Patents
Literature
77 results about "Heart failure cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heart failure cells are siderophages (hemosiderin-containing macrophages) generated in the alveoli of patients with left heart failure or chronic pulmonary edema, when the high pulmonary blood pressure causes red cells to pass through the vascular wall. Siderophages are not specific of heart failure. They are present wherever red blood cells encounter macrophages.
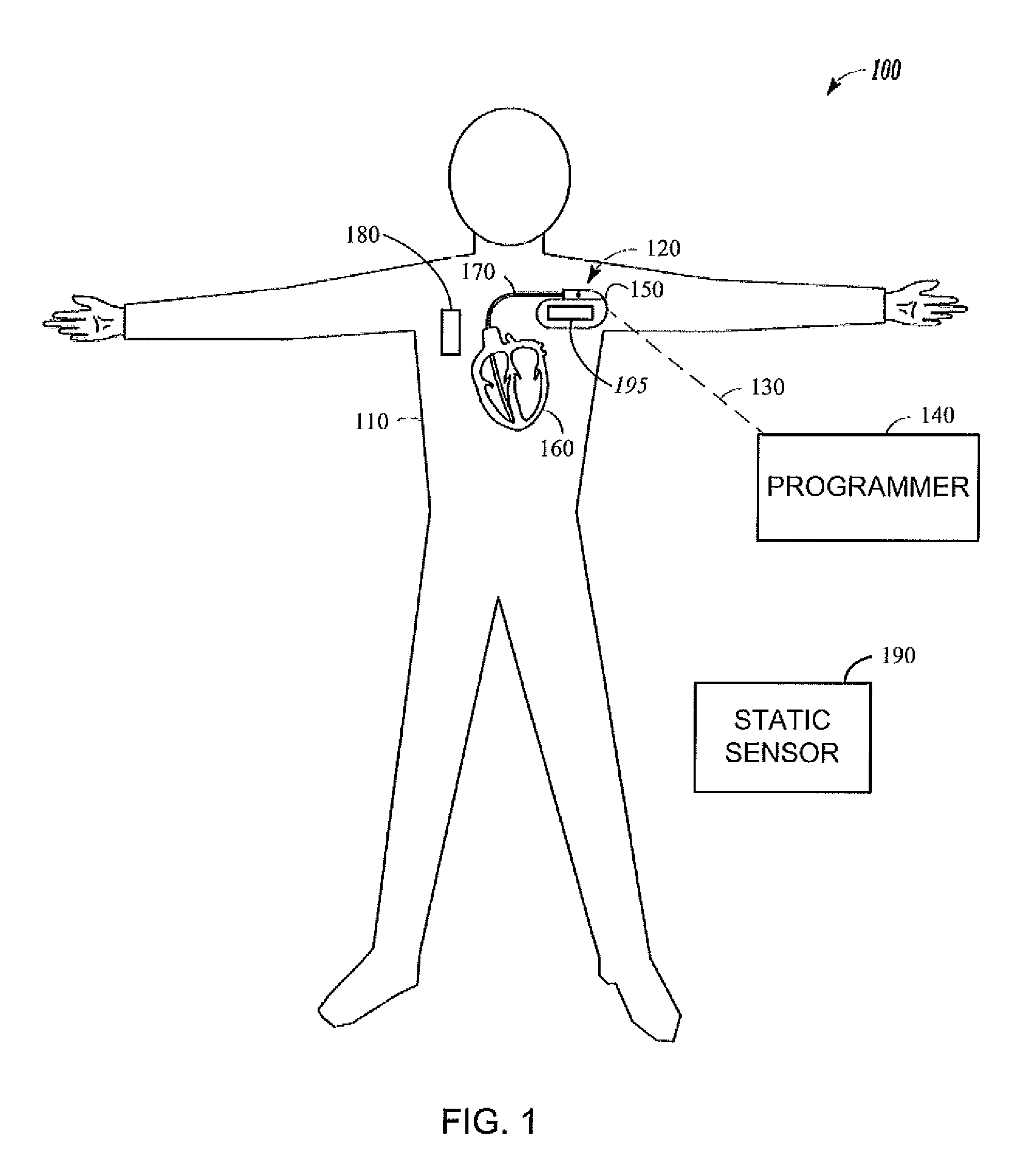
Heart failure/hemodynamic device
Owner:HRIDAYA
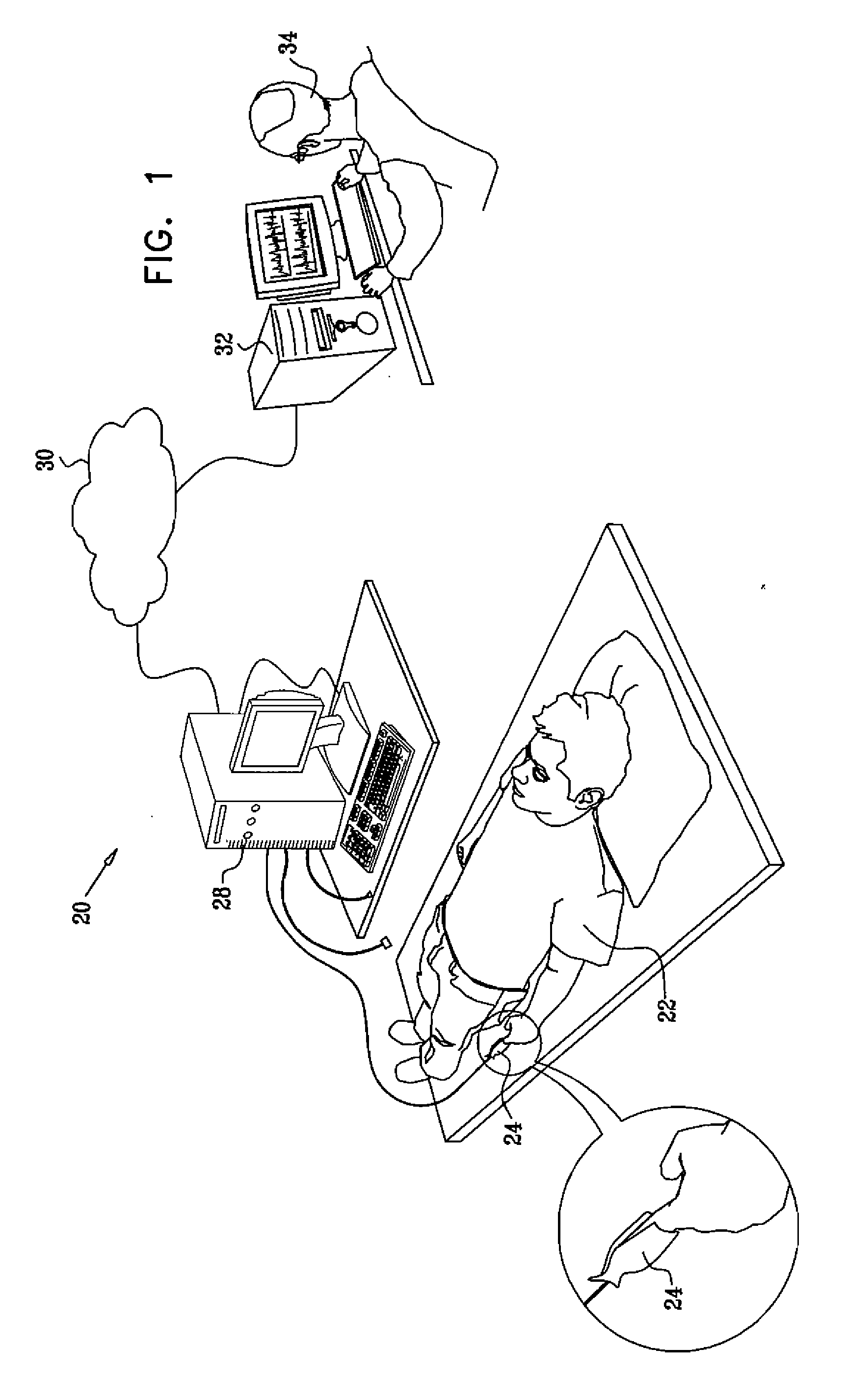
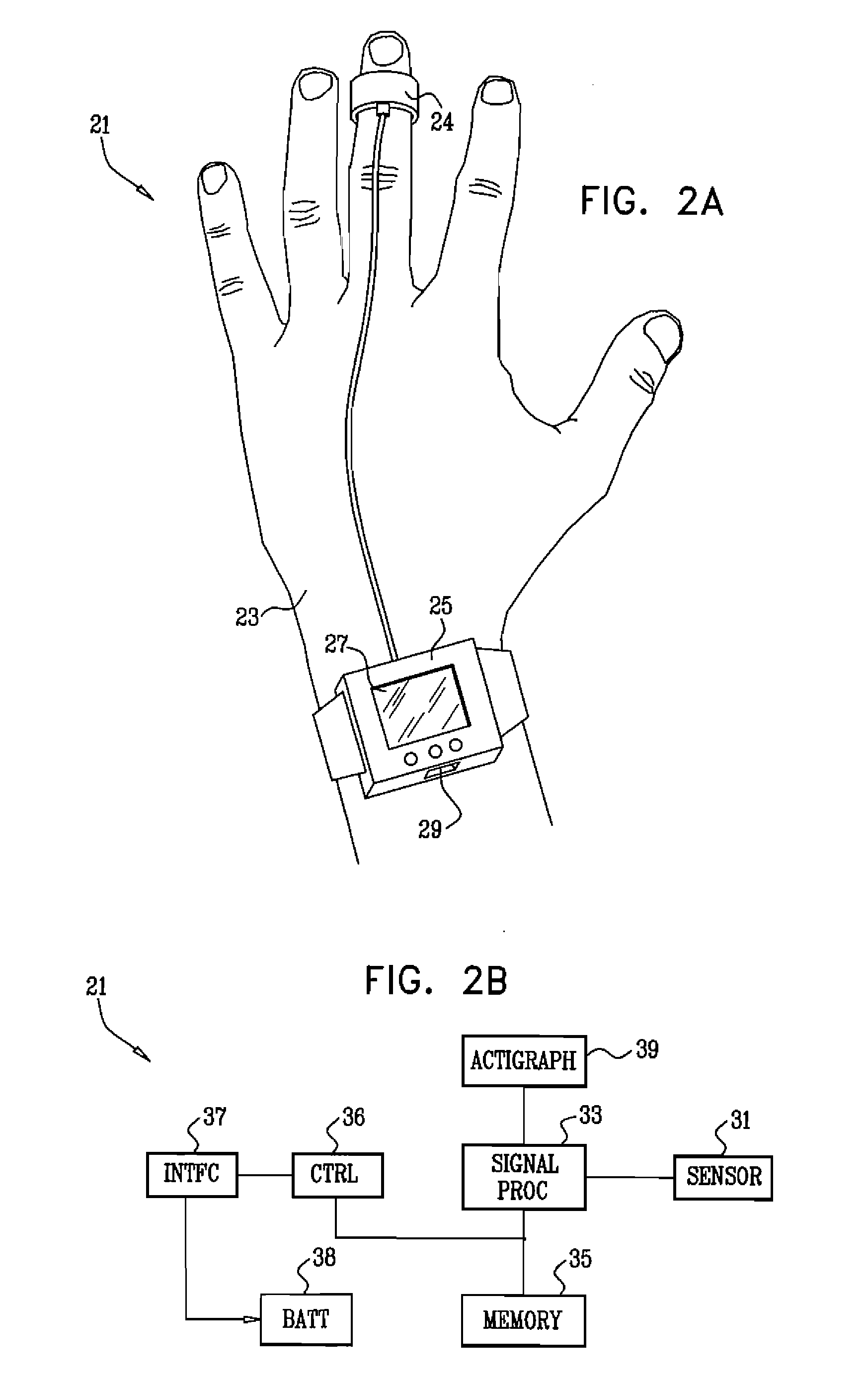
Detection of heart failure using a photoplethysmograph
ActiveUS20070213621A1Monitored comfortably and convenientlyHigh frequencyElectrocardiographyCatheterHeart failure cellRespiratory frequency
A method for diagnosis includes receiving a signal associated with blood oxygen saturation of a patient during sleep. The signal is filtered so as to eliminate signal components at frequencies equal to and greater than a respiratory frequency of the patient. The filtered signal is processed to detect a pattern corresponding to multiple cycles of periodic breathing.
Owner:WIDEMED
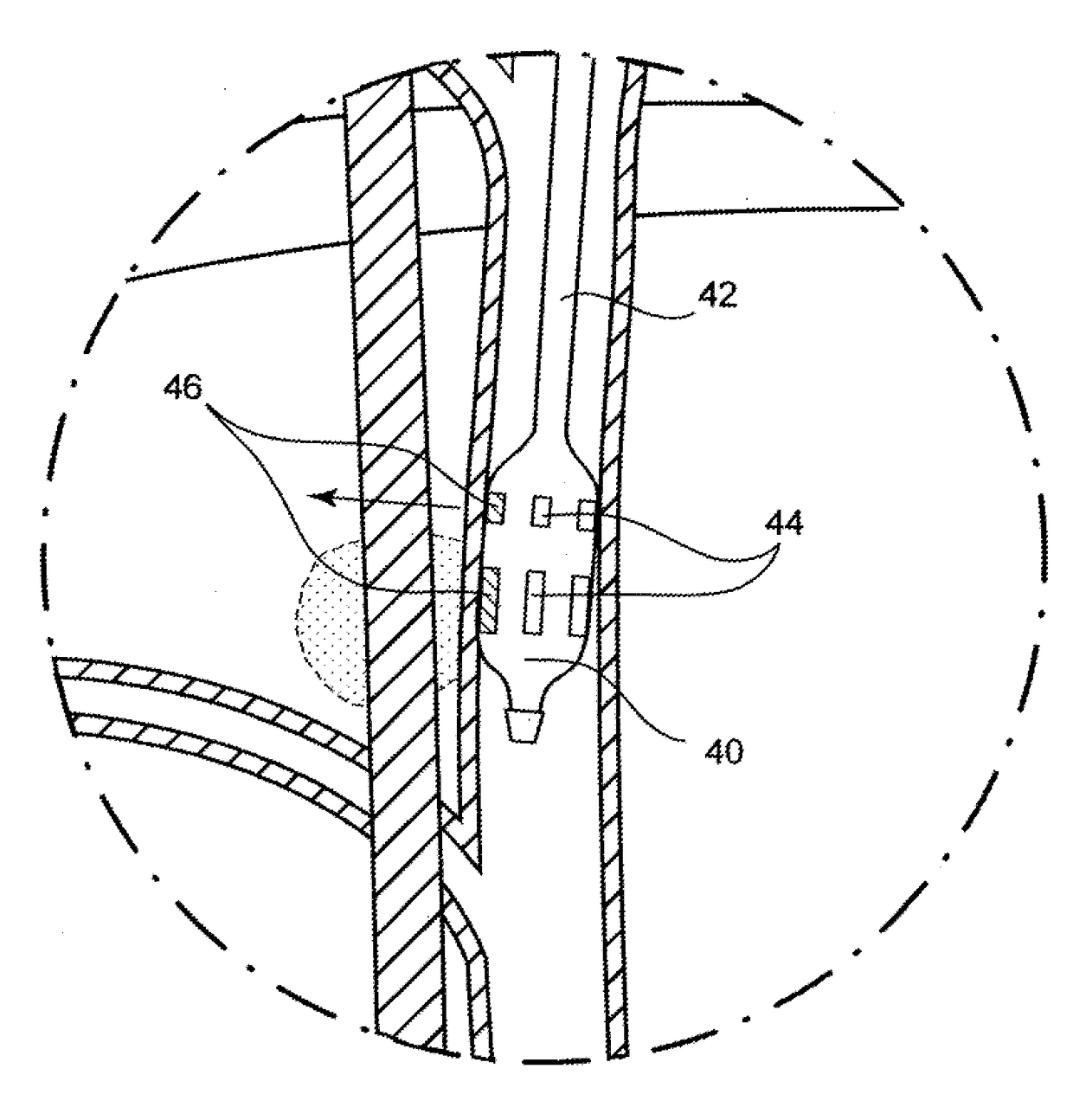
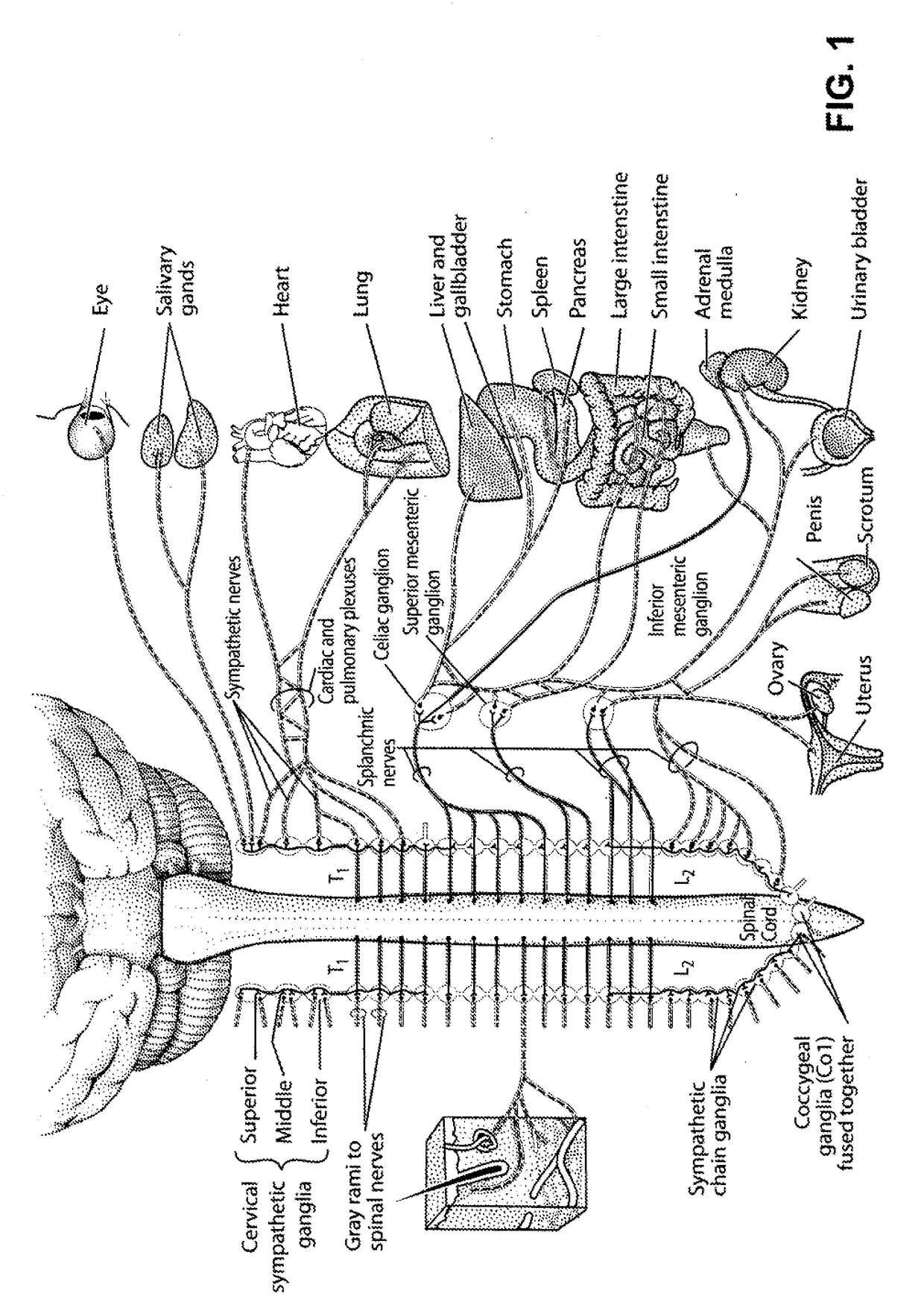
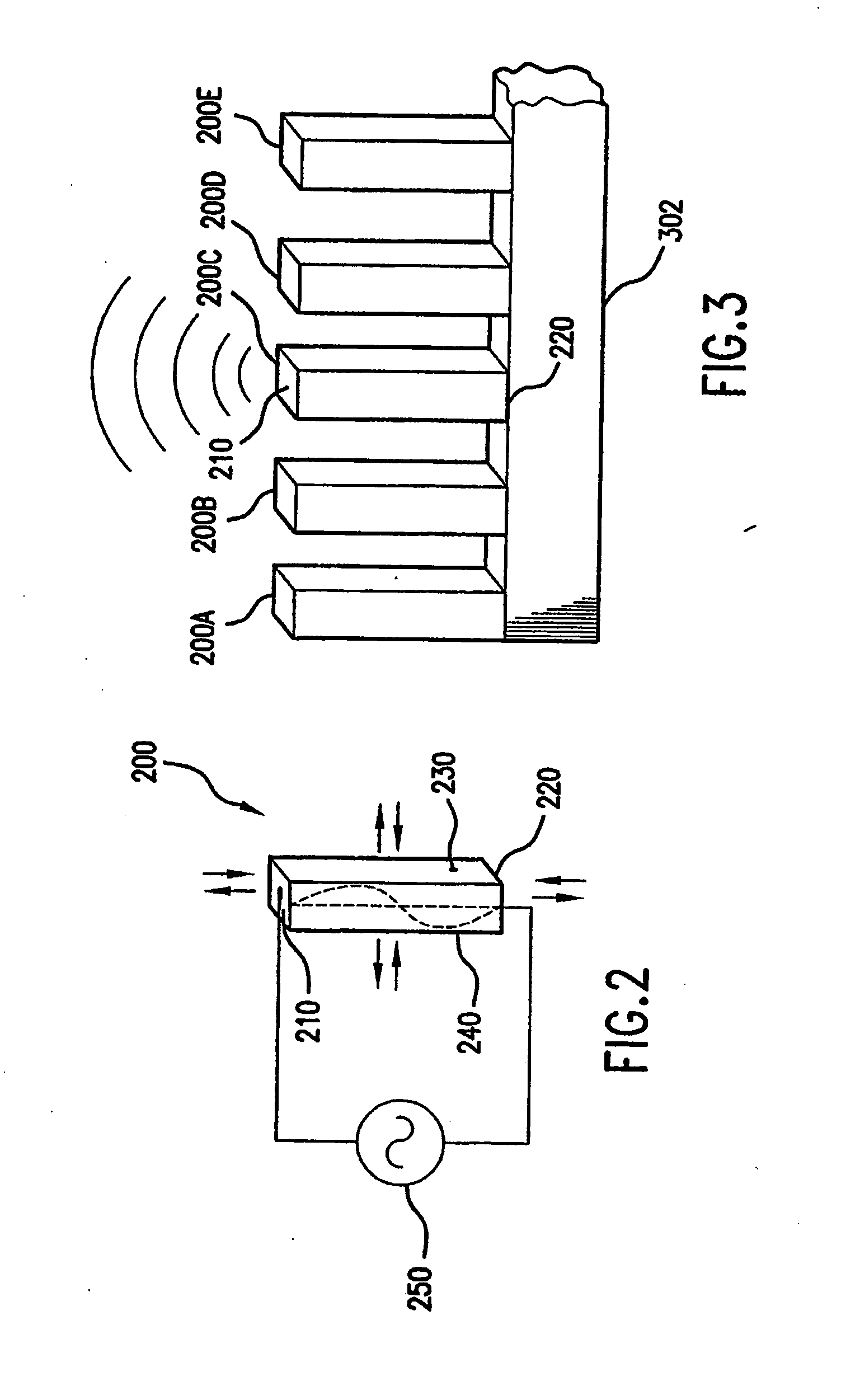
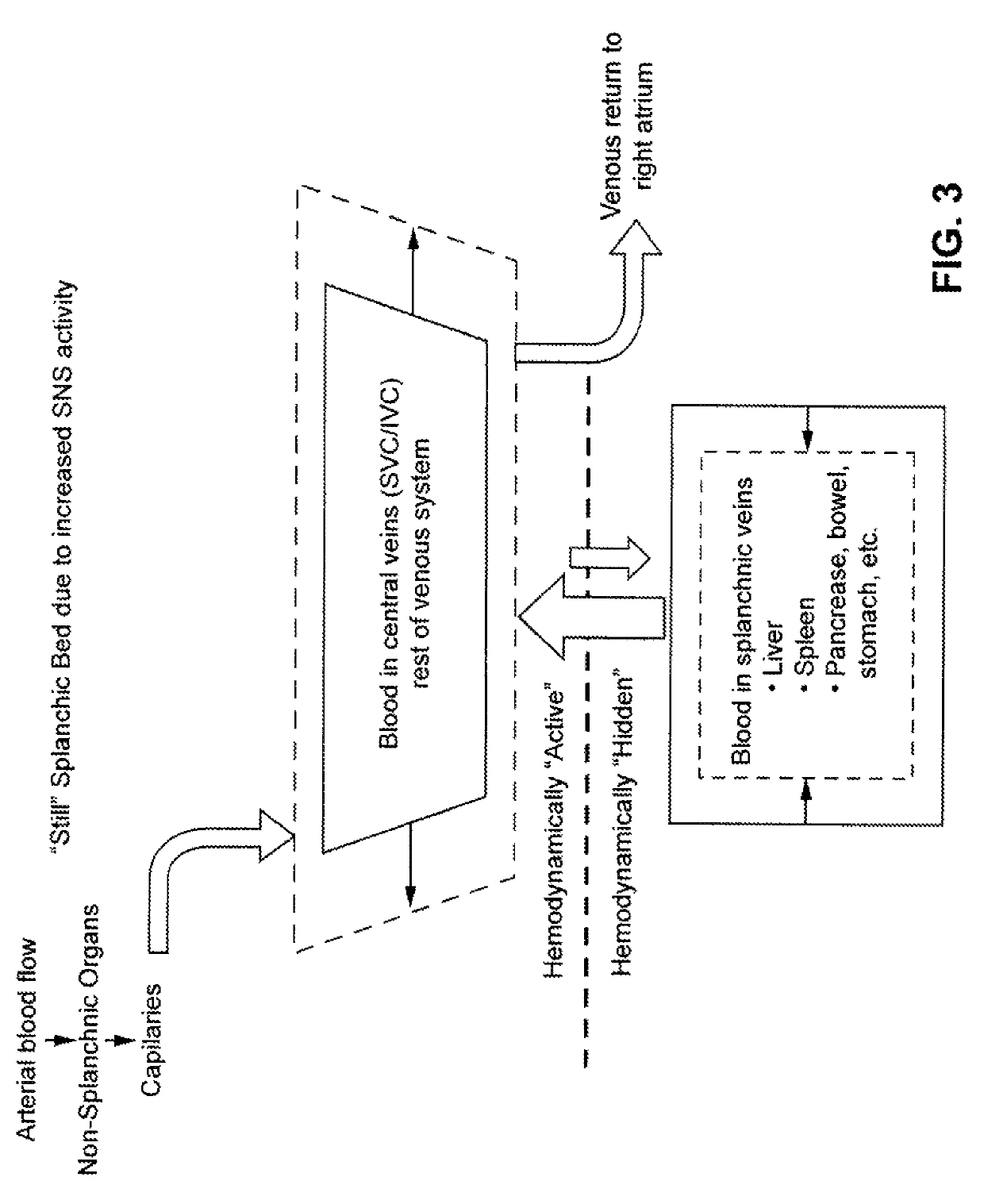
Devices and methods for treatment of heart failure by splanchnic nerve ablation
ActiveUS20180110561A1Add optionsLower blood pressureElectrotherapyDiagnosticsSplanchnic nervesHeart failure cell
A method for treating a heart failure patient by ablating a nerve of the splanchnic sympathetic nervous system to increase venous capacitance and reduce pulmonary blood pressure. A method including: inserting a catheter into a vein adjacent the nerve, applying stimulation energy and observing hemodynamic effects, applying ablation energy and observing hemodynamic effects, applying simulation energy after the ablation and observing hemodynamic effects.
Owner:AXON THERAPIES INC
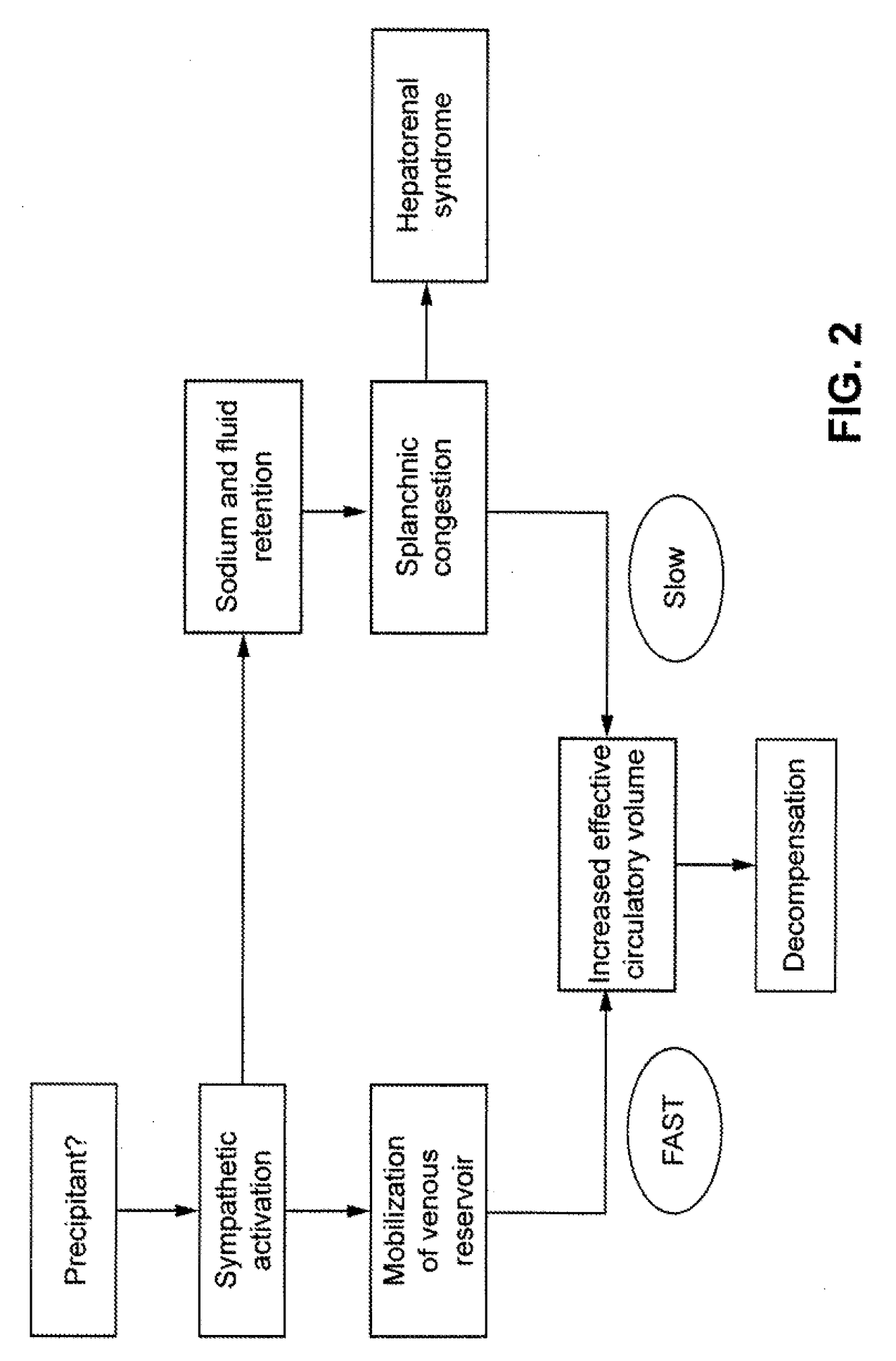
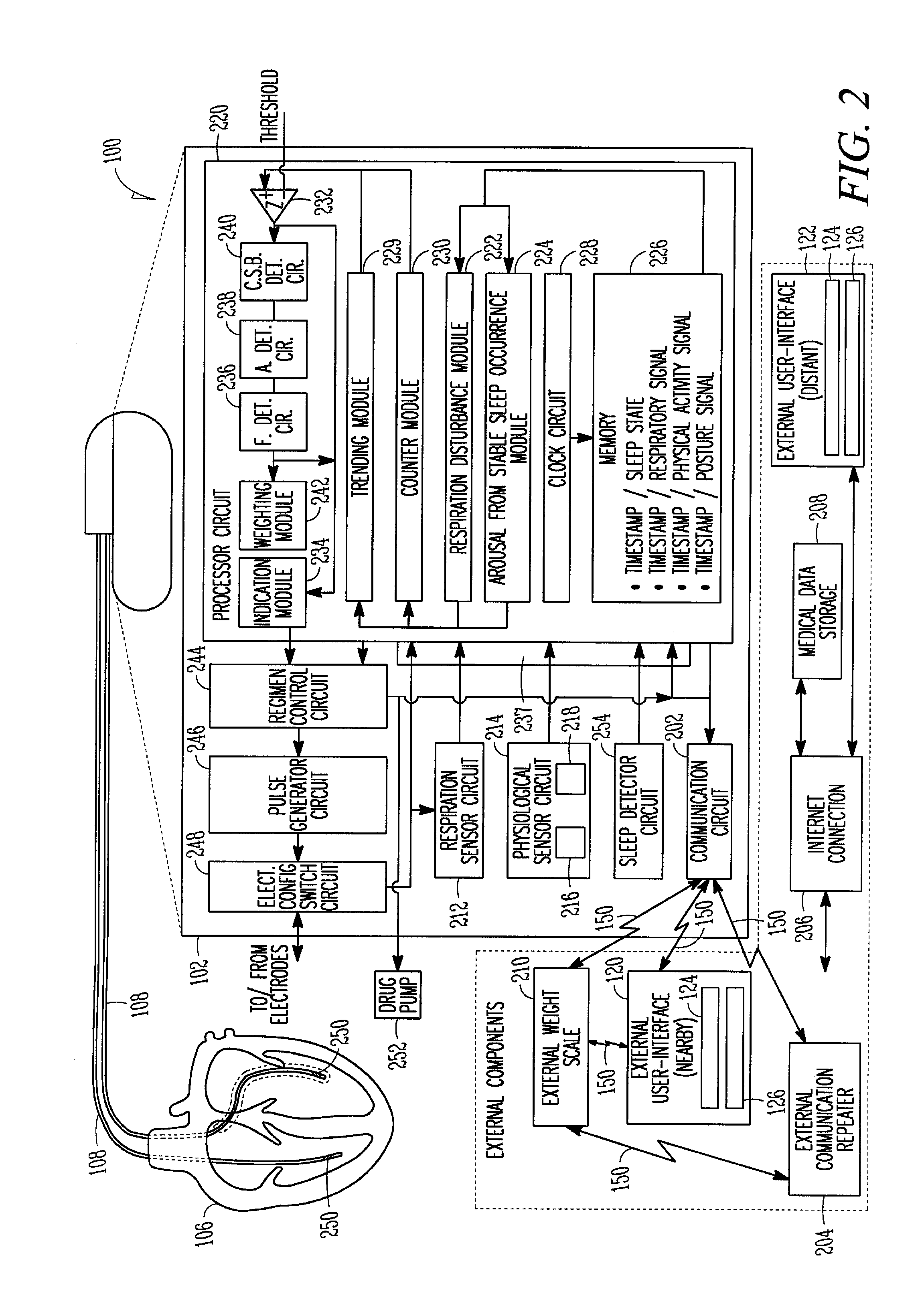
Using respiration distress manifestations for heart failure detection
Systems and methods for diagnosing one or more respiration distress manifestations by implantably recognizing their occurrence and evaluating information about the same to provide an indication of present or impending worsening heart failure are discussed. Using information produced by an implantable respiration sensor circuit and an implantable physiological sensor circuit, such as at least one of a physical activity sensor circuit or a posture sensor circuit, an implantable or external processor circuit may detect a respiration disturbance and an associated subsequent arousal from stable state occurrence and thereafter evaluate over time arousal from stable state occurrences to provide the indication of present or impending worsening heart failure. In one example, information about a fluid level within a subject is used in determining the indication of worsening heart failure. In various examples, a regimen is initiated or adjusted in response to the indication of present or impending worsening heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
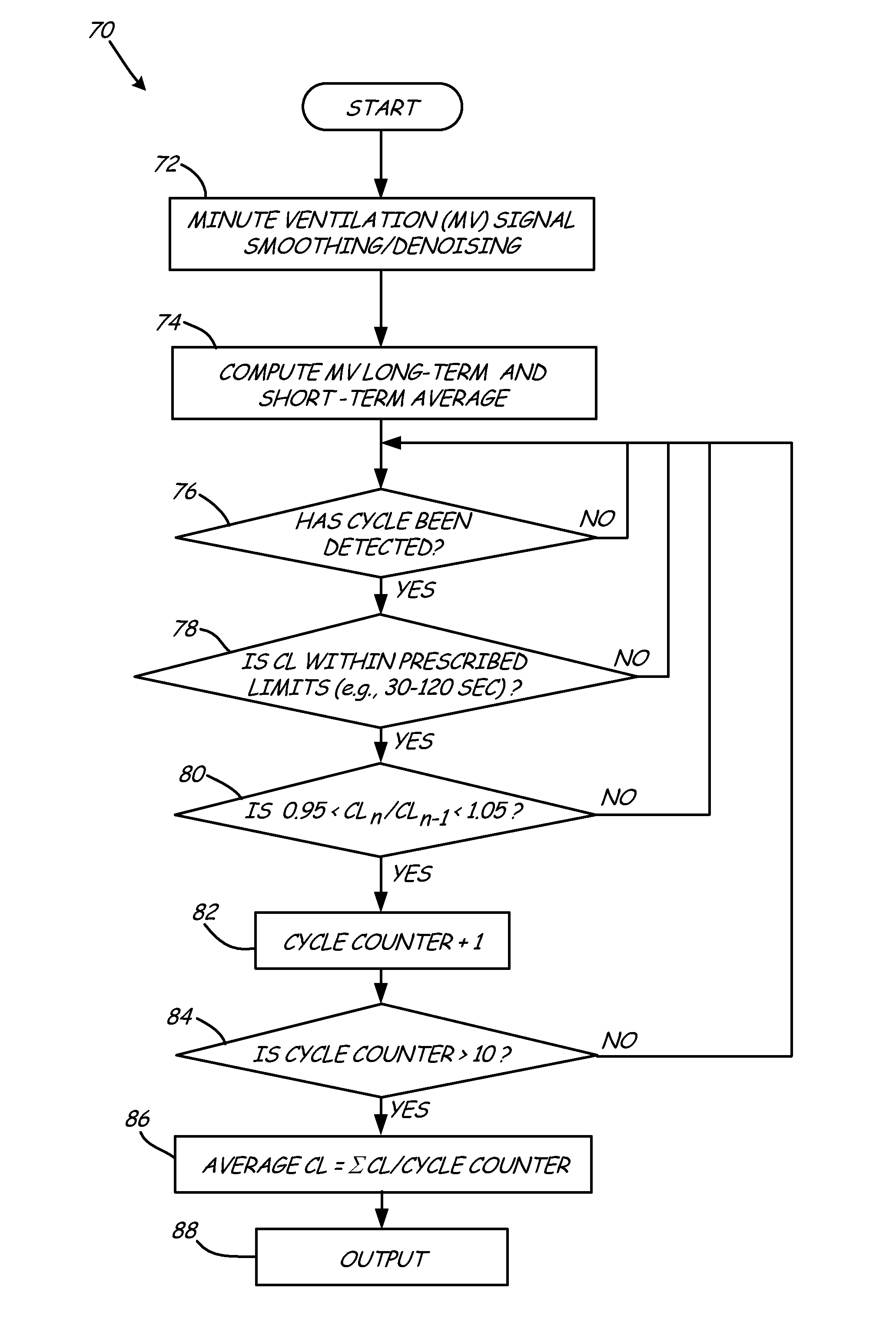
System and method for monitoring periodic breathing associated with heart failure
A system and method for monitoring in a patient includes producing sensor signals representative of a physiologic parameter associated with respiration. A periodic breathing cycle is detected based on the sensor signals. An output is produced as a function of the cycle length.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Detecting heart failure by monitoring the time seqence of physiological changes
Systems and methods for detecting heart failure by monitoring the time-sequence of physiological changes of a subject using a state machine circuit configured to receive information about physiological characteristics of the subject is described. The current state transitions between a first and a second state in response to a first transition trigger. The current state transitions between the second and first states in response to at least one of the expiration of a first timer or ceasing of the first transition trigger. The current state transitions between the second and third states in response to a second transition trigger. The current state transitions between the third and second states in response to at least one of expiration of a second timer or ceasing of the second transition trigger.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
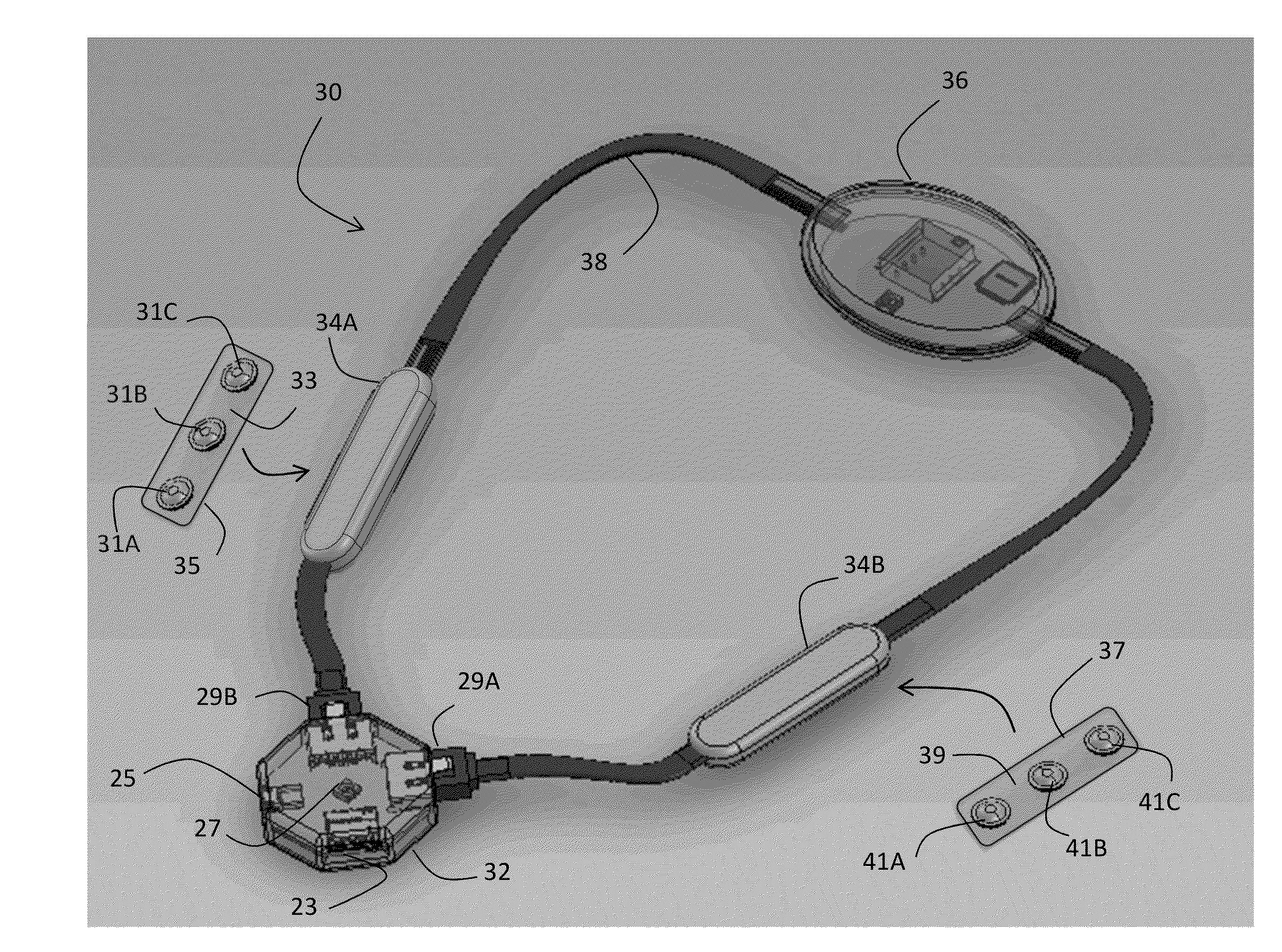
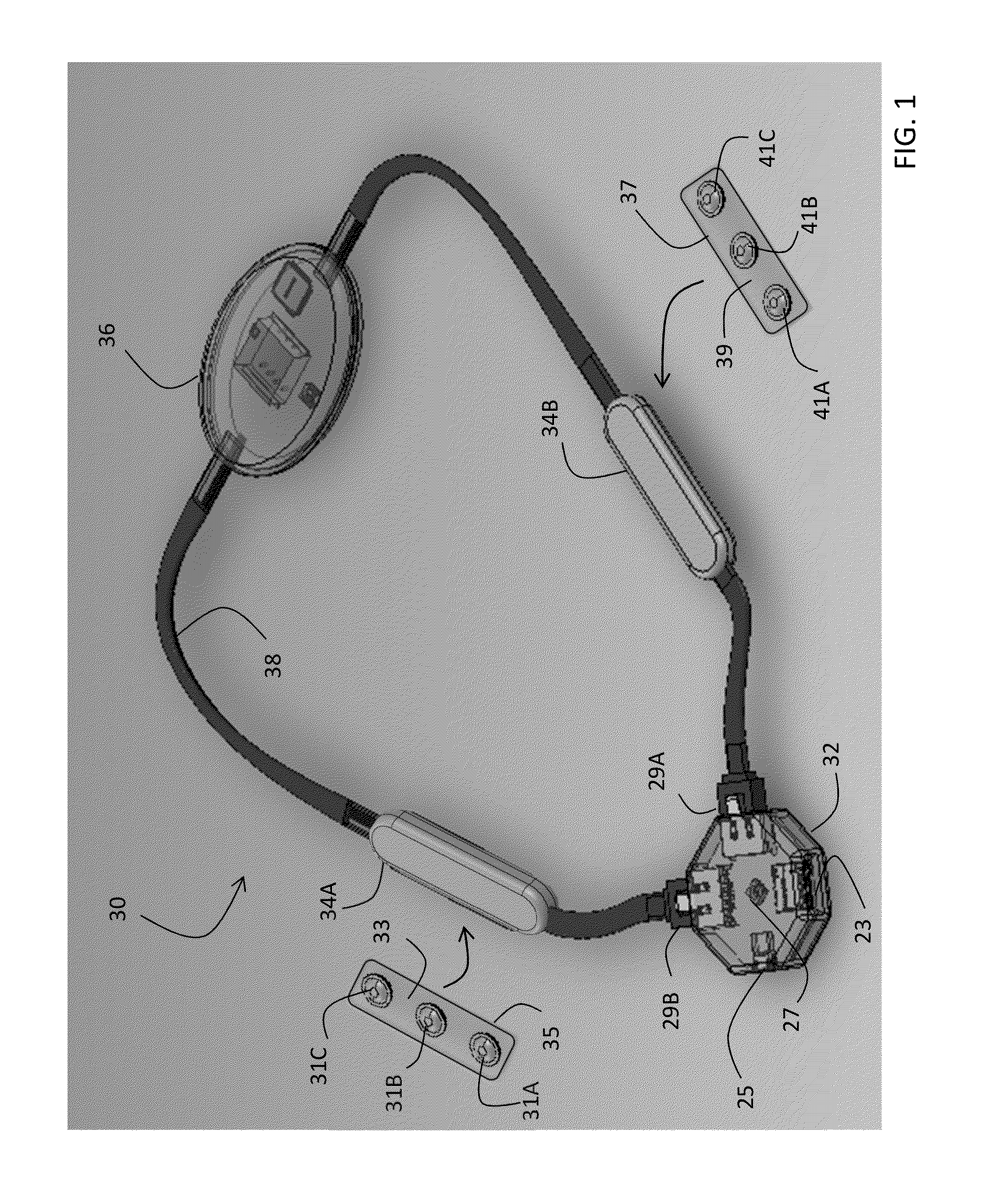
Body-worn sensor for characterizing patients with heart failure
ActiveUS20140187974A1Easy to coverSimple and low-costElectrocardiographyCatheterElectricityLeft heart failure
The invention provides a sensor for measuring both impedance and ECG waveforms that is configured to be worn around a patient's neck. The sensor features 1) an ECG system that includes an analog ECG circuit, in electrical contact with at least two ECG electrodes, that generates an analog ECG waveform; and 2) an impedance system that includes an analog impedance circuit, in electrical contact with at least two (and typically four) impedance electrodes, that generates an analog impedance waveform. Also included in the neck-worn system are a digital processing system featuring a microprocessor, and an analog-to-digital converter. During a measurement, the digital processing system receives and processes the analog ECG and impedance waveforms to measure physiological information from the patient. Finally, a cable that drapes around the patient's neck connects the ECG system, impedance system, and digital processing system.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Use of PDE iii inhibitors for the reduction of heart size in mammals suffering from heart failure
ActiveUS20140155338A1Reduction in mean heart sizeBiocideAnimal repellantsHeart failure cellHeart size
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
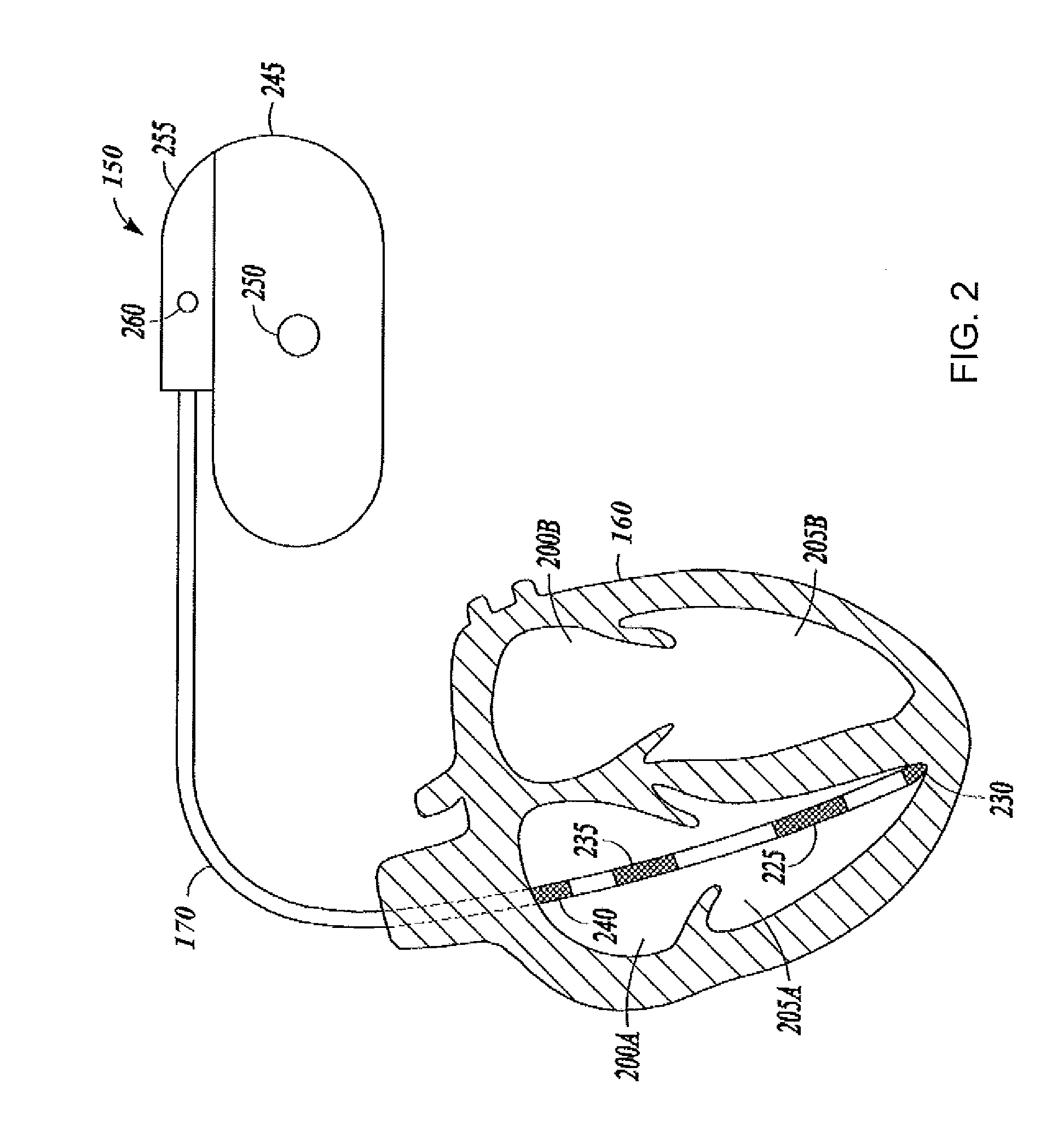
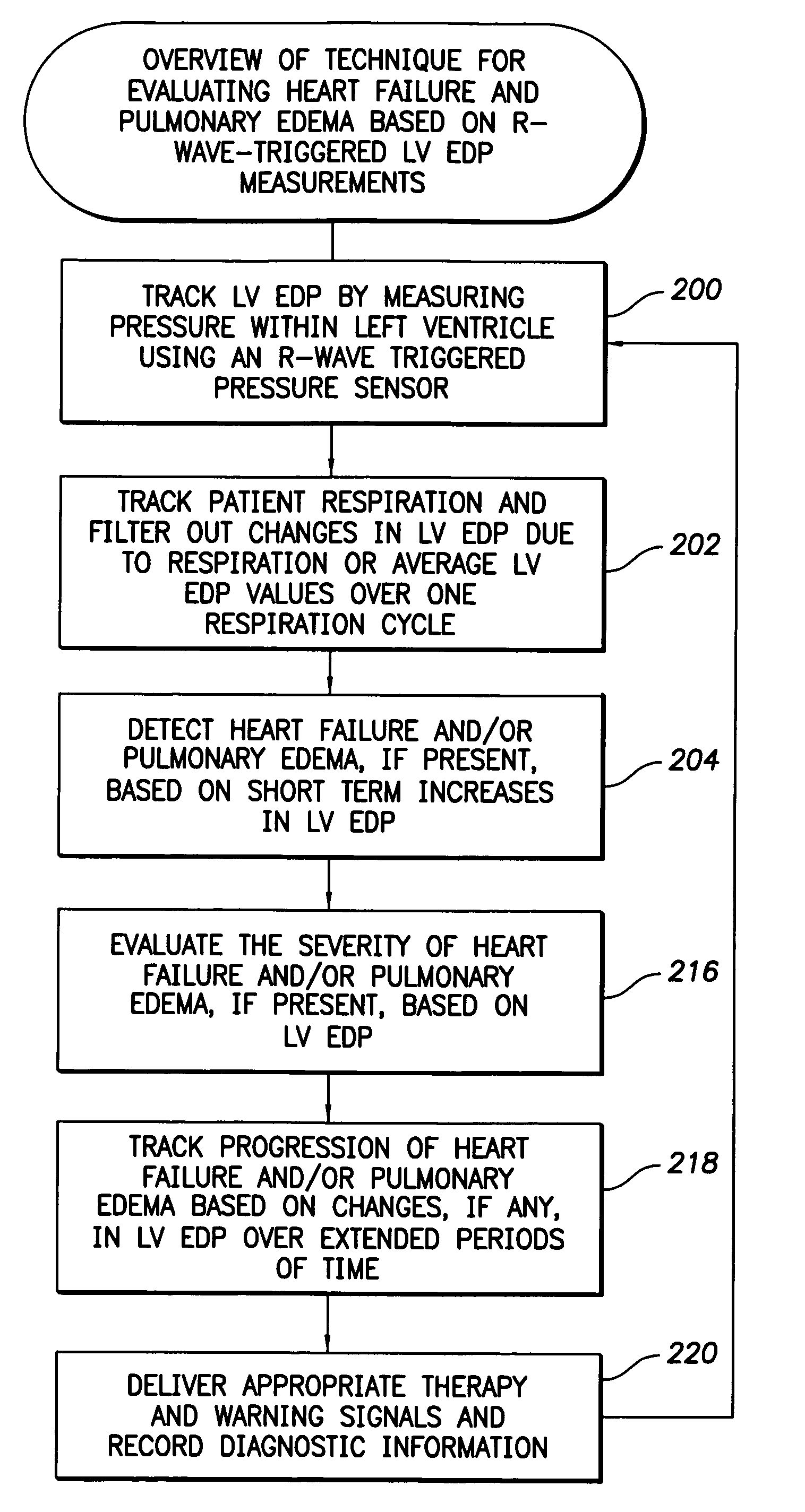
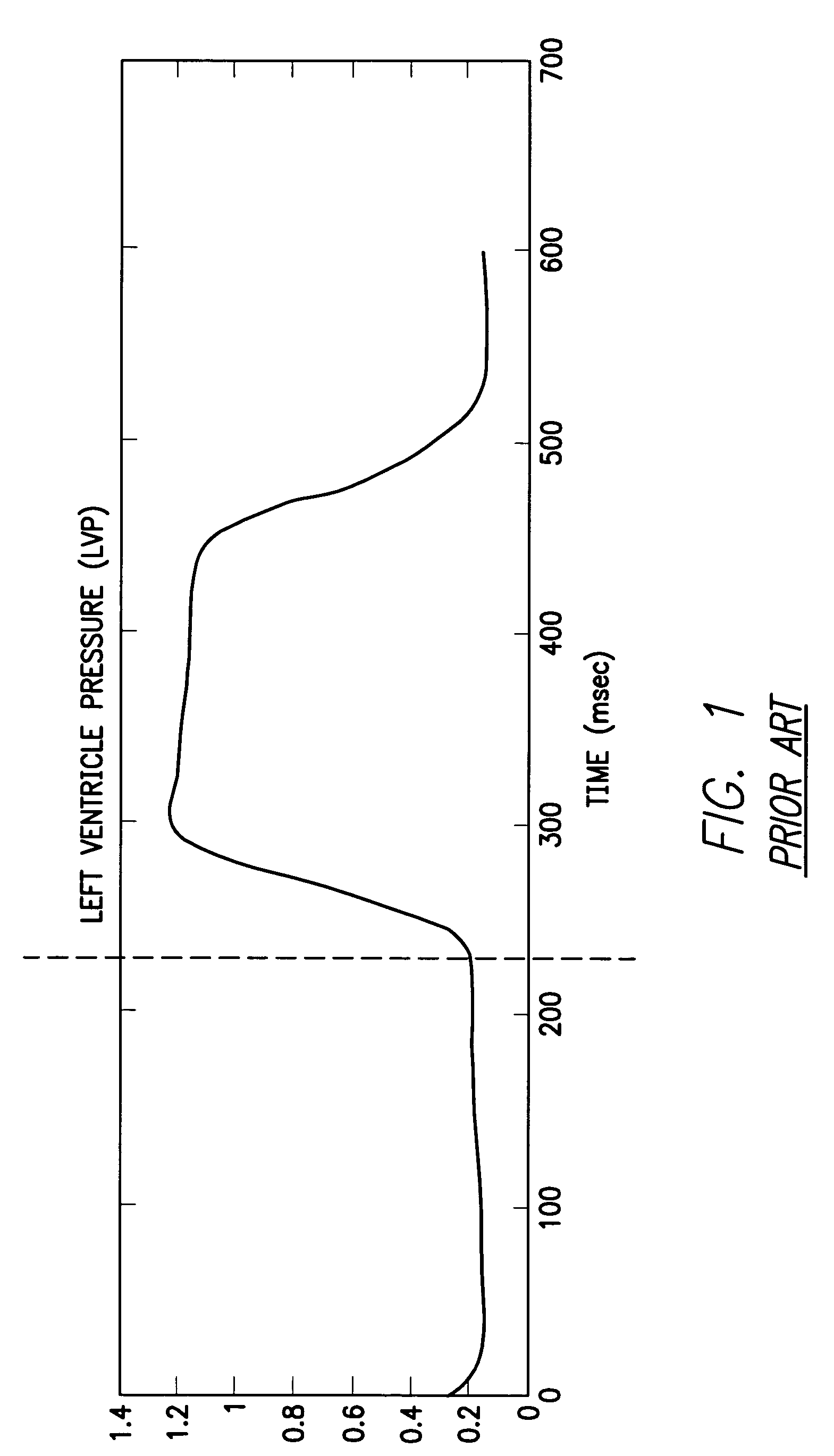
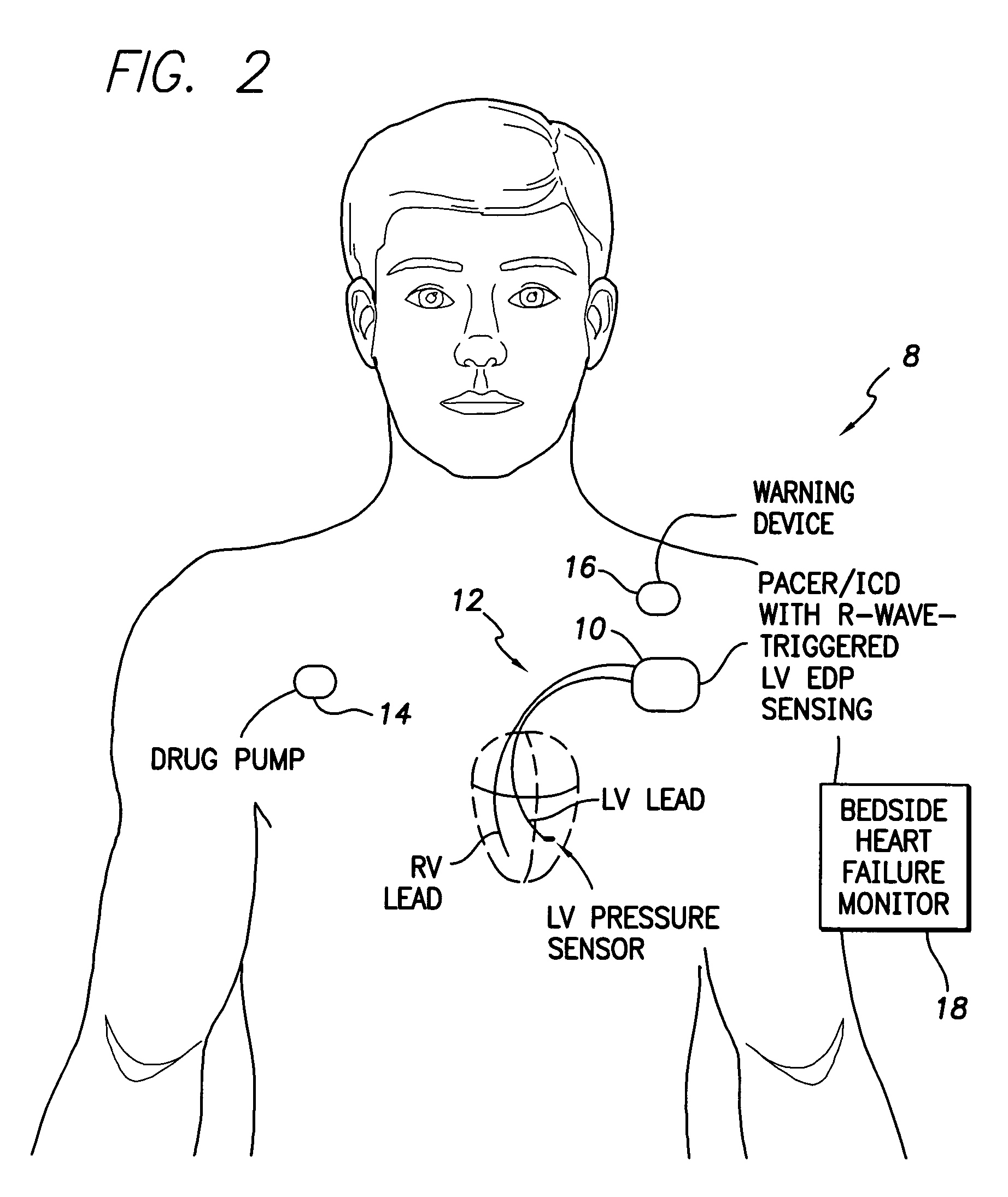
System and method for detecting heart failure and pulmonary edema based on ventricular end-diastolic pressure using an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for detecting left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LV EDP) using a pressure sensor implanted within the heart of a patient and for detecting and evaluating heart failure and pulmonary edema based on LV EDP. Briefly, the peak of the R-wave of an intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) is used to trigger the measurement of a pressure value within the left ventricle. This pressure value is deemed to be representative of LV EDP. In this manner, LV EDP is easily detected merely by measuring pressure at one point within the heartbeat—thereby eliminating any need to track ventricular pressure throughout the heartbeat. Techniques for detecting and evaluating heart failure and pulmonary edema based on the R-wave triggered LV EDP measurements are also set forth herein.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
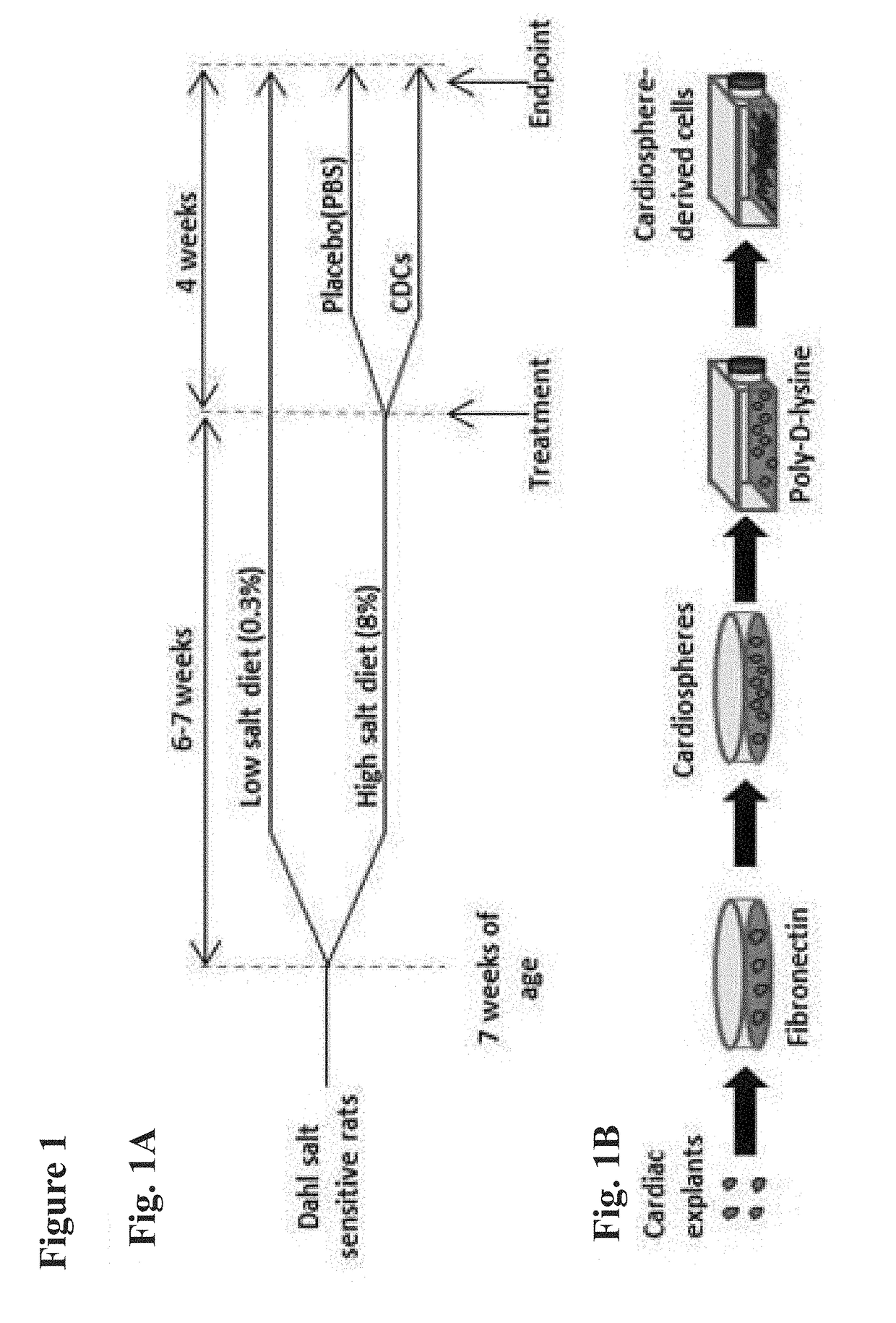
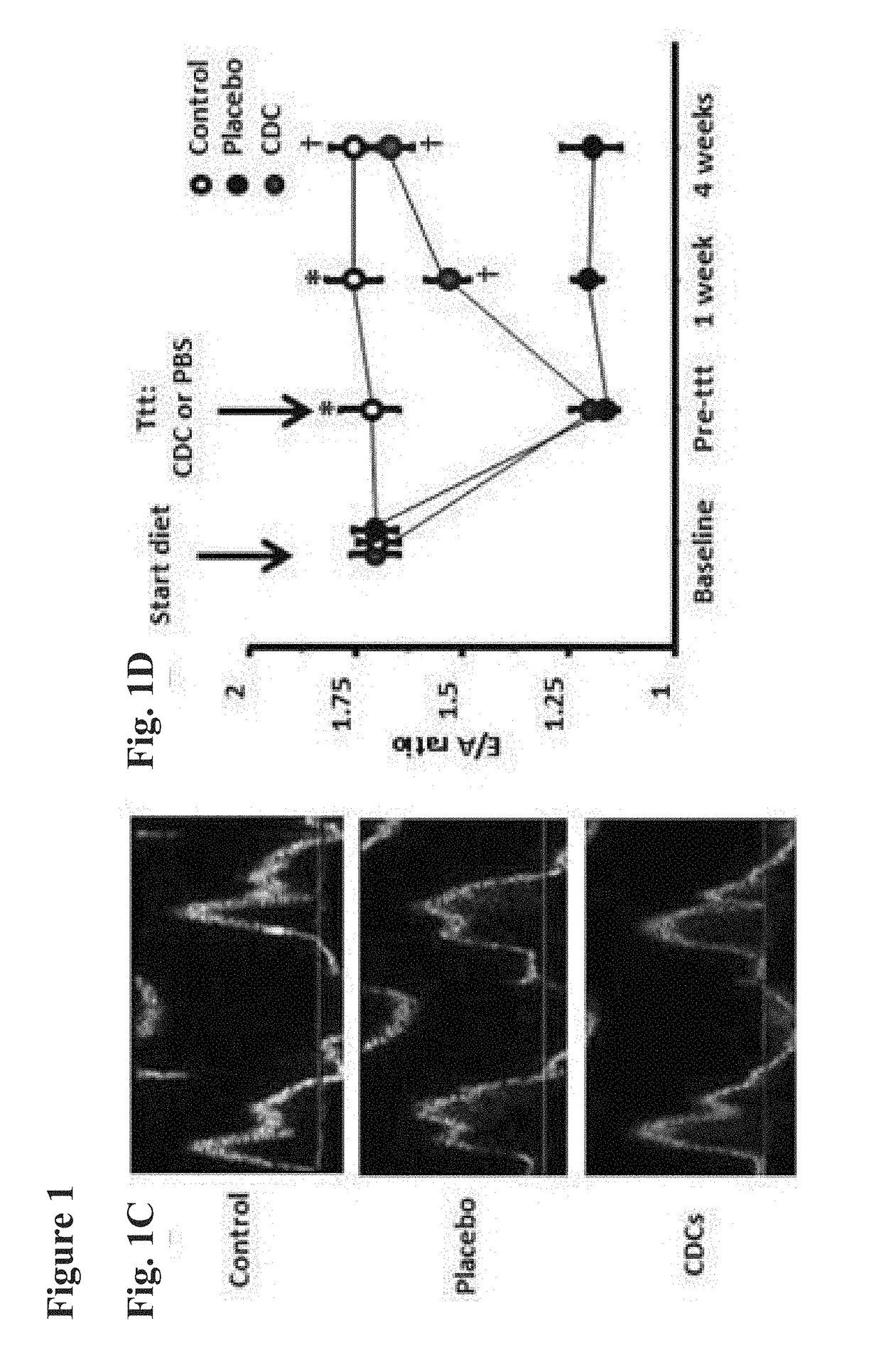
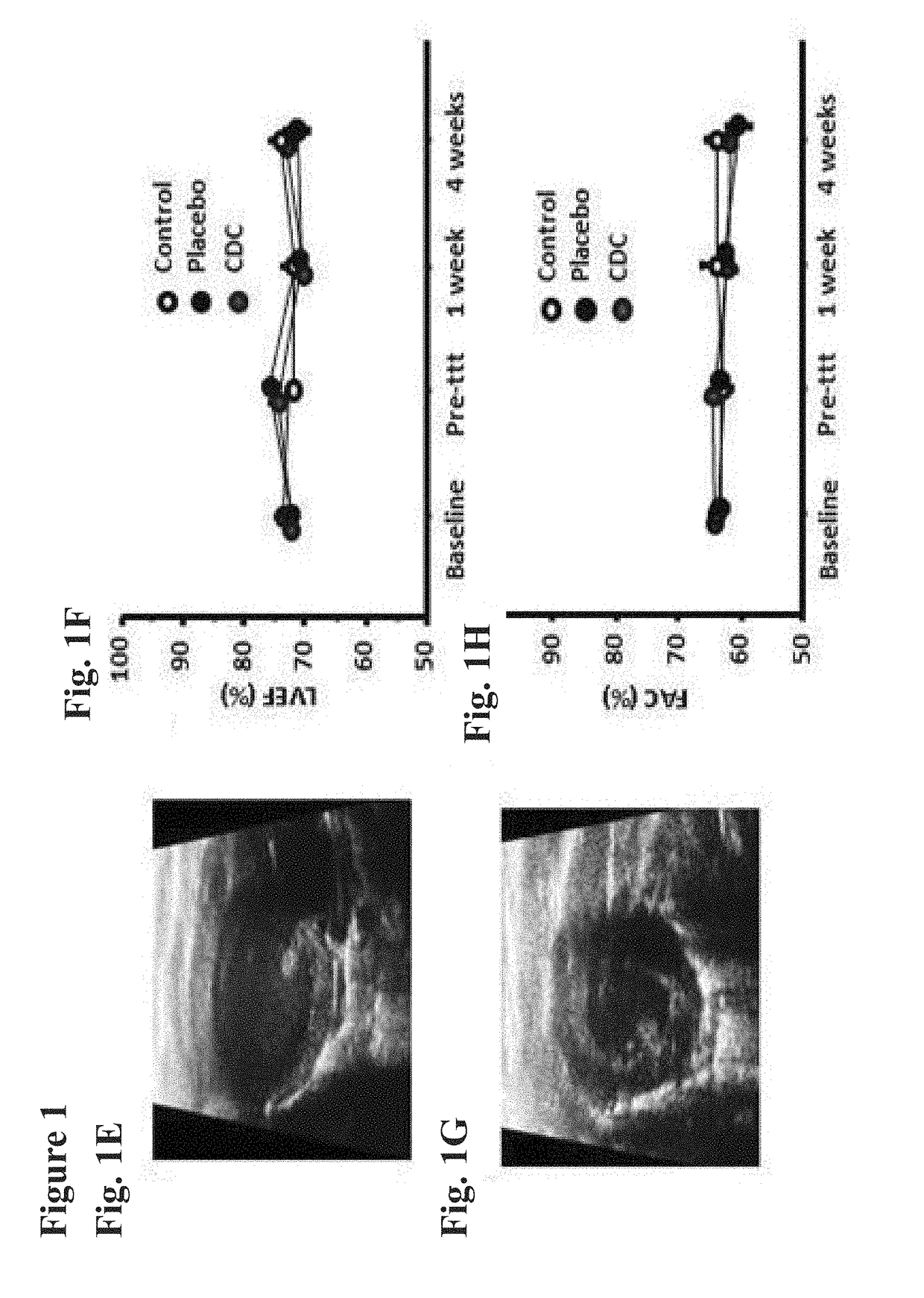
Cardiosphere-derived cells and exosomes secreted by such cells in the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
ActiveUS20190000888A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLower riskMortality rate
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a disease condition characterized by heart failure (HF) signs and symptoms, but with normal or near normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and is not responsive to standard therapy for treatment of HF. Described herein are compositions and methods related to use of cardiosphere derived cells (CDCs) and their exosomes to improve left ventricular structure, function and overall outcome. Administration of CDCs led to improved LV relaxation, lower LV end-diastolic pressure, decreased lung congestion and enhanced survival. Lower risk of arrhythmias in HFpEF was also observed following CDC administration. Improvement of diastolic dysfunction following administration of CDC-derived exosomes was observed, along with decreased mortality. In view of these salutary effects, CDCs and CDC-derived exosomes are beneficial in the treatment of HFpEF.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Myocardial infarction and heart failure magnetic microparticle microfluidic biochip and detection method
InactiveCN108663525AExtended rescue timeRealize finger blood detection functionLaboratory glasswaresDisease diagnosisSignal onImmune complex deposition
The invention relates to a myocardial infarction and heart failure magnetic microparticle microfluidic biochip, which belongs to the technical field of POCT detection. The myocardial infraction and heart failure magnetic microparticle microfluidic biochip comprises a PCB board, wherein the PCB board is provided with a microflow passage, a biosensor is arranged in the microflow passage, the biosensor consists of a wafer platform and a point sample antibody covered on the wafer platform, the point sample antibody can form an immune complex with a magnetic bead coupling antibody and a marker protein, and the concentration of the marker protein can be judged by determining a magnetic resistance signal on the wafer platform. In the technical scheme, the magnetic bead has a larger specific surface area, and by combining more antibodies, the detection sensitivity is improved, and the specificity is higher than that of a fourth-generation chemical luminescent method. The invention also provides a detection method using the biochip. The heart markers such as myocardial infarction and heart failure can be simultaneously and quantitatively detected, the detection lower limit can be improved,and the leakage detection and false negative phenomenon can be effectively avoided.
Owner:微粒云科技(北京)有限公司
Body-worn sensor for characterizing patients with heart failure
ActiveUS9332941B2Easy to coverSimple and low-costElectrocardiographySensorsLeft heart failureElectricity
The invention provides a sensor for measuring both impedance and ECG waveforms that is configured to be worn around a patient's neck. The sensor features 1) an ECG system that includes an analog ECG circuit, in electrical contact with at least two ECG electrodes, that generates an analog ECG waveform; and 2) an impedance system that includes an analog impedance circuit, in electrical contact with at least two (and typically four) impedance electrodes, that generates an analog impedance waveform. Also included in the neck-worn system are a digital processing system featuring a microprocessor, and an analog-to-digital converter. During a measurement, the digital processing system receives and processes the analog ECG and impedance waveforms to measure physiological information from the patient. Finally, a cable that drapes around the patient's neck connects the ECG system, impedance system, and digital processing system.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method for reducing hypertension and heart failure
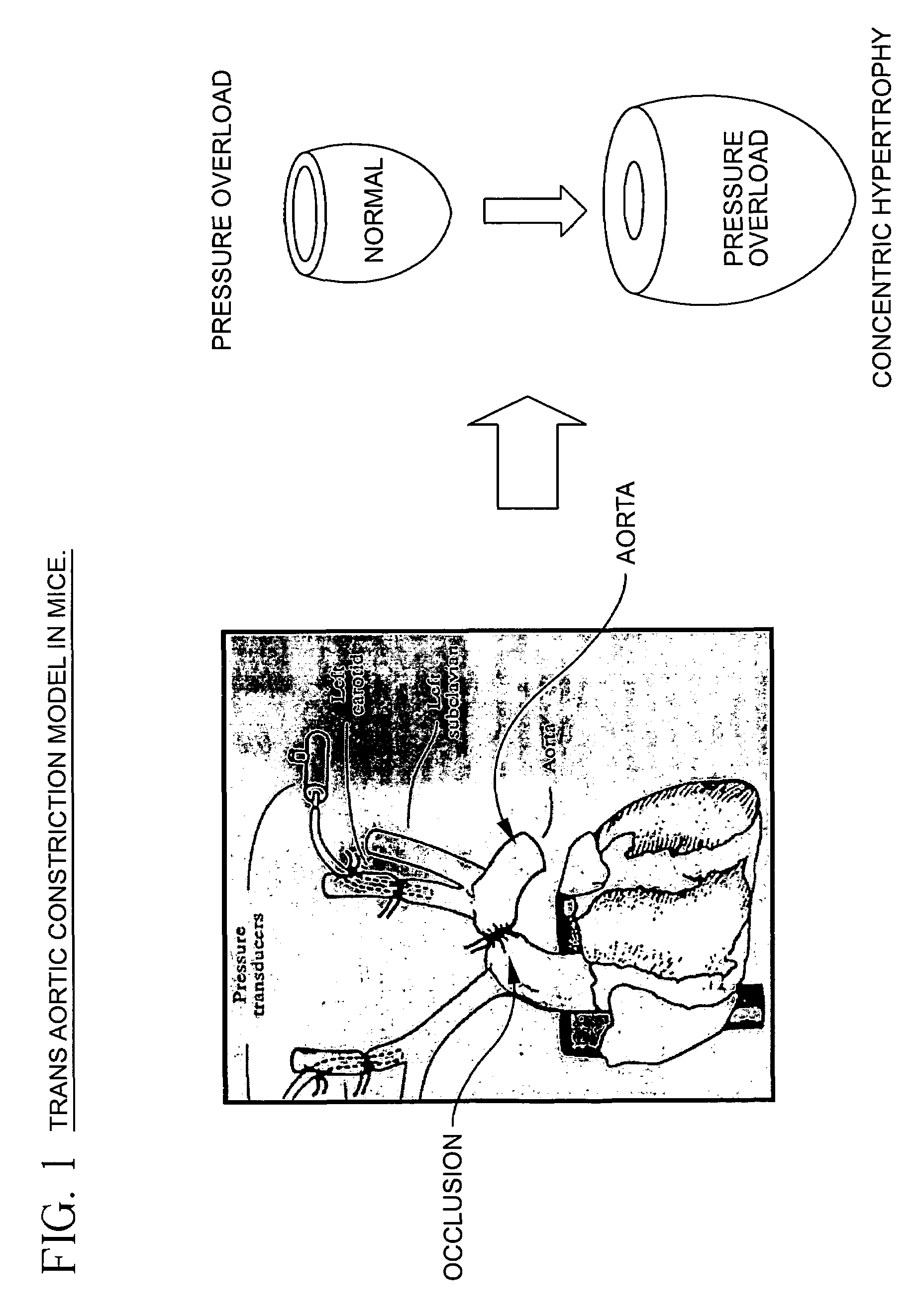
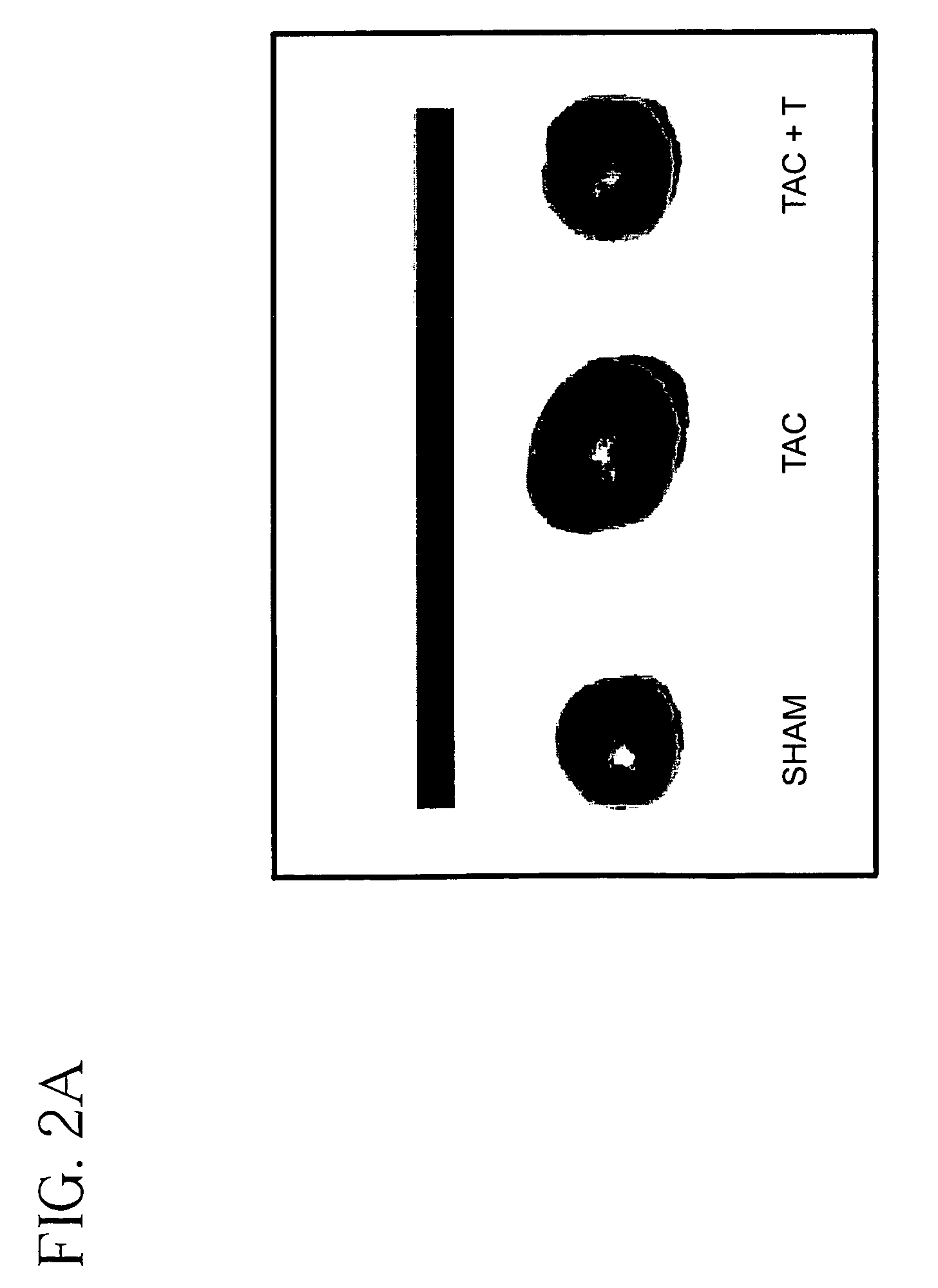
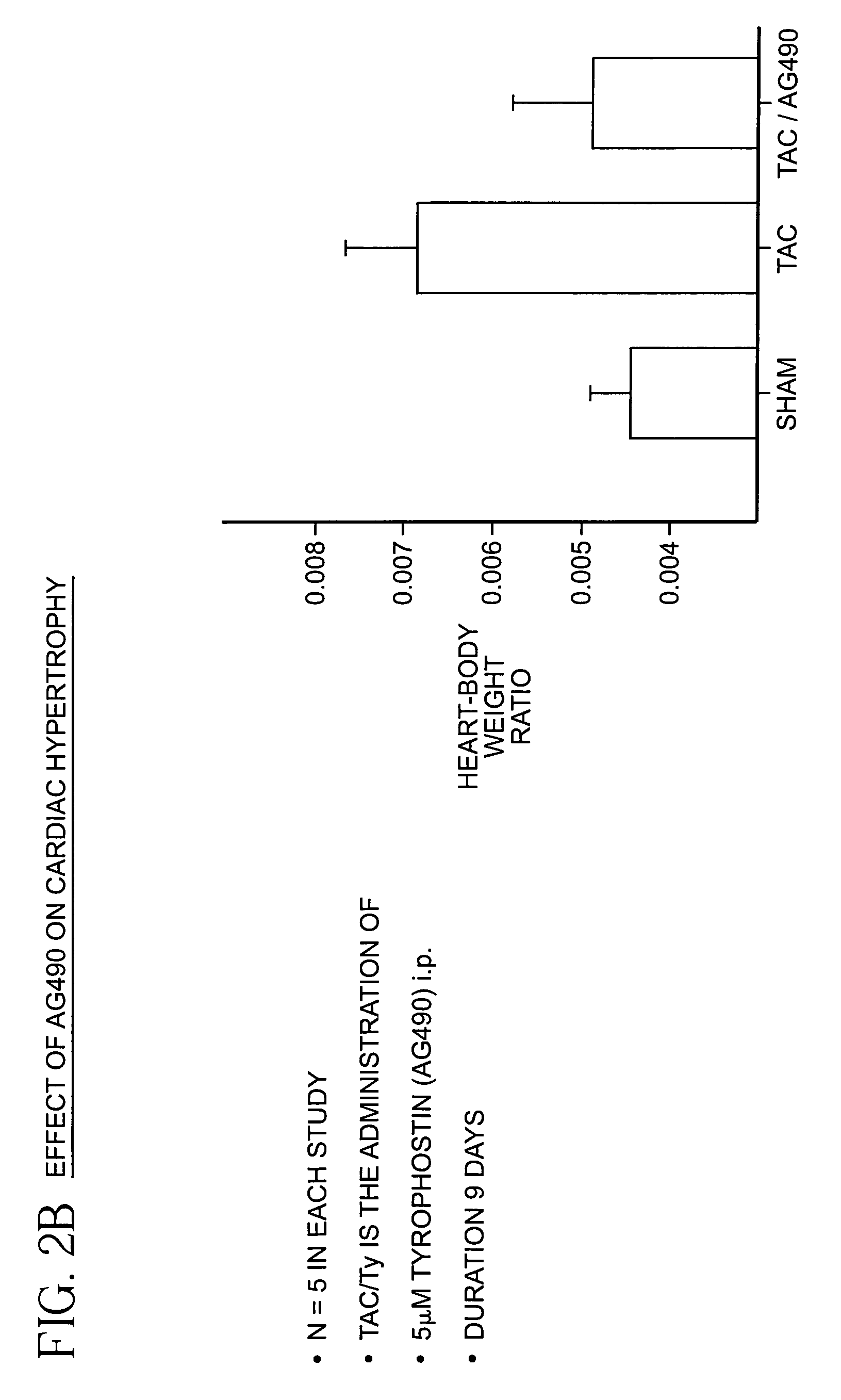
InactiveUS7235588B2Reducing hypertensionReduce hypertrophyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeart failure cellProtein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
A method is provided for reducing hypertension and / or heart failure in a mammal. Preferably, the method is used to treat or prevent tissue damage to a human heart. The method includes administering an effective amount of a Jak2 inhibitor, preferably a tyrphostin, such as AG490.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of pathological cardiac remodeling and heart failure
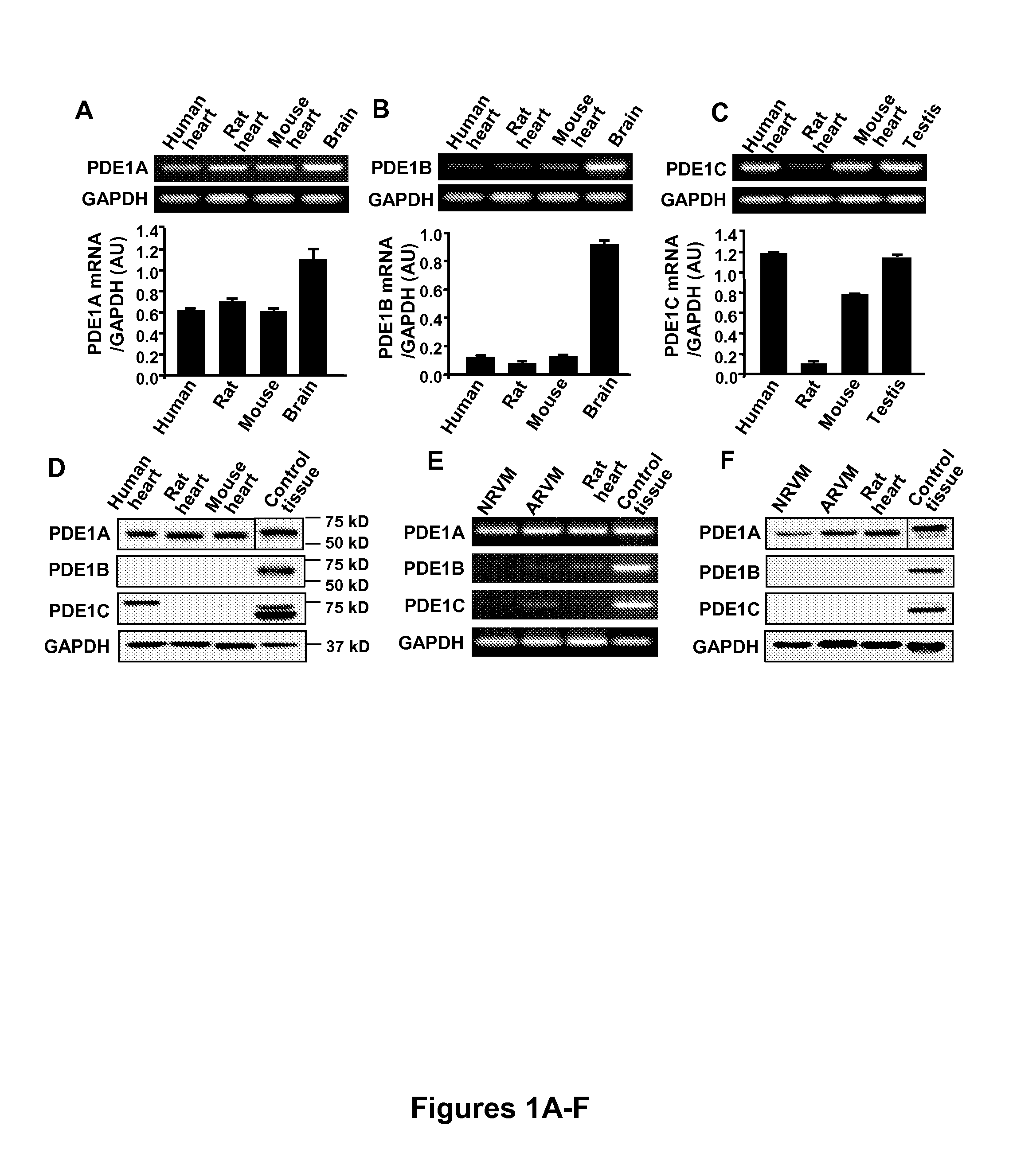
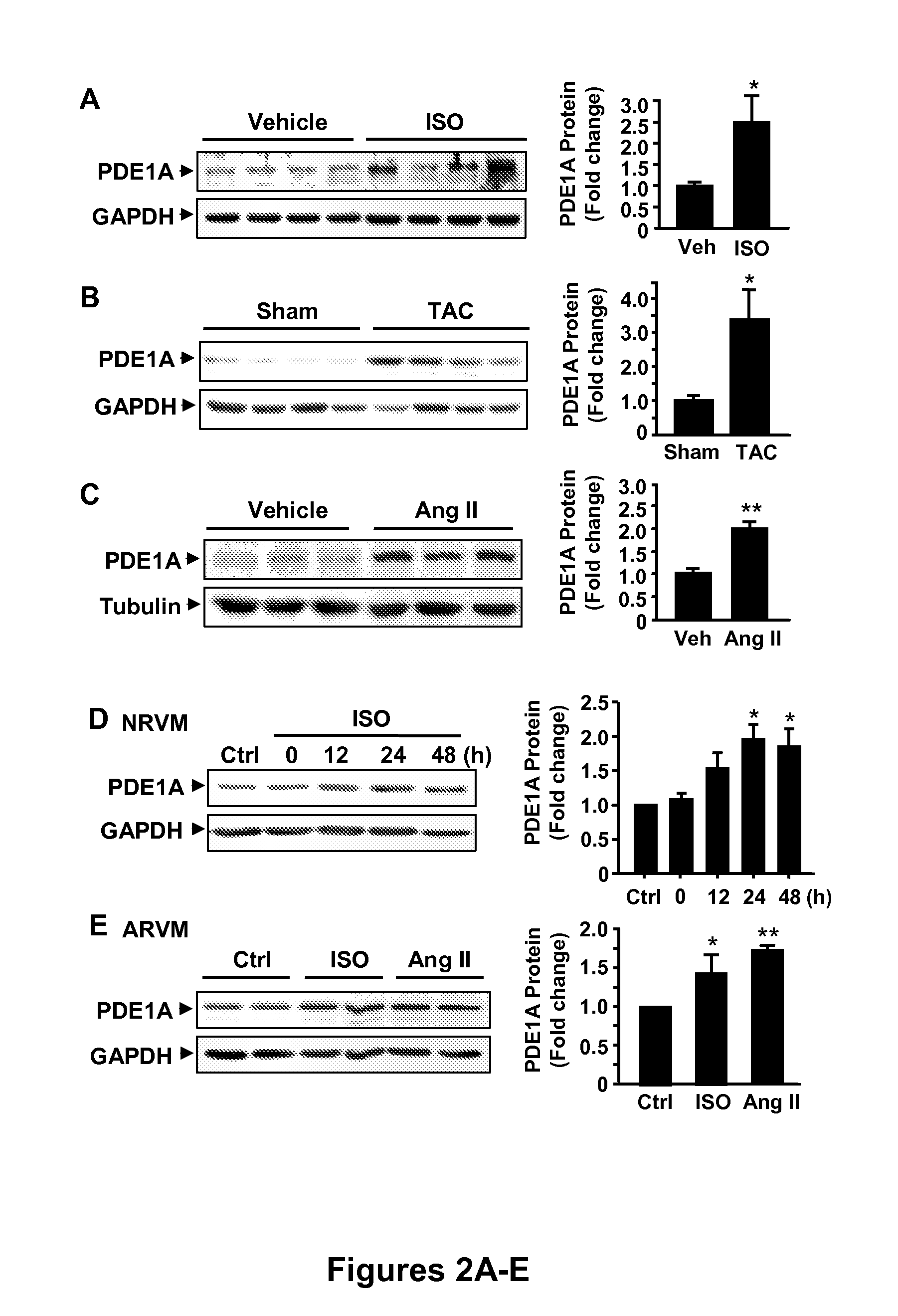
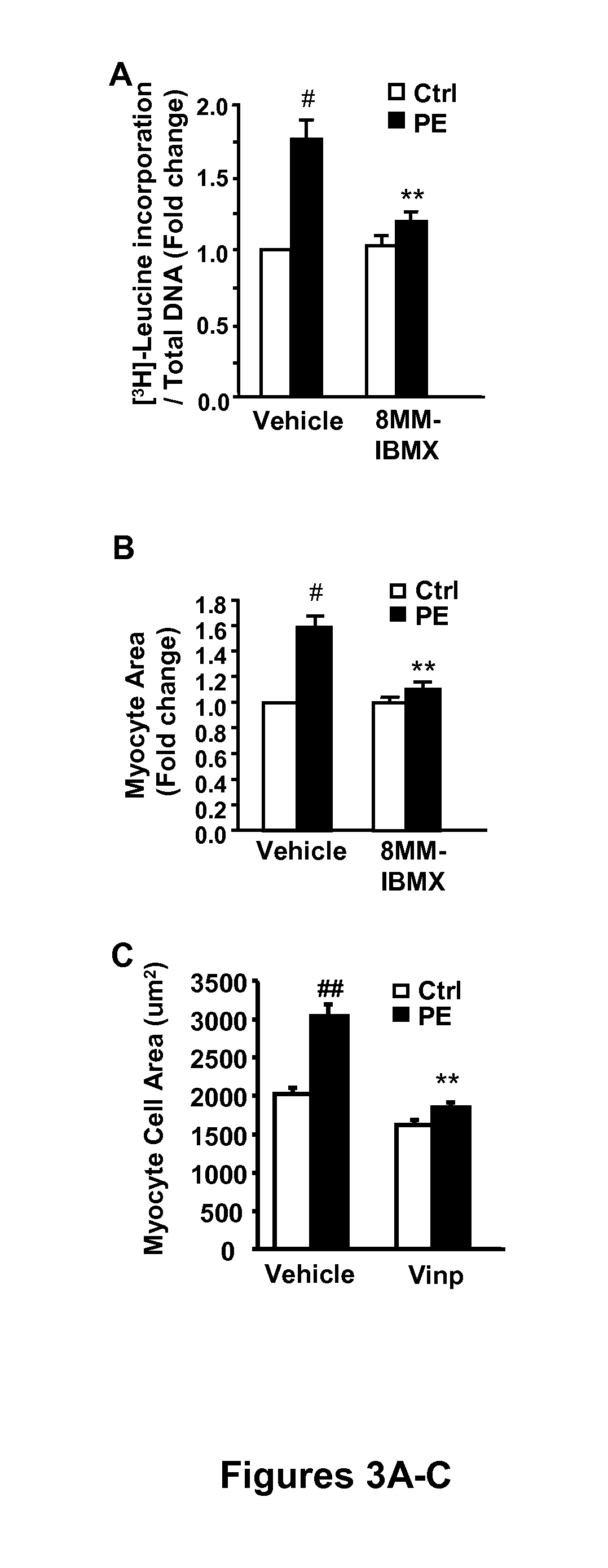
The invention relates to methods of treating or preventing pathological cardiac remodeling and / or preventing heart failure. These methods include the administration of a PDE1 inhibitor to a patient under conditions effective to treat or prevent pathological cardiac remodeling, and therefore heart failure that occurs as a result of such remodeling. Pharmaceutical compositions and delivery vehicles that can be used in the methods of the present invention are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
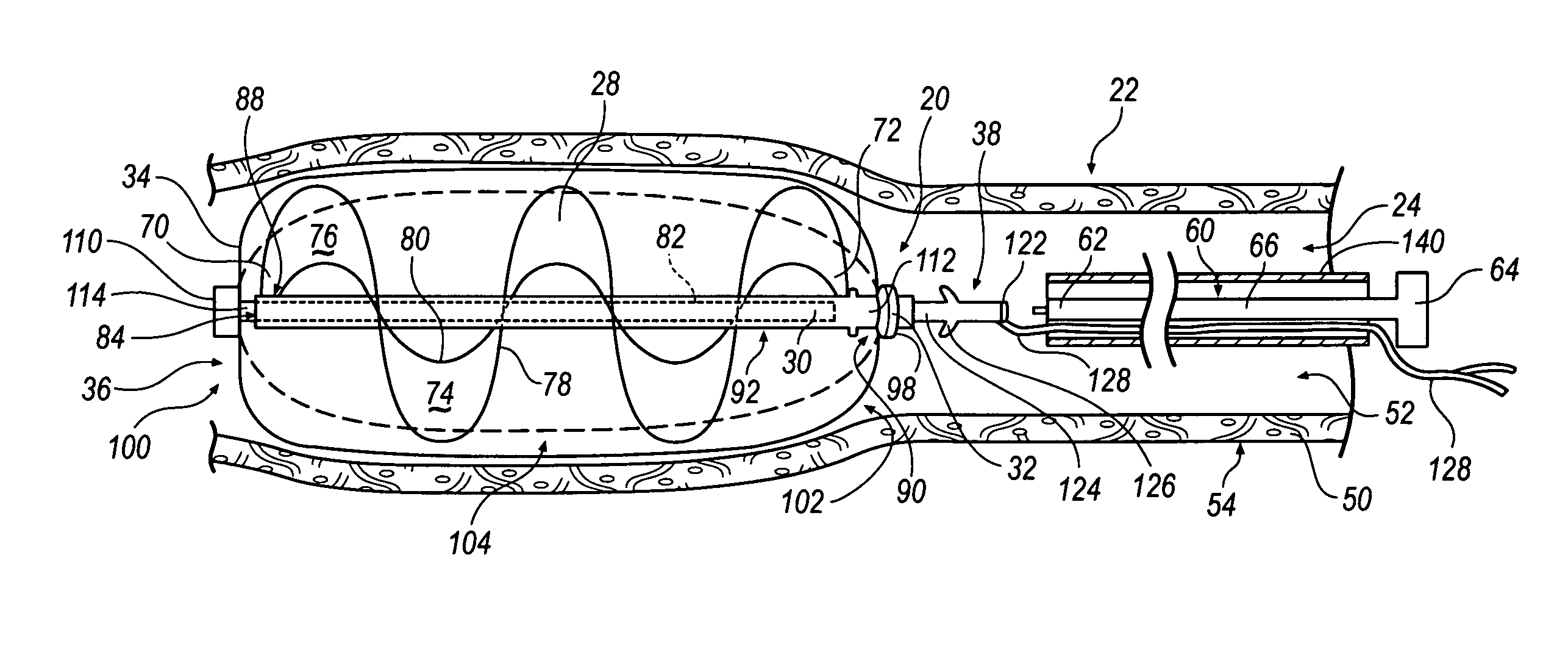
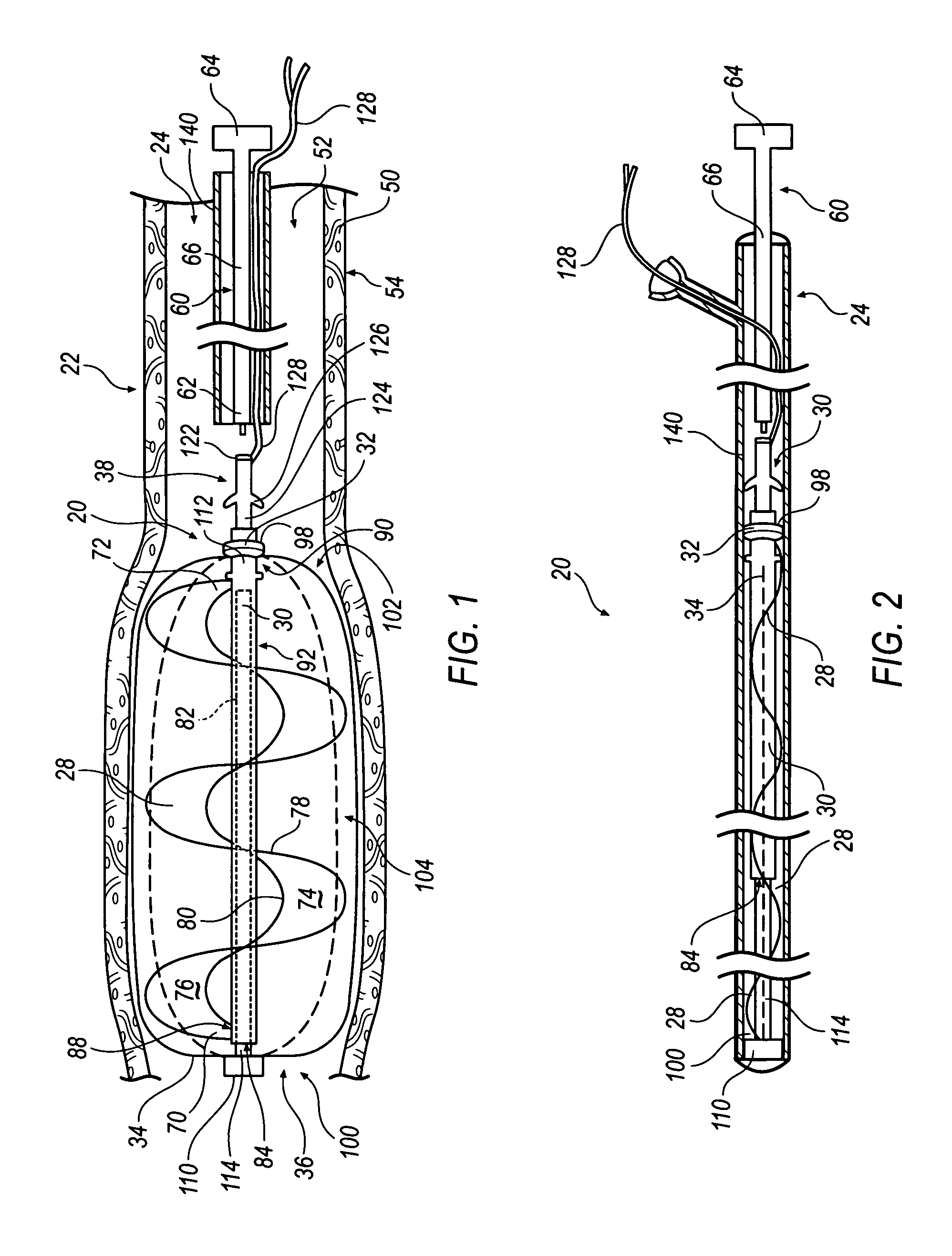
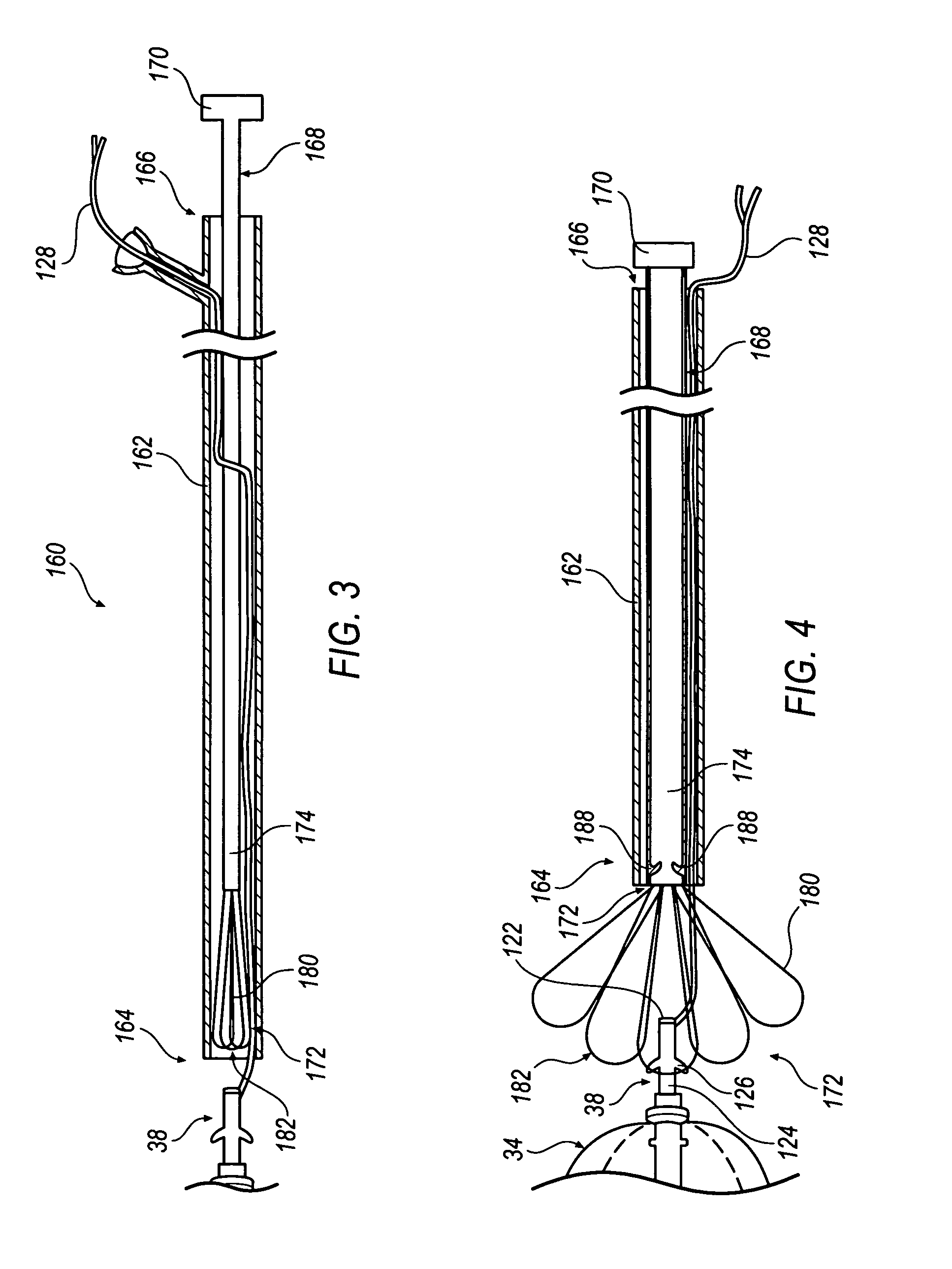
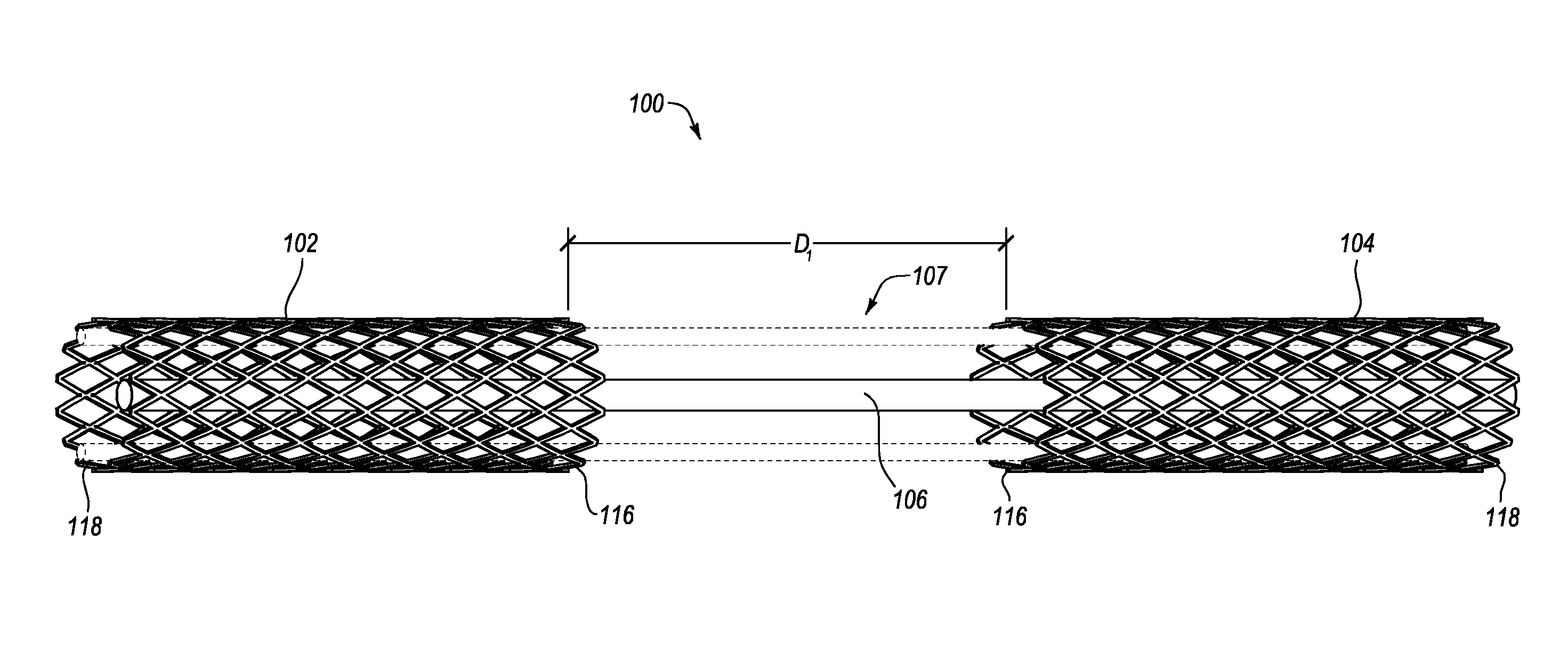
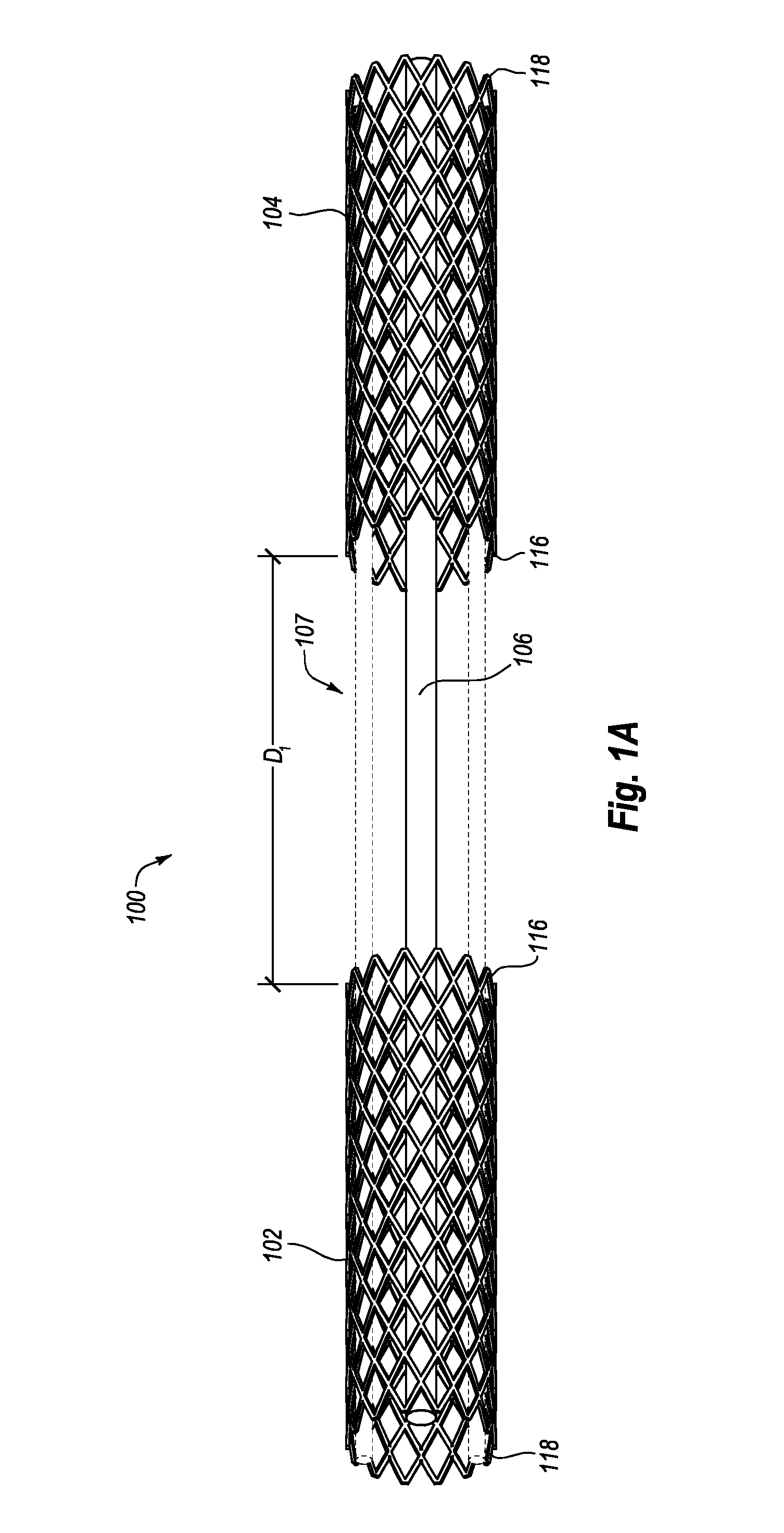
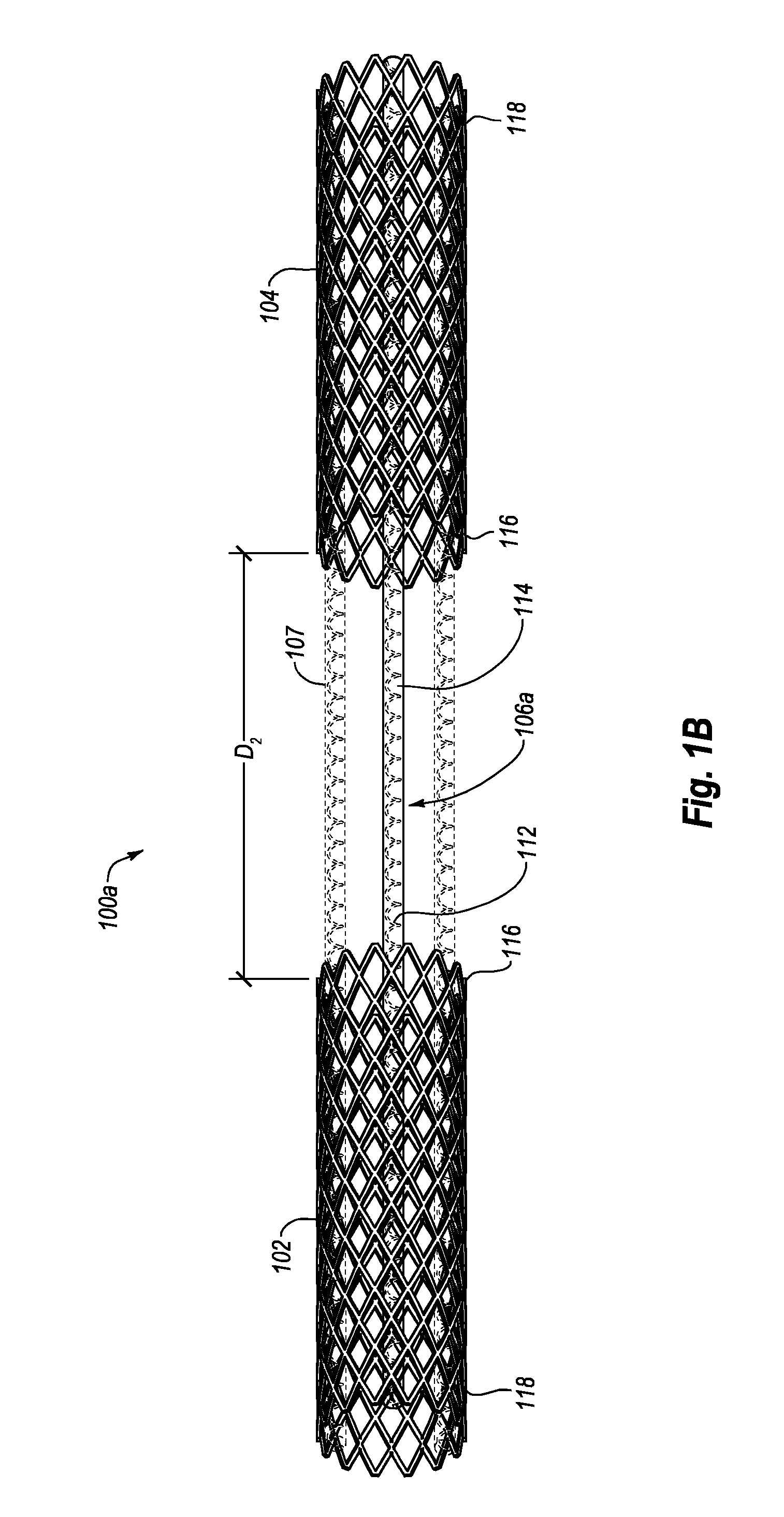
Intravascular cardiac restraining implants and methods for treating heart failure
Intravascular cardiac restraining implants designed for treatment of heart disease and heart failure and methods for their use. The disclosed implants can be used to reshape or reinforce a diseased, weakened or distended portion of a patient's heart to counteract heart disease and heart damage. An intravascular cardiac restraining implant may include a first tissue anchor configured for implantation in a first region of a coronary vein, a second tissue anchor configured for implantation in a second region of the coronary vein, and at least one elongate member coupled to the first tissue anchor and the second tissue anchor. In one embodiment, the at least one elongate member may be a spring or a similar device configured for biasing the first and second tissue anchors toward one another, thus reshaping or reinforcing a diseased, weakened or distended portion of a patient's heart.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
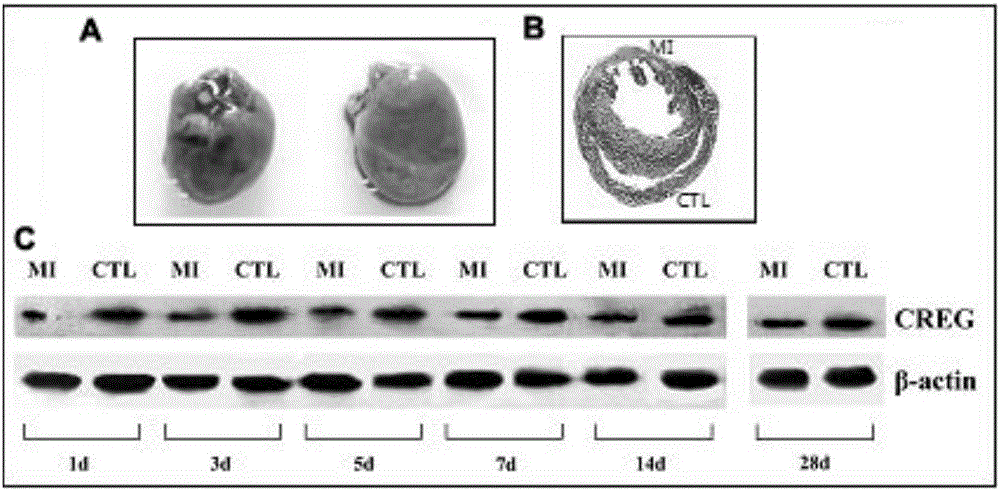
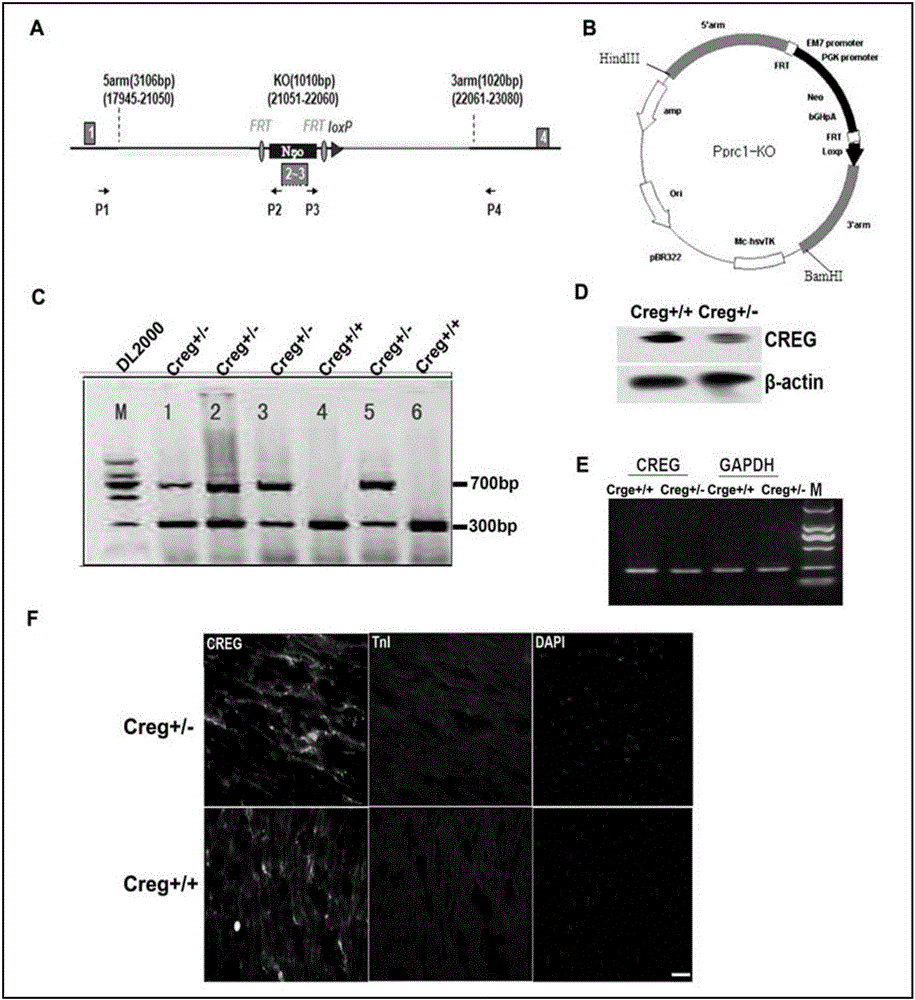
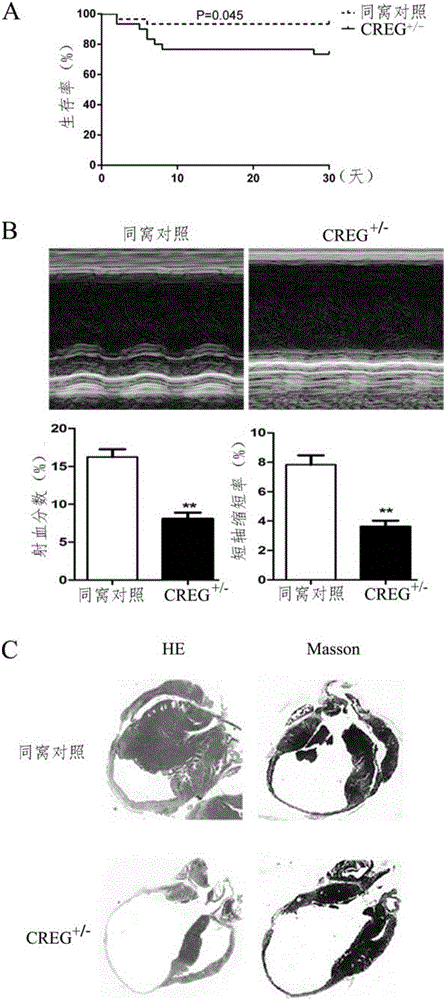
Medical application of CREG protein in preventing or treating myocardial infarction
ActiveCN105056208AEnhance regulatory moleculesGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeart failure cellCardiac muscle
The invention relates to application of E1A-simulated gene cellular repressor (CREG) protein, in particular to application of CREG protein or active fragment thereof in preparation of drug used for preventing and / or treating acute myocardial infarction, heart failure after acute myocardial infarction and / or ventricular remodeling after the same. The invention further relates to application of recombinant vector or recombinant cell expressing the CREG protein or the active fragment thereof in preparation of the drug used for preventing and / or treating acute myocardial infarction, heart failure after acute myocardial infarction and / or ventricular remodeling after the same.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF THE NORTHERN WAR ZONE OF THE CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Selected cell delivery for heart failure
InactiveUS7097833B2Increase blood flowPreventing heart failureBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsIncreased blood flowBlood vessel
This invention provides methods of increasing blood flow to tissue in a subject in need thereof, methods of regenerating tissue in a subject, methods of treating diseased tissue in a subject, methods of forming new blood vessels in tissue and new tissue, such as myocardial tissue, in a subject in need thereof, methods of increasing angiogenesis in diseased tissue in a subject, and methods of preventing heart failure in a subject, which methods comprise: a) isolating autologous mononuclear cells from the subject; b) selecting from the isolated autologous mononuclear cells of step (a) lineage negative (Lin−) mononuclear cells; and c) transplanting locally into or adjacent to the tissue an effective amount of the Lin− autologous mononuclear cells, resulting in formation of new blood vessels in the tissue and formation of new tissue. Additional methods provided for such uses further select from the isolated autologous mononuclear cells of step (a) lineage negative (Lin−) mononuclear cells a subset of Lin− mononuclear side population (SP) cells and transplant locally into or adjacent to the tissue an effective amount of the Lin− SP cells. In other aspects, methods using tissue other than mononuclear cells for these uses are provided, which comprise (a) obtaining a cell suspension from the tissue or a second tissue of the subject; (b) selecting from the cell suspension step (a) side population (SP) cells; and (c) transplanting locally into or adjacent to the tissue an effective amount of the SP cells, resulting in formation of new blood vessels in the tissue and formation of new tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Treatment of heart failure and related conditions
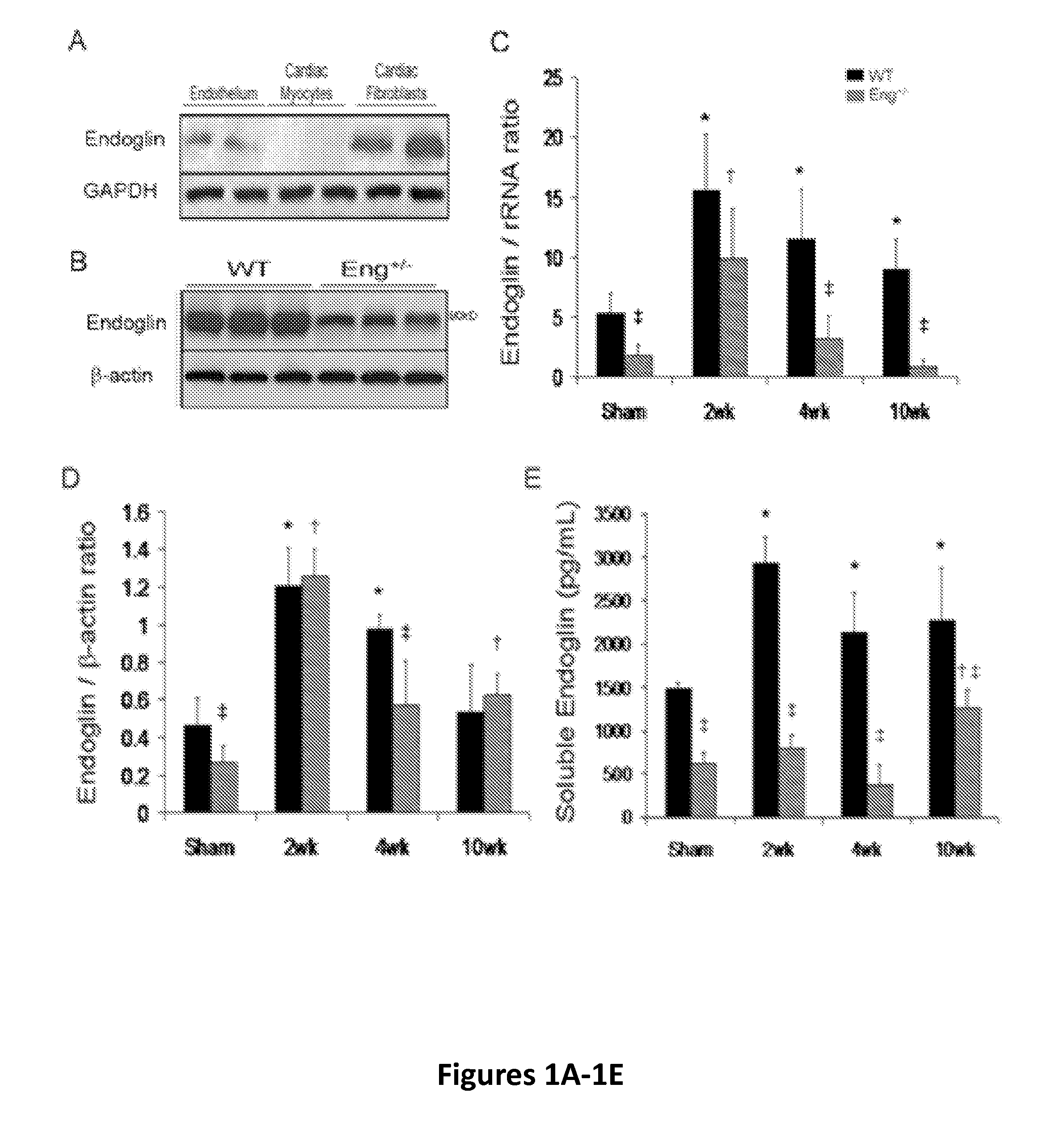
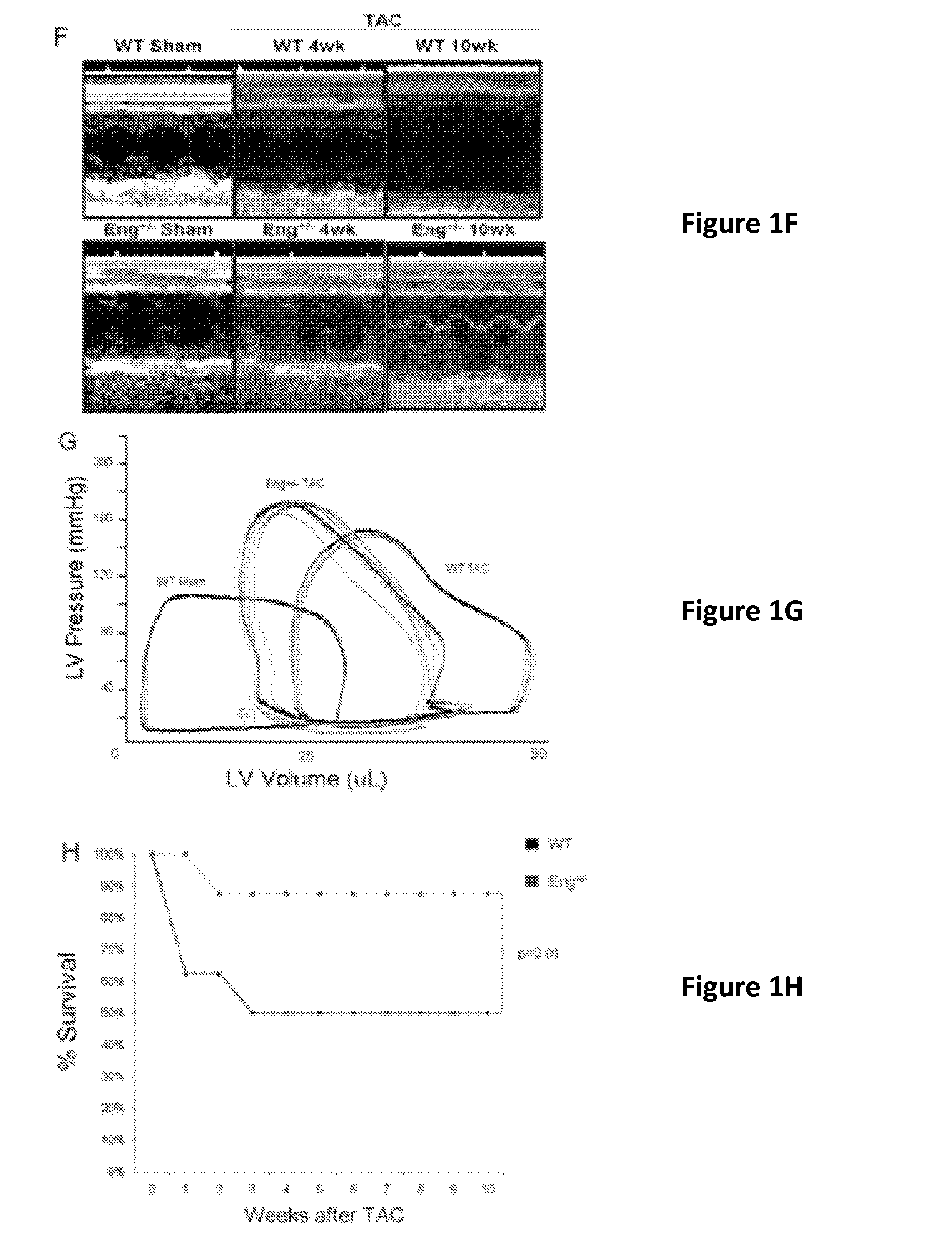
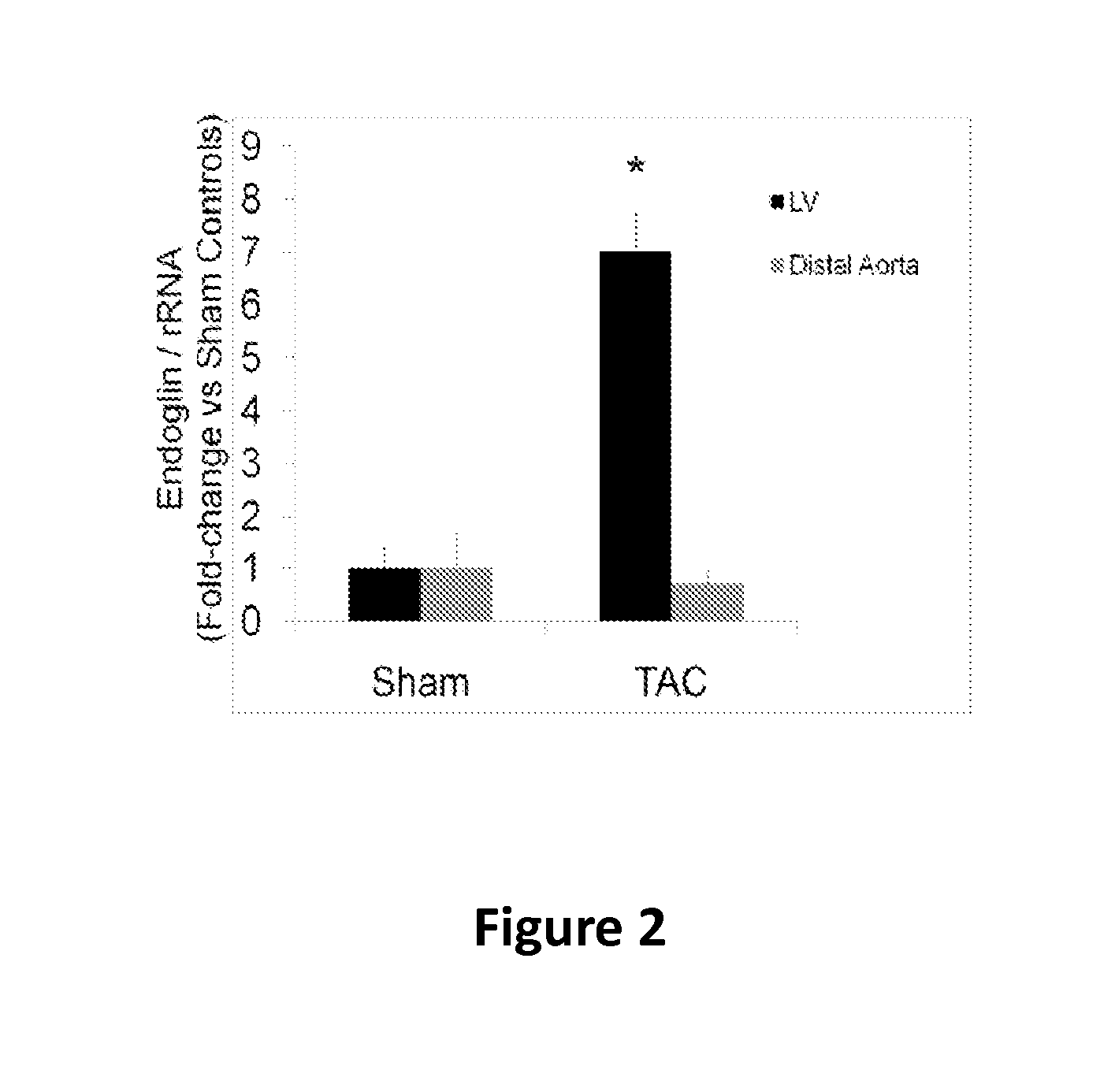
ActiveUS20140234319A1Easily damagedControlling signalOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac fibrosisDisease
Endoglin has now been shown to be an important target of therapy to reduce disease symptoms associated with heart failure, particularly cardiac fibrosis. Soluble Endoglin is identified as an anatogonist to TGFβ1 activity, while membrane-bound Endoglin is identified as a necessary component to promote TGFβ1 activity in heart failure. The present invention therefore features methods and kits for treatment of subject having heart failure or a related disorder by administering a composition that decreases TGFβ1 signaling through either direct inhibition of membrane-bound Endoglin or promoting expression of soluble Endoglin.
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
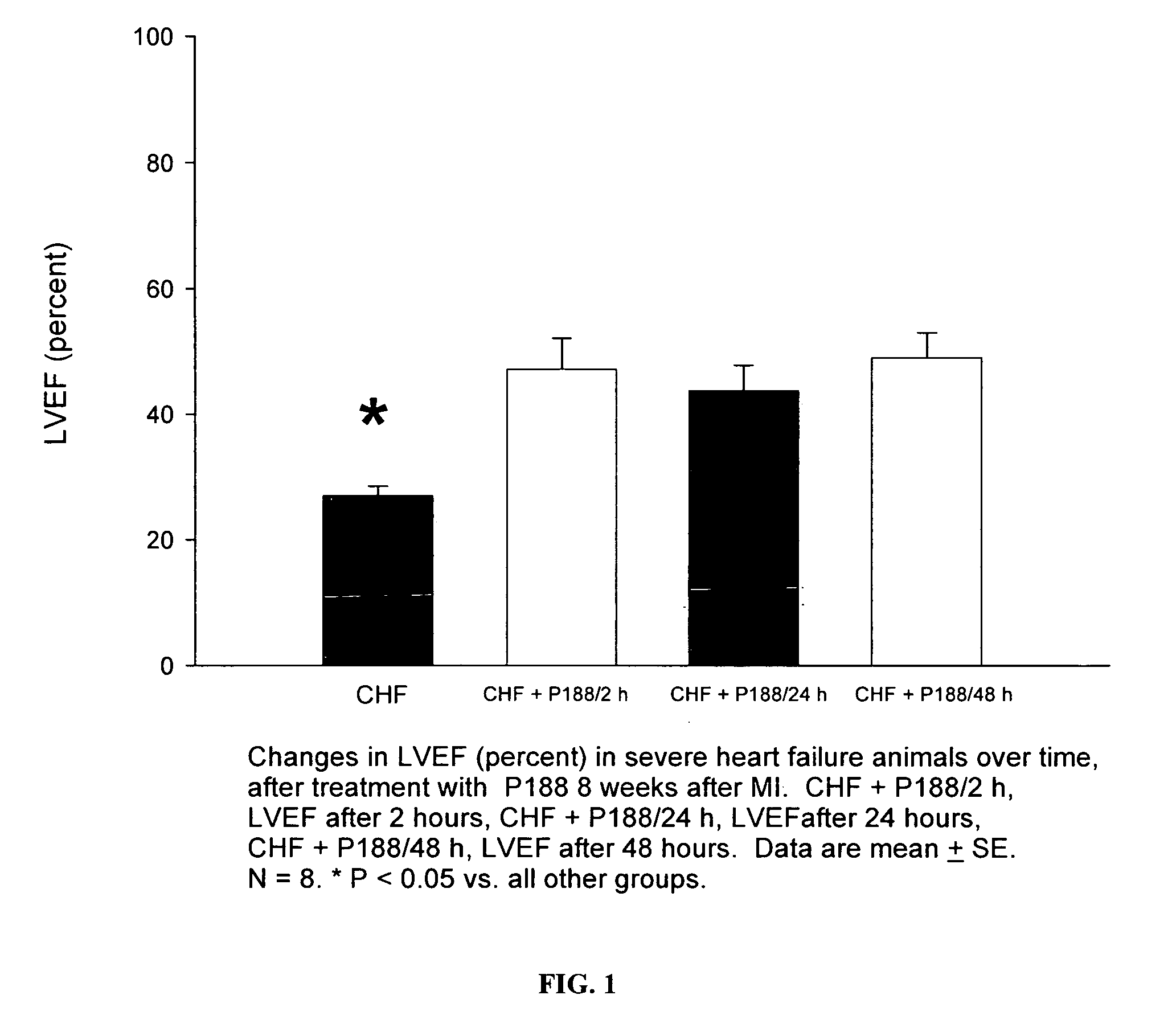
Compositions and methods for the treatment of heart failure
ActiveUS8372387B2Function increaseReduce pressurePharmaceutical delivery mechanismSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsHeart failure cellLeft ventricular ejection
Owner:PHRIXUS PHARMA
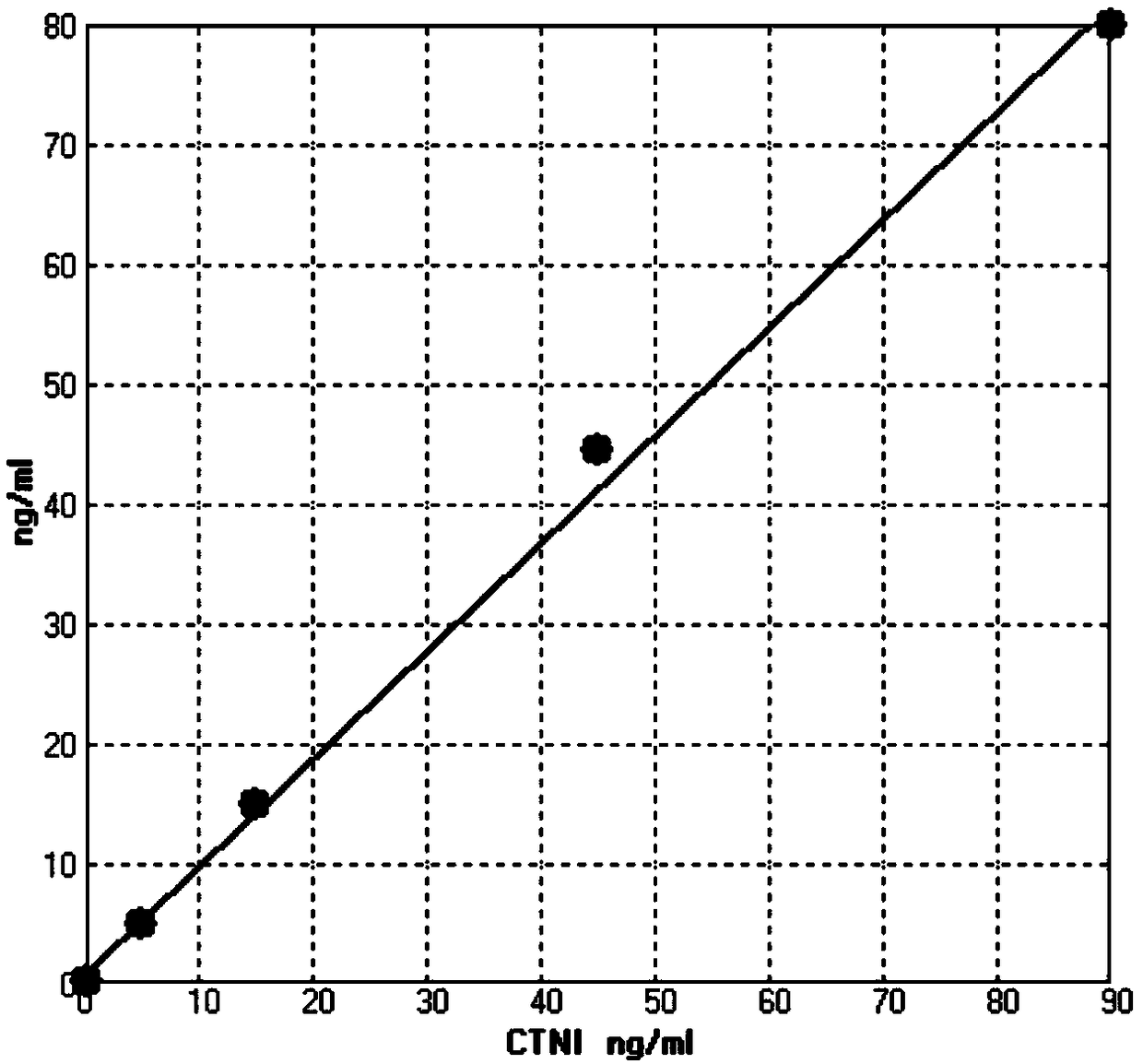
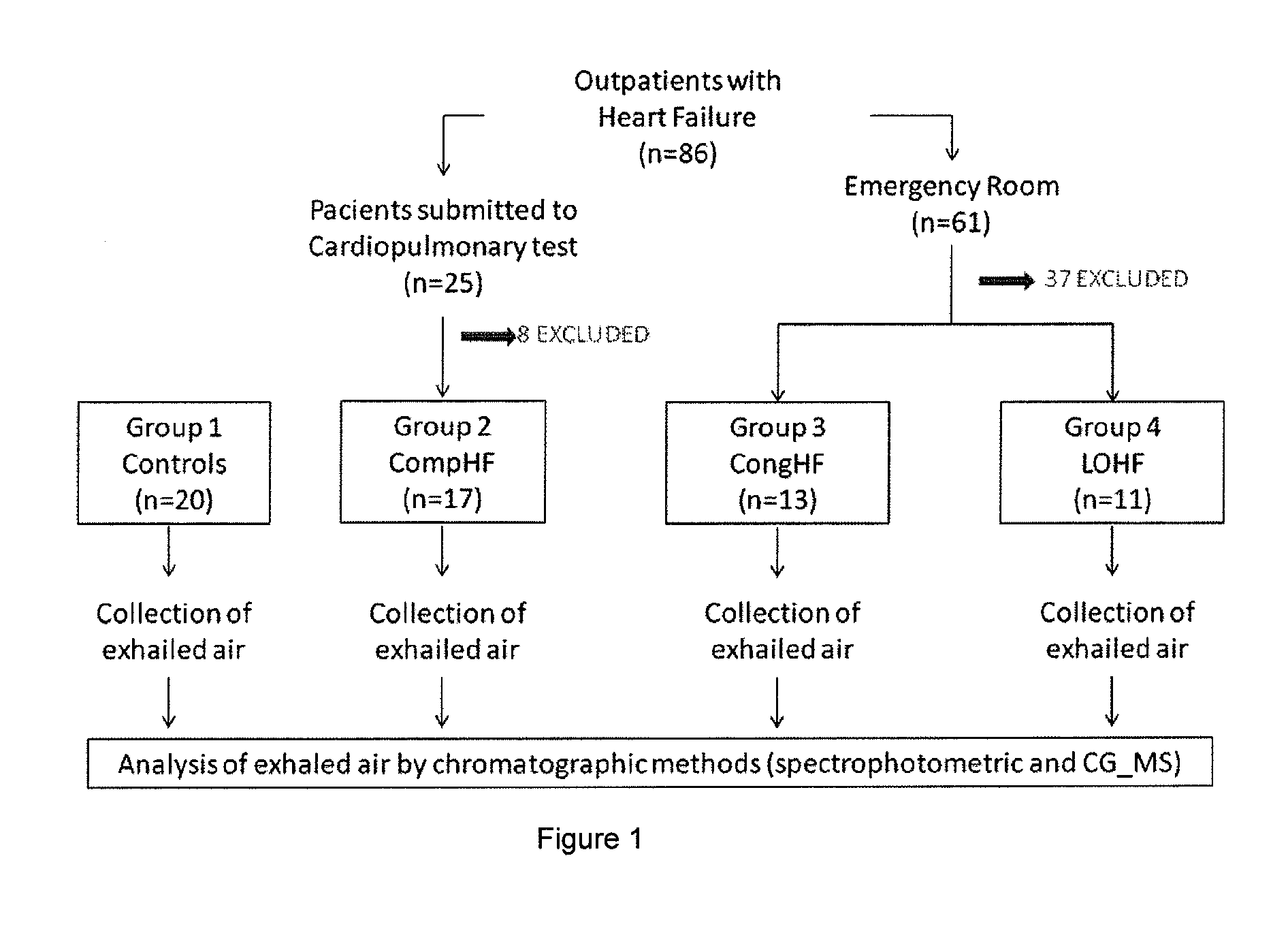
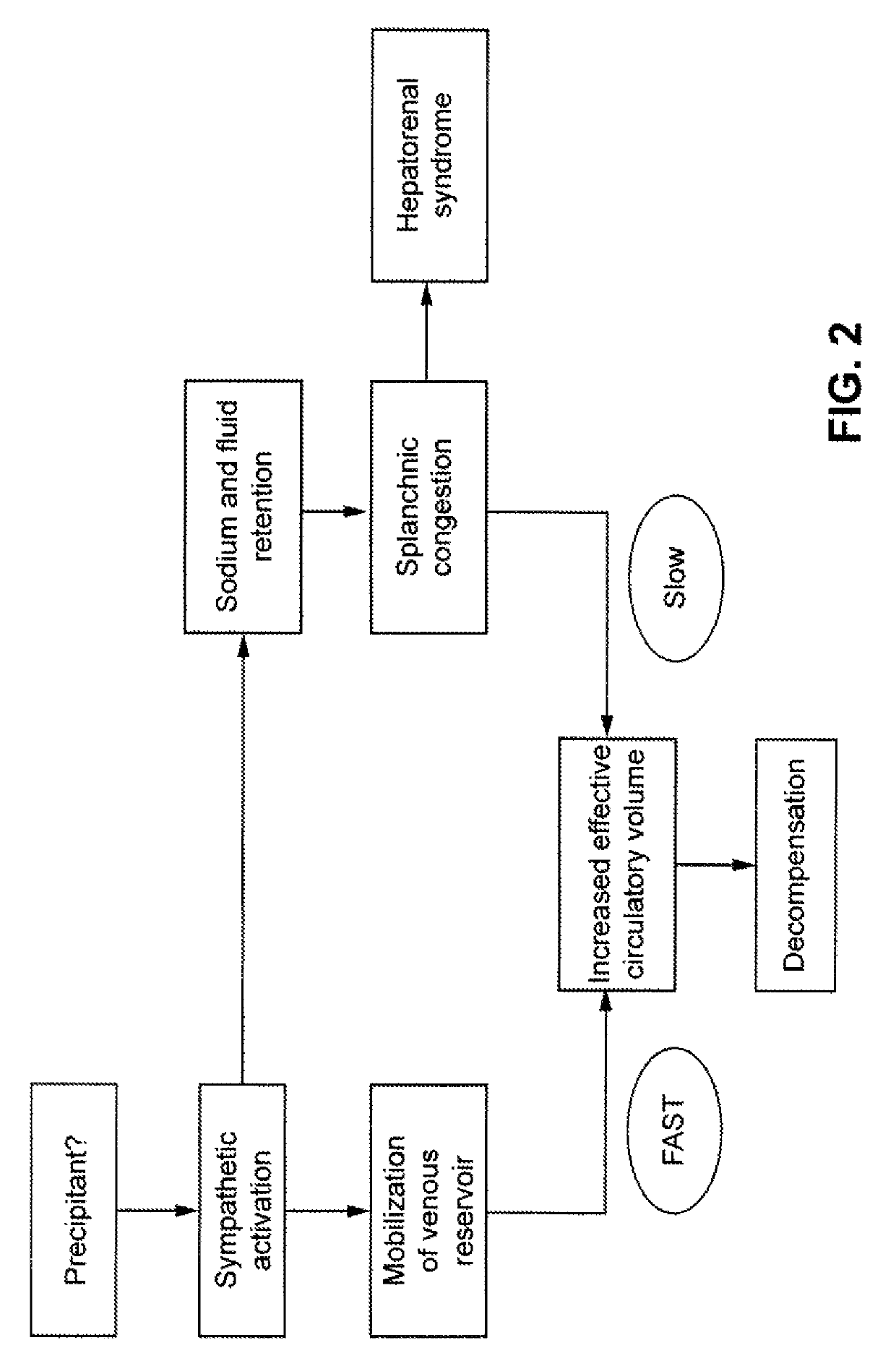
Non-invasive method for diagnosing the severity of heart failure, use of a biomarker for diagnosing decompensated heart failure, collector device for the heart failure biomarker from exhaled breath and a diagnosis kit
ActiveUS20120011918A1Improve retention efficiencyHigh affinityRadiation pyrometryOrganic chemistryDiseaseCell heart failure
The invention application presents a fast, efficient, reproductive alternative of a non-invasive method for diagnosing the severity of heart failure based on a specific biomarker. An additional object of the present invention is a collector device for the biomarker from exhaled breath that is portable, simple, low cost and does not need to run on electric power. This invention advantageously permits the replacement of invasive diagnosis methods, favoring the patient's comfort in addition to the agility and speed of medical attention at hospitals, and may become a standard method for all suspected cases of circulatory disease and heart failure and, more specifically, decompensated heart failure.
Owner:BRAGA FABIANA GOULART MARCONDES +3
Immunochromatographic test strip for detecting cardiac infarction and heart failure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107290529AAccurate readingLow cross-reactivityDisease diagnosisAgainst vector-borne diseasesHeart failure cellImmunofluorescence
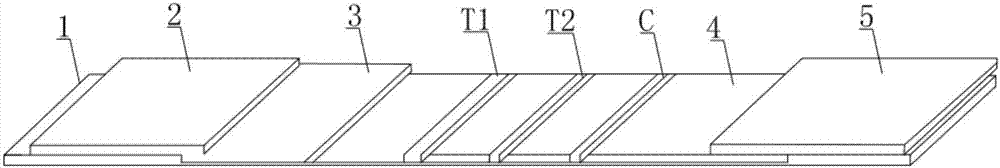
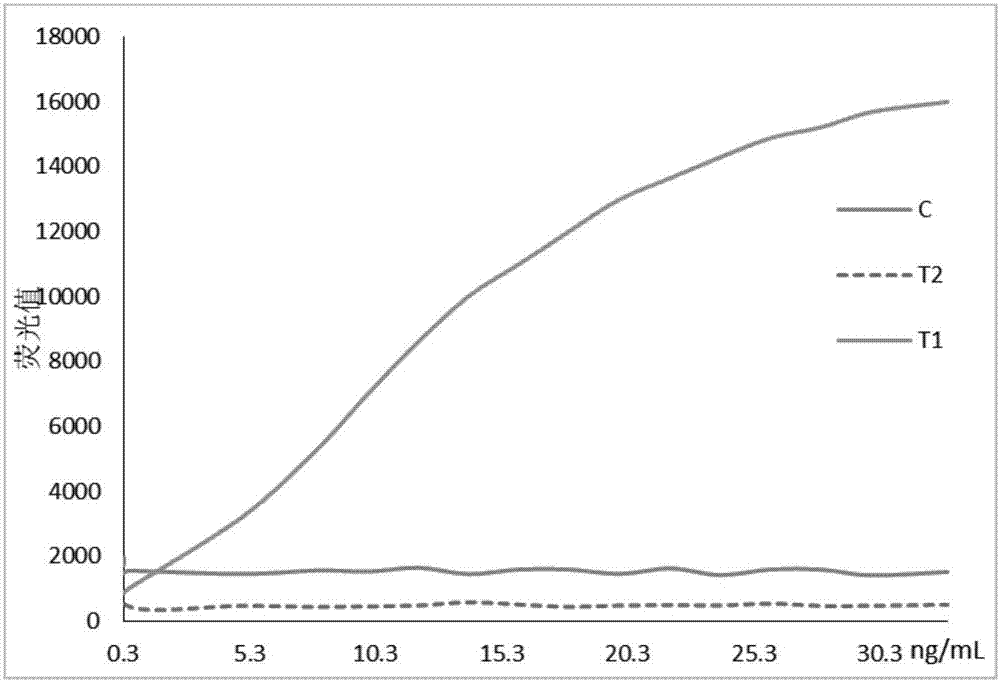
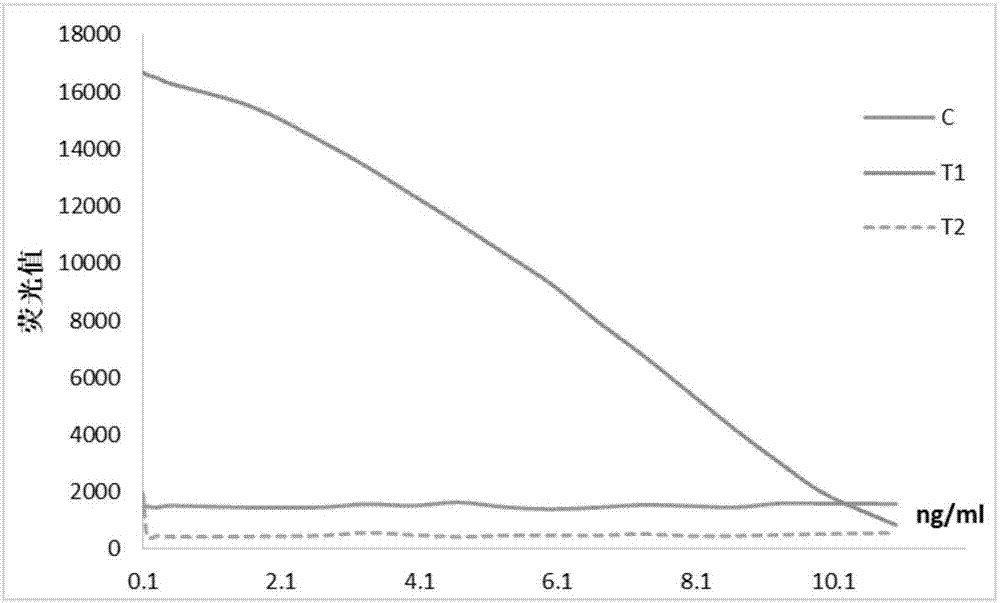
The invention discloses an immunochromatographic test strip for detecting cardiac infarction and heart failure and a preparation method thereof, and is intended to provide an immunochromatographic test strip that provides detection results accurately determinable and causes few cross reactions. The immunochromatographic test strip comprises a bottom board; a sample pad, a binding pad, a reaction film and an absorbing pad are linked to the bottom board; CRP (C-reactive protein) antibody and chicken IgY labeled by 300 nm immunofluorescence spheres are sprayed to the binding pad, and NT-proBNP antibody labeled by 200 nm immunofluorescence spheres is also sprayed thereto; the reaction film is parallelly provided with a C quality control line, a T1 detection line and a T2 detection line; the C quality control line is coated with goat anti-chicken IgY; the T1 detection line is coated with antigen CRP protein; the T2 detection line is coated with anti-NT-proBNP antibody.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WEIMI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
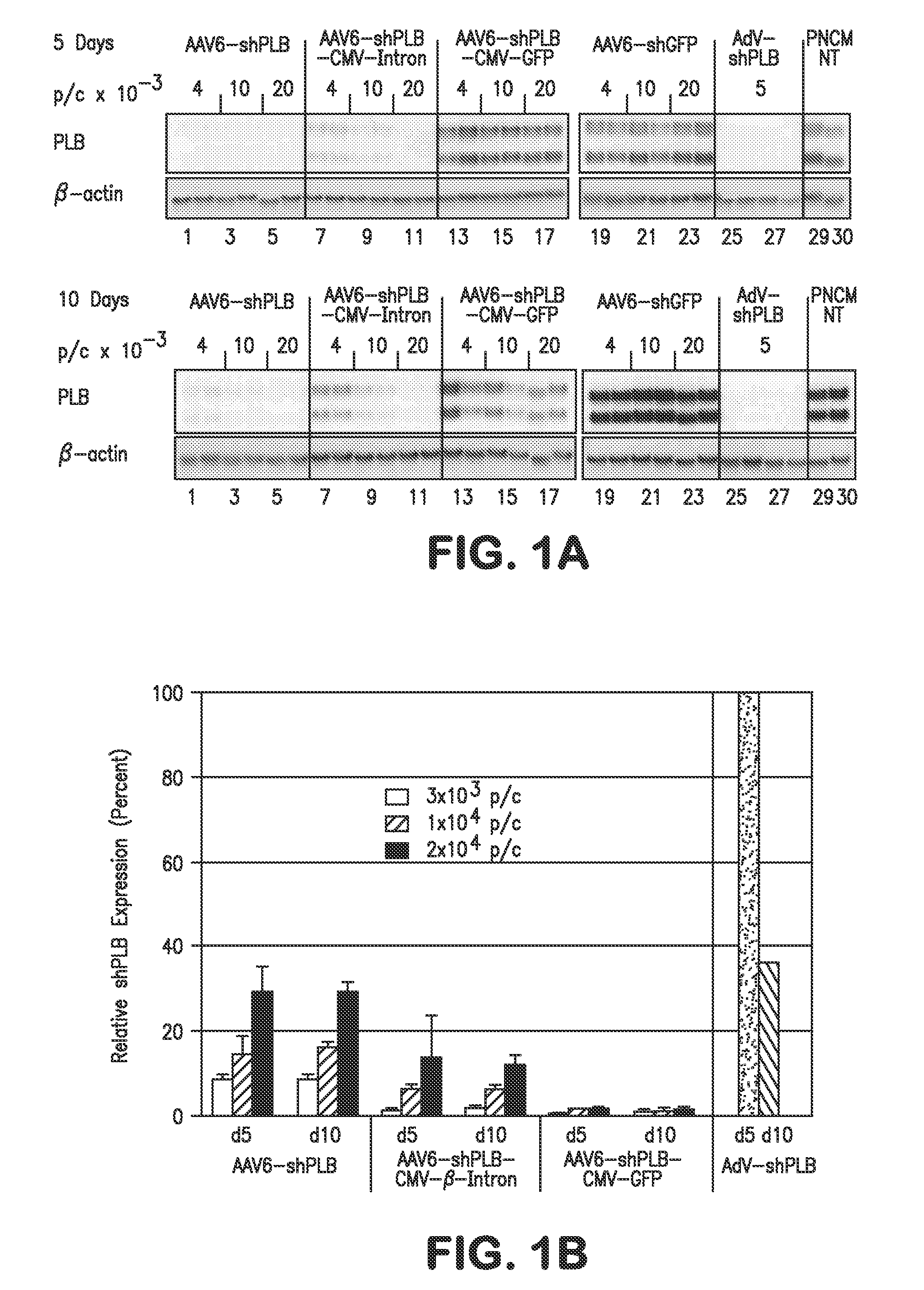
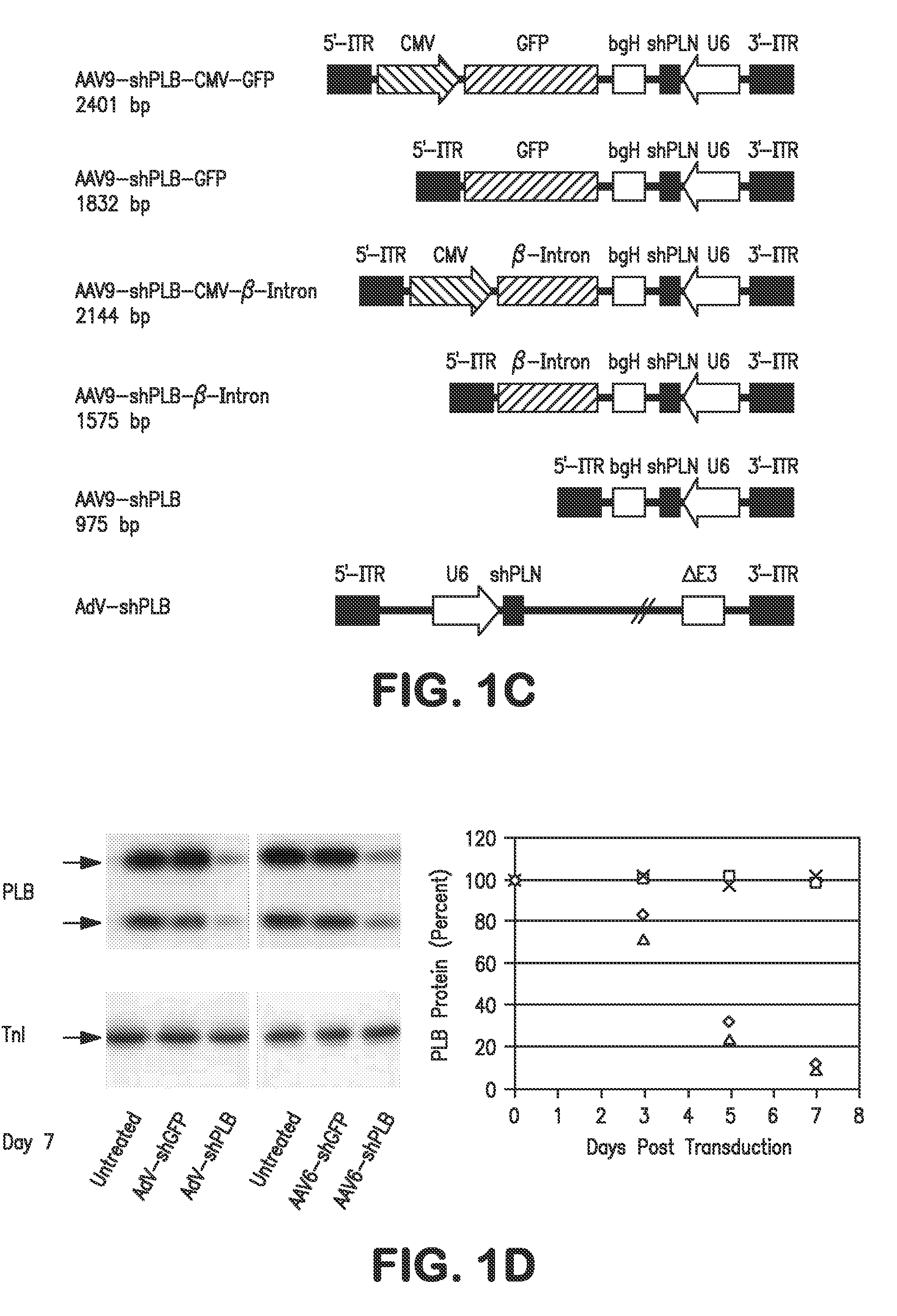
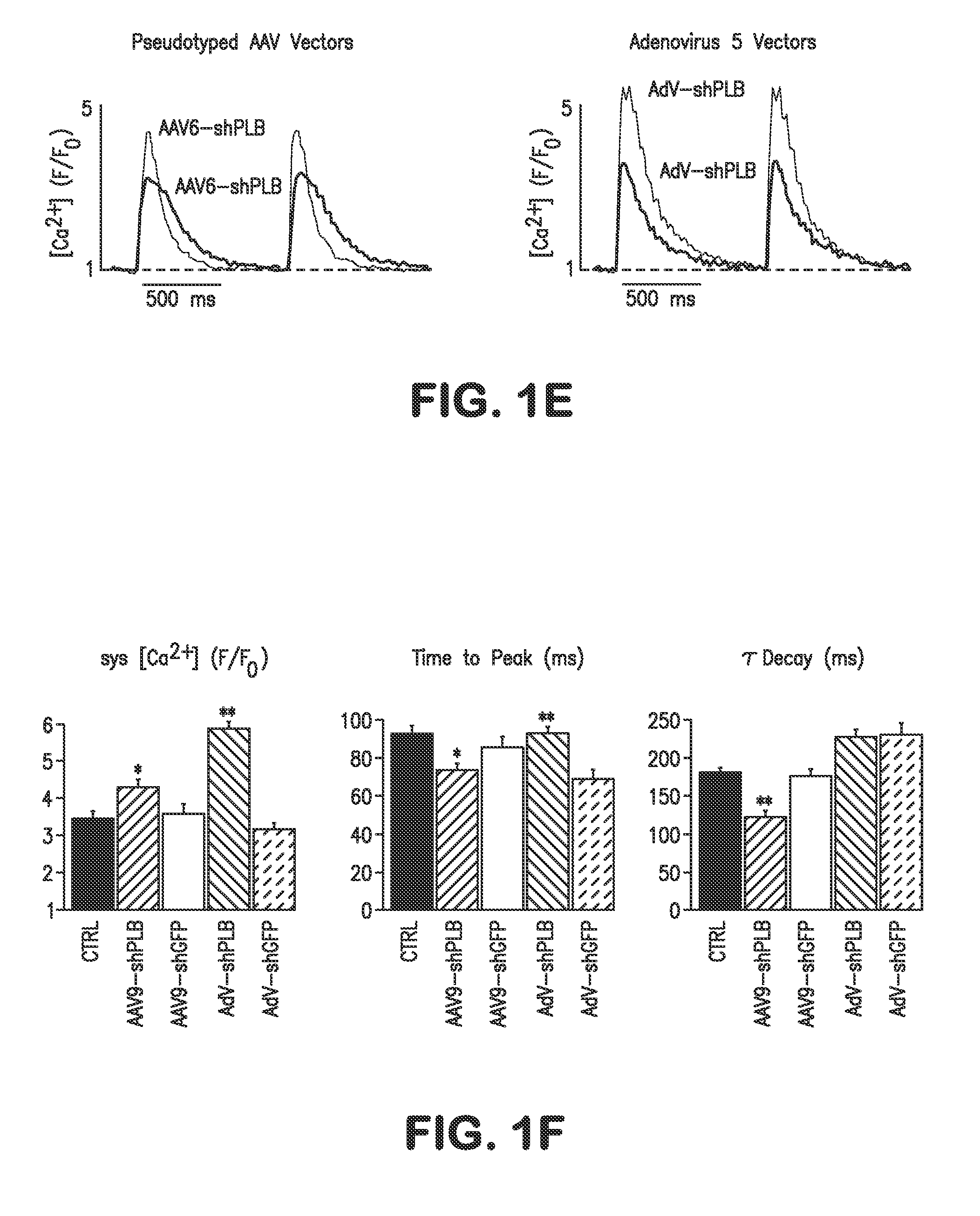
RNA Interference for the Treatment of Heart Failure
InactiveUS20110098338A1Improve survivalReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsTissue cultureHeart failure cellVentricular dysrhythmia
The present invention relates to targeted RNAi for the treatment of heart failure by modulating defective cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis via decreasing expression or activity of phospholamban (PLB) using adeno-associated virus (AAV) transfection of cardiomyocytes. Methods for decreasing ventricular arrhythmias, as well as methods for overall improvement of survival from heart failure in subjects are also disclosed. Further, the present invention provides methods which can be used to diagnose susceptibility to treatment by RNAi, and includes pharmaceutical compositions, kits and vectors including an RNAi sequence.
Owner:NANOCOR THERAPEUTICS +1
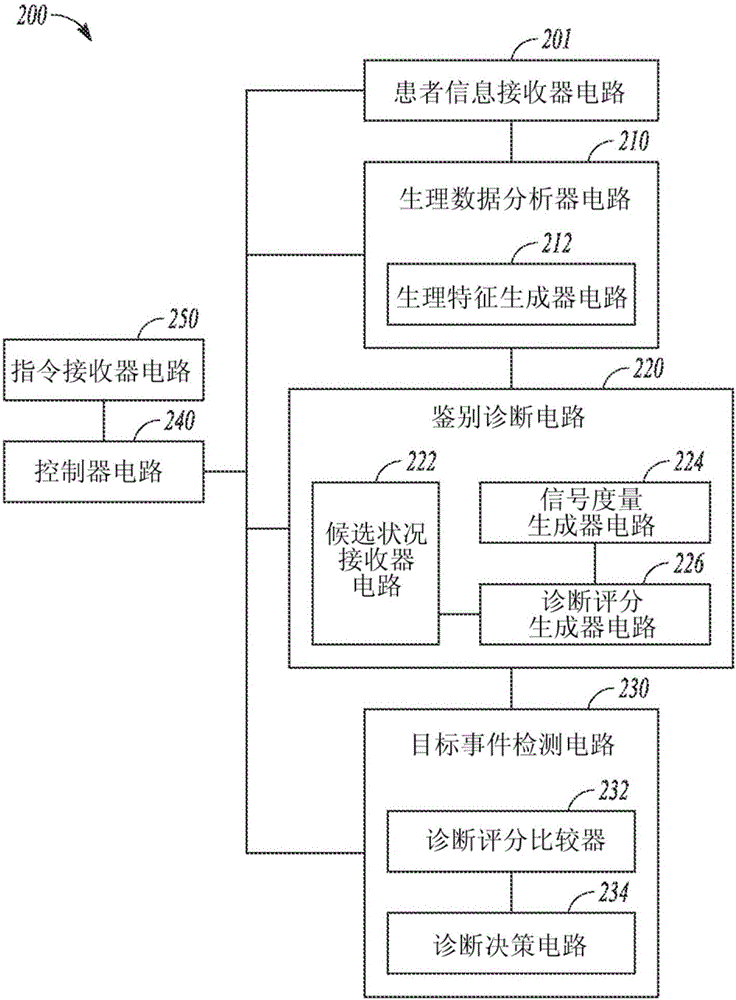
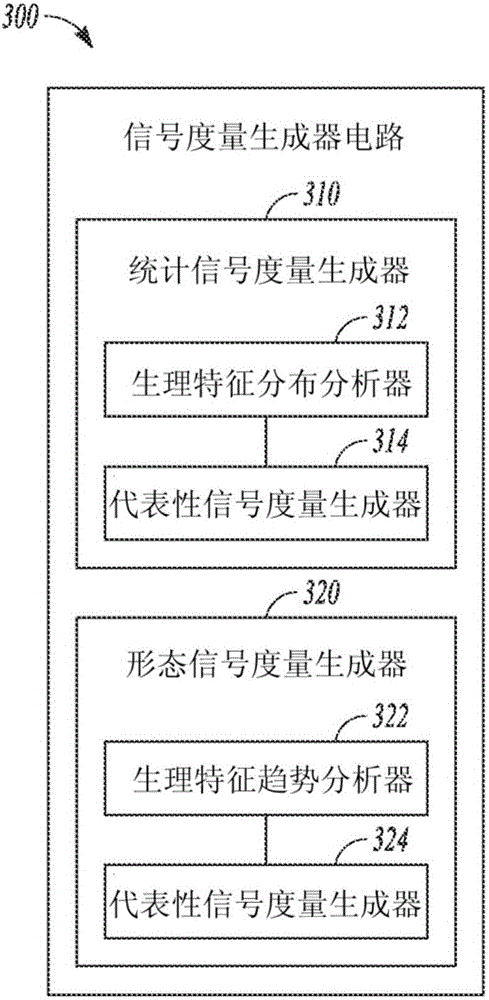
Automatic differential diagnosis of worsening heart failure
InactiveCN106455995APrevents HF exacerbationLow costHealth-index calculationStethoscopeDiseaseHeart failure cell
Devices and methods for differentially diagnosing between worsening heart failure (HF) and other diseases or medical conditions are described. A medical system can receive patient information including one or more physiologic signals, and detect a respective physiologic feature from each of the one or more received physiologic signals. The medical system can include a differential diagnosis circuit that generates one or more signal metrics, receive two or more candidate conditions associated with the change in patient physical or physiological status, and determine a respective diagnostic score for each of the candidate conditions. The diagnostic score can indicate likelihood the change in the patient physical or physiologic status being caused by the corresponding candidate condition. A user interface can be provided to generate a presentation of the detected physiologic features and the diagnostic scores associated with the candidate conditions.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
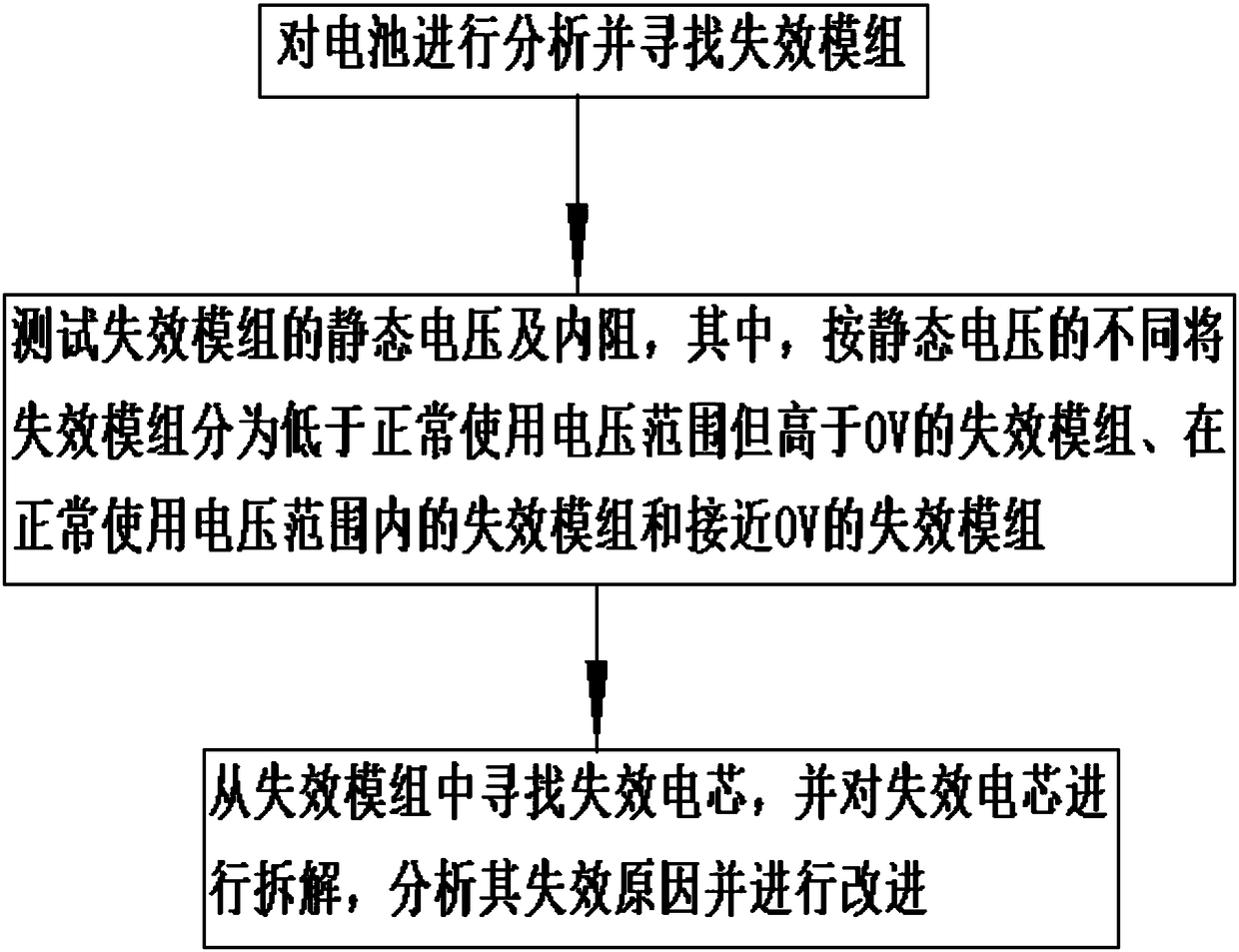
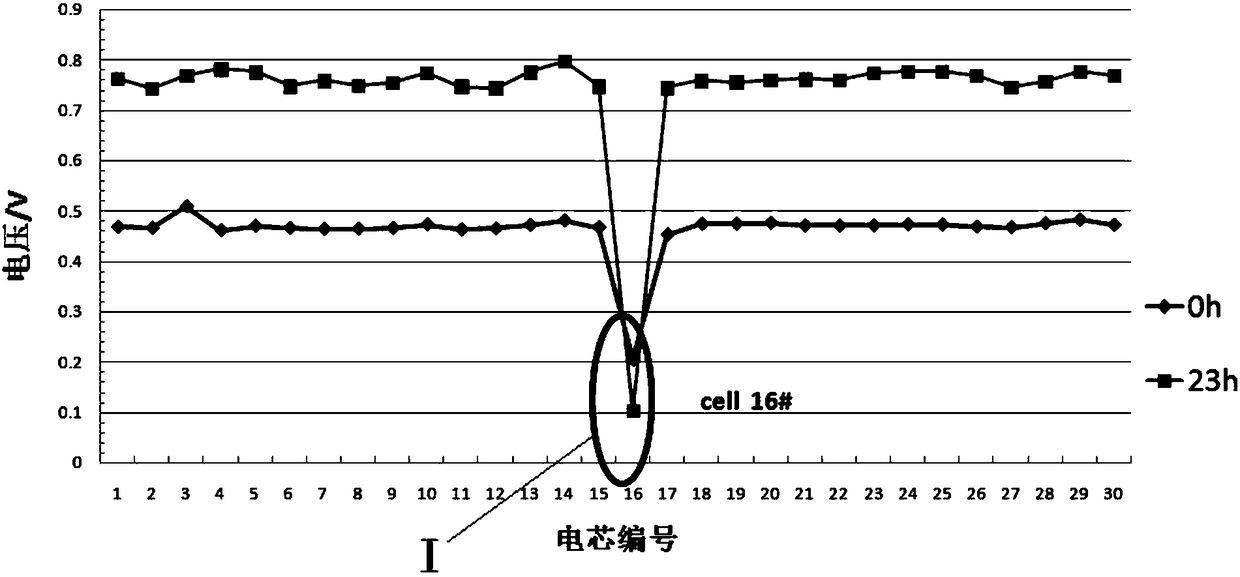
Analysis method for vehicle-mounted battery pack pressure difference problem
InactiveCN108089131AQuality improvementLow failure rateElectrical testingFailure rateHeart failure cell
The invention discloses an analysis method for a vehicle-mounted battery pack pressure difference problem. The method includes firstly, analyzing the battery and finding out a failure module; secondly, testing the static voltage and the internal resistance of the failure module, wherein the failure module is divided into a failure module which is lower than the normal use voltage range but is higher than 0V, a failure module in a normal use voltage range and a failure module close to 0V according to the different static voltages; finally, finding out the failure cell from the failure module, dissembling the failure cell, and analyzing the failure reason and making the improvement. The method has the beneficial effects that starting from the differential pressure large fault module, the failure cell of the failure module can be analyzed through the capacity, direct-current internal resistance, disassembly, self-discharge analysis aspects, and the root cause of the cell failure is foundthrough disassembly of the cell, the cell production is guided to improve the cell quality, and the failure rate of the battery pack pressure difference is fundamentally reduced.
Owner:SHANXI CHANGZHENG POWER TECH CO LTD
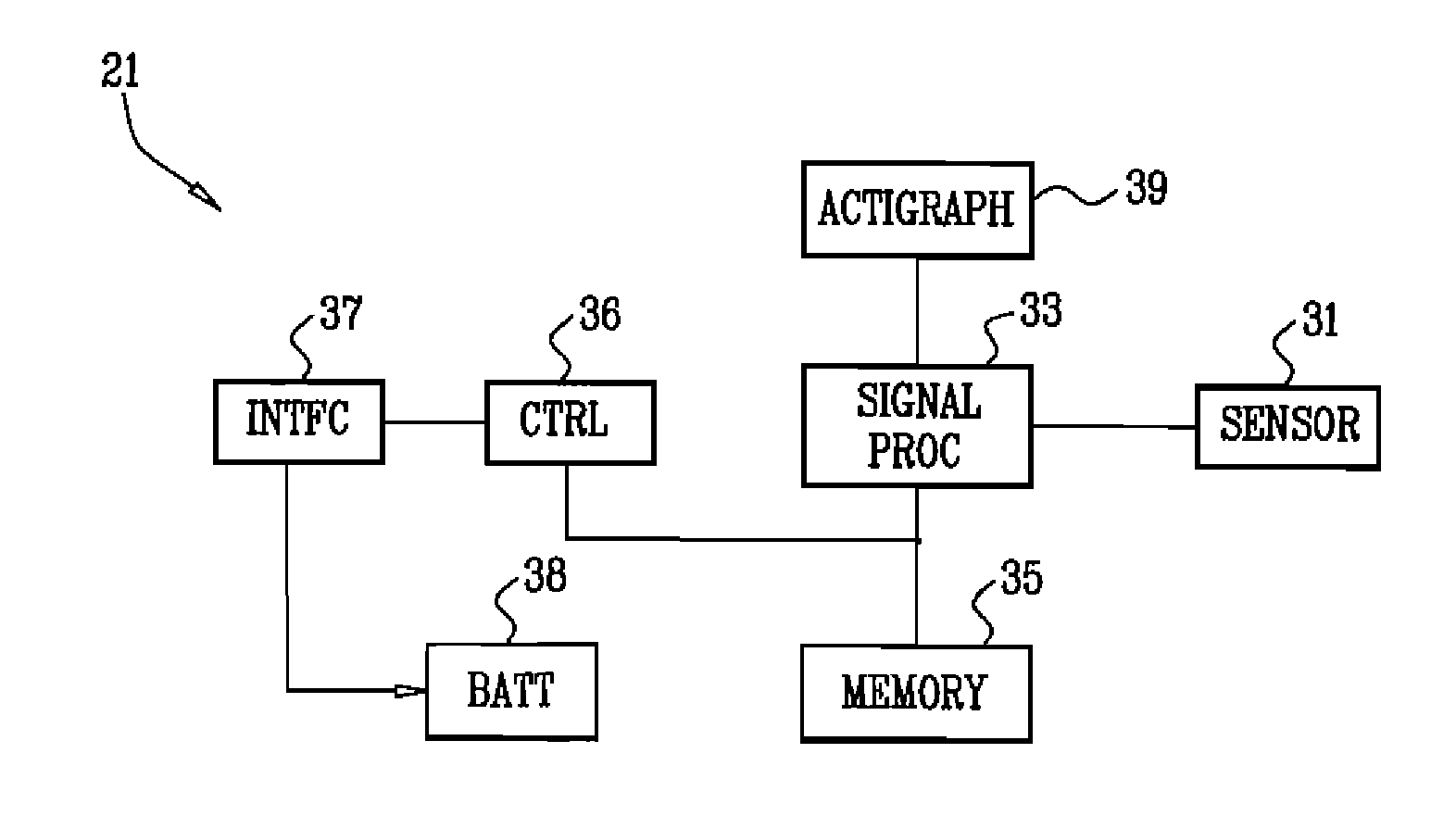
Absolute intrathoracic impedance based scheme to stratify patients for risk of a heart failure event
ActiveUS20170027474A1Quick confirmationAvoid and reduce probabilityHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMoving averageIntrathoracic impedance
A health care system acquires data determines whether a patient is at risk of hypervolemia or hypovolemia. The method comprises (a) acquiring from a device memory a patient's absolute intrathoracic impedance data over a pre-specified time period, (b) determining a running average of the intrathoracic impedance data over the pre-specified time period, and (c) determining by the system whether the running average of the intrathoracic impedance data over the pre-specified time period exceeds one of a first and second range, the first range being a higher value boundary of intrathoracic electrical impedance and the second range being a lower value boundary of intrathoracic electrical impedance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Neuregulin based methods for treating heart failure
ActiveUS20130079281A1Improves and protects deteriorationImprove survivalPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticNeuregulinHeart failure cell
The present invention features methods of treating patients with chronic heart failure by administering a neuregulin polypeptide within a dosage range which is both effective and safe.
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
Devices and methods for treatment of heart failure by splanchnic nerve ablation
Owner:AXON THERAPIES INC
A method of protecting against heart failure
InactiveCN102257392AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHeart failure cellCell heart failure
The present invention relates, in general, to heart failure, and, in particular to a method of reducing the risk of heart failure, particularly in patents with established cardiomyopathy.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
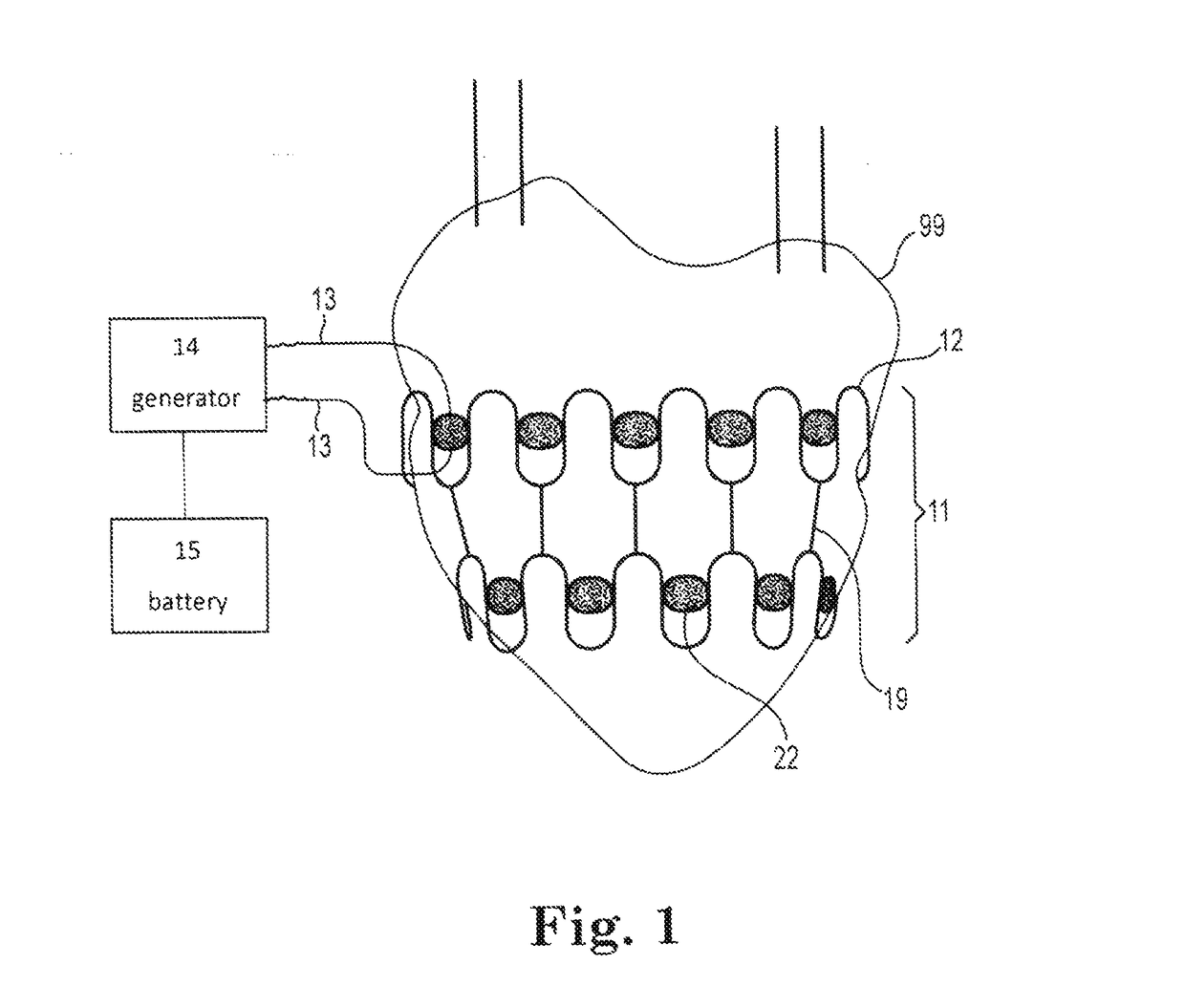
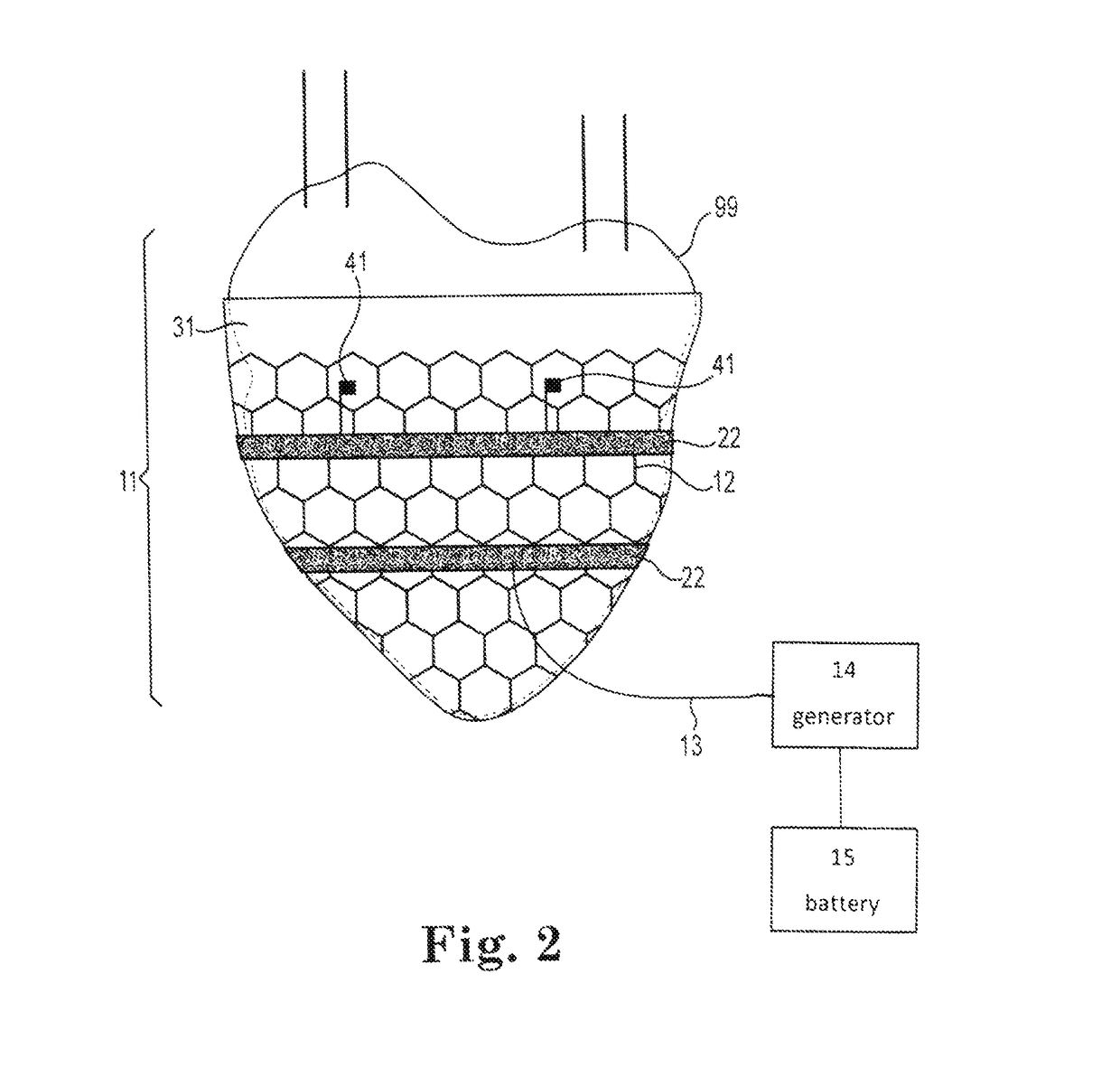
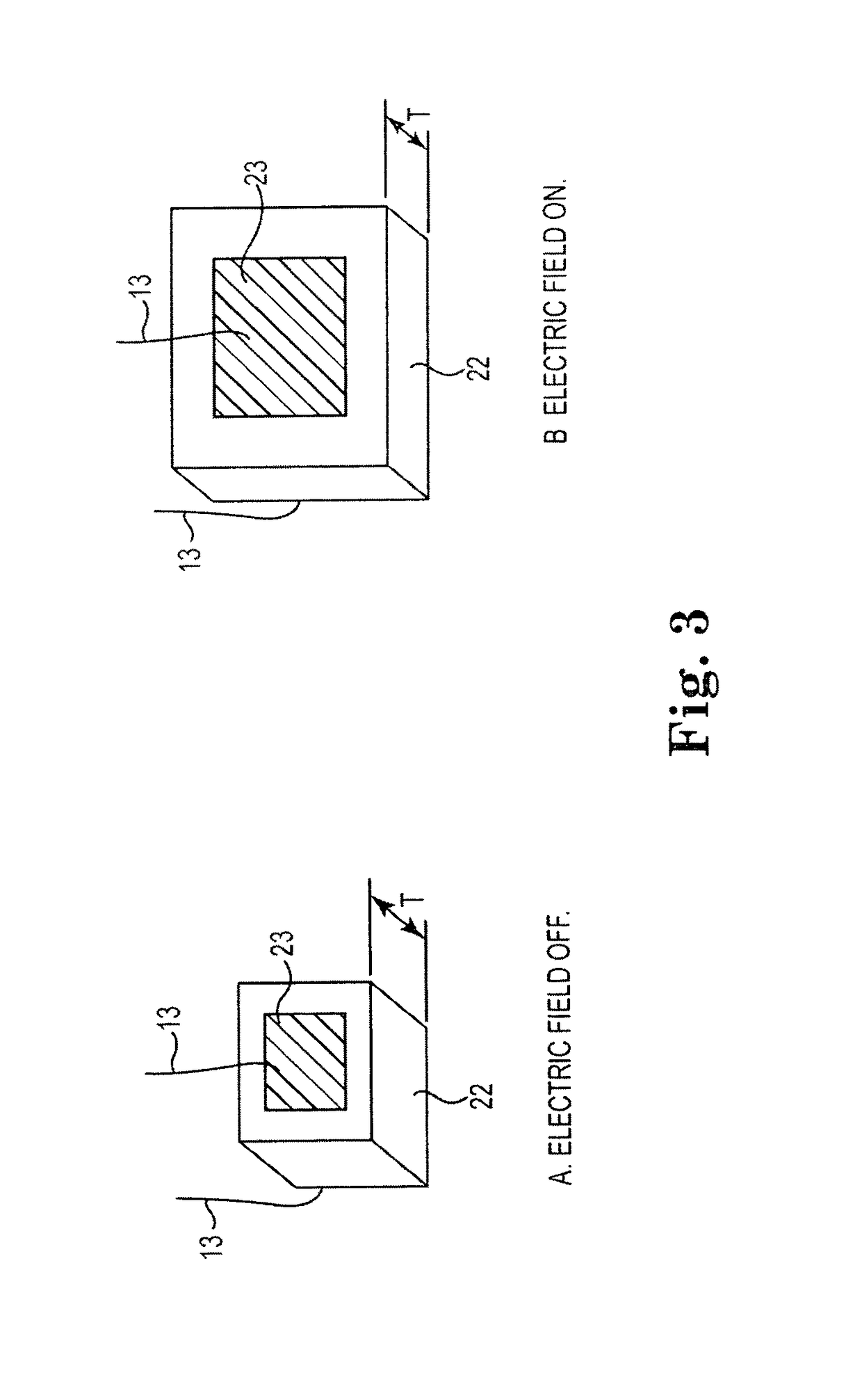
Implanted cardiac device to treat heart failure
New methods and devices for treating heart failure and other cardiac disease conditions. Devices include a cardiac jacket adapted to fit generally around at least a portion of the heart. The jacket in some embodiments includes an electroactive polymer to squeeze the exterior of the heart to assist contraction of one or more pumping chambers, preferably the left ventricle. The jacket may also include stem cells on an inner surface of the jacket. The stem cells differentiate into cardiac tissue and help treatment of heart failure. Some embodiments also involve delivering an electric field or an electric current to electrically conductive material in the jacket to establish an electromagnetic field at the surface of the heart effective to promote growth and differentiation of stem cells into cardiac tissue.
Owner:NEOCARDIAL TECH LLC
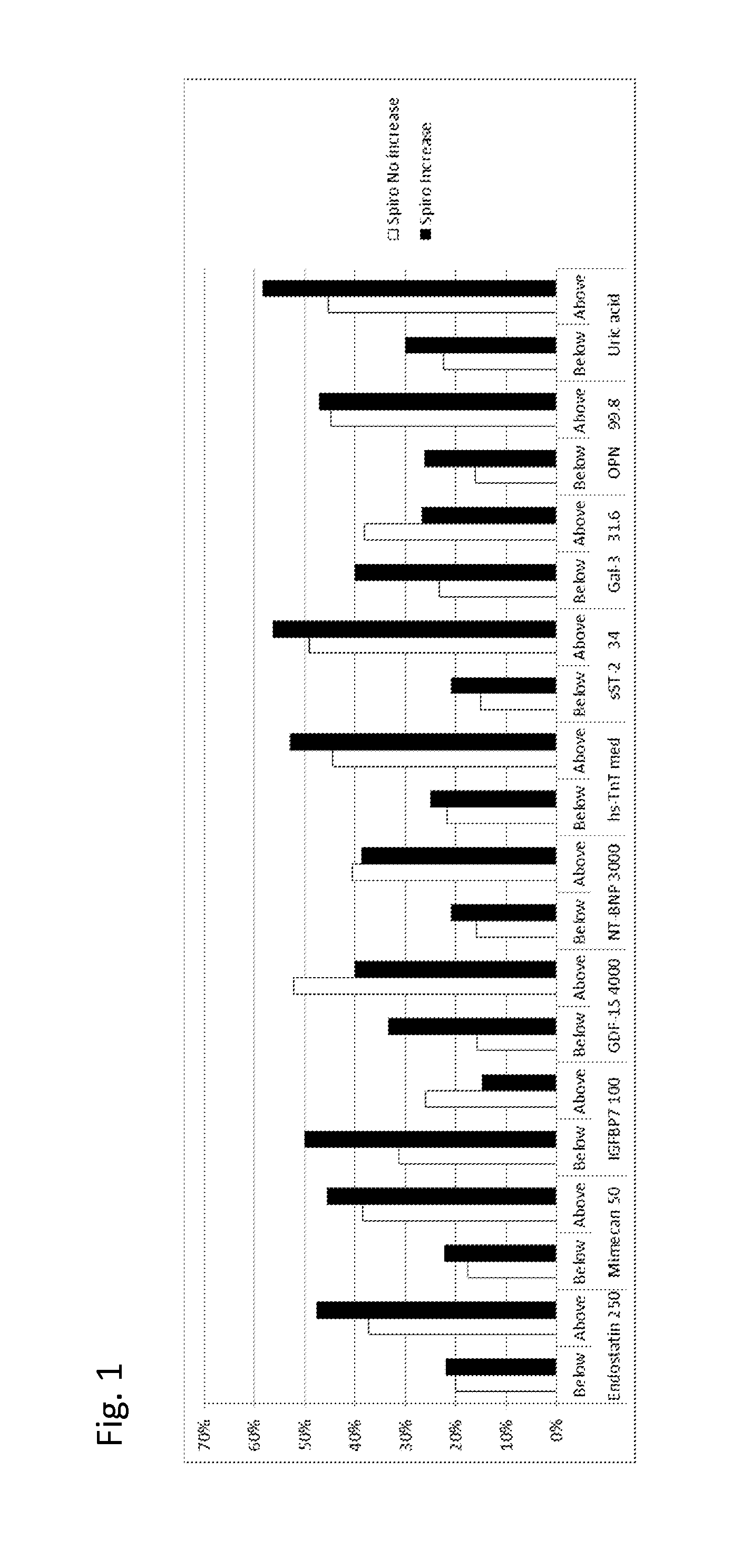
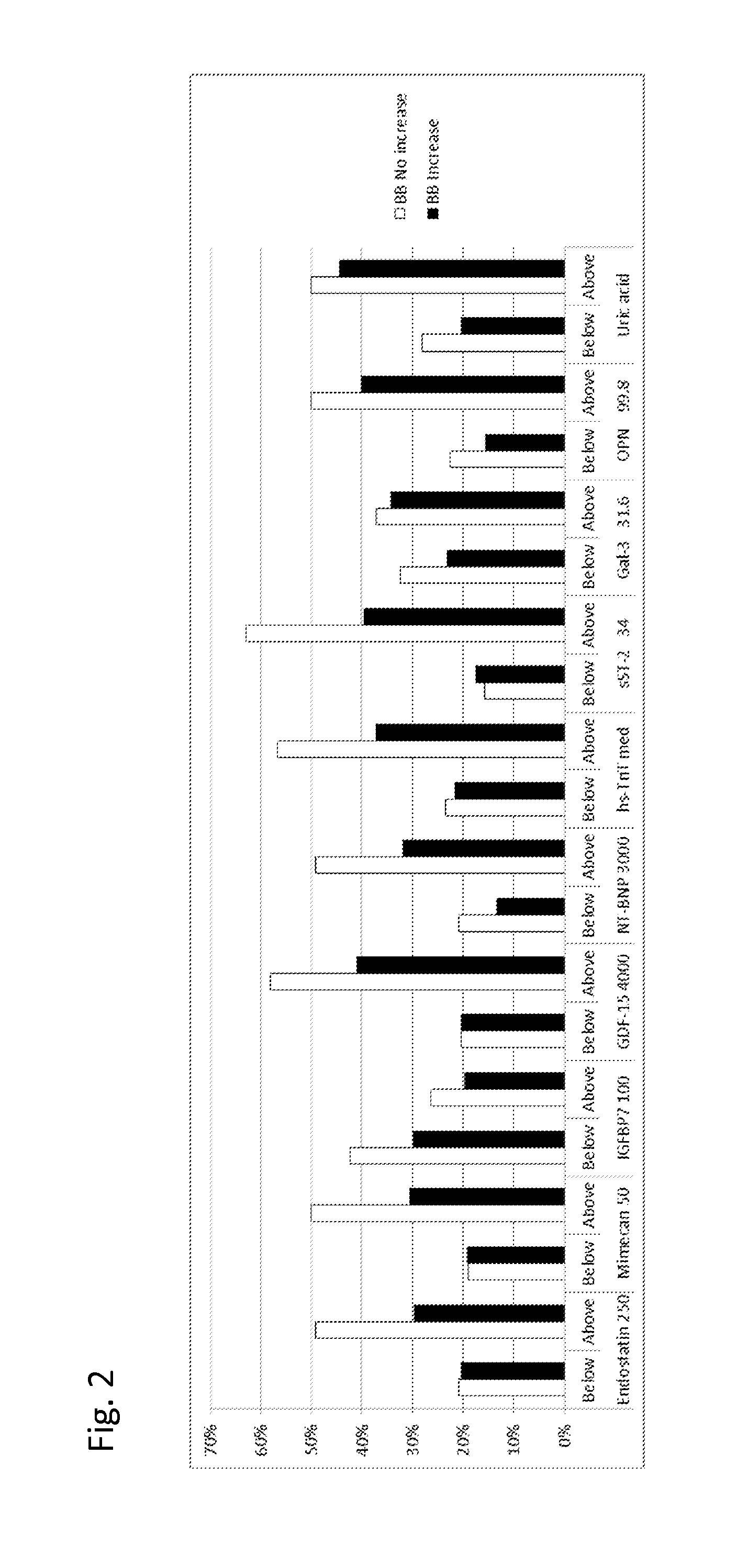
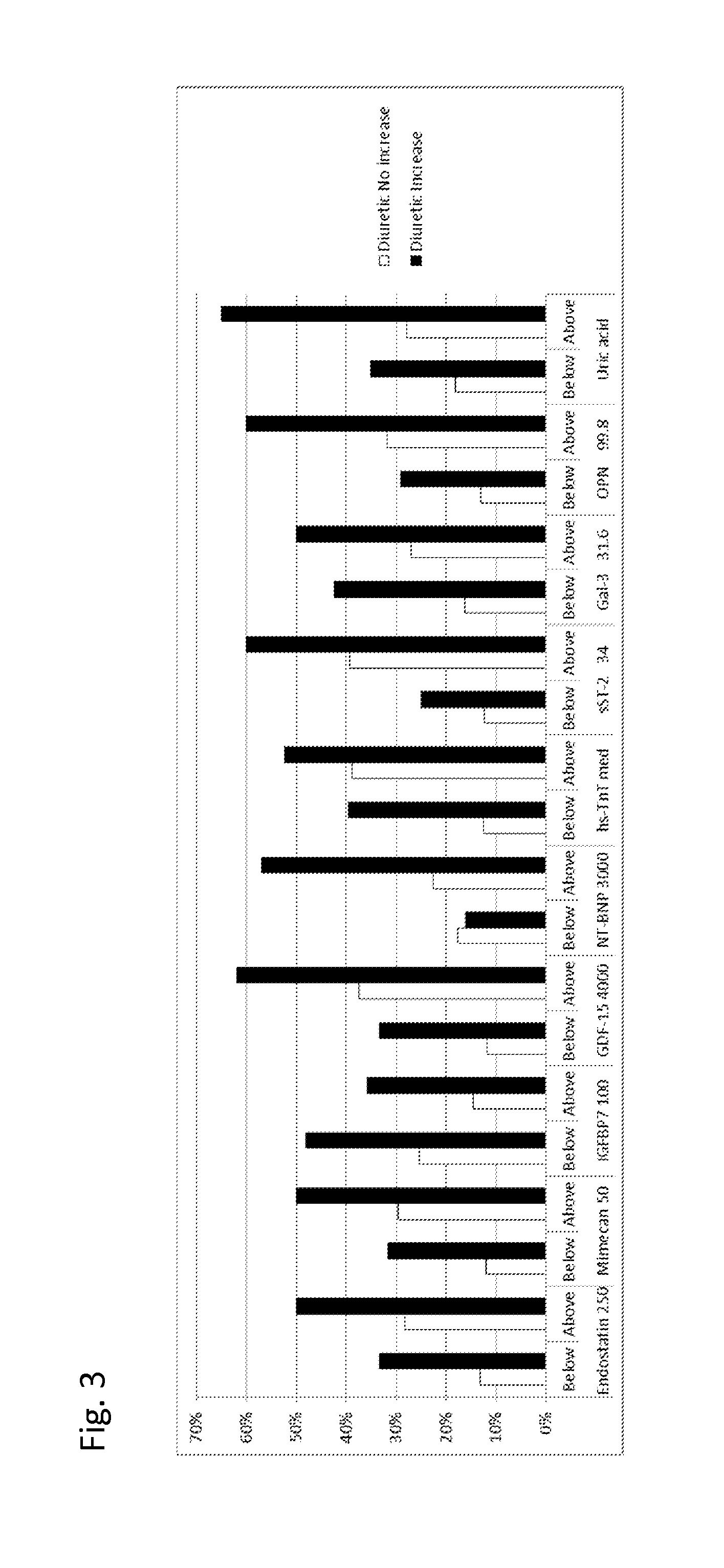
Biomarkers in the selection of therapy of heart failure
InactiveUS20150268251A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBeta blockerBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a subject being eligible to the administration of at least one medicament selected from the group consisting of a beta blocker, an aldosterone antagonist, a diuretic, and an inhibitor of the renin-angiotensin system. The method is based on the determination of the amount of at least one biomarker selected from the group consisting of GDF-15 (Growth Differentiation Factor 15), endostatin, mimecan, IGFBP7 (IGF binding protein 7), a cardiac Troponin, a BNP-type peptide, uric acid, Gal3 (Galectin-3), osteopontin, sST2 (soluble ST2), PlGF, sFlt-1, P1NP, Cystatin C, Prealbumin, and Transferrin in a sample from a subject suffering from heart failure. Further, the method comprises the step of comparing the, thus, determined amount with a reference amount. Further envisaged by the present invention are kits and devices adapted to carry out the method of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a system for identifying a subject being eligible to the administration of at least one medicament as disclosed herein and to reagents and kits used in performing the methods as disclosed herein.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com