Patents
Literature
1912 results about "Permanent magnet rotor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
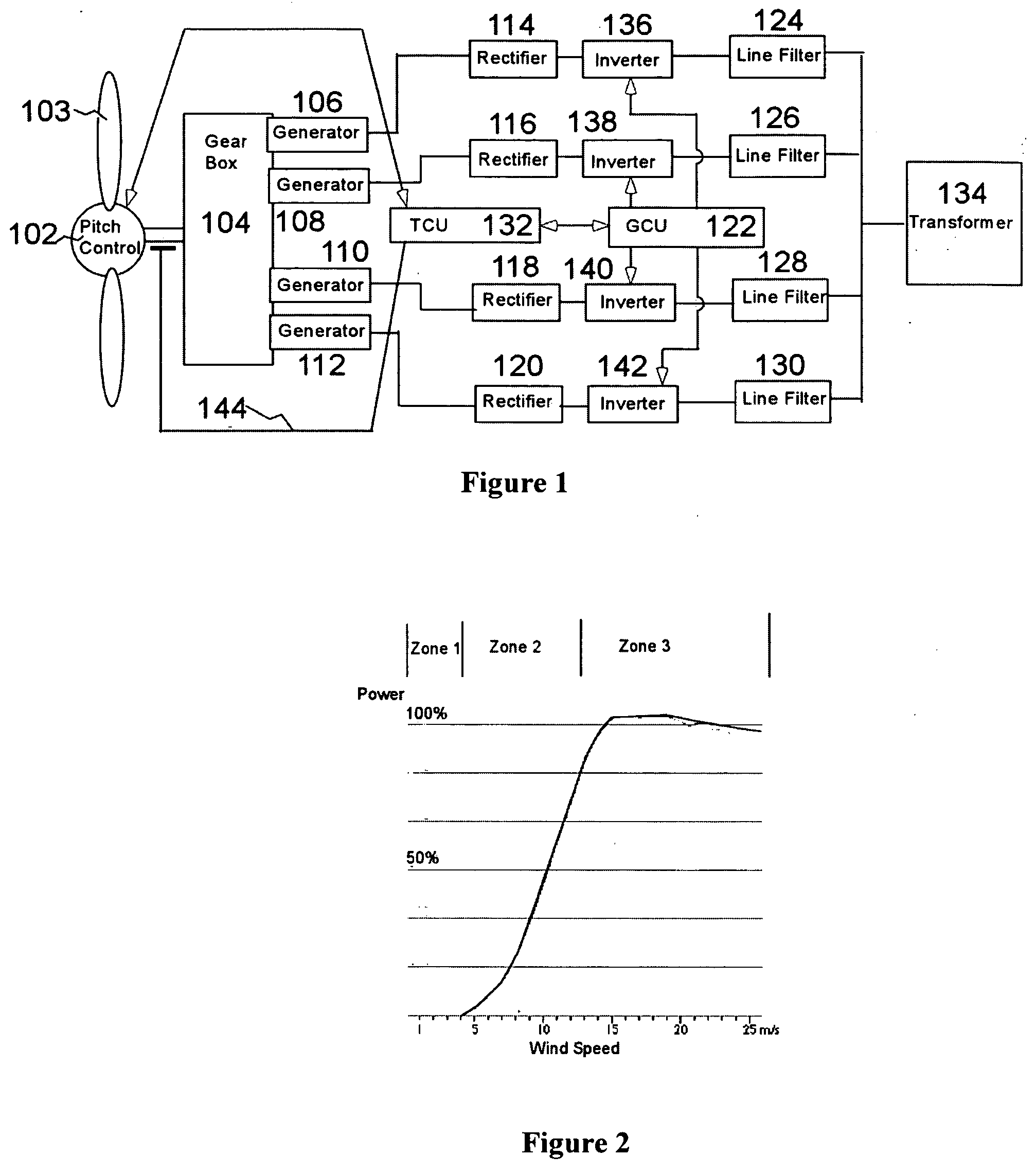
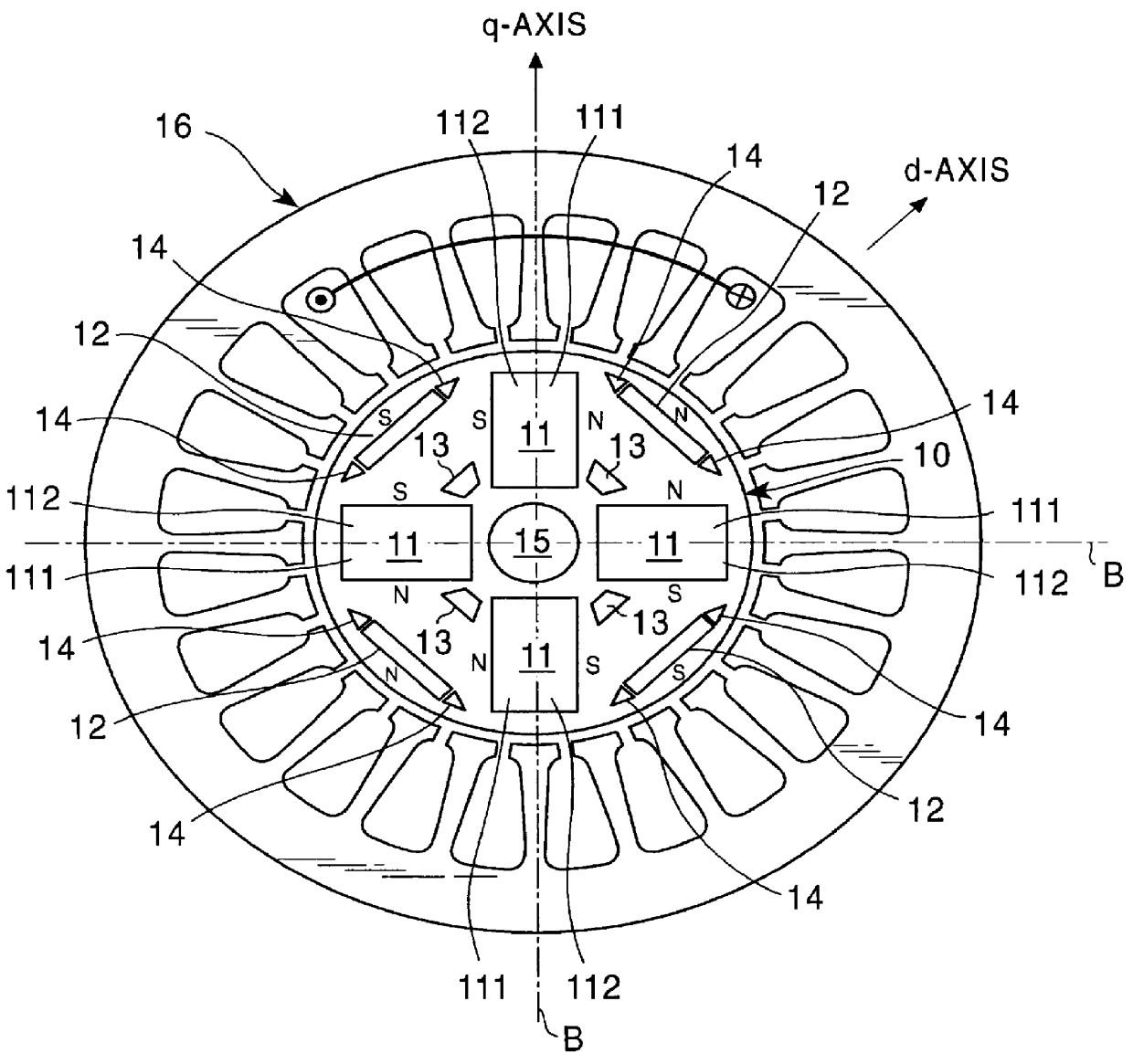
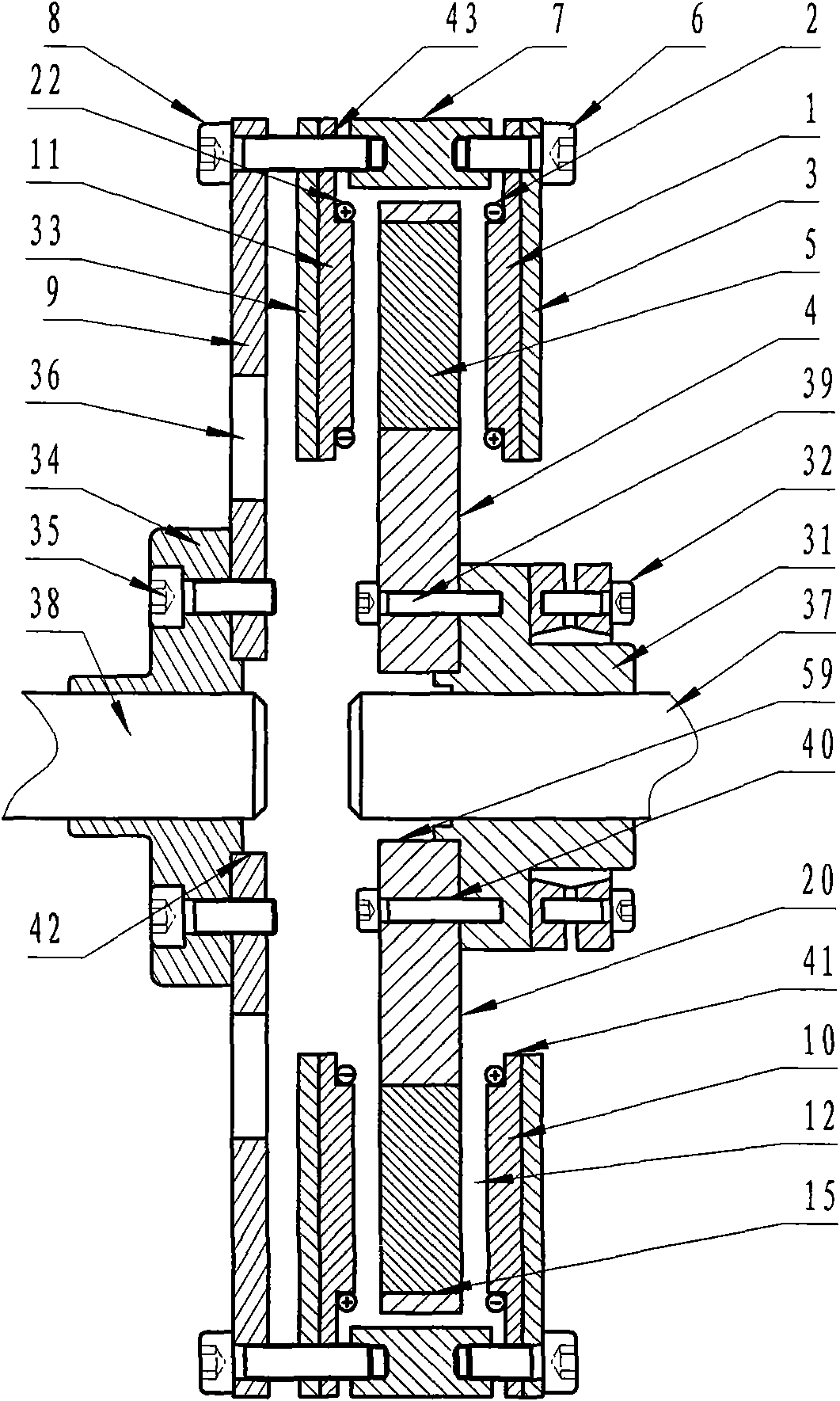
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS7042110B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPermanent magnet rotorDc current
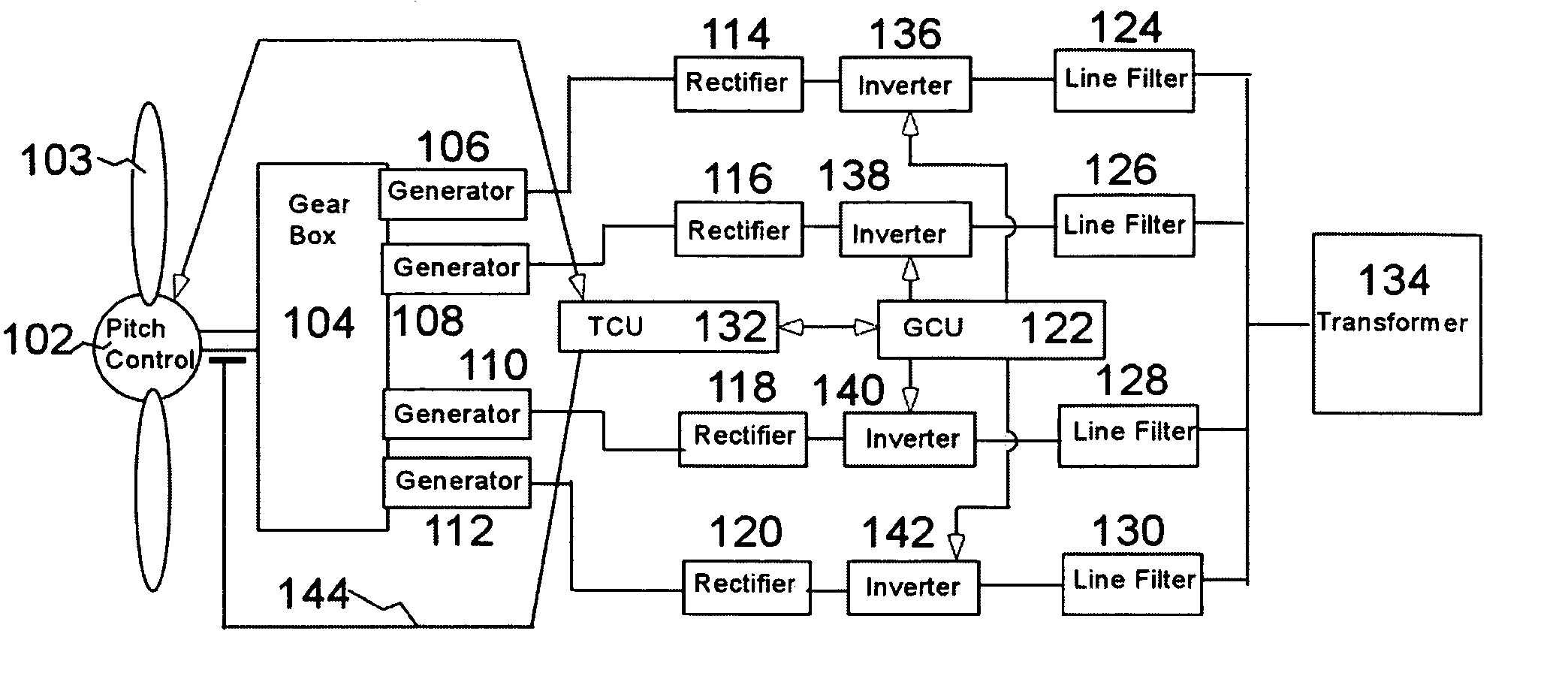
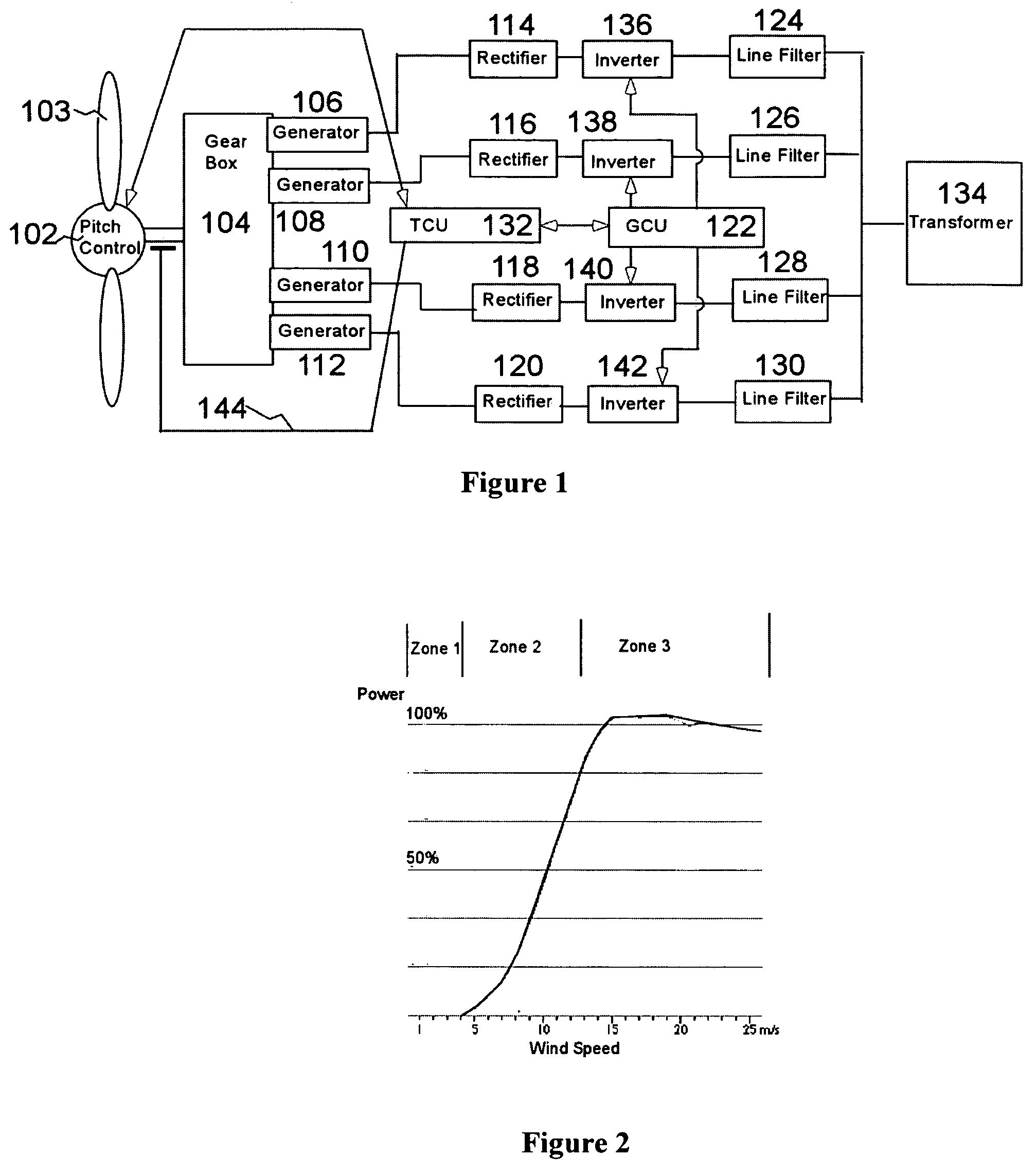
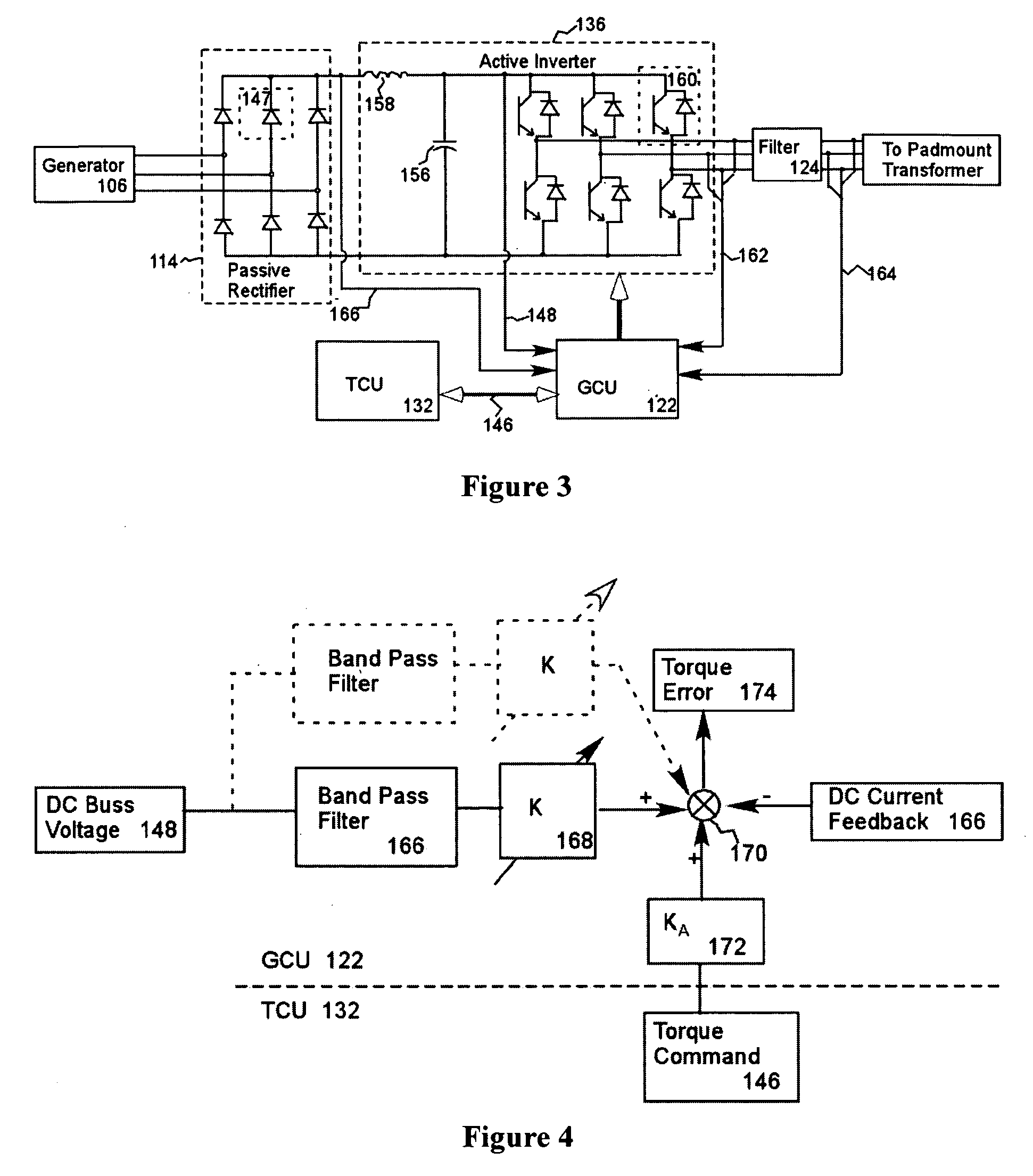
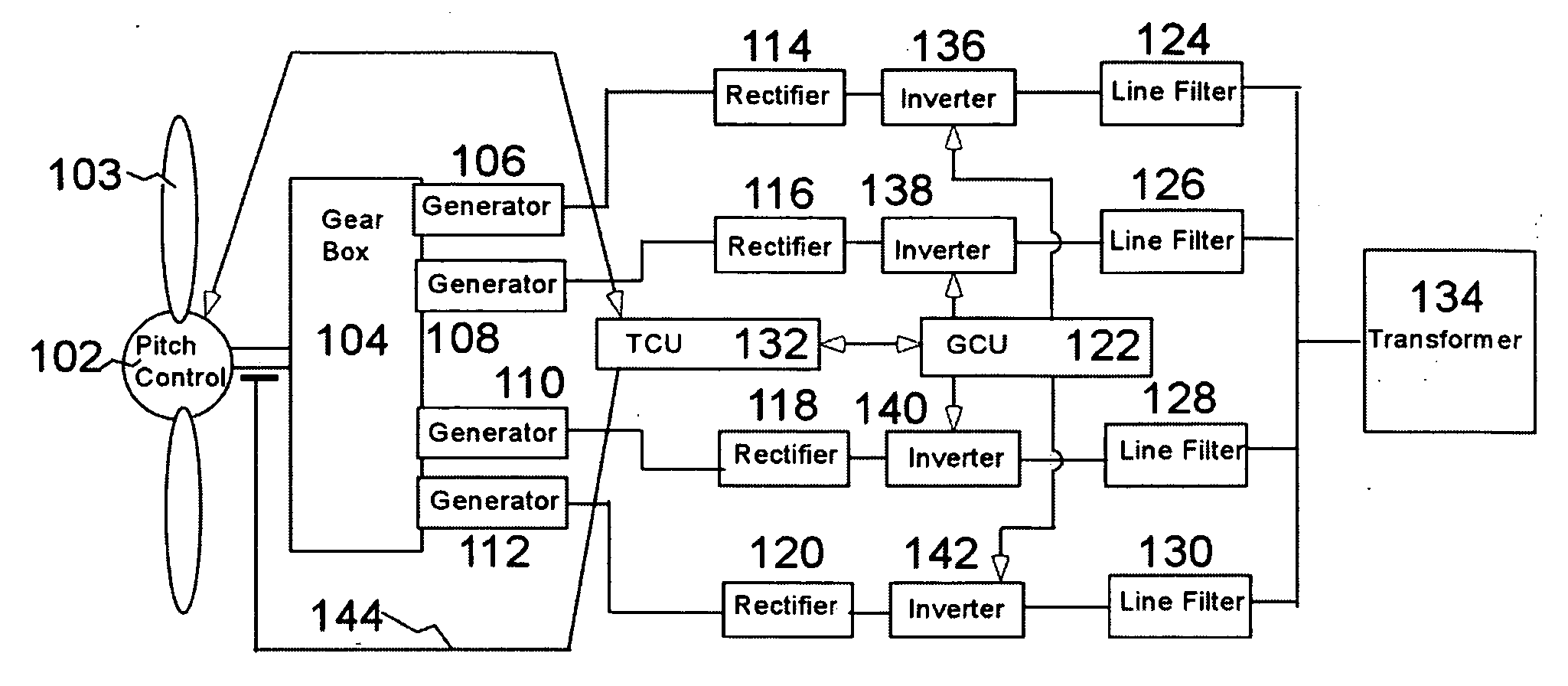
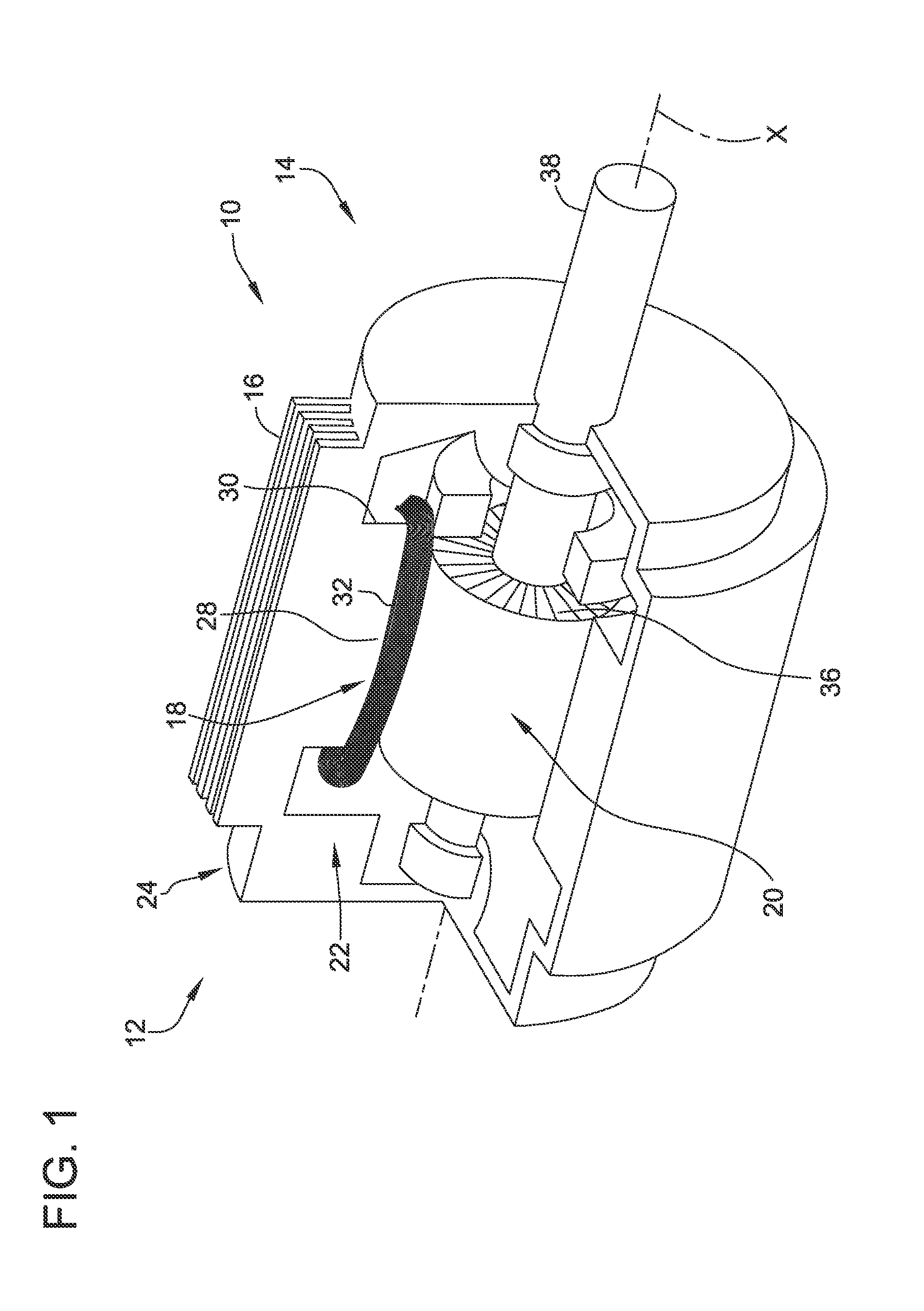
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Permanent magnet rotor type electric motor with different permanent magnet materials
InactiveUS6025667AMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
In an electric motor, such as a DC brushless motor or the like, having a permanent magnet in a rotor, each magnetic pole is formed of three permanent magnets, and the permanent magnets are made of at least two kinds of magnetic materials represented by ferrite magnet and rare-earth magnet. Thus, in a permanent magnet rotor type electric motor, a reluctance torque and a magnetic flux density can be selectively established, and cost is reasonable, corresponding to the quality.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Permanent magnet rotating electric machine and electric car using the same
ActiveUS7151335B2Reduce impactImprove efficiencySpeed controllerMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
A permanent magnet rotating electric machine comprises a stator having stator windings wound round a stator iron core and a permanent magnet rotor having a plurality of inserted permanent magnets in which the polarity is alternately arranged in the peripheral direction in the rotor iron core. The rotor iron core of the permanent magnets is composed of magnetic pole pieces, auxiliary magnetic poles, and a stator yoke, and furthermore has concavities formed on the air gap face of the magnetic pole pieces of the rotor iron core of the permanent magnets, gently tilting from the central part of the magnetic poles to the end thereof; resulting in a permanent magnet rotating electric machine effects of iron loss are reduced, and an electric car using highly efficient permanent magnet rotating electric machine are realized.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Polyphase transverse flux motor
InactiveUS6492758B1Synchronous motorsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet rotorTransverse flux
A tranverse flux motor having multiple stator phase windings which are electronically commutated to produce a rotating flux to drive a permanent magnet rotor located externally of the stator. The stator is formed by two complementary facing pieces each carrying half the stator poles, the latter preferably being of claw pole configuration. The stator windings are sandwiched between the stator pieces and wound about cores which magnetically couple the stator pieces. Preferably the number of motor phases (P) is selected from the series 2, 3, . . . , N, the number of windings per phase (W) is selected from the series 1, 2, . . . , M, the number of poles per winding (PW) is selected from the series 2, 4, . . . , L, and the number of stator poles (SP) is equal to the product P*WP*PW and the number of rotor poles is SP±W.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
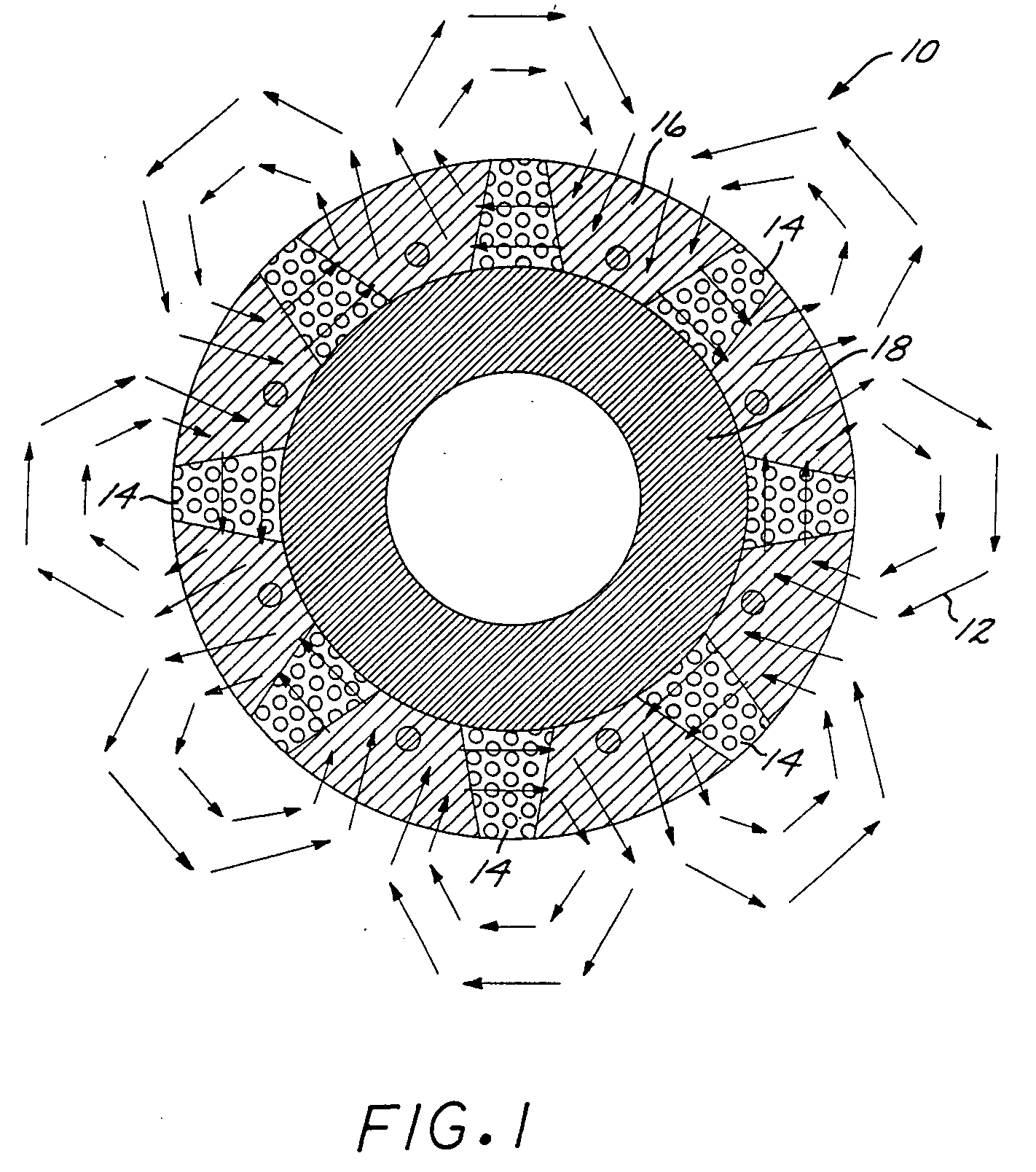
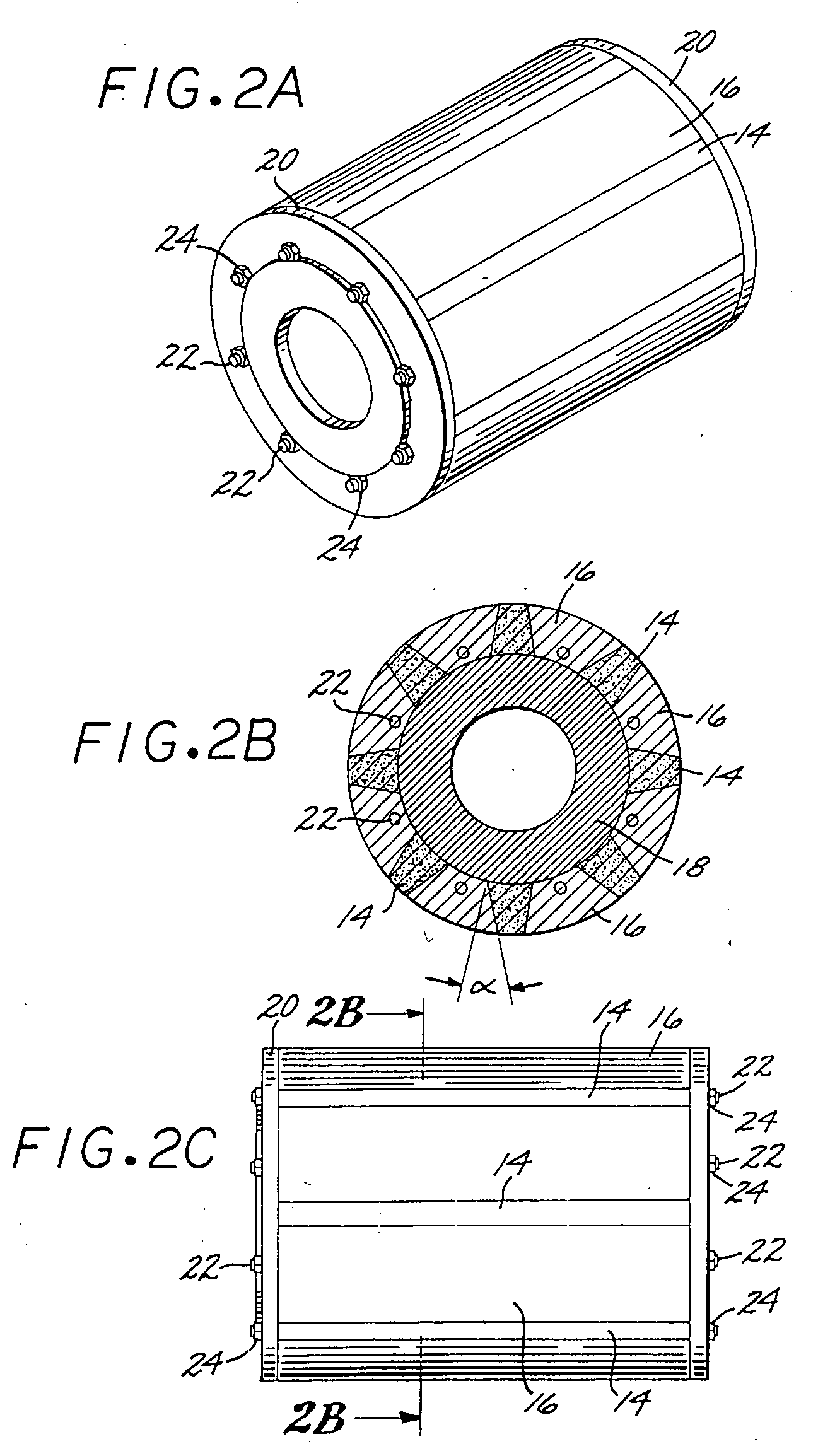
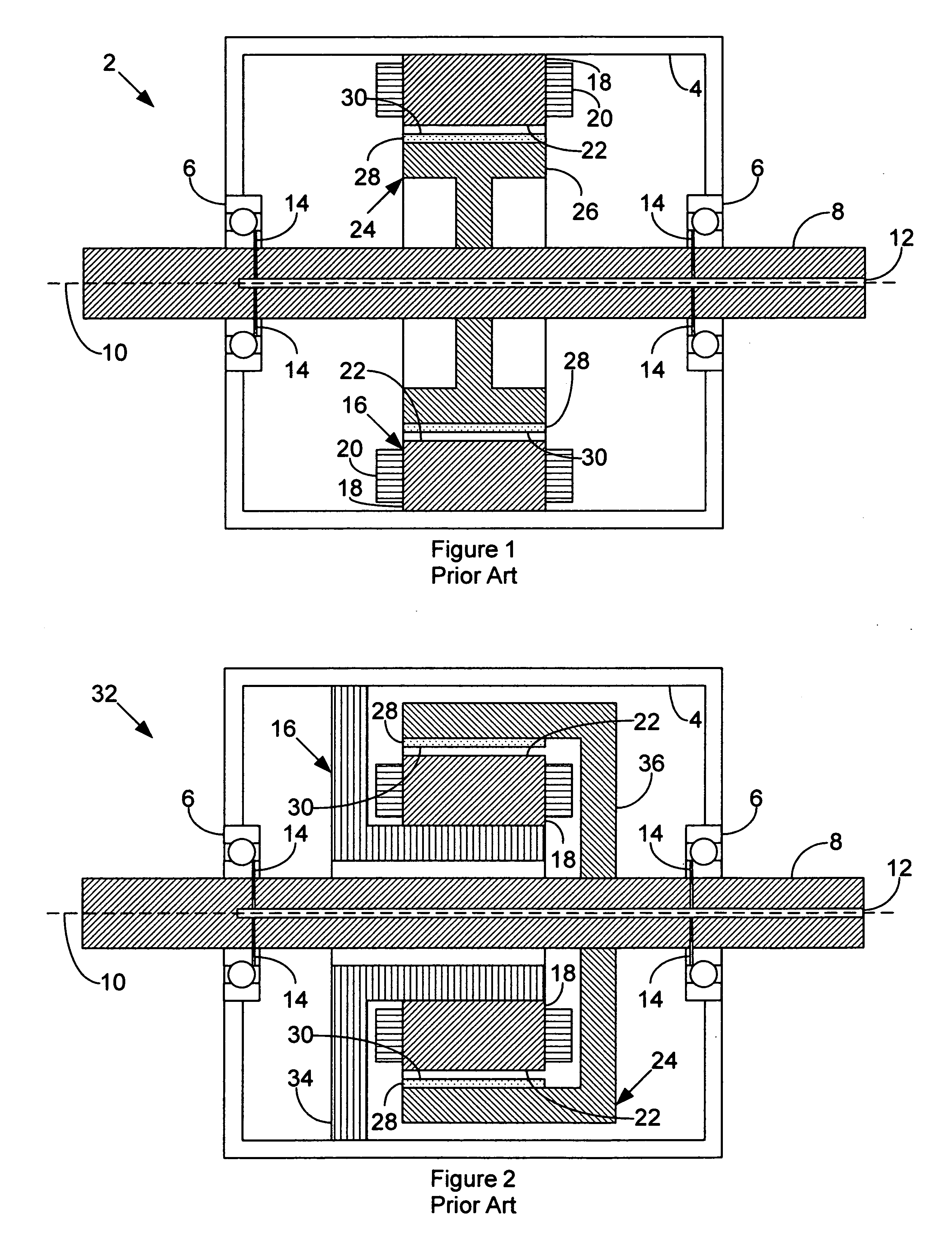
Sleeveless permanent magnet rotor construction
InactiveUS20050093391A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorMagnetic poles
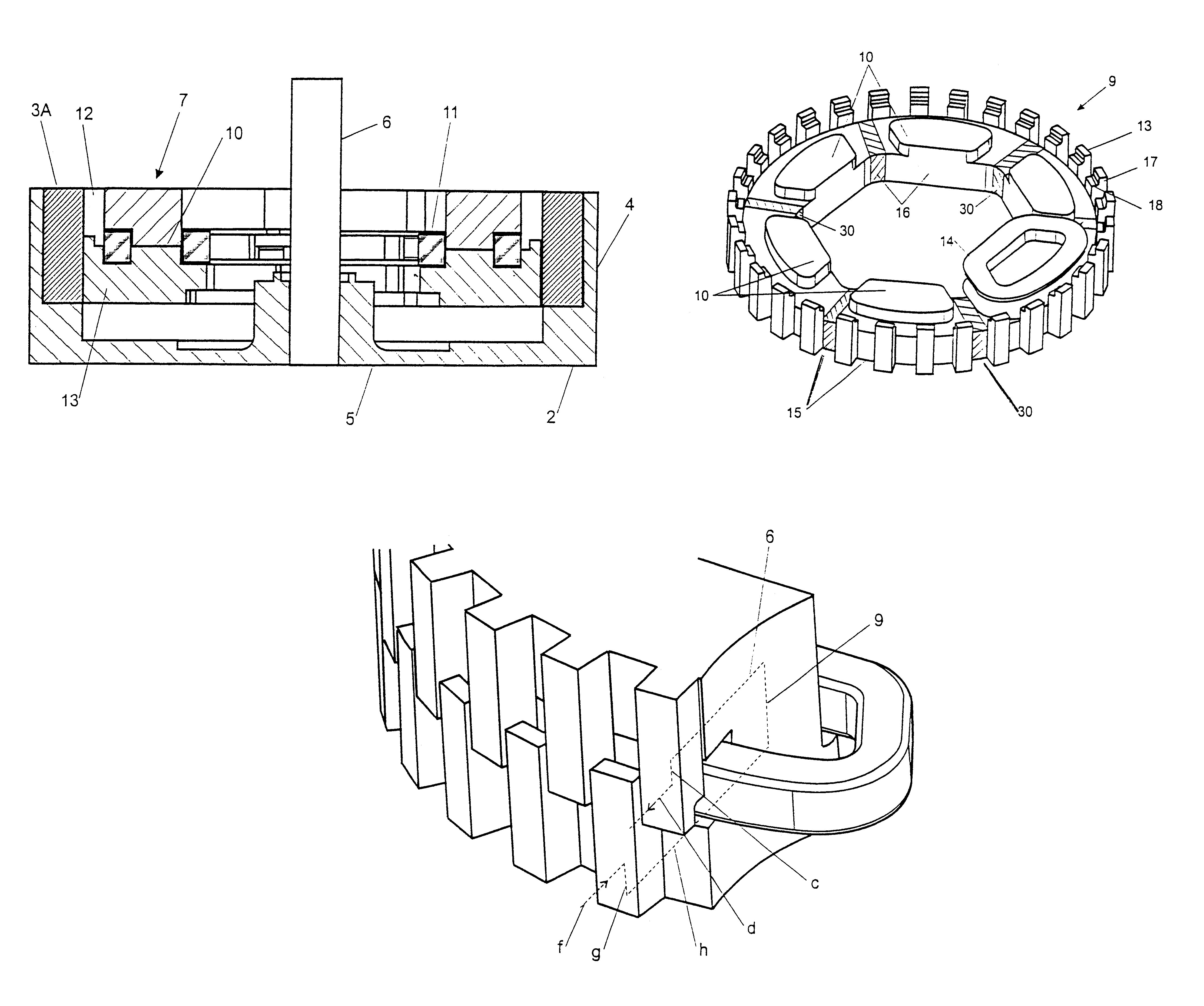
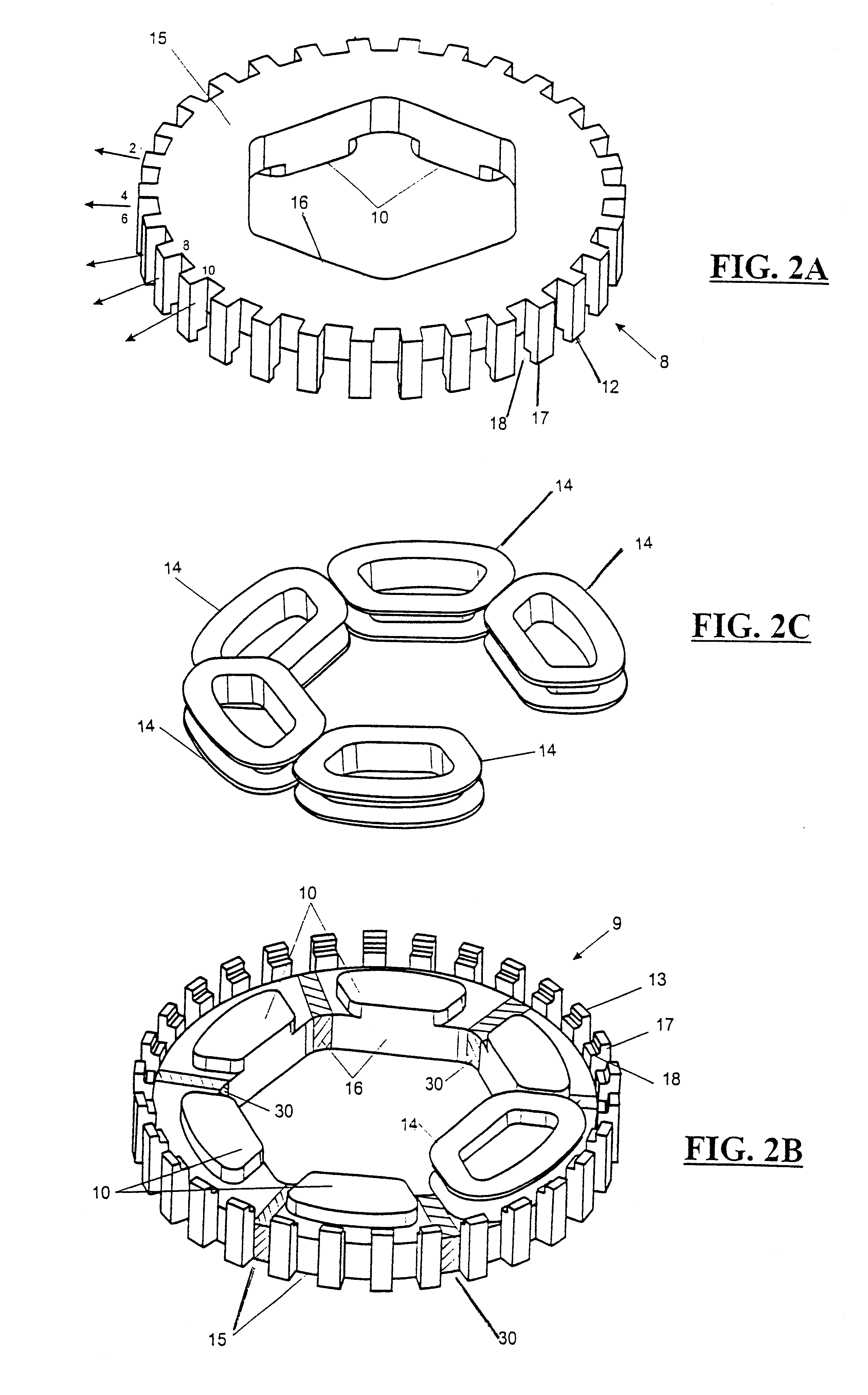
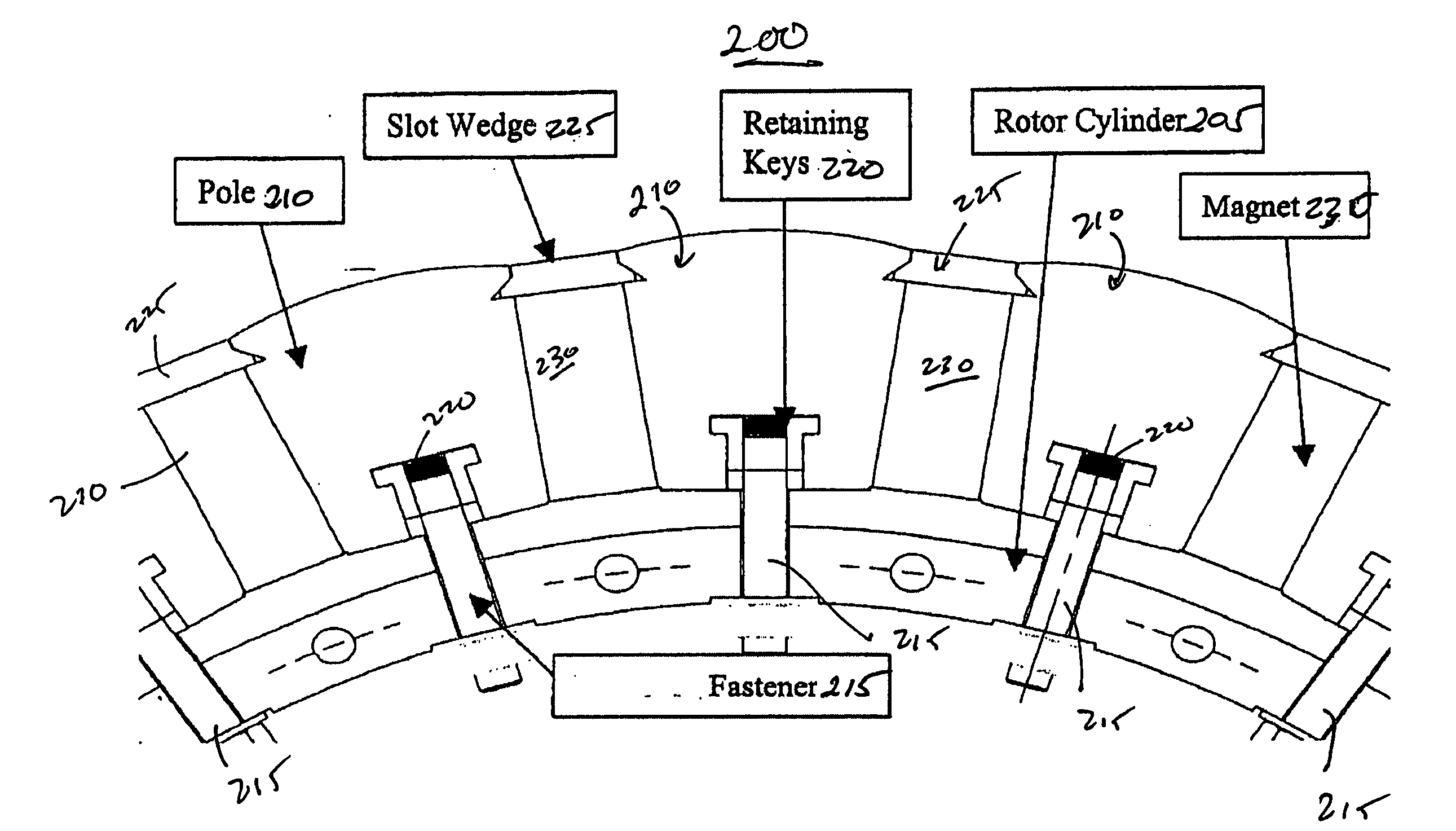
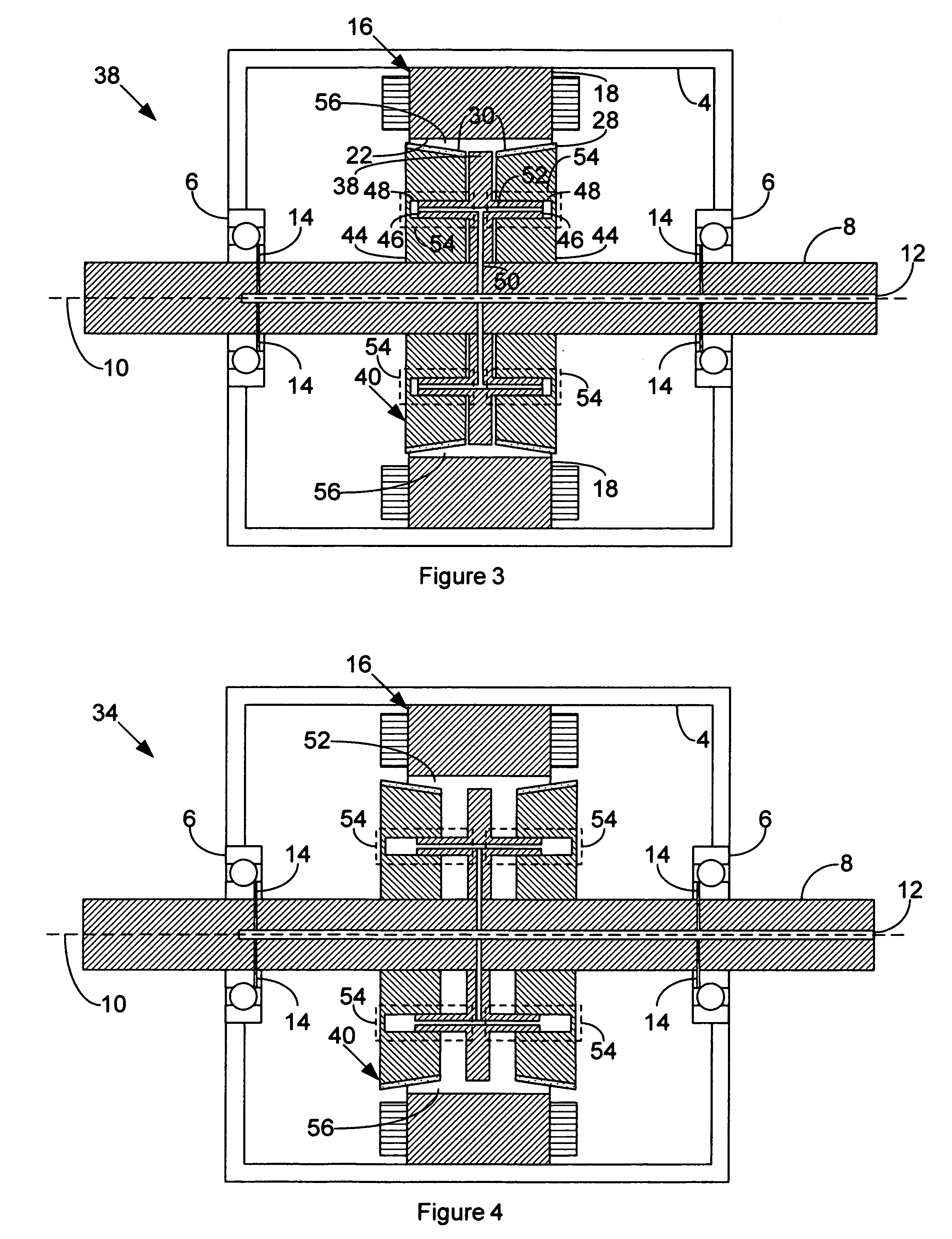
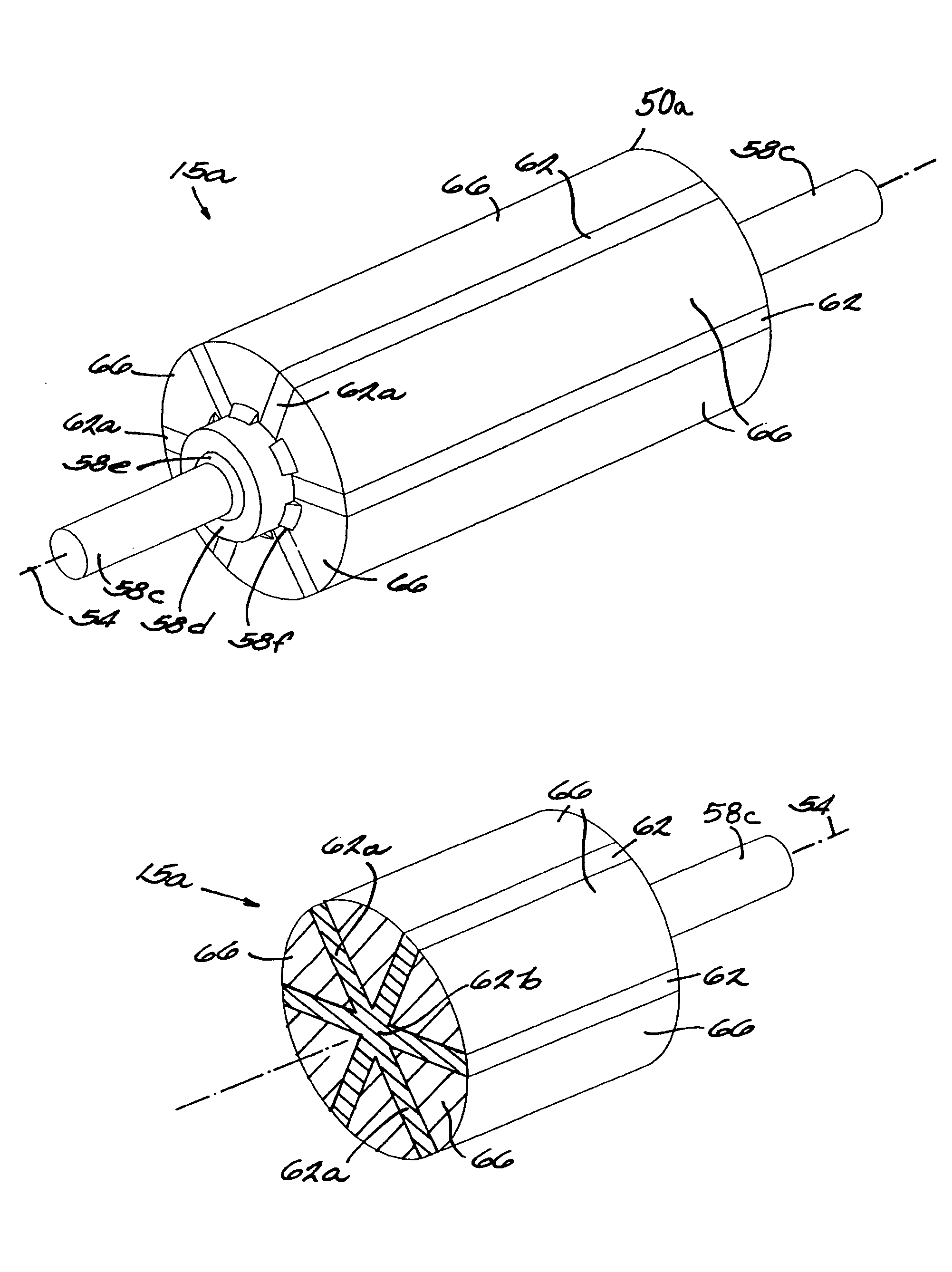
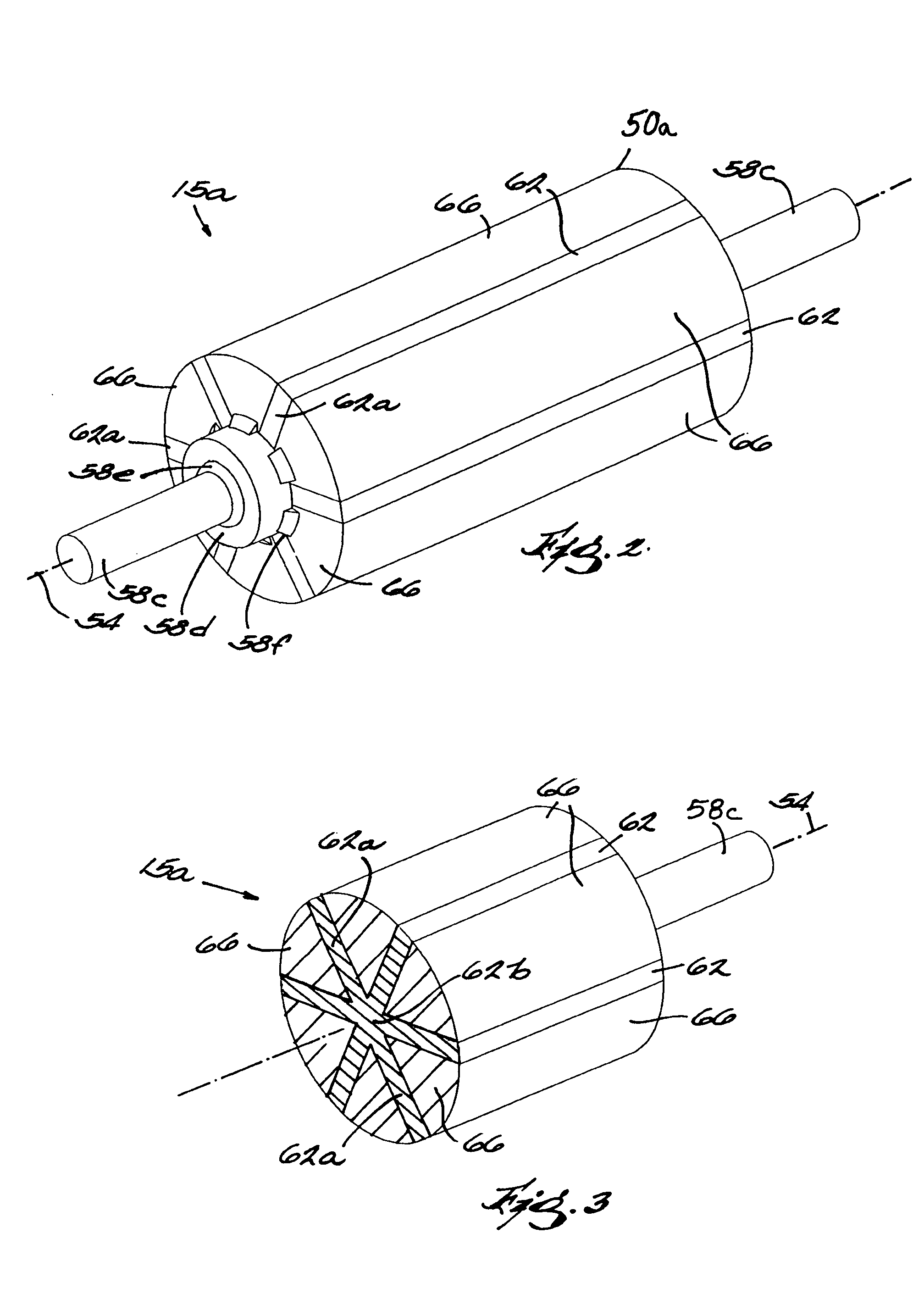
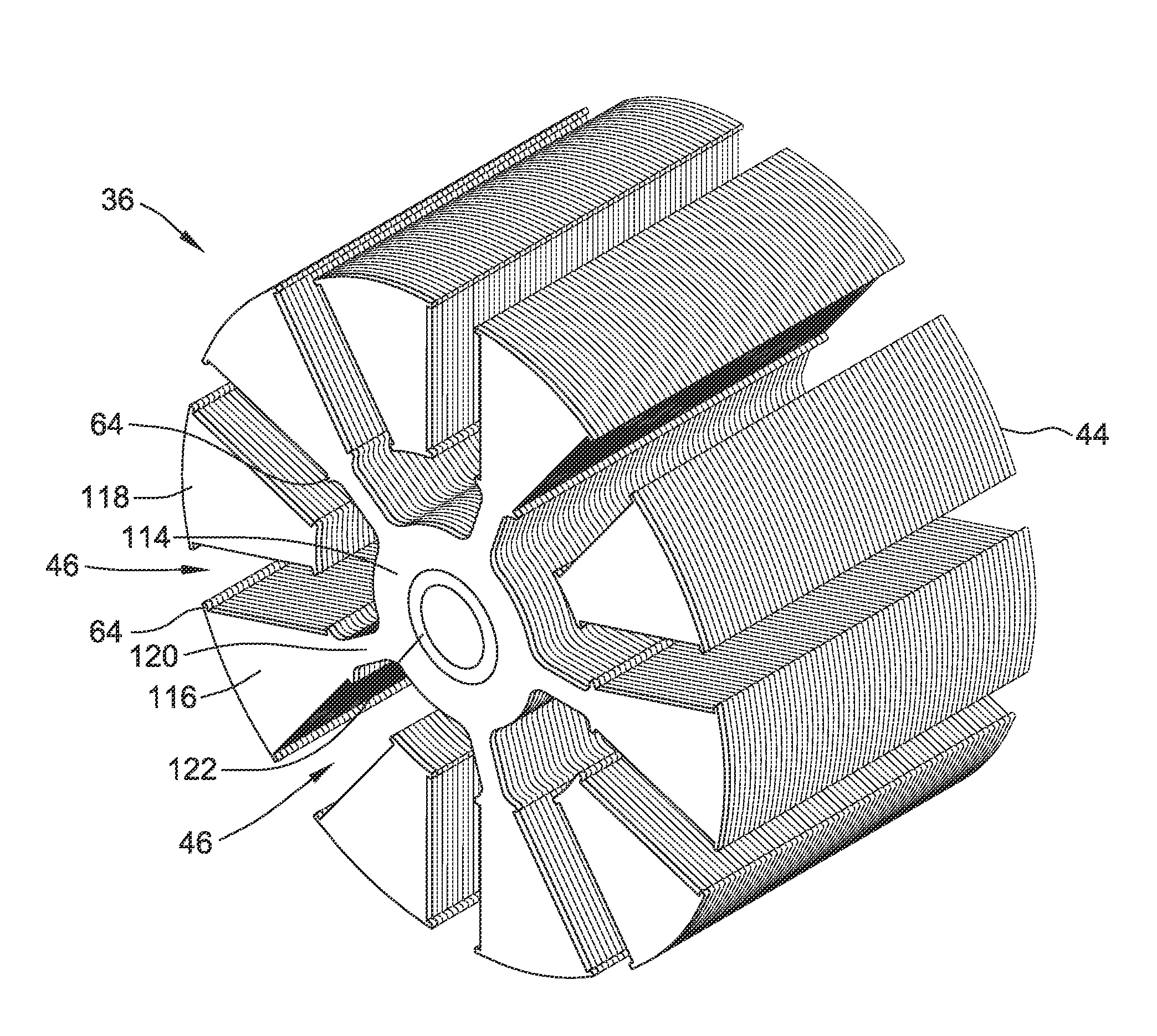
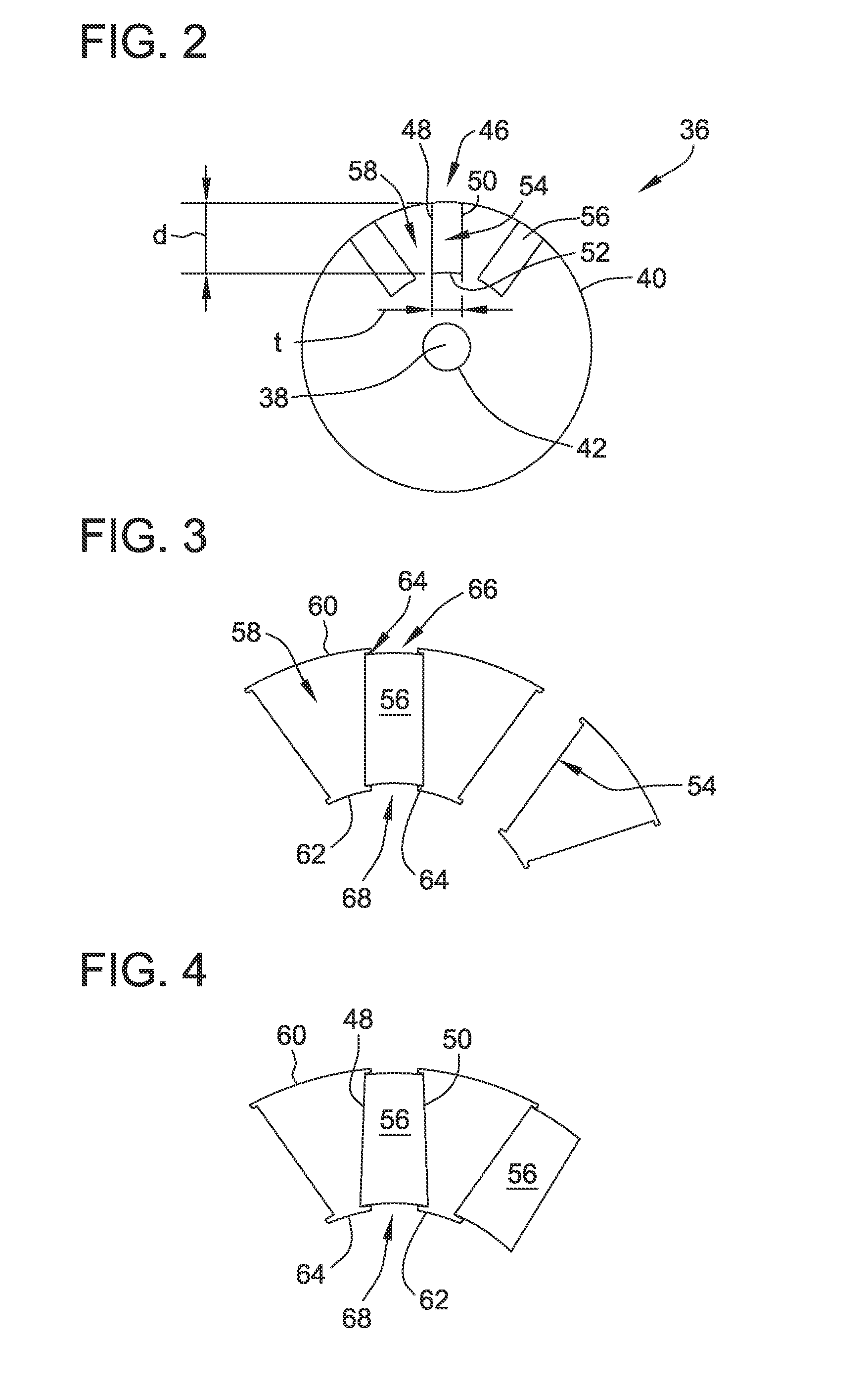
Method and apparatus for containing and protecting the magnets of a permanent magnet rotor spinning at high speeds without the use of a sleeve and is applicable to all permanent magnet rotors with two or more poles. Magnetic pole pieces are used to mechanically retain the magnets as well as provide a low reluctance path for the magnetic field to travel. The pole pieces and magnets are oriented radially on a hub made of a non-magnetic material such that the flux path of the magnets to the rotor poles is not shorted through the hub or shaft. The rotor poles have a taper angle and are secured to the rotor hub; the pole taper angle trapping the magnets, which have a matching taper angle. End cap pieces are provided to retain the rotor poles and the permanent magnets as an integral magnets / poles subassembly for use in a motor or generator.
Owner:CALNETIX
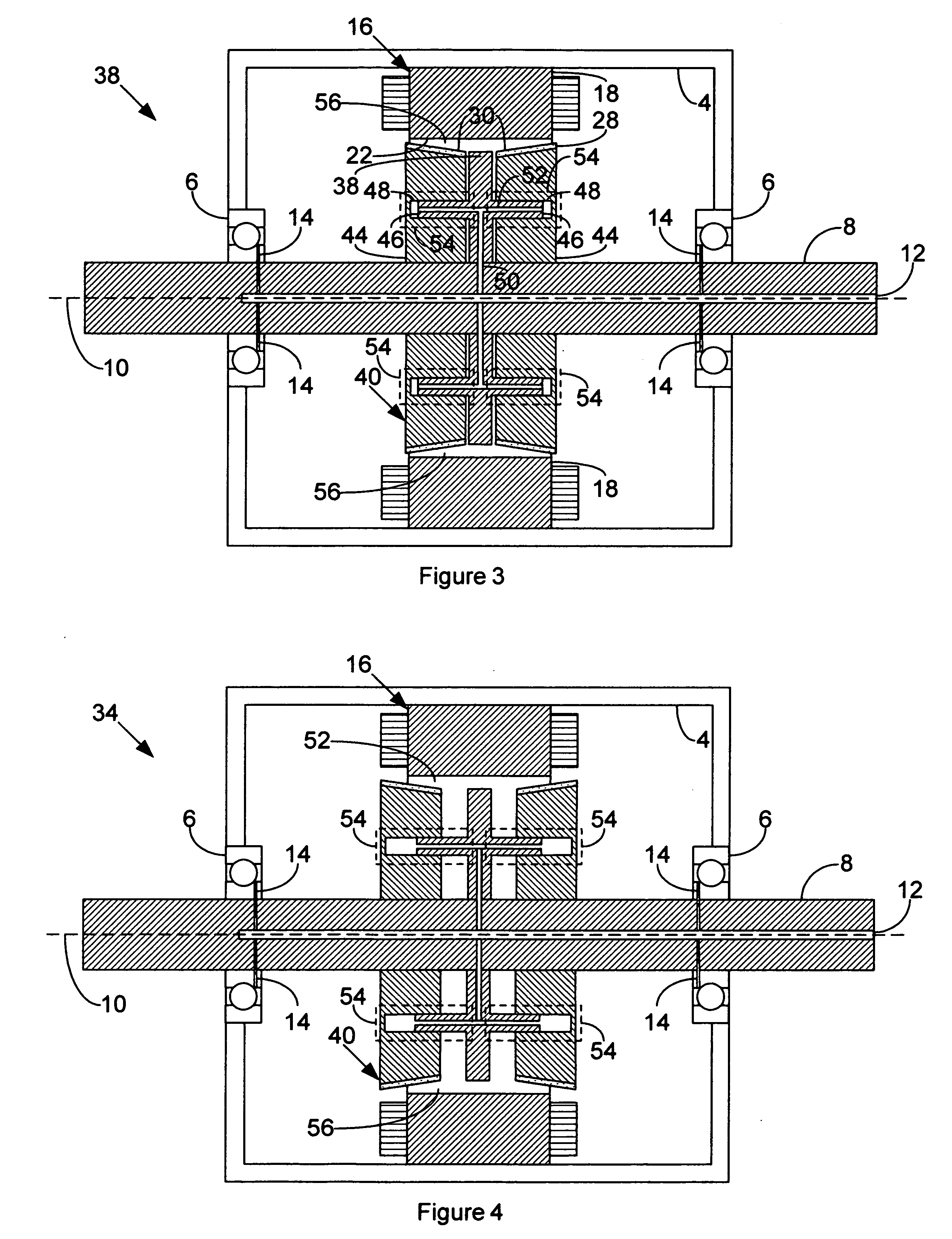
Permanent magnet rotor and magnet cradle
ActiveUS6933645B1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorNon magnetic
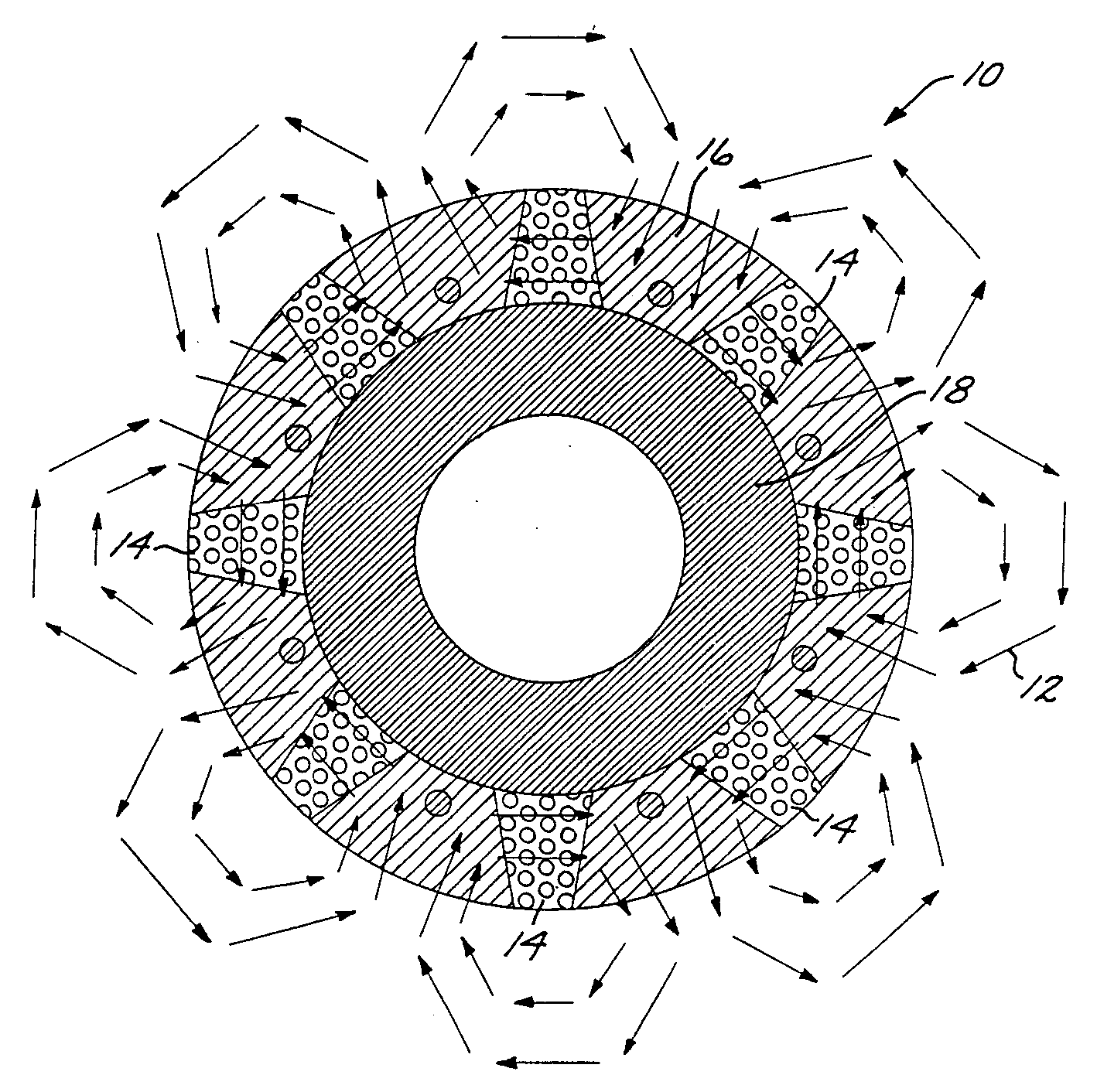
A magnet cradle for supporting a permanent magnet in an overhung recessed slot on the surface of a permanent magnet rotor having an axis of rotation. The cradle is non-magnetic and comprises a top and bottom wall abutting the permanent magnet. The cradle is sized to hold the permanent magnet within the overhung slots. Axial end walls generally perpendicular to the axis of rotation have circumferential edges configured to directly abut overhung portions of the slots. The total axial length of the top and bottom walls of the cradles in the axial direction are greater that the total axial length of the magnet, thereby permitting a magnet to fit between the axial end walls of the cradle without the cradle in the magnetic flux path of the magnet.
Owner:ELLIOTT CO
Permanent magnet rotor construction wherein relative movement between components is prevented
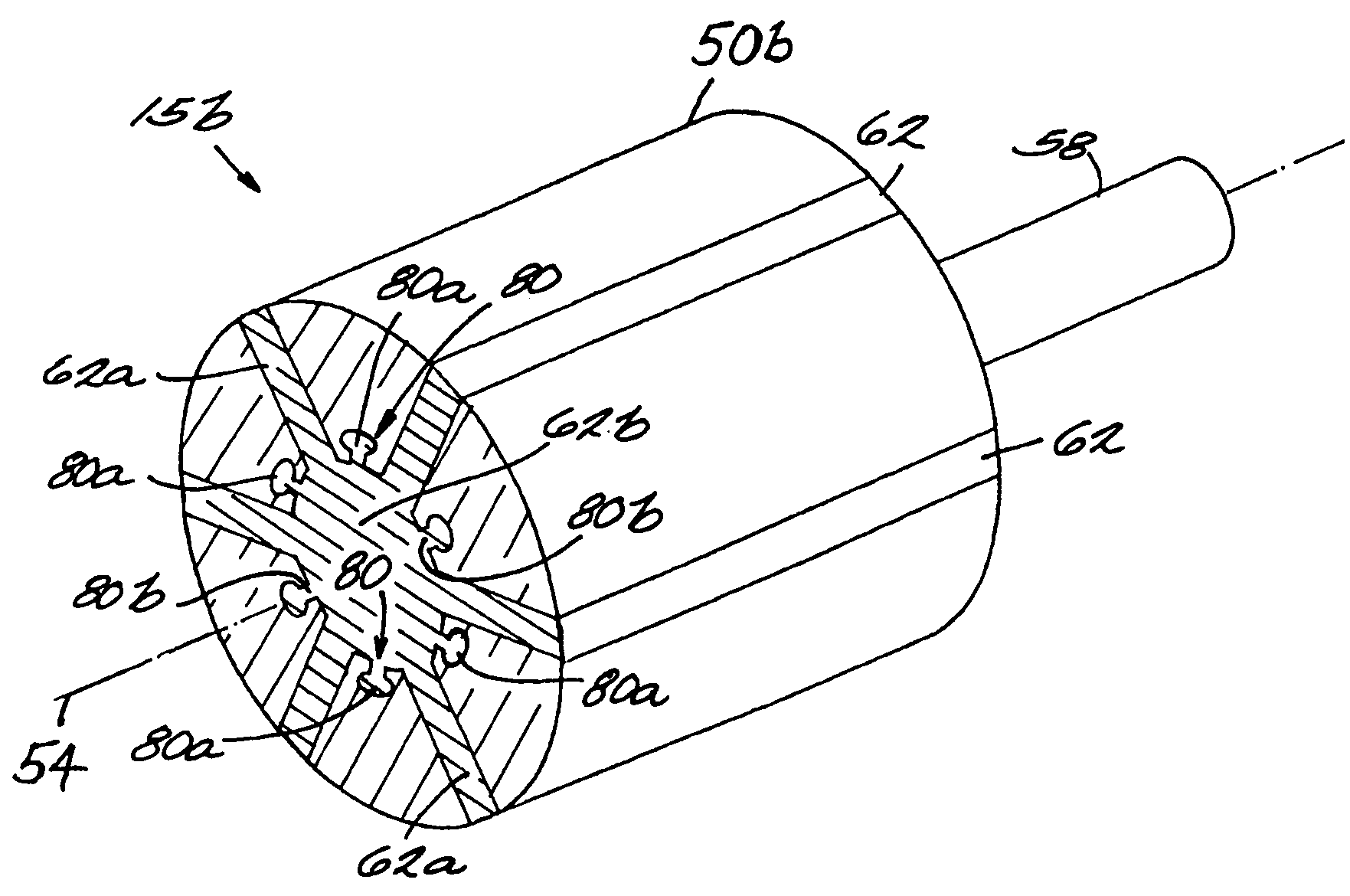
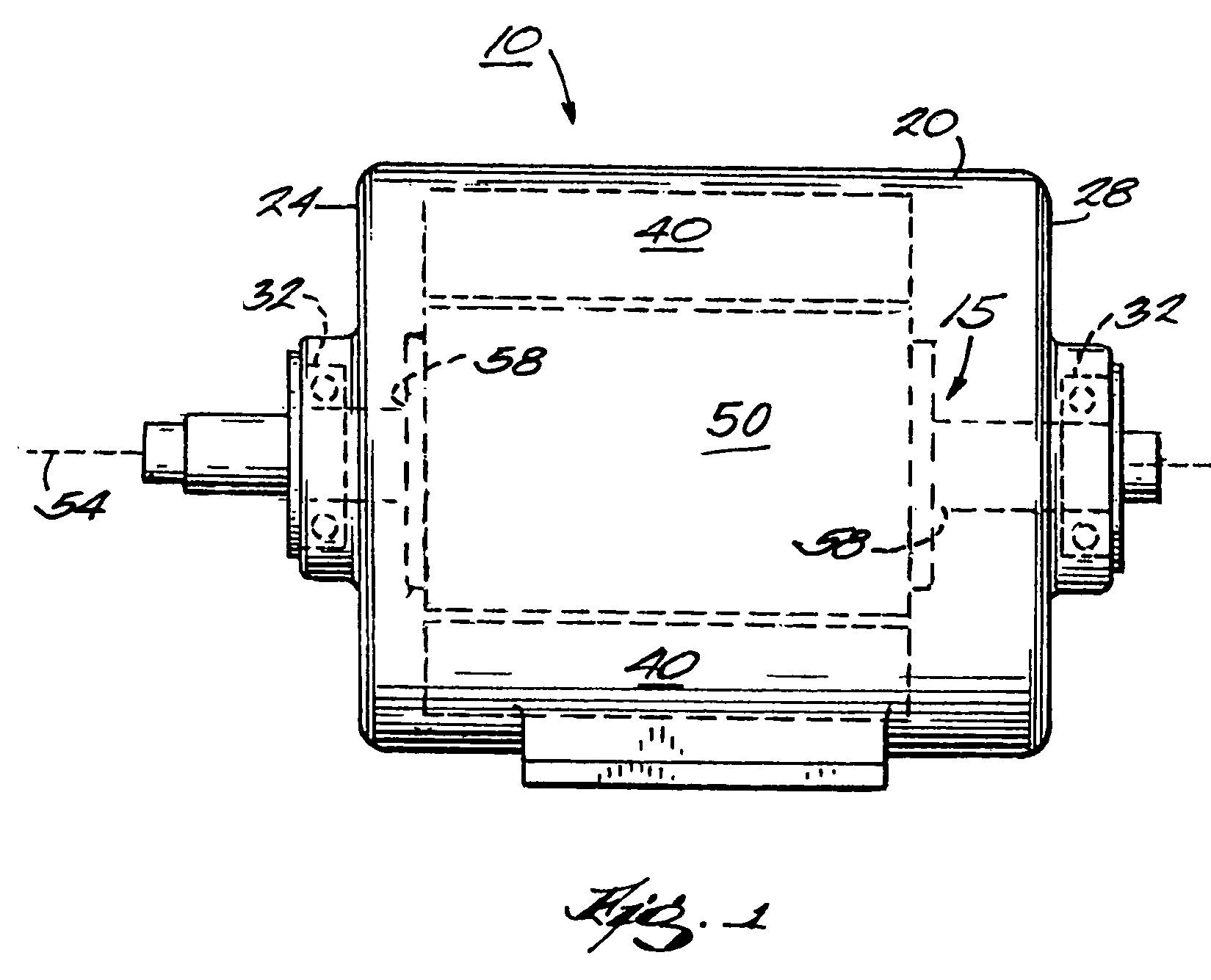
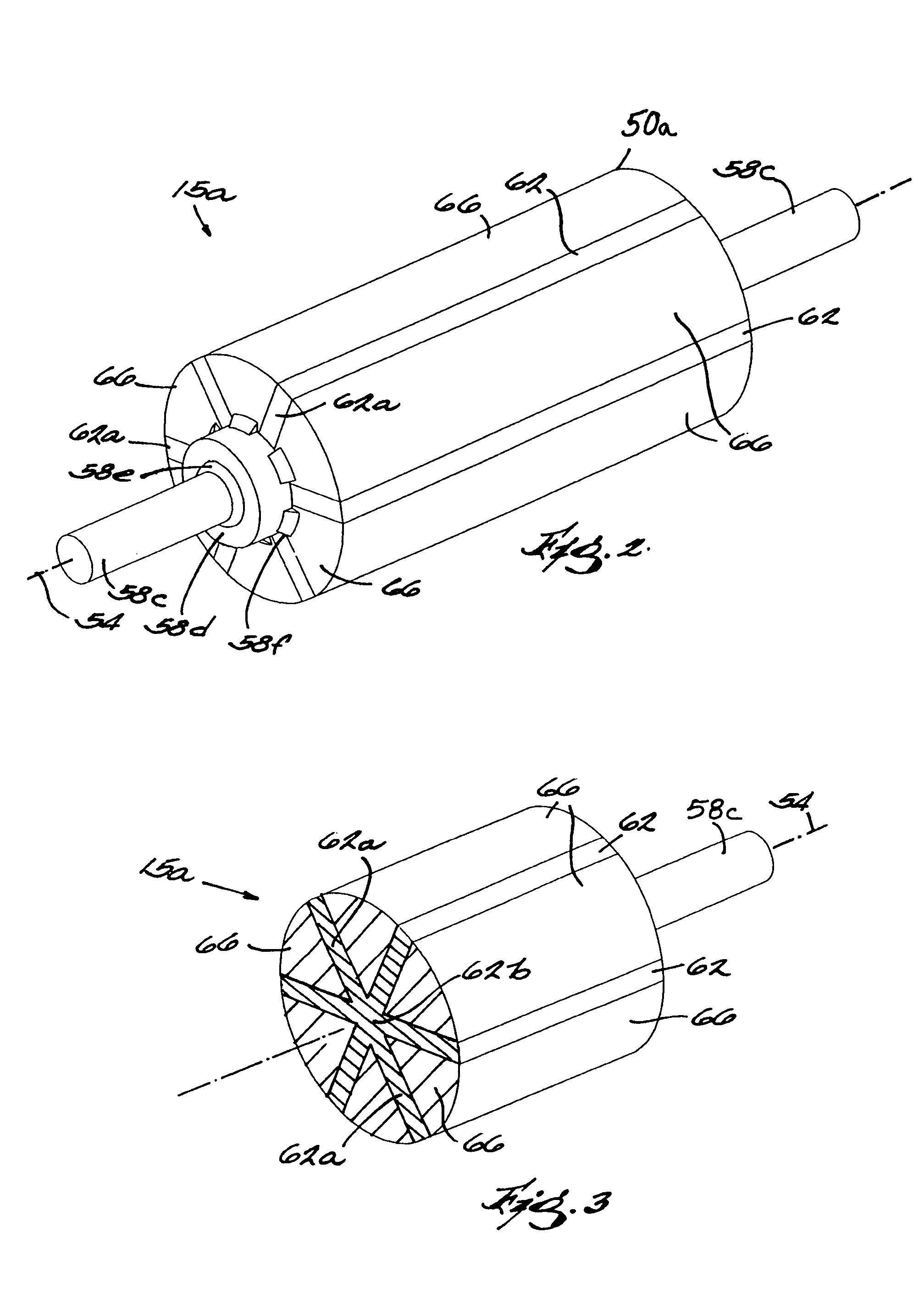
ActiveUS7042118B2Simple methodHigh strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsPropulsion systemsInterference fitPermanent magnet rotor
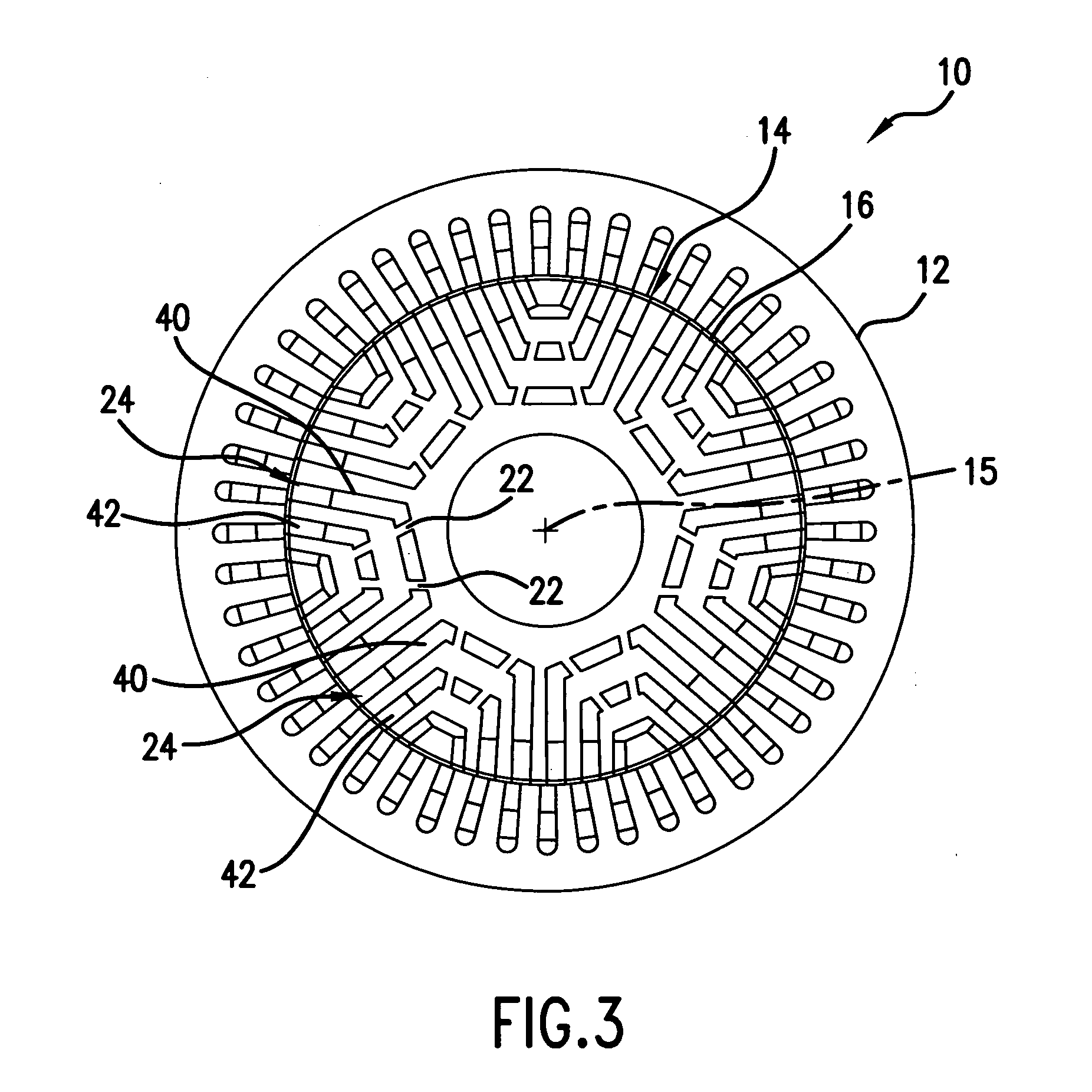
A rotor construction may comprise a rotor with a centrally located permanent magnet section having aligned magnet segments and having a central hole throughout its length. A thin rod of magnetic steel is located in this central hole to support the permanent magnets from within. At each end of the rod are located threaded sections for attachment to supporting end stubs. A high strength steel sleeve is interference fit over both the magnets and the end stubs to provide a mechanical link from stub to stub. The guide rod insures that the end stubs and central magnet are concentric during initial processing, prevents relative motion between the rotor components and provides support for the magnet once the sleeve is installed.
Owner:CALNETIX TECH
Efficient permanent magnet coupling device for transmission shaft
InactiveCN101931309ASignificant technological progressPermanent-magnet clutches/brakesPermanent magnet rotorDrive shaft
An efficient permanent magnet coupling device for a transmission shaft comprises armature winding rotor disks and adaptive armature winding disk shaft coupling mechanisms, permanent magnet rotor disks and adaptive permanent magnet disk shaft coupling mechanisms and input and output shaft couplings, wherein the armature winding rotor disks comprise armature windings and armature winding installing disks; the permanent magnet rotor disks comprise a group of permanent magnets and a permanent magnet installing disk; the permanent magnets are respectively assembled on the circumference of the permanent magnet installing disk, with N and S poles staggered; the armature winding rotor disks and the permanent magnet rotor disks are, face to face, coaxially installed and are coupled with the corresponding input and output shaft couplings by the adaptive disk shaft coupling mechanisms; and air gaps exist between the armature winding rotor disks and the permanent magnet rotor disks. The device has the characteristics of higher transmission efficiency, simple and reliable structure, convenient installation, resistance to severe environment, tolerance for shaft eccentricity, load isolation, reduction of vibration and noises, prolonging of equipment life, etc, and has the advantages of not damaging the motors and not affecting the safety of power grids.
Owner:林贵生
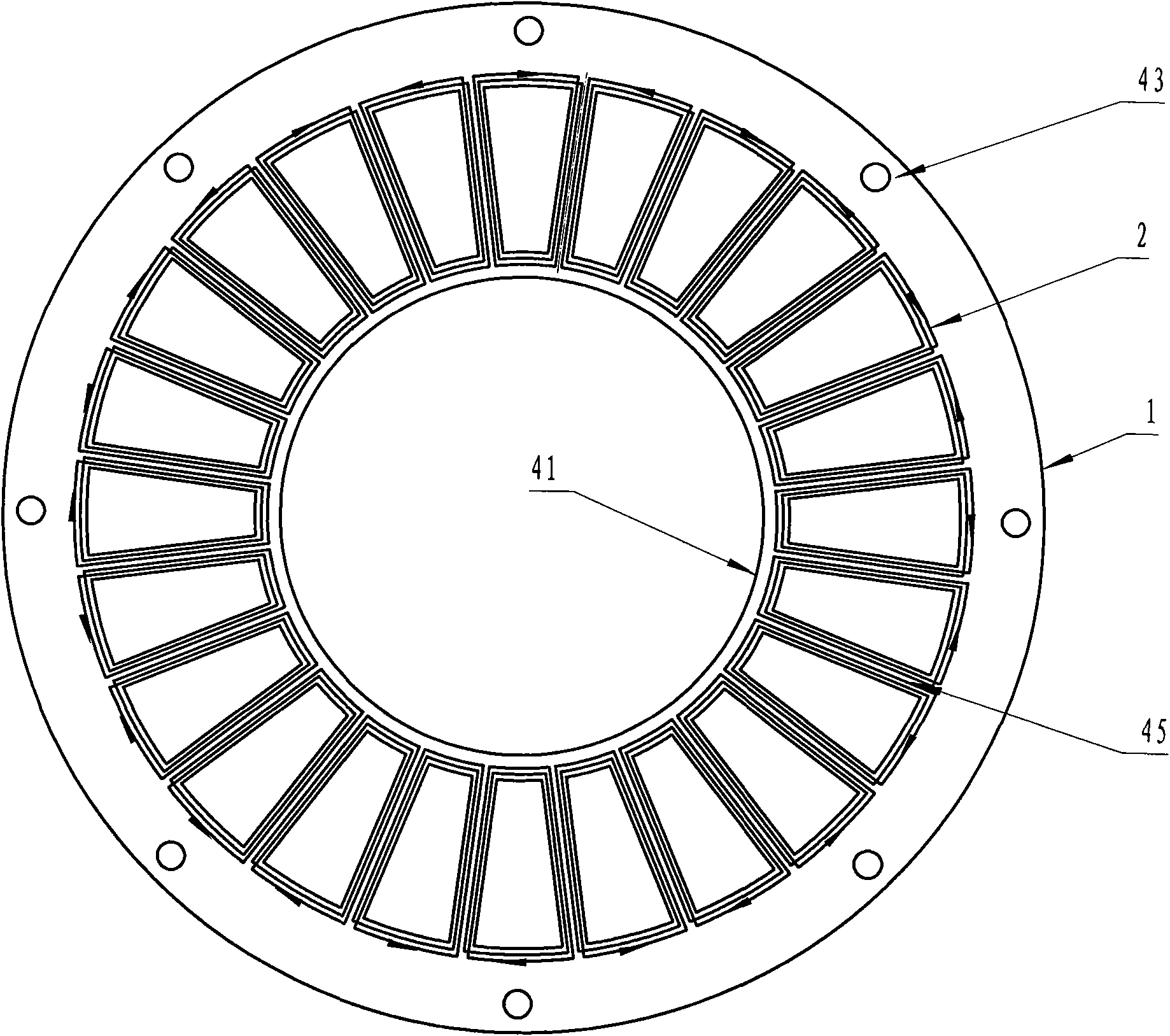
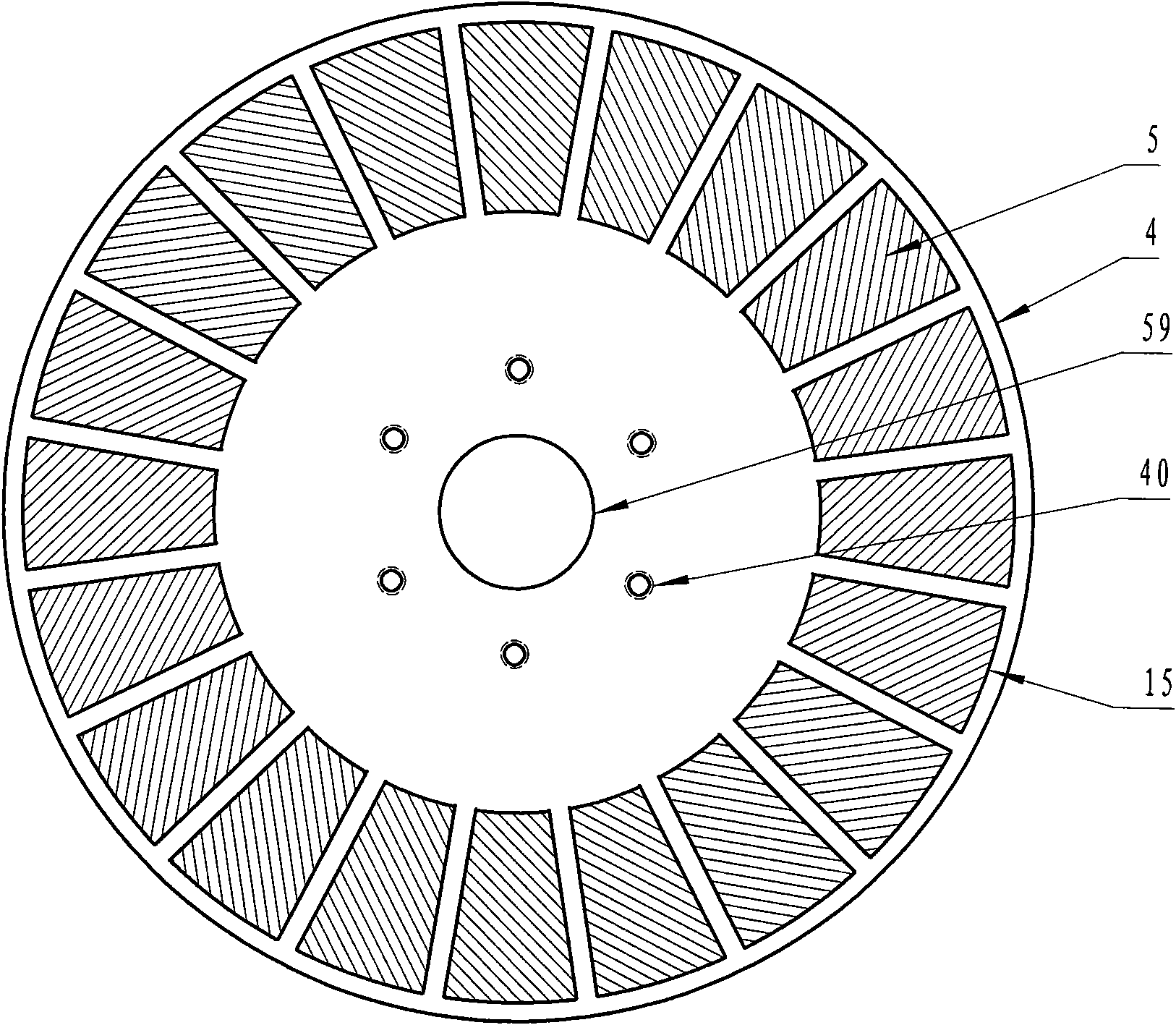
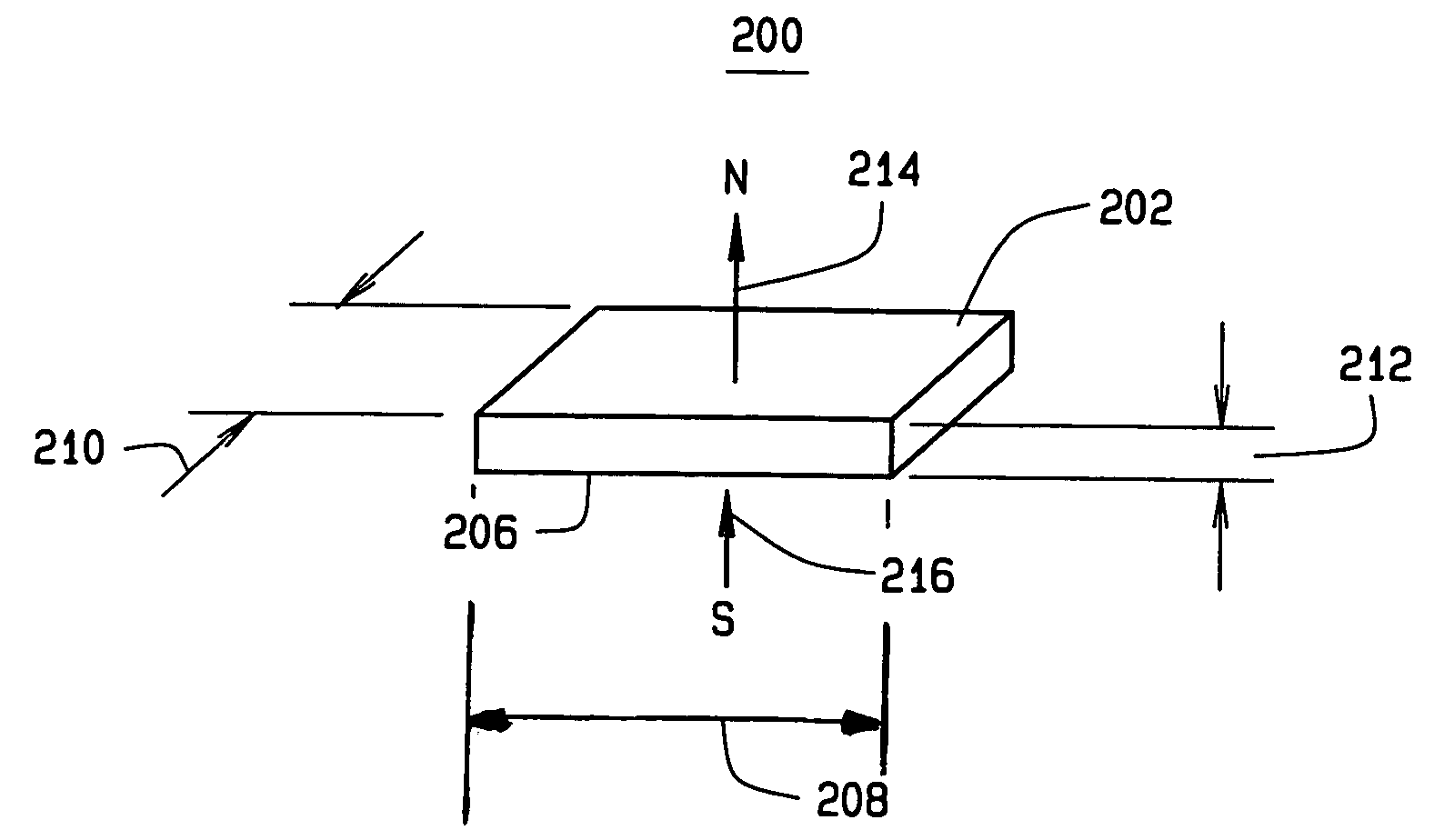
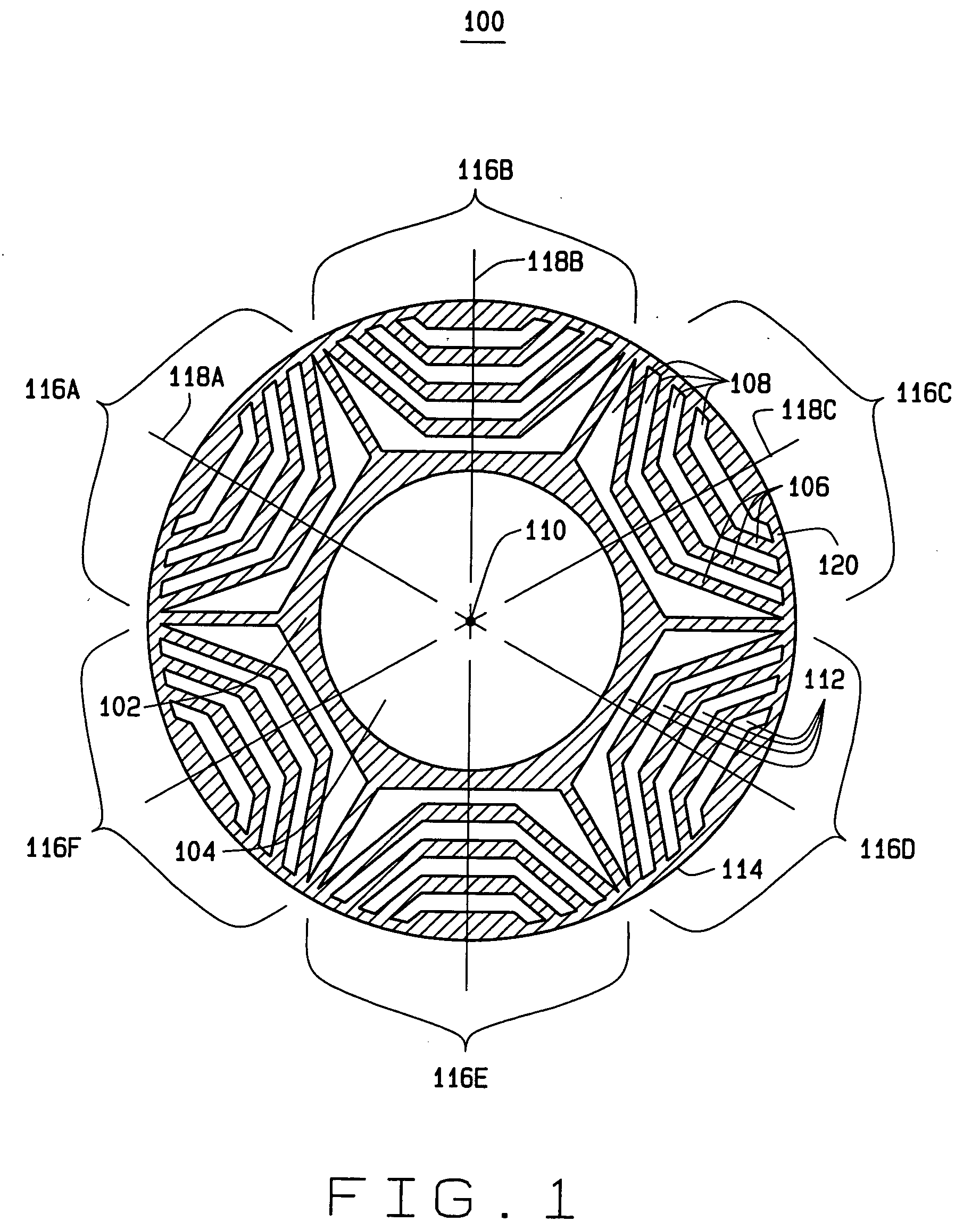
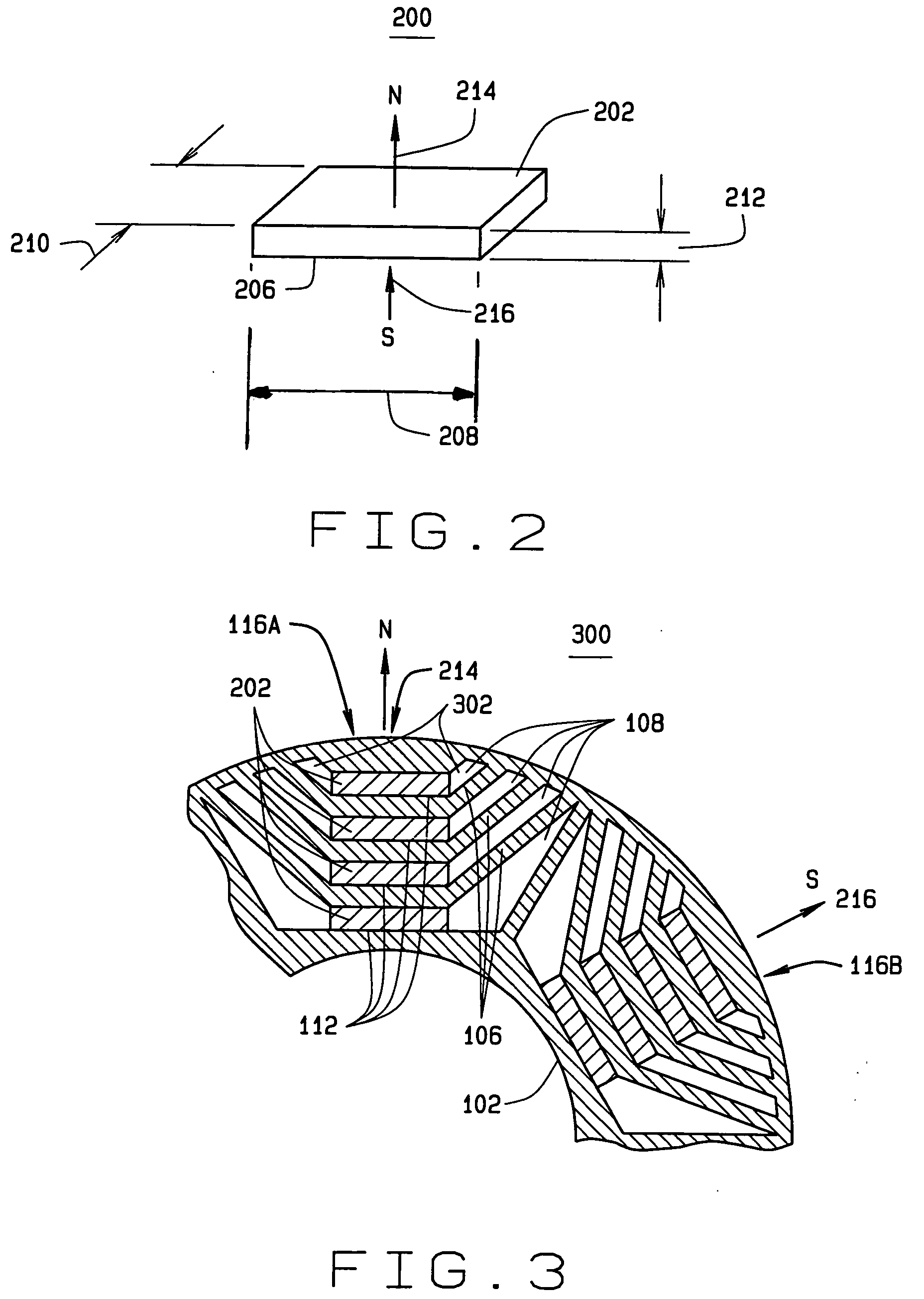
Interior permanent magnet rotors with multiple properties and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070228862A1Magnetic circuitManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesPermanent magnet rotorMagnetic poles
An armature for use in an electric traction motor comprises a rotor having a central portion and a peripheral portion with the peripheral portion having a plurality of cavities. Permanent magnets solidified from liquid magnetic material are disposed in the cavities to form poles of the rotor with at least a portion of the cavities having directly abutting permanent magnets comprised of at least first and second magnetic materials of different properties injected in liquid or mobile form into single cavities. In interface regions between the at least first and second magnetic materials the first and second magnetic materials are intermingled to form a transition zone. A method of making the armature includes injecting the magnetic materials simultaneously as well as injecting a subsequent magnetic material when the initial magnetic material is still fluidly mobile.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
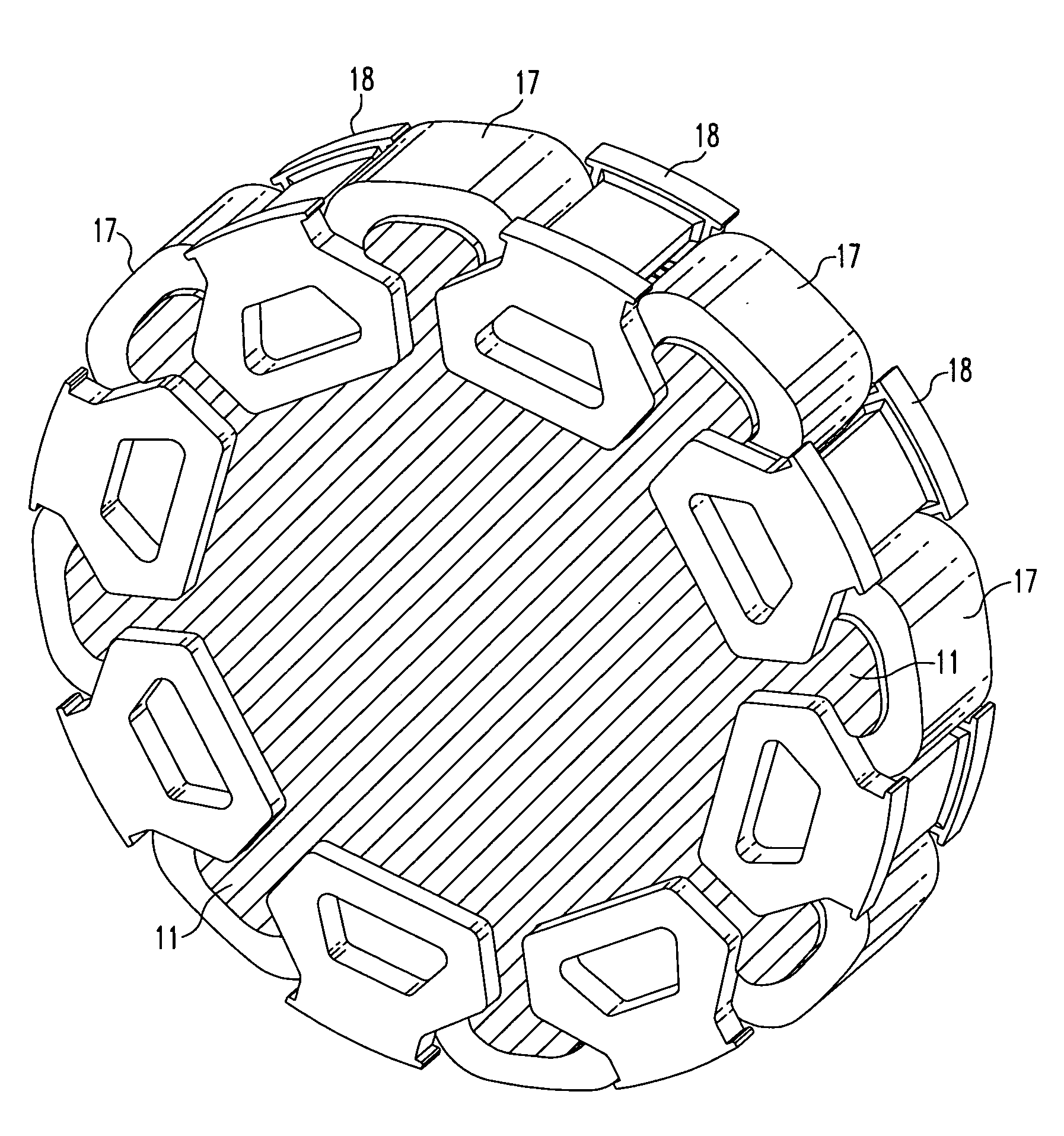
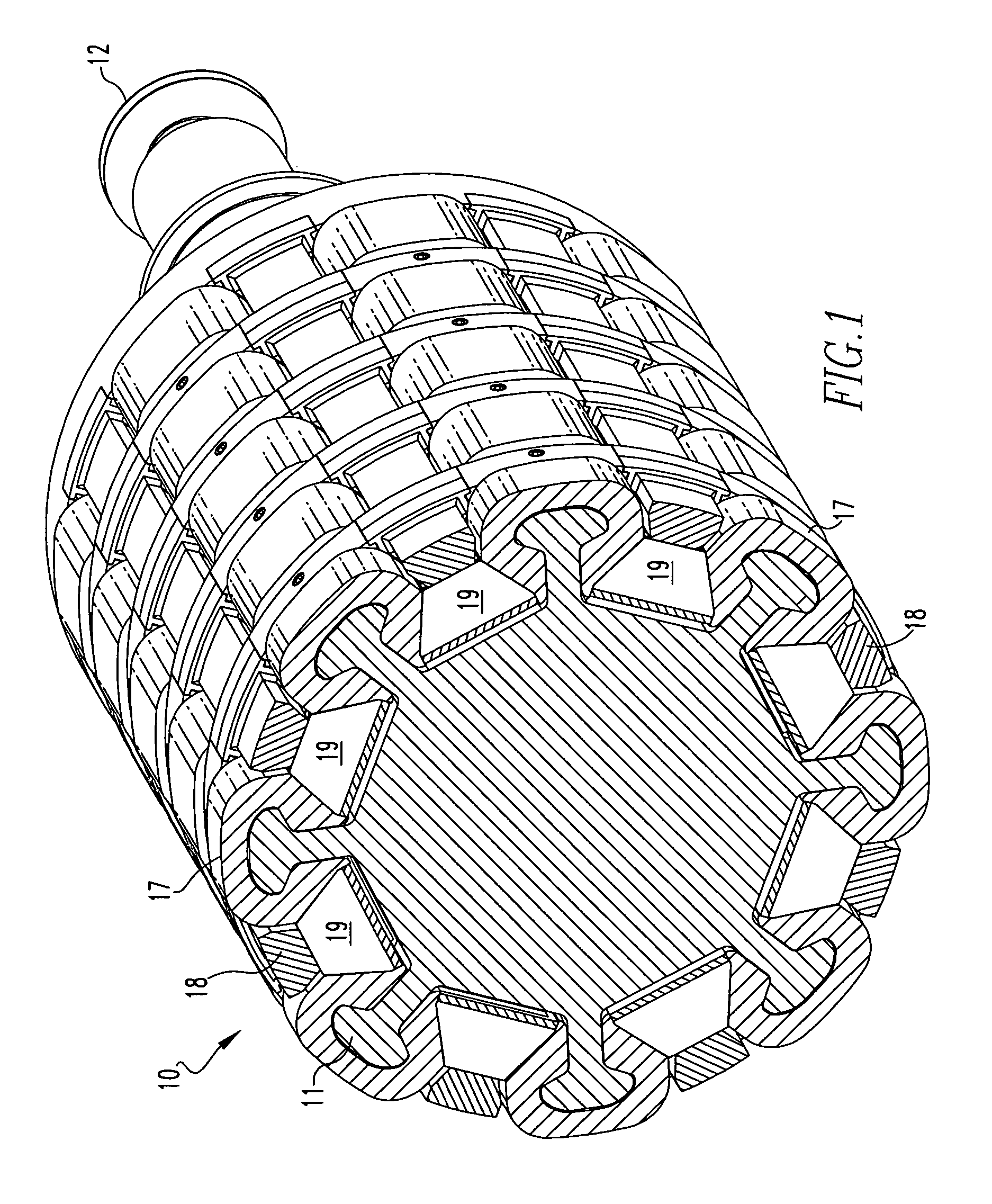
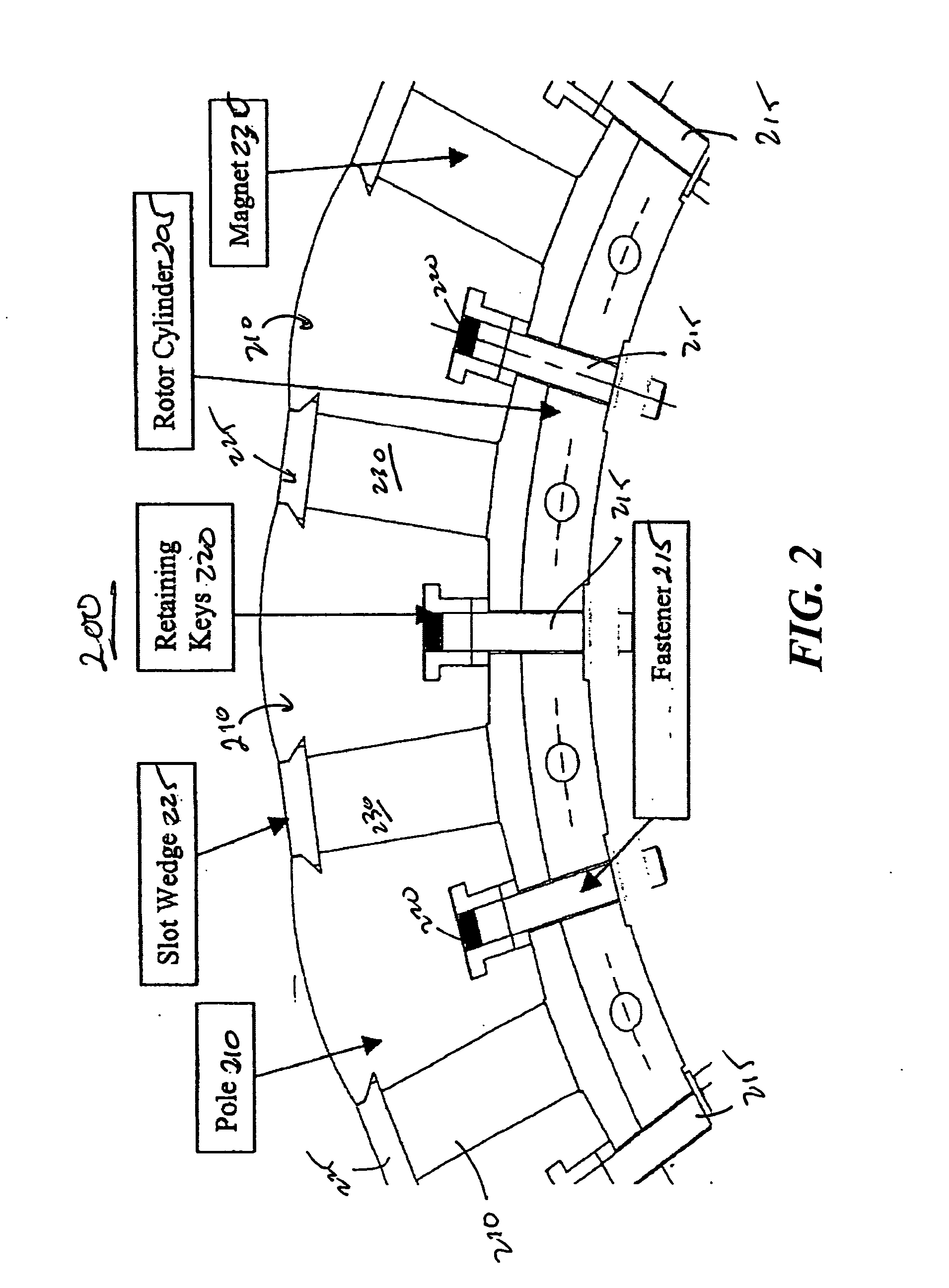
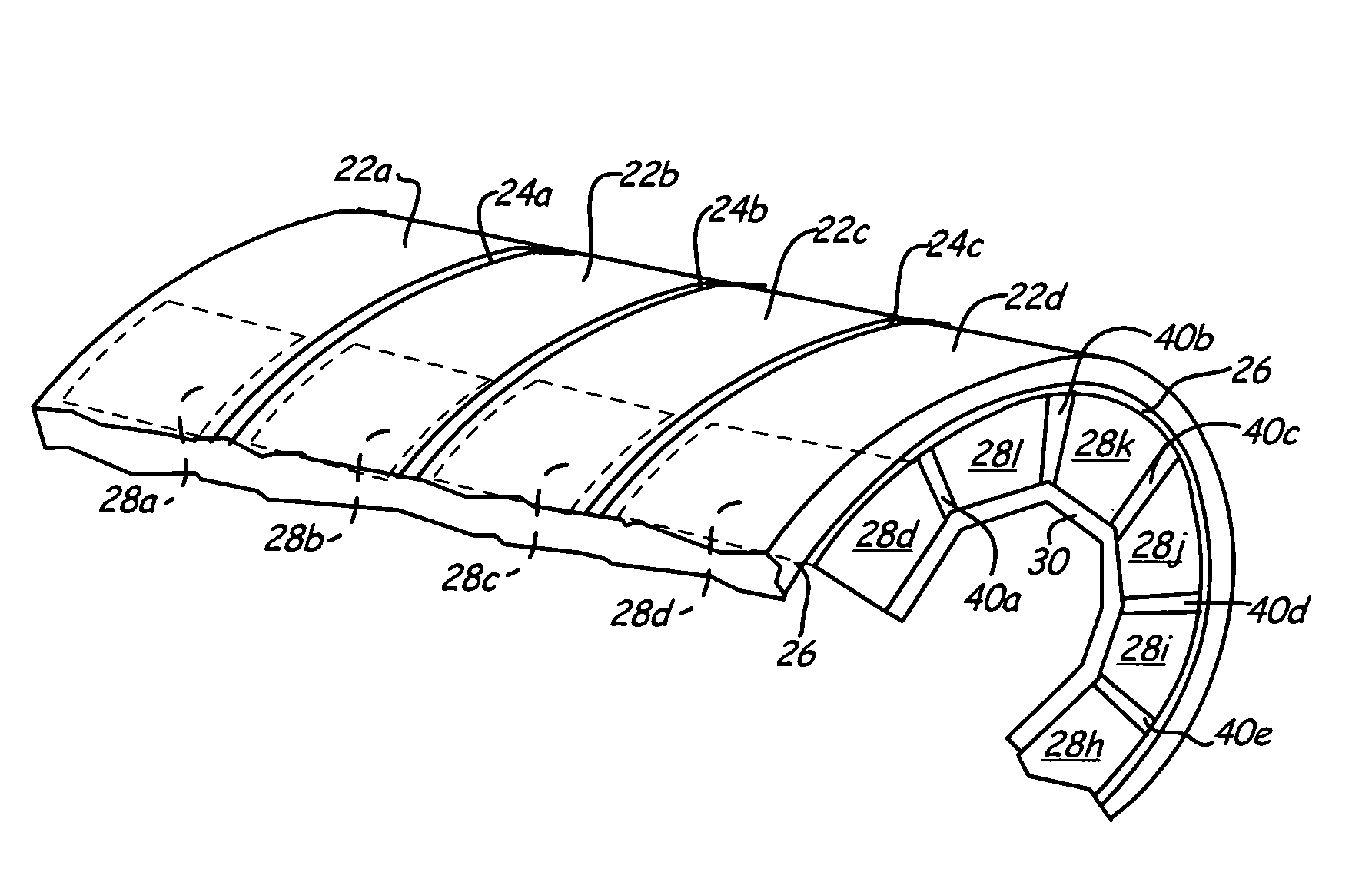
Apparatus for pole pieces
InactiveUS20060255679A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorPole piece
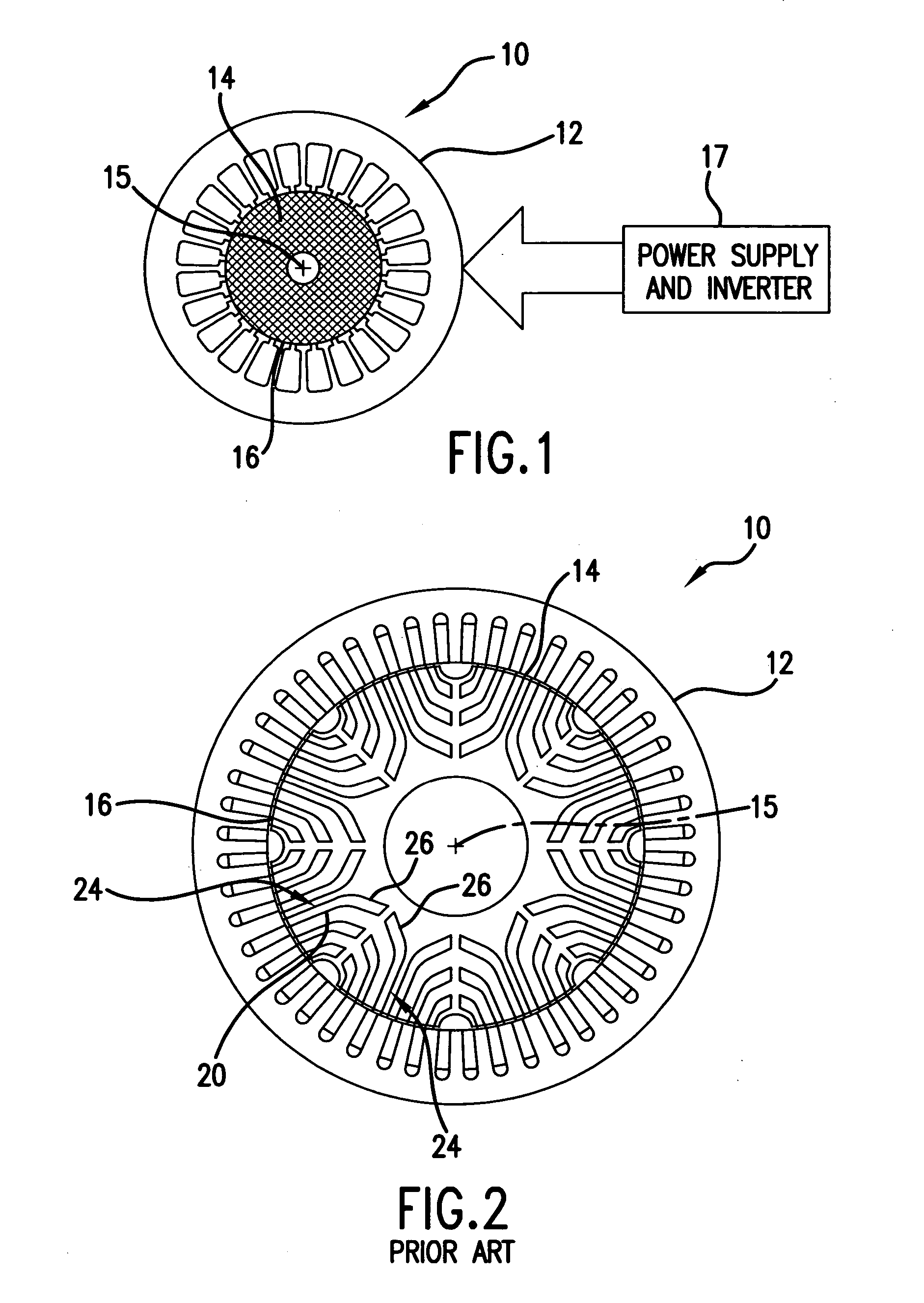
An embodiment generally relates to a permanent magnet rotor arrangement. The arrangement includes a rotor having a plurality of apertures, a plurality of pole pieces, a plurality of wedges, and a plurality of permanent magnets. Each magnet is held substantially secure against the rotor by a two pole pieces of the plurality of pole pieces and an associated wedge from the plurality of wedges. Each pole piece is connected to the rotor by a fastener pulled through an associated aperture.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS ELECTRIC BOAT CORP
Birotor permanent magnet motor and washing machine
ActiveCN103346655ASpeed effectAppropriate speedMagnetic circuit rotating partsOther washing machinesPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
The invention provides a birotor permanent magnet motor and a washing machine with the same. The birotor permanent magnet motor comprises an inner rotor, a stator and an outer rotator which are sequentially arranged from inside to outside, and is characterized in that both the inner rotor and the outer rotor are permanent magnet rotors, and the stator comprises a magnetic modulation ring and a stator winding arranged on the magnetic modulation ring in a wound mode. The birotor permanent magnet motor is based on the magnetic field modulation principle and has a birotor structure, the outer rotor and the inner rotor can rotate according to certain proportional relation, and high-performance output of the motor under operating conditions of a low speed and a high speed can be met at the same time. When the birotor permanent magnet motor drives the washing machine to operate, not only are design requirements for low-speed large torque output and high-speed small torque output of the motor under the optimal operating state met, but also the structures of a belt pulley, a reduction gearbox and the like in a traditional washing machine are eliminated, transmission efficiency of the motor is improved, and meanwhile the defects of high noise, machine body vibration and the like of the traditional washing machine are overcome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Permanent magnet dynamoelectric machine with axially displaceable permanent magnet rotor assembly
A dynamoelectric machine comprises: a stator that comprises a plurality of stator poles arranged around a stator surface of revolution with a stator axis for the stator surface of revolution; at least one rotor that comprises a plurality of permanent rotor magnets arranged around a rotor surface of revolution with a rotor axis for the rotor surface of revolution that is coincident with the stator axis and with the rotor surface of revolution adjacent the stator surface of revolution; a drive shaft with a drive shaft axis of rotation that is substantially coincident with the stator axis coupled to the rotor for rotating the rotor relative to the stator about the drive shaft axis of rotation; and a at least one actuator for axially displacing the rotor surface of revolution along the drive shaft relative to the stator surface of revolution to change magnetic flux interaction between the stator poles and the rotor magnets; wherein at least one of the surfaces of revolution tilts with respect to the drive shaft axis of rotation.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Segmented permanent magnet rotor for high speed synchronous machines
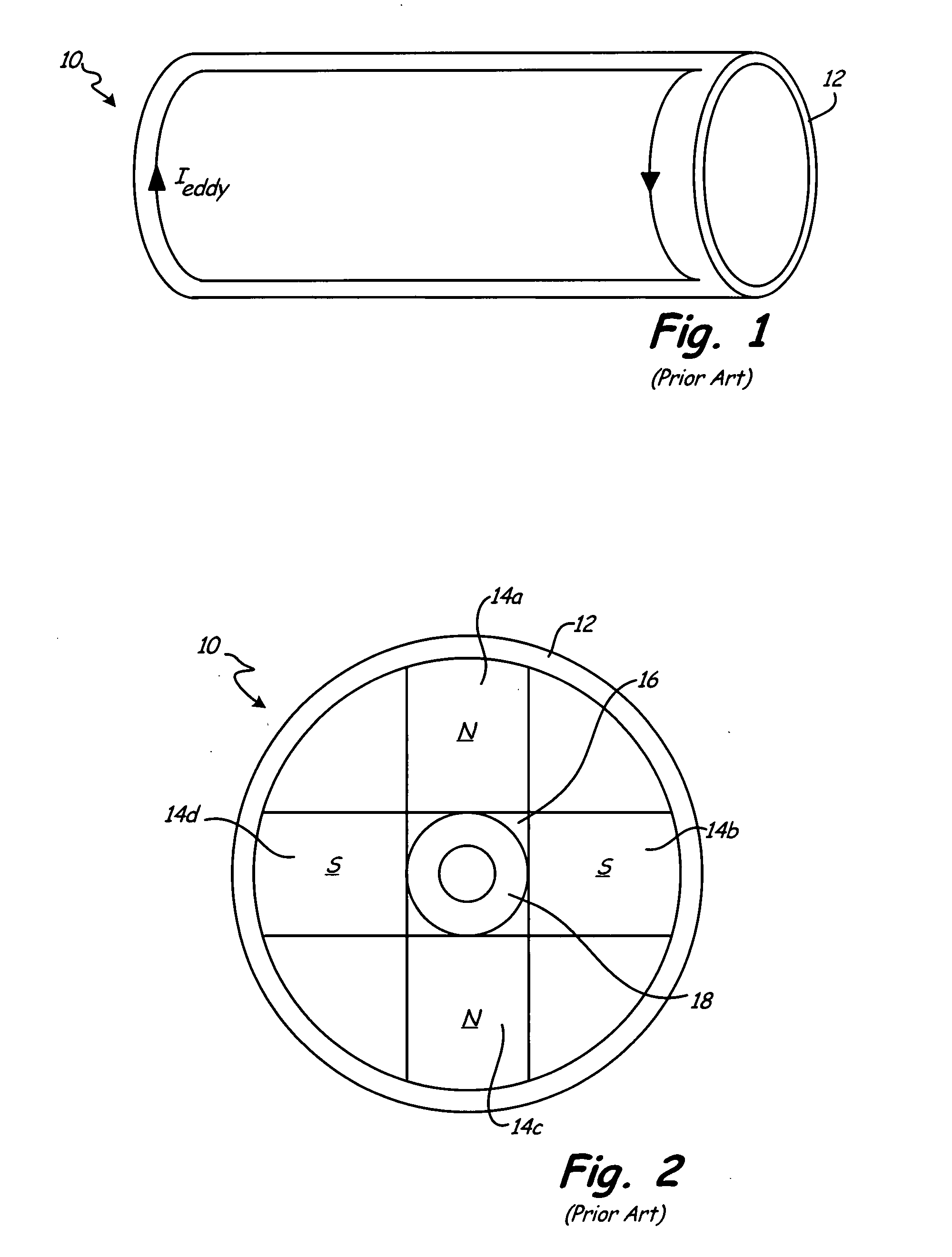
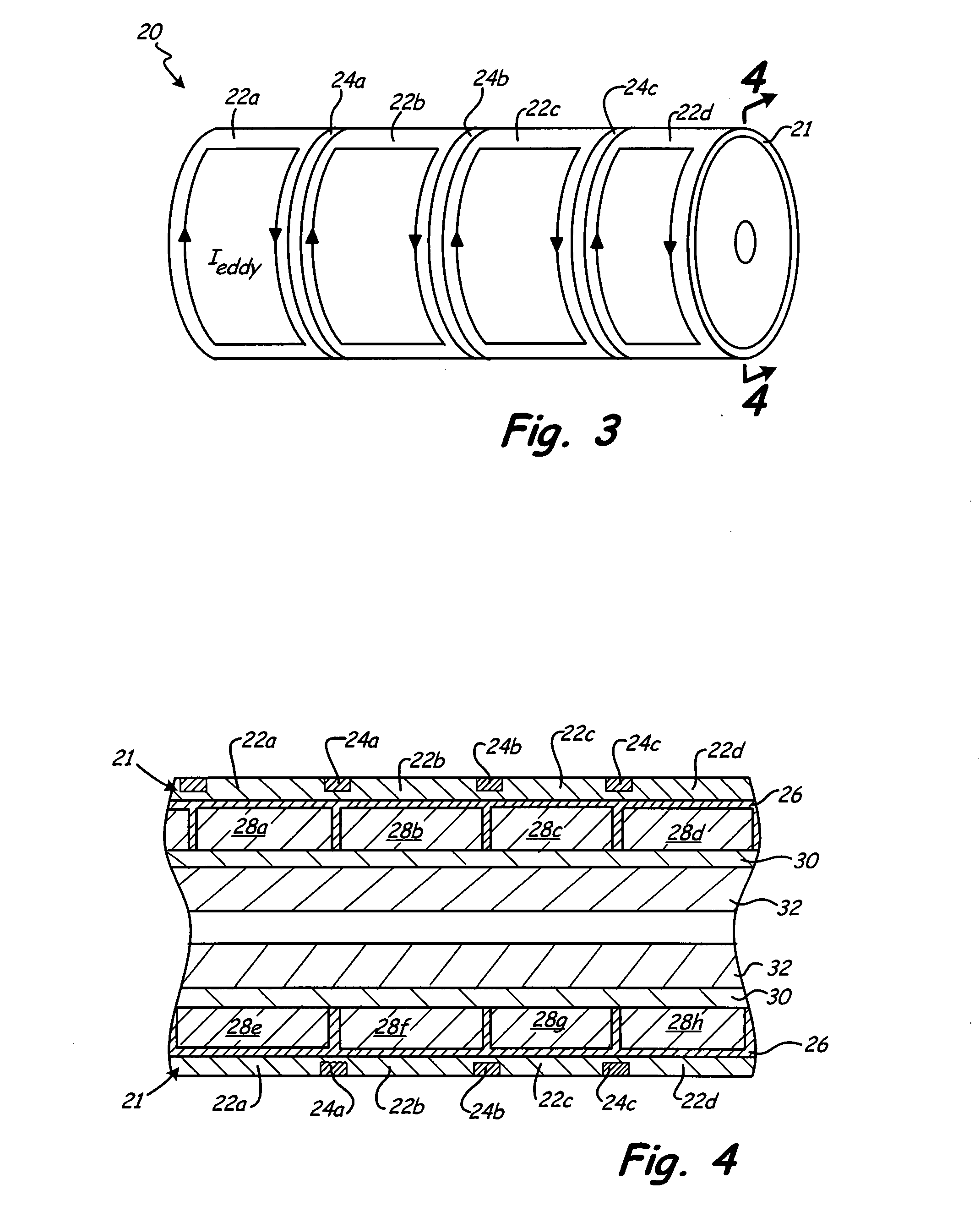
InactiveUS20080238234A1Reduce eddy-current lossReducing eddy current lossWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet rotorEngineering
The segmented permanent-magnet rotor for high-speed synchronous machines reduces eddy-current losses by axially segmenting the containment sleeve and the permanent magnets. The axial segmentation of the containment sleeve includes forming grooves circumferentially around the outer surface of the containment sleeve. The circumferential grooves disrupt the generation of eddy currents on the outer surface of the containment sleeve and therefore reduce eddy-current losses in the containment sleeve. Axial segmentation of the permanent magnets also disrupts eddy current formation, thereby reducing eddy current losses in the permanent magnets. In addition, the presence of an electrically insulating layer between the containment sleeve and the permanent magnets reduces eddy current migration from the containment sleeve to the permanent magnets, and therefore provides additional reduction of eddy-current losses.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Permanent magnet dynamoelectric machine with axially displaceable permanent magnet rotor assembly
A dynamoelectric machine comprises: a stator that comprises a plurality of stator poles arranged around a stator surface of revolution with a stator axis for the stator surface of revolution; at least one rotor that comprises a plurality of permanent rotor magnets arranged around a rotor surface of revolution with a rotor axis for the rotor surface of revolution that is coincident with the stator axis and with the rotor surface of revolution adjacent the stator surface of revolution; a drive shaft with a drive shaft axis of rotation that is substantially coincident with the stator axis coupled to the rotor for rotating the rotor relative to the stator about the drive shaft axis of rotation; and a at least one actuator for axially displacing the rotor surface of revolution along the drive shaft relative to the stator surface of revolution to change magnetic flux interaction between the stator poles and the rotor magnets; wherein at least one of the surfaces of revolution tilts with respect to the drive shaft axis of rotation.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
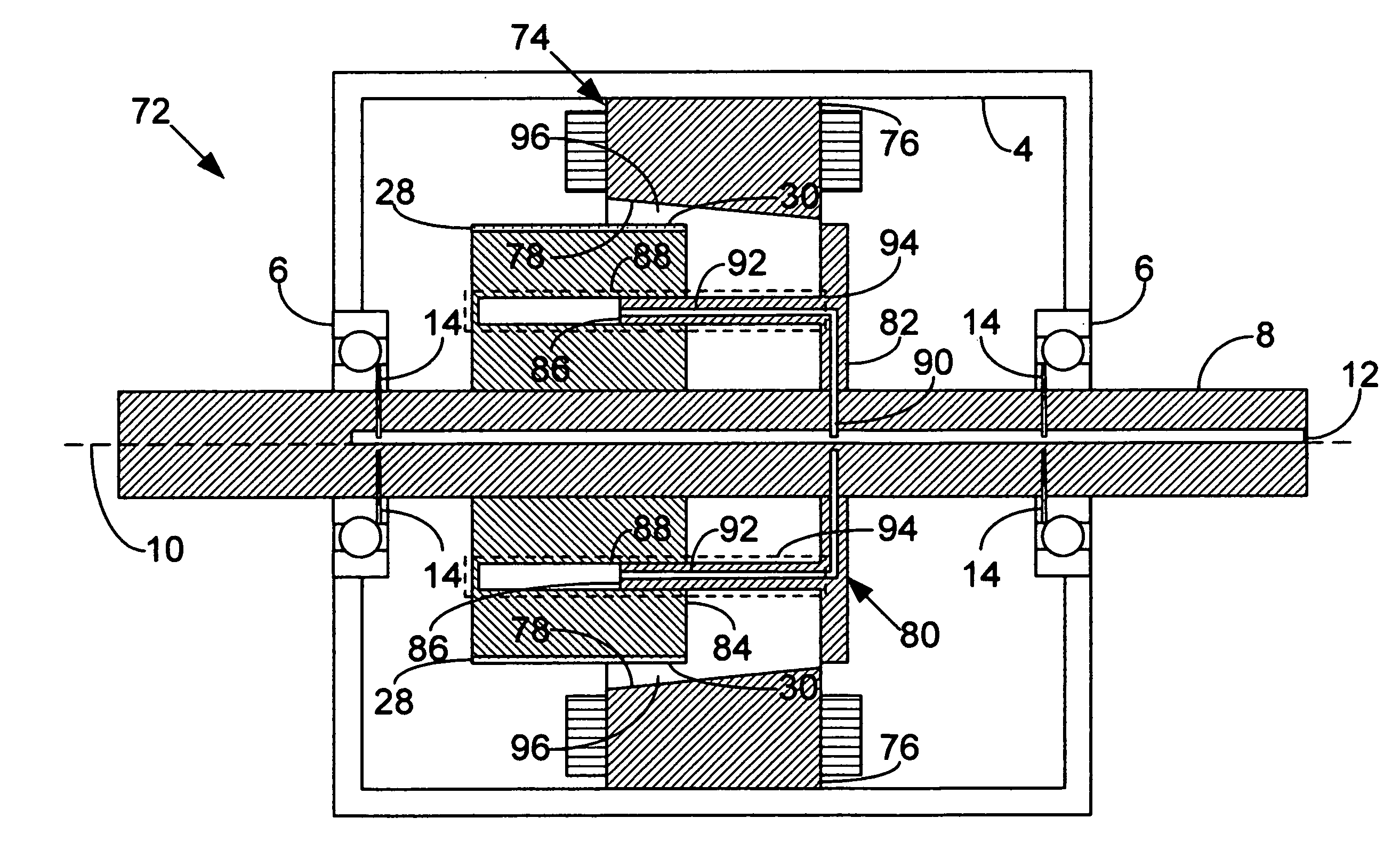
Spoke permanent magnet rotors for electrical machines and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20050088052A1Improve performanceLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
A rotor assembly for an electric motor includes a spoke permanent magnet rotor and a shaft connected thereto. The spoke permanent magnet rotor has an axis of rotation, permanent magnet material, and ferro-magnetic material. The permanent magnet material extends outwardly relative to the axis of rotation to form a plurality of outwardly extending spoke portions of permanent magnet material. The ferro-magnetic material is positioned adjacent to the outwardly extending spoke portions of permanent magnet material. The shaft supports the spoke permanent magnet rotor for rotation about the axis of rotation. The permanent magnet material may circumferentially surround the axis of rotation to form a center portion of permanent magnet material. Further, the axis of rotation may pass through the permanent magnet material. The spoke permanent magnet rotor may be formed using a compaction process and / or an injection molding process.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
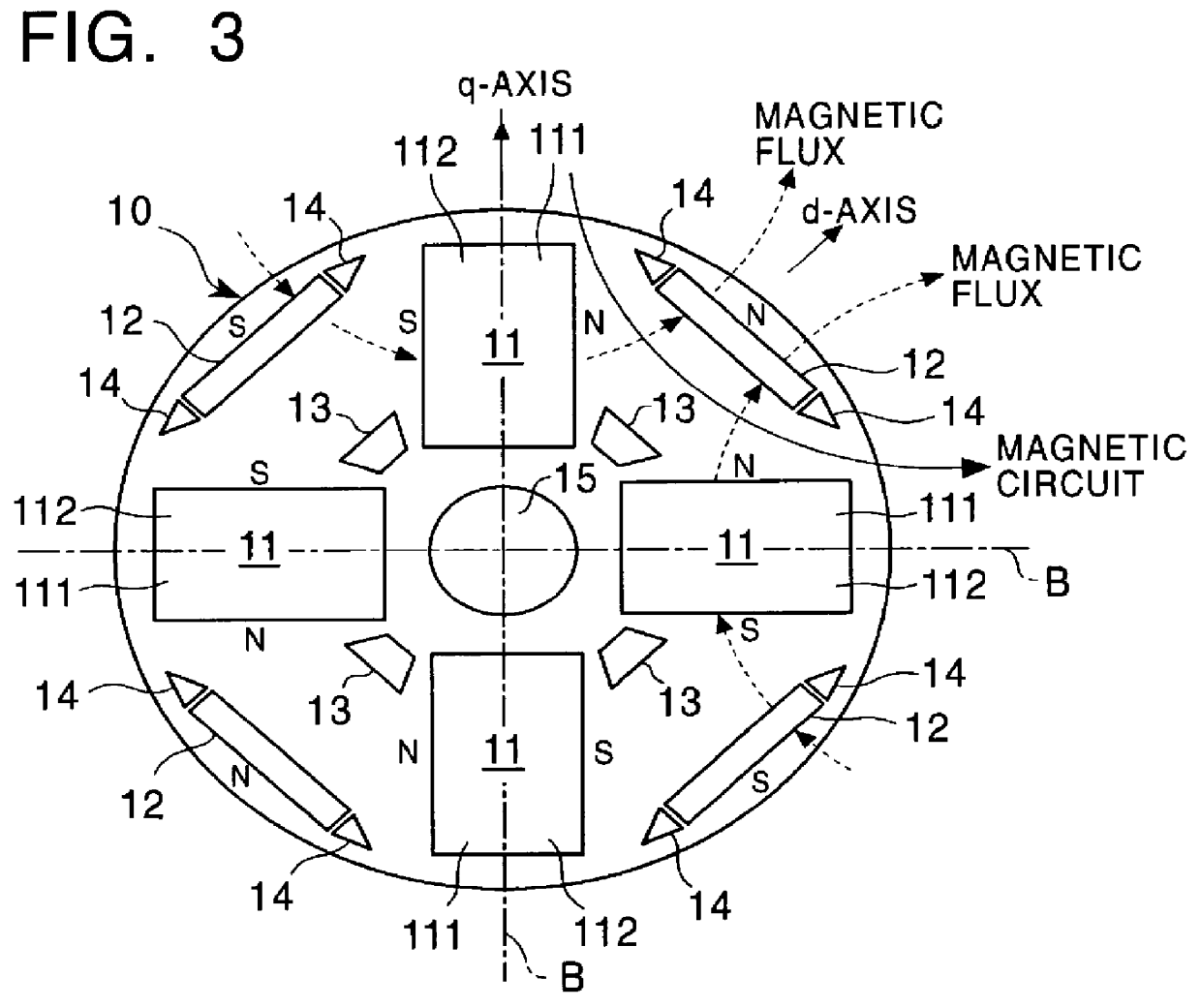
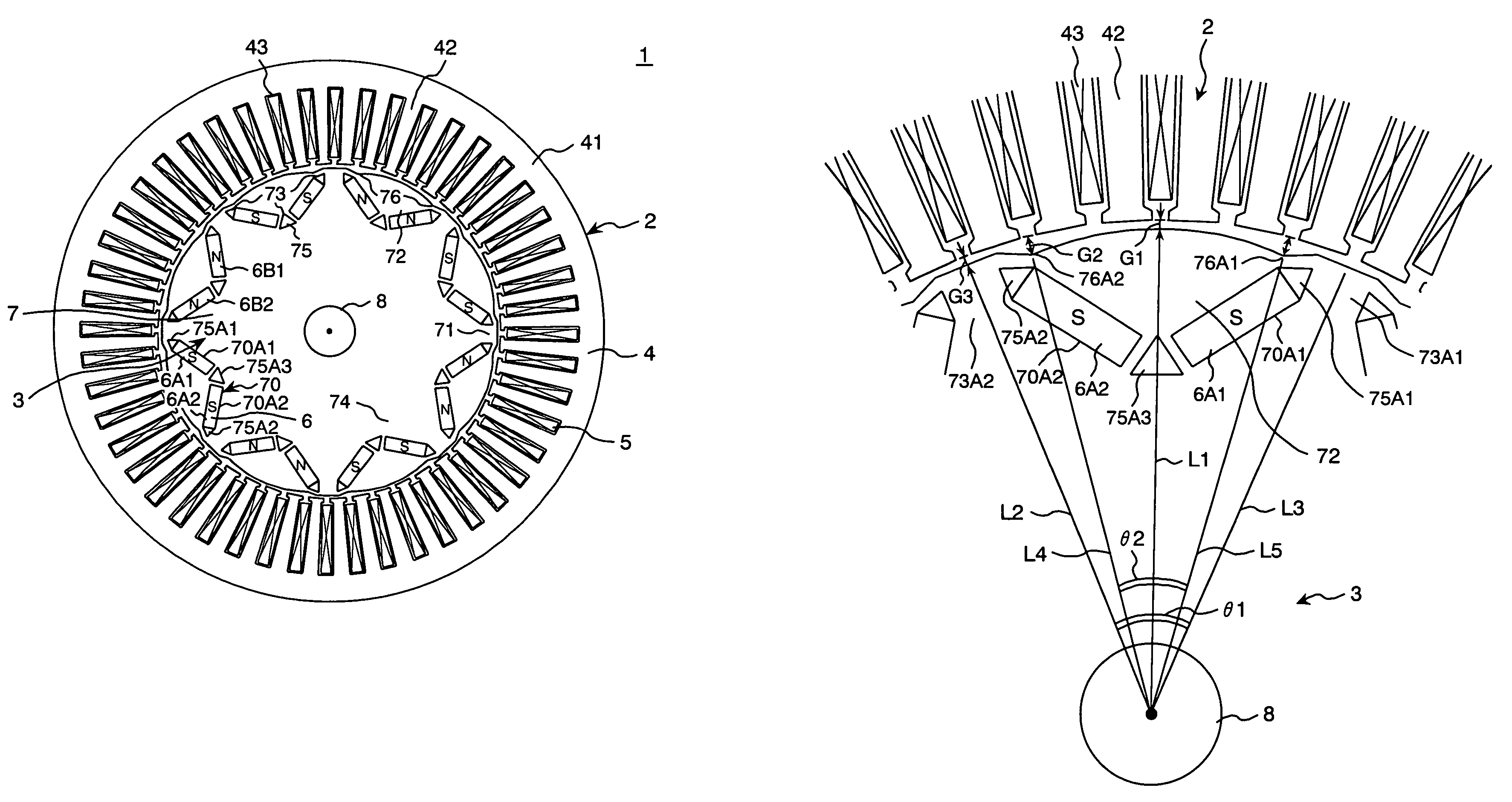
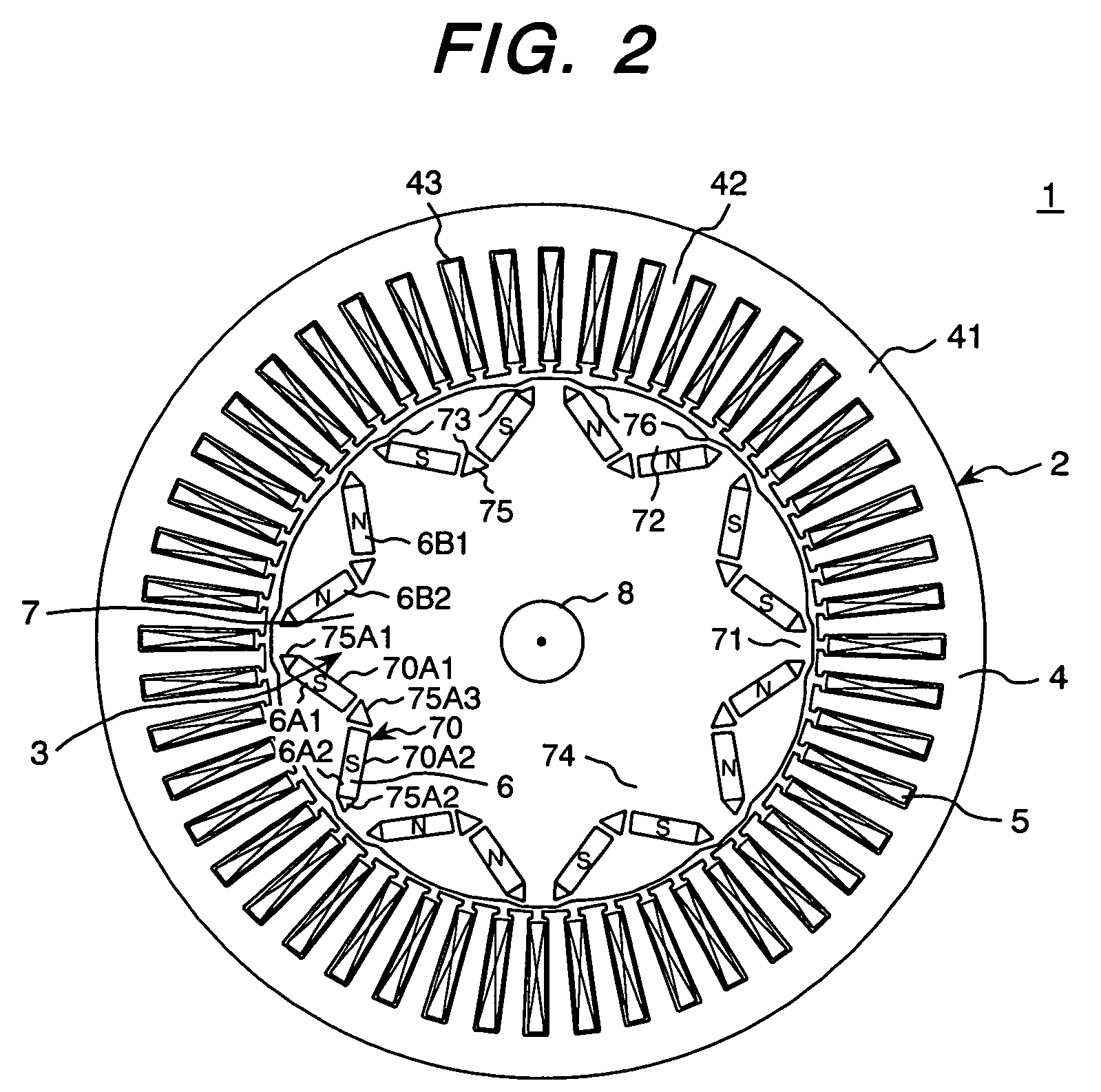
Internal permanent magnet rotor having improved configuration of magnetic flux barriers
InactiveUS20050269888A1High levelIncreased complexityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
At each permanent magnet in a rotor of an IPM rotary electric machine, each of a pair of flux barriers respectively disposed adjoining circumferentially opposed side faces of the magnet is formed with a trench portion that extends farther from a circumferential face of the rotor than a position on a corresponding side face that is located farthest, on that side face, from the rotor circumferential face. This prevents part of a flow of magnetic flux, from the stator through the rotor, from being diverted to flow into the magnet. Increased torque or output power is thereby achieved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Permanent magnet type electric rotating machine and wind turbine electric power generation system
InactiveUS20060071568A1Improve cooling efficiencyImprove cooling effectMagnetic circuit rotating partsWind motor controlPermanent magnet rotorTurbine
A permanent magnet type electric rotating machine comprises a stator having a distributed winding and a permanent magnet rotor, wherein the permanent magnet rotor is provided with a wind passage in an axial direction thereof.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Permanent magnet electrical rotating machine, wind power generating system, and a method of magnetizing a permanent magnet
ActiveUS20080129129A1Improve cooling effectStructural economyElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet rotorEngineering
A permanent magnet electrical rotating machine having a permanent magnet rotor and a stator, wherein:a plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in a rotor iron core of the permanent magnet rotor along a periphery of the rotor iron core, polarities thereof being alternately changed;a cooling airflow channel is formed between each pair of adjacent opposite poles on the rotor iron core; and the cooling airflow channel has an approximately trapezoidal shape on an outer periphery side of the rotor iron core; and extends from an end on a central side in a radial direction of the approximately trapezoidal shape to a radial center.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Centrifgal pump
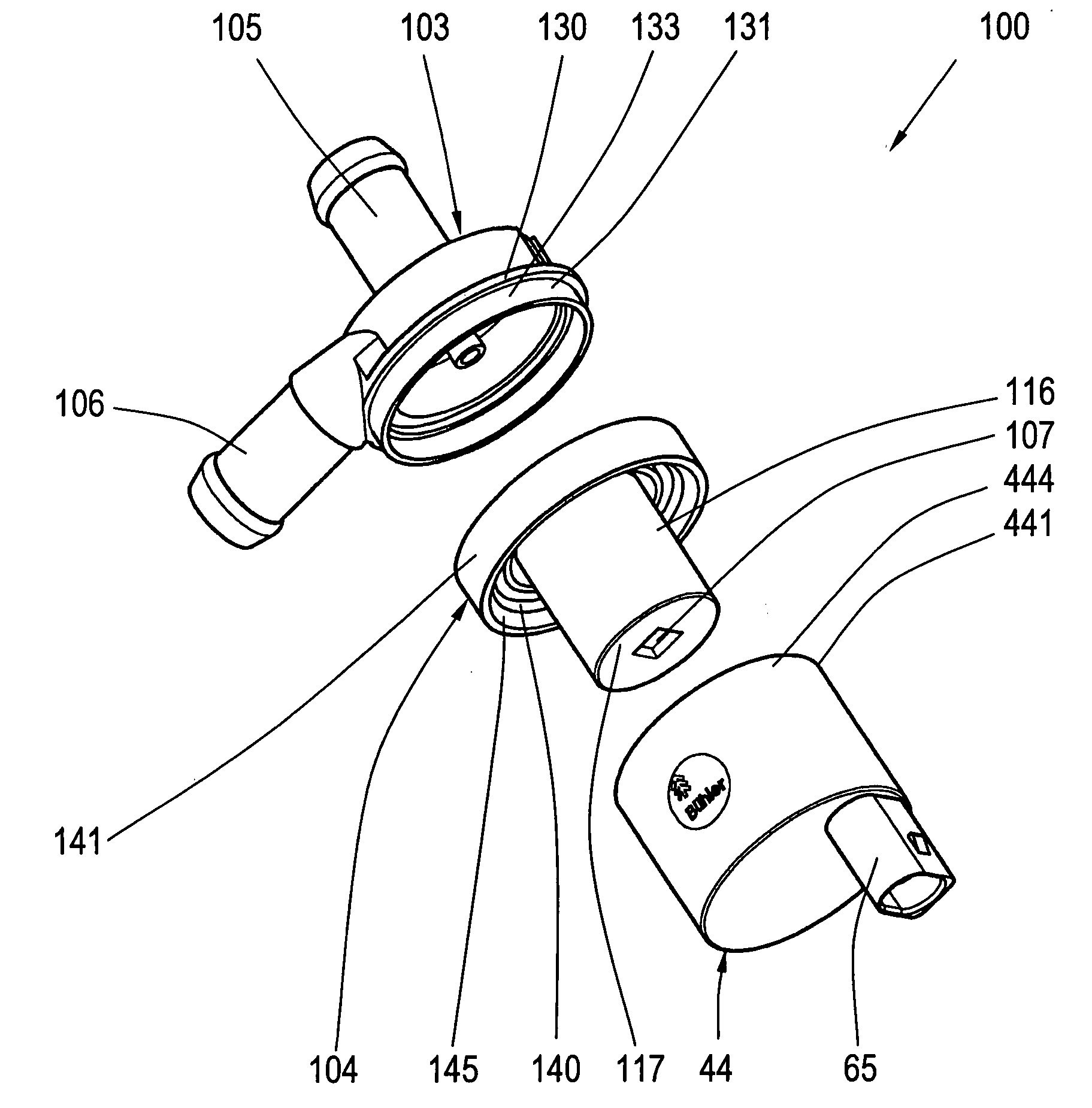
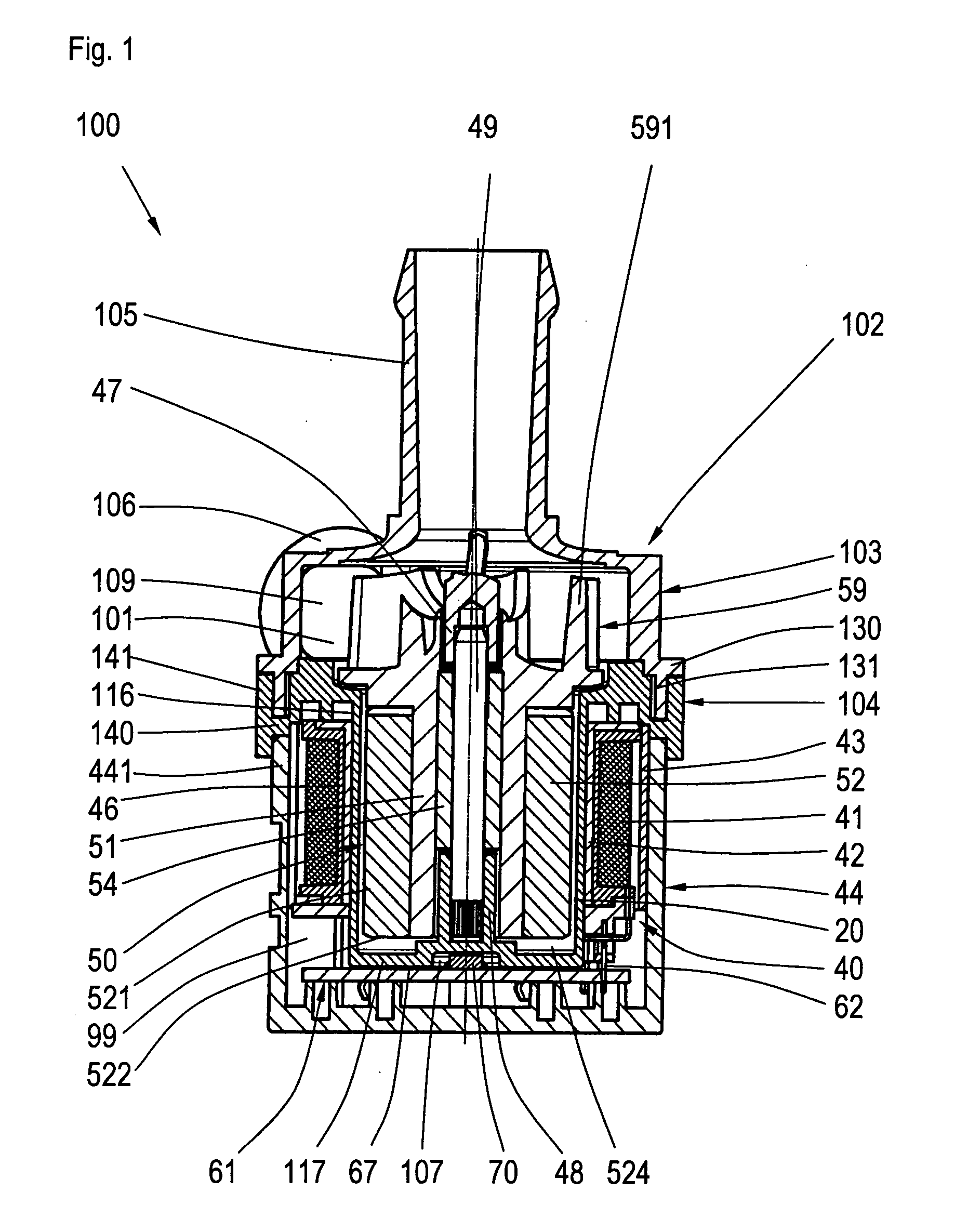
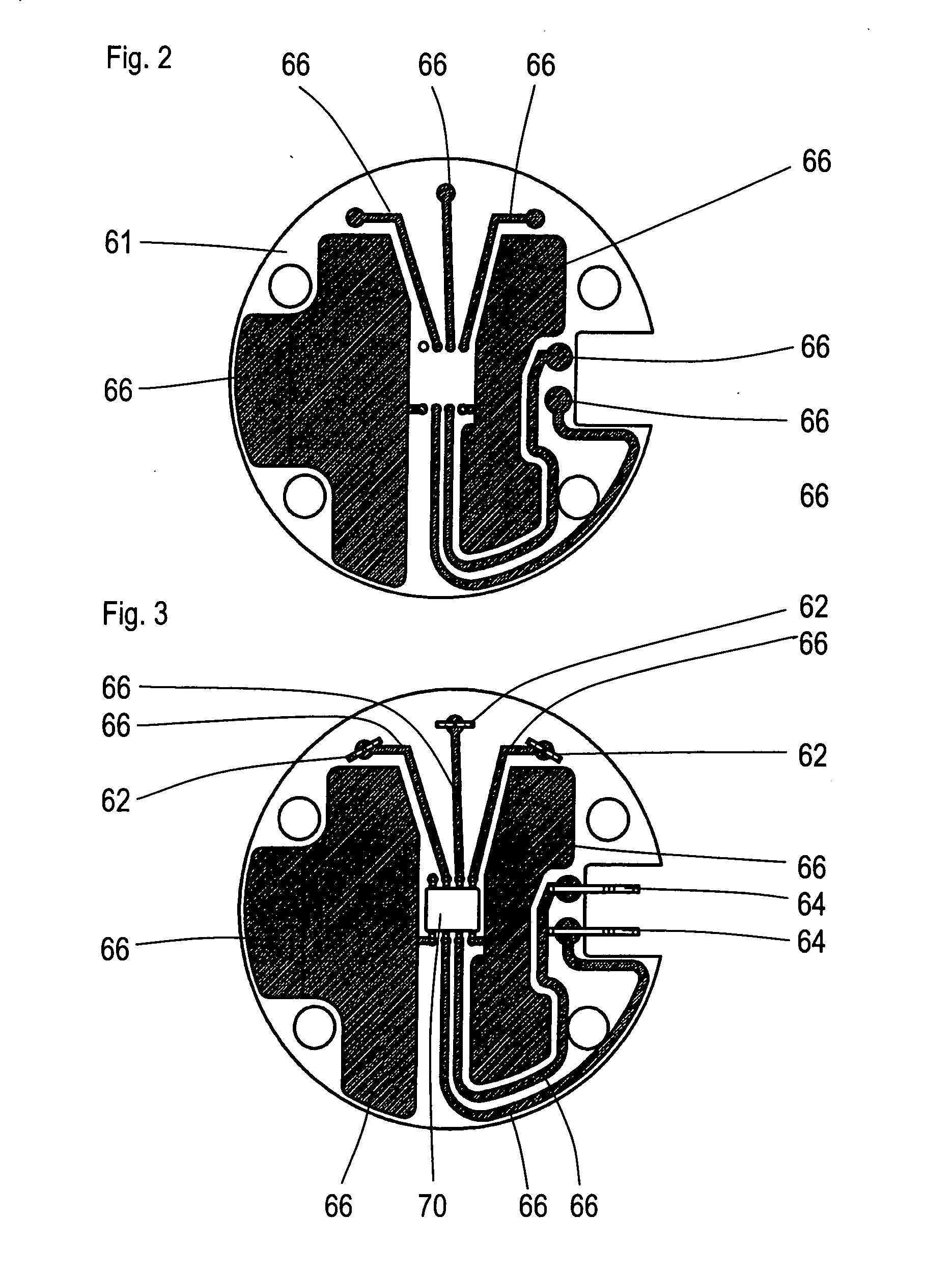
ActiveUS20070286723A1Improve cooling effectMounted easily and securelyPump componentsReaction enginesPermanent magnet rotorElectrical conductor
The invention is related to a centrifugal pump with an existing pump housing made of plastic material that can be processed through injection molding, having a first housing section, featuring a suction nozzle and a pressure nozzle, a second housing section supporting an electronically commutated DC motor and a split case, a motor housing section that closes a dry chamber separated from a wet chamber by the split case in which a stator and an electronic component are arranged, and a permanent magnet rotor that is mounted in the wet chamber in such a way that it can rotate, and drives a pump impeller that reaches into the pump chamber. The electronic components are arranged on an electronic circuit board aligned at right angles to an axle and parallel to a base of the split case. The electronic circuit board is in heat conducting contact with the base. The task of the invention is to cool electronic components sensitive to heat in a simple way and with a high degree of efficiency such that a simple installation of the electronic components is guaranteed and only a small number of parts is required, the construction space being as small as possible. According to the invention, this problem is solved by the fact that one or several conductors of the electronic circuit board are in heat conducting contact with the base.
Owner:BUHLER MOTOR GMBH
Permanent-magnet rotor for an inner rotor type electric rotary machine and magnet-saving type rotor for a synchronous motor
InactiveUS7105971B2Easily magnetizedSmall sizeMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
A total of three permanent magnets, installed in a rotor core closely to an outer cylindrical surface of the rotor core, are disposed at predetermined angular pitches in the circumferential direction of the rotor core. All of the permanent magnets are magnetized in such a manner that the direction of magnetization is the same when seen in the radial direction. A plurality of magnet-less holes, extending in the axial direction in the vicinity of the outer cylindrical surface of the rotor core, are provided between two adjacent permanent magnets.
Owner:DENSO CORP
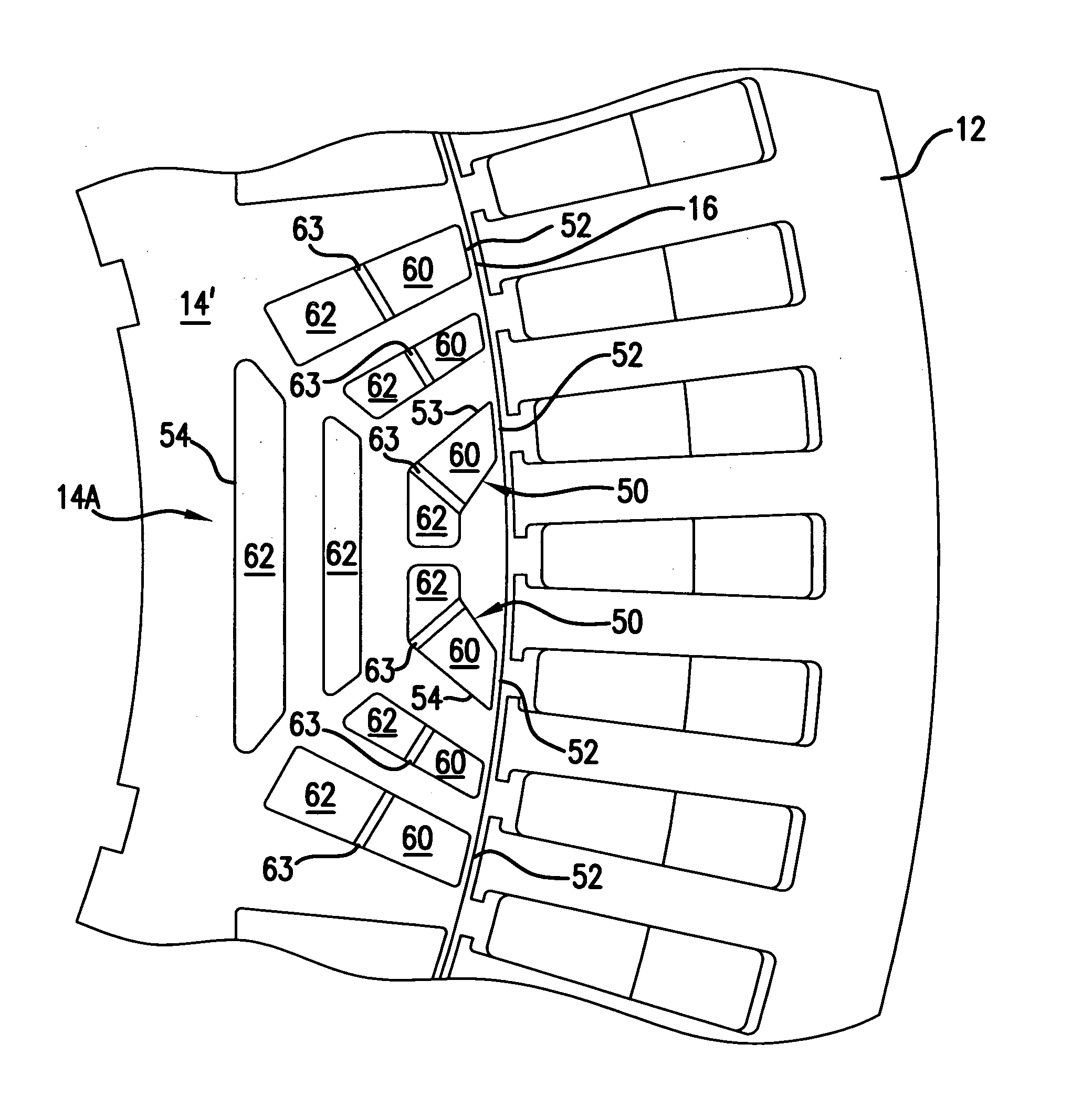
Permanent magnet rotor and brushless motor
InactiveUS6940199B2Large reluctance torqueImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
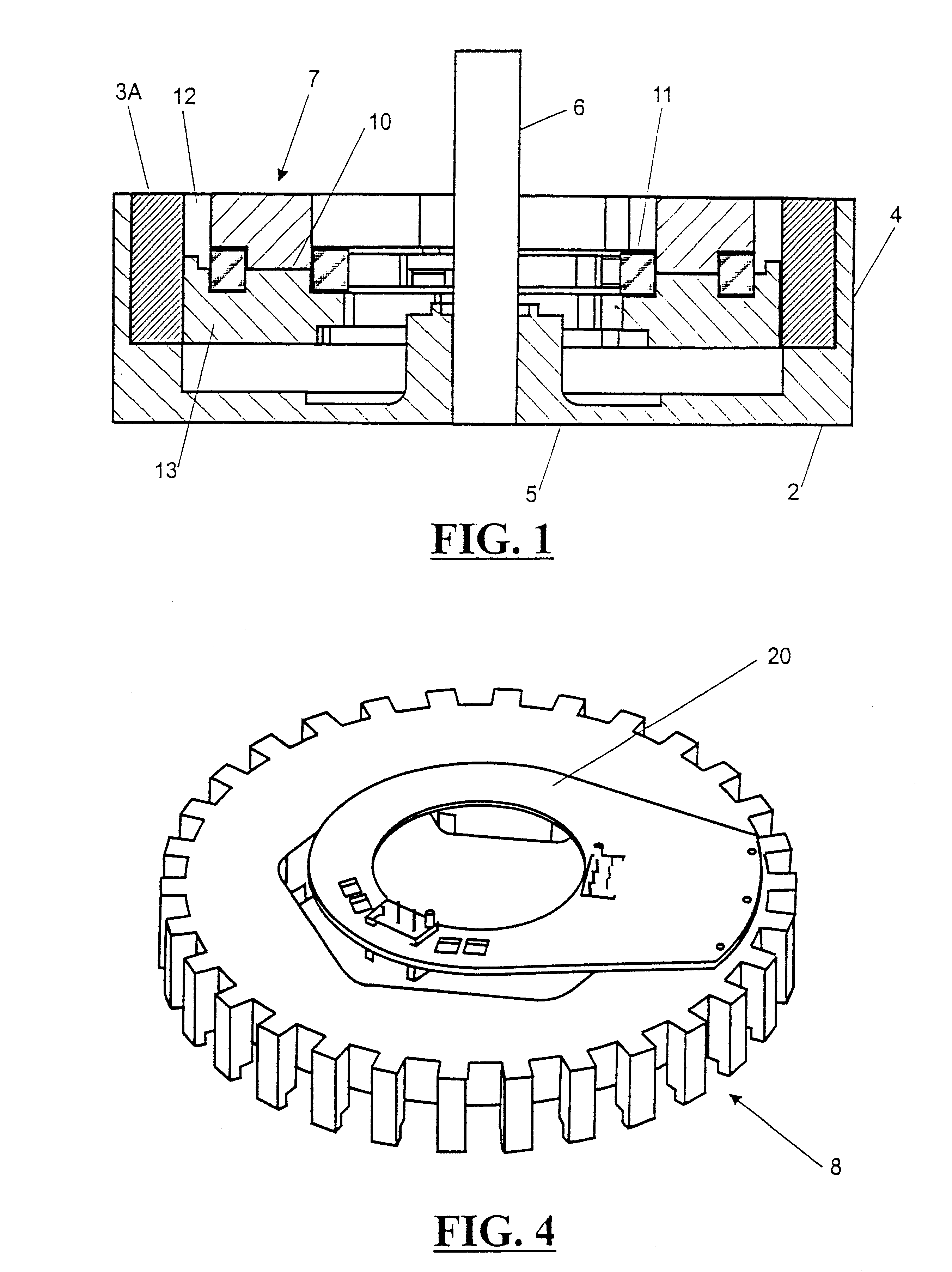
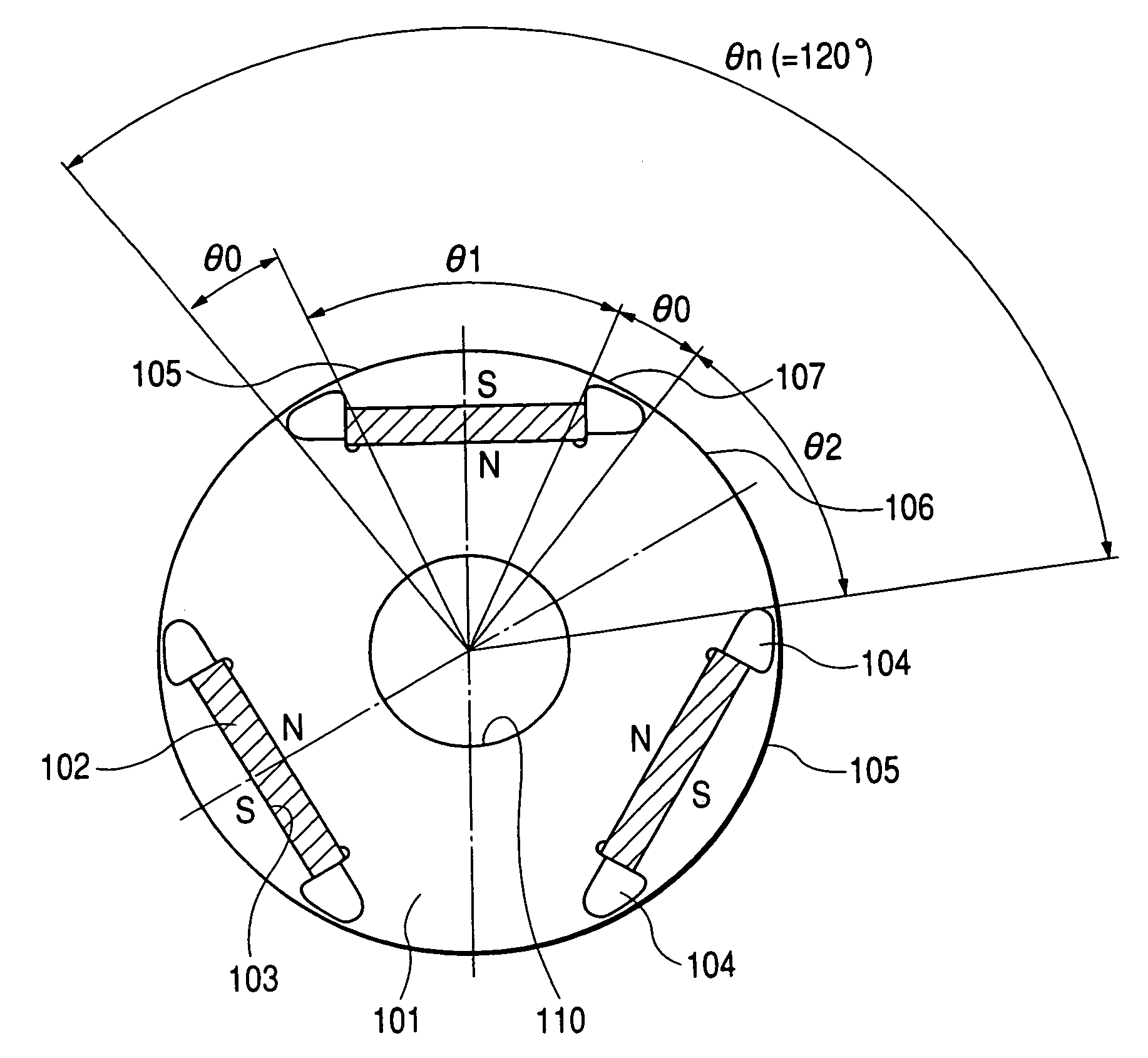
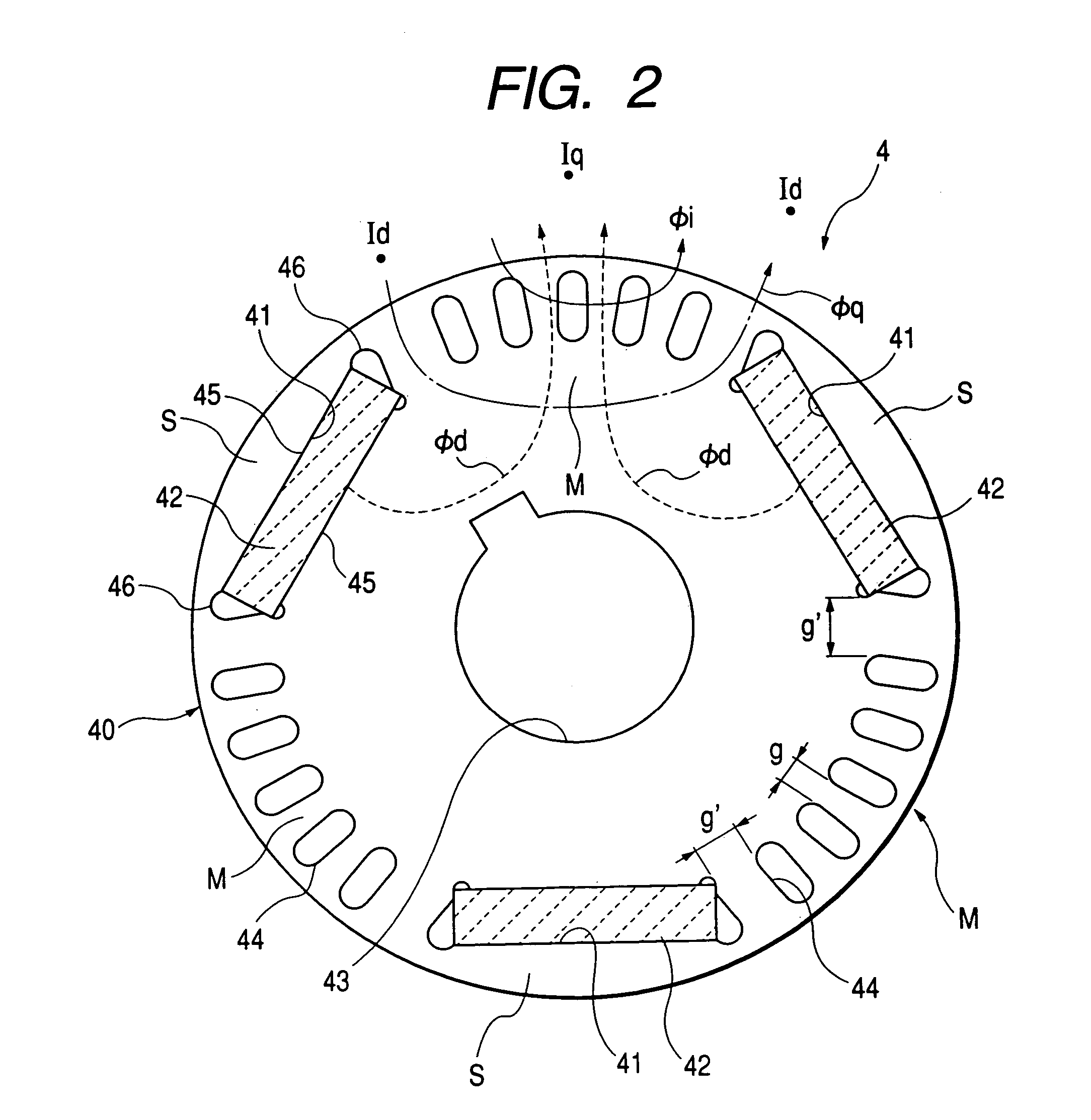
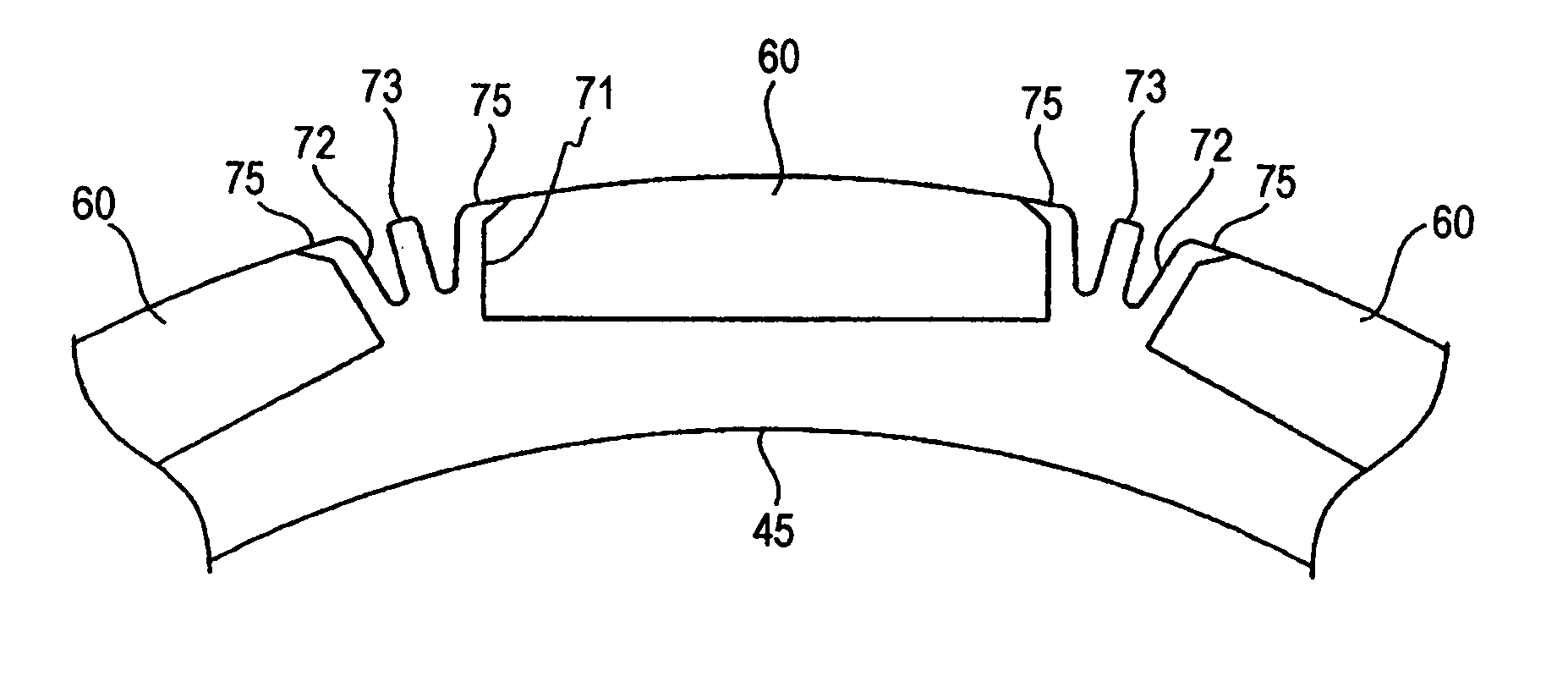
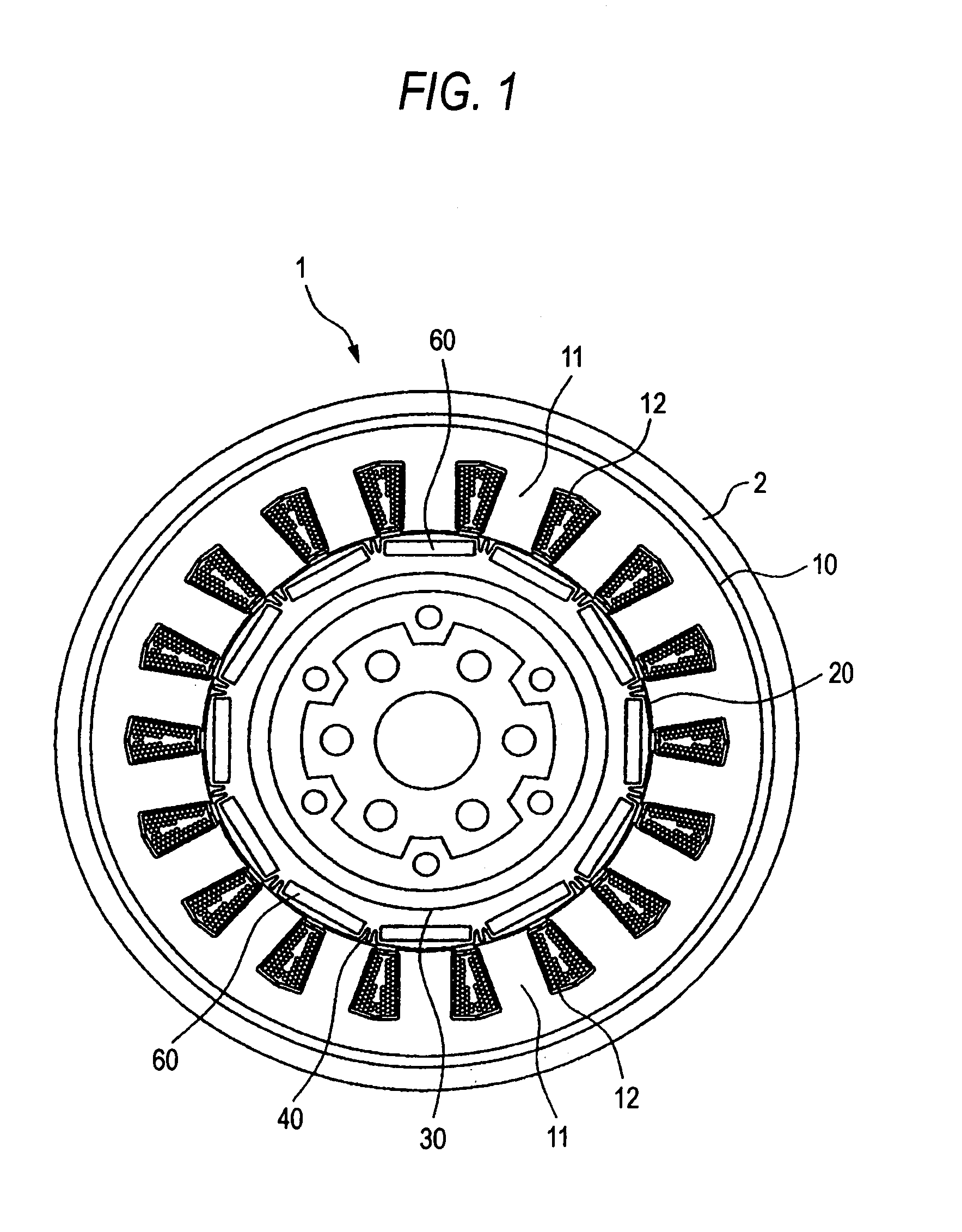
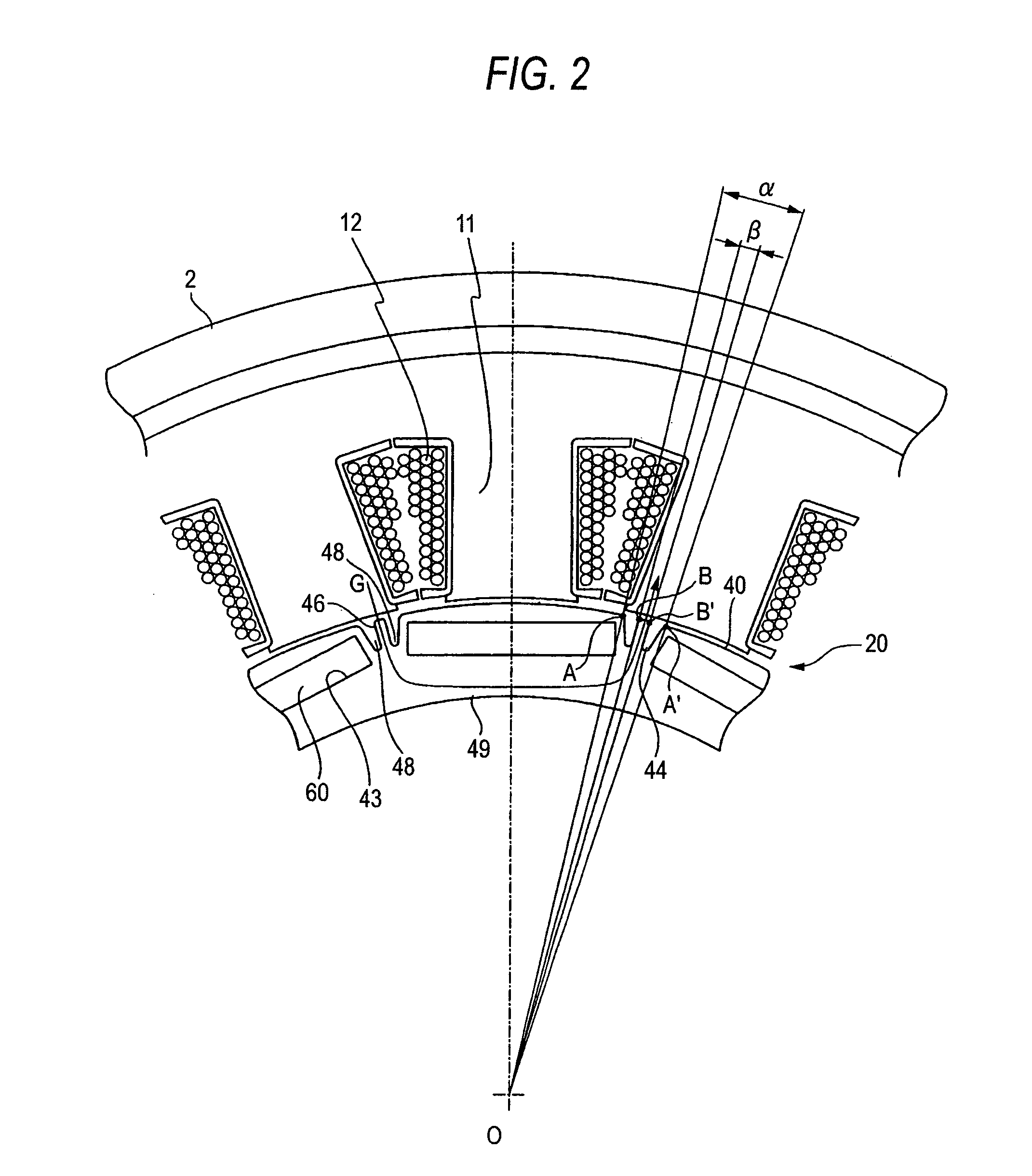
In a rotor 20 including a plurality of permanent magnet pieces 60 fixed in a plurality of magnet insertion slots 43 provided on the outer periphery of a rotor yoke 40, respectively, and the rotor yoke 40 having concaves 44 each provided between the permanent magnet pieces 60 adjacent to each other and protrusions 46 each provided in each the concaves 44 to protrude outwardly in the radial direction of the rotor yoke 40, between the sandwiching angle α formed by two sides connecting both outer ends A and A′ of each the concaves 44 to the center axis O of the rotor yoke 40 and the sandwiching angle β formed by two sides connecting both outer ends B and B′ of each the protrusions 46 to the center axis O of the rotor yoke 40, the following relationship is satisfied:0.3<β / α<0.5.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Permanent magnet brushless motor comprising rotor with dustproof structure
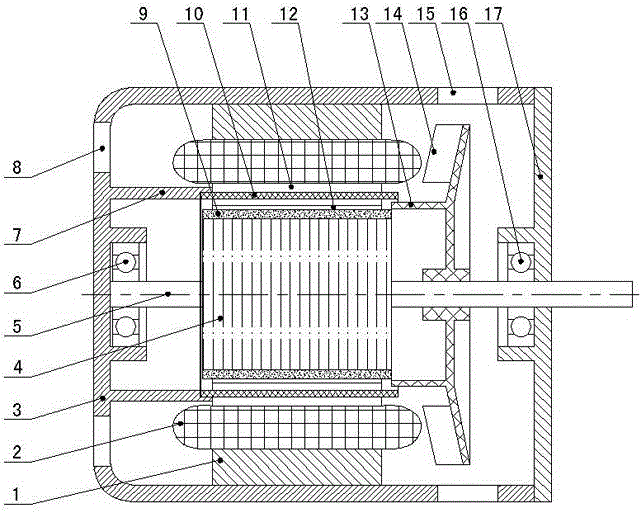
ActiveCN104539078AGuaranteed uptimeLong-term normal operationWindingsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet rotorBrushless motors
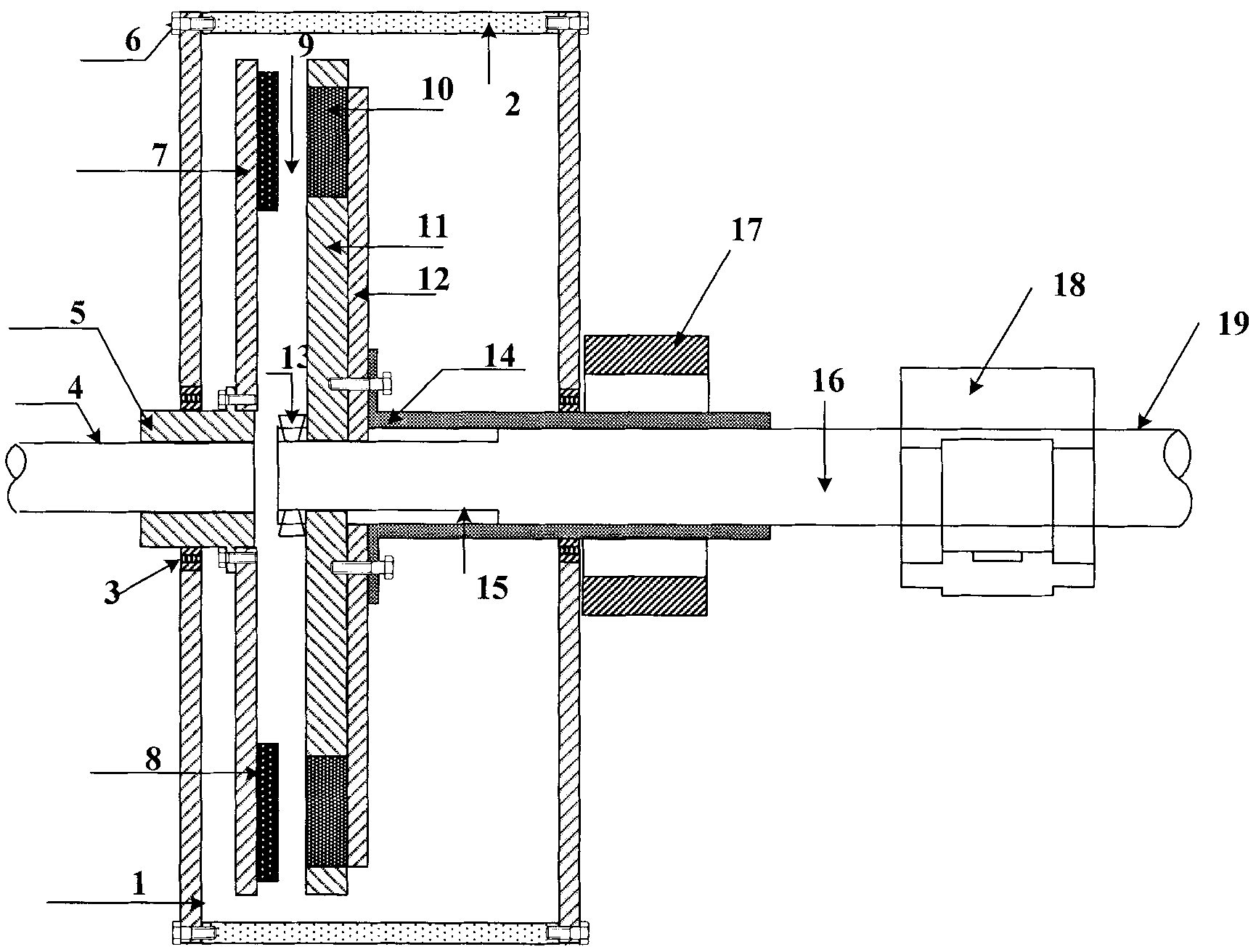
The invention discloses a permanent magnet brushless motor comprising a rotor with a dustproof structure, comprising a housing (3), a stator, a permanent magnet rotor (4), a rotor shaft (5), a cooling fan (14), and an end cap (17). The housing (3) is provided with an air inlet (8) and an air inlet (15). The stator includes a stator core (1) and an electromagnetic winding (2). The air inlet (8) side of the housing (3) is provided with a dust cover (7), and the dust cover (7) faces the end face of the stator core (1). The stator core (1) is provided with an isolating slot wedge (10) matched with openings of electromagnetic winding slots (11), and the isolating slot wedge (10) is made of insulating material. The isolating slot wedge (10) and the dust cover (7) are mutually sheathed, and the isolating slot wedge (10) and the teeth of all the electromagnetic winding slots (11) constitute a closed stator inner circle. By adopting the structure, the permanent magnet brushless motor of the invention has the advantages of simple and reasonable structure, convenient installation, good sealing performance of the rotor, capability of avoiding iron powder and iron filings adsorption on the surface of the permanent magnet rotor (4), long service life, and the like.
Owner:胡超
Radial magnetic field modulating brushless double-rotor motor
ActiveCN101951090AReduce volumeLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
The invention provides a radial magnetic field modulating brushless double-rotor motor, belonging to the field of motors. The invention aims to solve the following problem: rotating windings in the existing double-rotor motors need electric brushes and slip rings to introduce current, so that the operation efficiency and the reliability are reduced and the parts such as the electric brushes need to be frequently maintained. The motor is characterized in that stators of the motor are fixed on the inner side walls of a shell; a permanent magnet rotor is fixed on a permanent magnet rotor output shaft; a modulation ring rotor is arranged between the stators and the permanent magnet rotor; the permanent magnet rotor output shaft is connected with the shell and the modulation ring rotor in a rotary manner; one end of the permanent magnet rotor output shaft is fixed on the modulation ring rotor and is connected with the shell in a rotary manner; the stators are electrified to form 2p-numbered pole magnetic fields; 2n-numbered permanent magnet units of the permanent magnet rotor are uniformly distributed and arranged on the excircle surface of a permanent magnet rotor core along the circumferential direction; the permanent magnet rotor rotates to form 2n-numbered pole magnetic fields; q-numbered magnetic blocks and q-numbered insulating blocks interlace on the excircle surface of a support of the modulation ring rotor along the circumference direction; and p is equal to hn plus kq.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Controllable flux permanent magnetic synchronous motor of multiple pole number built-in mixed rotor magnetic path structure
InactiveCN1617422AChange the magnetizationMemoryMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
This invention provides a multiple integral hybrid rotor magnetic circuit structure controlled flux magnet synchronous motor including motor spindle, a stator winding, a stator iron core, AlNiCo magnet, A Nd FeB magent, a rotor iron core, a position sensor, a sensor cable, a motor cable and a converter. The permanent rotor is in an integral hybrid rotor magnetic circuit structure, the magnet in the rotor iron cover is set in U shape, the NdFeB is placed tangentially and the AlNiCo magnet is in radial position characterizing in being called a memory motor since it can apply an amplitude controlled d-axis current vector to change the magnetization intensity of the rotor magnet and remember the changed flux intensity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
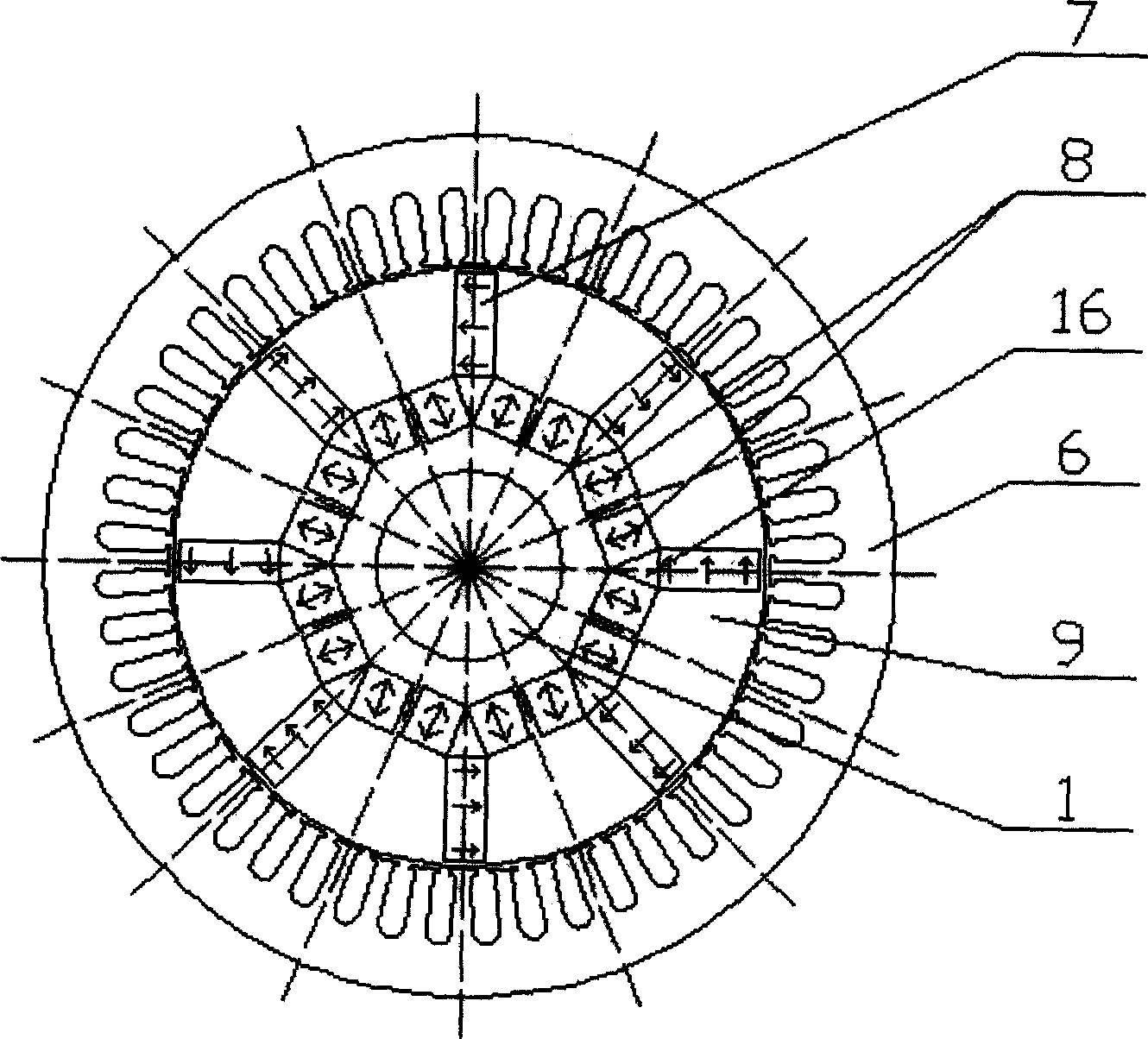
Permanent magnet rotor
InactiveUS20060103254A1Efficient use ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
A rotor for an electric machine has a rotor core with a plurality poles and a method of magnetizing the poles of a rotor. At least one of the poles includes a plurality of cavities spaced radially from one another with each of the cavities having a magnet portion. Each of a plurality of block magnets has substantially the same width and is positioned within one of the magnet portions of the cavities.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
Spoke permanent magnet rotors for electrical machines and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS7148598B2Improve performanceLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
A rotor assembly for an electric motor includes a spoke permanent magnet rotor and a shaft connected thereto. The spoke permanent magnet rotor has an axis of rotation, permanent magnet material, and ferro-magnetic material. The permanent magnet material extends outwardly relative to the axis of rotation to form a plurality of outwardly extending spoke portions of permanent magnet material. The ferro-magnetic material is positioned adjacent to the outwardly extending spoke portions of permanent magnet material. The shaft supports the spoke permanent magnet rotor for rotation about the axis of rotation. The permanent magnet material may circumferentially surround the axis of rotation to form a center portion of permanent magnet material. Further, the axis of rotation may pass through the permanent magnet material. The spoke permanent magnet rotor may be formed using a compaction process and / or an injection molding process.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
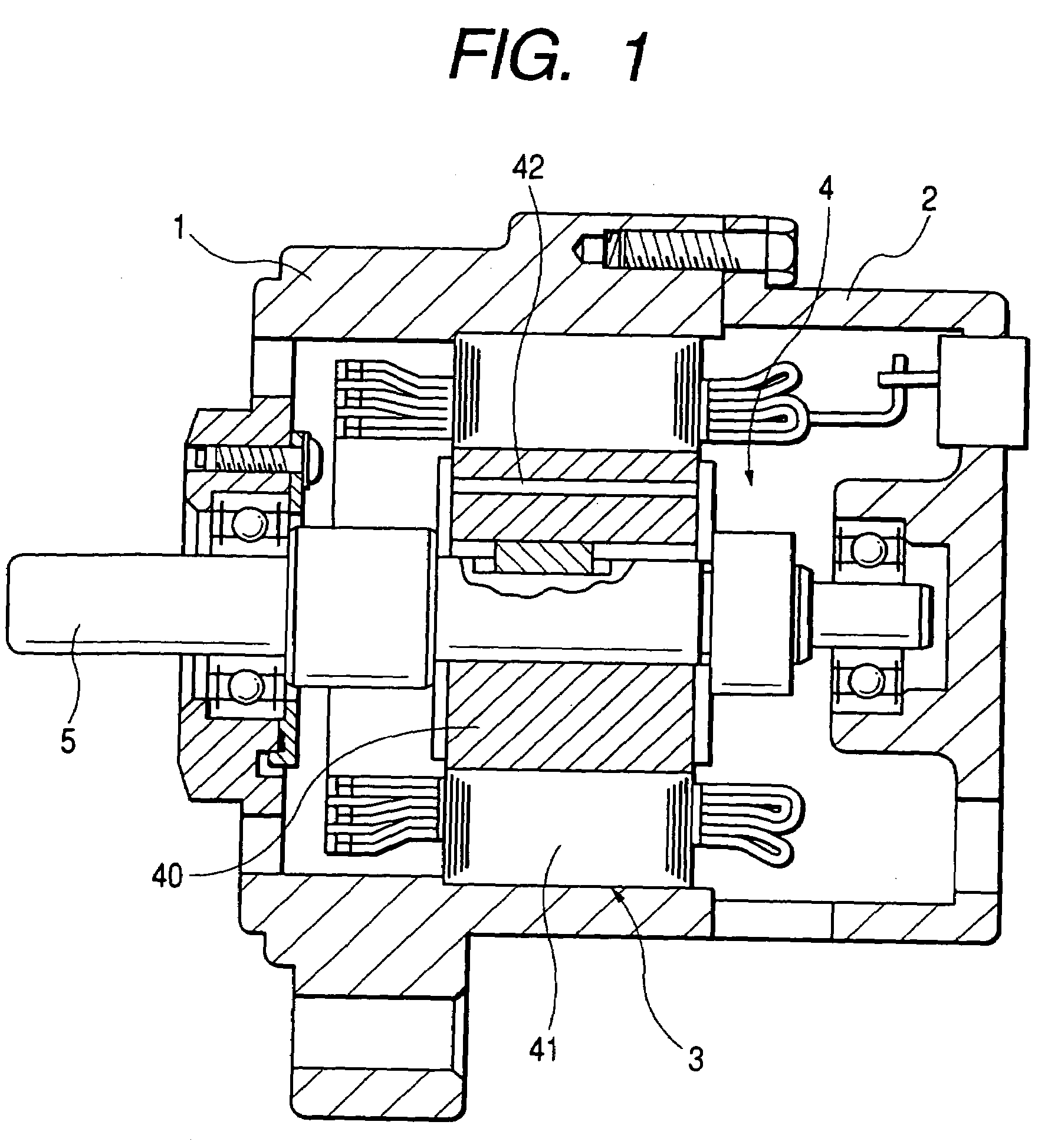
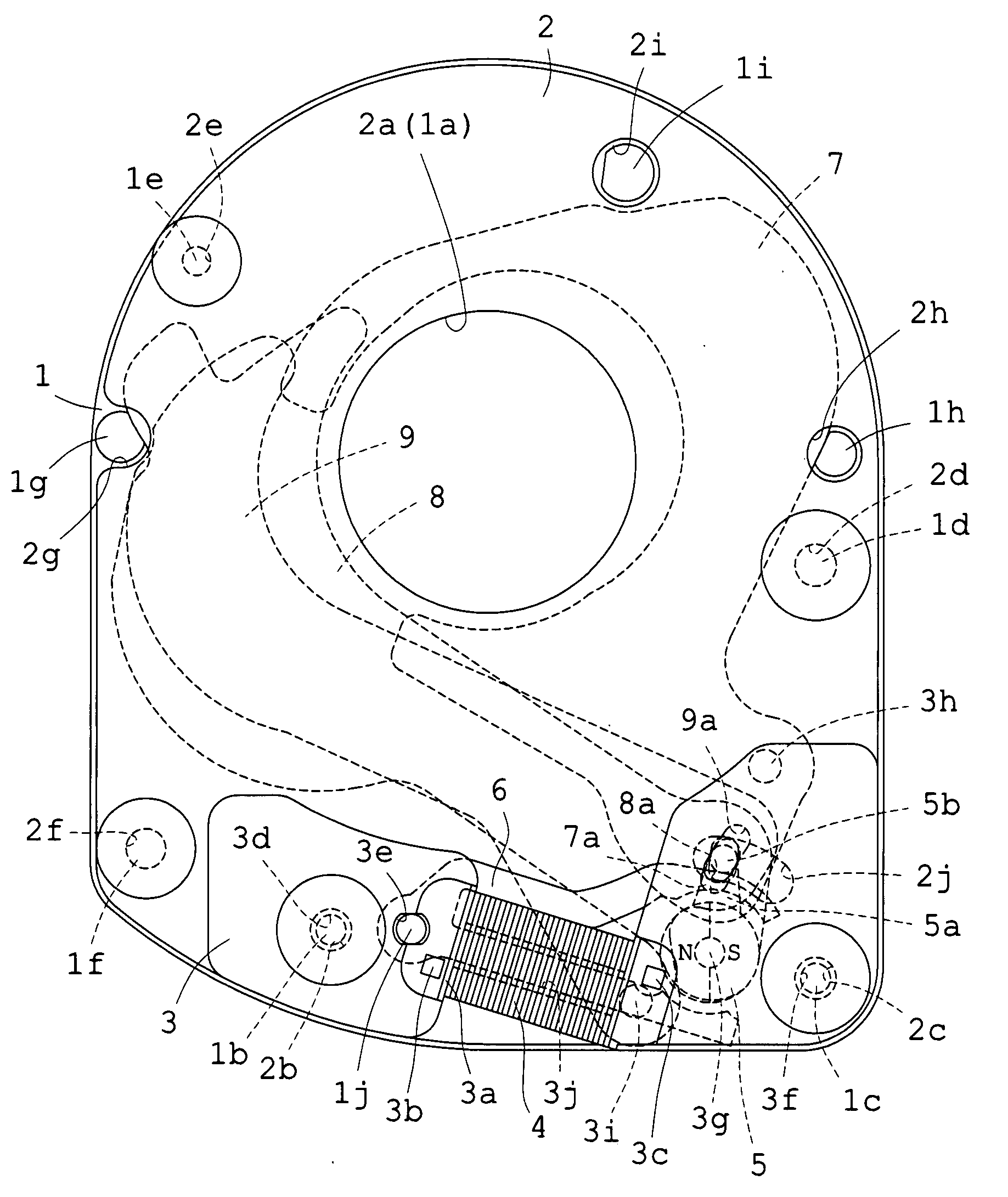
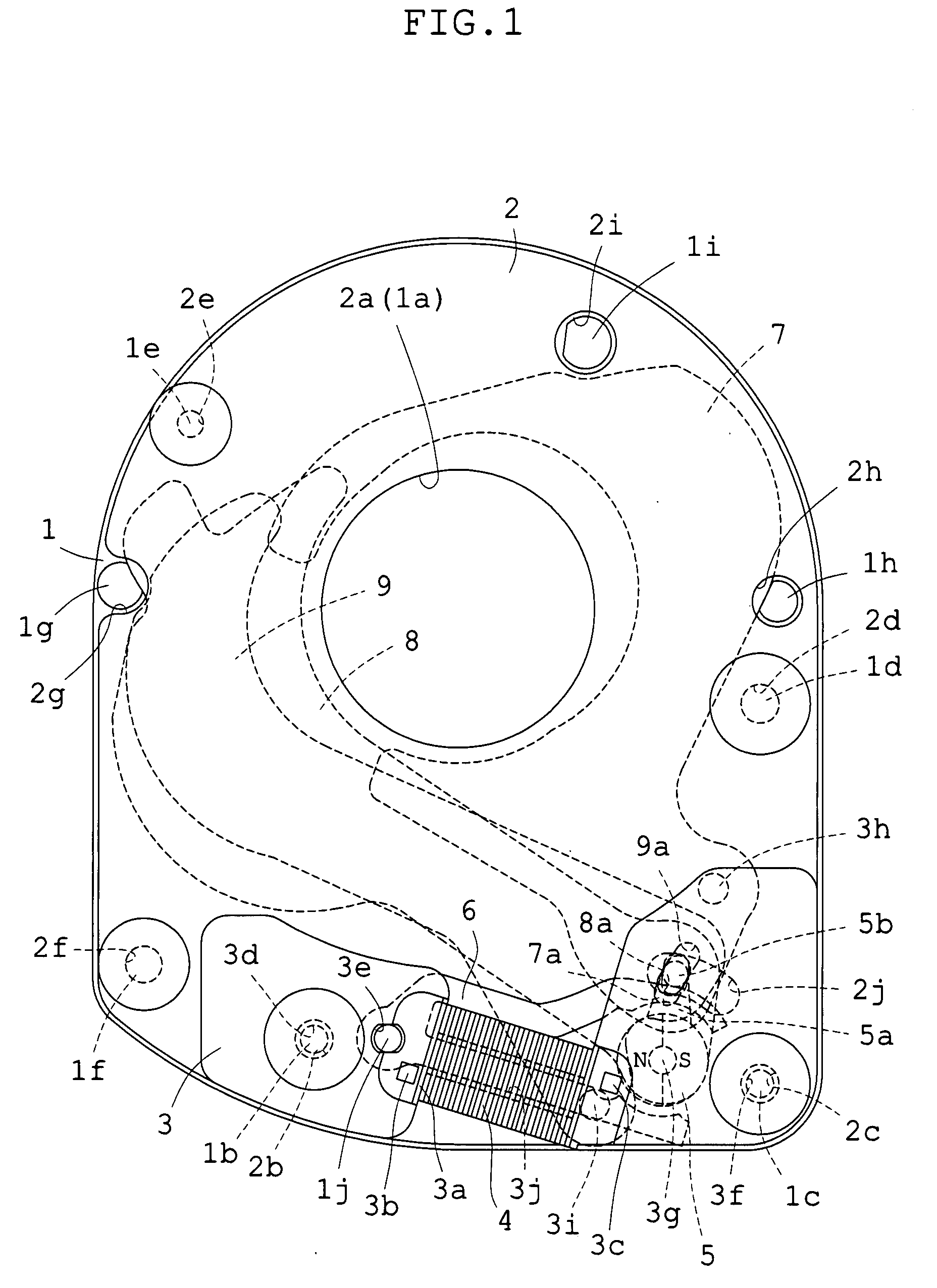
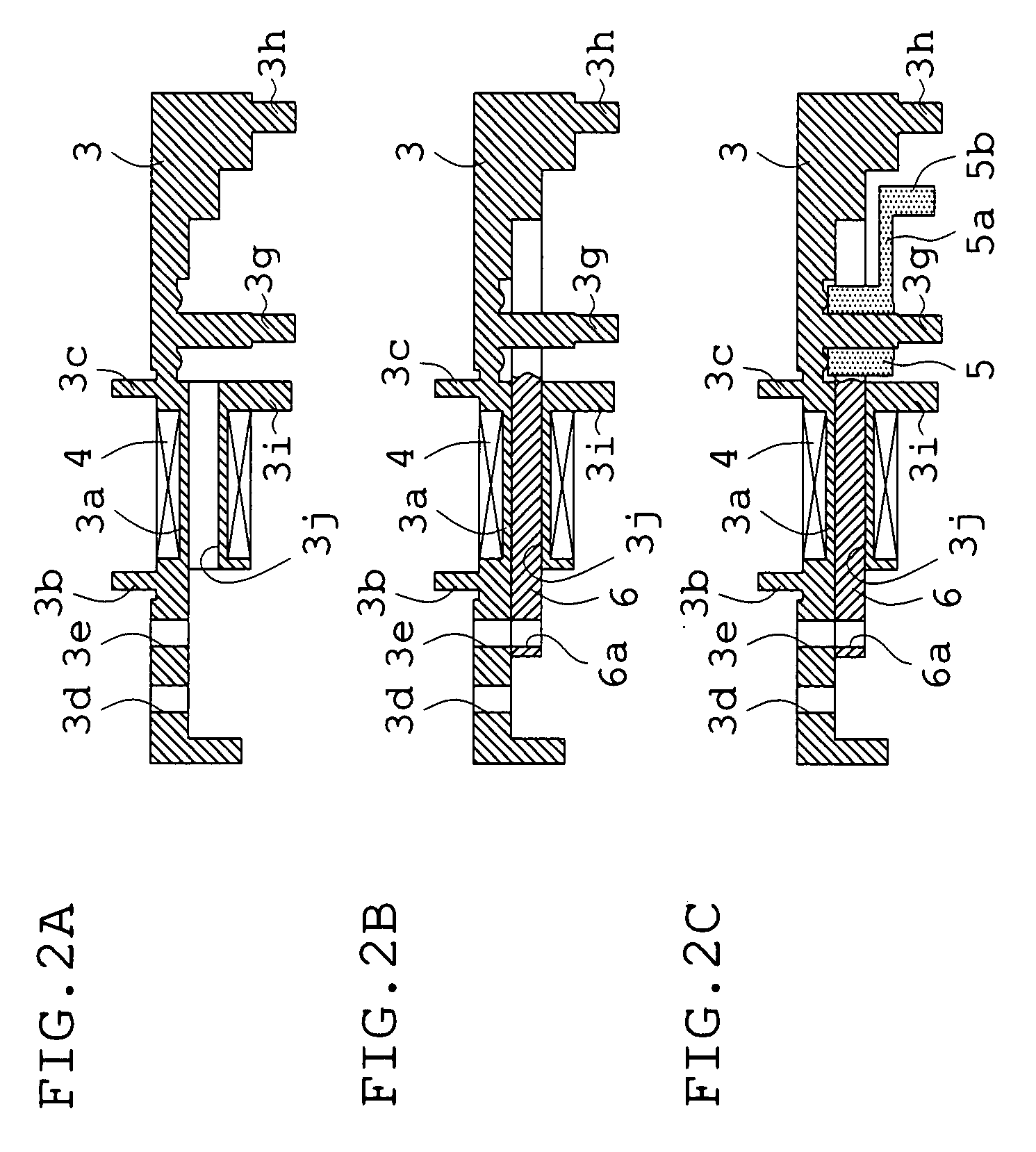
Blade driving apparatus for cameras
A blade driving apparatus for cameras includes a base plate having an aperture section for a photographing optical path; a partition plate having an aperture section for the photographing optical path so that a blade chamber is interposed between the base plate and the partition plate; a cover frame having an actuator chamber between the partition plate and the cover frame; a permanent magnet rotor rotatably mounted on the cover frame so that an output pin is introduced into the blade chamber; a yoke in which tops of two legs constructed as magnetic pole sections are opposite to the peripheral surface of the rotor in the actuator chamber and one of the two legs is fitted into a bobbin around which a coil is wound; and at least one blade rotatably mounted to a shank for at least one blade which is set upright on the cover frame and is introduced into the blade chamber, and introduced into, and removed from, the exposure aperture by the output pin.
Owner:COPAL CO LTD
Speed-adjusting-type permanent-magnet drive system
ActiveCN101867279ATo achieve the purpose of speed regulationAvoid harmonicsDynamo-electric gearsPermanent magnet rotorMagnetic tension force
The invention relates to a speed-adjusting-type permanent-magnet drive system, comprising a conductor rotor (a first rotor), a magnetic rotor (a second rotor) component and a lead screw regulator, wherein the conductor rotor (the first rotor) is arranged on an input shaft; the magnetic rotor (the second rotor) is arranged on an output shaft; the conductor rotor comprises a disk-shaped steel frame and a copper conducting ring; the surface of a steel plate is provided with the copper conducting ring; the opposite surfaces of a permanent-magnet rotor and the conductor rotor are embedded with permanent magnets; the gap of the opposite surfaces of the conductor rotor and the permanent-magnet rotor can adjust an axial air clearance; and the conductor rotor and the permanent-magnet rotor are coupled by the magnetic force. When the conductor rotor rotates, the permanent-magnet rotor also rotates along the same direction with the conductor rotor due to the coupling action of the magnetic force; the conductor rotor (the first rotor) is fixedly connected with the input shaft; the permanent-magnet rotor (the second rotor) is connected with the output shaft by a shaft section; the regulator is arranged on the shaft section; and the air clearance between the disk surfaces of the two rotors can be adjusted by the regulator, thus changing the torque and the rotating speed and achieving the purpose of speed adjustment.
Owner:ANSHAN QINYUAN ENERGY SAVING EQUIP MFG
Radially embedded permanent magnet rotor and methods thereof
InactiveUS20140103772A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesPermanent magnet rotorPole piece
In one embodiment, a permanent magnet rotor is provided. The rotor includes at least one permanent magnet and a substantially cylindrical rotor core including a plurality of stacked laminations, a hub having an inner edge defining a central opening, and a shaft inserted through the central opening, the shaft magnetically isolated from the hub. The rotor includes at least one connected pole piece coupled to the hub and at least one independent pole piece separated from the hub. The at least one permanent magnet is disposed between the at least one connected pole piece and the at least one independent pole piece.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com