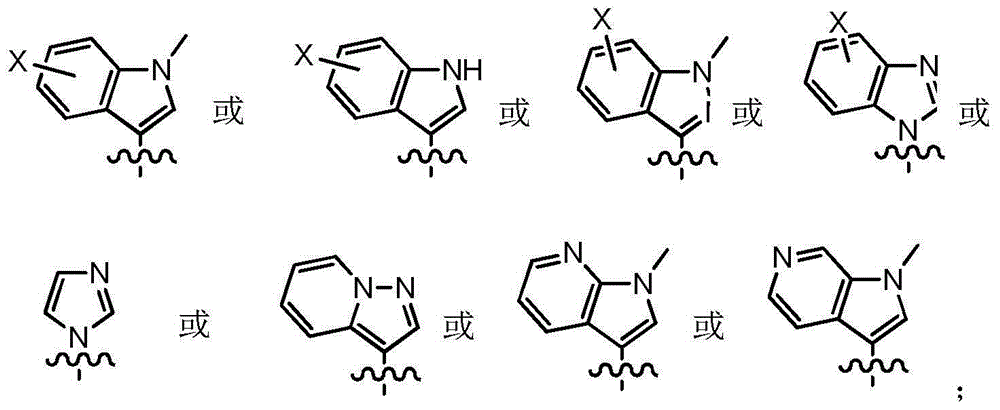
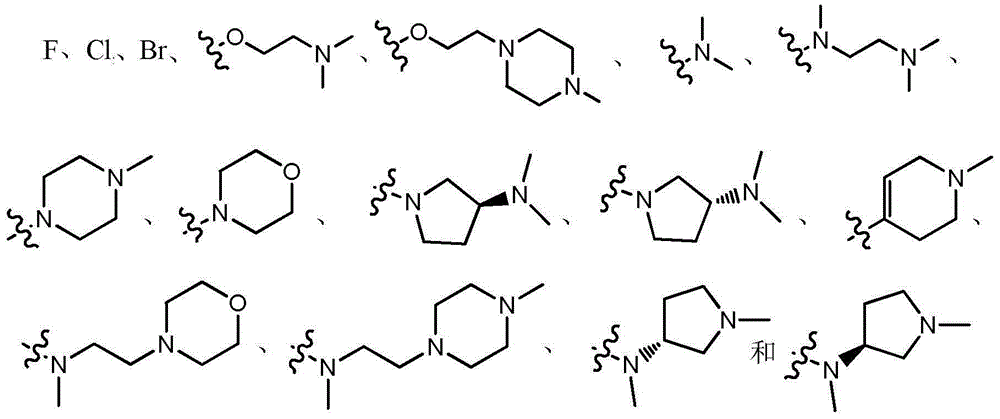
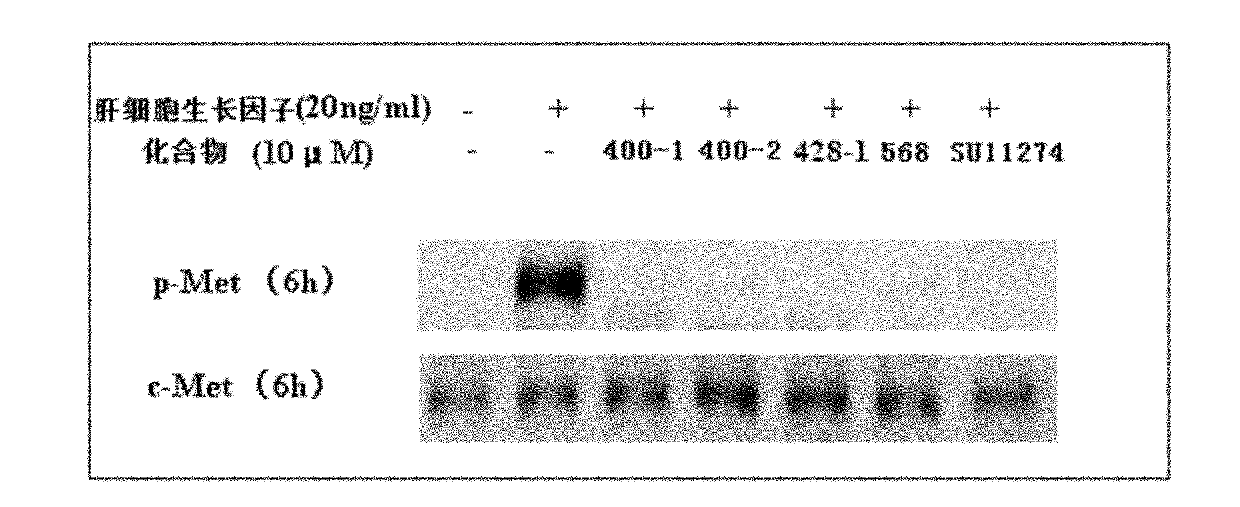
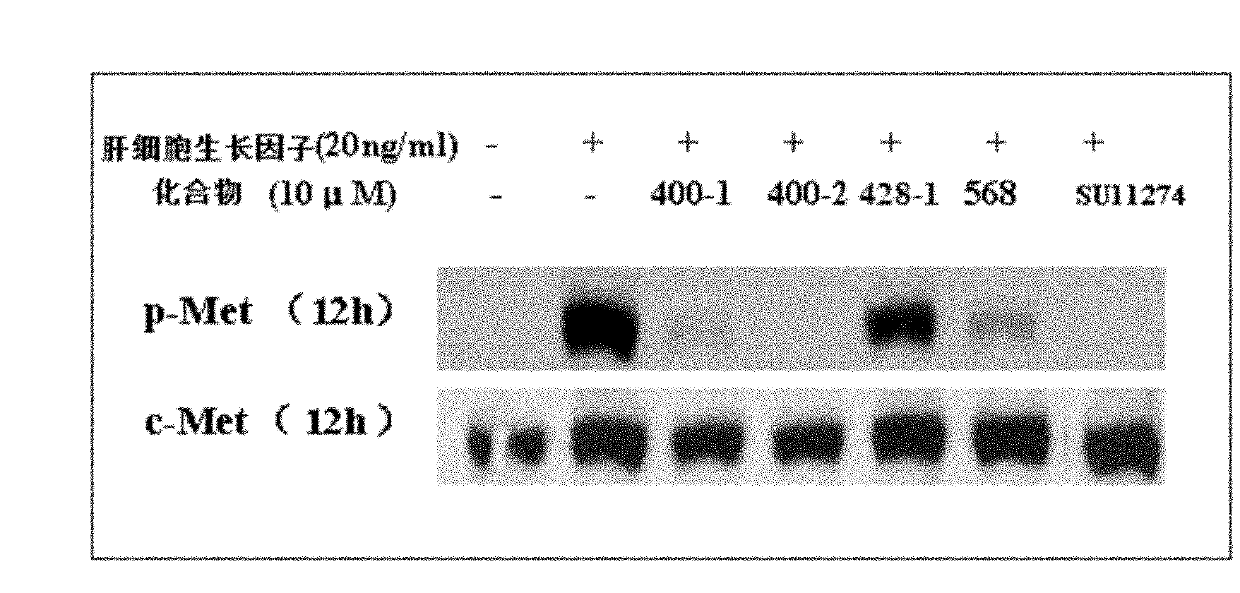
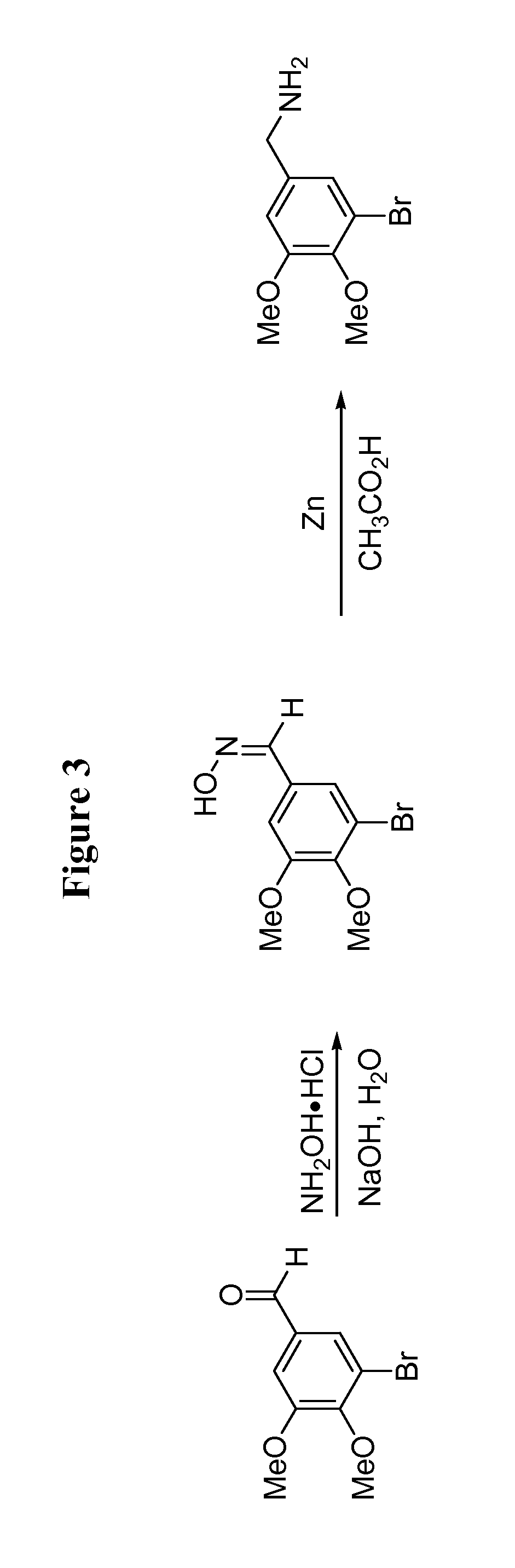
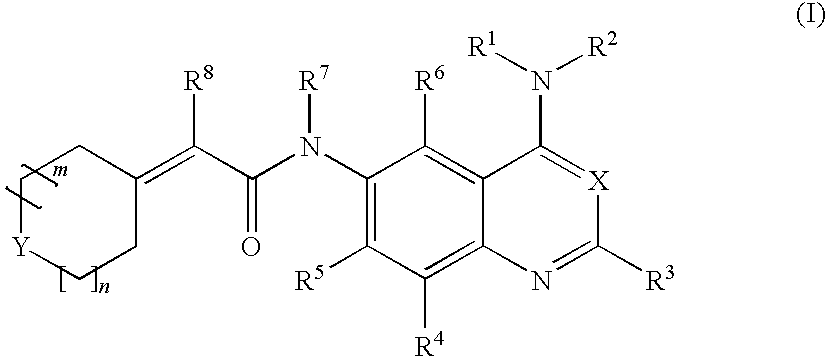
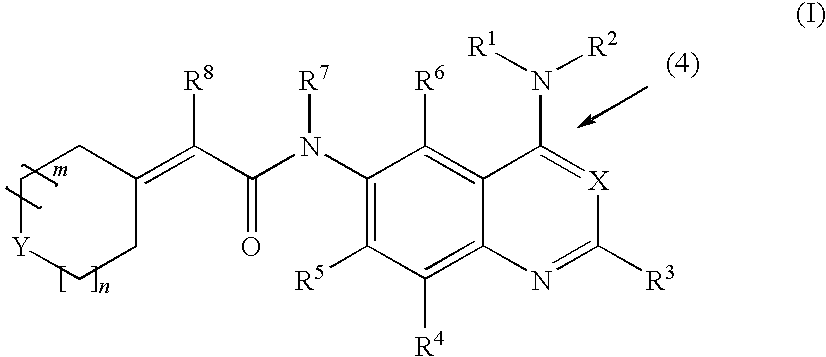
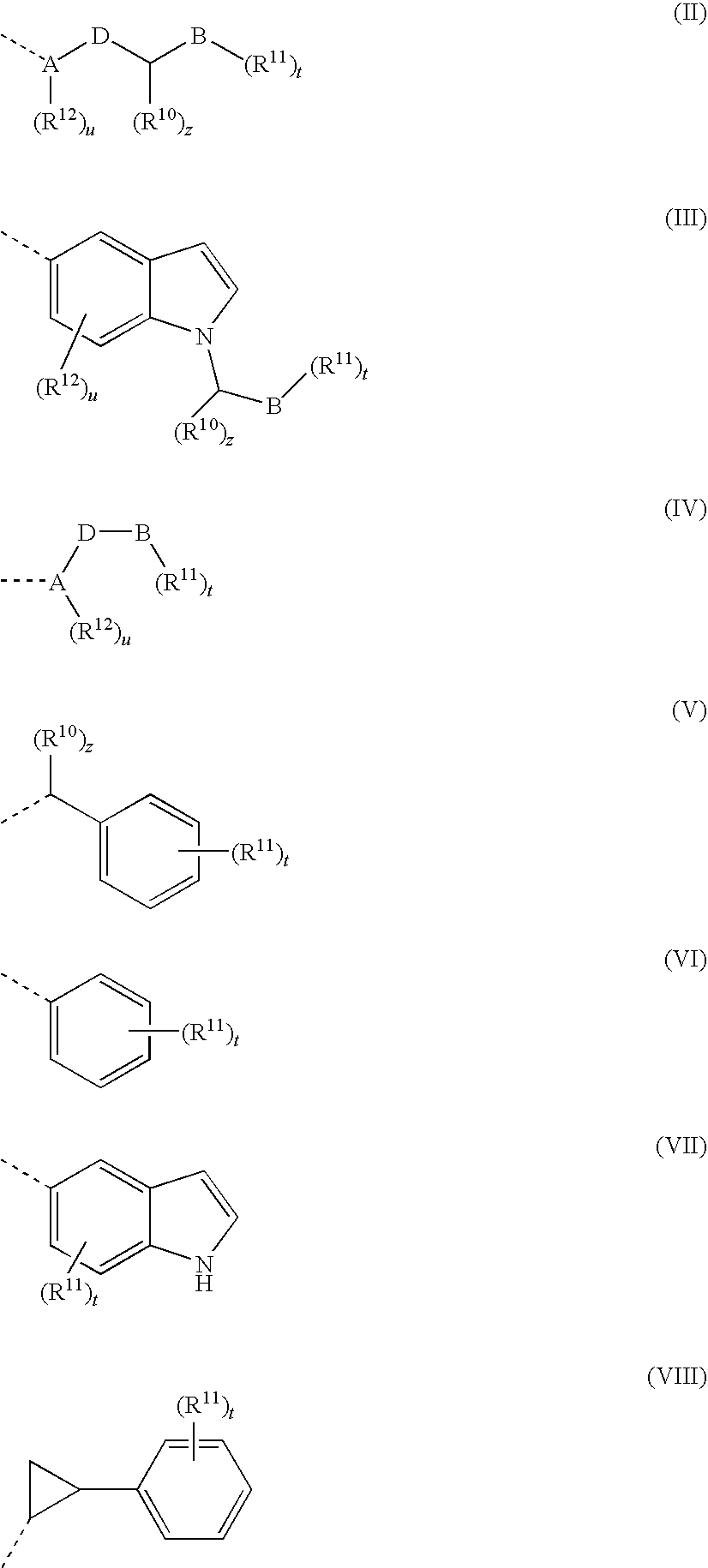
Patents
Literature
81 results about "Protein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation), a step that TKIs inhibit.
Method for designing protein kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS7070936B1Inhibits protein kinase activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPTK InhibitorsTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The present invention provides a method for identifying inhibitors of protein kinases. Methods are also provided for inhibiting protein kinase activity. Specific non-peptide protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor are provided. The protein kinases produced using the method of the present invention may be used to treat a number of conditions in patients, including cancer, psoriasis, arthrosclerosis, or immune system activity.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
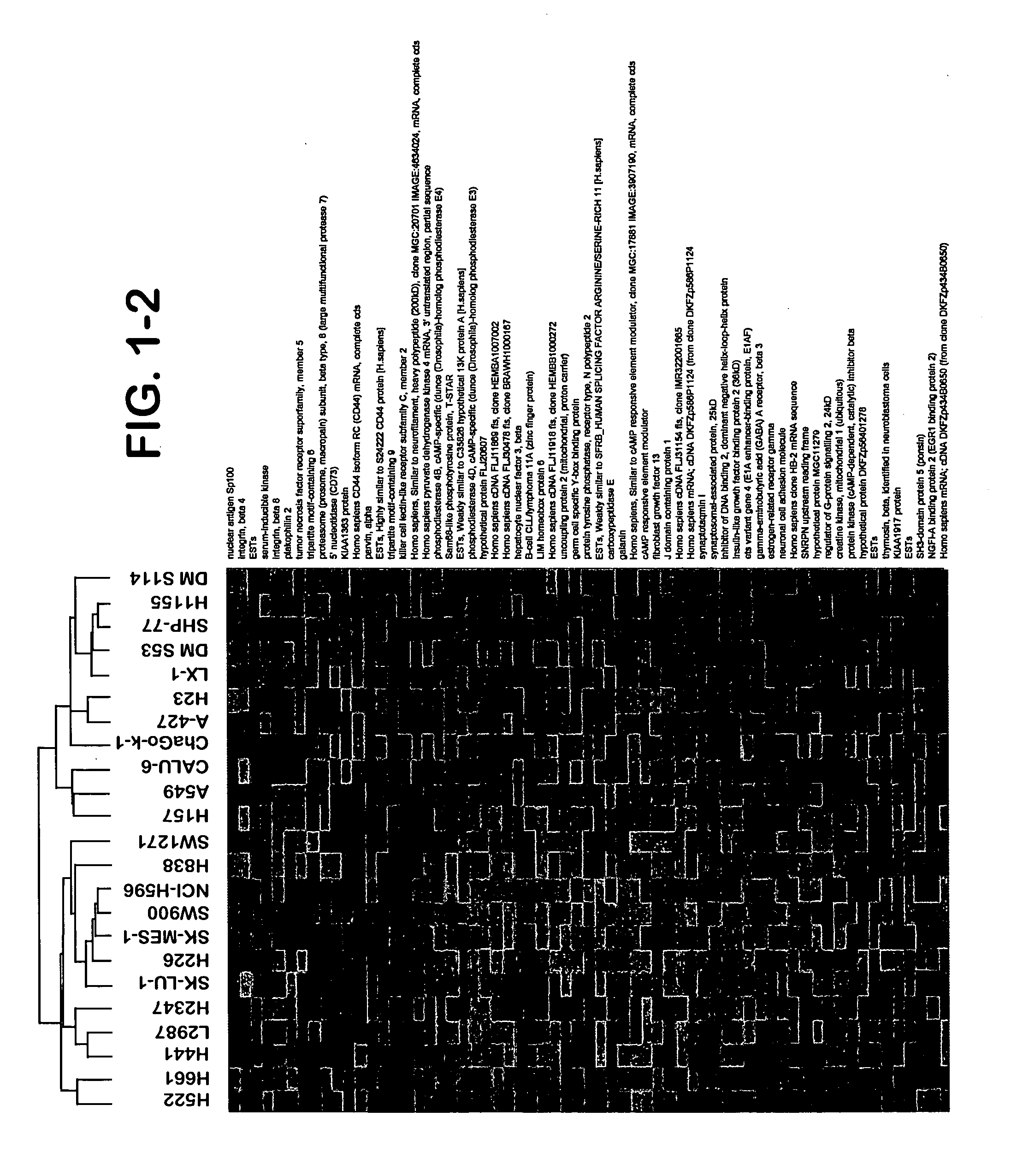
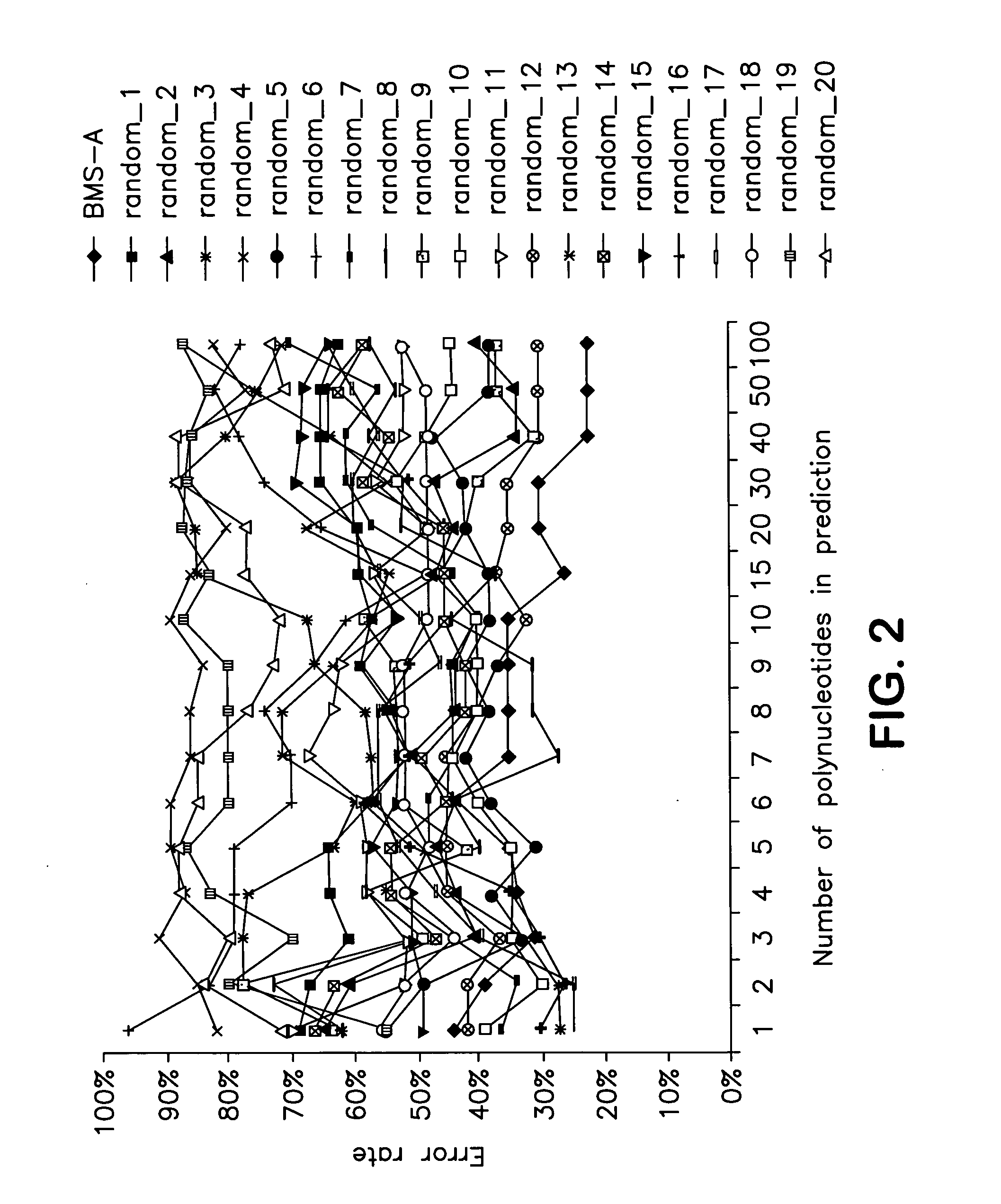
Identification of polynucleotides for predicting activity of compounds that interact with and/or modulate protein tyrosine kinases and/or protein tyrosine kinase pathways in lung cancer cells
InactiveUS20060019284A1Improved prognosisContinue treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsDisease areaProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention describes polynucleotides that have been discovered to correlate to the relative intrinsic sensitivity or resistance of cells, e.g., lung cell lines, to treatment with compounds that interact with and modulate, e.g., inhibit, protein tyrosine kinases, such as, for example, members of the Src family of tyrosine kinases, e.g., Src, Fgr, Fyn, Yes, Blk, Hck, Lck and Lyn, as well as other protein tyrosine kinases, including, Bcr-abl, Jak, PDGFR, c-kit and Ephr. These polynucleotides have been shown, through a weighted voting cross validation program, to have utility in predicting the resistance and sensitivity of lung cell lines to the compounds. The expression level of some polynucleotides is regulated by treatment with a particular protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor compound, thus indicating that these polynucleotides are involved in the protein tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathway, e.g., Src tyrosine kinase. Such polynucleotides, whose expression levels correlate highly with drug sensitivity or resistance and which are modulated by treatment with the compounds, comprise polynucleotide predictor or marker sets useful in methods of predicting drug response, and as prognostic or diagnostic indicators in disease management, particularly in those disease areas, e.g., lung cancer, in which signaling through the protein tyrosine kinase pathway, such as the Src tyrosine kinase pathway, is involved with the disease process.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
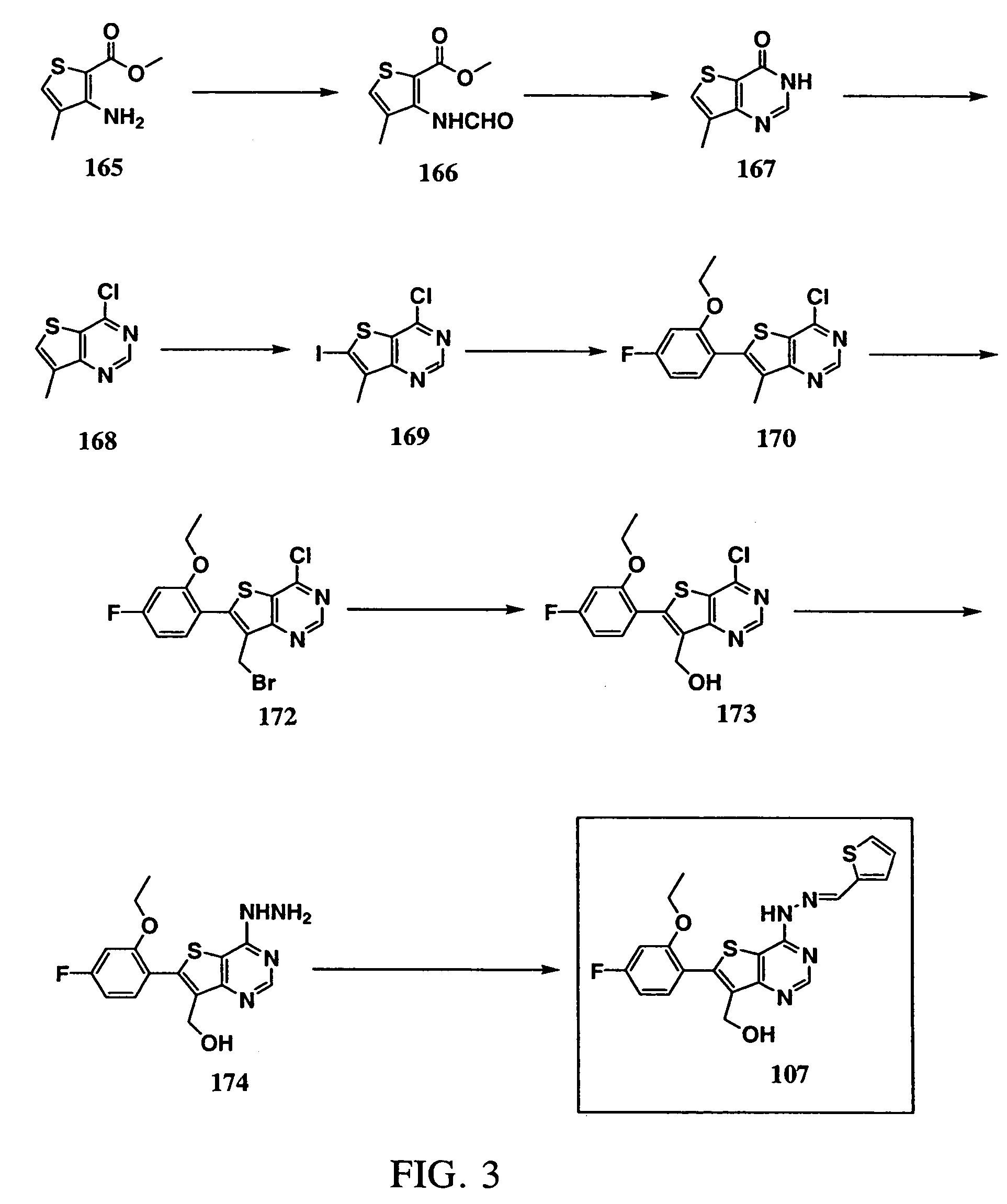
Small molecule thienopyrimidine-based protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20060004002A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsProtein-Tyrosine KinasesAutoimmune condition
Various thienopyrimidine-based analog compounds are able to selectively inhibit the Src family of tyrosine kinases. These compounds are useful in the treatment of various diseases including hyperproliferative diseases, hematologic diseases, osteoporosis, neurological diseases, autoimmune diseases, allergic / immunological diseases, or viral infections.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
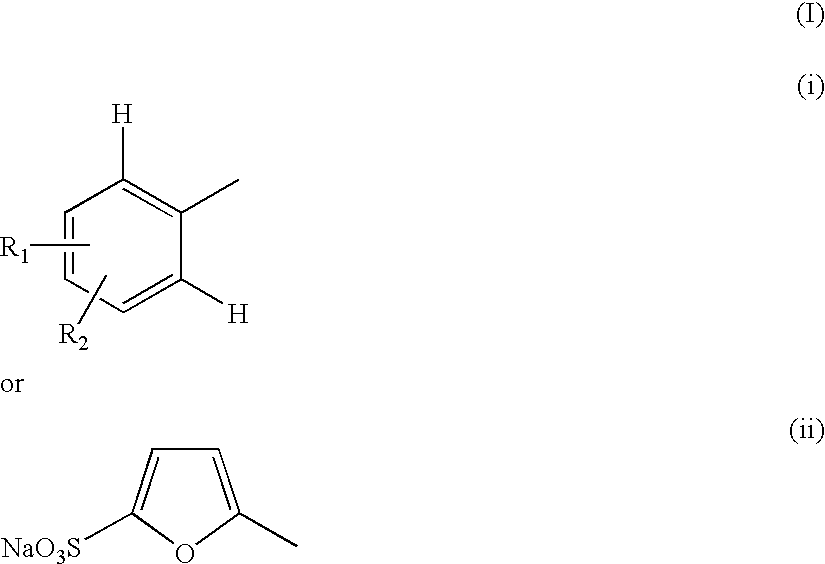
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising tyrphostins
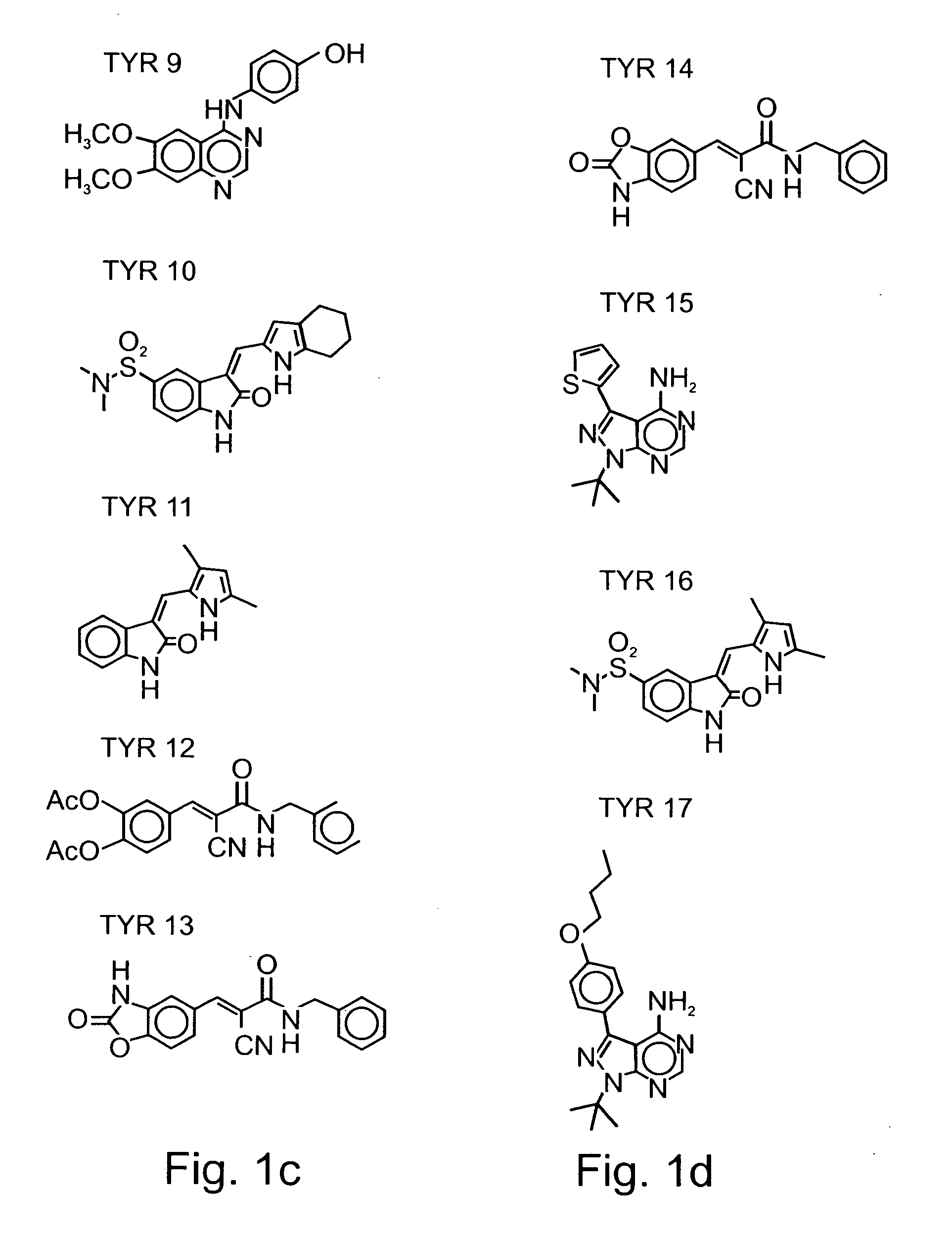
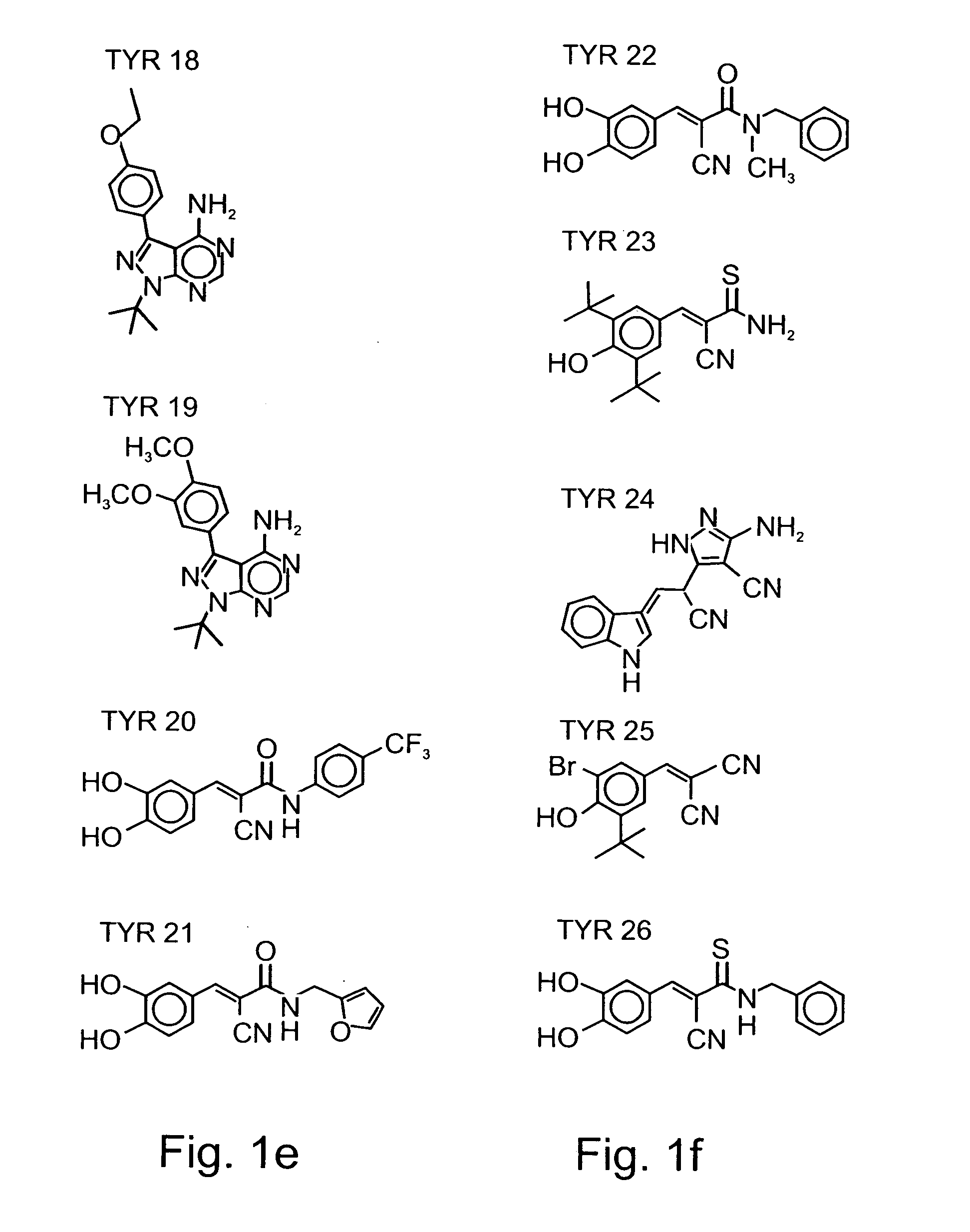
InactiveUS20030013748A1Good treatment effectConvenient treatmentBiocideOrganic chemistryProtein Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsTyrphostin Compound
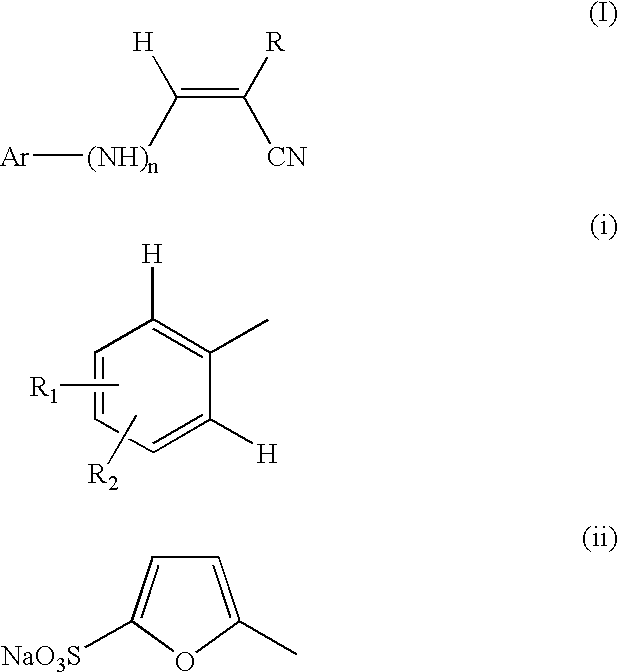
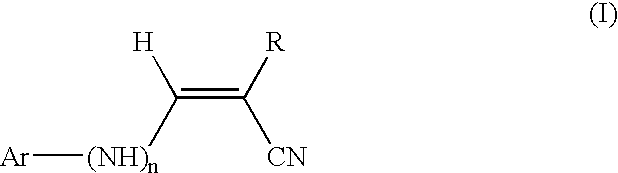
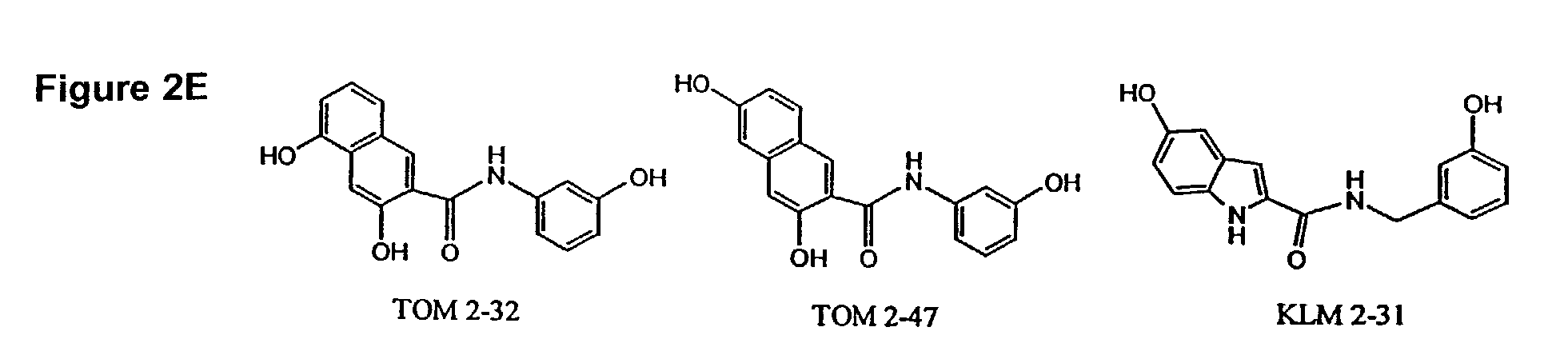
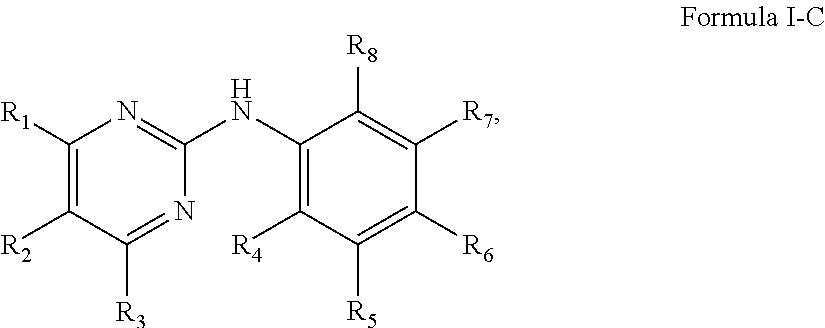
Compounds useful for countering undesired toxic effects to cells, tissues or organs having formula (I) wherein: Ar is a group of formulae (i) or (ii), n is O or, when Ar has formula (i) above, then n may also be 1, R is CN, -GC(S)NH2, -C(O)NHR3 or, when R1 is 4-NO2 and R2 is H or 3-OH, then R may also be a group of formulae (iii), (iv), (v), (vi) where R3 is H, phenyl, phenyl(lower alkyl) or pyridylmethyl; R1 and R2 are each independently H, OH, NO2 or, when R is CN, also CH3, F, or CF3, provided that both R1 and R2 are simultaneously H.
Owner:NOTOX
EGFR inhibitor and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105001208AStrong inhibitory activityGood inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention discloses an EGFR inhibitor. The EGFR inhibitor is of the structure shown in the formula (I) and is a compound including alpha, beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid amides. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a preparing method of the compound and the application of the compound serving as a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, especially the inhibiting function on T790M variant EGFR as the EGFR inhibitor, and the application on treating diseases such as the kidney cancer, the ling cancer, the prostate cancer, the pancreatic cancer the breast cancer and the spongiocytoma which are related to EGFR over expression. The structure is shown in the specification.
Owner:NANJING LEIKEXING BIOTECH CO LTD
Dicoumarol compound, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102558049ASimple structureEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsDicoumarolProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention relates to a dicoumarol compound shown in a general formula I, wherein definition of each substituent is described in the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the dicoumarol compound, and application of the dicoumarol compound serving as protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the field of tumor resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
PDGF receptor kinase inhibitory compounds, their preparation, purification and pharmaceutical compositions including same
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising tyrphostins
InactiveUS6426366B1Reducing inhibiting damageReduce harmBiocideOrganic chemistryProtein Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsTyrphostin Compound
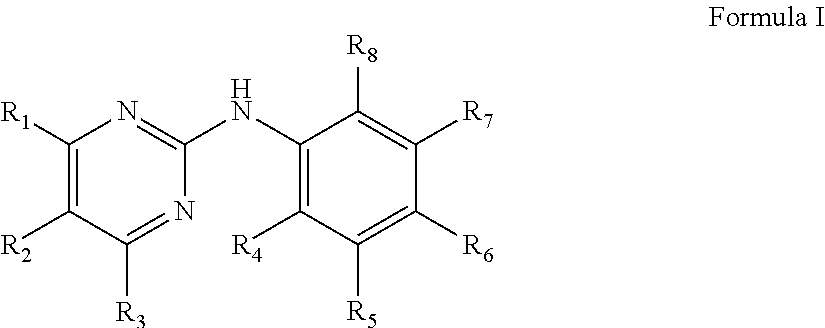
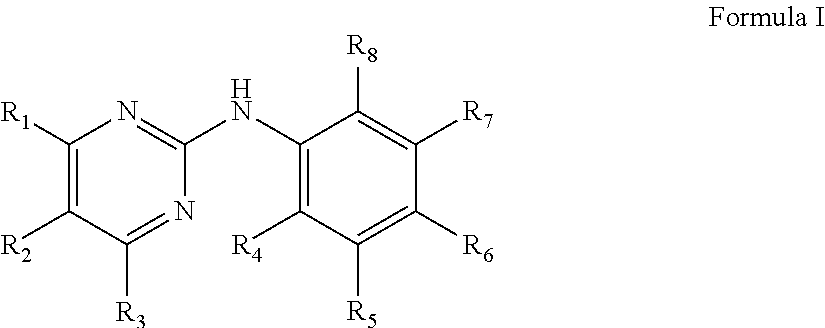
Compounds useful for countering undesired toxic effects to cells, tissues or organs having formula (I) wherein: Ar is a group of formulae (i) or (ii), n is 0 or, when Ar has formula (i) above, then n may also be 1, R is CN, -GC(S)NH2, -C(O)NHR3 or, when R1 is 4-NO2 add R2 is H or 3-OH, then R may also be a group of formulae (iii), (iv), (v), (vi) where R3 is H, phenyl, phenyl(lower alkyl) or pyridylmethyl; R1 and R2 are each independently H, OH, NO2 or, when R is CN, also CH3, F, or CF3, provided that both R1 and R2 are not simultaneously H.
Owner:NOTOX
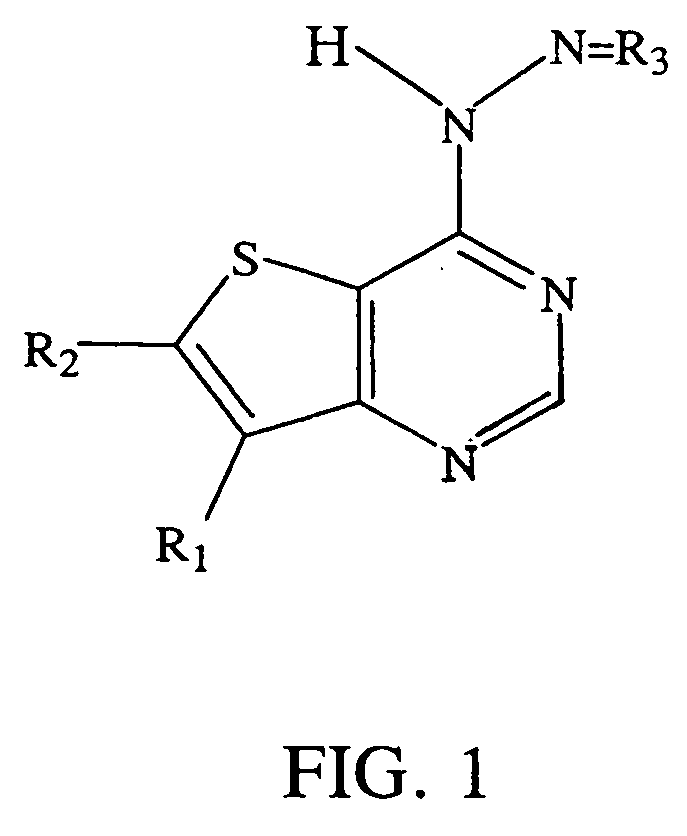
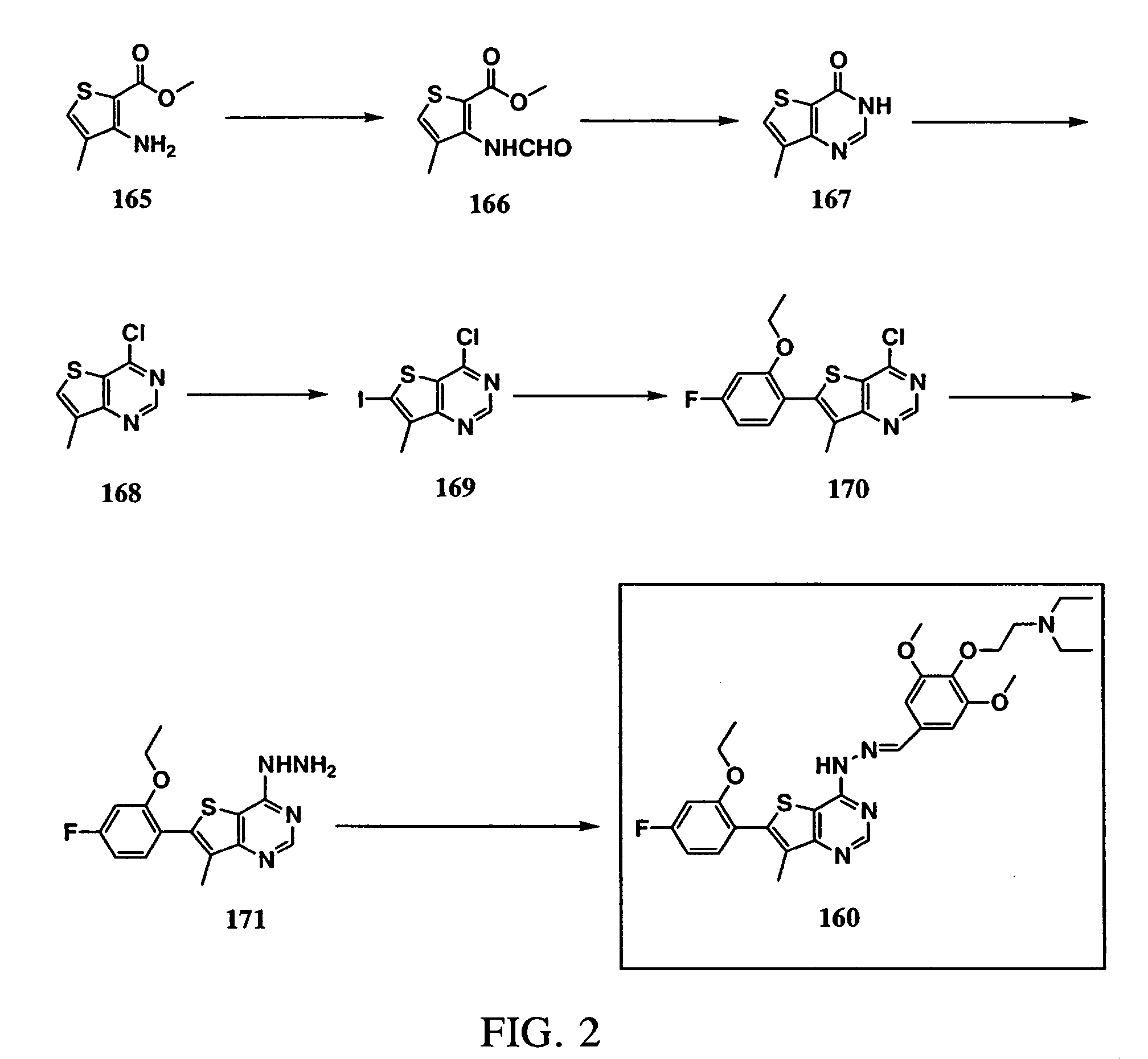
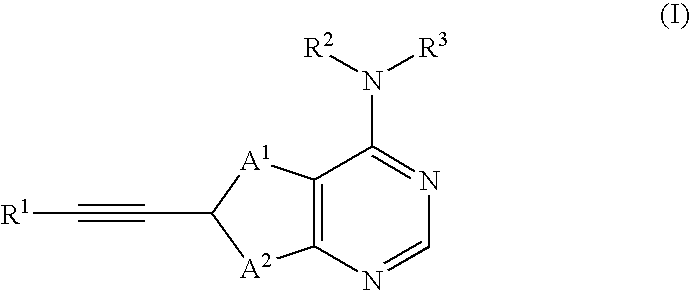
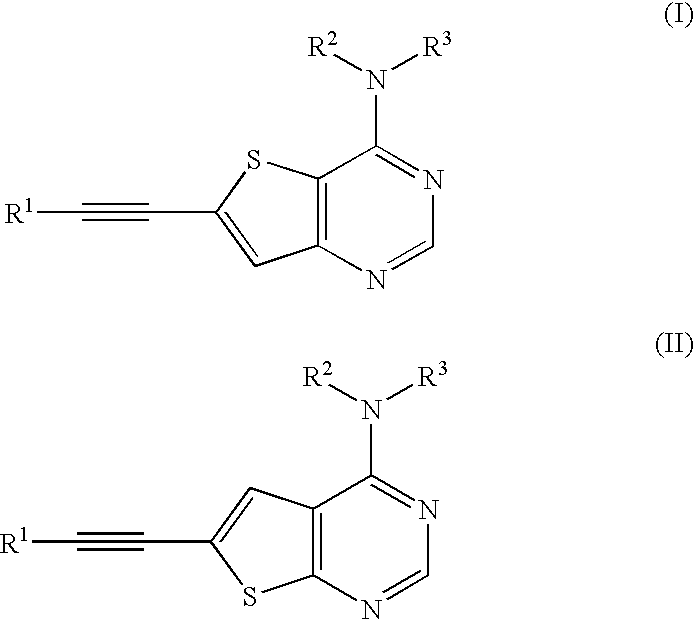
Thienopyrimidine compounds as protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20050009845A1Undesirable side-effectMinimizing potential side-effectsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention relates to thienopyrmidine compounds of formula (I) (one of A1 and A2 is S and the other is CH), salts thereof, as well as use and preparation of the same. These compounds are inhibitors of various protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) of the ErbB family and consequently are useful in the treatment of disorders mediated by aberrant activity of such kinases.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
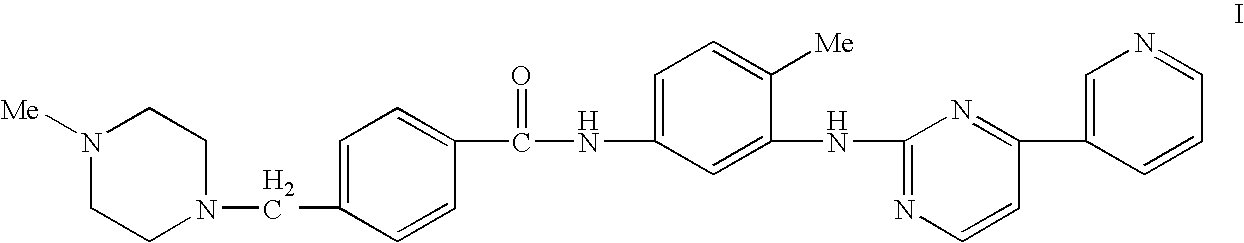
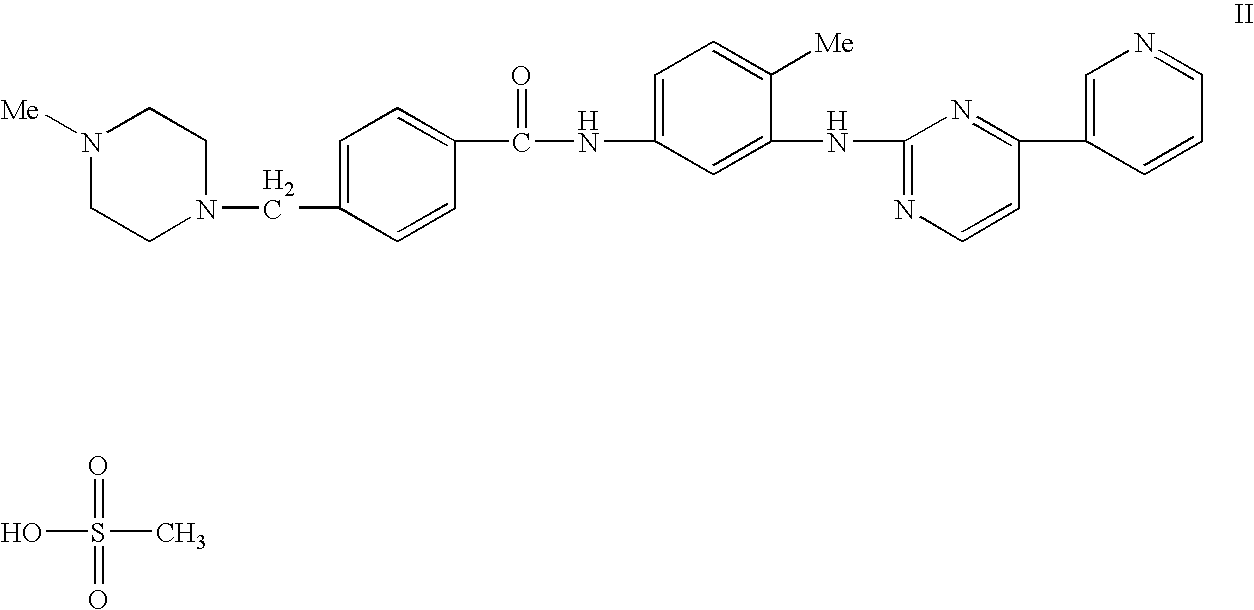
Medical devices comprising a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor to inhibit restonosis
Implantable medical devices having an anti-restenotic coatings are disclosed. Specifically, implantable medical devices having coatings of proteintyrosine kinase inhibitors are disclosed. The anti-restenotic protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor is 4+4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide methanesulfonate and pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof (imatinib mesylate). The anti-restenotic medial devices include stents, catheters, micro-particles, probes and vascular grafts. The medical devices can be coated using any method known in the art including compounding the protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a biocompatible polymer prior to applying the coating. Moreover, medical devices composed entirely of biocompatible polymer-protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor blends are disclosed. Additionally, medical devices having a coating comprising at least one proteintyrosine kinase inhibitor in combination with at least one additional therapeutic agent are also disclosed. Furthermore, related methods of using and making the antirestenotic implantable devices are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method of treatment of philadelphia chromosome positive leukaemia
InactiveUS20120244116A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitorLestaurtinib
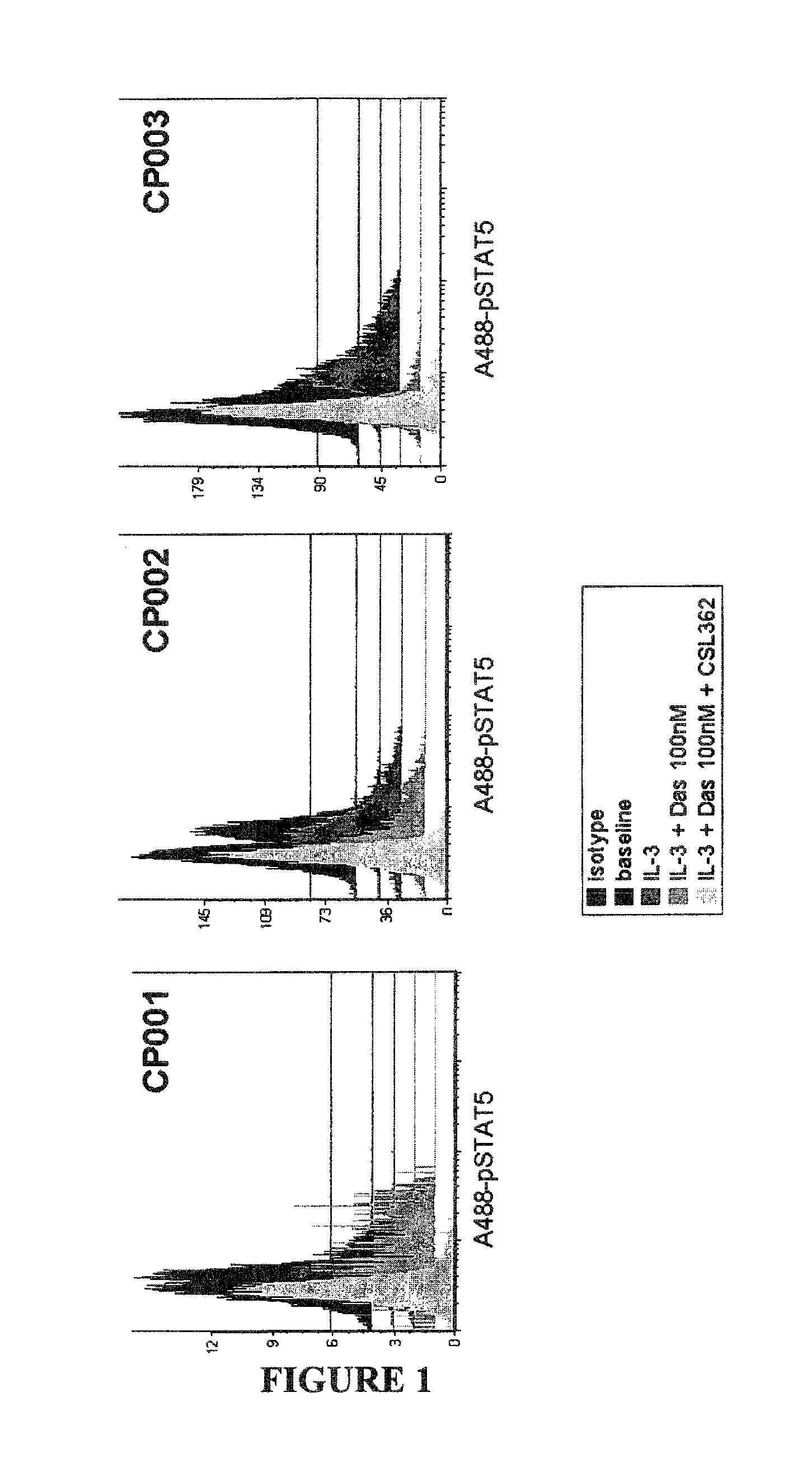
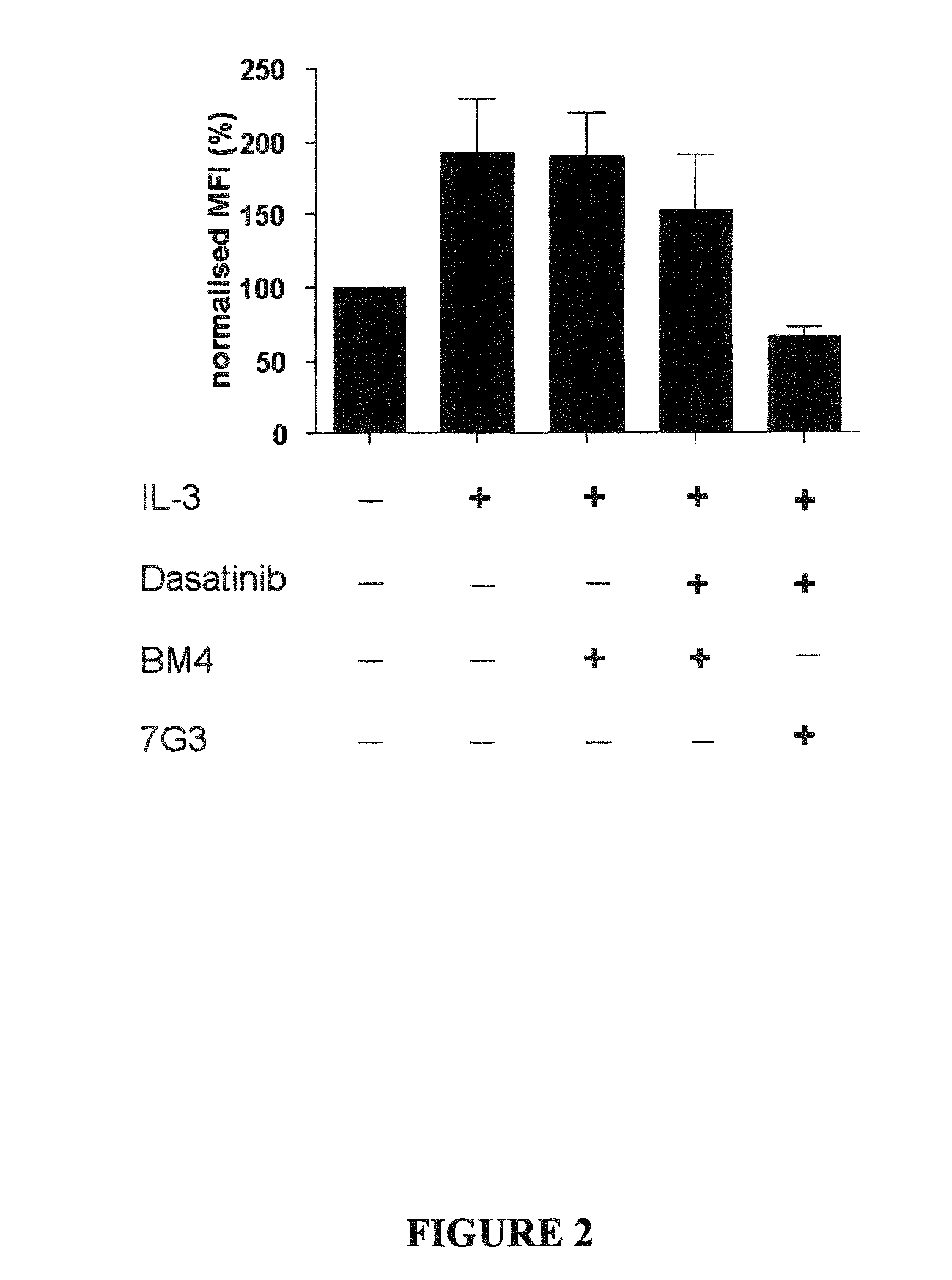
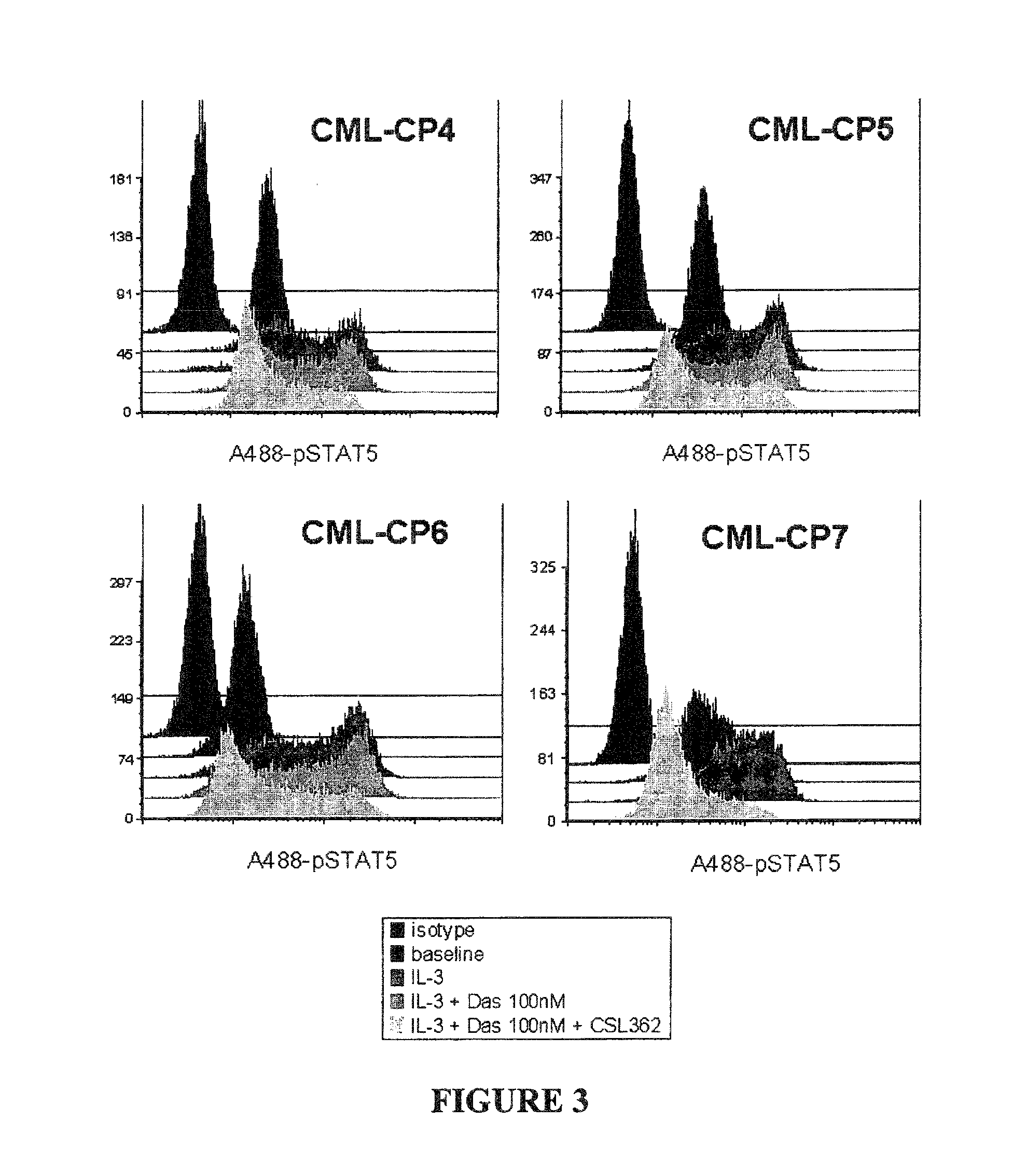
The invention provides a method for the treatment of Ph+ leukemia in a patient comprising administering to the patient (i) a BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and (ii) an agent which selectively binds to a cell surface receptor expressed on Ph+ leukemic stem cells. The invention further provides for the use of (i) and (ii) in, or in the manufacture of a medicament for, the treatment of Ph+ leukemia in a patient; and a composition for the treatment of Ph+ leukemia in a patient comprising (i) and (ii); and kits comprising (i) and (ii). In some embodiments, the tyrosine kinase inhibitor is or is not imatinib; or is selected from the group consisting of dasatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib, axitinib, cediranib, crizotinib, damnacanthal, gefitinib, lapatinib, lestaurtinib, neratinib, semaxanib, sunitinib, toceranib, tyrphostins, vandetanib, vatalanib, INNO-406, AP24534, XL228, PHA-739358, MK-0457, SGX393 and DC2036; or is selected from the group consisting of dasatinib and nilotinib. In some embodiments, the agent binds to a receptor involved in signalling by at least one of IL-3, G-CSF and GM-CSF. In some embodiments, the agent is a mutein selected from the group consisting of IL-3 muteins, G-CSF muteins and GM-CSF muteins. In some embodiments, the mutein is an IL-3 mutein. In some embodiments, the agent is a soluble receptor which is capable of binding to IL-3.
Owner:CSL LTD
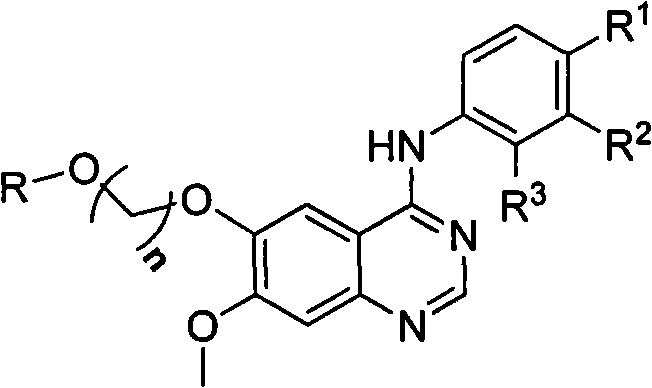
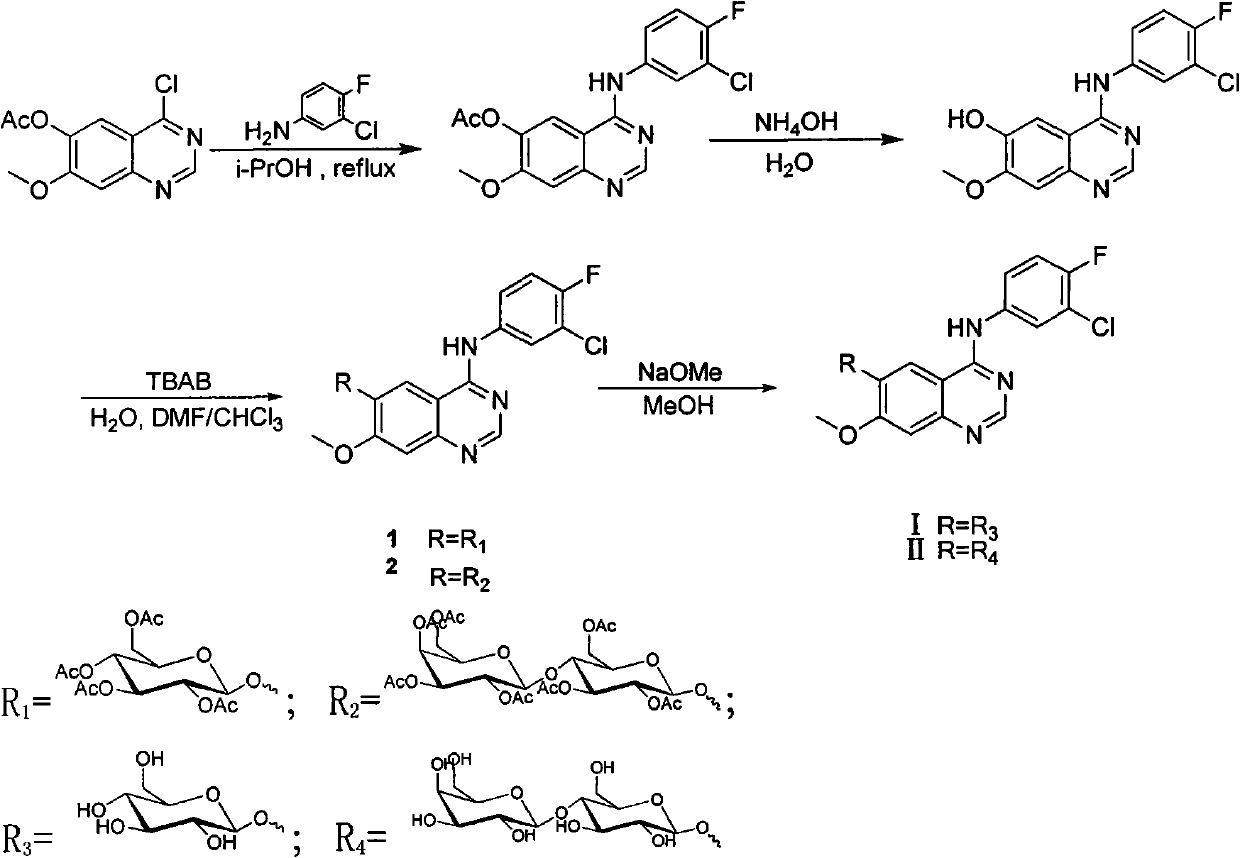
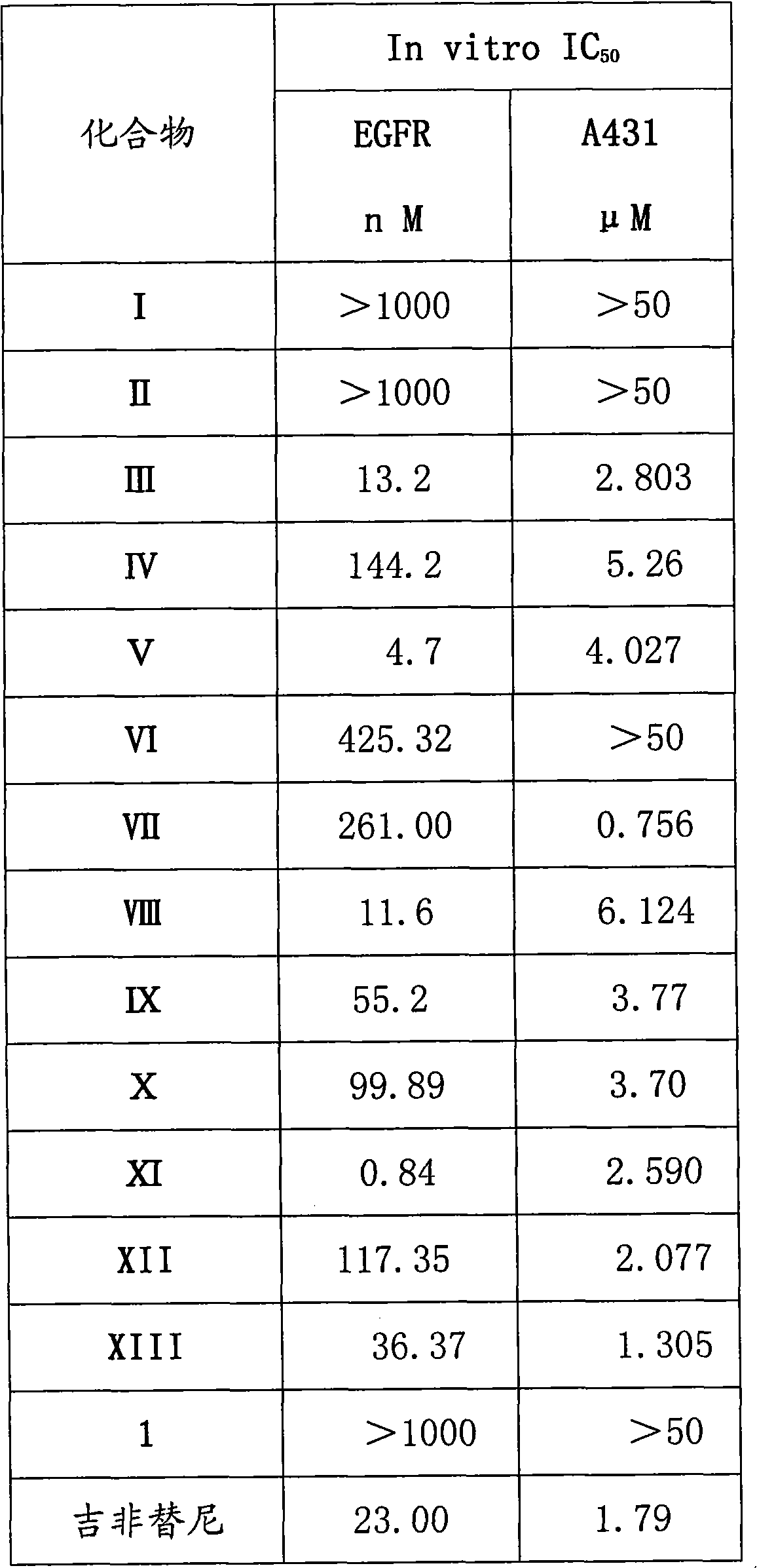
Series of quinazoline sugar derivatives used as protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101857618ASolve the problem of low activity of inhibiting tyrosine kinaseGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilityProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention provides a quinazoline sugar derivative and a preparation method and application thereof, which can solve the problem of low activity of inhibiting tyrosine kinase in the prior art. The prepared quinazoline sugar derivative has high water solubility and high activity of inhibiting human skin cancer cells A431, and can be used for preparing medicaments for preventing or treating tumors. The quinazoline sugar derivative provided by the invention is a kind of compounds which have novel structures and comprise abundant glycosyl group segments at a 6-bit side chain of a quinazoline parent ring, wherein the raw materials adopted in a method for performing glycosylation on quinazoline rings are readily available; the synthesis method is simple; the purification mode is simple and convenient and quick; and the quinazoline sugar derivative has high water solubility, high biological activity, particularly obvious activity of selectively inhibiting an EGFR, and obvious anti-tumor effect, so the kind of compounds has a wide application prospect in medicaments for preventing or curing tumors. The quinazoline sugar derivative comprises the following structural formula.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
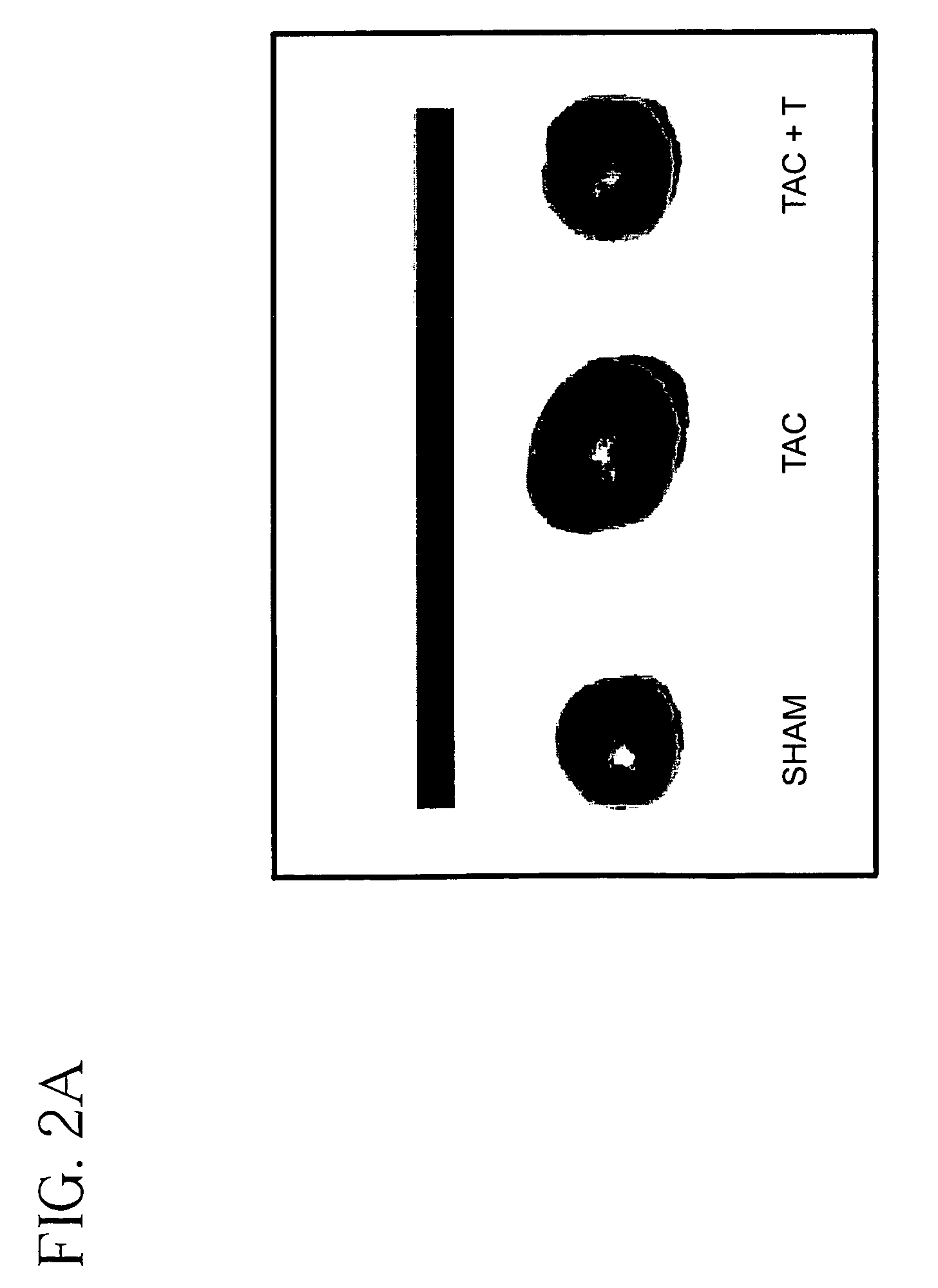
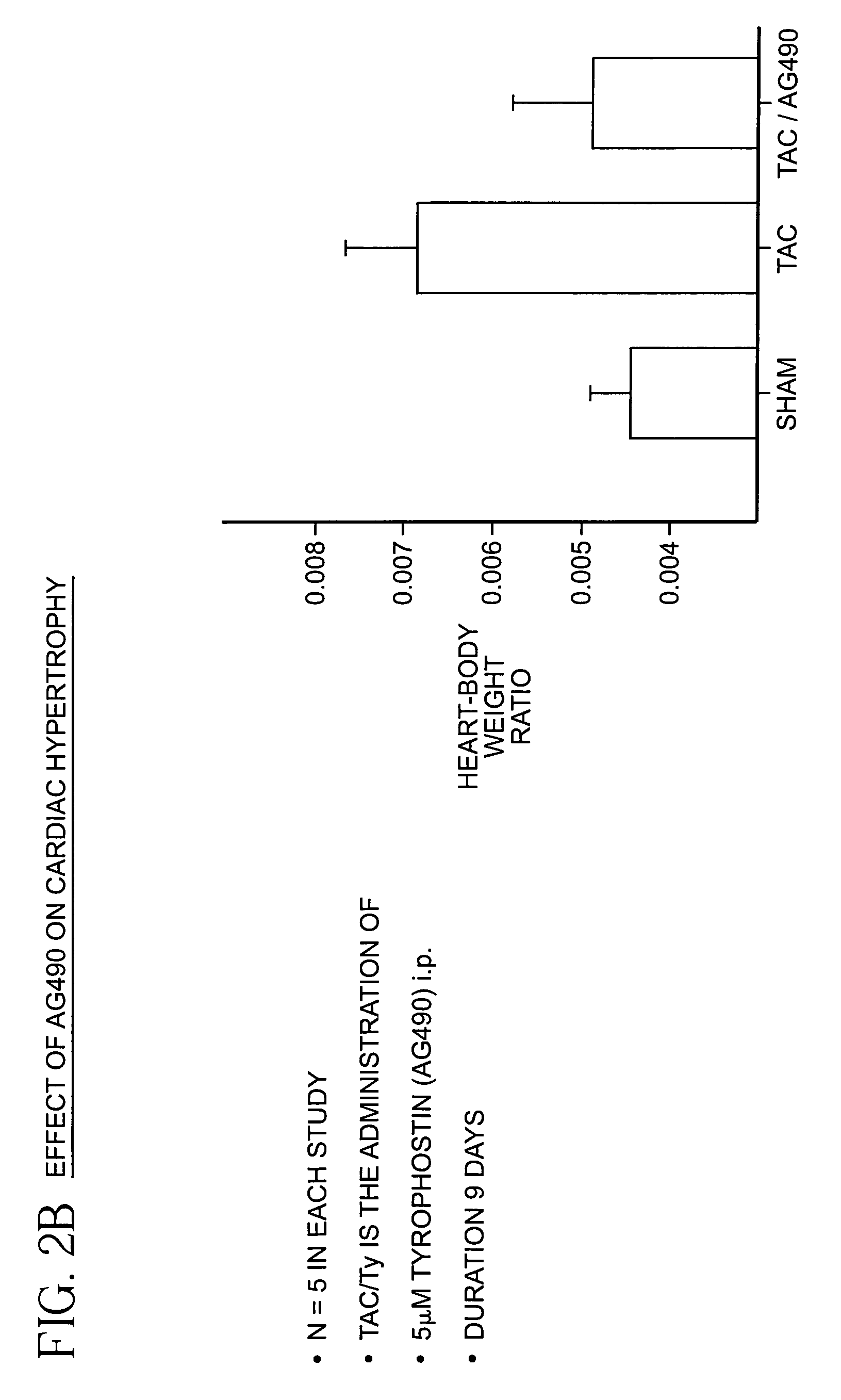
Method for reducing hypertension and heart failure
InactiveUS7235588B2Reducing hypertensionReduce hypertrophyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeart failure cellProtein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
A method is provided for reducing hypertension and / or heart failure in a mammal. Preferably, the method is used to treat or prevent tissue damage to a human heart. The method includes administering an effective amount of a Jak2 inhibitor, preferably a tyrphostin, such as AG490.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Protection against and treatment of hearing loss
InactiveUS20060172971A1Low toxicityIncrease doseBiocideSenses disorderProtein-Tyrosine KinasesProtein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
The present invention provides a method for protecting against or treating hearing loss in a subject. This method involves administering an effective amount of a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor to the subject to protect against or to treat hearing loss.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
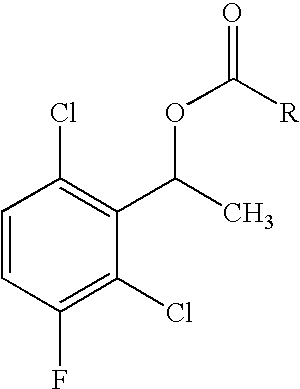
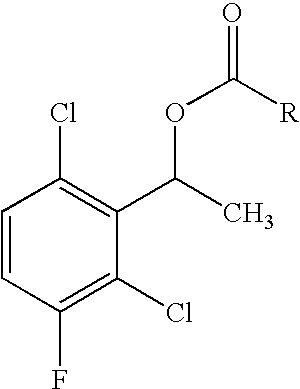
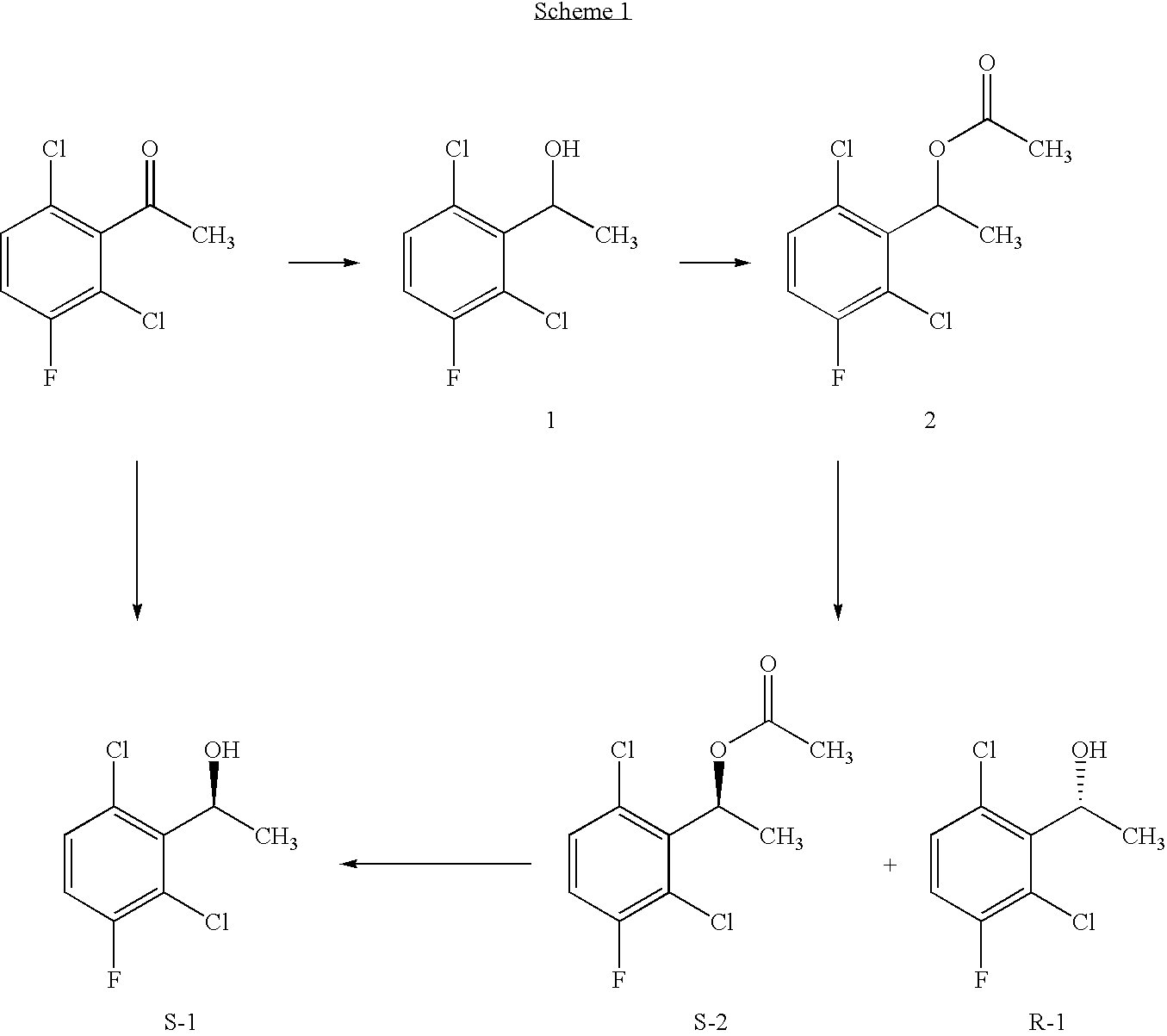
Enantioselective biotransformation for preparation of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor intermediates
Owner:AGOURON PHARMA INC
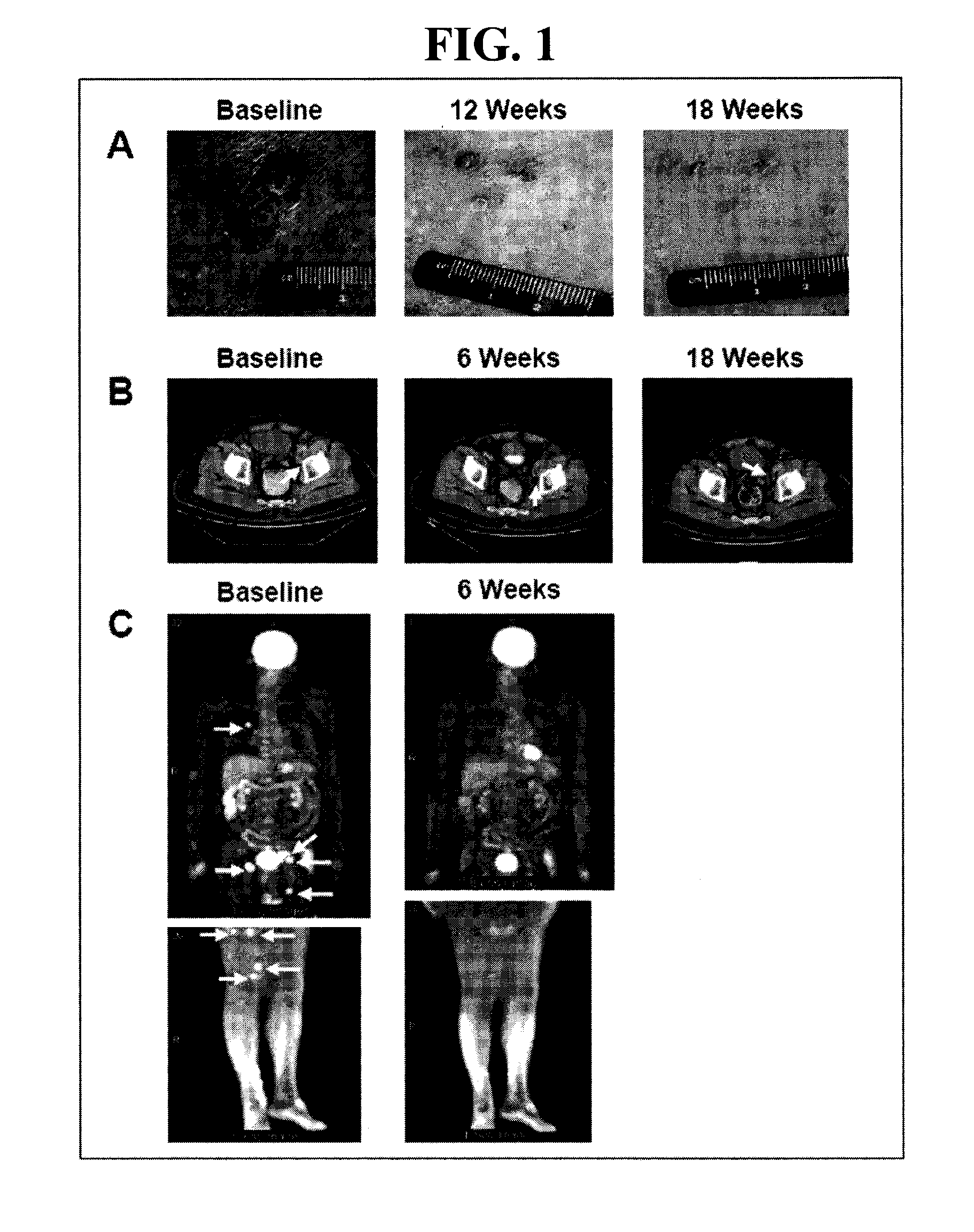
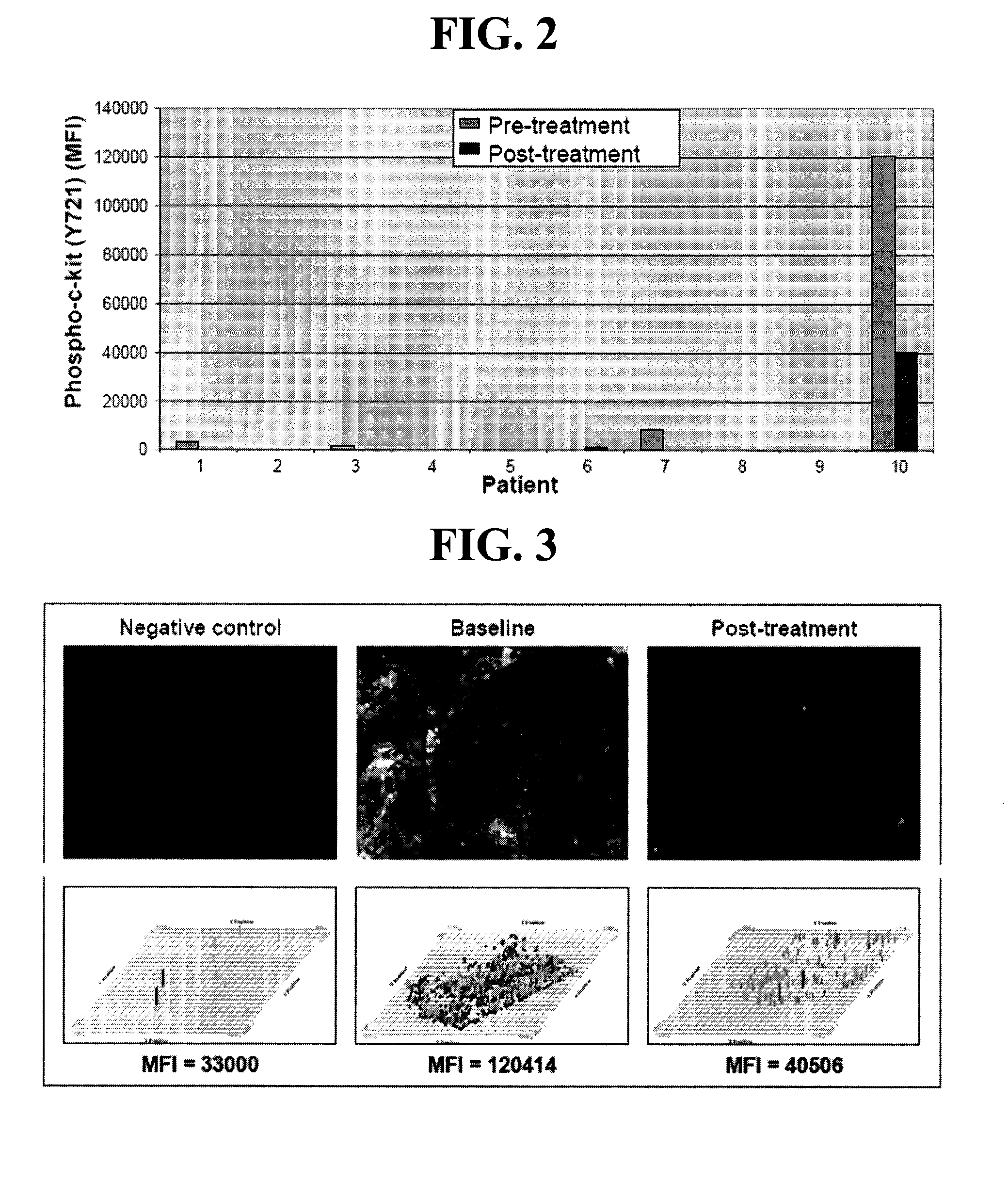
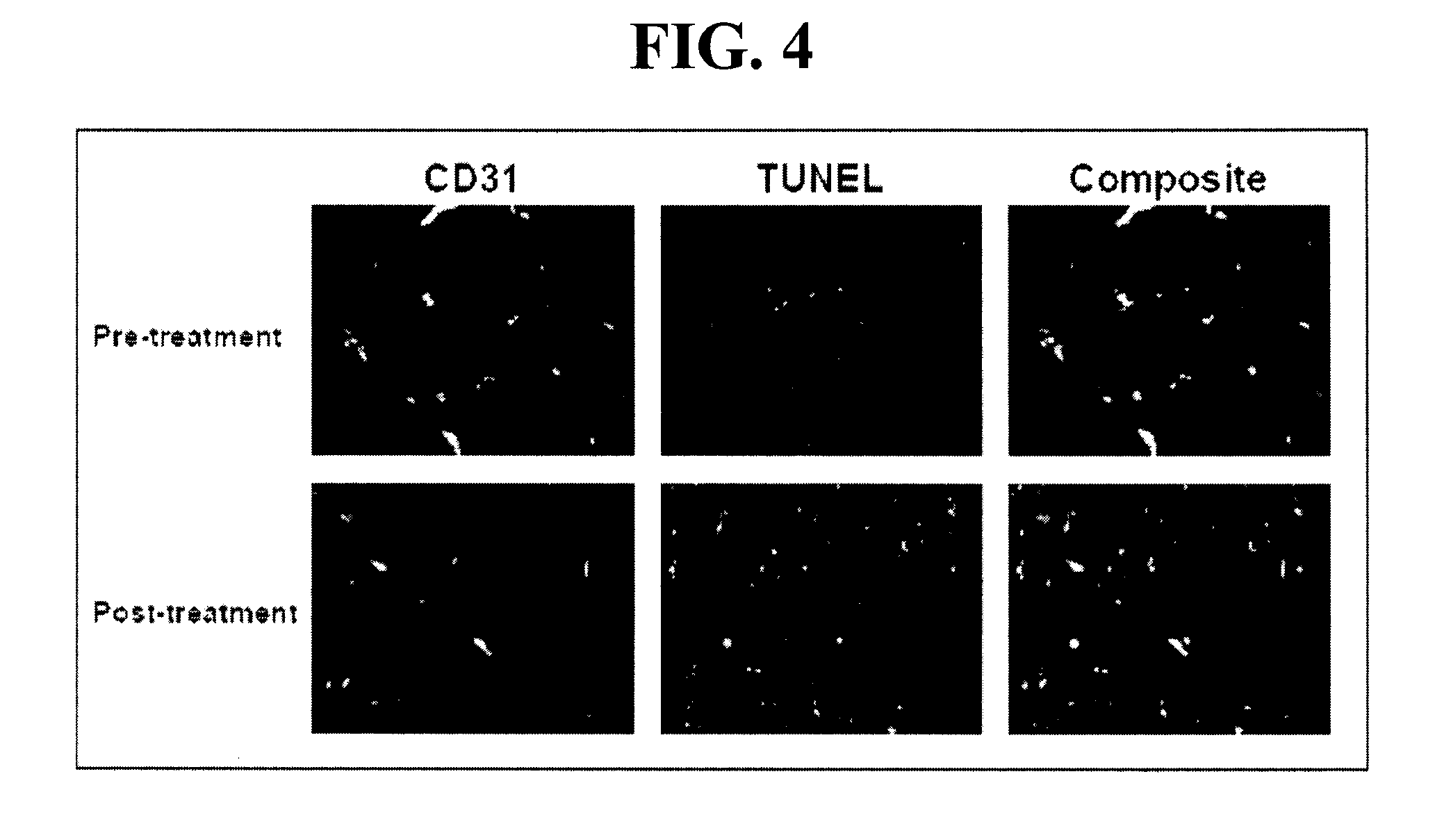
c-KIT Phosphorylation in Cancer
InactiveUS20100143935A1Inhibit phosphorylationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein phosphorylationTreatment use
An antibody is disclosed for the detection of phosphorylated c-KIT. A method of diagnosing and monitoring cancers responsive to treatment using an anti-phospho-c-KIT antibody are also disclosed. A diagnostic kit is also provided for the detection and monitoring of cancers responsive to tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor treatment.
Owner:APOCELL
Oligomer-Protein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Conjugates
The invention relates to (among other things) oligomer-PTK inhibitor conjugates and related compounds. A compound of the invention, when administered by any of a number of administration routes, exhibits advantages over PTK inhibitor compounds lacking a water soluble, non peptidic oligomer.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Protection against and treatment of hearing loss
InactiveUS7129225B2Low toxicityIncrease doseBiocideSenses disorderProtein-Tyrosine KinasesProtein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
The present invention provides a method for protecting against or treating hearing loss in a subject. This method involves administering an effective amount of a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor to the subject to protect against or to treat hearing loss.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC +1
Tricyclic protein kinase inhibitors
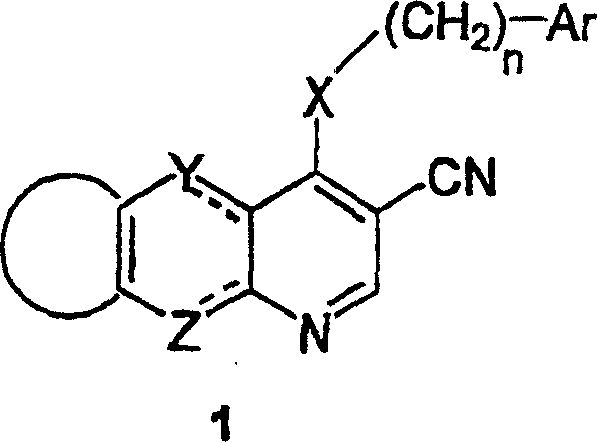
This invention provides compounds of formula (1) which are useful as inhibitors of protein tyrosine kinase and are antiproliferative agents.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Non-myeloablative tolerogenic treatment with tyrphostins
A method of inducing immune tolerance in a first mammal to antigens of a second, non-syngeneic, mammal, is disclosed. The method is utilized to minimize graft rejection and / or reduce graft-versus-host diseases in transplantation procedures and to produce hematopoietic mixed chimeras. Methods of determining the activity of tyrphostins and the optimal concentration thereof in this method are also disclosed.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
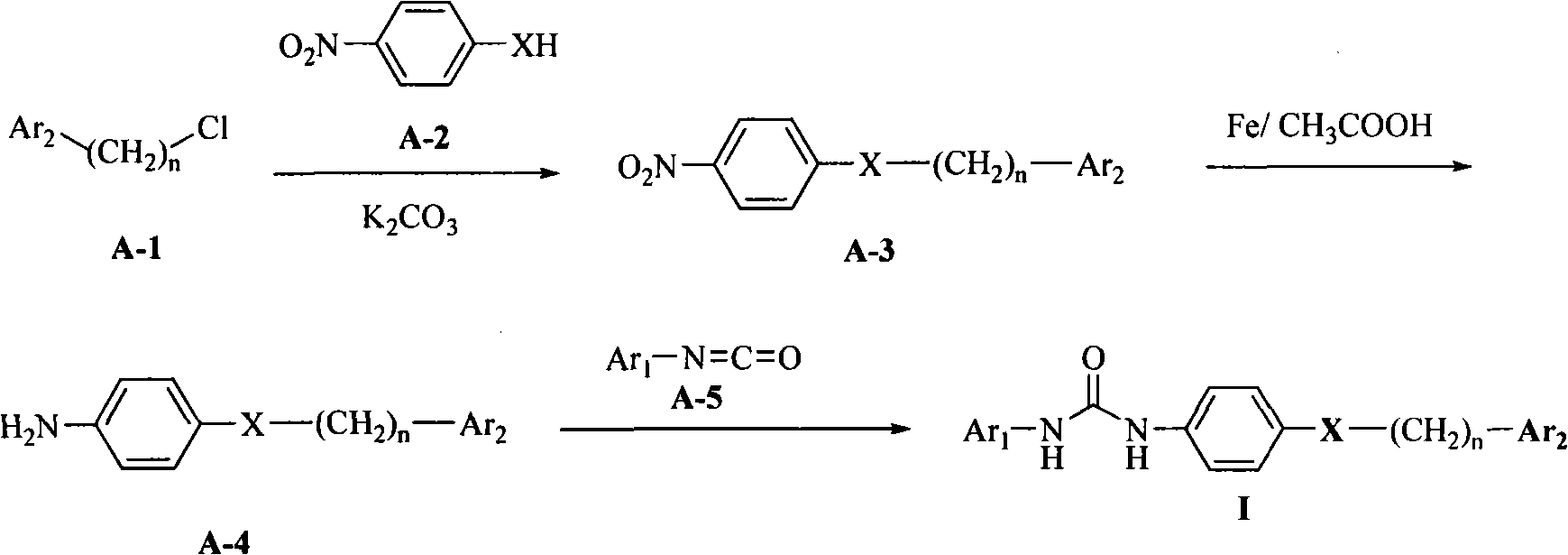
Diarylurea derivatives and application thereof used for preparing anti-neoplastic medicament
InactiveCN101550136AHas anticancer effectGood antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer preventionReceptor Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention belongs to the field of medical technology, which relates to diarylurea derivatives or salts accepted in medicine shown in formula I, wherein substituents of Ar1, Ar2, X and n have definitions given in an instruction. The derivatives shown in the formula I can be used for preparing receptor protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (RPTKI), and medicaments used for treating and / or preventingcancer or other proliferative diseases. The derivatives or salts accepted in medicine can be taken as active ingredients for preparing composition or different preparations used in clinical requirement mixed together with different carriers or excipient in medicine so as to be used for treating and / or preventing from various cancers.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Benzimidazole analogues and related methods
The invention relates to compounds of the formula (VIII) wherein the moieties R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are as defined in the specification, and salts thereof, as well as their use, methods of use for them, methods of their synthesis, and the like. The compounds are protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors and can be used in the treatment of various cancer diseases and cancer-associated pain.
Owner:UNIV FEDERICO II +1
Quinazoline and quinoline derivatives as irreversible protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20090105247A1Improve anti-tumor effectUnique structureBiocideOrganic chemistryKinase activityProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
A compound of formula (I), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, or hydrate thereof, and a method of preparing the same. A method of treating or preventing a physiological disorder caused by abnormal protein tyrosine kinase activity in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of formula (I).
Owner:TIANJIN HEMAY ONCOLOGY PHARMA CO LTD
Enzymatic measurement of imatinib mesylate
ActiveUS7300768B2Economical and simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesProtein-Tyrosine KinasesKinase
Owner:SALADAX BIOMEDICAL INC
Oligomer-protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor conjugates
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Anti-vascular and anti-proliferation methods, therapies, and combinations employing specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20070197538A1Good conditionImprove treatmentBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
This invention is directed to potent inhibitors of protein tyrosine kinase alone or in synergistic combination with antiangiogenic or chemotherapeutic agents for the abrogation of mature vasculature within chemotherapeutic refractory tumors, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds, and to the use of these compounds for treating a patient suffering from or subject to disorders / conditions involving cell proliferation, and particularly treatment of brain cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer prostate cancer, and human leukemias, such as CML, AML or ALL.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA SA (US)
Methods and agents for inhibiting dynamin-dependent endocytosis
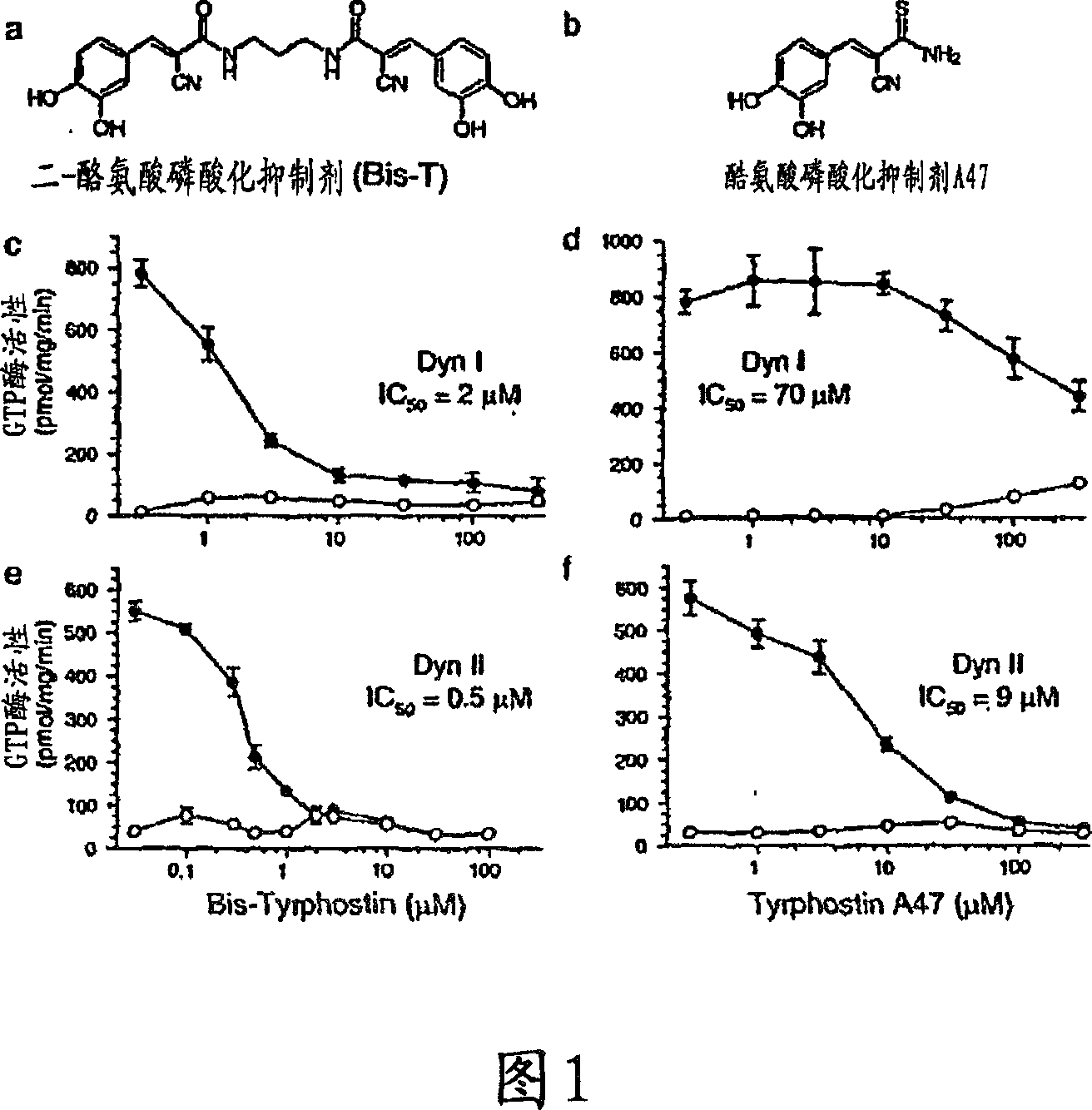
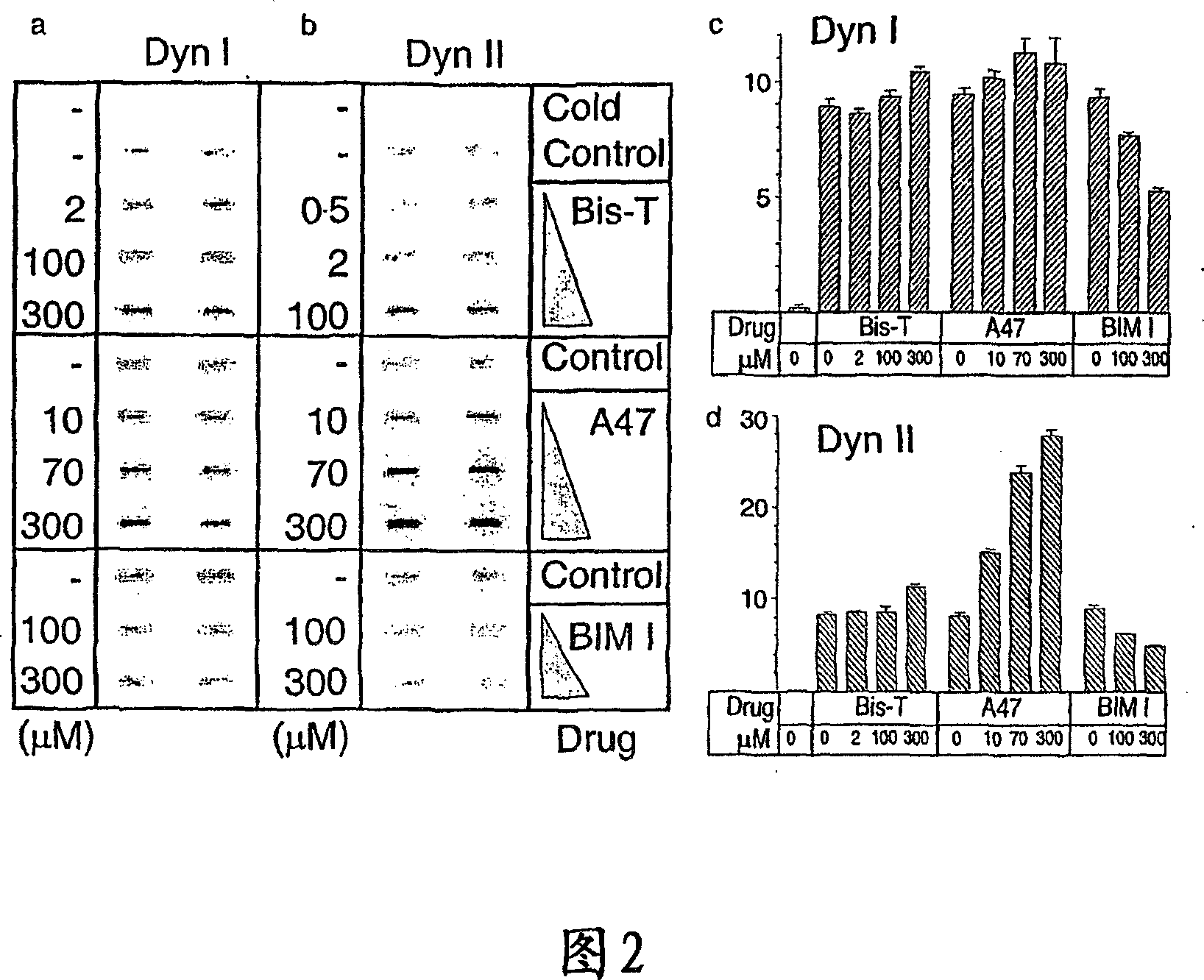
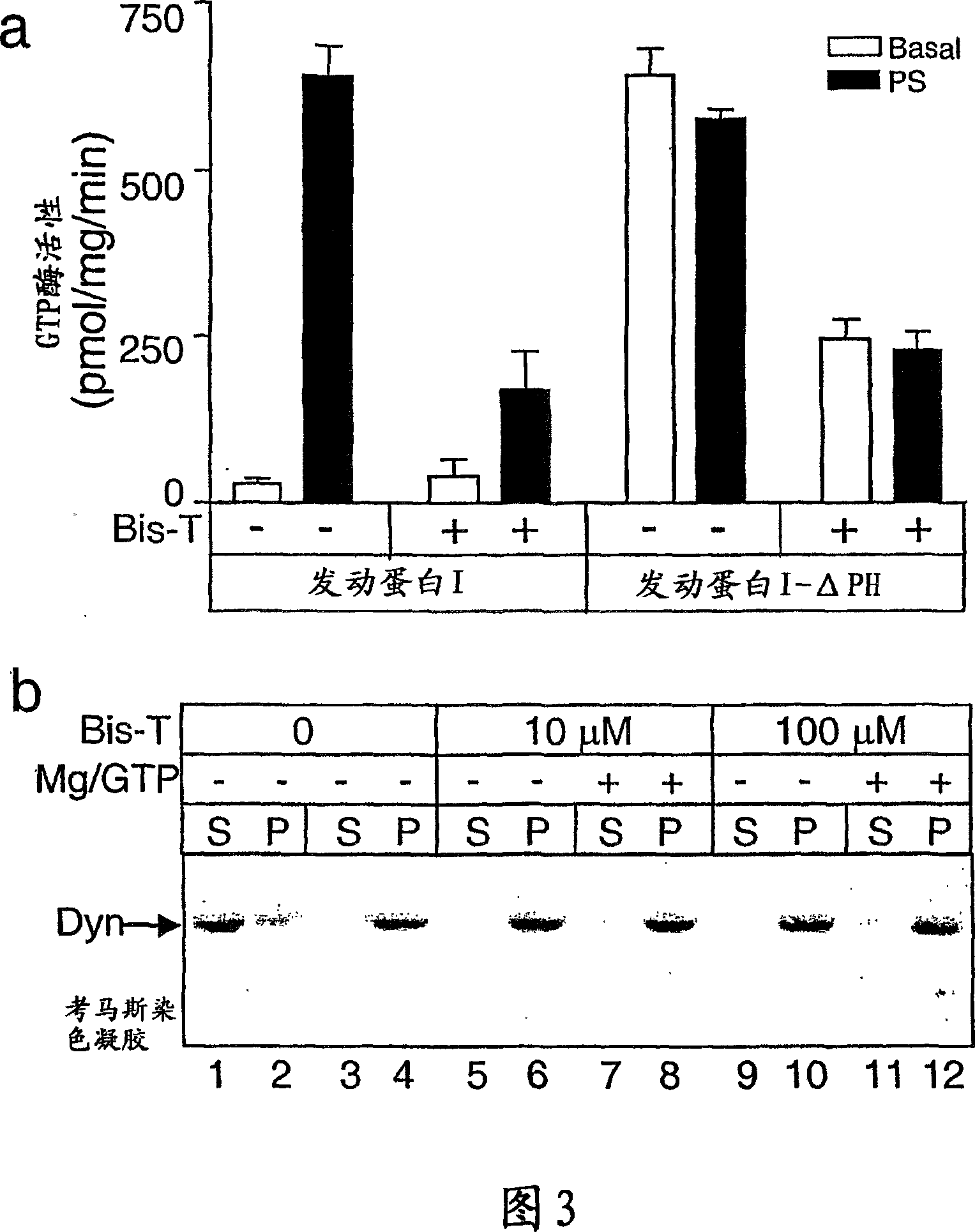
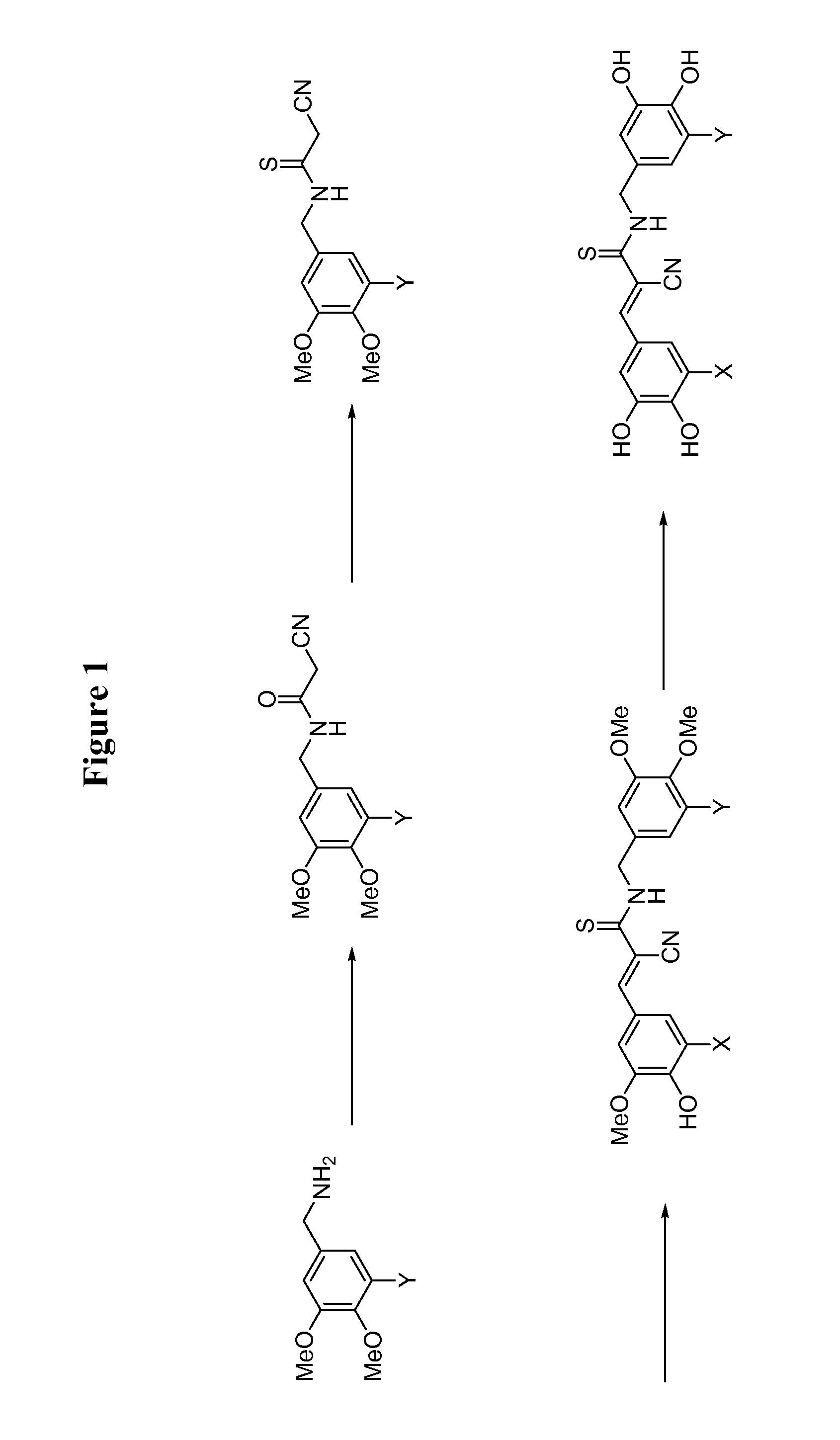
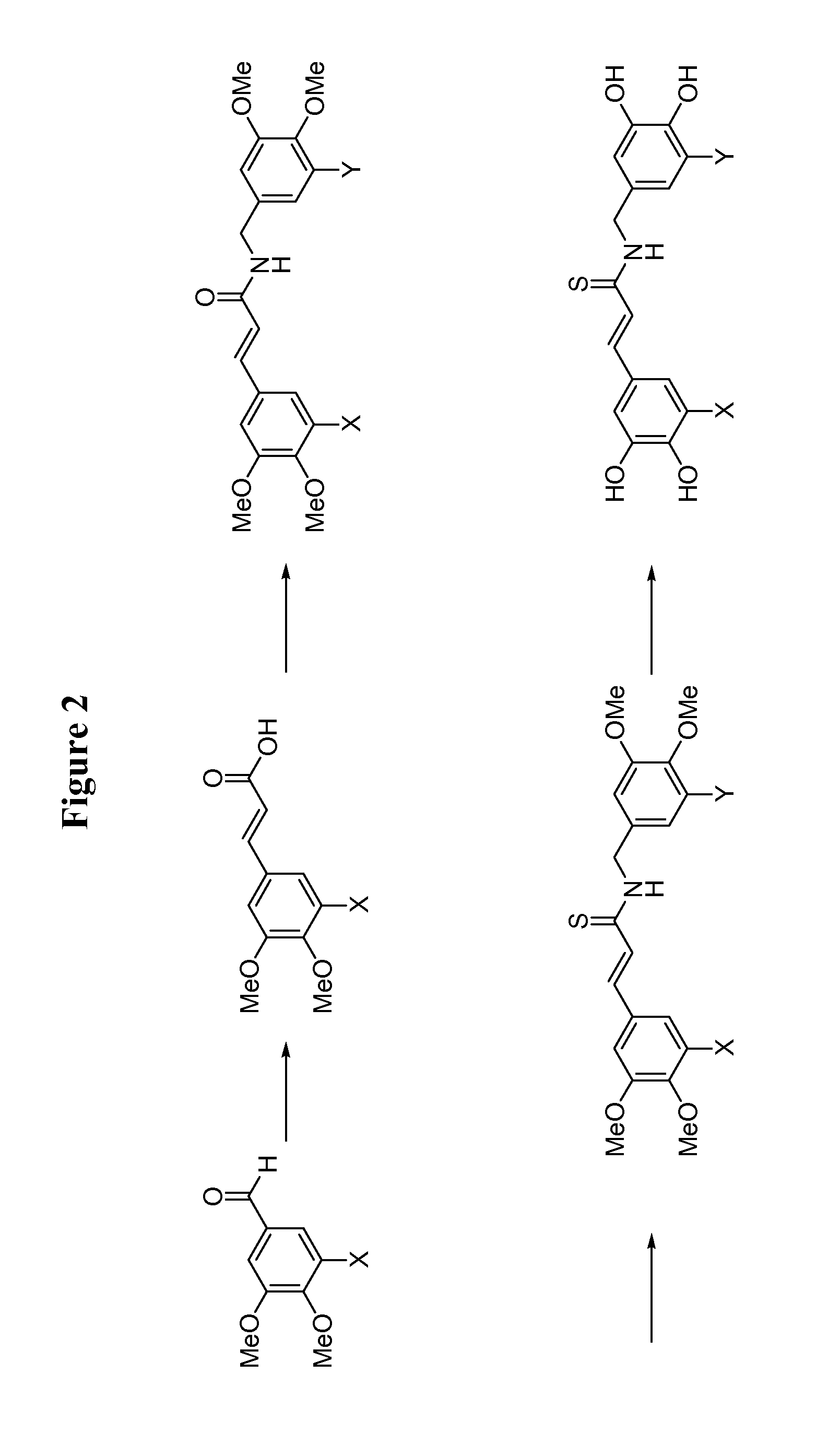
There are disclosed methods for inhibiting dynamin-dependent endocytosis in cells comprising treating the cells with an effective amount of a compound of formula (I), or a dimeric tyrphostin, physiologically acceptable salt, or prodrug thereof. Compounds useful in the methods described are also provided. The inhibition of dynamin-dependent endocytosis of cells is applicable to the treatment of epilepsy and neurological disorders and conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF NEWCASTLE RES ASSOCS +1
Novel protein kinase modulators and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS20120083528A1Improve suppression propertiesStrong inhibitory activityBiocideMetabolism disorderProtein-Tyrosine KinasesBiology
The present invention provides new tyrphostin derivatives acting as protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) inhibitors and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitors, and / or which directly or indirectly affect proteins in the PTK-mediated signal transduction pathway, methods of their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions including such compounds, and methods of using these compounds and compositions, especially as chemotherapeutic agents for preventions and treatments of PTK and RTK related disorders such as metabolic, fibrotic, and cell proliferative disorders, in particular psoriasis and cancer.
Owner:NOVOTYR THERAPEUTICS LTD
Quinazoline and quinoline derivatives as irreversibe protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors
ActiveUS8198301B2Improve anti-tumor effectUnique structureBiocideOrganic chemistryQuinolineQuinazoline
A compound of formula (I),a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, or hydrate thereof, and a method of preparing the same. A method of treating or preventing a physiological disorder caused by abnormal protein tyrosine kinase activity in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of formula (I).
Owner:TIANJIN HEMAY ONCOLOGY PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com