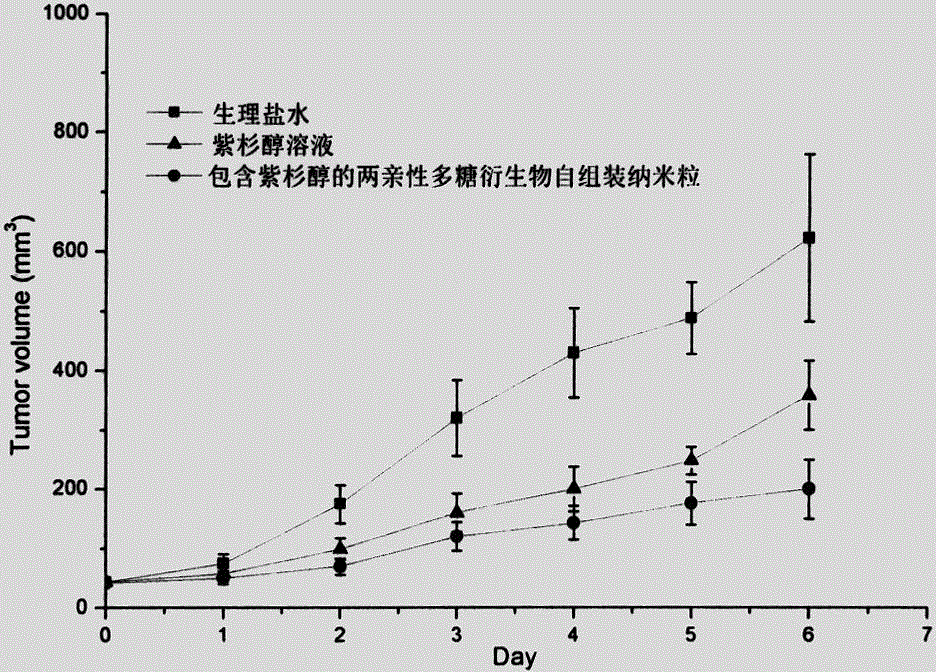
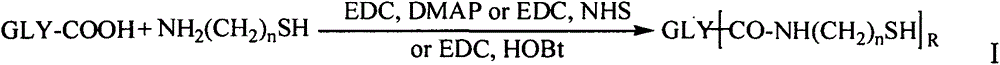Amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels as well as preparation and application of pharmaceutical composition of amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier
A technology of tumor neovascularization and amphiphilic polysaccharides, which is applied in the direction of anti-tumor drugs, drug combinations, and medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., which can solve the problems of low drug uptake rate, poor targeting of tumor blood vessels, and side effects And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1: Preparation of Esbp-disulfide-acetylated hyaluronic acid
[0063] 0.1mmol of hyaluronic acid, 1mmol of 2-aminoethanethiol, 1mmol of EDC and 1mmol of NHS were dissolved in formamide. After 24 hours of reaction, the hyaluronic acid intermediate was precipitated with acetone, filtered and dialyzed with distilled water for 72 hours (MWCO=3500), frozen Dry to obtain the hyaluronic acid intermediate of free one end mercapto group.
[0064] Dissolve 0.4mmol Esbp peptide and 0.1mmol hyaluronic acid intermediate in formamide, oxidize in natural air, and react for 24h. After the reaction was completed, it was dialyzed with excess distilled water for 72 hours (MWCO=3500), and freeze-dried to obtain the Esbp-disulfide-acetylated hyaluronic acid derivative carrier.
Embodiment 2
[0065]Embodiment 2: Preparation of Esbp-disulfide-propionylated chitosan
[0066] 0.1mmol chitosan was dissolved in a mixed solvent of water and methanol (v / v=1:1), 1mmol 3-mercaptopropionic acid, 0.5mmol EDC and 0.5mmol HOBt were added, reacted for 8h, methanol was removed by rotary evaporation, and distilled water was dialyzed for 72h (MWCO= 3500), freeze-dried to obtain the chitosan intermediate of a free end sulfhydryl.
[0067] 0.5mmol Esbp peptide and 0.1mmol chitosan intermediate were dissolved in a mixed solvent of water and methanol (v / v=1:1), ammonia water was used to adjust the pH value to 8.0, potassium ferricyanide (0.2mmol) aqueous solution was added dropwise, Reaction at room temperature for 2h. After the reaction was completed, the methanol was removed by rotary evaporation, dialyzed in distilled water for 72 hours (MWCO=3500), and freeze-dried to obtain the Esbp-disulfide-propionylated chitosan derivative carrier.
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Preparation of Esbp-disulfide-acetylated chondroitin sulfate
[0069] 0.1mmol of chondroitin sulfate, 1mmol of 2-aminoethanethiol, 0.5mmol of EDC and 0.5mmol of DMAP were dissolved in formamide, and after 12 hours of reaction, the chondroitin sulfate intermediate was precipitated with acetone, suction filtered and dialyzed with distilled water for 72 hours (MWCO=3500 ), freeze-dry to obtain the chondroitin sulfate intermediate of free one-end sulfhydryl.
[0070] Dissolve 0.2mmol Esbp and 0.1mmol chondroitin sulfate intermediate in a mixed solvent of N,N-dimethylformamide and water, add iodine solution (0.2mmol) dropwise for oxidation, and react for 30min. After the reaction, use excess acetone to precipitate, filter and vacuum dry to obtain the Esbp-disulfide-acetylated chondroitin sulfate derivative carrier.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com