Patents
Literature
16649results about "Reaction engines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
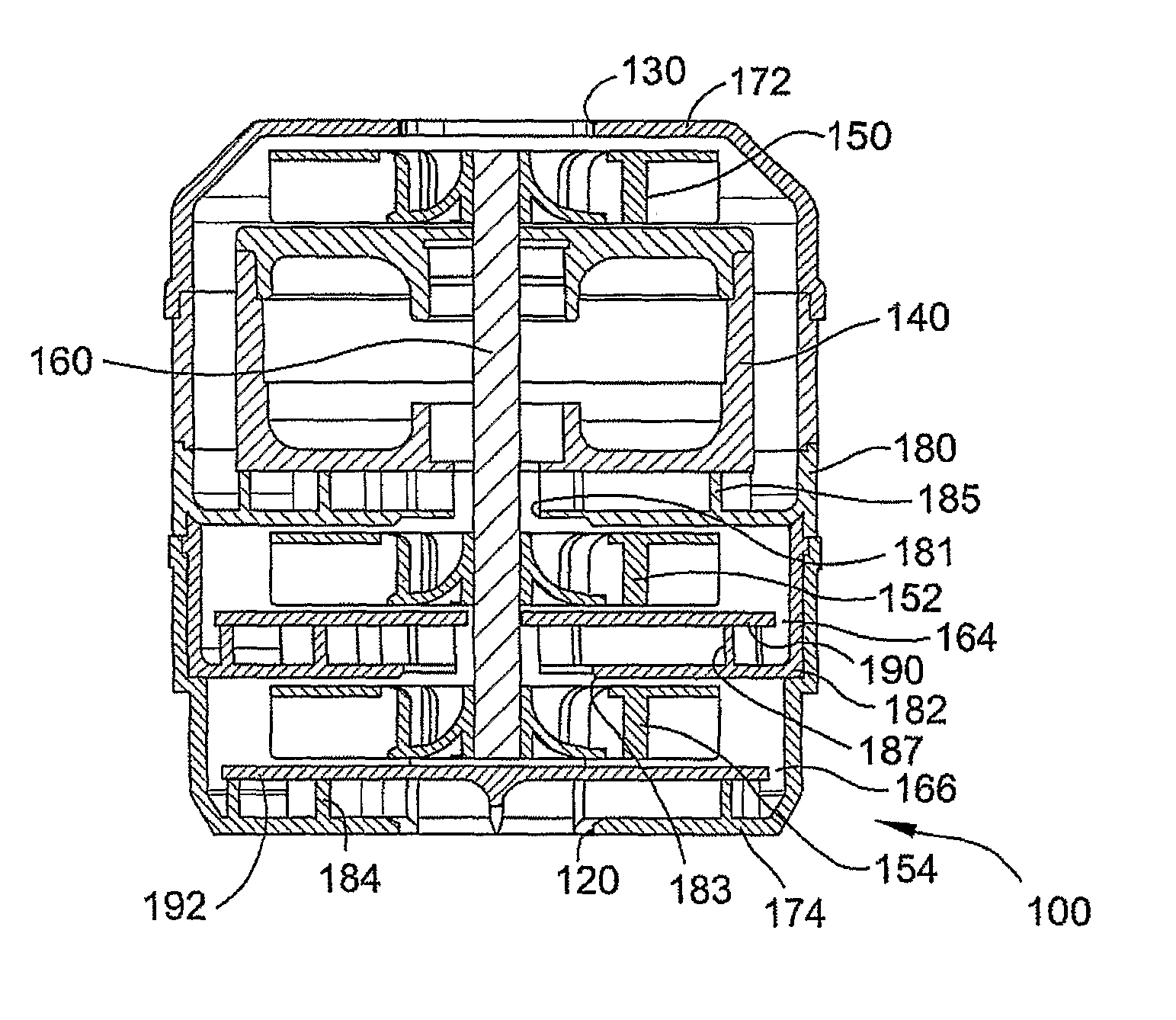
Compact low noise efficient blower for CPAP devices
Owner:RESMED MOTOR TECH
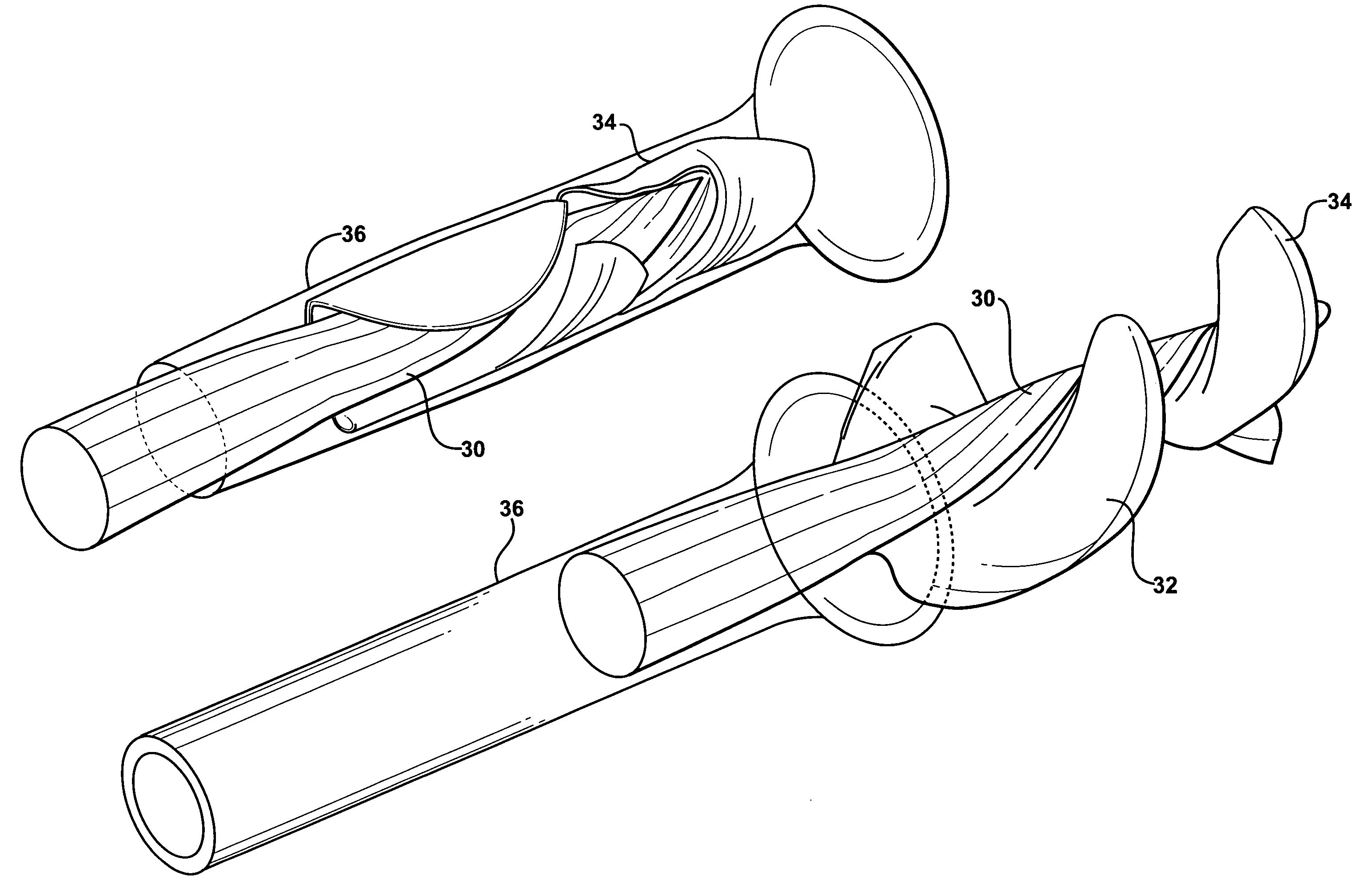
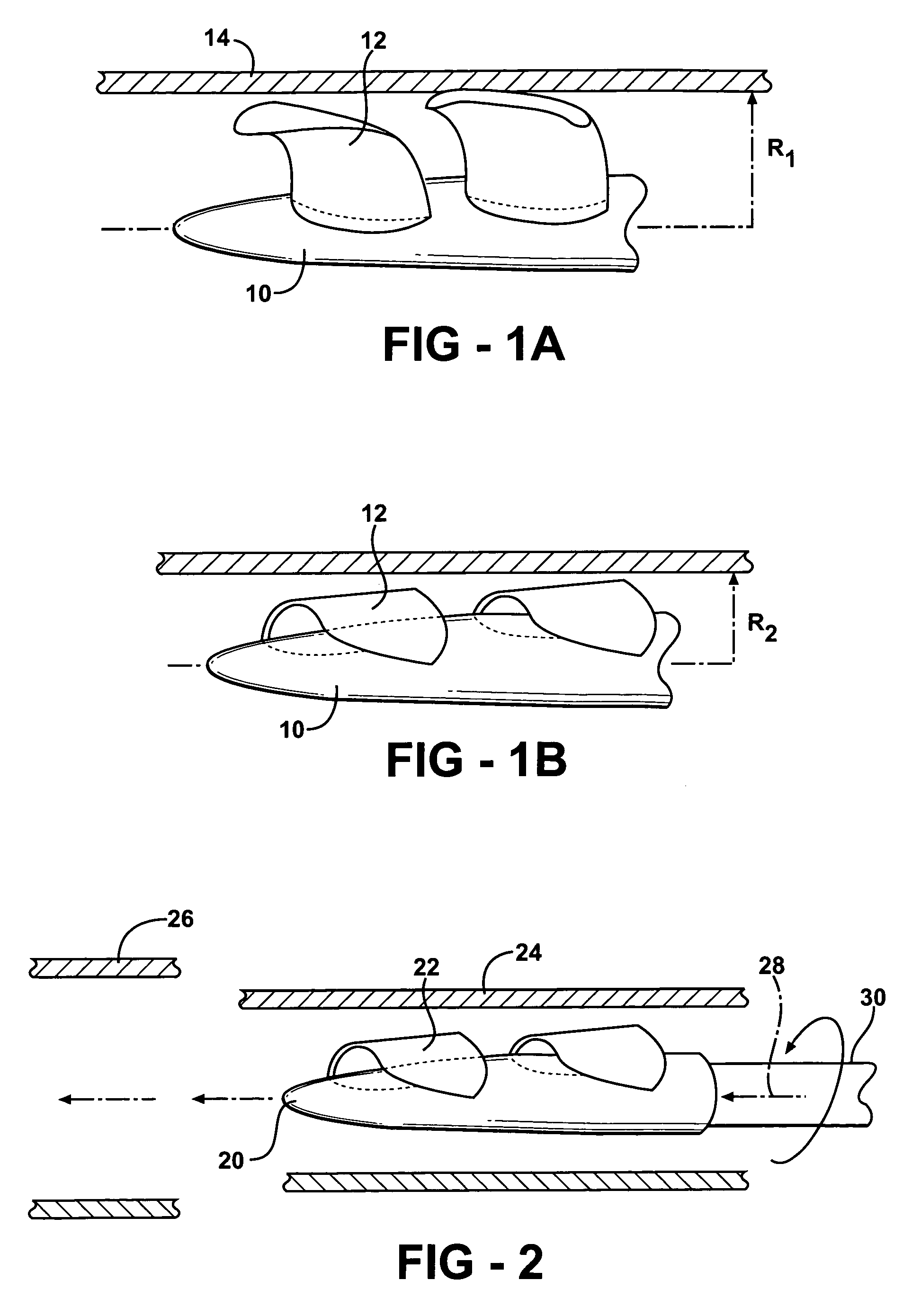
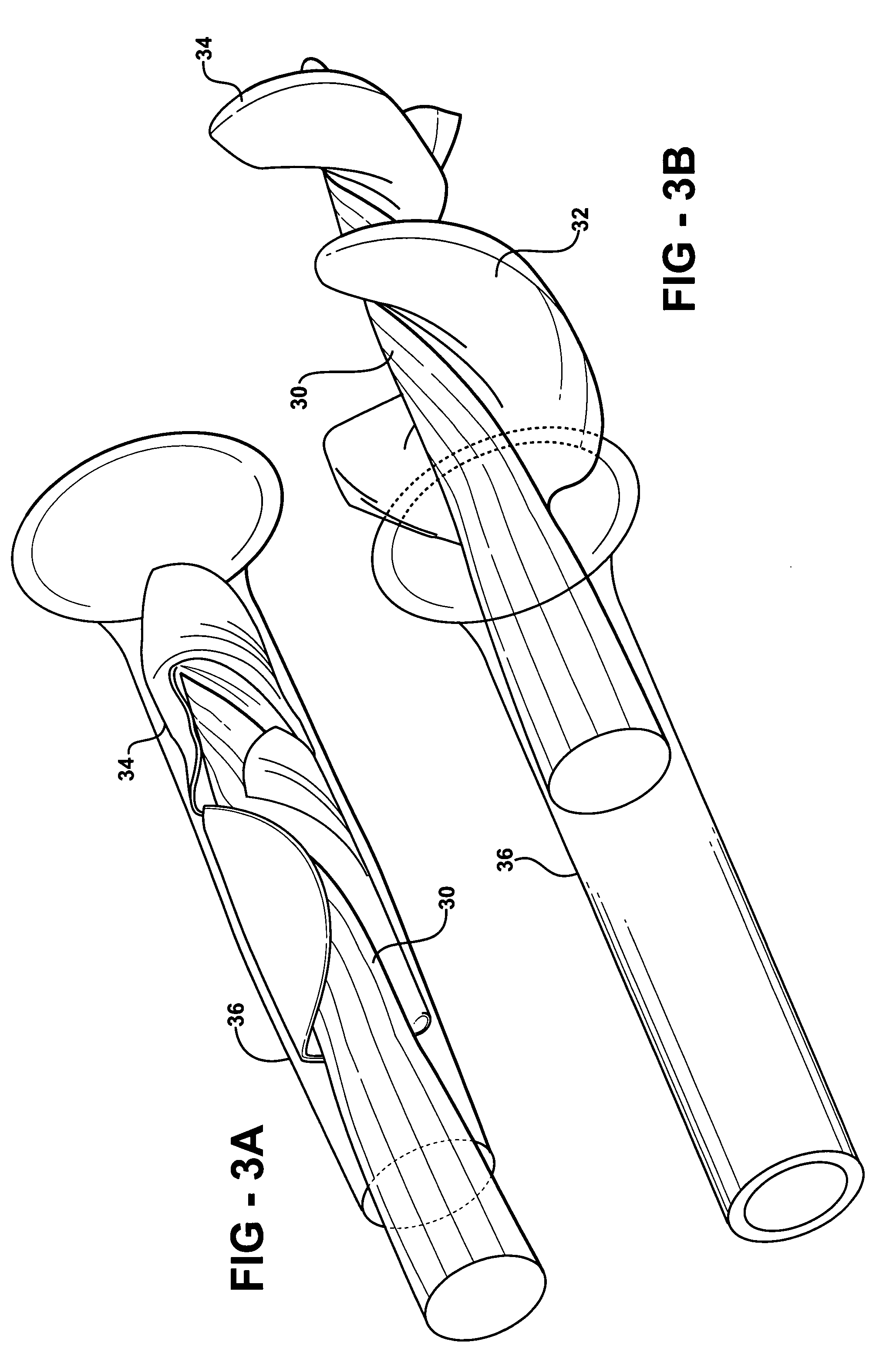
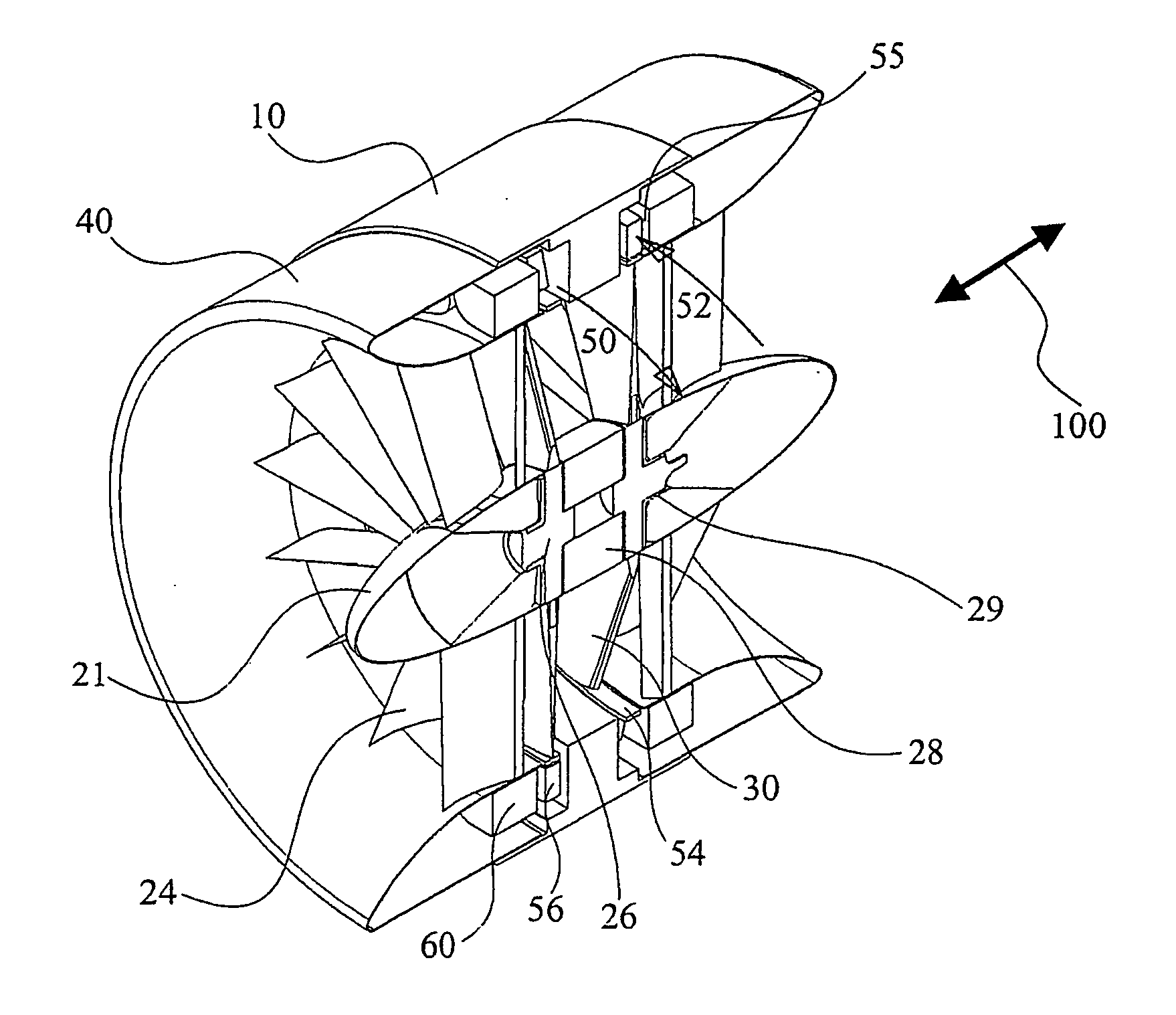
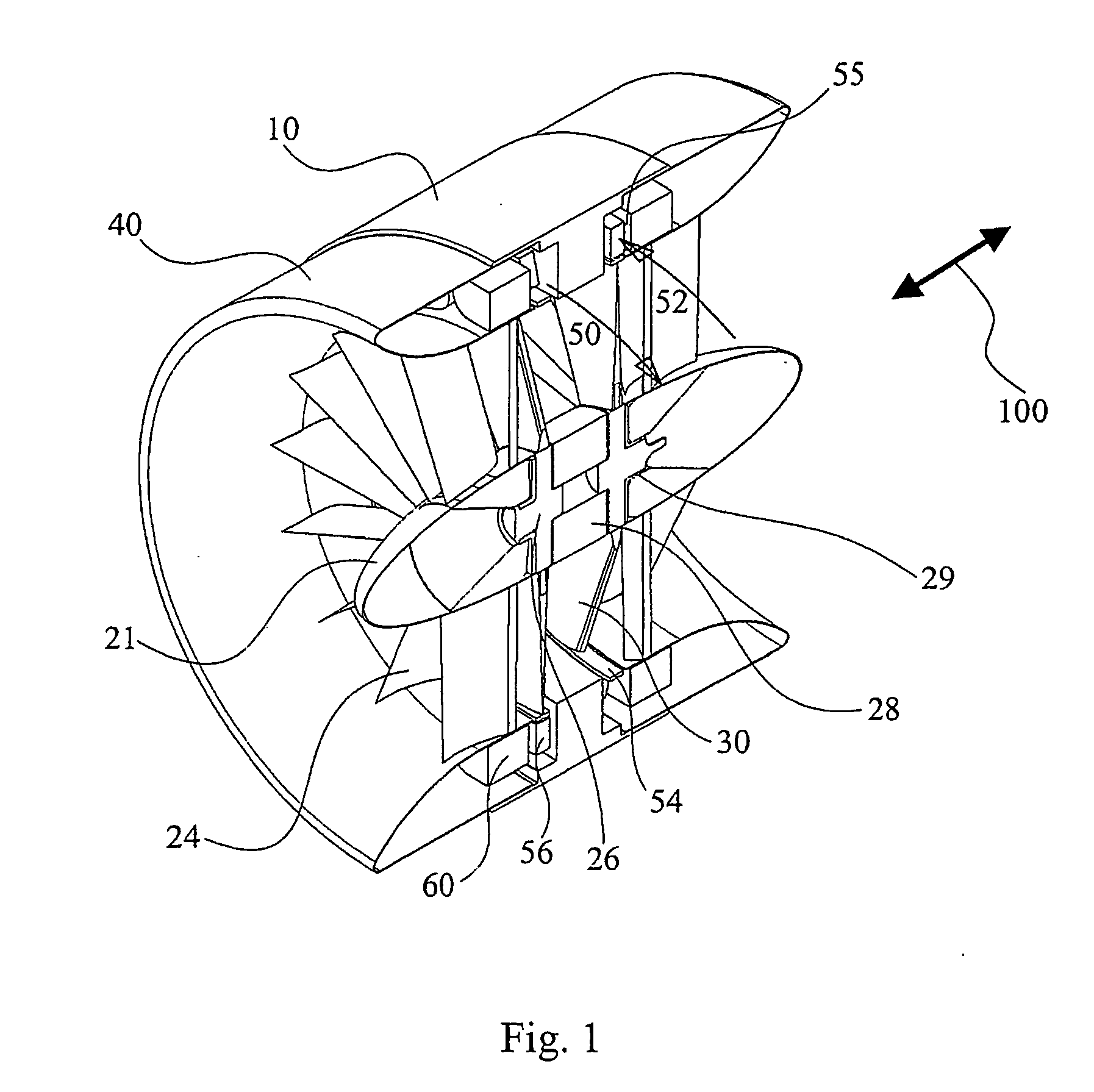
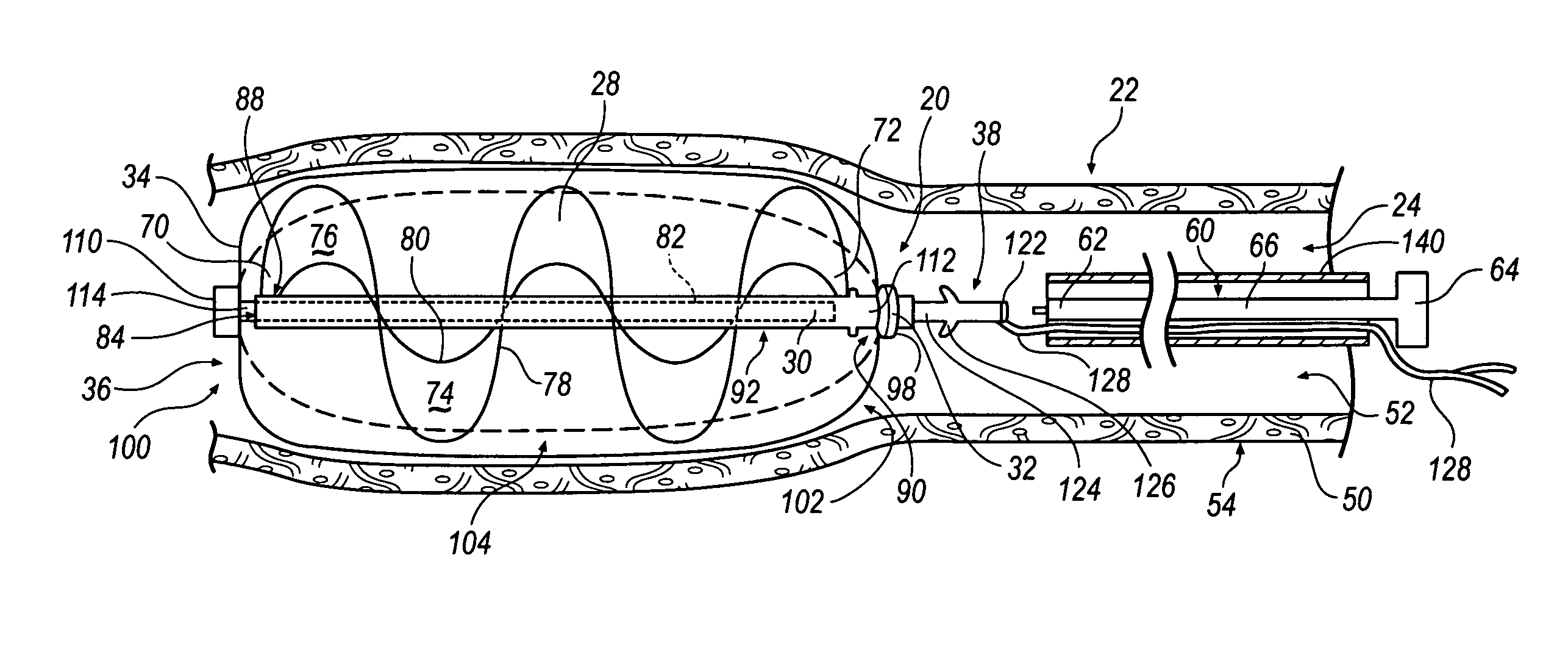
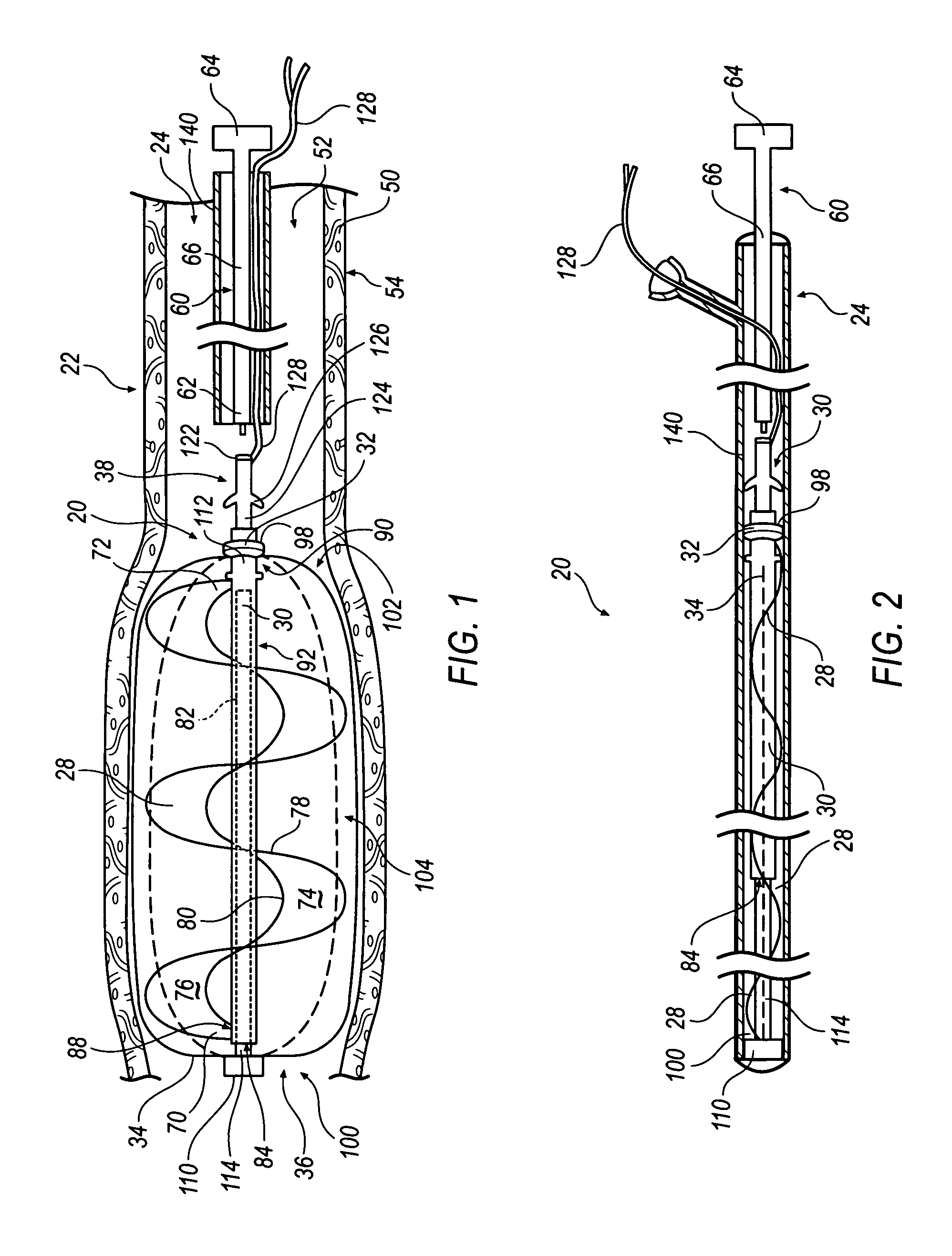
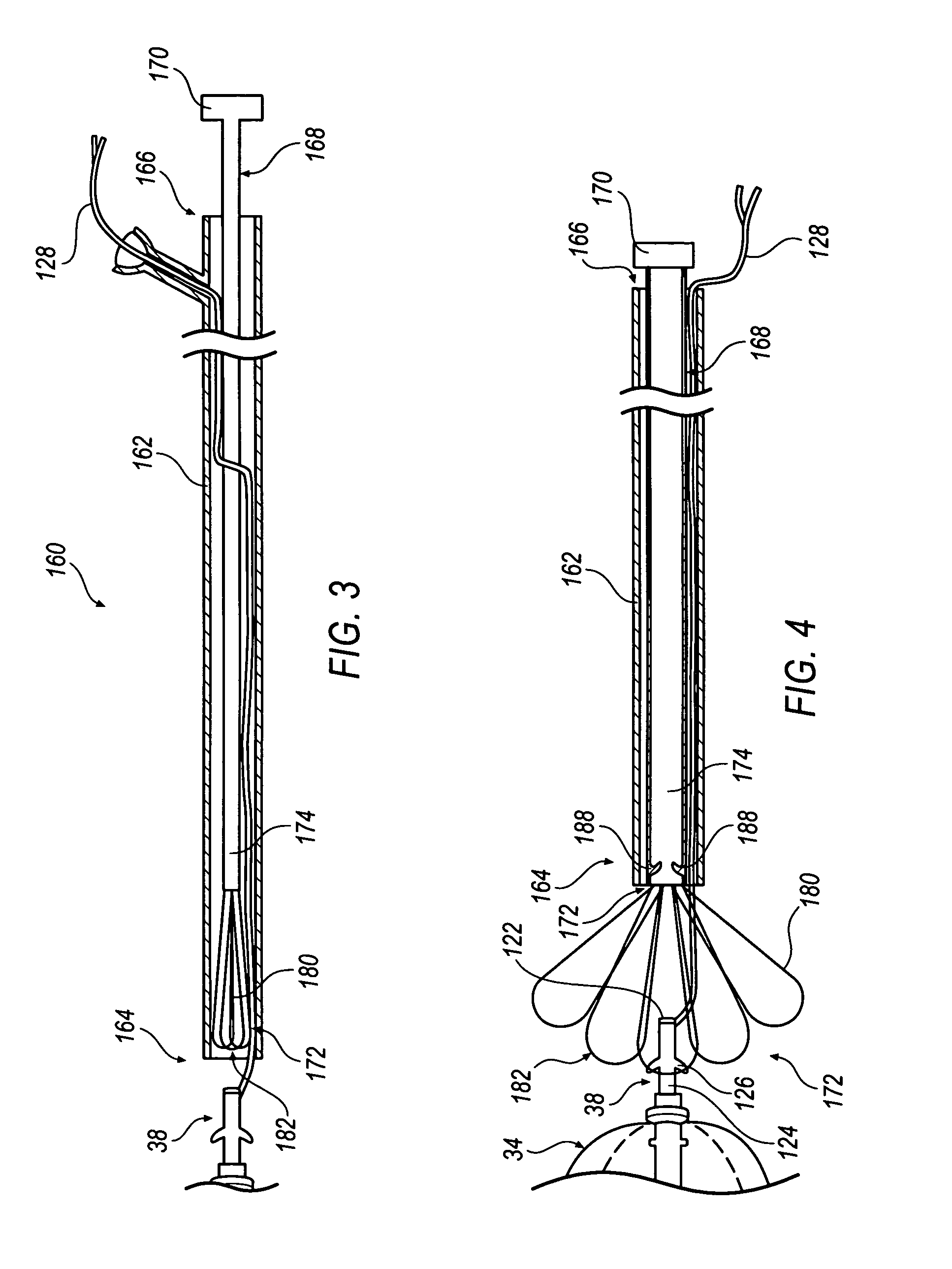
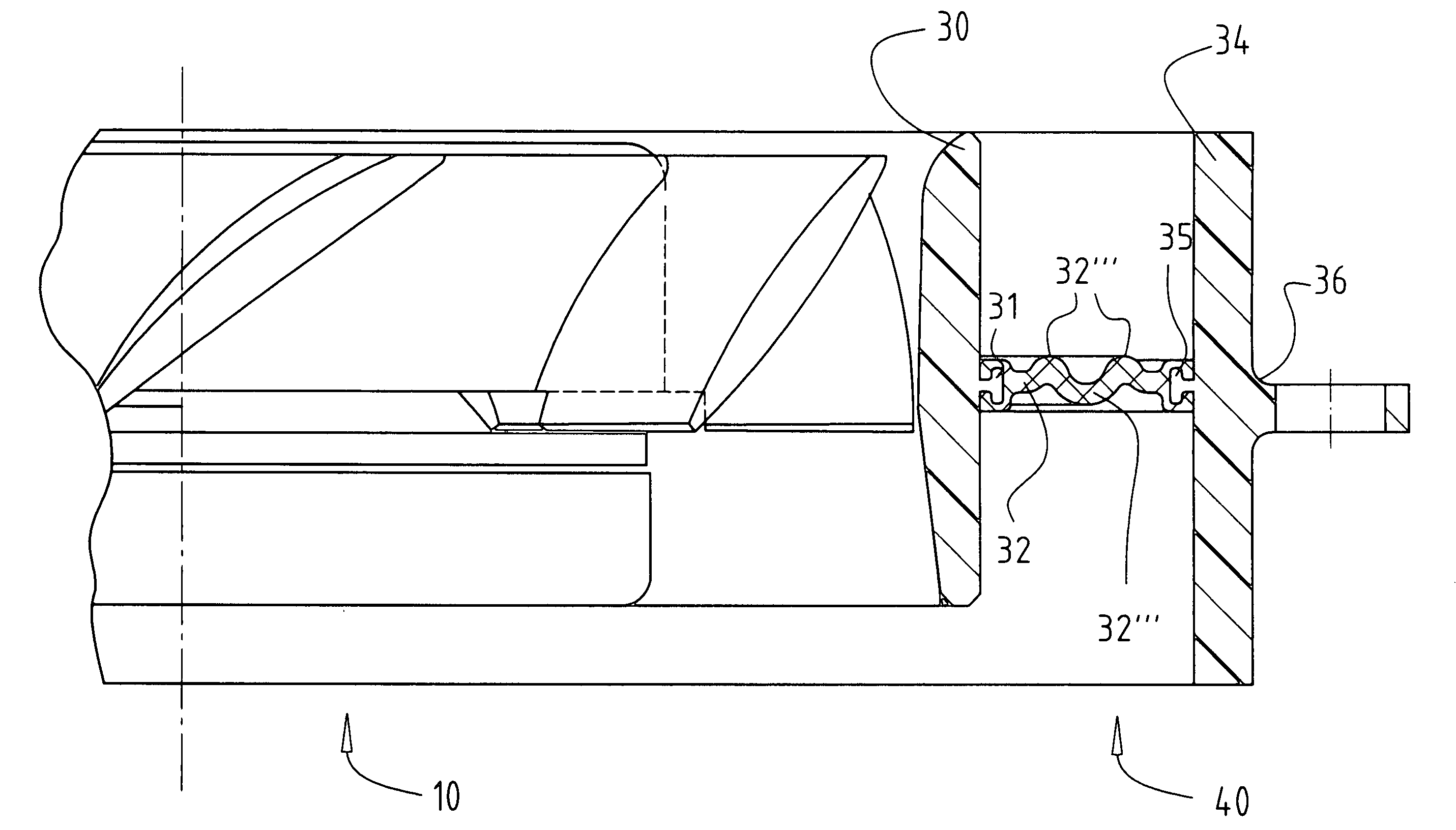
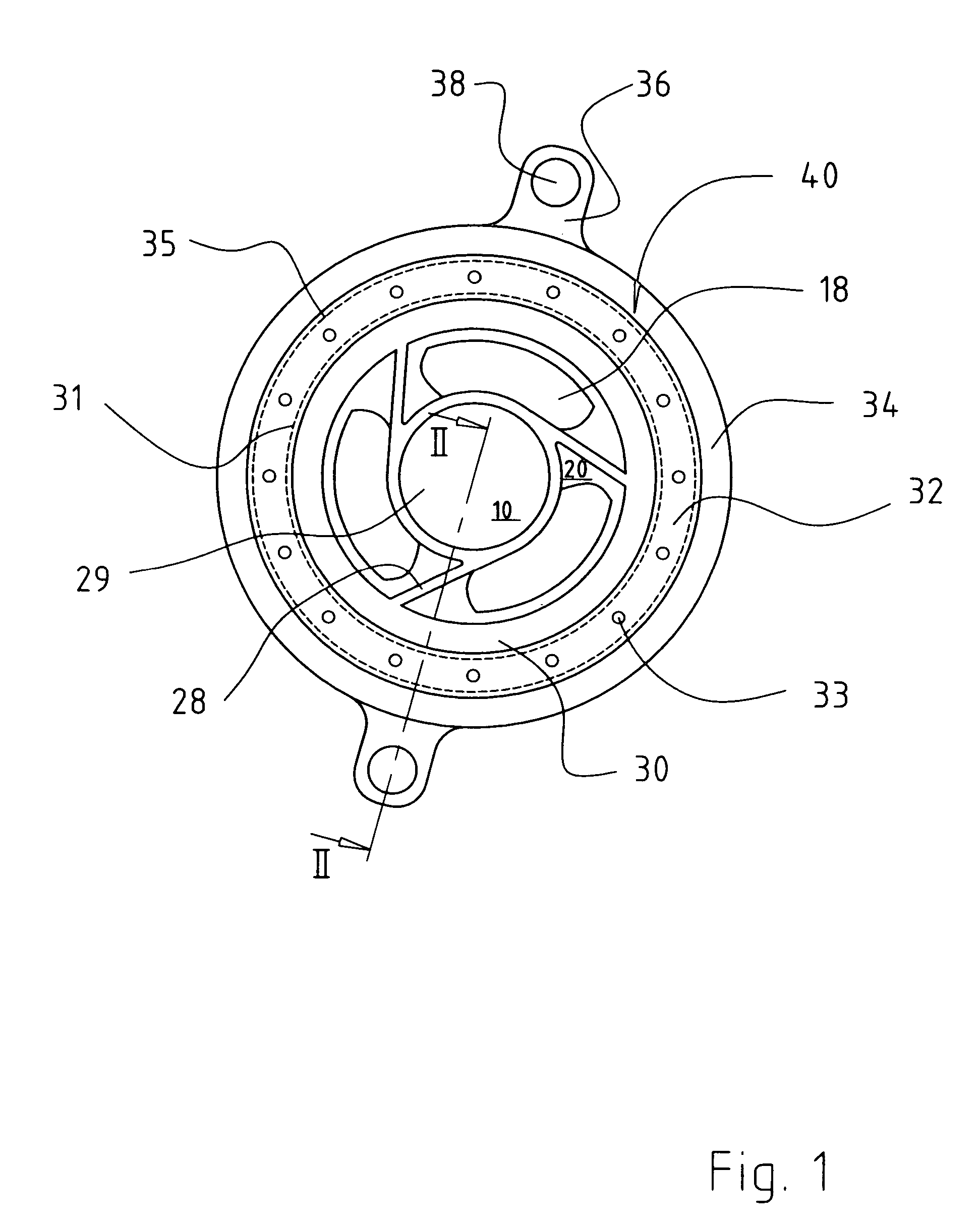
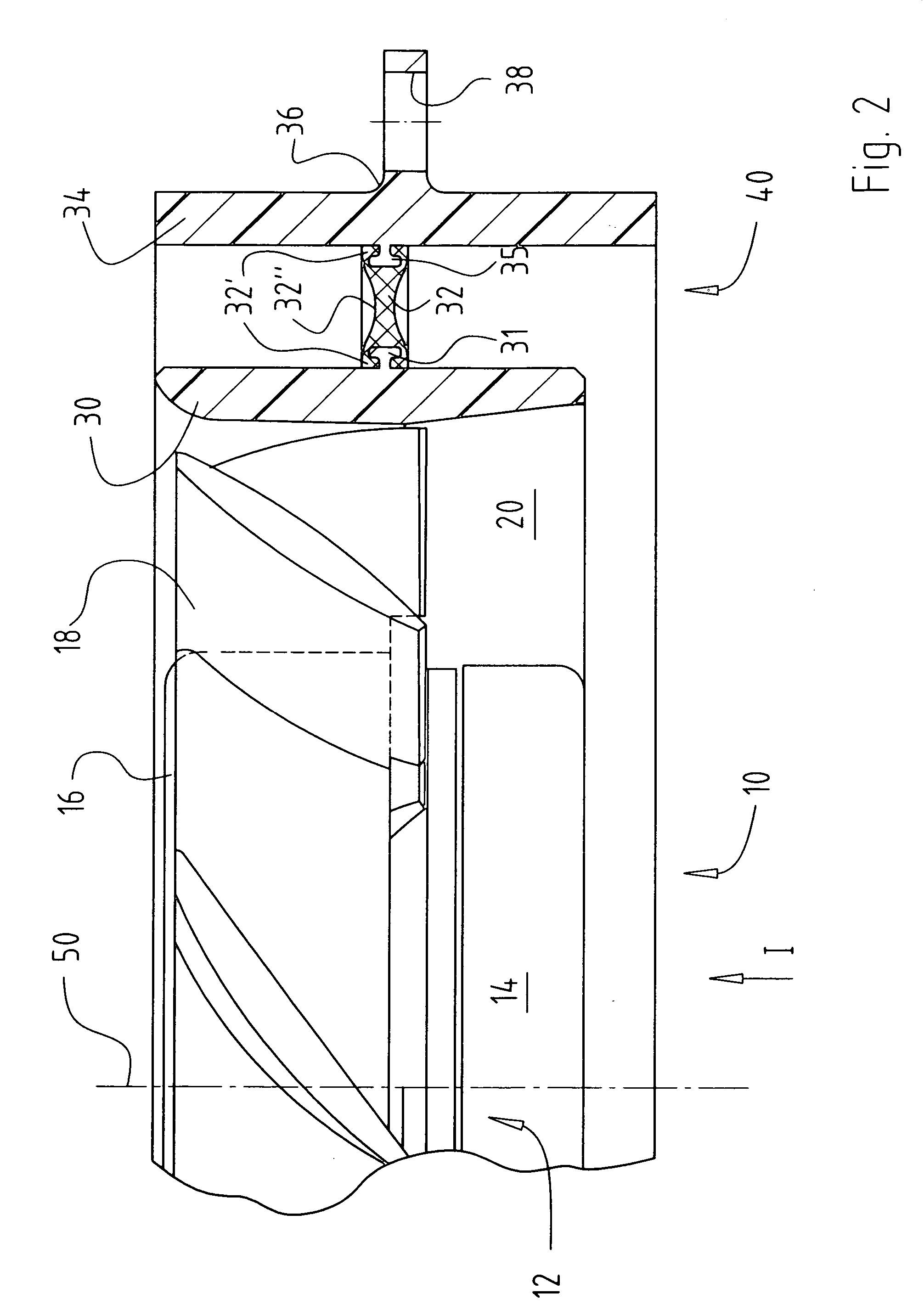
Expandable impeller pump
ActiveUS7393181B2Easy to compressReduced form requirementsPropellersEngine manufactureImpellerEngineering
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Heart assist device with expandable impeller pump
An impeller includes a hub and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a stored configuration in which the blade is compressed so that its distal end moves towards the hub, and a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub. The impeller may be part of a pump for pumping fluids, such as pumping blood within a patient. A blood pump may include a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller may reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula may have a compressed diameter which allows it to be inserted percutaneously into a patient. Once at a desired location, the expandable portion of the cannula may be expanded and the impeller expanded to the deployed configuration. A flexible drive shaft may extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
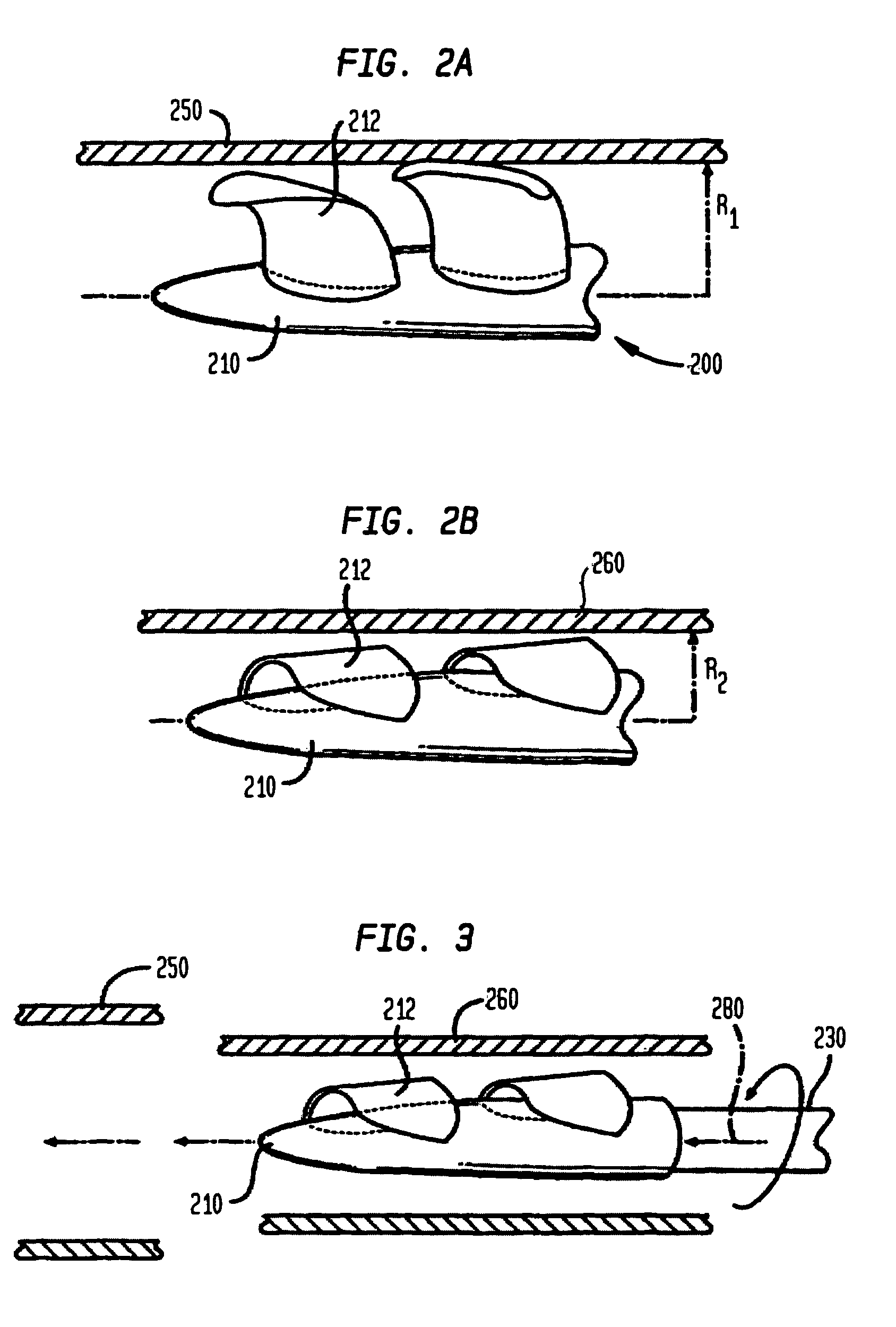
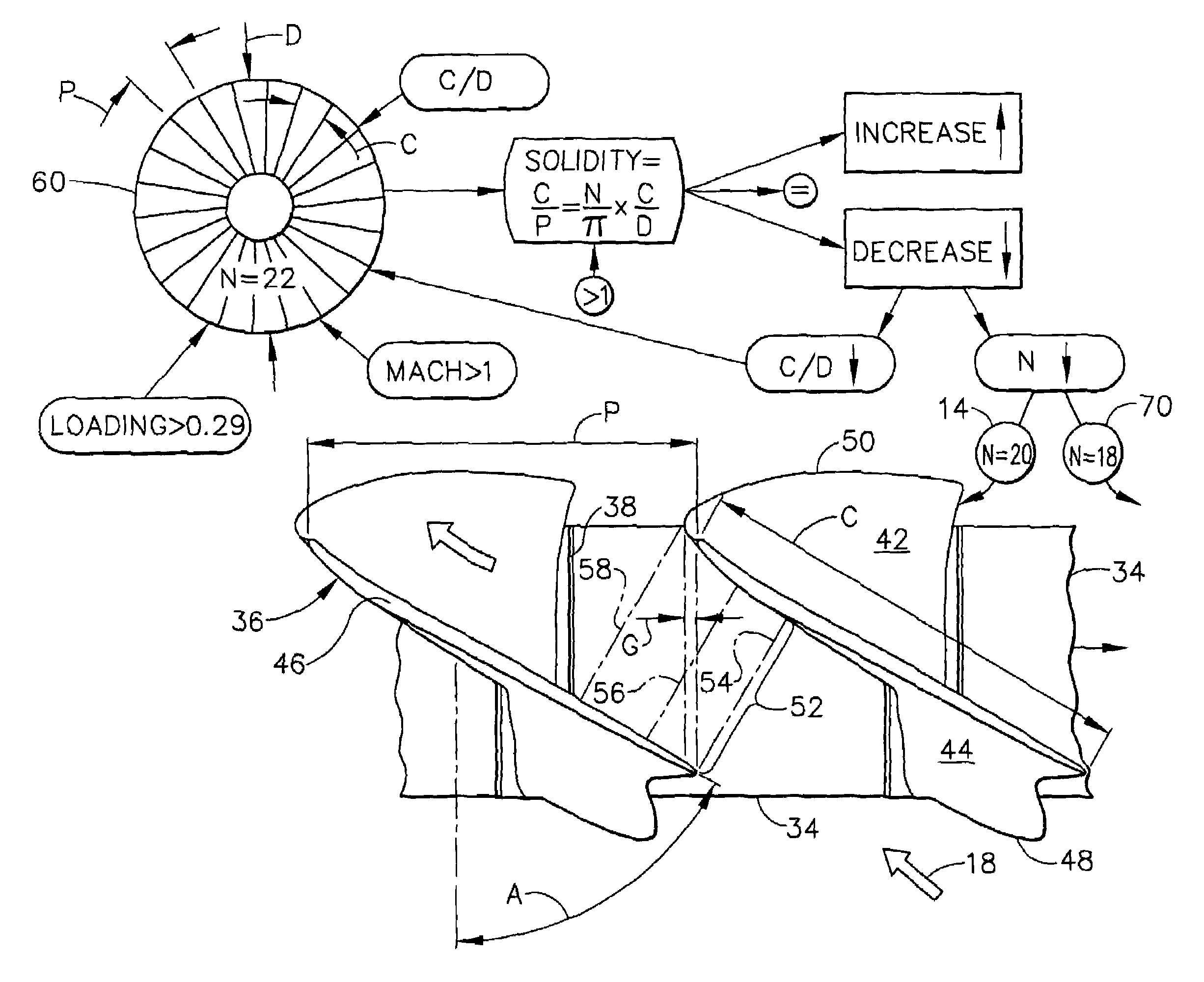
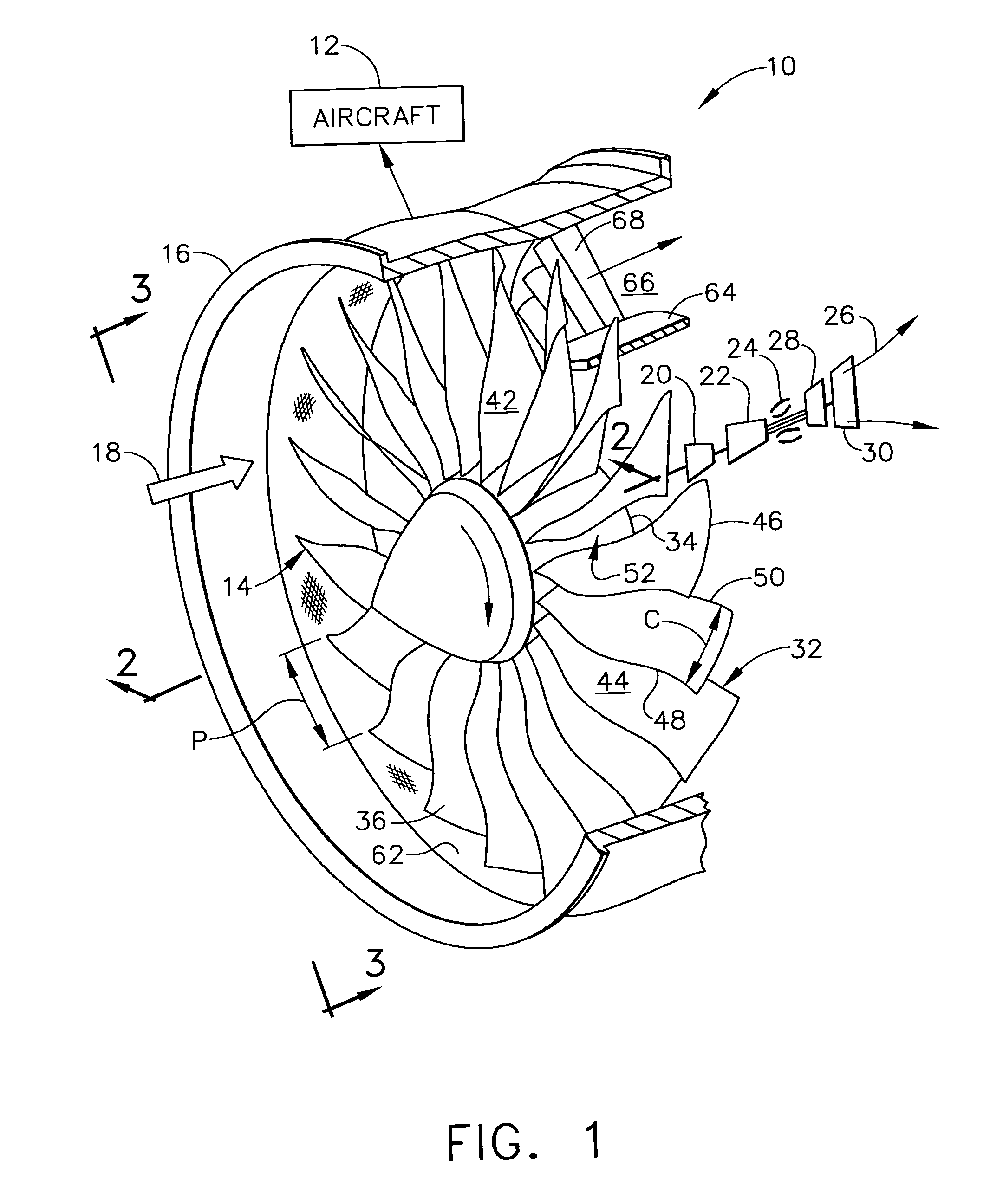
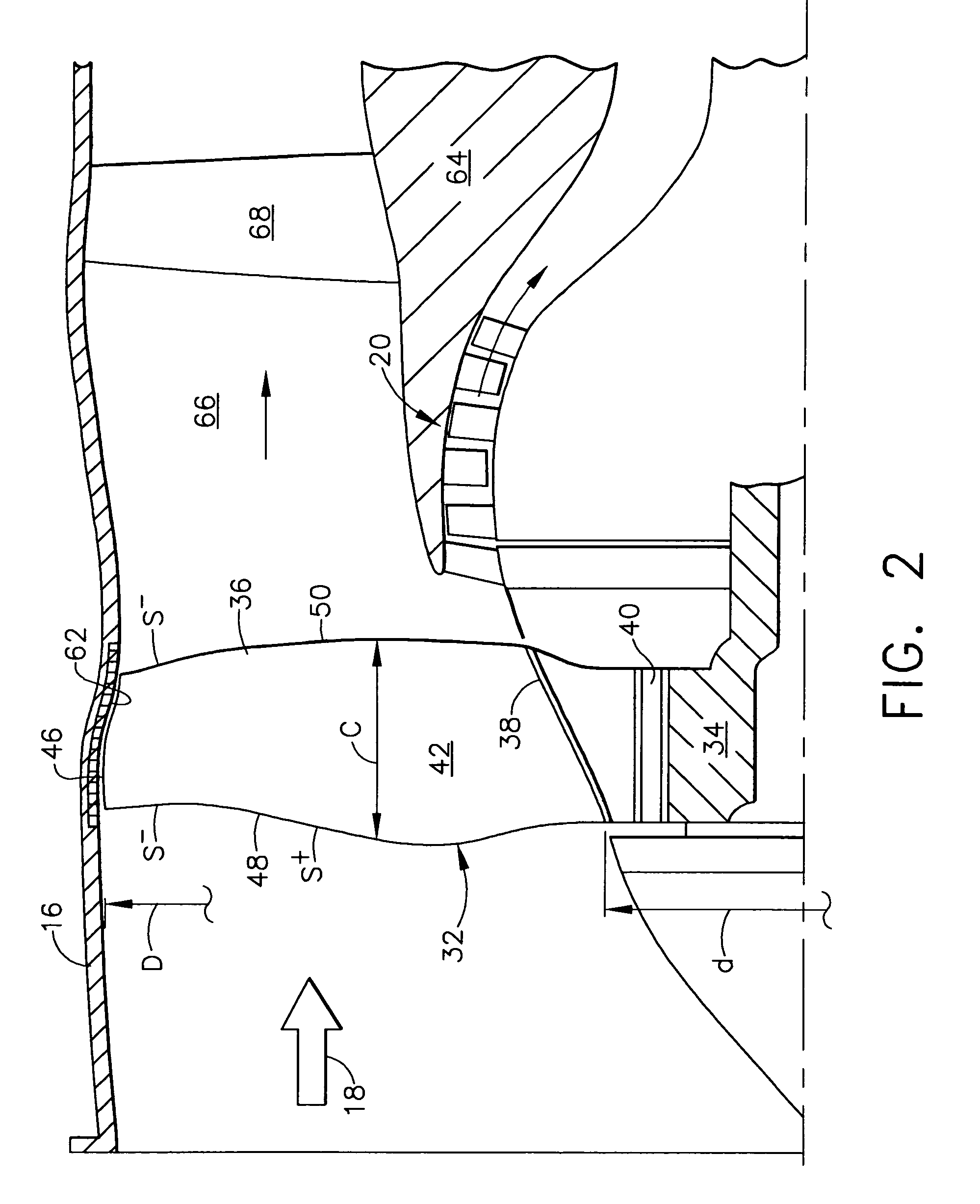
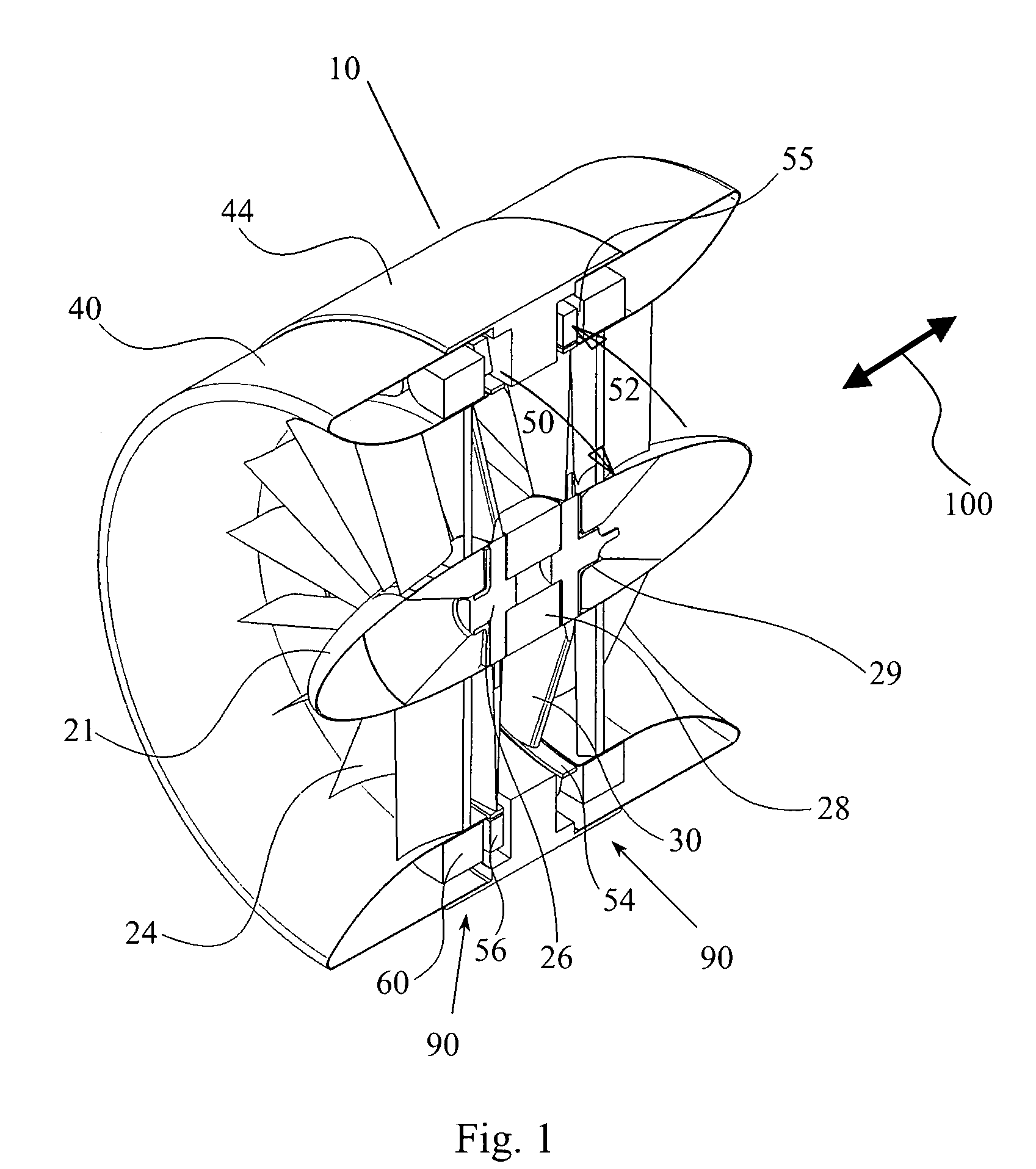
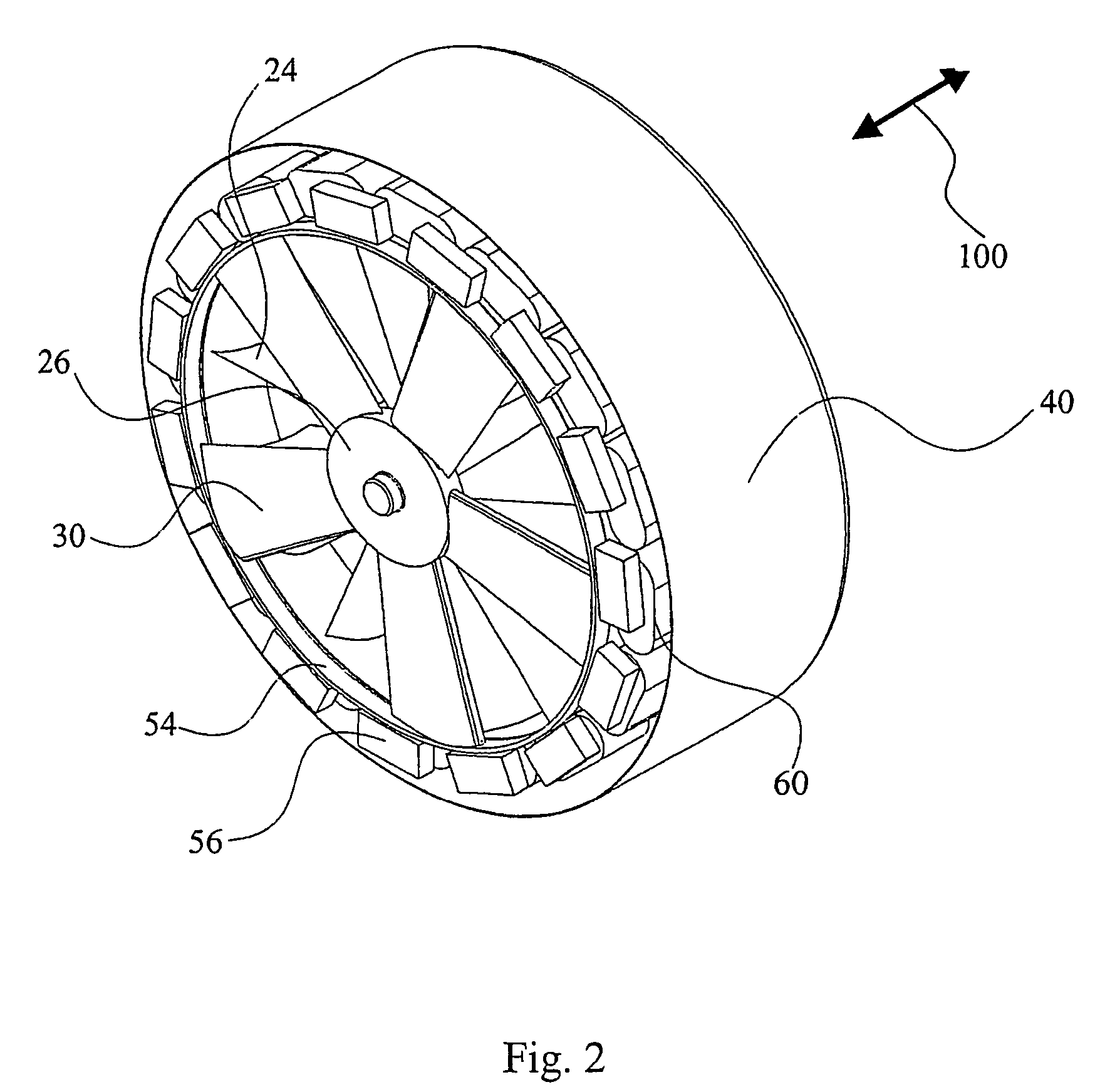
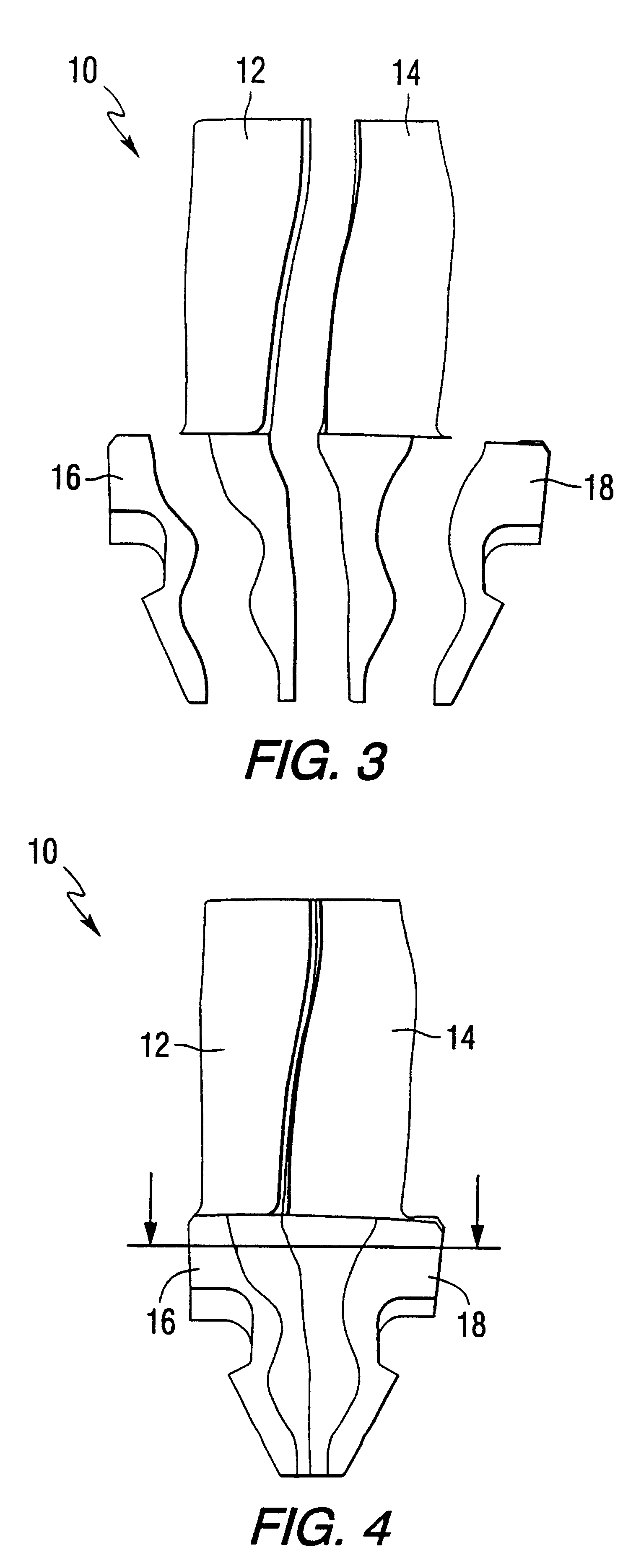
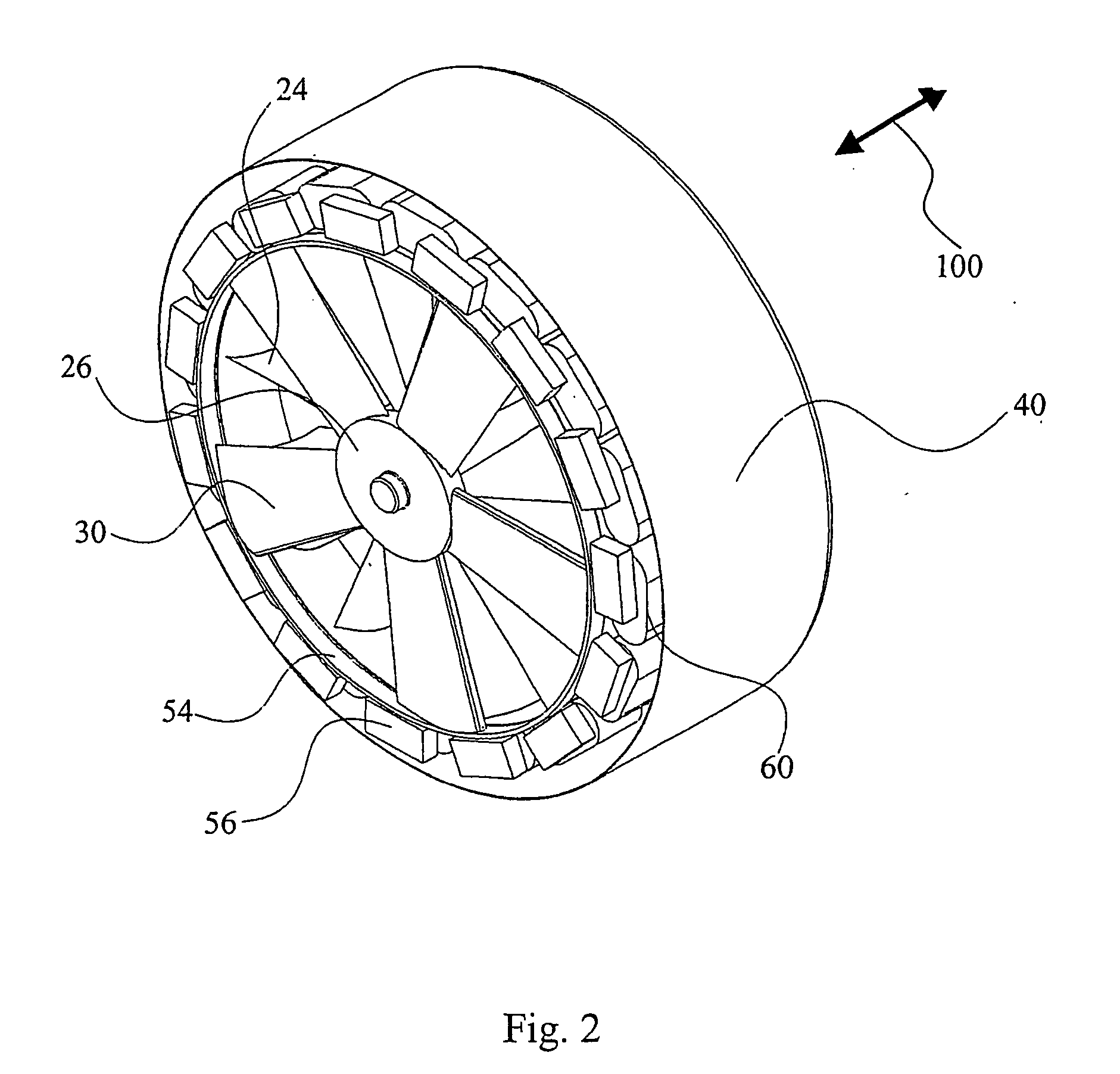
Low solidity turbofan
A turbofan includes a row of fan blades extending from a supporting disk inside an annular casing. Each blade includes an airfoil having opposite pressure and suction sides extending radially in span between a root and tip and axially in chord between leading and trailing edges. Adjacent airfoils define corresponding flow passages therebetween for pressurizing air. Each airfoil includes stagger increasing between the root and tip, and the flow passage has a mouth between the airfoil leading edge and the suction side of an adjacent airfoil and converges to a throat aft from the mouth. The row includes no more than twenty fan blades having low tip solidity for increasing the width of the passage throat.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
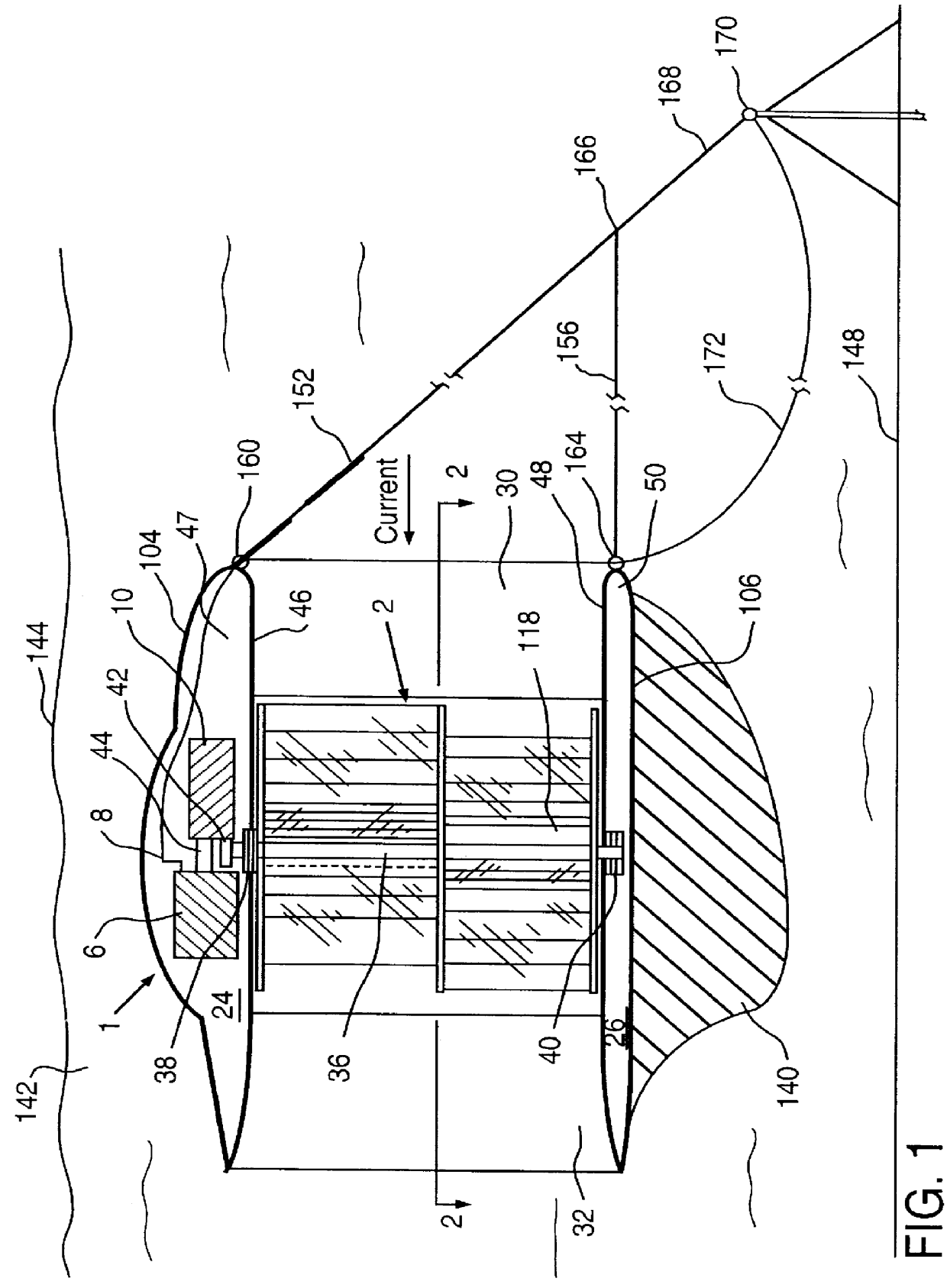
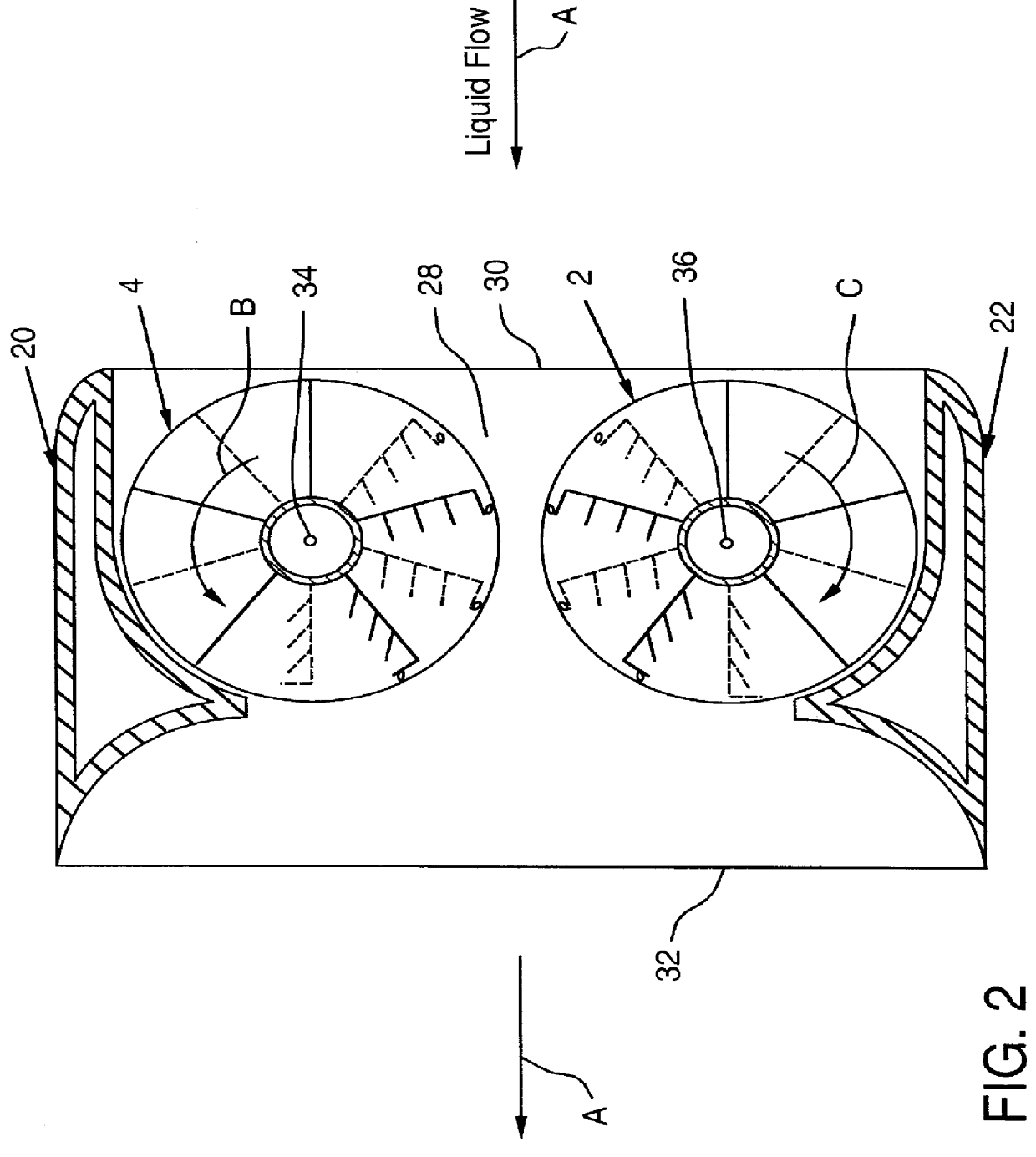
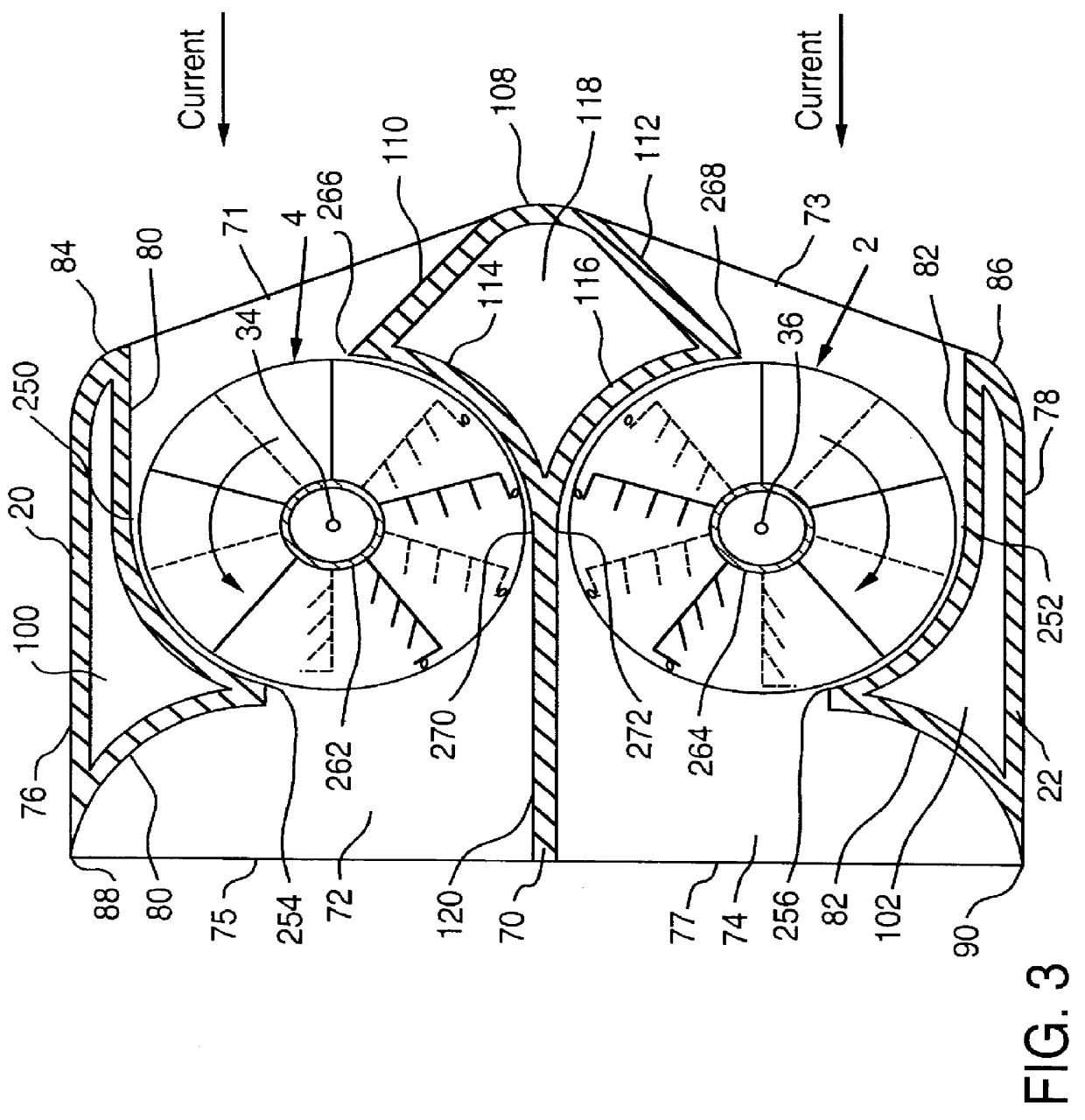
Submersible appartus for generating electricity and associated method
InactiveUS6109863AReduce the impactReduce impactCircumferential flow pumpsWind motor controlElectricityMarine engineering
A fully submersible apparatus for generating electricity from liquid flow as in an ocean or river current. A buoyant structure is fully submersible and has at least one pair of counter-rotating side-by-side motors with a plurality of angularly spaced radial vanes each having a plurality of rotatable subvanes such that current impinging upon the motor will impinge on a closed or solid vane to effect rotation of the motor and its shaft during a first phase of the rotational cycle and will impinge on open vanes for free passage therethrough on the return or second phase of rotation of the motor. Motors may also be provided with vanes in overlying and underlying relationship. An associated method is provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN LARRY D
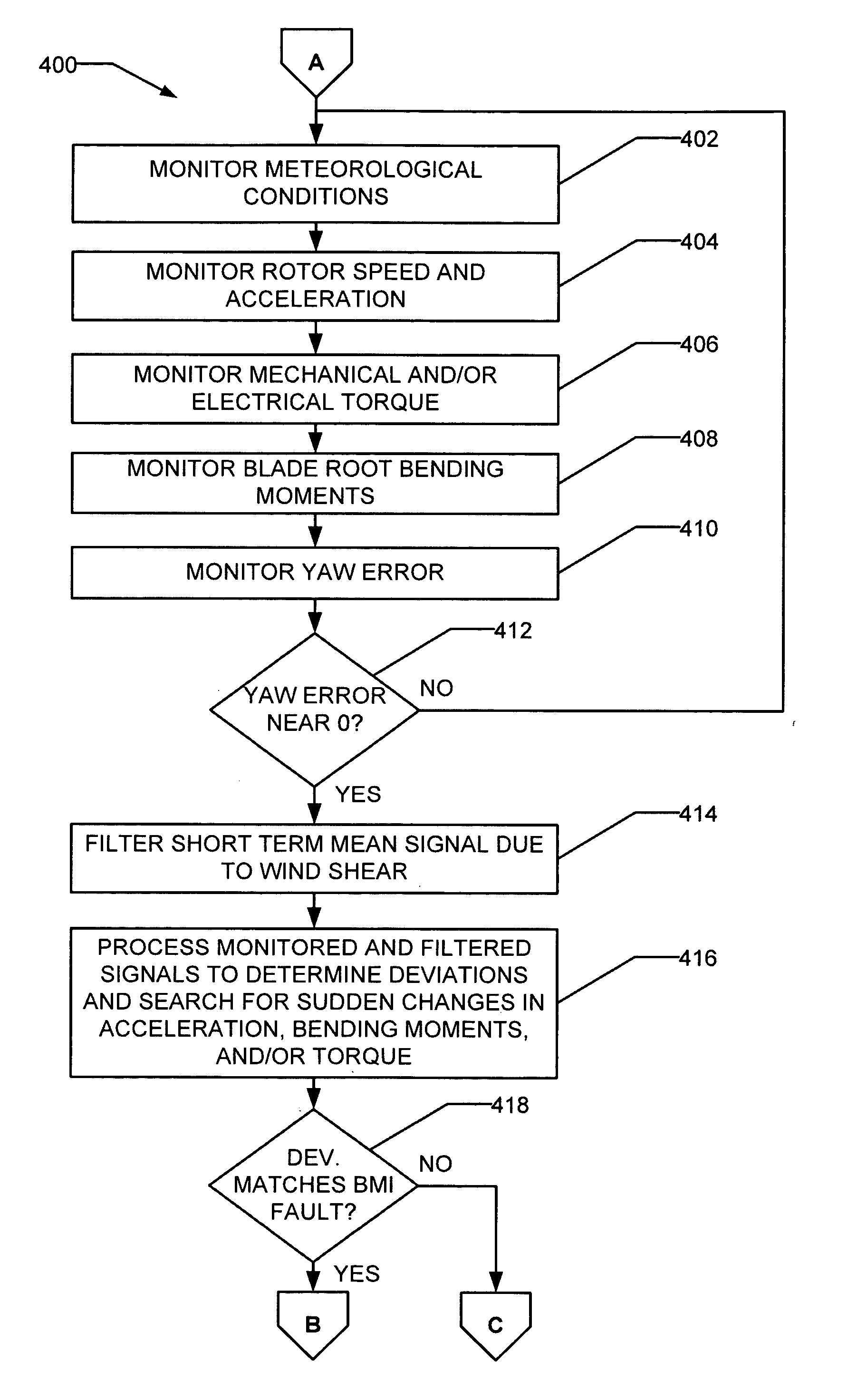
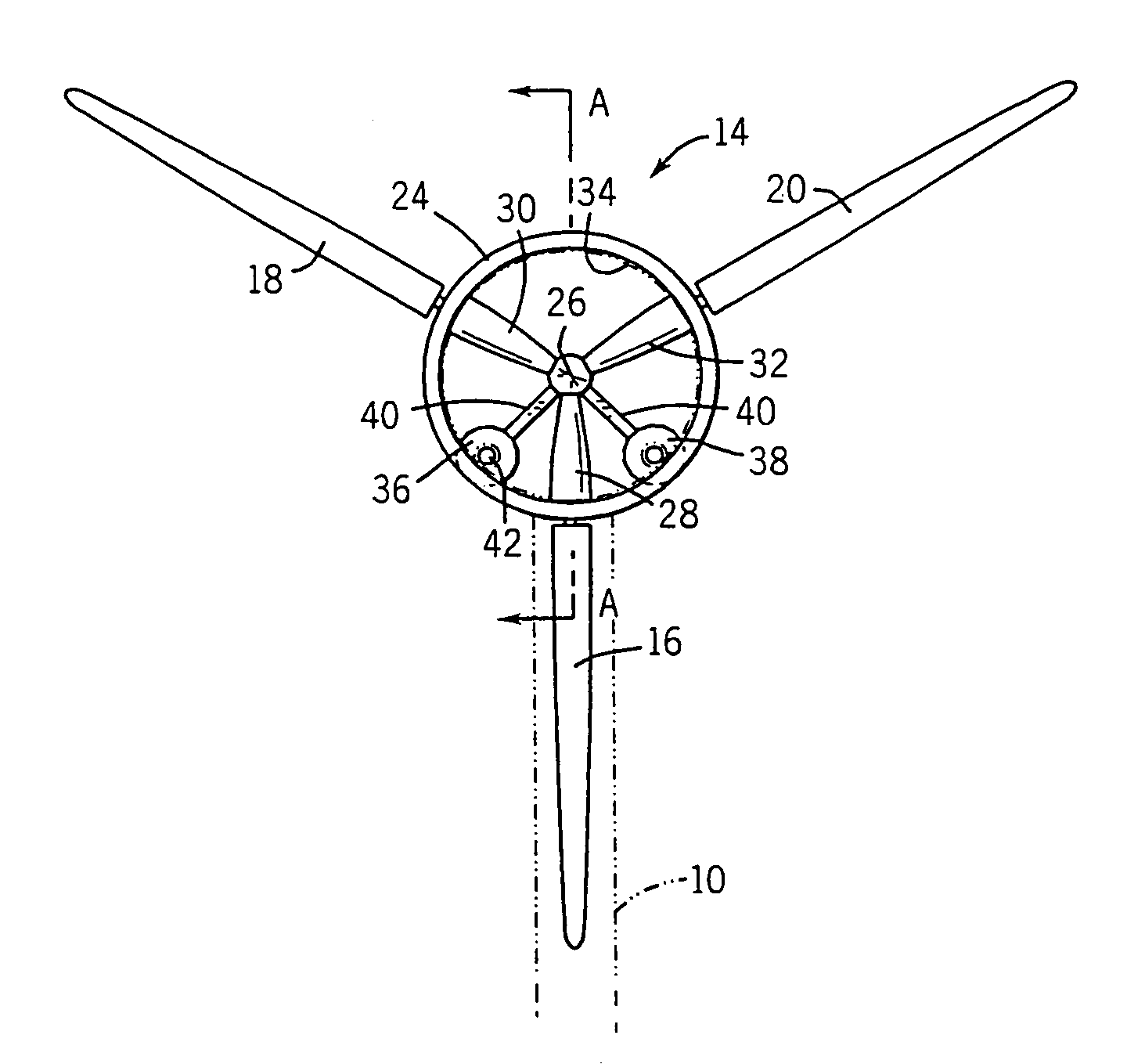
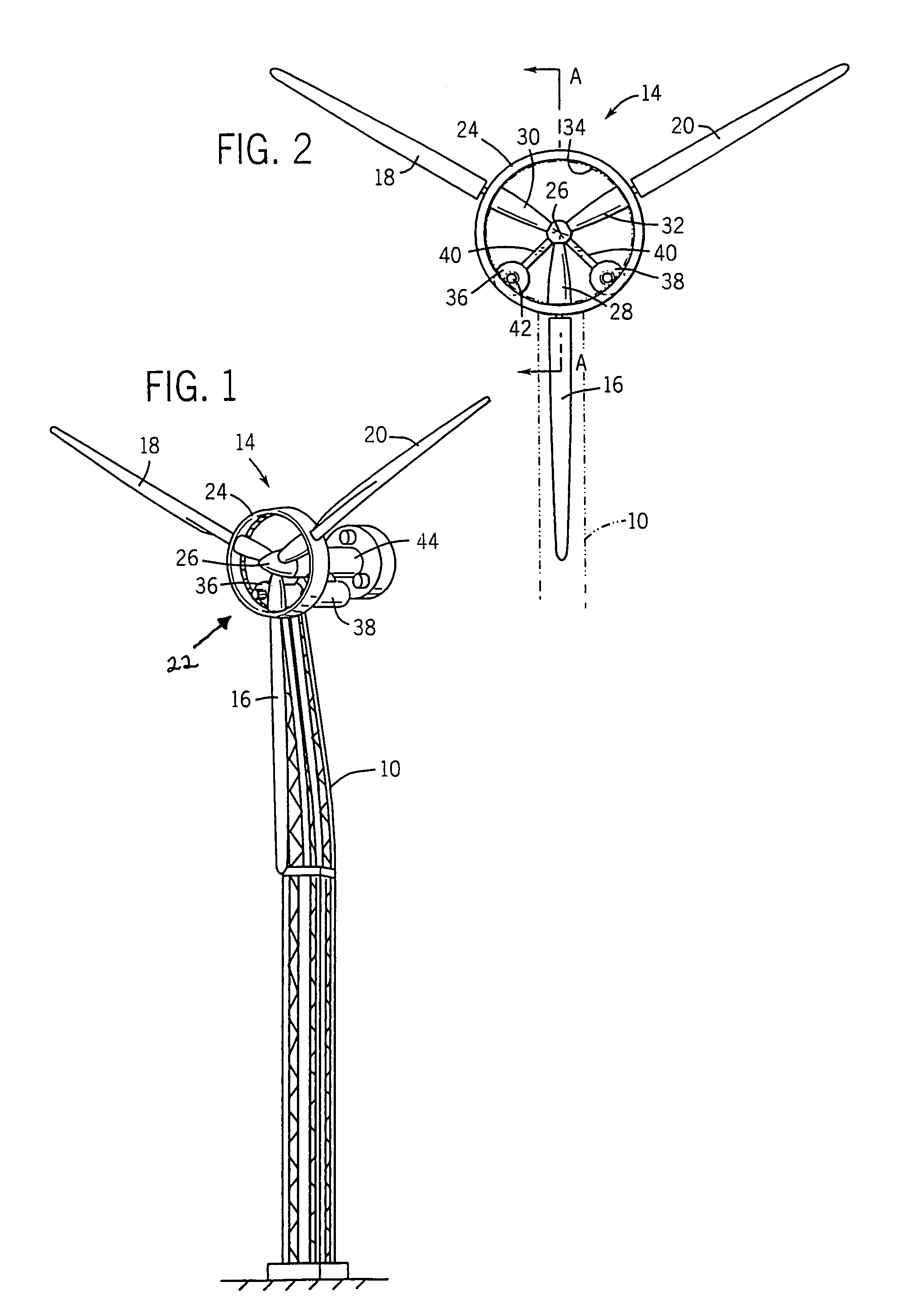
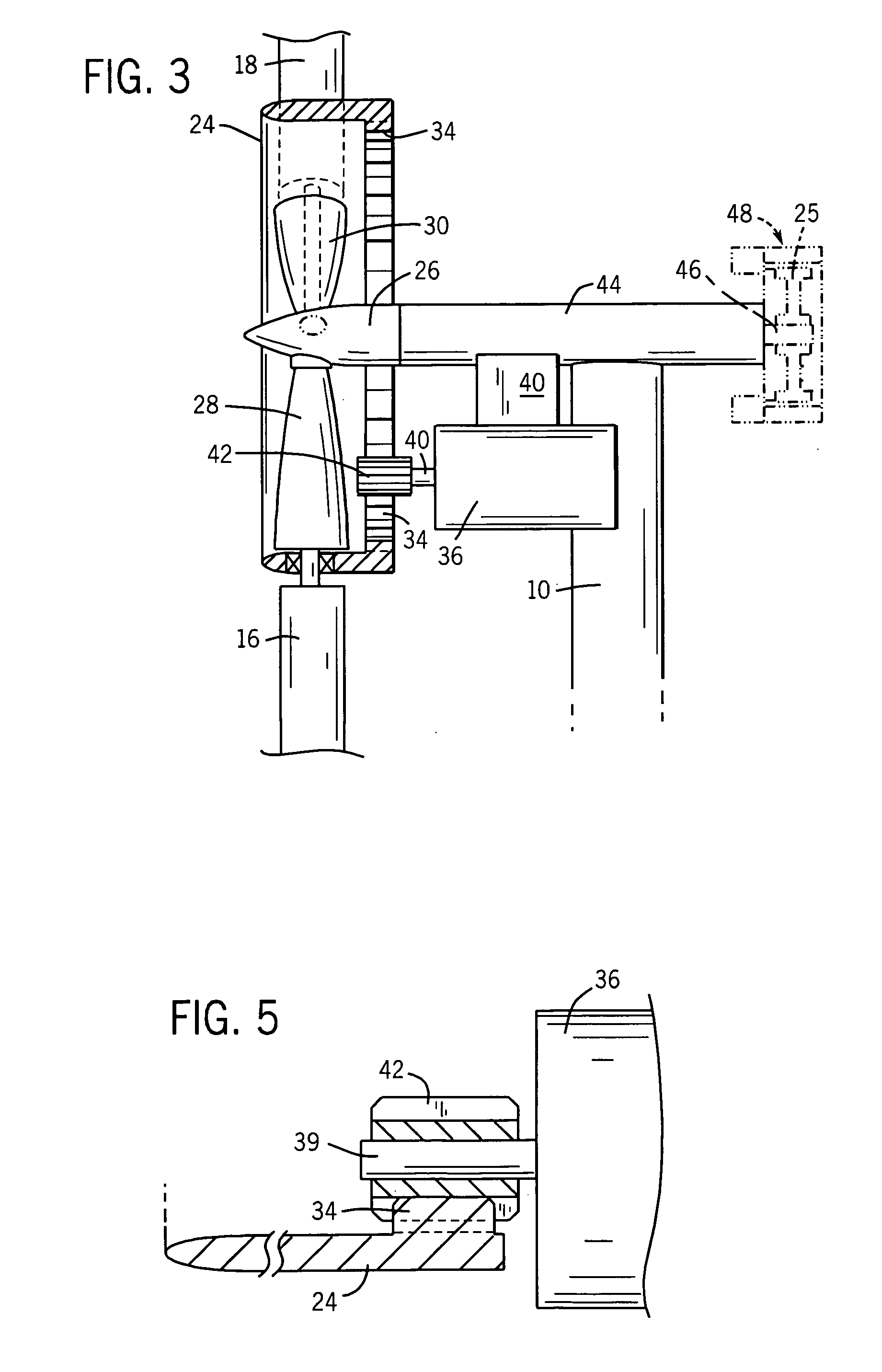
Methods and apparatus for rotor blade ice detection
ActiveUS20050276696A1Reduced lifting capabilityDiminished aerodynamic rotor blade performancePropellersWind motor controlIcing conditionsEngineering
A method for detecting ice on a wind turbine having a rotor and one or more rotor blades each having blade roots includes monitoring meteorological conditions relating to icing conditions and monitoring one or more physical characteristics of the wind turbine in operation that vary in accordance with at least one of the mass of the one or more rotor blades or a mass imbalance between the rotor blades. The method also includes using the one or more monitored physical characteristics to determine whether a blade mass anomaly exists, determining whether the monitored meteorological conditions are consistent with blade icing; and signaling an icing-related blade mass anomaly when a blade mass anomaly is determined to exist and the monitored meteorological conditions are determined to be consistent with icing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Deicing device for wind turbine blades
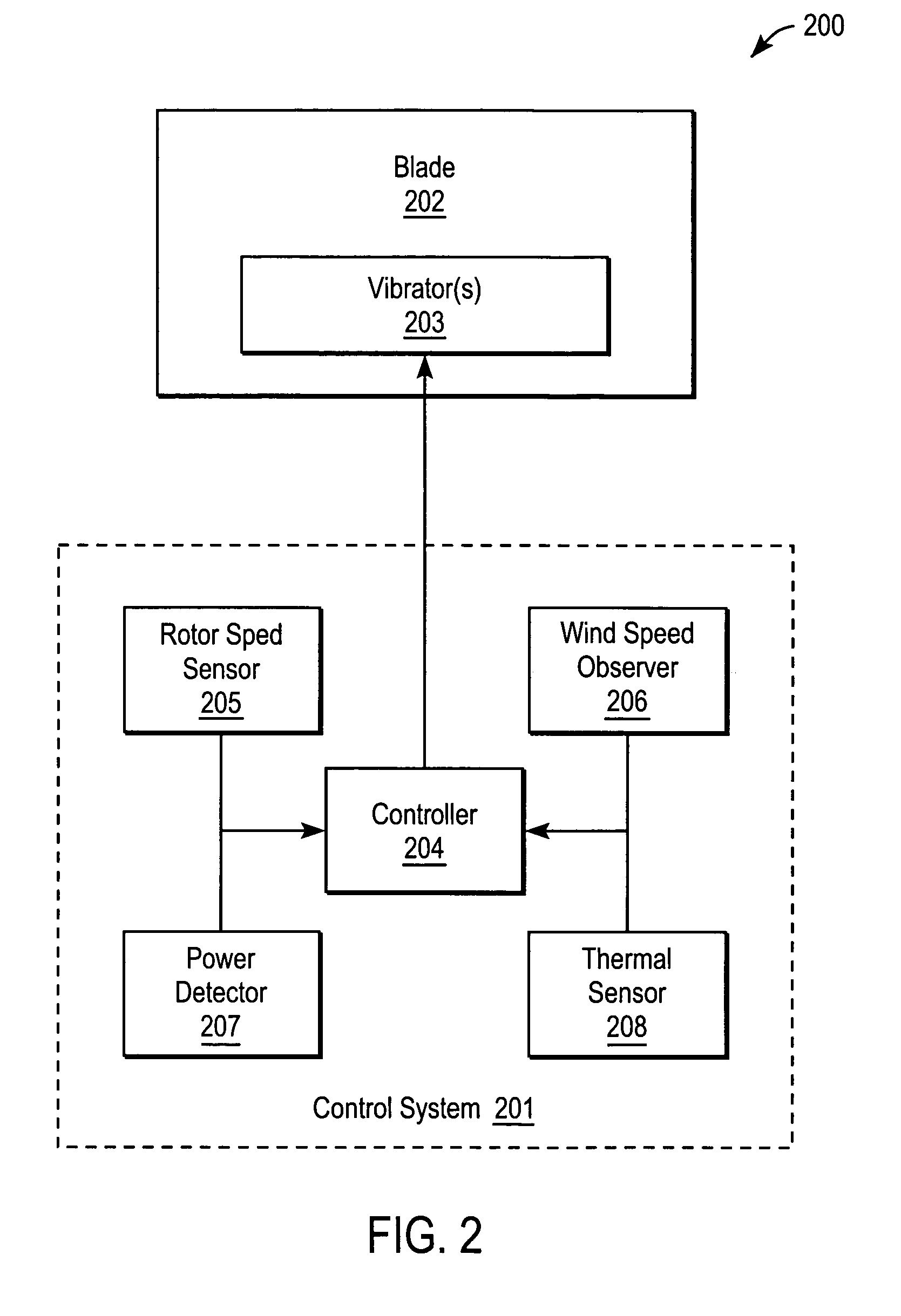
Methods and Apparatuses for deicing a wind turbine blade are described herein. In one embodiment, an exemplary process includes detecting an icy condition on a wind turbine blade and causing at least a portion of the wind turbine blade to vibrate, causing the ice built up on the wind turbine blade to break off.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
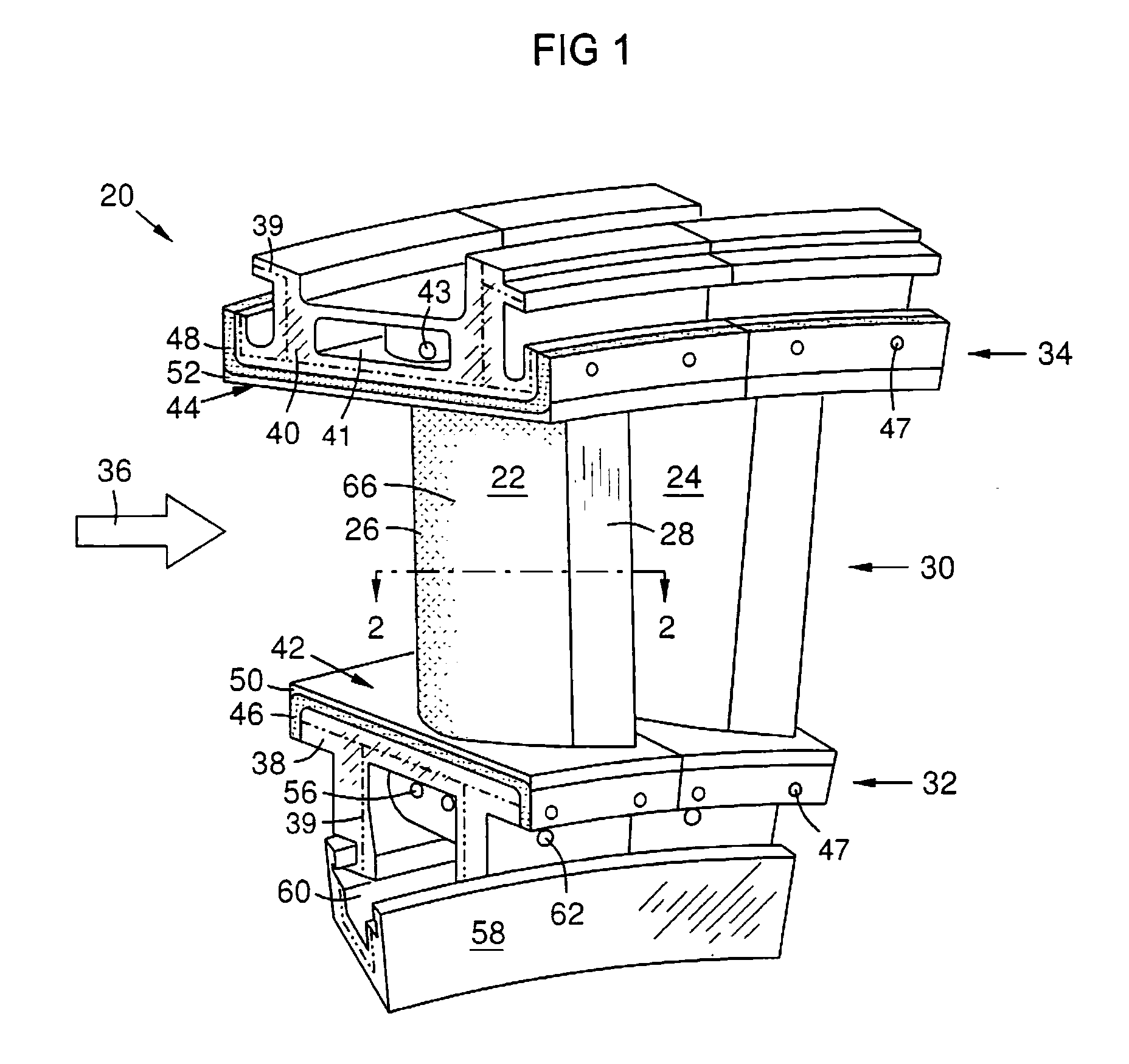
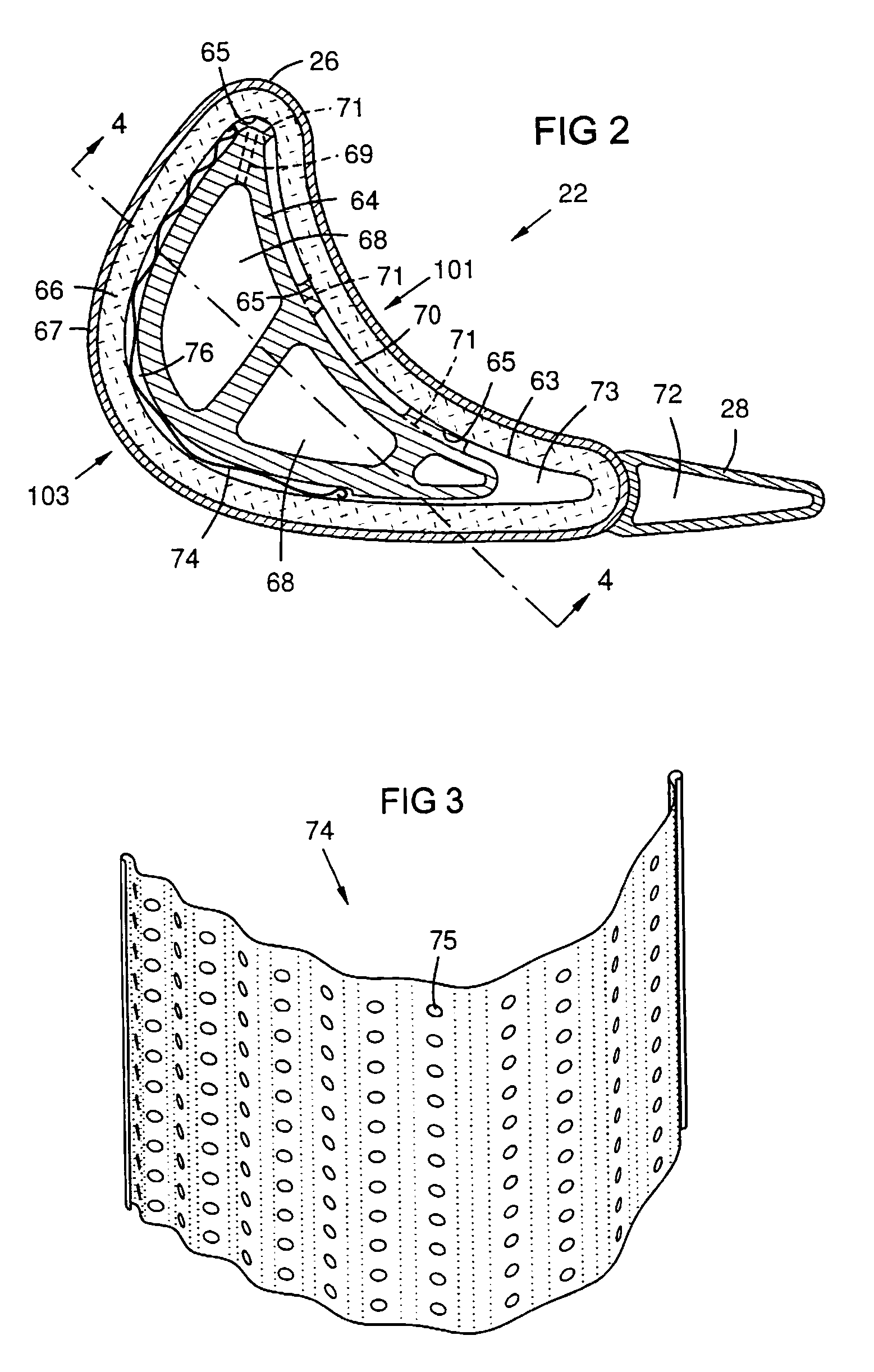
Double-ended blower and volutes therefor
InactiveUS6910483B2Faster pressure rise timeImprove reliabilityPropellersElement comparisonMotor speedImpeller
A double-ended variable speed blower for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) ventilation of patients includes two impellers in the gas flow path that cooperatively pressurize gas to desired pressure and flow characteristics. Thus, the double-ended blower can provide faster pressure response and desired flow characteristics over a narrower range of motor speeds, resulting in greater reliability and less acoustic noise.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and apparatus for radial exhaust gas turbine
A radial exhaust gas turbine apparatus has a gas turbine engine that includes a radial exhaust diffuser section and a casing apparatus consisting essentially of polygonal walls, substantially straight plates, and substantially straight sidewalls. The casing apparatus encloses the radial exhaust diffuser section and is configured to direct at least a substantial portion of the gas exiting the radial exhaust diffuser section to an exit in the casing apparatus via an approximately involute path.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Underwater ducted turbine
InactiveUS7471009B2Minimize loss of efficiencyThe process is stable and efficientEngine fuctionsWorking fluid for enginesUnderwaterStator coil
An apparatus is disclosed for a turbine for generating electrical power from water or air flow comprising at least one rotor disk having a plurality of hydrofoil blades, a guide vanes, a cylindrical housing, and a generator means. A rim generator comprising a magnet race rotor rim and fixed stator coils in the housing is used. The apparatus is fitted with a screen to stop the ingress of debris and marine life, and a skirt augmenter device to reduce the Betz effect. The apparatus is preferably for sub-sea deployment and driven by tidal currents, but may be powered by river current or wave driven air or by wind. The apparatus may be deployed on at least one telescoping pole, tethered to the sea-bed and kept buoyant by buoyant concrete in the housing, inserted in a dam, under a barge or in a tidal power array.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
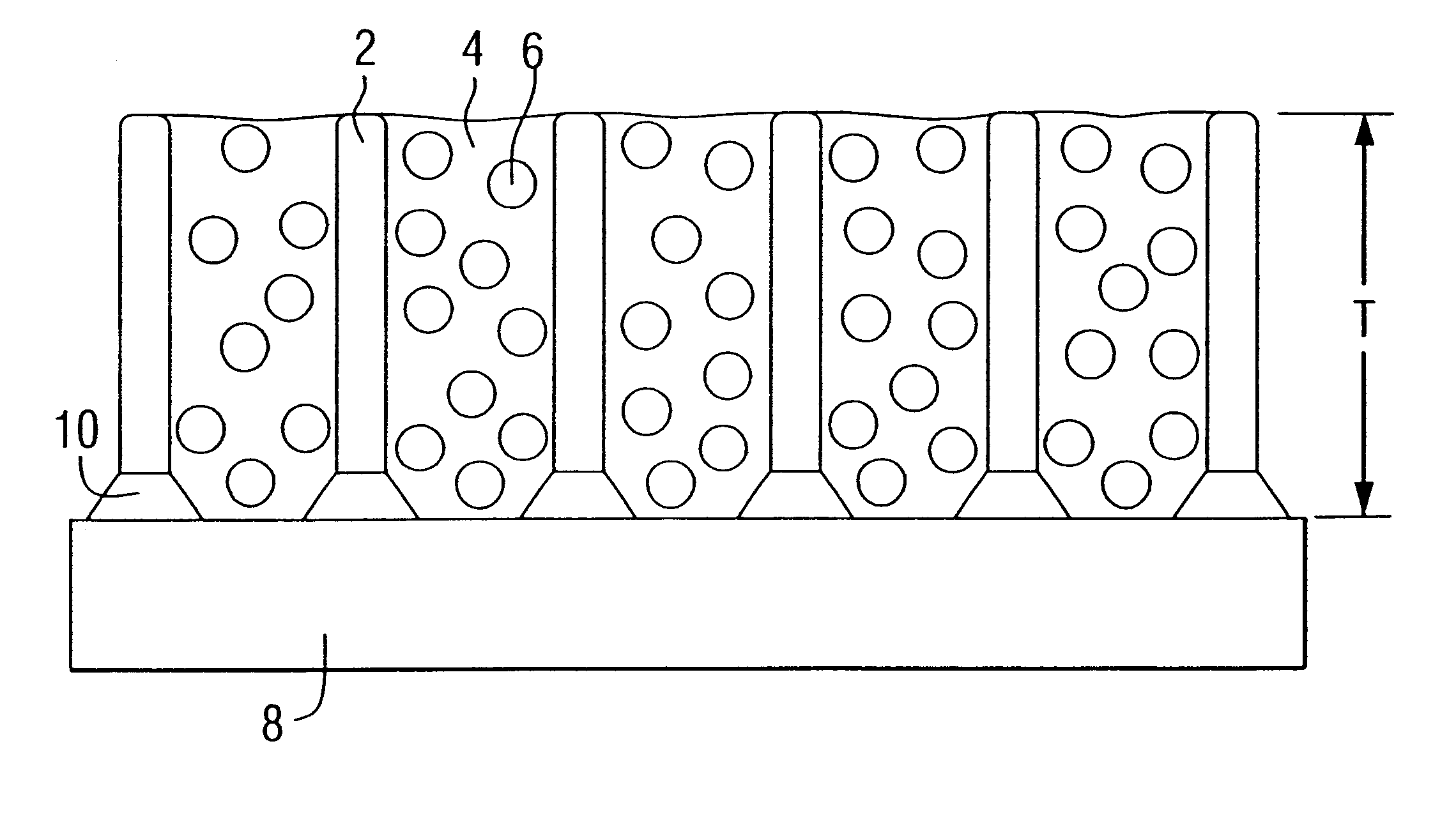
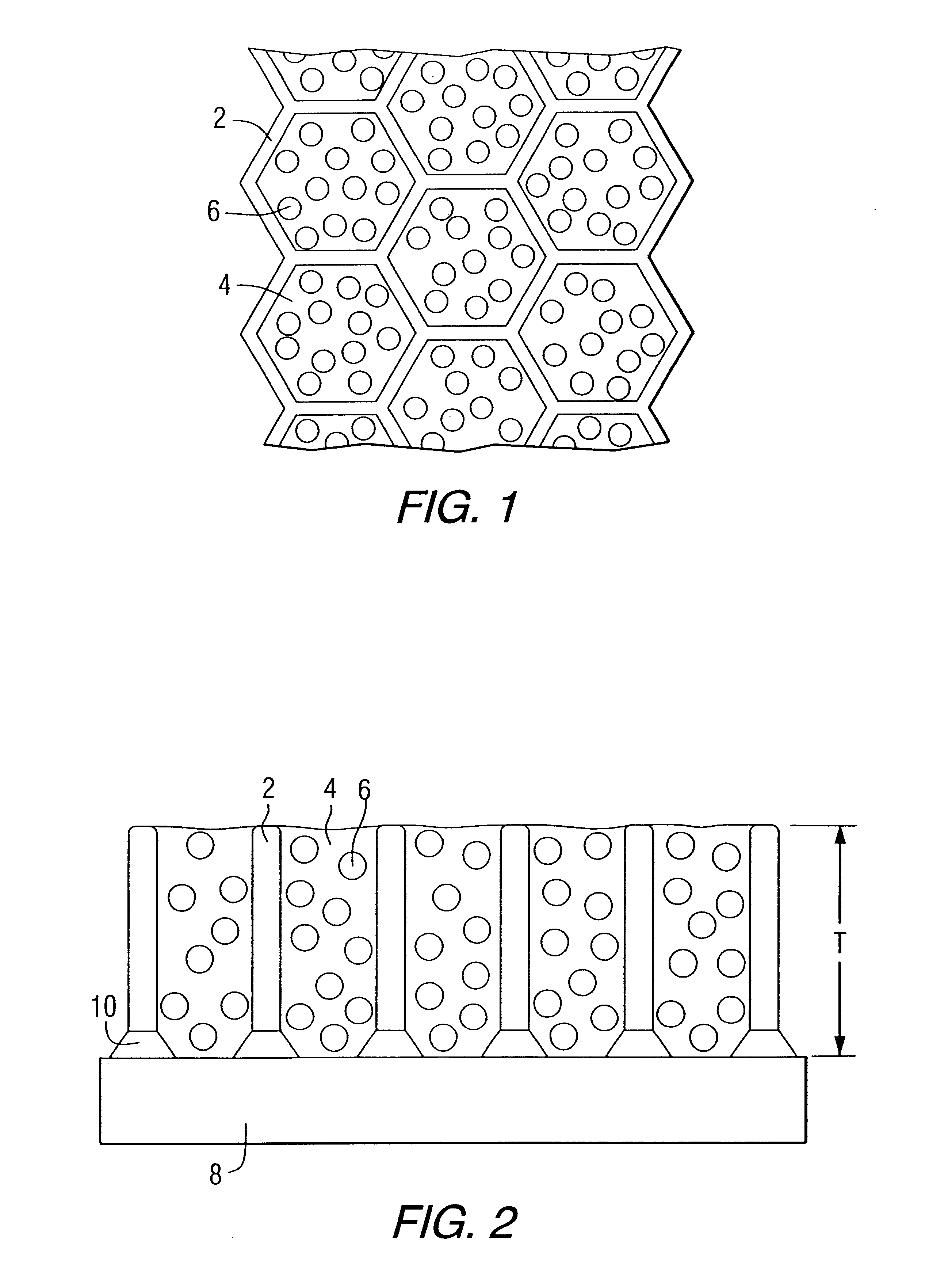
High temperature erosion resistant, abradable thermal barrier composite coating
InactiveUS6235370B1Improve wear resistanceImprove adhesionMolten spray coatingPump componentsCombustorHoneycomb
A composite thermal barrier coating system includes a honeycomb metallic structure filled with high thermal expansion ceramic hollow spheres in a phosphate bonded matrix. The composite thermal barrier coating system may be manufactured to thicknesses in excess of current thermal barrier coating systems, thereby imparting greater thermal protection. Superior erosion resistance and abrasion properties are also achieved. The composite thermal barrier coating is useful on combustion turbine components such as ring seal segments, vane segment shrouds, transitions and combustors.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Fluid energy converter
Embodiments include apparatus and methods of fluid energy conversion. One embodiment relates to a tube for a fluid energy converter. The tube may include a generally cylindrical and hollow body having an interior surface, an exterior surface, and a longitudinal axis. Another embodiment includes a fluid energy converter having a longitudinal axis and a rotatable tube coaxial about the longitudinal axis. In some embodiments, the rotatable tube converts kinetic energy in a fluid into rotating mechanical energy, or converts rotating mechanical energy into kinetic energy in a fluid.
Owner:VIRYD TECH
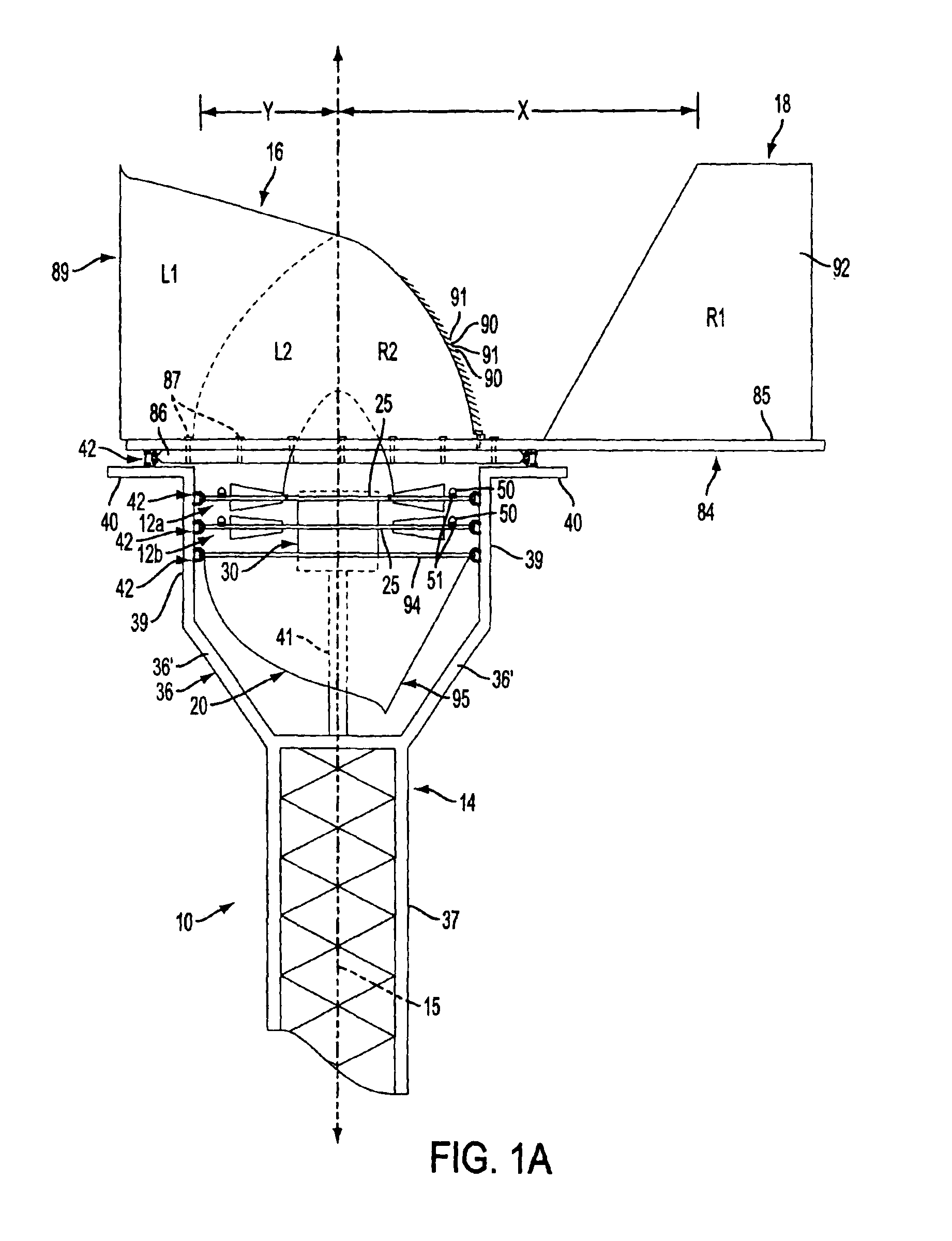
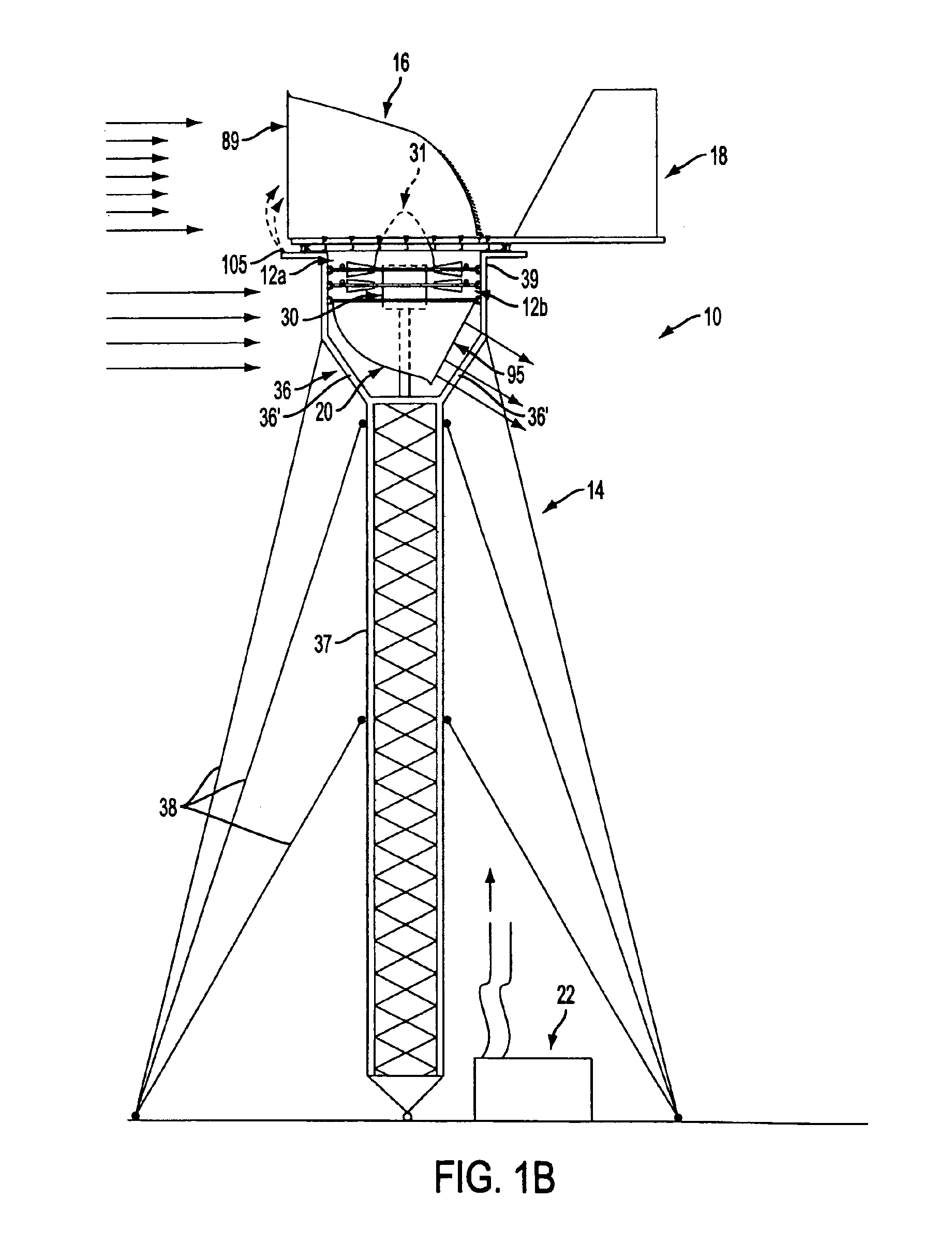
Variable geometry guide vane for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS7632064B2Improve load balancingImprove performancePropellersGas turbine plantsTurbineInlet flow
A variable geometry inlet guide vane for a gas turbine aircraft engine includes an aerodynamic shell for turning inlet flow to a turbine or compressor and an internal spar spaced from the airfoil shell by an air gap. A number of actuation mechanisms grounded to the spar and connected to the inner surface of the aerodynamic shell adjust the shape of the shell in response to varying operating conditions of the engine, imbalanced aerodynamic loading of the shell or vibration or other transient loads on the shell.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
CMC Vane Assembly Apparatus and Method
A metal vane core or strut (64) is formed integrally with an outer backing plate (40). An inner backing plate (38) is formed separately. A spring (74) with holes (75) is installed in a peripheral spring chamber (76) on the strut. Inner and outer CMC shroud covers (46, 48) are formed, cured, then attached to facing surfaces of the inner and outer backing plates (38, 40). A CMC vane airfoil (22) is formed, cured, and slid over the strut (64). The spring (74) urges continuous contact between the strut (64) and airfoil (66), eliminating vibrations while allowing differential expansion. The inner end (88) of the strut is fastened to the inner backing plate (38). A cooling channel (68) in the strut is connected by holes (69) along the leading edge of the strut to peripheral cooling paths (70, 71) around the strut. Coolant flows through and around the strut, including through the spring holes.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine blades made from multiple single crystal cast superalloy segments
InactiveUS6331217B1Improve bindingQuality improvementPropellersFrom frozen solutionsTurbine bladeSingle crystal
Large gas turbine blades made from separate cast segments of superalloys are disclosed. The turbine blade is designed such that bond lines between adjacent segments are placed in low stress regions of the blade. The cast superalloy segments of the blades are aligned and fitted together with specified tolerances. The turbine blade segments are then joined by transient liquid phase bonding, followed by a controlled heat treatment which produces the desired microstructure in the bond region. The method allows for the production of large, high quality turbine blades by joining small, high quality cast superalloy sections, in comparison with prior attempts to cast large turbine blades as single pieces which have produced very low yields and high individual component costs.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
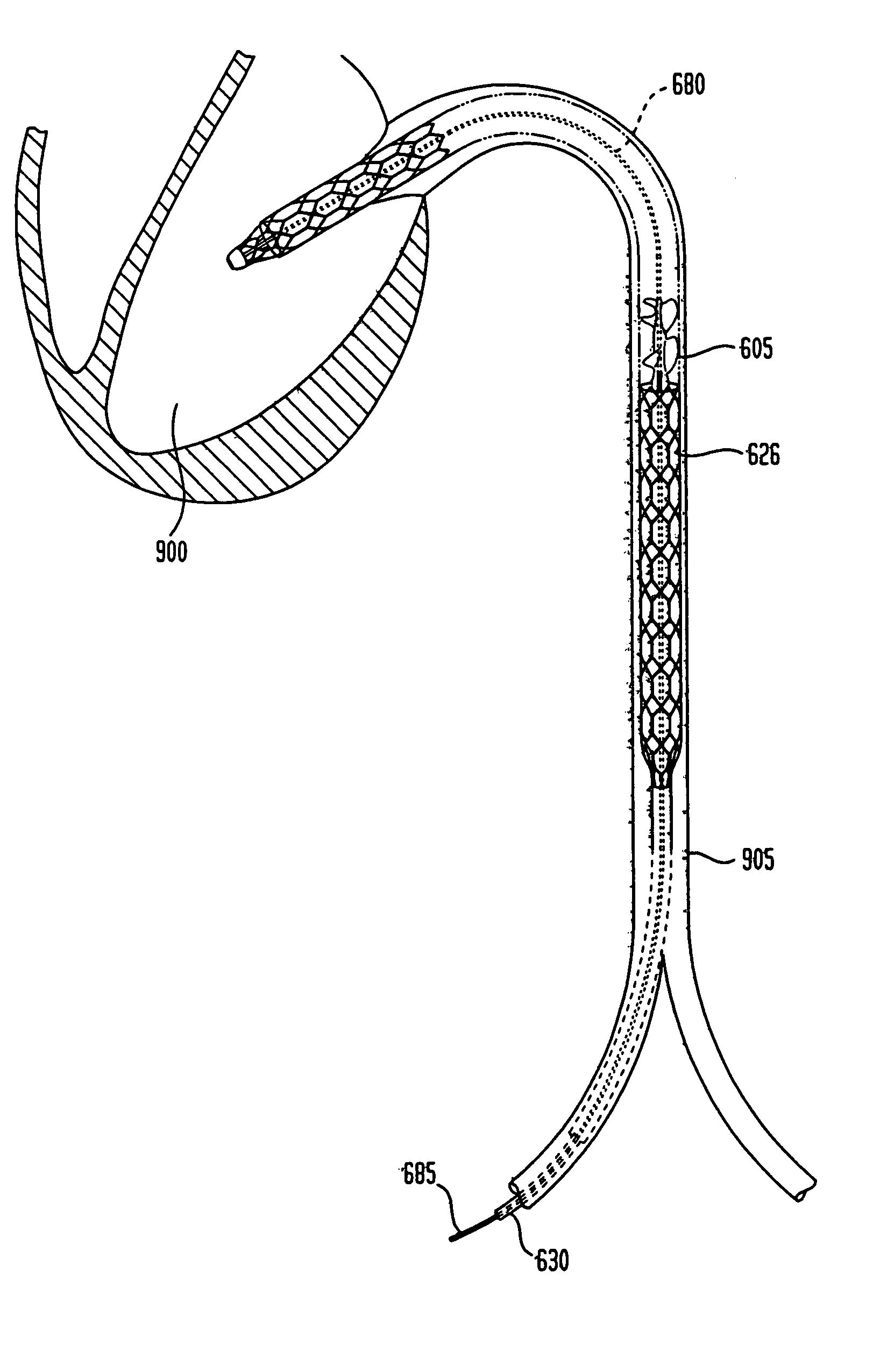
Rotary blood pump and control system therefor
Owner:TC1 LLC +1
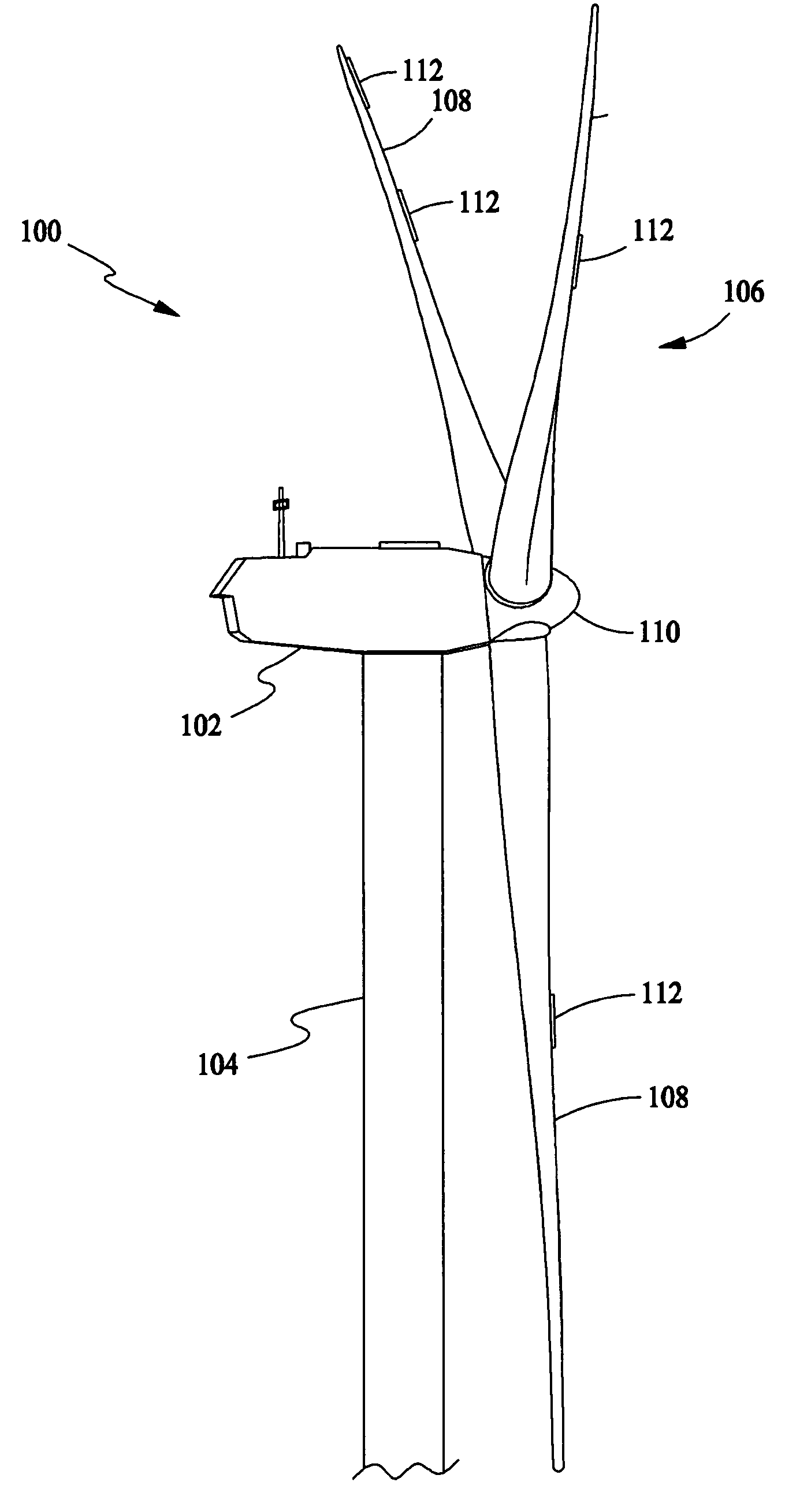
Wind energy conversion system
InactiveUS6952058B2Reduced weight and mass and costAdjustable sizePropellersWind motor supports/mountsWind energy conversionEngineering
A wind energy conversion system includes upper and lower wind turbines having counter-rotating blade assemblies supported for rotation about a vertical rotation axis, with each blade assembly carrying a rotor for rotation past a stator to produce an electrical output. The wind turbines are supported by a tower at an elevated position above the ground. Each wind turbine produces torque, and the wind energy conversion system provides for balancing the torques to avoid a net torque on the tower. Adjustment mechanisms are provided for adjusting blade pitch and for adjusting the size of an air gap between a stator and a rotor that comes into alignment with the stator as the rotor rotates therepast. The wind energy conversion system provides a hood for supplying intake air to a wind turbine and an exhaust plenum for exhausting air from the wind turbine, with the hood and the exhaust plenum being directionally positionable.
Owner:WECS
Hydro turbine generator
InactiveUS20050285407A1Minimize downstream efficiency lossMinimizing swirl lossEngine fuctionsWorking fluid for enginesStator coilEngineering
An apparatus is disclosed for a turbine for generating electrical power from water or air flow comprising at least one rotor disk having a plurality of hydrofoil blades, a guide vanes, a cylindrical housing, and a generator means. A rim generator comprising a magnet race rotor rim and fixed stator coils in the housing is used. The apparatus is fitted with a screen to stop the ingress of debris and marine life, and a skirt augmenter device to reduce the Betz effect. The apparatus is preferably for sub-sea deployment and driven by tidal currents, but may be powered by river current or wave driven air or by wind. The apparatus may be deployed on at least one telescoping pole, tethered to the sea-bed and kept buoyant by buoyant concrete in the housing, inserted in a dam, under a barge or in a tidal power array.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
Wind turbine ring/shroud drive system
InactiveUS6951443B1Easy to adaptEliminate structureWind motor controlPump componentsNacelleGear drive
A wind turbine capable of driving multiple electric generators having a ring or shroud structure for reducing blade root bending moments, hub loads, blade fastener loads and pitch bearing loads. The shroud may further incorporate a ring gear for driving an electric generator. In one embodiment, the electric generator may be cantilevered from the nacelle such that the gear on the generator drive shaft is contacted by the ring gear of the shroud. The shroud also provides protection for the gearing and aids in preventing gear lubricant contamination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
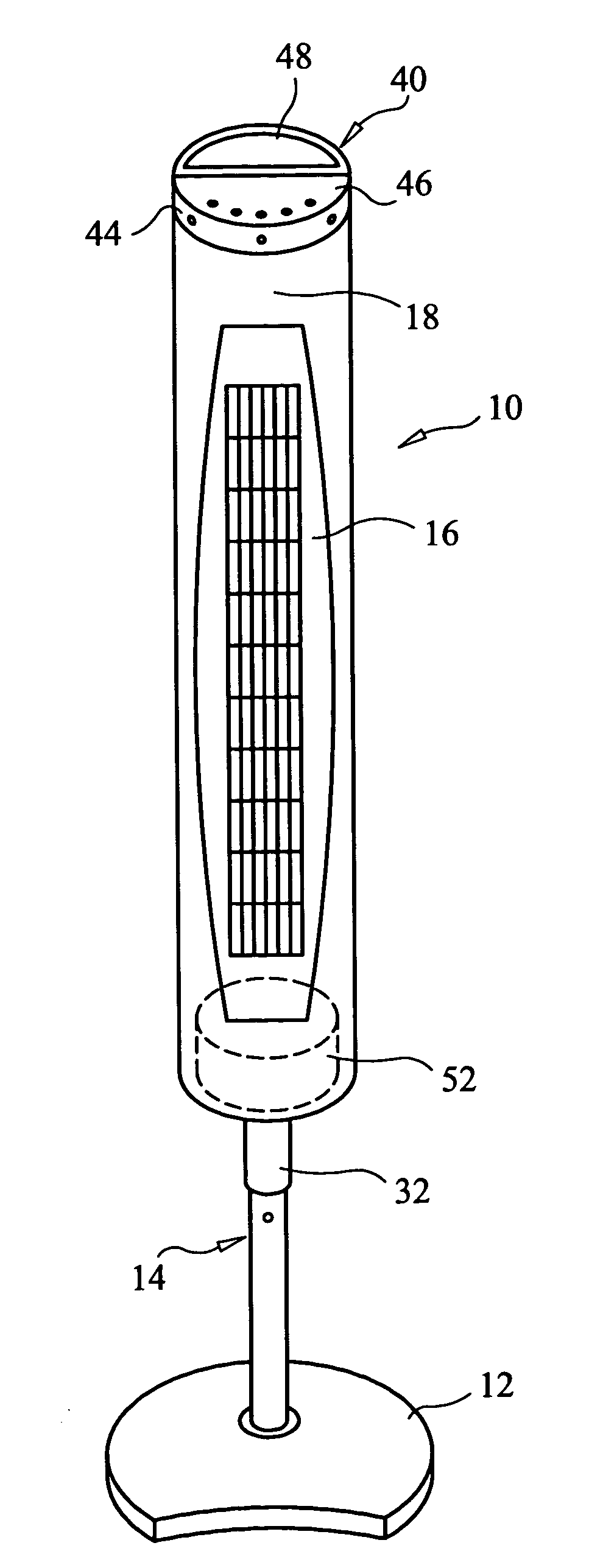
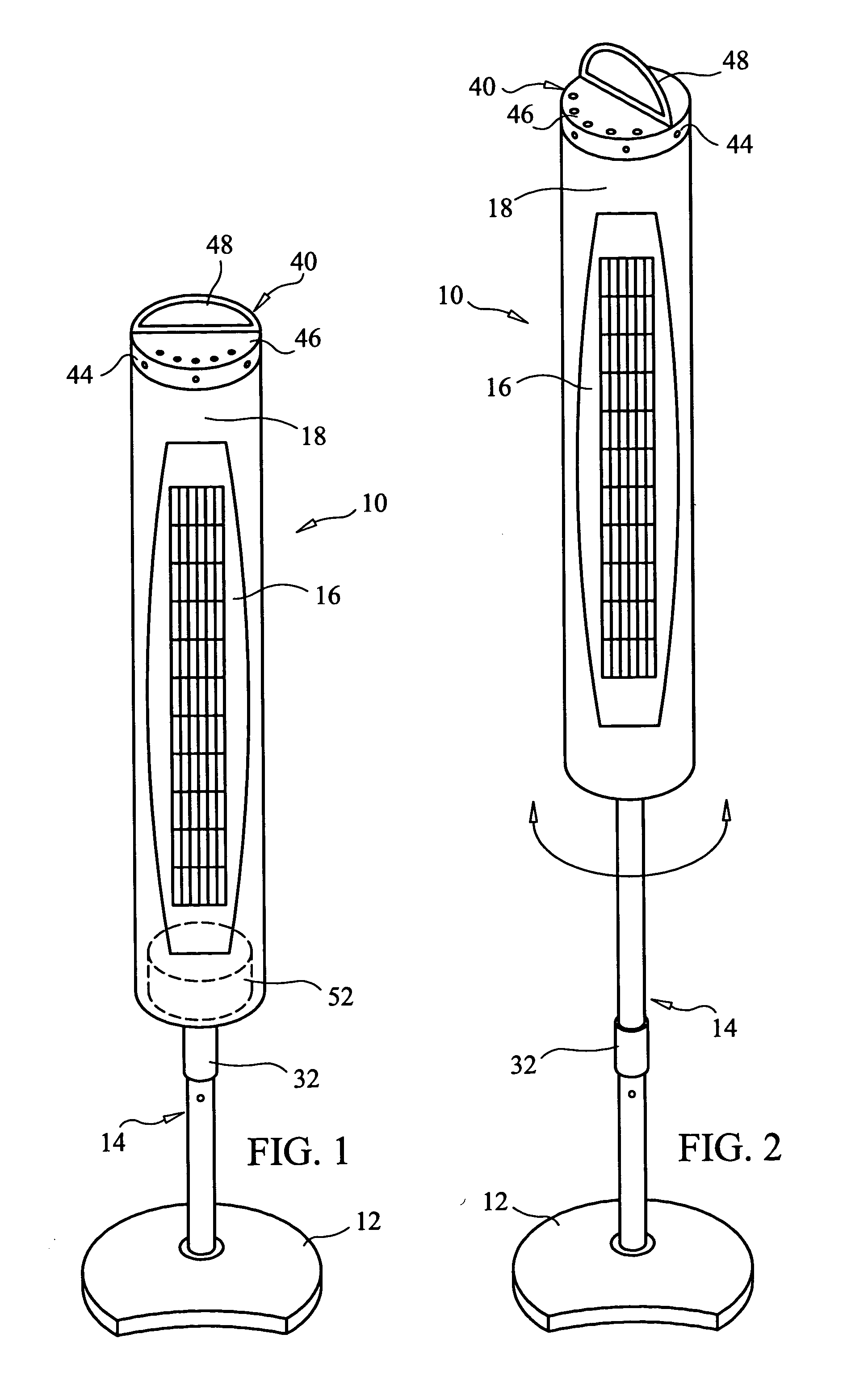
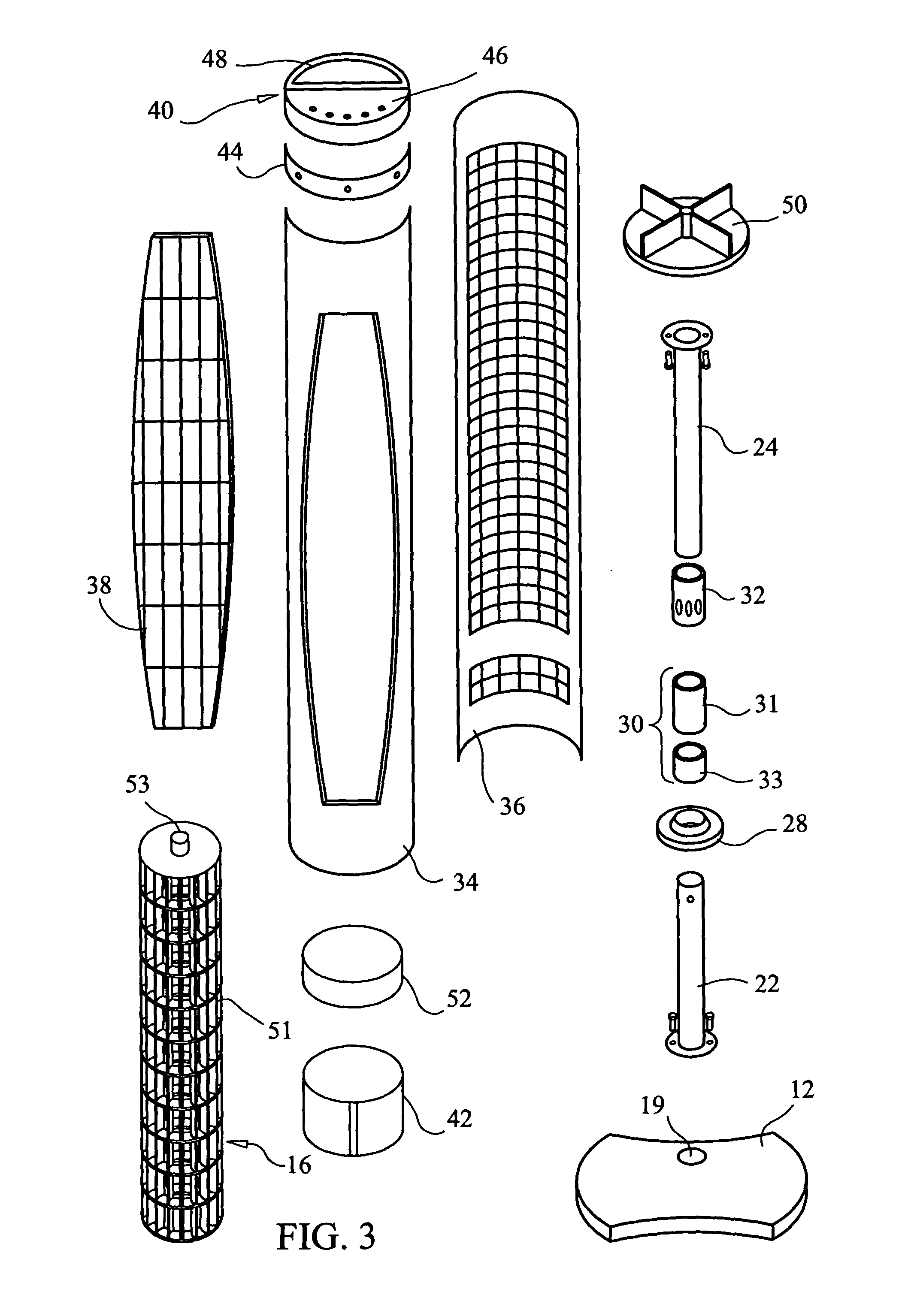
Tower fan assembly with telescopic support column
A vertical axis tower fan apparatus having an adjustable support column. The tower fan apparatus is comprised of a support base, a telescopic support column adjustable between fixed, retracted and extended positions, a vertical axis propeller encased within a housing, and a motor. The vertical axis propeller is contained within the cylindrical housing, wherein the housing is rotatably coupled to one end of the support column. The fan is rotatably connected to the top of the support column and is adapted to rotate freely thereon, when activated. The opposing end of the column is insertable into the support base. The telescopic column is comprised of a hollow pillar and an extendable member removably inserted within the hollow pillar. The column is manually adjustable to a variety of heights to provide cooling air to different target heights via the use of an adjustable locking sleeve. The sleeve may be loosened, to allow the extendable member to be extracted from within the hollow pillar and raised until the fan reaches a desirable height. Conversely, the extendable member may be retracted until the fan reaches another target height. When the desired height is reached, the sleeve is tightened thereby preventing the member from moving within the pillar. A keypad located in the housing cover, or a remote control unit allows the user to program the fan, via the use of a microcontroller within the fan housing, to achieve a variety of speeds and wind patterns, as well as activating an oscillation mode and a timer.
Owner:ATICO INT USA
Wind energy system with fluid-working machine with non-symmetric actuation
The invention relates to a wind energy system with hydraulic energy transmission with non-symmetric actuation. The non-symmetric actuation is caused by valve control and mechanical means for controlling the actuation of the pistons. A cylinder unit is provided comprising a drive unit and an output unit associated with two hydraulic connections. The drive and the output unit comprise a minimum of two cylinders, in which pistons are reciprocating. Some of the cylinders can be switched off during low wind speeds. The cylinders communicate with a low pressure manifold and a high pressure manifold. These manifolds are part of the hydraulic connections. Use of the fluid-working machine as transmission in wind energy systems increases the overall economical efficiency.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Double ended blower and volutes therefor
InactiveUS20030168064A1Faster pressure rise timeImprove reliabilityPropellersElement comparisonMotor speedImpeller
A double-ended variable speed blower for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) ventilation of patients includes two impellers in the gas flow path that cooperatively pressurize gas to desired pressure and flow characteristics. Thus, the double-ended blower can provide faster pressure response and desired flow characteristics over a narrower range of motor speeds, resulting in greater reliability and less acoustic noise.
Owner:RESMED LTD
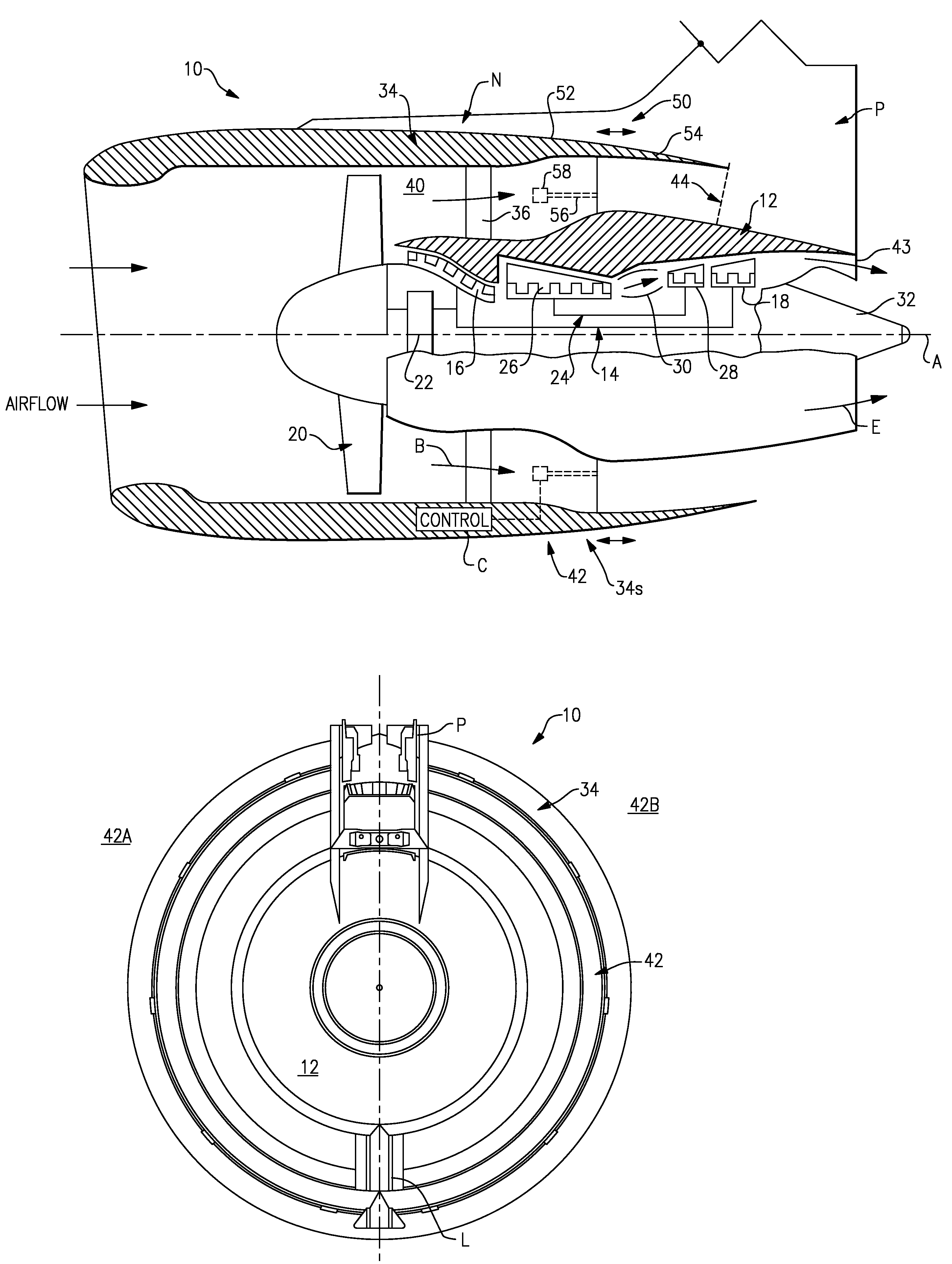
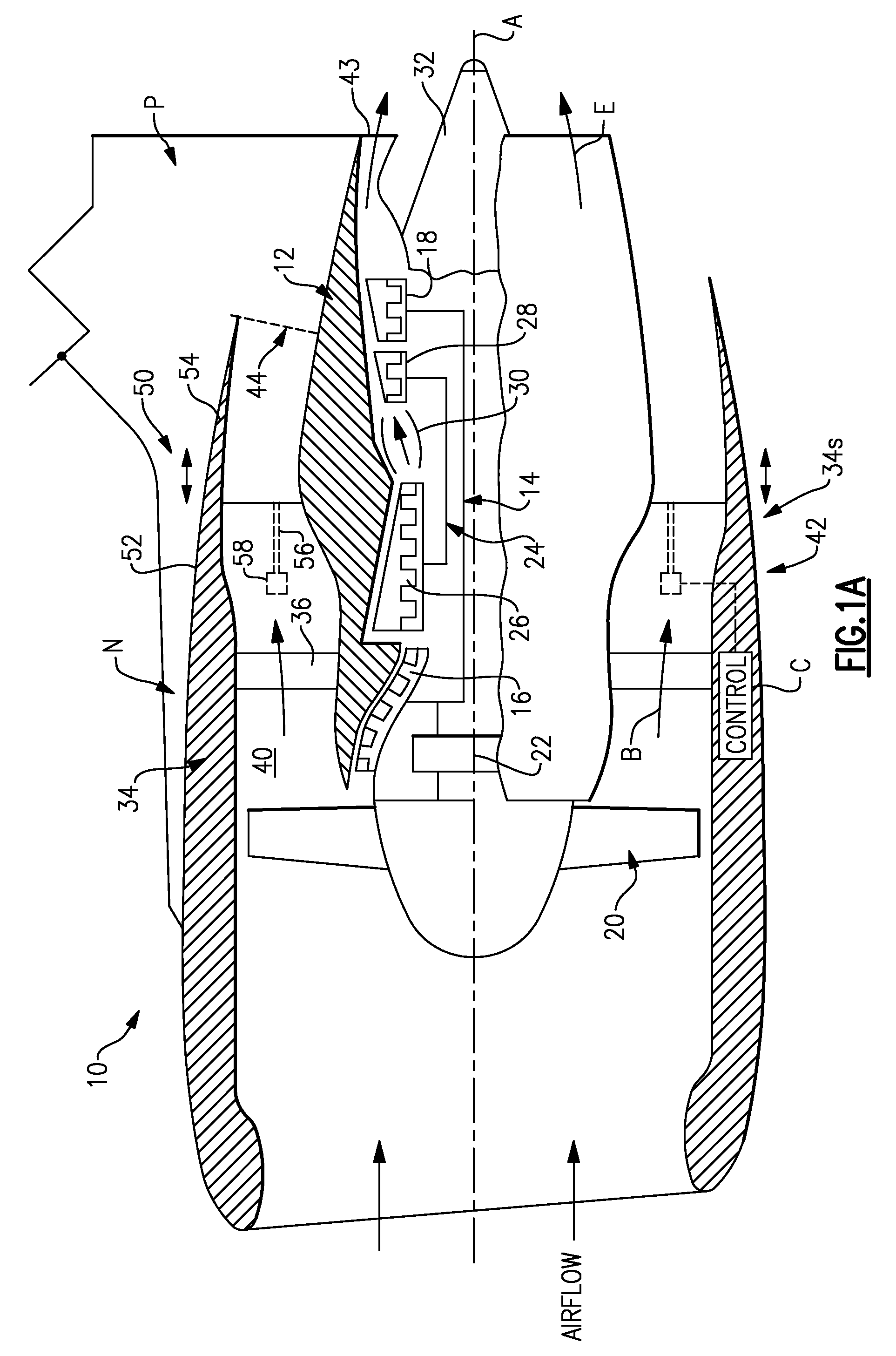
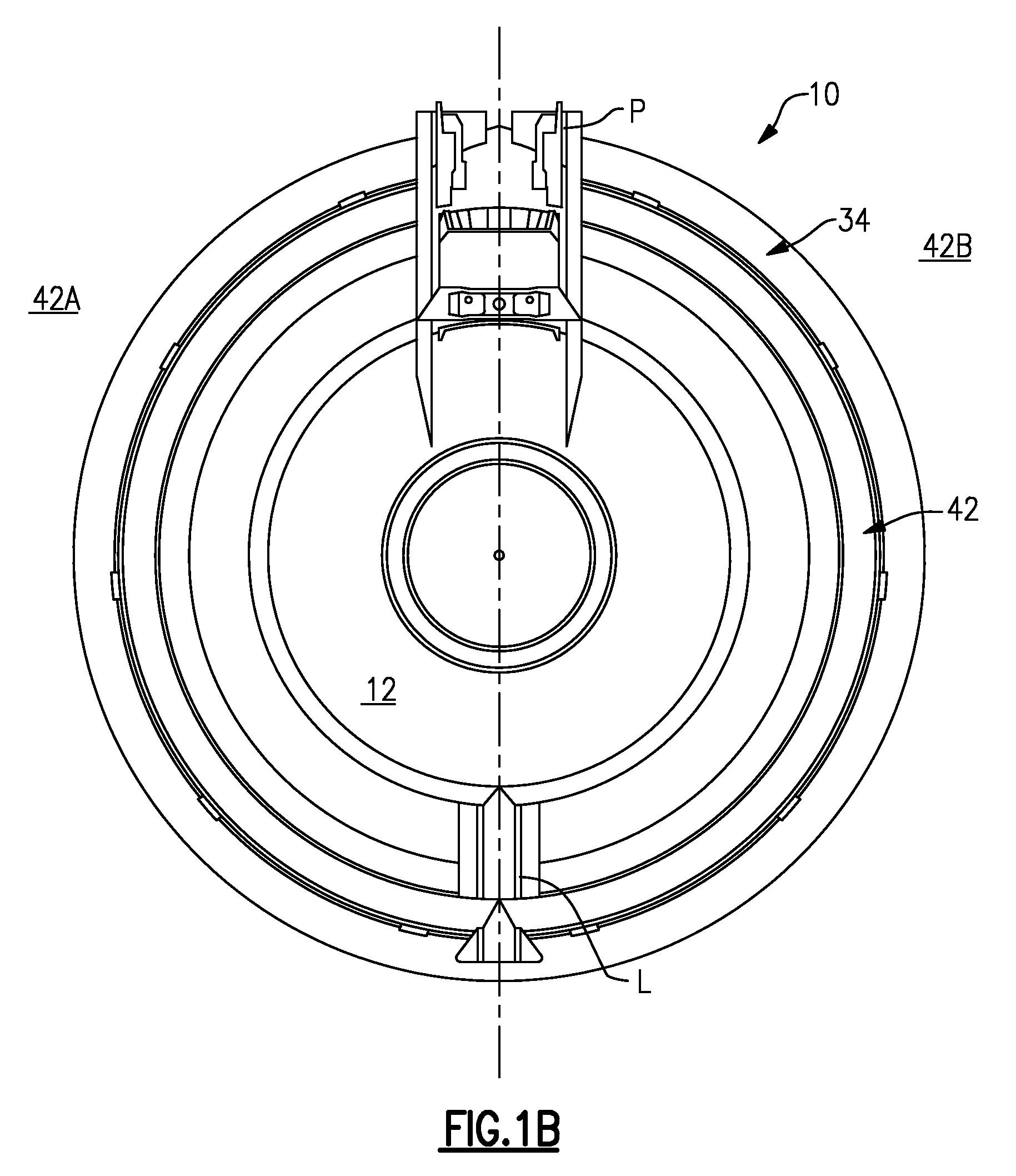
Gas turbine engine with axial movable fan variable area nozzle
ActiveUS20090053058A1Efficiency sometimes variesEnhanced ground operationPower plant exhaust arrangementsPump componentsNacelleTurbofan
A turbofan engine includes a fan variable area nozzle includes having a first fan nacelle section and a second fan nacelle section movably mounted relative the first fan nacelle section. The second fan nacelle section axially slides aftward relative to the fixed first fan nacelle section to change the effective area of the fan nozzle exit area.
Owner:RTX CORP
Methods and apparatus for rotor blade ice detection
ActiveUS7086834B2Lower performance requirementsPropellersWind motor controlIcing conditionsEngineering
A method for detecting ice on a wind turbine having a rotor and one or more rotor blades each having blade roots includes monitoring meteorological conditions relating to icing conditions and monitoring one or more physical characteristics of the wind turbine in operation that vary in accordance with at least one of the mass of the one or more rotor blades or a mass imbalance between the rotor blades. The method also includes using the one or more monitored physical characteristics to determine whether a blade mass anomaly exists, determining whether the monitored meteorological conditions are consistent with blade icing; and signaling an icing-related blade mass anomaly when a blade mass anomaly is determined to exist and the monitored meteorological conditions are determined to be consistent with icing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Airfoil shape for a turbine bucket
InactiveUS6854961B2Improve performanceReduction of thermalEngine manufactureOther chemical processesTurbine bladeEngineering
First stage turbine buckets have airfoil profiles substantially in accordance with Cartesian coordinate values of X, Y and Z set forth Table I wherein X and Y values are in inches and the Z values are non-dimensional values from 0 to 1 convertible to Z distances in inches by multiplying the Z values by the height of the airfoil in inches. The X and Y values are distances which, when connected by smooth continuing arcs, define airfoil profile sections at each distance Z. The profile sections at each distance Z are joined smoothly to one another to form a complete airfoil shape. The X, Y and Z distances may be scalable as a function of the same constant or number to provide a scaled up or scaled down airfoil section for the bucket. The nominal airfoil given by the X, Y and Z distances lies within an envelop of ±0.055 inches in directions normal to the surface of the airfoil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
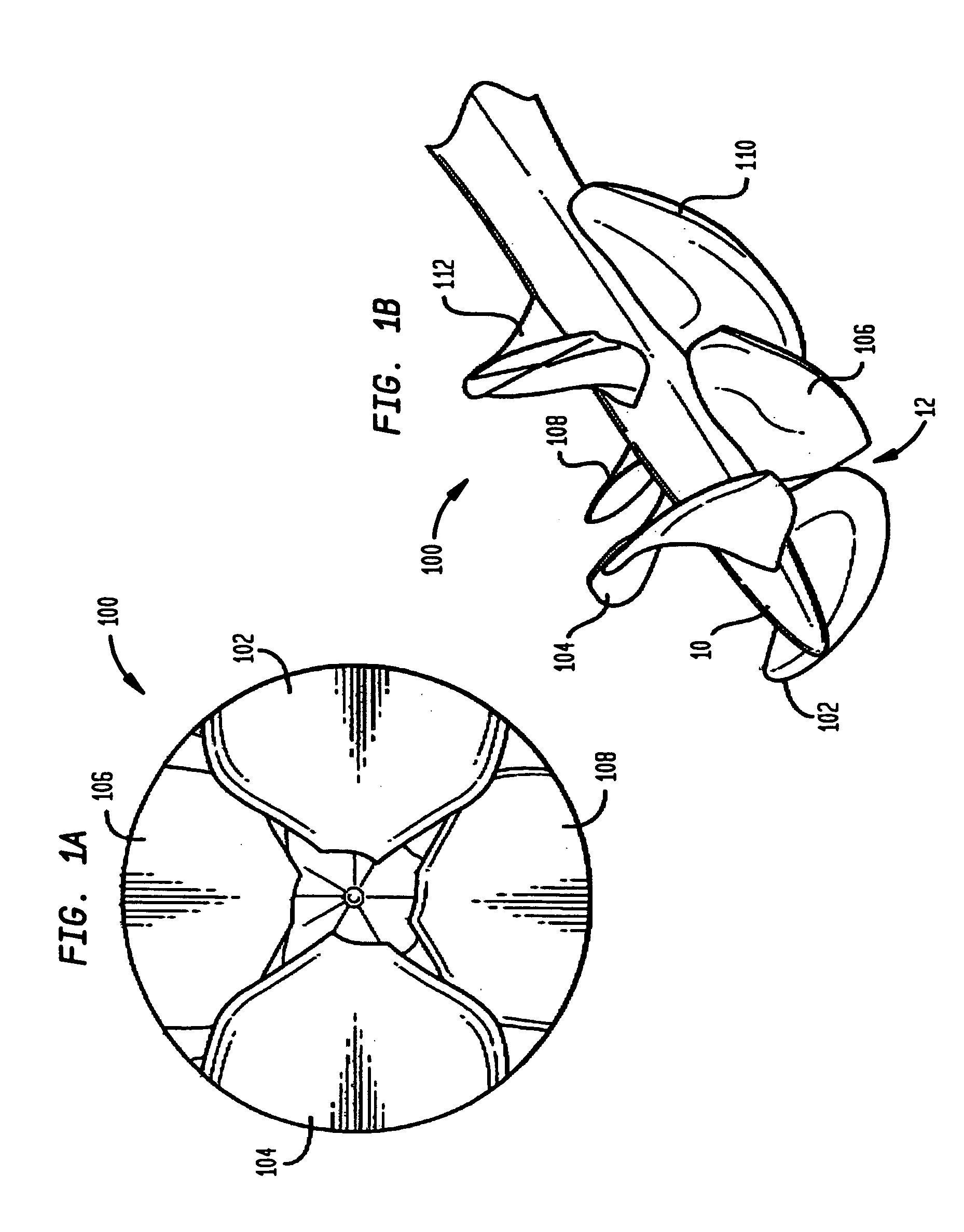
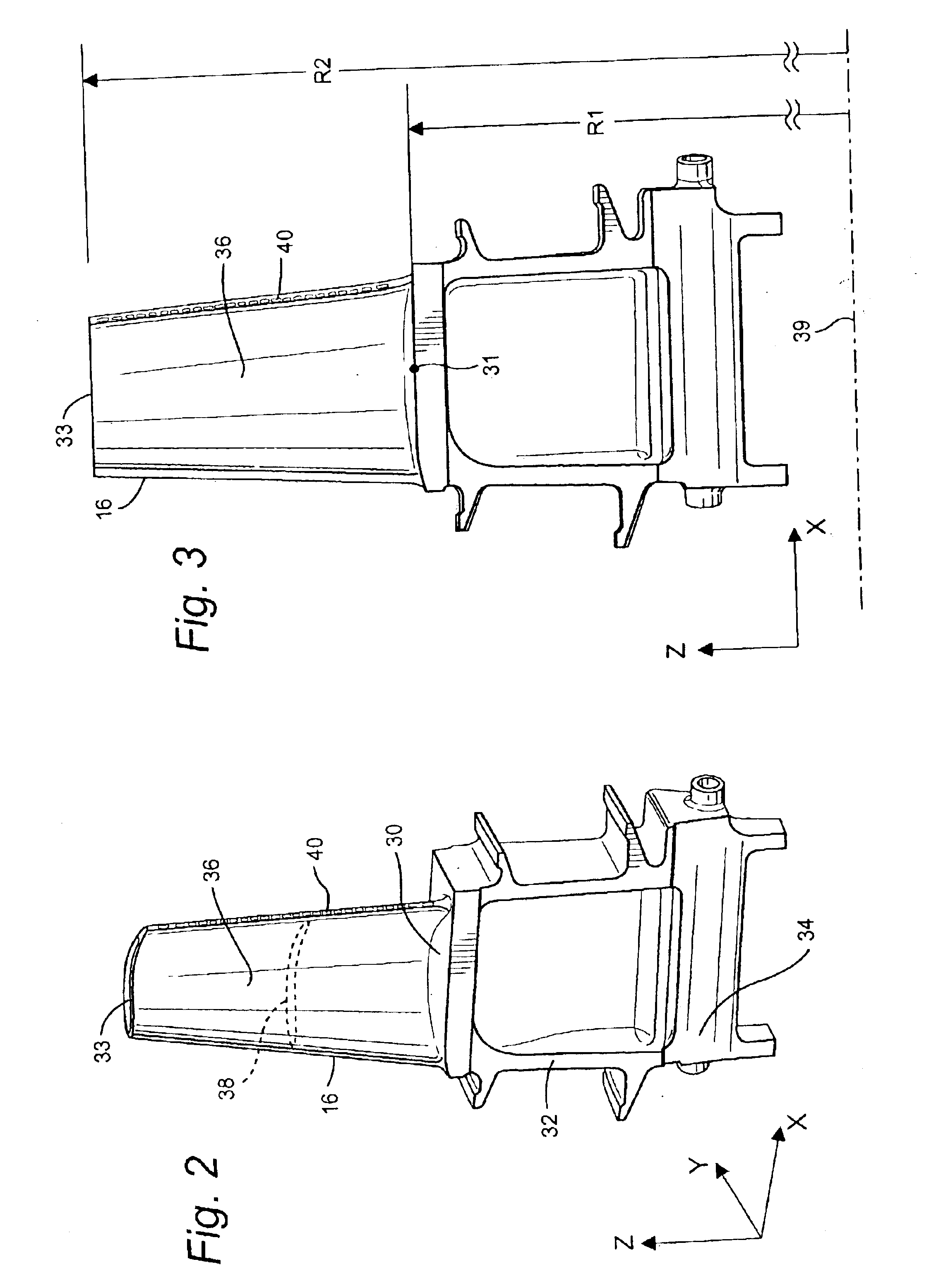
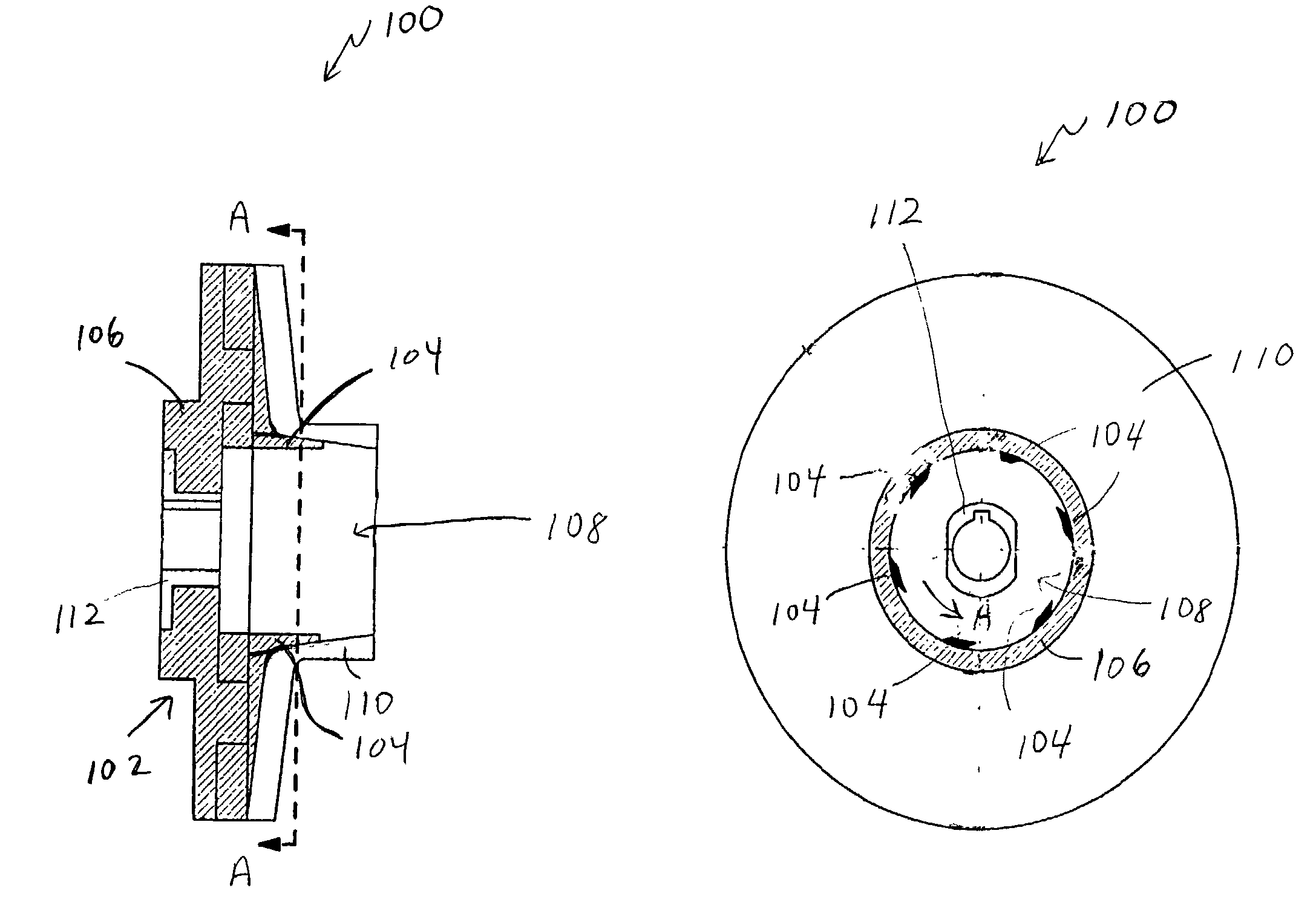
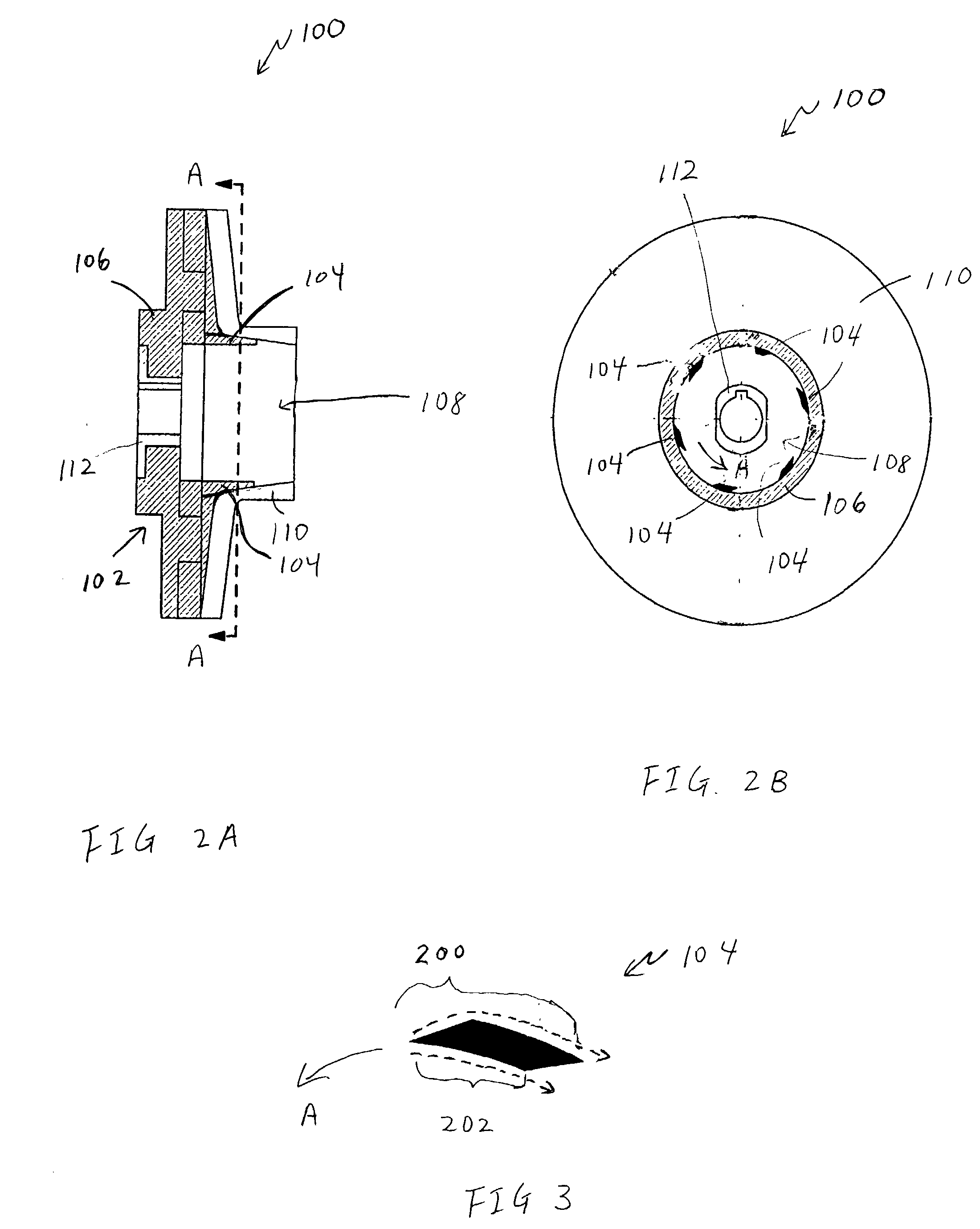
Impeller assembly for centrifugal pumps
InactiveUS20030231959A1Shorten the time periodExpedite evacuationPropellersRotary propellersEngineeringEye opening
An impeller assembly for centrifugal pumps that enables self-priming in a relatively short time period includes an impeller and at least one winglet (e.g., six winglets with a trapezium cross-sectional shape). The impeller includes an impeller body with an eye opening therein. The eye opening is configured for the passage of a fluid (e.g., water) therethrough when the impeller assembly is in use. The impeller body also includes at least one vane, with a leading end, disposed about the eye opening. The at least one winglet is positioned to protrude into the eye opening of the impeller body and may, for example, be coupled to the leading end of the vane.
Owner:HACKETT WILLIAM FRANKLIN JR
Heart failure/hemodynamic device
Owner:HRIDAYA
Fan mounting means and method of making the same
InactiveUS20050069407A1Quickly and reliably and economically manufacturedPump componentsNon-rotating vibration suppressionImpellerEngineering
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
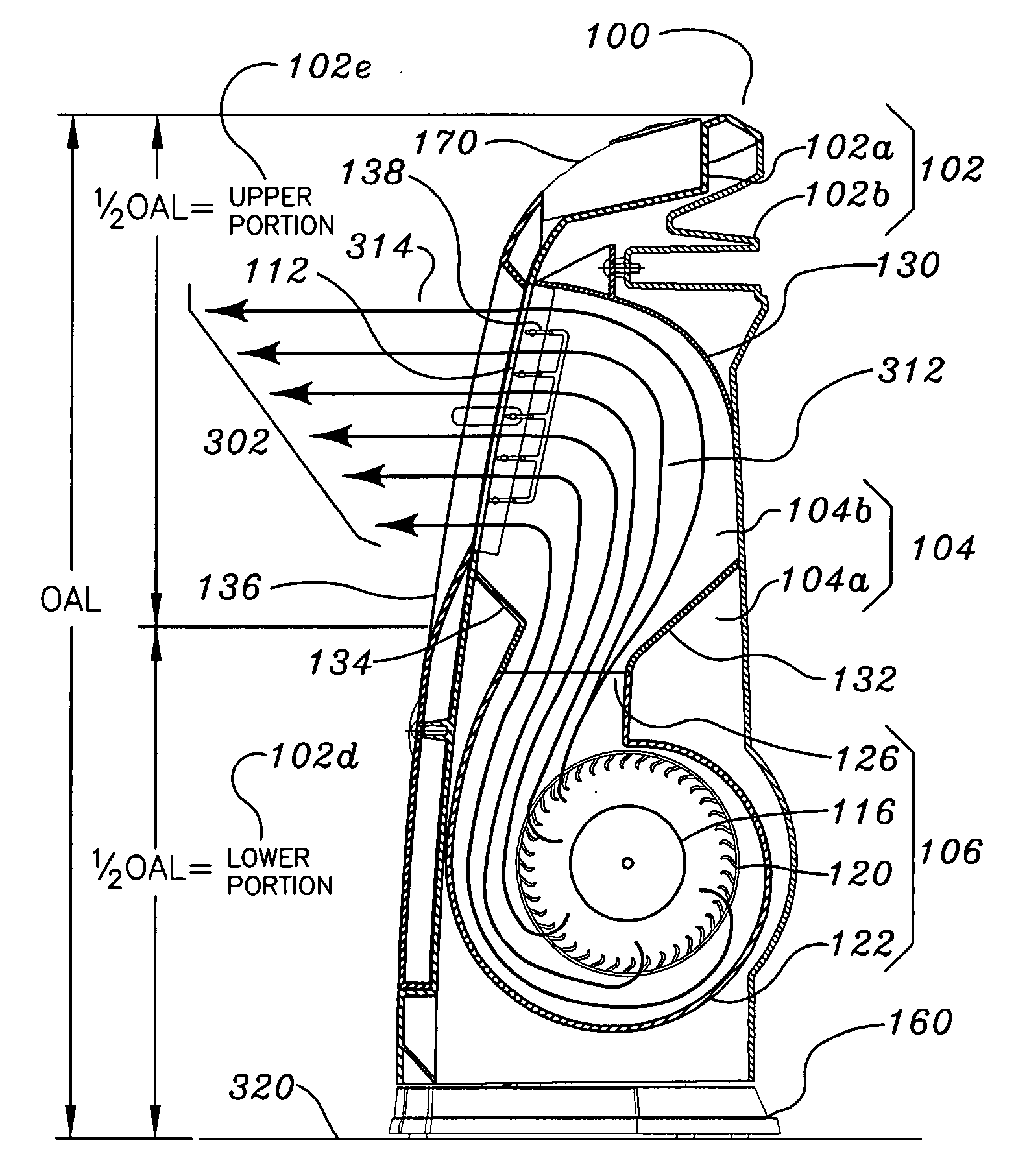
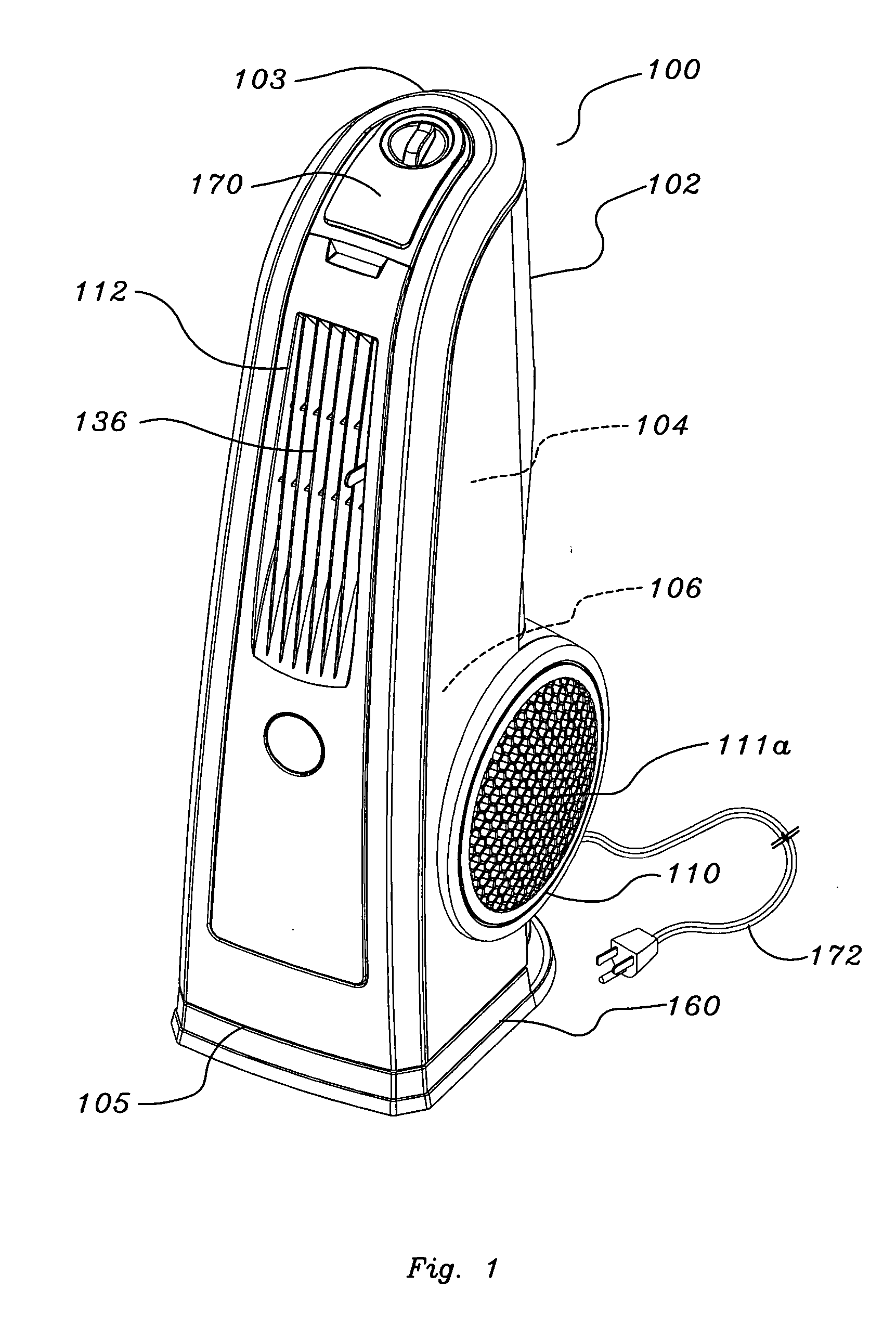
Portable air moving device
ActiveUS20050031448A1Maximize evaporationEfficiently impingePropellersPump componentsAir blowerSupport surface
A stable portable air moving device capable of generating an air stream elevated above a support surface allowing the air stream to be directed as desired by the user is provided. The device includes an air blower assembly located within an elongate housing generating an exhaust air stream that exits the elongate housing at an elevation above the air blower assembly.
Owner:LASKO OPERATION HLDG LLC
Centrifugal blood pump
The present invention provides a blood pump capable of substantially completely preventing thrombus from attaching to the inner bottom portion of the casing without lowering the anti-hemolytic characteristic of blood. A centrifugal blood pump in accordance with the present invention comprises a pump casing, a suction inlet disposed at the central portion on the upper side of the casing, a delivery outlet disposed at the bottom peripheral portion of the casing, a main impeller (D in diameter) for forming a centrifugal flow of blood supplied from the suction inlet in the range from the central portion to the peripheral portion to feed the blood to the delivery outlet, wherein the main impeller is provided with an stirring impeller, the surface of which is provided with one or more stirring elements (L in entire length) having the shape of a fin or a groove, and the dimensions of the stirring elements are determined to satisfy inequality (1): 0.43<LD<1.30 and inequality (2) 0.03<S / A<0.21, where S is the surface area of the blood contact surfaces of the stirring elements.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com