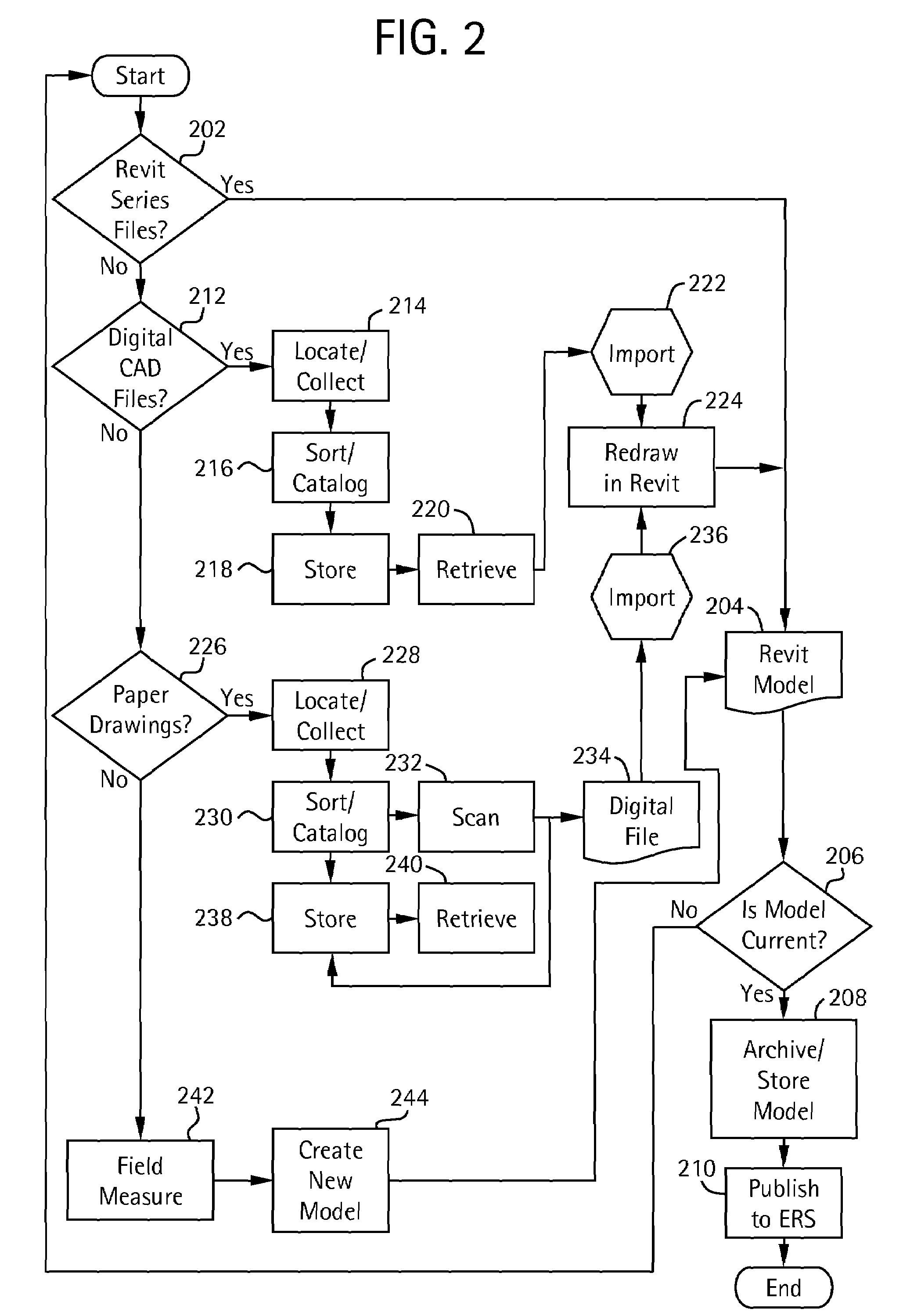
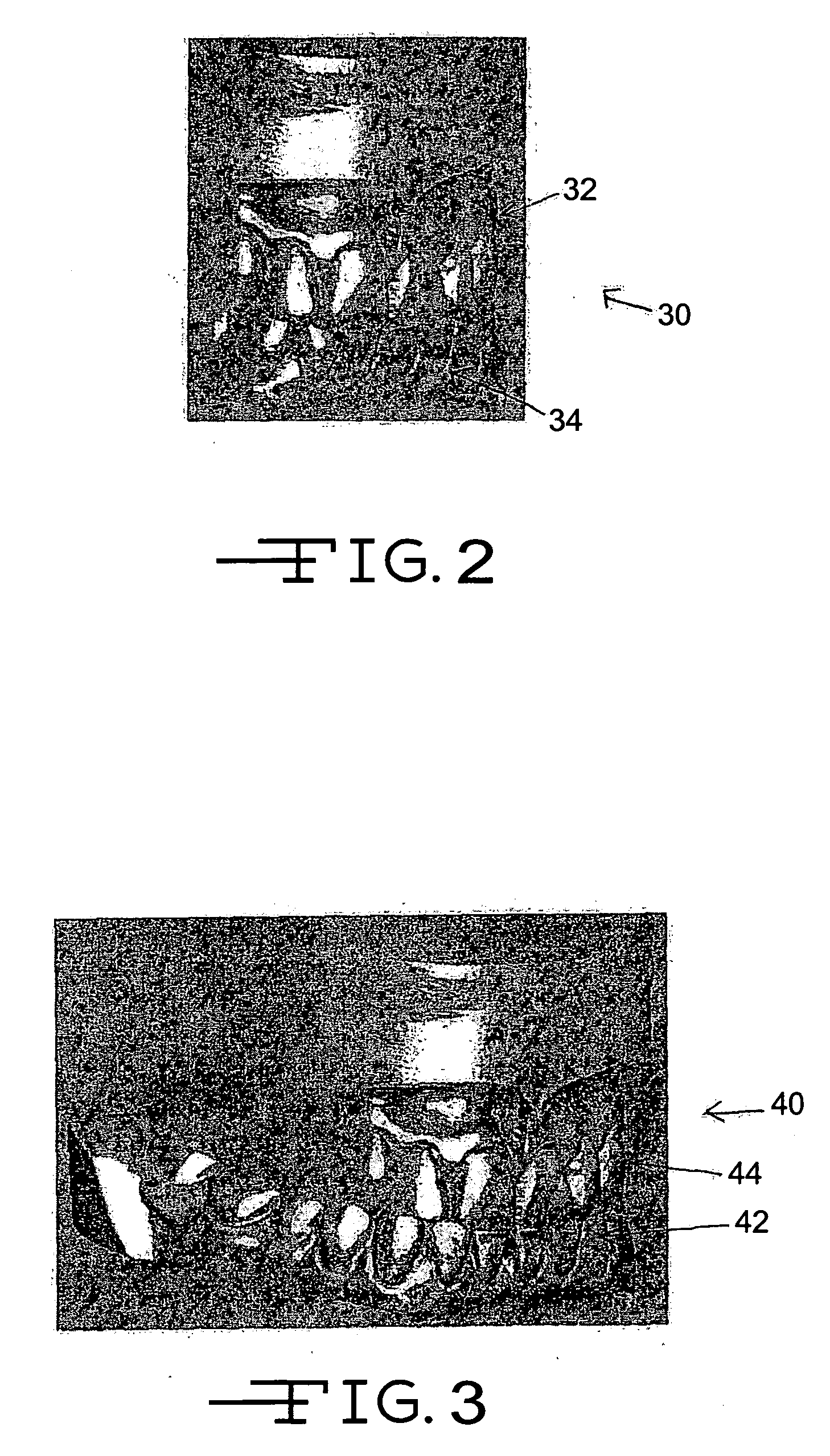
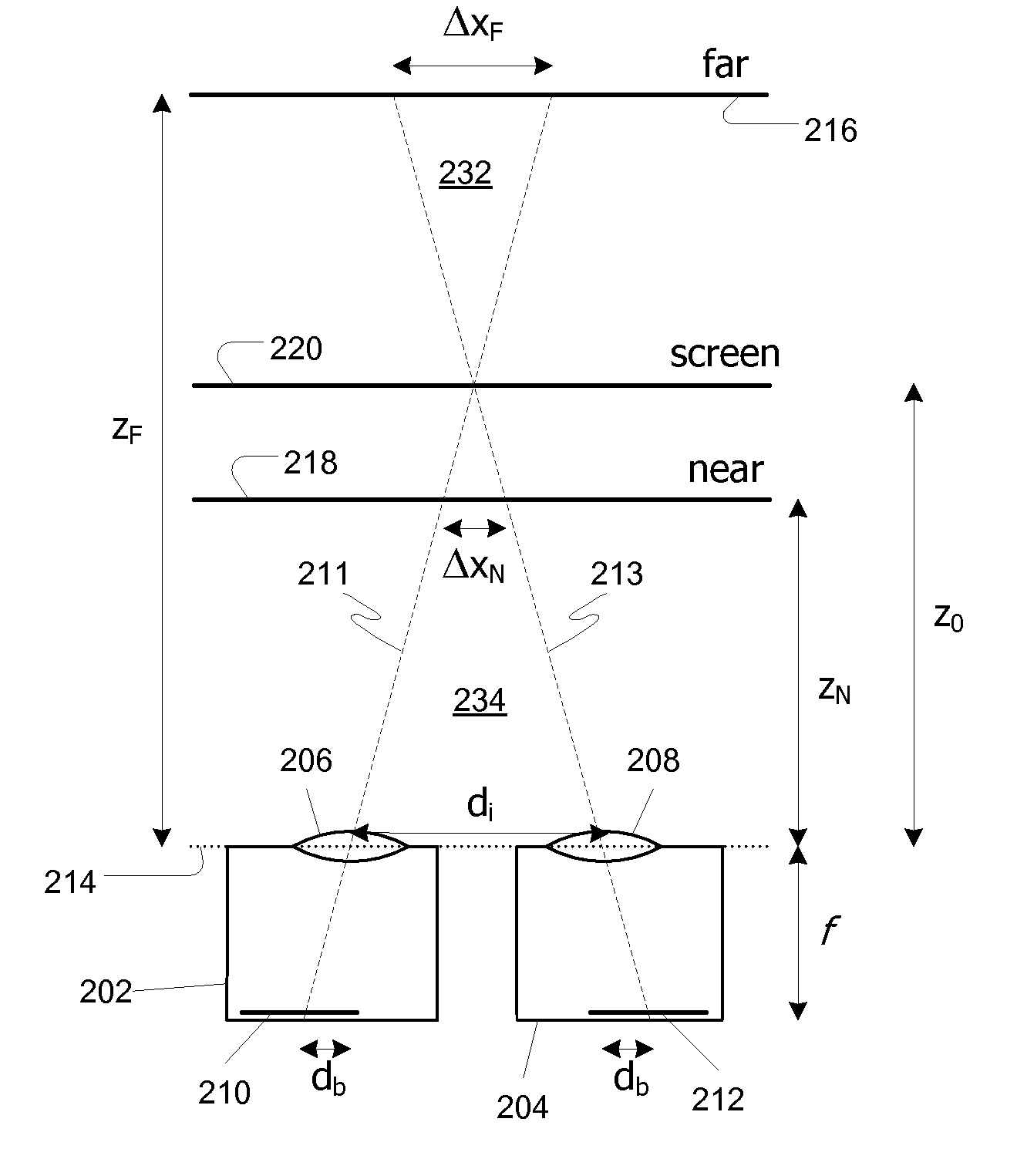
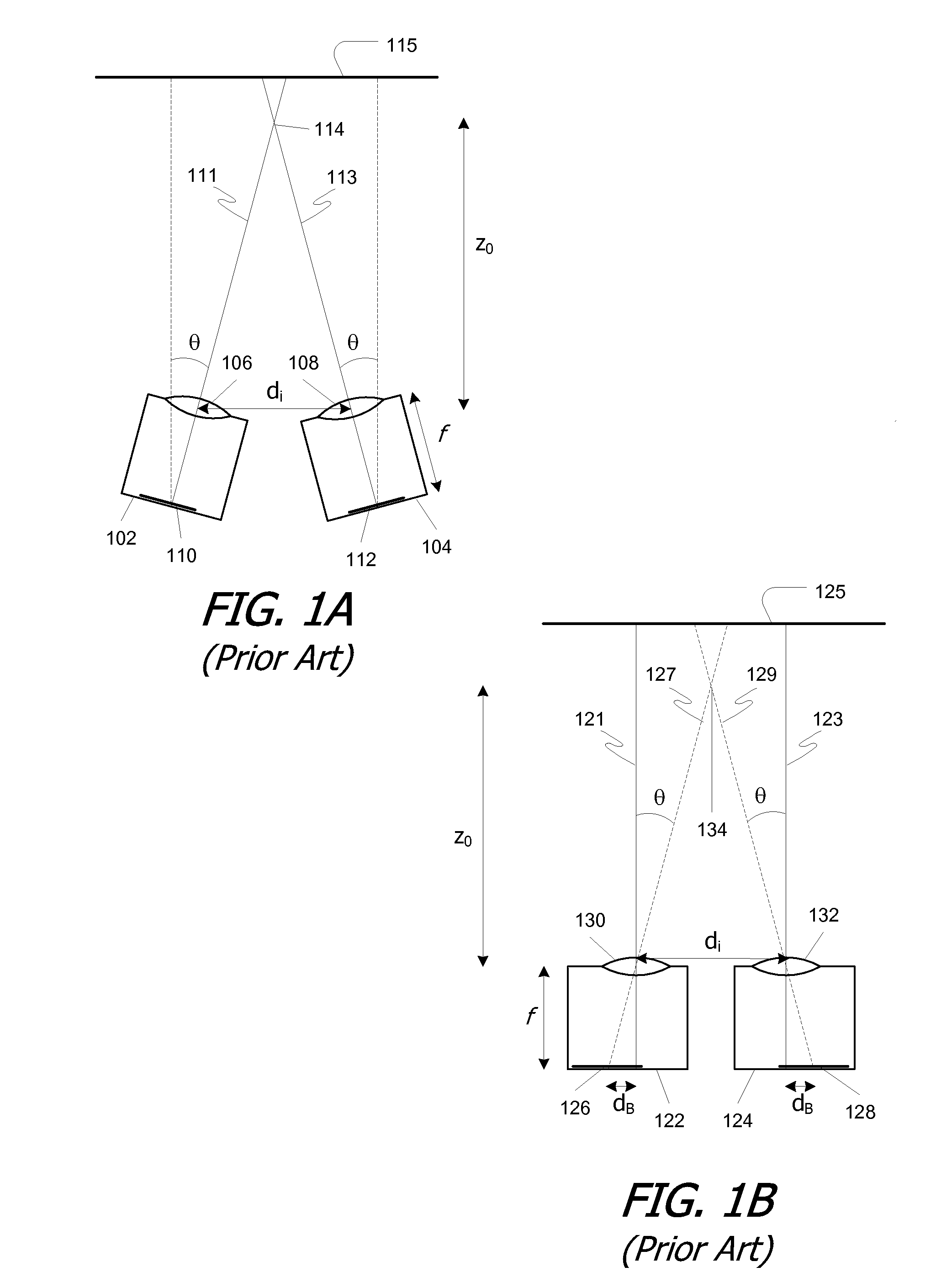
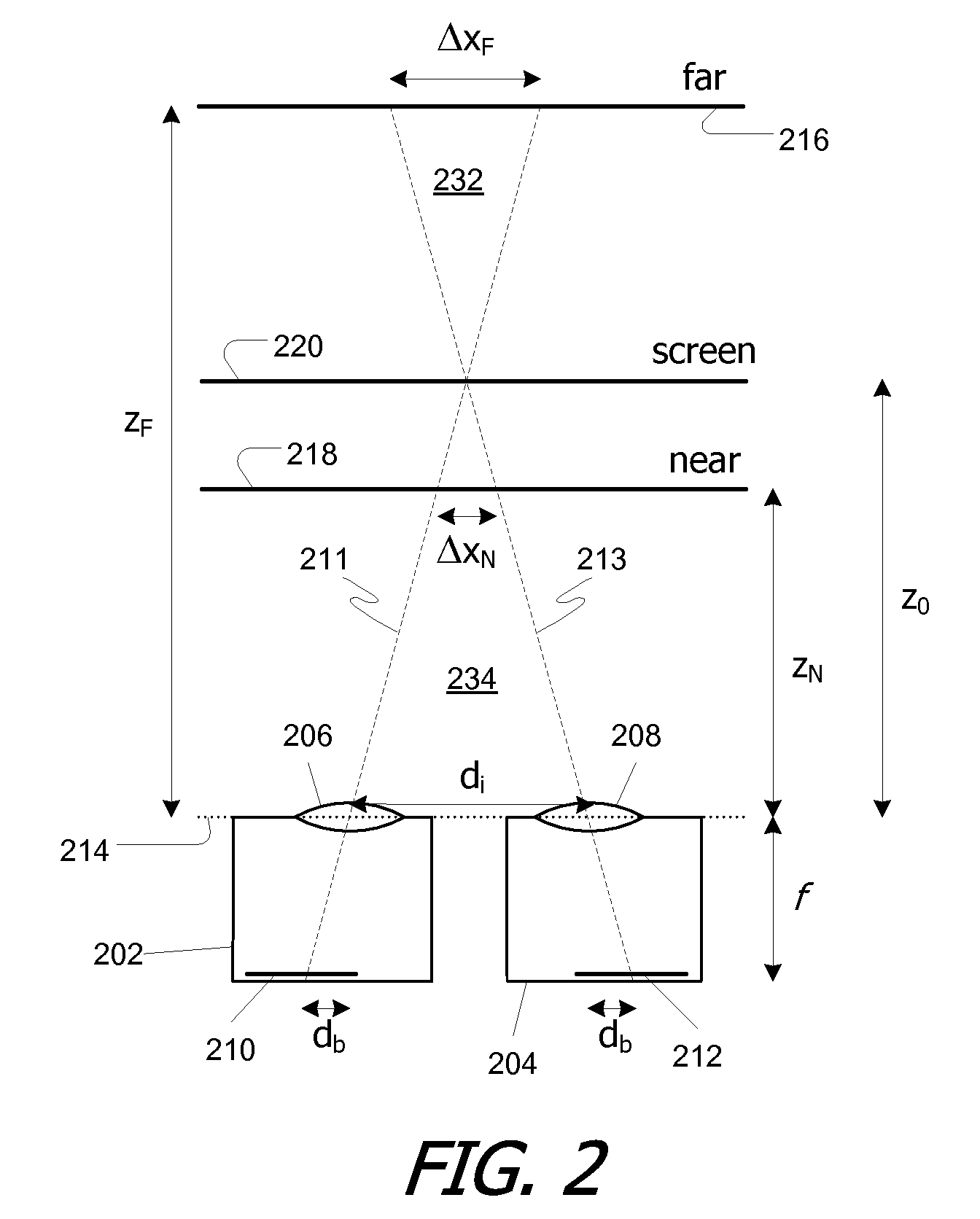
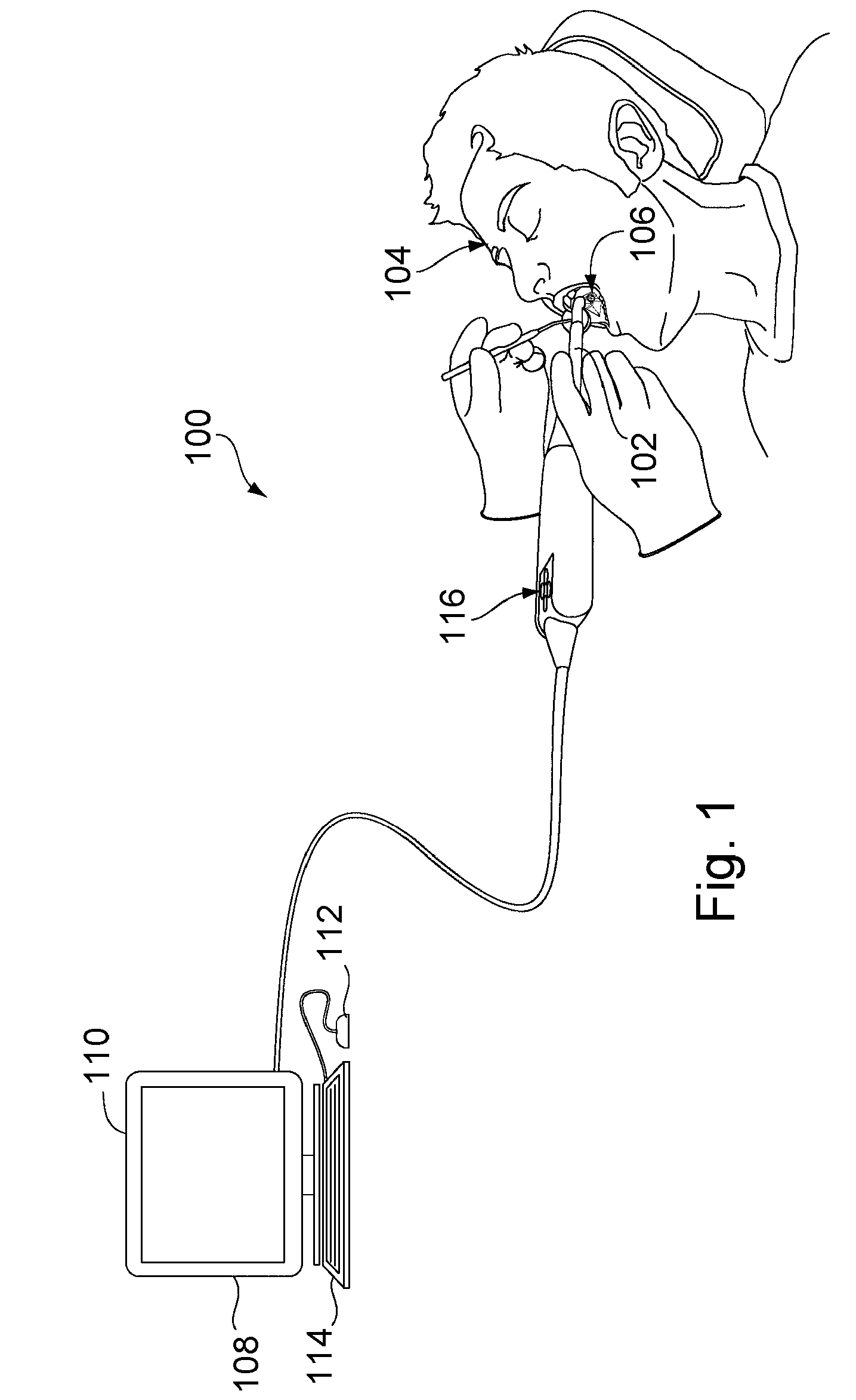
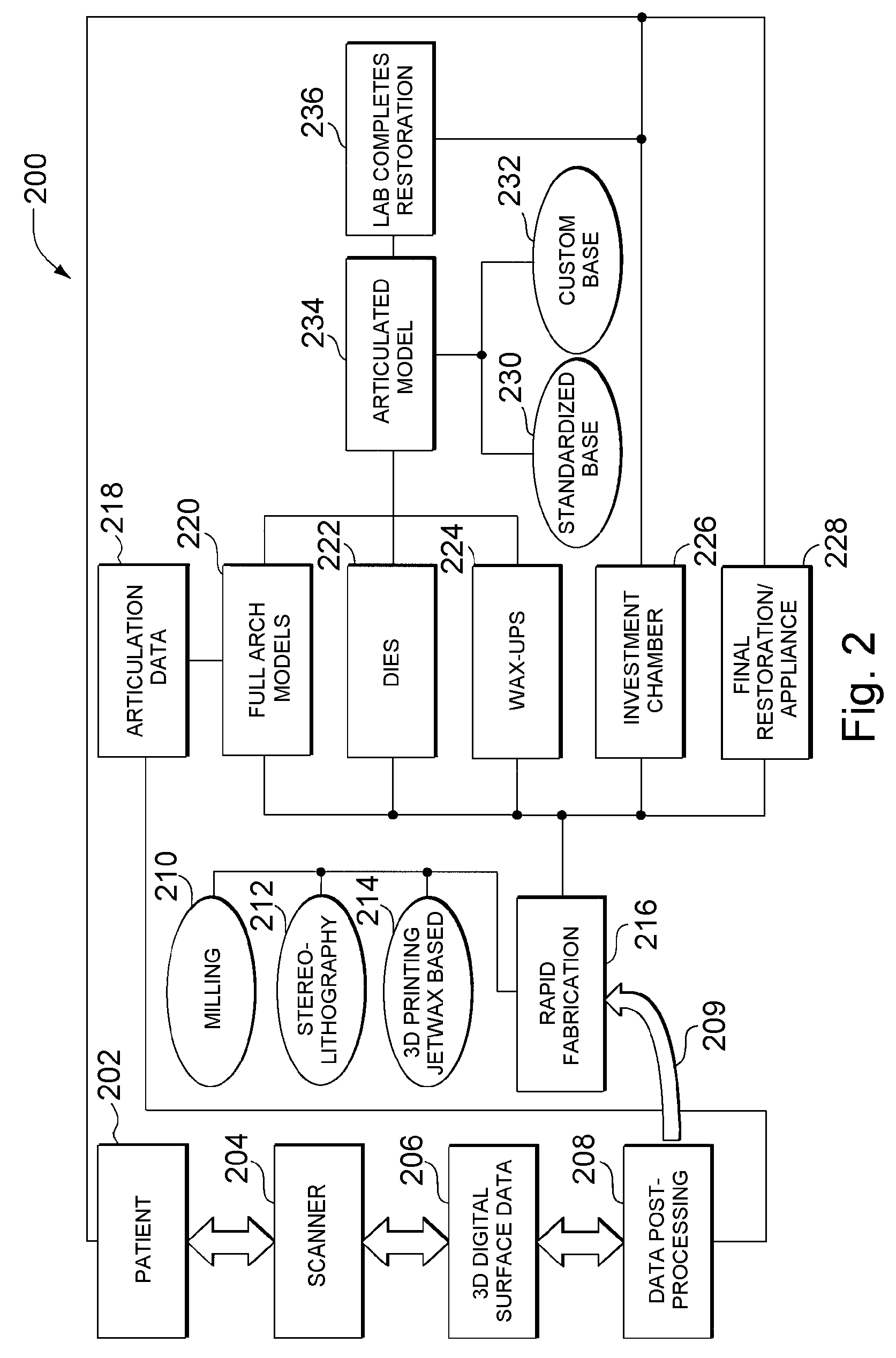
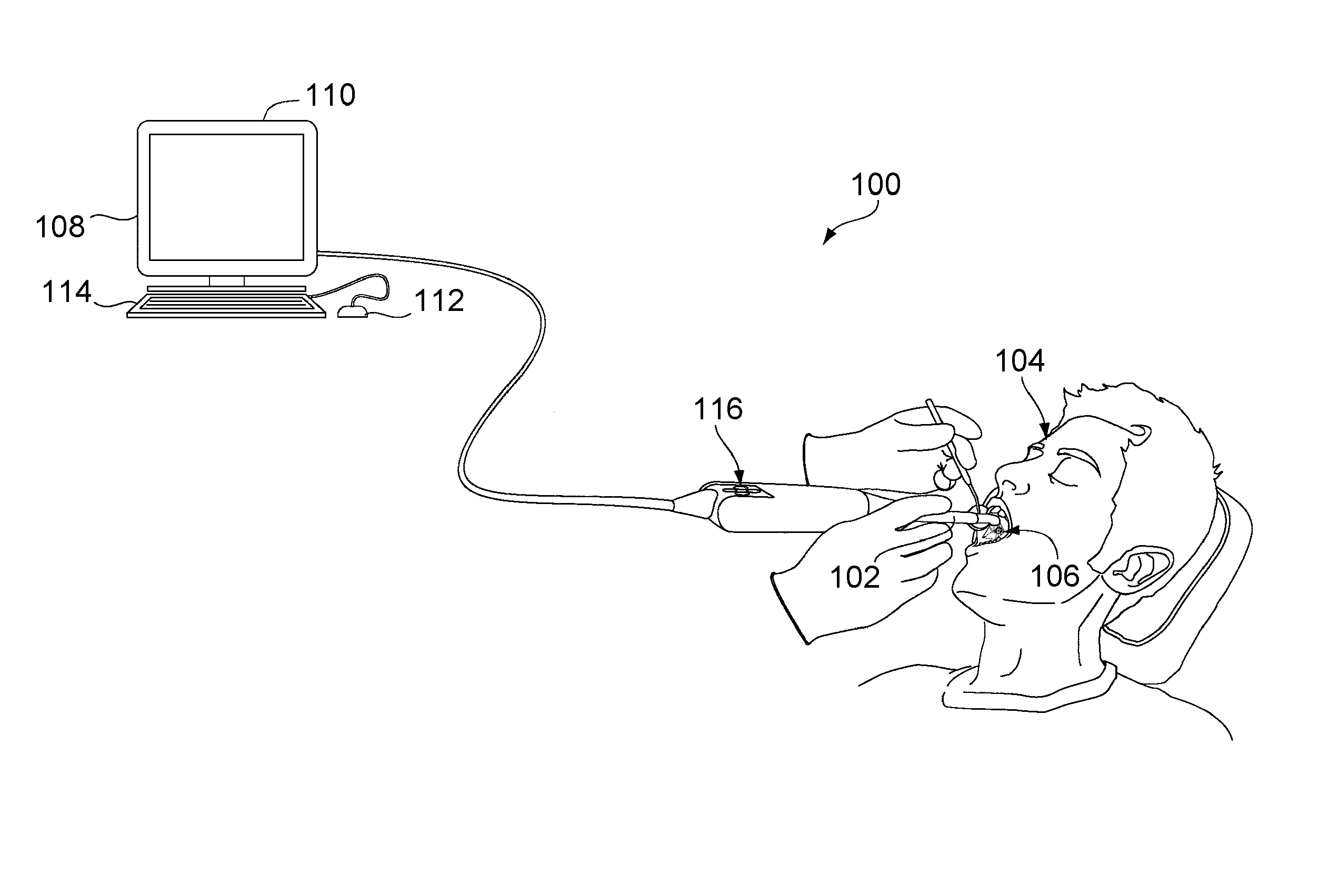
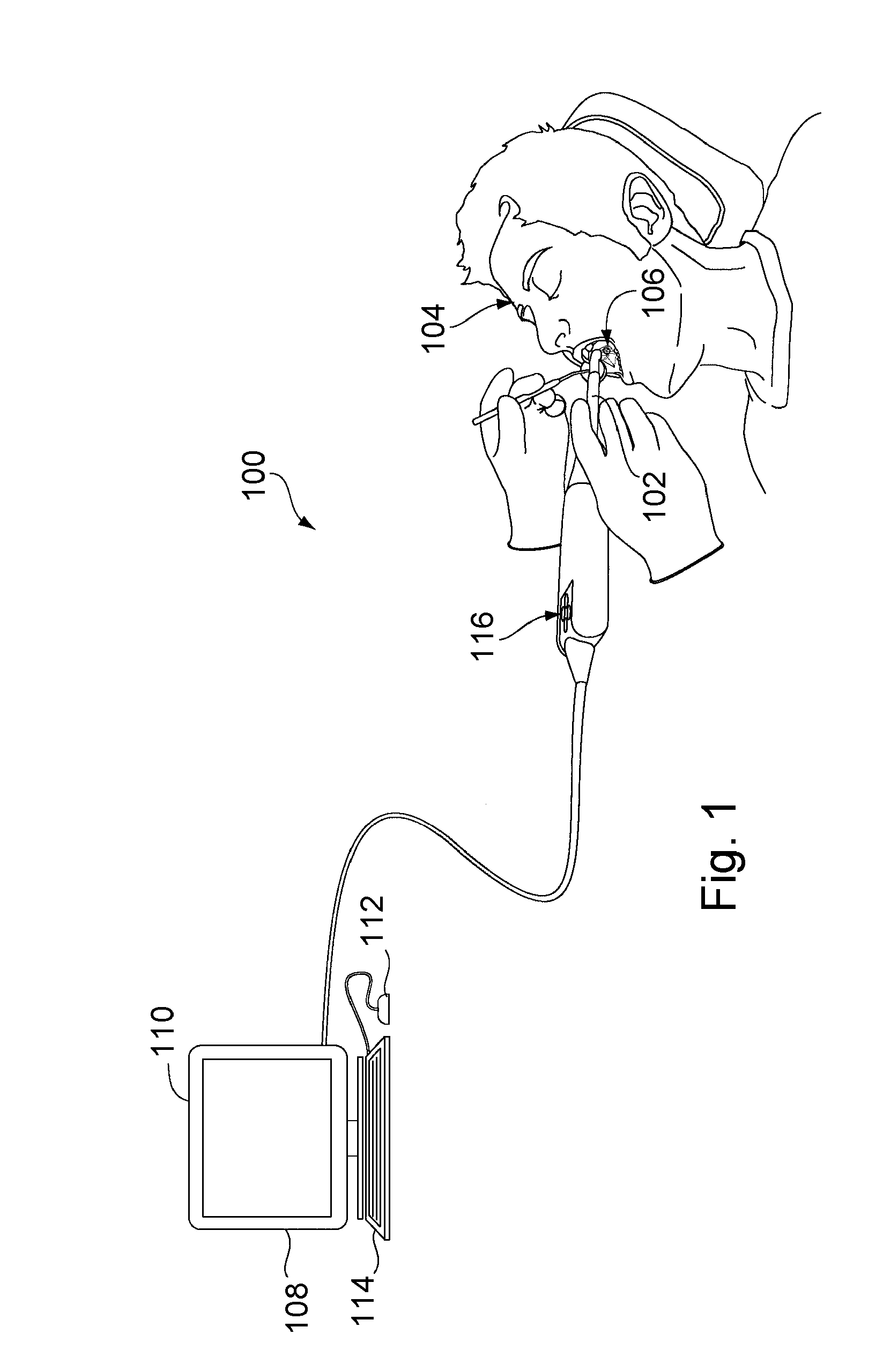
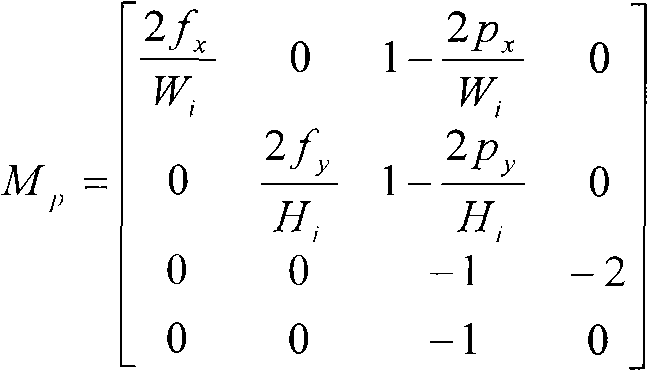Patents
Literature
5772 results about "Dimensional modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dimensional modeling (DM) is part of the Business Dimensional Lifecycle methodology developed by Ralph Kimball which includes a set of methods, techniques and concepts for use in data warehouse design. The approach focuses on identifying the key business processes within a business and modelling and implementing these first before adding additional business processes, a bottom-up approach. An alternative approach from Inmon advocates a top down design of the model of all the enterprise data using tools such as entity-relationship modeling (ER).
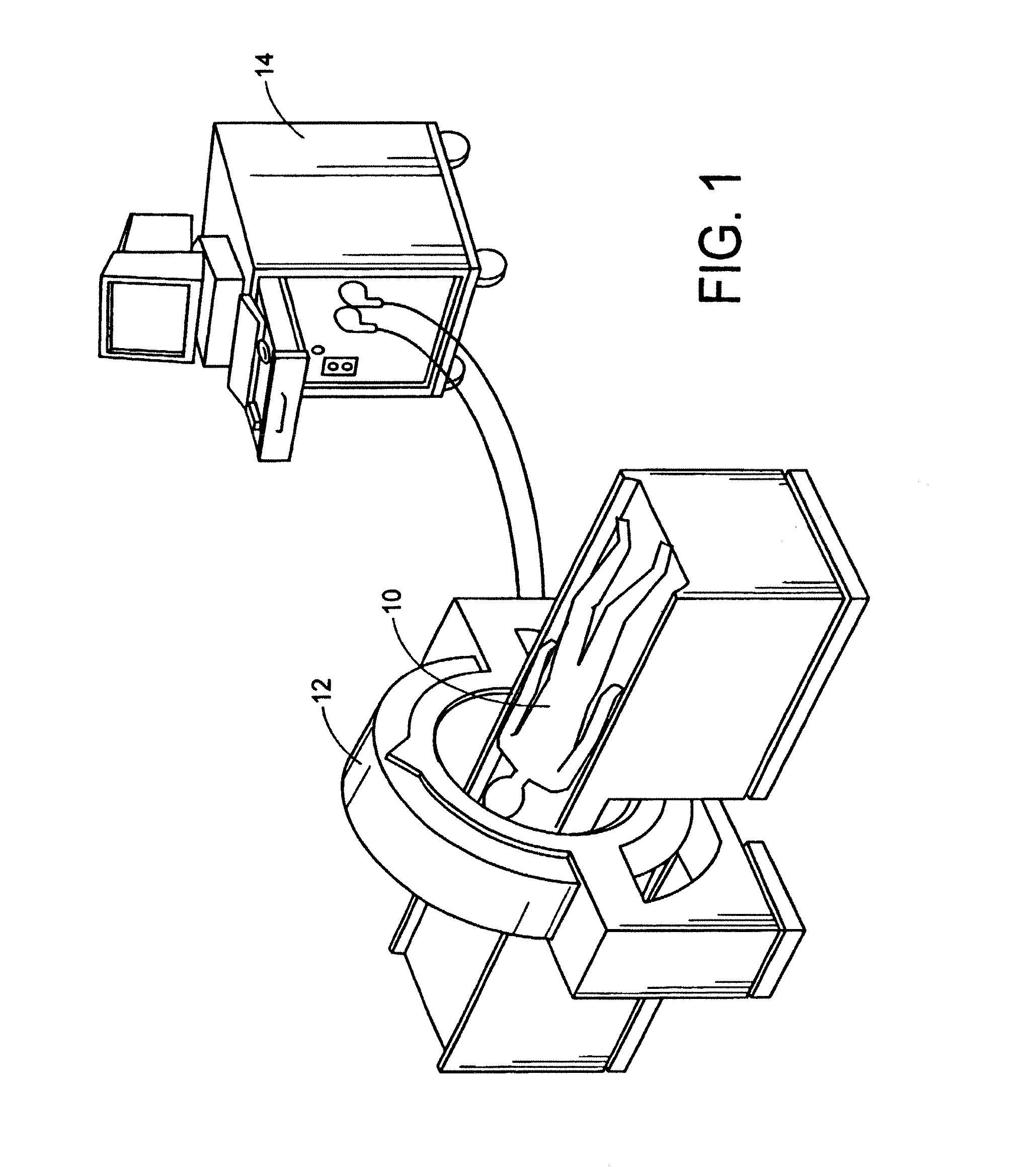
Three dimensional multibody modeling of anatomical joints
InactiveUS6161080AEasy to modifyPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesData selectionDimensional modeling
The present invention relates to a method of generating a three dimensional representation of one or more anatomical joints, wherein the representation comprises two or more movable bodies and one or more links, comprising the steps of inputting anatomically representative data of two or more movable bodies of the selected joint or joints; selecting one or more link types responsive to the representative data of the bodies; selecting link characteristics responsive to each selected link type; generating an equilibrium condition responsive to interaction between the bodies and the links; and displaying a three dimensional representation of the selected joint or joints responsive to the data generated from the equilibrium condition of the anatomical joint or joints. The present invention further relates to a system for generating a three dimensional representation of one or more anatomical joints, and a method of planning surgery of one or more anatomical joints.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
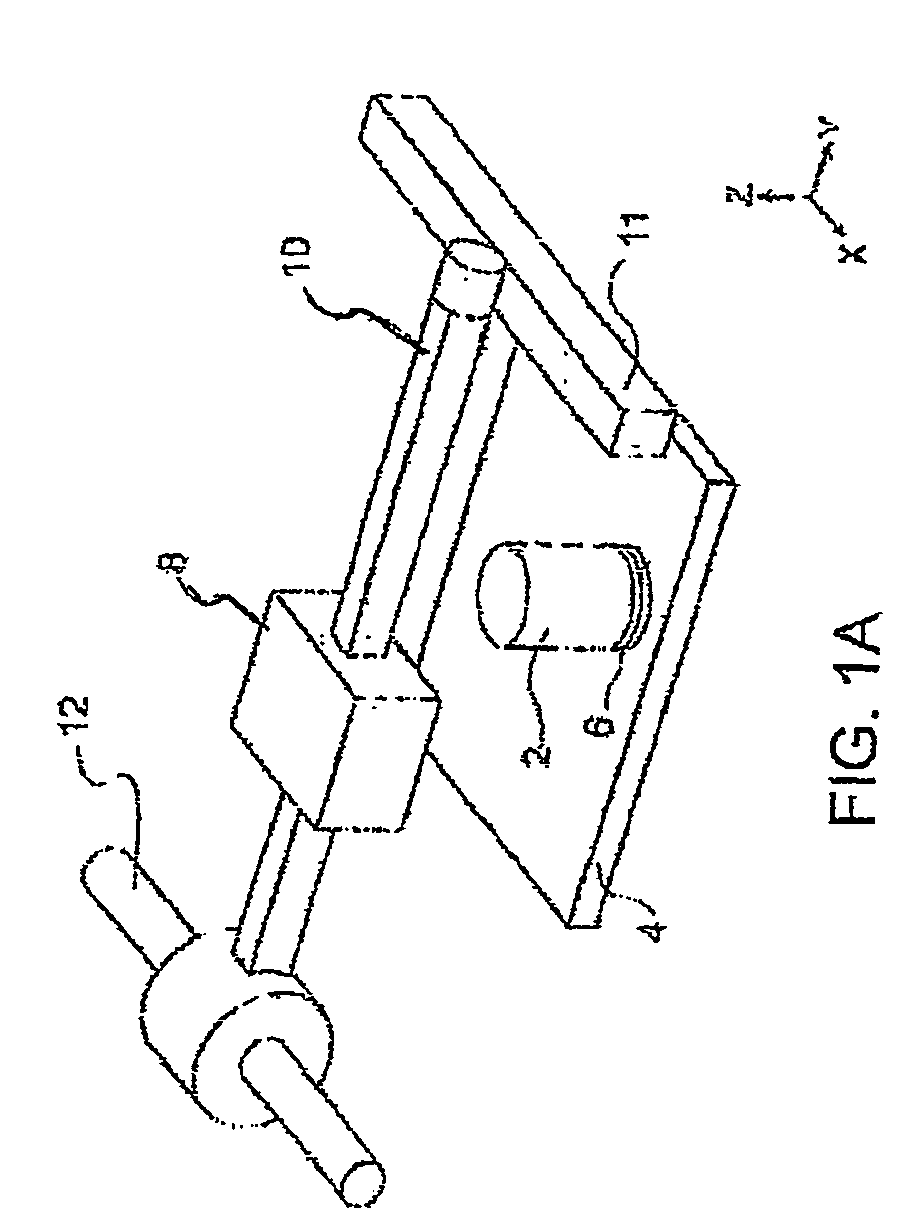
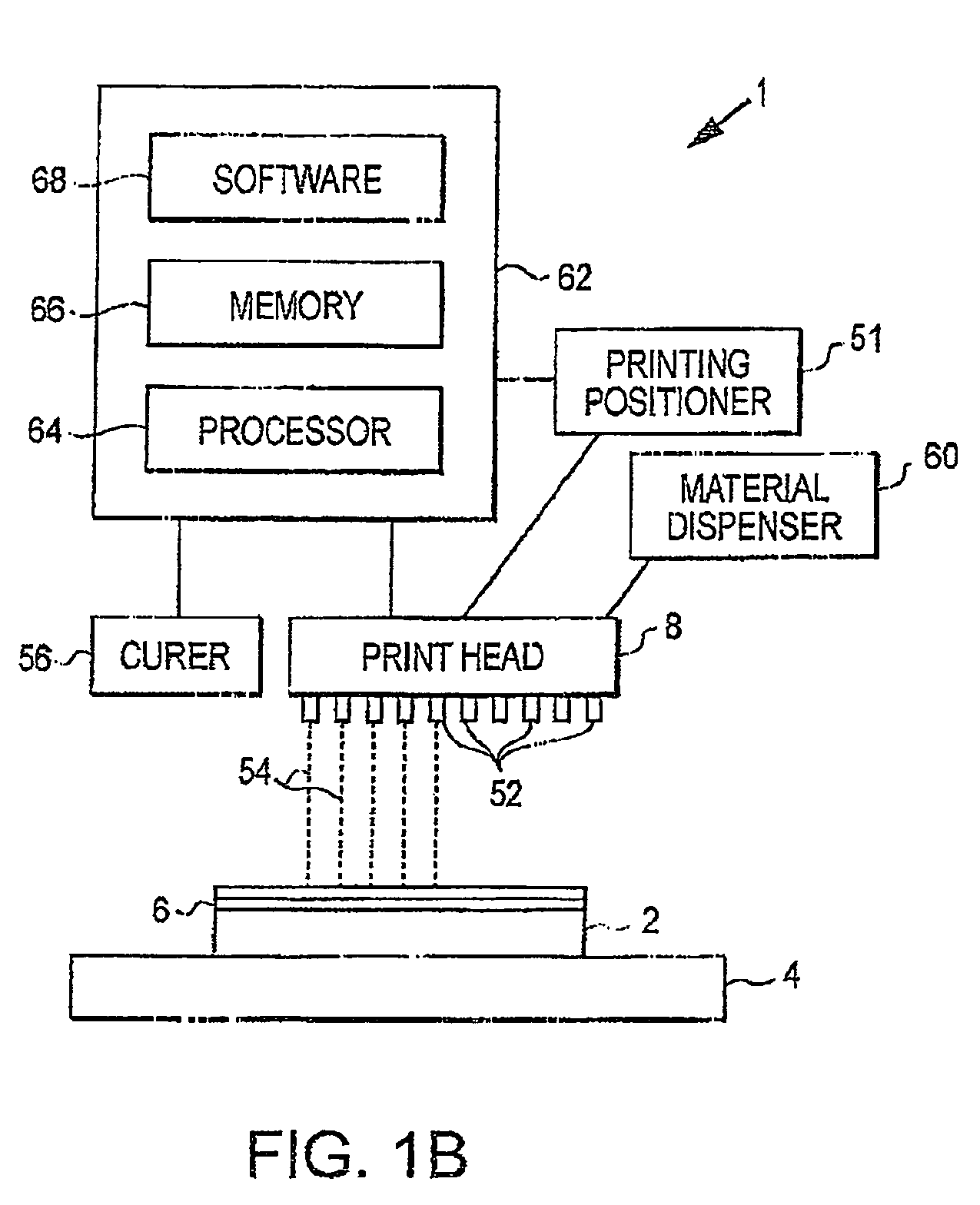
System and method for accurate printing of three dimensional models utilizing adjustment parameters
InactiveUS7209797B2Quality improvementAdditive manufacturing apparatusMeasurement apparatus componentsDimensional modeling3D modeling
A system and method for building three dimensional objects may adjust data used to build the objects to, for example, improve quality or correct for defects. A printer may, for example, accept data representing the object and modify the data according to an adjustment parameter; the printer may build the object according to the parameter. The parameter may be, for example, fixed in the printer, user entered, and / or calculated by the printer. In one embodiment, a support pedestal may be built of deposited material before the object is built.
Owner:STRATASYS LTD
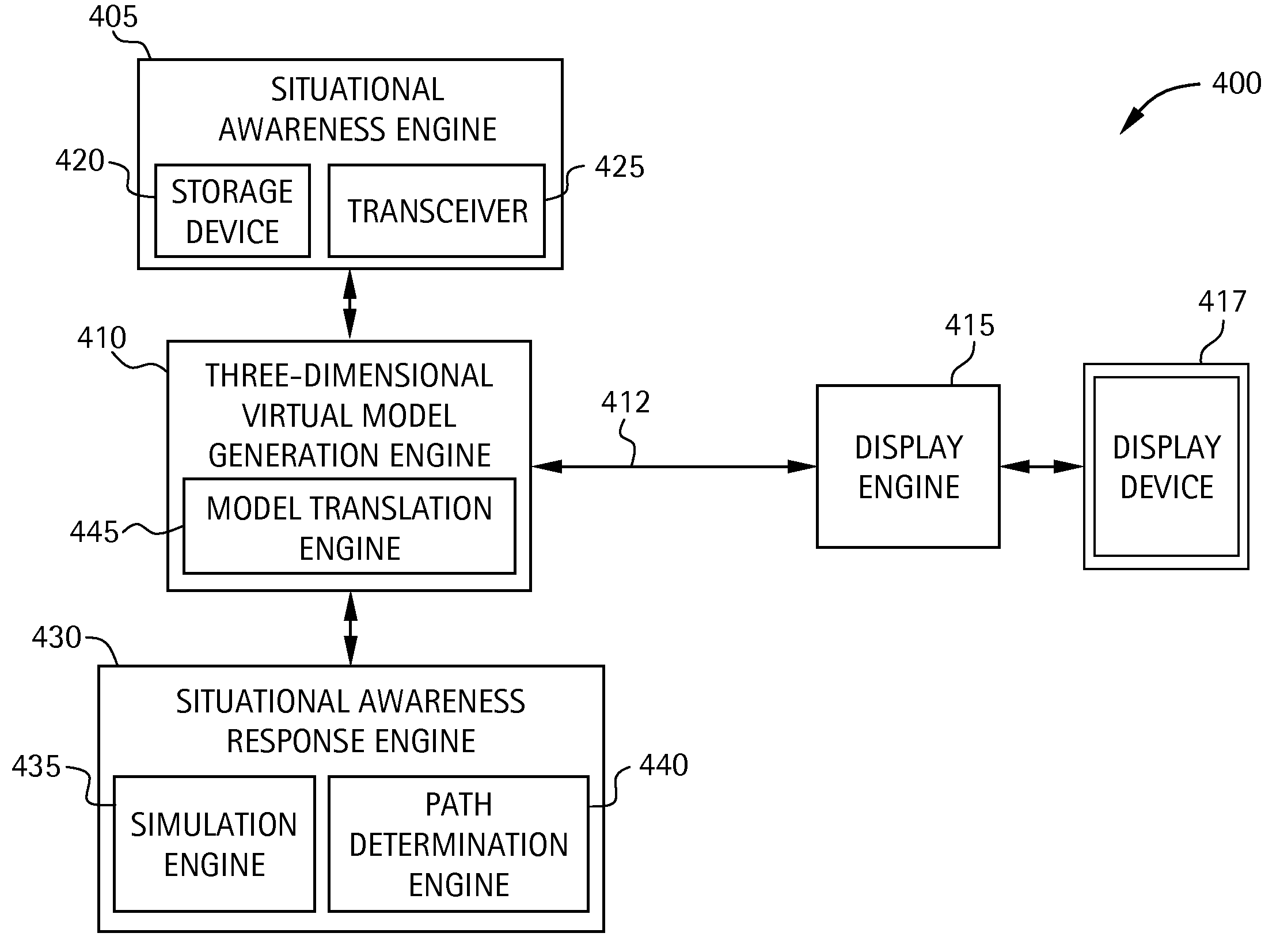
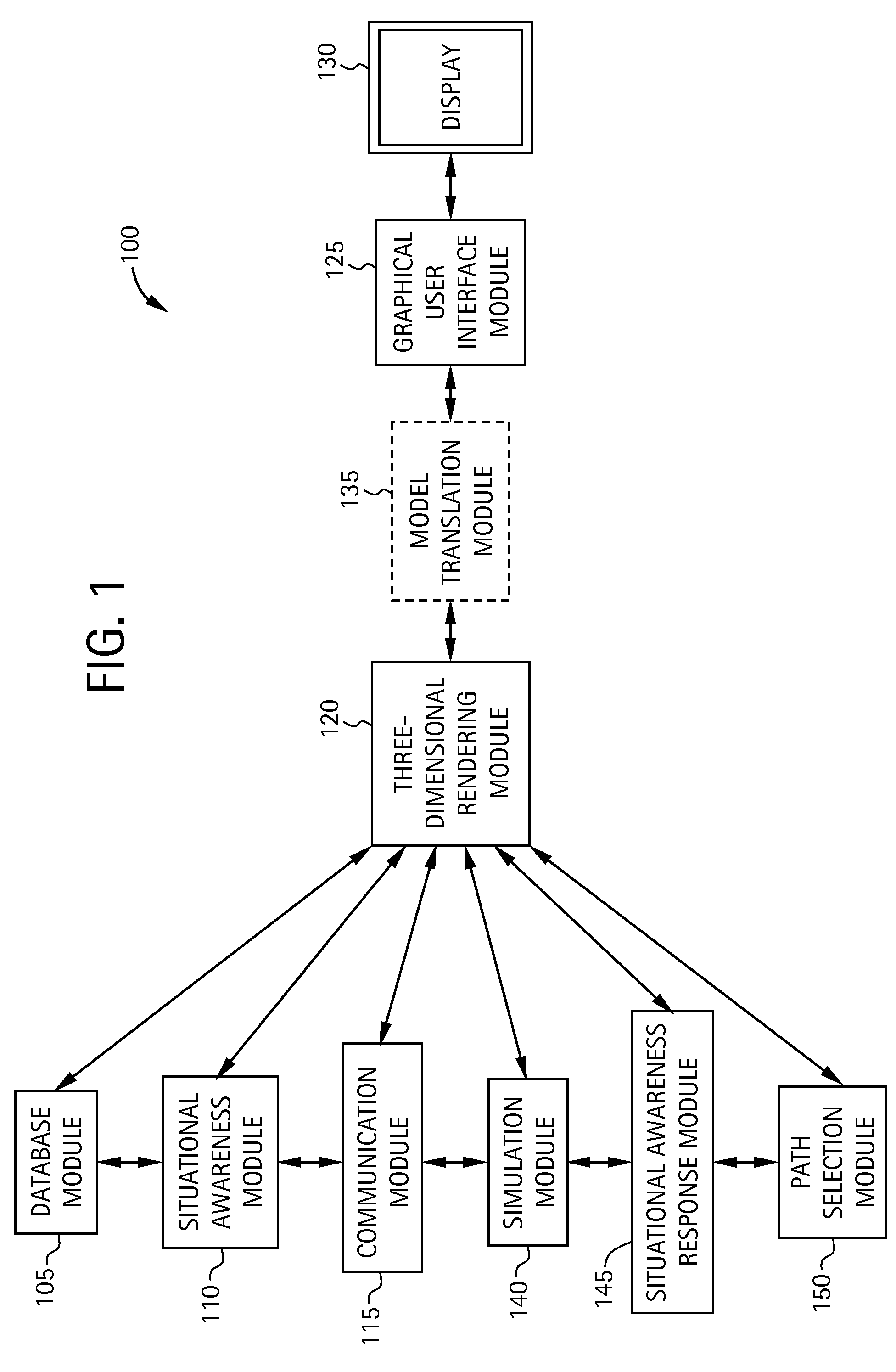
Computer-based system and method for providing situational awareness for a structure using three-dimensional modeling
InactiveUS20080062167A1Geometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system for providing real-time or near real-time situational awareness for a structure includes a database module for storing structural information associated with the structure. The system includes a situational awareness module for gathering situational awareness information associated with the structure. The system includes a three-dimensional (3-D) rendering module in communication with the database module and the situational awareness module for rendering a 3-D virtual model of the structure utilizing the structural information associated with the structure, and for integrating into the 3-D virtual model the situational awareness information associated with the structure. The system includes a graphical user interface module in communication with the 3-D rendering module for displaying to a user the 3-D virtual model of the structure integrating the situational awareness information associated with the structure.
Owner:ERIS TECH CORP
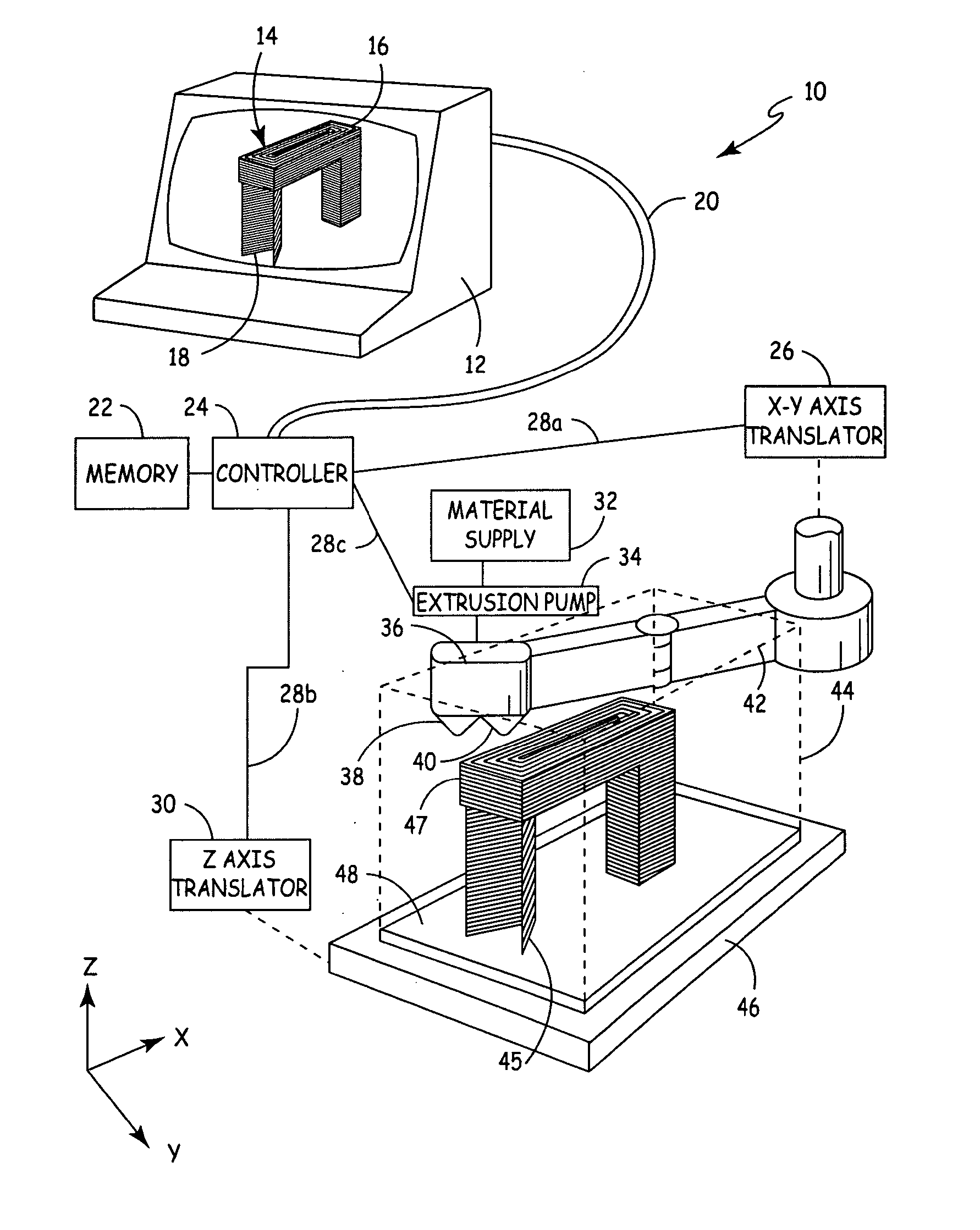
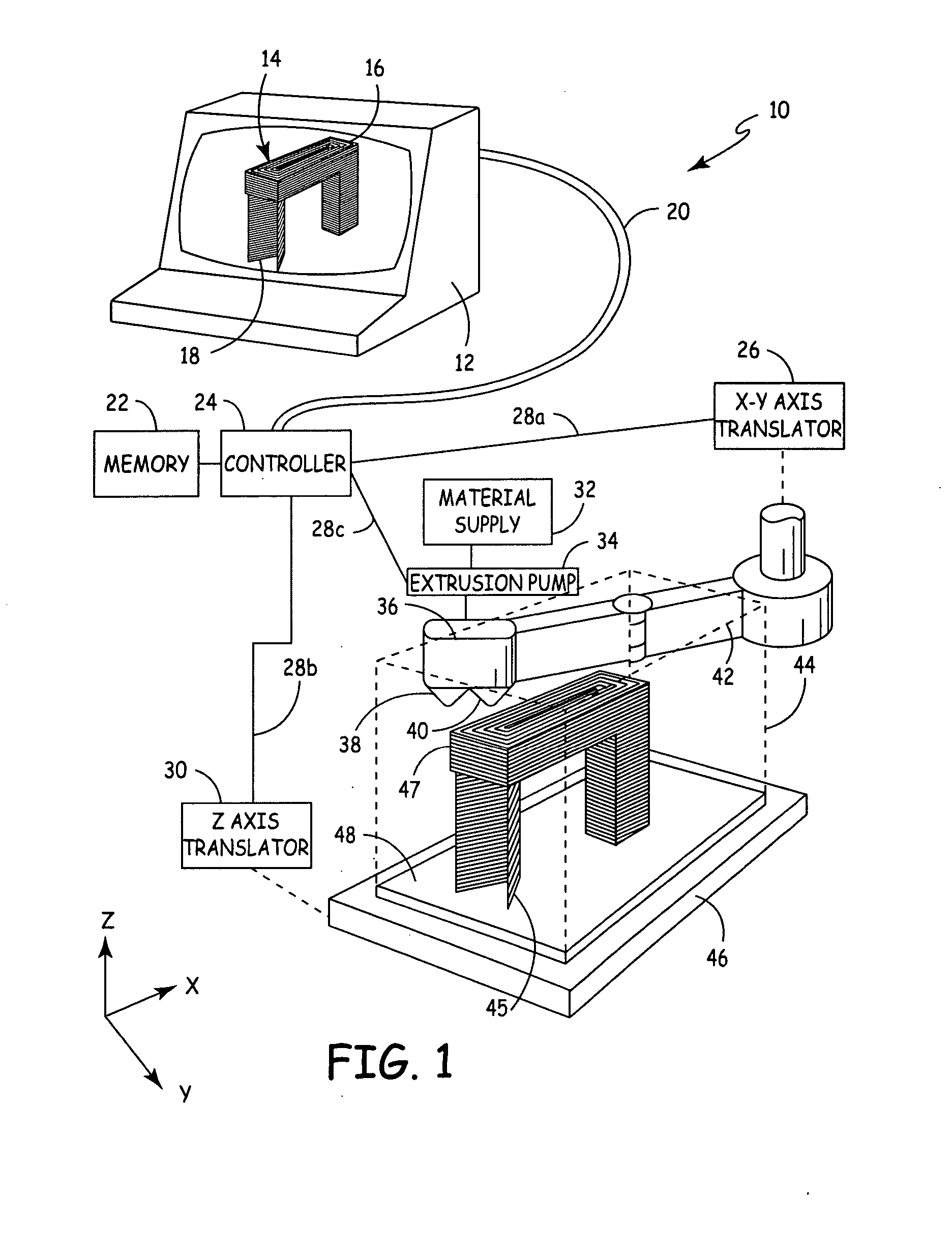
Auto tip calibration in an extrusion apparatus
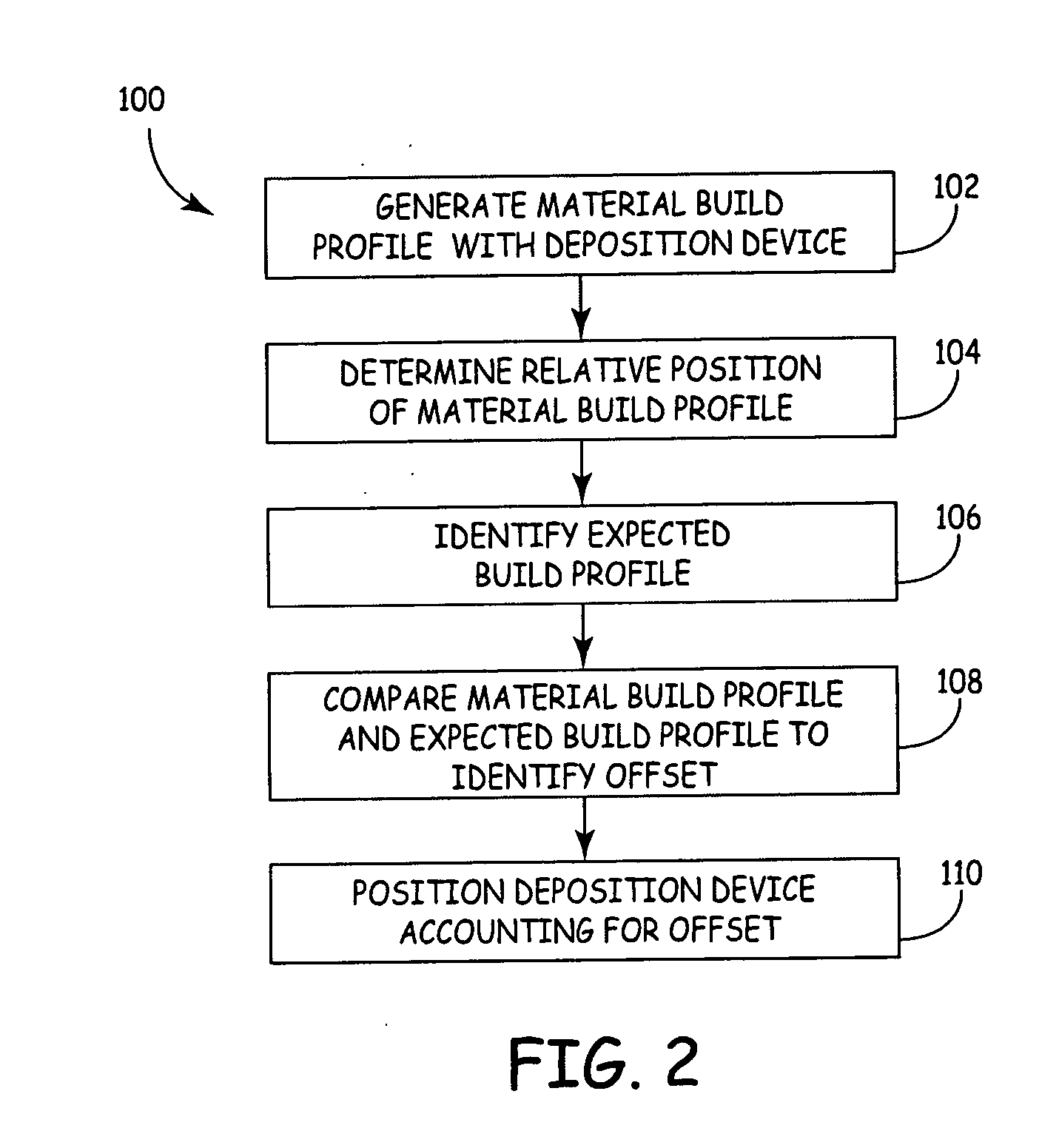
The present invention is a method for performing a calibration routine of a deposition device in a three-dimensional modeling machine that deposits a material to build up three-dimensional objects as directed by a controller on a substrate mounted on a platform. The method comprises generating a material build profile, which represents a three-dimensional structure at defined locations. A relative position of the material build profile is then determined. An expected build profile is identified and then compared to the determined relative position of the material build profile to identify any difference which represents an offset. The modeling system then positions the deposition device based upon the offset.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
High performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography and associated method of use
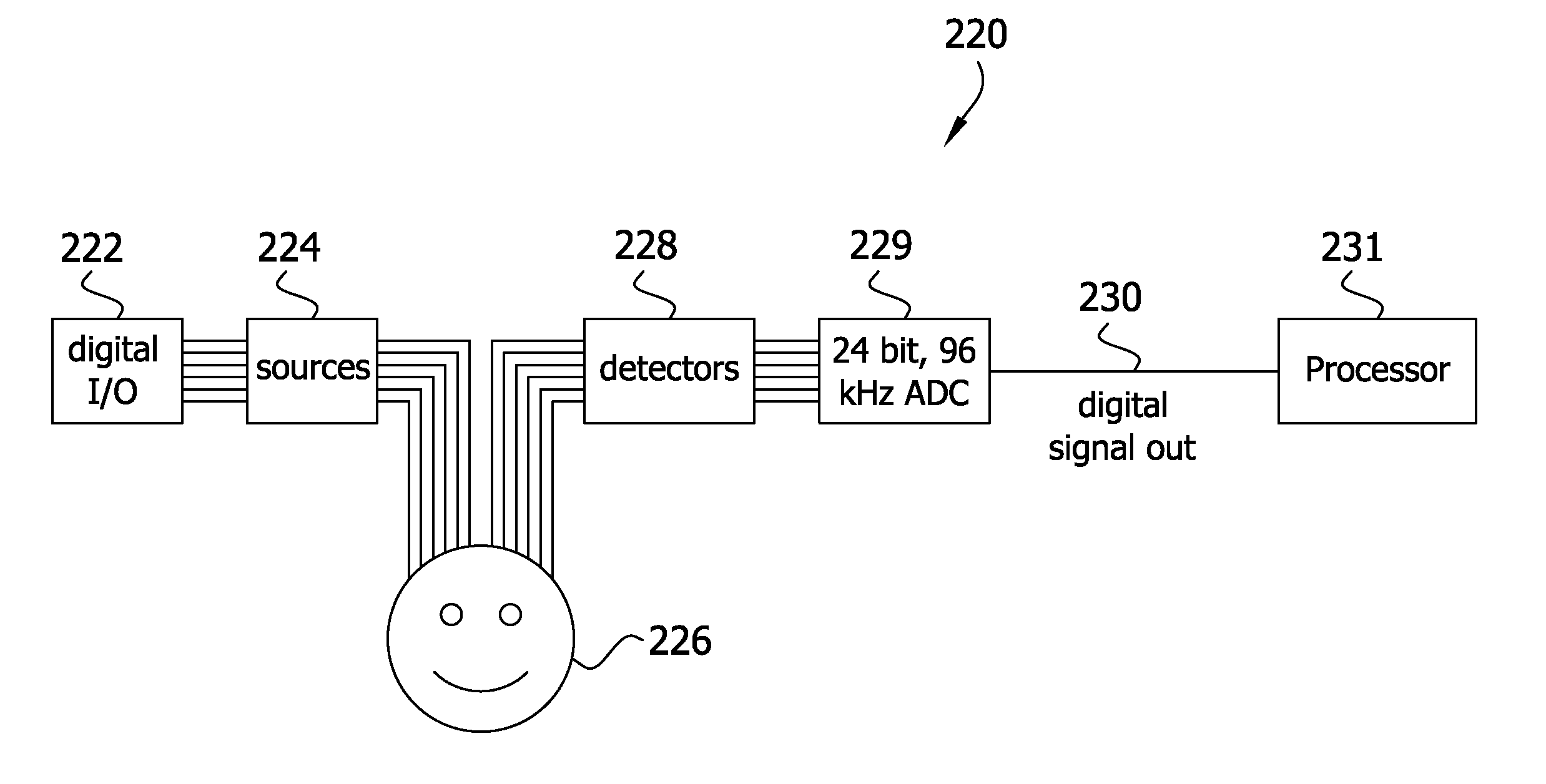
ActiveUS7983740B2High bandwidthImprove performanceDiagnostics using tomographySensorsOptical tomographyImaging quality
A high performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography is disclosed. A dense grid utilizing sources, e.g., light emitting diodes (“LEDs”), that achieve high performance at high speed with a high dynamic range and low inter-channel crosstalk are complemented by a system of discrete, isolated receivers, e.g., avalanche photodiodes (“APDs”). The source channels have dedicated reconfigurable encoding control signals, and the detector channels have reconfigurable decoding, allowing maximum flexibility and optimal mixtures of frequency and time encoding and decoding. Each detector channel is analyzed by dedicated, isolated, high-bandwidth receiver circuitry so that no channel gain switching is necessary. The resulting improvements to DOT system performance, e.g., increased dynamic range and decreased crosstalk, enable higher density imaging arrays and provide significantly enhanced DOT image quality. A processor can be utilized to provide sophisticated three dimensional modeling as well as noise reduction.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Filament loading system in an extrusion apparatus
InactiveUS6923634B2Protect environmentEasy loadingConfectionerySweetmeatsDrive wheelDimensional modeling
An apparatus which extrudes flowable material from a liquifier includes a system for loading filament supplied in a cassette. The cassette is loaded into a loading bay of the apparatus. A strand of filament from the cassette is engaged and advanced along a path to the liquifier using a drive wheel or roller pair. A conduit having an entrance in the loading bay guides the filament as it is advanced. The filament loading system of the present invention provides a convenient manner of loading and unloading filament in a three-dimensional modeling machine, and can be implemented in a manner that protects the filament from environmental moisture.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
System and method for three dimensional modeling
InactiveUS20050128196A1Remove redundant informationSimple modelImage analysisOptical rangefindersComputer graphics (images)Light beam
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Distributed lidar sensing system for wide field of view three dimensional mapping and method of using same
InactiveUS20150192677A1Low costWide field of viewOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationWide fieldRadar
A three-dimensional mapping system comprising a moderate number (typically 2 to 4) of moderate-beam-count (typically 8-beam to 16-beam) lidar sensors is proposed to achieve low cost systems with wide fields of view. Secondary advantages include compact sensors and a small minimum range (possible by optimal placement of each of a plurality of sensors).
Owner:QUANERGY SYST
Apparatus and method for production of three-dimensional models by spatial light modulator
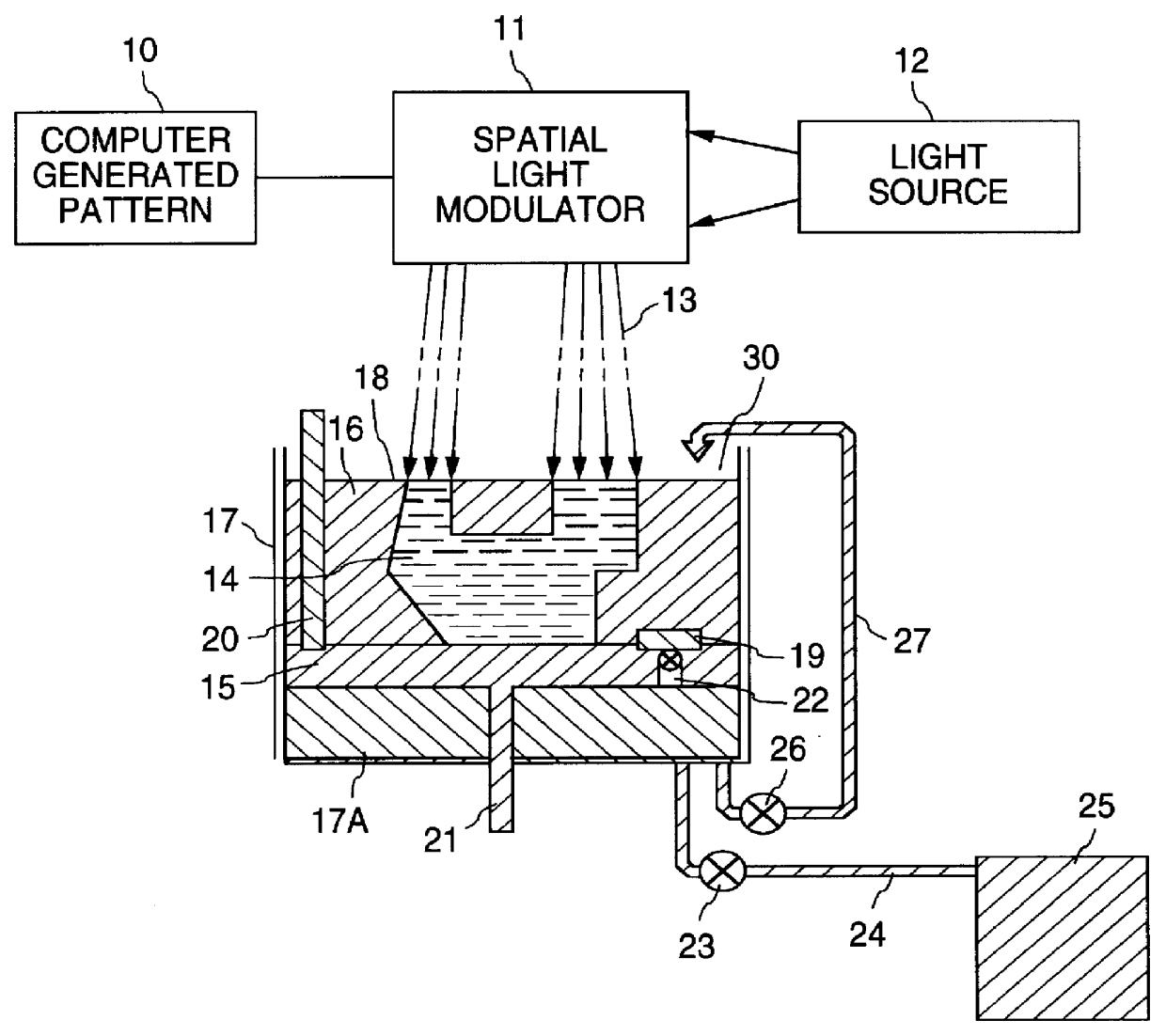
InactiveUS6051179AFacilitate cross-linkingHigh mechanical strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnalogue computers for control systemsSpatial light modulatorWide beam
An apparatus and the method of its operation for rapid prototyping of a three-dimensional object which includes a radiant energy source of a wide beam of radiant energy of suitable intensity and wavelength for curing a layer of photo-curable resin contained in an open vat, a spatial light modulator (SLM) having an array of pixel elements which are individually digitally controllable by a computer, for modulating the radiant energy beam projected from the radiant energy source on a pixel by pixel basis, to form a series of time sequential images of the cross-sectional laminae of the object, an optical system for focusing each image formed by the SLM, one at a time, onto successive layers of photo-curable resin for predetermined exposure times to thereby form stacked laminae of cured resin, each lamina of cured resin being in the shape of a different one of the cross-sectional laminae, and a piston support for lowering each lamina of cured resin after it is formed by the SLM and for depositing a layer of resin corresponding to the thickness of one cross sectional lamina of the three-dimensional object before the step of projecting a new image by the SLM. The SLM, the piston support for lowering, and the optical system operate repeatedly and sequentially until a complete copy of the object is thereby produced.
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
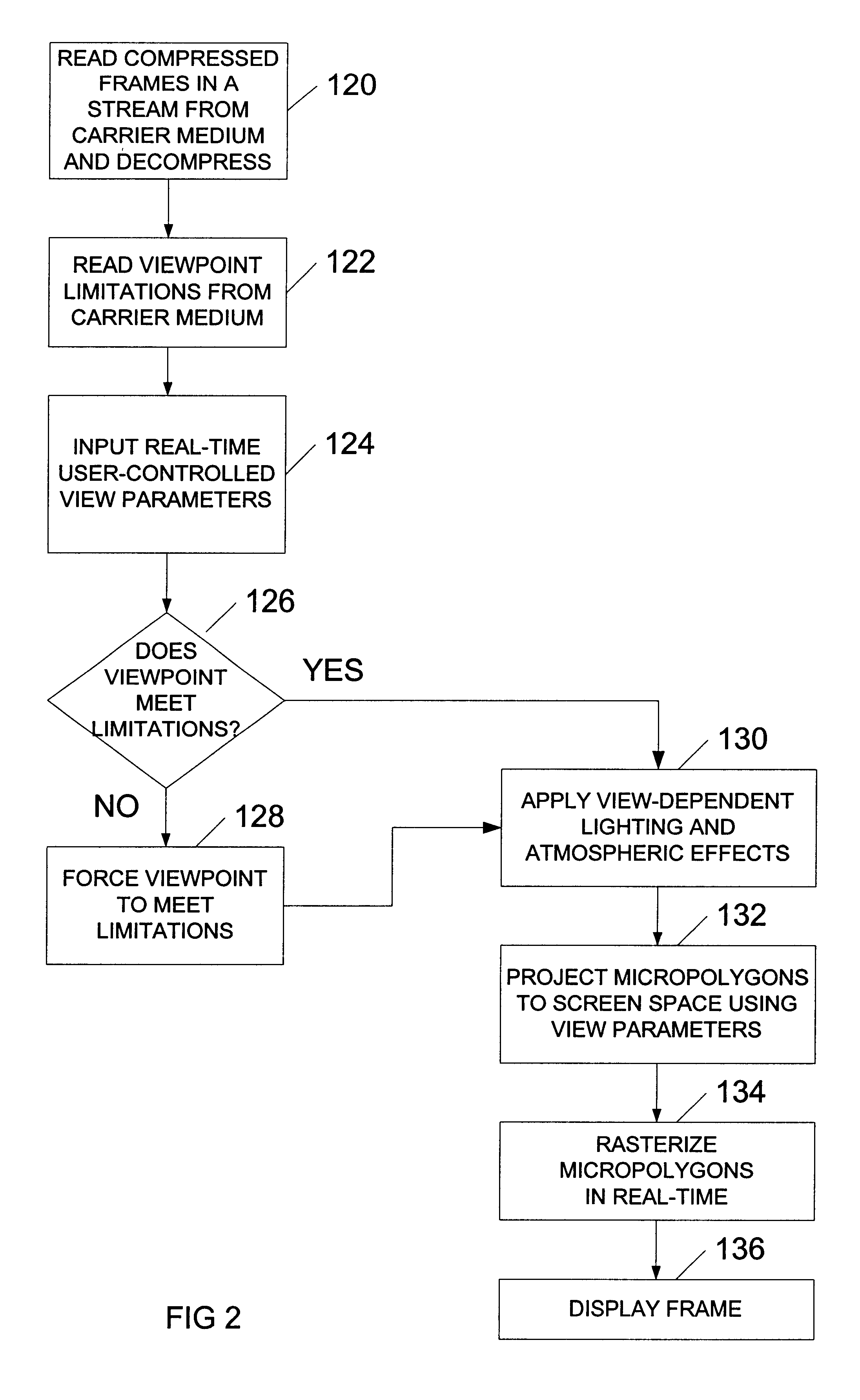
System and method for generating and playback of three-dimensional movies
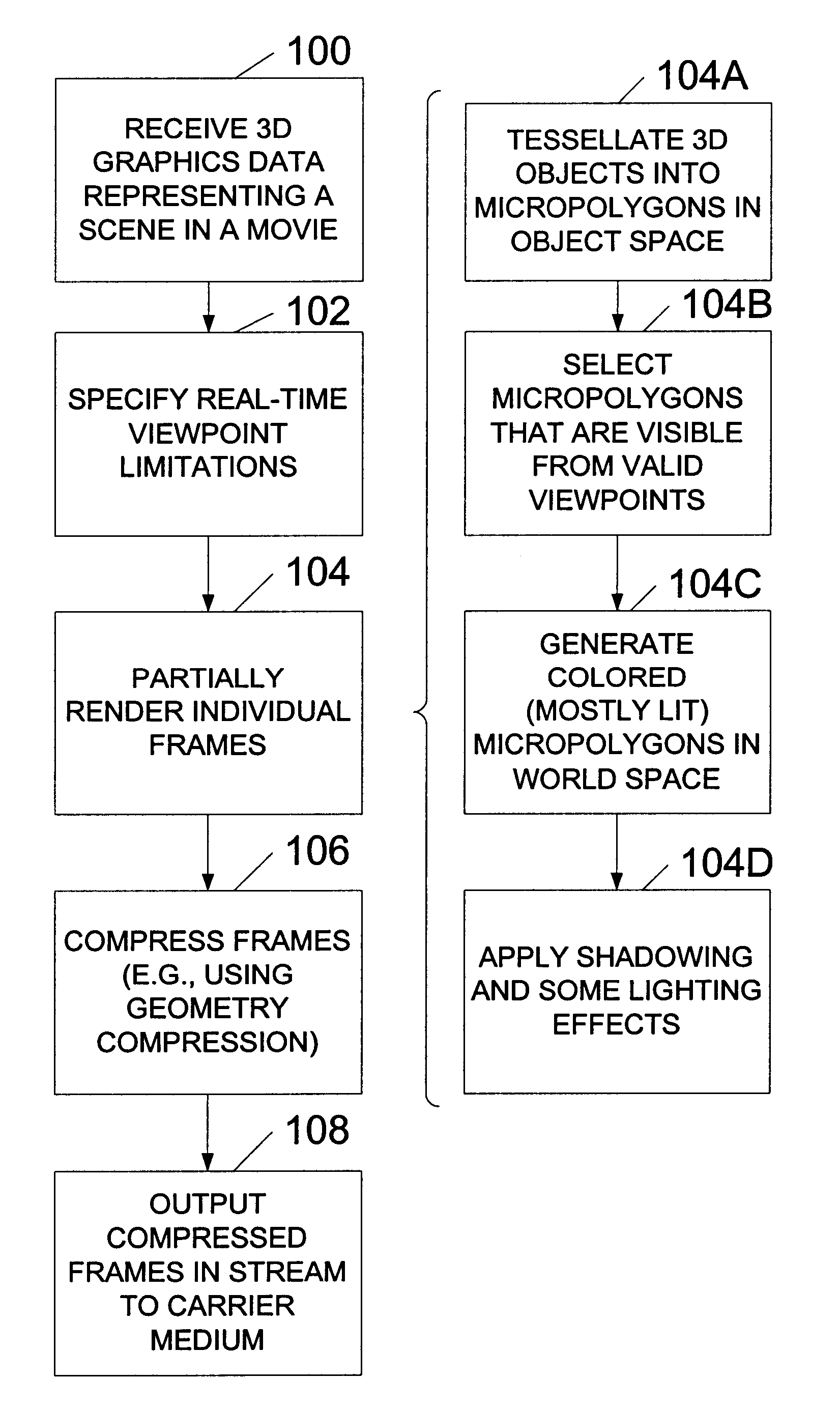
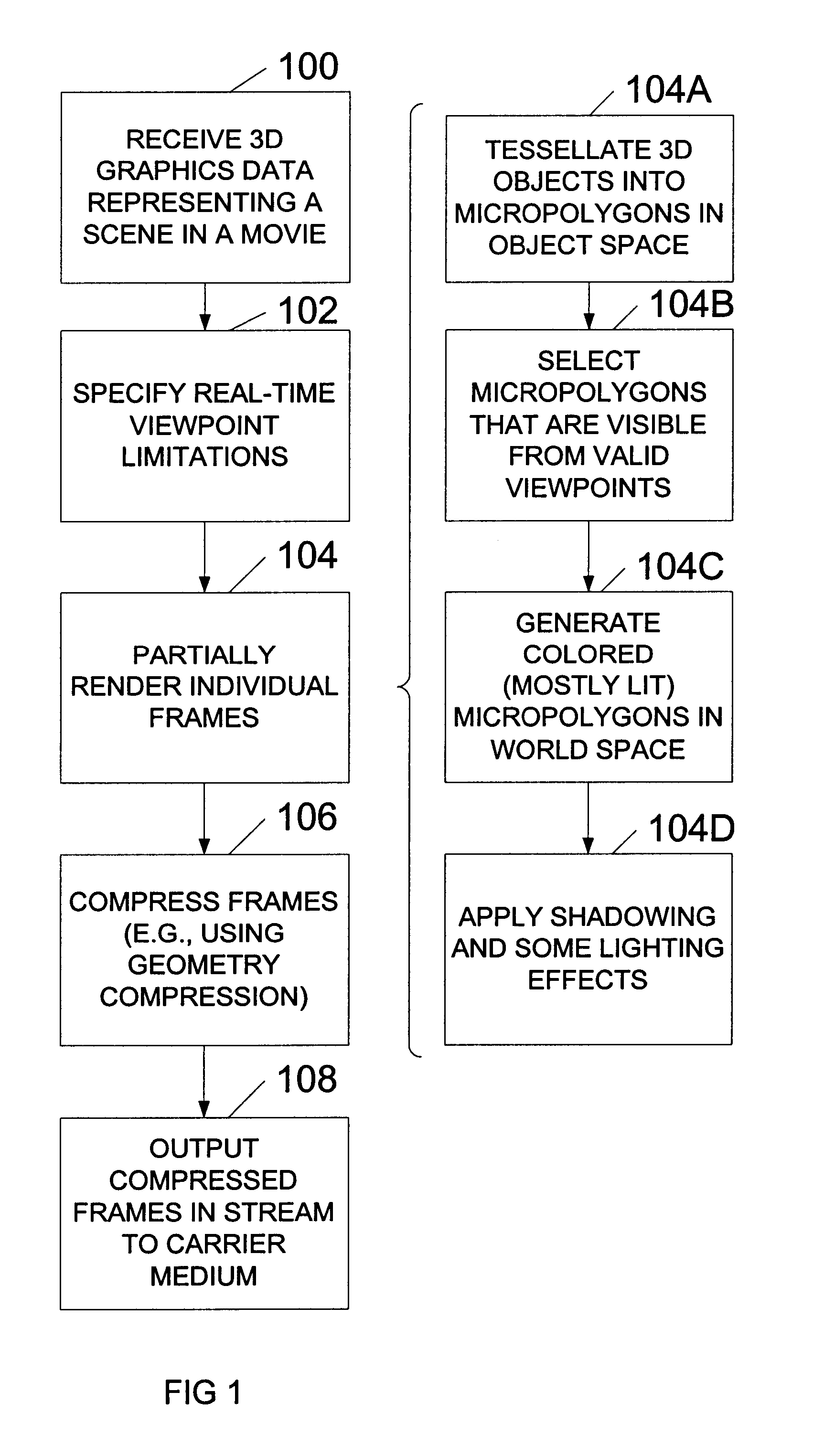
A system and method for generating and playing back three-dimensional (3D) movies are disclosed. The system is capable of partially rendering frames without relying upon exact viewpoint information. The partially rendered frames may be rendered to the extent possible without performing viewpoint-dependent processes, and then compressed and stored to a carrier medium. To reduce the amount of data to be stored, the viewer's possible viewpoints may be restricted (e.g., by defining a viewpoint-limiting volume or region). The resulting partially-rendered geometry data may be compressed using geometry compression. During playback, the compressed frames are read as a stream, and decompressed. Any final viewpoint-dependent rendering operations may then be performed (e.g., some lighting calculations and atmospheric effects, some fogging, specular highlighting, and reflections). A sensor such as a head-tracker may provide real-time viewpoint information that may be used by the playback system. After rendering, the frames are rasterized and then displayed in stereo.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Three-dimensional design and manufacturing systems
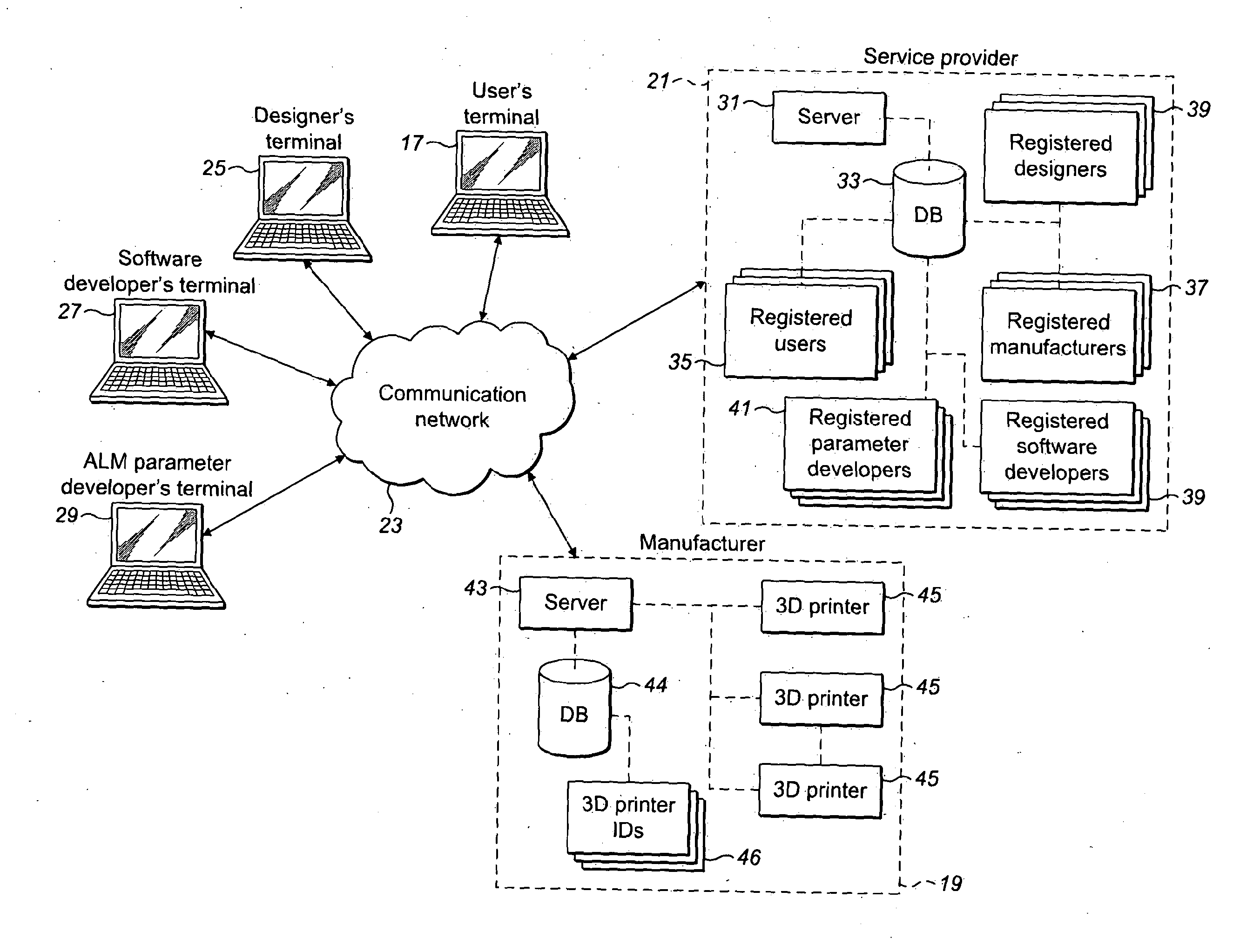
ActiveUS20140156053A1Use directlyMinimize amount of processingAdditive manufacturing apparatusData processing applications3d print3d design
A method of authenticating the printing of a three-dimensional (3D) article at a 3D printer according to a 3D print file describing a three-dimensional design is described. The method comprises: receiving an authentication request from a 3D print server that is associated with the 3D printer, the request comprising a unique design identifier associated with a 3D design file and a unique 3D printer identifier associated with a 3D printer, the received unique 3D design identifier being related to the received 3D printer ter identifier in accordance with a first relationship; using at least one of the received unique identifiers to access a verifying 3D design identifier and a verifying 3D printer identifier, the verifying identifiers being related to each other in accordance with a second relationship; comparing the first and second relationships between the received and verifying identifiers; generating an authentication signal if the first relationship corresponds with the second relationship; obtaining a decryption key associated with the received identifiers in response to the authentication signal; and transferring the decryption key to the 3D print server to authenticate and enable the printing of the 3D article on the 3D printer.
Owner:DNA AM LTD
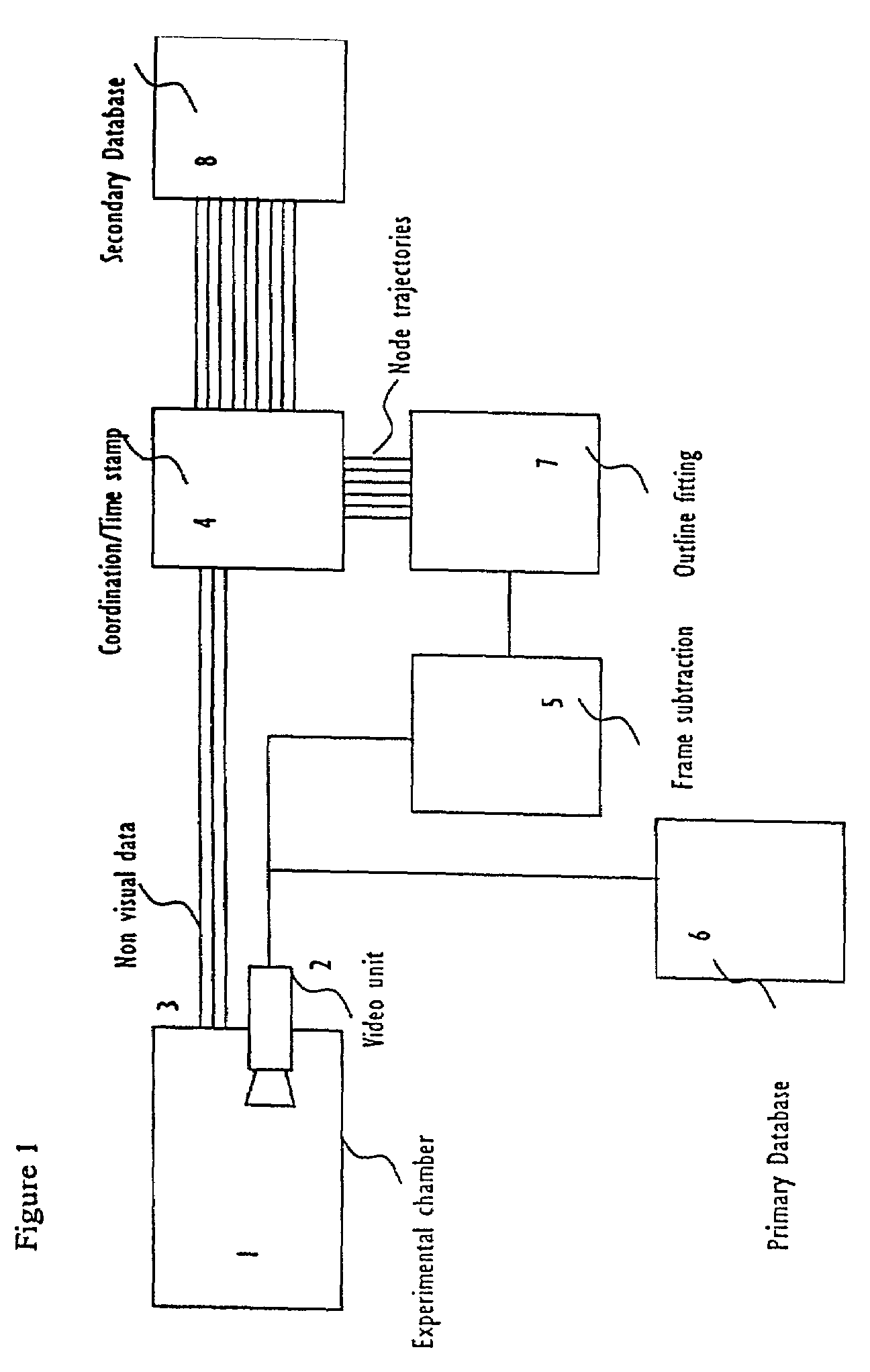
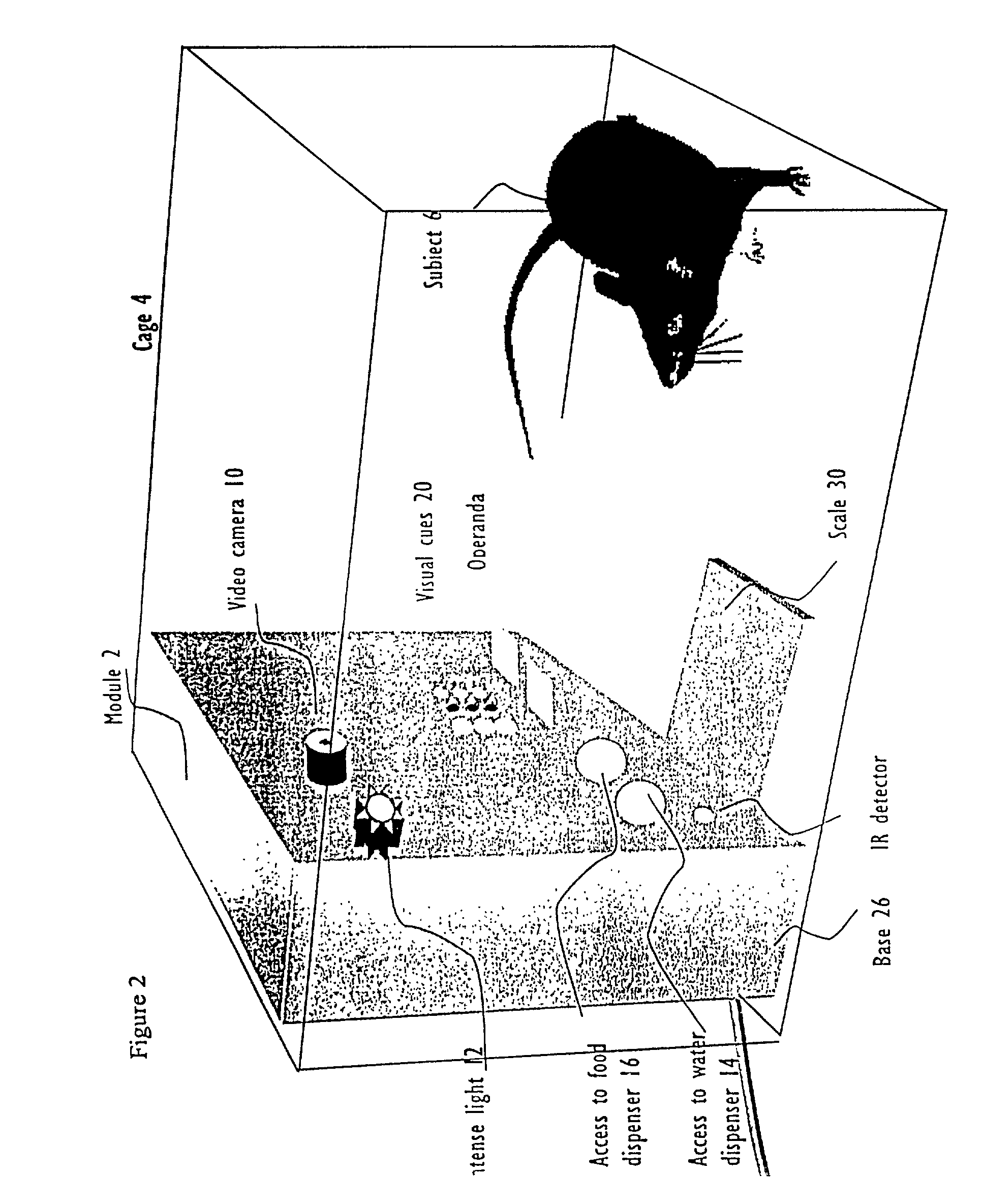
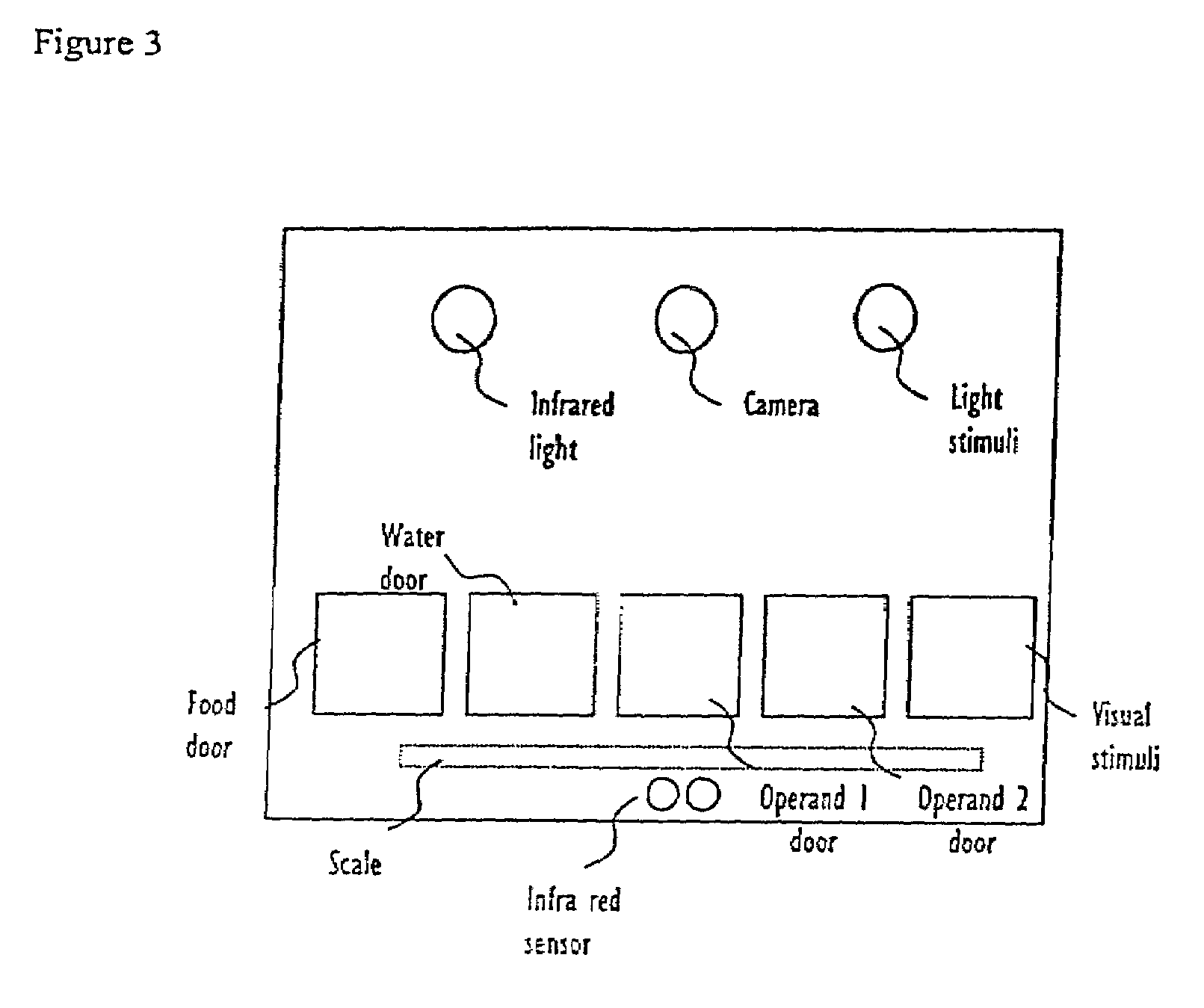
Systems and methods for monitoring behavior informatics
InactiveUS7269516B2Improve abilitiesIncrease powerDrug and medicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionBehavioral neurologyDiagnosis laboratory
A system and method used to assess animal behavior includes a module having sensors that collects a variety of physical and biological data from a test subject. Interpretation of the data is provided to assess the test subject's behavior, neurology, biochemistry and physiology. The module is useful in observing the effects of a drug on the test animal and providing information on the drug's signature. Another advantage is the module's portability that allows it to be used in standard laboratory cages. This portability allows the animal to be tested in its own habitat, that can reduce any erroneous data due to stressing the animal when removed to a test cage. Additionally, the module's design allows for parallel data collection and interpretation from several laboratory animals undergoing different experiments. Multi-dimensional modeling of the test subject based the system's interpretation of the data allows pattern recognition of the drug signature, and predictive drug analysis.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
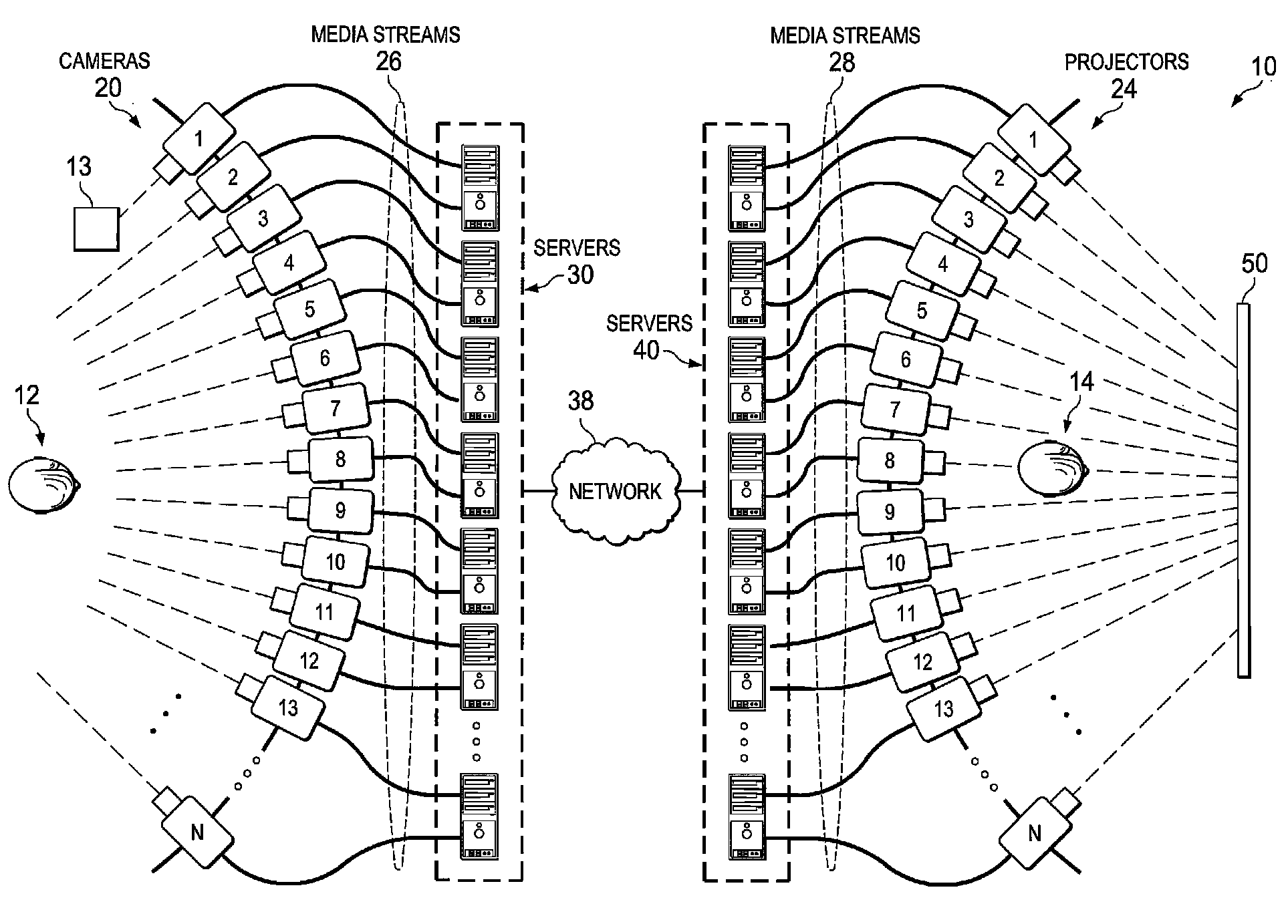
System and method for providing three dimensional imaging in a network environment
A method is provided in one example embodiment and includes receiving data indicative of a personal position of an end user and receiving image data associated with an object. The image data can be captured by a first camera at a first angle and a second camera at a second angle. The method also includes synthesizing the image data in order to deliver a three-dimensional rendering of the object at a selected angle, which is based on the data indicative of the personal position of the end user. In more specific embodiments, the synthesizing is executed by a server configured to be coupled to a network. Video analytics can be used to determine the personal position of the end user. In other embodiments, the method includes determining an approximate time interval for the synthesizing of the image data and then delaying audio data based on the time interval.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Extrusion method for three dimensional modeling
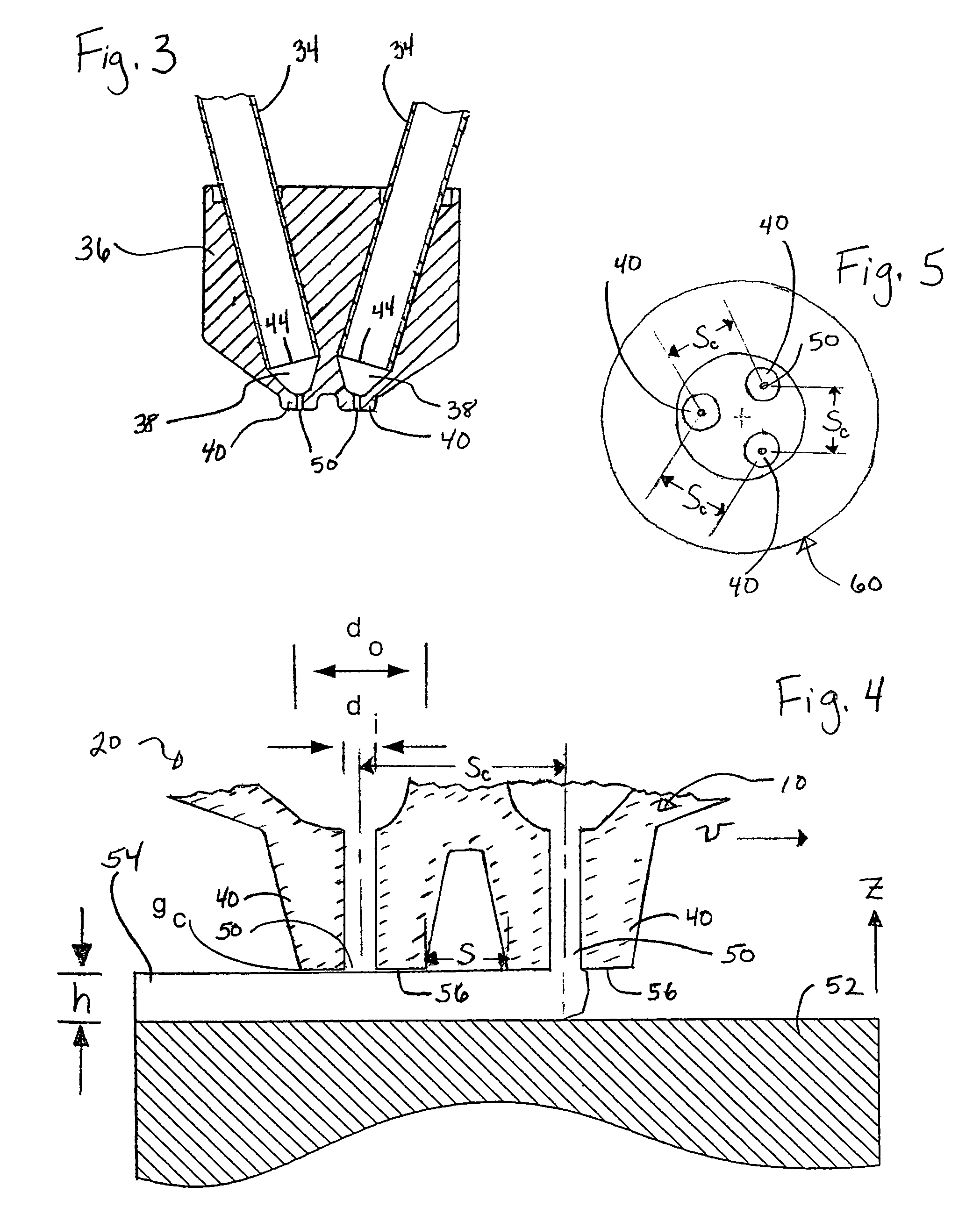
InactiveUS6998087B1Efficient productionLimited spaceAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusDimensional modelingEngineering
A multi-tip extrusion method and apparatus for building a three-dimensional object deposits modeling materials from distinct supply sources, each in a layerwise predetermined pattern, from dispensers having co-planar dispensing tips. The tip spacing is controlled so that a road of material extruded by a leading one of the tips will cool and shrink from the plane of the tips before a trailing one of the tips passes over the road. In this manner, smearing of the road by a trailing one of the tips is avoided.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Generating a three-dimensional model using a portable electronic device recording
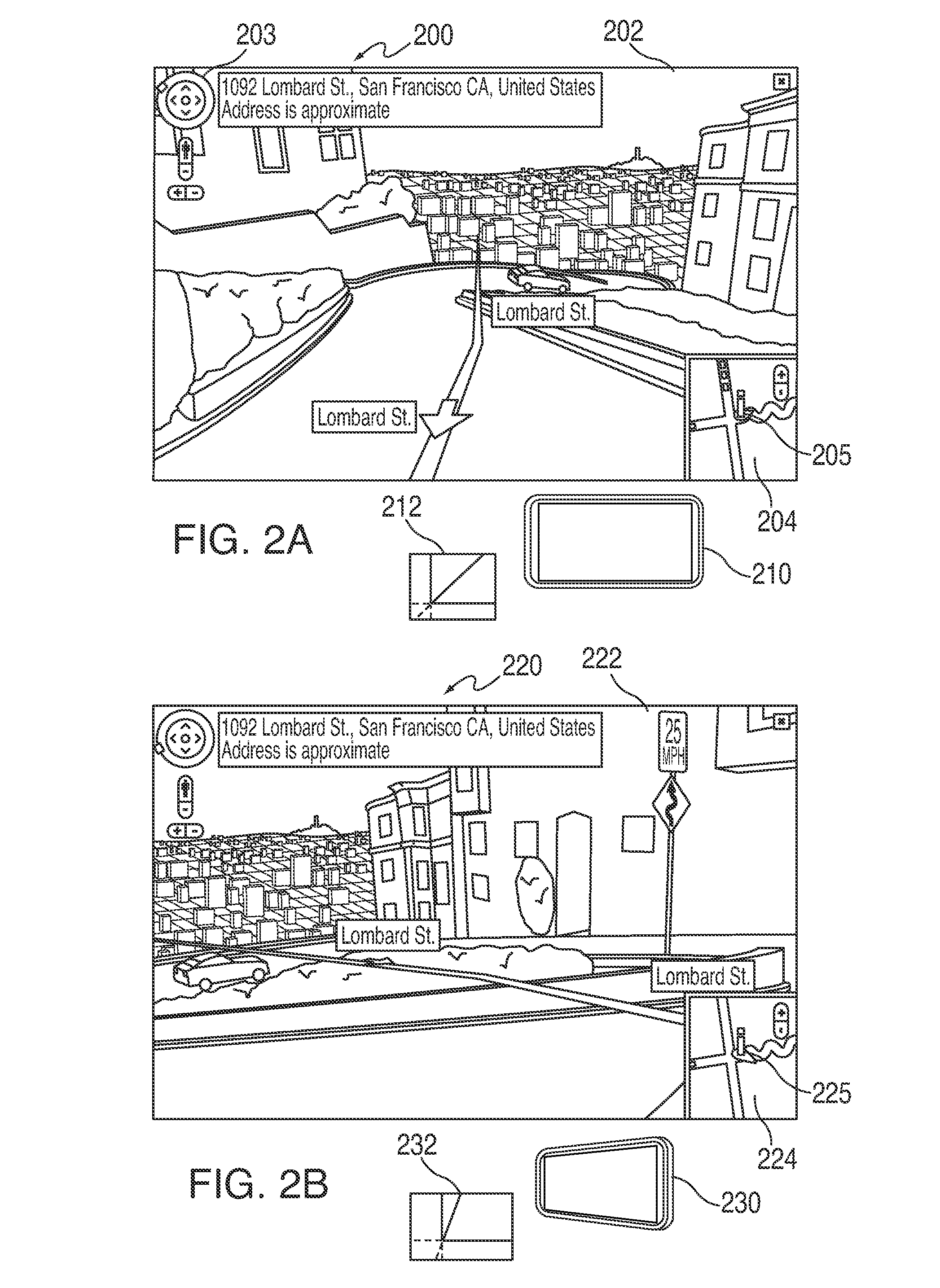
ActiveUS20100188503A1Navigational calculation instrumentsColor television detailsMotion sensingDimensional modeling
Systems and methods are providing for navigating a three-dimensional model using deterministic movement of an electronic device. An electronic device can load and provide an initial display of a three dimensional model (e.g., of an environment or of an object). As the user moves the electronic device, motion sensing components, positioning circuitry, and other components can detect the device movement and adjust the displayed portion of the three-dimensional model to reflect the movement of the device. By walking with the device in the user's real environment, a user can virtually navigate a representation of a three-dimensional environment. In some embodiments, a user can record an object or environment using an electronic device, and tag the recorded images or video with movement information describing the movement of the device during the recording. The recorded information can then be processed with the movement information to generate a three-dimensional model of the recorded environment or object.
Owner:APPLE INC
Modeling apparatus with tray substrate
ActiveUS7127309B2Reduce usageAdditive manufacturing apparatusLarge fixed membersDimensional modelingEngineering
A modeling apparatus includes a platform and a substrate, which are adapted to be releasably locked together to provide a surface for building up models in an additive-process three-dimensional modeling machine. The substrate comprises a substantially rigid, non-dusting tray providing a modeling surface. Male connectors extending from the tray are seated in female connectors in the platform, to engage the substrate to the platform. The engaged substrate is locked to the platform, maintaining accurate positioning of the substrate while a model is built. After modeling is complete, the substrate is released from the platform, the model is removed, and the substrate may be reused.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
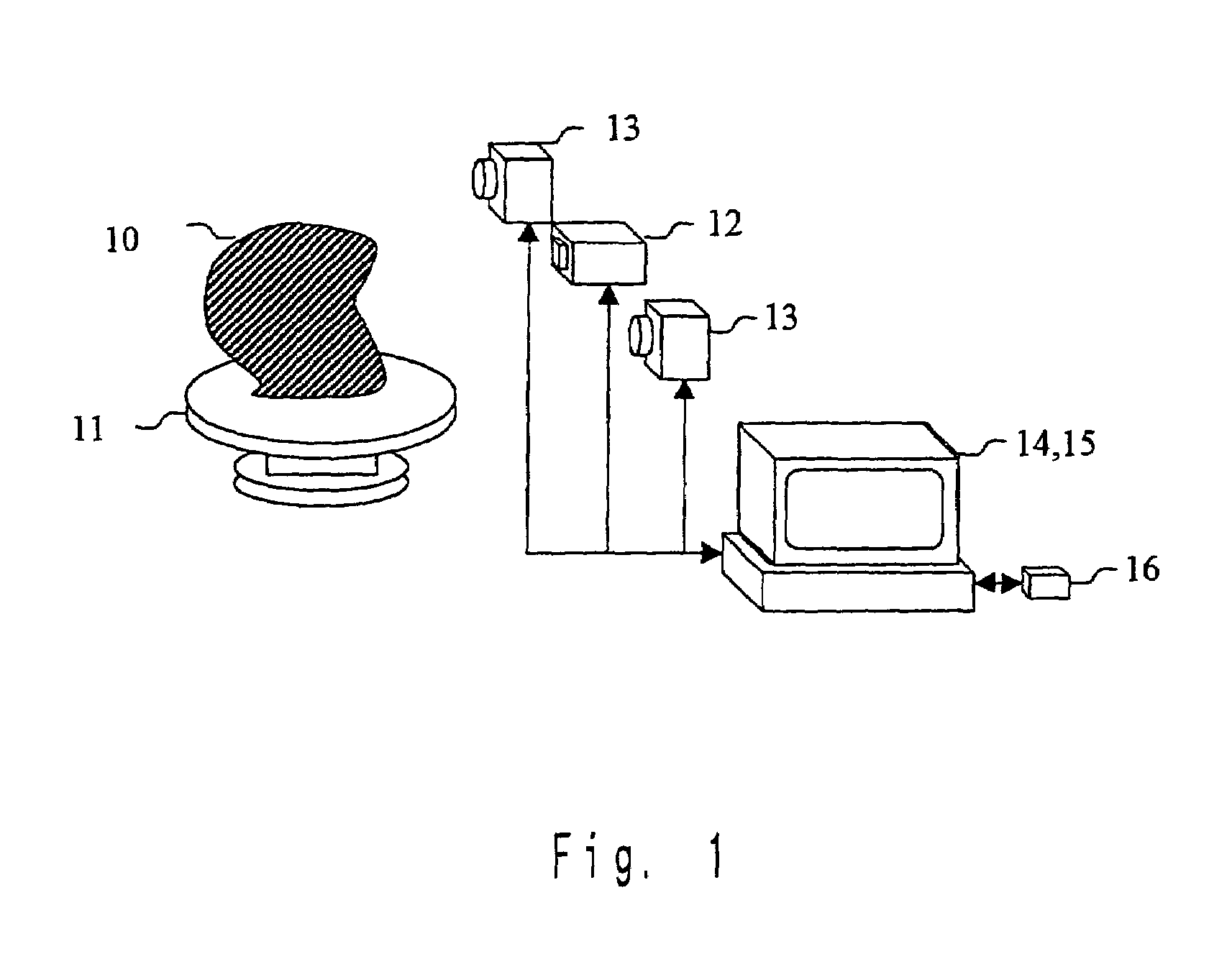
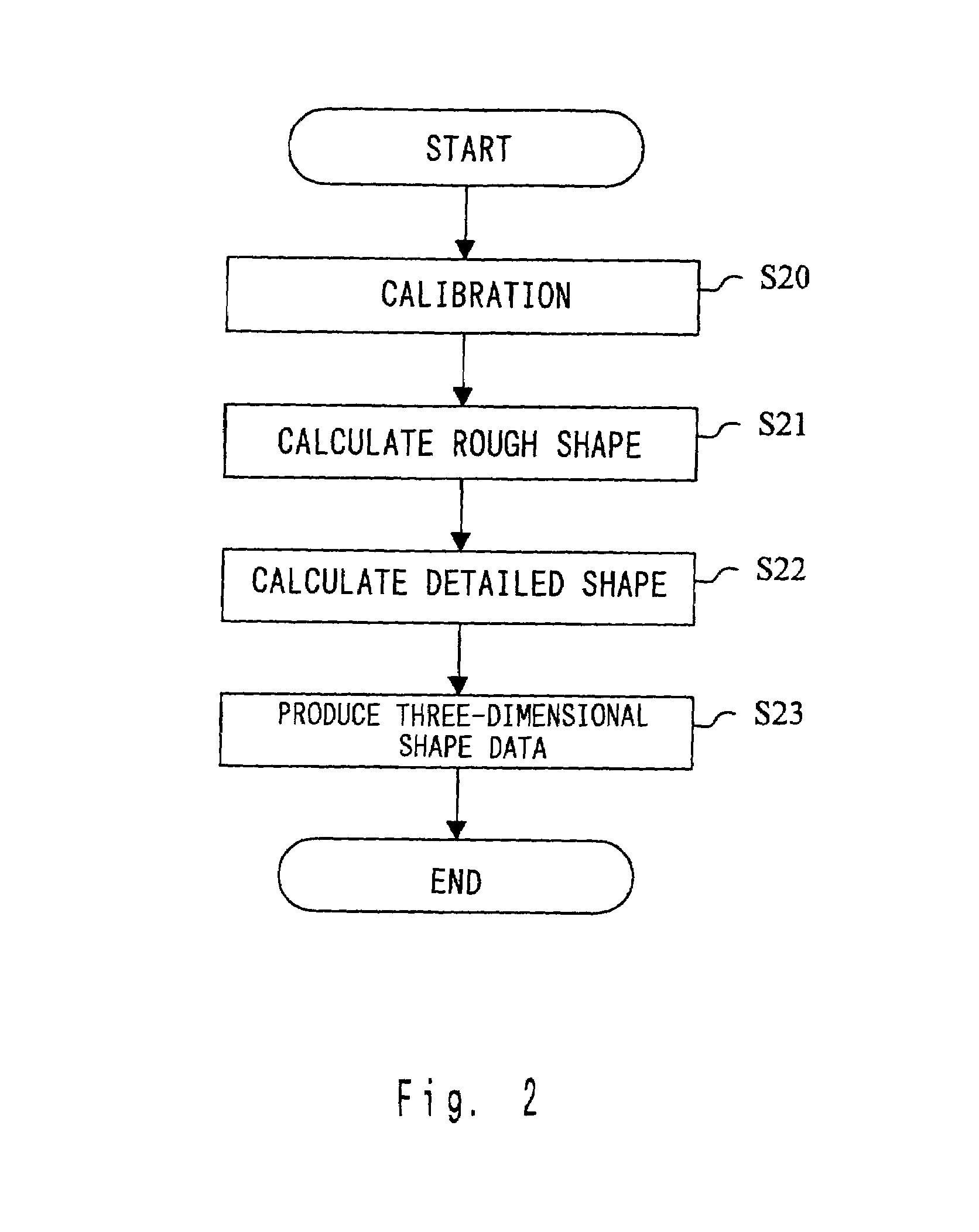
Three-dimensional modeling apparatus, method, and medium, and three-dimensional shape data recording apparatus, method, and medium
InactiveUS6965690B2Increase investmentOptical rangefindersFuel cell auxillariesTriangulationThree dimensional shape
A three-dimensional shape modeling of a real object that reduces the limitations on the target shape and color. The rough shape of the target object is determined by a silhouette method (which has limitation on the target shape) and, at the same time, the detailed shape of the target object is determined by a triangulation method or the like (which has limitation on the target color). By using both sets of information, the consistency between the rough and detailed shape information are checked. For the portions where the consistency is not satisfied (points where detailed shape information is absent or points where detailed shape section is present outside the rough shape), rough shape is assumed to be the final object information and for other portions, the detailed shape is taken as the final object information. In this manner, three-dimensional shape modeling with reduced limitations on the target shape and color can be performed.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
Automatic Scene Calibration
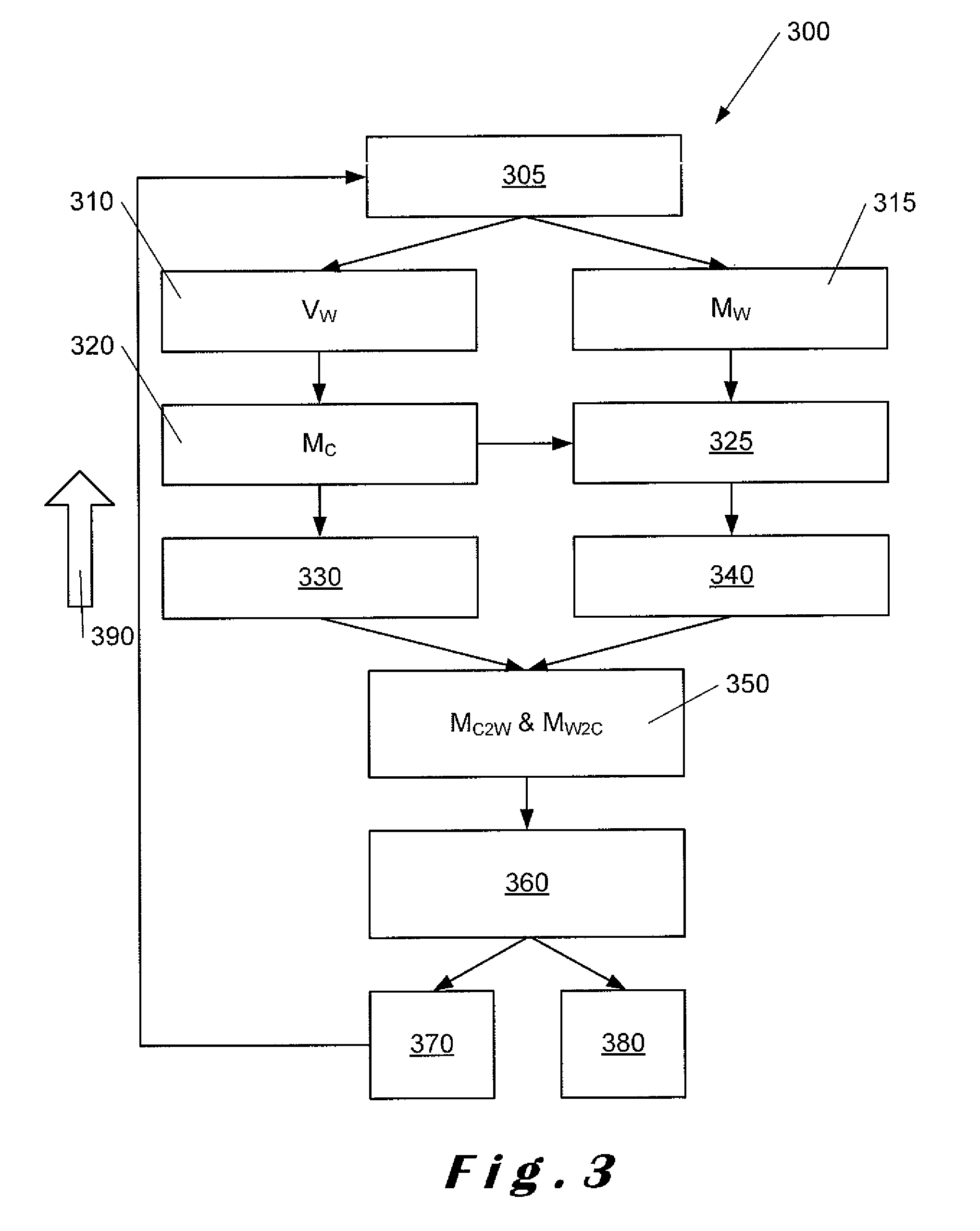
ActiveUS20150181198A1Improve visibilityImproving and automating calibration processImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual coordinate systemsDimensional modeling
Described herein is a method of calibrating a three-dimensional imaging system. During calibration, a position and an orientation of the three-dimensional imaging system is determined with respect to a first parameter comprising a real world vertical direction (Vw) and to a second parameter comprising an origin of a three-dimensional scene captured by the imaging system. The first and second parameters are used to derive a calibration matrix (MC2w) which is used to convert measurements from a virtual coordinate system (Mc) of the three-dimensional imaging system into a real coordinate system (Mw) related to the real world. The calibration matrix (MC2w) is used to rectify measurements prior to signal processing. An inverse calibration matrix (Mw2c) is also determined. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of the setup of the three-dimensional imaging system is carried out and the calibration matrix (Mc2w) and its inverse (Mw2c) are adjusted accordingly.
Owner:SOFTKINETIC SOFTWARE
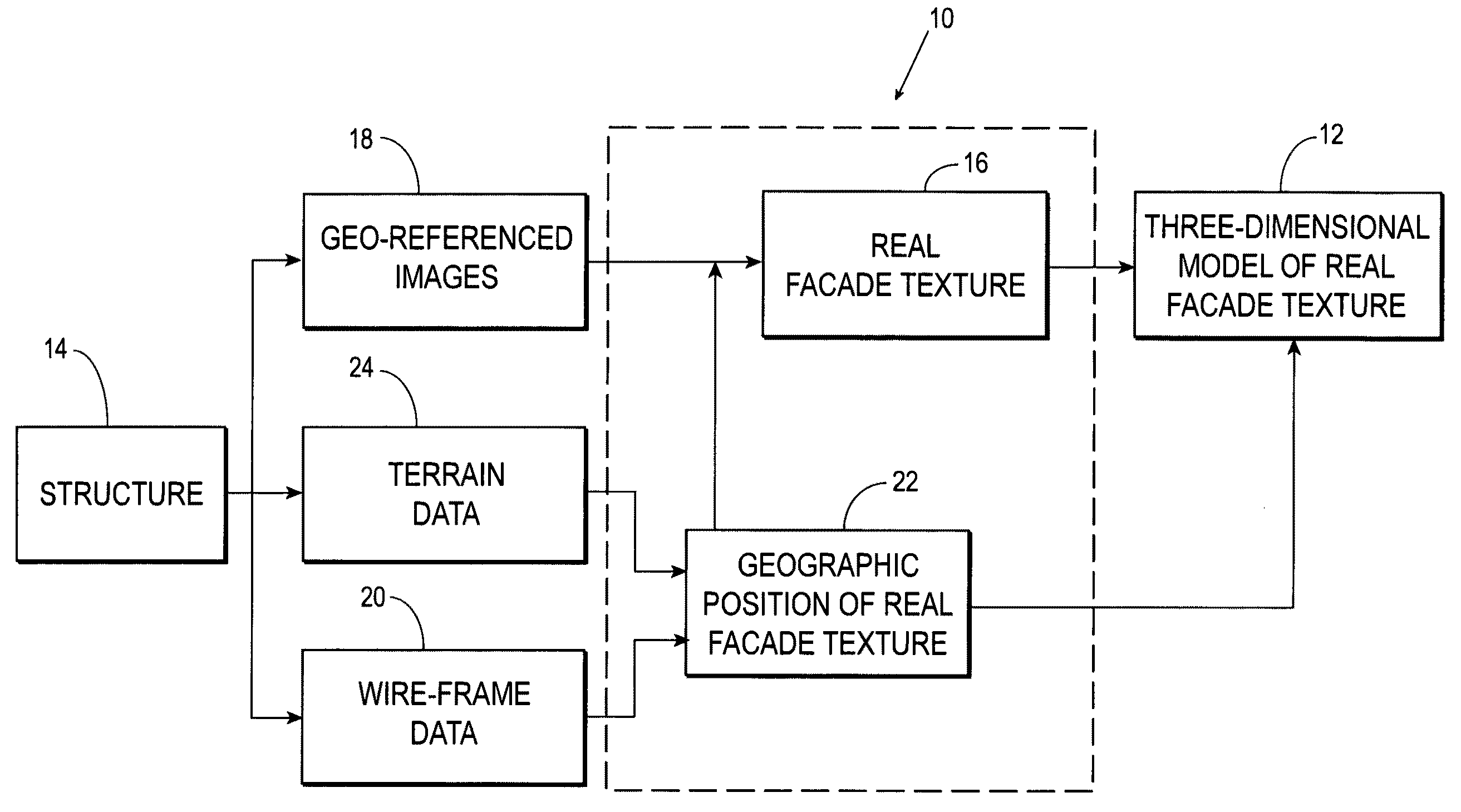
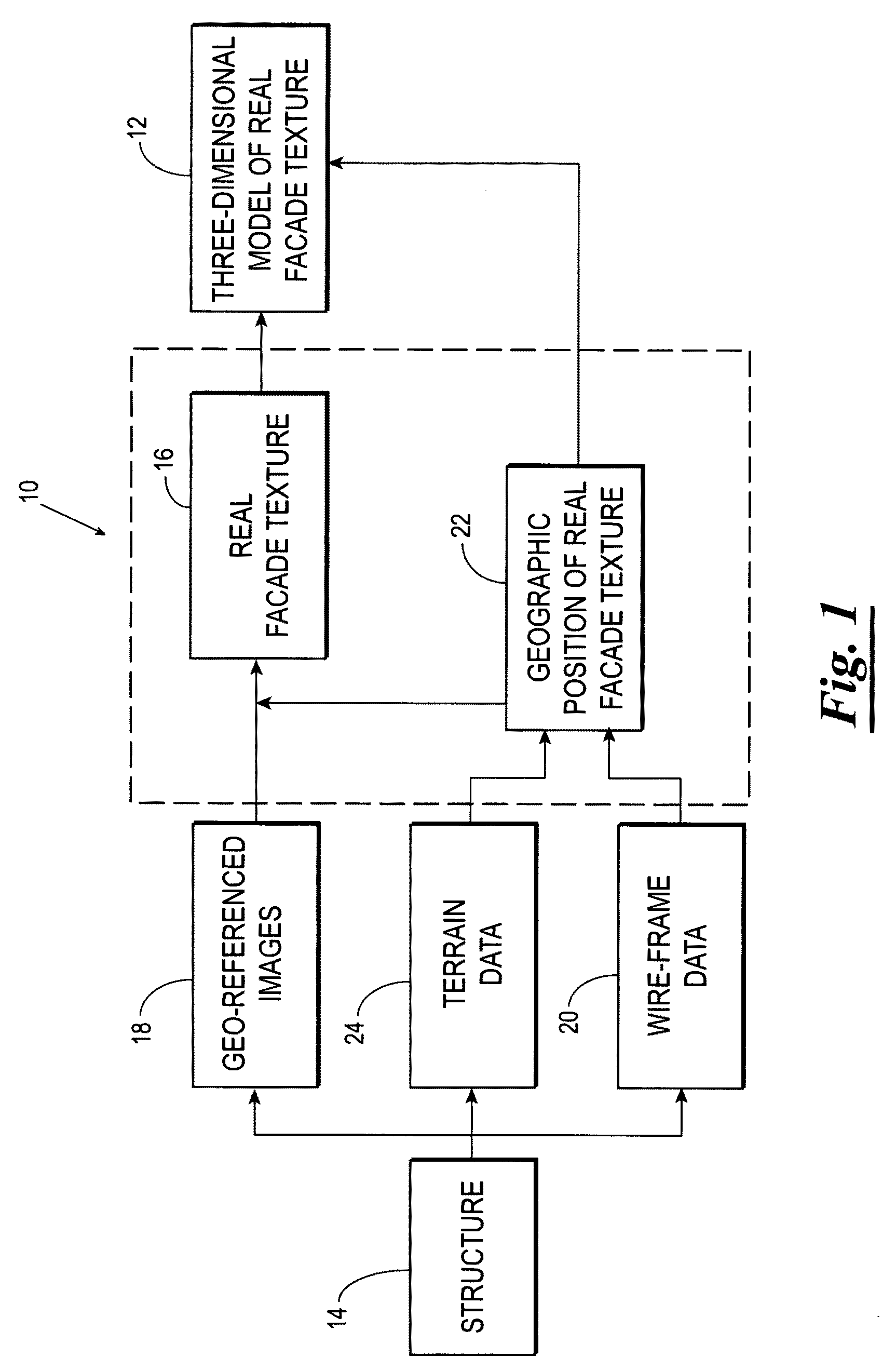
Systems and methods for rapid three-dimensional modeling with real facade texture
Owner:PICTOMETRY INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Fast multilevel imagination and reality occlusion method at actuality enhancement environment
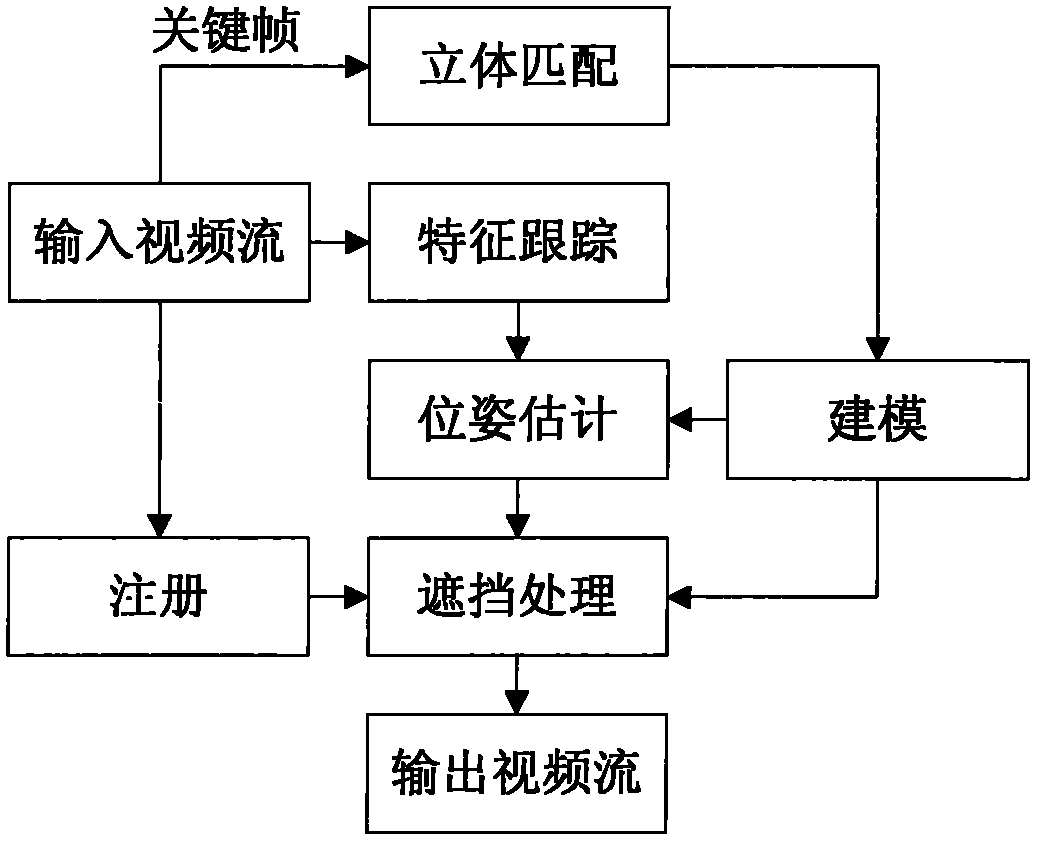
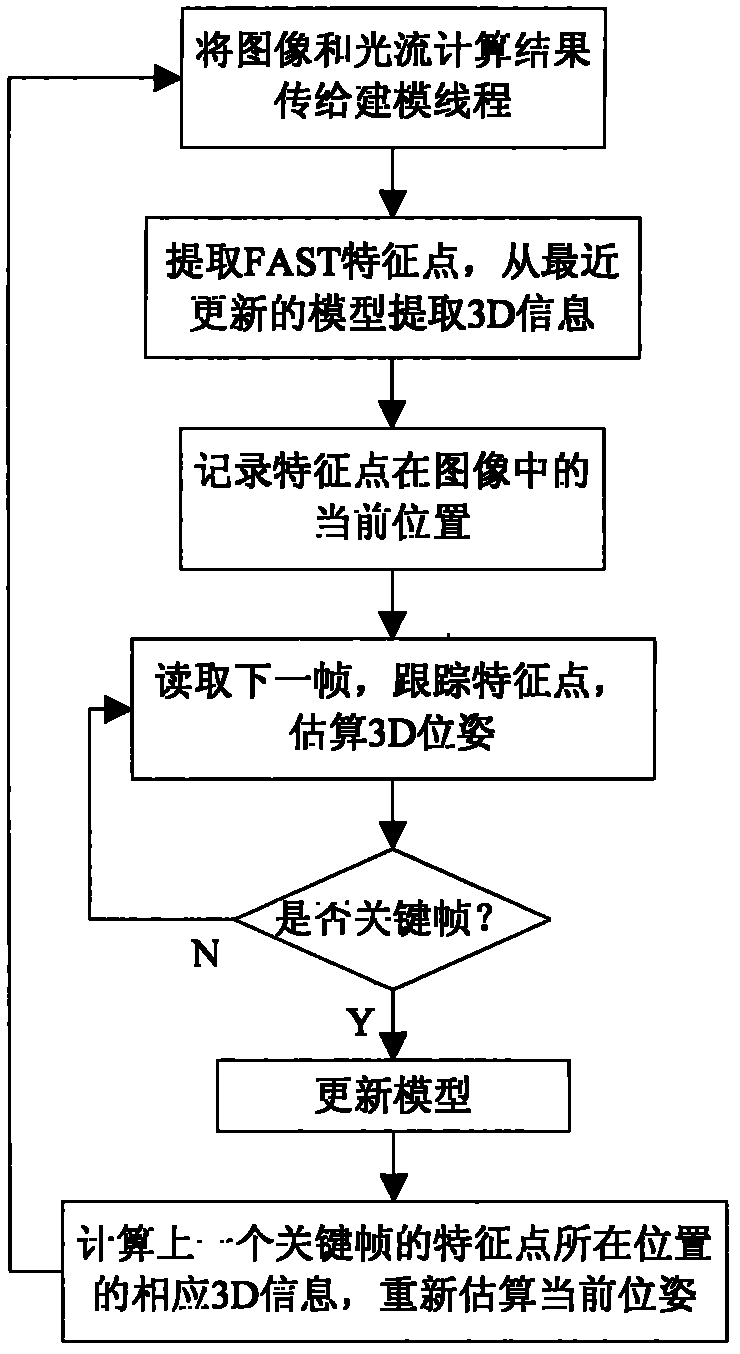
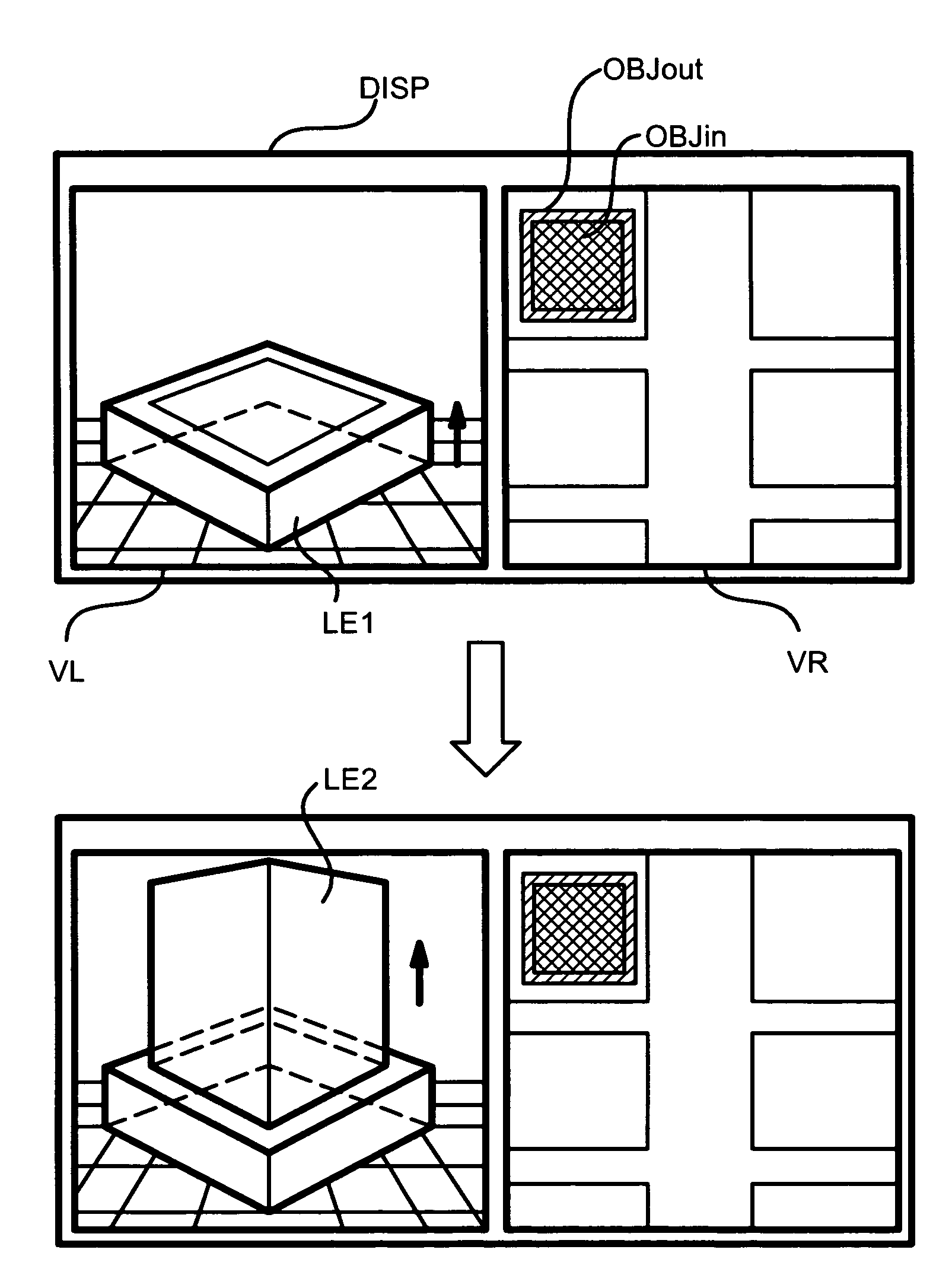
InactiveCN102129708AMeet real-time requirementsStrengthen the occlusionSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingDimensional modelingParallel processing
The invention relates to a fast multilevel imagination and reality occlusion method at an actuality enhancement environment, comprising the following steps of: acquiring videos of a real scene by using a two-path video camera; extracting a pair of keyframes from a two-path video stream at set intervals to carry out the resolving of a dense depth map, building a three-dimensional model of a real object participating in occlusion, and extracting sparse feature points; tracking the sparse feature points of all middle frames of the two-path video stream, and estimating the posture of a current camera by combining with the positions of the sparse feature points in an image; acquiring the three-dimensional information of the real object according to a model built for the last time; moving and rotating the model of the real object according to the posture of the current camera; carrying out depth relation comparison by utilizing the three-dimensional information of the recently regulated real object with a registered three-dimensional virtual object; and respectively processing the three-dimensional tracking of the middle frames and the three-dimensional reconstruction of the keyframes in parallel at different threads. The invention is suitable for unknown and variable environments without modeling in advance and can meet the requirements for real time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
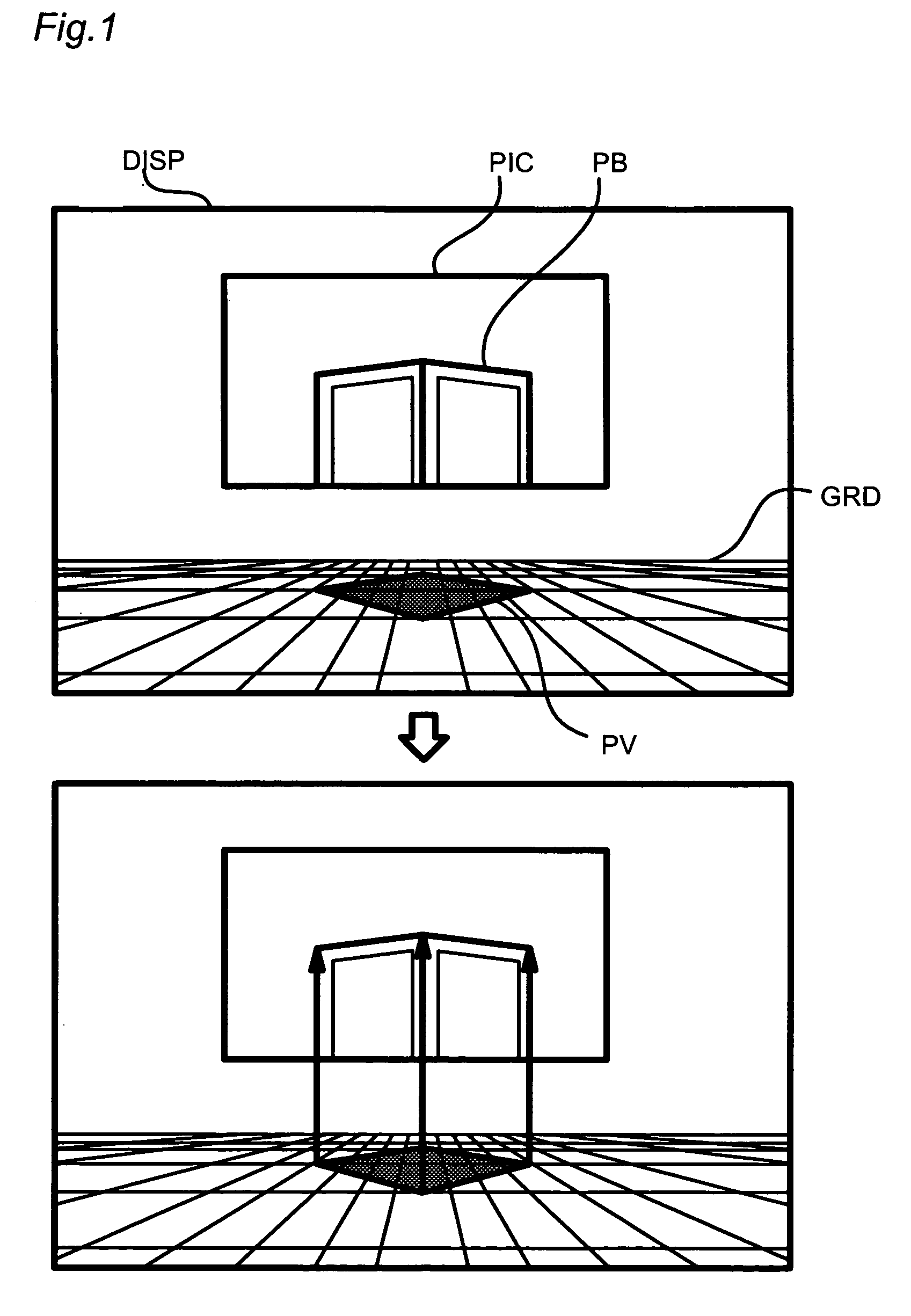
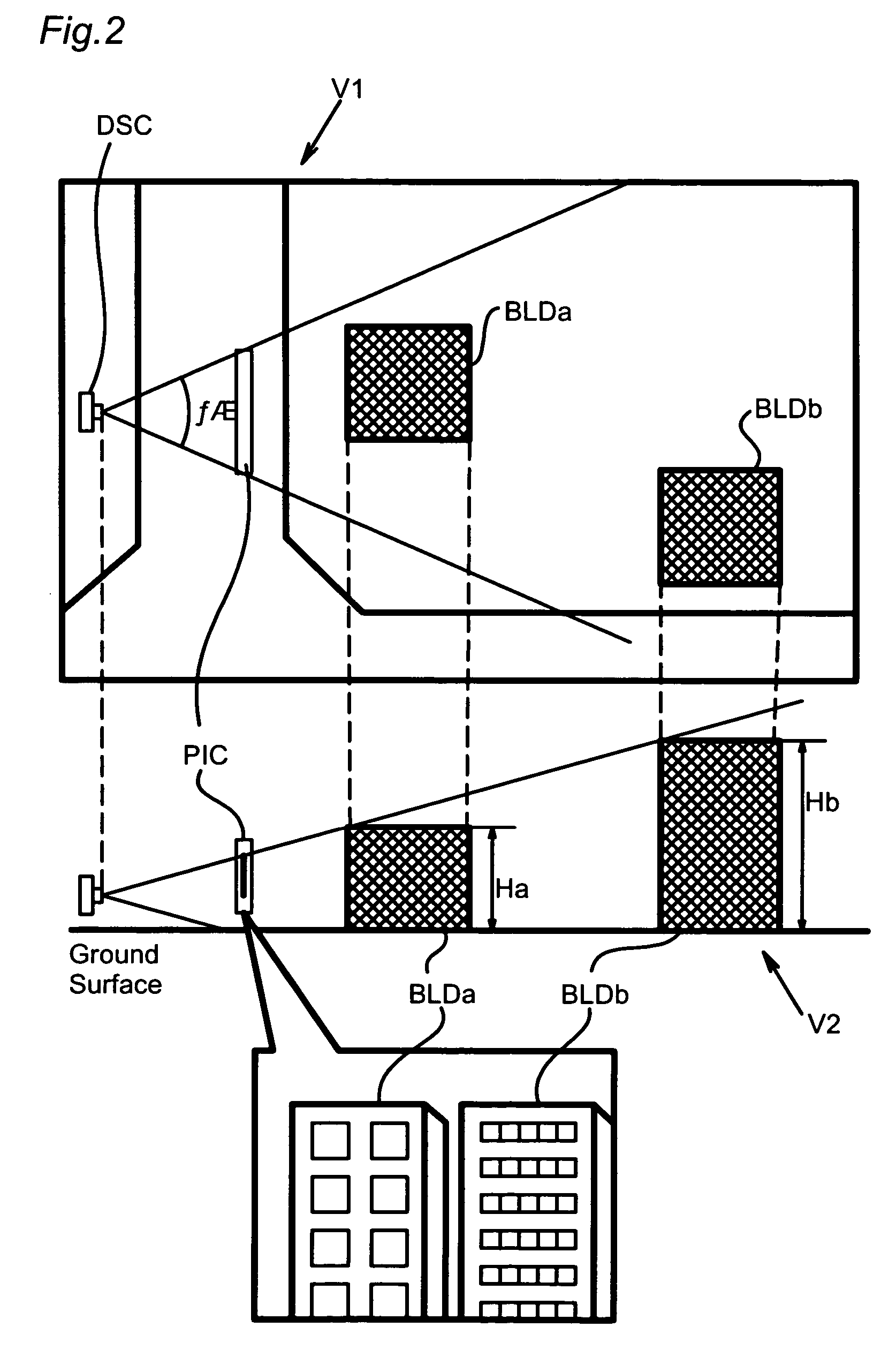
Three-dimensional electronic map data creation method
InactiveUS7343268B2Promote generationGeometric CADInstruments for road network navigationVirtual spaceDimensional modeling
When creating three-dimensional electronic map data, three-dimensional modeling of a building is performed as follows without measuring height of the building. Firstly, a building is photographed and the photographing position and photographing parameters (camera direction, angle of view) are recorded. Secondly, in a virtual space prepared on a computer, a photograph is arranged so as to reproduce the state upon the photographing according to these data. In combination with this, a plan view of the building is arranged according to the two-dimensional map data. Thirdly, the plan view is moved in the height direction until it is overlapped with the photograph, thereby modeling the building. Thus, it is possible to realize three-dimensional modeling without measuring the height.
Owner:ZENRIN
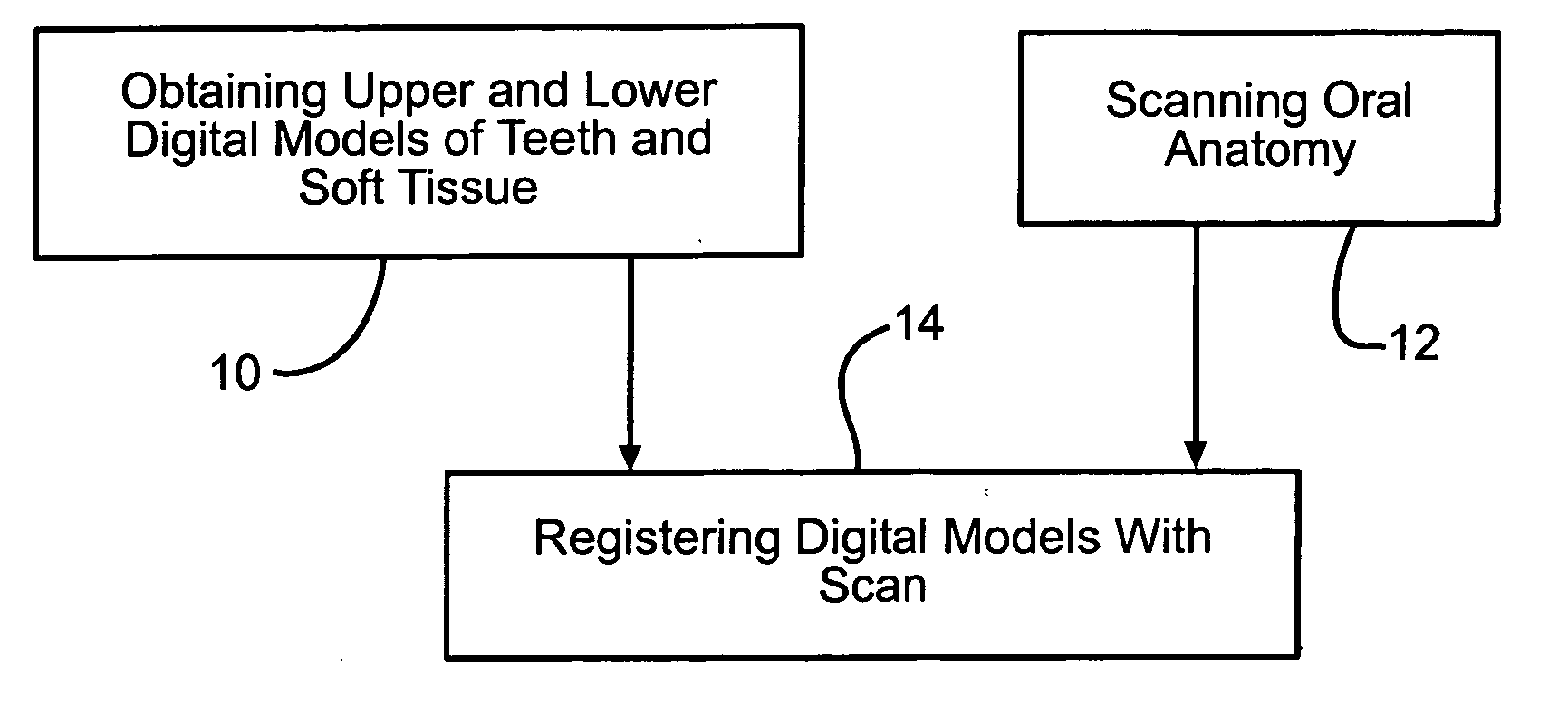
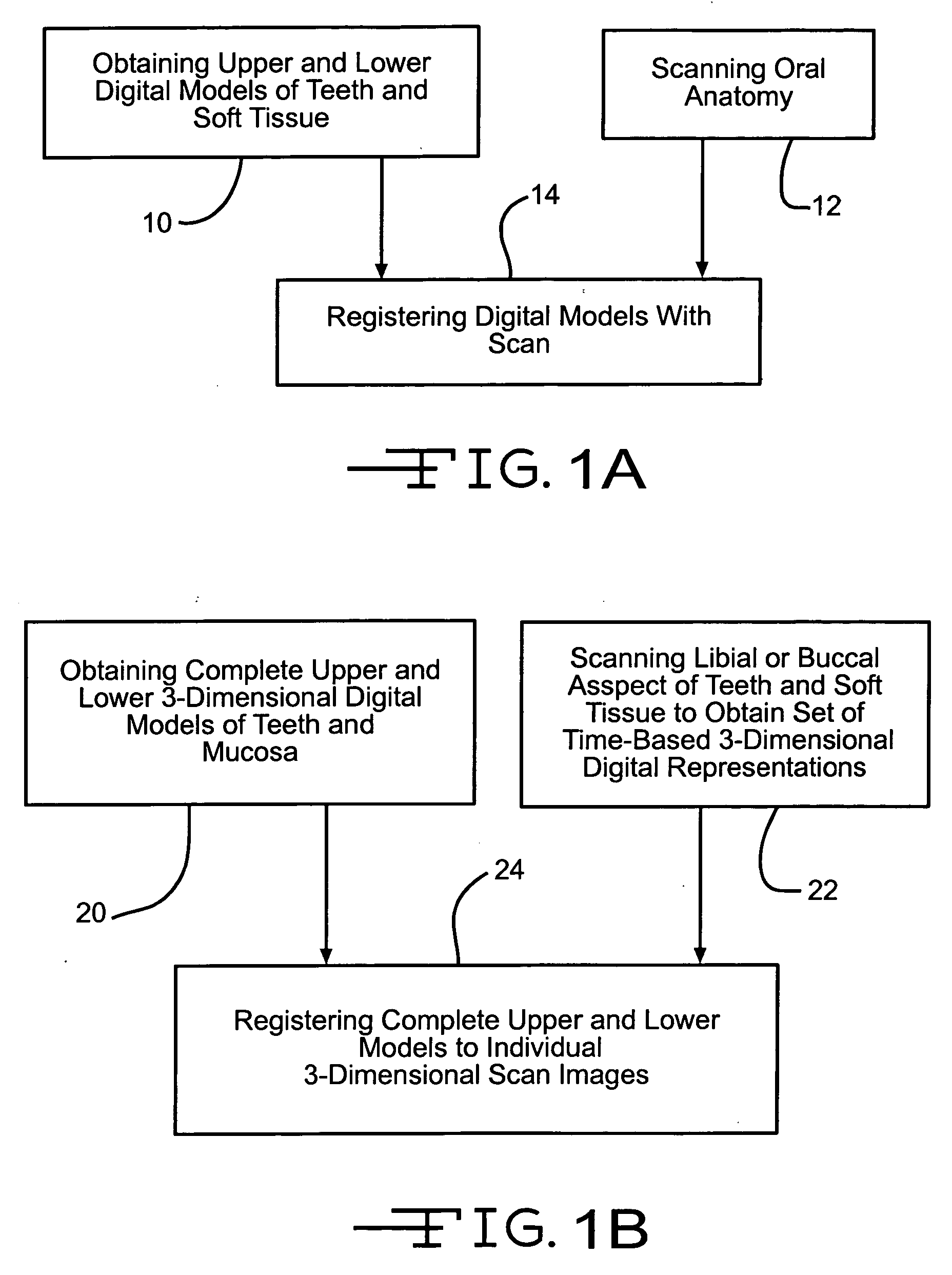
Four dimensional modeling of jaw and tooth dynamics
InactiveUS20070207441A1Impression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDimensional modelingTemporomandibular joint
Methods and systems are described to digitally model the 4-dimensional dynamics of jaw and tooth motion using time-based 3-dimensional data. Complete upper and lower digital models are registered to time-based 3-dimensional intra-oral data to produce a true 4-dimensional model. Diagnostic and clinical applications include balancing the occlusion and characterizing the geometry of the temporomandibular joint. The 4-dimensional model is readily combined with conventional imaging methods such as CT to create a more complete virtual patient model.
Owner:GREAT LAKES ORTHODONTICS
Generation of three-dimensional movies with improved depth control
ActiveUS20090160934A1Smooth changeEasy to controlCharacter and pattern recognitionStereoscopic photographyLive actionComputer graphics (images)
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Three-dimensional shape conversion system, three-dimensional shape conversion method, and program for conversion of three-dimensional shape
InactiveUS20090040224A1Improve accuracyAdequately consistentSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingThree dimensional shapeDimensional modeling
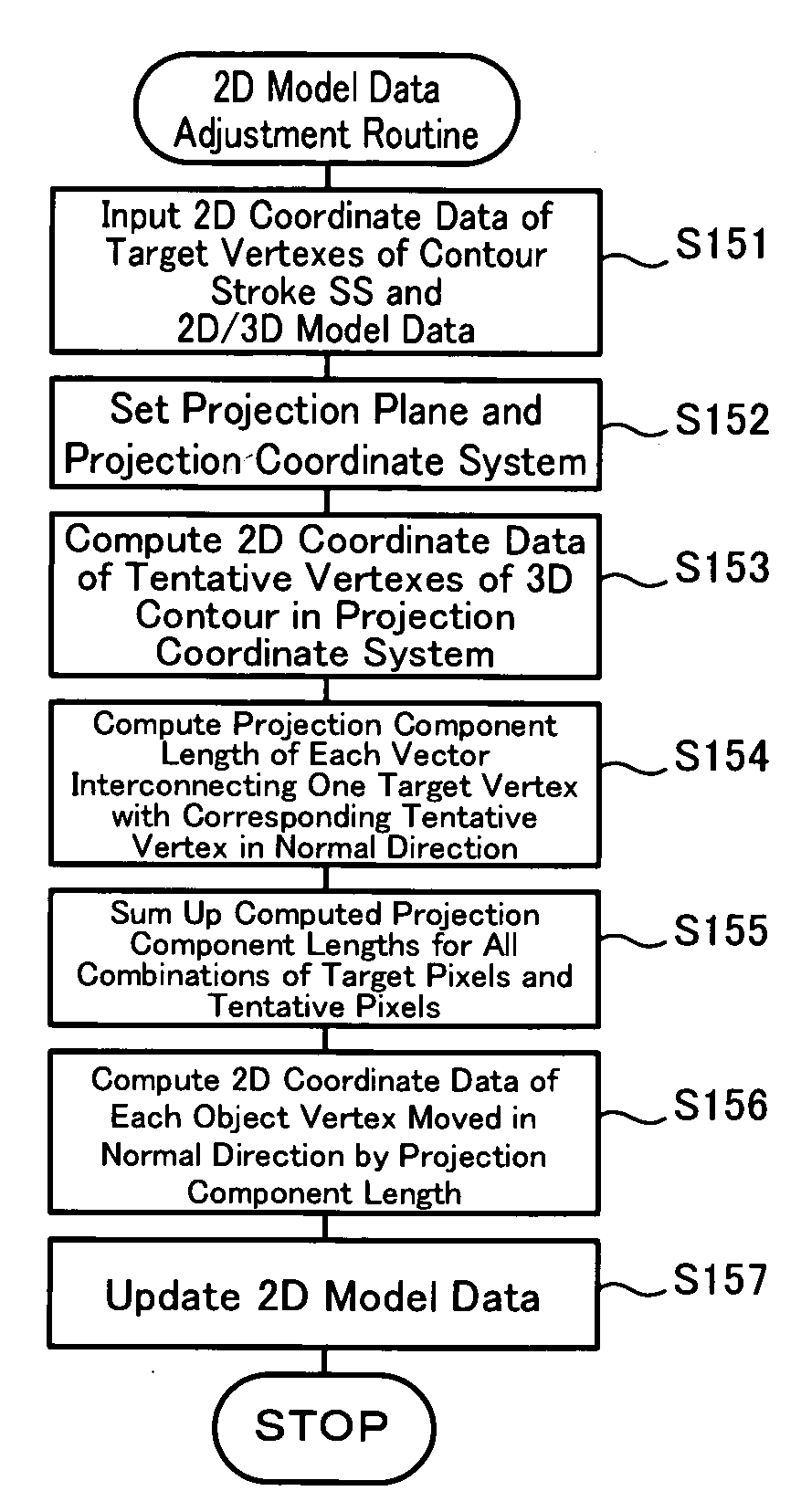
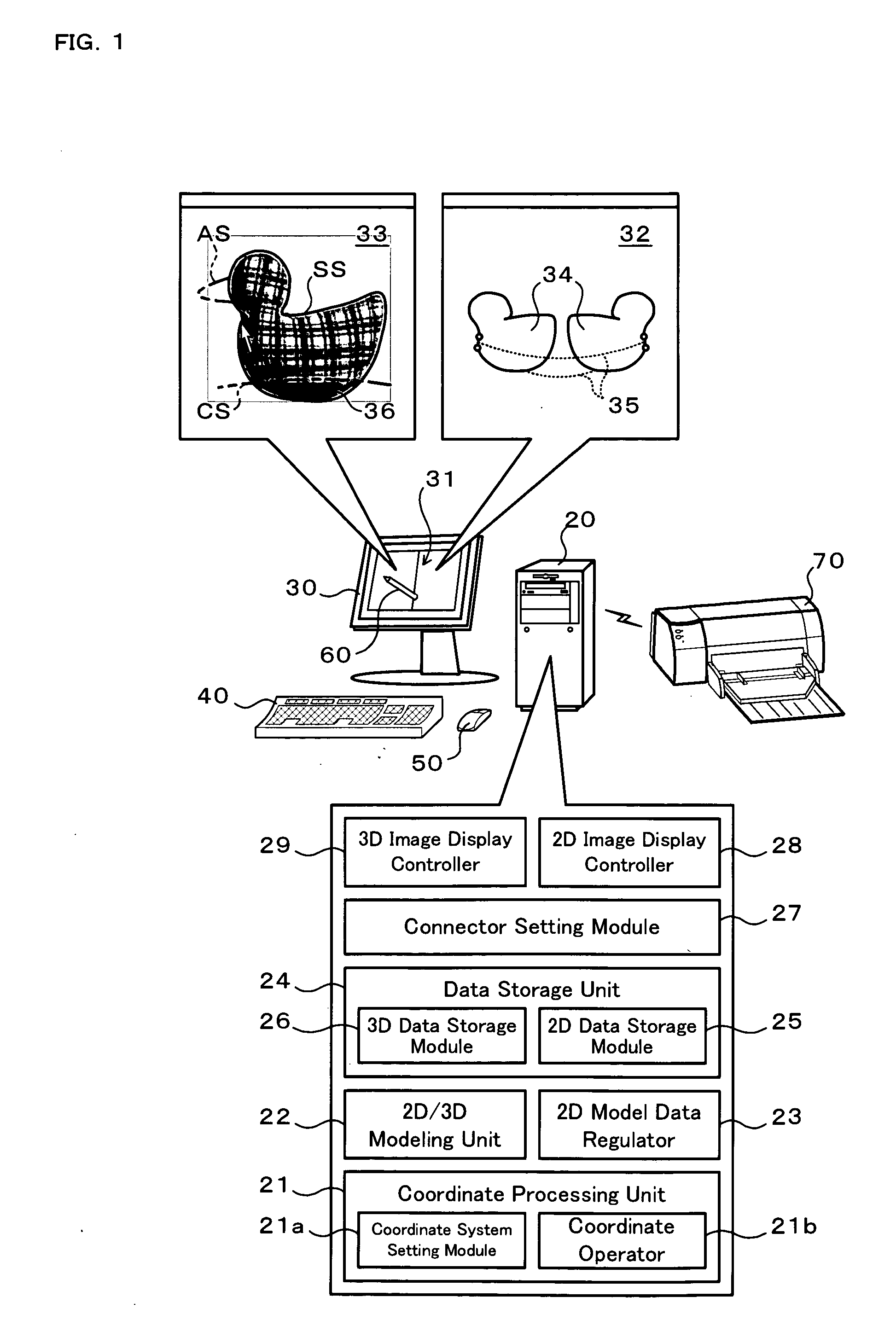
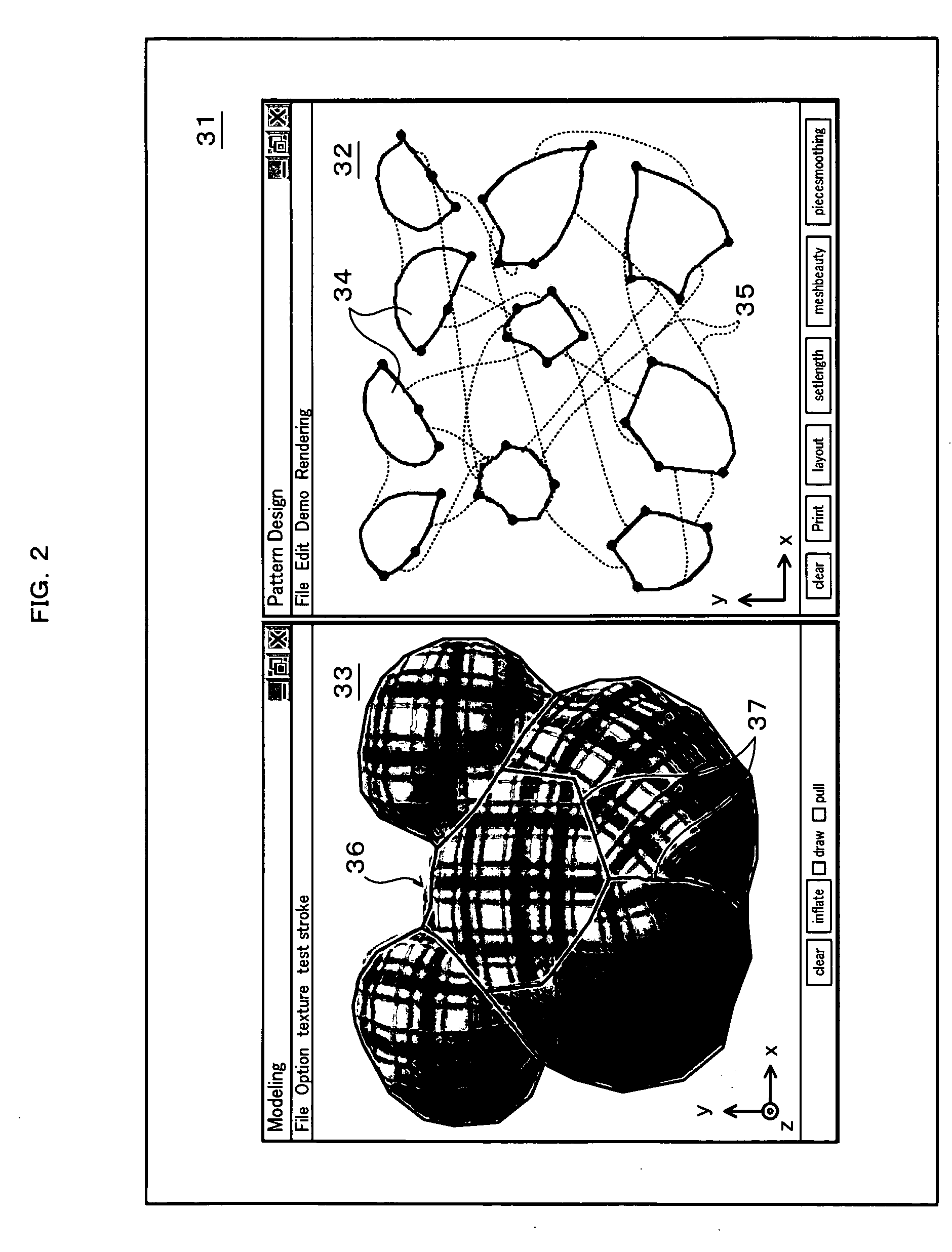
In a computer 20 with a three-dimensional shape conversion program installed therein, a coordinate processing unit 21 obtains two-dimensional coordinate data of a contour stroke SS input through the user's operation of a mouse 50 or another suitable input unit. A 2D / 3D modeling unit 22 performs two-dimensional modeling based on the obtained two-dimensional coordinate data and thereby generates two-dimensional model data regarding a two-dimensional pattern, while performing three-dimensional modeling based on the generated two-dimensional model data and generates three-dimensional model data regarding a three-dimensional shape obtained by expanding the two-dimensional pattern. A 2D model data regulator 23 adjusts the two-dimensional model data to make a corresponding contour of the three-dimensional shape defined by the three-dimensional model data substantially consistent with the input contour stroke SS.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
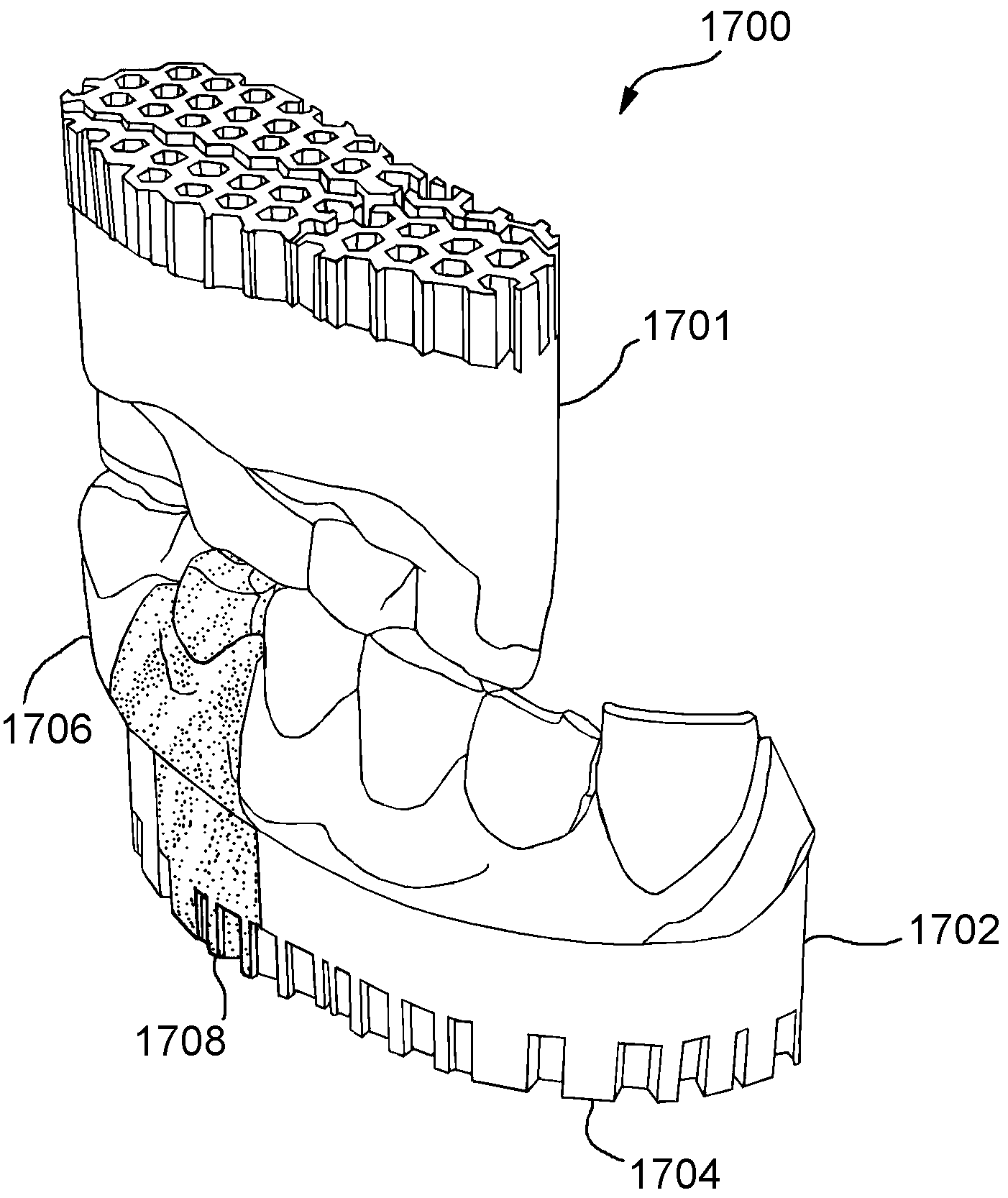
Local enforcement of accuracy in fabricated models
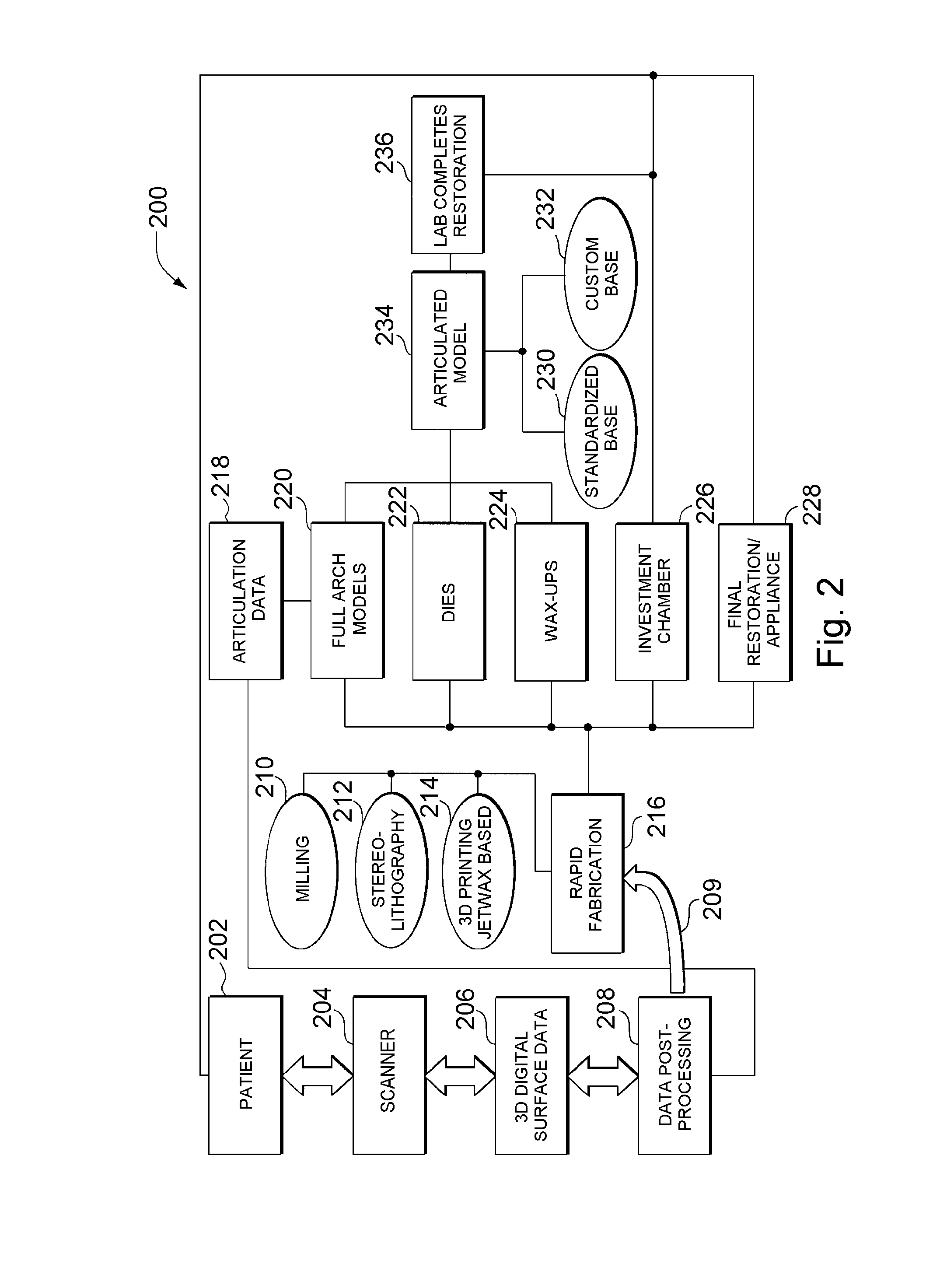
ActiveUS7698014B2Dental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusDental ArticulatorsDimensional modeling
The systems and methods disclosed herein employ a combination of digital three-dimensional modeling and rapid fabrication technologies to provide pre-indexed, pre-registered, and / or precut components for articulated dental models. Dental articulators and components of dental models as described herein use a positioning key to encode positional information for components of the dental model, and / or a reference grid on mounting surfaces to enforce local accuracy of fabricated parts against a fixed reference array.
Owner:MEDIT CORP
Local enforcement of accuracy in fabricated models
ActiveUS20080015727A1Additive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsDental ArticulatorsDimensional modeling
The systems and methods disclosed herein employ a combination of digital three-dimensional modeling and rapid fabrication technologies to provide pre-indexed, pre-registered, and / or precut components for articulated dental models. Dental articulators and components of dental models as described herein use a positioning key to encode positional information for components of the dental model, and / or a reference grid on mounting surfaces to enforce local accuracy of fabricated parts against a fixed reference array.
Owner:MEDIT CORP
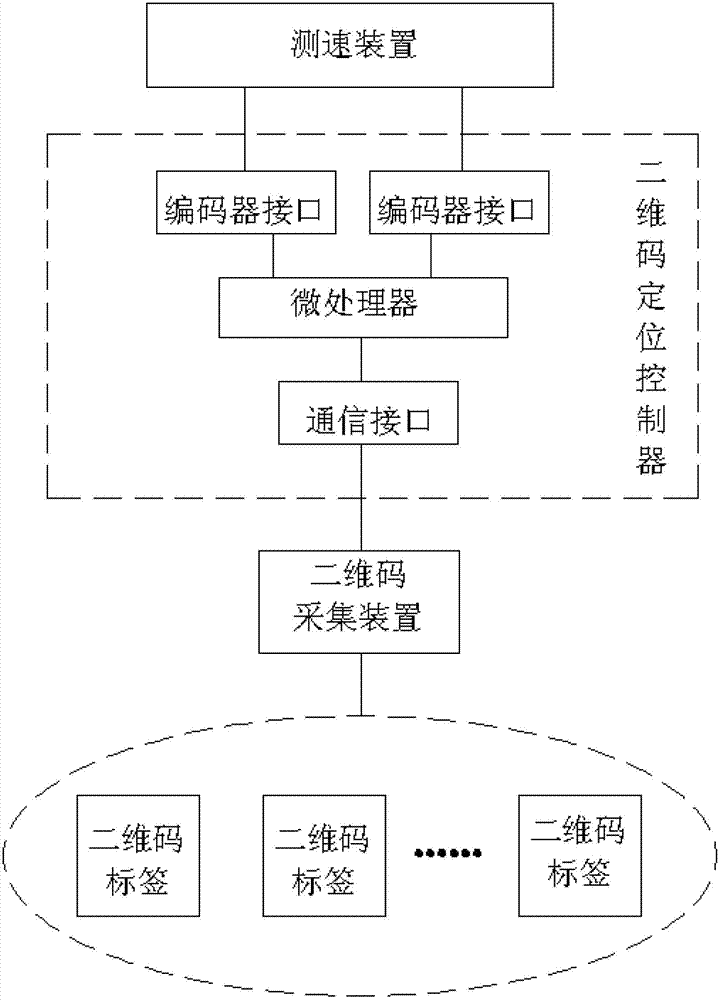
Indoor mobile robot positioning system and method based on two-dimensional code
ActiveCN102735235ASolve the speed problemFix the angle problemNavigation instrumentsCommunication interfaceImaging processing
The present invention relates to an indoor mobile robot positioning system and method based on two-dimensional code. The system includes a two-dimensional code positioning controller mounted on a mobile robot, a two-dimensional code acquisition device and a two-dimensional code label distributed in the indoor environment. The two-dimensional code positioning controller is composed of a microprocessor and a communication interface that are connected together. The microprocessor is connected with the two-dimensional code acquisition device through the communication interface and is used for controlling the two-dimensional code acquisition device to acquire two-dimensional code images, receive the two-dimensional code images acquired by the two-dimensional code image acquisition device and realize precise positioning function. The method acquires an actual position of the mobile robot through photographing the indoor two-dimensional code labels, transforming coordinates and mapping code values. The method of the invention organically combines visual positioning technique, two-dimensional code positioning technology and two degree of freedom measuring technology to realize the function of precise positioning of the mobile robot and solve problems of complex image processing and inaccurate positioning of a traditional vision positioning system.
Owner:爱泊科技(海南)有限公司
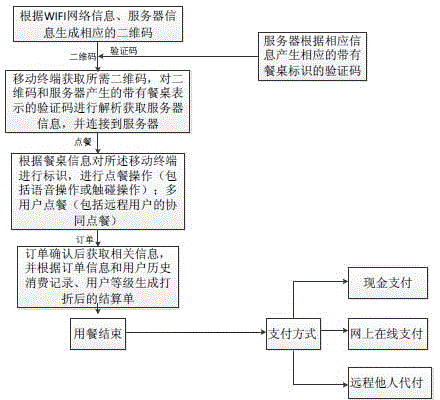
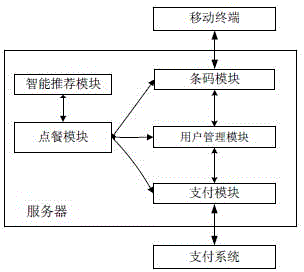
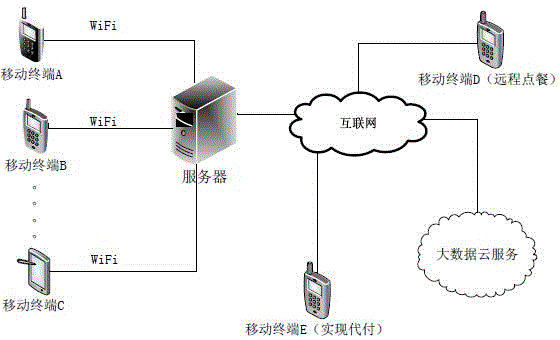
Two-dimensional code-based cooperative intelligent ordering method and system
InactiveCN104978697AOptimize dish informationAvoid the situation of "one dish is fried many times"Data processing applicationsTablet computerPayment
The invention discloses a two-dimensional code-based cooperative intelligent ordering method and system. The system comprises a mobile terminal with a two-dimensional code scanning function and a server supporting ordering and payment functions. The mobile terminal can be an intelligent mobile phone and a tablet computer. The server is used for processing ordering information, and mainly comprises a barcode module, an ordering module, a user management module, an intelligent recommendation module and a payment module; the barcode module mainly comprises two-dimensional code and verification code generation and verification functions; the ordering module is used for supporting ordering (including remote ordering) of multiple persons and voice ordering; the user management module is mainly used for automatically identifying user identities and storing user consumption information; the intelligent recommendation module is mainly used for providing big data cloud services for merchants, digging user consumption habits, tastes and the like according to user consumption records and providing personalized dish and service recommendations for users; and the payment module is mainly used for supporting transaction of cash, electronic payment (including remote payment for another) and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Producing a three dimensional model of an implant
InactiveUS8781557B2Quick assemblyProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusDimensional modelingMedical device
Determining a shape of a medical device to be implanted into a subject produces an image including a defective portion and a non-defective portion of a surface of a tissue of interest included in the subject. The tissue of interest is segmented within the image. A template, representing a normative shape of an external anatomical surface of the tissue of interest, is superimposed to span the defective portion. An external shape of an implant, is determined as a function of respective shapes of the defective portion as seen in the template, for repairing the defective portion.
Owner:OSTEOPLASTICS
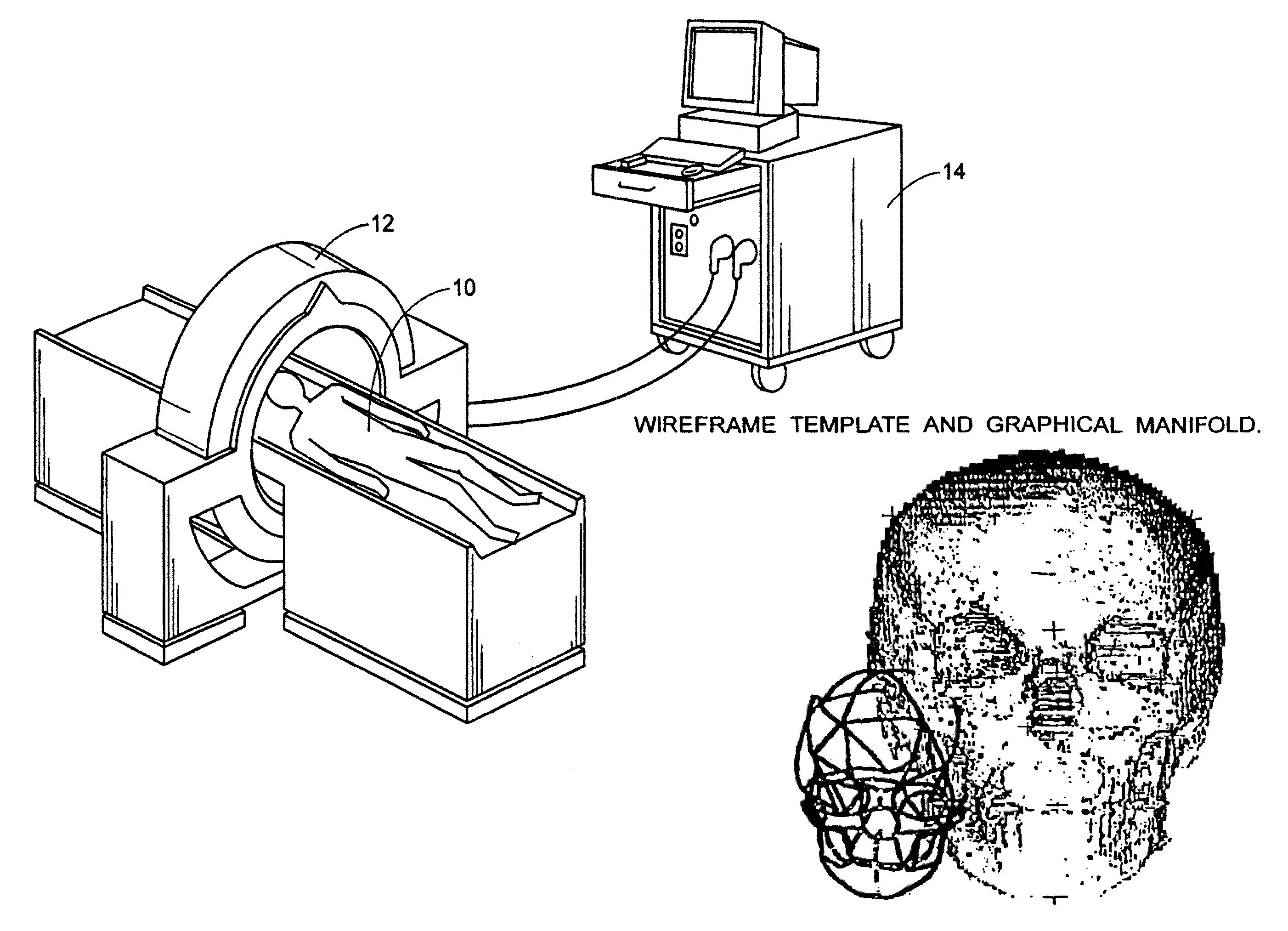
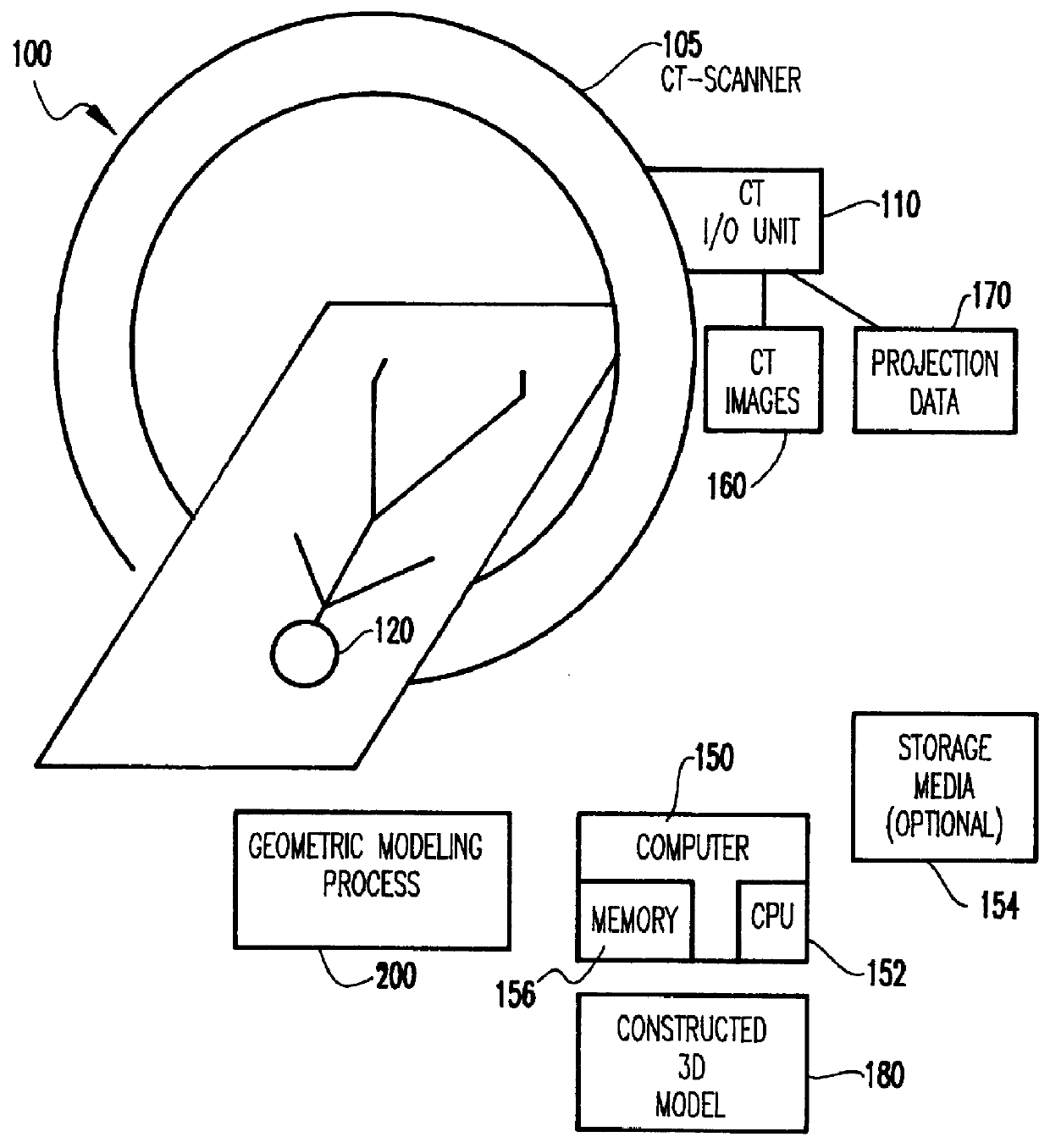
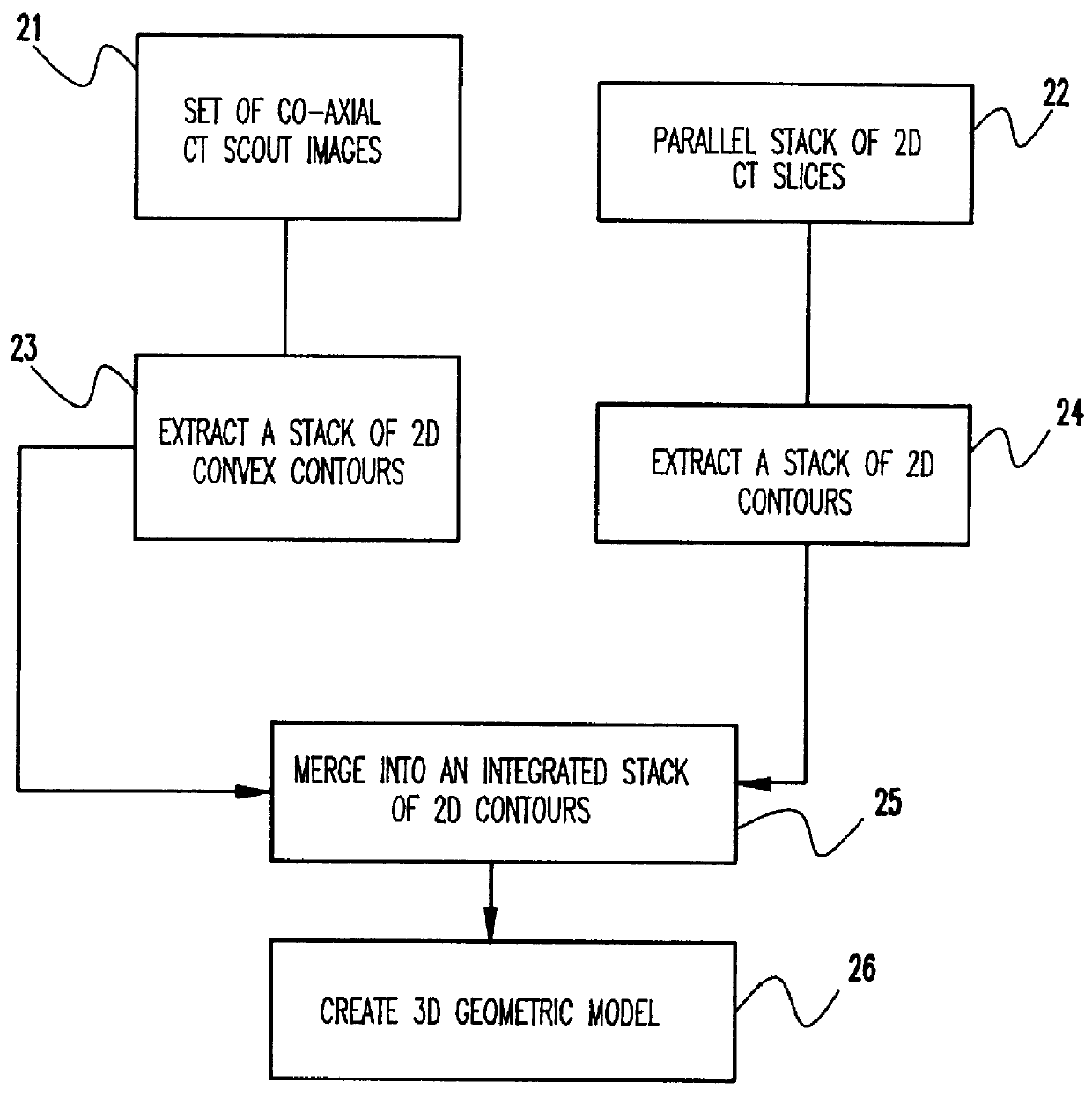
System and method for three-dimensional geometric modeling by extracting and merging two-dimensional contours from CT slice data and CT scout data
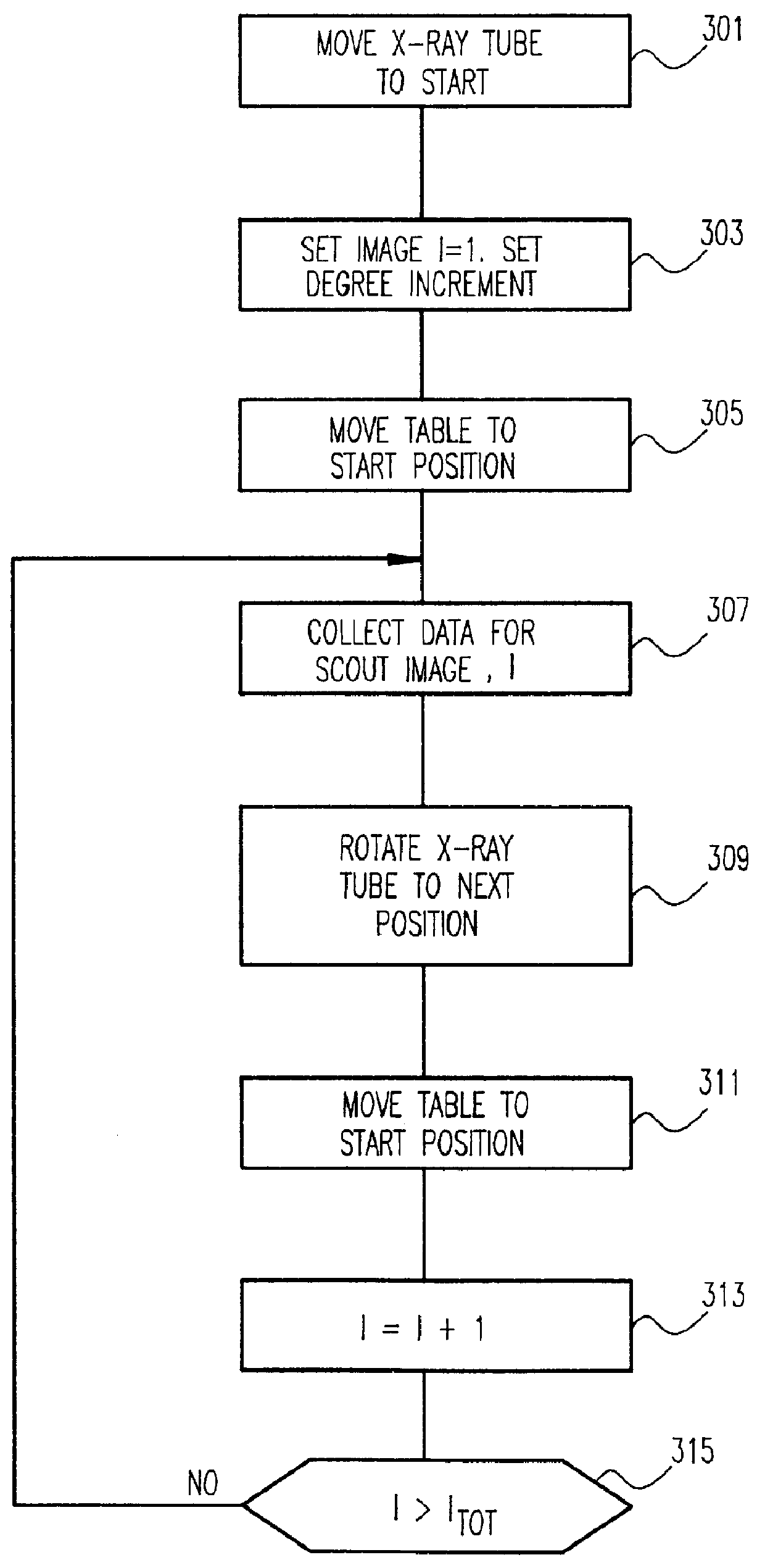
InactiveUS6028907AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersGeometric modeling
A computer system and method solve the problem of getting a useful three-dimensional representation of an object like the spine using a small amount of data. This is done by gathering three-dimensional data in the form of a set of 2D computer tomography (CT) slices of a patient's bones and a coaxial set of 2D CT scout images, which are digital two-dimensional X-ray images that can be produced by a CT scanner; extracting from each of these three-dimensional data sets a corresponding stack of 2D contours; and constructing a 3D geometric model of the object. The main features of spinal deformation are captured by integrating these two sets of three-dimensional data, and constructing from them a three-dimensional geometric model of the spine. Scouts are usually used to monitor CT scan acquisition. Here, they are also used as an essential source of data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com