Patents
Literature
88 results about "Femoral shaft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
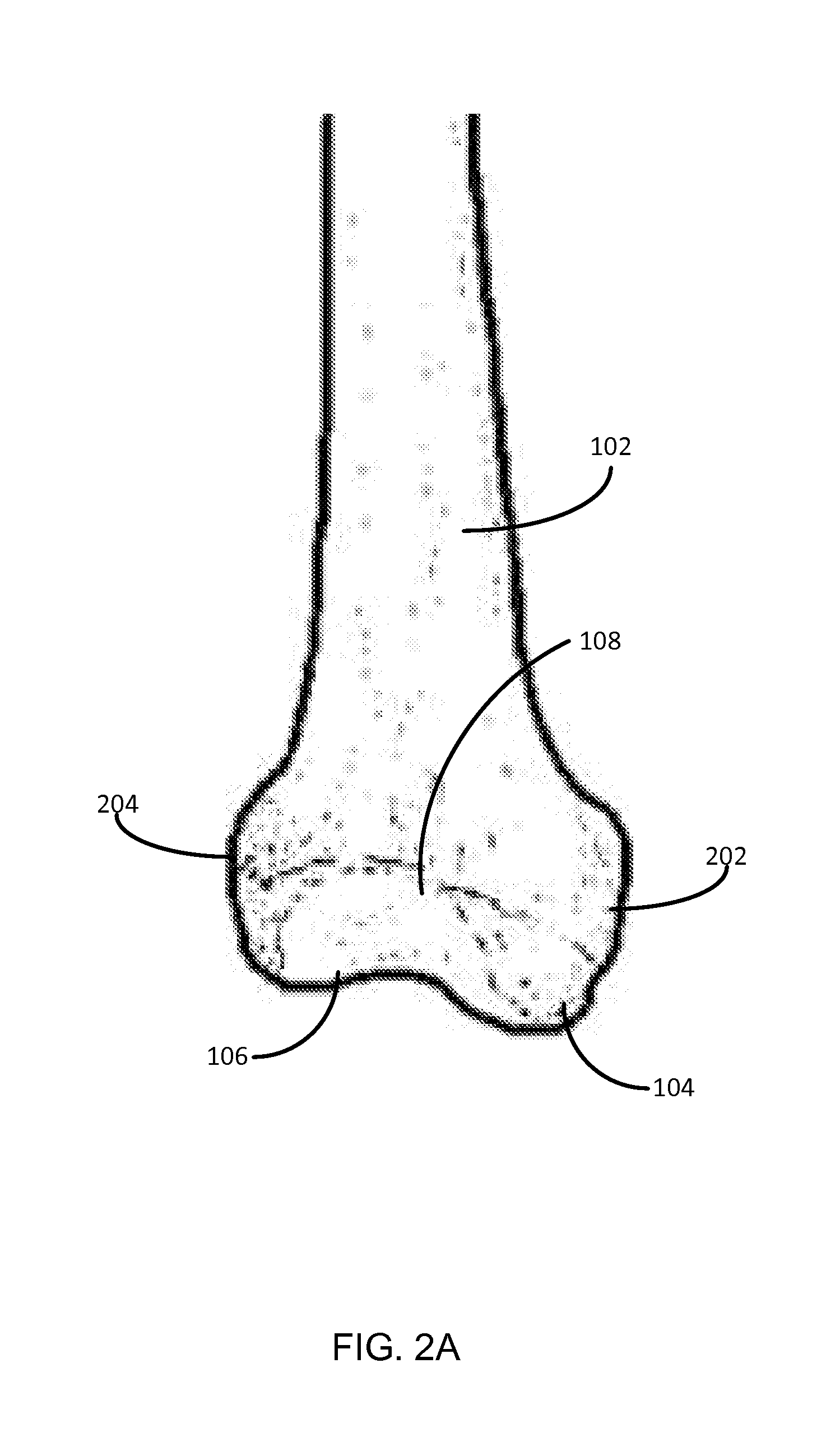
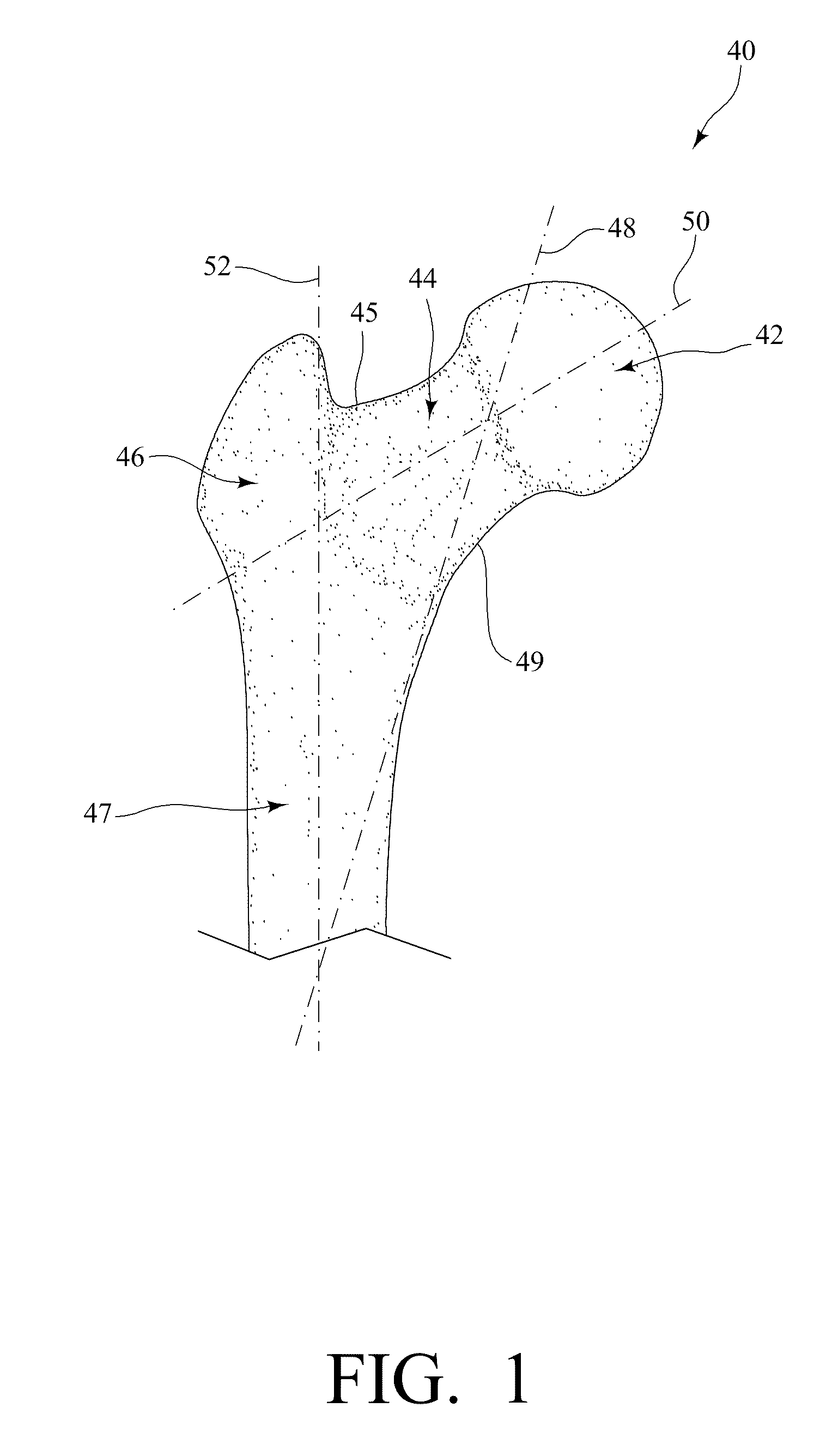
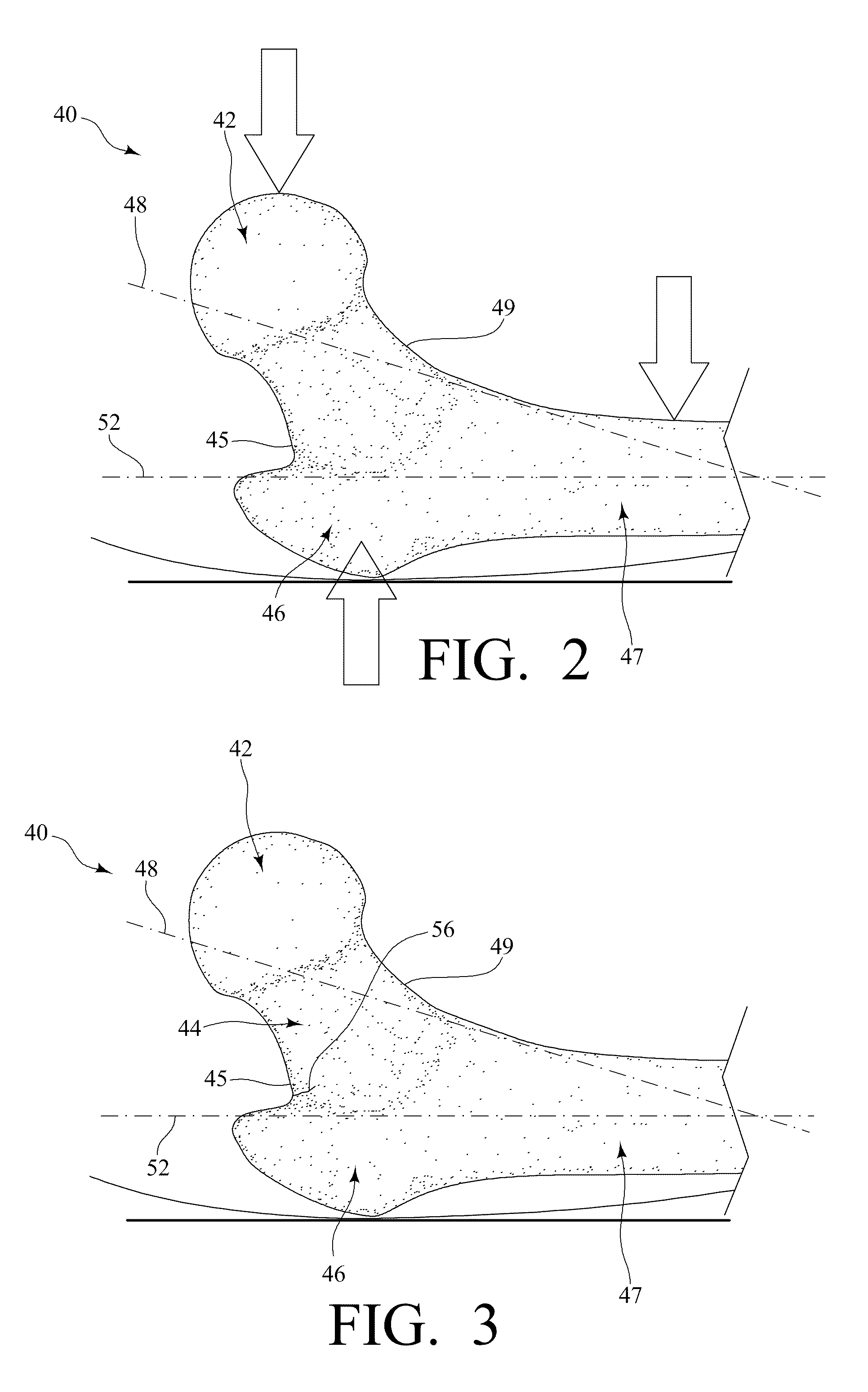
Femoral shaft is the elongated, straight part of the femur and any breakage or fracture along the length of this shaft is known as femoral shaft fracture. The femur is the strongest and longest bone in our body. As the femur is a very strong bone, it takes a lot of force to fracture or break it.
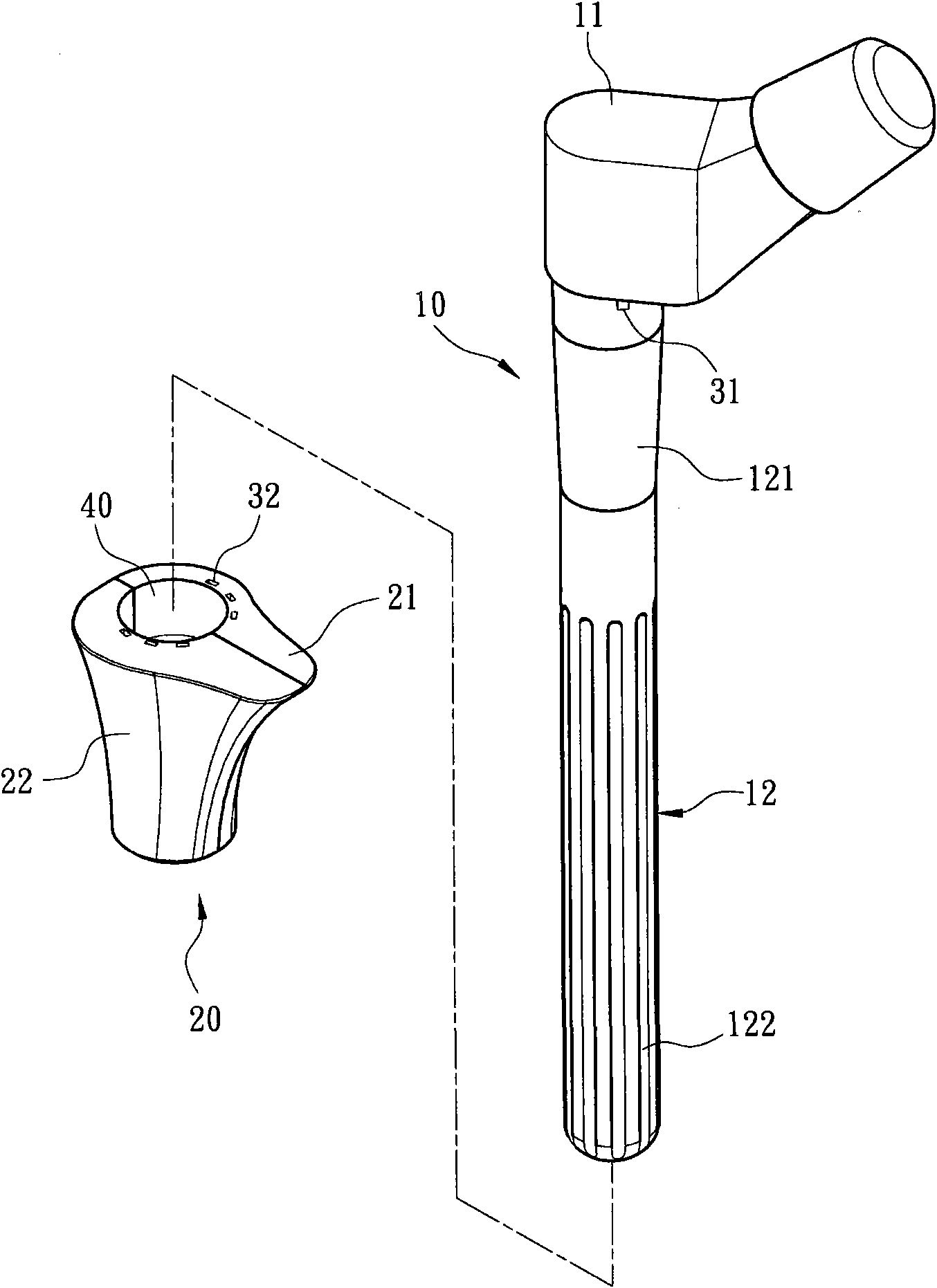
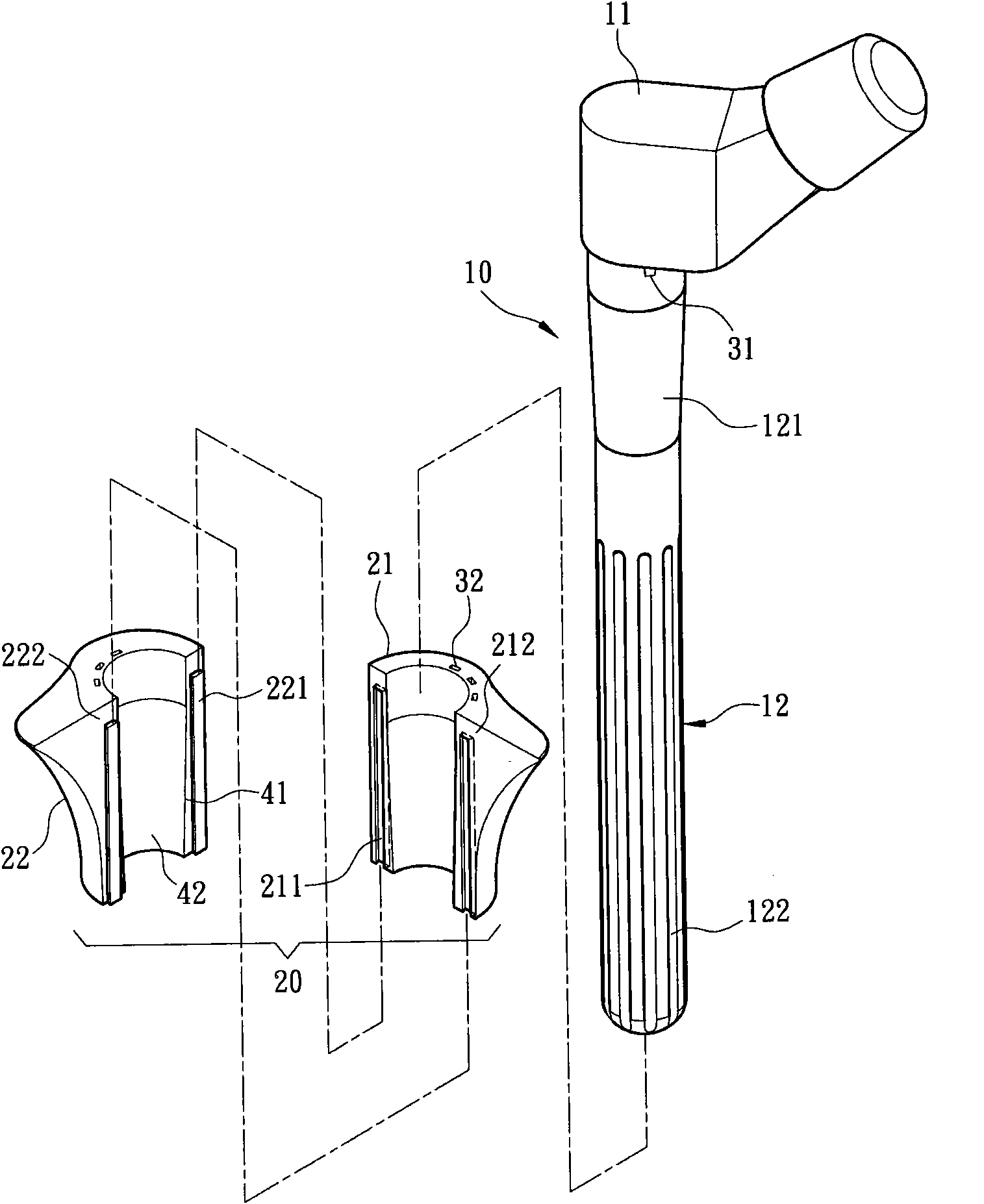
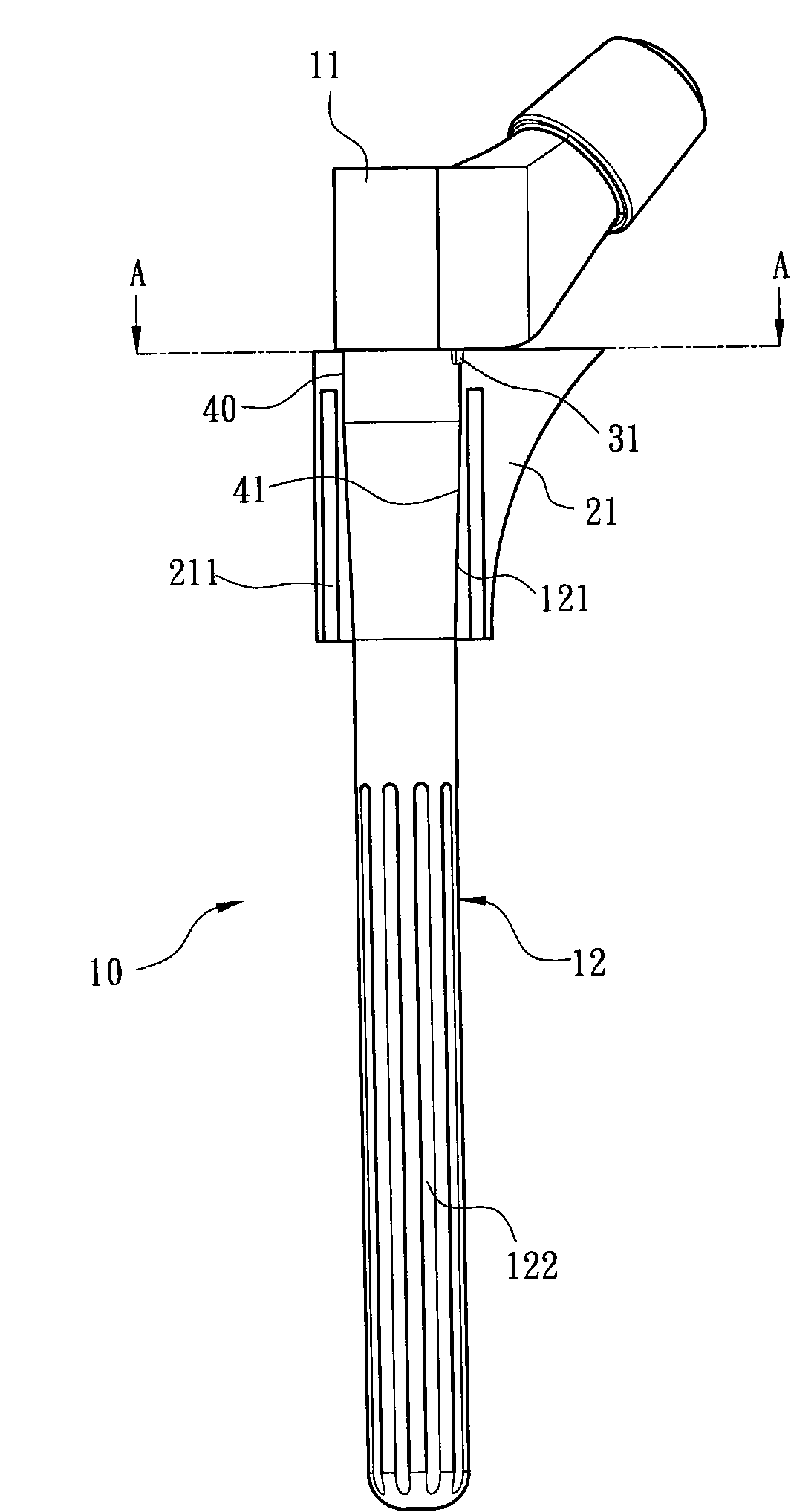
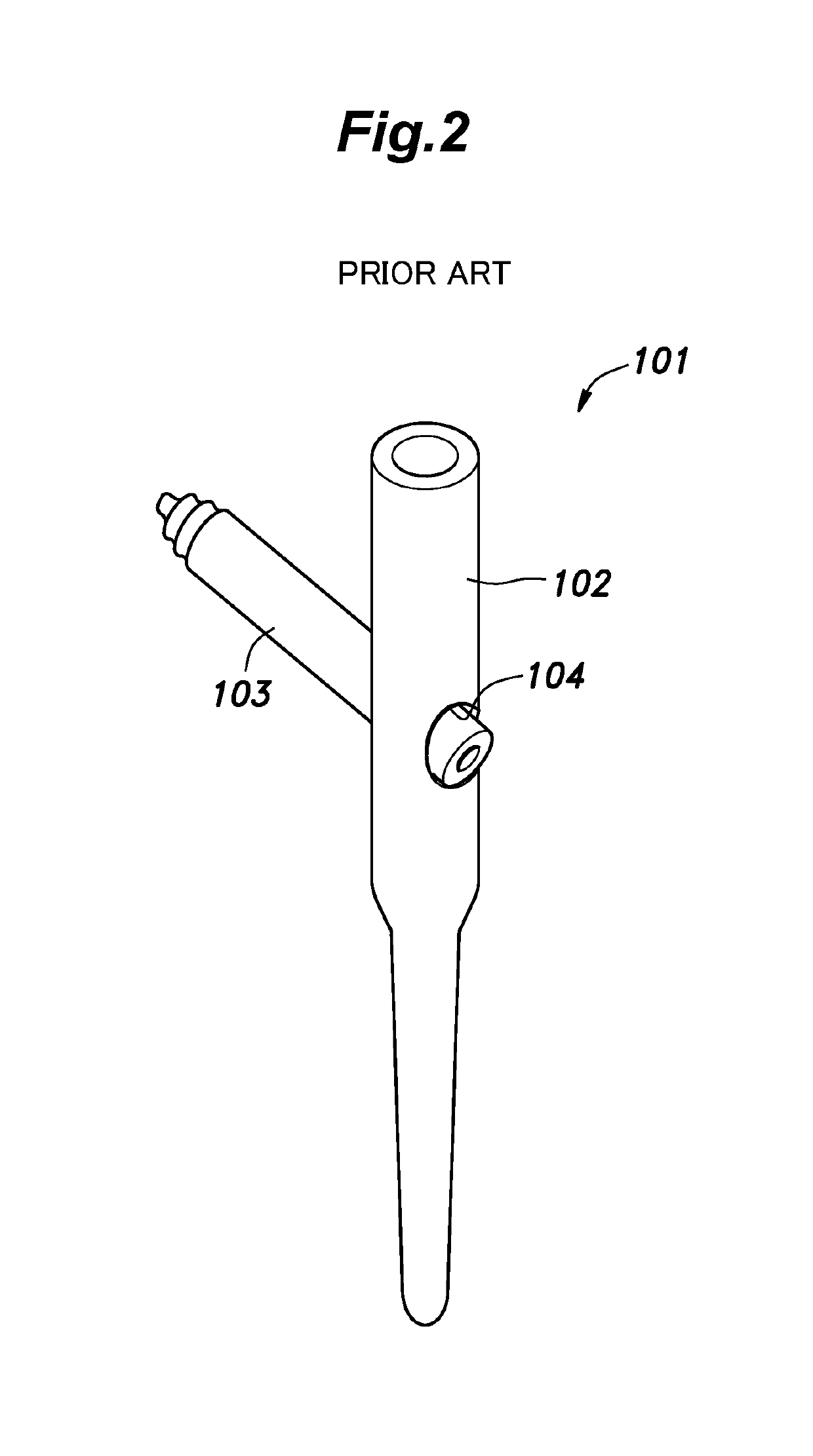
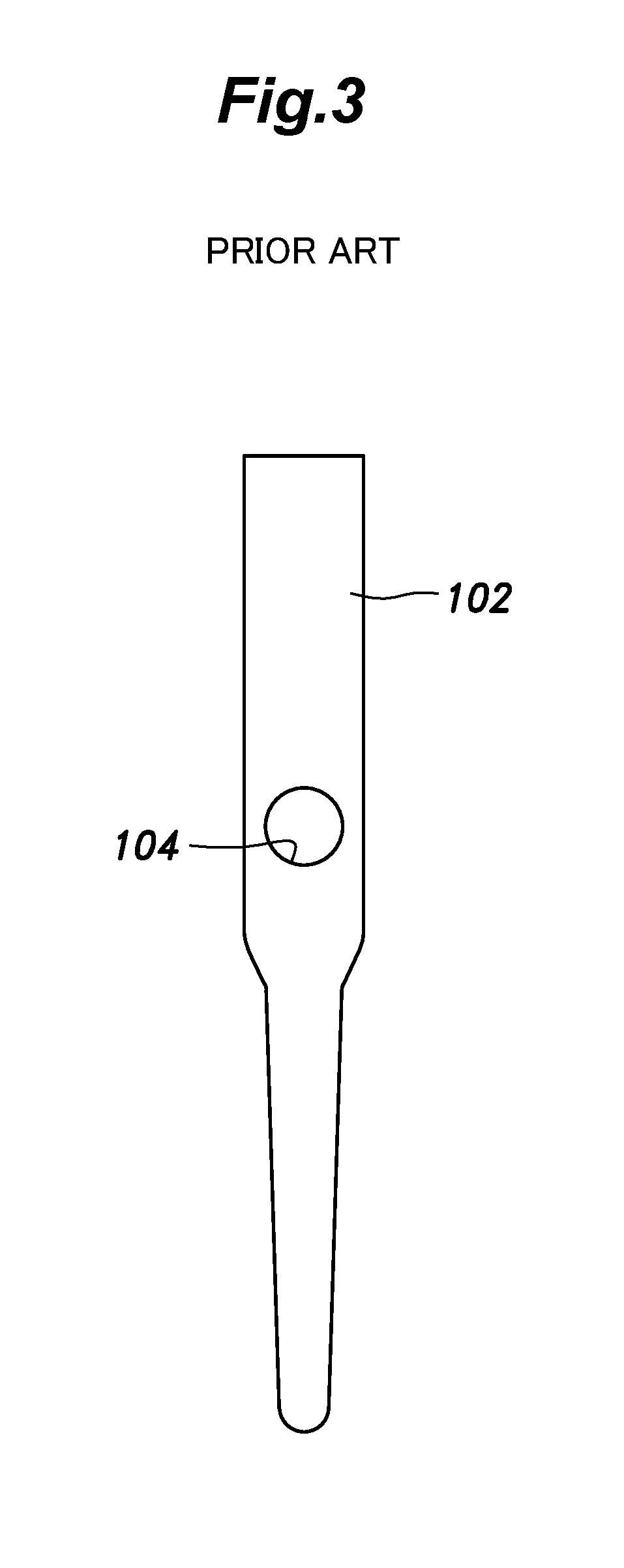
Method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
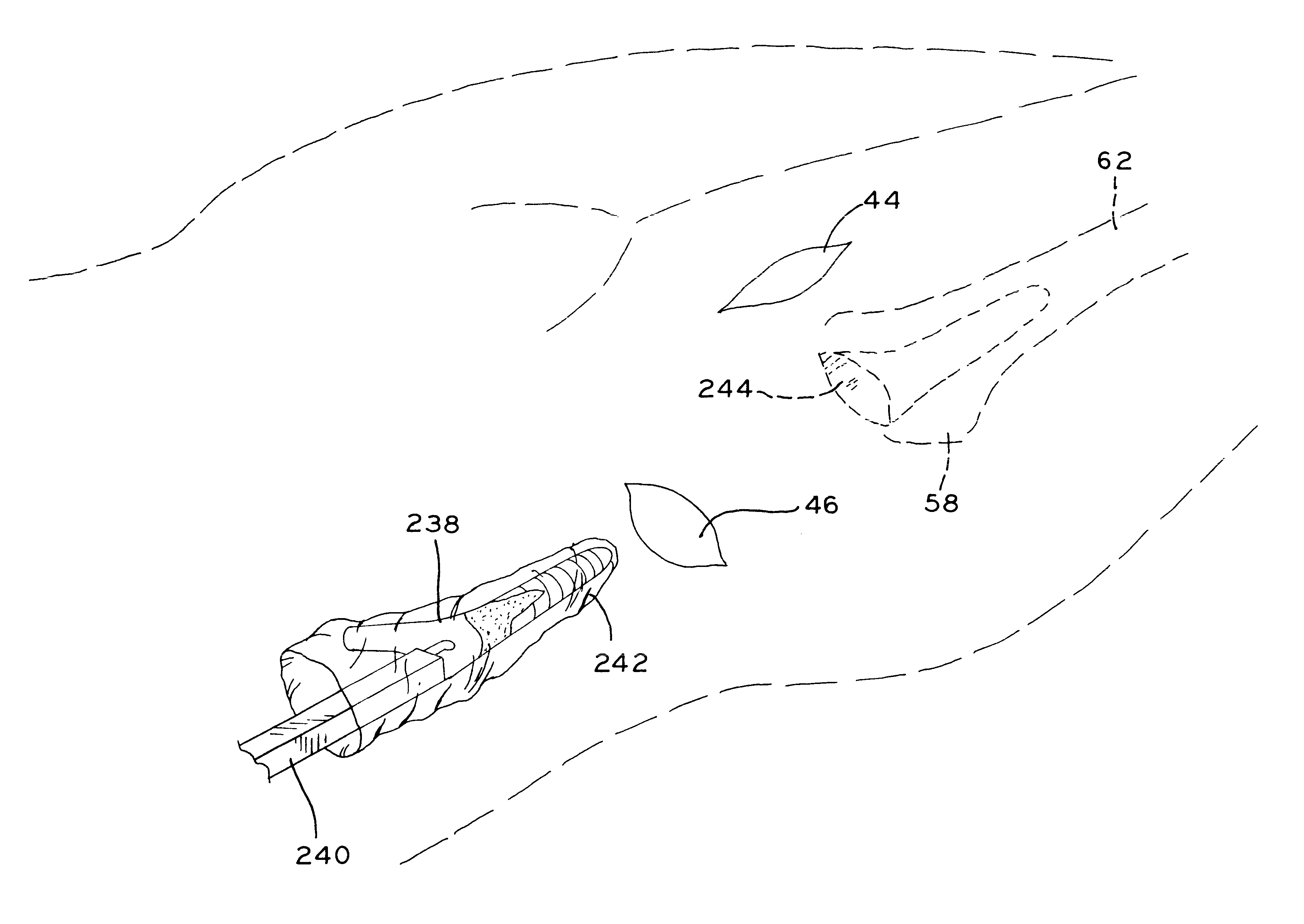
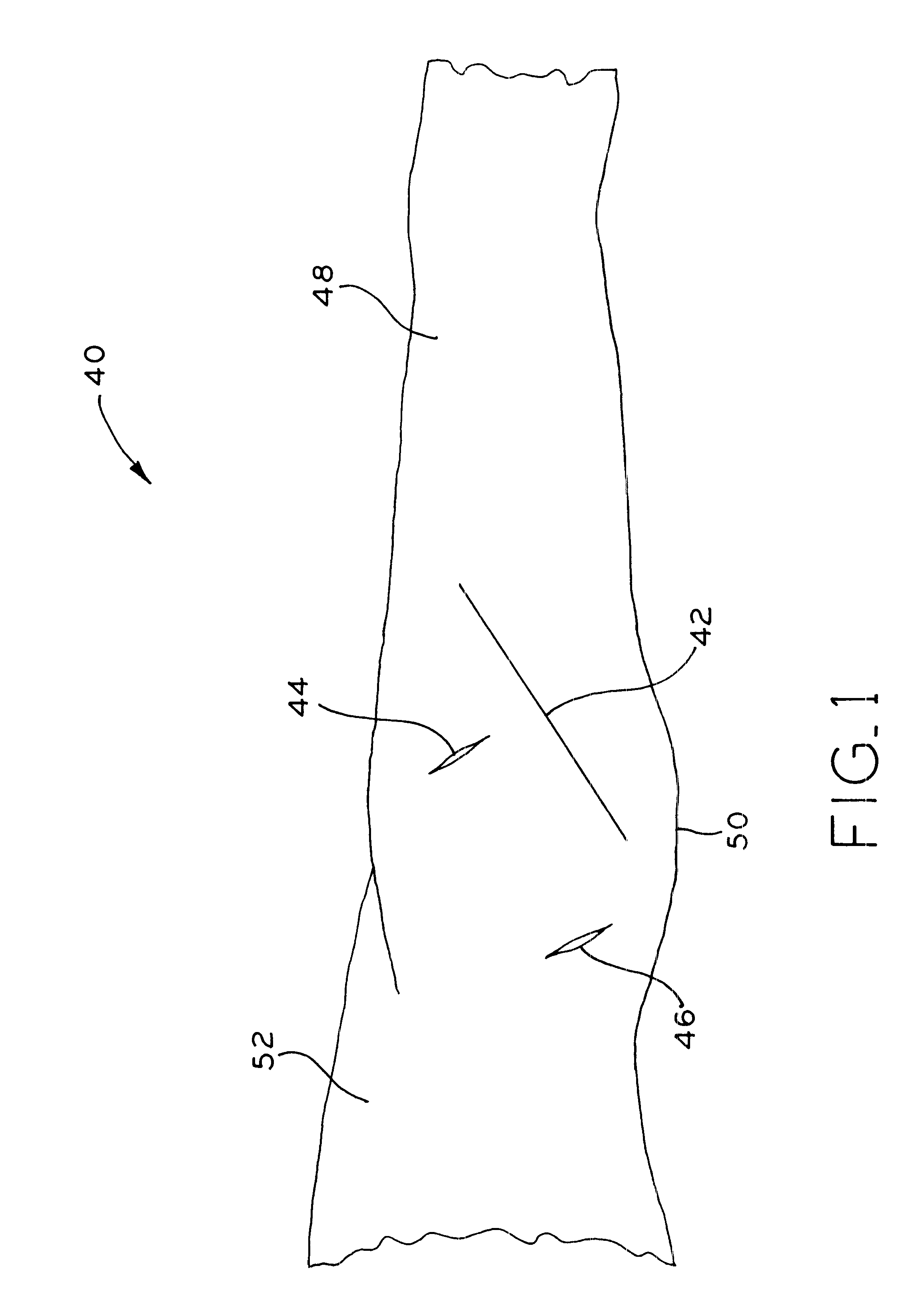
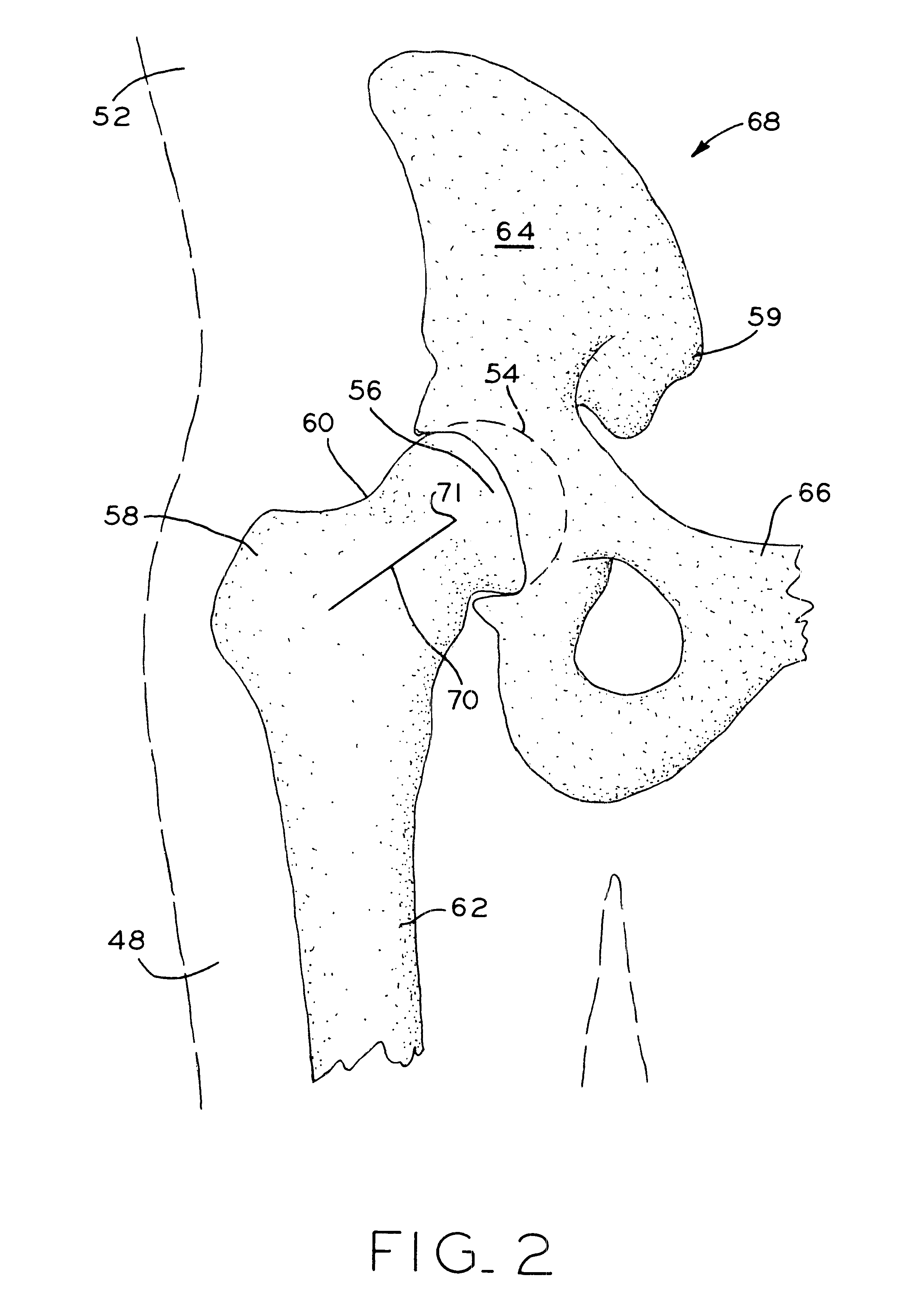
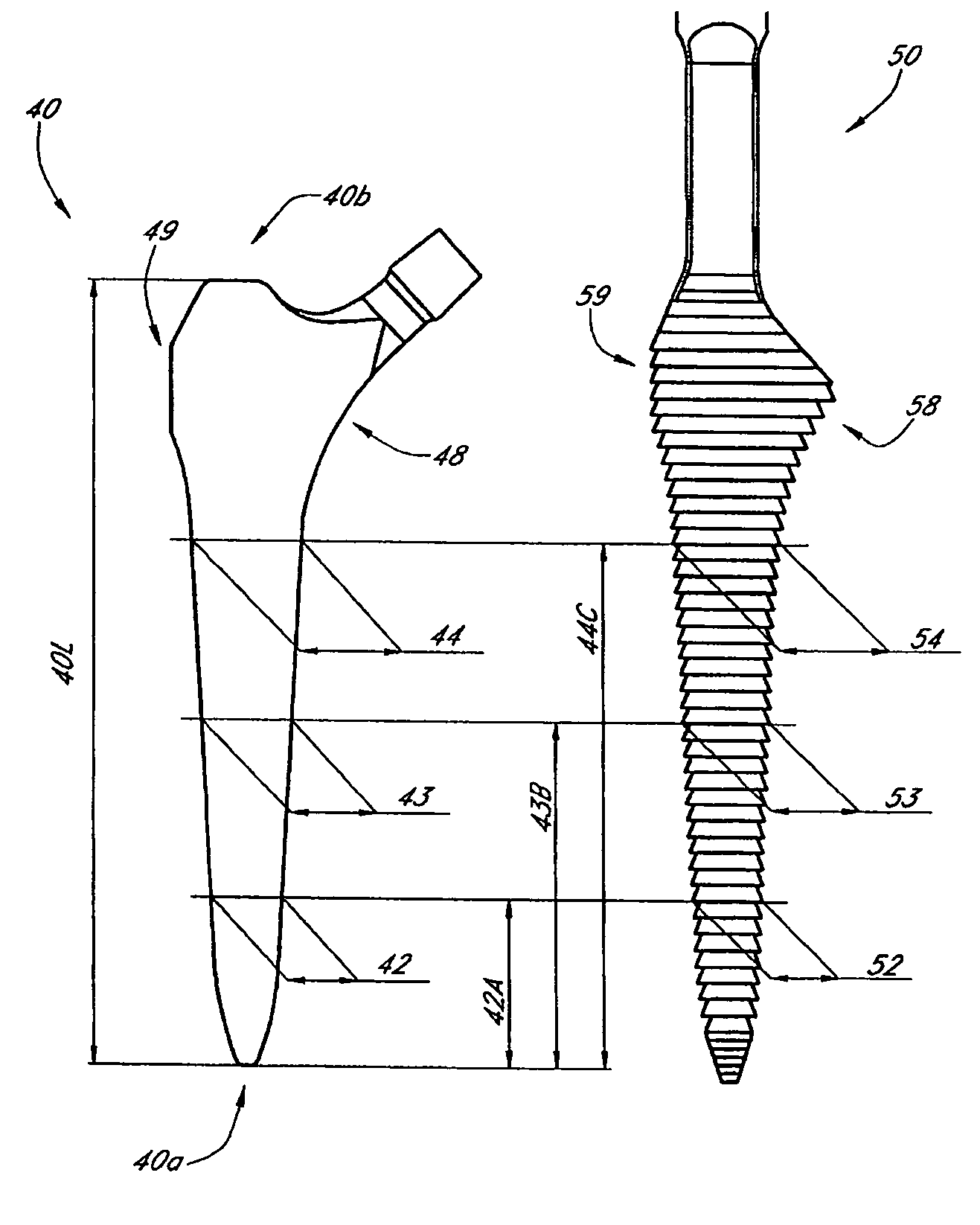
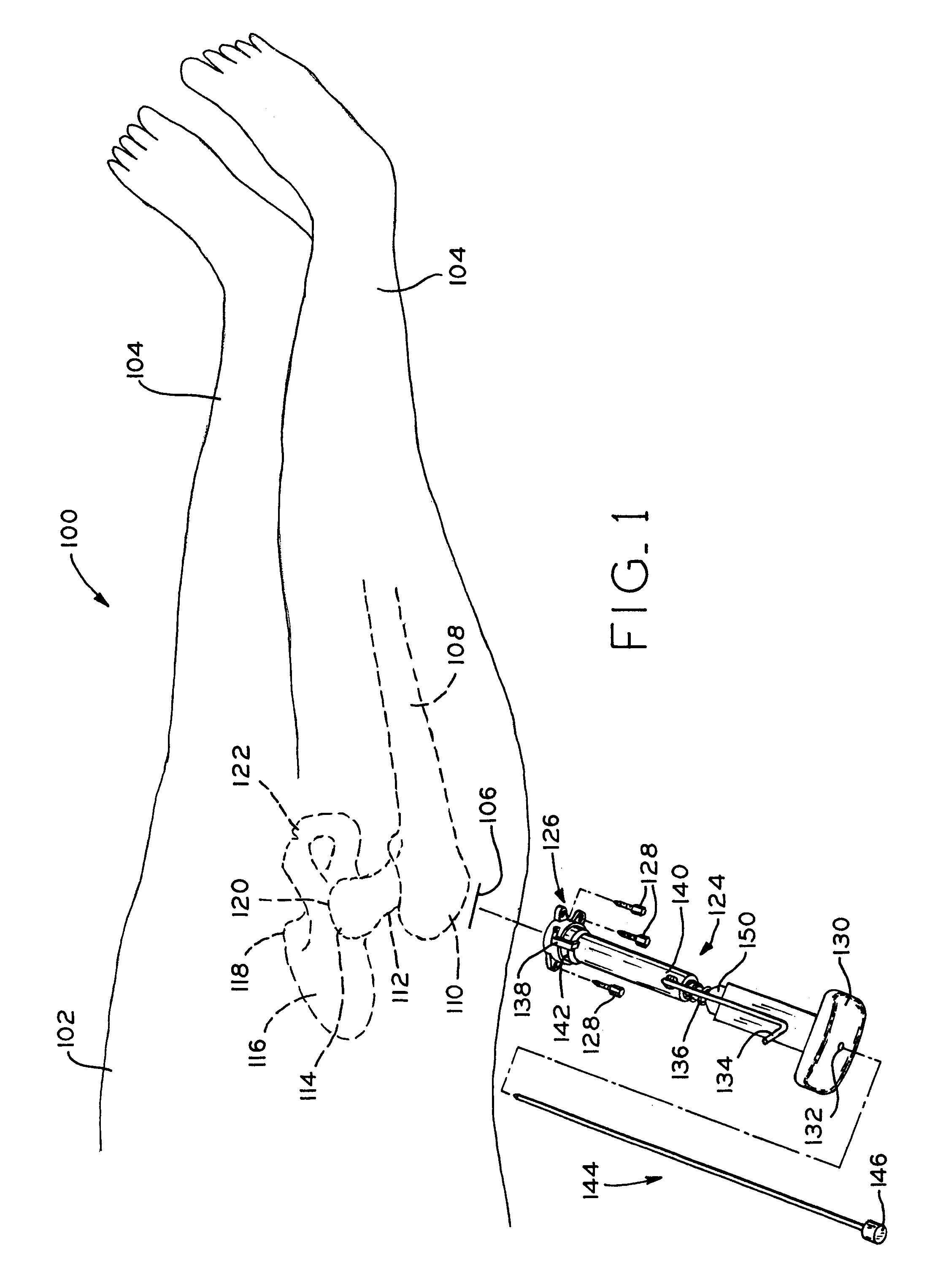
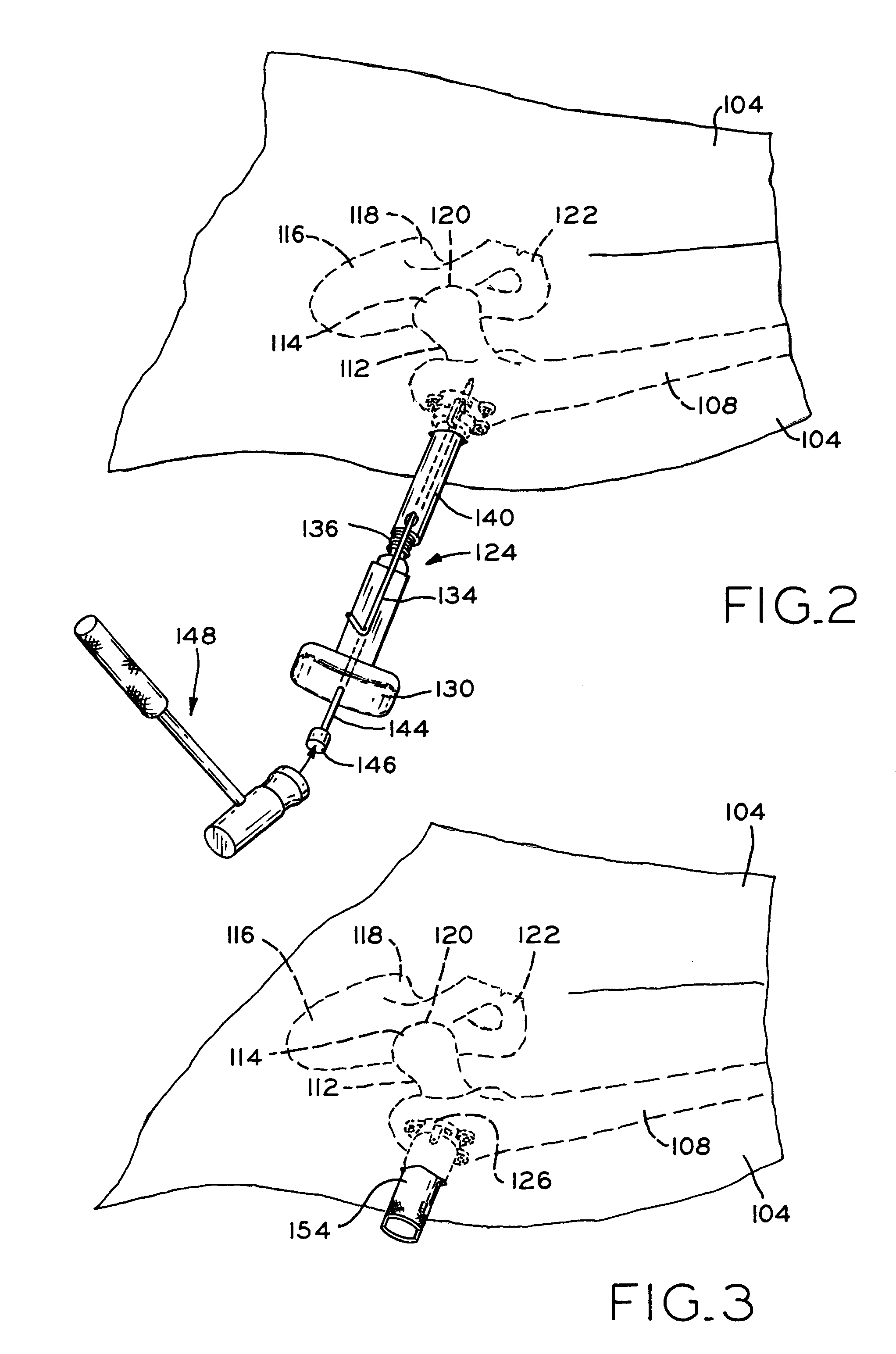
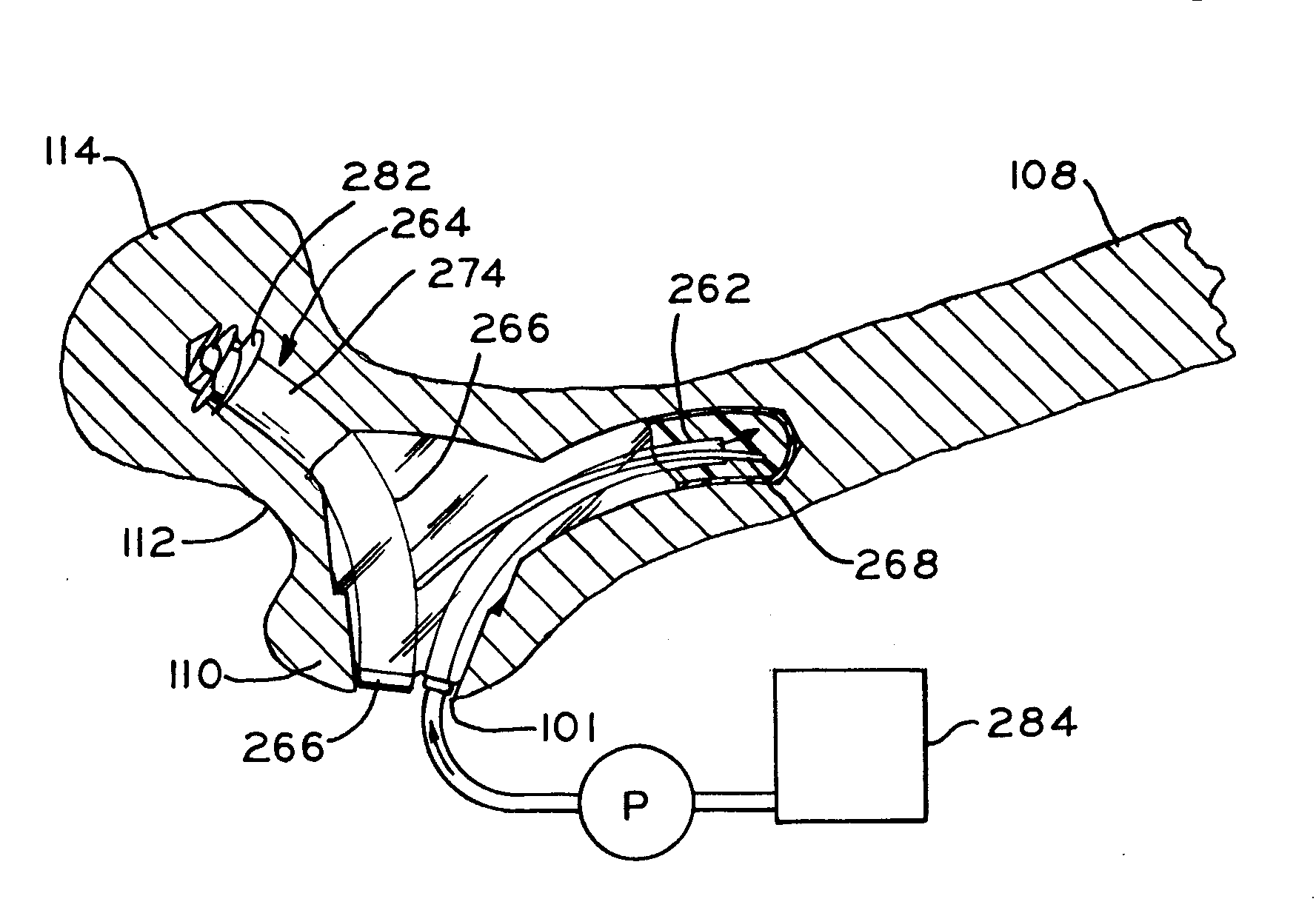
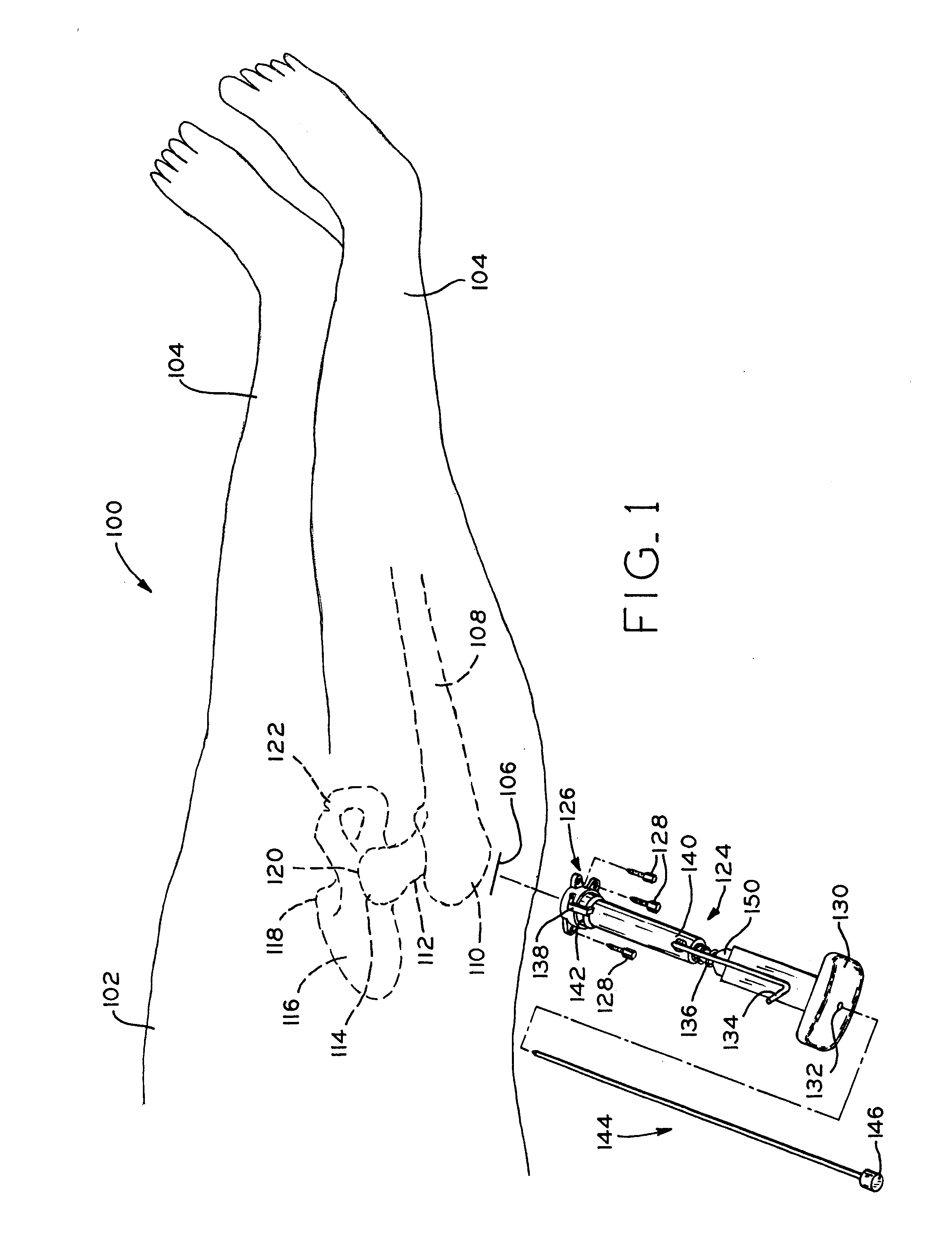
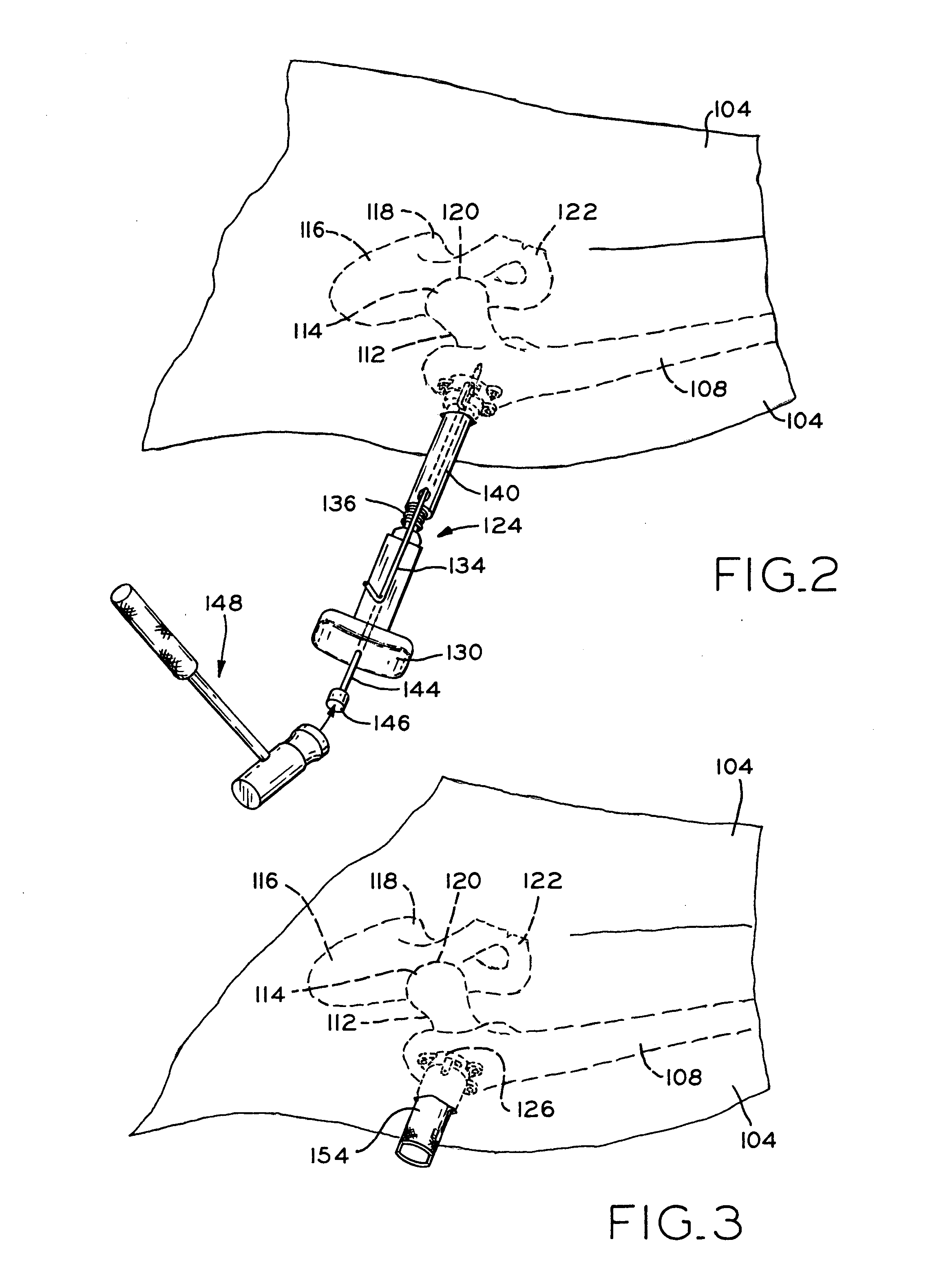
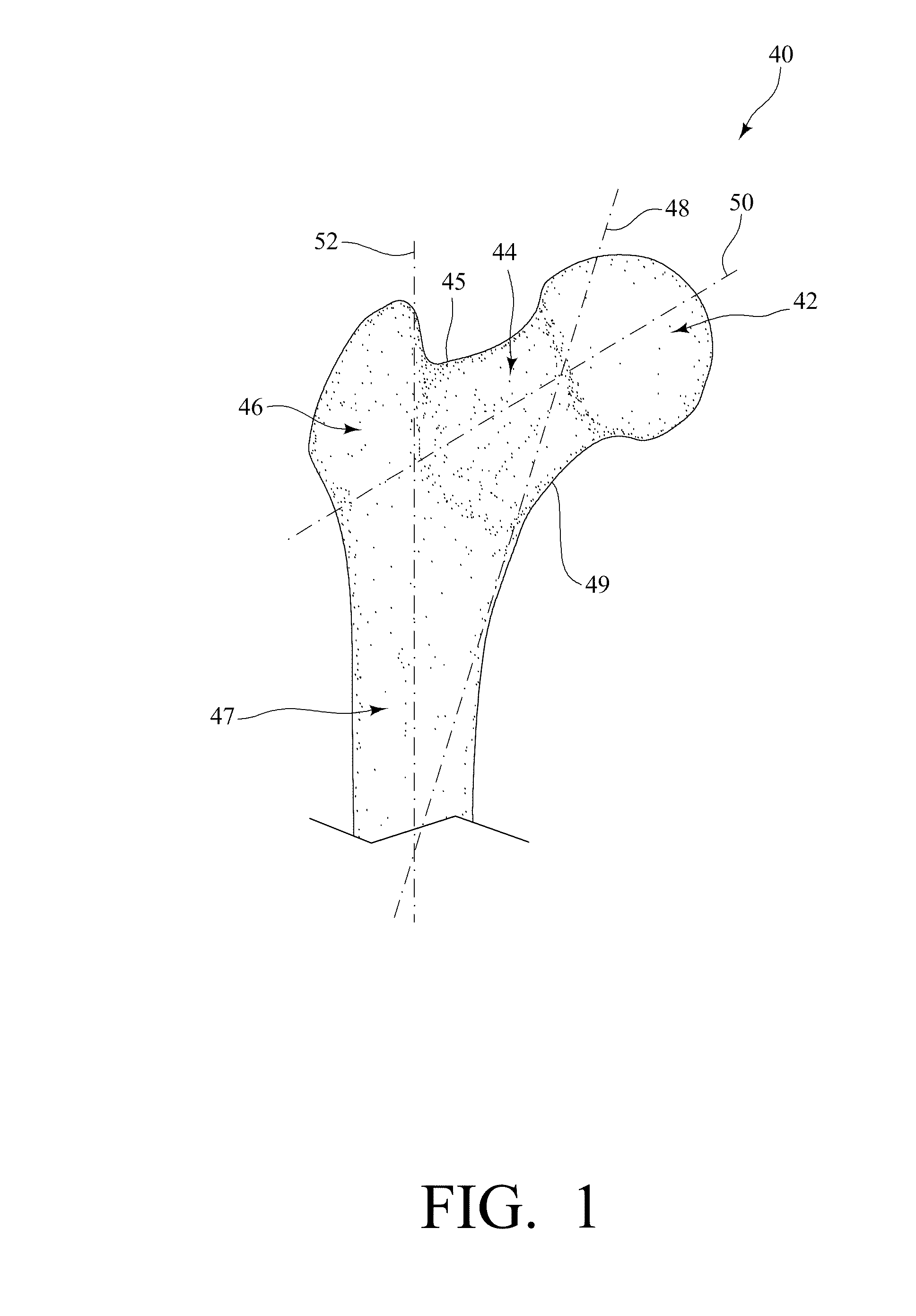
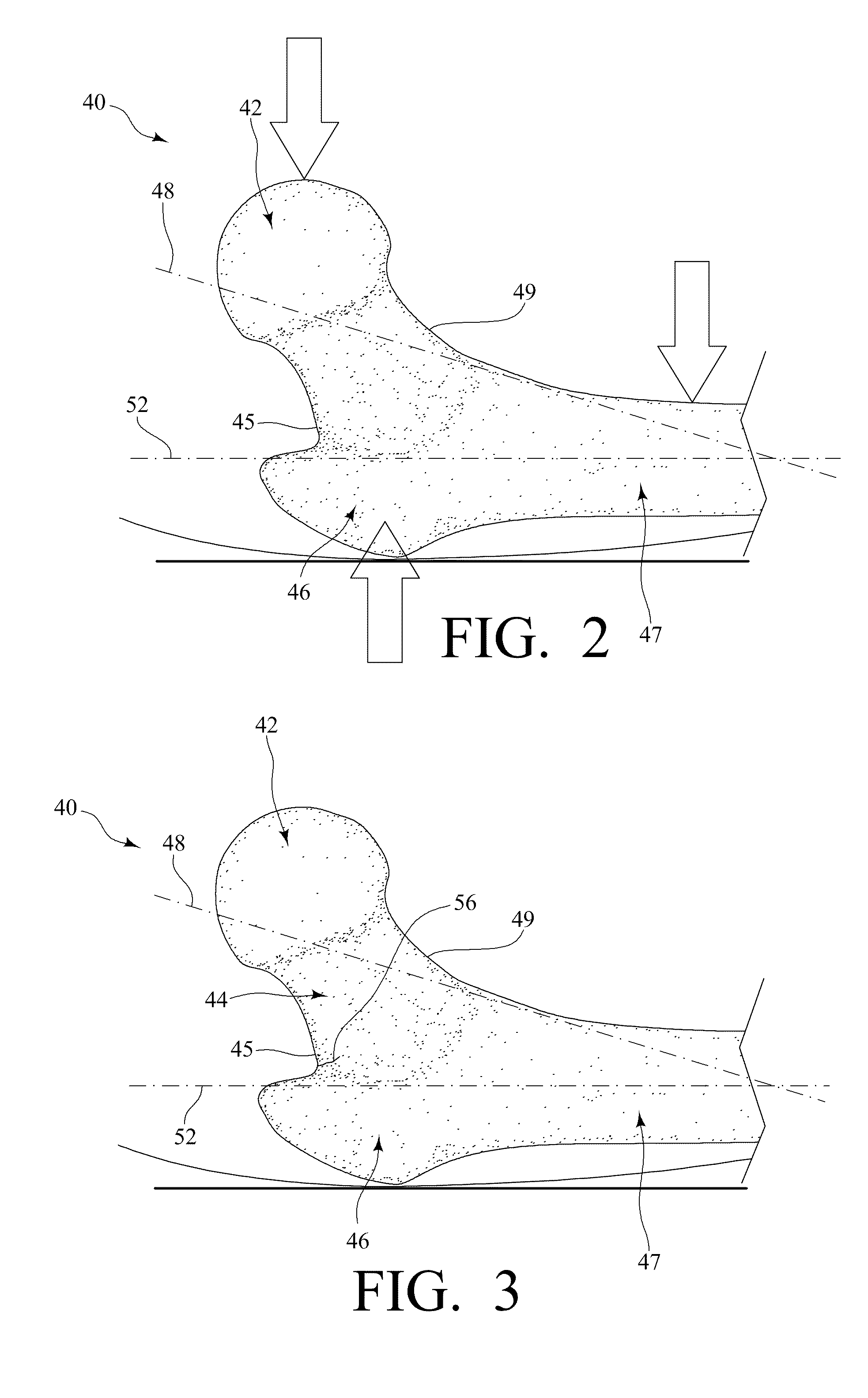
A method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. An approximately 3.75-5 centimeter (1.5-2 inch) anterior incision is made in line with the femoral neck. The femoral neck is severed from the femoral shaft and removed through the anterior incision. The acetabulum is prepared for receiving an acetabular cup through the anterior incision, and the acetabular cup is placed into the acetabulum through the anterior incision. A posterior incision of approximately 2.5-3.75 centimeters (1-1.5 inches) is generally aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft and provides access to the femoral shaft. Preparation of the femoral shaft including the reaming and rasping thereof is performed through the posterior incision, and the femoral stem is inserted through the posterior incision for implantation in the femur. A variety of novel instruments including an osteotomy guide; an awl for locating a posterior incision aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft; a tubular posterior retractor; a selectively lockable rasp handle with an engagement guide; and a selectively lockable provisional neck are utilized to perform the total hip arthroplasty of the current invention.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
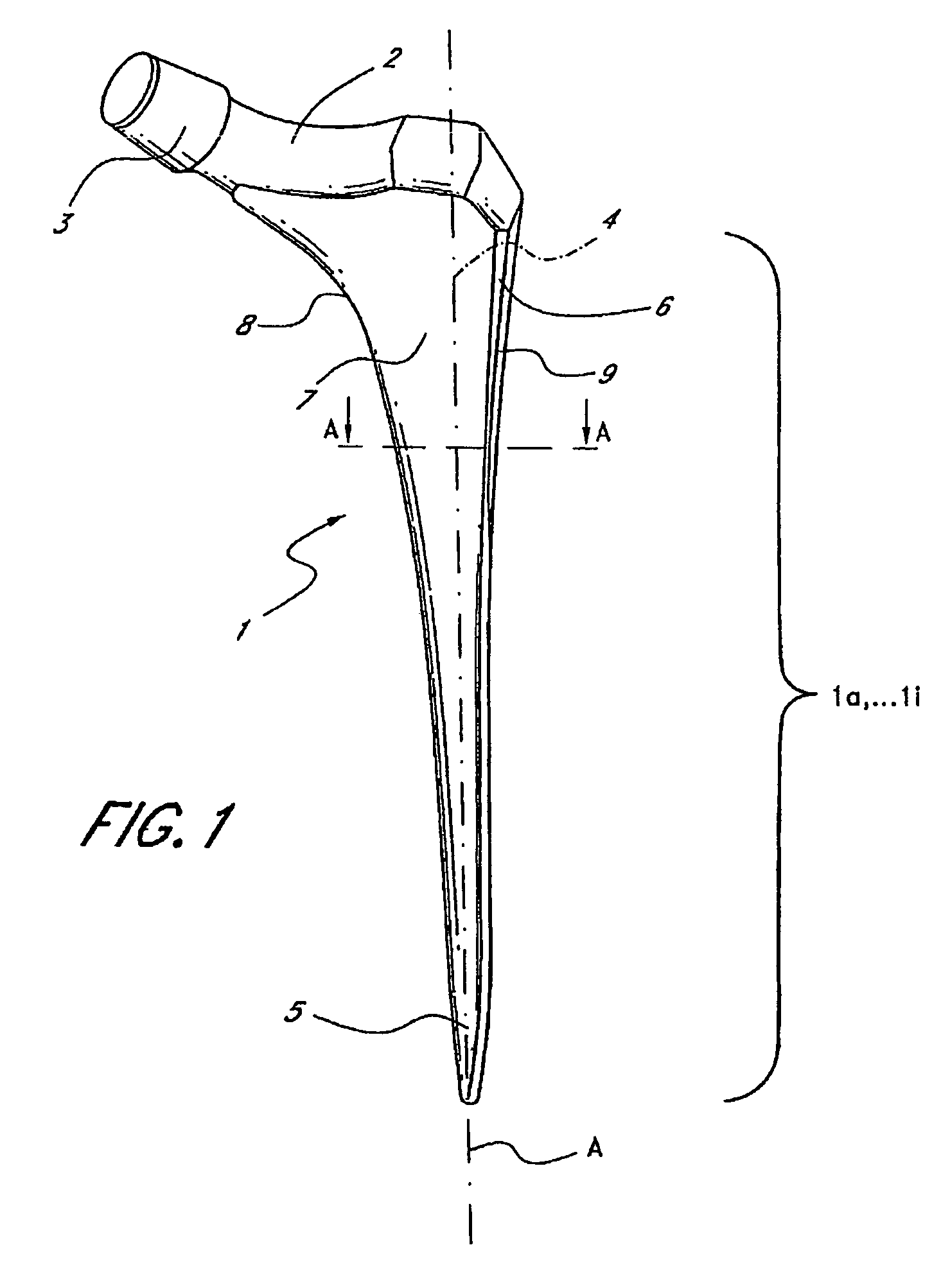
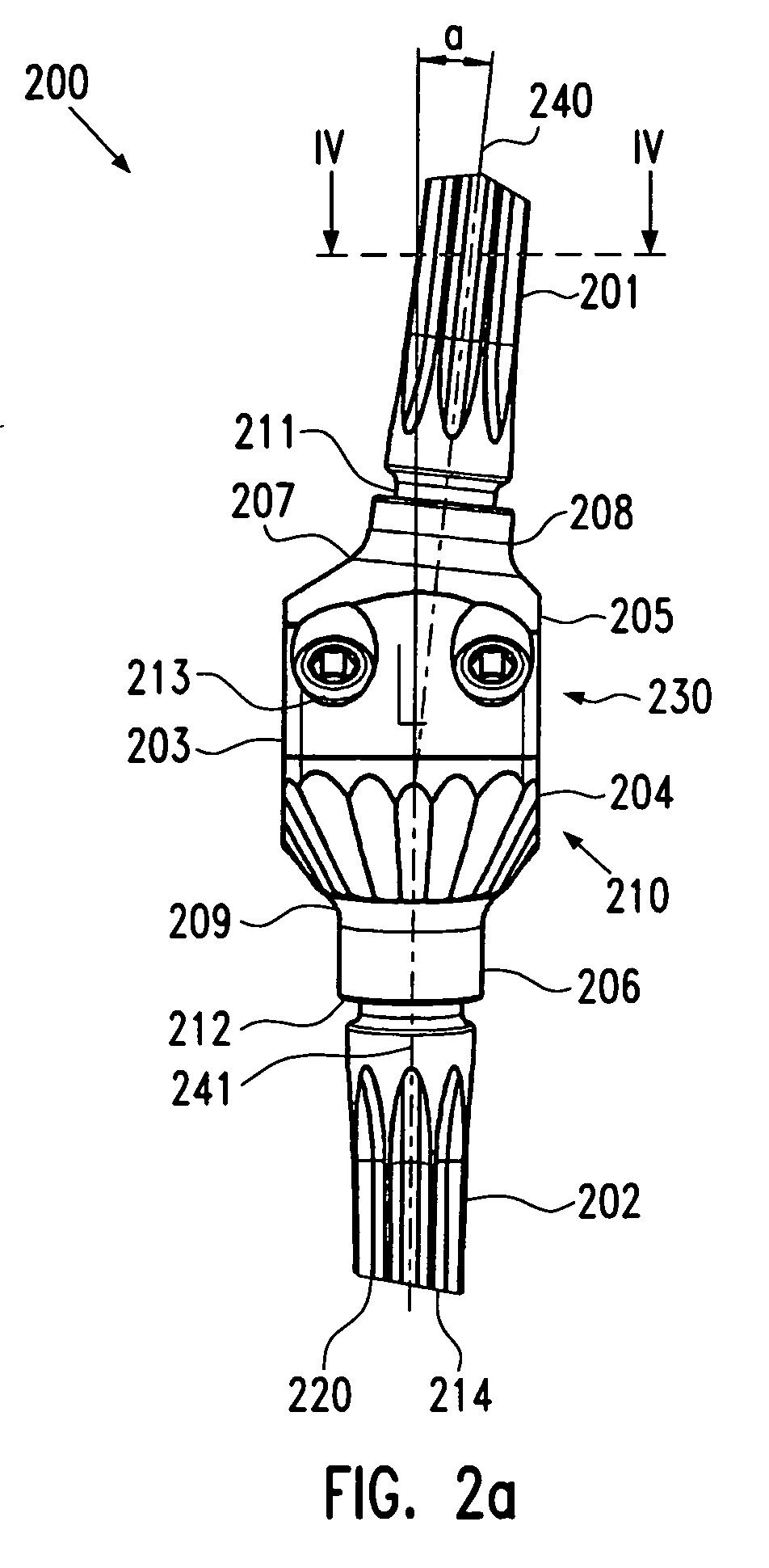
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
InactiveUS7494510B2Advantageous for revascularizationFacilitate revascularizationSurgeryJoint implantsRaspFemoral shaft
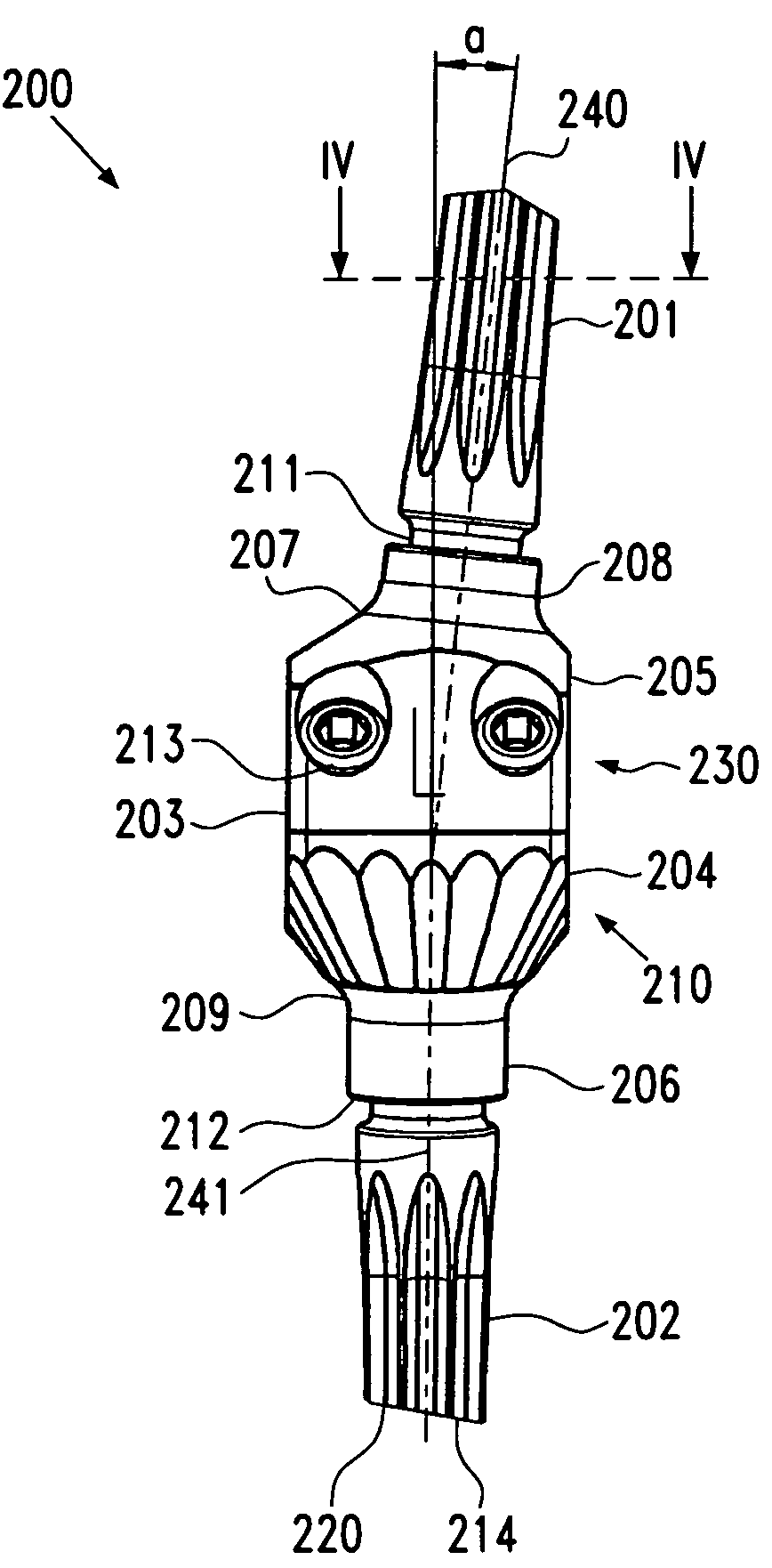
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to components of a hip-joint prosthesis. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to a leaf-like femoral shaft for use as part of a hip-joint prosthesis, and instruments (e.g., a rasp) and methods for implanting the shaft. The shaft includes an anchoring section extending between a proximal region and a distal end of the shaft. The shaft has a cross-sectional contour that defines a lateral side, a medial side, an anterior side and a posterior side. A corresponding rasp is preferably provided for each femoral shaft. The rasp is inserted into the femur to form a cavity having generally the same configuration as the rasp. The shaft is configured to be over-dimensioned in at least one of the anterior-posterior direction and medial-lateral direction relative to the rasped femur cavity. In one embodiment, the distance between diagonally opposite corner junctions of the shaft is substantially equal to the distance between corresponding diagonally opposite corner junctions of the femur cavity, so as to inhibit excess stress on the corticalis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
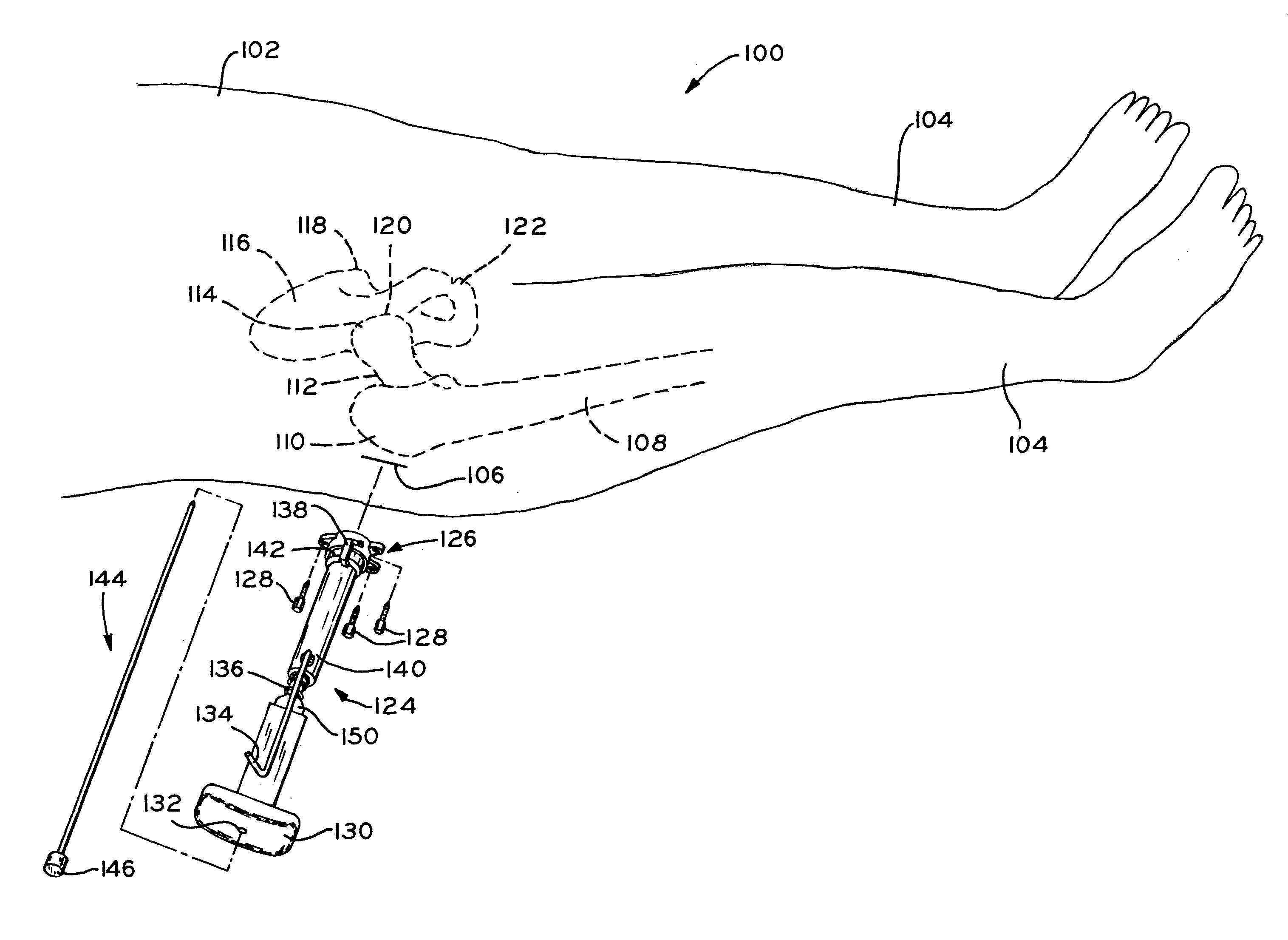
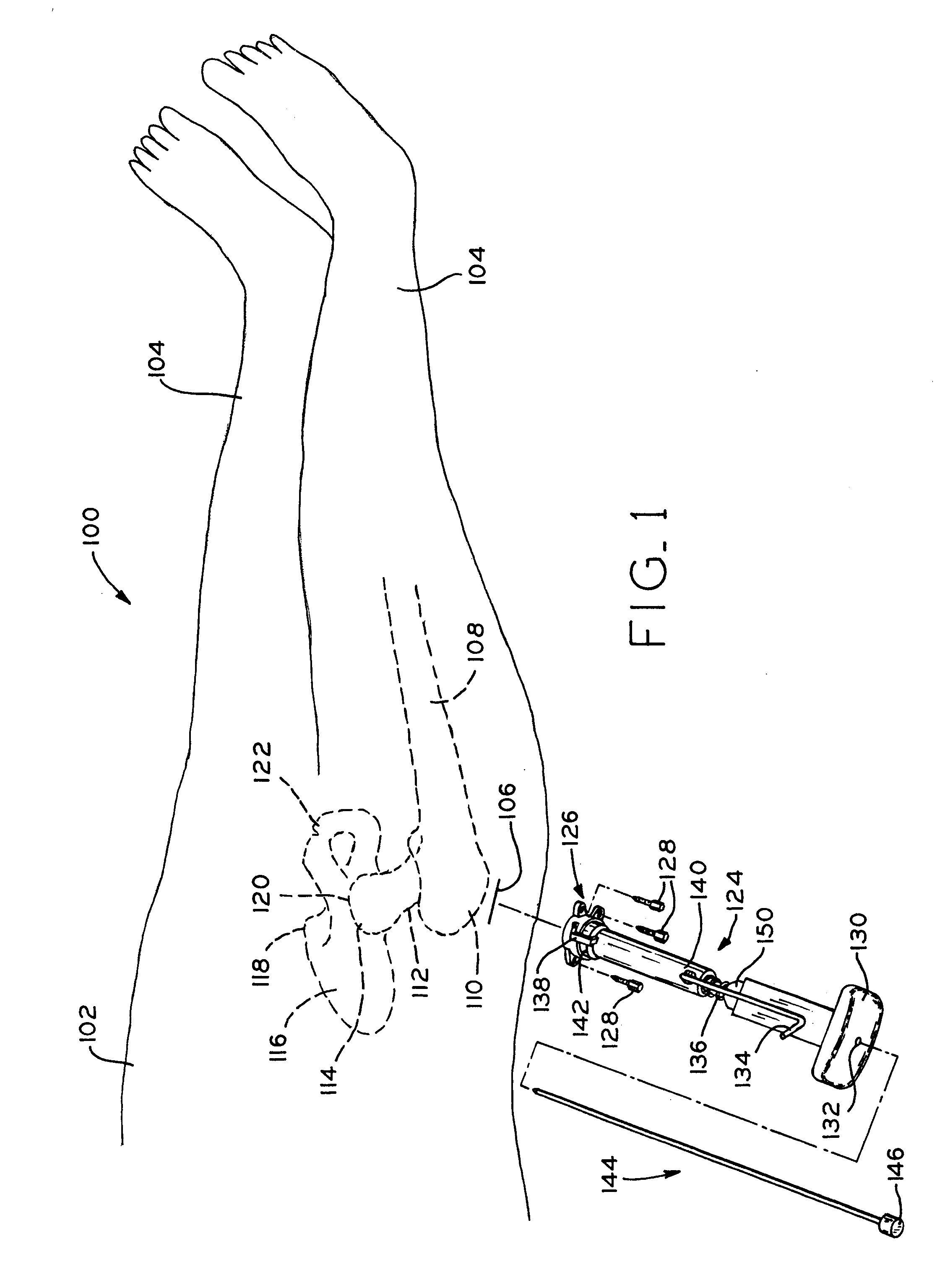
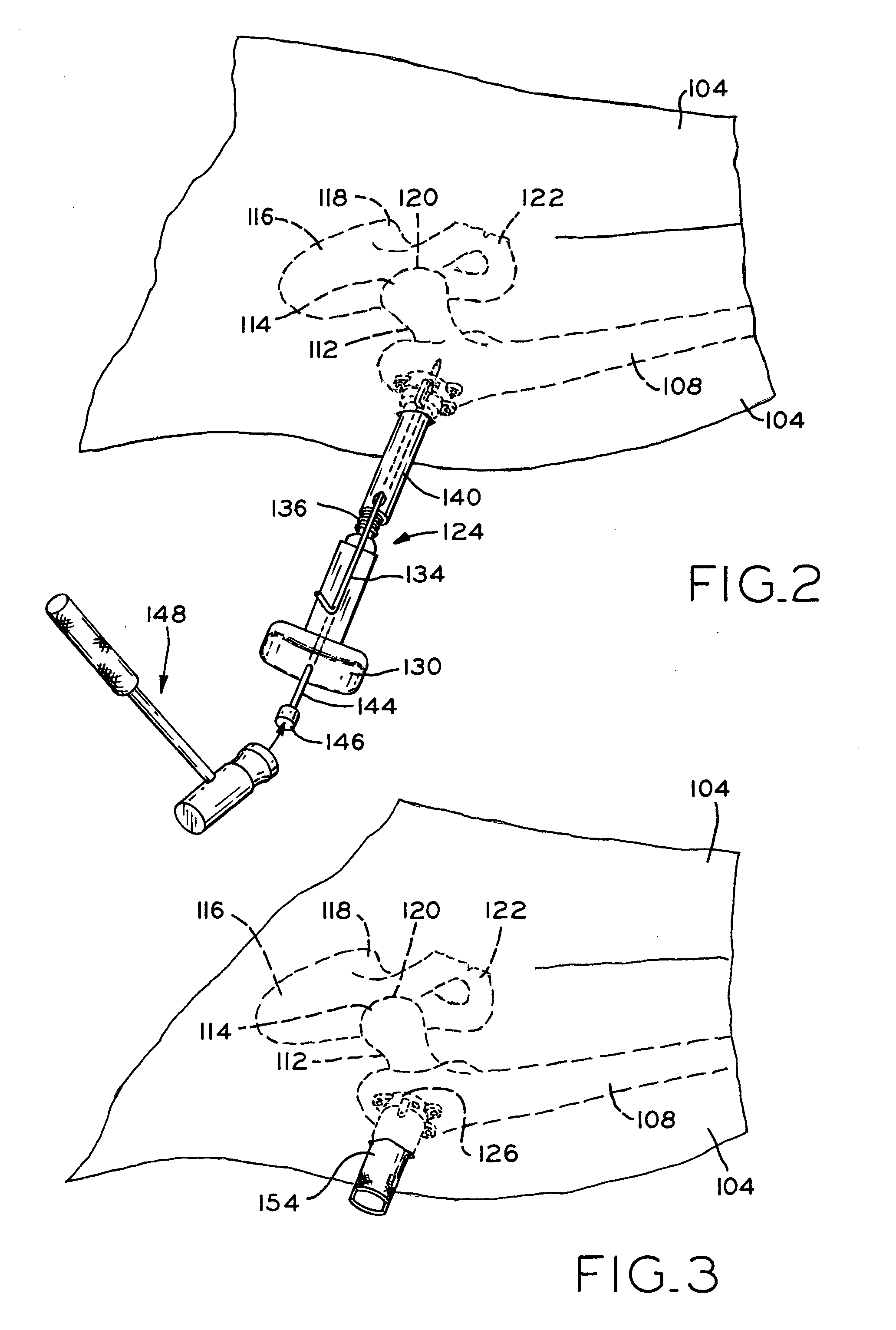
Method and apparatus for reducing femoral fractures
InactiveUS7258692B2Reducing a hip fracturePrevent escapeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headHip fracture
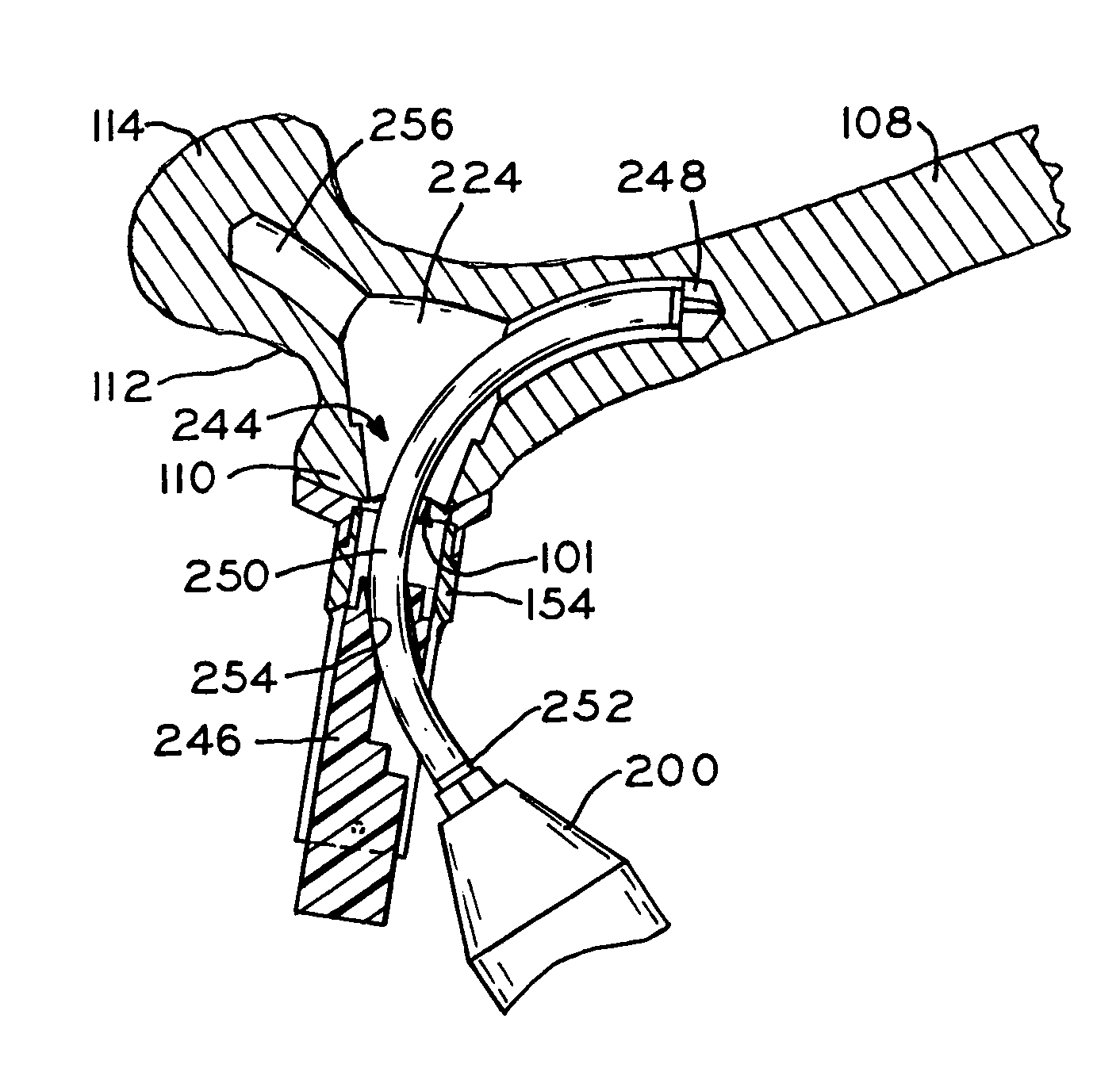
An improved method and apparatus for reducing a hip fracture utilizing a minimally invasive procedure which does not require incision of the quadriceps. A femoral implant in accordance with the present invention achieves intramedullary fixation as well as fixation into the femoral head to allow for the compression needed for a femoral fracture to heal. To position the femoral implant of the present invention, an incision is made along the greater trochanter. Because the greater trochanter is not circumferentially covered with muscles, the incision can be made and the wound developed through the skin and fascia to expose the greater trochanter, without incising muscle, including, e.g., the quadriceps. After exposing the greater trochanter, novel instruments of the present invention are utilized to prepare a cavity in the femur extending from the greater trochanter into the femoral head and further extending from the greater trochanter into the intramedullary canal of the femur. After preparation of the femoral cavity, a femoral implant in accordance with the present invention is inserted into the aforementioned cavity in the femur. The femoral implant is thereafter secured in the femur, with portions of the implant extending into and being secured within the femoral head and portions of the implant extending into and being secured within the femoral shaft.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Method and apparatus for reducing femoral fractures
InactiveUS20070225721A1Reducing a hip fractureHigh strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headHip fracture
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
A method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. An approximately 3.75-5 centimeter (1.5-2 inch) anterior incision is made in line with the femoral neck. The femoral neck is severed from the femoral shaft and removed through the anterior incision. The acetabulum is prepared for receiving an acetabular cup through the anterior incision and the acetabular cup is placed into the acetabulum through the anterior incision. A posterior incision of approximately 2-3 centimeters (0.8-1.2 inches) is generally aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft and provides access to the femoral shaft. Preparation of the femoral shaft including the reaming and rasping thereof is performed through the posterior incision, and the femoral stem is inserted through the posterior incision for implantation in the femur. A variety of novel instruments including an osteotomy guide an awl for locating a posterior incision aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft, a tubular posterior retracter, a selectively lockable rasp handle with an engagement guide; and a selectively lockabele provisional neck are utilized to perform the total hip arthroplasty of the current invention.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Device and method to prevent hip fractures
ActiveUS20100023012A1Prevent hip fracturesAvoid fracturesInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headHip fracture
A device for preventing a hip fracture includes: a shaft having a first end and a second end and an expanding means for engaging the femoral head at the first end. The shaft is positioned in a hole of a predetermined depth in a femur. The hole extends from the greater trochanter to the femoral head of the femur, such that the first end is positioned in the femoral head and the second end is positioned in the greater trochanter. The device is oriented substantially perpendicular to the long axis of the femoral shaft.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Arthrodesis module and method for providing a patient with an arthrodesis
An endoprothetical connection element for creating a knee arthrodesis comprises a coupling element that comprises a first fastener and a second fastener. The first fastener is adapted for connection with a first fastening element corresponding to the first fastener that is provided at a shaft insertable into a femur of a patient. The second fastener is adapted for connection with a second fastening element corresponding to the second fastener that is provided at a shaft insertable into a tibia of the patient. The coupling element is formed such that a first longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft connected to the first fastener and a second longitudinal axis of the tibial shaft connected to the second fastener include an angle different from 180 degrees which, when implanted into the body of the patient, is lying in a coronal plane of the patient.
Owner:BREHM PETER
Method and apparatus for reducing femoral fractures
InactiveUS20070123995A1Hastens patient recoveryReducing a hip fractureInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsHip fractureRight femoral head
An improved method and apparatus for reducing a hip fracture utilizing a minimally invasive procedure which does not require incision of the quadriceps. A femoral implant in accordance with the present invention achieves intramedullary fixation as well as fixation into the femoral head to allow for the compression needed for a femoral fracture to heal. To position the femoral implant of the present invention, an incision is made along the greater trochanter. Because the greater trochanter is not circumferentially covered with muscles, the incision can be made and the wound developed through the skin and fascia to expose the greater trochanter, without incising muscle, including, e.g., the quadriceps. After exposing the greater trochanter, novel instruments of the present invention are utilized to prepare a cavity in the femur extending from the greater trochanter into the femoral head and further extending from the greater trochanter into the intramedullary canal of the femur. After preparation of the femoral cavity, a femoral implant in accordance with the present invention is inserted into the aforementioned cavity in the femur. The femoral implant is thereafter secured in the femur, with portions of the implant extending into and being secured within the femoral head and portions of the implant extending into and being secured within the femoral shaft.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
An external proximal femoral prosthesis for total hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080004711A1Remove complicationsMaintain bone qualityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsAcetabular componentCalcar
An external proximal femoral prosthesis for total hip arthroplasty (THA) is described, which fundamentally comprises a shell configured a hollow, thin-wall, asymmetric bell shape and a plurality of tension anchor means. An inner transverse cross contour of the shell forms a cavity, which could be affixable to a profile of outer surface of the area of neck, trochantic bed and calcar of the proximal femur. A neck portion of the shell is compatible with acetabular components (ball and cup). The prosthesis is mechanically fastened by tension anchor means during the operation and further biologically secured by in-growing bone through the side holes on the shell wall and into its interior coating surface of implant wall thereafter. The loading force on the femoral head would be well transferred and distributed on the shell and then directly conducted into the cortical bone of the femoral shaft therearound.
Owner:LI XUE +2
Customized artificial semi-knee-joint and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101278866AReduce wearJoint implantsComputerised tomographsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Customized hemi-knee joint prosthesis and a preparation method thereof are provided. Firstly, the normal side knee joint femur condyle data of a patient is extracted by CT for the medical image three-dimensional image reconstruction. The three-dimensional anatomy model of patient femur condyle is obtained by an antagonizing model. A metal femur condyle joint is obtained according to the three-dimensional anatomy model. Then, a rolling pillar is arranged in the metal femur condyle joint. The two sides of the rolling pillar are respectively opened with a cylindrical groove. A rolling combined station is sheathed on the rolling pillar. The two sides of the rolling combined station are respectively equipped with a side-push plate with a lug boss. The lug bosses of the side-push plates are inserted in the grooves of the rolling pillars. As the rolling pillar is arranged inside the articular surface of the metal femur condyle of the hemi-knee joint prosthesis, the prosthesis upper part, namely the rolling combined station, and the lower part, namely the articular surface of the metal femur condyle, which are fixed on a femoral shaft move relatively within a certain angle. Being corresponding to a tibia platform, the lower part is static during the period. Therefore, the whole process of the knee joint bending is finished and the abrasion of the prosthesis on the cartilage surface of the joint is reduced.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Targeting device and method
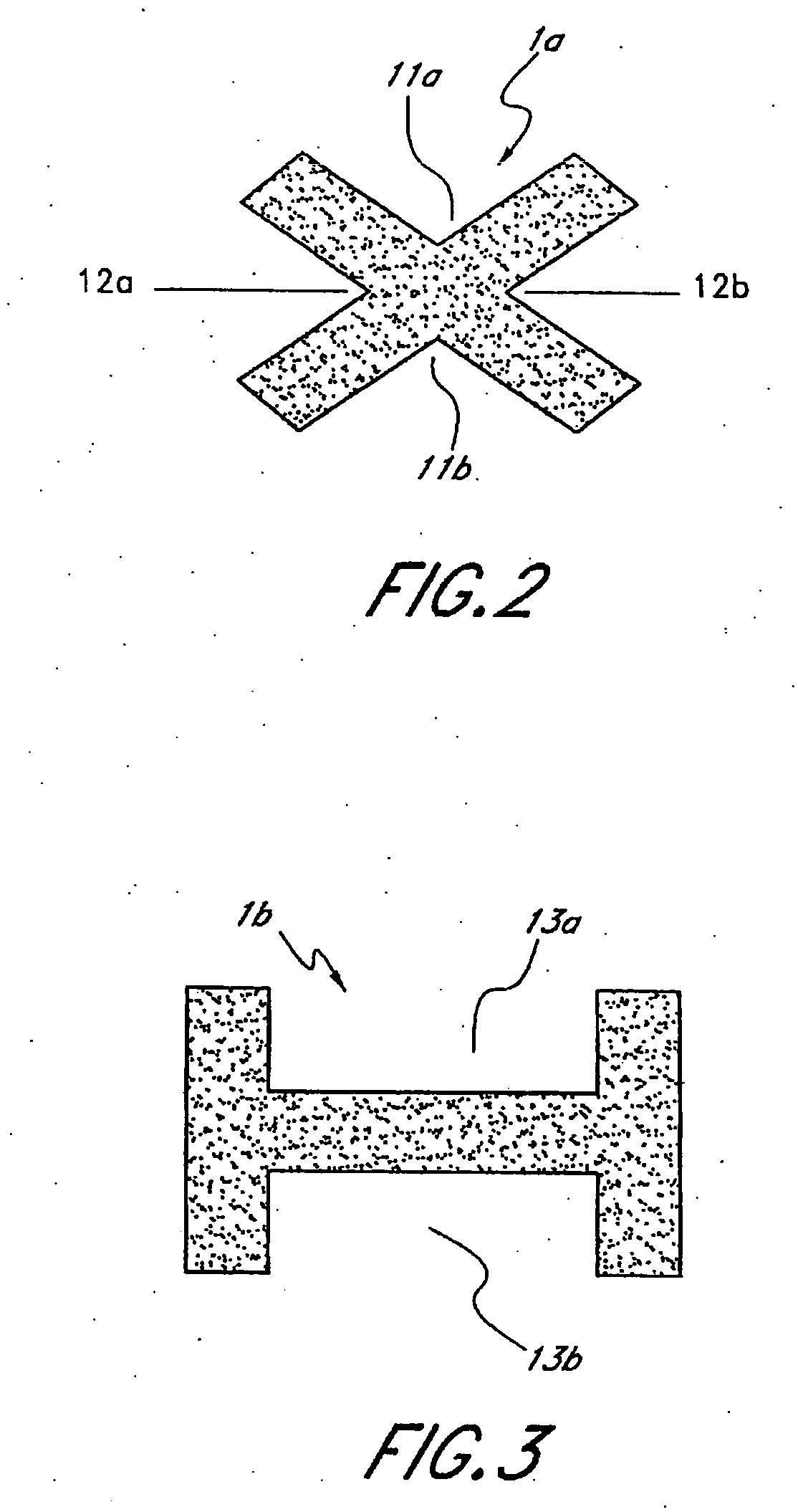
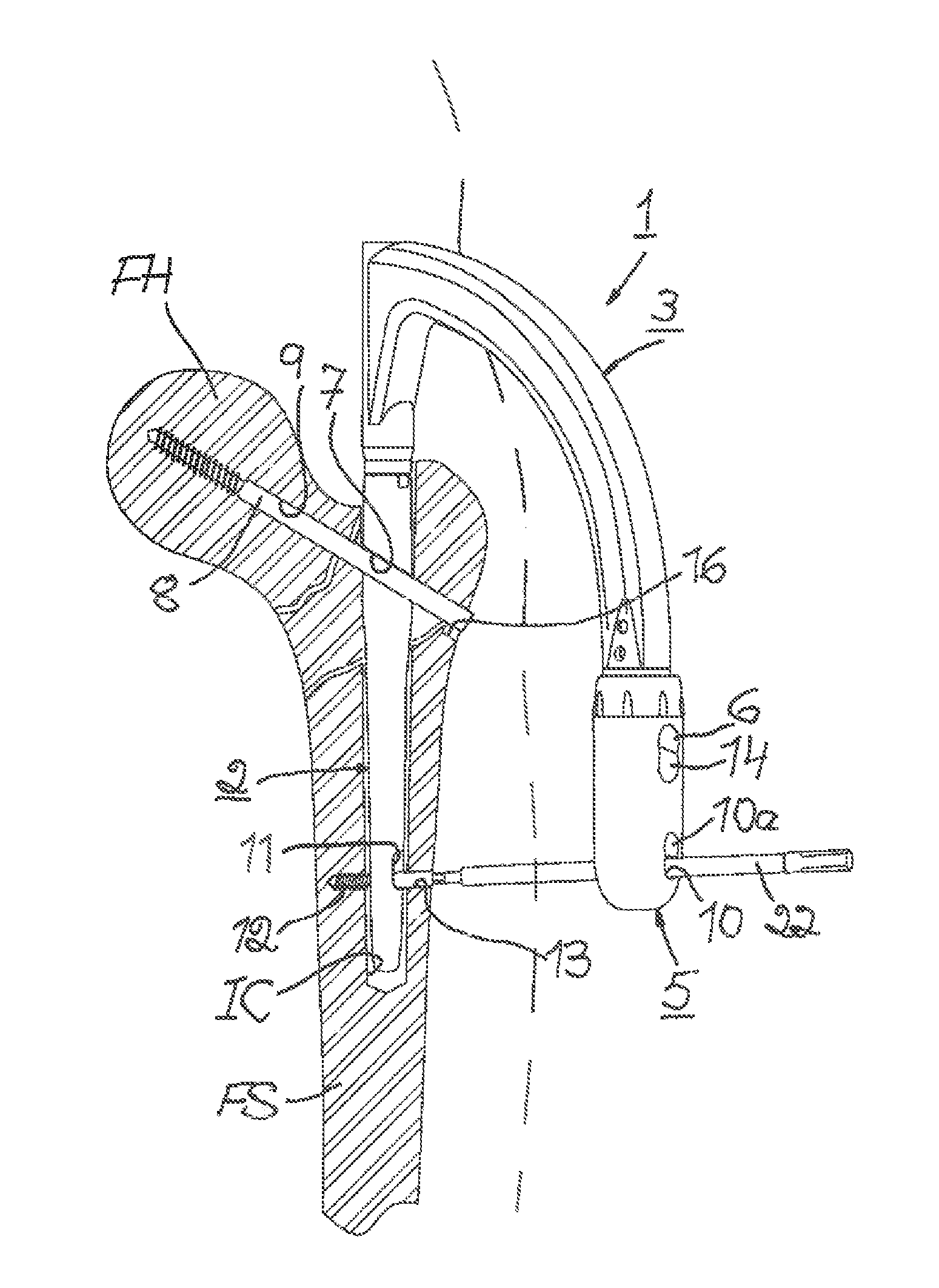
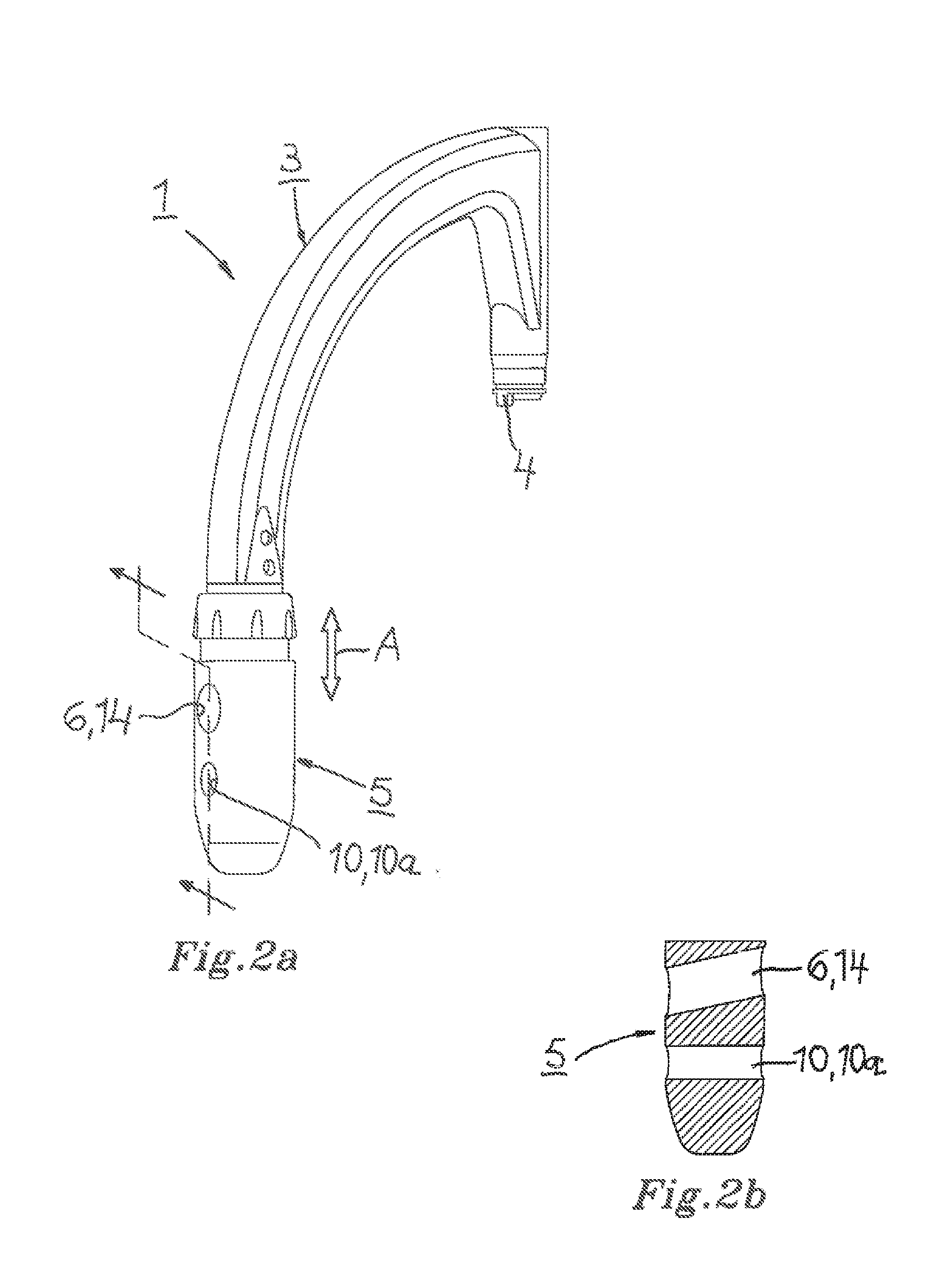
The present invention relates to a method for fixing an intramedullary cavity nail for the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures and to a targeting device for use in performing the steps of said method. According to the method, a recess (16) for a femur neck screw (8) for fixing the cavity nail (2) is provided in at least the lateral cortex of the femoral shaft (FS) in close distal proximity to a hole (9) for the femur neck screw such that bone fragment(s) located distally of the fracture and bone fragment(s) located proximally of the fracture relatively seen can be displaced towards each other. A targeting head (5) of the targeting device (1) is configured with a targeting bore (14) which is alignable with a point on the femoral shaft (FS) in close distal proximity to the hole (9) for the femur neck screw (8) for use in providing at said point, said recess (16) for the femur neck screw.
Owner:SWEMAC INNOVATION
Femoral intertrochanteric fracture double-sleeve type osteosynthesis device
InactiveCN104688311AAvoid displacementImprove versatilityInternal osteosythesisBone platesIntertrochanteric fractureFemoral shaft
The invention discloses a femoral intertrochanteric fracture double-sleeve type osteosynthesis device. The femoral intertrochanteric fracture double-sleeve type osteosynthesis device comprises an osteosynthesis plate, double-sleeve nails and a plurality of locking screws. The osteosynthesis plate is matched with the outer side of the femoral neck end in shape and the width and the thickness of the osteosynthesis plate decrease from top to bottom. The upper portion and the lower portion of the osteosynthesis plate are provided with a plurality of threaded locking holes and the middle portion of the osteosynthesis plate is fixedly connected to two sleeves. The double-sleeve nails comprise two half-threaded empty nails and the tail ends of the two half-threaded empty nails are sleeved in the two sleeves of the osteosynthesis plate. The locking screws are used for fixing the osteosynthesis to a femur through the locking holes. When the femoral intertrochanteric fracture double-sleeve type osteosynthesis device is used clinically, the two half-threaded empty nails are screwed along a guide needle, the sleeves sleeve the tail ends of the half-threaded empty nails, the upper portion of the osteosynthesis plate is fixed to a femoral greater trochanter with 3 or 4 locking screws, and the lower portion of the osteosynthesis plate is fixed to a femoral shaft. The femoral intertrochanteric fracture double-sleeve type osteosynthesis device can reduce the fracture line, improves stability and is quick in healing and suitable for diversity femoral neck fracture repair.
Owner:SUZHOU RUIHUA HOSPITAL
Method for knee resection alignment approximation in knee replacement procedures
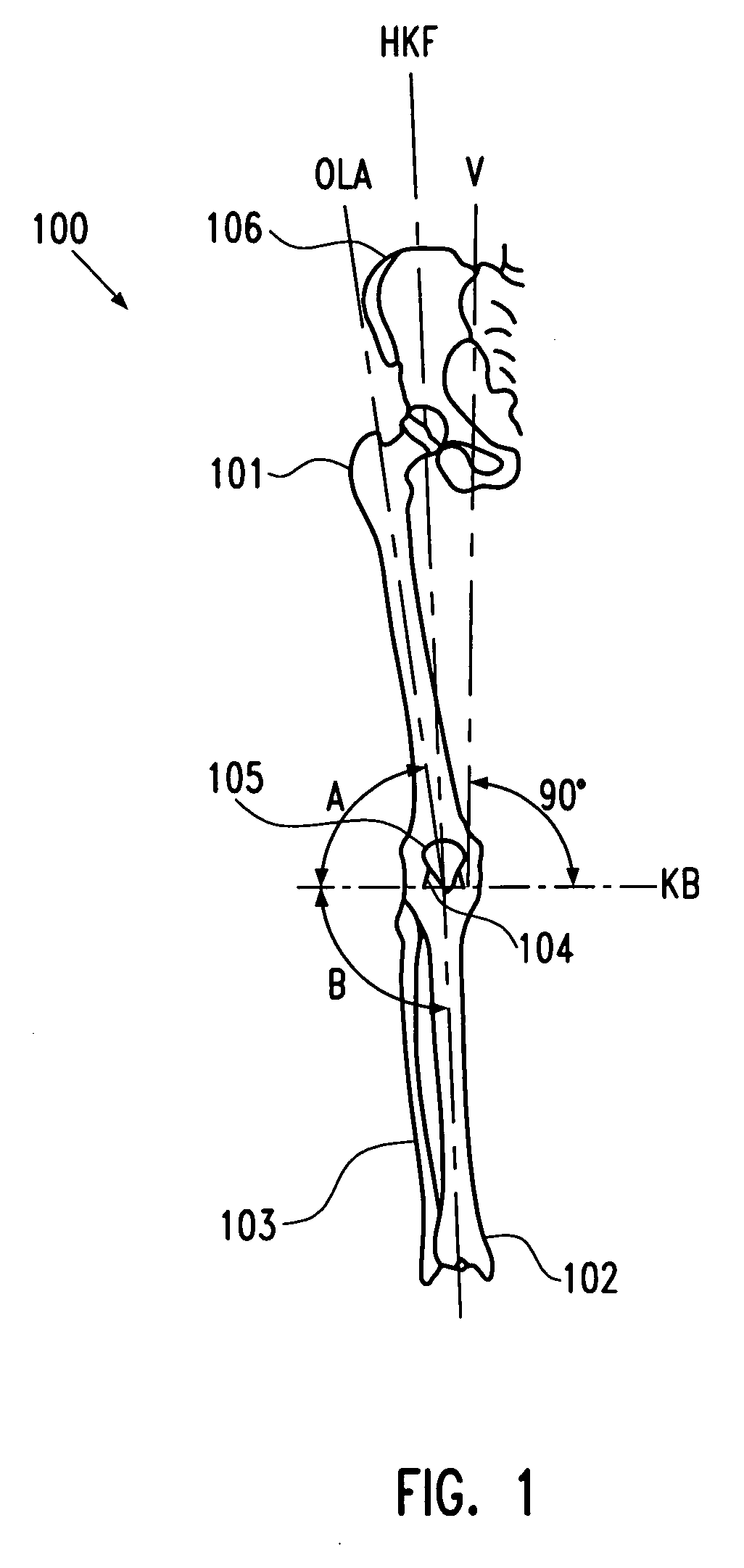
Aspects of the present disclosure involve systems, methods, computer program products, and the like, for utilizing a series of images of a patient's anatomy to determine a cut plane for use during a knee procedure. To determine a cut plane for use during a knee replacement procedure, the 2D images may be analyzed by a computer program to determine a femoral shaft axis reference line, a center of rotation of the knee, and the valley floor of the condyle notch. With these landmarks identified in the images, a cut plane through the femur for use during a TKA procedure may be determined. Further, the location of these features in the images may be determined by analyzing the gray scale value of one or more pixels around a selected point on the image. The pixel with the lowest gray scale value may then be assumed to be the edge of the cortical bone in the 2D image.
Owner:UNIK ORTHOPEDICS INC
Controllable and slidable locking compression plate for femoral neck
InactiveCN106388923AGood for maintaining lengthAdjust the sliding spaceBone platesThighAnatomical structures
The invention discloses a controllable and slidable locking compression plate for a femoral neck. The controllable and slidable locking compression plate for the femoral neck comprises a fixation steel plate, wherein the shape of a mounting surface of the fixation steel plate is matched with an anatomical structure at a near end of a thigh bone; a femoral shaft fixation hole, multiple screw thread locking holes and multiple sleeves are arranged on the fixation steel plate, a fixation screw is arranged in the femoral shaft fixation hole, the multiple sleeves correspond to multiple screw thread locking holes one by one, each sleeve is matched and connected with the corresponding screw thread locking hole and is coaxial with the screw thread locking hole, a slidable screw and a limit body used for limiting excessive looseness of the slidable screw are arranged in each sleeve, a sliding space exists between the limit body and the corresponding slidable screw, and the size of each sliding space can be controlled by regulating the length of the corresponding limit body. The controllable and slidable locking compression plate for the femoral neck has the advantages that continuous and sliding pressurization can be provided for a fracture end in a fracture healing early stage of the femoral neck, and excessive sliding produced by the screws in the sleeves also can be avoided, so that shortening of the femoral neck is reduced to the utmost extent while the fracture healing of the femoral neck is guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Device and method to prevent hip fractures
ActiveUS9452003B2Prevent hip fracturesAvoid fracturesInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headHip fracture
A device for preventing a hip fracture includes: a shaft having a first end and a second end and an expanding means for engaging the femoral head at the first end. The shaft is positioned in a hole of a predetermined depth in a femur. The hole extends from the greater trochanter to the femoral head of the femur, such that the first end is positioned in the femoral head and the second end is positioned in the greater trochanter. The device is oriented substantially perpendicular to the long axis of the femoral shaft.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
A kind of traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating fracture
InactiveCN102274370APromote regenerationGood curative effectAnthropod material medical ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsTibiaUlna
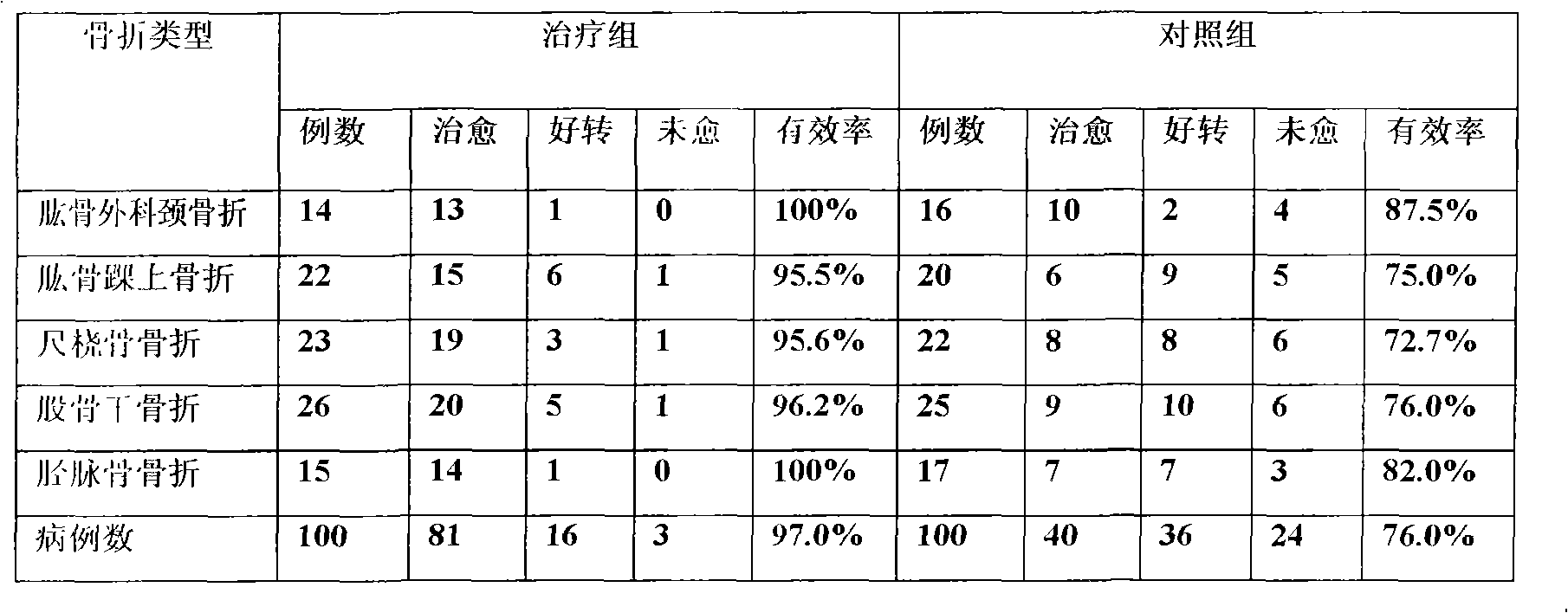
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating fracture, which is prepared from hemlock parsley, angelica, prepared rehmannia root, radix astragali, pseudo-ginseng, peach kernel, safflower, ground beetle, melon kernel, draconis sanguis, borneol, frankincense, myrrh and the like. The clinical test proves that the traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating fracture has good curative effects for fracture of surgical neck of humerus, supracondylar fracture of humerus, fracture of ulna and radius, fracture of femoral shaft, fracture of tibia and the like, and the effective rate is up to 97.0%. The traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating fracture can eliminate pain of patients with fracture or hairline fracture, and greatly shortens the recovery period, thereby relieving patients of pain.
Owner:支付亮
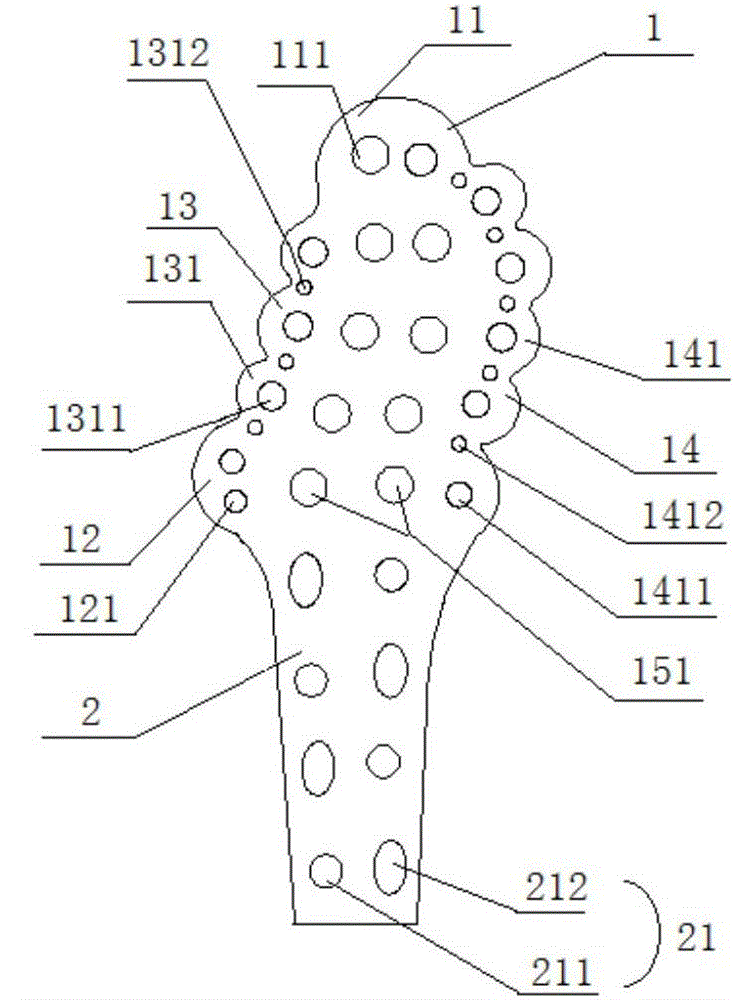
Anatomical femoral trochanter locking steel plate
The invention discloses an anatomical femoral trochanter locking steel plate, relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and aims to avoid the condition that the steel plate needs to be repeatedly bent for shaping before an operation and to simplify the operation. The main technical scheme is that the anatomical femoral trochanter locking steel plate comprises a trochanter part and a femoral part connected with the trochanter part, wherein the trochanter part is adaptive to the anatomical shape of the rear part of a human femoral trochanter, and the femoral part is adaptive to the anatomical shape of the rear part of a human femoral shaft; a big trochanter tongue flap, a small trochanter tongue flap, a first connecting part and a second connecting part are arranged on the trochanter part; the first connecting part is arranged between the big trochanter tongue flap and the small trochanter tongue flap; the second connecting part is arranged between the big trochanter tongue flap and the femoral part. The anatomical femoral trochanter locking steel plate is mainly used for fixing femoral trochanter fracture blocks.
Owner:陈继峰
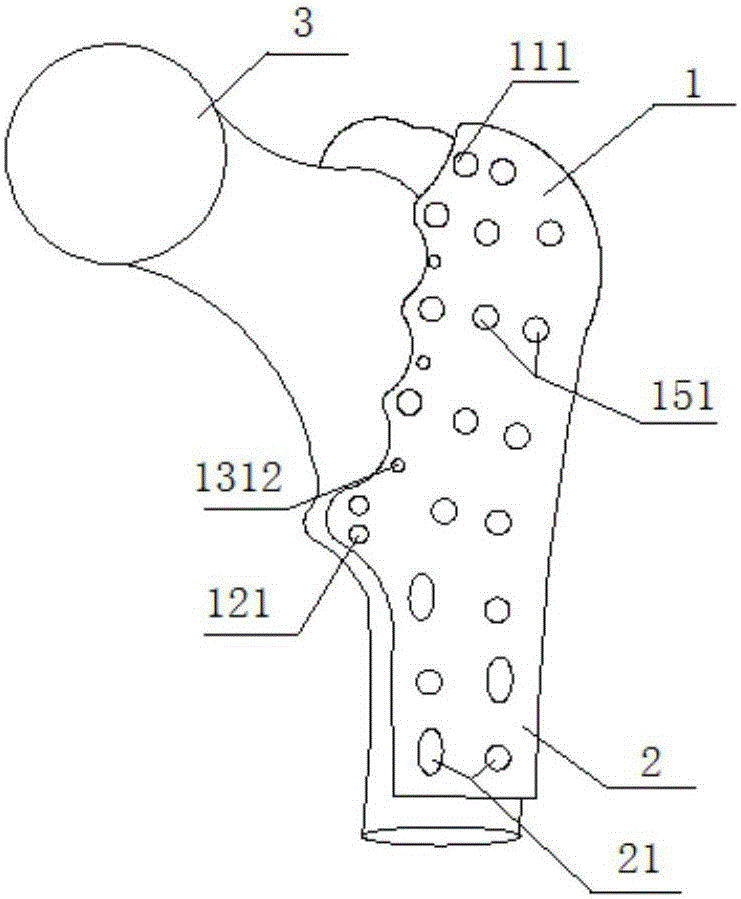
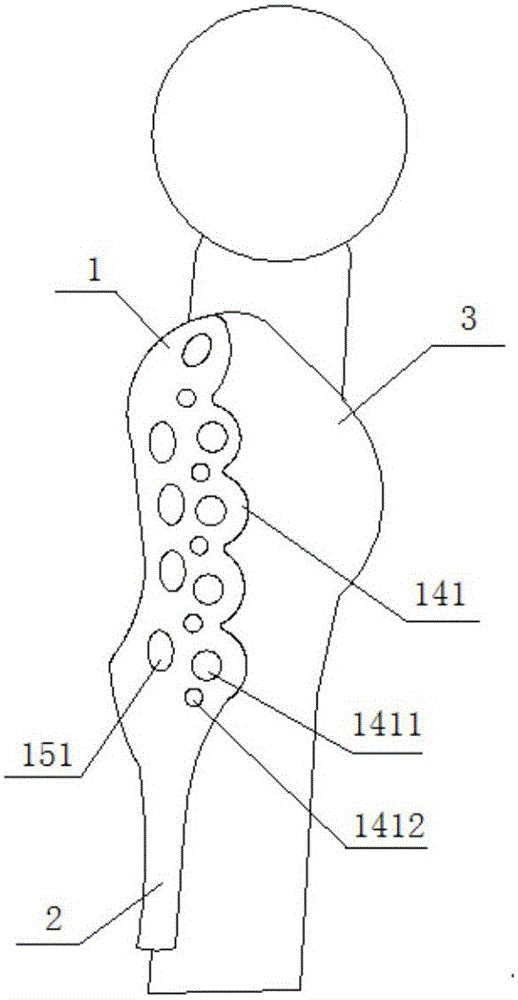
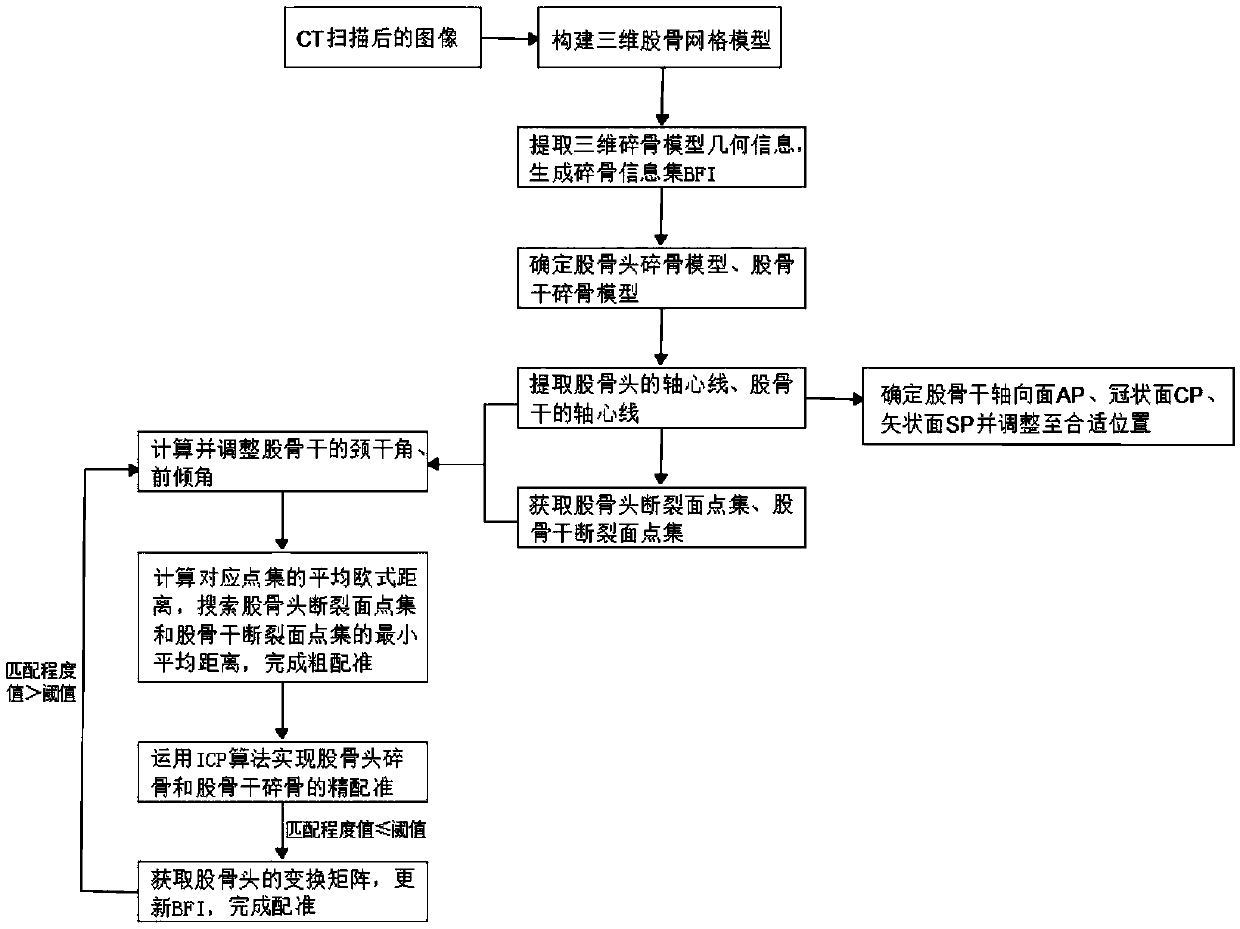
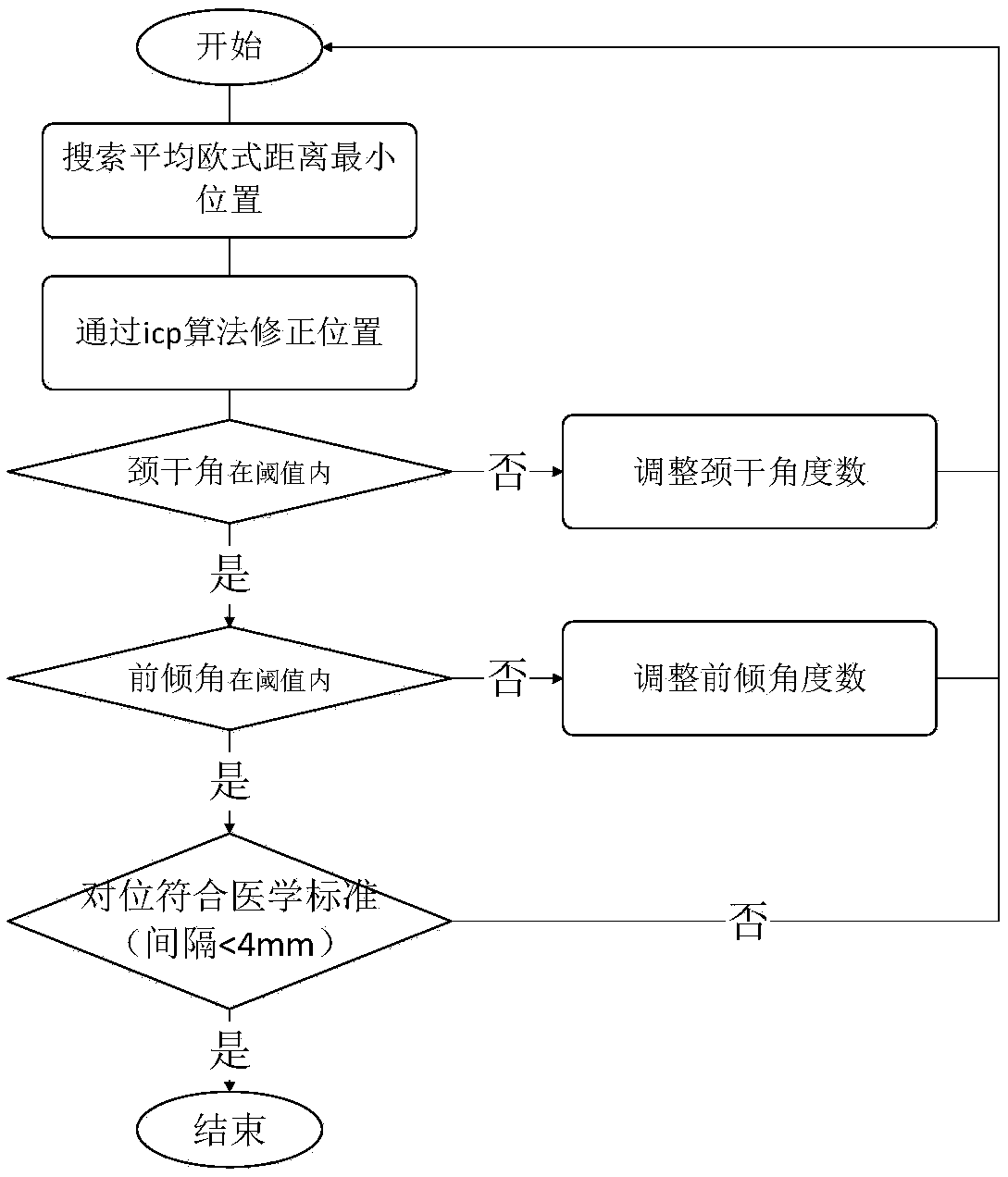
Computer-assistant femoral intertrochanteric fracture positional and alignment semi-automatic restoration method
InactiveCN109528305ASolve matching problemsSolve clinical problemsComputer-aided planning/modellingIntertrochanteric fractureRestoration method
The invention discloses a computer-assistant femoral intertrochanteric fracture positional and alignment semi-automatic restoration method including: 1) with the broken bone three-dimensional model generated by a CT image as an information input source, extracting the geometric information and topologic relationship of the three-dimensional network model; 2) extracting the fracture surface and related force lines of caput femoris and femoral shaft; 3) determining a restoration position required in clinical medicine by means of a positional-alignment iteration method to complete the semi-automatic restoration of the intertrochanteric fracture. In the invention, on the basis of basic requirement on the closed reduction of the femoral intertrochanteric fracture, medical requirement on the broken bone joint is satisfied; then by means of positional-alignment iteration for calculation, preoperative planning demand of medical personnel is satisfied and working efficiency is increased just through a less amount of human-computer interaction.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Modularized artificial hip joint femoral shaft
The invention relates to a modularized artificial hip joint femoral shaft, in particular to an artificial hip joint femoral shaft structure for replacement in human body medical treatment, which is used to be embedded in a proximal end femoral medullary cavity of a patient in a closely fit mode. The modularized artificial hip joint femoral shaft comprises a base body embedded in the proximal end femoral medullary cavity and provided with a through hole with a taper, and a support shaft inserted through the through hole, wherein the base body and the support shaft are provided with a positioning slot and a positioning key which correspond to each other respectively; one end of the support shaft is provided with a joint end, while the other end is provided with a femoral shaft end; and the femoral shaft end is provided with a taper segment which is correspondingly and closely pressed against the taper of the through hole. The modularized artificial hip joint femoral shaft is characterized in that the base body comprises a first element and a second element which are provided with a groove formed by the through hole respectively, wherein the first element is provided with a first assembly and the second element is provided with a second assembly in bond connection with the first assembly, so that the femoral shaft can be matched with diverse femoral medullary cavities and has the advantages of diversity and modularization.
Owner:FARMAR LICENSING
Internal fixator for bone fracture
ActiveUS20190336186A1Reduce riskSmooth connectionInternal osteosythesisRight femoral headFemoral shaft
A bone fracture internal fixator for repairing a bone fracture of a femoral neck that allows load to be applied to the associated bone parts evenly, and increases the connecting strength between the femoral head and femoral shaft while minimizing the risk of the femoral head being torn apart by the inner connecting member by increasing the diameter of the inner fixing member. The central axial line of the femoral head is offset from the central axial line of the intramedullary nail placed in the medullary cavity of the femoral shaft. In order to bring the inner fixing member such as a lag screw configured to be inserted through the femoral neck close to the central axial line of the femoral neck, the central axial line of the through hole for receiving the inner fixing member is offset from the central axial line of the intramedullary nail.
Owner:BFN RES KK
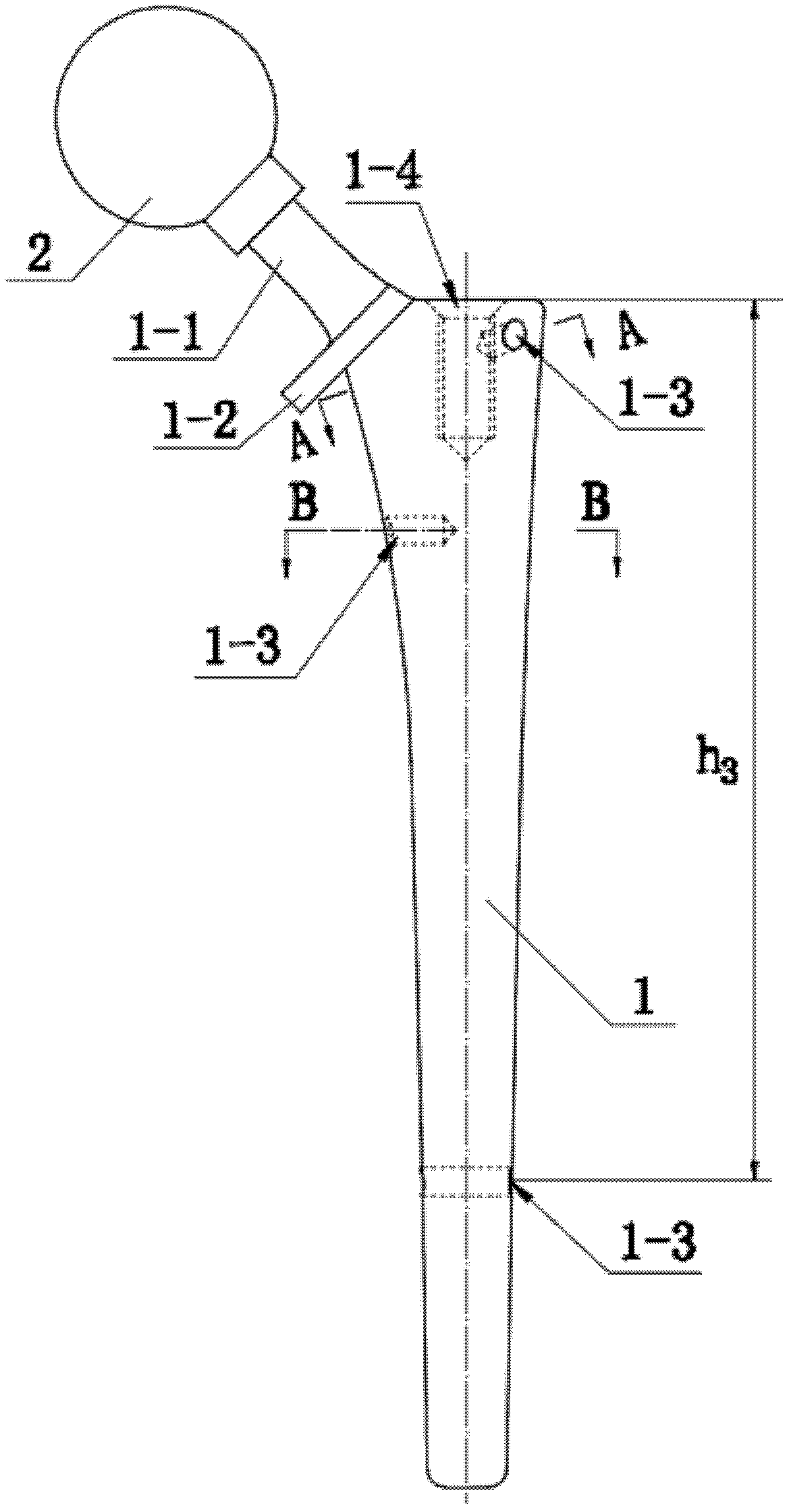
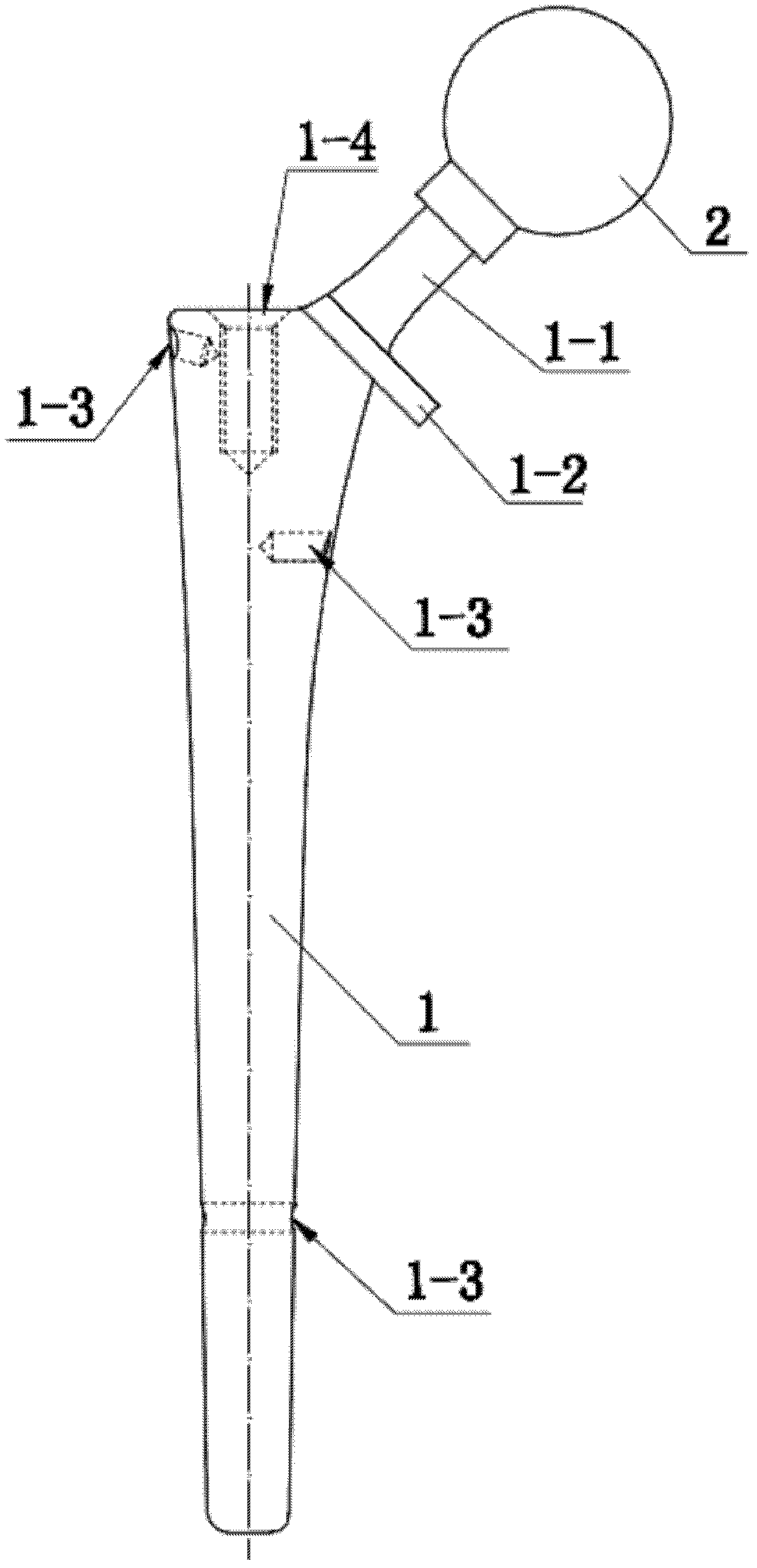
Artificial femoral stem for fracture surgery around hip joint prosthesis
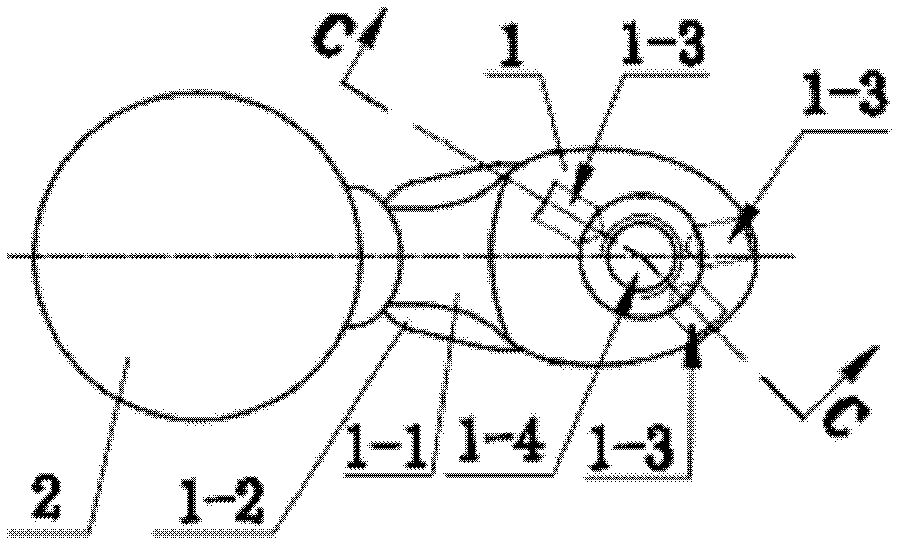
InactiveCN102551921ASmall woundOutstanding simplicityJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral shaftMuscles of the hip
The invention relates to an artificial femoral stem for a fracture surgery around a hip joint prosthesis, wherein a proximal end of a femoral shaft (1) of the artificial femoral stem is provided with at least one bolt hole (1-3) on the external wall; and a distal end is provided with one bolt hole (1-3) transversely penetrating through the femoral shaft (1). The invention also relates to a screw implant guiding frame for performing the fracture surgery around the hip joint prosthesis by the artificial femoral stem, wherein the screw implant guiding frame is constituted by a positioning arm (3), a positioning rod (7), an arc plate (4) below the positioning arm (3), and a guiding cylinder (5) which is installed on the arc plate (4) and is colinear with the bolt hole (1-3). The invention is applicable to secondary fracture surgery around the prosthesis after hip joint replacement surgery, and is beneficial for improving a fixation effect and improving the surgery quality.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Auxiliary device for intramedullary fixation of femoral intertrochanteric fracture
PendingCN110974385AAchieve connectionEasy to fixInternal osteosythesisBone platesIntertrochanteric fractureFemoral shaft
The invention discloses an auxiliary device for intramedullary fixation of femoral intertrochanteric fracture. The auxiliary device comprises a fixation bone plate; the proximal end of the fixation bone plate is provided with a first connecting part for connecting a greater trochanter; the distal end of the fixation bone plate is provided with a second connecting part for connecting a femoral shaft; the fixation bone plate is provided with a sliding hole corresponding to a fracture intramedullary fixation device; and one end of a connecting piece passes through the sliding hole and is connected with the fracture intramedullary fixation device, wherein the boundary dimension of the other end of the connecting piece is larger than that of the sliding hole. According to the invention, the fixation bone plate and the fracture intramedullary fixation device can be connected into a whole, so that reconstruction of a femoral proximal outer side wall and the internal intramedullary fixation can be integrated, firm fixation of the greater trochanter can be realized, and failure of the intramedullary fixing device can be effectively avoided.
Owner:首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院
Knee-joint activity and inertia-combined adjusting control outer fixer
ActiveCN103445843AImprove adaptabilitySimple and safe operationExternal osteosynthesisTibiaExternal fixator
A knee-joint activity and inertia-combined adjusting control outer fixer comprises an upper C-shaped hole ring arranged at a thighbone far end, and a lower C-shaped hole ring arranged at a tibia near end; the upper C-shaped hole ring is upwards connected with two upper tubular connection rods by a T-shaped connection plate; two dual-groove steel needle fixing clamps are fixed on the two upper tubular connection rods; point ends of two thread semi-needles are fixed on a femoral shaft; an arc arch is connected between the upper C-shaped hole ring and the upper tubular connection rods; the tail ends of the thread semi-needles are fixed with a single-groove steel needle fixing clamp on the arc arch; the point ends of the thread semi-needles are fixed on the femoral shaft. The upper C-shaped hole ring and the lower C-shaped hole ring are connected by a knee elbow joint device. The knee-joint activity and inertia-combined adjusting control outer fixer is firm in static fixing and balanced in dynamic fixing, can adjust and control the kneel joint gap, can promote the fracture healing and reduce or avoid the stiffness of the knee joint and is an advanced and excellent treatment method for the knee joint fracture, particularly the severe comminuted fracture.
Owner:JIANGSU GUANGJI MEDICAL TECH
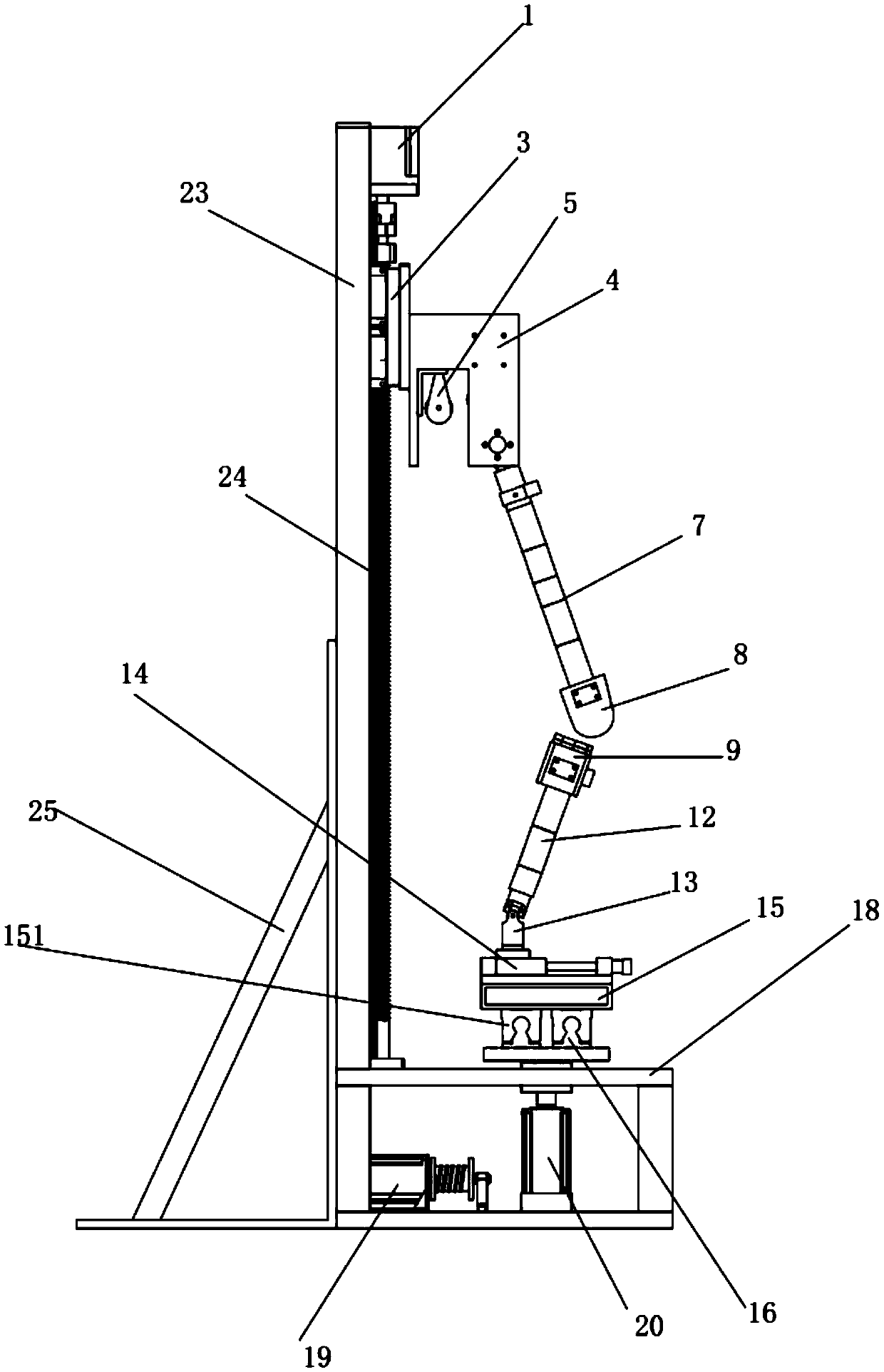
Squatting-type human lower limb joint biomimetic device
PendingCN111568613ANovel structureEasy to useJoint implantsApparatus for force/torque/work measurementHuman bodyGyroscope
The invention relates to a squatting-type human body lower limb joint biomimetic device. The technical scheme is as follows, a sliding table which is driven by a first motor and slides up and down oris fixed in the height direction of a vertical supporting plate is arranged on the vertical supporting plate, a horizontal fixed shaft is fixed on the sliding table, the middle part of the fixed shaftis connected to a femoral shaft through a first universal joint, the lower end of the femoral shaft is fixedly connected to a femur lower end simulation block, a steel wire rope is wound on a rotating shaft, on which a second motor is fixed, of a base, one end of the steel wire rope is fixed on the rotating shaft of the second motor, and the other end extends upwards, bypasses a fixed pulley block fixed on the sliding table and then is connected to the upper end of a patella ligament simulation belt. According to the invention, the condition of applying squatting force is acquired through a tension sensor, the motion trail signal in the squatting process is acquired through a gyroscope, and the stress of knee joints and soles is acquired through strain gauges, so that the motion trail andthe stress condition of squatting motion of the lower limbs of a human body under the condition of a certain stress curve are simulated.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
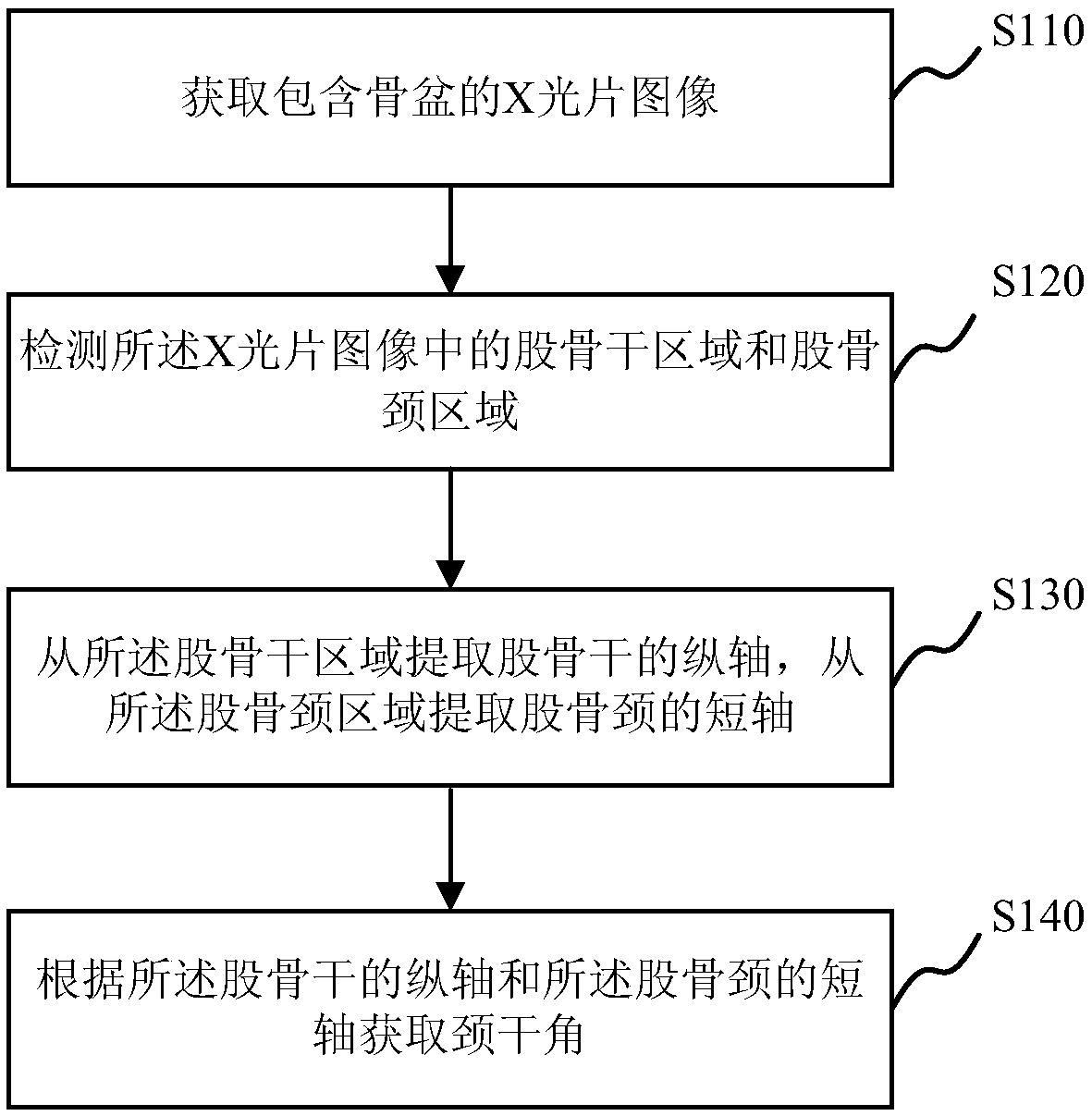
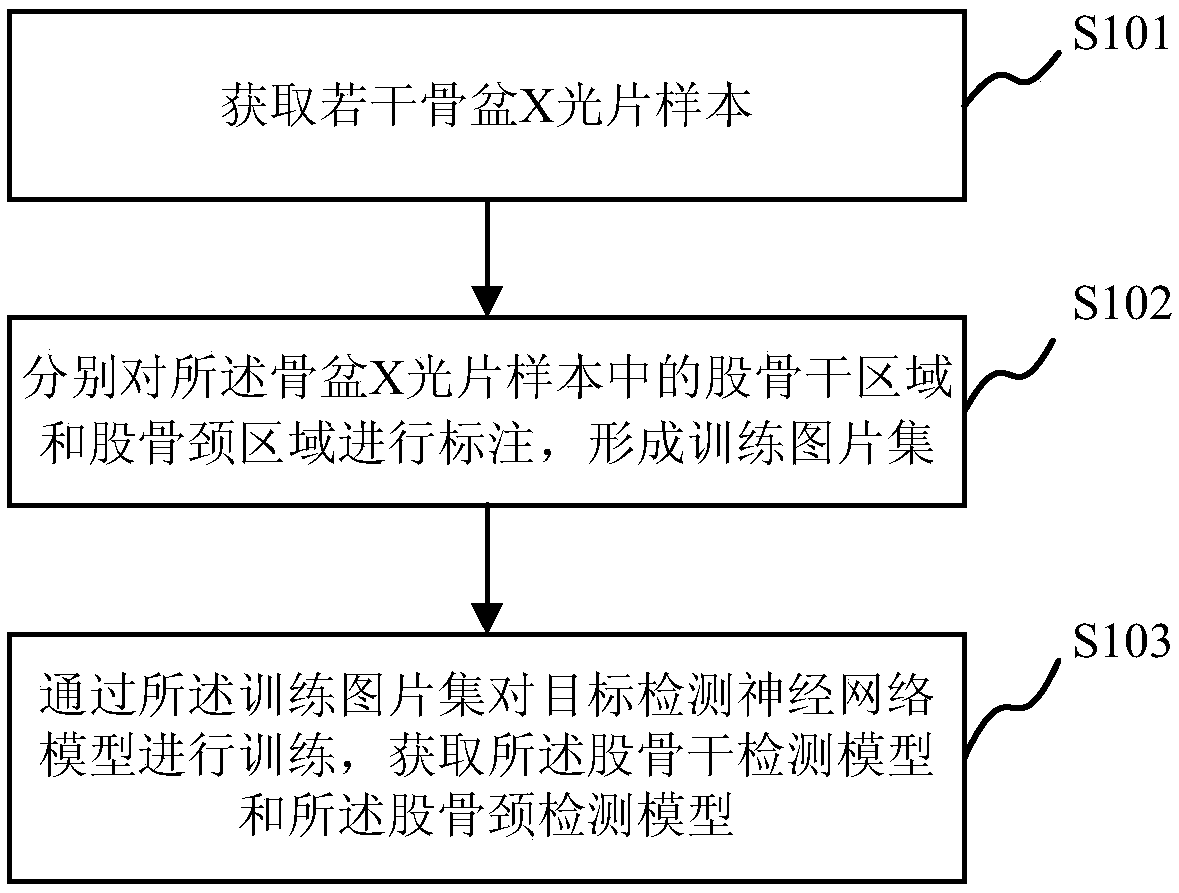
Method, system, apparatus and storage medium for measuring neck shaft angle in pelvic X-ray film
ActiveCN109242837AAccurate and automatic measurementEfficient automatic measurementImage enhancementImage analysisFemoral shaftX-ray
The invention provides a method, system, apparatus and storage medium for measuring neck shaft angle in pelvic X-ray film. The method for measuring neck shaft angle in pelvic X-ray film comprises thefollowing steps: acquiring X-ray film image including pelvis; Detecting a femoral shaft region and a femoral neck region in the X-ray image; Extracting a longitudinal axis of a femoral shaft from thefemoral shaft region and extracting a short axis of a femoral neck from the femoral neck region; obtaining the neck shaft angle according to the longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft and the short axis of the femoral neck. The invention can accurately and efficiently automatically measure the neck shaft angle in the pelvic X-ray film, and effectively solves the problem in the prior art that theneck shaft angle in the X-ray film is easy to misjudge by relying on the subjective observation of the medical personnel or the hand drawing method, which is time-consuming and laborious.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Internal fixation device for treating complex intertrochanteric fracture and application method thereof
PendingCN109171934APromote healingInternal osteosythesisFastenersRight femoral headIntertrochanteric fracture
The invention provides an internal fixation device for treating complex intertrochanteric fractures and an application method thereof, the device comprising a femoral shaft intramedullary main nail, afemoral neck main screw, a lateral steel plate, a femoral neck locking hollow nail, a distal main nail locking nail and a steel plate fixation screw, wherein the femoral shaft intramedullary main nail is inserted into a medullary cavity; the lateral plate is attached to the restored lateral wall of the great tuberosity. At least one femoral neck loc hollow nail is inserted and fix into that femoral head through the first locking hole. The head end of the femoral neck main screw is inserted into the femoral head through the femoral neck after pas through the sliding hole on the middle part ofthe lateral plate and the first lateral hole on the upper part of the femoral shaft main nail. The invention is used for internal fixation treatment of complex intertrochanteric fractures, has the advantages of good internal fixation effect, stability and less failure of internal fixation, and is particularly suitable for complex intertrochanteric fractures with comminuted lateral wall of great trochanter.
Owner:陆海波
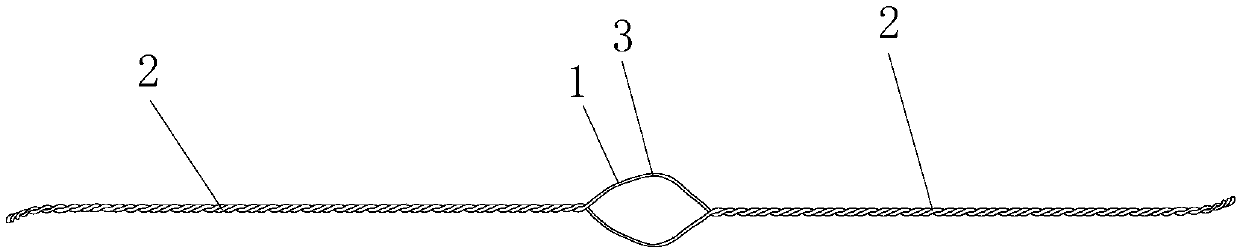
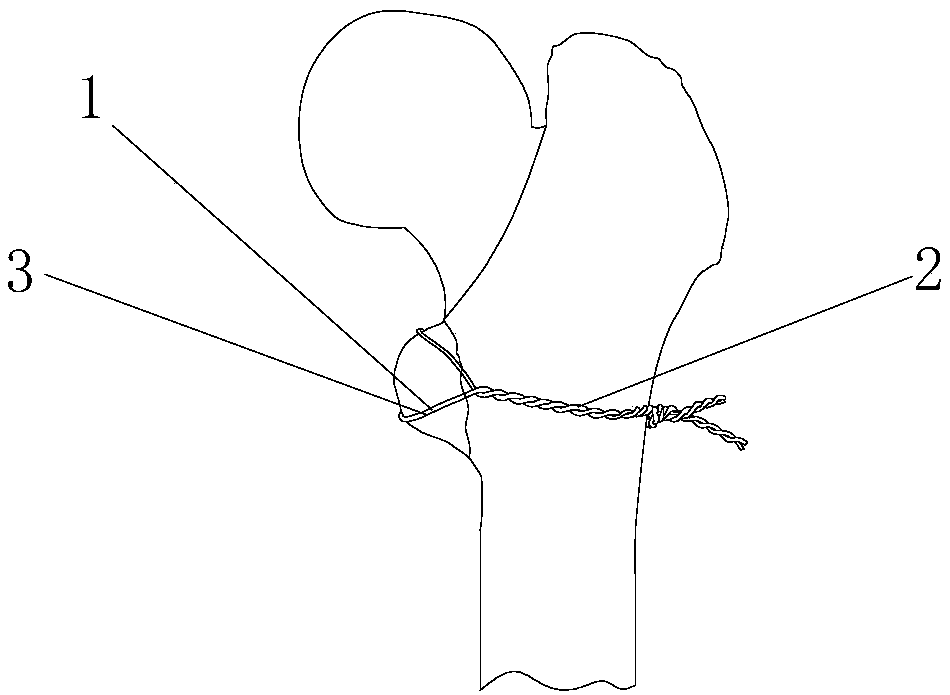
Fixing and binding band for femoral lesser trochanter bone fracture reduction
PendingCN108042194AReduce the impactLittle impact on operationInternal osteosythesisRight lesser trochanterDiaphysis
The invention discloses a fixing and binding band for femoral lesser trochanter bone fracture reduction. The band comprises a plurality of metal wires, the front and rear ends of the metal wires are woven to form binding band bodies, the middles of the metal wires are woven to form a fixing lantern ring, the binding band bodies are formed by twisting all the metal wires into a strand, the fixing lantern ring is formed by twisting the middle metal wires into two strands, and the metal wires are made of peptide alloy materials; a locking buckle is arranged on the binding band and comprises a main locking buckle body, the main locking buckle body is provided with two axial through holes, the inner side of the main locking buckle body is provided with four claws, and the binding band bodies atthe two ends are matched with the two through holes one to one; the cross section of the main locking buckle body is arc. The fixing and binding band has the advantages that the band is simple in structure and convenient to use and operate, the surgical traumas of patients are effectively alleviated, it is effectively ensured that the lesser trochanter cannot be displaced again due to binding looseness, the influence on the blood supply of the femoral shaft is small, the production cost is low, and the surgical cost of the patients is effectively reduced.
Owner:臧学慧
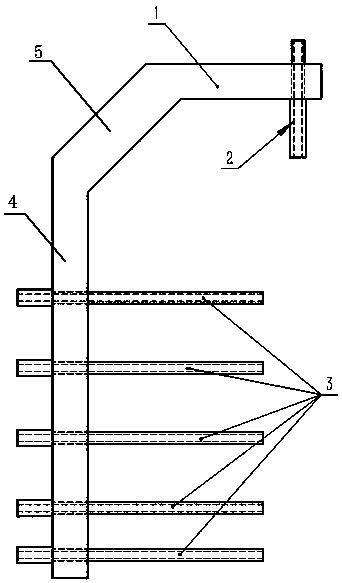
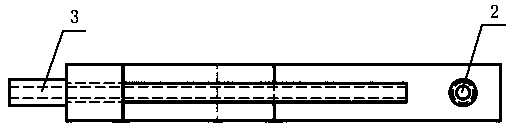
Femoral nail opening guider
The invention relates to medical devices, and provides a femoral nail opening guider. The guider comprises a long arm supporting bracket and a short arm supporting bracket which is perpendicular to the long arm supporting bracket, guiding holes are formed in the long arm supporting bracket and the short arm supporting bracket, a plurality of guiding holes perpendicular to the long arm supporting bracket are formed in the long arm supporting bracket, a plurality of guiding holes perpendicular to short arms are formed in the short arm supporting bracket, and the guiding holes are located on thesame section. The guider adopts the principle of two points and one line, when a long arm guiding tube is completely pressed against the outer side of the cortex of a femoral shaft, the intersection point of extension lines is located at the center of a femoral marrow cavity, the tip part of the femur trochanter or the pyriform sinus is used as the point of penetration, the structure is simple, the implementation is convenient, and the positioning is fast and accurate.
Owner:郁传江
Establishment method and induced differentiation application of human marrow mesenchymal stem cell strain
InactiveCN110283782AHigh purityHigh activityCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsFemoral shaftTreatment targets
The invention discloses an establishment method and an induced differentiation application of a human marrow mesenchymal stem cell strain. A marrow mesenchymal stem cell extracted from a femoral shaft marrow cavity is high in purity and good in activity and can completely meet a series of experiments of osteogenesis induced differentiation of stem cells, an extracted marrow mesenchymal stem cell of an osteoporosis patient has expression difference in transcriptomics as compared with that of normal persons, and a new thought and method are provided for further disclose the osteoporosis pathogenesis of the marrow mesenchymal stem cell and seek a new treatment target. Besides, as for samples with fewer marrow mesenchymal stem cells of osteoporosis and the like, the technology can effectively increase the cell obtaining amount after extraction, increase the number of adherent cells, promotes the cells to rapidly enter a logarithmic growth stage, reduce the culture time and reduce the culture cost and more easily keep the dryness of the marrow mesenchymal stem cell, so that a series of experiment demands of osteogenic differentiation, stem cell treatment and the like are met.
Owner:昆明医科大学第二附属医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com