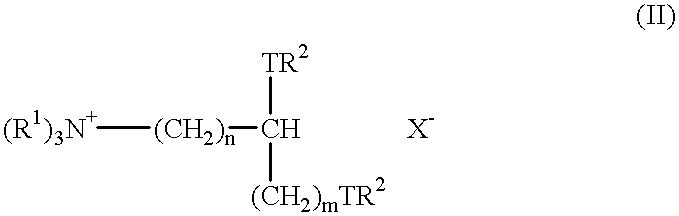
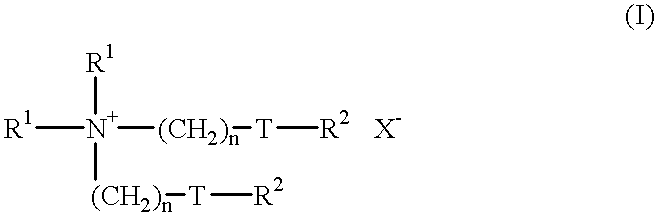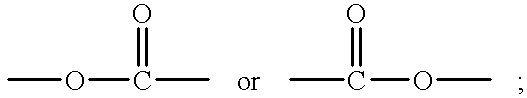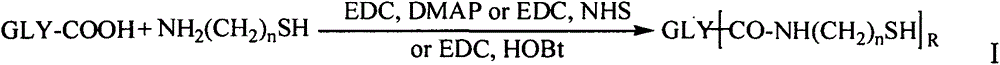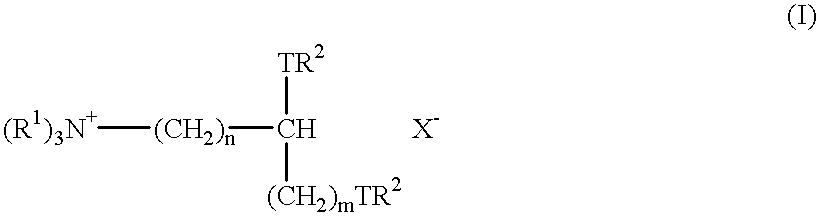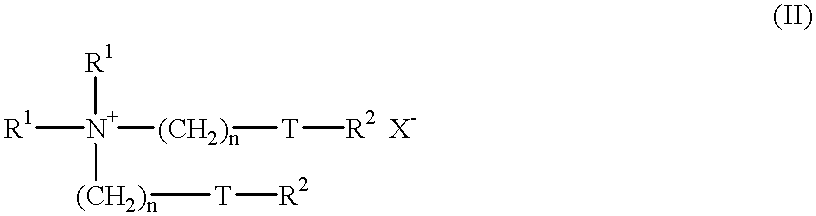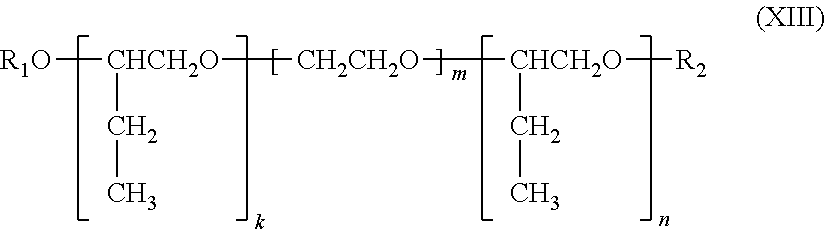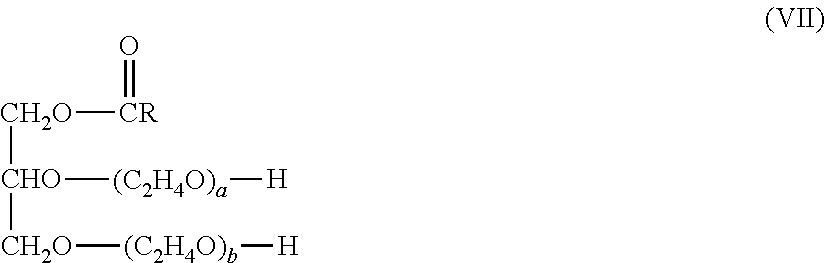Patents
Literature
65 results about "Sugar derivative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
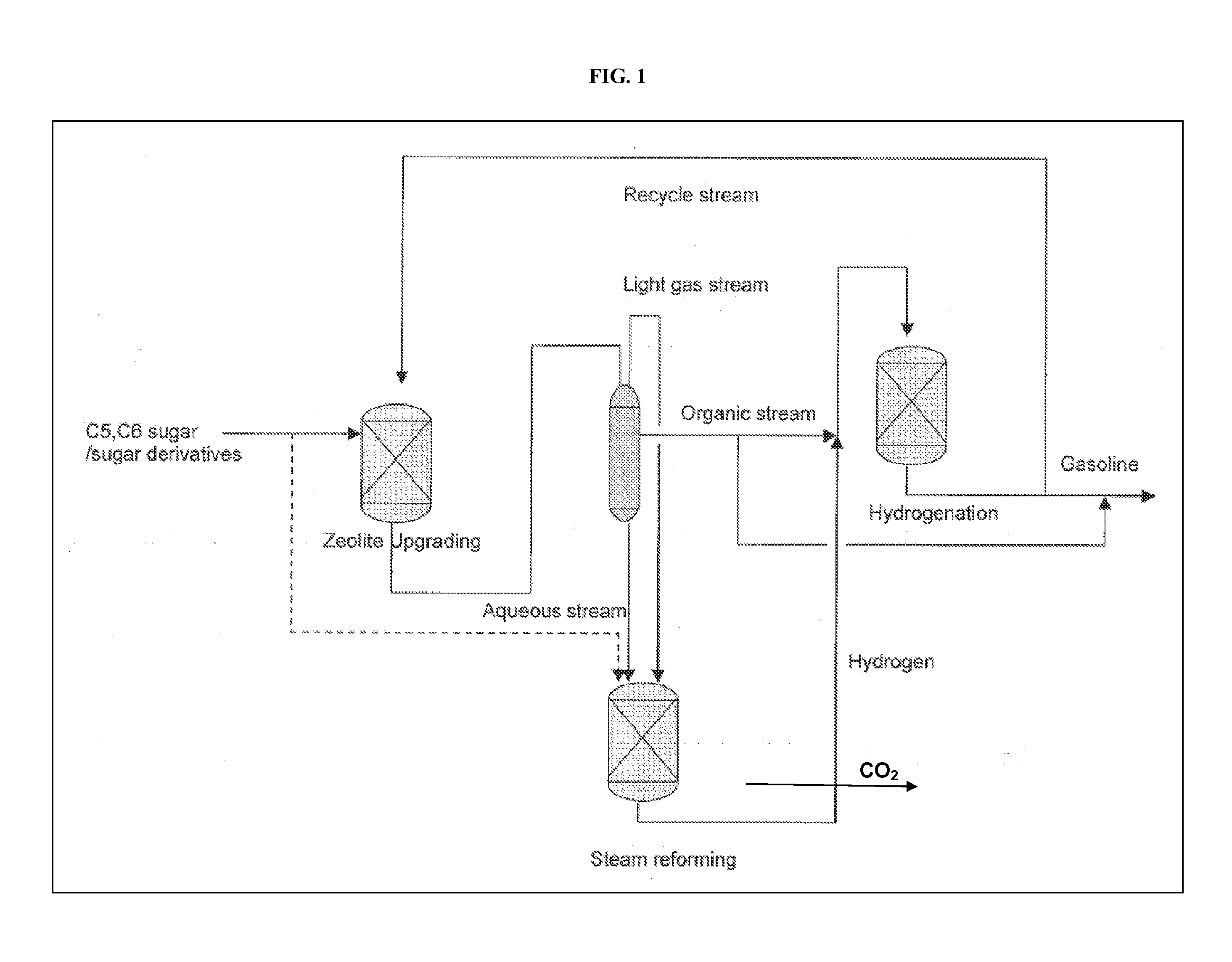
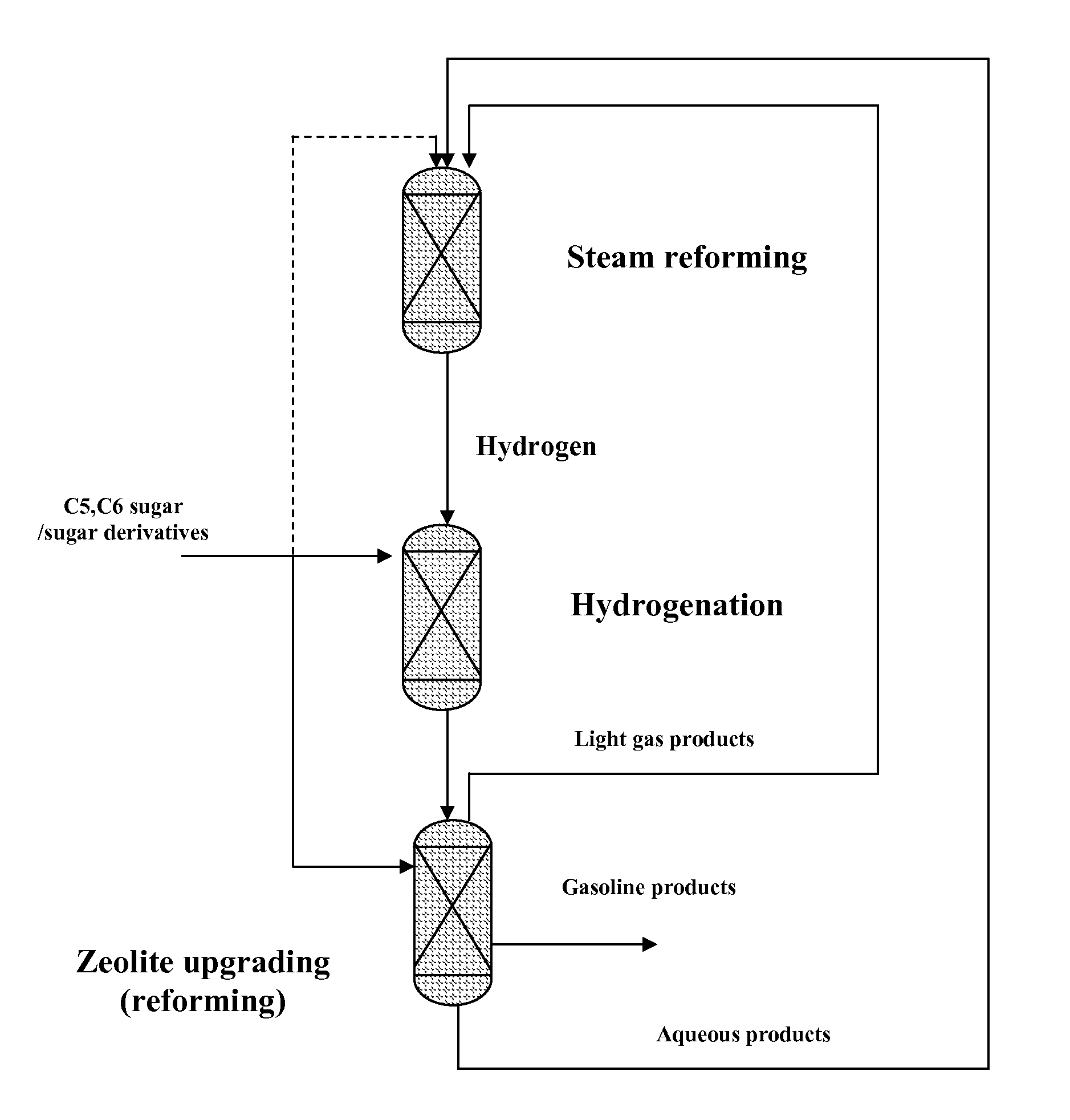
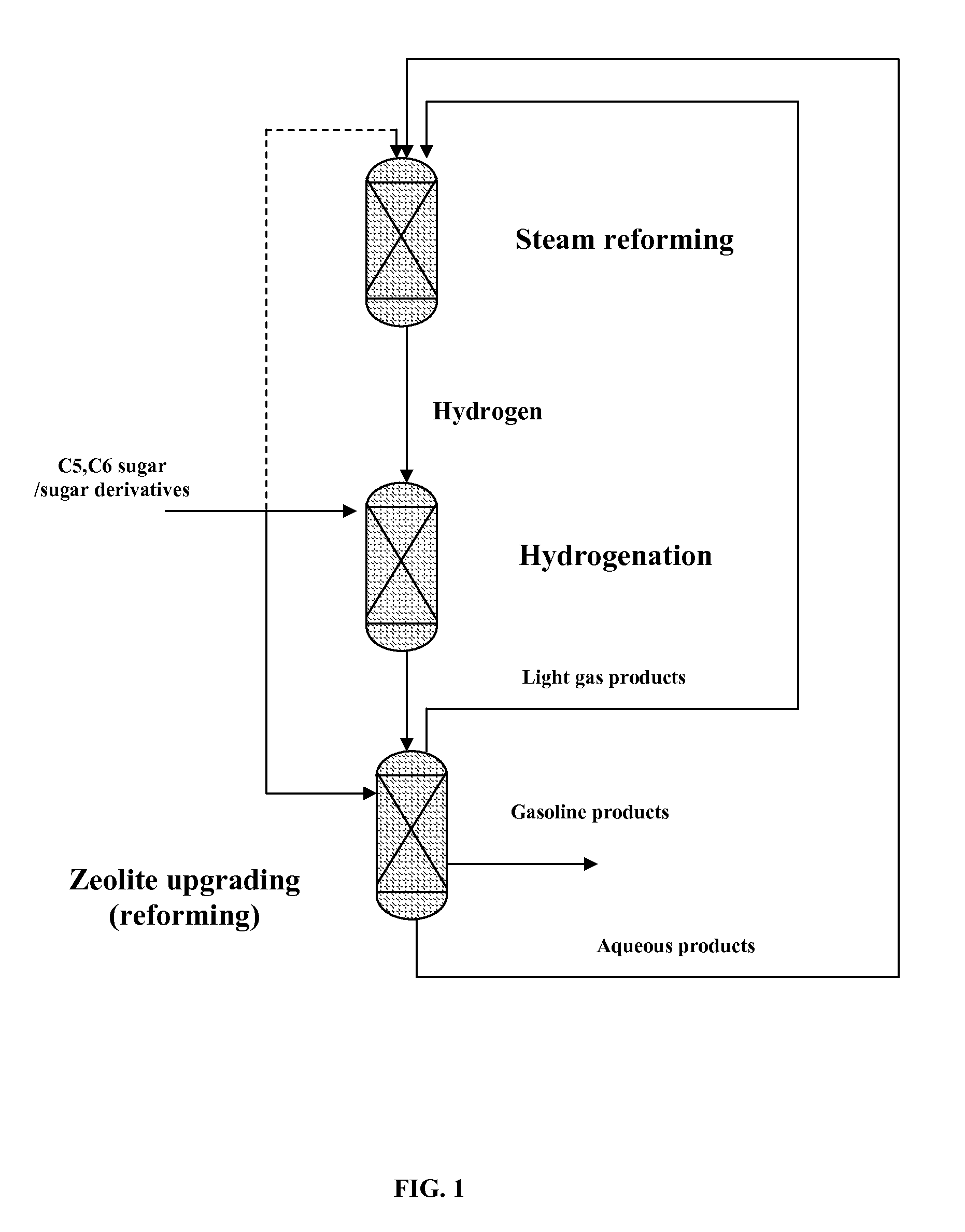
Carbohydrates upgrading and hydrotreating to hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20110263916A1Easy to convertReduced liquid yieldHydrogenBiofuelsCarbon footprintLiquid hydrocarbons
Technologies to convert biomass to liquid hydrocarbon fuels are currently being developed to decrease our carbon footprint and increase use of renewable fuels. Since sugars / sugar derivatives from biomass have high oxygen content and low hydrogen content, coke becomes an issue during zeolite upgrading to liquid hydrocarbon fuels. A process was designed to reduce the coke by co-feeding sugars / sugar derivatives with a saturated recycle stream containing hydrogenated products.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
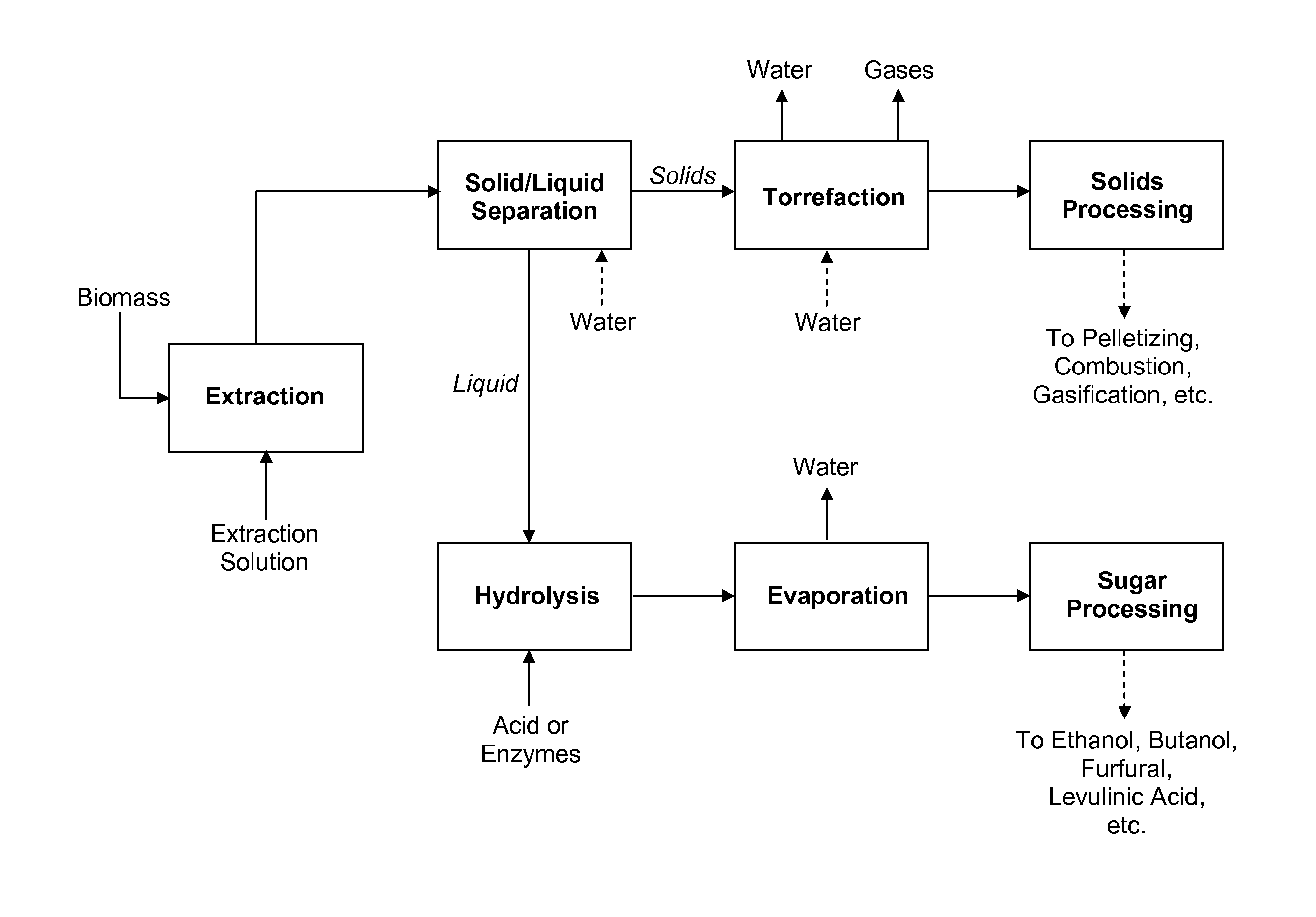
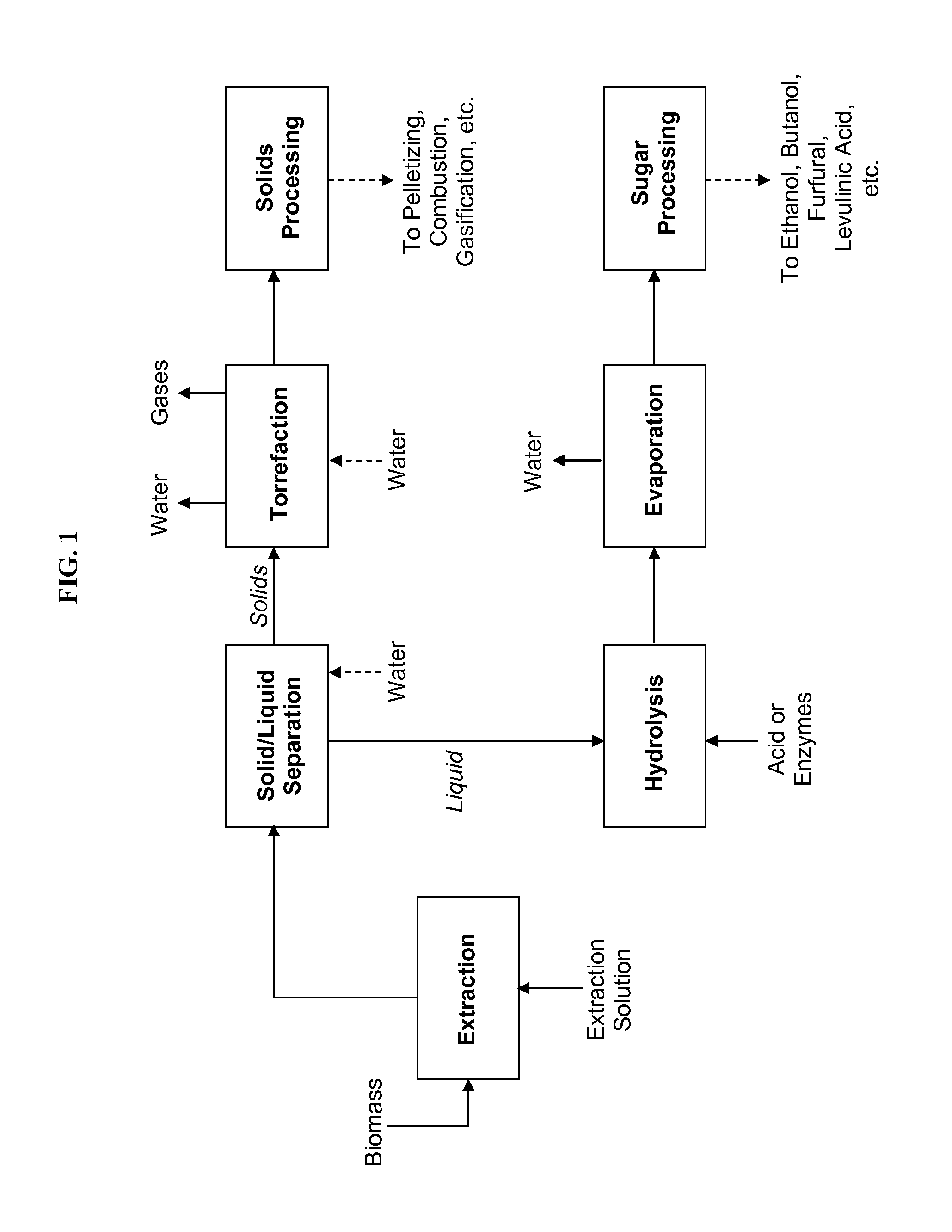
Processes for producing energy-dense biomass and sugars or sugar derivatives, by integrated hydrolysis and torrefaction
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Fabric softening compositions and compounds
The invention provides a fabric softening composition comprising; (i) at least one oily sugar derivative which is a liquid or soft solid derivative of a cyclic polyol or of a reduced saccharide, said derivative resulting from 35 to 100% of the hydroxyl groups it said polyol or in said saccharide being esterified or etherified, and wherein, the derivative has two or more ester or ether groups independently attached to alkyl or alkenyl chains derived from a fatty acid mixture comprising at least 50% by weight of a mixture of tallow fatty acid and oleyl fatty acid, and (ii) one or more deposition aid(s). The invention also provides a method of treating fabric by applying thereto the composition of the invention and the use of the aforementioned oily sugar derivatives within a fabric softening composition as a fabric softening aid that does not decrease the absorbency of the fabric. Also provided are the above mentioned oily sugar derivatives.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
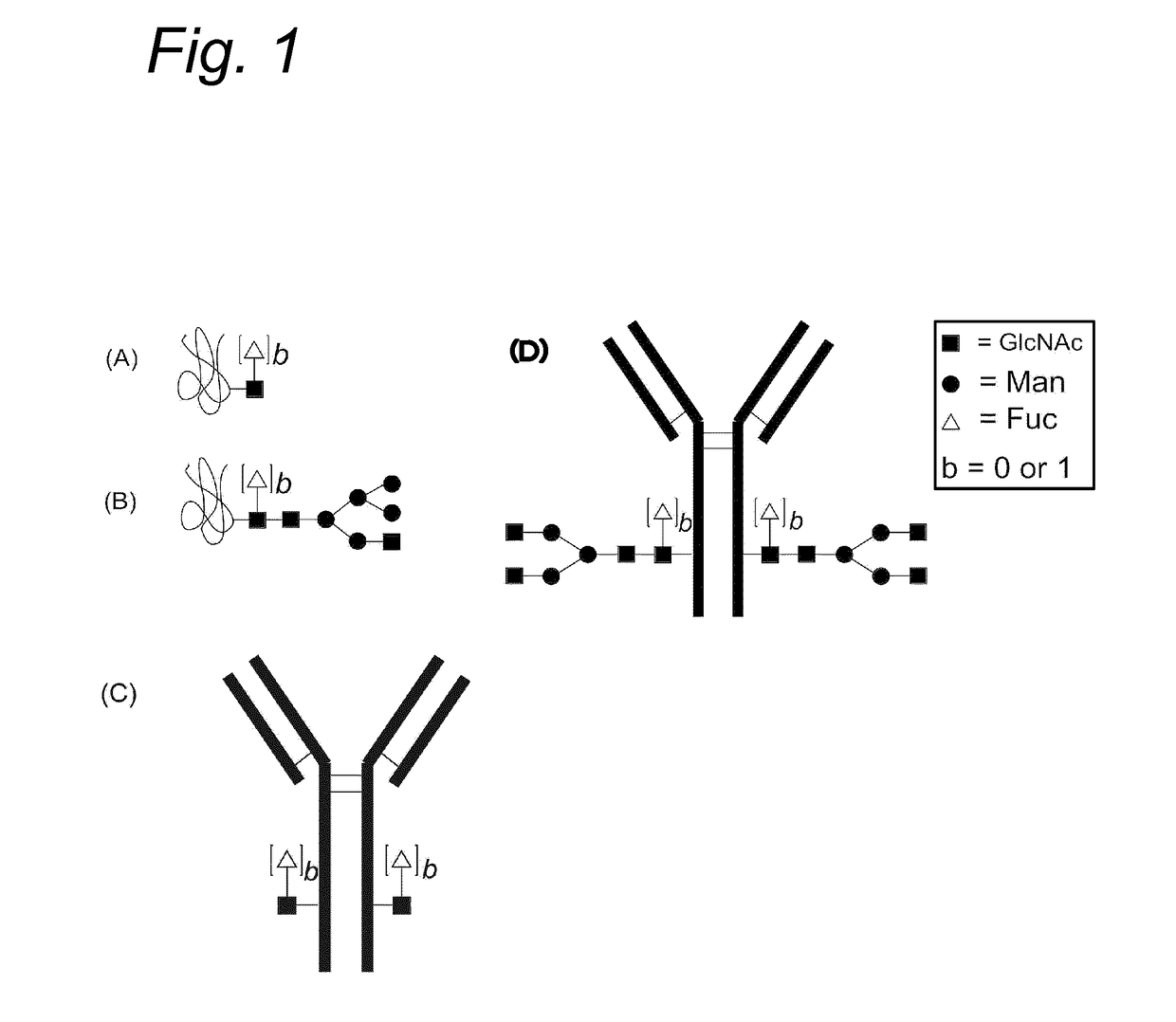
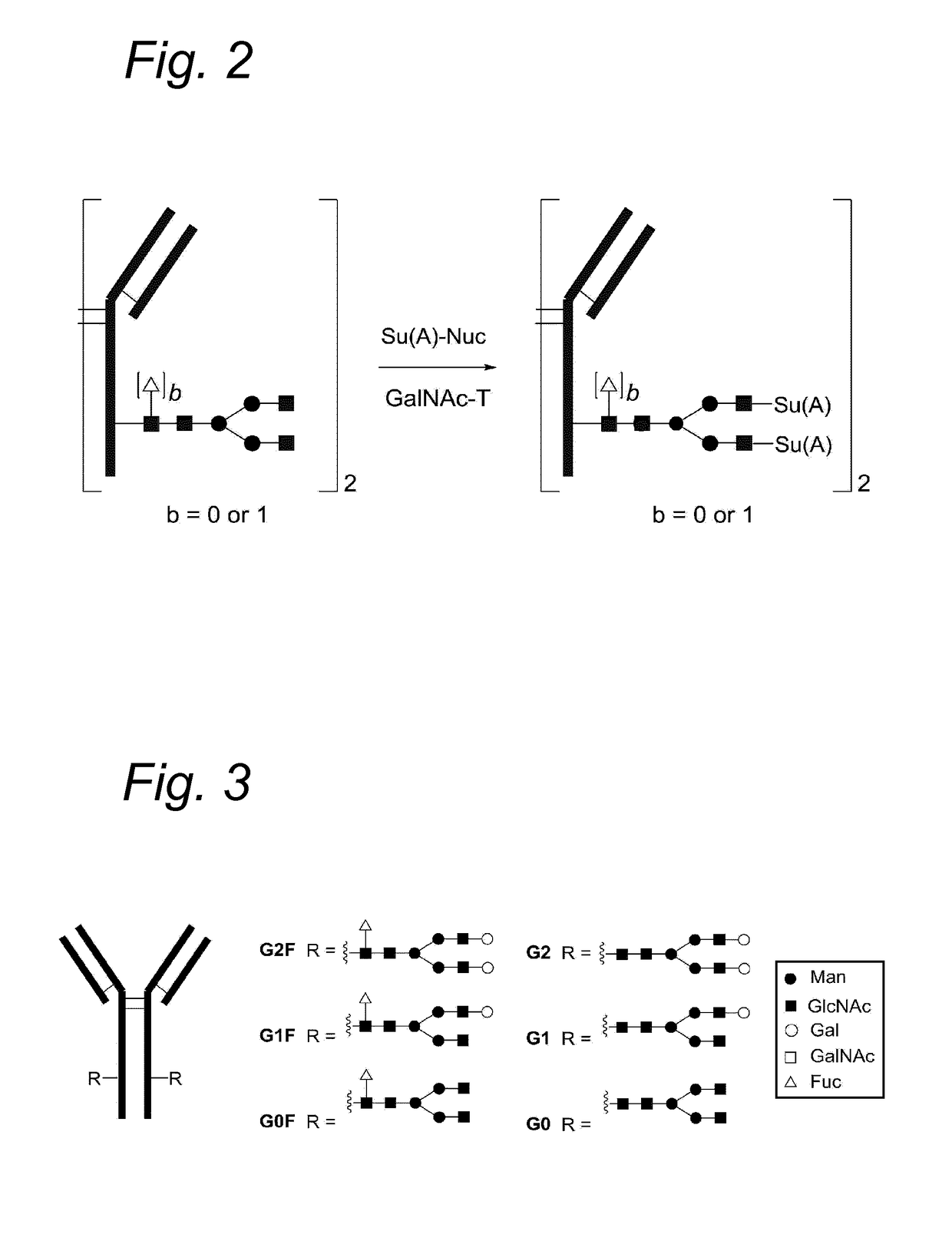
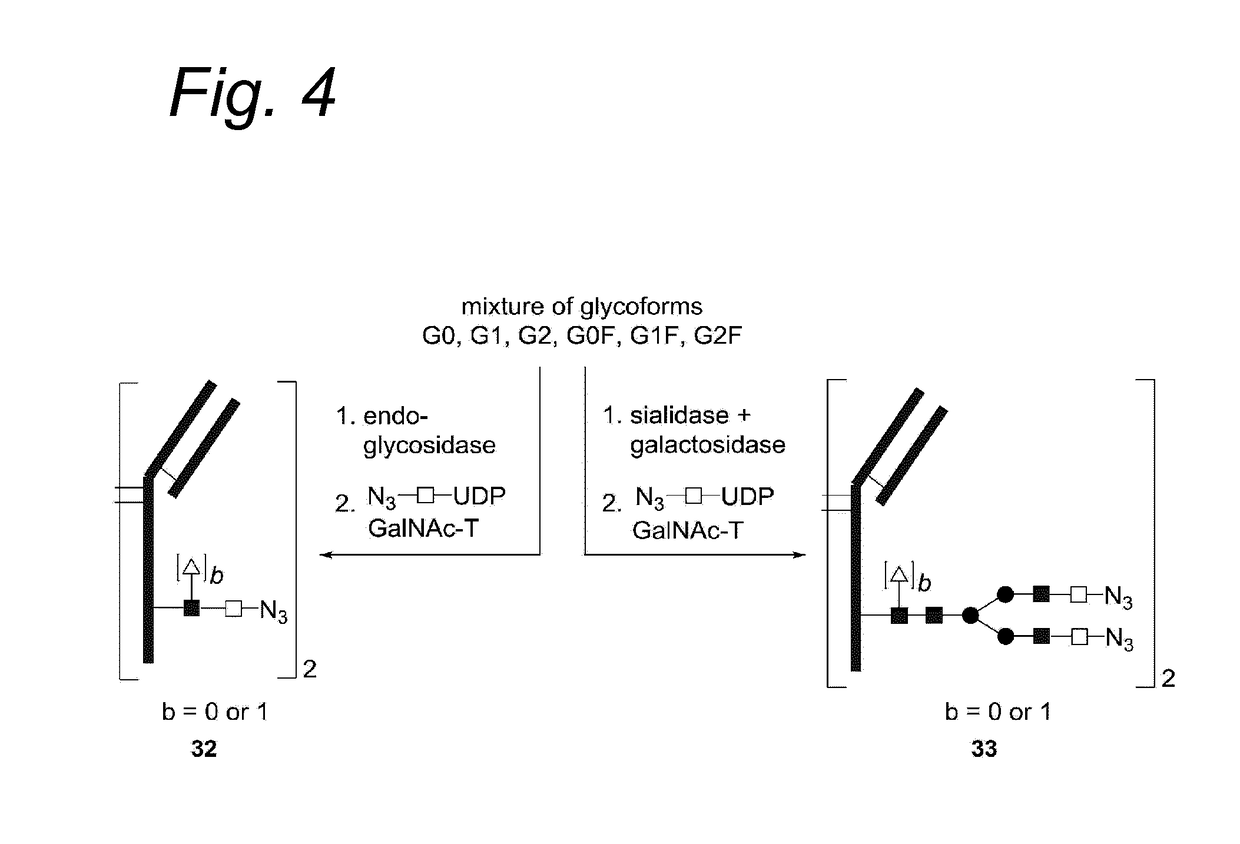
Modified glycoprotein, protein-conjugate and process for the preparation thereof
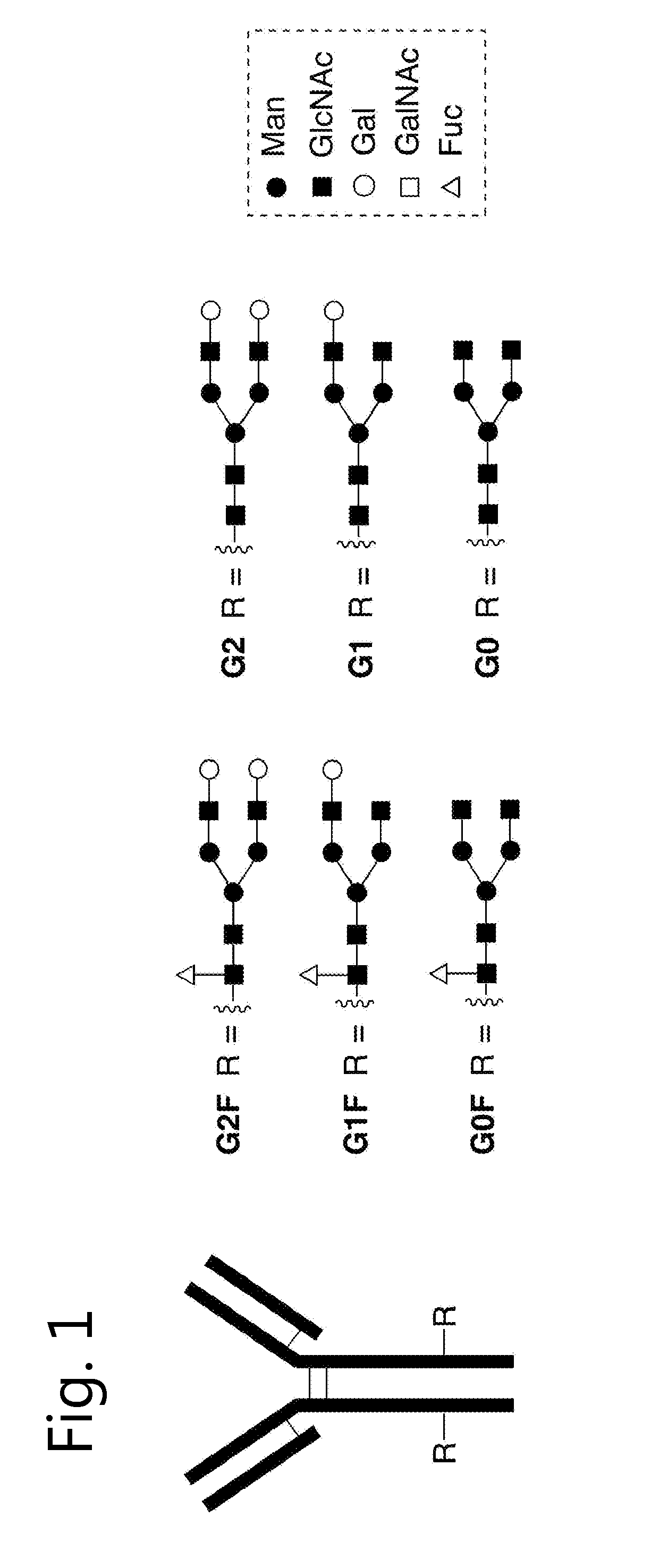
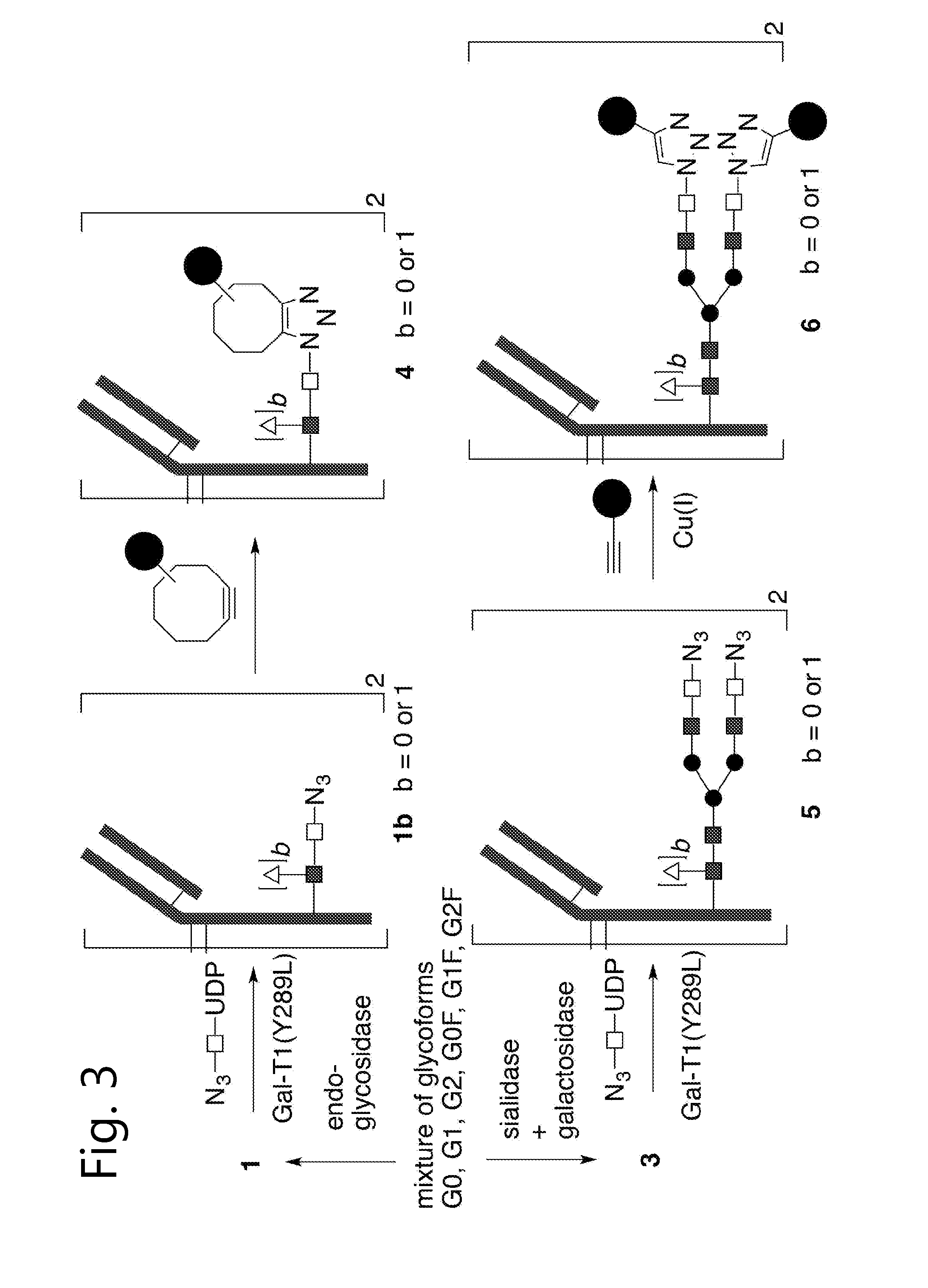
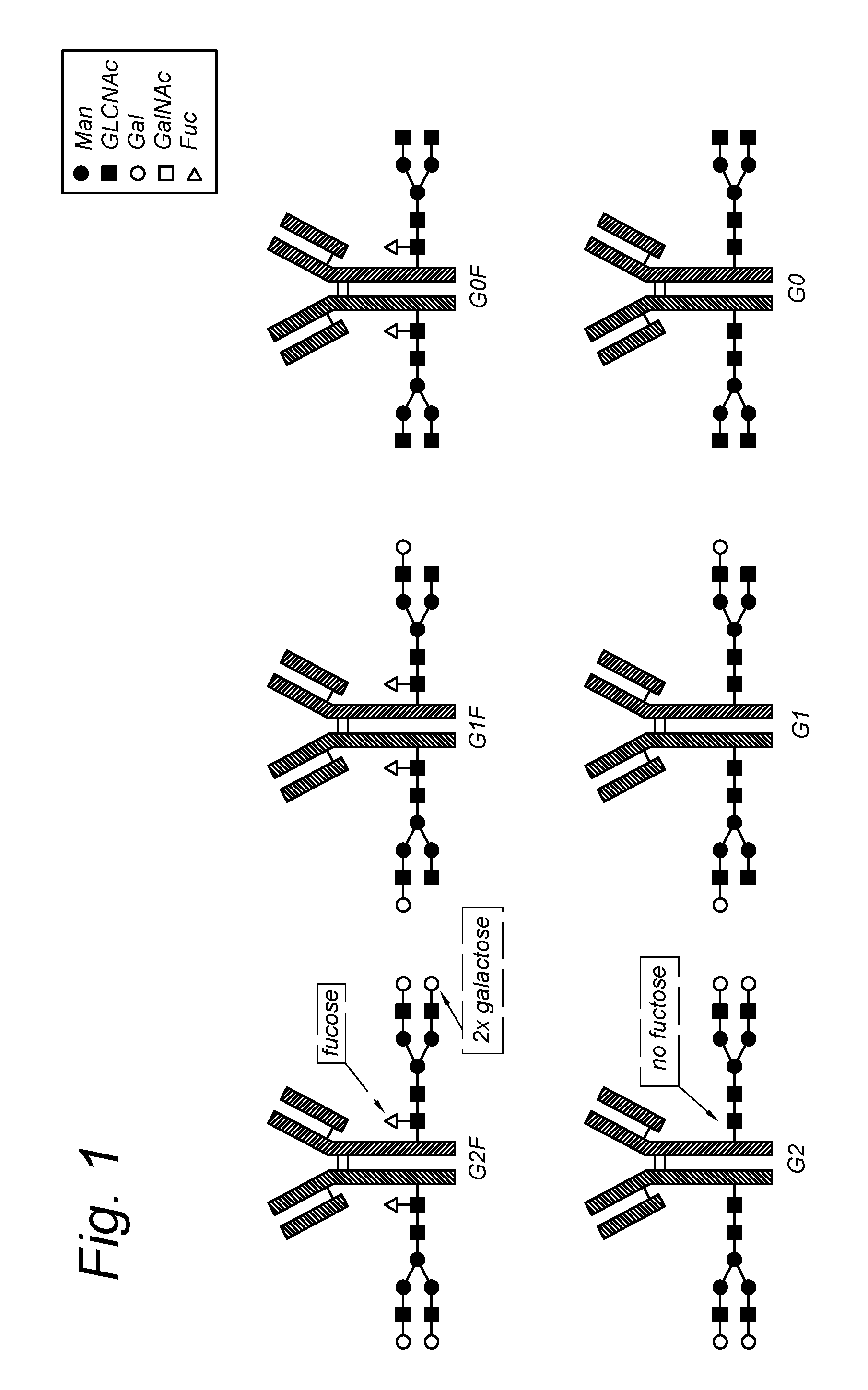
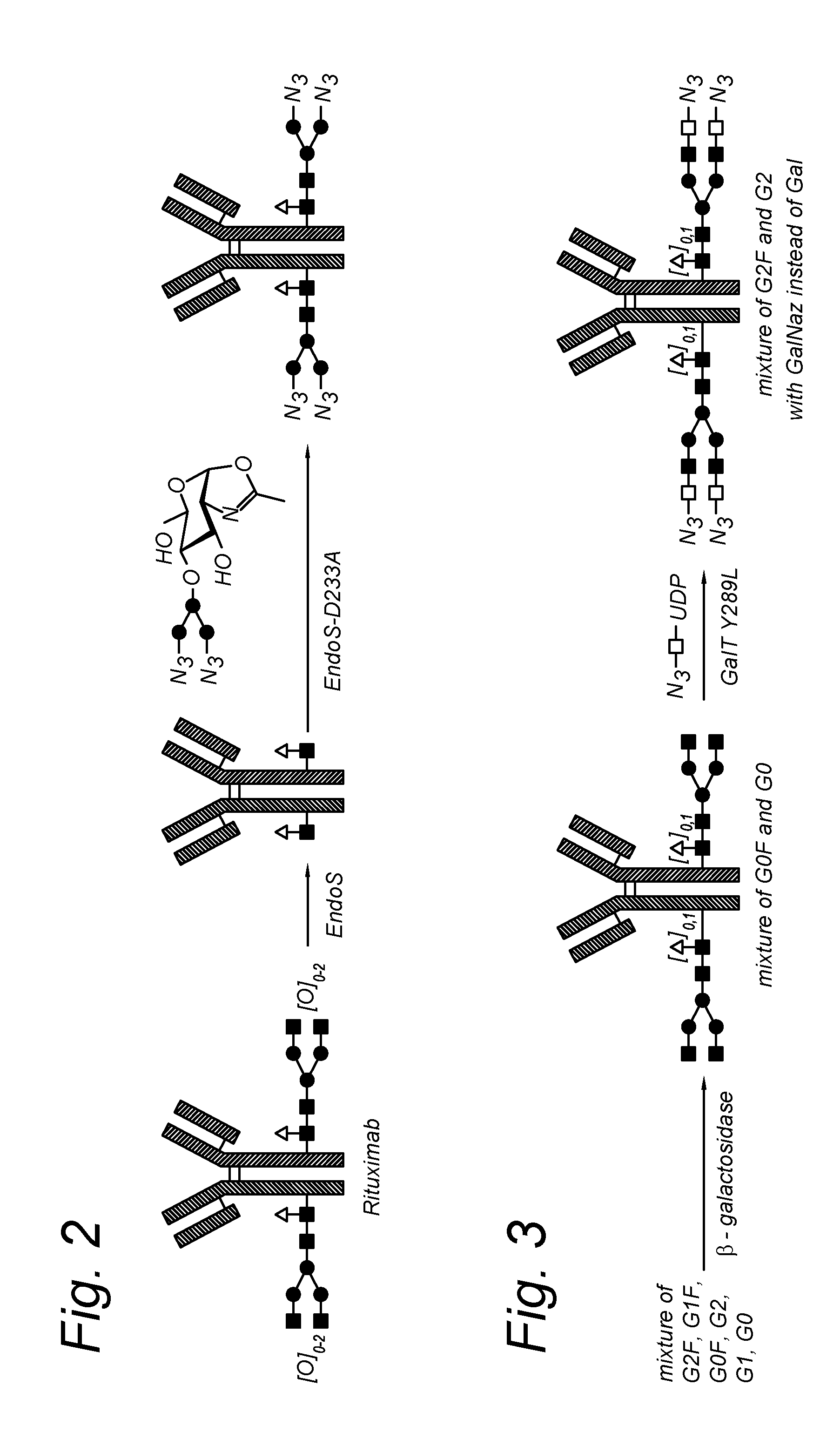
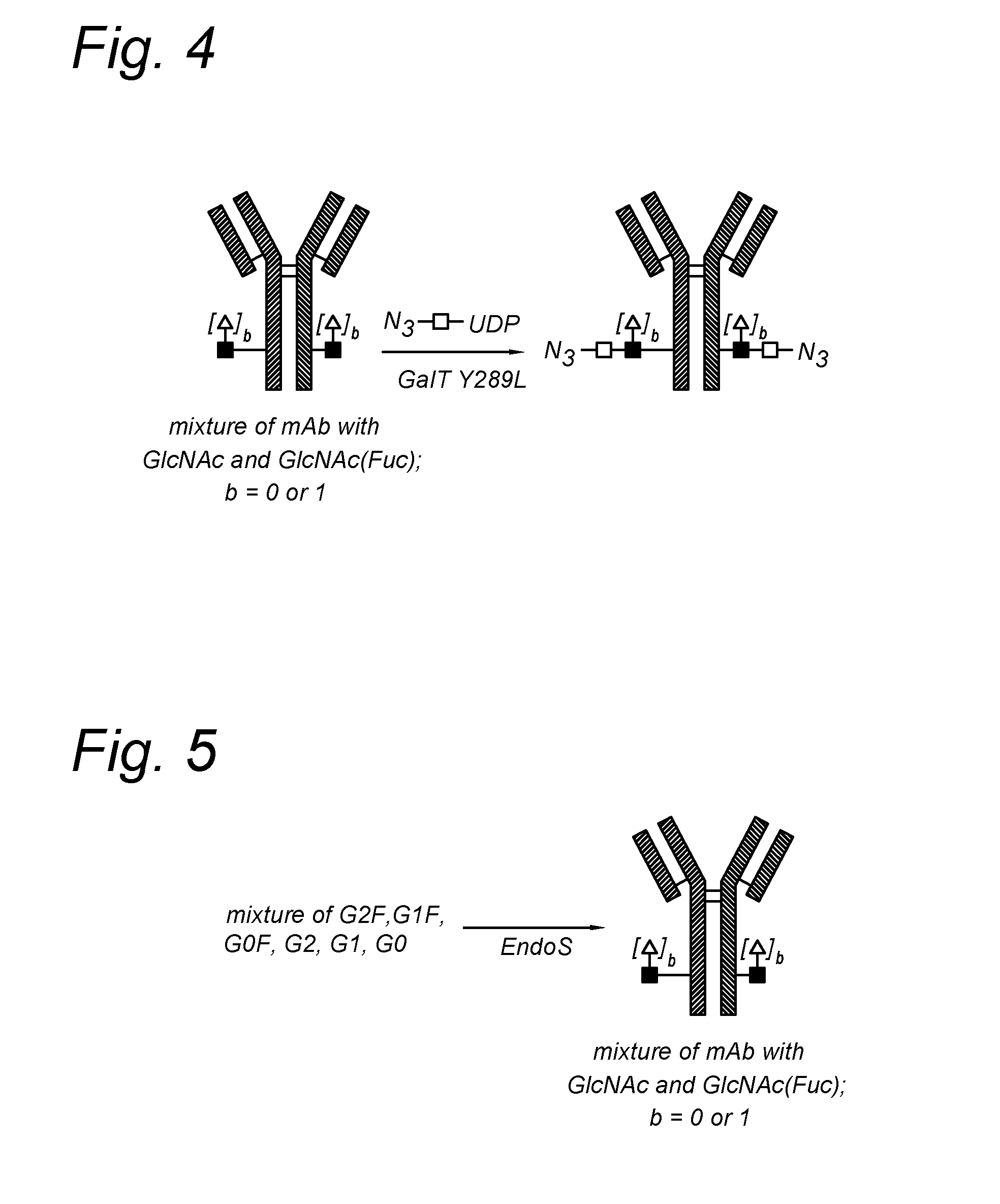
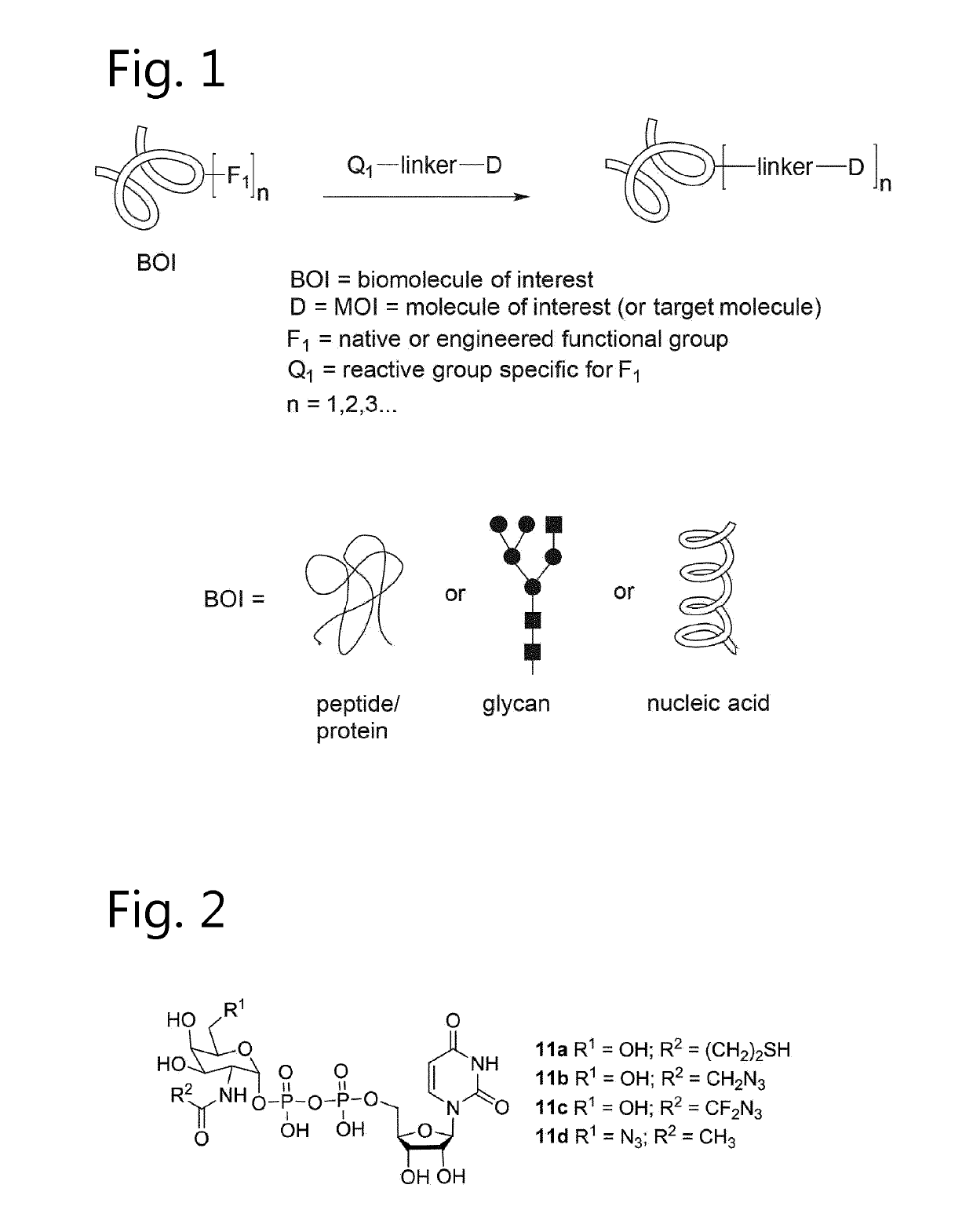
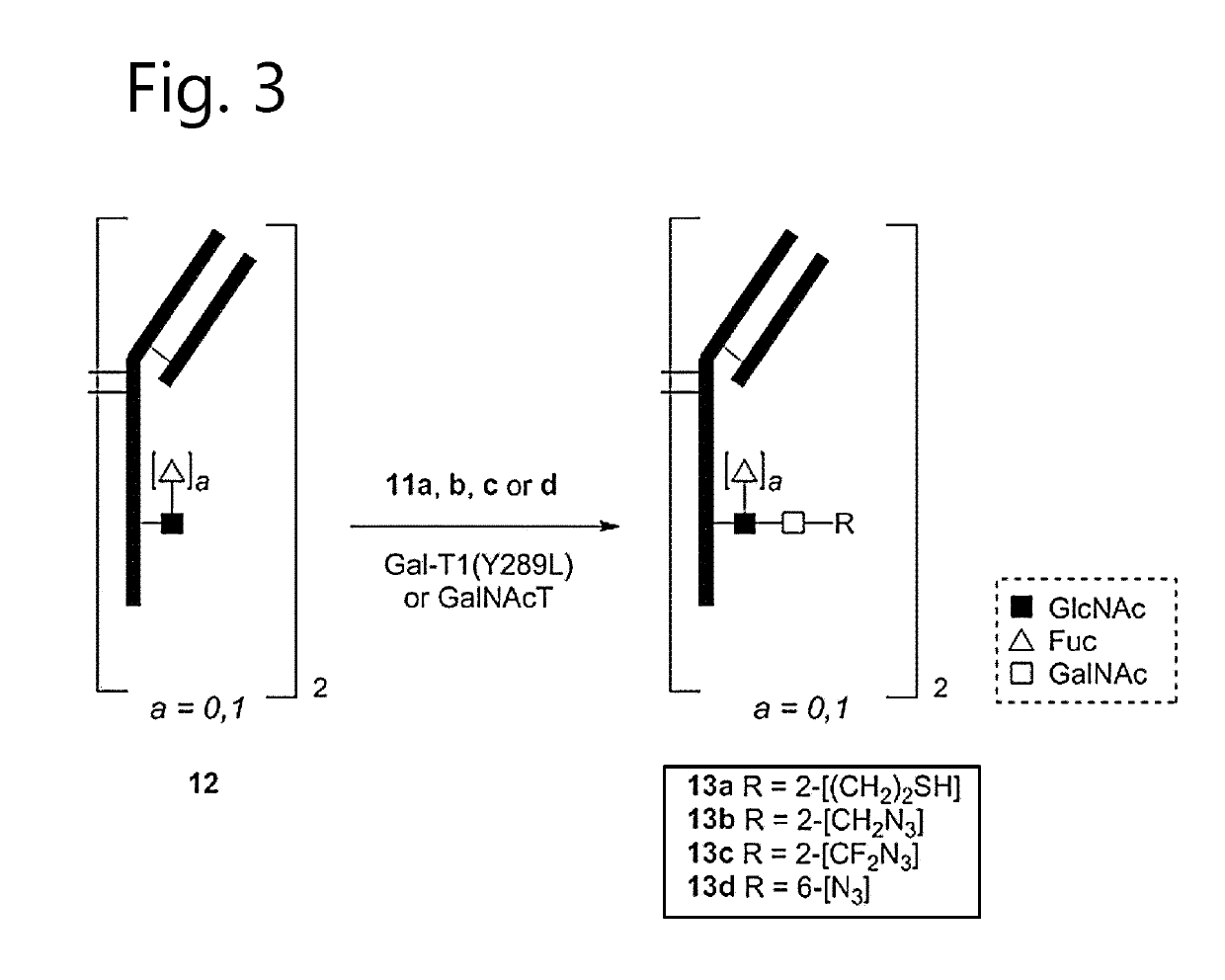
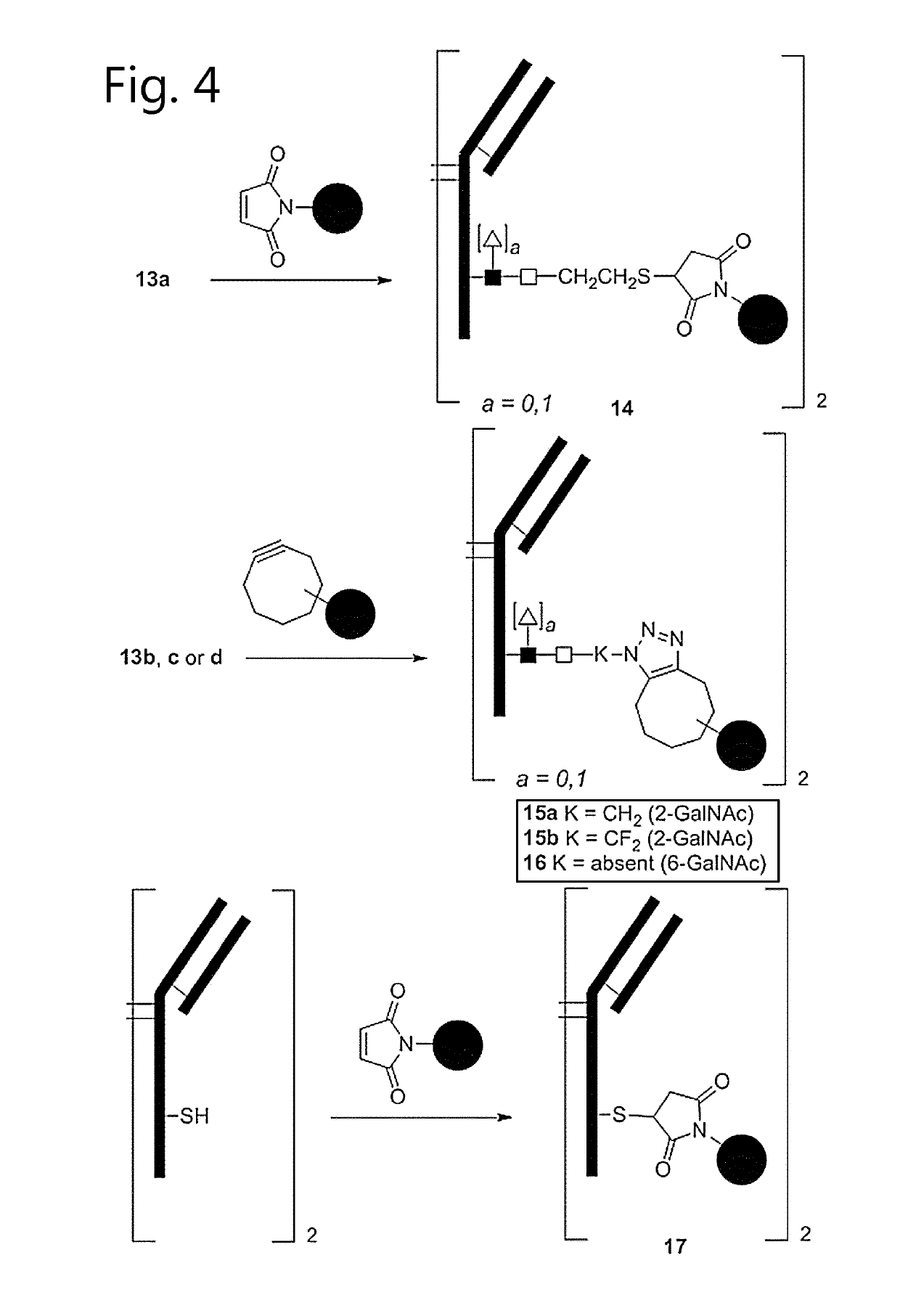
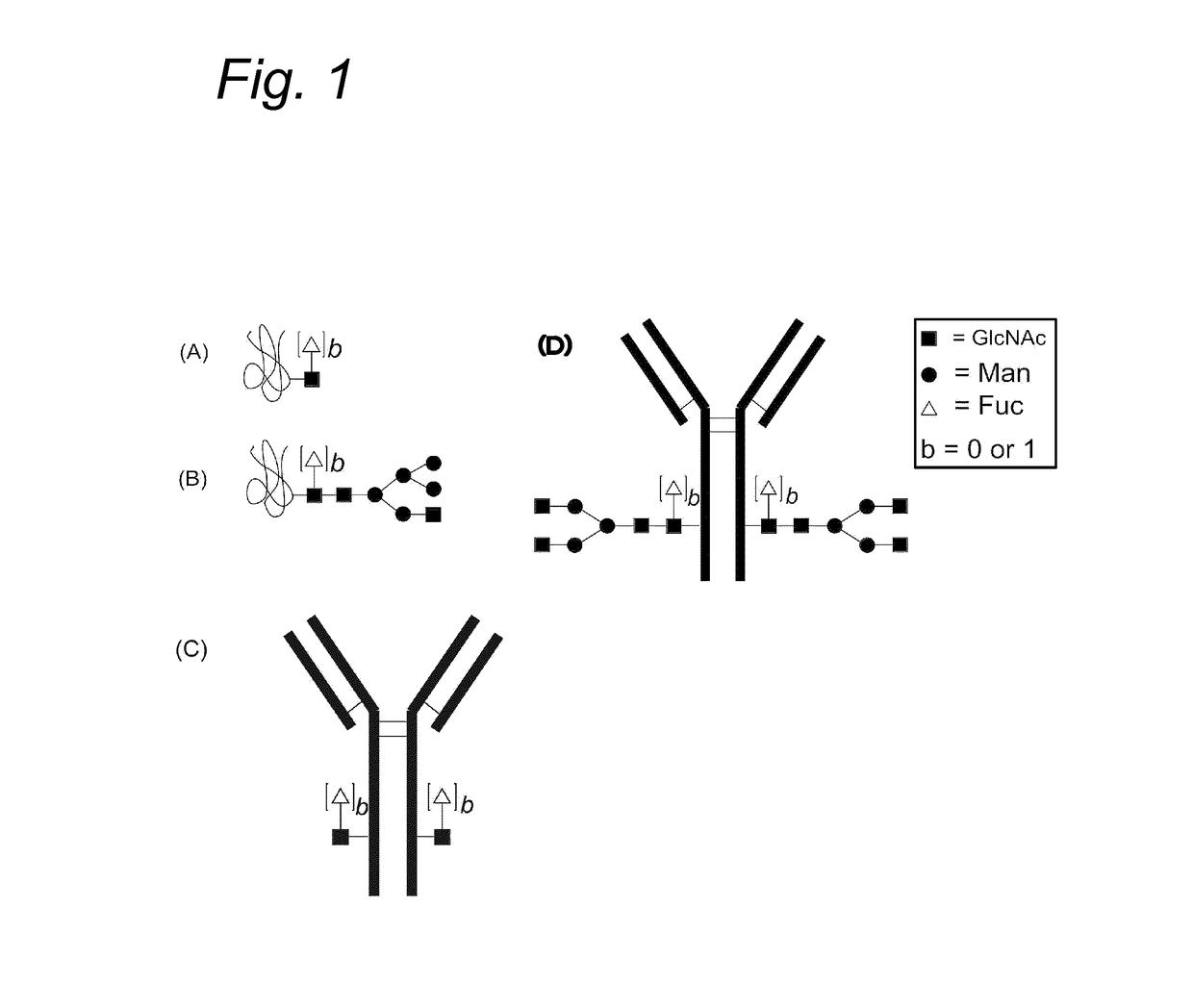
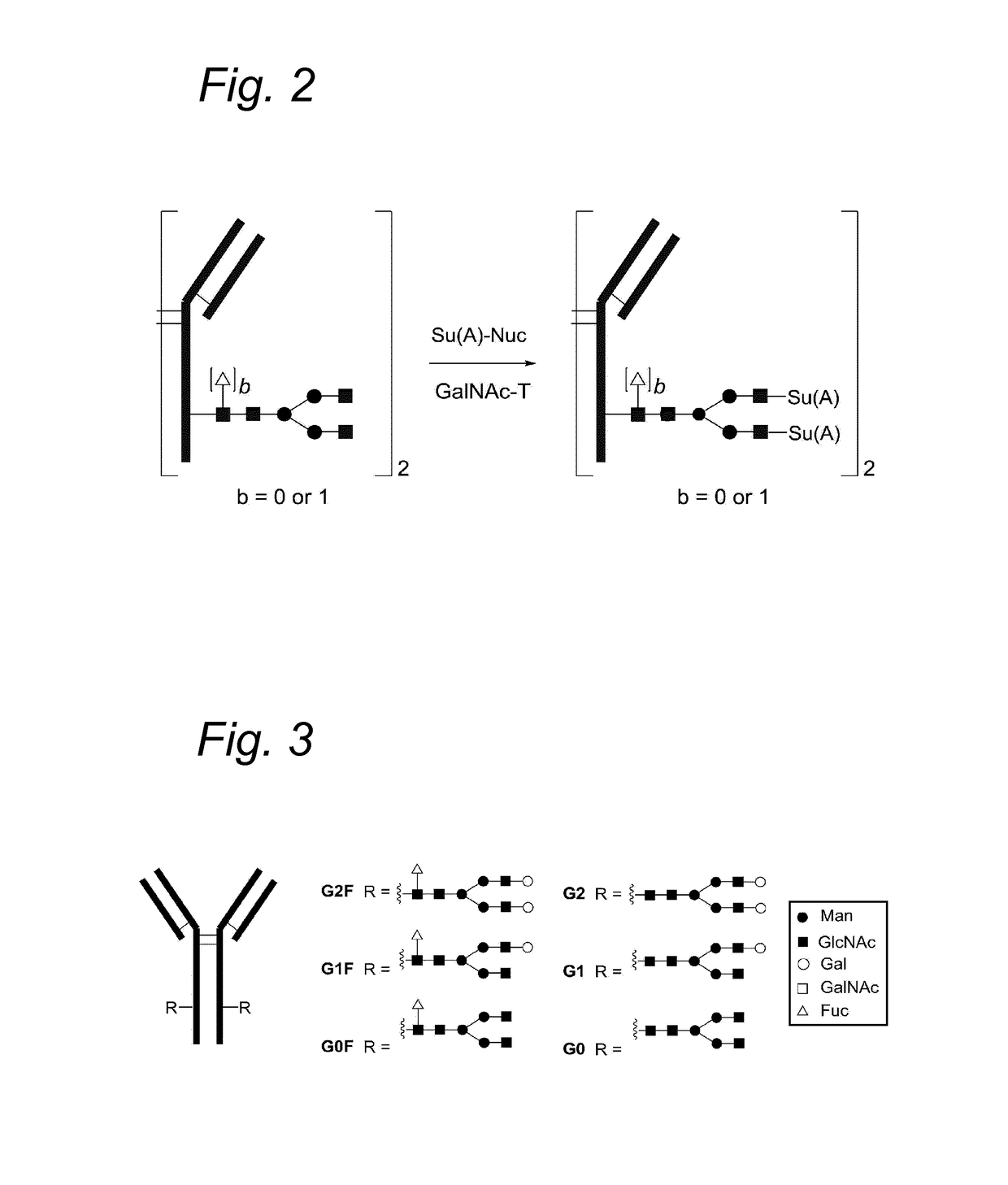
Glycoproteins comprising a glycan of the formula (102) are disclosed; wherein b is 0 or 1; the GlcNAc residue optionally fucosylated; and Su(A)x is a sugar derivative comprising x functional groups A, wherein x is 1, 2, 3 or 4 and A is independently selected from the group consisting of an azido group, a keto group, an alkynyl group, a thiol group, a halogen, a sulfonyloxy group, a halogenated acetamido group, a mercaptoacetamido group and a sulfonylated hydroxyacetamido group.Protein-conjugates having glycoproteins according to the invention conjugated to a molecule of interest (e.g., an active substance) are also disclosed. Examples include modified antibodies, antibody-conjugates, and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Processes for the preparation of the modified glycoproteins according to the invention and methods for the preparation of a protein-conjugate according to the invention are mentioned.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Polyol-modified silanes as precursors for silica
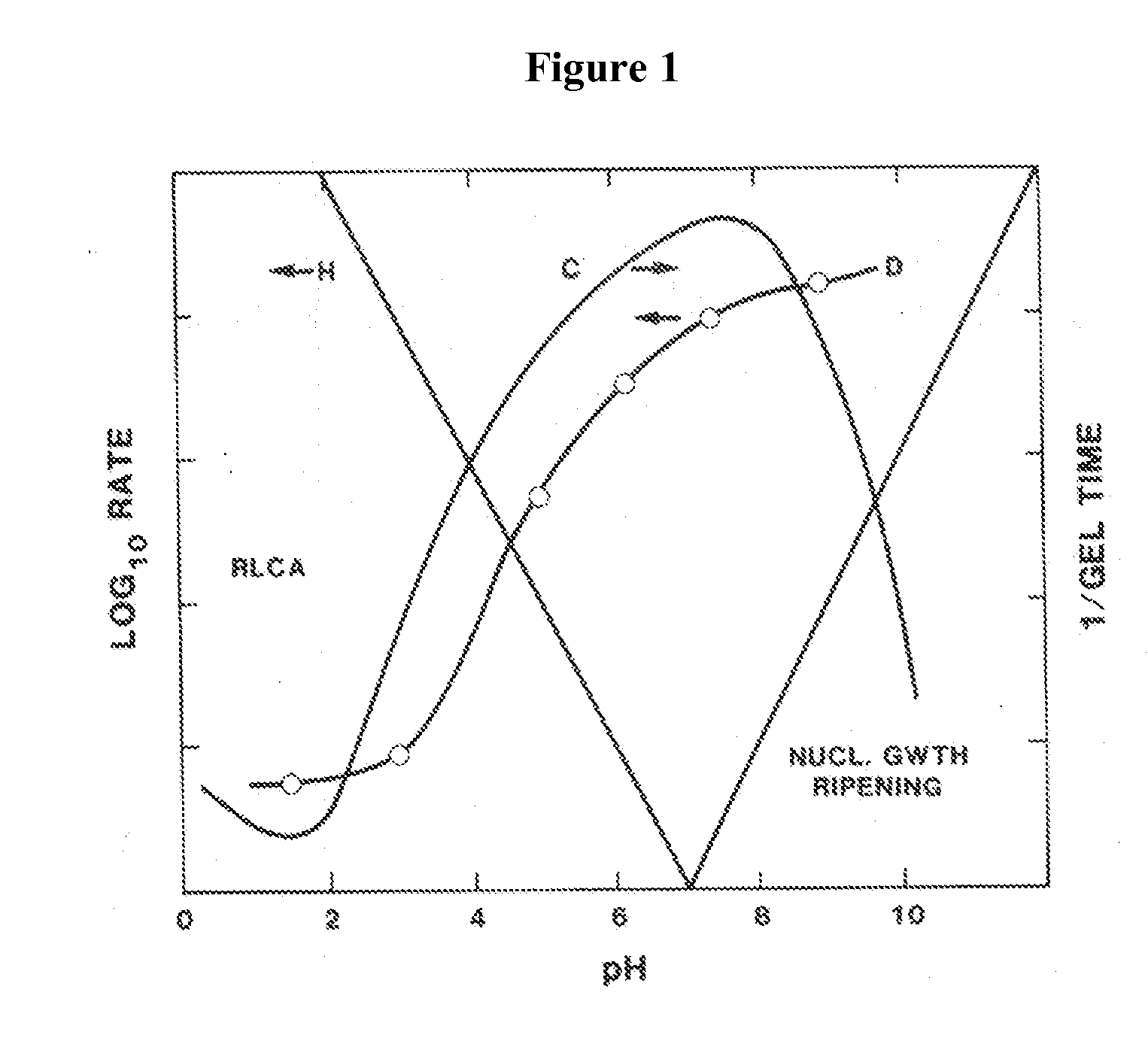
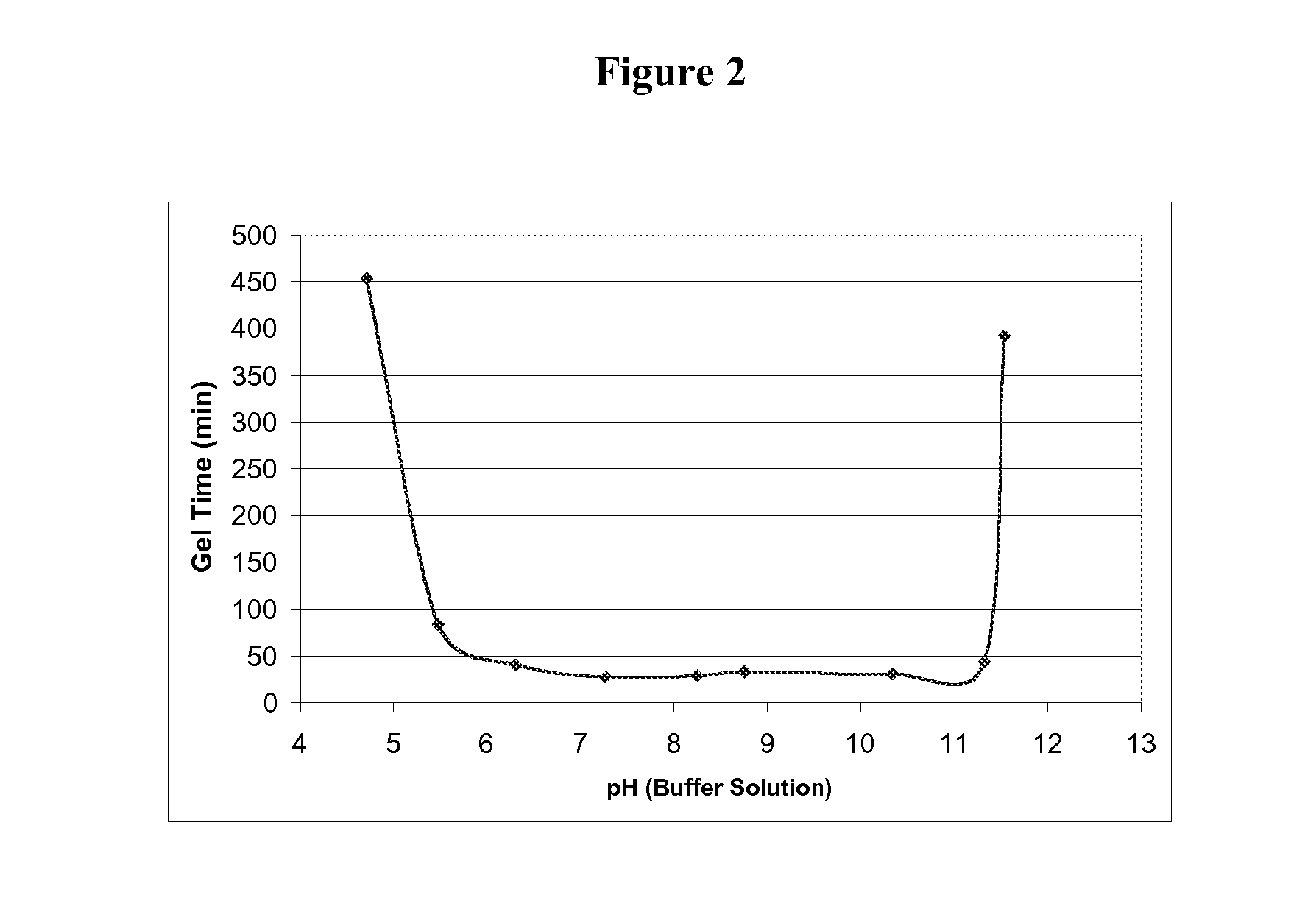
The invention relates to the preparation of monolithic silica under mild conditions from alkoxysilanes derived from sugars, sugar acids, sugar alcohols and polysaccharides including glycerol, sorbitol, mannose and dextran. Unlike the commonly used silica starting material TEOS (Si(OEt)4), the sol-gel hydrolysis and cure of the sugar derivatives are not very sensitive to pH as similar rates of gelation were observed over a pH range of about 5.5-11. The morphology of the resulting silicas could be varied using specific additives, including multivalent ions and hydrophilic polymers.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
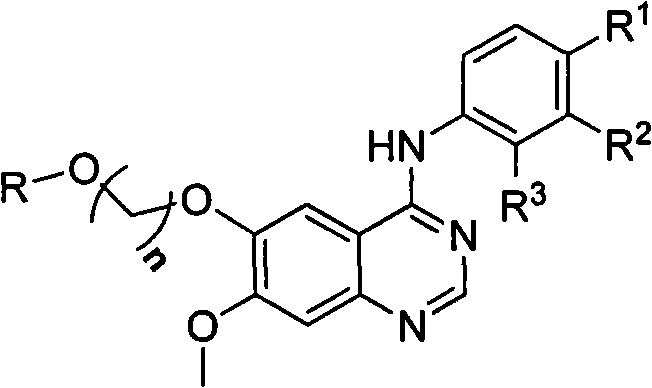
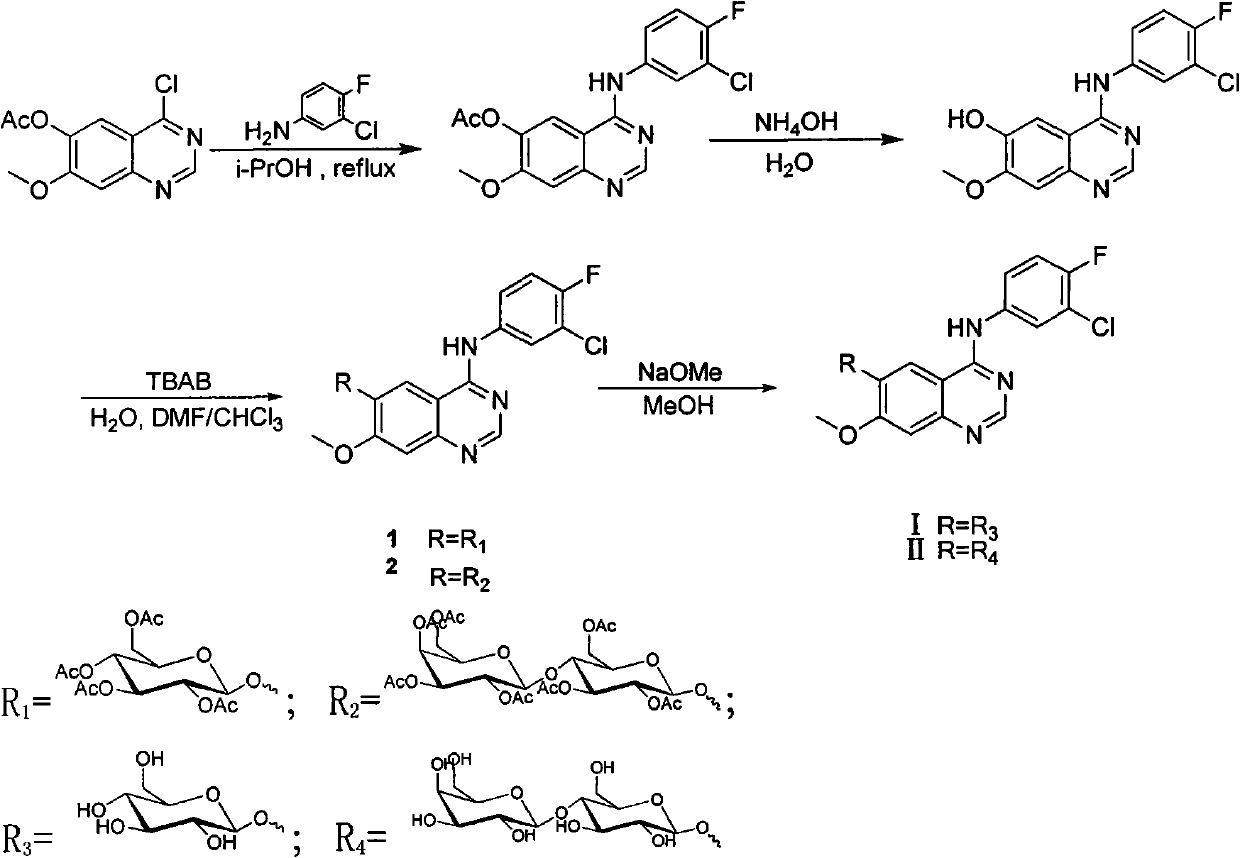
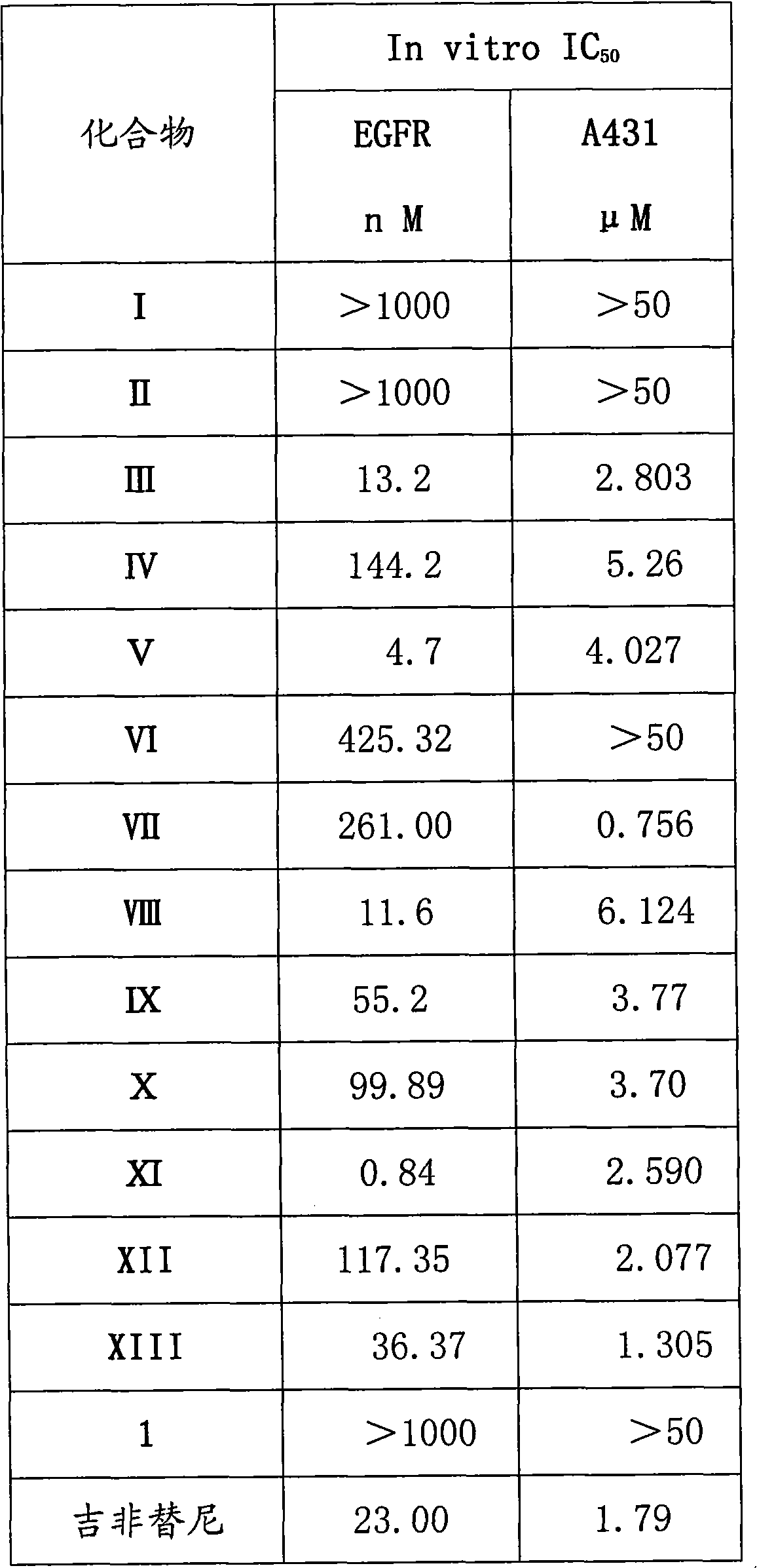
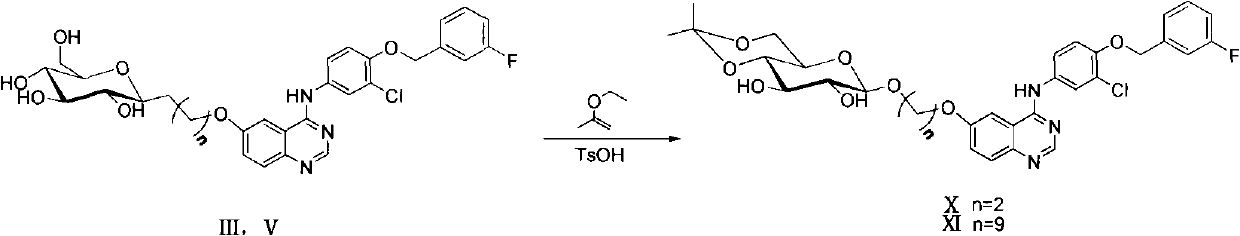
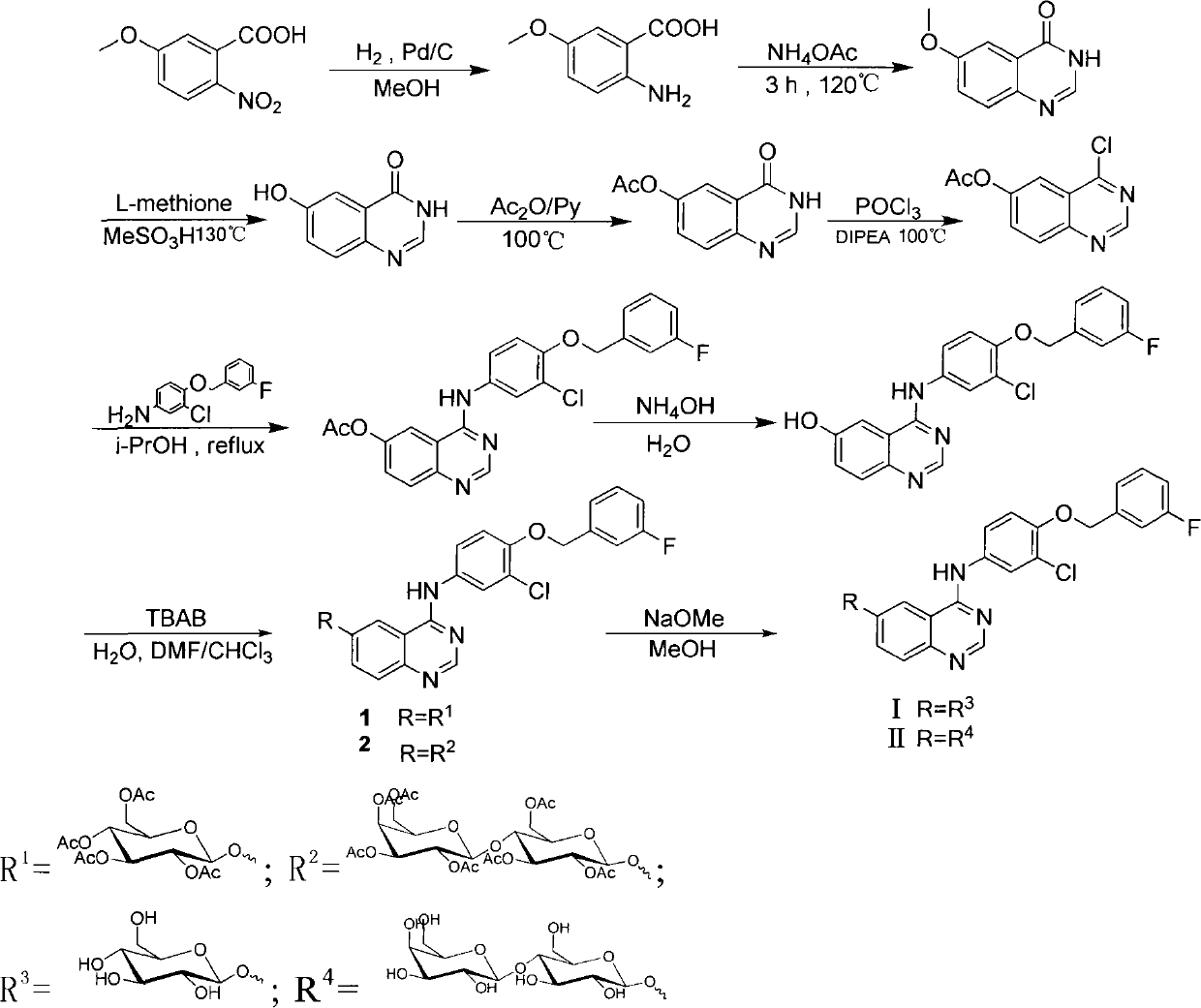
Series of quinazoline sugar derivatives used as protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101857618ASolve the problem of low activity of inhibiting tyrosine kinaseGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilityProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
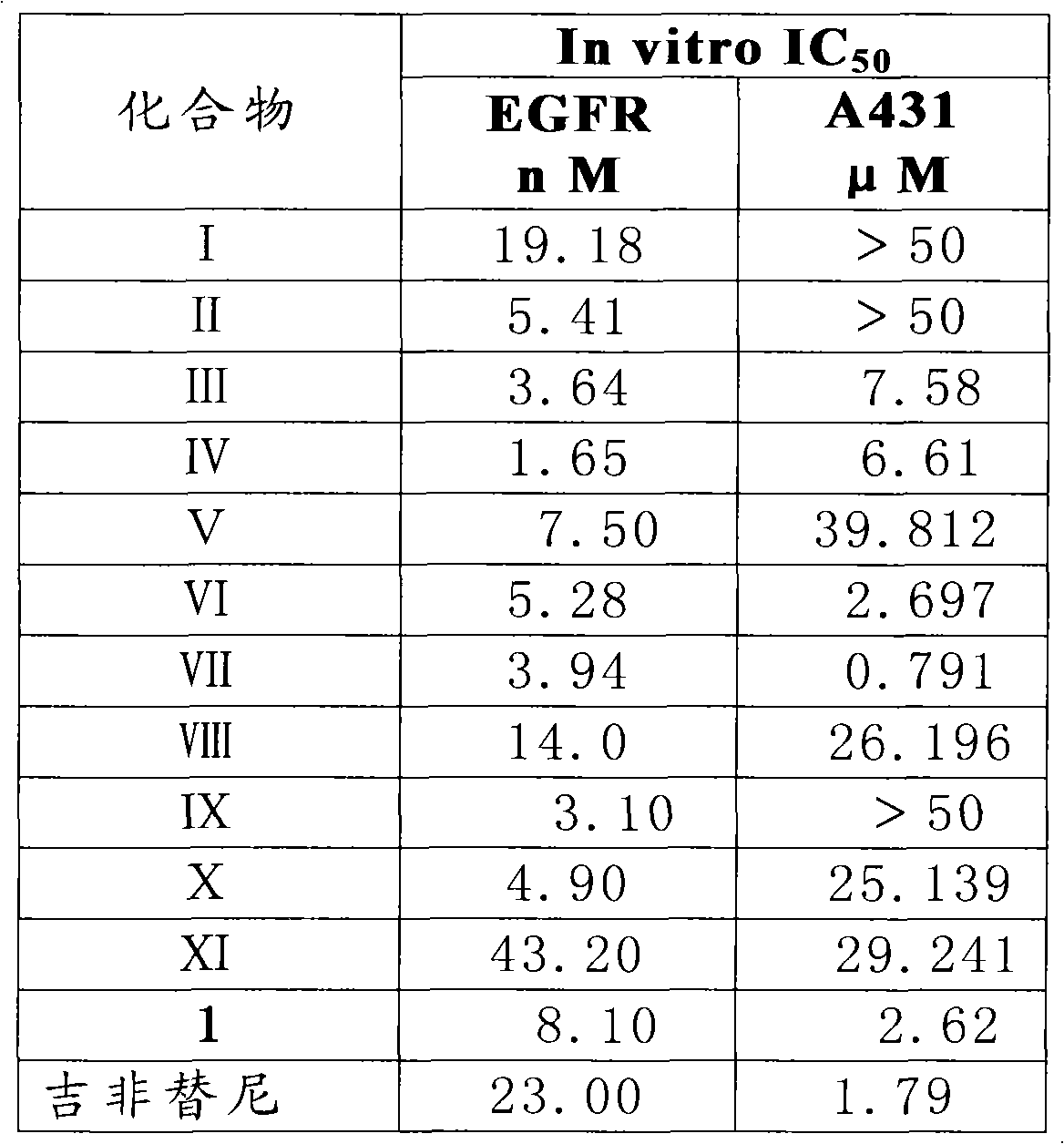
The invention provides a quinazoline sugar derivative and a preparation method and application thereof, which can solve the problem of low activity of inhibiting tyrosine kinase in the prior art. The prepared quinazoline sugar derivative has high water solubility and high activity of inhibiting human skin cancer cells A431, and can be used for preparing medicaments for preventing or treating tumors. The quinazoline sugar derivative provided by the invention is a kind of compounds which have novel structures and comprise abundant glycosyl group segments at a 6-bit side chain of a quinazoline parent ring, wherein the raw materials adopted in a method for performing glycosylation on quinazoline rings are readily available; the synthesis method is simple; the purification mode is simple and convenient and quick; and the quinazoline sugar derivative has high water solubility, high biological activity, particularly obvious activity of selectively inhibiting an EGFR, and obvious anti-tumor effect, so the kind of compounds has a wide application prospect in medicaments for preventing or curing tumors. The quinazoline sugar derivative comprises the following structural formula.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Combination of zeolite upgrading with hydrogenation upgrading to produce renewable gasoline from biomass
ActiveUS20120095274A1Low vapor pressureReduce cokingMolecular sieve catalystsRaney catalystAlkaneParaffin wax
Technologies to convert biomass to liquid hydrocarbon fuels are currently being developed to decrease our carbon footprint and increase use of renewable fuels. Since sugars / sugar derivatives from biomass have high oxygen content and low hydrogen content, coke becomes an issue during zeolite upgrading to liquid hydrocarbon fuels. A self-sustainable process was designed to reduce the coke by co-feeding sugars / sugar derivatives with the paraffin products from hydrogenation of sugars / sugar derivatives. Paraffins without complete conversion result in products with less aromatics and relatively low density compared with the products directly from zeolite upgrading. Thus, the process is more economically favorable.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Process for the modification of a glycoprotein using a glycosyltransferase that is or is derived from a ß(1,4)-n-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
ActiveUS20170130256A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsN-AcetylgalactosaminyltransferasesN-Acetylgalactosamine
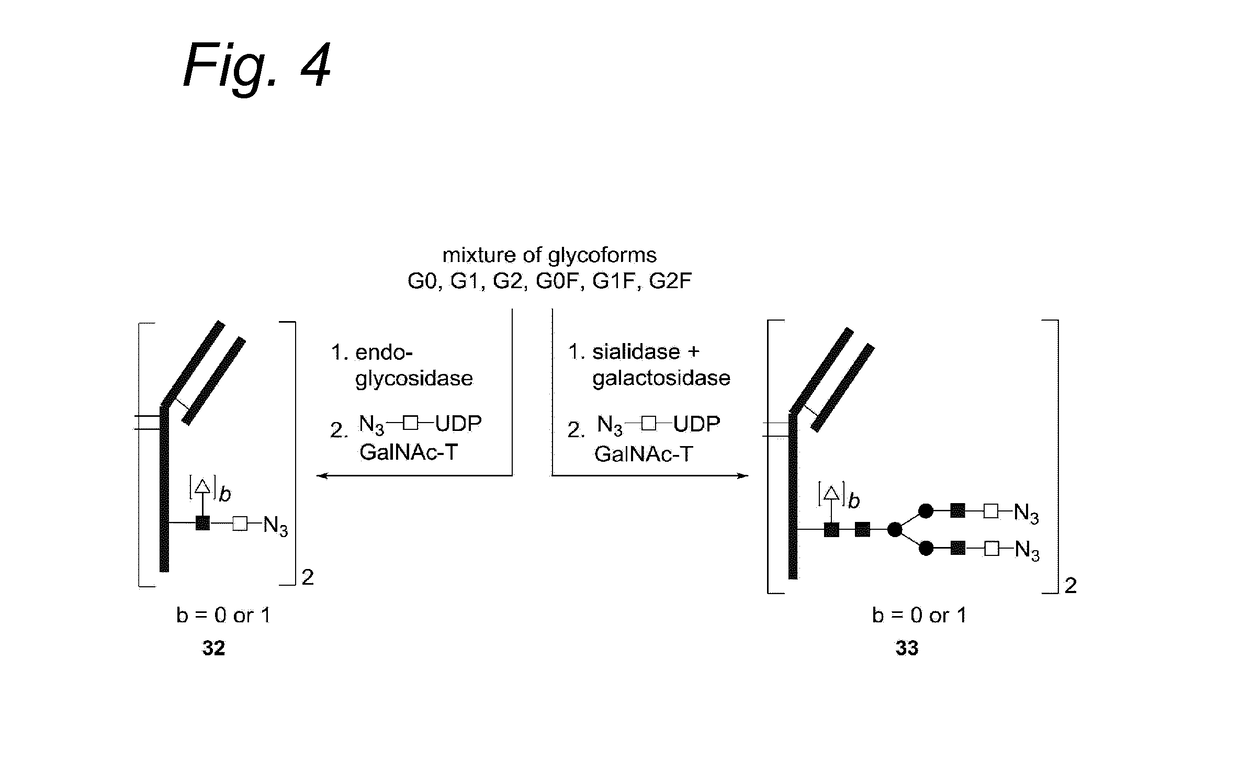
The present invention relates to a process for the enzymatic modification of a glycoprotein. The process comprises the step of contacting a glycoprotein comprising a glycan comprising a terminal GlcNAc-moiety, in the presence of glycosyltransferase that is, or is derived from, a β-(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, with a non-natural sugar-derivative nucleotide. The non-natural sugar-derivative nucleotide is according to formula (3): wherein A is selected from the group consisting of —N3, —C(O)R3, —(CH2)iC≡C—R4, —SH, —SC(O)R8, —SC(0)OR8, —SC(S)OR8, —F, —CI, —Br —I, —OS(O)2R5, terminal C2-C24 alkenyl groups, C3-C5 cycloalkenyl groups, C4-C8 alkadienyl groups, terminal C3-C24 allenyl groups and amino groups. The invention further relates to a glycoprotein obtainable by the process according to the invention, to a bioconjugate that can be obtained by conjugating the glycoprotein with a linker-conjugate, and to β-(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases that can be used in preparing the the glycoprotein according to the invention.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels as well as preparation and application of pharmaceutical composition of amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier
ActiveCN104971353AImprove stabilityImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWater insolubleVascular endothelium
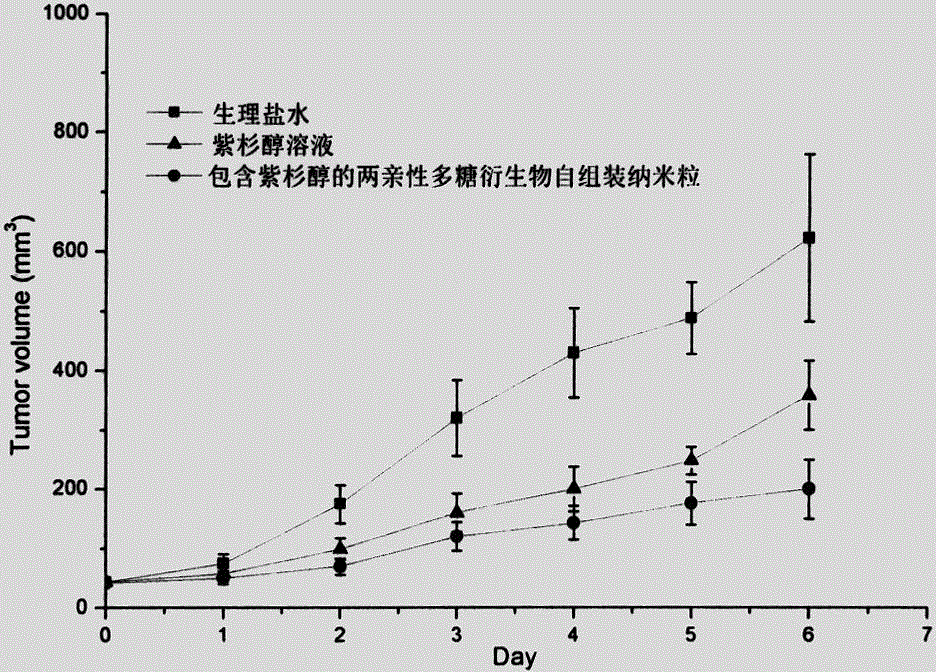
The invention relates to an amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels. According to the derivative, a polysaccharide skeleton is coupled with functional polypeptide targeting E-selectin by virtue of a disulfide bond to ensure that polysaccharide has amphipathy, and is assembled into nano particles for targeting the tumor new blood vessels after carrying an antitumor drug or a tumor new blood vessel inhibitor in an aqueous medium. The nano particles deliver medicines to the tumor new blood vessels in an active targeting manner by virtue of the high affinity between the functional polypeptide targeting the E-selectin and the E-selectin on the surface of the tumor new blood vessels, then a disulfide bond connecting arm can be specifically degraded by a strong reducing environment in endothelial cells of the tumor new blood vessels to cause that the functional polypeptide targeting the E-selectin is separated from polysaccharide, and the medicines are quickly released to treatment target points, so that the concentration of free medicines at tumor new blood vessel parts can be significantly improved and the antitumor curative effect is enhanced. An auxiliary material can be used as a carrier for water-insoluble, indissolvable or amphiphilic antitumor drugs and the tumor new blood vessel inhibitor, and is administrated by injecting into blood vessels or muscles, or is administrated orally or externally. The amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier provided by the invention is simple in preparation method, mature in process and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Quinazoline sugar derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101857617AHigh activityNovel structureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilitySynthesis methods
The invention provides a quinazoline sugar derivative and a preparation method and an application thereof, which are capable of solving the problems of low selection inhibitory activity and water solubility of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the prior art. The glycosylation method of the quinazoline sugar derivative to quinazoline ring in the invention has easily-obtained raw materials, simple synthesis method, simple and convenient purification mode, better bioactivity, especially obvious inhibitory activity on EGFR, and remarkable anti-tumor effect so that the compound has wide prospect in medicines to prevent or cure tumors. The quinazoline sugar derivative has a structure formula as shown in the specification.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Use of fabric conditioning compositions for ironing benefits
InactiveUS20010006938A1Non-ionic surface-active compoundsDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesPolyolEther
The present invention provides the use of a fabric treatment composition to provide anti-creasing properties and / or ease or ironing benefits to a fabric wherein said composition comprises; (i) an oily sugar derivative which is a liquid or soft solid derivative of a cyclic polyol or of a reduced saccharide, said derivative resulting from 35 to 100% of the hydroxyl groups in said polyol or in said saccharide being esterified or etherified, wherein said derivative has two or more ester or ether groups independently attached to a C8-C22 alkyl or alkenyl chain, and (ii) one or more deposition aid(s). According to a further aspect the present invention provides a method of reducing the creasing of fabric by applying thereto during a laundering operation the composition defined above, and a method of providing ease of ironing benefits by applying thereto during a laundering operation the composition defined above.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
Agent for enhancing collagen production and utilization of the same
InactiveCN101232891APrevent agingGuaranteed continuous useCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTTrehalose
It is intended to provide a means exerting a prolonged effect of enhancing the production of collagen. This object can be achieved by an agent for enhancing collagen production which contains, as the active ingredient, alpha, alpha-trehalose and / or a sugar derivative of alpha, alpha-trehalose, or a composition for enhancing collagen production which contains the agent for enhancing collagen production as described above.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
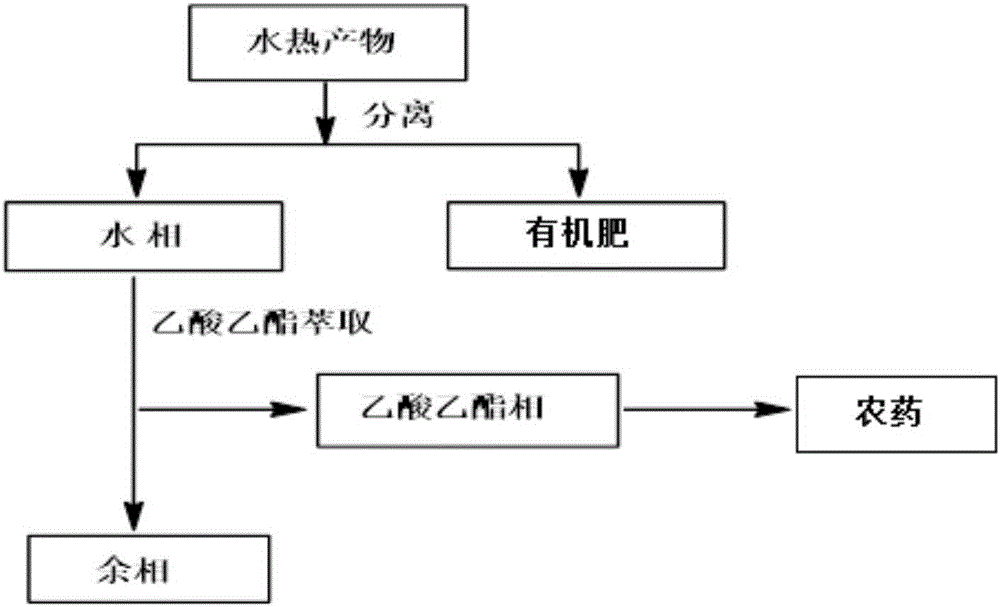
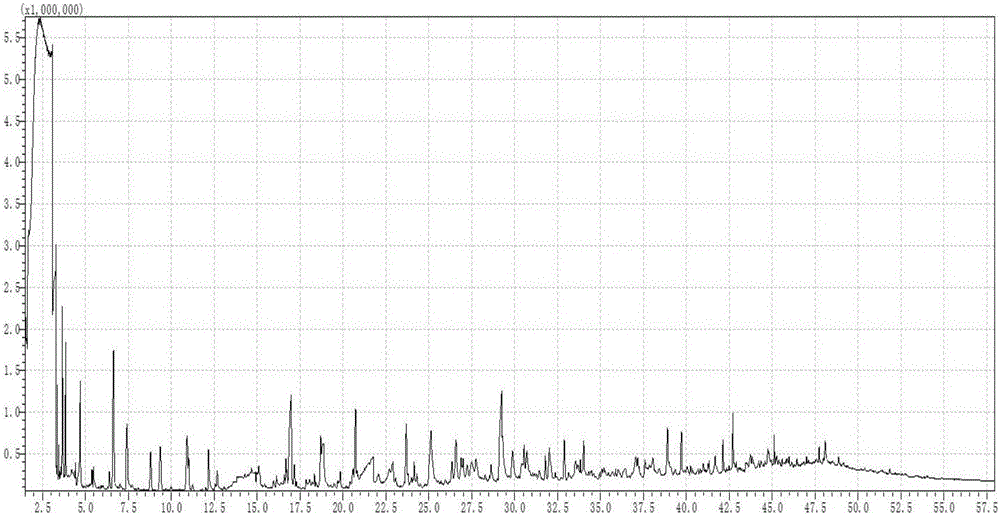
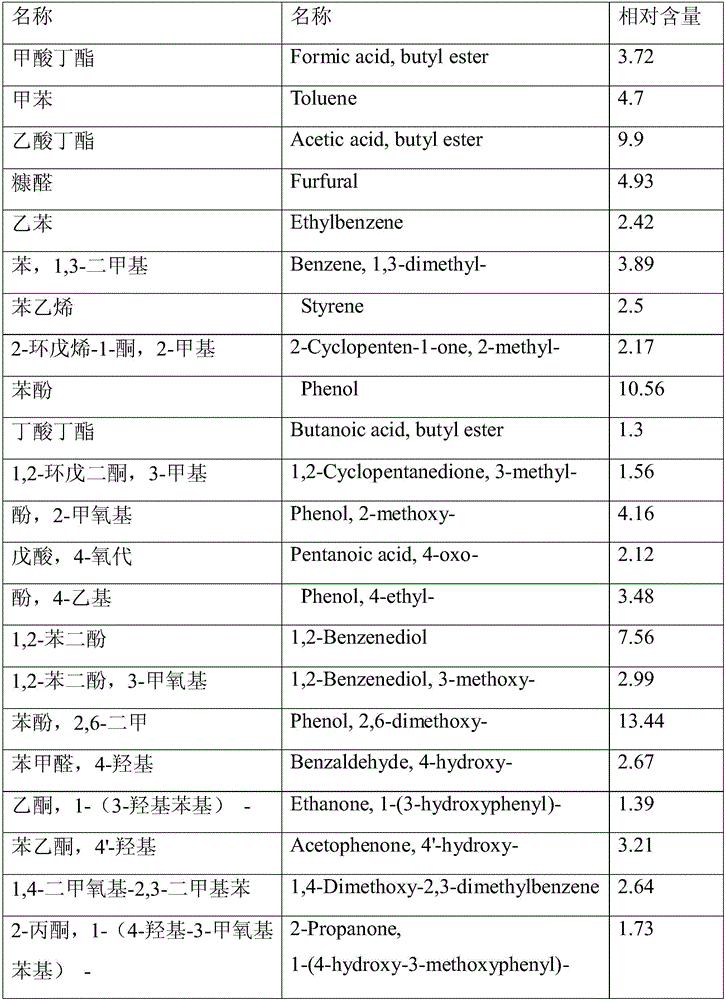
Method for preparing pesticide by using biomass hydrothermal carbonization liquid phase and preparing organic fertilizers by using solid phase
InactiveCN105900984AFix instabilitySimple reactivityBiocideBiofuelsResource utilizationHigh pressure
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomass resource utilization, and discloses a method for preparing pesticide by using biomass hydrothermal carbonization liquid phase and preparing organic fertilizers by using solid phase. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing biomass raw materials with water to obtain a biomass aqueous solution; then adding the biomass aqueous solution in a high-pressure reactor; replacing air in the reactor by using inert gas or hydrogen; heating to the temperature of 200-300 DEG C; carrying out constant-temperature hydrothermal carbonization reaction under the condition of stirring; filtering or centrifugally separating a reaction product; extracting the liquid phase with ethyl acetate and then preparing the pesticide; and drying the solid phase and then preparing the organic fertilizers. Compared with the traditional method for preparing pesticide and organic fertilizers by using biological oil water-phase component sugar and sugar derivatives, the method has the advantages of low energy consumption, mild reaction conditions, simple technological process, easiness in separation of the reaction products, environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process for dry-grinding a polysaccharide derivative
ActiveUS20120187225A1Energy optimizationHigh energyGrain treatmentsWet separationParticulatesPolysaccharide
In a process for producing a particulate polysaccharide derivative by dry-grinding a moist polysaccharide derivative the median length of the particles after dry-grinding is controlled by controlling the moisture content of the polysaccharide derivative prior to dry-grinding. Advantageously the median length of the particles after dry-grinding is adjusted to a first value by a first moisture content of the polysaccharide derivative prior to dry-grinding and is adjusted to a second value by a second moisture content.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 1 LLC
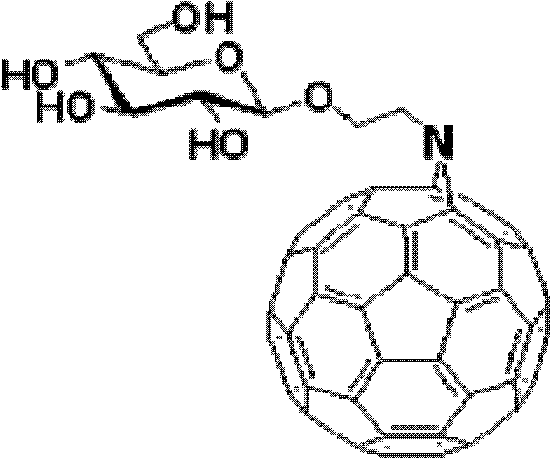
Fullerene polysaccharide derivative and its preparation method
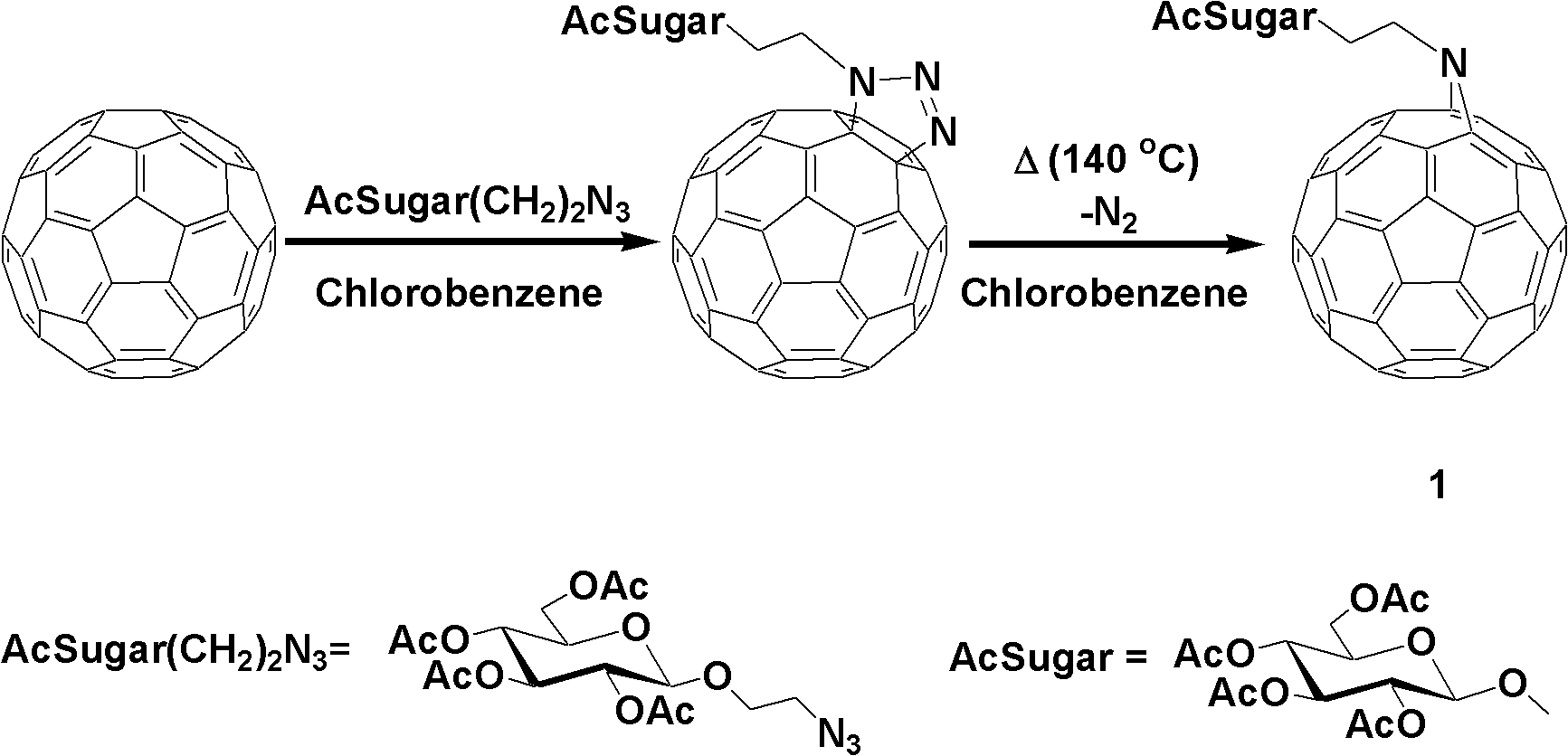
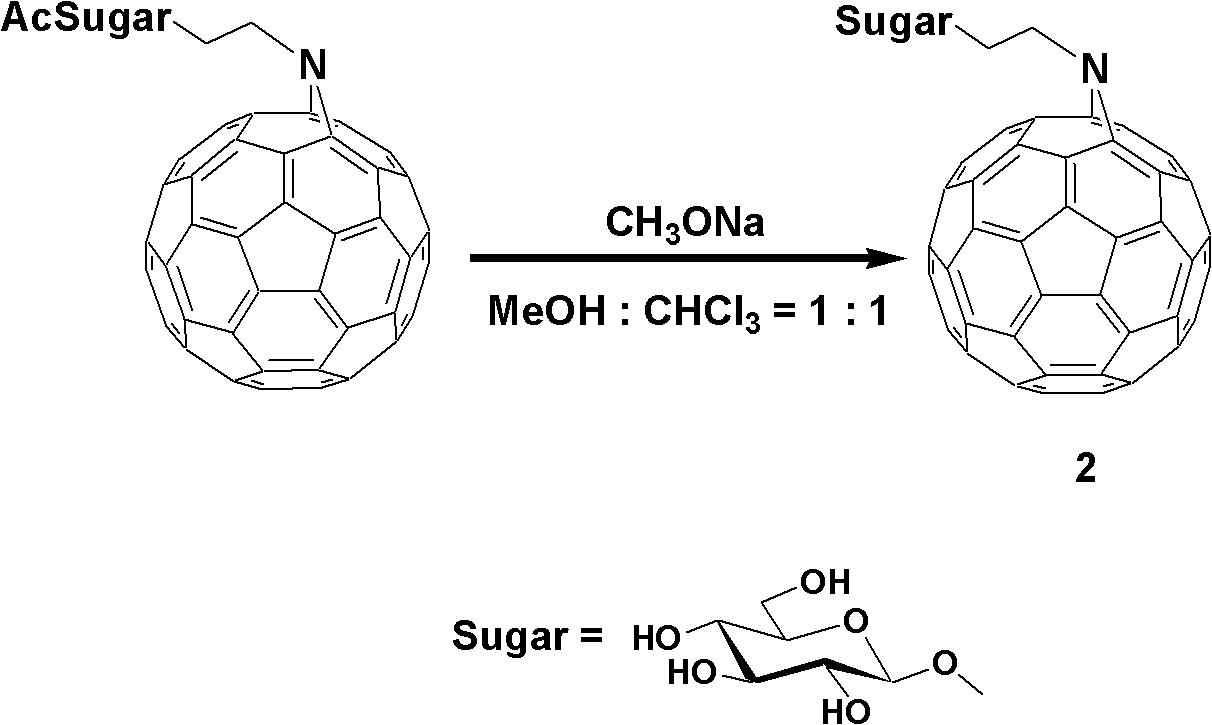
InactiveCN102627267AGood choiceImprove expectationsEnergy modified materialsFullerenesSodium methoxideChlorobenzene
The invention provides a fullerene polysaccharide derivative and its preparation method. The method comprises: adding 2-azidoethyl-2, 3, 4, 6-tetra-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside and fullerene in a mole ratio of 1:1, dissolving them with chlorobenzene, conducting shading stirring for 12h at a temperature of 140DEG C and under inert gas protection; carrying out reduced pressure distillation so as to obtain tawny powder; dissolving the obtained tawny powder in a mixed solvent of chloroform and methanol that are in a ratio of 1:1, adding sodium methoxide until the pH reaches 9, and performing stirring for 30min under a temperature of 60DEG C; implementing neutralization with 25% acetic acid, then standing the mixture under refrigeration; and conducting filtration, then carrying out washing with methanol as well as vacuum drying, thus obtain the fullerene polysaccharide derivative. With fullerene and glucose as raw materials, the method of the invention synthesizes the fullerene polysaccharide derivative with nontoxicity to human bodies and good biological compatibility. The unique cancer cell-killing capability of the derivative can substantially improve the medical treatment level of mankind in treating bladder cancers.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Process for preparing flavonoids
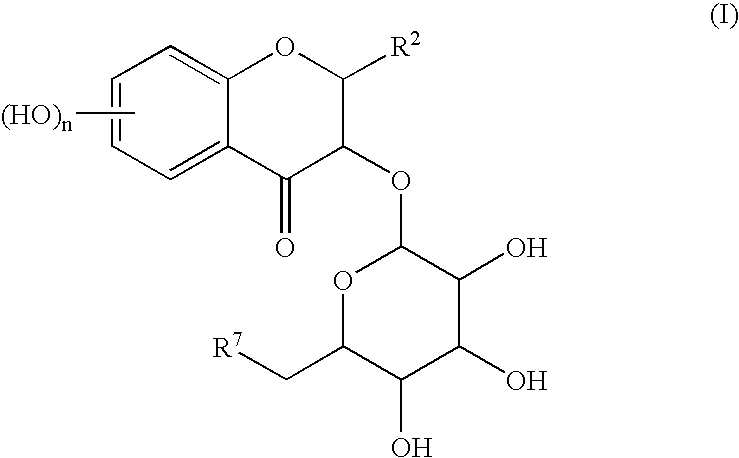
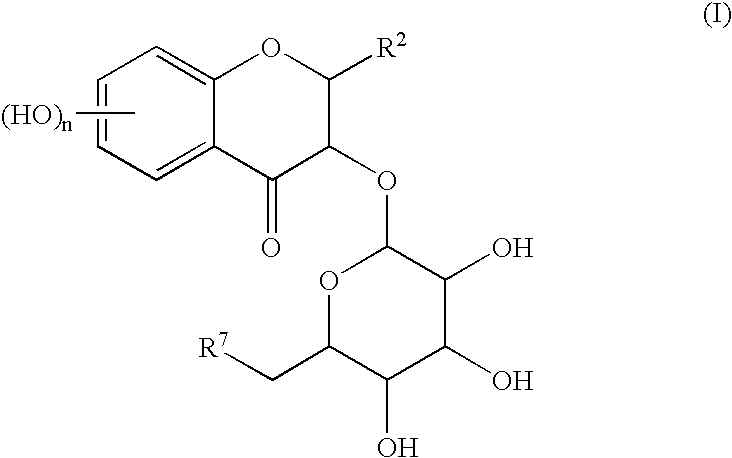
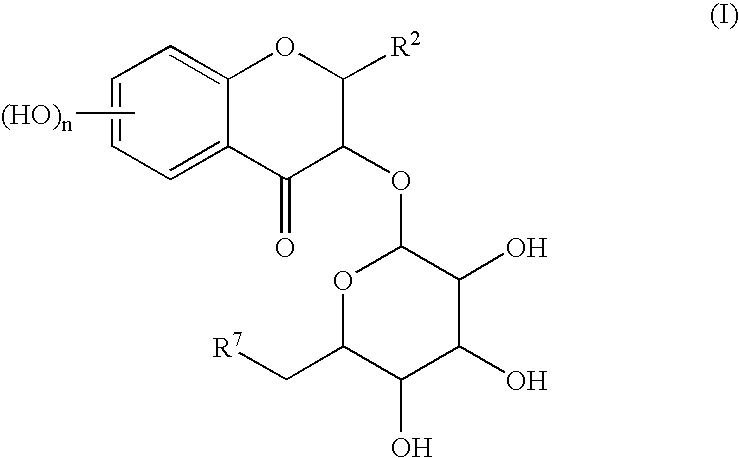
InactiveUS6706865B2High yieldPresent invention is superior oneSugar derivativesGlycosidesPhenyl groupActive oxygen
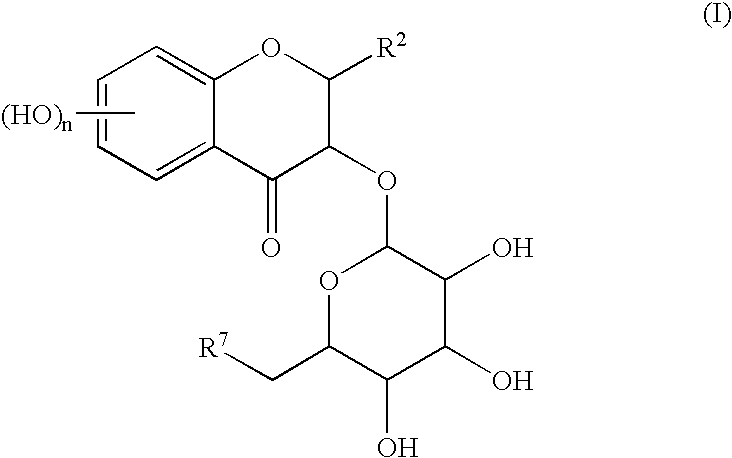
A simple and easy process for preparing pharmacologically useful flavonoid compound having reductase inhibitory effect, active oxygen extinguishing effect, carcinogenesis promotion inhibitory effect, anti-inflammatory effect, and so on. Particularly, a process for preparing the compound of the formula (I):wherein, R<2 >is a substituted or un-substituted phenyl group; R<7 >is a hydrogen atom or a hydroxyl group; and n is an integer of 1 to 4;by bonding a sugar derivative to catechins as the starting compound selectively via O-glycoside bond and then oxidizing the 4-position of flavanoid skeleton of the obtained compound.
Owner:DAIICHI SUNTORY PHARMA CO LTD
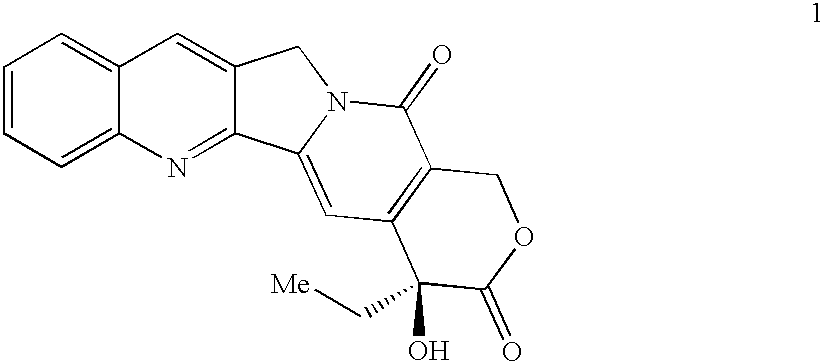
Topoisomerase I selective cytotoxic sugar derivatives of indolopyrrolocarbazoles
The present invention relates to fluoro sugar and other sugar derivatives of indolopyrrolocarbazoles, their salts and hydrates, which exhibit selective topoisomerase I (topo I) activity, are useful in inhibiting the proliferation of tumor cells and exhibit an antitumor effect, as well as processes for their preparation.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Modified antibody, antibody-conjugate and process for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20150320882A1Reduced potencyDamage bindingImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody conjugateN-Acetylglucosamine
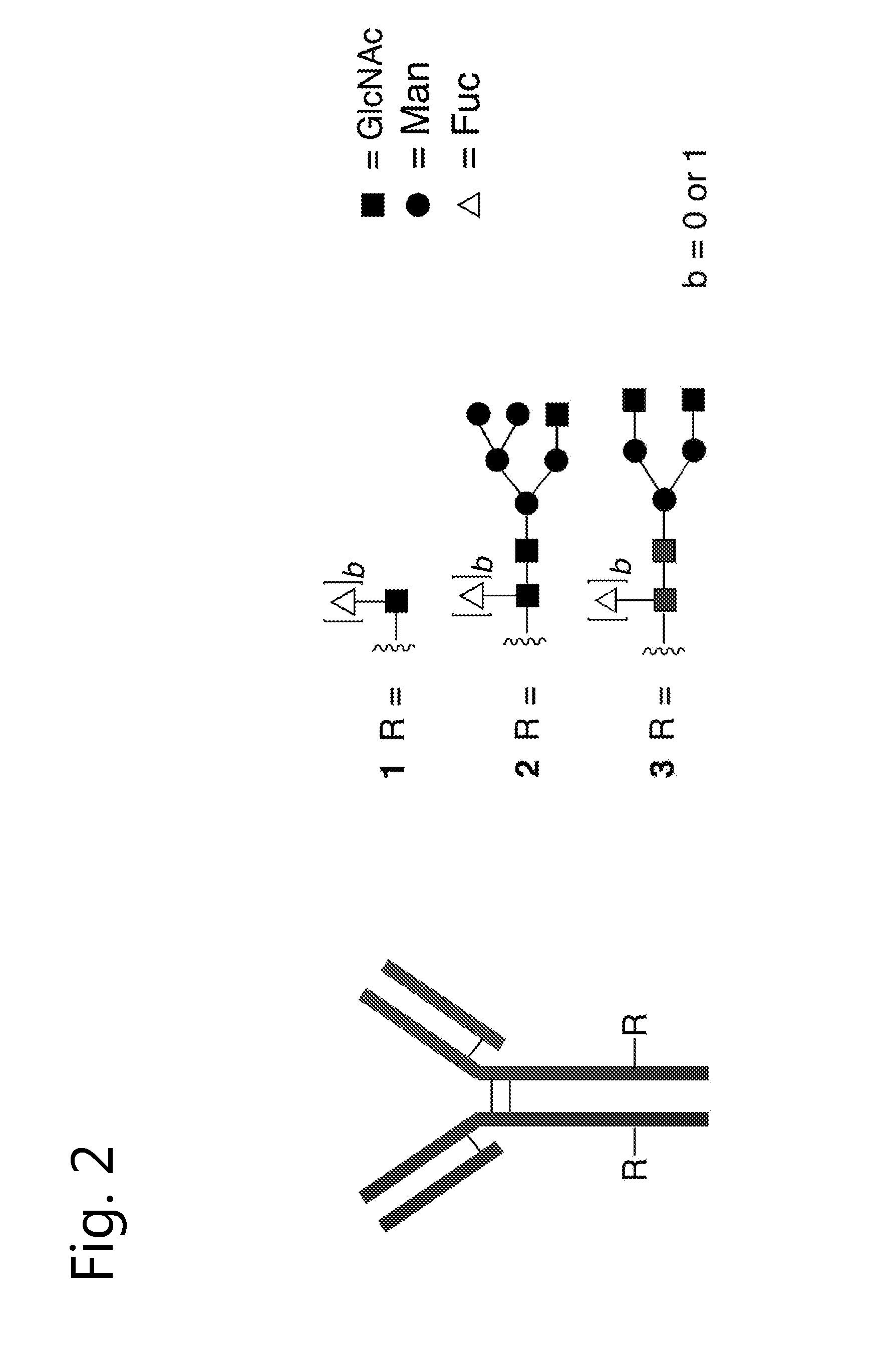
An antibody comprising a GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent is disclosed, wherein S(A)x is a sugar derivative comprising x functional groups A wherein A is independently selected from the group consisting of an azido group, a keto group and an alkynyl group and x is 1, 2, 3 or 4, wherein said GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent is bonded to the antibody via C1 of the N-acetylglucosamine of said GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent, and wherein said N-acetylglucosamine is optionally fucosylated. Also disclosed is an antibody-conjugate, in particular to an antibody-conjugate according to the Formula (20) or (20b), wherein AB is an antibody, S is a sugar or a sugar derivative, D is a molecule of interest, and wherein said N-acetylglucosamine is optionally fucosylated (b is 0 or 1).Also disclosed is a process for the preparation of a modified antibody, to a process for the preparation of an antibody-conjugate, and to said antibody-conjugate for use as a medicament.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Hair Styling Cosmetic Composition
InactiveUS20130164246A1Maintain good propertiesLow viscosityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsInorganic saltsAlcohol sugars
To provide a hair styling cosmetic composition which is excellent in hair styling property and hair restyling property, even though having a low viscosity, and is excellent in non-stickiness, smoothness, and light finish of the hair. A hair styling cosmetic composition comprising (a) one or more substances being solid at room temperature (25° C.) selected from among (a1) a sugar alcohol, (a2) a sugar, (a3) a polyalkylene glycol polymer, and (a4) an inorganic salt, in an amount of from 0.1 to 20 by mass, (b) a sugar derivative and / or a sugar alcohol derivative being liquid at room temperature in an amount of from 0.1 to 25 by mass, (c) one or more film-forming polymers selected from among acrylic and vinylic film-forming polymers (but excepting ampholytic polymers) and urethanic polymers, in an amount of from 0.1 to 12 by mass, and (d) an aqueous solvent, wherein the viscosity of the system is at most 10,000 mPa·s (at 25° C. with B-type viscometer).
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
Antibody-conjugates with improved therapeutic index for targeting cd30 tumours and method for improving therapeutic index of antibody-conjugates
ActiveUS20190262468A1High indexGreat therapeutic indexTetrapeptide ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody conjugatePhosphoric acid
The present invention concerns novel and improved antibody-conjugates for targeting CD30. The inventors found that when antibody-conjugates were prepared using a specific mode of conjugation, they exhibit an improved therapeutic index. The mode of conjugation comprises a first step (i) of contacting a glycoprotein comprising 1-4 core N-acetylglucosamine moieties with a compound of the formula S(F1)x-P in the presence of a catalyst, wherein S(F1)x is a sugar derivative comprising x functional groups F1 capable of reacting with a functional group Q1, x is 1 or 2 and P is a nucleoside mono- or diphosphate, and wherein the catalyst is capable of transferring the S(F1)x moiety to the core-GlcNAc moiety, to obtain a modified antibody; and a second step (ii) of reacting the modified antibody with a linker-conjugate comprising a functional group Q1 capable of reacting with functional group F1 and a target molecule D connected to Q1 via a linker L2 to obtain the antibody-conjugate wherein linker L comprises S—Z3-L2 and wherein Z3 is a connecting group resulting from the reaction between Q1 and F1. The invention also relates to a use for improving the therapeutic index of an antibody-conjugate and to a method for targeting CD30-expressing cells.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
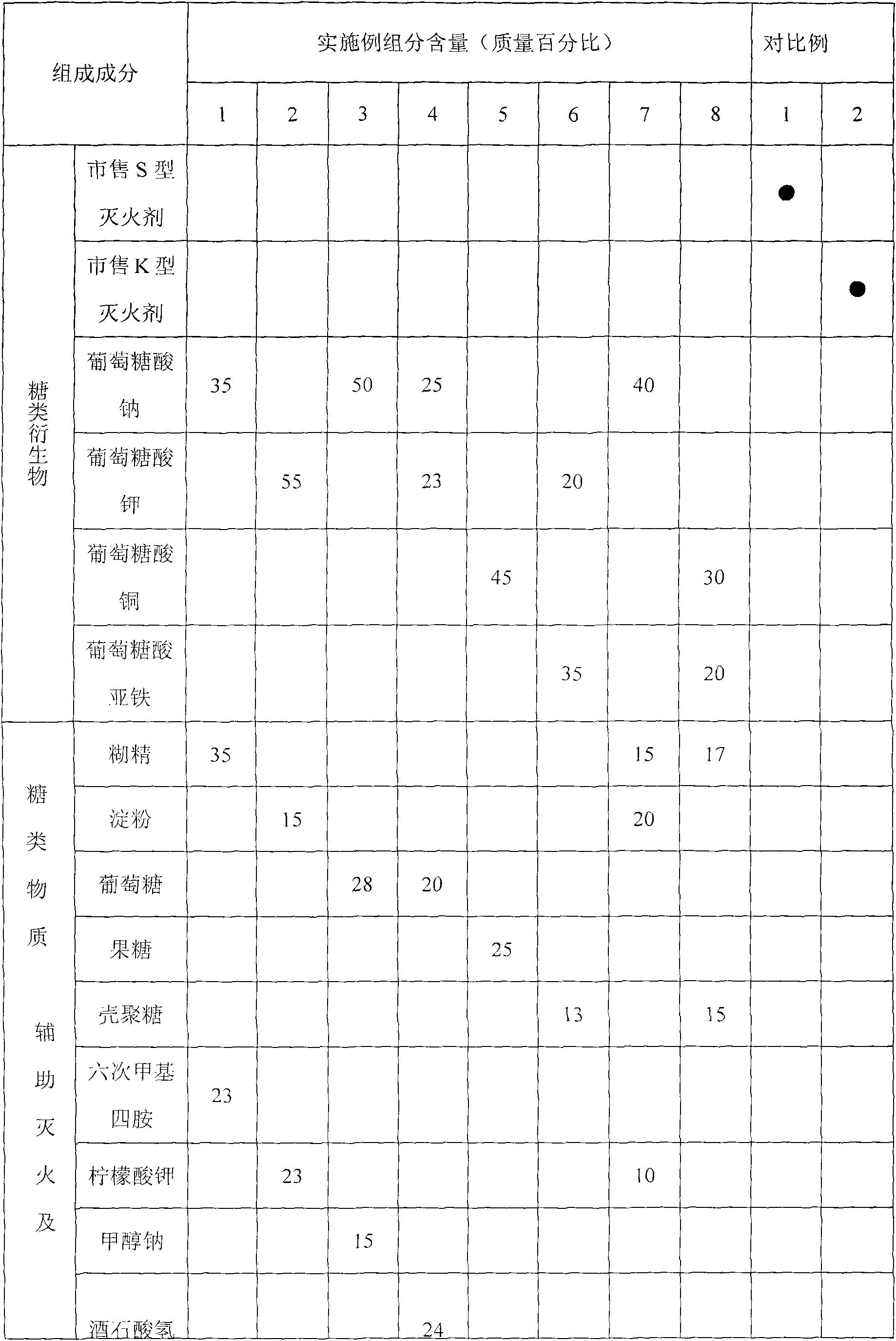
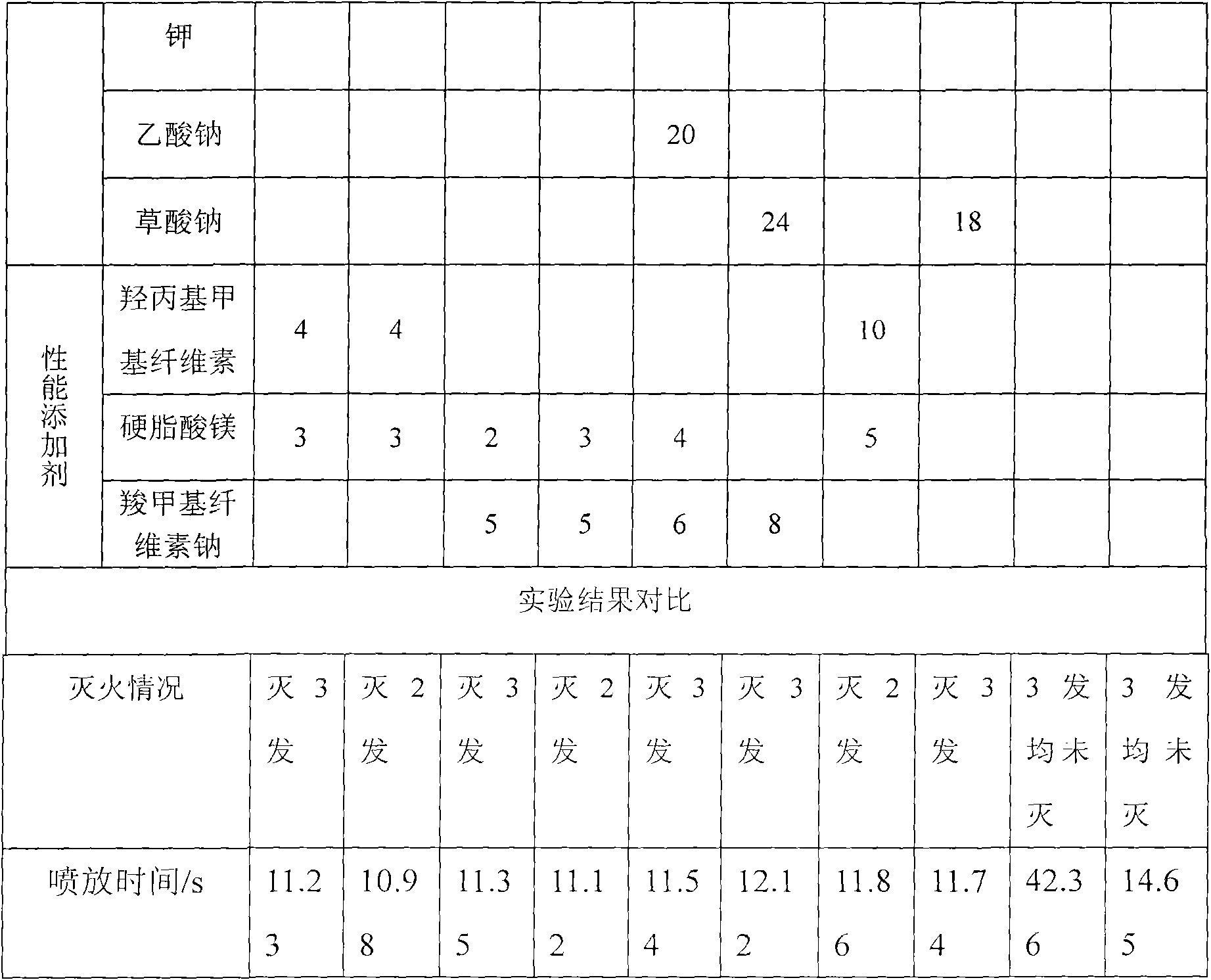
Fire-extinguishing composition containing sugars and sugar derivatives
ActiveCN103170087AImprove fire extinguishing effectNo pollution in the processFire rescueFire extinguisherCombustionFireworks
The invention relates to a fire-extinguishing composition containing sugars and sugar derivatives. The fire-extinguishing composition comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 30-60% of sugar derivatives, 10-40% of sugars and 10-30% of assistant fire-extinguishing agent. In the fire-extinguishing composition, fireworks drug is used as heat source and power source; the fireworks drug is driven to decompose or react in heating by the high temperature of the combustion of the firework drug, and the generated fire-extinguishing substances are sprayed out together with the fireworks drug so as to extinguish fire. In the fire-extinguishing composition, sugars and sugar derivatives are used as the main materials, and fireworks drug is used as the heat source and power source, so that the fire-extinguishing composition is easy to decompose and generate nontoxic and harmless gas in heating, and is pollution-free after being sprayed; the effective using rate of each component is high, and the decomposed materials also can extinguish fire so as to generate synergistic function to the fireworks drug, therefore, the fire-extinguishing efficiency of the whole fire-extinguishing composition is improved.
Owner:YICHANG JI AN DUN FIRE FIGHTING TECH CO LTD
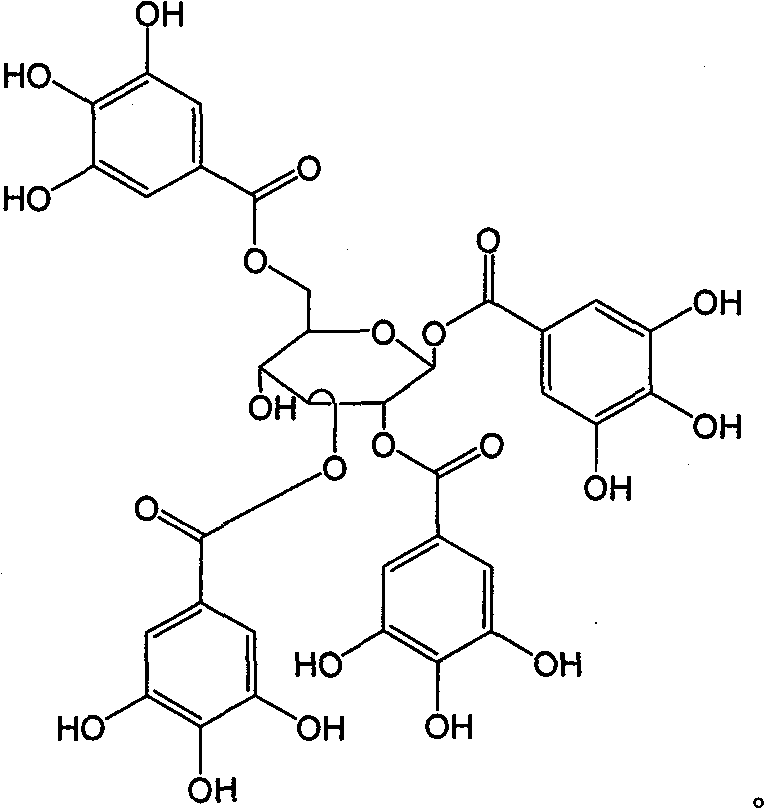
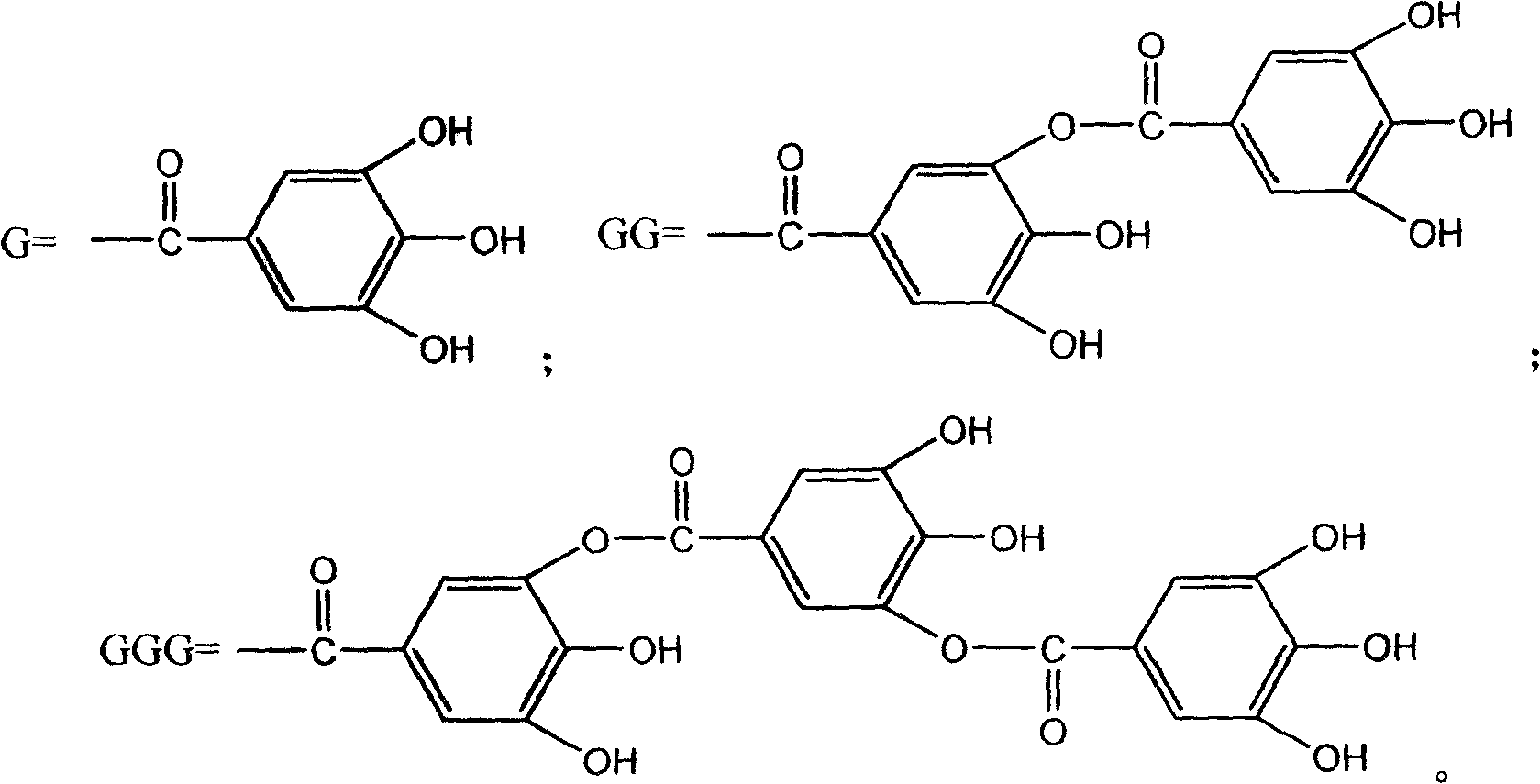
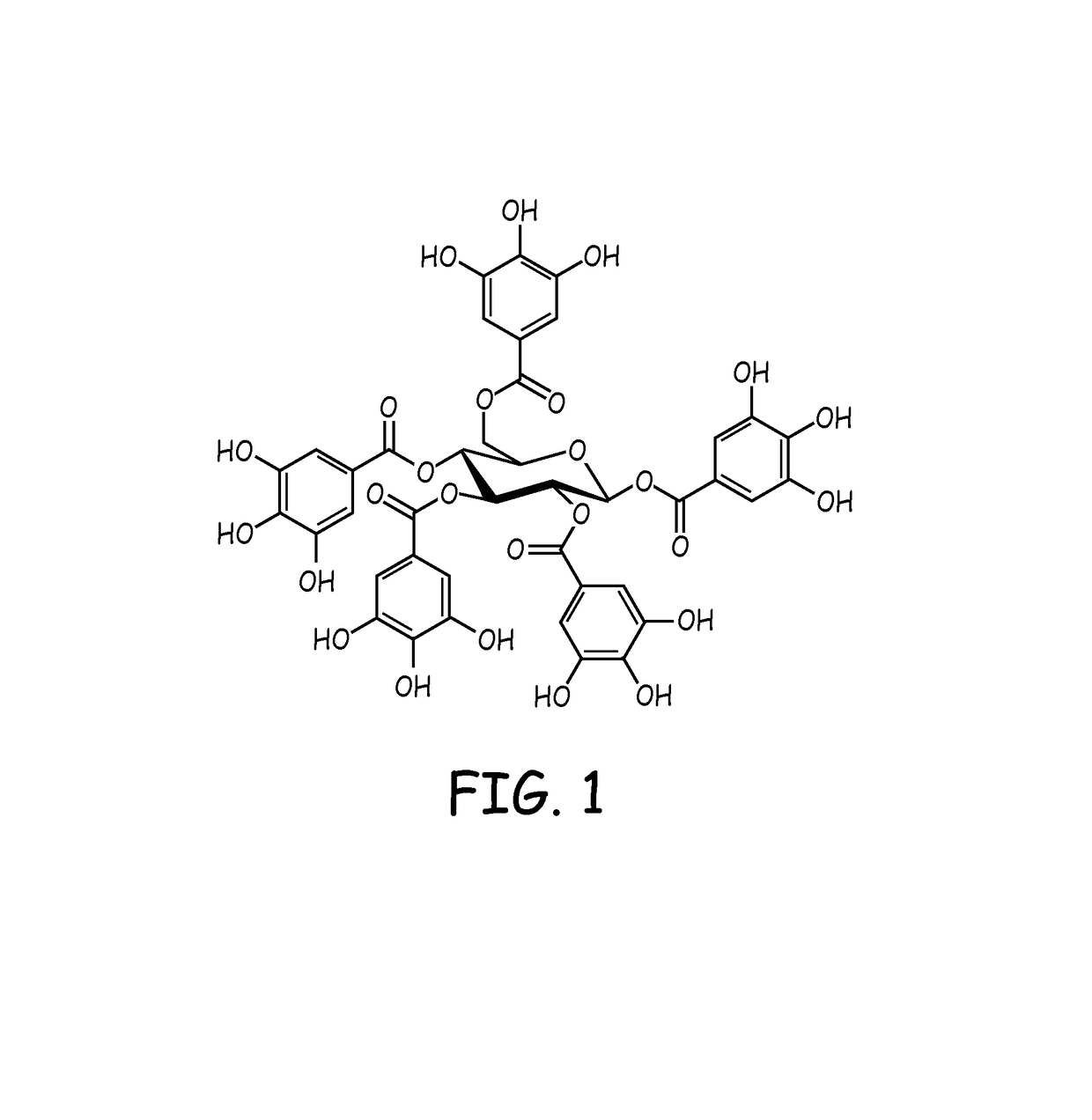
New use of polyhydroxy galloyl-beta-D-glucose derivatives
The invention relates to a usage of polyhydroxy galloyl-Beta-D-glucose derivatives or the medicinal salts in anti-helicobacter pylori, and the invention also relates to a usage of drugs which contain at least one extract of polyhydroxy galloyl-Beta-D-glucose derivative used for the prevention and / or treatment of diseases which are caused by helicobacter pylori.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD
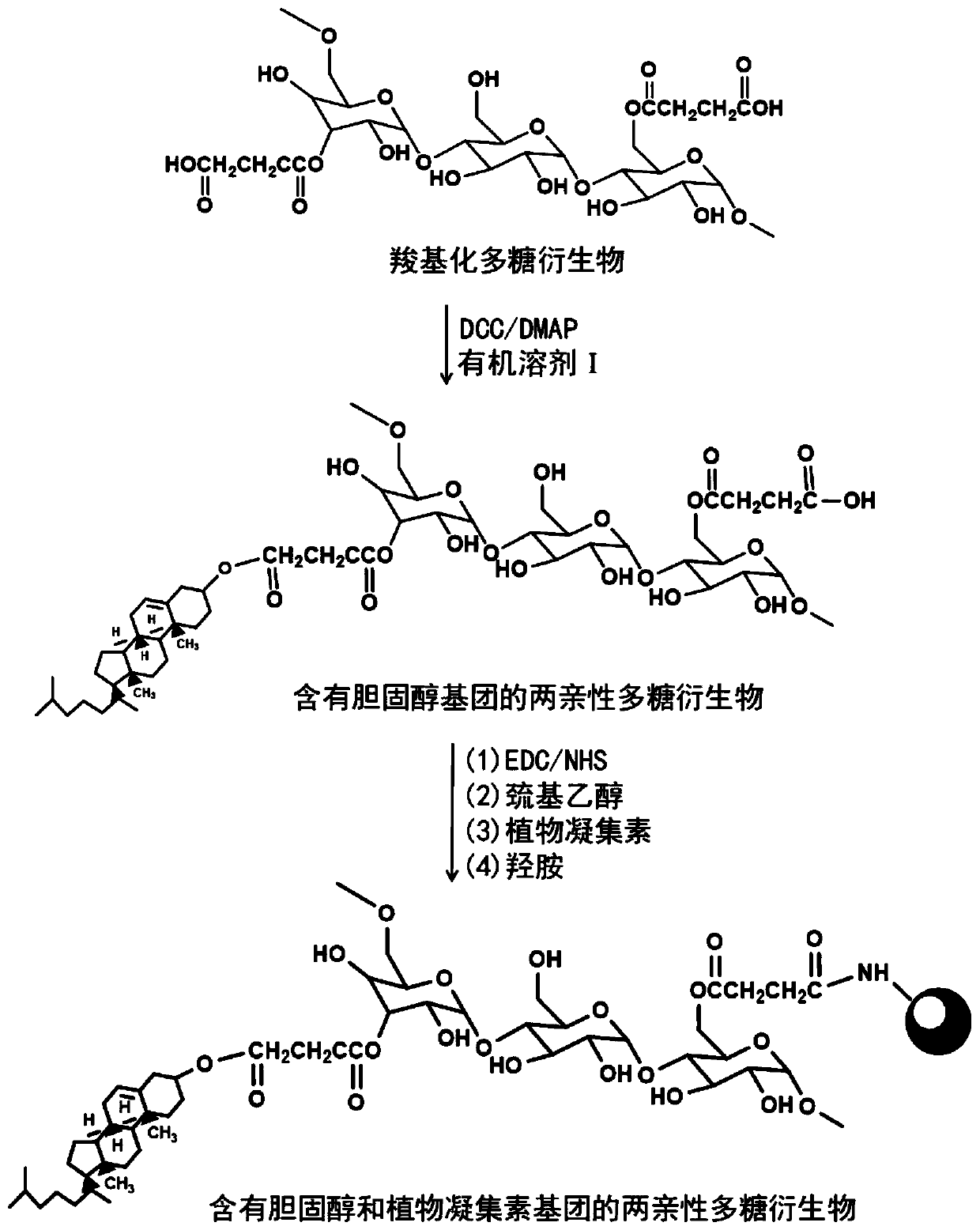
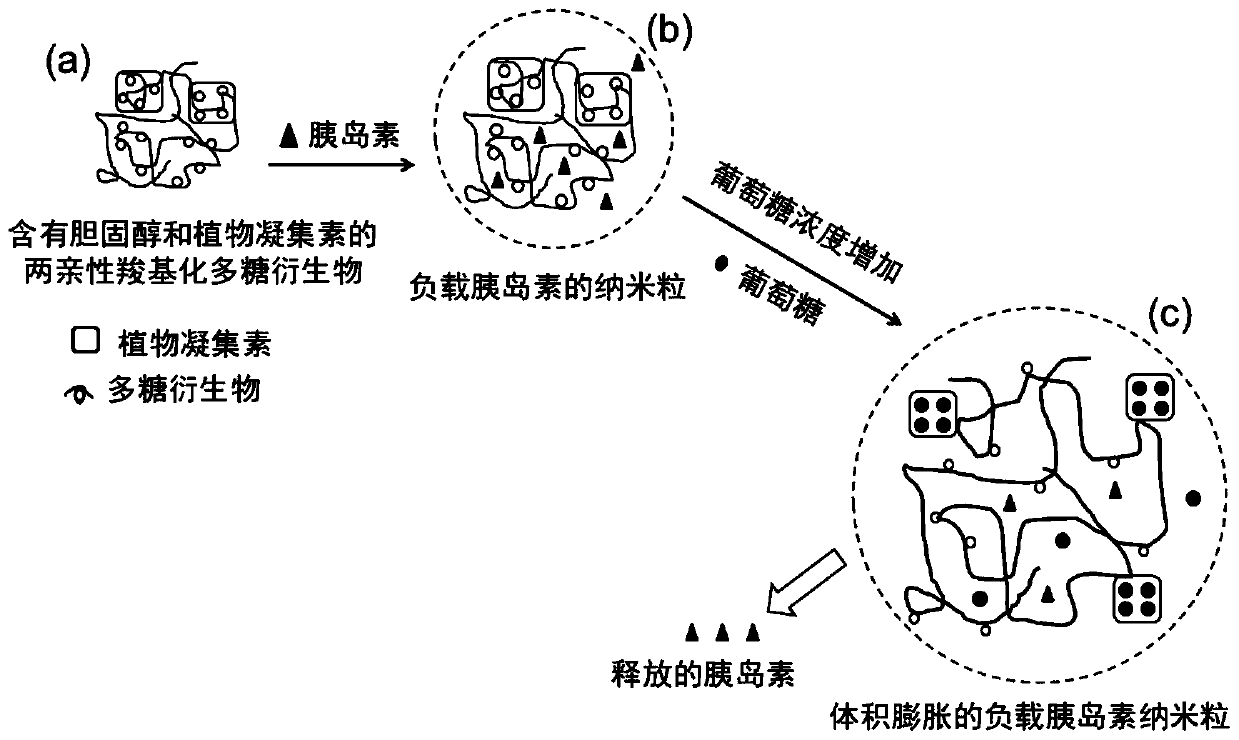
Amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative containing cholesterol and phytolectin group as well as preparation method and application of amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative
ActiveCN109879977ARelease intelligenceIncrease in sizePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCholesterolBlood sugar
The invention discloses an amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative containing cholesterol and phytolectin group as well as a preparation method and application of the amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative. According to the invention, firstly, an amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative containing cholesterol and a phytolectin group is synthesized; and further an insulin-loaded amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative nanoparticle with glucose responsiveness is synthesized. The capability of combining free glucose molecules in the surrounding environment of the phytolectin group in the nanoparticle ishigher than that of combining glucose groups on polysaccharide chains, so that the chain segments of the amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative become loose, the size of the nanoparticles is increased,insulin is released, and intelligent regulation and control are realized. The preparation conditions of the amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative and the nanoparticle are mild, the used raw materialsare safe, and the activity of specific binding of phytolectin to glucose molecules and the structural stability and biological activity of insulin are maintained. The amphiphilic nanoparticle for intelligently regulating and controlling insulin release prepared by the invention is expected to be used as an insulin delivery carrier, and can intelligently regulate and control insulin release according to the change of the blood glucose level in the body of a diabetes patient, so that the amphiphilic nanoparticle has a certain application prospect in the aspect of diabetes treatment.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
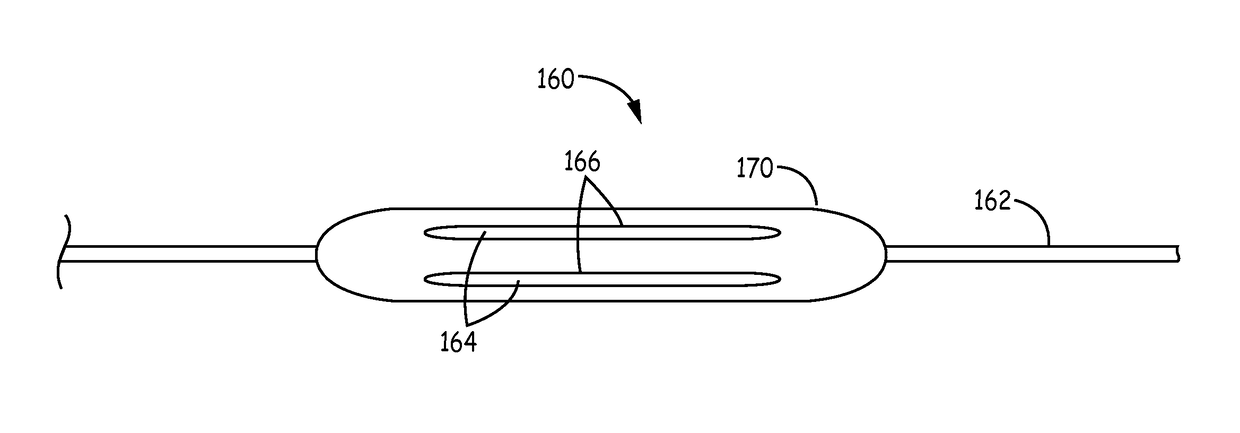
Coated balloons for blood vessel stabilization
A coated balloon device for stabilizing a section of a blood vessel in a living subject is disclosed. The coating layer of the coated balloon comprises a phenolic compound having a plurality of phenolic groups connected to form a hydrophobic core with peripheral phenolic hydroxyl groups. The coating layer of the coated balloon may contain a hydrophilic polymer to facilitate the release of the phenolic compound. The balloon in general is made of a compliant polymer for atraumatic contact with the blood vessel. In some embodiments, the coating of the coated balloon device further comprises a hydrophilic undercoat layer between the balloon and the coating layer. In some embodiments, the coated balloon device further comprises a sacrificial top coating that dissolves upon delivery into the section of the blood vessel and comprises a hydrophilic composition including sugar, sugar derivatives, or a combination thereof.
Owner:VATRIX MEDICAL INC
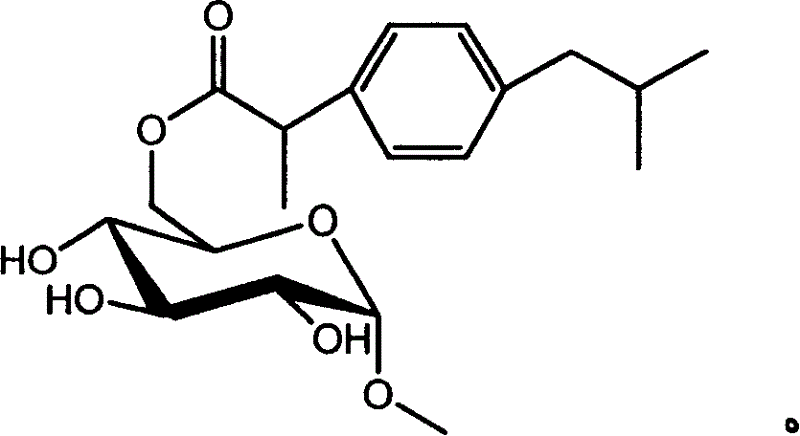
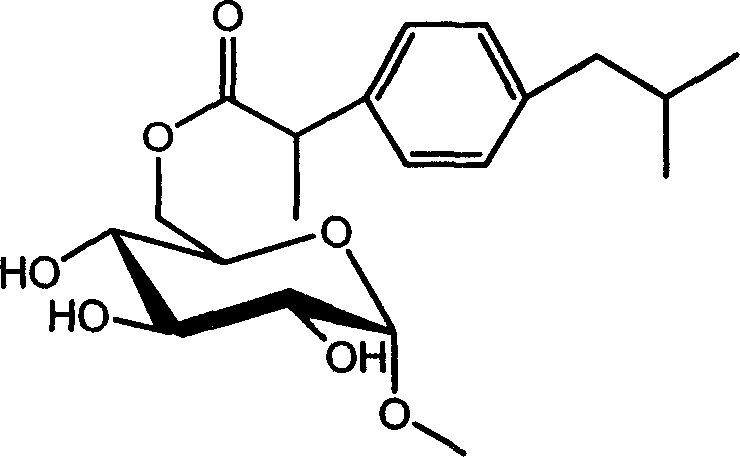
Ibuprofen sugar derivative and its preparing process and use
InactiveCN1683385AOvercome the disadvantages of complicated steps in the preparation methodOvercome the disadvantages of cumbersome stepsEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsPropanoic acidAlpha-methyl-D-glucoside
The present invention relates to ibuprofen sugar derivative and its preparation process and application. The present invention prepares the target compound through crosslinking unprotected alpha-methyl-D-glucoside and 2-(4'-isobutylphenyl)-propanoic acid with immobilized lipase. The present invention has simplified operation steps, mild reaction condition and high product purity, and may be used in industrial production. The ibuprofen sugar derivative of the present invention may be used in preparing medicine for treating rheumarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Its general structural expression is also given.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for comprehensive utilization of wood fiber all components
The invention discloses a method for comprehensive utilization of wood fiber all components. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, separating hemicellulose components by carrying out CO2-assisted hydrothermal liquefaction and mainly hydrolyzing the hemicellulose components into C5 sugar and a C5 sugar derivative; converting lignin into a phenolic product through a catalytic hydrogenation process; finally, dissolving out small amount of hemicellulose and lignin left in the wood fiber residues by carrying out alkaline hydrogen peroxide treatment, thus finally obtaining high-purity cellulose. In situ weak acid carbonic acid is formed by pressurizing carbon dioxide; a reactant is gradually acidized due to the dissociation of the carbonic acid; by use of the pressurization effect of the carbon dioxide, the permeability of a solvent to the wood fiber can be greatly improved. According to the method disclosed by the invention, various products of wood fiber components are obtained by separating and further the comprehensive utilization of the wood fiber all components is realized.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
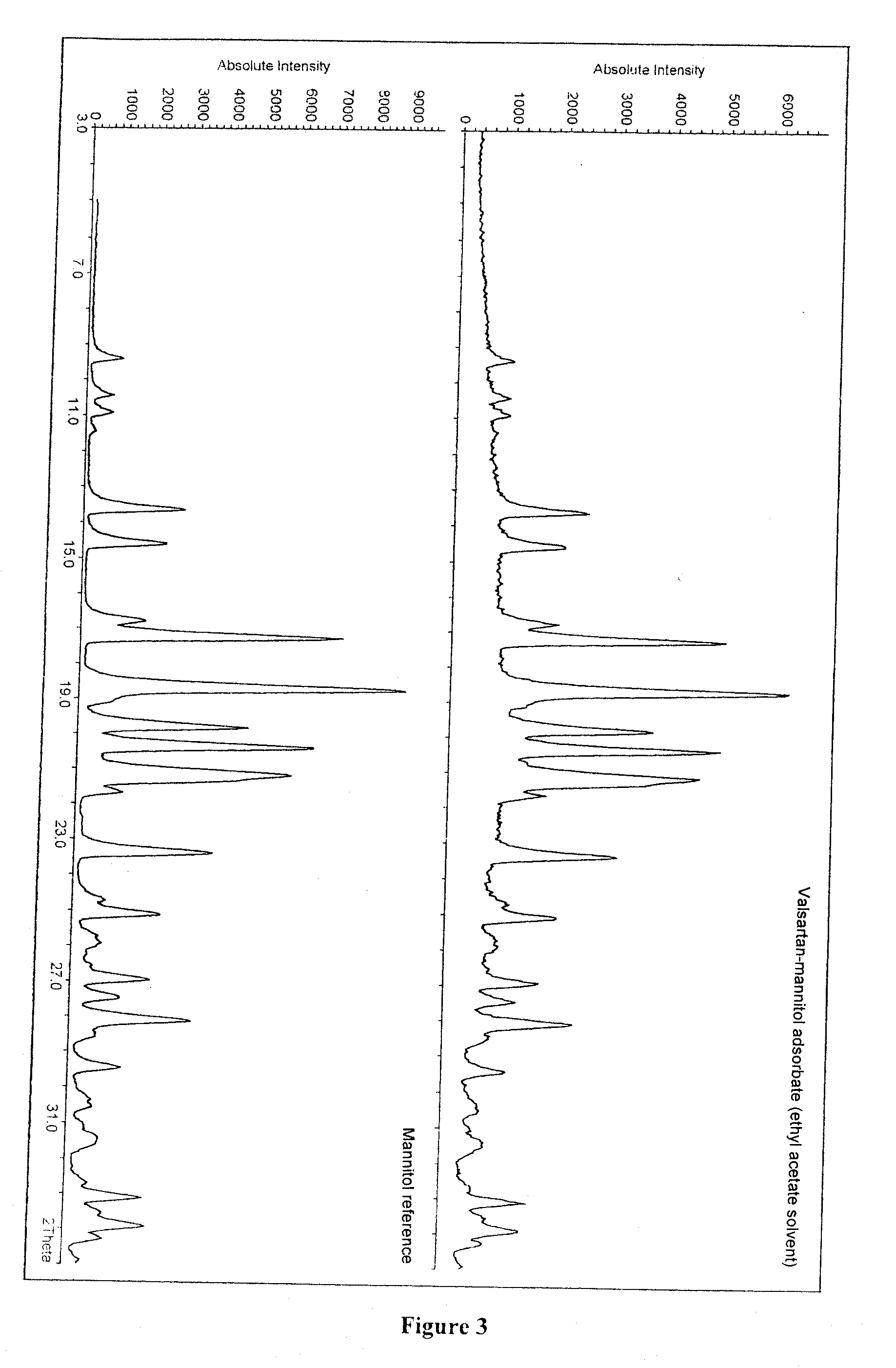
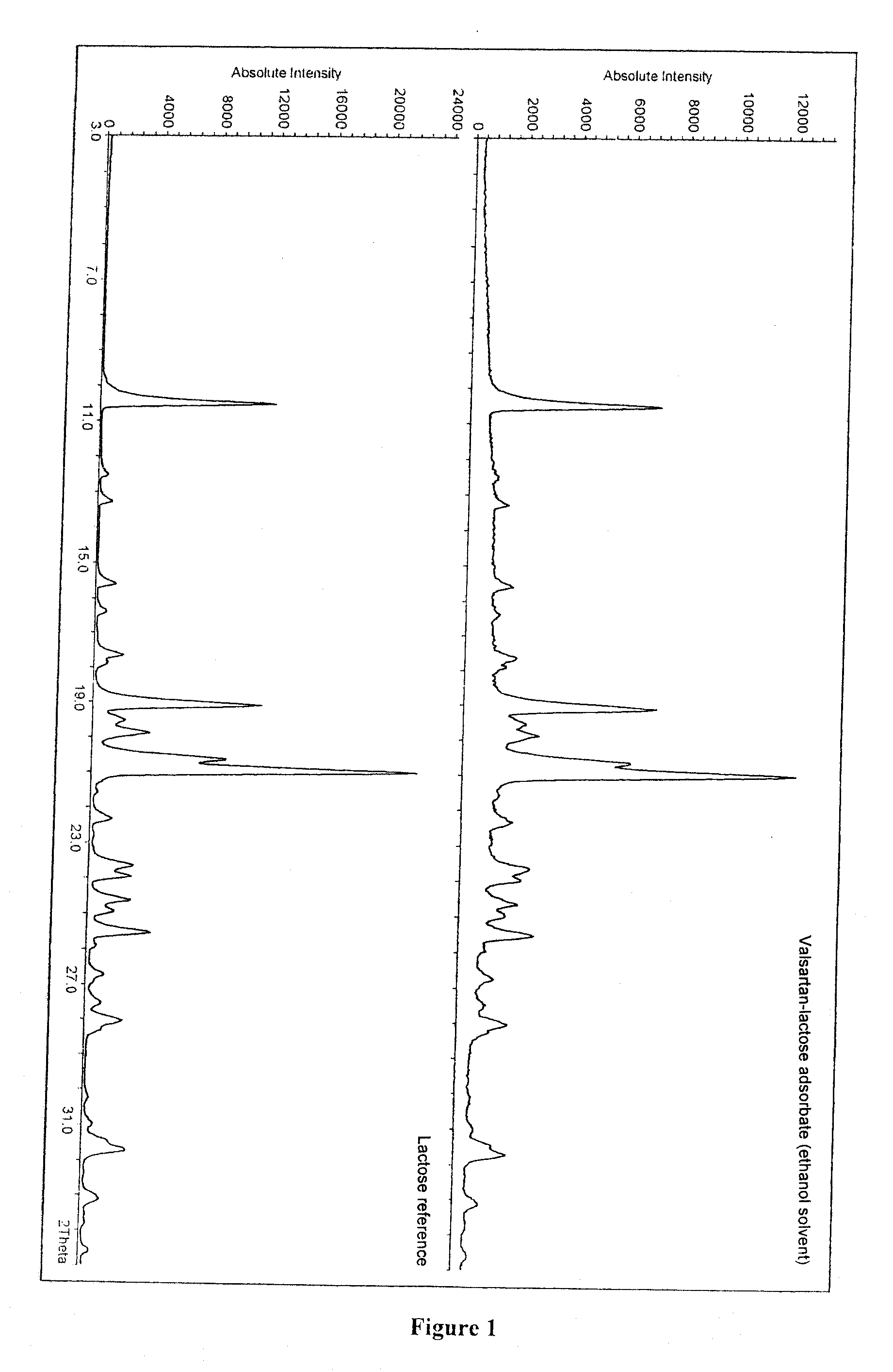
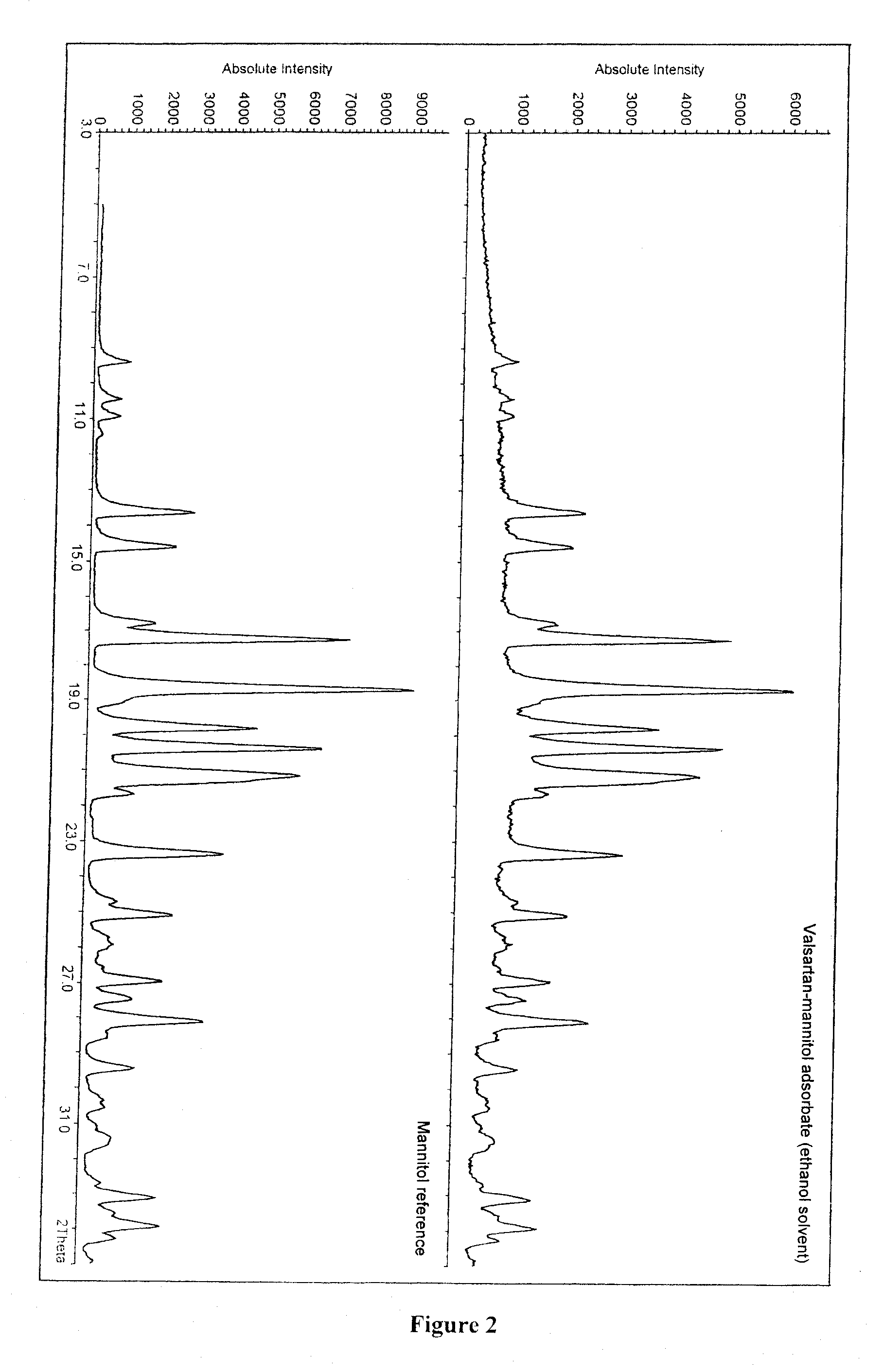
Process for the preparation of adsorbates of valsartan and/or its solvates or hydrates
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of adsorbates of valsartan and / or its solvates or hydrates wherein one starts with a solution of valsartan or of one of its pharmaceutically acceptable salts and / or their solvates or hydrates in at least one organic solvent where the total water content of the solvent is not higher than 15% by volume, preferably not higher than 5% by volume, disperses therein an adsorbing material selected from the group consisting of celluloses, cellulose derivatives, polyols, sugars, sugar derivatives, maltodextins, cyclodextrins, starches, polydextroses, or their mixtures, and removes the solvent. The invention further relates to valsartan adsorbates that can be prepared with the processes precited, as well as pharmaceutical formulations for the preparation of which the valsartan adsorbates are employed.
Owner:GLAENZER KLAUS
Method for selectivelly removing isopropyl from diisoprop ketal sugar derivative
InactiveCN101029063AHigh selectivityEasy to makePhysical/chemical process catalystsSugar derivativesAcetonitrileAqueous solution
A process for selectively removing isopropylidene from diisopropylidene ketalose derivative includes such steps as immersing nano-TiO2 in the solution of sulfuric acid, filtering, drying calcining to obtain the catalyst SO4 / TiO2, dissolving diisopropylidene ktalose derivative in the aqueous solution of methanol or ethanol or acetonitrile, adding said catalyst, reacting at 10-40 deg.C for 10-20 hr, and purifying.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process for preparing flavonoids
InactiveUS20030162728A1High yieldPresent invention is superior oneBiocideSugar derivativesPhenyl groupActive oxygen
A simple and easy process for preparing pharmacologically useful flavonoid compound having reductase inhibitory effect, active oxygen extinguishing effect, carcinogenesis promotion inhibitory effect, anti-inflammatory effect, and so on. Particularly, a process for preparing the compound of the formula (I): wherein, R2 is a substituted or un-substituted phenyl group; R7 is a hydrogen atom or a hydroxyl group; and n is an integer of 1 to 4; by bonding a sugar derivative to catechins as the starting compound selectively via O-glycoside bond and then oxidizing the 4-position of flavanoid skeleton of the obtained compound.
Owner:DAIICHI SUNTORY PHARMA CO LTD
Process for the modification of a glycoprotein using a glycosyltransferase that is or is derived from A β(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
ActiveUS9988661B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsN-AcetylgalactosaminyltransferasesNucleotide
The present invention relates to a process for the enzymatic modification of a glycoprotein. The process comprises the step of contacting a glycoprotein comprising a glycan comprising a terminal GlcNAc-moiety, in the presence of glycosyltransferase that is, or is derived from, a β-(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, with a non-natural sugar-derivative nucleotide. The non-natural sugar-derivative nucleotide is according to formula (3): wherein A is selected from the group consisting of —N3, —C(O)R3, —(CH2)iC≡C—R4, —SH, —SC(O)R8, —SC(O)OR8, —SC(S)OR8, —F, —CI, —Br —I, —OS(O)2R5, terminal C2-C24 alkenyl groups, C3-C5 cycloalkenyl groups, C4-C8 alkadienyl groups, terminal C3-C24 allenyl groups and amino groups. The invention further relates to a glycoprotein obtainable by the process according to the invention, to a bioconjugate that can be obtained by conjugating the glycoprotein with a linker-conjugate, and to β-(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases that can be used in preparing the the glycoprotein according to the invention.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com