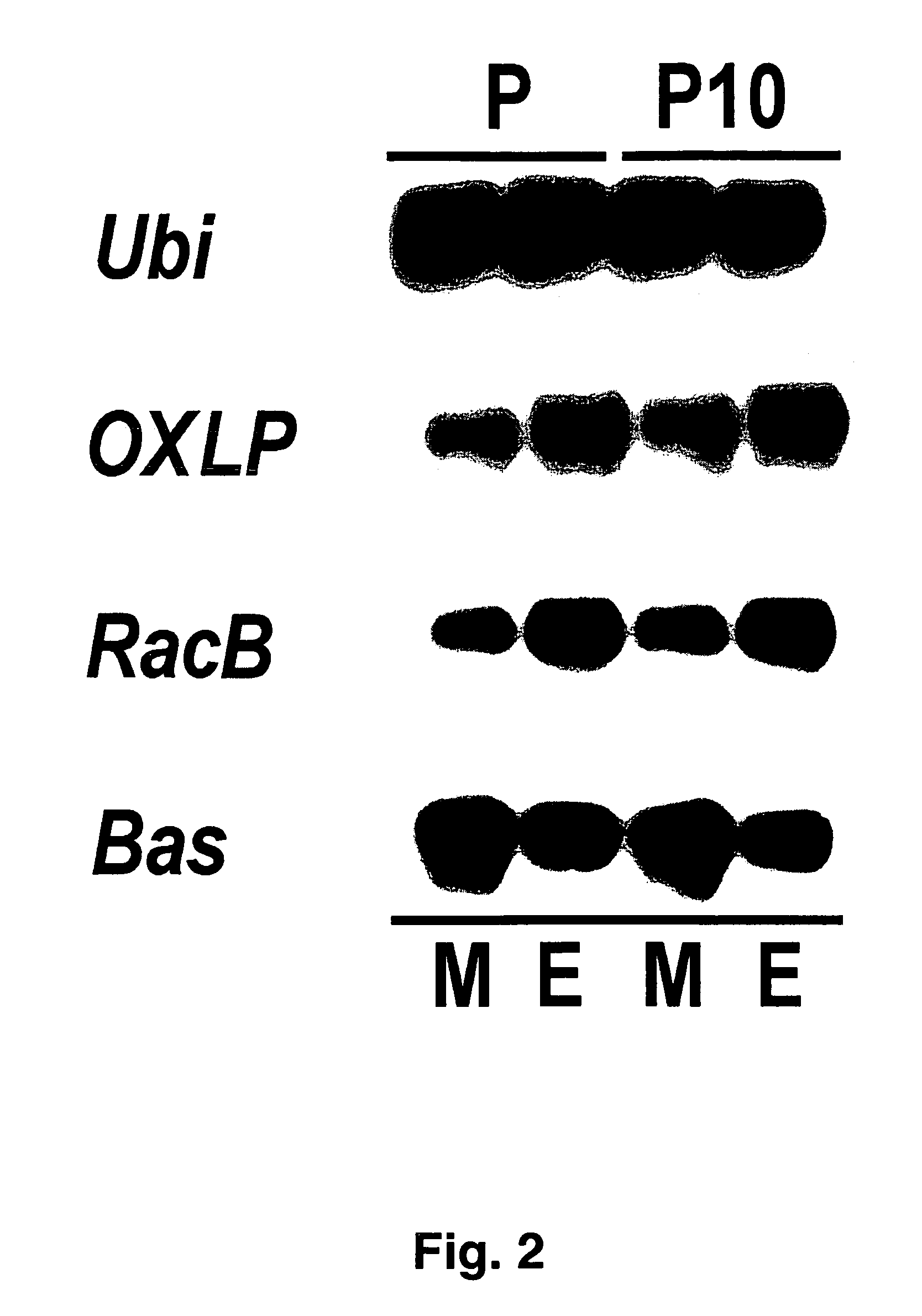Patents
Literature
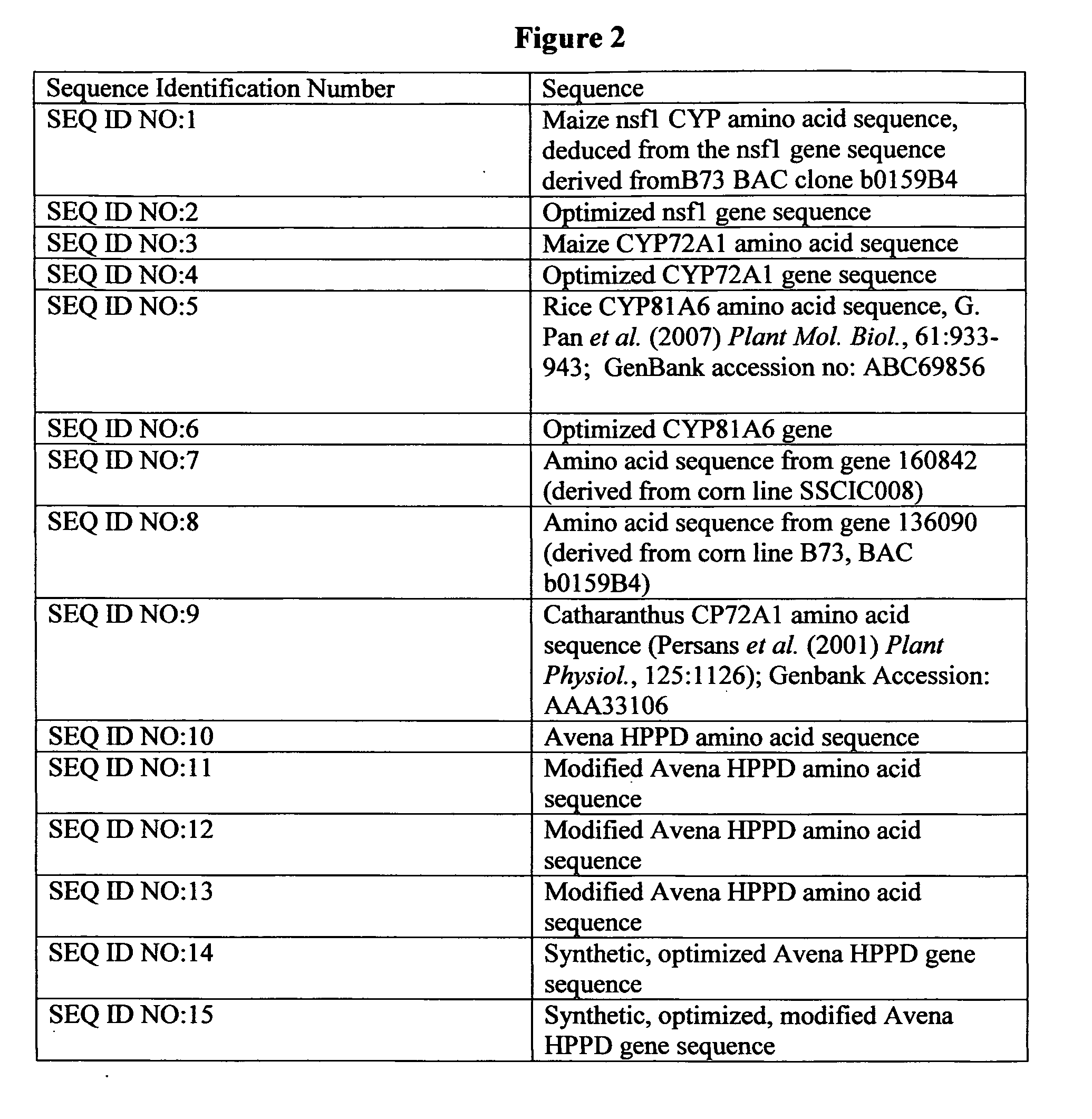
157results about How to "Confer resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
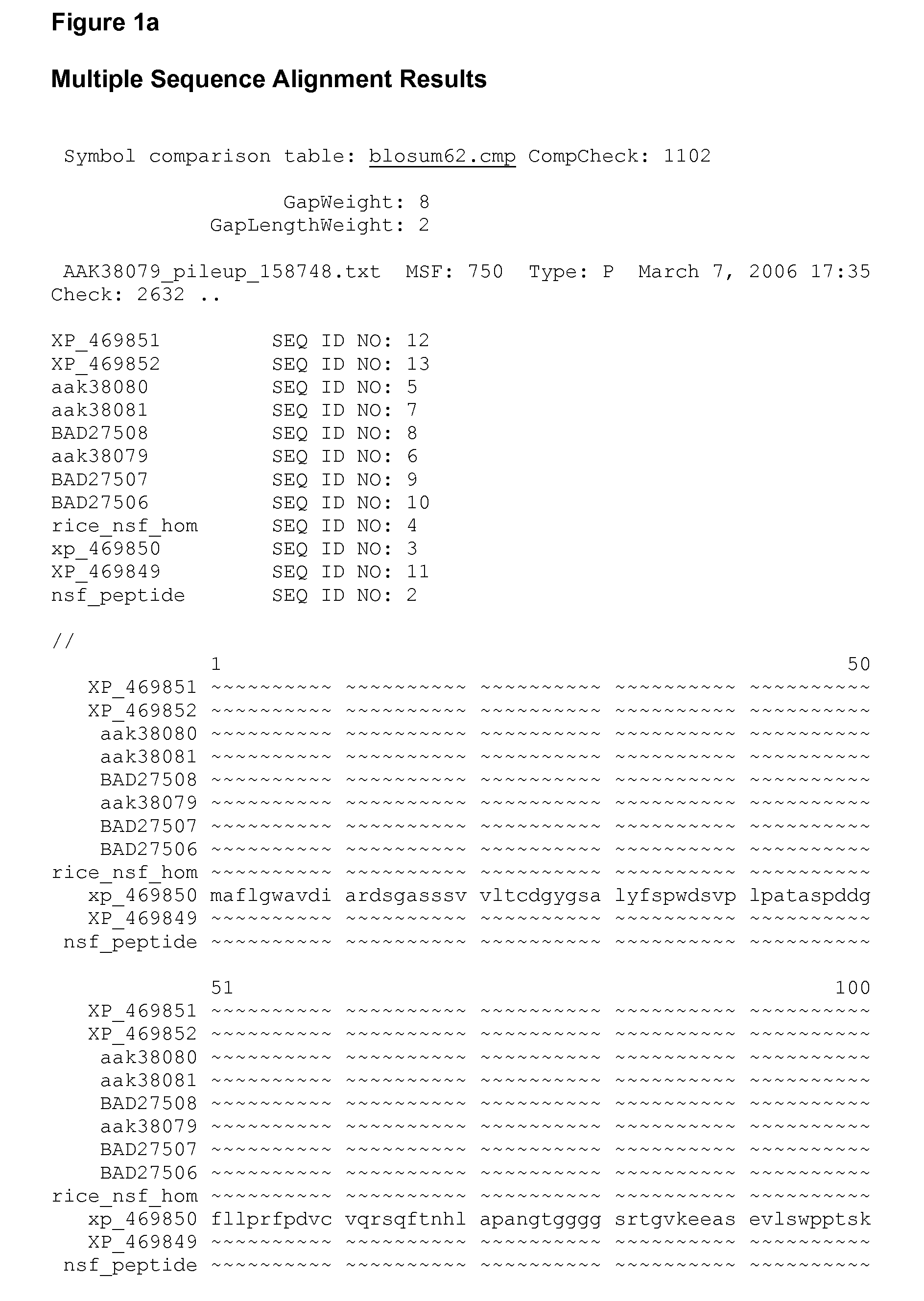
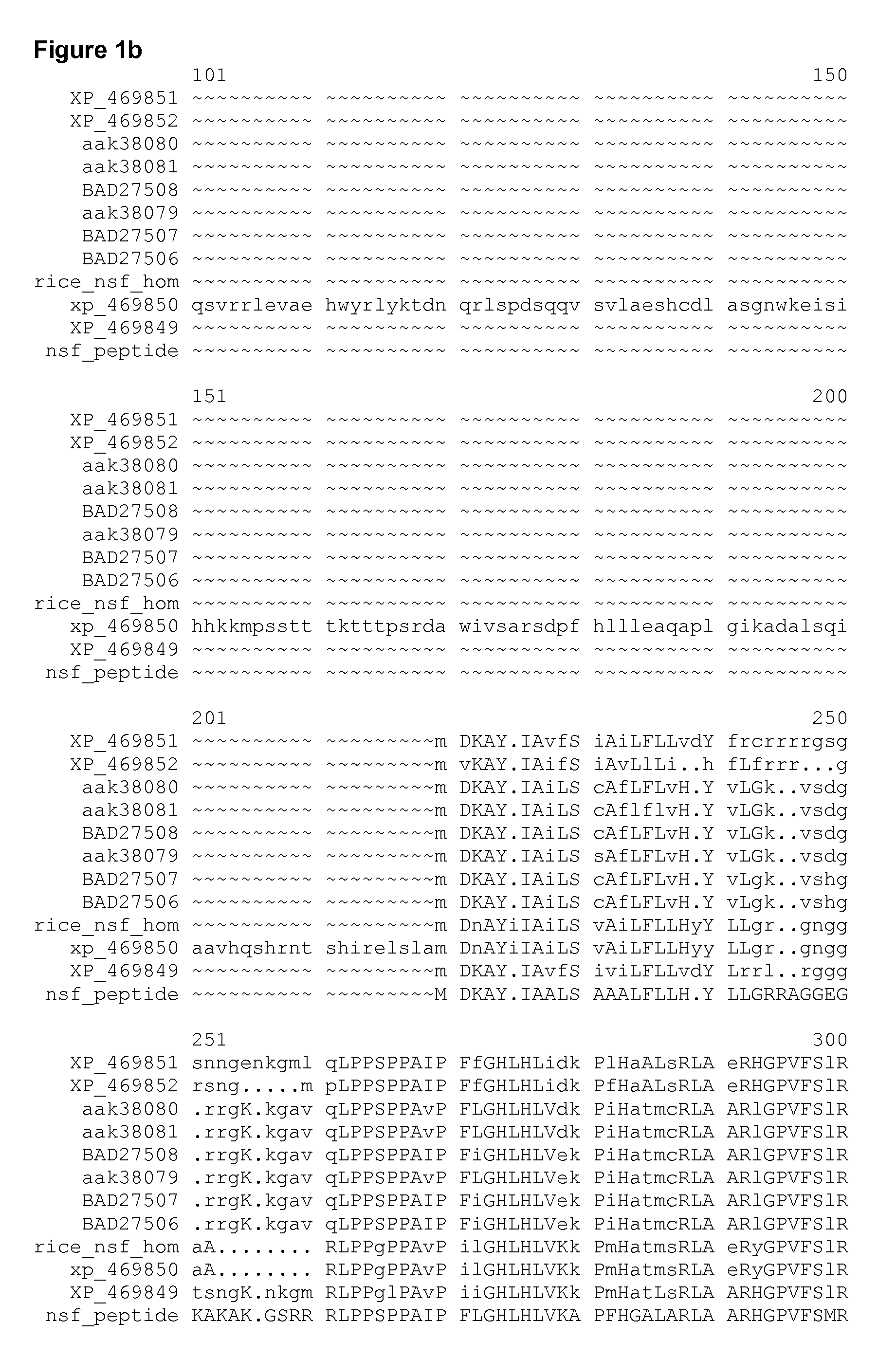
Axmi-031, axmi-039, axmi-040 and axmi-049, a family of novel delta endotoxin genes and methods for their use
ActiveUS20070294787A1Confer resistanceProduct can be usedBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a delta-endotoxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated delta-endotoxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed, and antibodies specifically binding to those amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, or 38, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, or 37, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Methods and compositions for improved enzyme activity in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20070289031A1Increase enzyme activityConfer resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant cell
Compositions and methods for increasing enzyme activity across a broad physiological spectrum in plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include plants or plant parts comprising two or more polynucleotides encoding polypeptides that are active across a broader physiological spectrum than when either polynucleotide is expressed alone. Vectors comprising these polynucleotide molecules as well as host cells comprising the vectors are further provided. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In addition, methods are provided for producing the plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds of the invention. Methods for increasing plant yield and methods for conferring resistance to an herbicide in a plant are further provided.
Owner:ATHENIX
Peptides and peptidomimetics with structural similarity to human P53 that activate P53 function
InactiveUS6245886B1Improve the immunityLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsP53 proteinWild typeP53 Mutation
The present invention provides peptides and peptidomimetics corresponding to part or to the entirety of the region encompassed by residues 360-386 of human p53, said peptides and peptidomimetics characterized by the ability to activate DNA binding of wild-type p53 and to select tumor-derived p53 mutants. Pharmaceutical compositions of the compounds of the invention and methods of using these compositions therapeutically are also provided.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
Methods and compositions for controlling plant pests
InactiveUS20100226951A1Confer resistanceProduct can be usedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibodyNucleic acid molecule
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a delta-endotoxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated delta-endotoxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed, and antibodies specifically binding to those amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:13-24, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1-12 and 25-44, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
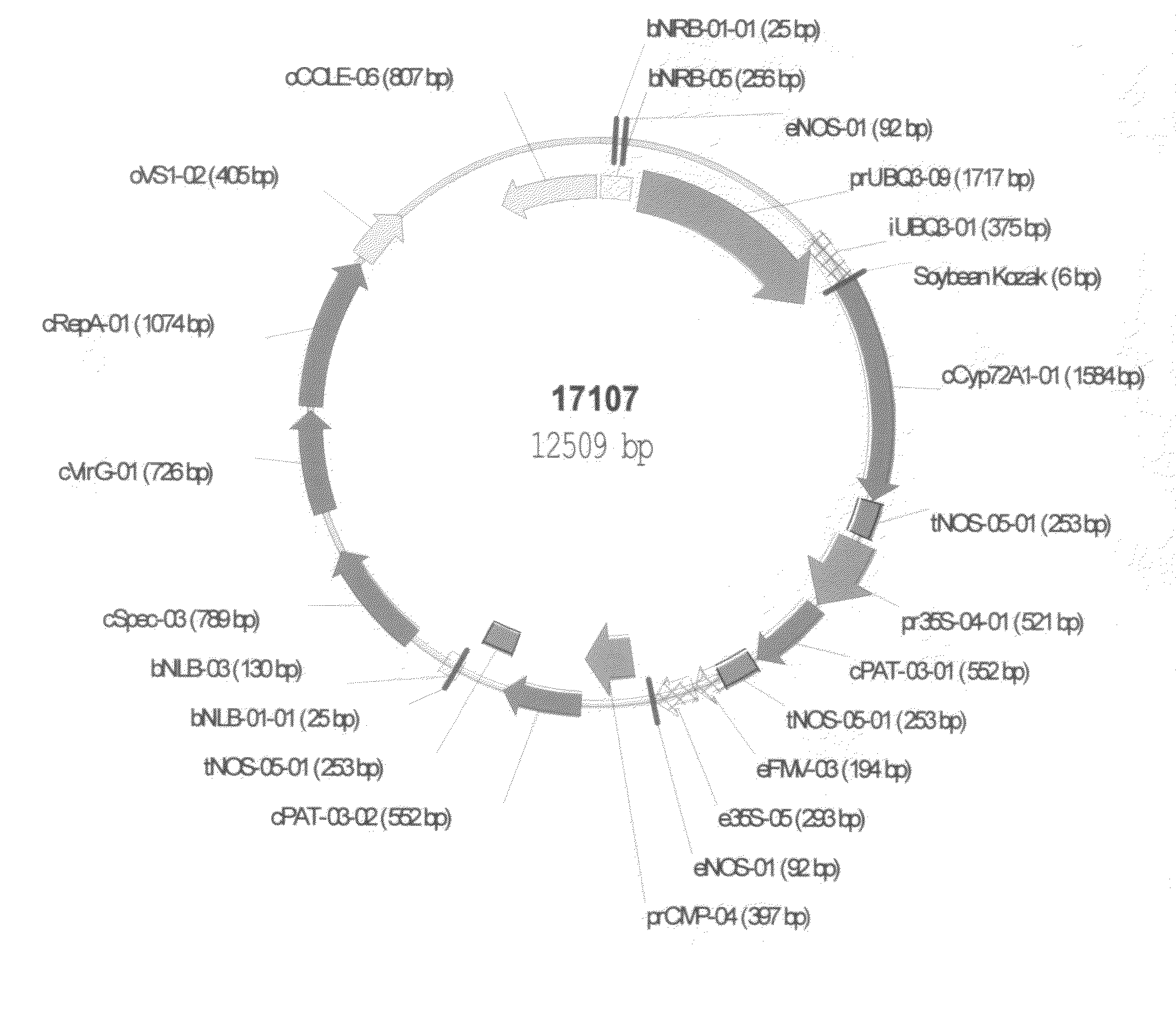
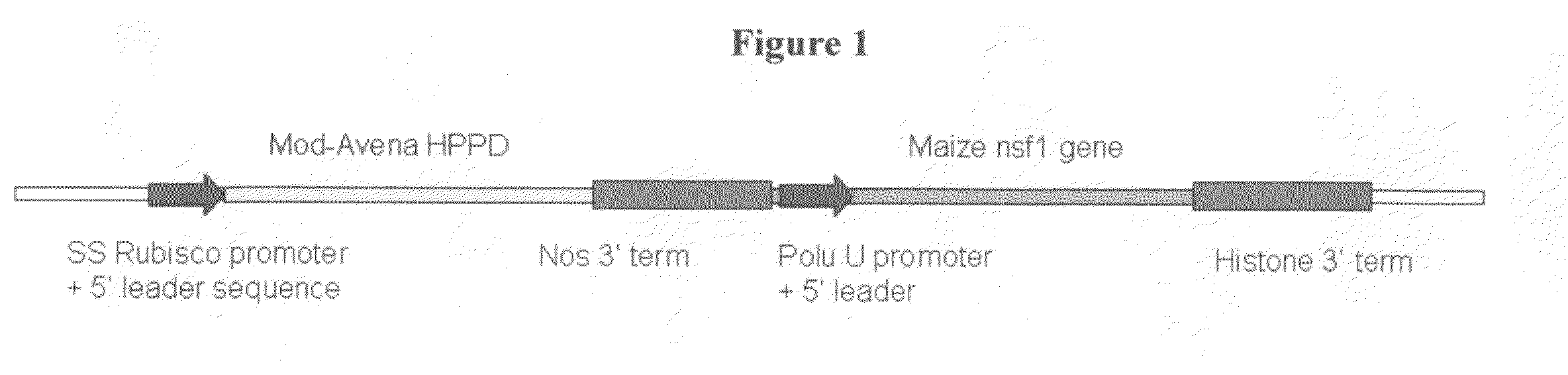
Polynucleotide encoding a maize herbicide resistance gene and methods for use
InactiveUS20070214515A1Confer resistanceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotidePolynucleotide
This invention relates to polynucleotide sequences encoding a gene that can confer resistance to at least one herbicide. It further relates to plants and seeds of plants carrying chimeric genes comprising said polynucleotide sequences, which enhance or confer resistance to at least one herbicide, and methods of making said plants and seeds. The invention further presents sequences that can be used as molecular markers that in turn can be used to identify the region of interest in corn lines resulting from new crosses and to quickly and efficiently select the best lines for breeding strategies by avoiding sensitive lines.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Cytochrome P450 genes conferring herbicide resistance
ActiveUS20090011936A1Without damageReduce residue levelsBiocideOther foreign material introduction processesGMO PlantsBiology
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include transgenic plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds that have been transformed with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a cytochrome P450 or variant thereof that confers herbicide resistance or tolerance, alone or in combination with one or more additional nucleic acid molecules encoding polypeptides that confer desirable traits. In particular, the cytochrome P450 or variant thereof confers resistance or tolerance to HPPD inhibitors, benzothiadiazinones, sulfonylureas, and other classes of herbicides. The additional polypeptide may also confer resistance or tolerance to an herbicide, including HPPD inhibitors and other herbicides. Methods are also provided for the production and use of the herbicide resistant or tolerant plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds of the invention.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Human regulatory molecules
The invention provides human regulatory molecules and polynucleotides (collectively designated HRM) which identify and encode them. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, agonists, antibodies and antagonists. The invention further provides methods for diagnosing, preventing, and treating disorders associated with expression of human regulatory molecules.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
AXMI-192 Family of Pesticidal Genes and Methods for Their Use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a toxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated toxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed, and antibodies specifically binding to those amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:28-62, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1-27, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Extracellular adhesive proteins
InactiveUS20010010913A1High viscosityHighly concentrated solutionAntibacterial agentsFungiExtracellularAgonist
The invention provides human extracellular adhesive proteins (EXADH) and polynucleotides which identify and encode EXADH. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating or preventing disorders associated with expression of EXADH.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Polynucleotides and polypeptides derived from corn tassel
InactiveUS20010051335A1Desirable propertyLong half-lifeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesNucleotideTassel
The present invention provides purified, corn tassel-derived polynucleotides (cdps) which encode corn tassel-derived polypeptides (CDPs). The invention also provides for the use of cdps or their complements, oligonucleotides, or fragments in methods for determining altered gene expression, to recover regulatory elements, and to follow inheritance of desirable characteristics through hybrid breeding programs. The invention further provides for vectors and host cells containing cdps for the expression of CDPs. The invention additionally provides for (i) use of isolated and purified CDPs to induce antibodies and to screen libraries of compounds and (ii) use of anti-CDP antibodies in diagnostic assays.
Owner:INCYTE +1
Transgenic plants containing ligninase and cellulase which degrade lignin and cellulose to fermentable sugars
InactiveUS7049485B2Stress resistantConfer resistanceBiofuelsOther foreign material introduction processesLignin-modifying enzymeFermentable sugar
The present invention provides transgenic plants which after harvest degrade the lignin and cellulose therein to fermentable sugars which can further be fermented to ethanol or other products. In particular, the transgenic plants comprise ligninase and cellulase genes from microbes operably linked to a DNA encoding a signal peptide which targets the fusion polypeptide produced therefrom to an organelle of the plant, in particular the chloroplasts. When the transgenic plants are harvested, the plants are ground to release the ligninase and cellulase which then degrade the lignin and cellulose of the transgenic plants to produce the fermentable sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Extracellular signaling molecules
InactiveUS20020187523A1Efficiently translatedImprove expression efficiencyFungiBacteriaENCODEAntibody
The invention provides human extracellular signaling molecules (EXCS) and polynucleotides which identify and encode EXCS. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with expression of EXCS.
Owner:INCYTE
Pesticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS20100298207A1Confer resistanceProduct can be usedAntibacterial agentsBiocideDNA constructNucleotide
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a toxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated toxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed, and antibodies specifically binding to those amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:50-96, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1-47, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
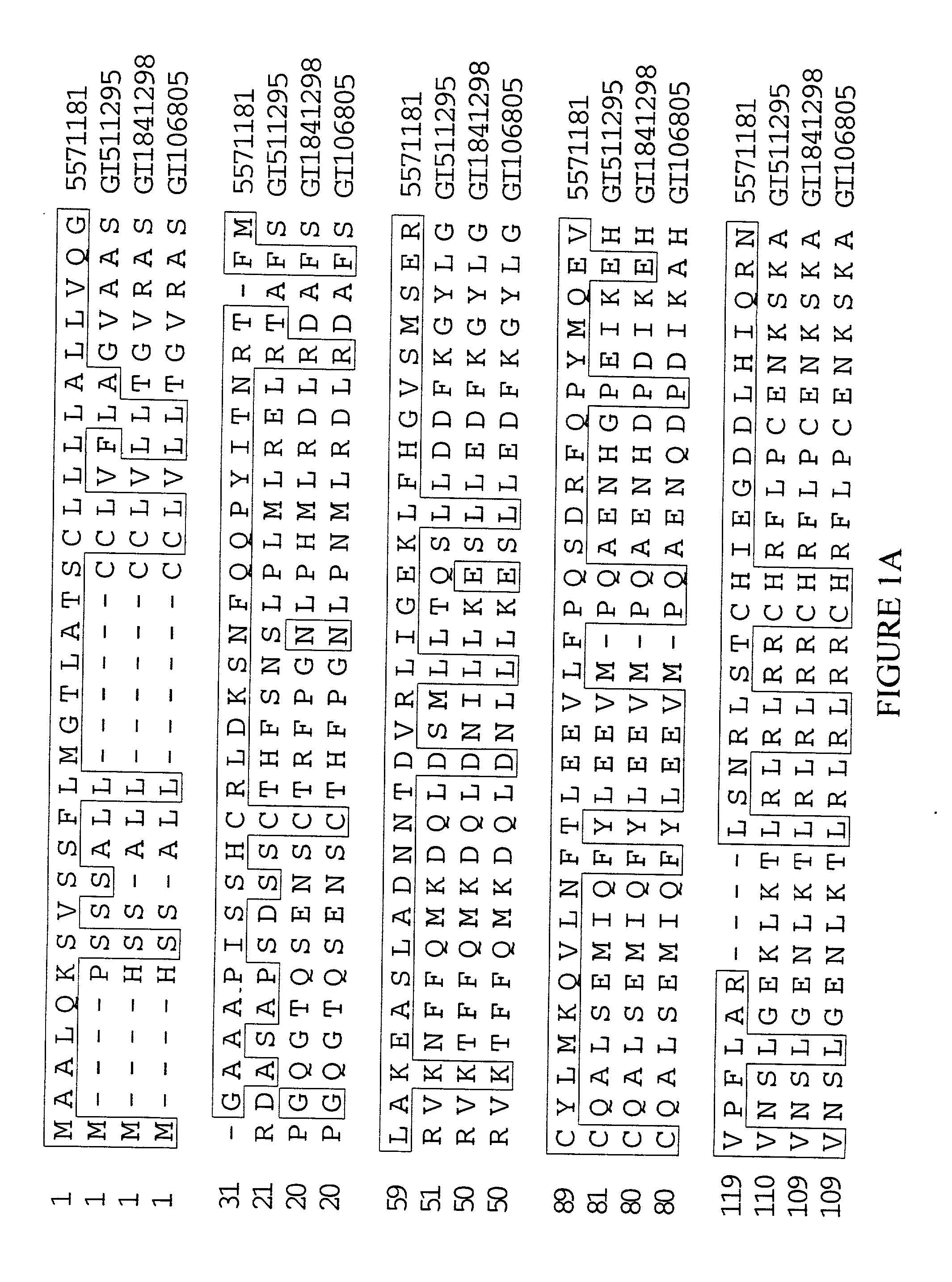
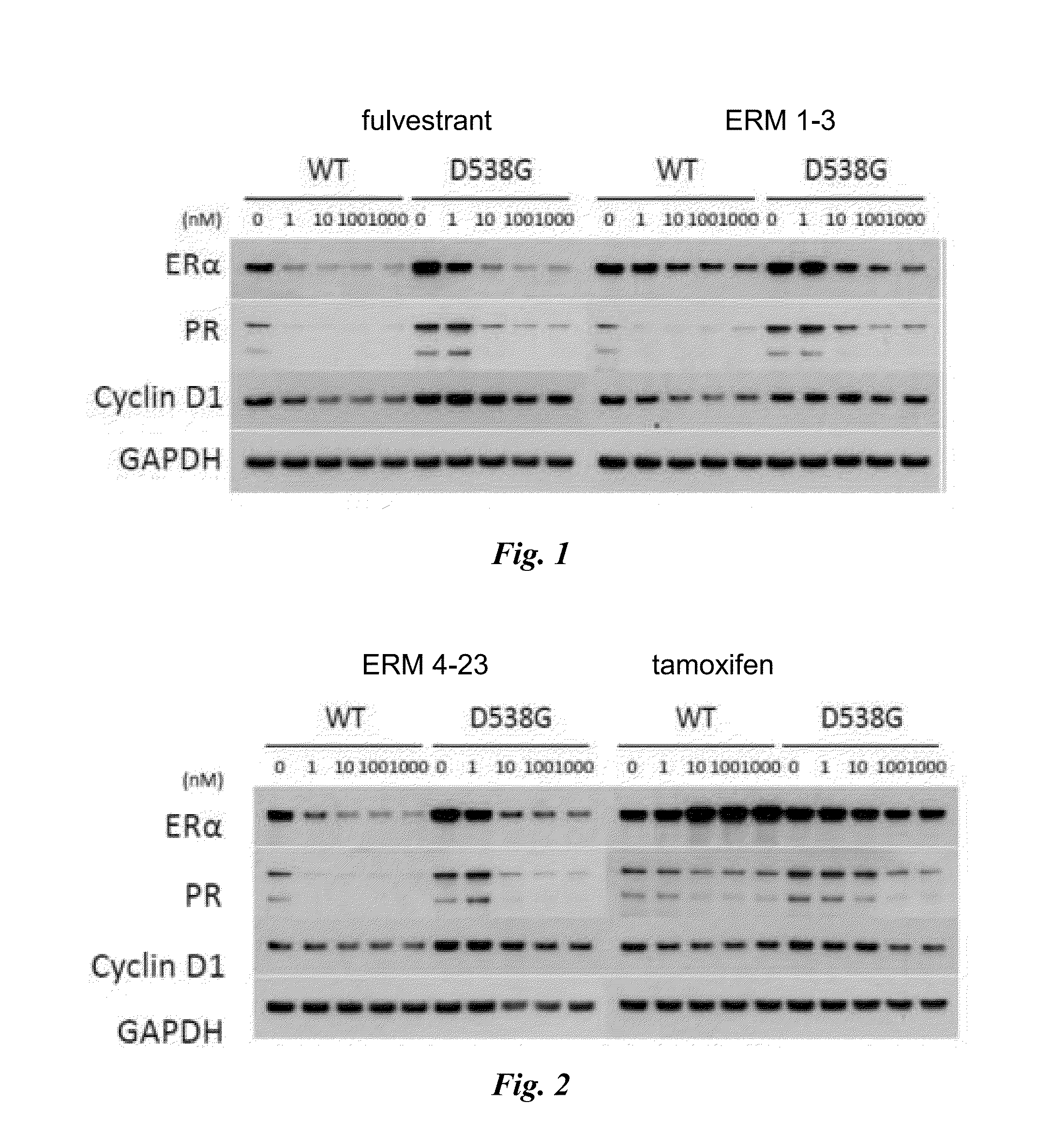
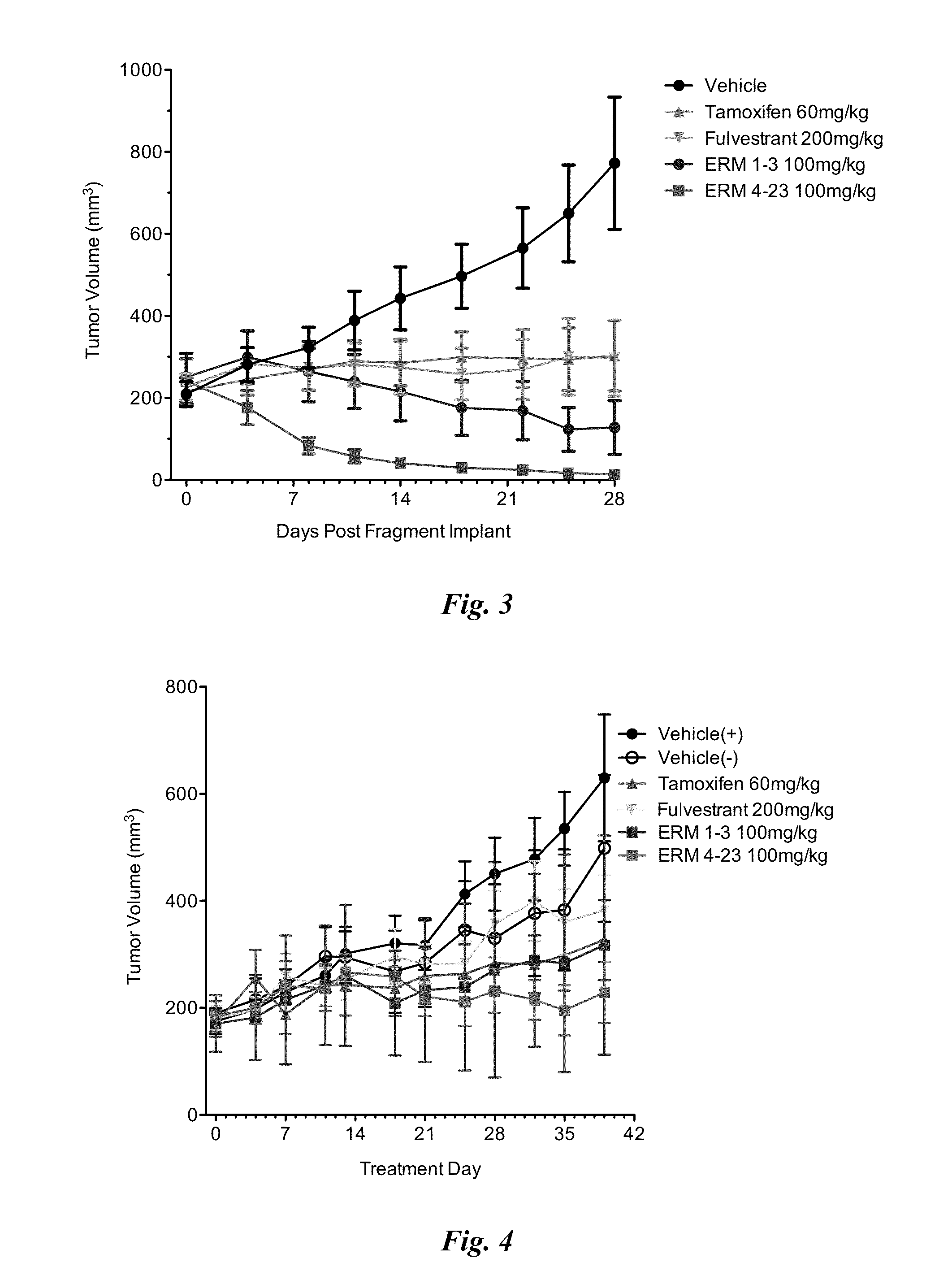
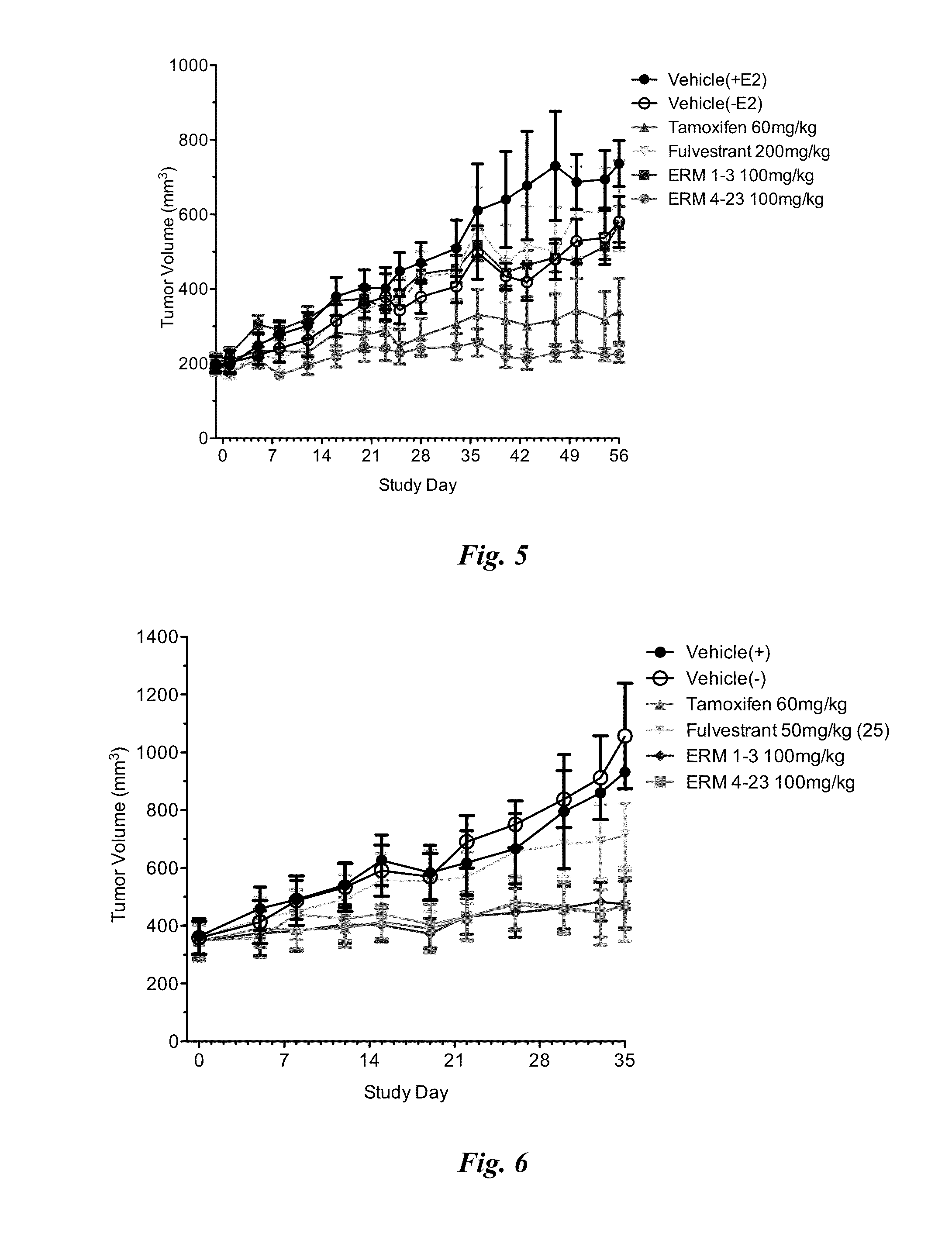
Methods and compositions for modulating estrogen receptor mutants
InactiveUS20150258099A1Altered interactionImprove treatment outcomesBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEstrogen receptor modulator
Described herein are methods and compositions for treating an ER-related disease condition characterized by a mutation in the ESR1 gene by administering an estrogen receptor modulator. Also described herein are methods of treating hormone resistant-estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancers characterized by a mutation in the ESR1 gene by administering an estrogen receptor modulator.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Plastid transformation in Arabidopsis thaliana
InactiveUS6376744B1High expressionImprove stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyEtioplasts
The invention provides methods and compositions for obtaining transplastomic Arabidopsis plants. Specifically, the method provides culturing protocols and compositions that facilitate the regeneration of transformed plants following delivery of exogenous DNA molecules.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
AXMI-028 and AXMI-029, a family of novel delta-endotoxin genes and methods for their use
InactiveUS20070044178A1Confer resistanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid moleculeBacteria
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a delta-endotoxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated delta-endotoxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, 15, 17, or 19, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 14, 16, or 18, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Human immune system associated molecules
InactiveUS6135941AConfer resistanceAvoid the needSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsAgonistPolynucleotide
The invention provides human immune system associated proteins (HISAP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode HISAP. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for treating or preventing disorders associated with expression of HISAP.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Human eosinophil-derived basic protein
The present invention provides a human eosinophil-derived basic protein (EBPH) and polynucleotides which identify and encode EBPH. The invention also provides genetically engineered expression vectors and host cells comprising the nucleic acid sequences encoding EBPH and a method for producing EBPH. The invention also provides for use of EBPH and agonists, antibodies or antagonists specifically binding EBPH, in the prevention and treatment of diseases associated with expression of EBPH. Additionally, the invention provides for the use of antisense molecules to polynucleotides encoding EBPH for the treatment of diseases associated with the expression of EBPH. The invention also provides diagnostic assays which utilize the polynucleotide, or fragments or the complement thereof, and antibodies specifically binding EBPH.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
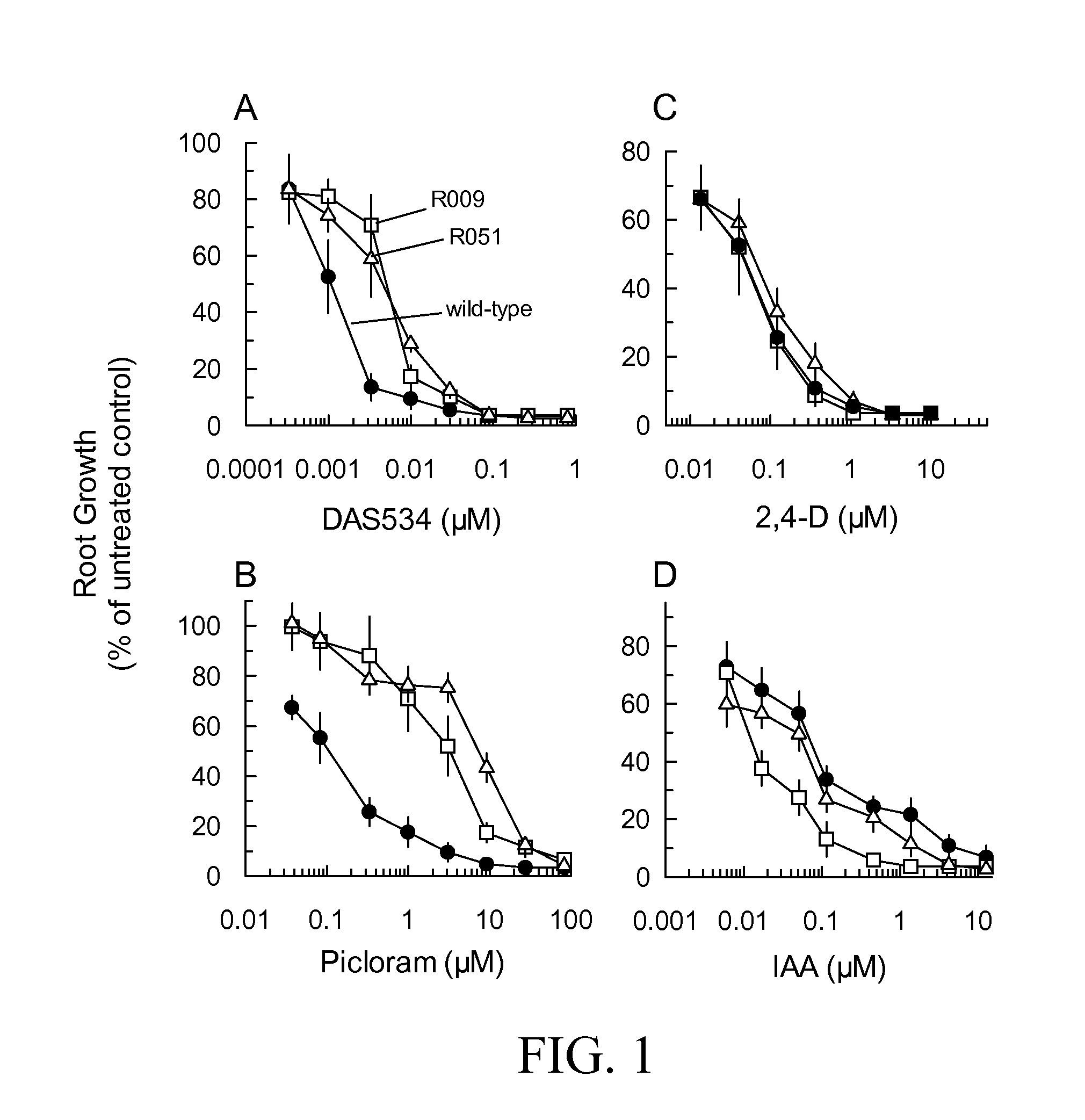
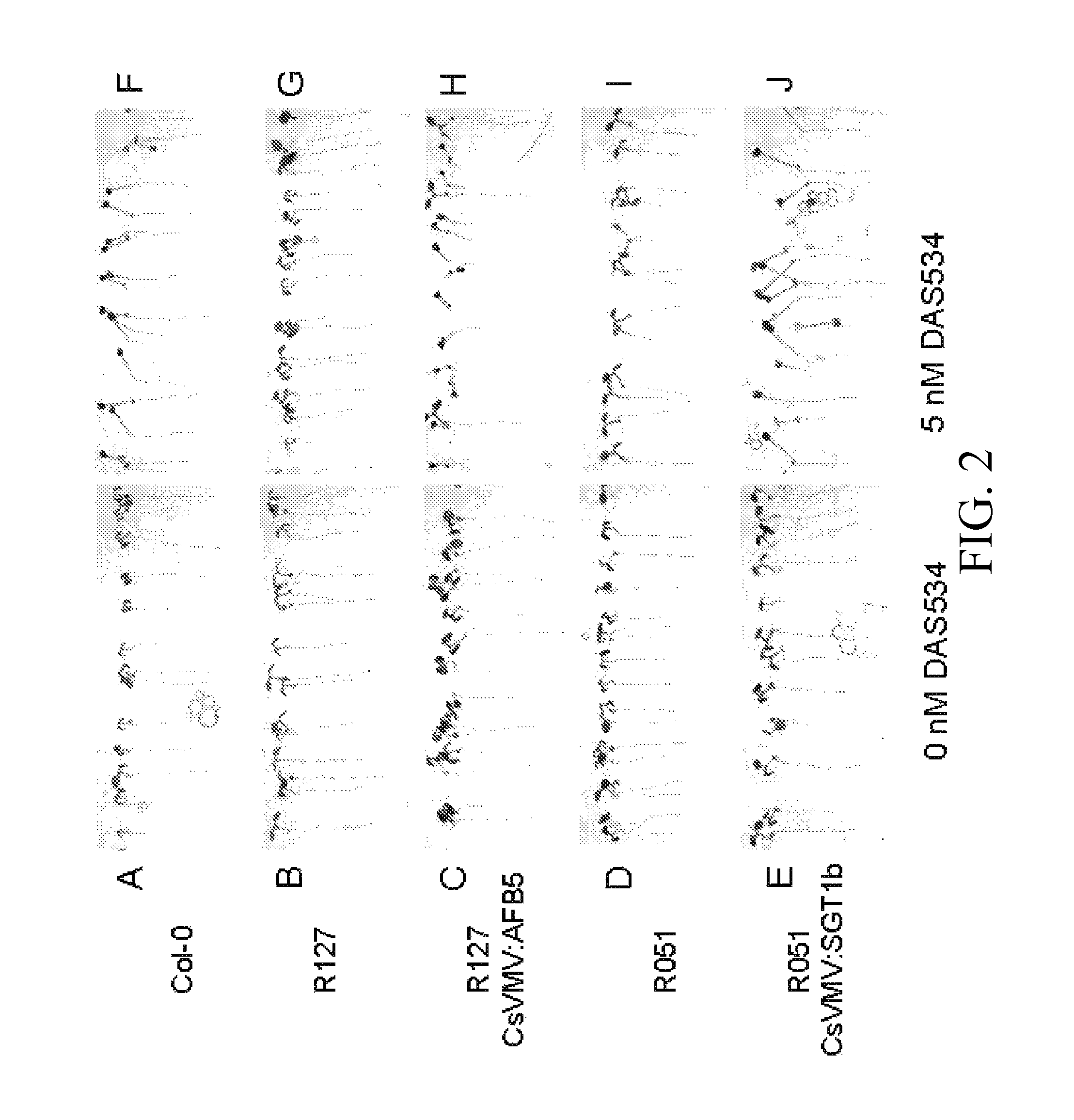
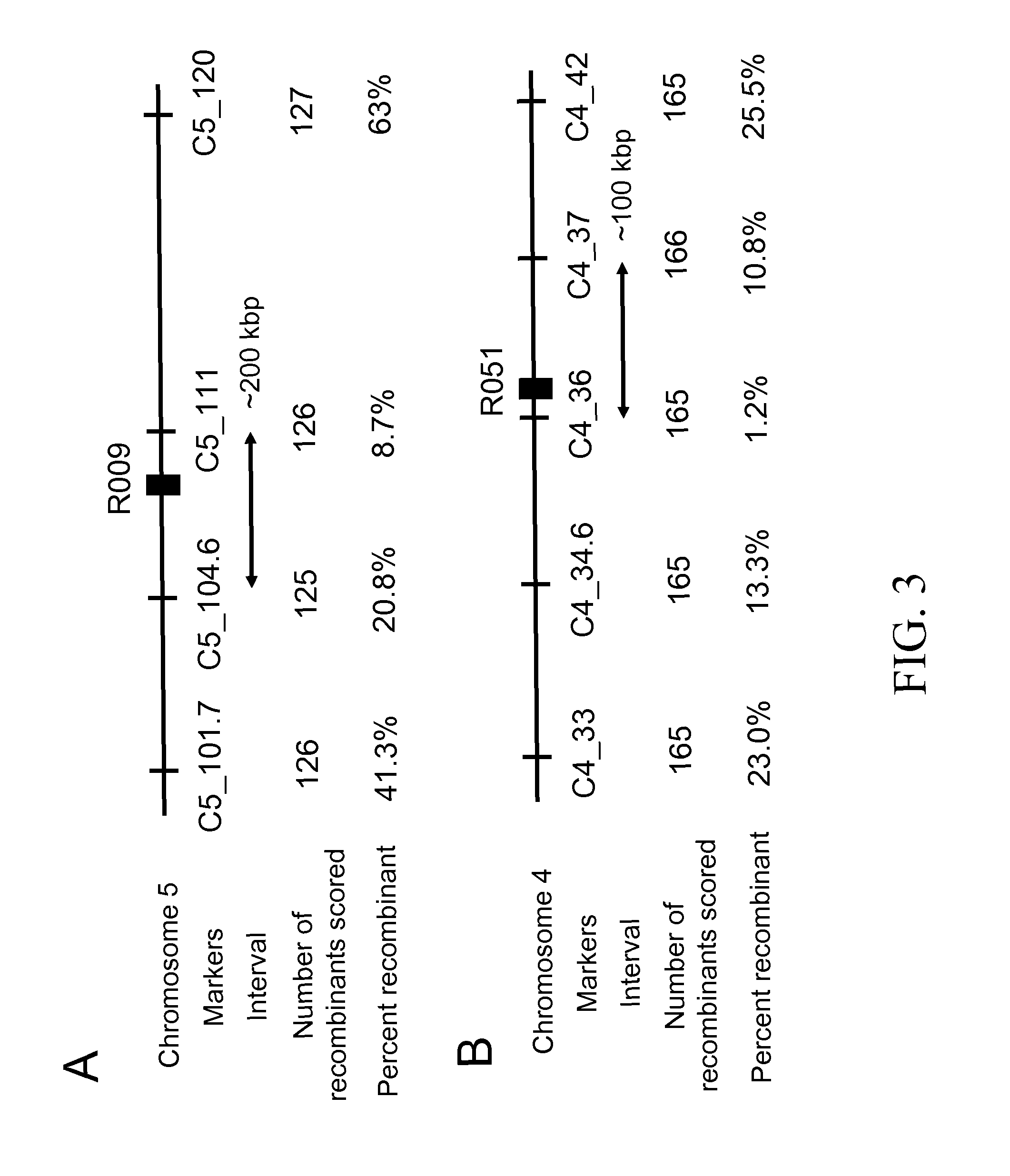
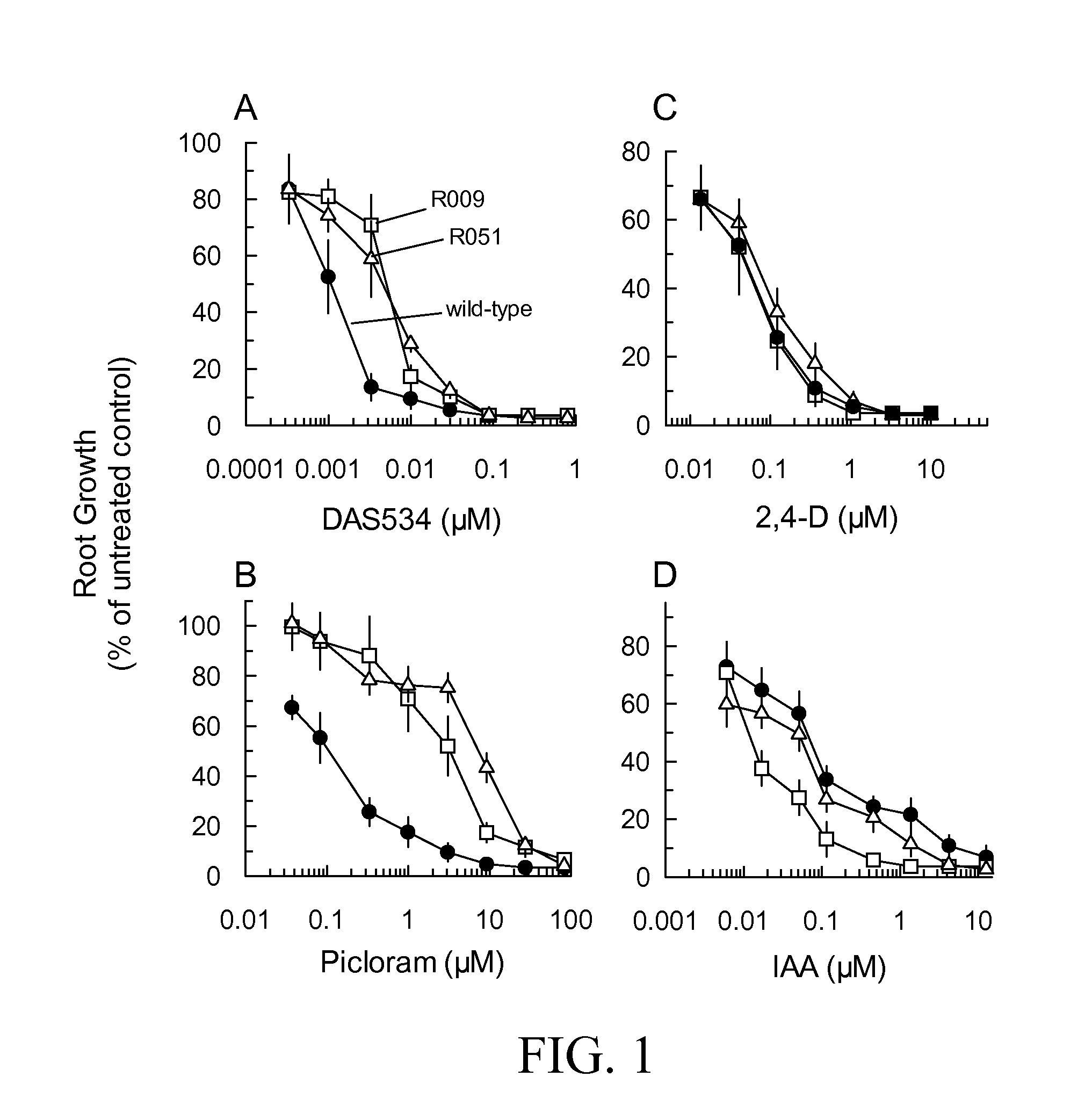
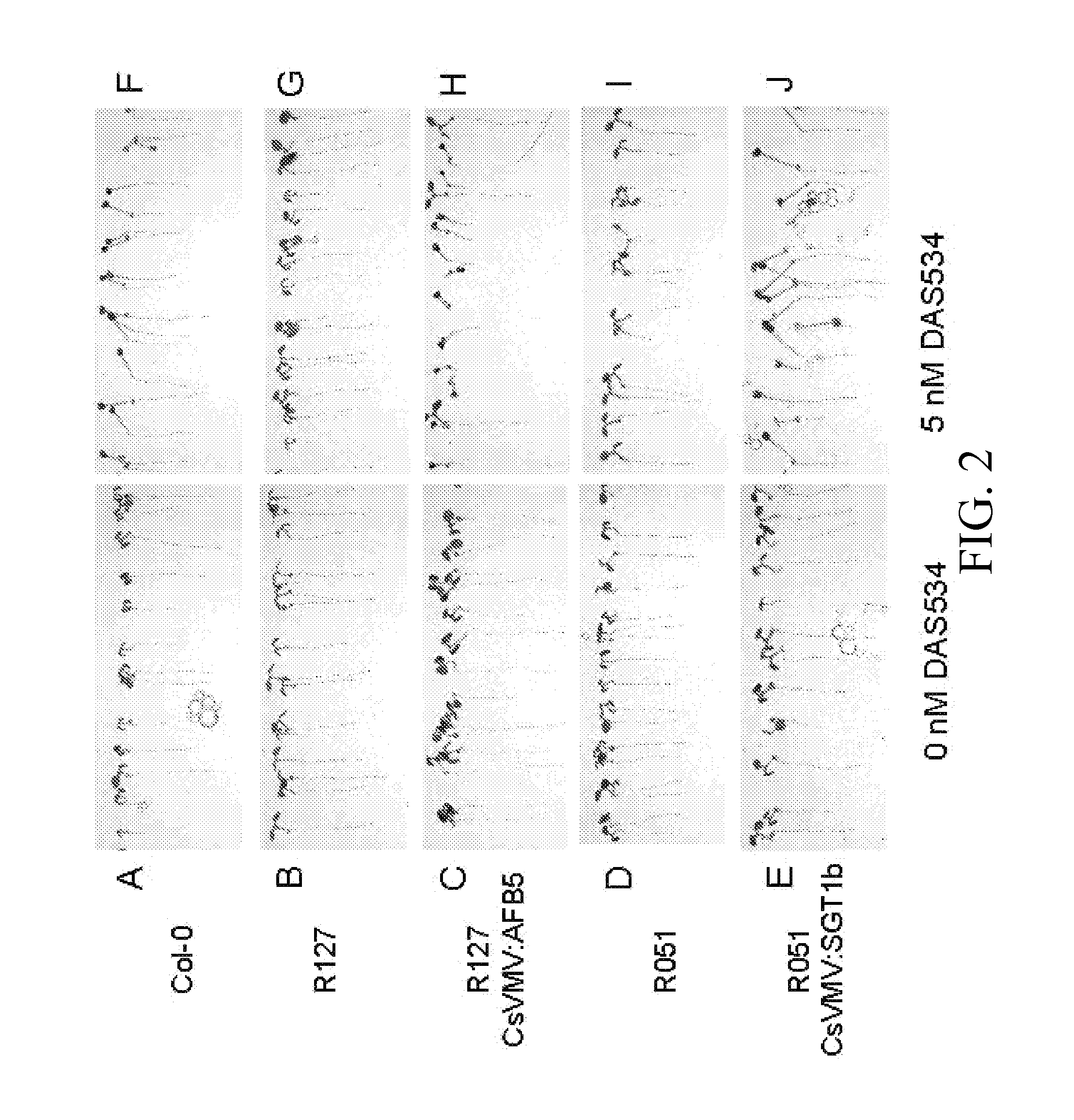
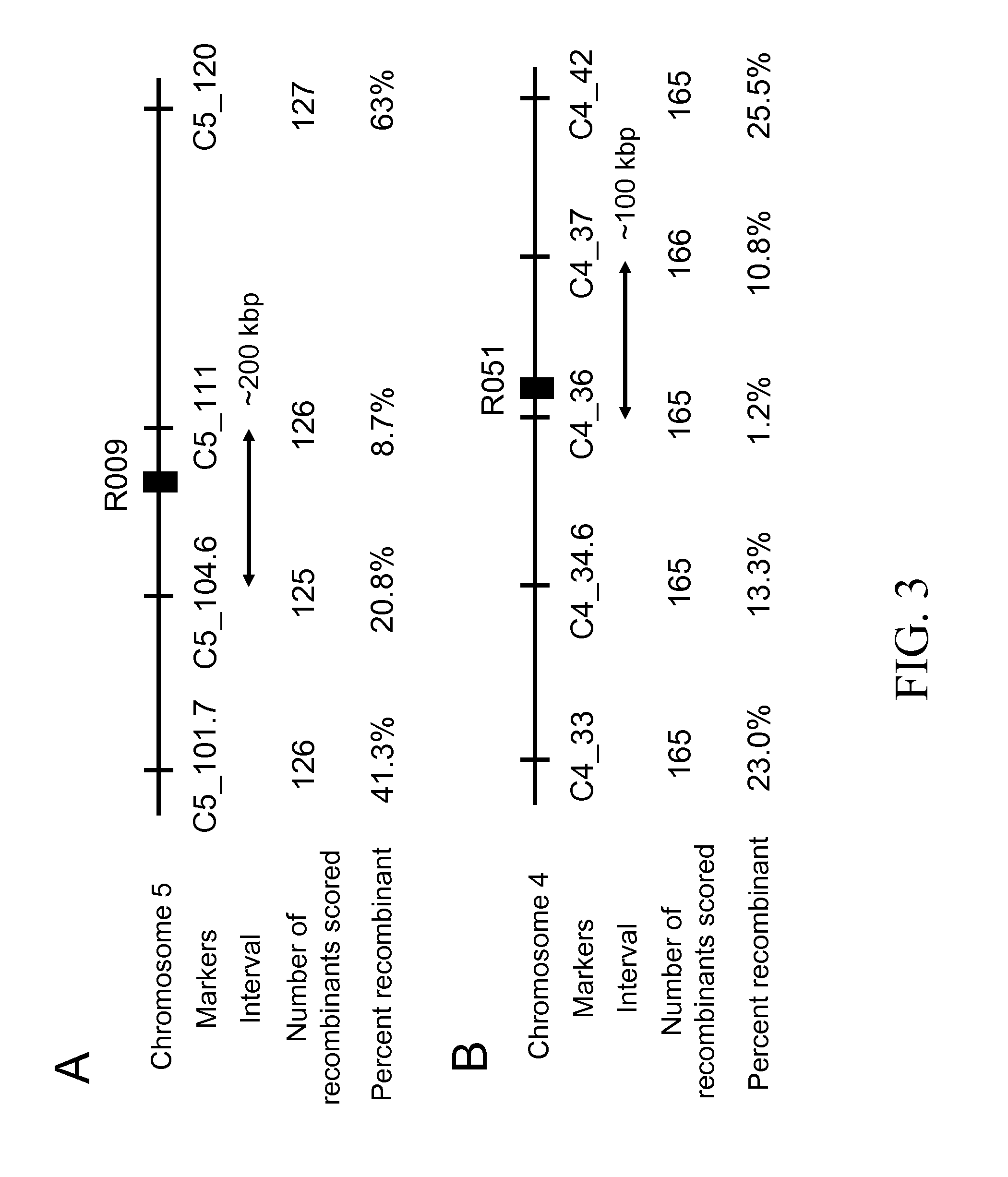
Resistance to auxinic herbicides
ActiveUS7820883B2Confer resistanceBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesGrowth plantMolecular binding
The invention provides methods of identifying herbicidal auxins. The invention further provides auxin-herbicide-resistant plants and genes conferring auxin-herbicide resistance. This invention also provides a method of identifying other proteins that bind picolinate auxins from additional plant species. The invention further provides a method to identify the molecular binding site for picolinate auxins. The invention also includes the use of the picolinate herbicidal auxin target site proteins, and methods of discovering new compounds with herbicidal or plant growth regulatory activity. The invention also includes methods for producing plants that are resistant to picolinate herbicidal auxins. Specific examples of novel proteins associated with herbicide binding include AFB5, AFB4, and SGT1b.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
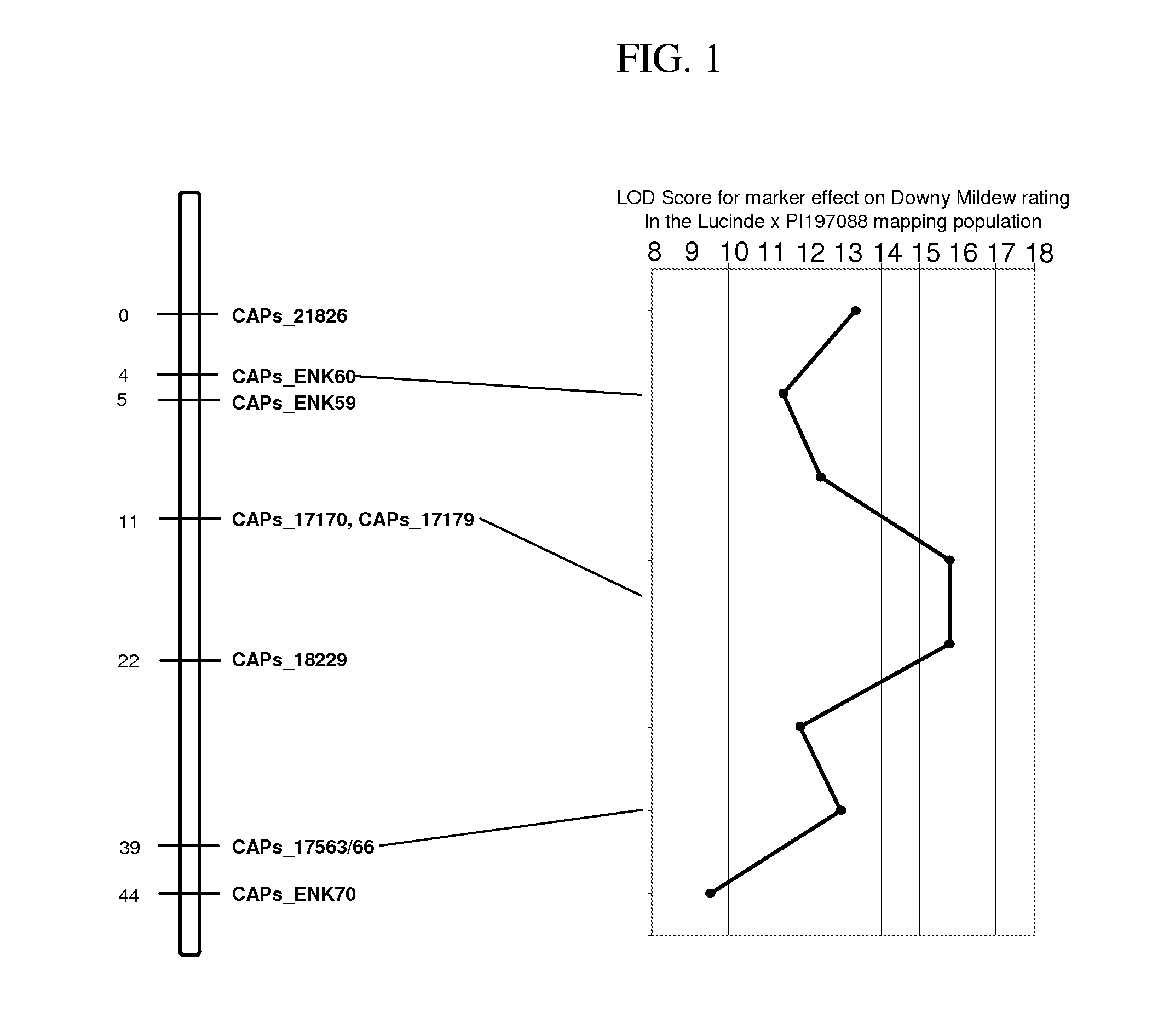
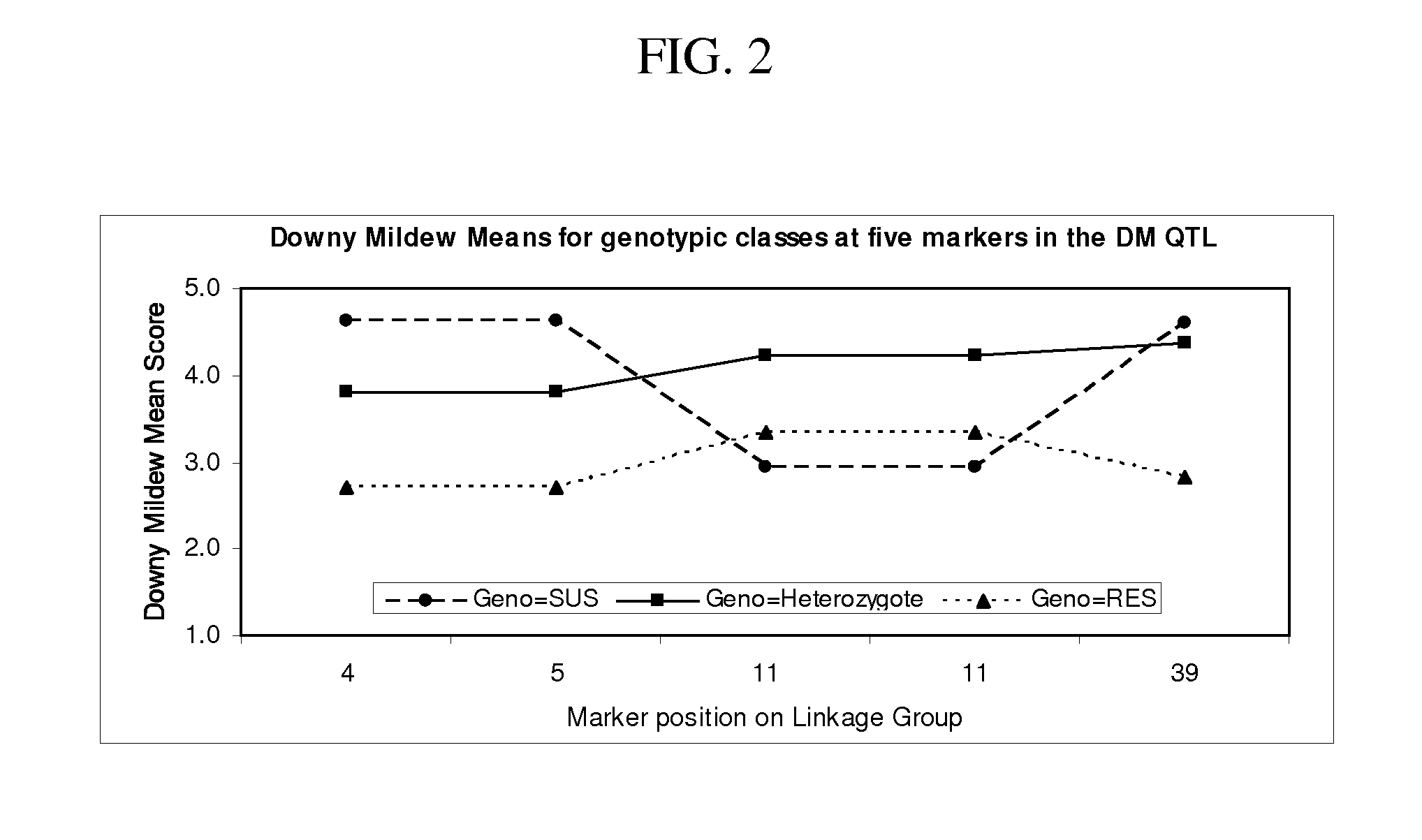
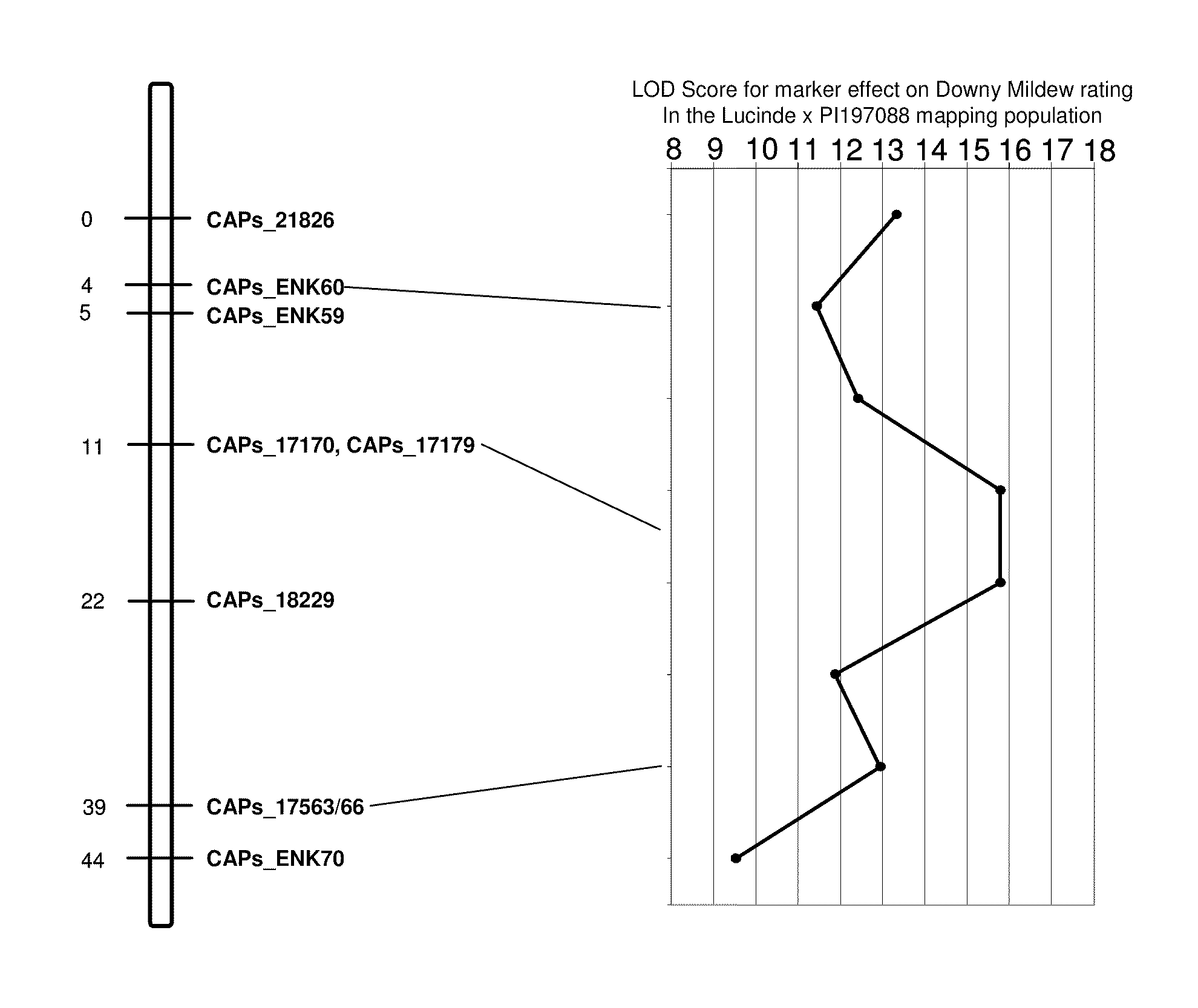
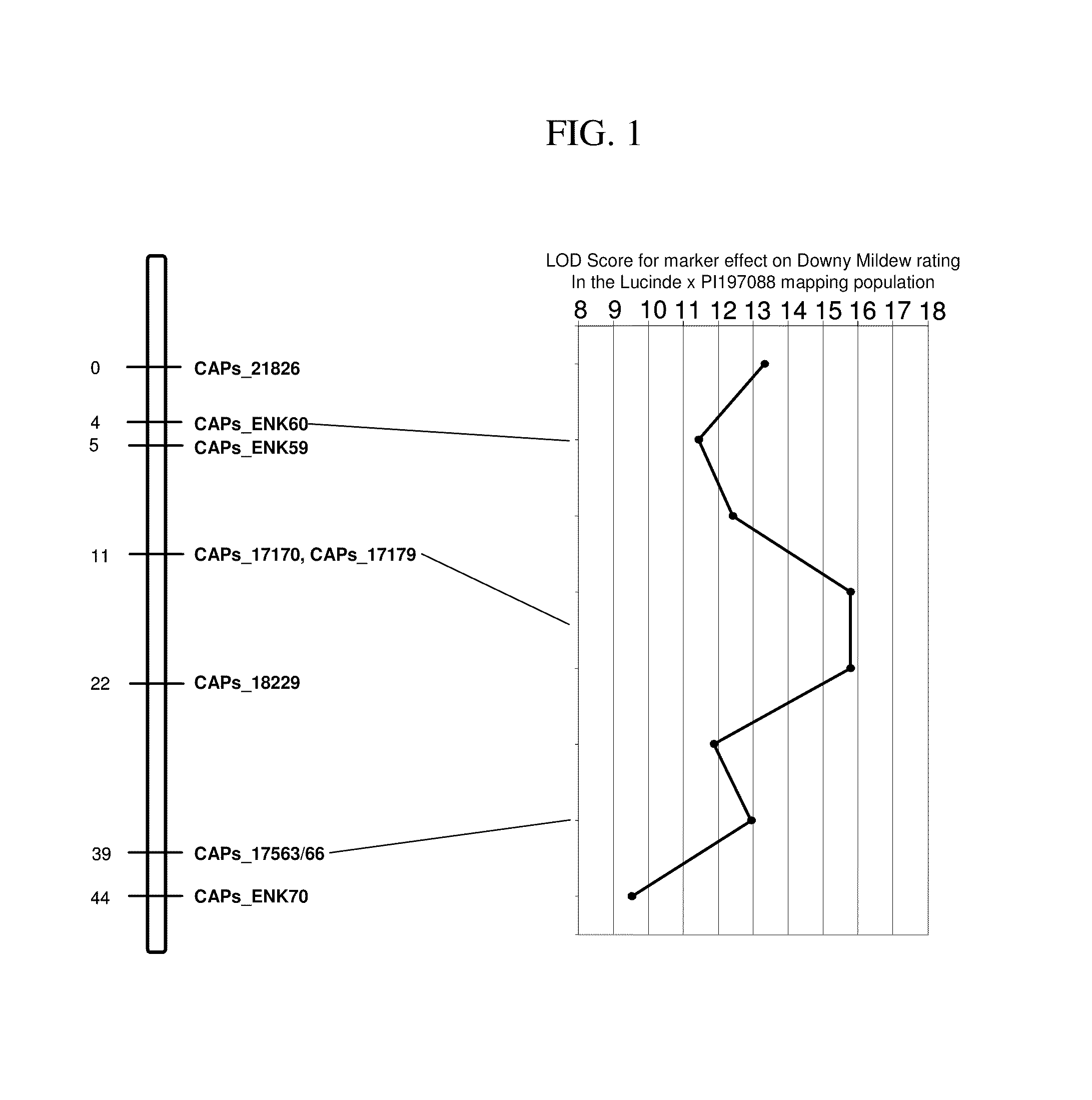
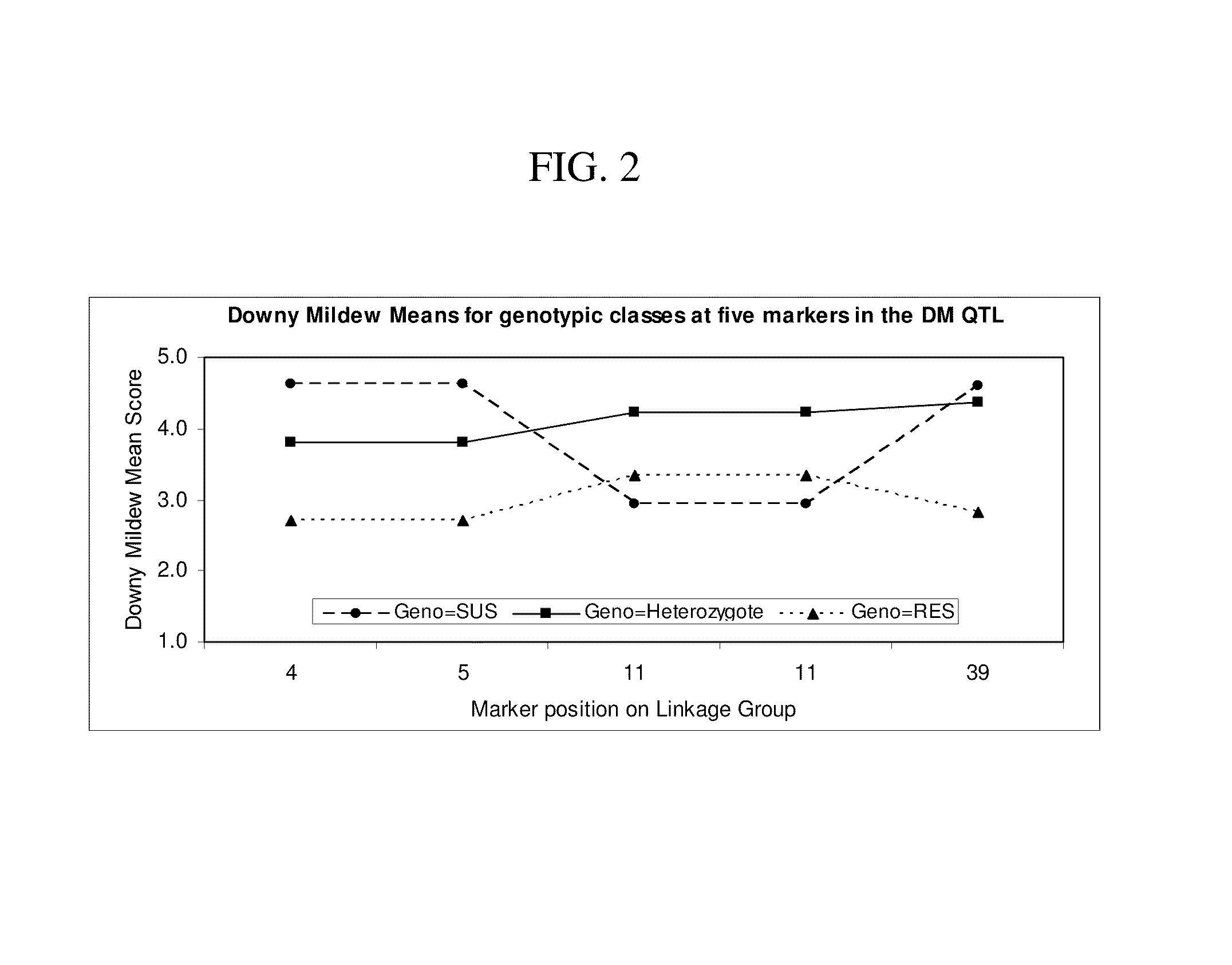
Methods and compositions for identifying downy mildew resistant cucumber plants
ActiveUS20110126309A1Reduction of foliar symptomConfer resistanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The present invention relates to methods for identifying cucumber lines having increased resistance to Downy Mildew, and identification of genetic markers linked to gene(s) conditioning such increased disease resistance. The present invention also relates to methods of breeding cucumber plants from lines having increased Downy Mildew resistance by marker-assisted selection, compositions including nucleic acid probes or primers which are useful for such marker assisted selection, and plants and plant parts produced by such methods.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
Cytochrome P450 genes conferring herbicide resistance
ActiveUS8097774B2Reduce residue levelsConfer resistanceBiocideOther foreign material introduction processesSulfonylureaPlant cell
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include transgenic plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds that have been transformed with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a cytochrome P450 or variant thereof that confers herbicide resistance or tolerance, alone or in combination with one or more additional nucleic acid molecules encoding polypeptides that confer desirable traits. In particular, the cytochrome P450 or variant thereof confers resistance or tolerance to HPPD inhibitors, benzothiadiazinones, sulfonylureas, and other classes of herbicides. The additional polypeptide may also confer resistance or tolerance to an herbicide, including HPPD inhibitors and other herbicides. Methods are also provided for the production and use of the herbicide resistant or tolerant plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds of the invention.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Resistance to auxinic herbicides
ActiveUS20070220629A1High elongationImprove responseBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesGrowth plantMolecular binding
The invention provides methods of identifying herbicidal auxins. The invention further provides auxin-herbicide-resistant plants and genes conferring auxin-herbicide resistance. This invention also provides a method of identifying other proteins that bind picolinate auxins from additional plant species. The invention further provides a method to identify the molecular binding site for picolinate auxins. The invention also includes the use of the picolinate herbicidal auxin target site proteins, and methods of discovering new compounds with herbicidal or plant growth regulatory activity. The invention also includes methods for producing plants that are resistant to picolinate herbicidal auxins. Specific examples of novel proteins associated with herbicide binding include AFB5, AFB4, and SGT1b.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
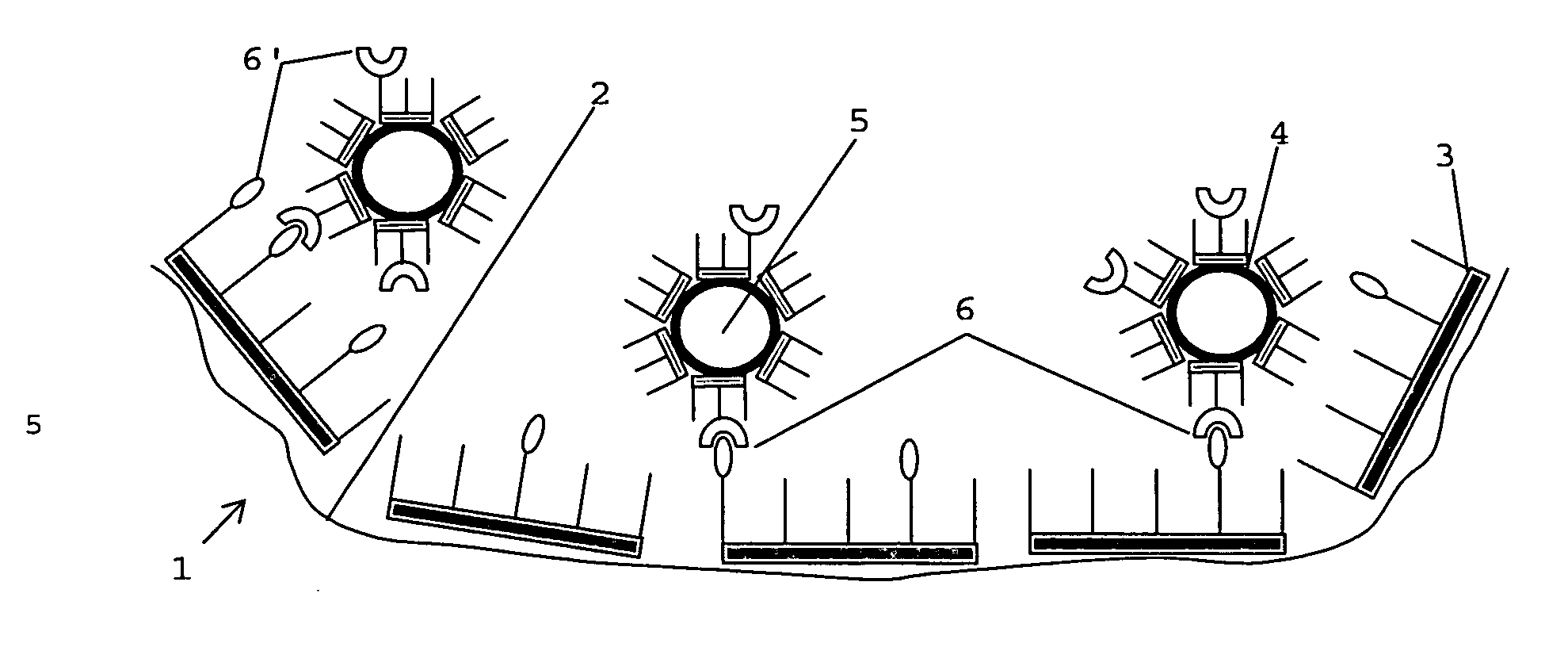
Cell selective implant surface with controlled release of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20070190107A1Heal fastPreventing acuteMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseActive agent
The present invention relates to an implant (1) with at least partially a roughened surface (2), which is at least partially covered by an organic or polymeric intermediate layer (3) and attached thereto a top layer (4). The top layer (4) provides for a controlled release of at least one bioactive agent. A kit for preparing such an implant is also described.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Methods and compositions for identifying downy mildew resistant cucumber plants
ActiveUS8809622B2Reduction of foliar symptomConfer resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationDiseaseMarker-assisted selection
The present invention relates to methods for identifying cucumber lines having increased resistance to Downy Mildew, and identification of genetic markers linked to gene(s) conditioning such increased disease resistance. The present invention also relates to methods of breeding cucumber plants from lines having increased Downy Mildew resistance by marker-assisted selection, compositions including nucleic acid probes or primers which are useful for such marker assisted selection, and plants and plant parts produced by such methods.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
Human S100 proteins
InactiveUS6103497AAvoid the needIncrease ratingsSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsS100 proteinAgonist
The invention provides two human S100 proteins designated individually as S100P1 and S10OP2 and collectively as S100P, and polynucleotides which identify and encode S100P. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, agonists, antibodies and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for treating disorders associated with expression of S100P.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Actinobacillus succinogenes shuttle vector and methods of use
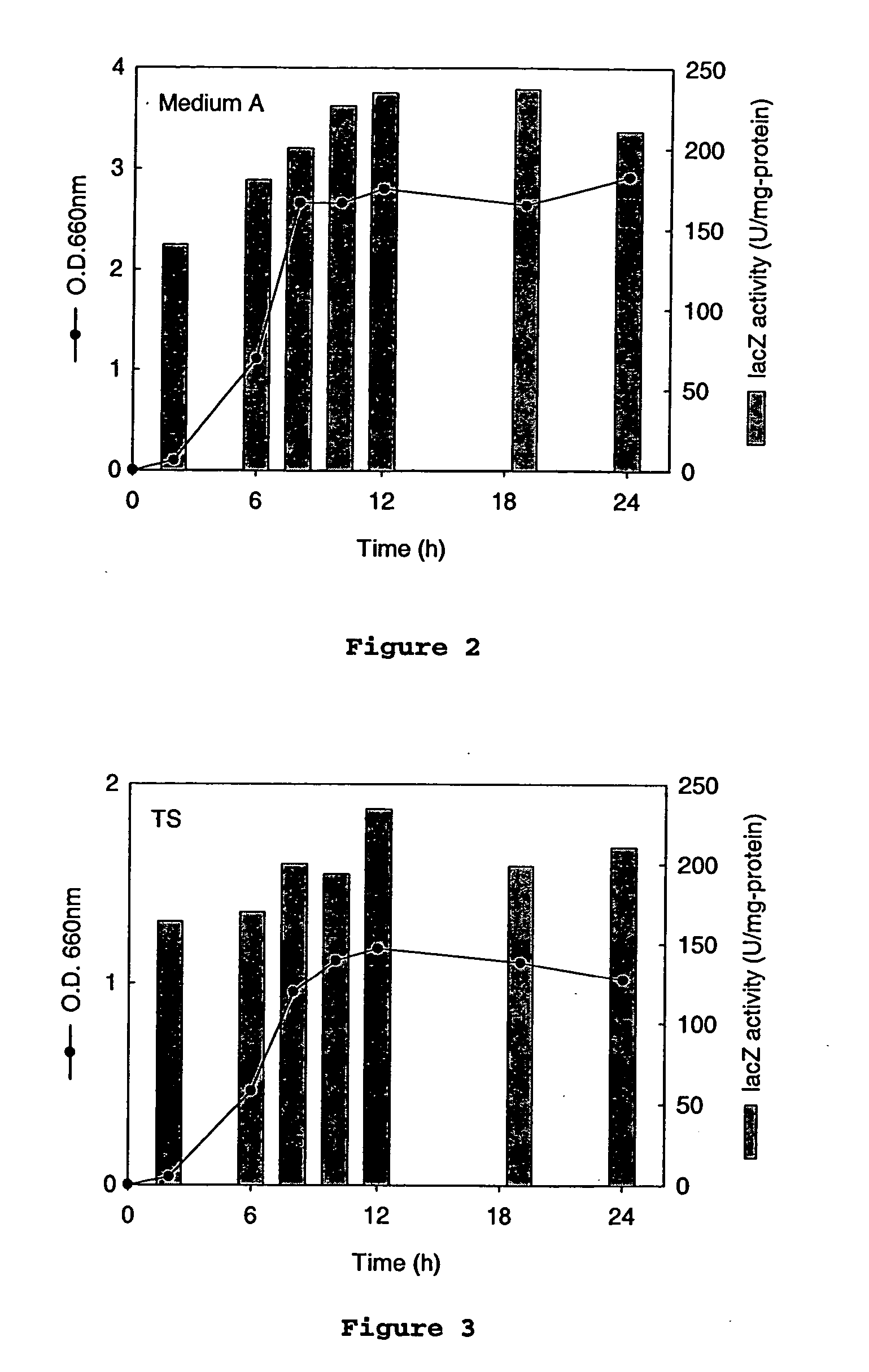
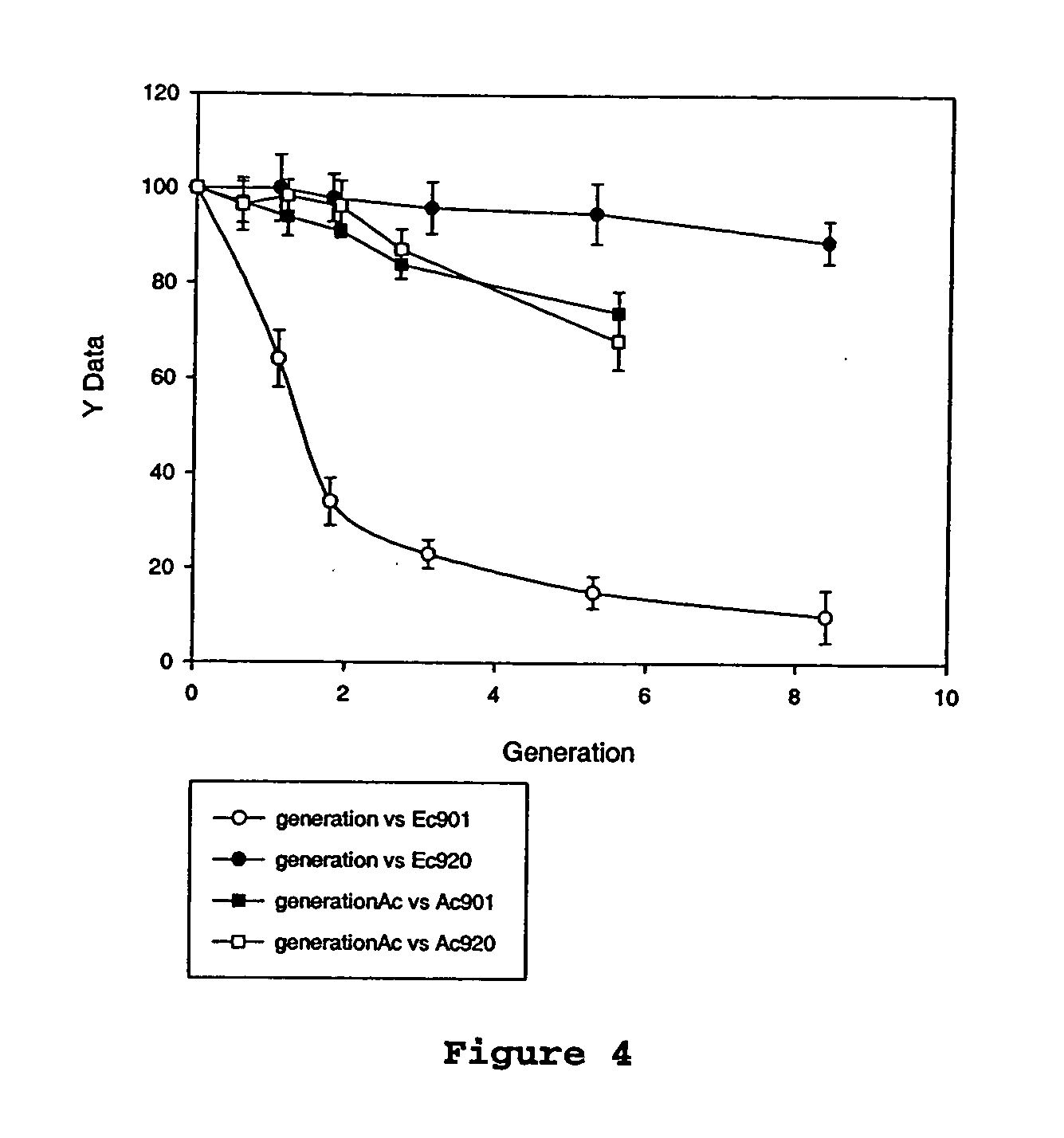
An Actinobacillus succinogenes plasmid vector which provides a means to overexpress proteins in A. succinogenes. The plasmid can be transformed efficiently by electroporation, and replicates in a stable manner in A. succinogenes. The plasmid comprises at least one marker gene, operably linked to a first promoter functional in Actinobacillus succinogenes, an origin of replication functional in Actinobacillus succinogenes, a second promoter isolated from Actinobacillus succinogenes, and a cloning site downstream from the second promoter. Plasmids pLGZ901, pLGZ920, pLGZ921, and pLGZ922 are disclosed. The pckA gene polypeptide sequence and nucleic acid sequence of Actinobacillus succinogenes, including the promoter and ribosome binding site, is disclosed. Furthermore, a method for producing a recombinant Actinobacillus succinogenes is described, including a method of transformation. Additionally, a recombinant Actinobacillus succinogenes is disclosed and a method for producing succinate utilizing this recombinant Actinobacillus succinogenes is described.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Methods of creating dwarf phenotypes in plants
InactiveUS20020194646A1Increase ratingsDesirable propertyClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNicotiana tabacumTobacco product
The invention is directed to the application of gene sequences which cause a dwarf phenotype in plants to the fields of forestry plants, ornamental horticultural plants, medicinal plants, and Nicotiana plants which are used for purposes other than for traditional tobacco products. The invention provides cDNAs identified by the polynucleotide sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-122 that may be used to create transfected or transgenic plants exhibiting a dwarf phenotype. The invention also provides methods of creating a transfected or transgenic plant exhibiting a dwarf phenotype by expressing in the plant DNA or mRNA identified by the sequences SEQ ID NO:1-122.
Owner:LARGE SCALE BIOLOGY
Immunomodulatory agents for treatment of inflammatory diseases
InactiveUS20070123455A1Conferring oxidation resistancePrevent dimerizationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides methods and compositions suitable for treating inflammatory disorders such as allergy, asthma, artherosclerosis, autoimmune disease, infection, injury, meningitis, psoriasis, and transplant rejection. In particular, the present invention provides methods and compositions comprising human S100A8 and / or S100A9 for reducing inflammation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nucleic acid sequences and their use in methods for achieving pathogen resistance in plants
InactiveUS7456335B2Confer resistanceReduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingGMO Plants
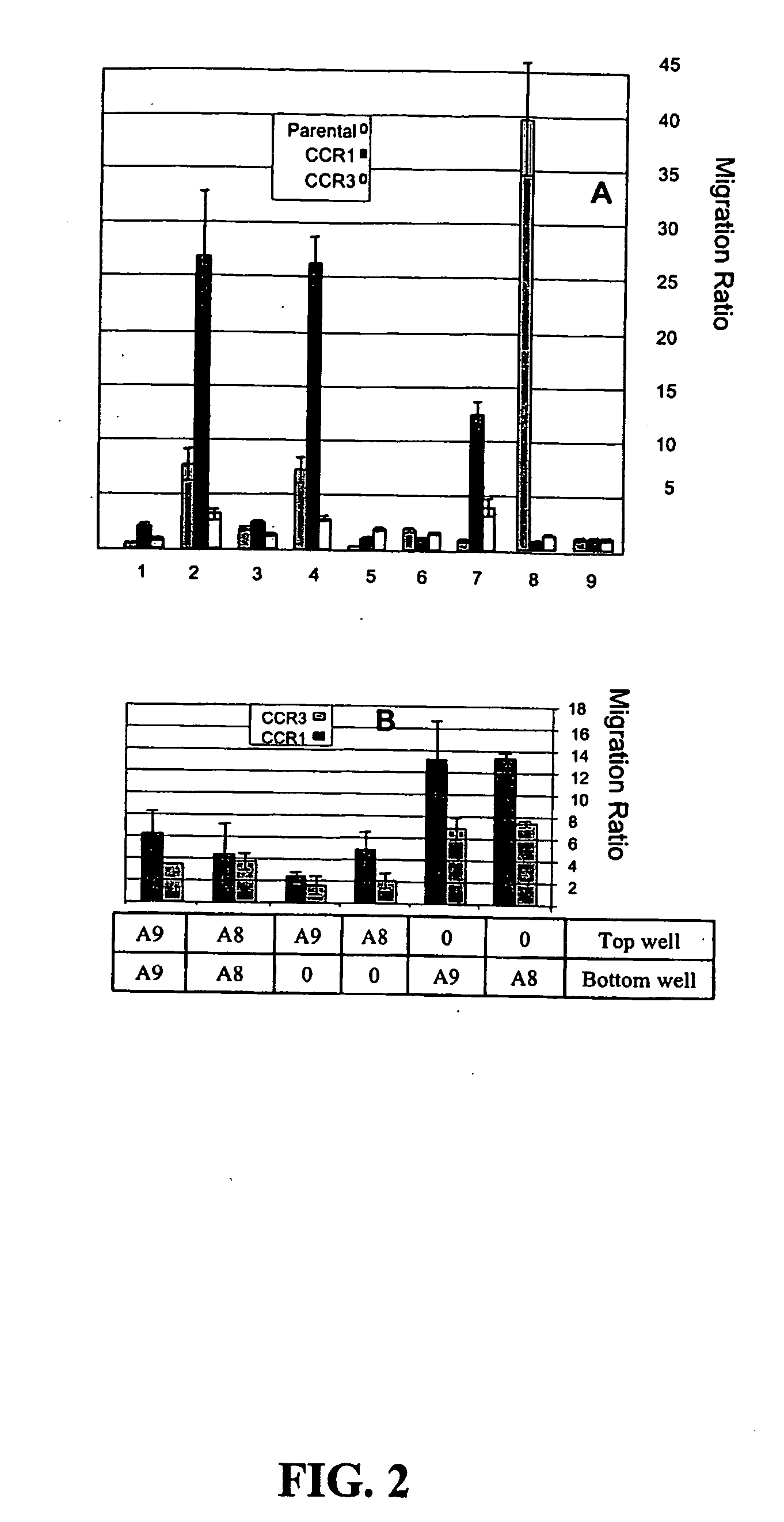
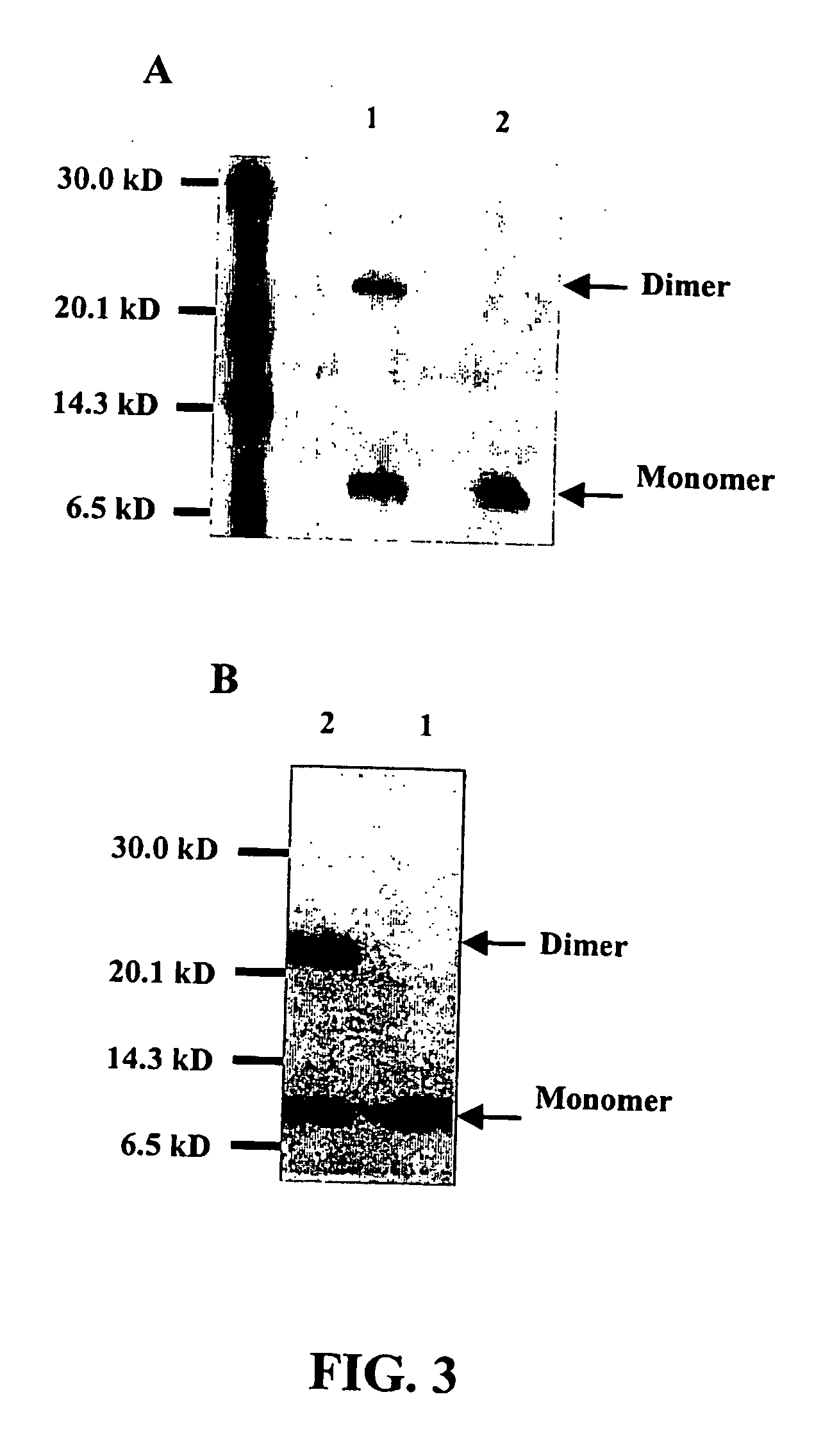
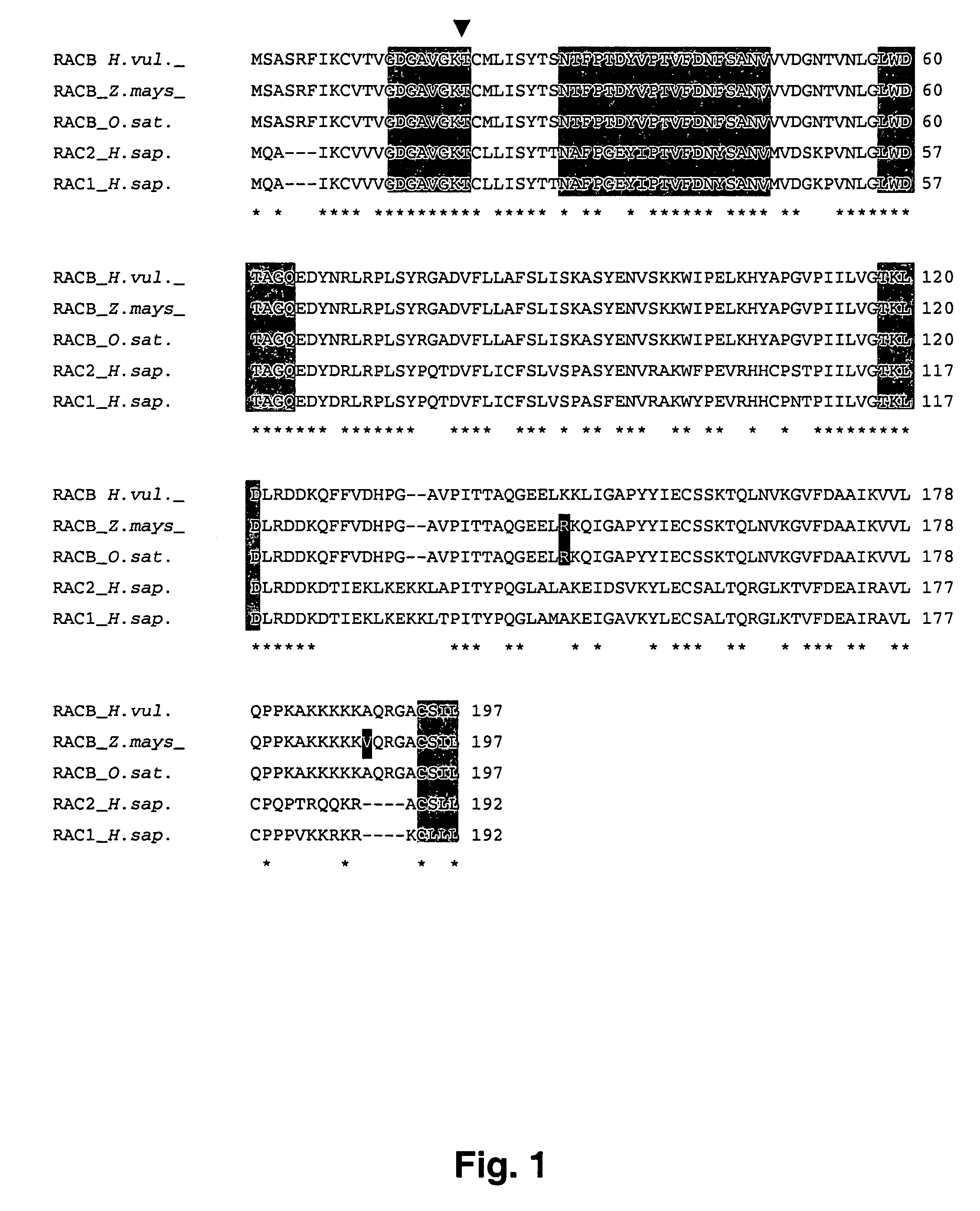
The invention relates to novel RacB cDNA sequences from barley and to expression cassettes and vectors comprising these promoter sequences. The invention furthermore relates to transgenic plants transformed with these expression cassettes or vectors, to cultures, parts or transgenic propagation material derived from them, and to their use for the production of foodstuffs, feeding stuffs, seed, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals. The invention furthermore relates to methods of generating or increasing a pathogen resistance in plants by reducing the expression of an RacB protein or of a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Polynucleotides and polypeptides derived from corn seedling
InactiveUS20020013958A1High degree of certaintyNot be correctSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideGene expression
The present invention provides purified, corn seedling-derived polynucleotides (cdps) which encode corn seedling-derived polypeptides (CDPs). The invention also provides for the use of cdps or their complements, oligonucleotides, or fragments in methods for determining altered gene expression, to recover regulatory elements, and to follow inheritance of desirable characteristics through hybrid breeding programs. The invention further provides for vectors and host cells containing cdps for the expression of CDPs. The invention additionally provides for (i) use of isolated and purified CDPs to induce antibodies and to screen libraries of compounds and (ii) use of anti-CDP antibodies in diagnostic assays.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com