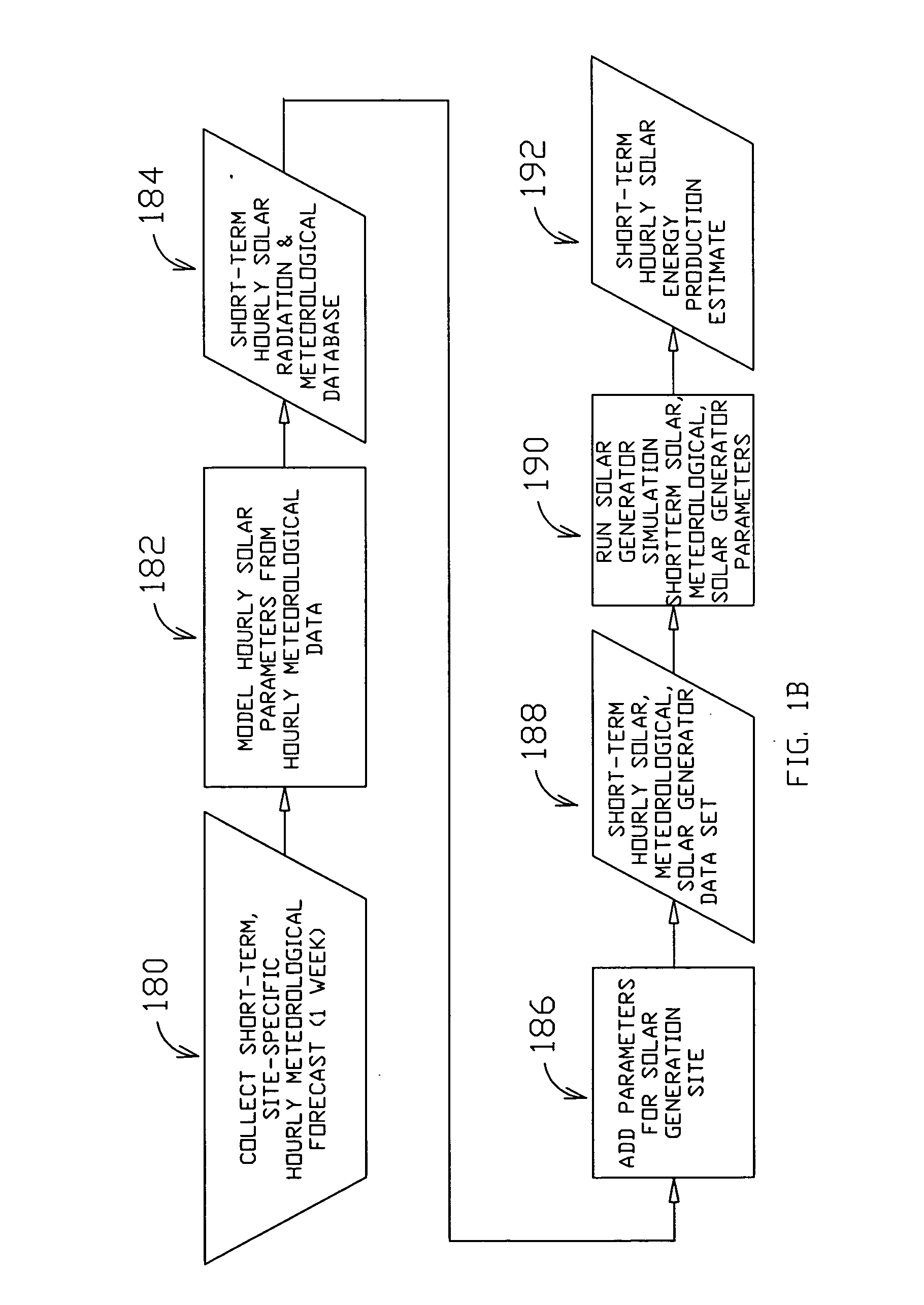
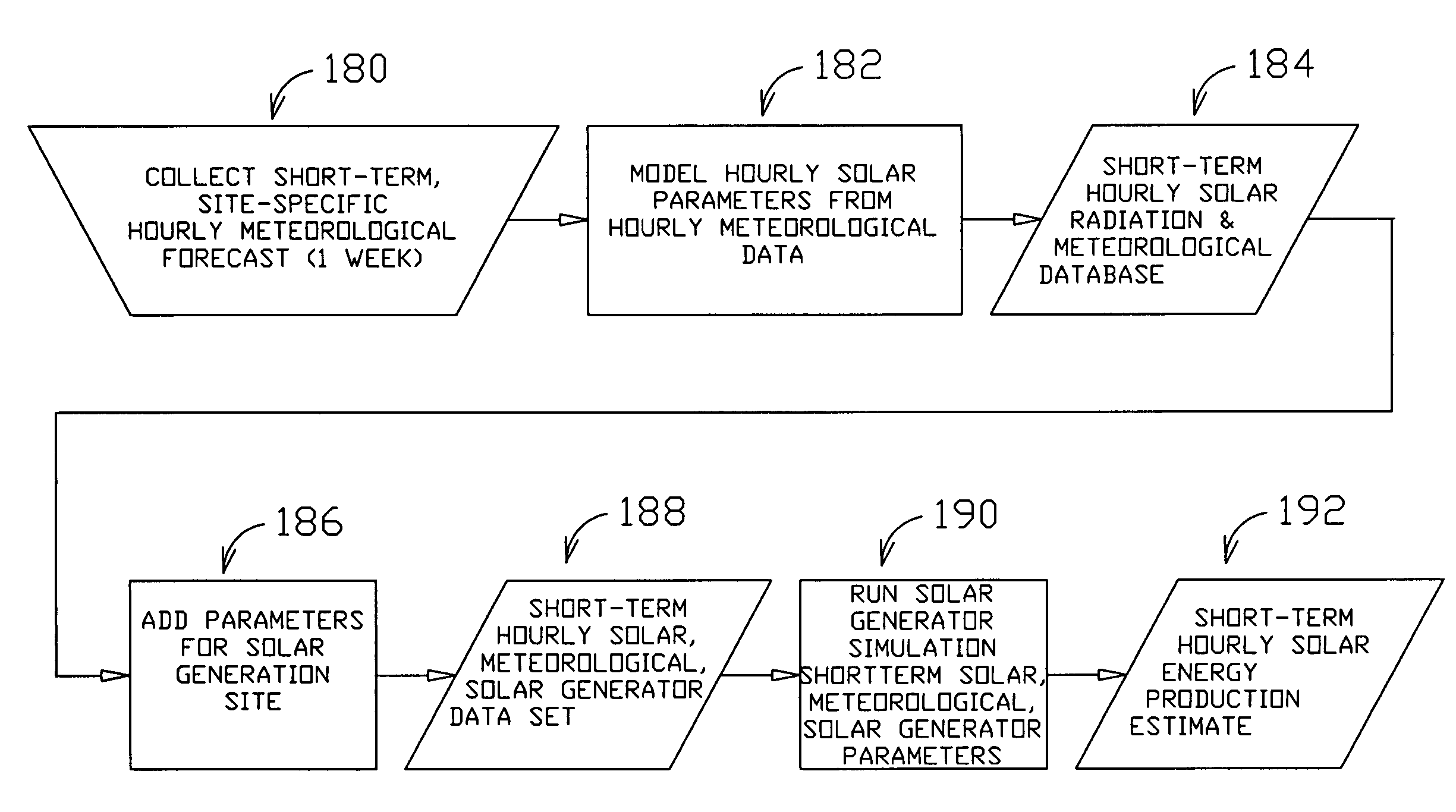
Method and system for predicting solar energy production
A system, method and computer program product to assist in managing the physical plant mechanisms and market finances for a deregulated electricity grid or regulated utility grid, populated with solar electric generation capacity. This system provides tools to assist grid operators in the scheduling and dispatch of generation resources in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity, a week in advance, on an hourly basis. It also provides tools to assist companies engaged in generation, distribution and energy marketing, in the electrical power industry, to manage their contractual supply obligations in the day-ahead hourly wholesale market and the spot market, in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity. This process can also be used to predict solar loading of building structures, using forecast irradiance data as inputs to common building energy modeling programs, a week in advance, on an hourly basis.
Owner:NEO VIRTUS ENG
Wireless Automated Vehicle Energizing System
A wireless recharging system for battery or hybrid vehicles having an in-road magnetic power transmission assembly that interconnects to a magnetic power reception assembly onboard the vehicle. As the vehicle stops or passes over the in-road magnetic power transmission assembly, magnetic coupling transfers power to the magnetic power reception assembly which, in turn, is used to recharge the vehicle battery. The in-road magnetic power transmission assembly may be powered from the electrical grid or designated electrical generators and is preferably designed to build the powering magnetic field in response to the detection of an authorized vehicle in proximity to the transmission assembly.
Owner:STEELE DANIEL W
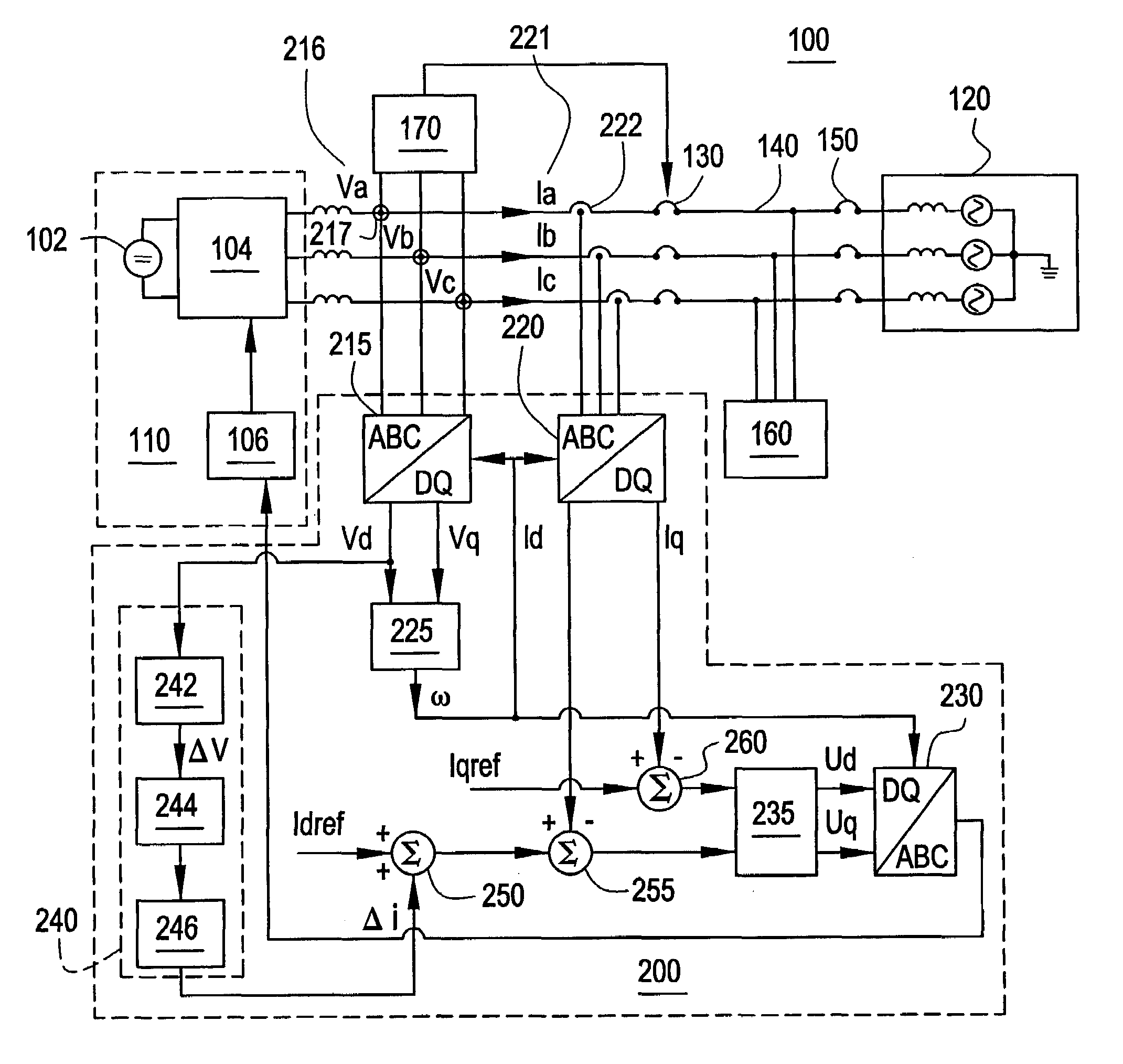
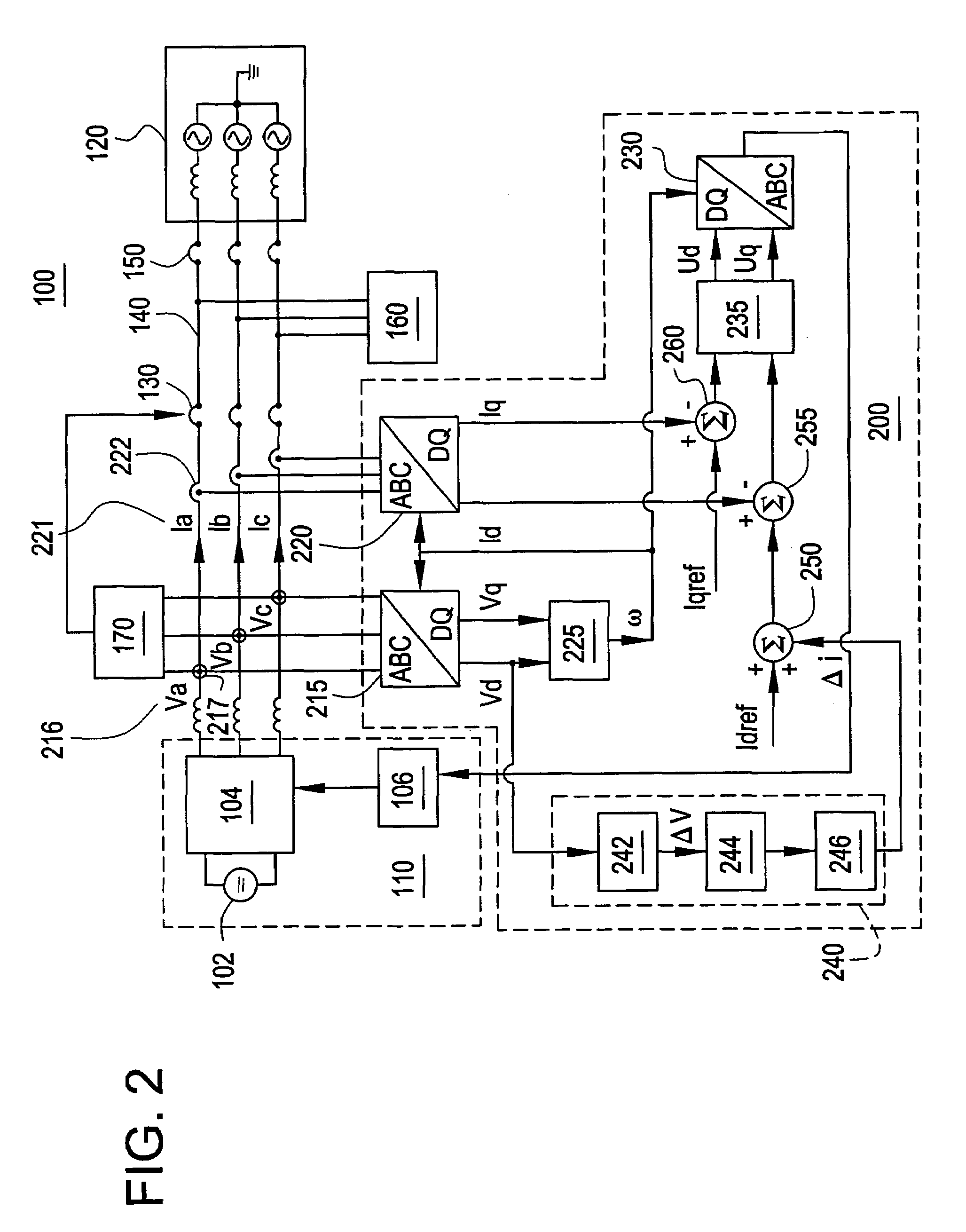
Frequency responsive charge sustaining control of electricity storage systems for ancillary services on an electrical power grid
ActiveUS7839027B2Circuit monitoring/indicationElectric power transfer ac networkElectricityState of charge
Systems, apparatus, and methods are provided for maintaining the state of charge of energy storage devices such as batteries, flywheel, capacitors, or other technologies that are energetically coupled with the electricity grid to support ancillary services. To reliably respond to requests to regulate the grid, the charge on the energy storage device is sustained or restored to a specified range in a manner that optimizes the readiness of the energy storage device to supply ancillary services in light of the condition of the grid. A state of charge (SOC) of the energy storage device and the grid frequency may be monitored. When a request from the operator to regulate the grid frequency is not being serviced, the charge of the energy storage device may be increased or decreased so that the charge may be sustained within the specific range. Once the SOC falls outside of the first range, charge may be added to or removed from the energy storage device when the grid frequency has appropriate values, e.g. if the grid frequency is respectively above a first setpoint or below a second setpoint.
Owner:FLUENCE ENERGY LLC
Method and apparatus for anti-islanding protection of distributed generations
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
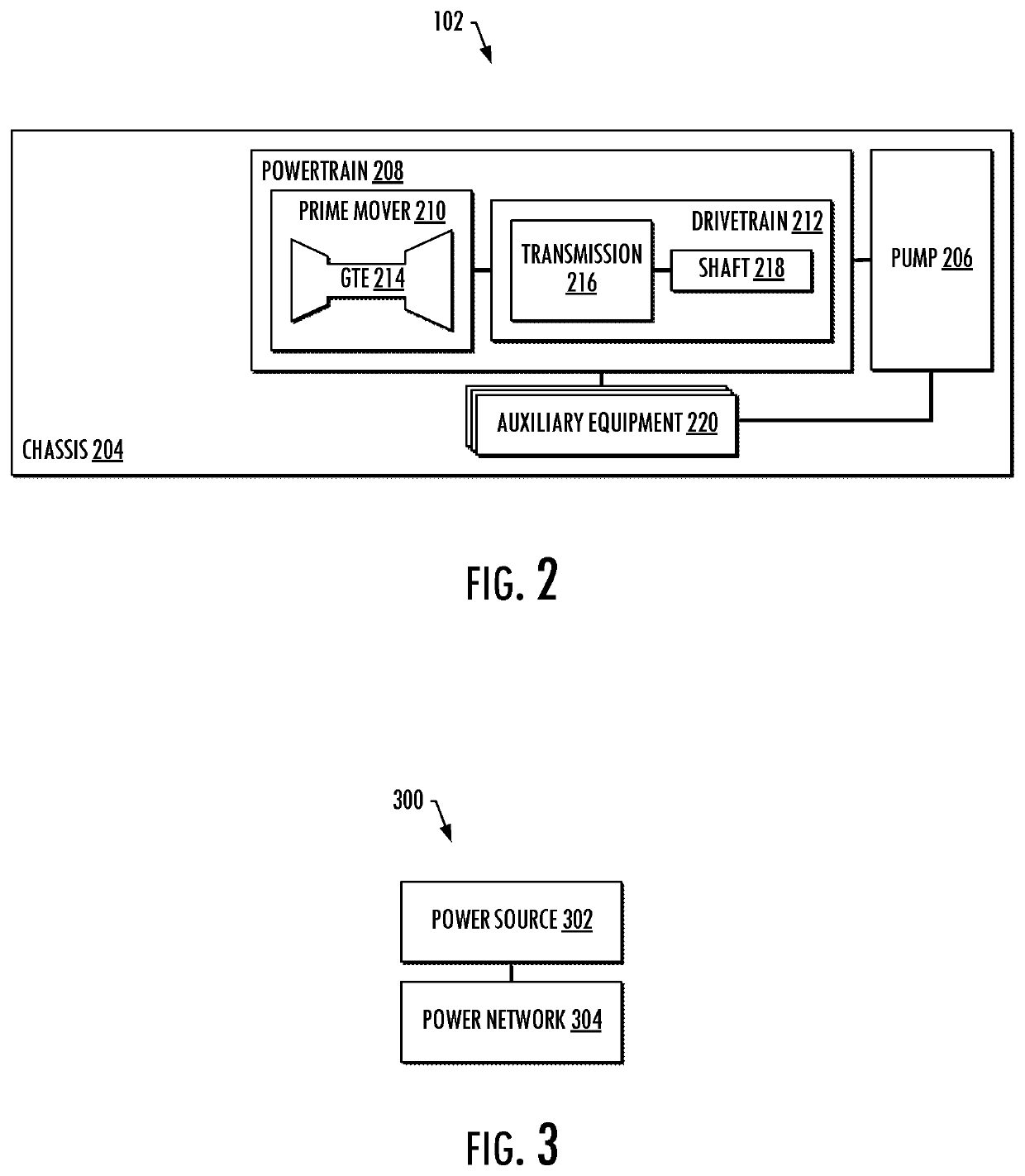
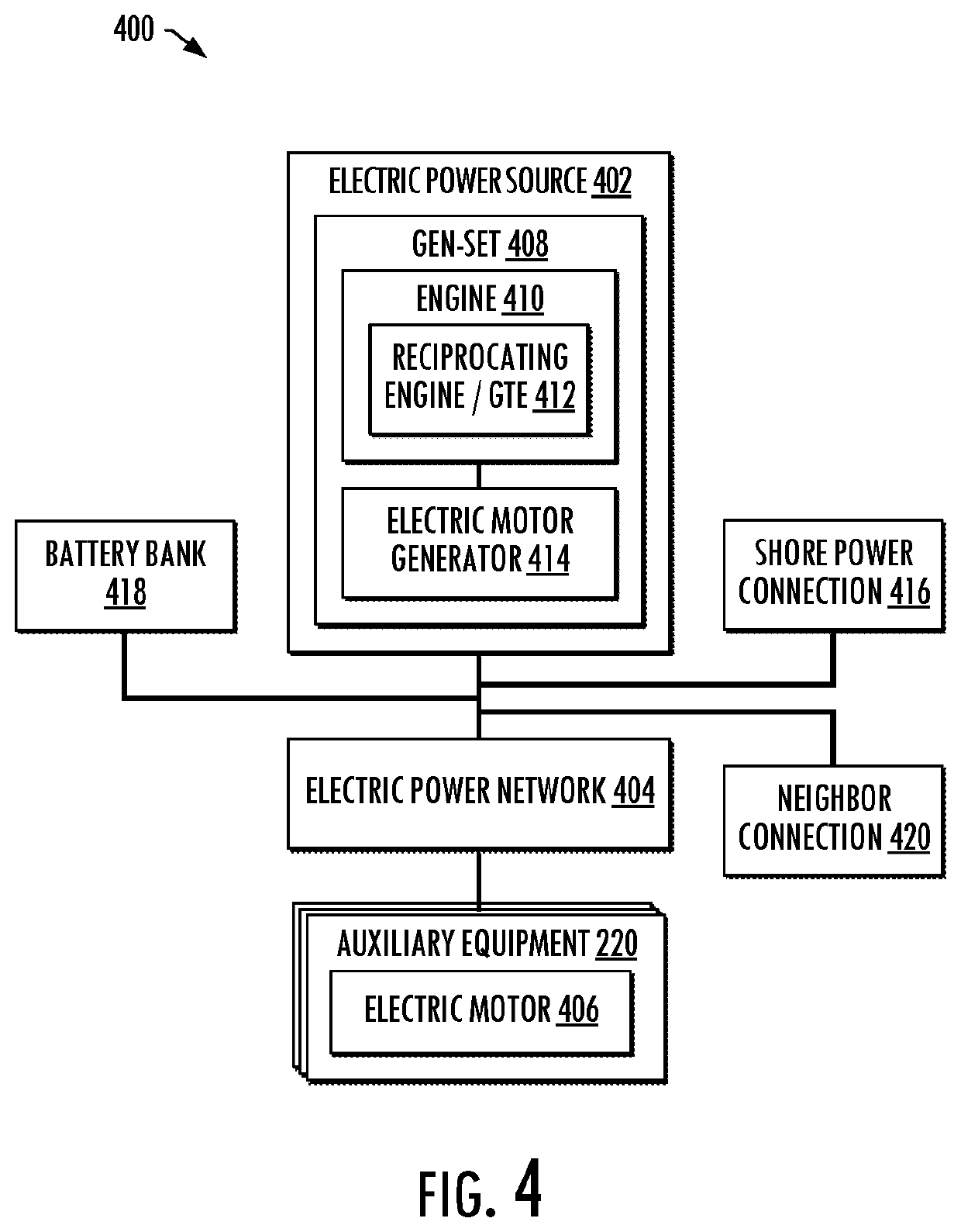
Power sources and transmission networks for auxiliary equipment onboard hydraulic fracturing units and associated methods
Embodiments of systems and methods disclosed provide a hydraulic fracturing unit that includes a reciprocating plunger pump configured to pump a fracturing fluid and a powertrain configured to power the reciprocating plunger pump. The powertrain includes a prime mover and a drivetrain, the prime mover including a gas turbine engine. The hydraulic fracturing unit also includes auxiliary equipment configured to support operation of the hydraulic fracturing unit including the reciprocating plunger pump and the powertrain. A power system is configured to power the auxiliary equipment. The power system includes a power source and a power network. The power source is configured to generate power for the auxiliary equipment. The power network is coupled to the power source and the auxiliary equipment, and configured to deliver the power generated by the power source to the auxiliary equipment. Associated systems including a plurality of hydraulic fracturing units are also provided.
Owner:BJ ENERGY SOLUTIONS LLC
Method And System To Charge Batteries Only While Vehicle Is Parked
InactiveUS20100320964A1Avoid chargingAvoid flowBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsSolenoid valveOn board
Electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle derive all, or at least some, of their power from the electrical grid. The vehicle is provided with a receptacle into which a 110 Volt AC power cord can be plugged. According to the present disclosure, coupling of the external power supply and / or charging are prevented when the vehicle is not in a parked condition. The parked condition is based on the application of a vehicle parking brake and / or a gear shift selector being in a parked position. If a parked condition is not detected, one of the following measures is taken: a relay in the battery charger on board the vehicle is opened thereby disallowing charging; an access door to the receptacle is locked by an access door solenoid; and a plug ejector prevents insertion of a plug into the receptacle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Charging profiles for a storage device in an energy generation system
InactiveUS20160322835A1Prolong lifeTime of use is limitedComputer controlEnergy storageSocial mediaPower grid
A computer-implemented method for an energy generation site includes detecting an energy storage device and its storage capacity, detecting an electrical grid operatively coupled to the energy generation site, and receiving event data corresponding to an event affecting the electrical grid. The method further includes determining a probability that the electrical grid will experience a power outage based on the event data, and charging the storage device according to a first charging profile or a second charging profile based on the probability. A maximum charge set point of the storage device for the first charging profile is less than the maximum storage capacity of the storage device, and the maximum charge set point for the second charging profile is at the maximum storage capacity of the storage device. The event data can be weather data, geological data, social media, or local alert data.
Owner:SOLARCITY
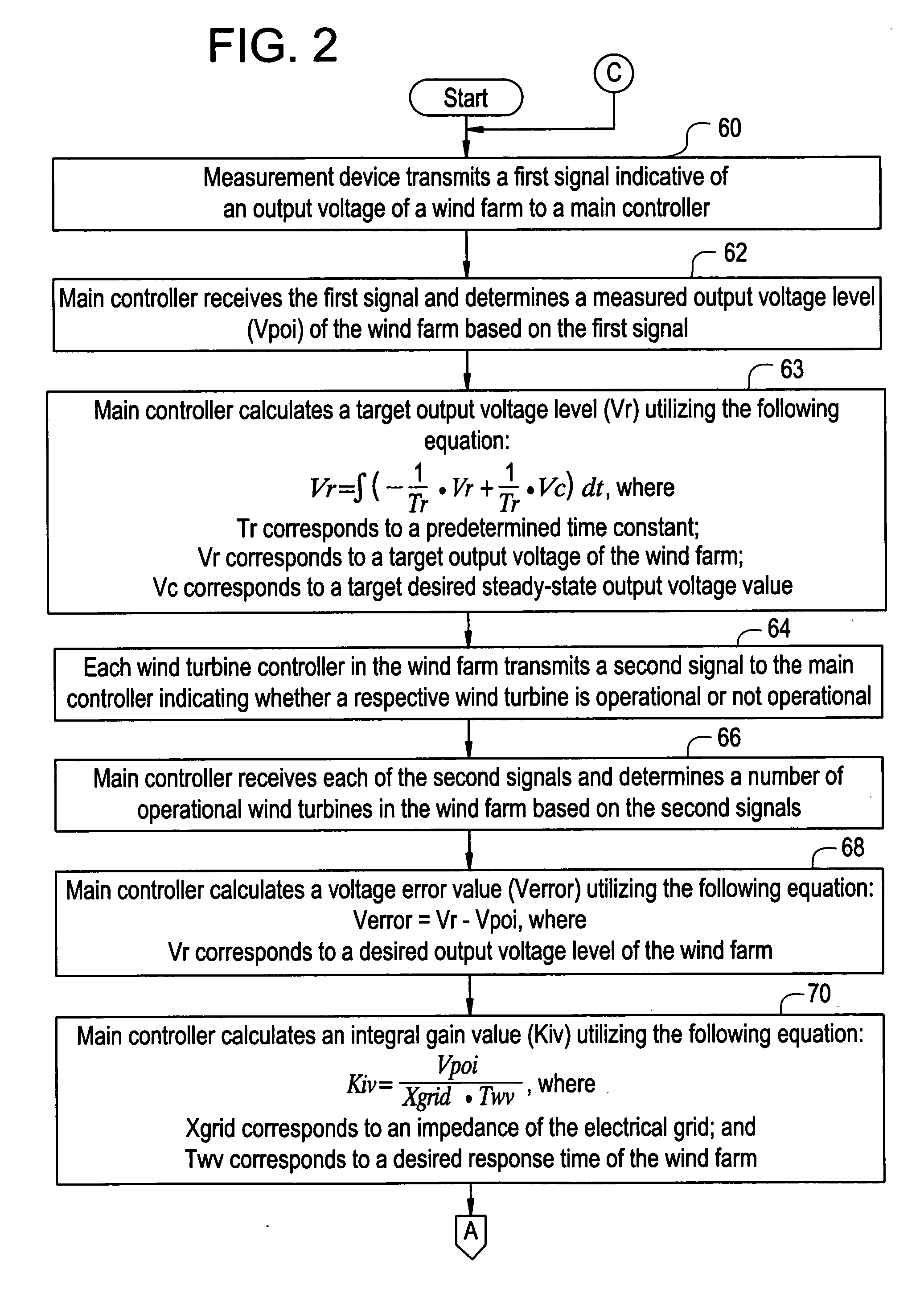
System, method, and article of manufacture for controlling operation of an electrical power generation system
A system, a method, and an article of manufacture for controlling operation of an electrical power generation system are provided. The electrical power generation system has a plurality of electrical generators electrically coupled to an electrical grid. The method includes obtaining a first output parameter value associated with the electrical power generation system. The method further includes determining an error value indicative of a difference between the first output parameter value and a desired output parameter value. The method further includes determining a first gain value based on at least one of the first output parameter value and a time-varying operational parameter of the electrical power generation system. The method further includes determining a first power value based on the error value and the first gain value. The method further includes determining a second gain value based on at least one of the first output parameter value, the time-varying operational parameter, and a reference value. The method further includes determining a second power value based on the error value and the second gain value. The method further includes generating a desired power command for the electrical power generation system based on the first and second power values.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
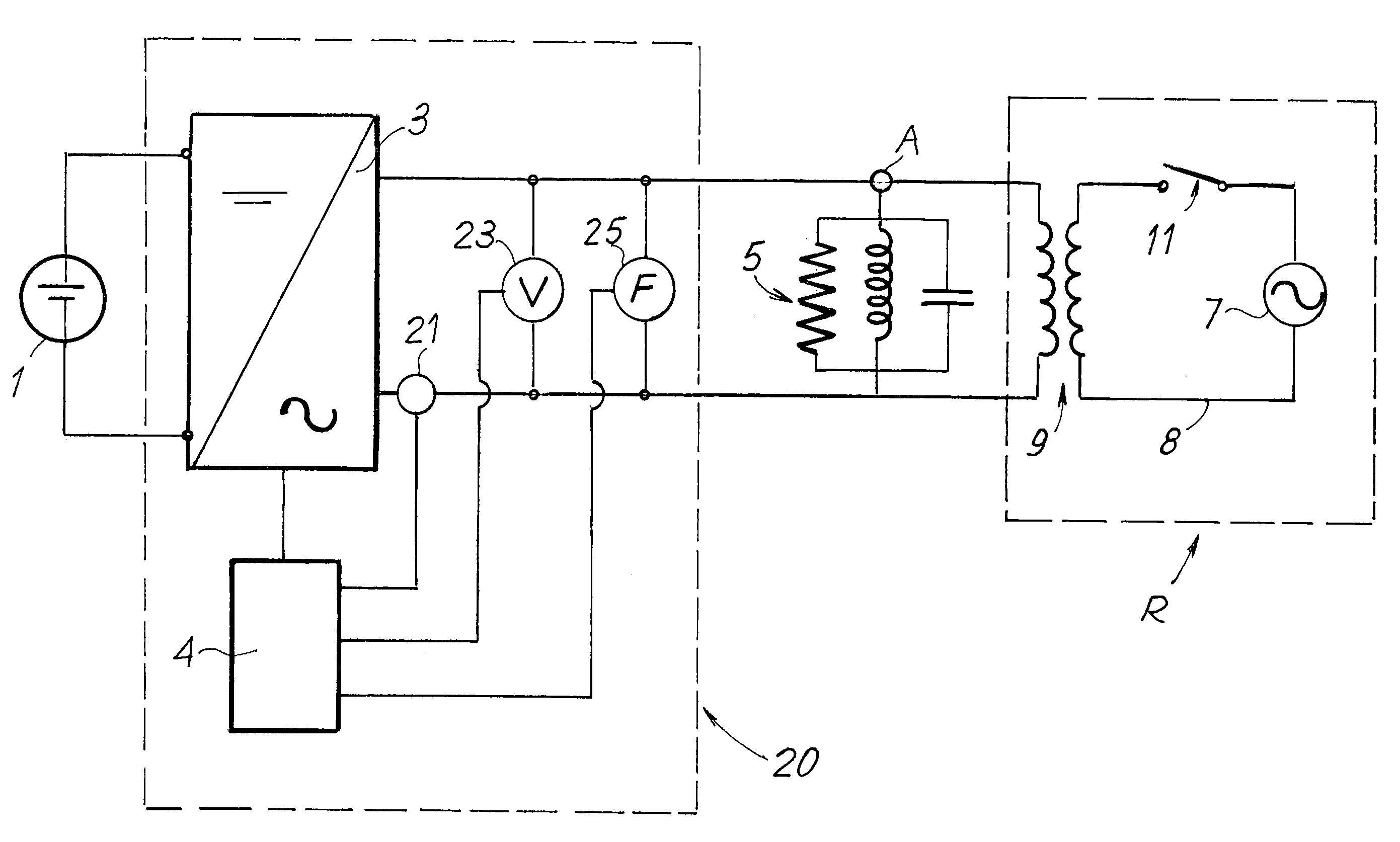
Anti-islanding method and system for distributed power generation systems
ActiveUS7408268B1Quick changeReduce power levelDc network circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityIslanding
An electrical power supply system connected to an electrical grid, includes at least one source of electrical power, an inverter which receives power from the electrical source and delivers power to a local load, and a connection to the electrical grid. The system also includes a control unit for controlling the inverter, which interrupts the delivery of power by the inverter when at least one electrical parameter of the system exceeds a threshold value. The system also includes anti-islanding logic which detects at least one symptom of an islanding condition of the system and, when the symptom is detected, to cause a variation in the power level delivered by the inverter.
Owner:MARICI HLDG THE NETHERLANDS BV
Electrical network command and control system and method of operation
A system is provided that allows the aggregation of a plurality of inputs from an electrical grid and the display of the plurality of inputs on a single integrated display for a network operator. The system accepts signals from electrical loads and generation devices and analyzes the inputs to determine potential issues or trends, including fault predictions and recommends contingency plans. The system presents these potential issues and possible corrective actions to the network operator. The network operator may initiate actions, such as dispatching loads or activating generation capacity for example, in response.
Owner:CONSOL EDISON OF NEW YORK
Apparatus, method and article for authentication, security and control of power storage devices, such as batteries
ActiveUS20140028089A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesCoin-freed apparatusElectrical batteryEngineering
A network of collection, charging and distribution machines collect, charge and distribute portable electrical energy storage devices (e.g., batteries, supercapacitors or ultracapacitors). To charge, the machines employ electrical current from an external source, such as the electrical grid or an electrical service of an installation location. By default, each portable electrical energy storage device is disabled from accepting a charge unless it receives authentication information from an authorized collection, charging and distribution machine, other authorized charging device, or other authorized device that transmits the authentication credentials. Also, by default, each portable electrical energy storage device is disabled from releasing energy unless it receives authentication information from an external device to which it will provide power, such as a vehicle or other authorization device.
Owner:GOGORO
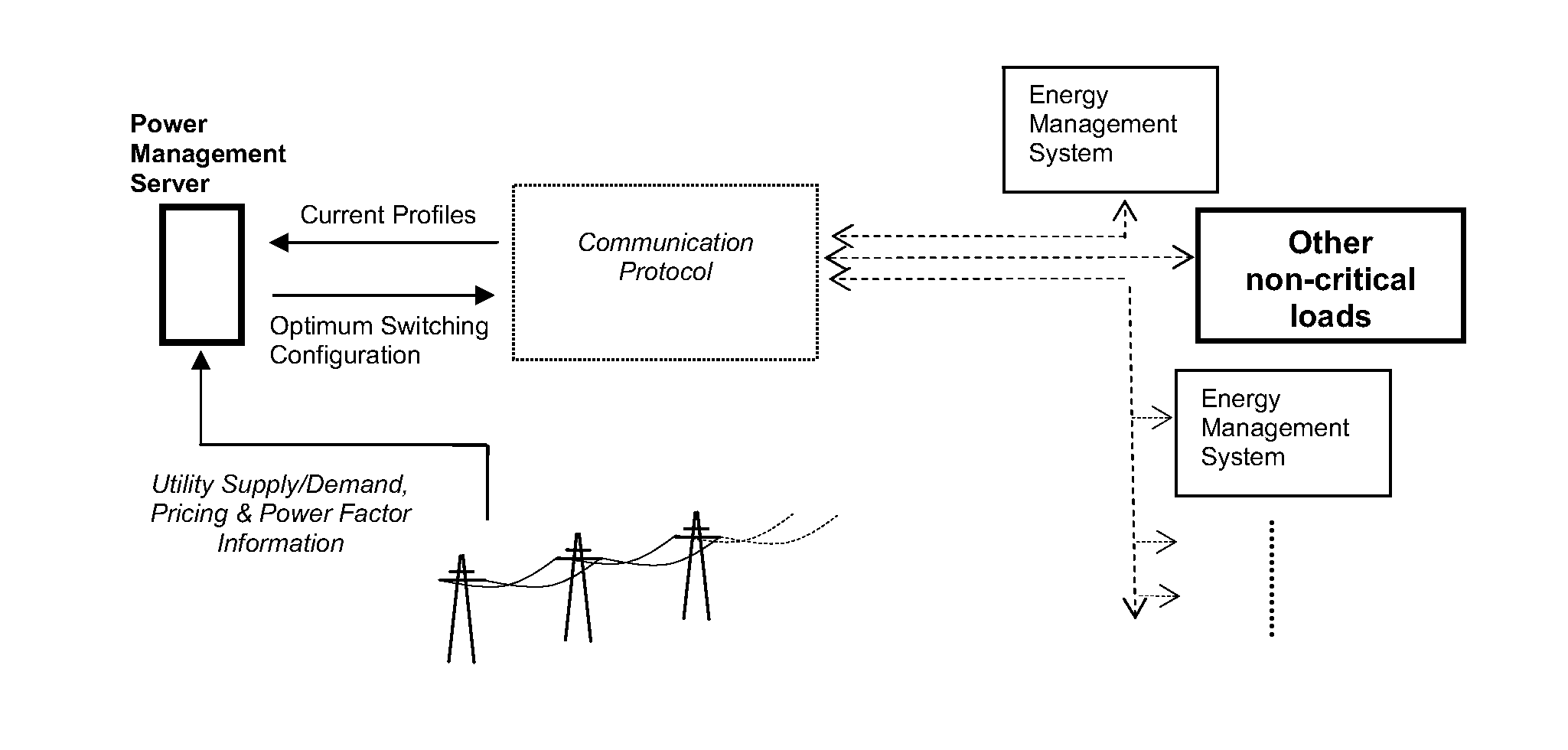
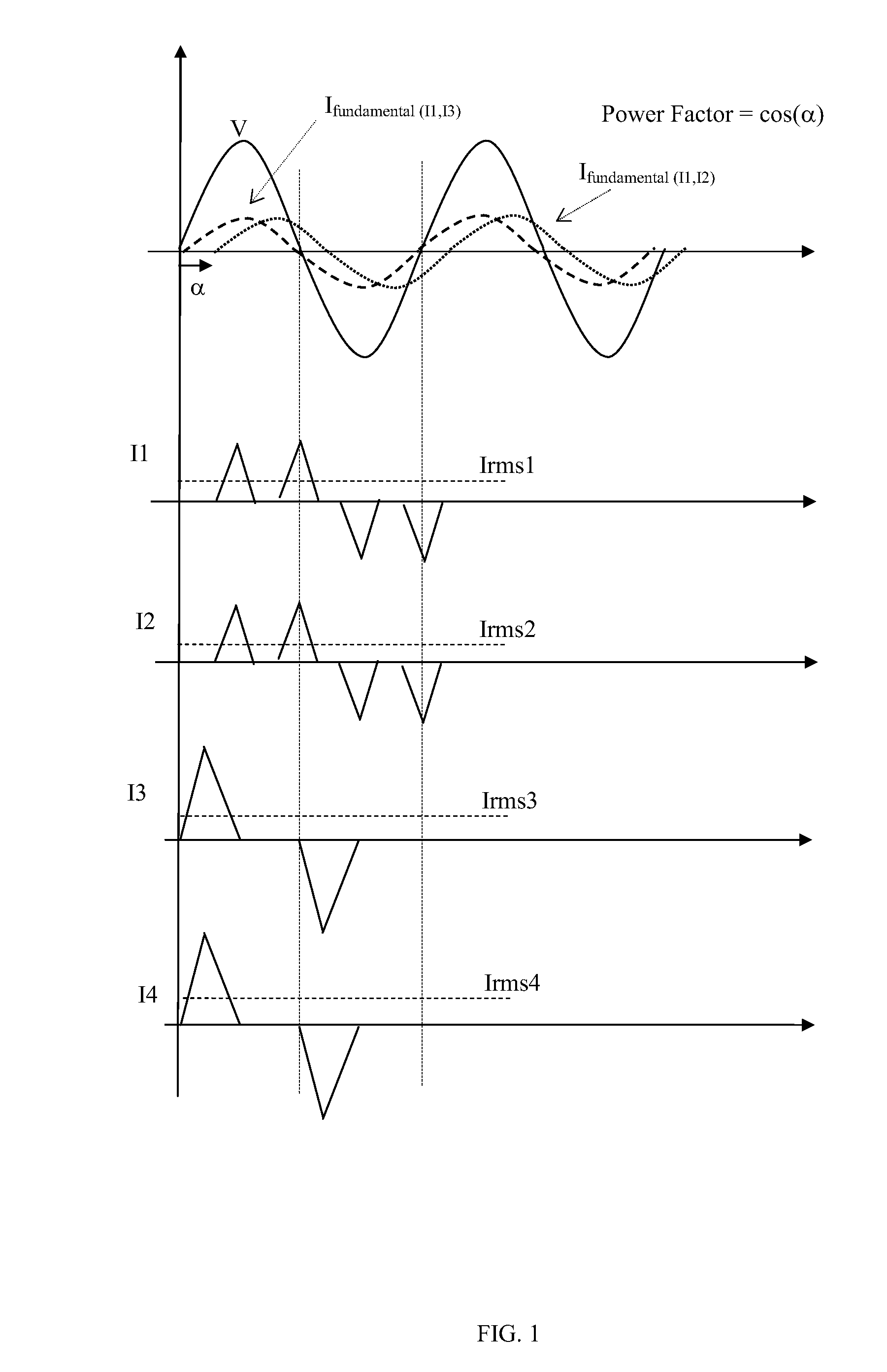
Smart-grid adaptive power management method and system with power factor optimization and total harmonic distortion reduction
A method and system of power factor optimization and total harmonic distortion are provided under the premise of efficient power management and distribution on an electrical grid. The method and system include a novel optimization technique based on a novel current profiling methodology enabling real-time power management with power factor correction as a function of the optimization. The optimization can be performed under dynamic current constraints. When deployed on an electrical grid, the method and system can provide a new technique for power management targeting an efficiency of the electrical grid. The method and system can thus provide for reduced costs of energy production and reduced carbon emissions into the atmosphere.
Owner:VOLTA ENERGY
Method and system for predicting solar energy production
ActiveUS7580817B2Financial riskGeneration forecast in ac networkFinanceSolar powerLoad following power plant
A system, method and computer program product to assist in managing the physical plant mechanisms and market finances for a deregulated electricity grid or regulated utility grid, populated with solar electric generation capacity. This system provides tools to assist grid operators in the scheduling and dispatch of generation resources in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity, a week in advance, on an hourly basis. It also provides tools to assist companies engaged in generation, distribution and energy marketing, in the electrical power industry, to manage their contractual supply obligations in the day-ahead hourly wholesale market and the spot market, in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity. This process can also be used to predict solar loading of building structures, using forecast irradiance data as inputs to common building energy modeling programs, a week in advance, on an hourly basis.
Owner:NEO VIRTUS ENG
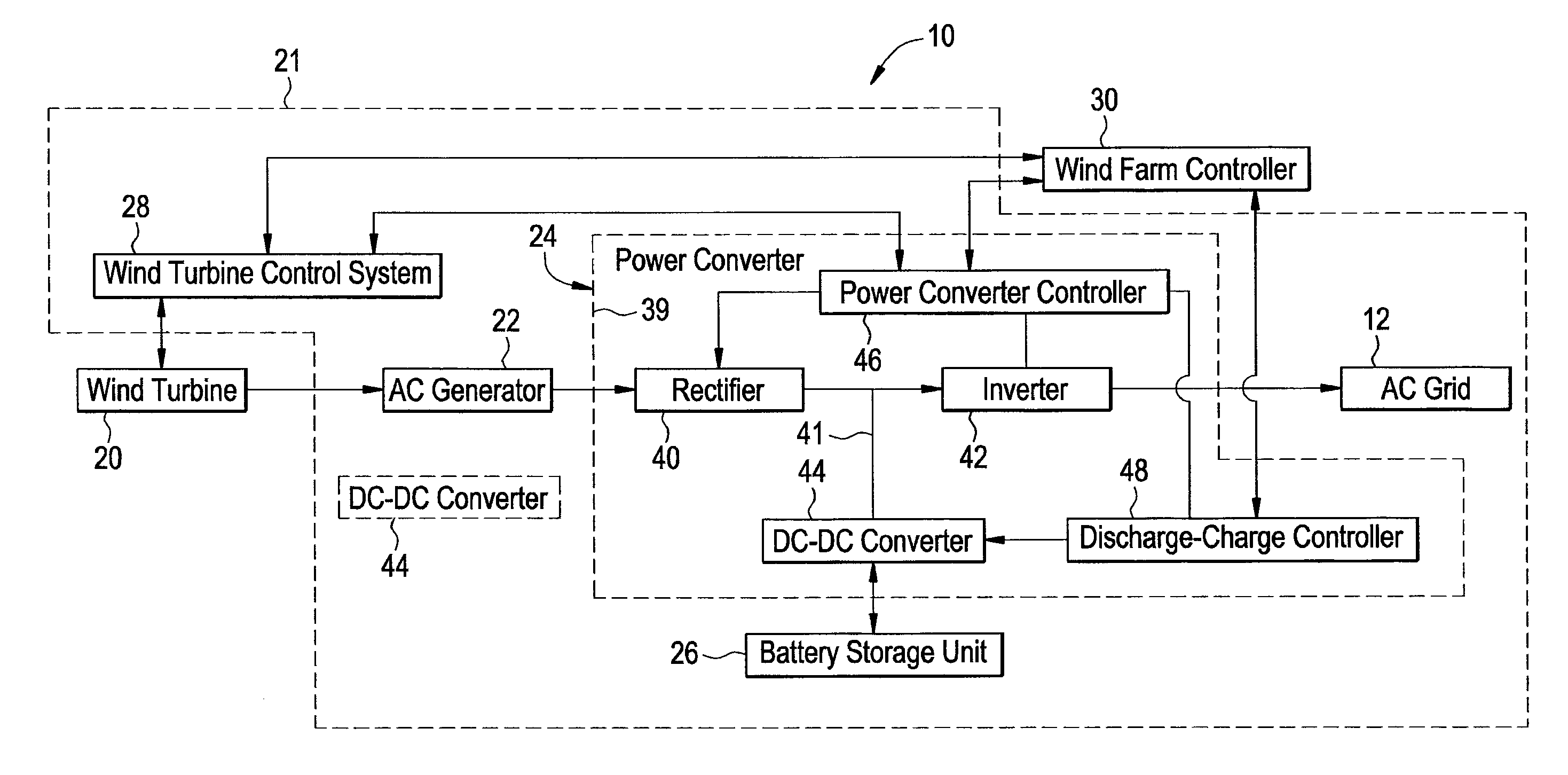
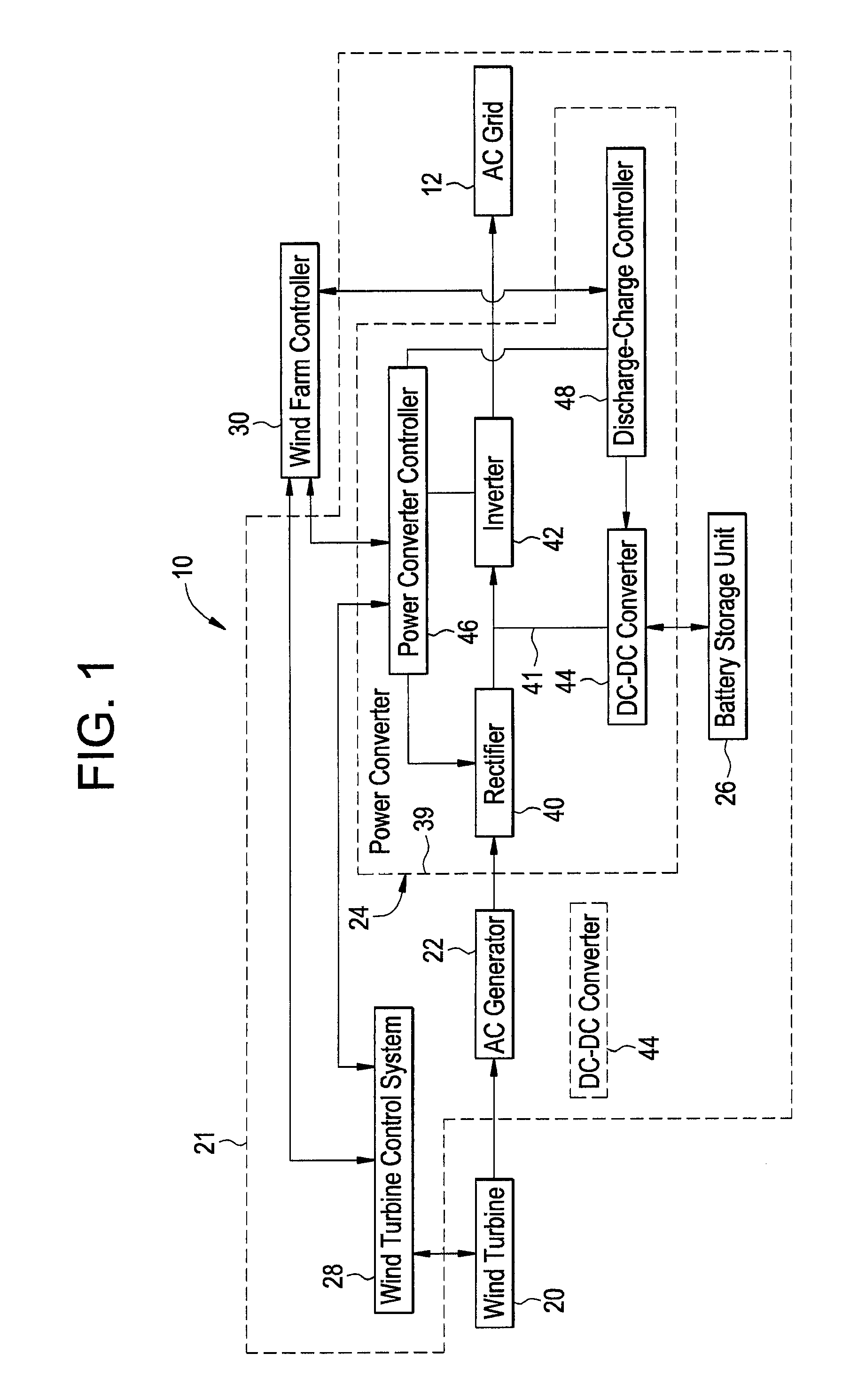
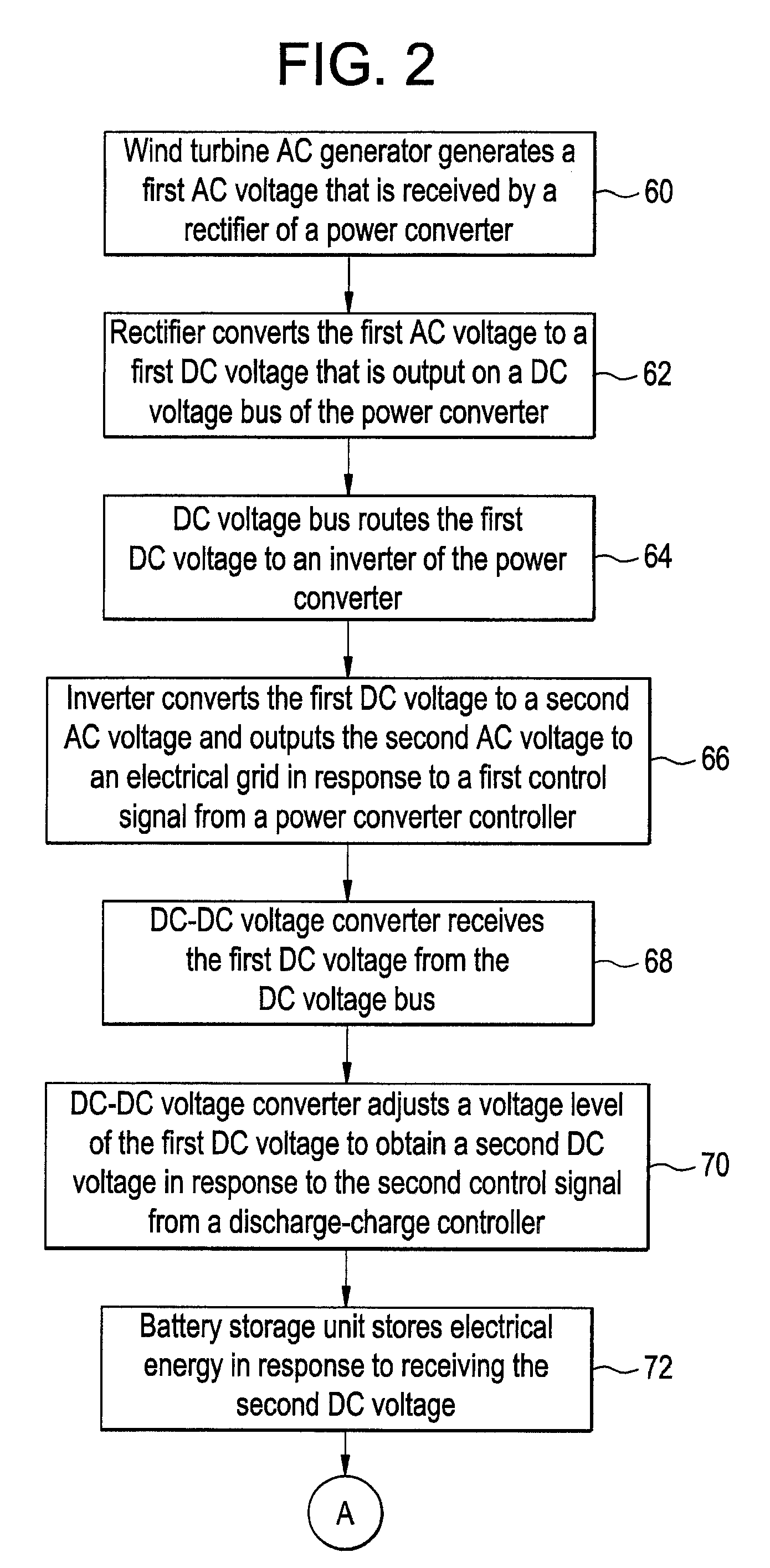
Power generation system and method for storing electrical energy
ActiveUS7608937B1Batteries circuit arrangementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc dc converterControl signal
A power generation system and a method for storing electrical energy are provided. The method includes generating a first AC voltage from a wind turbine generator and converting the first AC voltage to a first DC voltage, utilizing a rectifier. The method further includes routing the first DC voltage through a DC voltage bus to an inverter of the power converter, and converting the first DC voltage to a second AC voltage utilizing the inverter and outputting the second AC voltage to an electrical grid in response to a first control signal from a power converter controller. The method further includes receiving the first DC voltage from the DC voltage bus at a DC-DC converter operably coupled to the DC voltage bus, and storing electrical energy from the first DC voltage in a battery storage unit utilizing the DC-DC converter in response to a second control signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com