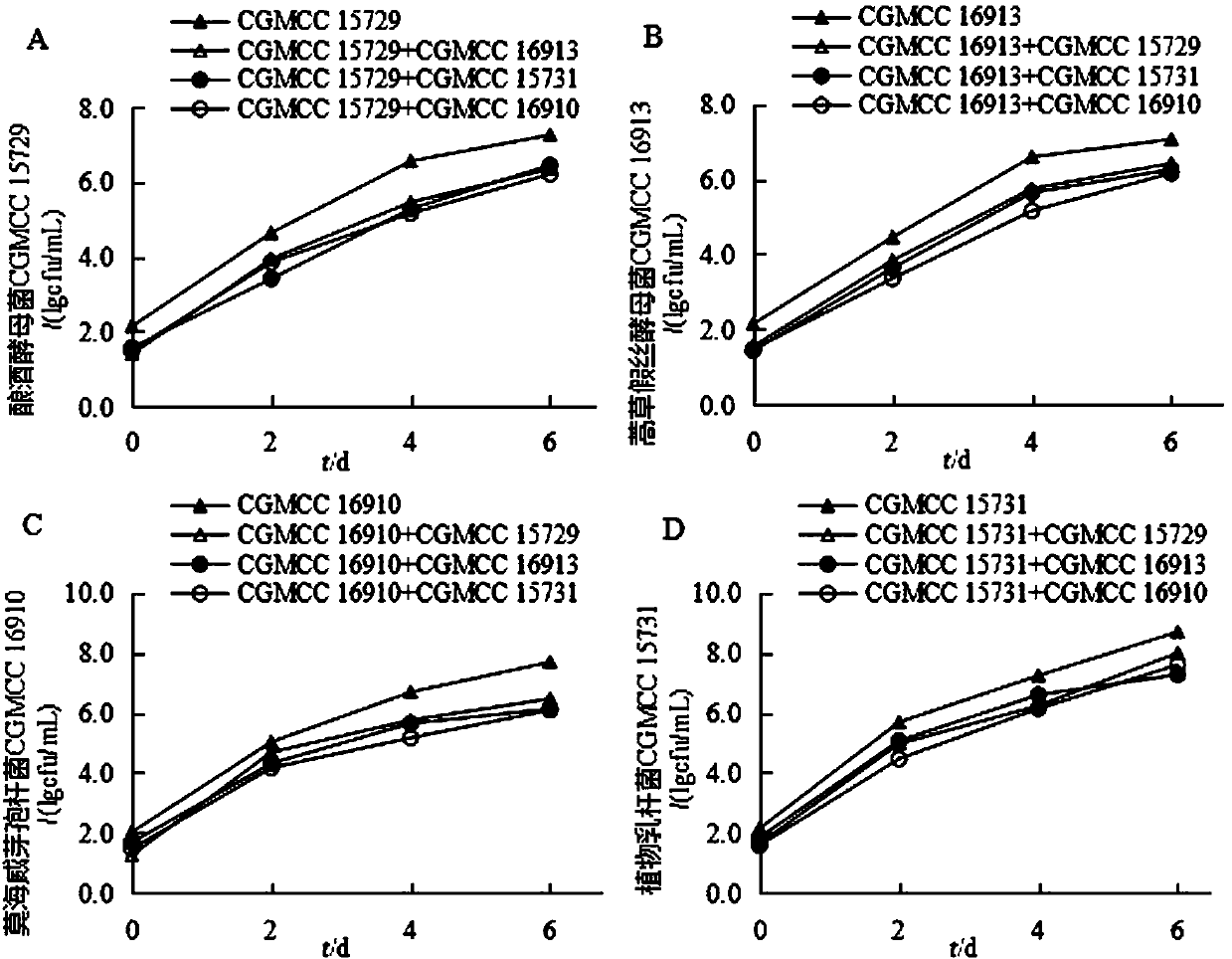
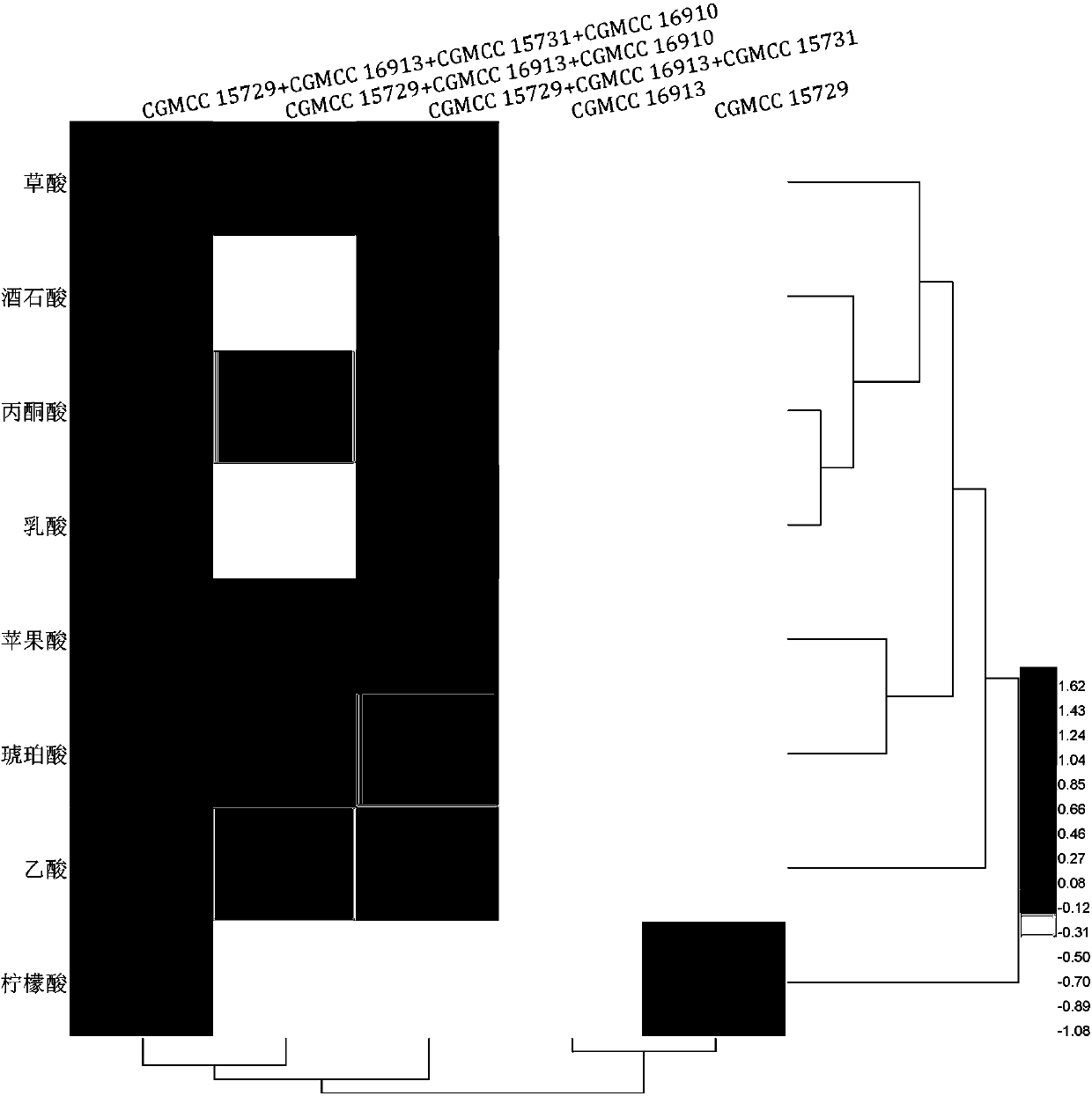
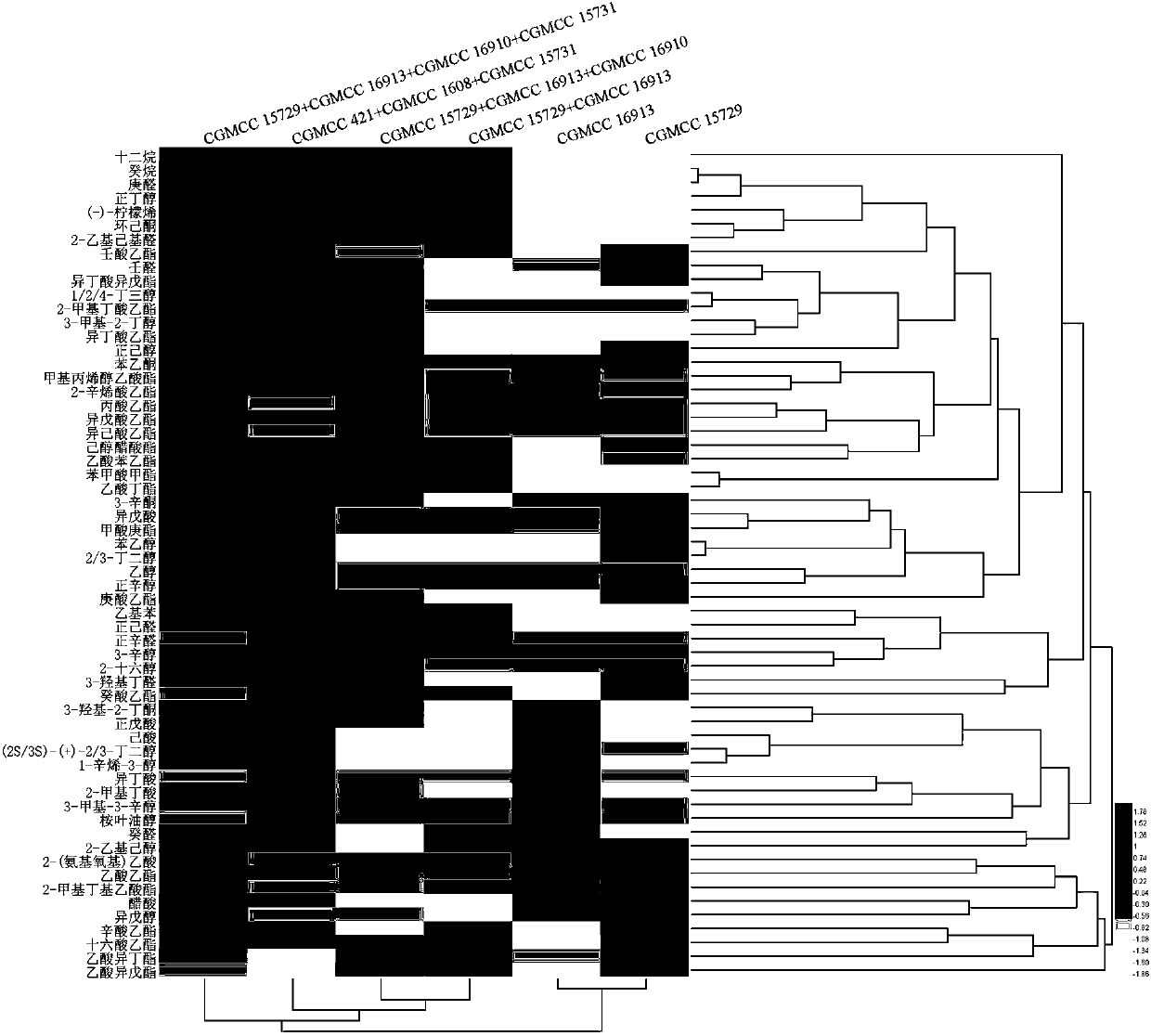
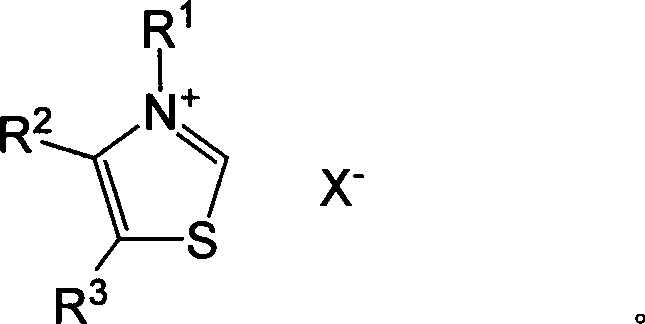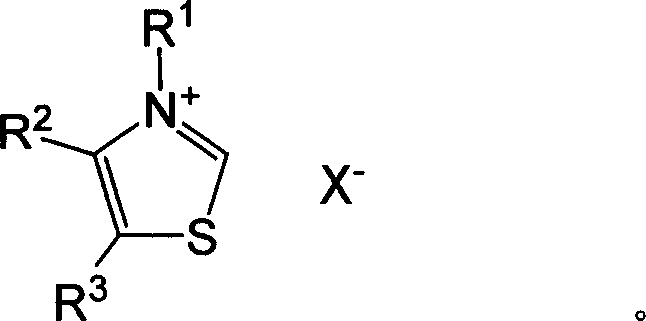Patents
Literature
205 results about "Acetoin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
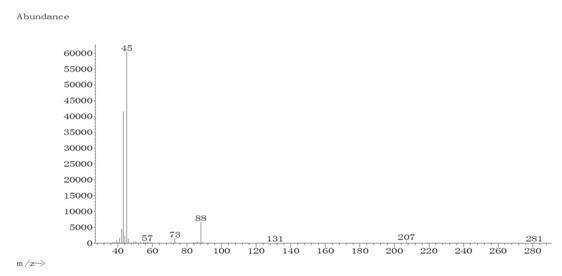
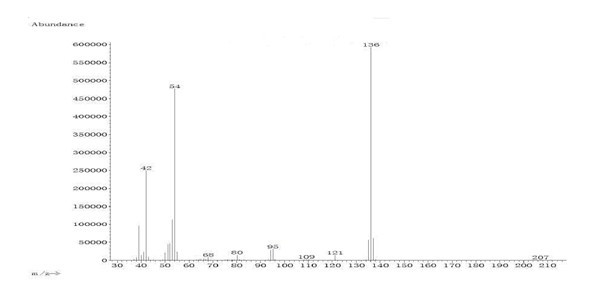
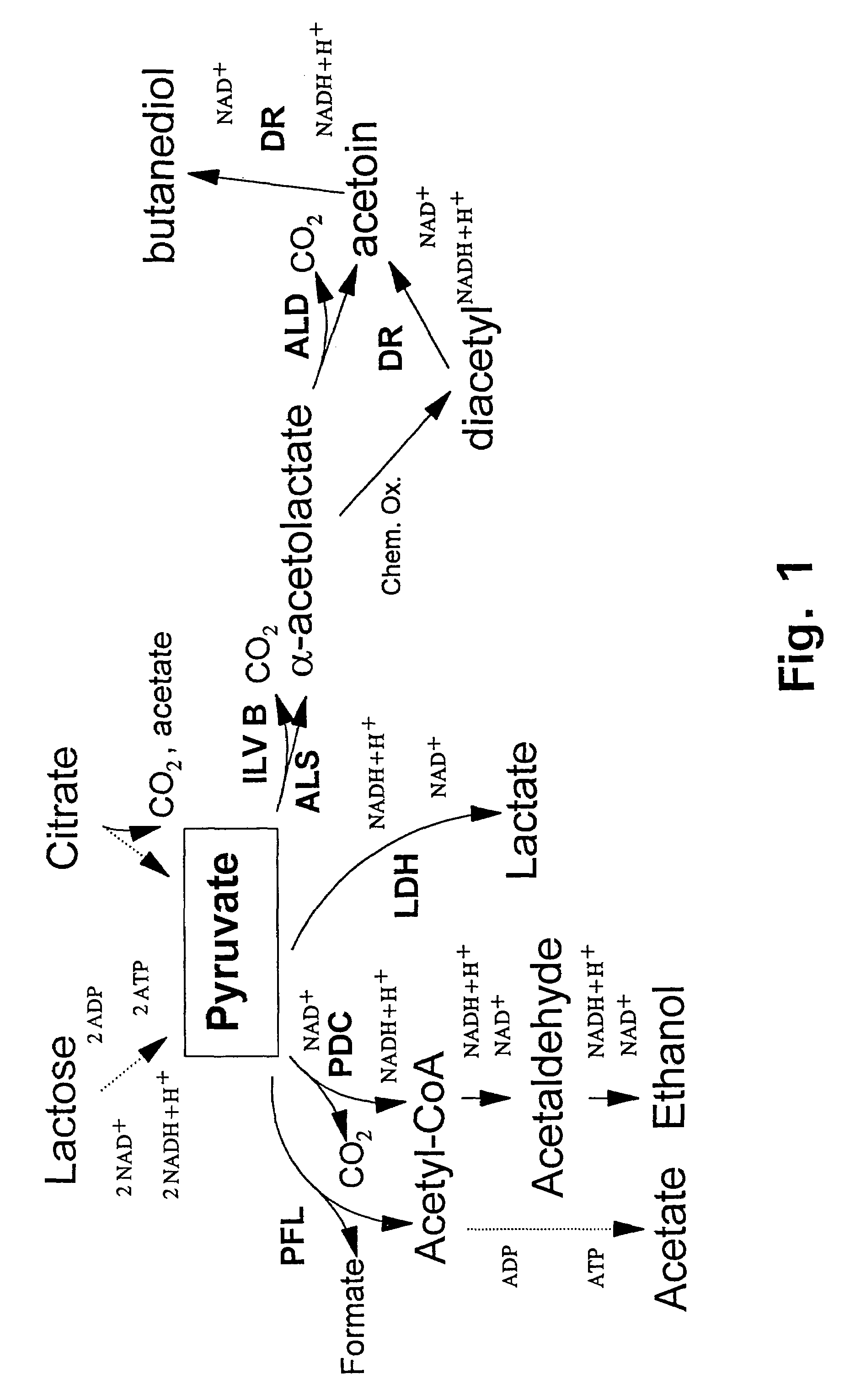
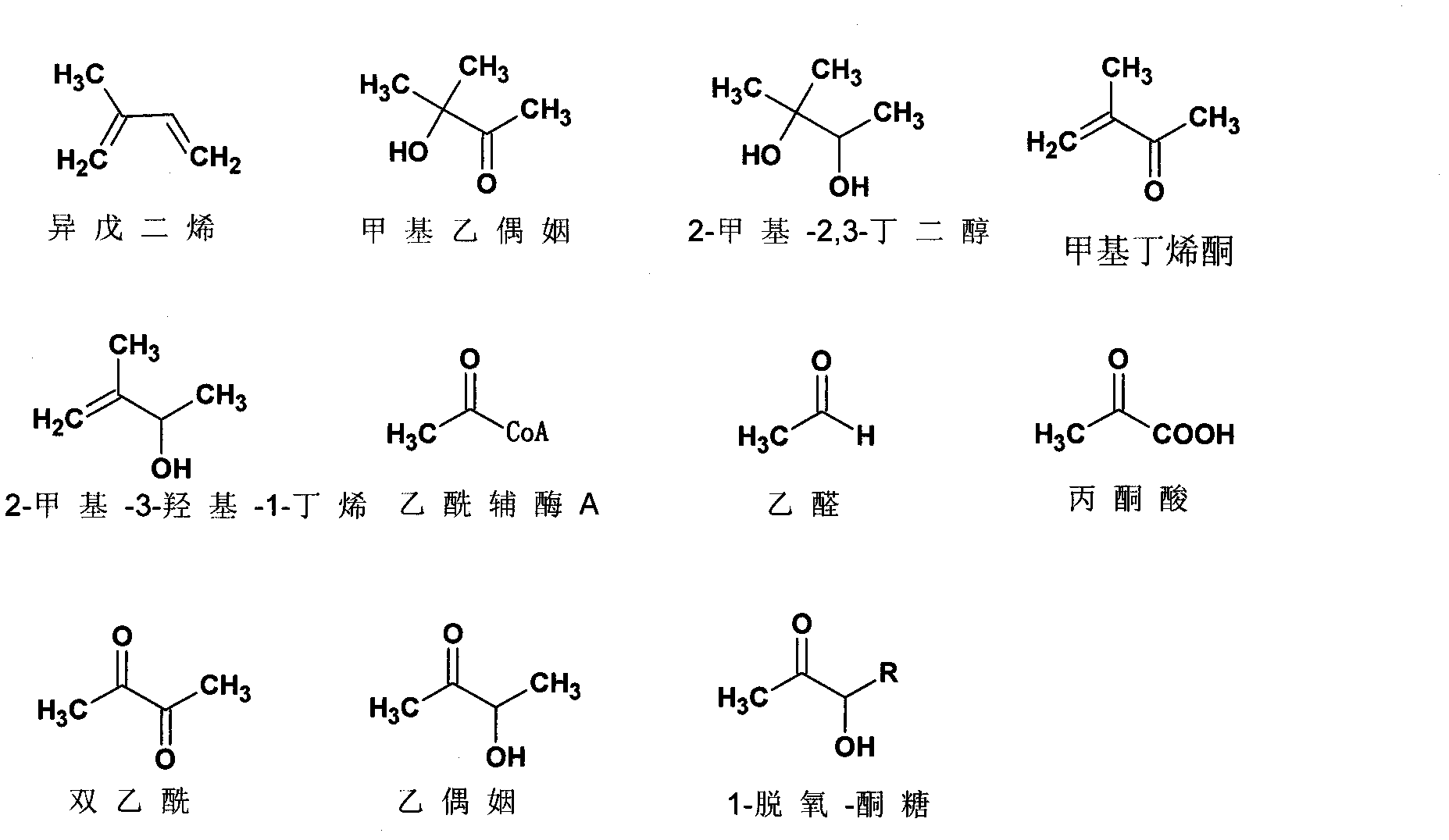
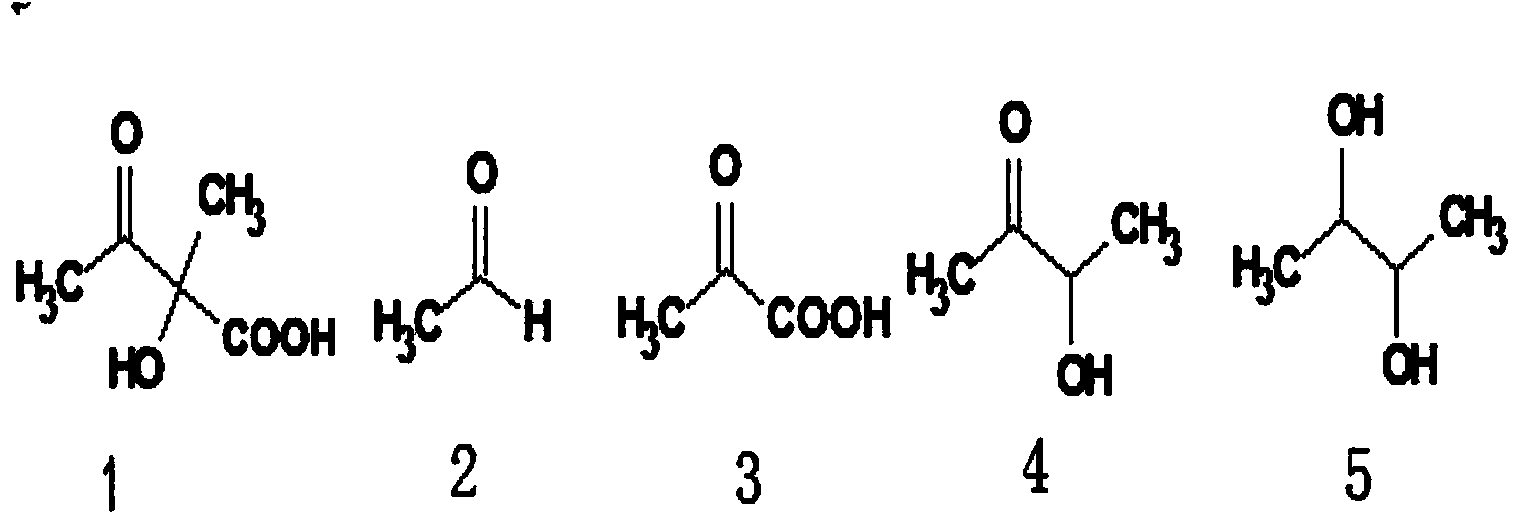
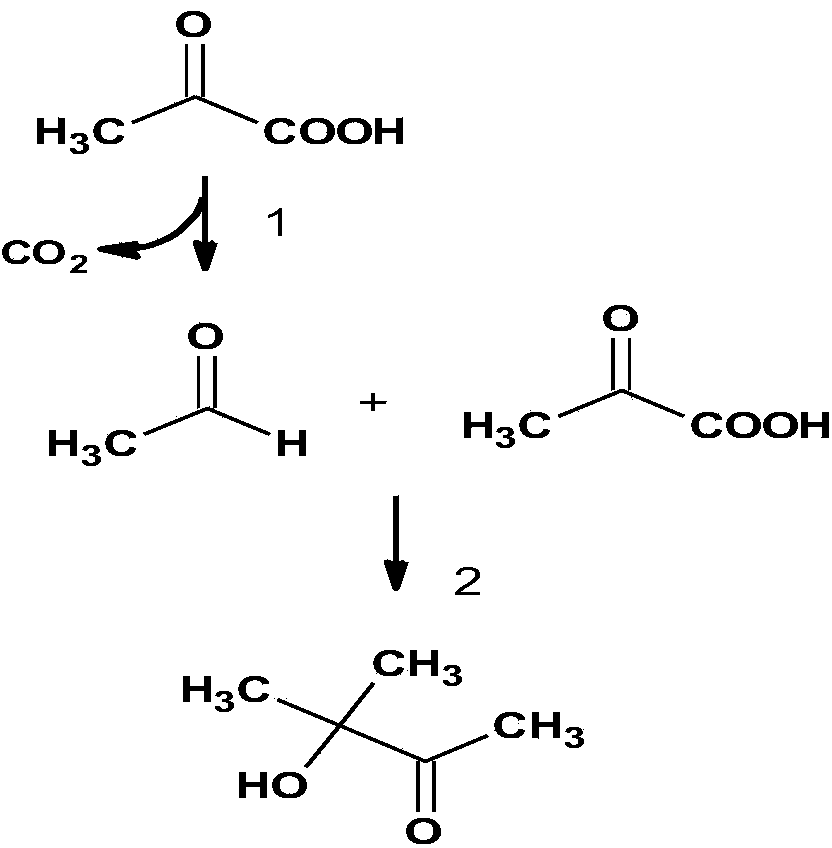
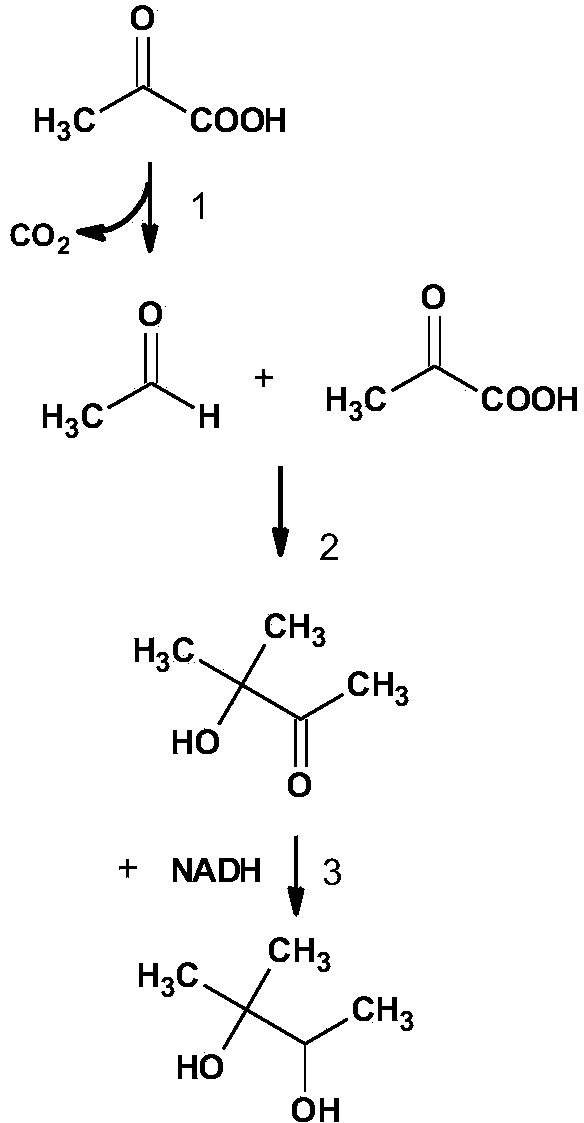
Acetoin, also known as 3-hydroxybutanone or acetyl methyl carbinol, is an organic compound with the formula CH₃CH(OH)C(O)CH₃. It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant, buttery odor. It is chiral. The form produced by bacteria is (R)-acetoin.
Methods for promoting plant health
ActiveUS20100260735A1Promoting health of plantImprove pathogen resistanceBiocideKetone active ingredientsGrowth plantBiofilm
A method for promoting the health of a plant comprises administering malic acid to the plant or the soil in an amount effective to recruit plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) to the plant. Administration of malic acid promotes biofilm formation of PGPR on the plant's roots, thereby restricting entry of a foliar pathogen through stomatal pores present in the leaves. Another method for promoting the health of a plant comprises administering acetoin to the plant or the soil in an amount effective to increase pathogen resistance in aerial parts of the plant.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Method and strain for producing tetramethylpyrazine
InactiveCN101955980APromote rapid proliferationRich sourcesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisHigh concentration
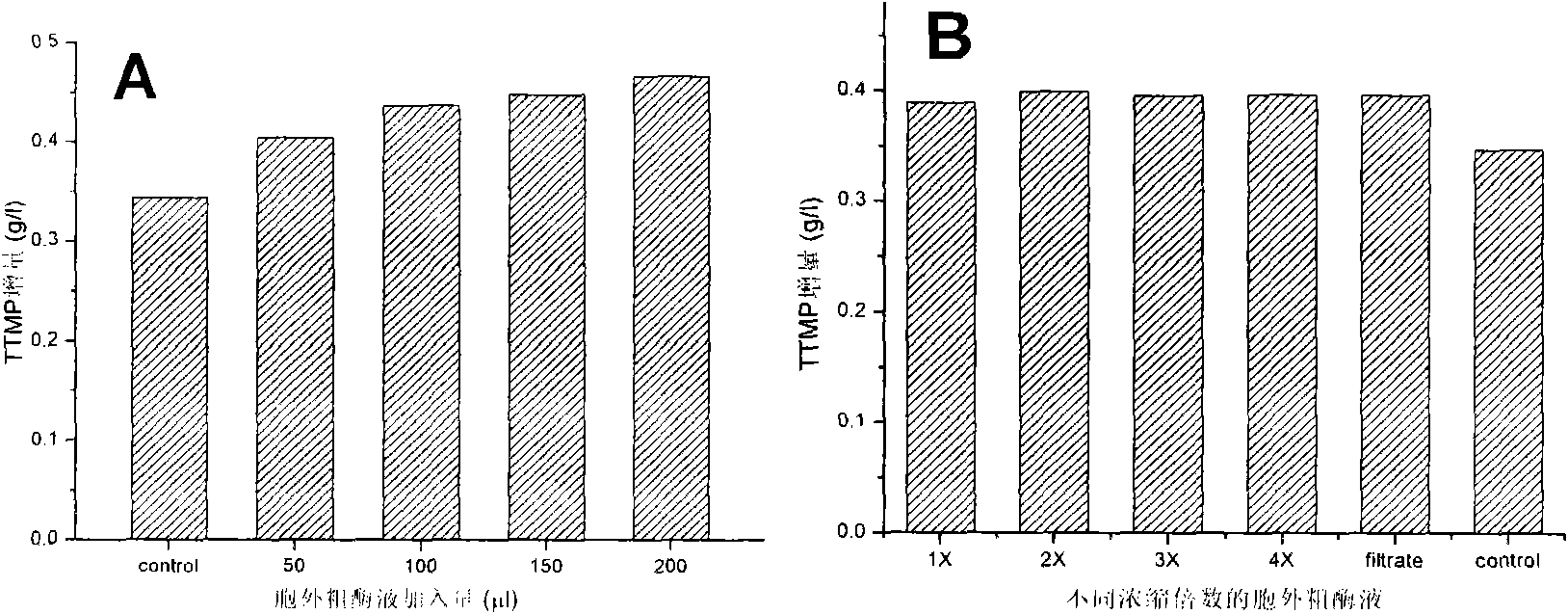
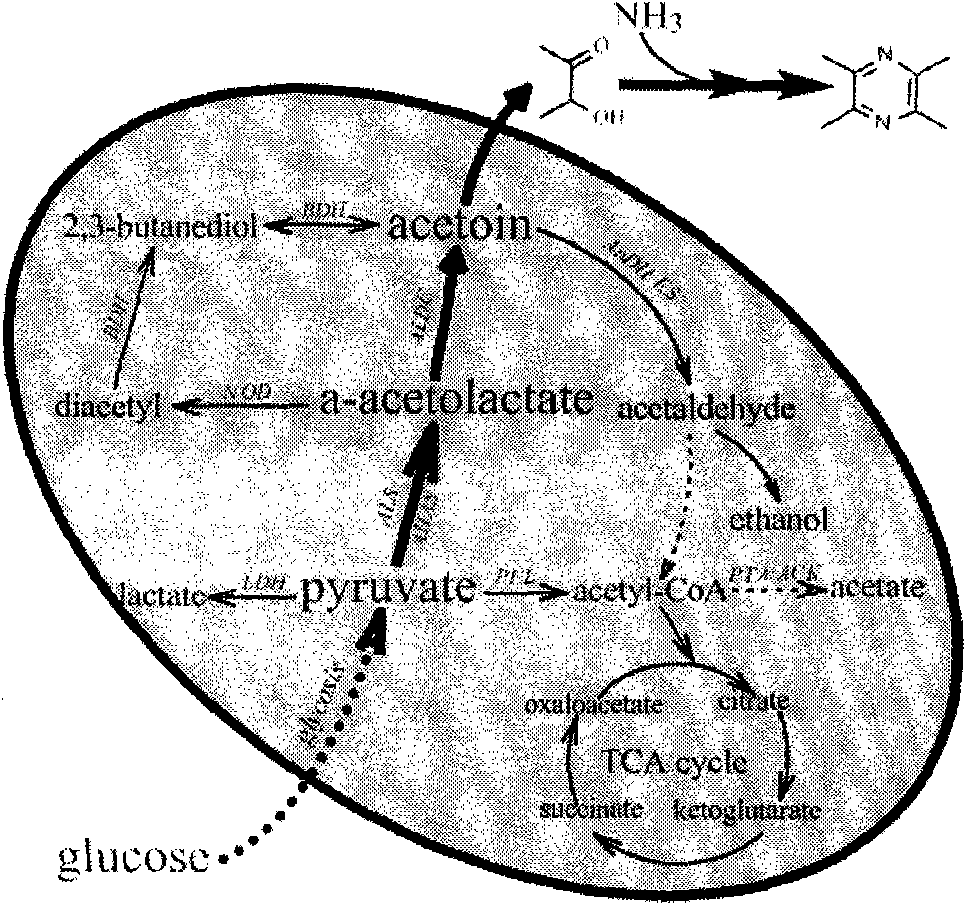
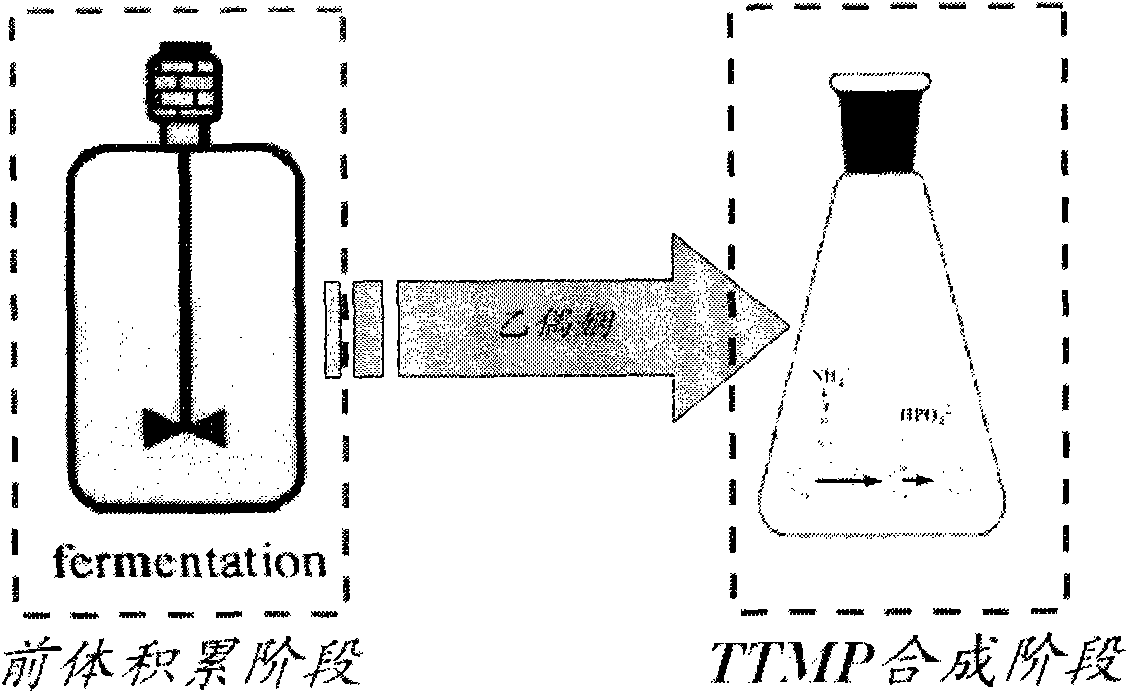
The invention discloses a method and a strain for producing tetramethylpyrazine (TTMP), in particular a two-step production process that a microorganism accumulates precursor acetoin by using the fermentation of reducing sugar and the acetoin and ammonia undergo a non-enzymatic reaction to synthesize the TTMP, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The microorganism is any one of bacillus subtilis (CCTCC NO:M 208157), bacillus licheniformis (CGMCC NO:3961), bacillus licheniformis (CGMCC NO:3962) and bacillus licheniformis (CGMCC NO:3963). The strain obtains biomass and accumulates endogenous precursor acetoin by using the fermentation of the reducing sugar, and the acetoin and the ammonia in a fermentation system undergo the non-enzymatic reaction to synthesize the TTMP. The method has the advantages that: the obtained bacteria quantity is higher, the accumulation amount of the acetoin is effectively improved (38 to 44g / L); the high-concentration endogenous precursor acetoin and the ammonia can quickly react under proper conditions to form the TTMP (16 to 20g / L); and the use ratio (40.3 percent) of precursors is obviously improved due to the accumulation of endogenous acetoin and an in-situ fermentation environment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Taste-Masking Compositions, Sweetener Compositions and Consumable Product Compositions Containing the Same
Owner:CELANESE SALES GERMANY
Method for synthesizing Yiyuyin through catalysis of acetaldehyde
InactiveCN1562934AHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationDistillationSolvent
Ethyl aldehyde is directly synthesized into ethyl acyloin under catalyst of thiazol salt, needing no solvents. This invention process has advantages of: low by-product, high pureness (after simple distillation the product ethyl acyloin is obtd. with pureness of 98.7%), high selectivity of 99%, and suitable for use to produce essences with types of butter, milchigs, leben and strawberry etc.
Owner:大连金菊化工厂
Biofuel and chemical production by recombinant microorganisms via fermentation of proteinacious biomass
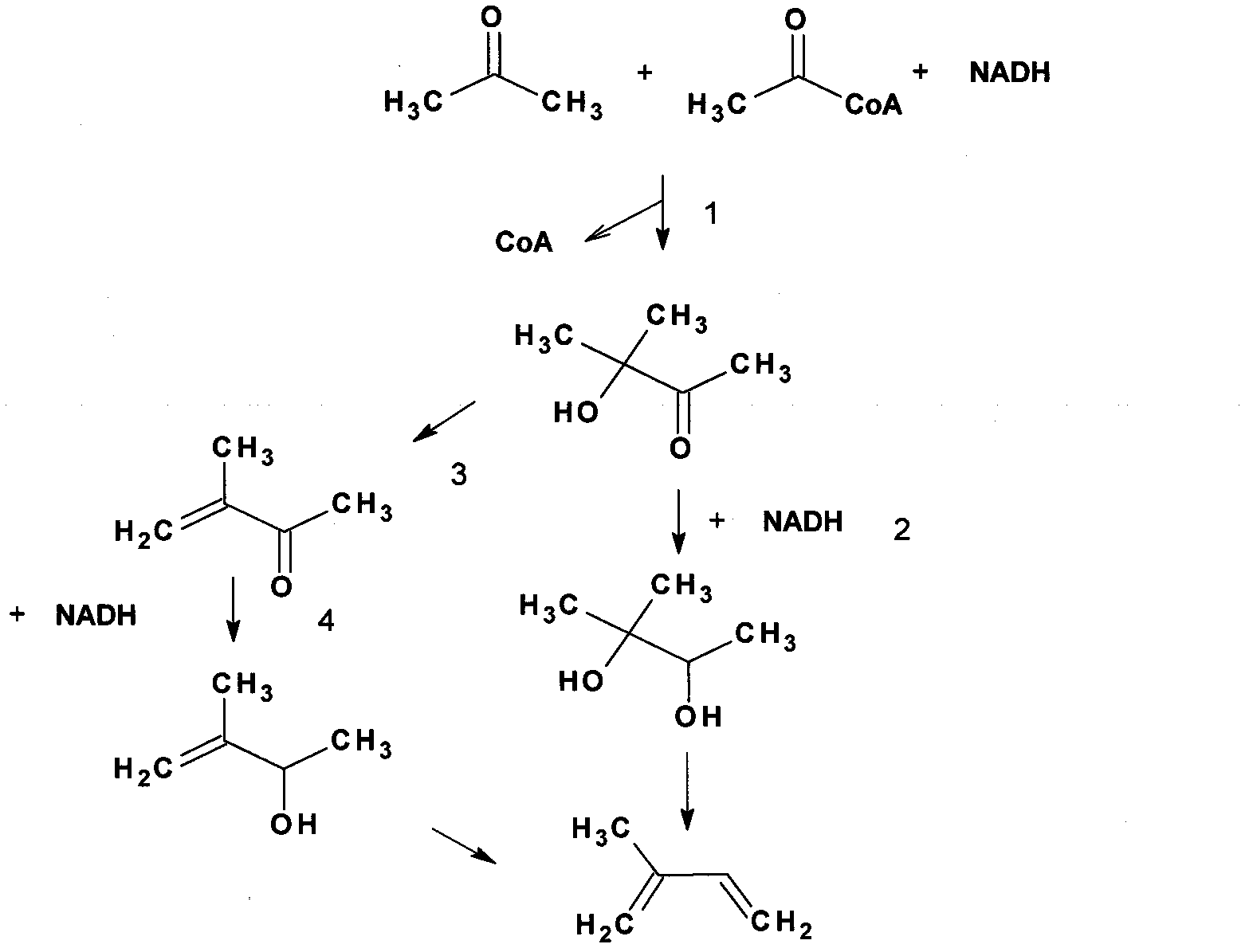
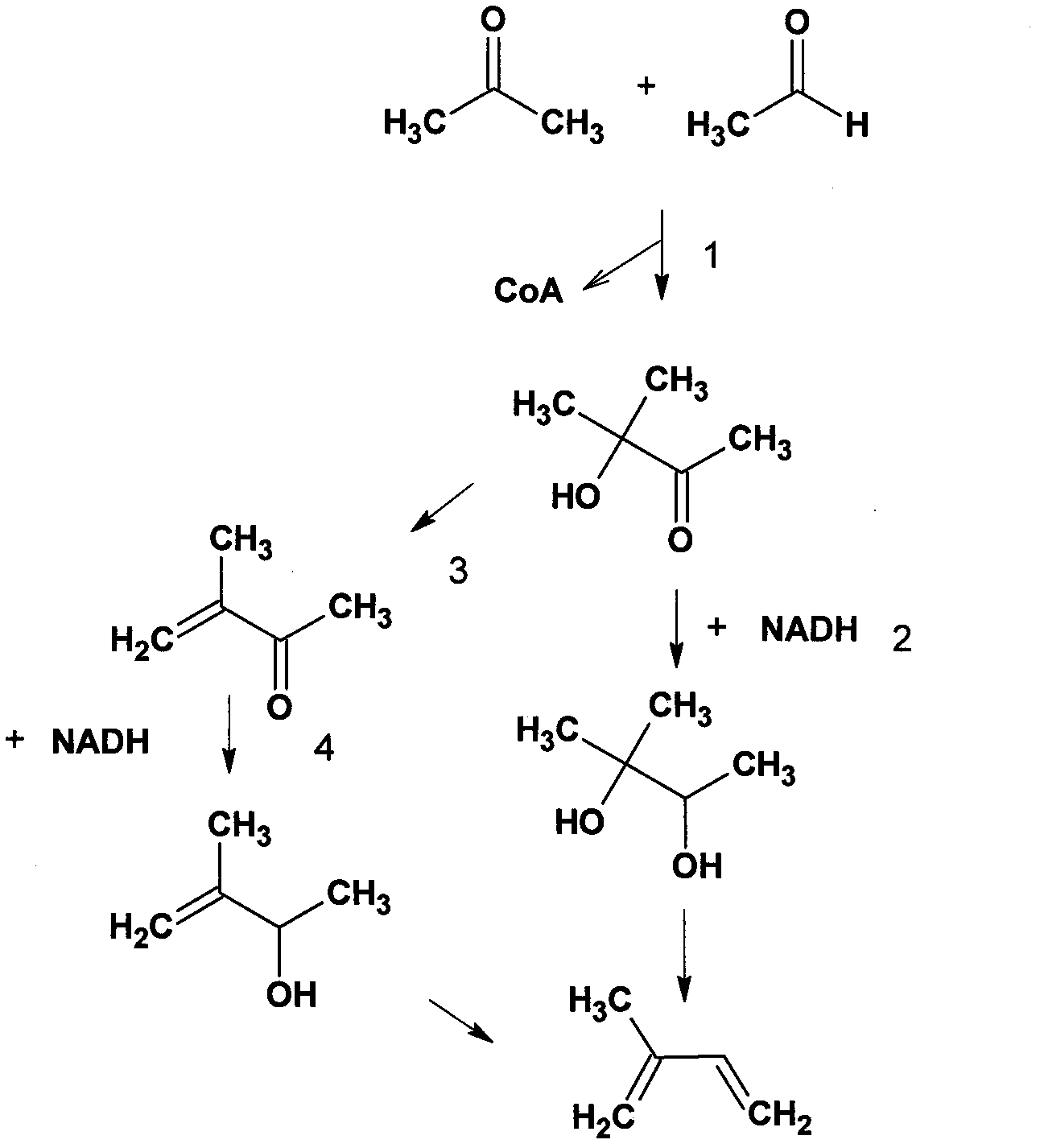
Provided herein are metabolically modified microorganisms characterized by having an increased keto-acid flux when compared with the wild-type organism and comprising at least one polynucleotide encoding an enzyme, and causing the production of a greater quantity of a chemical product when compared with the wild-type organism. The recombinant microorganisms are useful for producing a large number of chemical compositions from various nitrogen containing biomass compositions and other carbon sources. More specifically, provided herein are methods of producing alcohols, acetaldehyde, acetate, isobutyraldehyde, isobutyric acid, n- butyraldehyde, n-butyric acid, 2-methyl-l-butyraldehyde, 2-methyl-l -butyric acid, 3- methyl-l-butyraldehyde, 3 -methyl- 1 -butyric acid, ammonia, ammonium, amino acids, 2,3-butanediol, 1,4-butanediol, 2-methyl-l, 4-butanediol, 2-methyl- 1,4-butanediamine, isobutene, itaconate, acetoin, acetone, isobutene, 1,5-diaminopentane, L-lactic acid, D- lactic acid, shikimic acid, mevalonate, polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), isoprenoids, fatty acids, homoalanine, 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA), succinic acid, malic acid, citric acid, adipic acid, p-hydroxy-cinnamic acid, tetrahydrofuran, 3-methyl-tetrahydrofuran, gamma-butyrolactone, pyrrolidinone, n-methylpyrrolidone, aspartic acid, lysine, cadeverine, 2-ketoadipic acid, and / or S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM), from a suitable nitrogen rich biomass.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bacillus subtilis for highly producing D-ribose and co-producing acetoin
InactiveCN101974444AAvoid damageHigh mutation rateBacteriaMutant preparationBacterial strainButanediol
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis for highly producing D-ribose and co-producing acetoin, which is preserved in a China general microbiological culture collection center with CGMCC No.3720 and the preservation data of April eighth, 2010. The invention also discloses a method for producing the D-ribose and co-producing the acetoin by fermenting the bacillus subtilis. The selected bacterial strains can produce produce the D-ribose and co-produce the acetoin by using the fermentation of a plurality of types of carbon and nitrogen sources, the operation is convenient and simple, the conditions of culture are extensive, and the industrialization is easy. In the invention, an organic acid is added to a fermentation medium, therefore, the yield of the D-ribose is improved by 64.5g / L compared with the original strains, and the acetoin is improved by 17.3g / L. The bacillus subtilis has higher capability for synthetizing the D-ribose and the acetoin, and the yield of reduced by-products of 2,3-butanediol of the acetoin is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing 2,3-butanediol by using starch raw materials
InactiveCN101565721AWide variety of sourcesLow priceMicroorganism based processesFermentationK pneumoniaeAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a method for producing 2,3-butanediol by using starch raw materials, which comprises the following steps: subjecting the starch raw materials to treatment by alpha-amylase and maltogenic amylase; and producing the 2,3-butanediol by carrying out separate hydrolysis and fermentation or simultaneous sacchrification and fermentation under an aseptic condition, using saccharification liquid or liquefaction liquid as a fermentable substrate and using Klesiella pneumoniae as a fermentable strain. Finally the concentration of the 2,3-butanediol reaches 43 to 112g / L, and the final concentration of acetoin and the final concentration of the 2,3-butanediol reach 45 to 121g / L. The method has the advantages of using the starch raw materials to produce a high-value platform compound by fermentation, reducing the raw material cost of the production of the 2,3-butanediol by the fermentation and establishing the optimal fermentation condition for the production of the 2,3-butanediol by the sacchrification and fermentation of the starch raw materials. The production of the 2,3-butanediol by the simultaneous sacchrification and fermentation of the invention can save energy and equipment investment, reduce fermentation period and improve production efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Screening method of strain capable of producing acetoin and acetoin production method based on strain fermenting method
InactiveCN102634563AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention describes a screening method of a strain capable of producing acetoin and an acetoin production method based on a strain fermenting method, belonging to the technical field of the biological engineering. A soil sample of the strain is dried, suspended, diluted, coated, and then qualitatively analyzed and screened by a Voges-Proskauer(V-P) experiment, and then the screened strain is subject to physiological and biochemical and molecular biological identification, and a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens capable of producing the acetoin with high yield is obtained by using a high-performance liquid chromatography method. The invention also discloses an acetoin production method based on the strain, wherein the yield of the acetoin is 35g / L after fermenting lasts for 72 hours.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing acetoin by vinasse fermentation and producing tetramethylpyrazine by acetoin transformation
ActiveCN102618587AIncrease added valueEfficient use ofMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a method for producing biological aromatics: acetoin and tetramethylpyrazine by taking vinasse as a raw material by utilizing microbial fermentation and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: supplementing a proper amount of glucose (0-100g / kg) into fresh vinasse of which the acidity is regulated; adding a seed culture cultured by any one of bacillus subtilis (CCTCCNO: M208157) or bacillus licheniformis (CGMCC3961, 3962, 3963); then, fermenting for 1-3 days at the temperature of 37 DEG C to produce a great amount of one of the biological aromatics: the acetoin; and on the basis, adding ammonium salt to the fermentation product to produce the other biological aromatic: the tetramethylpyrazine by acetoin transformation. The method for selectively producing the biological aromatics: the acetoin and the tetramethylpyrazine under control by taking the vinasse as the raw material through whether the ammonium salt is added or not has the outstanding advantages that not only can the biological aromatics with different high additional values be selectively obtained but also the vinasse is prevented from polluting the environment and the utilization value of the vinasse is promoted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacillus subtilis mutant strain and a fermentation method for producing acetoin using this organism
ActiveUS20080182306A1High yieldHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
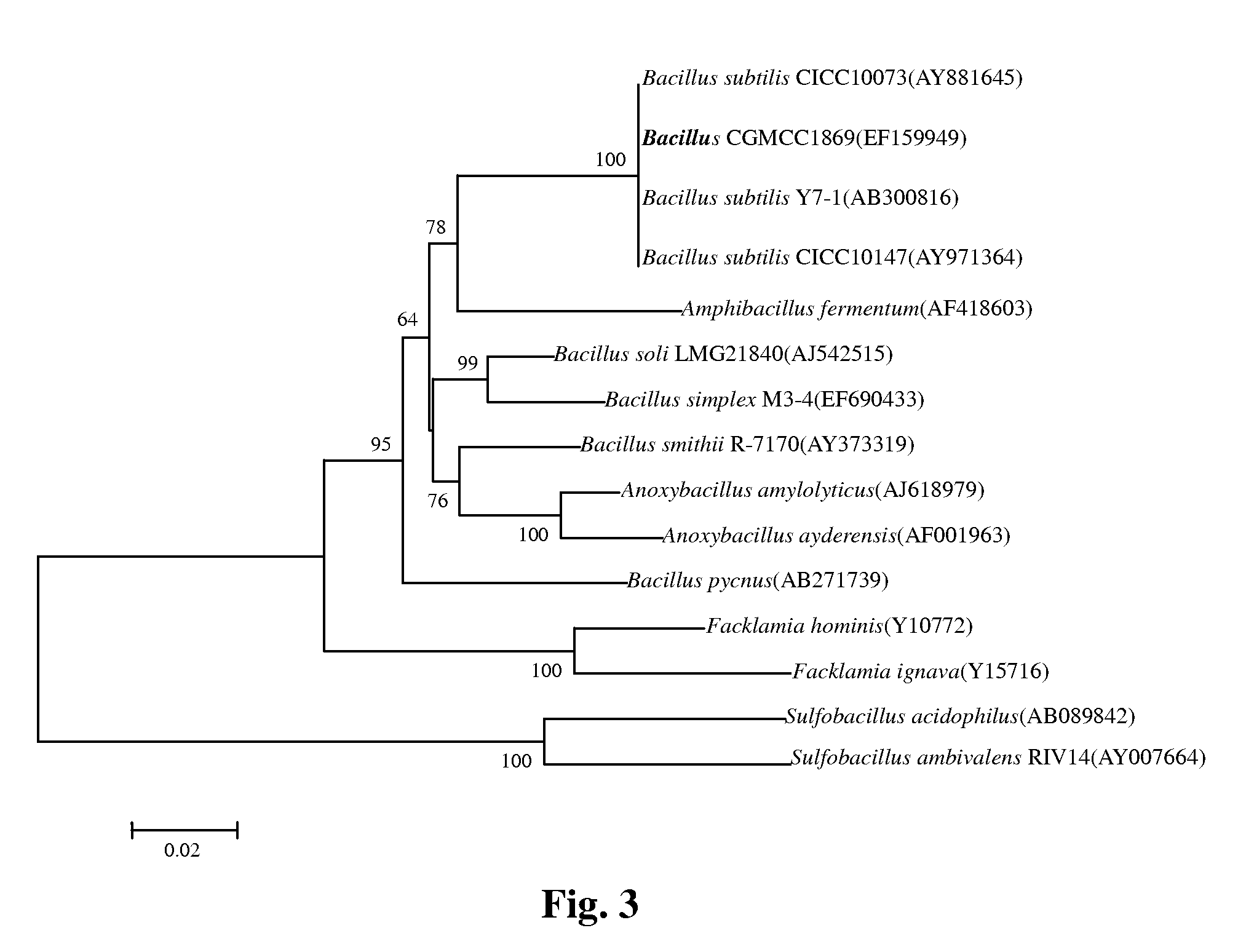
The present invention provides a mutant strain of Bacillus subtilis SFA-H31 and includes an optimized method for producing of acetoin using this strain. The advantage of this method to produce acetoin has been defined by its high-yield without mixture with diacetyl or 2,3 butanedinol, both of which are usually accompanied with acetoin in other strain. This Bacillus subtilis mutant strain has been deposited in China General Microbilogical Culture Collection (CGMCC) and the accession number is CGMCC No. 1869, in which the process of fermentation for acetoin production is composed of (1) strain activation, (2) seed culture, (3) fermentation, (4) quantification of substrates and products. Based on current method, the concentration of acetoin in the ferment broth can reach to 35-55 g / L and the conversion rate of glucose to acetoin is in the range of 40-50%.
Owner:FOOD FERMENTATION IND RES & DESIGN INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE +1
Metabolically engineered lactic acid bacteria and their use
InactiveUS7465575B2Reduced growth rateReduce probabilityBiocideBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseLactic bacteria
Mutants of lactic acid bacteria including Lactococcus lactis which are defective in pyruvate formate-lyase production and / or in their lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh) production and methods of isolating such mutants or variants are provided. The mutants are useful in the production of food products or in the manufacturing of compounds such as diacetyl, acetoin and acetaldehyde and as components of food starter cultures.
Owner:NILSSON DAN
Method for producing acetoin through high-efficiency fermentation by appropriately expressing novel bacillus subtilis NADH oxidizing enzyme
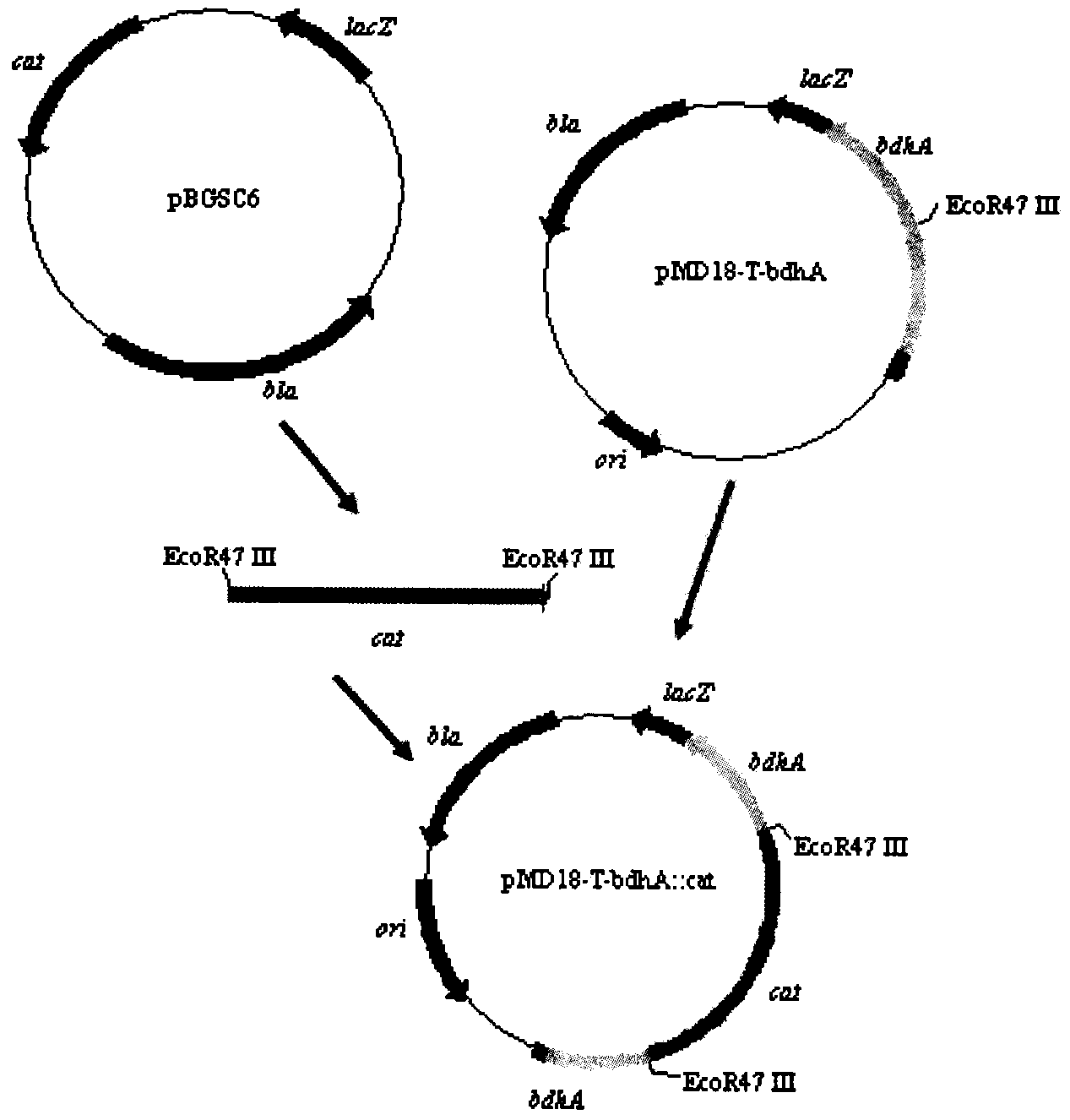
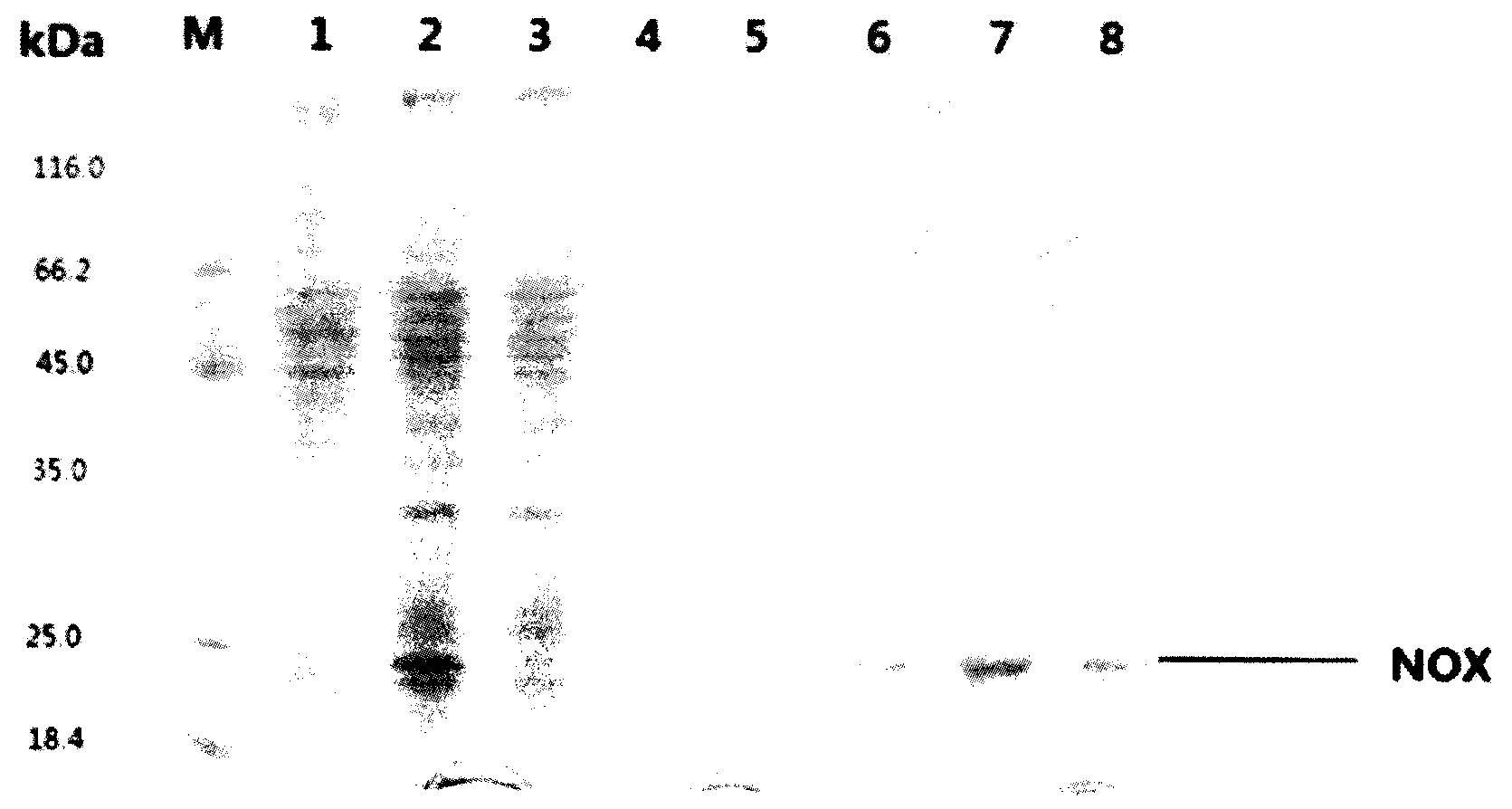
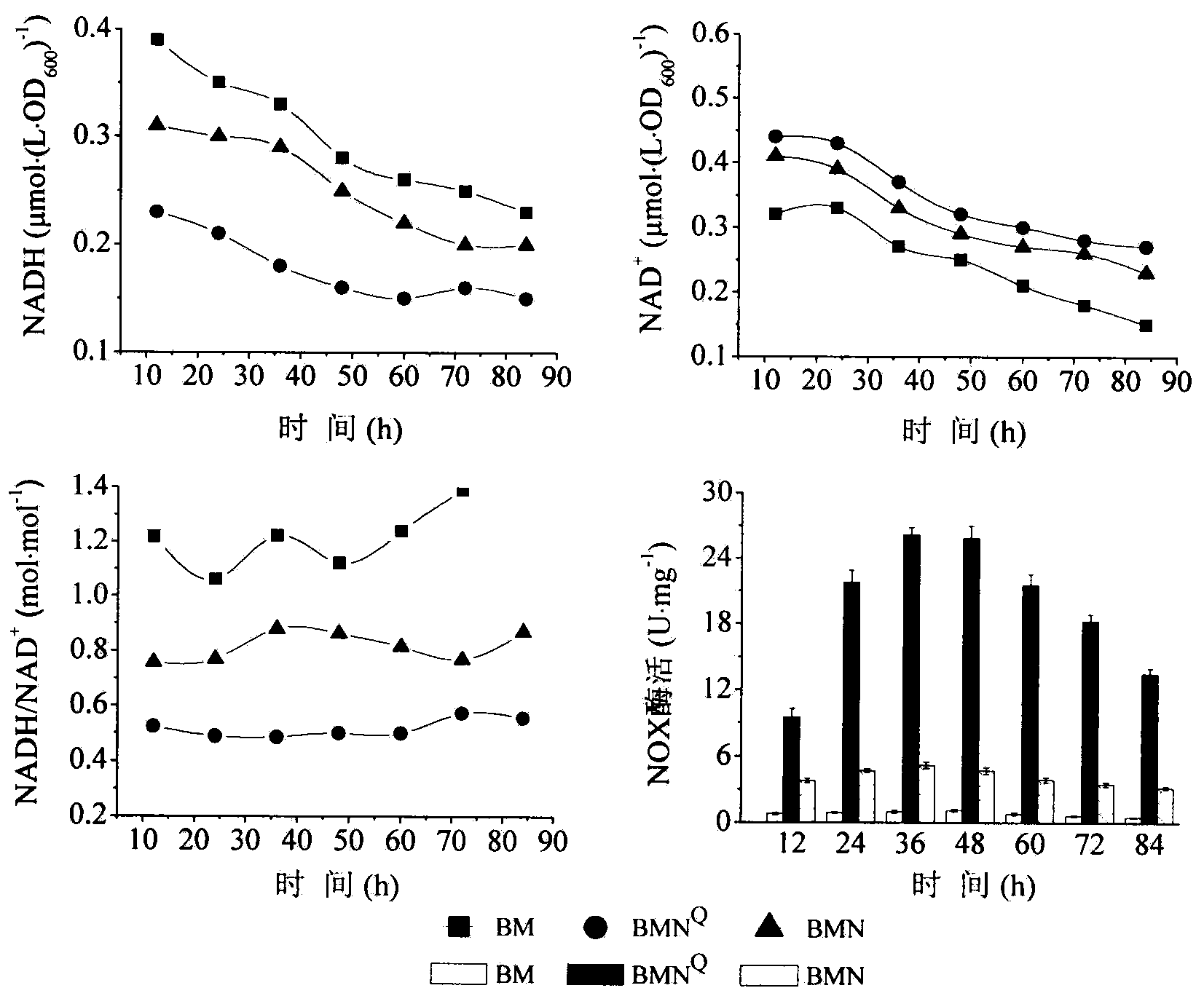
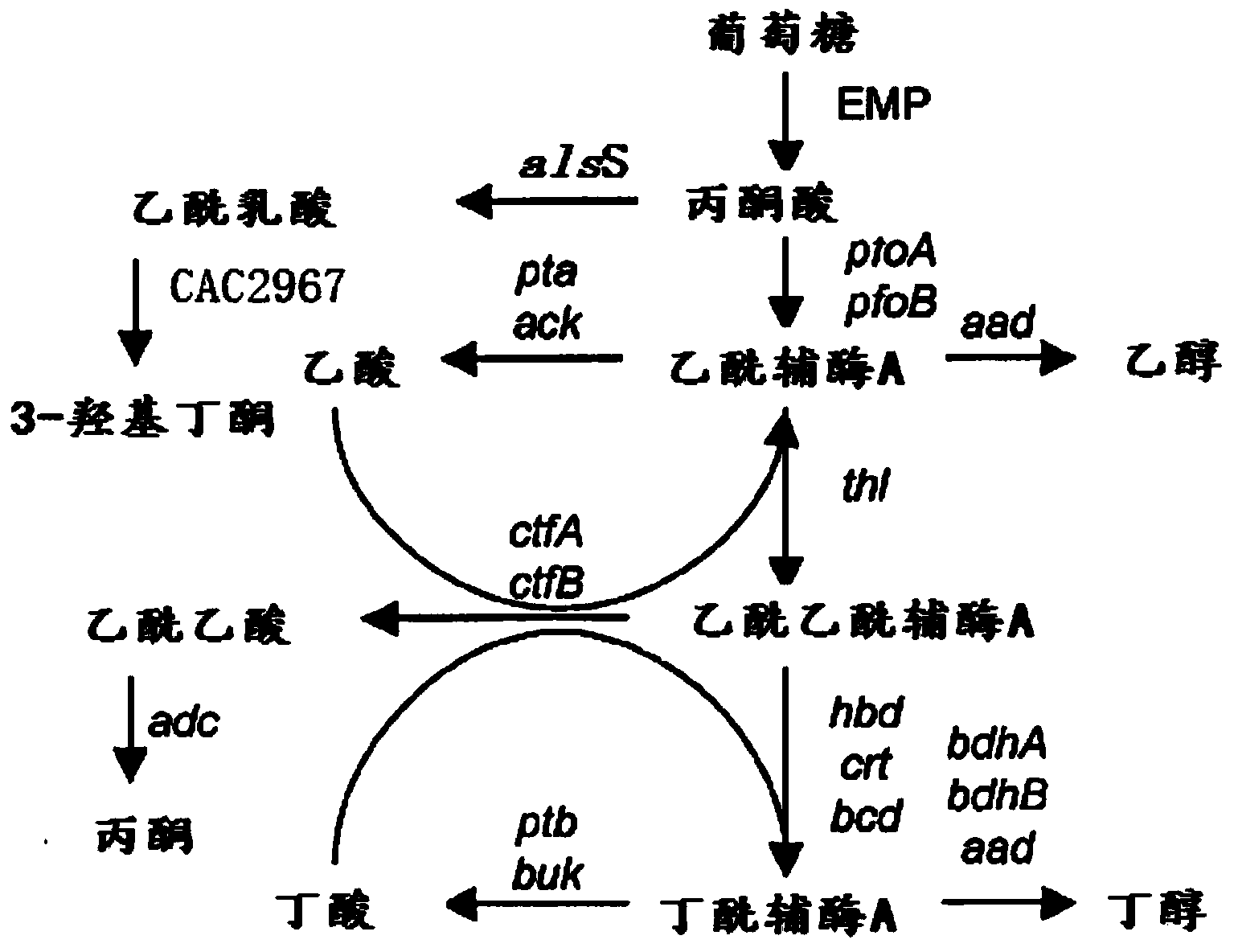
InactiveCN104017758AEfficient productionShorten the fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIntellectual propertyBacterial strain
The invention relates to a method for producing acetoin through high-efficiency fermentation by appropriately expressing a novel bacillus subtilis NADH oxidizing enzyme and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. According to the method, the noval bacillus subtilis NADH oxidizing enzyme is found for the first time in genome of a high-yield acetoin bacterial strain B.subtilis JNA which is autonomously screened by a laboratory and has independent intellectual property, the enzymatic property of the noval bacillus subtilis NADH oxidizing enzyme is determined while an NADH oxidizing enzyme is expressed in bdhA gene deleted bacillus subtilis by appropriately expressing a carrier pMA5-PbdhA, finally the acetoin is produced through fermentation by utilizing recombinant bacteria modified by metabolic engineering, about 56.7g / L acetoin and 1.2g / L of 2,3-butanediol are obtained, the contents of 2,3-butanediol, lactic acid and acetic acid are respectively reduced by about 92.3%, 70.1% and 75.0%, the production efficiency of the acetoin is increased to 0.68g / (L.h), and a fermentation period is shortened for 1.7 times compared with the original bacterial strain; NADH regulation in bacillus subtilis is utilized for producing the acetoin for the first time at home and abroad, and the aims of shortening the fermentation period and reducing a NADH-dependent by-product are realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Taste-masking compositions, sweetener compositions and consumable product compositions containing the same
Owner:CELANESE SALES GERMANY
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing acetoin as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103436479AIncrease productionIncreased acetoin productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenetically engineered
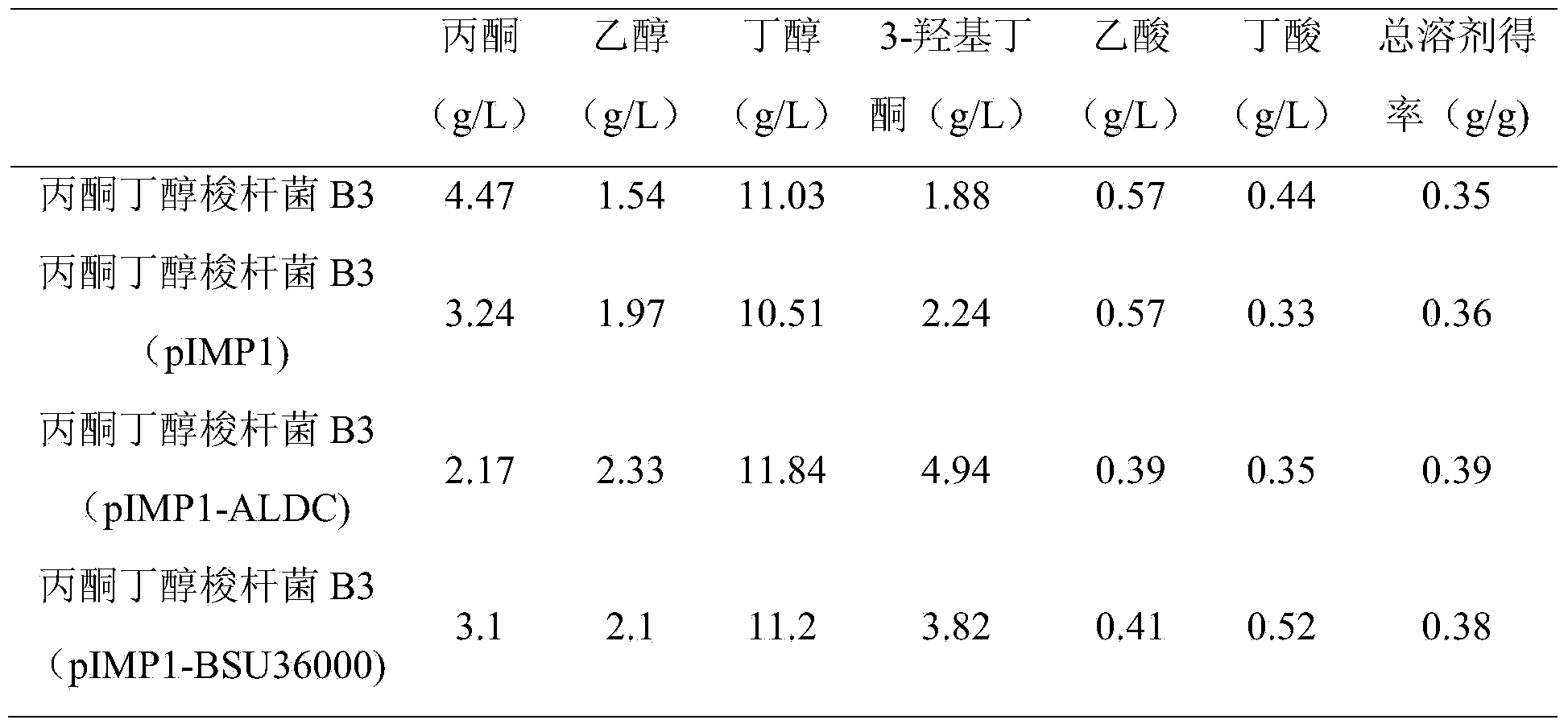
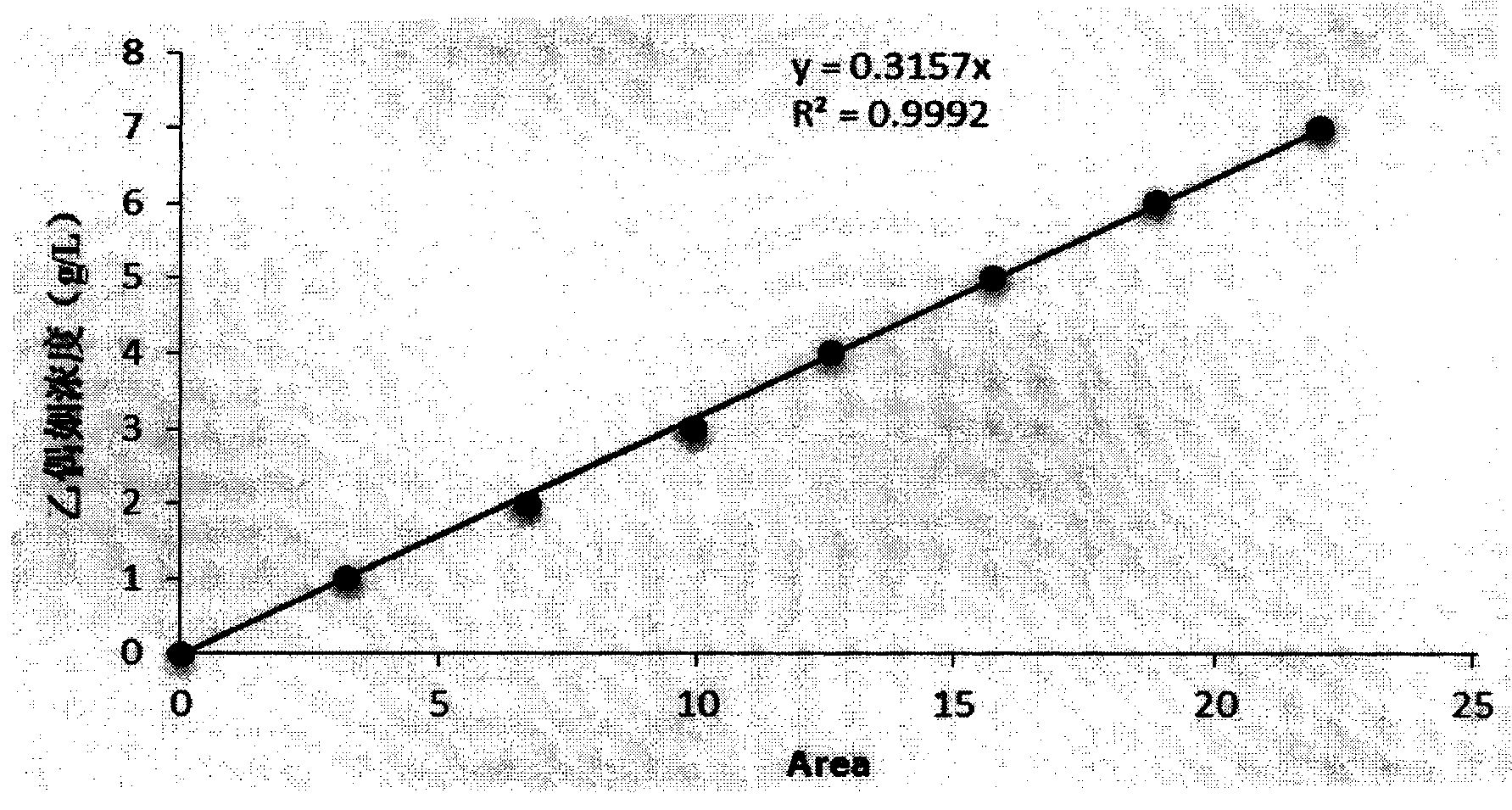
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing acetoin. The genetically engineered bacterium is clostridium into which a coding gene of acetolactate decarboxylic reaction enzyme is imported. The invention also discloses a construction method and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium. By adopting the method, the average yield of acetoin produced from clostridium acetobutylicum is about 5g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
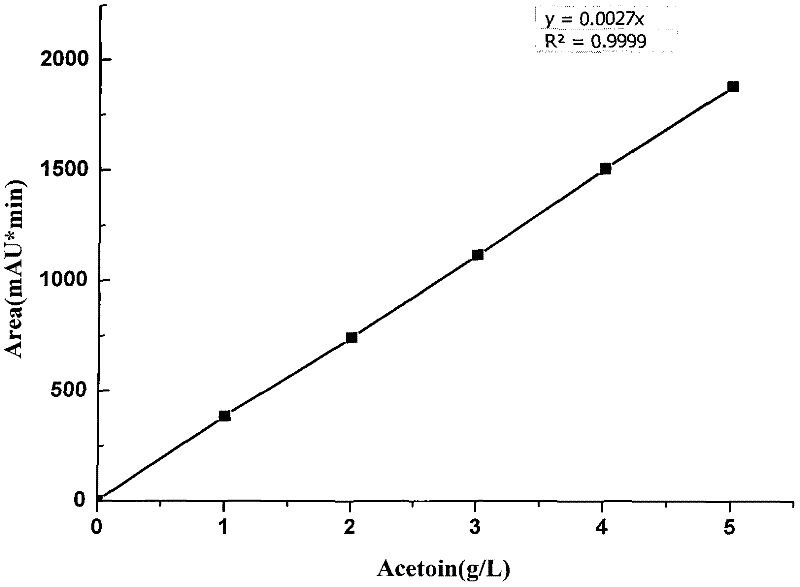
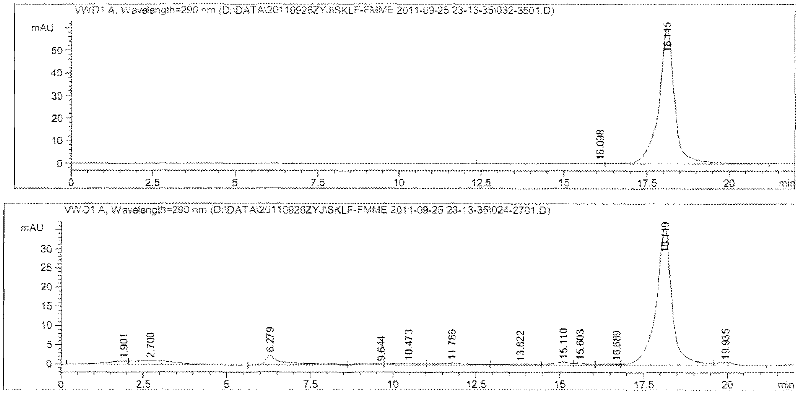
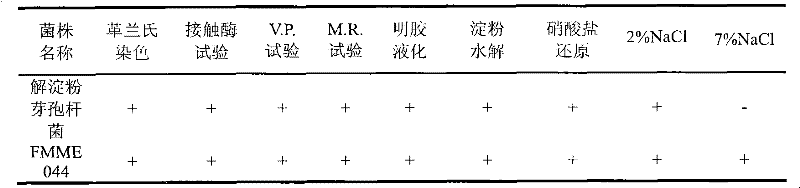
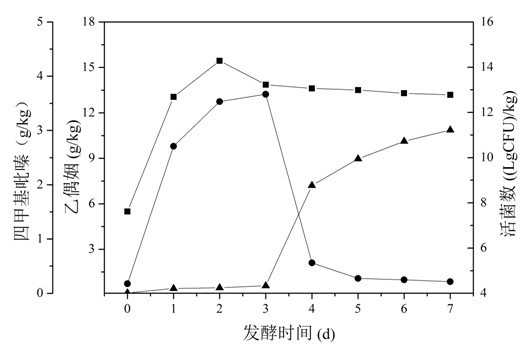
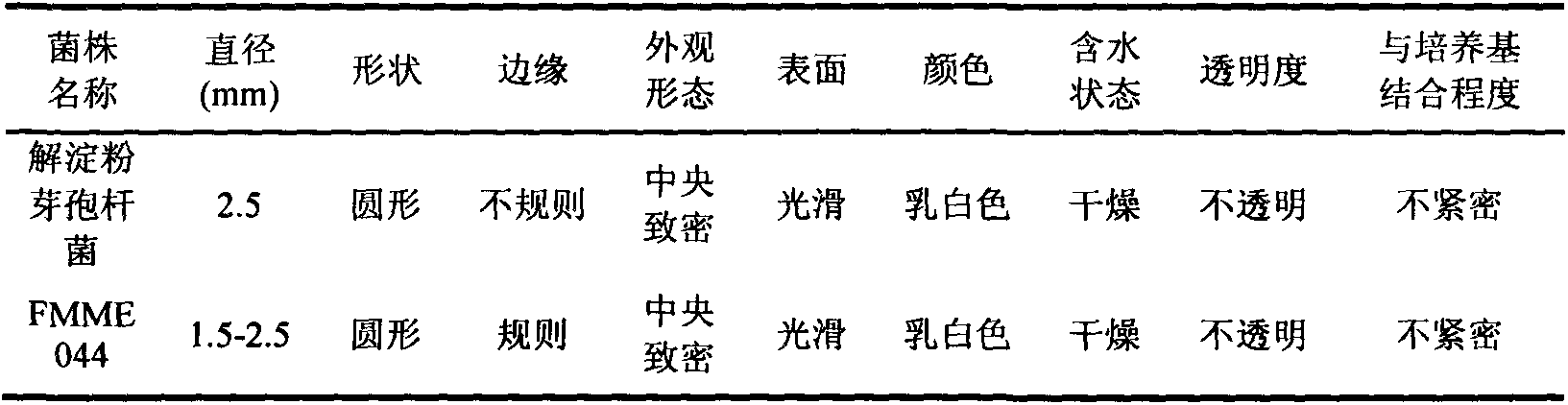
Breeding of acetoin high-tolerance bacterial strain and acetoin fermentation production with bacterial strain
The invention discloses breeding of an acetoin high-tolerance bacterial strain and acetoin fermentation production with the bacterial strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering (the field of microorganism). The breeding procedures are as follows: (1) nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis: taking Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FMME044 screened and stored by the laboratory as an original strain to prepare a bacterial suspension, taking reaction with nitrosoguanidine in different concentrations, after a while, stopping reaction and then carrying out post-cultivation; (2) domestication: adding acetoin with different concentrations in domestication culture media to prepare acetoin fermentation liquors with different concentrations, gradually increasing the acetoin concentrate to carry out domesticating cultivation, and directly coating the domesticated bacterial suspensions on a panel containing high-concentration acetoin; (3) screening: obtaining the acetoin high-tolerance bacterial strain which is the single colonies grown on the panel containing the high-concentration acetoin, and then selecting the single colonies to carry out fermentation verification, performing secondary verification on the high-producing strains to screen out a bacterial strain with higher concentration of acetoin than the original strain, and naming the bacterial strain B. amyloliquefaciens E-11. The invention further discloses a method for producing acetoin with the bacterial strain. The yield of acetoin produced by the method with 40 h fermentation is 63 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant cell and method for synthesizing methyl acetoin and derivative compounds thereof by using biological method
The invention provides a method, a recombinant cell and an enzyme system relevant to the production of methyl acetoin and derivative compounds thereof, and particularly provides nucleic acid, polypeptide, a host cell, the method and material for producing the methyl acetoin and the derivative compounds thereof by using a biological method.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
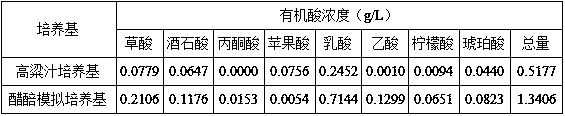
Development and multi-stage strengthening method for Shanxi mature vinegar composite bacterial agent based on bacteria strain interaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and provides a development and multi-stage strengthening method for a Shanxi mature vinegar composite bacterial agent based on bacteriastrain interaction. Shanxi mature vinegar native high-yield alcohol saccharomyces cerevisiae, high-yield ester wormwood candida, high-yield acetoin, bacillus mojavensis of high ester production capacity, high-yield non-volatile acid lactobacillus plantarum, high-yield acid, acetoin and acetobacter pasteurianus of high tolerance are subjected to an interaction experiment. The saccharomyces cerevisiae, the wormwood candida, the bacillus mojavensis and the lactobacillus plantarum are prepared into a compound direct vat set in the alcoholic fermentation stage, the bacillus mojavensis, the lactobacillus plantarum and the acetobacter pasteurianus are prepared into a compound direct vat set in the fermentation stage for strengthening production of Shanxi mature vinegar, according to new pour vinegar, the content of total acid is 6.23 g / 100mL, the content of involatile acid is 2.68 g / 100 mL, the content of total ester is 5.88 g / 100 mL, the content of ligustrazine is 335.6-5 micrograms / mL, andthe spectrogram and content of organic acid and volatile aroma are enriched.
Owner:山西不老泉食品有限公司
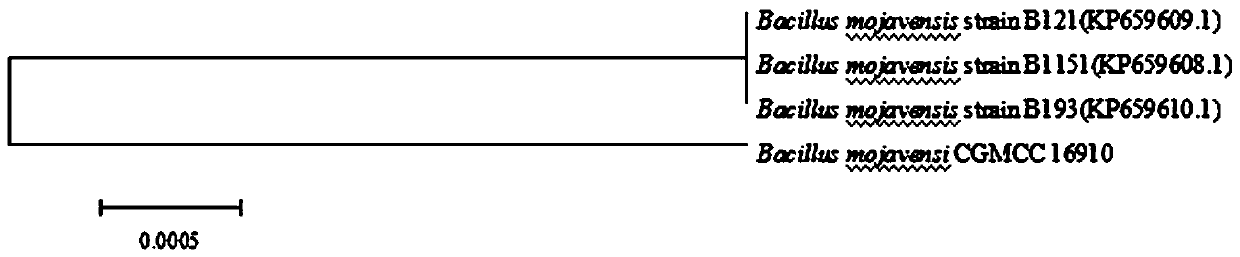
Preparation method of direct fermentation agent of high-yield acetoin and aromatized mohevea bacillus and application of direct fermentation agent in production of Shanxi mature vinegar
ActiveCN109666616AEnhancement of physiological function componentsIncrease contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiological Techniques
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and provides a preparation method of a direct fermentation agent of high-yield acetoin and aromatized mohevea bacillus and an application of the direct fermentation agent in production of Shanxi mature vinegar. The method comprises the following steps of: separating and screening a strain of mohevea bacillus which has strong acetoin production, fragrance production and polyphenol production capabilities from the fermentation process of Shanxi mature vinegar, and preserving the strain of the mohevea bacillus in a common microorganism center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC 16910. The direct fermentation agent of the aromatized mohevea bacillus CGMCC16910 is forcedly used to the production of Shanxi mature vinegar, the ligustrazine is 266.47micro g / mL and the polyphenol is 514micro g / mL in the final new vinegar, the physiological function components areobviously improved, the contents of the total acid, non-volatile acid and total ester are also obviously improved, compared with the control, the method has the advantages that the contents of the total acid, non-volatile acid and total ester are improved by 59.04%, 77.89% and 74.32% respectively, and the volatile aroma spectrum and content are enriched.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Acetoin high-yield strain and application thereof in fermentation to produce acetoin
ActiveCN108251339AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
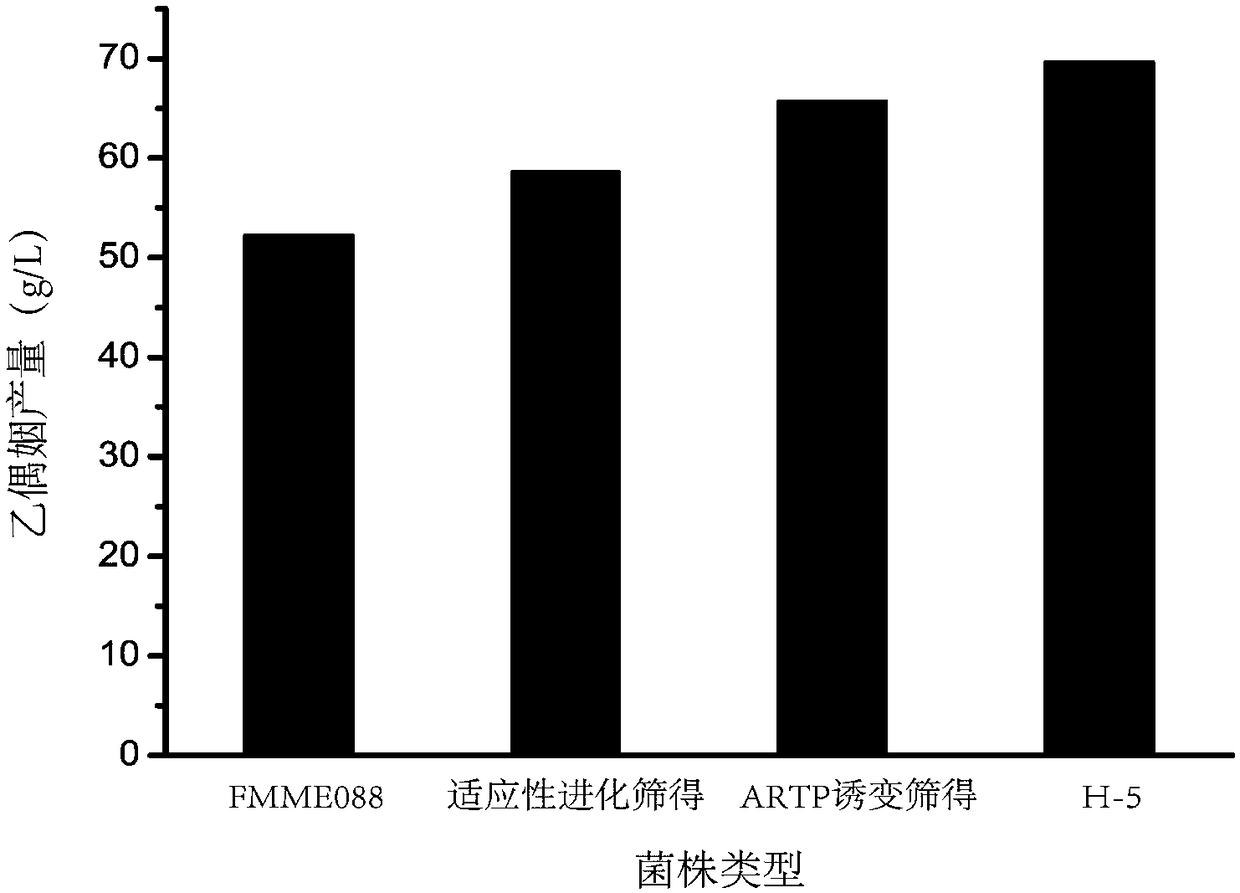
The invention discloses an acetoin high-yield strain and application thereof in fermentation to produce acetoin and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H-5 disclosed by the invention is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on 15th November 2017, a preservation address is Wuhan university in Wuhan of China, and a preservation number is CCTCCNO:M 2017694. Acetoin tolerance capacity of the acetoin high-yield strain H-5 disclosed by the invention can reach 90g / L. The H-5 is amplified and cultured on a 30L fermenting tank, culturing time is52h, an acetoin yield can reach 85.24g / L, and the acetoin yield is the maximum yield for an existing microbiological fermenting method to produce the acetoin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
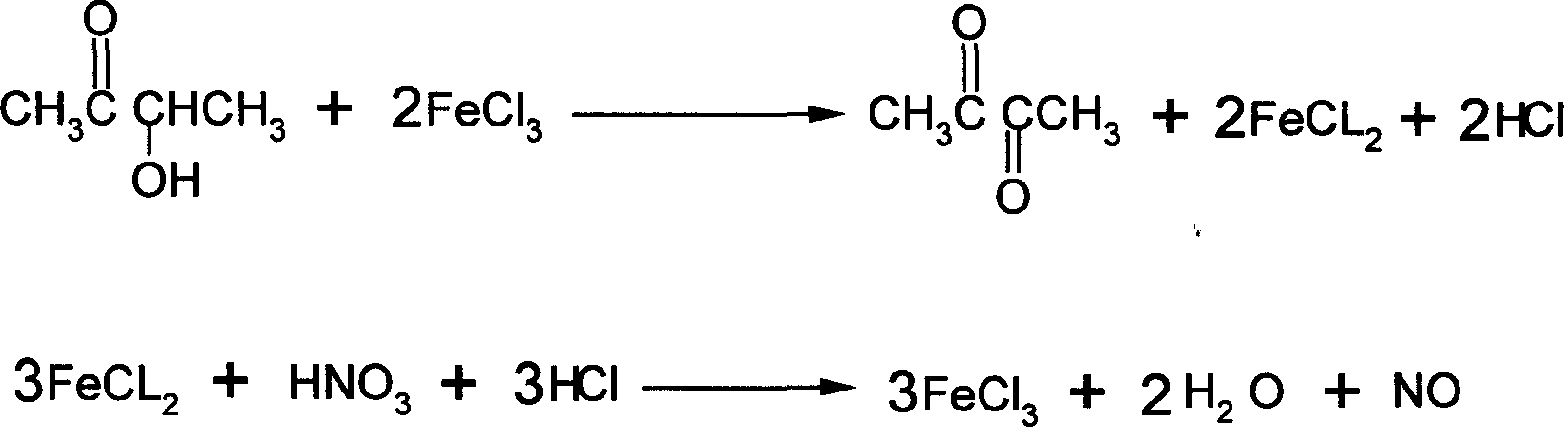
Method for preparing butanedione through oxidating acetylmethylcarbinol
InactiveCN1686992AReduce manufacturing costEasy to operateCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationAcetoinAcetylmethylcarbinol
The present invention relates to a new method for preparing butanedione by utilizing acetoin. Said invention uses acetoin as raw material, and utilizes iron trichloride to produce chemical oxidation so as to obtain butanedione, then make sit undego the process of simple treatment, so that the pure butanedione product whose purity can be up to 99% can be obtained. The oxidant iron trichloride can be converted into iron dichloride, said iron dichloride can be oxidated by nitric acid, and can be reformed into iron trichloride, after the iron trichloride is concentrated, it can be circularly used.
Owner:DALIAN LAIKE FINE CHEM CO LTD
Wine regulator for regulating color, smell and taste of wine
The invention relates to a wine regulator for regulating color, smell and taste of wine. The wine regulator is characterized by being made from the following raw materials by weight: 0.08-1 part of carbonyl compound, 1-3 parts of organic alcohol and 0.5-3 parts of xylitol; wherein, the organic alcohol comprises isoamyl alcohol, isobutyl alcohol, glycerol, 2,3-butylene glycol; the carbonyl compound comprises acetaldehyde, acetal, diacetyl and acetoin. The wine regulator for regulating the color, smell and taste of the wine is nontoxic and harmless, and has ecological environmental protection function, and health care function on human body. The wine regulator can be eaten frequently to achieve the functions of regulating blood sugar level, protecting liver, preventing dental caries, inhibiting infection of lung, regulating internal secretion and the like. The wine regulator can be used together with other additives and has good synergetic action.
Owner:TIANJIN JINGUIGU XYLITOL
Acid-resistant bacillus velezensis DQA21 for producing acetoin and application
ActiveCN112251379AAcid resistantConducive to metabolic engineeringBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyConcentrations glucose
The invention discloses acid-resistant bacillus velezensis DQA21 for producing acetoin and application. The acid-resistant bacillus velezensis DQA21 was preserved in the China Center for Type CultureCollection (CCTCC) with the preservation number being CCTCC NO:M 2020360 on July 27, 2020. The fermentation conditions of the strain are optimized, and the optimal fermentation conditions are as follows: the glucose concentration is 80 g / L, the pH is 5.46, the temperature is 37.31 DEG C, the liquid loading amount is 49.17 mL, the inoculation amount is 5%, and the rotating speed is 210 r / min. Underthe conditions, the average yield of the acetoin fermented by a strain shake flask is 25.60 g / L, and is improved by 39.36% compared with the yield of 18.37 g / L of the strain before optimization. Thestrain has the advantages of high acetoin yield, high fermentation speed and the like, can be used for producing baijiu, and can be used for increasing the content of the acetoin in the baijiu, improving the mouthfeel and flavor and enhancing the quality of the baijiu.
Owner:WULIANGYE +1
Bacillus siamensis and application thereof in acetoin-rich table vinegar
ActiveCN112795519AIncrease profitIncreased acetoin contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmylase
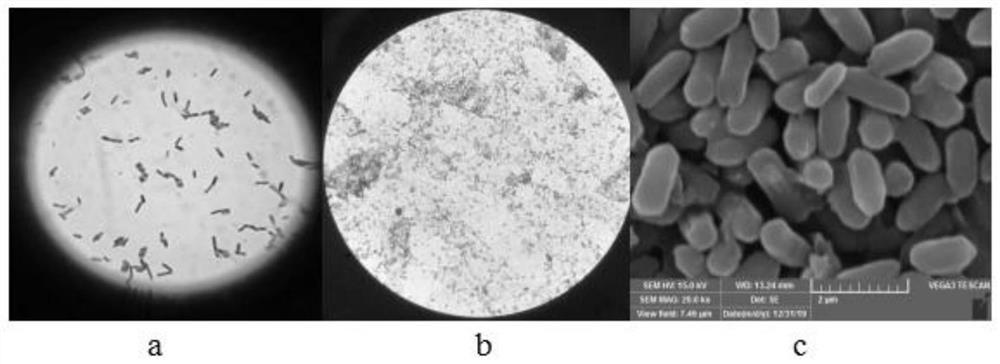
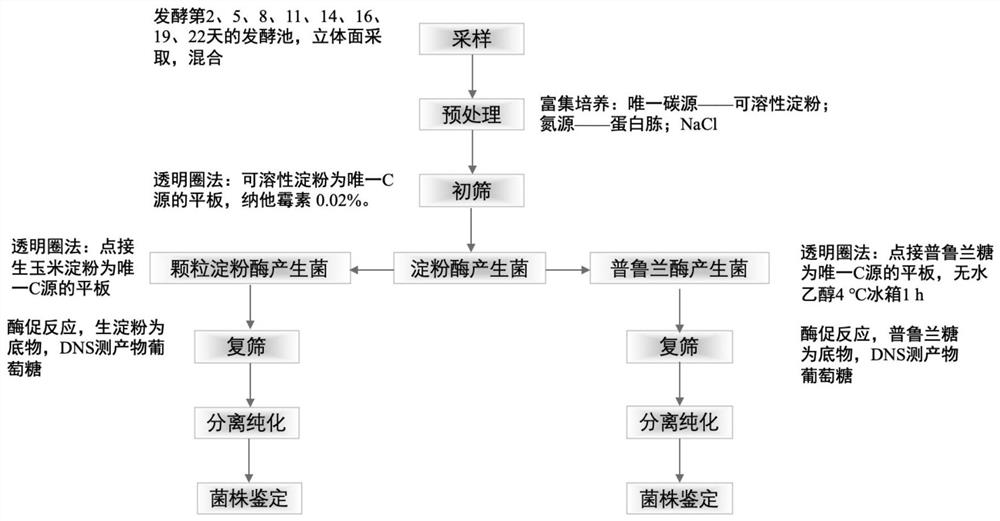
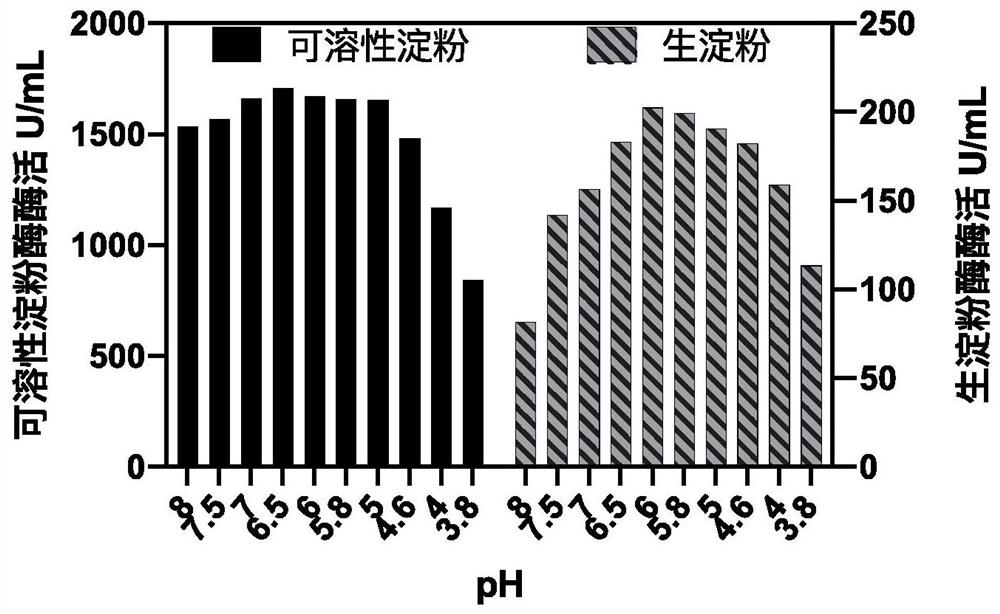
The invention discloses bacillus siamensis and application thereof in acetoin-rich table vinegar, bacillus siamensis QH-20009 can grow and metabolize under an acidic condition and produce amylase, granular amylase, pullulanase and protease at the same time, is applied to the field of food, and can remarkably improve the starch utilization rate and the nonvolatile acid content of a table vinegar brewing raw material, so that the yield of the vinegar is increased, and the production cost is reduced. The problem that the raw material utilization rate is not high in the vinegar brewing process can be solved, full utilization of grains is guaranteed, the amino acid content in the vinegar is increased, carbohydrates can be metabolized to produce acetoin, the acetoin content in the brewed vinegar can be increased, the flavor of the brewed vinegar can be improved, and the vinegar product quality can be improved.
Owner:QIANHE CONDIMENT & FOOD CO LTD
Coffee essence
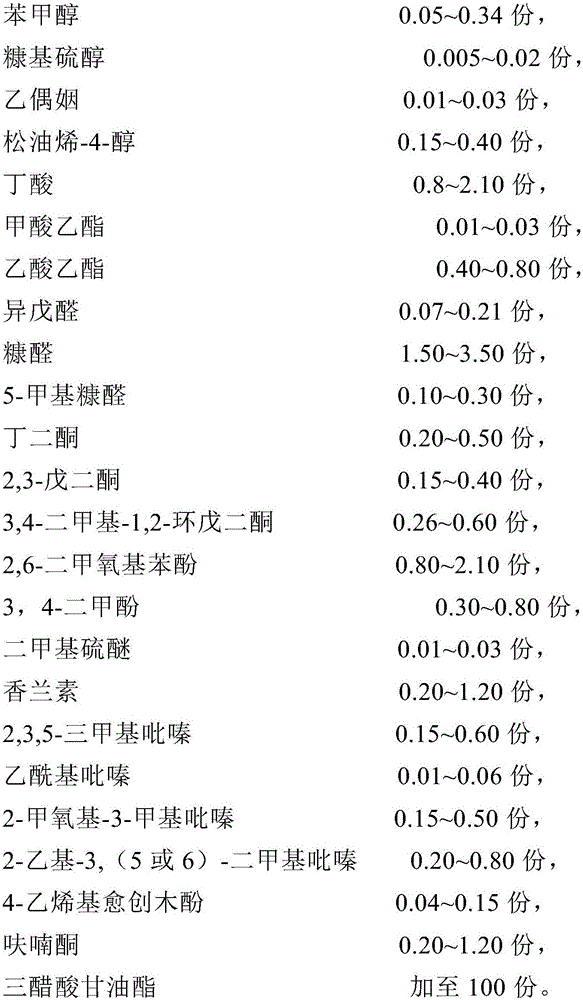
The invention relates to coffee essence. The coffee essence is prepared from an essence base, solvent, surfactant, auxiliary surfactant, 10-50 parts of coffee extracts and a carrier. The essence base is prepared from benzyl alcohol, furfuryl mercaptan, acetoin, terpinen-4-ol, butyric acid, ethyl formate, ethyl acetate, isovaleraldehyde, furfural, 5-methylfurfural, butanedione, 2,3-pentanedione, 3,4-dimethyl-1,2-cyclopentanedione, 2,6-dimethoxy benzene, 3,4-xylenol, dimethyl sulfide, vanillin, 2,3,5-trimethyl pyrazine, 2-acetylpyrazine, 2-methoxy-3-methylpyrazine, 2-ethyl-3,(5 or 6)-dimethyl pyrazine, 4-vinyl guaiacol, furanone and glycerol triacetate. Spices with natural equivalent components having high affinity on coffee beverages are adopted as raw materials of the coffee essence formula, so the natural feeling of beverages and other food containing the coffee essence is enhanced, and the coffee essence has natural aroma and taste.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAIRUN INVESTMENT HLDG GRP CO LTD
Method of preparing 2,3-butanediol by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of corncob residues
ActiveCN102643869ARealize high value utilizationReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationDry weightKlebsiella oxytoca
The invention discloses a method of preparing 2,3-butanediol by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of corncob residues with xylose extracted from corncobs and belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering. The method includes the steps of using the corncob residues as a carbon source and carbamide as a nitrogen source, using klebsiella pneumoniae CICC 10011, klebsiella oxytoca CICC 21518, bacillus polymyxa CICC 10010, bacillus cloacae CICC 10014 and a mixed bacterium solution to perform the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, and enabling the weight of the 2,3-butanediol and acetoin to reach 19.59%-36.13% of the dry weight of the corncob residues. According to the method of preparing 2,3-butanediol by the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of the corncob residues, the corncob residues are used as the carbon source, so that production cost is effectively reduced, high value utilization of resources is achieved, and huge economic benefits and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for synthesizing acetoin and derivative thereof through biological method
ActiveCN103725718AAddresses depletion affecting acetoinSolve productivityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEmulsion2,3-Butanediol
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing acetoin and a derivative thereof through a biological method, which belongs to the technical field of the molecular biology. The method comprises the steps of introducing pyruvate decarboxylase genes and genes with acetoin enzyme activity into host bacteria to obtain recombination bacteria, producing the acetoin by fermenting the recombination bacteria, and further producing 2,3-butanediol on the basis of the acetoin. By adopting the method, the acetoin and the 2,3-butanediol are successfully generated by fermenting the recombined bacteria strain, and the problem that the yield of the acetoin and the 2,3-butanediol is influenced by the consumption of an intermediate product acetyl emulsion in the natural production process can be solved.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methylotrophic bacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN103361288AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides methylotrophic bacillus which can produce acetoin at high yield. The methylotrophic bacillus is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) and has the collection number of CGMCCC No.7485. When the methylotrophic bacillus is fermented under a certain conditions, acetoin with the concentration of 15.71g / L can be obtained. The production capacity of most of the reported acetoin producing bacteria is lower than or equivalent to that of the methylotrophic bacillus CGMCCC No.7485; however, according to the strain, except the glucose concentration is preliminarily optimized, other culture conditions and medium components are not subjected to breeding transformation. Thus, after the methylotrophic bacillus is subjected to further breeding transformation and condition optimization, the acetoin yield is further improved. Therefore, the methylotrophic bacillus has wide application prospects.
Owner:青岛诺森生物技术有限责任公司
Method for increasing yield of paenibacillus polymyxa 2,3-butanediol by using vitamin C
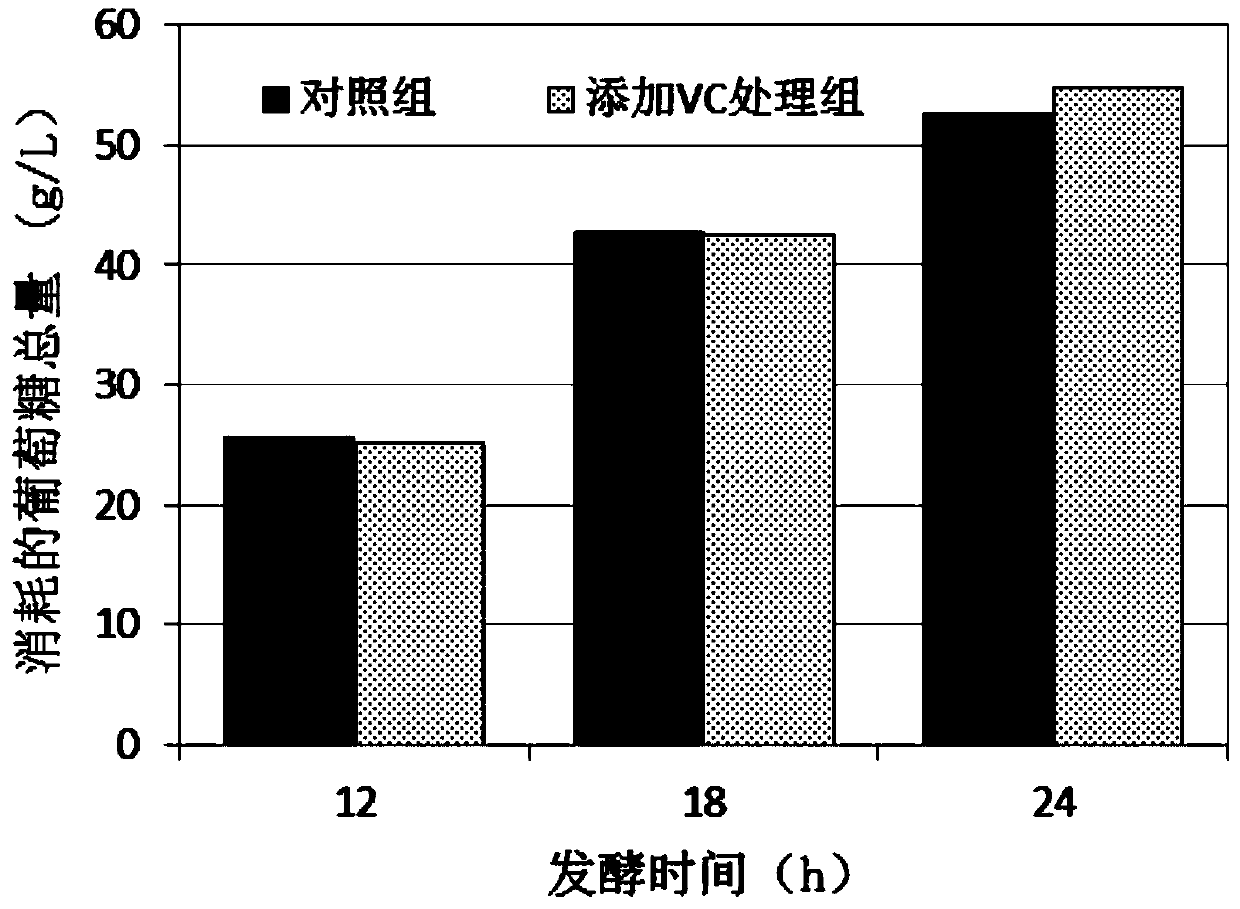
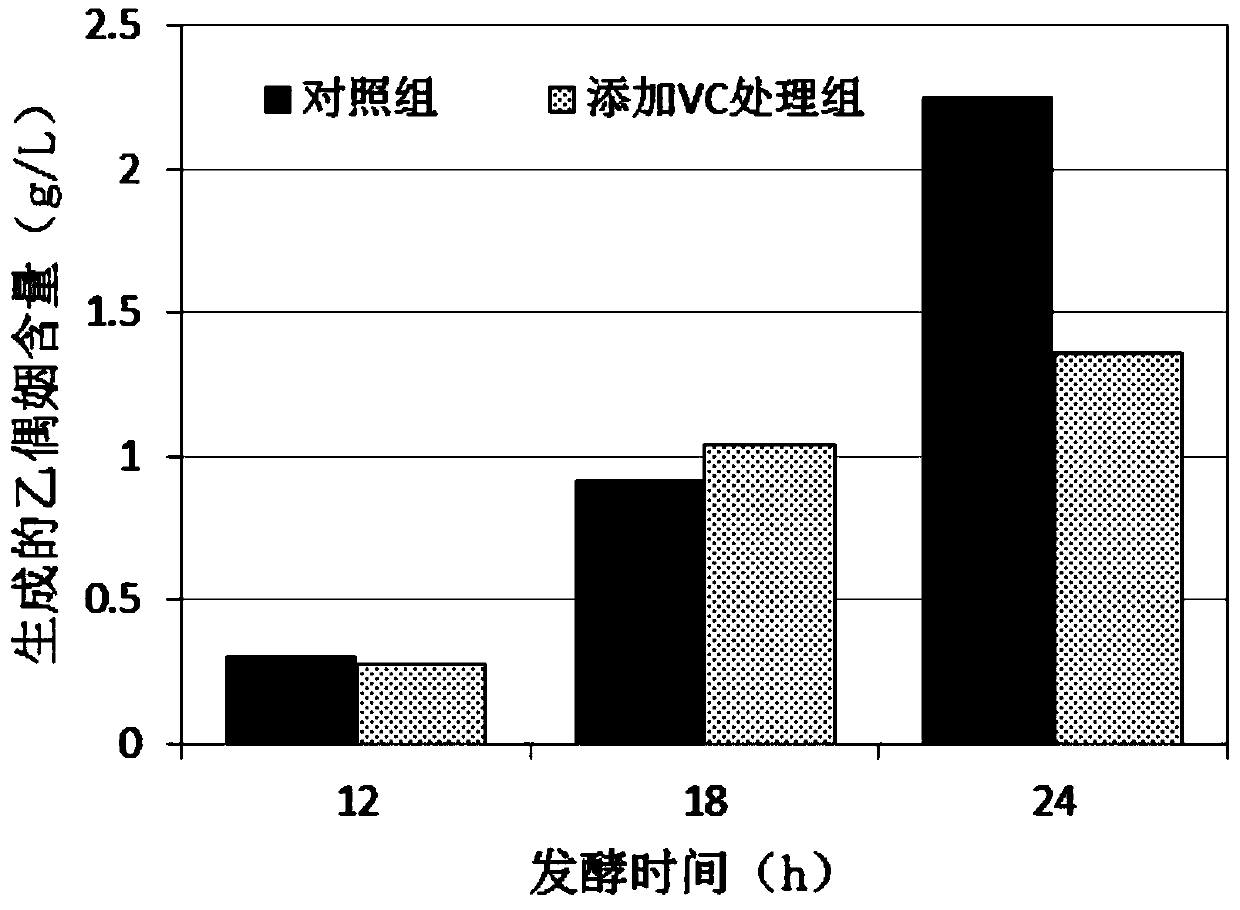
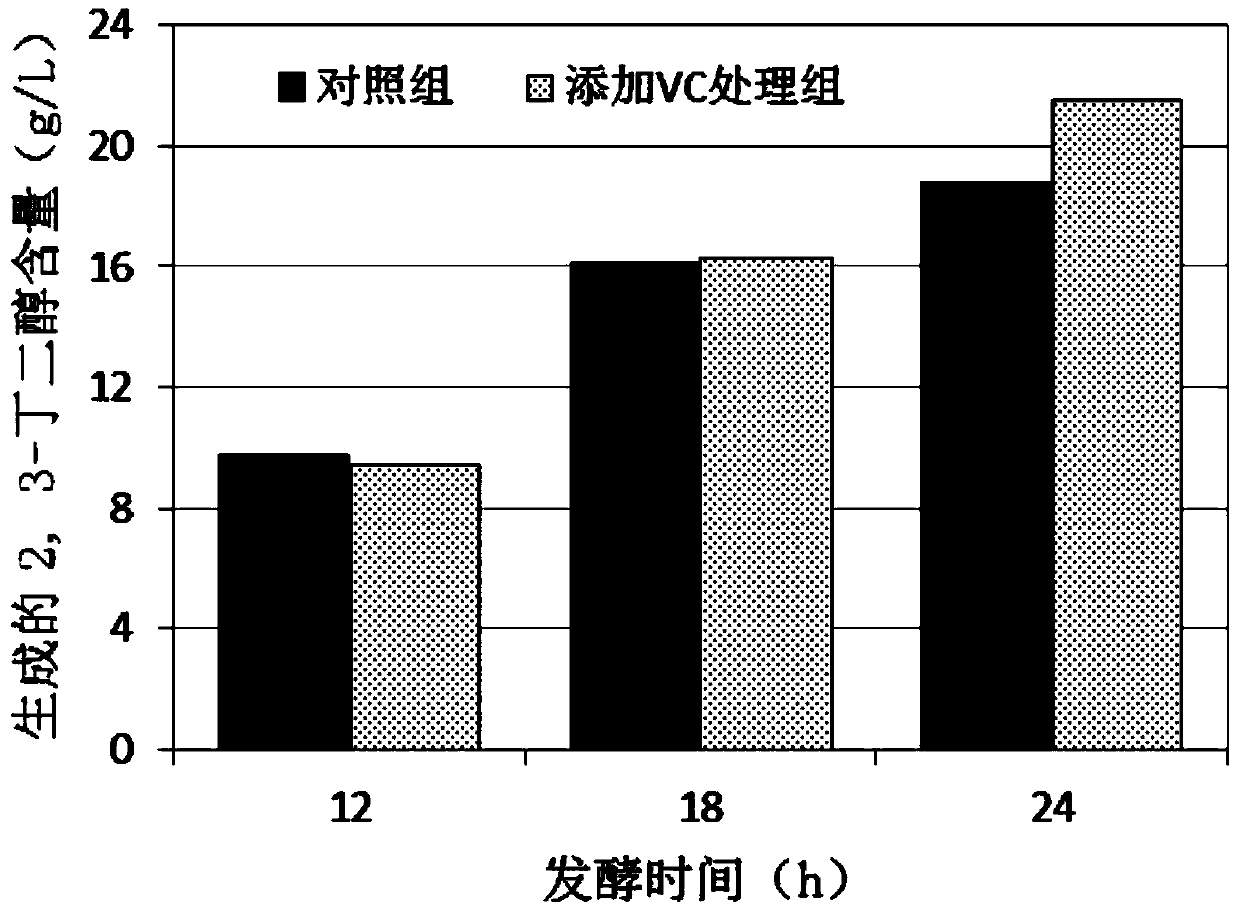
InactiveCN103695477AReduce the impact of hindered accumulationIncrease consumptionMicroorganism based processesFermentationVitamin CConcentrations glucose
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of paenibacillus polymyxa 2,3-butanediol by using vitamin C. The method comprises the following steps: (1) seed culture; (2) fermentation culture: inoculating secondary seeds into a fermentation culture medium, performing fermentation under the conditions that the ventilatory capacity is 0.1-0.8vvm, the stirring rotating speed is 300-500rpm and the temperature is 32-42 DEG C for 12-24 hours, and adding 80-160g / L vitamin C solution when the concentration of glucose in the fermentation culture medium is reduced to 2-10g / L. By the adoption of a method for continuously adding a reducing agent, the method disclosed by the invention is favorable for maintenance of a redox situation of an external environment in which bionts exist in the whole fermentation process, so that consumption of the glucose in fermentation liquid and conversion of acetoin are finally promoted, and the accumulation of (R,R)-2,2- butanediol is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Multi-strain liquid fermented vinegar rich in lactic acid and acetoin and brewing method thereof
InactiveCN110079433AIncrease umamiRich tasteMicroorganism based processesVinegar preparationSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a multi-strain liquid fermented vinegar rich in lactic acid and acetoin produced through multi-strain fermentation. A brewing method comprises the following steps: during a brewing process, firstly, soaking and cooking rice or sticky rice; adding water and then adding liquifying enzyme and saccharifying enzyme, thereby acquiring a saccharification liquid; inoculating with abrewer yeast for fermenting, thereby acquiring wine with dregs; mixing bran with water, and then filtering, thereby acquiring a bran leachate; inoculating lactobacillus helveticus, thereby acquiringa lactic acid fermented liquor; mixing the lactic acid fermented liquor with the wine with dregs, and inoculating with pasteur acetate and acetobacter gluconicum for acetic fermentation, thereby acquiring a vinegar liquor rich in acetoin; adding saccharose and inoculating lactobacillus acidophilus for anaerobic fermentation, thereby acquiring the liquid fermented vinegar rich in lactic acid and acetoin. The increasing of lactic acid content is capable of enhancing softness of vinegar and reducing excitement; in an ageing stage, acetoin is capable of reacting with the free amino acid in the bran leachate, thereby generating ligustrazine, so that the multi-strain liquid fermented vinegar has a fragrance of baking nuts and has healthcare effects of protecting heart and cerebral vessels, resisting against oxidation, softening blood vessels, and the like; besides, the free amino acid in the bran leachate is beneficial to enhancing freshness of liquid vinegar.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for improving yield of acetylglucosamine and building method of recombinant bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN106148262AIncrease productionIncrease extracellular accumulationBacteriaStable introduction of DNABacillus subtilisAcetoin
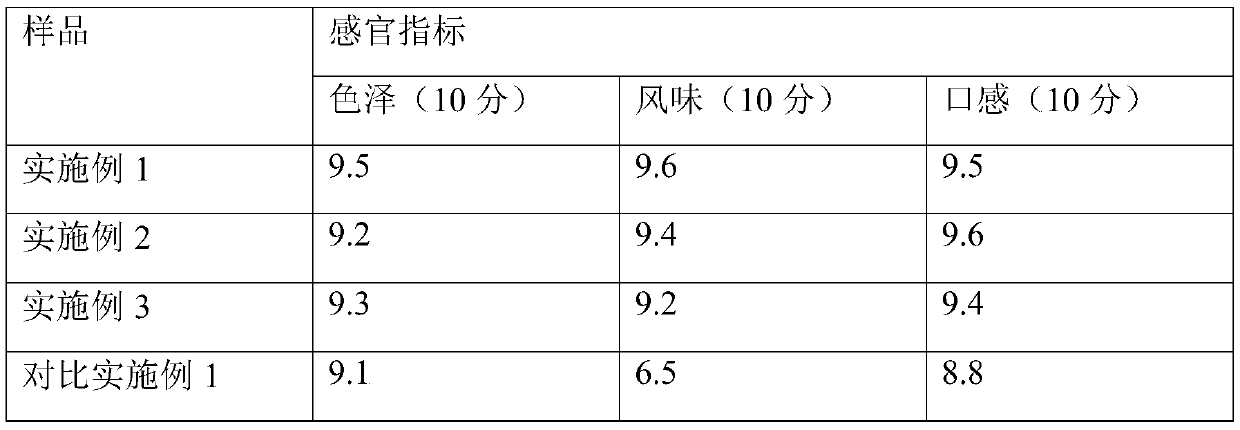
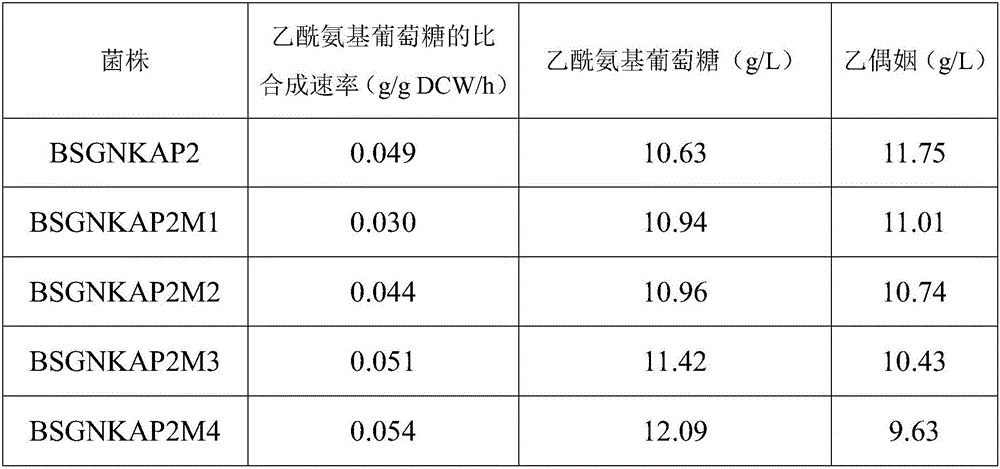
The invention provides recombinant bacillus subtilis for improving the yield of acetylglucosamine. Malic dehydrogenase coding genes are knocked out from bacillus subtilis. The invention further provides a building method of the recombinant bacillus subtilis. The method comprises the steps that a malic dehydrogenase coding gene knock-out frame is built; malic dehydrogenase coding genes ytsJ, ywkA, malS and mleA are knocked out from a bacillus subtilis genome, and the recombinant bacillus subtilis for improving the yield of the acetylglucosamine is obtained. Compared with original strains, according to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, the acetylglucosamine extracellular accumulation amount is improved, and the yield of the by-product acetoin is reduced. The building method of the recombinant bacillus subtilis is simple, convenient to use and good in application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com