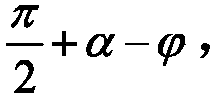Patents
Literature
117 results about "Equilibrium conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Conditions for equilibrium are as follows: (1) the reaction must occur in a closed system; (2) the rates of the forward and reverse reactions must be equal; (3) as a result of the forward and reverse reactions occurring at equal rates, the concentrations of both the products and reactants tend to be constant. Equilibrium can occur in both chemical and physical changes.
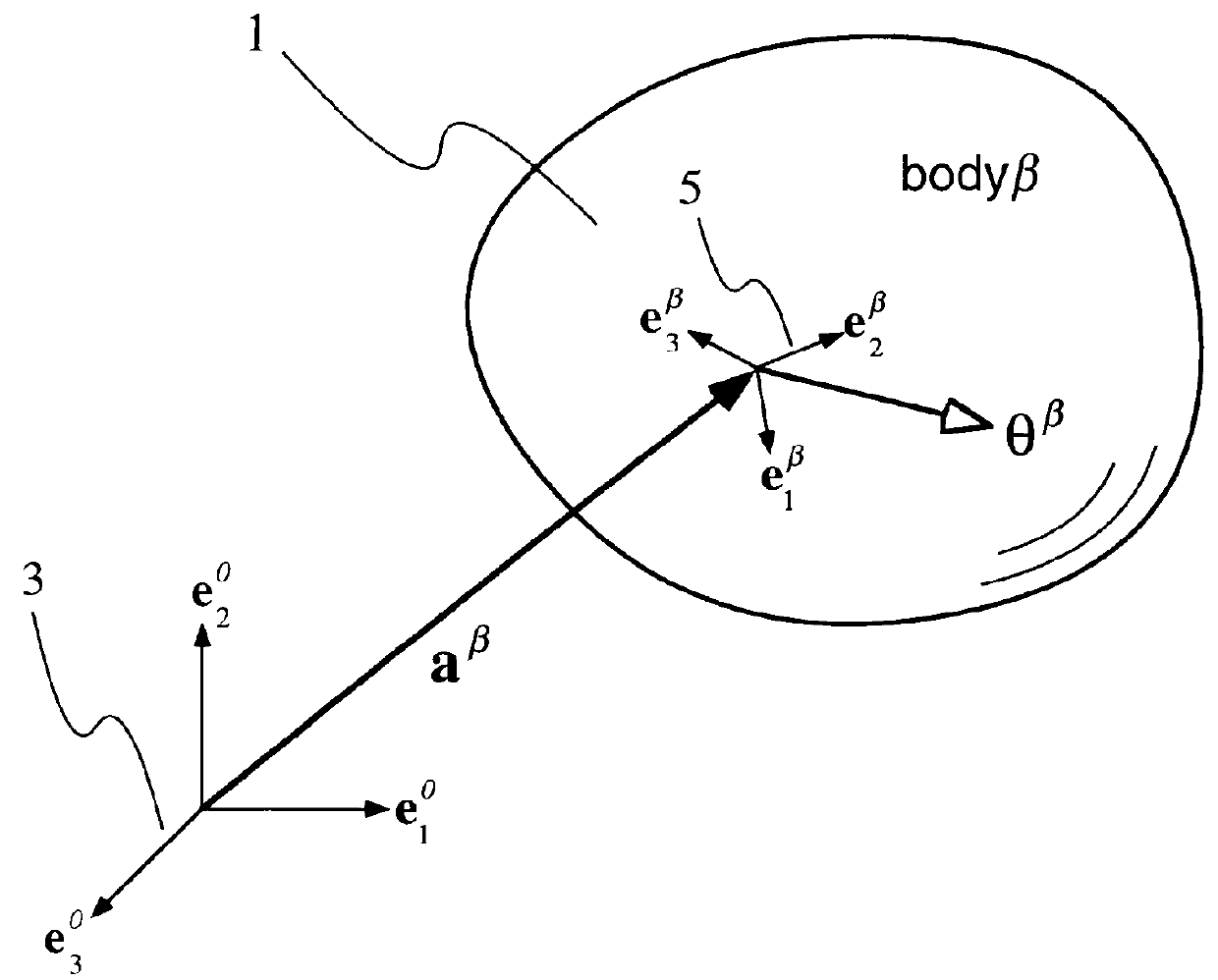
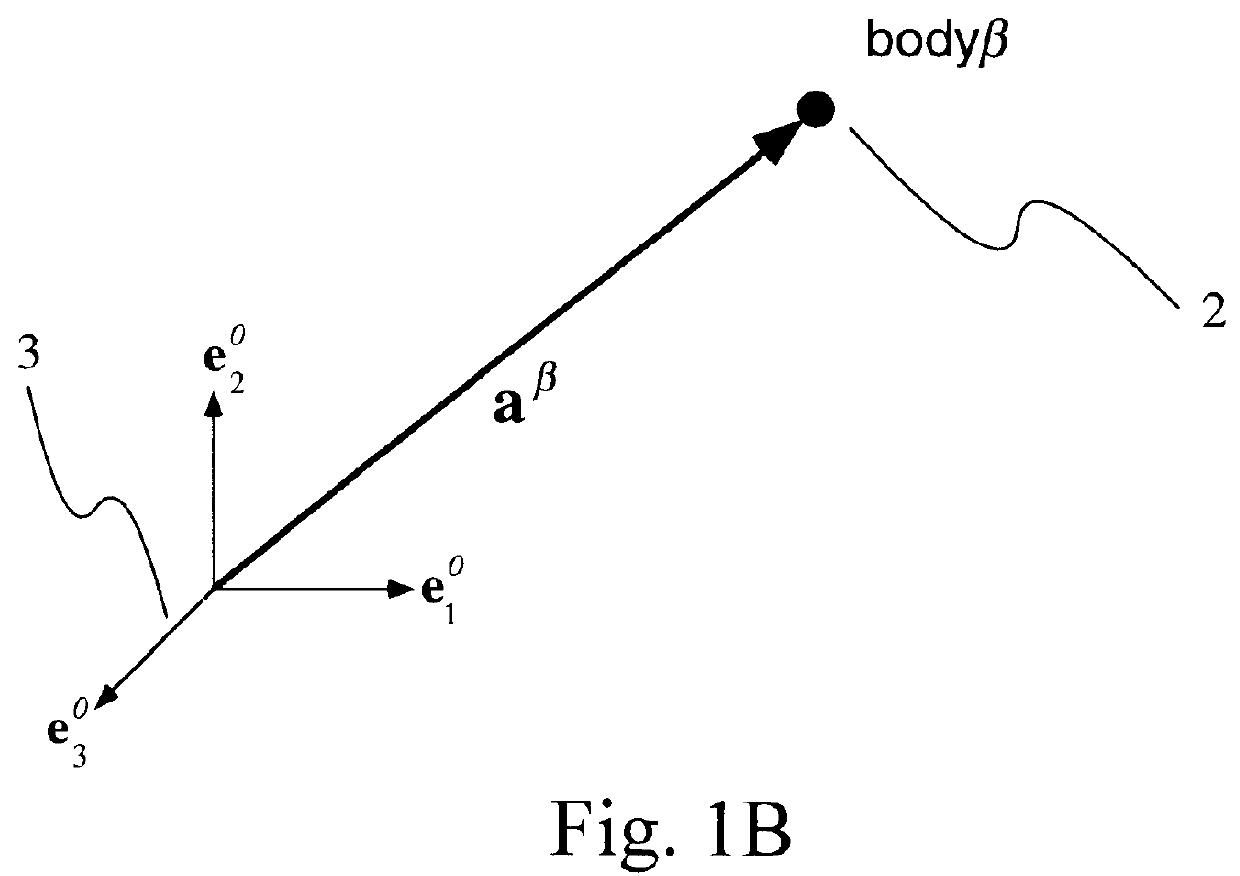
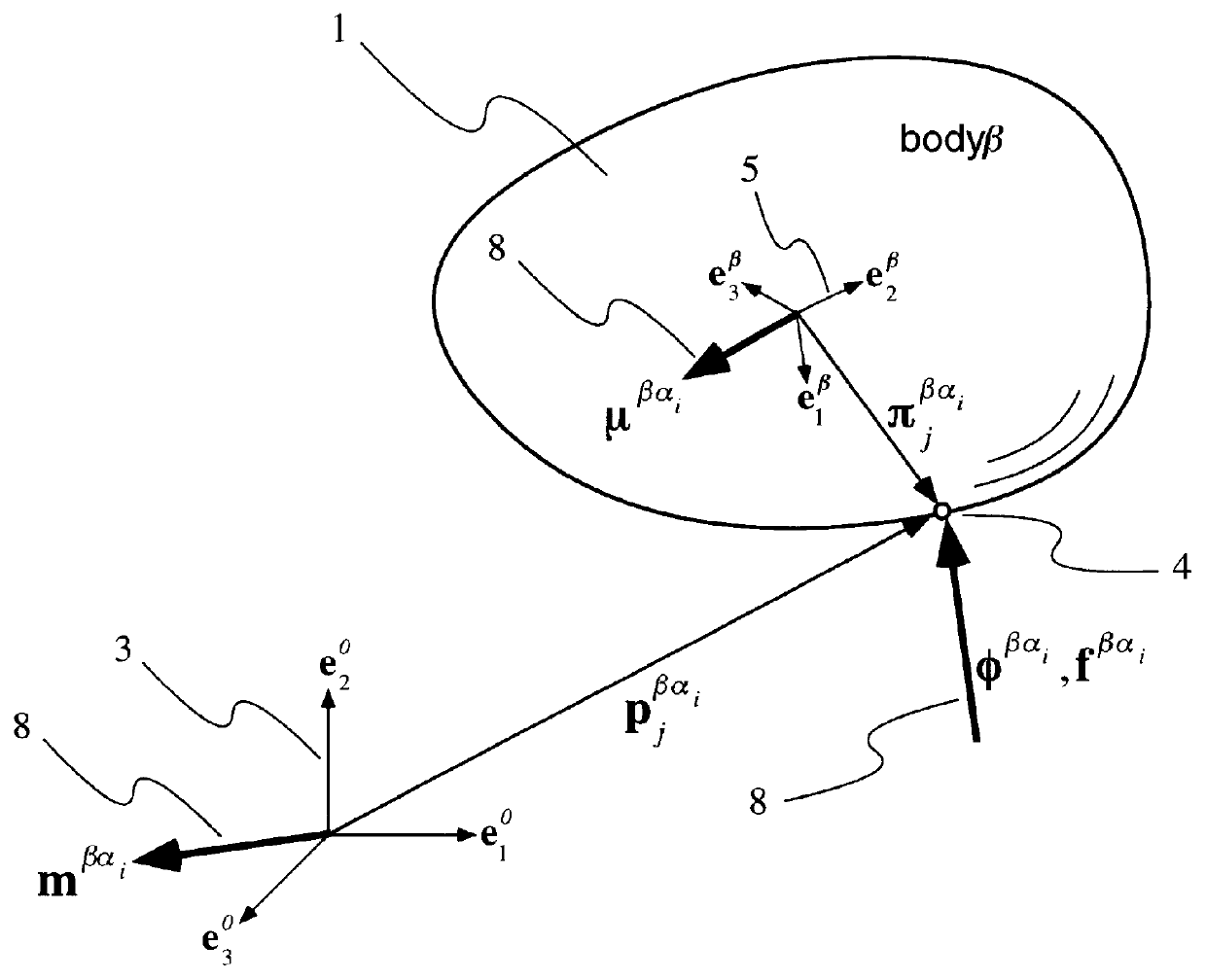
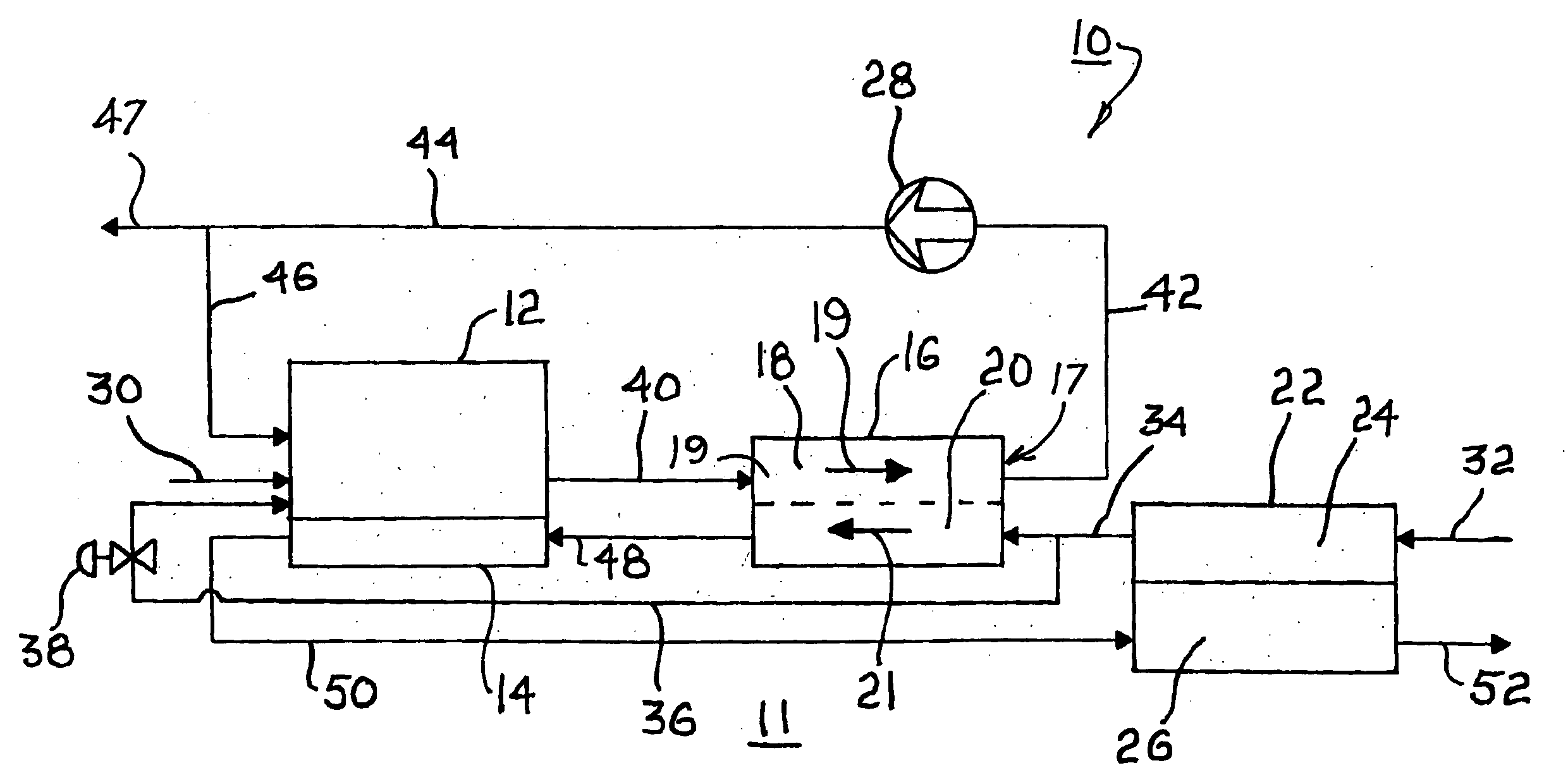
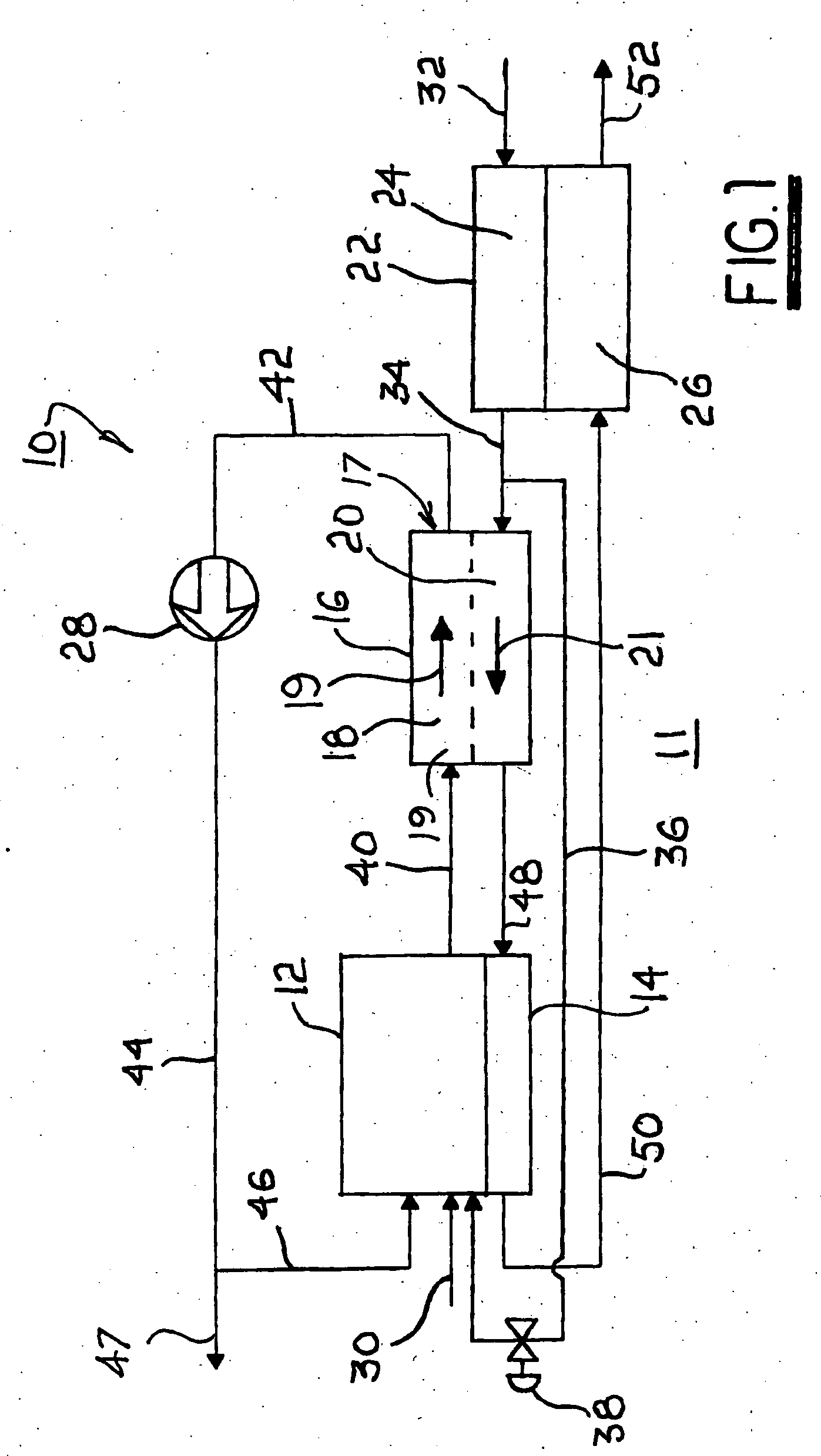
Three dimensional multibody modeling of anatomical joints
InactiveUS6161080AEasy to modifyPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesData selectionDimensional modeling
The present invention relates to a method of generating a three dimensional representation of one or more anatomical joints, wherein the representation comprises two or more movable bodies and one or more links, comprising the steps of inputting anatomically representative data of two or more movable bodies of the selected joint or joints; selecting one or more link types responsive to the representative data of the bodies; selecting link characteristics responsive to each selected link type; generating an equilibrium condition responsive to interaction between the bodies and the links; and displaying a three dimensional representation of the selected joint or joints responsive to the data generated from the equilibrium condition of the anatomical joint or joints. The present invention further relates to a system for generating a three dimensional representation of one or more anatomical joints, and a method of planning surgery of one or more anatomical joints.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
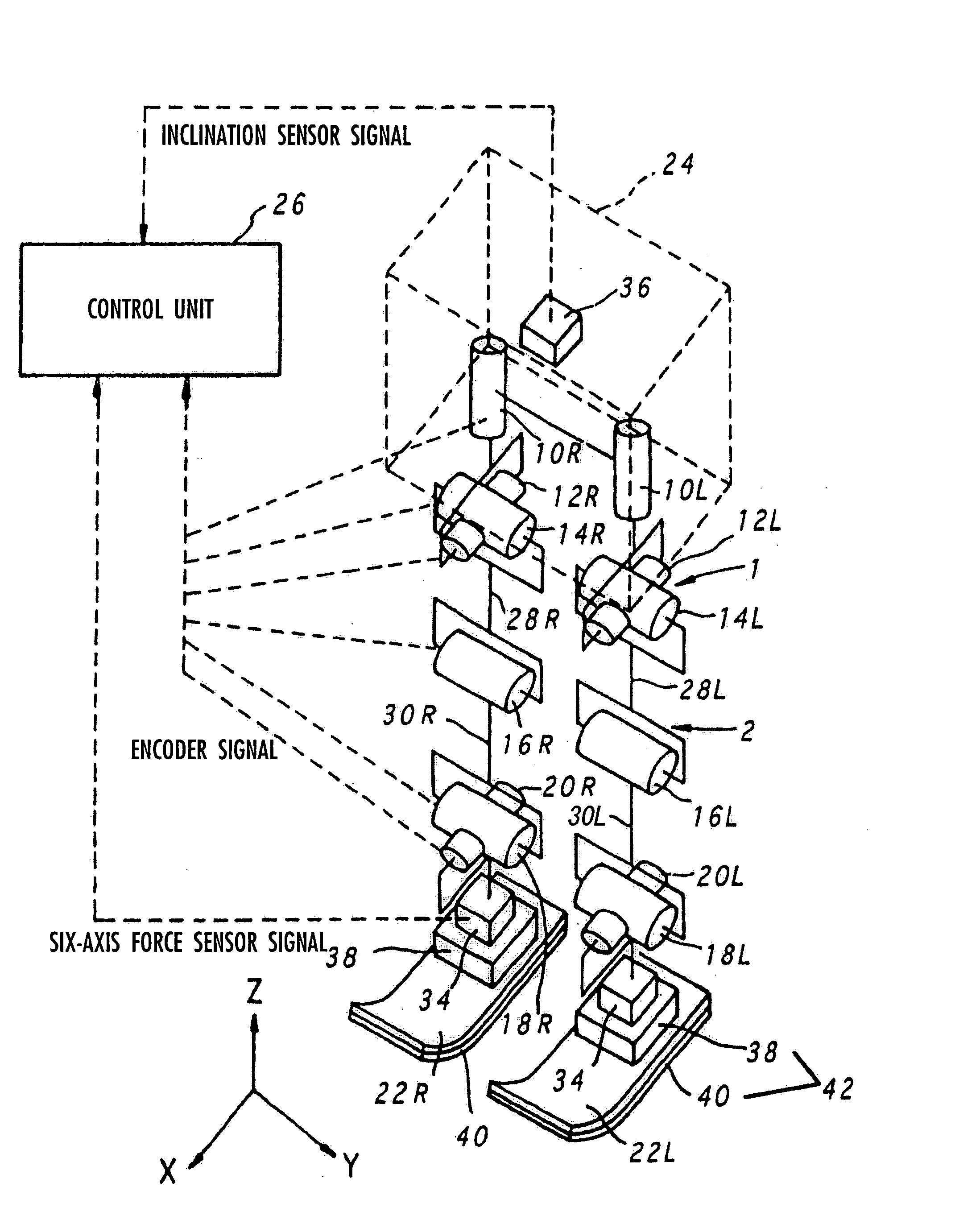
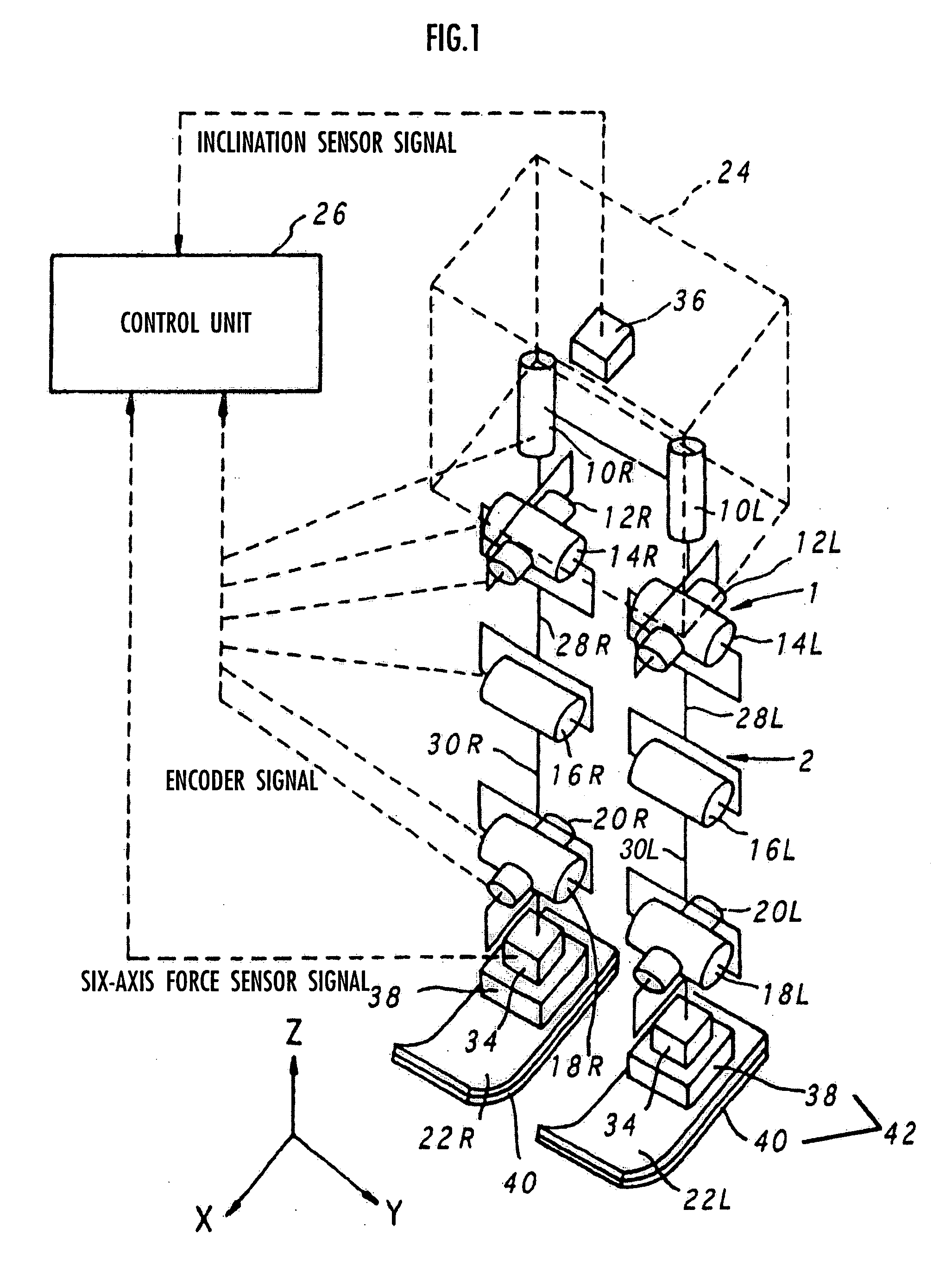
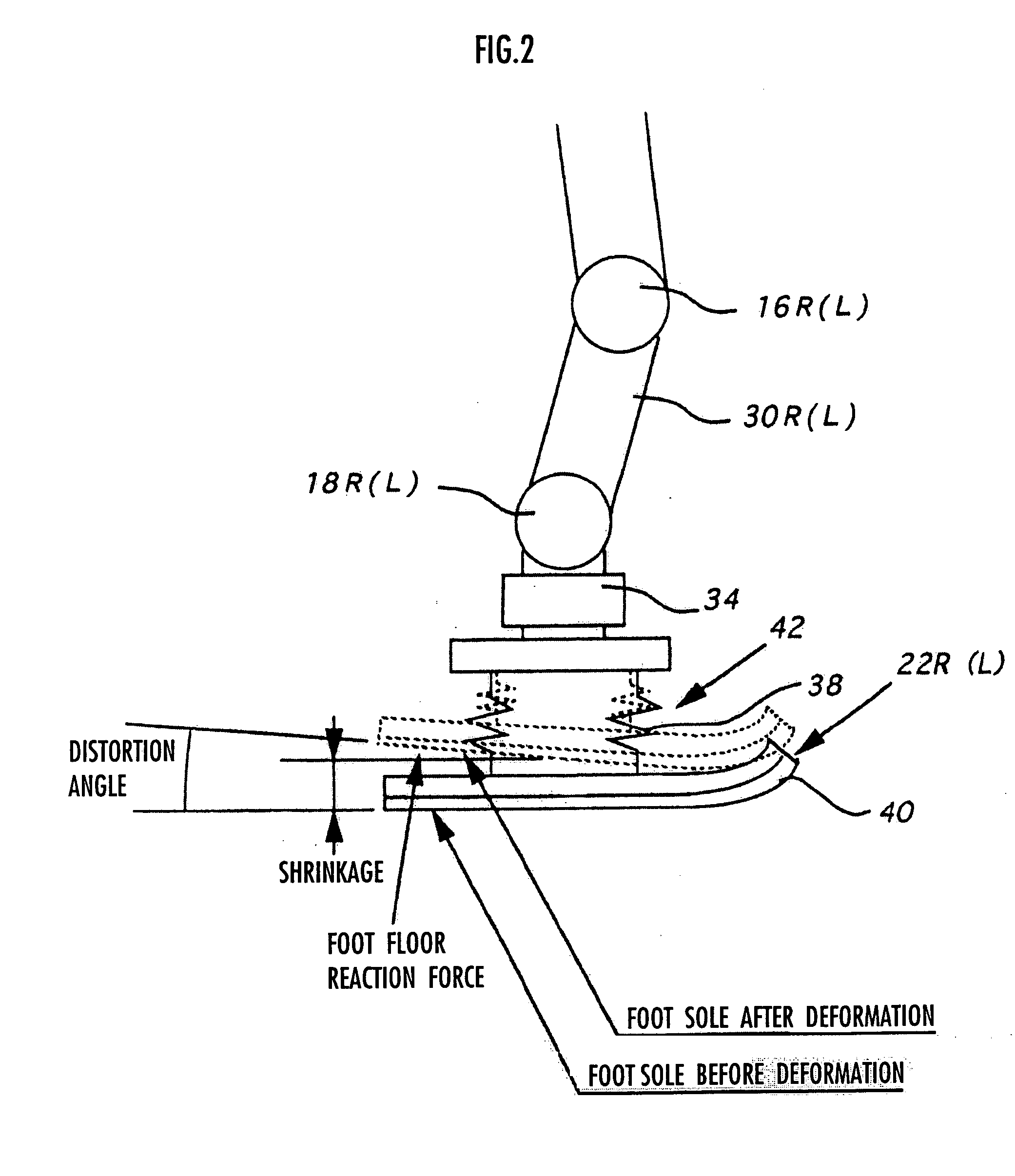
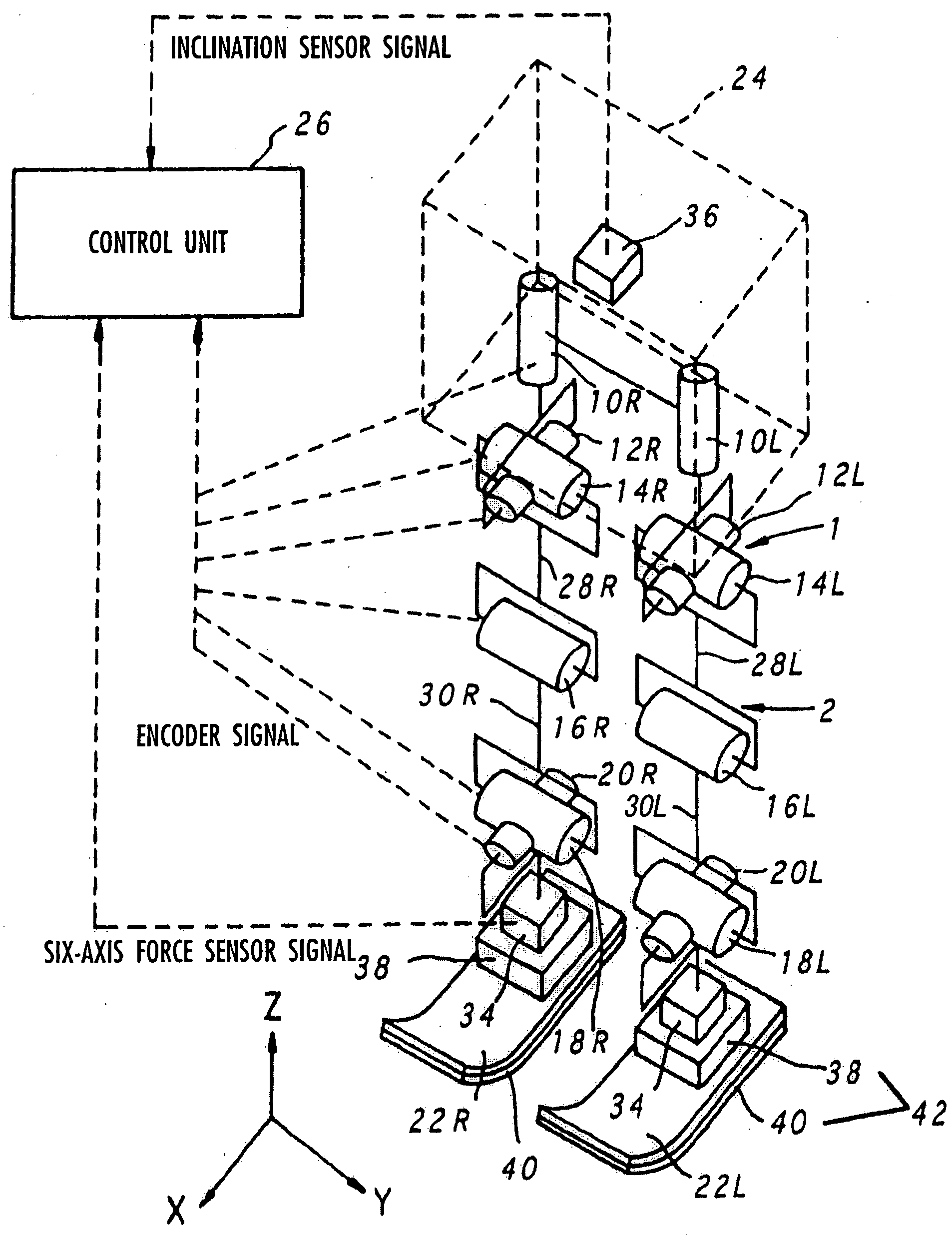
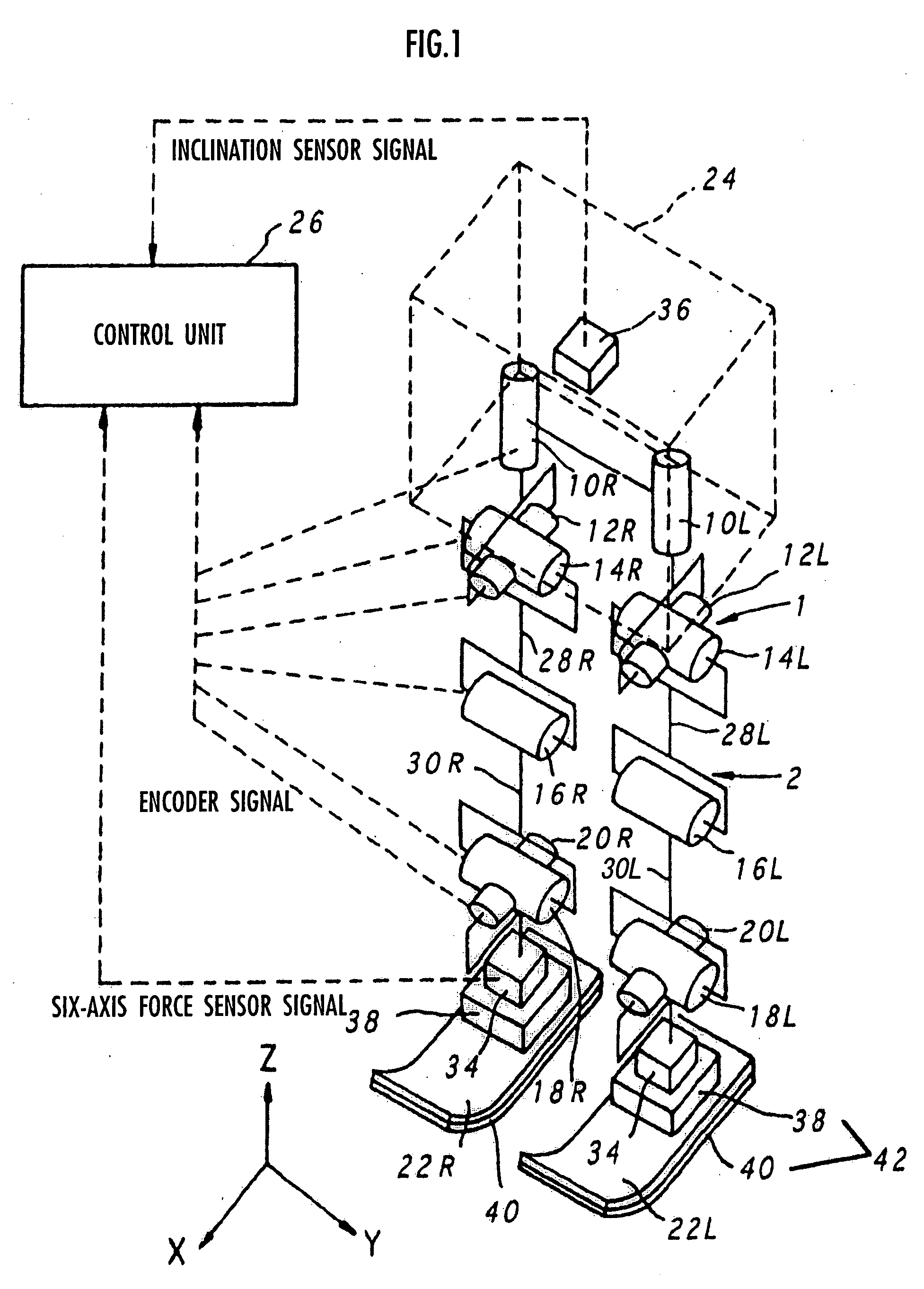
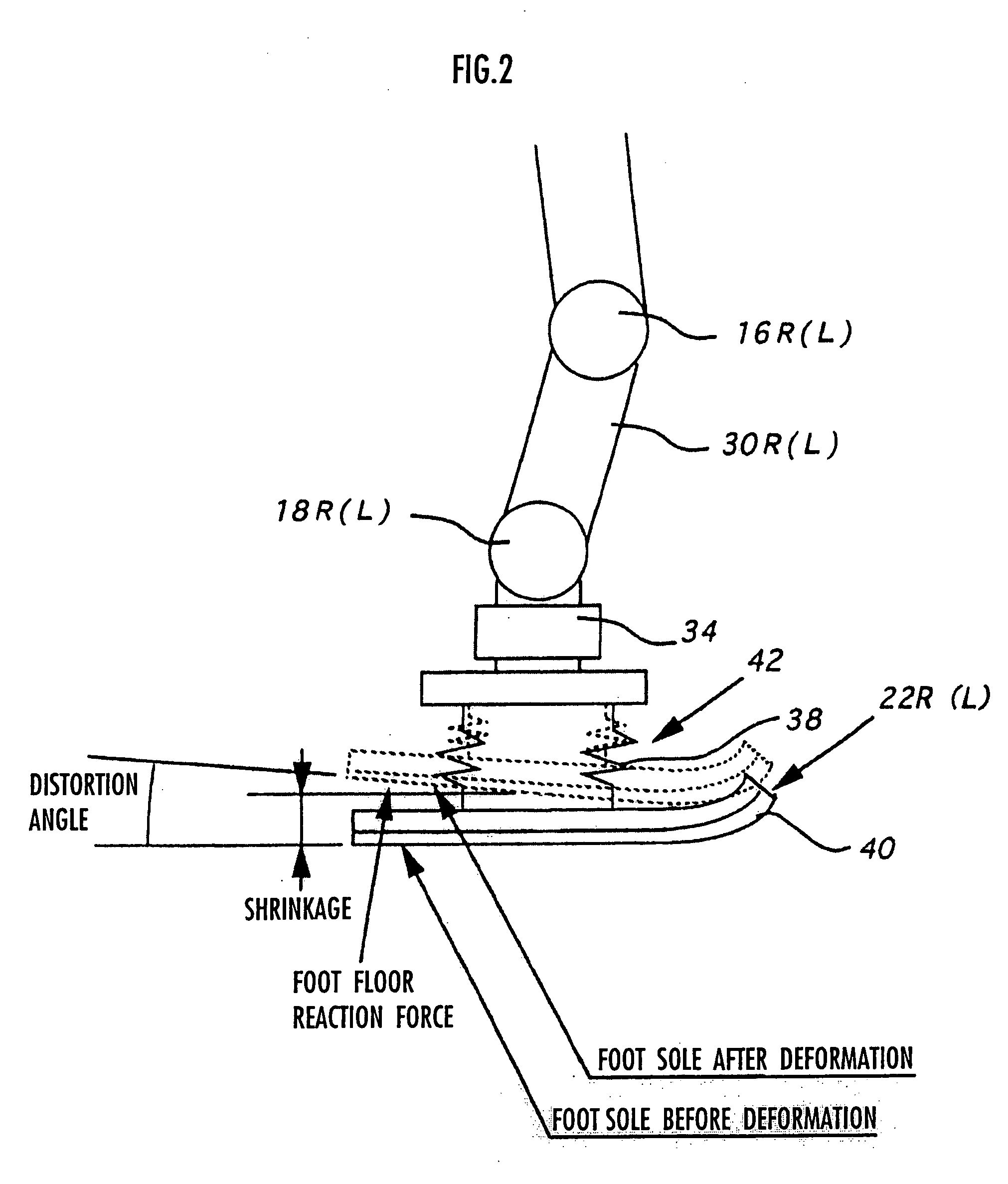
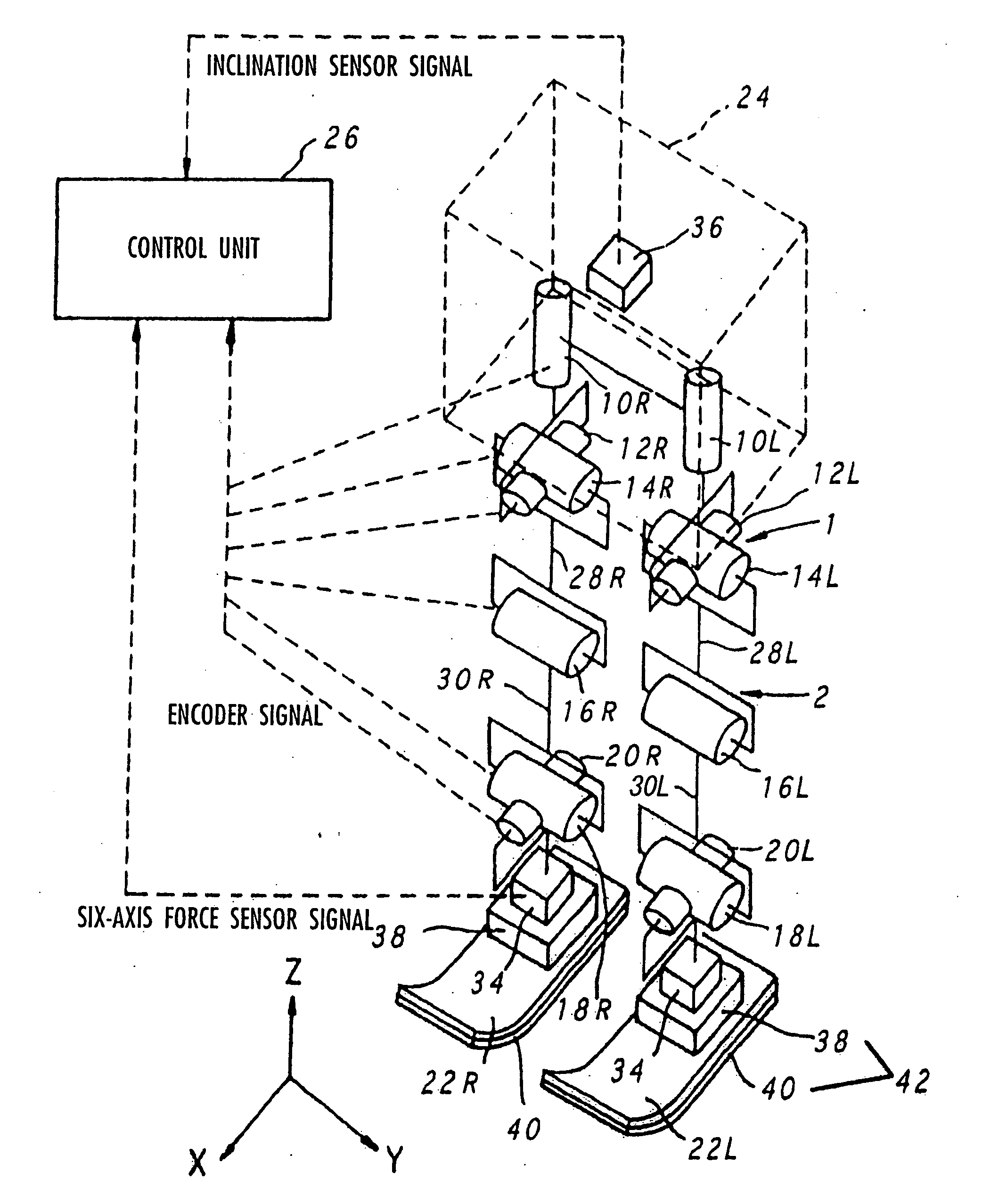
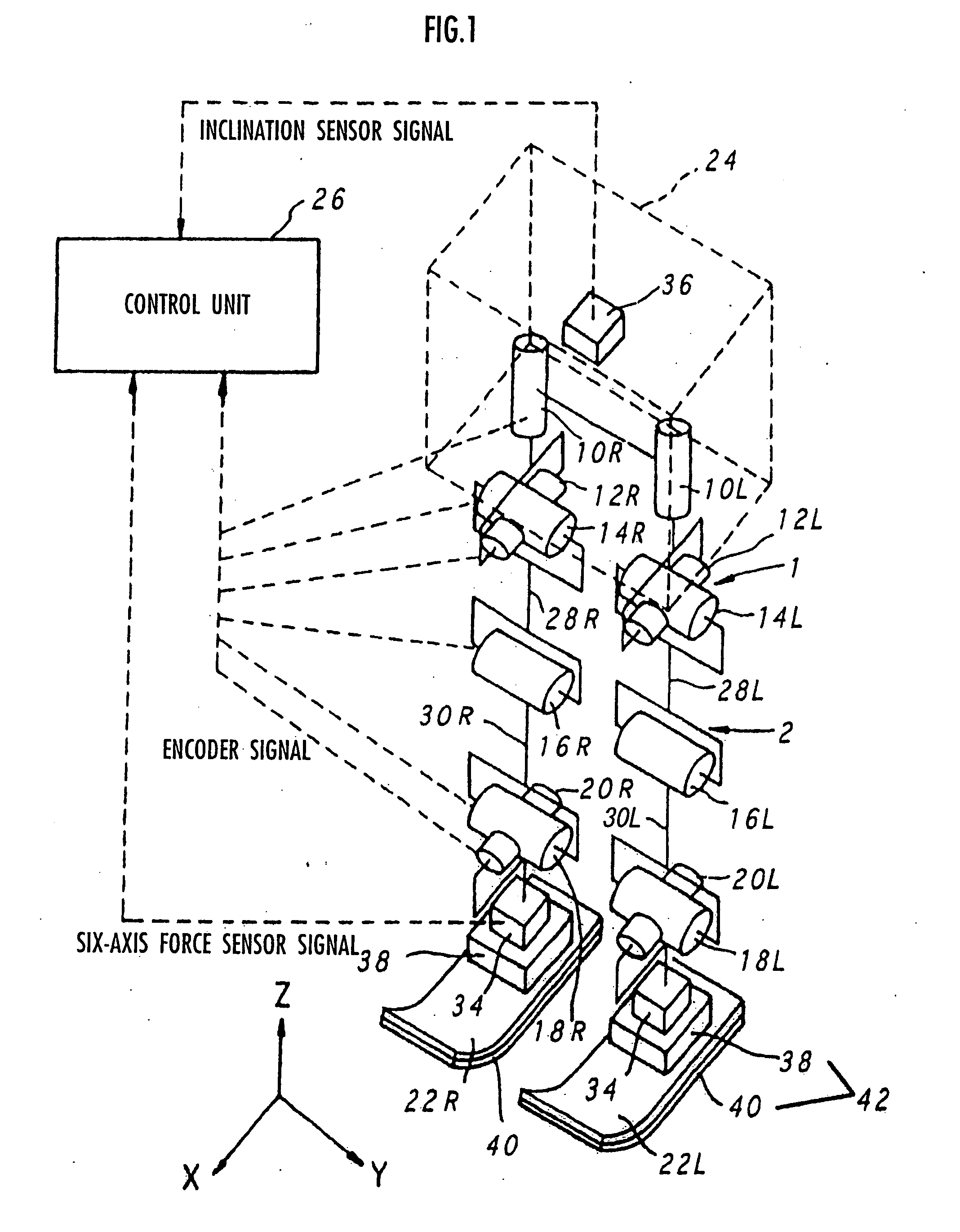
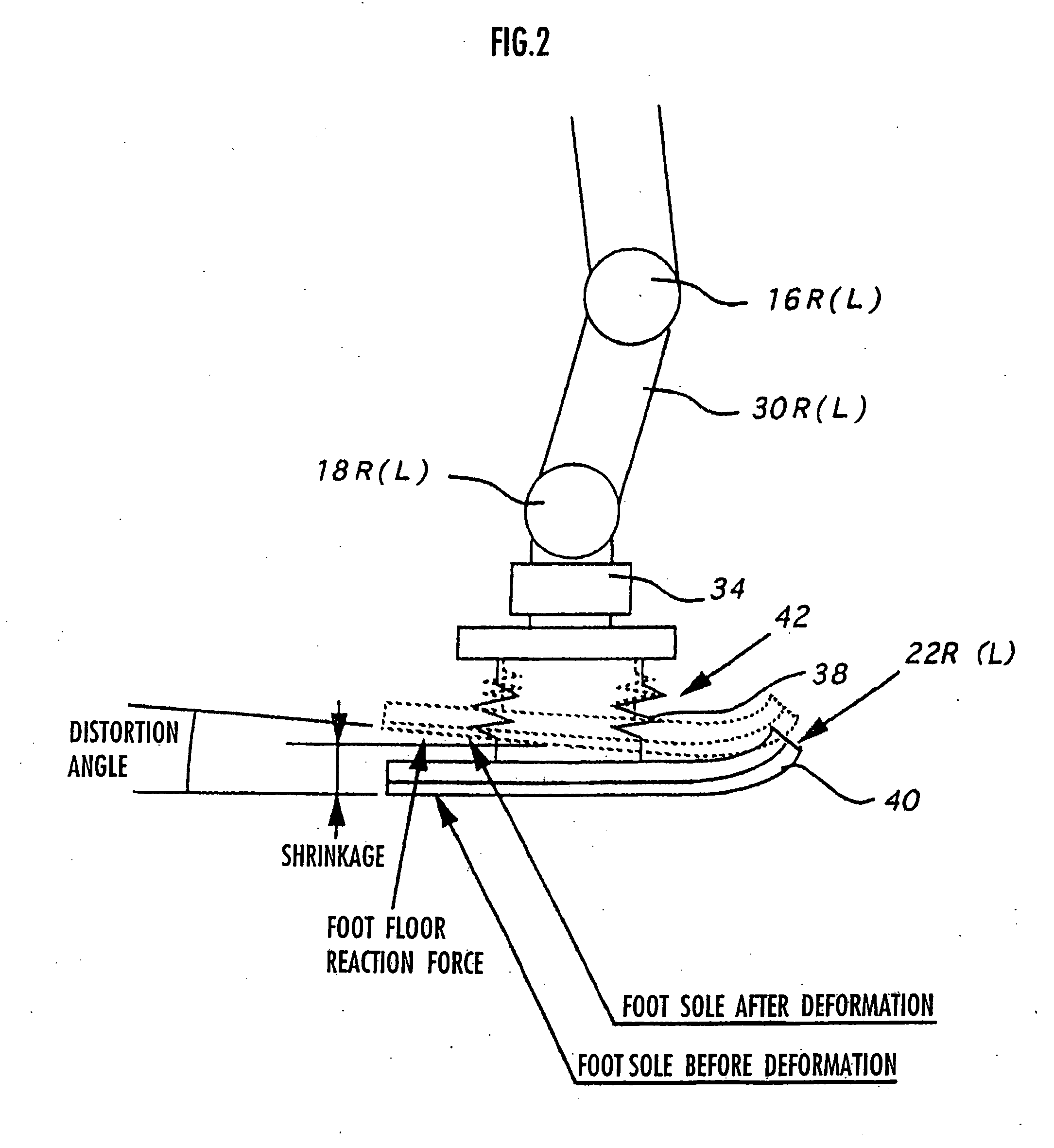
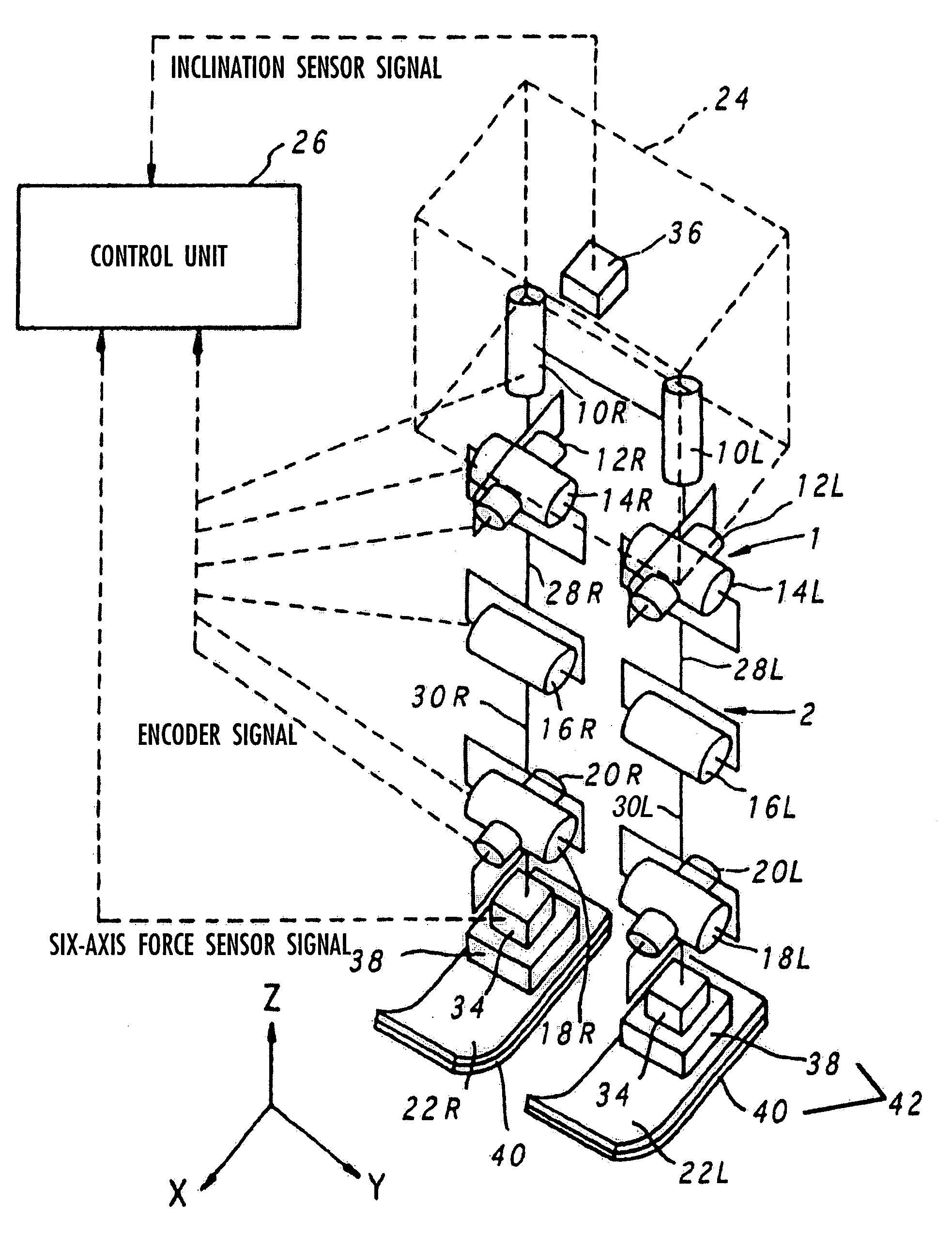
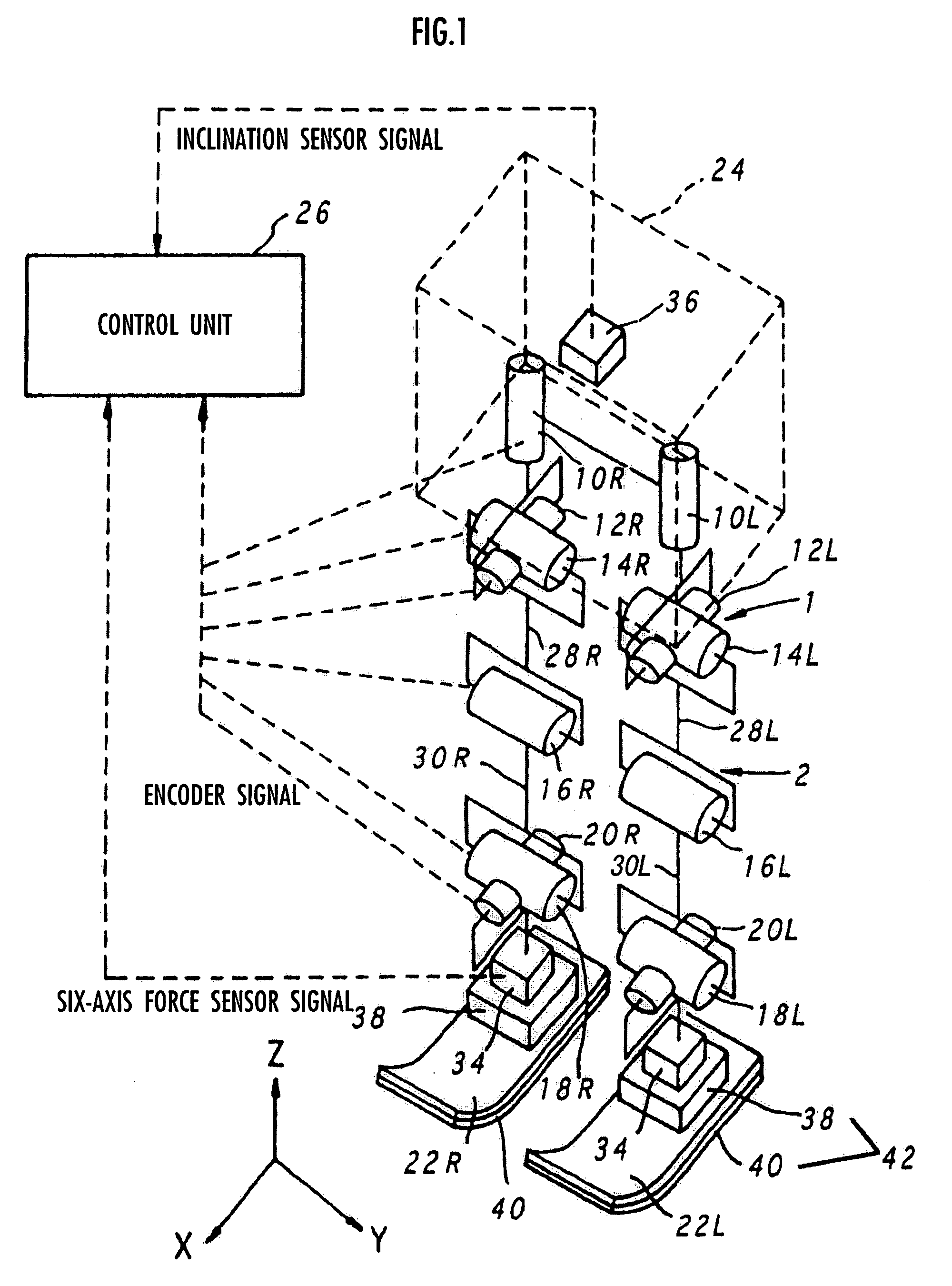
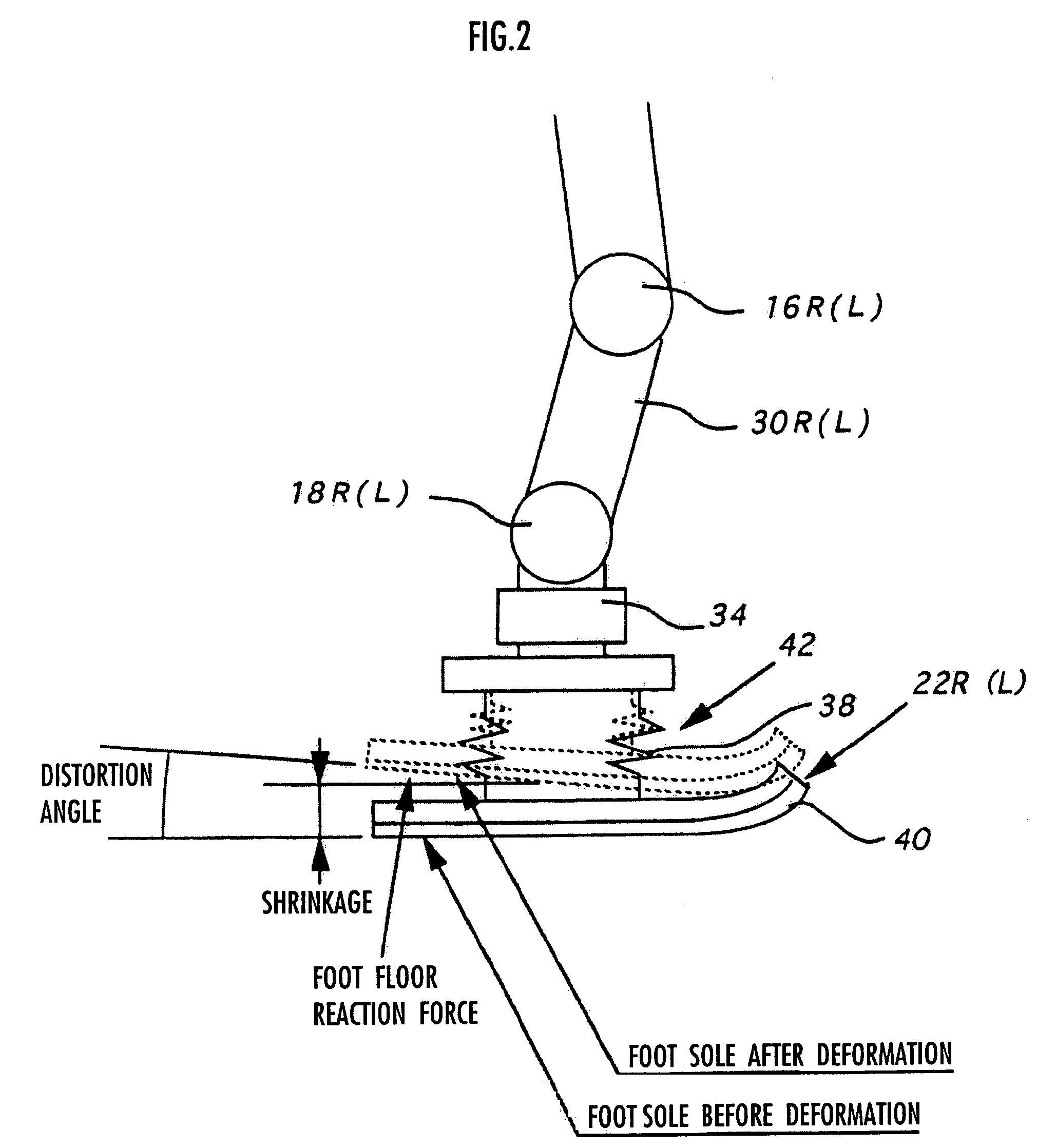
Gait generation device for legged mobile robot
ActiveUS20050075755A1Reduce coefficient of frictionGenerate lotProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlDynamic modelsEngineering
A gait generation device includes means for setting a translation floor reaction force's horizontal component (component concerning a friction force) applied to a robot 1, a limitation-target quantity, such as a ZMP, and an allowable range, means for determining at least a provisional instantaneous value of a desired floor reaction force and a provisional instantaneous value for a desired movement of the robot 1, and means that receives at least the provisional instantaneous value for the desired movement and determines a model floor reaction force instantaneous value with the aid of a dynamics model. Based on the difference between the model floor reaction force instantaneous value and the provisional instantaneous value of the desired floor reaction force or the allowable range of the limitation-target quantity, the provisional instantaneous value for the desired movement is corrected so that the limitation-target quantity falls within the allowable range and a dynamical equilibrium condition on the dynamics model is satisfied, thereby determining a desired instantaneous value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Gait producing device for leg type movable robot
ActiveUS20050021176A1Easy to optimizeMove continuously and stablyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringFriction force
An allowable range of a frictional force component, such as a horizontal component of a translation floor reaction force, applied to a legged mobile robot 1 is set, and a provisional movement with a current time gait of the robot 1 is determined so as to satisfy a condition concerning the allowable range and a dynamical equilibrium condition that a moment produced about a point of application of a provisional desired floor reaction force substantially agrees with a provisional desired floor reaction force moment. The provisional movement is determined by adjusting movements in two movement modes which are different in ratio between the translation floor reaction force and the floor reaction force moment. Based on the final state of the provisional movement, the current time gait is determined by correcting the provisional movement and at least one of the point of application of the provisional desired floor reaction force and the provisional desired floor reaction force moment in such a manner that the current time gait is connected to or brought close to a normal gait. The correction is performed when the frictional force component is unlikely to exceed the allowable range.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
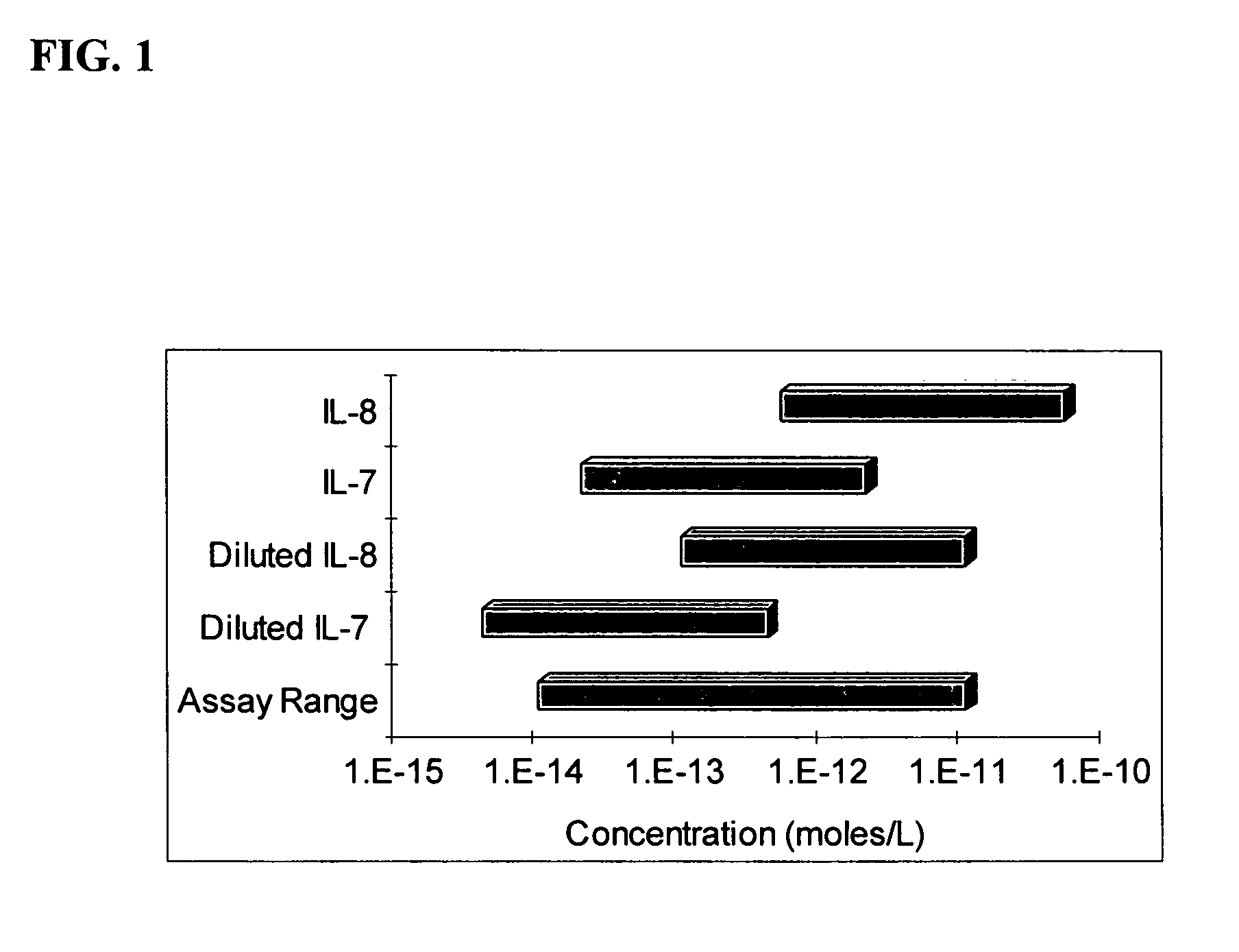
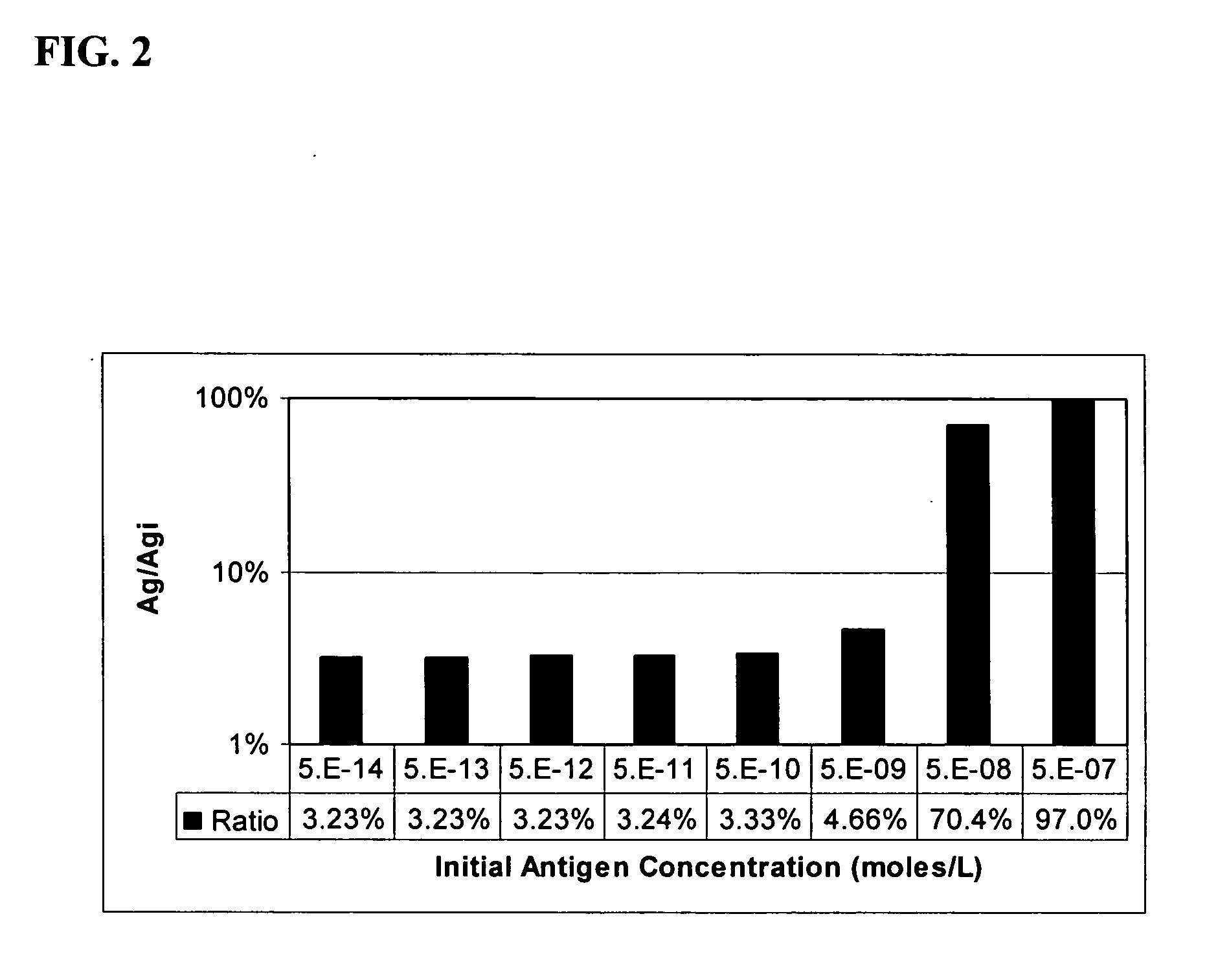
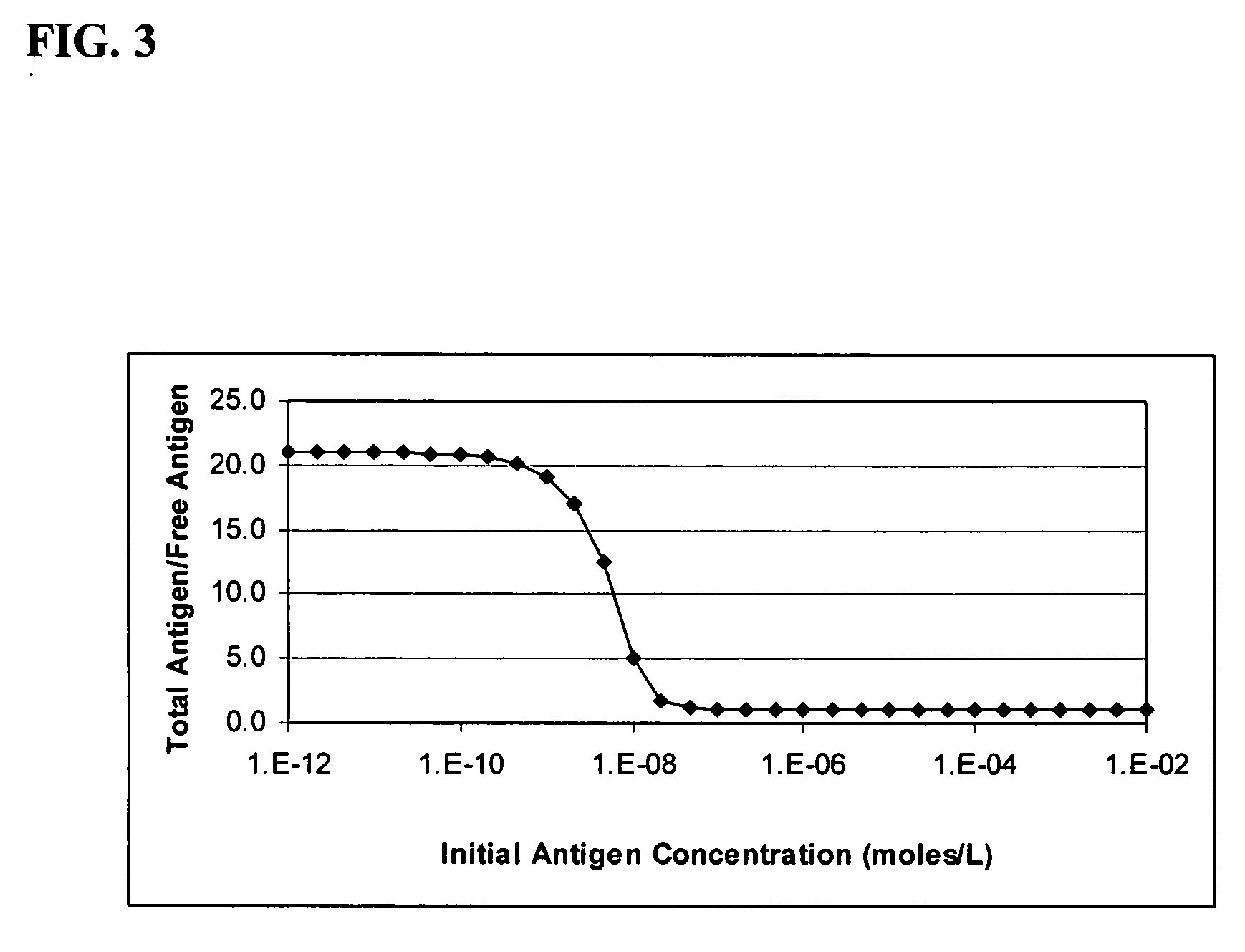
Method of adjusting the working range of a multi-analyte assay
InactiveUS20060177873A1Reduce available analyte concentrationHinder availabilityBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsHigh concentrationMulti analyte
The invention features a method of adjusting the concentration of at least one but not all of a plurality of analytes in a fluid sample to match a known working range of detection of an analyte assay system, where each of the plurality of analytes may or may not be present within an expected initial concentration range having a high end and a low end, and at least one analyte has a high end expected concentration range that exceeds the high end of the working range of the assay system. The expected concentration of the high concentration analyte is adjusted by a proportional scaling constant, α, so that the high end of the adjusted expected concentration range is less than or equal to the high end of the working range, without adjusting the expected concentration range of at least one other of the plurality of analytes. Adjustment is preferably accomplished by adding to the solution phase of the assay one or more scaling agents, each scaling agent binding with specificity to an analyte and thereby preventing it from being detected by the assay system, e.g., by competing with binding to immobilized capture agent. This scaling method contrasts with prior methods, in which a concentration of available analyte is offset by a fixed amount to adjust the detectable threshold of the assay. Here, the amount of scaling agent is proportional to a scaling coefficient, and the scaling agent is present in the solution phase of the assay at high concentrations relative to analyte. Due to the equilibrium conditions established by the laws of mass transfer, the amount of free analyte remaining in solution in the presence of scaling agent is predictable and finite, and can be measured as a quantitative indicator of the initial concentration of the analyte in the sample.
Owner:COURTAGEN LIFE SCI
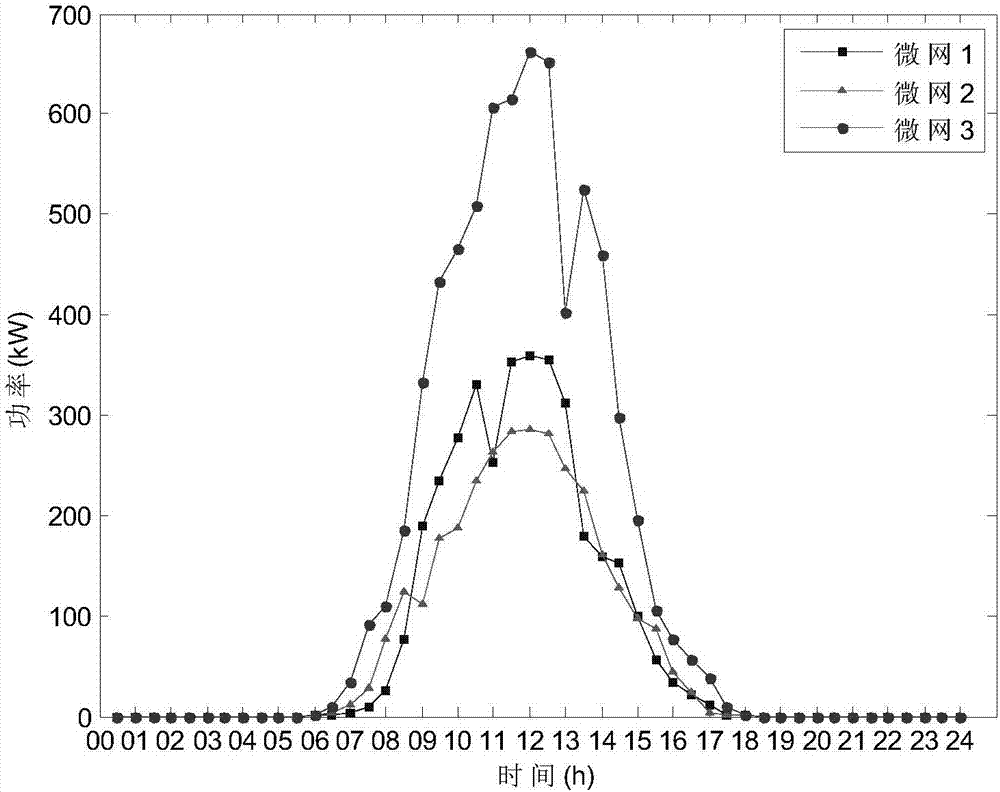
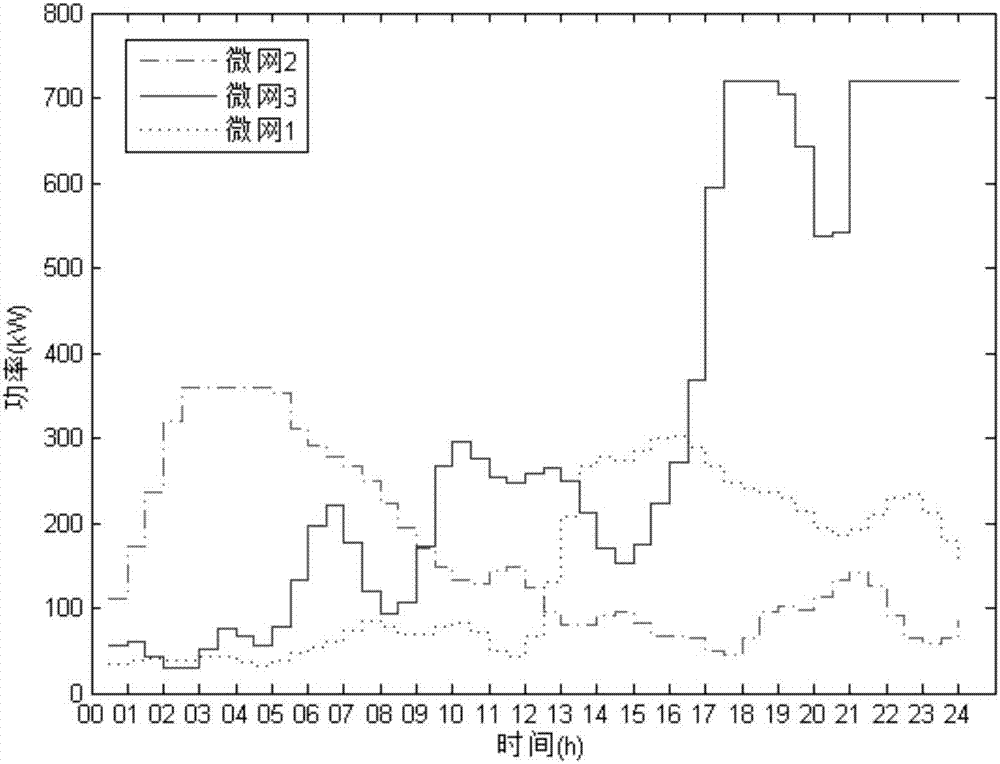
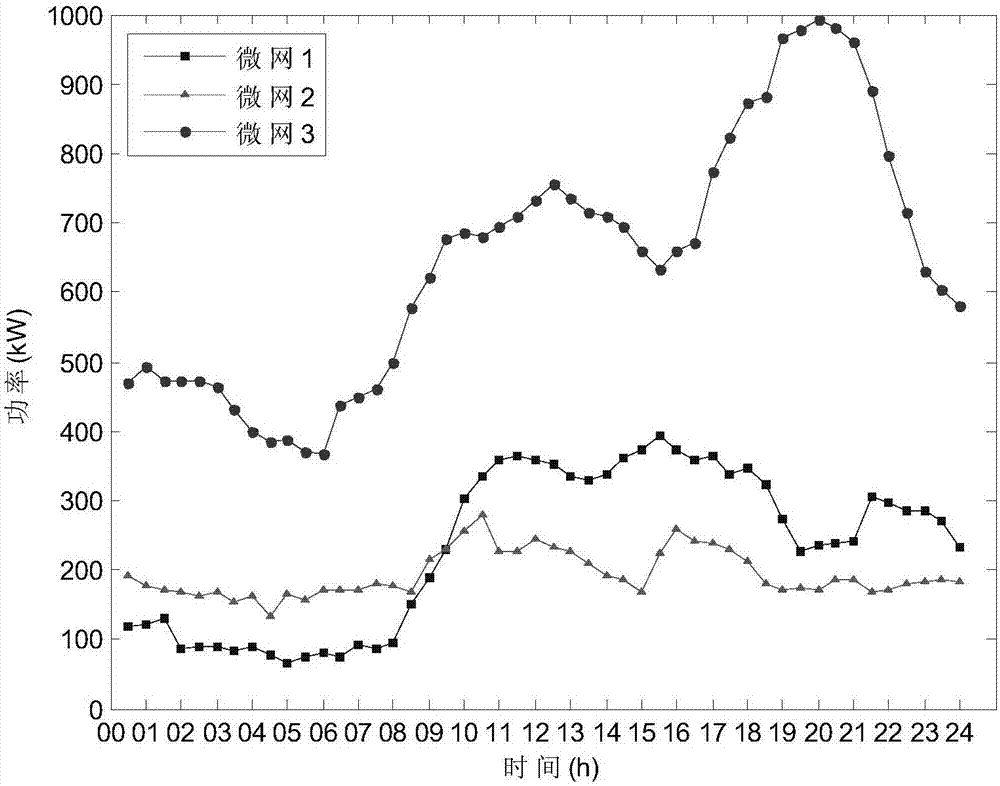
Game theory-based multi-micro-grid interconnection running optimization method
ActiveCN107545325AImprove absorption capacityImprove load characteristicsForecastingPower gridSystem stability
The invention discloses a game theory-based multi-micro-grid interconnection running optimization method. The method includes the following steps: analyzing load demand response characteristics of allmicro-grids, and constructing a micro-grid group model; then initializing a system, establishing a day-ahead game model, and calculating a net load of the i-th micro-grid in a j-th period and a totalnet load amount of the system by day-ahead forecast data; obtaining respective optimal strategies by solving by all the micro-grids according to initial status, carrying out information exchange in amicro-grid group, sharing respectively obtained best strategy information, and updating status information; judging, by a system control center, whether Nash equilibrium is reached, and if the systemmeets an equilibrium condition, ending a game, and outputting a final optimization strategy set; and otherwise, turning ahead to carry out optimization again according to updated status information.The method can give consideration to both the stability and the economy of the system, and realize individual benefit maximization and optimal group running of the micro-grids at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
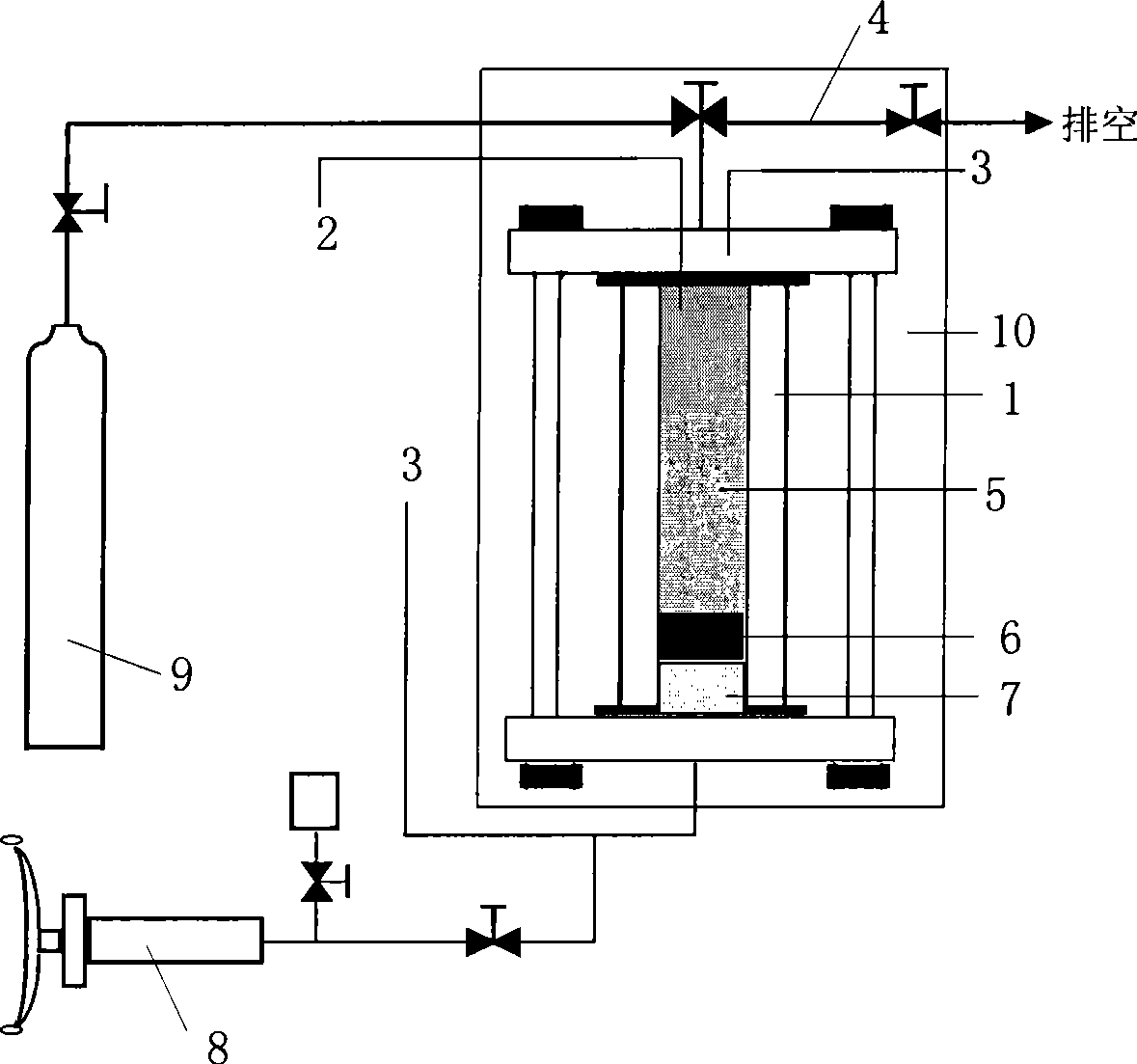
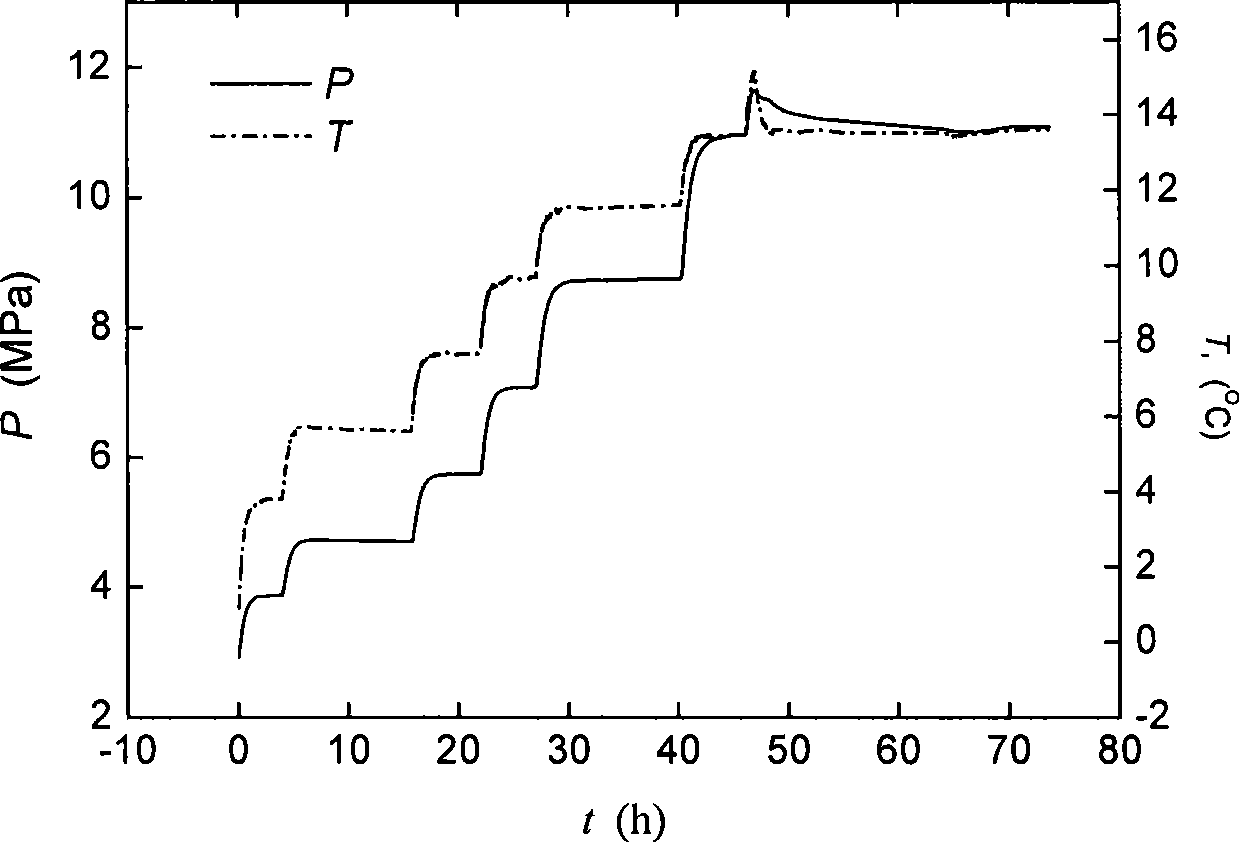
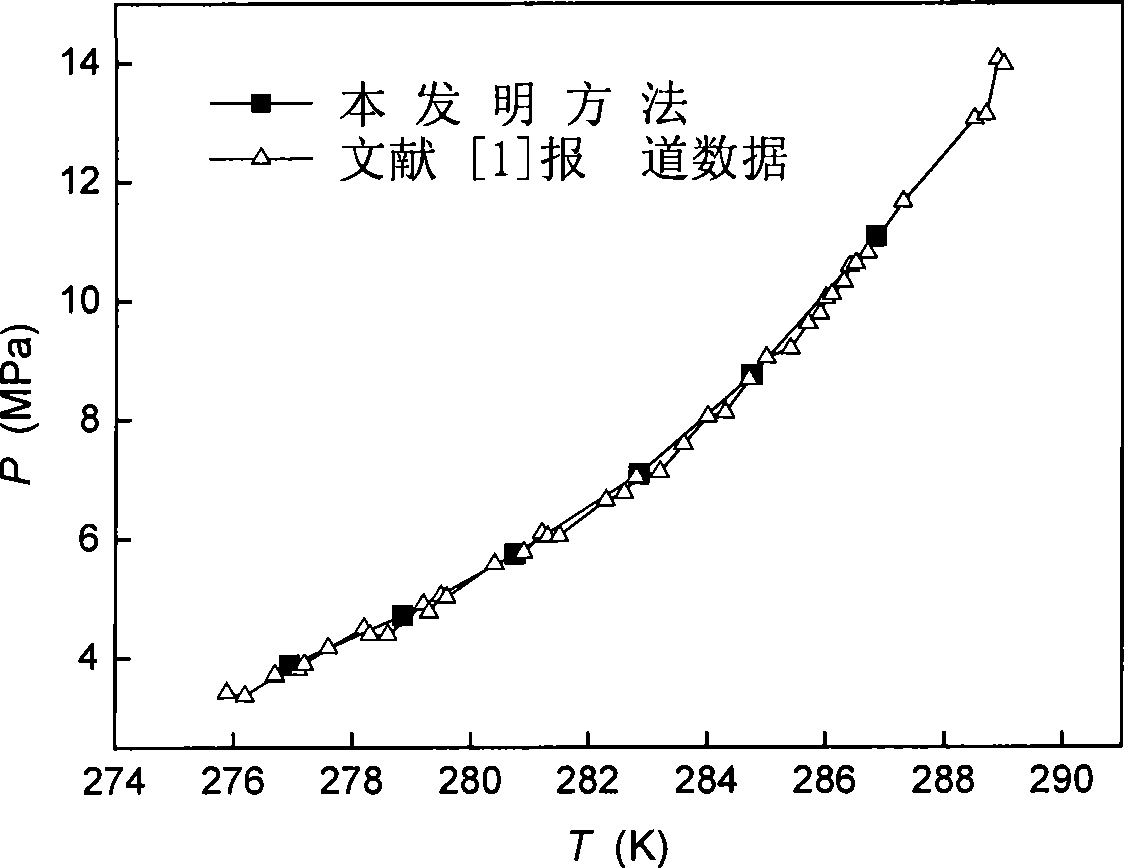
Method for measuring gas hydrate phase balance condition
InactiveCN101377478AImprove measurement accuracyAvoid cloggingInvestigating phase/state changeGas phasePorous medium
The invention provides a method for determining the phase balance condition of gas hydrates, which mainly has the procedures: gas to be measured is caused to generate hydrates in a reaction kettle which is provided with a temperature measurement system, a pressure measurement system and an exhaust system; gas-phase space in the reaction kettle is compressed; system temperature in the reaction kettle is regulated to the temperature of the phase balance condition to be measured to exhaust the gas and lower the pressure, as well as the exhaust system is closed when the pressure in the reaction kettle rises at once because the exhaust is stopped, thus the reaction kettle is caused to become a closed system; the variation of the pressure in the reaction kettle is observed, if the pressure keeps invariant for a long time, three-phase balance is considered to be reached, at this time, the corresponding temperature and the corresponding pressure are a set of phase balance condition for the hydrates. The system temperature can further rise to the next balance temperature to be measured, the pressure variation is continuously recorded until the hydrates in the reaction kettle is completely decomposed, therefore, a series of phase balance condition data of the hydrates can be obtained. Adopting the method, the phase balance condition of the gas hydrates in a free water system or a porous media can be measured, and the measurement accuracy is high.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
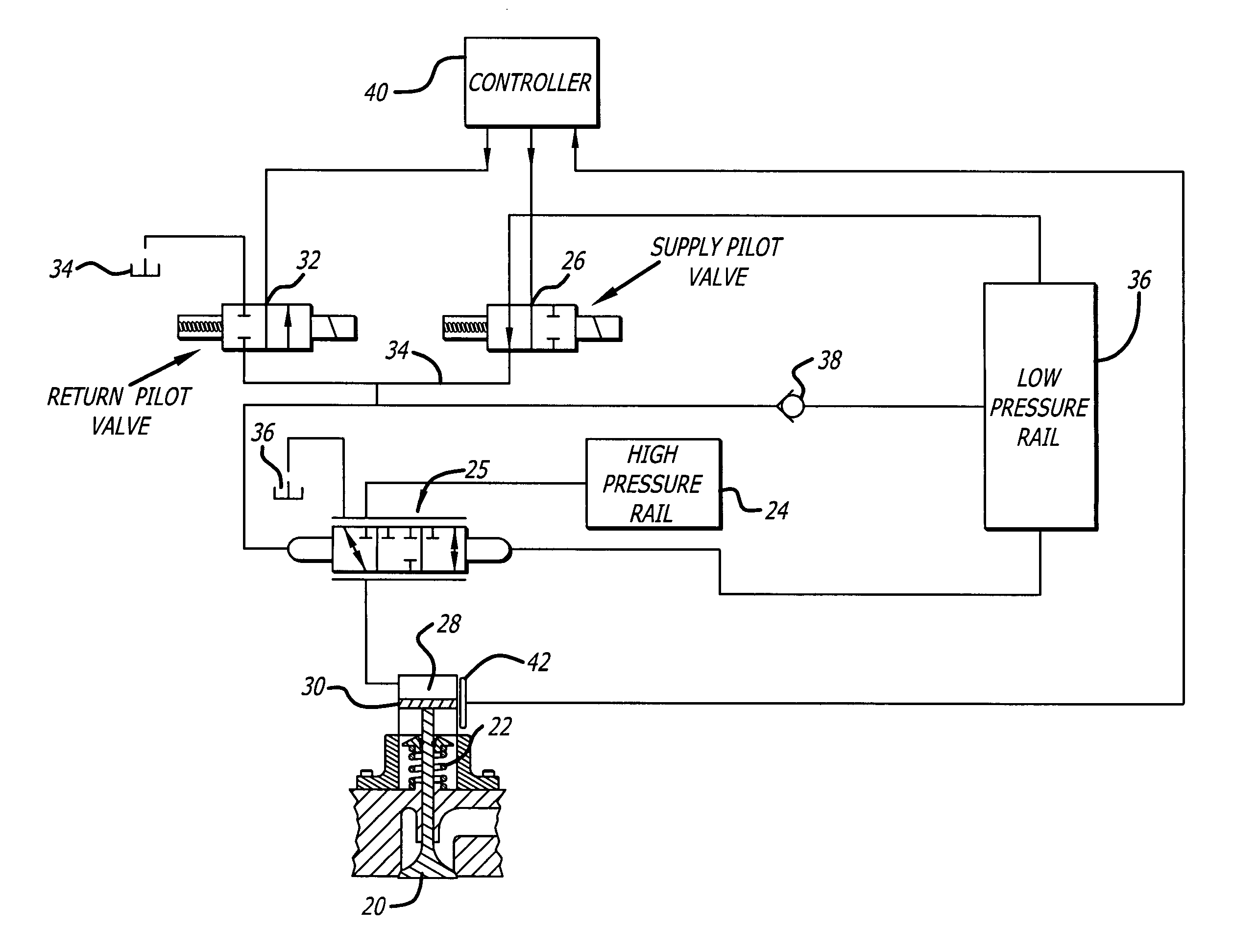
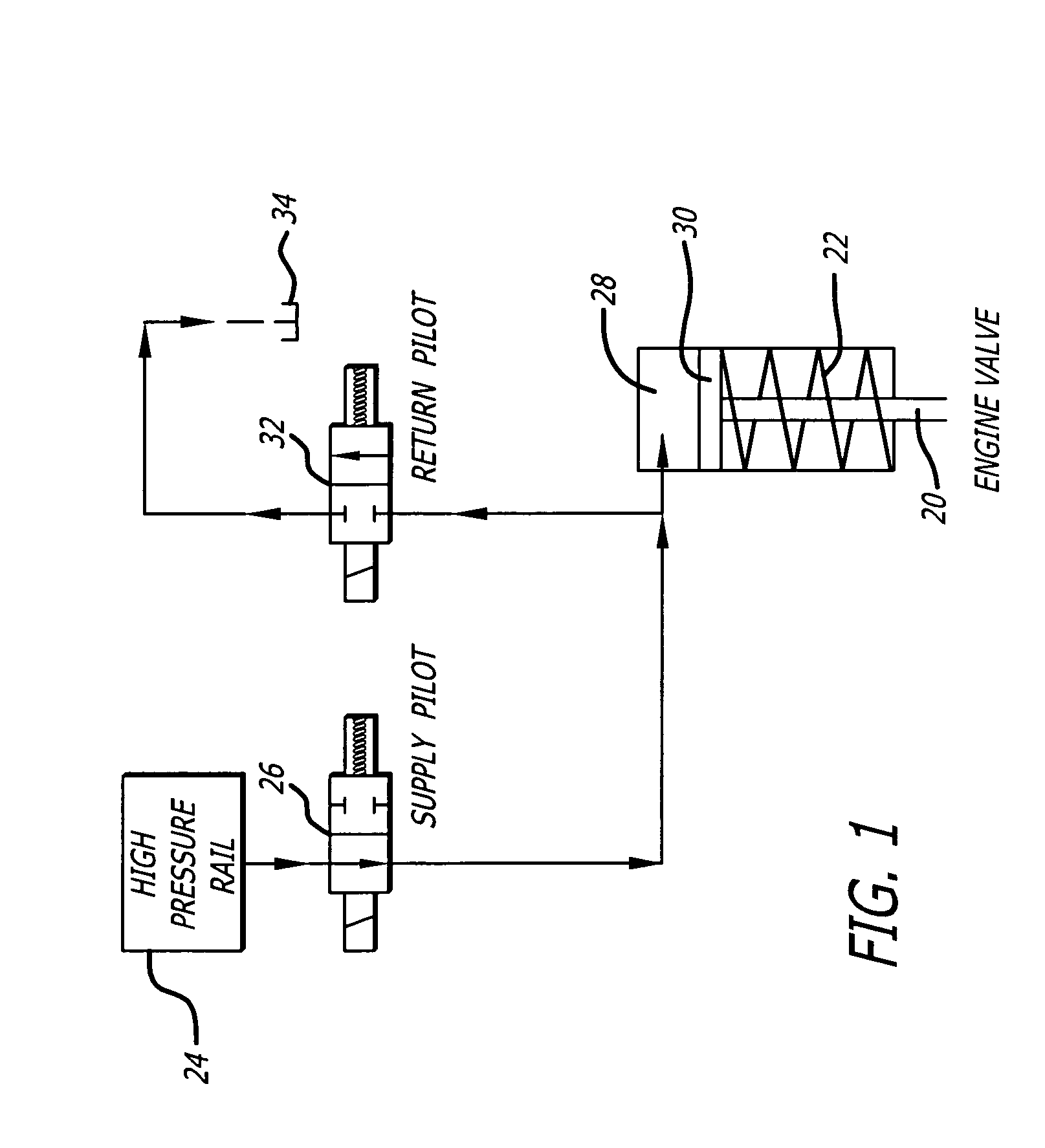
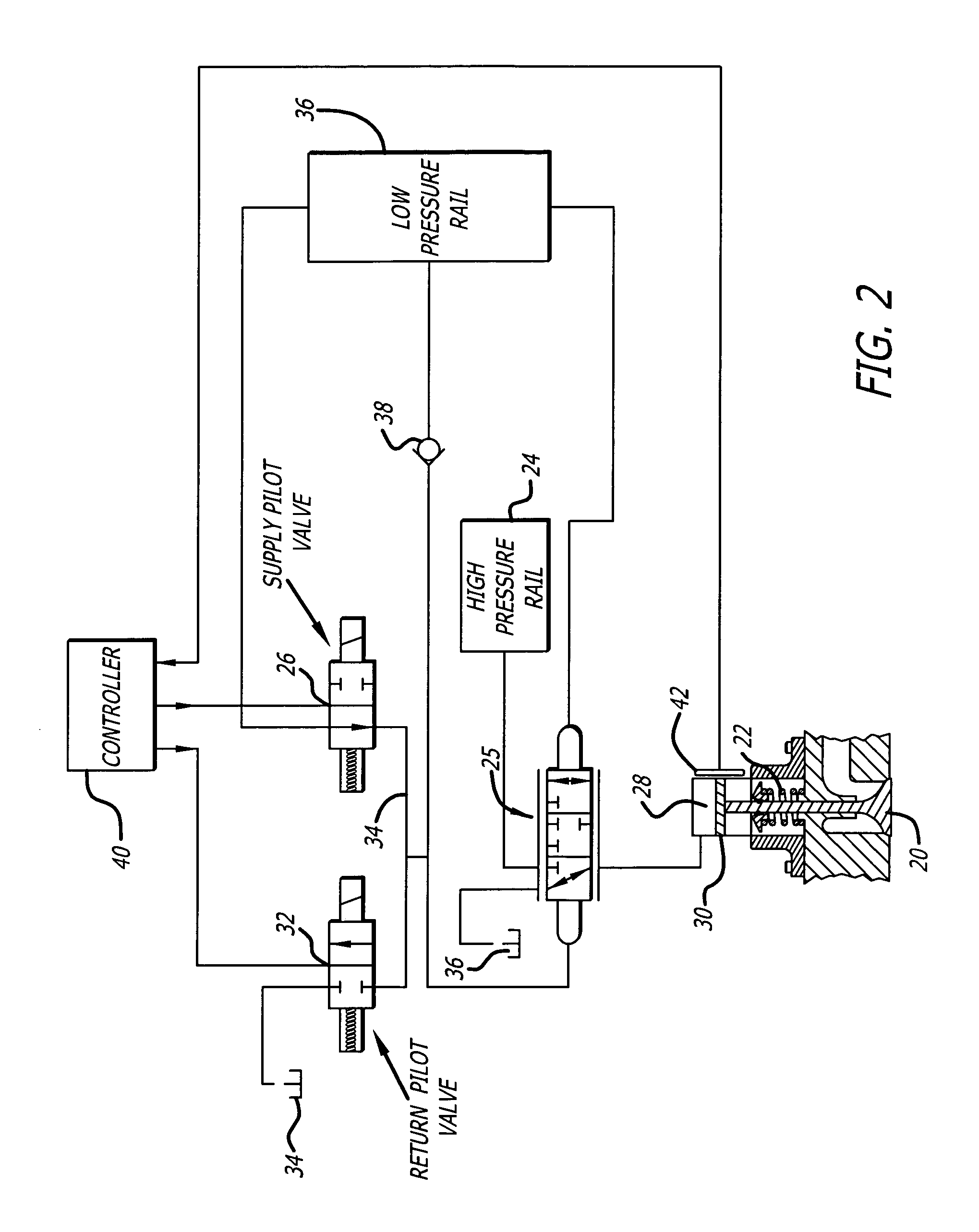
Hydraulic valve actuation methods and apparatus
InactiveUS7025326B2Improve energy efficiencySave energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesCombustionValve actuator
Hydraulic engine valve actuation methods for internal combustion engines having improved energy efficiency. In hydraulic engine valve operating systems using spring returns for valve closure, the spring force is a minimum when the valve is closed and a maximum at the maximum lift. The present invention takes advantage of this difference by using a valve opening hydraulic force which is greater than the spring force when the valve is closed and less than the spring force when the valve is open at its maximum lift. The valve actuator is controlled to allow the valve, when opening, to overshoot the equilibrium condition. During the overshoot, the hydraulic actuator backfills with actuating fluid at it normal actuating pressure. When the valve velocity decays to zero or near zero, the flow of hydraulic fluid to (and from) the valve actuator may be cut off, capturing the valve substantially at the overshoot position.
Owner:STURMAN INDS
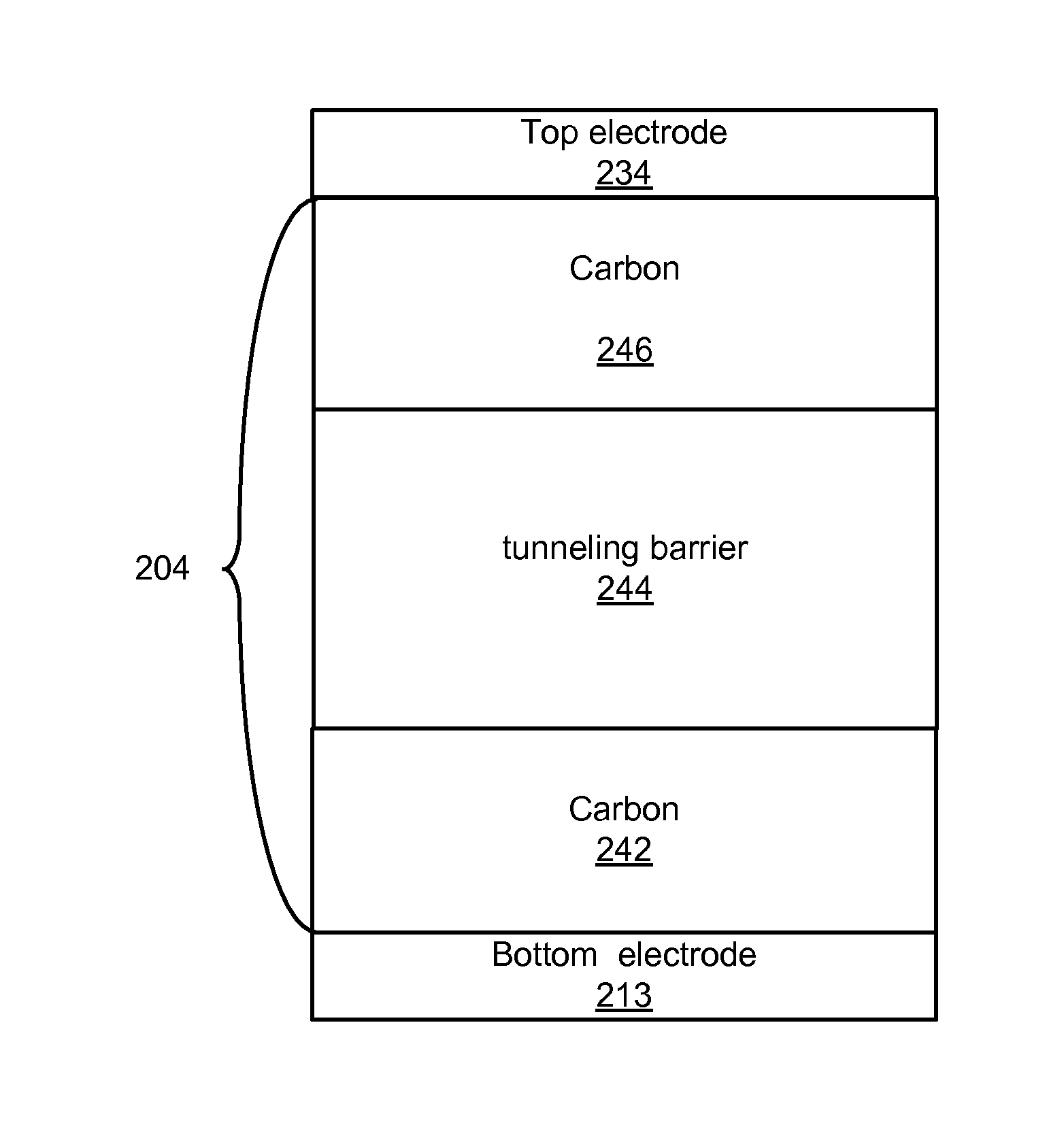
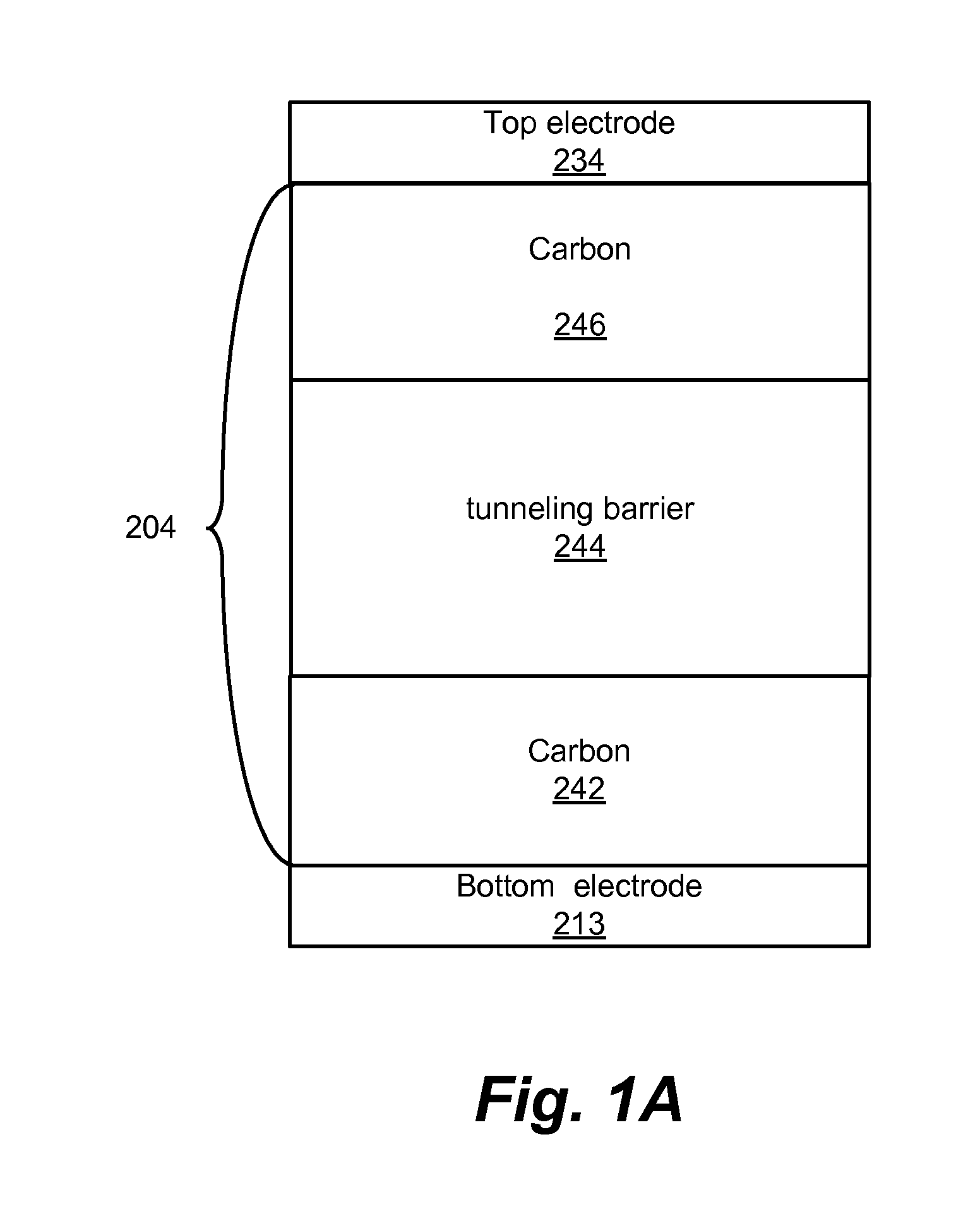
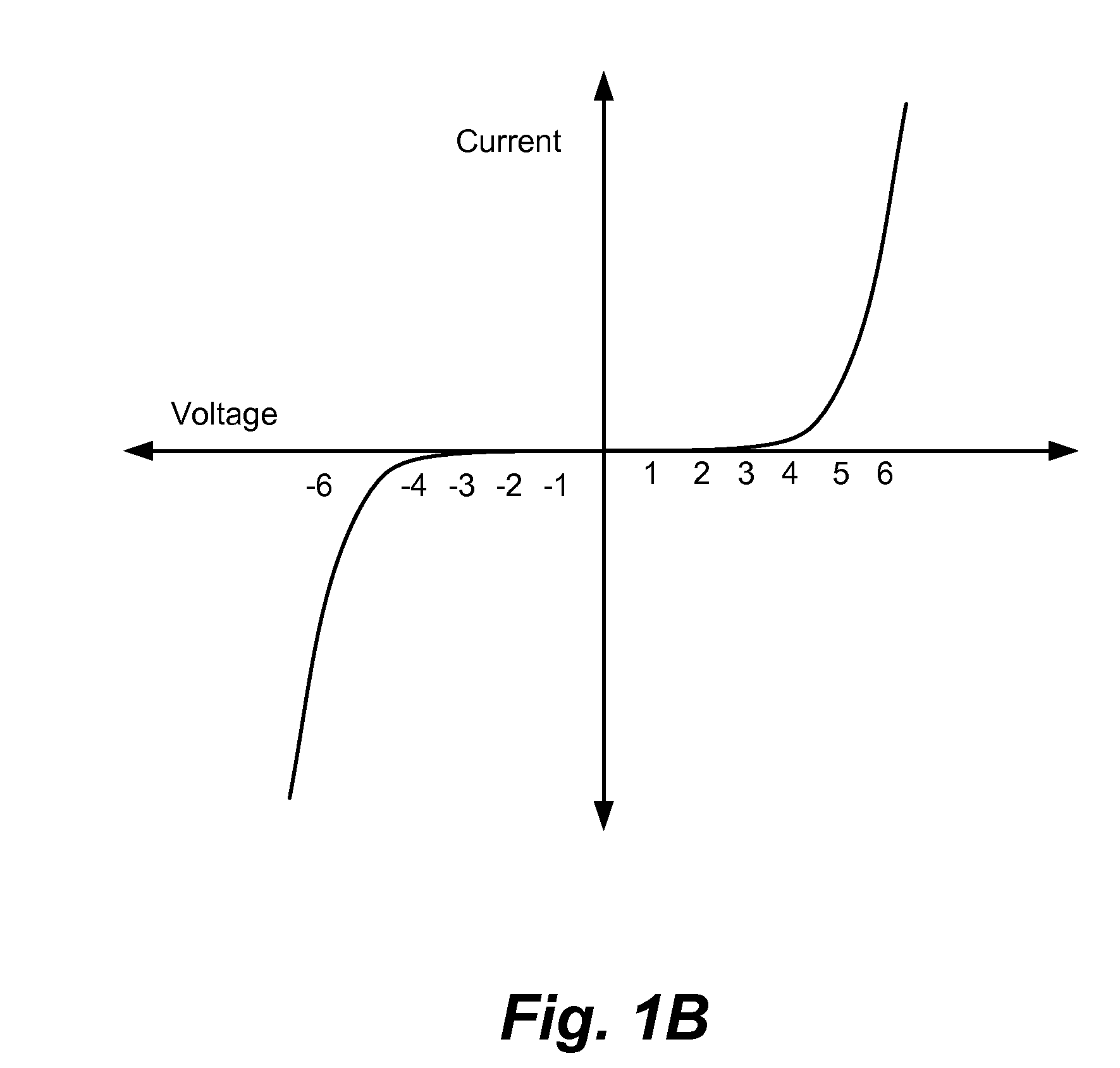
Carbon/tunneling-barrier/carbon diode
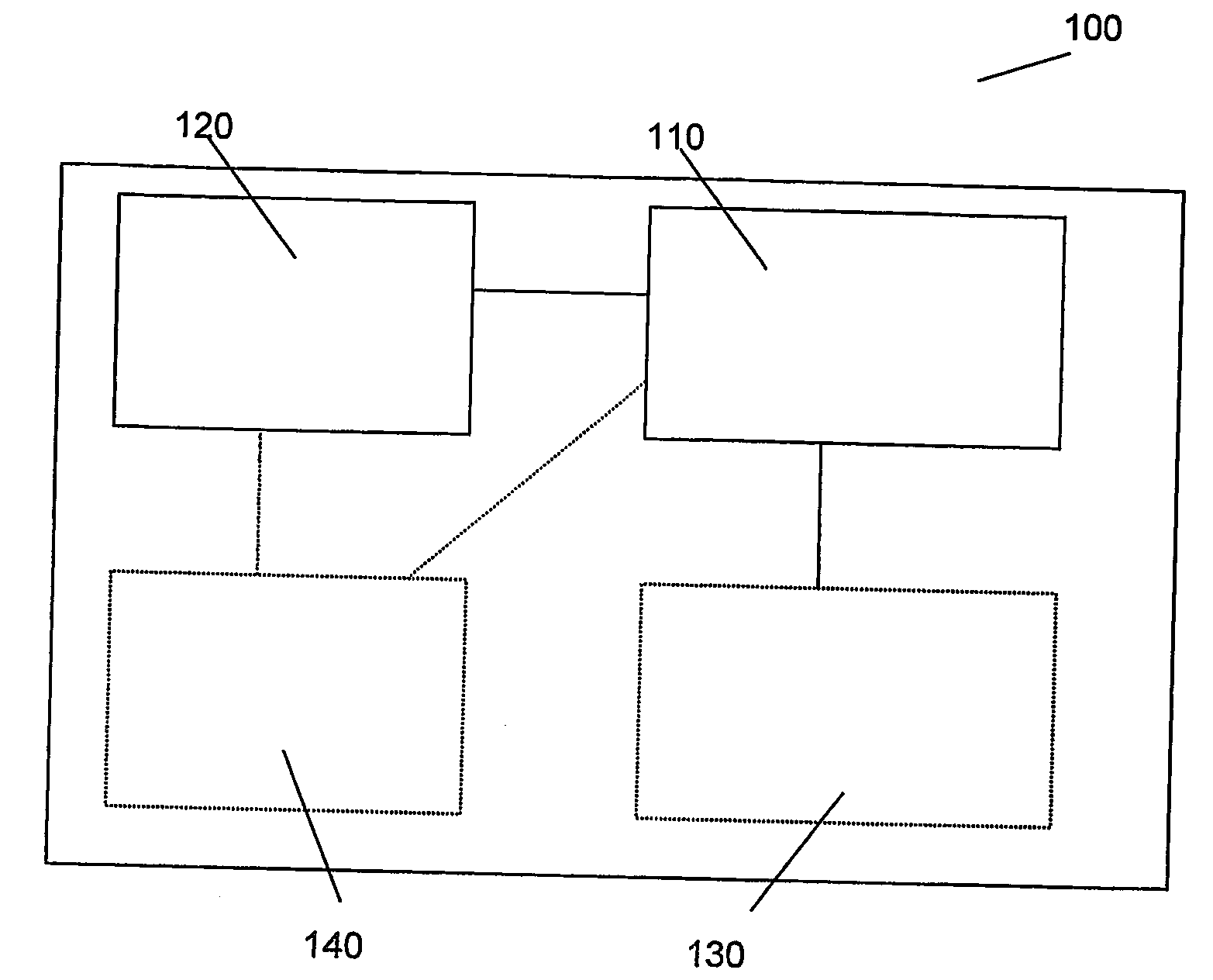
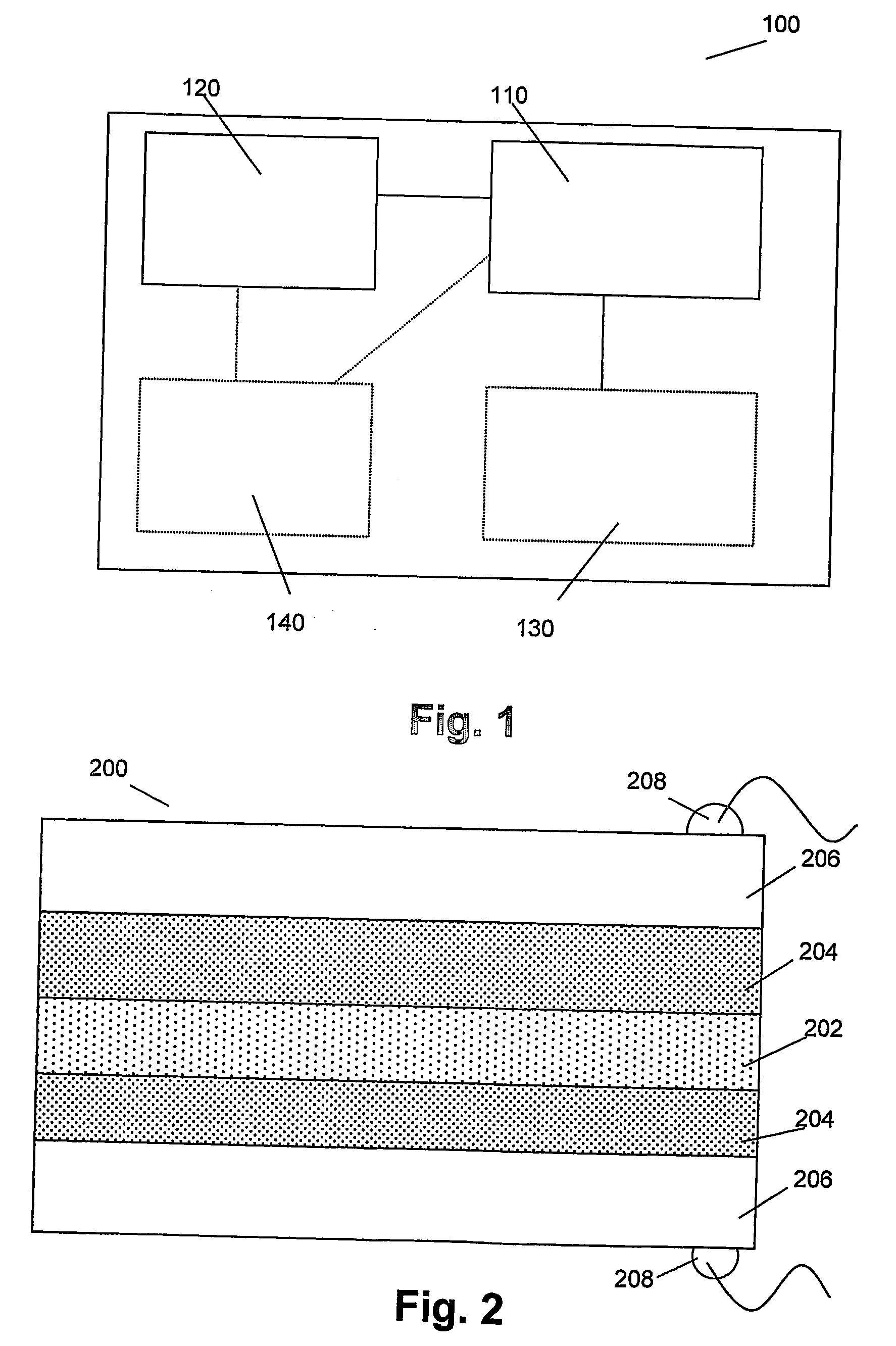
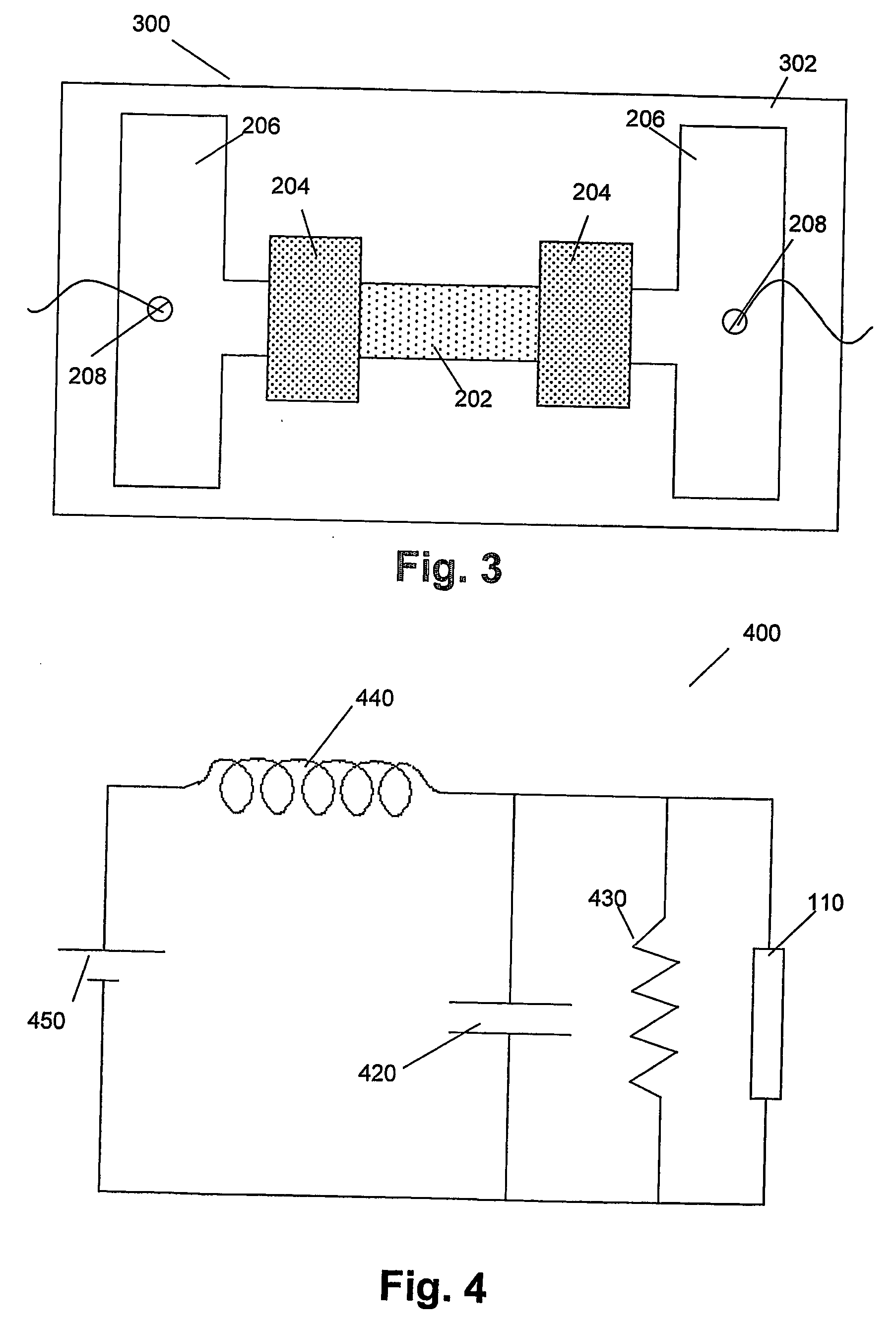
ActiveUS20110140064A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringEquilibrium conditions
A carbon / tunneling-barrier / carbon diode and method for forming the same are disclosed. The carbon / tunneling-barrier / carbon may be used as a steering element in a memory array. Each memory cell in the memory array may include a reversible resistivity-switching element and a carbon / tunneling-barrier / carbon diode as the steering element. The tunneling-barrier may include a semiconductor or an insulator. Thus, the diode may be a carbon / semiconductor / carbon diode. The semiconductor in the diode may be intrinsic or doped. The semiconductor may be depleted when the diode is under equilibrium conditions. For example, the semiconductor may be lightly doped such that the depletion region extends from one end of the semiconductor region to the other end. The diode may be a carbon / insulator / carbon diode.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method and device for load balancing
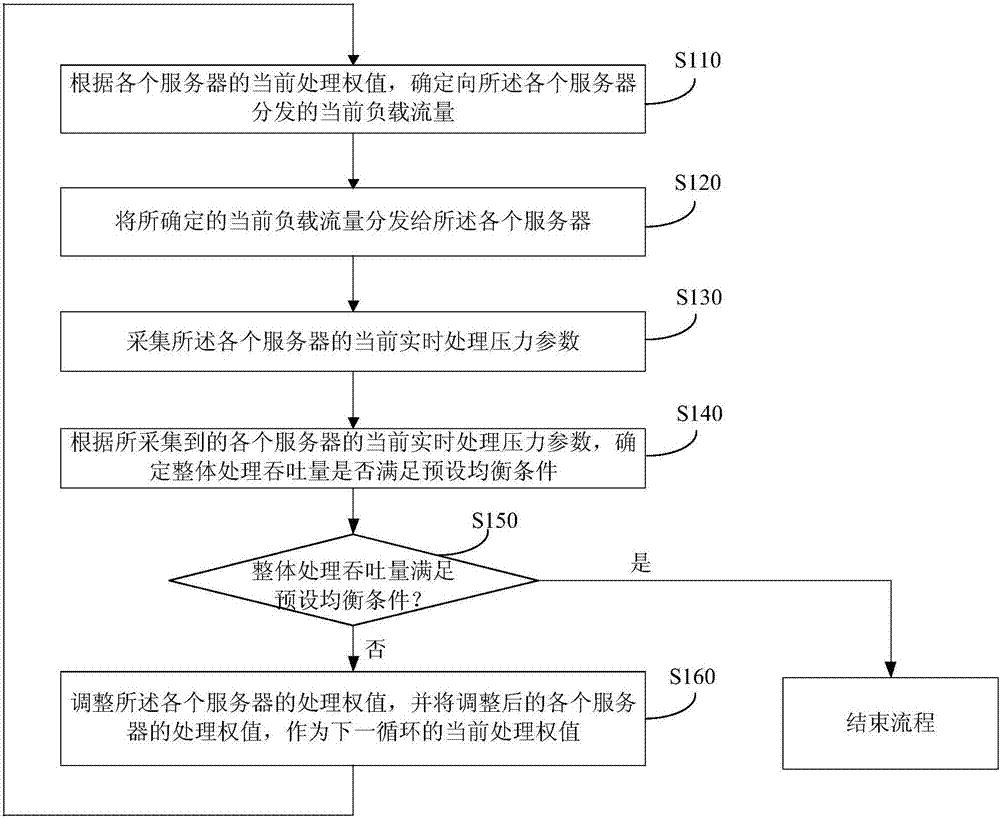
The invention discloses a method and a device for load balancing. The method includes the following steps: circularly executing the following steps until that the overall processing throughput meets a preset equilibrium condition is determined; determining the current load flow distributed to each server according to the current processing weight of each server; distributing the determined current load flow to each server; collecting the current real-time processing pressure parameter of each server; determining whether the overall processing throughput meets the preset equilibrium condition according to the collected current real-time processing pressure parameter of each server; and when determining that the overall processing throughput meets the preset equilibrium condition, adjusting the processing weight of each server, and taking the processing weight of each server after adjustment as the current processing weight in next cycle. Through the technical scheme provided by the embodiments of the invention, the problem that the whole back-end processing cluster cannot function best and even some machines may be overloaded in the current network or machine environment is solved.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Customized bus pricing method considering system optimization
InactiveCN107330716AIncrease share rateEase traffic pressureMarketingTraffic networkSystem optimization
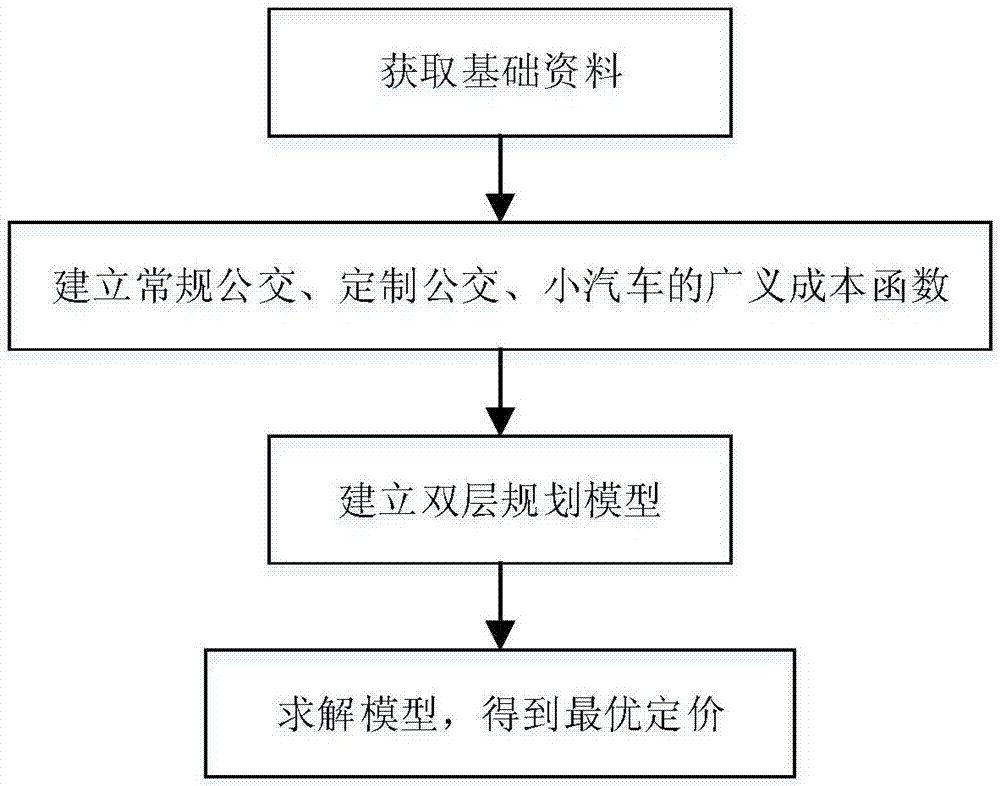
The invention discloses a system-optimized custom public transport pricing method, which comprises the steps of: obtaining planning basic data; respectively establishing generalized travel cost functions of conventional public transport, customized public transport and cars; establishing a lower layer according to the equilibrium condition of a multi-mode traffic network, etc. The multi-mode stochastic user balance model of price, and consider the optimal model of the system to establish the upper model, so as to build a two-level programming model to describe the customized bus pricing problem under the optimal situation of the system; The planning model is solved to obtain the optimal pricing of customized public transport under the optimal condition of the system. Compared with the previous traditional pricing mode, the present invention is more scientific, can effectively reduce the total cost of the system, attract travelers to travel by public transport through scientific pricing, can effectively increase the share rate of public transport, and reduce the share rate of cars.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Gait producing device for leg type movable robot, and control device
ActiveUS20050051368A1Reduce loadVelocity increasesComputer controlSimulator controlEngineeringGravity center
A desired trajectory of a vertical component of a translation floor reaction force of a legged mobile robot 1, a vertical component of a total center-of-gravity acceleration or a body acceleration's vertical component of the robot 1 is determined, and a desired vertical position of a total center-of-gravity or body of the robot 1 is determined in such a manner that the vertical component of the translation floor reaction force, the vertical component of the total center-of-gravity acceleration or the body acceleration's vertical component agrees with the desired trajectory (that is, a dynamical equilibrium condition in the vertical direction is satisfied). Since the movement of the total center-of-gravity or the like in the vertical direction is determined after the desired trajectory of the vertical component of the translation floor reaction force or the like, a desired gait for the robot 1 suitable not only for walking but also for running can be generated.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
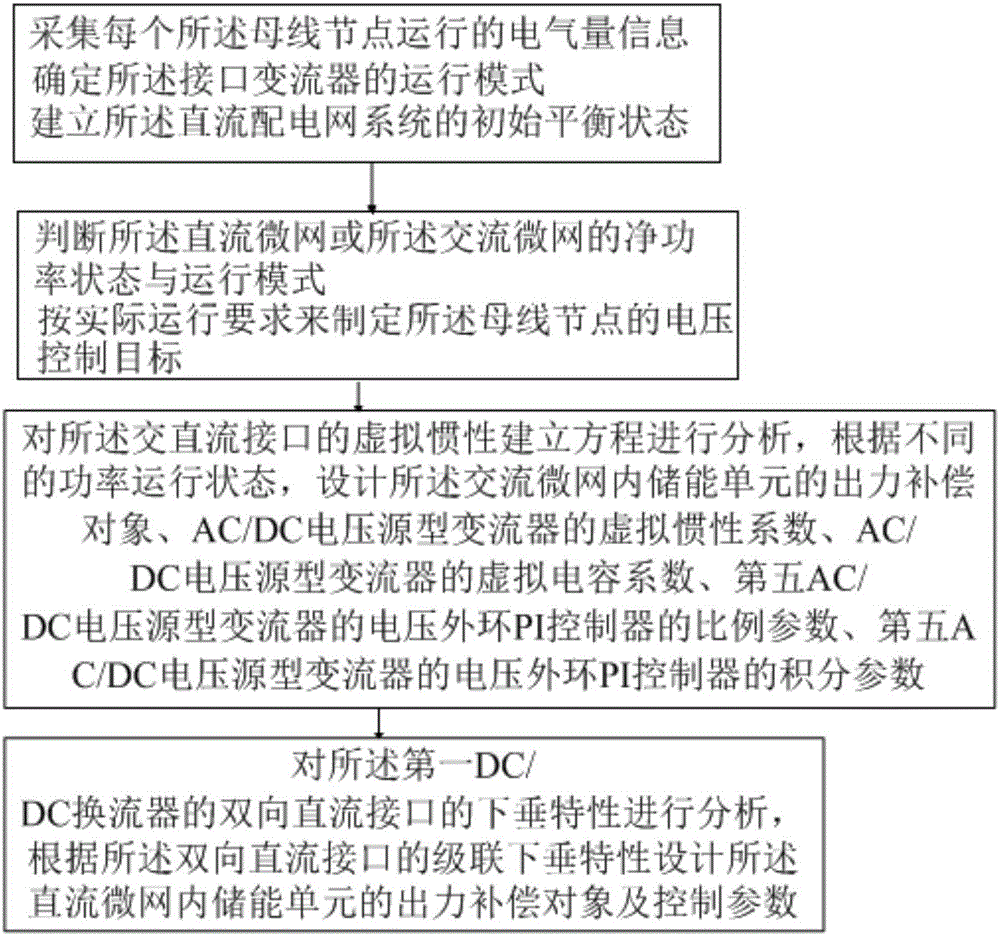
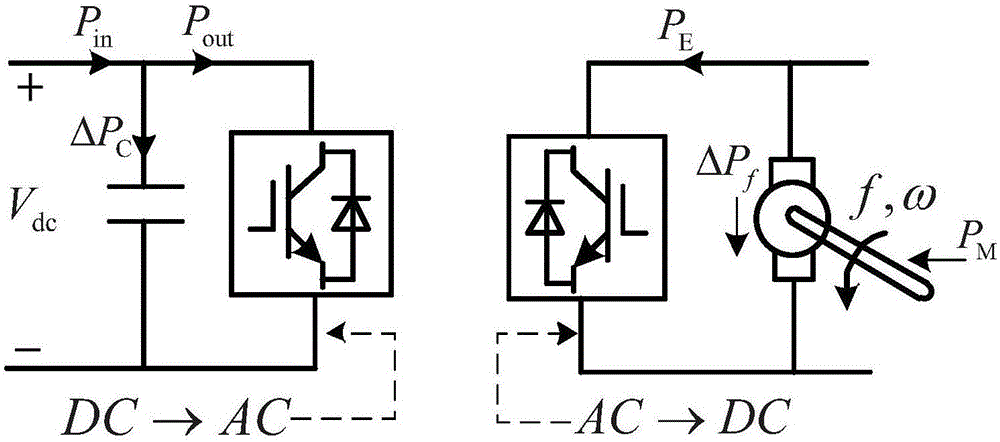
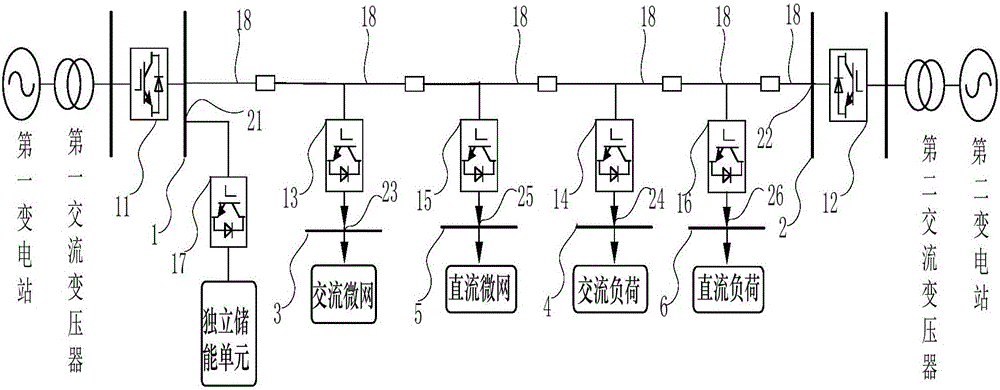
Voltage flexible control method of direct current distribution network system
ActiveCN106849106AImprove dynamic stabilityReduce difficultyElectric power transfer ac networkAc network voltage adjustmentMicrogridEngineering
The invention discloses a voltage flexible control method of a direct current distribution network system. The method comprises the following steps of collecting operation electric quantity information of each bus node, determining an operation mode of an interface converter, and building an initial equilibrium condition of the direct current distribution network system; judging a net power state and an operation mode of a direct current microgrid or an alternating current microgrid, and forming a voltage control target of the bus node according to an actual operation requirement; establishing an equation for virtual inertia of an alternating current and direct current interface for analysis, and according to different power operation states, designing parameters of the interface converter and an electricity using unit; and analyzing drooping characteristics of a bidirectional direct current interface of a first DC / DC converter, and according to cascading drooping characteristics of the bidirectional direct current interface, designing an output compensation object and a control parameter of an inner energy-storing unit of the direct current microgrid. By a voltage flexible control way, the stability, convenience and reliability of control on a direct current distribution network are improved, energy-storing adjustment is fully used, and power fluctuation is reduced.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Gait generation device for legged mobile robot
ActiveUS7319918B2Reduce coefficient of frictionGenerate lotProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlDynamic modelsEngineering
A gait generation device for setting a translation floor reaction force's horizontal component (component concerning a friction force) applied to a robot 1, a limitation-target quantity, such as a ZMP, and an allowable range, for determining at least a provisional instantaneous value of a desired floor reaction force and a provisional instantaneous value for a desired movement of the robot 1, that receives at least the provisional instantaneous value for the desired movement and determines a model floor reaction force instantaneous value with the aid of a dynamics model. Based on the difference between the model floor reaction force instantaneous value and the provisional instantaneous value of the desired floor reaction force or the allowable range of the limitation-target quantity, the provisional instantaneous value for the desired movement is corrected so that the limitation-target quantity falls within the allowable range and a dynamical equilibrium condition on the dynamics model is satisfied, thereby determining a desired instantaneous value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
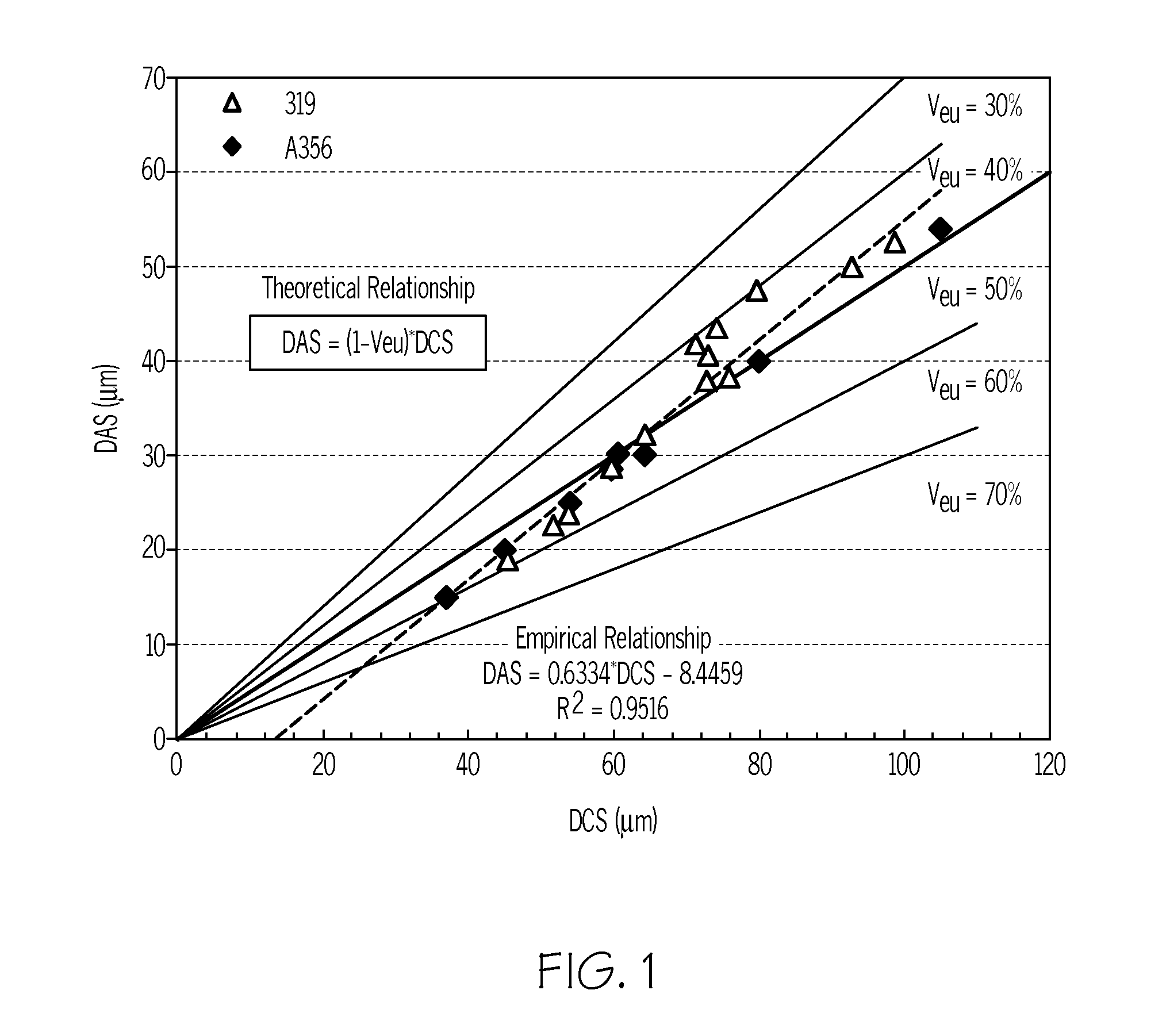
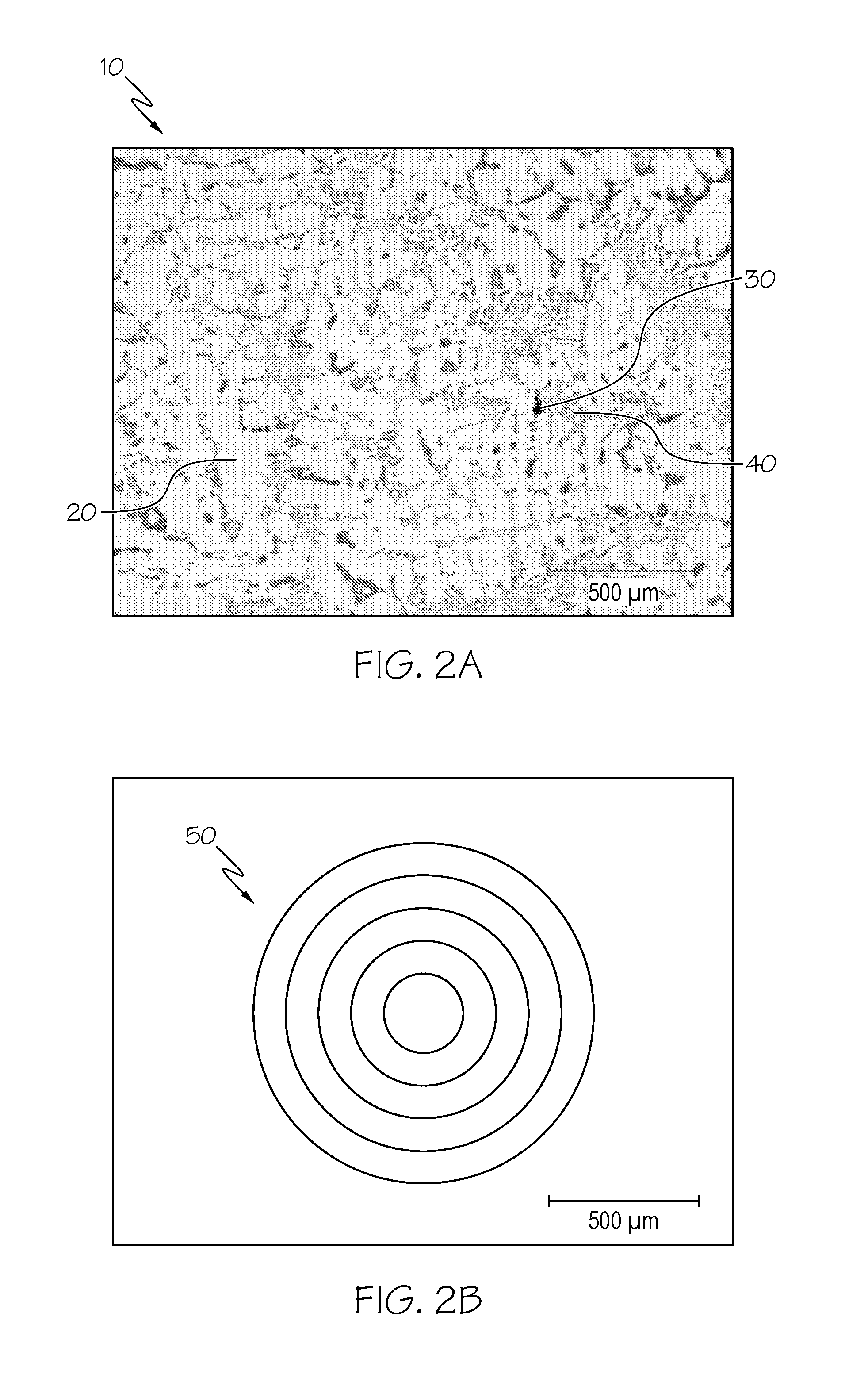
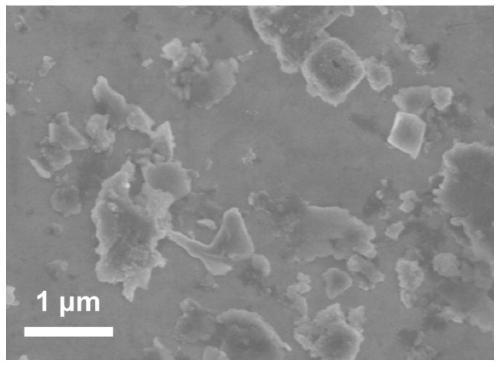
Method for automatic quantification of dendrite arm spacing in dendritic microstructures
A method to automatically quantify dendrite arm spacing in dendritic microstructures. Once a location of interest in a cast material specimen has been identified, the information contained in it is automatically analyzed to quantify dendrite cell size information that is subsequently converted into a quantified dendrite arm spacing through an empirical relationship or a theoretical relationship. In one form, the relationship between DCS and DAS is such that the DAS in dendritic structure of cast aluminum alloys may be automatically determined from the measurement of one or more of dendrite cell size and the actual volume fraction of the eutectic phases in the local casting microstructure. Non-equilibrium conditions may be accounted for in situations where a theoretical volume fraction of a eutectic phase of the alloy in equilibrium condition is appropriately modified. Thus, in situations where equilibrium conditions—such as those where the casting is cooled very slowly during solidification—does not apply (such as during rapid cooling and consequent solidification), the eutectic measured in the non-equilibrium condition, which can be smaller than the theoretical value in equilibrium, can be accounted for.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
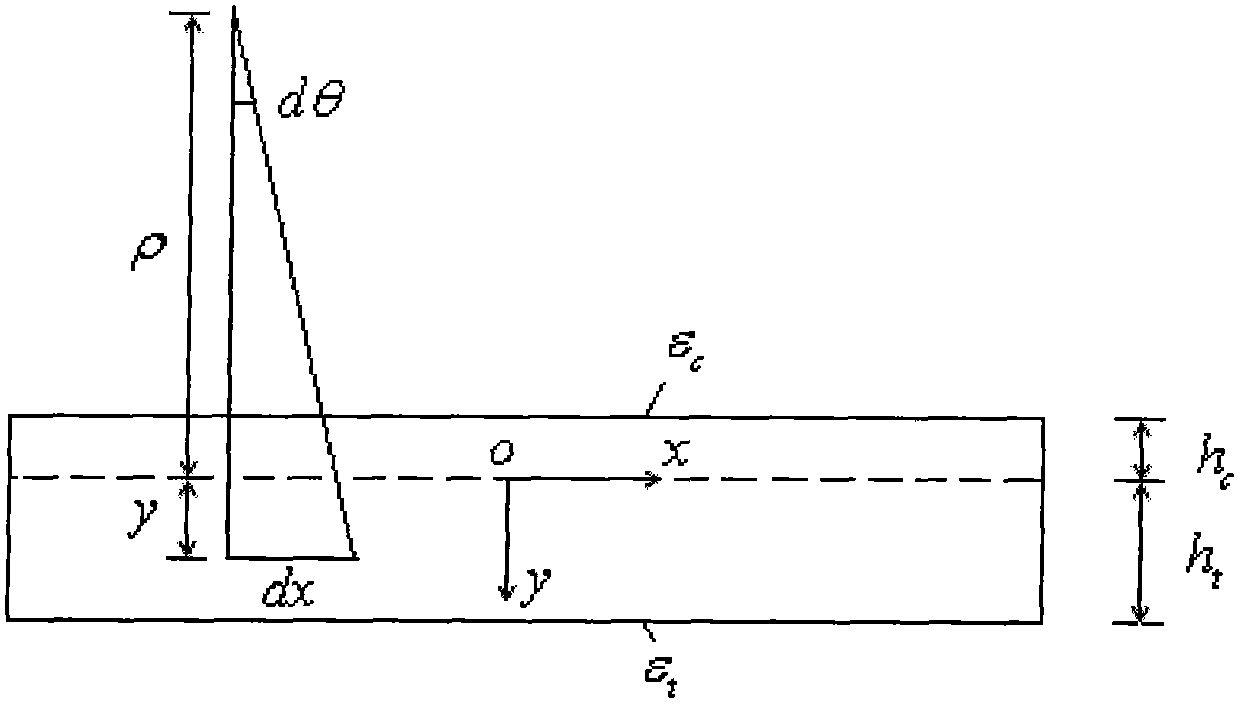
Method for adopting bend test to test tensile elasticity modulus of material
InactiveCN103018112ASolve test problemsReduce workloadMaterial strength using steady bending forcesEngineeringGreek letter epsilon
The invention discloses a method for adopting a bend test to test the tensile elasticity modulus of a material. A compressive elasticity modulus Ec of a material is supposed to be known, and the pure bending or transverse bending small transformation experiment is carried out in a linear elastic range of the material; axial strain values epsilon c and epsilon t of an optional position on upper and lower surfaces of the pure bending section of a sample or axial strain values epsilon c and epsilon t on the upper and lower edges of any cross section of the transverse bending section are measured in an experiment; a relation of the pressure-pulling elasticity modulus ratio and the pulling compressive strain ratio of the material is deduced through an equilibrium condition of a cross section, thereby determining the tensile elasticity modulus Et of the material according to the formulae shown in the specification. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the theory is correct, a computing formula is concise, the parameter is easy to measure, and the tensile elasticity modulus of the material can be accurately measured.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
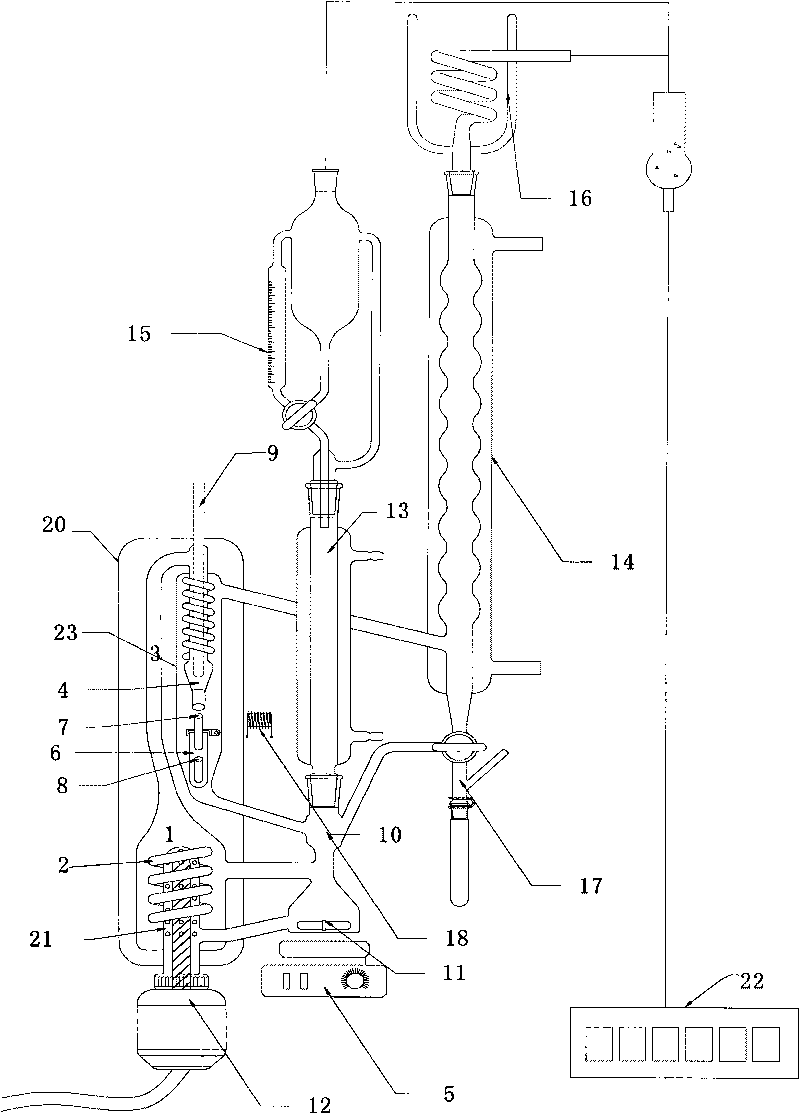
Gas-liquid-liquid equilibrium data measurement device
InactiveCN101726507AFully contactedAccurate measurementLaboratory glasswaresInvestigating phase/state changeMeasurement deviceThree-phase
The invention discloses a gas-liquid-liquid equilibrium data measurement device. An equilibrium still comprises three circulation loop structures for accelerating the circular mixing of fluid. The liquid phase in a hating still is homogenized by an ultrasonic homogenizer for improving the mass transfer rate and rapidly achieving the equilibrium. The separation is performed through stirring and heating. A liquid-liquid split phase tube is arranged in a gas-liquid separation chamber, so the liquid-liquid split phase experiment condition is the same as the gas-liquid equilibrium condition. The still is used for performing gas-liquid-liquid equilibrium measurement; gas-liquid-liquid three phase samples accurately representing gas-liquid-liquid equilibrium components can be obtained, time consumption is low, the equilibrium components and equilibrium temperature are accurately measured, and the experimental operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Apparatus and method for operation of a high temperature fuel cell system using recycled anode exhaust
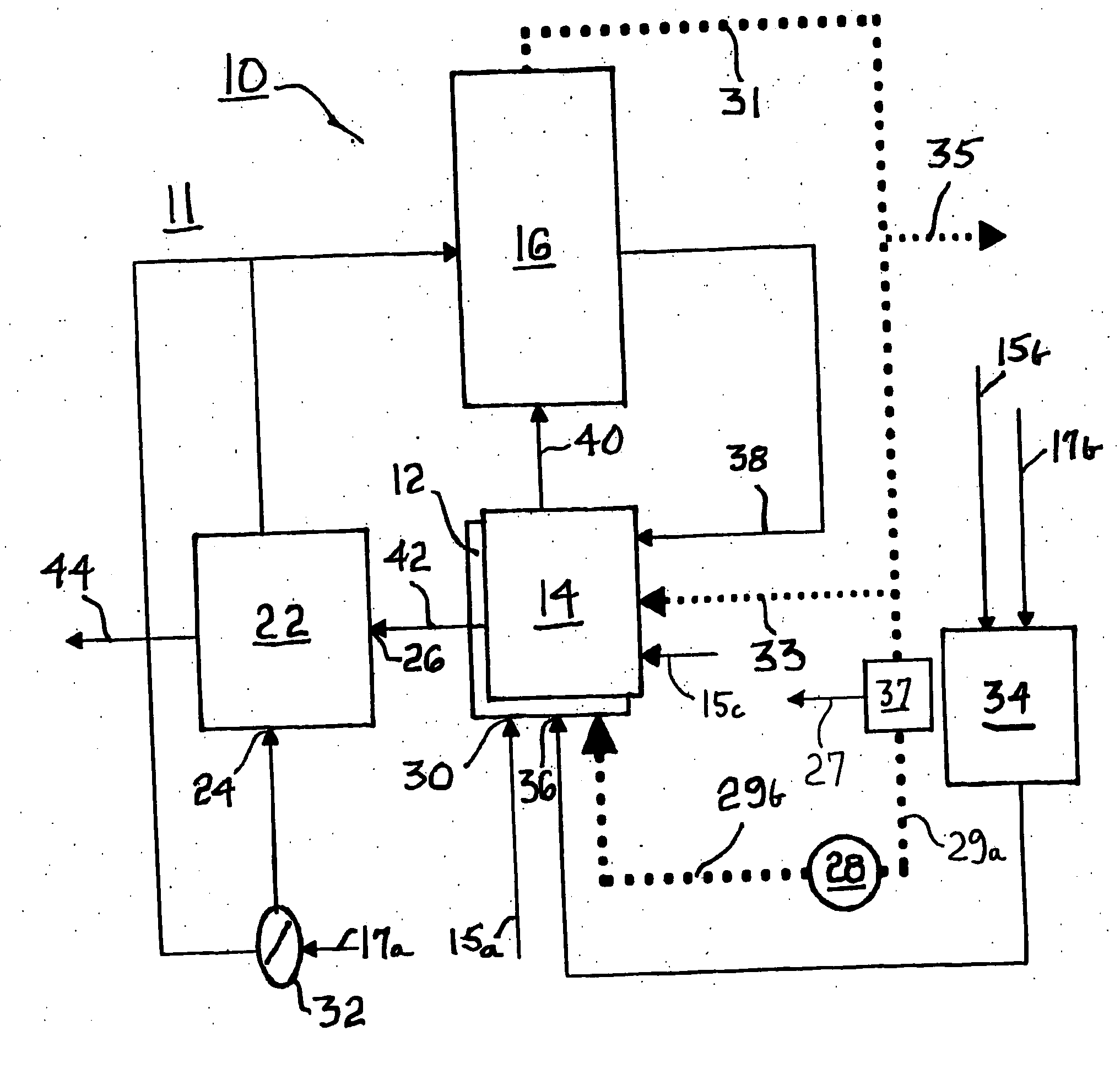
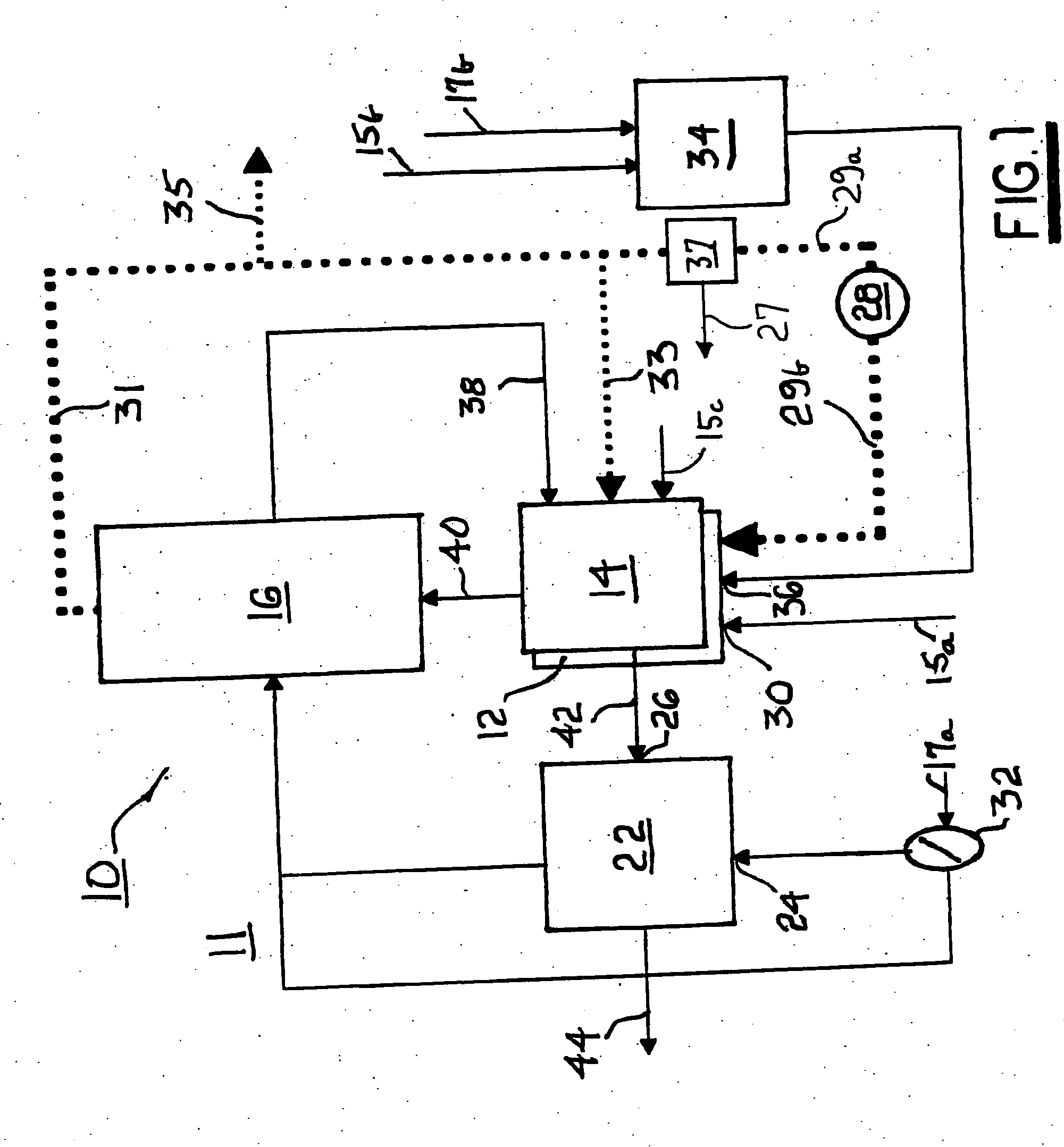
ActiveUS7326482B2Improve efficiencyEliminate needAuxillary drivesFuel cells groupingFuel efficiencyOxygen
A method for improving the efficiency of a hydrocarbon catalytic reformer and close-coupled fuel cell system by recycling a percentage of the anode exhaust syngas directly into the reformer in a range between about 20% and about 60%. Oxygen is supplied to the reformer at start-up. Under equilibrium conditions, oxygen required for reforming of hydrocarbon fuel is derived entirely from endothermic reforming of water and carbon dioxide in the recycled syngas. Recycling of anode syngas into the reformer increases fuel efficiency, adds excess water to the reformate to increase protection against anode coking, and protects the fuel cell stack against air- and water-borne contaminants. A method for producing an excess amount of syngas for exporting for other purposes is also provided.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Apparatus and method for high efficiency operation of a high temperature fuel cell system
ActiveUS7674538B2High atomic oxygen/carbonReduce the temperatureAuxillary drivesFuel cell heat exchangeSyngasFuel cells
Apparatus and method for operating a fuel cell system including a hydrocarbon catalytic reformer and close-coupled fuel cell stack by recycling anode syngas into the reformer in a range between 60% and 95% of the total syngas. At equilibrium conditions, oxygen required for reforming of hydrocarbon fuel is derived from endothermically reformed water and carbon dioxide in the syngas. Reforming temperature is between about 650° C. to 750° C. The stack exit temperature is about 800° C. to 880° C. such that the required endotherm can be provided by the sensible heat of the recycled syngas. The stack has approximately equal anode and cathode gas flows in opposite directions, resulting in cooling from both the anodes and cathodes.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
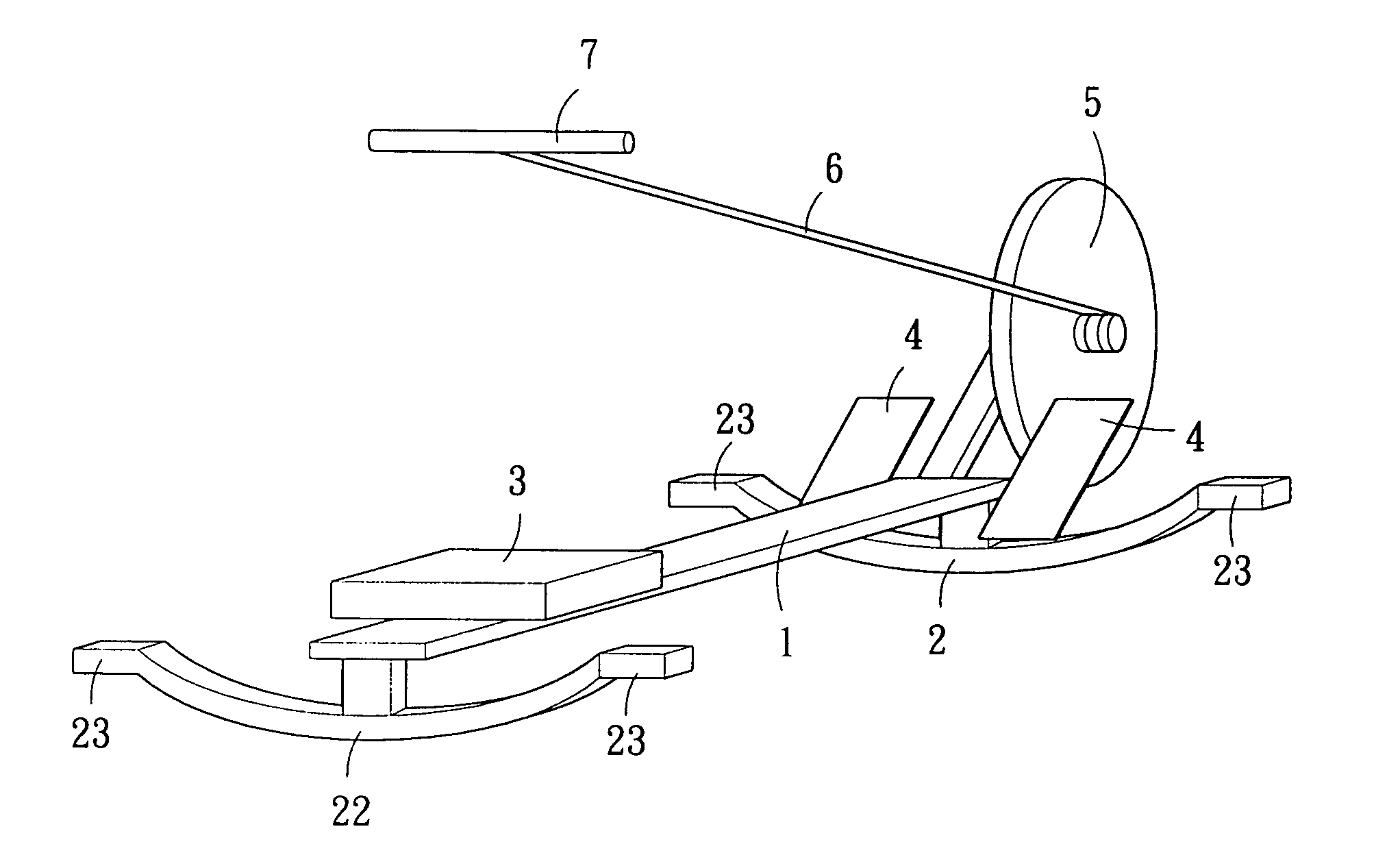
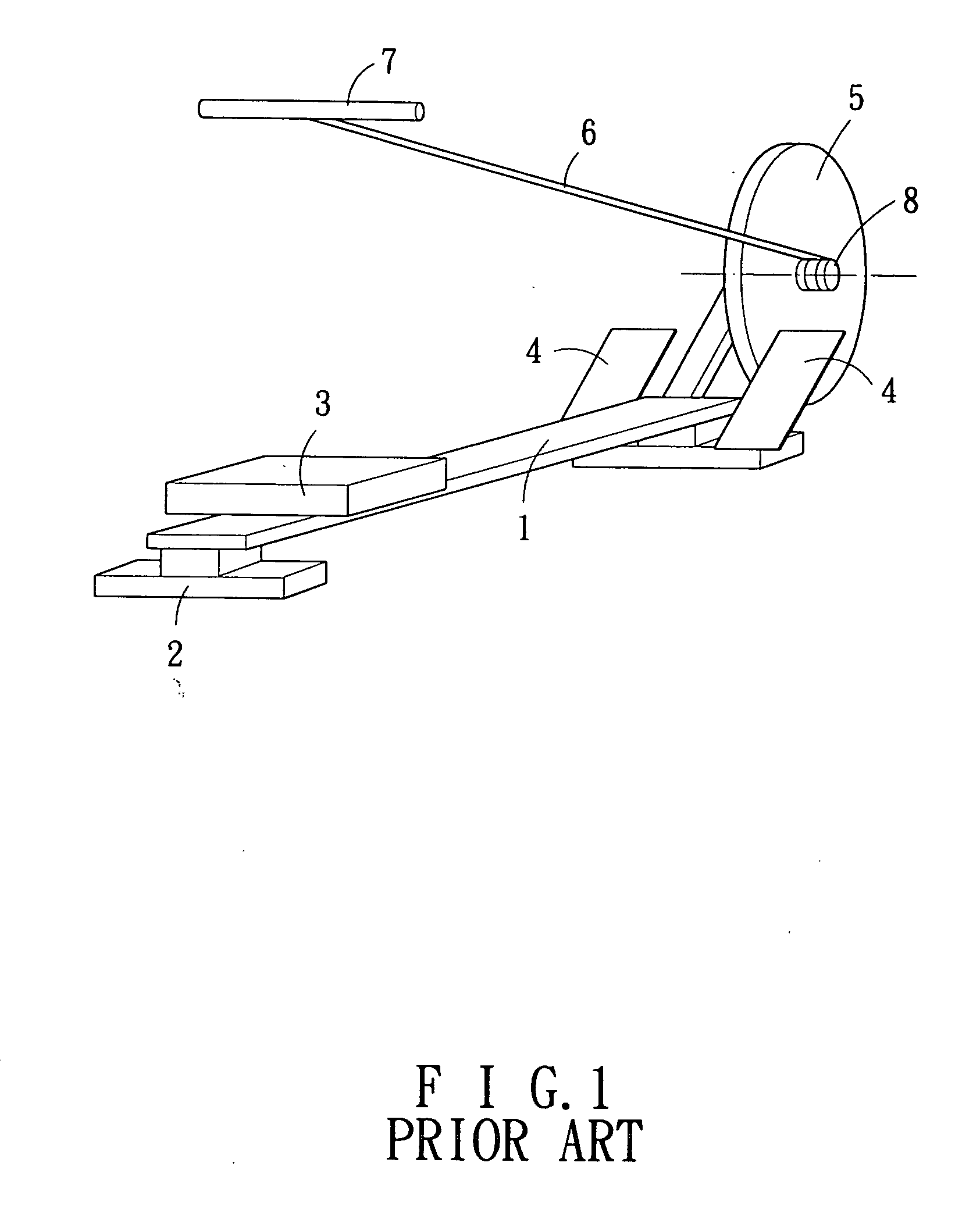
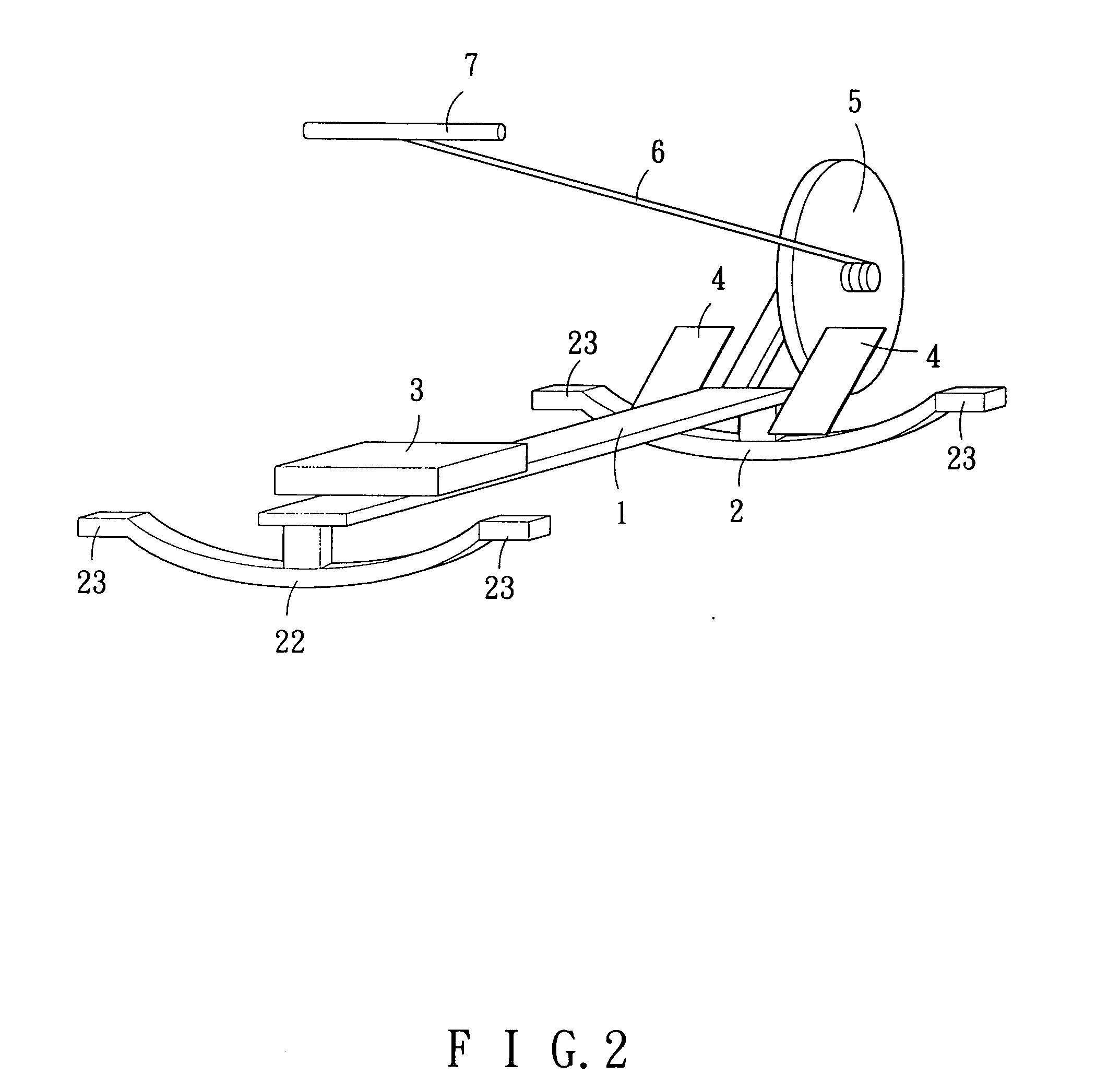
Swinging implement for simulating rowing exercises
A swinging implement for simulating a rowing exercise comprises a supporting framework, which can be caused to bear on a floor by supporting elements, and including a seat plane, which can freely slide along the supporting framework, characterized in that said swinging implement comprises moreover swinging means for causing said supporting framework to swing with respect to a floor, thereby inducing a user to search equilibrium conditions during the exercise.
Owner:GRAMACCIONI FEDERICO
IpDFT-based frequency estimation method of non-equilibrium electric power system
ActiveCN108020721AImprove estimation accuracyImprove stabilitySpectral/fourier analysisFrequency measurement arrangementComputation complexityElectric power system
The present invention discloses an IpDFT(Interpolation Discrete Fourier Transform)-based frequency estimation method of a non-equilibrium electric power system. The problem of non-circular signal employed frequency estimation in a non-equilibrium condition is solved based on modeling of complex-valued signals deduced from a three-phase voltage through orthogonal [Alpha][Beta]transformation. The newest progress obtained through enhanced complex-valued second-order statistics is employed, and in a non-equilibrium condition, the complex-valued signals are second-order non-circular signals. In theinvention, interpolation Fourier transform is employed to estimate frequency of the signals, the non-circular signals are converted to sinusoidal signals through simple calculation, positive and negative frequency components are considered, and therefore, the estimation accuracy of the frequency is improved and the calculation is simple. Compared to traditional linear adaptive estimation, the method is more suitable for the non-equilibrium system, gives out unbiased frequency estimation, and is not sensitive to frequency change. The method is more stable and low in calculation complexity, andis improved in robustness anti-noise performance and estimation precision.
Owner:南京福致通电气自动化有限公司 +1
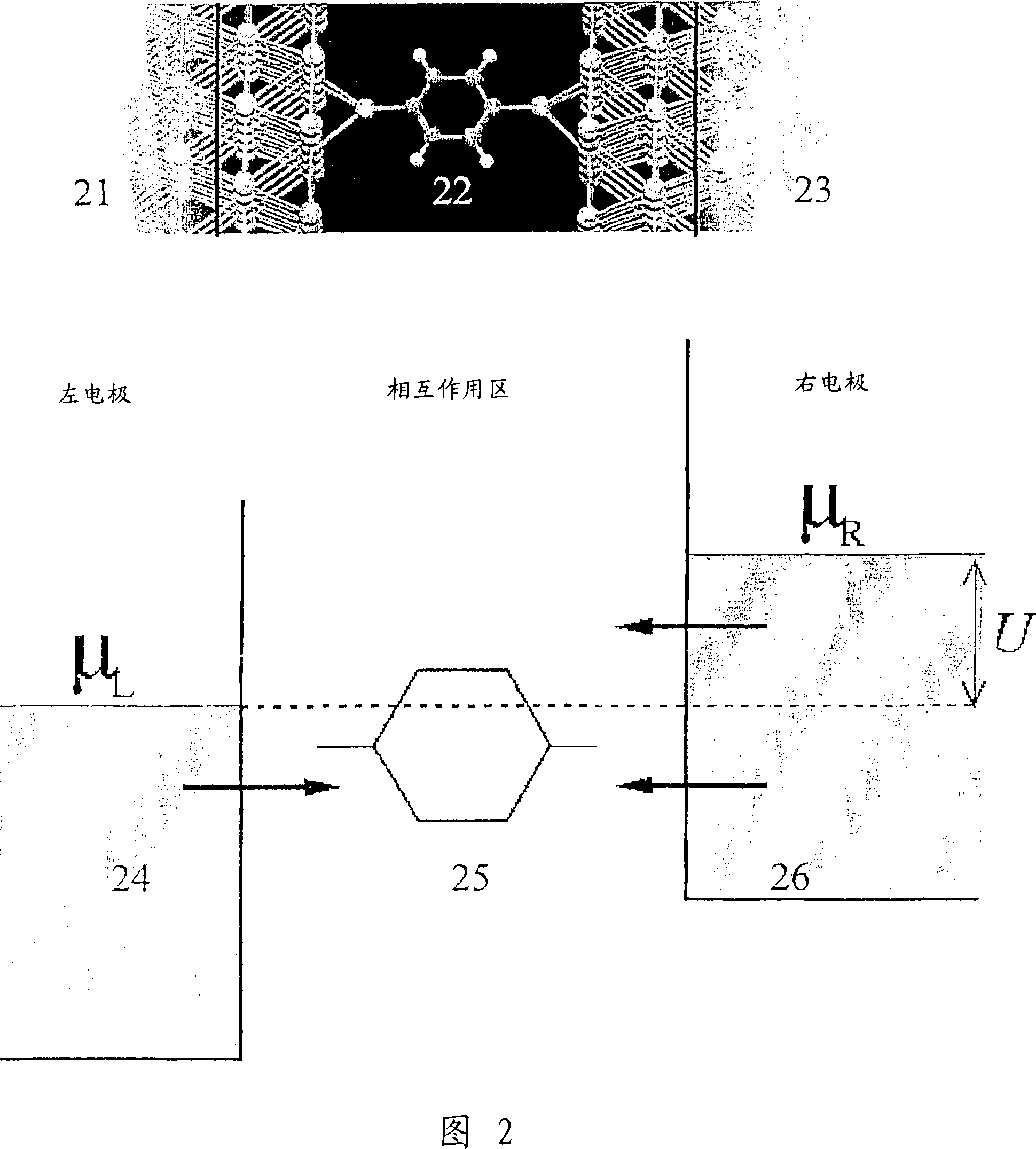
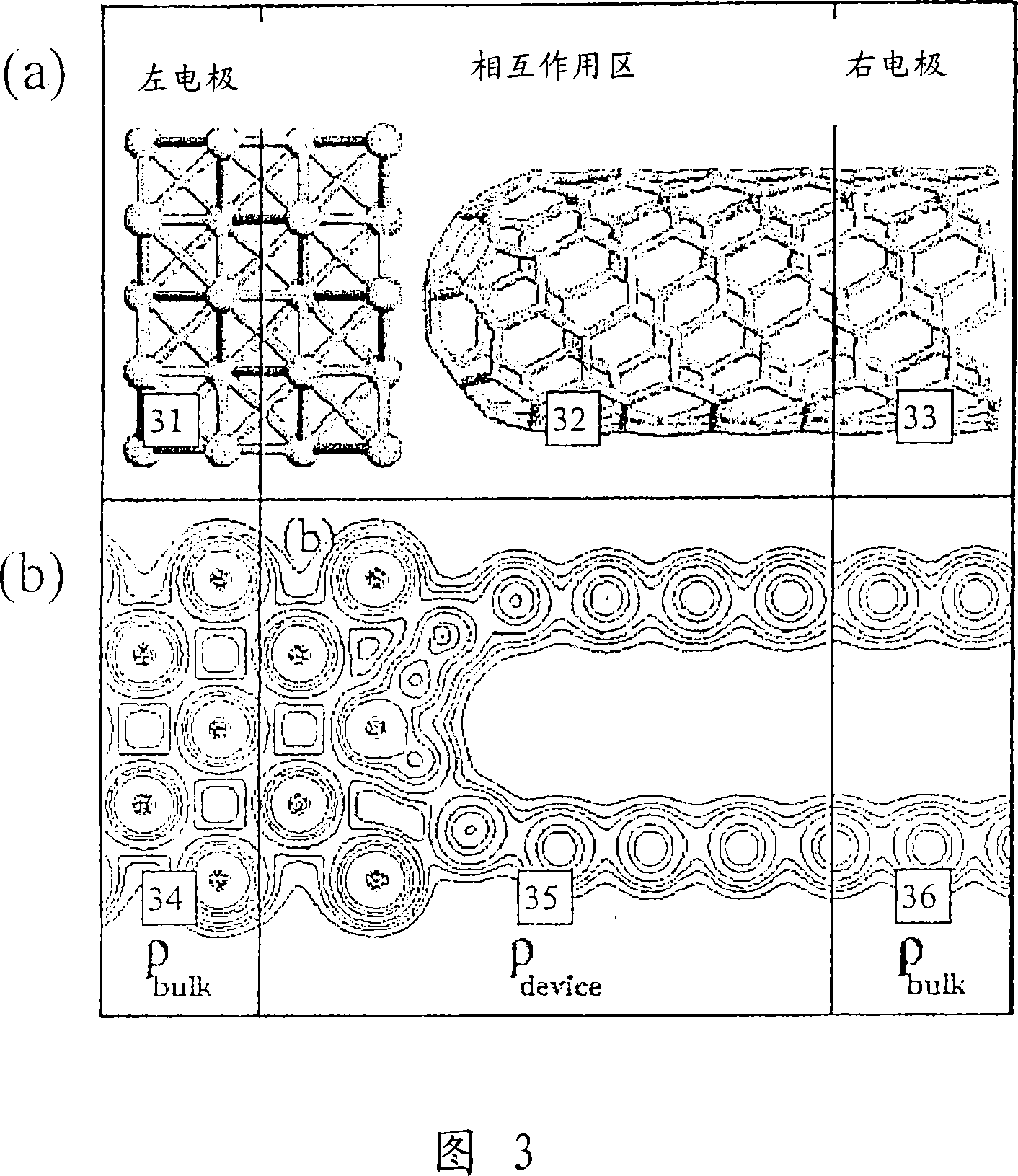
Method and computer system for quantum chemical modelling of molecules under non-equilibrium conditions
InactiveCN101019122ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic structureQuantum chemistry
Owner:ATOMISTIX
A method for calculating earthquake earth pressure of gravity embankment retaining wall
ActiveCN109101774AAvoid destructionHigh precisionGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsCalculation methodsRetaining wall
The invention discloses a method for calculating earthquake earth pressure of gravity embankment retaining wall, which comprises the following steps: according to the basic assumption of Coulomb earthpressure theory, a theoretical model calculation diagram is established according to the limit equilibrium state of a quadrilateral sliding soil wedge; considering the static equilibrium condition ofsoil wedge, the equilibrium diagram of force system is established; gravity G and seismic inertia force F are synthesized to obtain F combination and simplifying force system equilibrium diagram; according to the sinusoidal theorem, the seismic active earth pressure of gravity embankment retaining wall is calculated. A method for calculating earth pressure of gravity embankment retaining wall under earthquake condition features that a shaking table test is carried out to compare that theoretical calculation result with the actual measurement result, and the theoretical calculation result is proved to have high accuracy and the applicability of the calculation method is verified.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
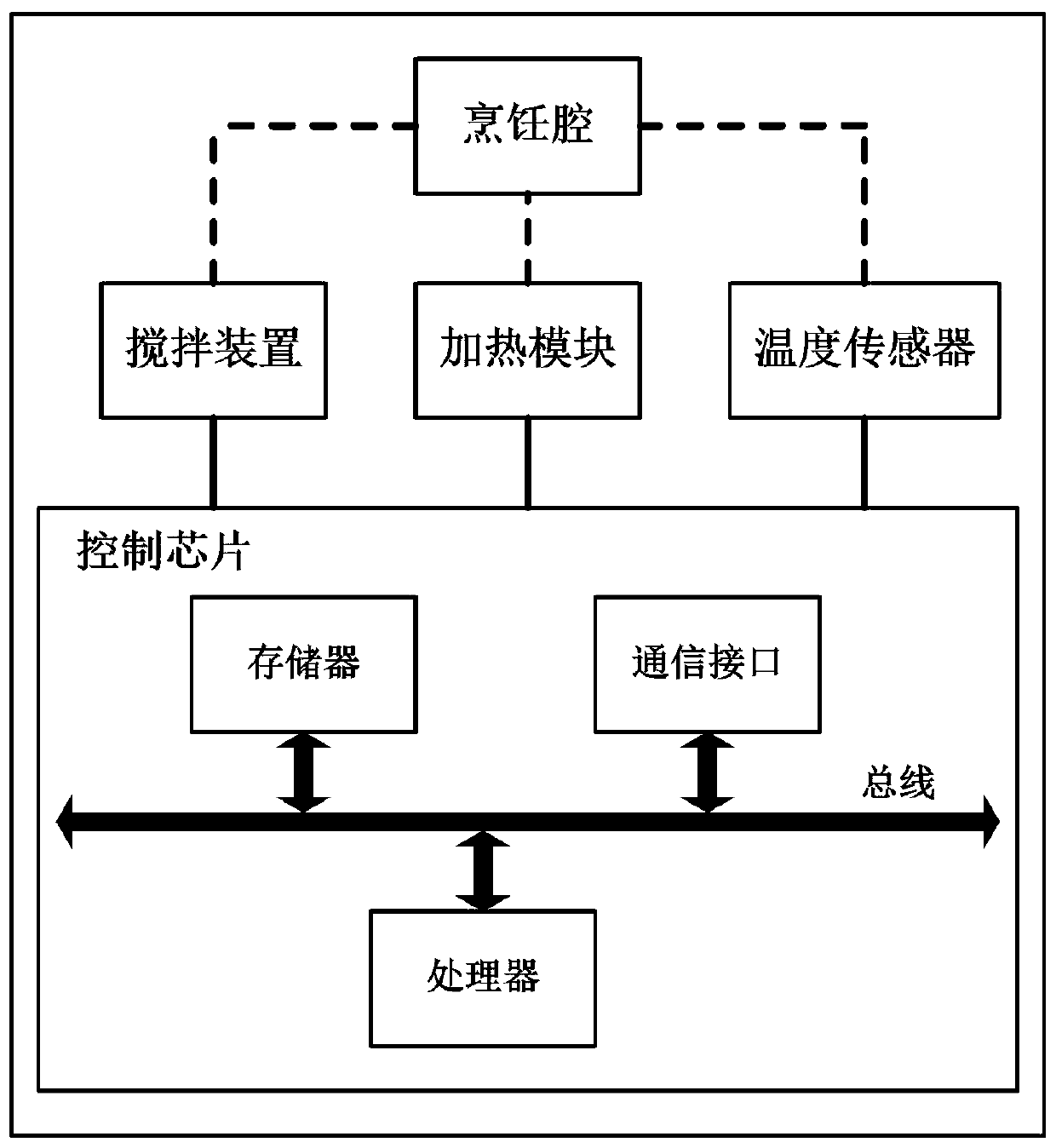
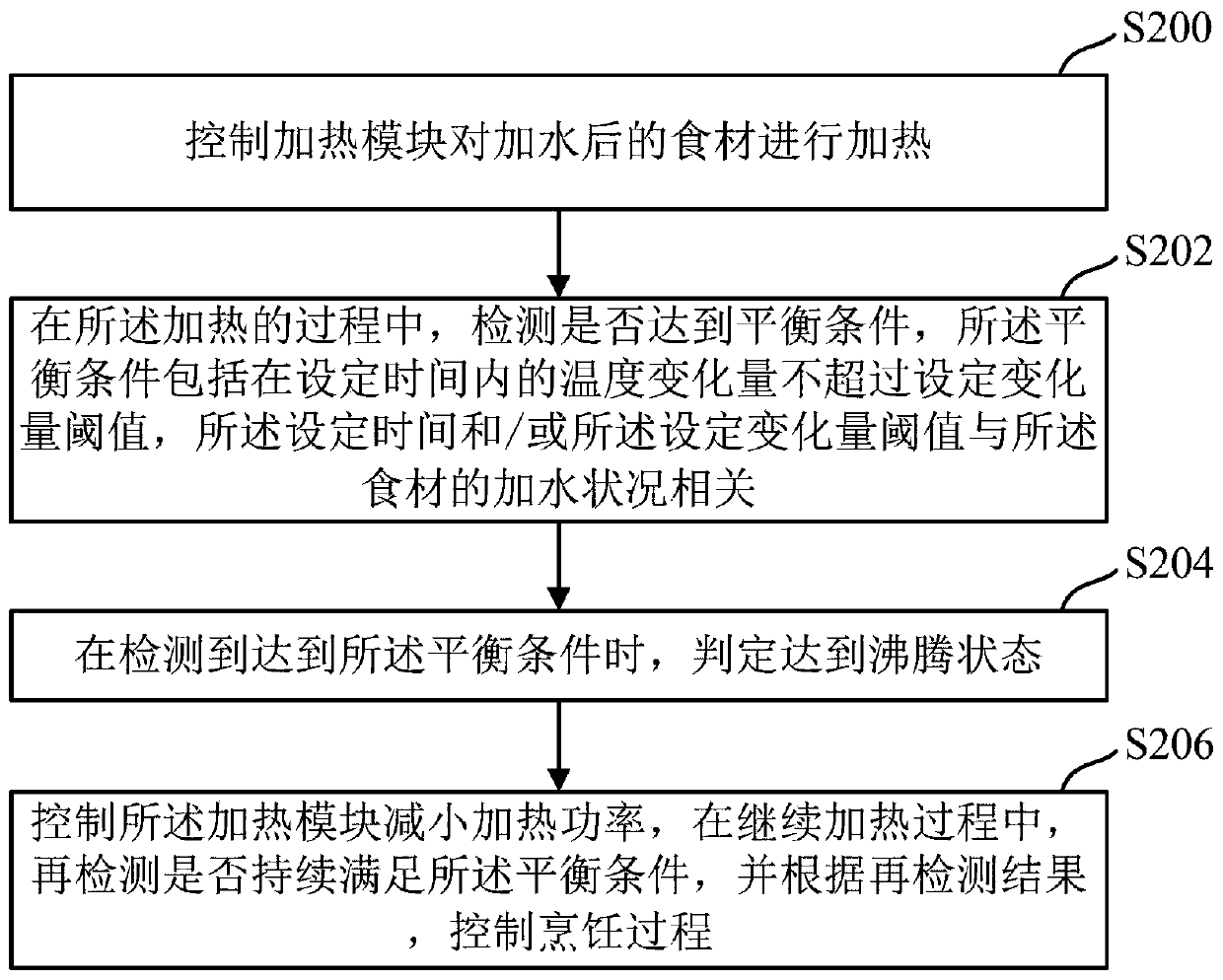
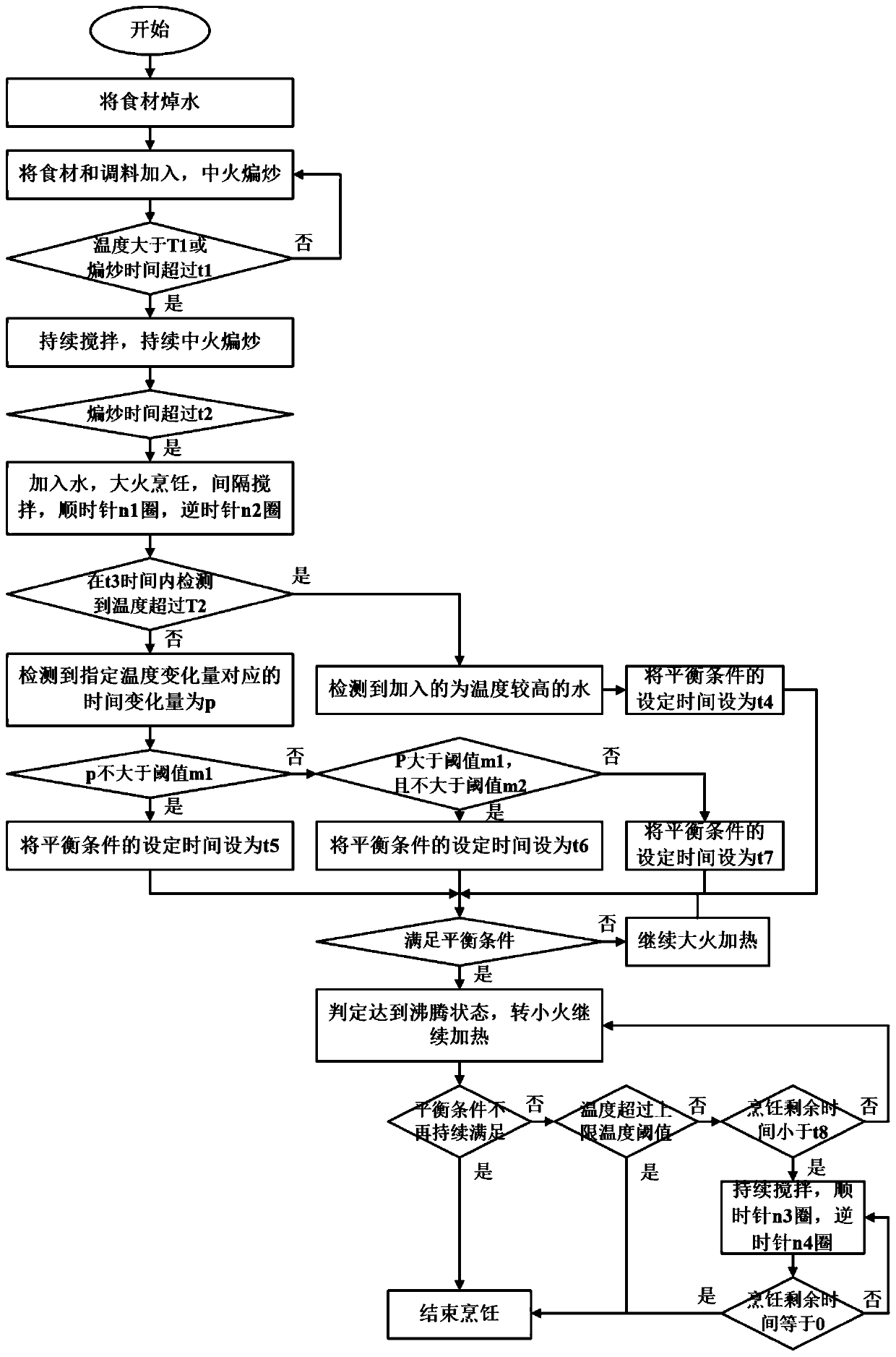
Cooking control method and cooking appliance
PendingCN110558852AReduce the burden onAvoid sticky pot phenomenonTime-controlled ignitorsAdditive ingredientProcess engineering
The present application discloses a cooking control method and a cooking appliance. The method comprises: controlling a heating module to heat watered ingredients; in a heating process, detecting whether an equilibrium condition is satisfied, wherein the equilibrium condition comprises that the temperature change amount within a set time does not exceed the set change amount threshold, and the settime and / or the set change amount threshold is related to the watering condition of the ingredients; when detecting that the equilibrium condition is satisfied, determining that a boiling state is satisfied; and controlling the heating module to reduce the heating power, during the continuously heating process, detecting whether the equilibrium condition is satisfied, and controlling the cookingprocess according to a re-detection result. According to the technical scheme of the present application, an equilibrium condition that is compatible with the watering condition of the ingredients isset, on one hand, the timing of converting a boiling state into a low-heat state can be automatically determined according to the equilibrium condition, and on the other hand, after entering the low-heat state, the cooking process is controlled according to the equilibrium condition once again, so that the phenomenon of over cooking due to less watering can be prevented, the burden on the user canbe reduced in a facilitated manner, and a better cooking result can be obtained.
Owner:JOYOUNG CO LTD
Apparatus and method for operation of a high temperature fuel cell system using recycled anode exhaust
ActiveUS20050196653A1Improve efficiencyEliminate needAuxillary drivesFuel cells groupingSyngasFuel cells
A method for improving the efficiency of a hydrocarbon catalytic reformer and close-coupled fuel cell system by recycling a percentage of the anode exhaust syngas directly into the reformer in a range between about 20% and about 60%. Oxygen is supplied to the reformer at start-up. Under equilibrium conditions, oxygen required for reforming of hydrocarbon fuel is derived entirely from endothermic reforming of water and carbon dioxide in the recycled syngas. Recycling of anode syngas into the reformer increases fuel efficiency, adds excess water to the reformate to increase protection against anode coking, and protects the fuel cell stack against air- and water-borne contaminants. A method for producing an excess amount of syngas for exporting for other purposes is also provided.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
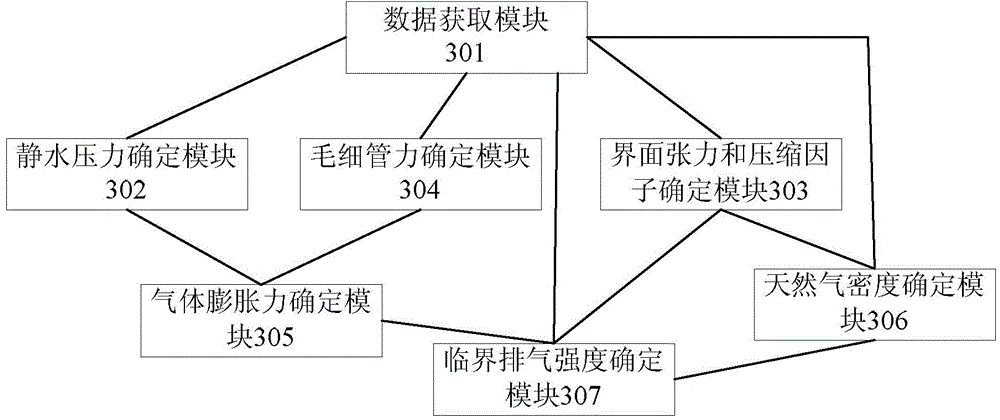
Method and device used for determining critical exhaust strength of tight sandstone gas reservoir exhaust source rocks
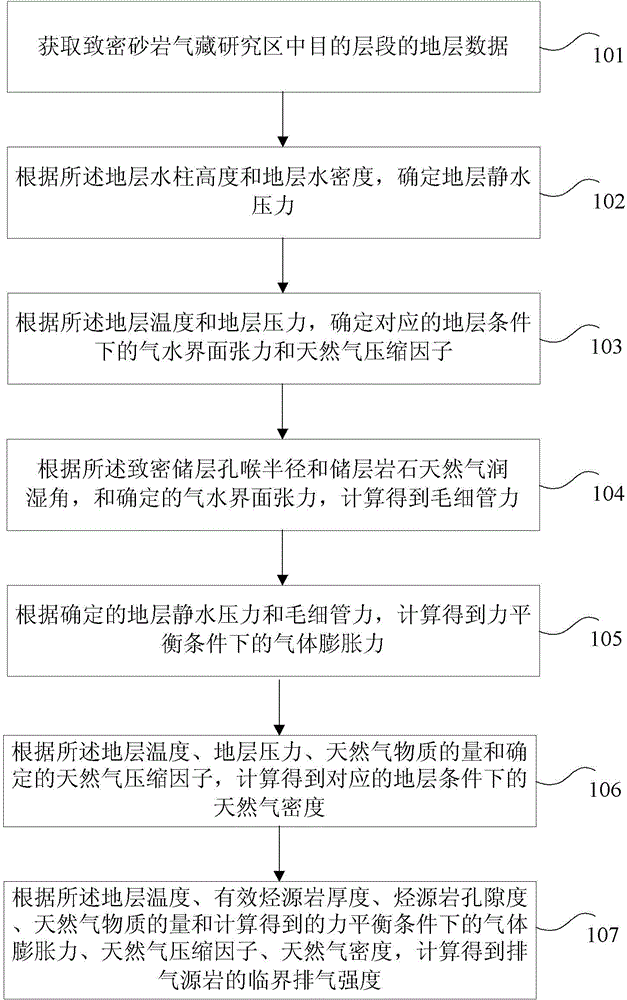
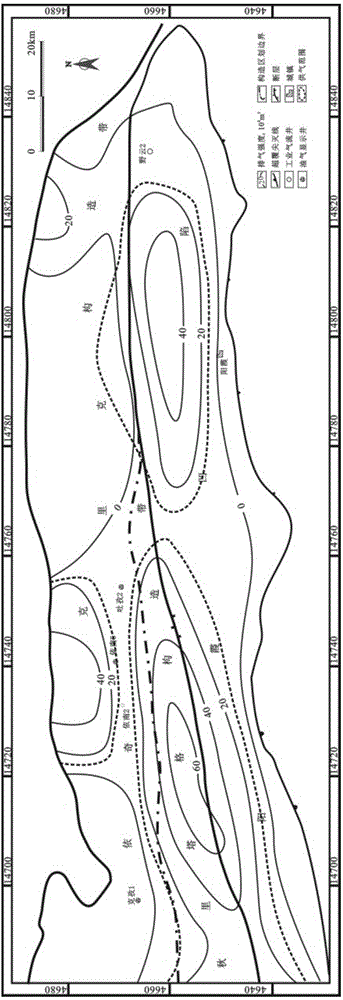
InactiveCN104483715AImprove exploration efficiencyReduce exploration riskGeological measurementsPorosityHydrostatic pressure
The invention provides a method and a device used for determining critical exhaust strength of tight sandstone gas reservoir exhaust source rocks. The method comprises steps that, stratum data of a target interval of a tight sandstone gas reservoir research zone is acquired, stratum hydrostatic pressure, gas water interface tension force under the stratum condition, natural gas compression factors and capillary force are determined according to the acquired stratum data, gas bulging force under the force balance condition is calculated, and the critical exhaust strength is calculated according to the stratum temperature, effective hydrocarbon source rock thickness, hydrocarbon source rock porosity and natural gas substance amount of the acquired stratum data, and the natural gas compression factors and natural gas density acquired through calculation. The method solves a technical problem of difficulty in quantitatively predicting the critical exhaust strength of the tight sandstone gas reservoir exhaust source rocks in an oil gas basin in the prior art, improves exploration efficiency of tight sandstone gas and reduces risks in exploring tight sandstone gas reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method for preparing monocrystalline CaTiO3 dendrite
ActiveCN102242400AControl dendrite morphologySimple process routePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsDistilled waterTitanium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a monocrystalline CaTiO3 dendrite by using a hydrothermal method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly dissolving a titanium compound in an ethanol solvent to obtain an A solution; then mixing calcium chloride dihydrate, distilled water and an ethanol solvent to obtain a B solution; and slowly and dropwisely adding the A solution into the B solution, adjusting the pH value to 10-11, stirring and mixing, placing the mixture in a hydrothermal kettle, and keeping the temperature at 180-260 DEG C for 1-36 hours to obtain the CaTiO3 dendrite. Through the method, the pure CaTiO3 dendrite is prepared by a one-step hydrothermal method by using inexpensive butyl titanate and calcium chloride dihydrate as the raw materials and water-ethanol as the solvent under low-temperature non-equilibrium conditions, the process route is simple, and the morphology of the CaTiO3 dendrite can be conveniently controlled by adjusting the process parameters.
Generation of electric oscillations by continuous, supercooled superconductors under a voltage
InactiveUS20060097809A1Increase output powerLess brittleOscillations generatorsSmall amplitudeSuperconductor classification
The essence of the invention is the use of supercooled superconductors for generation of high-frequency electric oscillations. The superconductor is supercooled, i.e. in the normal phase at a temperature lower than the critical transition temperature for superconductivity, under an applied electric energy source. In such non equilibrium conditions the superconductor can have negative differential conductivity which can be used as an active medium in generators of electric ( current and voltage) oscillations. Such generators can be used in the superconducing electronics. Oscillation can be modulated by the change of bias voltage, electrostatic doping by a gate electrode, or by light. When small amplitude oscillations are stabilized near to the critical temperature the generator can be used as a bolometer. The supercooled superconductors can be used also as transistors and frequency mixers. The negative differential conductivity of superconductor is created by the excess conductivity of fluctuation Cooper pairs. This behavior is predicted by the solution of the Boltzmann kinetic equation of the metastable in the normal phase Cooper pairs. Boltzmann equation for fluctuation Cooper pairs is derived as a state-of-the-art application of the microscopic theory of superconductivity.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
Metal material and metal material surface in-situ dissolution modification method
InactiveCN110230019AEasy to operateWide range of usesMolten spray coatingTransportation and packagingMetal catalystRoom temperature
The invention discloses a metal material surface in-situ dissolution modification method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, substrate metal is fully mixed with modified metal powder toobtain raw material powder; 2, the raw material powder obtained in step 1 is prepared into a metal material by a preparation means under a non-equilibrium condition; and 3, the metal material preparedin step 2 is subjected to heat treatment so that the metal material can reach a balanced state, and after the metal material is cooled to room temperature, a doped phase is dissolved out of the surface of the metal material to obtain the modified metal material. The modification method is simple to operate, only a small amount of modified metal needs to be doped and mixed for preparation as raw materials, then heat treatment is used later, and therefore a modified metal catalyst can be obtained The method is wide in application range and high in application value.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF NEW MATERIALS
Pile net for landslide or rockfall disaster protection and design method thereof
InactiveCN107988925APortable and reasonable structureEasy to buildGeometric CADProtective constructionSoil massSoil arching
The invention discloses a pile net for landslide or rockfall disaster protection and a design method thereof. The pile net for landslide or rockfall disaster protection includes at least two anti-slide piles arranged adjacent to a rock and soil mass and deepened in a stable rock stratum under a sliding surface. Flexible protective nets whose two sides are fixed on the anti-slide piles through a plurality of pull rings are arranged between the two adjacent anti-slide piles. The design method of the pile net includes an arch axis equation corresponding to an arch when forming a soil arching effect of the rock and soil mass; according to the static balance of the soil arch, the axial pressure on the arch axis is calculated; when the axial pressure has the maximum value, a failure surface of the soil arch can be obtained according to an arch distance corresponding to the maximum axial pressure; when the pile is in a static equilibrium condition, the angle between the failure plane and a horizontal plane is calculated; based on the principle that a trapezoidal compression zone at the failure surface is not destroyed and the Kulun strength theorem, the pile distance of the two adjacent anti-slide piles is calculated; according to the collapse amount of empty soil between the piles, the strength of the flexible protective nets is calculated.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Apparatus and method for high efficiency operation of a high temperature fuel cell system
ActiveUS20050196652A1High atomic oxygen/carbonReduce the temperatureAuxillary drivesFuel cell heat exchangeHydrocotyle bowlesioidesOxygen
Apparatus and method for operating a fuel cell system including a hydrocarbon catalytic reformer and close-coupled fuel cell stack by recycling anode syngas into the reformer in a range between 60% and 95% of the total syngas. At equilibrium conditions, oxygen required for reforming of hydrocarbon fuel is derived from endothermically reformed water and carbon dioxide in the syngas. Reforming temperature is between about 650° C. to 750° C. The stack exit temperature is about 800° C. to 880° C. such that the required endotherm can be provided by the sensible heat of the recycled syngas. The stack has approximately equal anode and cathode gas flows in opposite directions, resulting in cooling from both the anodes and cathodes.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com