Patents
Literature
1713results about How to "Simple system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
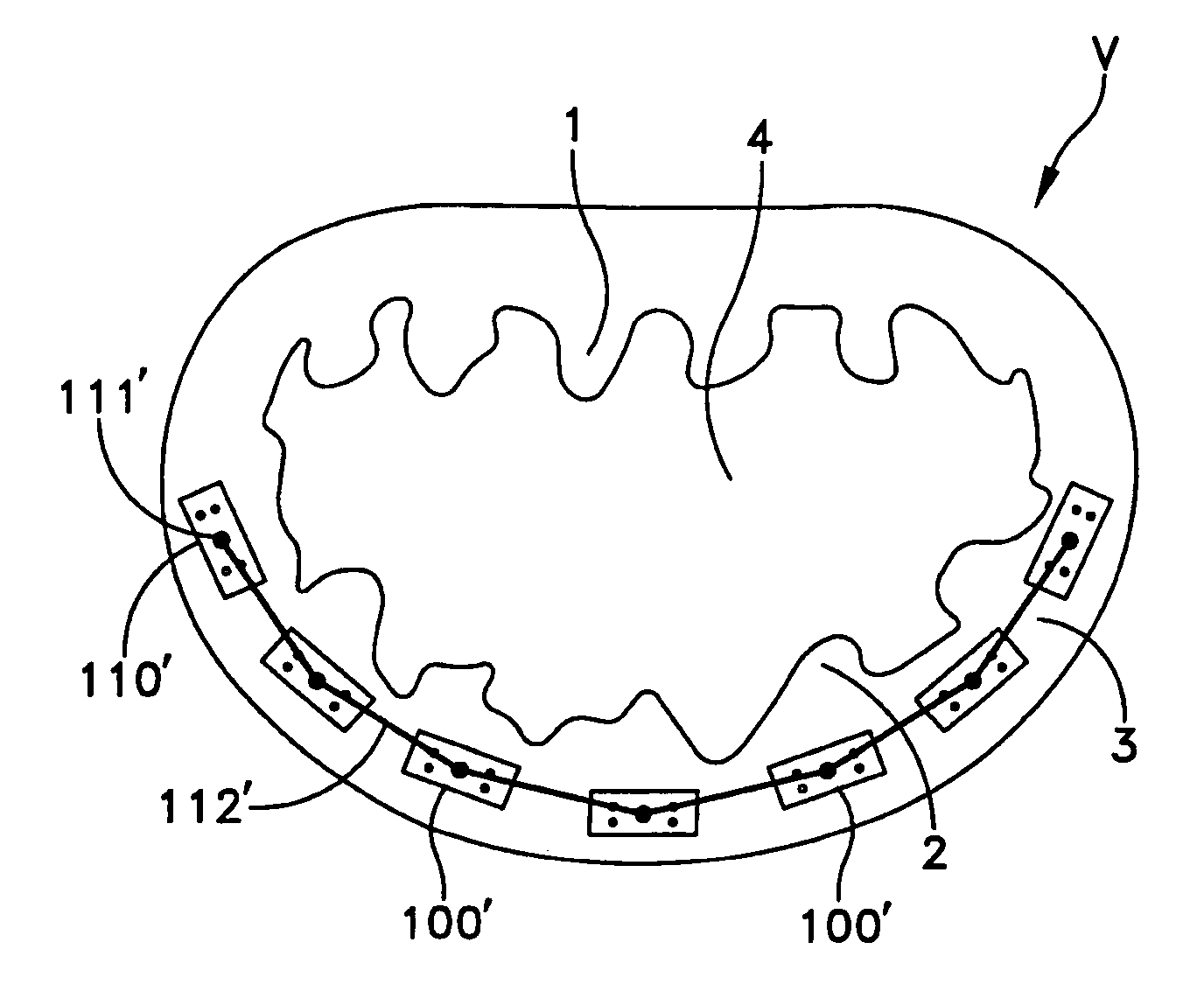
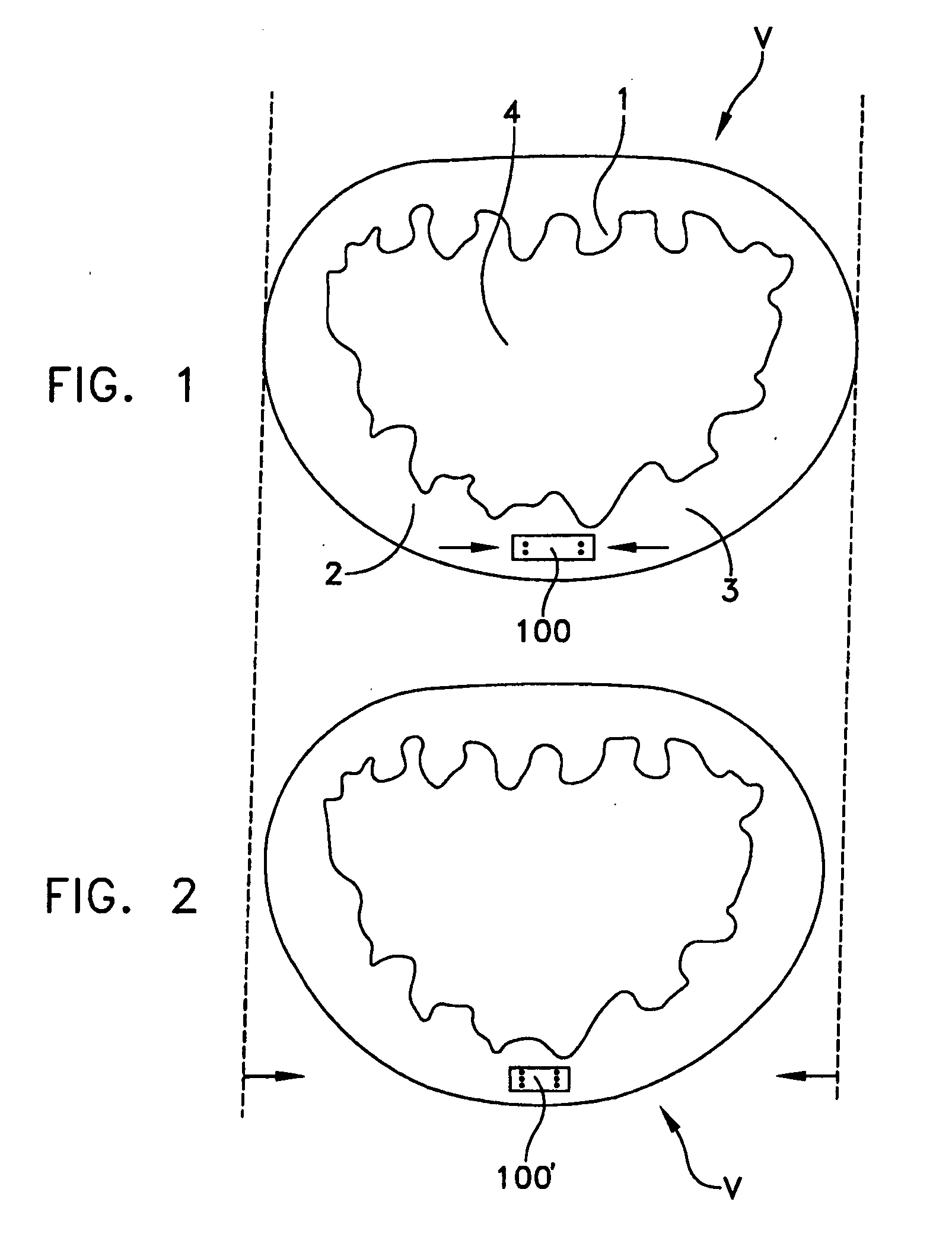
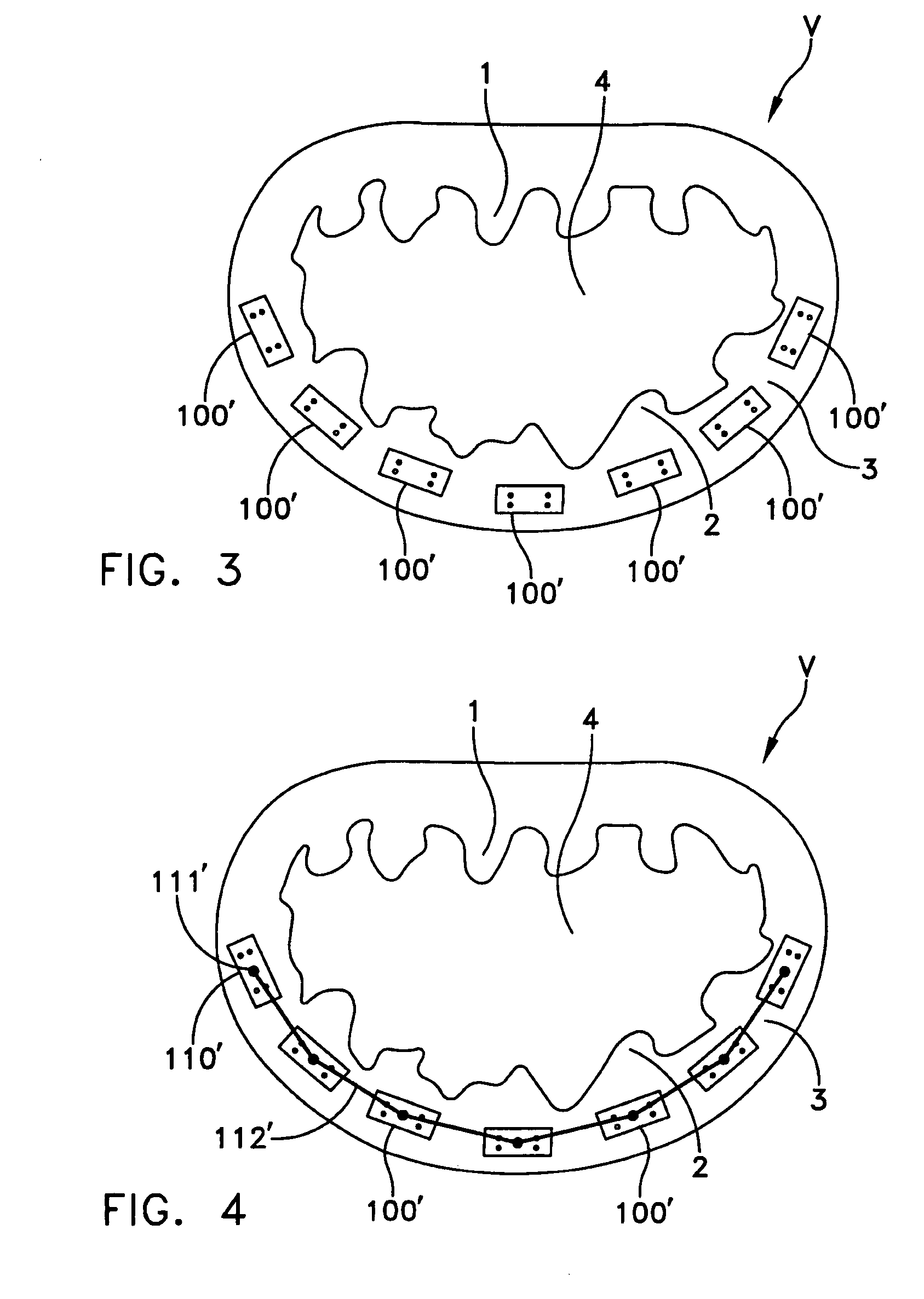
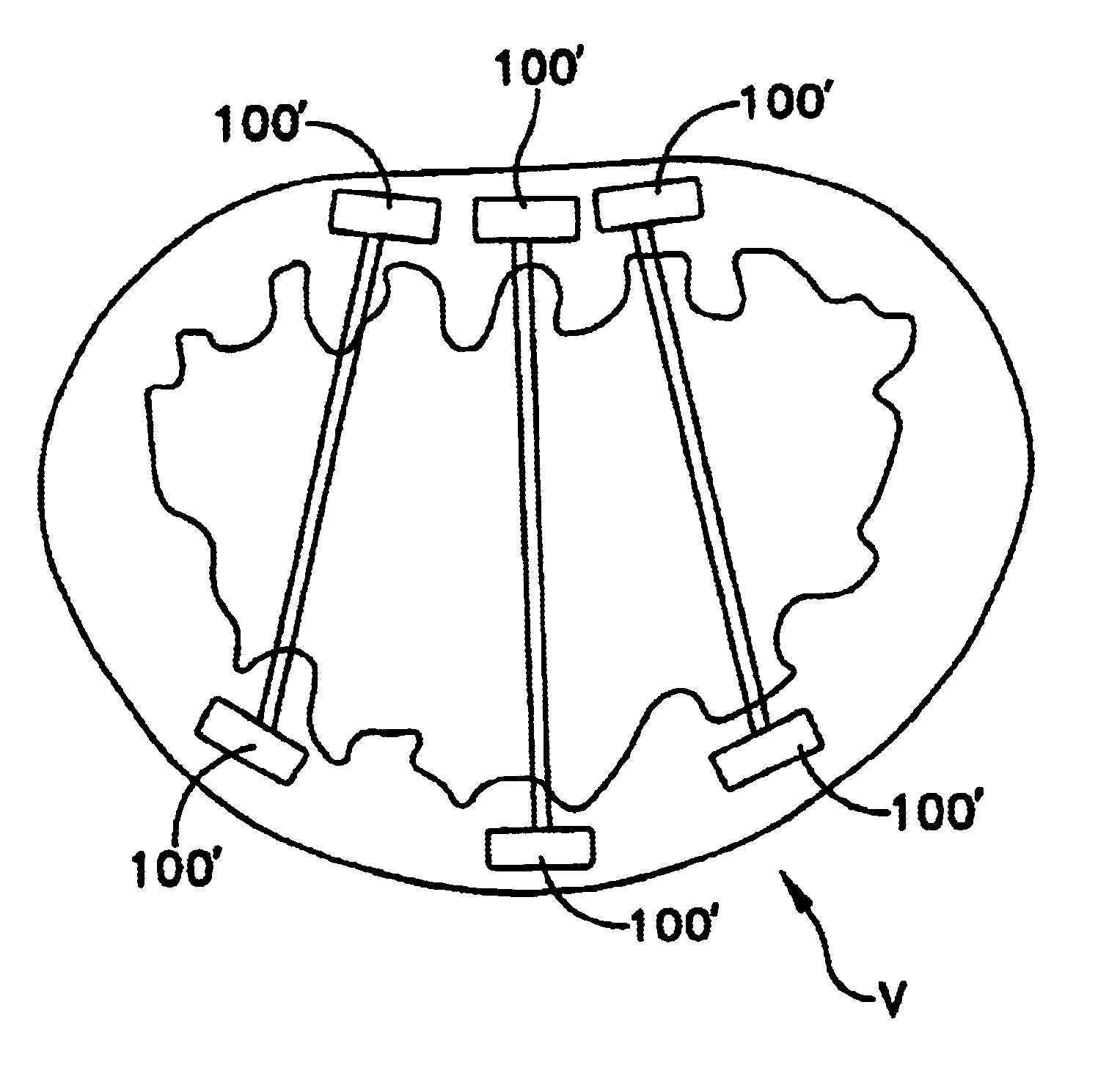
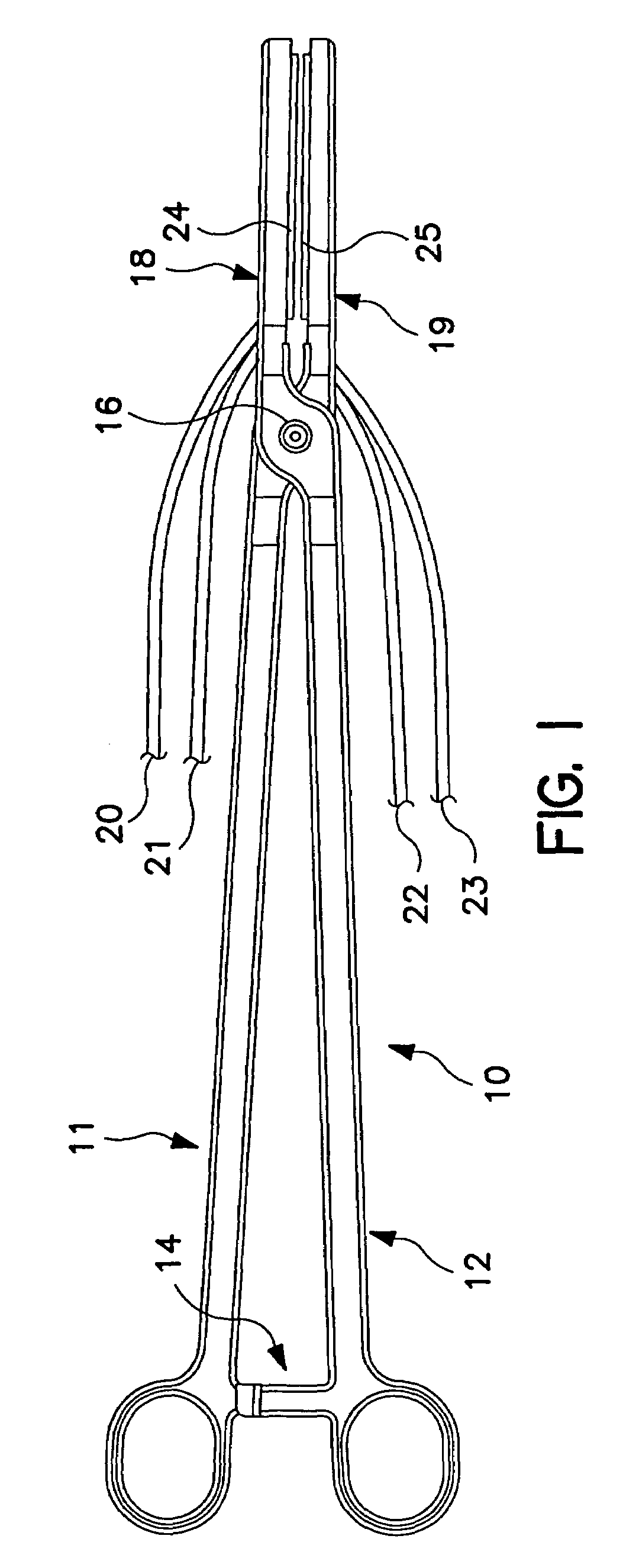
Automated annular plication for mitral valve repair
InactiveUS20060020336A1Reducing mitral regurgitationImprove efficiencyAnnuloplasty ringsSurgical staplesCoronary sinusMitral valve leaflet
A method for reducing mitral regurgitation comprising: providing a plication assembly comprising a first anchoring element, a second anchoring element, and a linkage construct connecting the first anchoring element to the second anchoring element; positioning the first anchoring element in the coronary sinus adjacent to the mitral annulus, and positioning the second anchoring element in another area of the mitral annulus so that the linkage construct extends across the opening of the mitral valve and holds the mitral valve in a reconfigured configuration so as to reduce mitral regurgitation. An apparatus for reducing mitral regurgitation comprising: a plication assembly comprising a first anchoring element, a second anchoring element, and a linkage construct connecting the first anchoring element to the second anchoring element; and a catheter adapted to deliver the first anchoring element to the coronary sinus.
Owner:VIACOR INC
Automated annular plication for mitral valve repair
InactiveUS6913608B2Stabilize and improve left ventricular functionAvoid developmentSuture equipmentsBone implantMitral valve leafletMitral valve operation
A novel system for performing a heart valve annuloplasty. The system involves the use of a plication band. In one embodiment, the annulus of the valve is reduced by constriction of the plication band itself. More particularly, each plication band enters the tissue at two or more points which are spaced from one other by a distance which is dictated by the geometry of the plication band. Subsequent constriction of the plication band causes these points to move toward each other, thereby constricting the tissue trapped between these points and thus reducing the overall circumference of the valve annulus. In a second embodiment, the annulus of the valve is reduced by linking multiple plication bands to one other, using a linkage construct, and then using a shortening of the length of the linkage construct between each plication band so as to gather the tissue between each plication band, whereby to reduce the overall circumference of the valve annulus.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
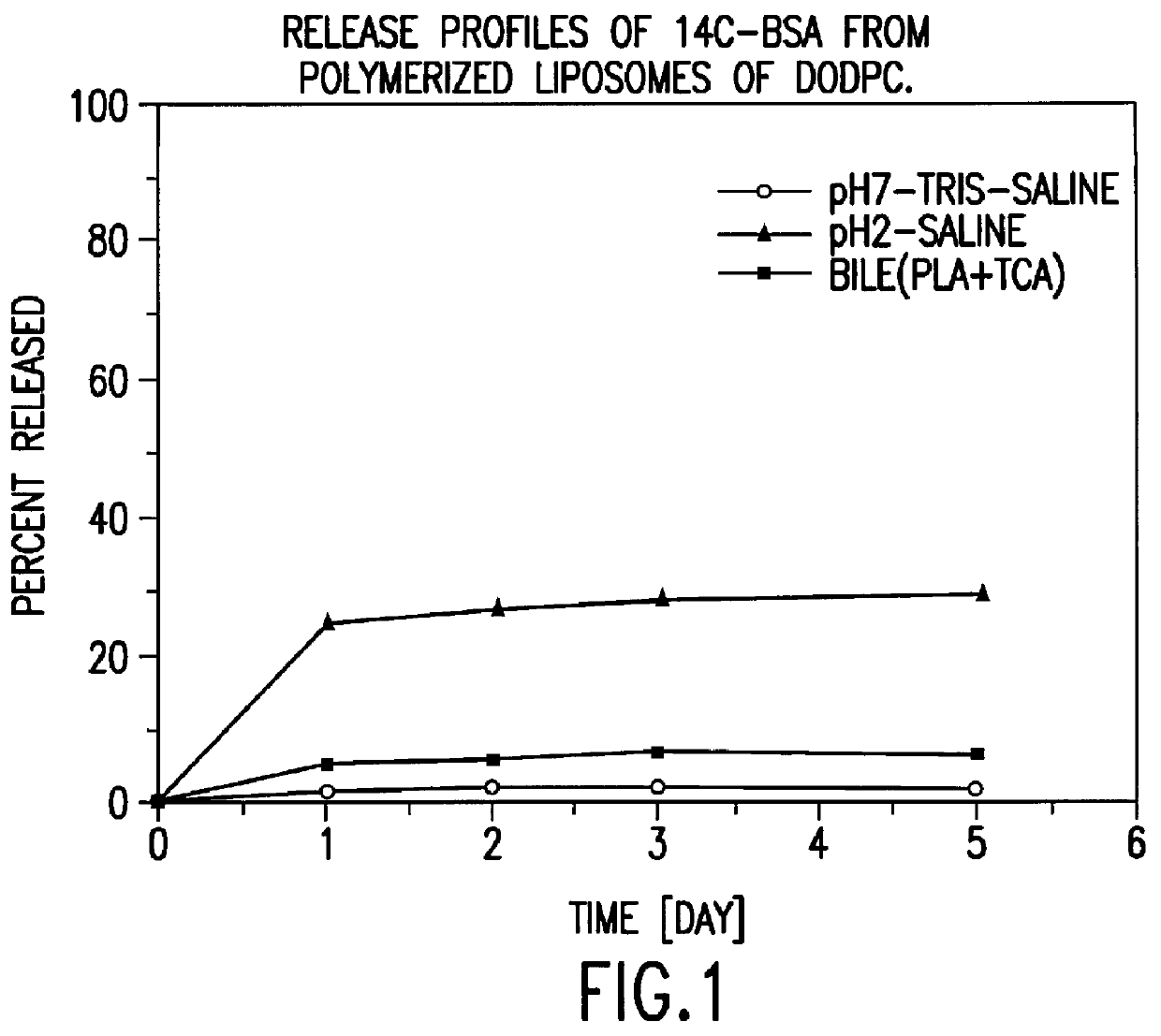
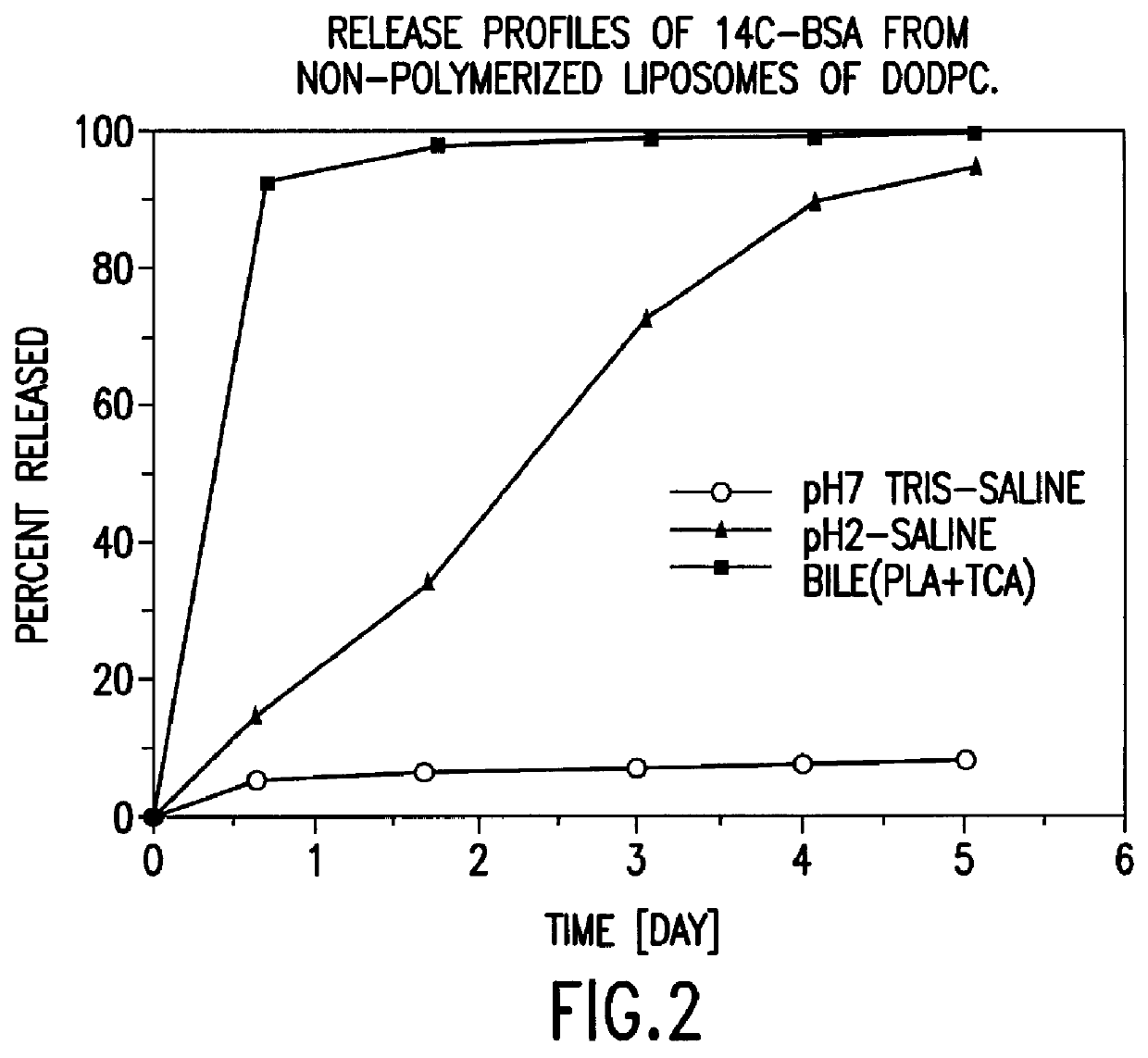
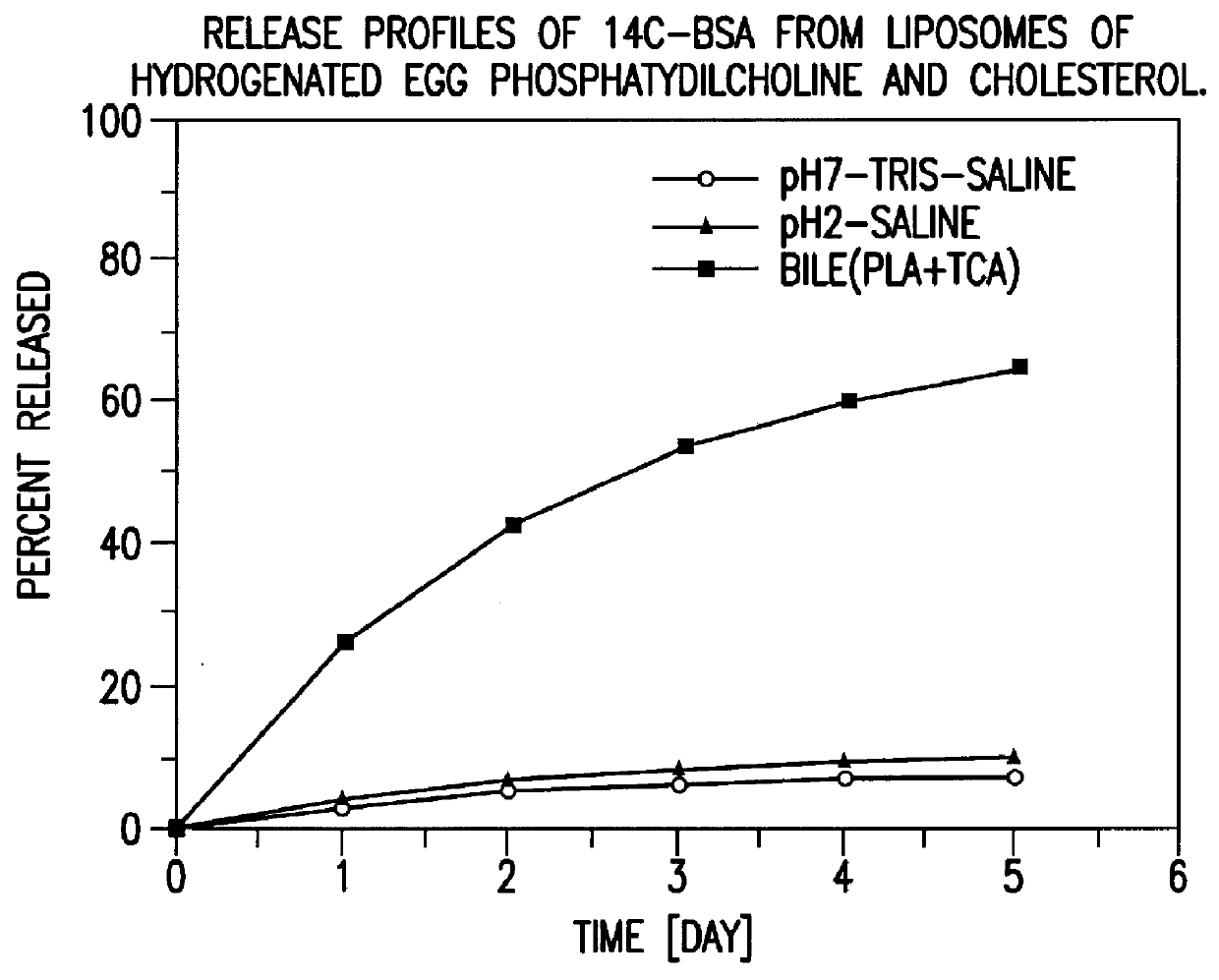
Polymerized liposomes targeted to M cells and useful for oral or mucosal drug delivery
InactiveUS6060082ALessContainment leakBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell typeLiposome
The present invention relates to targeted polymerized liposomes for oral and / or mucosal delivery of vaccines, allergens and therapeutics. In particular, the present invention relates to polymerized liposomes which have been modified on their surface to contain a molecule or ligand which targets the polymerized liposome to a specific site or cell type. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of polymerized liposomes modified to contain a carbohydrate or lectin on their surface.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
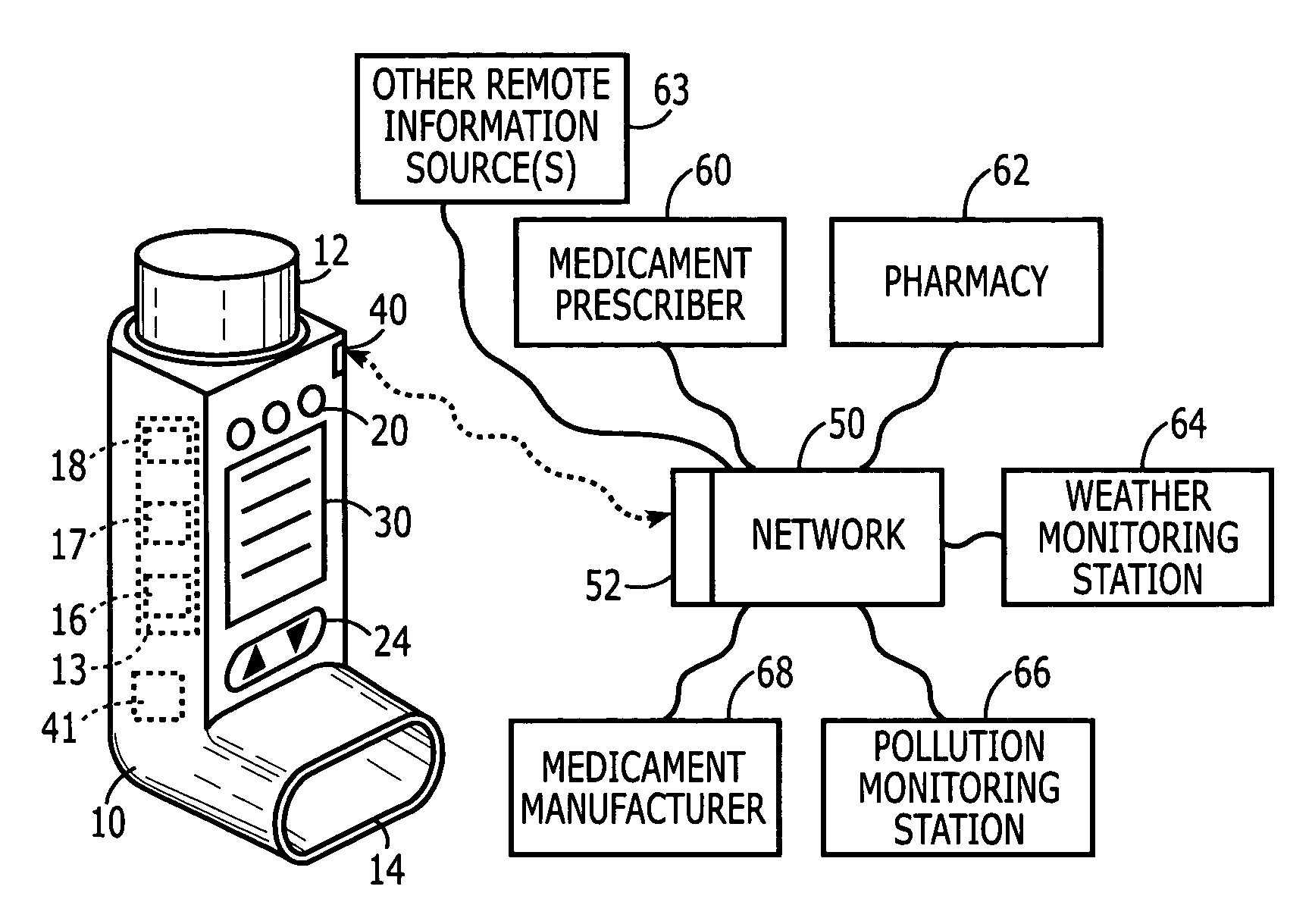
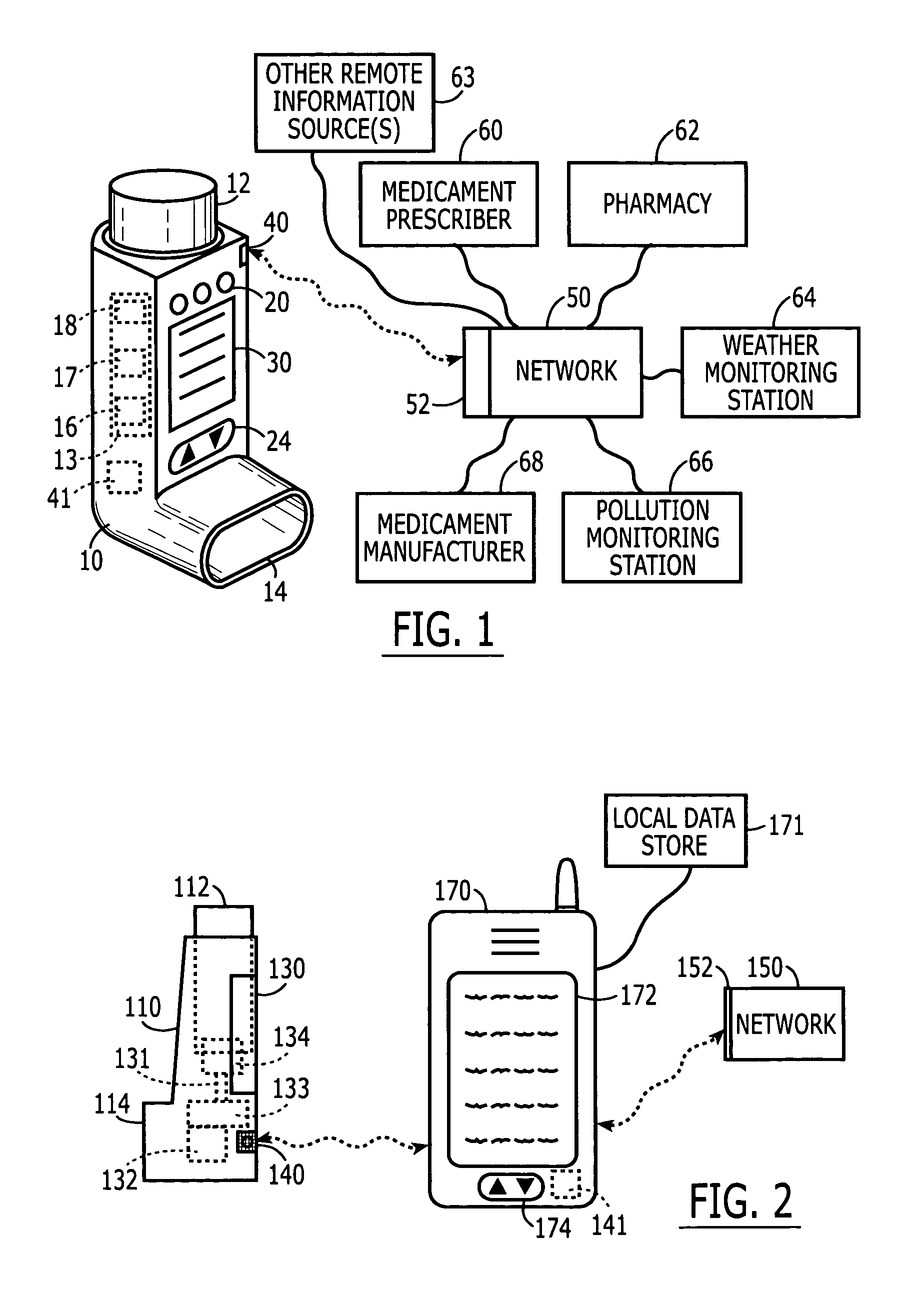
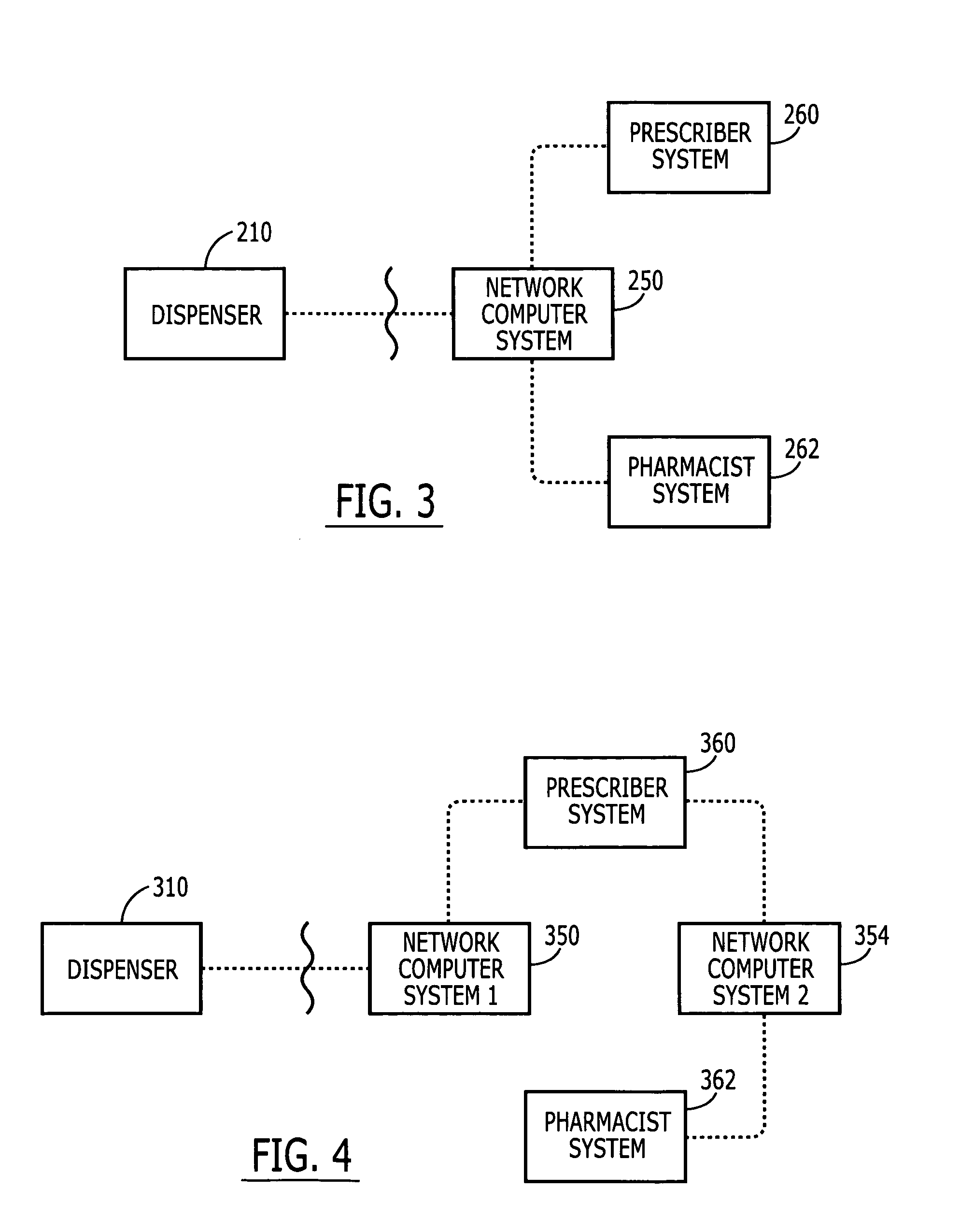
Medicament delivery system
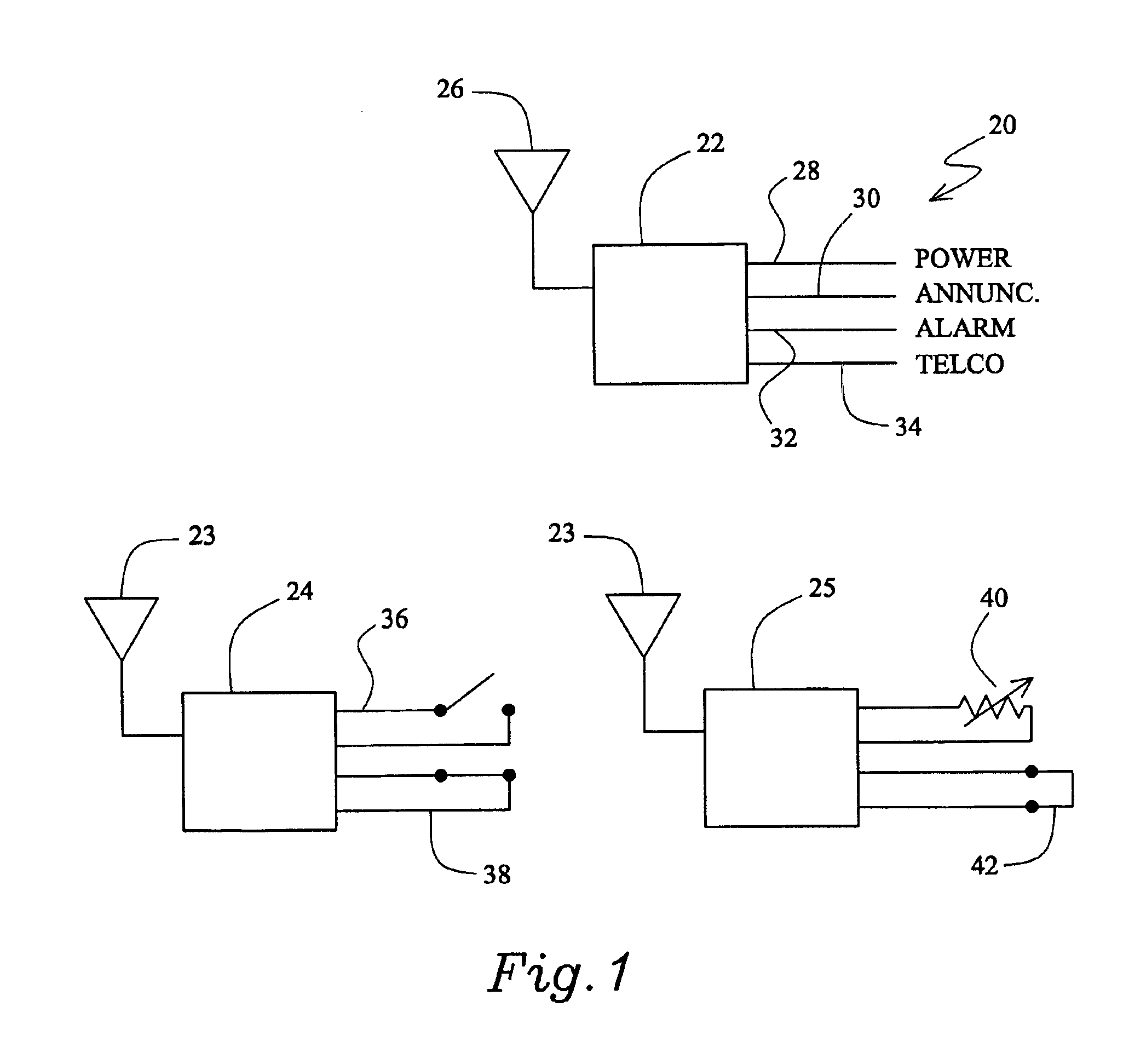
InactiveUS6958691B1Simple systemEasy accessDigital data processing detailsDrug and medicationsComputer scienceDelivery system
There is provided a system for the delivery of medicament comprising a medicament container; a dispensing mechanism for dispensing medicament from the medicament container; an electronic data management system; and a communicator for wireless communication with a network computer system to enable communication of data between the network computer system and the electronic data management system. The electronic data management system comprises a memory for storage of data; a microprocessor for performing operations on the data; and a transmitter for transmitting a signal relating to the data or the outcome of an operation on the data.
Owner:GLAXO WELLCOME INC
Method and apparatus providing secure initialization of network devices using a cryptographic key distribution approach
ActiveUS7181620B1Efficiently establishedCommunication securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey scheduleKey distribution
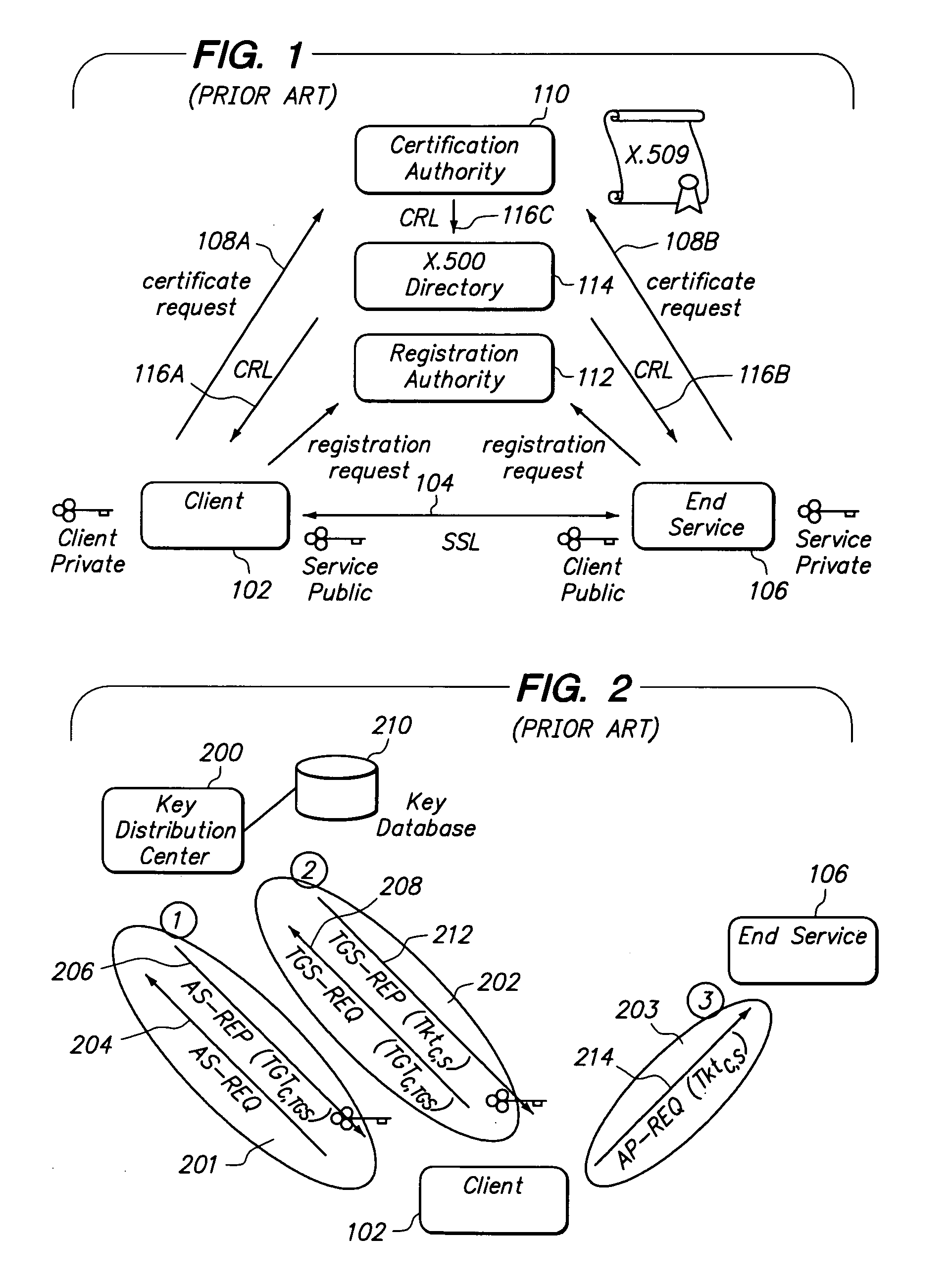
Registration of non-configured network devices in a distributed network is facilitated by a method of distributing cryptographic keys. A non-configured first device seeking to communicate securely with a second device acquires knowledge of a trusted registration service. The first device registers with the registration service and obtains a longer-lived symmetric key. Using the longer-lived key, the first device authenticates itself to a key management service, and receives a shorter-lived symmetric key encapsulated in a ticket that includes policy information. A second device carries out the same preparatory process. Using its ticket containing the shorter-lived key, the first device requests the second device to obtain a session key on behalf of both. The second device presents its own ticket and that of the first device to the key management service to authenticate the shorter-lived key, and then obtains a session key for use in communications among the first and second devices. The first device and second device then communicate by encrypting communications with the session key, and without further contact with the key management or registration services or any other online authoritative server or key database. Thus newly deployed network devices may be positively identified, registered in the network, and subjected to key schedule or other key management policies.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
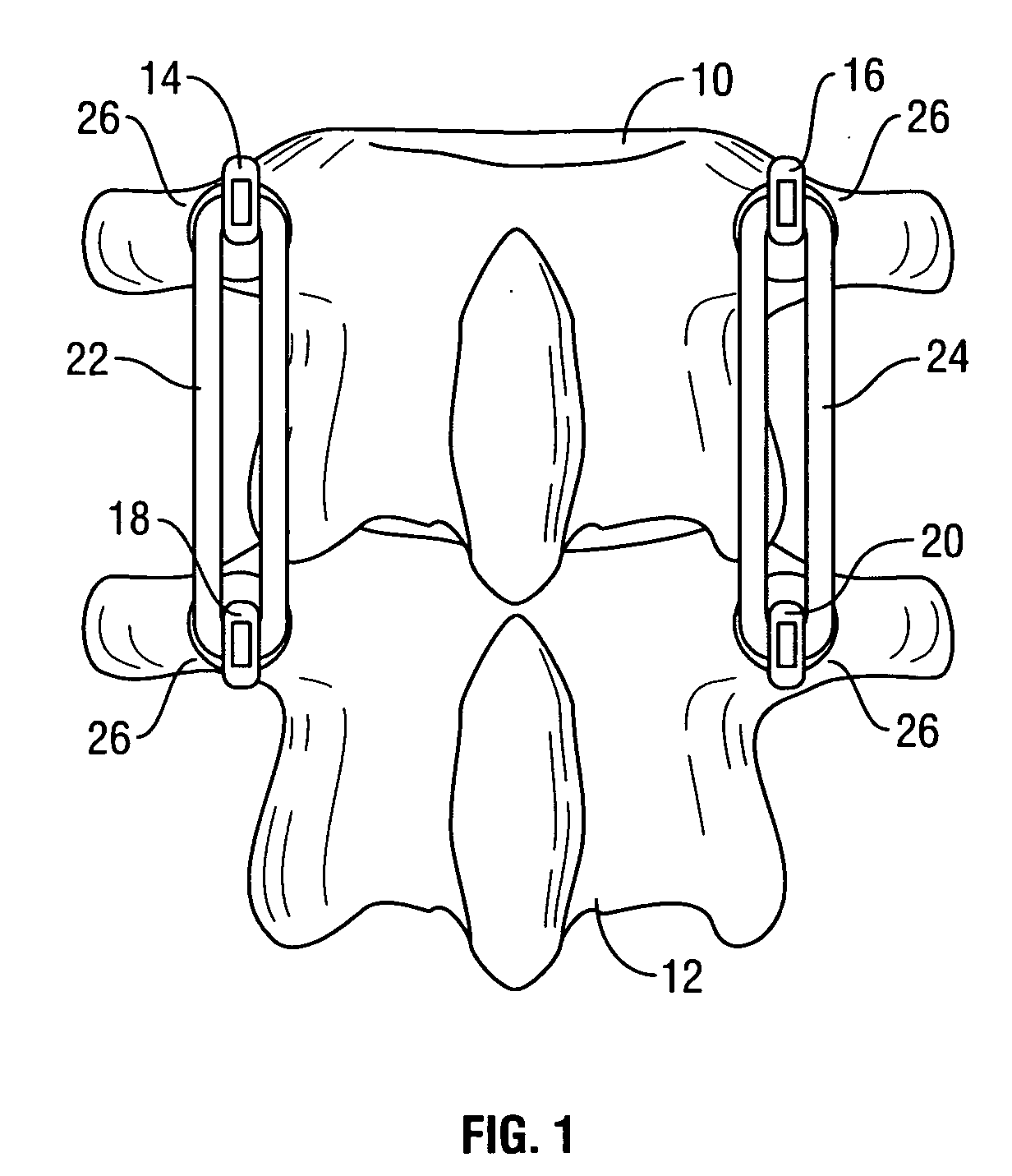
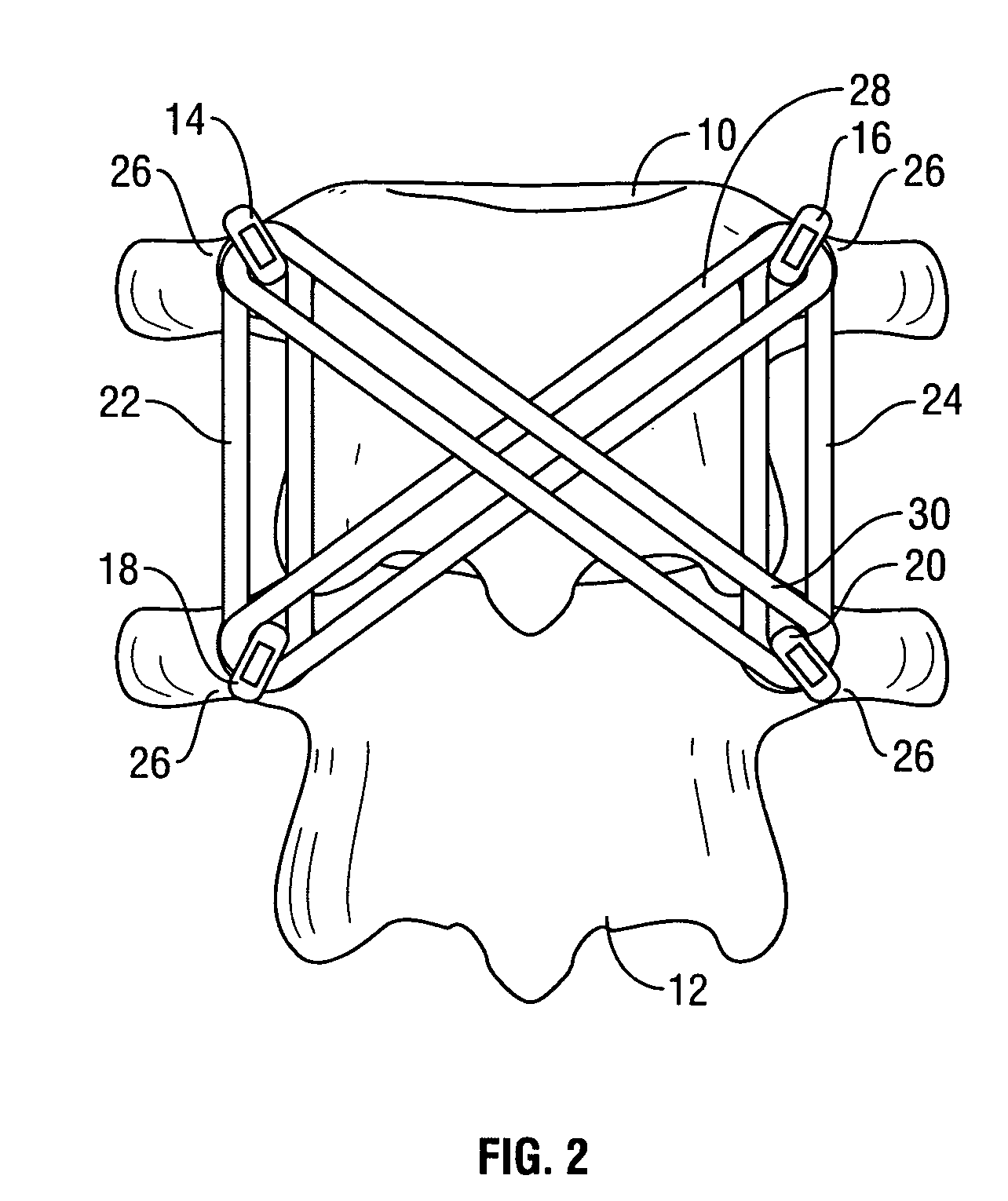
Spinal stabilization system to flexibly connect vertebrae
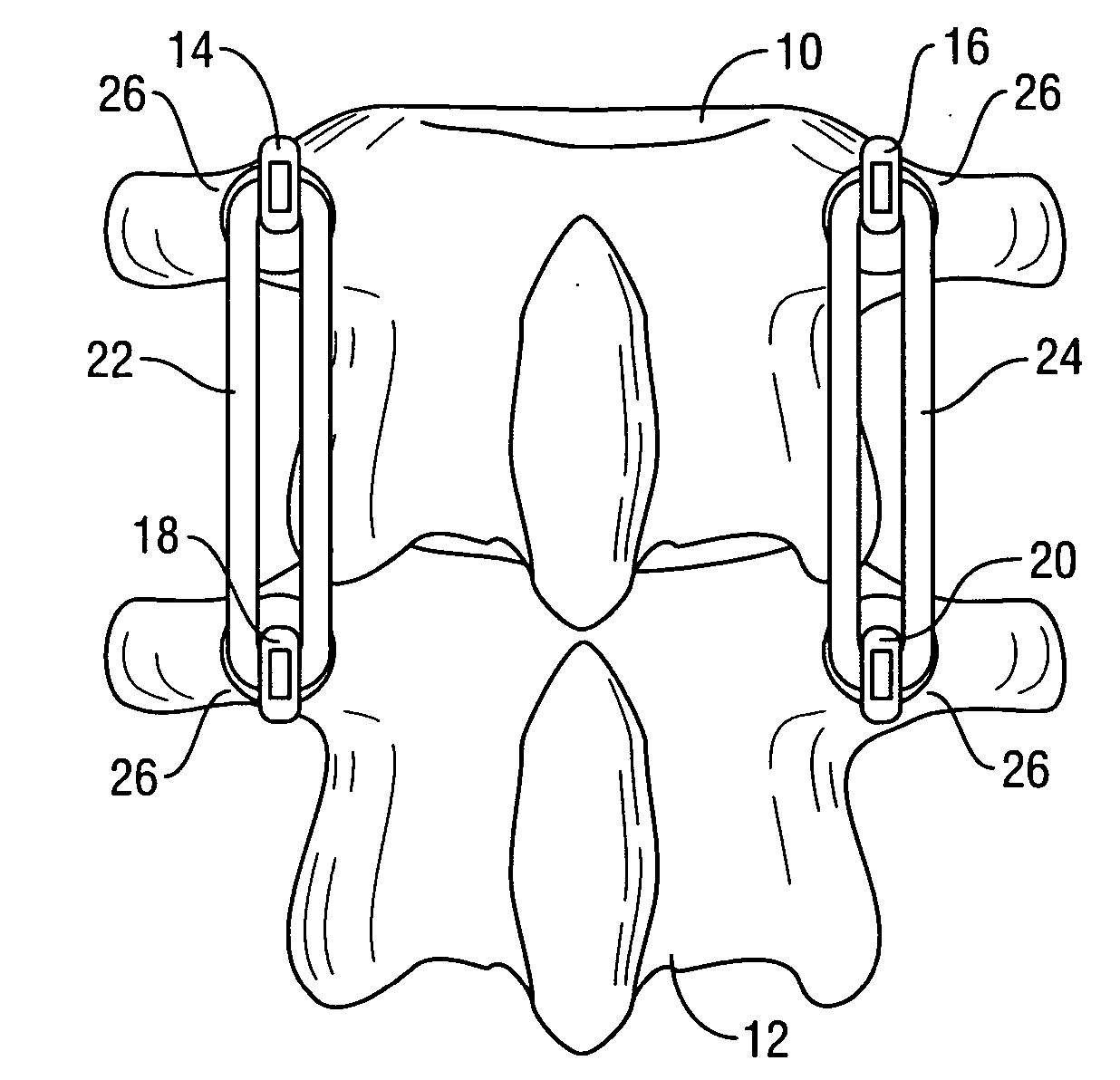
InactiveUS20050267470A1Preventing excessive motionPrecise alignmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDeformity
A surgically implanted spinal stabilization system uses posterior anchor hooks attached to vertebrae to retain elastic bands to retain flexibility and mobility while maintaining alignment and preventing excessive motion and deformity. The elastic bands may parallel the longitudinal axis of the spine, or, for enhanced promotion of alignment, they may also arranged in a diagonally crossing configuration. Multi-level fixation can be achieved using the spinal stabilization system with longer elastic bands. A method of applying the spinal stabilization system using an elastic band application tool facilitates simple, rapid application of the system to a patient.
Owner:MCBRIDE DUNCAN Q
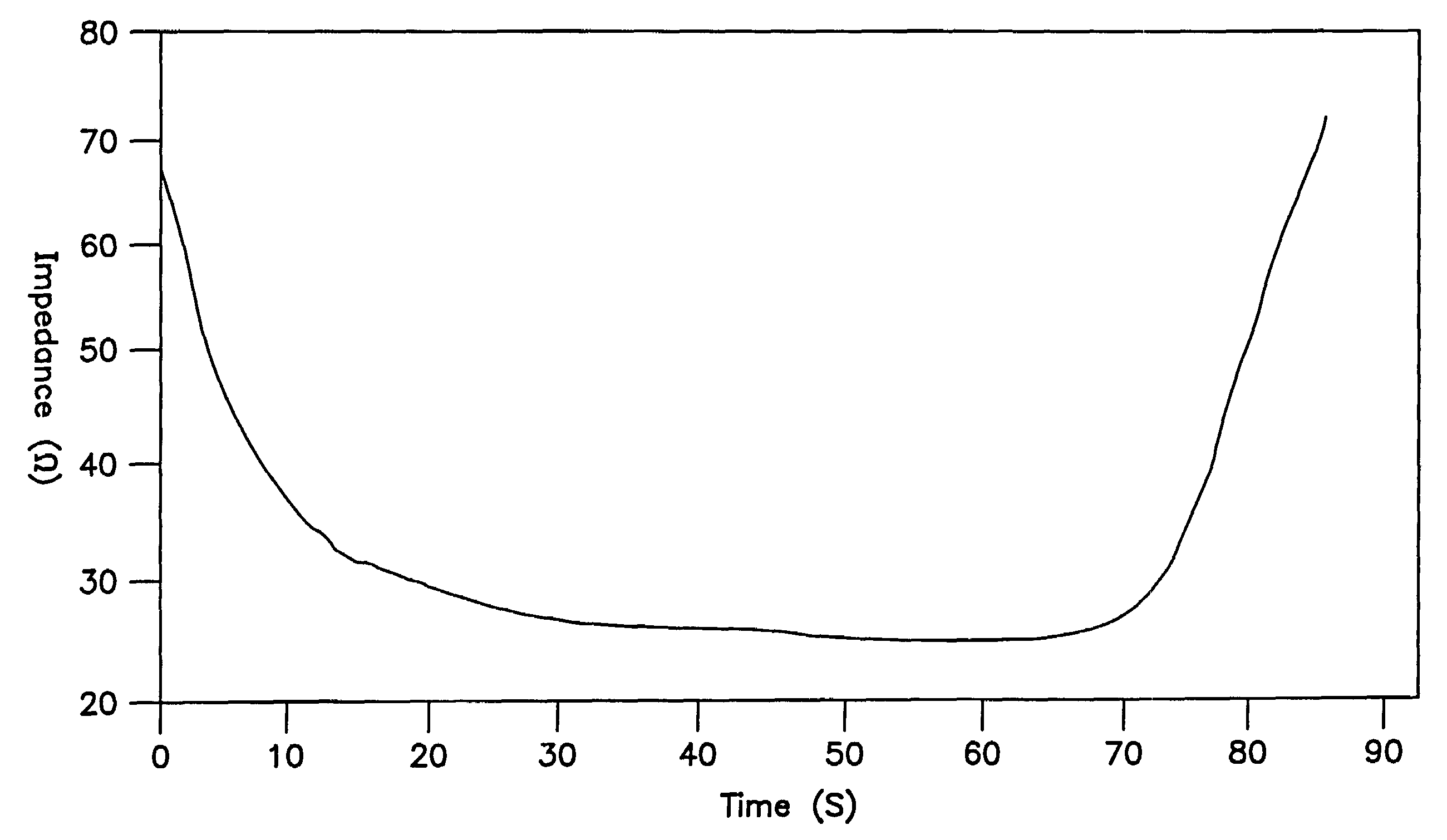
Ablation system
A system for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the impedance of the tissue to be ablated. Rather than attempting to detect a desired drop or a desired increase impedance, completeness of a lesion is detected in response to the measured impedance remaining at a stable level for a desired period of time, referred to as an impedance plateau. The mechanism for determining transmurality of lesions adjacent individual electrodes or pairs may be used to deactivate individual electrodes or electrode pairs, when the lesions in tissue adjacent these individual electrodes or electrode pairs are complete, to create an essentially uniform lesion along the line of electrodes or electrode pairs, regardless of differences in tissue thickness adjacent the individual electrodes or electrode pairs.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Selective surveillance system with active sensor management policies
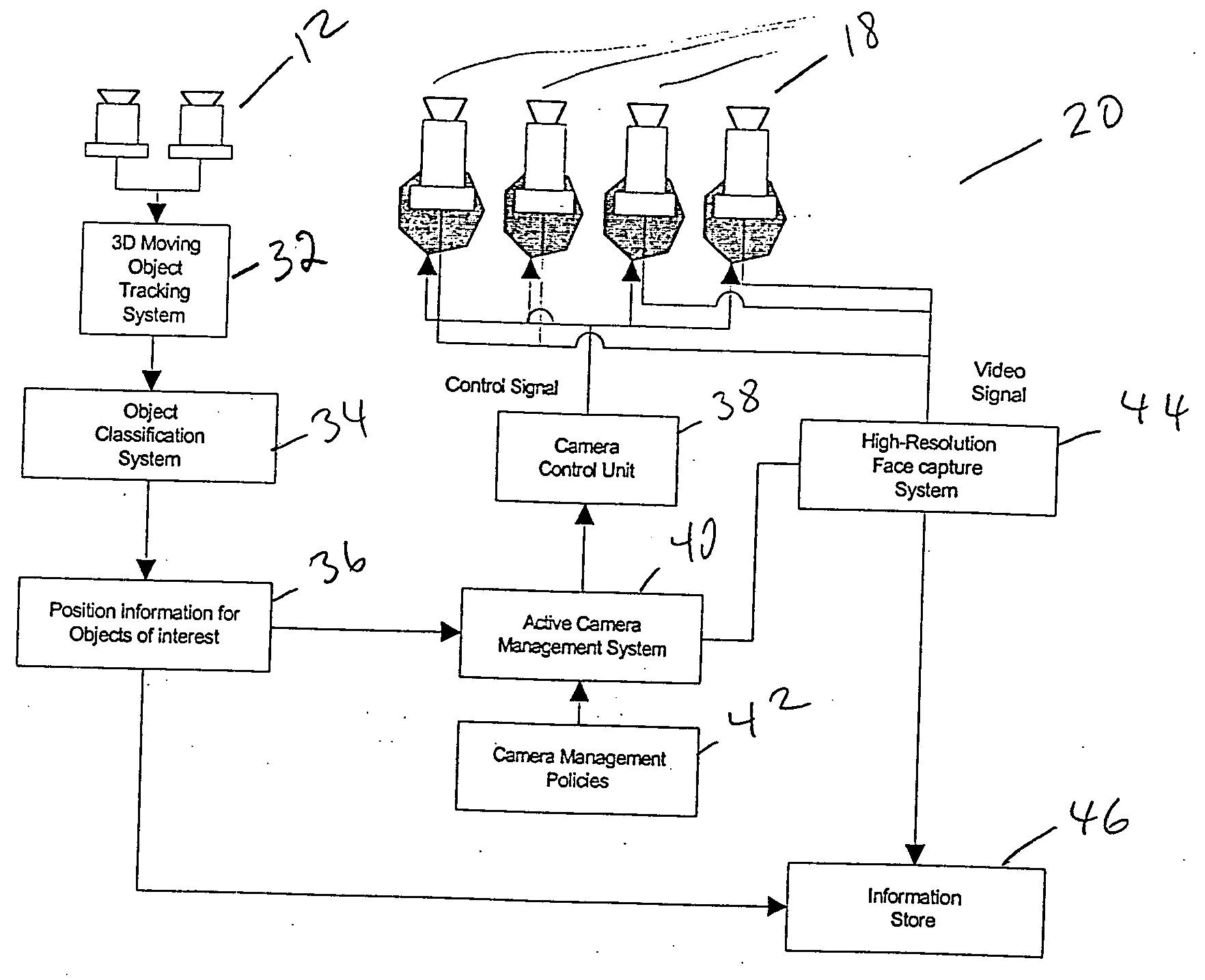
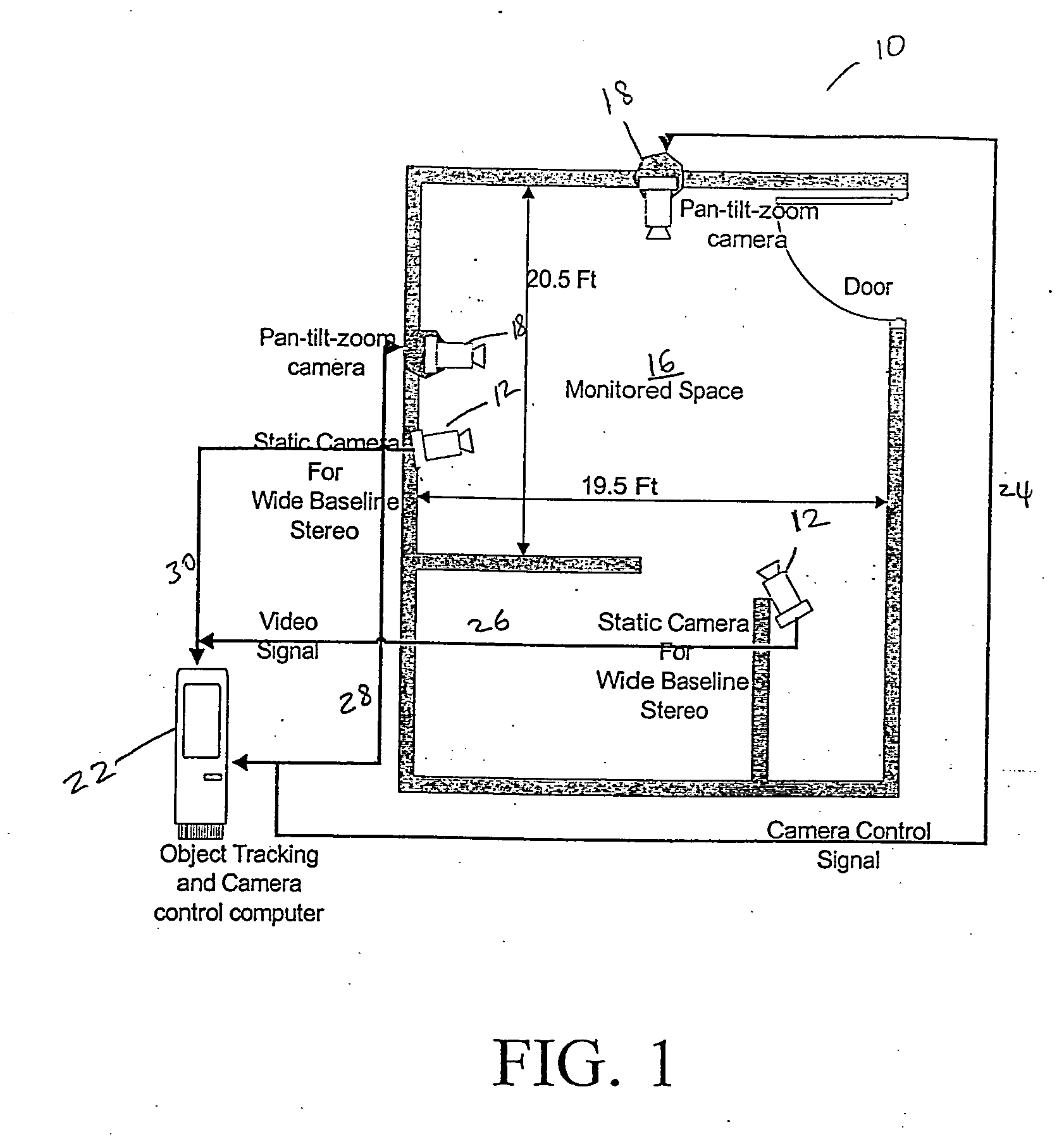
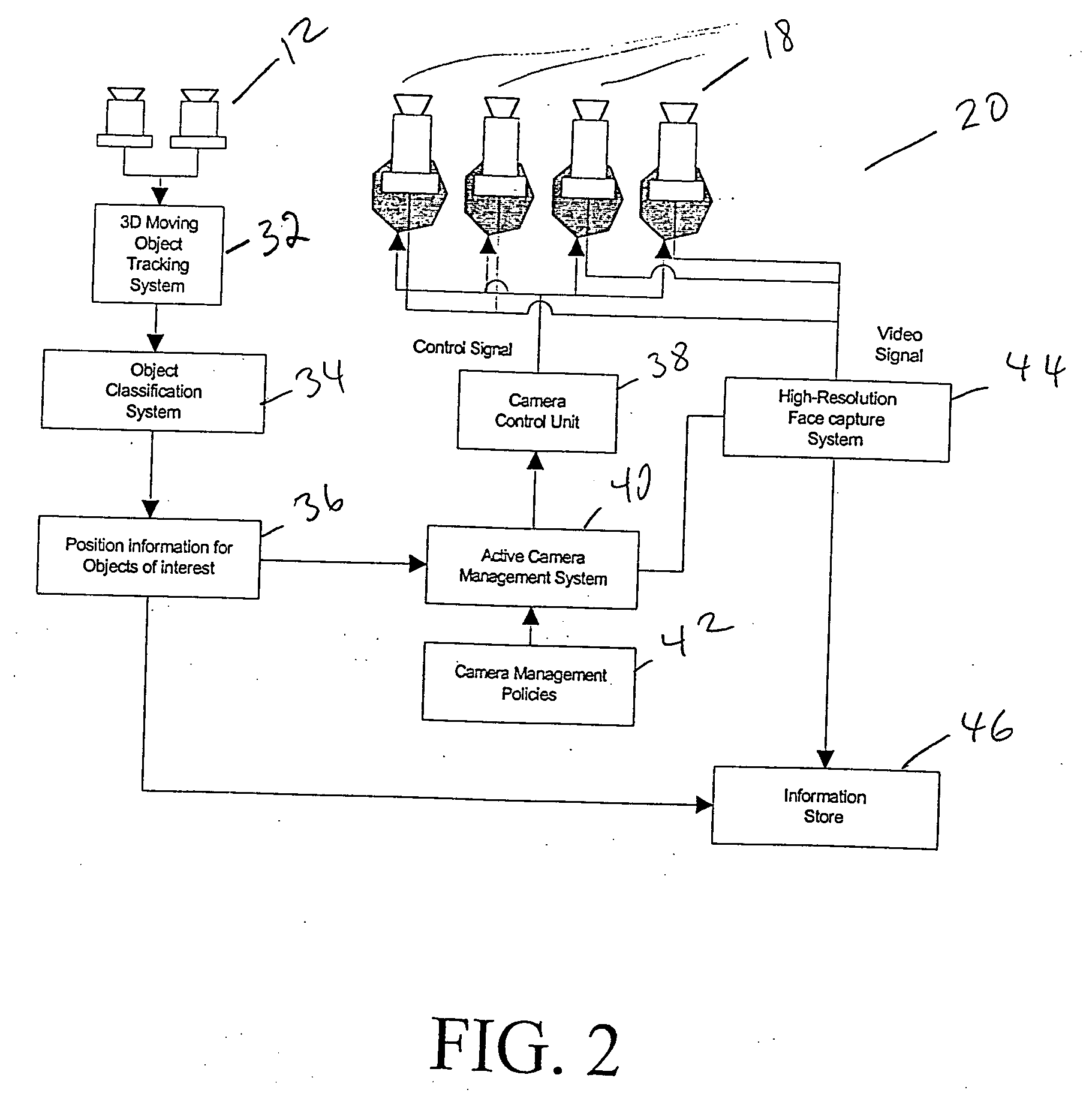
InactiveUS20050012817A1Simple systemAvoid maintenanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsThree-dimensional spaceMonitoring system
A system and method for selectively monitoring movement of one or more objects having one or more object attributes in a three dimensional space. The method is achieved by following the steps of detecting a position of the one or more objects in the three dimensional space by collecting information from one or more static sensors; selecting each detected object for monitoring; uniquely identifying selected objects and assigning one or more variable sensors to monitor the uniquely identified object. The method further requires gathering information from the variable sensors for each identified object; detecting a direction of each identified object in the three dimensional space; and controlling the one or more variable sensors to continuously point to the assigned uniquely identified object.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and apparatuses for controlling the appearance of a user interface
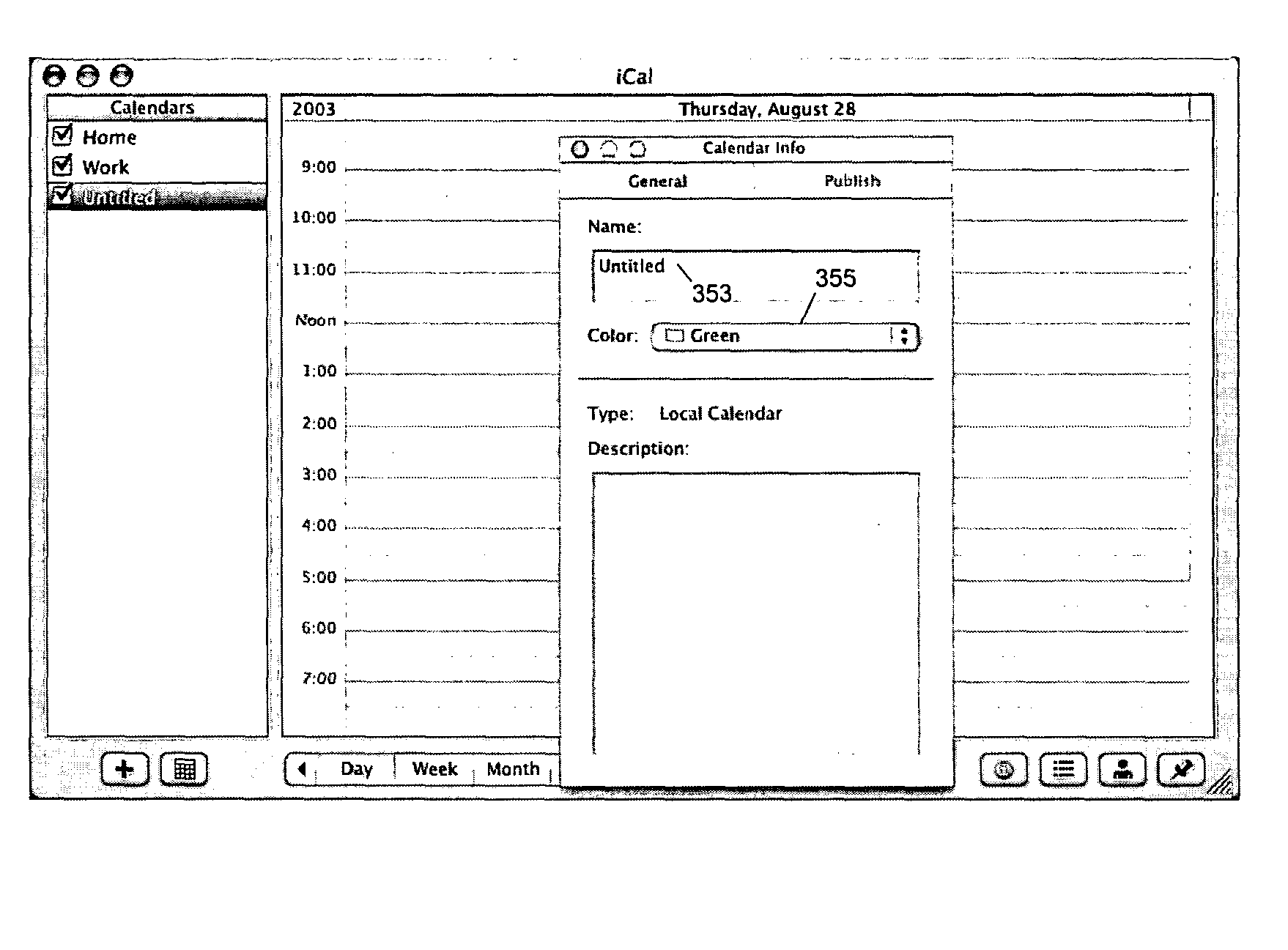
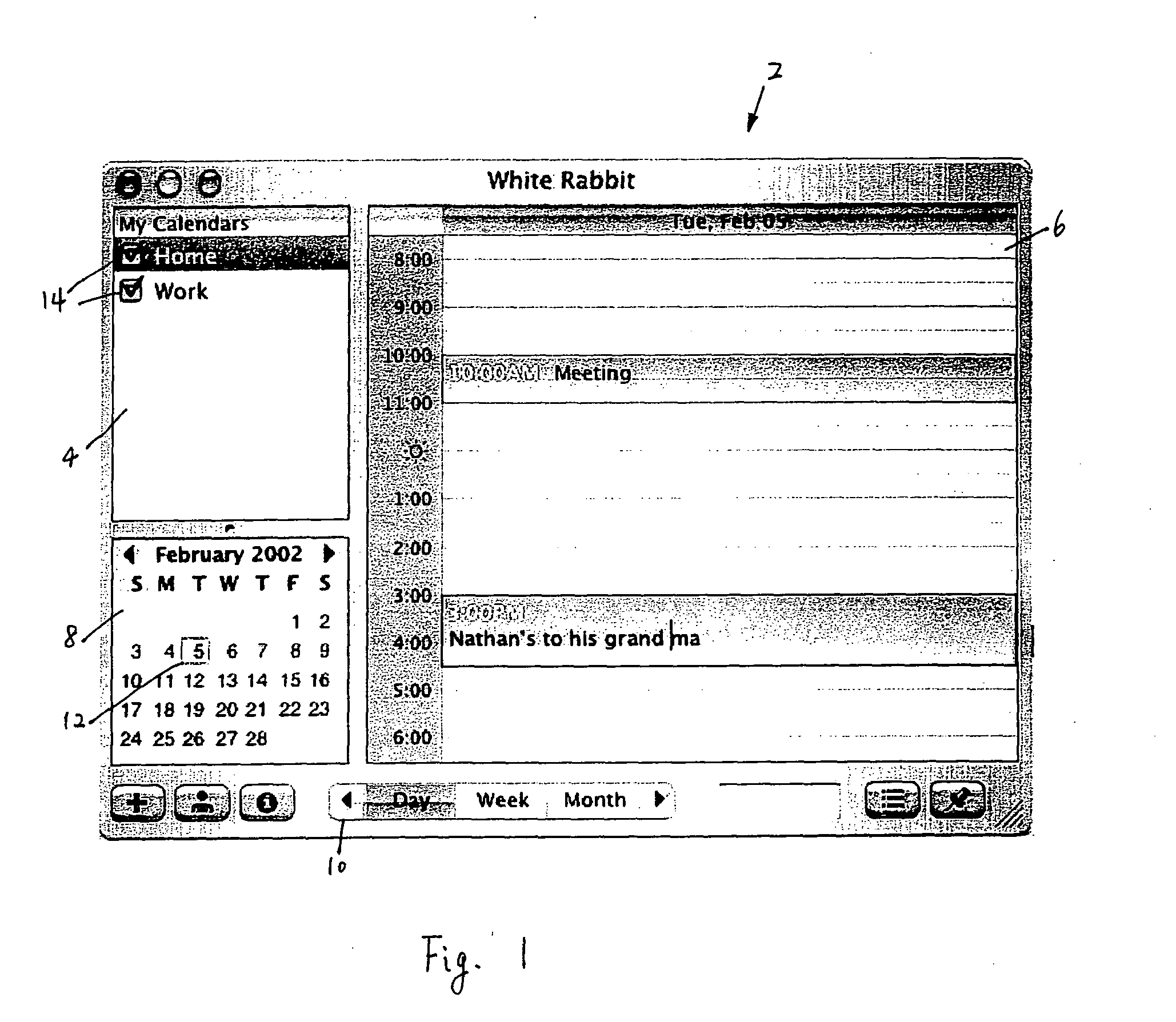
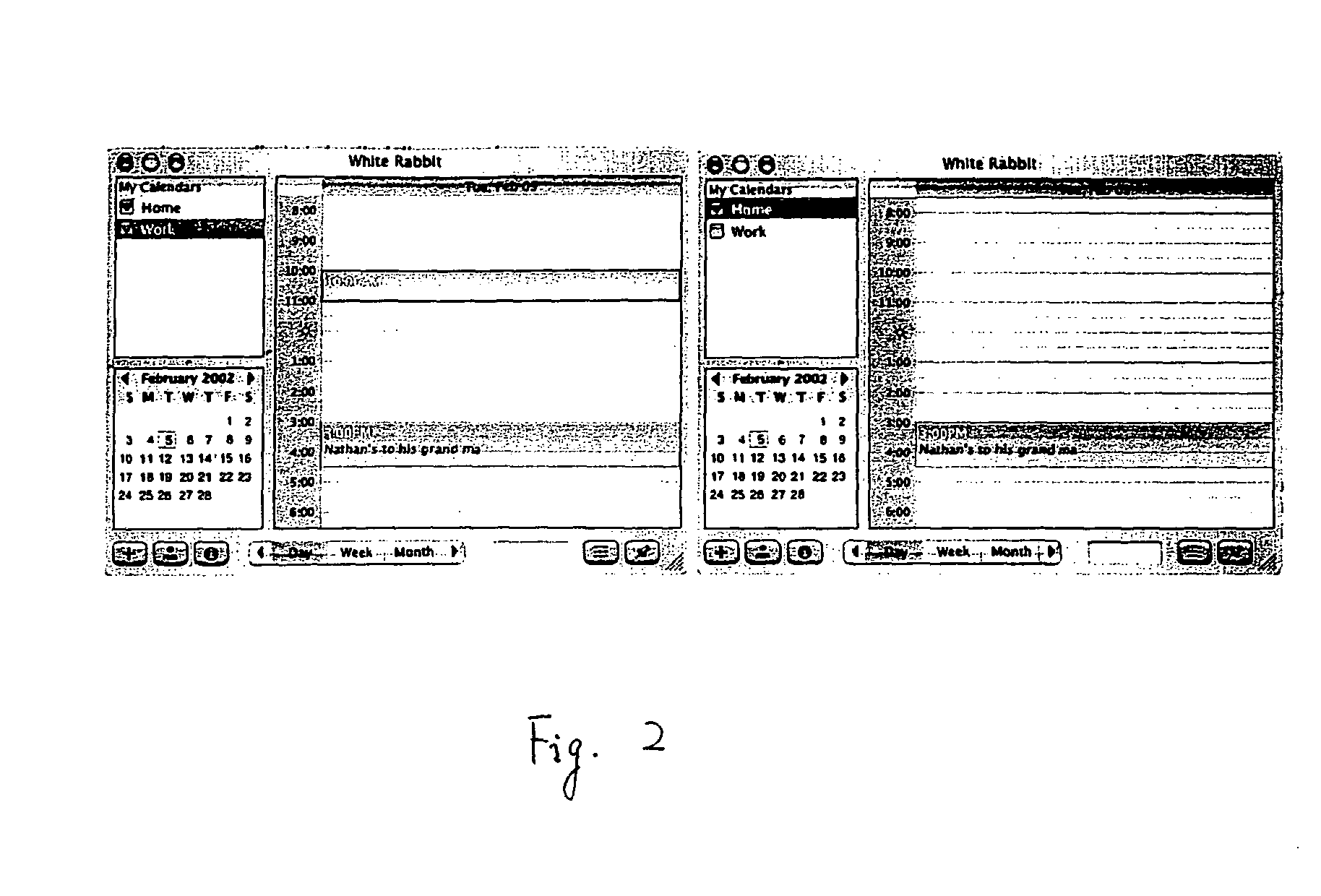
ActiveUS20050039142A1Simple systemCathode-ray tube indicatorsOffice automationData processing systemDisplay device
Methods, systems and machine readable media for displaying (e.g., information from multiple calendars) using different secondary colors generated according to primary colors in a data processing system. In one exemplary method, a calendar interface is displayed on a display device, wherein the calendar interface is capable of displaying calendar events for a user, and a control interface is displayed, which control interface allows the user to selectively display calendar events simultaneously from at least two calendars of the user in the calendar interface. Each of the calendars can have a primary color for display; and, secondary colors are automatically determined based on the primary color for the user interface elements associated with a calendar.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and systems for automating the control of objects within a defined human environment
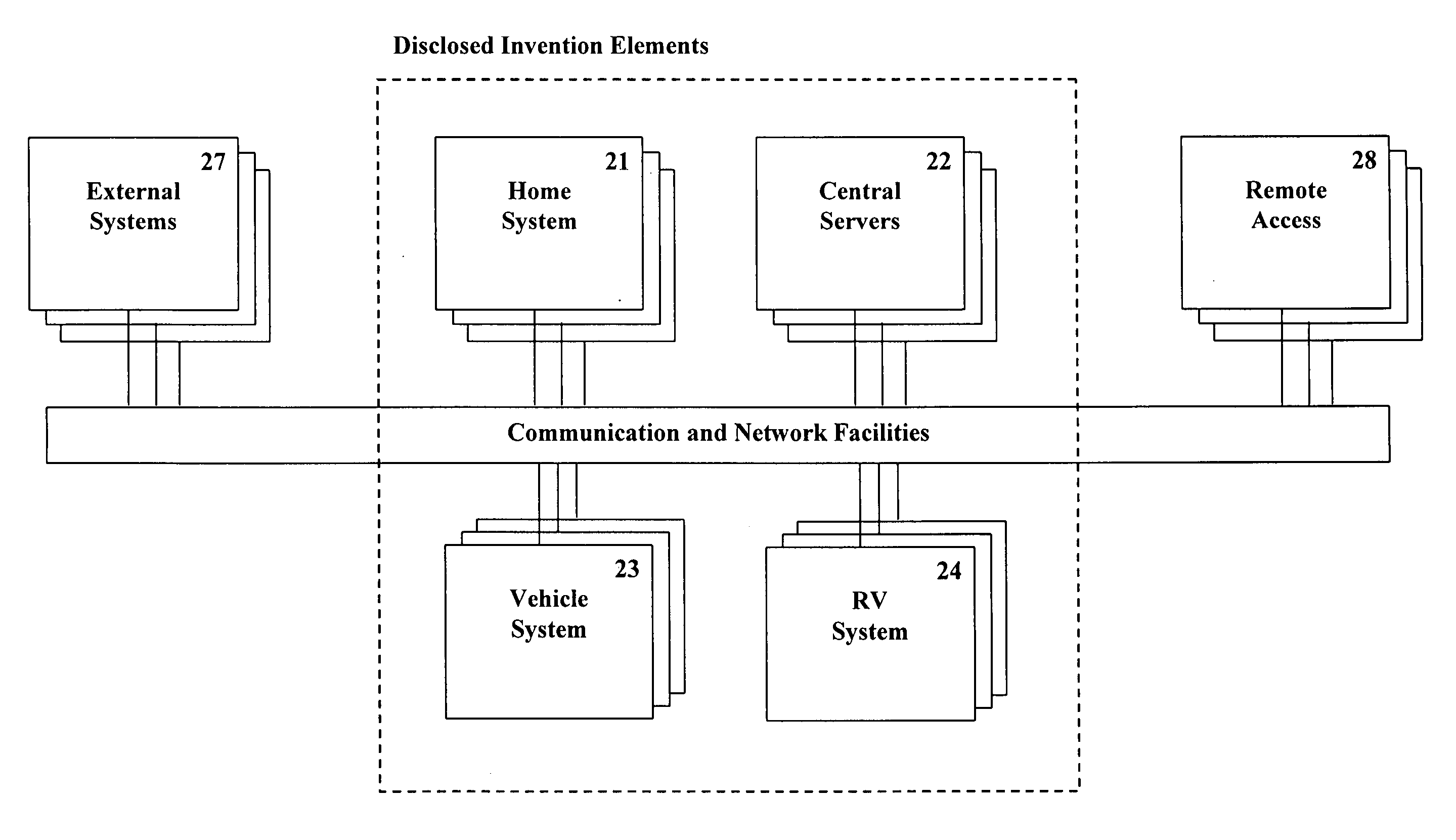
InactiveUS20060218244A1Reduce system costSimple systemMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionAutomatic controlAction function
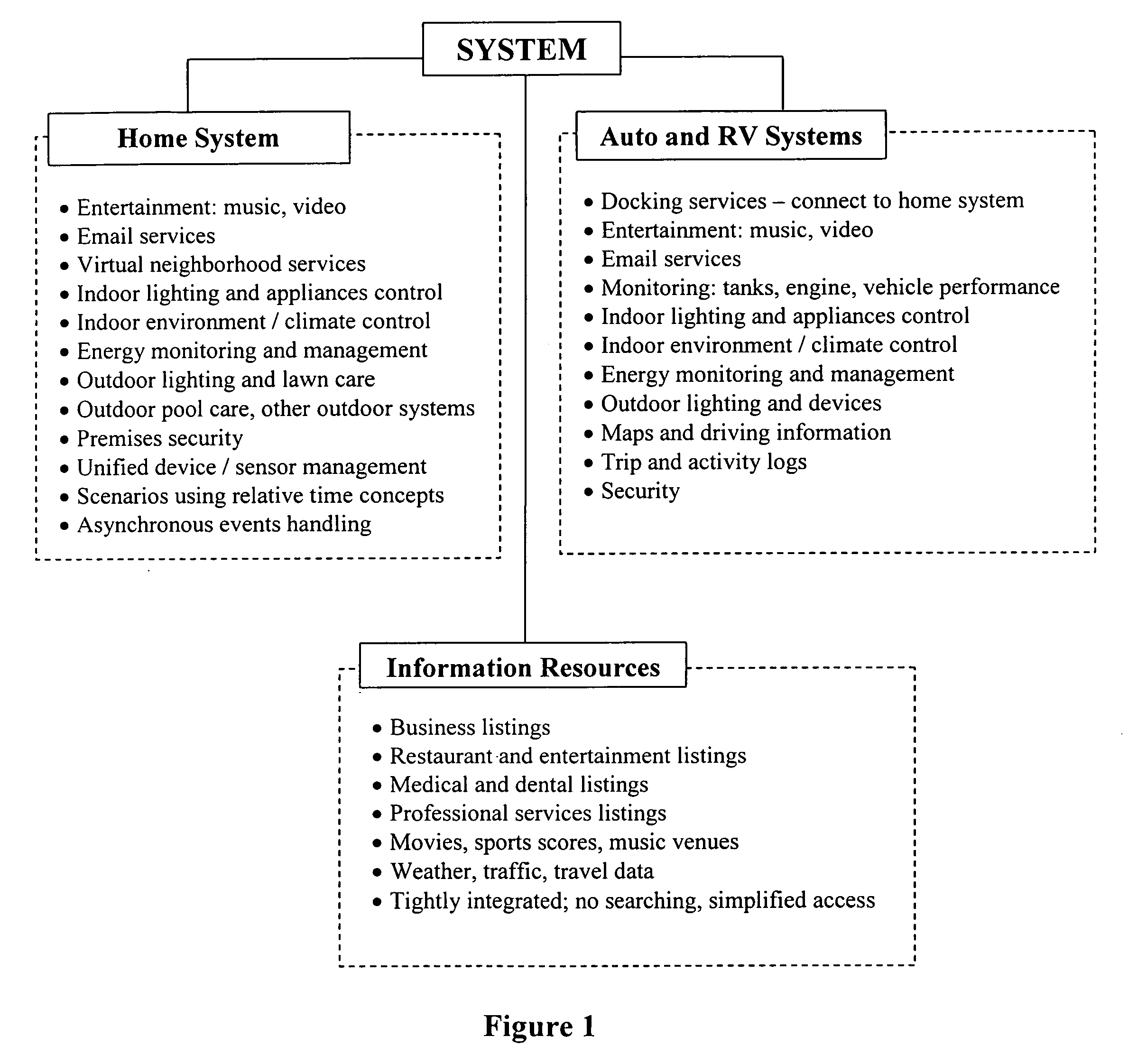
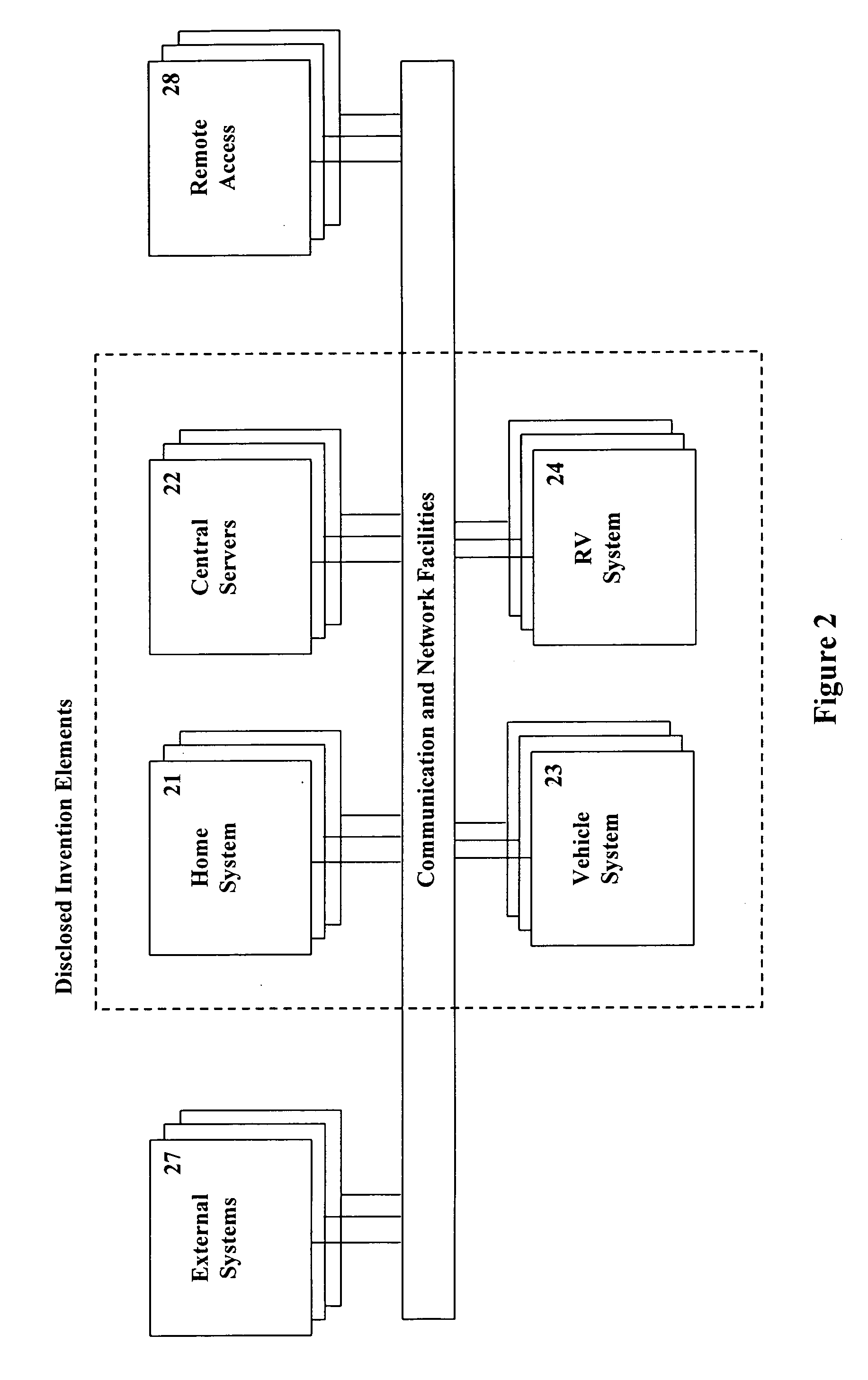
Methods and systems are described for the automation of a human living environment such as a home, an apartment, a workplace, or a vehicle. The methods and systems are directed to the control of various groups of objects within the human living environments according to defined criteria and defined object groupings, in a manner that establishes operational themes and scenarios within the environment. The methods and systems utilize devices for characterizing the environment (sensors), making decisions about actions appropriate in the environment (processors), and effecting actions and activities within the environment (switches, controls and actuators). The automation operates on multiple levels including; responsive safety functionality, one time action functionality, sporadically initiated timed action functionality, and periodically scheduled action functionality. The systems integrate with off-site information and action routing services that increase the decision making ability of the individuals within the environment.
Owner:RASMUSSEN JUNG A +1
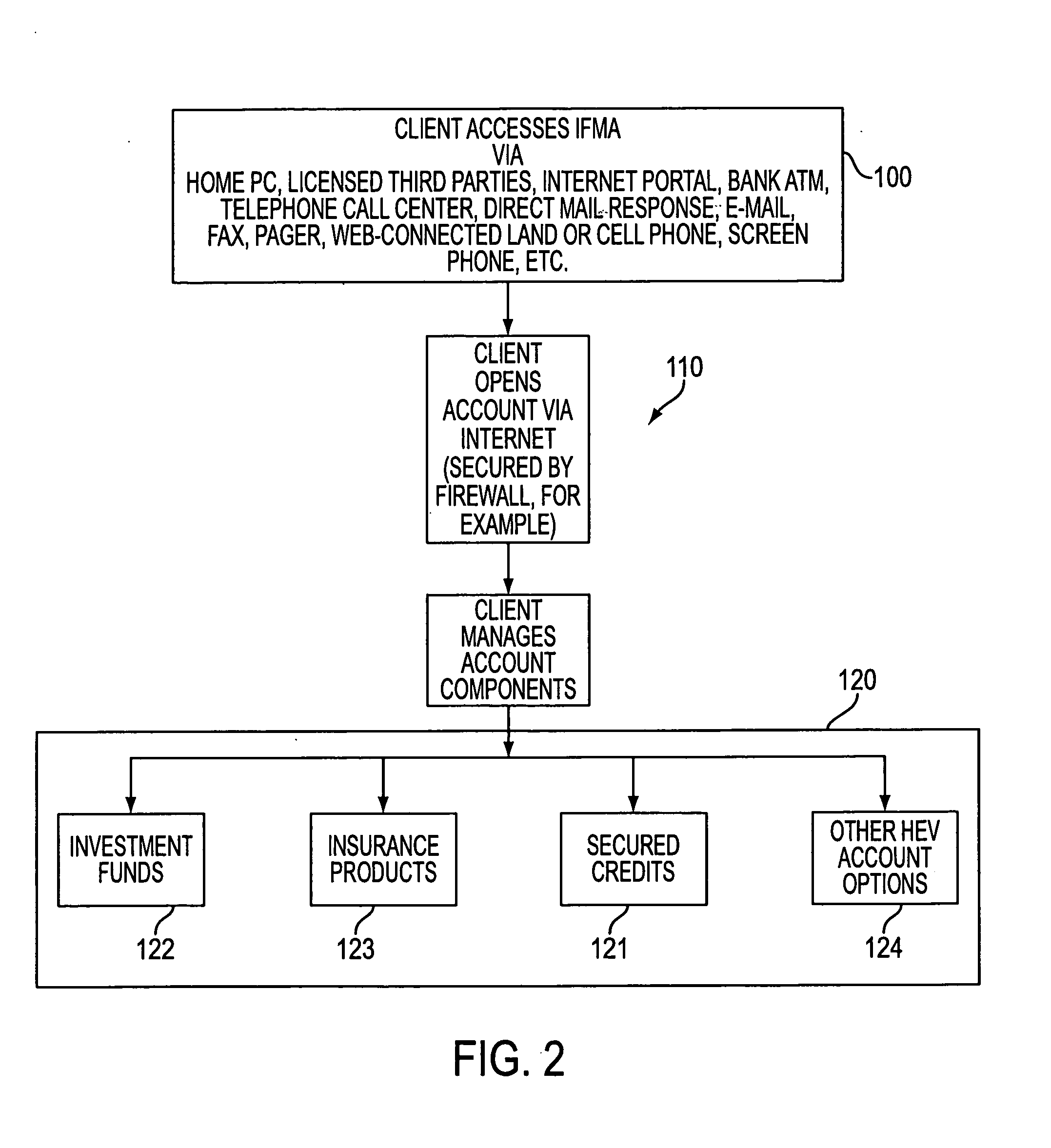
Method and system for internet banking and financial services
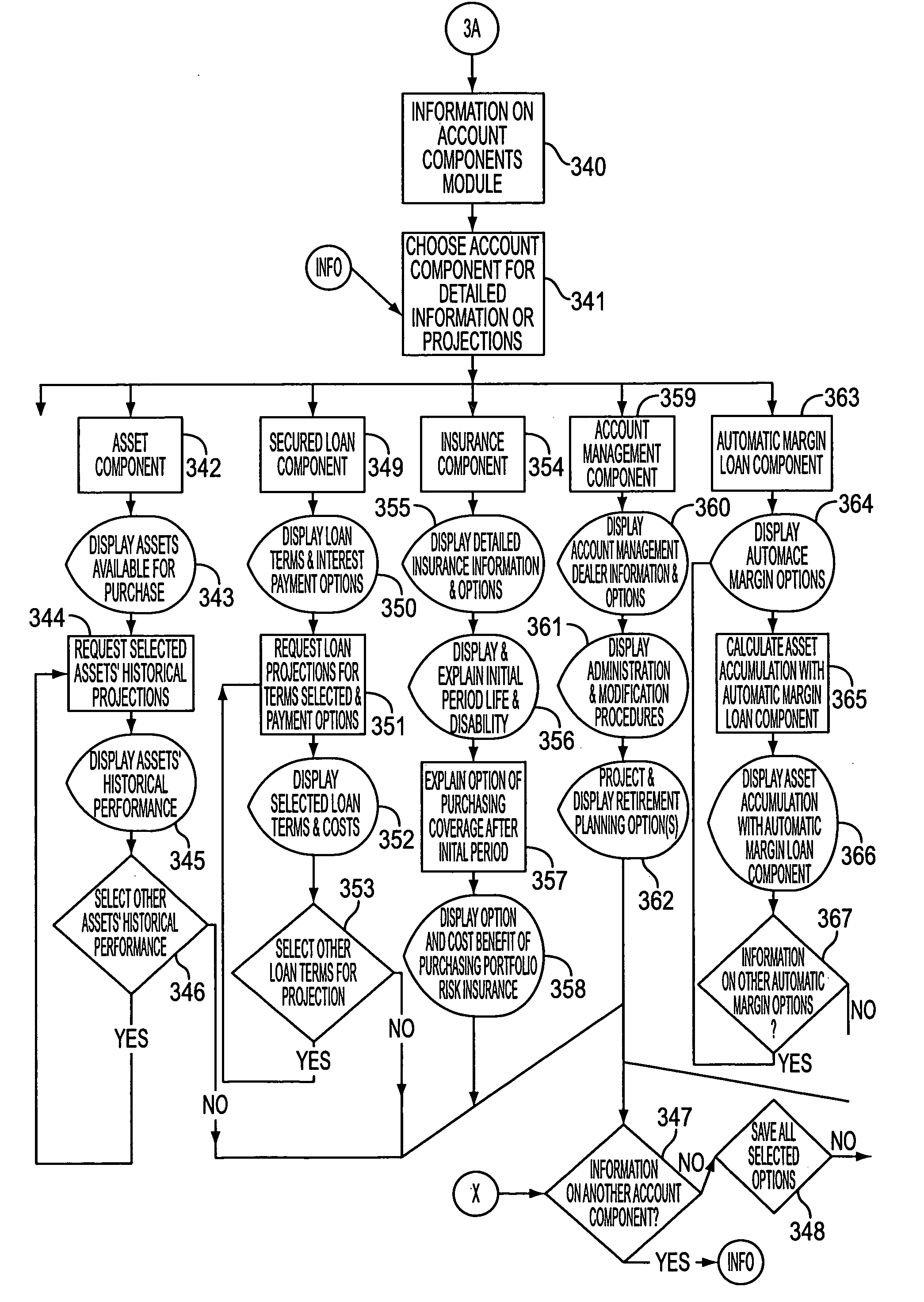
A computer implemented method of providing a client with an integrated financial management account, including receiving application data for an integrated financial management account and setting up the integrated financial account with a loan component data, an investment component data, and an insurance component, all associated with an account file. Thereby qualifying the client for a loan in the loan component of the integrated financial management account and associating the qualification information with the account file, disbursing the proceeds of the loan component into the investment component by recording a proceed value in the investment component data associated with the account file, and purchasing investment assets using the proceeds of the loan component and associating purchased investment assets to the investment component data associated with the account file.
Owner:NOLAND CATHLEEN
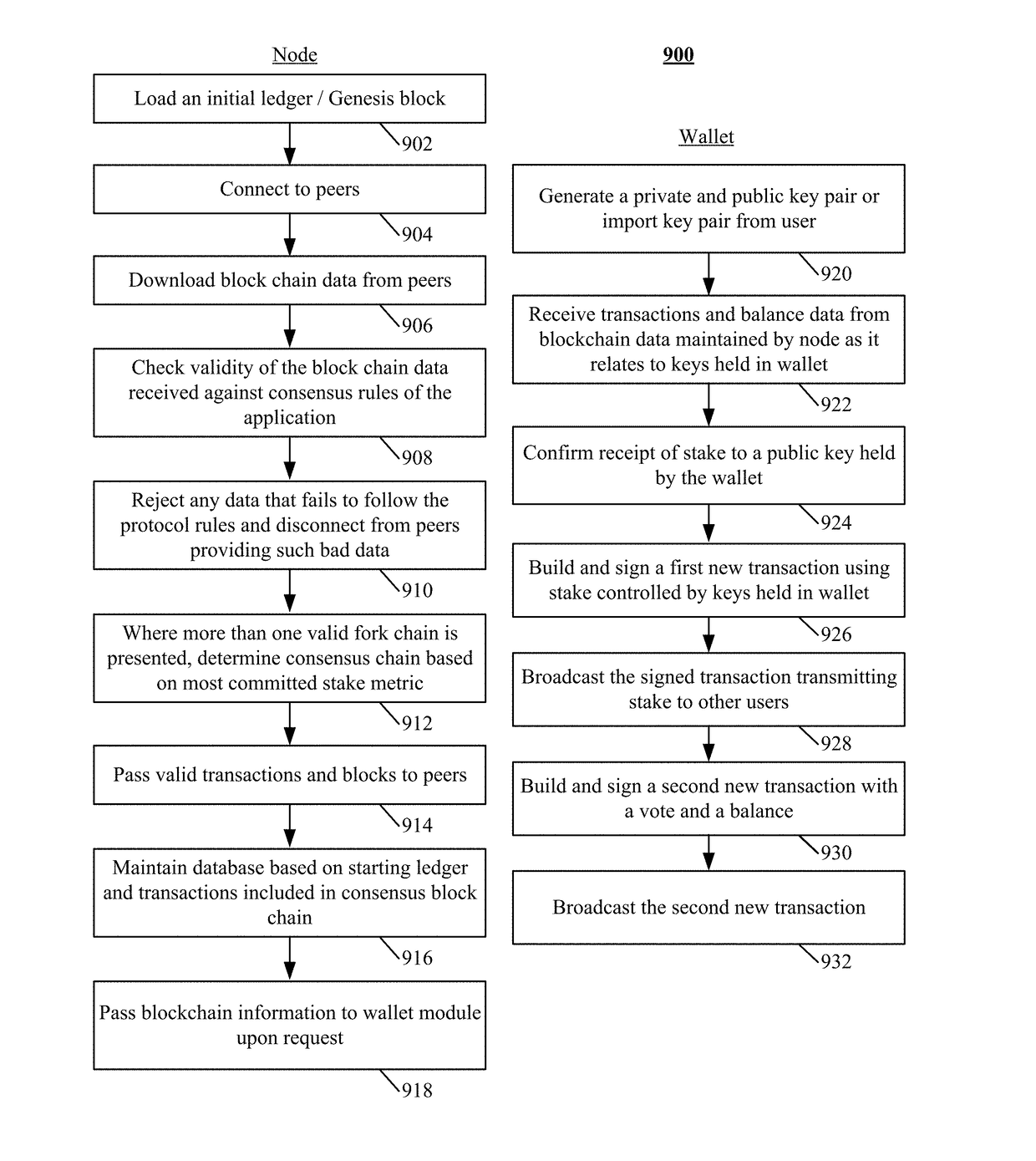
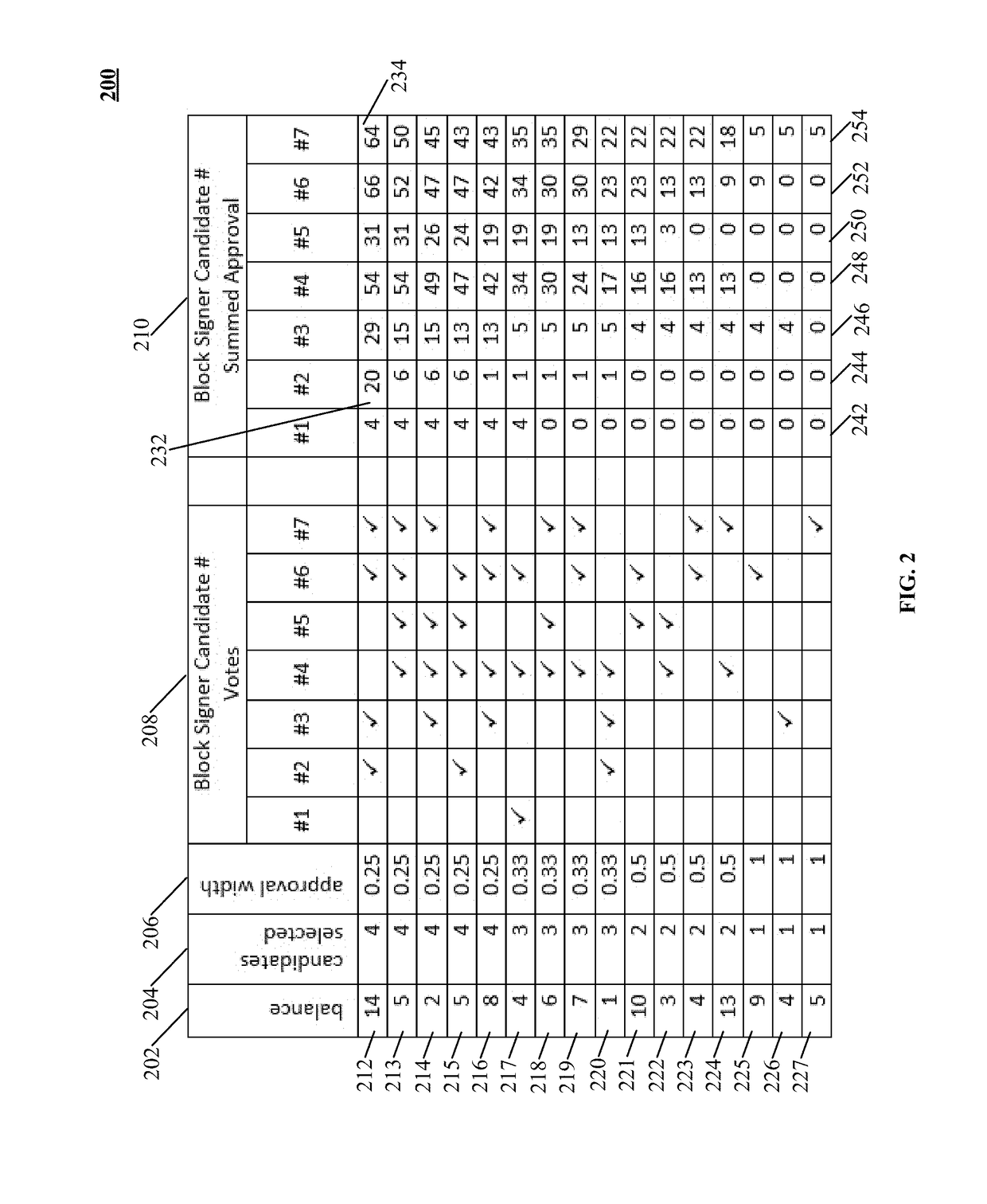
Consensus system for tracking peer-to-peer digital records
ActiveUS9875510B1Improve trustReduce overheadComplete banking machinesFinanceDigital recordingData Corruption
The disclosure describes a peer-to-peer consensus system and method for achieving consensus in tracking transferrable digital objects. The system achieves consensus on a shared ledger between a plurality of peers and prevents double spending in light of network latency, data corruption and intentional manipulation of the system. Consensus is achieved and double spending is prevented via the use of the most committed stake metric to choose a single consensus transaction record. A trustable record is also facilitated by allowing stakeholders to elect a set of trusted non-colluding parties to cooperatively add transactions to the consensus record. The voting mechanism is a real-time auditable stake weighted approval voting mechanism. This voting mechanism has far reaching applications such as vote directed capital and providing a trusted source for data input into a digital consensus system. The system further enables digital assets that track the value of conventional assets with low counterparty risk.
Owner:KASPER LANCE
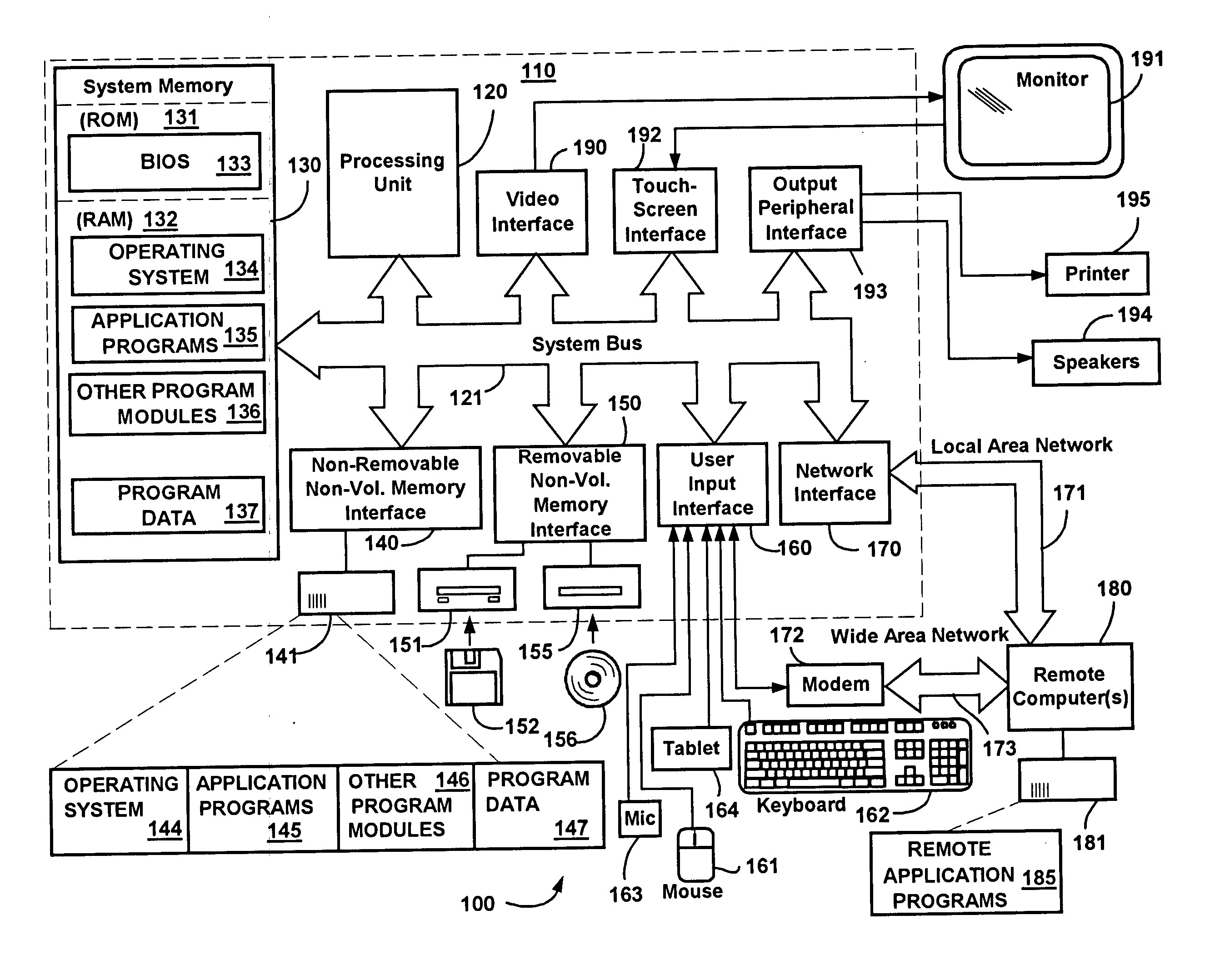
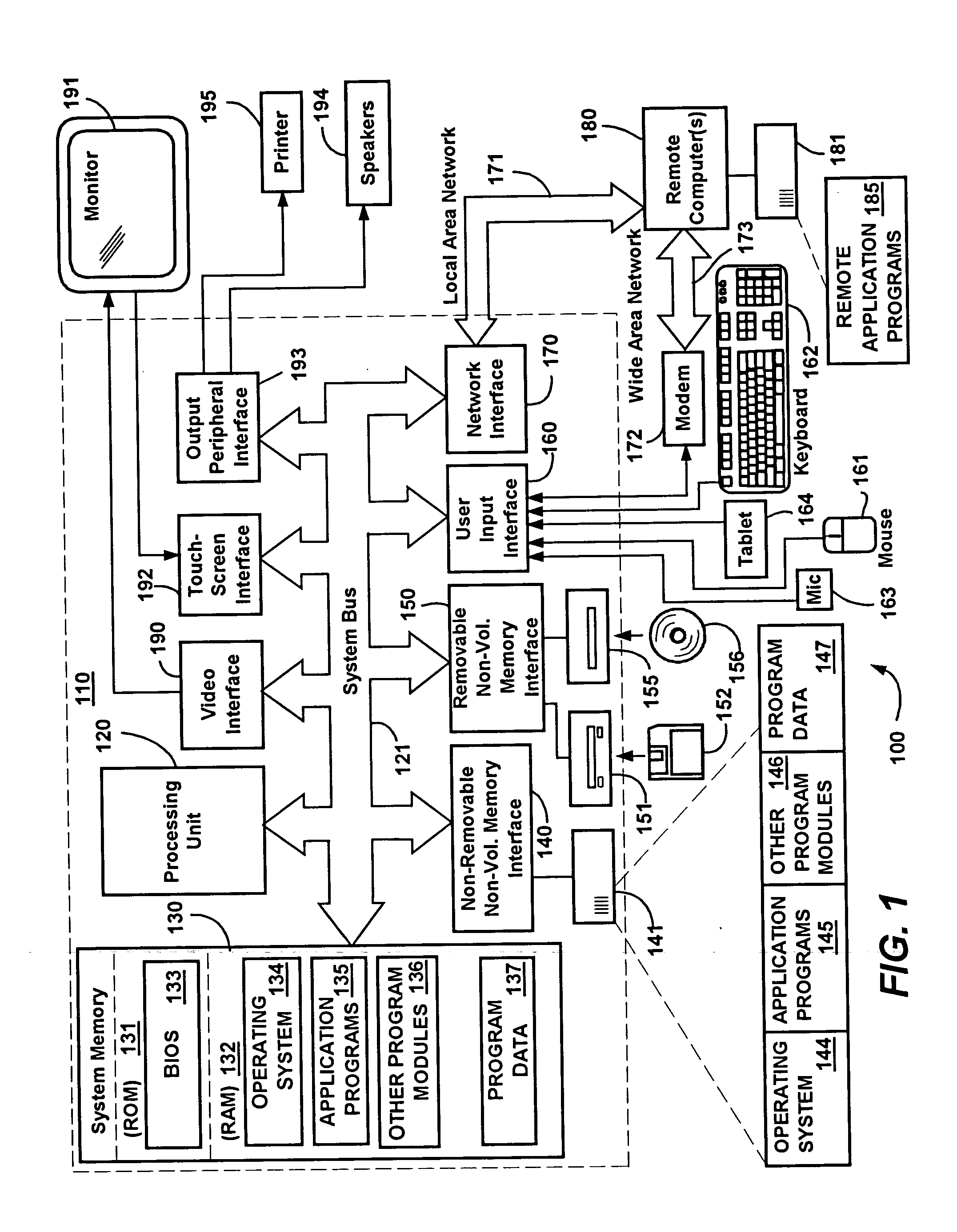
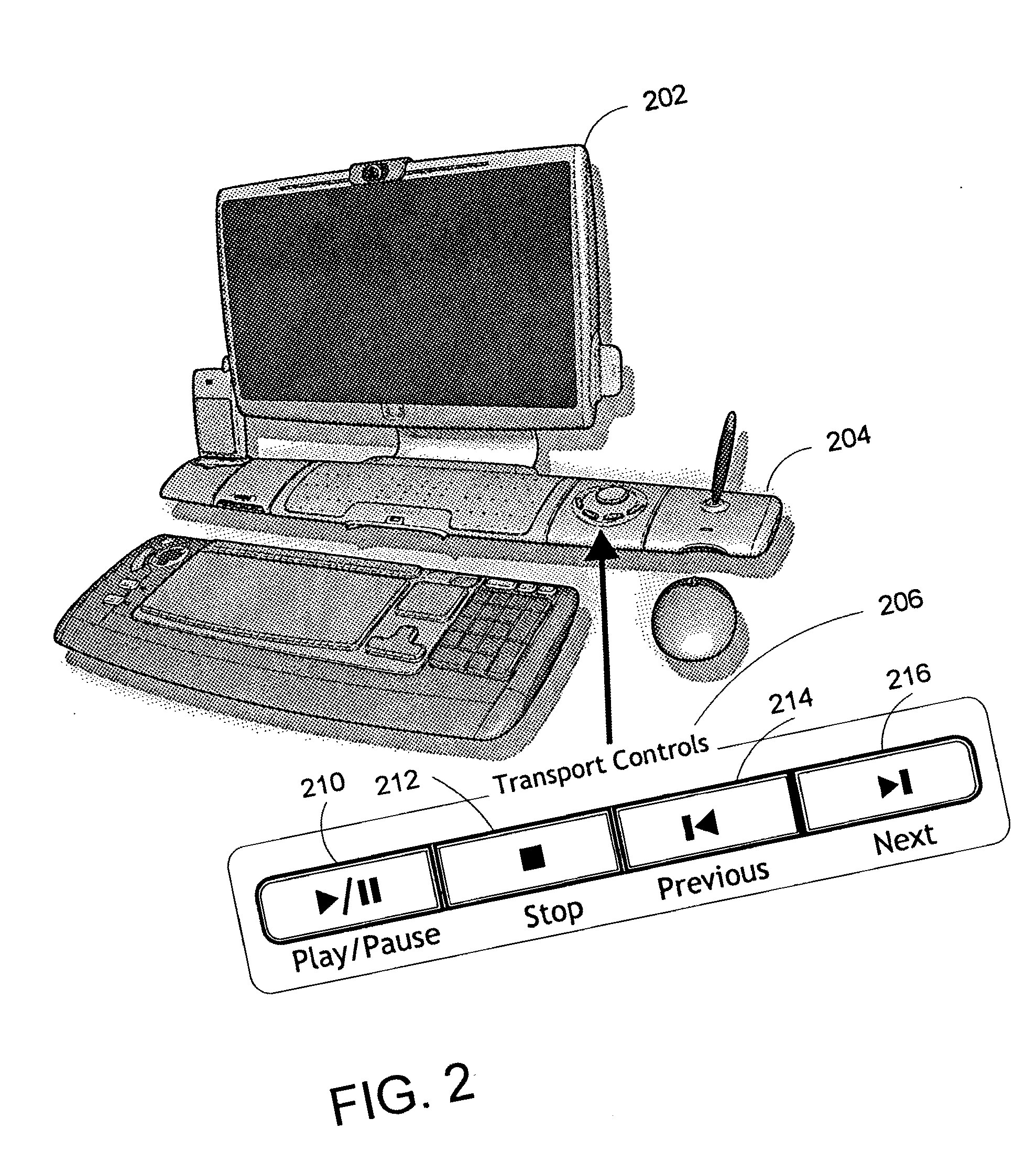
Method and system for navigation using media transport controls
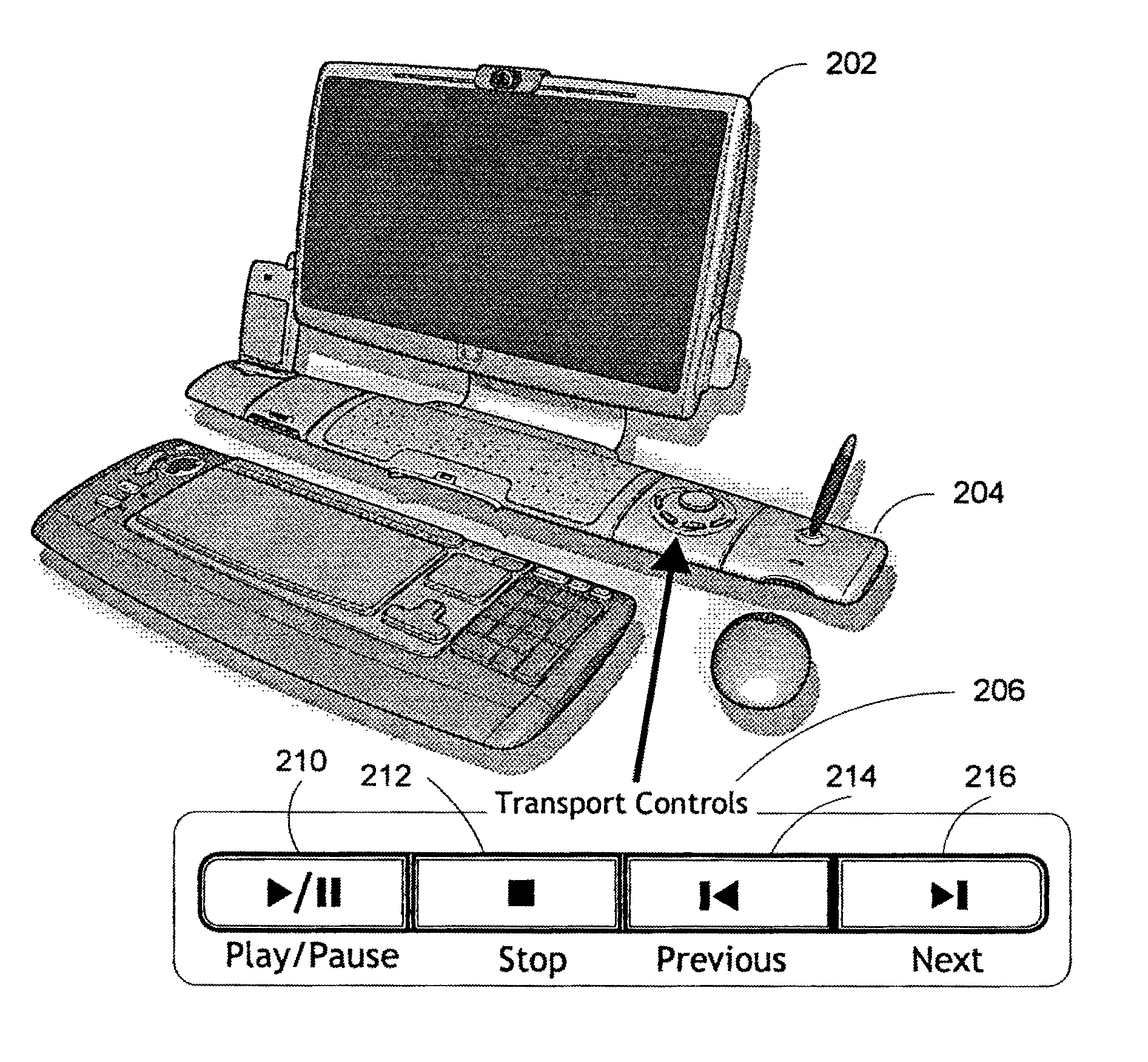
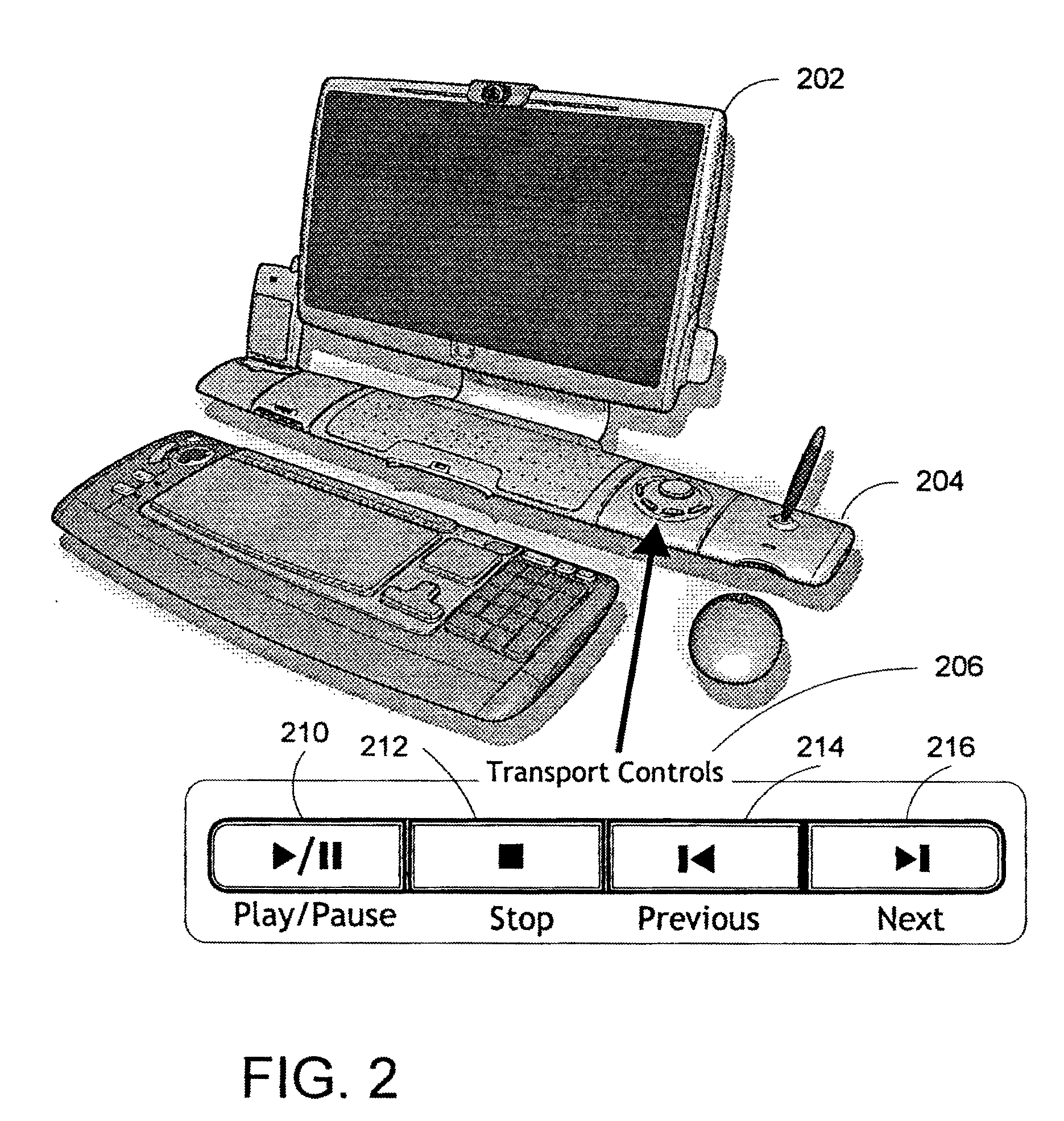
ActiveUS20050071437A1Improve playbackSimple systemInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital computer detailsRemote controlElectronic form
A system and method for improved navigation and access of computer media content using media transport controls is provided. These transport controls may be placed in various locations such as on the computer housing, on a keyboard, on a monitor or a remote control. With these controls, a user may easily play multimedia content and navigate to individual tracks or segments of an audio and / or video stream. The transport controls include a play / pause button, a stop button, a previous button, and a next button. A user may intuitively activate and interact with media content in a variety of applications using these transport controls. For example, users may play recordings such as voice mail and review their recorded replies using the transport controls. Users may similarly play and / or review multimedia annotations made to any application files, including traditional computer files such as spreadsheets, documents and presentations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
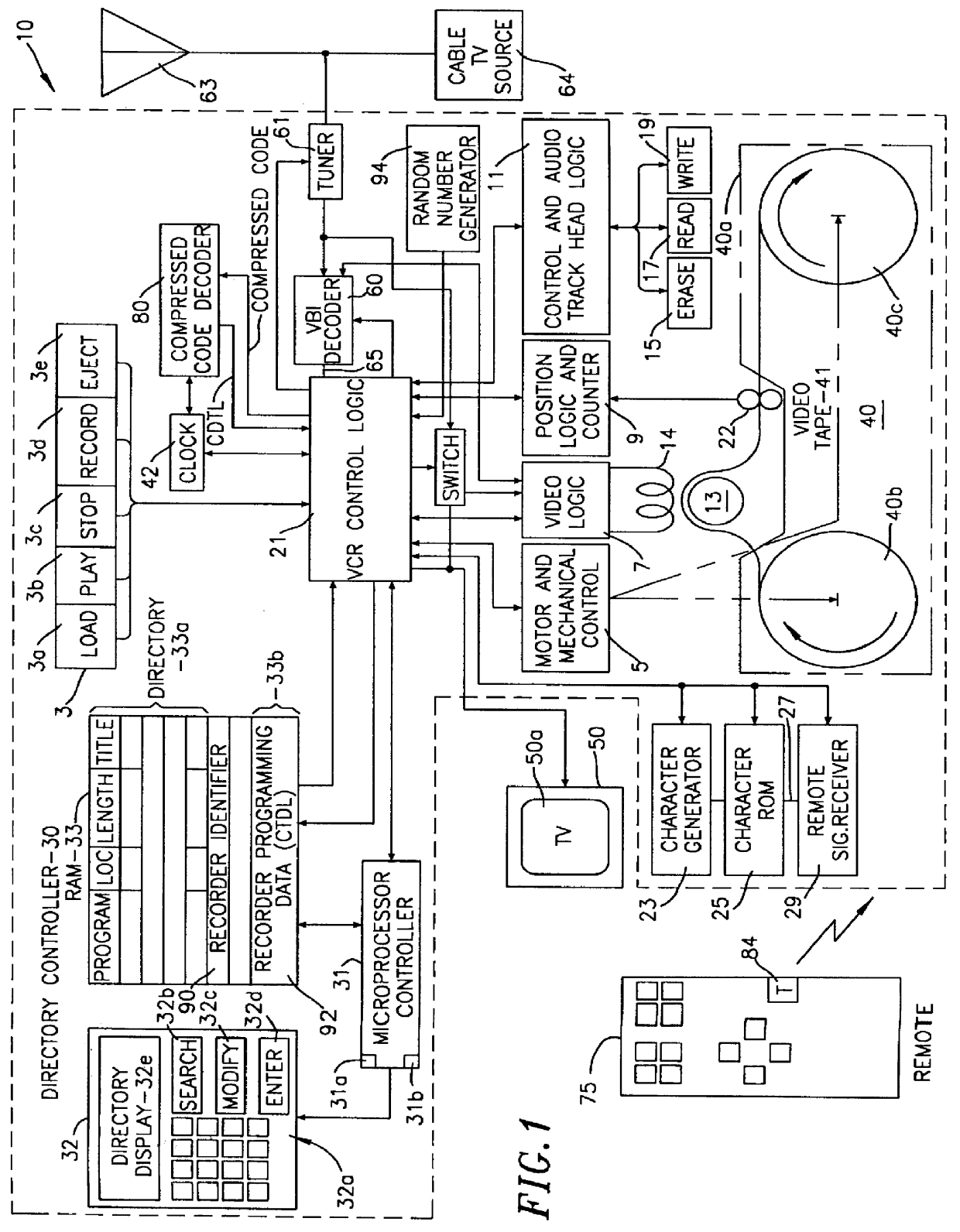
Identifier generation and remote programming for individually addressable video cassette recorders
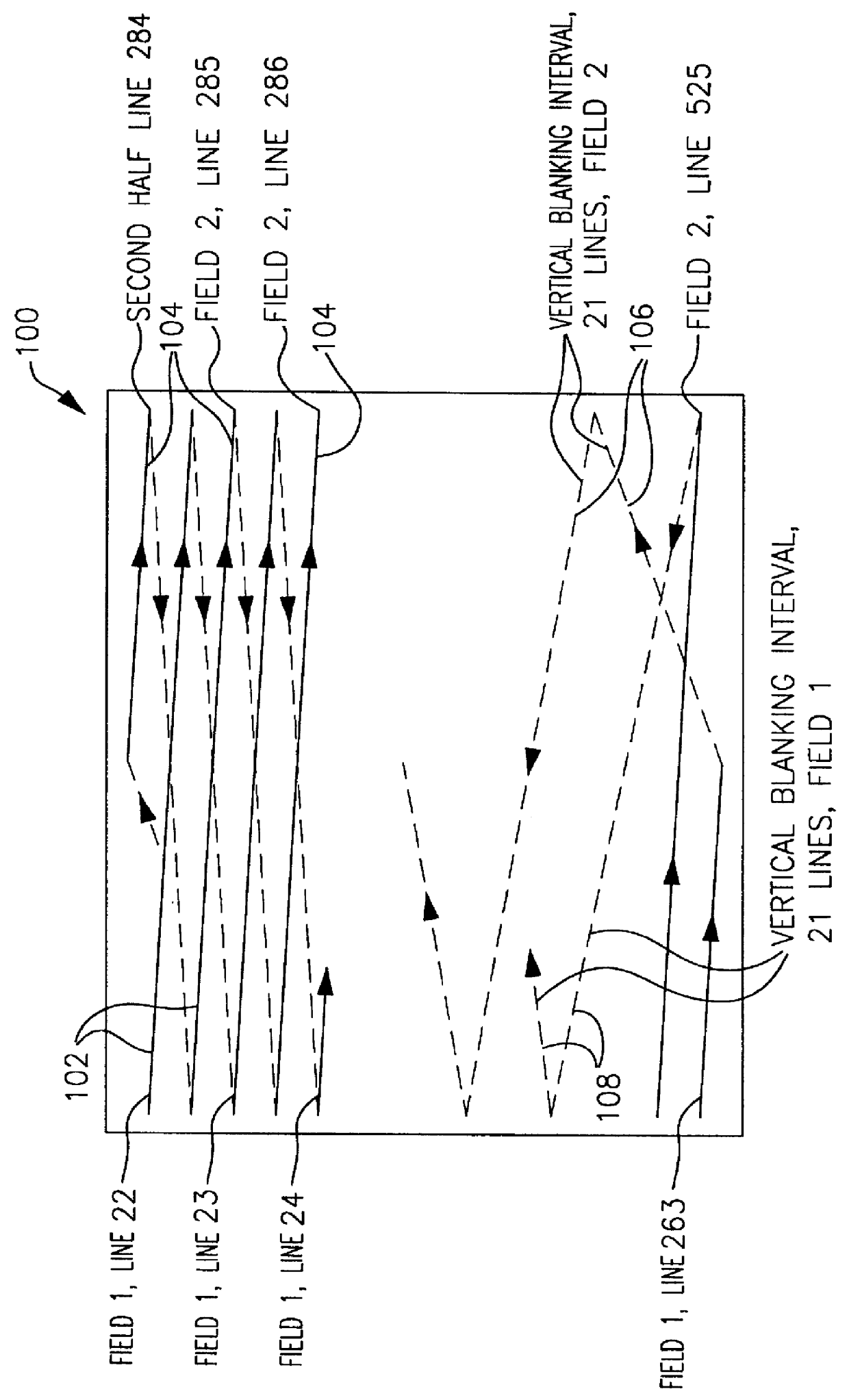
InactiveUS6058238ASimple systemTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web carriers operation controlVideocassette recorderVertical blanking interval
Apparatus and methods are provided for controlling recording of video programs. In one embodiment an apparatus for controlling the recording of video programs includes a device for retrieving a recorder identifier and recorder programming data from a television signal received from a television signal source, a device for determining whether the retrieved recorder identifier matches a first identifier for the apparatus, a device for storing the recorder programming data, if the retrieved recorder identifier matches the first identifier for the apparatus, and a device for using the stored recorder programming data to control recording. The device for retrieving a recorder identifier and recorder programming data from a television signal includes a vertical blanking interval decoder.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Method of improving the stability of active matrix OLED displays driven by amorphous silicon thin-film transistors
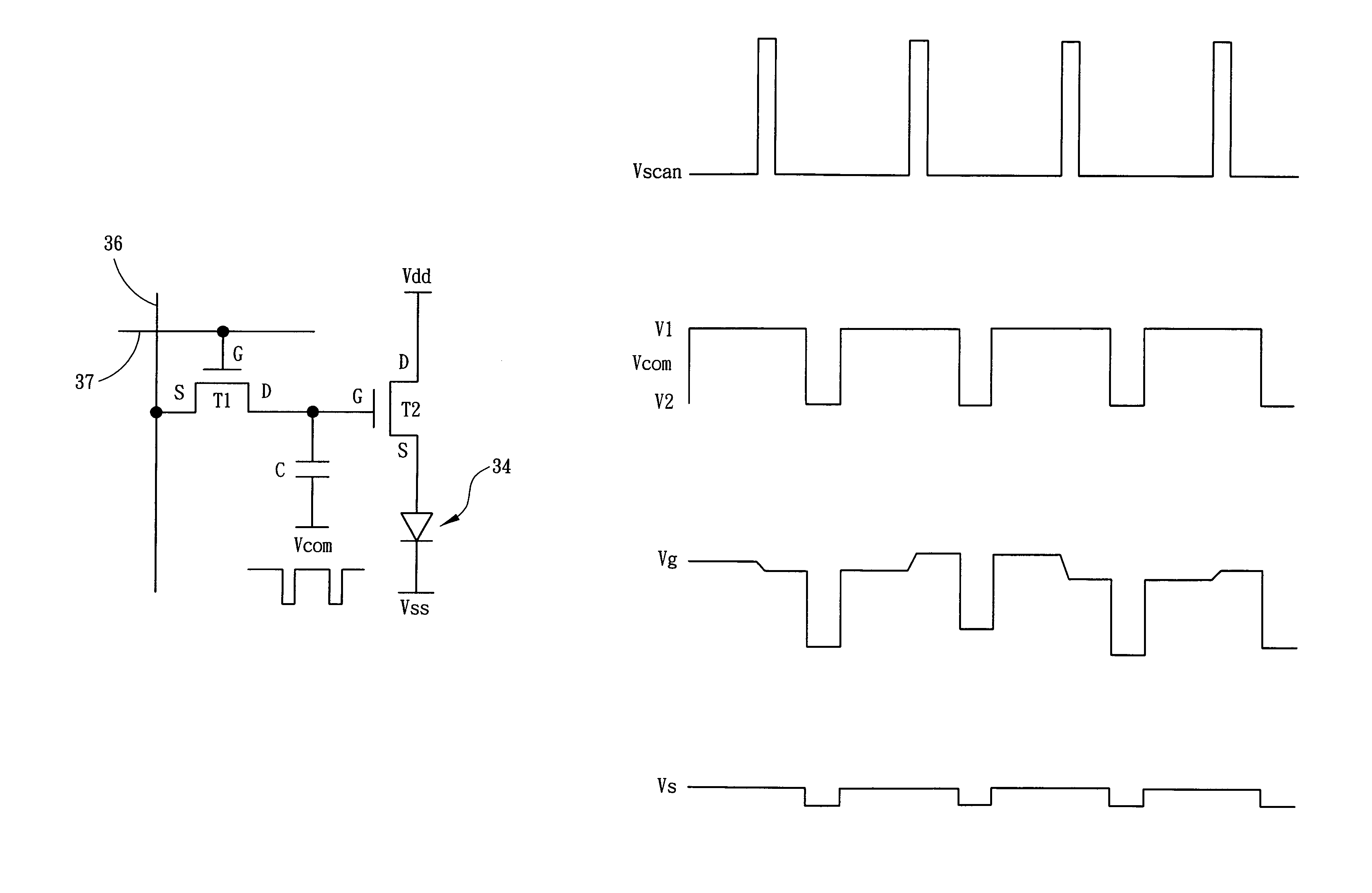
InactiveUS7116058B2Improve driving stabilityEliminate unevennessElectrical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitanceDriver circuit
A method of improving the stability of organic light emitting diode (OLED) display devices driven by amorphous silicon thin-film transistors, in which the driving circuitry within each sub-pixel includes a driving transistor for driving organic light emitting diode (OLED), a scanning transistor and a storage capacitance. An end of the capacitance is connected to the signal resetting line, which a resetting time pulse of high potential and low potential are supplied. Since the resetting signals within the sub-pixels are synchronized, a single voltage of the resetting signal can control the positive and negative stresses for each transistor in the sub-pixels on the panel.
Owner:WINTEX
Method and system for navigation using media transport controls
ActiveUS7194611B2Improve playbackSimple systemInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital computer detailsRemote controlElectronic form
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automated annular plication for mitral valve repair
InactiveUS20060004443A1Improve efficiencySimple systemSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsMitral valve operationBiomedical engineering
A novel system for performing a heart valve annuloplasty. The system involves the use of a plication band. In one embodiment, the annulus of the valve is reduced by constriction of the plication band itself. More particularly, each plication band enters the tissue at two or more points which are spaced from one other by a distance which is dictated by the geometry of the plication band. Subsequent constriction of the plication band causes these points to move toward each other, thereby constricting the tissue trapped between these points and thus reducing the overall circumference of the valve annulus. In a second embodiment, the annulus of the valve is reduced by linking multiple plication bands to one other, using a linkage construct, and then using a shortening of the length of the linkage construct between each plication band so as to gather the tissue between each plication band, whereby to reduce the overall circumference of the valve annulus.
Owner:LIDDICOAT JOHN R +3
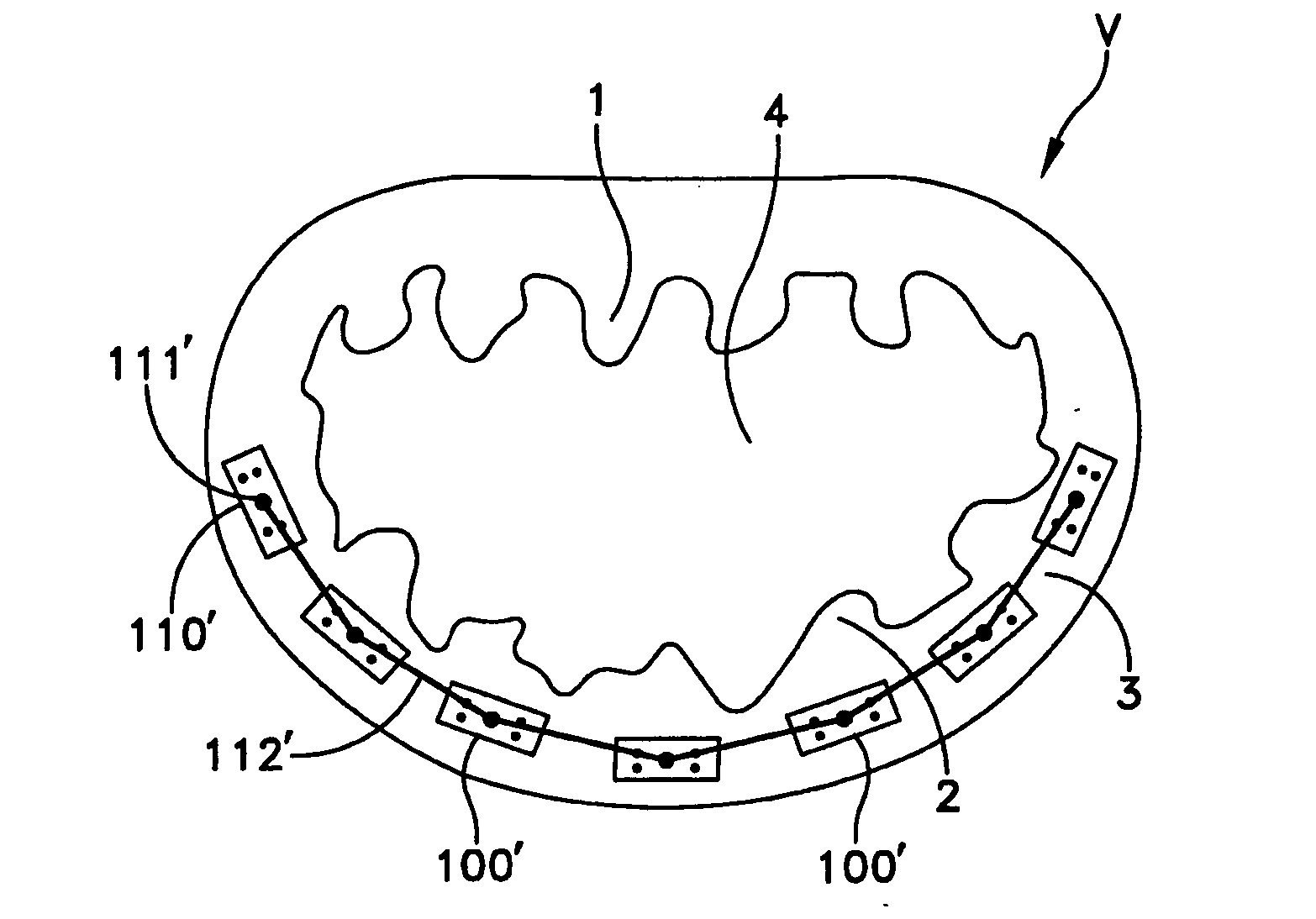
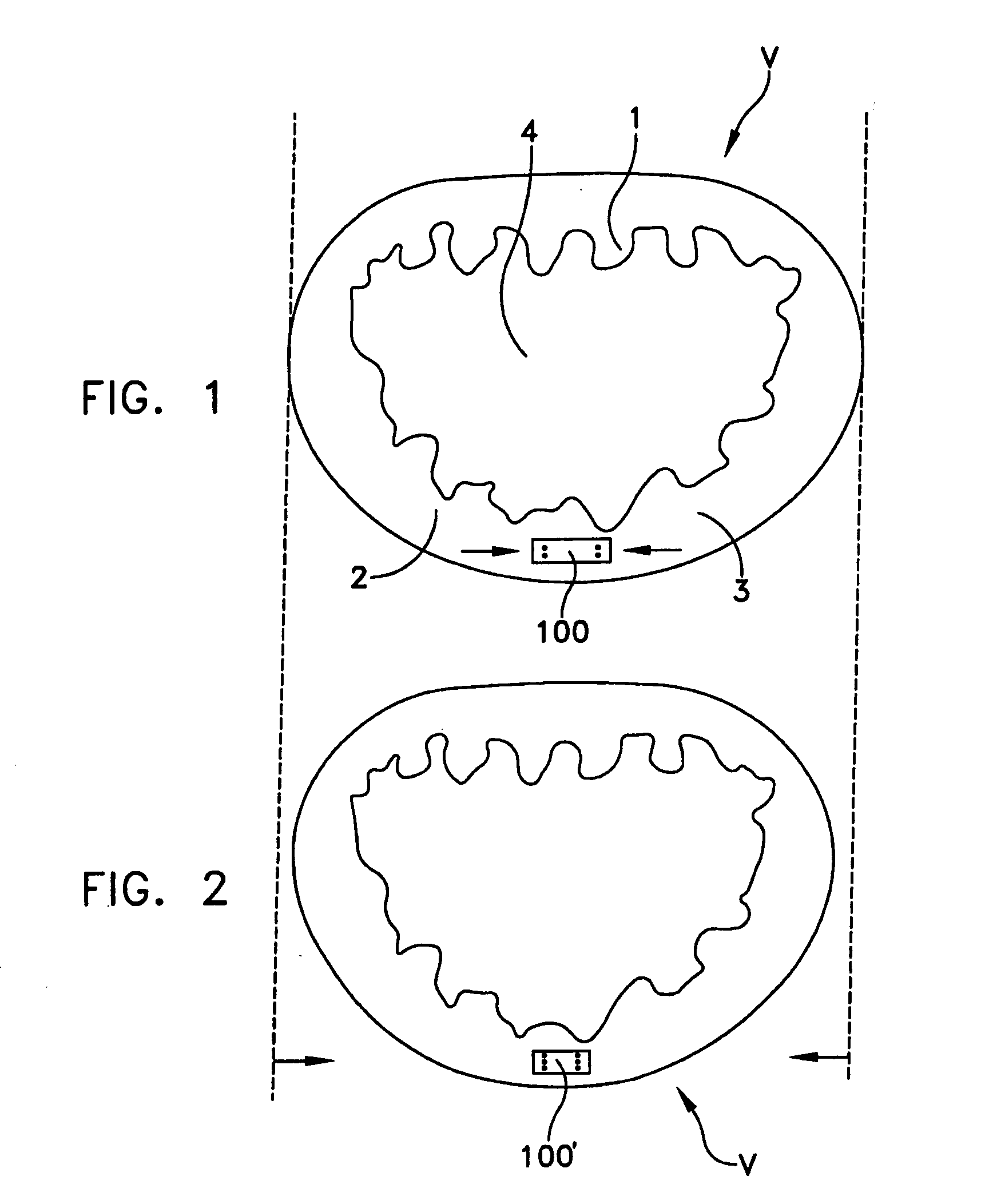
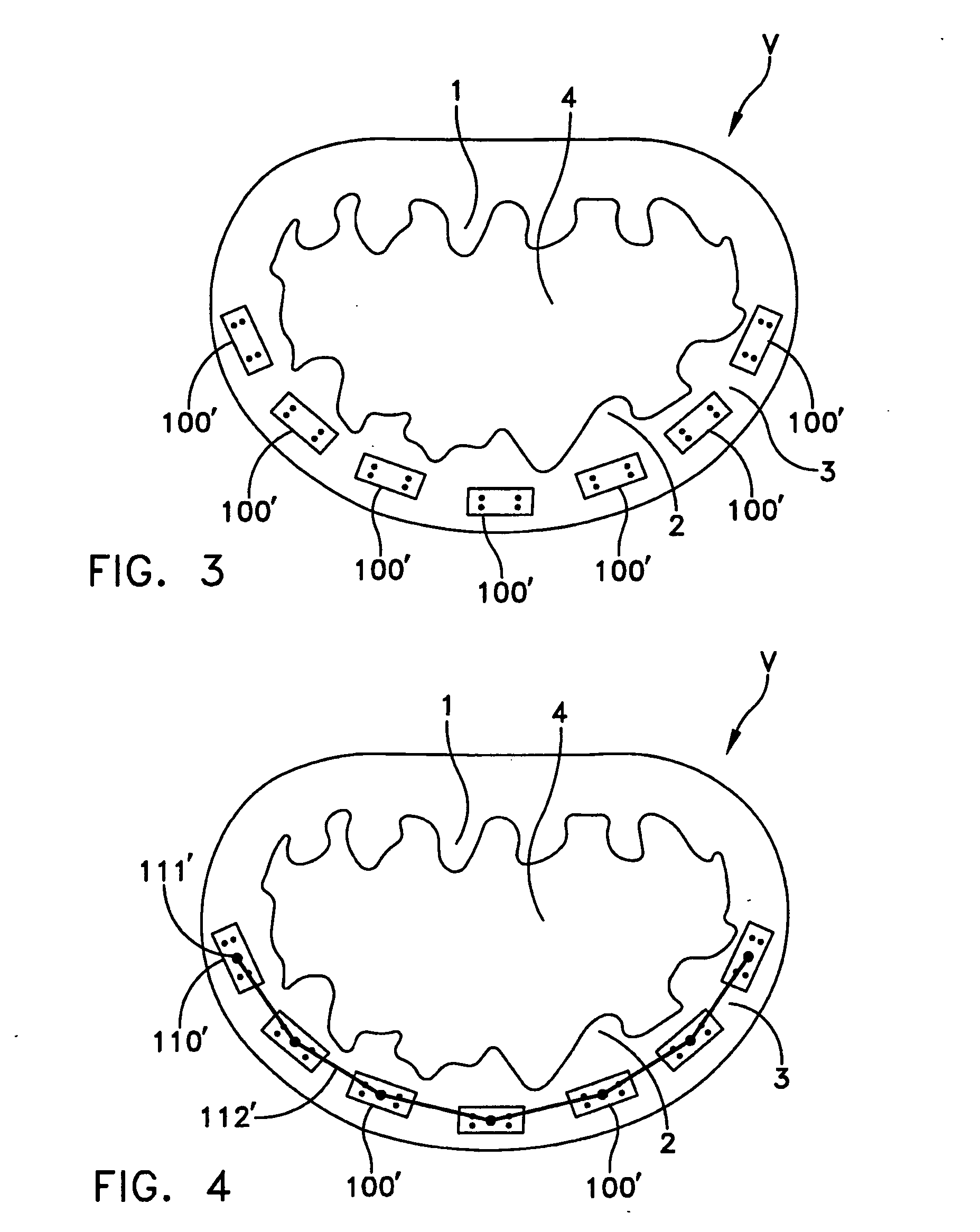
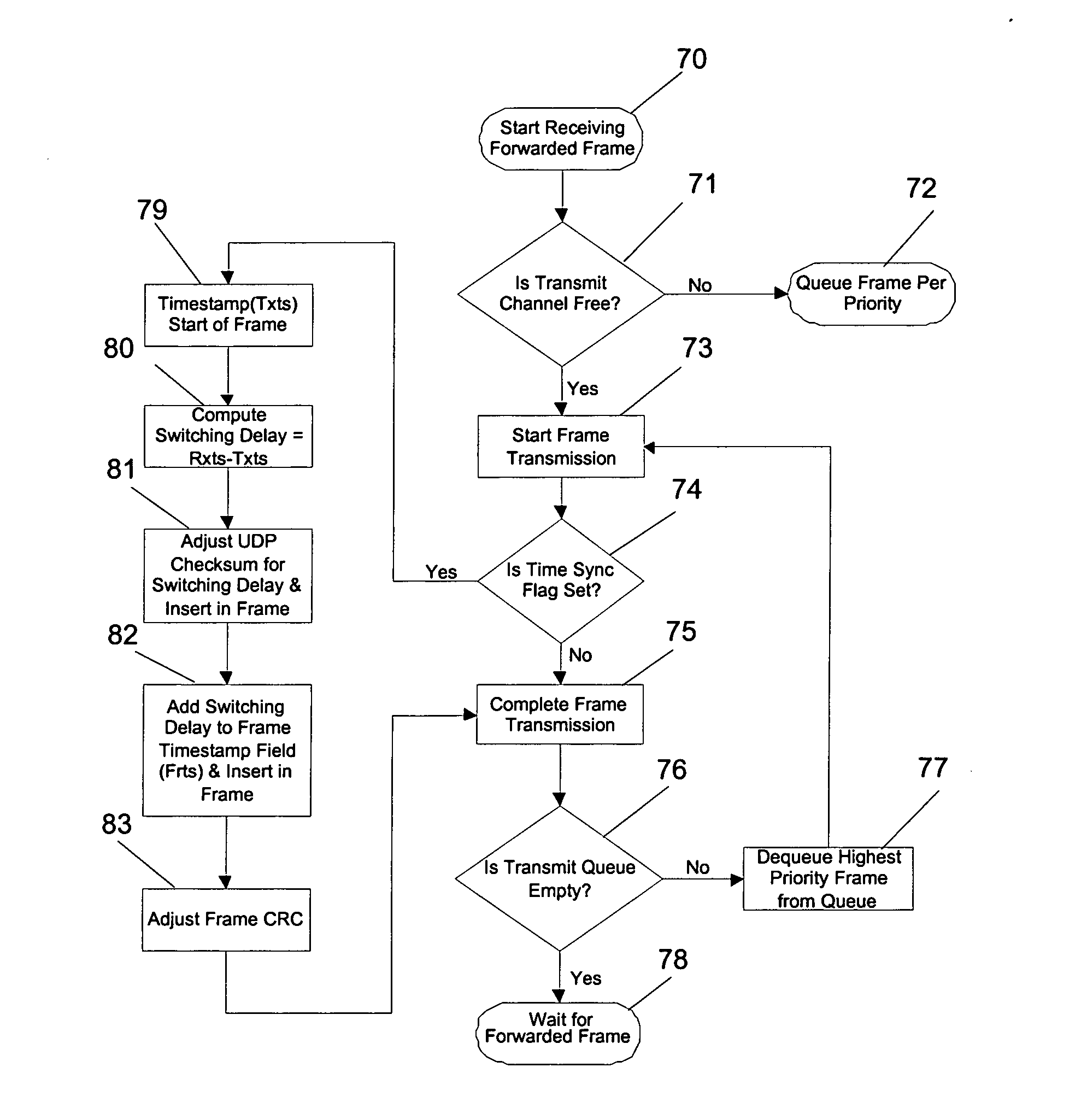
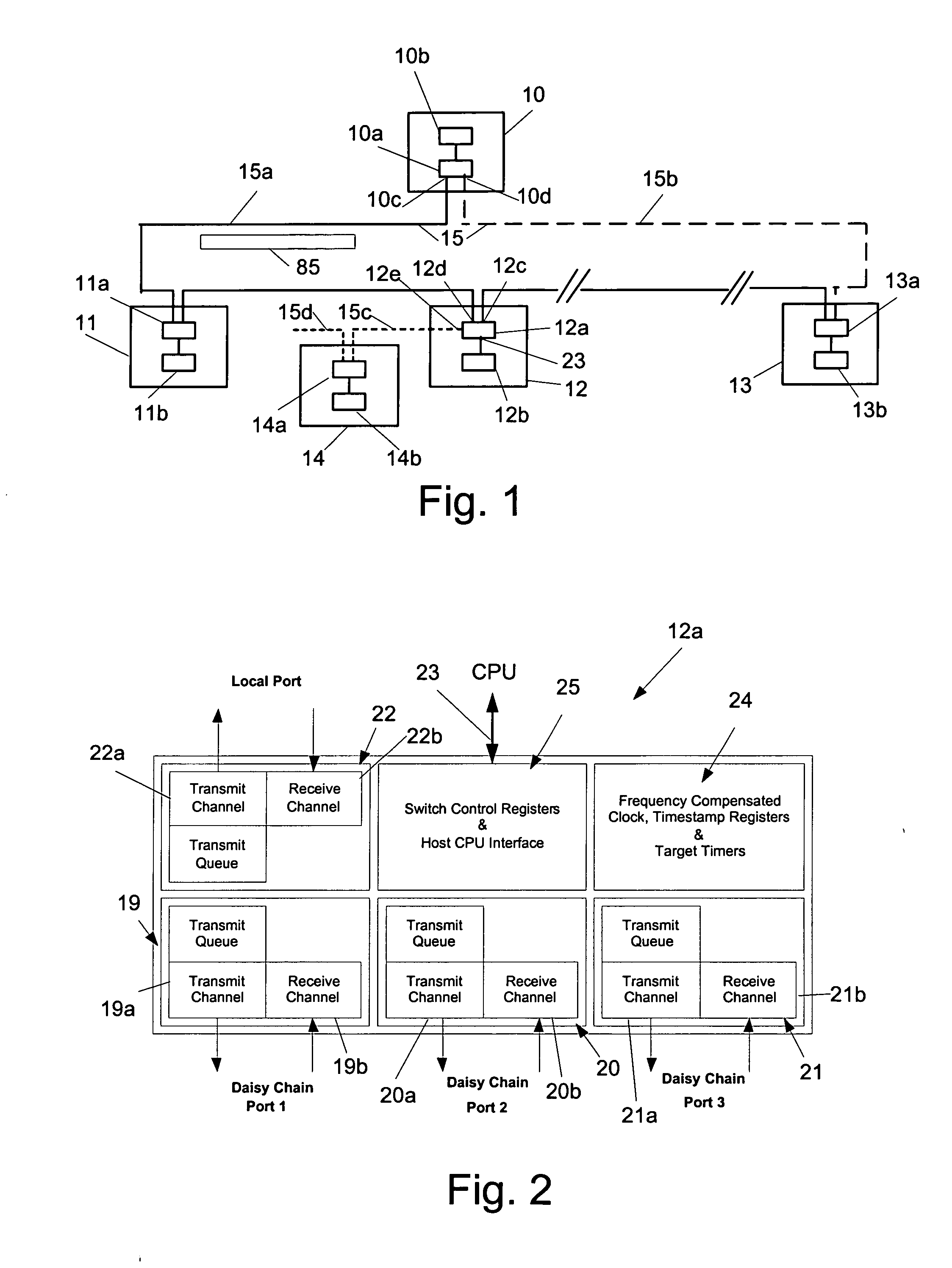
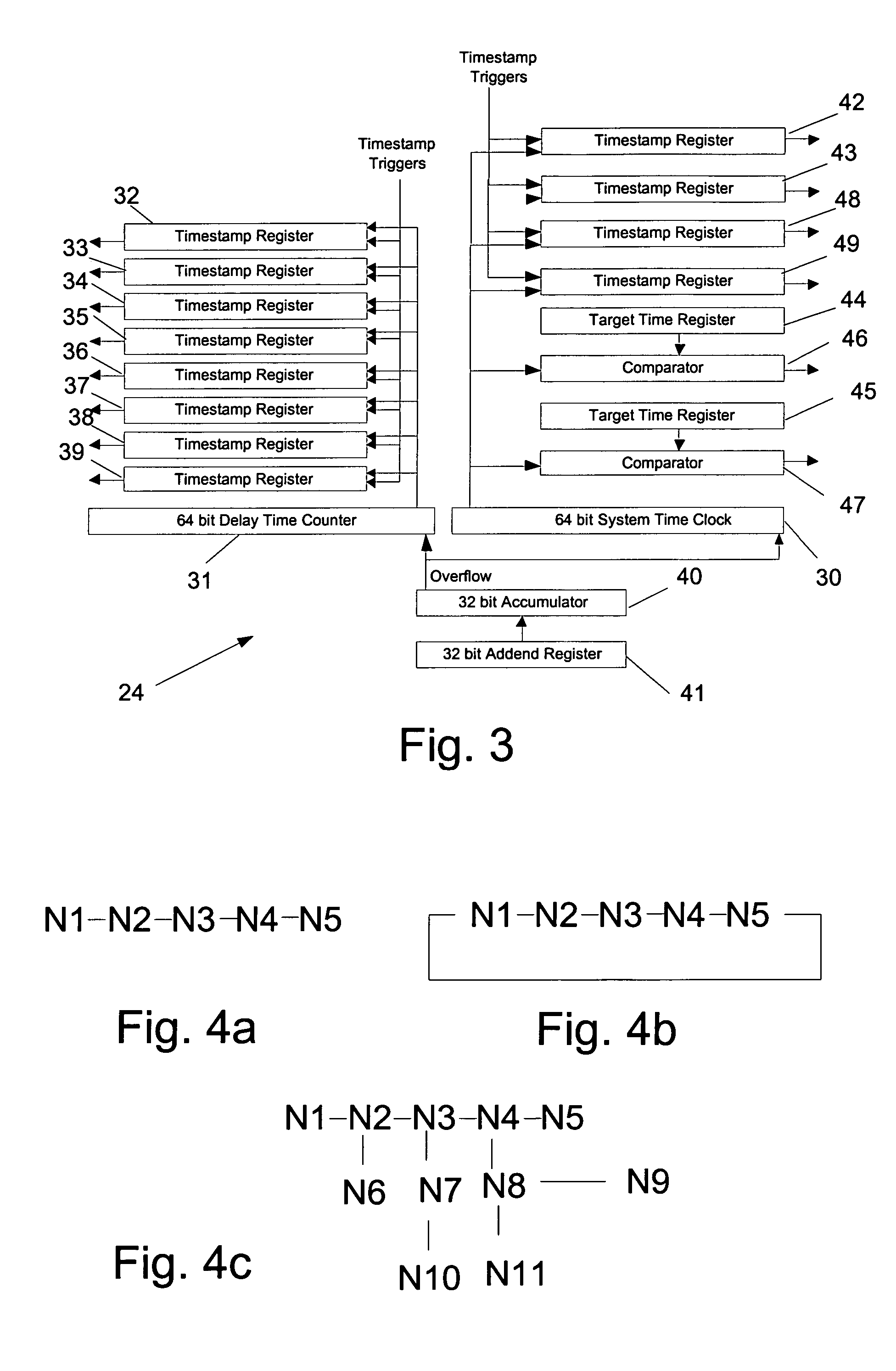
Time synchronization, deterministic data delivery and redundancy for cascaded nodes on full duplex ethernet networks
ActiveUS20060245454A1Accurate accountingSimple systemTime-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsTimestampStandard protocol
A method and circuit for precisely synchronizing clocks in separate nodes on a communication network is provided by adjusting timestamps and related data in network messages. The circuit will allow a daisy-chain connection of the nodes and will forward time synchronization frames while accounting for delays in a manner that does not use boundary clocks, but does not depart from the IEEE 1588 standard protocol. The delays will be added on the fly to synchronization packets and the IP checksum and frame CRC will be adjusted. Deterministic data delivery and redundant data paths are also provided in a full duplex Ethernet network.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Respiratory monitoring during gas delivery
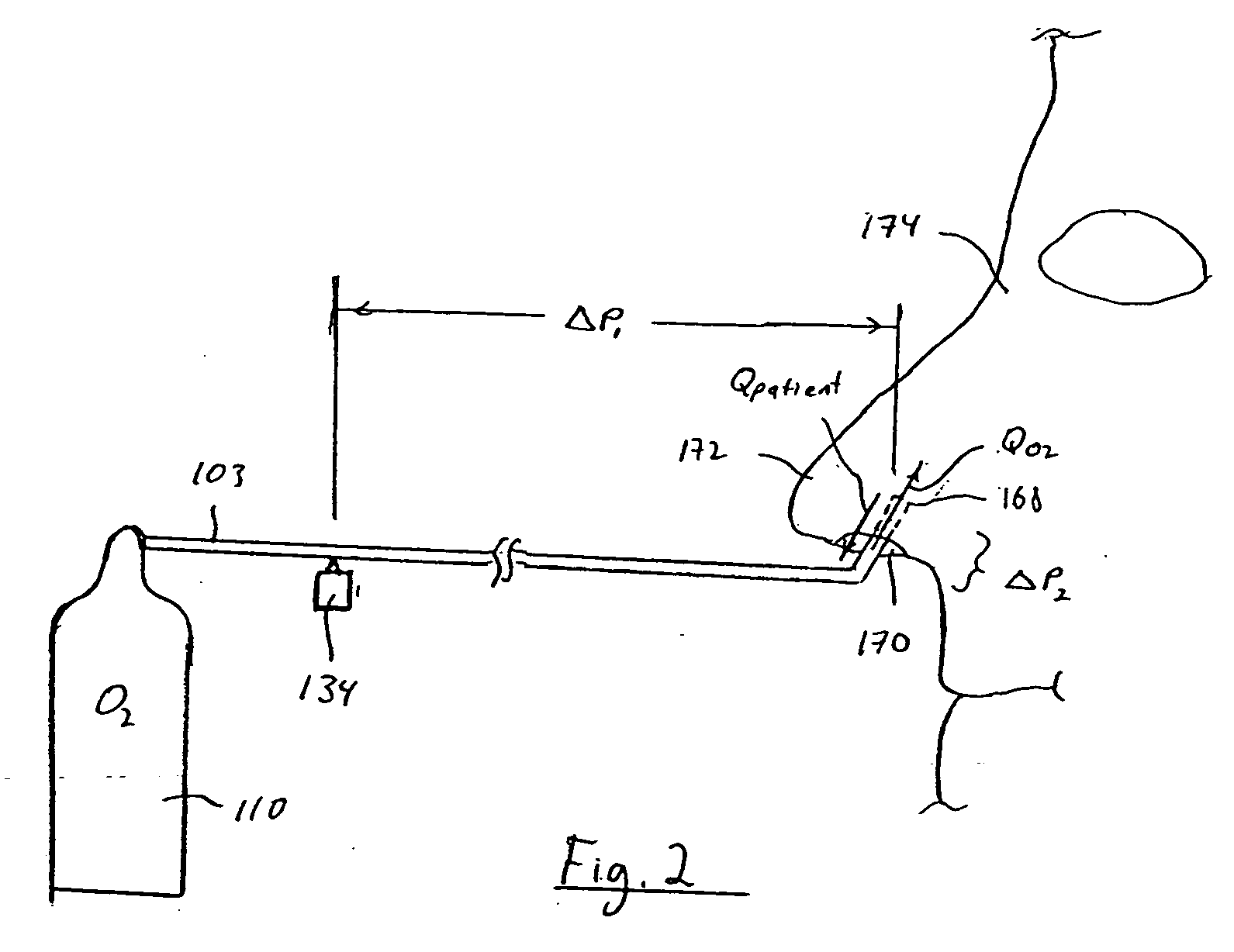
InactiveUS20050121033A1Simple systemOvercomes shortcomingTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesContinuous flowRespiratory monitoring
A method and apparatus for monitoring a patient's respiratory status during the delivery of gases, such as supplemental oxygen. In one embodiment, a conduit carries a continuous flow of gas to an airway of a patient over a plurality of respiratory cycles and a gas flow characteristic of the gas in the conduit is monitored using a pressure sensor, a flow sensor, or both. The gas flow characteristic is used to determine a respiratory variable for the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
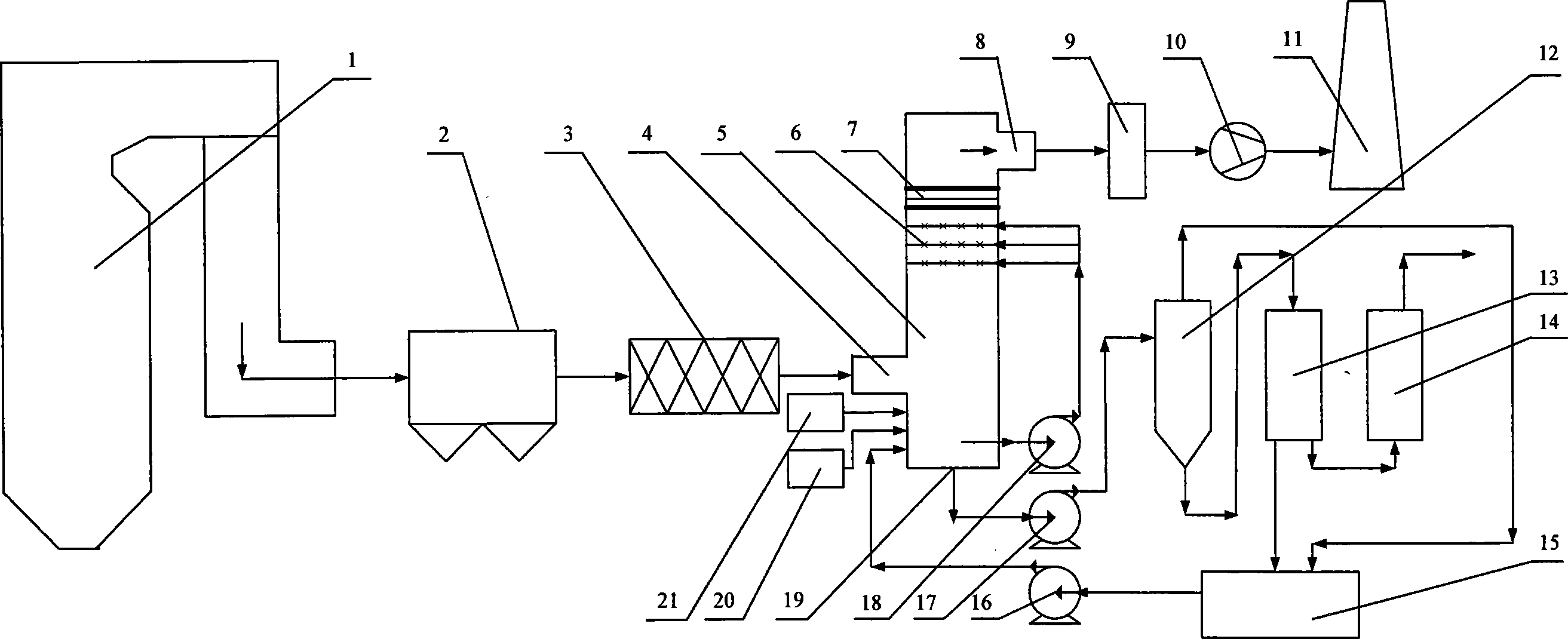
Simultaneously desulfurization and denitration wet ammonia flue gas cleaning technology and system thereof
InactiveCN101053747ASimple processSmall footprintDispersed particle separationFertilizerNitric oxide
A wet ammonium flue gas cleaning process for desulfurizing and denitrifying and a system thereof are disclosed. The process oxidates NO in the flue gas to be NO2, makes SO2 and NO2 in the flue gas react with ammonium to product ammonium sulfite, ammonium nitrate and ammonium nitrite, then oxidates ammonium sulfite and ammonium nitrite therein to product the byproduct that is ammiaonia sulfate and ammonium nitrate, and lastly gets the clear flue gas after demisting to the desulfurizing and denitrifying flue gas. The system comprises a dust pre-collector, a hydrogen peroxide or ozone sprayer, and a desulfurizing and denitrifying tower, which are connected in turns, wherein ammonia replenishment system and an air feeding device are mounted at the bottom of the desulfurizing and denitrifying tower, sprinkling layer which can cycle sprinkle is mounted at the middle, and a demister is mounted at the upper. The invention has a simple process, a simplified system, a low investment and operation cost. The invention not only has a high efficiency in desulfurizing and denitrifying, but also a high utilance of desulfurizing and denitrifying absorbent, and byproduct of desulfurization and denitration can be utilized as chemical fertilizer of ammiaonia sulfate and ammonium nitrate.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ELECTRIC POWER ENVIRONMENTAL
Method and apparatus for separating particles by size
InactiveUS7108137B2Easy to manufactureLow costWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsParticle size analysisUltrasonic radiationHigh pressure
A method and apparatus for separating a mixture of particles of various sizes in a capillary tube into groups by size using multiple forces of controlled amplitude. Ultrasonic radiation at a first selected frequency is applied to set up a standing pressure wave in the capillary tube, resulting in a first aggregating force which causes particles of all sizes to aggregate at positions within the capillary tube which correspond to nodes or anti-nodes of the standing wave. Transverse vibrations are also applied to the capillary tube. The frequency of the ultrasonic radiation is adjusted to reduce the magnitude of the first aggregating force. Inertial forces resulting from the transverse vibrations then cause the particles to separate by size. The apparatus and method allows a mixture of particles to be separated by size quickly, without requiring the use of high voltages.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Optical computational system
In optical filter systems and optical transmission systems, an optical filter compresses data into and / or derives data from a light signal. The filter way weight an incident light signal by wavelength over a predetermined wavelength range according to a predetermined function so that the filter performs the dot product of the light signal and the function.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC +1
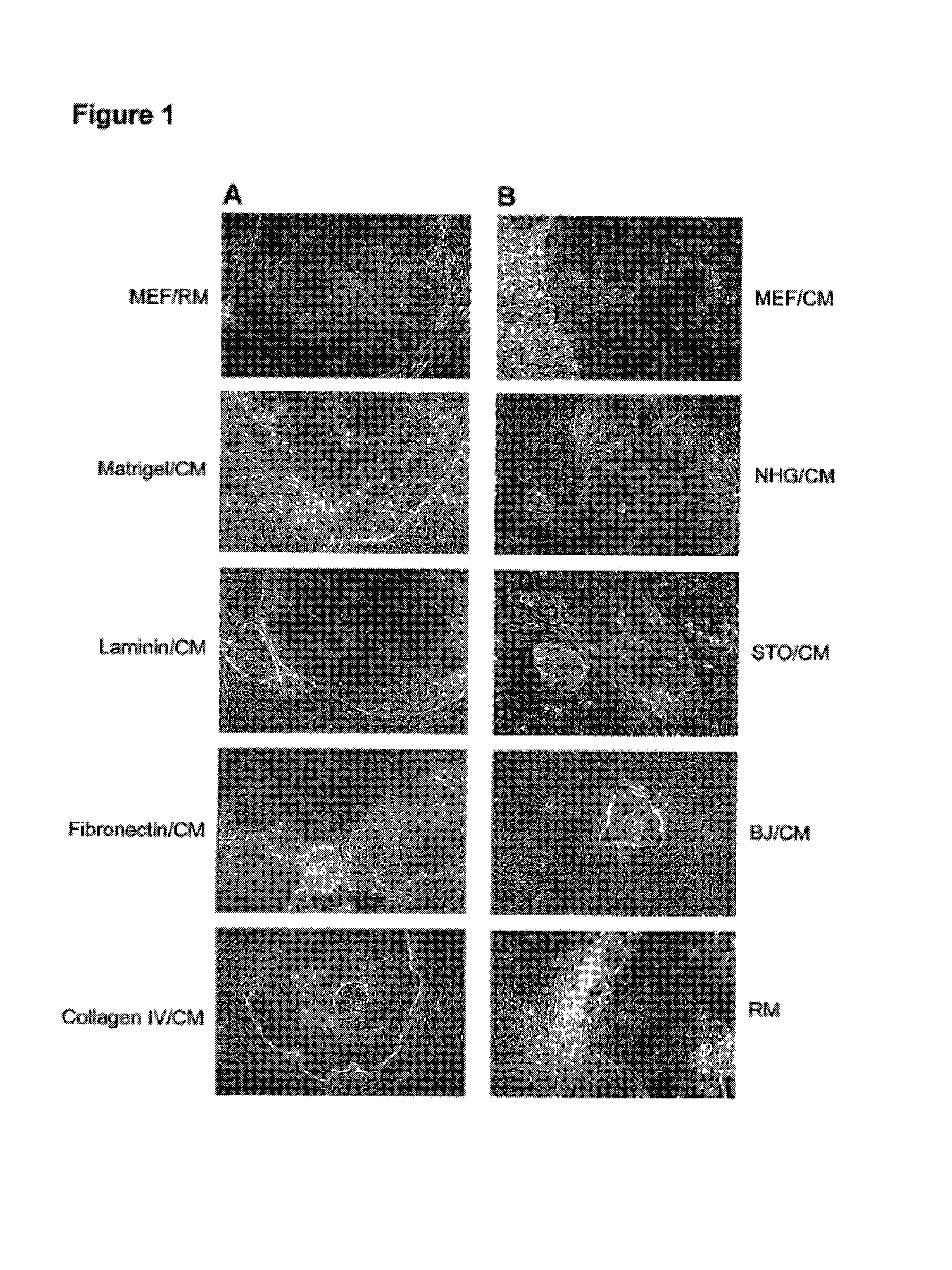
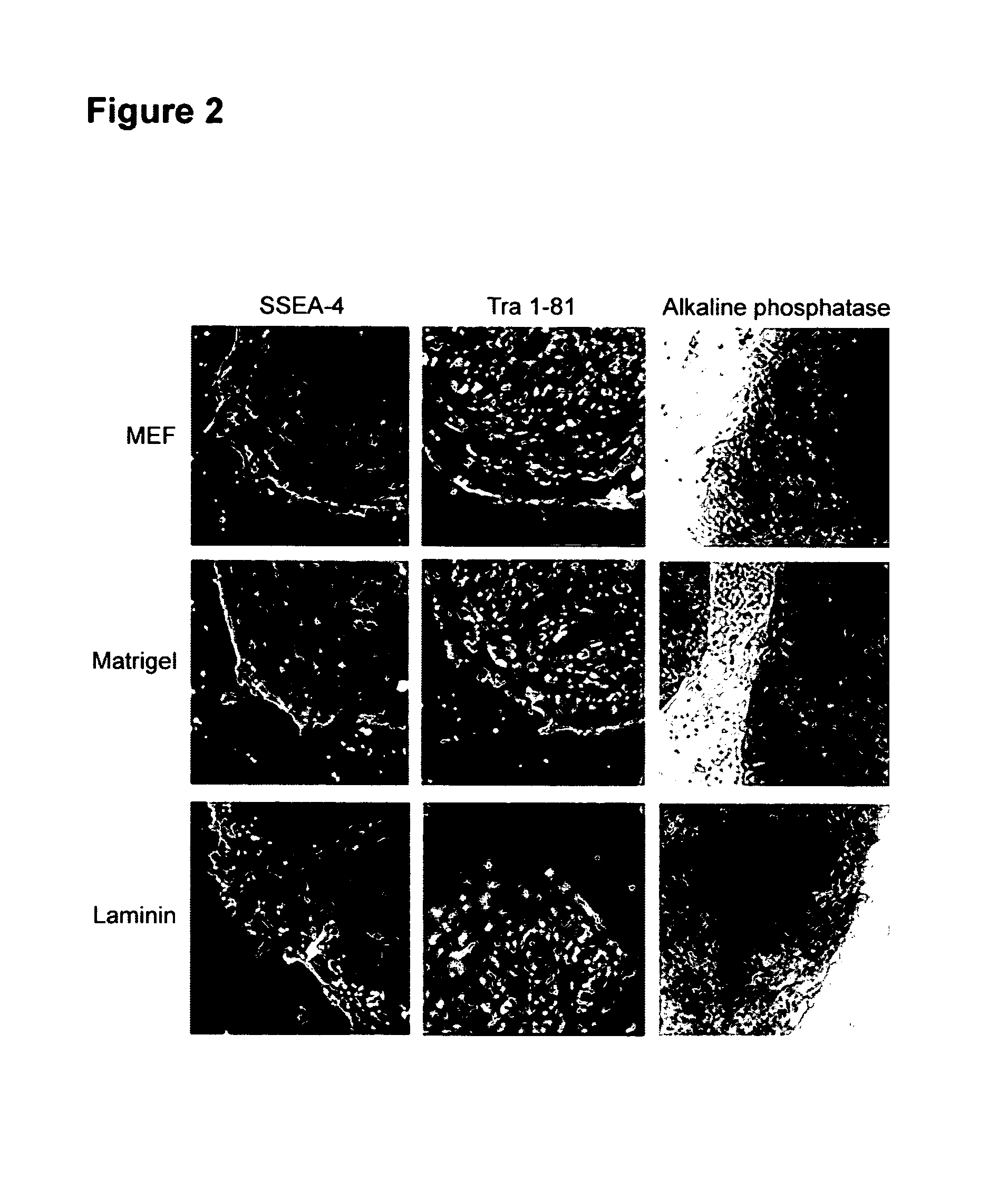
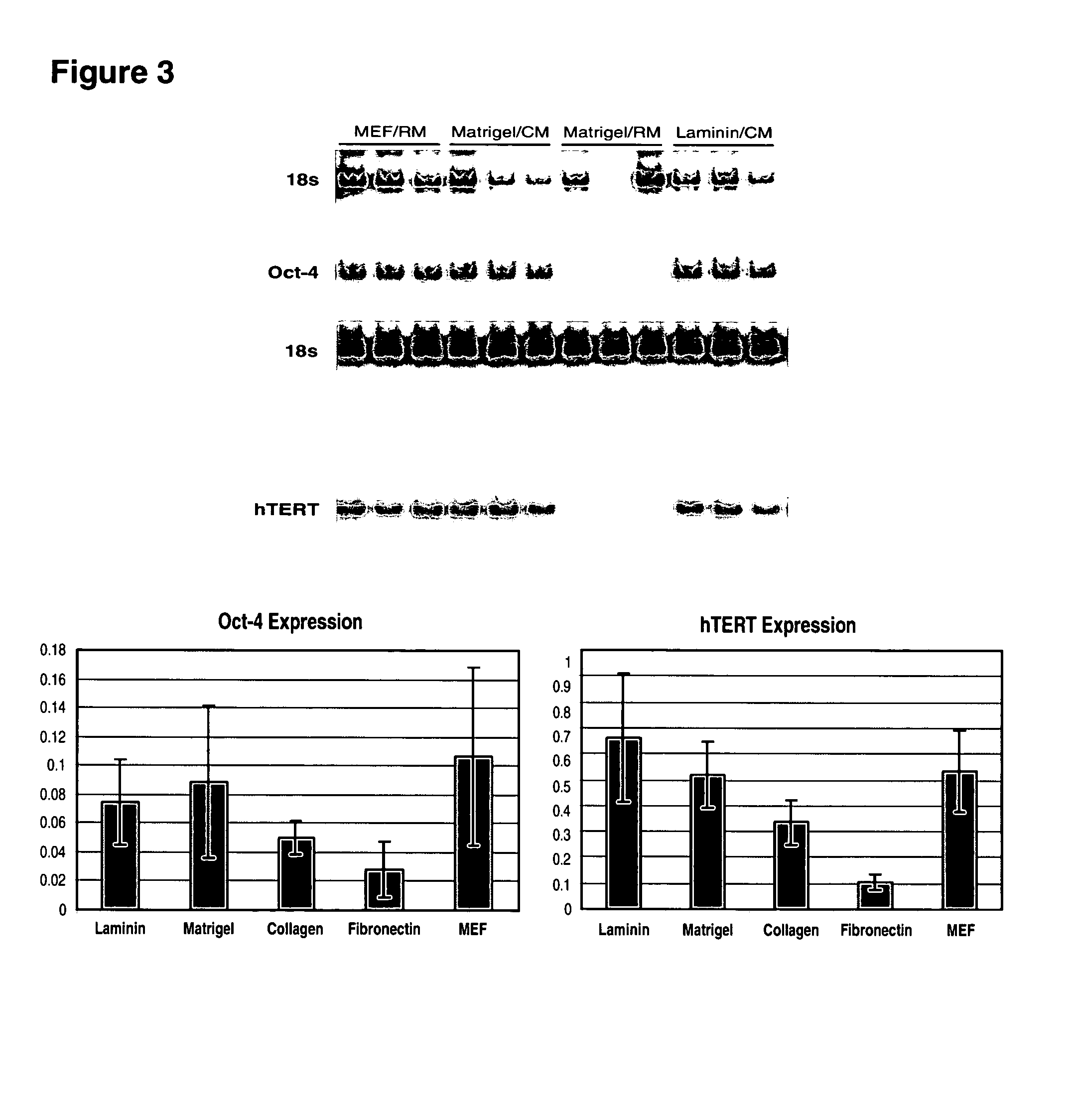
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7297539B2Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerFiber
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
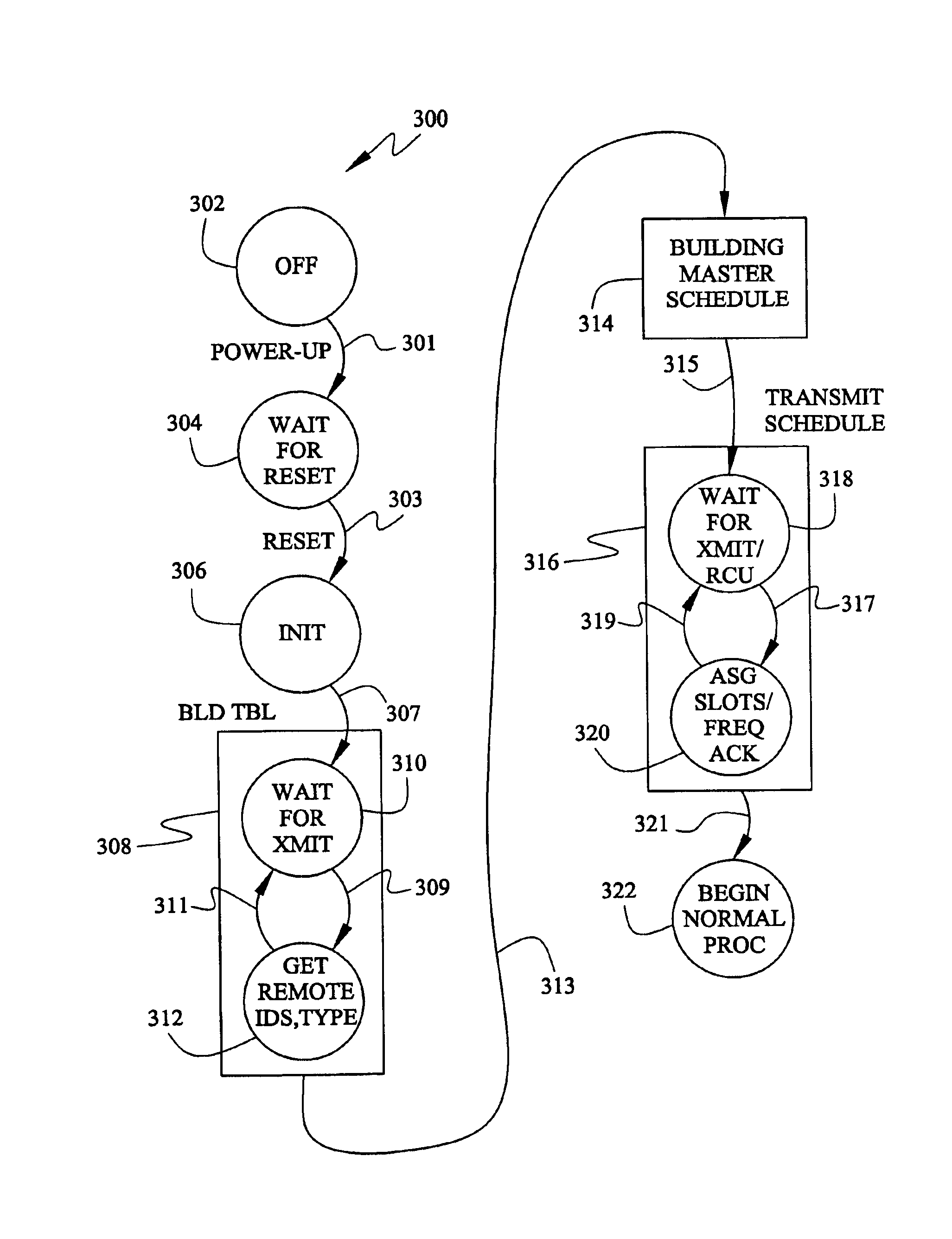
Wireless control network with scheduled time slots
InactiveUS6901066B1Easy to optimizeImprove update rateTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsElectric testing/monitoringWireless controlMonitoring system
A building monitoring system is disclosed that includes a bi-directional radio link between a master and a number of remote units, wherein the master unit schedules the transmission times of the remote units to avoid collisions.
Owner:HONEYWELL INC
Wireless communication system having a guest transmitter and a host receiver
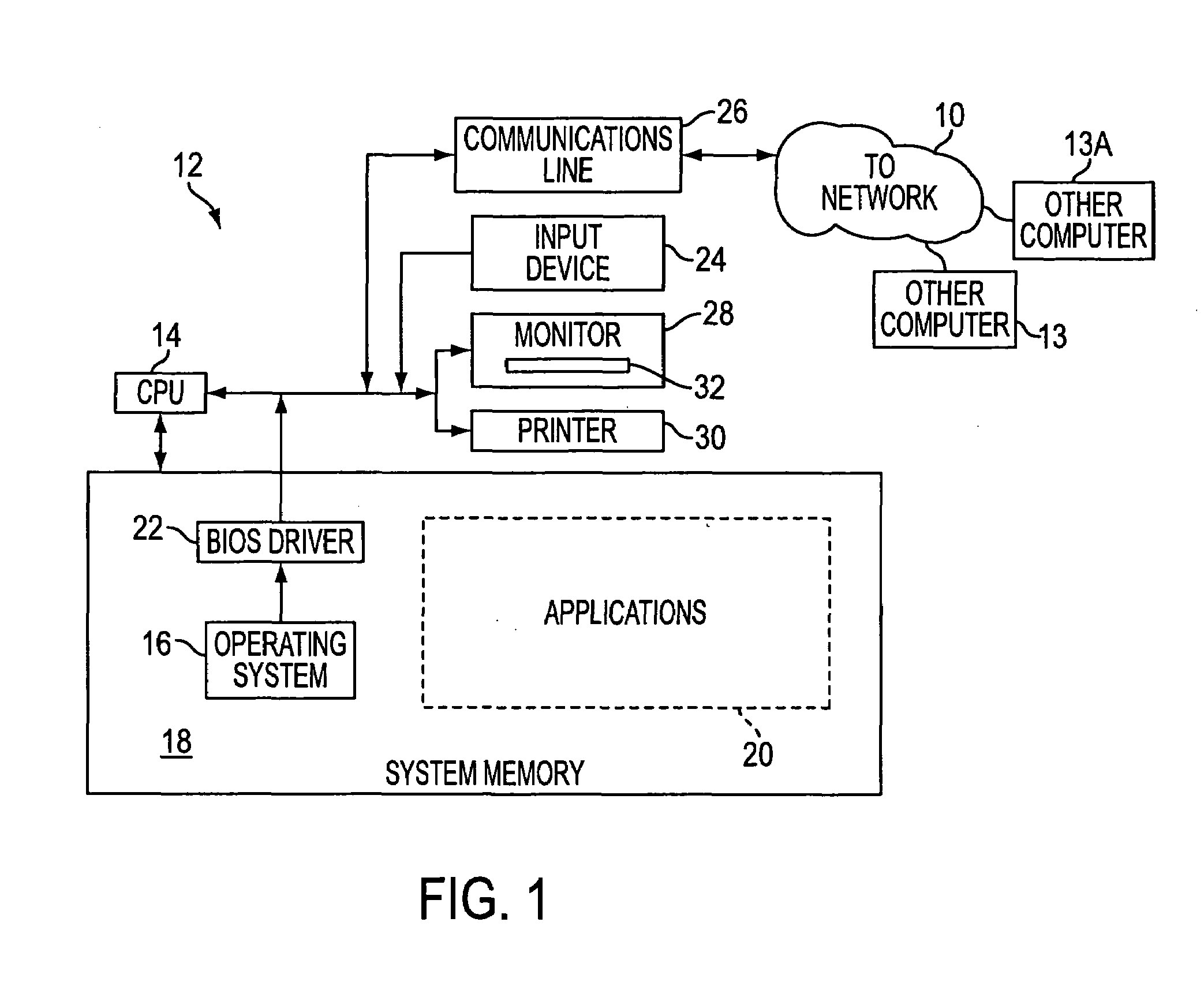
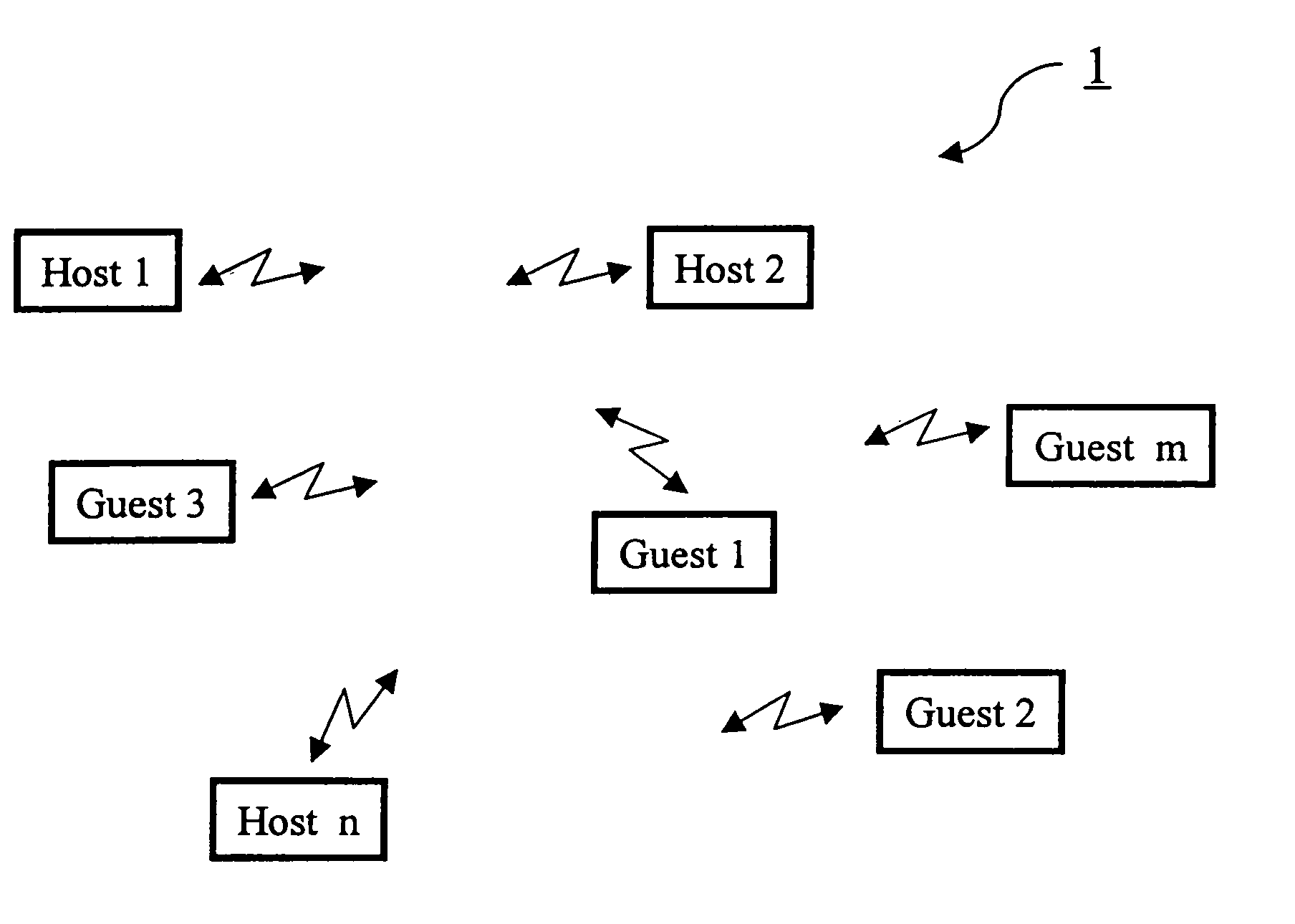
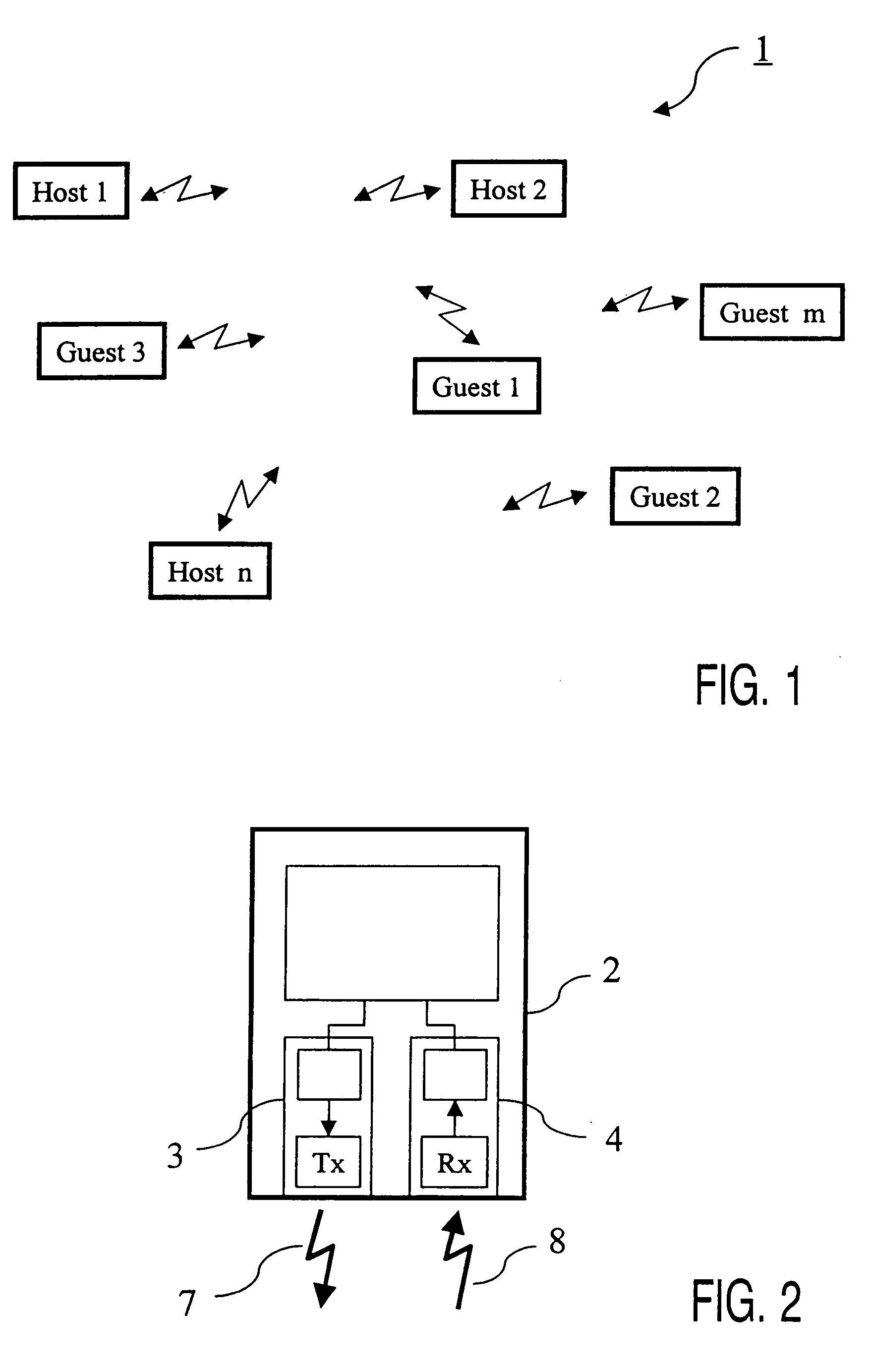
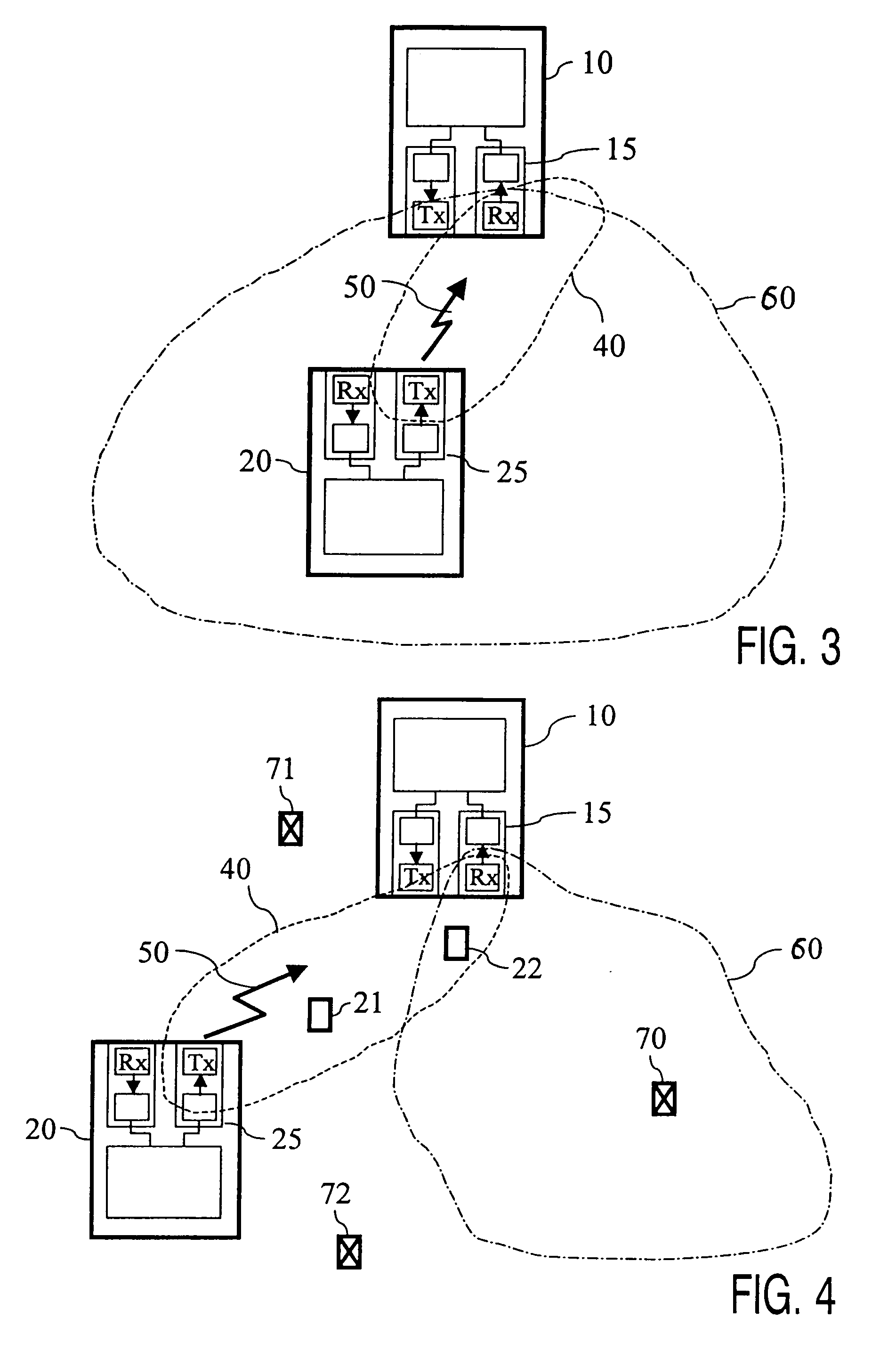
ActiveUS7092694B2Simple processSimple systemAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemEngineering
A system including at least one host and at least one guest communicating with each other via a wireless medium and having structure for linking a selected host (10) to a selected guest (20). In order to be able to perform such selection and such linking in a simplified manner, the host (10) has structure for establishing the link on the double condition that the guest (20) transmits a declaration signal (50) and that this declaration signal (50) is transmitted from within a declaration area (40) of the host (10) which differs substantially from the normal operating area (60) of the guest / host pair. The selection and the linking of the host (10) and the guest (20) is performed simply by putting the selected guest (20) within the declaration area (40) of the selected host (10) and by triggering the transmission of a declaration signal (50) by the selected guest (20) from within this declaration area (40).
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Capacitance fluid volume measurement
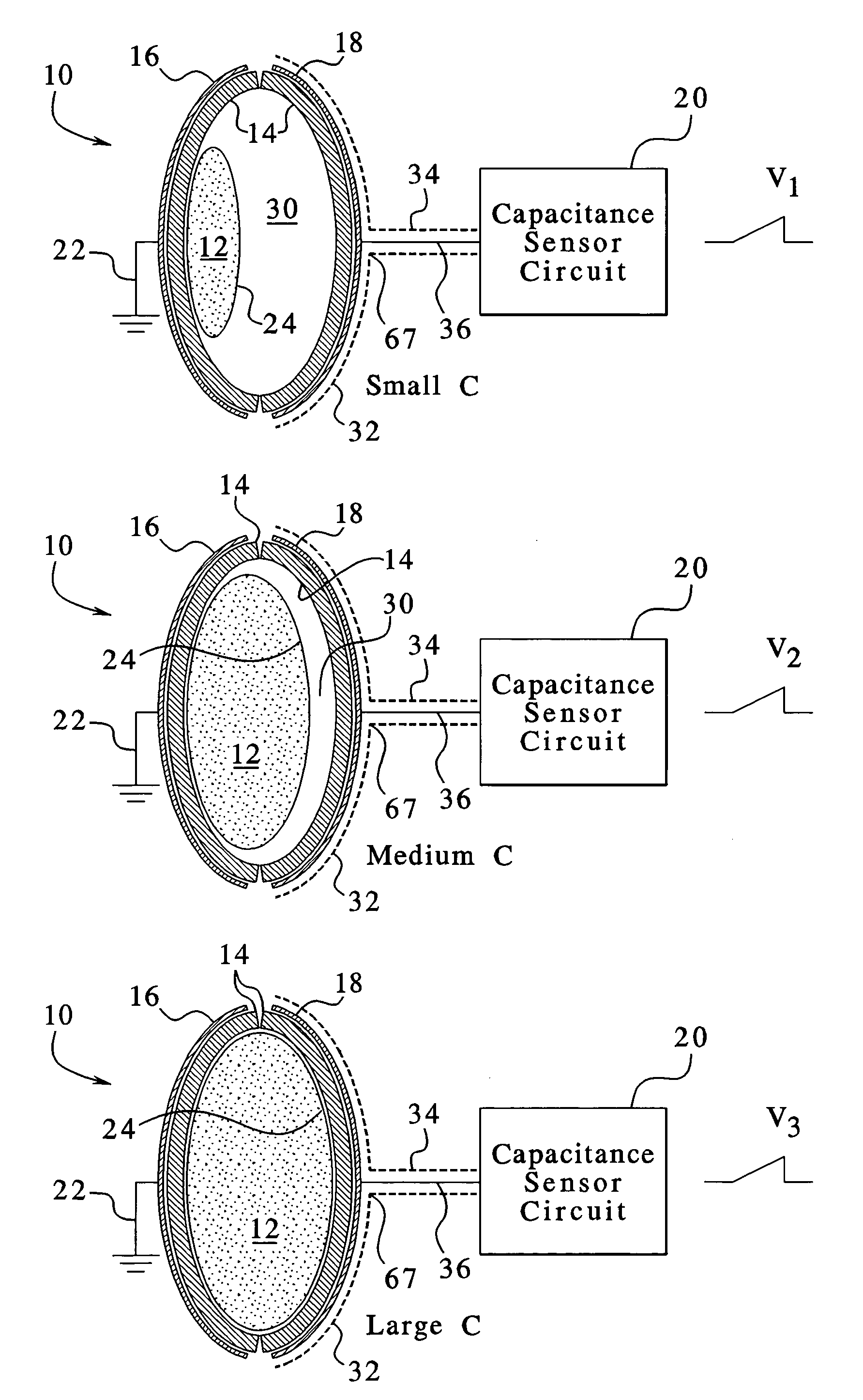
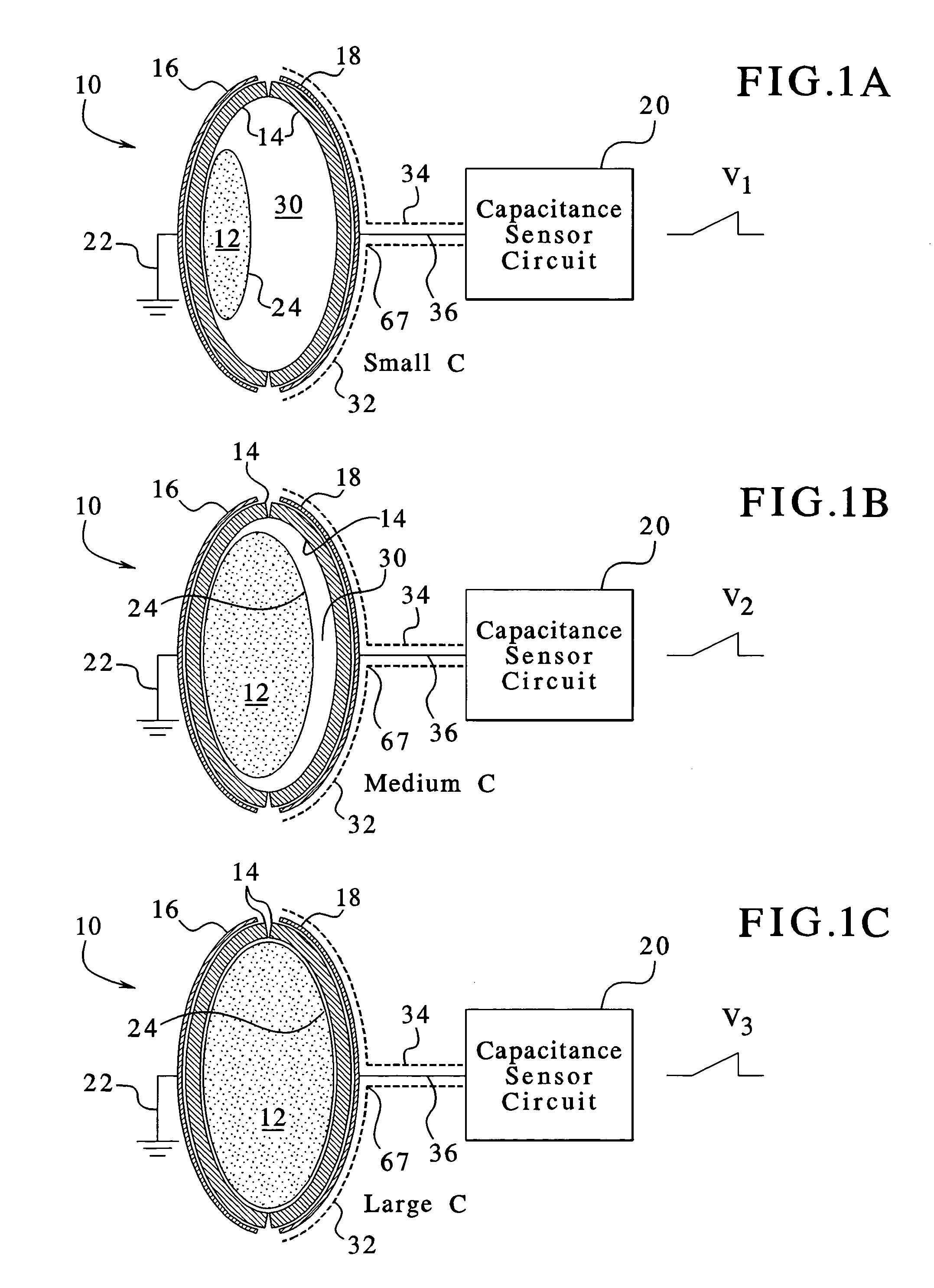
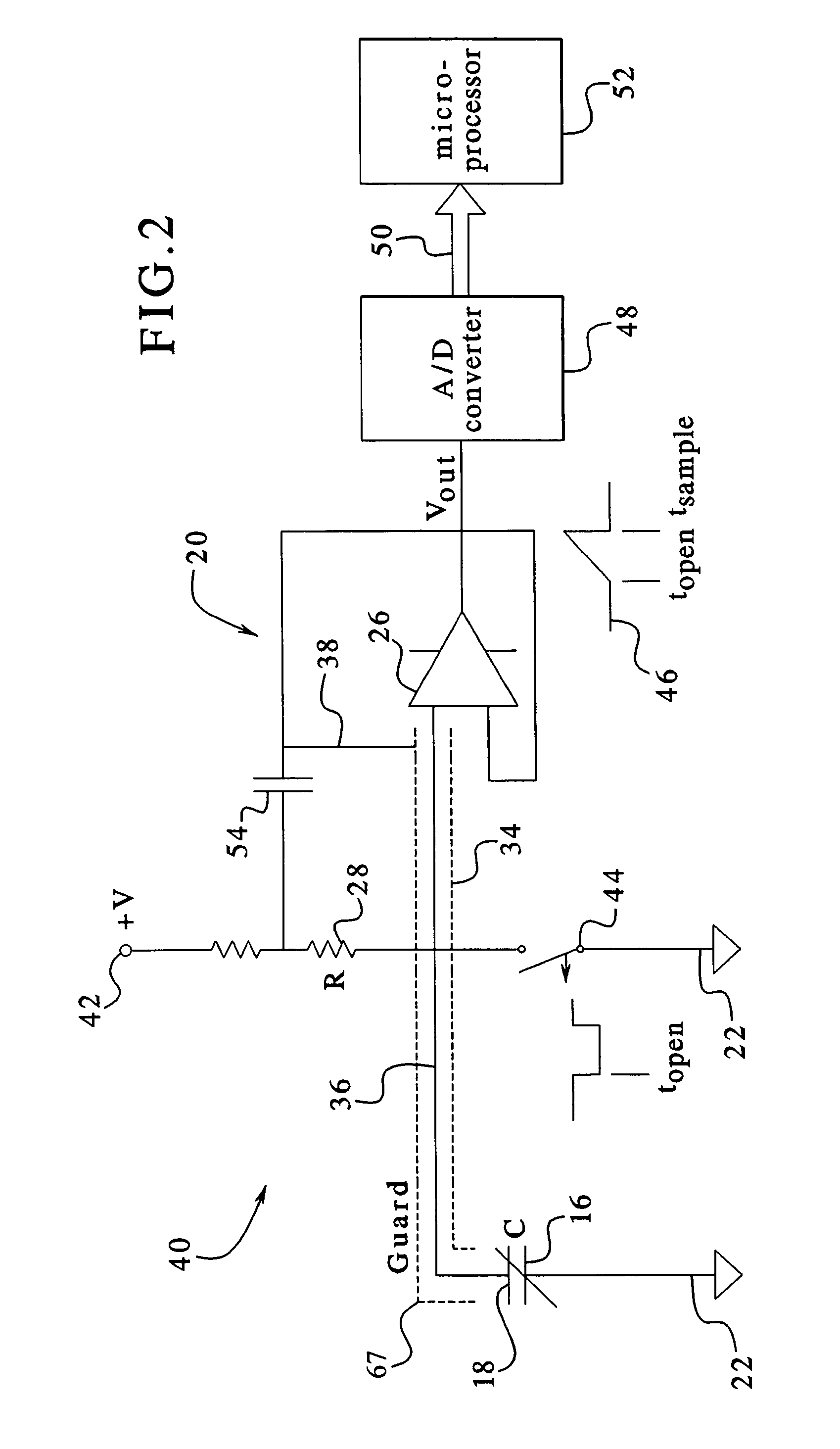
InactiveUS7107837B2Simple systemSimple methodVolume/mass flow measurementMedical devicesPump chamberEngineering
A fluid volumetric pumping system has a fluid pump and capacitor plates disposed around a pump chamber of the fluid pump. The capacitance between the capacitor plates changes as the volume of fluid in the pump chamber changes. An electrical circuit measures a change in the capacitance between the plates and outputs a signal indicative of the volume of fluid in the pump chamber. The pump having the capacitance sensor of the present invention fluidly connects to a patient. In an embodiment, a peritoneal dialysis system provides dialysate to the patient via the pump, and the capacitance sensor measures the volume of dialysate supplied to and drained from a peritoneal cavity of the patient.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method and System for Performing Video Flashlight
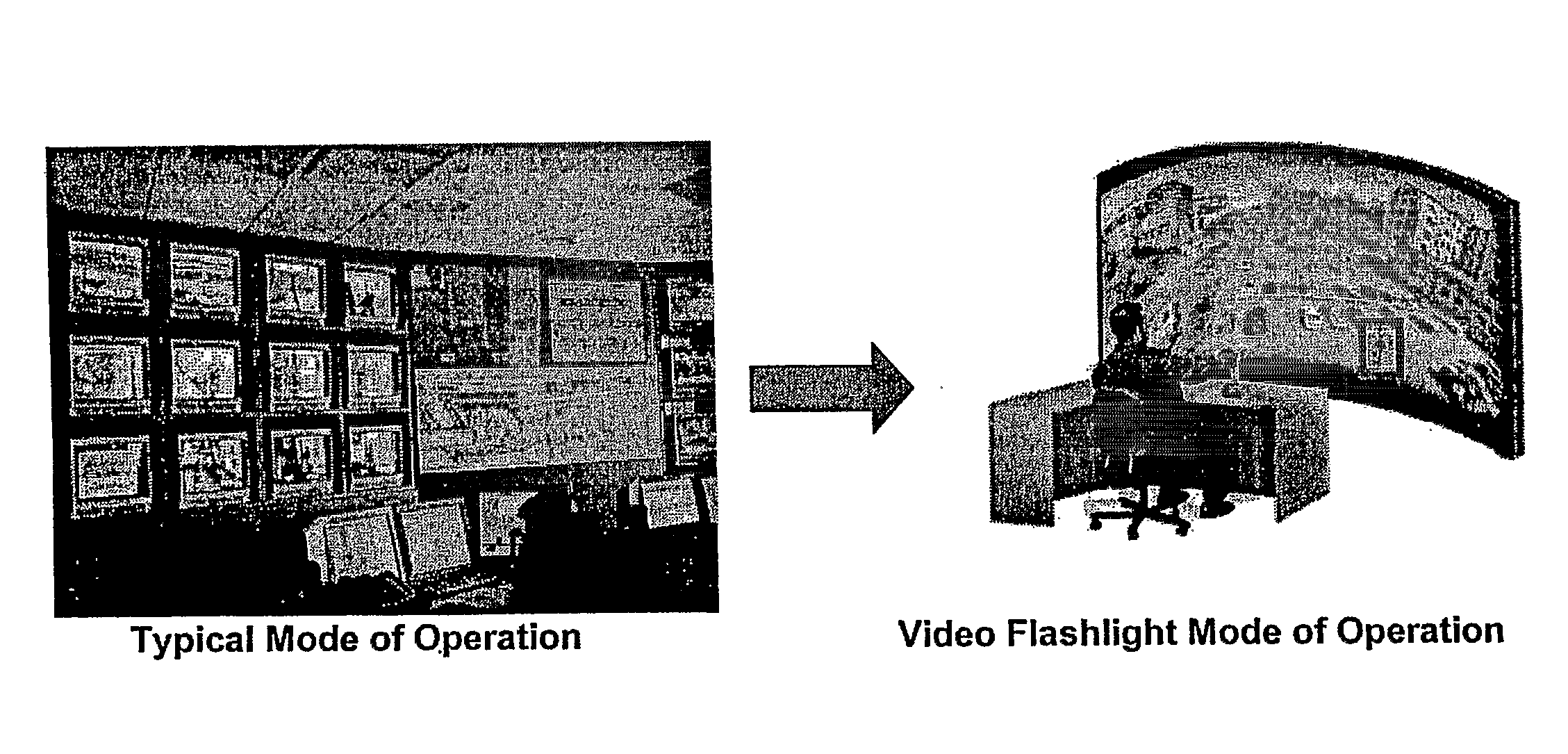
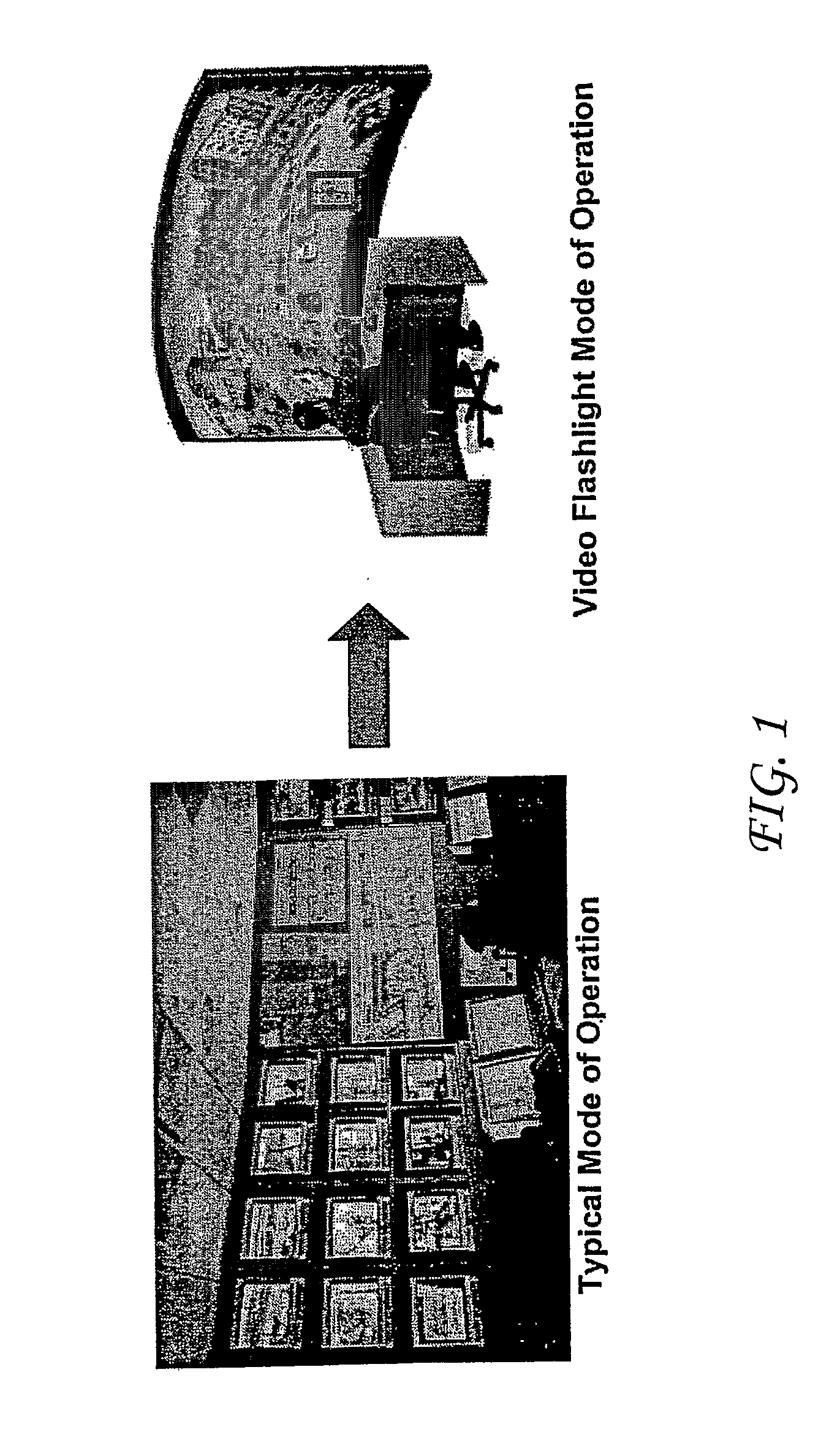
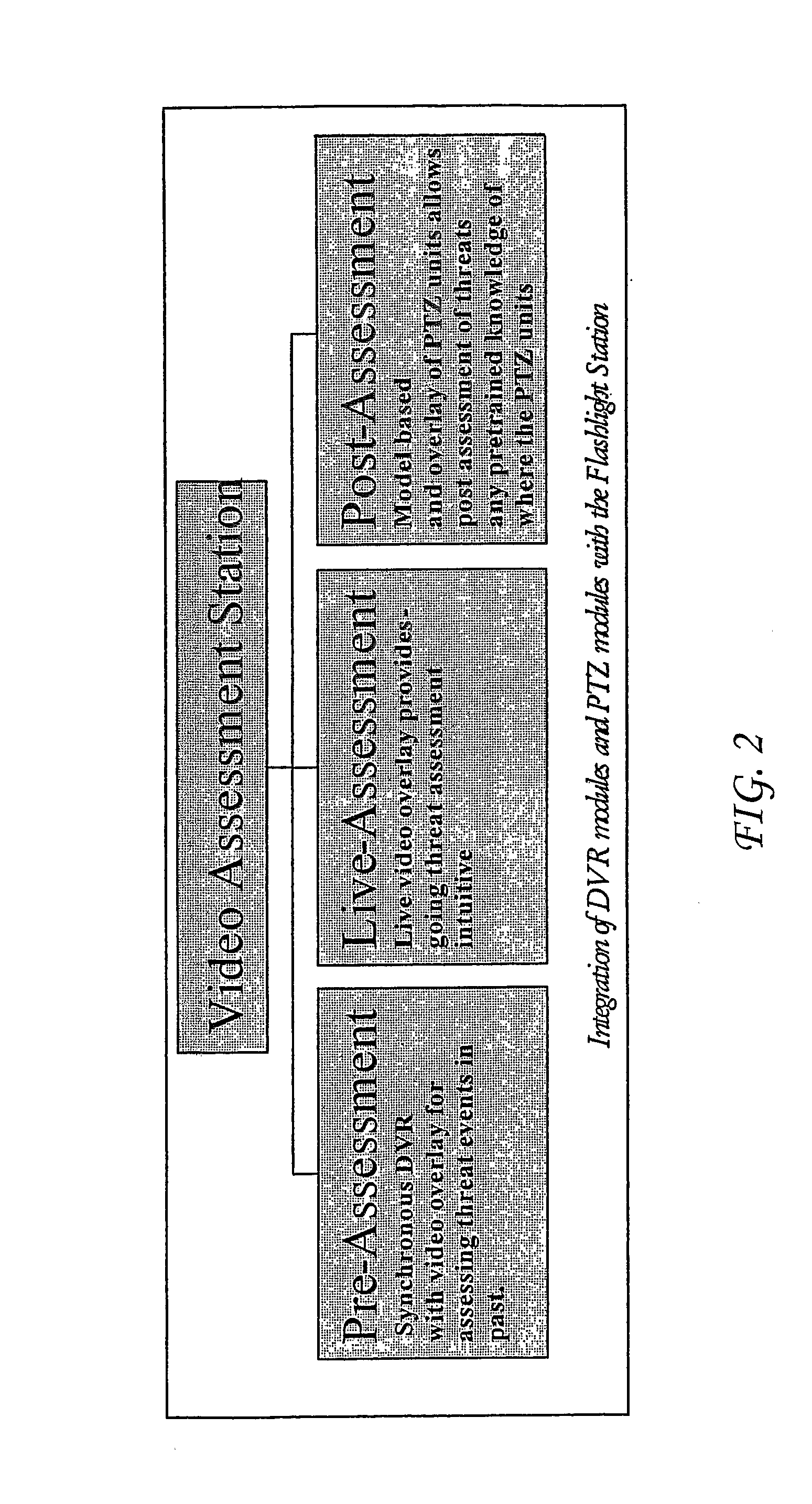
InactiveUS20080291279A1Simple systemReduce data volumeClosed circuit television systemsBurglar alarmViewpointsControl system
In an immersive surveillance system, videos or other data from a large number of cameras and other sensors is managed and displayed by a video processing system overlaying the data within a rendered 2D or 3D model of a scene. The system has a viewpoint selector configured to allow a user to selectively identify a viewpoint from which to view the site. A video control system receives data identifying the viewpoint and based on the viewpoint automatically selects a subset of the plurality of cameras that is generating video relevant to the view from the viewpoint, and causes video from the subset of cameras to be transmitted to the video processing system. As the viewpoint changes, the cameras communicating with the video processor are changed to hand off to cameras generating relevant video to the new position. Playback in the immersive environment is provided by synchronization of time stamped recordings of video. Navigation of the viewpoint on constrained paths in the model or map-based navigation is also provided.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
System for distributing and controlling color reproduction at multiple sites
InactiveUS7075643B2Provide accuratelyMinimize involvementImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryMeasuring instrumentSpectrograph
In the color imaging system, multiple rendering devices are provided at different nodes along a network. Each rendering device has a color measurement instrument for calibrating the color presented by the rendering device. A rendering device may represent a color display in which a member surrounds the outer periphery of the screen of the display and a color measuring instrument is coupled to the first member. The color measuring instrument includes a sensor spaced from the screen at an angle with respect to the screen for receiving light from an area of the screen. A rendering device may be a printer in which the measuring of color samples on a sheet rendered by the printer is provided by a sensor coupled to a transport mechanism which moves the sensor and sheet relative to each other, where the sensor provides light from the sample to a spectrograph. The color measuring instruments provide for non-contact measurements of color samples either displayed on a color display, or printed on a sheet, and are self-calibrating by the use of calibration references in the instrument.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
Extension -mode angular velocity sensor
ActiveUS20110061460A1SimplerLow costAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAngular rate sensorAngular velocity
An angular velocity sensor including a drive extension mode. In one aspect, an angular rate sensor includes a base and at least three masses disposed substantially in a plane parallel to the base, the masses having a center of mass. At least one actuator drives the masses in an extension mode, such that in the extension mode the masses move in the plane simultaneously away or simultaneously towards the center of mass. At least one transducer senses at least one Coriolis force resulting from motion of the masses and angular velocity about at least one input axis of the sensor. Additional embodiments can include a linkage that constrains the masses to move in the extension mode.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Method and apparatus for detecting doubled bills in a currency handling device
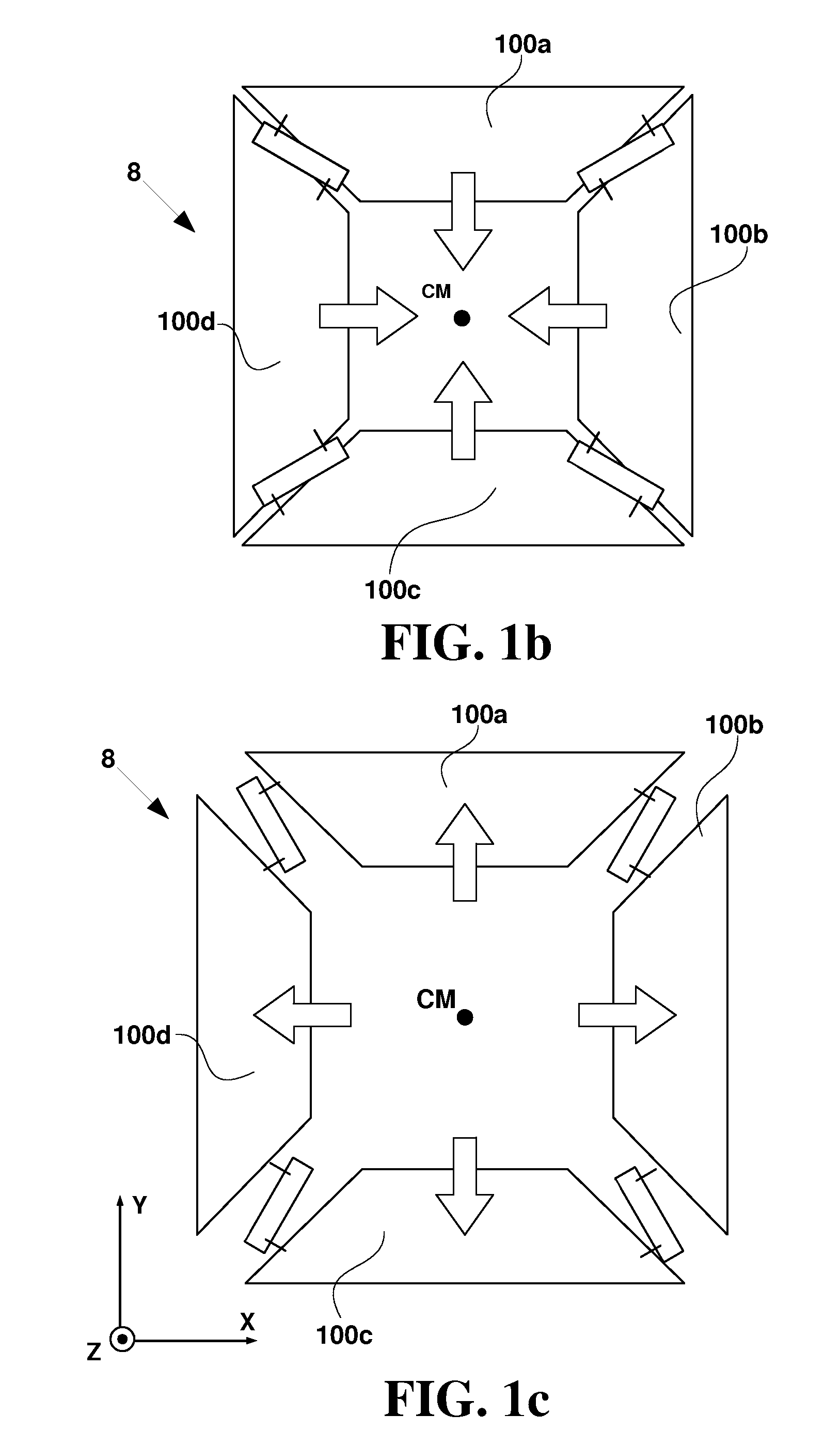
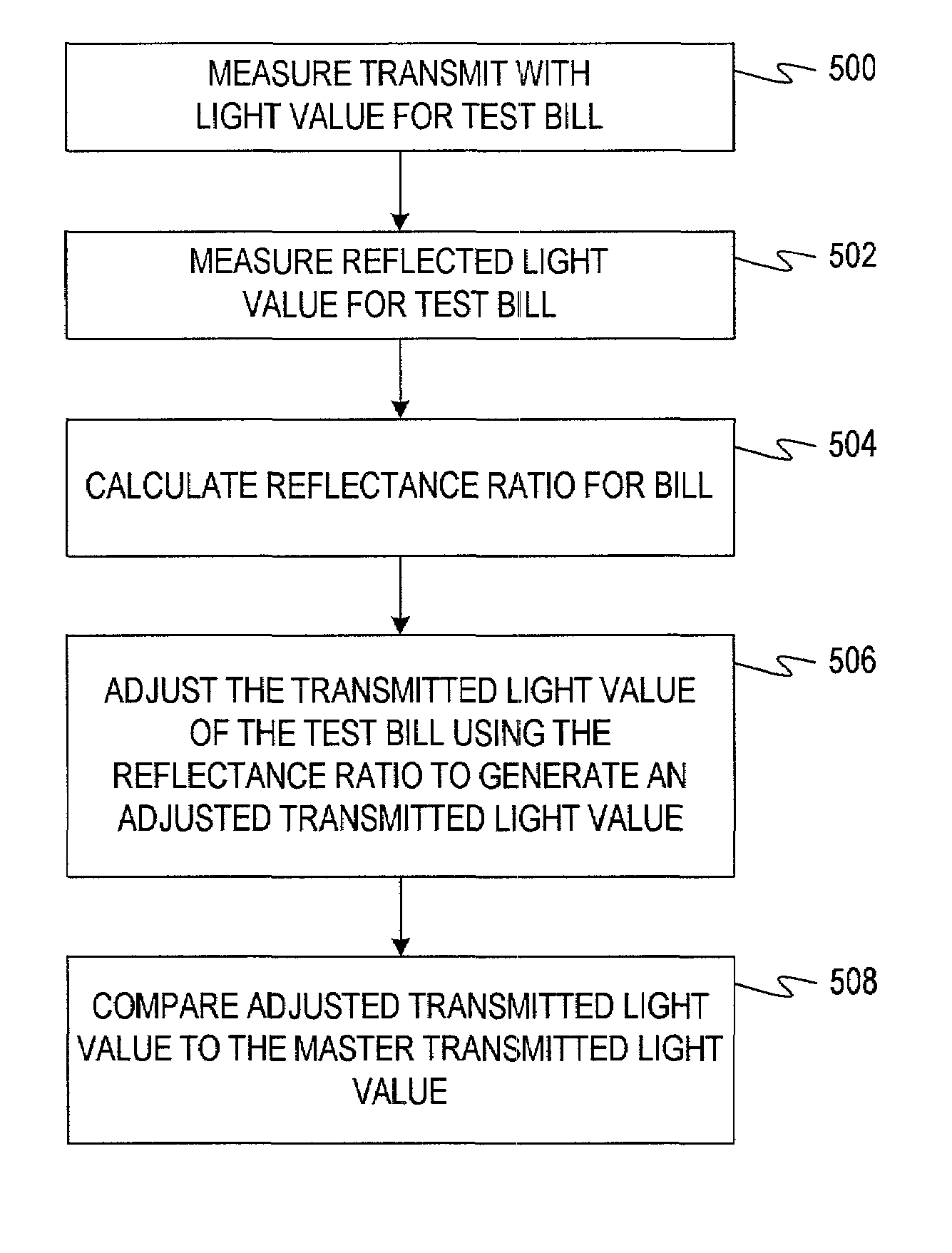
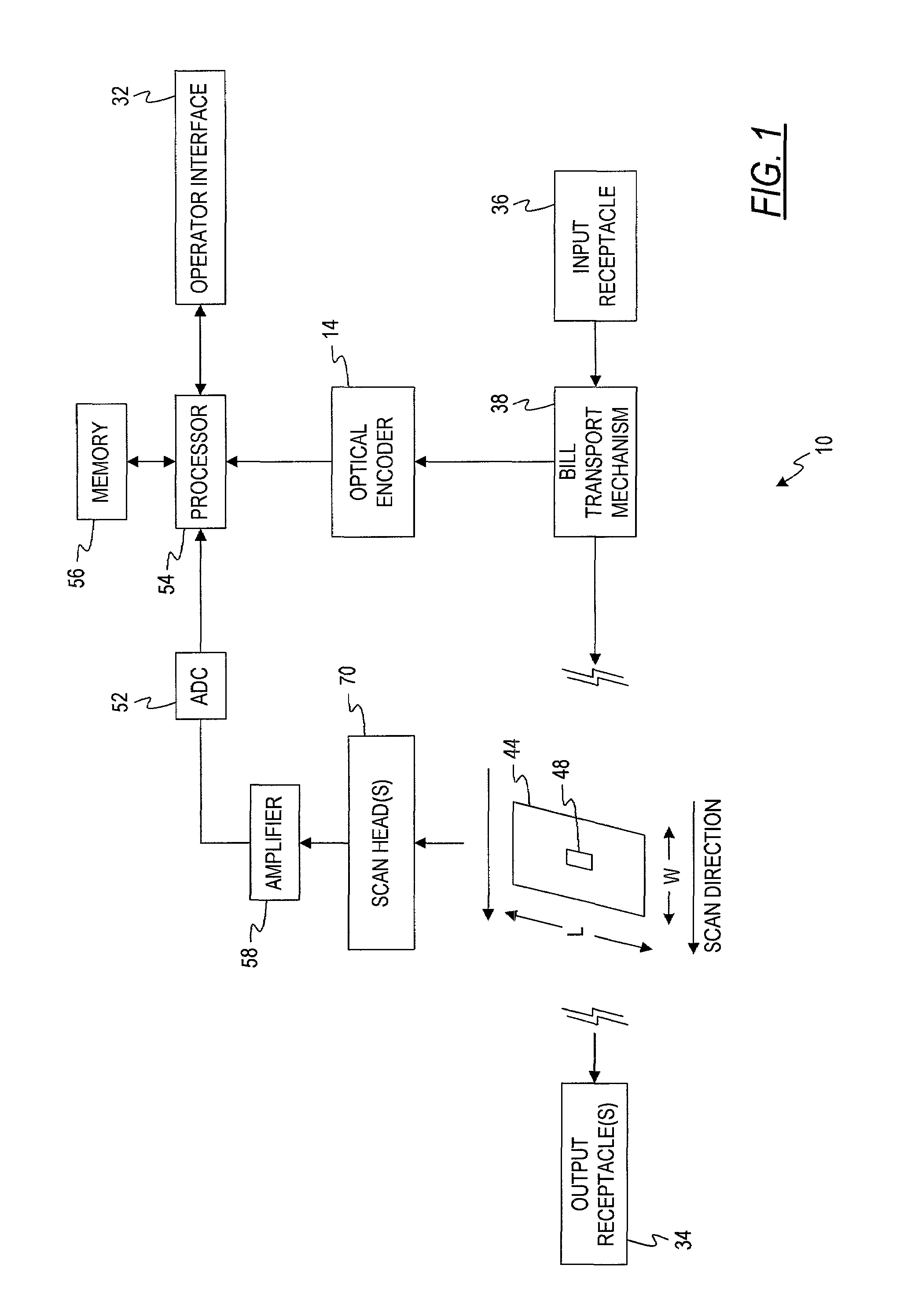
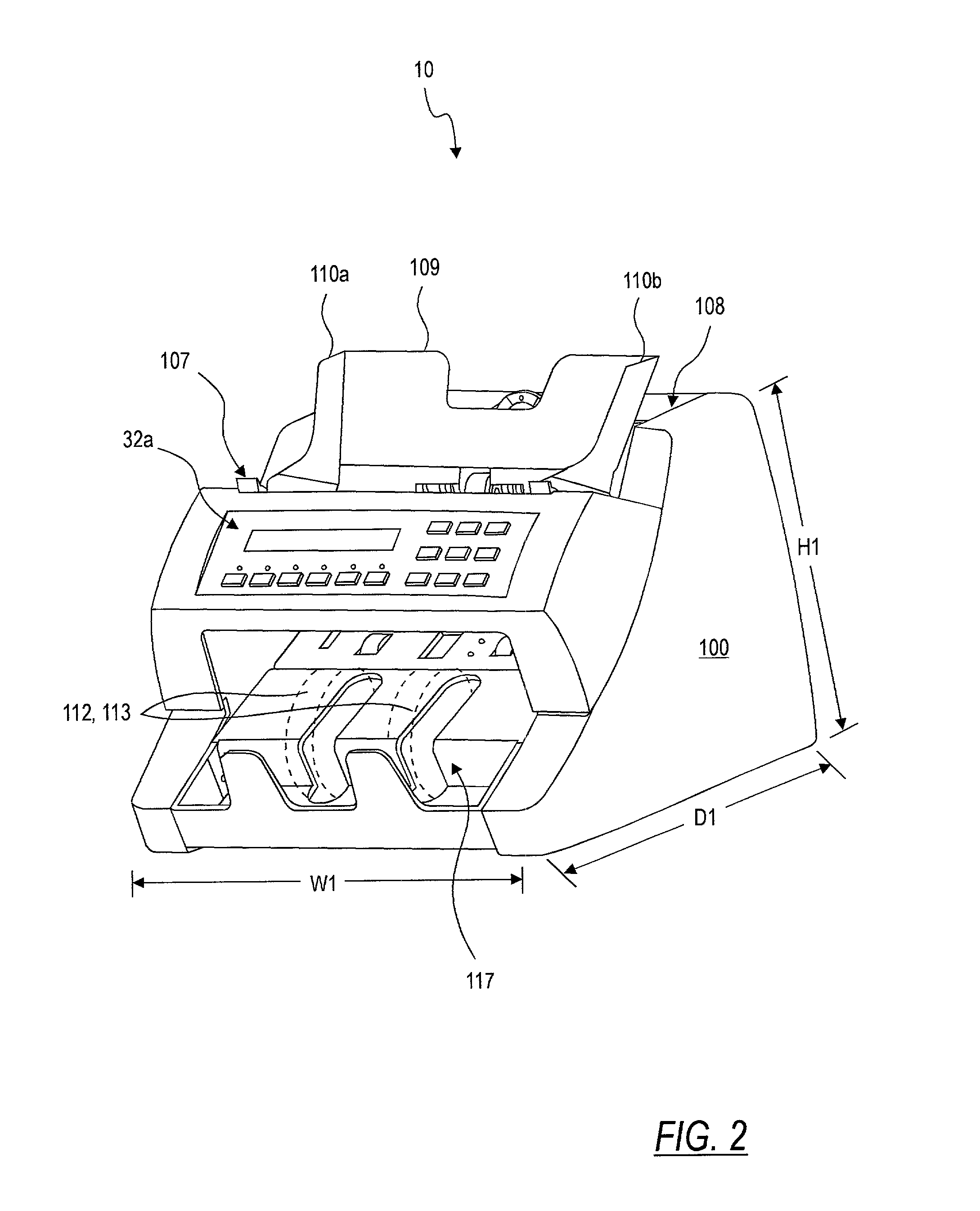
InactiveUS7103206B2Simple systemEfficient detectionPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionReflectivityLight source
A doubles detection system for detecting doubled documents. The system comprises one or more light sources disposed on a first side of a test document and one or more reflected light sensors disposed along the first side of the test document. The reflected light sensors are adapted to generate reflected light signals. The system also comprises one or more transmitted light sensors disposed along a second side of the test document which are adapted to generate transmitted light signals. The system also comprises a memory having a master reflected light value and a master transmitted light value stored therein. The system comprises a processor adapted to receive the reflected light signal, generate a reflected light value for the test document, and calculate a reflectance ratio between the reflected light value of the test document and a master reflected light value. The processor is also adapted to receive the transmitted light signal, generate a transmitted light value for the test document, and adjust the transmitted light value for the test document based on the reflectance ratio. The processor is adapted to compare the adjusted transmitted light value for the test document to the master transmitted light value and generate a doubles signal if the comparison of the adjusted transmitted light value for the test document with the master transmitted light value indicates that more than one document is present.
Owner:CUMMINS-ALLISON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com