Patents
Literature
102 results about "Normal gait" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
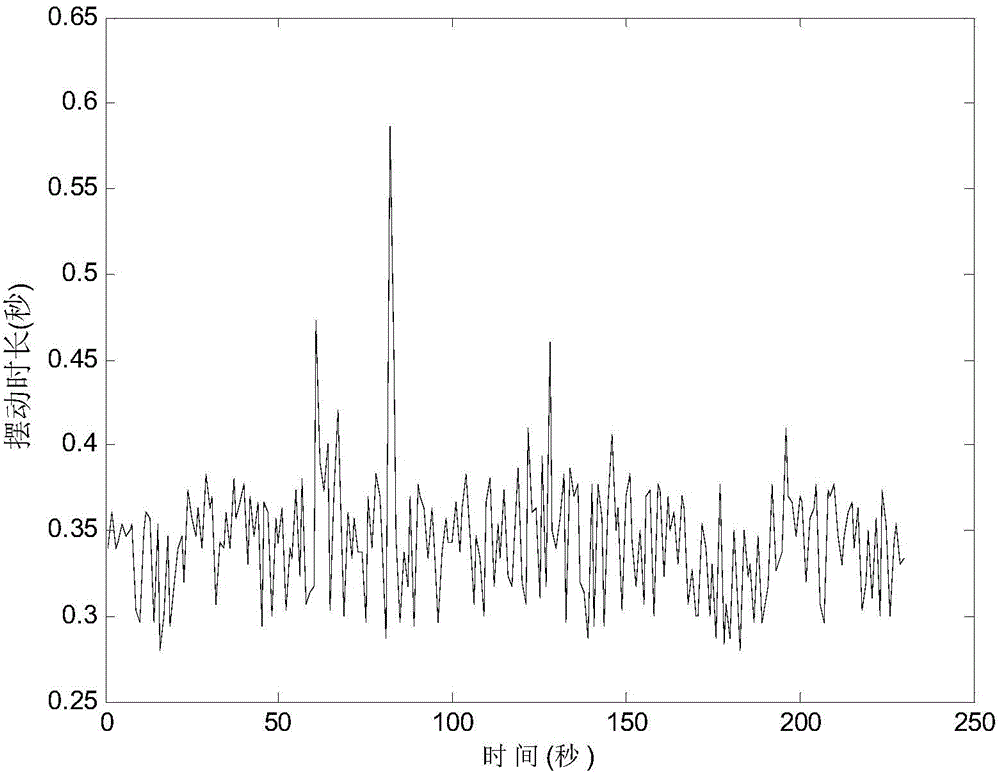
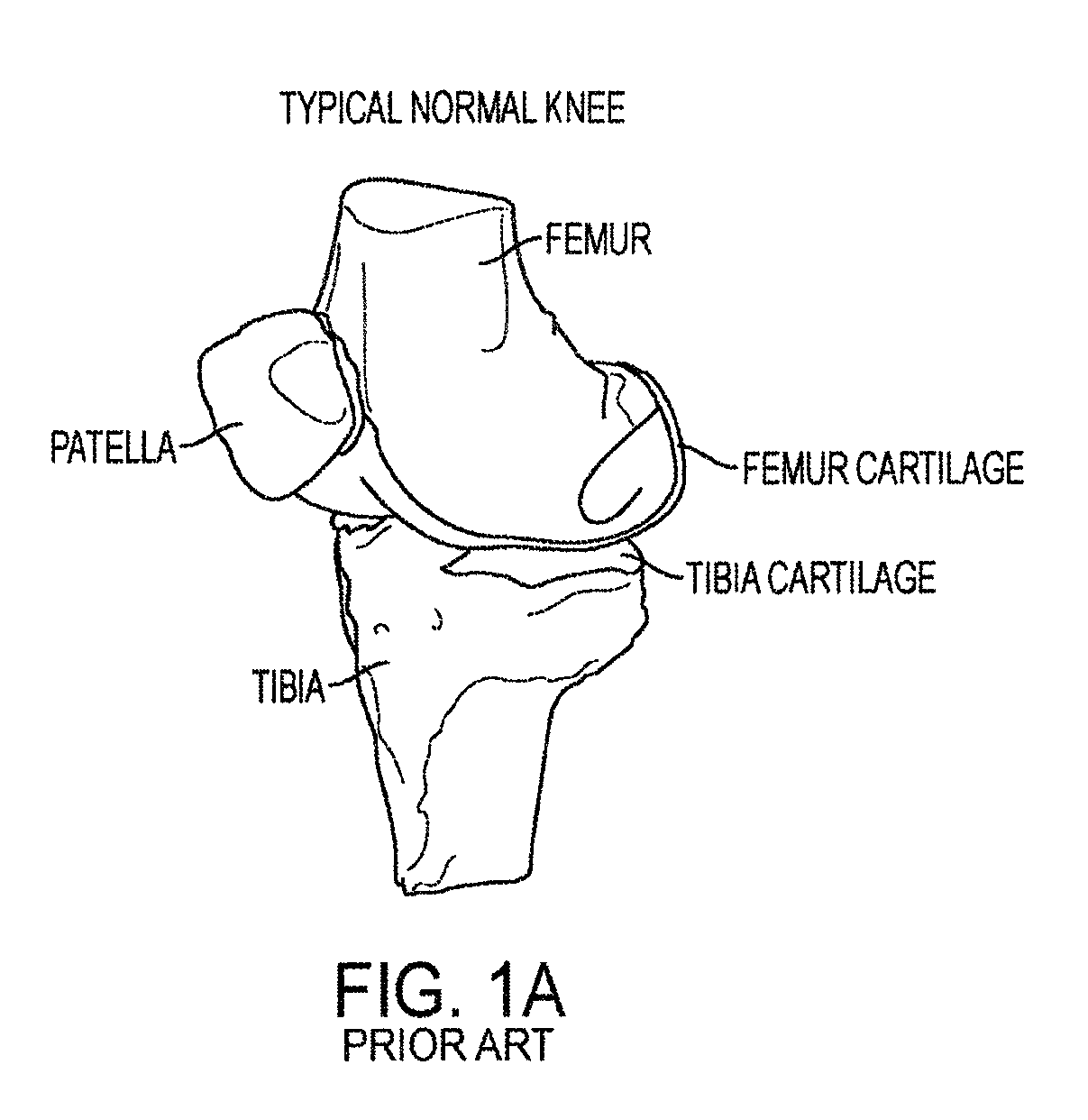
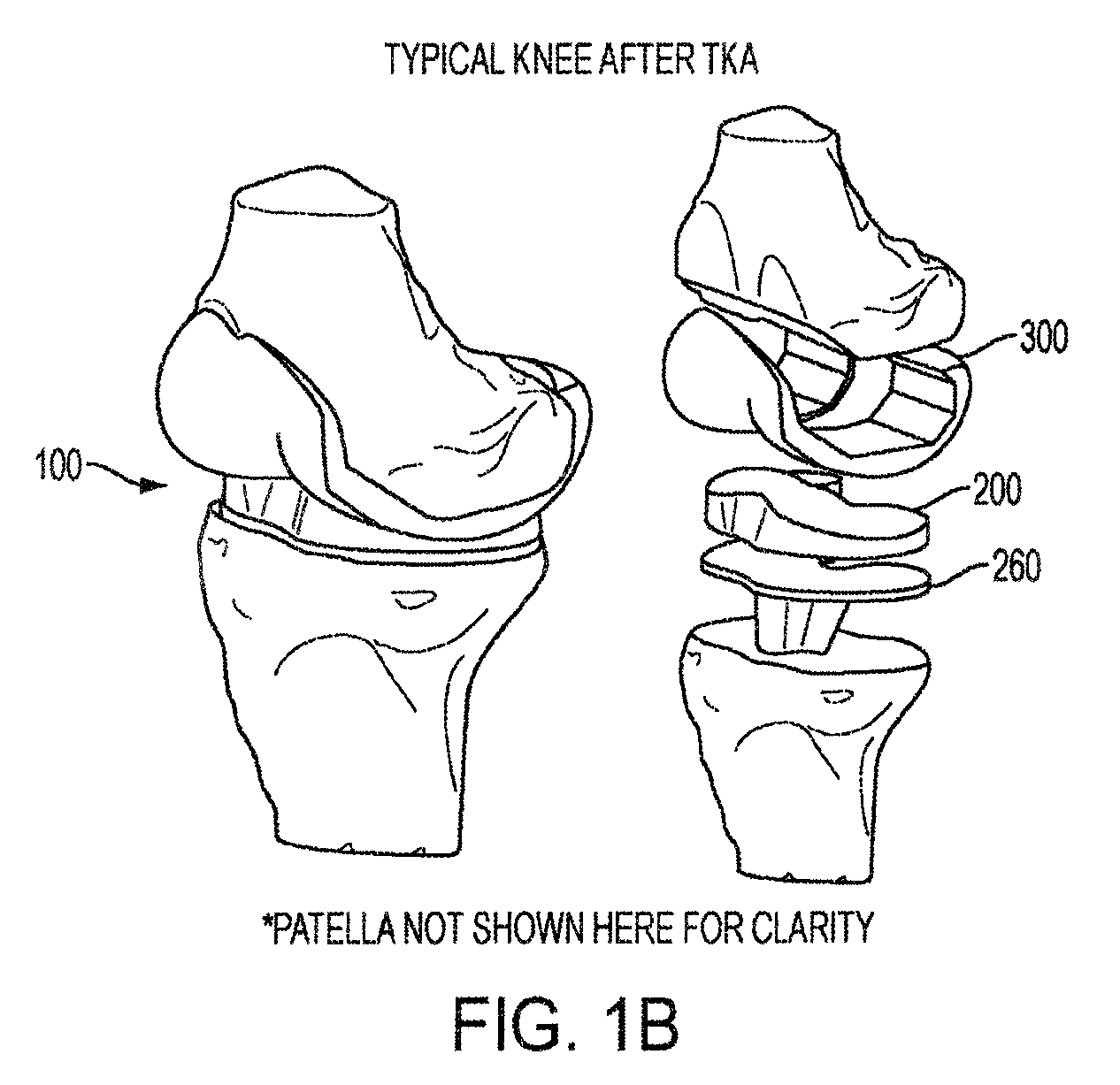
The stance phase of a normal gait comprises about 60% of the entire walking cycle, and less for a running cycle. It progresses from the moment a heel touches the ground to the moment the big toe leaves the ground. In a proper gait, the heel will strike the floor on the outside back — that is, the outer posterior — of the foot.
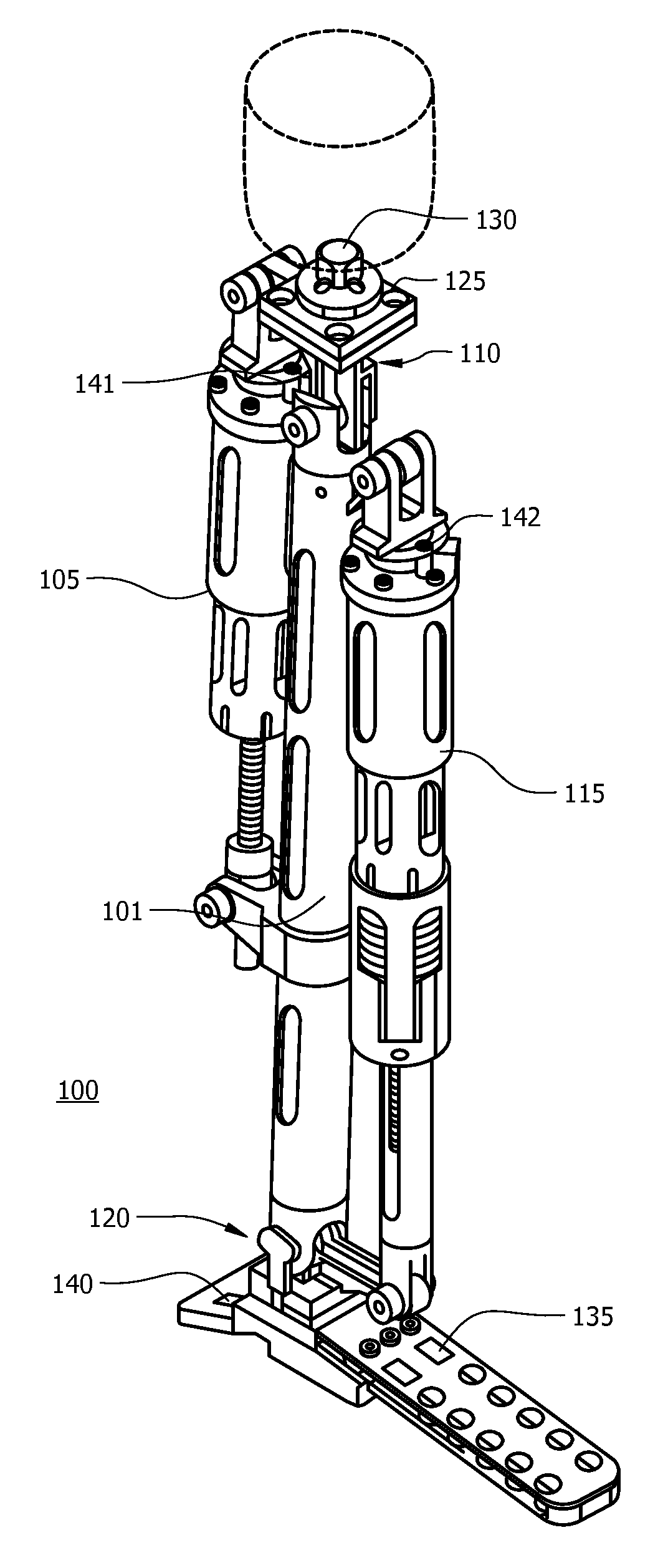
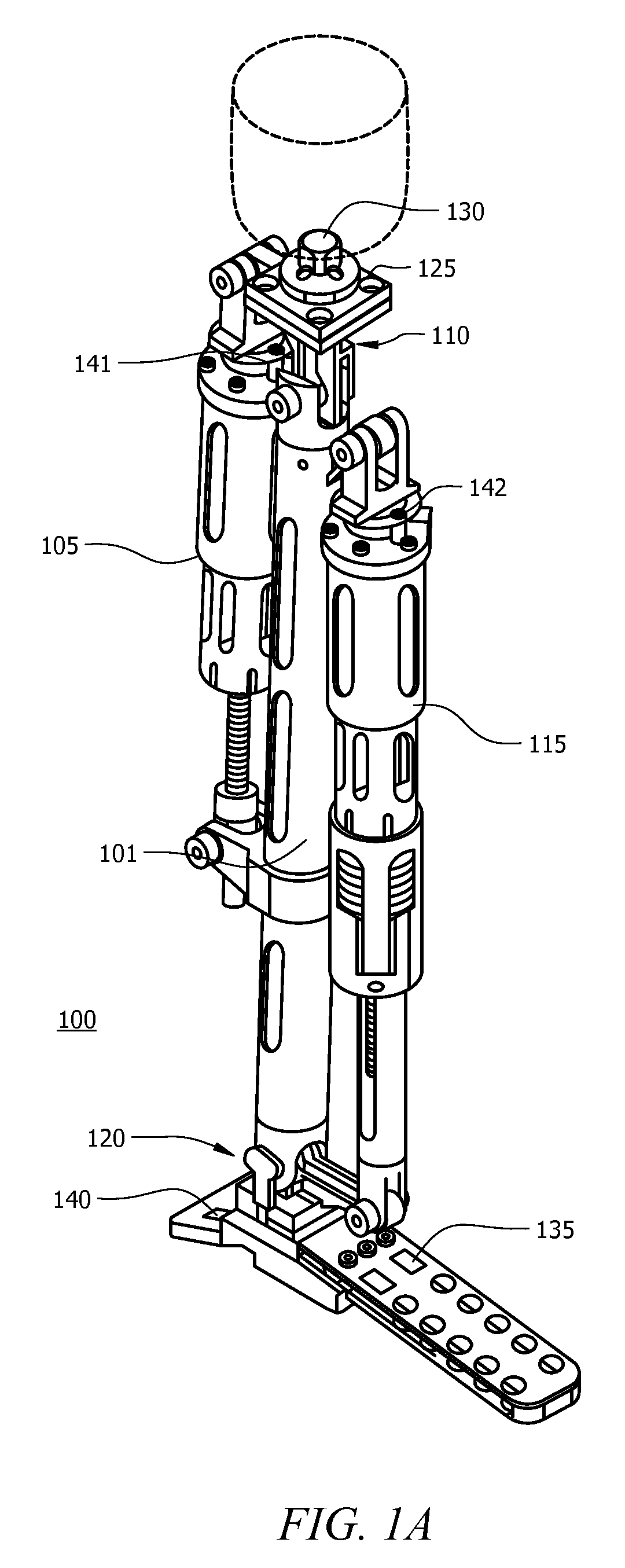
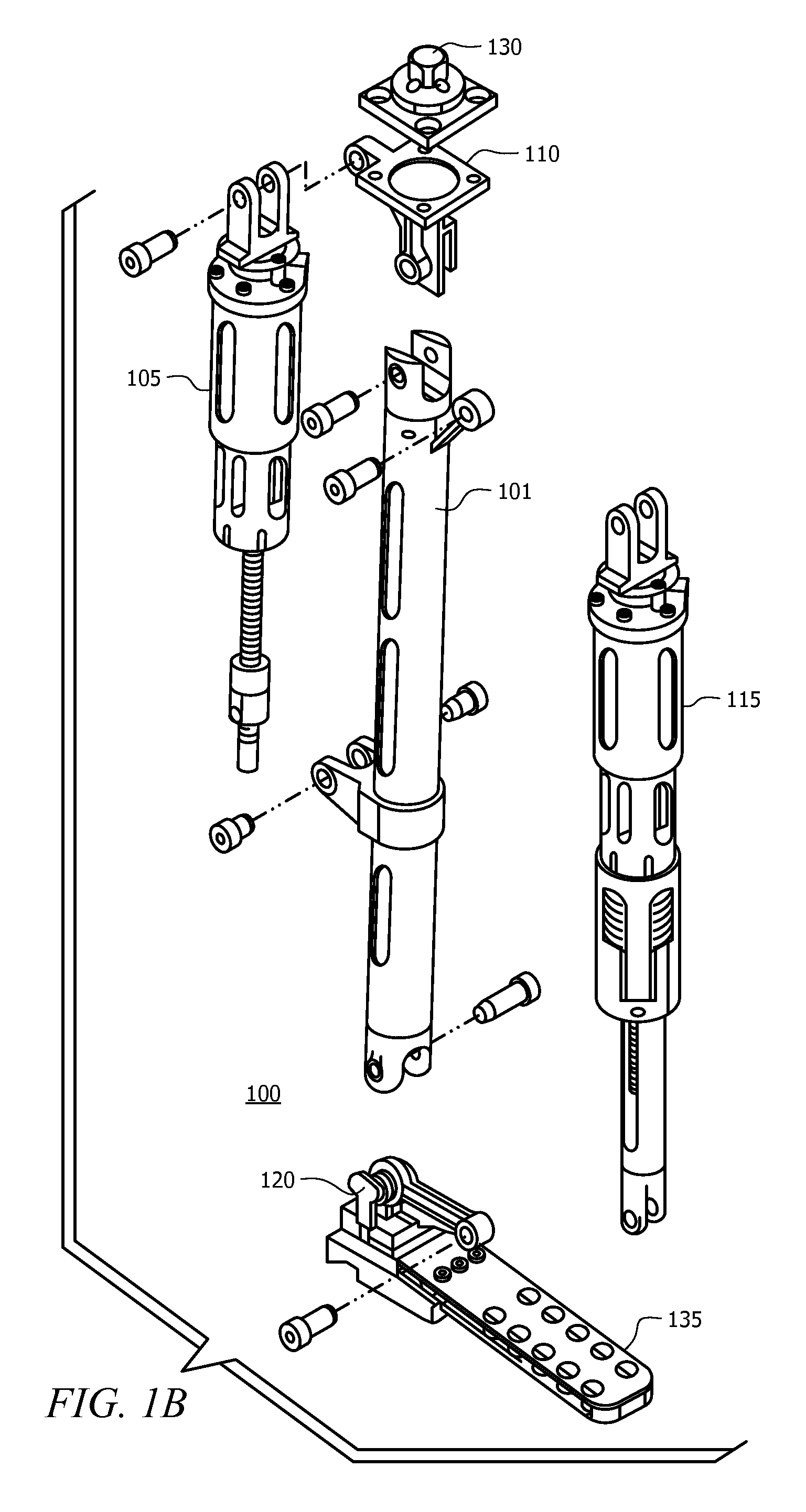
Powered leg prosthesis and control methodologies for obtaining near normal gait
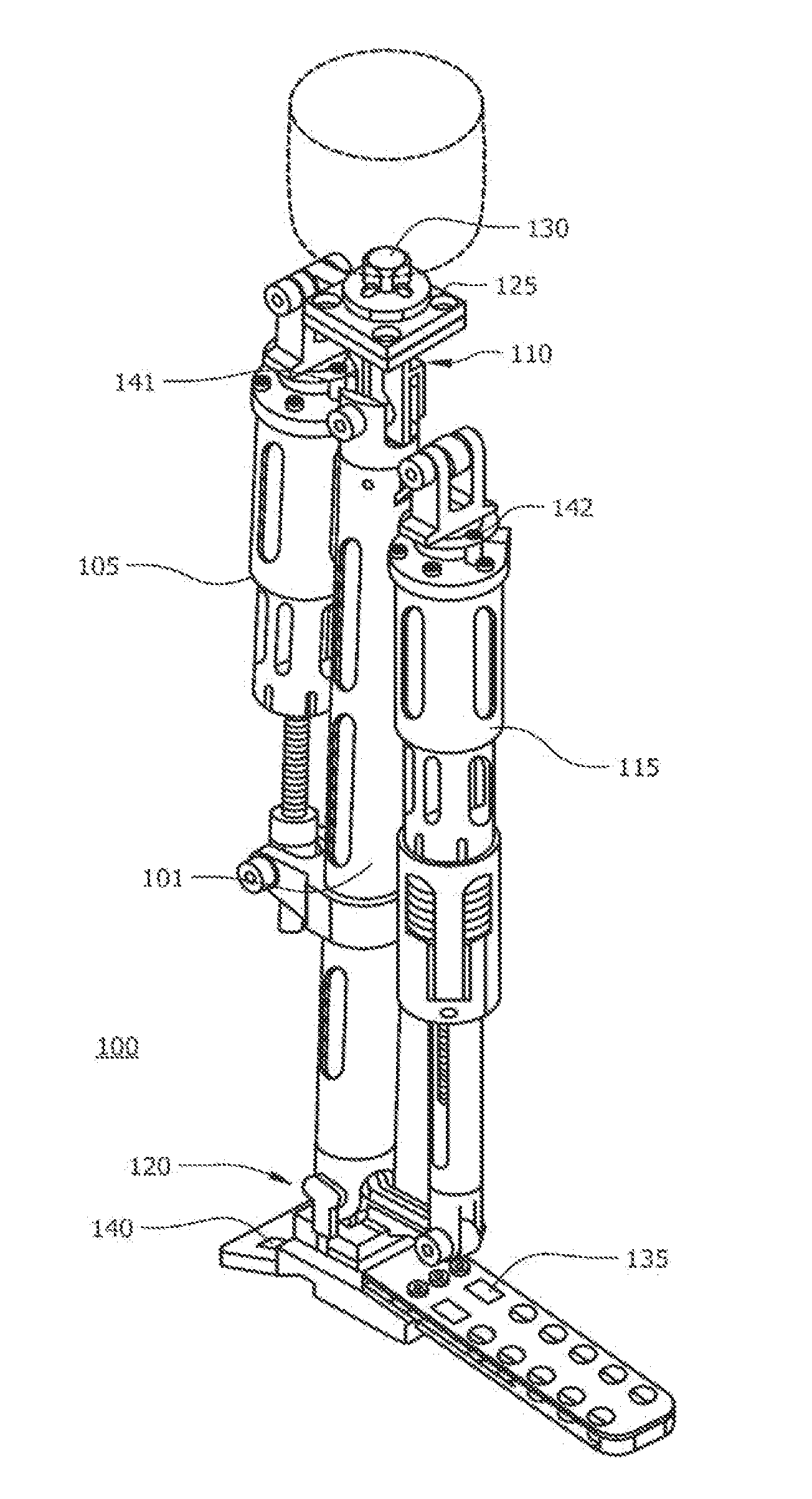
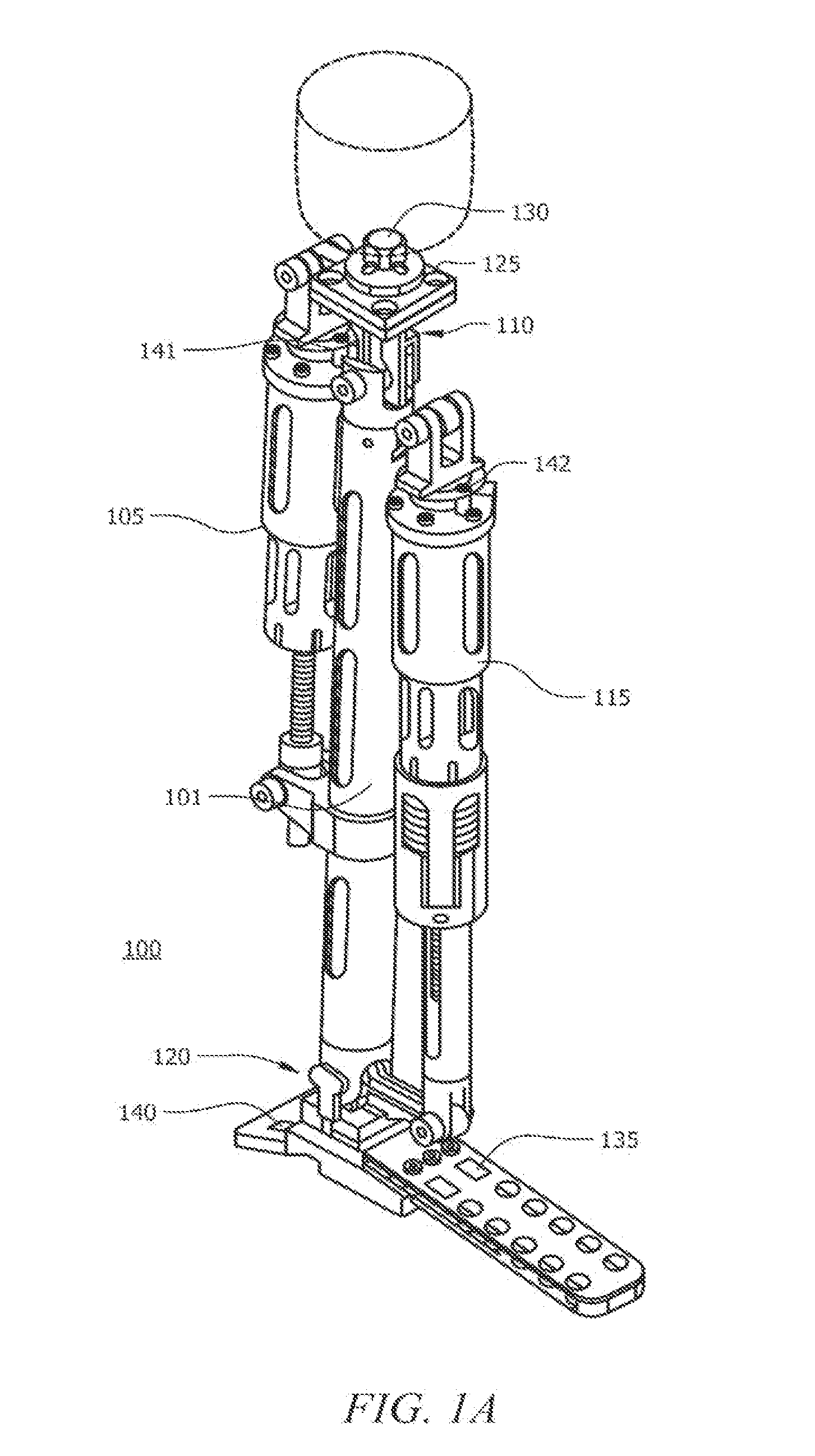
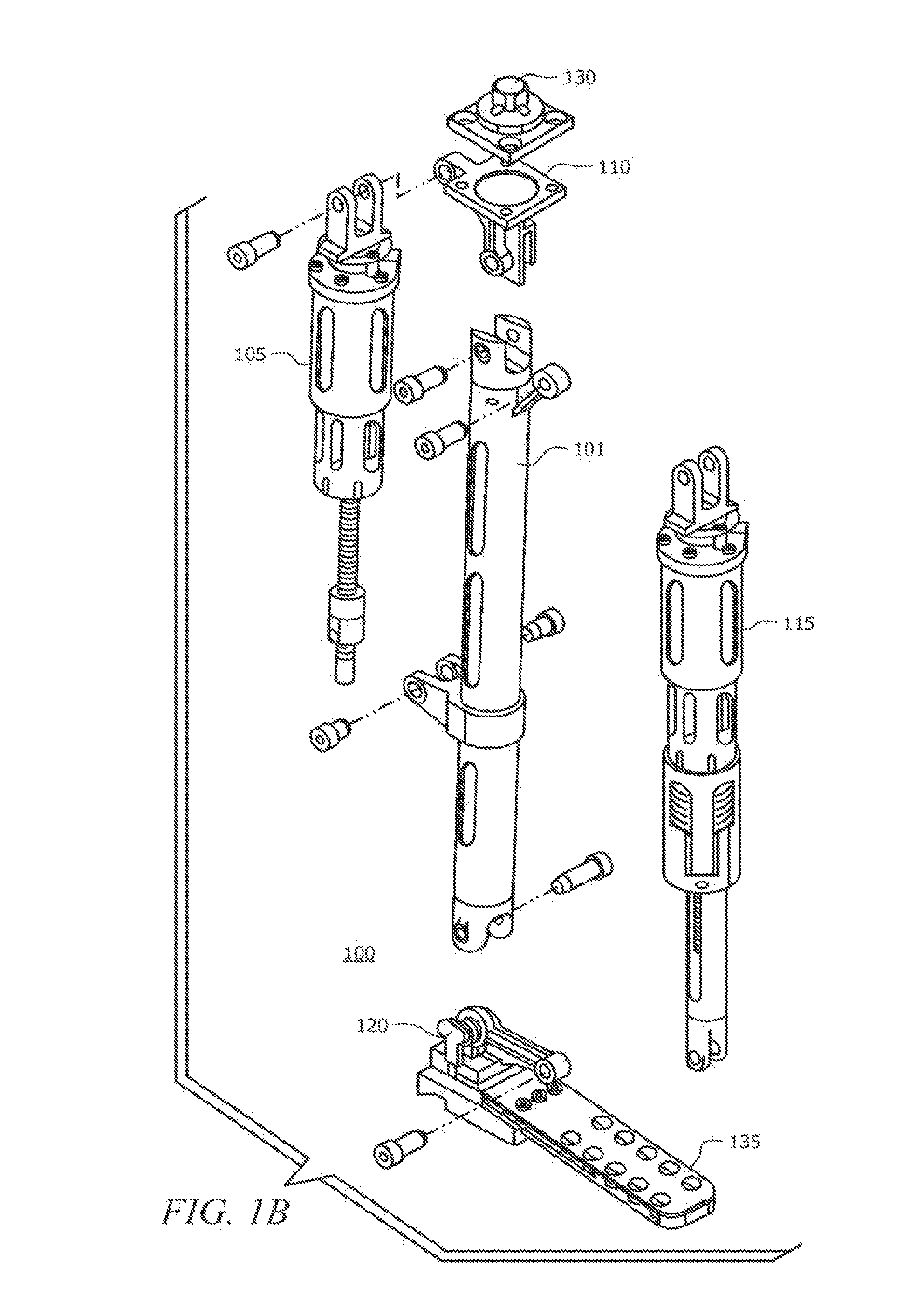
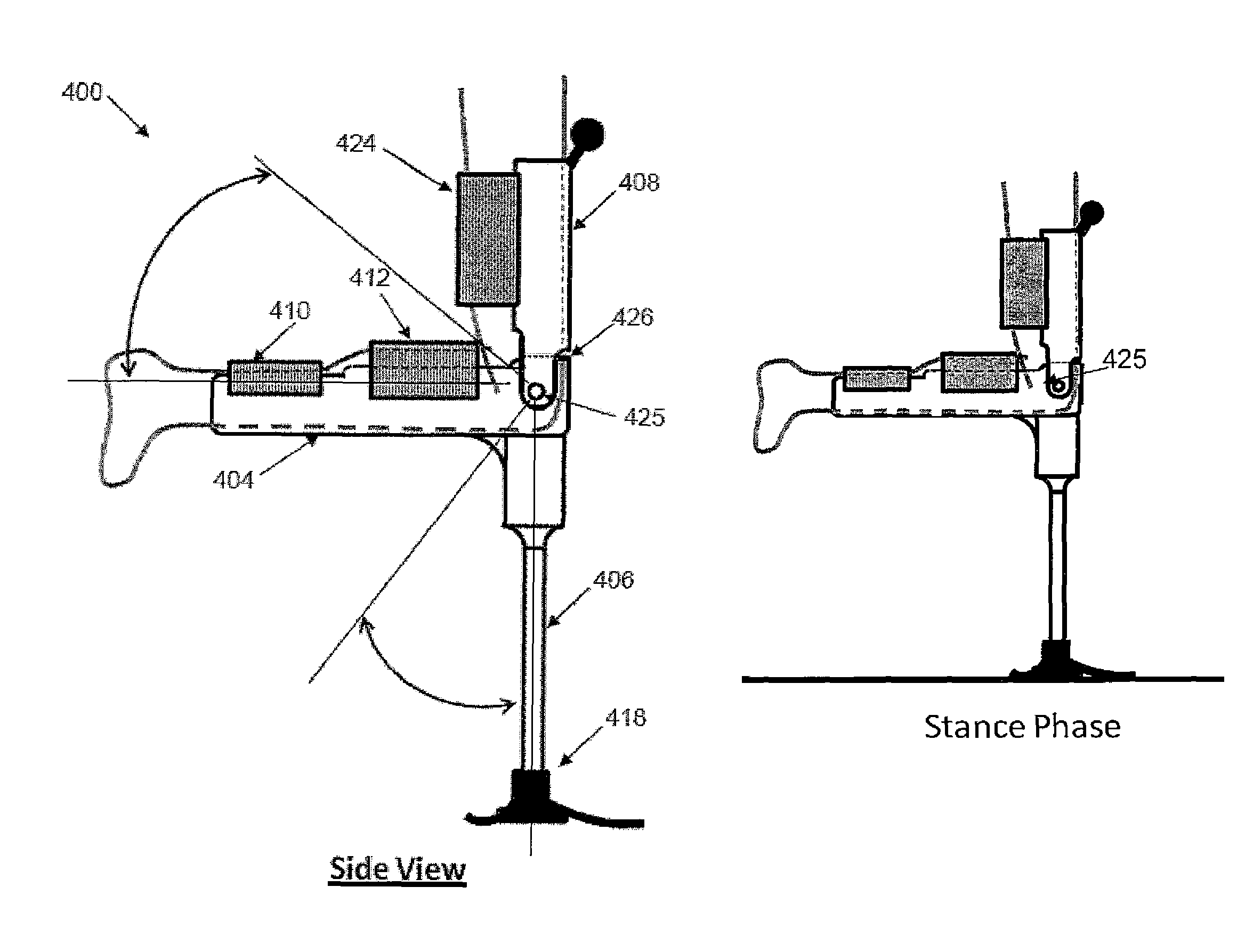
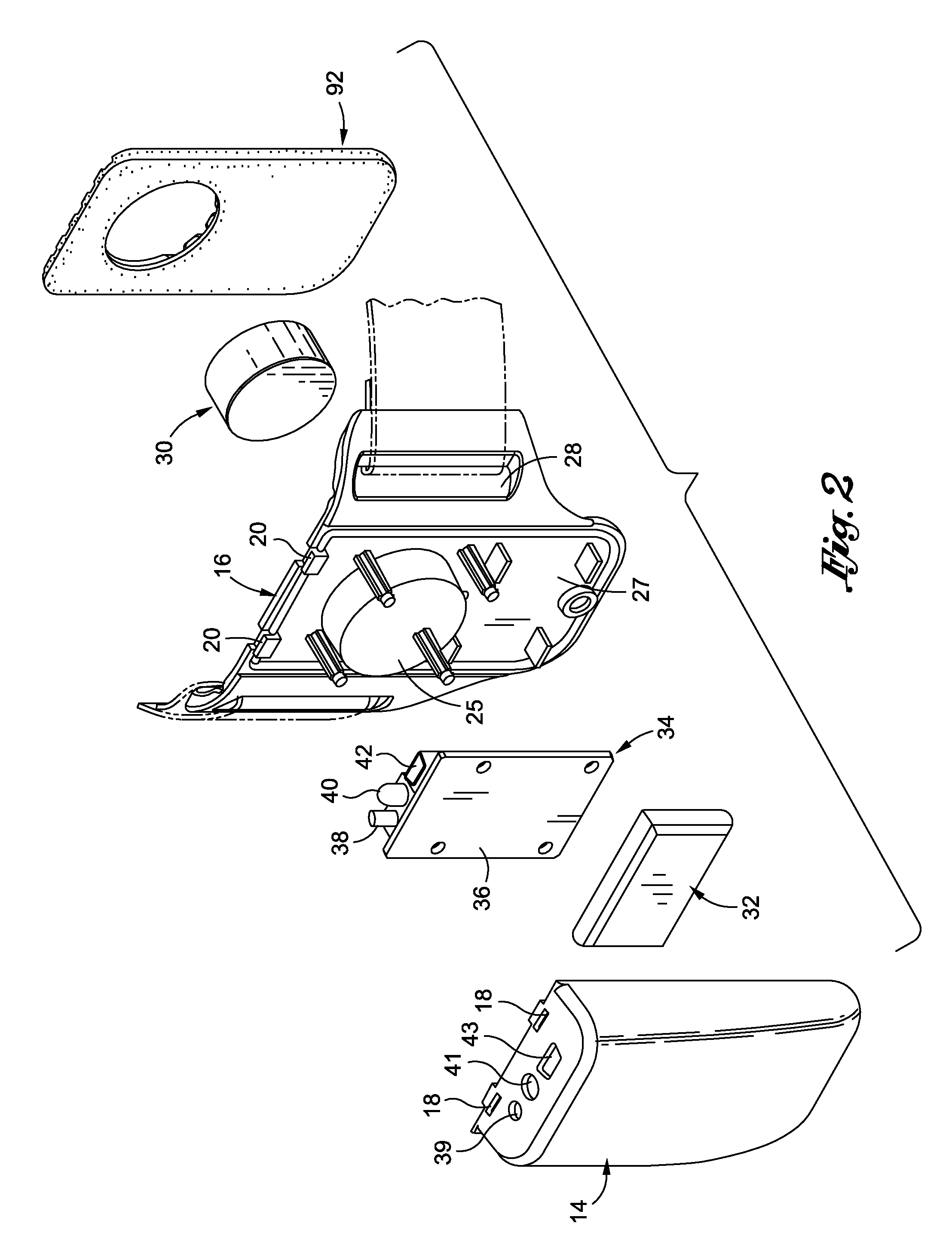
A powered leg prosthesis includes powered knee joint comprising a knee joint and a knee motor unit for delivering power to the knee joint. The prosthesis also includes a prosthetic lower leg having a socket interface coupled to the knee joint and a powered ankle joint coupled to the lower leg opposite the knee joint comprising an ankle joint and an ankle motor unit to deliver power to the ankle joint. The prosthesis further includes a prosthetic foot coupled to the ankle joint, at least one sensor for measuring a real-time input, and at least one controller for controlling movement of the prosthesis based on the real-time input.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
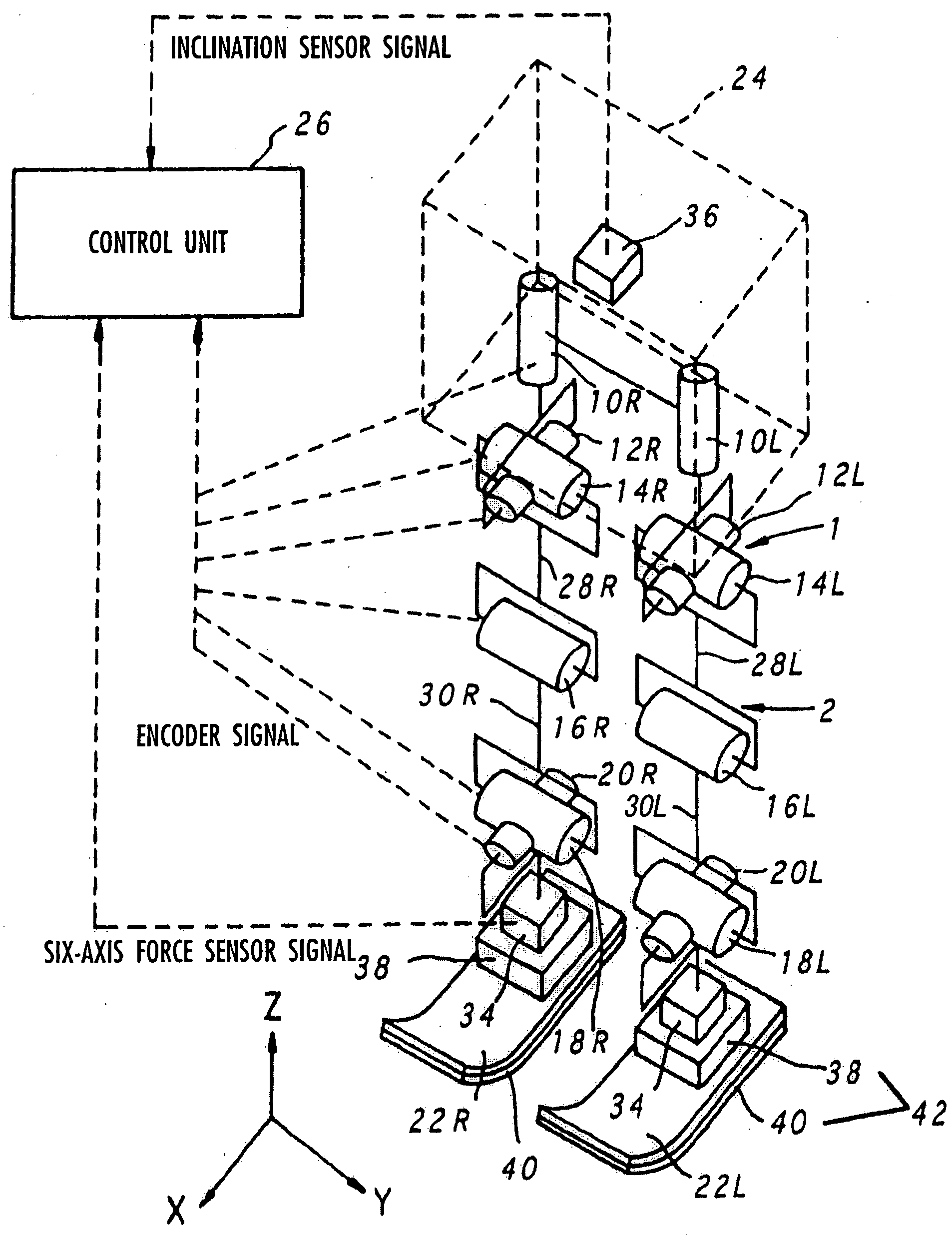
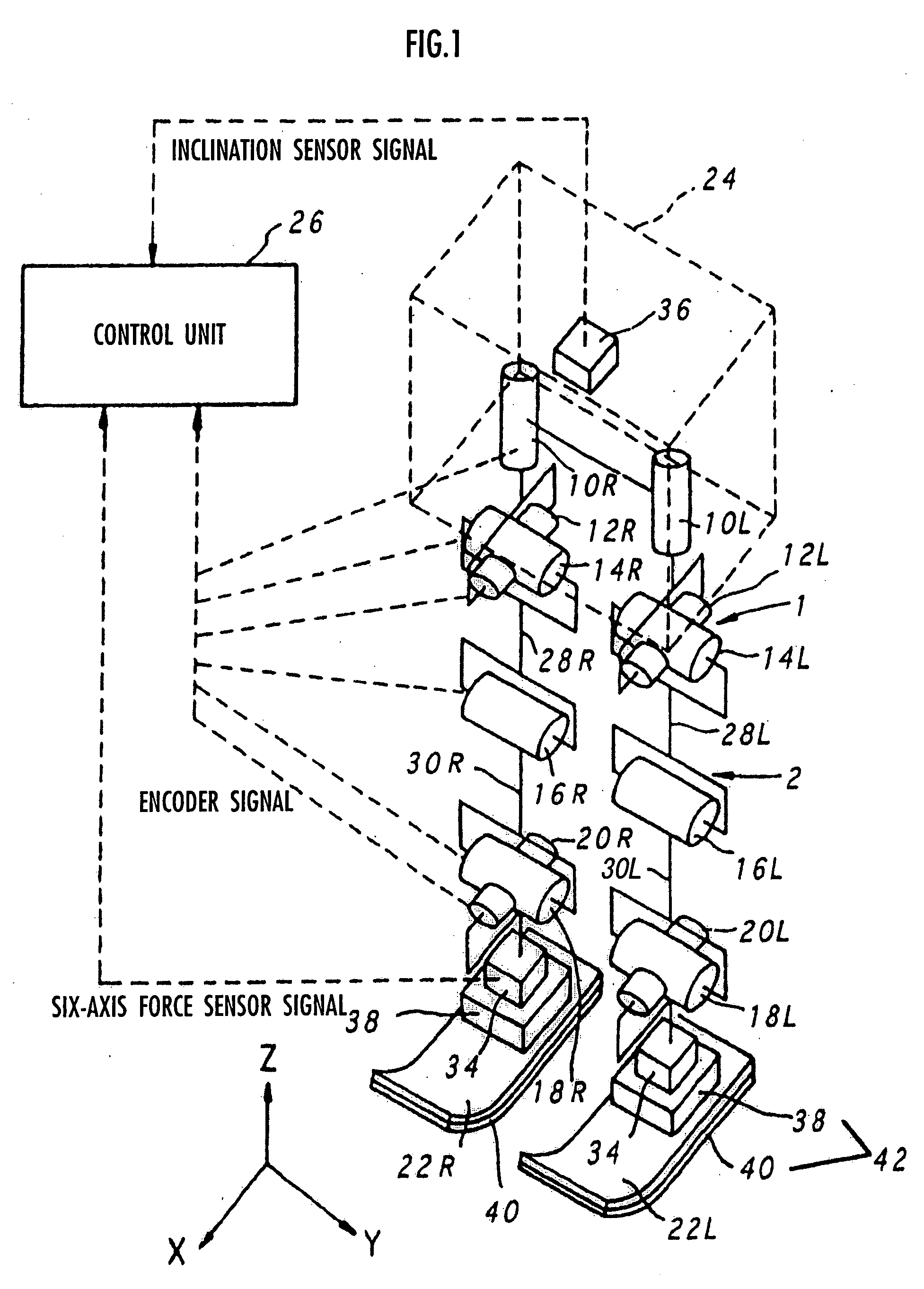
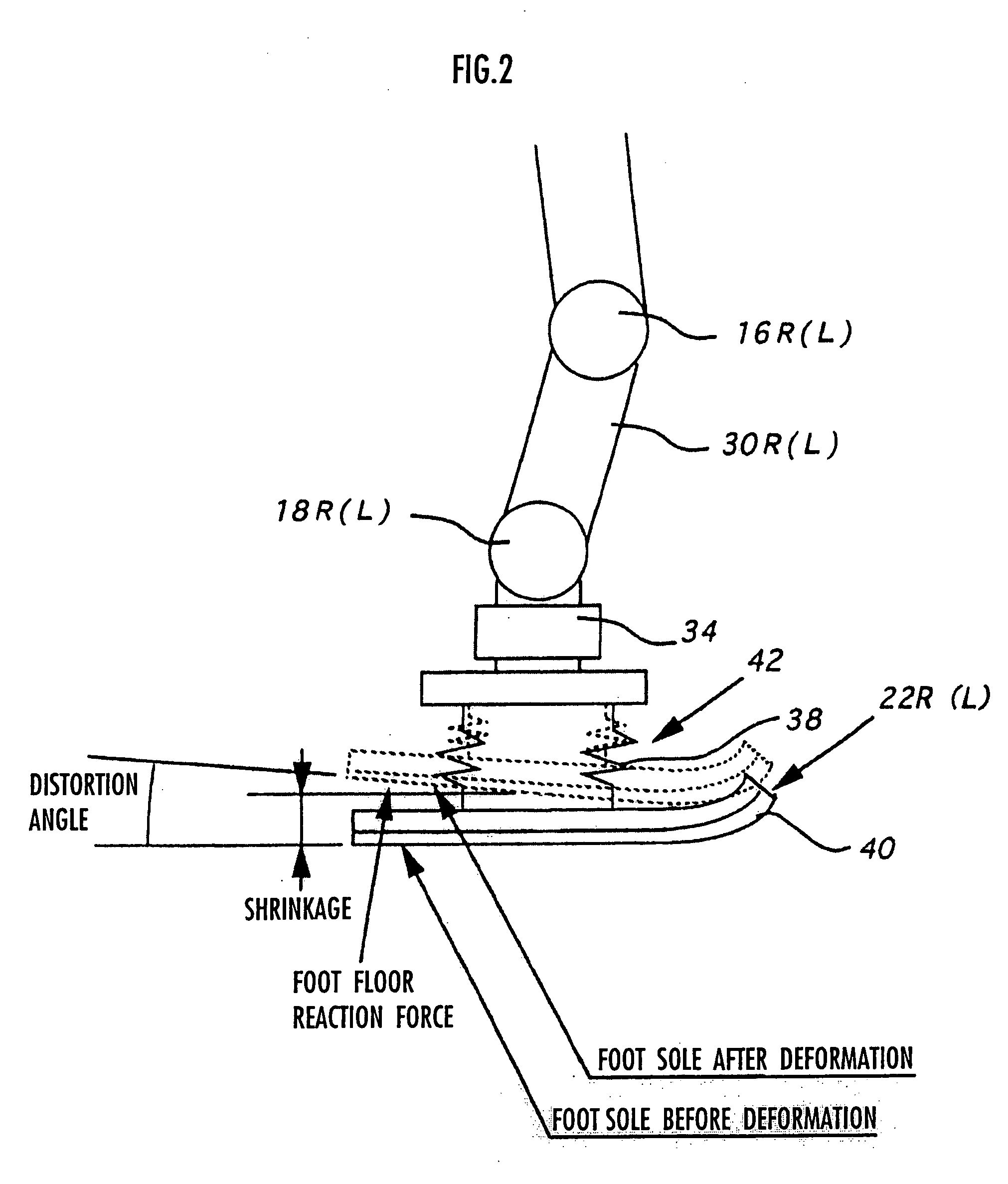
Gait producing device for leg type movable robot
ActiveUS20050021176A1Easy to optimizeMove continuously and stablyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringFriction force
An allowable range of a frictional force component, such as a horizontal component of a translation floor reaction force, applied to a legged mobile robot 1 is set, and a provisional movement with a current time gait of the robot 1 is determined so as to satisfy a condition concerning the allowable range and a dynamical equilibrium condition that a moment produced about a point of application of a provisional desired floor reaction force substantially agrees with a provisional desired floor reaction force moment. The provisional movement is determined by adjusting movements in two movement modes which are different in ratio between the translation floor reaction force and the floor reaction force moment. Based on the final state of the provisional movement, the current time gait is determined by correcting the provisional movement and at least one of the point of application of the provisional desired floor reaction force and the provisional desired floor reaction force moment in such a manner that the current time gait is connected to or brought close to a normal gait. The correction is performed when the frictional force component is unlikely to exceed the allowable range.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
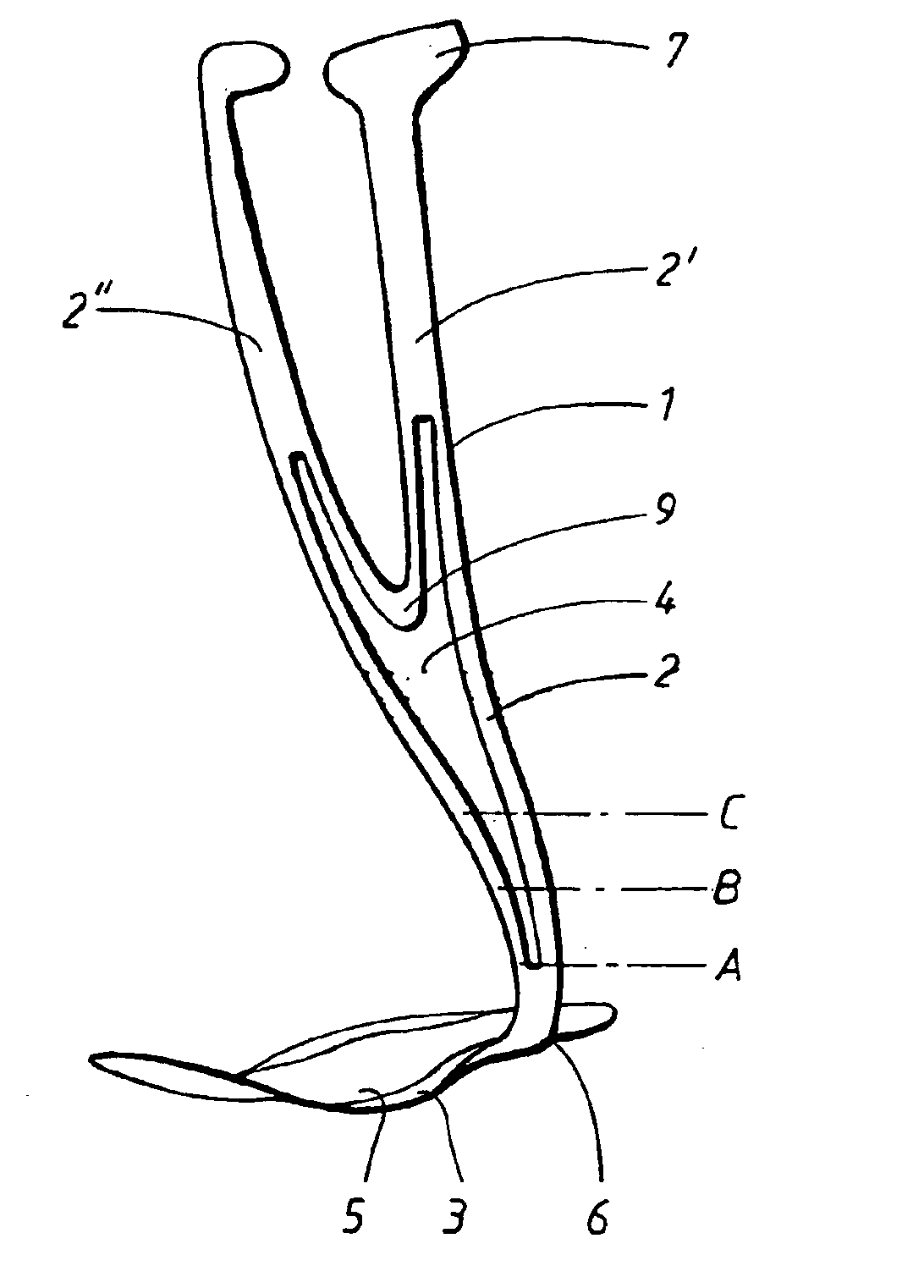
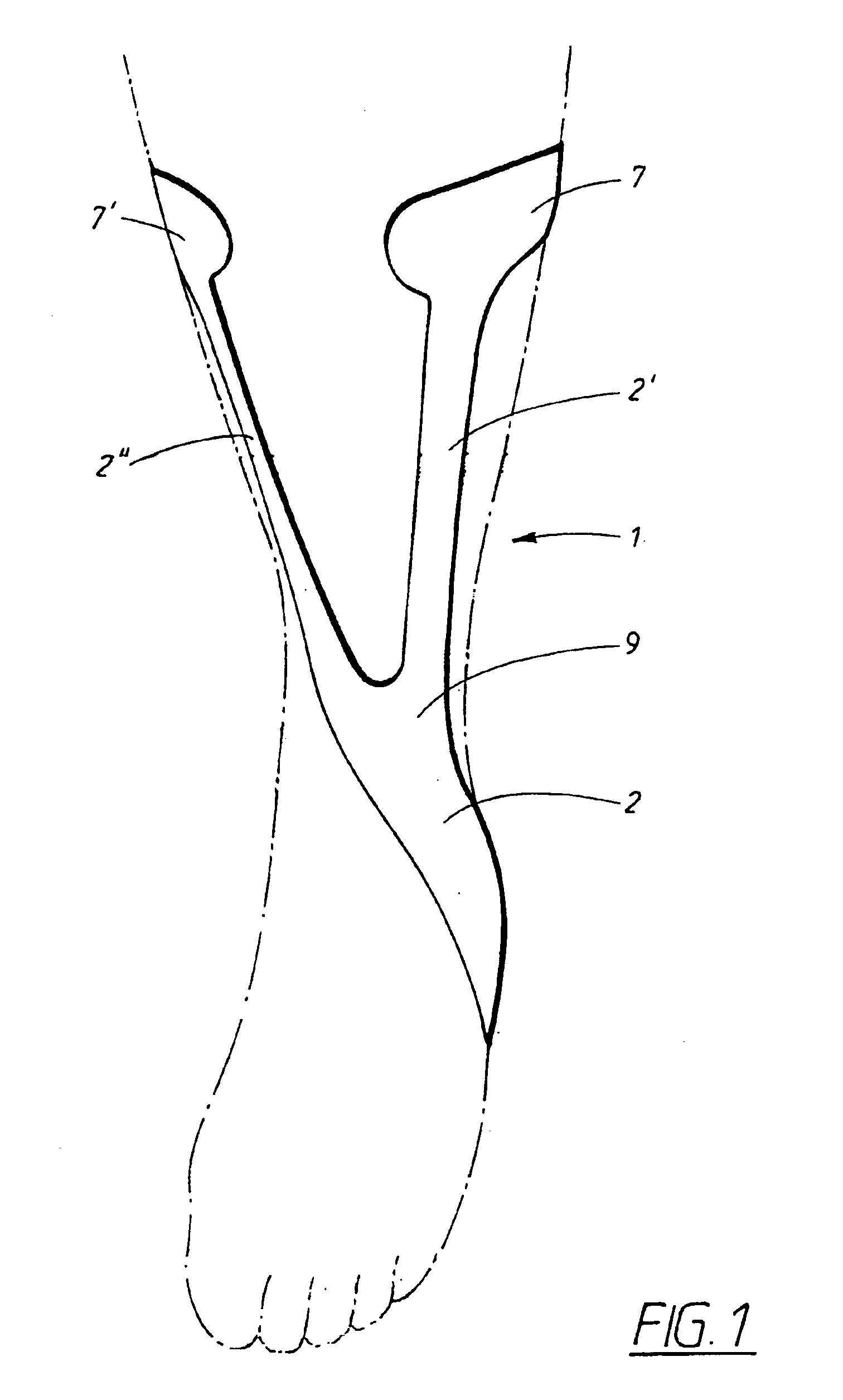
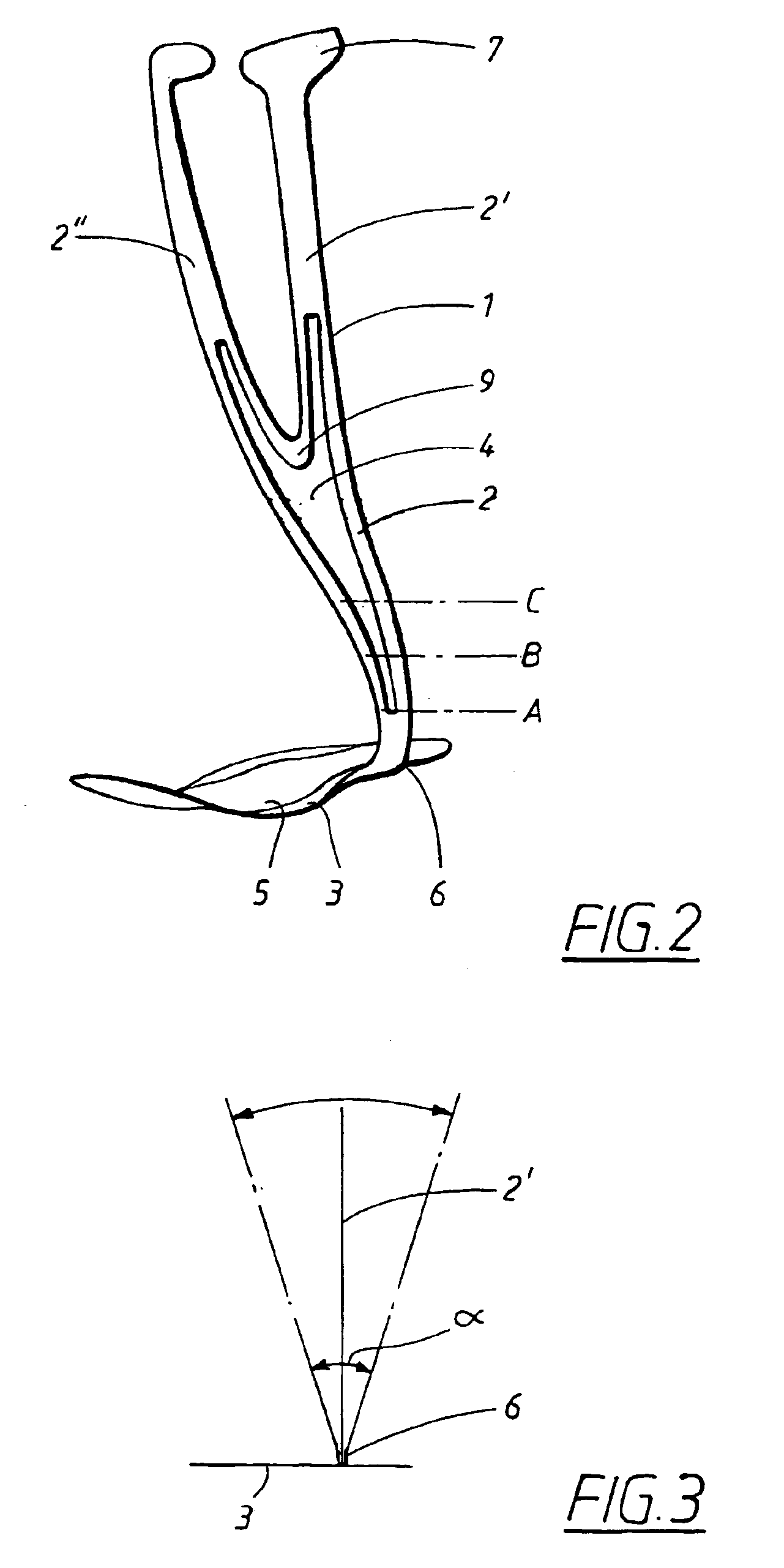
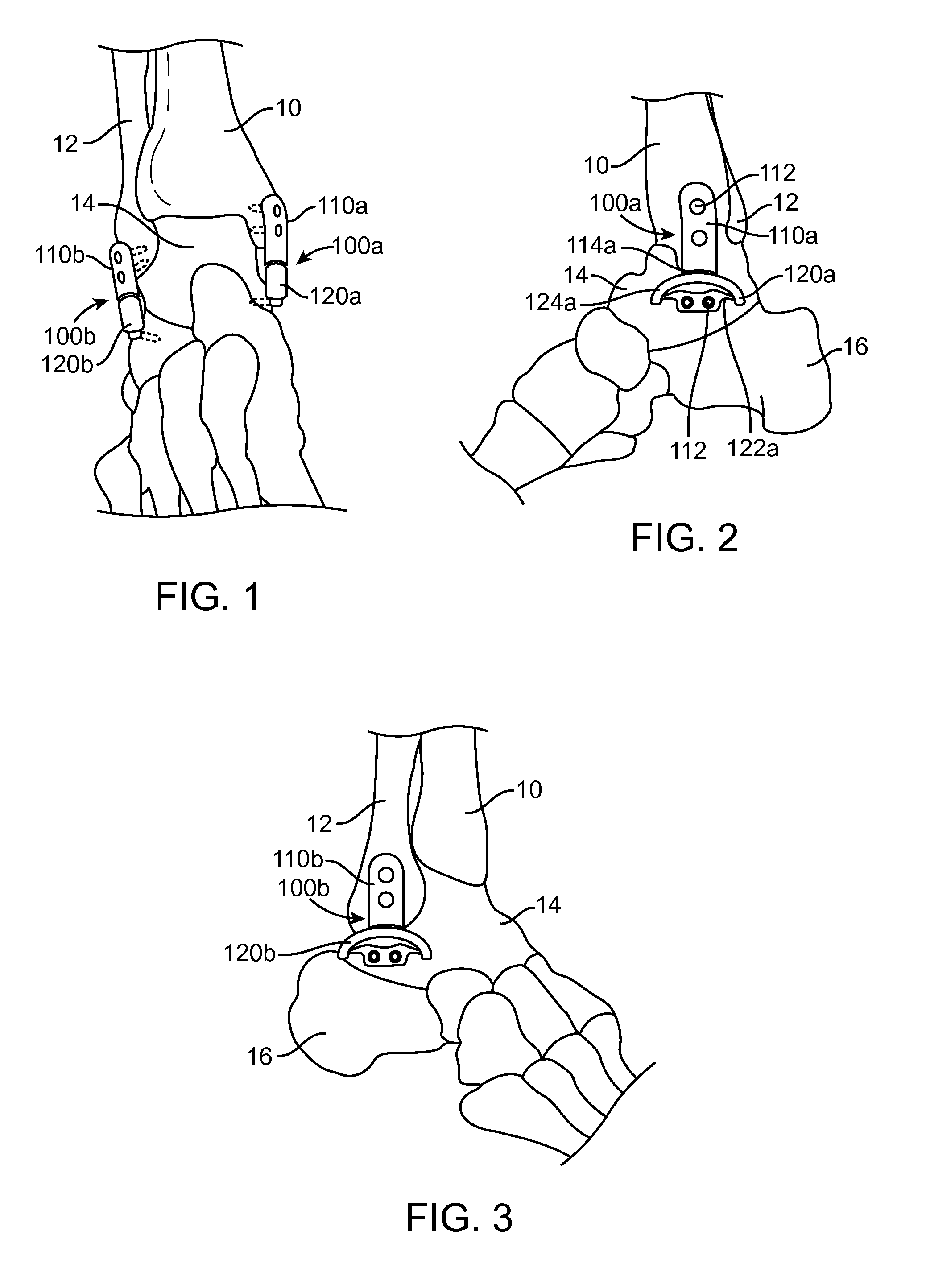
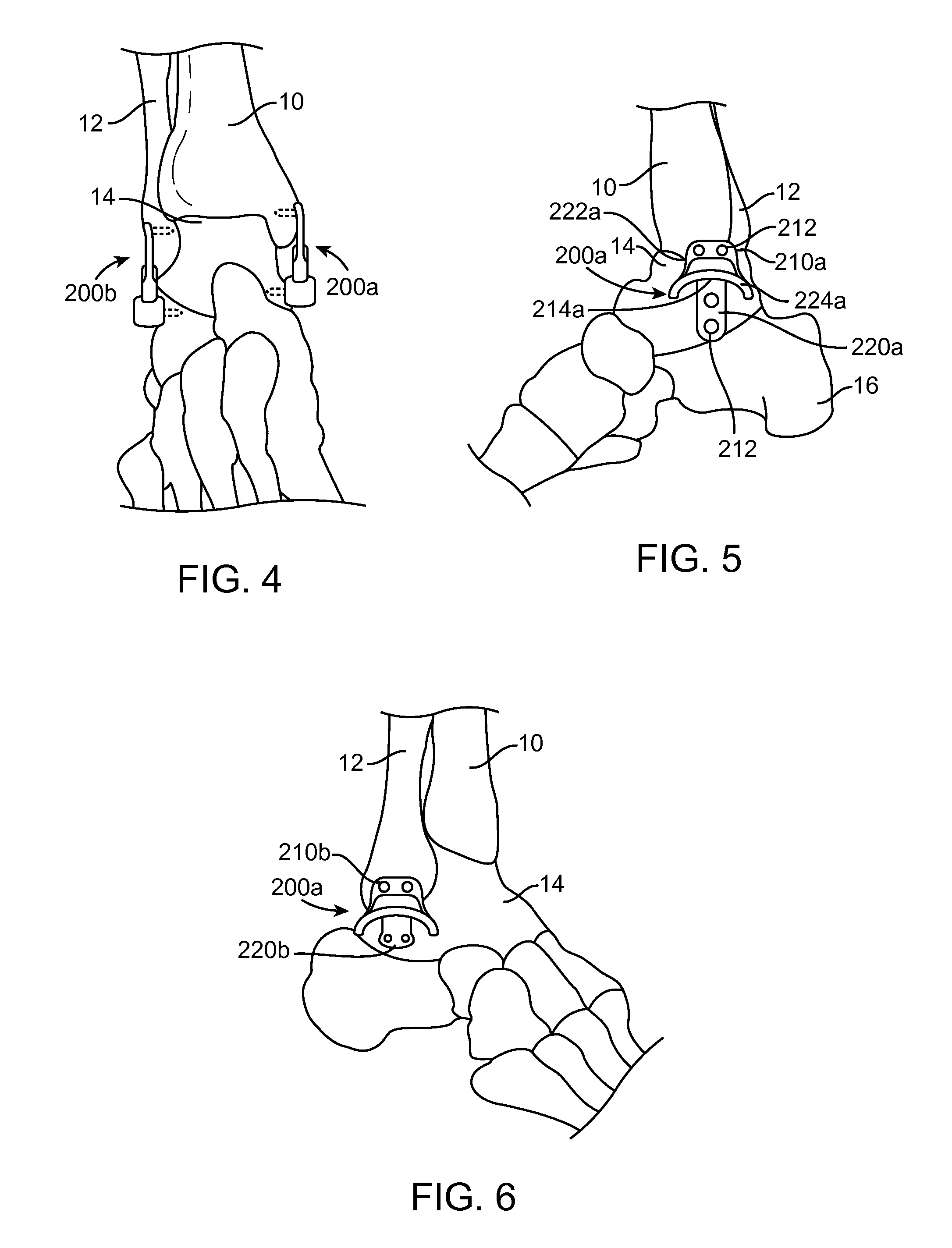
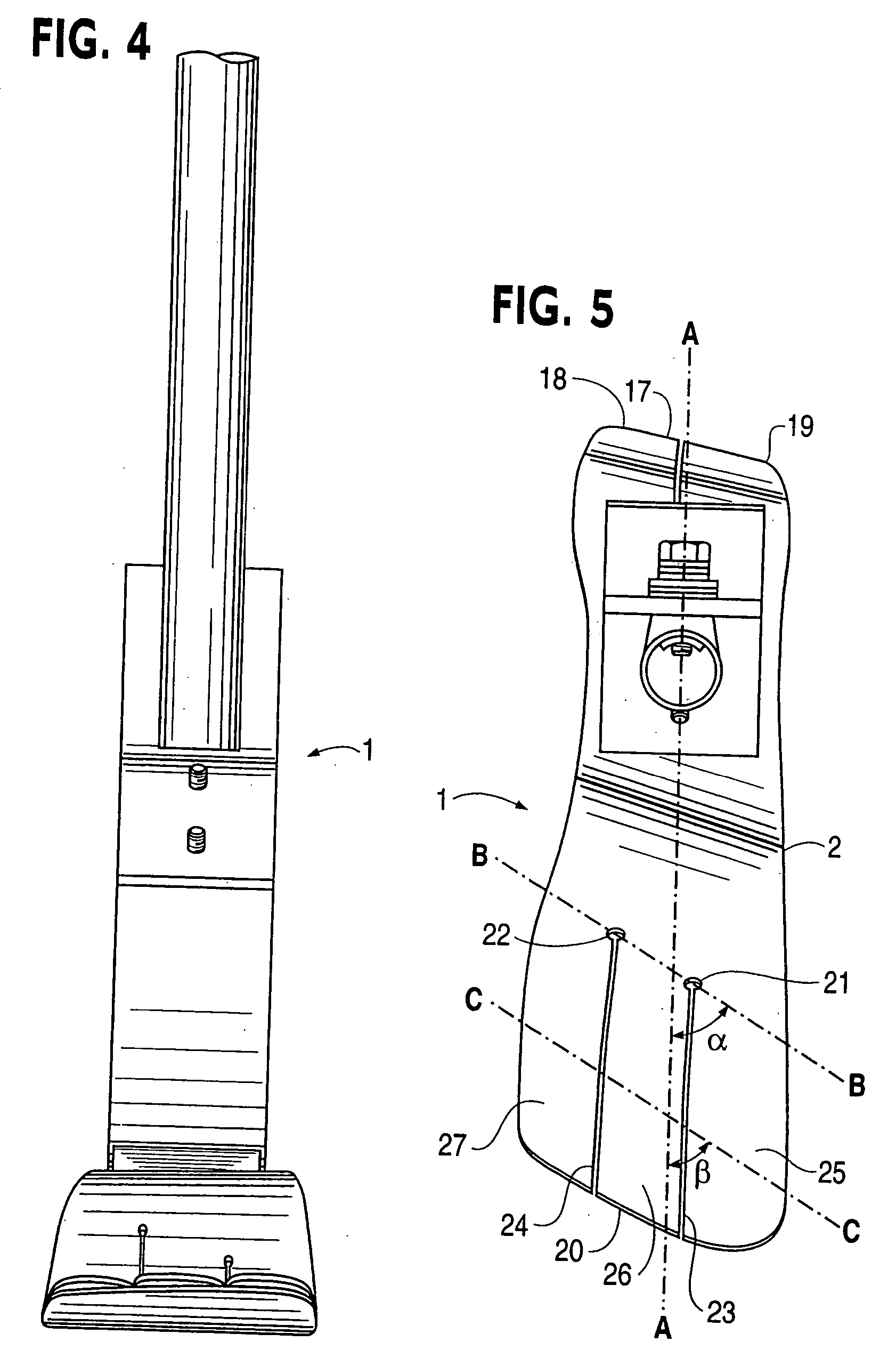
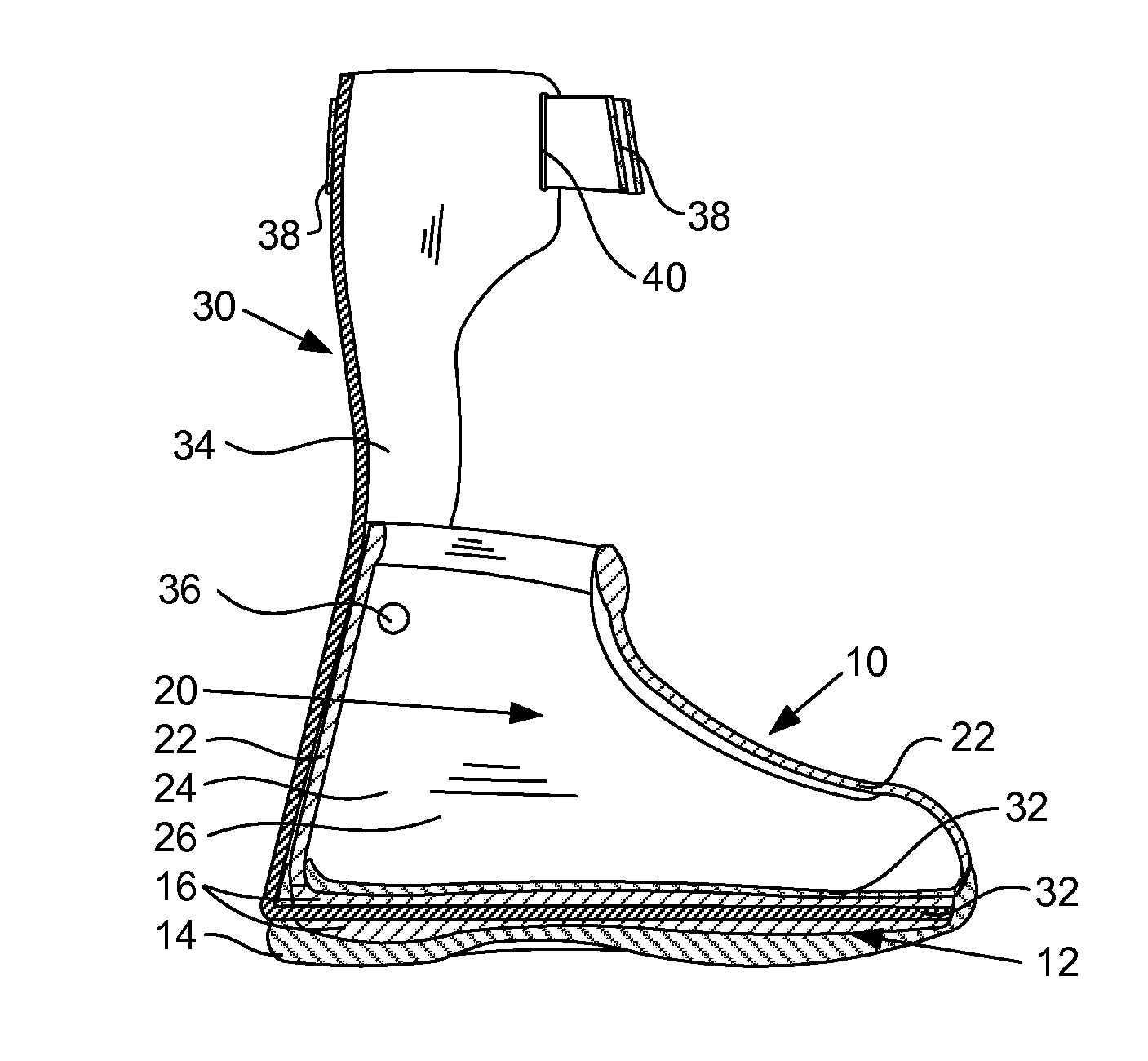
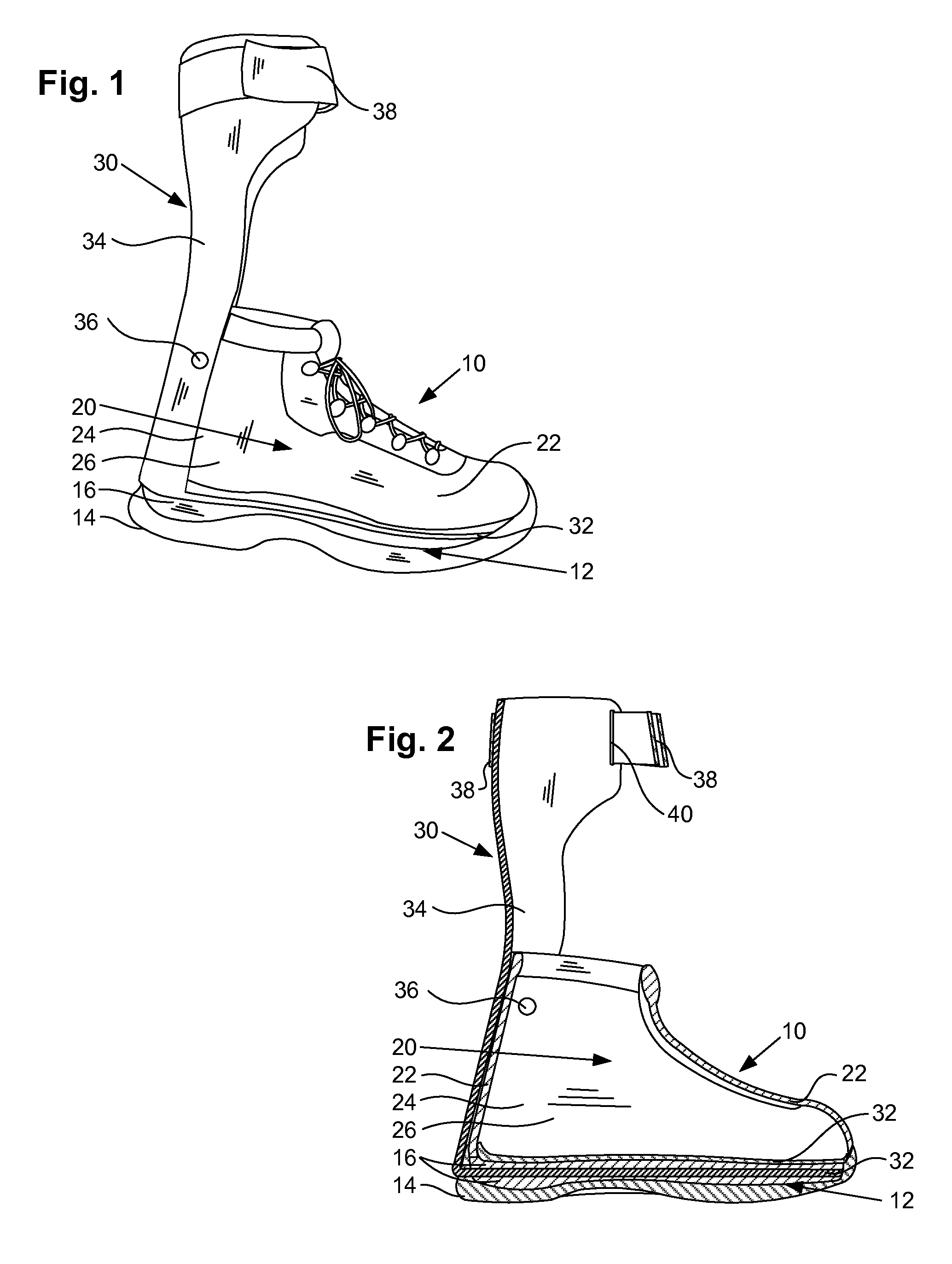
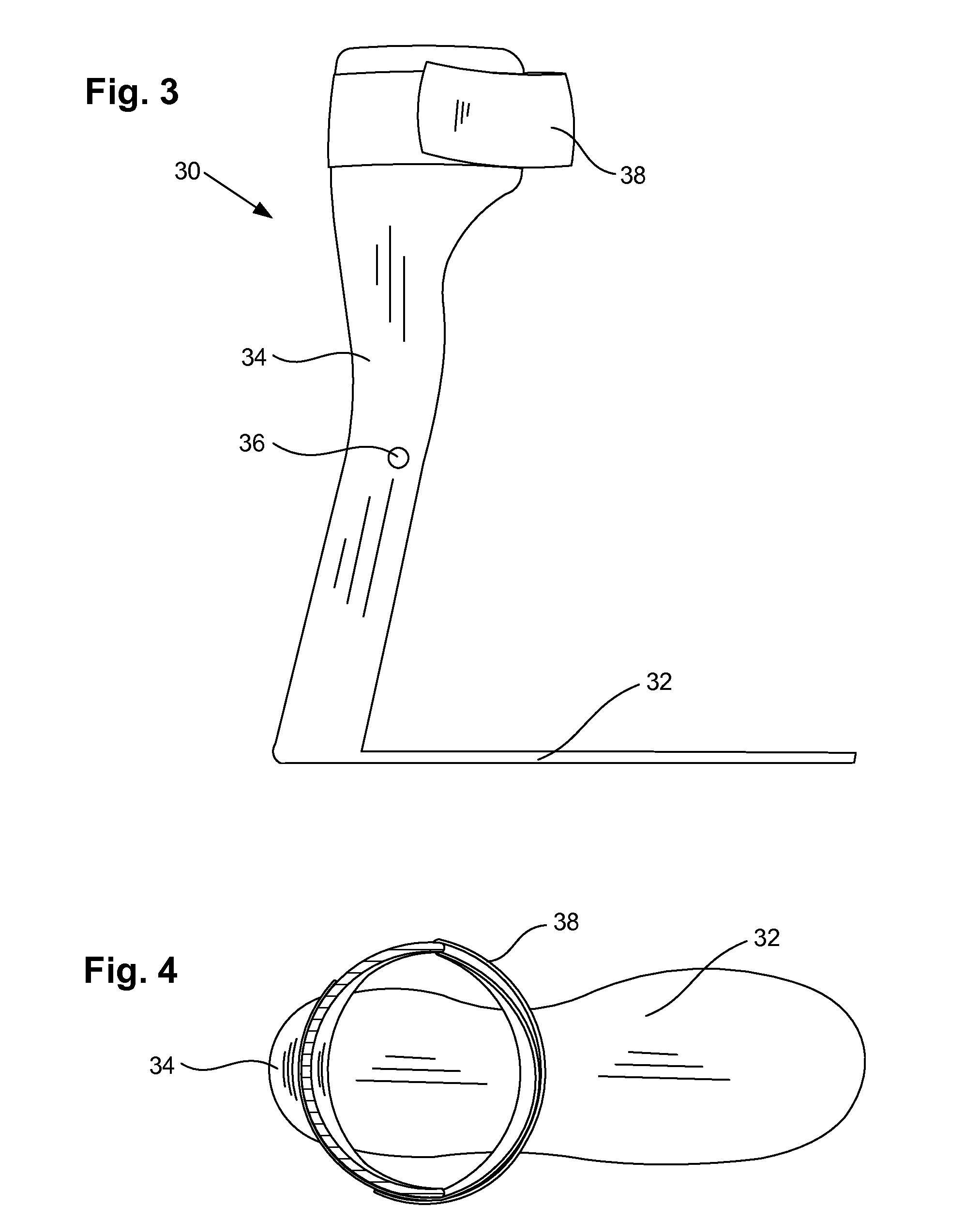
Ankle-foot orthosis
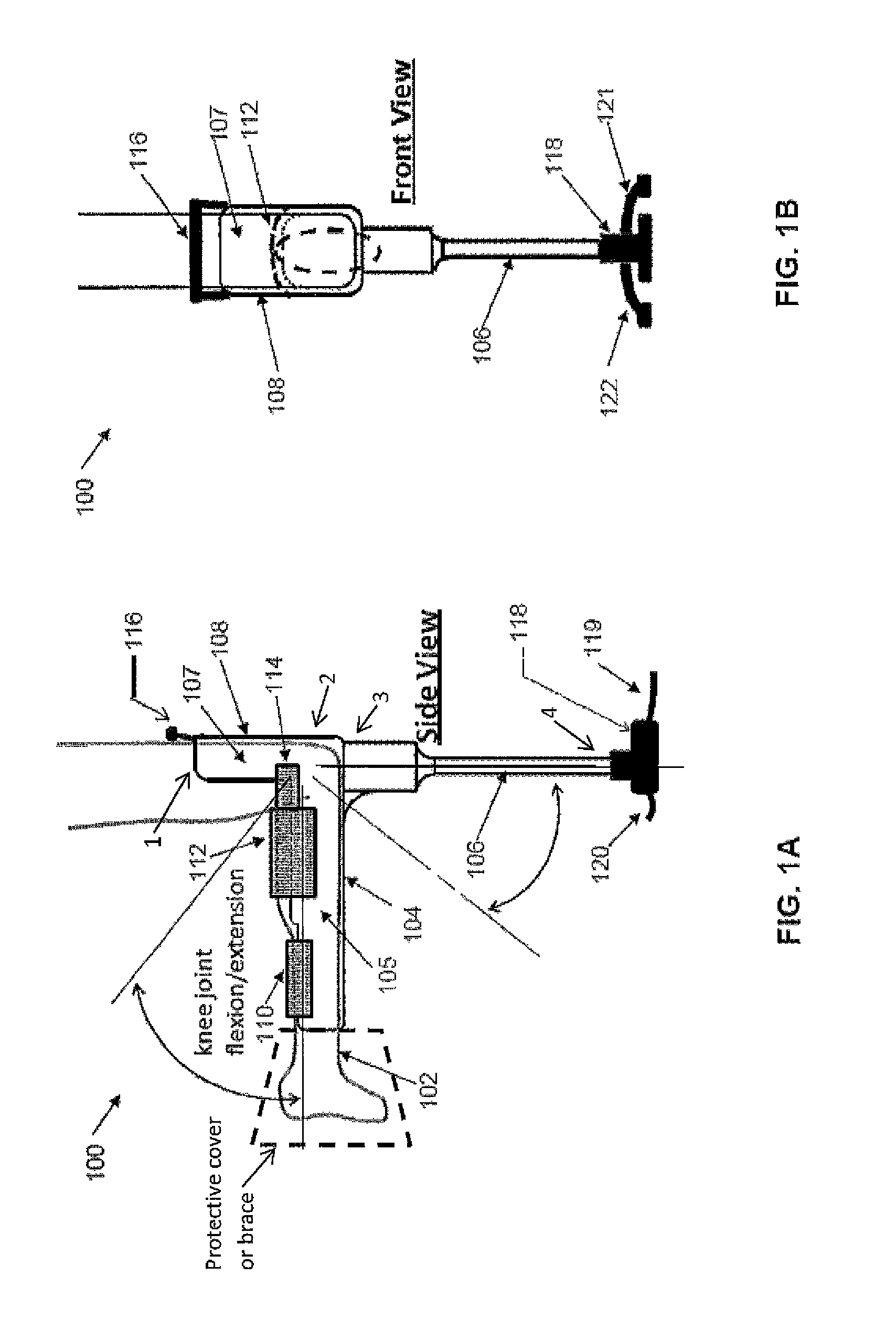
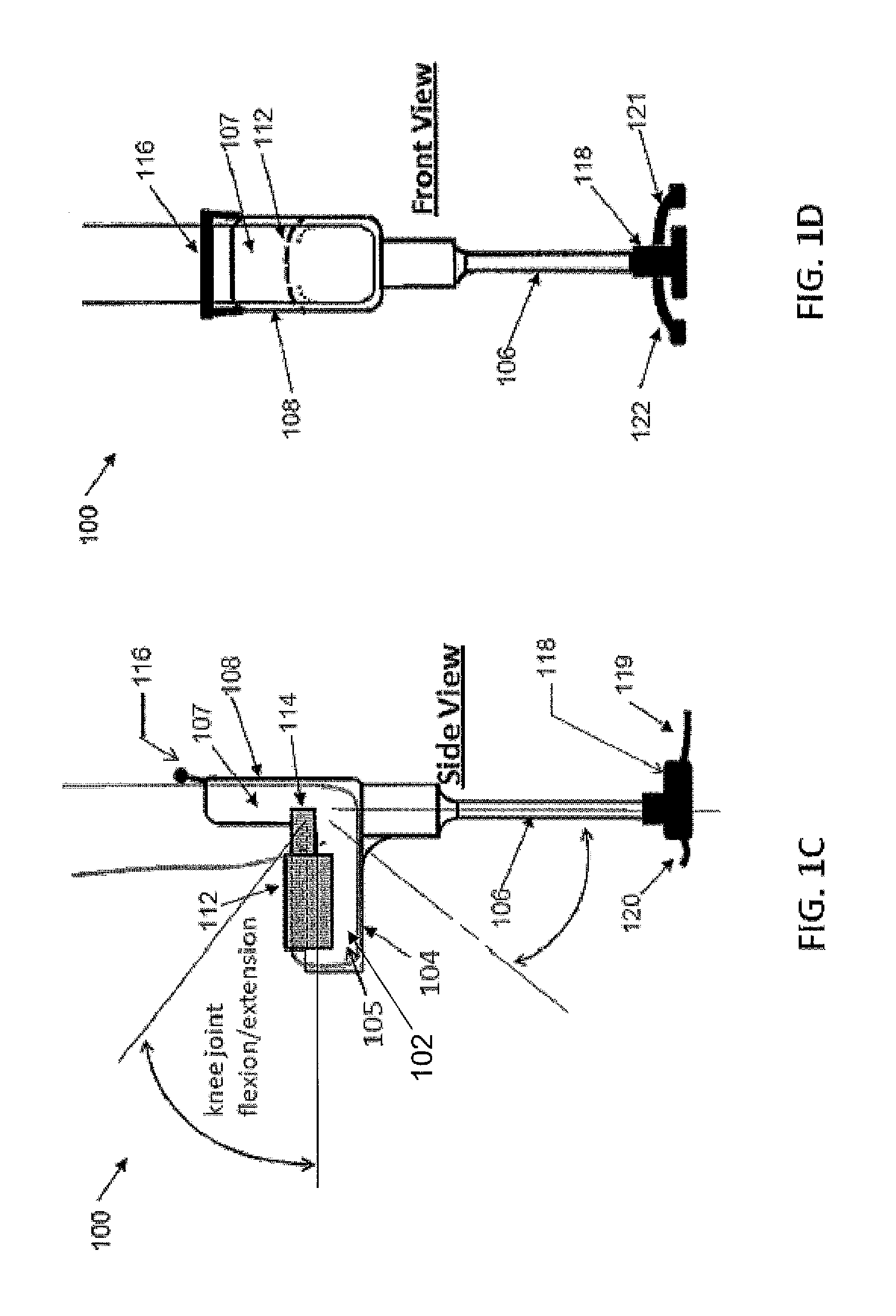
The present invention provides an ankle-foot orthosis (1) that comprises a strut (2) extending over the front of the lower leg and anterior of the lateral ankle, a foot plate (3) extending beneath the sole of the foot and a fastening means for the fastening the orthosis (1) to the leg. The strut comprises a bifurcation zone (9) and two strut branches (2′, 2″) arranged to extend on the outside of the lower leg on each side of the tibia. Thus the present invention provides an orthosis (1) with high resistance against wear and tear, high wear comfort for the patient and an orthosis (1) enabling an almost normal gait.
Owner:CAMP SCANDINAVIA
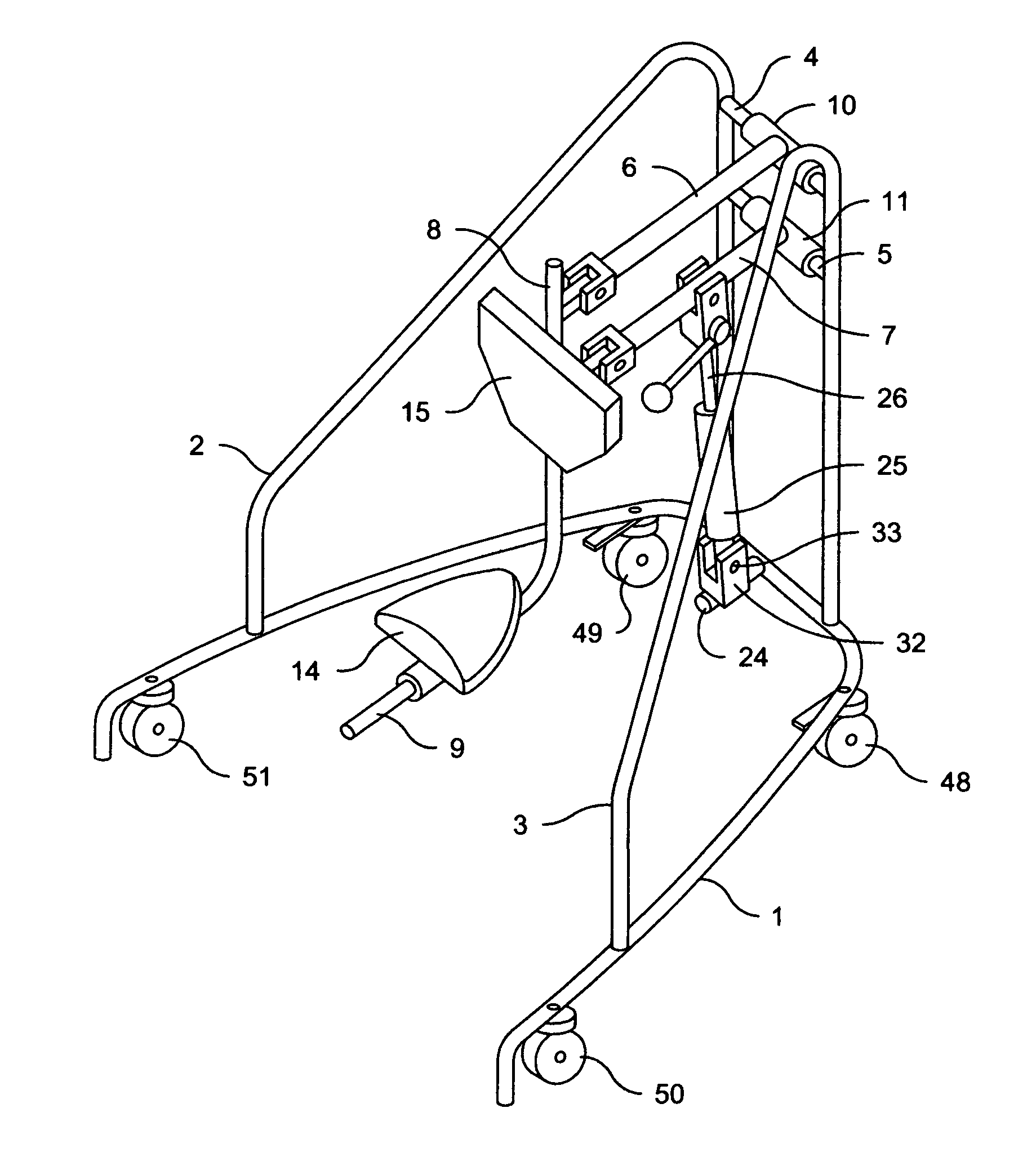
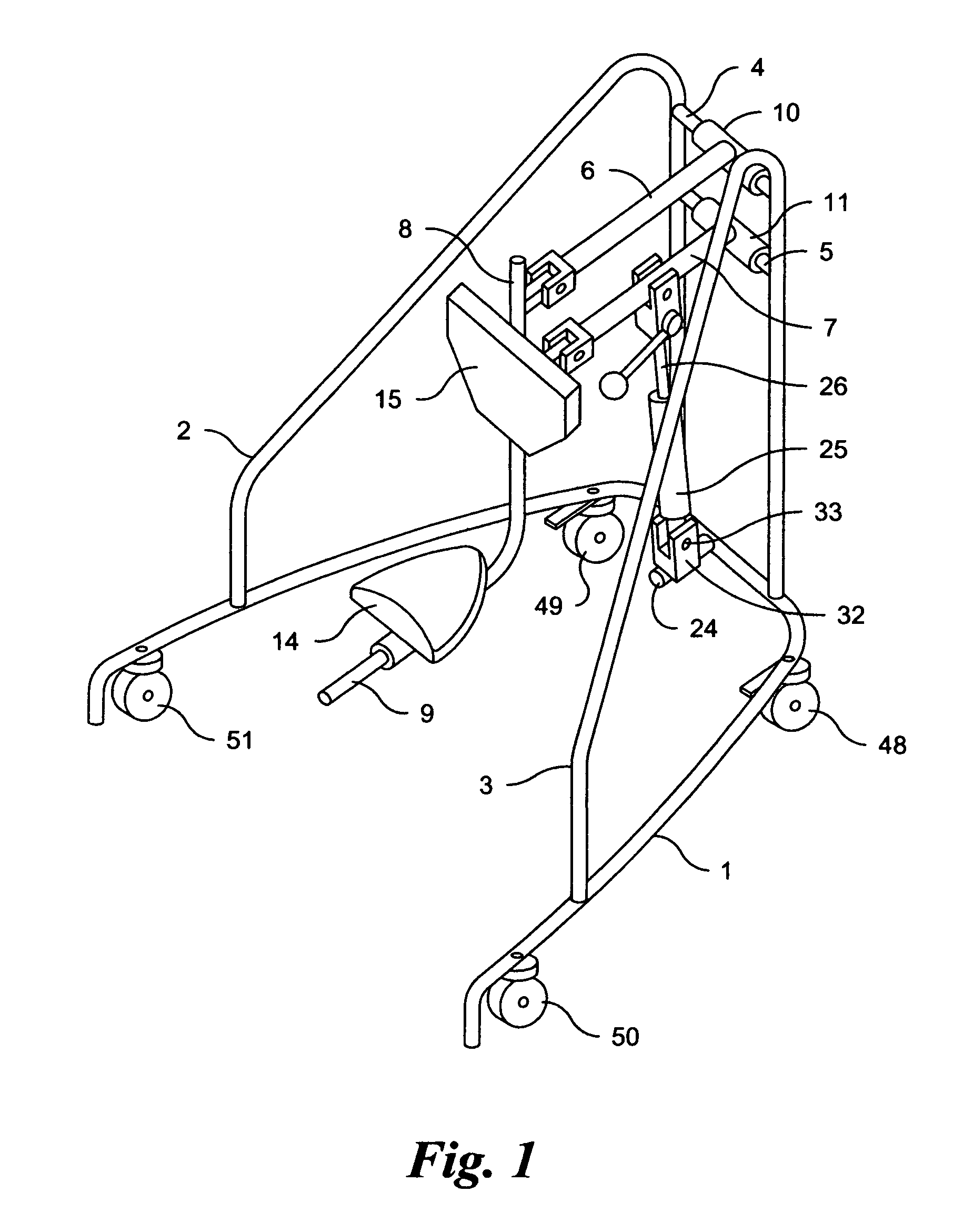
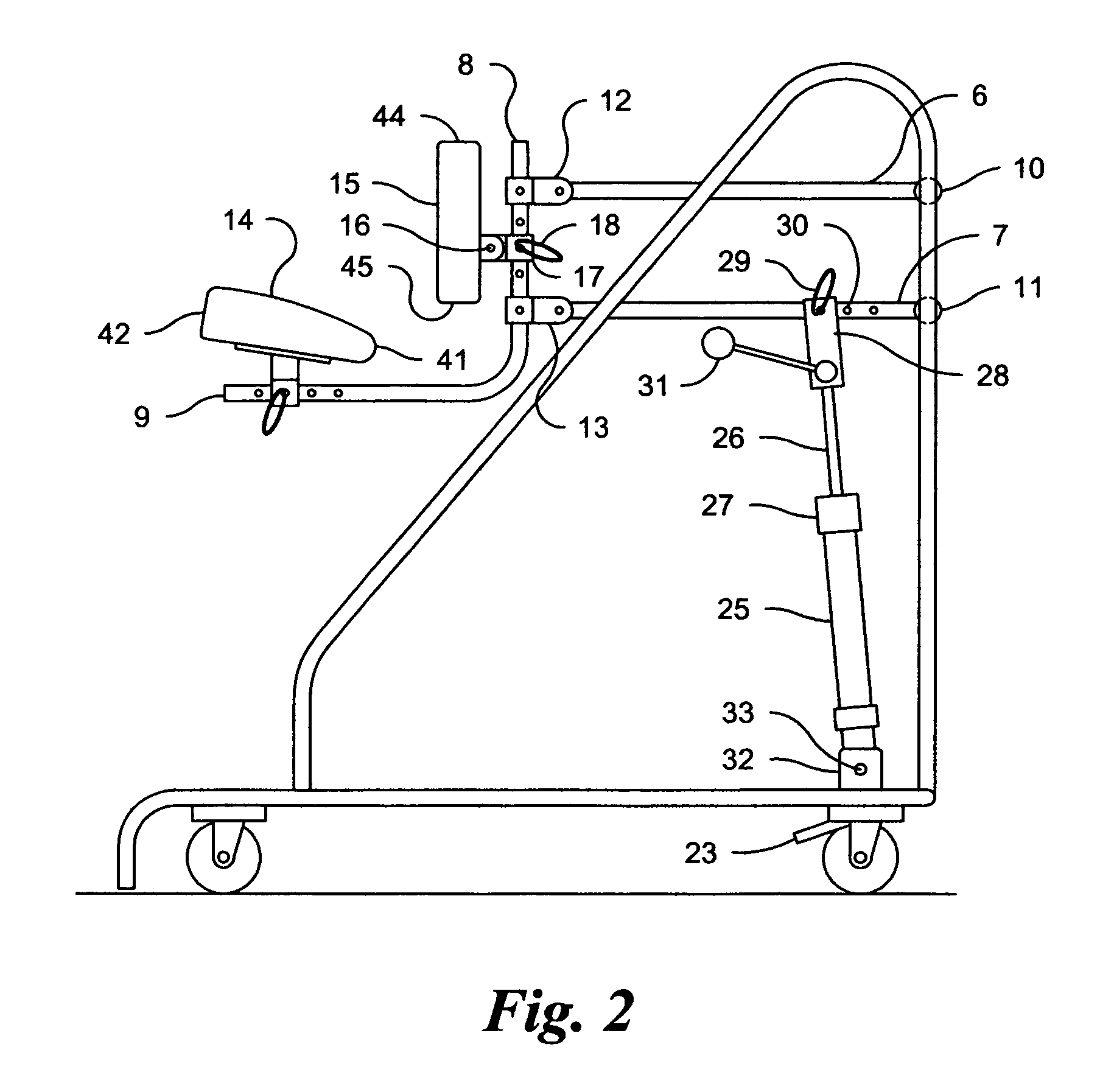
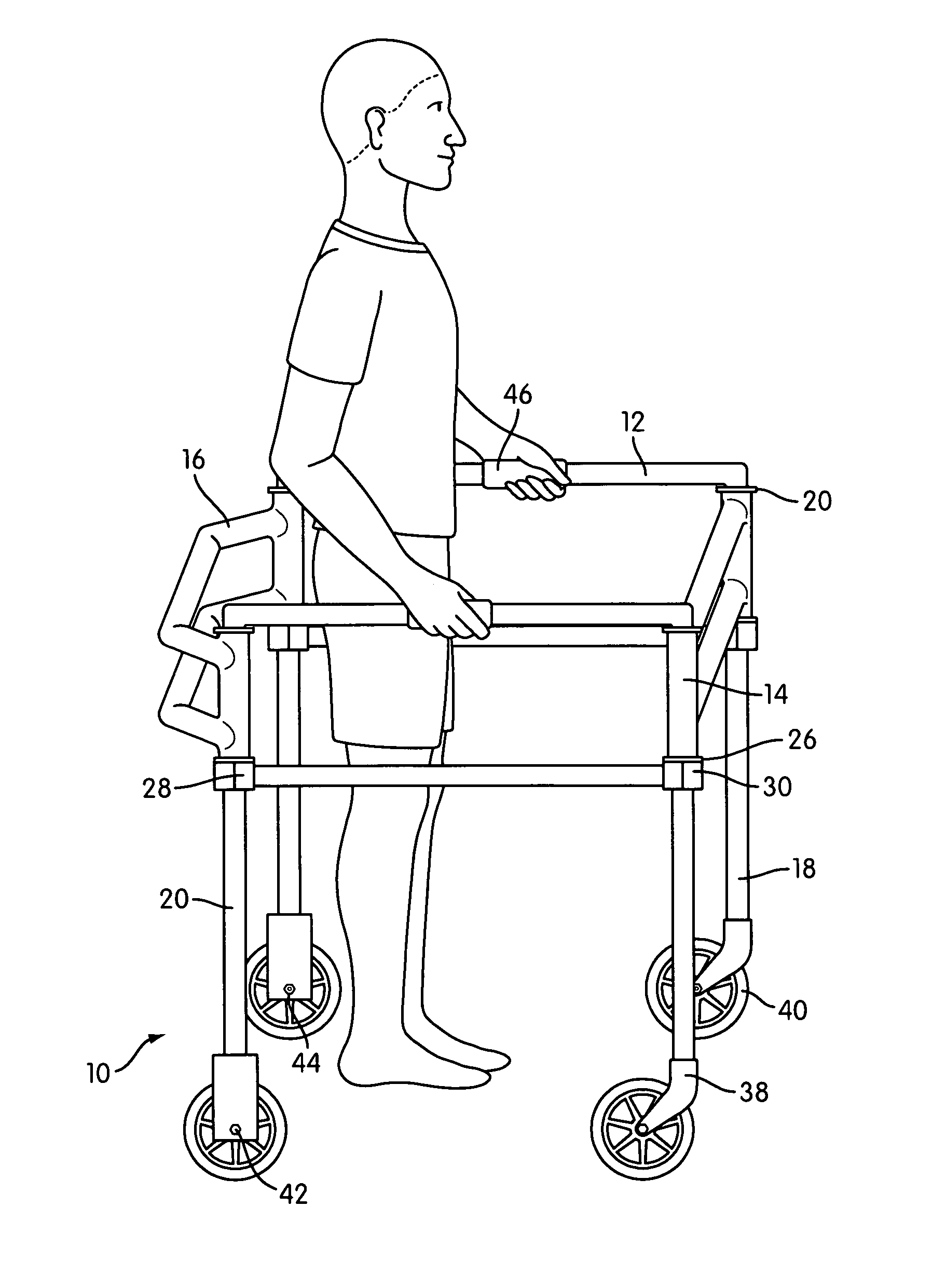
Sit down and stand up walker with seat assembly
ActiveUS8151812B2Loss of balanceEfficiently enableWalking sticksOperating chairsHand heldFull weight bearing
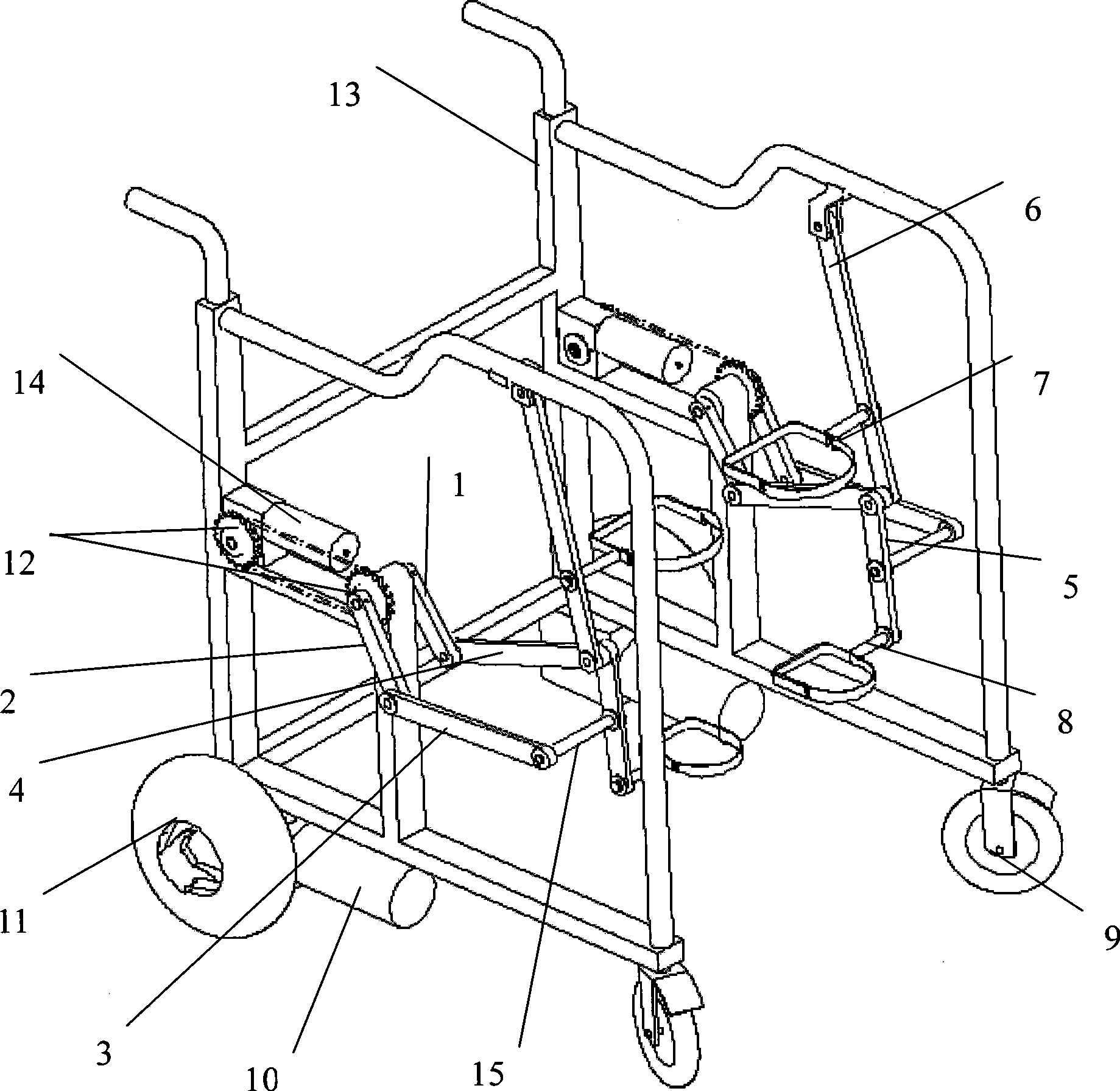
A sit down and stand up walker for assisting a user during walking and when not walking in a standing, partially standing or sitting positions with partial or full weight bearing support and with means to change from standing, partially standing to sitting positions with partial weight bearing support to a fixed elevation with full weight bearing support in any varied or repeated sequence. The partial or full weight bearing means supports a seat assembly which includes a seat and front body support with adjustable positioning to provide pelvic stability. The angle of the seat assembly relative to a flat ground surface is maintained at any elevation of the seat assembly between a standing and sitting position. The weight bearing means is responsive to the variable force supplied by the user as the user walks, stands or sits allowing the seat assembly to move up or down. The weight bearing means in a preferred embodiment is an enclosed gas spring cylinder with piston rod that can be locked at differing elevations or released to respond to a user's body force as the user walks, stands or sits. The walker is intended to be moved without the user's hands holding onto the frame thereby promoting a normal gait and posture. The walker enables the user to expend less energy as the body's center of gravity with partial or full weight bearing support rises and falls with each stride. The walker facilitates transfers from a sitting to standing positions and vice versa by the user independently without the intervention of caregivers.
Owner:RAZON ELI
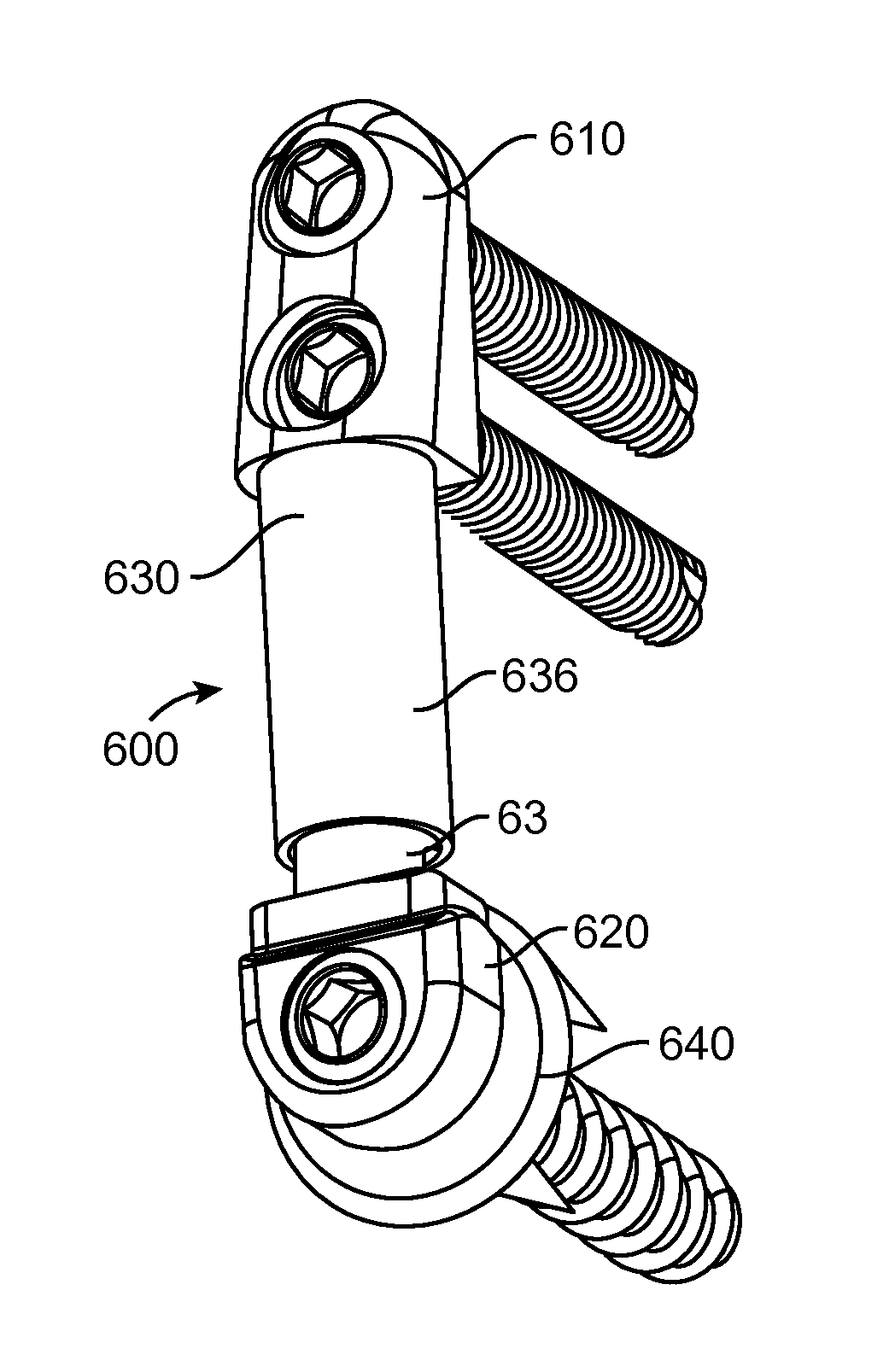
Implantable Device For Relieving Ankle Pain
An apparatus and related method for controlling a load on a human ankle joint during normal gait while preserving motion. The approach is intended to treat osteoarthritis and pain of the ankle without substantially resisting an angular displacement associated with full mobility of the ankle joint.
Owner:MOXIMED INC
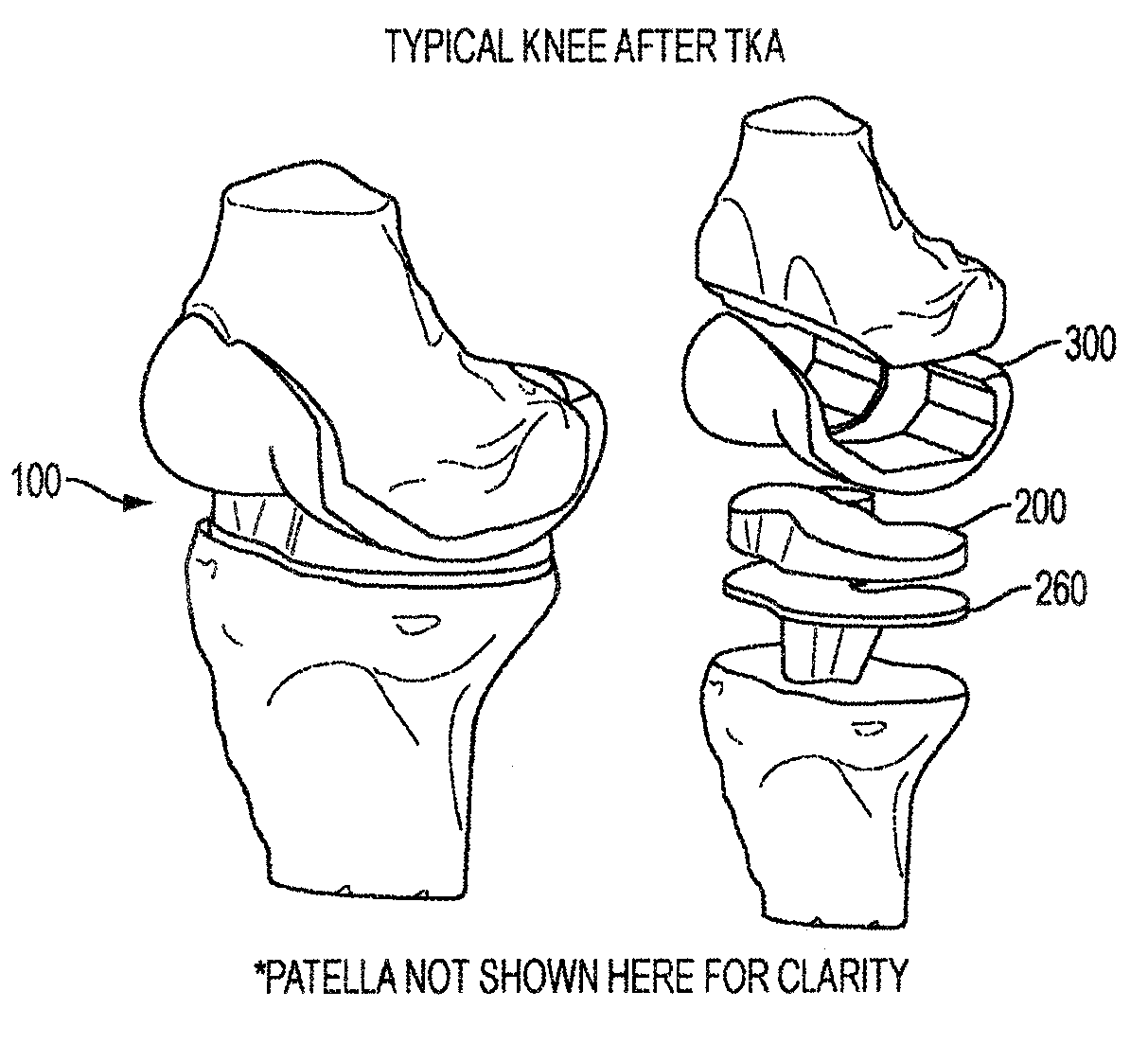
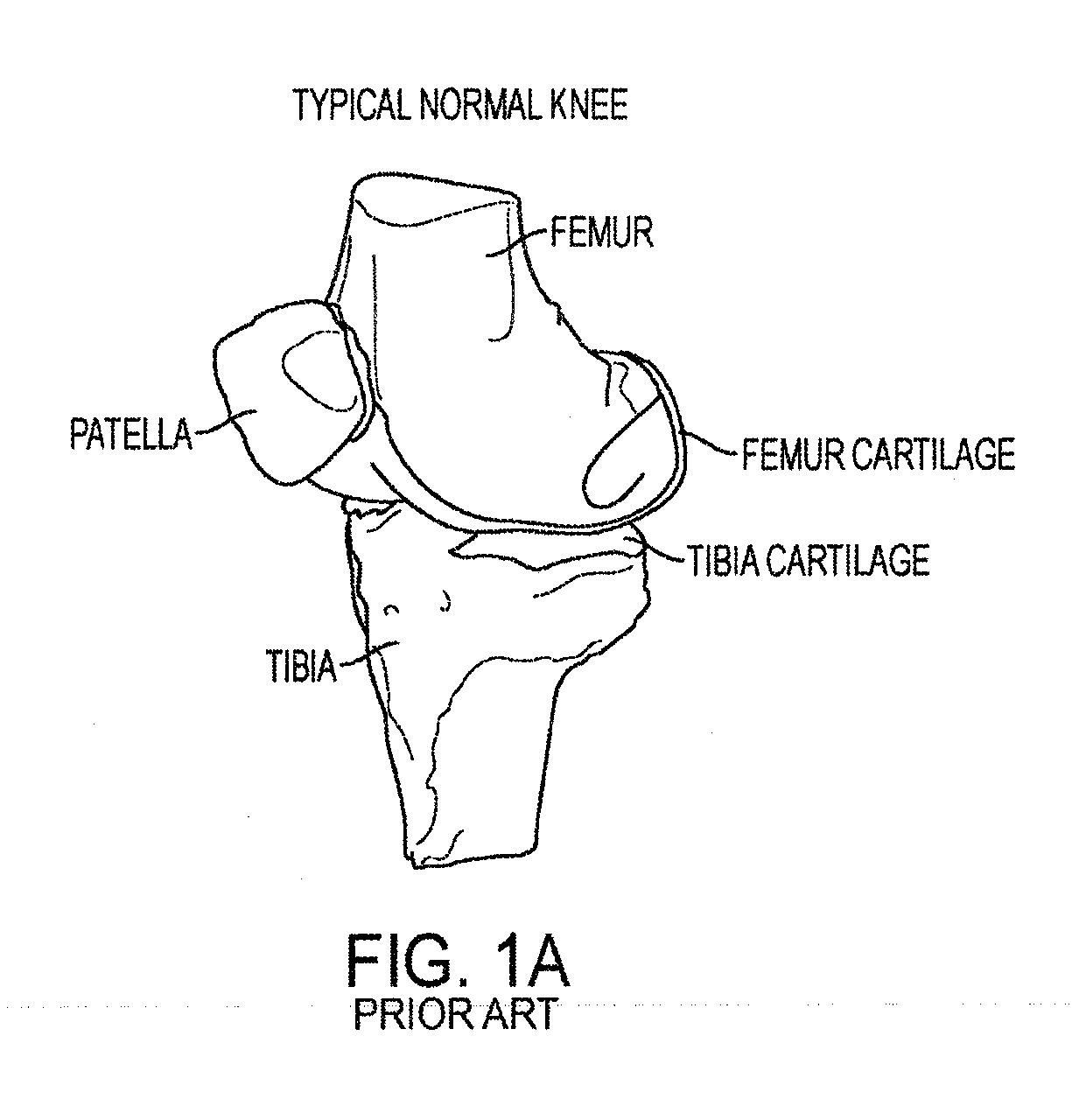
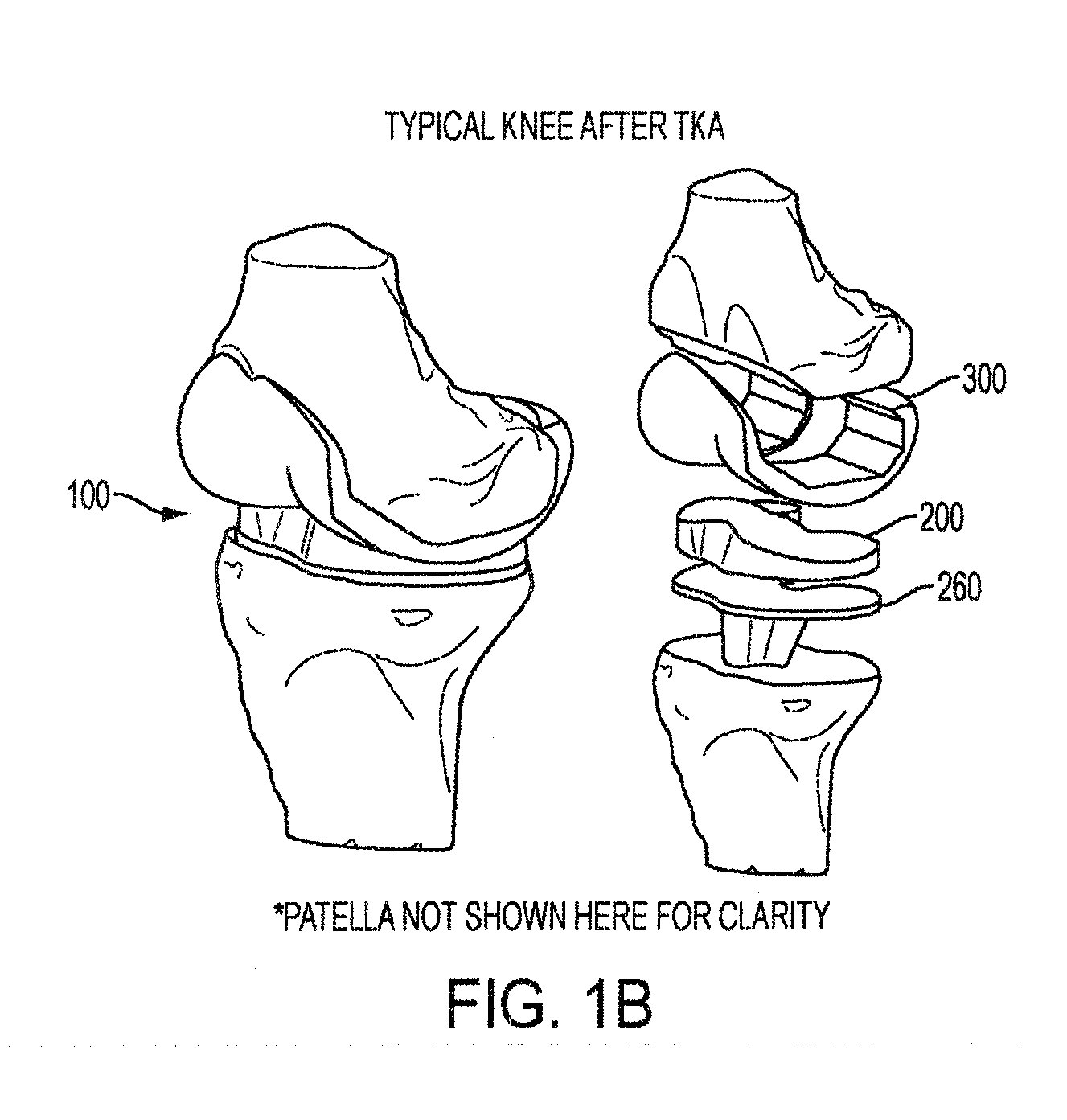
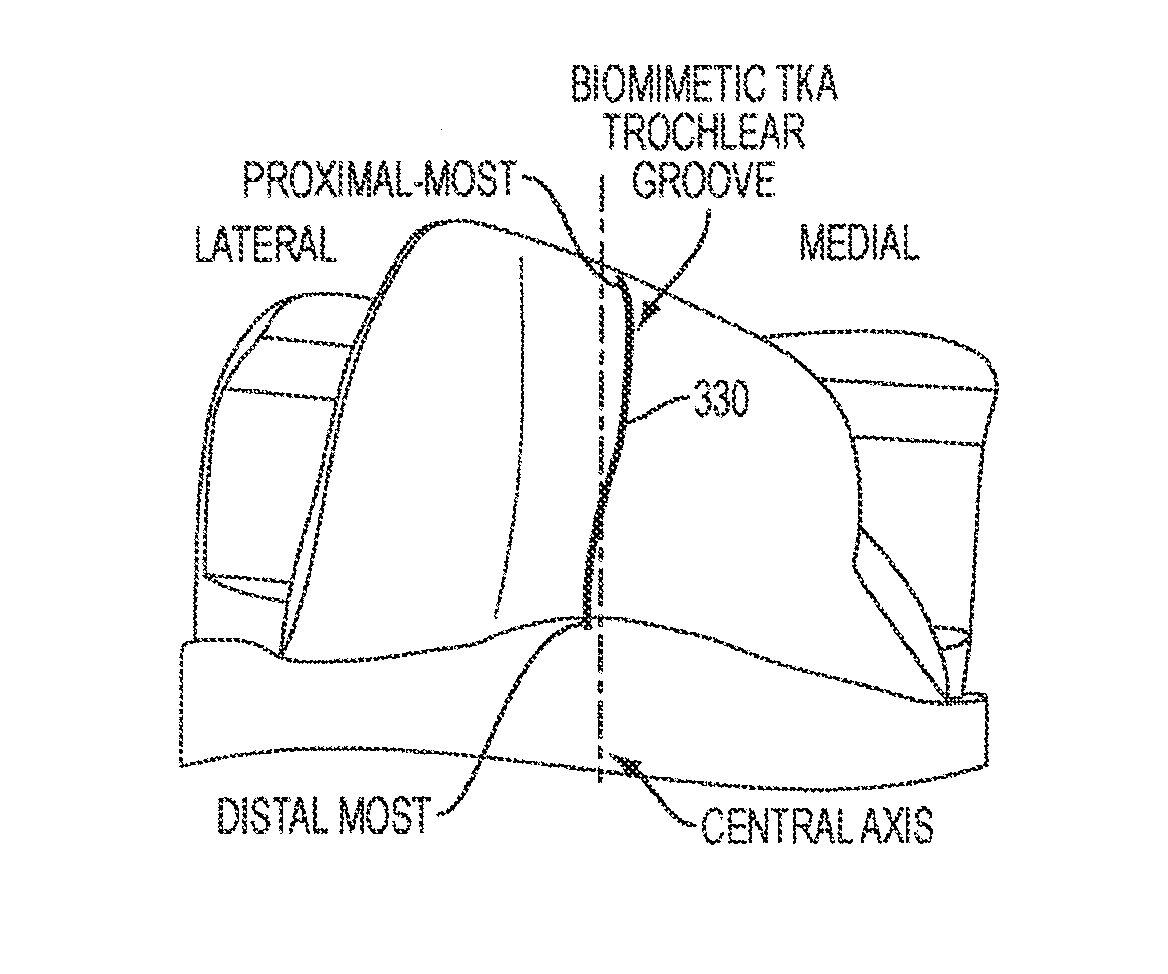
Implant for restoring normal range flexion and kinematics of the knee
ActiveUS20120310362A1Prevent subsidenceHigh strengthJoint implantsKnee jointsForce equilibriumArticular surface
Embodiments of the invention provide knee prostheses which more faithfully and closely replicate the function, anatomy and physiology of the normal human knee yielding a number of advantages. Among other things, such prostheses can provide an increased range of motion and function more normally particularly in extension, deep flexion and during normal gait. Knee prostheses according to various aspects of the invention recognize that during movement of the knee, particularly during flexion, the kinematics of the bones of the knee are a result of achieving equilibrium of the forces that cause motion of the knee. In addition, the shape of the articular surfaces acting in combination with forces imposed by various muscles, ligaments and tendons, determines the direction of the large contact forces.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Prosthetic foot with tunable performance
InactiveUS20060030950A1High level of functionHigh level of performanceCapsule deliveryArtificial legsKeelCoupling
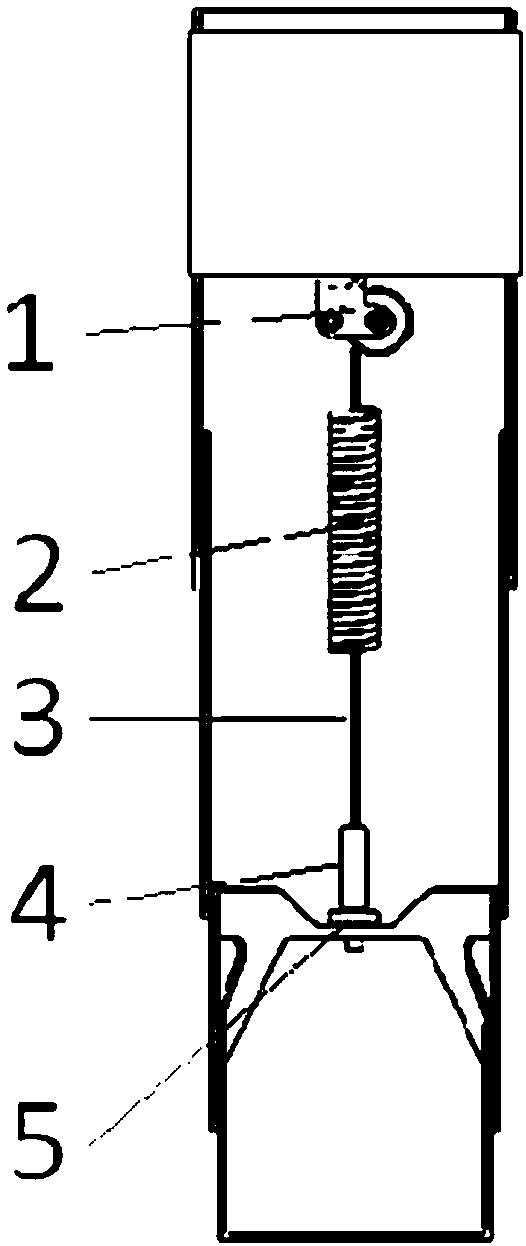
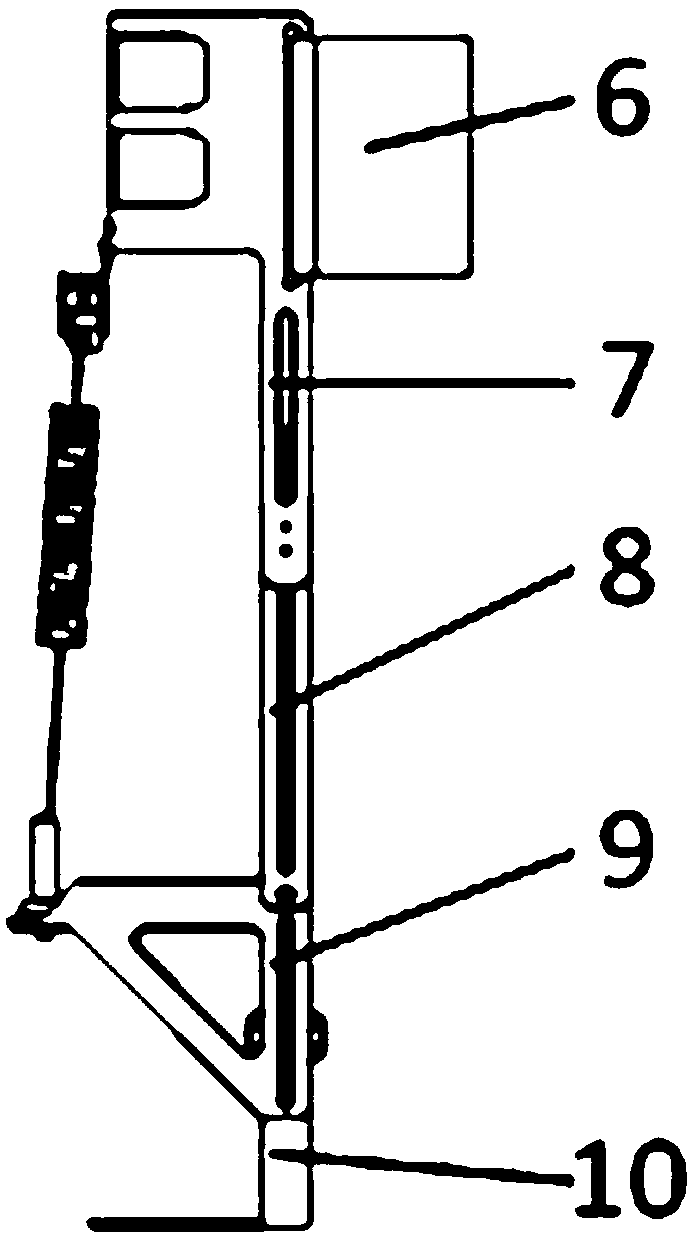
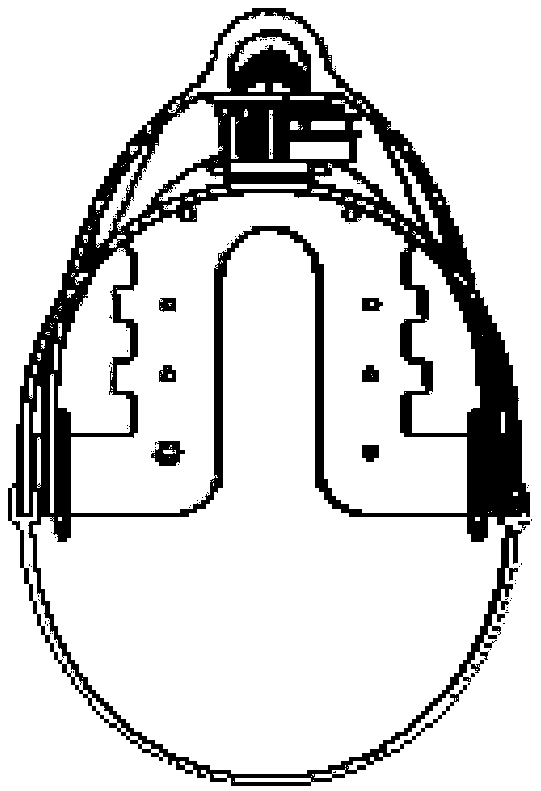
A prosthetic foot (190) incorporates a foot keel (192) and a resilient calf shank (193) with its lower end connected to the foot keel to form an ankle joint of the prosthetic foot. The calf shank extends upward from the foot keel by way of an anterior facing convexly curved portion (195) of the shank, and is secured to the foot keel by way of a coupling element (194). The lower end of the shank is reversely curved (196) and housed by a reversely curved portion of the coupling element. A posterior calf device (191) has a cable (204) which is untensioned in a normal gait cycle but tensioned by a force loading on the prosthesis greater than 120% of body weight of the user to limit, e.g. stop, further anterior motion of the upper end of the shank.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Abnormal gait identification method capable of facilitating screening Parkinsonism
InactiveCN104834888AEnables assisted screening testingRealize daily gait monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkPressure sense
The invention discloses an abnormal gait identification method capable of facilitating screening Parkinsonism. The method is characterized in that the gait plantar pressure characteristics can be extracted, and the modeling and the identification of the neural network of the gait system of the normal healthy people and the patients suffering from the Parkinsonism can be dynamically carried out; the constant neutral network can be established; a dynamic estimator can be built by using the constant neutral network, and based on the difference between the gait modes of the normal healthy people and the patients suffering from the Parkinsonism in the gait system dynamics, the abnormal gait caused by the Parkinsonism and the normal gait of the normal healthy people can be distinguished according to the minimum error principle, and the screening detection of the Parkinsonism can be facilitated. By arranging a pressure sensing floor system or wearing the special shoes provided with the pressure sensor insole, the plantar pressure characteristics can be acquired, and the abnormal gait caused by the Parkinsonism and the normal gait of the normal healthy people can be distinguished conveniently, simply, and non-invasively, and therefore the daily gait monitoring of the family members can be realized, and the screening detection of the Parkinsonism can be facilitated.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
Dual-mode passive ankle power-assisted exoskeleton
ActiveCN109093596AWalking with a natural gaitReduce energy consumptionProgramme-controlled manipulatorDual modeEngineering
The invention relates to a dual-mode passive ankle power-assisted exoskeleton, and belongs to the technical field of wearable power-assisted machinery. The dual-mode passive ankle power-assisted exoskeleton solves the technical problems that the walking gait of a wearer is unnatural due to the fact that an existing exoskeleton exerts additional load on a human body due to the own weight and an elastic element of the exoskeleton exerts resistance to movement of an ankle joint. The dual-mode passive ankle power-assisted exoskeleton comprises a calf mechanism, a mode switching device, a calf length adjusting rod, a spring, a rope, a pre-tightening mechanism, a tension sensor, an ankle joint mechanism and a sole support plate. The mode switching device is arranged on the calf mechanism, and the calf mechanism is connected with the ankle joint mechanism through the calf length adjusting rod. The sole support plate is disposed under the ankle joint mechanism. The spring is connected with themode switching device and the pre-tightening mechanism through the rope, and the pre-tightening mechanism is disposed on the ankle joint mechanism. The dual-mode passive ankle power-assisted exoskeleton can provide assistant power for an ankle, reduces the metabolic energy consumption of the human body, and does not affect the normal gait of the wearer.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Assistive ambulatory device
InactiveUS8573612B1Reduce weightConvenient heightWalking aidsChildren furnitureAmbulatoryWeight-bearing
A method of producing a natural gait by a patient using an ambulatory device having a patient positioned in the middle of the ambulatory device to allow for an upright trunk, minimizing abnormal lower extremities kinematics and weight bearing on arms. By having hinged corners with an adjustable friction the device allows reciprocal arm swing when unlocked. The use of four wheels permits a continuous stepping motion that does not disrupt normal gait kinematics. Having an adjustable height allows the ambulatory device to have an optimal height for placement of patient hands that minimizes weight bearing on arms.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
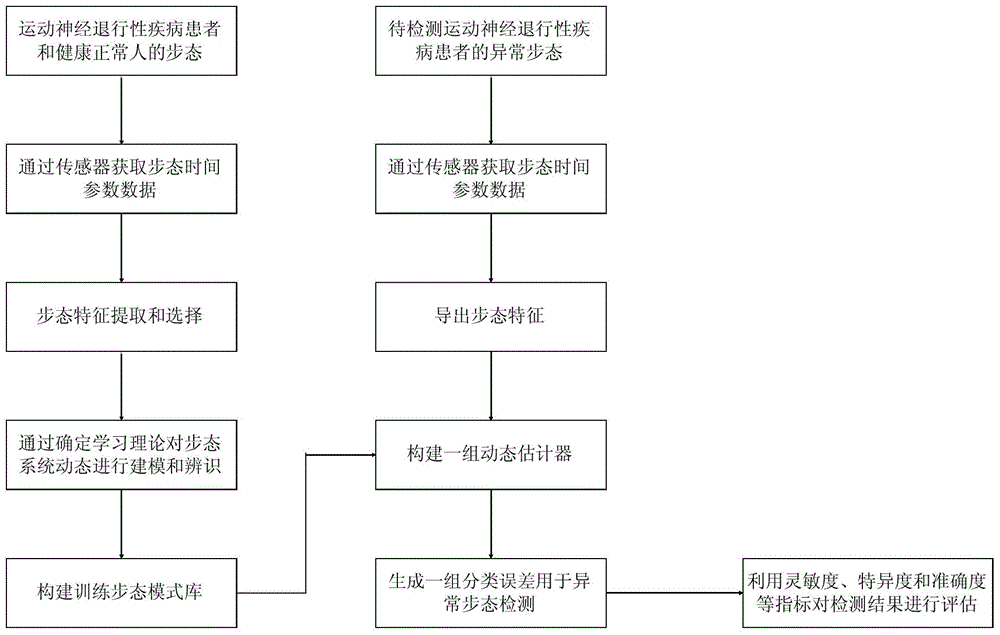
Abnormal gait detection method based on determined learning theory
ActiveCN104091177ARapid Classification DetectionRealize daily gait monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseHome environment
The invention discloses an abnormal gait detection method based on a determined learning theory. The abnormal gait detection method based on the determined learning theory includes the steps that features are extracted, neural network modeling and identification are dynamically carried out on a gait system of healthy and normal people and patients with motor neurodegenerative diseases of different types on the basis of the extracted gait features, a constant neural network is built, a dynamic estimator is built by the utilization of the constant neural network, and abnormal gaits caused by the motor neurodegenerative diseases are distinguished from normal gaits of the general healthy people according to the minimum error principle on the basis of differences between the gait mode of the healthy and normal people and the gait mode of the patients with the motor neurodegenerative diseases of different types on the gait system dynamics, so that the abnormal gaits are detected accurately and a detection result is evaluated. The abnormal gait detection method based on the determined learning theory has the advantages that the method is convenient and easy to implement and is in a non-invasion mode, and under the intelligent home environment, daily gait monitoring on family members can be achieved by mounting a pressure sensing floor system or wearing special shoes with sensor insoles.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Powered leg prosthesis and control methodologies for obtaining near normal gait
A powered leg prosthesis includes powered knee joint comprising a knee joint and a knee motor unit for delivering power to the knee joint. The prosthesis also includes a prosthetic lower leg having a socket interface coupled to the knee joint and a powered ankle joint coupled to the lower leg opposite the knee joint comprising an ankle, joint and an ankle motor unit to deliver power to the ankle joint. The prosthesis further includes a prosthetic foot coupled to the ankle joint, at least one sensor for measuring a real-time input, and at least one controller for controlling movement of the prosthesis based on the real-time input.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Limb prosthesis
Disclosed are limb prostheses for use when normal use of the lower leg is temporarily or permanently lost due to lower leg injury or disease, including below-knee amputation. Disclosed prostheses provide full body weight support and allow a wearer to maintain the use of the hands and arms during ambulation. In addition, a wearer can maintain use of their own knee to flex and extend during ambulation, thereby better controlling the prosthesis during motion and providing a more normal gait as compared to previously known devices. In the event of permanent loss of the lower leg due to below-knee amputation, the disclosed prosthesis provides an alternative to socket-type prosthetic devices.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIVERSITY
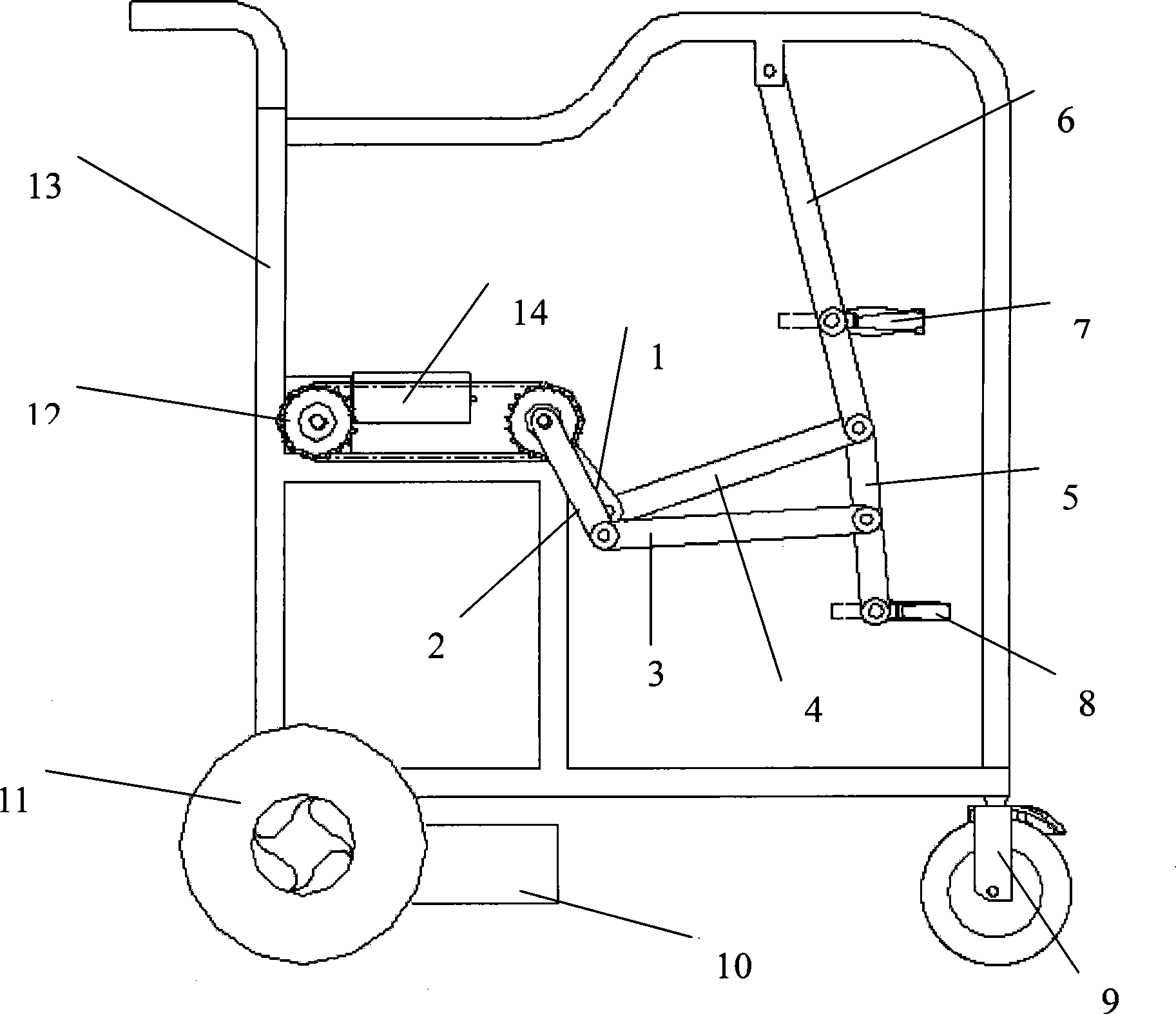
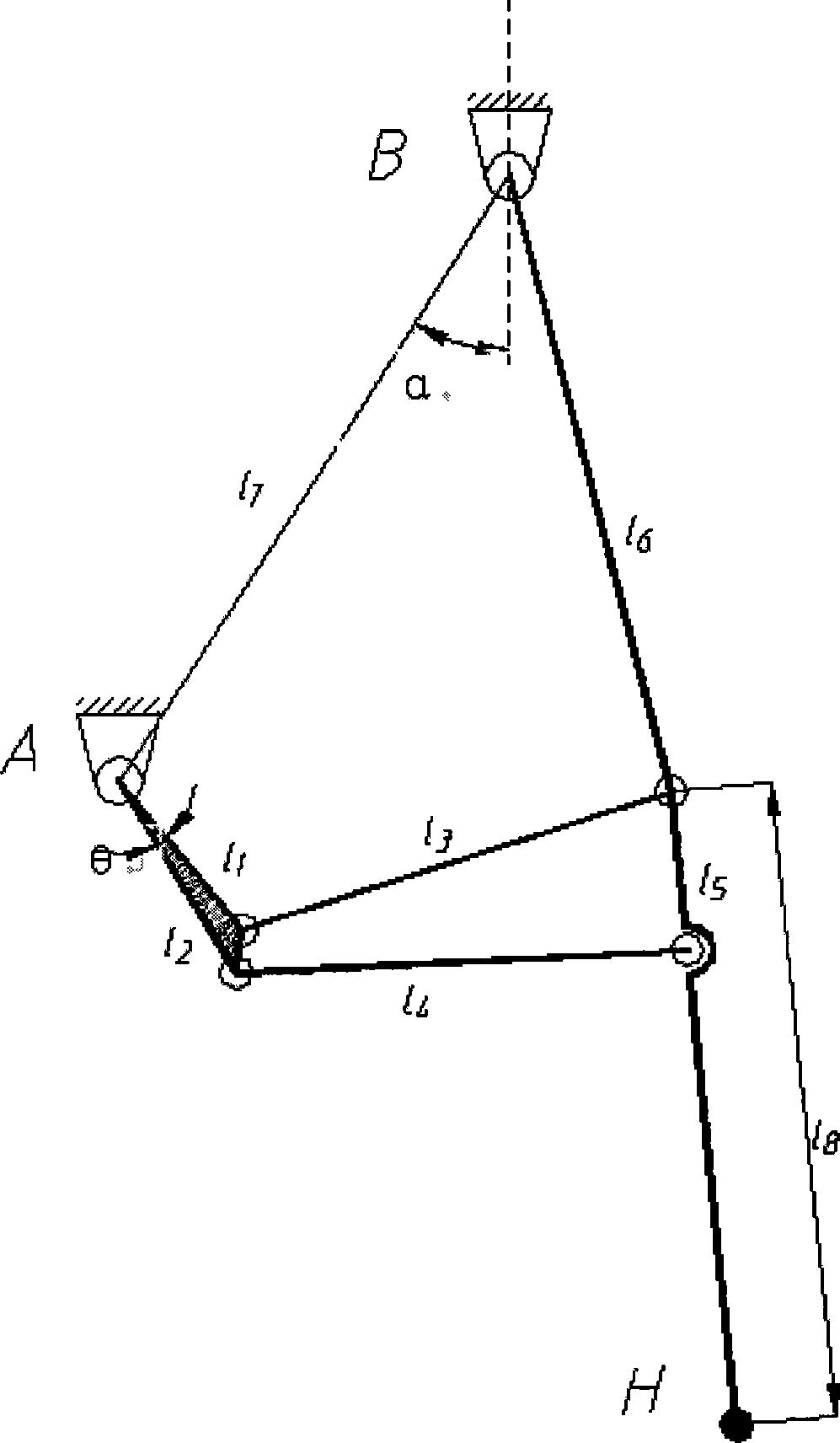
Six-lever apery gait power-assistant running mechanism
The invention provides a six-rod assisted walking mechanism simulating the human gaits, which comprises a vehicle body, driving wheels and universal wheels at the bottom of the vehicle body, and a driving wheel motor arranged on the vehicle body and connected with the driving wheels. A six-rod mechanism with single freedom of motion and a rod mechanism driving device are respectively arranged at the left and the right sides of the vehicle body; the rod mechanism driving device consists of a rod driving motor, a driving sprocket, a driven sprocket and a chain; the six-rod mechanism with single freedom of motion is provided with a short crank rod, a long crank rod, a connecting rod I, a connecting rod II, a thigh rod and a shank rod. When the cranks are driven to rotate by the rod driving motor, the six-rod mechanism moves according to a specific rule, rendering the constraining parts on the thigh rod and shank rod to constrain the thigh and shank of the patient so as to enable the patient to move in accordance with the rules of natural human gaits. At the same time, the driving wheels drive the vehicle body to move at a walking speed, enabling the patients with extremity dysfunction to walk according to the normal gait tracks. The assisted walking device simulating the human gaits has the advantages of simple structure, excellent controllability and low cost.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for determining abnormal gait
InactiveUS20150230733A1Accurately determine abnormalityPerson identificationSensorsEngineeringFuzzy membership function
The invention relates to a method for determining abnormal gait comprising the following steps: (a) measuring ground reaction force generated during walking by a plurality of sensors arranged on the left-foot and the right-foot respectively; (b) applying measurements from each of the plurality of sensors to a predetermined fuzzy membership function to transform the measurements into the first fuzzy values; (c) applying the first fuzzy values to a predetermined fuzzy logic to generate the second fuzzy values for a plurality of gait phases; and (d) comparing the second fuzzy values with pre-stored data of normal gait to determine whether it is abnormal gait or not. Therefore, it is possible to determine abnormal gait more accurately even with fewer sensors.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
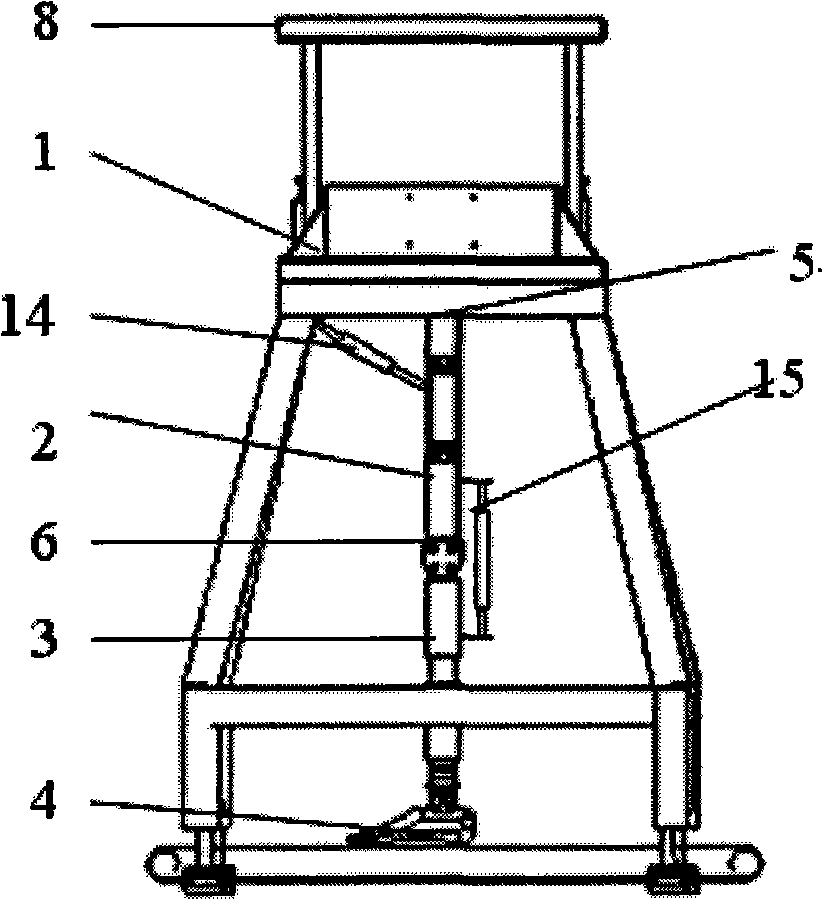
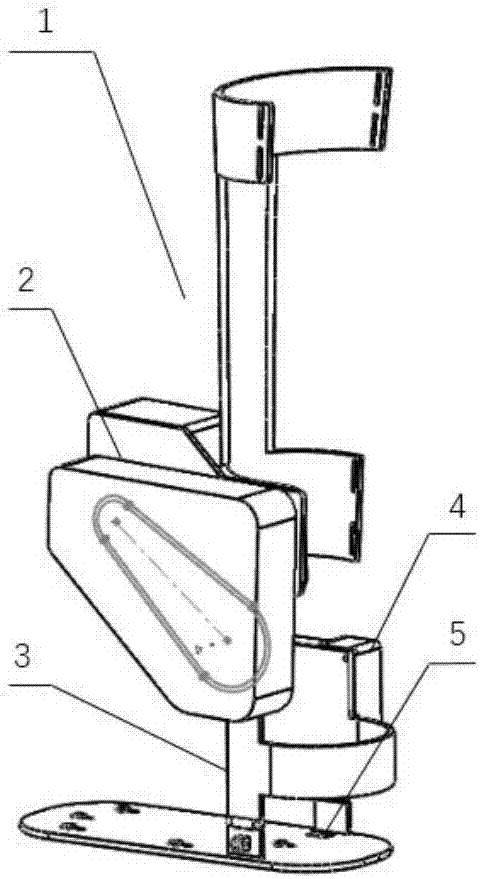
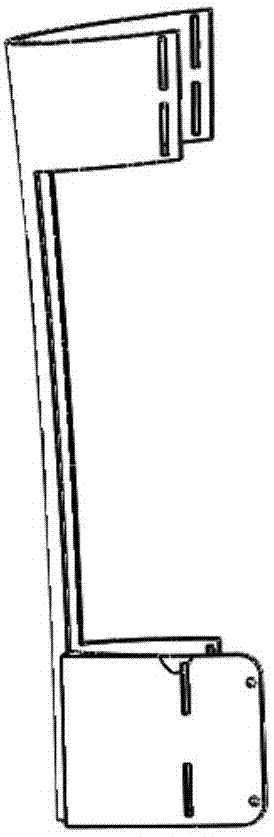
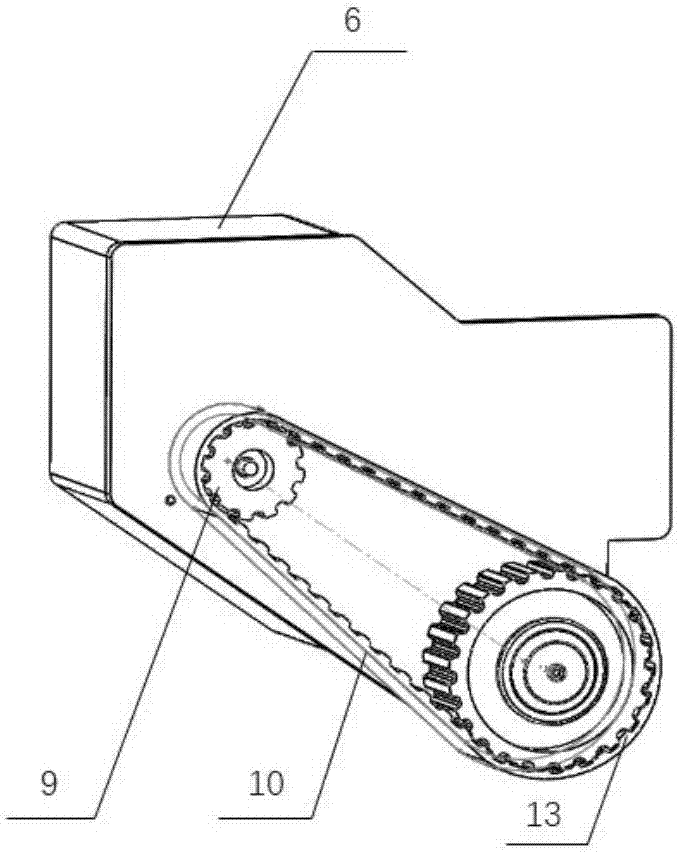
Rehabilitation training robot capable of achieving normal gait pattern
ActiveCN105456002AReduce manufacturing costReduce in quantityChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesSupporting systemUser needs
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
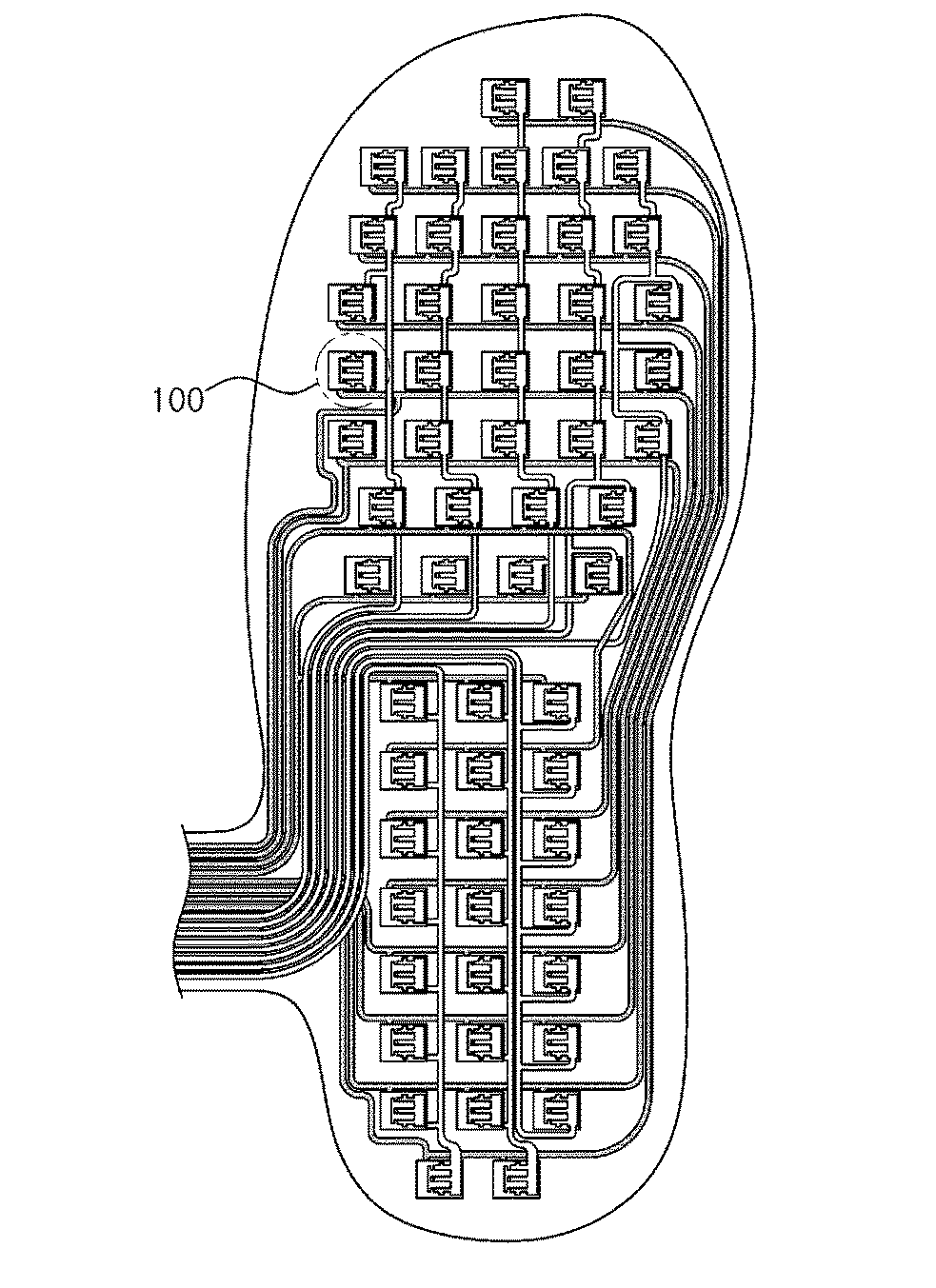
Wearable intelligent insole with health consultation function
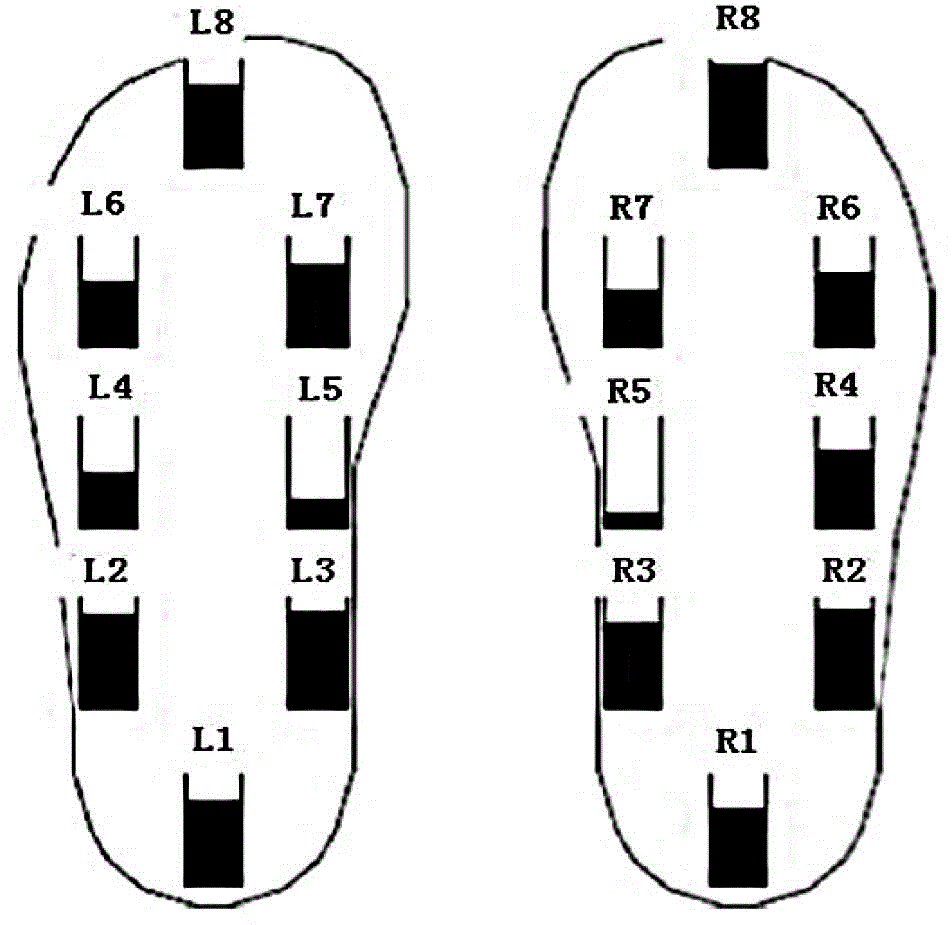
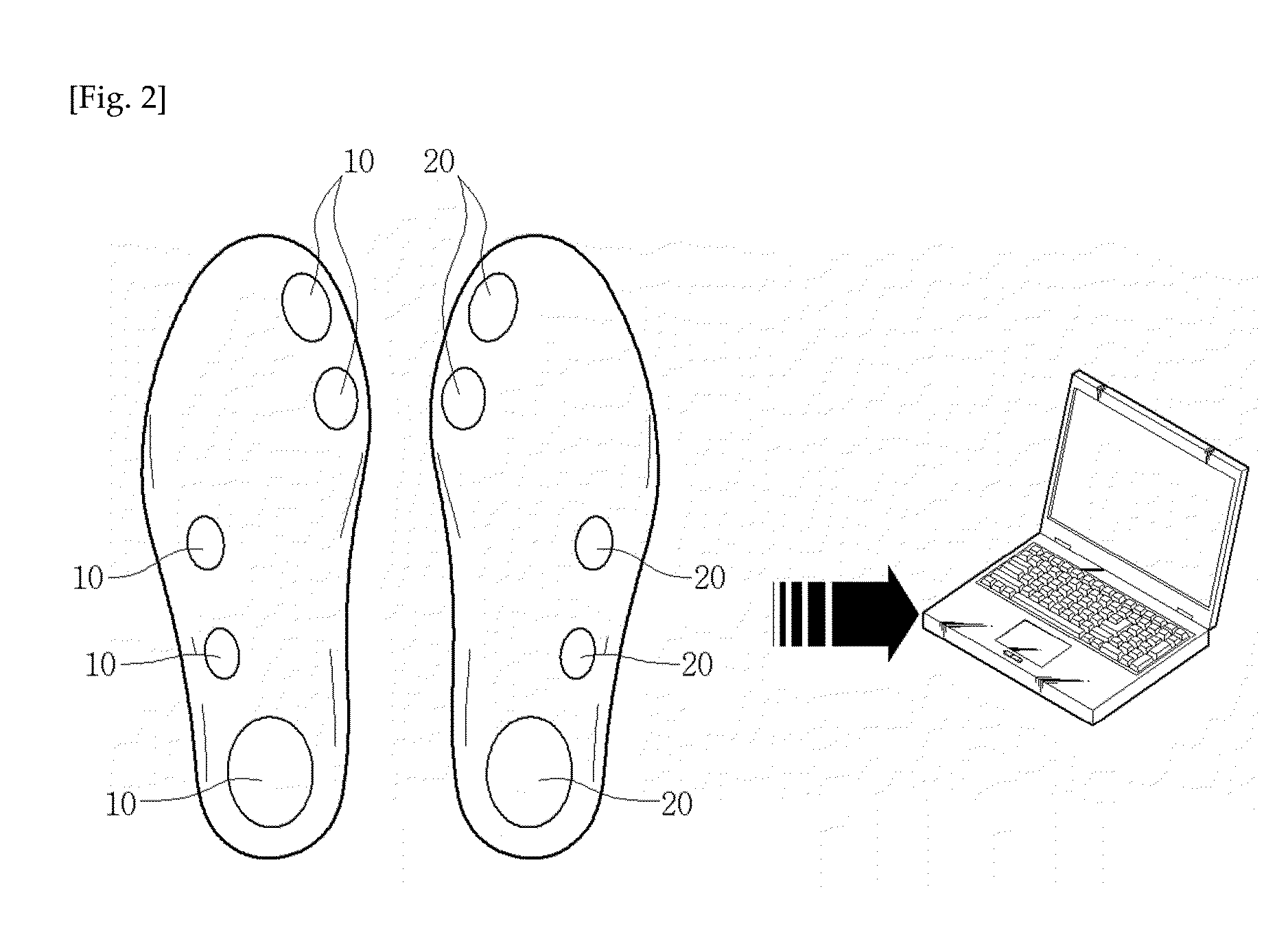
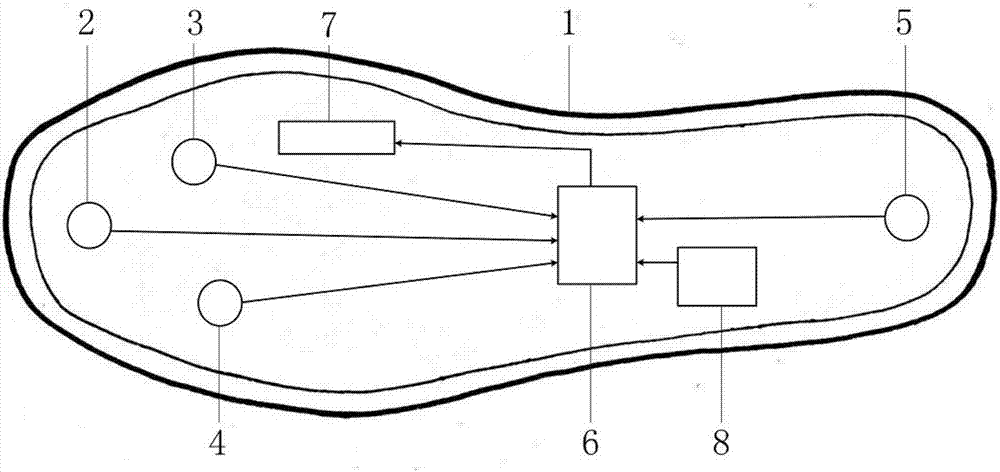
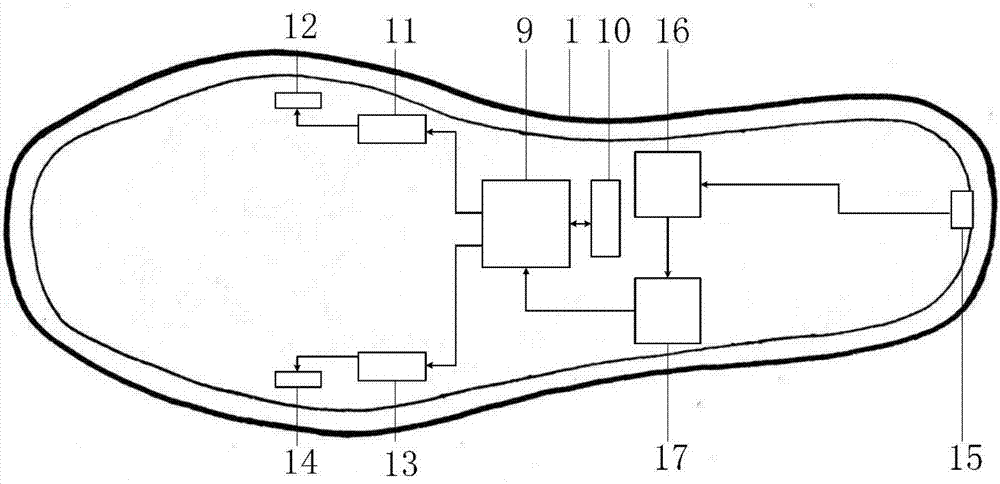
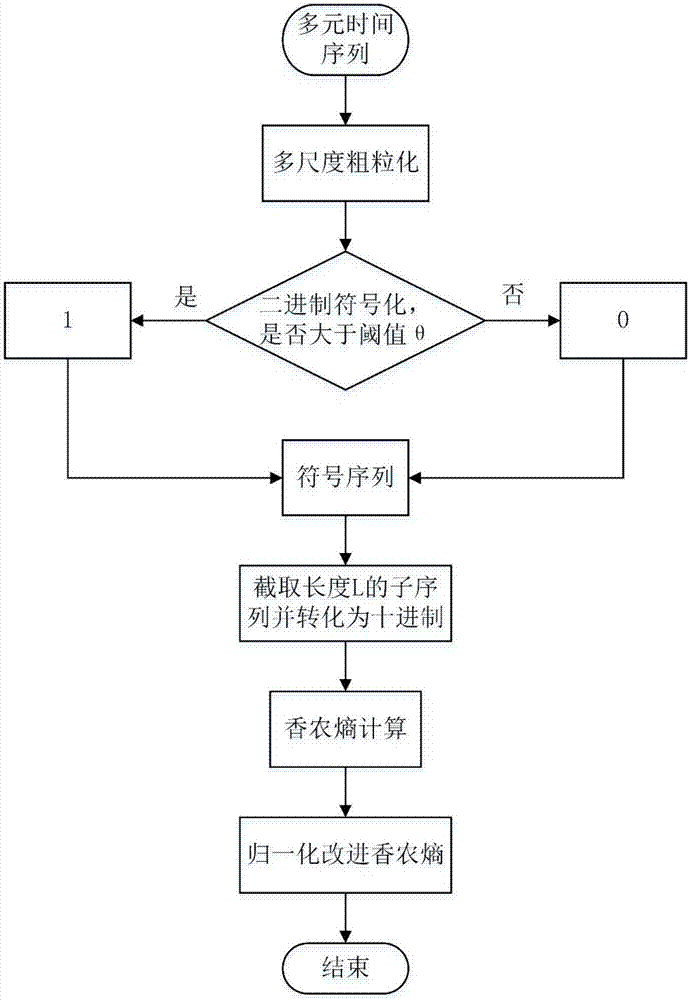
The invention discloses a wearable intelligent insole with the health consultation function. The wearable intelligent insole with the health consultation function comprises an insole base layer, flexible pressure sensors, a control circuit, a signal transmission circuit and a power supply device, wherein the flexible pressure sensors, the control circuit, the signal transmission circuit and the power supply device are arranged in the insole base layer. The flexible pressure sensors are put on corresponding positions of a tiptoe, a first metatarsophalangeal joint, a fourth metatarsophalangeal joint and a heel respectively, the signal output ends of the flexible pressure sensors are connected with the input end of the control circuit, the output end of the control circuit is connected with the input end of the signal transmission circuit, and the power supply device is connected with the control circuit for supplying power to the flexible pressure sensors. A main chip of the control circuit is integrated with the multi-ary-and-multi-scale-symbolic-entropy data analysis method, and the movement condition, the gait characteristics and the healthy condition of the human body are analyzed according to multiple pressure signals of the foot sole. According to the wearable intelligent insole with the health consultation function, signals of the abnormal gait and the healthy normal gait can be analyzed, processed and identified, and limitation of small data points is met; meanwhile, the coupling relationship between pressure signals of different parts of the foot sole is achieved, the accuracy and the efficiency of gait identification are improved, and the human health is conveniently and remotely monitored.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Apparatus for controlling a load on a hip joint
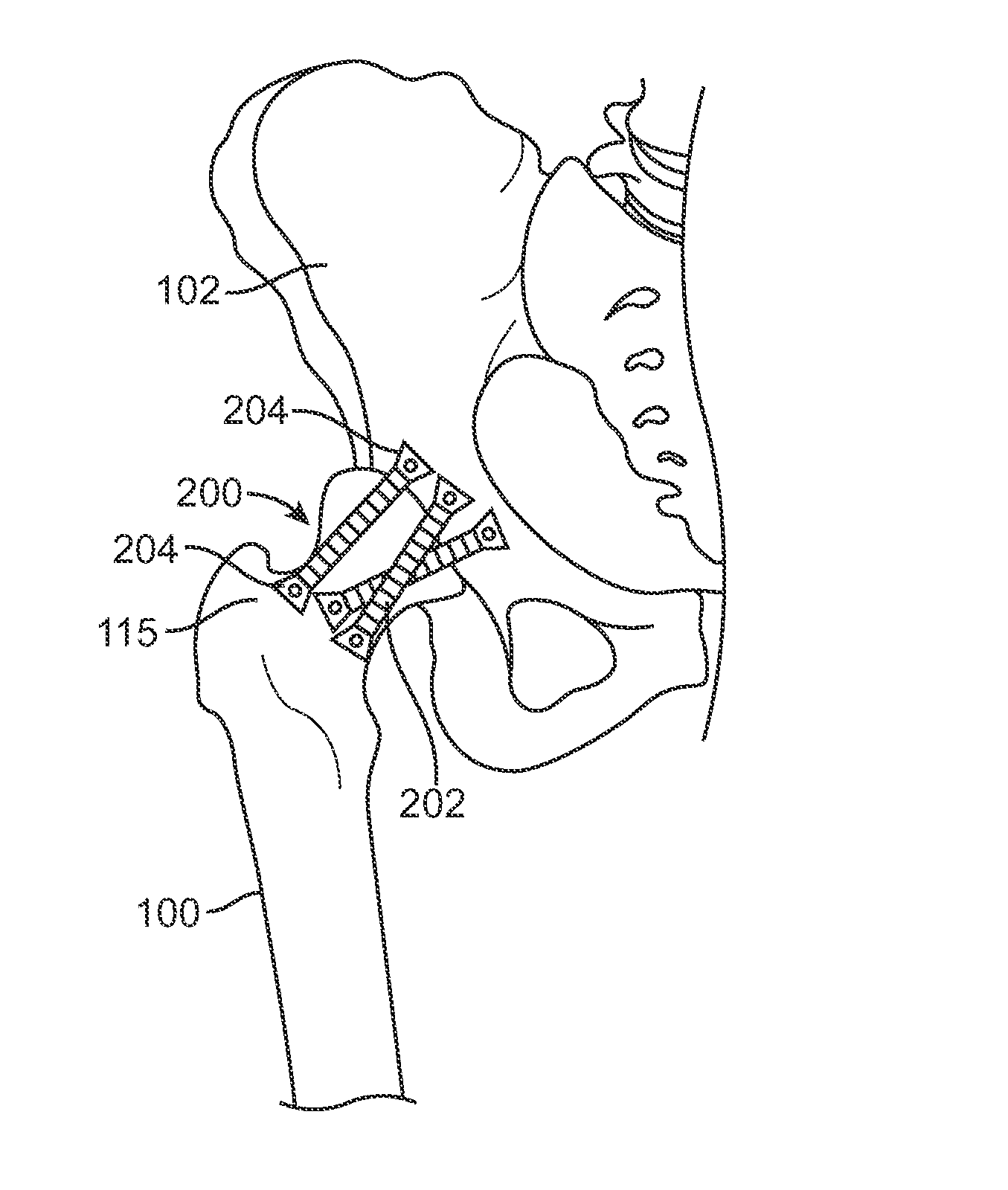
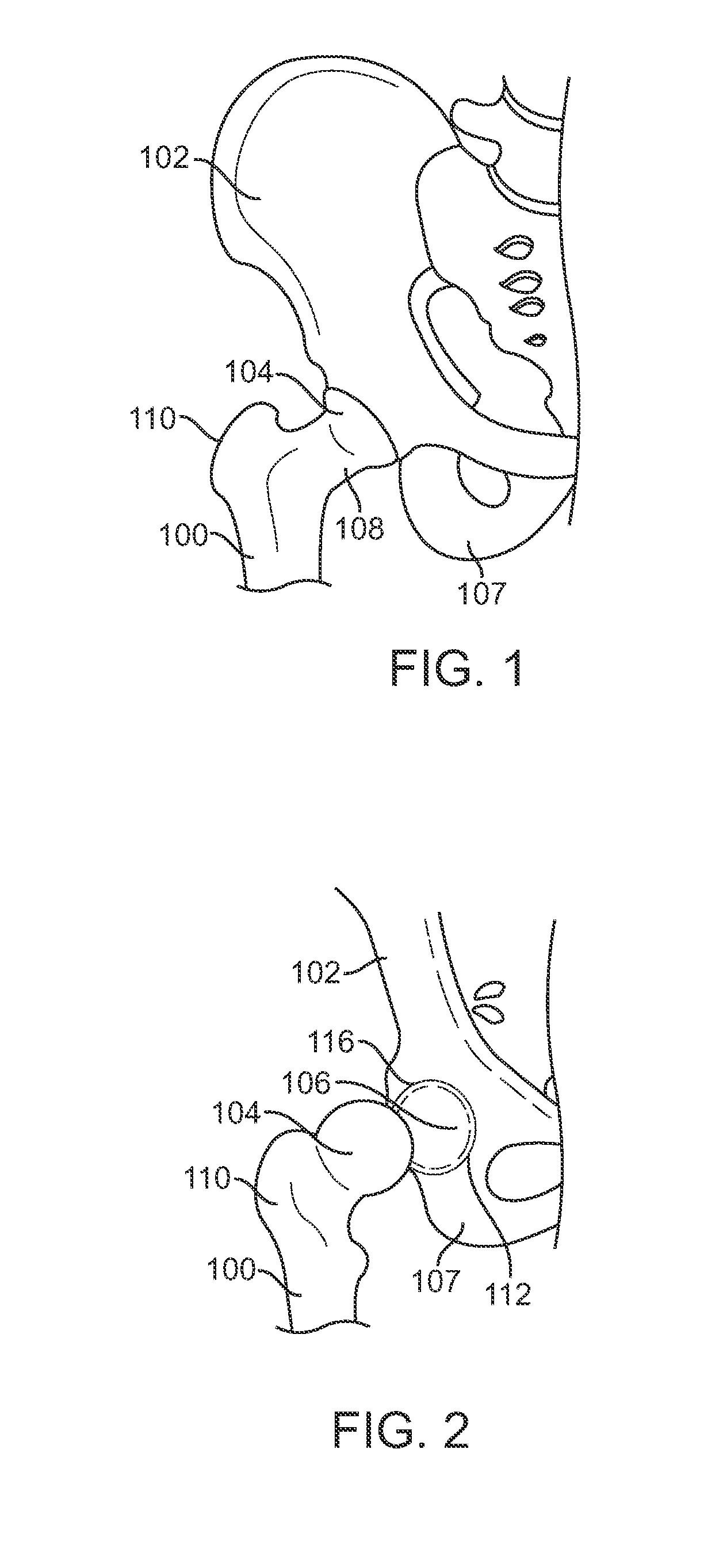
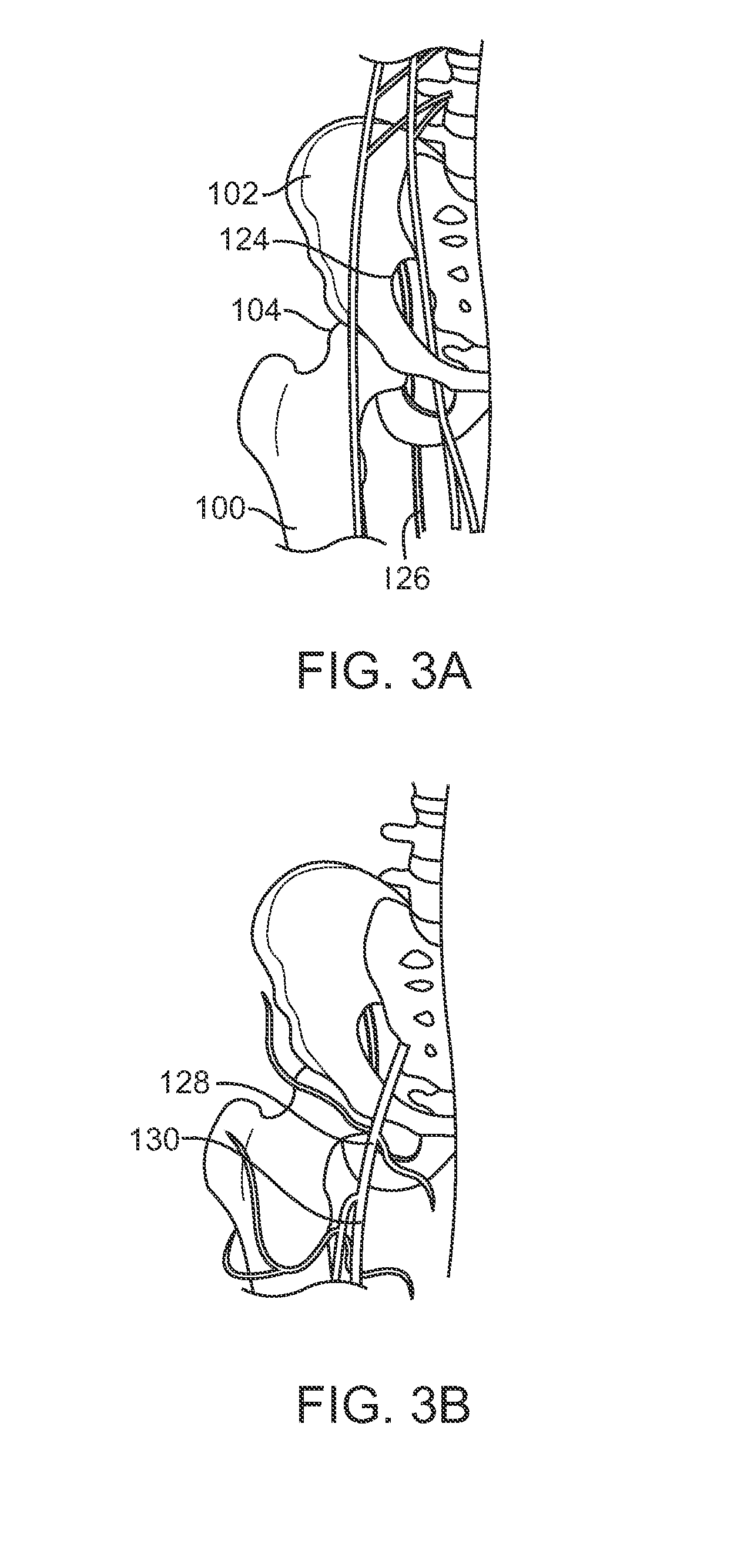
InactiveUS20120046754A1Reduce pressureResisting mobilitySurgeryJoint implantsMuscles of the hipPelvis
An apparatus and related method for controlling a load on a human hip joint during normal gait while preserving motion. The approach is intended to treat osteoarthritis of the hip without substantially resisting an angular displacement associated with full mobility of the pelvis and femur bones.
Owner:MOXIMED INC
Artificial leg gait test system
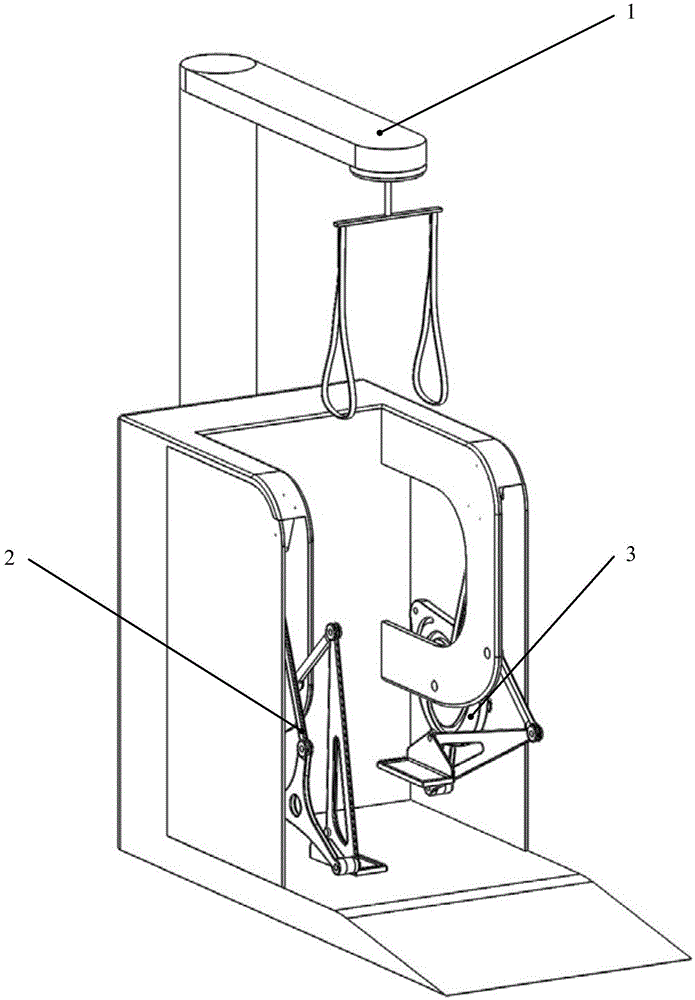
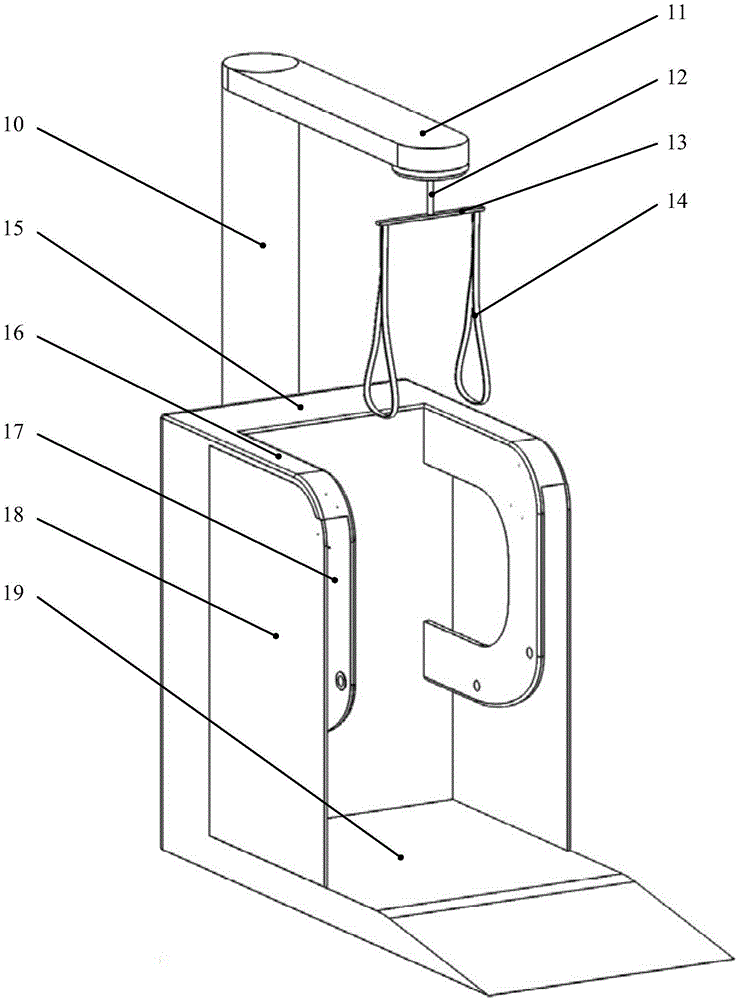
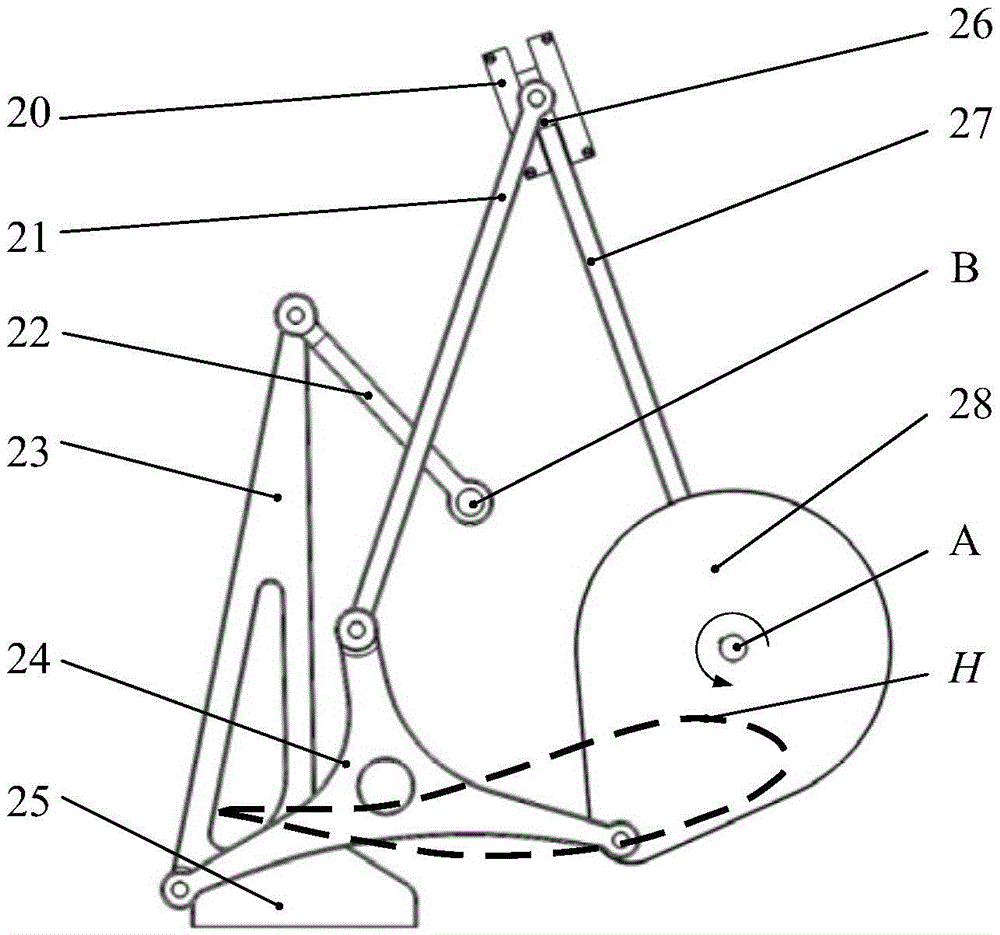
The invention relates to a lower limb prostheses gait testing system, consisting of a simulation leg, a power source, a transmission device and a measurement and control system; the measurement and control system comprises a four-corner displacement sensor, a data collecting module, a motion control card and a computer processing system; wherein, the computer processing system is fixed on an external box body on the ground surface by a bracket; the four-corner displacement sensor is respectively arranged at two hip joints and two knee joints and used for collecting and simulating the joint angle change of the gait, and transmits the collected signal to the computer processing system by a data collecting module; furthermore, by the software of the control system and the collecting system, the collected gait joint angle data in the whole gait period when human walks normally is used as the control signal; the power source is controlled by a motion control card; the output of the power source drives the motion of the simulation leg by the transmission device, thus realizing the simulation of the normal human walking gait. The system of the invention can basically simulate the normal gait of the human body, can provides feasible testing platform for the objective evaluation of the prostheses performance.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Active intention control-based portable ankle joint rehabilitation robot
The invention relates to an active intention control-based portable ankle joint rehabilitation robot comprising a leg protection fixing mechanism, a walking-assisting mechanism connected to the leg protection fixing mechanism, a foot plate mechanism arranged on the leg protection fixing mechanism to be connected with the walking-assisting mechanism, and a gait correction mechanism connected to thefoot plate mechanism. A pressure sensor and a microprocessor are integrated on the foot plate mechanism. With a plantar pressure sensing system, a plantar pressure signal of a testee can be processedduring the test and active motion intention of the testee can be captured; the active motion intention is converted into a control instruction and the walking-assisting mechanism can be controlled and ankle dorsal flexure and plantar flexion rehabilitation and normal gait walk can be assisted for the testee; and the gait correction mechanism can be controlled and ankle inward turn and outward turn rehabilitation training can be completed. Reliable foundation is laid for the rehabilitation evaluation system and the training system; and the active intention control-based portable ankle joint rehabilitation robot has high overall control precision and great real-time control capability.
Owner:深圳睿瀚医疗科技有限公司
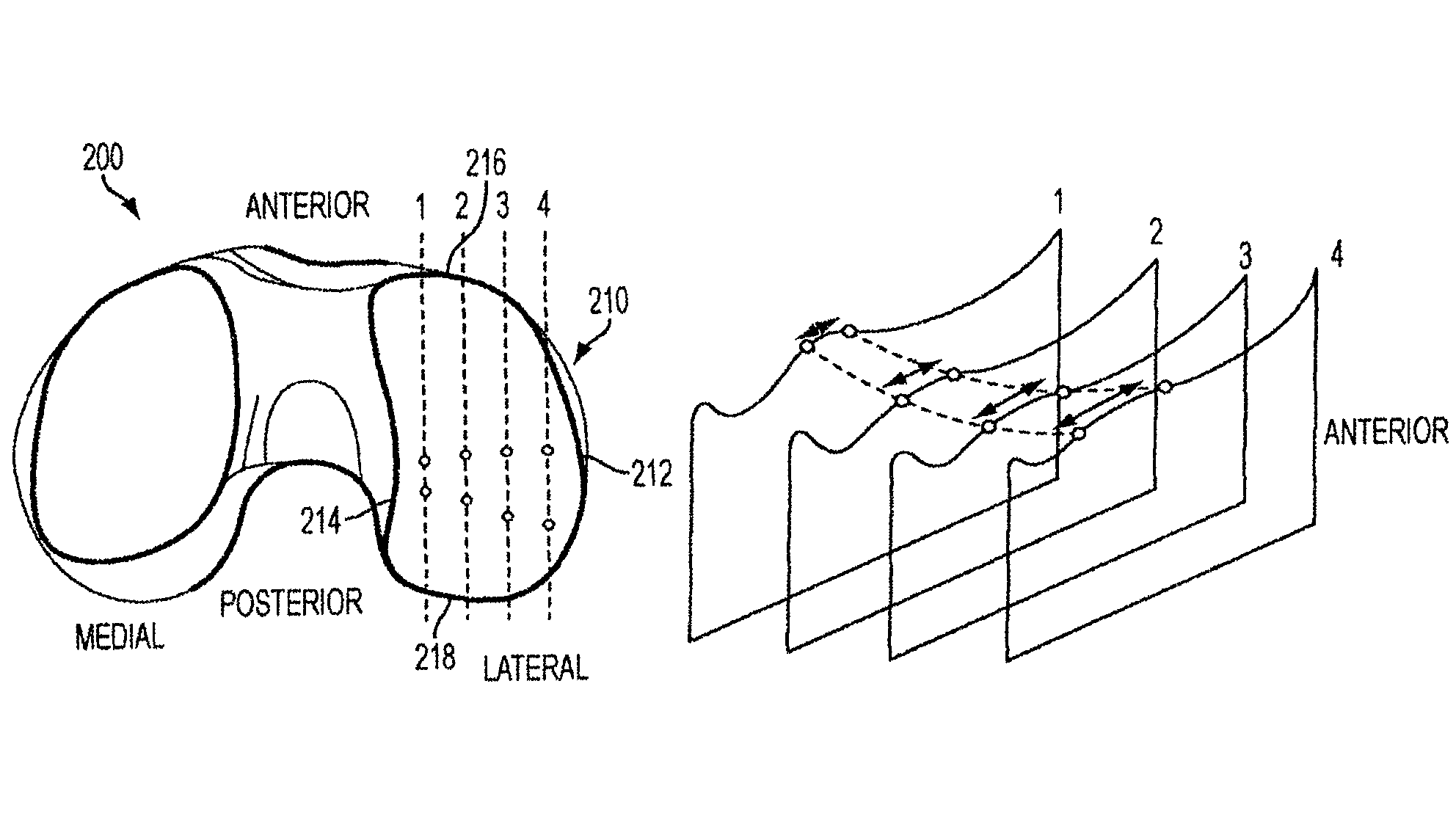
Implant for restoring normal range flexion and kinematics of the knee
ActiveUS8911502B2Reduced radiusAvoid collisionJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesForce equilibrium
Embodiments of the invention provide knee prostheses which more faithfully and closely replicate the function, anatomy and physiology of the normal human knee yielding a number of advantages. Among other things, such prostheses can provide an increased range of motion and function more normally particularly in extension, deep flexion and during normal gait. Knee prostheses according to various aspects of the invention recognize that during movement of the knee, particularly during flexion, the kinematics of the bones of the knee are a result of achieving equilibrium of the forces that cause motion of the knee. In addition, the shape of the articular surfaces acting in combination with forces imposed by various muscles, ligaments and tendons, determines the direction of the large contact forces.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
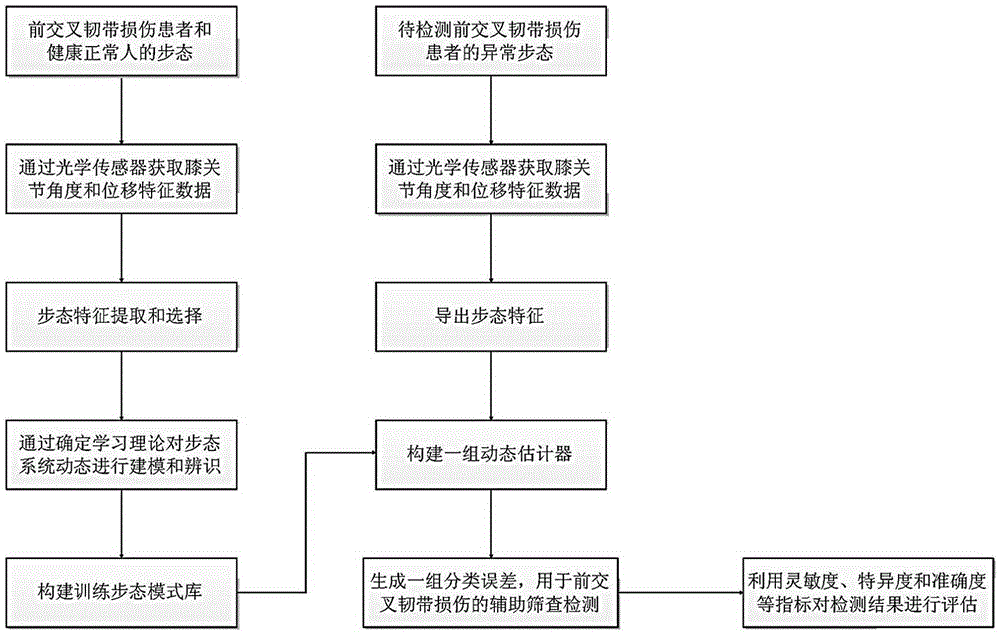
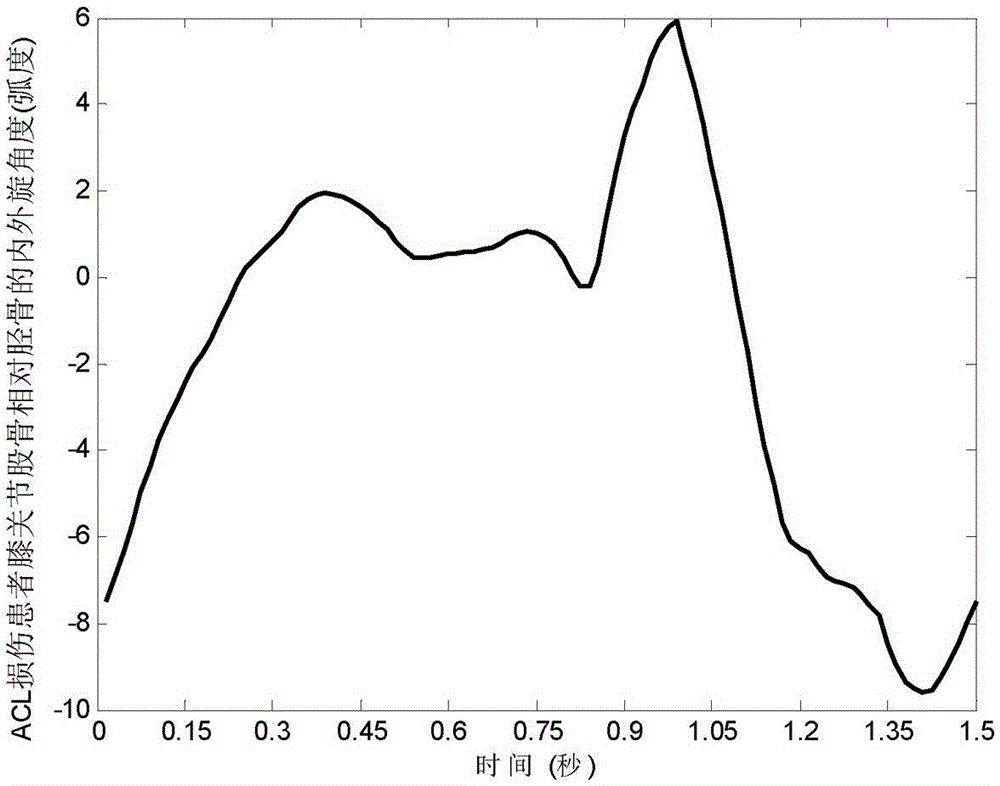
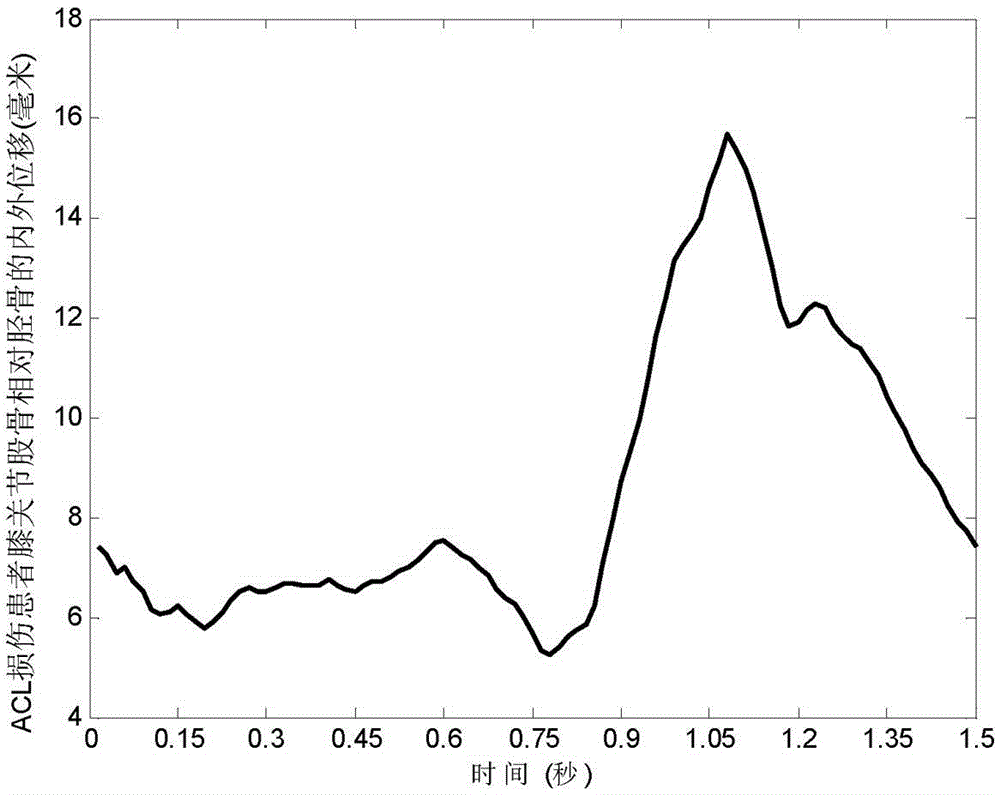
Gait analysis method for auxiliary screening of injury of anterior cruciate ligament
InactiveCN105286875AEnables assisted screening testingShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsArthroscopic procedureNerve network
The invention discloses a gait analysis method for auxiliary screening of injury of anterior cruciate ligament. The method comprises the following steps: based on the gait characteristics of the extracted knee joint angle and displacement, carrying out neural network modeling and identification on gait system dynamics of healthy normal persons and patients with injury of anterior cruciate ligament; establishing a constant neural network; constructing a dynamic estimator by utilizing the constant neural network; and based on the difference between gait modes of the healthy normal persons and the patients with injury of anterior cruciate ligament in gait system dynamics, distinguishing the abnormal gait caused by the injury of anterior cruciate ligament from the normal gait of the healthy persons according to the minimum error principle, thereby realizing auxiliary screening detection of the injury of anterior cruciate ligament. According to the invention, the gait characteristic data of the knee joint angle and displacement is acquired through an optical sensor, so that the abnormal gait caused by the injury of anterior cruciate ligament and the normal gait of the healthy persons can be conveniently, simply and non-intrusively distinguished; and compared with the screening means, such as magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic surgery, the method disclosed by the invention can realize non-invasive screening and can save time and cost.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
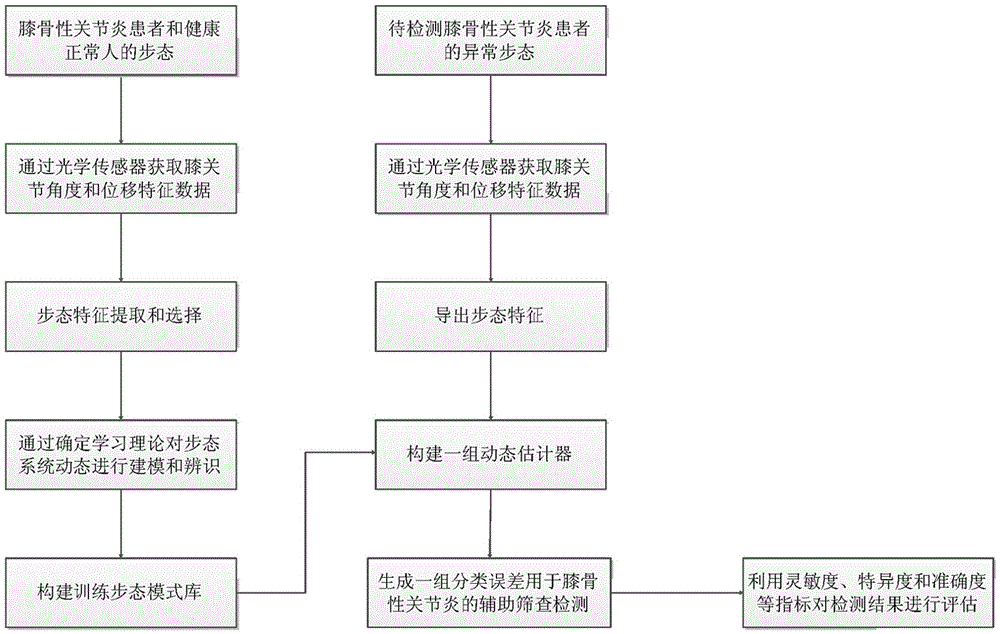
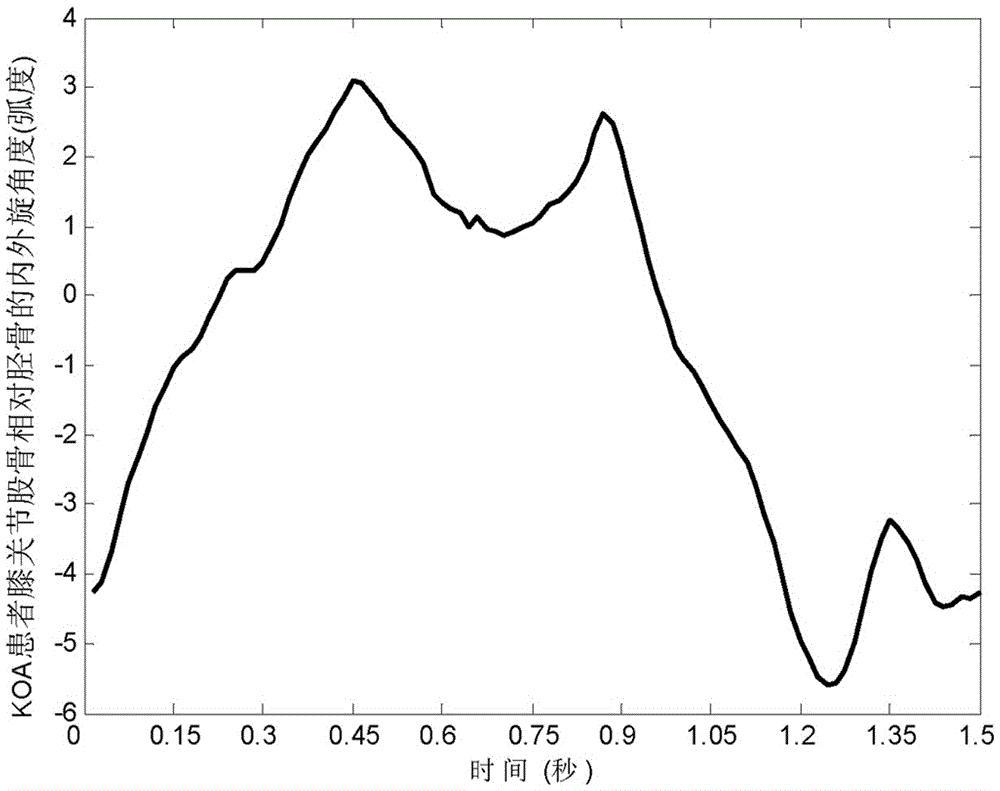
Gait analysis method capable of carrying out auxiliary screening on knee osteoarthritis
InactiveCN105468908ARealize non-invasive auxiliary screening detectionEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsNeural learning methodsNerve networkKnee Joint
The invention discloses a gait analysis method capable of carrying out auxiliary screening on knee osteoarthritis. The gait analysis method comprises the following steps: on the basis of the gait characteristic data of an extracted knee joint angle and displacement, dynamically carrying out neural network modeling and identification on the gait system of healthy normal people and the gait system of knee osteoarthritis patients; establishing a constant value neural network; and utilizing the constant value neural network to construct a dynamic estimator, distinguishing abnormal gaits caused by the knee osteoarthritis and the normal gaits of general healthy crowd according to a minimum error principle on the basis of differences between the gait modes of the healthy normal people and the knee osteoarthritis patients on an aspect of gait system dynamics to realize the auxiliary screening detection of the knee osteoarthritis. An optical sensor obtains the gait characteristic data, and the abnormal gaits caused by the knee osteoarthritis and the normal gaits of the general healthy crowd can be conveniently and simply distinguished in a non-intrusive way. Compared with screening means including magnetic resonance imaging, arthroscopic surgeries and the like, the gait analysis method can realize the noninvasive screening of the knee osteoarthritis and saves time and cost.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
Power-assisted lower limb exoskeleton device
ActiveCN110394783AImprove energy utilizationImprove applicabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorThighKnee Joint
The invention discloses a power-assisted lower limb exoskeleton device. The power-assisted lower limb exoskeleton device comprises a waistband, thigh binding bands and shank binding bands, wherein thewaistband, the thigh binding bands and the shank binding bands are sequentially arranged from top to bottom, hip joint devices are arranged between the waistband and the thigh binding bands, knee joint devices are arranged between the thigh binding bands and the shank binding bands, the waistband is connected with the hip joint devices through a waist support, the hip joint devices are connectedwith the knee joint devices through a thigh support, and the knee joint devices are connected with the shank binding bands through a shank support. According to the power-assisted lower limb exoskeleton device, the power-assisted lower limb exoskeleton device is designed according to gait characteristics of a human body, the energy generated by the hip movement and the knee movement is stored through the hip joint devices and the knee joint devices correspondingly, then the whole device and the human body gait work in a cooperating mode through cooperation between a hip and knees, the energy capable of being generated in the normal gait of the human body can be fully stored and released, so that the energy utilization rate is improved, the power-assisted lower limb exoskeleton device is worn on the human body through the waistband and the binding bands, and the wearing applicability is greatly improved.
Owner:THE QUARTERMASTER RES INST OF THE GENERAL LOGISTICS DEPT OF THE CPLA
Ankle-Foot Orthosis
An Ankle-Foot Orthosis, or AFO, has a vertical portion and a horizontal portion joined together. The horizontal portion is fixed to a shoe, which is selected by a user, by separating at least part of the sole such that the horizontal portion can be adhered near or between a midsole of the sole of a shoe. The horizontal portion provides the necessary structure needed to connect a shoe to the vertical portion of the AFO such that a user suffering with a weakness or deformity can walk with a more normal gait. In an alternate embodiment, the AFO is removable from a shoe such that it can be replaced onto the same or a different shoe.
Owner:SCHWARTZ NATHAN
Implant for Restoring Normal Range Flexion and Kinematics of the Knee
ActiveUS20150088264A1Reduced radiusAvoid collisionJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Embodiments of the invention provide knee prostheses which more faithfully and closely replicate the function, anatomy and physiology of the normal human knee yielding a number of advantages. Among other things, such prostheses can provide an increased range of motion and function more normally particularly in extension, deep flexion and during normal gait. Knee prostheses according to various aspects of the invention recognize that during movement of the knee, particularly during flexion, the kinematics of the bones of the knee are a result of achieving equilibrium of the forces that cause motion of the knee. In addition, the shape of the articular surfaces acting in combination with forces imposed by various muscles, ligaments and tendons, determines the direction of the large contact forces.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Non-invasive, vibrotactile medical device to restore normal gait for patients suffering from peripheral neuropathy
InactiveUS9452101B2Restore balanceChiropractic devicesInertial sensorsVibrotactile stimulationTouch Perception
Owner:WALKJOY
Method for controlling adaptive iterative learning of knee joints of lower prostheses
ActiveCN103750927AGood control requirementsReduce tracking errorProsthesisHuman bodyKnee joint movement
The invention discloses a method for controlling movement of knee joints of lower prostheses of human bodies, and particularly relates to a method for controlling adaptive iterative learning when human bodies with double-rigid-body and two-degrees-of-freedom lower prostheses walk on flat grounds. The method includes firstly, analyzing normal gait features of the human bodies and control requirements of the lower prostheses of the human bodies; secondly, kinetically analyzing the normal gait features of the human bodies and the control requirements of the lower prostheses of the human bodies by the aid of Newton-Euler algorithms and building a movement system model of the double-rigidity-body and two-degrees-of-freedom lower prostheses; thirdly, applying an algorithm for controlling adaptive iterative learning to the movement system model. Flow of the algorithm for controlling adaptive iterative learning includes describing problems; analyzing convergence; solving the boundedness of a first expression; solving the progressive increase property of a second expression; solving the progressive increase property of the first expression. The method has the advantages that knee joint movement tracking errors can be stably reduced within a certain time, and accordingly an excellent tracking effect can be realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Lower limb rehabilitation training elliptical machine device
ActiveCN105167958ARealize rehabilitation trainingEffective rehabilitationChiropractic devicesSingle degree of freedomRest frame
The invention provides a lower limb rehabilitation training elliptical machine device which comprises a device rack, a driving transmission unit, an elliptical trajectory implementation unit and pedal plate connecting units, wherein the device rack comprises an arm-rest frame, a base and vertical plates; the driving transmission unit mainly comprises a drive motor, a small belt wheel, a big belt wheel and a synchronous belt; the elliptical trajectory implementation unit comprises a rotating disc, an elliptical sliding groove, a sliding block, a linear sliding rail and a group of guide wheels; the pedal plate connecting units comprise connecting pieces, pedal plates, flange plates and a bearing. According to the lower limb rehabilitation training elliptical machine device, provided by the invention, a patient is driven to be rehabilitated along the elliptical trajectory, which is more aligned with normal gait of people; besides, as the synchronous belt is in transmission connection with the linear guide rail, and the sliding block is matched with the elliptical sliding groove, the lower limbs can perform rehabilitation training along the elliptical trajectory, the machine device is compact in structure, the mechanism that forms the elliptical trajectory is driven in a single degree-of-freedom manner, and a better lower limb rehabilitation training effect is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Ankle rehabilitation system capable of simulating walking based on VR
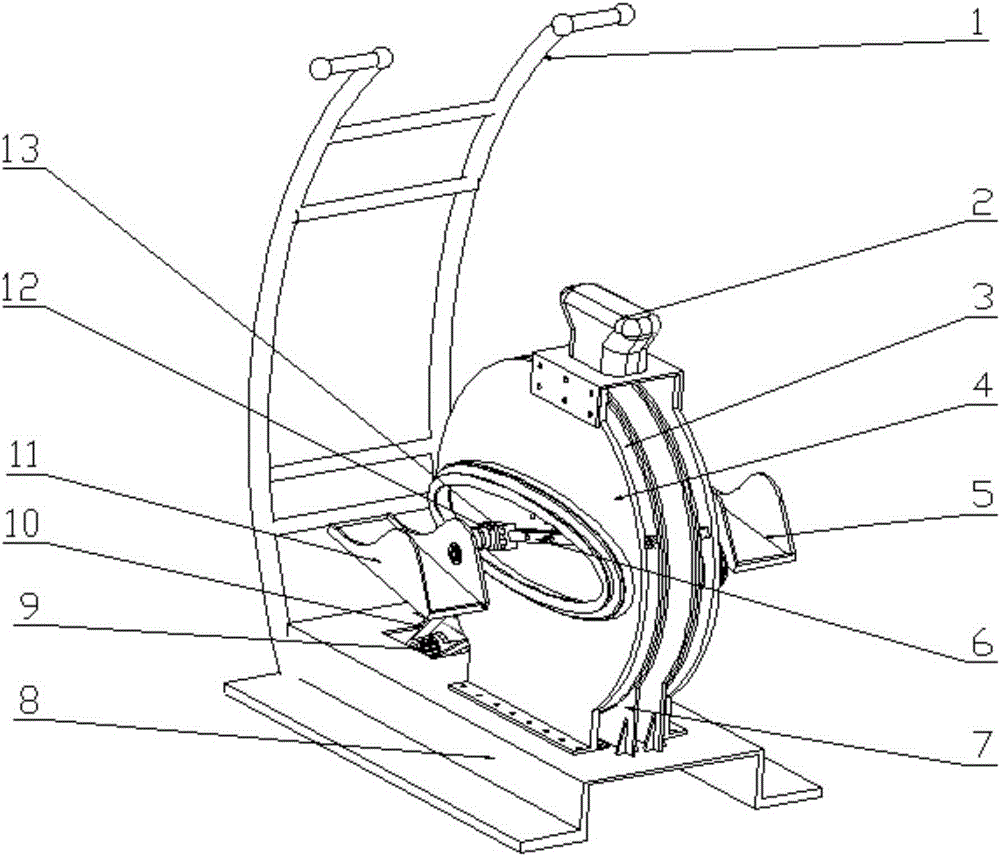
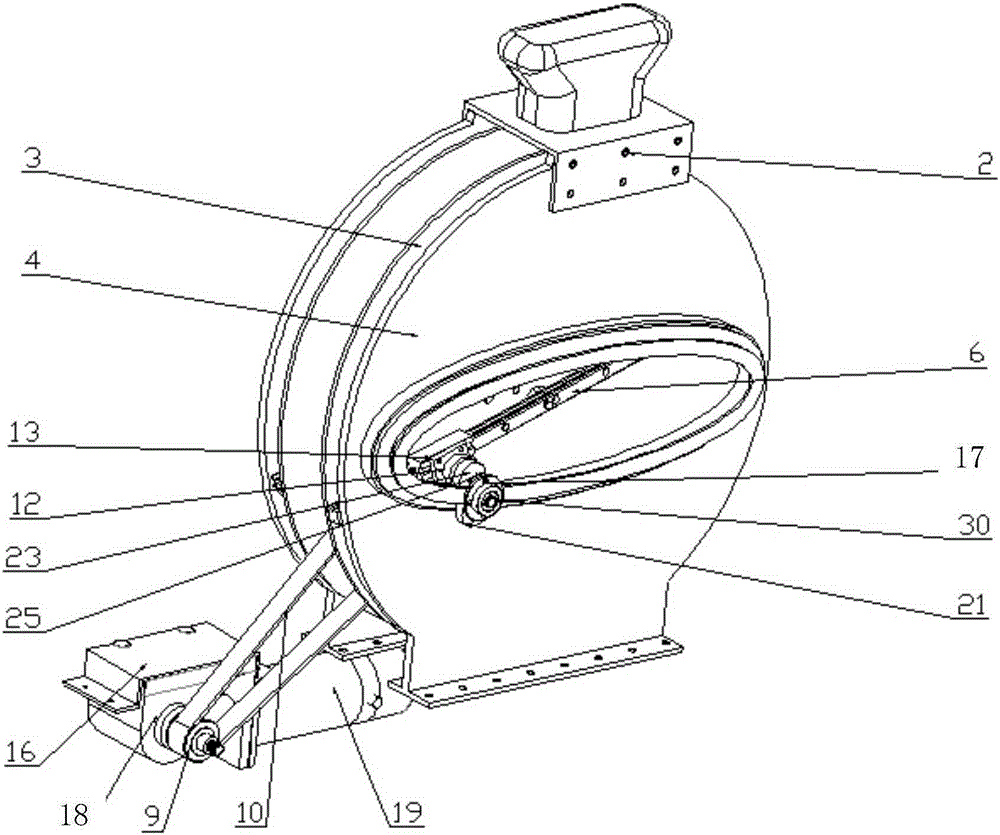
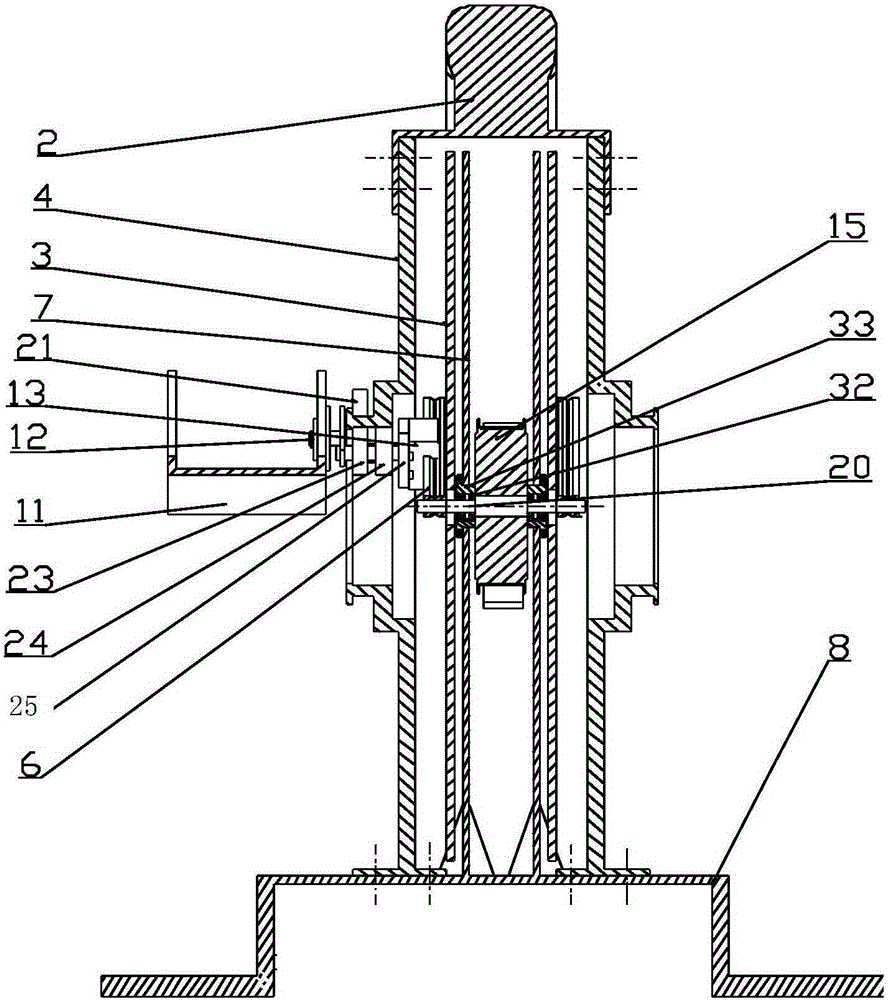
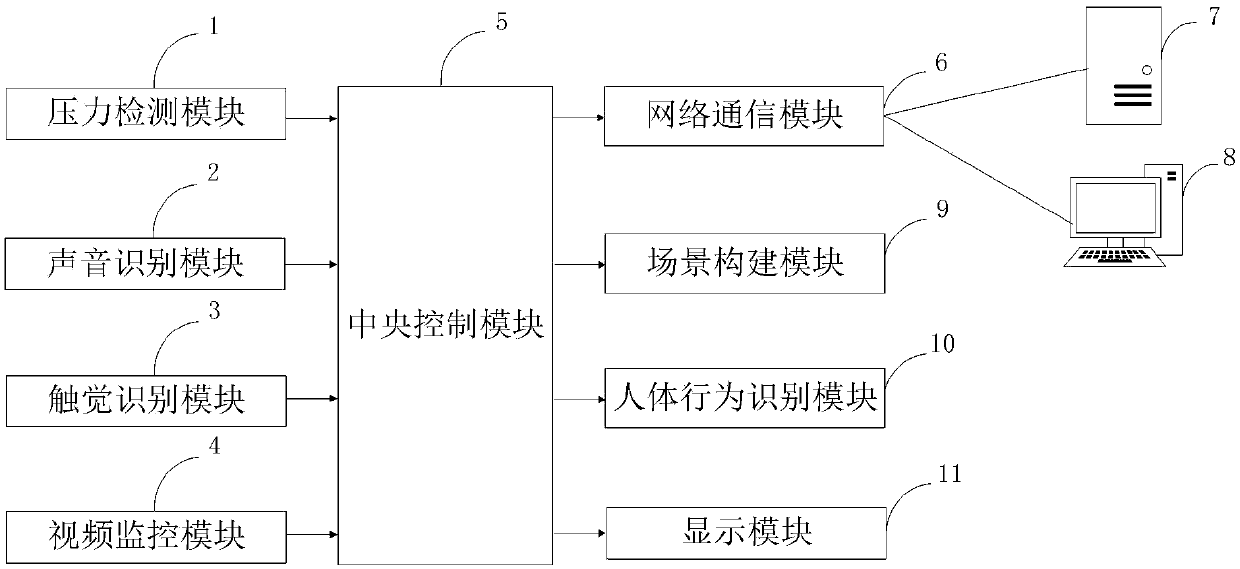
PendingCN109545323AImprove walking abilityImprove recovery efficiencyPhysical therapies and activitiesCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringHuman behavior
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical rehabilitation, and discloses an ankle rehabilitation system capable of simulating walking based on VR. The system comprises a pressure detection module, a voice recognition module, a touch recognition module, a video monitoring module, a central control module, a network communication module, a server, a computer, a scene construction module, a human behavior recognition module, and a display module. The system provided by the invention is more advantageous for a user to actively carry out rehabilitation training of an ankle in a scene through a scene reconstruction module; can simulate the walking state of a patient through the visual feedback of the VR, feeds back and corrects a pathological walking mode, and forms a normal gait, thereby improving walking ability. Compared with the traditional walking rehabilitation training, the system has the effects of shortening the rehabilitation process, improving the rehabilitation efficiency and improving the rehabilitation effect. Through human behaviors, the system determines the moving significance area via the idea that a severe moving region provides more discriminating information in the behavior recognition, and assists the rehabilitation of the ankle.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUIZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com