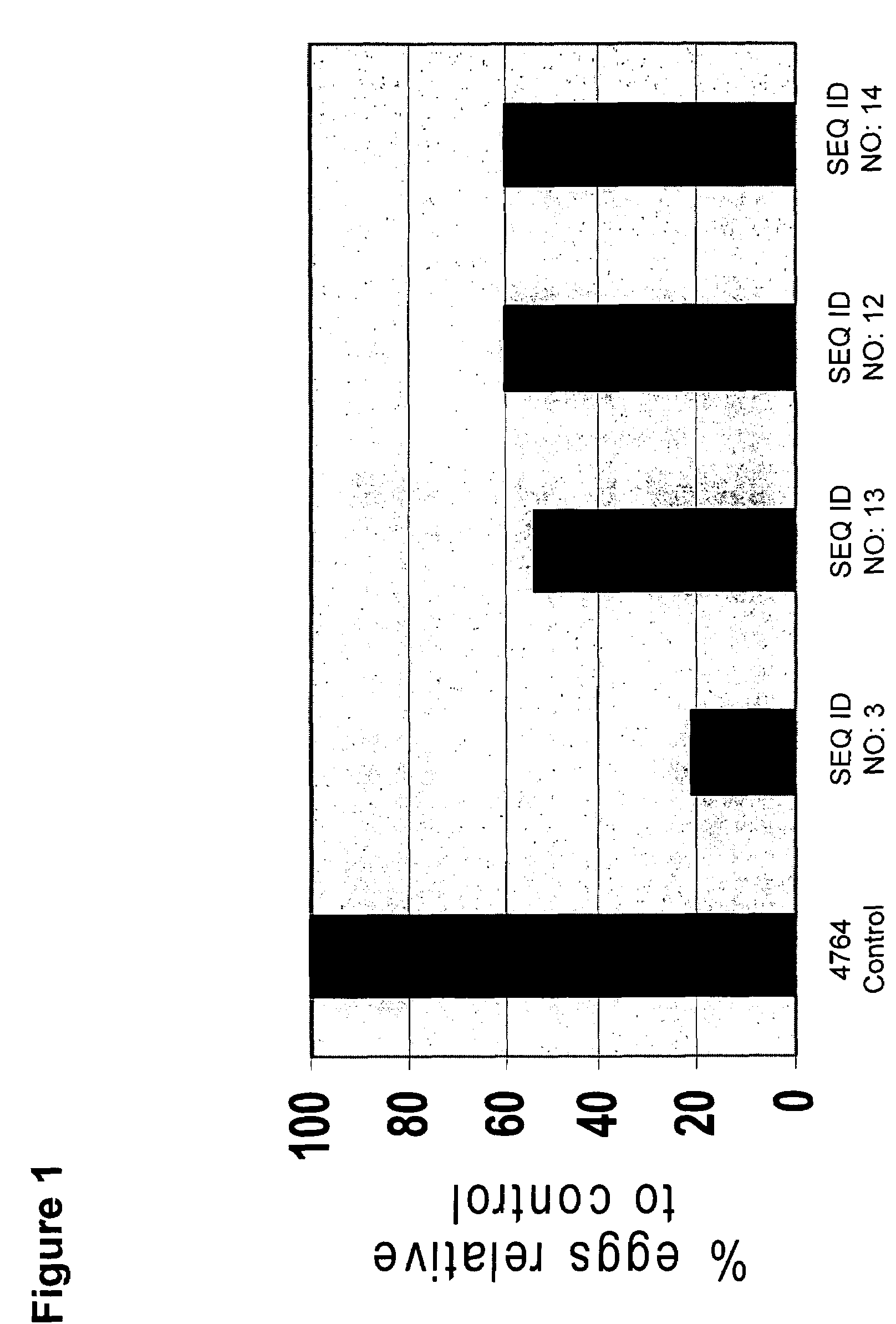
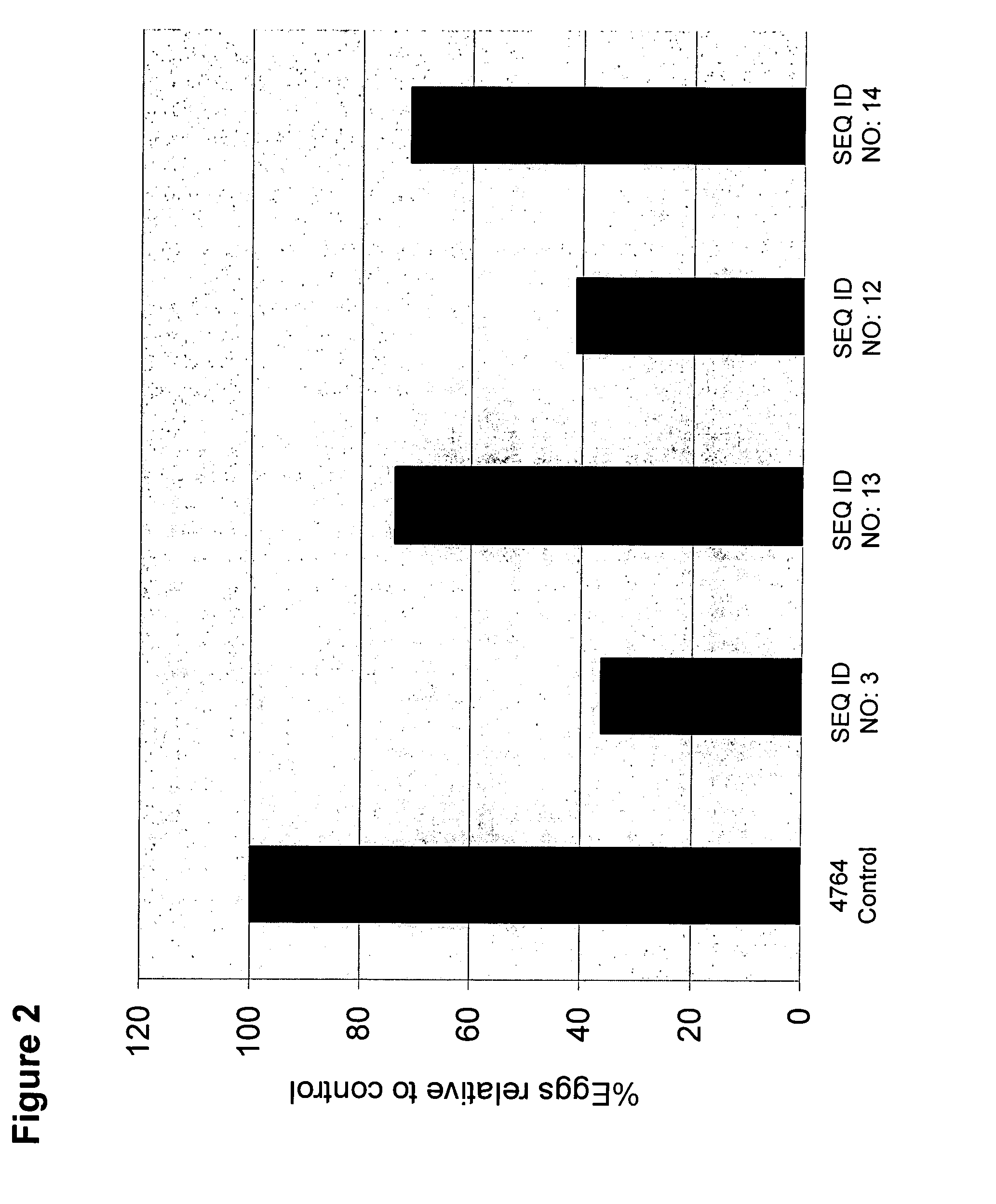
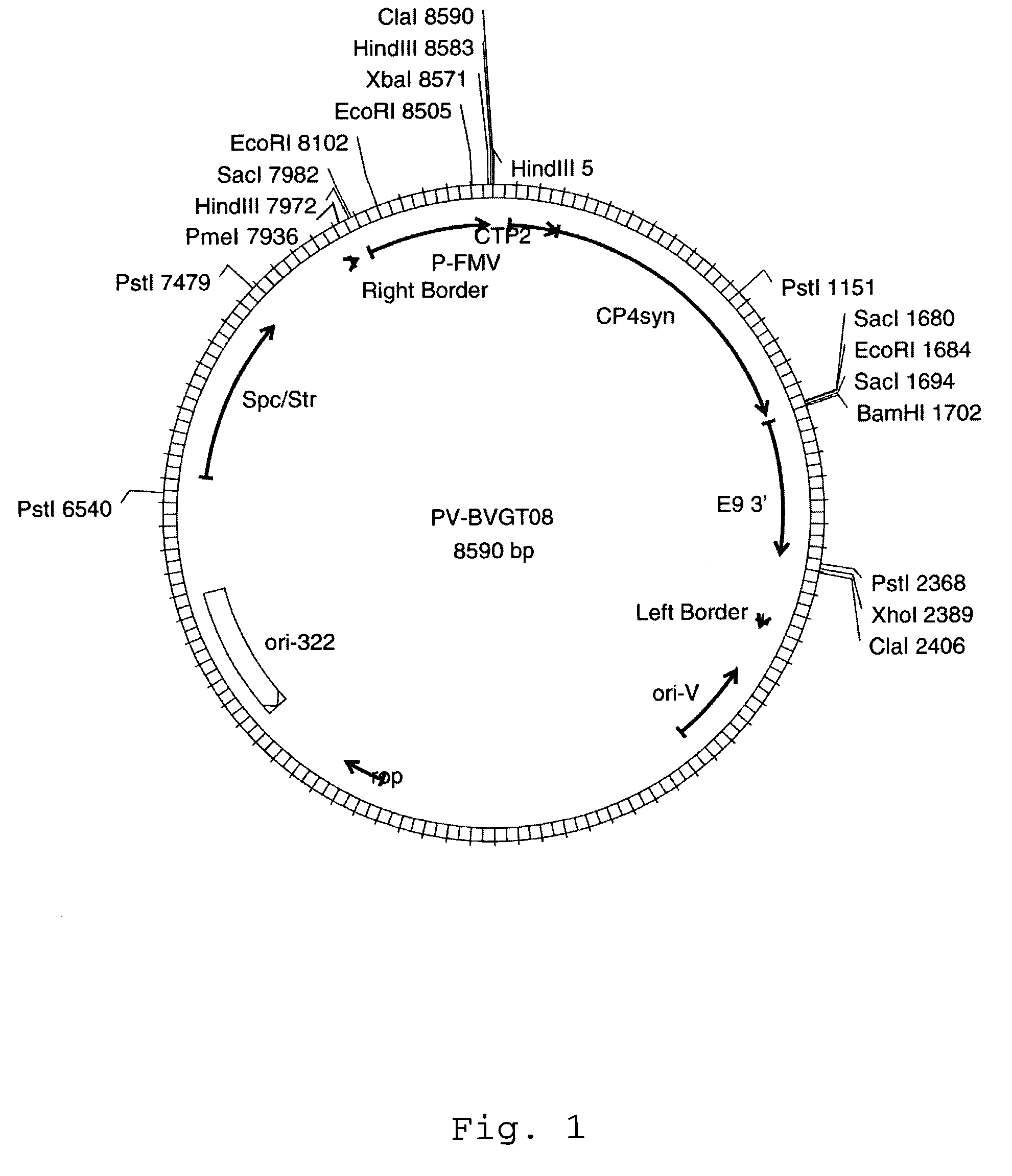
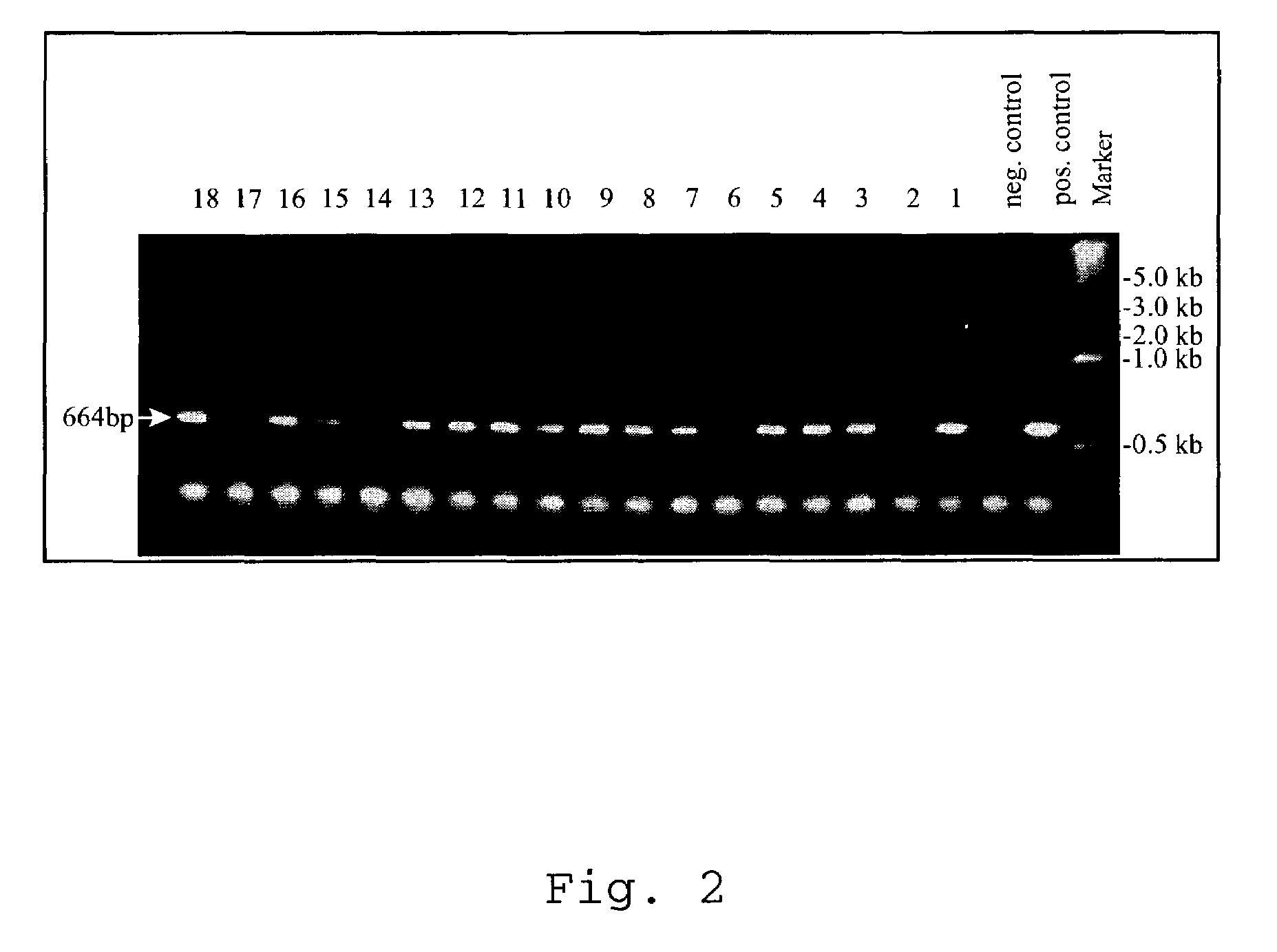
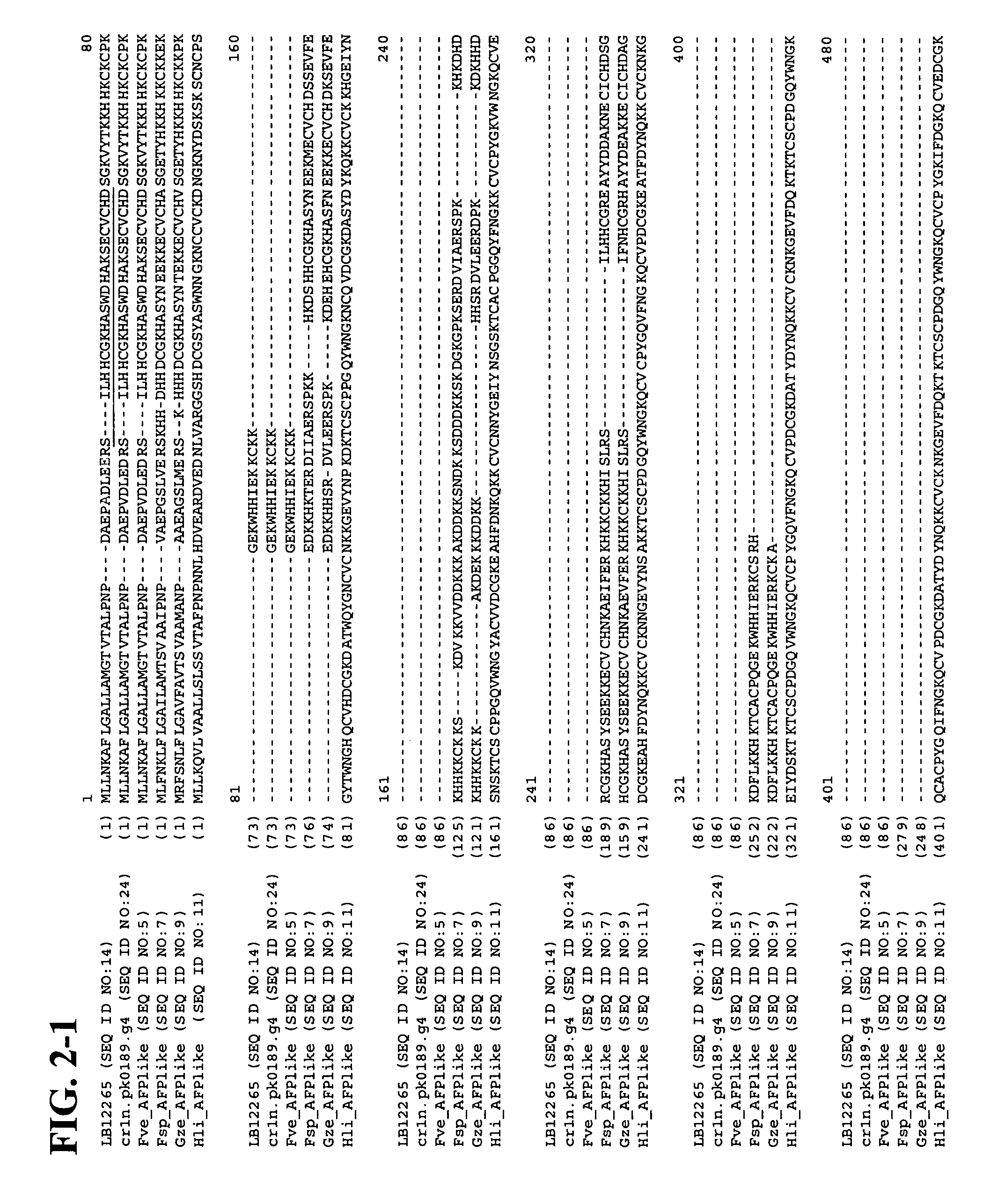
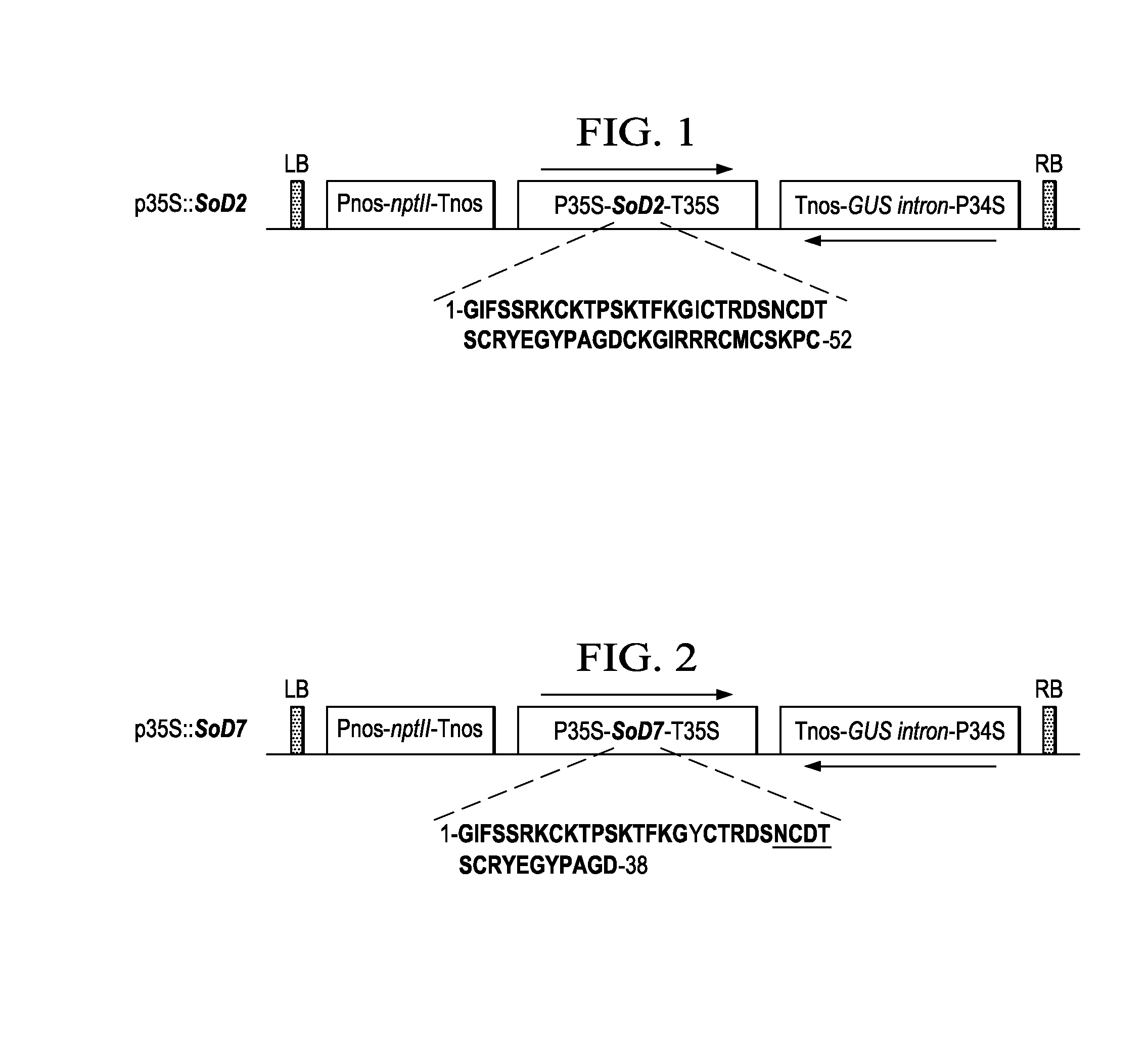
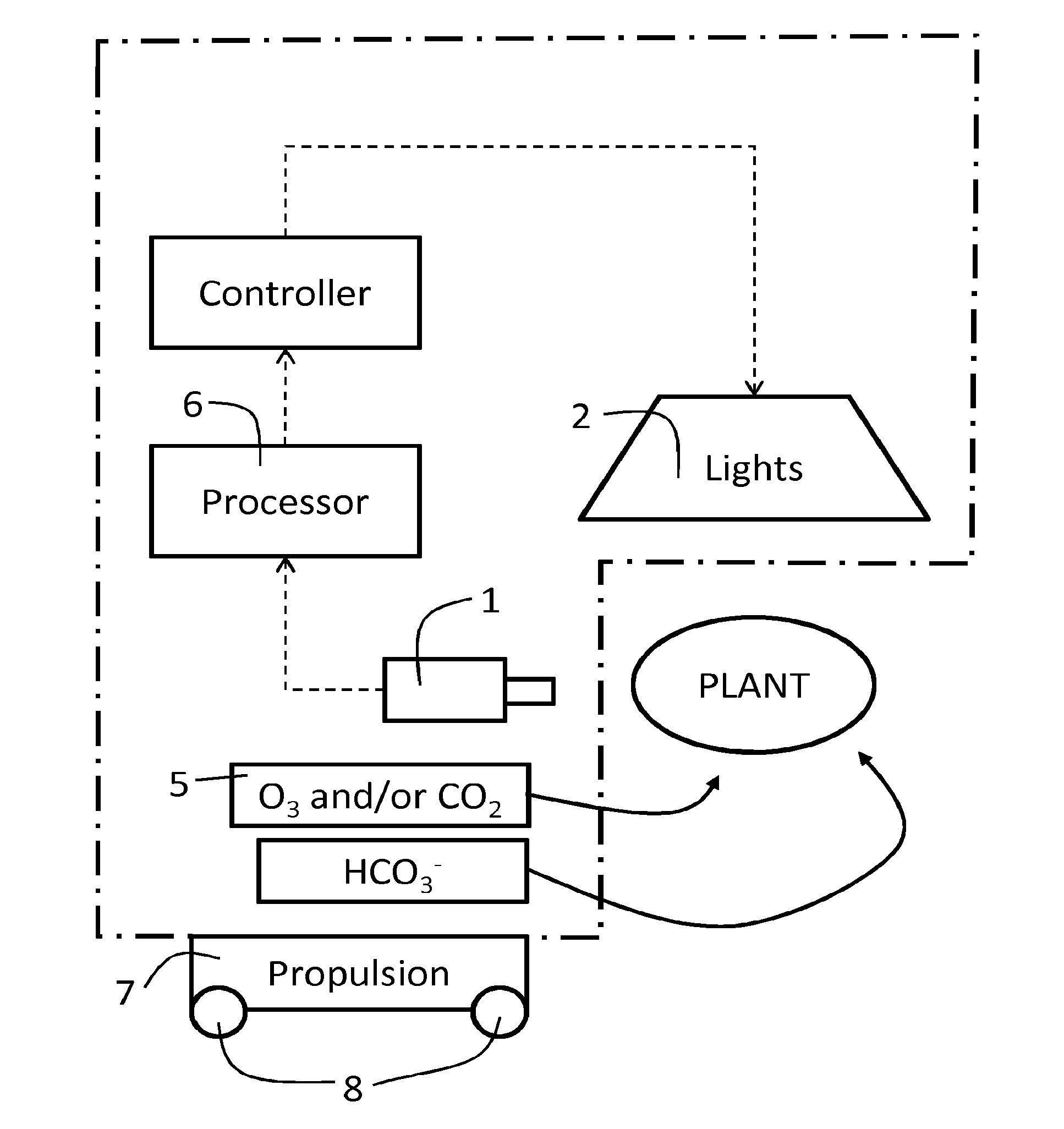
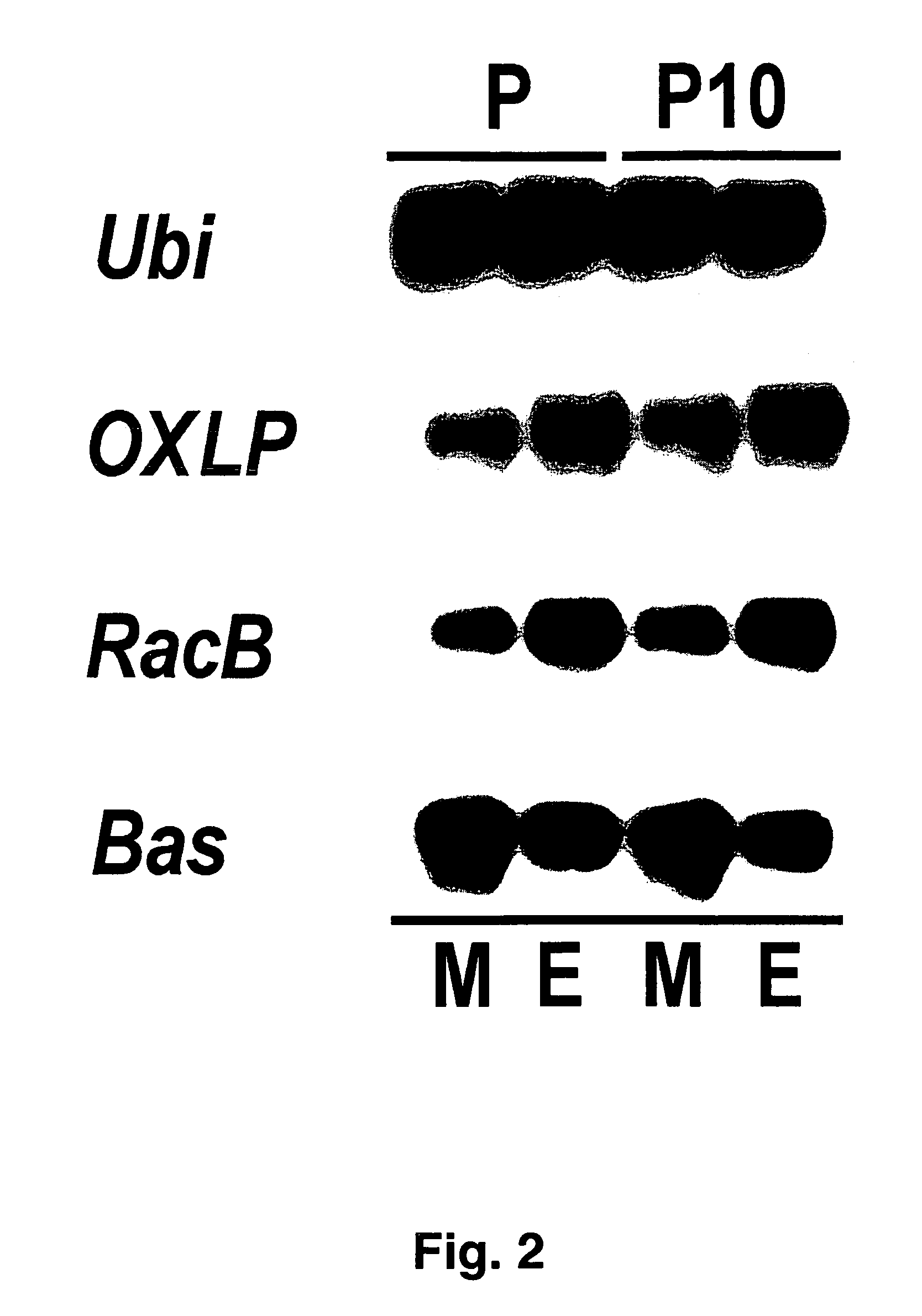Patents
Literature
199 results about "Pathogen resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Resistance to external pathogens by an organism’s immune system has been strongly debated by life scientists for many years. Mainly observed in plants, antibody-mediated pathogen resistance is achieved when the expression of certain antibodies or antibody fragments causes the external pathogen to be inactivated via antibody attachment.
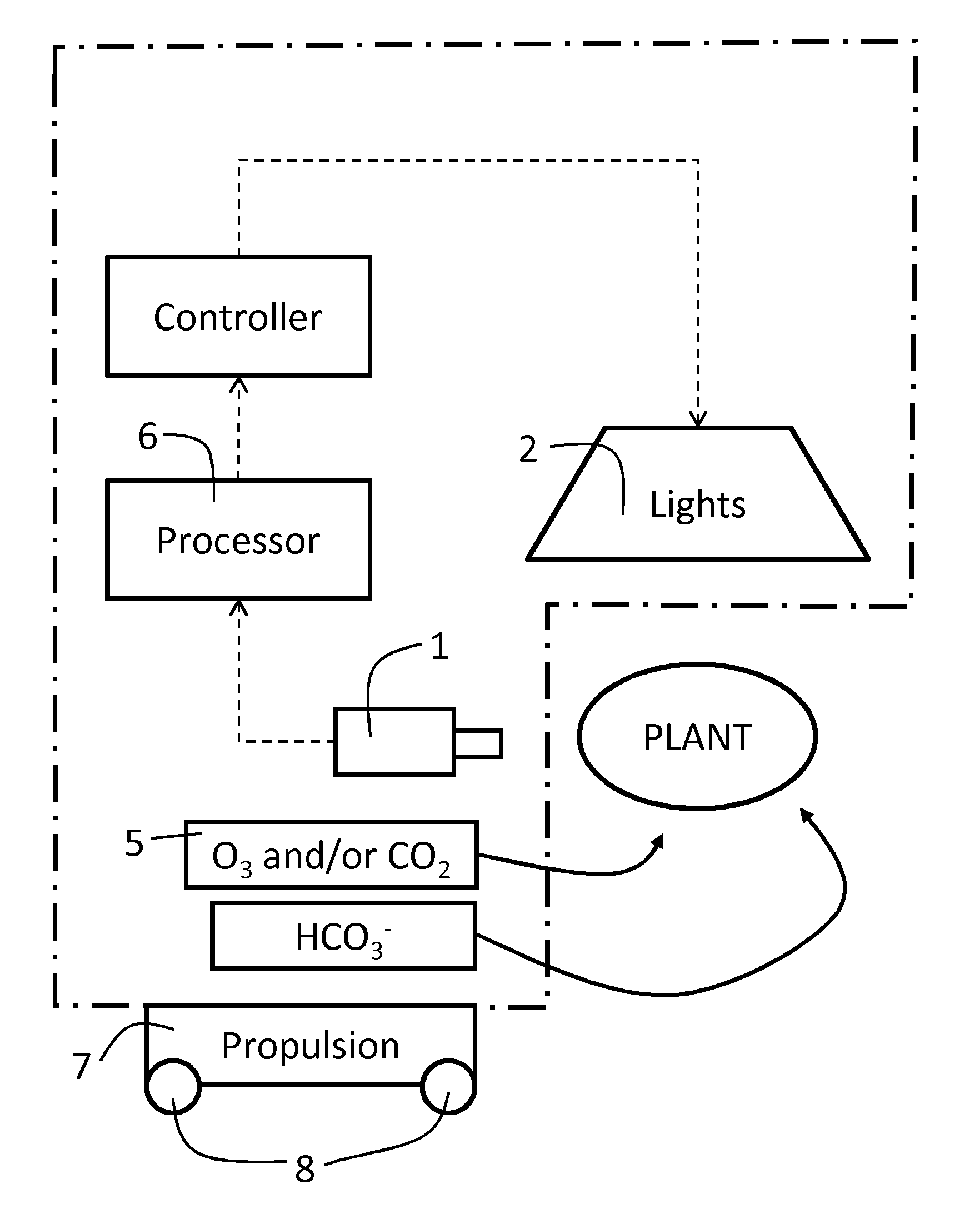
Method for facilitating pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20030150017A1Convenient researchImprove developmentClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructNucleotide
Methods are provided for the genetic control of pathogen infestation in host organisms such as plants, vertebrate animals and fungi. Such methods utilize the host as a delivery system for the delivery of genetic agents, preferably in the form of RNA molecules, to a pathogen, which agents cause directly or indirectly an impairment in the ability of the pathogen to maintain itself, grow or otherwise infest a host plant, vertebrate animal or fungus. Also provided are DNA constructs and novel nematode nucleotide sequences for use in same, that facilitate pathogen resistance when expressed in a genetically-modified host. Such constructs direct the expression of RNA molecules substantially homologous and / or complementary to an RNA molecule encoded by a nucleotide sequence within the genome of a pathogen and / or of the cells of a host to effect down-regulation of the nucleotide sequence. Particular hosts contemplated are plants, such as pineapple plants, and particular pathogens are nematodes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND +1
Methods for promoting plant health
ActiveUS20100260735A1Promoting health of plantImprove pathogen resistanceBiocideKetone active ingredientsGrowth plantBiofilm
A method for promoting the health of a plant comprises administering malic acid to the plant or the soil in an amount effective to recruit plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) to the plant. Administration of malic acid promotes biofilm formation of PGPR on the plant's roots, thereby restricting entry of a foliar pathogen through stomatal pores present in the leaves. Another method for promoting the health of a plant comprises administering acetoin to the plant or the soil in an amount effective to increase pathogen resistance in aerial parts of the plant.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Methods of protecting plants from pathogenic fungi and nematodes
Methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a pathogenic fungus or nematode, are provided. A method for enhancing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant an expression cassette comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the embodiments, or variant or fragment thereof, are also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Antifungal polypeptides
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include novel amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for antipathogenic polypeptides that were isolated from microbial fermentation broths. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides of the invention are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant an expression cassette comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a transformed microorganism comprising a nucleic acid of the invention in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention, or variant or fragment thereof, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Maize Antifungal RNAse NE Homolog Gene Sequence Encoding an Antimicrobial Protein Useful for Enhancing Plant Resistance to Pathogens
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include novel amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for antipathogenic polypeptides that were isolated from maize. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides of the embodiments are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant a DNA construct comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the embodiments. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a transformed microorganism comprising a nucleic acid of the embodiments in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the embodiments, or variant or fragment thereof, are also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Glyphosate tolerant sugar beet
InactiveUS7335816B2Easy to detectHigh level of tolerance against glyphosateMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesGlyphosateSugar beet
The invention relates to glyphosate tolerant sugar beet plants, plant material and seeds. It is the object of the invention to provide a transgenic sugar beet plant event that shows a high level of tolerance against glyphosate, but is not impaired in other important agronomic properties such as growth, yield, quality, pathogen resistance etc.
Owner:KWS SAAT SE
Antifungal polypeptides
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include an amino acid sequence, and variants and fragments thereof, for an antipathogenic polypeptide that was isolated from a fungal fermentation broth. Nucleic acid molecules that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides of the invention, and antipathogenic domains thereof, are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant an expression cassette comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a transformed microorganism comprising a nucleic acid of the invention in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +2
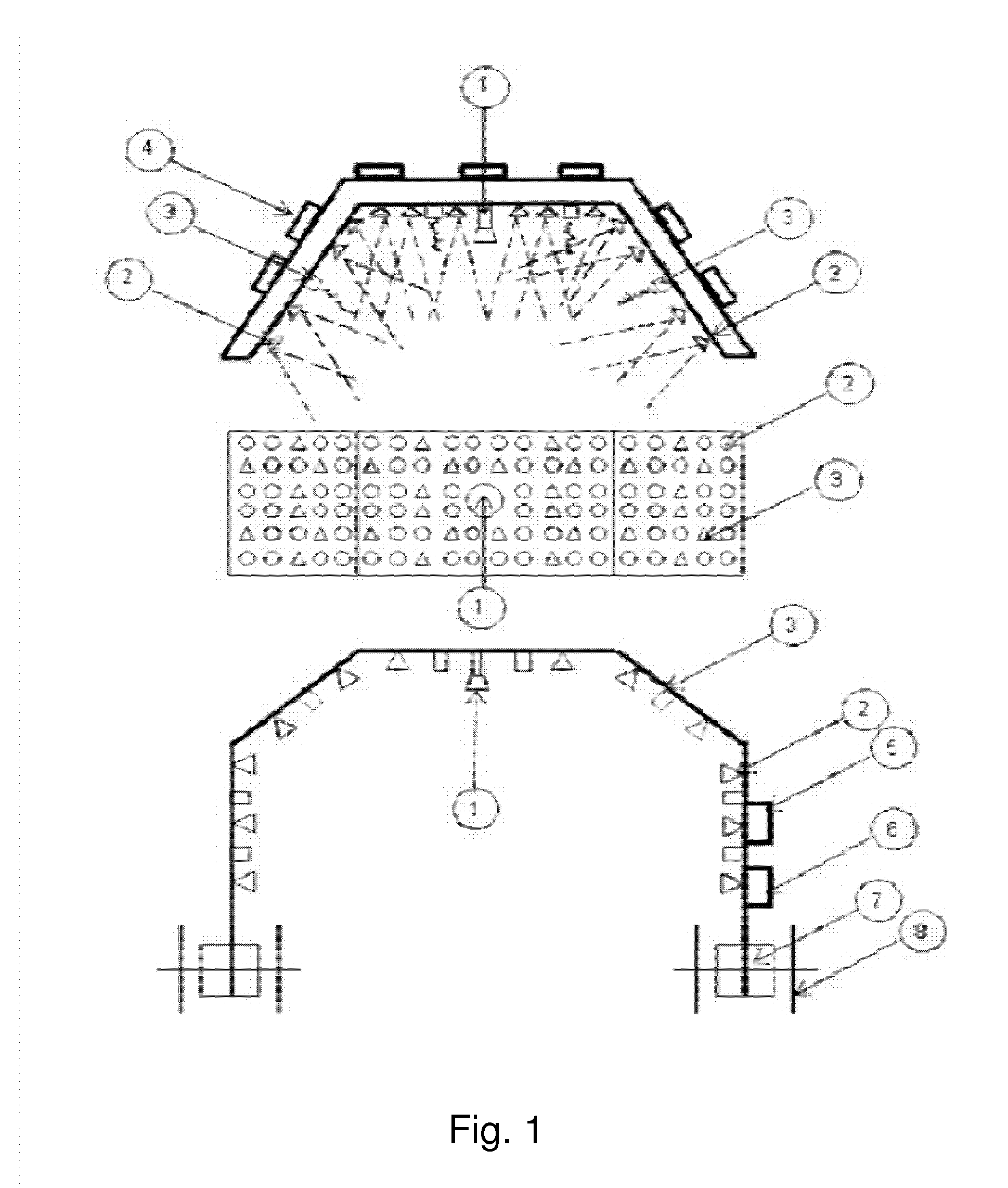
Method and apparatus for plant protection
InactiveUS20130255150A1Improve pathogen resistanceReduce infectionRoot feedersSaving energy measuresHigh intensityLength wave
A method of improving the growth and / or pathogen resistance of a plant, comprising the step of exposing at least part of the plant to a transient period of high intensity illumination providing a photon flux at the plant surface having at least one of the following characteristics: (a) a red photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square metre per second, and having a wavelength of between 600 and 700 nm; (b) a blue photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square metre per second, having a wavelength of between 420 and 480 nm. The Invention also provides apparatus for providing such conditions to growing plants.
Owner:KARPINSKI STANISLAW +1
Polynucleotides and methods for making plants resistant to fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20060223102A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesAnthriscus caucalisPolynucleotide
This invention relates to polynucleotide sequences encoding a gene that can confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, which causes anthracnose stalk rot, leaf blight and top dieback in corn and other cereals. It further relates to plants and seeds of plants carrying chimeric genes comprising said polynucleotide sequences, which enhance or confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, and processes of making said plants and seeds. The invention further presents sequences that can be used as molecular markers that in turn can be used to identify the region of interest in corn lines resulting from new crosses and to quickly and efficiently introgress the gene from corn lines carrying said gene into other corn lines that do not carry said gene, in order to make them resistant to Colletotrichum and resistant to stalk rot.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +2
Bifidobacterium possessing characteristic for anti pathogenesis bacterium in intestinal tract and antioxidation, and application
InactiveCN1796540AHave adhesive propertiesInhibitoryBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsEscherichia coliDisease
This invention describes a bifidobacterium, i.e., bifidobacterium longum BM358 that can resist intestinal pathogens as well as resist oxidation. The bifidobacterium longum has such properties as high security, outstanding acid and bile resistance, adhesion to intestinal epithelial cells, outstanding intestinal pathogen resistance and oxidation resistance. The bifidobacterium longum can be used to prevent and treat gastritis, gastrelcosis and duodenitis caused by pylorus helicobacteria, and enteritis, acute diarrhea and enterogastric disorder caused by colibacillus and other intestinal pathogens.
Owner:王敖喜 +1
Polynucleotides and methods for making plants resistant to fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20060225151A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnthriscus caucalisPolynucleotide
This invention relates to polynucleotide sequences encoding a gene that can confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, which causes anthracnose stalk rot, leaf blight and top dieback in corn and other cereals. It further relates to plants and seeds of plants carrying chimeric genes comprising said polynucleotide sequences, which enhance or confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, and processes of making said plants and seeds. The invention further presents sequences that can be used as molecular markers that in turn can be used to identify the region of interest in corn lines resulting from new crosses and to quickly and efficiently introgress the gene from corn lines carrying said gene into other corn lines that do not carry said gene, in order to make them resistant to Colletotrichum and resistant to stalk rot.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE +2
Engineered bacteriocins and bacteriocin combinations and methods for treating bacterial based infections
InactiveUS20060229244A1High specific activity against the bacterial infectionReduce infectionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHigh specific activityBiology
A method for treating bacterial infections in a patient is provided. The method includes the step of administering a therapeutically effective amount of a single naturally-occurring or engineered bacteriocin, or combinations thereof, designed to have high specific activity against the bacterial infection to the patient so that a rate of resistance to the bacteriocin in the patient is decreased. The colicins and other bacteriocins or combinations of colicins and other bacteriocins target and kill specific bacterial pathogens in a manner that results in a high specific killing activity and decreased incidence of pathogen resistance. To this end, the characteristics of existing colicins and other bacteriocins are modified in order to enhance and amplify their therapeutic value.
Owner:DORIT ROBERT +1
Methods and materials for conferring resistance to pests and pathogens of plants
InactiveUS20060095987A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyVermin
Methods and materials for conferring pest resistance to plants are provided. Plants are transformed with a silencing construct homologous to a gene of a plant pest that is essential for the survival, development, or pathogenicity of the pest. This results in the plant producing RNAi to the selected gene, which, when ingested by the pest results in silencing of the gene and a subsequent reduction of the pest's ability to harm the plant. In other embodiments, the pest's reduced ability to harm the plant is passed on to pest progeny. Methods and materials for depathogenesis of pests is also provided.
Owner:VENGANZA
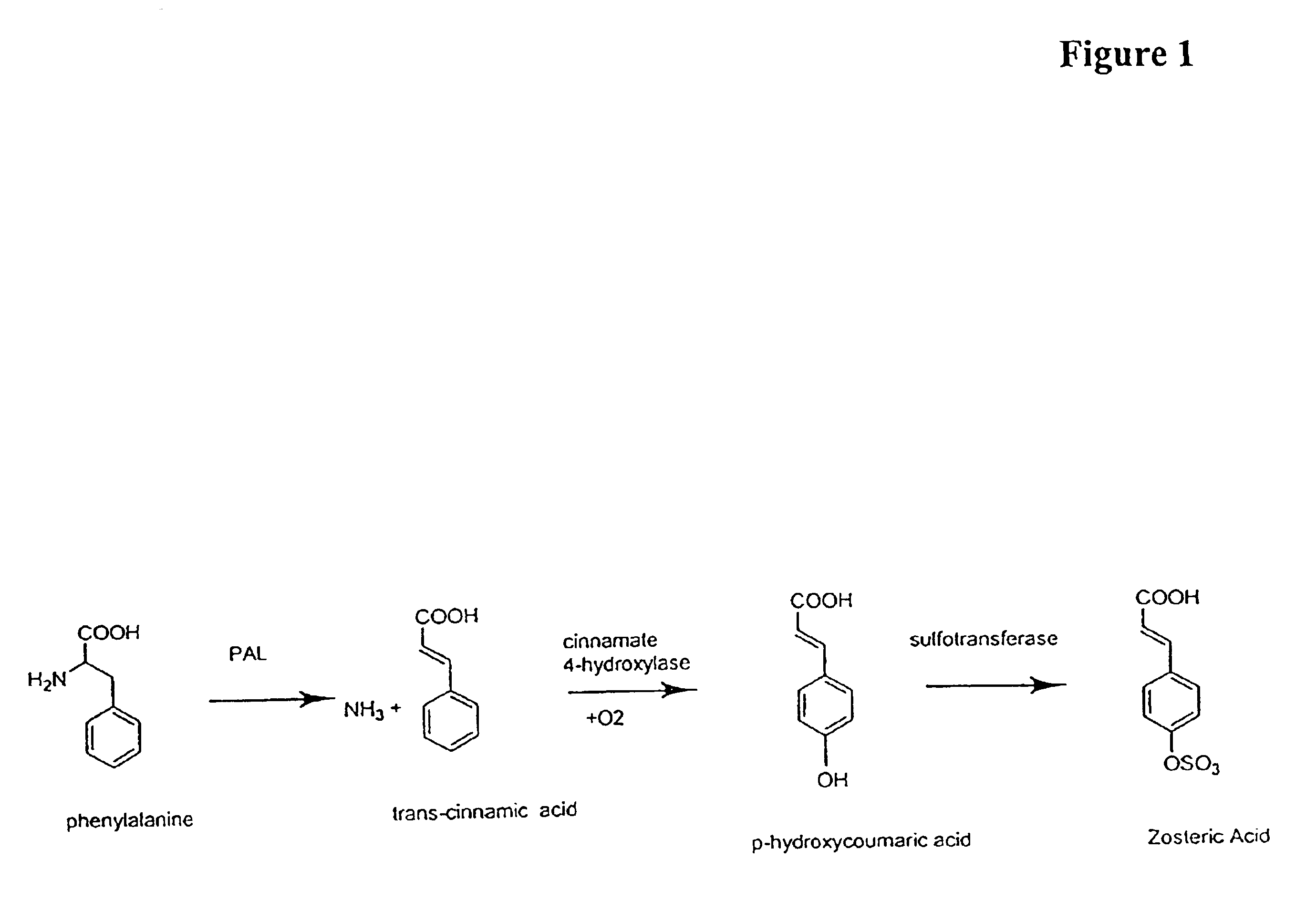
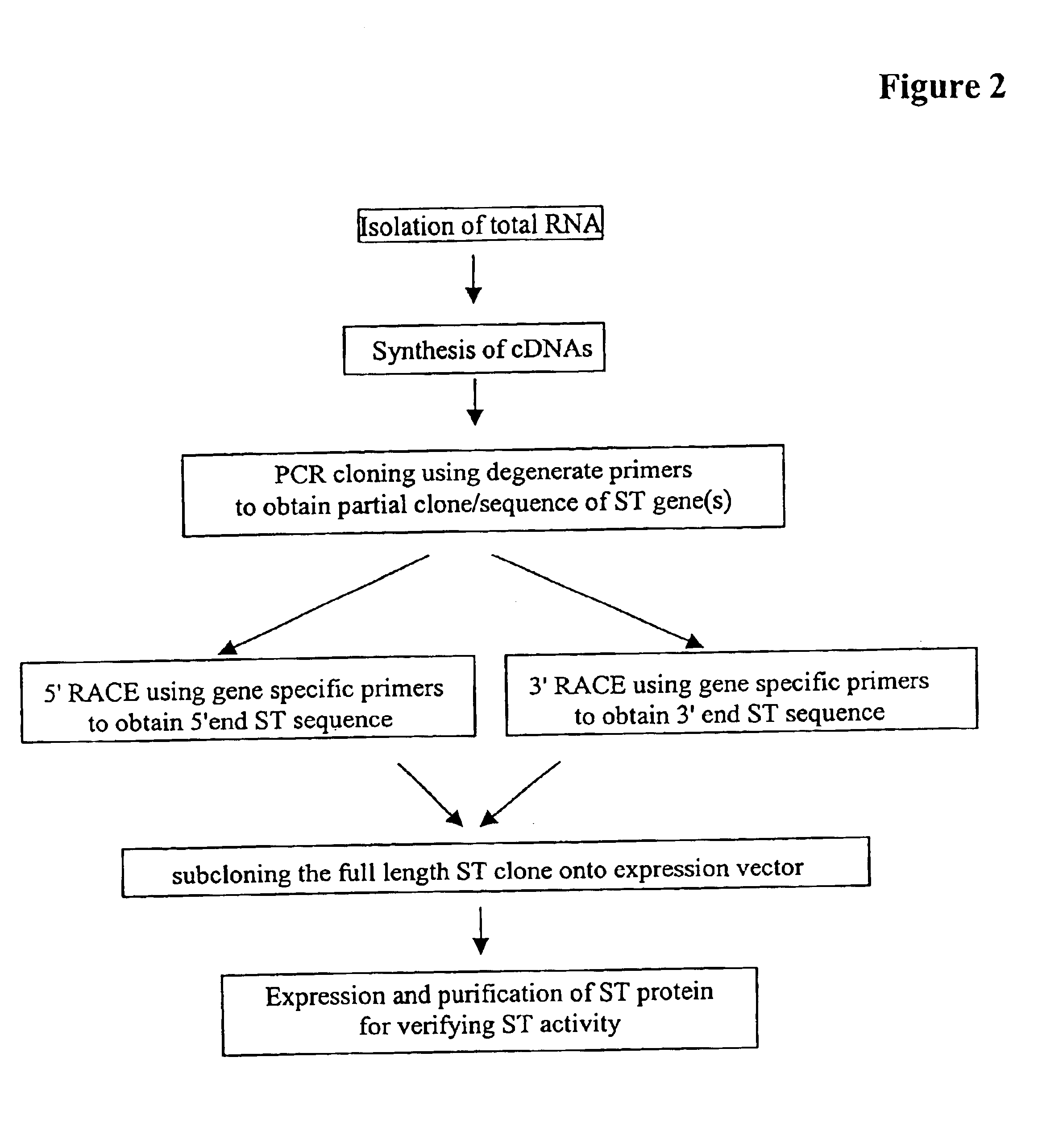
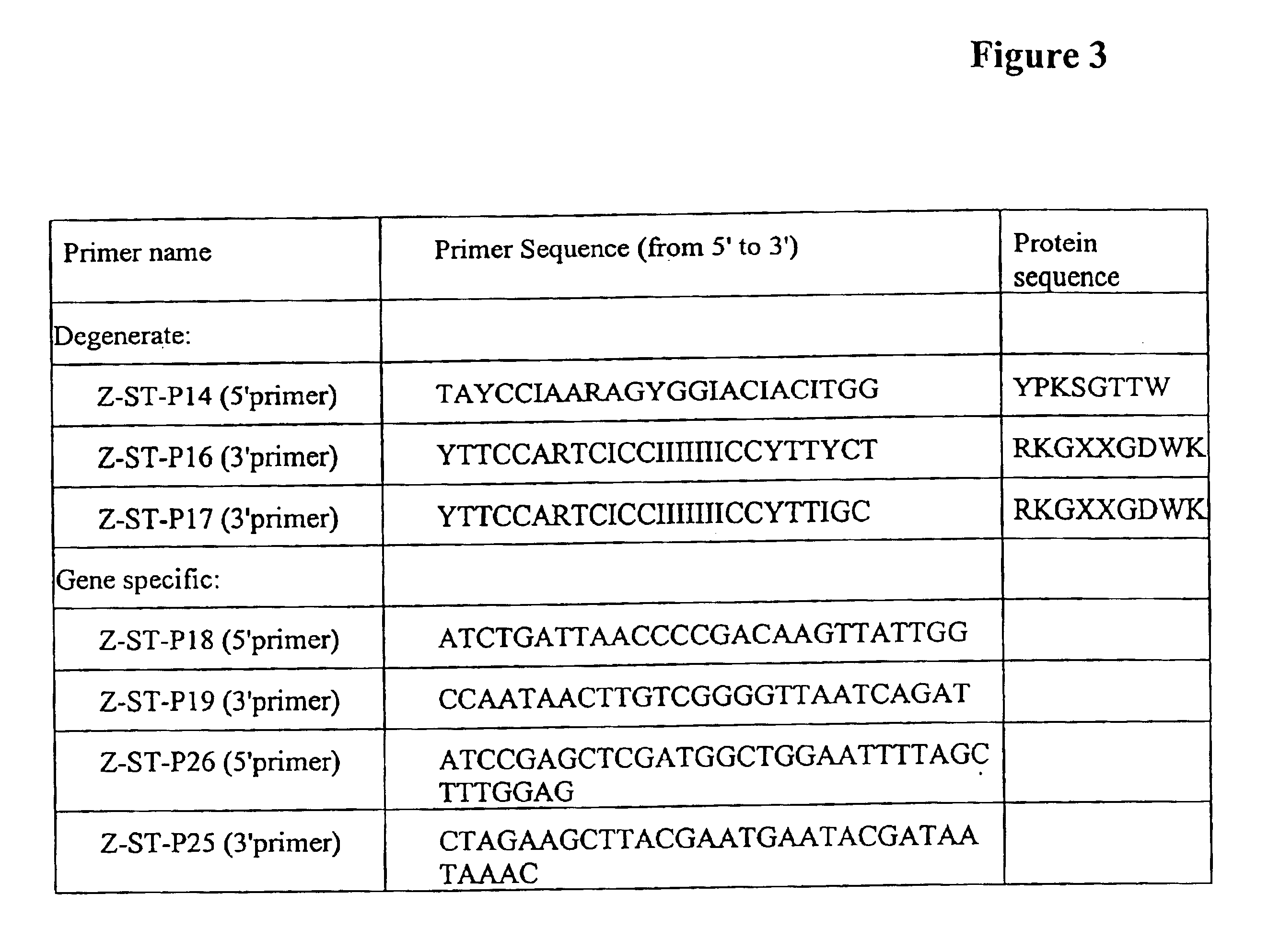
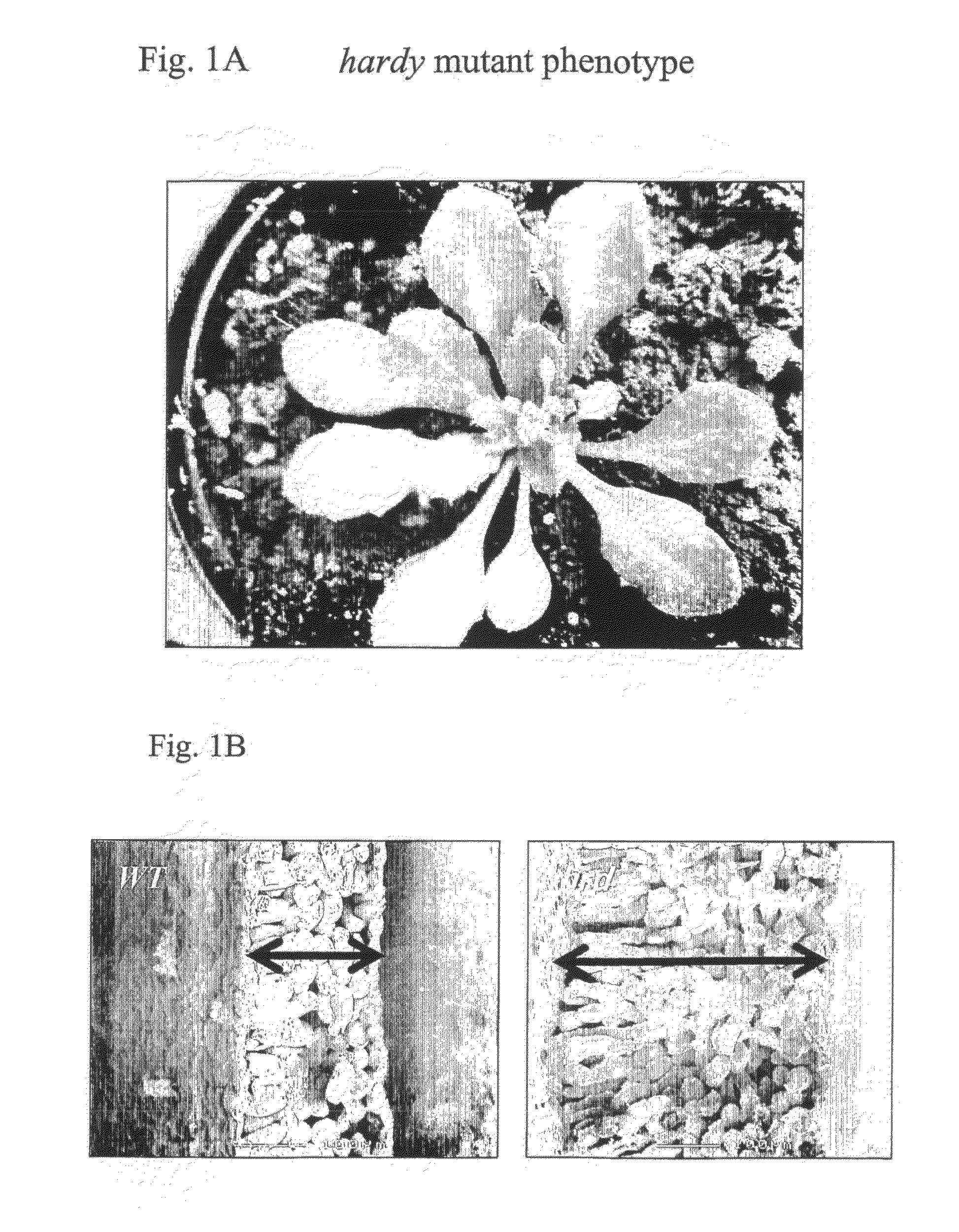
Transgenic plants incorporating traits of zostera marina
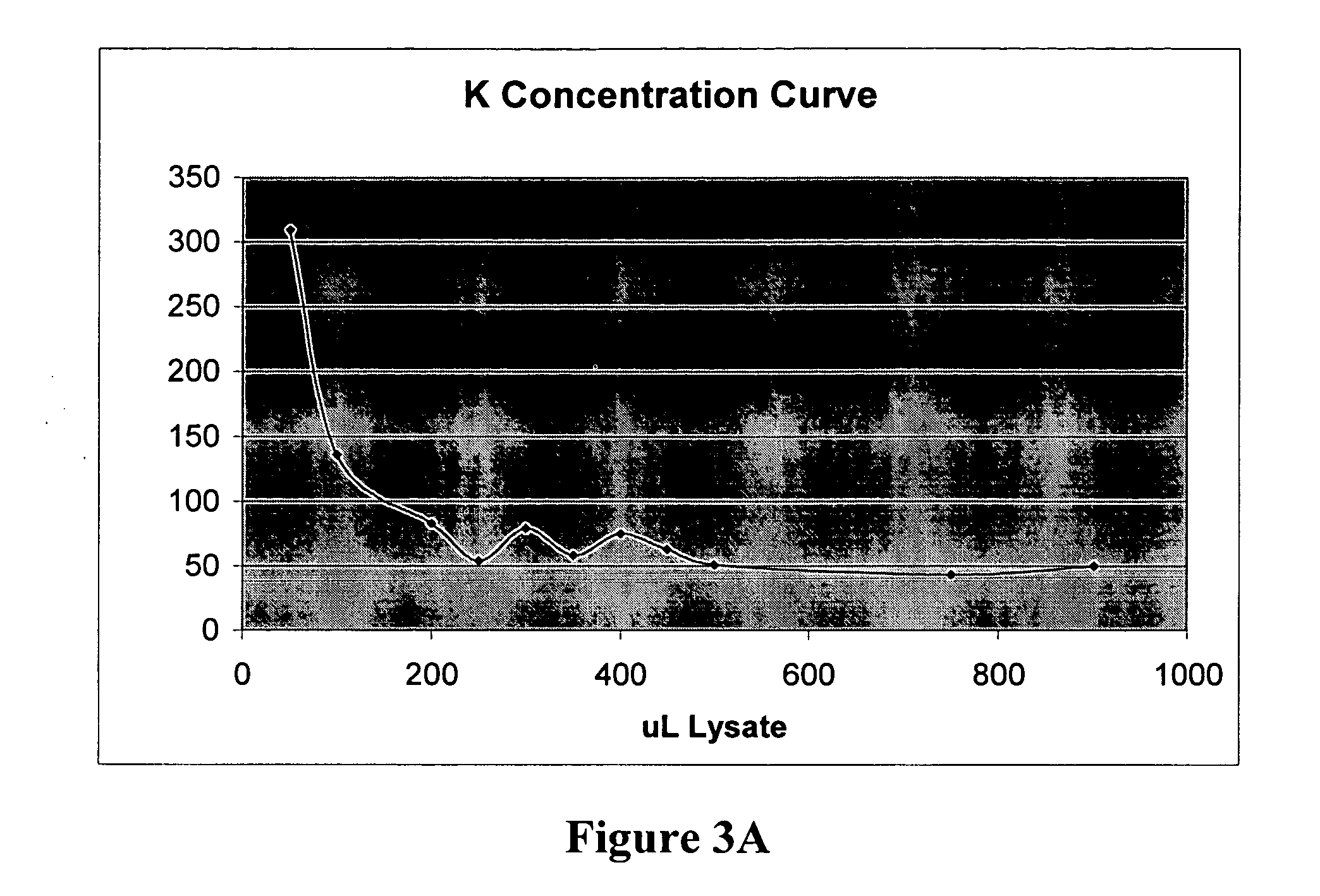
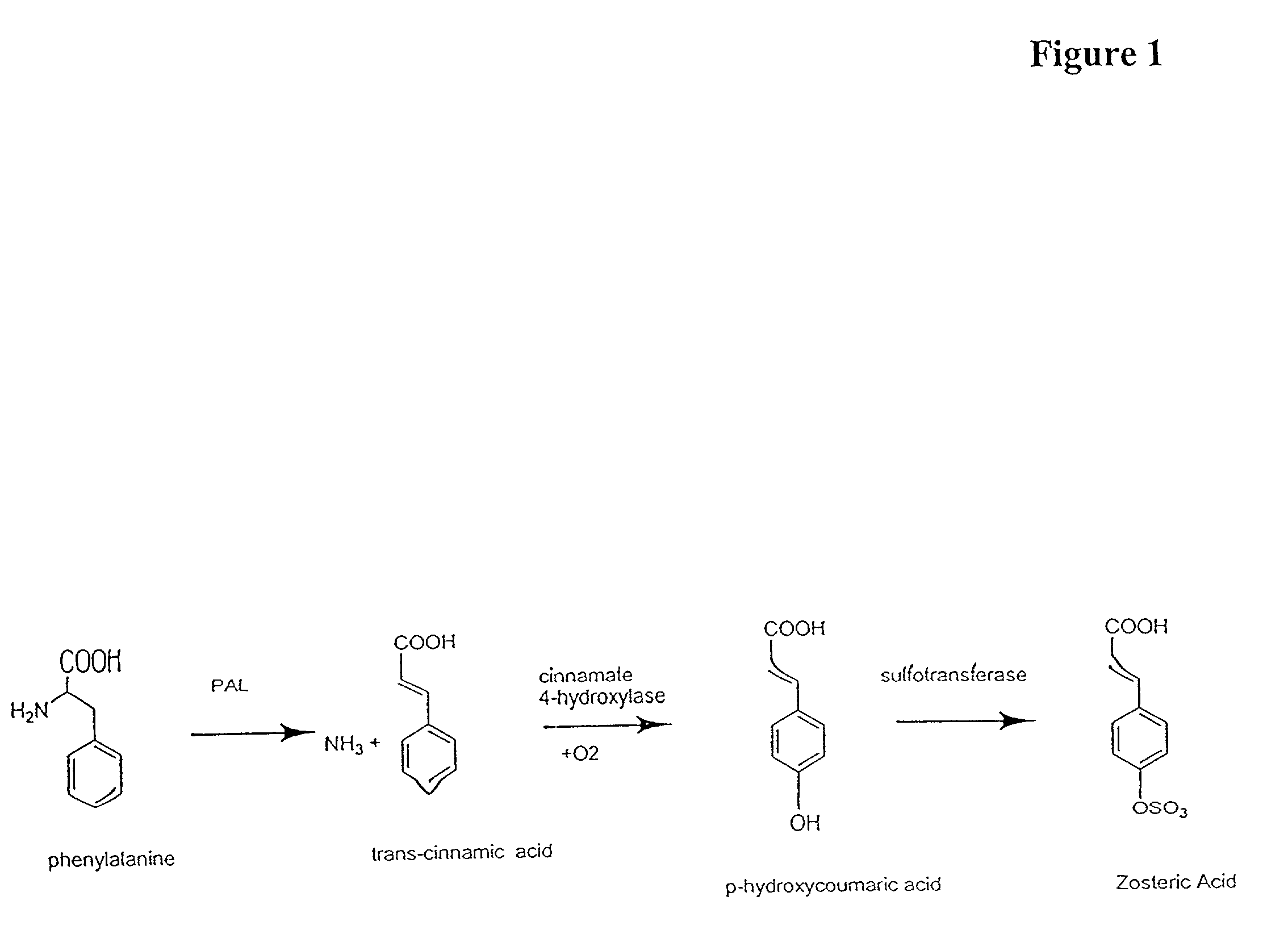
The invention provides methods and compositions related to transgenic plants which incorporate genetic traits of the marine eelgrass Zostera marina. These traits include pathogen resistance, which may be conferred by stimulating zosteric acid biosynthesis, and root anoxia resistance, which may be conferred by introducing one or more anoxia-induced or anoxia-resistance genes.
Owner:CERNOFINA
Transgenic plants expressing dermaseptin peptides providing broad spectrum resistance to pathogens
InactiveUS6835868B1Improve stabilityImprove purification effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOther foreign material introduction processesDermaseptinDermaseptin peptide
Transgenic plants that express dermaseptin peptides are disclosed. In certain embodiments, these plants have enhanced, broad-spectrum pathogen resistance and are useful as agricultural or horticultural crops. In other embodiments, the plants are used to produce large quantities of the dermaseptin peptides.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA +1
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improvedresistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including speciessuch as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
Sterilization composition containing Dufulin
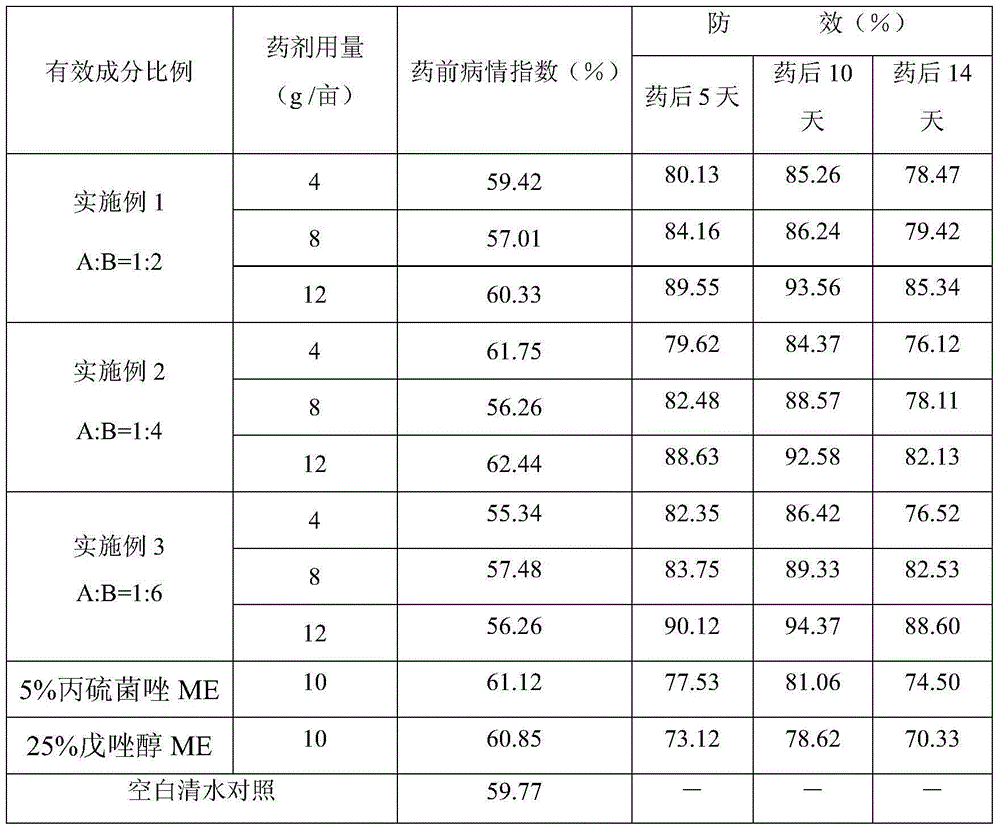
ActiveCN102726444AOvercoming and delaying drug resistanceGood synergyBiocideFungicidesMedicineSuspending Agents
The present invention discloses a sterilization composition containing Dufulin, wherein the active ingredient is prepared by compounding Dufulin A and a strobilurins sterilant B, the strobilurins sterilant B is one selected from azoxystrobin, kresoxim-methyl, pyraclostrobin, and picoxystrobin, a weight ratio of the Dufulin A to the strobilurins sterilant B is 50:1-1:50, the total weight of the Dufulin A and the strobilurins sterilant B is 5-80% of the total weight of the sterilization composition, and the sterilization composition can be prepared into a wettable powder agent, a suspending agent, water-dispersible granules and other conventional formations. The composition of the present invention is used for prevention and treatment of crop plant diseases, and has advantages of high efficiency, low environment pollution, delaying of pathogen resistance generation, and the like.
Owner:GAUNGXI TIANYUAN BIOCHEM
Transgenic plants incorporating traits of Zostera marina
The invention provides methods and compositions related to transgenic plants which incorporate genetic traits of the marine eelgrass Zostera marina. These traits include pathogen resistance, which may be conferred by stimulating zosteric acid biosynthesis.
Owner:CERNOFINA
Transgenic Plant Having Enhanced Drought Tolerance
InactiveUS20110209247A1Improve drought toleranceImprove disease resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellGMO Plants
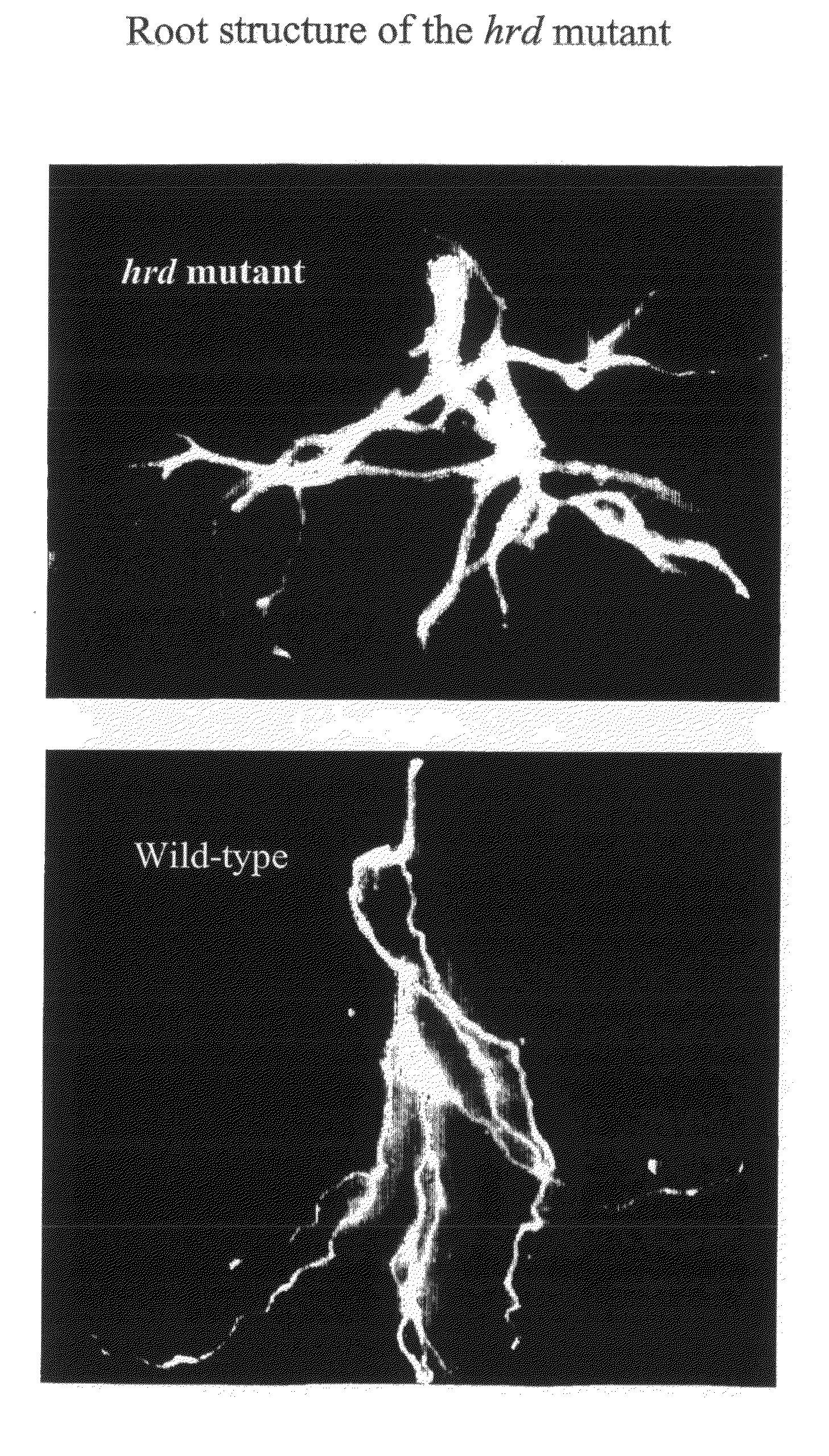
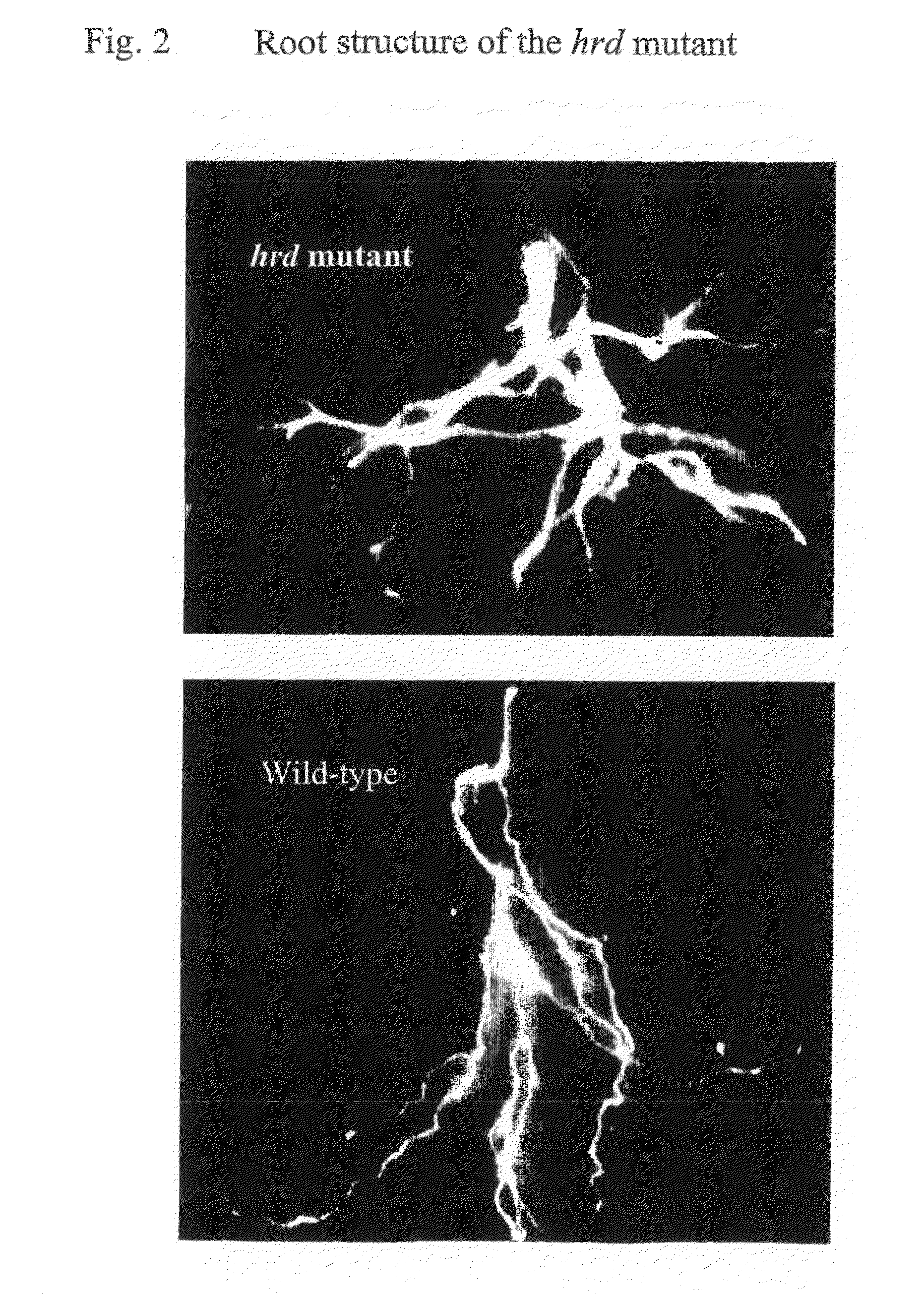
The present invention relates to the field of transgenic plants with novel phenotypes, especially plants with enhanced drought and pathogen resistance. Provided are transgenic crop plants comprising integrated in their genome a chimeric gene, characterized by said chimeric gene comprising a transcription regulatory sequence active in plant cells operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a protein having the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 or a protein at least 70% identical to SEQ ID NO: 3, or an ortholog protein or a functional fragment thereof. In addition to enhanced drought tolerance the transgenic plants may show enhanced disease resistance and enhanced root structure.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
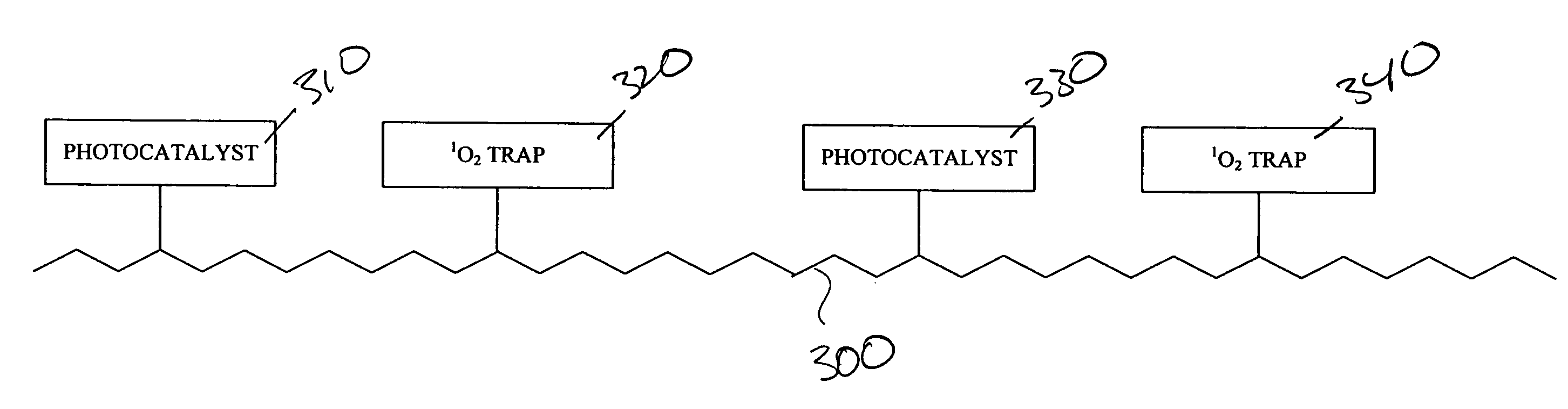
Pathogen-resistant coatings
InactiveUS7915197B2Low costEffectively “ hardens ”Alkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCatalyst protectionSinglet oxygenAmbient air
A pathogen-resistant coating comprising one or more photocatalysts capable of generating singlet oxygen from ambient air. The pathogen-resistant coating may optionally include one or more singlet oxygen traps.
Owner:LOMBARDI JOHN L
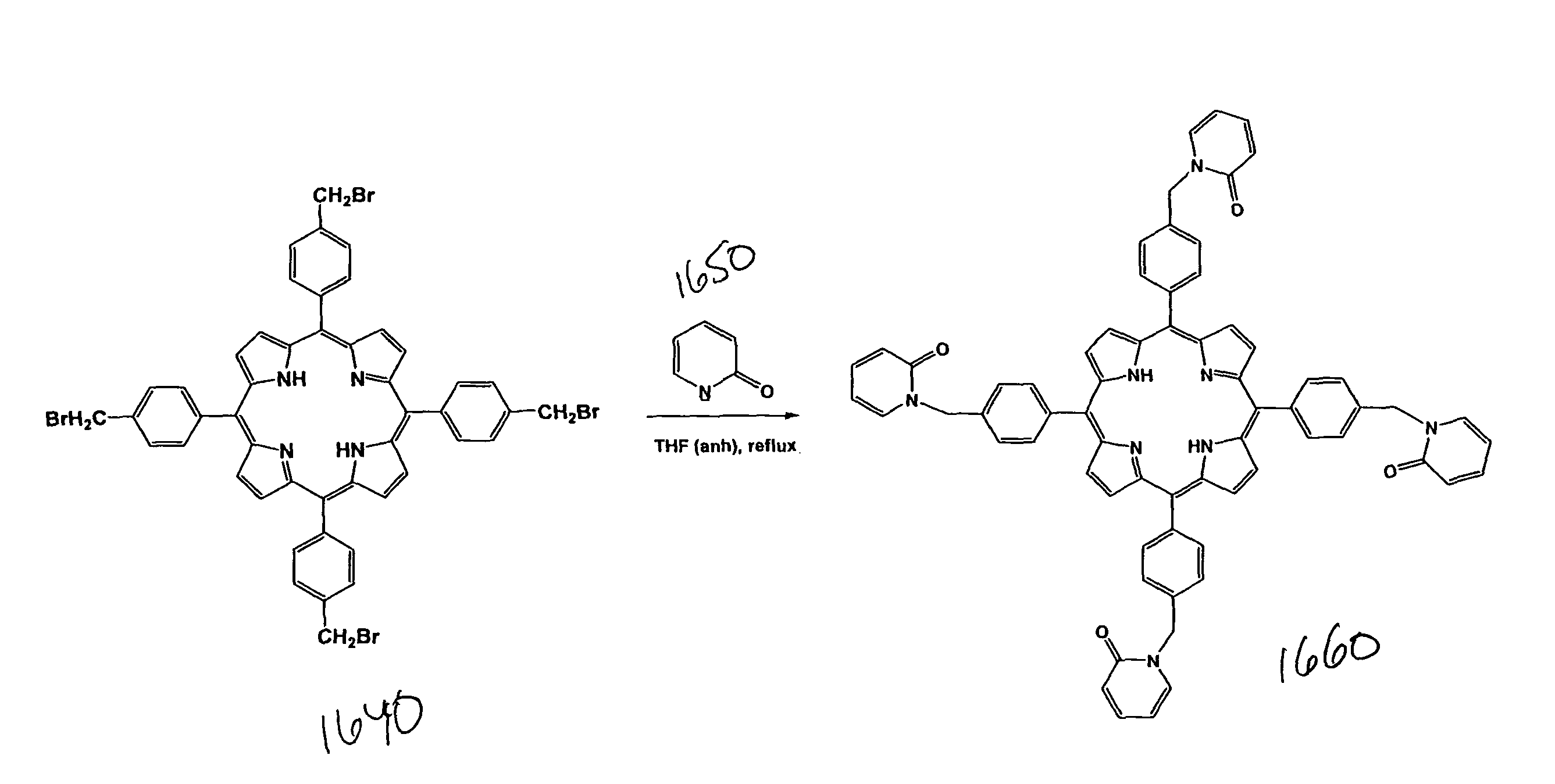
Nucleic acid sequences and their use in methods for achieving pathogen resistance in plants
InactiveUS7456335B2Confer resistanceReduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingGMO Plants
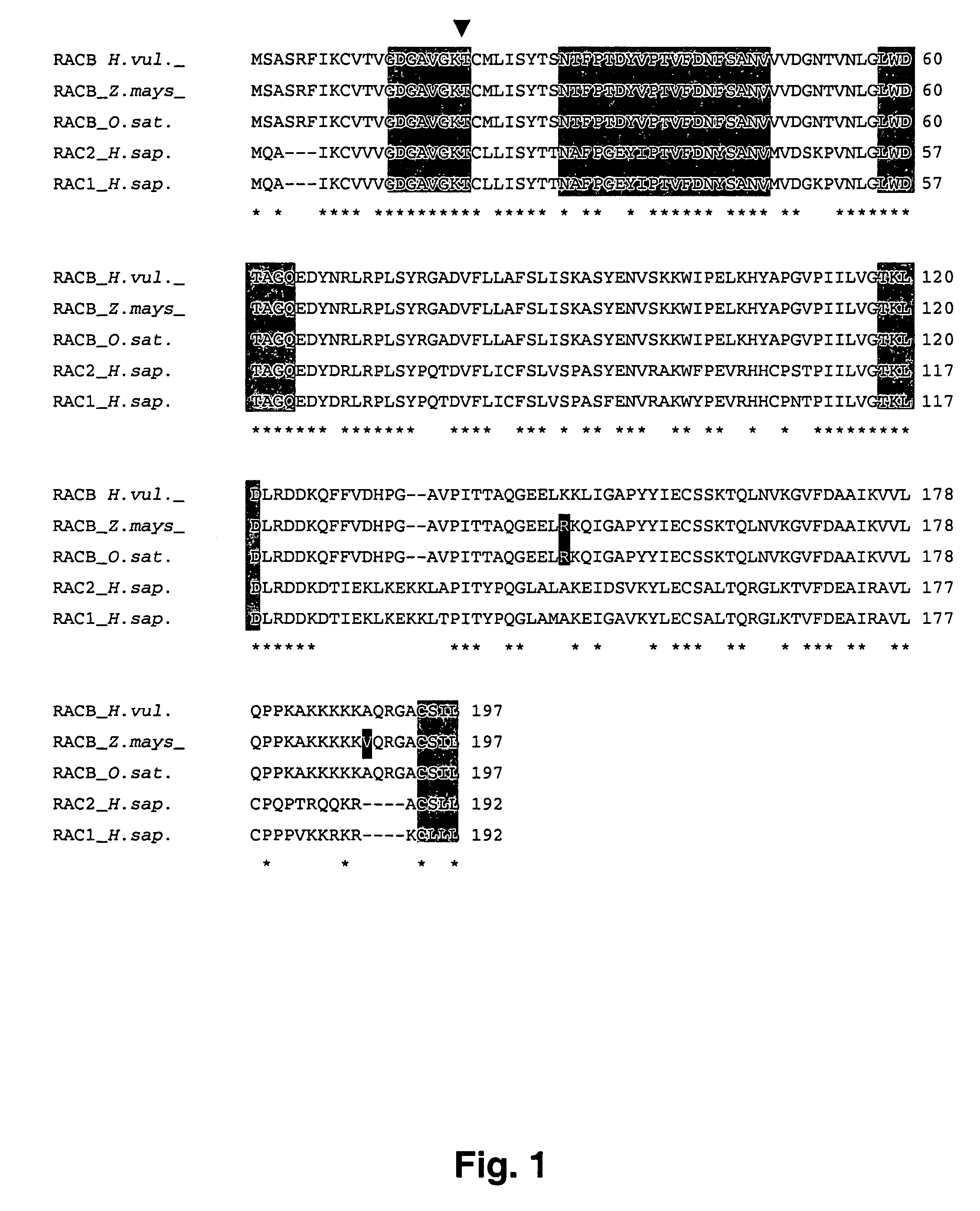
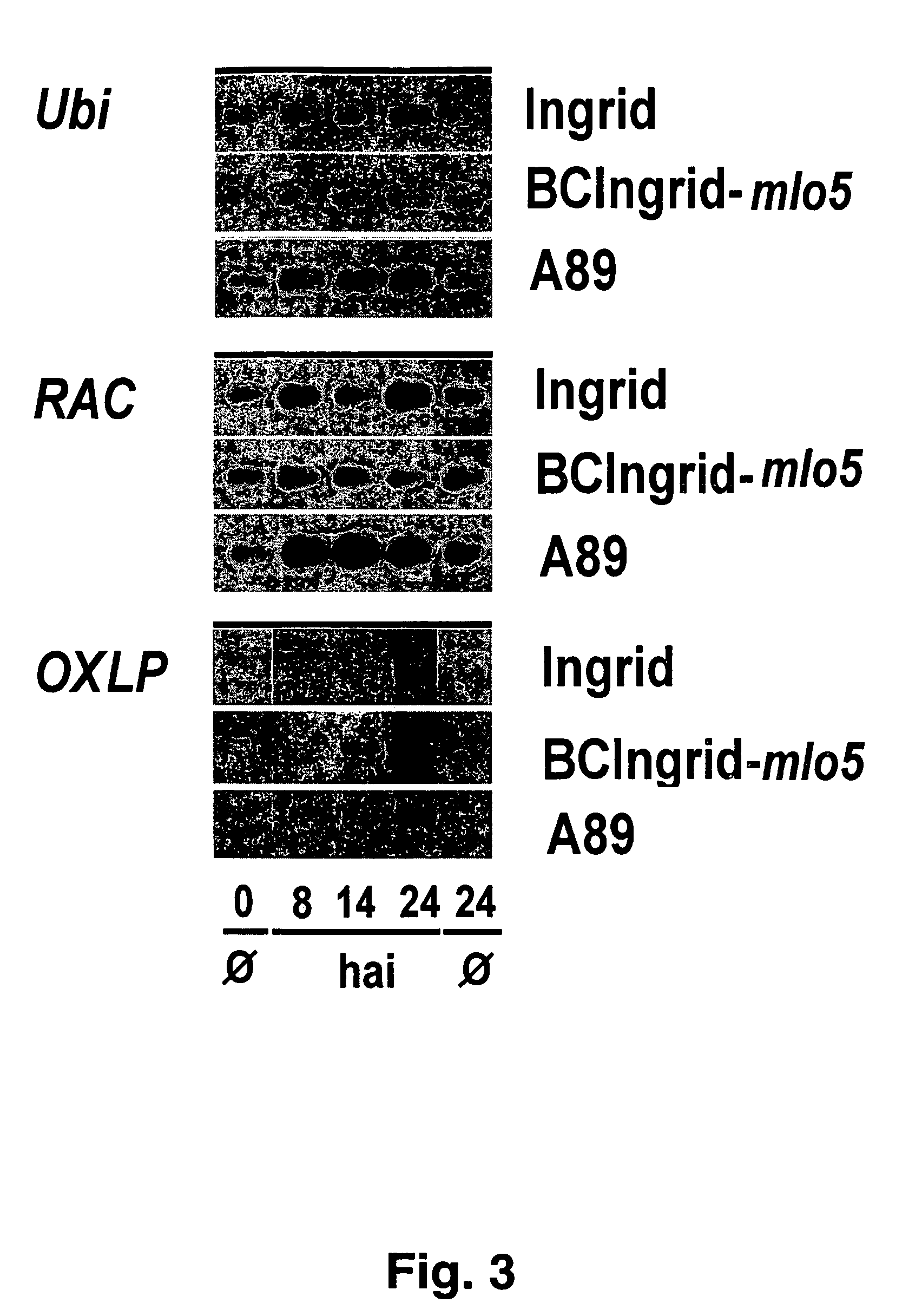
The invention relates to novel RacB cDNA sequences from barley and to expression cassettes and vectors comprising these promoter sequences. The invention furthermore relates to transgenic plants transformed with these expression cassettes or vectors, to cultures, parts or transgenic propagation material derived from them, and to their use for the production of foodstuffs, feeding stuffs, seed, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals. The invention furthermore relates to methods of generating or increasing a pathogen resistance in plants by reducing the expression of an RacB protein or of a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
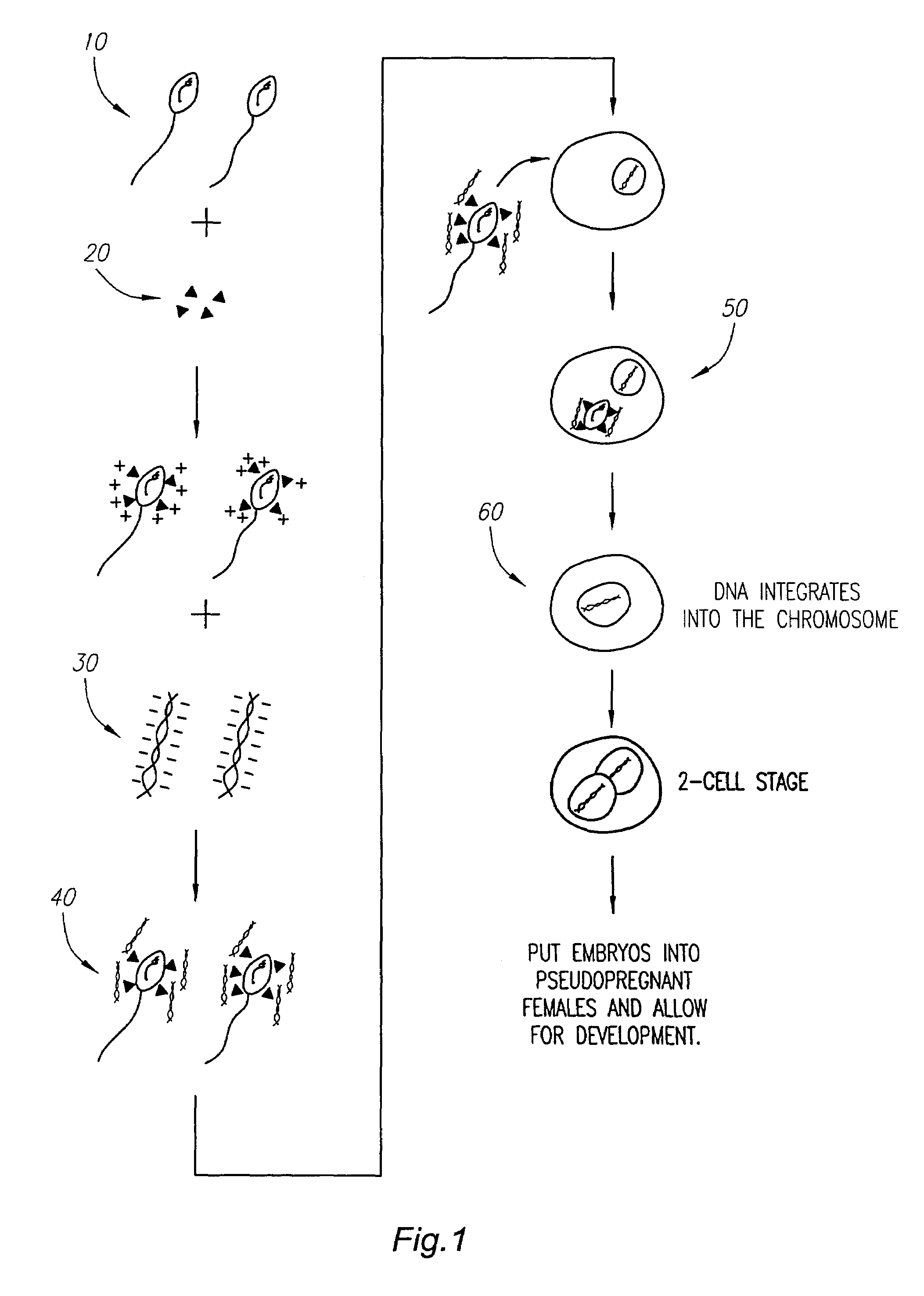
Vector for genetically modifying non-human animals
InactiveUS7067308B1High productHigh speedMammal material medical ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseLiposome
The present invention is directed to a vector and its use to generate genetically modified animals and cells. One aspect of this invention involves a vector that comprises a sperm cell and one or more polynucleotide molecules bound to a sperm cell through one or more non-liposome based linkers. In a preferred embodiment of this invention, the linker is a protein or polypeptide, preferably sperm specific such as an antibody that binds with the external surface of the sperm cell. In another aspect of the present invention, genetically modified cells or animals are derived from the fertilization of an animal egg cell with the vector described. In one preferred embodiment, genetic modification occurs with the polynucleotide molecule integrating, wholly or partially, into the cell or animal's genome. Another aspect of the present invention includes cells, such as sperm cells or egg cells, and cell lines that are derived from these genetically modified animals or their descendants. In another aspect of the present invention, the genetically modified animals derived from the use of the sperm vector described above possess certain desired characteristics. Examples of these characteristics include faster growth rates, disease or pathogen resistance, high production of certain proteins in milk, and organs suitable for animal to human xenotransplantation.
Owner:KWANG HUA DEV & INVESTMENT
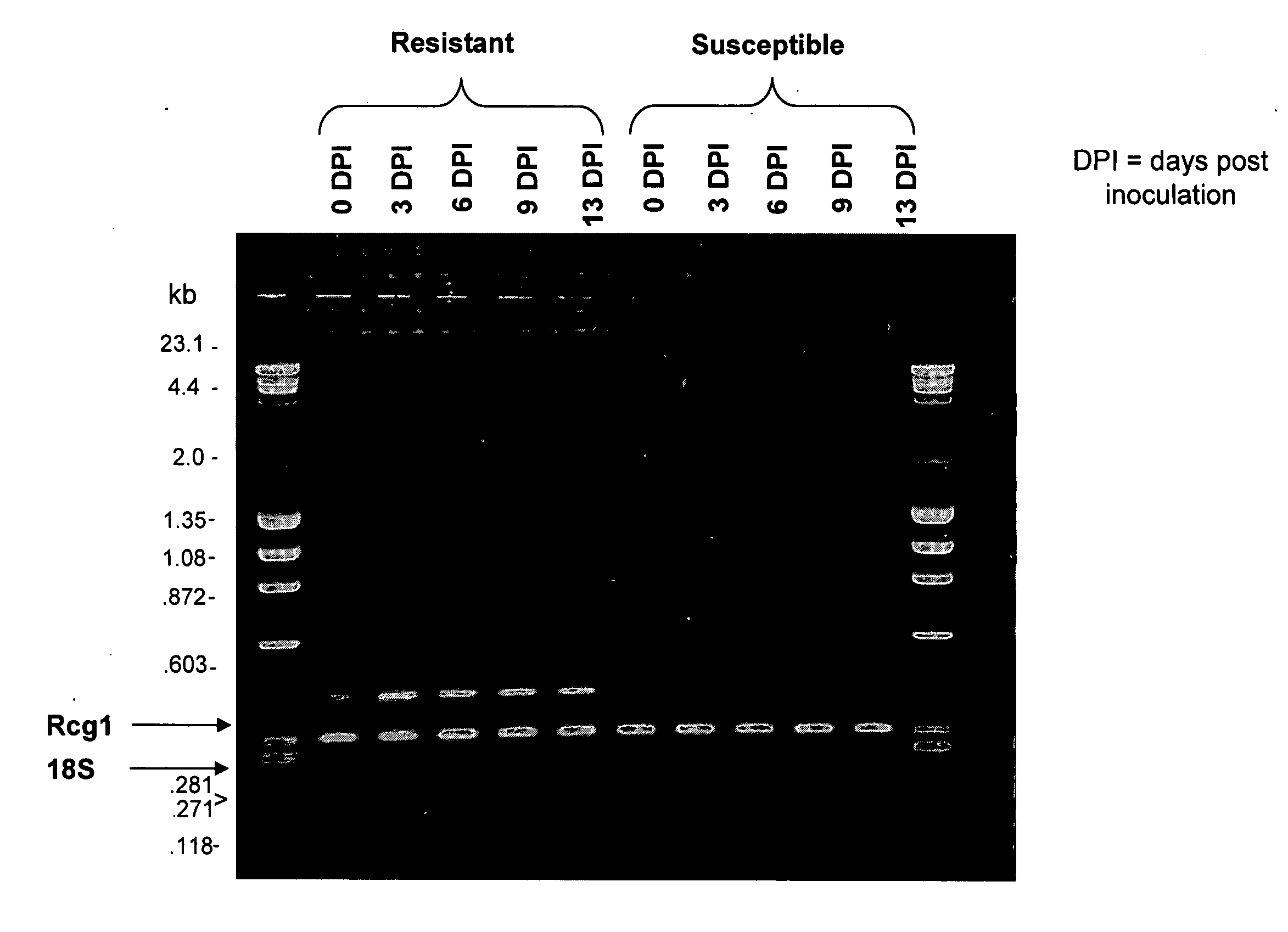
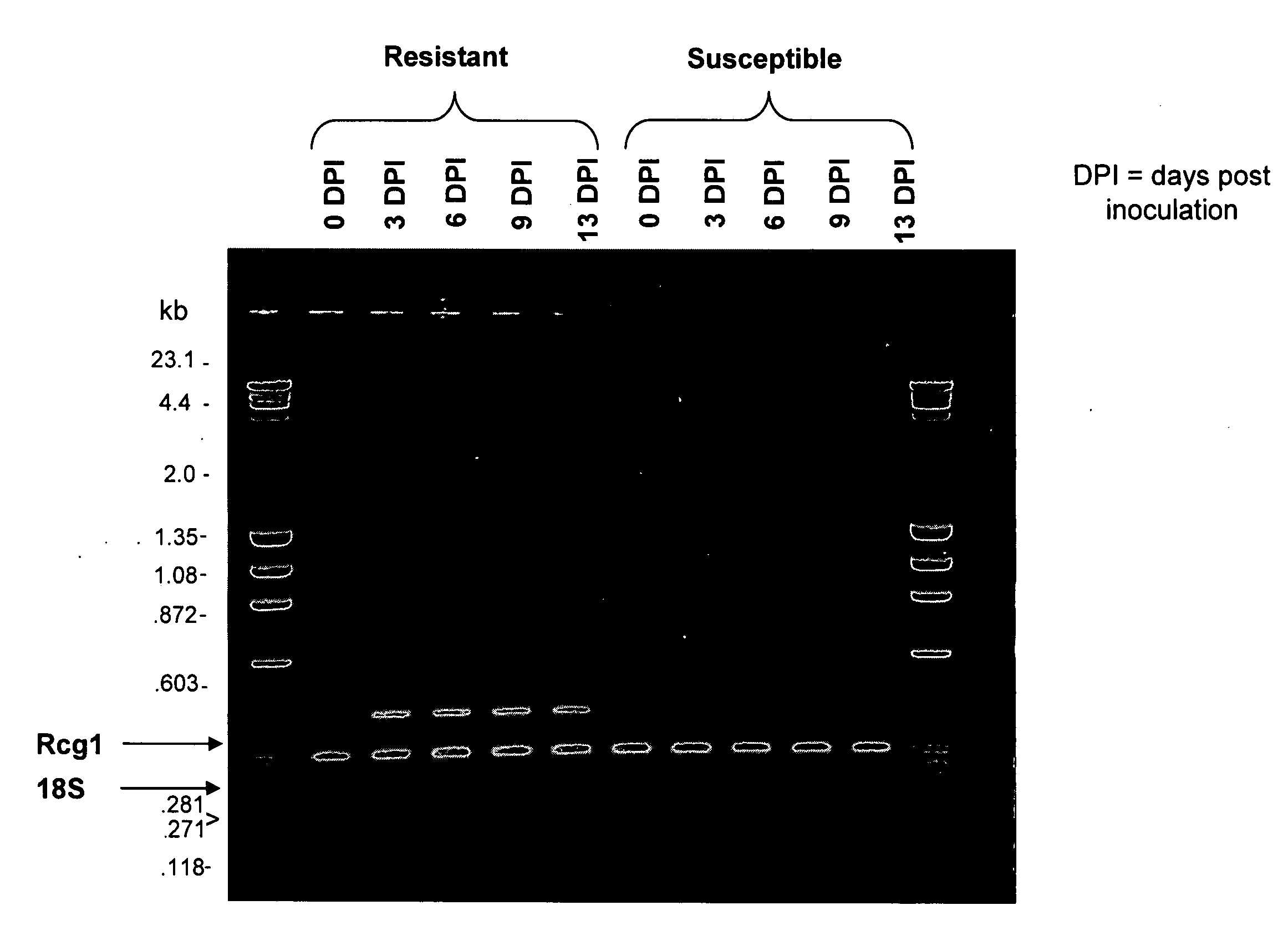
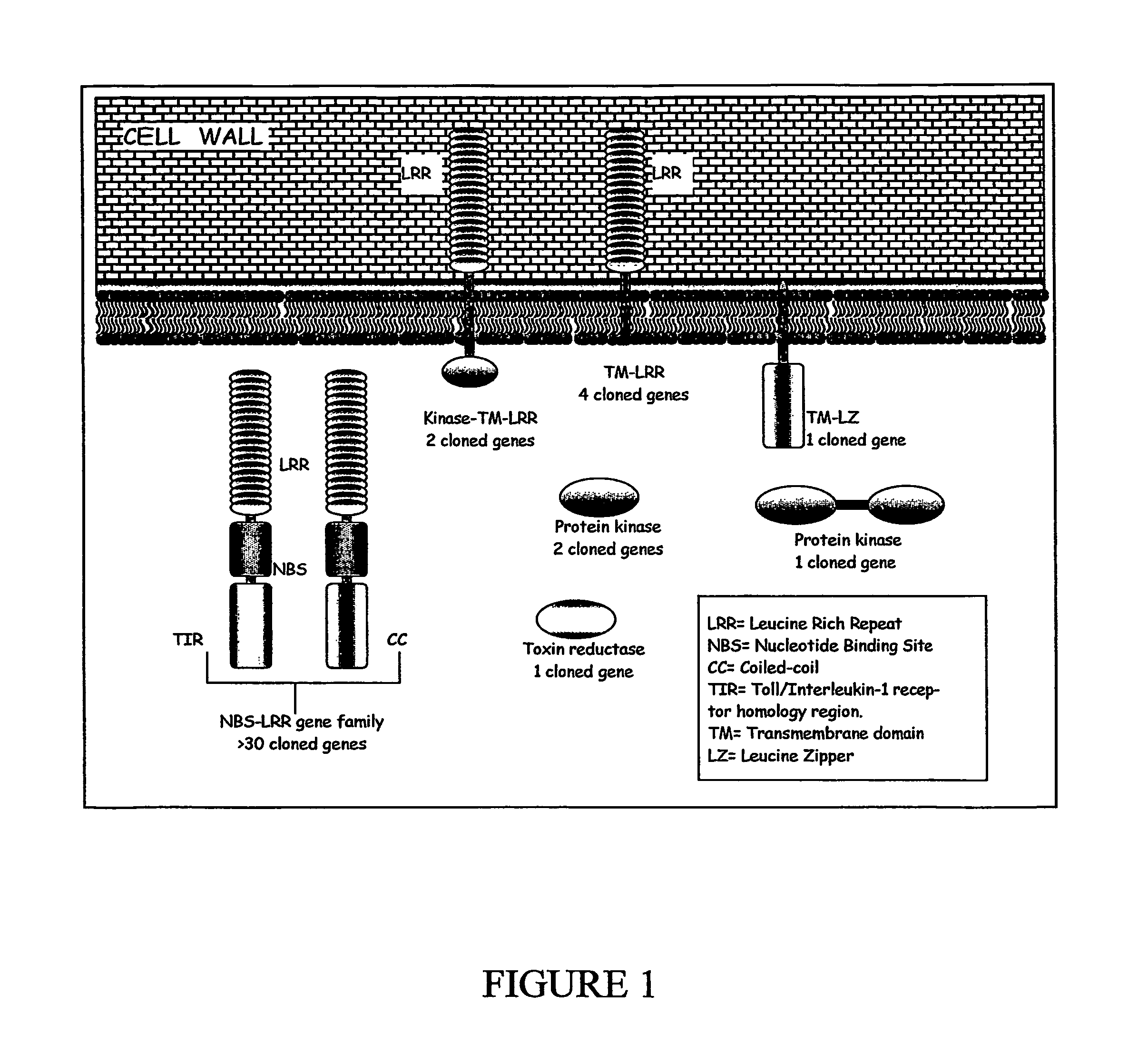
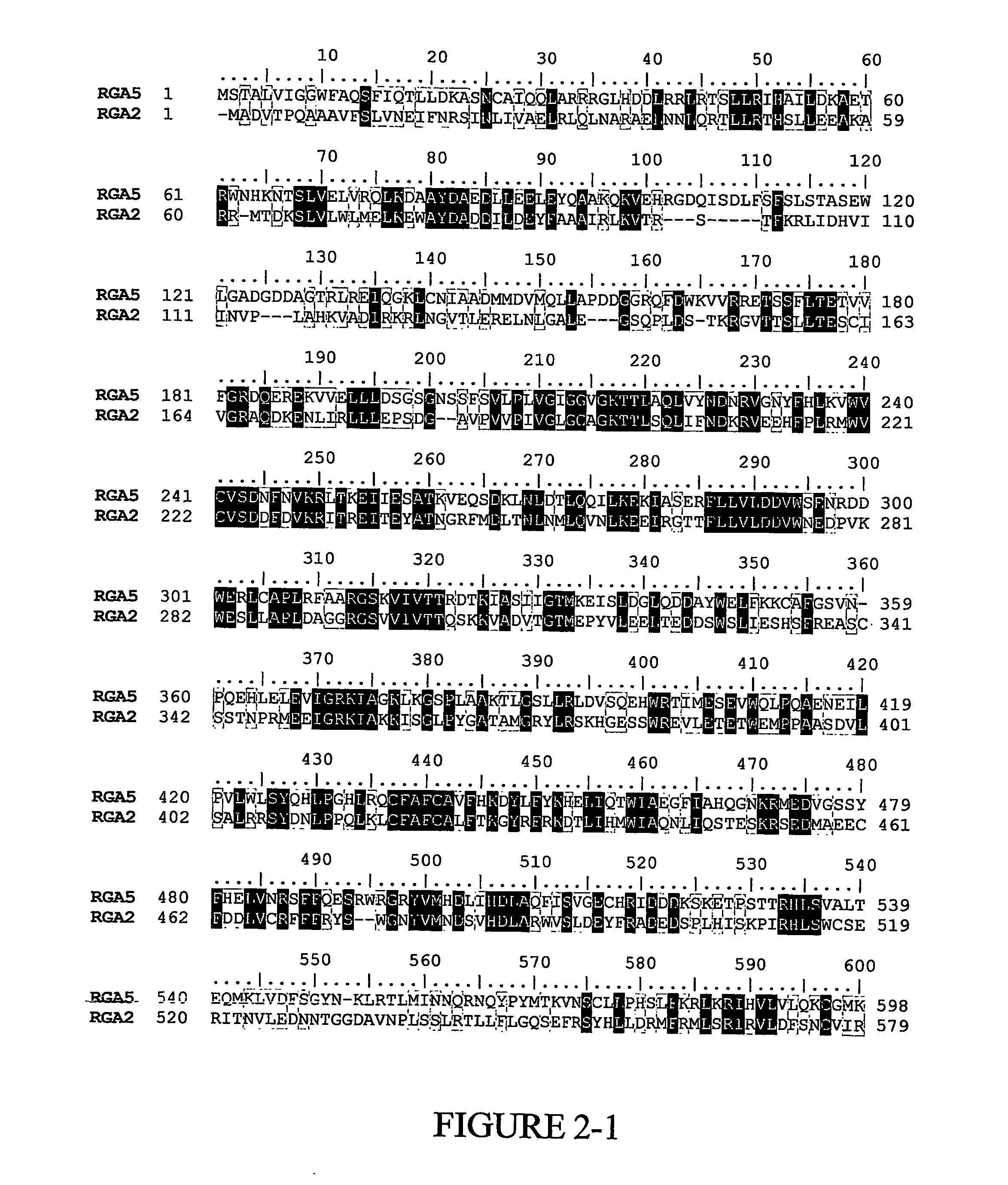
Banana Resistance Genes And Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20070204368A1Low and medium and high stringencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBanana PlantFungal microorganisms
The present invention relates to pathogenic resistance. More particularly the present invention relates to polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences involved in the resistance mechanism of banana plants to fungal pathogens particularly, the soil born Fusarium fungi. Two banana resistance genes, RGA5 and RGA2 are isolated and characterised. The invention also relates to the use of these sequences for modulating plant resistance and for producing genetically modified plants having modified pathogen resistance characteristics.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
Pathogen resistant citrus compositions, organisms, systems, and methods
The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to pathogen resistant citrus compositions, organisms, systems, and methods. For example, a composition may comprise a peptide (e.g., a defensin peptide) and / or a nucleic acid (e.g., a defensin nucleic acid). A pathogen resistant citrus plant may comprise, in some embodiments, a defensin peptide and / or an expressable nucleic acid encoding a defensin peptide.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for improving growth and/or pathogen resistance of a plant using transient high-intensity illumination
InactiveUS9131645B2Induce dormancyAccelerated deathSaving energy measuresHorticulture methodsHigh intensitySquare meter
A method of improving the growth and / or pathogen resistance of a plant, comprising the step of exposing at least part of the plant to a transient period of high intensity illumination providing a photon flux at the plant surface having at least one of the following characteristics: (a) a red photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square meter per second, and having a wavelength of between 600 and 700 nm; (b) a blue photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square meter per second, having a wavelength of between 420 and 480 nm. The Invention also provides apparatus for providing such conditions to growing plants.
Owner:KARPINSKI STANISLAW +1
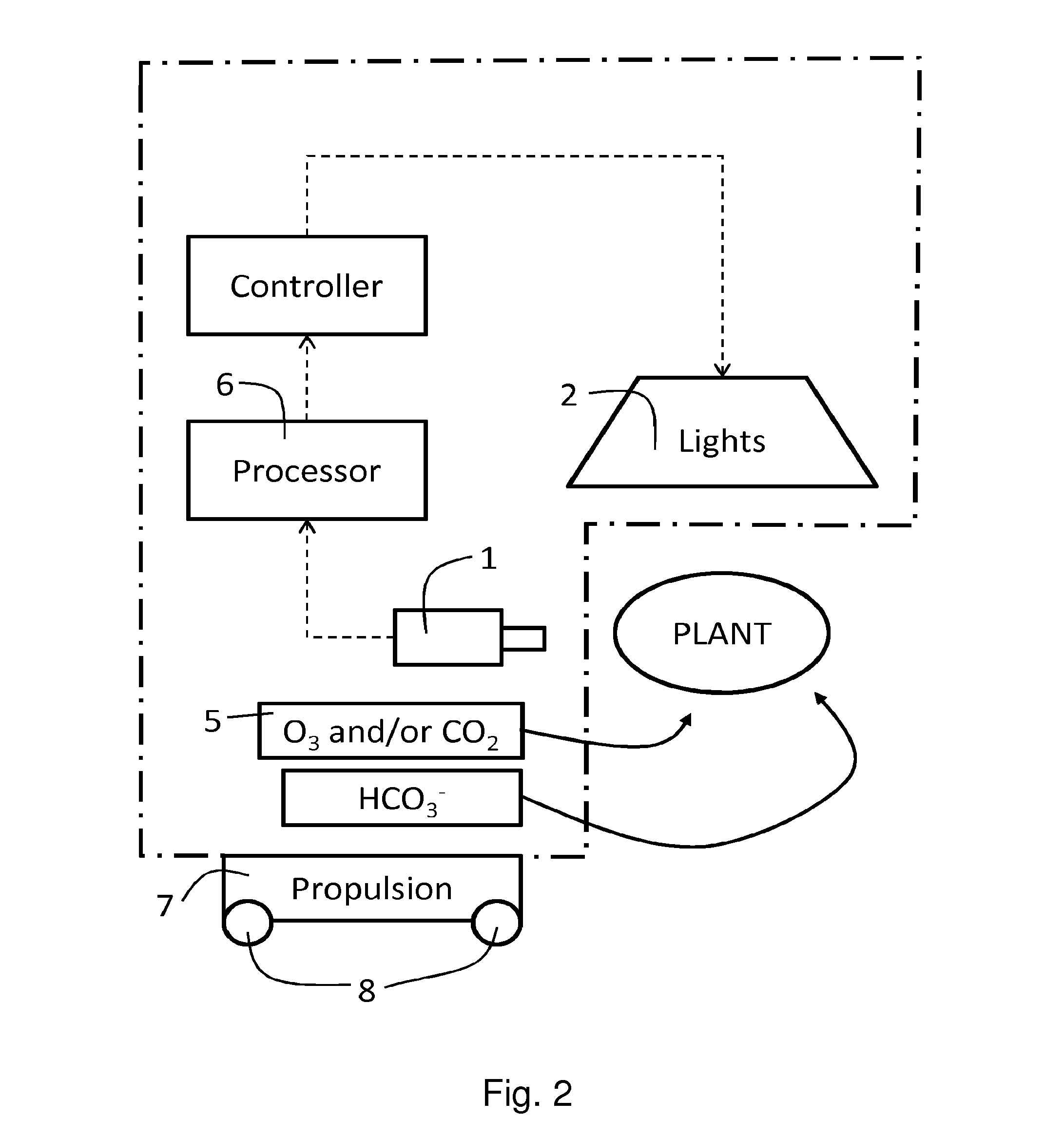
Water that expresses pathogen-resistance genes (pr gene clusters) to encode plant immunoproteins, a method of preventing plant diseases using the water, and a device for producing the water
InactiveUS20110212185A1Induce expressionReduced responseBiocideInorganic active ingredientsDiseaseResistant genes
Disclosed is a method of preventing diseases in plants which can bring about a redox reaction in the inside of plant cells thus inducing the expression of pathogen-resistance genes in the plant cells. There is no possibility that residual contents remain in soils. It is also possible to cultivate plants which are strong against diseases. By bringing water which contains reactive oxygen species and allows the reactive oxygen species to be held and to function for a long period into contact with plants, the expression of the pathogen-resistance genes which the plants possess is induced. Accordingly, the water containing reactive oxygen is absorbed into the plants to prevent diseases in plants.
Owner:K2R
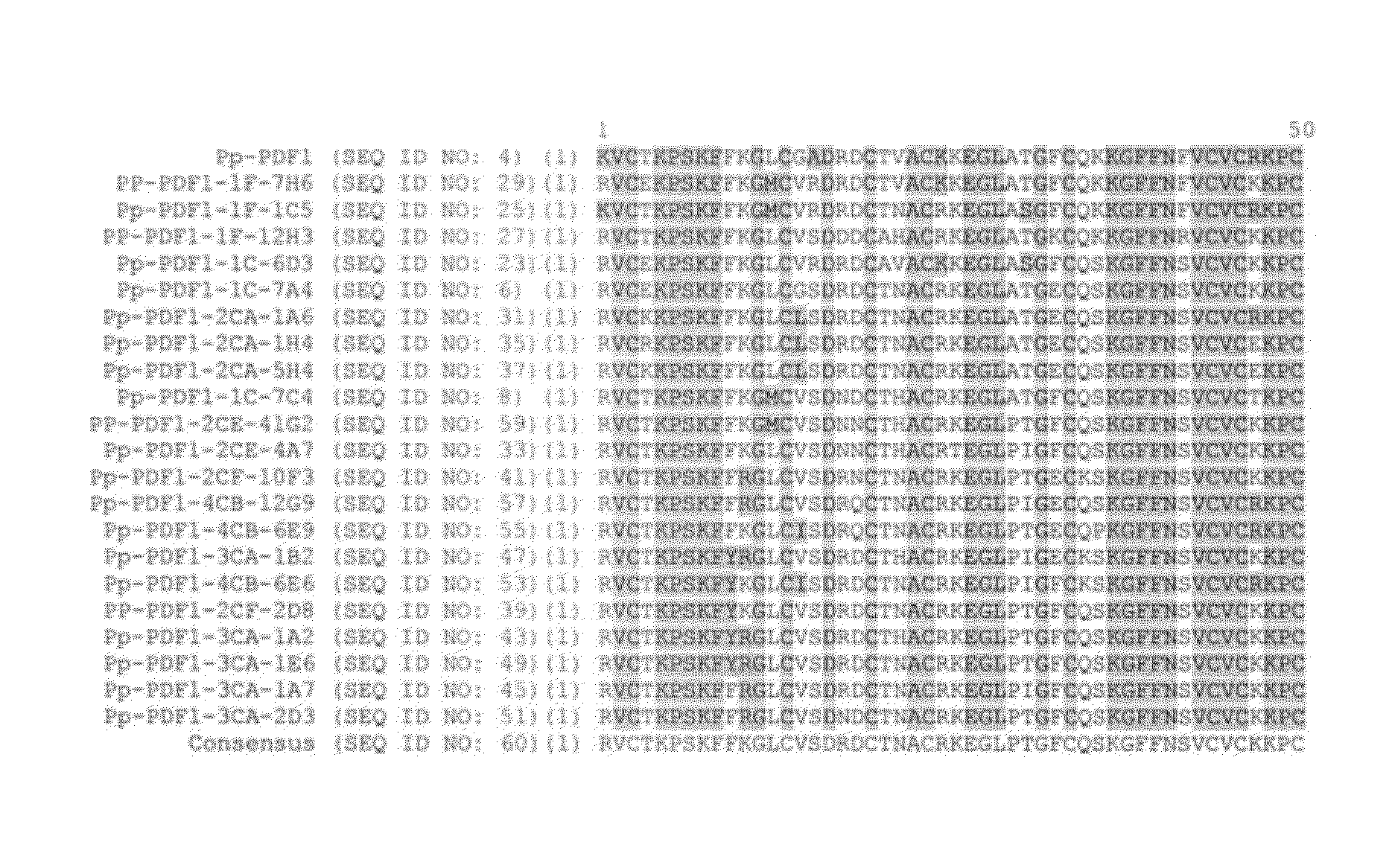
Defensin variants and methods of use
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
Bactericidal composition containing prothioconazole and tebuconazole and application thereof
InactiveCN104642331AOvercoming and delaying drug resistanceExpand the spectrum of prevention and treatmentBiocideFungicidesFungal diseaseFruit tree
The invention discloses a bactericidal composition containing prothioconazole and tebuconazole and application thereof. The bactericidal composition uses prothioconazole and tebuconazole as the main effective components. The insecticidal composition can be applied to control of diseases of cereal, fruit trees and vegetables, has high synergetic effects and overcomes and delays pathogen resistance; and the bactericidal composition has the advantages of high insecticidal speed, long effective period, reduced application cost and control effect obvious better than that of single dose usage. The insecticidal composition can be used for control of fungal diseases on crops, in particular for control of powdery mildew, sheath blight, wilt, leaf spot, rust, stalk break, net blotch, scald, botrytis, black spot, brown blotch, black shank and smut, and has better effect than single dose usage.
Owner:NANJING HUAZHOU PHARMA
Pathogen-resistant coatings
InactiveUS20080171803A1Low costEffectively “ hardens ”Alkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCatalyst protectionSinglet oxygenAmbient air
A pathogen-resistant coating comprising one or more photocatalysts capable of generating singlet oxygen from ambient air. The pathogen-resistant coating may optionally include one or more singlet oxygen traps.
Owner:LOMBARDI JOHN L
Method for artificially culturing Chinese medicinal plant of Chinese pulsatilla root
InactiveCN101702981AImprove germination rateRegular artificial cultivation operationsSeed and root treatmentHorticultureMedicinal herbsToxic material
The invention belongs to a culture technique of Chinese medical plants, relating to a method for artificially culturing Chinese medicinal plant of Chinese pulsatilla root. The Chinese pulsatilla root is commonly used traditional Chinese medicine, and has the functions of antibiosis, pathogen resistance, dampness elimination, insect control, body immunity enhancement, cancer resistance, anti-inflammatory, poison resistance, heat and toxic material clearing, blood cooling and diarrhea stopping, calmness, pain relieving, endotoxemia resistance and the like. Currently, Chinese medicinal plants of Chinese pulsatilla root all around the world grow widely; the artificially cultured Chinese medicinal plant of Chinese pulsatilla root in the invention comprises the techniques such as seed cold storage, gibberellin seed soaking, wet sand pregermination, seeding and field management, and Chinese medical plant harvest. The invention has the advantages that the artificial culturing technique of Chinese pulsatilla root is integral; the culturing measurement is simple, practical and reliable, the rate of germination is improved, and the saponin content of Chinese pulsatilla root is ensured, thereby improving medicinal material therapy.
Owner:时维静
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com