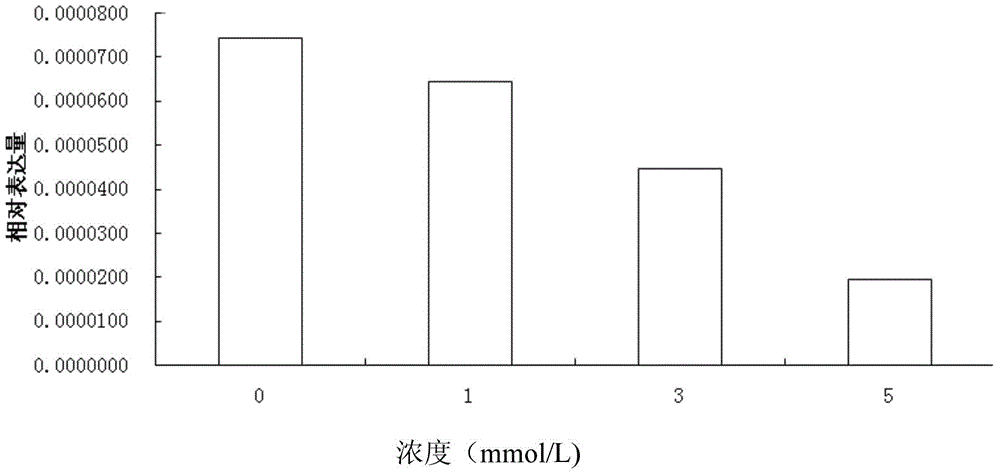
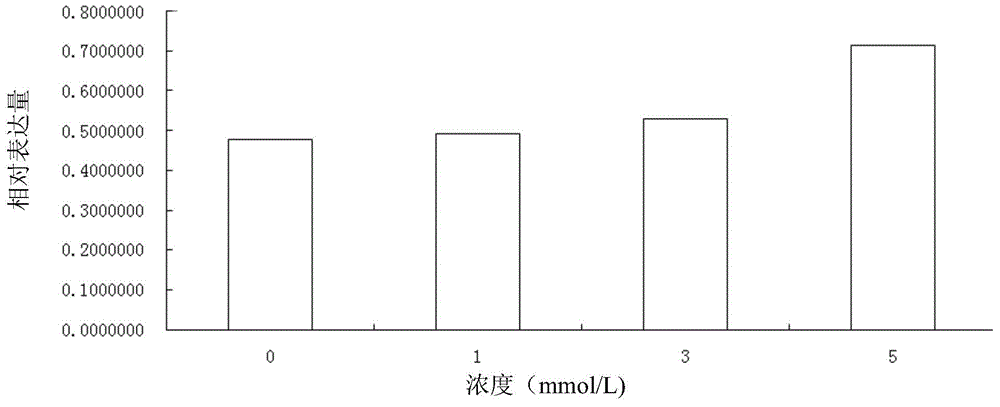
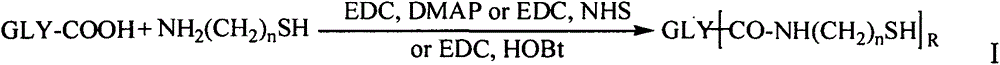Patents
Literature
70 results about "Blood vessel part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
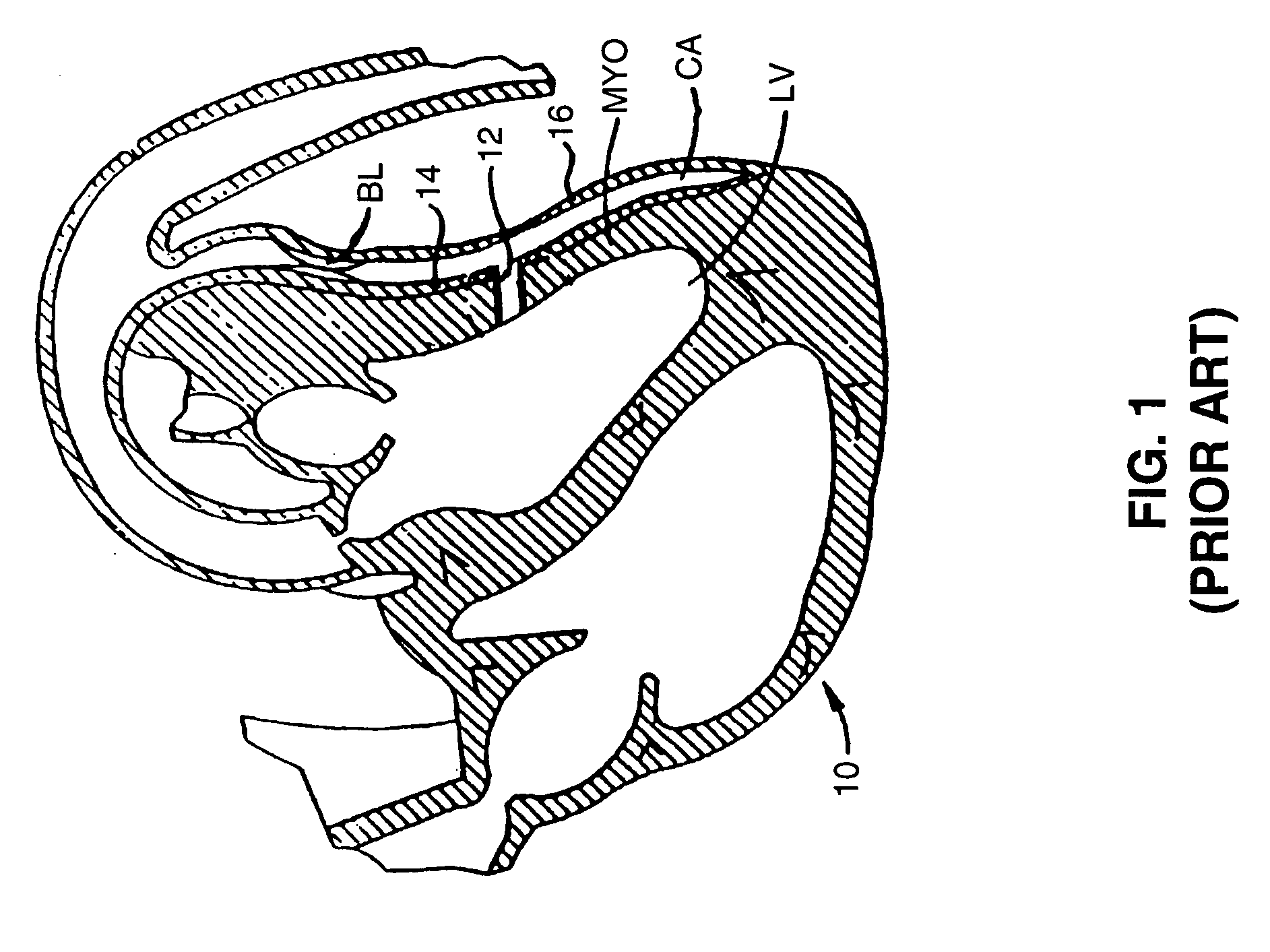
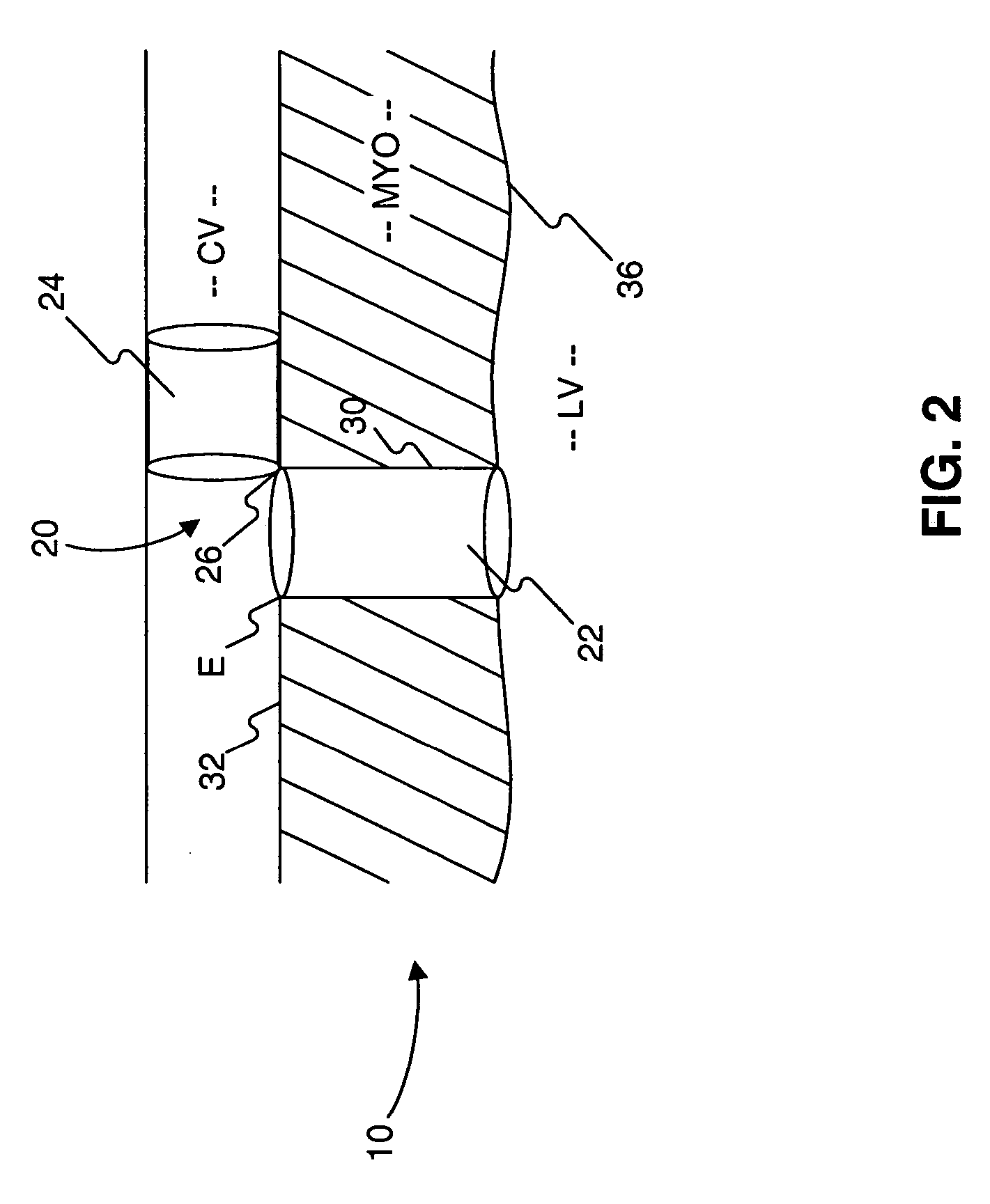
System and Method of Use for Revascularizing Stenotic Bypass Grafts and Other Blood Vessels
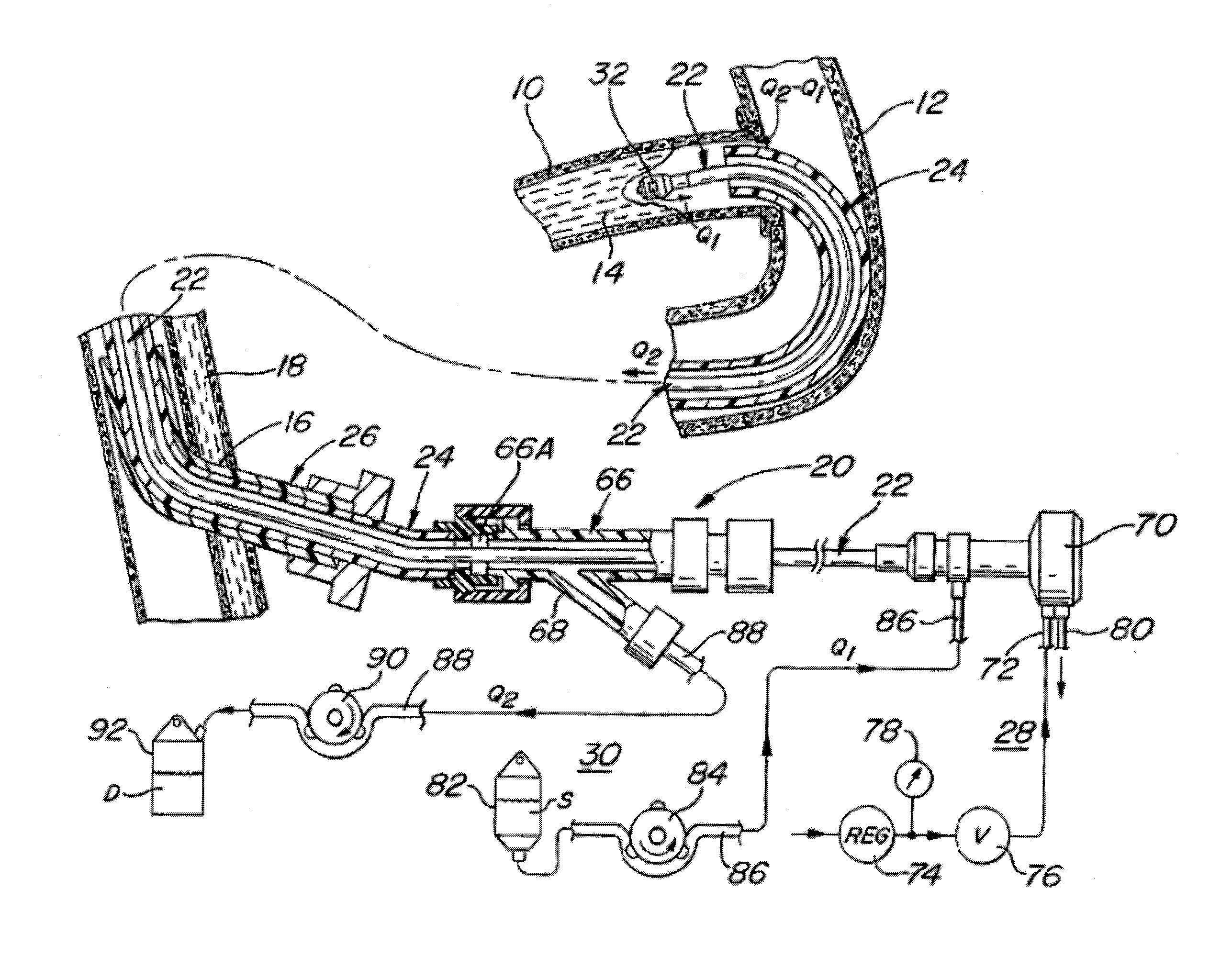
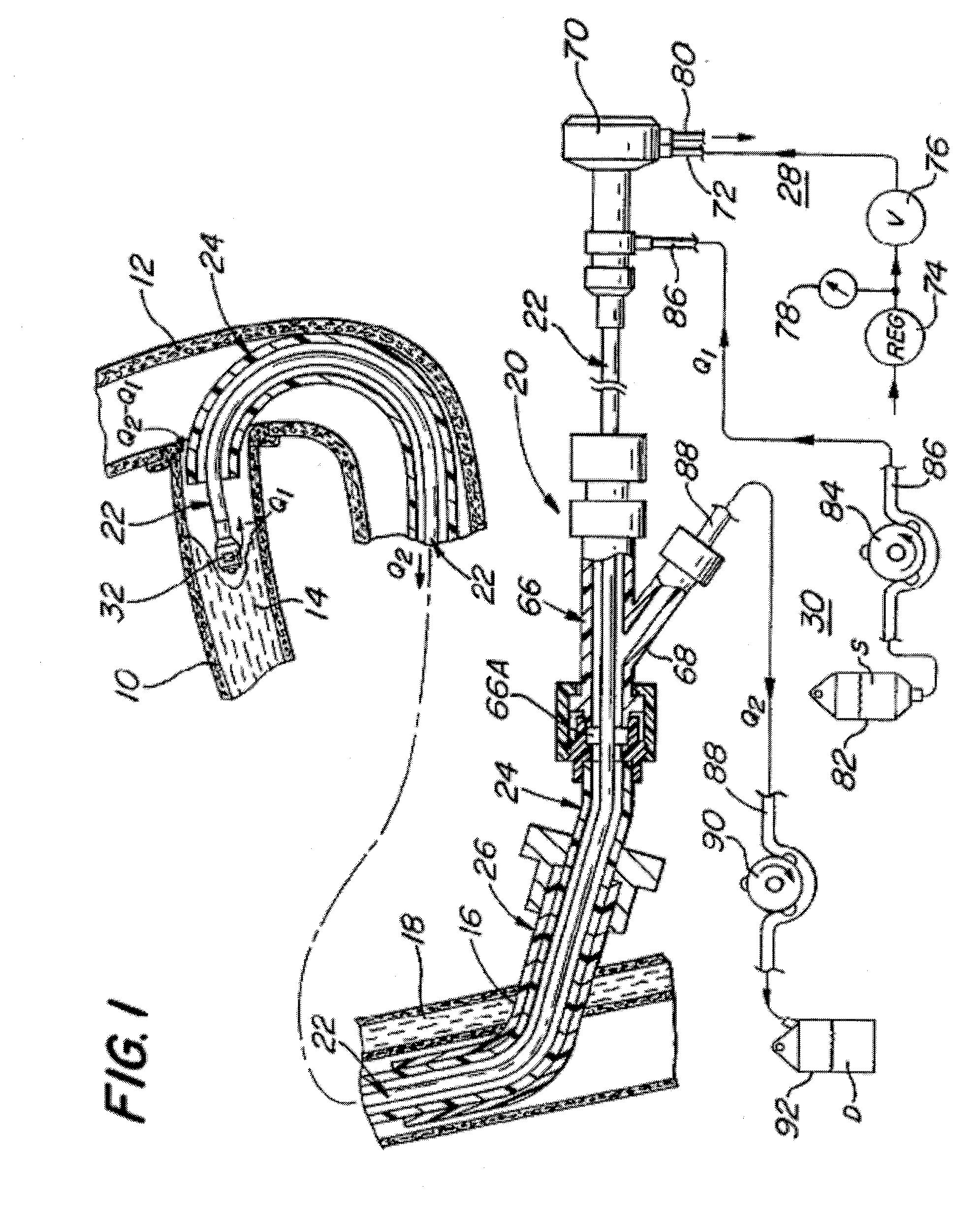
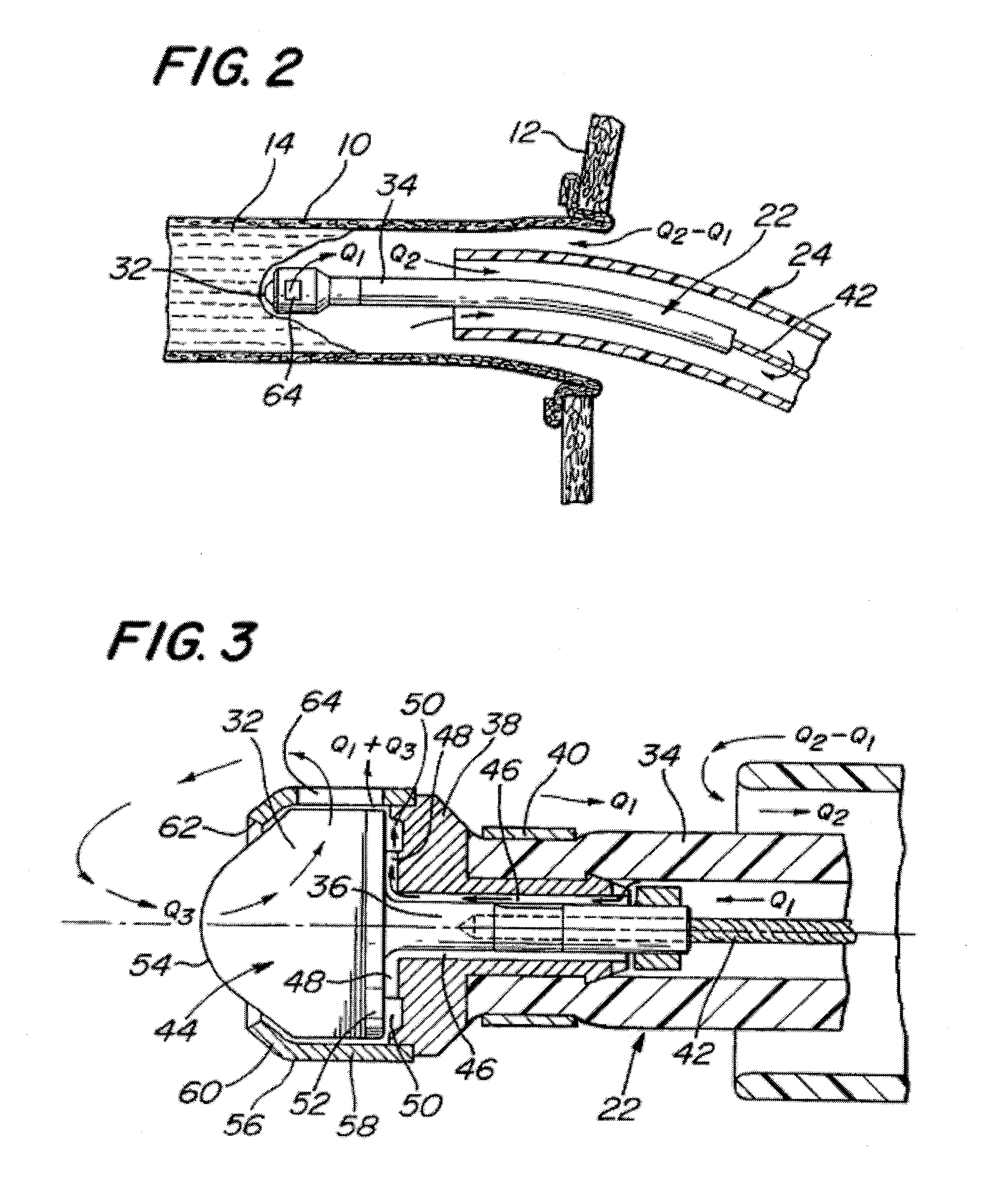
InactiveUS20070118072A1Avoid flowEffectively revascularizingCannulasMedical devicesCoronary arteriesBypass grafts
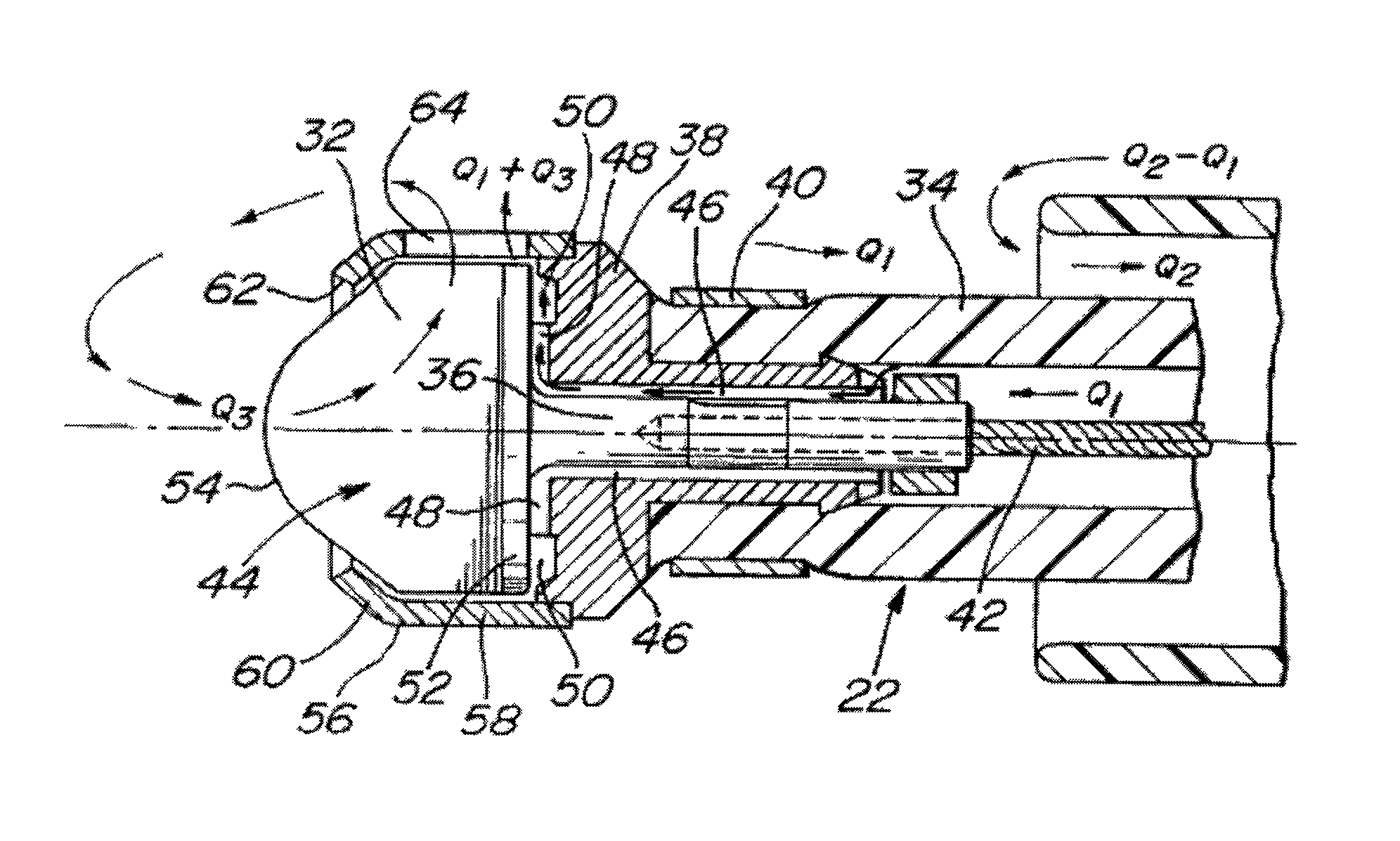
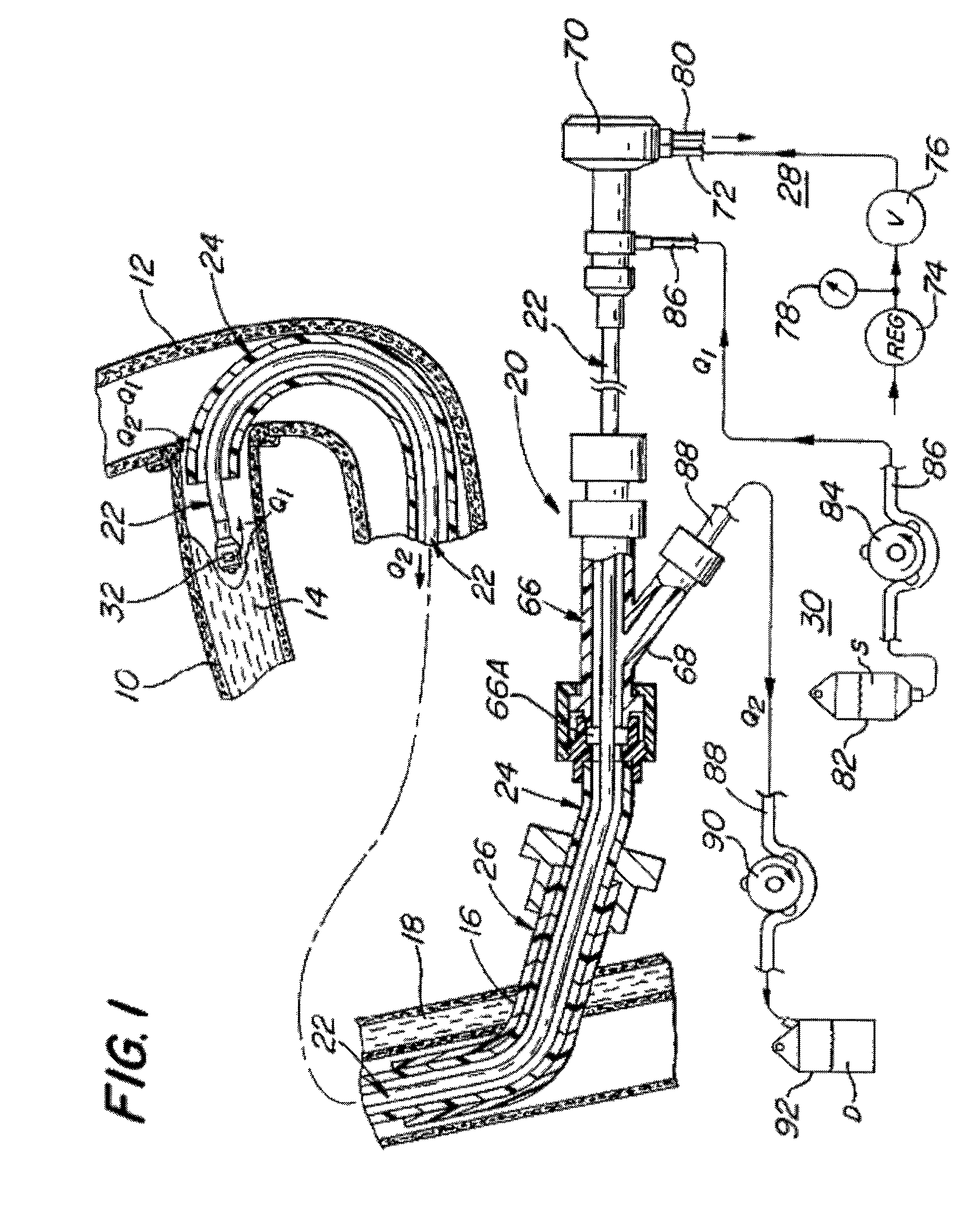
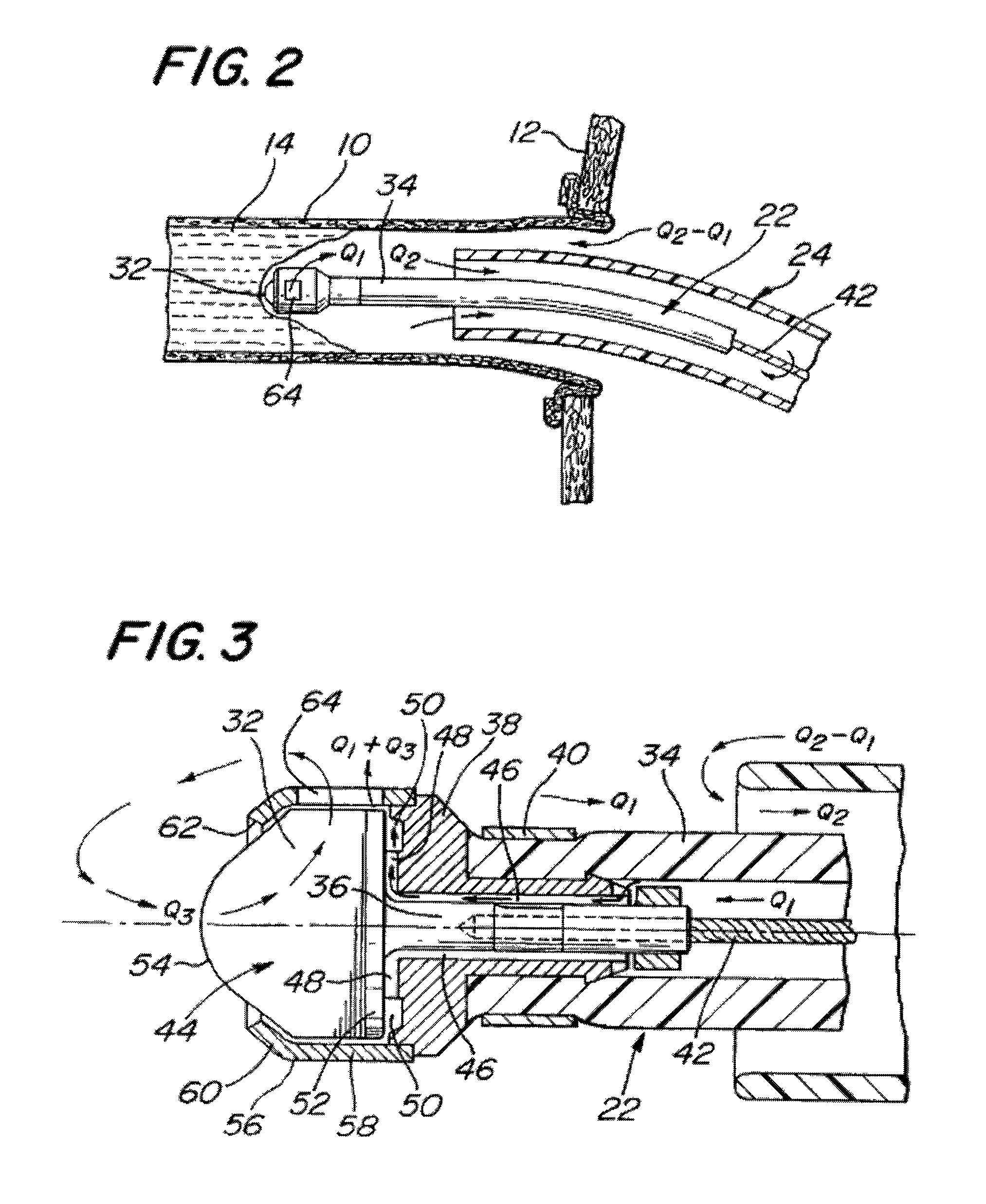
A system and method for opening a lumen in an occluded blood vessel, e.g., a coronary bypass graft, of a living being's vascular system. The system introduces an infusate liquid at a first flow rate to the occluded portion of the blood vessel, and withdraws that liquid and some blood at a second and higher flow rate. This action creates a differential flow in the occluded blood vessel portion and thereby prevent particles of occlusive material from flowing into any upstream blood vessel or downstream blood vessel in said living being's vascular system.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Hinged tissue implant and related methods and devices for delivering such an implant
InactiveUS20070005127A1Increased complexityReduce deliveryStentsHeart valvesCardiac muscleSacroiliac joint
A device for treating a heart may comprise a myocardial section configured to be positioned in a heart wall between a coronary vessel and a chamber of the heart and a vessel section configured to be positioned in the coronary vessel. The vessel section may be connected to the myocardial section and be configured to articulate relative to the myocardial section. The myocardial section and the vessel section may form an integral, single piece structure.
Owner:PERCARDIA INC
Method and apparatus for performing intra-operative angiography
Method for assessing the patency of a patient's blood vessel, advantageously during or after treatment of that vessel by an invasive procedure, comprising administering a fluorescent dye to the patient; obtaining at least one angiographic image of the vessel portion; and evaluating the at least one angiographic image to assess the patency of the vessel portion. Other related methods are contemplated, including methods for assessing perfusion in selected body tissue, methods for evaluating the potential of vessels for use in creation of AV fistulas, methods for determining the diameter of a vessel, and methods for locating a vessel located below the surface of a tissue.
Owner:NOVADAG TECH INC
System and method of use for revascularizing stenotic bypass grafts and other blood vessels
A system and method for opening a lumen in an occluded blood vessel, e.g., a coronary bypass graft, of a living being's vascular system. The system introduces an infusate liquid at a first flow rate to the occluded portion of the blood vessel, and withdraws that liquid and some blood at a second and higher flow rate. This action creates a differential flow in the occluded blood vessel portion and thereby prevent particles of occlusive material from flowing into any upstream blood vessel or downstream blood vessel in said living being's vascular system.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
SVM (support vector machine)-based medical image blood vessel recognition method
InactiveCN106530283AKeep the forkKeep the intersectionImage enhancementImage analysisManual segmentationImaging processing
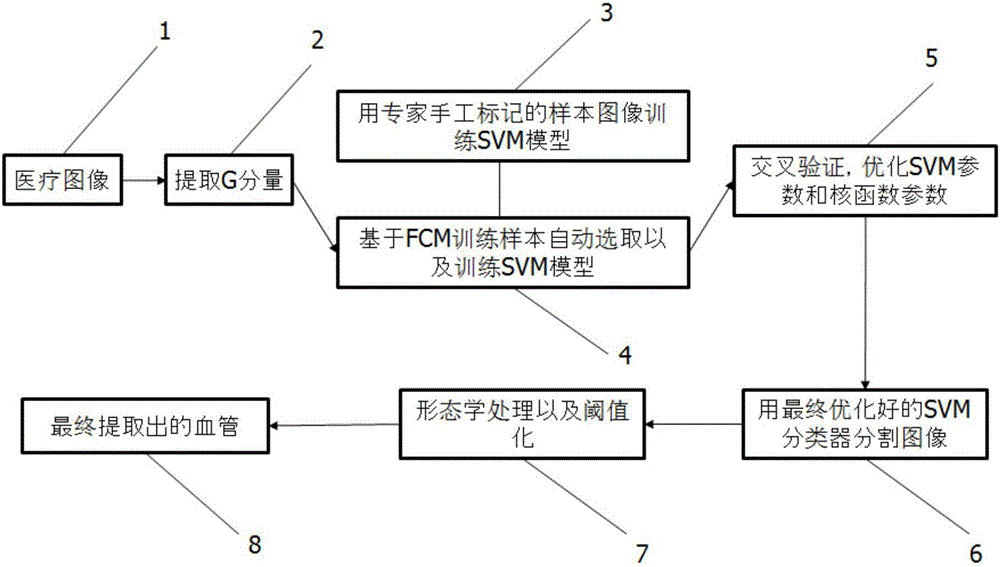
The invention discloses an SVM (support vector machine)-based medical image blood vessel recognition method. The method includes the following steps that: since an SVM classifier is obtained after cross validation and optimization are performed on an SVM model trained by samples automatically selected by an FCM by using an SVM model which is trained by samples obtained through the manual segmentation of experts, segmentation results are more accurate; the SVM is adopted to segment a blood vessel, namely, pixels are divided into a foreground (blood vessels) and a background (other parts), and the blood vessel part is extracted out; morphological processing and thresholding are performed, and therefore, a blood vessel network can be enhanced, the branches and intersections of the blood vessels are reserved; and an obtained image is converted into a binary image, so that blood vessel distribution can be reflected more directly. According to the method of the invention, the FCM, the SVM and the morphological image processing are combined together, so that a recognition effect is better.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Anastomosis Device and Method
InactiveUS20070250082A1Risk minimizationWithout any risk for defaultSurgical staplesWound clampsEngineeringMechanical engineering
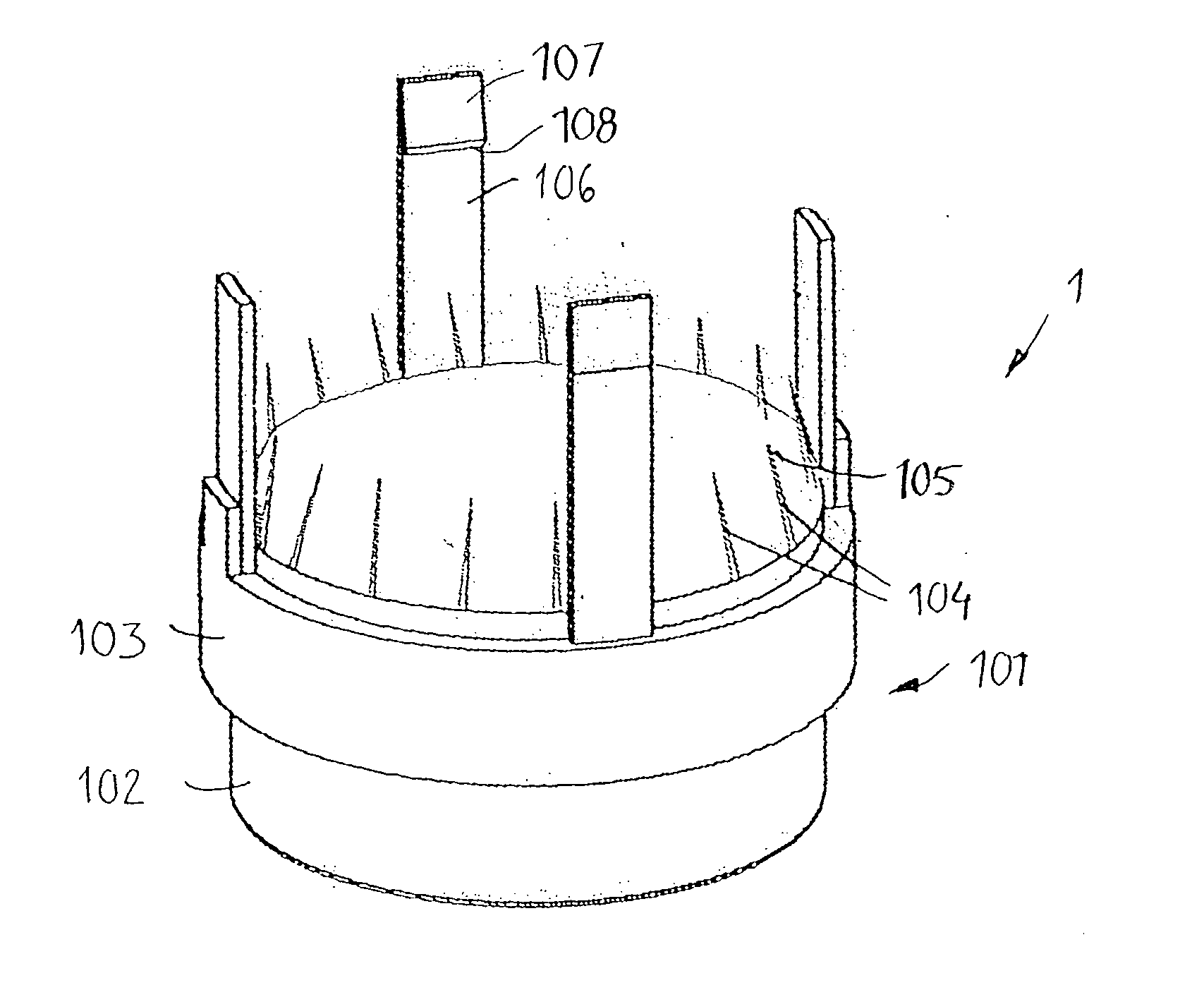
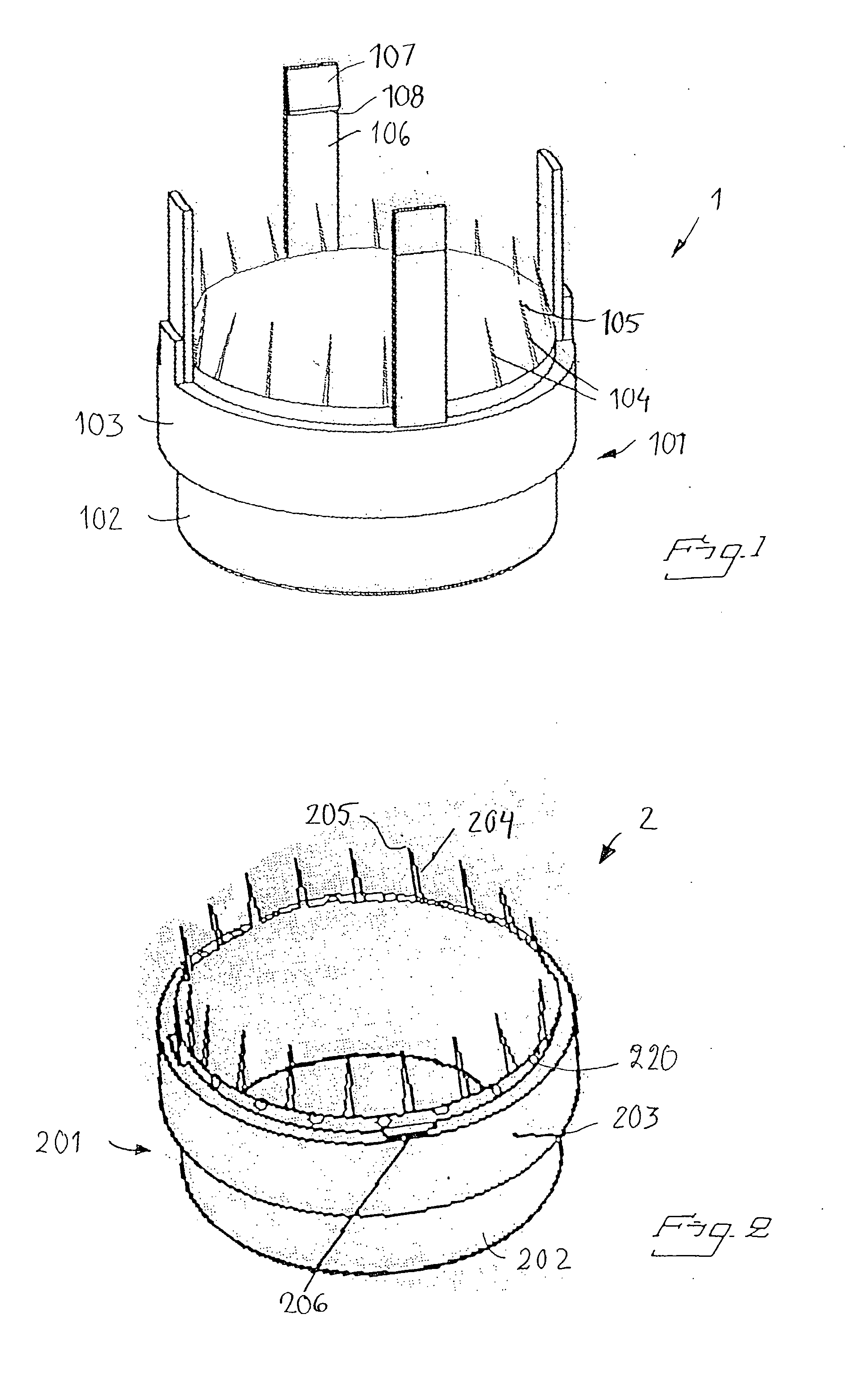
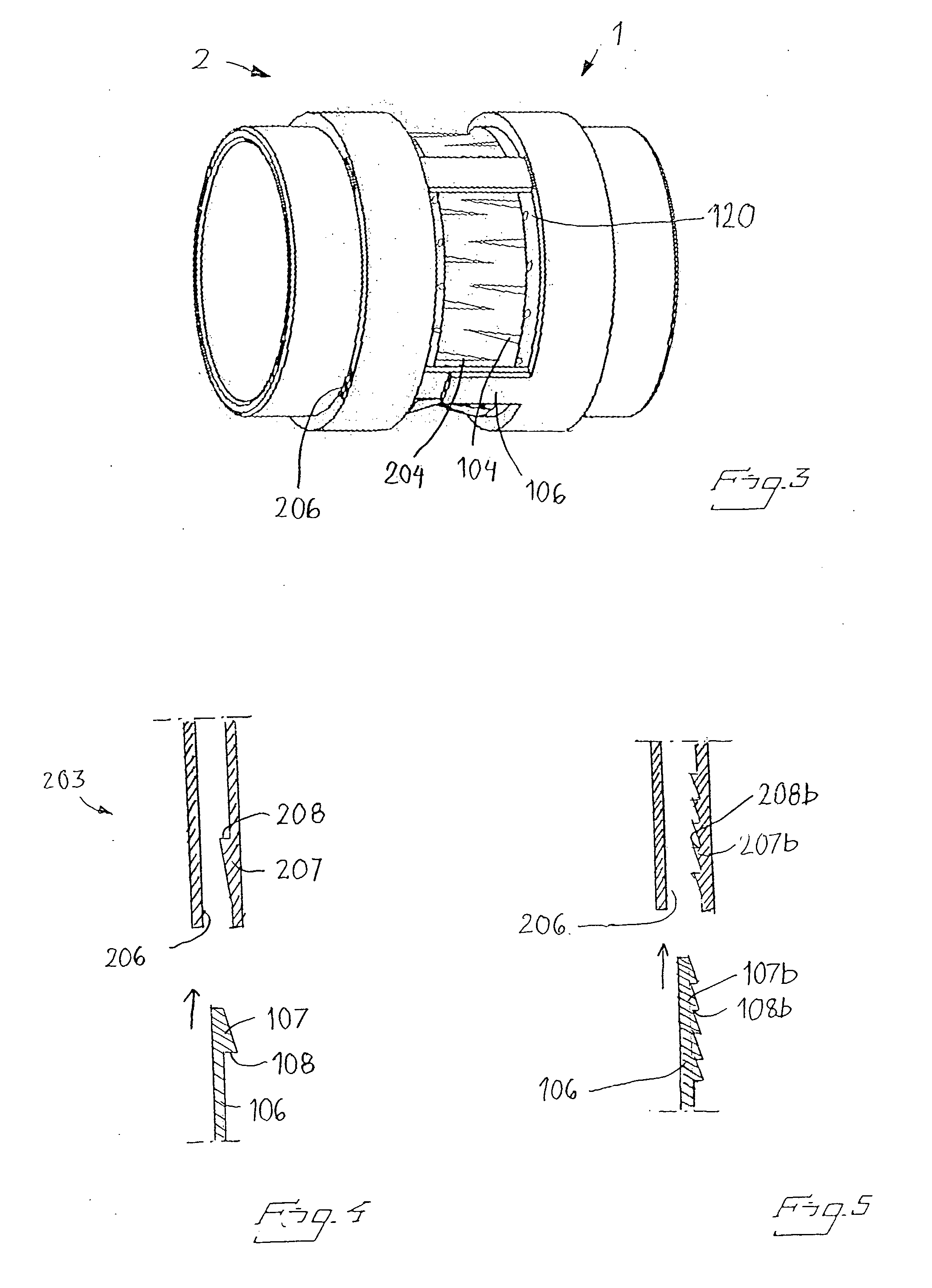
The invention relates to an anastomosis device for anastomosing the end of two vessel parts together. It includes two attachment units attachable to a respective end of the vessel parts. The units are connectable to each other. Each unit has a through-hole defining a central axis. According to the invention the device has at least two connection means. Each connection means includes an axially extending member having a free end, which member is provided on any of the attachment units and a receiving opening provided on the other of the attachment units. The receiving opening is arranged to axially receive the free end of the member. The member is arranged to snap into a locking position in the receiving opening in which the member is axially locked. The invention also relates to a method for anatomising of ends of two vessel parts together and to a use of the device.
Owner:PROZEO VASCULAR IMPLANT
Vascularizing tissue structure with microfluid passage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103767804AEnsure stabilityHelps to attachEnzyme production/based bioreactorsBlood vesselsSynthetic Polymeric MacromoleculesIn vivo
The invention relates to a vascularizing tissue structure with a microfluid passage and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of tissue engineering and forming of composite material. The vascularizing tissue structure comprises a tissue structure body, branch blood vessel parts, a capillary layer and a protecting layer. The vascularizing tissue structure has the advantages that the composite forming of thin solution, cells and water gel is realized; the tissue structure body is formed by spraying the water gel containing the cells, and the thin solution containing or not containing the cells is distributed among the grids of the water gel; a branch blood vessel hole passage is reserved by the water gel containing the cells, the thin solution containing or not containing the cells is distributed in the hole passage, and the wall of each branch blood vessel is a porous structure; the capillary layer is formed by coating or spraying the polymer thin solution, or the thin solution containing the cells; the support part and the protecting part are formed by stacking synthetic or natural polymer solution; the two ends of the formed structure body are provided with blood vessel joints or a plurality of opened type passages, and can be used for in-vivo implanting or in-vitro culturing, so as to promote the development of vascularizing.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of stripping diseased blood vessels from the human body
InactiveUS20050021068A1Diminishes trauma associateReduce traumaSurgerySuction devicesHuman bodyVaricose veins
A surgical device and method for using it to strip blood vessels, such as varicose veins, or other tubular structures from the body utilizing an endovenous cable that is passed through the vein section to be removed. Once the endovenous cable reaches the end of the section of blood vessel to be stripped, a head is attached to the endovenous cable. The head may have at its leading edge, rounded, streamlined shoulders, a leading edge and a central cavity to retain the end of the vein. On the trailing end of the stripper head are one or more structures capable of receiving and retaining a surgical drain. As the vein is tripped the drain is automatically pulled into the body. The drain will lie in the leg precisely where the vein had been, and the limit the common complication of retained post surgical bleeding.
Owner:JS VASCULAR
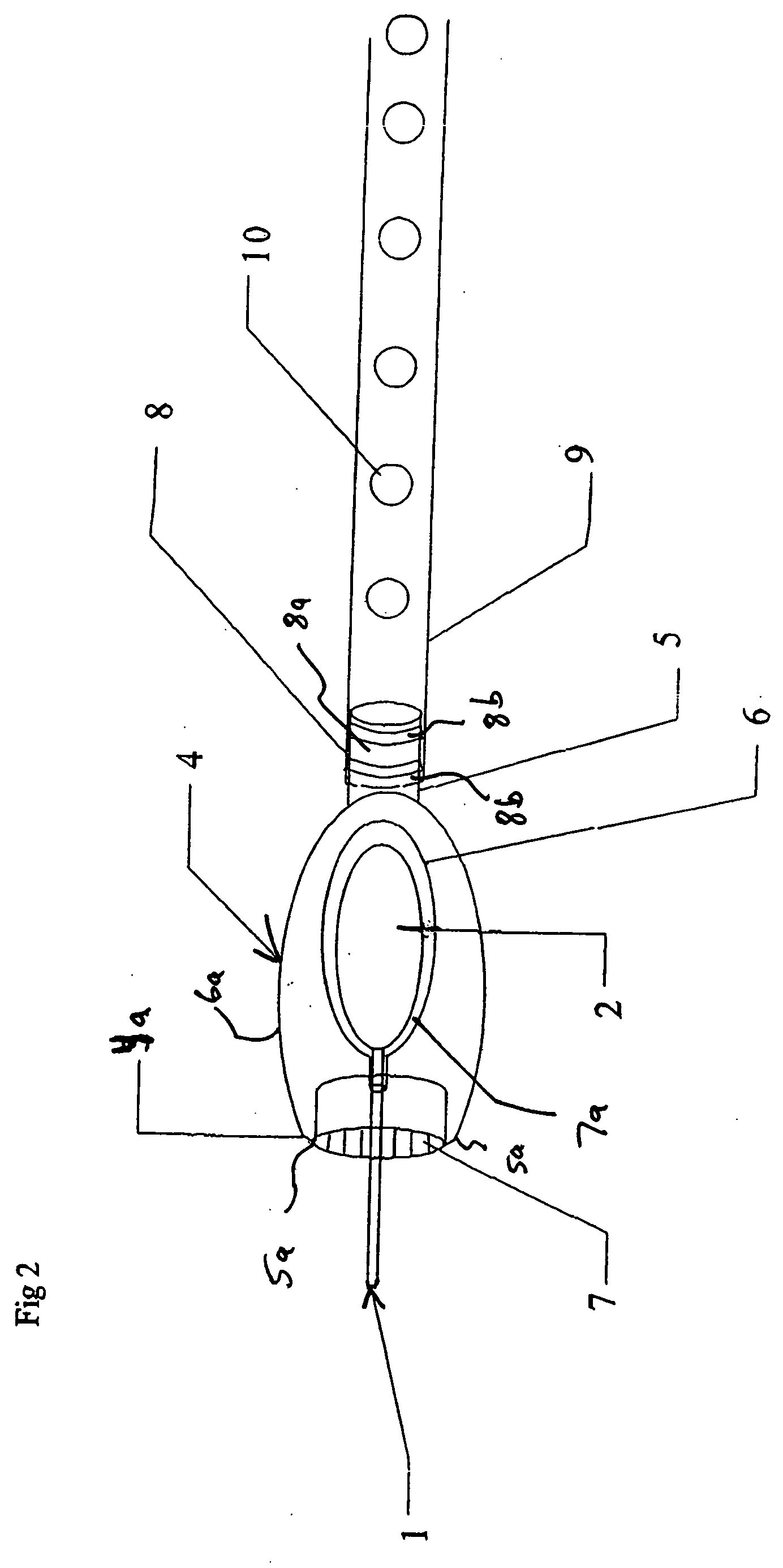
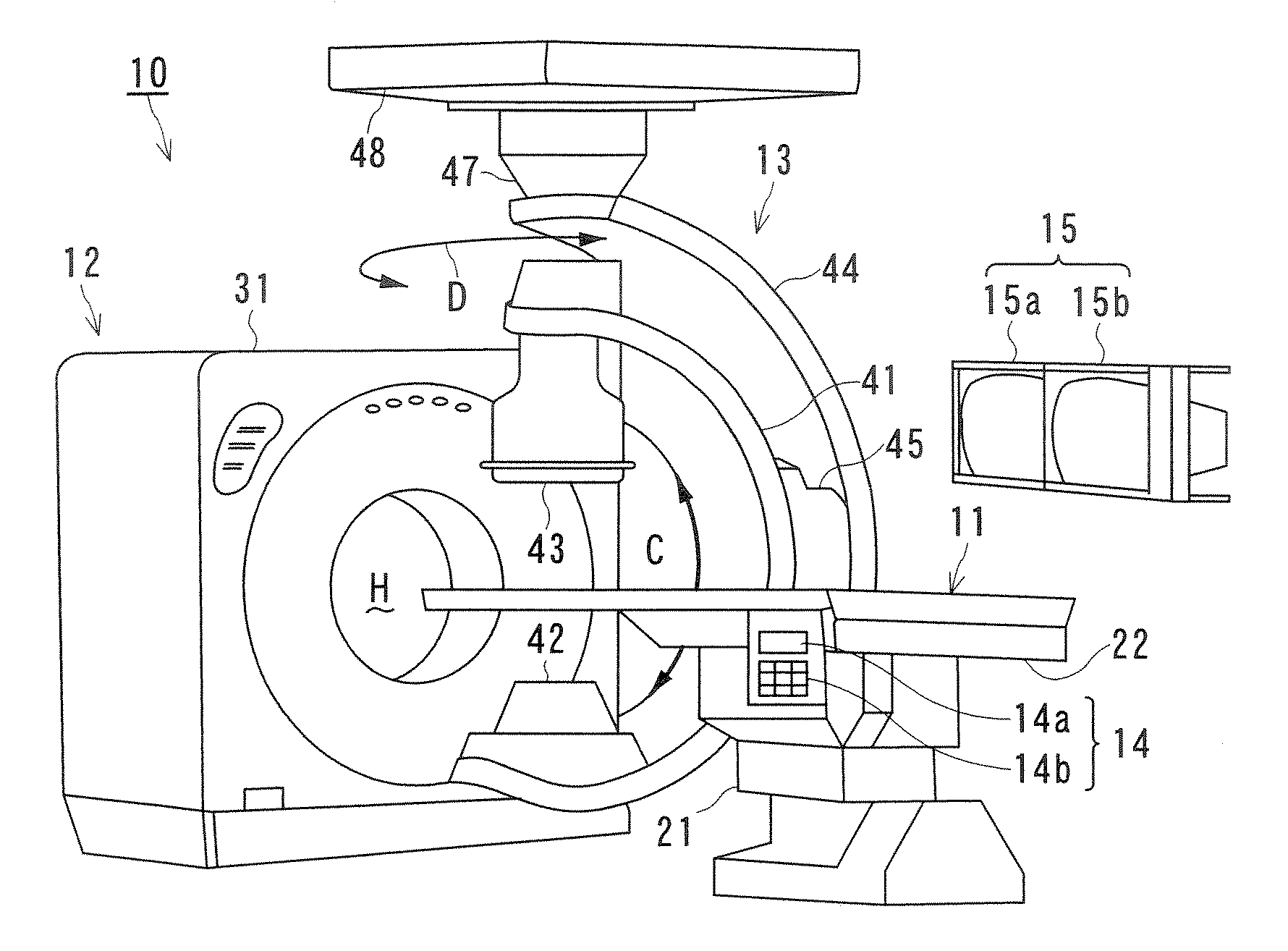
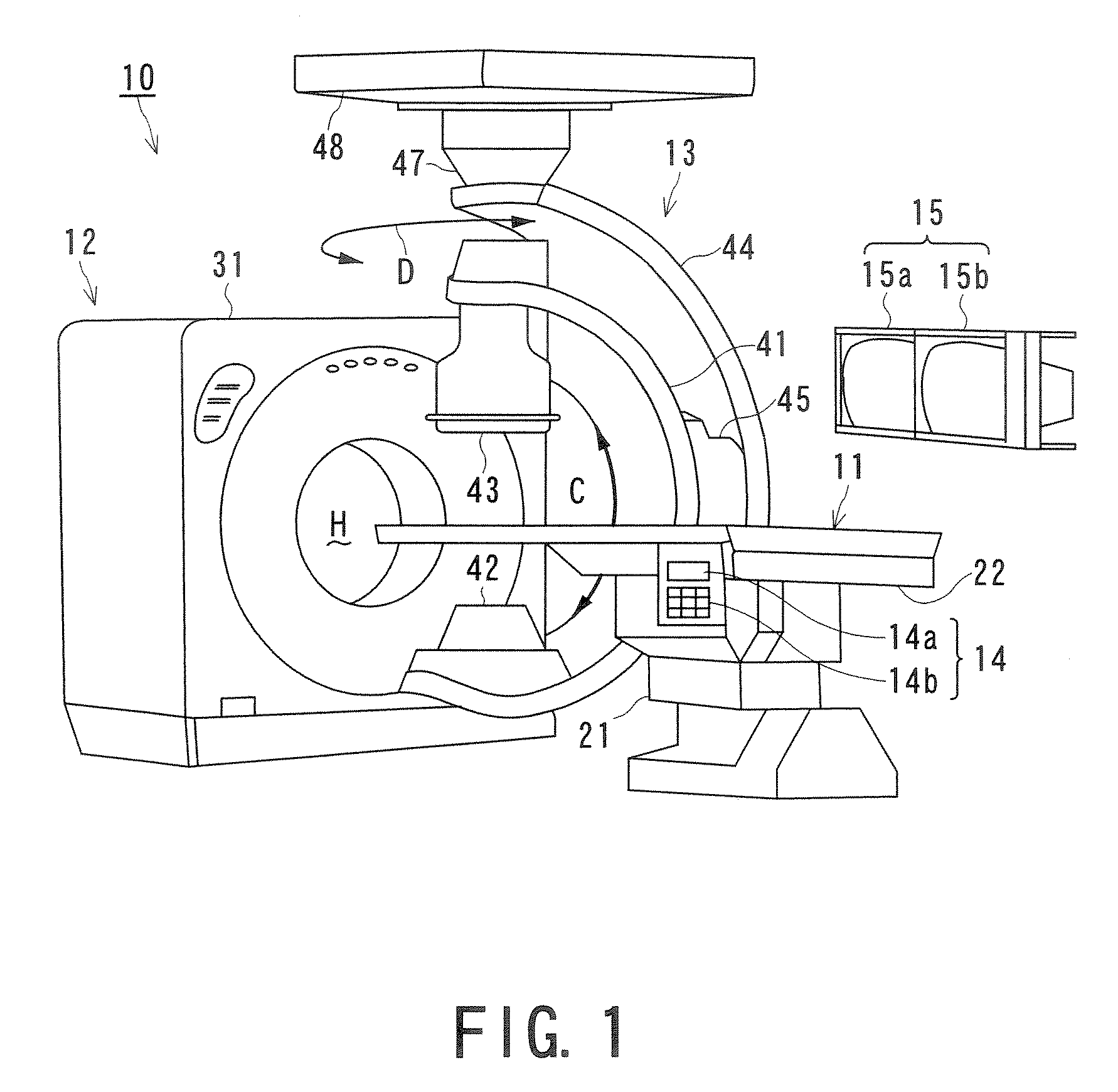
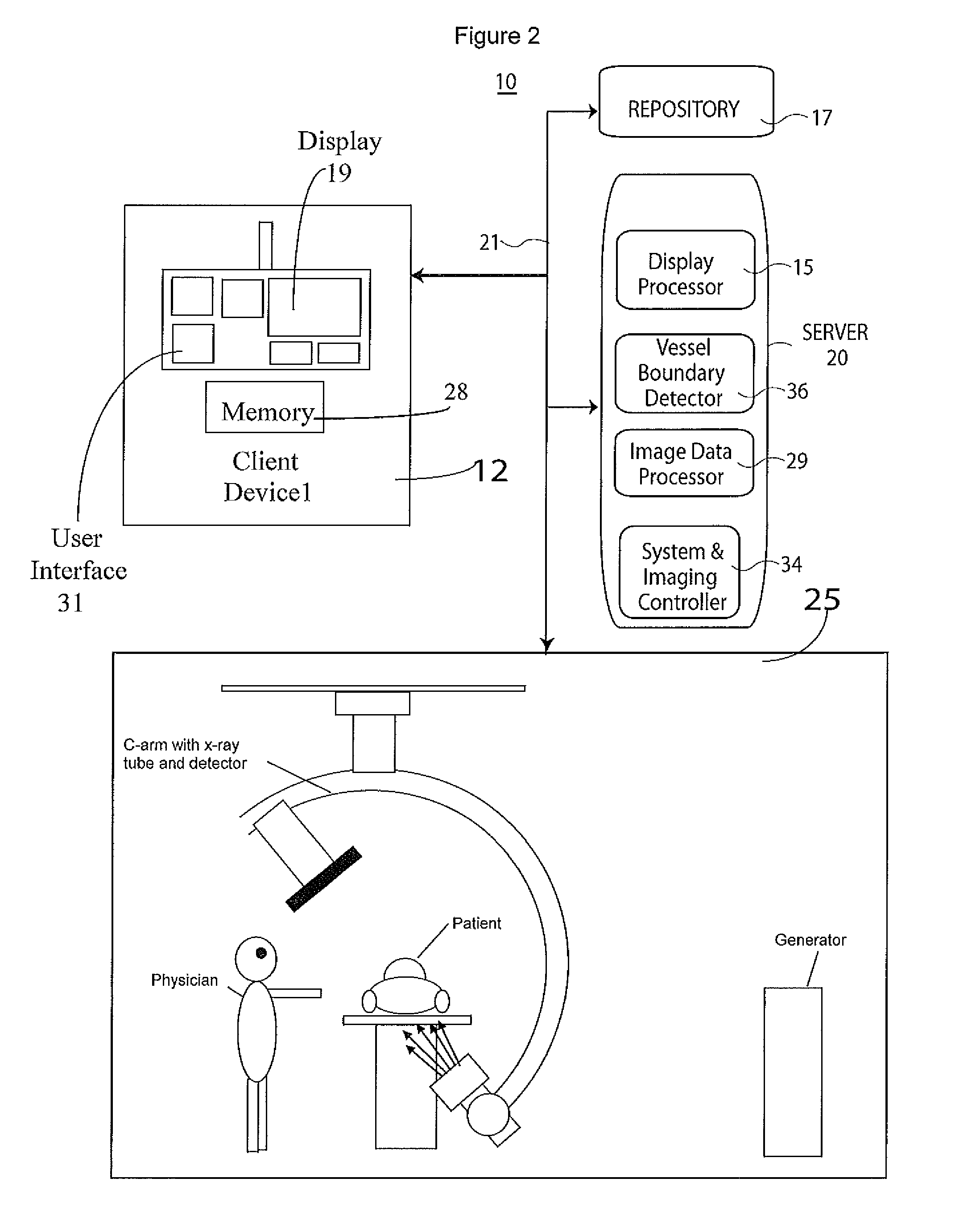
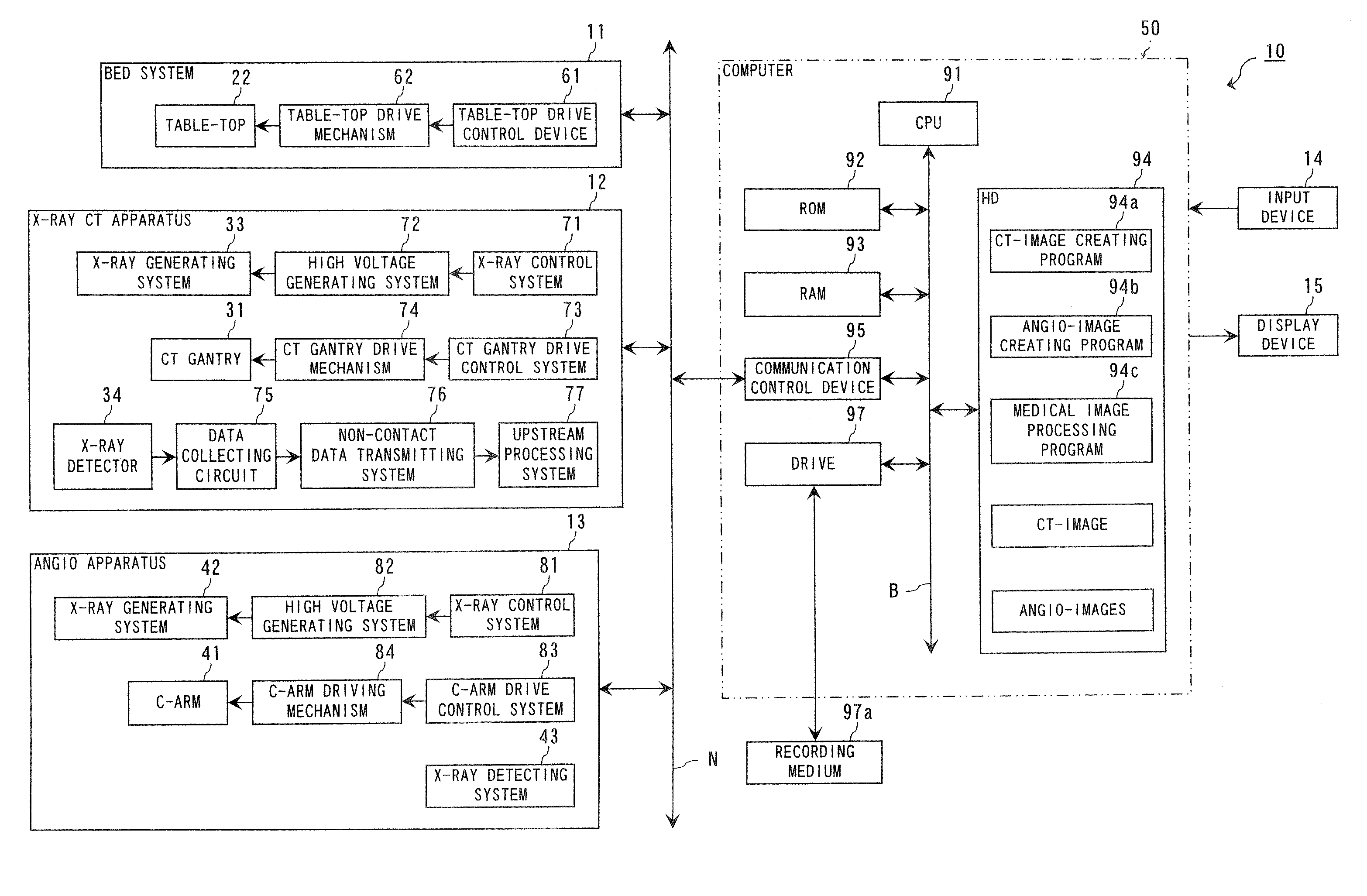
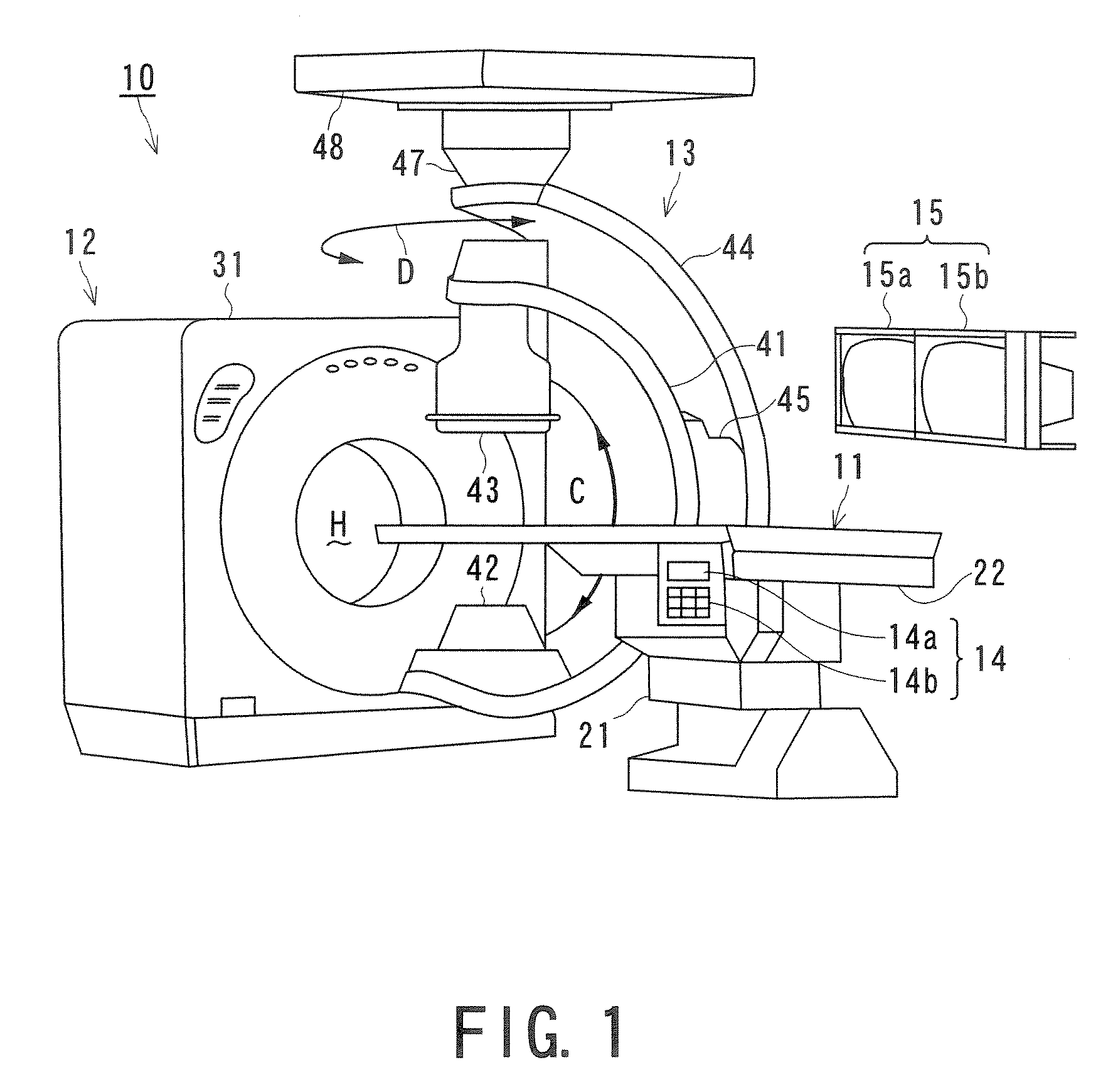
Medical image processing system and medical image processing method
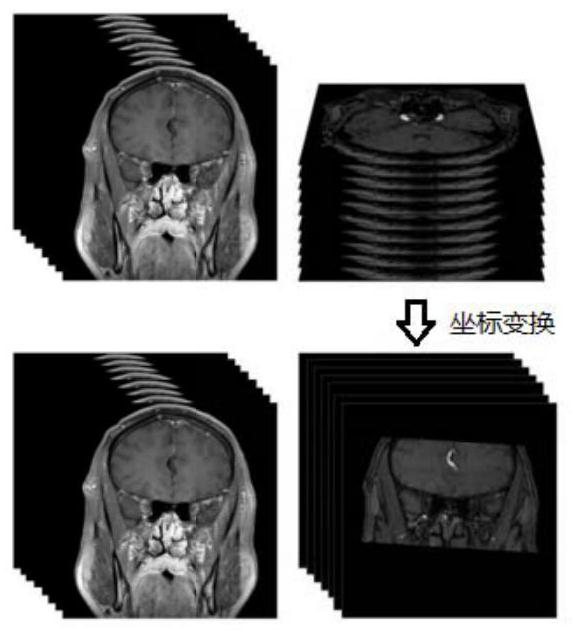
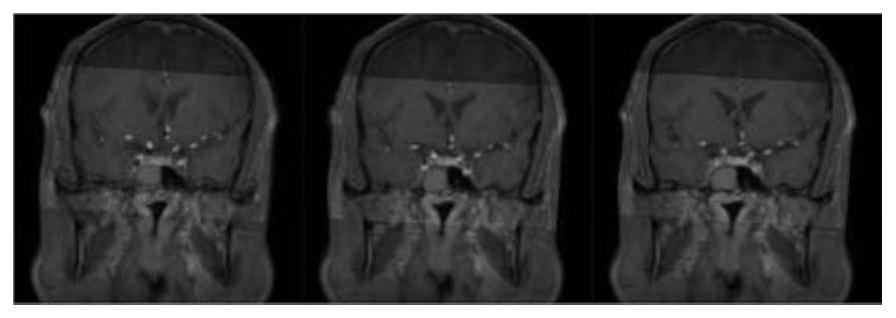
ActiveUS20070092067A1Accurate assessmentShort operating timeCharacter and pattern recognitionTomographyThree dimensional ct3D projection
IVR-CT apparatus has an angio-image obtaining unit, an angio-image imaging direction obtaining unit, a CT-image obtaining unit, a blood vessel part extracting unit, a projected image generating unit and a display control unit. The angio-image obtaining unit obtains a required angio-image from multiple chronological angio-images. The angio-image imaging direction obtaining unit obtains a direction of imaging as incidental information included in data on the required angio-image. The CT-image obtaining unit obtains a three-dimensional CT-image corresponding to the required angio-image. The blood vessel part extracting unit extracts a blood vessel part in the three-dimensional CT-image. The projected image generating unit generates a three-dimensional projected image by projecting the blood vessel part, and a three-dimensional projected image corresponding to a direction of a projection after a manual operation operates the direction of the projection. The display control unit makes display the three-dimensional projection image and the angio-image one over another.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method for utilizing 3D printing technology to manufacture intravascular inner wall stent and product thereof
InactiveCN106214296AShorten production timeIncrease flexibilityStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusHuman bodyMedicine
The invention discloses a method for utilizing a 3D printing technology to manufacture an intravascular inner wall stent and a product thereof. The method comprises the steps that a human body scanning device is utilized to scan the human body blood vessel part of the intravascular inner wall stent to be manufactured so as to preliminarily obtain a 3D model figure of the part needing the stent; computer drawing software is utilized to draw the rudiment of the intravascular inner wall stent needed to be erected in the obtained 3D model figure, then the stent rudiment is isolated and taken from the model figure, then finishing processing is performed, and finally the stent rudiment is converted into a file format which can identified by a 3D printer to be output; 3D printer software is utilized to read and identify a file as a main body of a model; then, the software is utilized to perform model stenting body establishment so as to obtain a model section file to be printed; a main body material and a supporting body material are loaded into two consumable chambers of the 3D printer, printing parameters are arranged for printing, then the established supporting body is removed to obtain the intravascular inner wall stent. The stent is low in cost and is more suitable for an individual.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
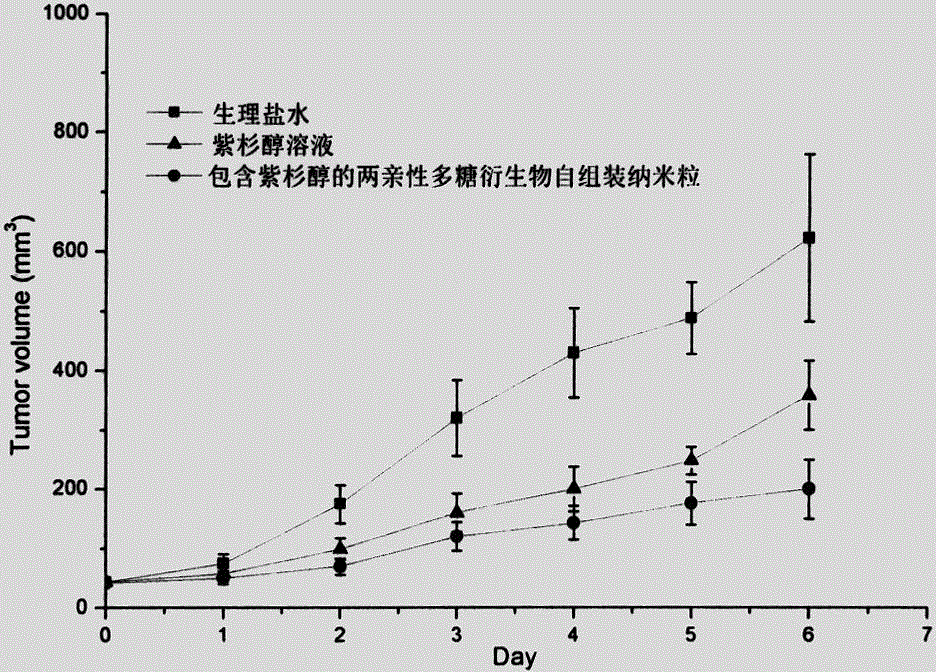
Amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels as well as preparation and application of pharmaceutical composition of amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier
ActiveCN104971353AImprove stabilityImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWater insolubleVascular endothelium
The invention relates to an amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels. According to the derivative, a polysaccharide skeleton is coupled with functional polypeptide targeting E-selectin by virtue of a disulfide bond to ensure that polysaccharide has amphipathy, and is assembled into nano particles for targeting the tumor new blood vessels after carrying an antitumor drug or a tumor new blood vessel inhibitor in an aqueous medium. The nano particles deliver medicines to the tumor new blood vessels in an active targeting manner by virtue of the high affinity between the functional polypeptide targeting the E-selectin and the E-selectin on the surface of the tumor new blood vessels, then a disulfide bond connecting arm can be specifically degraded by a strong reducing environment in endothelial cells of the tumor new blood vessels to cause that the functional polypeptide targeting the E-selectin is separated from polysaccharide, and the medicines are quickly released to treatment target points, so that the concentration of free medicines at tumor new blood vessel parts can be significantly improved and the antitumor curative effect is enhanced. An auxiliary material can be used as a carrier for water-insoluble, indissolvable or amphiphilic antitumor drugs and the tumor new blood vessel inhibitor, and is administrated by injecting into blood vessels or muscles, or is administrated orally or externally. The amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier provided by the invention is simple in preparation method, mature in process and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
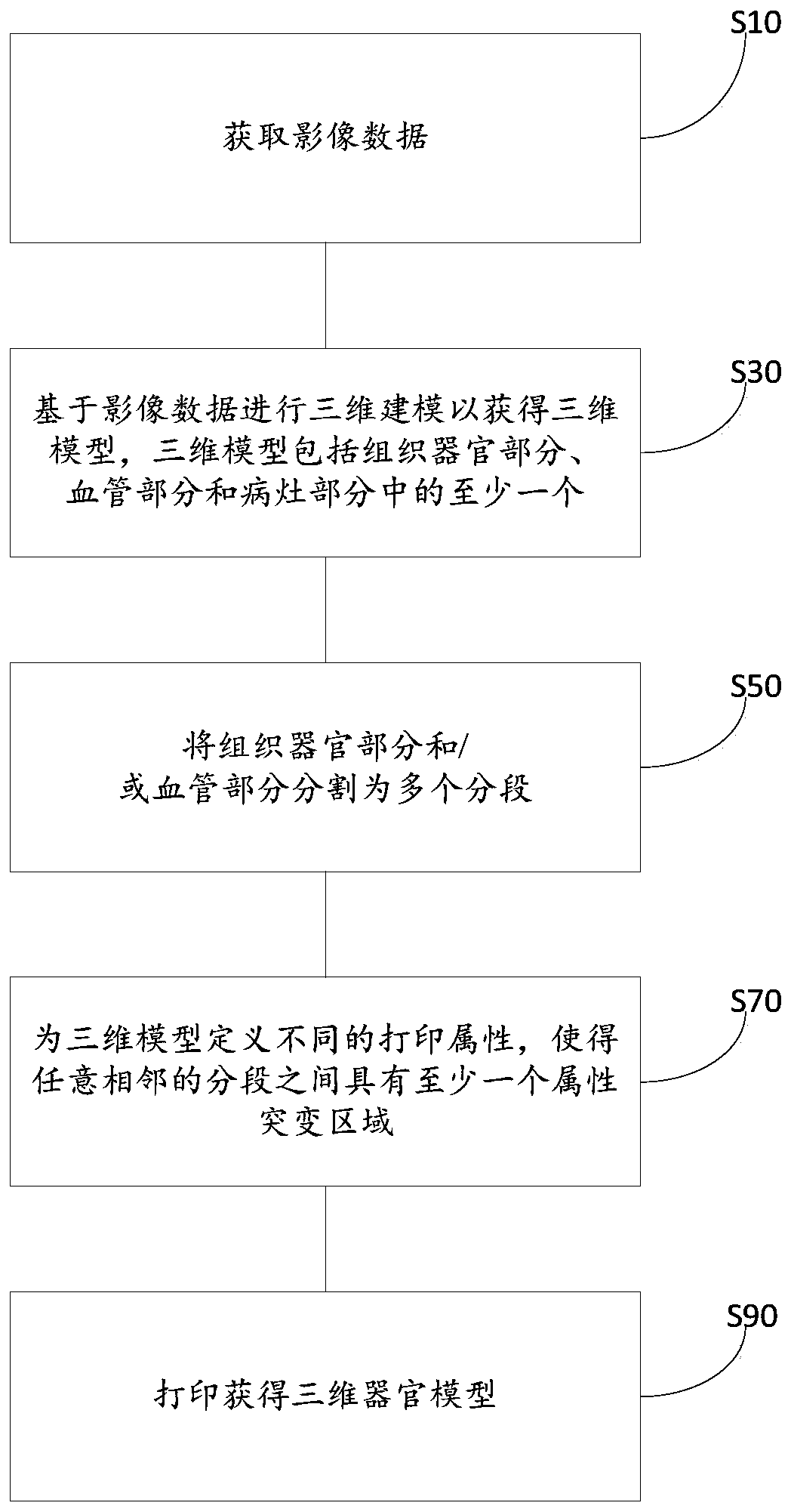
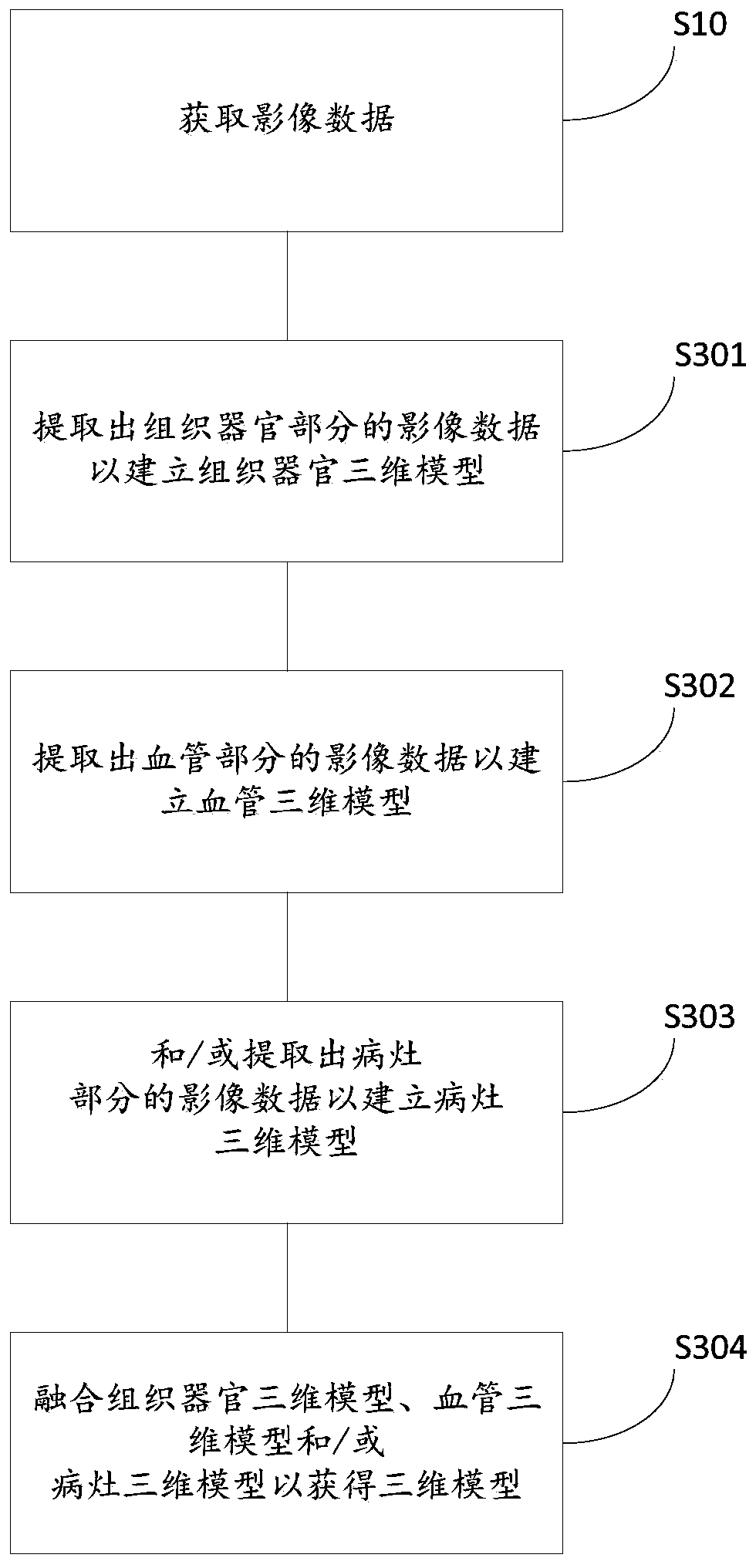
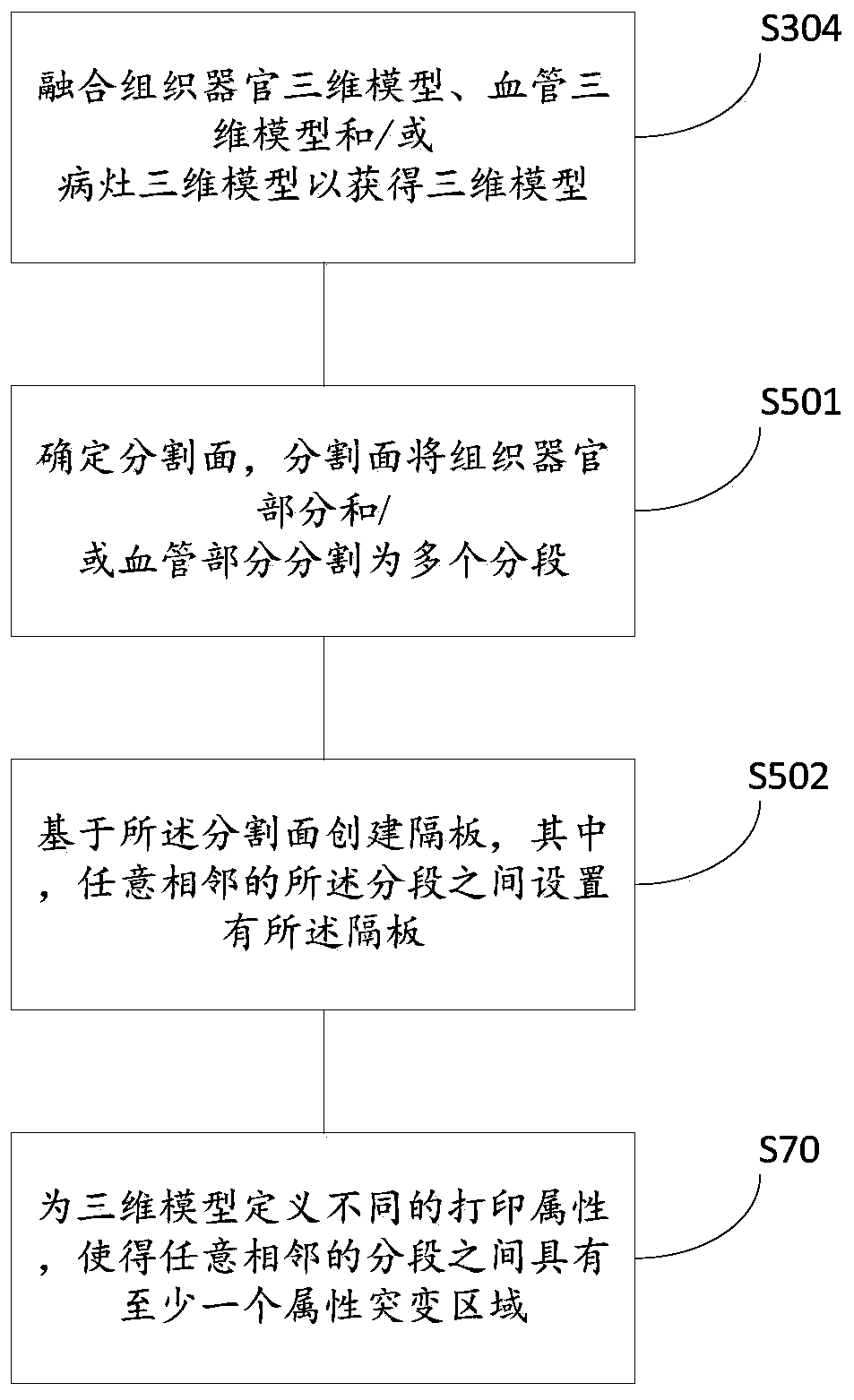
Three-dimensional organ model and printing method, device and equipment of three-dimensional organ model
ActiveCN110605853AIntuitive identificationAccurate identificationAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsOrgan ModelDimensional modeling
The invention relates to the technical field of printing and particularly relates to a three-dimensional organ model and a printing method, device and equipment of the three-dimensional organ model. The printing method of the three-dimensional organ model comprises the steps that image data are obtained; three-dimensional modeling is carried out based on the image data to obtain a three-dimensional model, wherein the three-dimensional model comprises at least one of a tissue organ part, a blood vessel part and a lesion part; the tissue organ part and / or the blood vessel part are / is divided into a plurality of sections; different printing attributes are defined for the three-dimensional model to make at least one attribute mutation area exist between any adjacent sections; and printing is carried out to obtain the three-dimensional organ model. By means of the three-dimensional organ model, the printing method, device and equipment of the three-dimensional organ model, all the sectionscan be visually and accurately distinguished, an operation path can be better planned, operation risks can be better reduced, and the purpose of precise medical treatment can be achieved.
Owner:ZHUHAI SAILNER 3D TECH CO LTD
Embolization polymer, novel blood vessel embolization chemotherapy composite as well as preparation and application of novel blood vessel embolization chemotherapy composite
InactiveCN109053953AImprove solubilityThe polymerization process is easy to controlOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesDiseaseCross-link
The invention provides an embolization polymer. The embolization polymer is prepared by performing polymerization reaction initiated by free radicals on micromolecule monomer containing unsaturated double bonds, monomer containing unsaturated double bonds and an optional cross-linking agent; the cross-linking agent is polyfunctionality water-soluble acrylate or acrylamide. The embolization polymeris an ion exchange microsphere carrier and has higher deformation ability and higher drug trapping efficiency and drug loading capacity; meanwhile, a slow release effect is better. The invention further provides a novel blood vessel embolization chemotherapy composite. The embolization chemotherapy composite disclosed by the invention can jointly deliver an embolization agent and chemotherapy drug to a target blood vessel part through a catheter, so that a curative effect of the chemotherapy drug is fully played, peripheral normal tissues are prevented from being damaged, and disease relapsing is reduced.
Owner:深圳市比德泰克生物医药科技有限公司
Device and method for creating retinal fundus maps
ActiveUS8073205B2Reduce volumeEasy to judgeImage analysisSubcutaneous biometric featuresData graphRadiology
A device has means for computing and obtaining blood vessel extraction images by extracting blood vessel portions from two or more fundus images, means for computing and obtaining a corner data image having corner portions of the blood vessel portions detected from the obtained blood vessel extraction image, means for computing and obtaining a probability distribution diagram for the corner data image by convolving the corner data image with a window function, means for computing a matching probability score when executing a matching processing between two or more fundus images on the basis of the probability distribution diagram corresponding to each fundus image obtained and the corner data image, and means for creating a retinal fundus map by superimposing two or more fundus images on the basis of the obtained matching probability score.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
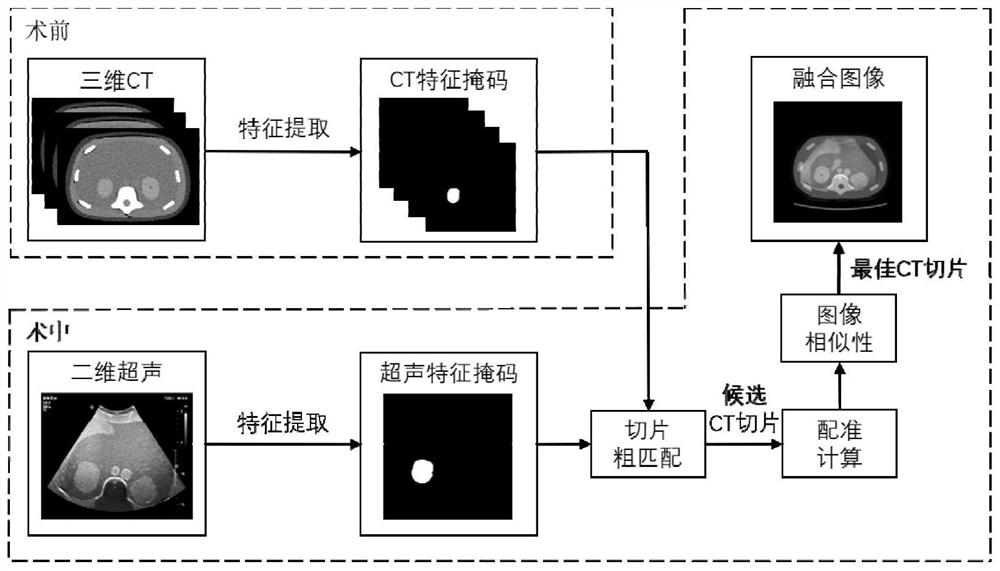
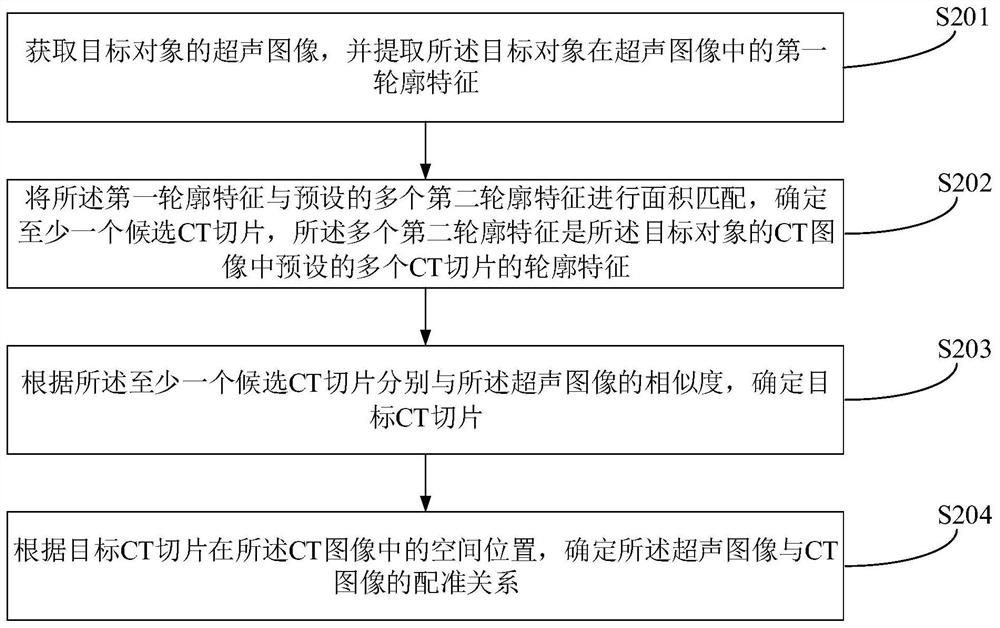
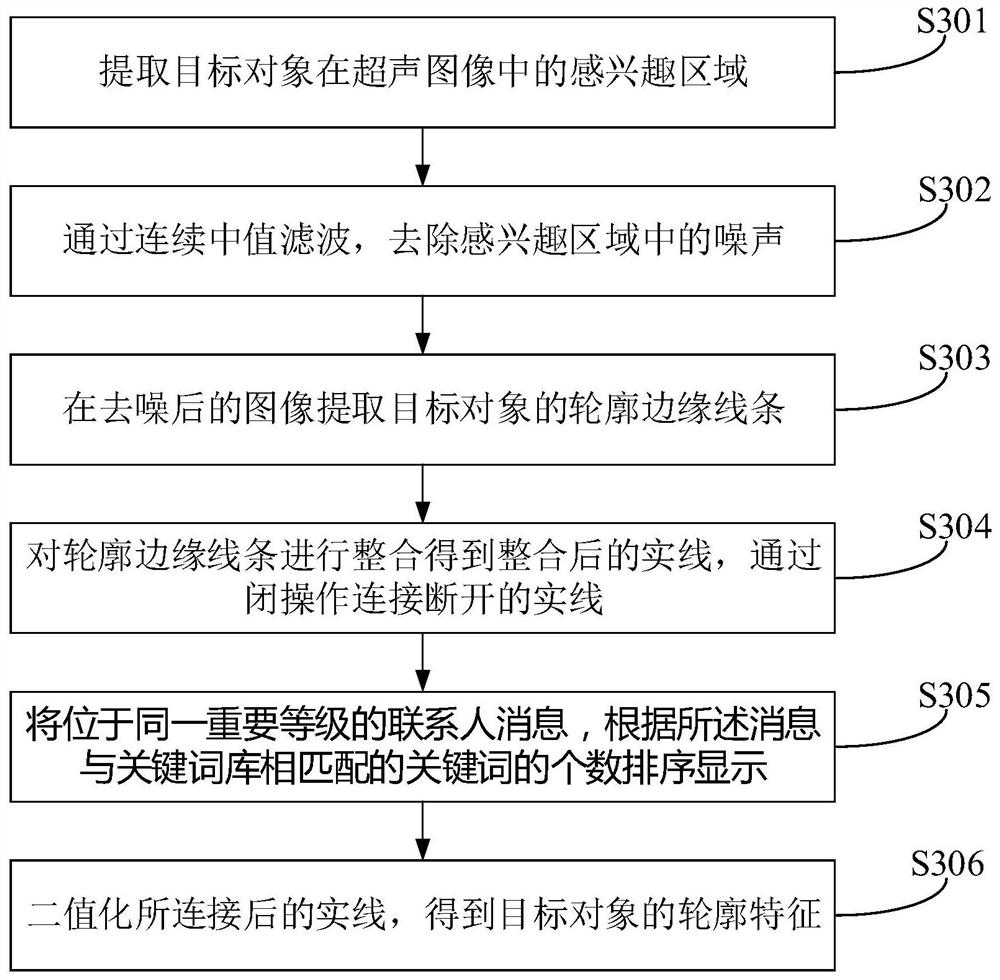
Ultrasonic image and CT image registration method, device and equipment
PendingCN112184781AReduce in quantityNot limited to rich partsImage enhancementImage analysisNuclear medicineImaging data
The invention belongs to the field of image data processing, and provides an ultrasonic image and CT image registration method, device and equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an ultrasonic image of a target object, and extracting a first contour feature of the target object in the ultrasonic image; performing area matching on the first contour feature and a plurality ofpreset second contour features, and determining at least one candidate CT slice; determining a target CT slice according to the similarity between the at least one candidate CT slice and the ultrasonic image; and determining a registration relationship between the ultrasonic image and the CT image according to the spatial position of the target CT slice in the CT image. The registration relation between the CT image and the ultrasonic image is determined only through the candidate CT slices, so that the number of CT slices needing registration calculation can be greatly reduced, the real-timeperformance of registration can be improved, the registration method is not limited to rich blood vessel parts, and the application range of the registration method can be widened.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
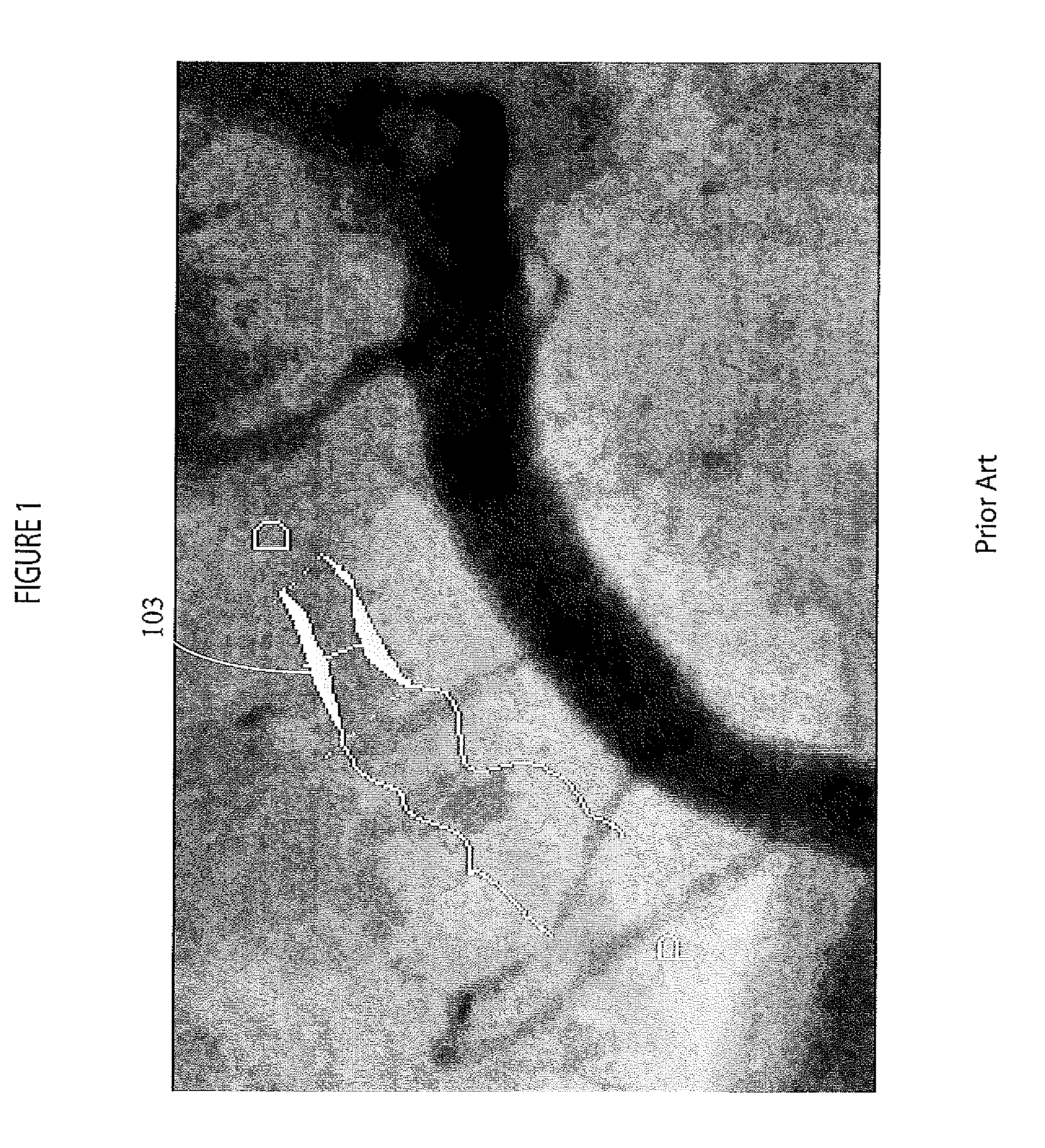
Automated system for anatomical vessel characteristic determination
ActiveUS8553954B2Prevent false detectionImage enhancementImage analysisNuclear medicineComputer science
A system enables a user to mark a ROI of a vessel portion having detected boundaries and extend the detection of vessel boundaries into a region identified by the user. An anatomical blood vessel detection and display system includes a user interface enabling a user, via a display of an image presenting anatomical vessels, to, mark a region of interest in a vessel identified by detected boundaries in the image and extend the marked region of interest of the vessel. A detector automatically detects a boundary of the vessel in the extended marked region of interest by detecting an edge representing a change in luminance in data representing the image. An image data processor identifies a minimum vessel diameter in the extended marked region of interest between the detected boundaries and initiates identification of the location of the minimum vessel diameter in the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Targeting antitumor drug using magnetic micro-nano material to destroy tumor blood vessels under driving of alternating magnetic field or radio frequency
ActiveCN105641695AHas a therapeutic effectAvoid harmPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsMicro nanoTumor target
The present invention discloses a novel use of a magnetic micro-nano material. The new use is application of the magnetic micro-nano material in manufacture of a targeting tumor treatment drug, the magnetic micro-nano material has all the following properties: (1) the magnetic micro-nano material is magnetic, sol that the magnetic micro-nano material can produce mechanical destructive effects on tumor blood vessel endothelial cells under driving of an alternating magnetic field or radio frequency; (2) the magnetic micro-nano material has a hydrophilic surface; (3) the magnetic micro-nano material has certain electronegativity on surface; and (4) the particle size range of the magnetic micro-nano material is 10-500nm, so that the magnetic micro-nano material has rigidity (namely, is not easy to deform). The magnetic micro-nano material can be specifically gathered and retained in tumor blood vessel parts by EPR effect after intravenous injection, and the mechanical destructive effects produced under driving of the alternating magnetic field or radio frequency can act on the tumor blood vessel endothelial cells highly selectively to further destroy tumor blood vessels to lead to tumor rapid necrosis and achieve the efficient tumor targeting treatment purpose.
Owner:赤峰福纳康生物技术有限公司 +1
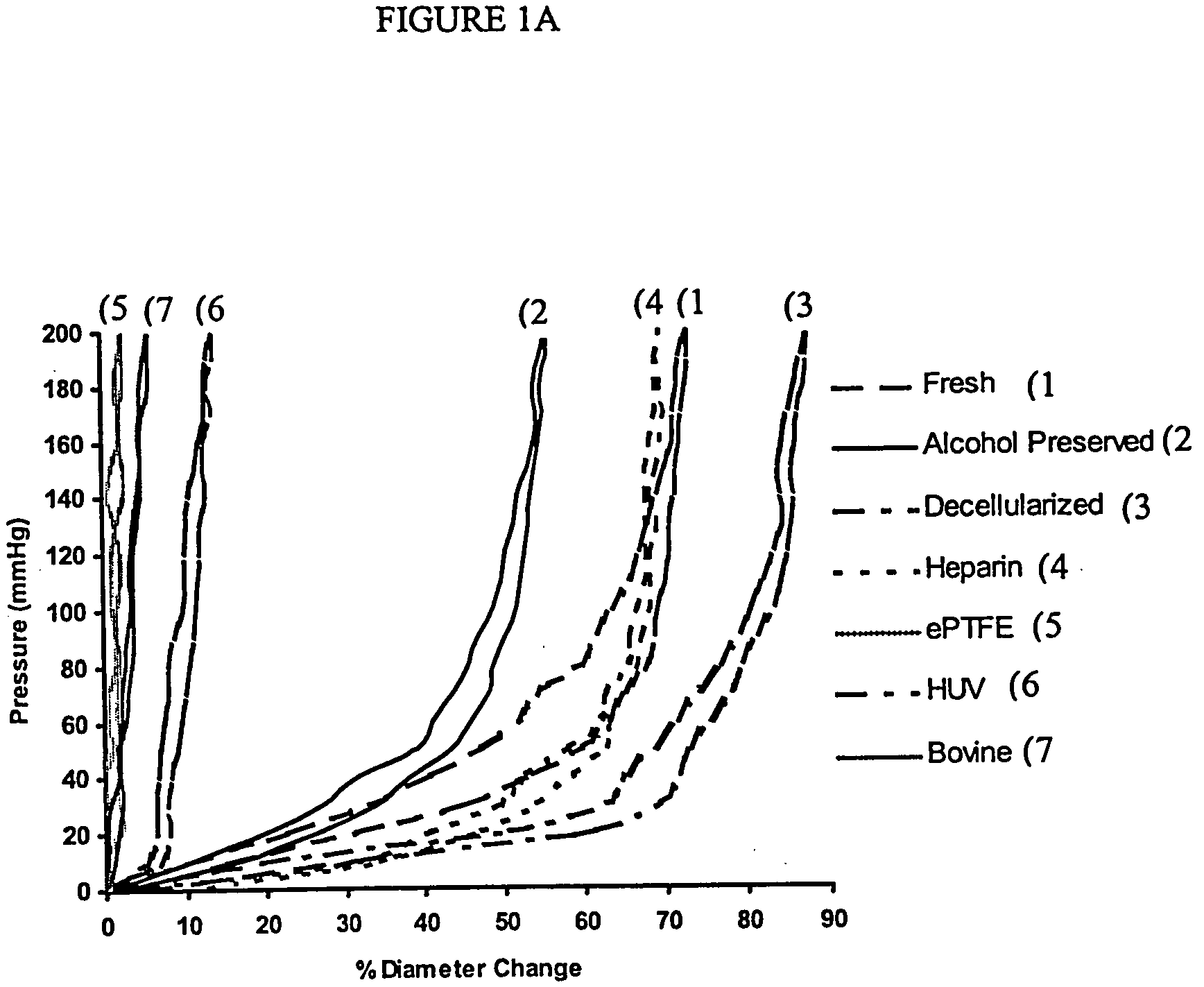
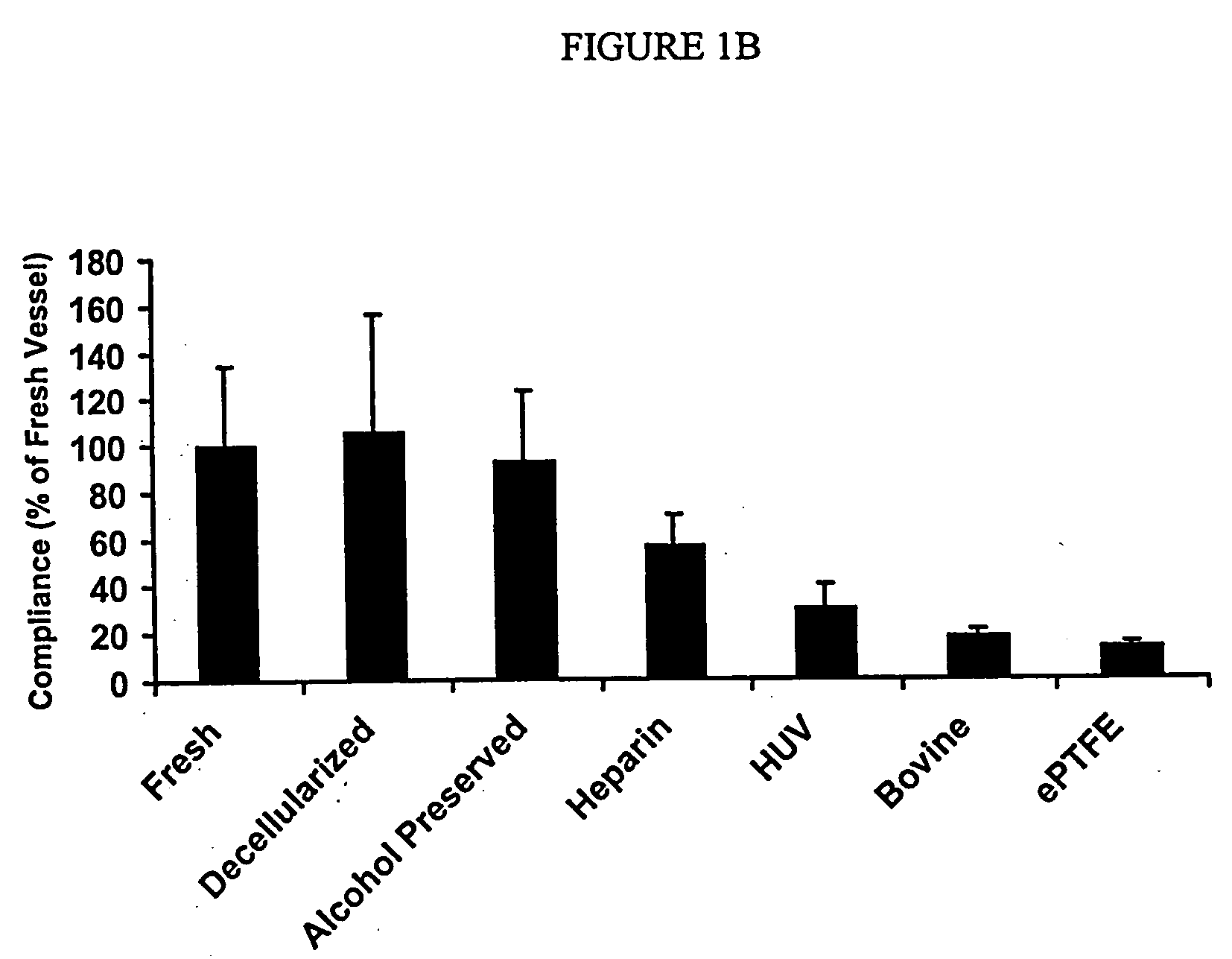
Decellularized vascular prostheses resistant to thrombus occlusion and immunological rejection
The present invention relates to decellularized vascular prostheses that are resistant to thrombus occlusion and have a low level of immunogenicity. The vascular prostheses are denuded of cells, and coated with an anti-thrombogenic agent and a growth factor that promotes recellularization and further reduces the immunogenicity. The prostheses have high mechanical strength, resist aneurysm rupture, and allow for secure surgical sutures while maintaining structural integrity. The present invention provides vascular prostheses that are blood vessels, valves or portions of vessels containing valves. The present invention is also useful for coating synthetic vascular stents.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Strontium chondroitin sulfate and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to strontium chondroitin sulfate and a preparation method thereof. The molecular formula of the strontium chondroitin sulfate is H2O(C14H19NSrO14S)x, wherein x is an integer of 60-100. According to the strontium chondroitin sulfate, the problems of petechiae and hematoma caused by calcium deposition of blood vessel parts and blood capillary parts can be avoided, and osteoporosis and osteoarthritis can be better treated in an aid way.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Medical image processing system and medical image processing method
ActiveUS7697740B2Evaluated more accuratelyAccurate assessmentCharacter and pattern recognitionTomographyThree dimensional ctImaging processing
IVR-CT apparatus has an angio-image obtaining unit, an angio-image imaging direction obtaining unit, a CT-image obtaining unit, a blood vessel part extracting unit, a projected image generating unit and a display control unit. The angio-image obtaining unit obtains a required angio-image from multiple chronological angio-images. The angio-image imaging direction obtaining unit obtains a direction of imaging as incidental information included in data on the required angio-image. The CT-image obtaining unit obtains a three-dimensional CT-image corresponding to the required angio-image. The blood vessel part extracting unit extracts a blood vessel part in the three-dimensional CT-image. The projected image generating unit generates a three-dimensional projected image by projecting the blood vessel part, and a three-dimensional projected image corresponding to a direction of a projection after a manual operation operates the direction of the projection. The display control unit makes display the three-dimensional projection image and the angio-image one over another.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
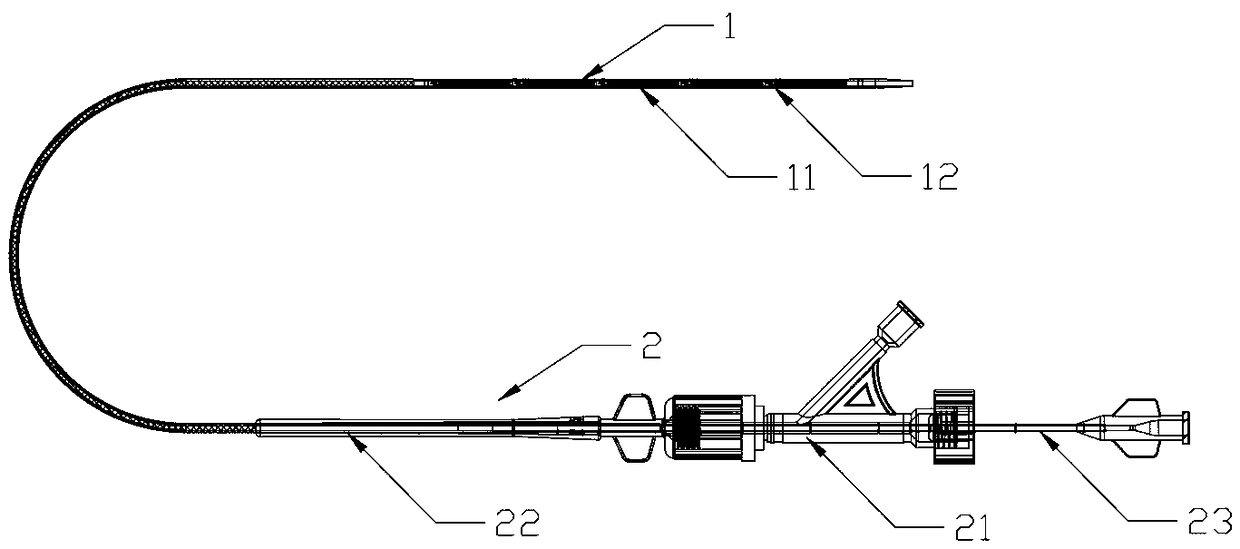
Systems and methods for delivering an implantable device
ActiveUS10772565B2Prevent movementBalloon catheterDiagnostic recording/measuringExternal catheterImplanted device
The delivery system may include, for example, an outer catheter having a distal tip and an inner support member, such as an inner catheter, disposed within the outer catheter. The inner support member includes an anchor member adjacent a distal tip of the inner support member and a support portion axially inward of the anchor member. The support portion is configured for supporting an implantable device thereon. A diameter of the anchor member corresponds to a diameter of a portion of a vessel in which the anchor member is to be disposed. The anchor member is configured to be lodged in the portion of the vessel to locate an intended position of the anchor member and to prevent movement of the inner support member relative to the vessel during release of the implantable device.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Blood vessel identifying method and device
InactiveCN1564191AImprove stabilityEasy to useCharacter and pattern recognitionInfraredPattern recognition
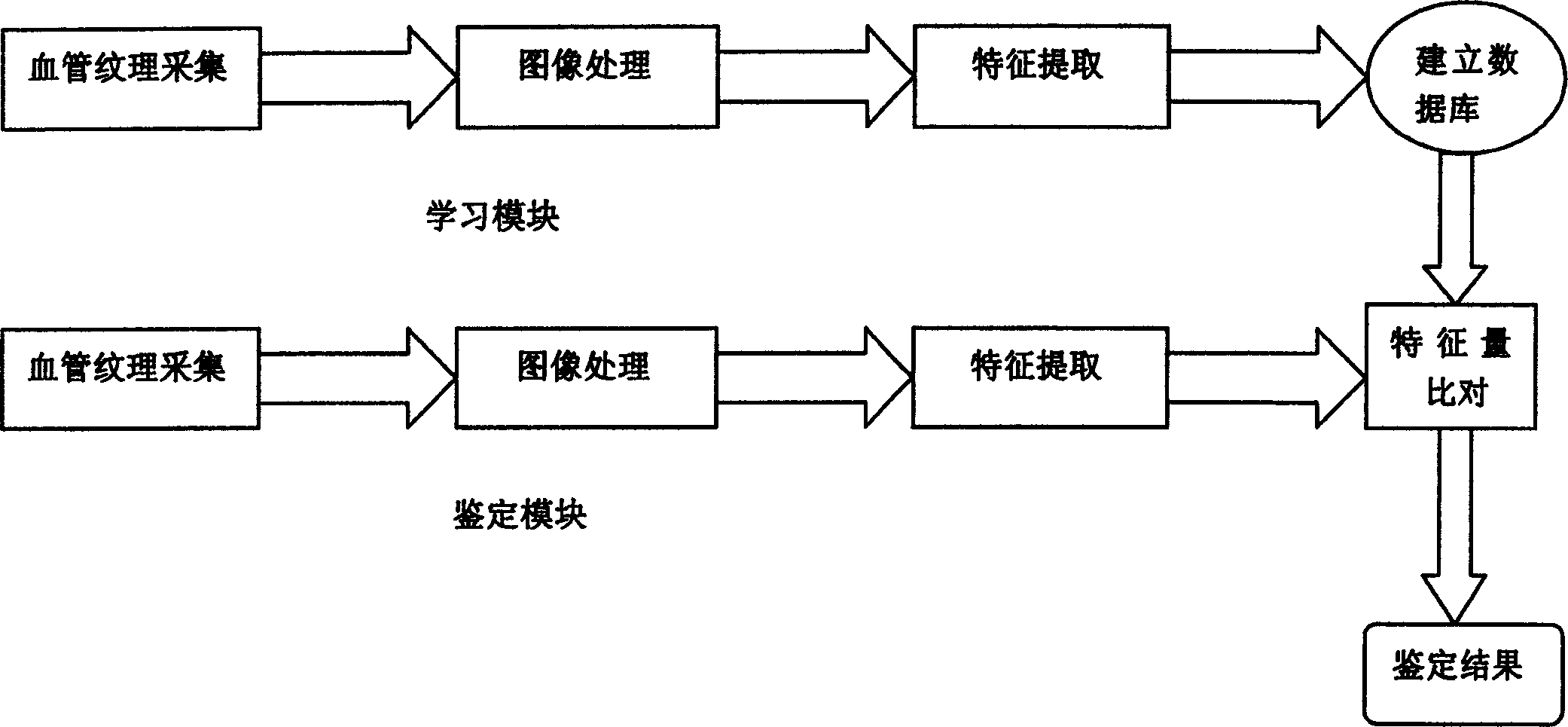
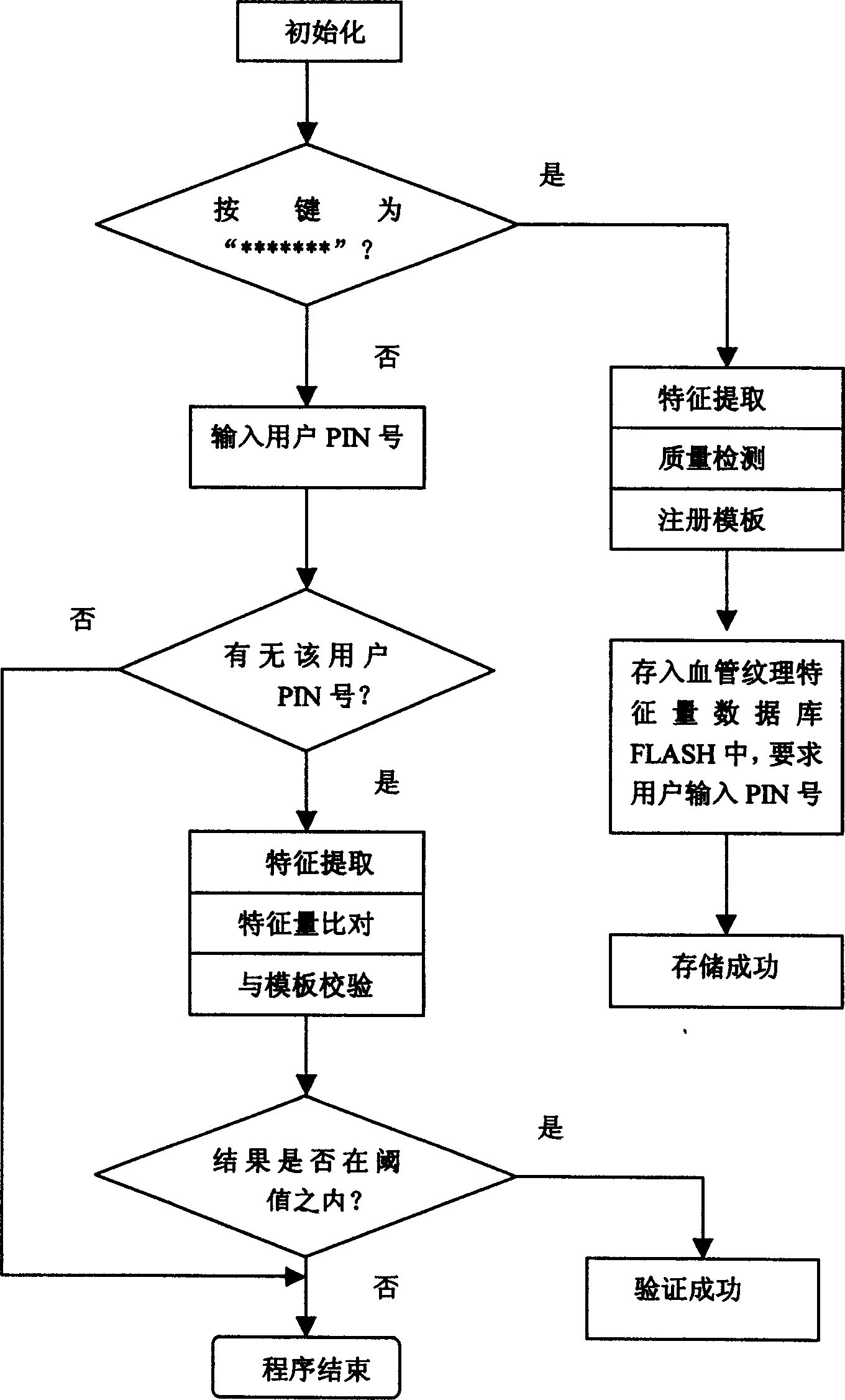
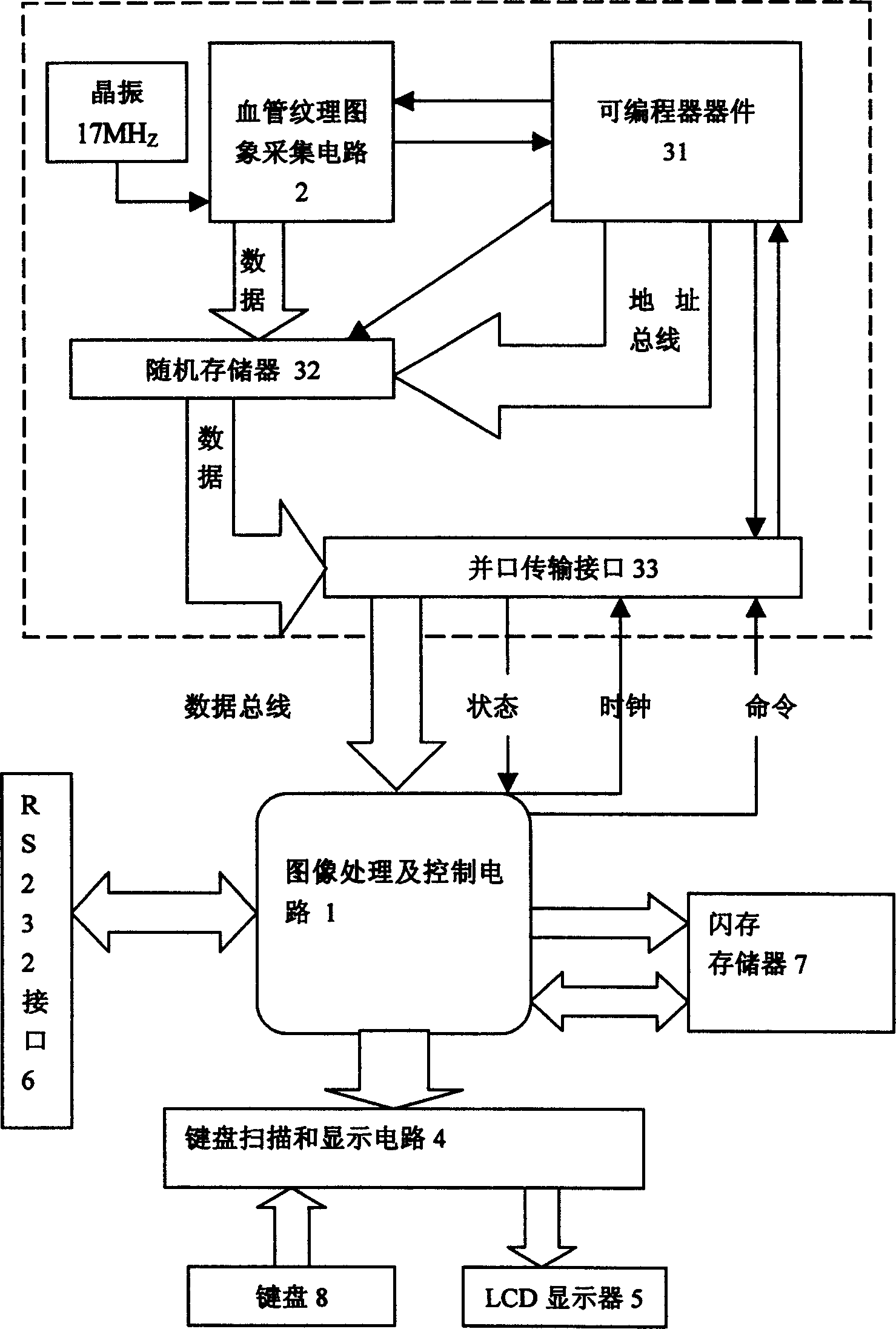
The invention relates to method for recognizing human id by using bioassay technique. Operation steps are as following: (1) irradiating blood vessel part to be tested by using near infrared auxiliary light to collect texture image of blood vessel; (2) pretreatment of texture image including: carrying separation of background by using threshold tracking method of standard deviation to determine foreground and back ground, and removing noise through bilevel, then thinning operation; (3) distinguish out singular points, converting issue of authenticating vessel texture into the issue of dot mode matching; (4) converting point coordinates of singular point to polar coordinates, which is stored into database as template filed; (5) characteristic matching: locking reference position first, then carrying out comparison; in comparison template stored in database and user's PID number constitutes original template of characteristic data.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Cubic cyclodextrin framework-RGD composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111440253AImprove securityGood biocompatibilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCyclodextrin
The invention provides a cubic cyclodextrin framework-RGD composition (RGD-COF) and a preparation method thereof. Specifically, the cyclodextrin framework-RGD composition of the present invention contains a cyclodextrin framework (COF) having a cubic structure and RGD. The cubic cyclodextrin framework-RGD composition disclosed by the invention can avoid phagocytosis and elimination of macrophages,enhance the mobility and the adhesion to damaged blood vessels and efficiently target and gather at activated blood platelets at the damaged blood vessel parts, and has great application prospects ontargeted diagnosis and treatment of vascular related diseases such as out-of-control hemorrhage, atherosclerosis and cerebral apoplexy. The invention provides a nanoscale cubic cyclodextrin framework-RGD composition which can be used for intravenous injection or a micron-scale cubic cyclodextrin framework-RGD composition which can be used for local external application by utilizing the advantagethat the size of a cyclodextrin-metal organic framework (CD-MOF) is controllable.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
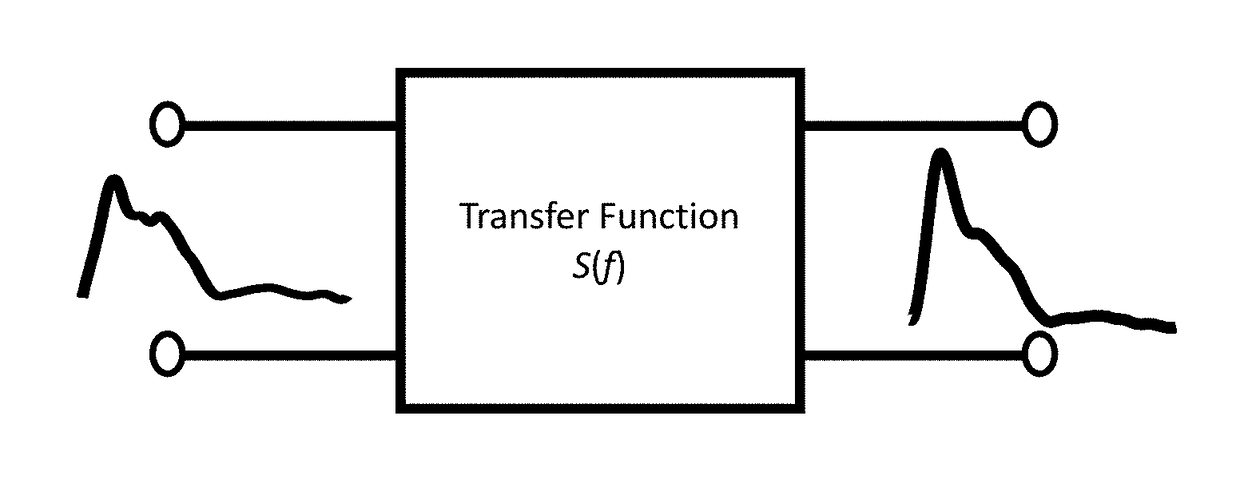
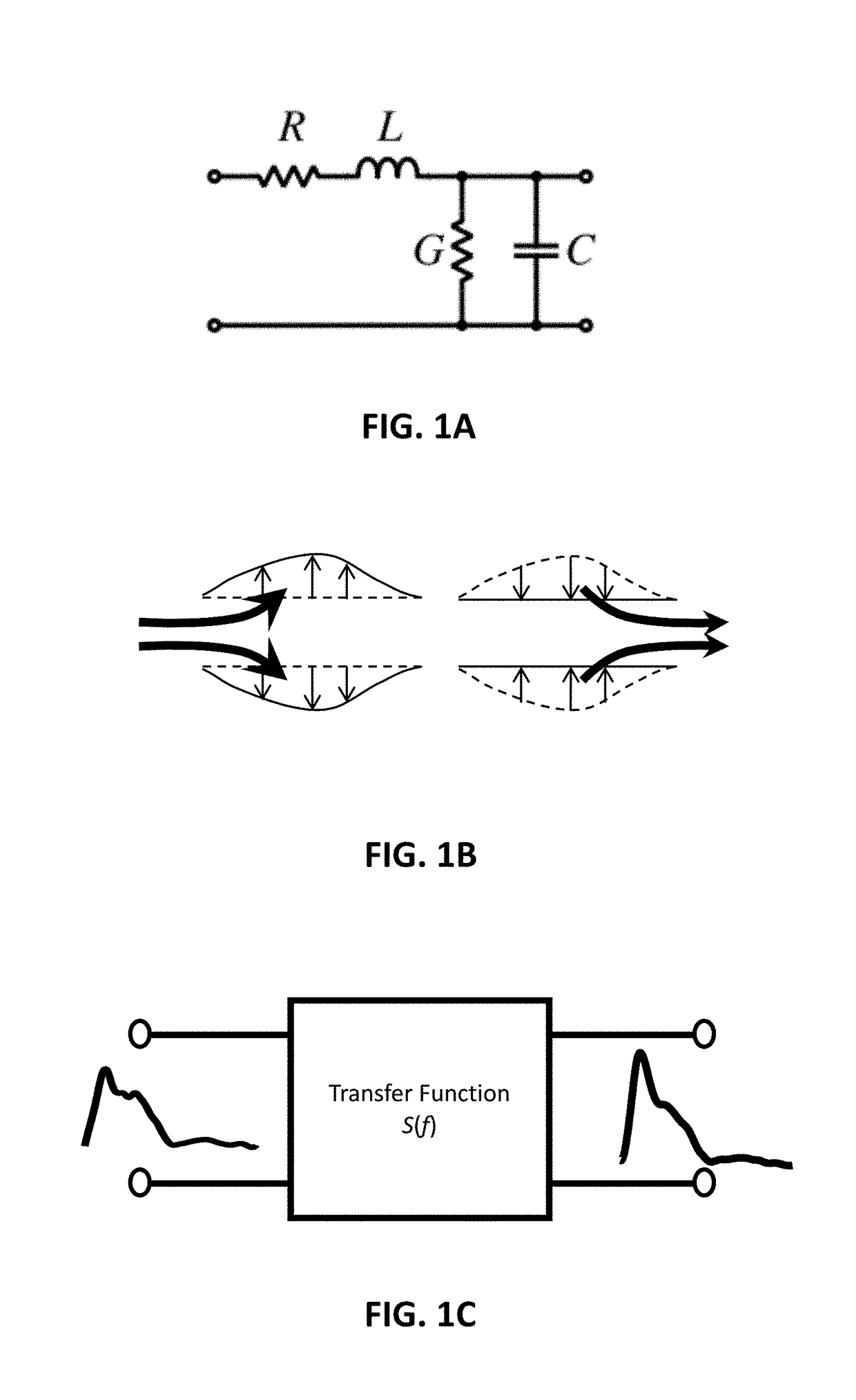
Method and system for evaluating blood vessel
ActiveUS20180125376A1Organ movement/changes detectionEvaluation of blood vesselsCOPDCoronary arteries
A method and system for evaluating physiological properties of a segment of blood vessel is provided. The method includes: acquiring a first measurement and a second measurement respectively at the first point and the second point; obtaining a transfer function configured to produce an output given an input, using the first measurement and the second measurement as the input and the output respectively; and determining the physiological properties of the section of the blood vessel based on the transfer function. The transfer function can be a velocity transfer function based on the blood velocity waveforms, or can be a pressure transfer function based on the blood pressure waveforms. The method and system can be used to non-invasively diagnose PH, COPD, and PA impedance in a pulmonary artery, and to detect a stenosis in a coronary artery.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
Vascular intervention operation simulator
PendingCN111081126ASimulate the realTo achieve the effect of observation operationCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsCoronary arteriesBlood flow
The invention provides a vascular interventional operation simulator which is used for simulating an operation object of a medical vascular interventional operation. The whole equipment is composed ofa blood circulation simulation system, a basic blood vessel and a focus blood vessel. The blood vessel circulation simulation system is composed of a water pump, a simulation liquid, a return pipe and a pressure and flow velocity sensor and simulates human blood flow conditions. A basic blood vessel is composed of a heart, a peripheral blood vessel and a local limb section which are made of transparent materials and used for simulating a blood vessel passage of an interventional operation, focus blood vessels comprise a coronary artery blood vessel and a common branch blood vessel, are used for simulating diseased blood vessel parts of a human body and can be connected to the basic blood vessel in a replaceable mode. The device can truly simulate the distribution conditions of blood vessels, blood flow and focuses of a human body, can be used for medical personnel to simulate the operation of a vascular interventional operation, and is particularly suitable for interventional operation training of the medical personnel novice, so that the medical personnel can be familiar with the operation process of the operation within a short time at zero risk. In addition, the vascular interventional operation simulator can also be used for research and development experiments of vascular interventional operation equipment, and the practicability of the equipment can be conveniently verified.
Owner:博联众科(武汉)科技有限公司
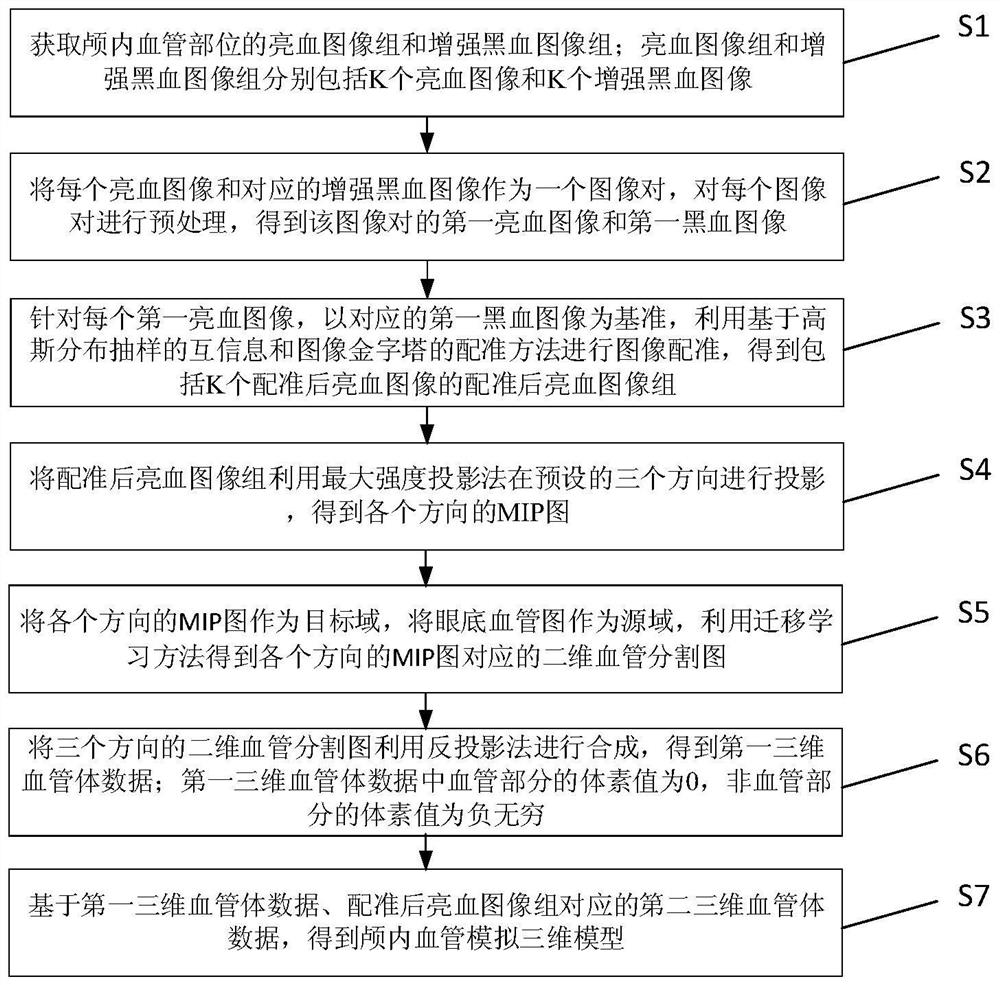
Method for quickly establishing intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional model based on transfer learning
PendingCN112562058ARealize 3D visualizationImprove registration efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisVascular bodyBlack blood
The invention discloses a method for quickly establishing an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model based on transfer learning. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a bright blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group of an intracranial blood vessel part; preprocessing each bright blood image and the corresponding enhanced black blood image to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image; performing image registration on the first bright blood image by using mutual information based on Gaussian distribution sampling and a registration method of an image pyramid; utilizing a maximum intensity projection method to obtain MIP images in all directions from the registered bright blood image groups; taking the MIP image as atarget domain, taking the fundus blood vessel image as a source domain, and obtaining a two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation image by using a transfer learning method; performing back projectionsynthesis on the two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation images in the three directions to obtain first three-dimensional blood vessel body data; and obtaining an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the second three-dimensional blood vessel body data corresponding to the registered bright blood image group. According to the method, the whole state of the intracranial blood vessel can be simply, conveniently, quickly and visually obtained clinically.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Sealing-type self-expanding unit stent
PendingCN108852570ASatisfies the situation where multiple stents are required for one interventionShorten operation timeStentsInsertion stentMulti segment
The invention discloses a sealing-type self-expanding unit stent. The unit stent includes a main body segment and a developing mark part connected to one end of the main body segment; the main body segment is of a tubular structure and has a shrinking state and an expansion state, wherein under the shrinking state, the main body segment is conveniently put into a blood vessel; under the expansionstate, the main body segment expands in the blood vessel. The main body segment includes triangular waveform units which are connected with one another into a whole part in the circumferential and axial directions of the stent under the shrinking state. Each triangular waveform unit is provided with an octagonal sealing frame body formed under the expansion state. The multi-segment stent can be distributed in a lesion blood vessel part for supporting; after being implanted, compared with stents of the same kind, the sealing-type self-expanding unit stent has the advantages that positioning isstable, a rejection effect on the human body is small, and bloodstream interference is small.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BARTY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Embedded controllable blood vessel shutting device
The invention relates to an embedded controllable blood vessel shutting device. The device comprises a shell, an actuator and a control module, the shell can be freely opened or closed, and the bloodvessel can be partly contained or moved out of the shutting device when the shell is opened; the control module is used for providing electric energy and control signals for the actuator; the actuatoris located between an inner tube and the shell, and the actuator is powered on and can expand, deform and compress the blood vessel, so that the tube wall of the inner tube is deformed and then the blood vessel which is contained in the inner tube is compressed. The embedded controllable blood vessel shutting device is designed aiming at the requirements for treating intracranial aneurysm, skullbase neoplasms or other brain diseases and the defects of an existing method that the lesion blood supply internal carotid is cut off in advance. The device can be completely implanted into the humanbody and can wrap the blood vessel, and the internal carotid can be controllably and slowly shut. In the gradual shutting process, the brain tissue for blood supply of the internal carotid can obtaincompensatory blood supply of other blood vessels and get rid of the dependence of the internal carotid, cerebral infarction cannot be caused when the internal carotid is cut off, and conditions are created for disease treatment.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Artificial blood vessel for realizing zero-angle bypass grafting
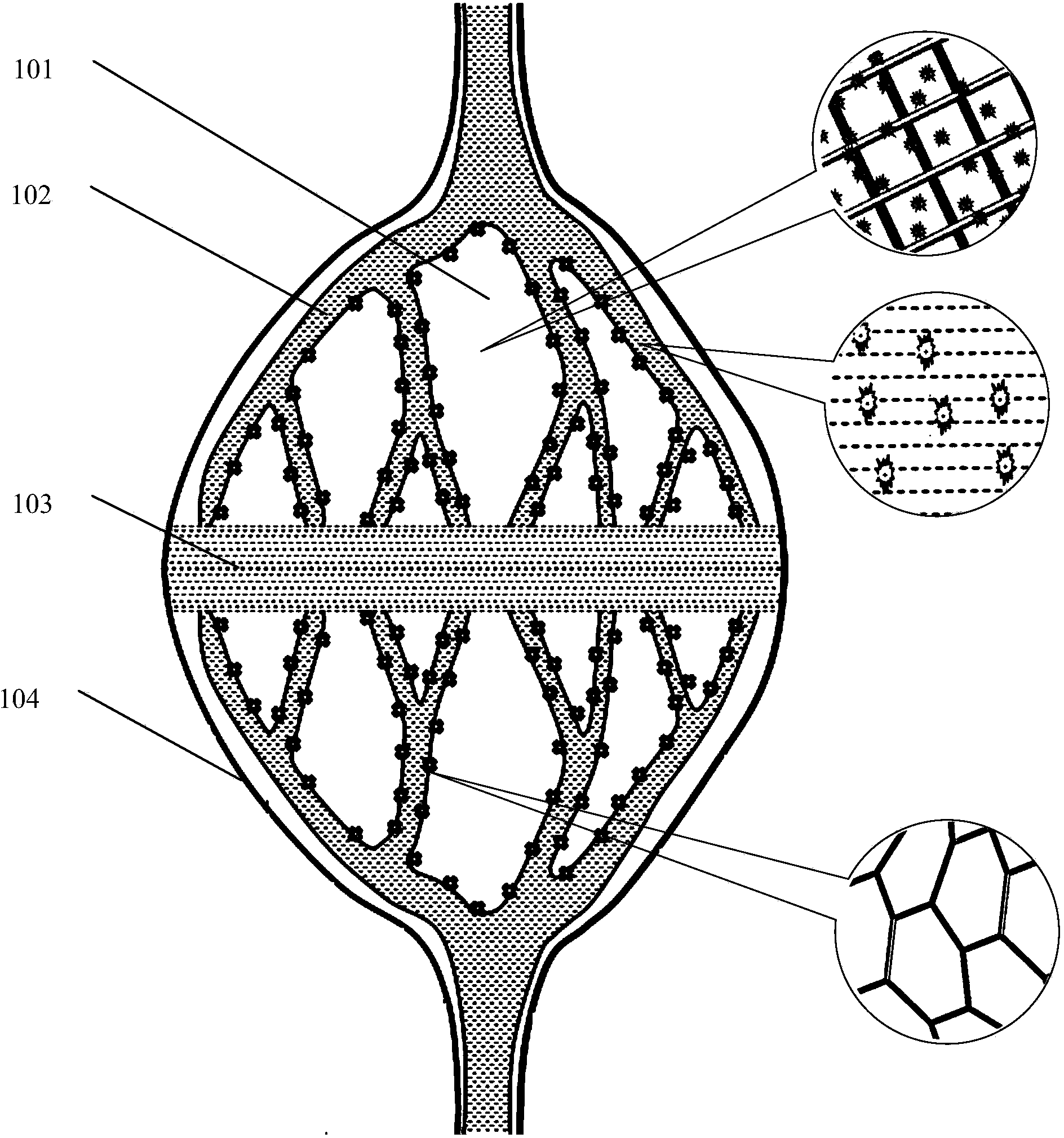
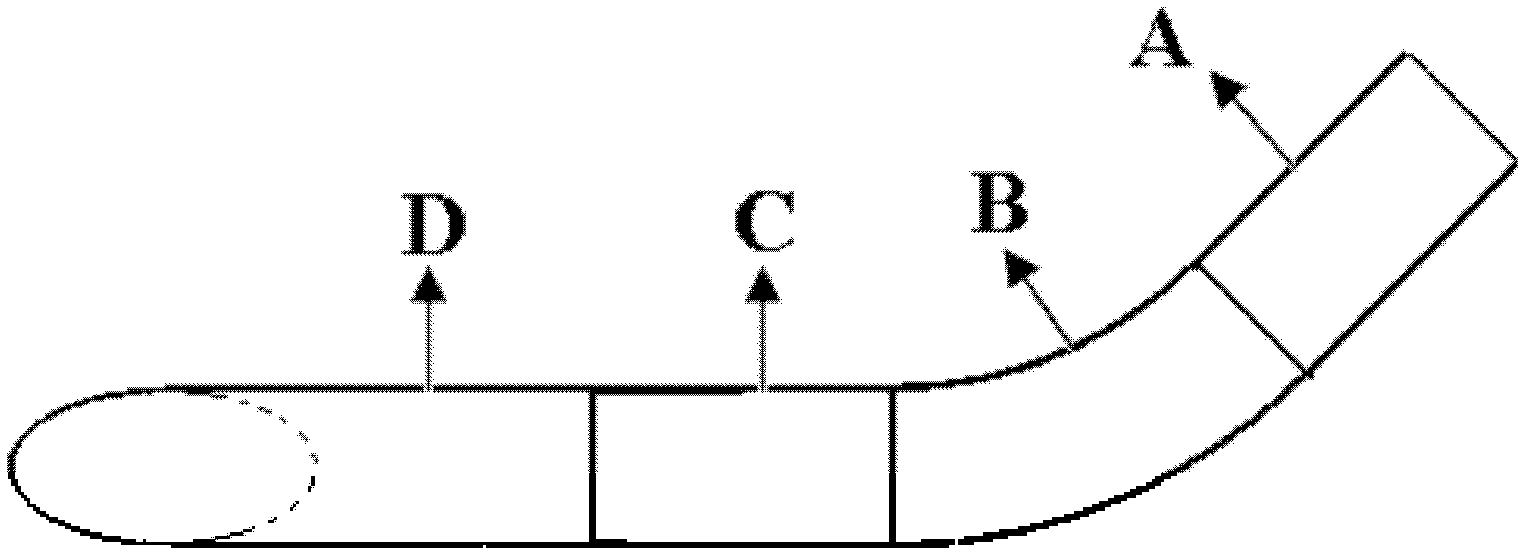
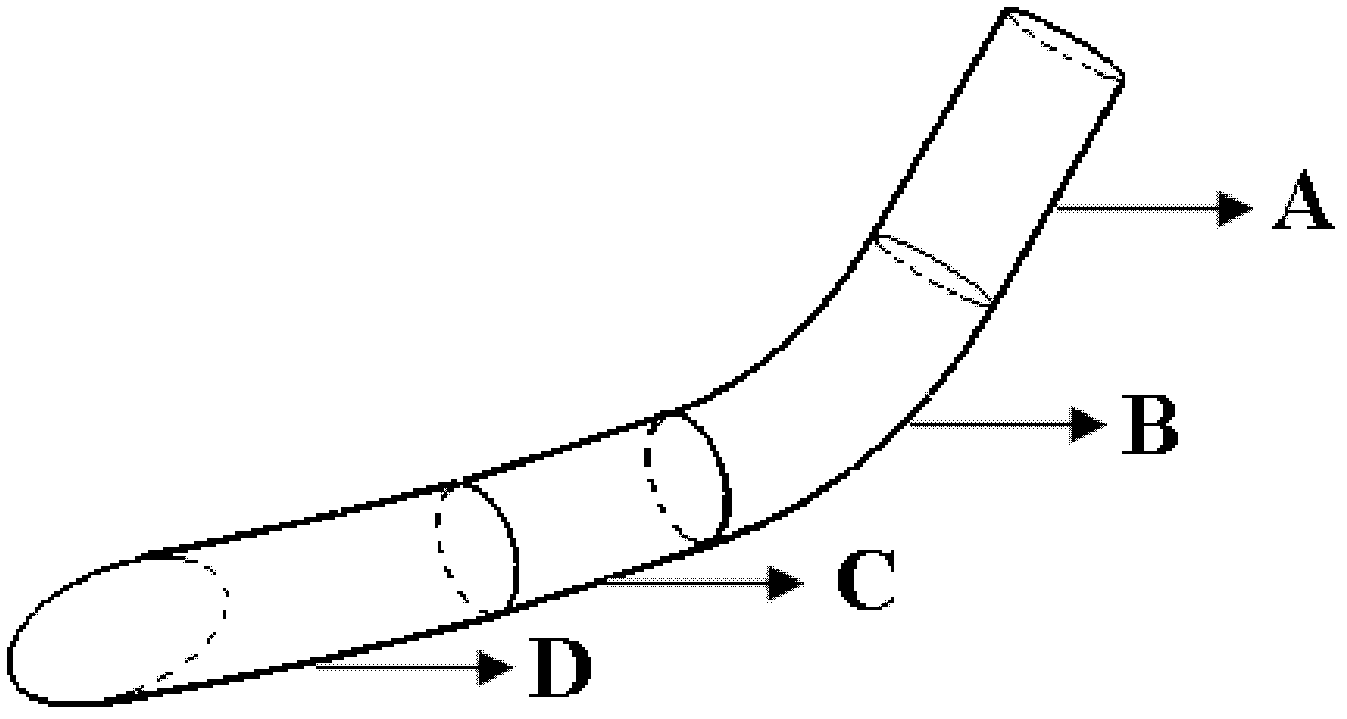
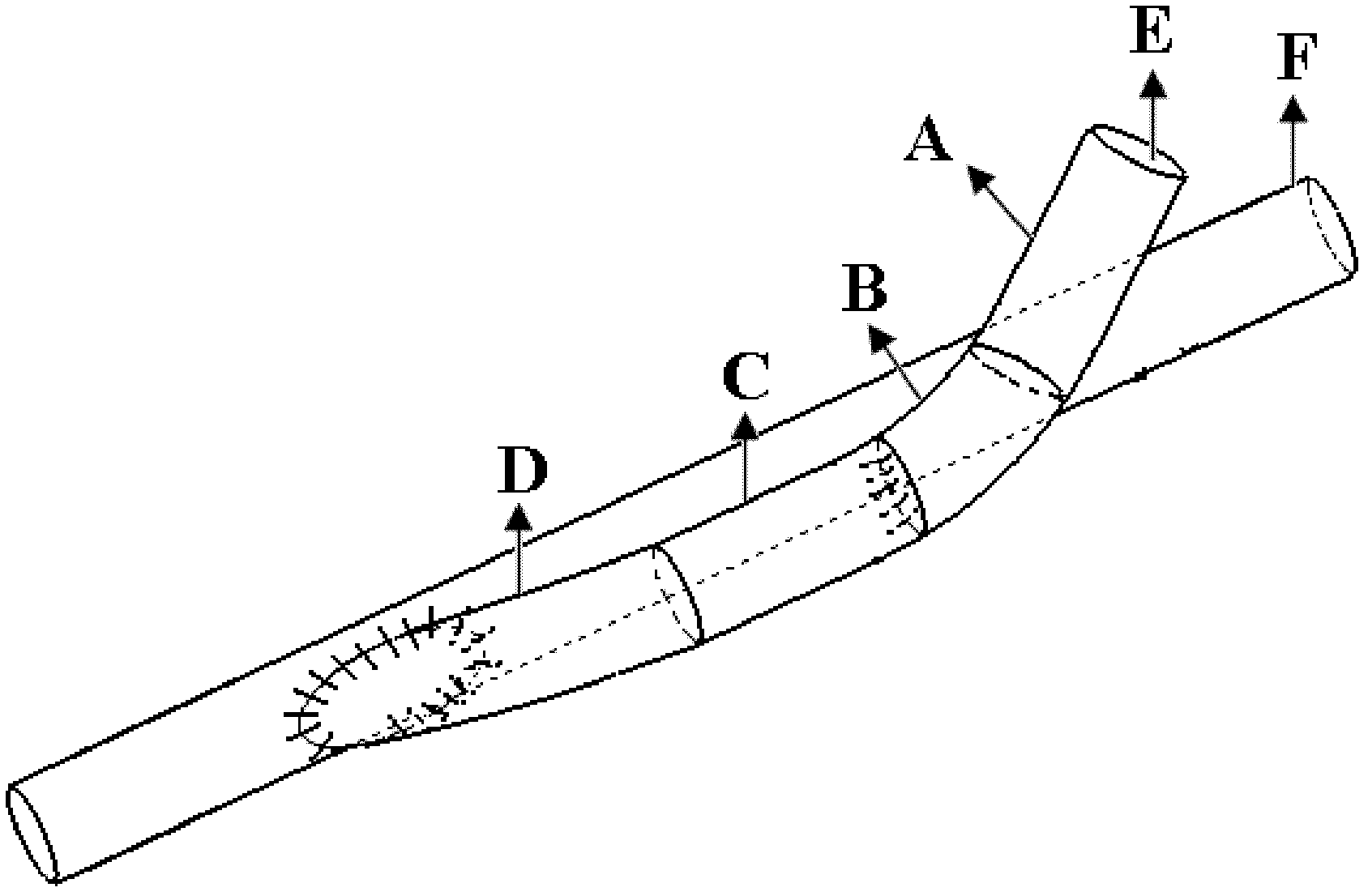
InactiveCN102198023AReduce disturbanceImprove the hemodynamic environmentBlood vesselsPercent Diameter StenosisBypass grafts
The invention discloses an artificial blood vessel for realizing zero-angle bypass grafting, which is characterized by comprising an artificial bypass grafting blood vessel (E part in a figure), a common artificial blood vessel part (A in the figure), round-cornered transition part (B in the figure), a parallel blood vessel part (C in the figure) and a tail end stitched edge (D in the figure), wherein the four parts are combined into a whole. An F part in the figure is a sketch map of a blood vessel to be grafted with a bypass. Compared with the conventional artificial bypass grafting blood vessel, the artificial blood vessel has a round-cornered part which allows the blood flowing direction in the bypass grafting blood vessel to gradually reduce an included angle with the axial direction of the blood vessel to be grafted with the bypass to zero degree and to be parallel to the axial direction of the blood vessel, so that the bypass grafting blood vessel is stitched with the blood vessel to be grafted with the bypass in a zero-angle mode; therefore, the disturbance of blood flow in a bypass grafting stitching part is minimized, and the restenosis of blood vessel after the bypass grafting is inhibited effectively.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for diagnosing and positioning coronary artery stenosis by using computer
InactiveCN114359140AAdd depthImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesComputer vision
The invention relates to a method for diagnosing and positioning coronary artery stenosis by using a computer, which comprises the following steps of: processing a first multi-dimensional coronary artery matrix depth information image through calculation, and calculating and processing a first stenosis area blood vessel part Kt in the first multi-dimensional coronary artery matrix depth information image through a first calculation unit to obtain a first image A; and performing first image instance segmentation Go on the first image A to obtain a segmented second coronary artery blood vessel image.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com