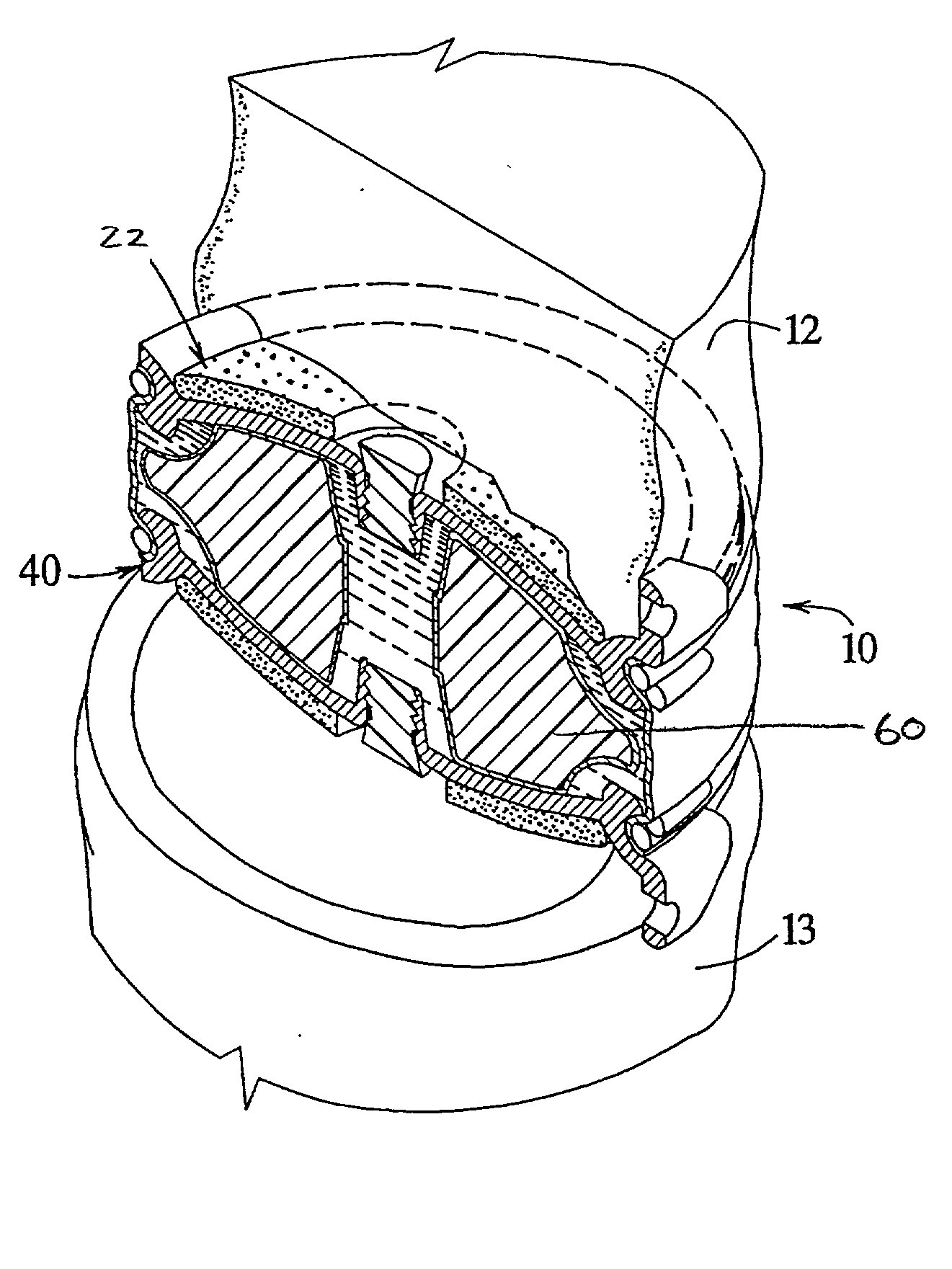
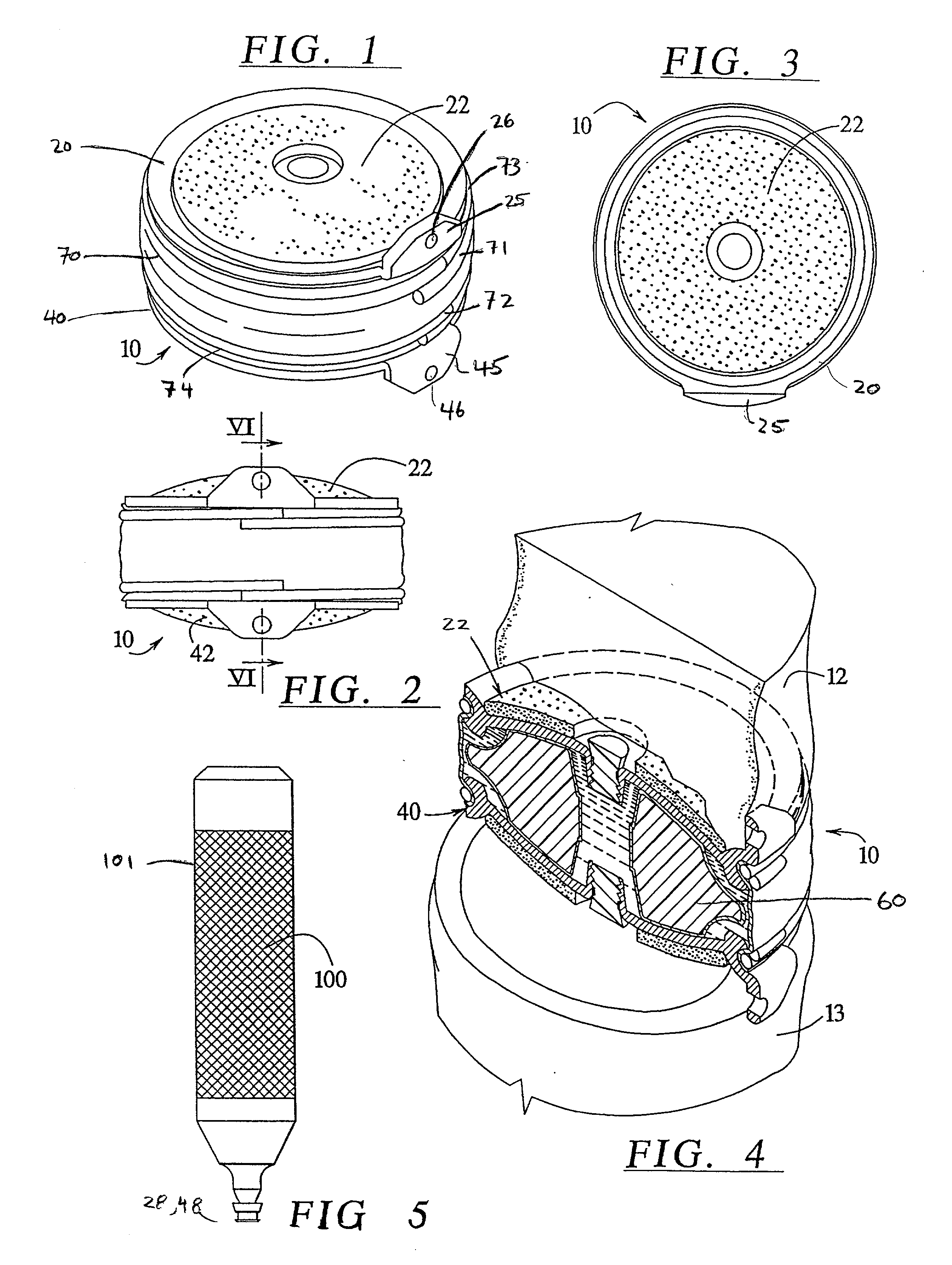
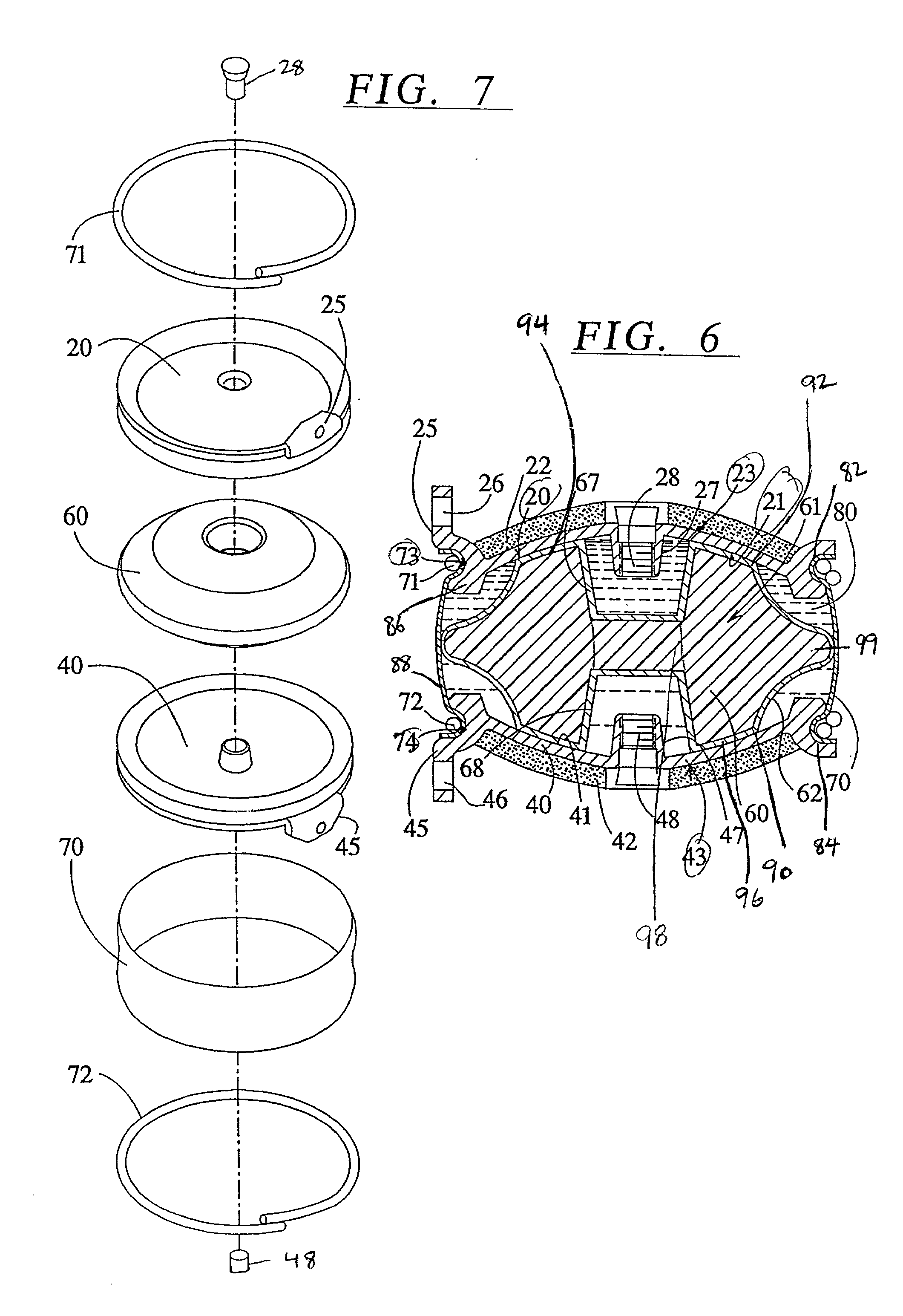
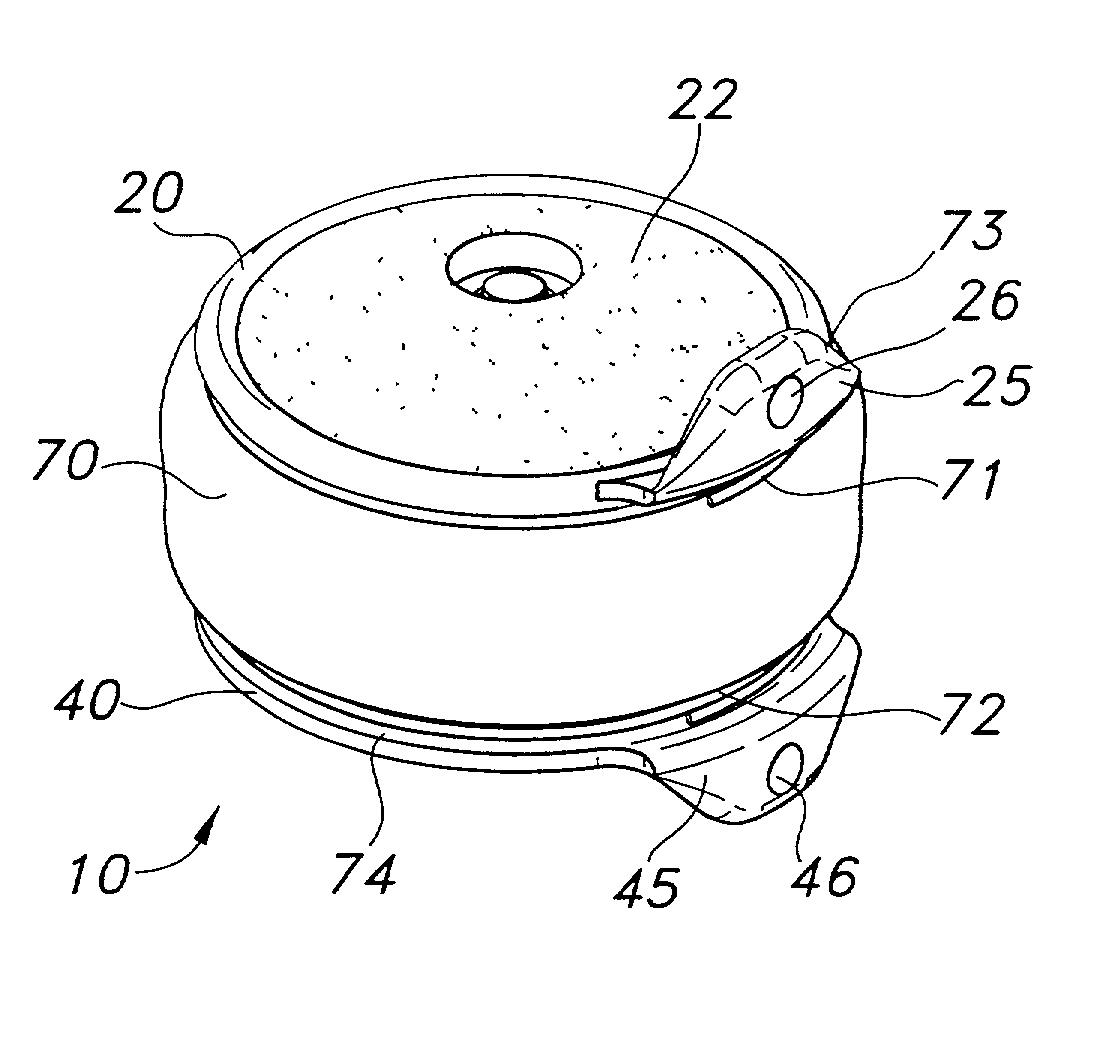
Patents
Literature
649 results about "Joint prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
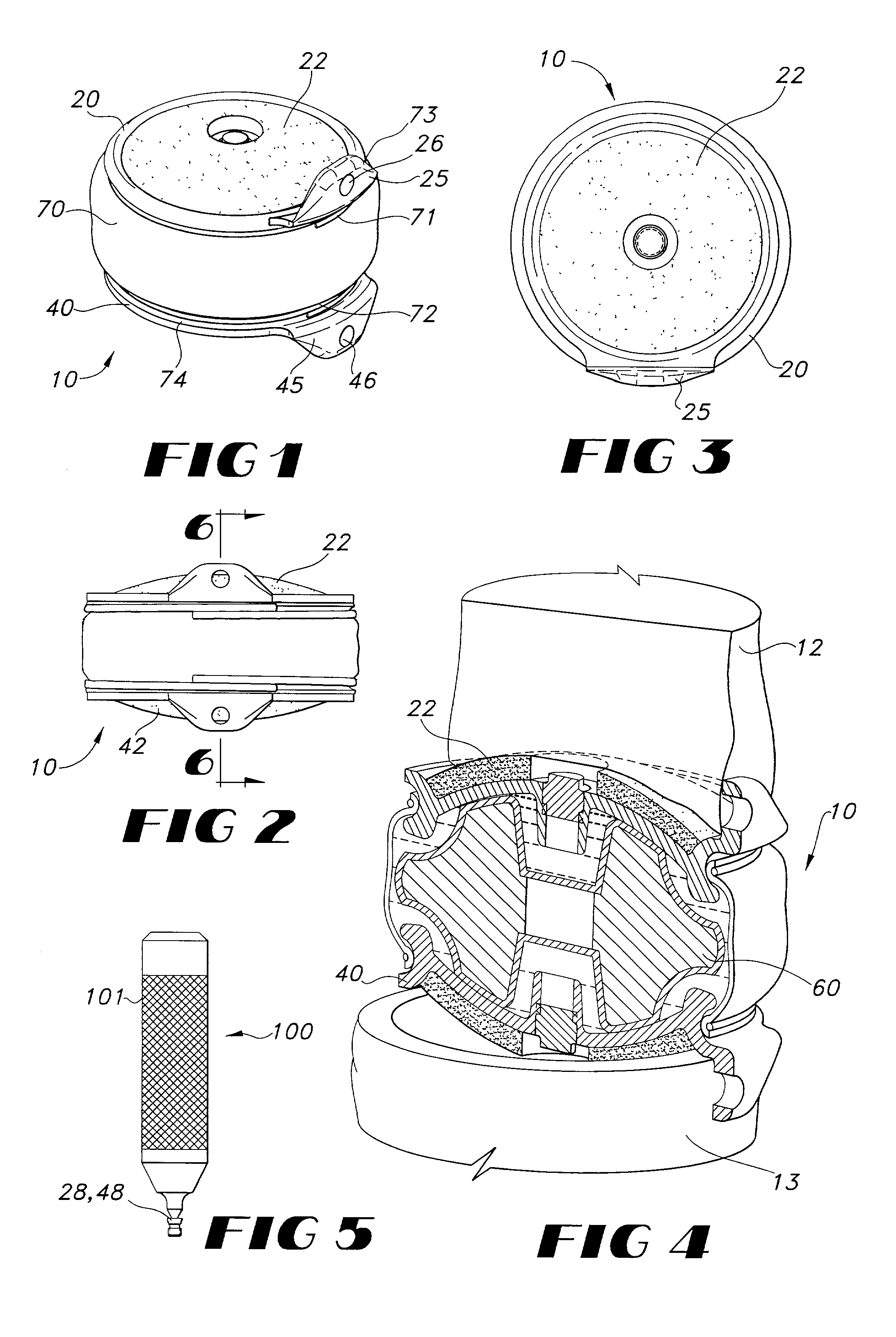
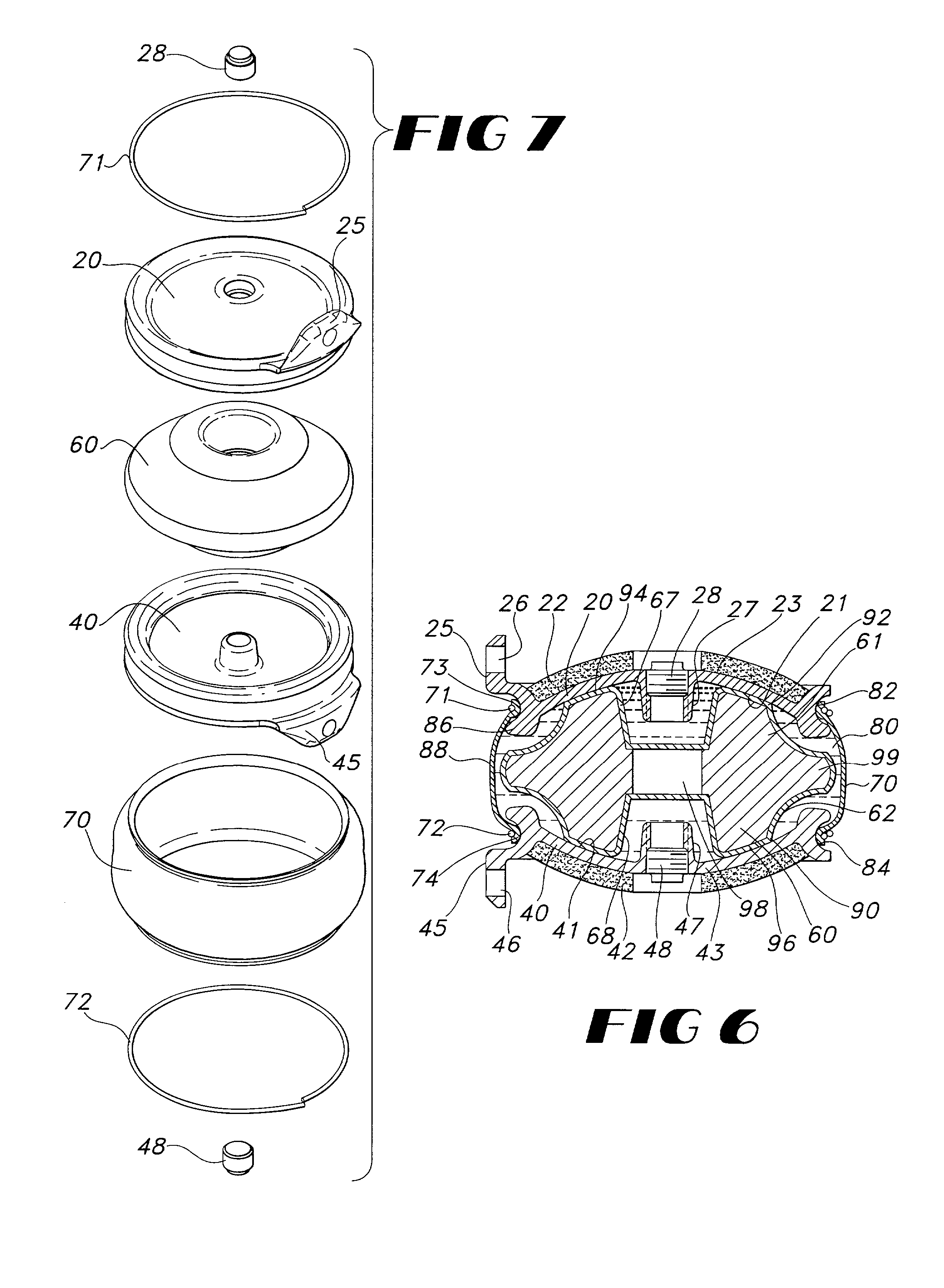
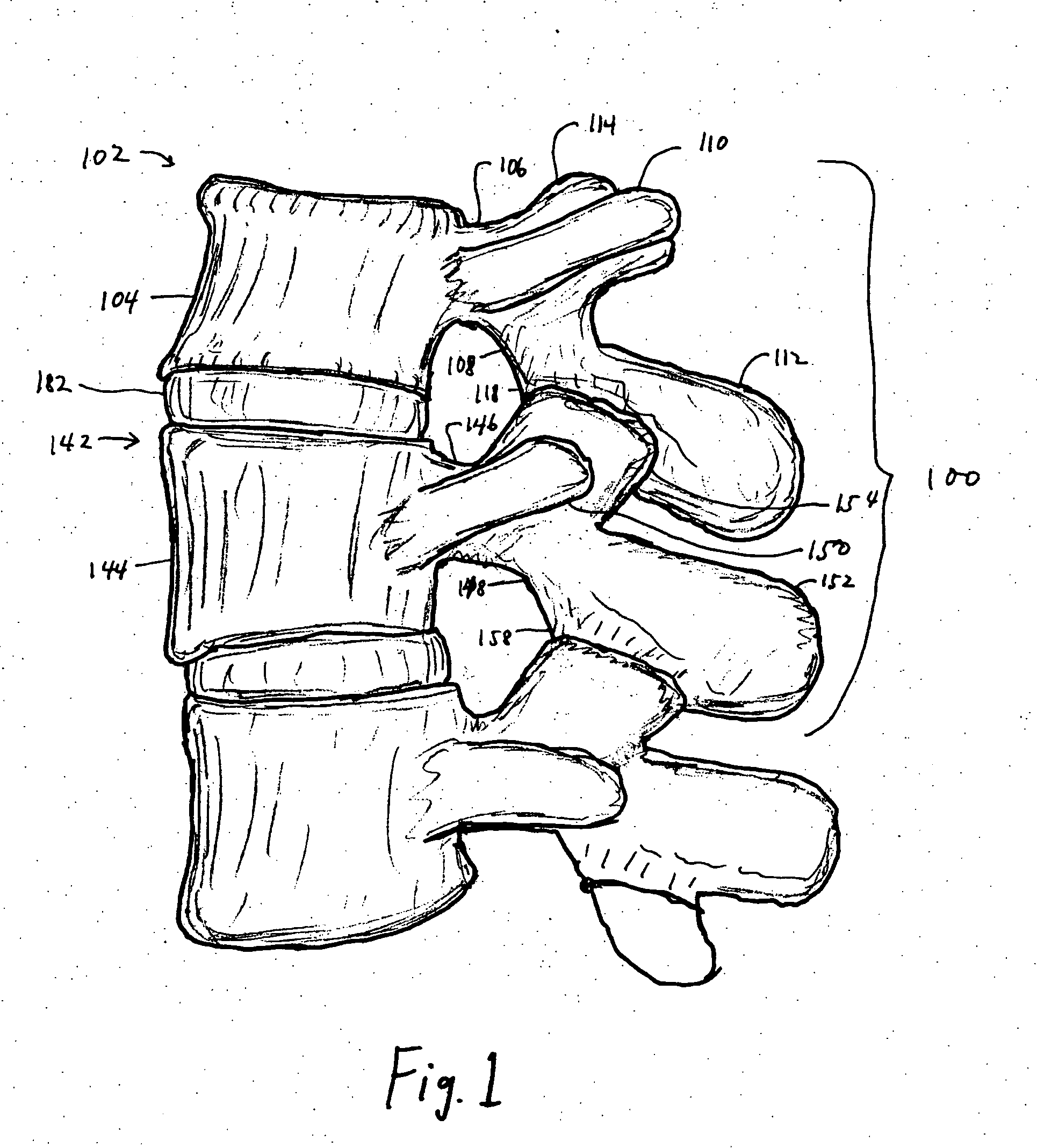
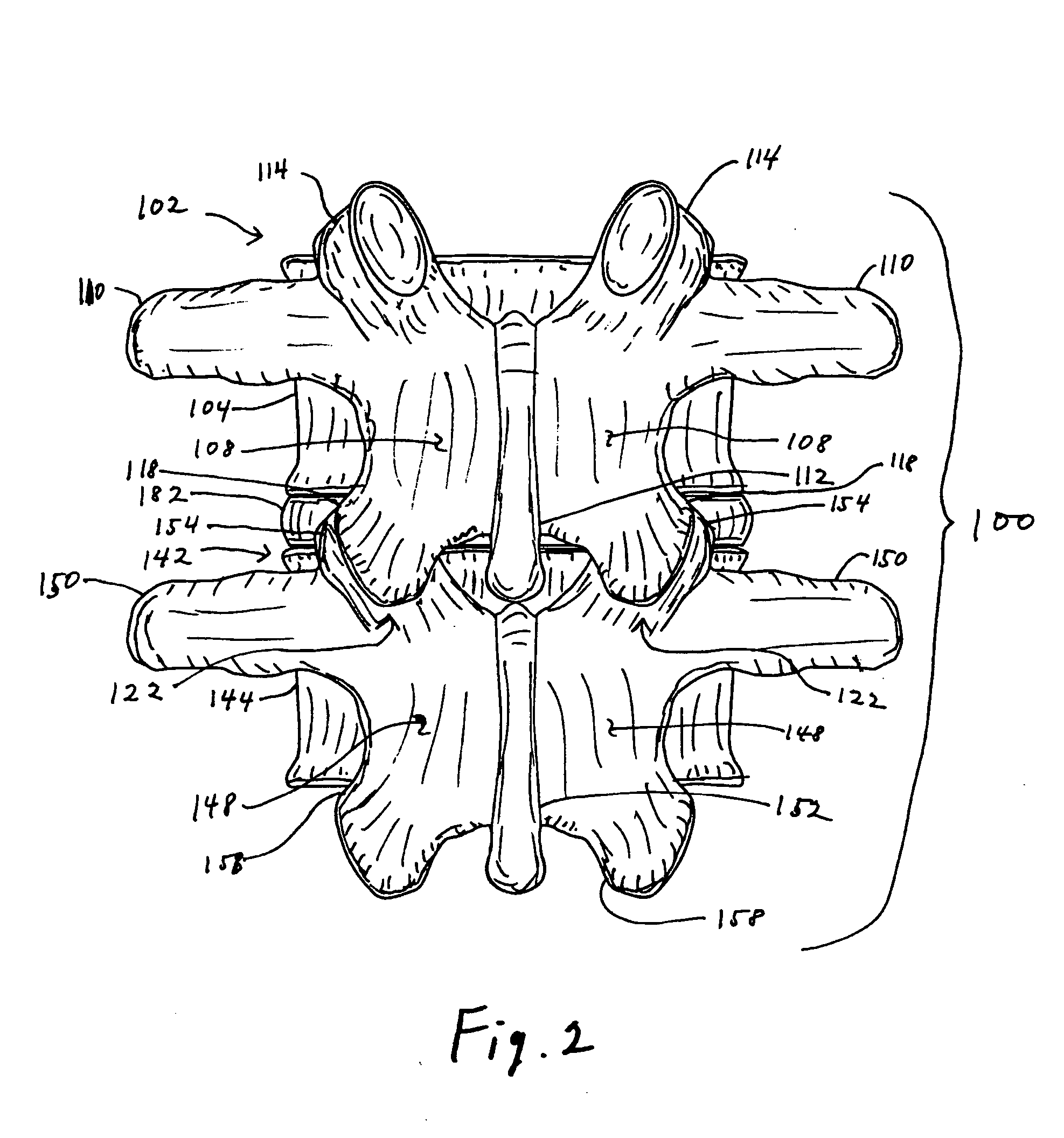
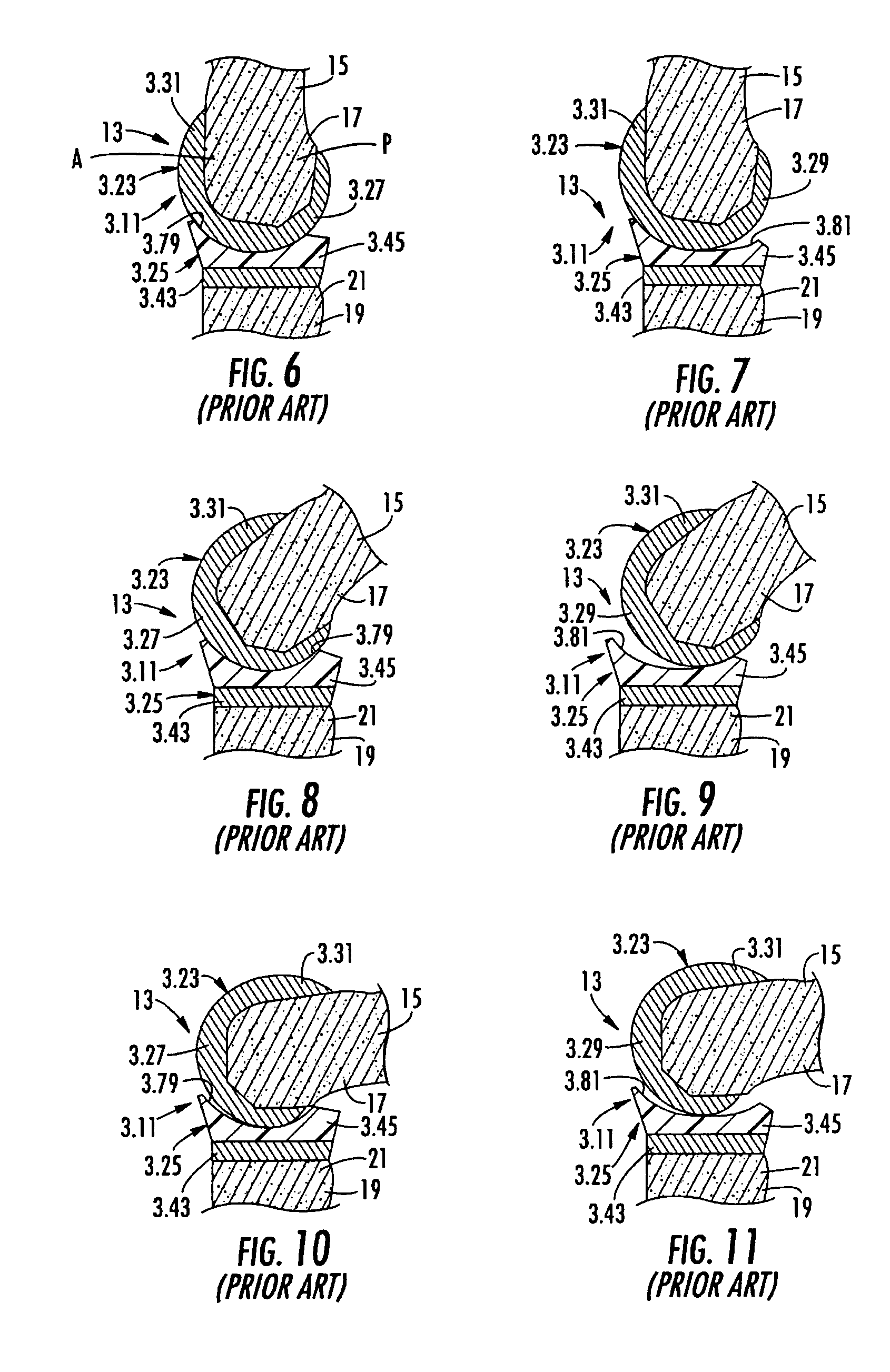
Implantable joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20020035400A1Improve wear resistanceImprove tribological propertiesDiagnosticsJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:SPINAL DYNAMICS CORP
Implantable joint prosthesis
ActiveUS20020128715A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityDiagnosticsJoint implantsIntervertebral discSurgical implant
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:COMPANION SPINE LLC
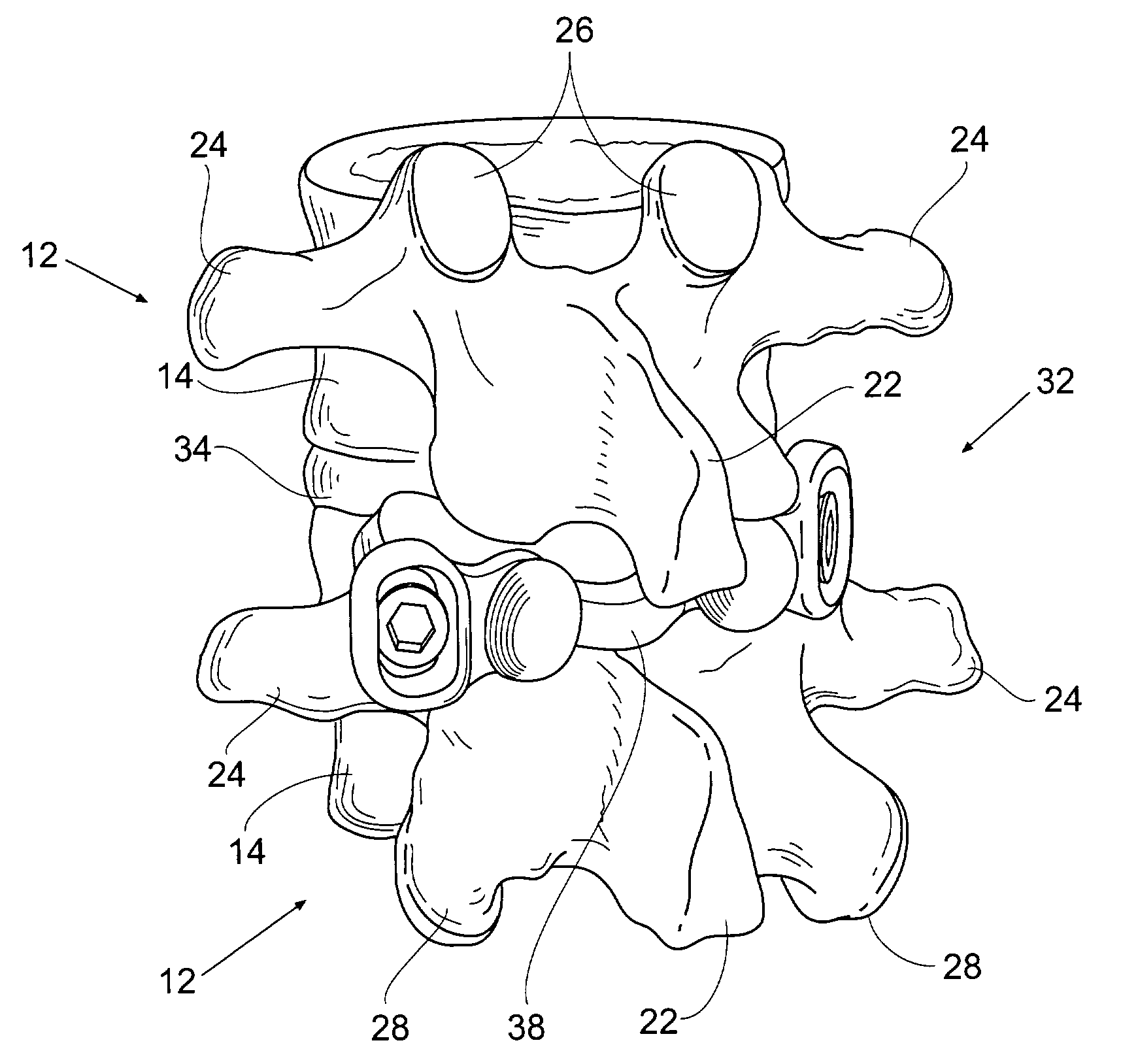
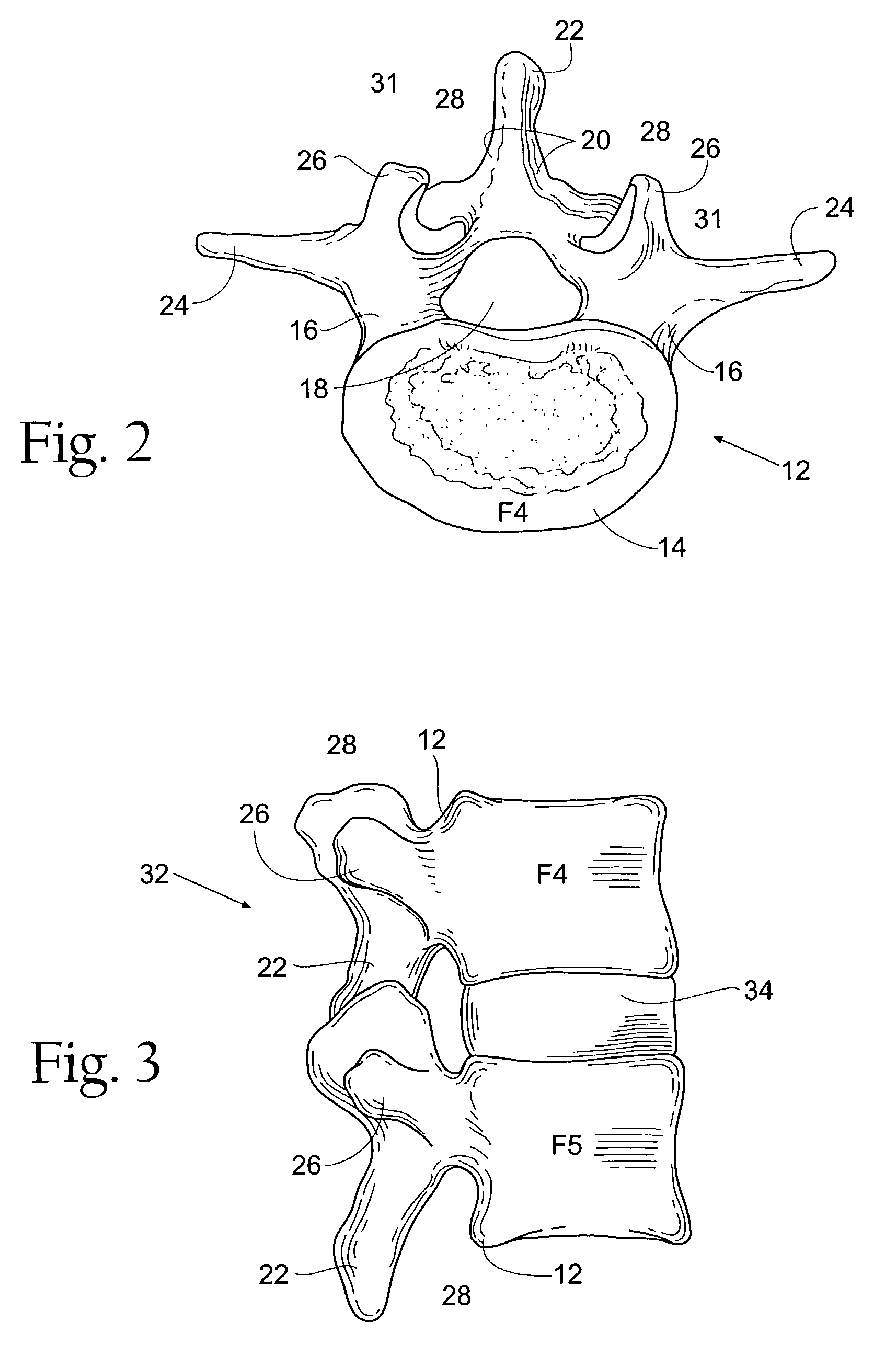
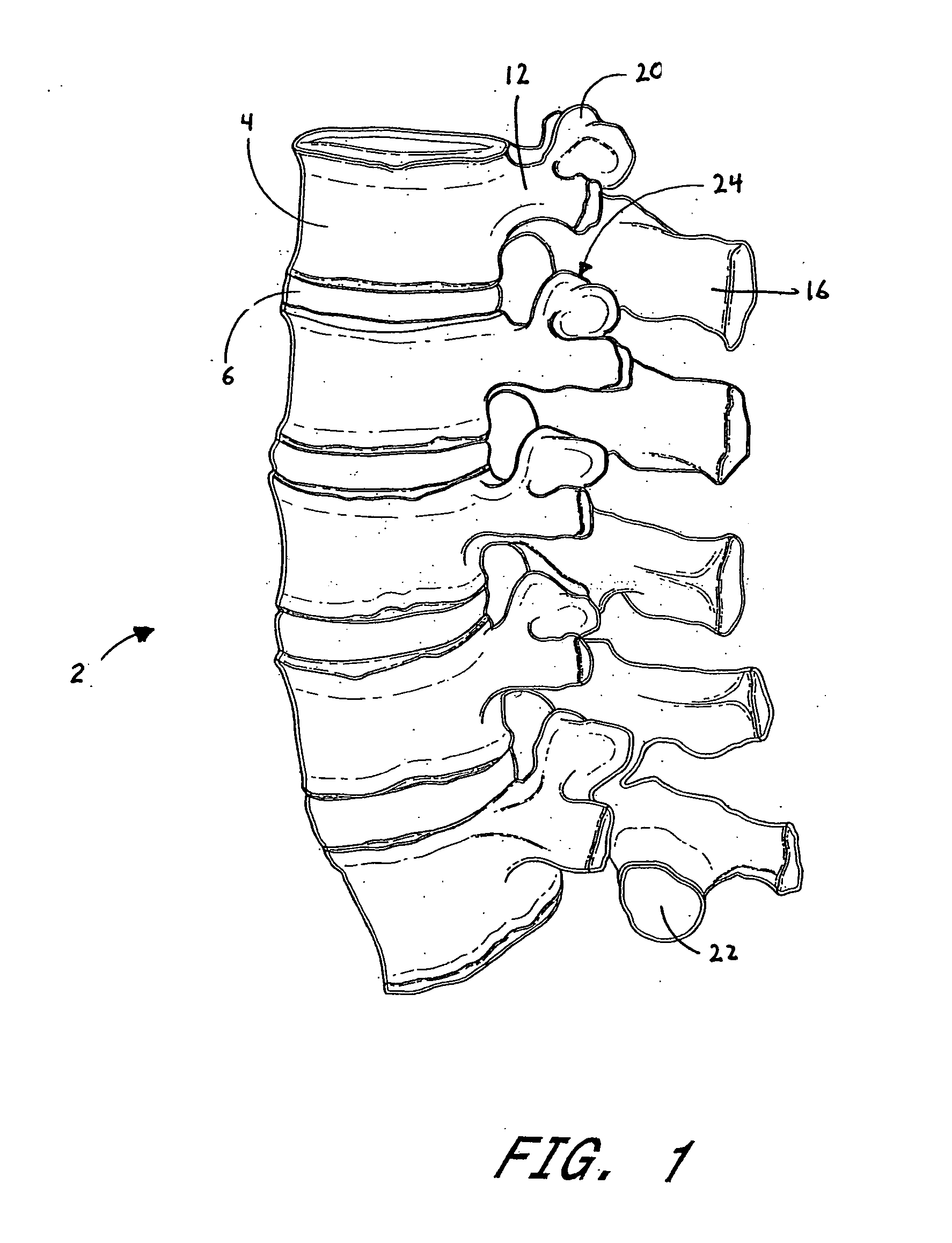
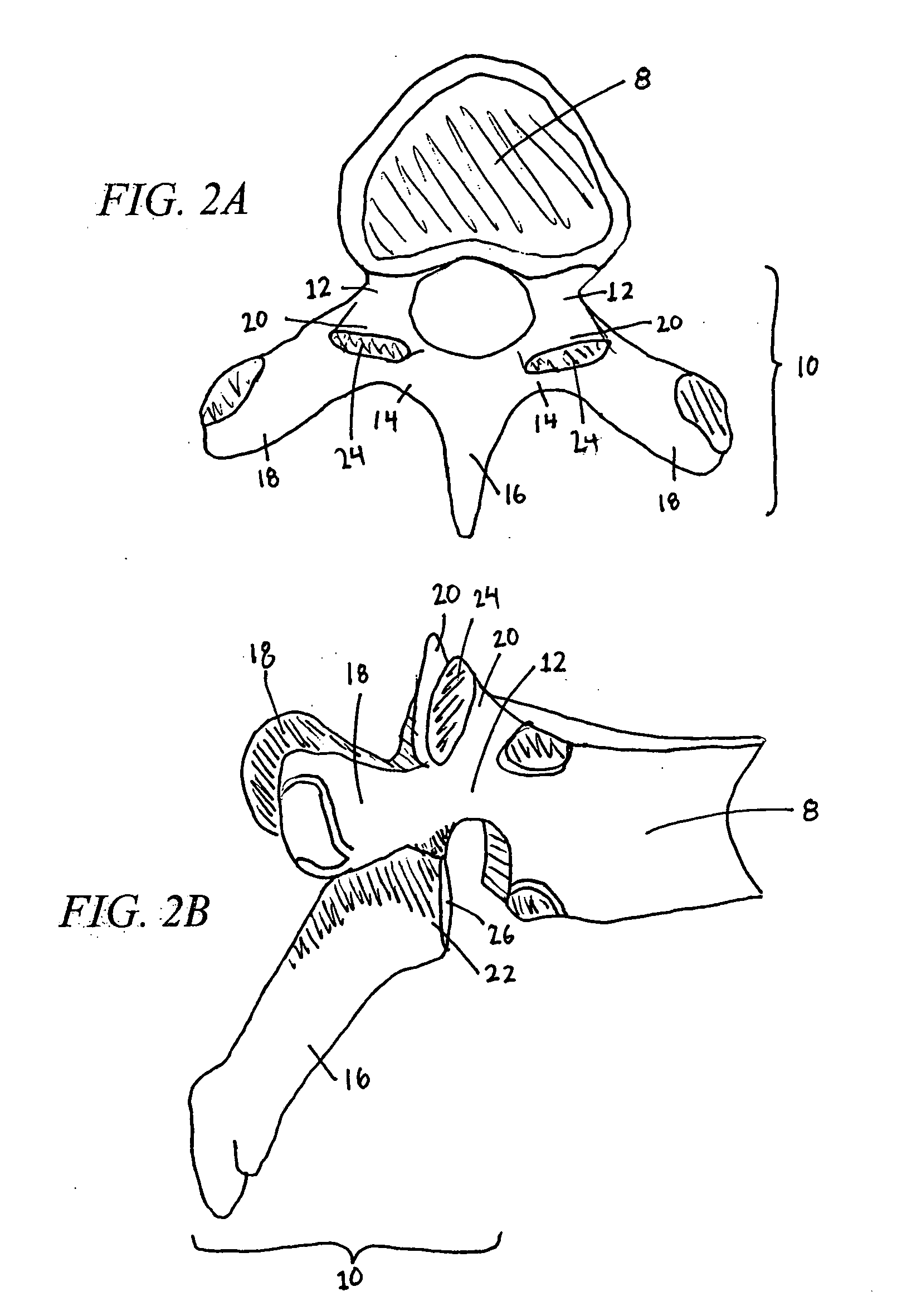
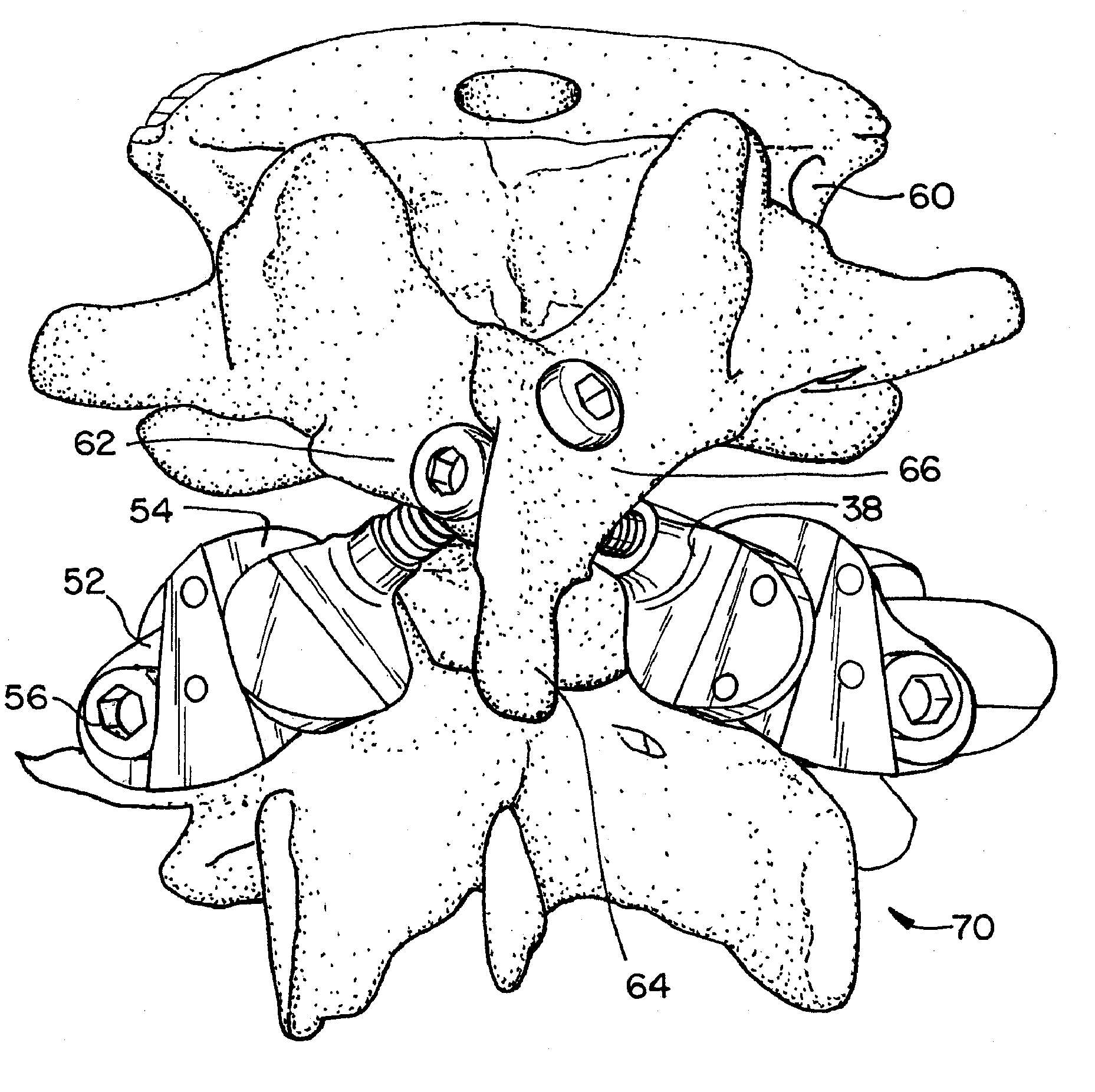
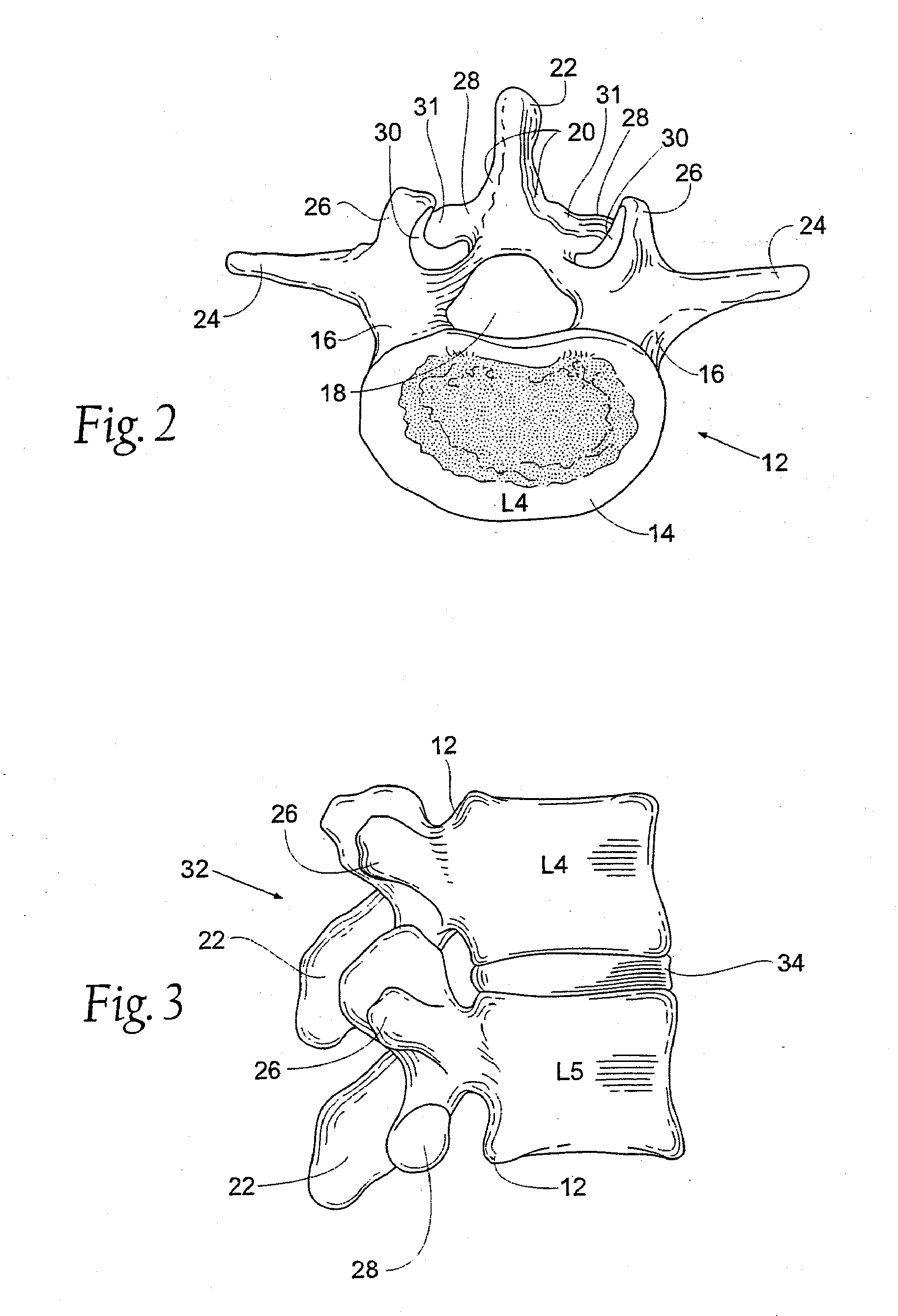
Prostheses, systems and methods for replacement of natural facet joints with artificial facet joint surfaces
InactiveUS6974478B2Desired range of mobilityLessen and alleviate spinal painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesSpinal column
Cephalad and caudal vertebral facet joint prostheses and methods of use are provided. The prostheses provide an artificial facet joint structure including an artificial articular configuration unlike the preexisting articular configuration. The radii and material stress values of the prostheses are configured to sustain contact stress. The cephalad prosthesis provides for posterior-anterior adjustment. Both prostheses permit lateral adjustment and adjustment to accomodate interpedicle distance. Further, the prostheses may be customized to provide a pre-defined lordotic angle and a pre-defined pedicle entry angle.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
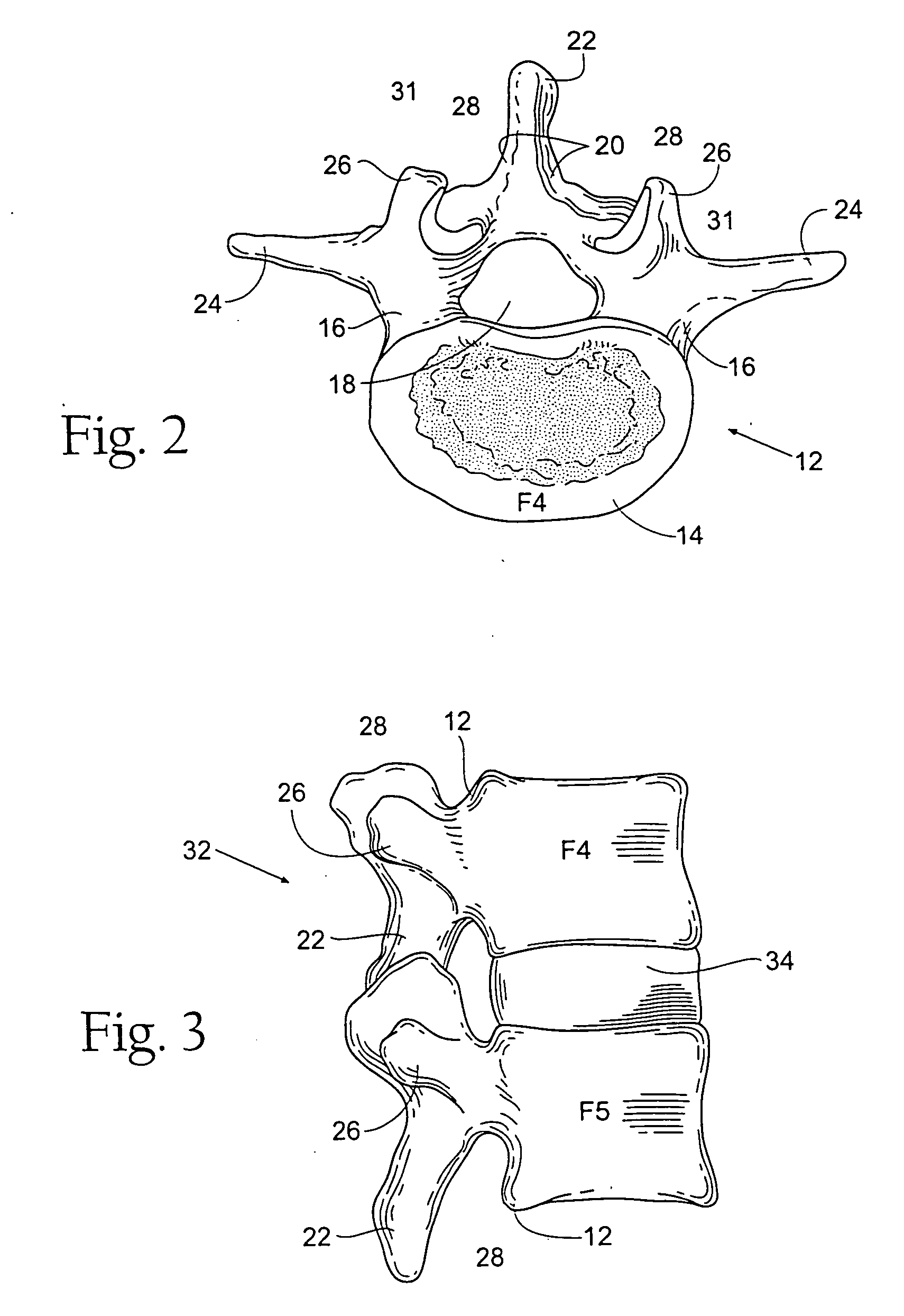
Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation
ActiveUS20050177240A1Reduce contactMaintain liquidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFacet joint prosthesisArticular processes
Devices and methods for altering the spacing and motion at the facet joints of the vertebral column are provided. One embodiment of the invention comprises a prosthesis with surfaces configured to articulate with the facets of the facet joint. A retaining member for anchoring the prosthesis within the facet joint is optionally included. Methods for surgically and less invasively implanting the prosthesis and securing the prosthesis to the articular processes or surrounding soft tissue are also provided.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Modular knee prosthesis
A modular prosthetic knee system used to replace the natural knee. The system includes a femoral knee prosthesis and a tibial knee prosthesis. Both prostheses are formed of modular components that are connectable in-vivo to form the prosthetic knee system. The femoral knee prosthesis includes two separate components, a lateral condyle and medial condyle; and the tibial knee prosthesis includes a multiple separate components, a medial baseplate, a lateral baseplate, a medial insert, and a lateral insert. The medial and lateral baseplate are connectable to form a complete baseplate with the medial and lateral inserts connectable to the complete baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Prostheses, tools and methods for replacement of natural facet joints with artificial facet joint surfaces
ActiveUS20050010291A1Lessen and alleviate spinal painRelieving sourceJoint implantsSpinal implantsFacet joint prosthesisArticular surfaces
Cephalad and caudal vertebral facet joint prostheses and methods of use are provided. The cephalad prostheses are adapted and configured to be attached to a lamina portion of a vertebra without blocking a pedicle portion of the cephalad vertebra. In some embodiments, the prosthesis is attached with a non-invasive support member, such as a clamp. In other embodiments, a translaminar screw may be used for additional fixation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
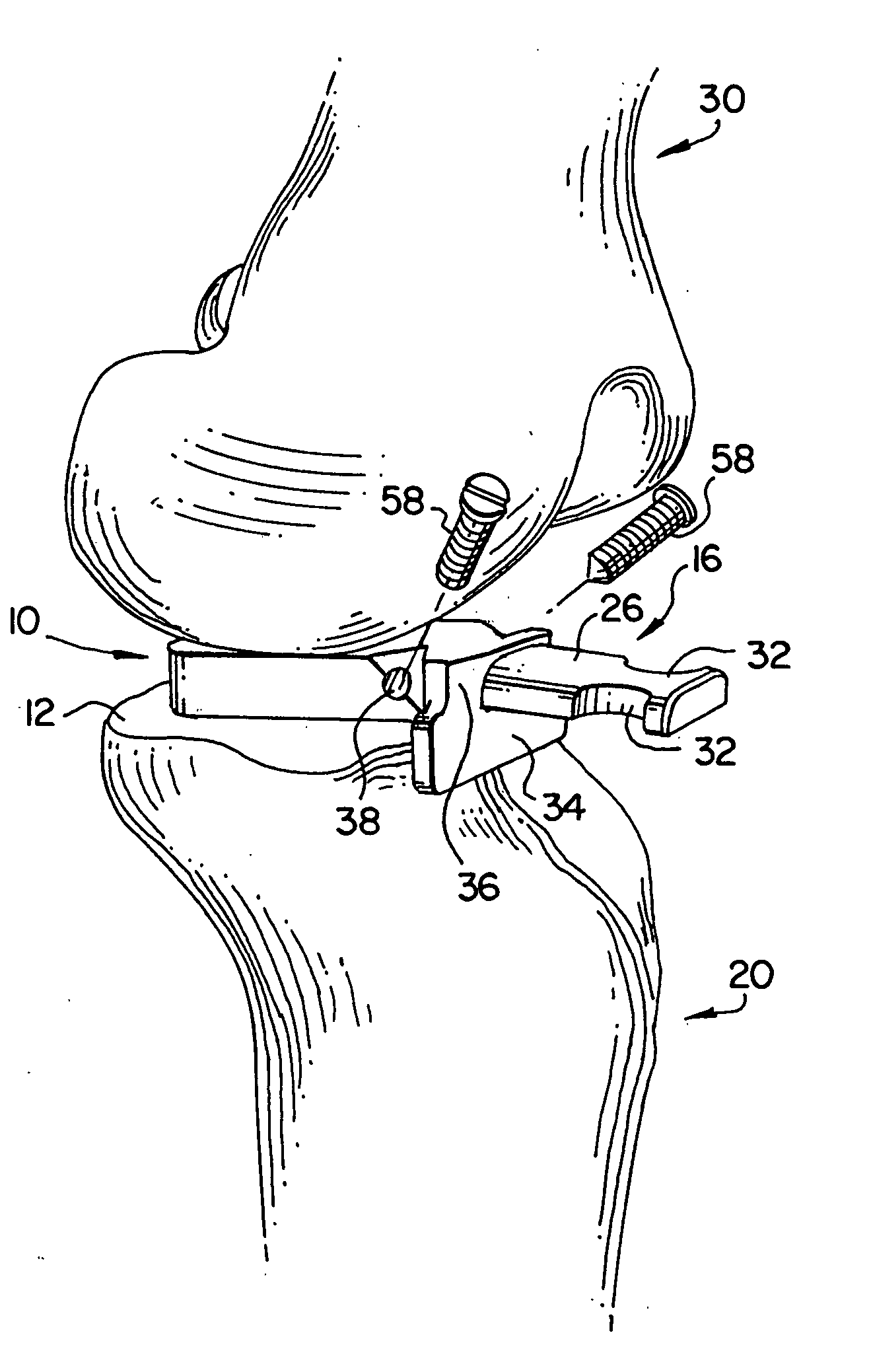
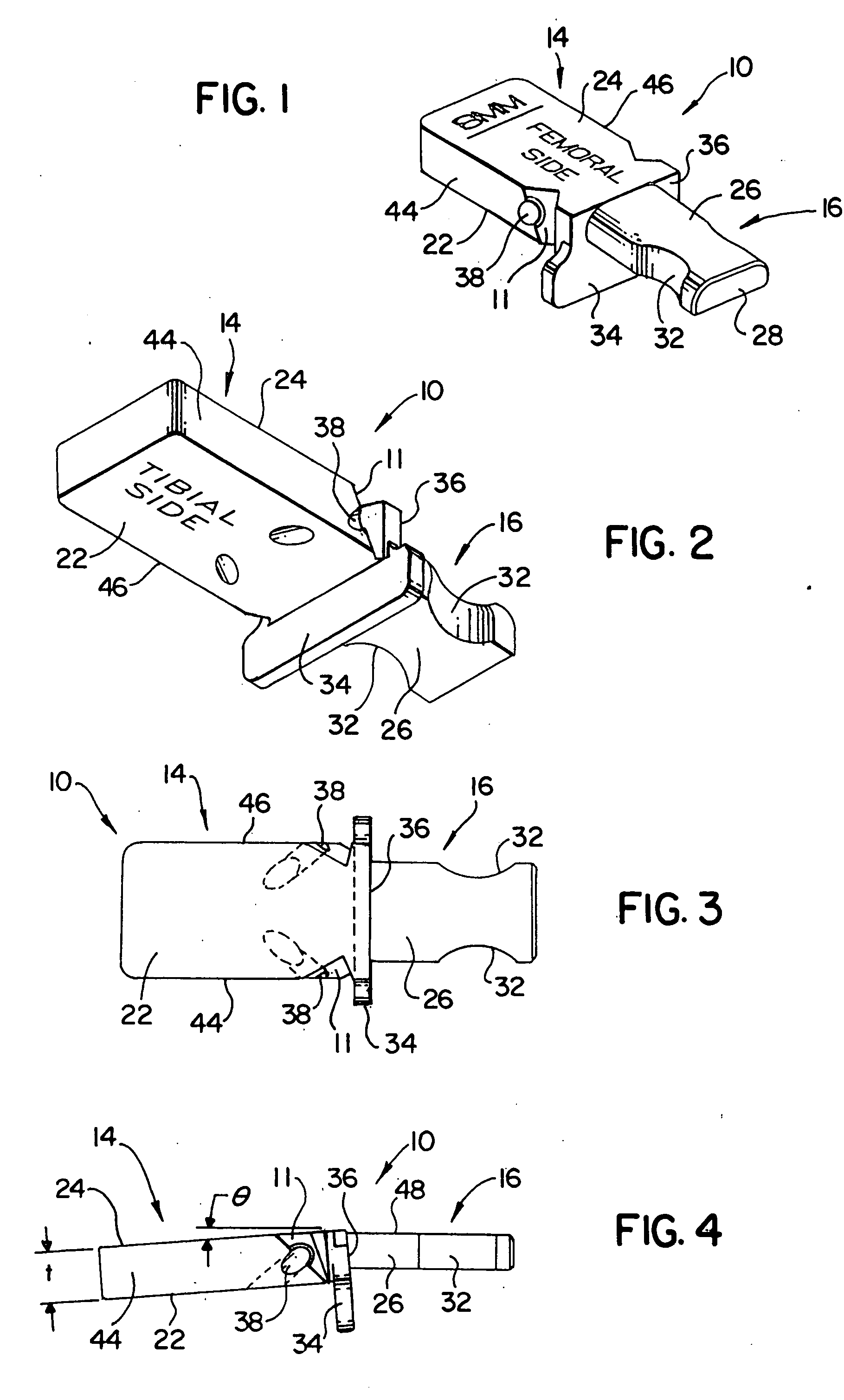
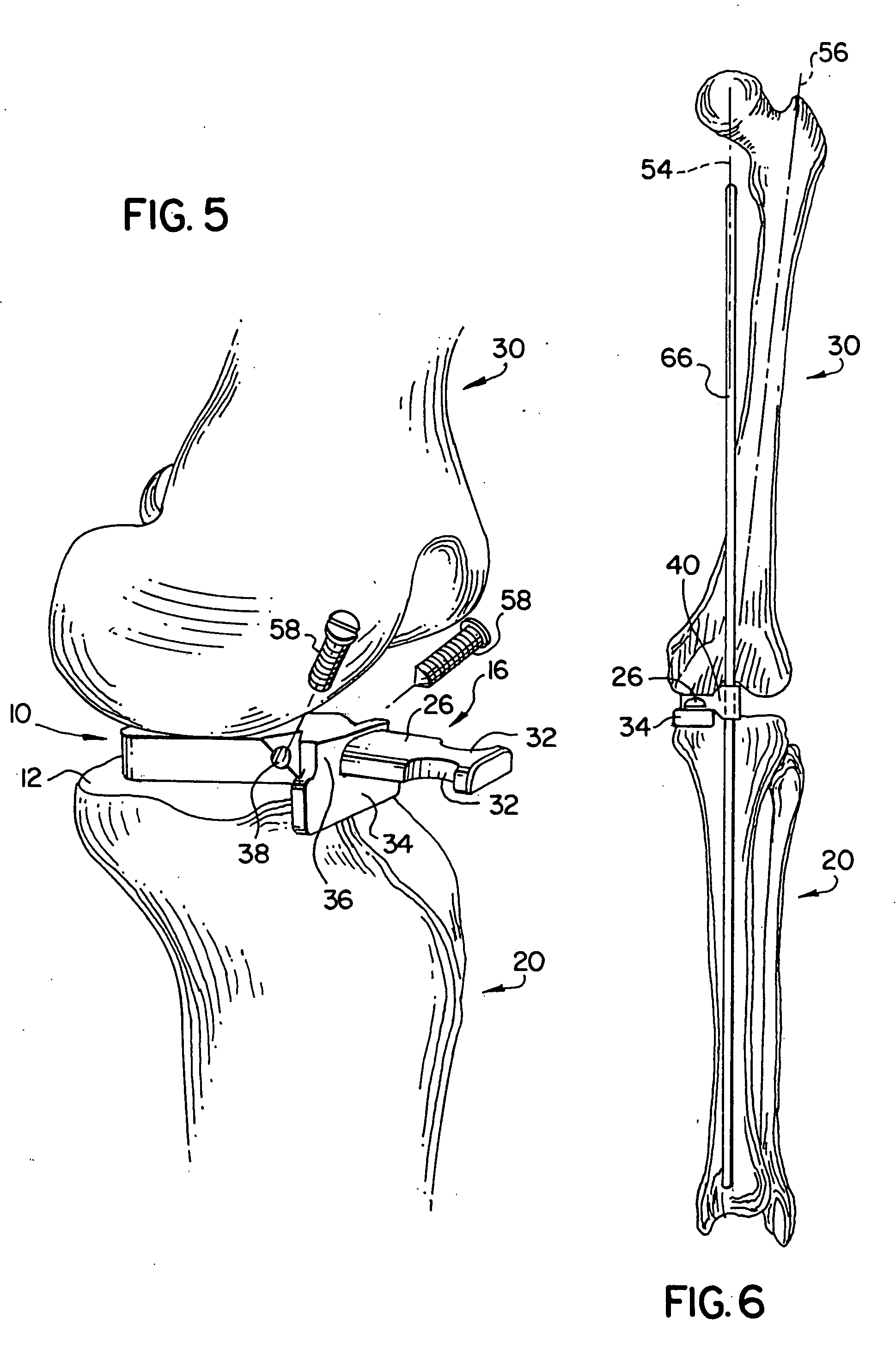
Posterior vertebral joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20050015146A1Easy to slideConserve high degree of mobilityJoint implantsSpinal implantsProsthesisVertebral Joint
The present invention relates to a posterior vertebral joint prosthesis. The left or right posterior vertebral joint prosthesis of the invention presents a smooth bearing surface and said surface presents antero-posterior curvature.
Owner:LOUIS CHRISTIAN +1
Orthopedic and dental implant devices providing controlled drug delivery
Implantable prosthetic devices are provided for controlled drug delivery, for orthopedic and dental applications. The device may include a prosthetic device body having at least one outer surface area; two or more discrete reservoirs located in spaced apart positions across at least a portion of the outer surface area, the reservoirs formed with an opening at the surface of the device body and extending into the device body; and a release system disposed in the reservoirs which comprises at least one therapeutic or prophylactic agent, wherein following implantation into a patient the therapeutic or prophylactic agent is released in a controlled manner from the reservoirs. The prosthetic device body preferably is a joint prosthesis or part thereof, such as a hip prosthesis, a knee prosthesis, a vertebral or spinal disc prosthesis, or part thereof. Optional reservoir caps may further control release kinetics.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
Prostheses, tools and methods for replacement of natural facet joints with artifical facet joint surfaces
ActiveUS20050143818A1Minimize sizeMinimize extentInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsArticular surfacesFacet joint prosthesis
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Facet joint prosthesis
A prosthetic implant for replacing a facet joint of a spinal motion segment includes a generally conical superior component adapted to be implanted at a surgically prepared site on a lower articular process of a cephalad vertebra of a spinal motion segment, and a cup-shaped inferior component adapted to be implanted at a surgically prepared site on a superior articular process of a caudad vertebra of the spinal motion segment.
Owner:RE SPINE
Implantable device for facet joint replacement
InactiveUS20050267579A1Desired range of mobilityLessen and alleviate spinal painInternal osteosythesisBone implantFacet joint structureProsthesis
Cephalad and caudal vertebral facet joint prostheses and methods of use are provided. The prostheses provide an artificial facet joint structure including an artificial articular configuration unlike the preexisting articular configuration. The radii and material stress values of the prostheses are configured to sustain contact stress. The cephalad prosthesis provides for posterior-anterior adjustment. Both prostheses permit lateral adjustment and adjustment to accomodate interpedicle distance. Further, the prostheses may be customized to provide a pre-defined lordotic angle and a pre-defined pedicle entry angle.
Owner:FACET SOLUTIONS
Modular knee prosthesis
A modular prosthetic knee system used to replace the natural knee. The system includes a femoral knee prosthesis and a tibial knee prosthesis. Both prostheses are formed of modular components that are connectable in-vivo to form the prosthetic knee system. The femoral knee prosthesis includes two separate components, a lateral condyle and medial condyle; and the tibial knee prosthesis includes a multiple separate components, a medial baseplate, a lateral baseplate, a medial insert, and a lateral insert. The medial and lateral baseplate are connectable to form a complete baseplate with the medial and lateral inserts connectable to the complete baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
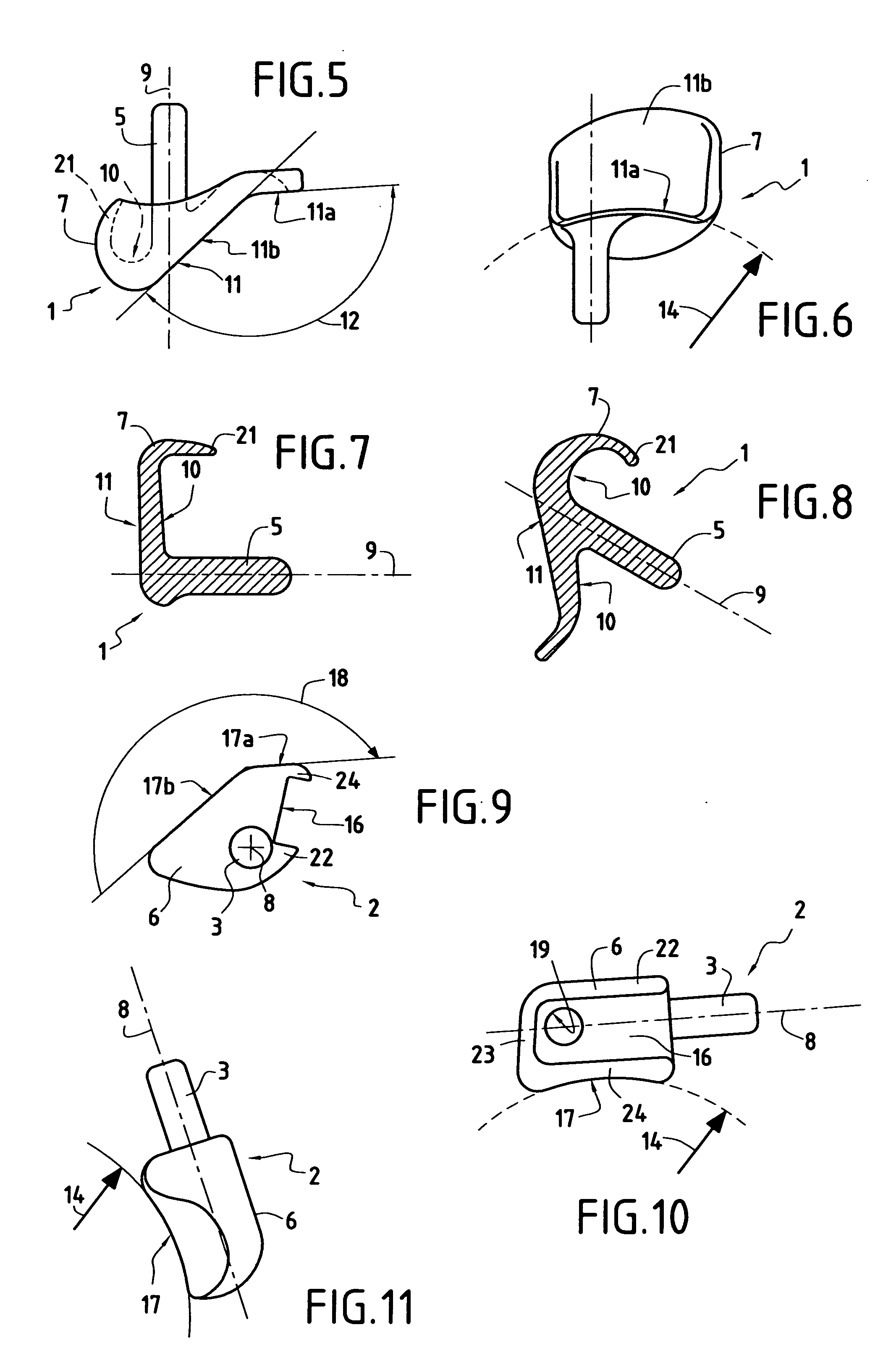
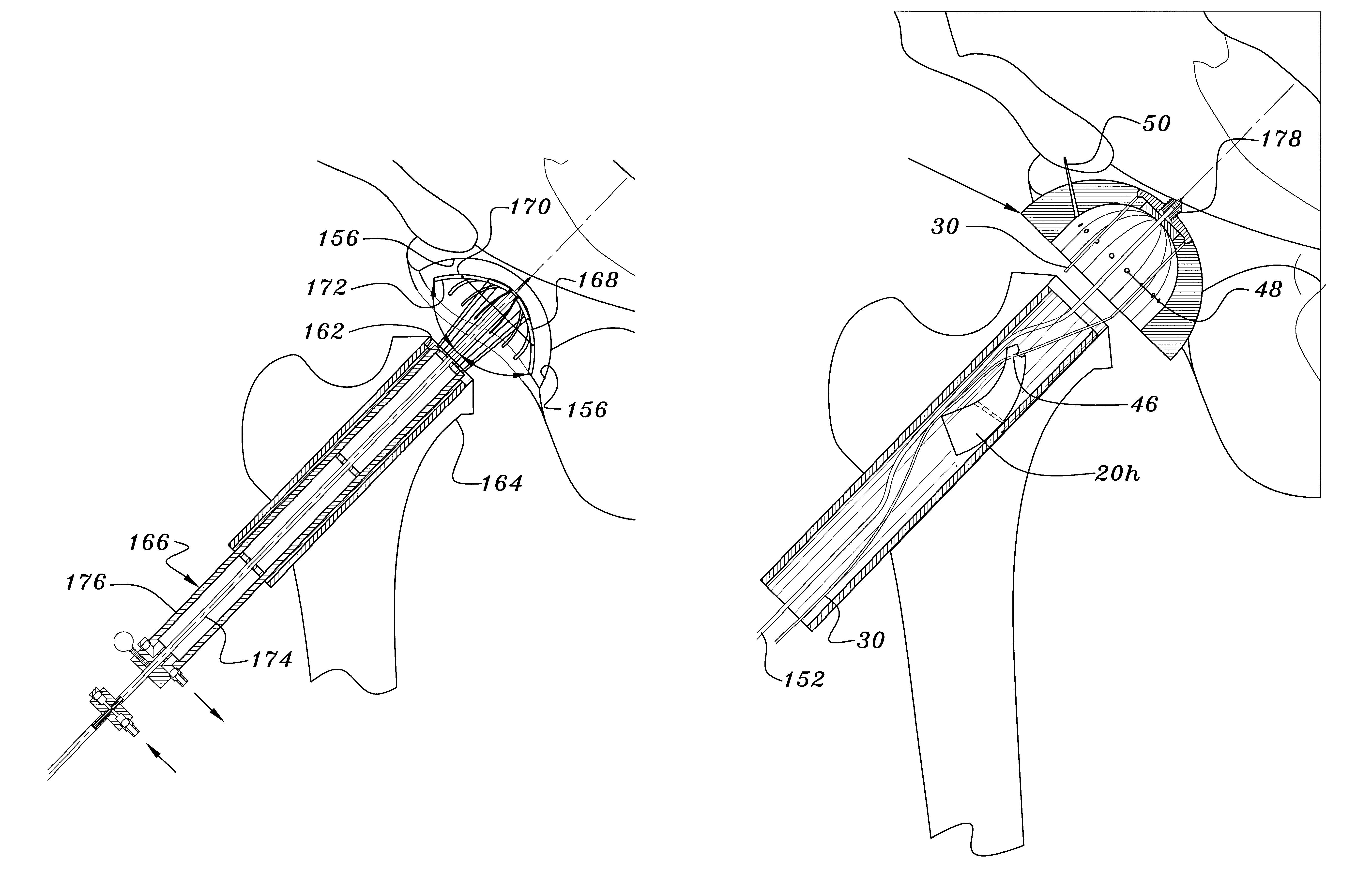
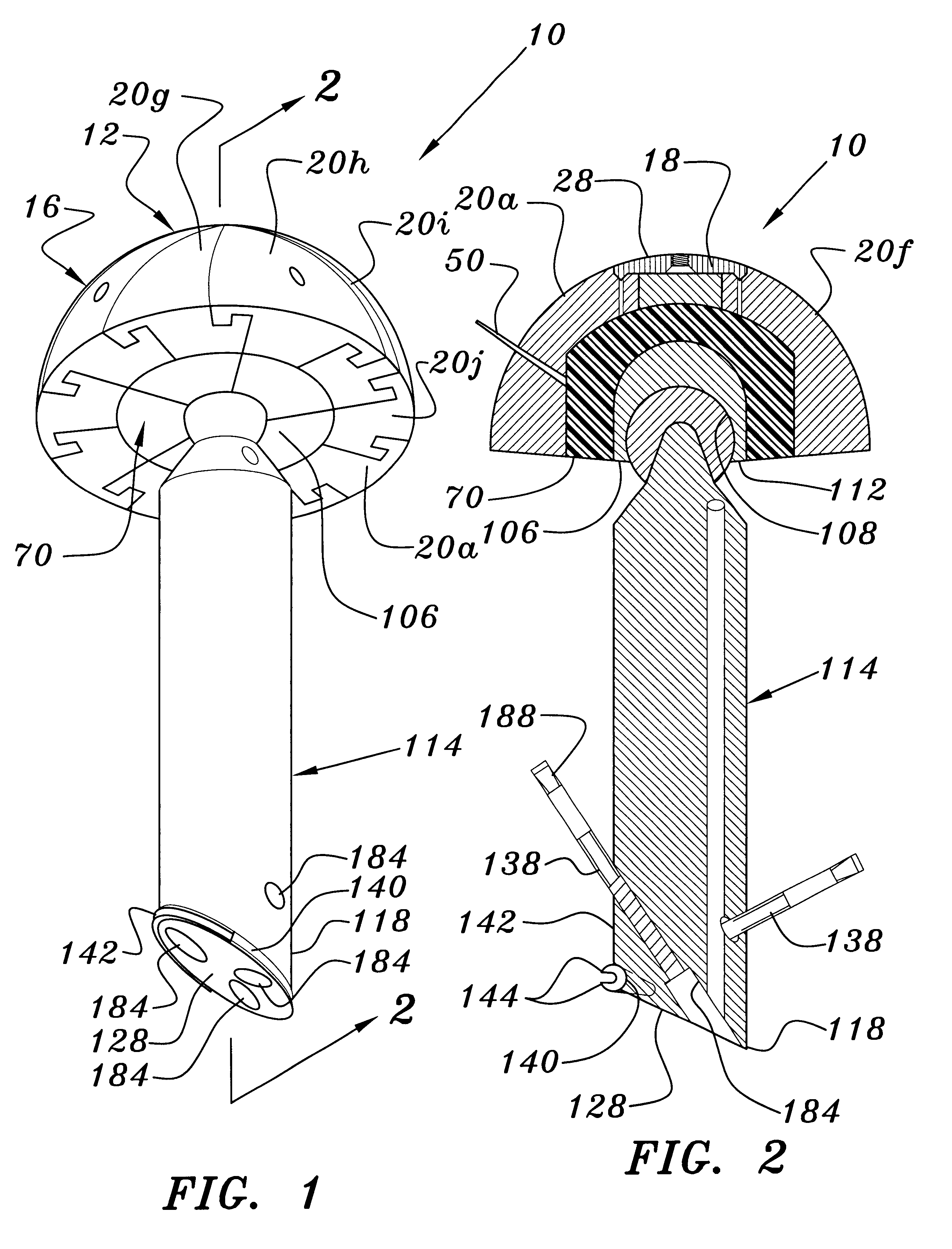
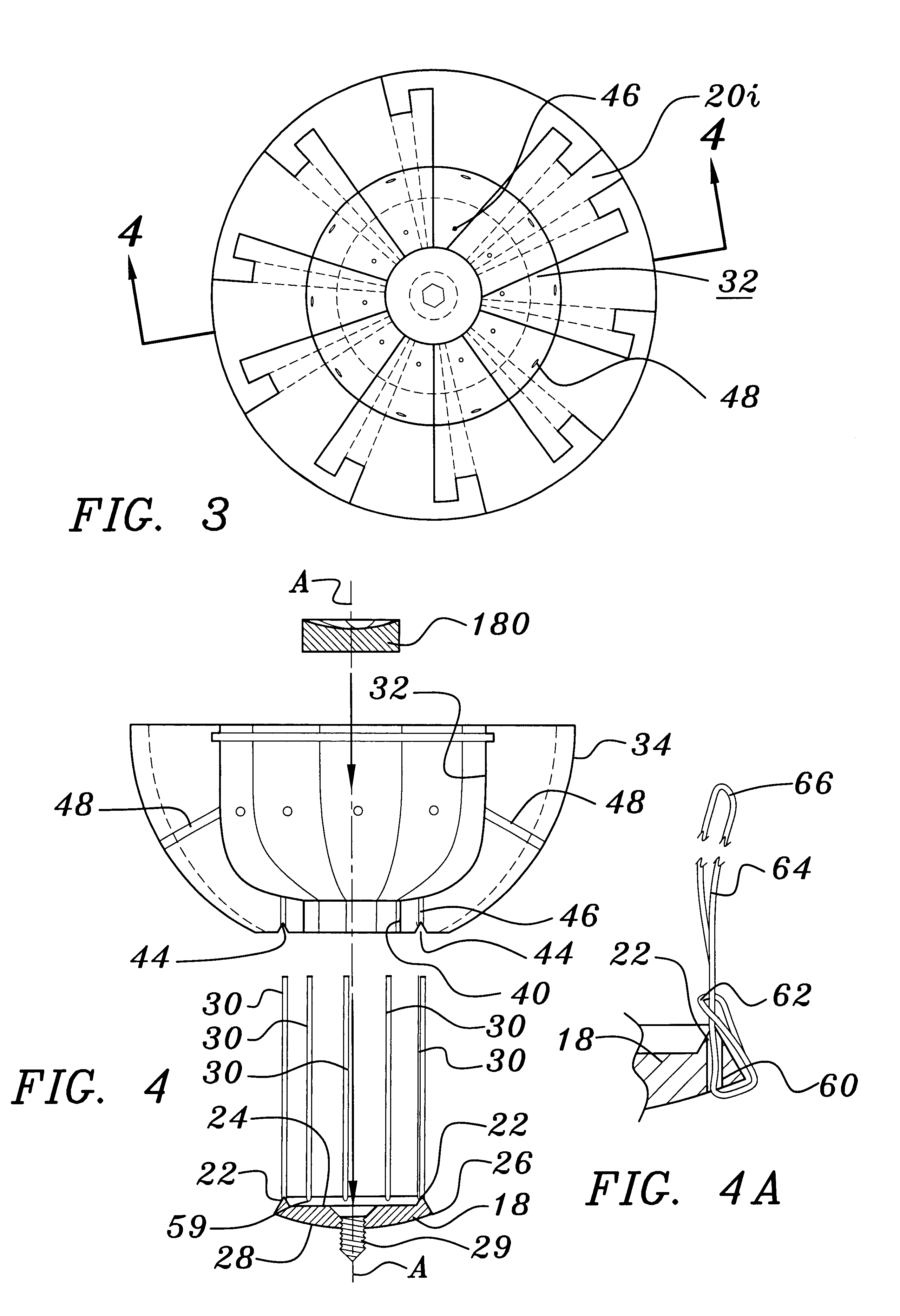
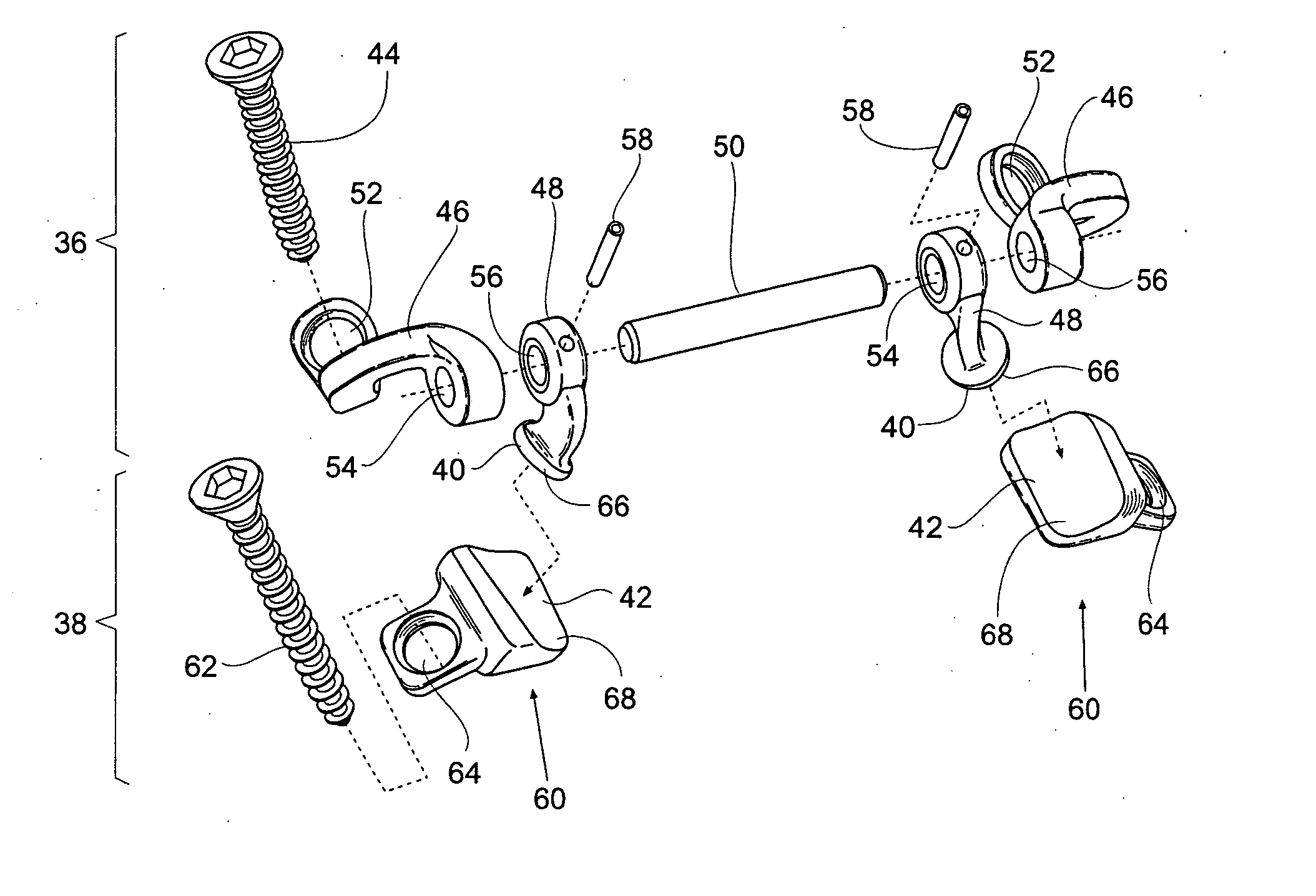
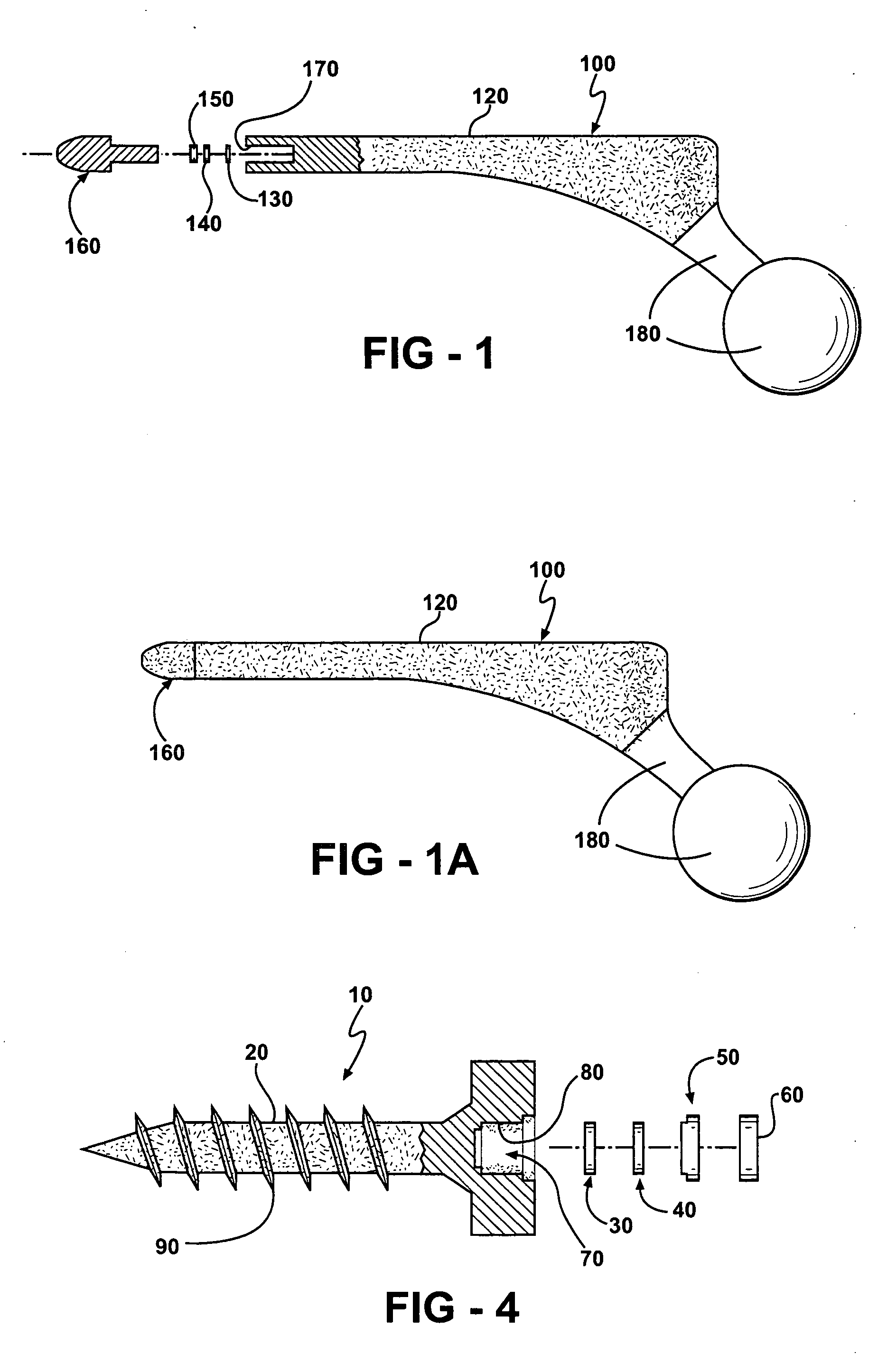
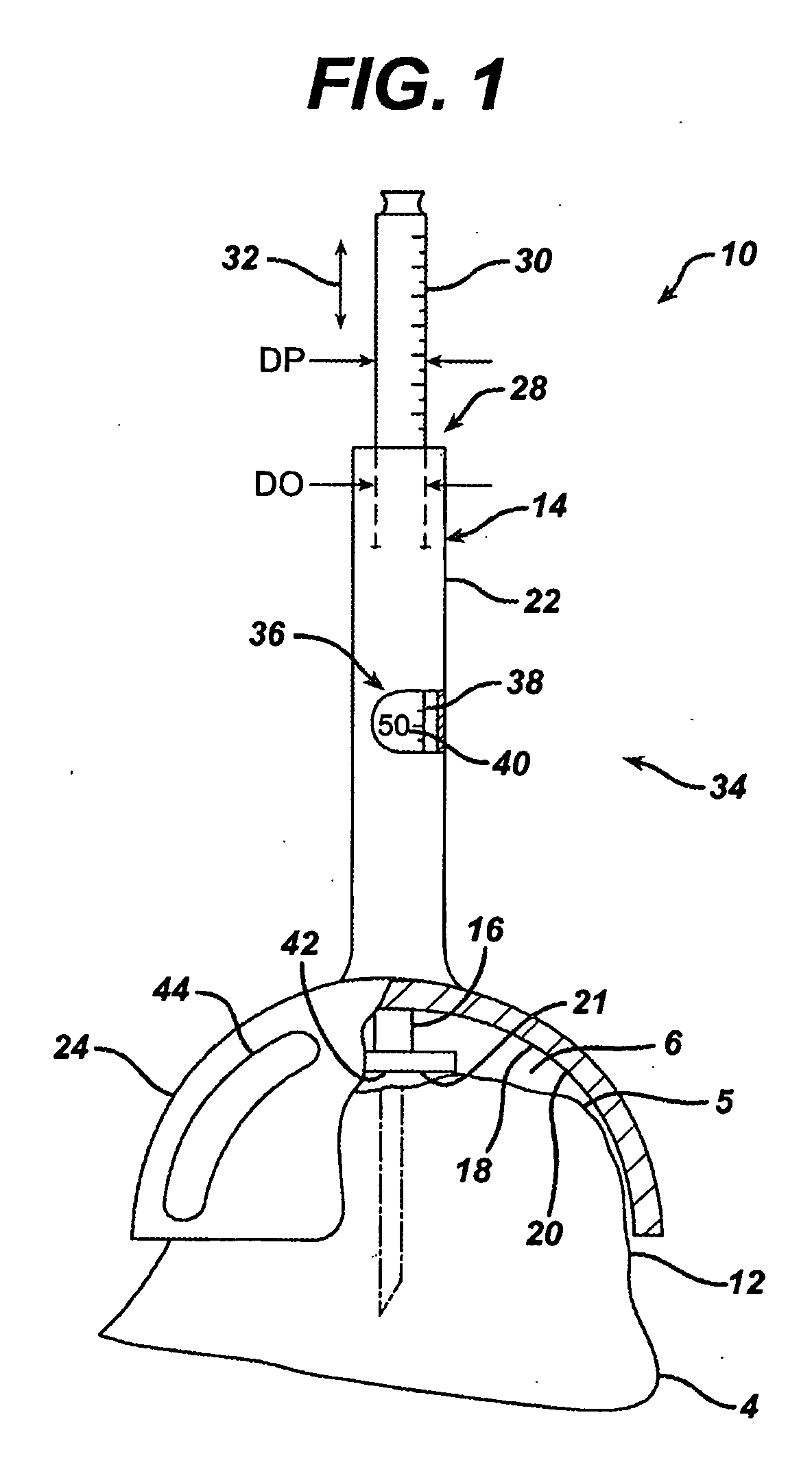
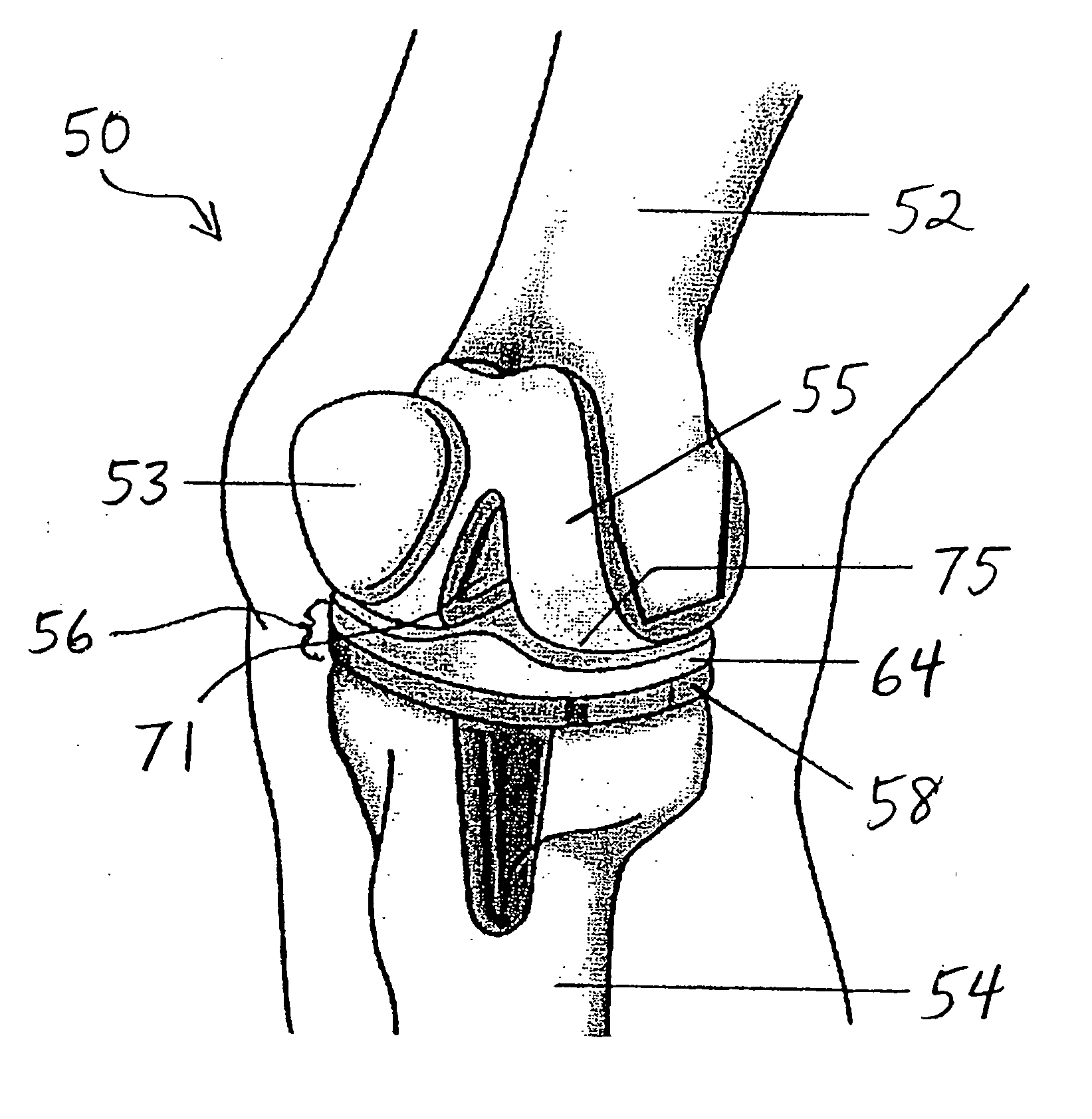
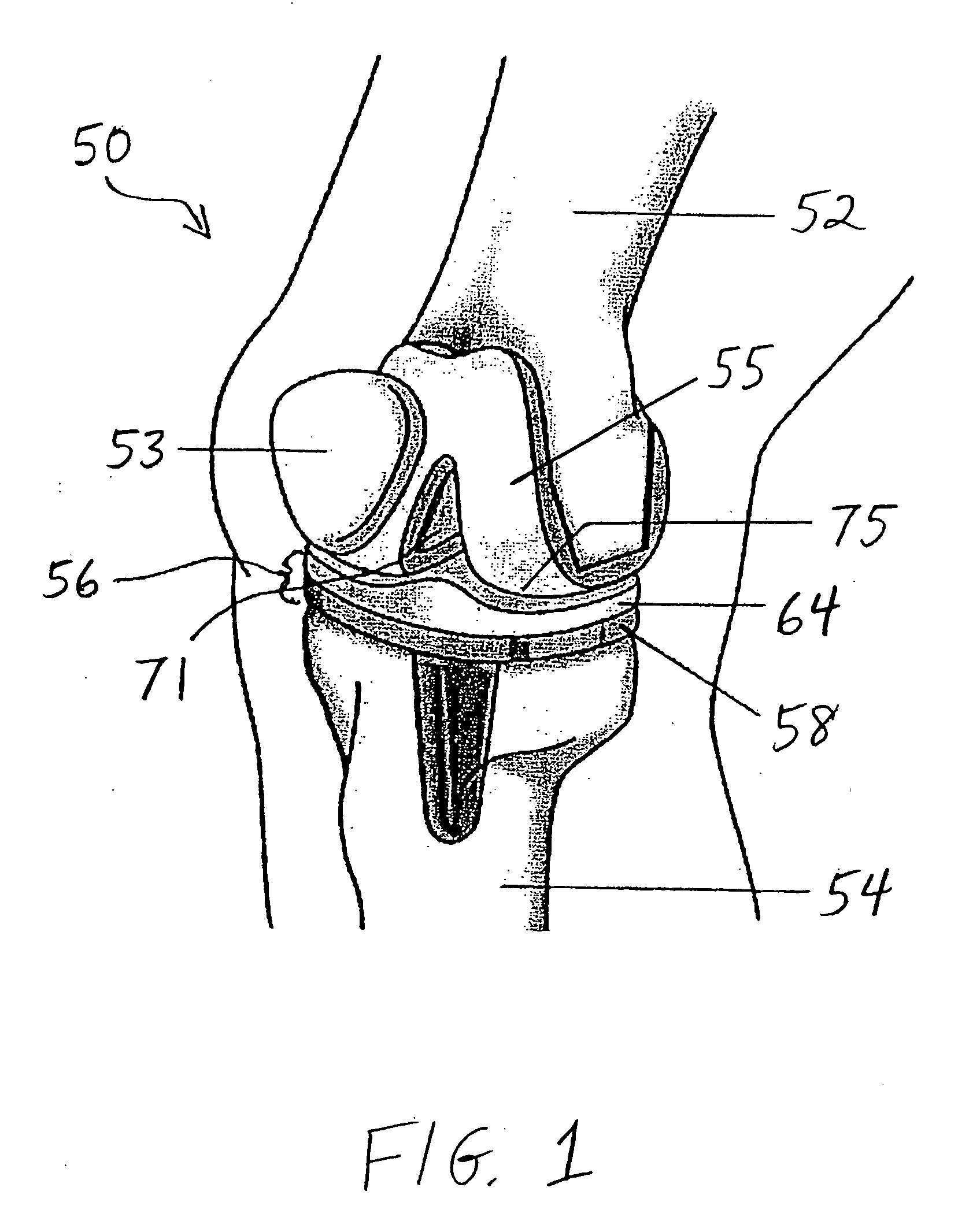
Joint prosthesis and method for placement
A prosthesis for replacement of a ball and socket joint in the human body. The prosthetic components comprise a plurality of separate parts which may be inserted through a hole in the femur of the patient and assembled and attached to the prepared acetabulum of the hip bone to form a cup-shaped first shell. A cup is also passed through the hole in the femur and attached to the first shell to form the socket portion of the joint. A shaft having a first end with a ball formed thereon is inserted in the hole through the femur so that the ball engages the cup for movement therein.
Owner:TARABISHY IMAD ED
Prostheses, systems and methods for replacement of natural facet joints with artificial facet joint surfaces
InactiveUS20050119748A1Secure durable attachmentProcess safety and stabilityInternal osteosythesisBone implantFacet joint prosthesisArticular surfaces
Cephalad and caudal vertebral facet joint prostheses and methods of use are provided. A pair of fixation elements are adapted to be secured within a vertebra in an orientation that best assures a secure and durable attachment to cortical and / or cancellous bone. Artificial facet joint surfaces are mounted on the fixation elements, either directly or with the aid of a support. The artificial facet joint structure may be carried by an arm. The artificial facet joint structure is adapted for articulation with a complementary natural or artificial facet joint structure. Bilateral prostheses may by coupled by a brace to further secure and stabilize the prostheses.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Tibial knee prosthesis
A knee prosthetic including a tibial component defining medial and lateral concavities shaped to receive medial and lateral femoral condyles of the femur. The concavities have first portions for contact with the condyles during normal knee flexion and second portions for contact with the condyles during deep, or high, knee flexion. The medial concavity can include a conforming boundary that encompasses at least the first and second portions, wherein an area inside the conforming boundary has a generally flat surface. The flat surface allows the medial femoral condyle to slide and rotate posteriorly during high knee flexion. The conforming boundary can have a generally triangular shape with an apex extending anteriorly and a relatively wider base extending posteriorly, wherein the apex includes the first portion and the base includes the second portion. The relatively wider base portion advantageously allows additional area for posteriorly directed articulating contact during high knee flexion.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS HLDG INC
Prophylactic bactericidal implant
InactiveUS20060004431A1Prevent microbial infectionSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyProtozoaSurgical operation
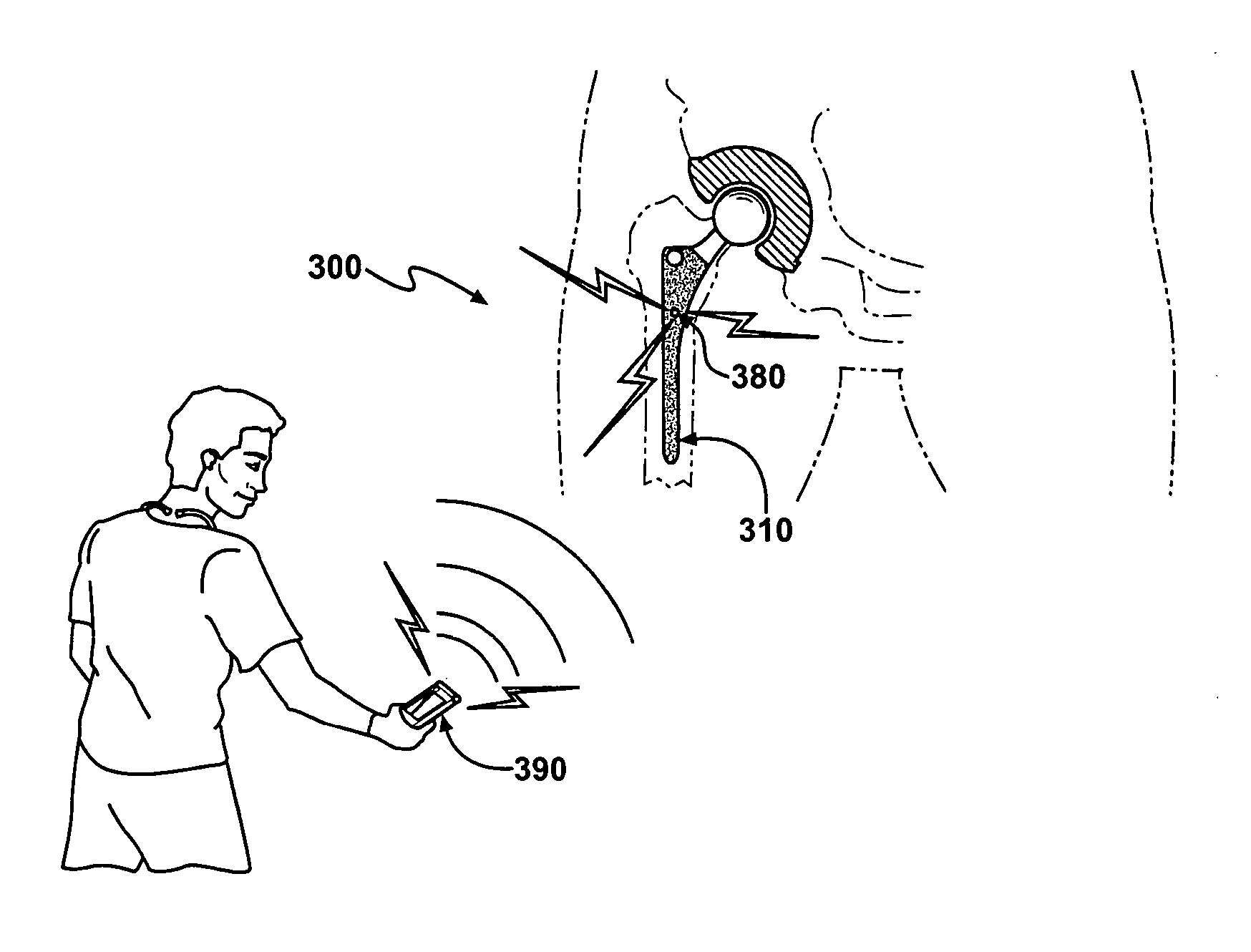
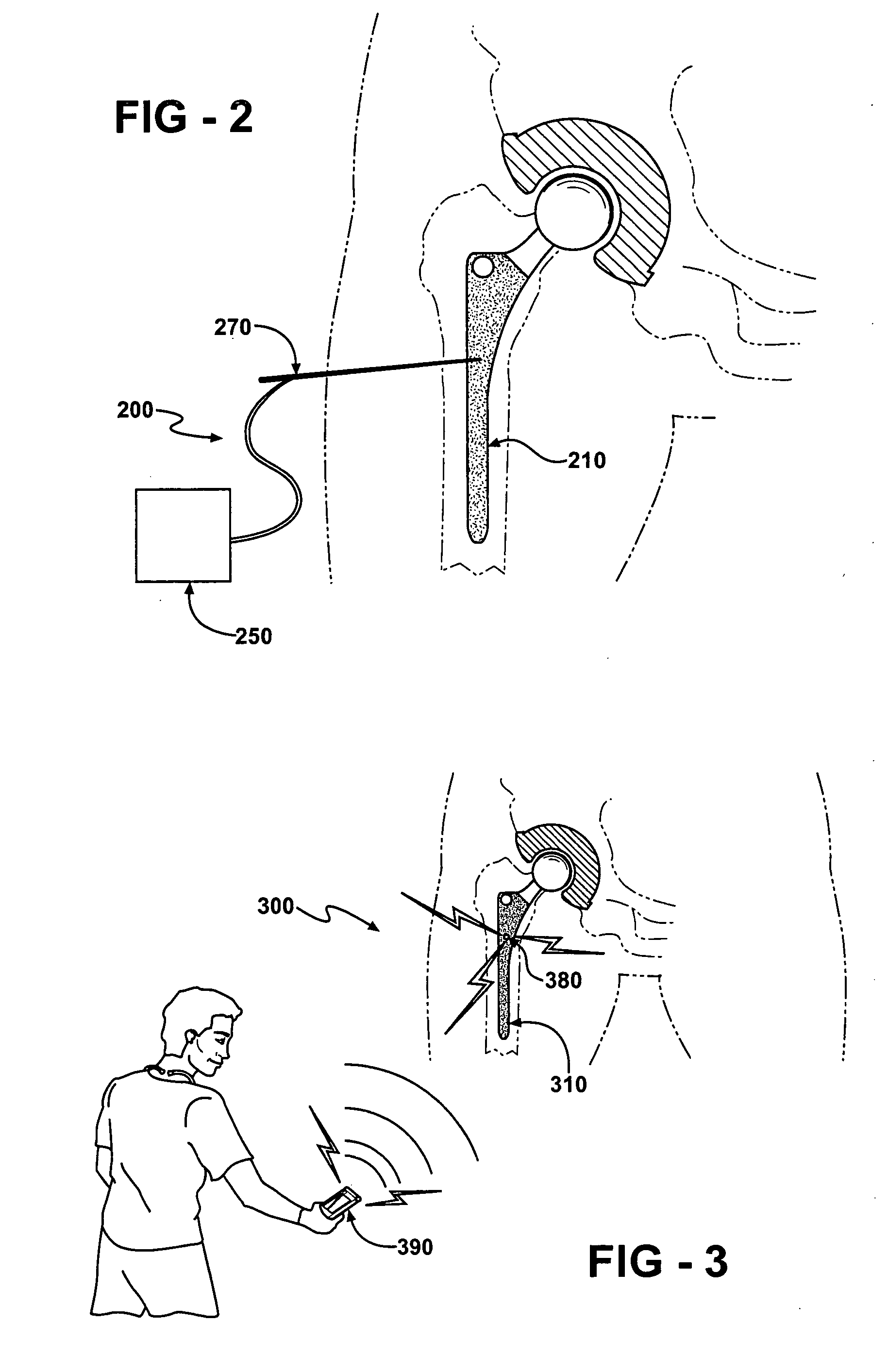
A medical implant system is described for inhibiting infection associated with a joint prosthesis implant. An inventive system includes an implant body made of a biocompatible material which has a metal component disposed on an external surface of the implant body. A current is allowed to flow to the metal component, stimulating release of metal ions toxic to microbes, such as bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and viruses. One detailed system is completely surgically implantable in the patient such that no part of the system is external to the patient while the system is in use. In addition, externally controlled devices are provided which allow for modulation of implanted components.
Owner:AIONX ANTIMICROBIAL TECH INC
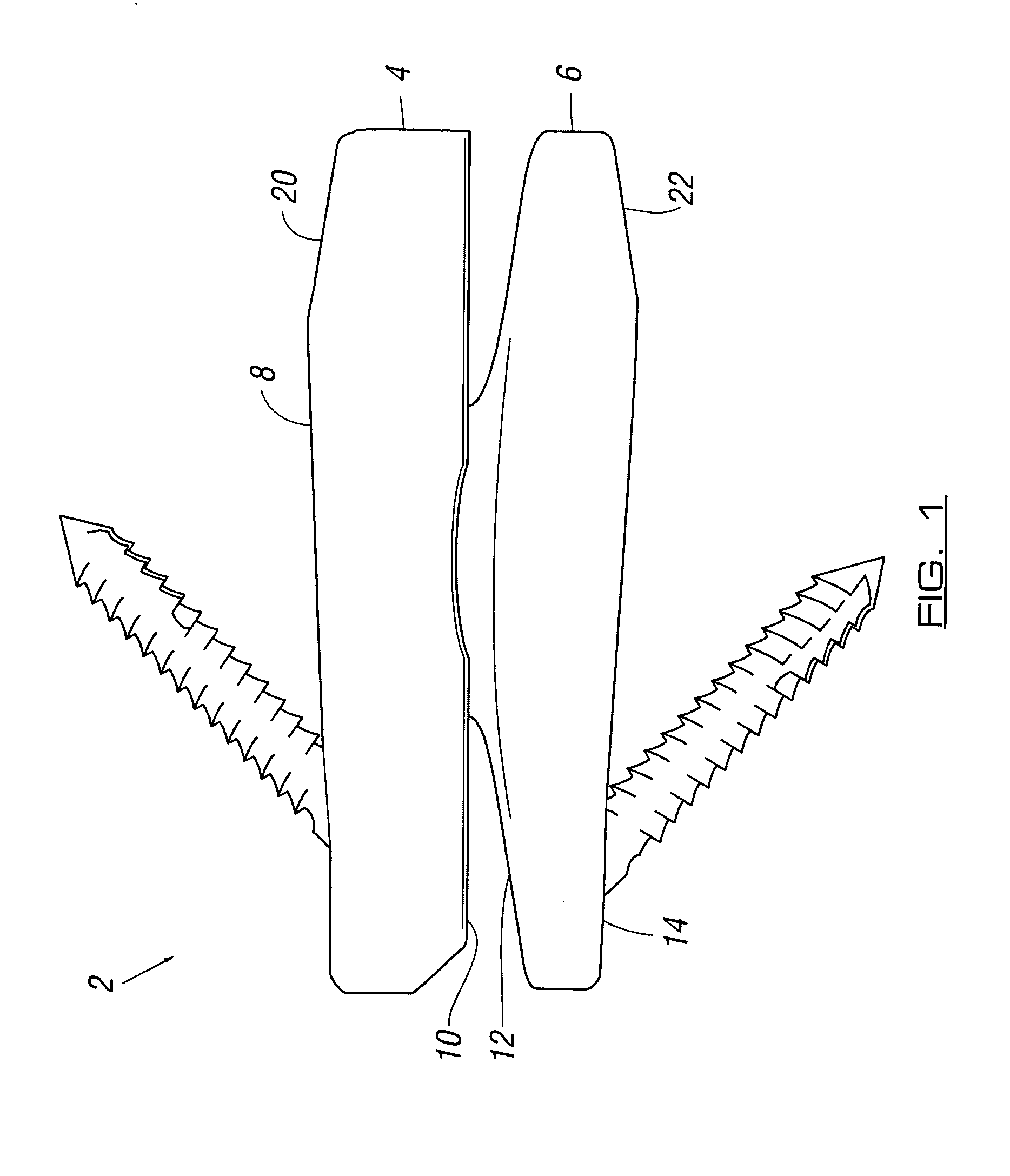
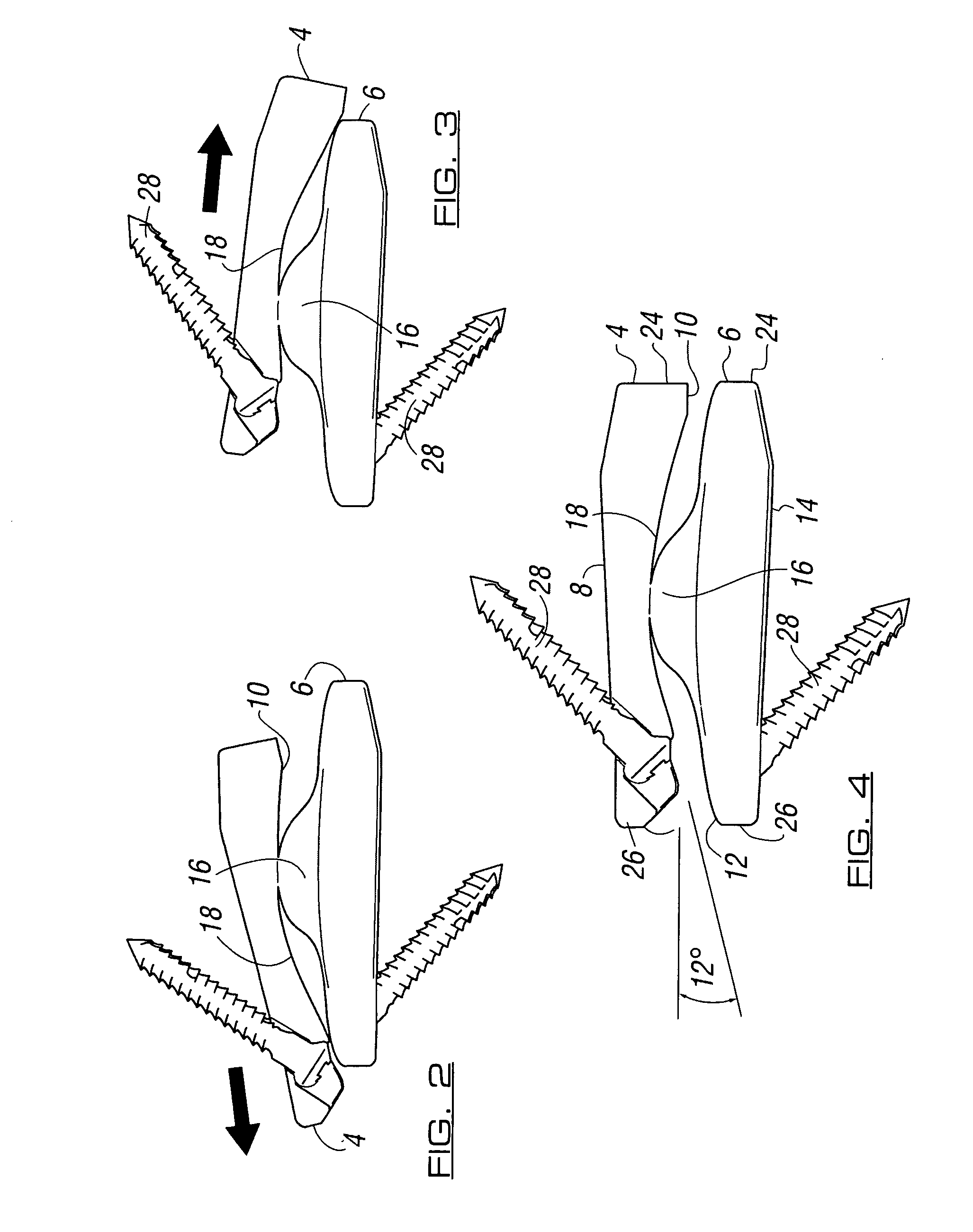
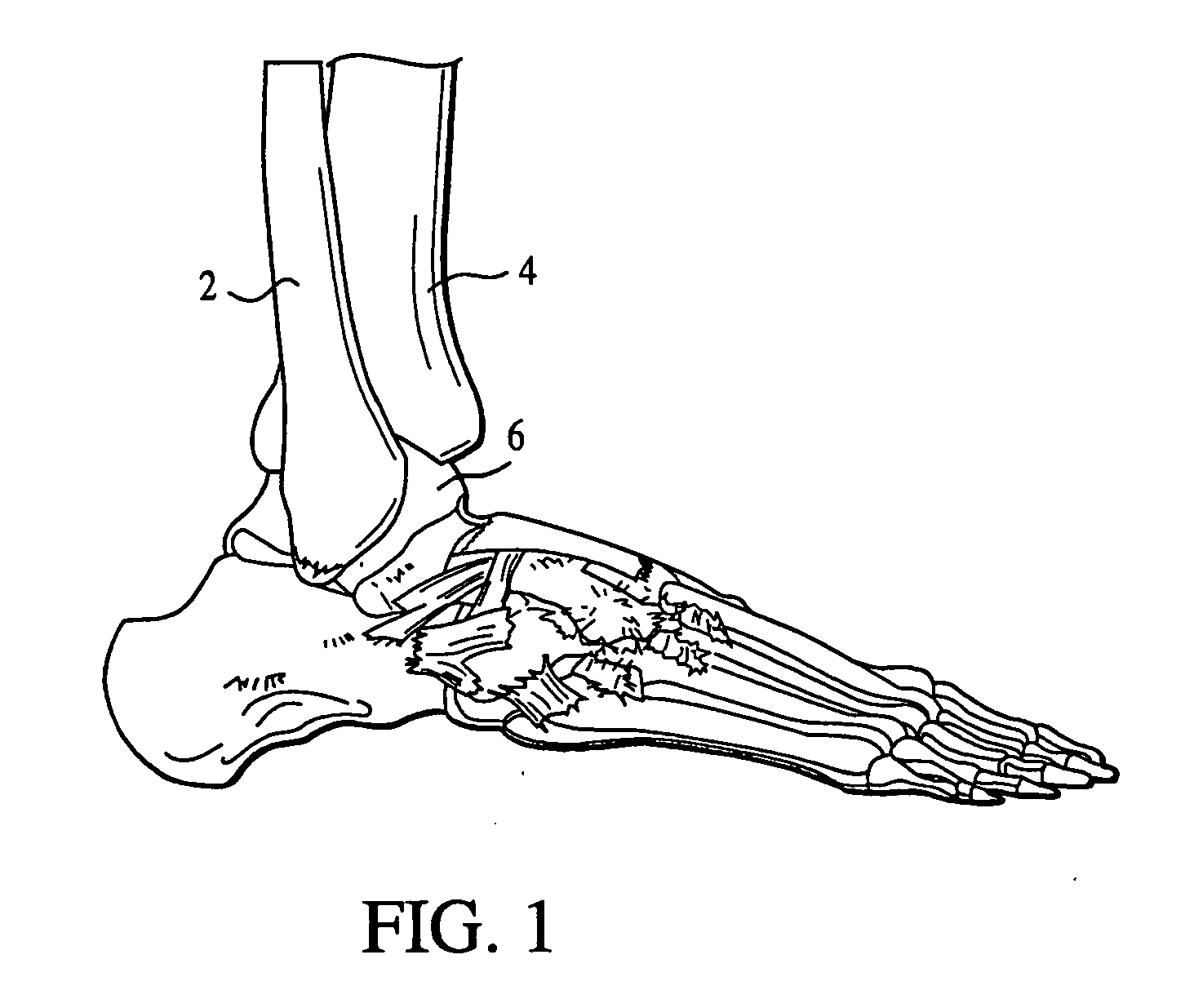
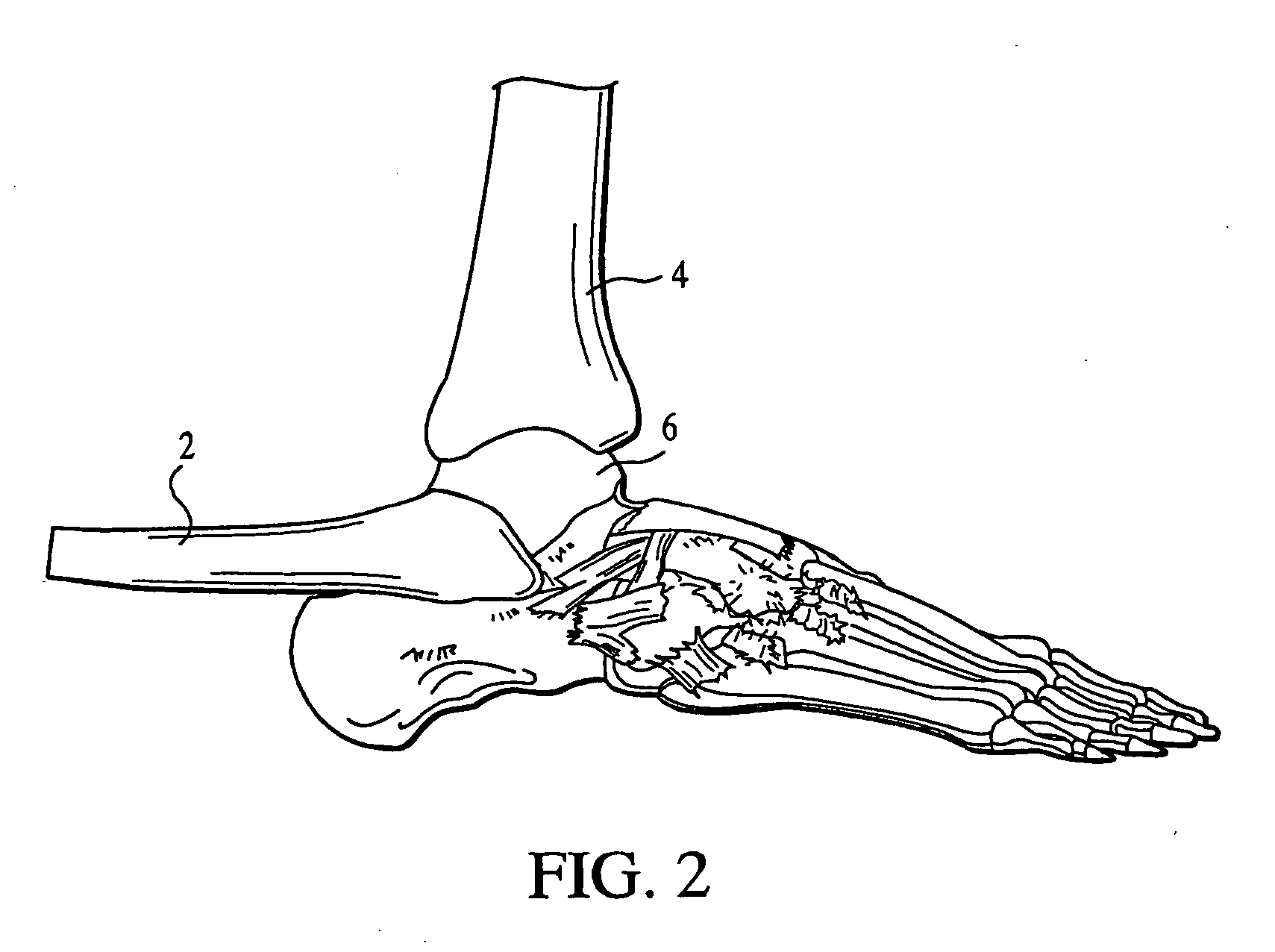
Ankle prosthesis
InactiveUS6409767B1Preventing uncontrolled deformationImprove the situationInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsTibiaBase of the sacrum
The invention provides an ankle prosthesis for use in the field of orthopedic prostheses comprising a talus implant for implanting in or on the talus and a top element including a tibia implant for implanting in or on the base of the tibia. The top element and the talus implant being mounted to move relative to each other by friction on a contact interface so as to allow the ankle to move. The contact interface presents a friction surface that can be considered as being a fraction of a substantially frustoconical surface. When implanted, the substantially frustoconical surface is oriented so that its larger radius portion is directed substantially towards the outside of the ankle.
Owner:EURON FOOT PLATFORM
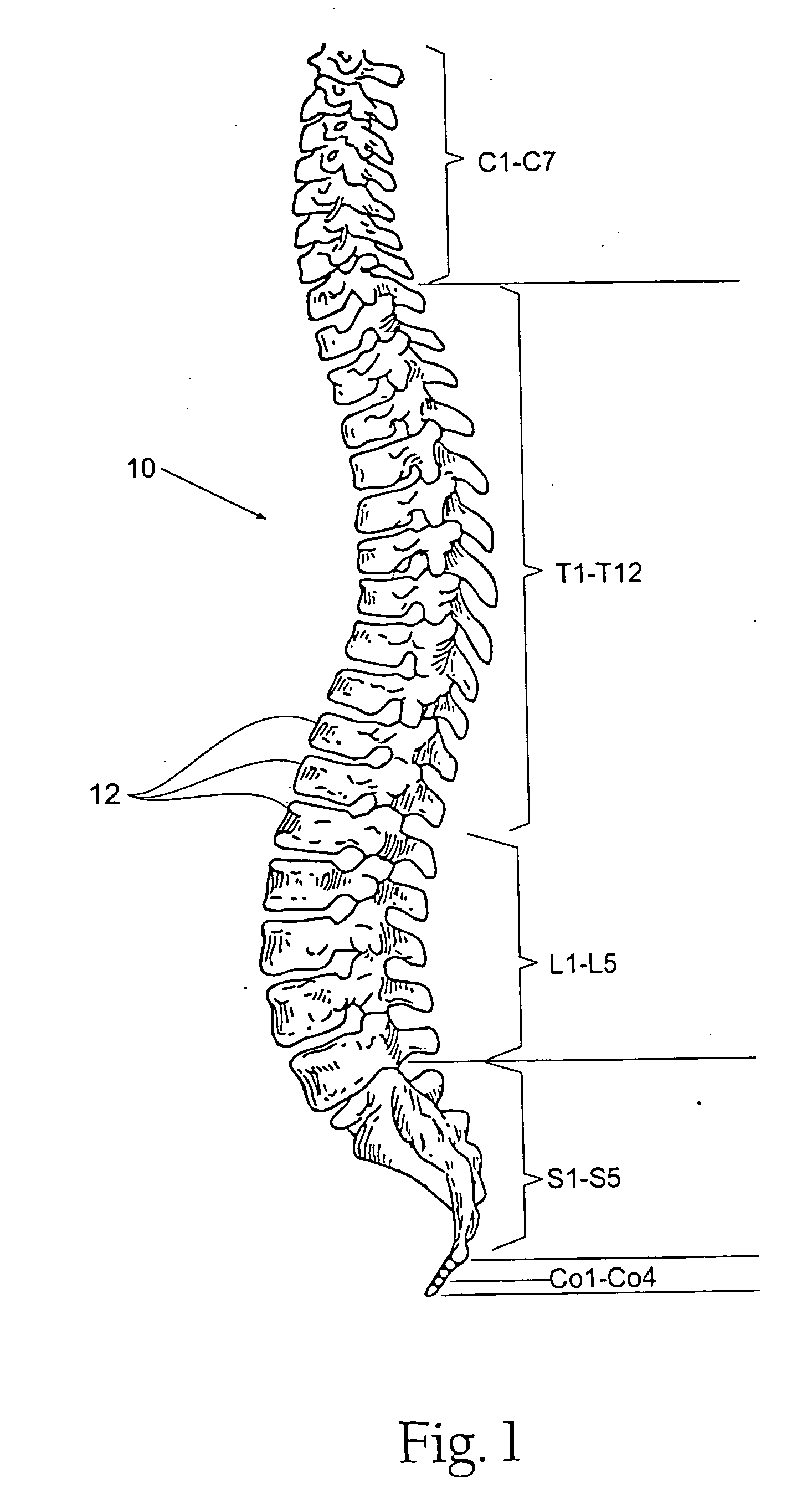
Joint Arthroplasty Kit and Method
A method for providing joint arthroplasty includes providing a gauge for making a measurement of the contour of a long bone, making a measurement of the contour of a long bone with the gauge, providing a plurality of joint prostheses, selecting one of the plurality of joint prostheses based upon the measurement of the contour, resecting a long bone, and implanting the selected one prosthesis onto the long bone. A kit is also provided for selecting one of a plurality of joint implants for use in joint arthroplasty on a bone. The kit includes a first gauge and a second gauge.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
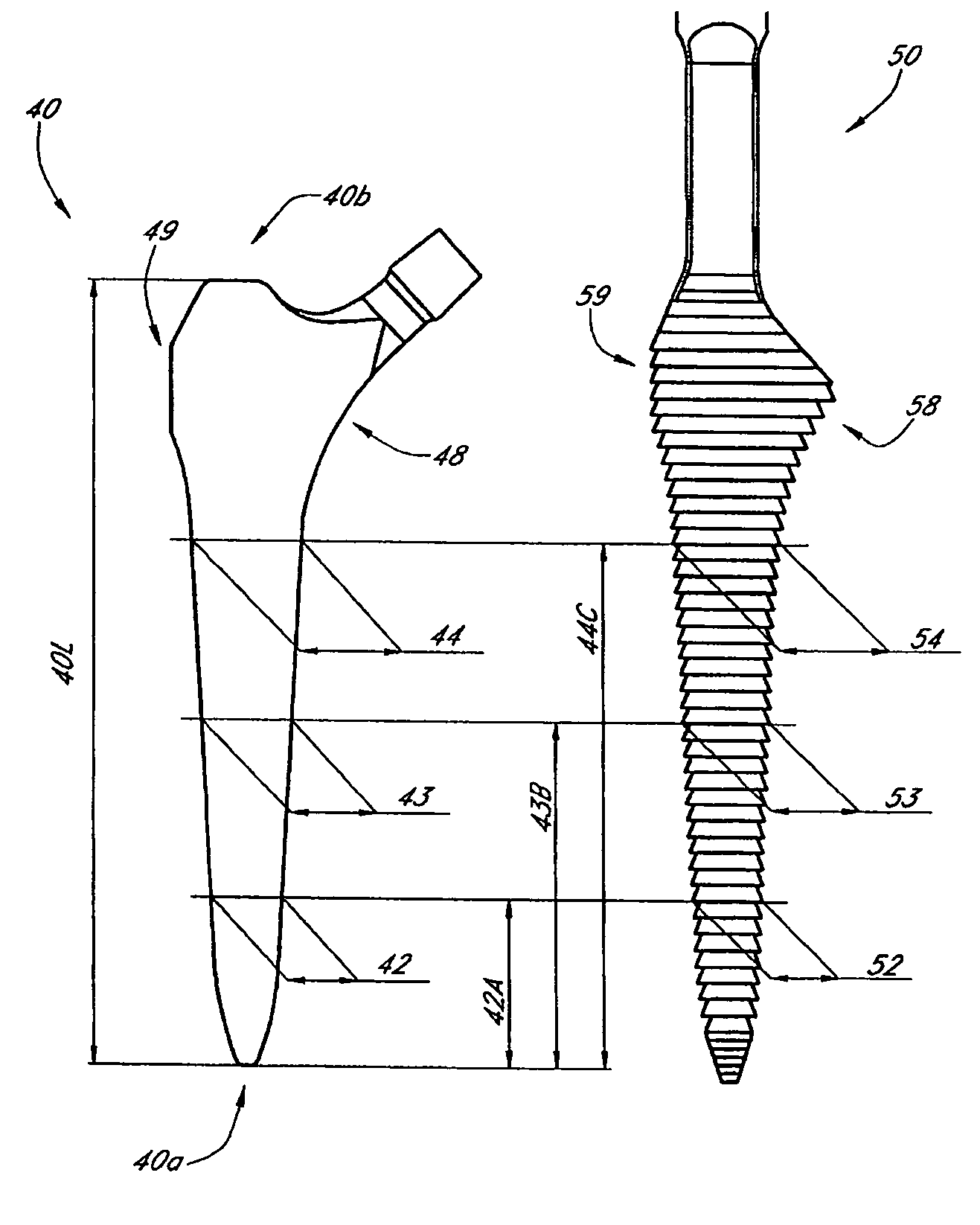
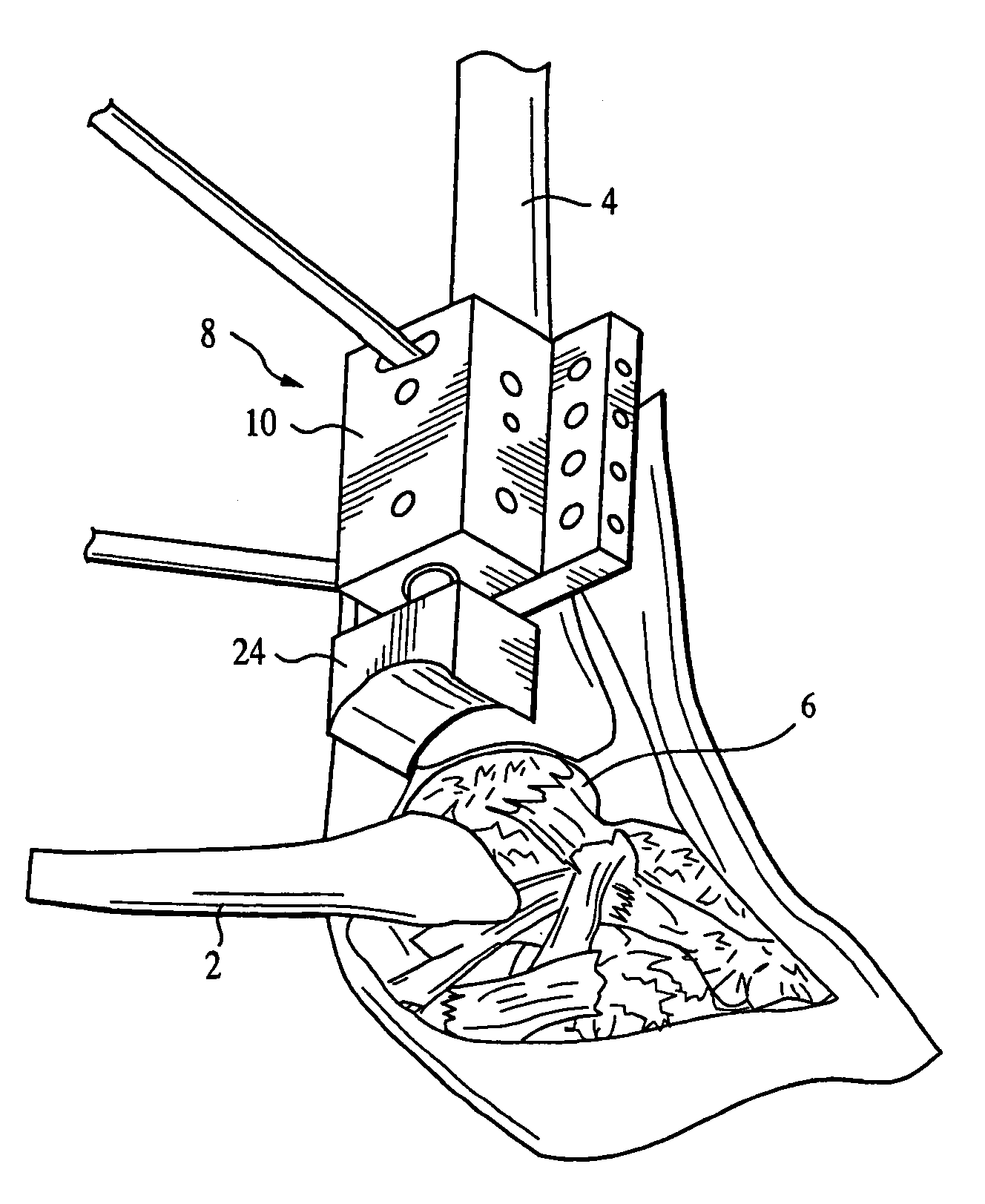
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
InactiveUS7494510B2Advantageous for revascularizationFacilitate revascularizationSurgeryJoint implantsRaspFemoral shaft
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to components of a hip-joint prosthesis. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to a leaf-like femoral shaft for use as part of a hip-joint prosthesis, and instruments (e.g., a rasp) and methods for implanting the shaft. The shaft includes an anchoring section extending between a proximal region and a distal end of the shaft. The shaft has a cross-sectional contour that defines a lateral side, a medial side, an anterior side and a posterior side. A corresponding rasp is preferably provided for each femoral shaft. The rasp is inserted into the femur to form a cavity having generally the same configuration as the rasp. The shaft is configured to be over-dimensioned in at least one of the anterior-posterior direction and medial-lateral direction relative to the rasped femur cavity. In one embodiment, the distance between diagonally opposite corner junctions of the shaft is substantially equal to the distance between corresponding diagonally opposite corner junctions of the femur cavity, so as to inhibit excess stress on the corticalis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
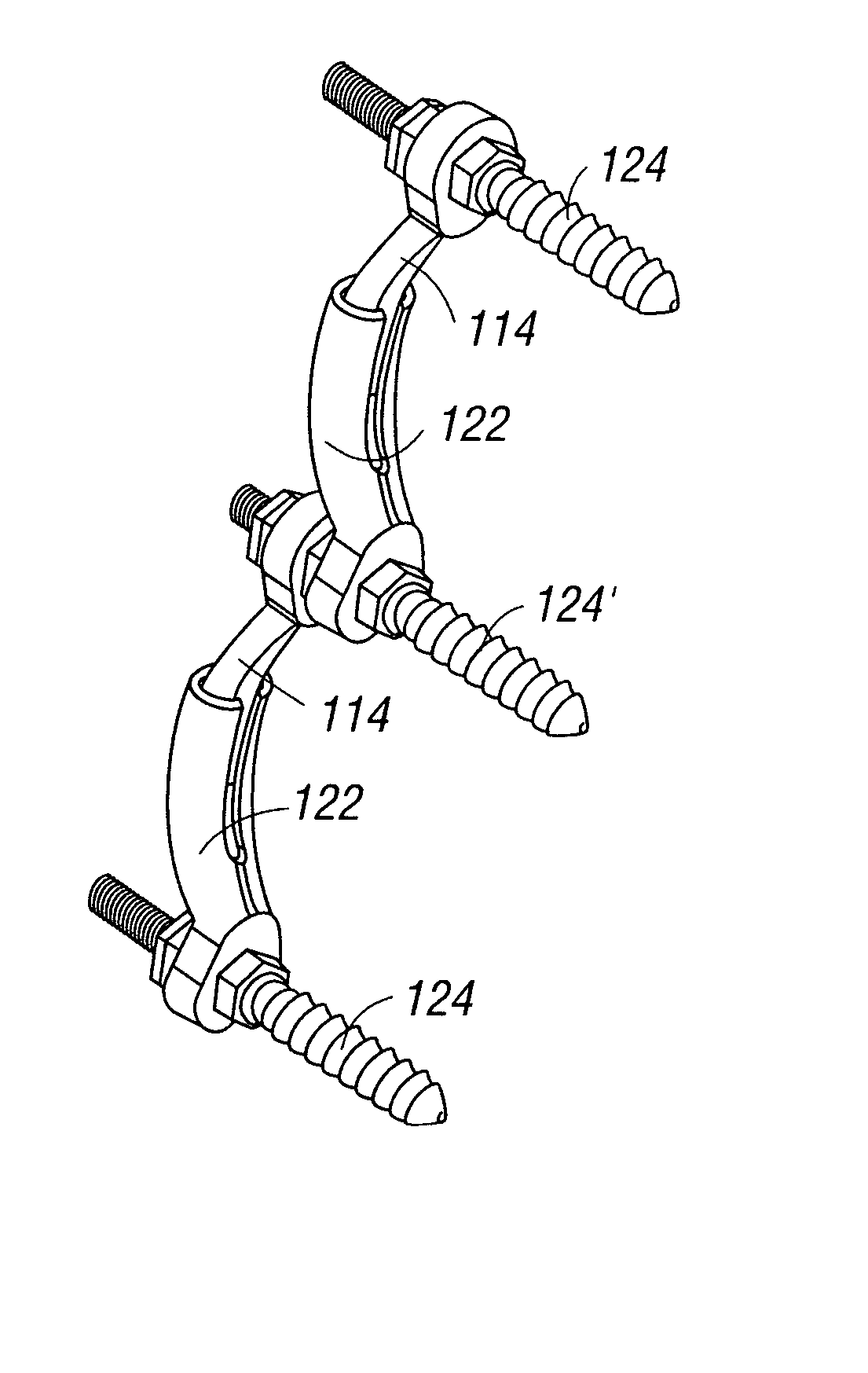
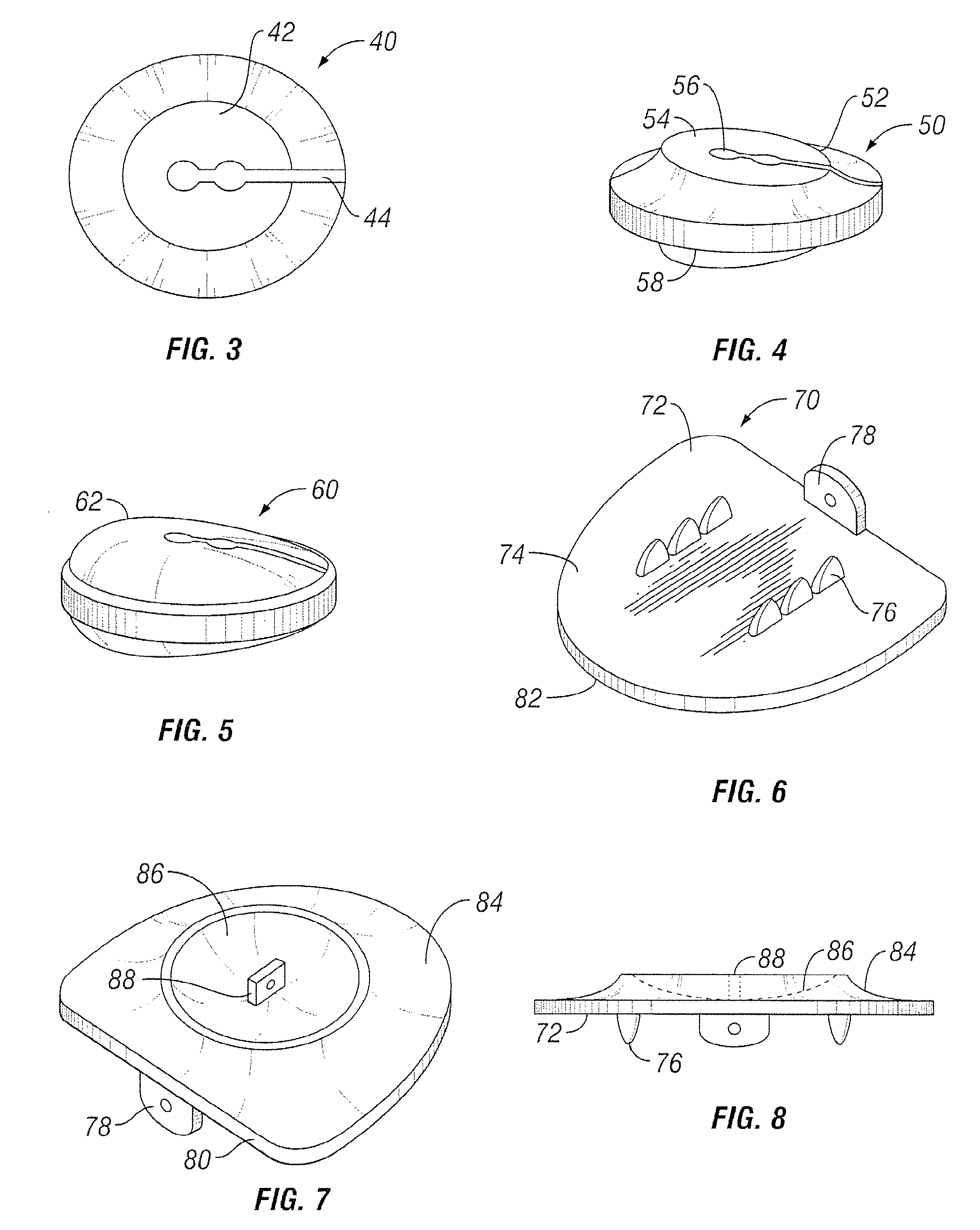
Crossbar spinal prosthesis having a modular design and related implantation methods
InactiveUS20070093833A1Maintaining their functionalityInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic markersSpinal columnFacet joint prosthesis
An adaptable spinal facet joint prosthesis, including a pedicle fixation element; a laminar fixation element; and a facet joint bearing surface having a location adaptable with respect at least one of the pedicle fixation element and the laminar fixation element. The invention also includes a method of implanting an adaptable spinal facet joint prosthesis including the steps of determining a desired position for a facet joint bearing surface; and attaching a prosthesis comprising a facet joint bearing surface to a pedicle portion of a vertebra and a lamina portion of a vertebra to place the facet joint bearing surface in the desired position. The invention also provides a facet joint prosthesis implant tool including a tool guide adapted to guide a vertebra cutting tool; and first and second fixation hole alignment elements extending from the saw guide.
Owner:FACET SOLUTIONS
Posterior spinal arthroplasty-development of a new posteriorly inserted artificial disc, a new anteriorly inserted artifical disc and an artificial facet joint
InactiveUS20060265074A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnFacet joint prosthesis
A lumbar disc prosthesis is provided including a pair of disc members. The first member of the disc pair has a vertebral disc contact surface and a recessed portion on an opposing surface thereof. The second member of the disc pair has a vertebral disc contact surface and a protruding portion on an opposing surface thereof. The protruding portion of the second member engages with the recessed portion of the first member in use. Each of the first and second disc members are provided with at least three sections; a middle section and two end sections. The recessed and protruding portions are provided in the middle section of the respective disc members and each of the two end sections have a narrowing taper towards the ends of the disc members. The facet joint prosthesis includes a first member for attachment to a first posterior lumbar disc in use and a second member for attachment to a second posterior lumbar disc in use. At least a part of the first member is telescopically mounted in at least a part of the second member in use.
Owner:SPINADYNE
Prostheses, Tools And Methods For Replacement Of Natural Facet Joints With Artificial Facet Joint Surfaces
InactiveUS20060149375A1Lessen and alleviate spinal painRelieving sourceJoint implantsSpinal implantsFacet joint prosthesisSacroiliac joint
Owner:GMEDELAWARE 2
Prostheses, tools and methods for replacement of natural facet joints with artificial facet joint surfaces
ActiveUS20060100707A1Relieving sourceLessen and alleviate spinal painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisFacet joint prosthesisArticular surfaces
Cephalad and caudal vertebral facet joint prostheses and methods of use are provided. The cephalad prostheses are adapted and configured to be attached to a lamina portion of a vertebra without blocking a pedicle portion of the cephalad vertebra. In some embodiments, the prosthesis is attached with a non-invasive support member, such as a clamp. In other embodiments, a translaminar screw may be used for additional fixation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Tibial component
A tibial knee joint prosthesis for attachment to a suitably prepared tibial bone, providing bearing portions in the lateral and medial compartments. The lateral and medial bearing surfaces of the component are inclined at different angles in the anterior to posterior direction of the knee, so that when mounted to the tibia, the lateral bearing surface of the prosthesis is higher than the medial bearing surface to the posterior side of the knee. In this way the lateral ligament is tightened progressively more than the medial ligament as the knee moves from extension to flexion, resulting in increased stability in the lateral compartment.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Application of neural networks to prosthesis fitting and balancing in joints
The present invention provides systems and methods for prosthesis fitting in joints that employ a trained neural network to predict at least one unknown set of data, such as position and contact force. The unknown data is predicted based on at least one known sensor value that is obtained intraoperatively. The predicted neural network data is made available to a physician and aids in the determination of whether to resect additional bone, release soft tissues, and / or select sizes for prosthetic components. Advantageously, increased data may be provided to a physician without the need to acquire numerous samples from a patient, and fewer sensors may be employed.
Owner:ORTHO SENSING TECH
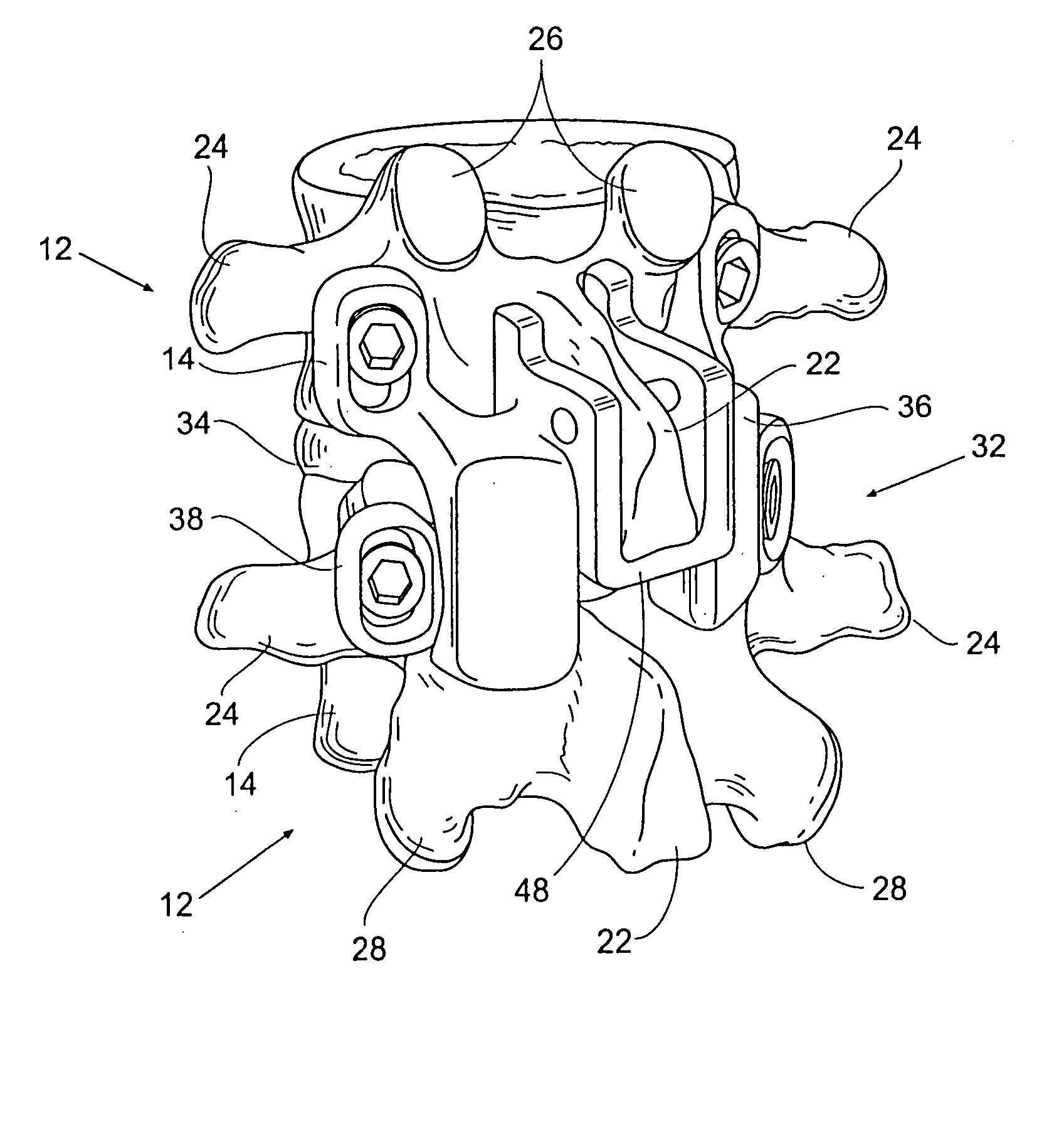
Blade for resection of bone for prosthesis implantation, blade stop and method
InactiveUS6875222B2Few instrumentsReduce in quantityMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesProsthesis ImplantationSacroiliac joint
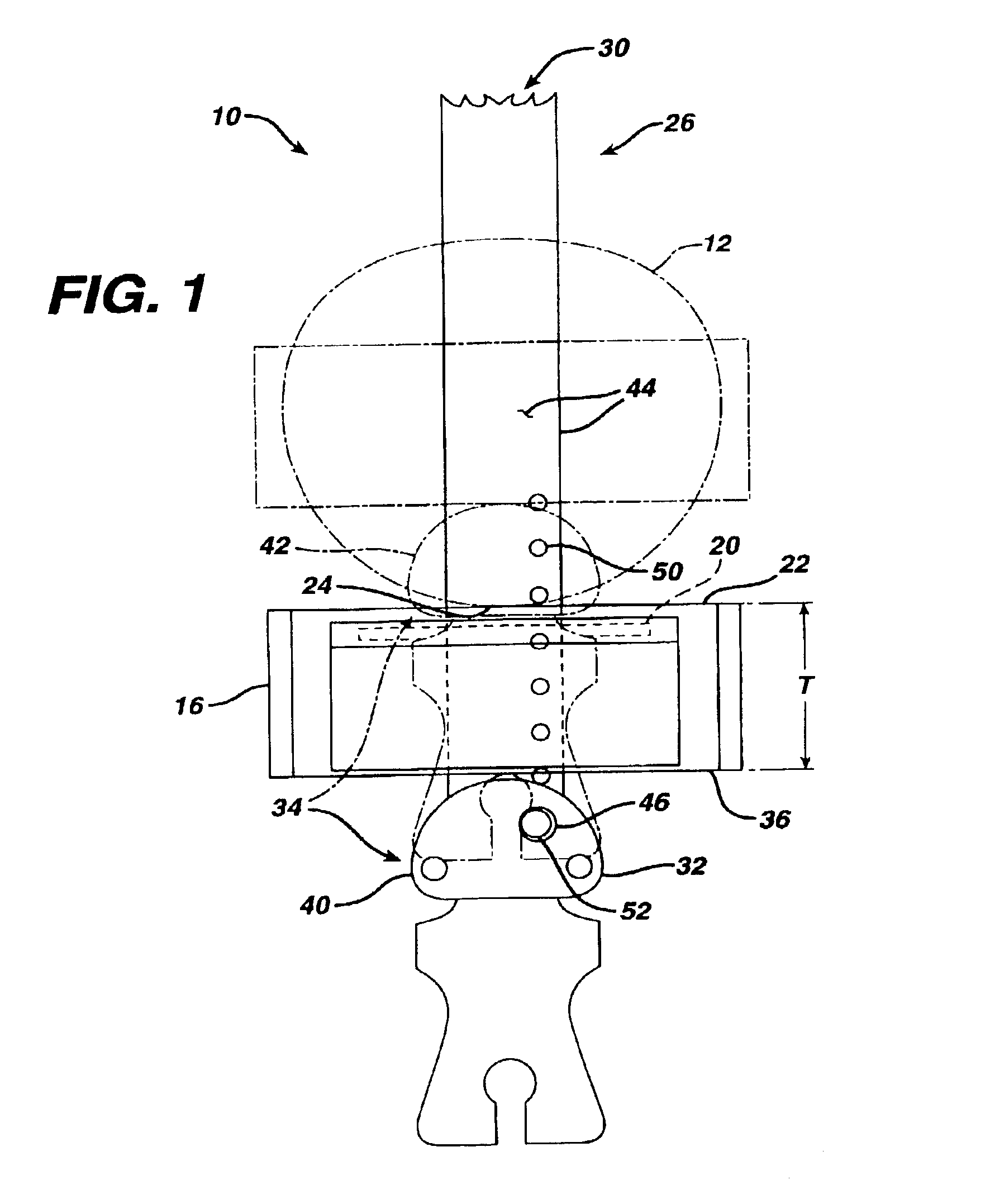
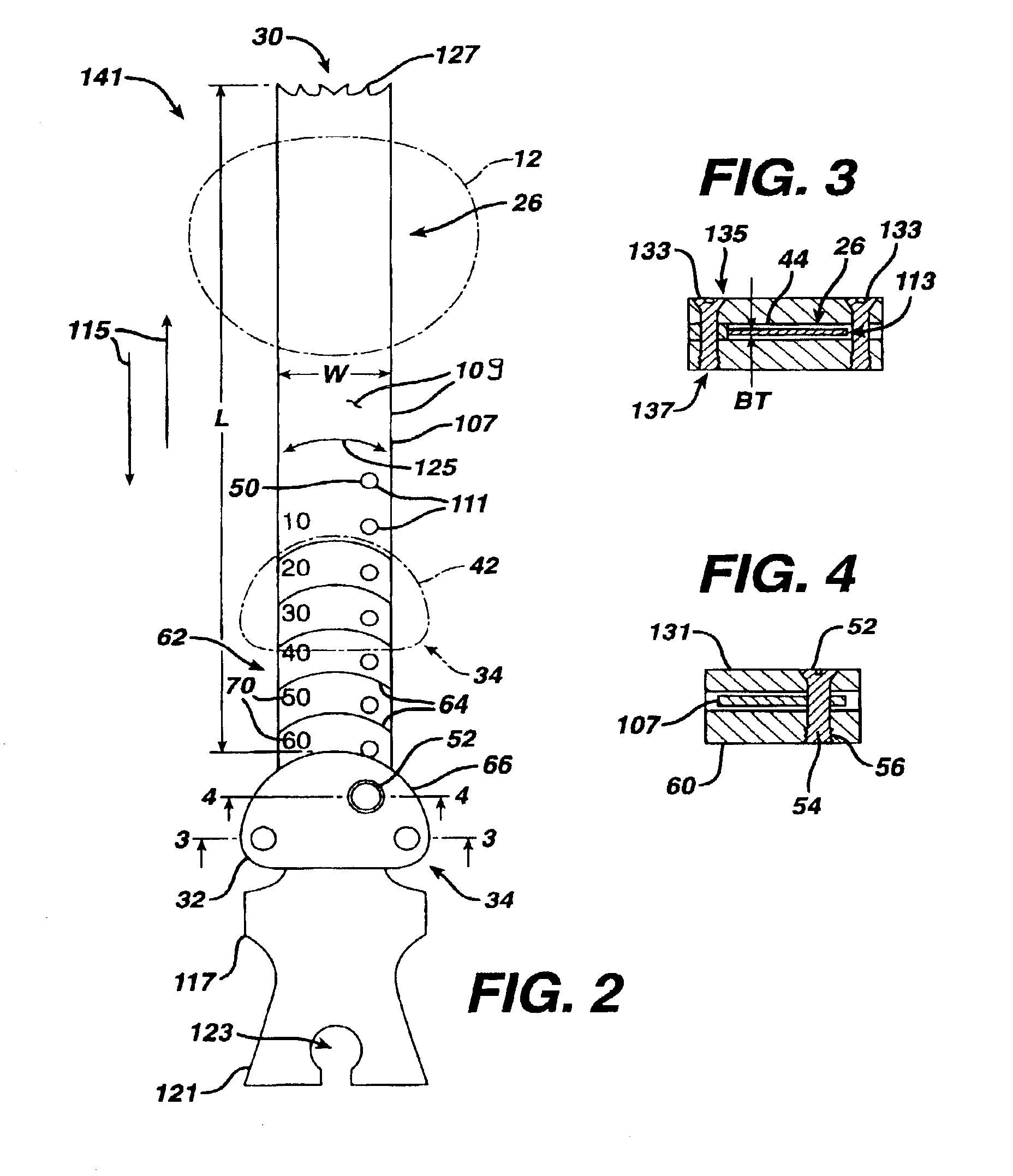
A kit (10) for resection of bone (12) for use in implantation of a joint prosthesis (14) is provided. The kit (10) includes a guide (16), a tool (26) and a stop (32). The guide (16) defines an opening (20) through the guide (16). The guide (16) is in cooperation with the bone (12). The tool (26) may be constrained within the opening (20) of the guide (16). The tool (26) includes a cutting edge (30) for resection of bone (12). The stop (32) cooperates with the guide (16) and the tool (26) to limit the movement of the tool (26) within the guide (16) so that the position of the cutting edge (30) with respect to the bone (12)m may be controlled. The stop (32) includes a plurality of positions (34) with respect to the tool (26) and the guide (16).
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
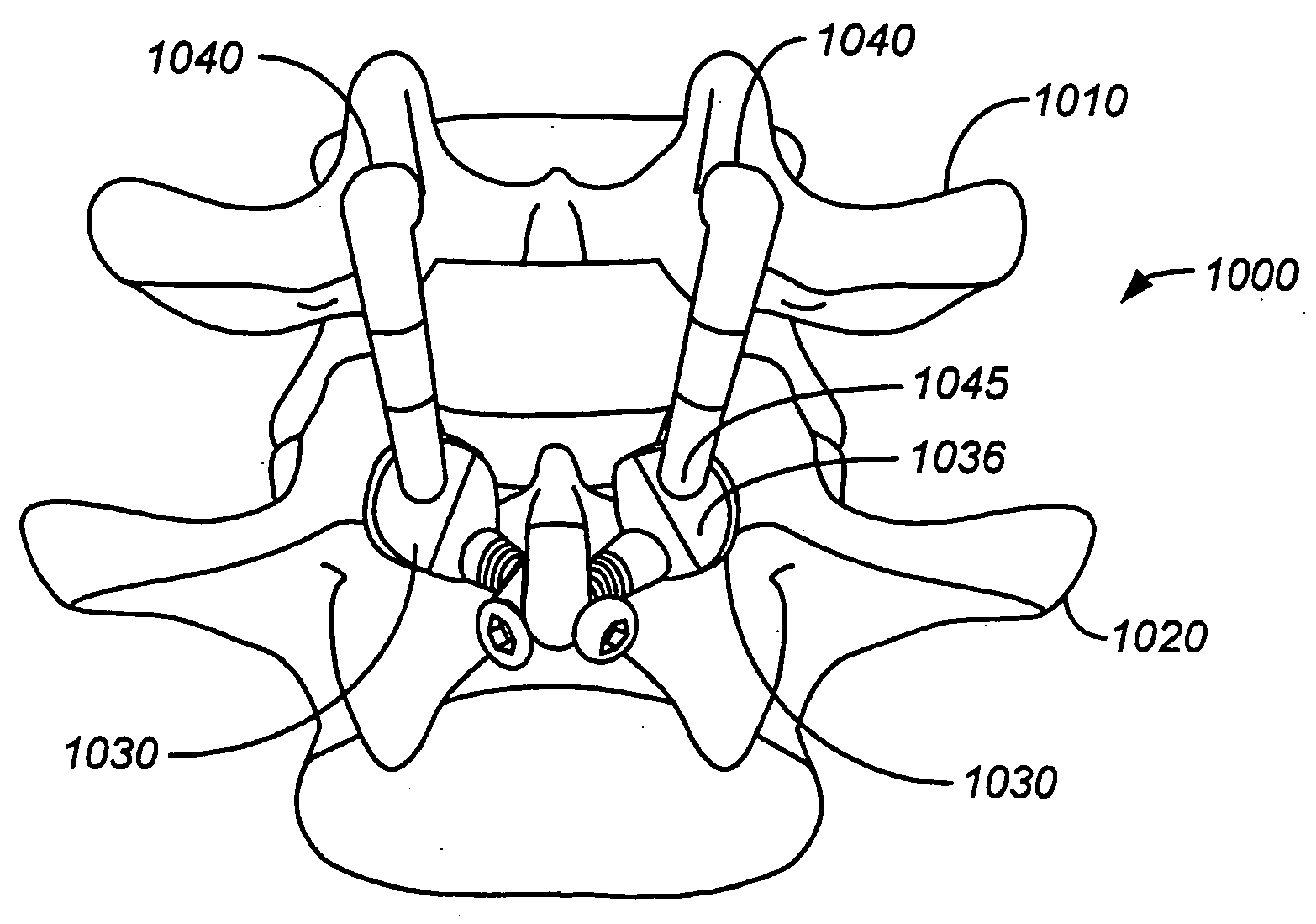
Joint Prostheses
ActiveUS20080215156A1Prevent hard stopPreventing posterior migration (expulsion)Finger jointsAnkle jointsSacroiliac jointBearing surface
The present invention provides an implantable joint prosthesis configured to replace a natural joint, and methods for implantation. The prosthesis may include a first component implantable in a first bone, having a first bearing surface, and a second component implantable in a second bone, having a second bearing surface which corresponds to the first bearing surface. Each bearing surface may include a flattened section such that when the bearing surfaces are placed in cooperation with one another in a preferred orientation, the flattened sections are aligned. Alternatively, the bearing surfaces may have and asymmetric configuration, with non-congruent surfaces that may enable correction of deformity. Several types of implantable joint prostheses are disclosed, including: carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, metatarsophalangeal, distal interphalangeal, proximal interphalangeal, ankle, knee, shoulder, and hip.
Owner:SYNERGY SPINE SOLUTIONS INC
Tibial spacer blocks and femoral cutting guide
The present invention relates to one or more tibial spacer blocks used during knee arthroplasty, each configured to be temporarily positioned upon a resected proximal portion of a tibia (essentially mimicking the tibial component of the knee prosthesis), for performing a range of motion analysis and for checking flexion and extension gaps prior to cutting the distal or posterior femur. Preferably, the spacer blocks each include an attachment arrangement configured and arranged to mate with a complementary attachment arrangement of an alignment tower and / or a femoral cutting guide. The alignment tower, which is configured to be used with an alignment rod, is used for verifying the alignment of the limb's mechanical axis when the spacer block is positioned between the tibia and the femur. The femoral cutting guide is used for guiding a cutting member into proper orientation for resecting a distal or posterior portion of a femur.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
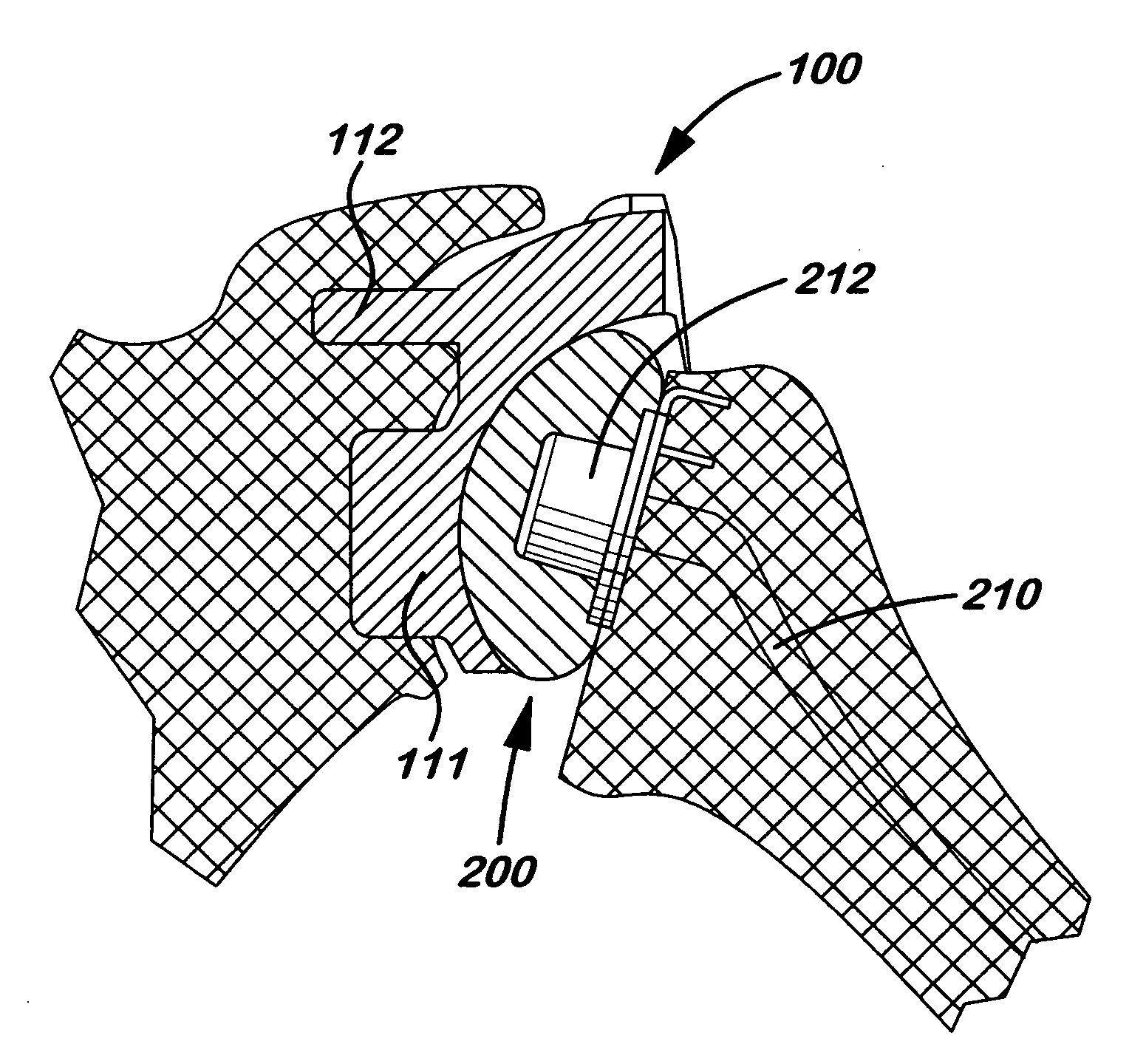
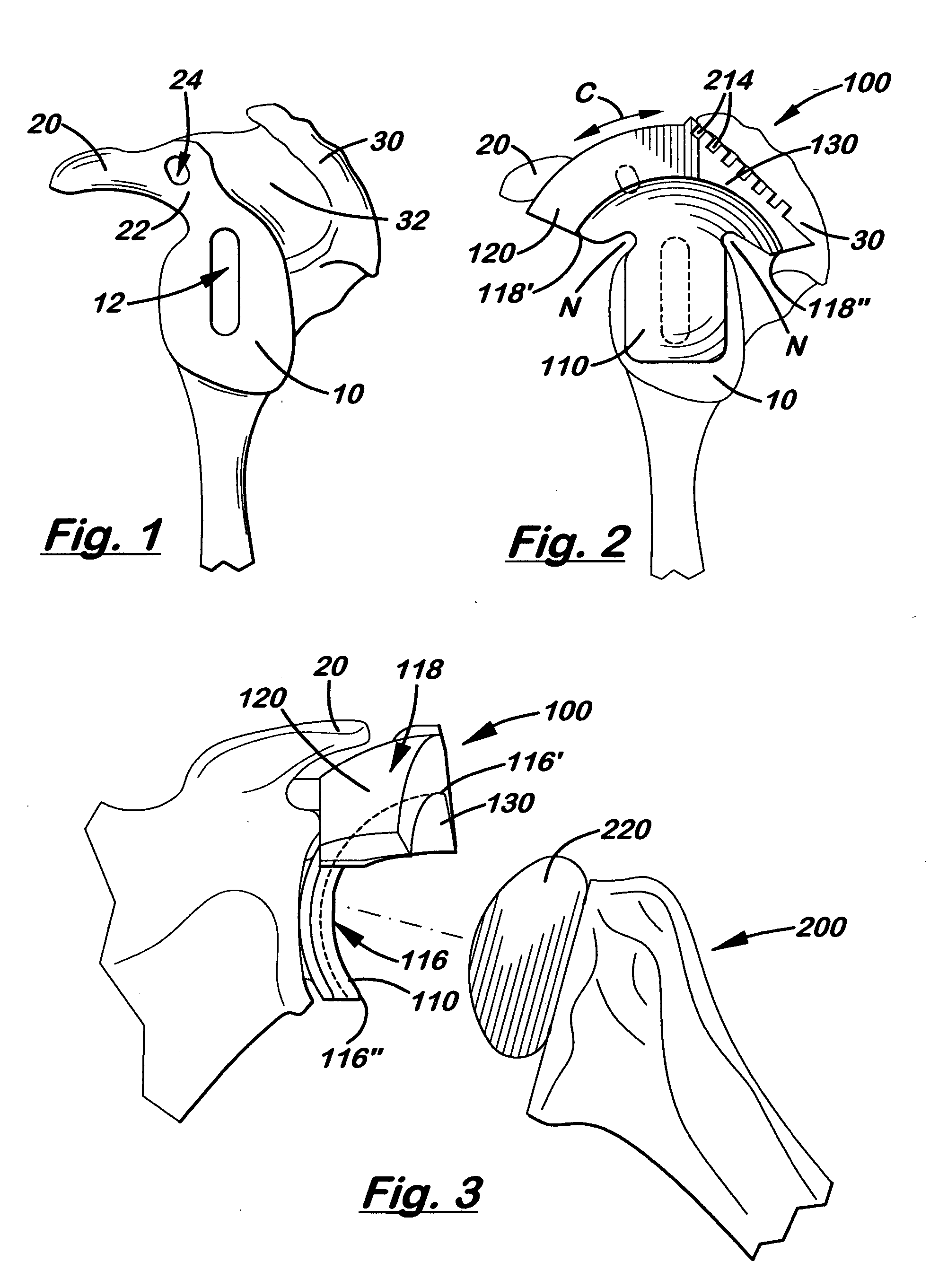
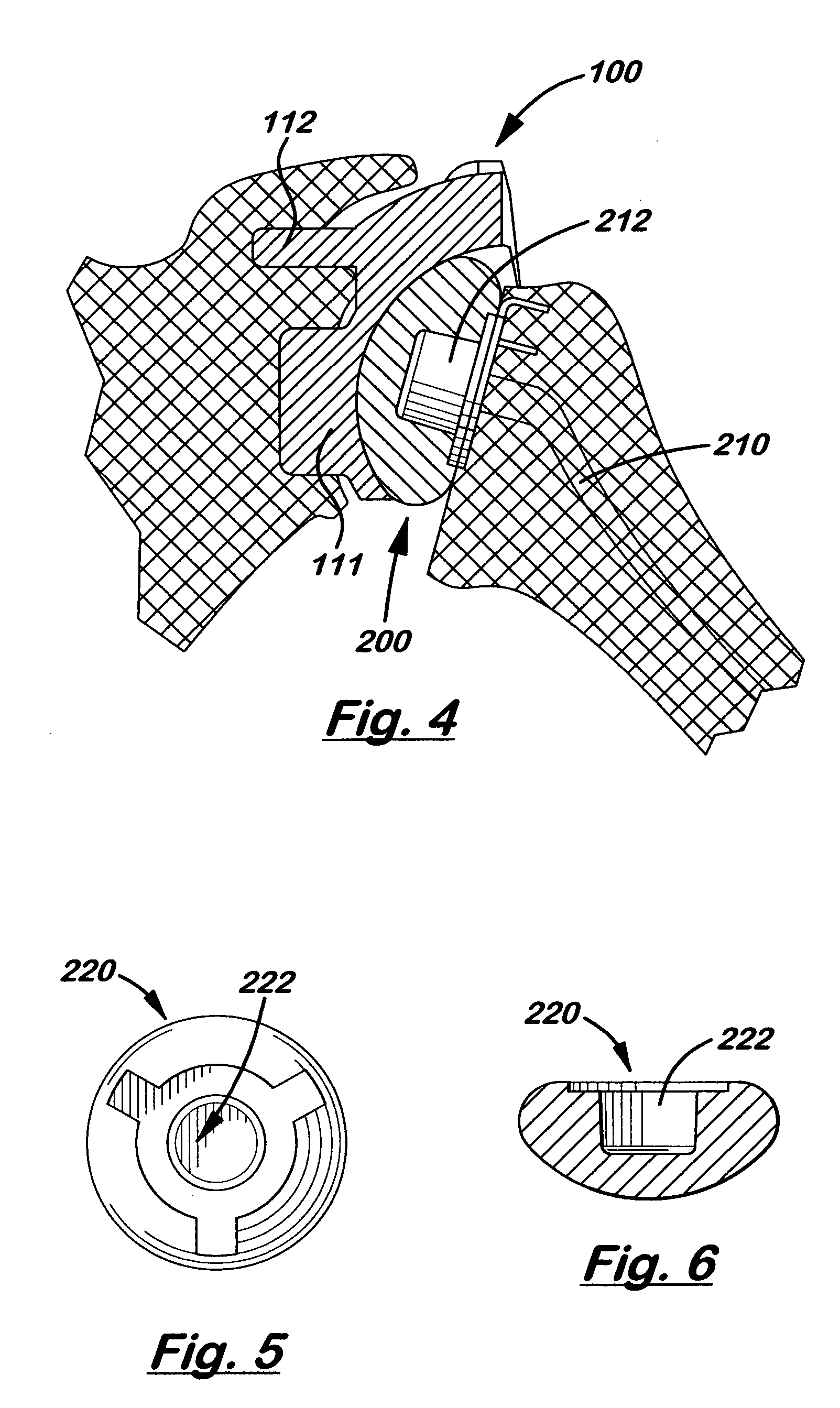
Semiconstrained shoulder prosthetic for treatment of rotator cuff arthropathy
InactiveUS20060079963A1Inhibition of translationProvide stabilityJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKeelAcromion
A glenoid component for treatment of rotator cuff arthropathy includes attachment to the coracoid process by a pin or post imbedded into a hole formed in the coracoid process. The glenoid component preferably also has a keel for extending into the glenoid fossa and protrusions such as ridges cemented to the acromion process. This way, an attachment point is preferably provided in / on the coracoid process, the acromion process, and the glenoid fossa, and at least two of the attachment points include a protrusion extending into a hole / slot drilled or otherwise formed in the bone. A jig is used for guiding / drilling into the bone, wherein the jig has both a glenoid fossa drill guide and a coracoid drill guide. The coracoid drill guide includes structure that abuts against opposing sides of the base of the coracoid process to prevent rotation of the jig relative to the scapula.
Owner:HANSEN REGAN
Semi-constrained ankle joint prosthesis and its method of implantation
The ankle joint prosthesis adapted to involve the patient's distal tibia and talus has, according to the present invention, tibial, talar and mobile or semi-constrained bearing components that are laterally to medially implanted in the patient. The tibial component's top surface has convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the distal tibia; its bottom surface being approximately flat. The talar component's top surface has saddle-shaped, convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane, it's bottom surface has concave curvature and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the talus. The mobile or semi-constrained bearing components have embodiments that comprise a wide variety of geometric shapes. A method for implanting such a prosthesis is also disclosed.
Owner:SCHON LEW C +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com