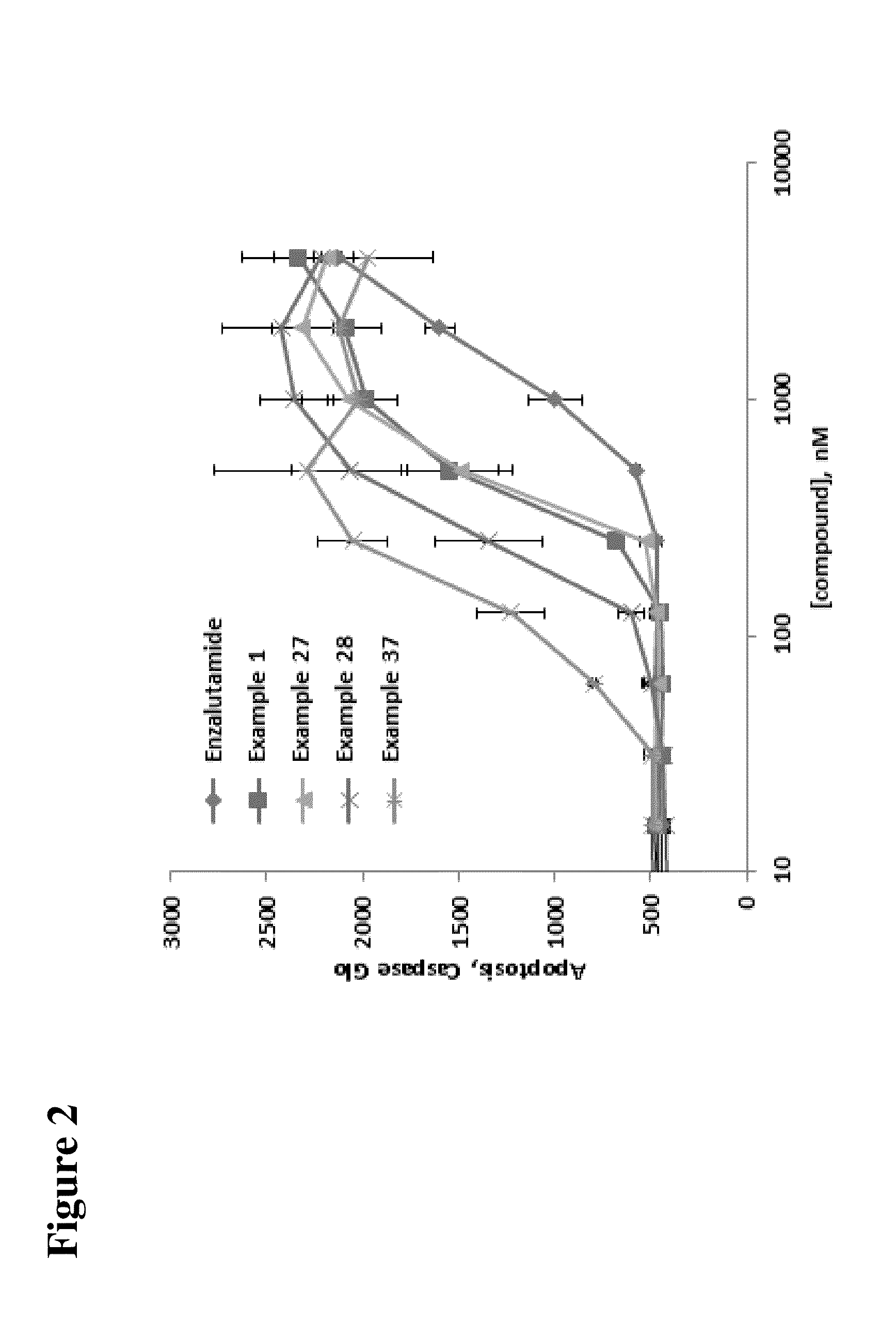
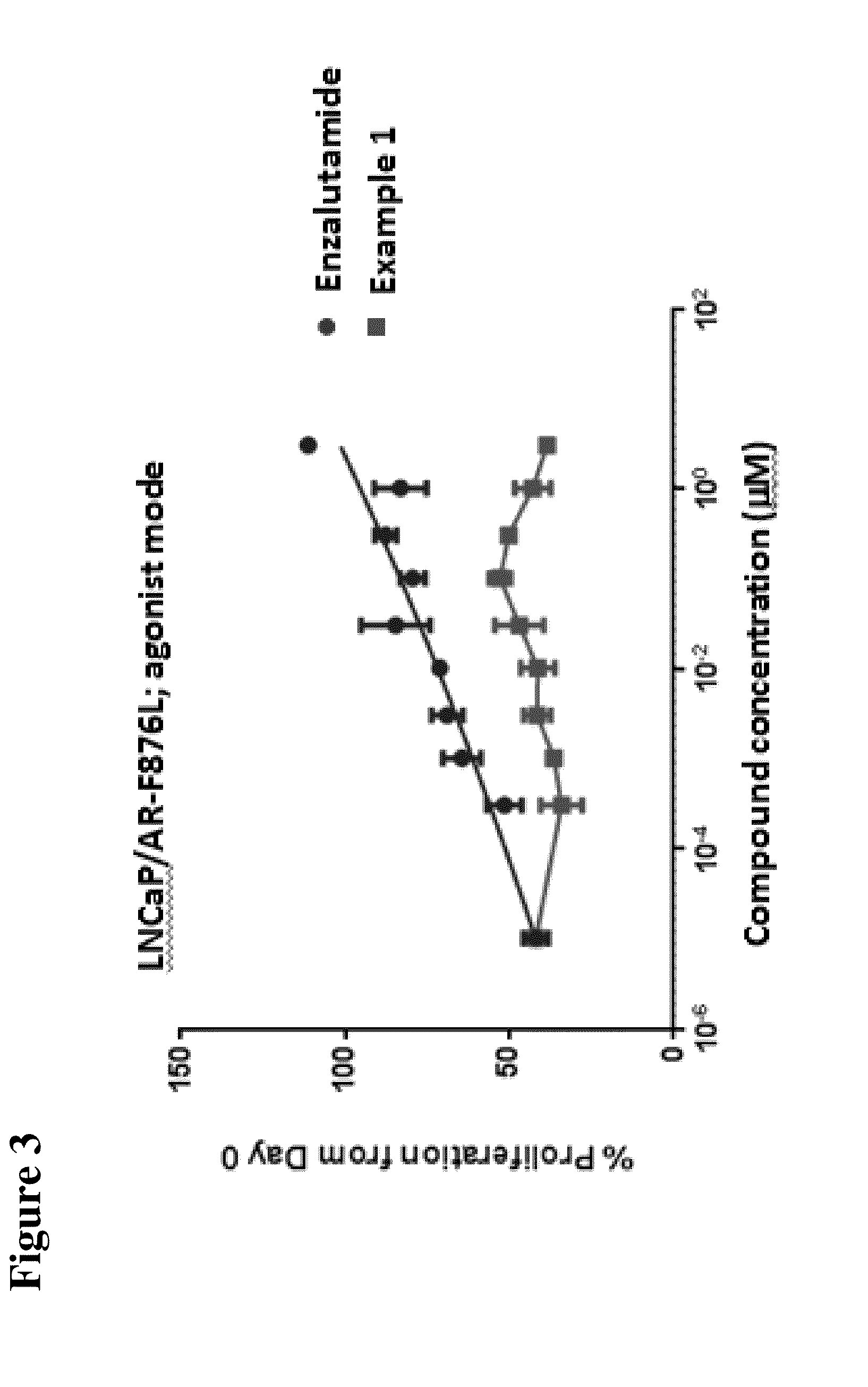
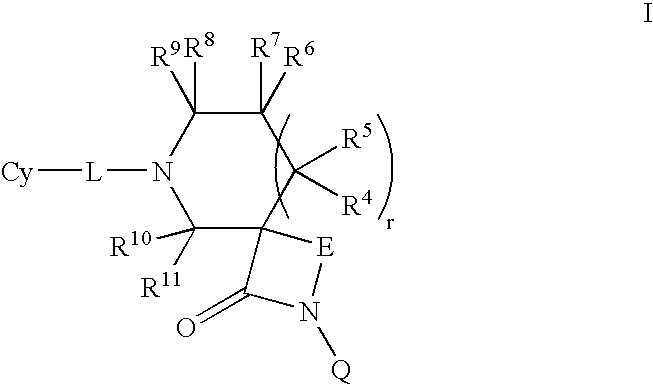
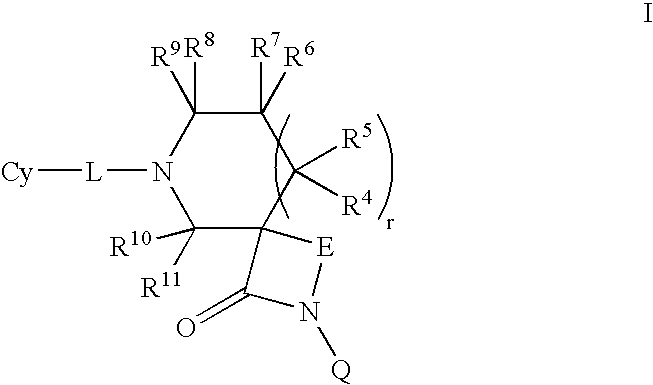
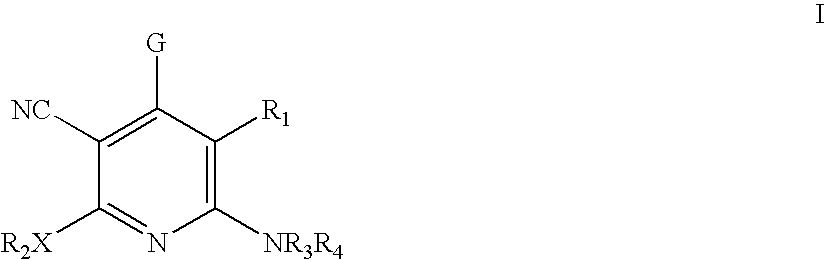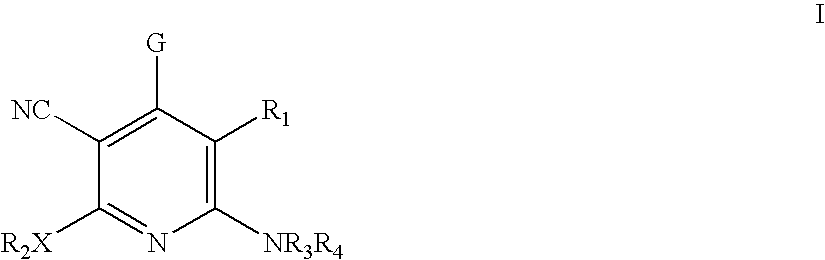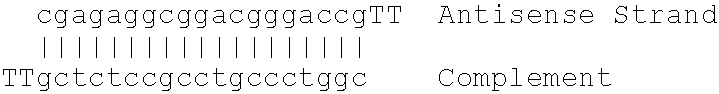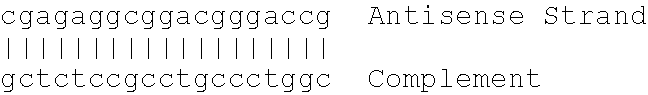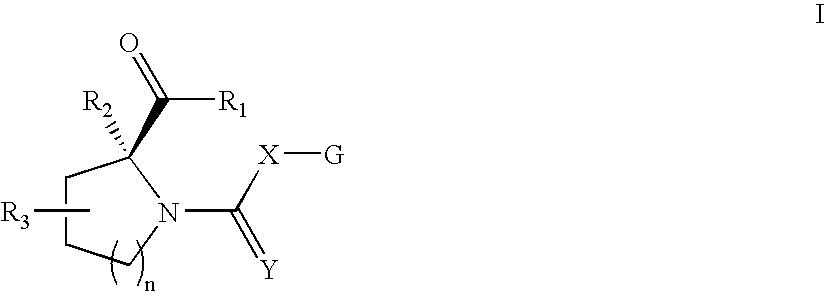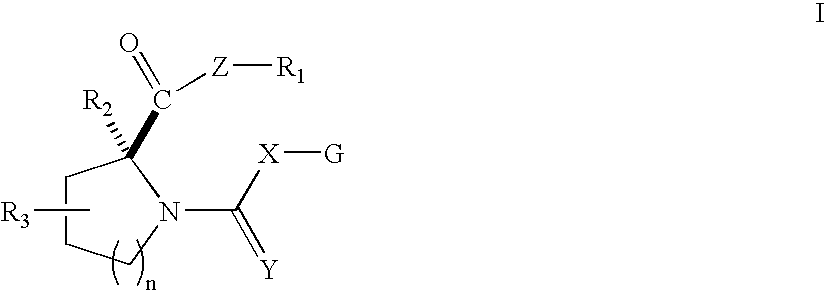Patents
Literature
727 results about "Hormone receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A hormone receptor is a receptor molecule that binds to a specific hormone. Hormone receptors are a wide family of proteins made up of receptors for thyroid and steroid hormones, retinoids and Vitamin D, and a variety of other receptors for various ligands, such as fatty acids and prostaglandins. There are two main classes of hormone receptors. Receptors for peptide hormones tend to be cell surface receptors built into the plasma membrane of cells and are thus referred to as trans membrane receptors. An example of this is insulin. Receptors for steroid hormones are usually found within the cytoplasm and are referred to as intracellular or nuclear receptors, such as testosterone. Upon hormone binding, the receptor can initiate multiple signaling pathways, which ultimately leads to changes in the behavior of the target cells.
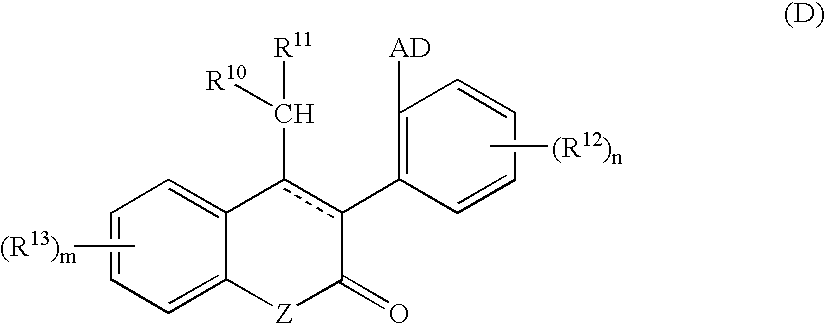
Method of using 3-cyano-4-arylpyridine derivatives as modulators of androgen receptor function
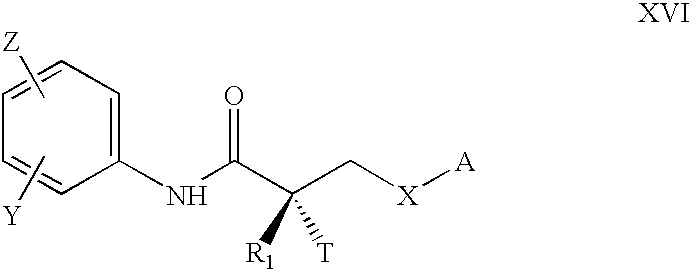
A method is provided for treating androgen receptor-associated conditions such as age-related diseases, for example sarcopenia, employing a compound of the structure wherein R1 is CN or H; X is O or S;R2 is alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; R3 and R4 are the same or different and are independently selected from H, C(O)R2a, alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; R2a is alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; G is aryl or heteroaryl, or aryl or heteroaryl substituted with one, two, three, four or five, where possible, of the substituents selected from the group consisting of hydrogen (H), halo, NO2, CN, OR2b, OH, CF3, NR3aR4a; wherein R3a and R4a, and R2b are the same or different and are independently selected from alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a prodrug ester thereof.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
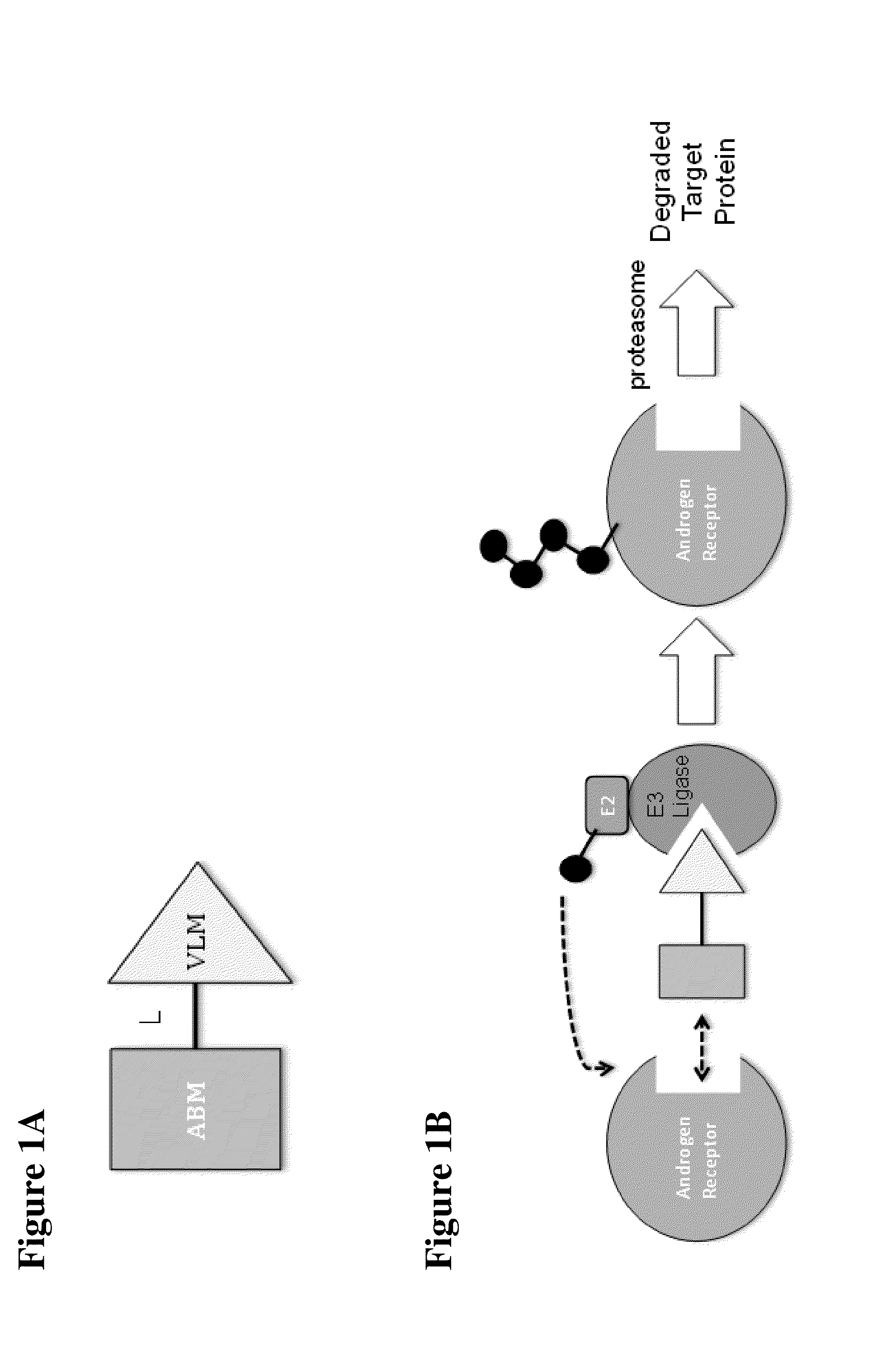
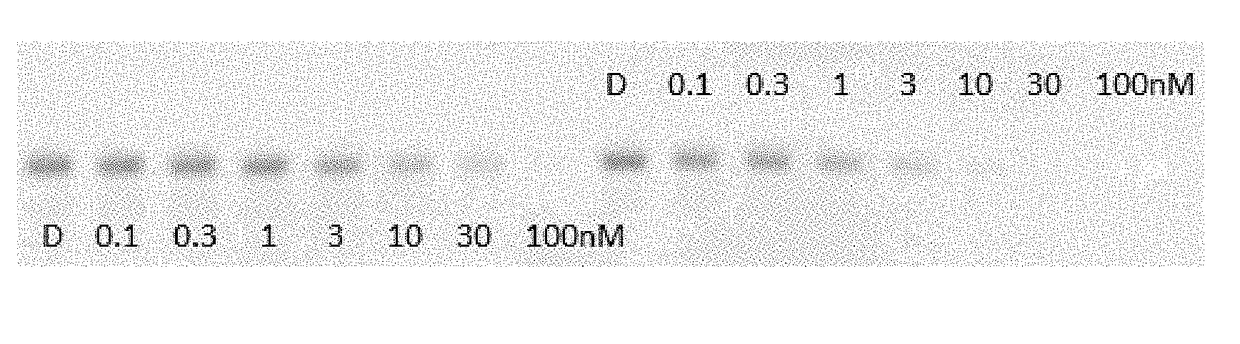
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
ActiveUS20160214972A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderAndrogen Receptor GeneUbiquitin ligase
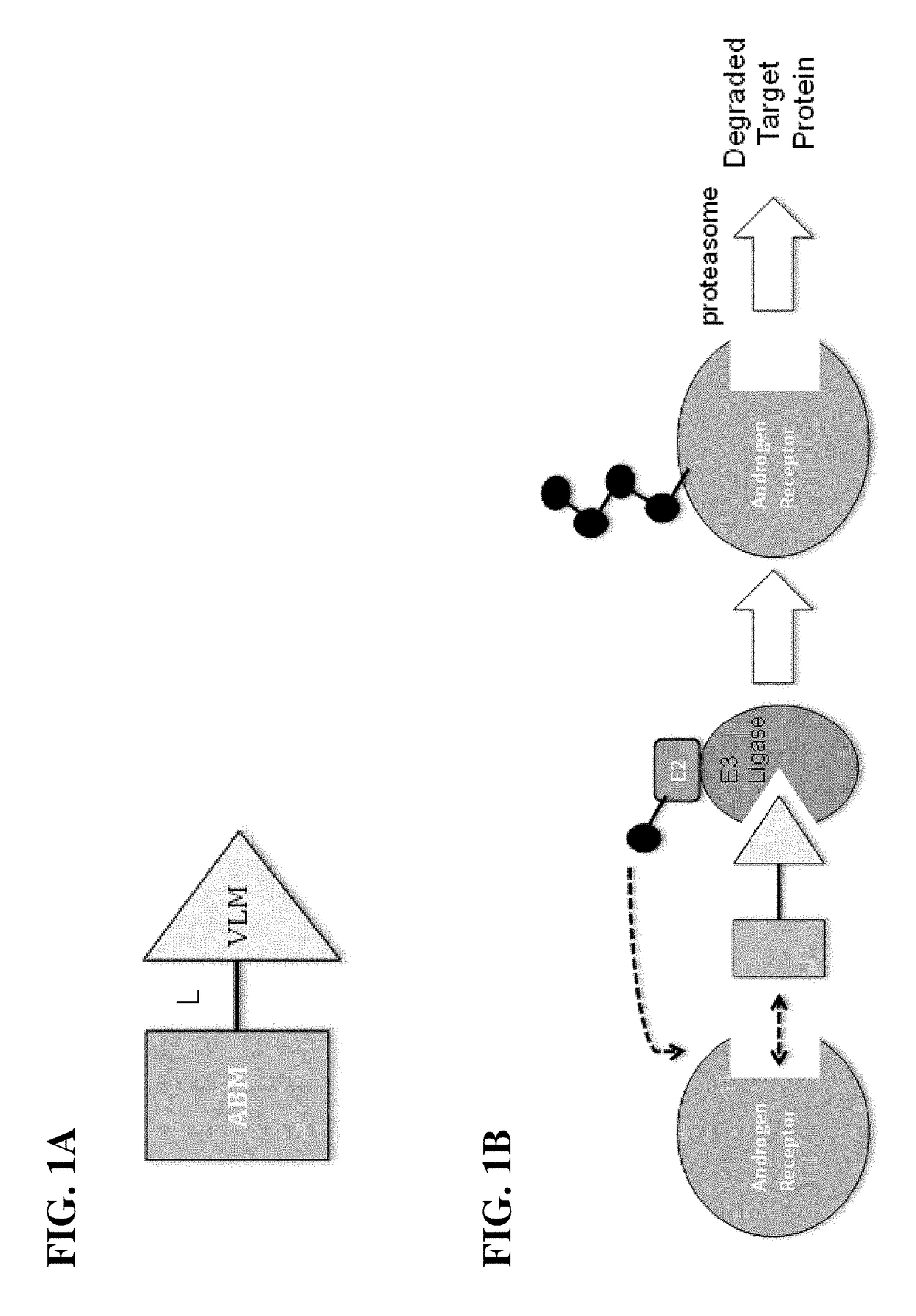
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade and (inhibit) Androgen Receptor. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds Androgen Receptor such that Androgen Receptor is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of Androgen Receptor. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of Androgen Receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Lactam compounds and their use as pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS20060116382A1Avoid conversionInhibit productionBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMineralocorticoid receptor
The present invention relates to inhibitors of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1, antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. The compounds of the invention can be useful in the treatment of various diseases associated with expression or activity of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1 and / or diseases associated with aldosterone excess.
Owner:INCYTE
Glucocorticoid mimetics, methods of making them, pharmaceutical compositions, and uses thereof
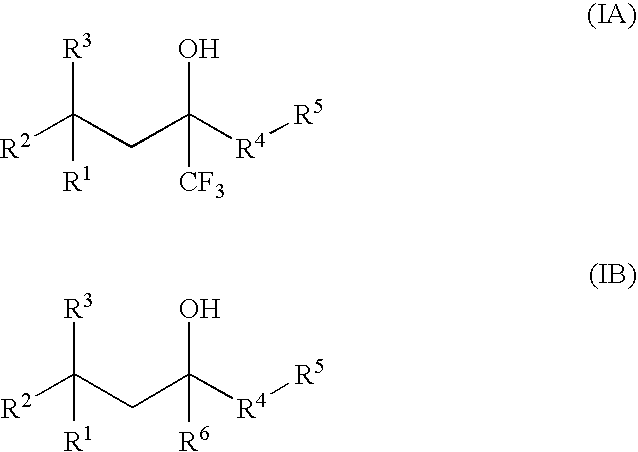
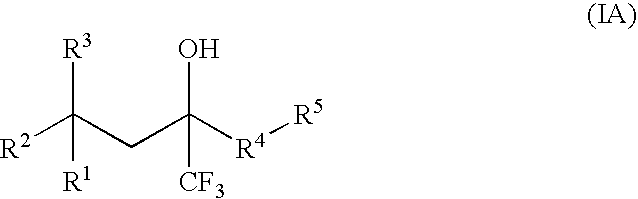
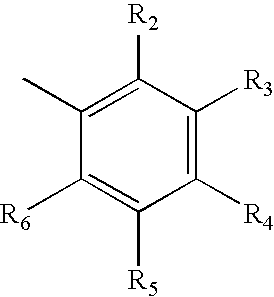
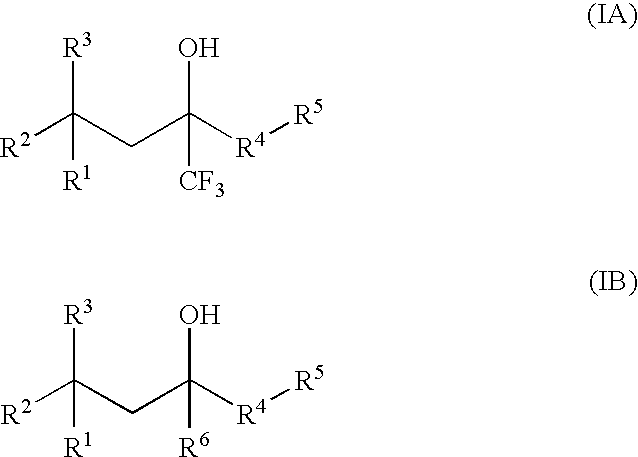
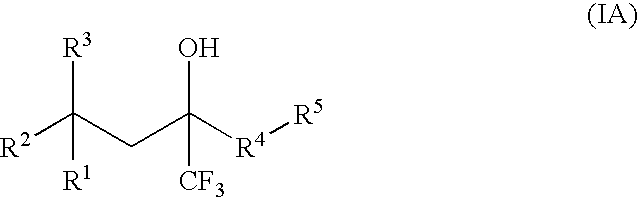
Compounds of Formula (IA) and Formula (IB) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and R6 are as defined herein for Formula (IA) or Formula (IB), or a tautomer, prodrug, solvate, or salt thereof; pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and methods of modulating the glucocorticoid receptor function and methods of treating disease-states or conditions mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor function or characterized by inflammatory, allergic, or proliferative processes in a patient using these compounds.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions for stimulating osteoblast proliferation or treating malignant cell proliferation and methods for selecting osteoblast proliferation stimulants
InactiveUS20030119791A1Overcome limitationsPromote growthBiocideOrganic chemistryStimulantHormones regulation
The present invention relates to pharmacologically active compounds which are capable of binding to nuclear hormone receptors and are useful for the stimulation of osteoblast proliferation and ultimately bone growth. This invention also relates to the use of such compounds for the treatment or prevention of diseases and / or disorders associated with nuclear hormone receptor families.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Beta-catenin is a strong and independent prognostic factor for cancer
InactiveUS20030064384A1Poor prognosisStrong and independent prognostic factor in cancerGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTransactivationFactor ii
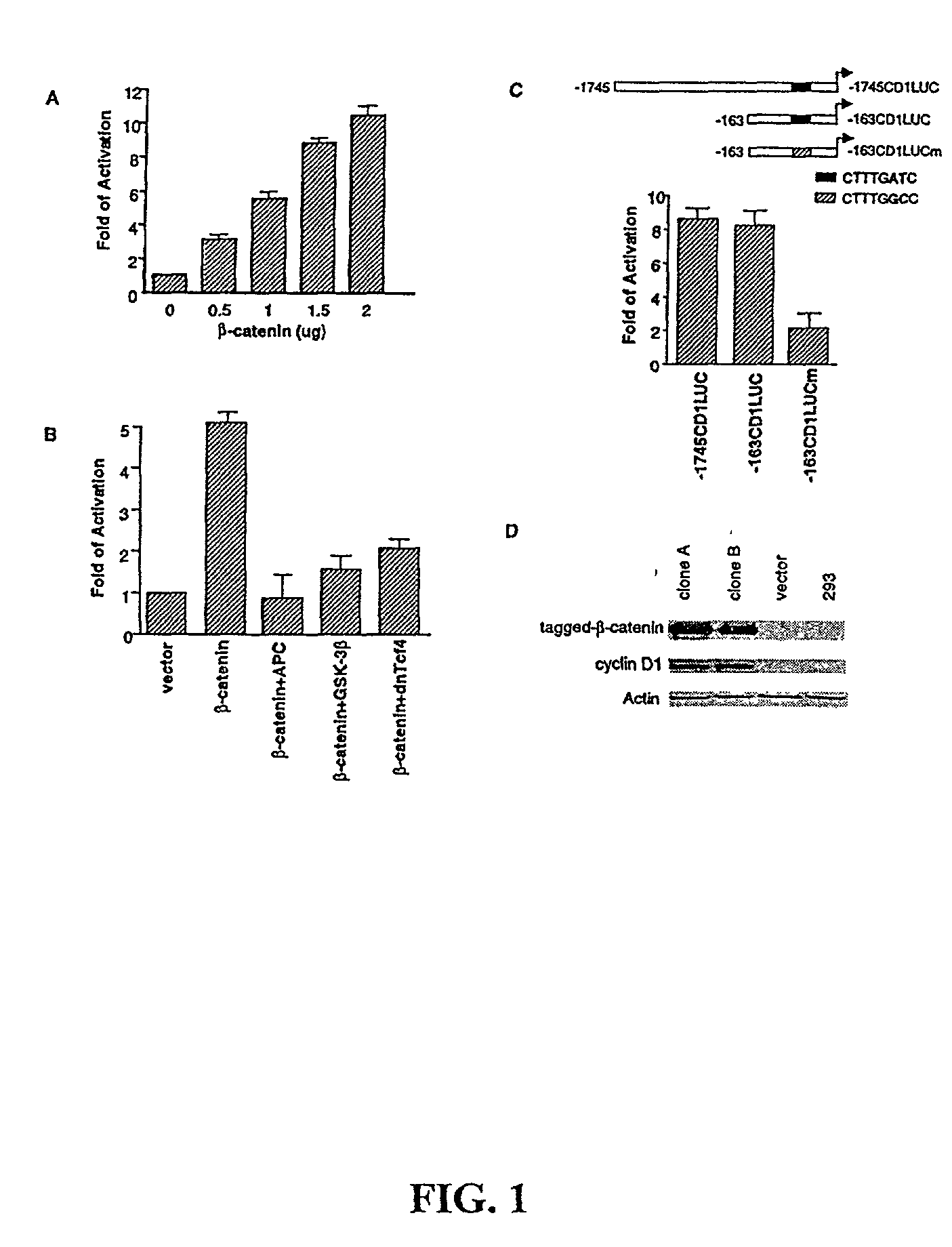
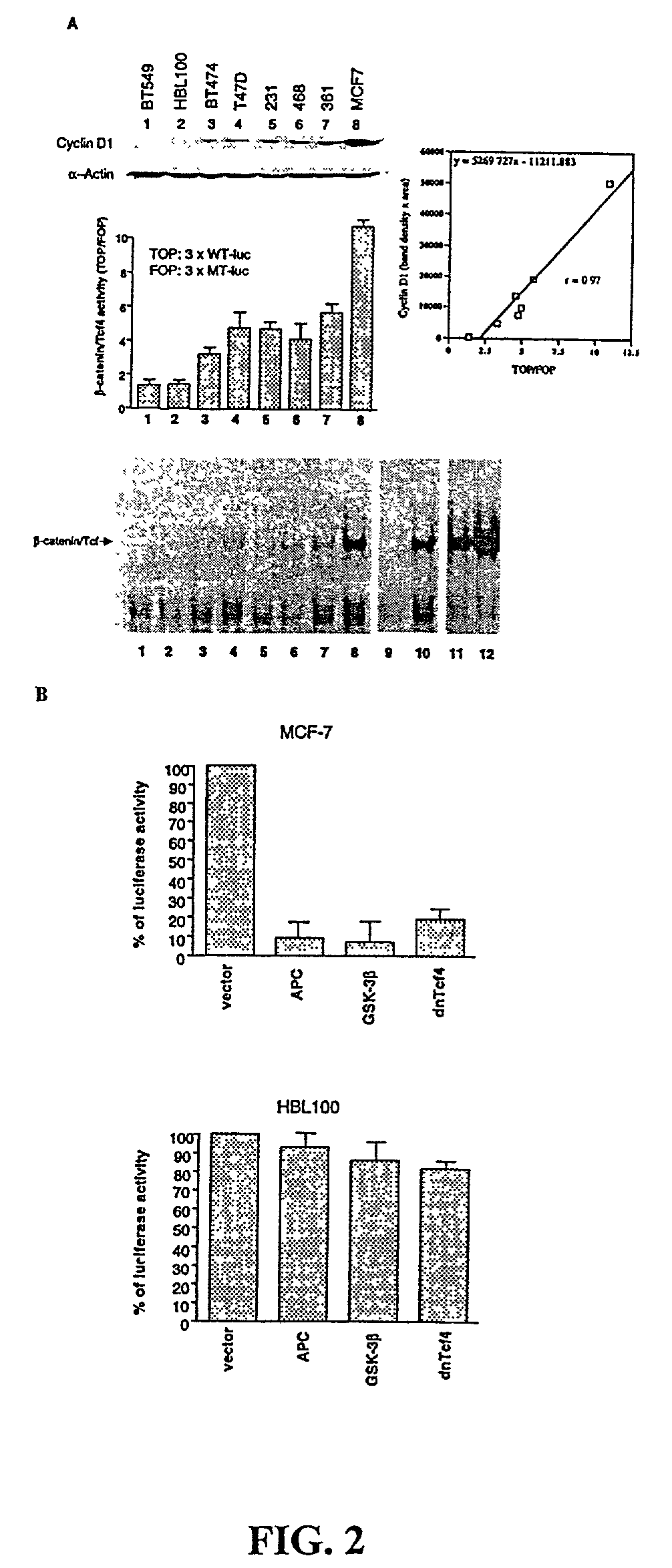
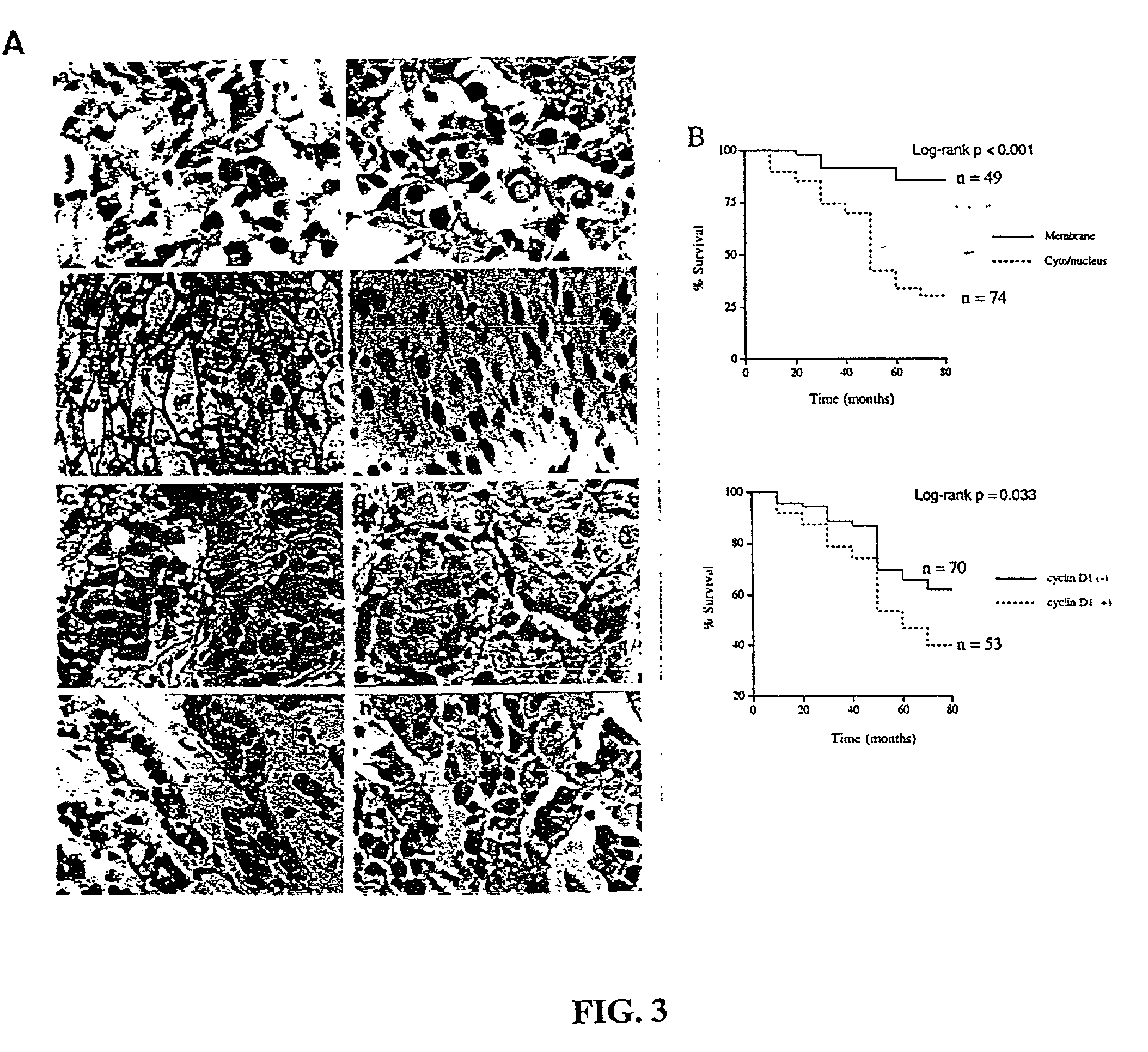
Cyclin D1 is one of the targets of beta-catenin in breast cancer cells. Transactivation of beta-catenin correlated significantly with cyclin D1 expression both in eight breast cell lines in vitro and in 123 patient samples. More importantly, high beta-catenin activity significantly correlated with poor prognosis of the patients and is a strong and independent prognostic factor in breast cancer (p<0.001). Moreover, by multivariate analyses, the inventors found that activated beta-catenin is a strong prognostic factor which provided additional and independent predictive information on patients survival rate even when other prognostic factors, including lymph node metastasis, tumor size, estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status, were taken into account (p<0.001). This invention demonstrates that beta-catenin is involved in breast cancer formation and / or progression and may serve as a target for breast cancer therapy.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
PendingUS20170327469A1Organic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAndrogen Receptor GeneUbiquitin ligase
The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade (and inhibit) Androgen Receptor. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds Androgen Receptor such that Androgen Receptor is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of Androgen Receptor. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of Androgen Receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Monocyclic N-aryl hydantoin modulators of androgen receptor function
The present invention relates to novel compounds useful in the treatment of androgen receptor associated conditions, such as age-related diseases, pharmaceutical compositions containing at least one of the compounds of the present invention and methods of treating a patient in need of therapy for an androgen receptor associated condition by administering a therapeutically effective amount of at least compound of the present invention.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Inhibitor oligonucleotides and their use for specific repression of a gene
A method of treating a disease resulting from the expression of a harmful gene is described. The method includes the step of administering a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition having at least one double stranded oligonucleotide including two complementary oligonucleotide sequences forming a hybrid. Each oligonucleotide sequence comprises at one of their 3′ or 5′ ends one to five unpaired nucleotides forming single-strand ends extending beyond the hybrid. One of the oligonucleotide sequences is substantially complementary to a target sequence belonging to a DNA or messenger RNA molecule of a gene coding a mutated or nonmutated androgen receptor.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Hormone receptor functional dimers and methods of their use
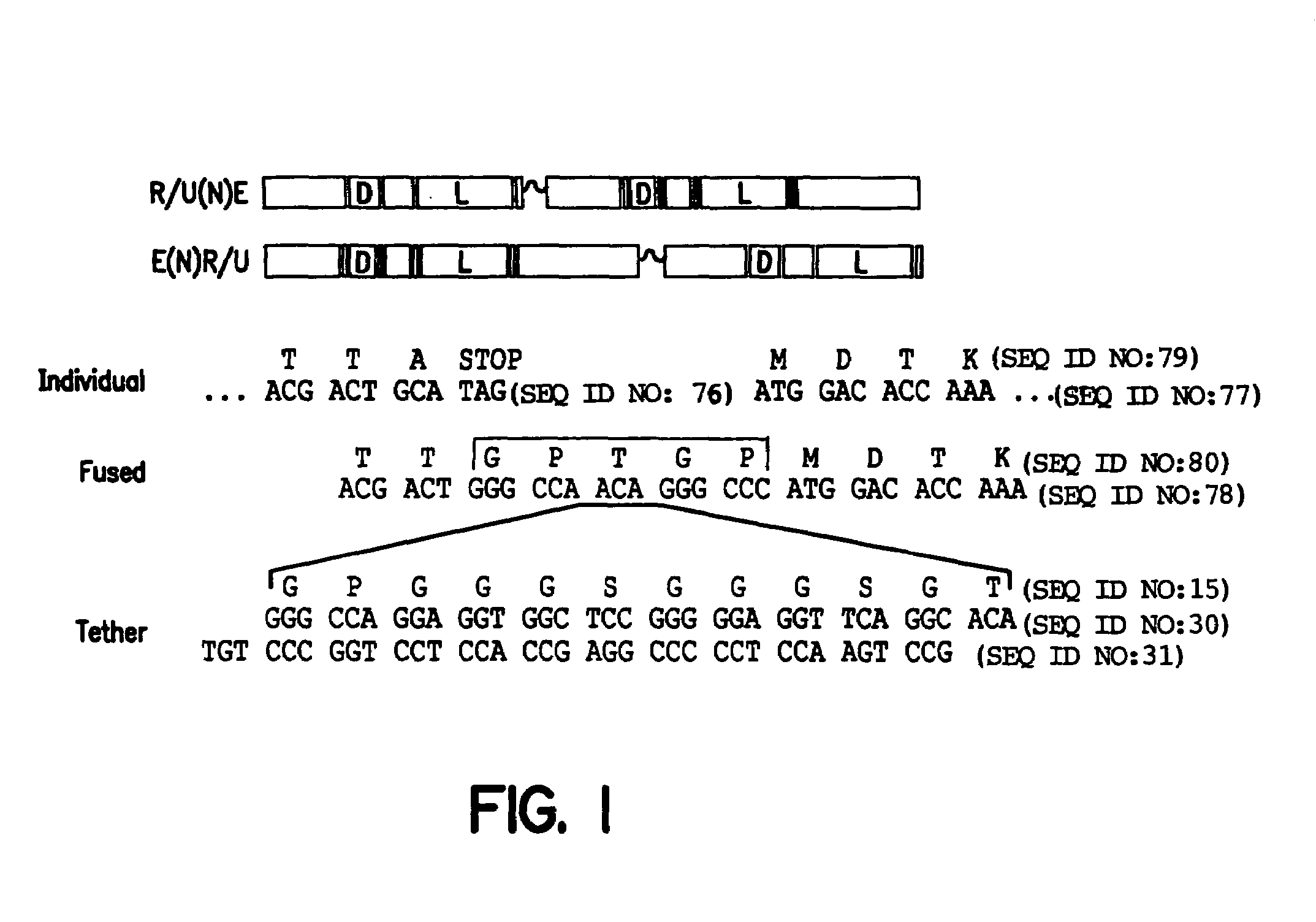
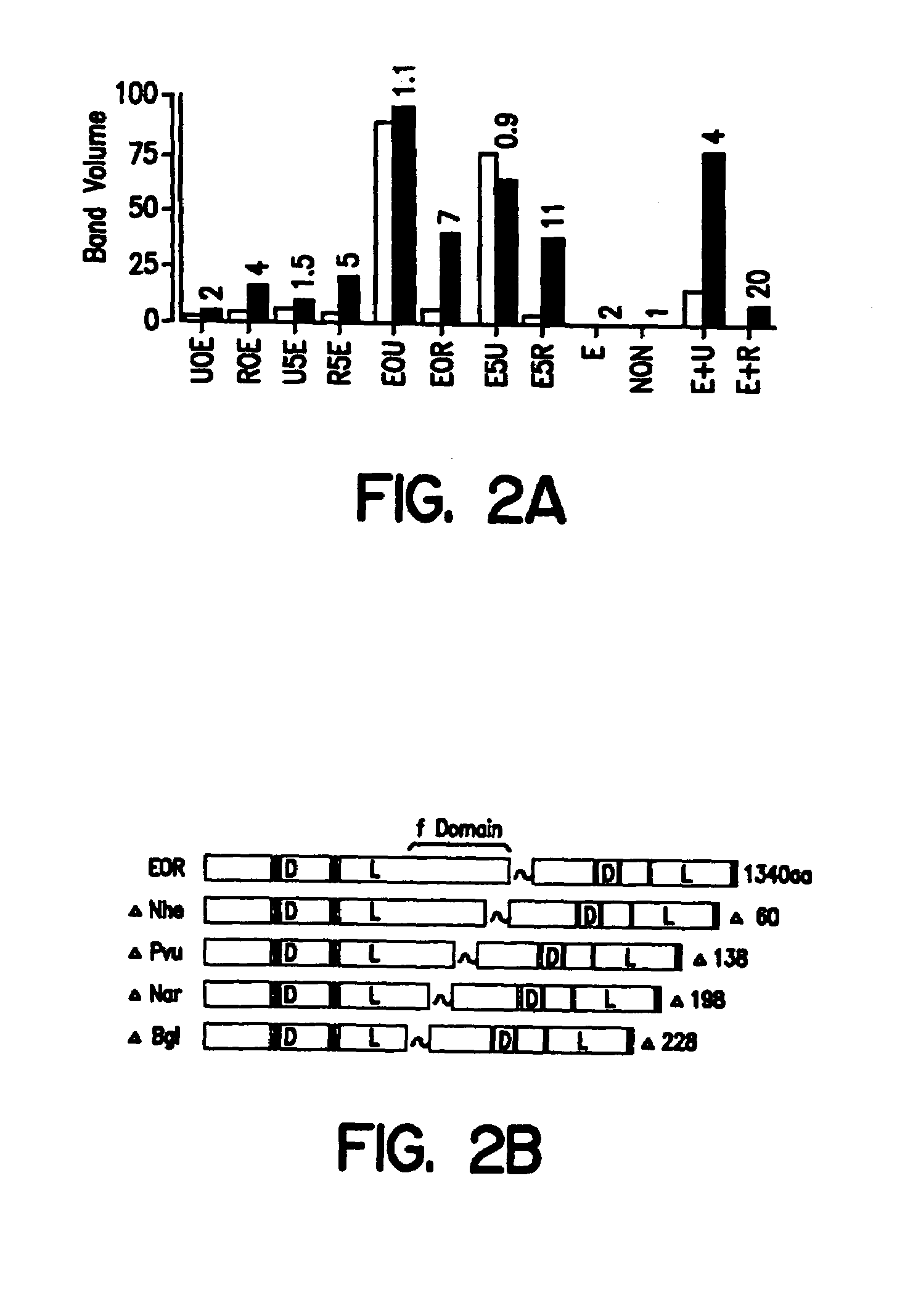
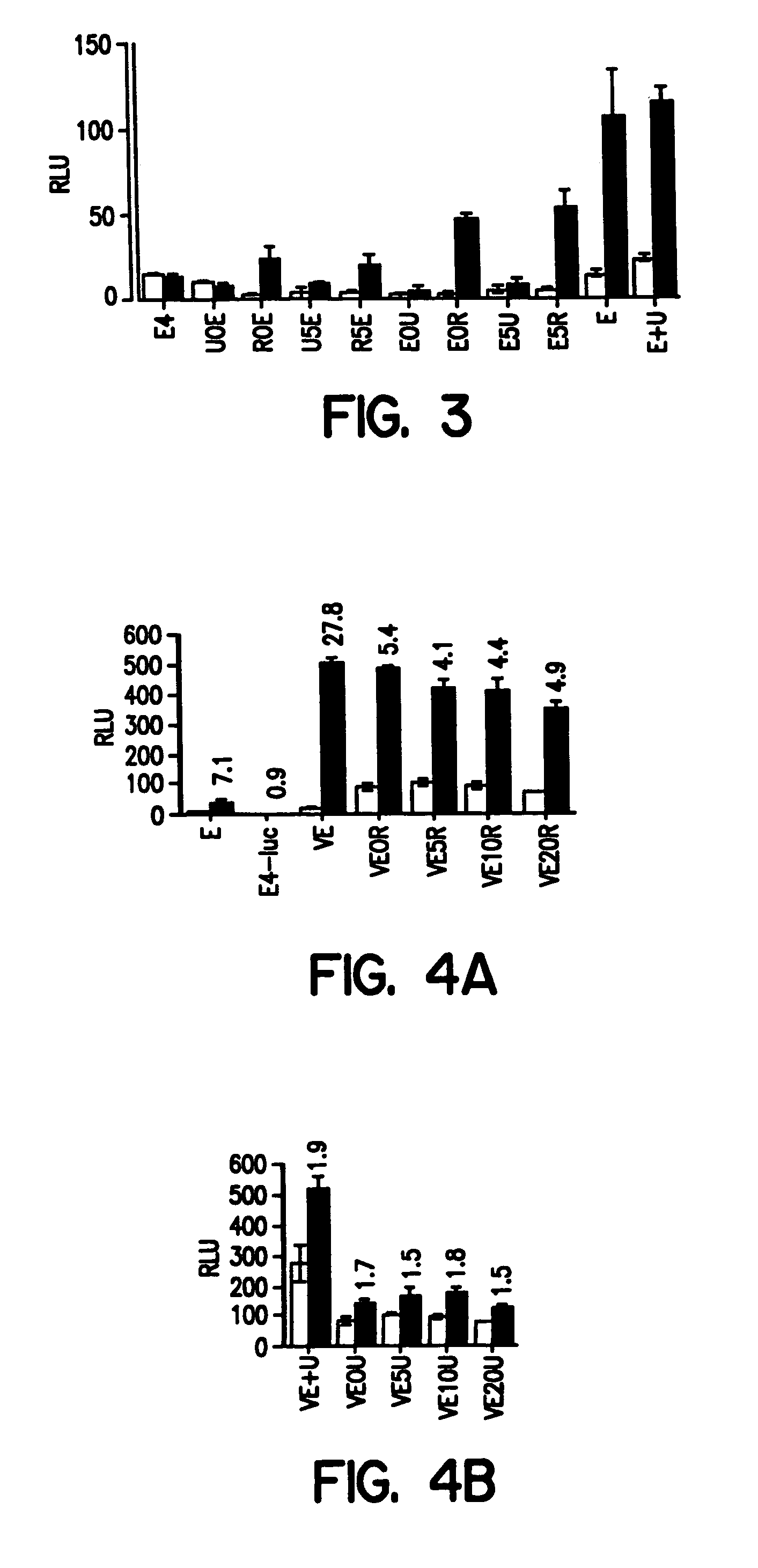
InactiveUS7057015B1Enhance possibility of producingIncrease flexibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesADAMTS ProteinsProtein Unit
The invention provides chimeric proteins having at least two functional protein units, each containing the dimerization domain of a member of the steroid / thyroid hormone nuclear receptor superfamily. The chimeric proteins can fold under crystallization conditions to form functional entities. The functional entities optionally contain a novel flexible peptide linker of variable lengths between at least two of the protein units. In a preferred embodiment, the linker is designed to be increased in increments of 12 amino acids each to aid in preparation of variant chimeric proteins. The DNA binding characteristics of the invention functional entities differ from those of wild-type complexes formed between “monomeric” receptors and their binding partners. Some functional entities, e.g. dimers expressed as fusion proteins, transactivate responsive promoters in a manner similar to wild-type complexes, while others do not promote transactivation and function instead essentially as constitutive repressors. The invention further provides nucleotide sequences encoding the invention chimeric proteins, cells containing such nucleotide sequences, and methods for using the invention chimeric proteins to modulate expression of one or more exogenous genes in a subject organism. In addition, isolated protein crystals suitable for x-ray diffraction analysis and methods for obtaining putative ligands for the invention chimeric proteins are provided.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
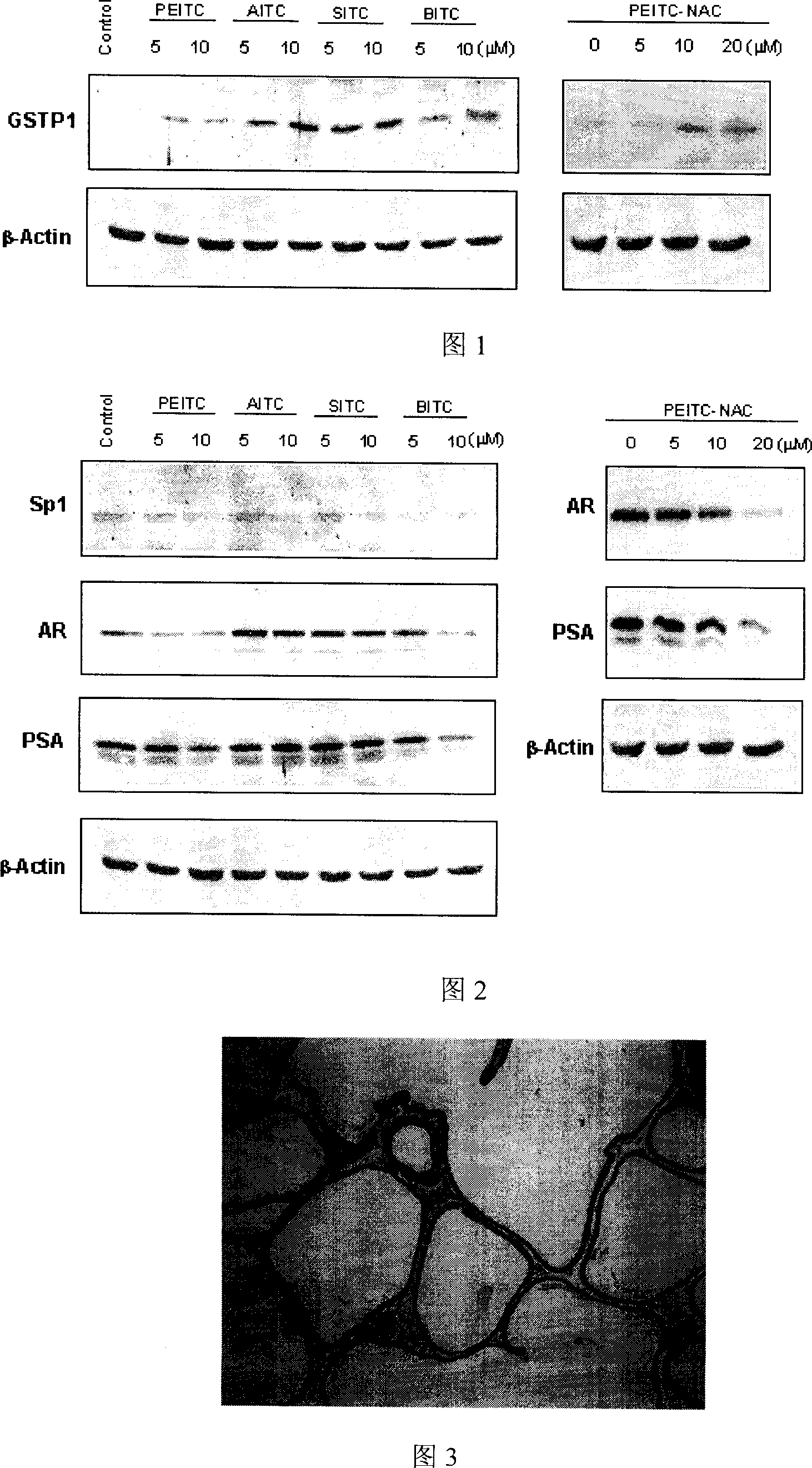
Application of compounds in isorhodanic ester classes for treating diseases of prostate and skin cancer
ActiveCN101091705AIncreased ability to remove harmful substancesImprove in vitro dissolutionUrinary disorderEster active ingredientsDiseaseProstate cancer cell
The present invention relates to a method capable of using natural and artificial synthetic isosulfocyanate compound or its derivative to prevent and cure prostatic diseases and skin carcinoma. The internal tests show that various isosulfocyanate compounds or their derivatives can induce prostatic cell II phase drug metabolic detoxication enzyme-glutathione transferase so as to can inhibit the hyperplasia of prostate and inflammation, and can prevent and cure prostatic carcinoma and skin carcinoma.
Owner:JC (WUXI) CO INC
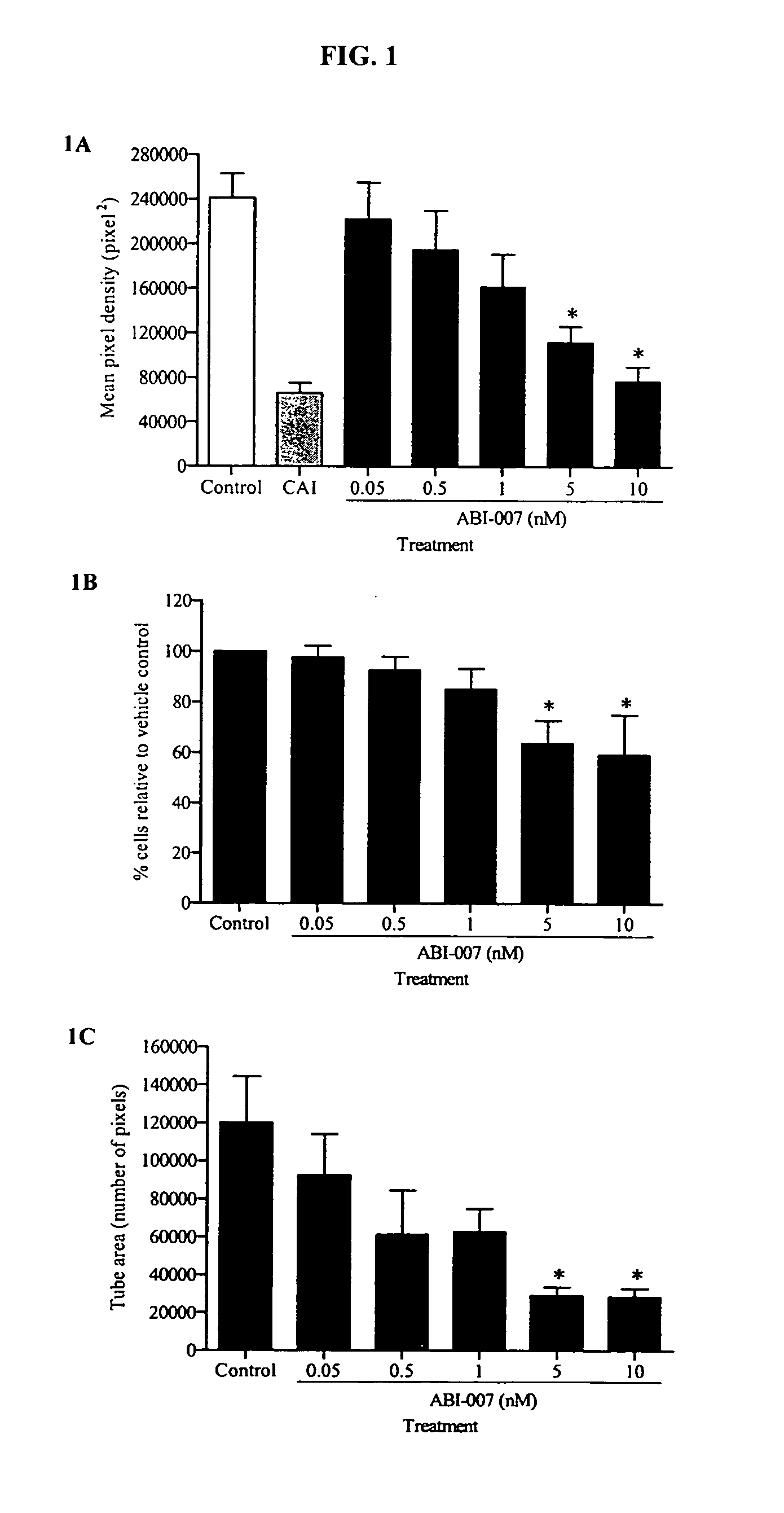
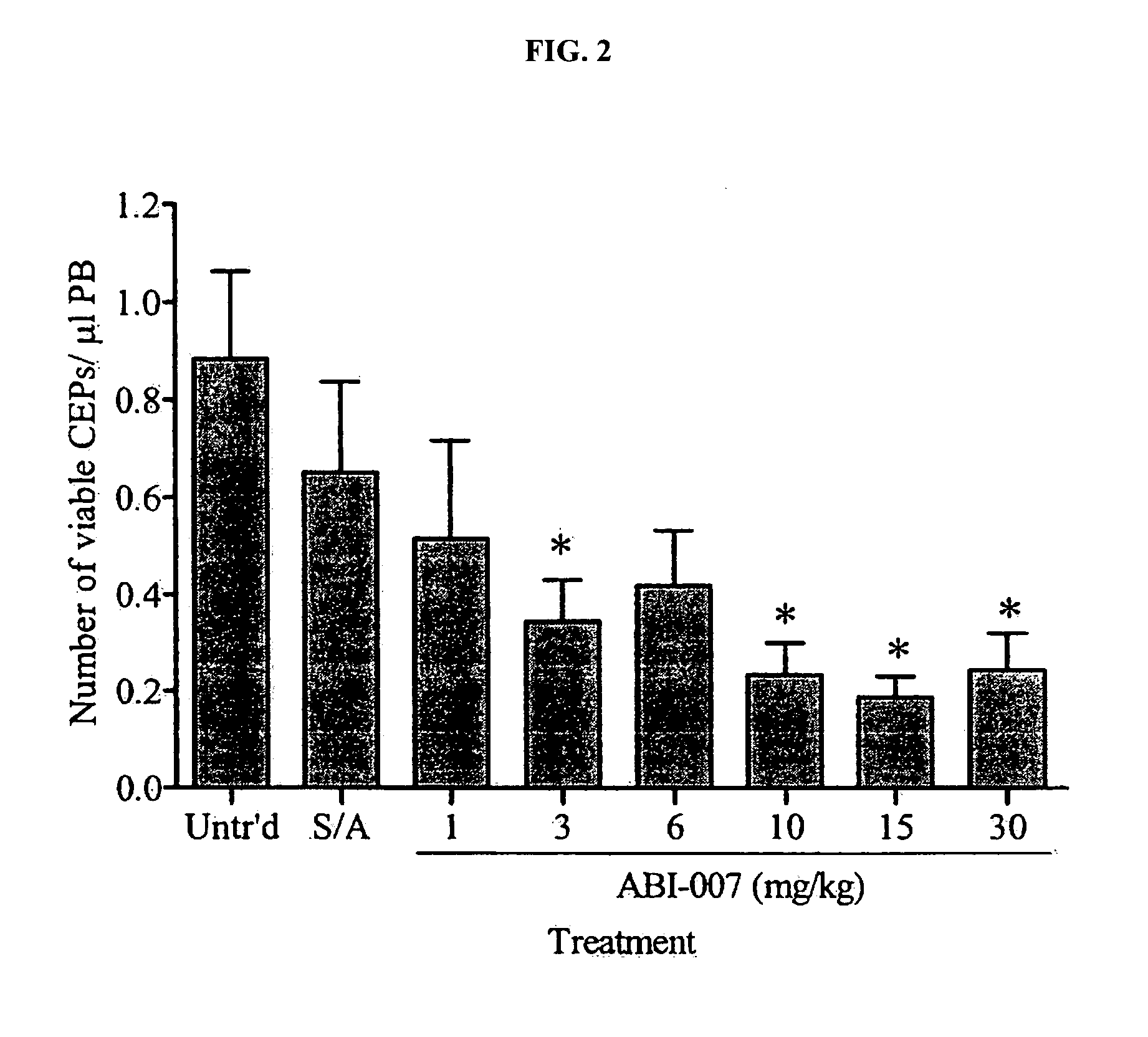
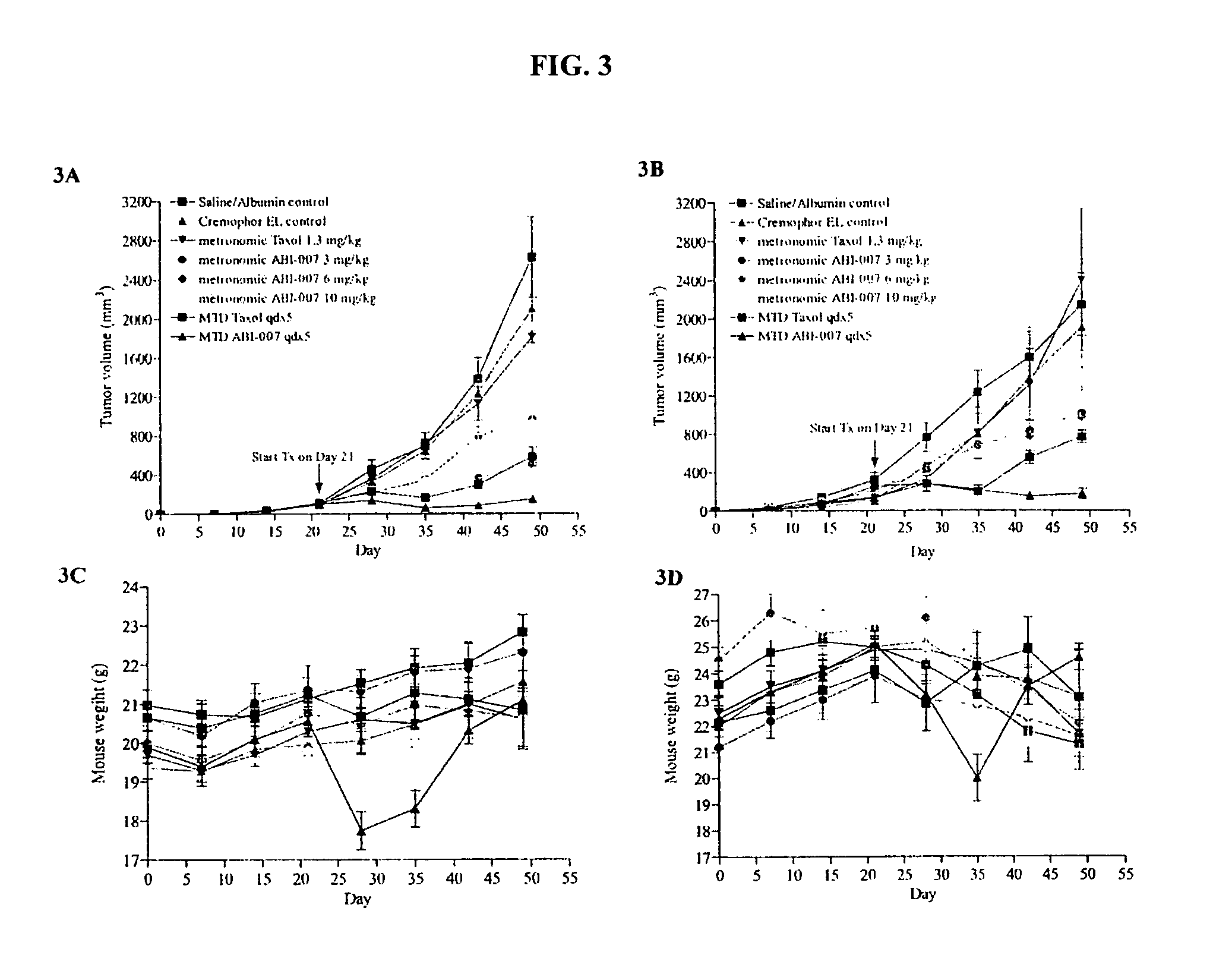
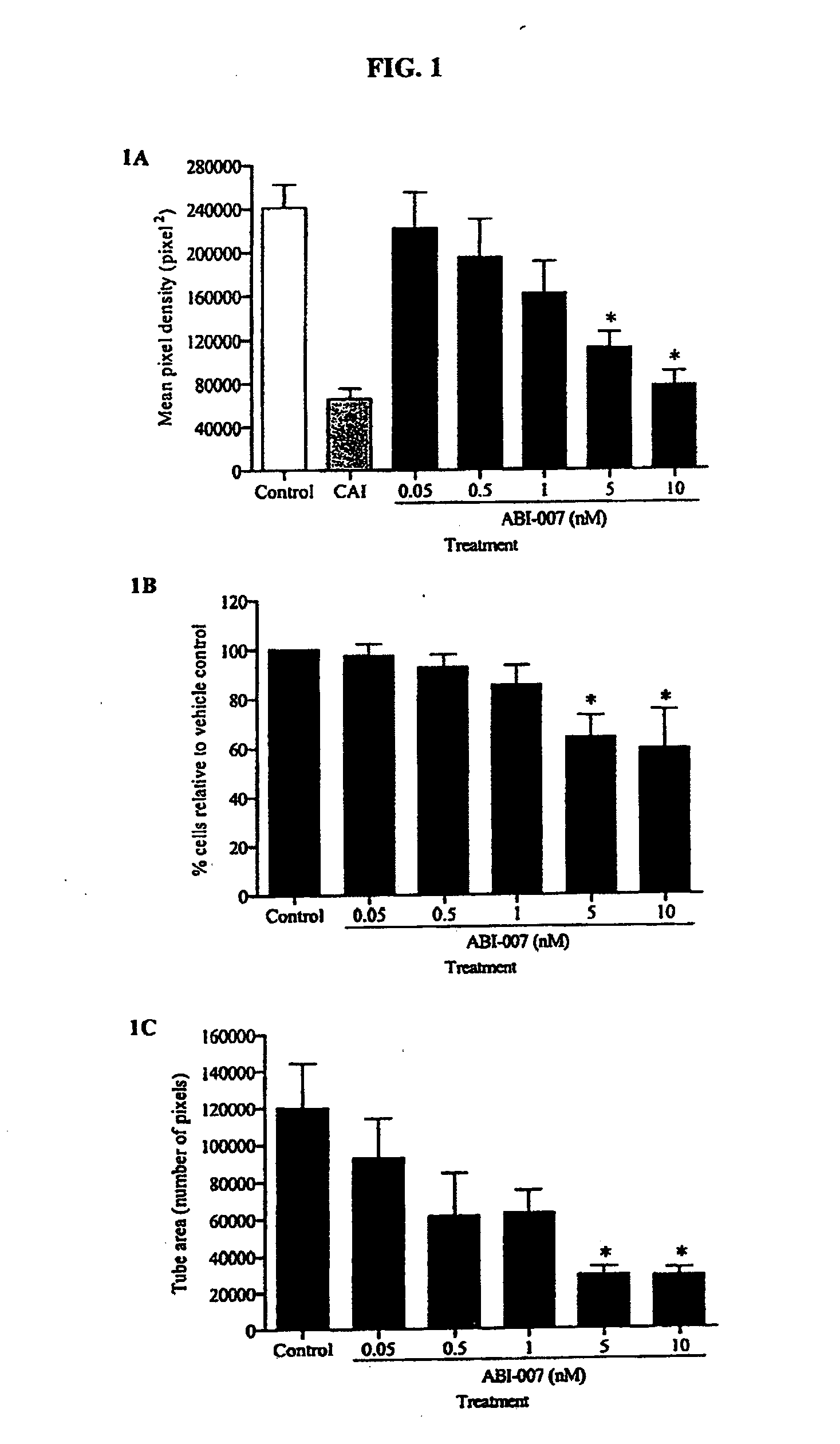
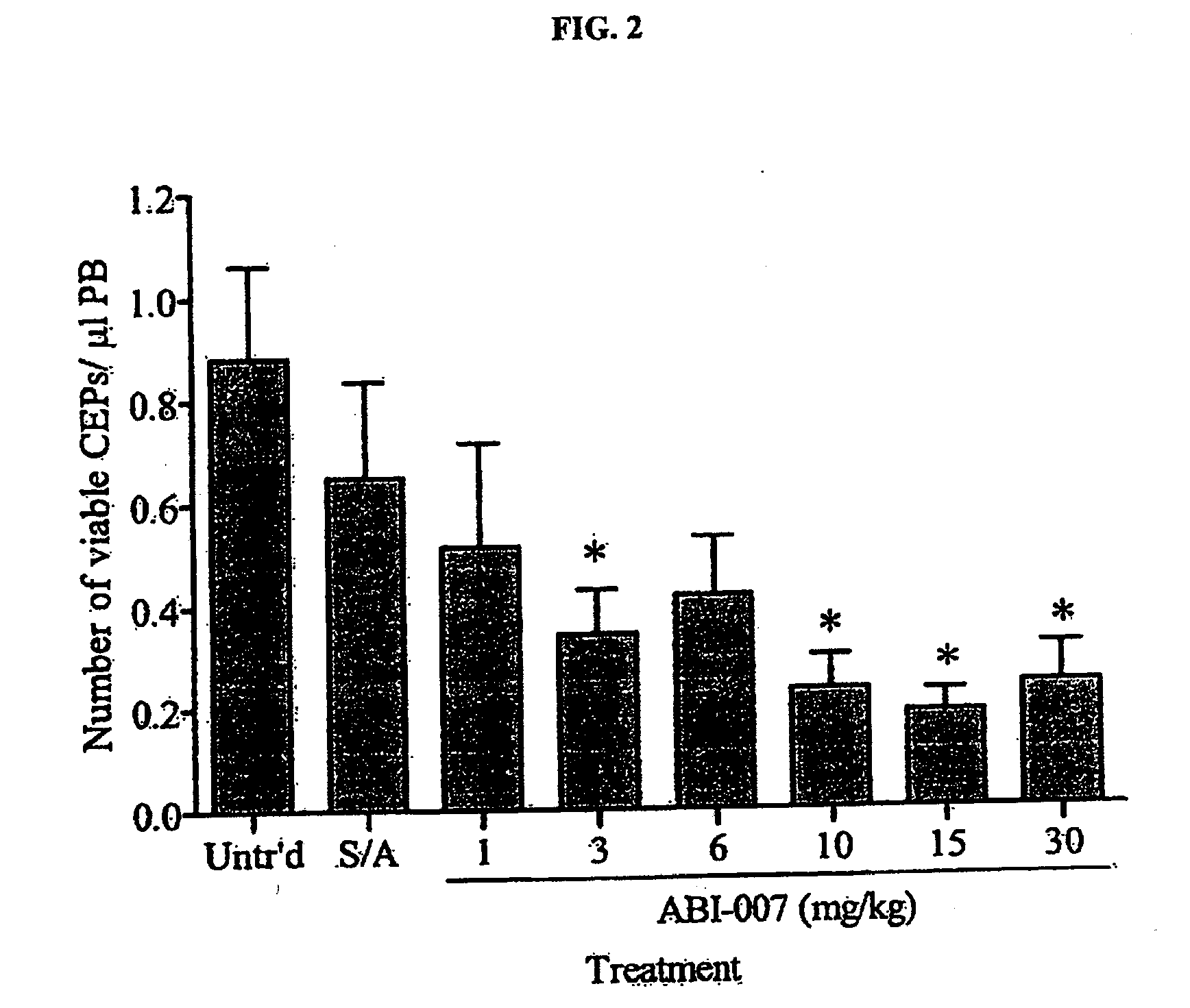
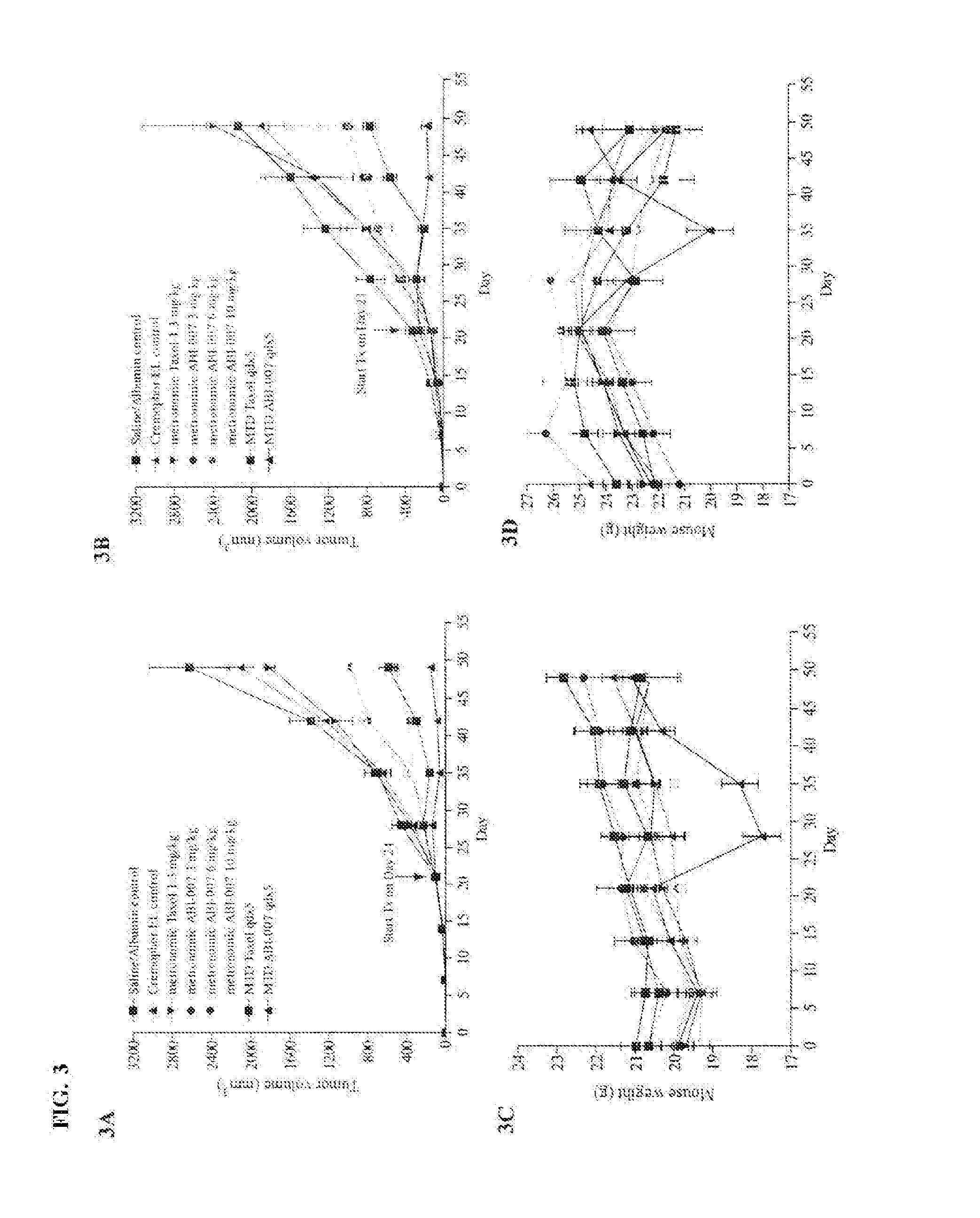
Breast cancer therapy based on hormone receptor status with nanoparticles comprising taxane
ActiveUS20100048499A1BiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsPR - Progesterone receptorNanoparticle
The present invention relates to methods and kits for the treatment of breast cancer based on hormone receptor status of progesterone receptor and estrogen receptor comprising the administration of a taxane alone, in combination with at least one other and other therapeutic agents, as well as other treatment modalities useful in the treatment of breast cancer. In particular, the invention relates to the use of nanoparticles comprising paclitaxel and albumin (such as Abraxane®) either alone or in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents or radiation, which may be used for the treatment of breast cancer which does not express estrogen receptor and / or progesterone receptor.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Tricyclic quinolinone and tricyclic quinoline androgen receptor modulator compounds and methods
Owner:LIGAND PHARMA INC
Amido compounds and their use as pharmaceuticals
The present invention relates to inhibitors of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1, antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. The compounds of the invention can be useful in the treatment of various diseases associated with expression or activity of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1 and / or diseases associated with aldosterone excess.
Owner:INCYTE HLDG CORP
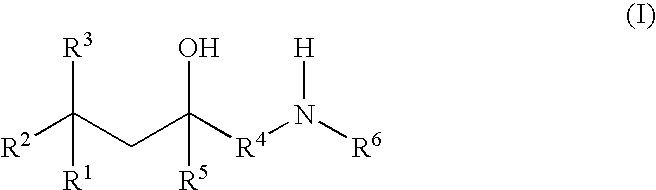
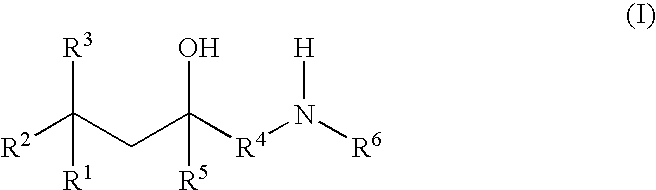
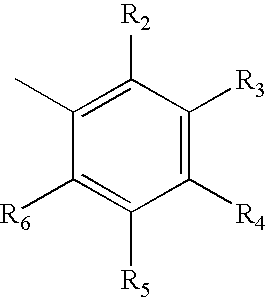
Glucocorticoid mimetics, methods of making them, pharmaceutical formulations, and uses thereof
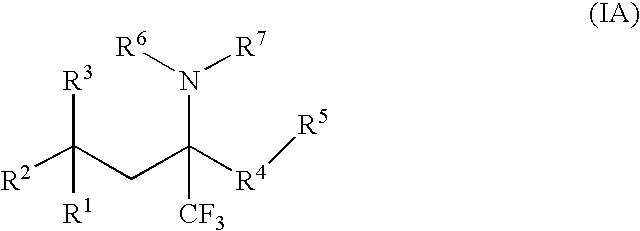
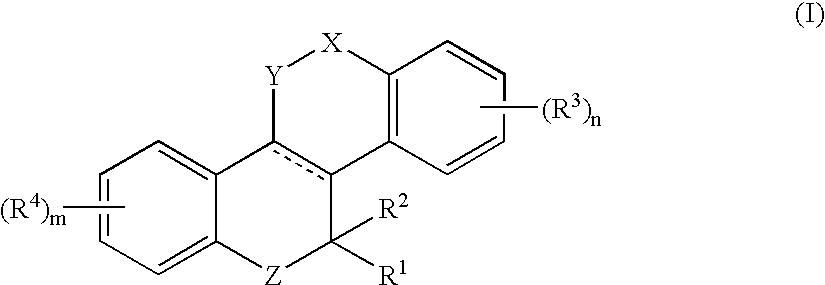
A compound of Formula (I) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and R6 are as defined herein, or a tautomer, prodrug, solvate, or salt thereof, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and methods of modulating the glucocorticoid receptor function and methods of treating disease-states or conditions mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor function or characterized by inflammatory, allergic, or proliferative processes in a patient using these compounds.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
Nucleic acid arrays for monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes
InactiveUS20050221354A1Reagent cost per experimentRobust overall probe set signal valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDrug targetPolynucleotide
The present invention provides nucleic acid arrays and methods of using the same for detecting or monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes. Non-limiting examples of drug target genes include kinase genes, phosphatase genes, protease genes, G-protein coupled receptor genes, nuclear hormone receptor genes, and ion channel genes. The present invention also provides methods of using nucleic acid arrays for the identification or validation of drugs or drug targets. In one embodiment, a nucleic acid array of the present invention is concentrated with probes for drug target genes. These probes constitute a substantial portion of all of the polynucleotide probes that are stably attached to the nucleic acid array, and can hybridize under stringent or nucleic acid array hybridization conditions to the tiling sequences selected from Attachment C, or the complements thereof.
Owner:WYETH
Glucocorticoid mimetics, methods of making them, pharmaceutical compositions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060014787A1Modulate it functionBiocideSenses disorderGlucocorticoid receptorDisease cause
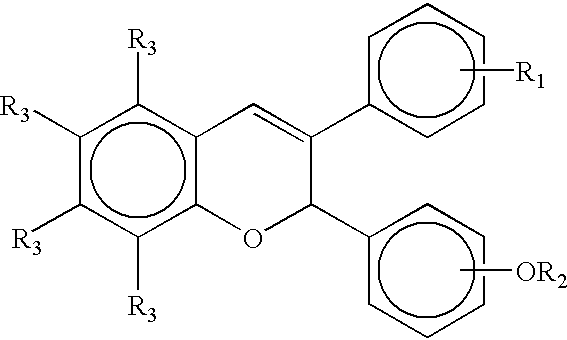
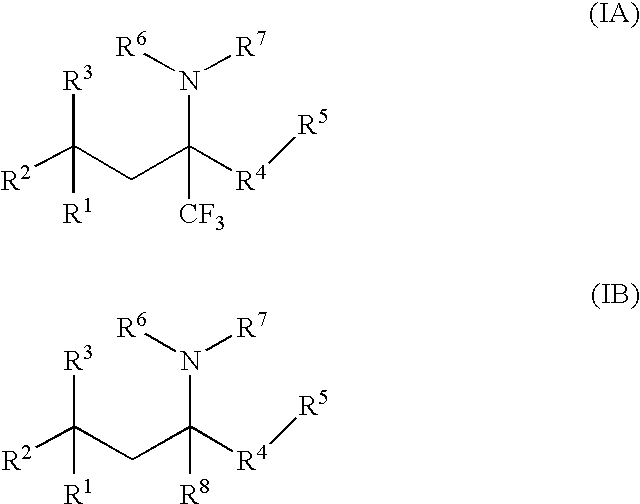
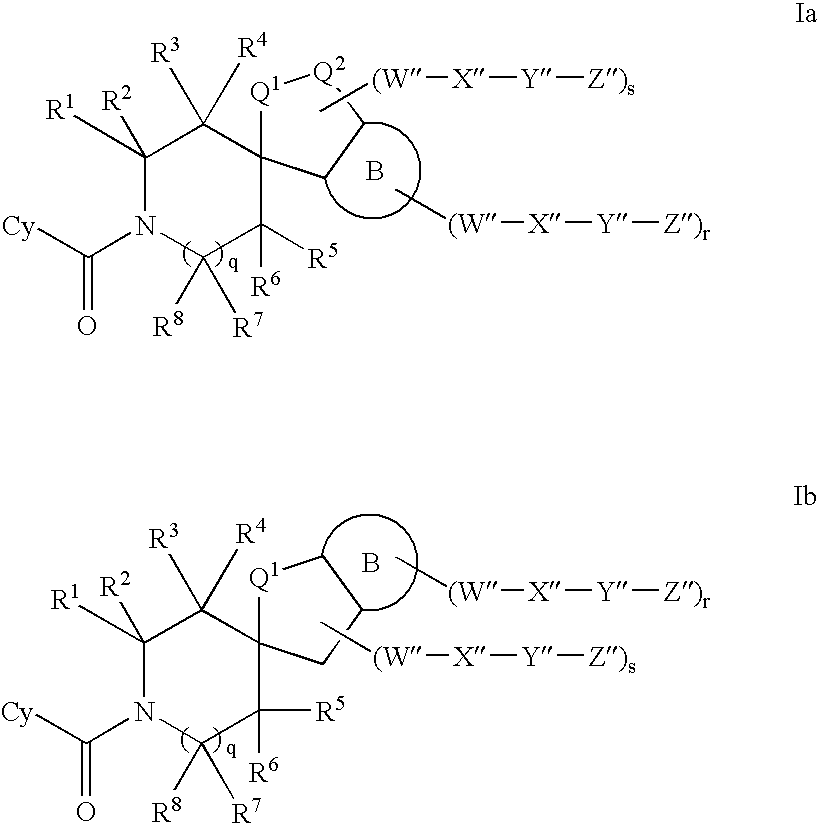
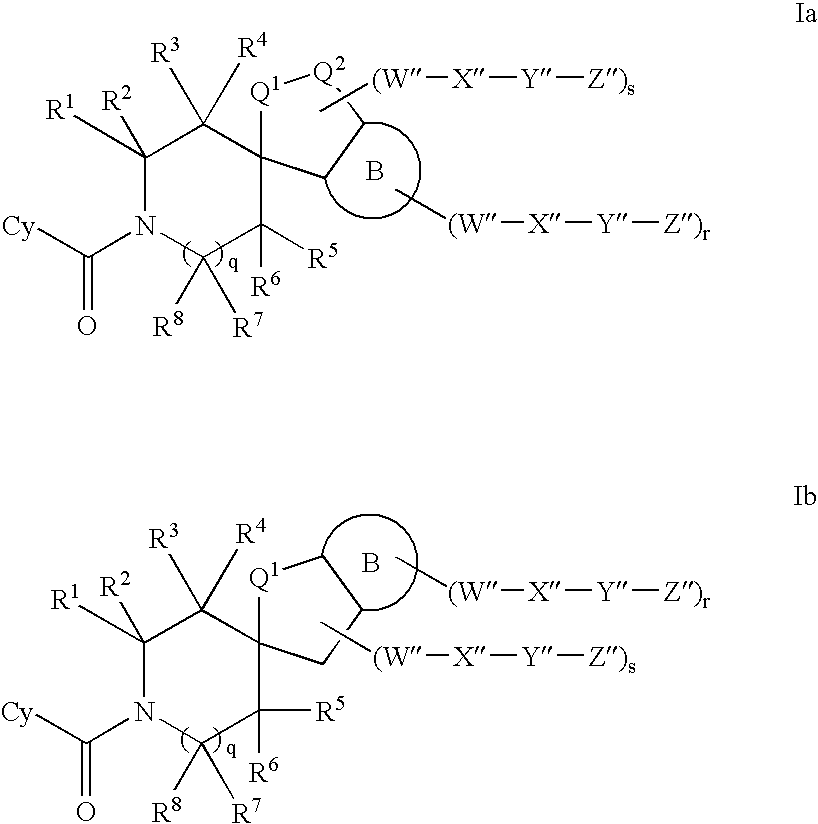
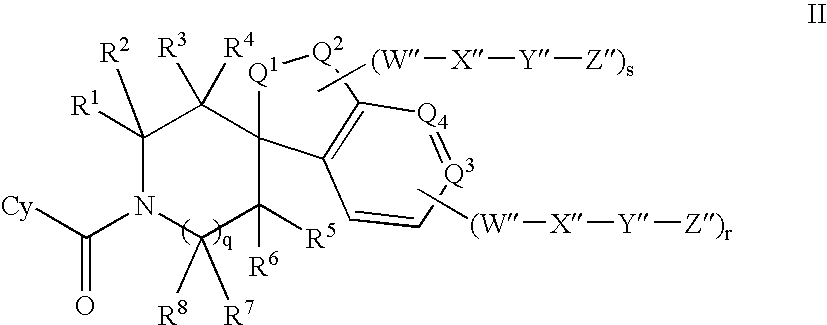
A compound of Formula (IA) or Formula (IB) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7 and R8 are as defined herein, or a tautomer, prodrug, solvate, or salt thereof; pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and methods of modulating the glucocorticoid receptor function and methods of treating disease-states or conditions mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor function or characterized by inflammatory, allergic, or proliferative processes in a patient using these compounds.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
Inhibitors of 11-beta hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type I and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060122210A1Improve actionReduce releaseBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMineralocorticoid receptor
The present invention relates to inhibitors of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1, antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. The compounds of the invention can be useful in the treatment of various diseases associated with expression or activity of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1 and / or diseases associated with aldosterone excess.
Owner:INCYTE
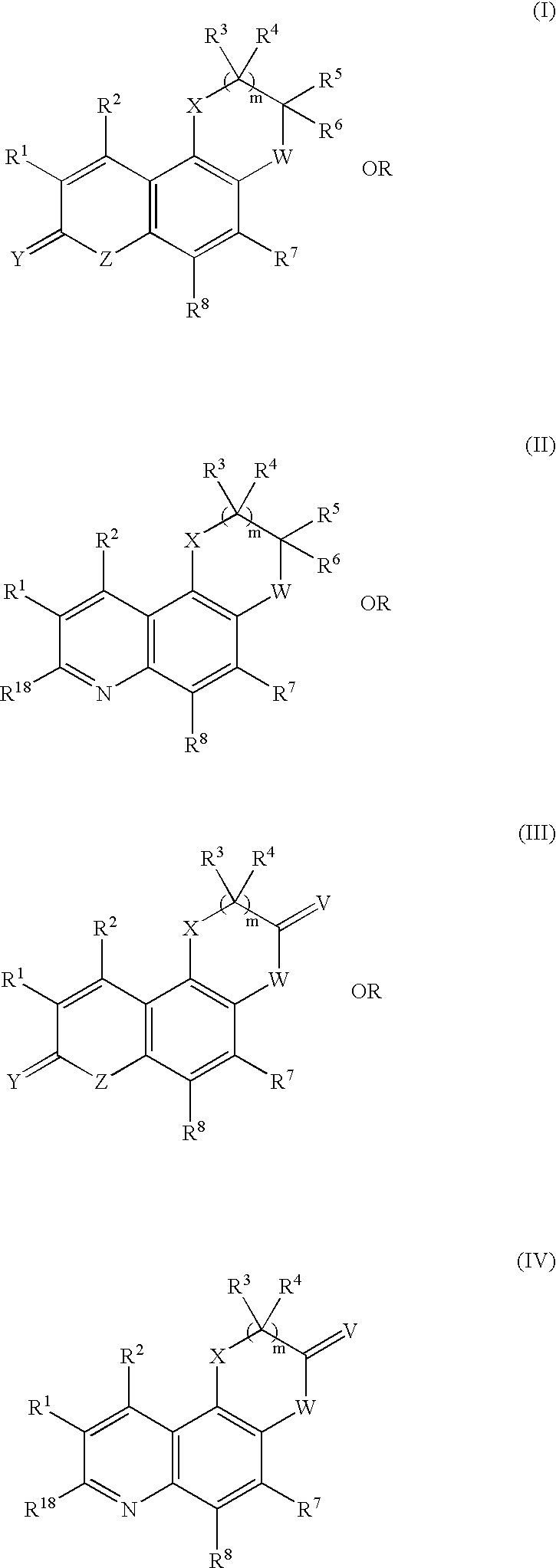
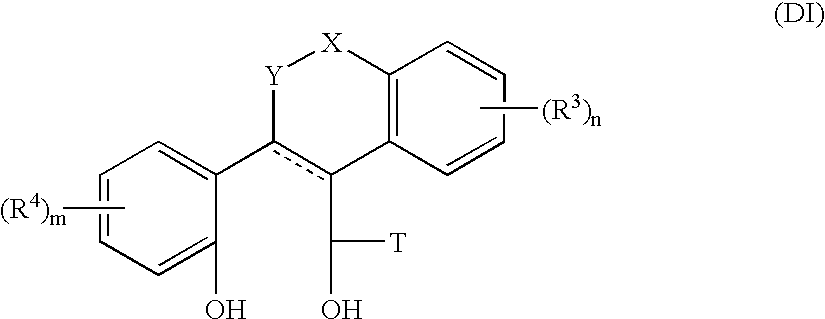
Heteroatom containing tetracyclic derivatives as selective estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention is directed to novel heteroatom containing tetracyclic derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, their use in the treatment and / or prevention of disorders mediated by one or more estrogen receptors and processes for their preparation. The compounds of the invention are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of disorders associated with the depletion of estrogen such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, osteopenia and osteoporosis; hormone sensitive cancers and hyperplasia of the breast, endometrium, cervix and prostate; endometriosis, uterine fibroids, osteoarthritis and as contraceptive agents, alone or in combination with a progestogen or progestogen antagonist.
Owner:ORTHO MCNEIL PHARM INC
Selective androgen receptor modulators
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
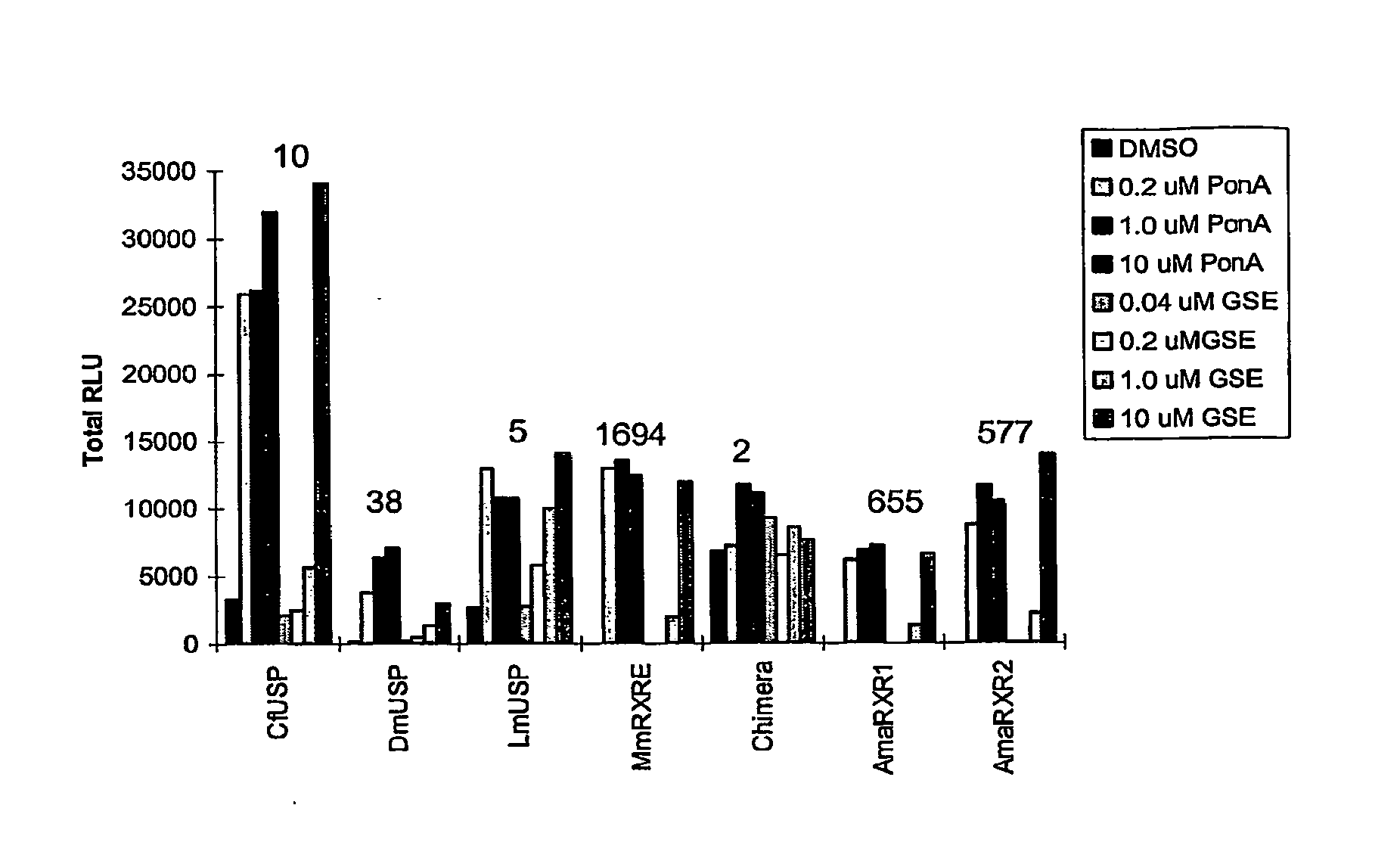
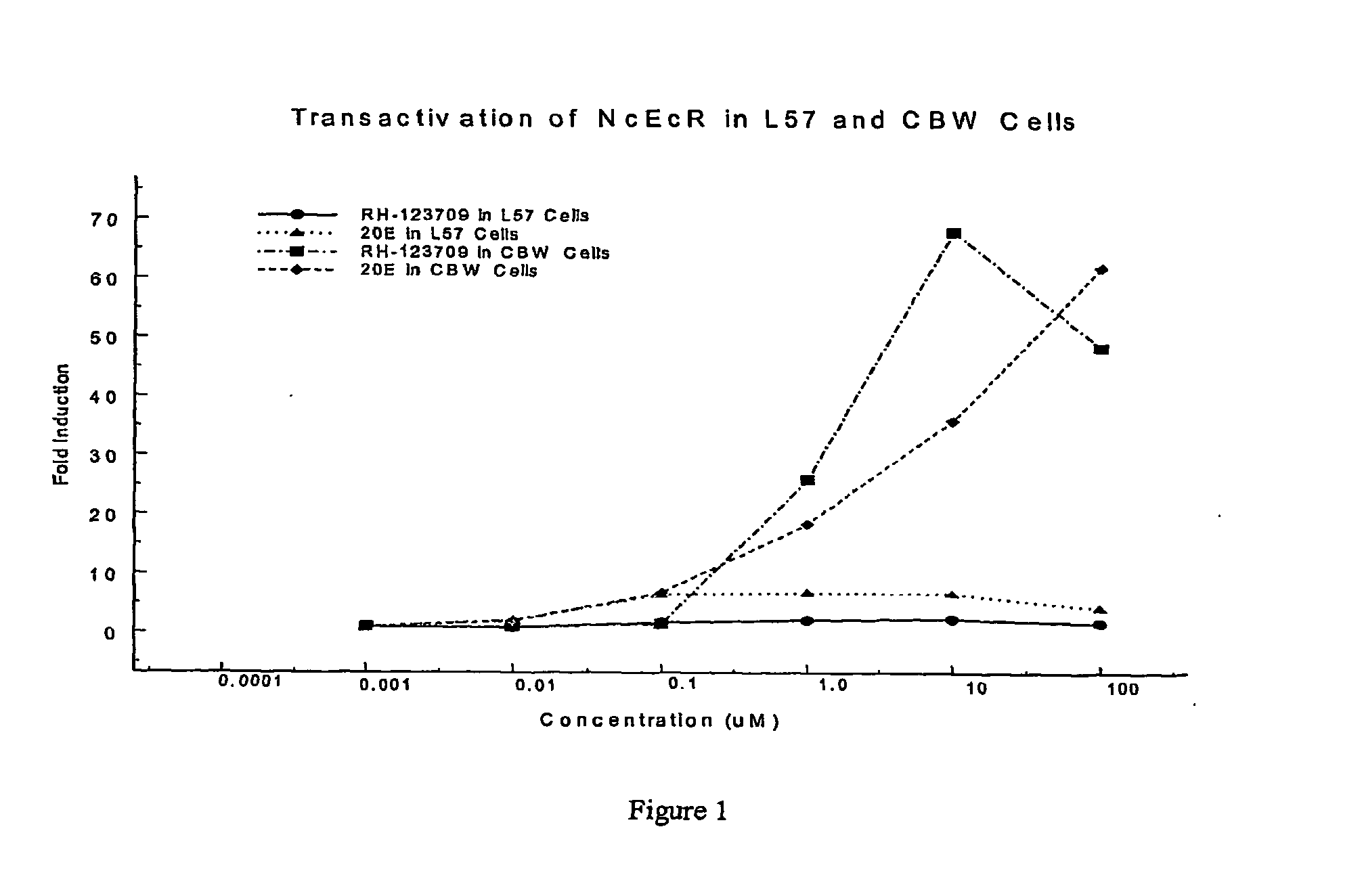
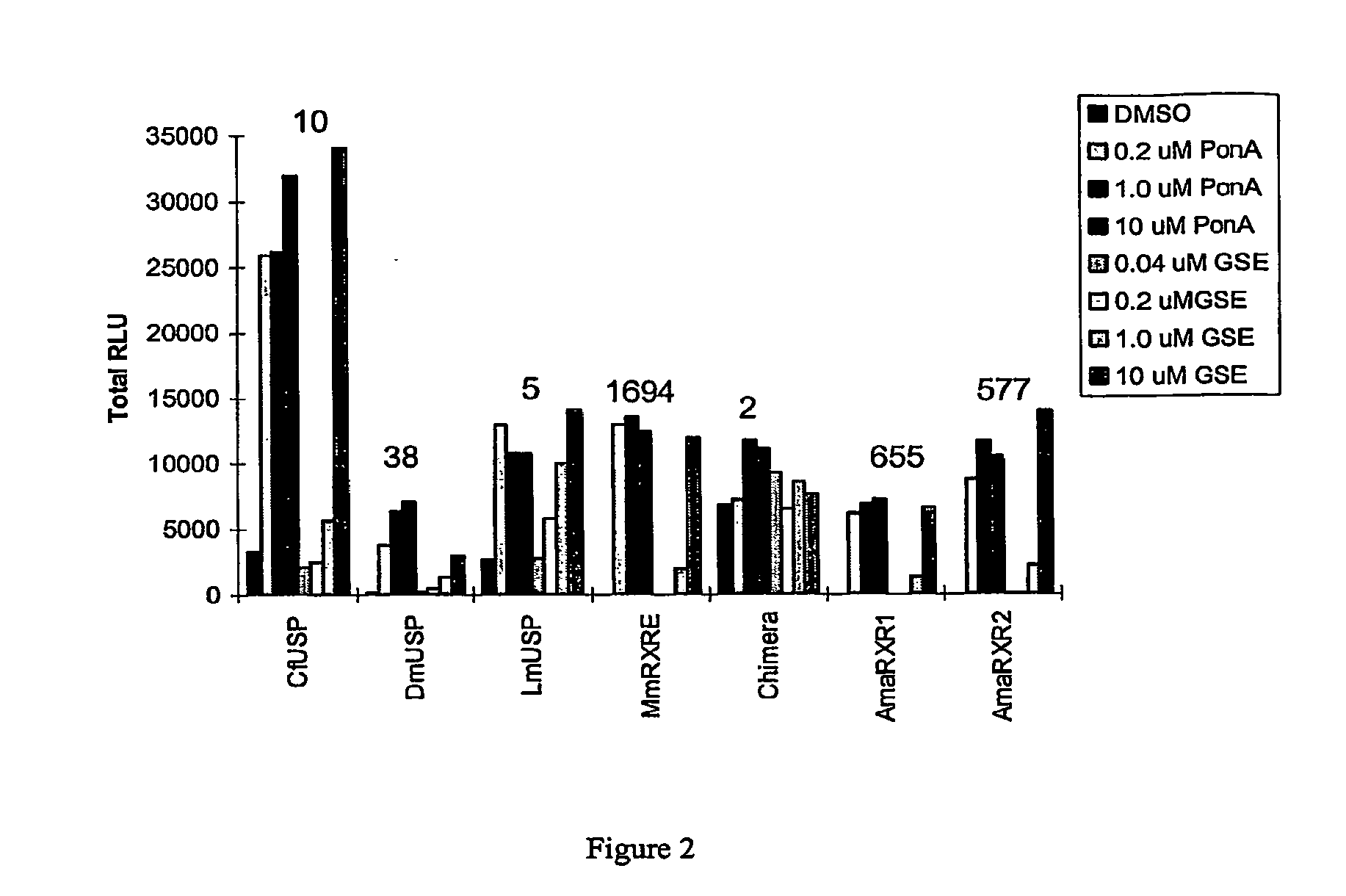
Leafhopper ecdysone receptor nucleic acids, polypeptides, and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a novel isolated leafhopper ecdysone receptor polypeptide. The invention also relates to an isolated nucleic acid encoding the leafhopper ecdysone receptor polypeptide, to vectors comprising them and to their uses, in particular in methods for modulating gene expression in an ecdysone receptor-based gene expression modulation system and methods for identifying molecules that modulate leafhopper ecdysone receptor activity.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Methods and compositions for modulating estrogen receptor mutants
InactiveUS20150258099A1Altered interactionImprove treatment outcomesBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEstrogen receptor modulator
Described herein are methods and compositions for treating an ER-related disease condition characterized by a mutation in the ESR1 gene by administering an estrogen receptor modulator. Also described herein are methods of treating hormone resistant-estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancers characterized by a mutation in the ESR1 gene by administering an estrogen receptor modulator.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Selective androgen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to androgen receptor targeting agents (ARTA) which demonstrate androgenic and anabolic activity, which are nonsteroidal ligands for the androgen receptor. The selective androgen receptor modulators (SARM) are useful for a) male contraception; b) treatment of a variety of hormone-related conditions, for example conditions associated with Androgen Decline in Aging Male (ADAM), such as fatigue, depression, decreased libido, sexual dysfunction, erectile dysfunction, hypogonadism, osteoporosis, hair loss, anemia, obesity, sarcopenia, osteopenia, osteoporosis, benign prostate hyperplasia, alterations in mood and cognition and prostate cancer; c) treatment of conditions associated with Androgen Decline in Female (ADIF), such as sexual dysfunction, decreased sexual libido, hypogonadism, sarcopenia, osteopenia, osteoporosis, alterations in cognition and mood, depression, anemia, hair loss, obesity, endometriosis, breast cancer, uterine cancer and ovarian cancer; d) treatment and / or prevention of chronic muscular wasting; e) decreasing the incidence of, halting or causing a regression of prostate cancer; f) oral androgen replacement and / or other clinical therapeutic and / or diagnostic areas.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Breast cancer therapy based on hormone receptor status with nanoparticles comprising taxane
ActiveUS20130280337A1BiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsGynecologyPR - Progesterone receptor
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Multi-gene classifiers and prognostic indicators for cancers
InactiveUS20110130296A1Increase doseIncrease frequencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary breast cancerOncology
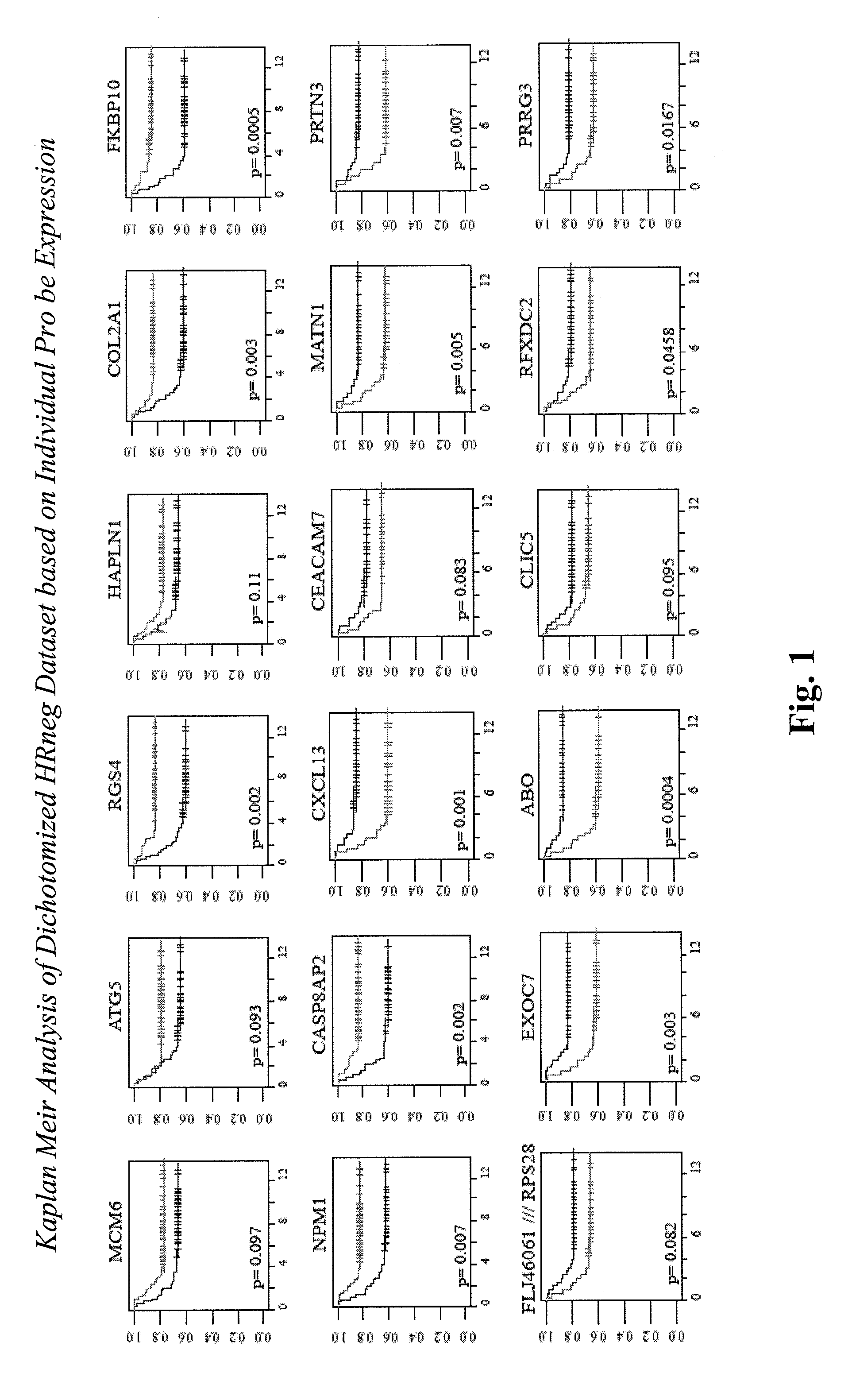
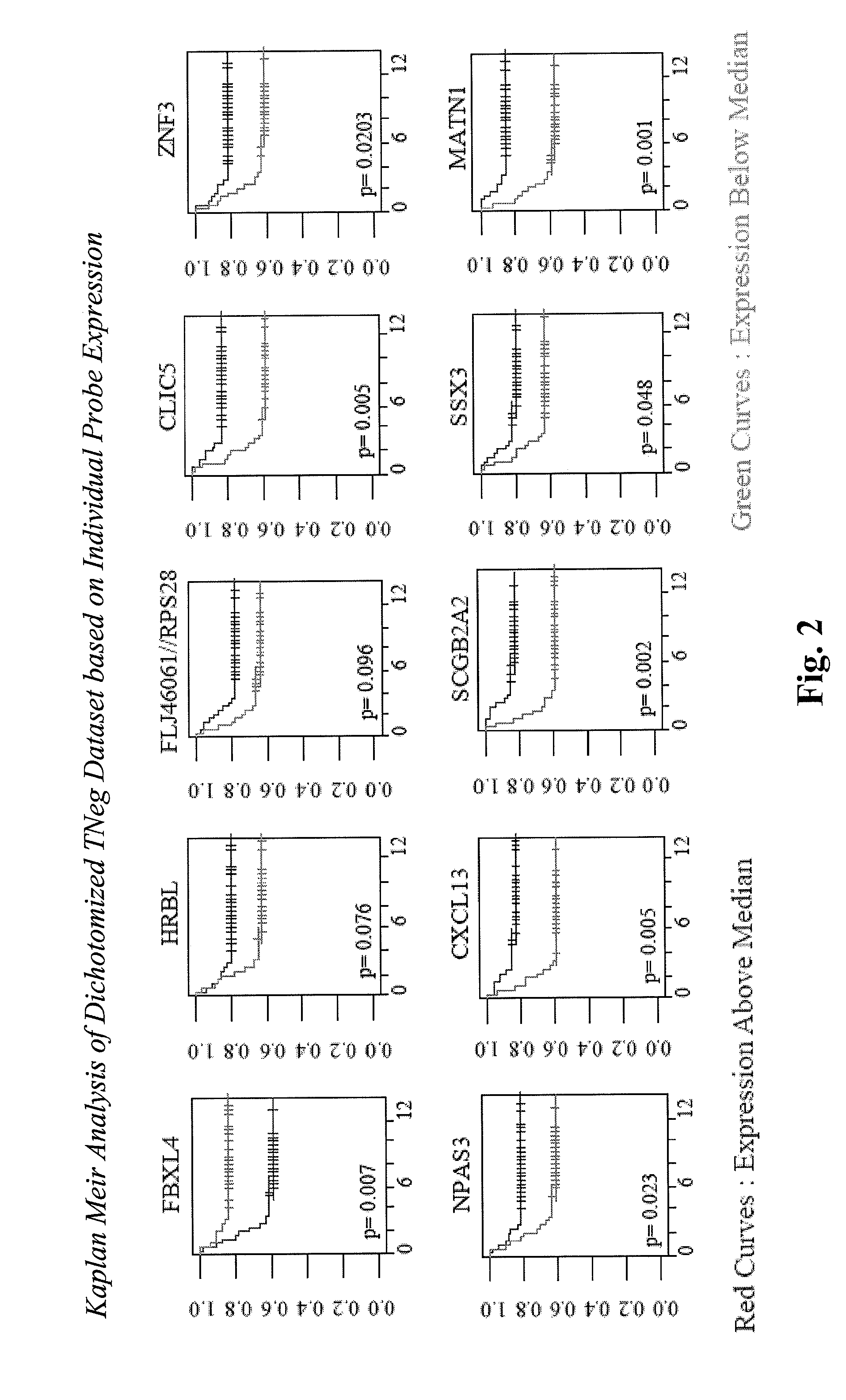
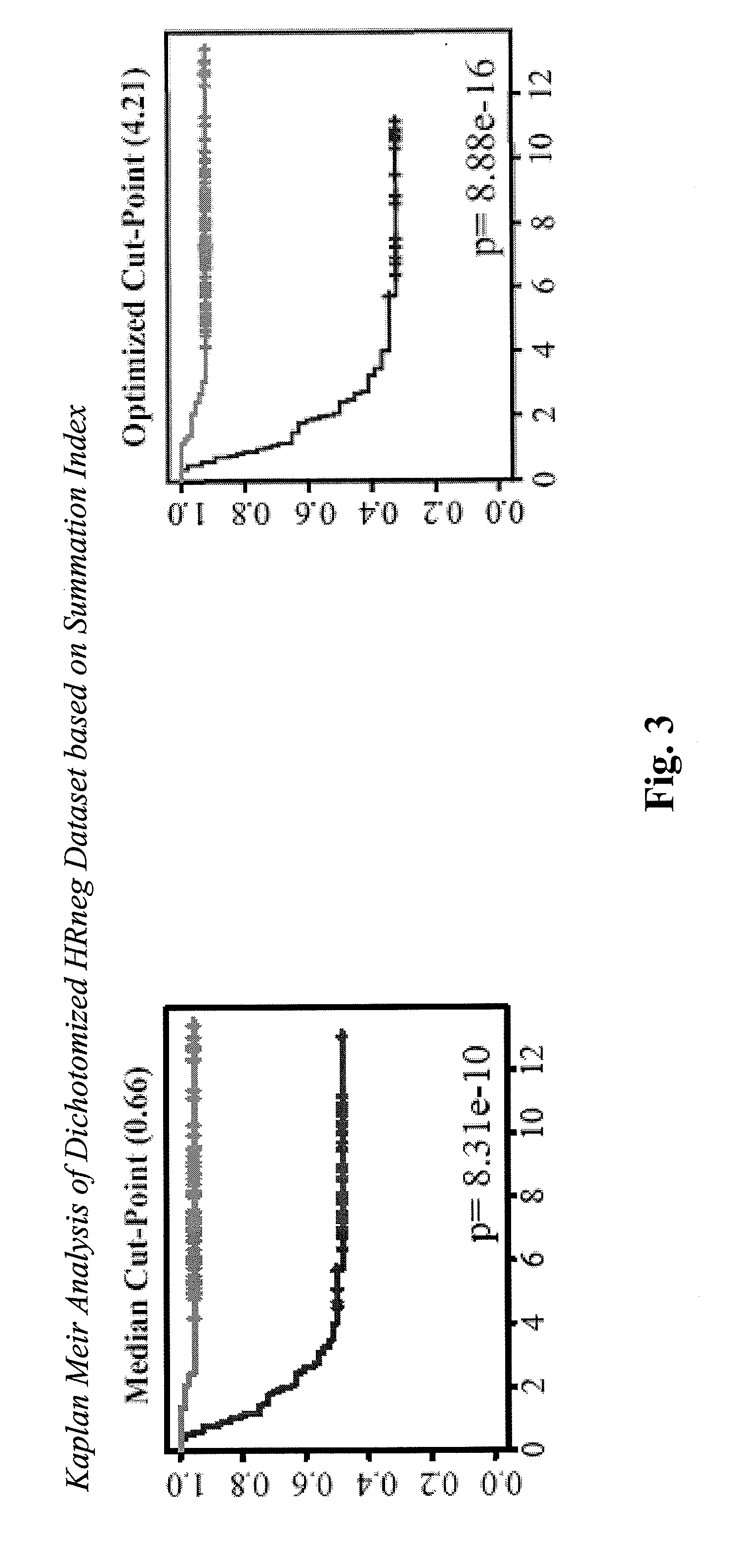
The present invention relates to the identification of marker genes useful in the diagnosis and prognosis of clinically problematic subsets of primary breast cancers. More specifically, the invention relates to the identification of two sets of marker genes that are differentially expressed in and useful for the diagnosis and prognosis of subsets of hormone receptor-negative (HRneg; i.e., ER and PR negative) and triple-negative (Tneg; i.e., ER, PR and HER2 negative) primary breast cancers at highest risk for early metastatic relapse. The invention further provides methods for determining the best course of treatment for patients having one of these clinically problematic subsets of primary breast cancers. The invention also provides methods for identifying compounds that prevent or treat a subtype of breast cancer based on their ability to modulate the activity or expression level of one or more marker genes identified herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
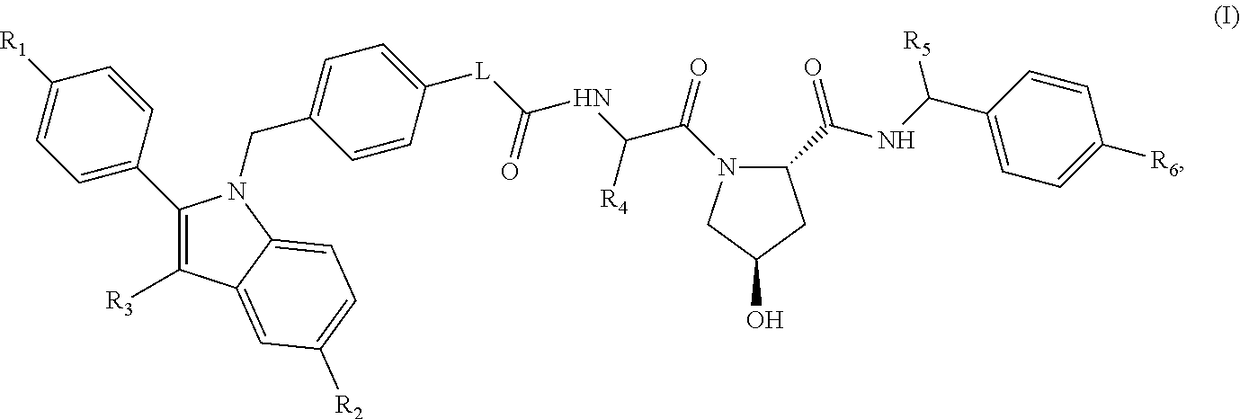
Indole derivatives as estrogen receptor degraders
The present disclosure relates to compounds and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, compositions, combinations and medicaments containing the compounds, and processes for their preparation. The disclosure also relates to the use of the compounds, combinations, compositions and medicaments, for example as inhibitors of the activity of the estrogen receptor, including degrading the estrogen receptor, the treatment of diseases and conditions mediated by the estrogen receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Modulation of growth hormone receptor expression and insulin-like growth factor expression
Compounds, compositions and methods are provided for modulating the expression of growth hormone receptor and / or insulin like growth factor-I (IGF-I). The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acid encoding growth hormone receptor. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of growth hormone receptor expression and for diagnosis and treatment of disease associated with expression of growth hormone receptor and / or insulin-like growth factor-I are provided. Diagnostic methods and kits are also provided.
Owner:ANTISENSE THERAPEUTICS LTD +1
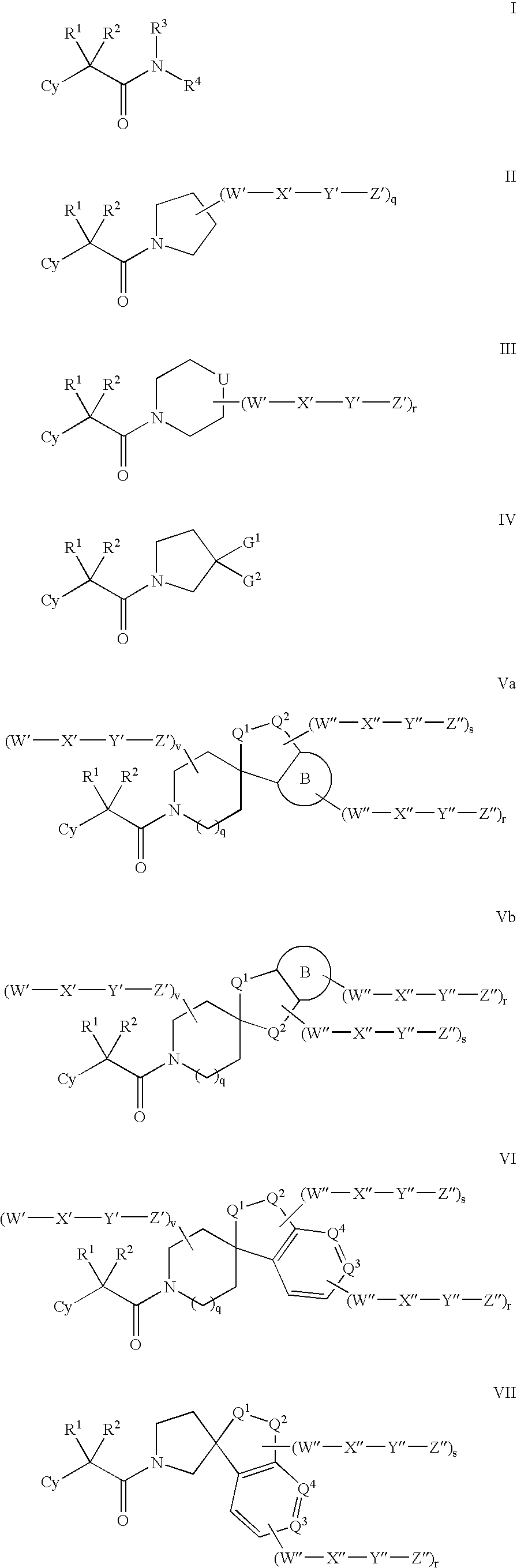
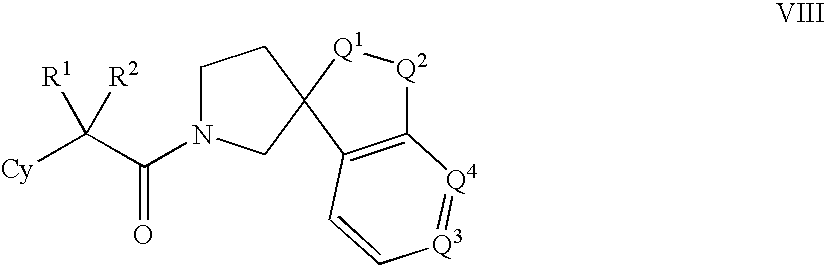
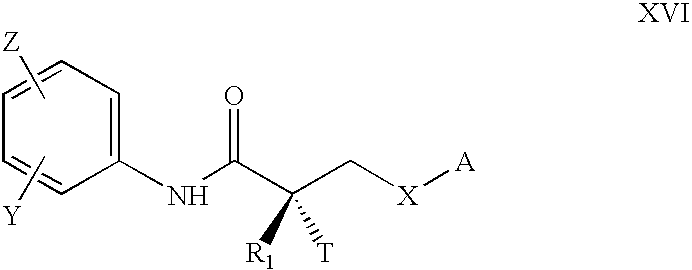
Open-chain prolyl urea-related modulators of androgen receptor function
There are provided nuclear hormone receptor modulating compounds of formula I wherein R1, R2, R3, X, Y, n and G are as described herein. Further provided are methods of using such compounds for the treatment of nuclear hormone receptor-associated conditions, such as age related diseases, for example sarcopenia, and also provided are pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Anti aromatase compounds pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof
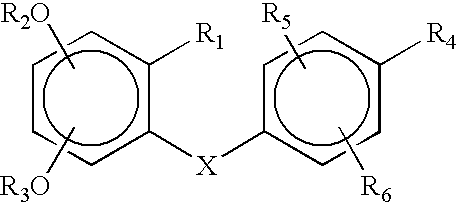
Compounds of Formula (I) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and R6 are as defined herein for Formula (IA) and Formula (IB), or a tautomer, prodrug, solvate, or salt thereof, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and methods of modulating estrogen receptor activity in a cell or patient or treating an estrogen receptor-mediated disorder, particularly breast and other cancers, in a patient in need thereof by administering an effective amount of compound of the invention thereto.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com