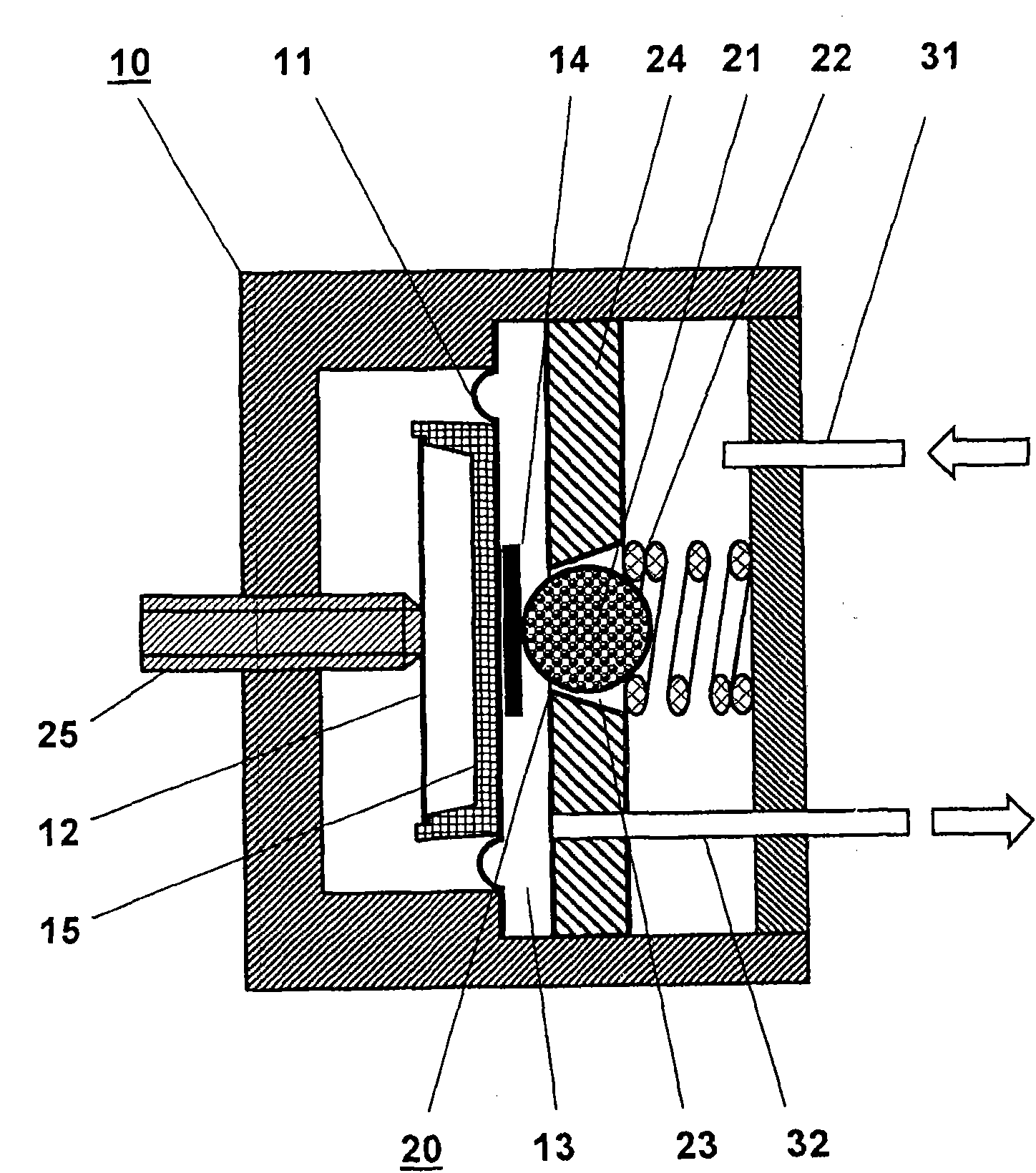
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Force equilibrium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
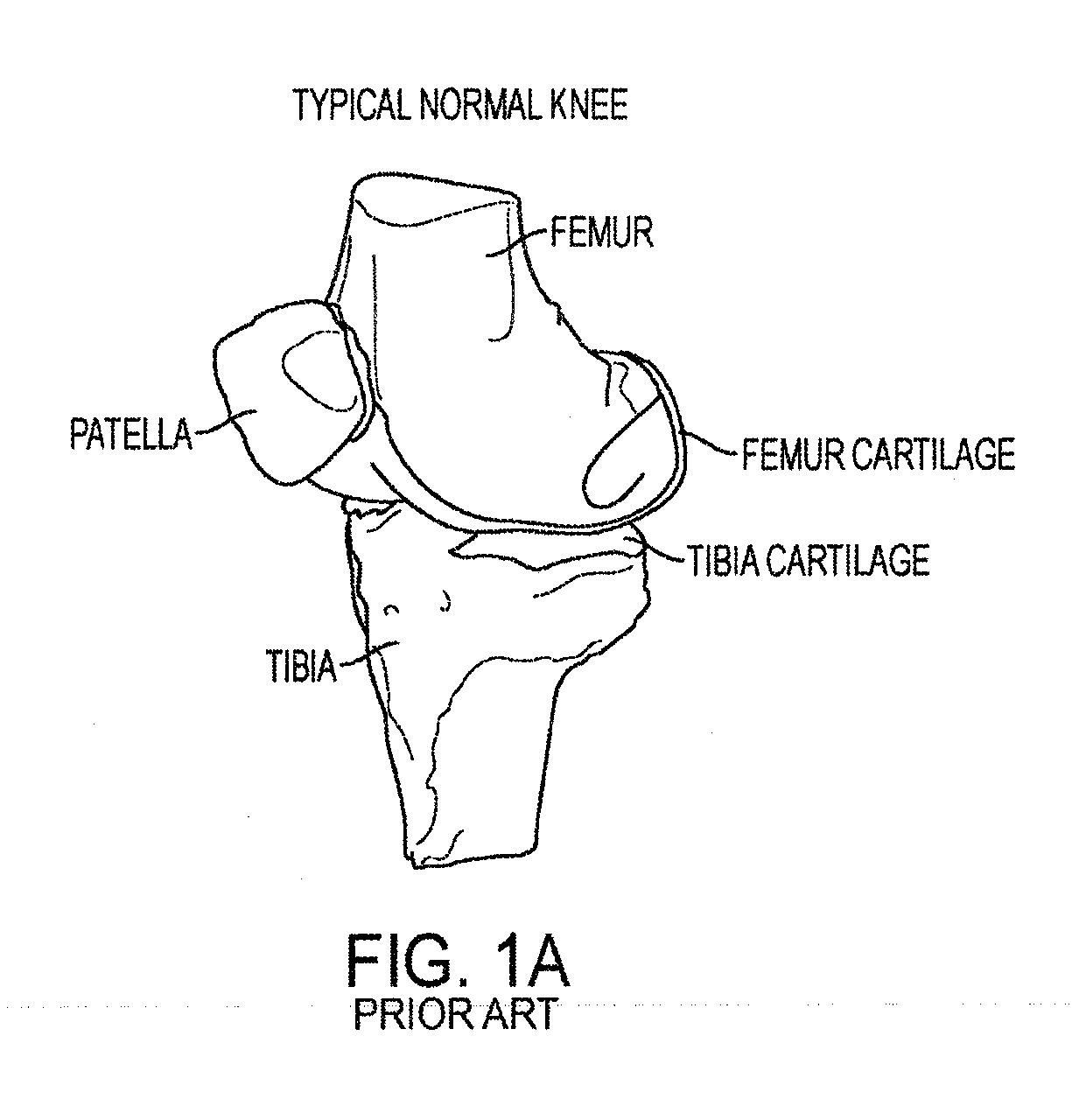
EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCE EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCES An object is in equilibrium when it is not accelerated, that is there is no force acting on it in any direction. For a body in equilibrium, the forces acting on it are so related in magnitude and direction that no acceleration results.
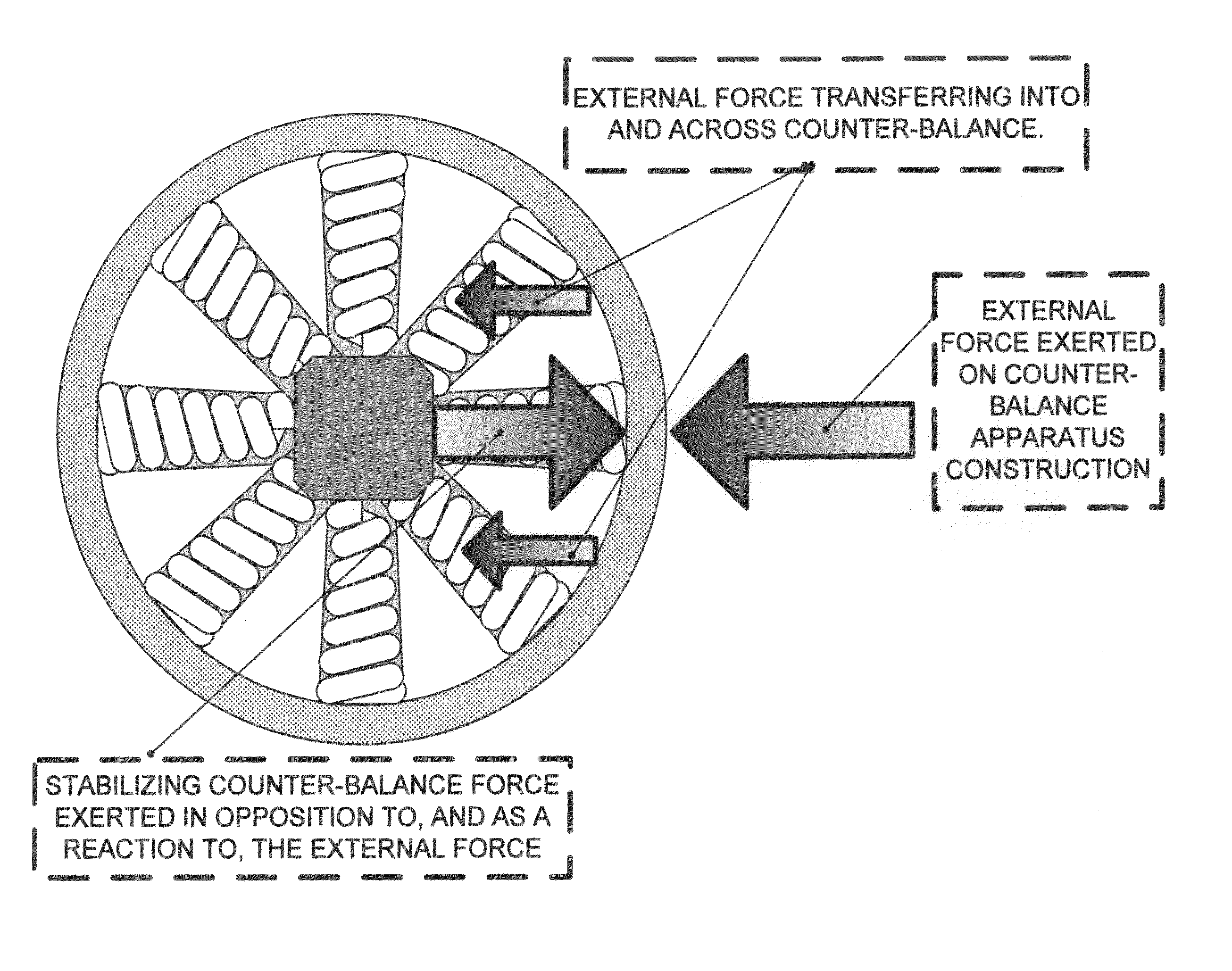
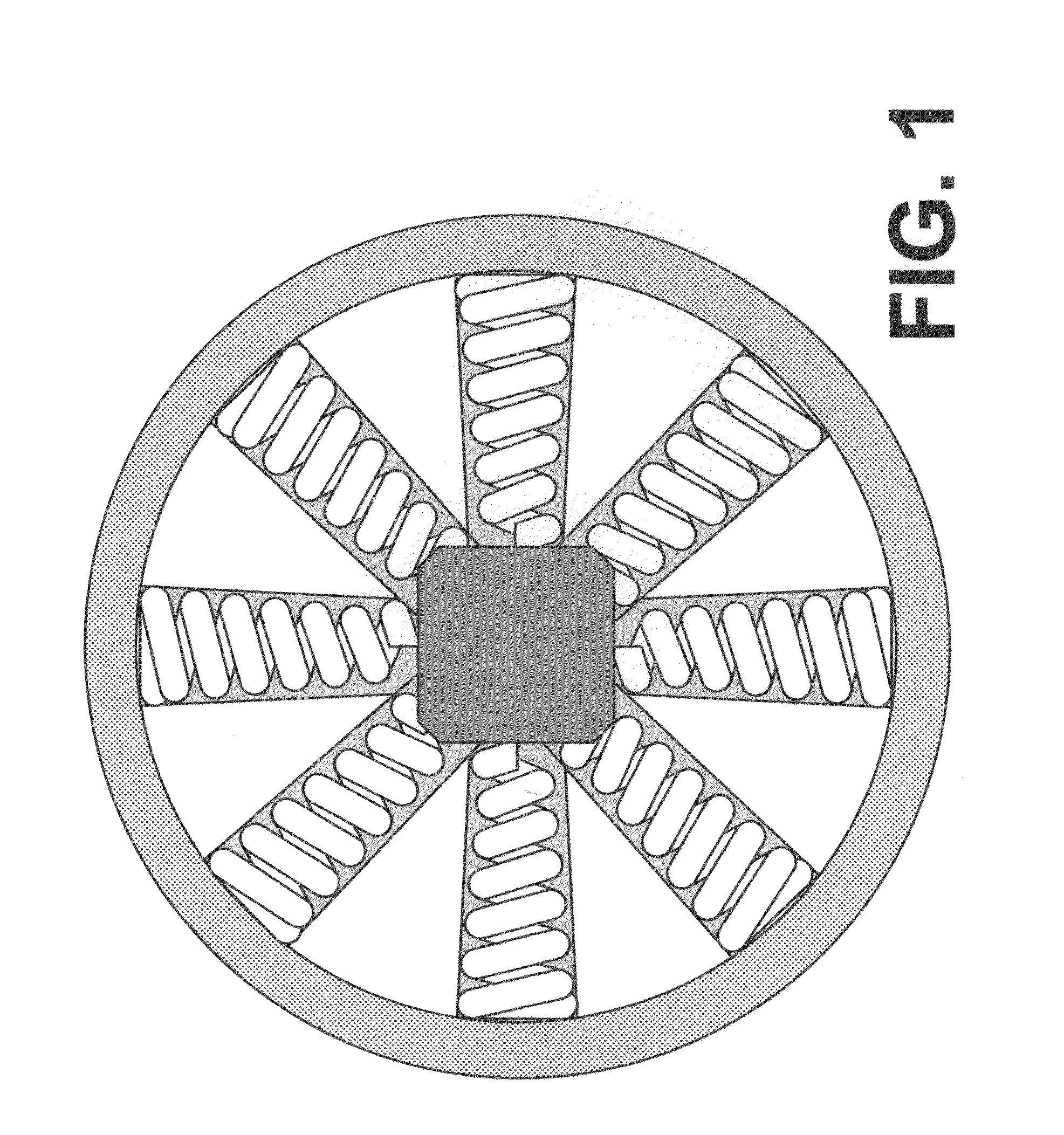
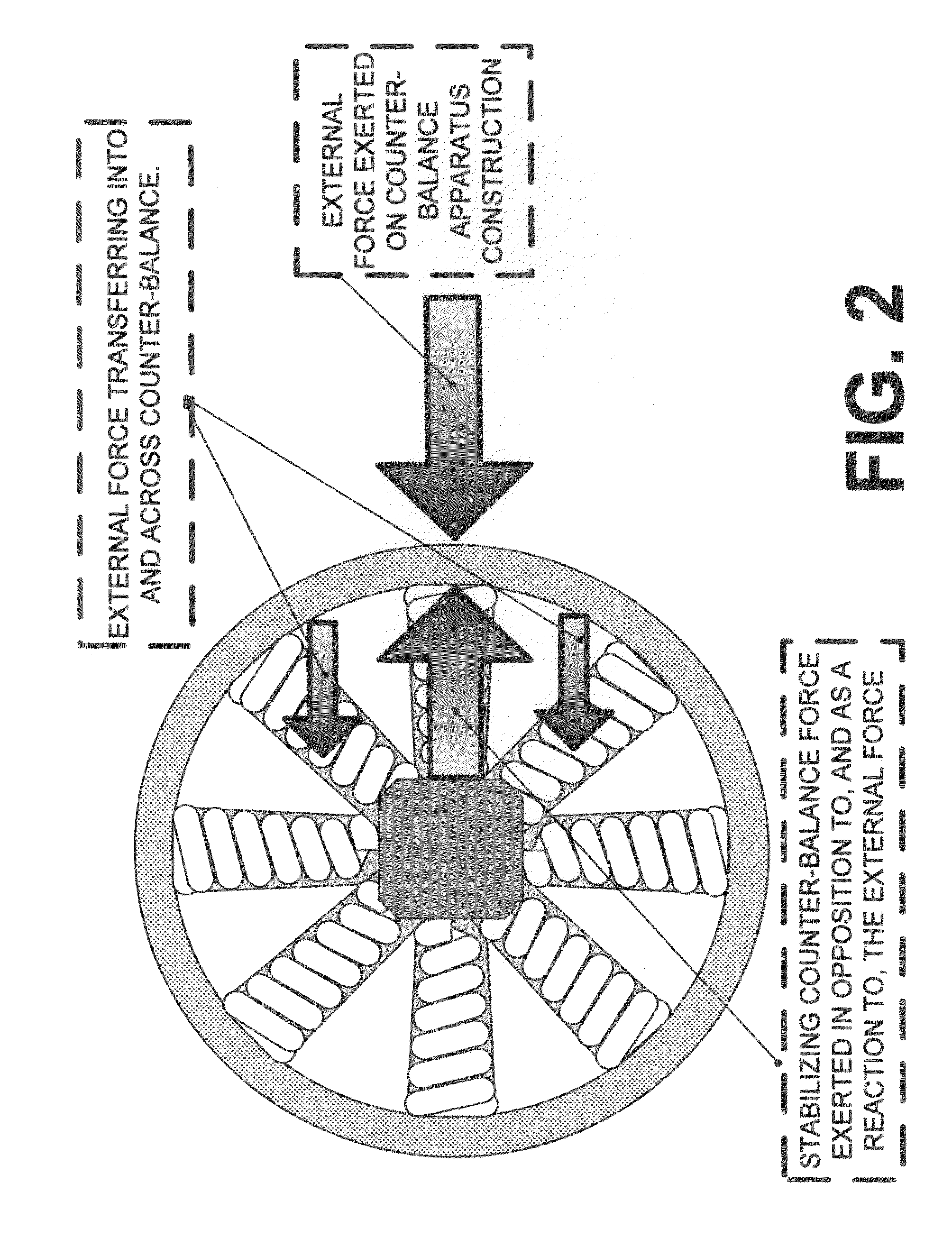
Counter-balance apparatus and method for providing a stabilizing force
InactiveUS20100263167A1Change effectNon-rotating vibration suppressionBuilding braking devicesForce equilibriumEngineering
A counter-balance apparatus and method, including configurable weights, suspensions, and supports, upon which an external force can be exerted, and as a result, will react as a counter-balance to said external force as a means to provide force resistance and stability; wherein the construct may be encapsulated, varied in materials, size, and substance, enabling said counter-balance with a predictable and known effect to be produced at scale, readily installed, moved, or manipulated, to address a plethora of stabilization applications, and which further comprises fastener(s) and / or band(s) to secure it to immobile, mobile, or in-motion objects, and computational and communications capabilities to dynamically adjust to external factors.
Owner:FOX SEYMOUR IAN
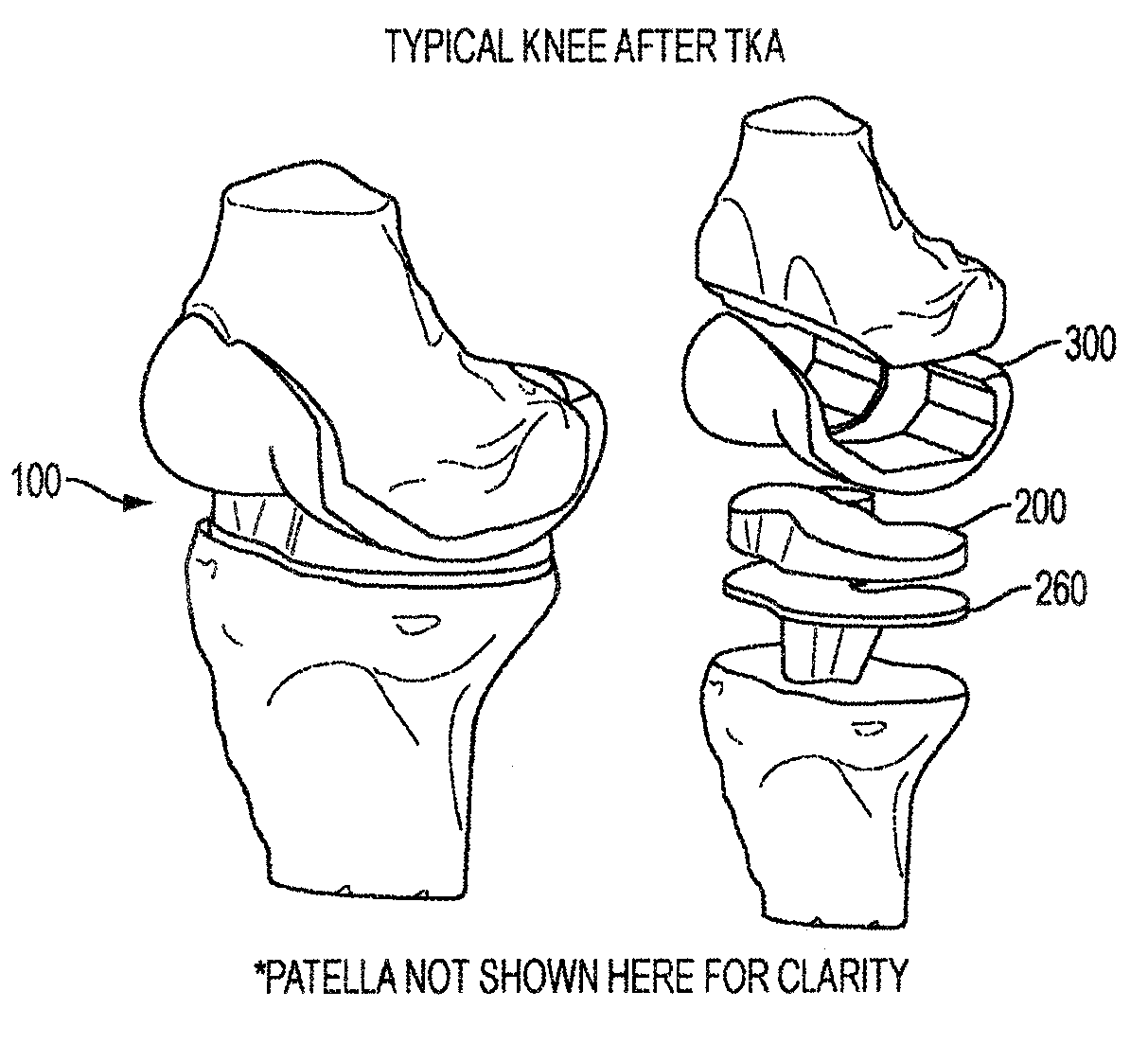
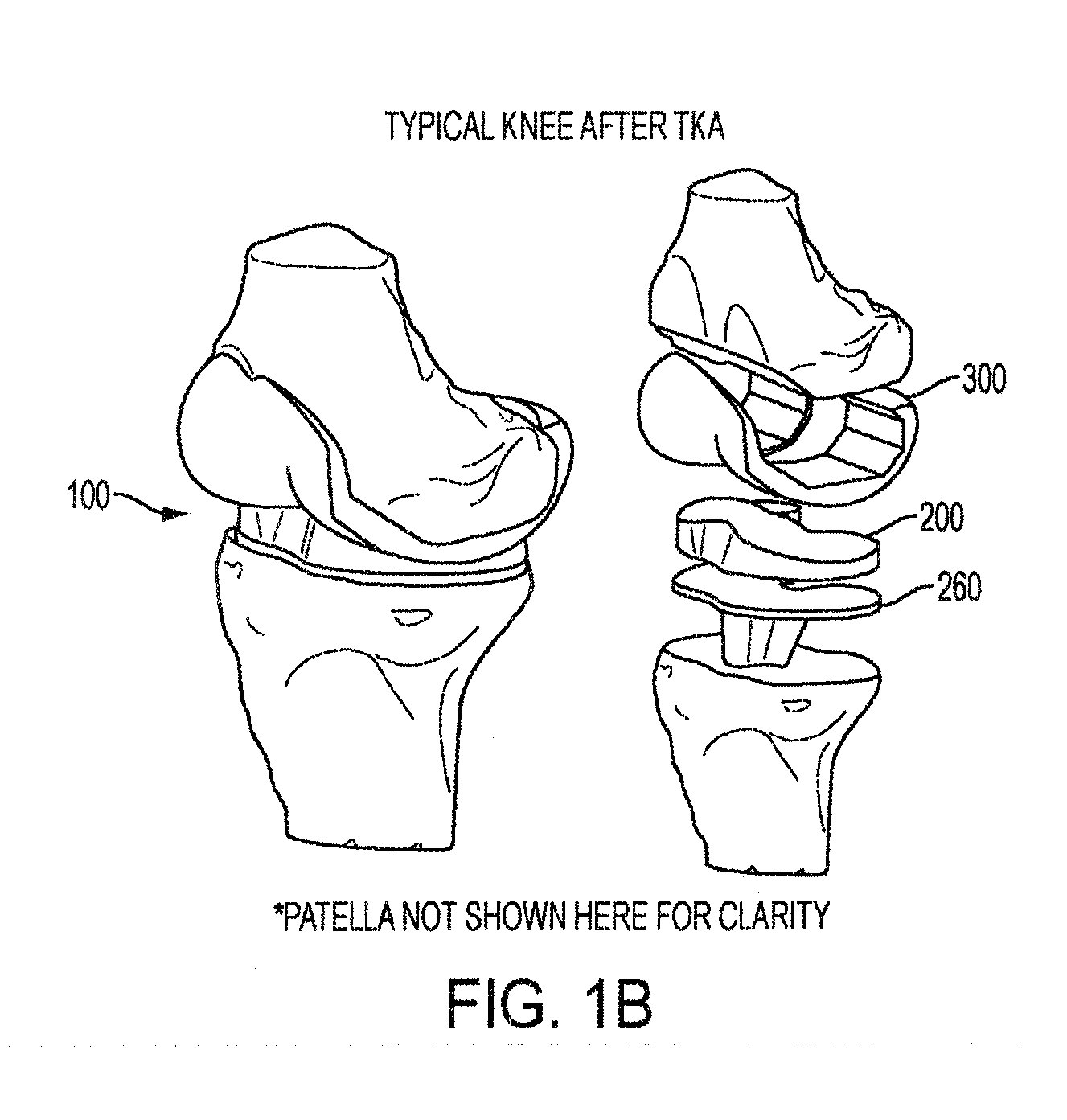
Implant for restoring normal range flexion and kinematics of the knee
ActiveUS20120310362A1Prevent subsidenceHigh strengthJoint implantsKnee jointsForce equilibriumArticular surface
Embodiments of the invention provide knee prostheses which more faithfully and closely replicate the function, anatomy and physiology of the normal human knee yielding a number of advantages. Among other things, such prostheses can provide an increased range of motion and function more normally particularly in extension, deep flexion and during normal gait. Knee prostheses according to various aspects of the invention recognize that during movement of the knee, particularly during flexion, the kinematics of the bones of the knee are a result of achieving equilibrium of the forces that cause motion of the knee. In addition, the shape of the articular surfaces acting in combination with forces imposed by various muscles, ligaments and tendons, determines the direction of the large contact forces.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
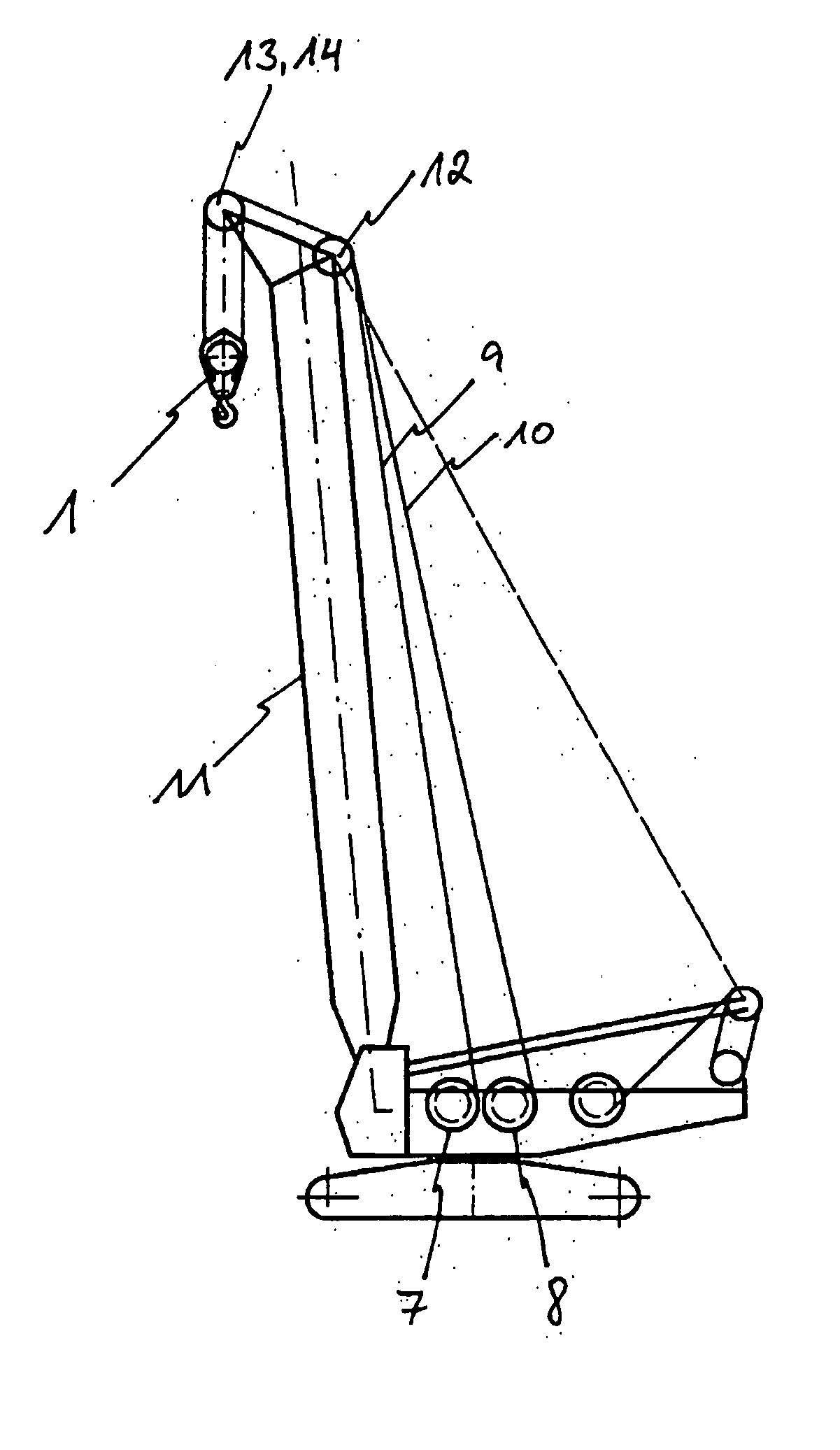
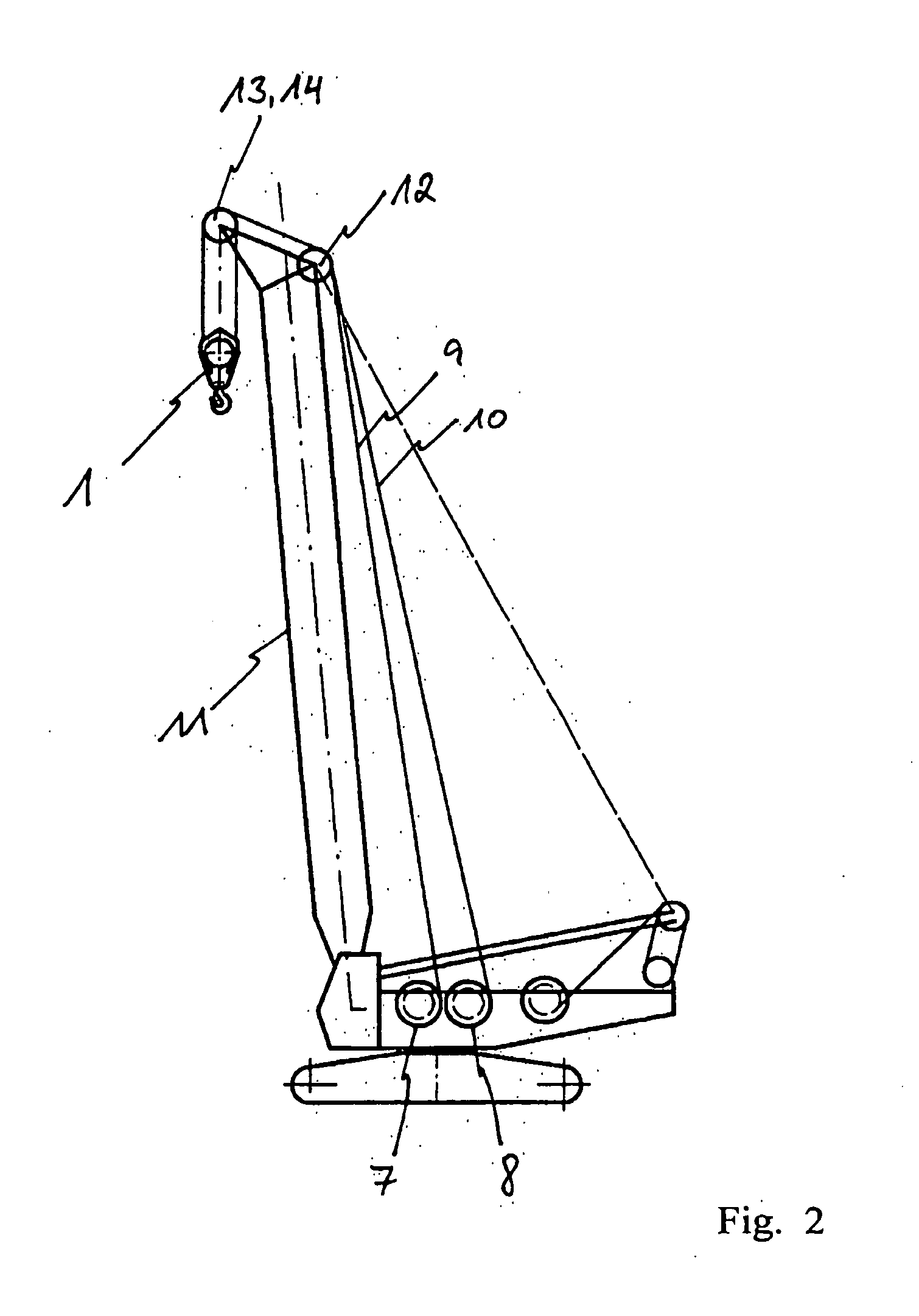
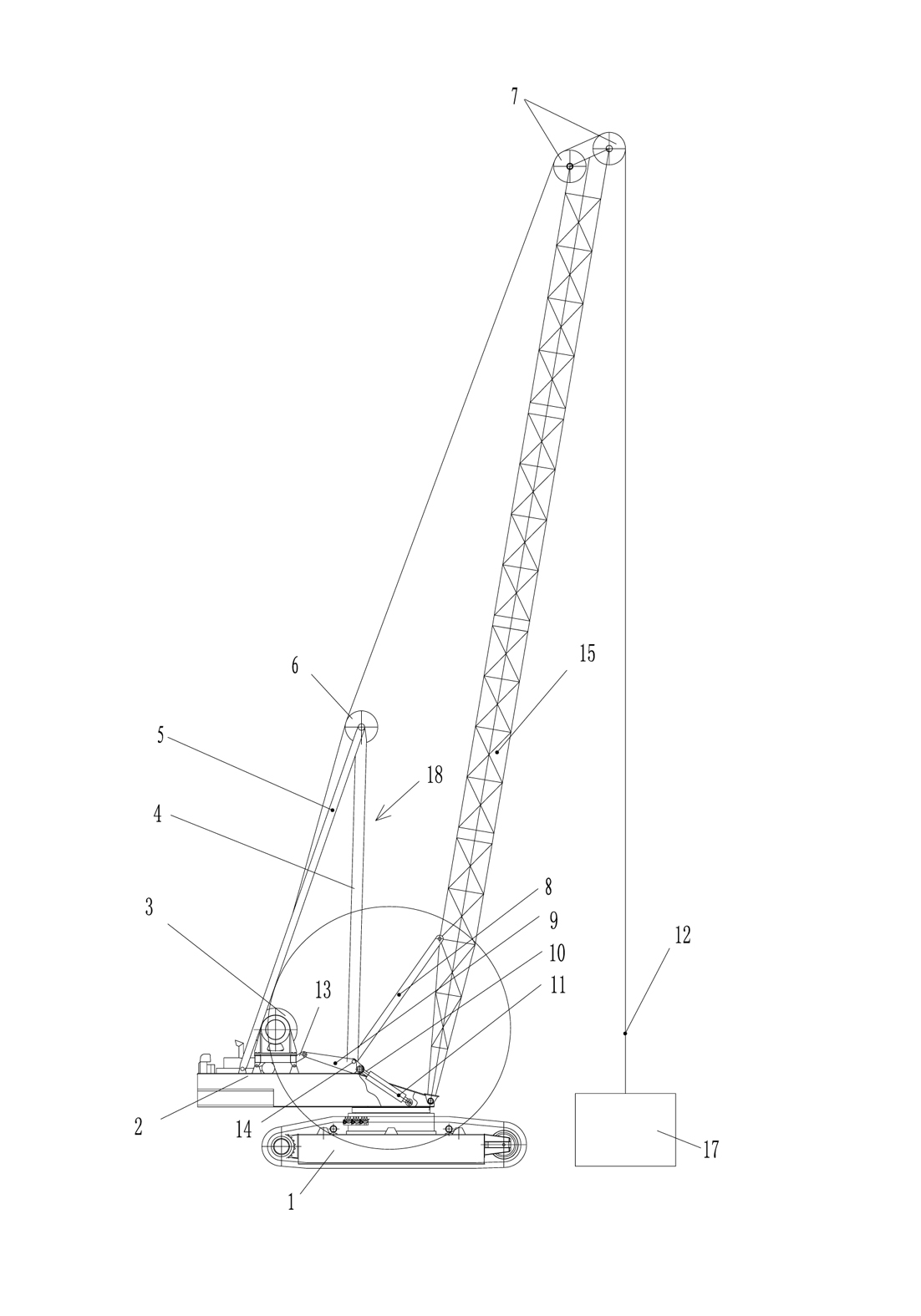
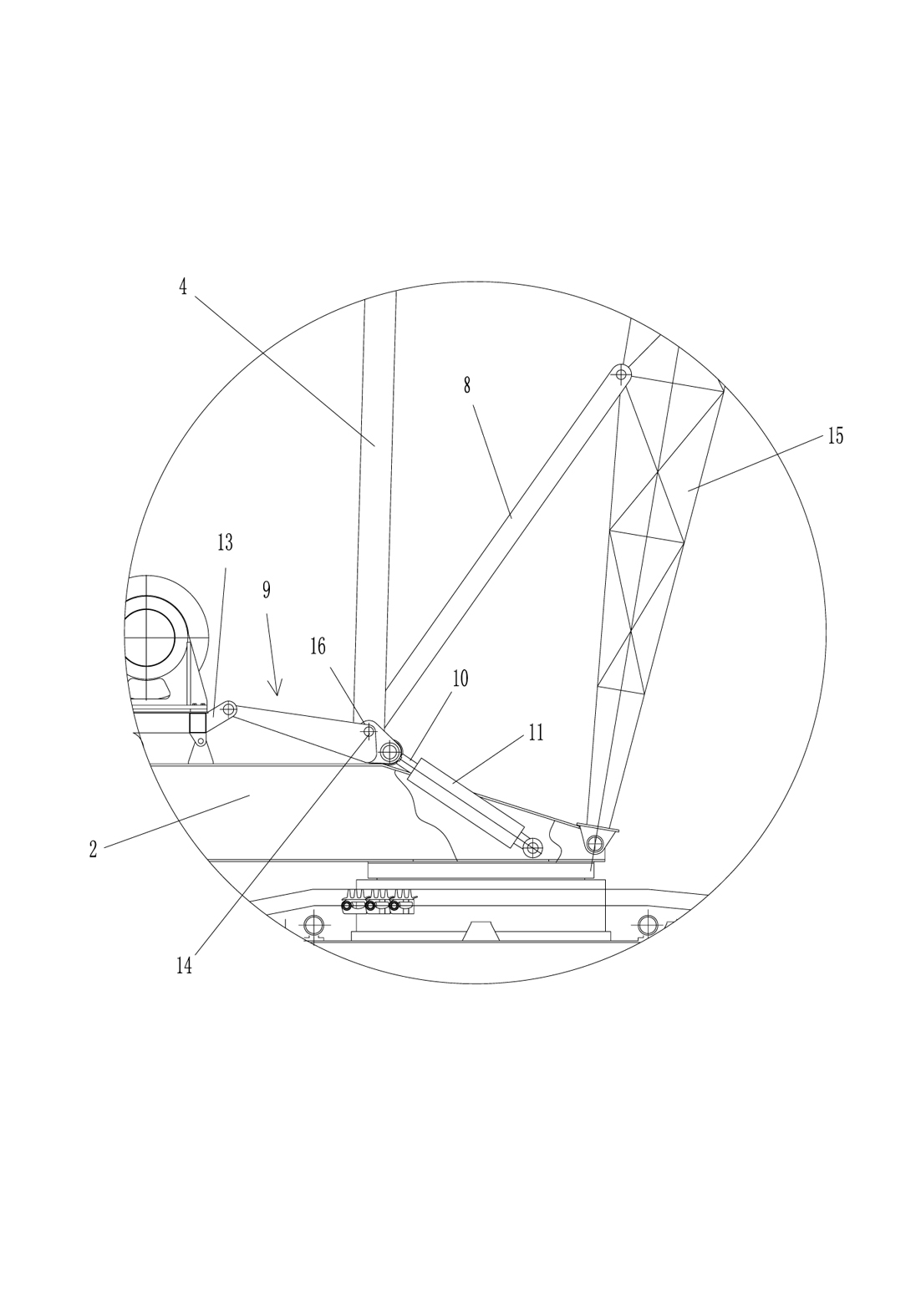
Hoisting-Cable Drive Comprising a Single Bottom-Hook Block and Two Winches
ActiveUS20070290182A1Easy to handleSolid and difficult to handlePortable liftingWinding mechanismsForce equilibriumDouble bottom
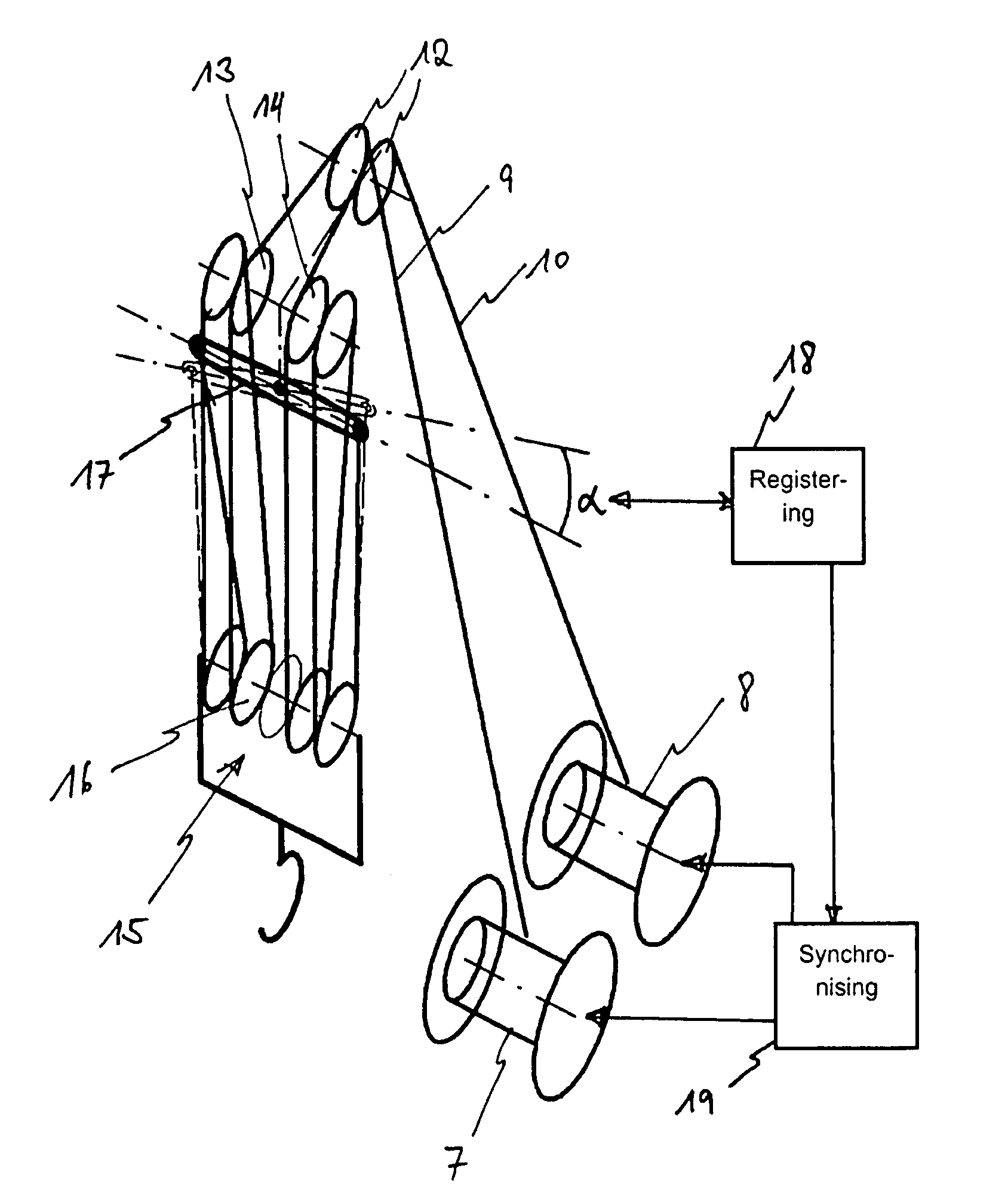
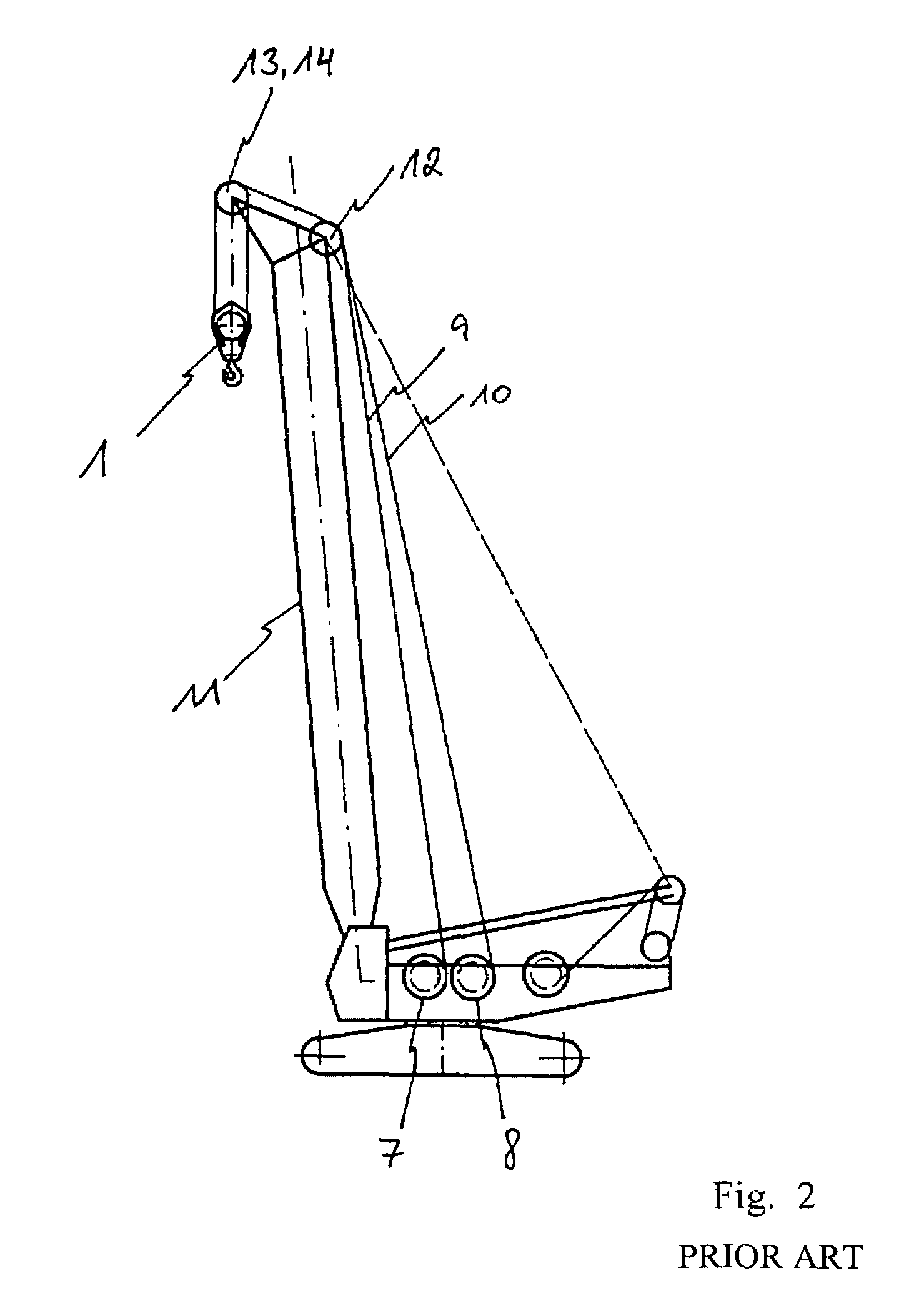
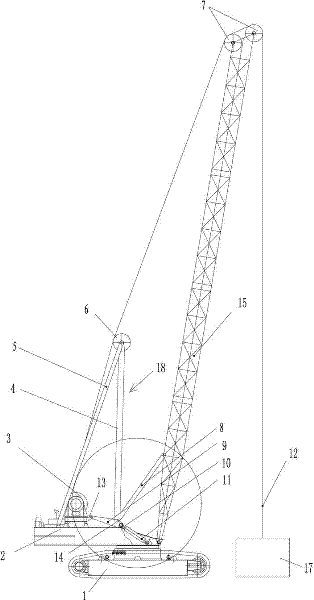
The invention proposes a hoisting-cable drive for a mobile crane, which hoisting-cable drive uses a single bottom-hook block (15) instead of a known double bottom-hook block. However, to prevent this single bottom-hook block (15) from tilting in the two cable lines (9, 10), for example due to possible variations in the elongation of the two cable drives, the hoisting-cable drive according to the invention comprises a kinematic force equilibrium device (17, 21), which can equalize such differences. To this effect, another embodiment of the hoisting-cable drive according to the invention uses a hoisting-cable load pickup (21) within each cable line arrangement so that the rotary speed of the winches (7, 8) can be varied, taking into account any load differences in the individual hoisting-cable lines (9, 10). Furthermore, the invention also proposes that the rotary speed of the winches (7, 8) be adjusted, taking into account the geometric winch states and crane states.
Owner:TADANO DEMAG GMBH
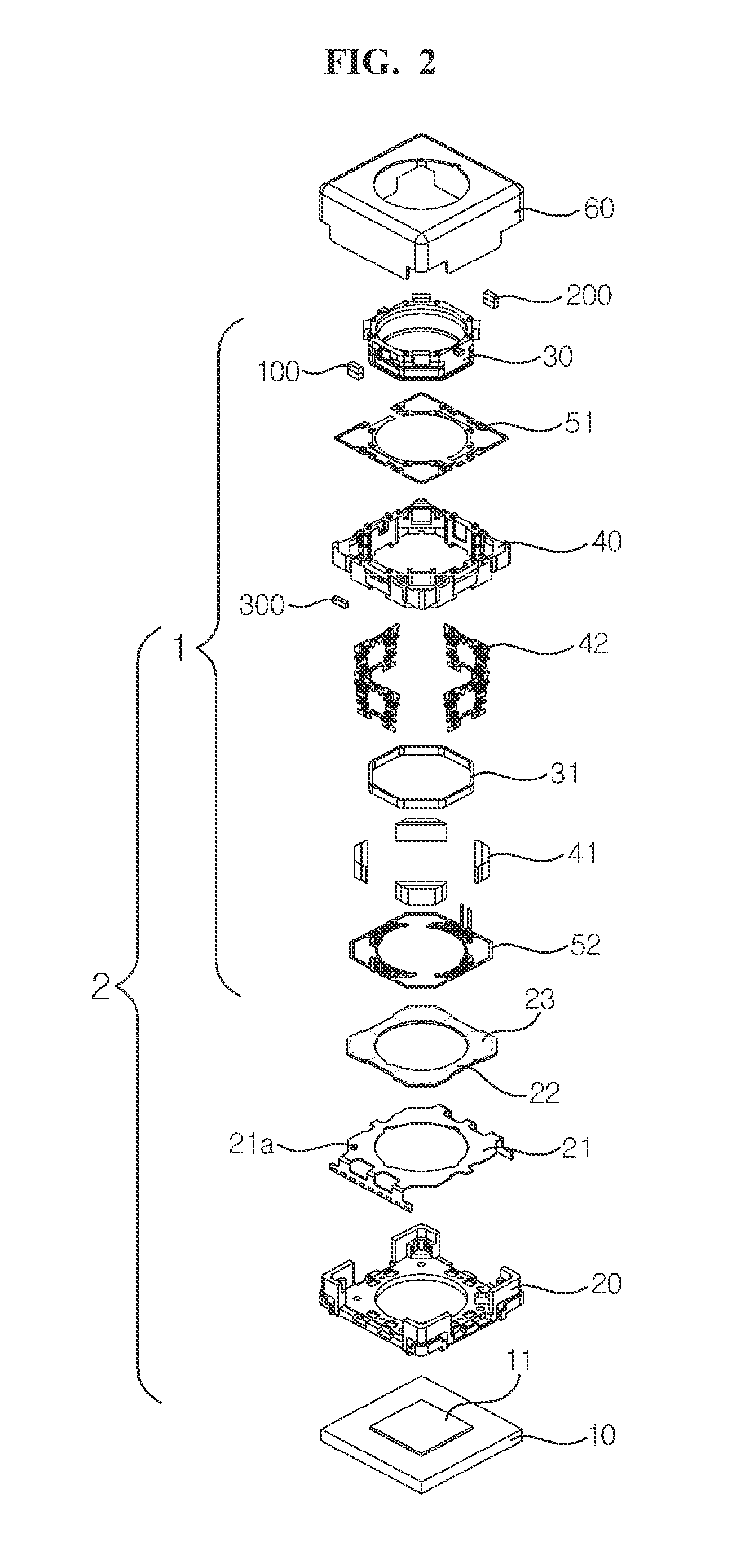
Lens Moving Device, Camera Module and Optical Apparatus
ActiveUS20150362696A1Accurate detectionProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensMagnetic tension force
A lens moving device is provided. The lens moving device includes: a bobbin; a first driving unit coupled to the bobbin; a second driving unit configured to move the first driving unit through an electromagnetic interaction with the first driving unit; a sensing magnet disposed on one side of the bobbin; a location detection sensor configured to sense a location of the sensing magnet; and a correction magnet disposed on an opposite side of the bobbin.According to the present disclosure, static tilt and dynamic tilt of the bobbin, to which a lens module is to be coupled, may be enhanced by a sensing magnet and a correction magnet which establish magnetic force equilibrium with each other.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Hoisting-cable drive comprising a single bottom-hook block and two winches
ActiveUS7416169B2Easy to handleSolid and difficult to handleWinding mechanismsLoad-engaging elementsForce equilibriumDouble bottom
The invention proposes a hoisting-cable drive for a mobile crane, which hoisting-cable drive uses a single bottom-hook block (15) instead of a known double bottom-hook block. However, to prevent this single bottom-hook block (15) from tilting in the two cable lines (9, 10), for example due to possible variations in the elongation of the two cable drives, the hoisting-cable drive according to the invention comprises a kinematic force equilibrium device (17, 21), which can equalize such differences. To this effect, another embodiment of the hoisting-cable drive according to the invention uses a hoisting-cable load pickup (21) within each cable line arrangement so that the rotary speed of the winches (7, 8) can be varied, taking into account any load differences in the individual hoisting-cable lines (9, 10). Furthermore, the invention also proposes that the rotary speed of the winches (7, 8) be adjusted, taking into account the geometric winch states and crane states.
Owner:TADANO DEMAG GMBH
Folding structure of carrier
ActiveUS7354058B2Easy and laborsavingCarriage/perambulator accessoriesCarriage/perambulator with multiple axesForce equilibriumMechanical engineering
Owner:LINK TREASURE
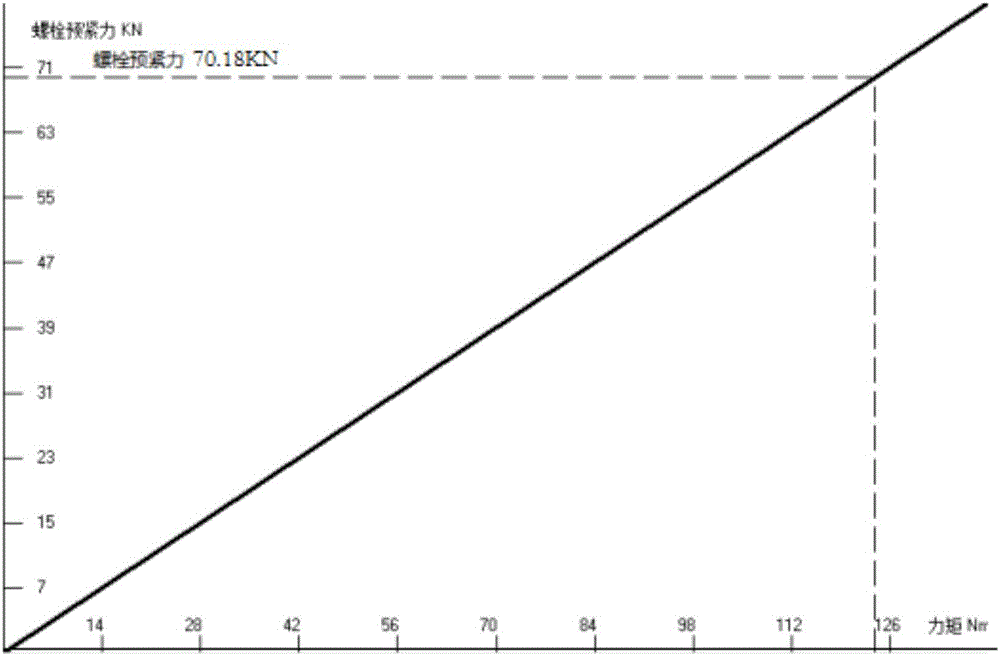
Prediction method for discrete pre-tightening force of bolt rotation angle method
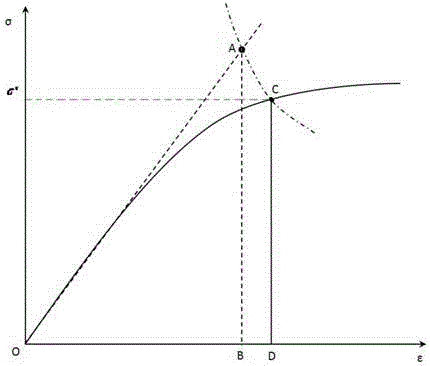
The invention discloses a prediction method for discrete pre-tightening force of a rotation angle method, and the prediction method is mainly used for design and assembling processes of main bolts of engines. The method is divided into two conditions of: in an elastic range, carrying out force balance on a bolt connection pair by utilizing a generalized Hooke's law: a combined computation of <Sigma> F=0 and deformation compatibility <Theta>=(<Delta>Lpull+<Delta>Lpush)*360 / P, so as to obtain pre-tightening force distribution of the rotation angle method; and if plastic deformation occurs to the bolt connection pair, adopting a law of conservation of energy: obtaining a false stress greater than real stress and a false strain less than the real strain under elastic assumption, obtaining a real stress and a real strain by adopting the law of conservation of energy, and finally obtaining the pre-tightening force distribution of the rotation angle method through nonlinear iterative computations of force balance and deformation compatibility. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple in computation and well-organized.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Implant for restoring normal range flexion and kinematics of the knee
ActiveUS8911502B2Reduced radiusAvoid collisionJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesForce equilibrium
Embodiments of the invention provide knee prostheses which more faithfully and closely replicate the function, anatomy and physiology of the normal human knee yielding a number of advantages. Among other things, such prostheses can provide an increased range of motion and function more normally particularly in extension, deep flexion and during normal gait. Knee prostheses according to various aspects of the invention recognize that during movement of the knee, particularly during flexion, the kinematics of the bones of the knee are a result of achieving equilibrium of the forces that cause motion of the knee. In addition, the shape of the articular surfaces acting in combination with forces imposed by various muscles, ligaments and tendons, determines the direction of the large contact forces.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Dynamic compactor capable of realizing amplitude-variable followup of A-bracket with arm support
ActiveCN102002936AReasonable forceAchieve balanceSoil preservationForce equilibriumDynamic compaction
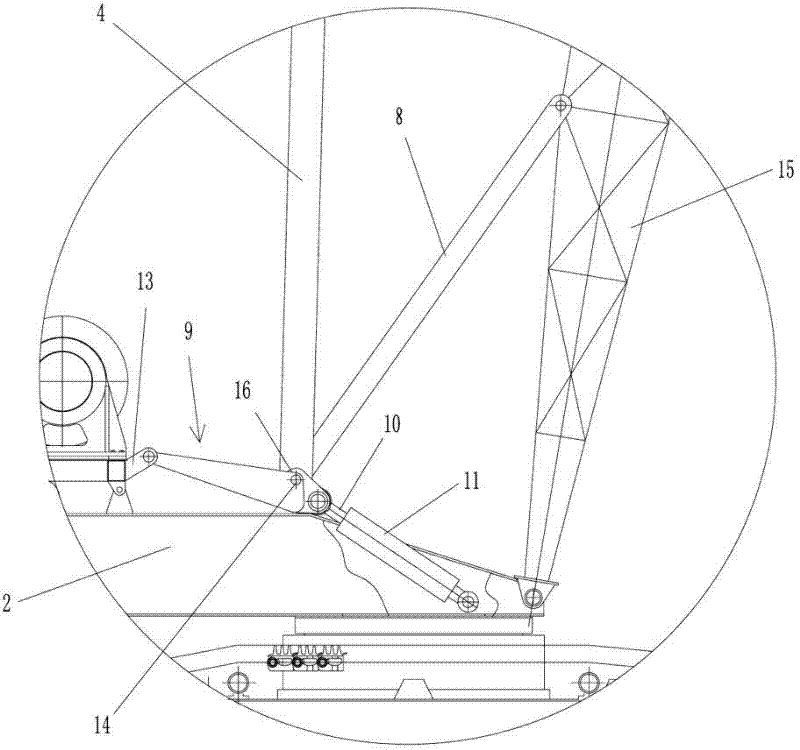
The invention relates to a dynamic compactor capable of realizing the amplitude-variable followup of an A-bracket with an arm support, which is characterized in that a followup A-bracket is mounted on a dynamic compactor rotating platform, an amplitude-variable draw rod is arranged between an inner diagonal rod and an arm support, a swing arm mechanism is arranged at the lower parts of the amplitude-variable draw rod and the inner diagonal rod, the swing arm mechanism is composed of a swing arm rack and a telescopic oil cylinder, and the followup A-bracket forms linkage with the amplitude-variable draw rod by the swing arm mechanism. Wire ropes of a hoisting mechanism are connected with a dynamic compactor weight through a pulley at the top end of the followup A-bracket and a pulley at the top end of the arm support, so that the quantity of front wire ropes at the top end of the arm support is the same with that of back wire ropes at the top end of the arm support. When the amplitude-variable draw rod drives the arm support to realize an amplitude-variable process, the swing arm mechanism connected with the followup A-bracket synchronously drives the followup A-bracket to swing. The amplitude-variable followup of the followup A-bracket with the arm support is realized, so that the stress on the arm support of the dynamic compactor is more reasonable, the stress balancing of the arm support can be realized to the greatest extent, the structural stress of the arm support can be improved, the self-weight of the arm support can be reduced, and the dynamic compaction operating performance of the arm support and the complete machine can be improved.
Owner:CHINA ZHONGHUA GEOTECHN ENG
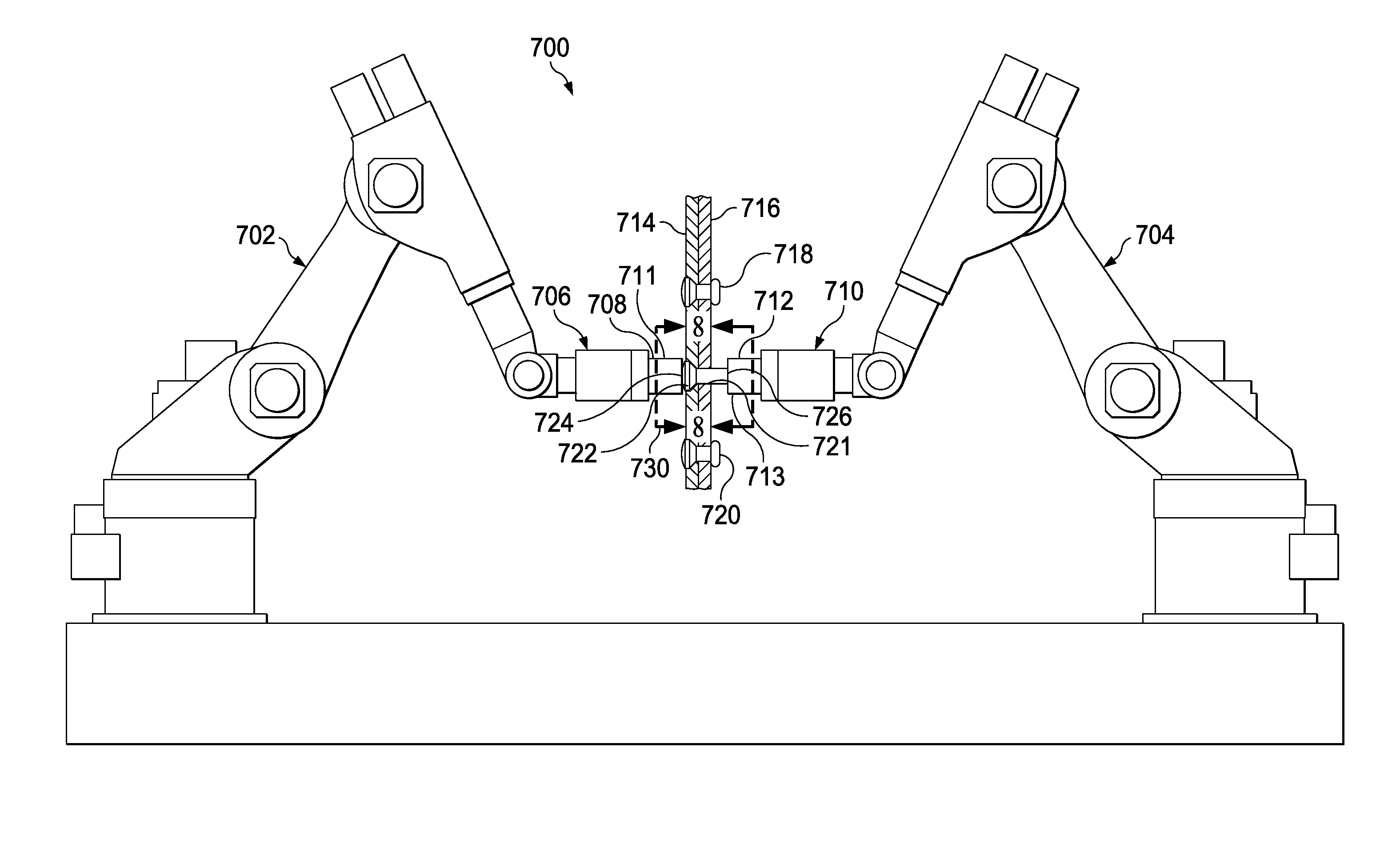
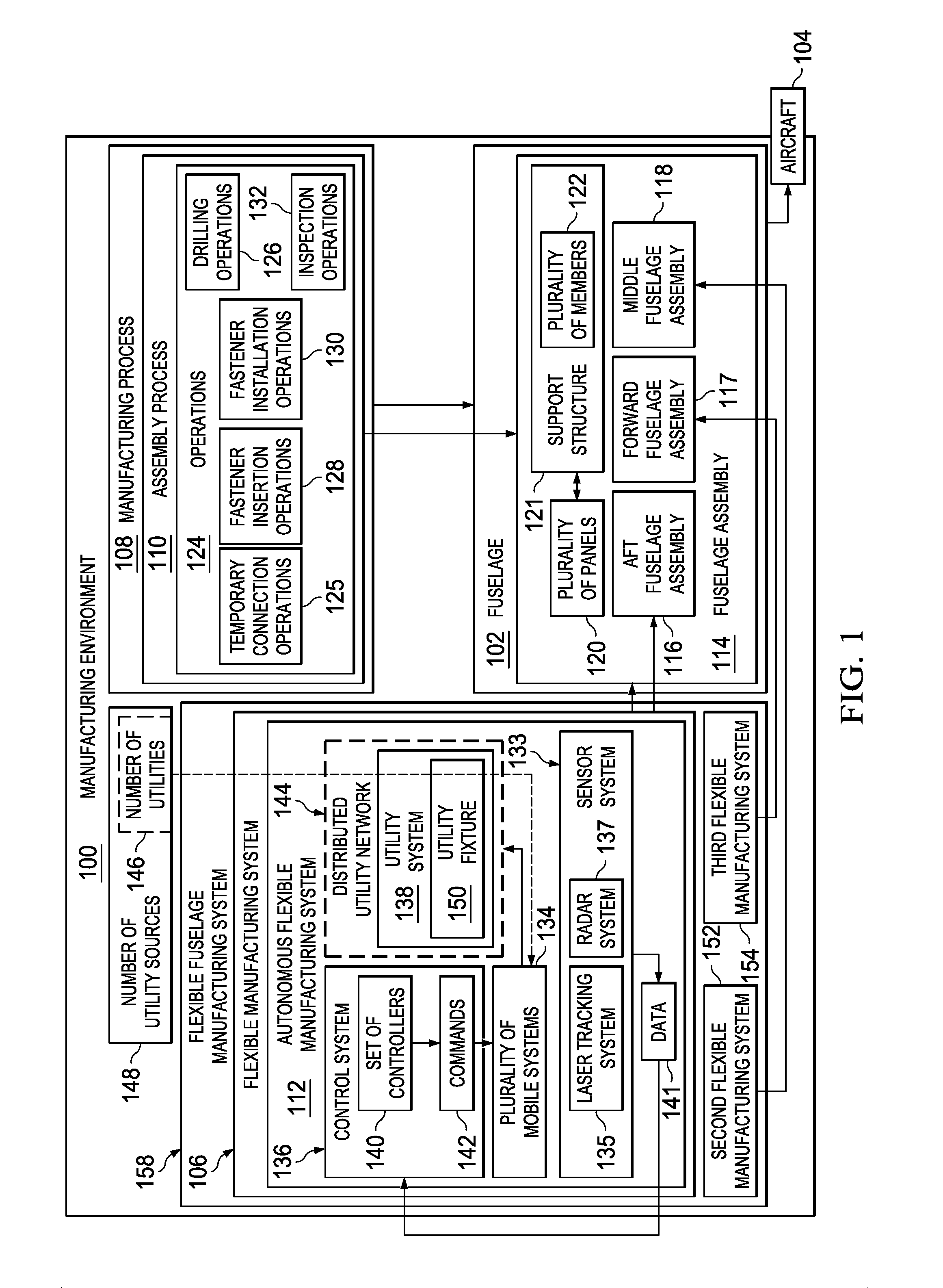
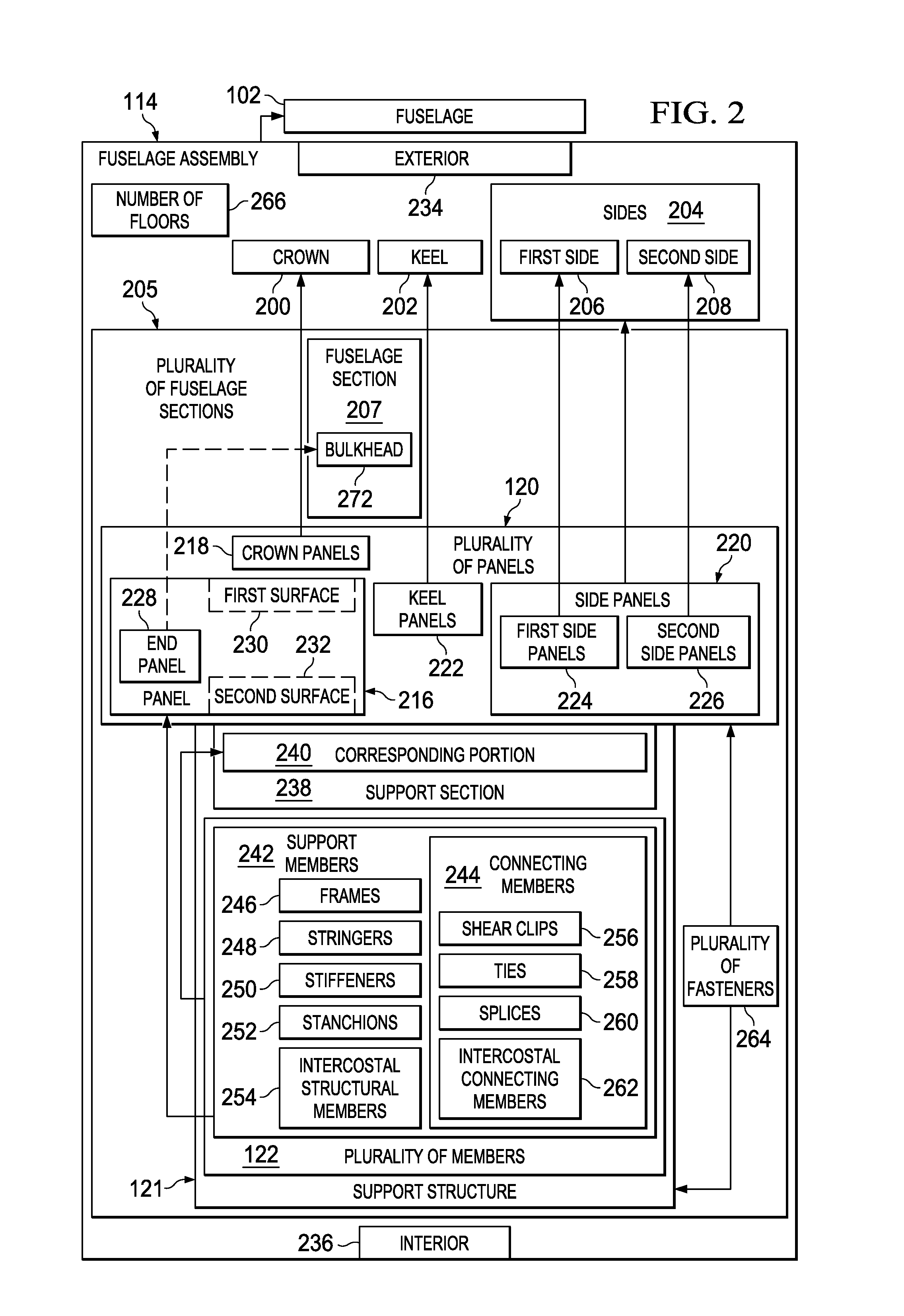
Two-Stage Riveting
ActiveUS20160008869A1Maintain forceProgramme-controlled manipulatorFuselage framesInterference fitForce equilibrium
A method and apparatus for fastening two parts together. An initial interference fit may be created between a fastener and at least a portion of a hole extending through the two parts while maintaining a force equilibrium. A final interference fit may be created between the fastener and the hole, while maintaining a new force equilibrium.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
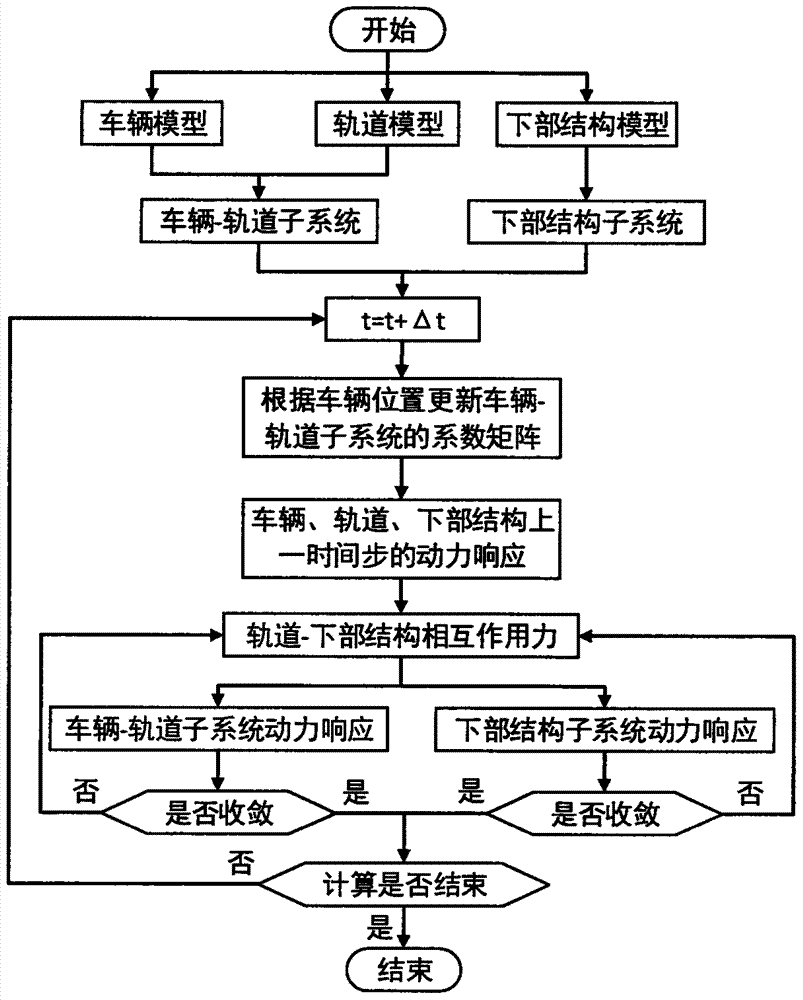
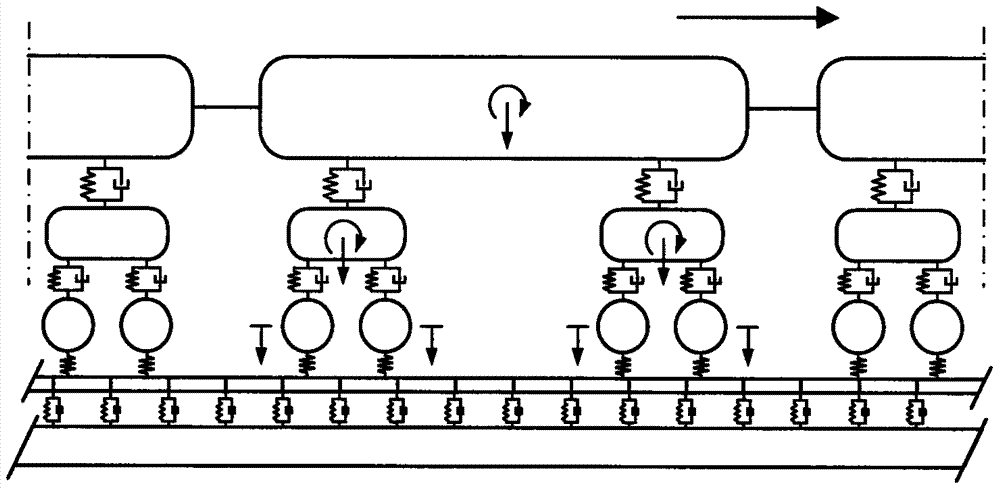
Efficient dynamic analysis method for train-rail-structure coupling system
InactiveCN107451384AImprove the efficiency of dynamic analysisSave bandwidthInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsForce equilibriumCoupling system
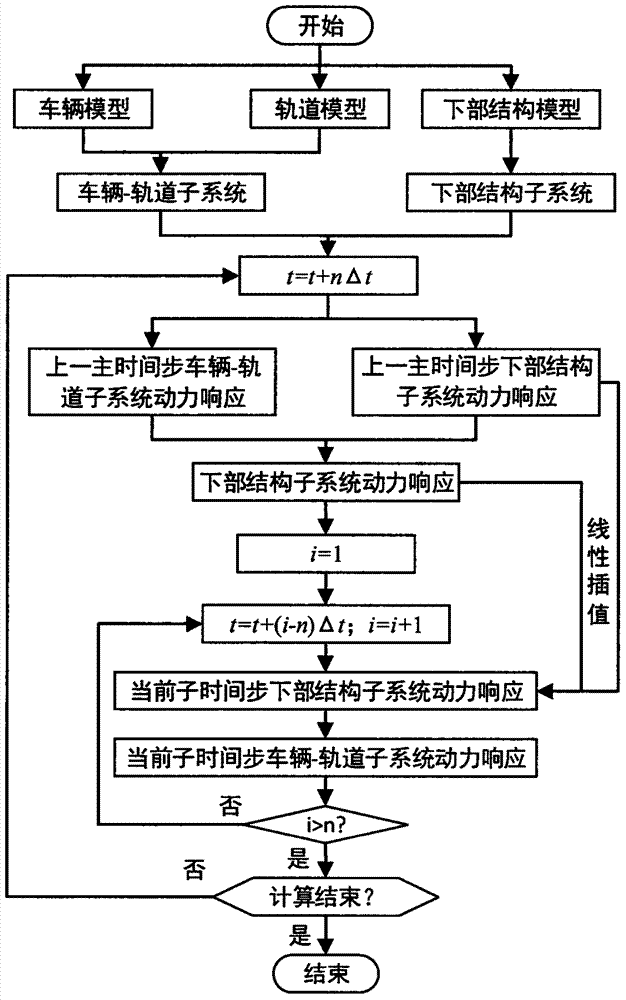
The invention discloses an efficient dynamic analysis method for a train-rail-structure coupling system. The method is characterized by comprising a train structure model module, a rail structure model module, a lower structure model module, a wheeltrack dynamic contact model module between wheels and a rail steel rail, a rail unsmooth module and a dynamic mutual action model module between the rail and a lower structure, wherein the train structure model module and the rail structure model module are coupled into an integral time-varying train-rail subsystem through a wheeltrack contact relationship, and the lower structure is a lower structure subsystem; and the train-rail subsystem and the lower structure subsystem are coupled through a mutual action force equilibrium condition between the rail and the lower structure; and in each time step, the train-rail subsystem and the lower structure subsystem are subjected to equilibrium iteration solving to realize the equilibrium convergence calculation of the mutual action force. By use of the method, the dynamic analysis efficiency of the train-rail-structure coupling system can be effectively improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Forced balanced system
ActiveUS7878272B2Valuable rig timeSuitable for useDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsForce equilibriumRadial position
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Bacillus subtilis strain for producing high-purity chiral meso-2,3-butanediol as well as construction method and application of strain
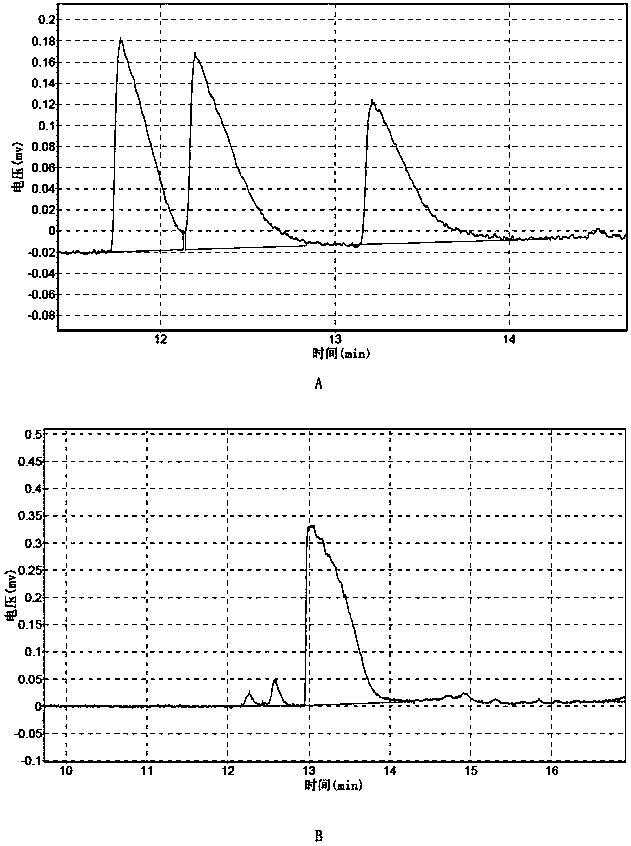
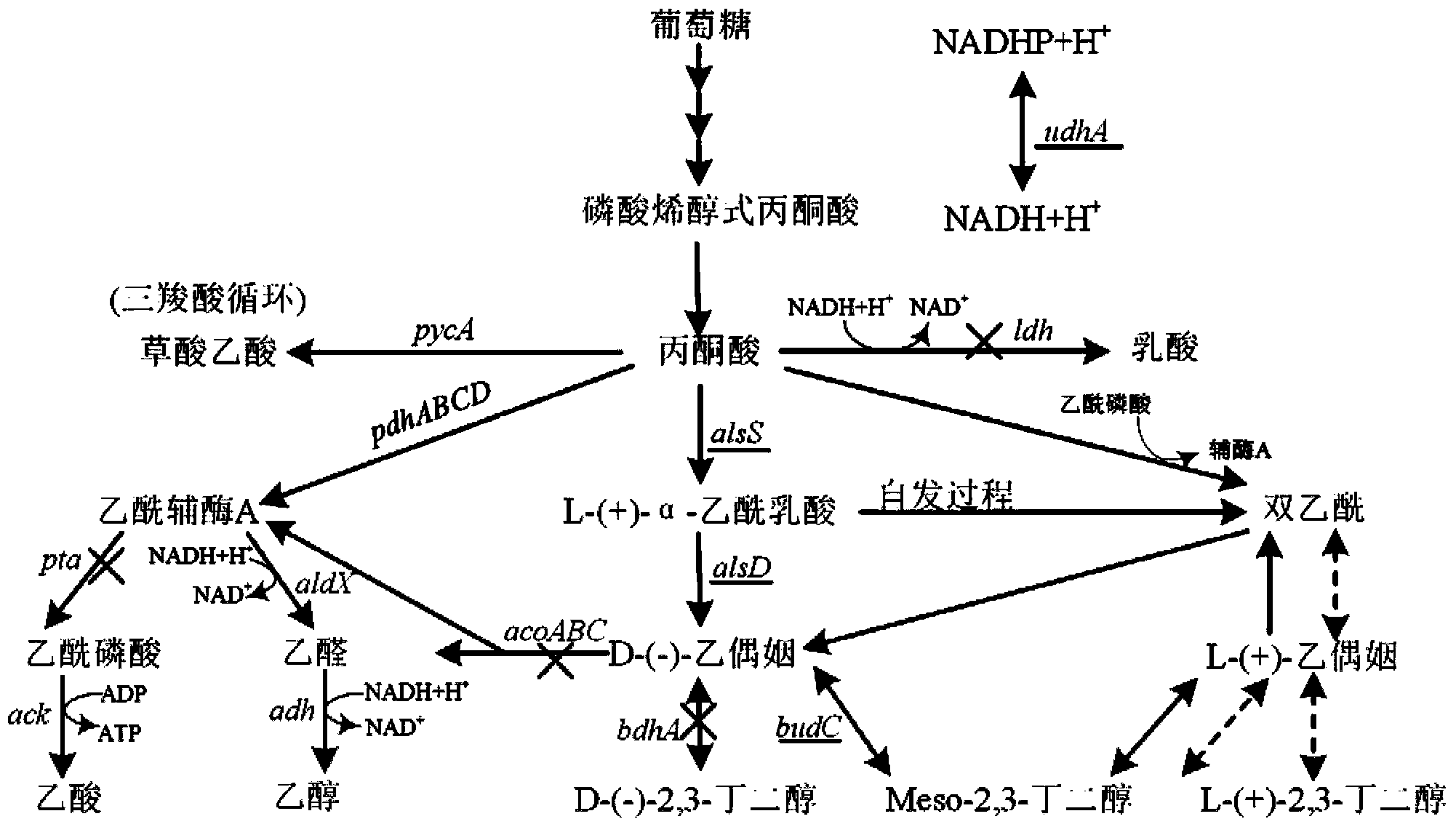
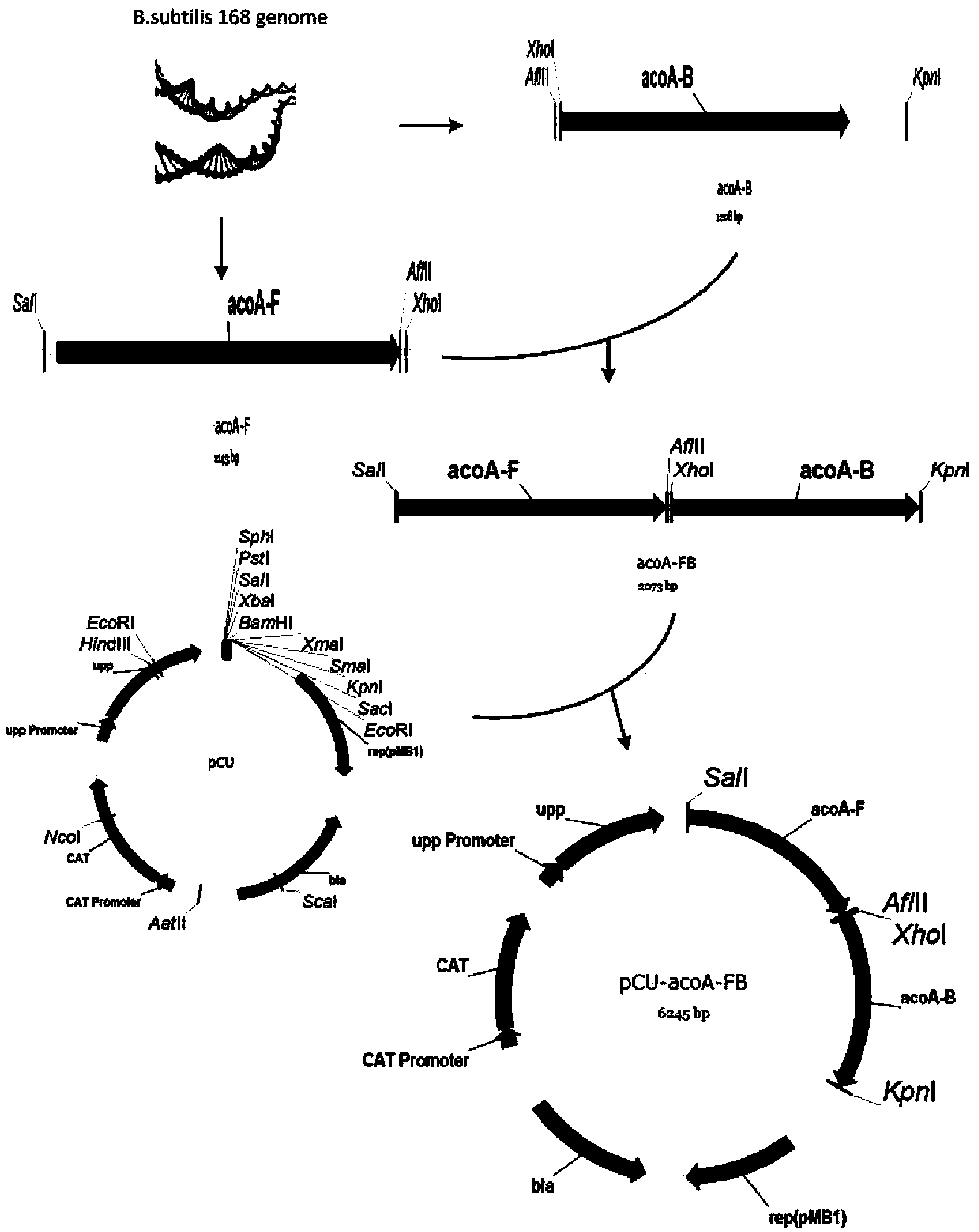
ActiveCN103451141AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesForce equilibriumAcetic acid
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis strain for producing high-purity chiral meso-2,3-butanediol as well as a construction method and application of the strain. The construction method comprises the steps of knocking out an acoA gene of a direct substrate of 2,3-butanediol, acetoin in a degradation pathway, from bacillus subtilis, knocking out an acetoin reductase coding gene bdhA, knocking out a pta gene in a byproduct acetic acid formation path and knocking out a 1dh gene in a byproduct lactic acid formation path, over-expressing a synthesis branch a1sSD promoter through a P43 strong promoter, over-expressing meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase coding gene budC through a P43 strong promoter, and over-expressing a transhydrogenase coding gene udhA in a reducing force equilibrium process through a P43 strong promoter. The constructed bacillus subtilis engineering strain is safe and harmless, and can produce meso-2,3-butanediol with chiral purity greater than 99% by taking glucose as a substrate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
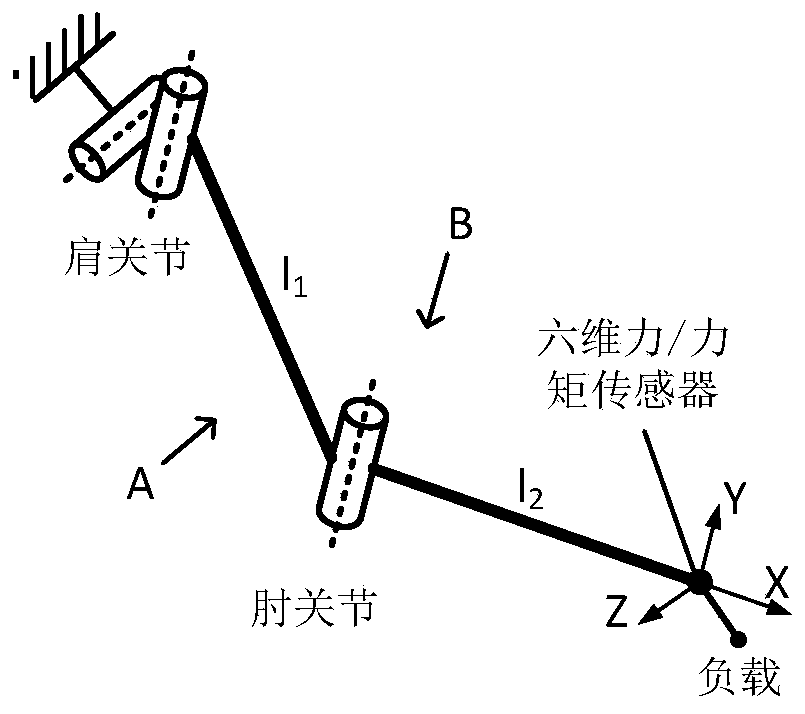
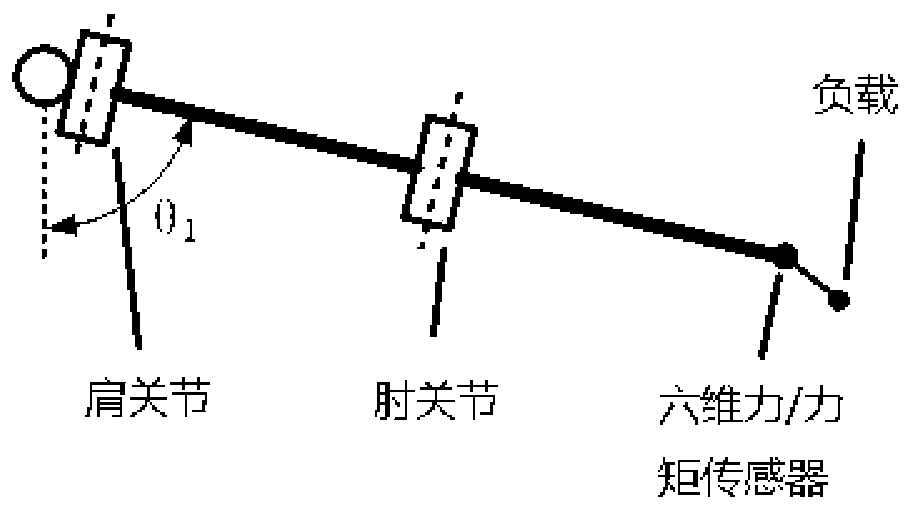
Dynamic load information calculation method for exoskeleton robot
ActiveCN109746901AAvoid the phenomenon that large numbers \"eat\" small numbersAvoid errorsProgramme-controlled manipulatorForce equilibriumD'Alembert's principle
The invention discloses a dynamic load information calculation method for an exoskeleton robot. The dynamic load information calculation method comprises the steps that 1, a six-dimensional force / moment sensor is arranged between an elbow joint and an end effector, and the force and moment information of the load is measured; angle sensors are arranged at the joints of the upper limb exoskeleton;2, the force and torque data of the load and the angle data of each joint are collected; 3, the driving torque of each joint is calculated according to the angle data of each joint and the inertia tensor matrix, and then the driving torque and the force and moment date of the load are utilized to construct a force and moment balance equation of the position at which the six-dimensional force / moment sensor is located through a d'alembert's principle; 4, the equilibrium equation of two force with the largest change and the equilibrium equation of two moments with the largest change under no-loadcondition are selected; and 5, the four equations obtained in step 4 are solved, and the load weight m and the position information x<m>, y<m> and z<m> of the load center of gravity relative to the six-dimensional force / moment sensor are obtained. The dynamic load information calculation method can quickly and effectively calculate the dynamic load information of the exoskeleton robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for determining the sensitivity of an acceleration sensor or magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS8461833B2Easy to operateAvoid failureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesForce equilibriumSeismic mass
A method for determining the sensitivity of a sensor provides the following steps: a) first and second deflection voltages are applied to first and second electrode systems of the sensor, respectively, and first and second electrostatic forces are exerted on an elastically suspended seismic mass of the sensor by the first and second electrode systems, respectively, and a restoring force is exerted on the mass as a result of the elasticity of the mass, and a force equilibrium is established among the first and second electrostatic forces and the restoring force, and the mass assumes a deflection position characteristic of the force equilibrium, and an output signal characteristic of the force equilibrium and of the deflection position is measured; and b) the sensitivity of the sensor is computed on the basis of the first and second deflection voltages.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Rotary blade-box rub-impact force determining method
ActiveCN103500287AResponse failure characteristicsImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsForce equilibriumMechanical energy
The invention discloses a rotary blade-box rub-impact force determining method and belongs to the technical field of machinery dynamics. The method includes the following steps of establishing a function equation Ue+Uc=W between a blade and a box at a certain moment according to the conservation law of mechanical energy; establishing the force equilibrium relation between the blade and the box and obtaining the expression of the radial force Fn in the position of a blade tip; decomposing the blade tip radial force Fn according to the normal direction and the tangential direction of the blade tip according to the bending deformation of the blade, wherein -FL=-Fncos[v'(L,t)], and -FT=Fnsin[v'(L,t)]; and finally, composing the stress on the blade tip.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for identifying granular system power transmission chain
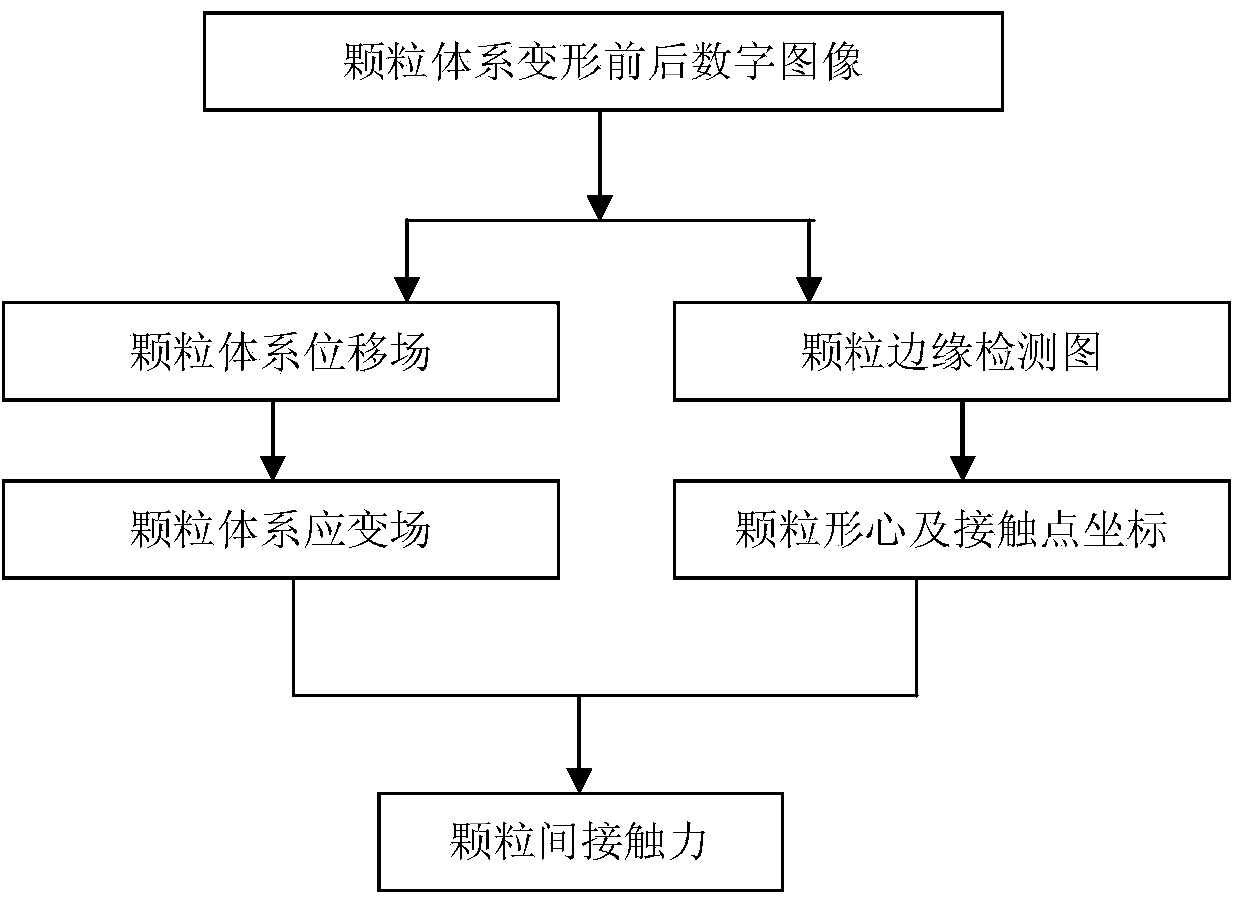
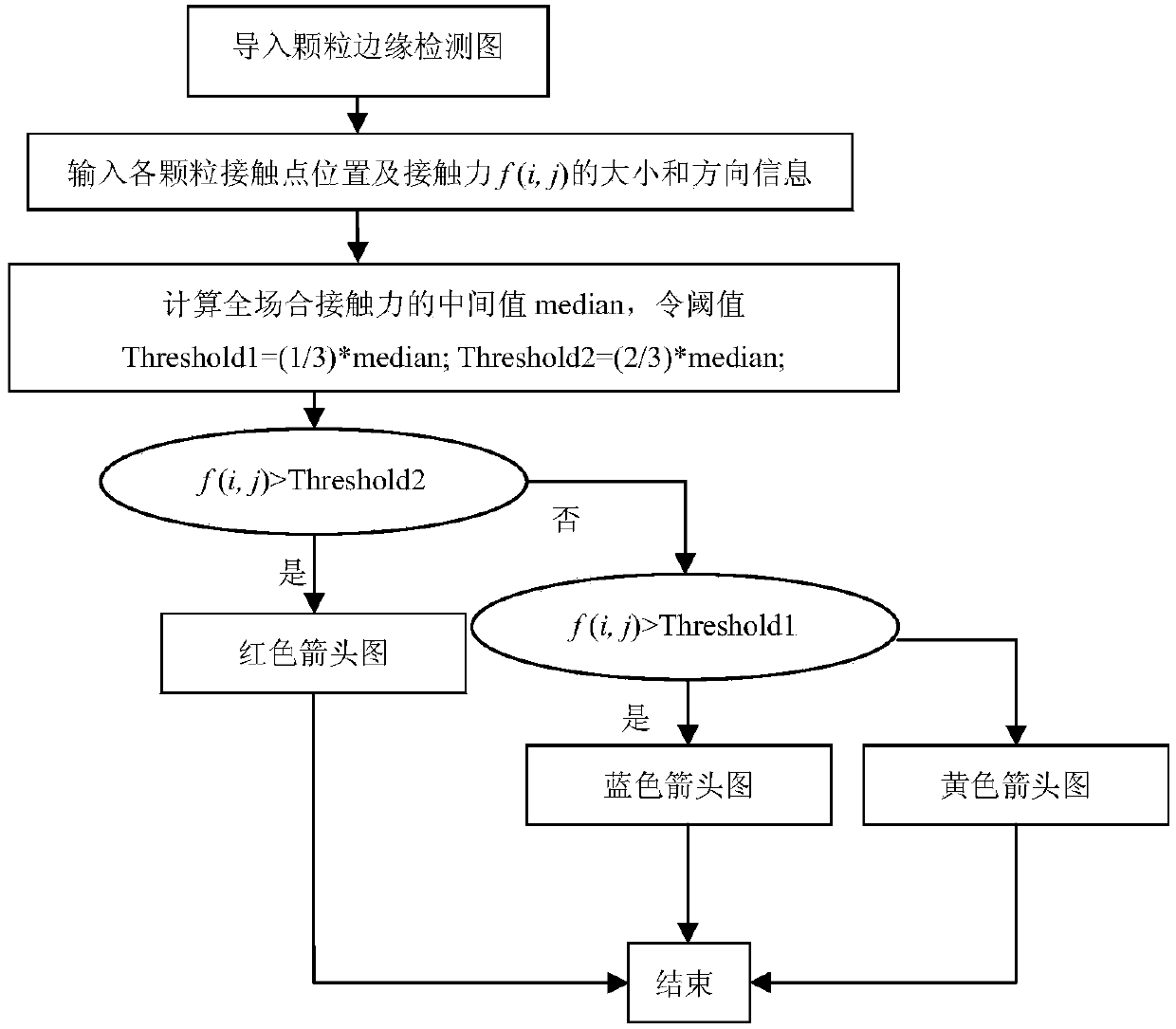
ActiveCN104007047APromote research progressSimple methodImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsForce equilibriumGraphics
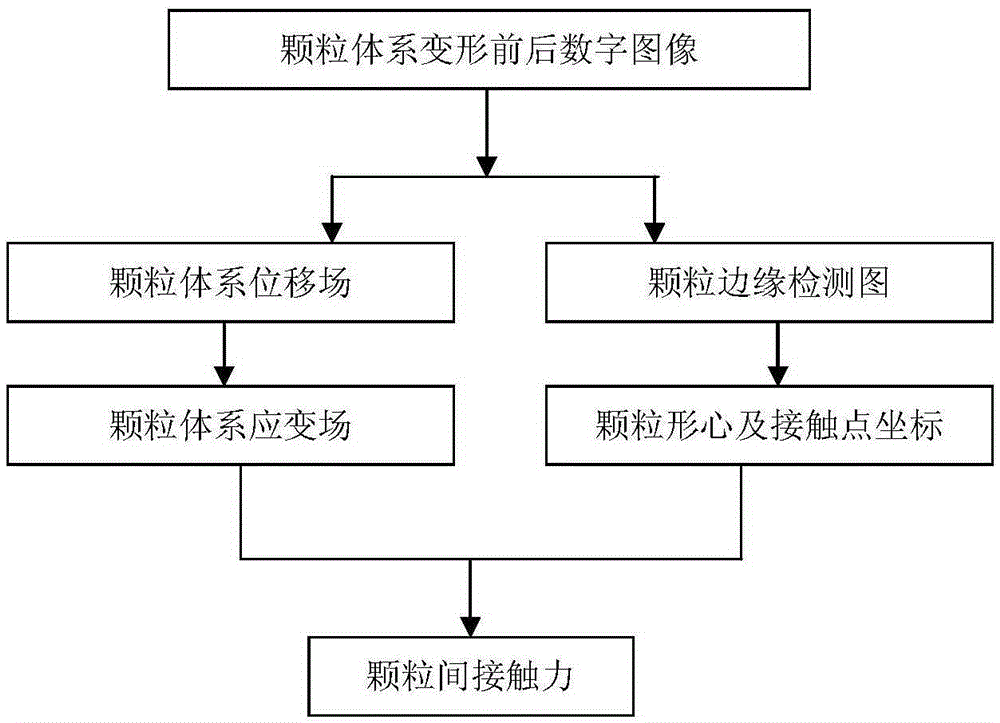
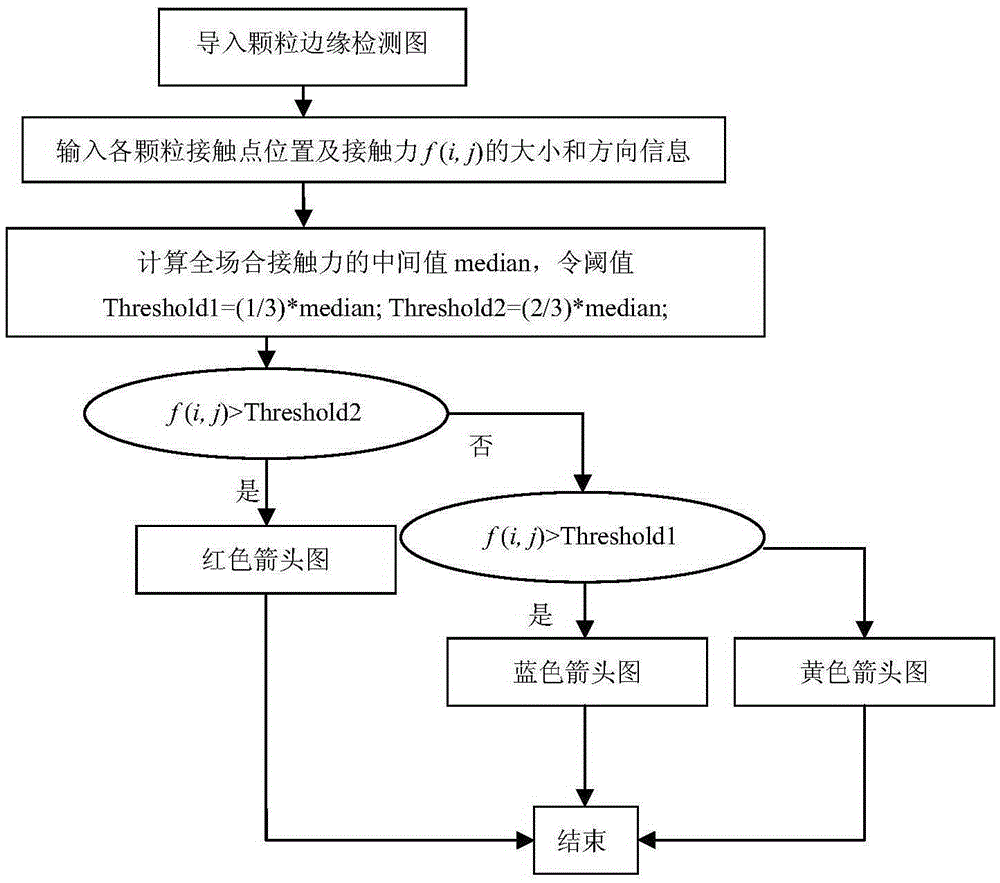
The invention belongs to the technical field of granular system power transmission chain identification, and relates to a method for identifying a granular system power transmission chain. The method includes the steps that firstly, a granular system is loaded, and granular system images before and after deformation are collected to be used as an original image and a target image respectively; then, the original image and the target image are analyzed, and after a displacement field and a strain field in the granular system surface of the target image at the corresponding moment are obtained, the stress of each point is obtained according to the strain of each point in the strain field; afterwards, image edge detection is conducted on the target image, granular centroids are identified, the coordinates of the granular centroids and the position coordinates of contact points of all granules are read, a force equilibrium and torque equilibrium equation is established for each granule, and the size and orientation of contact force at different contact points on all the granules are acquired through calculation; at last, the contact force of each granule is drawn, and the graph which is continuously represented by the contact force between adjacent granules is the path of the power transmission chain. The method is simple, scientific in principle, convenient and flexible to use, high in practicability, large in development prospect and wide in applied range.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Electric actuating mechanism for dynamic force equilibrium positioning
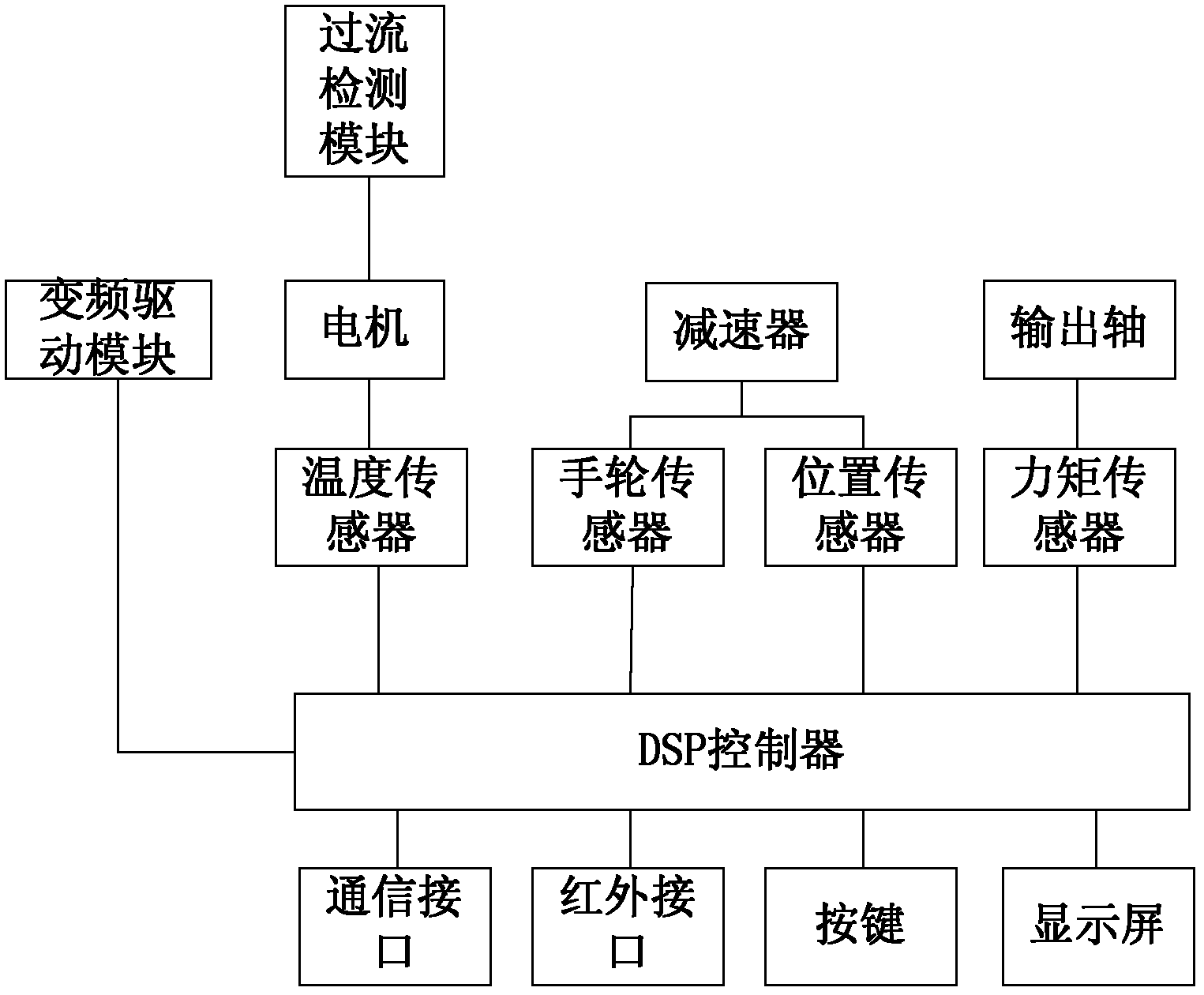
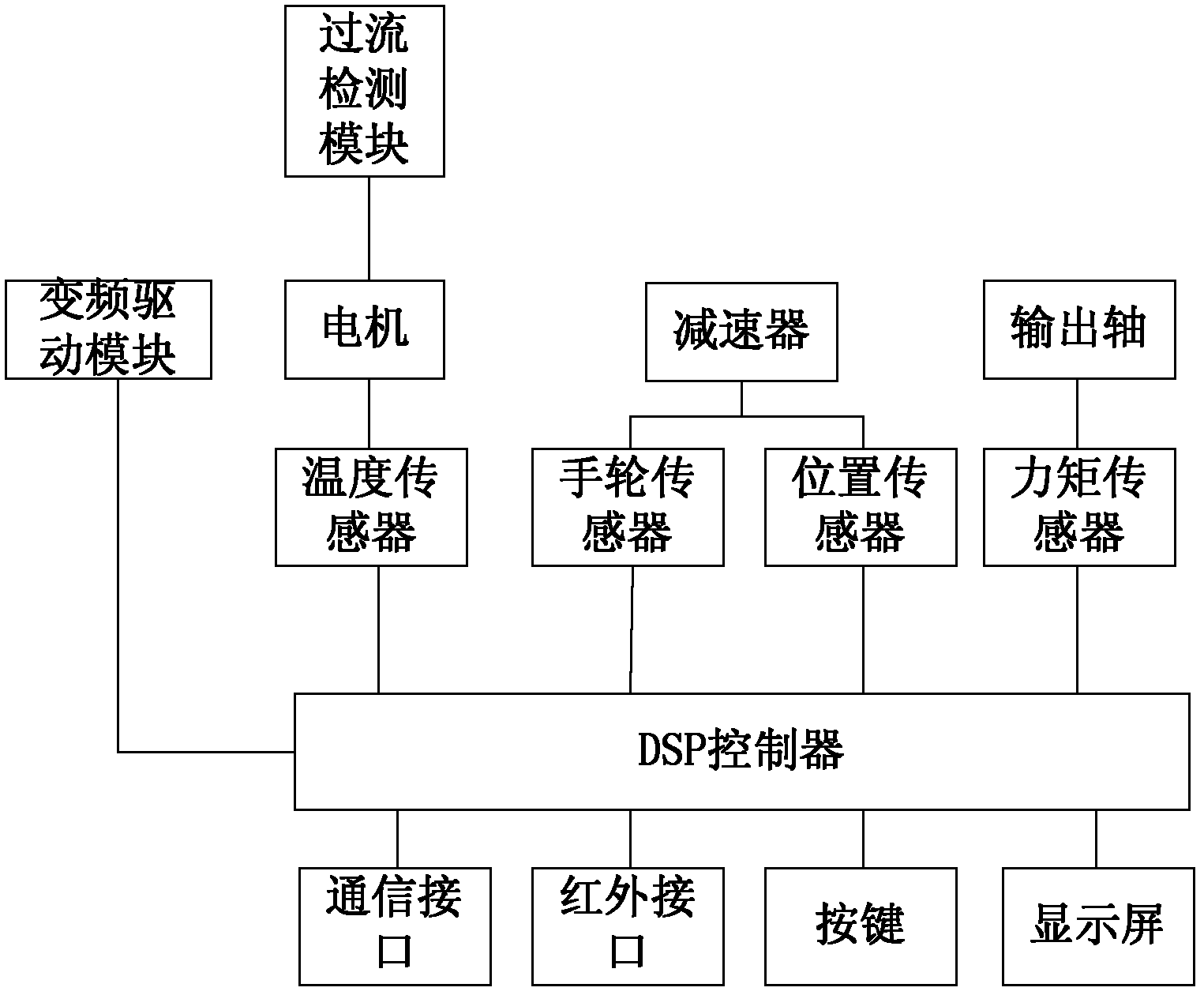
ActiveCN102361432AImprove reliabilityExtended service lifeAC motor controlForce equilibriumReduction drive
The invention relates to the technical field of actuating mechanisms, and provides an electric actuating mechanism for dynamic force equilibrium positioning. The electric actuating mechanism can realize dynamic force equilibrium output. The electric actuating mechanism for dynamic force equilibrium positioning comprises a power supply, a motor, an output shaft and a speed reducer, wherein a handwheel sensor and a position sensor are arranged on the speed reducer; and a torque sensor is arranged on the output shaft. The electric actuating mechanism also comprises a digital signal processor (DSP) processing system and a variable frequency drive module, wherein a signal input end of the DSP processing system is electrically connected with signal output ends of the handwheel sensor, the position sensor and the torque sensor to acquire the output torque and the speed of the electric actuating mechanism and feed the output torque and the speed back to the variable frequency drive module so as to adjust the running of the motor in real time.
Owner:CHONGQING CHUANYI AUTOMATION
Laboratory determination method of sulfate erosion depth in concrete
The invention discloses a laboratory determination method of sulfate erosion depth in concrete, and belongs to the concrete testing field. The laboratory determination method of sulfate erosion depth in concrete includes the following steps: manufacturing a concrete column test block: pre-pasting a foil gauge on the surface of a plain round steel bar, and pouring concrete by taking the plain round steel bar as the center to manufacture a concrete column test block, wherein the length of the concrete column test block is equal to the length of the plain round steel bar; immersing the concrete column test block in a barrel with sulfate liquor; using a pressure testing machine to perform an axle pressure test on the test block: disposing the barrel with the concrete column test block on the pressure testing machine, performing an axle pressure test with the specified constant pressure on the upper and lower surfaces of the concrete column test block, wherein the test time is not less than half a year, and the steel bar strain epsilons is obtained through the foil gauge on the plain round steel bar, and then through force equilibrium, by means of three formulas, the depth DeltaL that the concrete is eroded by sulfate can be derived; and changing the specified constant pressure, calculating the depth DeltaL that the concrete is eroded by sulfate in different pressure and in different time.
Owner:河北思动环保科技有限公司
Screw pump
ActiveCN105370563AExtended service lifeImprove equalization performanceRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesForce equilibriumMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to the technical field of engineering machinery, and discloses a screw pump, which comprises a rotor and a stator, wherein the stator is wrapped on the outer side of the rotor, the stator and the rotor form a screw pair, the inner wall of the stator and the outer wall of the rotor are connected in a sealed manner, a plurality of sealed cavities are formed between the inner side of the stator and the outer side of the rotor, the screw pump further comprises a pre-tightening force adjustment device, the pre-tightening force adjustment device comprises a plurality of clamping mechanisms wrapped on the outer side of the stator and aligned along the axial center line direction of the stator, and each clamping mechanism can be separately adjusted, ie., the action forces of each clamping mechanism on the stator can be controlled separately. With the technical scheme of the present invention, the action forces of each clamping mechanism on the stator can be adjusted so as to improve the pre-tightening force equilibrium between the stator and the rotor in the screw pair of the screw pump, such that the wear is generated between the stator and the rotor so as to prolong the service lives of the rotor and the stator.
Owner:ZOOMLION HEAVY IND CO LTD
Electropneumatic transducer with a pneumatic pressure-regulating valve
InactiveCN101900139ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costFluid pressure control with auxillary non-electric powerTransducersForce equilibriumTransducer
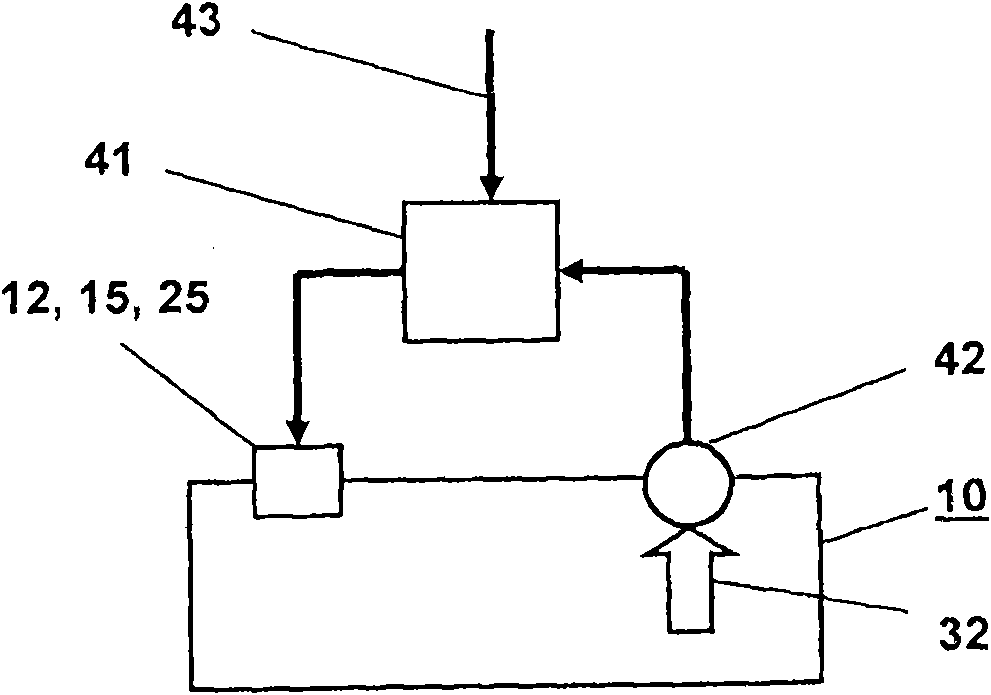
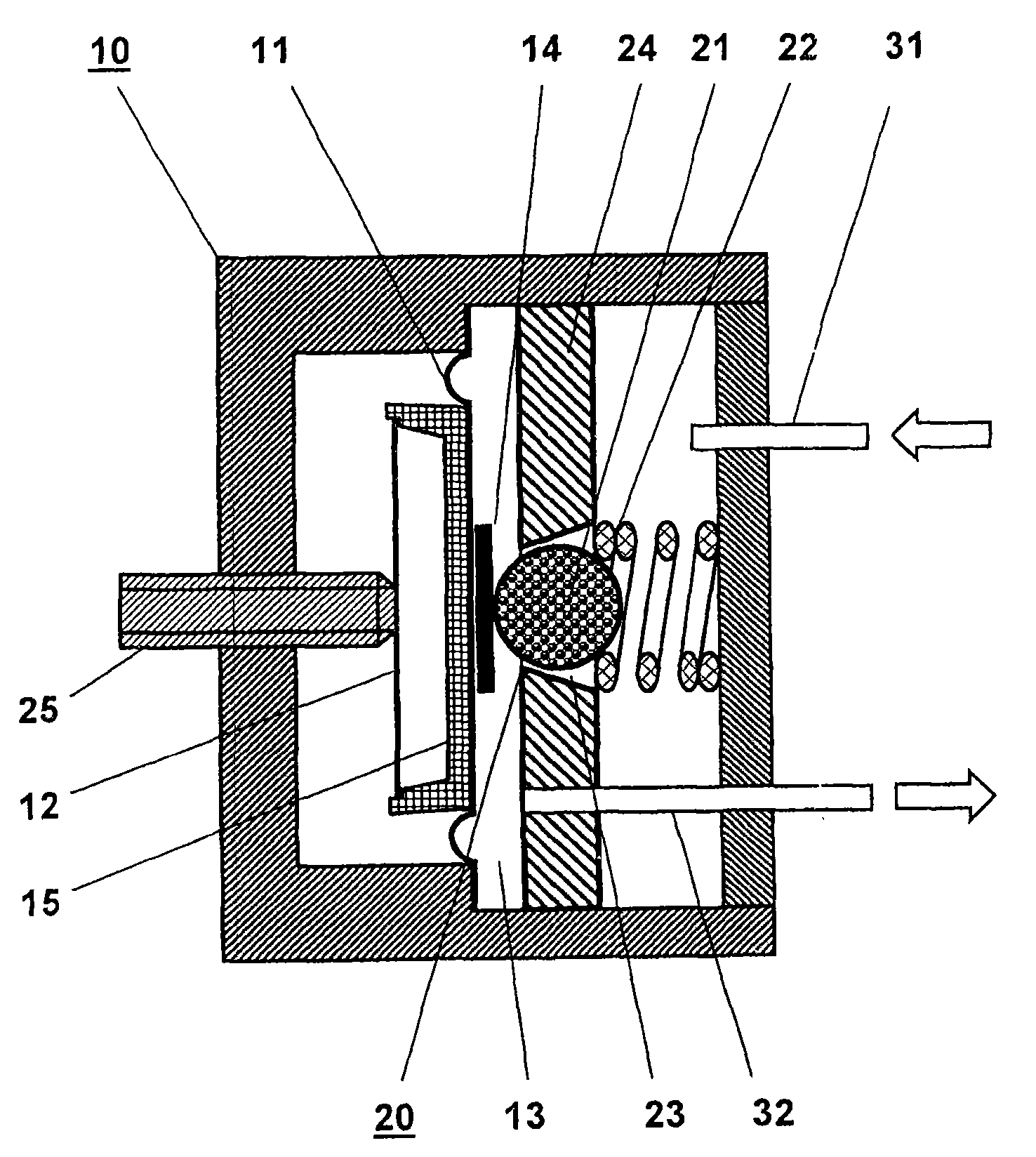
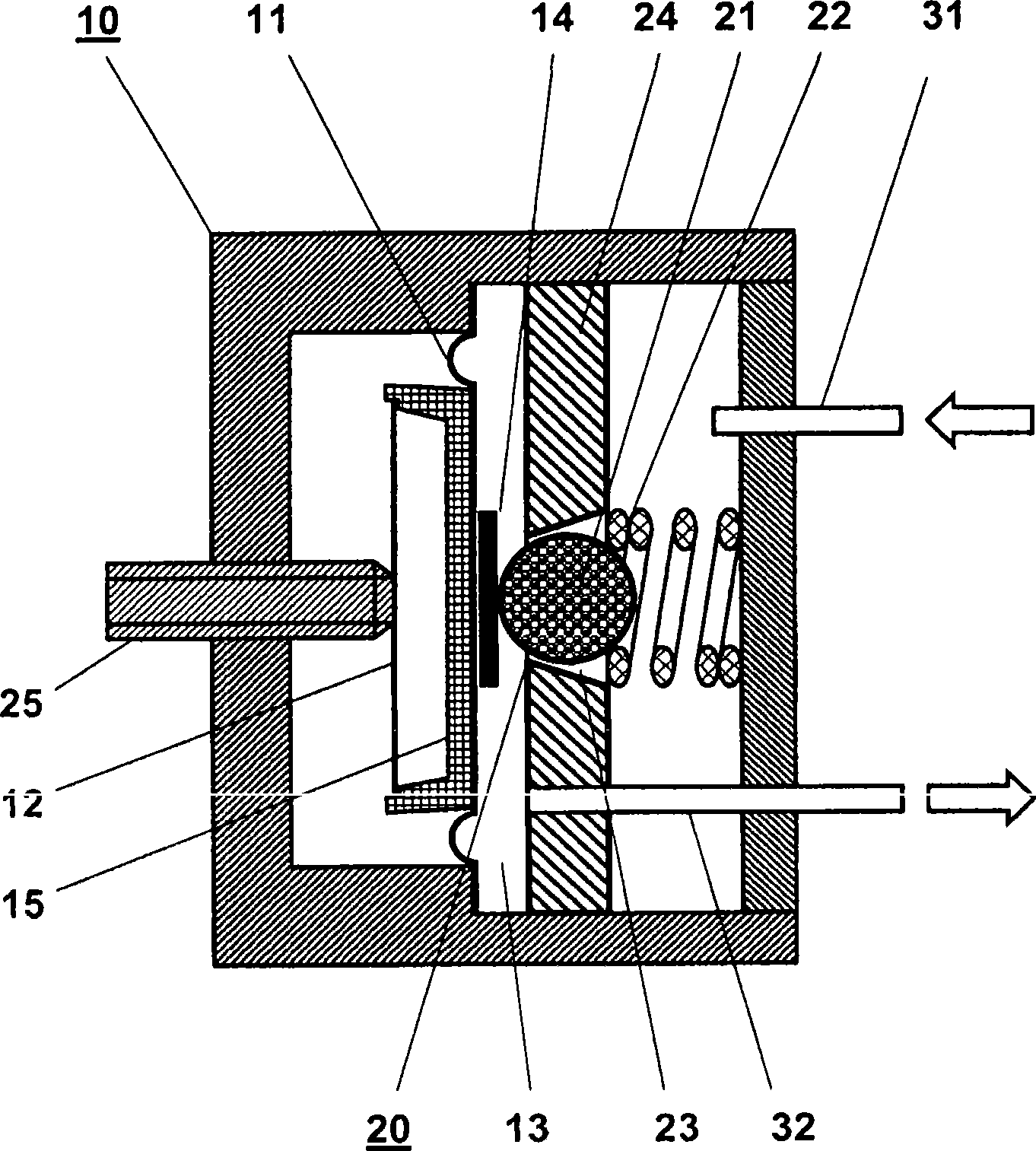
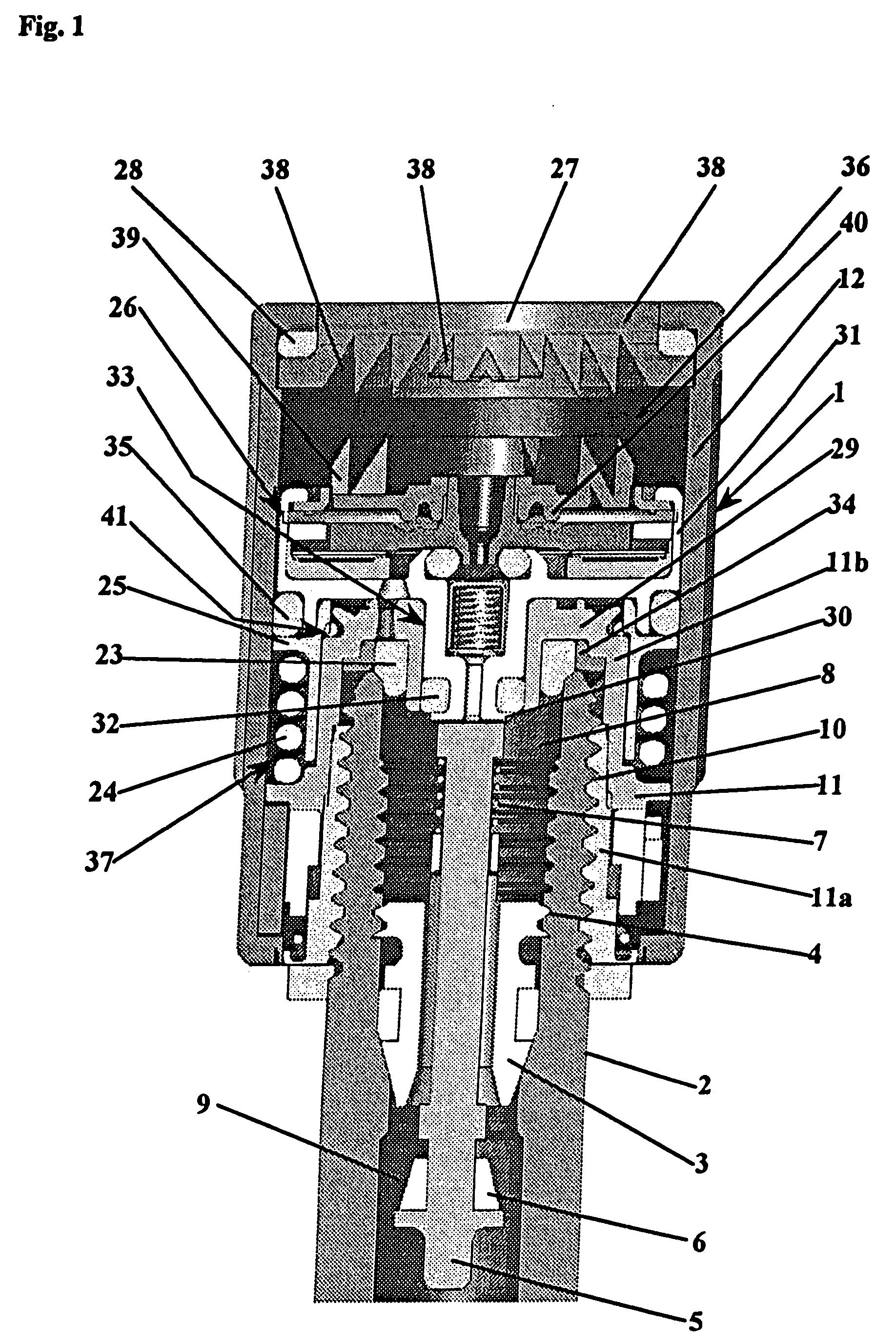
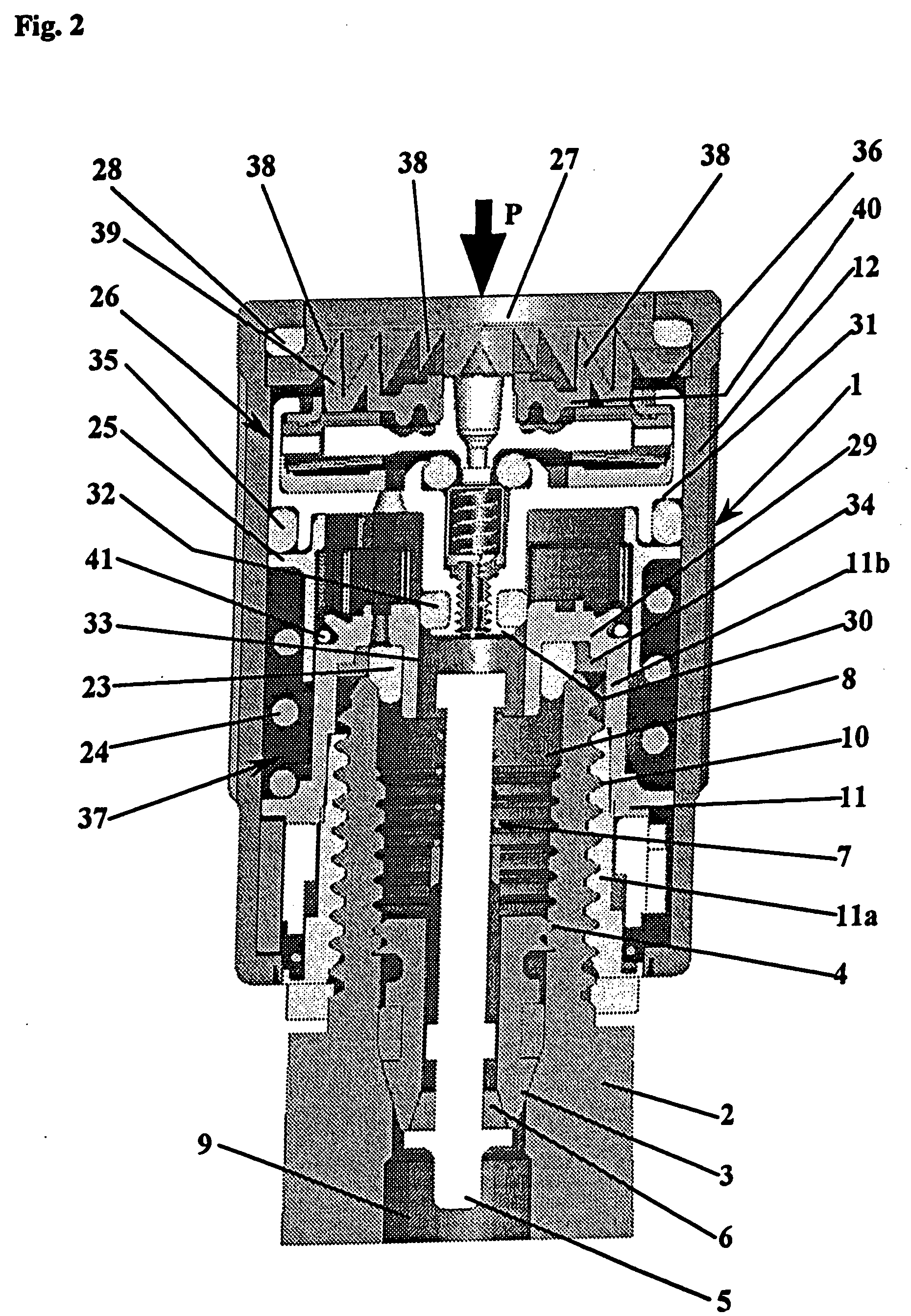
An electropneumatic transducer is disclosed having a pneumatic pressure-regulating valve for regulating a control pressure in a pressure chamber by a regulator diaphragm, which rests on (e.g., against a counter-bearing). The counter-bearing can include at least one pressure disk, a regulator spring and an adjusting screw, the regulator diaphragm being held in force equilibrium by the regulator spring and the control pressure. The regulator diaphragm can be coupled to a control valve such that the control valve opens or closes as a function of actual control pressure. The counter-bearing can include an electrically drivable actuator.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
A Method for Identifying Kinetic Chain of Granular System
ActiveCN104007047BPromote research progressSimple methodImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsForce equilibriumContact force
The invention belongs to the technical field of granular system power transmission chain identification, and relates to a method for identifying a granular system power transmission chain. The method includes the steps that firstly, a granular system is loaded, and granular system images before and after deformation are collected to be used as an original image and a target image respectively; then, the original image and the target image are analyzed, and after a displacement field and a strain field in the granular system surface of the target image at the corresponding moment are obtained, the stress of each point is obtained according to the strain of each point in the strain field; afterwards, image edge detection is conducted on the target image, granular centroids are identified, the coordinates of the granular centroids and the position coordinates of contact points of all granules are read, a force equilibrium and torque equilibrium equation is established for each granule, and the size and orientation of contact force at different contact points on all the granules are acquired through calculation; at last, the contact force of each granule is drawn, and the graph which is continuously represented by the contact force between adjacent granules is the path of the power transmission chain. The method is simple, scientific in principle, convenient and flexible to use, high in practicability, large in development prospect and wide in applied range.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Lens moving device, camera module and optical apparatus
ActiveUS9720251B2Accurate detectionProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementMagnetic tension forceCamera lens
A lens moving device is provided. The lens moving device includes: a bobbin; a first driving unit coupled to the bobbin; a second driving unit configured to move the first driving unit through an electromagnetic interaction with the first driving unit; a sensing magnet disposed on one side of the bobbin; a location detection sensor configured to sense a location of the sensing magnet; and a correction magnet disposed on an opposite side of the bobbin.According to the present disclosure, static tilt and dynamic tilt of the bobbin, to which a lens module is to be coupled, may be enhanced by a sensing magnet and a correction magnet which establish magnetic force equilibrium with each other.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Pneumatic pressure regulator
InactiveCN101498942AImprove stabilitySimple structureFluid pressure control without auxillary powerThin material handlingForce equilibriumEngineering
The disclosure relates to a pneumatic pressure regulator (10) for pressure adjustment (32) of a regulating pressure in a pressure chamber (13) with a regulator membrane (11) which is held in force equilibrium by a regulator spring (12) and the regulating pressure (32), wherein the regulator membrane (11) is coupled with a control valve (20) in such a way that the control valve (20) opens or closes in dependence upon the actual regulating pressure (32). For increasing the stability and the constancy of the regulating pressure it is proposed to form the control valve (20) by a dimensionally stable ball (21) which is seated in a loaded manner by means of a spring in a conical bore (23) which tapers in the direction of the regulator membrane (11) and is in a housing wall which lies opposite the regulator membrane (11) with regard to the pressure chamber (13), the regulator membrane (11) having a reinforcement in the contact region with the ball, and the ball following the movement of the regulator membrane in its normal direction. The diameter of the ball is relative to the conicity of the bore, which allows one segment of the bore to expend into the pressure chamber along the adjustment direction of the membrane.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Different-step-size efficient dynamic analysis method for train-rail-structure coupling system
InactiveCN107451305AAvoid short-term disadvantagesGuaranteed accuracyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsForce equilibriumCoupling system
The invention discloses a different-step-size efficient dynamic analysis method for a train-rail-structure coupling system. The method comprises a train structure model module, a rail structure model module, a lower structure model module, a wheeltrack dynamic contact model module between wheels and a rail steel rail, a rail unsmooth module and a dynamic mutual action model module between the rail and a lower structure, wherein the train structure model and the rail structure model are coupled into a train-rail subsystem through a wheeltrack contact relationship, and the lower structure is a lower structure subsystem; the train-rail subsystem and the lower structure subsystem are coupled through a mutual action force equilibrium condition between the rail and the lower structure; and the train-rail subsystem and the lower structure subsystem adopt different time integral step sizes, the train-rail subsystem adopts a sub step size of the small time integral step size, and the integral step size of the lower structure subsystem adopts a main step size of the large time integral step size, wherein the main step size is the integer multiple or non-integer multiple of the sub step size.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Apparatus and method for reducing shear loading on elements connecting an axle and a chassis of a vehicle
ActiveUS7383914B2Reduce and straighten out of warpageReduce and straighten out of and distortionUnderstructuresEndless track vehiclesForce equilibriumAbutment
Referring more particularly to FIG. 4, the present invention red ices such shear loading on the bolts, by utilizing a wedge member or a tapered block 106, inserted and wedged into a space 108 between wedge surfaces 70 and 88, and having oppositely facing outer surfaces 110 and 112 thereby placed into abutment with those surfaces, respectively, so as to exert a fore and aft directed force against those surface, denoted by arrows C, effectively acting to push those surfaces apart and counteracting the shear loads B. Such forces will also act in opposition to and reduce tensile loads acting on bolts 100. Tapered block 106 has at least one passage 114 therethrough (FIG. 3) for the passage of bolts 104 therethrough, to allow insertion of those bolts into threaded holes 98 and tightening those bolts to exert compressive forces against tapered block 106, denoted by arrows D, for holding that block in position. This may also be sufficient to apply a tensile load bolts 100, which are preferably at least generally longitudinally aligned therewith as shown. As a result, a force equilibrium condition can be achieved, which can significantly and predictably reduce and control shear forces acting against the bolts or other connectors for connecting axle housing 74 to the side plates 24 of chassis 22.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
System for predetermining the operating threshold of a device surveying the radial deformation state of a tire
InactiveUS20050166662A1Solve the real problemDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateForce equilibriumBelleville washer
A system for predetermining the operating threshold of a device surveying the radial deformation state of a tire comprises means capable of regulating the push due to the pressure of the tire on a closing mechanism and members capable of regulating the equilibrating counter push of the thrust of Belleville washers, helical springs and axially compressed seals.
Owner:GIOVANNI BARBANTI
Dynamic compactor capable of realizing amplitude-variable followup of A-bracket with arm support
ActiveCN102002936BReduce bending momentReasonable forceCranesSoil preservationForce equilibriumDynamic compaction
The invention relates to a dynamic compactor capable of realizing the amplitude-variable followup of an A-bracket with an arm support, which is characterized in that a followup A-bracket is mounted on a dynamic compactor rotating platform, an amplitude-variable draw rod is arranged between an inner diagonal rod and an arm support, a swing arm mechanism is arranged at the lower parts of the amplitude-variable draw rod and the inner diagonal rod, the swing arm mechanism is composed of a swing arm rack and a telescopic oil cylinder, and the followup A-bracket forms linkage with the amplitude-variable draw rod by the swing arm mechanism. Wire ropes of a hoisting mechanism are connected with a dynamic compactor weight through a pulley at the top end of the followup A-bracket and a pulley at the top end of the arm support, so that the quantity of front wire ropes at the top end of the arm support is the same with that of back wire ropes at the top end of the arm support. When the amplitude-variable draw rod drives the arm support to realize an amplitude-variable process, the swing arm mechanism connected with the followup A-bracket synchronously drives the followup A-bracket to swing. The amplitude-variable followup of the followup A-bracket with the arm support is realized, so that the stress on the arm support of the dynamic compactor is more reasonable, the stress balancing of the arm support can be realized to the greatest extent, the structural stress of the arm support can be improved, the self-weight of the arm support can be reduced, and the dynamic compaction operating performance of the arm support and the complete machine can be improved.
Owner:CHINA ZHONGHUA GEOTECHN ENG
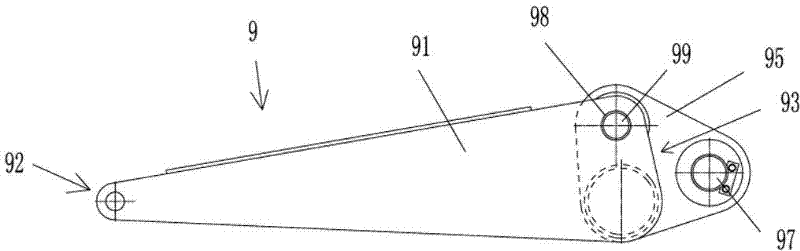
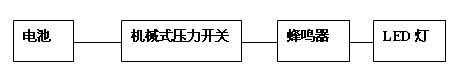
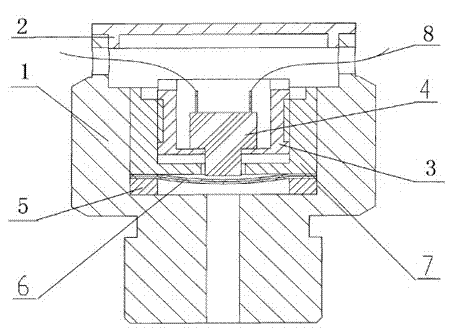
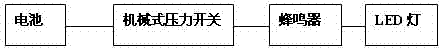
Simple tire pressure monitoring alarm device
The invention discloses a simple tire pressure monitoring alarm device. The simple tire pressure monitoring alarm device in the invention comprises a mechanical pressure switch, a cell and a buzzer; the mechanical pressure switch comprises a pressure sensing element and a microswitch which is cascaded in a connection loop of the cell and the buzzer. Preferably, the mechanical pressure switch is a force equilibrium type mechanical pressure switch. The invention also discloses a small electric car which comprises tires, and the tire is provided with the simple tire pressure monitoring alarm device provided in the invention; the pressure sensing element of the mechanical pressure switch is installed in the tire, the buzzer is fixed at the exterior of the tire. The simple tire pressure monitoring alarm device provided in the invention has the advantages of simple construction and low cost, and is especially applicable to transportation vehicles such as small electric cars and motorcycles.
Owner:SUQIAN XINYU TIRE
Hydrostatic valve arrangement, hydrostatic transmission gear having valve arrangement, and hydrostatic drive device having transmission gear
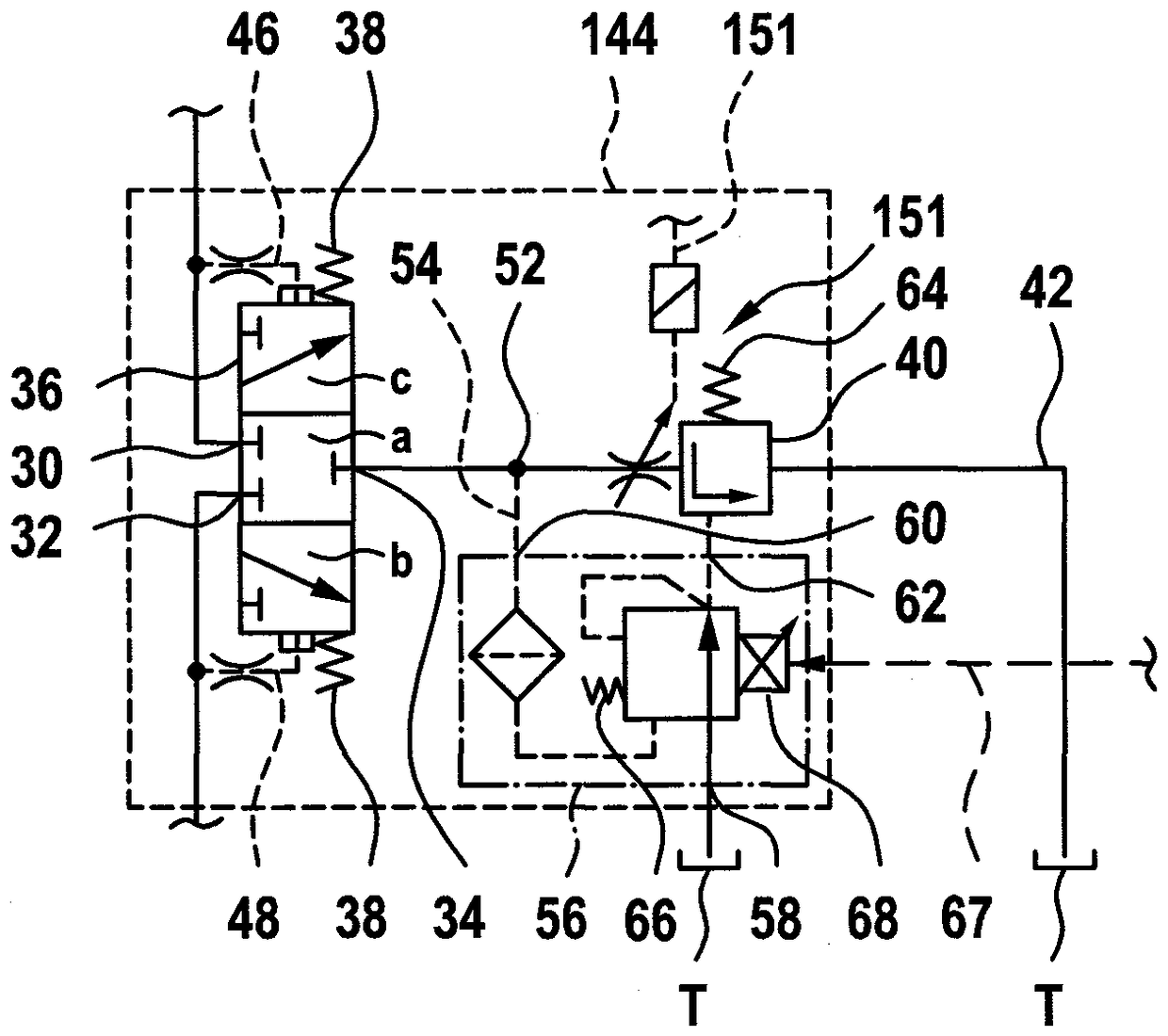
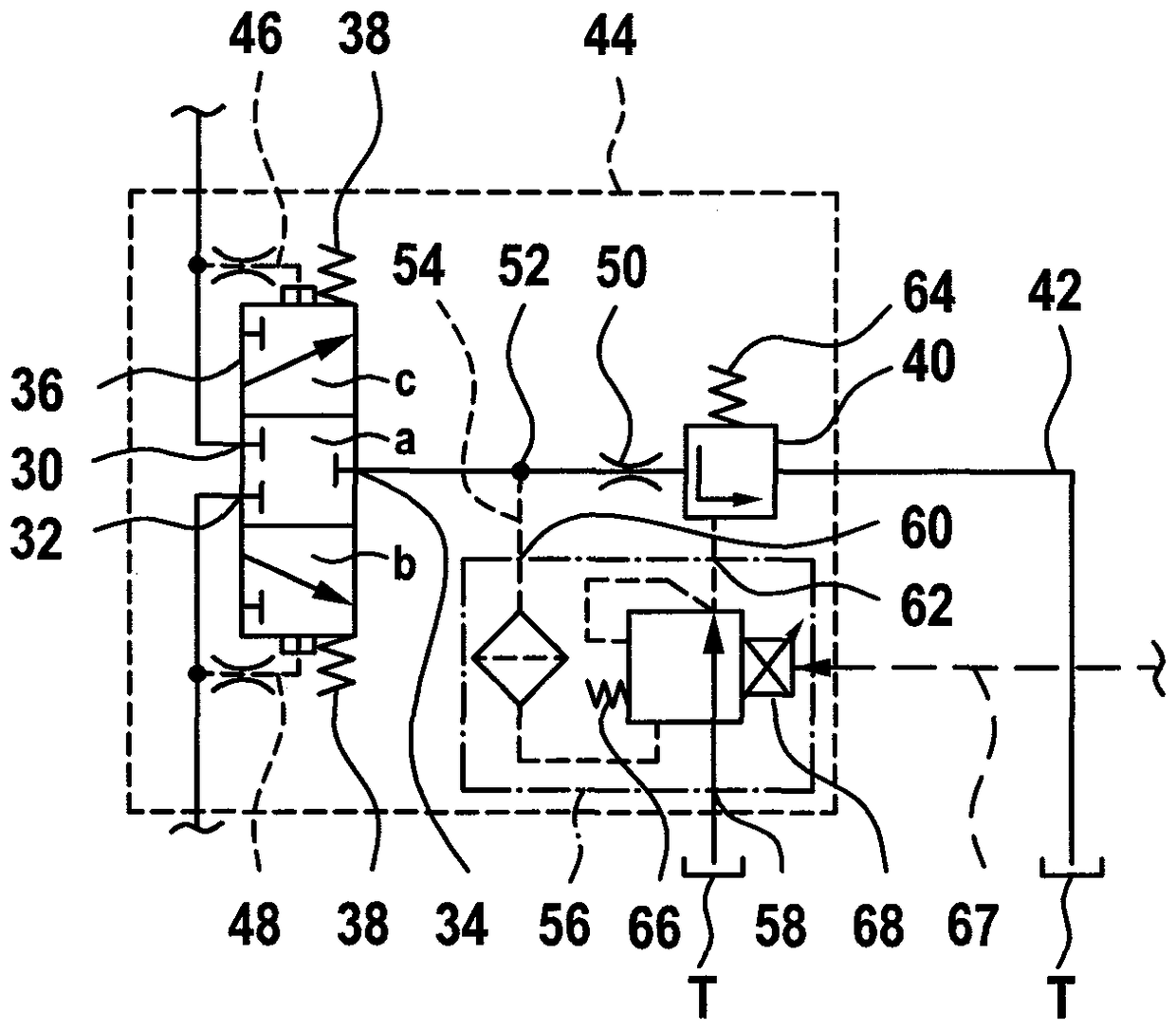
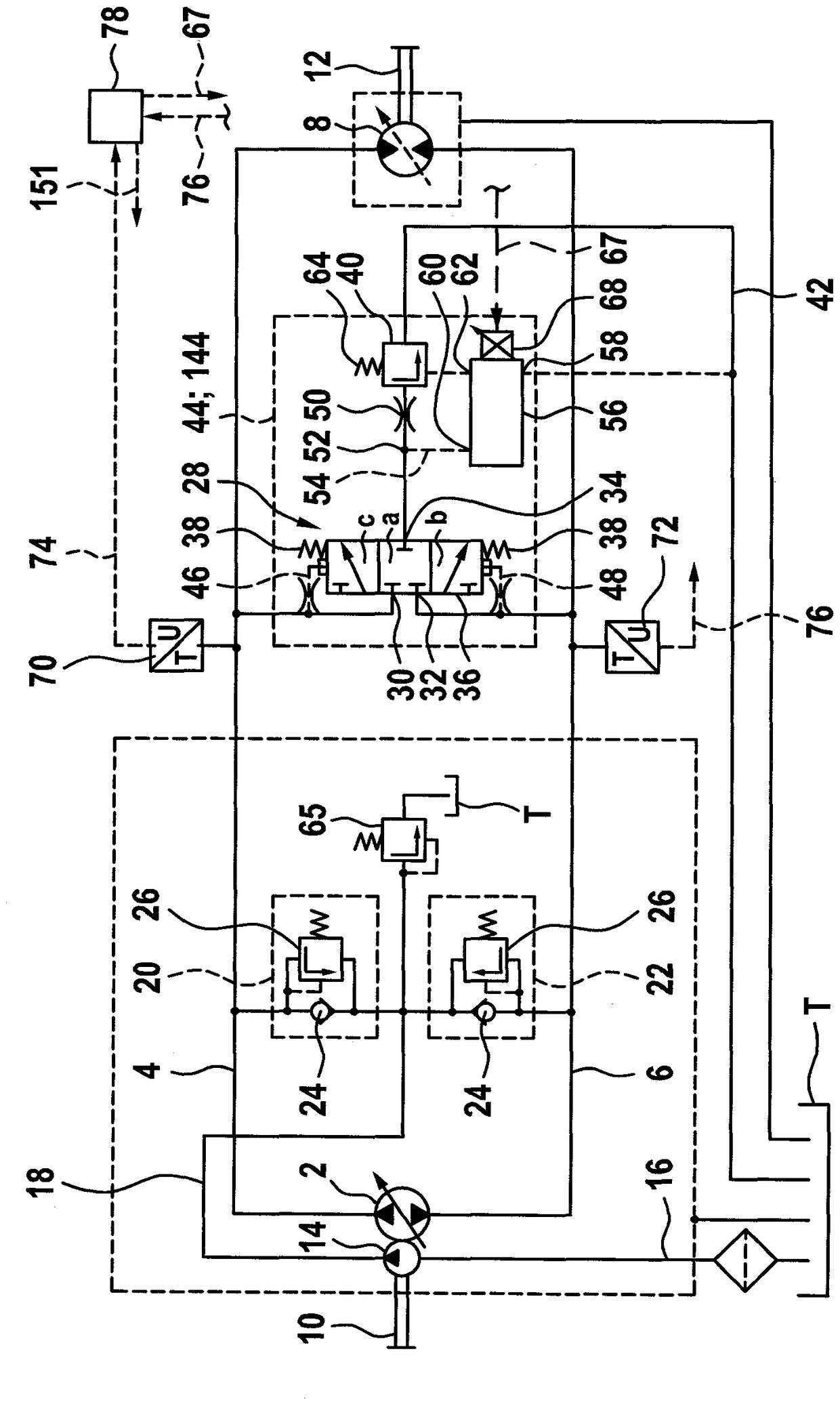
ActiveCN109469665ARelieve pressureOpen pressure dropServomotor componentsTelemotorsForce equilibriumHydraulic circuit
The invention relates to a hydrostatic valve arrangement for flushing a pressure medium from a working line of a hydraulic circuit includes a flushing valve with a first flushing connection for connecting to a first working line and an output connection for connecting to a pressure medium sink. The arrangement also includes a pressure valve arranged in a pressure medium flow path of the arrangement from the output connection in the direction of the pressure medium sink. The pressure valve has a valve body on which a force equilibrium is formed. The force equilibrium includes a pressure equivalent that acts on the valve body in a direction that blocks the pressure medium flow path and an opening pressure that acts in a direction that opens the pressure medium flow path and is dependent on the pressure at the output connection. The arrangement further includes an adjusting device for shifting the force equilibrium.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com