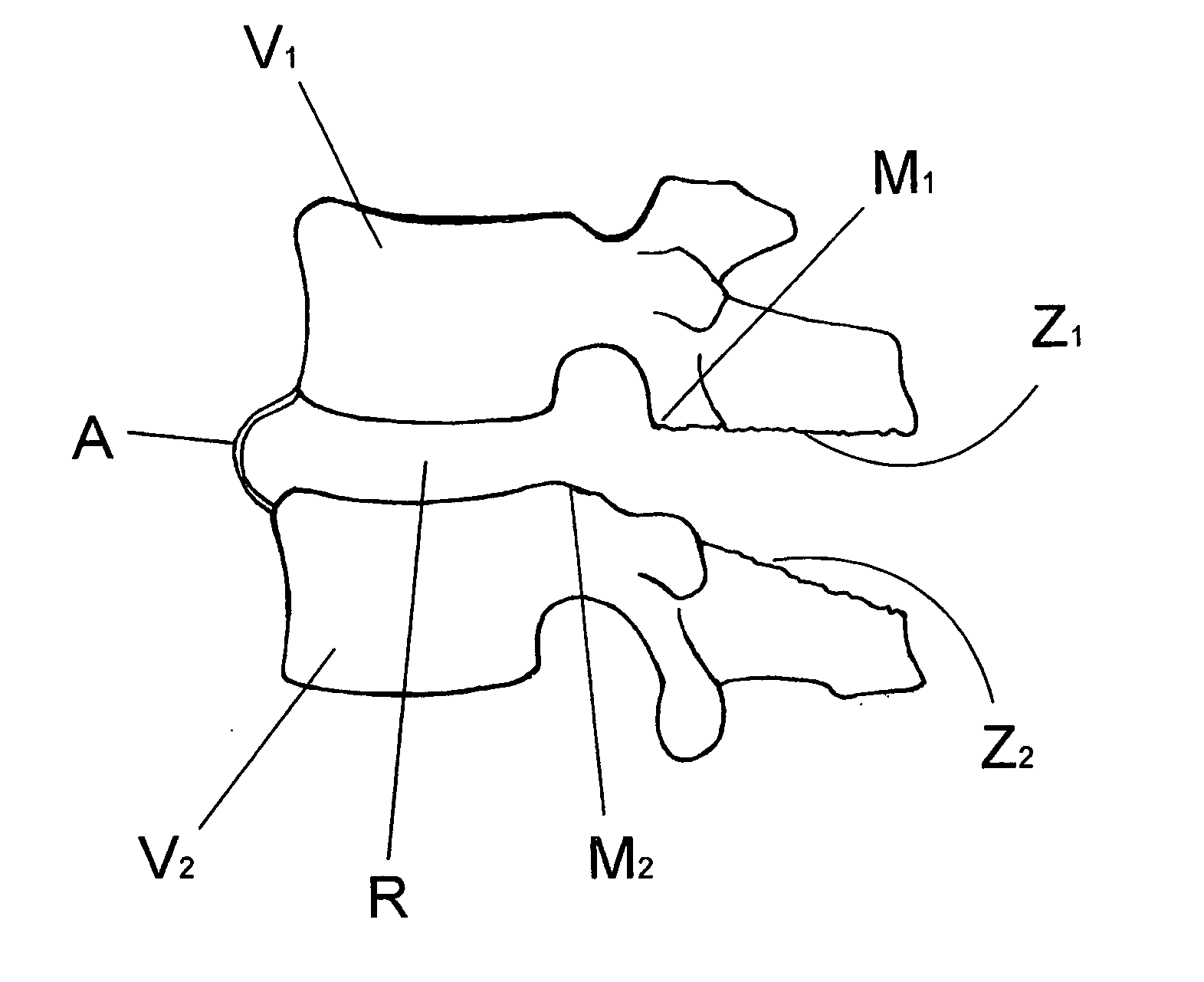
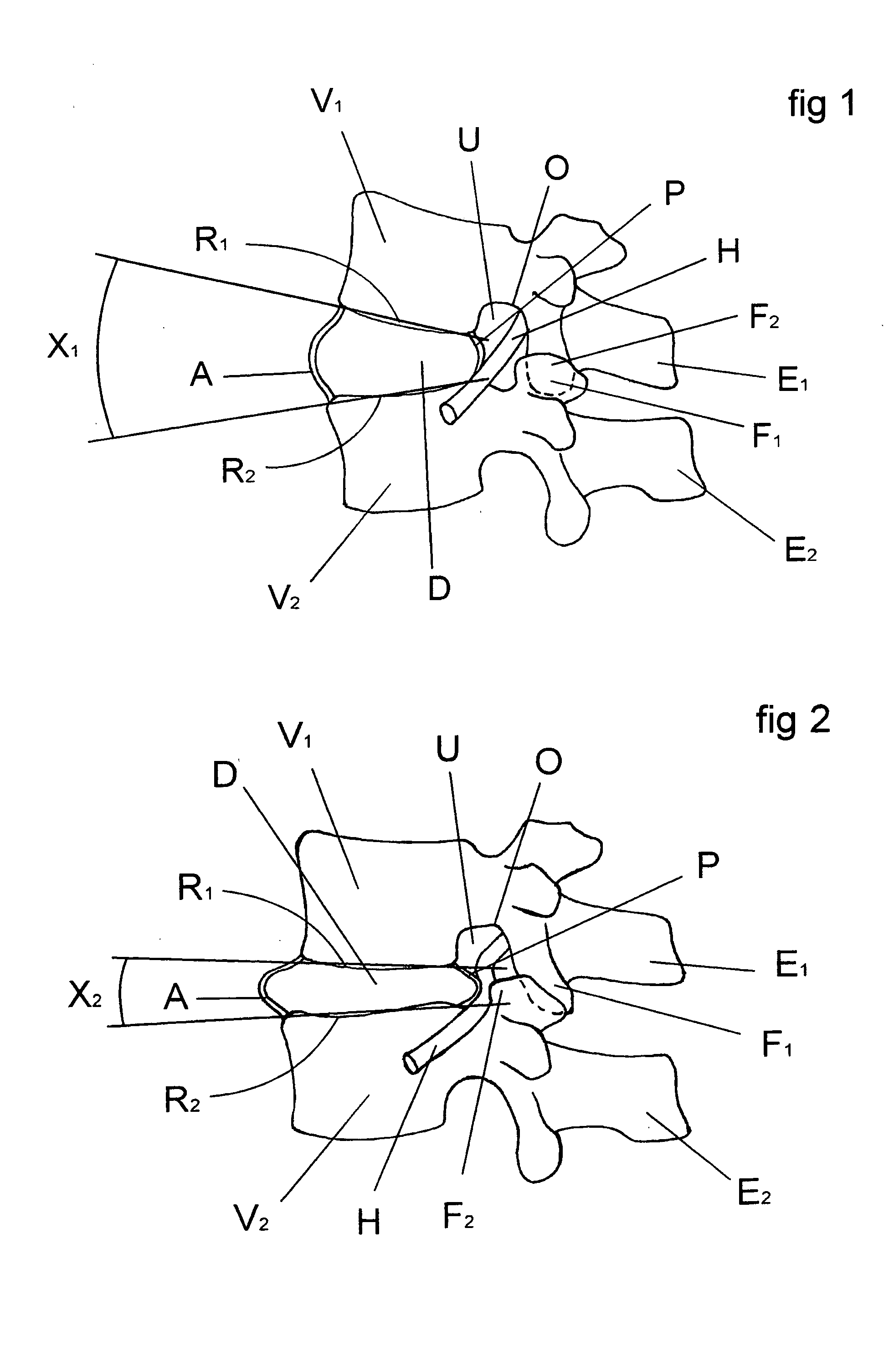
Patents
Literature
642 results about "Deformity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
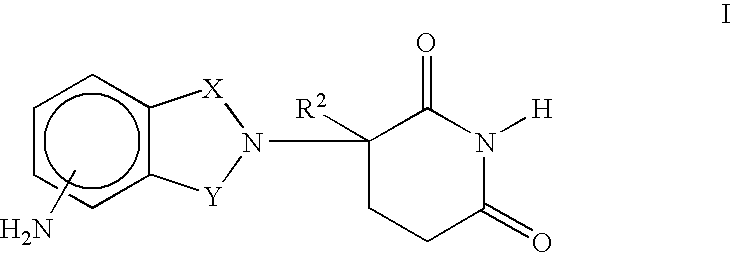
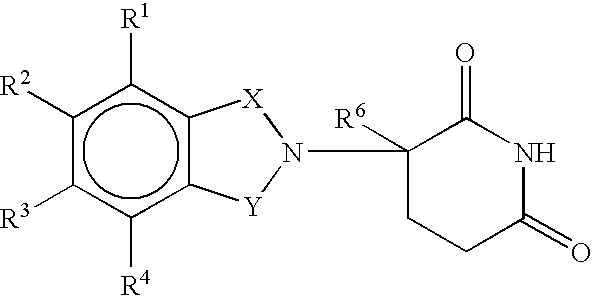
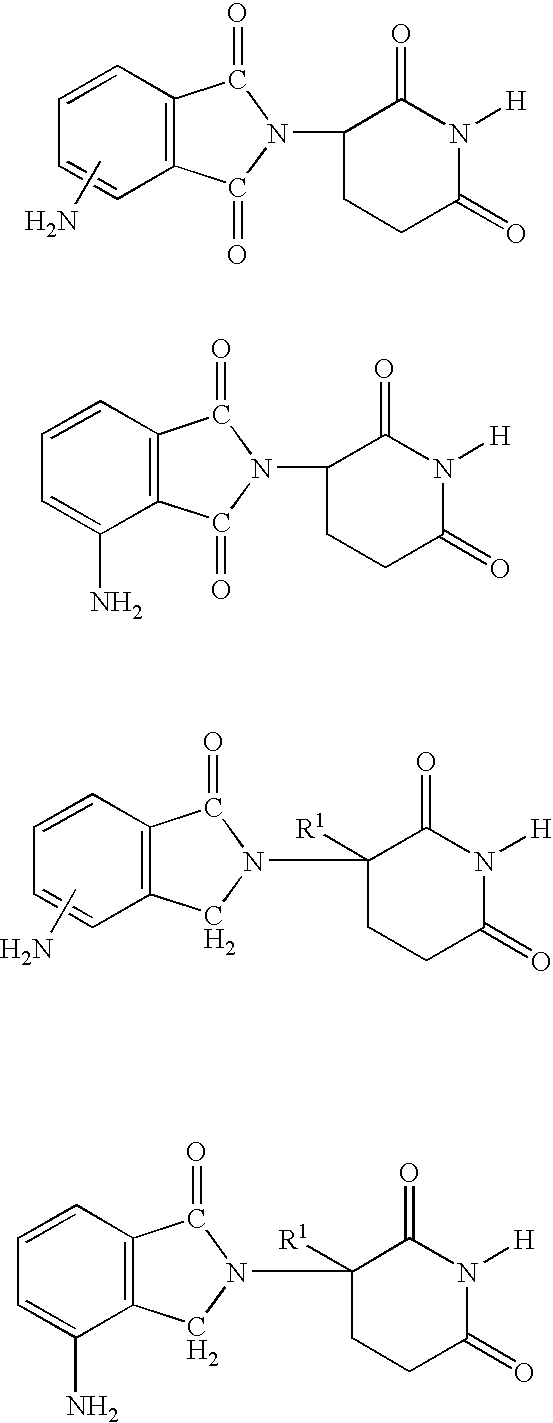
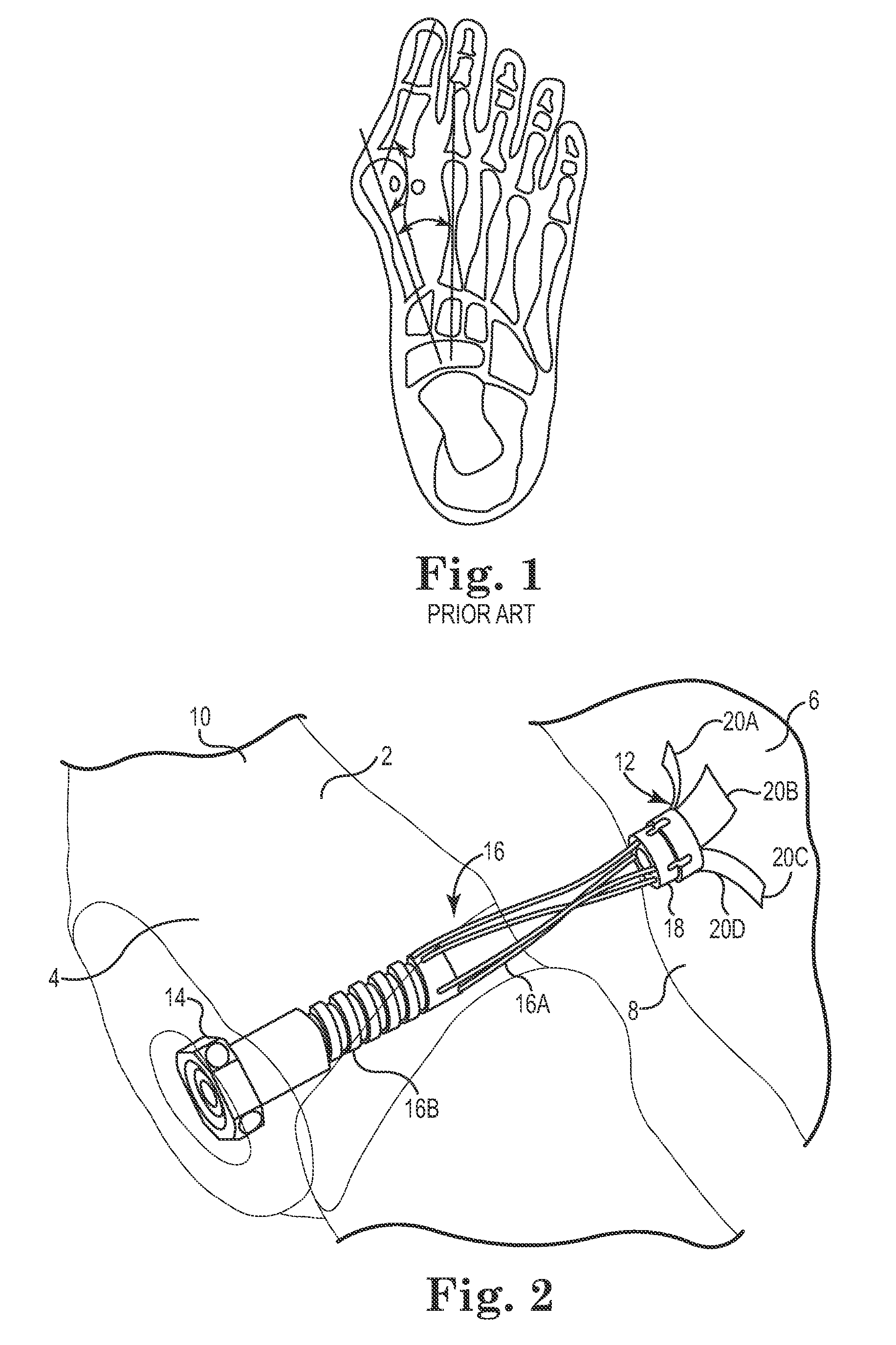
A deformity, dysmorphism, or dysmorphic feature is a major abnormality in the shape of a body part or organ compared to the normal shape of that part.
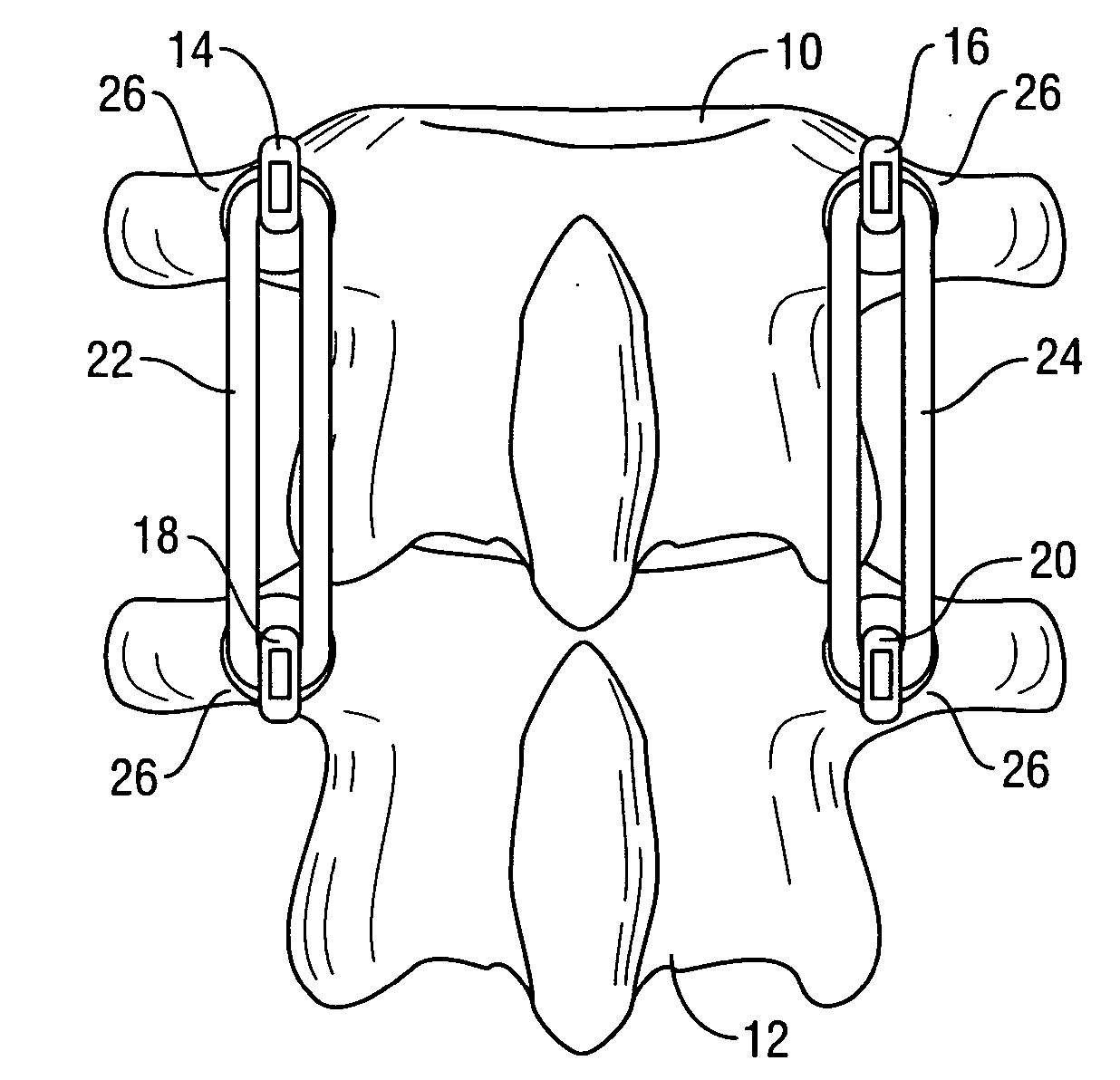
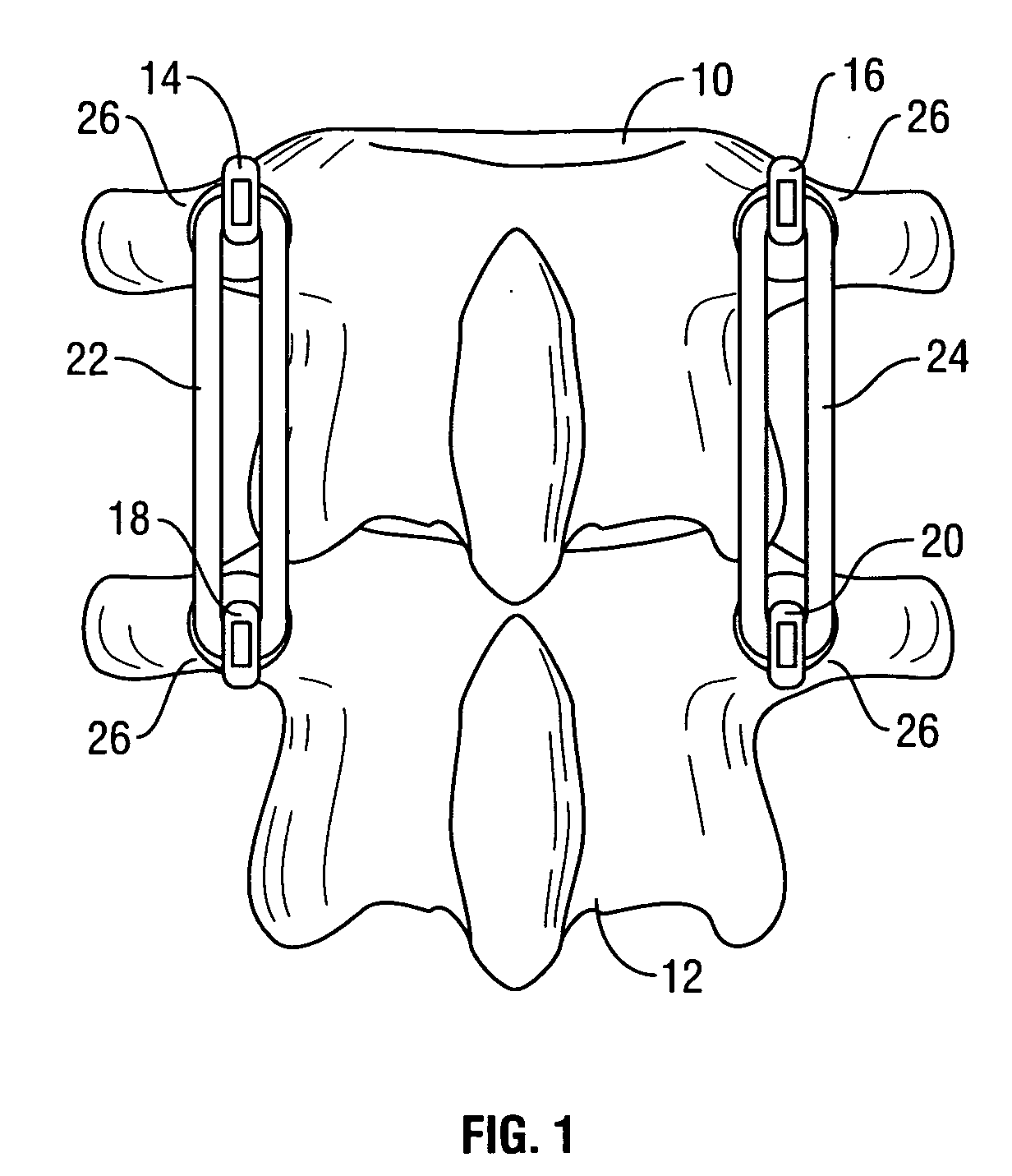
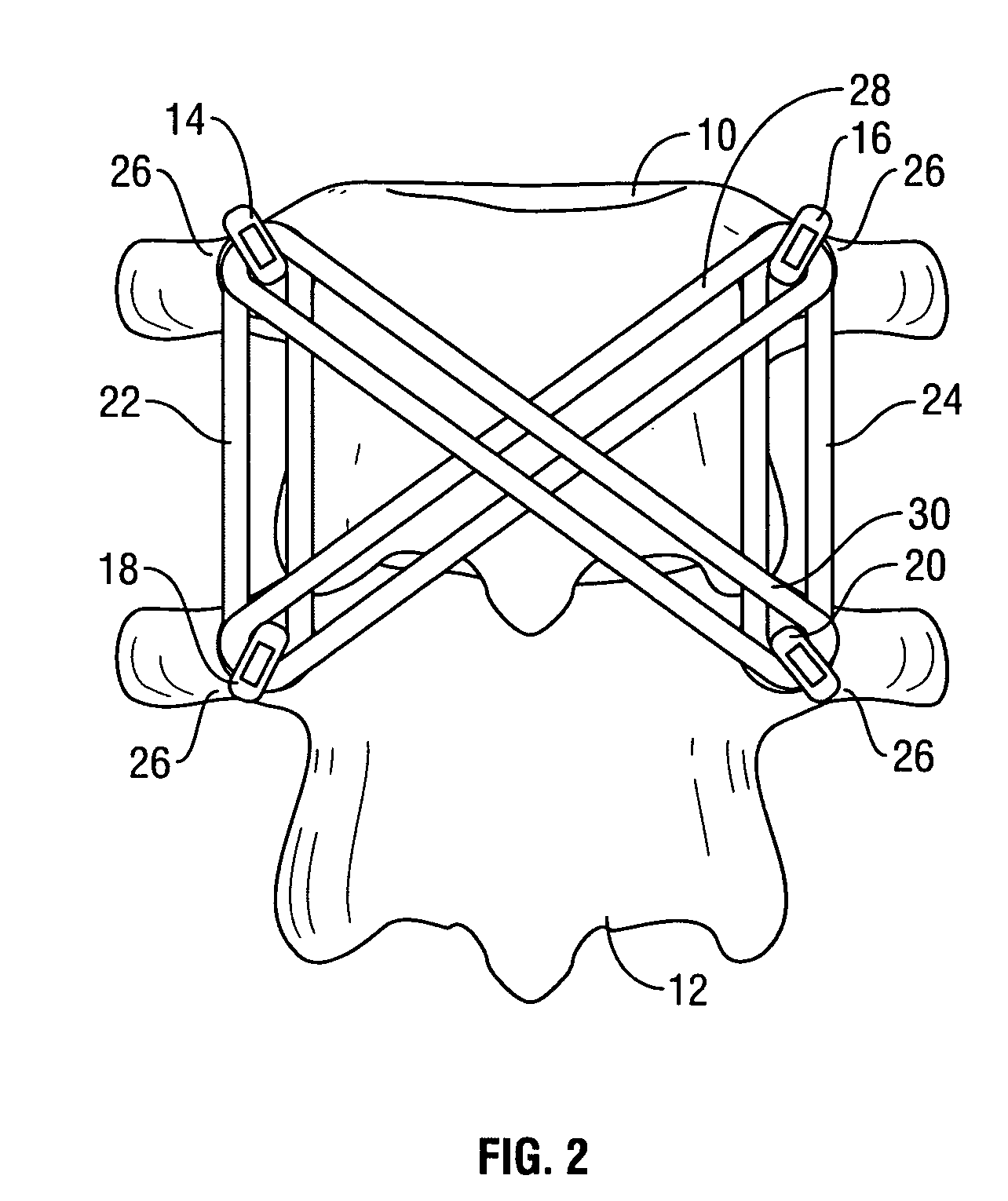
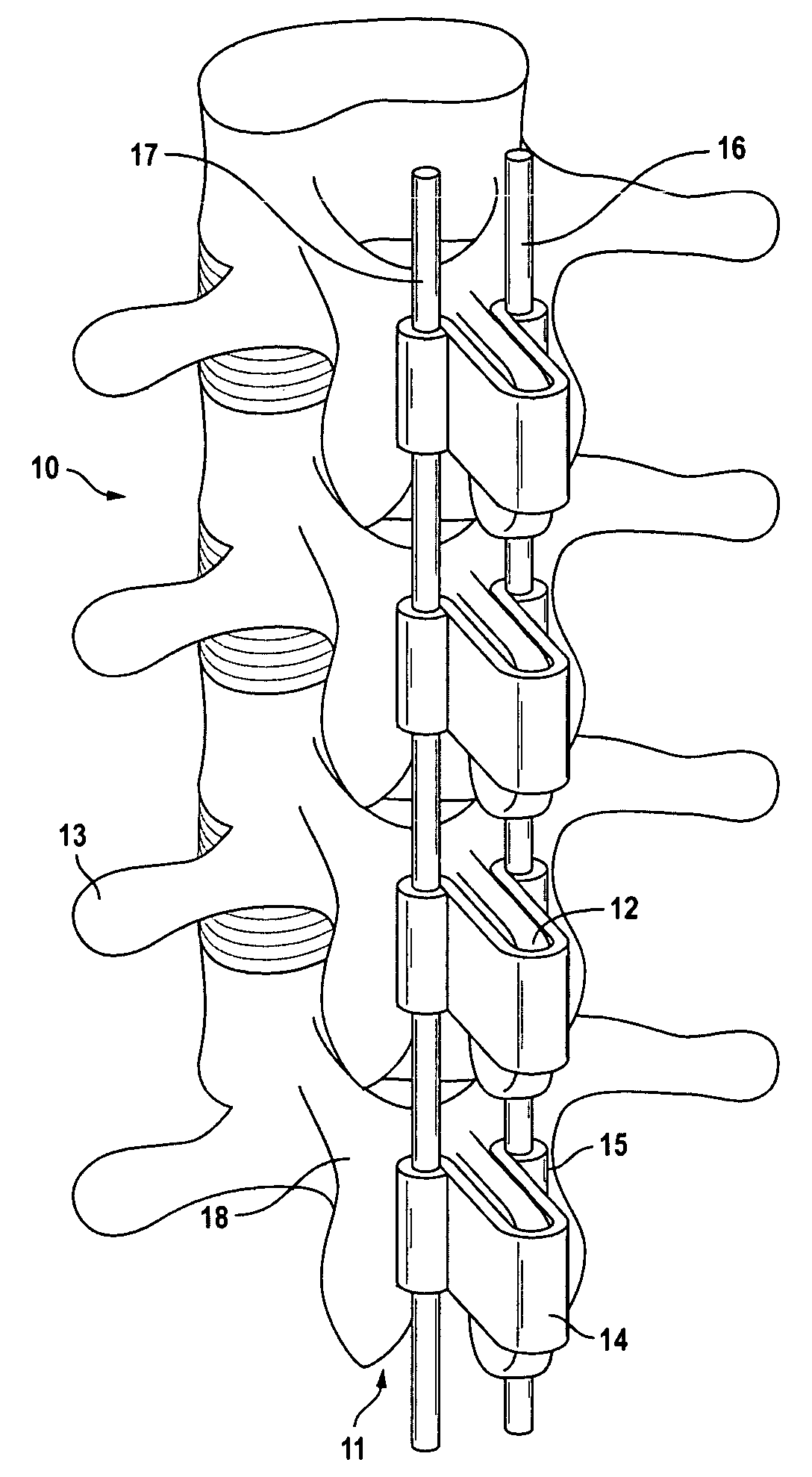
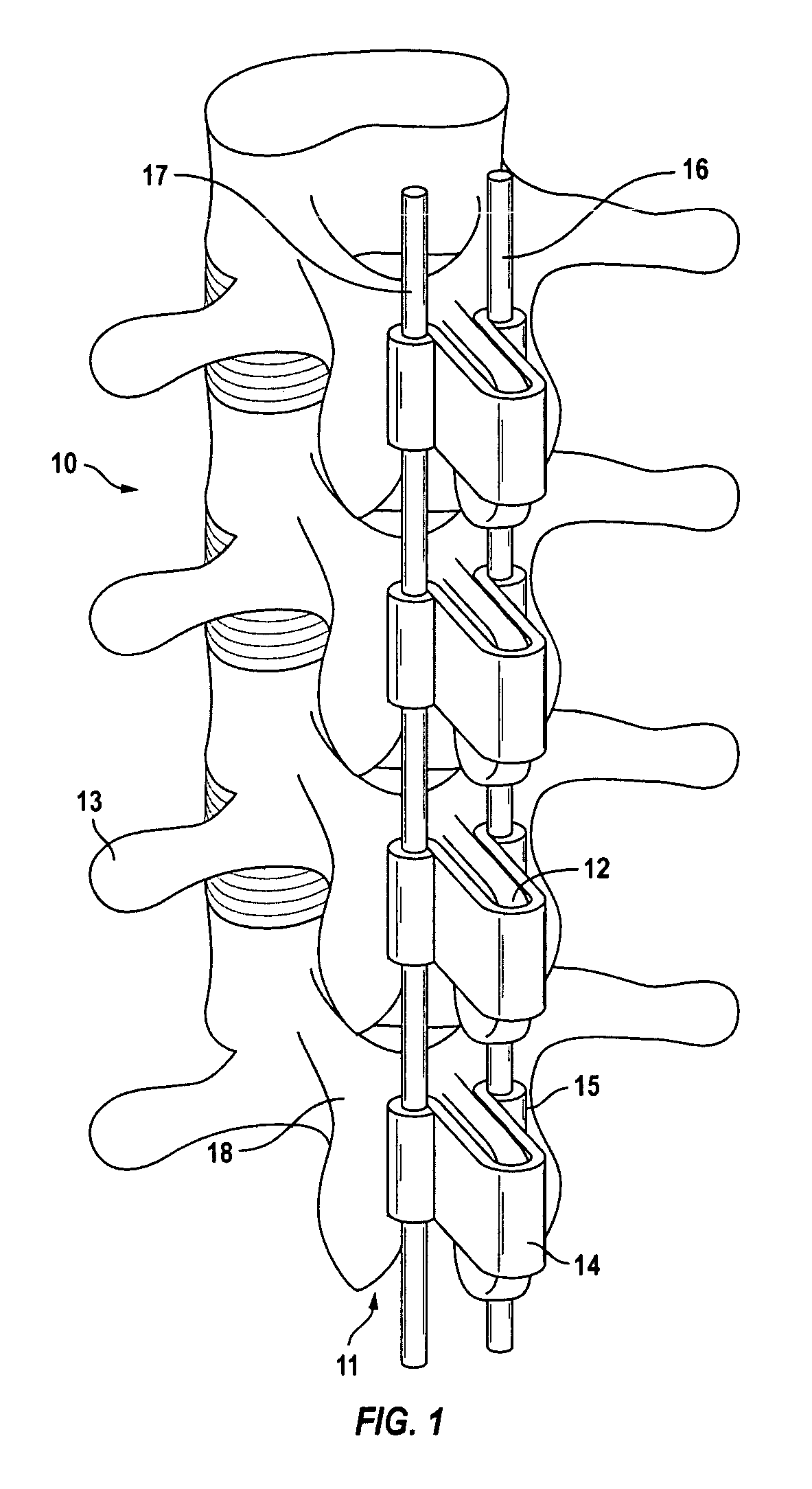
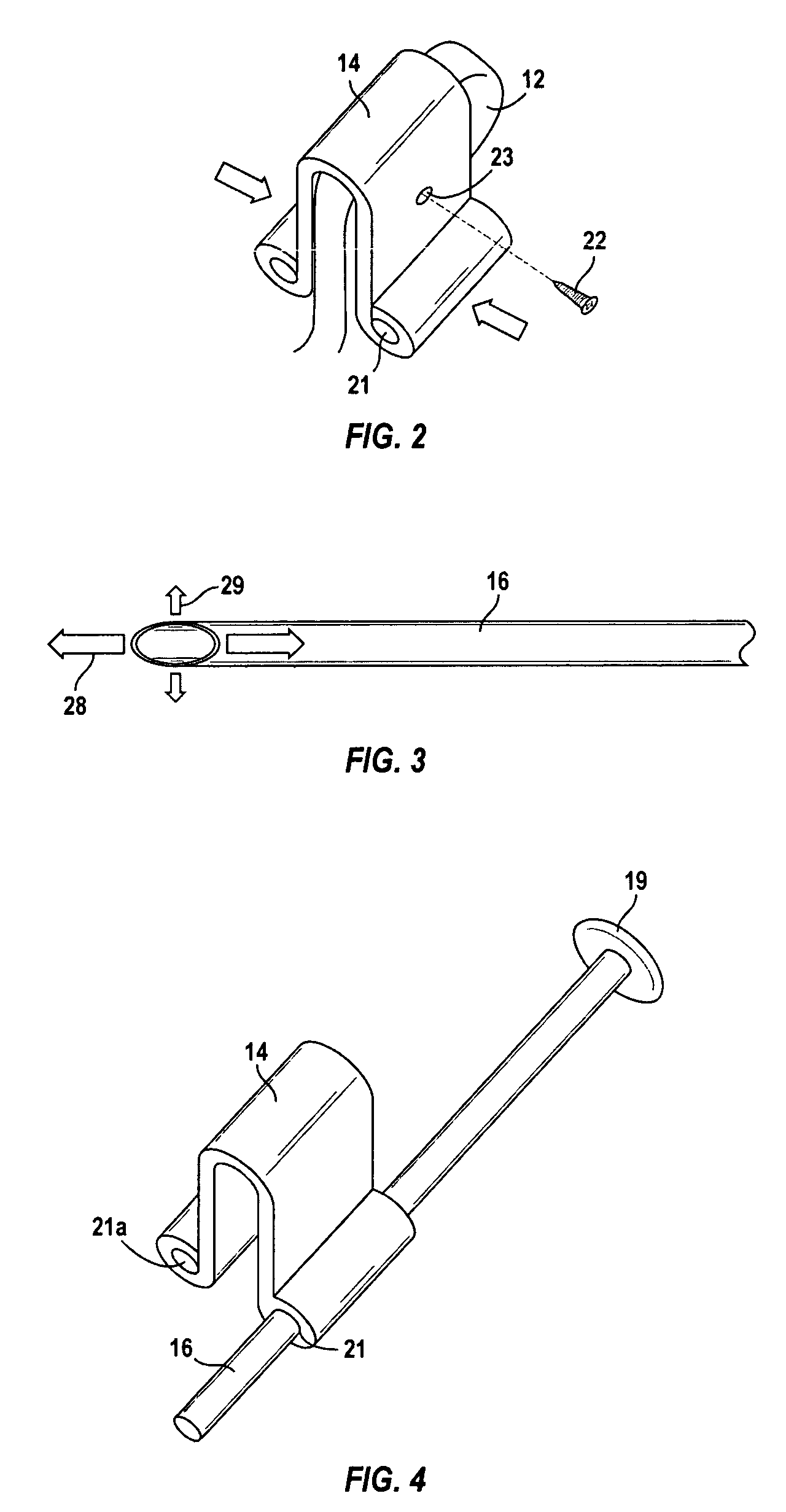
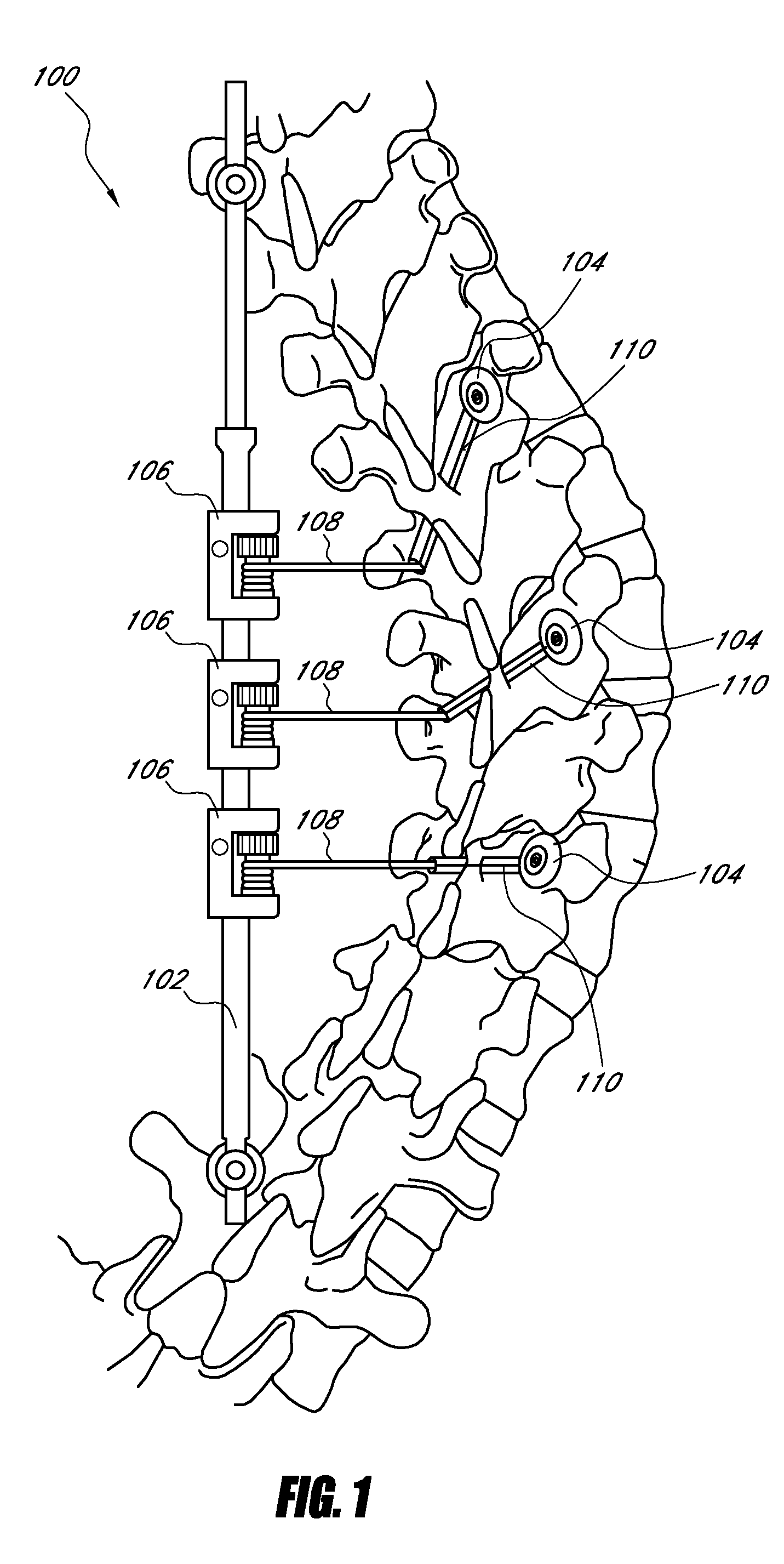
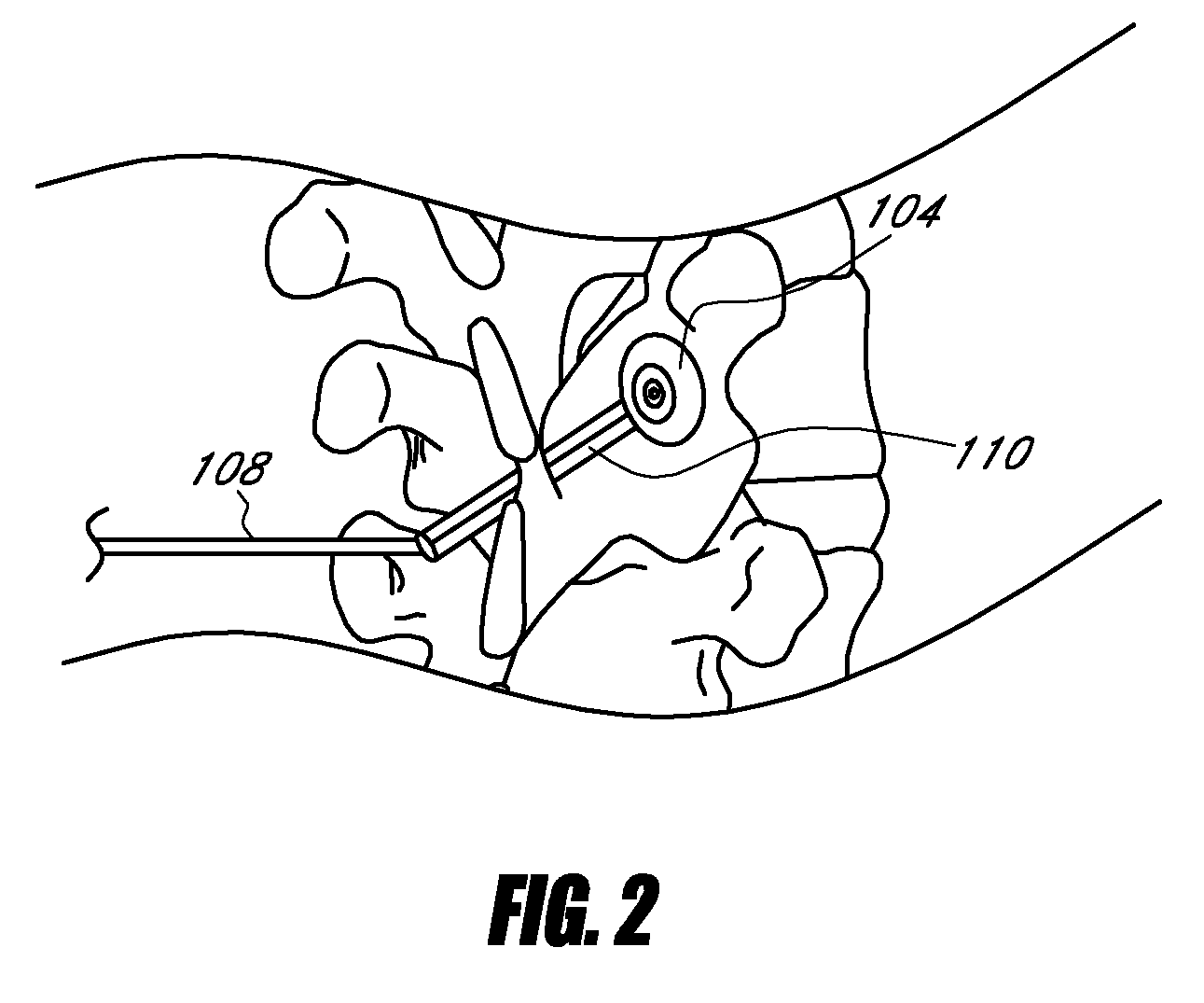
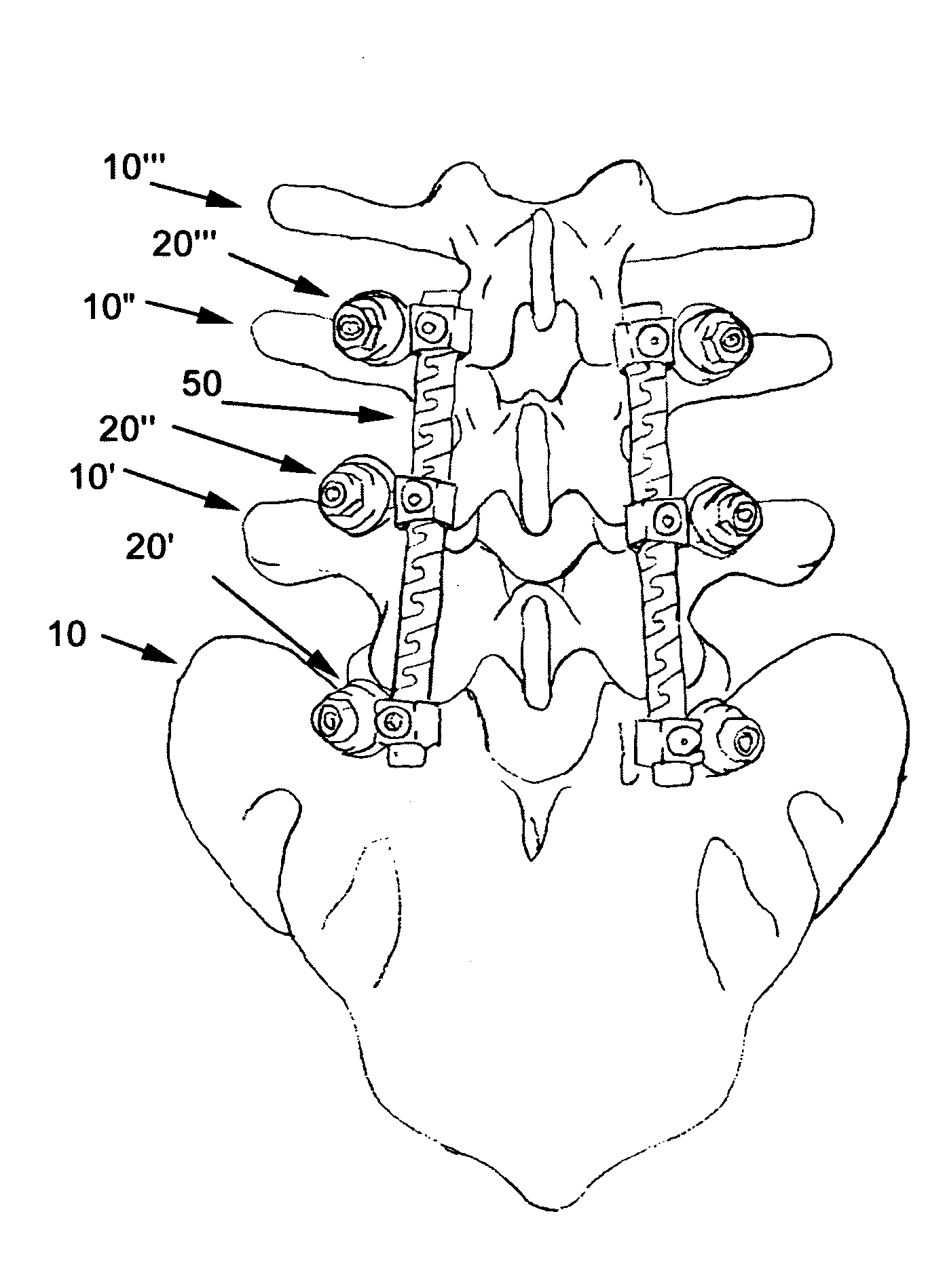
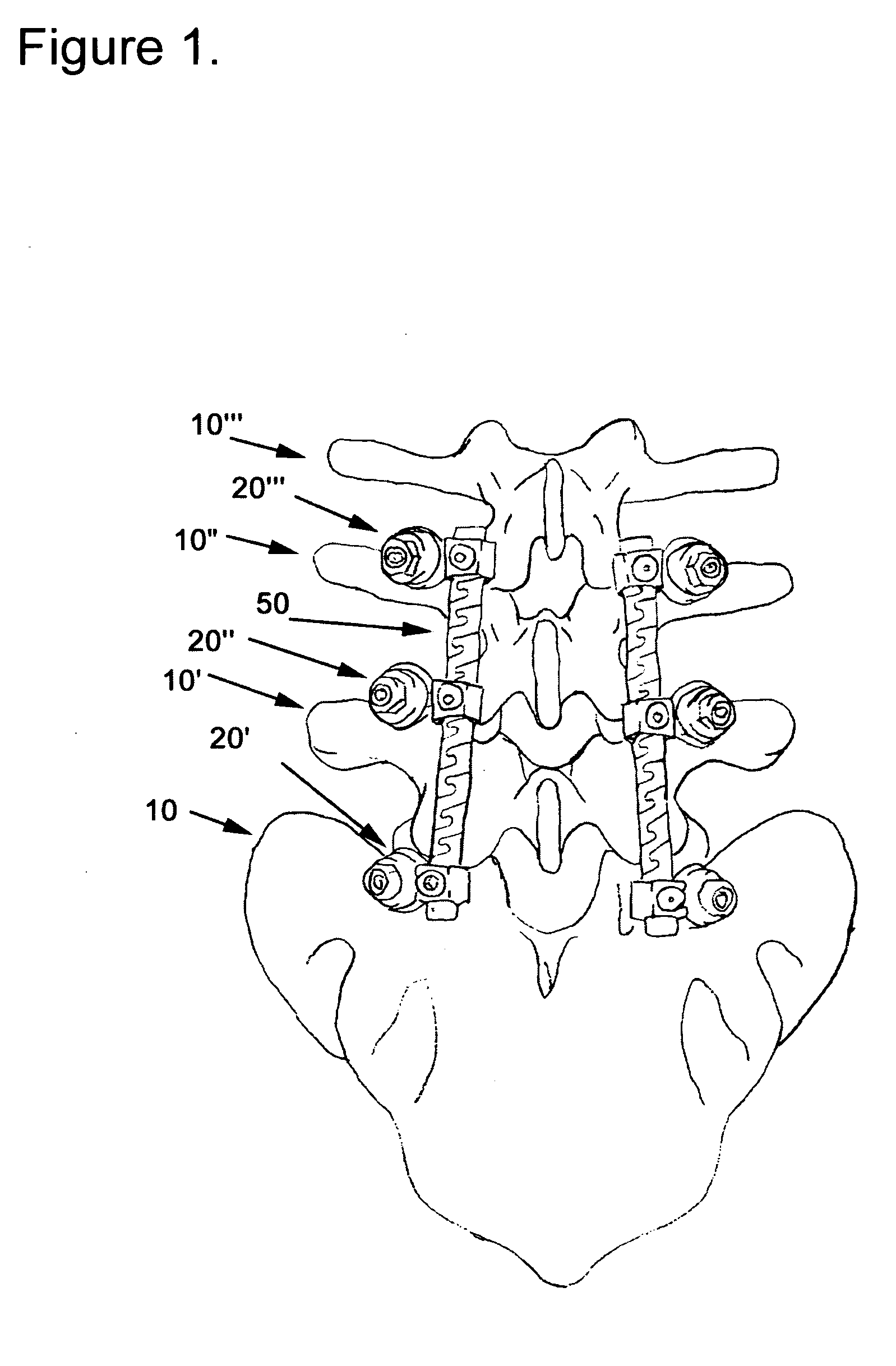
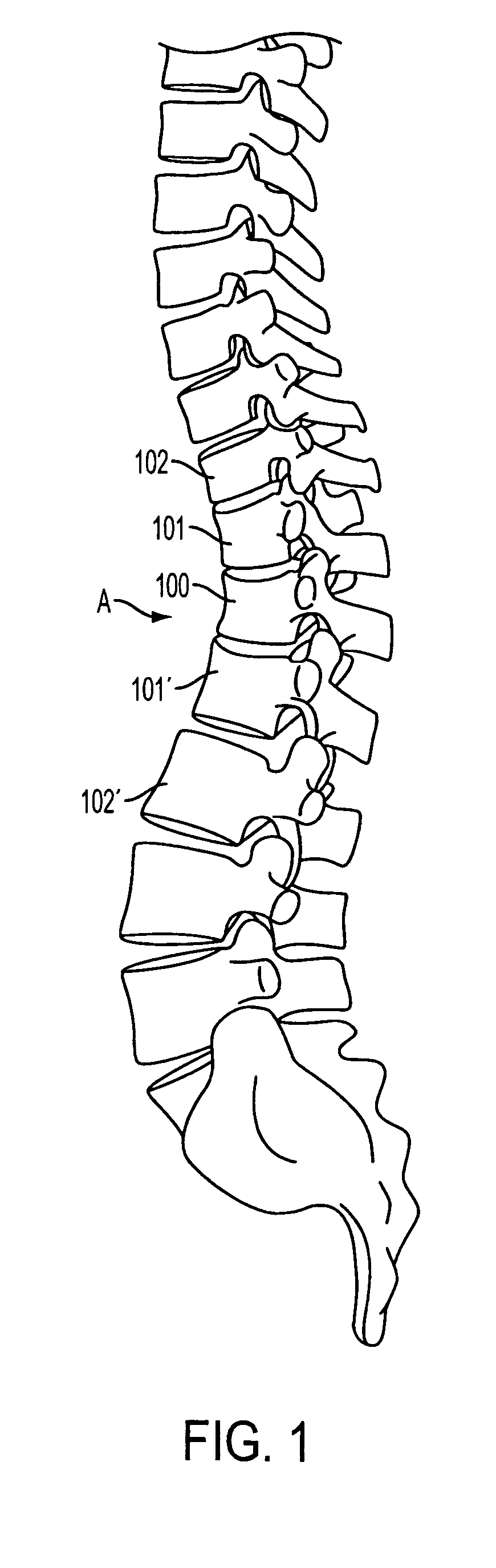
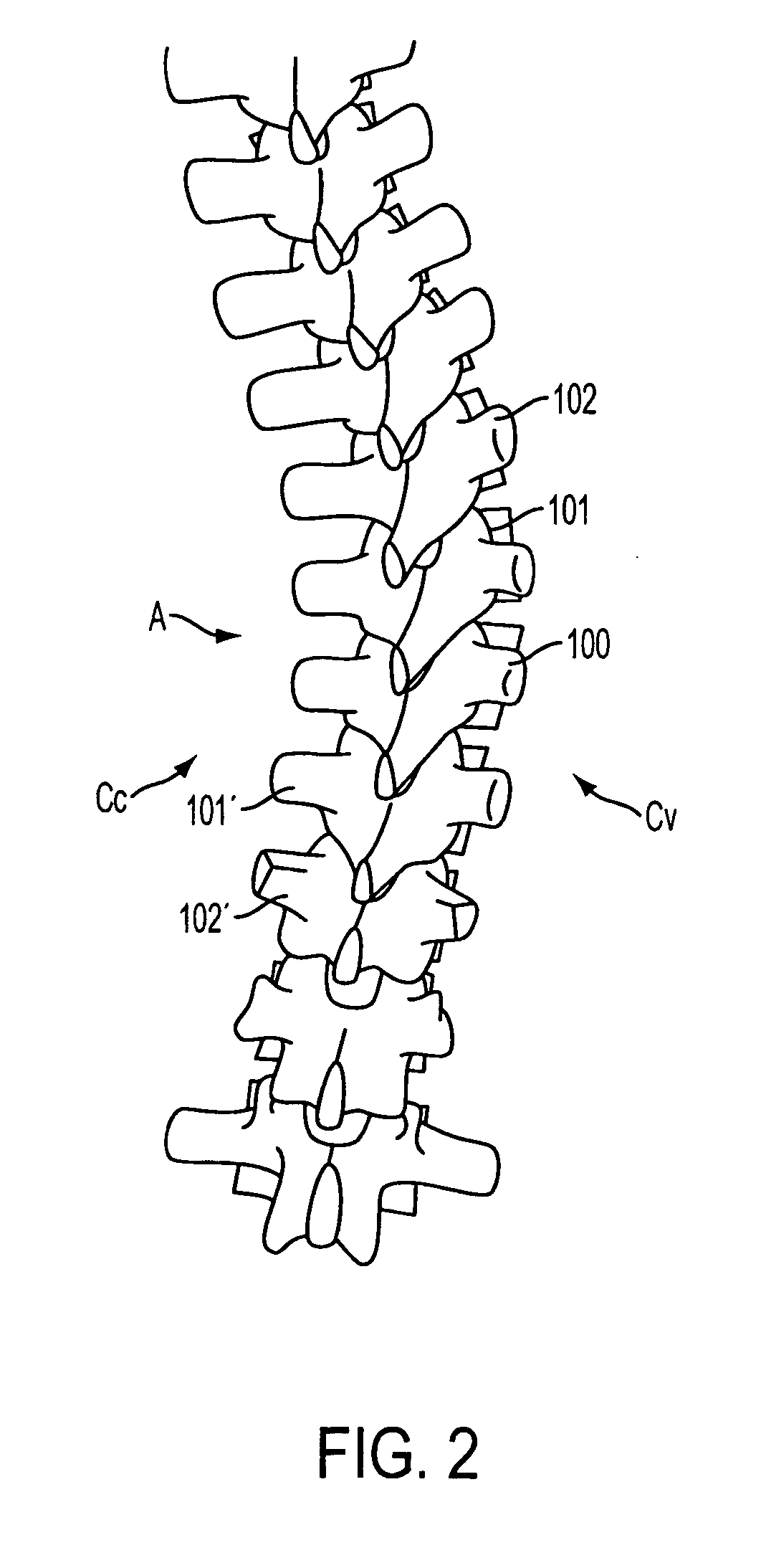
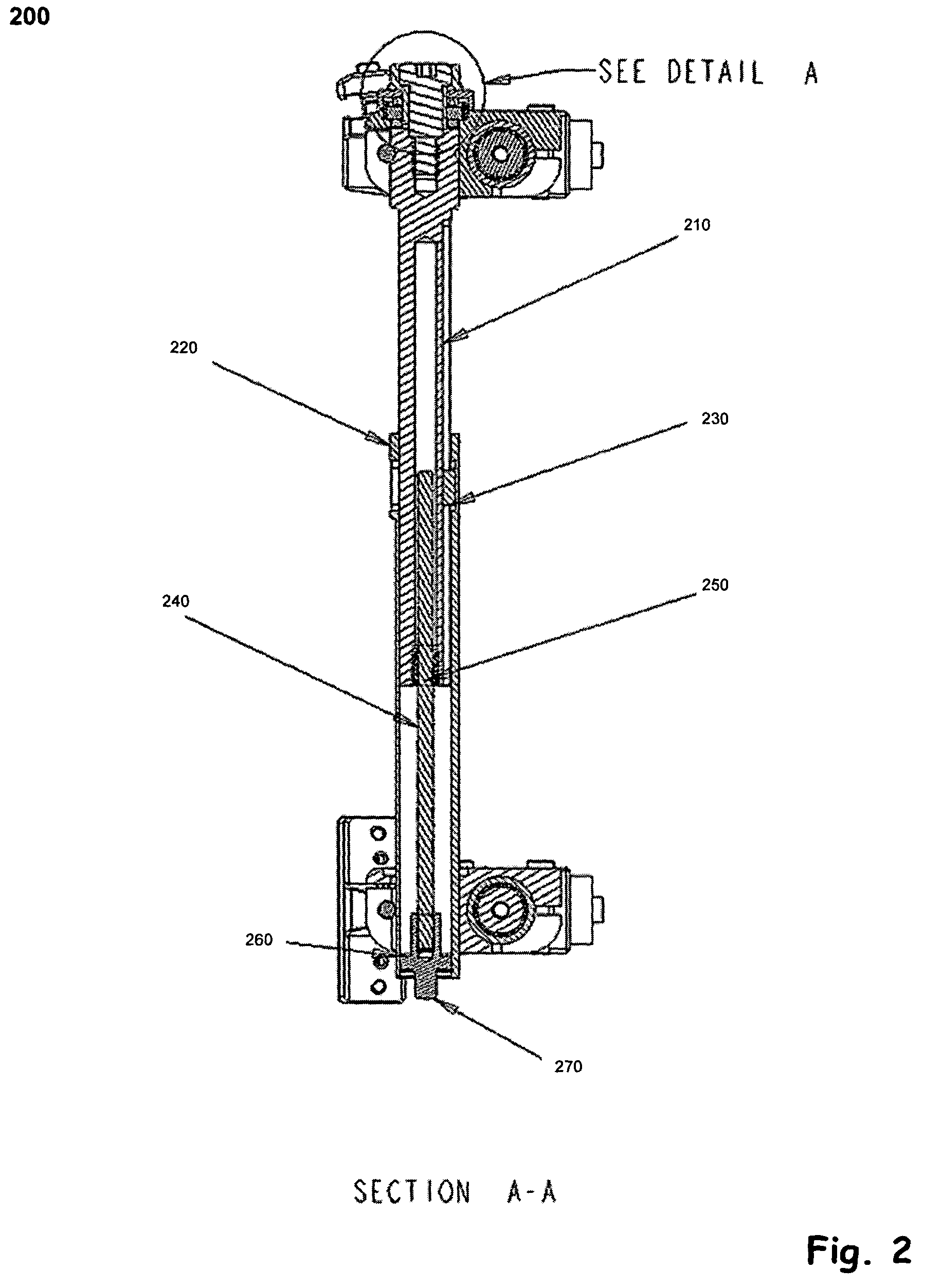
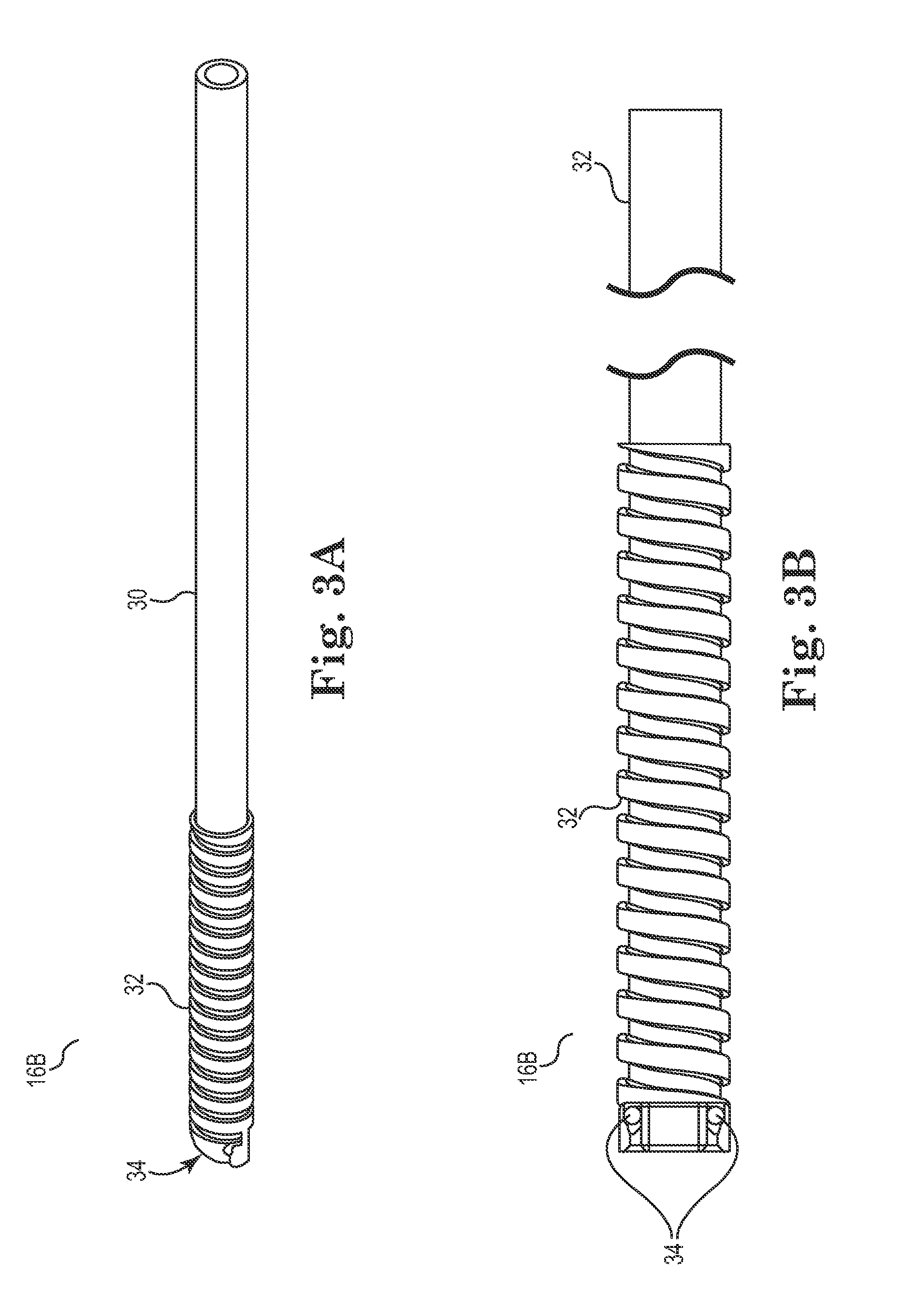
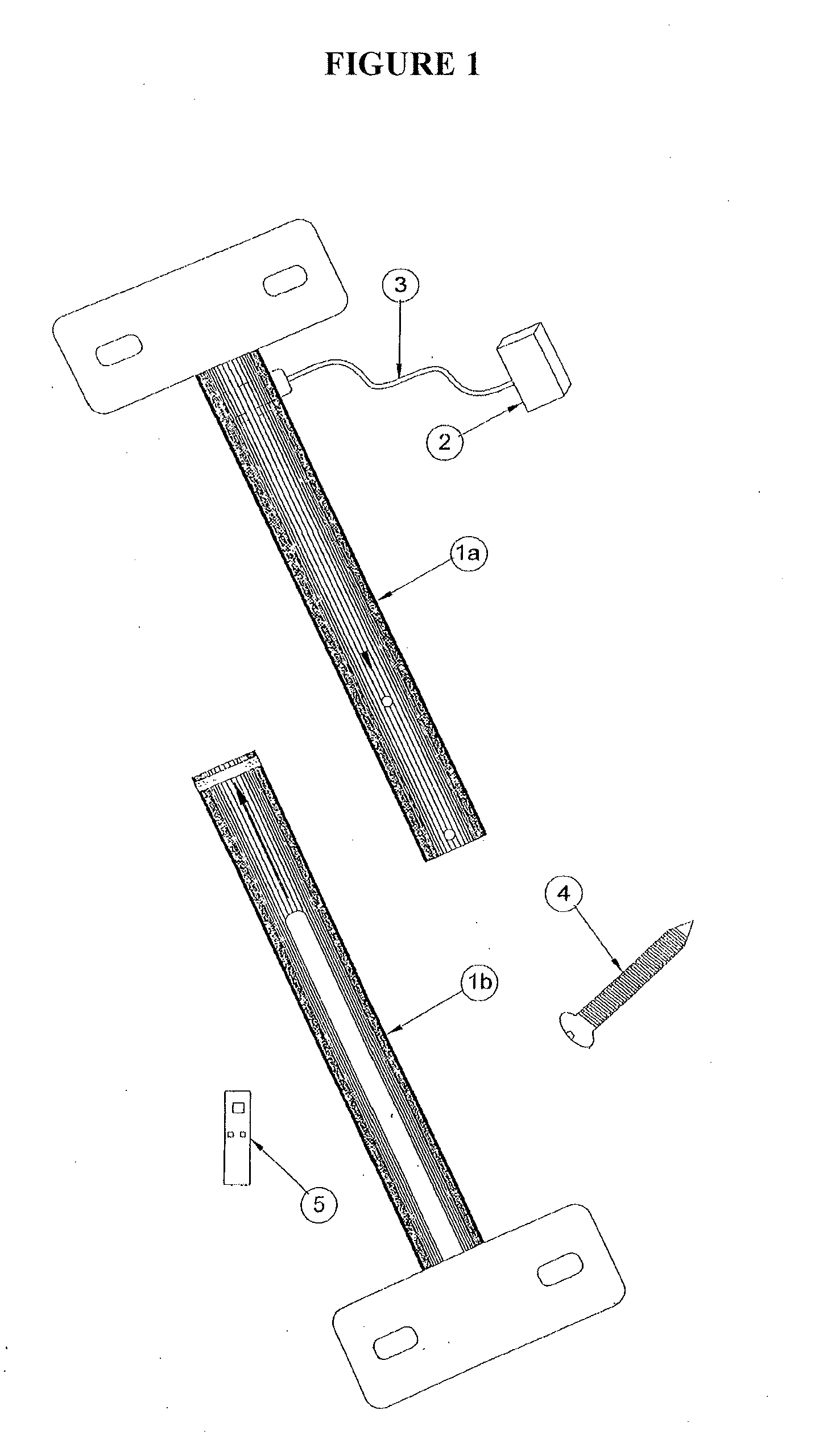
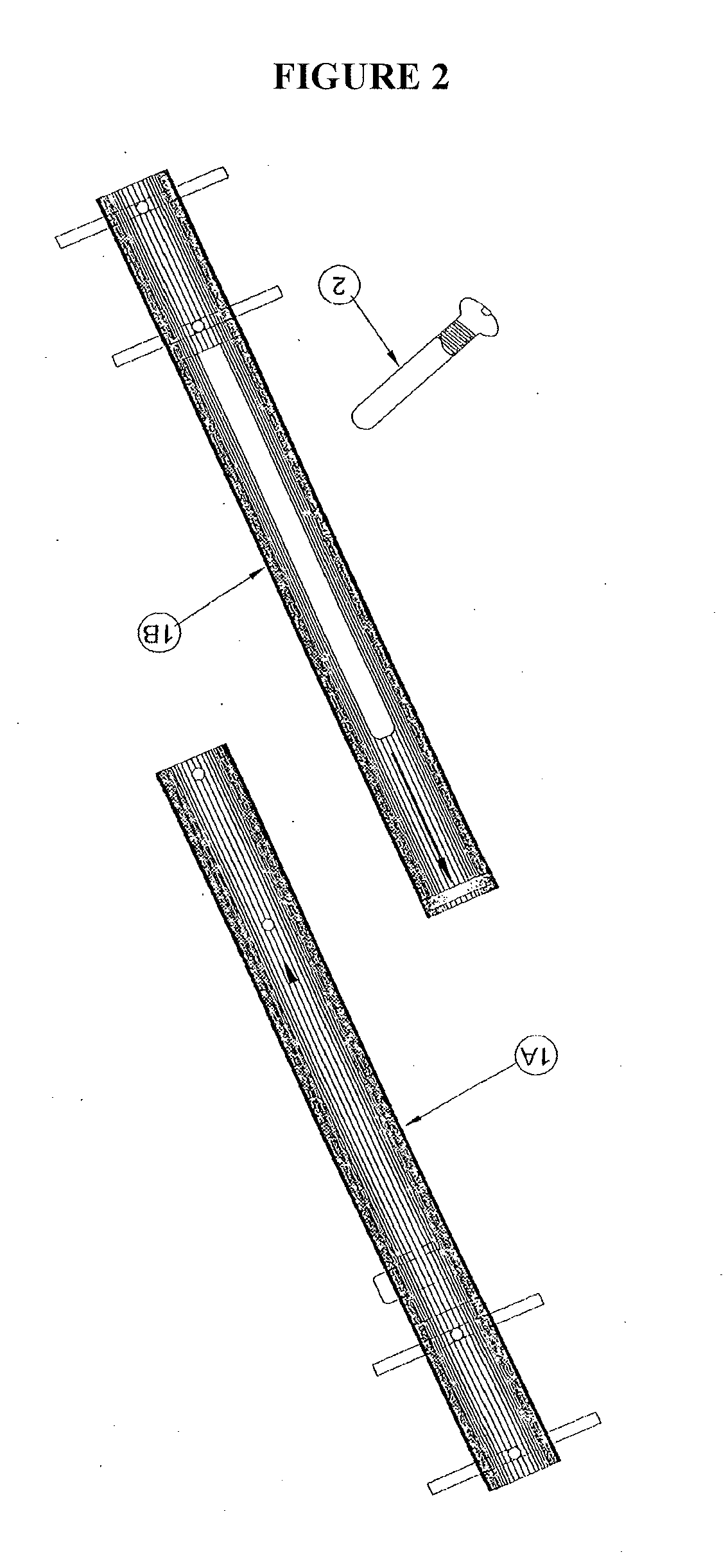
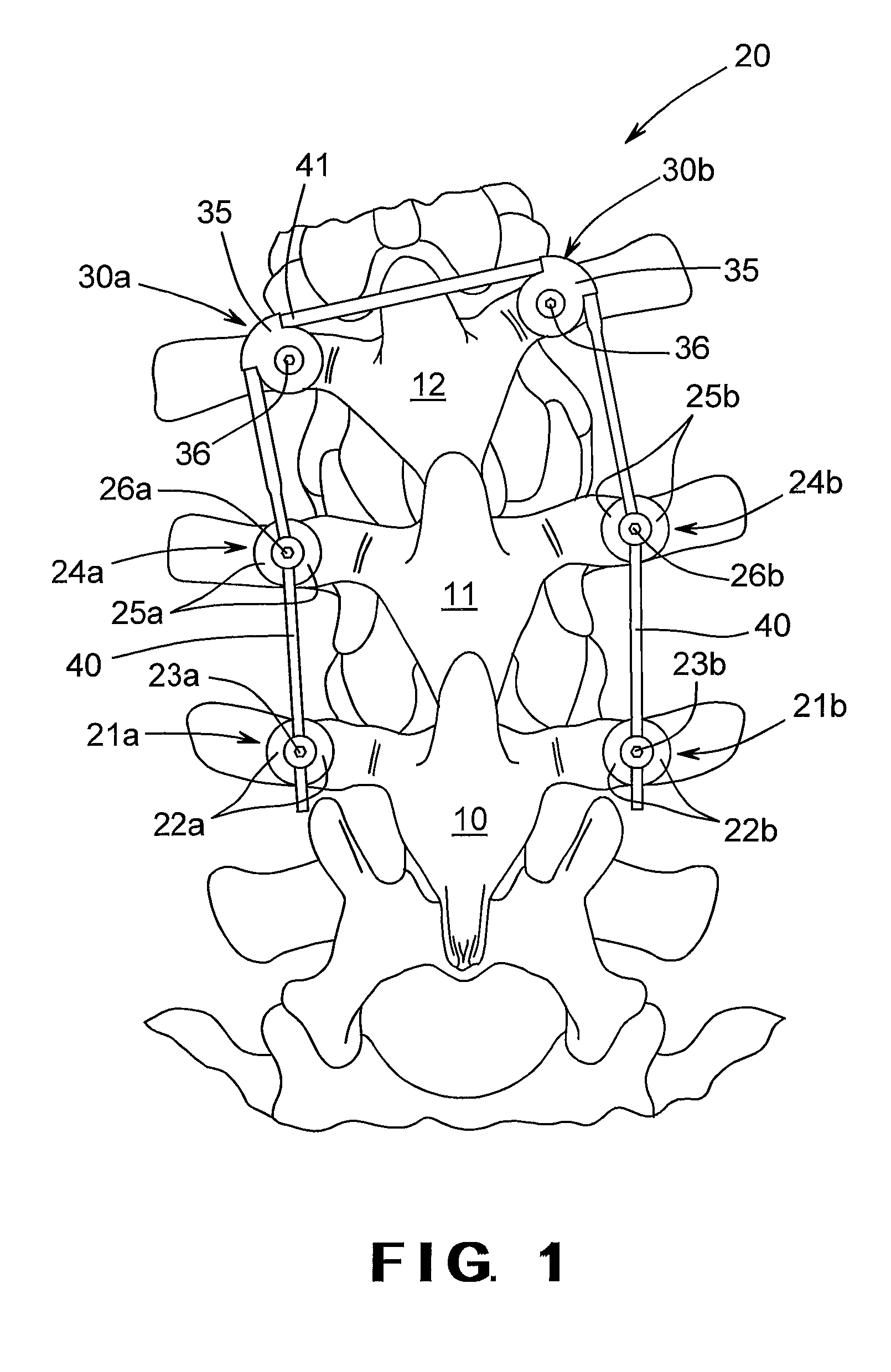
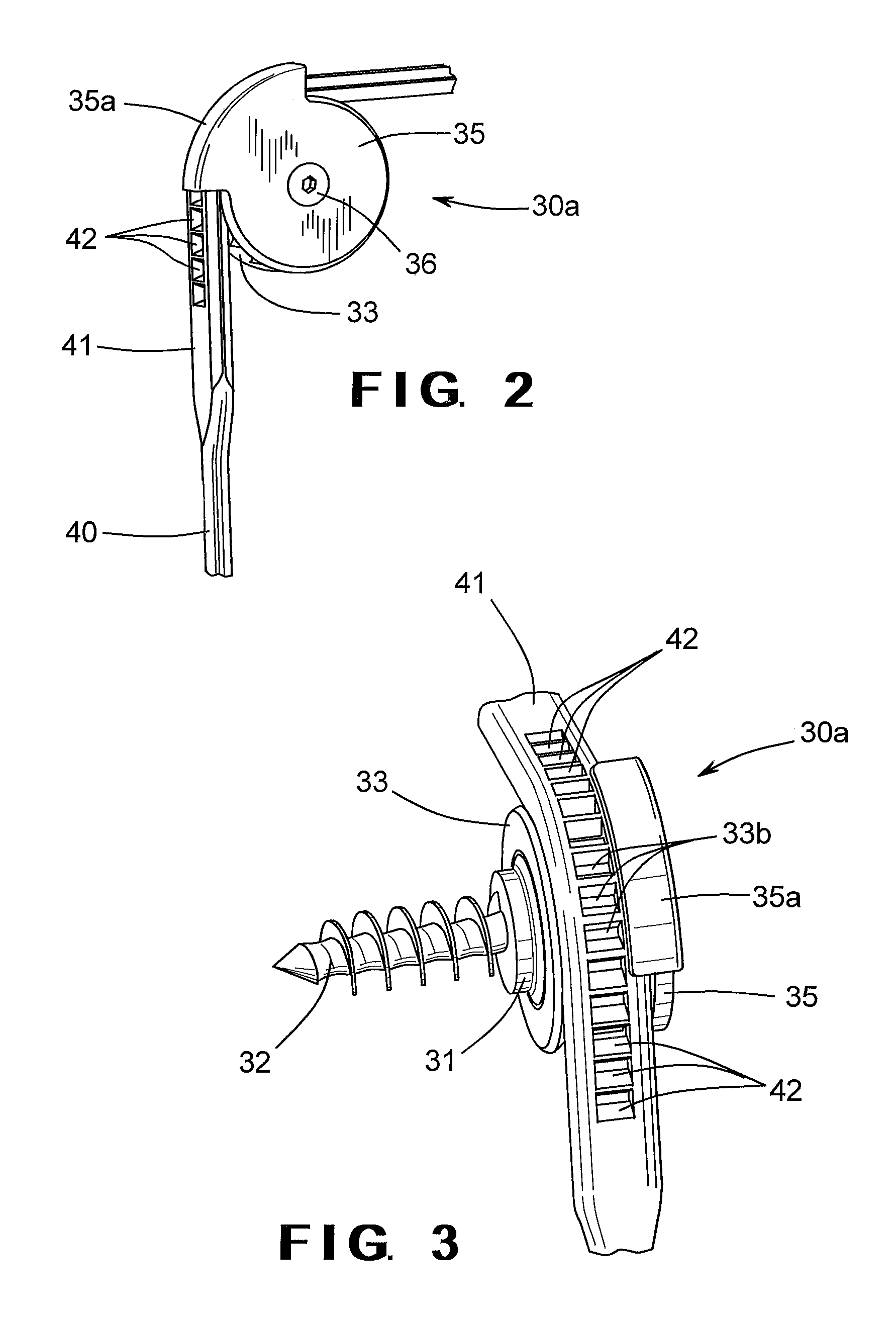
Spinal stabilization system to flexibly connect vertebrae
InactiveUS20050267470A1Preventing excessive motionPrecise alignmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDeformity
A surgically implanted spinal stabilization system uses posterior anchor hooks attached to vertebrae to retain elastic bands to retain flexibility and mobility while maintaining alignment and preventing excessive motion and deformity. The elastic bands may parallel the longitudinal axis of the spine, or, for enhanced promotion of alignment, they may also arranged in a diagonally crossing configuration. Multi-level fixation can be achieved using the spinal stabilization system with longer elastic bands. A method of applying the spinal stabilization system using an elastic band application tool facilitates simple, rapid application of the system to a patient.
Owner:MCBRIDE DUNCAN Q
Anchoring systems and methods for correcting spinal deformities
ActiveUS20050277919A1Correction of spinal deformityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDeformity
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
Sacral or iliac cross connector
InactiveUS20080021456A1Help positioningInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCross connectionLocking mechanism
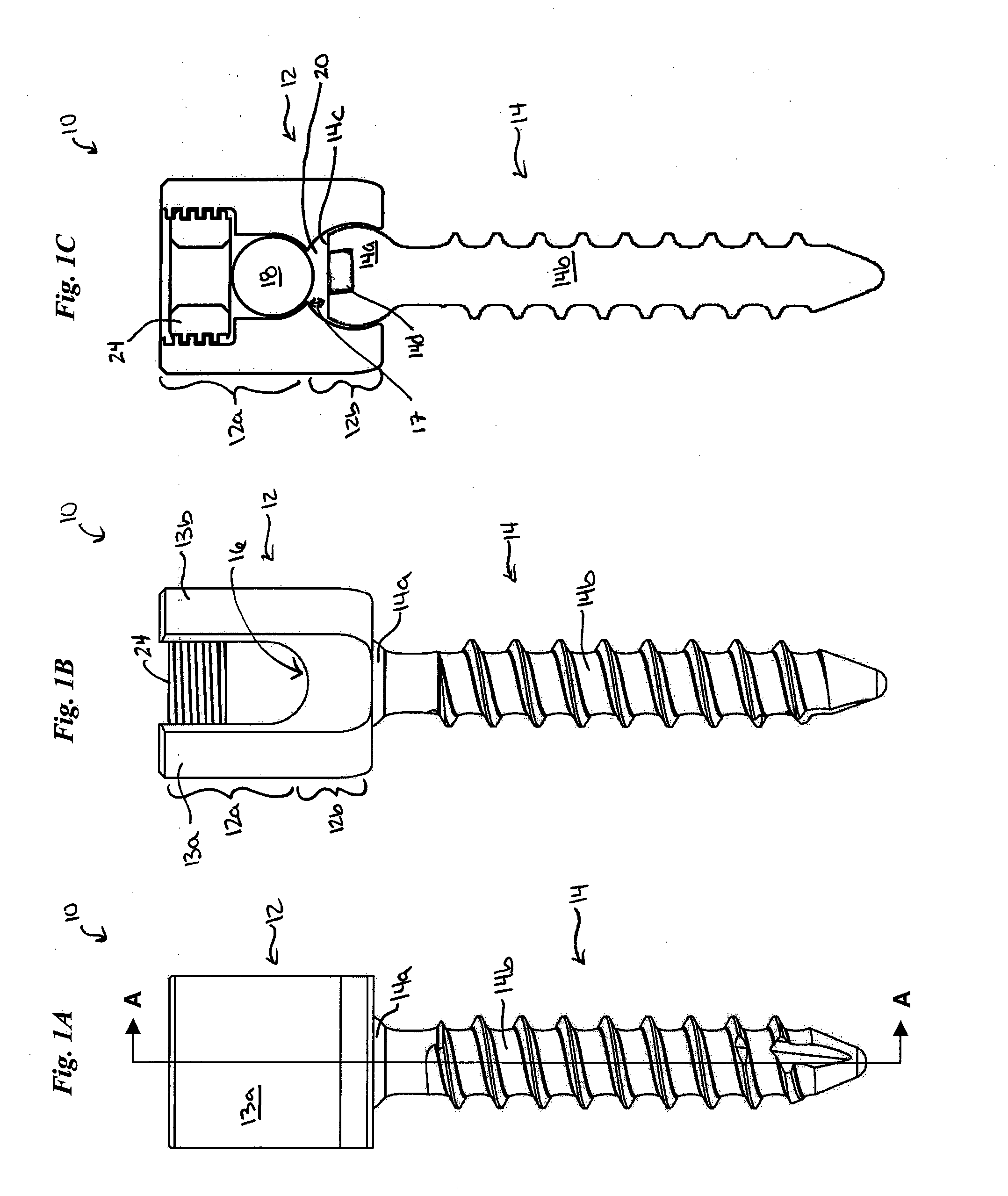
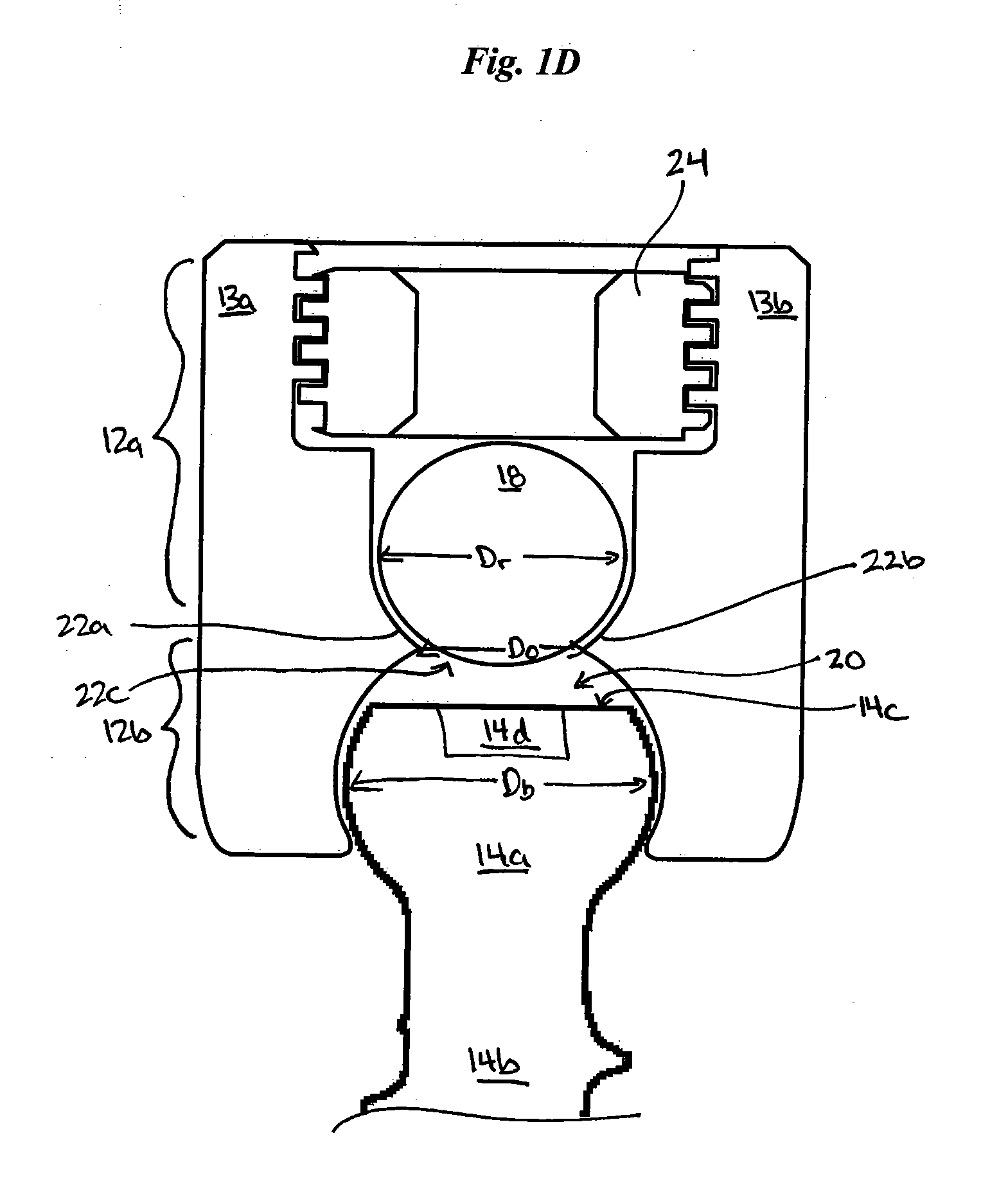
Implantable devices and methods for correcting spinal deformities or degeneration are disclosed. The devices and methods have particular application in the spinopelvic region and on the sacrum or ilium. In one embodiment, a cross connector is provided and can include a cross member with a connector head slidably disposed thereon. The cross member can be adapted for attachment to one or more anchoring elements, and the sliding connector head can include a first receiving portion defined by an opening through the connector head for receiving the cross member, and a second receiving portion defined by a recess between first and second opposed arms for receiving a spinal fixation element, such as a spinal rod. A guide channel can optionally be provided on the cross member for guiding the movement of the sliding connector head. In other embodiments, the device can include a locking mechanism for locking a spinal fixation element within the connector head, and for securing the connector head in place on the cross member.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Repair of tympanic membrane using placenta derived collagen biofabric
The present invention provides a method of repairing a tympanic membrane deformity, such as a tympanic membrane perforation, commonly referred to as tympanoplasty or myringoplasty, using a collagen biofabric. The collagen biofabric is preferably laminated. The invention further provides kits comprising one or more pieces of collagen biofabric, for example laminated collagen biofabric, for the repair of a tympanic membrane.
Owner:ANTHROGENESIS CORP
Orthosis to correct spinal deformities
An orthosis for correcting spinal deformities by urging spinal vertebrae toward a vertical axis. The orthosis includes a series of retaining clamps fixed onto the spinous process of said vertebrae, each of said retaining clamps having guides for retaining at least one elastic rod.
Owner:REDUCTION TECH
Valve prosthesis including a prosthetic leaflet
InactiveUS20050038509A1Improve effectivenessIncreased durabilityBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsProsthetic valveProsthesis
A prosthesis for repairing a damaged valve such as a heart mitral valve is disclosed. The prothesis comprises a prosthetic valve leaflet mounted on a frame. When implanted in a mitral valve, the leaflet replaces the function of an endogenous valve leaflet and coapts with an opposed endogenous valve leaflet. The prosthesis may further comprise a strut or other member to which the edge of an opposed valve leaflet can be sutured, and which can be used to correct deformities of a ventricle wall. Further disclosed is a method of repairing a damaged heart valve by providing a prosthetic valve leaflet or by providing a prosthetic valve leaflet and prosthetic attachment points for an opposed valve leaflet.
Owner:ASHE KASSEM ALI
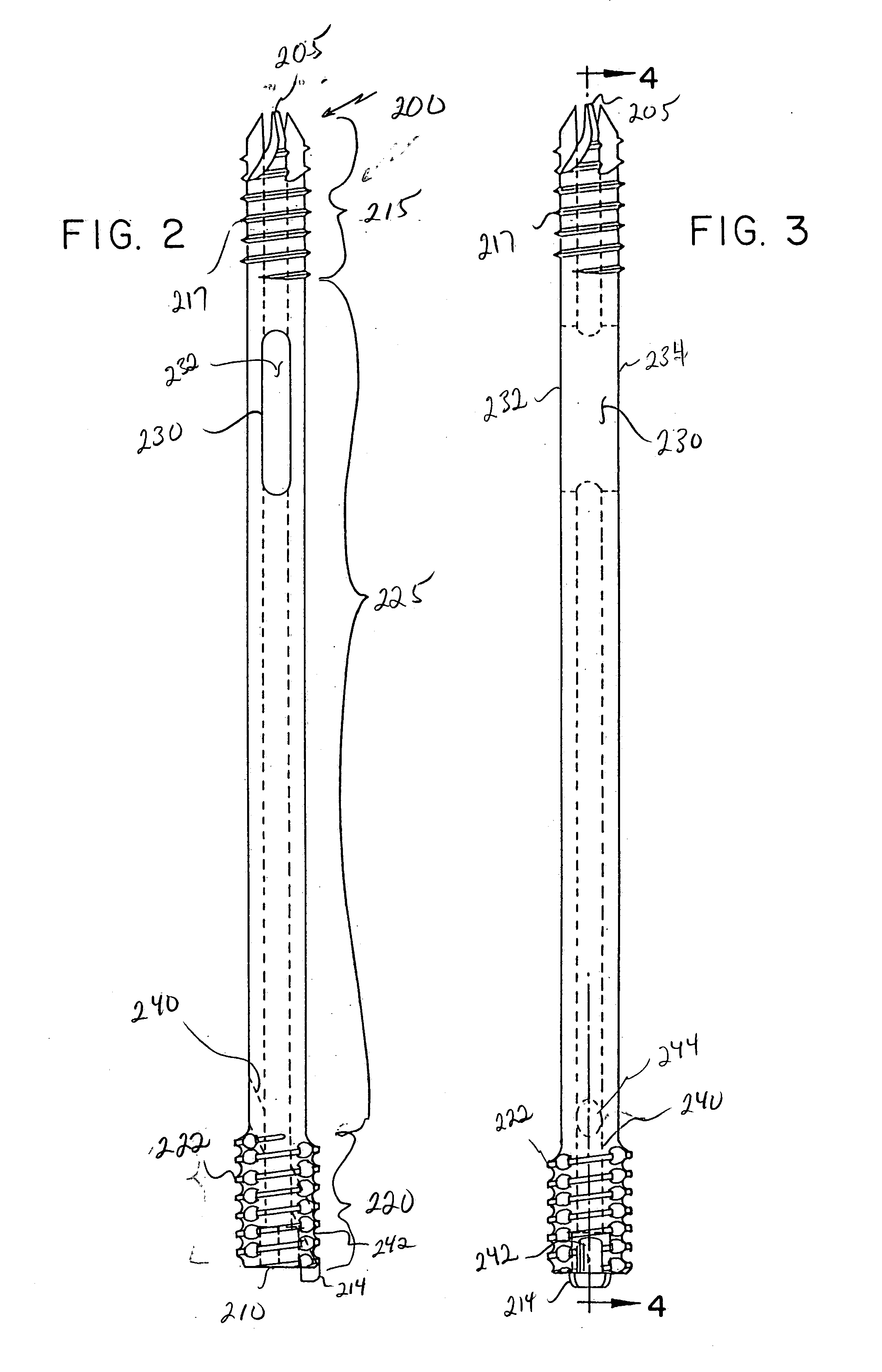
Intramedullary locked compression screw for stabiliziation and union of complex ankle and subtalar deformities
InactiveUS20050107791A1Easy to installReduce exposureInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsJOINT MALFORMATIONEngineering
An intramedullary lockable compression screw for stabilization and reconstruction of deformities of the ankle and subtalar joints, and which is particularly suitable for stabilization and fusion of the tibiotalar, talocalcaneal, tibiocalcaneal and / or tibiotalocalcaneal, is provided. The compression screw includes an elongated tubular member extending along a substantially straight first longitudinal axis between the leading end and the trailing end of the member. The tubular member includes a threaded leading end portion proximate the leading end, a threaded trailing end portion proximate to the trailing end, and an unthreaded shaft portion interconnecting the threaded leading end and the threaded trailing end portions. The diameter of the threaded leading end portion is smaller than the diameter of the threaded trailing end portion. A through-hole extends along a straight second longitudinal axis between a first opening, in a first area of an outer periphery of the tubular member proximate to the trailing end, and a second opening, in a second area of the outer periphery of the tubular member distal to the trailing end. The through hole is formed such that the second longitudinal axis intersects the first longitudinal axis at an angle of other than 90 degrees and so as to accommodate a locking screw.
Owner:MANDERSON EASTON L
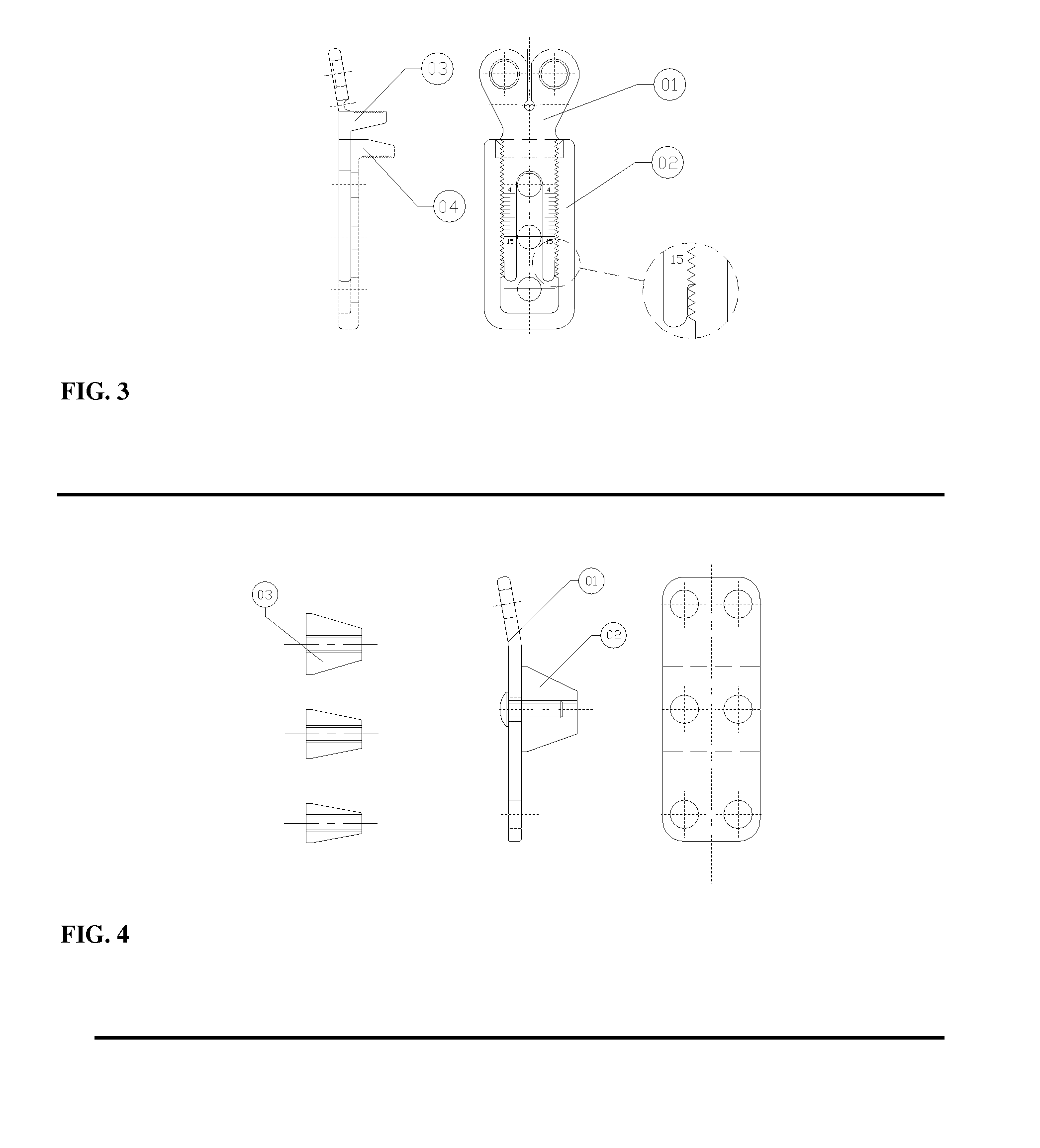
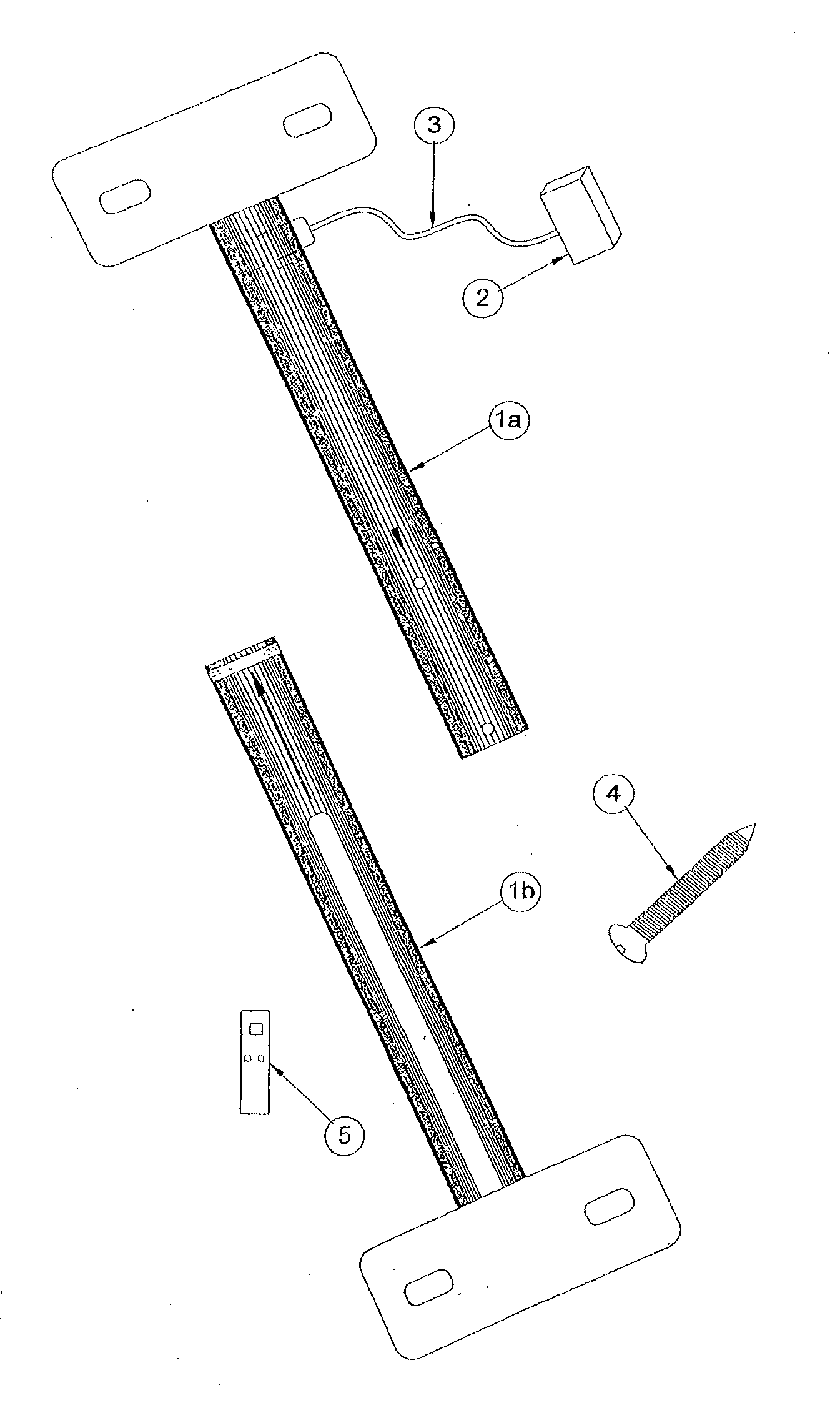
Multi-adjustable plate for osteotomy
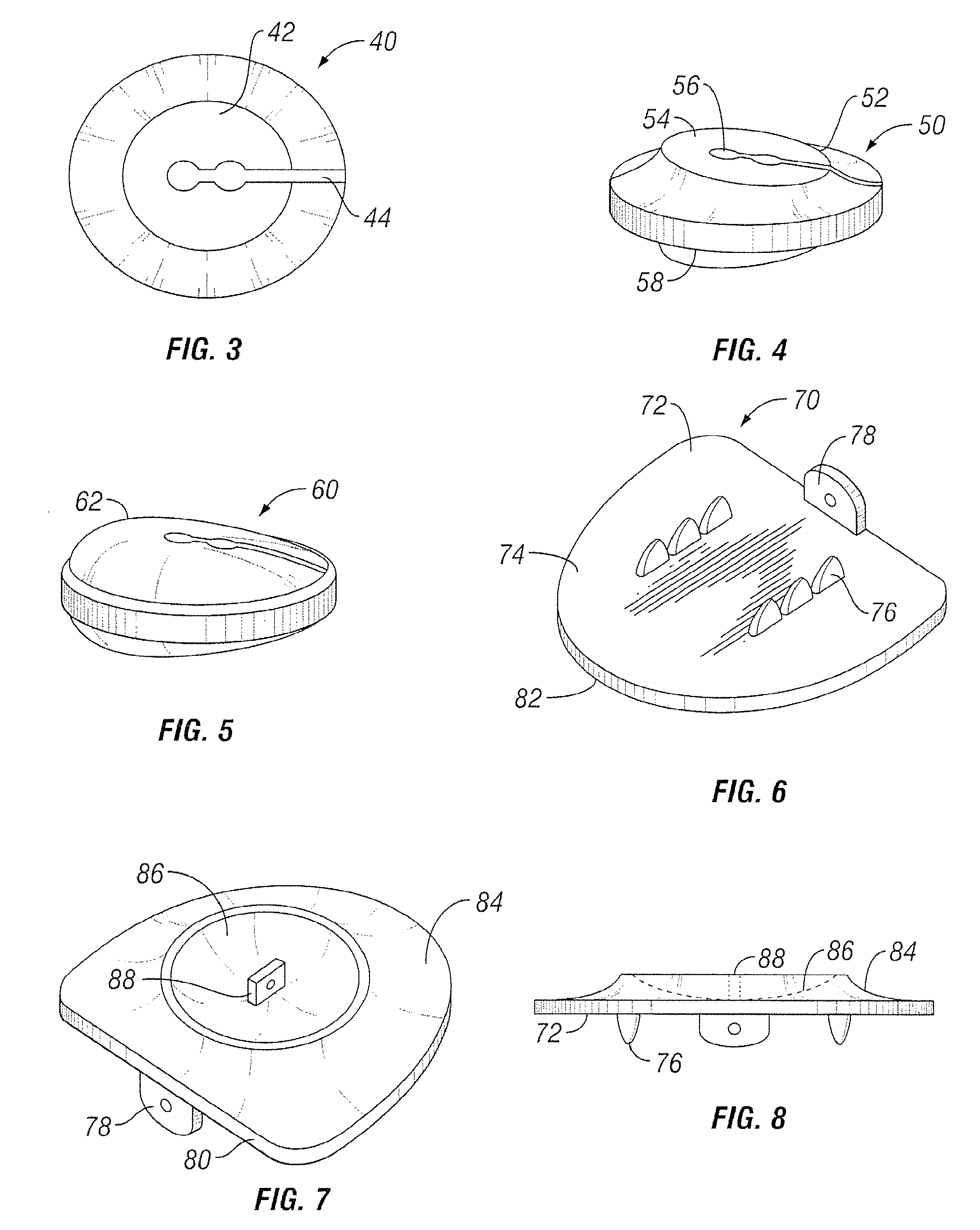
The invention relates to a mechanical device intended for correcting a malformation of the bones of the body. The device is continuously adjustable, making the surgeon's work easier and reducing surgery time, thus reducing the risk of infection and, above all, guaranteeing the desired precision for surgery. The device comprises a top plate (1) suitable for sliding over a bottom plate (2) by means of a guide (7). Said plates can be screwed on either side of an angled notch made in the bone. The plates comprise respectively top (5) and bottom (6) bearings of the notch of the bone. Said bearings form an acute-angle bevel which substantially matches the surfaces of the notch. One of the plates is provided with an adjustment screw (4) for continuous adjustment of the relative positions of the plates. The device also comprises a locking screw (3) suitable for maintaining the open position of the device and, consequently, the final angle of the notch of the bone in the desired position. The Top bearing of the notch of the bone having angular adjustment is suitable for correcting the angle of the bevelled surface of the bearing, in particular the tibial slope, by means of a tapered screw (8) adjustment an angular space in the bearing.
Owner:RIBEIRO CHRISTIANO HOSSRI +1
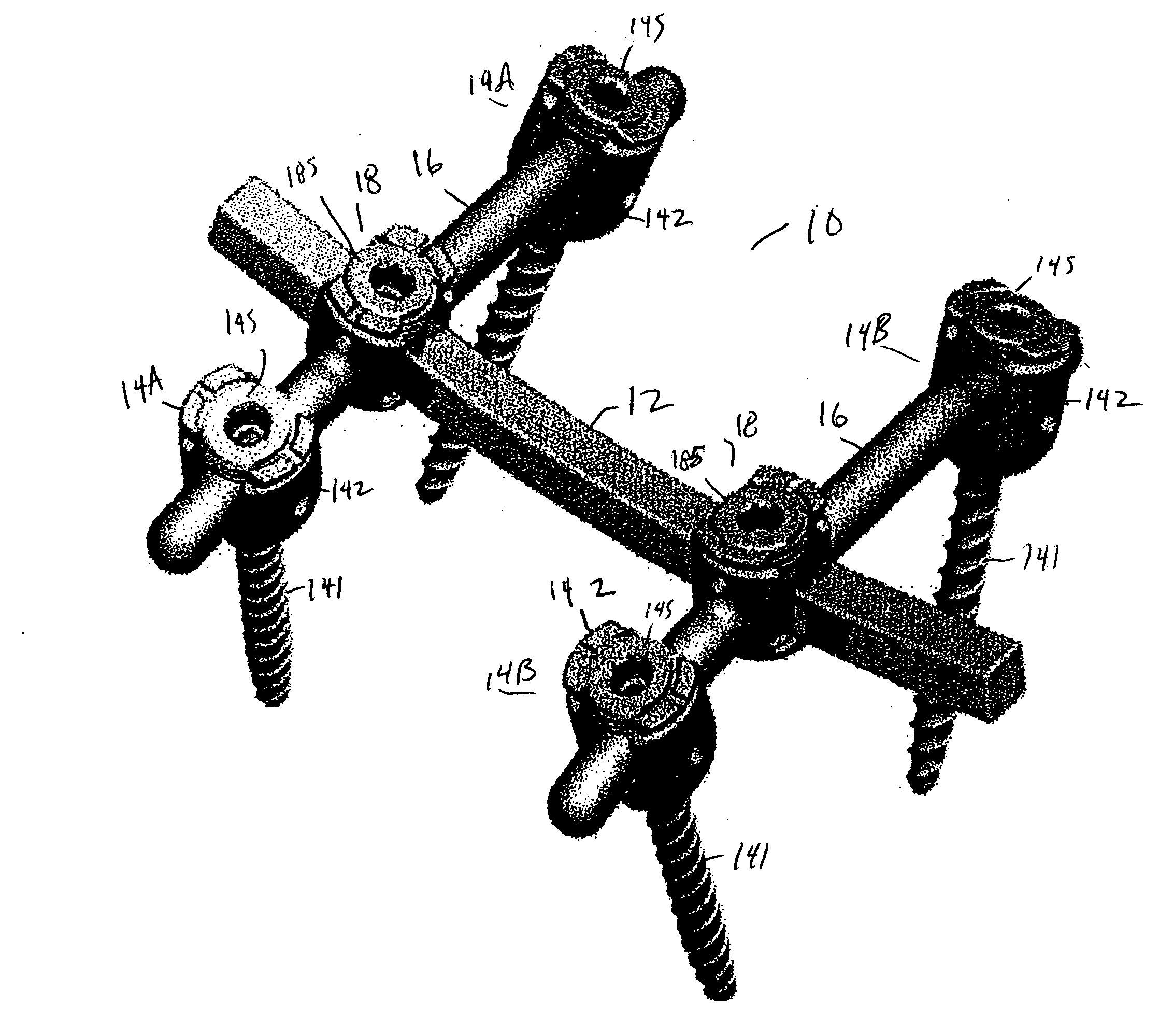
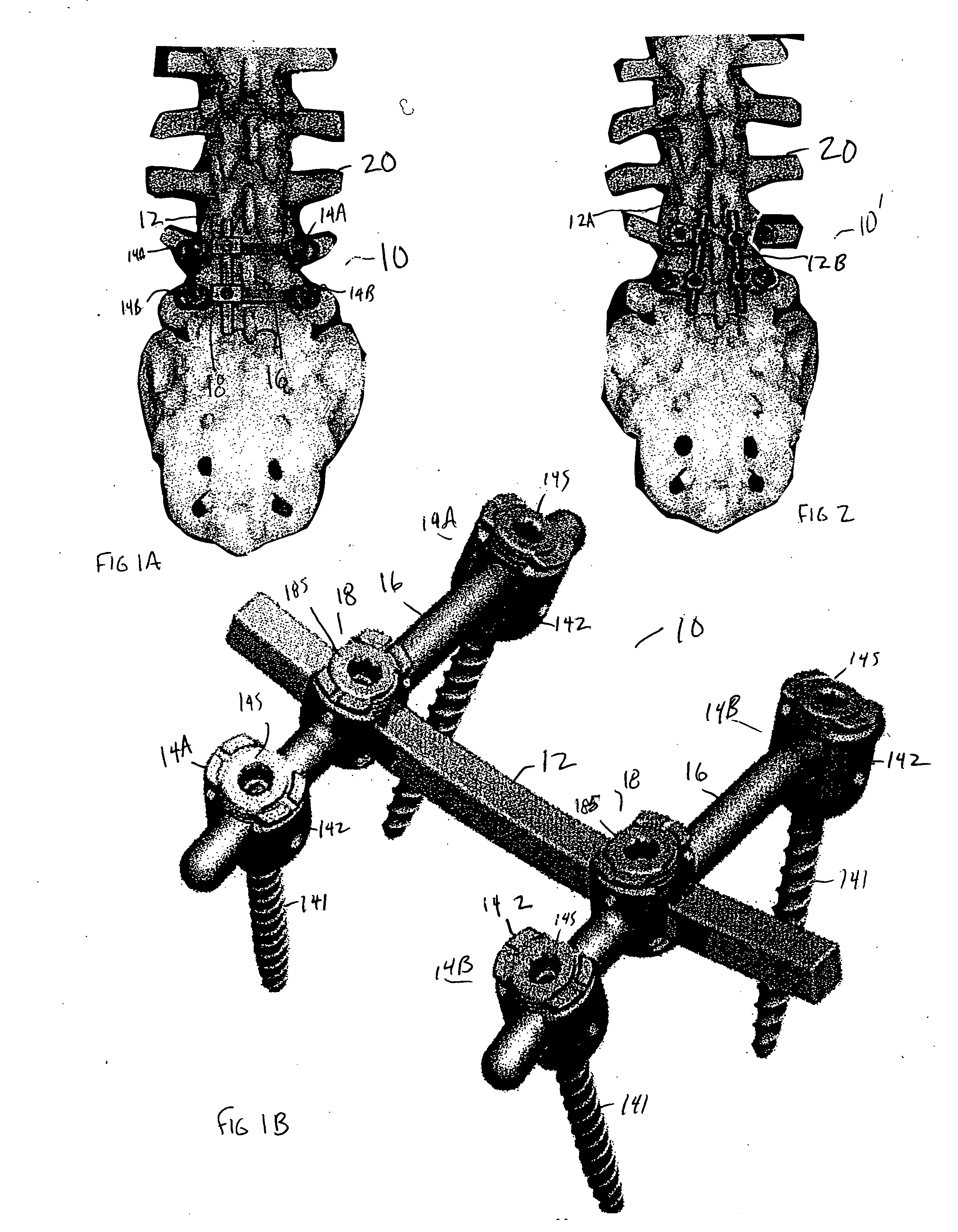
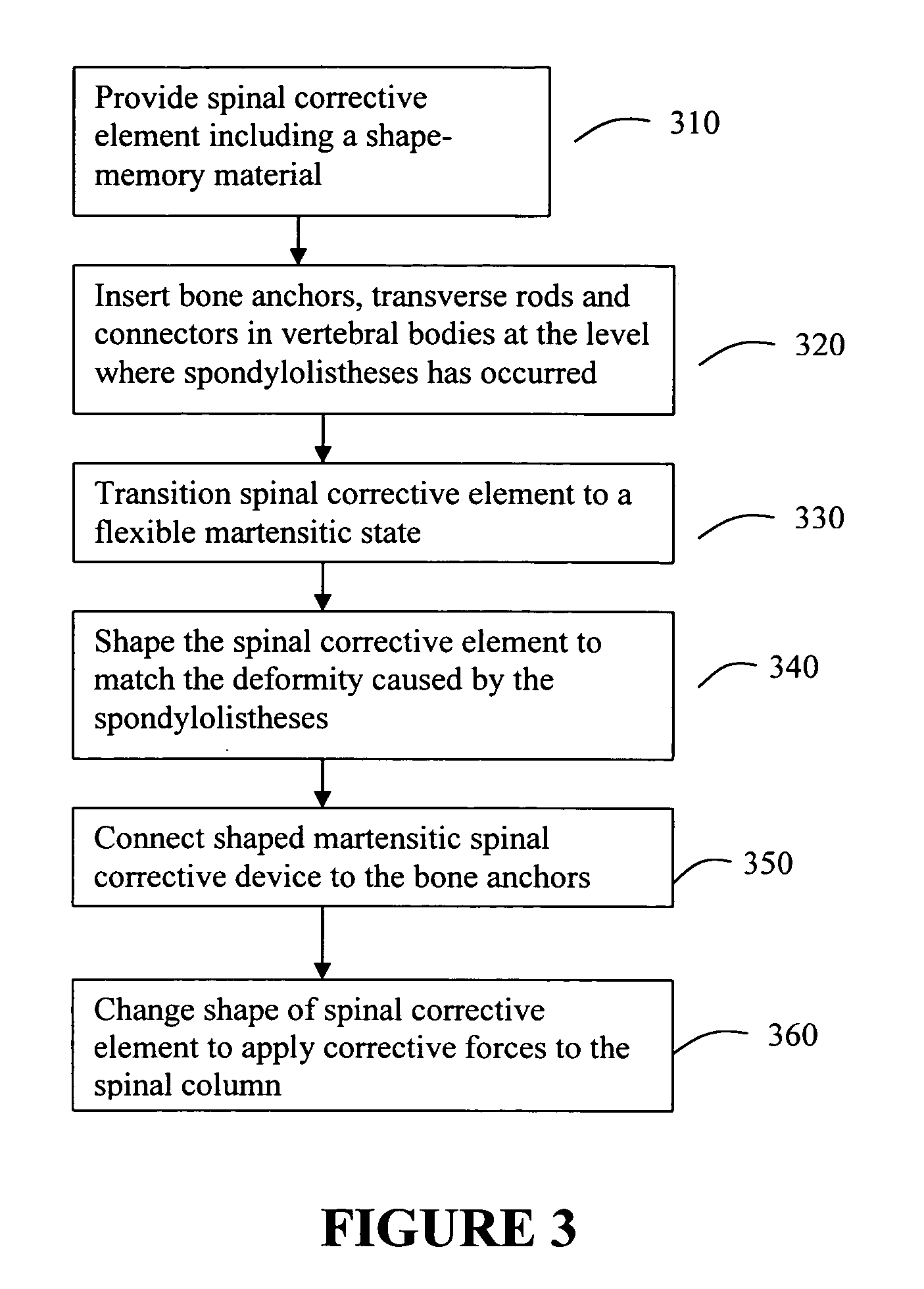
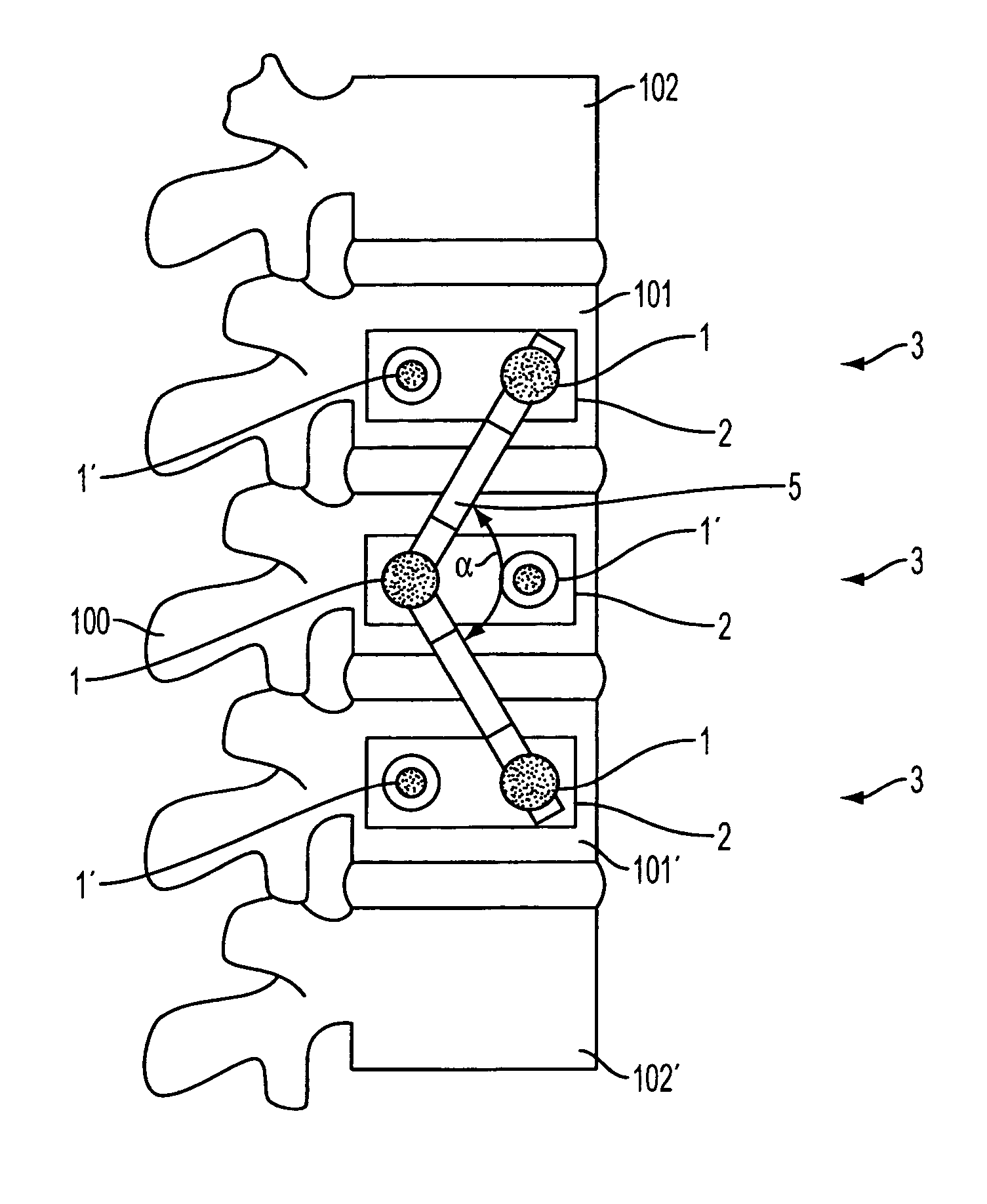
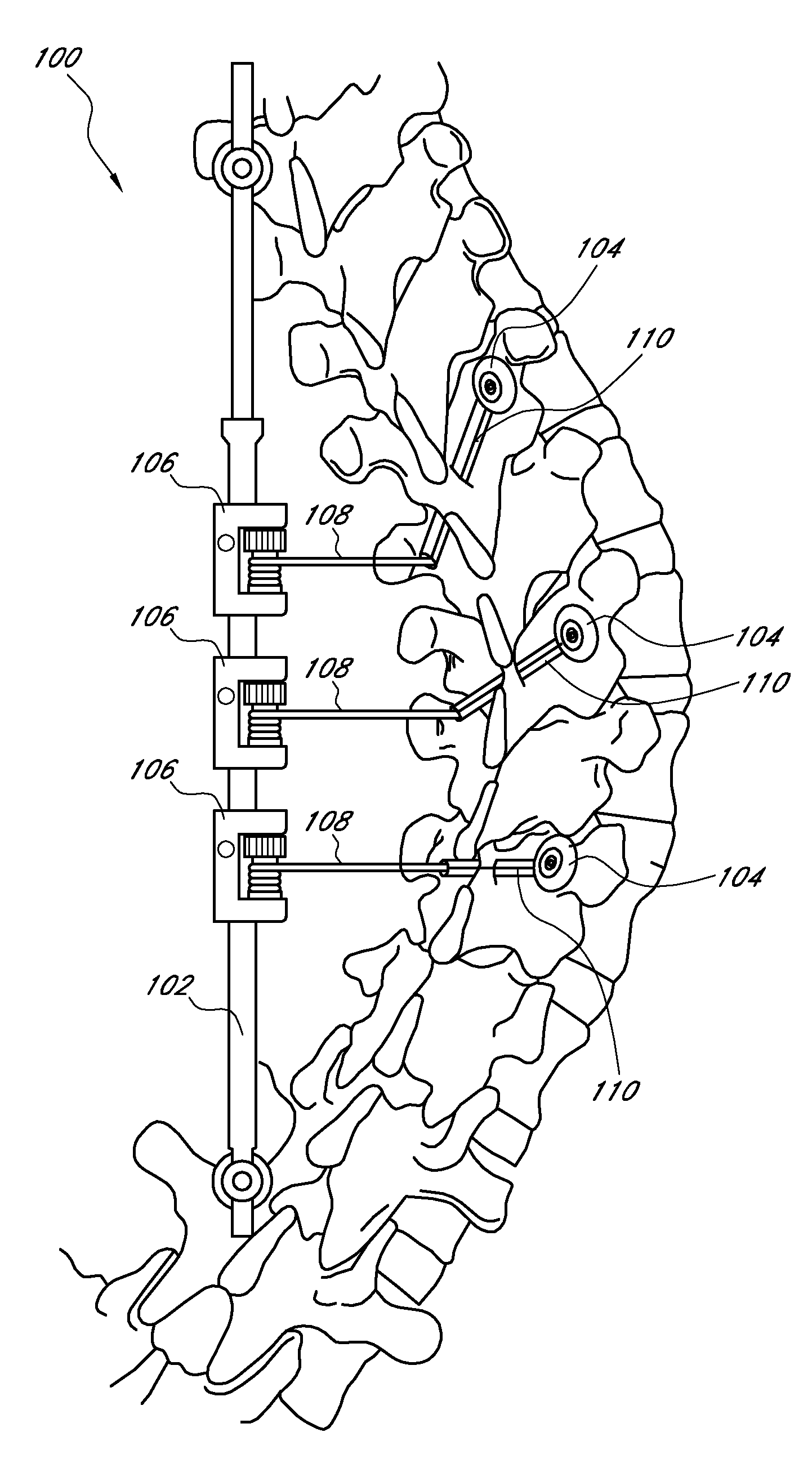
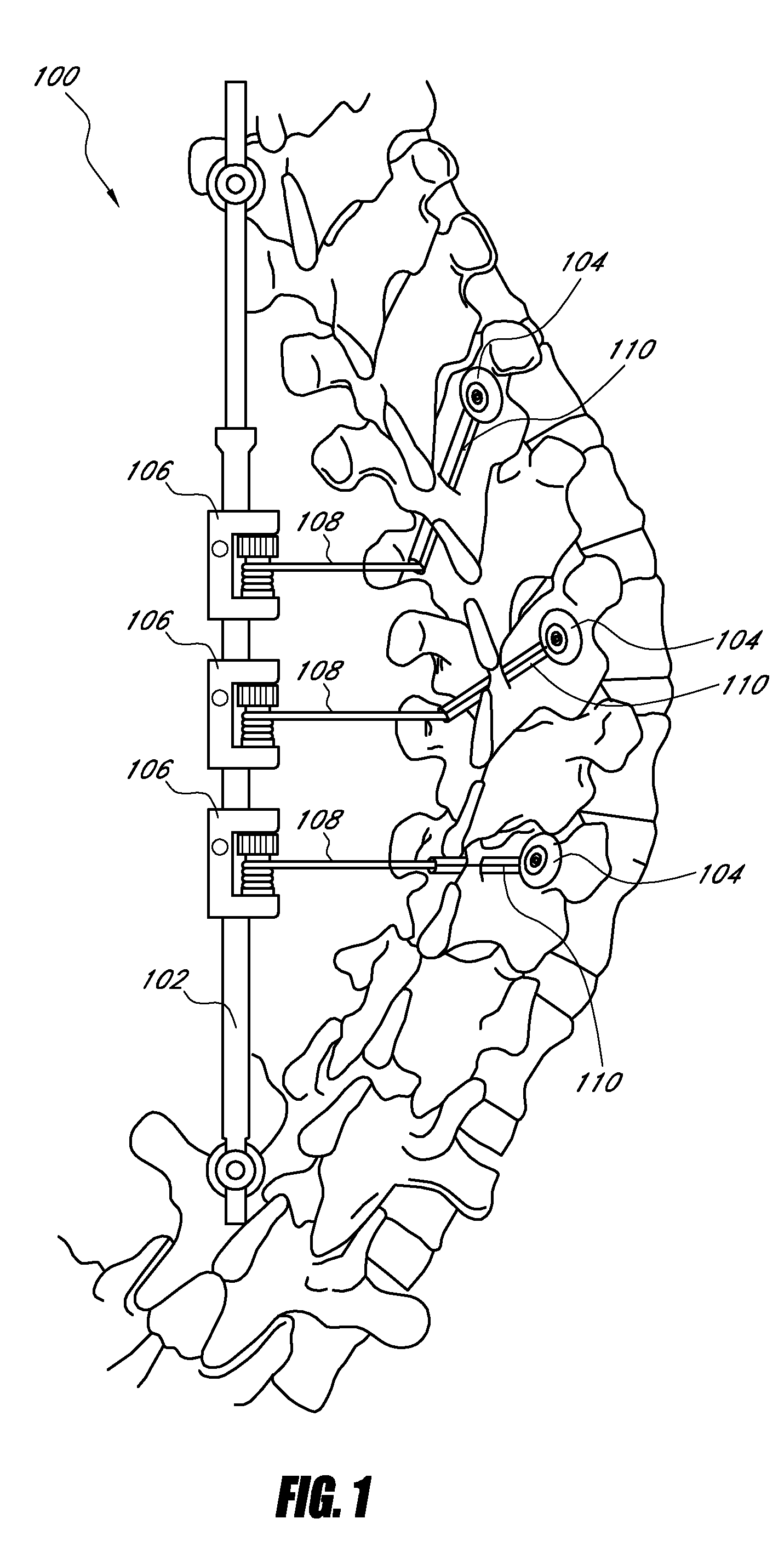
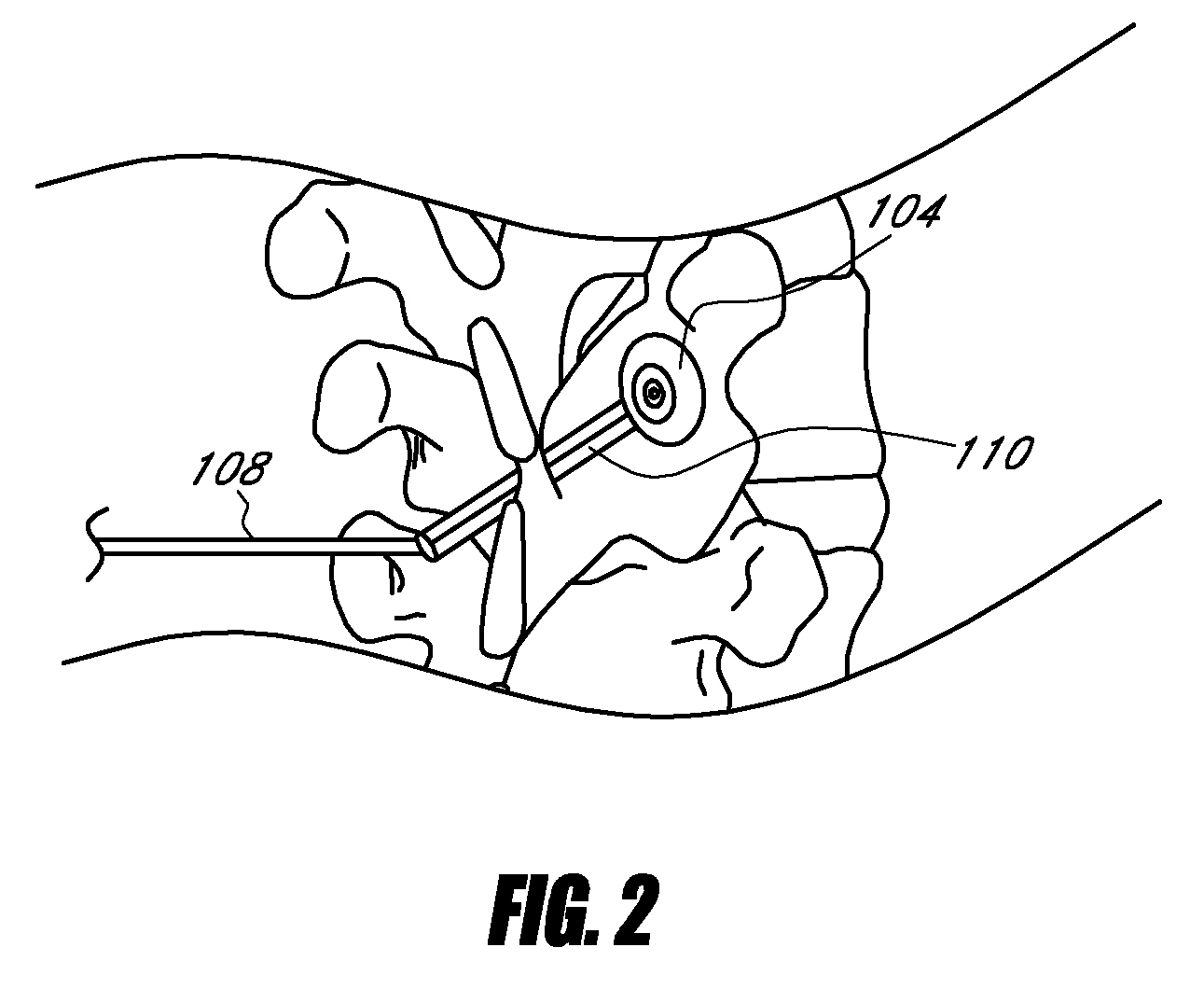
Spondylolistheses correction system and method of correcting spondylolistheses
InactiveUS20070173828A1Reduce spondylolisthesesInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnMedicine
A spinal correction element in a device and method of correcting spondylolistheses in a patient transitions between a first shape and a second shape while having a first portion fixed to a forwardly displaced vertebra and a second portion fixed to an undeformed portion of the spinal column to apply a corrective force bringing a displaced vertebra into alignment with the rest of the spinal column. A shape memory material in the spinal correction element transitions from a flexible martensitic state, in which the spinal correction element matches the shape of the deformity caused by the spondylolistheses, to a rigid austenitic state, in which the spinal correction element has the shape of an expected corrected spine, to apply a corrective force to the vertebral bodies fixed to the spinal correction element, thereby correcting the deformity caused by spondylolistheses. The shape memory material is induced to transition between the rigid austenitic state and the flexible martensitic state by changing the temperature, pressure, stress, chemistry and / or another parameter of the shape memory material.
Owner:DUPUY INT LTD
Medical device and method to correct deformity
ActiveUS20090012565A1Correction of spinal deformitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringMedical device
A system for correcting a spinal deformity includes an implant fixed to one side of a vertebra and a rod extending along an axis of the spine on a second side of the vertebra. An adjustment member, which may include a reel, is coupled to the rod. A force directing member, such as a cable, extends between the rod and the adjustment member. The force directing member is retractable toward and extendible from the adjustment member. A method of correcting spinal deformity includes providing an implant, a rod, an adjustment member coupled to the rod, and a force directing member extending between the rod and the adjustment member. The adjustment member can be retractable toward and extendible from the adjustment member.
Owner:K2M
Joint Prostheses
ActiveUS20080215156A1Prevent hard stopPreventing posterior migration (expulsion)Finger jointsAnkle jointsSacroiliac jointBearing surface
The present invention provides an implantable joint prosthesis configured to replace a natural joint, and methods for implantation. The prosthesis may include a first component implantable in a first bone, having a first bearing surface, and a second component implantable in a second bone, having a second bearing surface which corresponds to the first bearing surface. Each bearing surface may include a flattened section such that when the bearing surfaces are placed in cooperation with one another in a preferred orientation, the flattened sections are aligned. Alternatively, the bearing surfaces may have and asymmetric configuration, with non-congruent surfaces that may enable correction of deformity. Several types of implantable joint prostheses are disclosed, including: carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, metatarsophalangeal, distal interphalangeal, proximal interphalangeal, ankle, knee, shoulder, and hip.
Owner:SYNERGY SPINE SOLUTIONS INC
Apparatus and methods for magnetic alteration of deformities
Methods and apparatus for incrementally manipulating an internal body member of a patient are disclosed. The apparatus has a magnetic implant adapted to be received on a location of the body member, a platform external to the patient, and a magnetic member coupled to the platform, wherein the magnetic member generates a magnetic force between the implant and the platform to incrementally manipulate the body member. The implant and external magnetic member are preferably rare earth magnets or an array of rare earth magnets, and are configured to generate an attractive or repulsive force between the implant and the platform to reposition, reorient, deform, or lengthen the body member.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
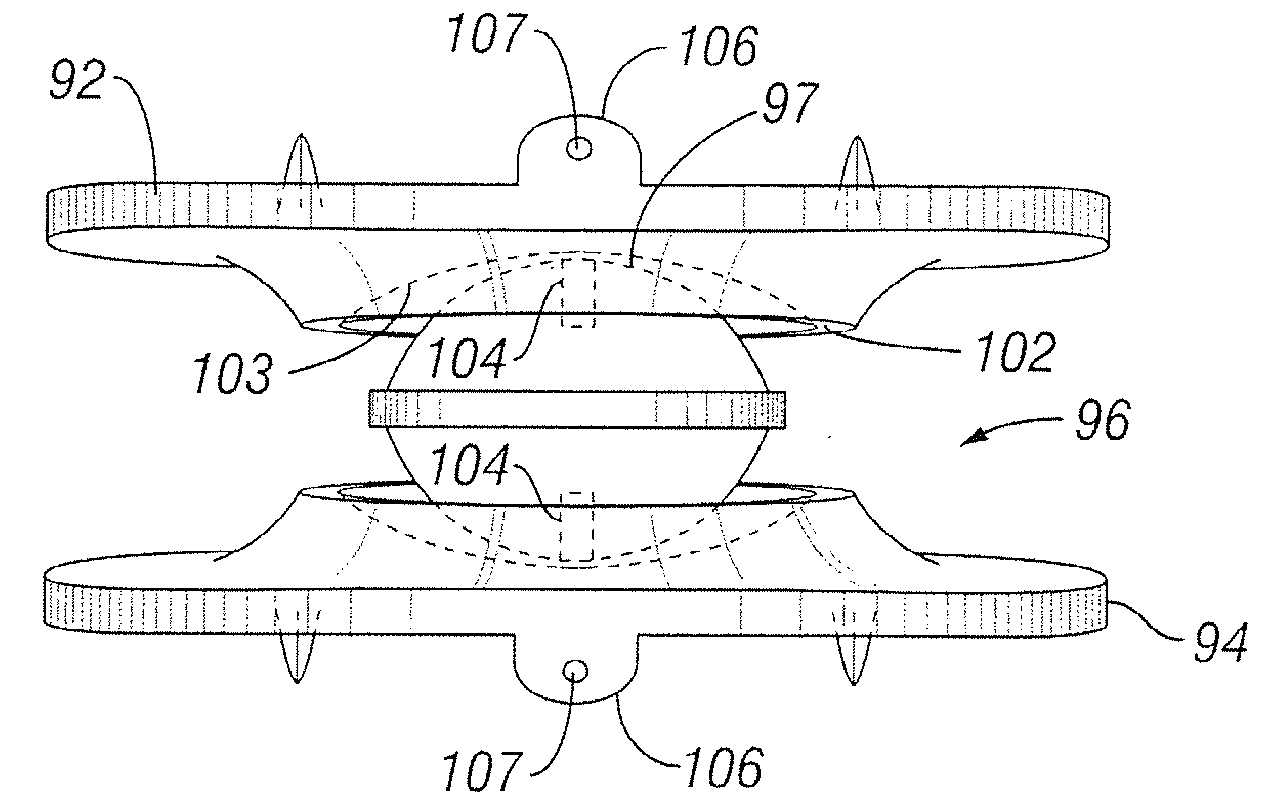
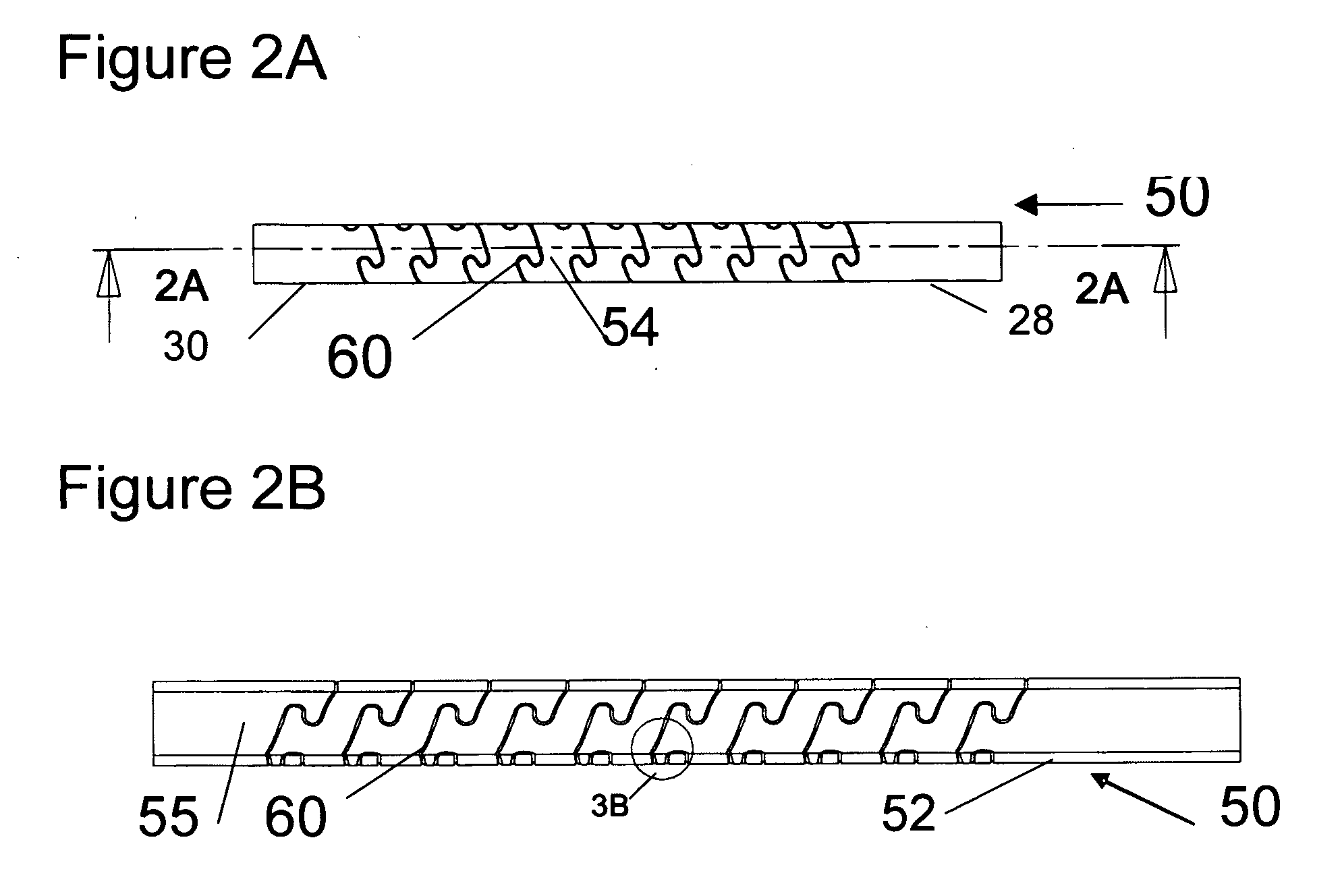
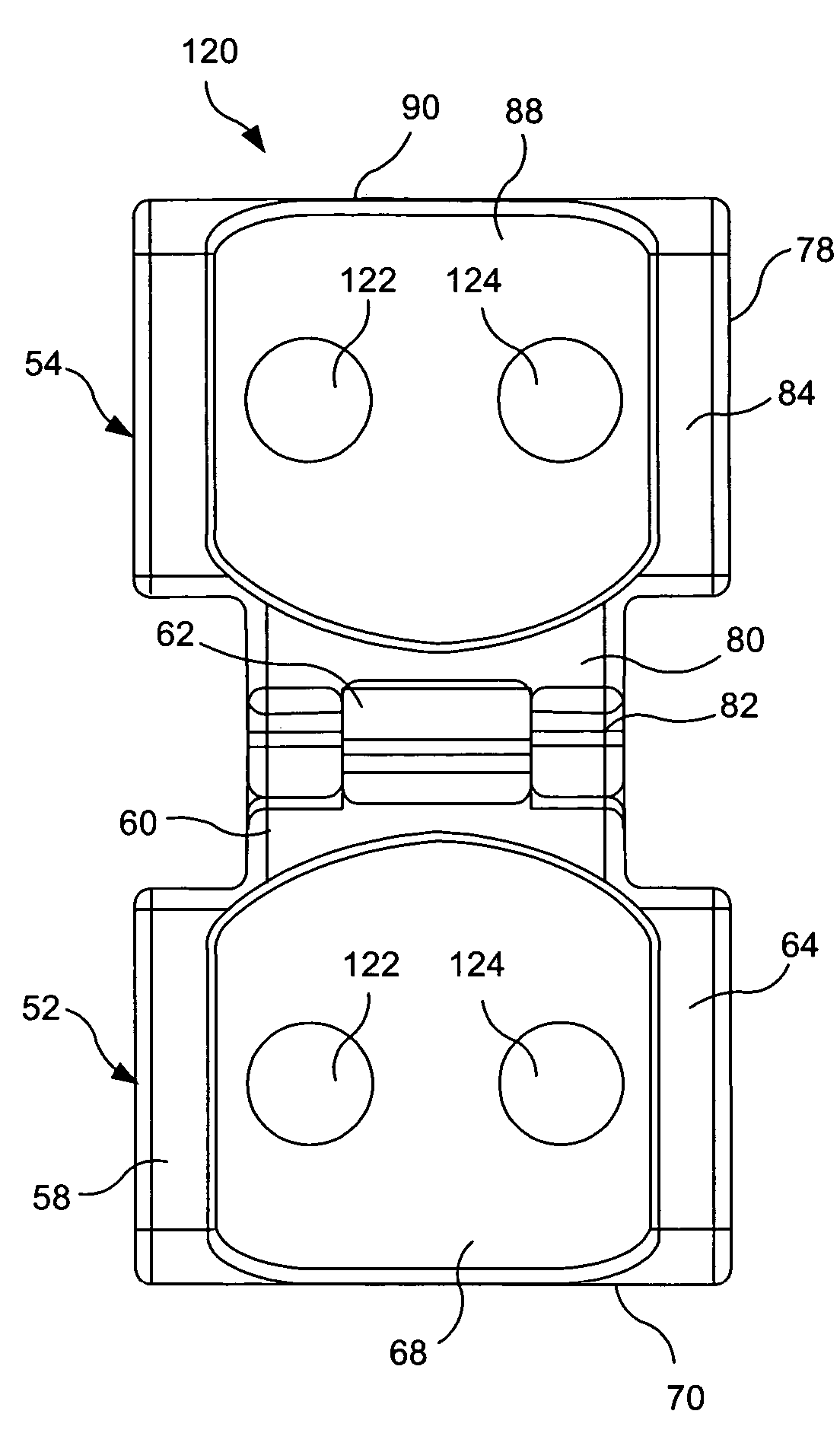
Flexible spine components
ActiveUS20080221620A1Increase flexibilityReduced flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisElastomerDeformity
An improved flexible component used for dynamic stabilization of spinal segments for the treatment of vertebrae deformities and injuries and for the replacement of a complete or segment of the body of a vertebra in the spine is described. The flexible component is comprised of a solid, suitable implant material with a longitudinal bore the entire length and an appropriately formed slot which extends spirally around the shaft either continuously or segmentally. The flexible component may be encapsulated, fully or partially, in a suitable implant grade elastomeric resilient material. When used for a dynamic stabilization device, the component is attached to the vertebral bodies by pedicle screws know to those in the art. When used as a vertebral replacement device, attached to the component's opposite ends are members for attachment to the adjacent vertebra that allow for height and angular adjustment.
Owner:FLEX TECH
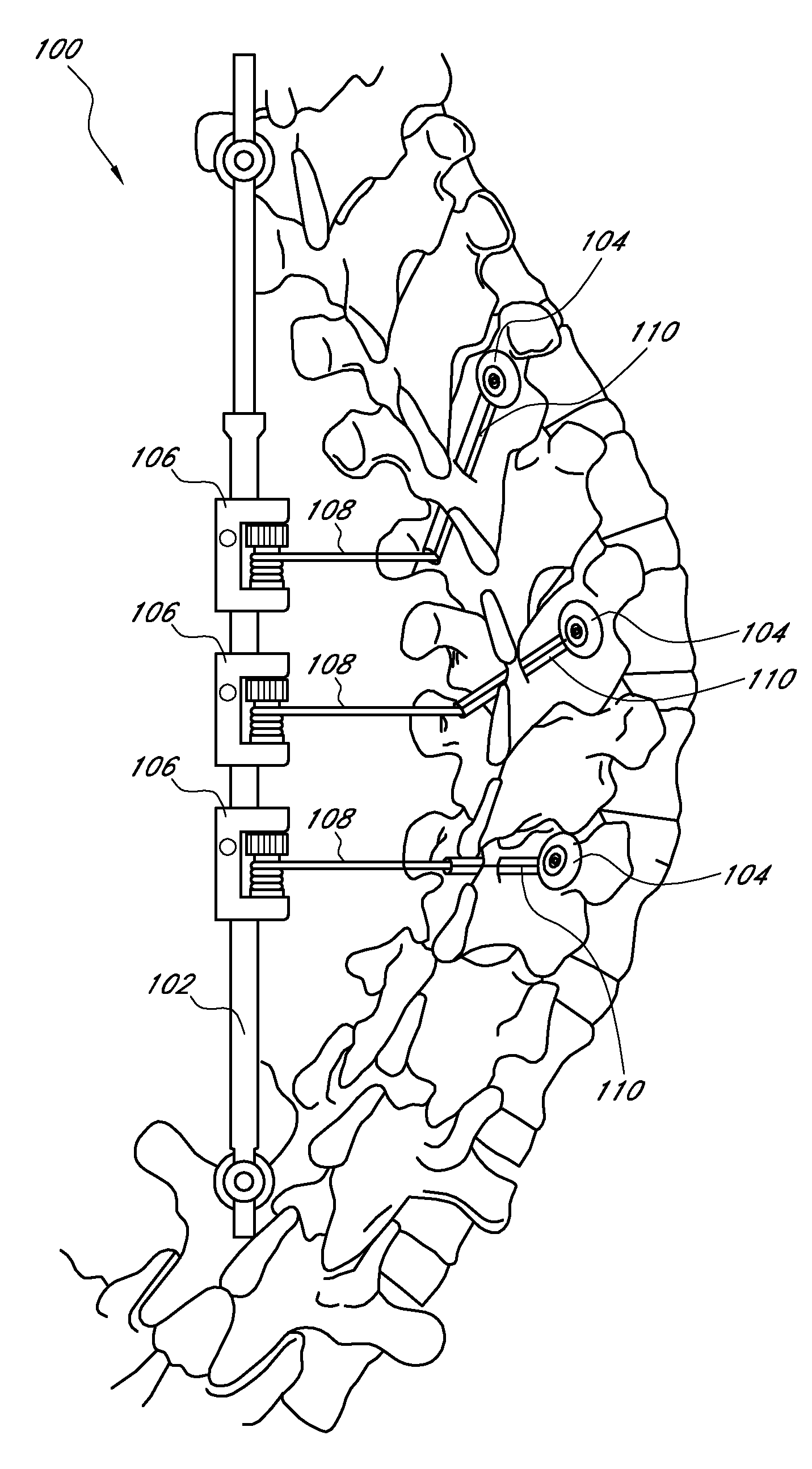
Device and method for dynamic spinal fixation for correction of spinal deformities
ActiveUS20050216004A1Easy to implementCorrection of deformitiesInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDeformity
Embodiments described herein relate to a method and system for dynamic spinal fixation for the correction of spinal deformities, and more specifically pertains to a method and system permitting a correction of spinal deformity without rigid fixation of the vertebral bodies. The embodiments are useful in correcting spinal deformities, including all types of scoliosis or other misalignments affecting the vertebral column. The positioning of devices and elements permits a gradual correction of a three dimensional spinal deformity through operative intervention and / or the natural growth of the vertebrae and spinal column.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Unilateral fixator
InactiveUS7282052B2Great advantageDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingExternal fixatorGear wheel
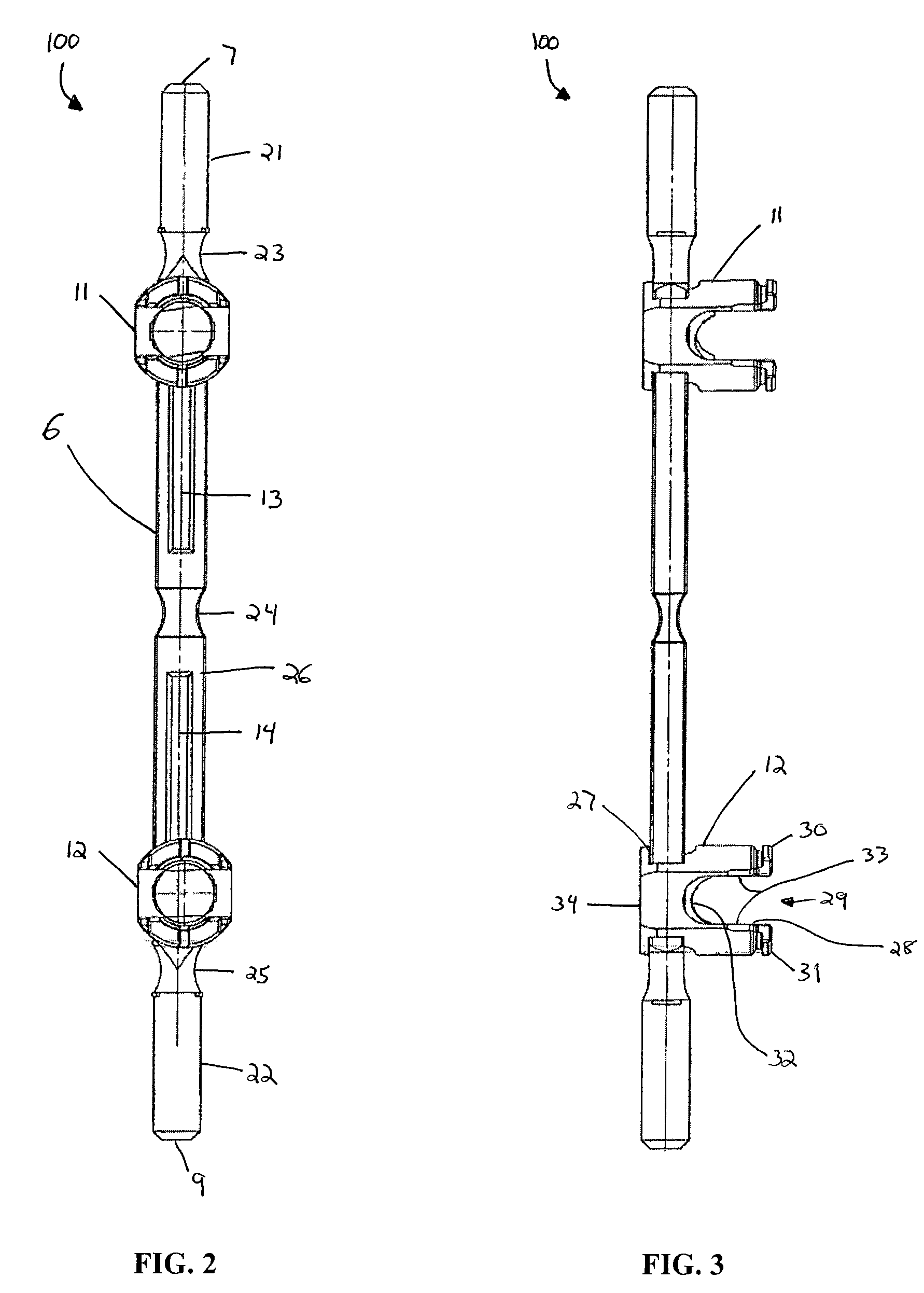
A unilateral external fixator device that allows for gross manipulation and fine adjustment of deformities in six degrees of freedom. The device may comprise a strut assembly and two compound movable joints, one at each end of the strut assembly. One compound movable joint may comprise two revolute joints, each containing a gear reduction mechanism and may rotate about the strut. The second compound movable joint may contain two revolute joints, each containing a gear reduction mechanism, and may move along the length of the strut assembly. The gear reduction mechanisms may comprise helical spline assemblies that allow for gross and fine adjustment of the fixator.
Owner:AMDT HLDG INC
Orthopedic device and method for correcting angular bone deformity
InactiveUS20060142767A1Correct angular deformationPromote growthJoint implantsBone platesBone structureEngineering
An orthopedic device and method for correcting angular deformation of a bone structure having a growth plate. The device includes first and second hinge members connected together at a hinge joint. The device is adapted for mounting the orthopedic device to the bone structure with the pivot joint positioned over the growth plate. Alignment of the pivot joint with the growth plate promotes asymmetric growth of the growth plate to thereby correct the angular deformation.
Owner:GREEN DANIEL W +1
Methods and Devices for Treating Hallux Valgus
The various embodiments disclosed herein relate to implantable devices for the treatment of structural bone and joint deformity, including hallux valgus. More specifically, the various embodiments include systems, devices, and methods for implantation of an implantable device having at least one bone anchor with deployable prongs for treating such deformity.
Owner:TARSUS MEDICAL
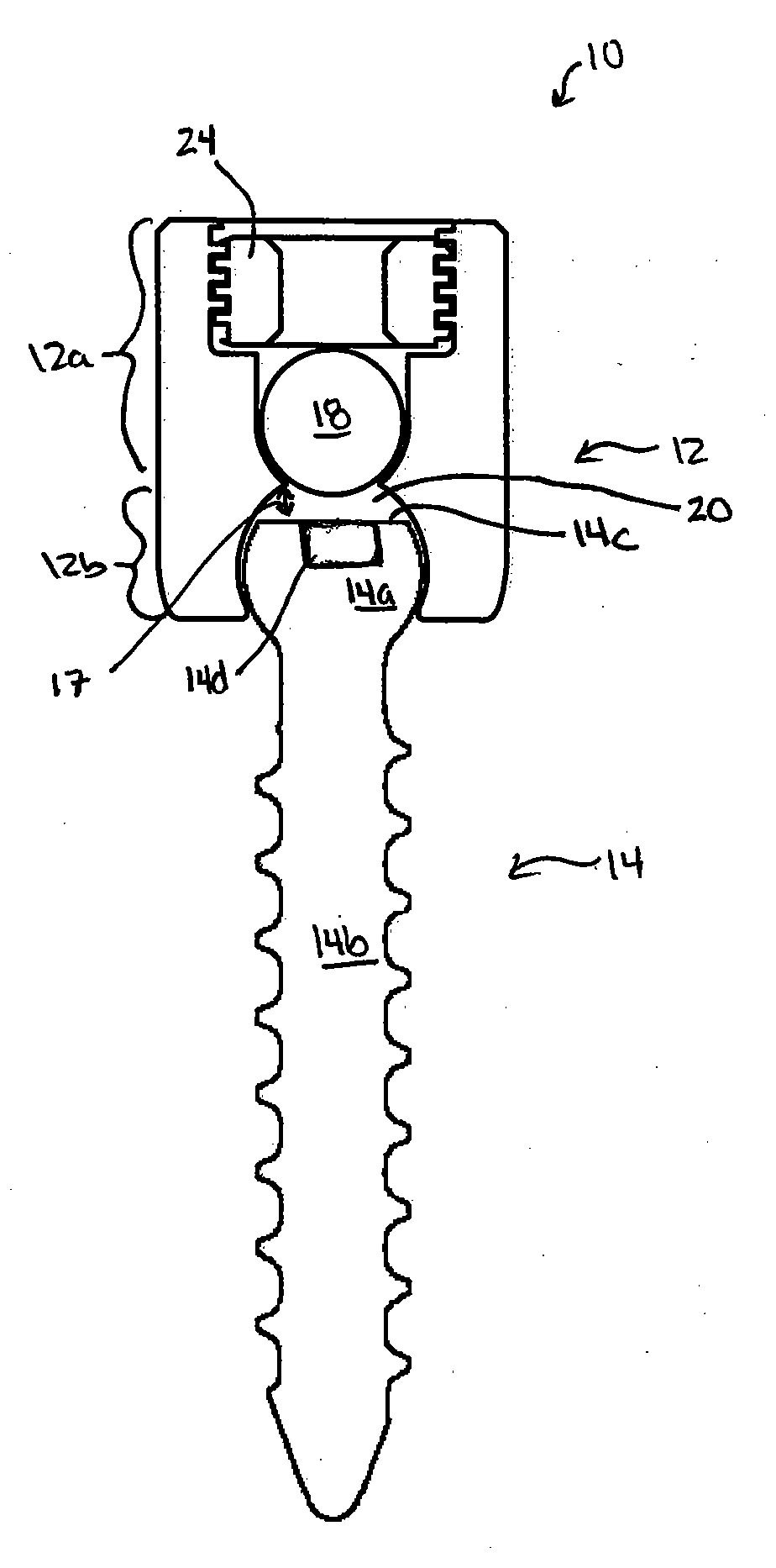
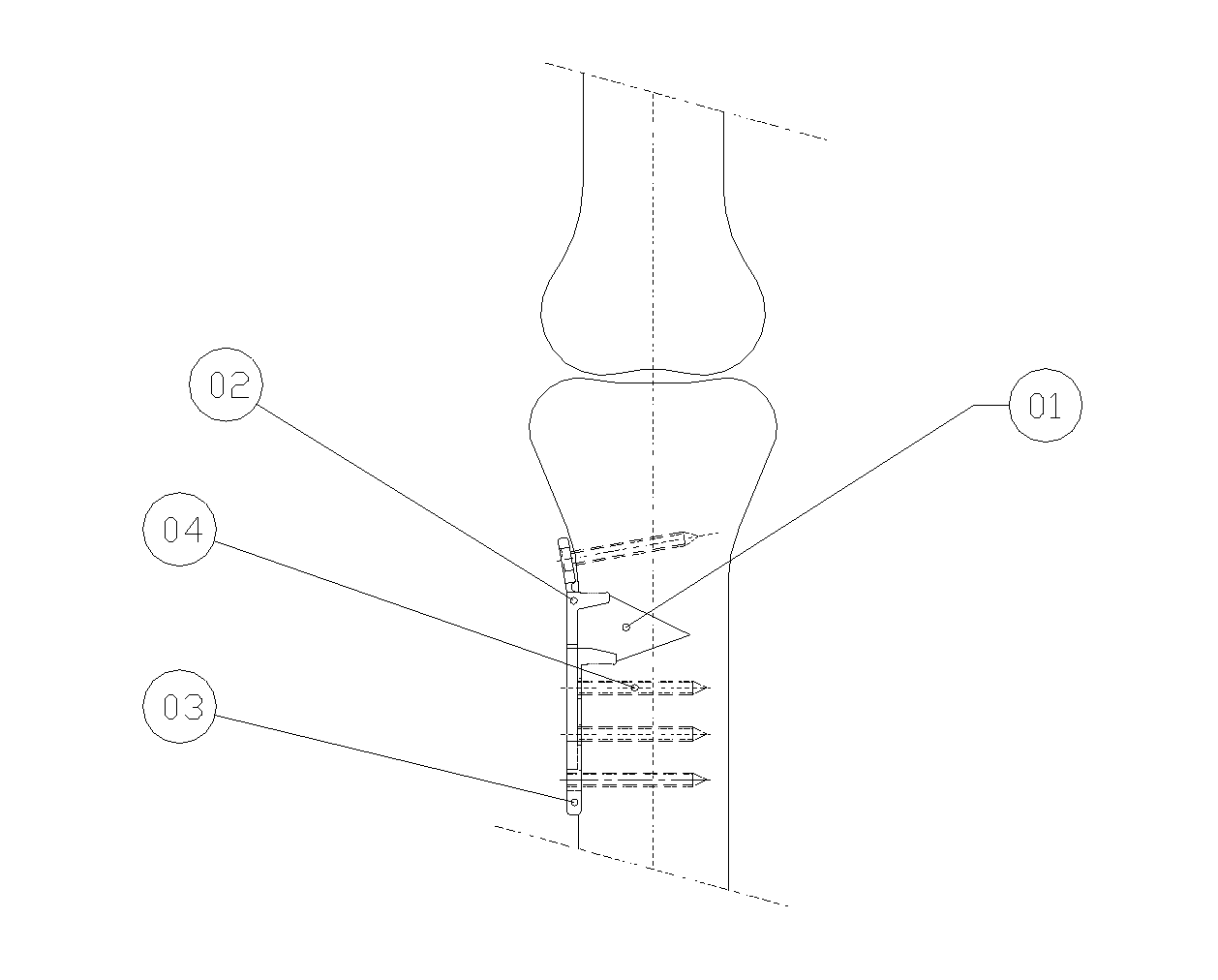
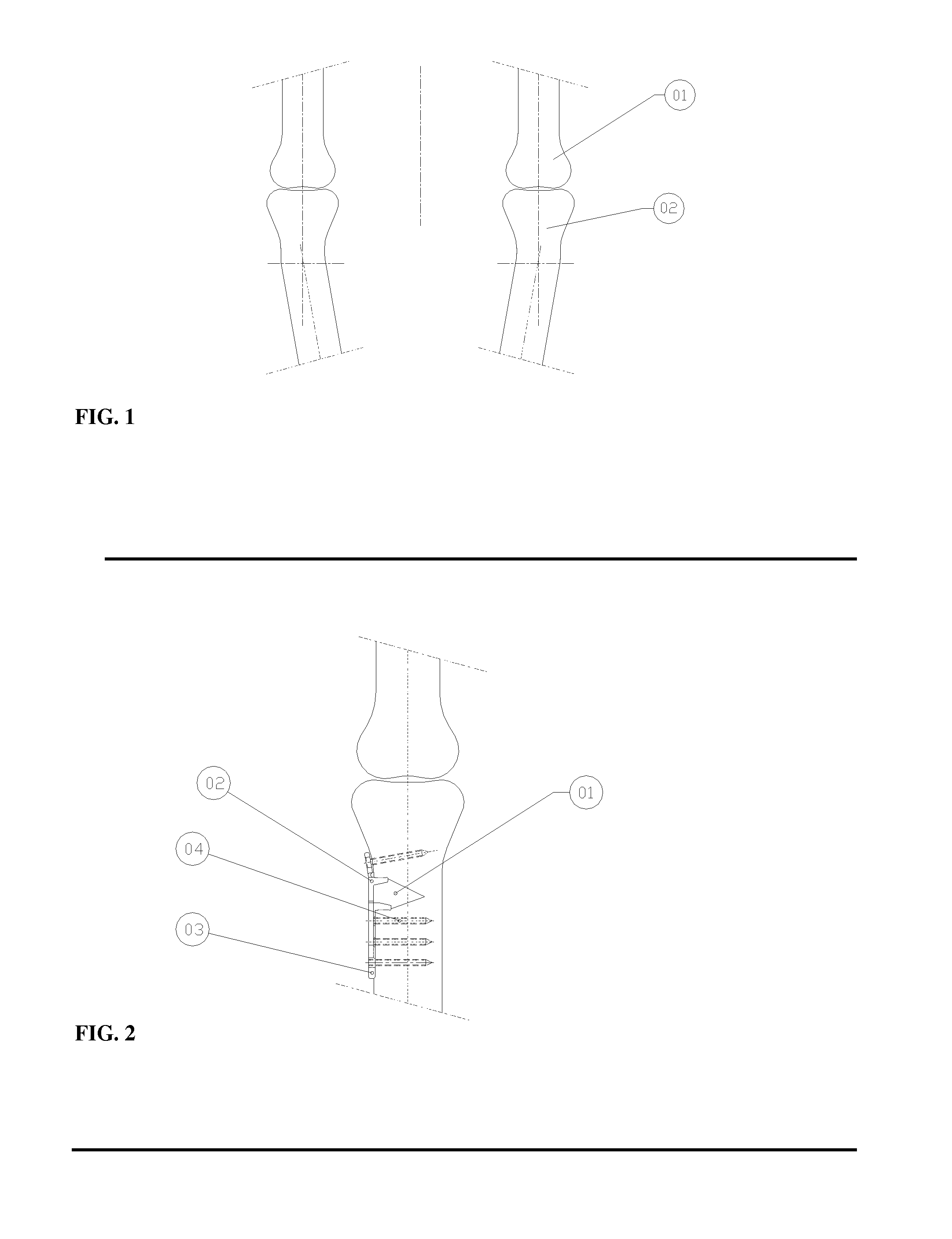
Deformity reduction instrument and method
InactiveUS20060111730A1Efficient and convenient to useInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsScrew threadMedical device
The present invention provides a medical device for reducing a rod towards a bone fastener, the medical device having a shaft defining a proximal end and a distal end, where the shaft further defines a first threaded portion. A gripper assembly may be coupled to the distal end of the shaft, where the gripper assembly is engageable with the bone fastener. The medical device also includes a slide element slideably disposed on the shaft and coupled to the gripper assembly, with the slide element defining a second threaded portion. A pusher element is slideably coupled to shaft, whereby the pusher element defines an aperture engageable with the rod. A shaft grip can be rotatably engaged with the first threaded portion of the shaft, and the shaft grip can abut at least a portion of the pusher element. The medical device can also include a jaw nut coupled to the shaft, with the jaw nut rotatably engaging the second threaded portion of the slide element, as well as a lever assembly pivotably coupled to the shaft, the lever assembly defining a rod channel engageable with the rod, and further including a latch mechanism for releasably securing the lever assembly to the shaft.
Owner:MEDICAL INNOVATORS
Methods and devices for treating a structural bone and joint deformity
The various embodiments disclosed herein relate to implantable devices for the treatment of a structural bone and deformity. More specifically, the various embodiments include systems, devices, and methods for implantation of a flexible or tension band for treating such a deformity, including hallux valgus.
Owner:TARSUS MEDICAL
Method for correcting a deformity in the spinal column and its corresponding implant
InactiveUS20050010292A1Correction of spinal deformityCausing an increase in the spine curvatureInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnBase of the sacrum
This invention relates to an implant to be inserted in the disc space between two adjacent vertebrae for the correction of the vertebral spine curvature. The configuration (lateral view) of the invention is basically a wedge or acute-angled isosceles trapeze, wherein the area opposite the shorter base or opposite to the vertex is a rounded pyramid-like surface, and the upper and lower surfaces of the trapeze include fixation protuberances to the vertebral plates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:CARRASCO MAURICIO RODOLFO
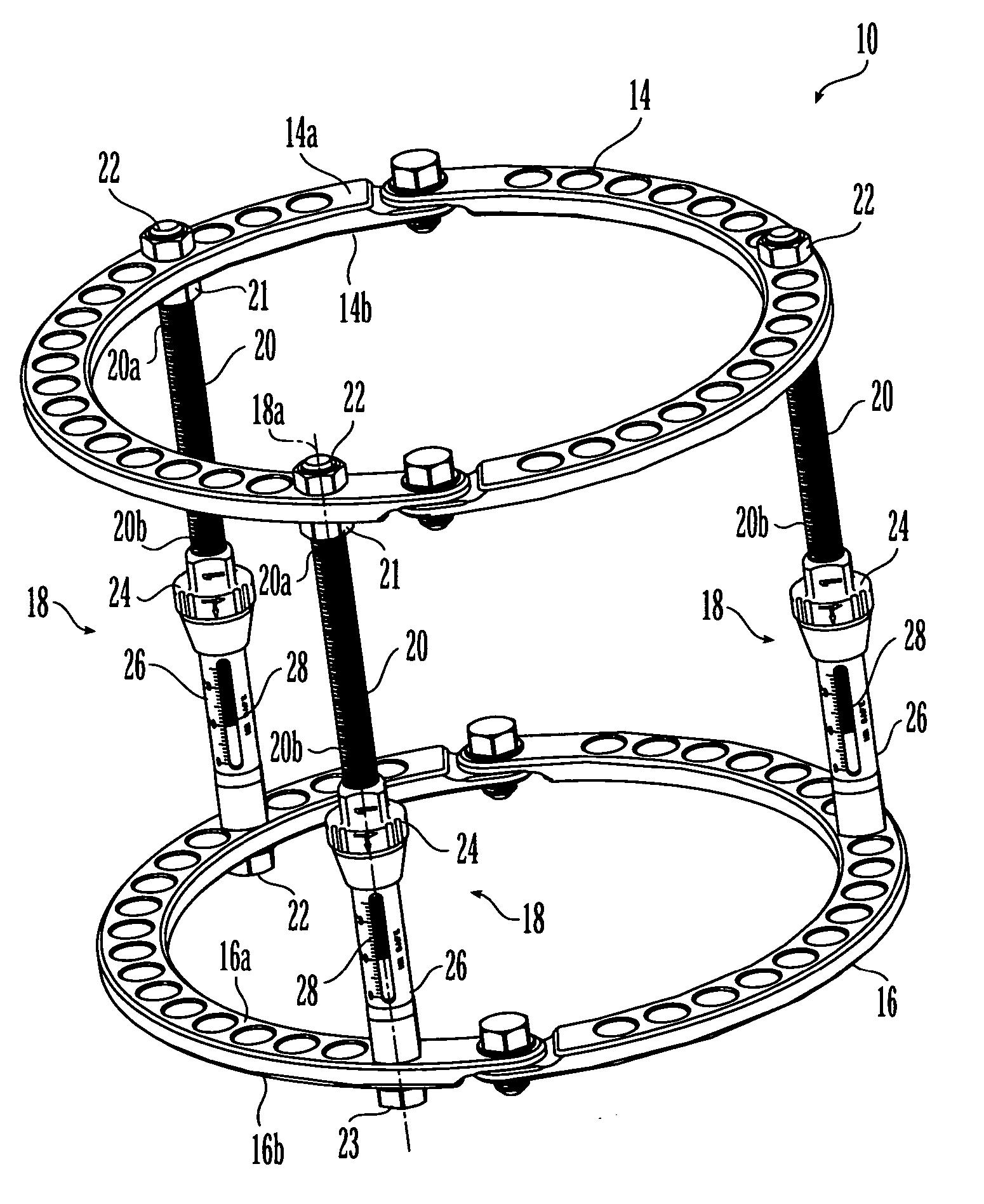
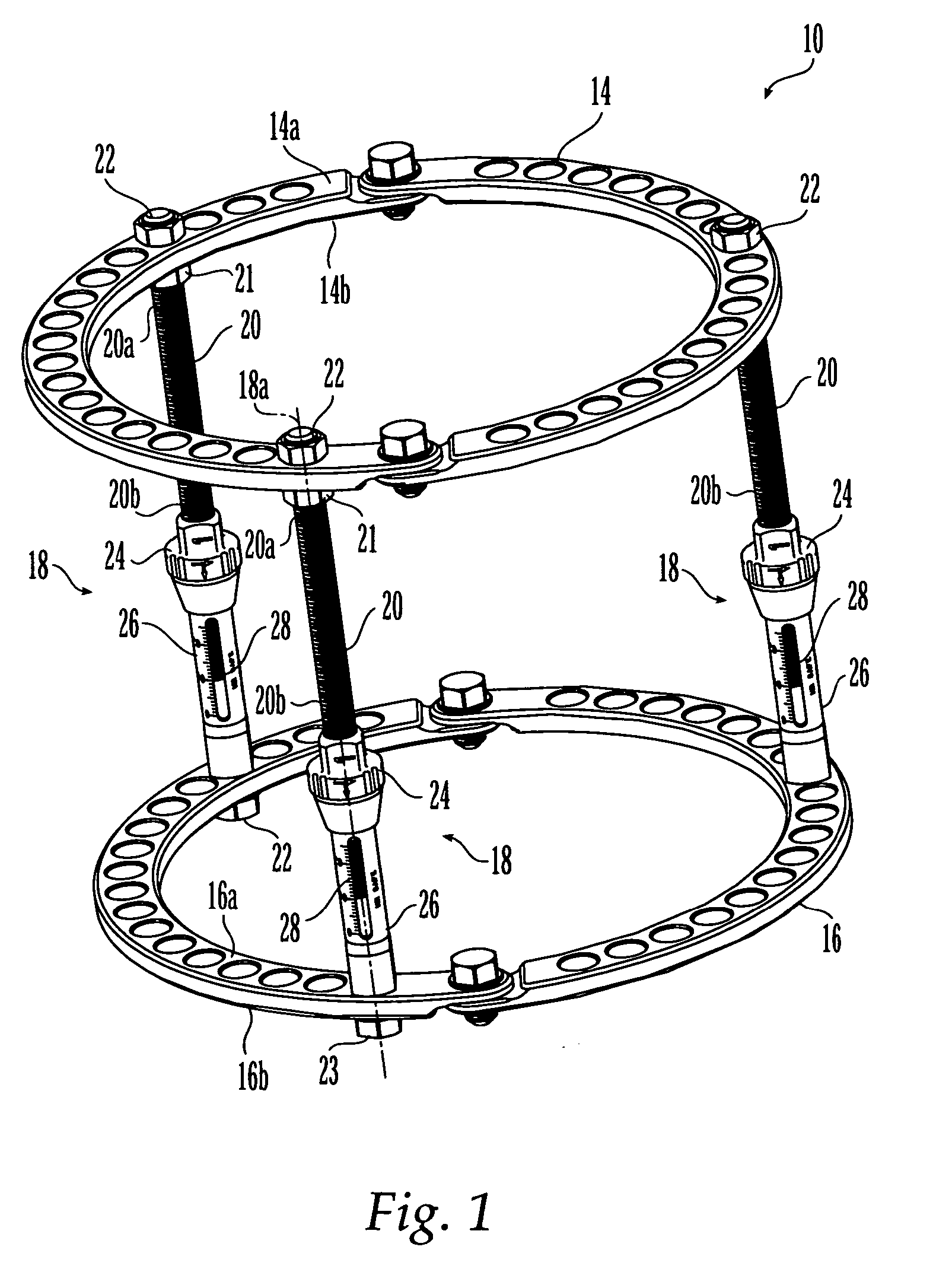
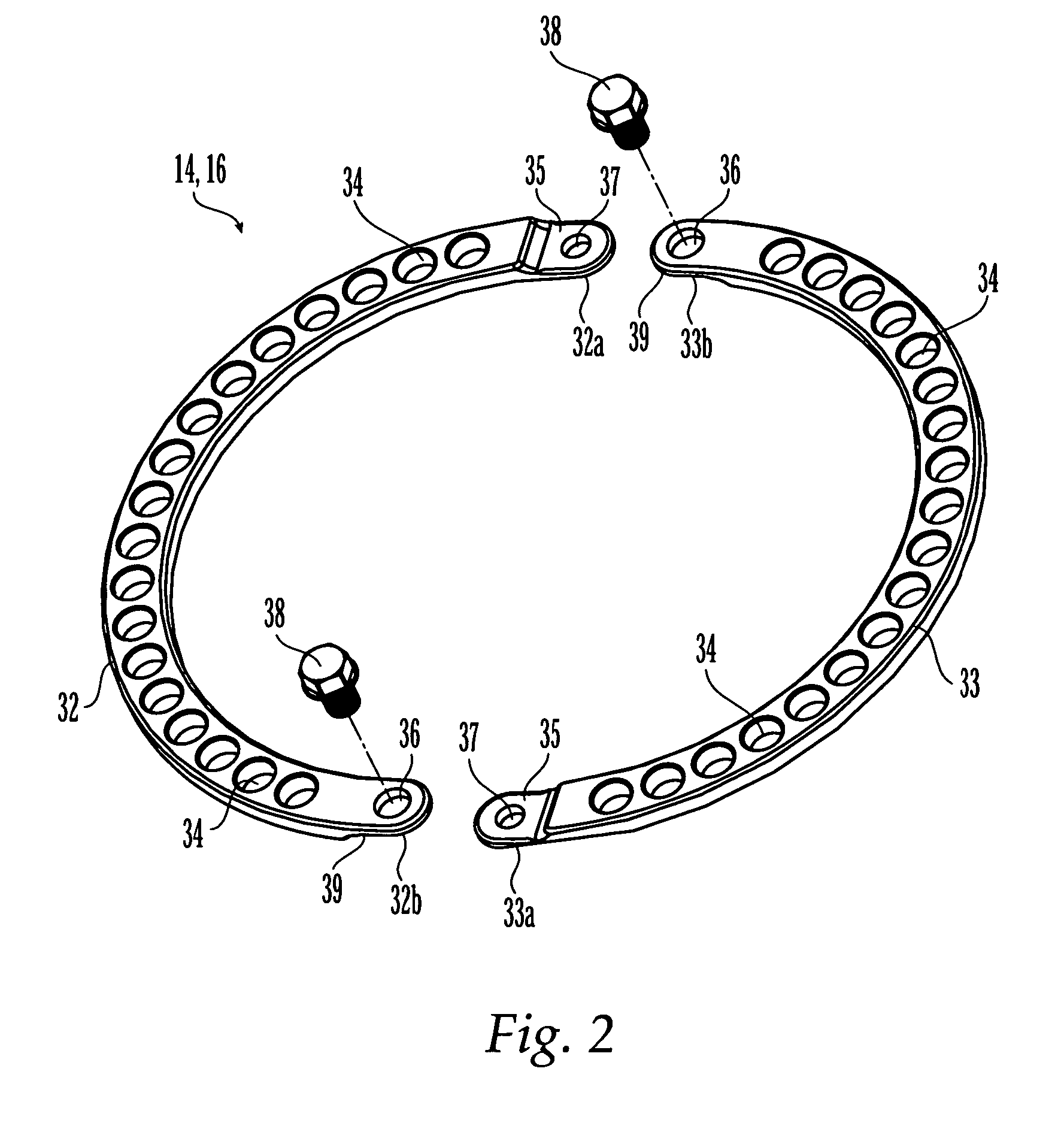
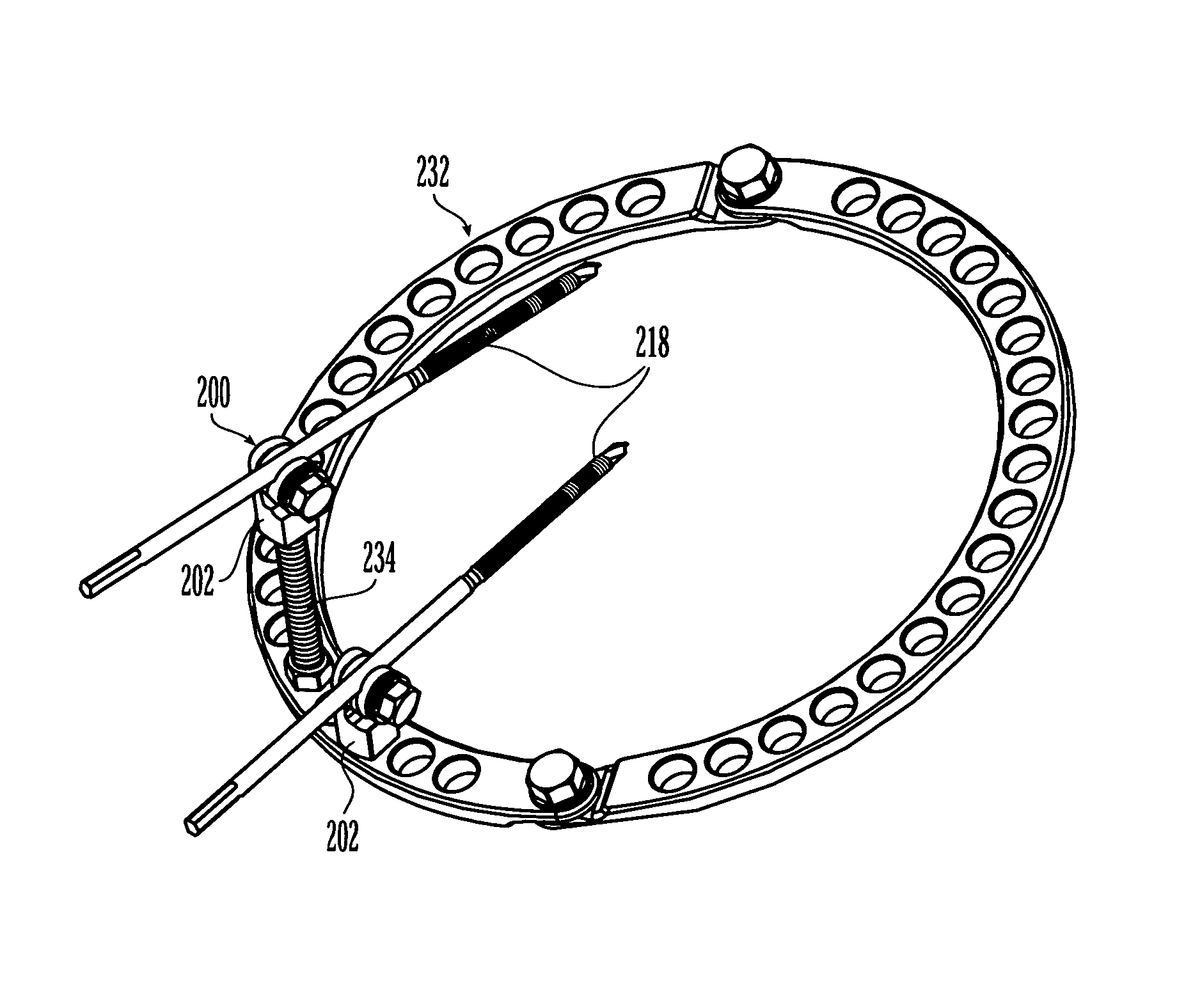
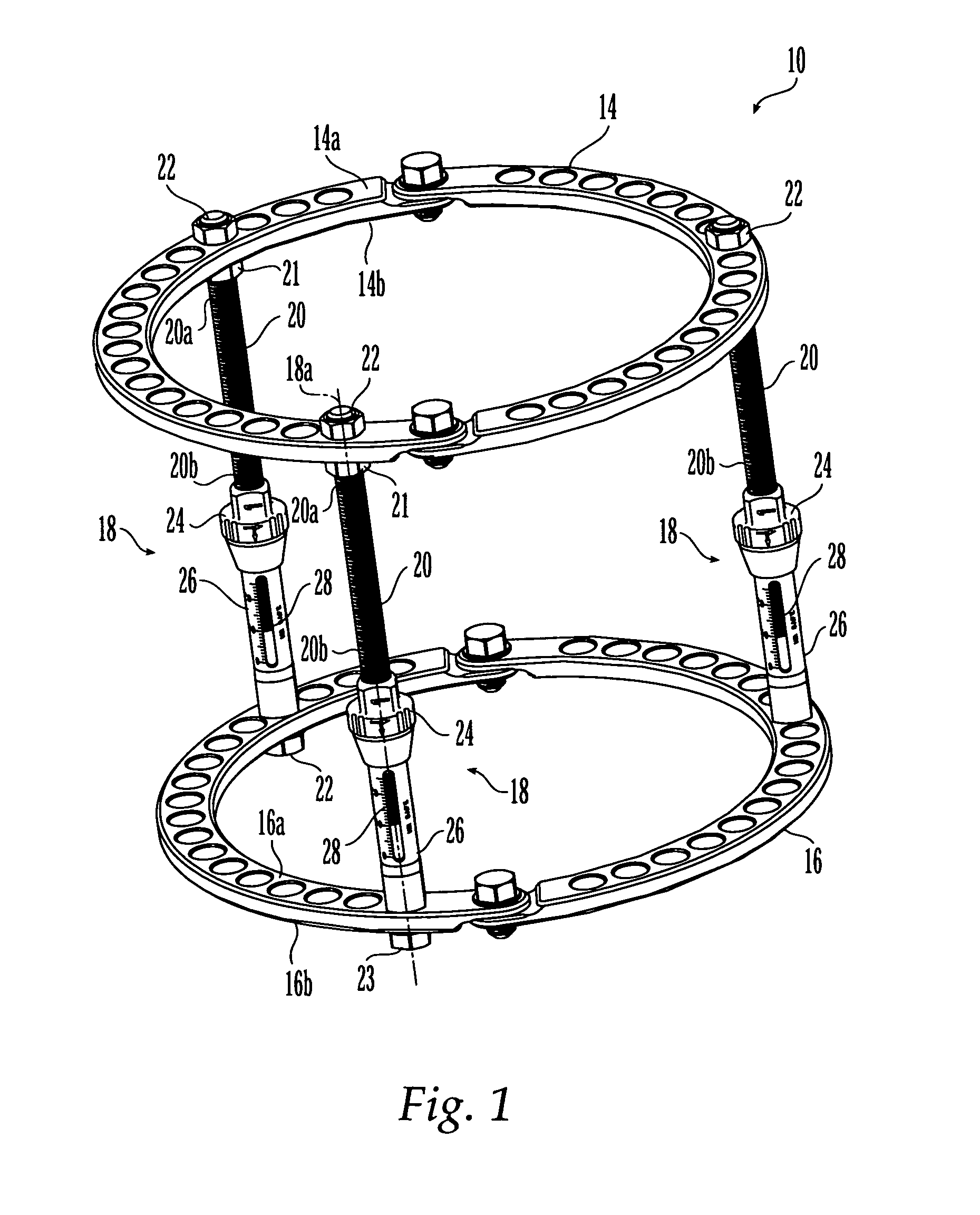
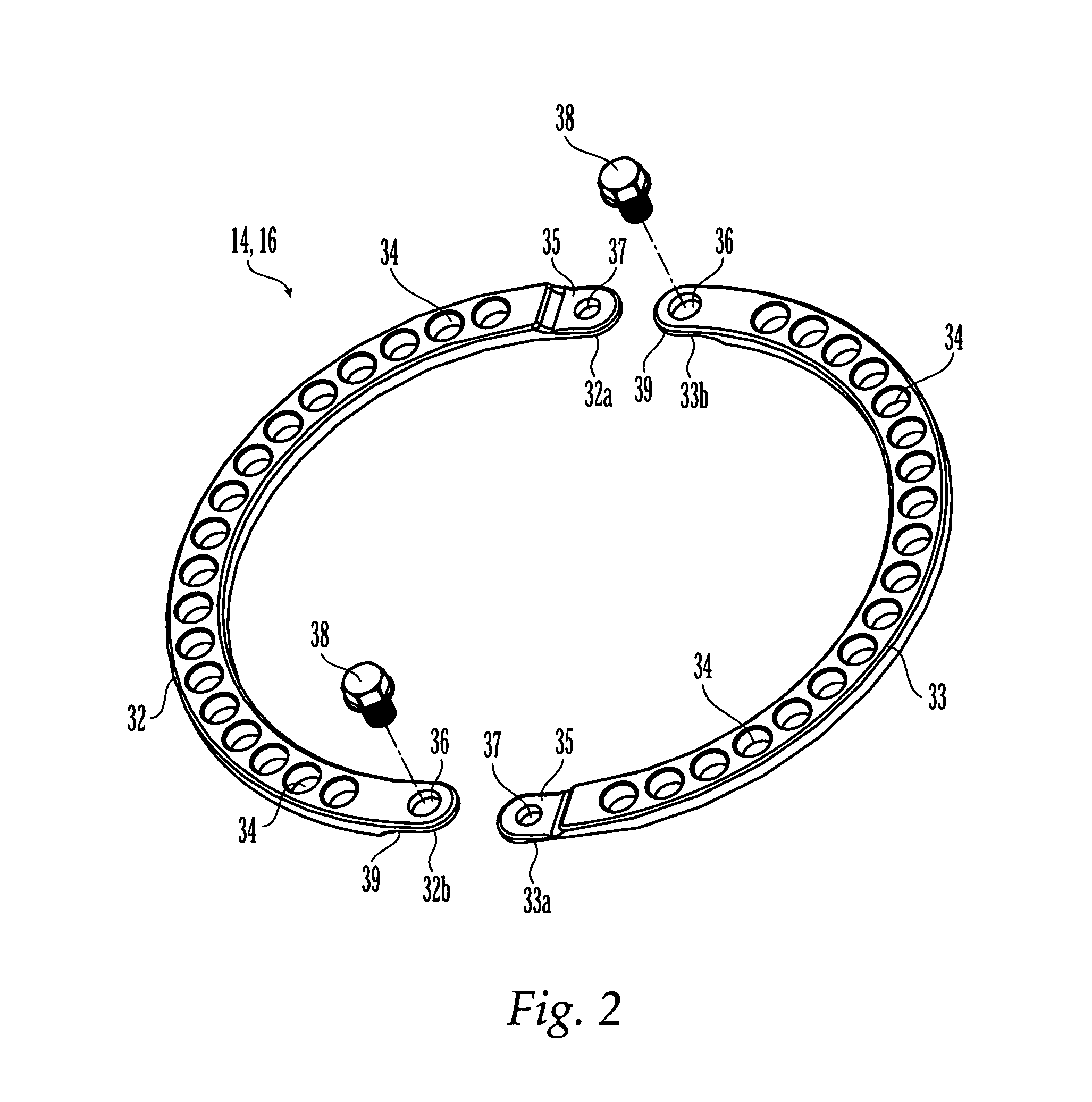
External fixation system and method of use
ActiveUS20070049930A1Distraction/reduction/compression of bone or bone segmentsMove quicklyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionDeformity
An external fixation system for connecting one or more bone segments together to facilitate healing of bone. The system may include one or more rings and / or ring segments. One or more linear distractors and / or angular distractors may connect the rings to each other so as to allow for distraction and / or reduction / compression of a bone. Linear distractors may enable an operator to move the rings towards and away from each other, while angular distractors may enable an operator to angle the rings relative to each other. In an embodiment using angular distractors, one or more angular separation assemblies may be positioned between the rings. These separation assemblies may have joints which may two portions which may be angled relative to each other and connected directly or indirectly to the rings. Various fasteners (e.g., nuts) and / or tightening members may configured for quick movement along and selective tightening to various components. Moreover, clamps may be attached to the rings and may engage pins, wire, rods, which may be inserted into bone to hold bone segments to each other. The components of the external fixation system may be provided in sets or kits so that the a surgeon may select various combinations of components to create an external fixation system which is configured specifically for the particular needs of a patient and the bone fracture / deformity.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
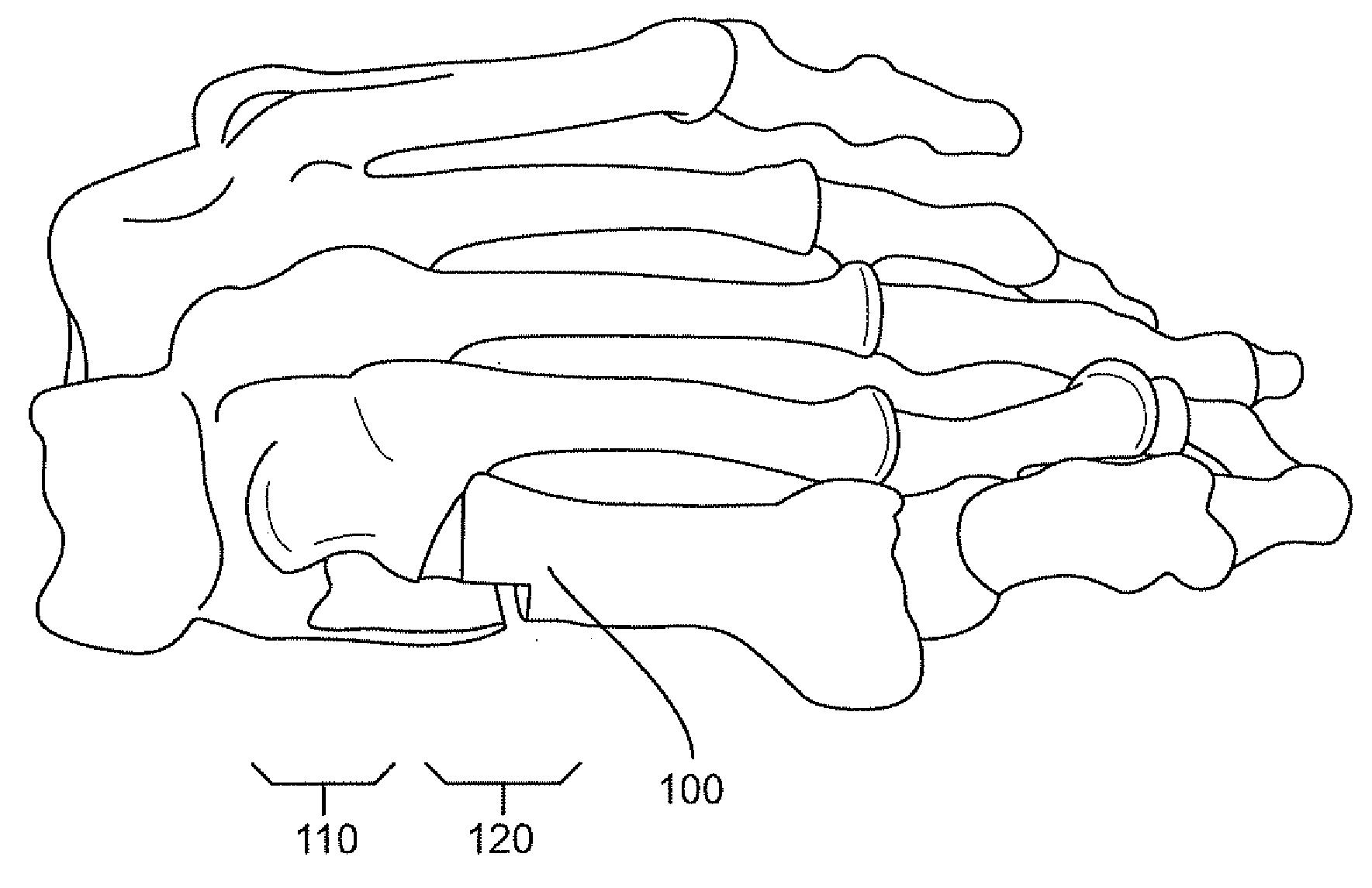
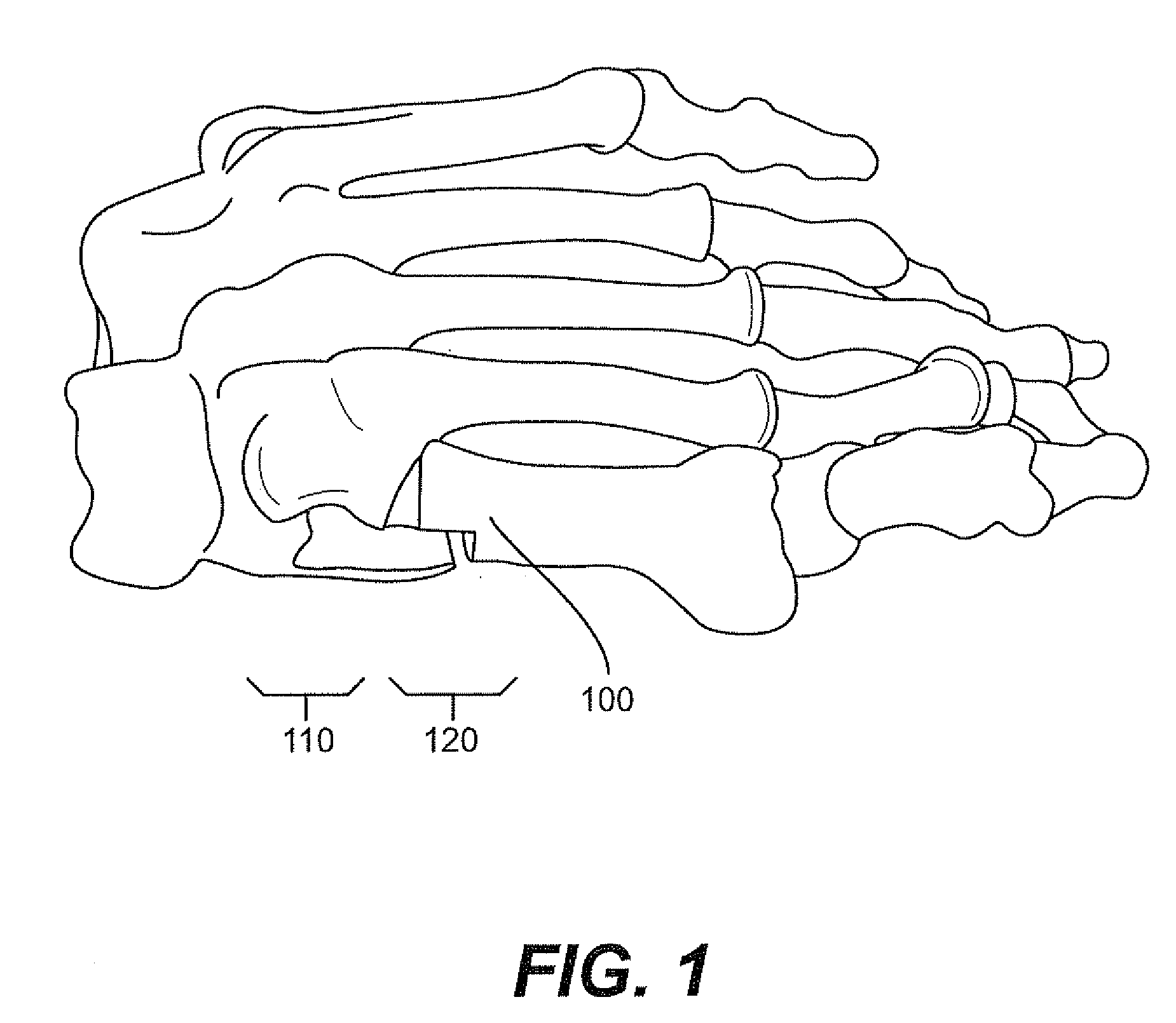
Implant for correcting skeletal mechanics
Deformities present on the end of a bone, for example the end of the metatarsal bone making up part of the metatarsocuneiform joint, can lead to deformities such as bunions. These deformities are treatable with an implant that comprises a plate with a wedge extending perpendicular from the plate. Following removal of cartilage from the joint, deformed portions at the end of the bone are removed and the wedge is inserted in the joint and held in place when the plate is attached to the bones flanking the joint. This effectively fuses the two bones together. The wedge can be shaped in various ways depending on the particular deformity present.
Owner:GRAHAM MICHAEL
Apparatus and methods for magnetic alteration of deformities
Methods and apparatus for incrementally manipulating an internal body member of a patient are disclosed. The apparatus has a magnetic implant adapted to be received on a location of the body member, a platform external to the patient, and a magnetic member coupled to the platform, wherein the magnetic member generates a magnetic force between the implant and the platform to incrementally manipulate the body member. The implant and external magnetic member are preferably rare earth magnets or an array of rare earth magnets, and are configured to generate an attractive or repulsive force between the implant and the platform to reposition, reorient, deform, or lengthen the body member.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
External fixation system and method of use
ActiveUS8029505B2Distraction/reduction/compression of bone or bone segmentsMove quicklyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDeformityBiomedical engineering
An external fixation system for connecting one or more bone segments together to facilitate healing of bone. The system may include one or more rings and / or ring segments. One or more linear distractors and / or angular distractors may connect the rings to each other so as to allow for distraction and / or reduction / compression of a bone. Linear distractors may enable an operator to move the rings towards and away from each other, while angular distractors may enable an operator to angle the rings relative to each other. In an embodiment using angular distractors, one or more angular separation assemblies may be positioned between the rings. These separation assemblies may have joints which may two portions which may be angled relative to each other and connected directly or indirectly to the rings. Various fasteners (e.g., nuts) and / or tightening members may configured for quick movement along and selective tightening to various components. Moreover, clamps may be attached to the rings and may engage pins, wire, rods, which may be inserted into bone to hold bone segments to each other. The components of the external fixation system may be provided in sets or kits so that the a surgeon may select various combinations of components to create an external fixation system which is configured specifically for the particular needs of a patient and the bone fracture / deformity.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Remote-controlled internal hydraulic osseous distractor
Owner:SAYAGO RUBEN FERNANDO
Preparation method for cellfree intestinum tenue submucosa biological material
ActiveCN101366975ARepair defectRepair membranous defectsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingIntestinal submucosa
The invention relates to a method for preparing a biomaterial of acellular small intestinal submucosa, which comprises the steps of preposition treatment, acellular treatment, enzyme treatment, preparations of membranous products and particle products. Compared with the prior art, the biomaterial has higher bioactivity and biocompatibility, no obvious immune rejection and no toxic effect on cells; besides, the biomaterial has a certain mechanical strength and toughness, and variable shape, size and thickness, thereby being convenient for clinical suturing and fixing. At the same time, the preparation method has the advantages of unlimited raw material source, cell-free residues, no ethical issues and being capable of effectively inactivating virus. The prepared products are applicable to the biomedical engineering fields, such as repairing defections of body tissue, serving as tissue filling materials, repairing facial depression deformity, serving as tissue reinforcements to replace fascia, repairing membranous defections and malnourished and infected surfaces of wound, serving as materials for biodegradable stents, and serving as injectable filling materials.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
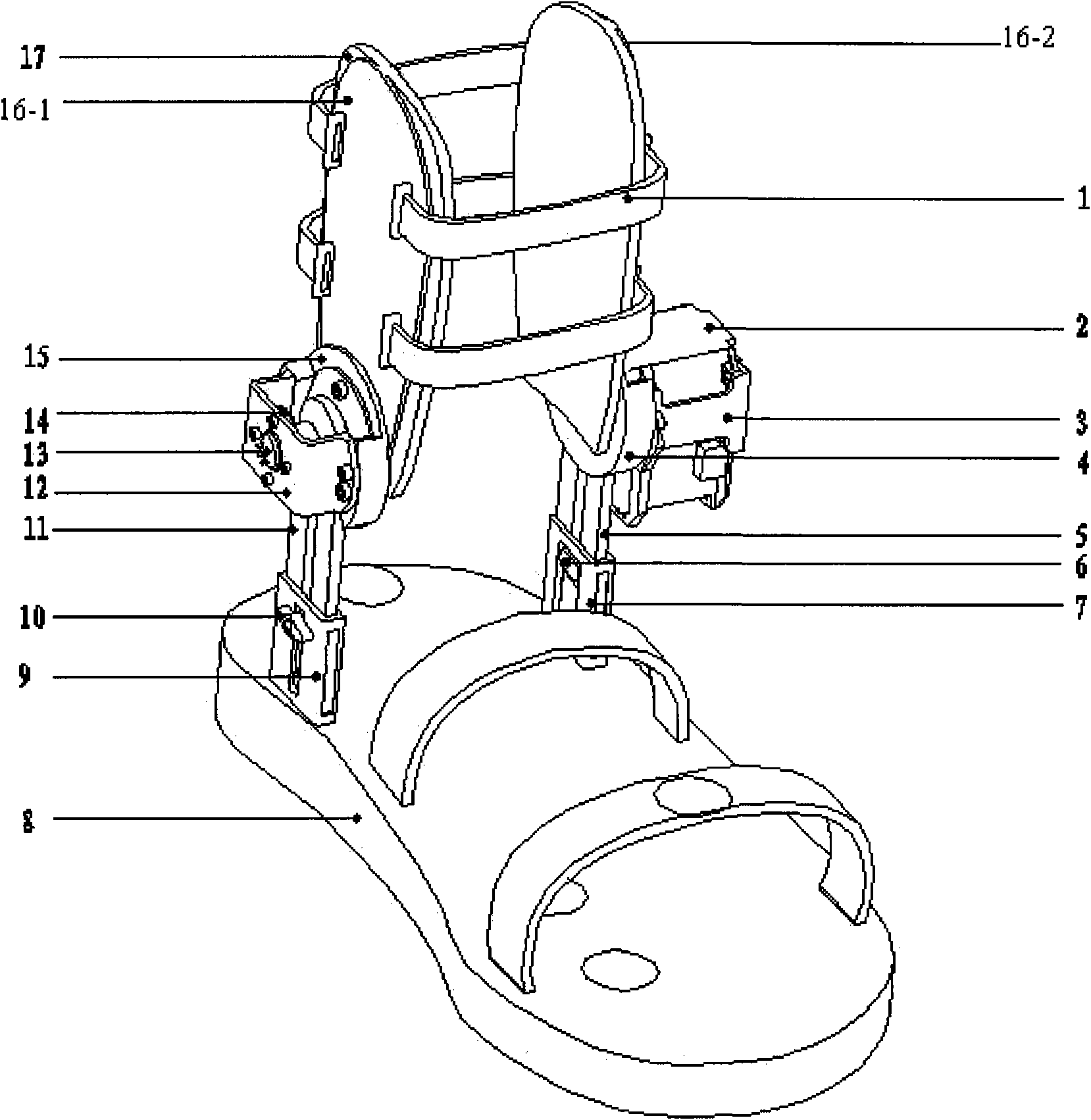
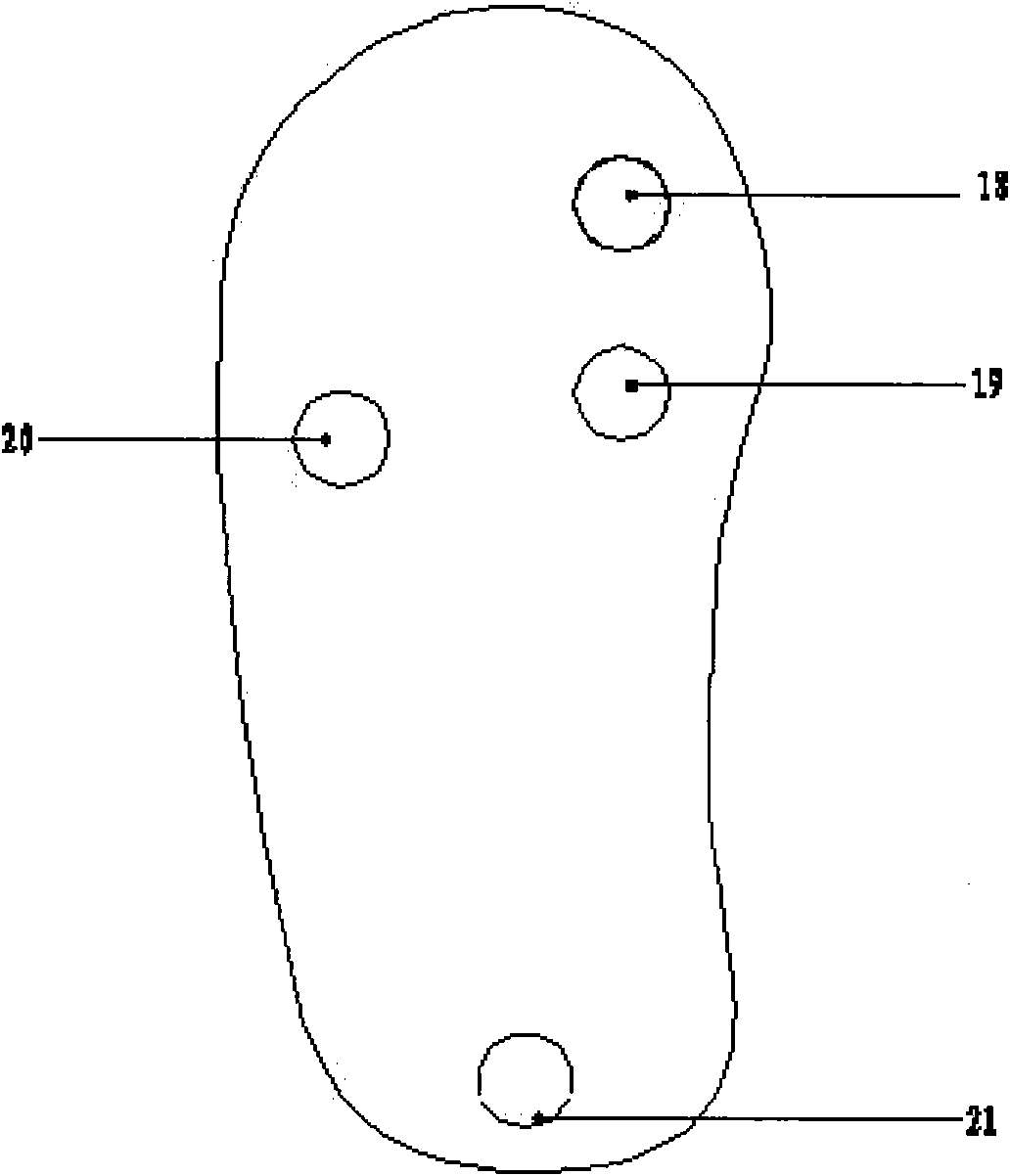
Gait phase detection apparatus with ankle joint angle self-rectification function
InactiveCN101548925ASimple structureEasy to useChiropractic devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringGait trainingDeformity
The invention discloses a gait phase detection apparatus with ankle joint angle self-rectification function, which comprises a shank fixing mechanism, a ankle joint angle control mechanism, a ankle joint angle measuring mechanism and a thenar pressure measuring footwear. The invention can control ankle joint motor rotation angle according to thenar pressure signal, regulate ankle joint angle for foot drop patient in weight reduction walking training, prevent the damage to foot due to the towing and impacting caused by foot drop, and improve the dorsiflexion ability of foot drop patient; a pressure sensor and an angle sensor collects thenar pressure signal and ankle joint angle signal timely, an upper computer performs fuzzy logic algorithm to realize to detect gait phase smoothly and submissively. patient with walking ability defects or normal person with some degree of gait deformity can wear the invention while walking, detect the gait phase information in walking, estimate gait recovery degree scientifically, and optimize gait training strategy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
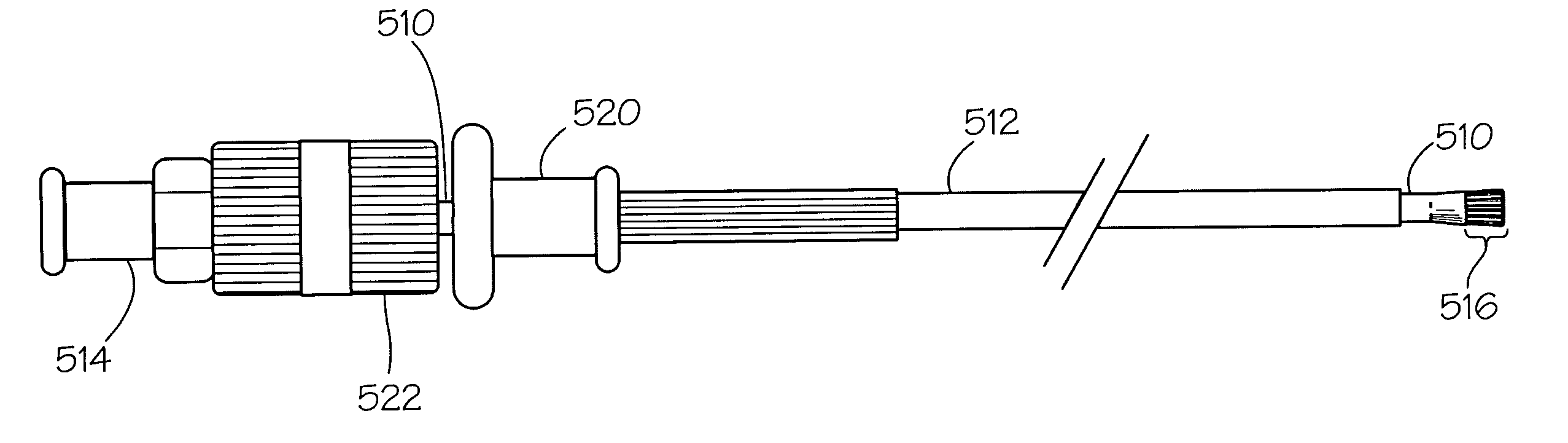
Medical liquid delivery device
Disclosed herein are novel liquid delivery catheters, and methods and kits implementing the same. The disclosed catheters are particularly useful for localized delivery of a liquid caustic agent to treat various defects associated with malformations and injuries resulting in chronic or acute bleeding, or to ablate tumors, occlude fistulae or other luminal structures. The disclosed devices have uses in a number of medical disciplines, and specific examples are provided pertaining to treatment of defects, malformations, and injuries, or bleeding due to medical procedures, in and along the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:MOULIS HARRY
Unidirectional rotatory pedicle screw and spinal deformity correction device for correction of spinal deformity in growing children
ActiveUS8394124B2Prevent soft tissue ingrowthPrevent cables from gettingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal deformity correctionEngineering
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com