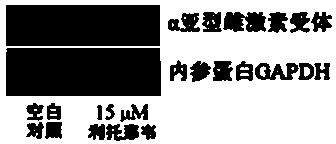Patents
Literature
68 results about "Estrogen receptor modulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pomegranate products useful in improving health and methods of use thereof
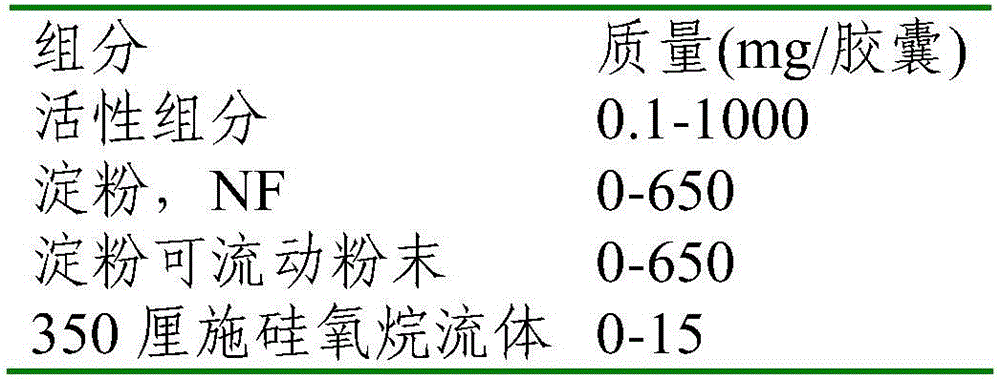
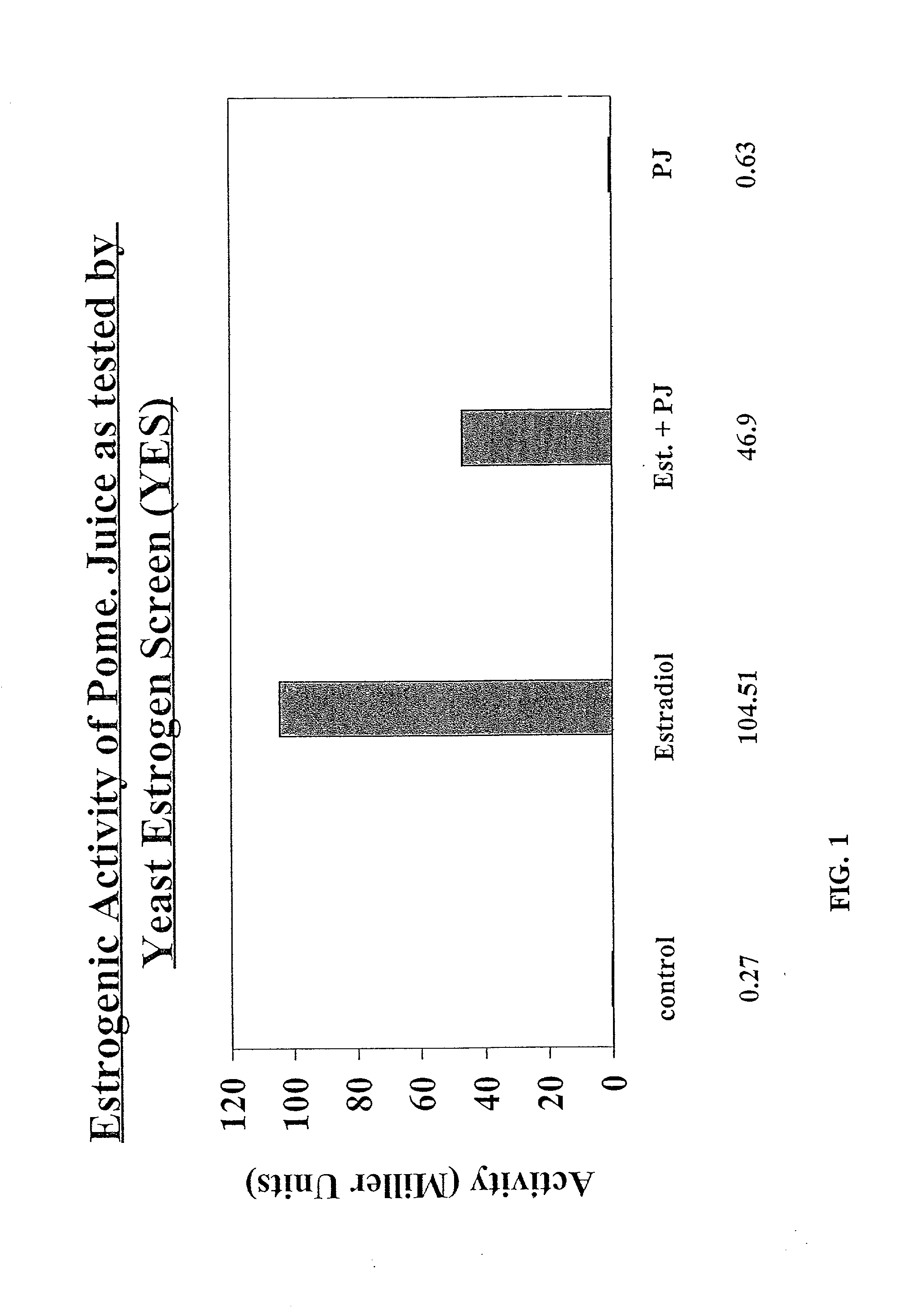
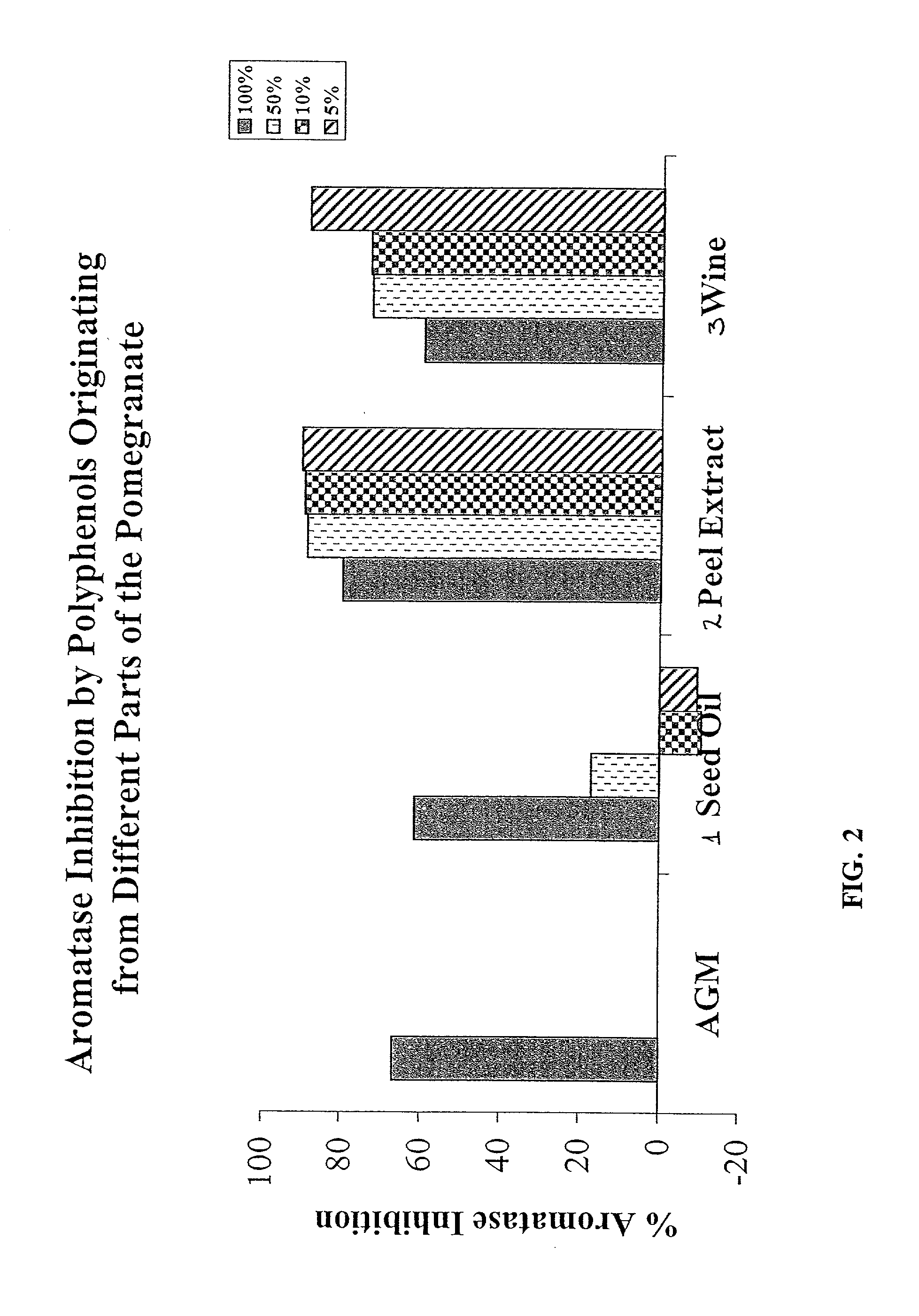
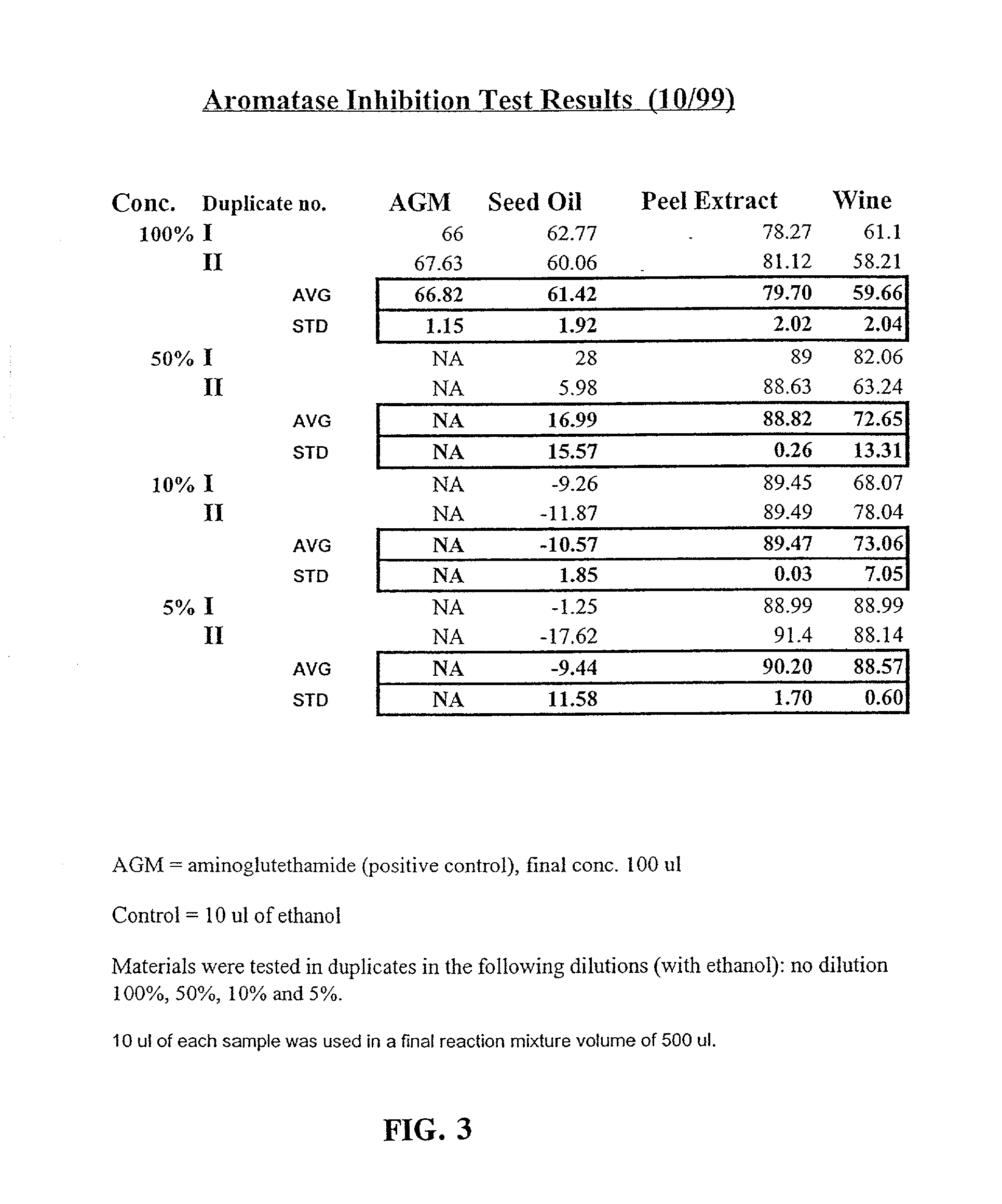
A mixture of a pomegranate seed oil product and a pomegranate juice product and a pharmaceutical composition containing same. The mixture, which is a cancer chemopreventive, includes a pomegranate seed oil product and pomegranate juice product. The pharmaceutical composition includes physiologically active amounts of pomegranate seed oil product, a pomegranate juice product and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. According to some disclosed embodiments, a pomegranate peel product is further included. Further disclosed is a selective estrogen receptor modulator and other biologically active compounds derived from pomegranates as well as methods of use thereof.
Owner:RIMONEST
Methods and compositions for modulating estrogen receptor mutants
InactiveUS20150258099A1Altered interactionImprove treatment outcomesBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEstrogen receptor modulator
Described herein are methods and compositions for treating an ER-related disease condition characterized by a mutation in the ESR1 gene by administering an estrogen receptor modulator. Also described herein are methods of treating hormone resistant-estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancers characterized by a mutation in the ESR1 gene by administering an estrogen receptor modulator.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS6291505B1Unexpected and surprising activity in modulating estrogen receptor activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEstrogen receptor activityEstrogen receptor modulator
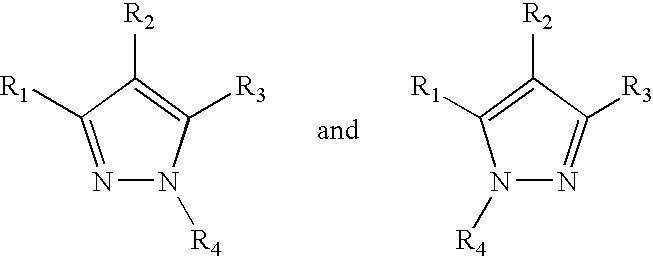
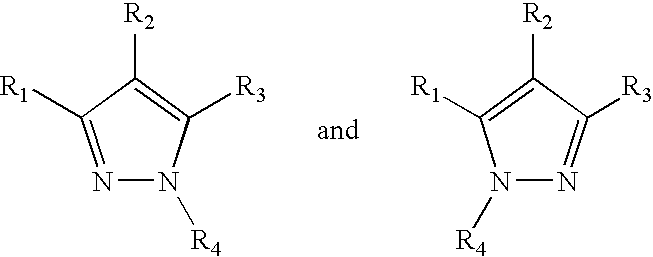
Estrogen receptor-modulating pyrazole compounds are described in addition to methods and compositions for treating or preventing estrogen receptor-mediated disorders. The compounds described have been found to have unexpected and surprising activity in modulating estrogen receptor activity. Thus, the compounds of the present invention have utility in preventing or treating estrogen receptor-mediated disorders such as osteoporosis, breast and endometrial cancers, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS7157604B2Urea derivatives preparationBiocideHormone Receptor ModulatorsPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS6387920B2Unexpected and surprising activity in modulating estrogen receptor activityBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseEstrogen receptor activity
Isoxazole estrogen receptor agonist and antagonist compounds having unexpected and surprising activity in modulating estrogen receptor activity are described. In addition, methods and compositions for treating or preventing estrogen receptor-mediated disorders are disclosed. The compounds, methods, and compositions of the invention have utility in preventing or treating estrogen receptor-mediated disorders such as osteoporosis, breast and endometrial cancers, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
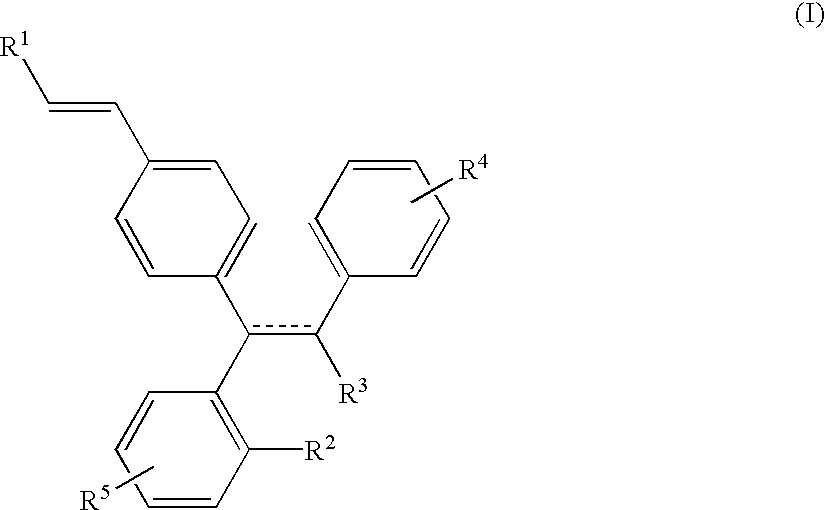
InactiveUS20030105148A1Improve patient acceptanceContinuous releaseBiocideNervous disorderSelective androgen receptor modulatorProstate cancer
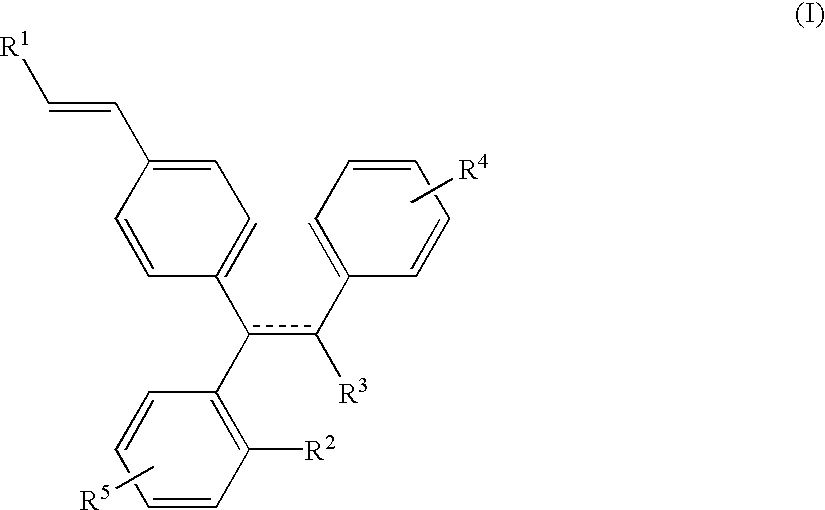
The present invention provides, inter alia, triphenylethylene derivatives, such as, 3-{4-[6-(3-Methoxy-phenyl)-8,9-dihydro-7H-benzocyclohepten-5-yl]-phenyl}-acrylic acid, as selective estrogen receptor modulators. Also provided are methods for the treatment and / or prevention of estrogen stimulated diseases in mammals including breast, uterine, ovarian, prostrate and colon cancer, osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and benign proliferative disorders, as well as pharmaceutical compositions of the compounds of the present invention.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restinosis, gynacomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
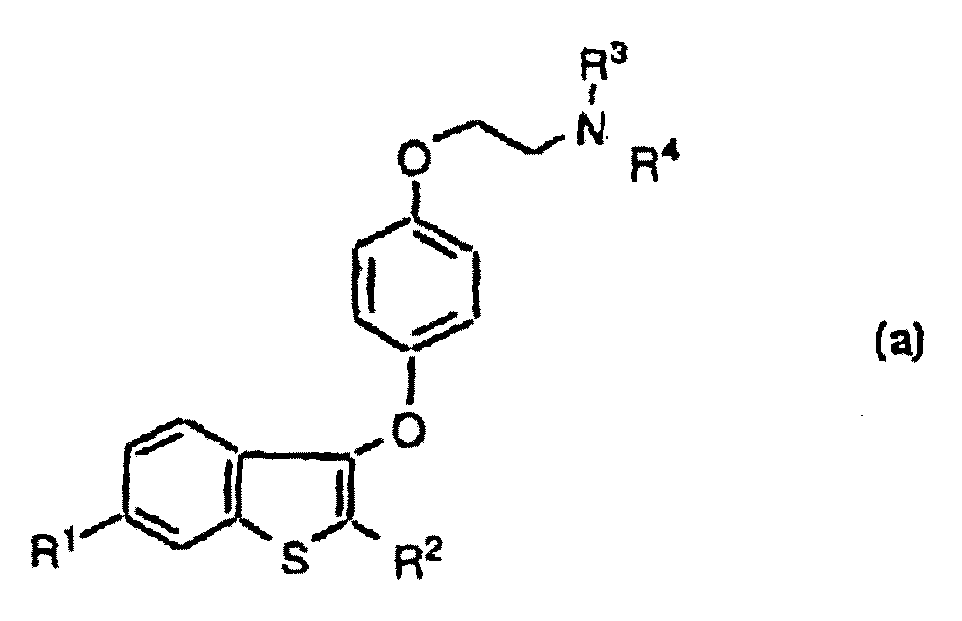
Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers
InactiveUS6891070B2BiocideOrganic compound preparationEstrogen receptor modulatorCombinatorial chemistry
A new method for the preparation of a selective estrogen receptor modulator and its isomers. Also disclosed is the preparation of new intermediates and their use in the preparation of the selective estrogen receptor modulator.
Owner:FORENDO PHARMA LTD
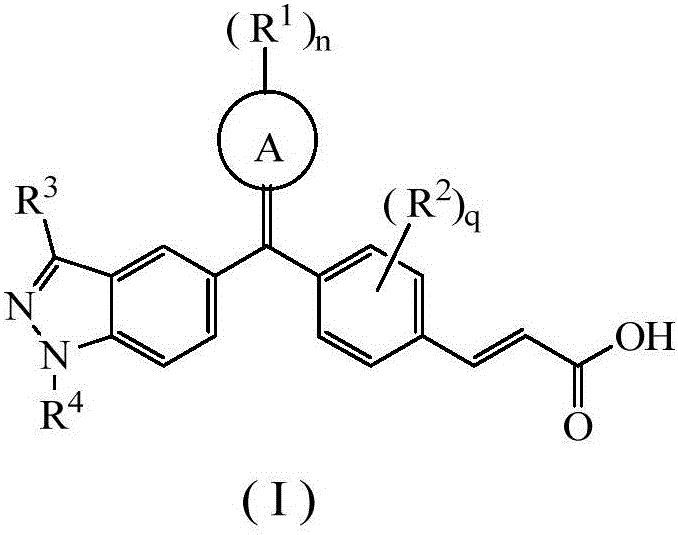
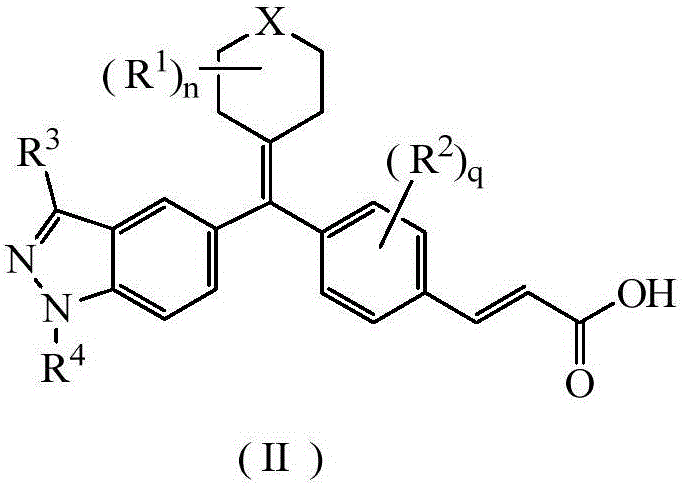
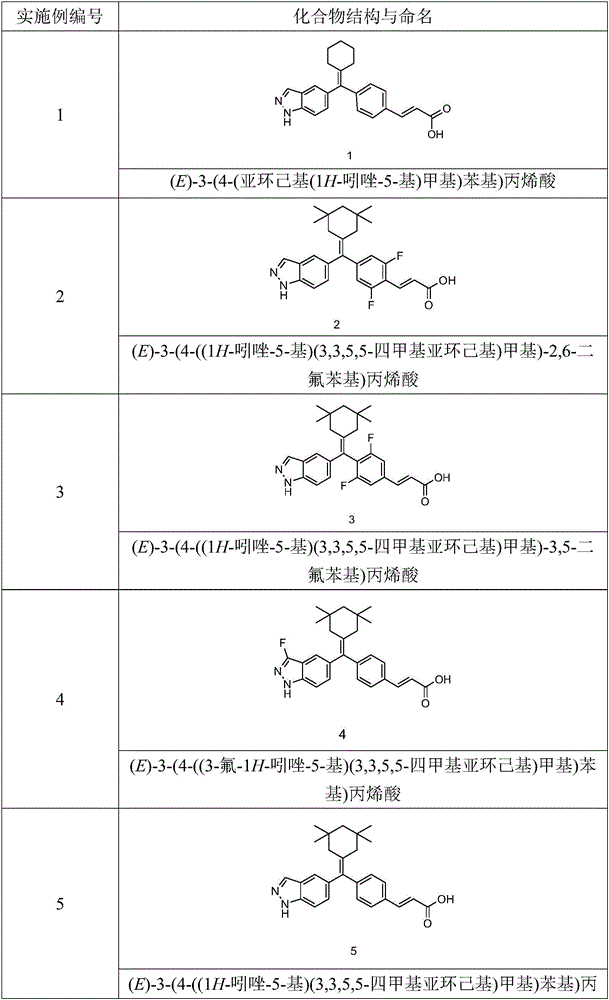
Acrylic acid derivative, preparation method therefore and medical application of acrylic acid derivative
The invention relates to an acrylic acid derivative, a preparation method thereof and medical application of the acrylic acid derivative. Particularly, the invention relates to the acrylic acid derivative as shown in a general formula (I) defined in the description, the preparation method thereof, a pharmaceutical composition containing the derivative and application of the derivative serving an estrogen receptor modulator for treating estrogen receptor mediated or dependent diseases or symptoms, and the disease of a breast cancer is particularly preferable. All substituents of the formula (I) are the same as the definition in the description.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGRUI MEDICINE CO LTD +1
Estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their cynthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compound of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid desease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholestterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muschle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
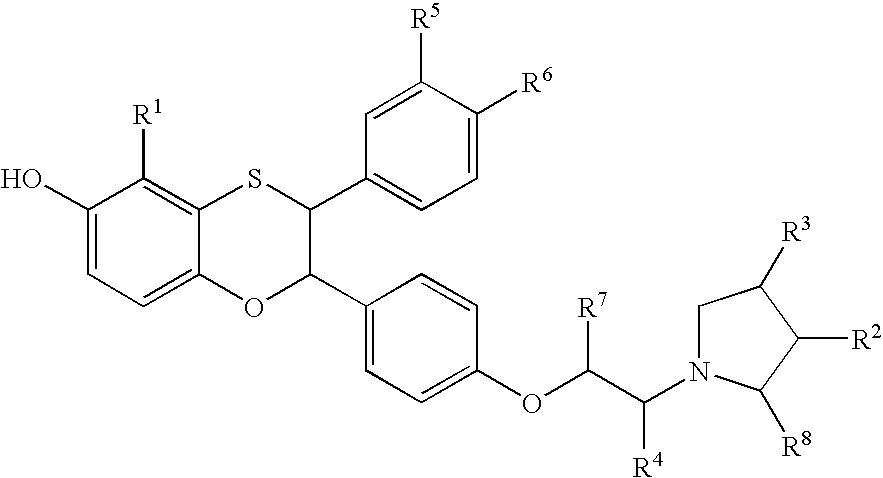
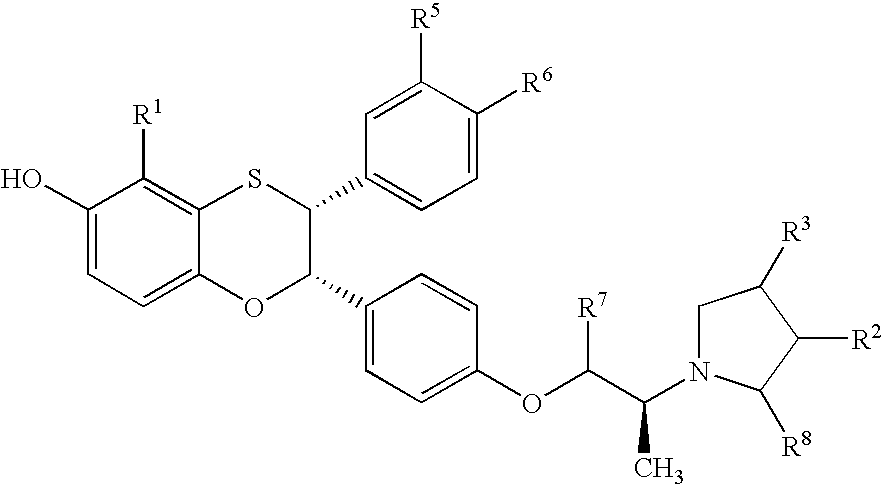
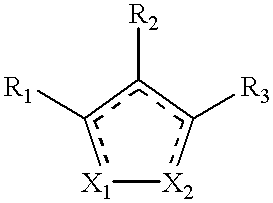
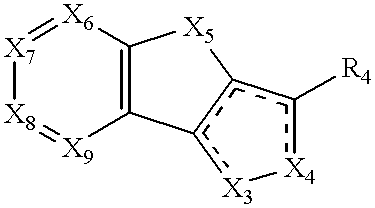
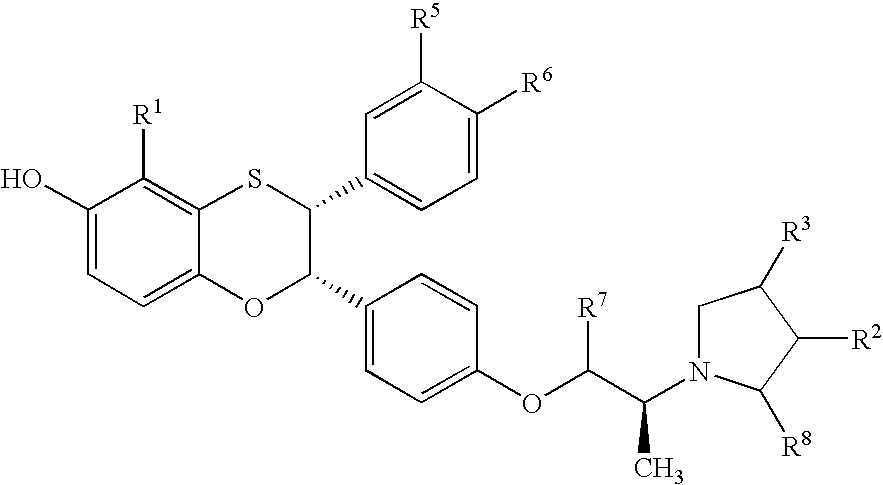
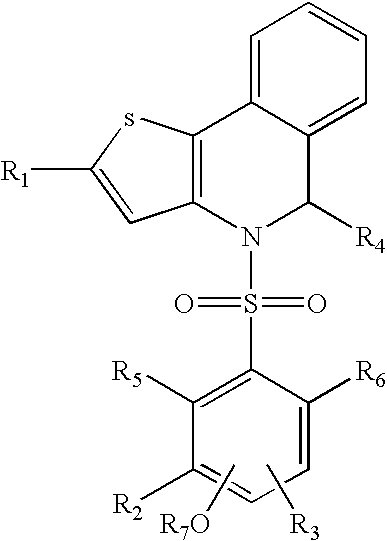
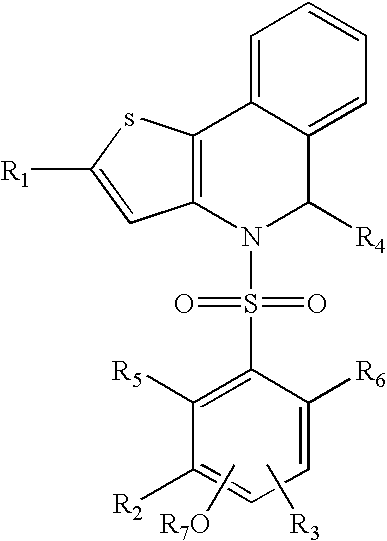
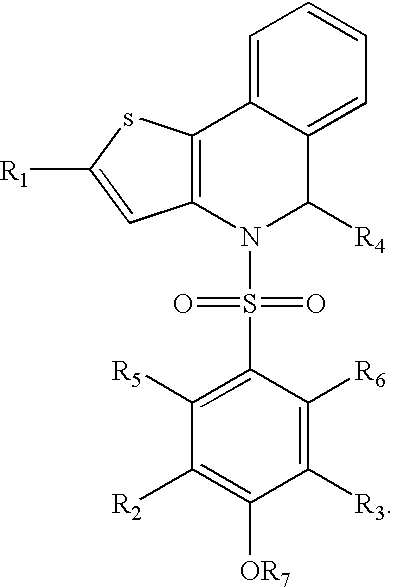
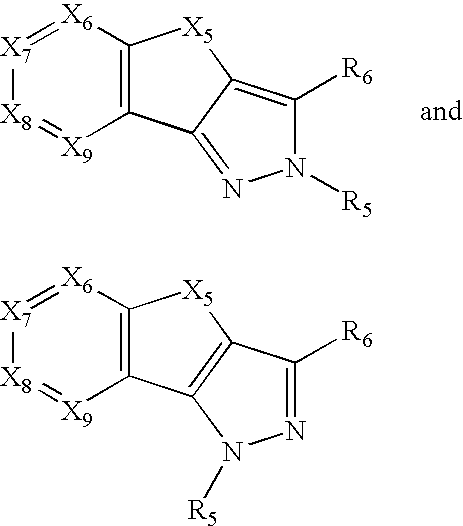
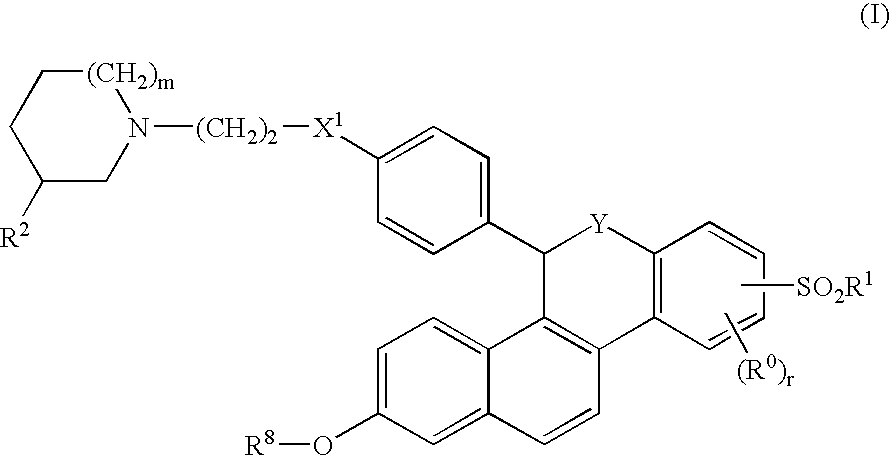
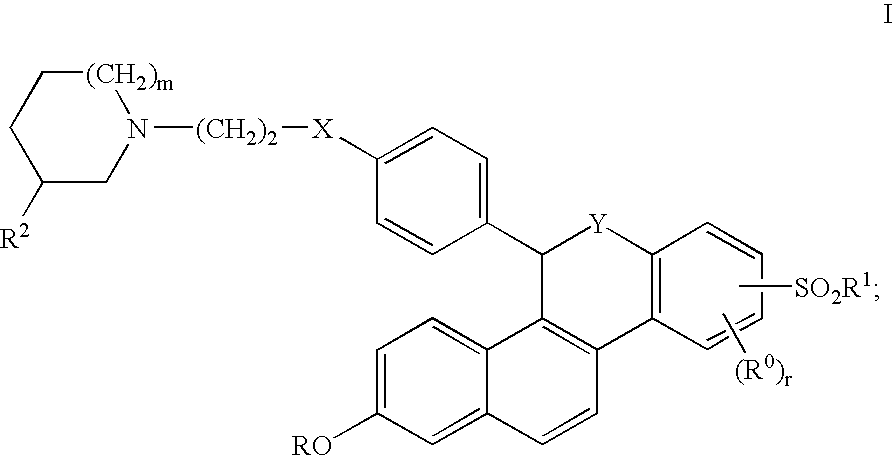
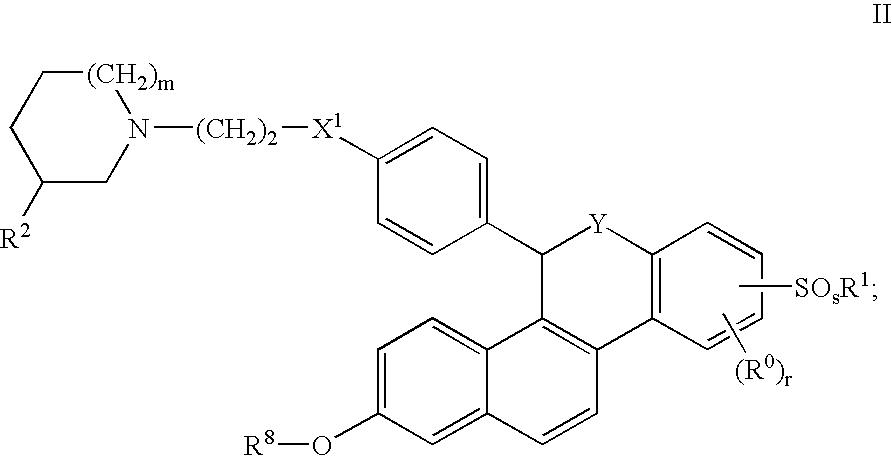
Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents
InactiveUS20060160815A1Lower Level RequirementsBiocideNervous disorderEstrogen receptor modulatorPyrrole
Owner:WYETH LLC
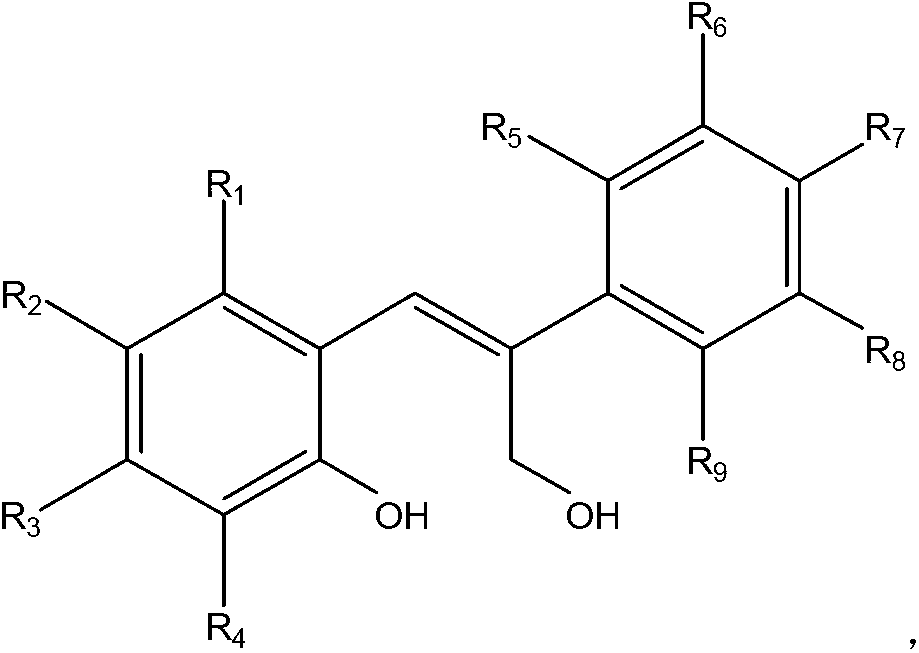
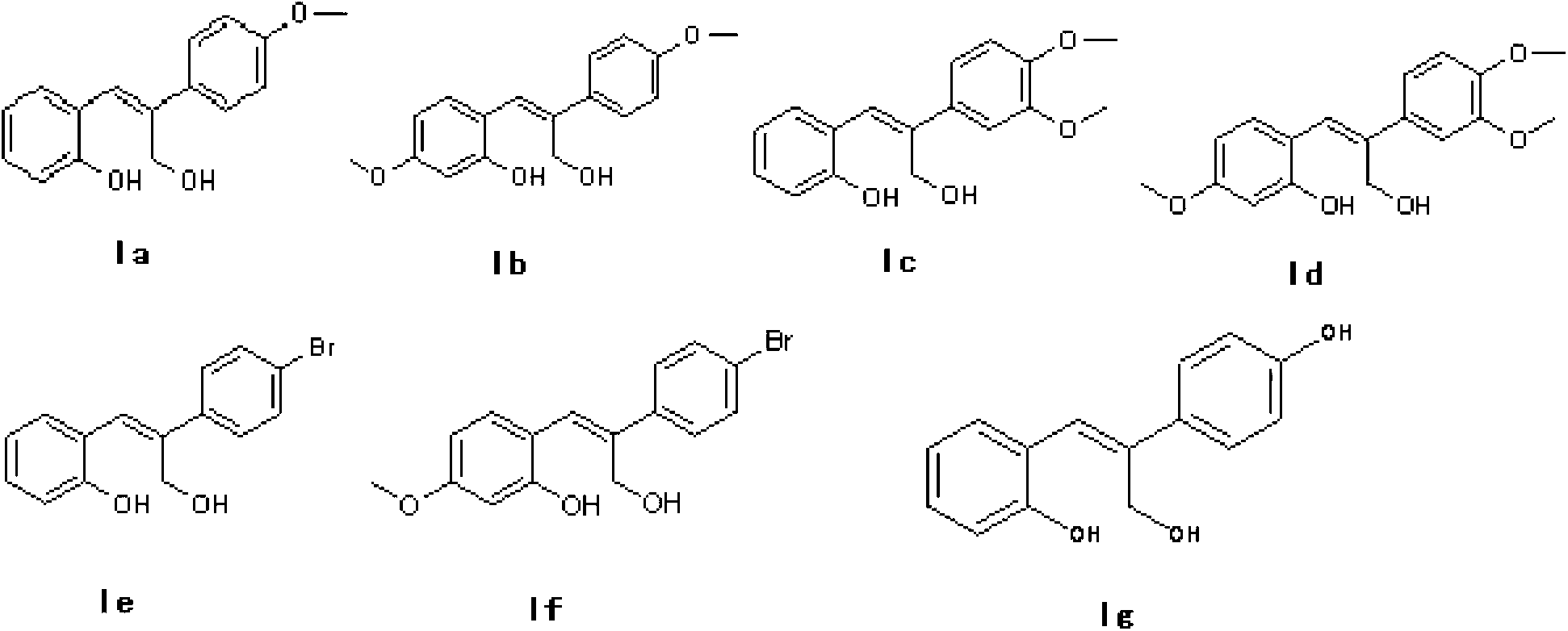
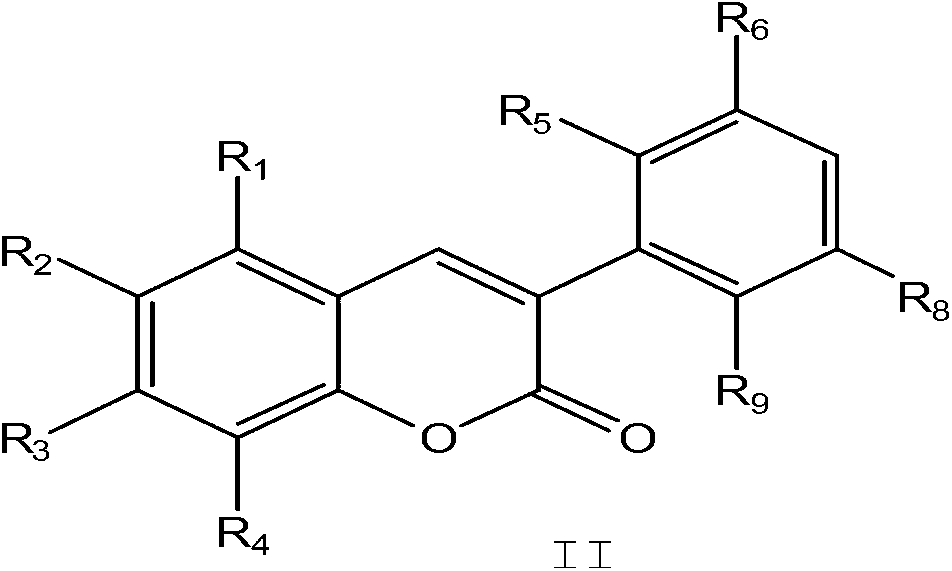
Application of selective estrogen receptor modulator
InactiveCN103058832AWide variety of sourcesLow costOrganic chemistryHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseInfertility
The invention discloses a stilbene compound, a preparation method and application of the stilbene compound. According to the invention, a substituted coumarin is adopted and used as a raw material, and the raw material is processed by reduction reaction in an organic solvent so as to the stilbene compound. The preparation method of the stilbene compound has the characteristics that the raw material is wide in source and low in cost, the method is simple in operation and mild in condition. The stilbene compound has combinability respect to ER Alpha higher than that respect to ER Beta and is relatively high in selectivity, some compounds show antagonistic effect to the ER Alpha and show partial agonistic action to ER Beta, therefore, the stilbene compound can be applied to preparation of a pharmaceutic preparation for preventing or treating diseases caused by estrogen deficiency or relative lack of estrogen, such as breast cancers, premature ovarian failure, climacteric syndrome, osteoporosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome and infertility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
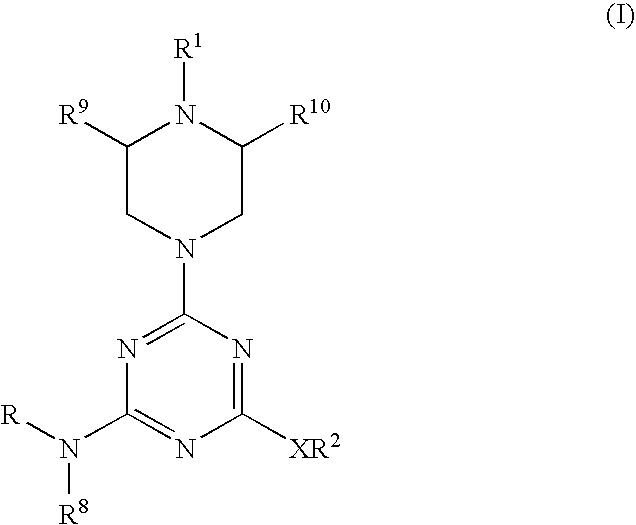
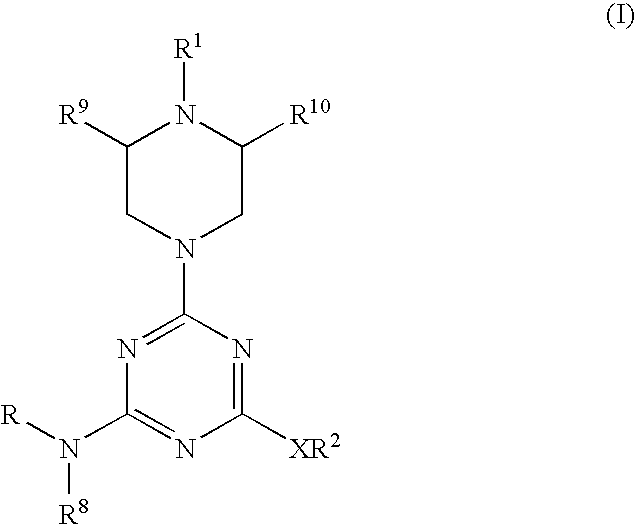
Piperazinyltriazines as estrogen receptor modulators
Triazine derivatives of formula (I), which exhibit pharmacological activity at estrogen receptors alpha (ER alpha) and beta (ER beta) are described herein. The described invention also includes compositions and medicaments containing the triazine derivatives as well as processes for the preparation and use of such compounds, compositions and medicaments.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Dibenzo chromene derivatives and their use as ERbeta selective ligands
InactiveCN1946707AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEstrogen receptor modulatorStereochemistry
Owner:WYETH LLC
Treatment of central nervous system disorders with selective estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention provides a method of treating depression, mood swings, or Alzheimer's disease in a patient in need of such treatment by administering a selective estrogen receptor modulating compound of the formula in which R1 and R2 are independently hydroxy and alkoxy of one to four carbon atoms; and R3 and R4 are independently methyl or ethyl, or R3 and R4, taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached, form a pyrrolidino, methyl-pyrrolidino, dimethylpyrrolidino, piperidino, morpholino, or hexamethyleneimino ring.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
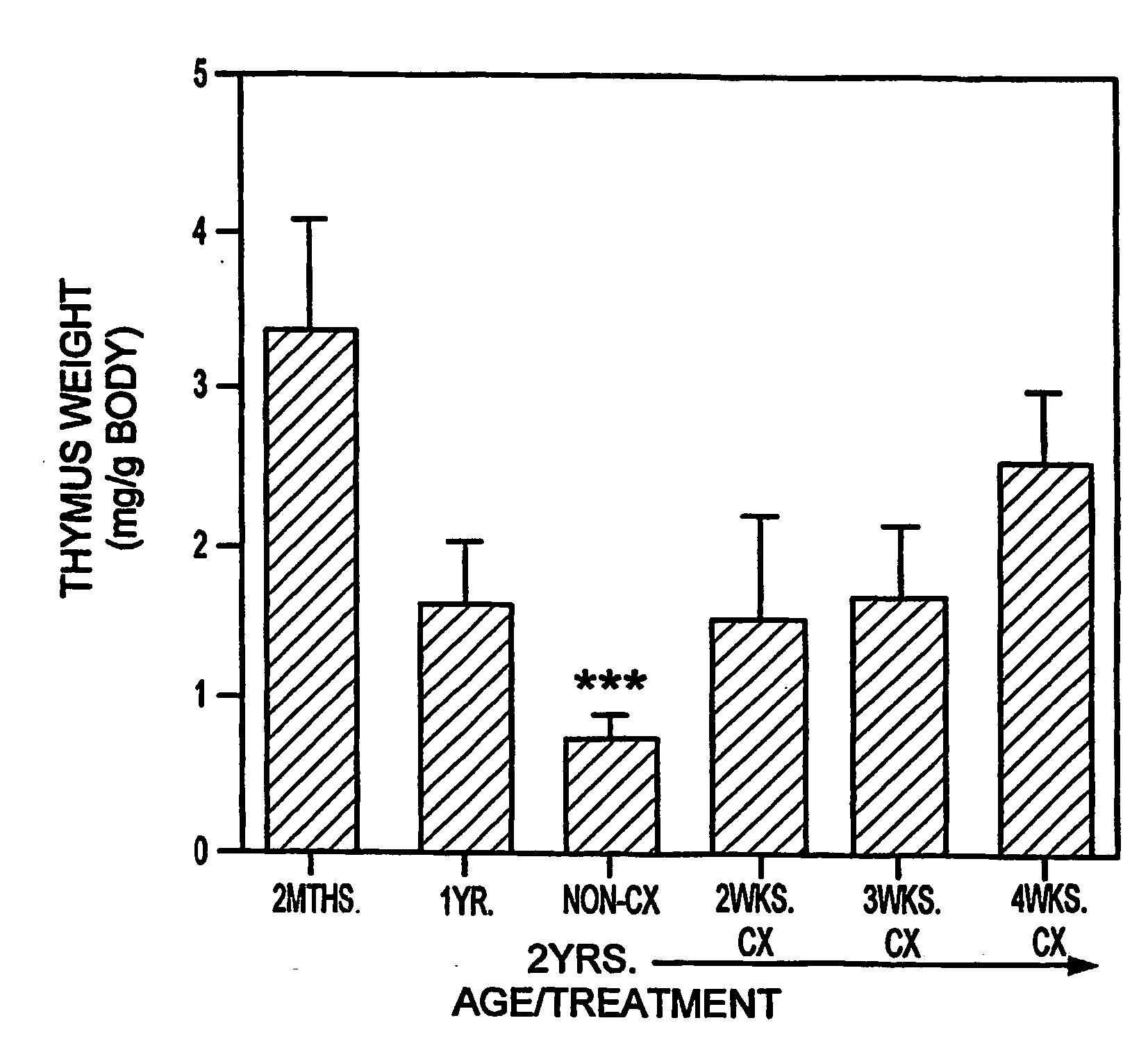
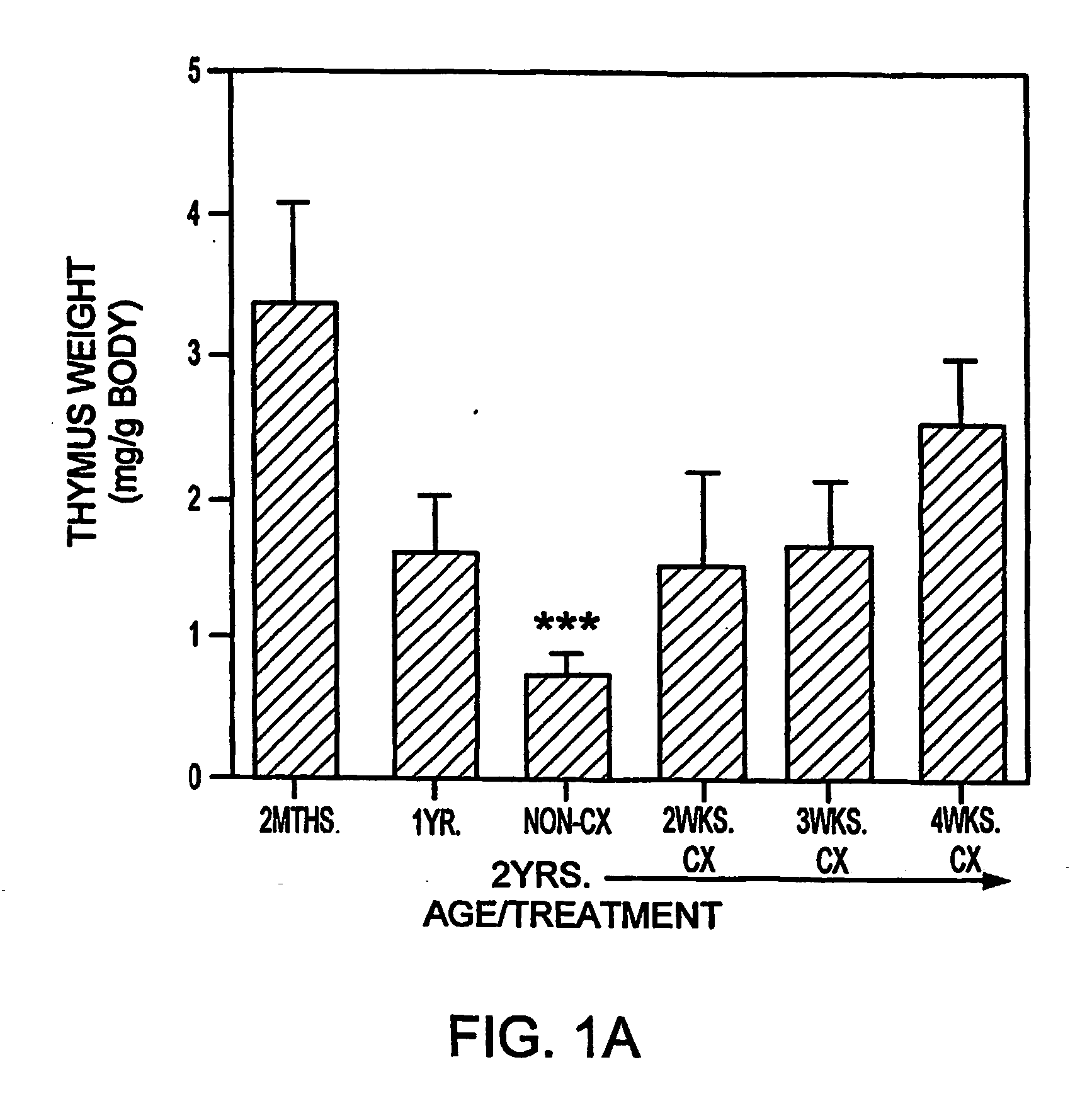
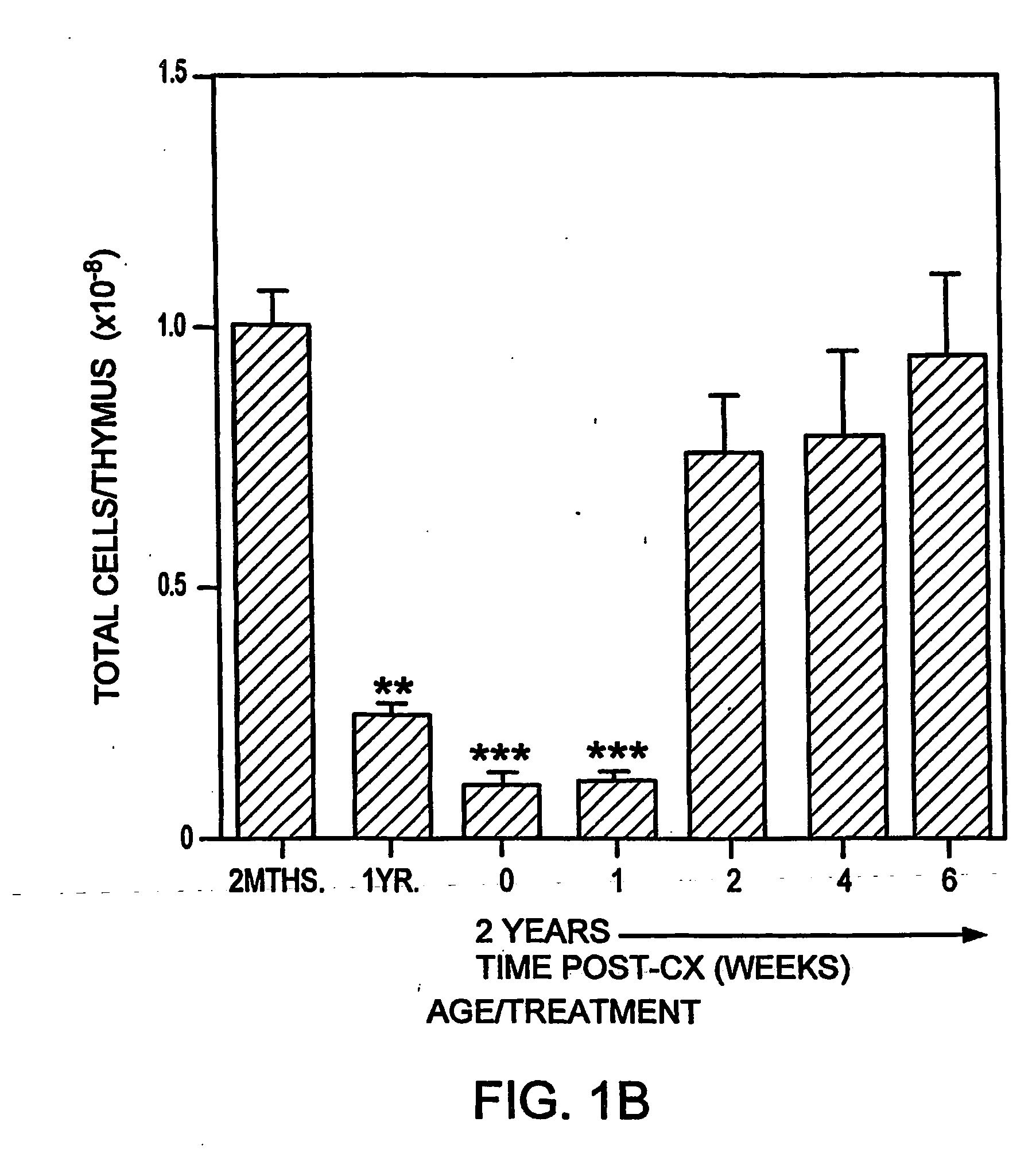
Tolerance to Graft Prior to Thymic Reactivation
InactiveUS20070274946A1Enhanced graft acceptanceFunction increaseBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTolerabilitySterol
The present disclosure provides methods for inducing tolerance in a recipient to a mismatched graft of an organ, tissue, and / or cells, by disrupting sex steroid signaling in the patient, wherein the bone marrow and other immune cell functionality is improved without, prior to, or concurrently with, thymic regeneration. In some embodiments, sex steroid signaling in the patient, is interrupted or ablated by the administration of LHRH agonists, LHRH antagonists, anti-LHRH receptor antibodies, anti-LHRH vaccines, anti-androgens, anti-estrogens, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), selective progesterone response modulators (SPRMs), ERDs, aromatase inhibitors, or various combinations thereof.
Owner:NORWOOD IMMUNOLOGY
Estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS20040077701A1Unexpected and surprising activity in modulating estrogen receptor activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideEstrogen receptor activityEstrogen receptor modulator
Estrogen receptor-modulating pyrazole compounds are described in addition to methods and compositions for treating or preventing estrogen receptor-mediated disorders. The compounds described have been found to have unexpected and surprising activity in modulating estrogen receptor activity. Thus, the compounds of the present invention have utility in preventing or treating estrogen receptor-mediated disorders such as osteoporosis, breast and endometrial cancers, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
The present invention relates to a selective estrogen receptor modulator of formula I: I; or a pharmaceutical acid addition salt thereof; useful, e.g., for treating endometriosis and uterine leiomyoma.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
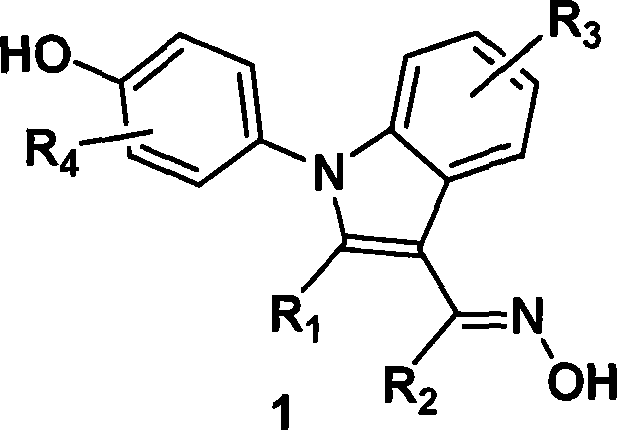
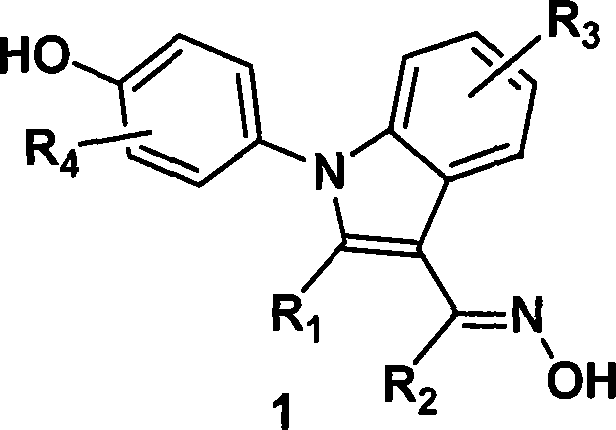
(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1h-indole-3-carbaldehyde oxime derivative as estrogenic agents
InactiveCN1867329AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryIndole-3-carbaldehydeEstrogen receptor modulator
Owner:WYETH LLC
Preparation of 6-oxa-8alpha-steroid estrogen analogues - a new group of unnatural estrogens and their use in medicine
The invention is related to the area of new 6-Oxa-8α-steroid estrogen analogues and the synthesis of these new biological active steroid estrogen analogues, namely, to the preparation of 6-oxa-8α-steroid estrogens and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. These new estrogen analogues are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for the treatment and prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning. These conditions include bone and cartilage disorders, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular diseases, impairment of cognitive function, cerebral degeneration disorders, endometriosis and other types of inflammation, the metabolic syndrome, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:TOPASS
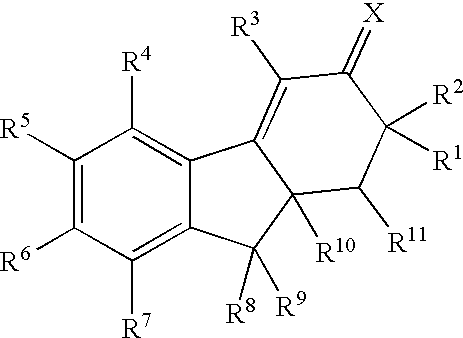
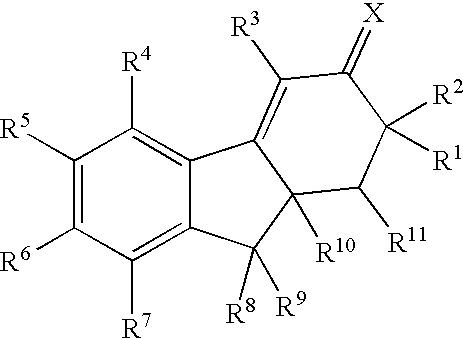
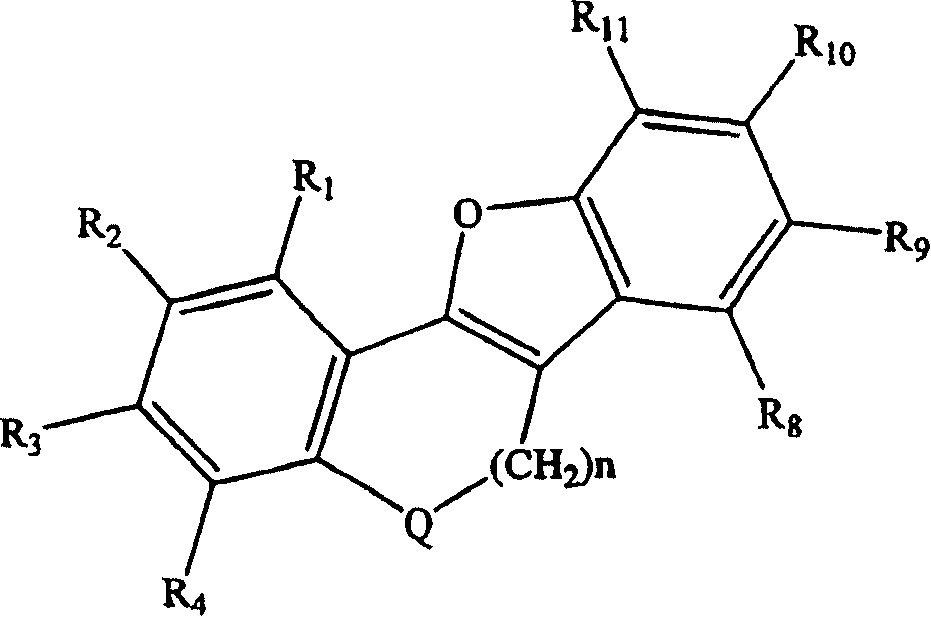
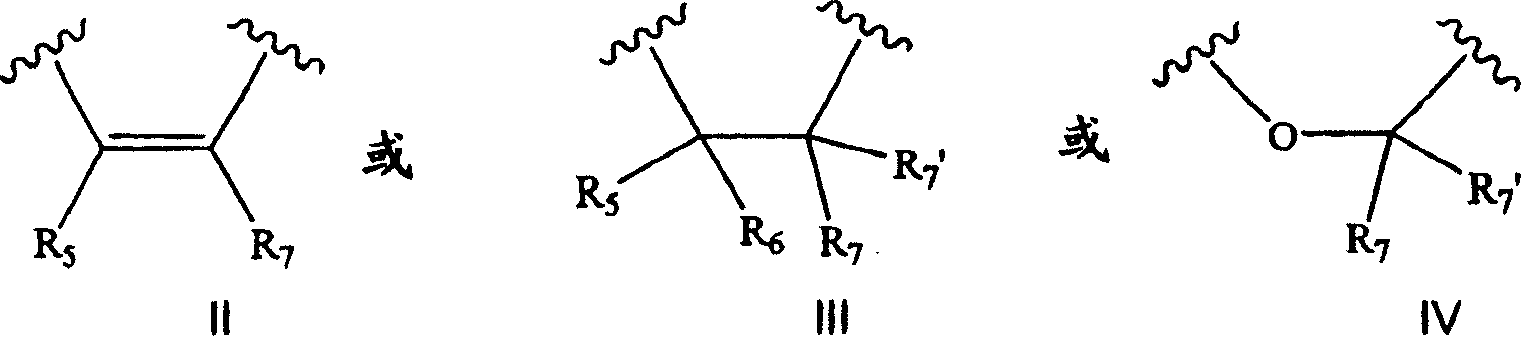
Tetracyclic compounds as estrogen ligands
InactiveCN1993343AEasy to useAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEstrogen receptor modulatorStereochemistry
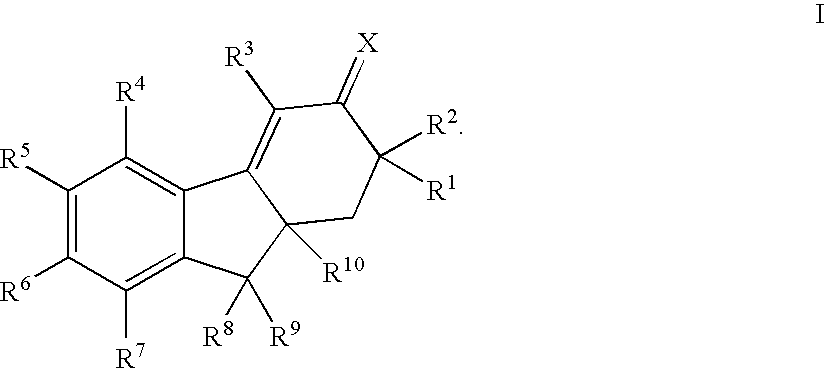
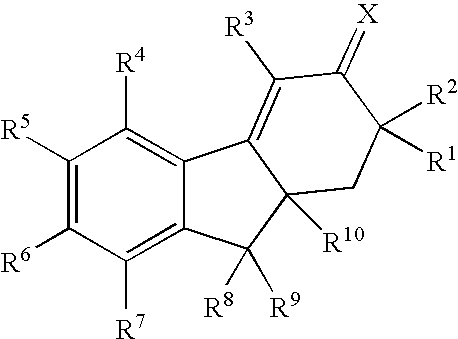
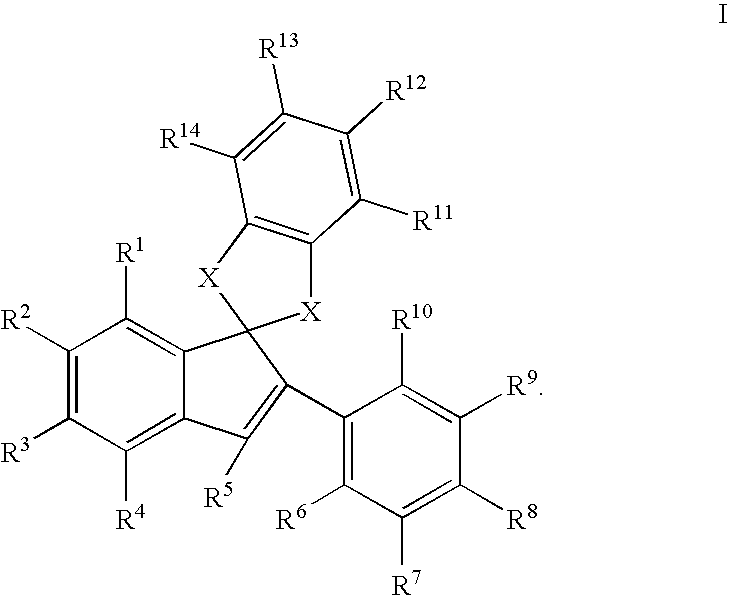
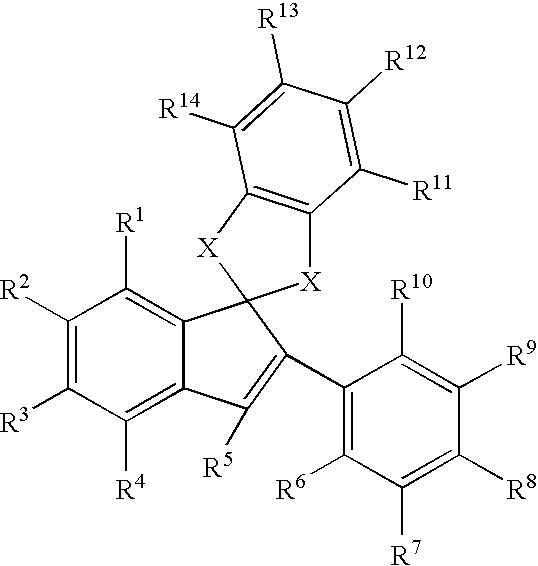
This invention provides estrogen receptor modulators having the structure (I), wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, Q, n, R8, R9, R10, and R11 have been defined in the specification; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The invention further provides methods for the preparation and use of the compounds.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Estrogen receptor modulators
ActiveUS10400006B2Organic active ingredientsEstrane derivativesEstrogen receptor modulatorEndocrinology
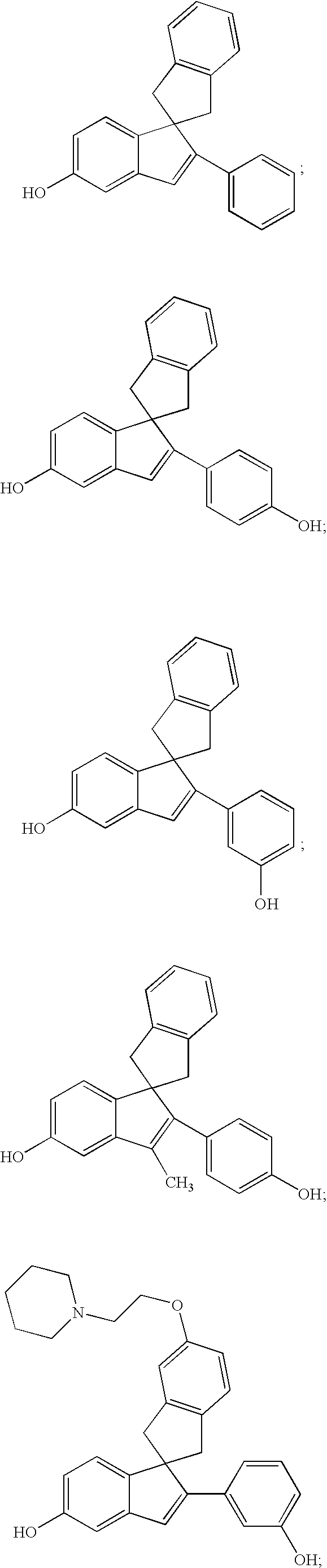
Described herein, inter alia, are compositions and methods for treating or preventing hyperproliferative disorders, including cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
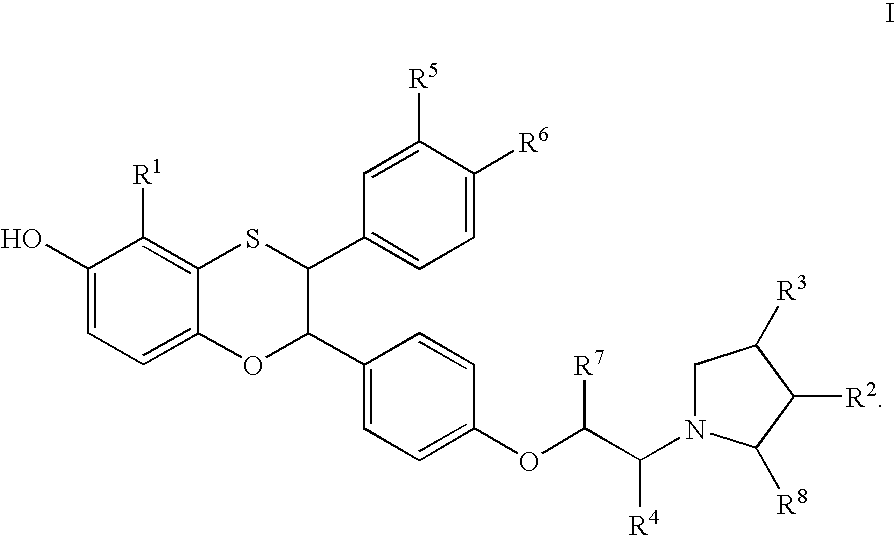
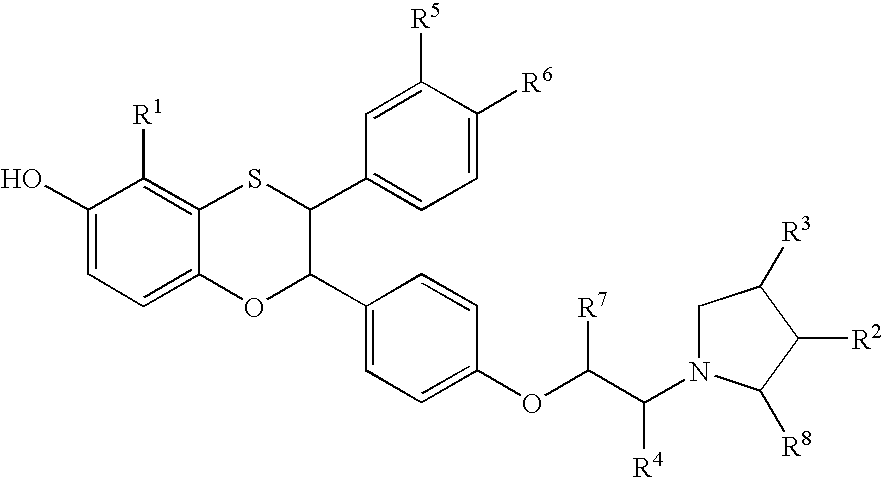
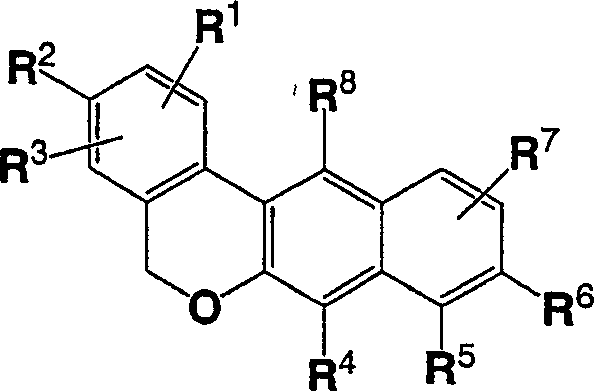
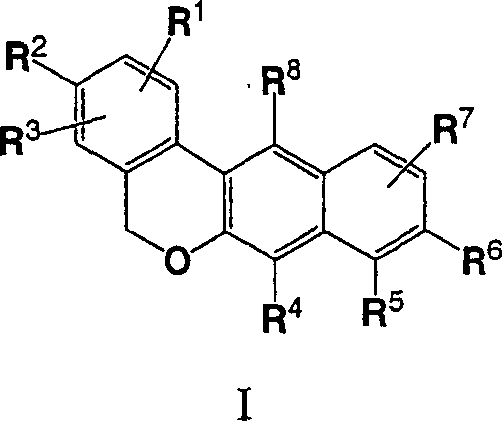
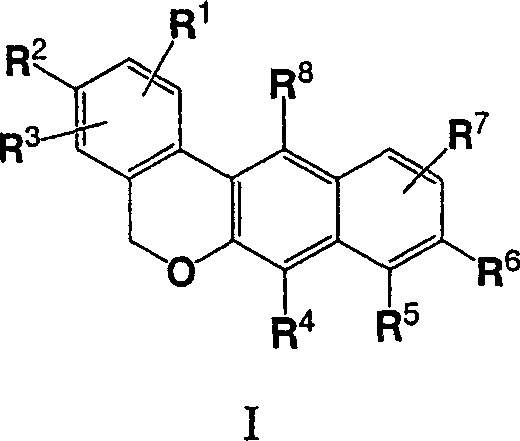
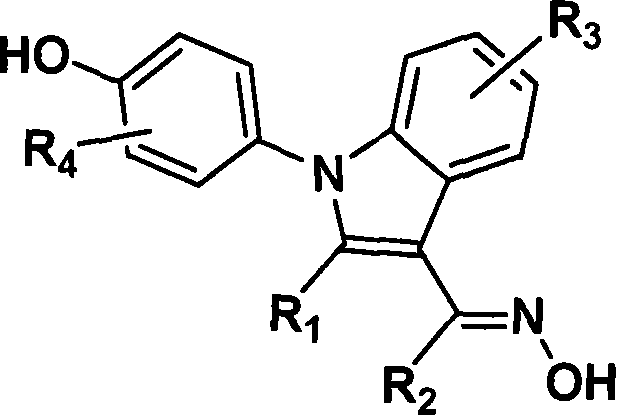
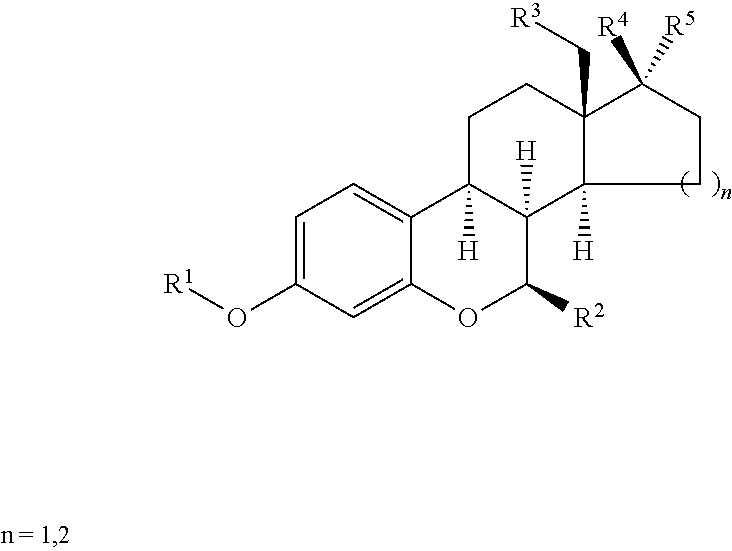
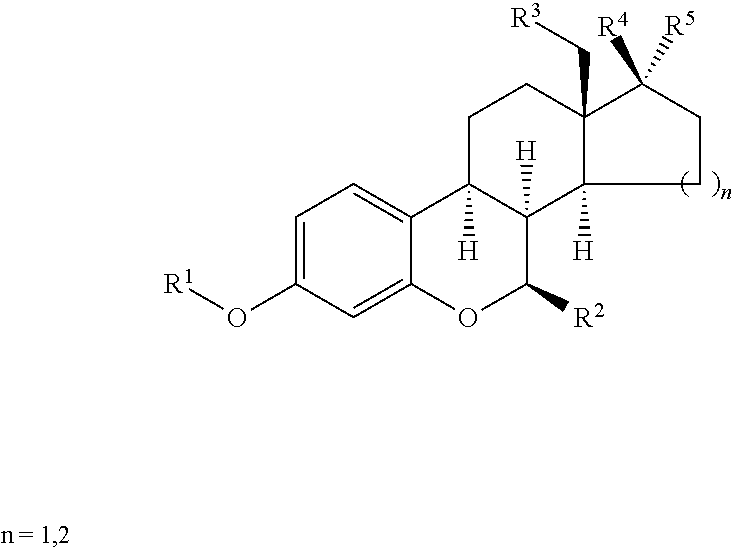
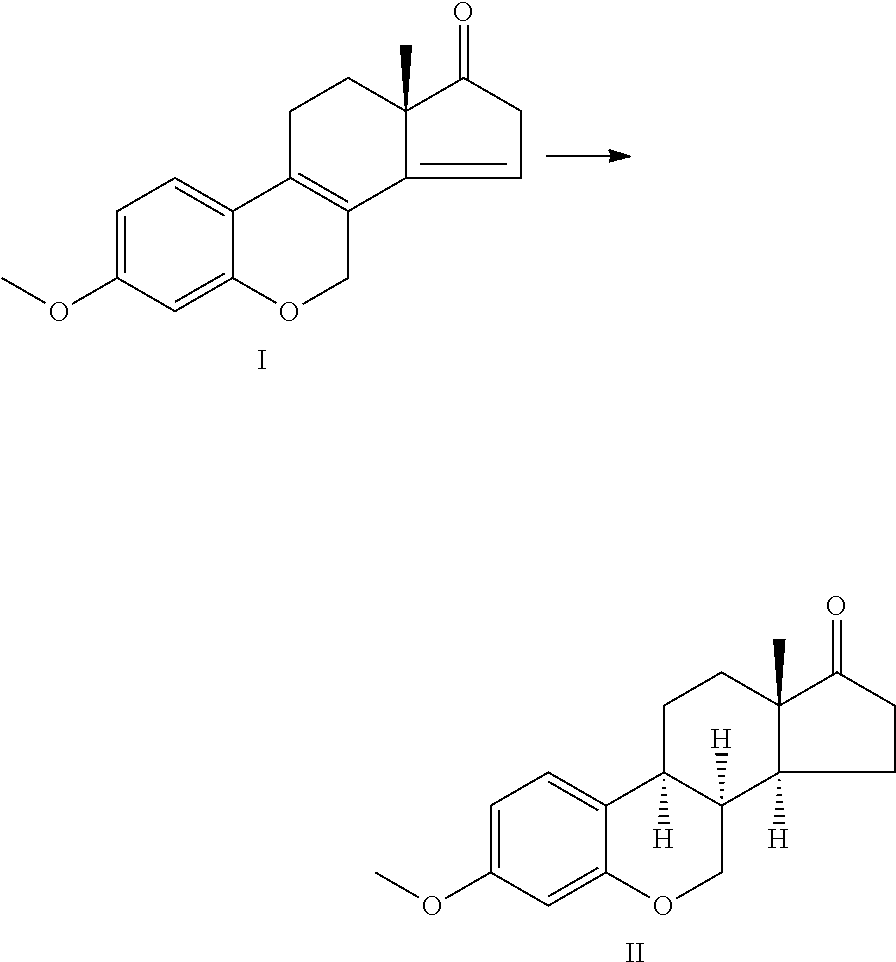
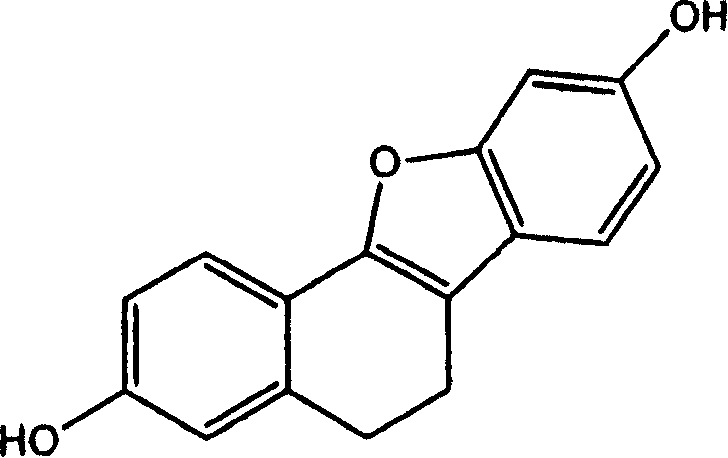
Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS8877949B2Good effect in prevention and treatment of estrogen-related diseaseHigh yieldBiocideSenses disorderFuranEstrogen receptor modulator
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
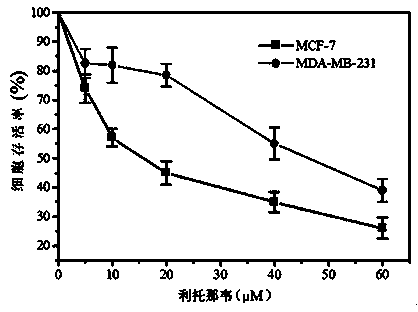
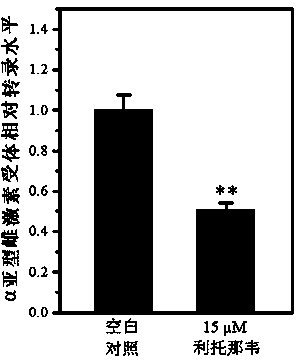
Application of ritonavir as estrogen receptor modulator
InactiveCN103816151ASignificant effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPromoter activityMetabolite
The invention discloses novel applications of ritonavir, and metabolite thereof and / or a metabolite derivative and / or a structural analogue of ritonavir as an estrogen receptor modulator. An inhibition effect of ritonavir to tumor cells is partially depended on an estrogen receptor. Ritonavir down-regulates protein expression level and gene transcription level of an alpha subtype estrogen receptor of the tumor cells; ritonavir inhibits F promoter activity of the alpha subtype estrogen receptor; interactive experiments of rotonavir and the alpha subtype estrogen receptor-ligandb inding domain demonstrate that ritonavir is a selective antagonist of the alpha subtype estrogen receptor, belongs to the estrogen receptor modulator, and can bind the estrogen receptor and modulate transcription and expression level of the estrogen receptor, thereby generating effects of inhibiting growth of the tumor cells and increasing cell mortality rate. Reposition of conventional drugs can reduce risks and reduce research cost. The drug is expected to be used for preparing tumor-treating drugs for drug resistance and chemotherapy resistance of conventional antitumor drugs.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Therapeutic combinations of (selective) estrogen receptor modulators (SERM) and growth hormone secretagogues (GHS) for treating musculoskeletal frailty
InactiveCN1301160AImprove bone qualityIncrease bone densityDigestive systemSkeletal disorderMedicineEstrogen receptor modulator
This invention is directed to pharmaceutical combination compositions and methods containing (-)-cis-6-phenyl-5-(4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2-ol or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and 2-amino-N-(2-(3a(R)-benzyl-2-methyl-3-oxo-2,3, 3a, 4,6,7-hexahydro-pyrazolo-[4,3-c]pyridin-5-yl)-1(R)-benzyloxymethyl-2-oxo-ethyl)-isobutyramide or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, methods of using such compositions and kits containing such compositions. The compositions are useful for treating musculoskeletal frailty, including osteoporosis, osteoporotic fracture, low bone mass, frailty and low muscle mass.
Owner:PFIZER PRODS ETAT DE CONNECTICUT
Aurones as estrogen receptor modulators and their use in sex hormone dependent diseases
InactiveUS20100267822A1Reduce and eliminate componentBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseEstrogen receptor modulator
The invention relates to aurones and extracts comprising them useful in the prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment of an animal (including a human) with an estrogen receptor (ER) related disease or condition of the animal or human body, as well as methods, uses and other inventions related thereto.
Owner:BIOTROPICS MALAYSIA BERHAD
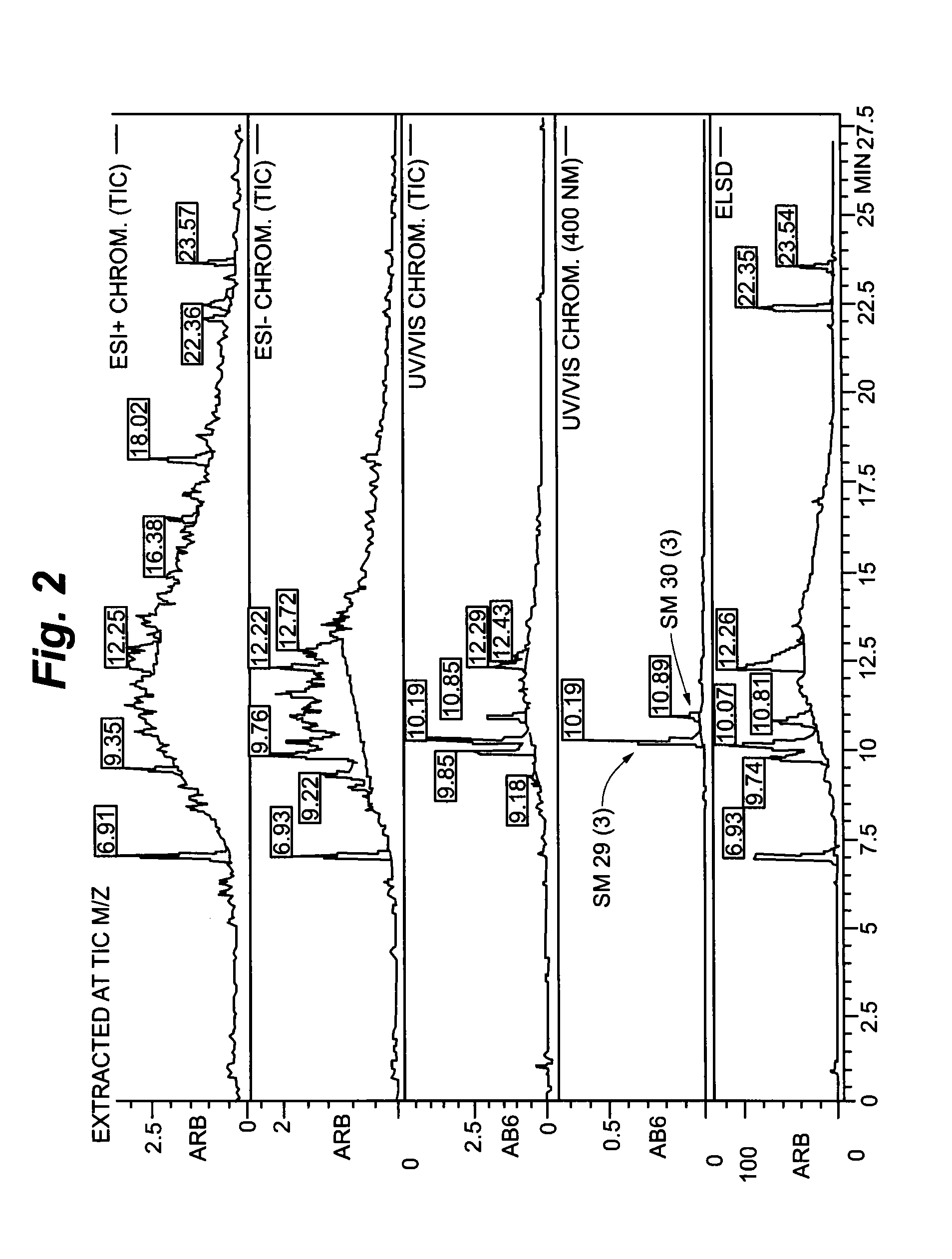
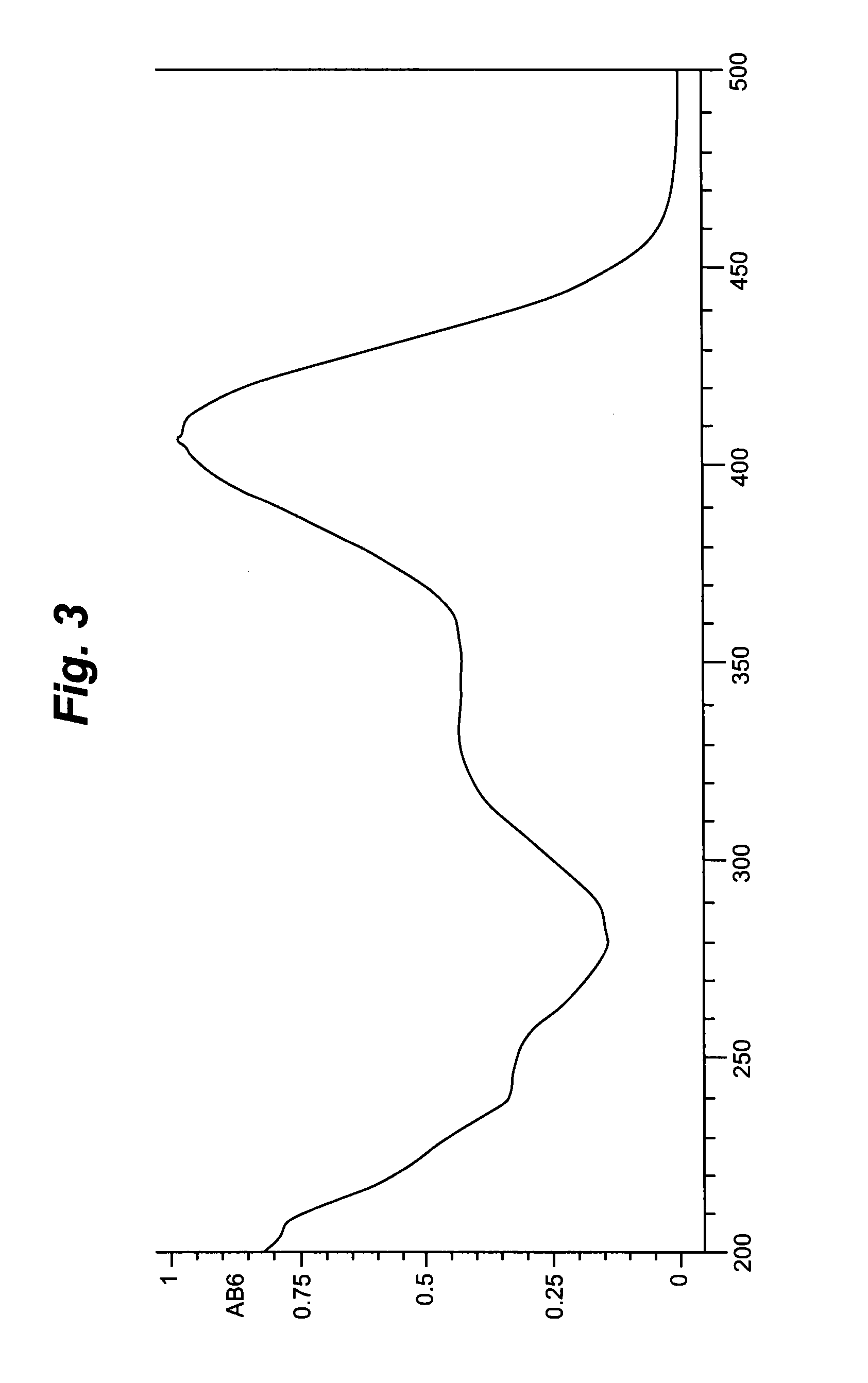
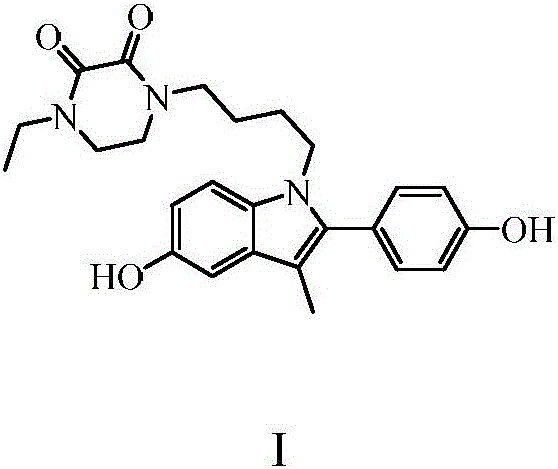
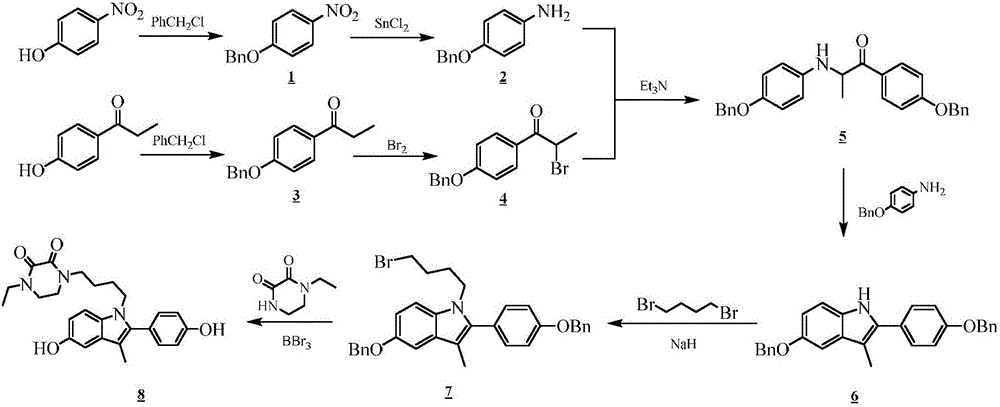
Piperazinone compounds and application thereof
ActiveCN105801564AEasy to prepareHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHormone Receptor ModulatorsHectic fever
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and relates to 1-ethyl-4-[4-[5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1H-indole-1-yl]butyl]piperazine-2,3-dione as well as a medical application, a stereoisomer and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The structural formula of 1-ethyl-4-[4-[5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1H-indole-1-yl] butyl]piperazine-2,3-dione is represented in the specification; 1-ethyl-4-[4-[5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1H-indole-1-yl]butyl]piperazine-2,3-dione and pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt of the compound can be combined with existing drugs or can be independently used as an estrogen receptor modulator for treating or preventing various estrogen function related diseases such as bone loss, fracture, osteoporosis, hectic fever, LDL cholesterol level rise, cardiovascular disease, cognitive impairment, brain degeneration disease and anxiety, as well as depression, sexual dysfunction, hypertension, retinal degeneration and cancer caused by estrogen deficiency, especially osteoporosis.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
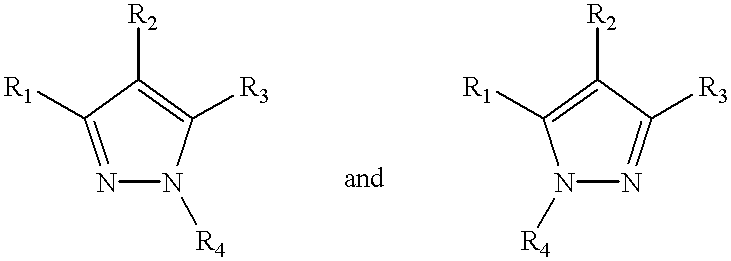
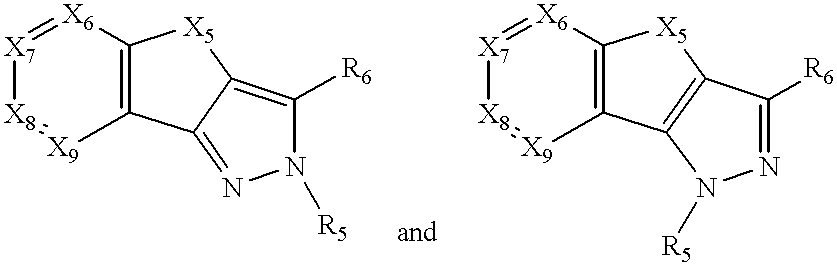
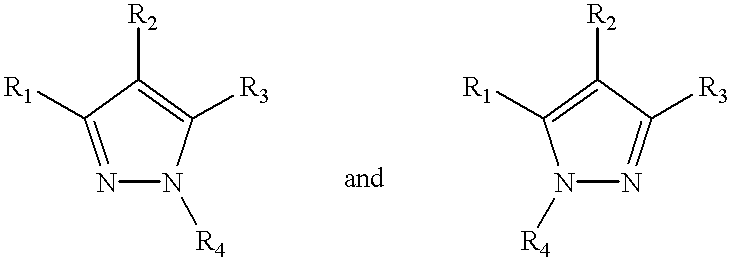

![Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/79fd2cae-e8f3-4a25-9386-d56340c40fbc/US06891070-20050510-C00001.png)
![Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/79fd2cae-e8f3-4a25-9386-d56340c40fbc/US06891070-20050510-C00002.png)
![Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers Method for the preparation of 2-{2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethanol and its isomers](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/79fd2cae-e8f3-4a25-9386-d56340c40fbc/US06891070-20050510-C00003.png)
![Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/14e46de8-0c90-4626-bf0e-645d9199b841/US20060160815A1-20060720-C00001.png)
![Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/14e46de8-0c90-4626-bf0e-645d9199b841/US20060160815A1-20060720-C00002.png)
![Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-5-(4H)-yl)sulfonyls and carbonyls and their use as estrogenic agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/14e46de8-0c90-4626-bf0e-645d9199b841/US20060160815A1-20060720-C00003.png)
![Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/02811518-b836-487d-9379-8fa2483caab9/US08877949-20141104-C00001.png)
![Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/02811518-b836-487d-9379-8fa2483caab9/US08877949-20141104-C00002.png)
![Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof Furo[3,2-g]chromene compounds and uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/02811518-b836-487d-9379-8fa2483caab9/US08877949-20141104-C00003.png)