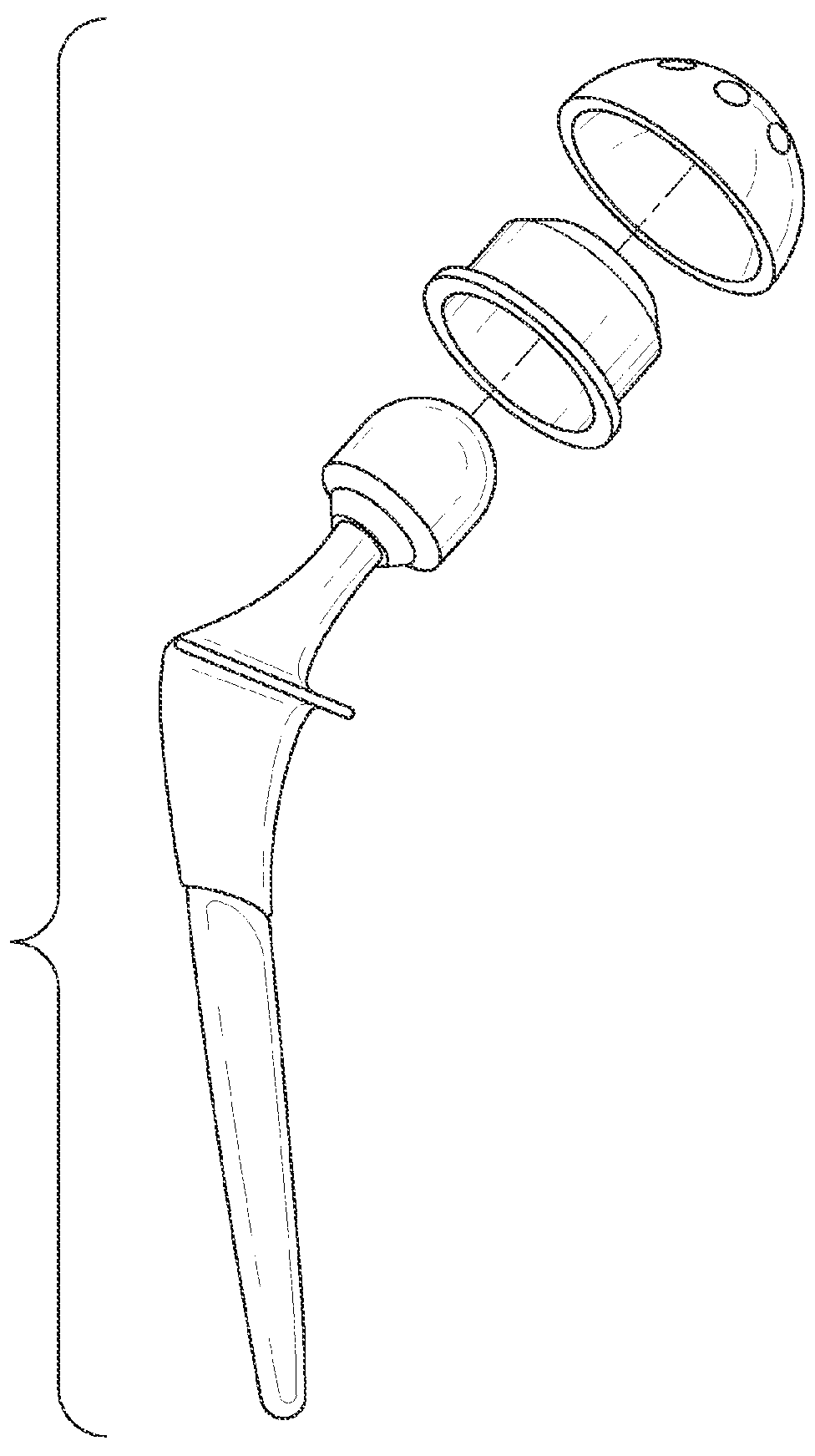
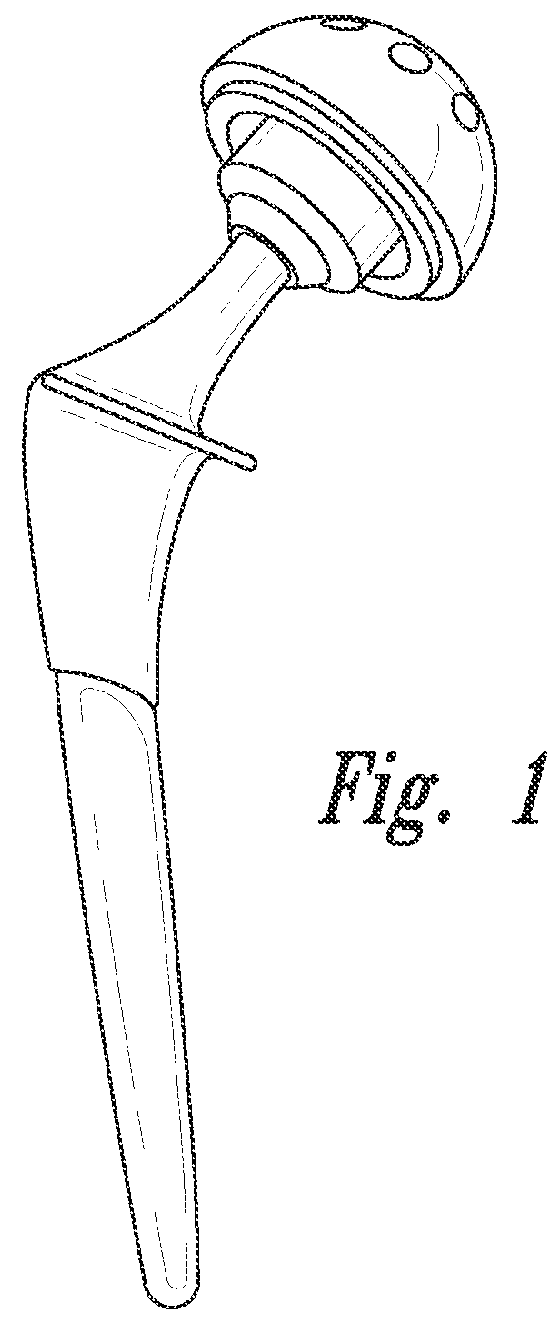
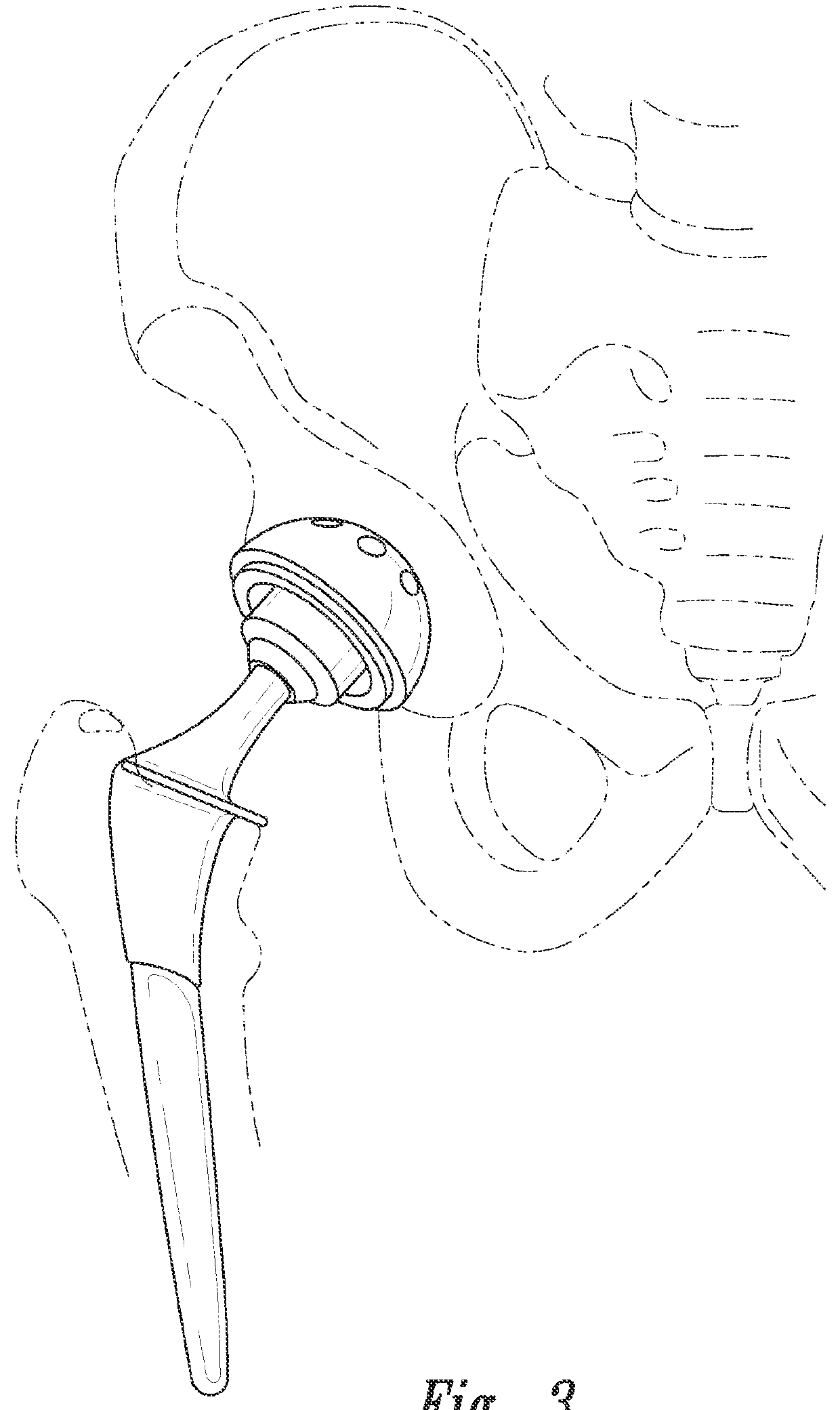
Patents
Literature
231 results about "Hip joint replacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
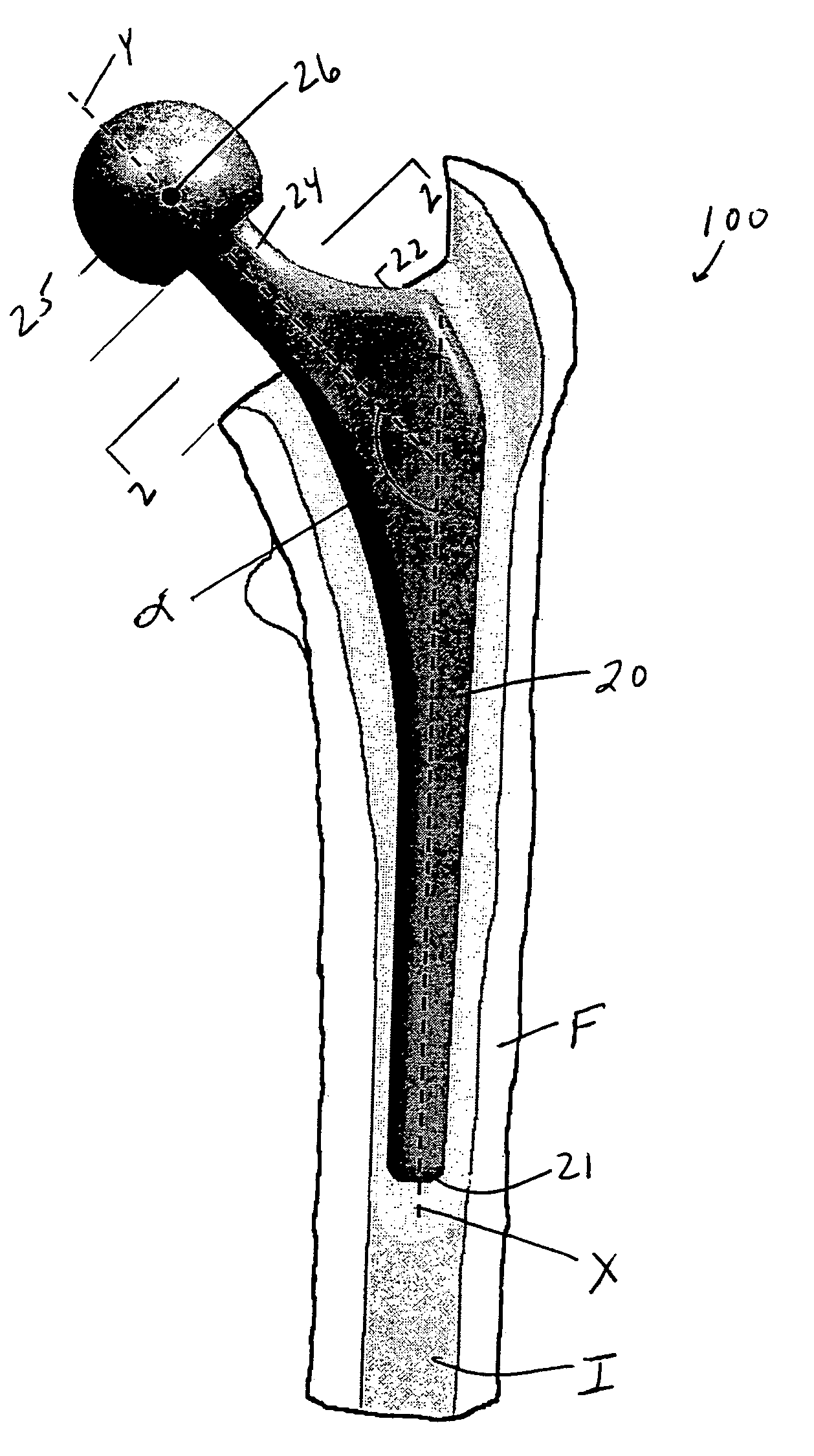
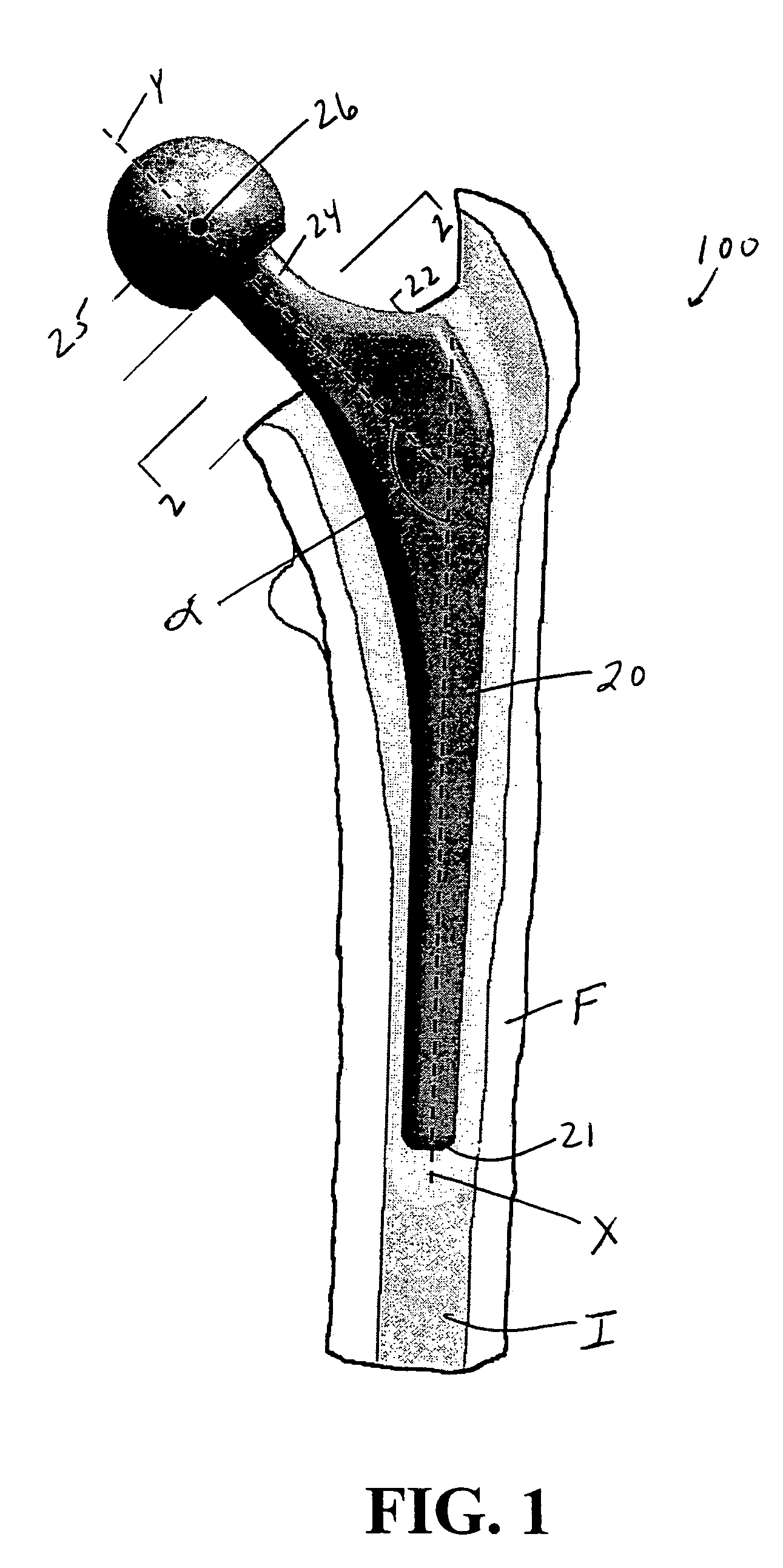
For instance, they’re sometimes used if a tumor grows in the hip joint. Hip replacements may also be used in an emergency to fix a fracture in the hip joint or the thighbone. A condition called avascular necrosis of the hip often requires a total hip replacement.
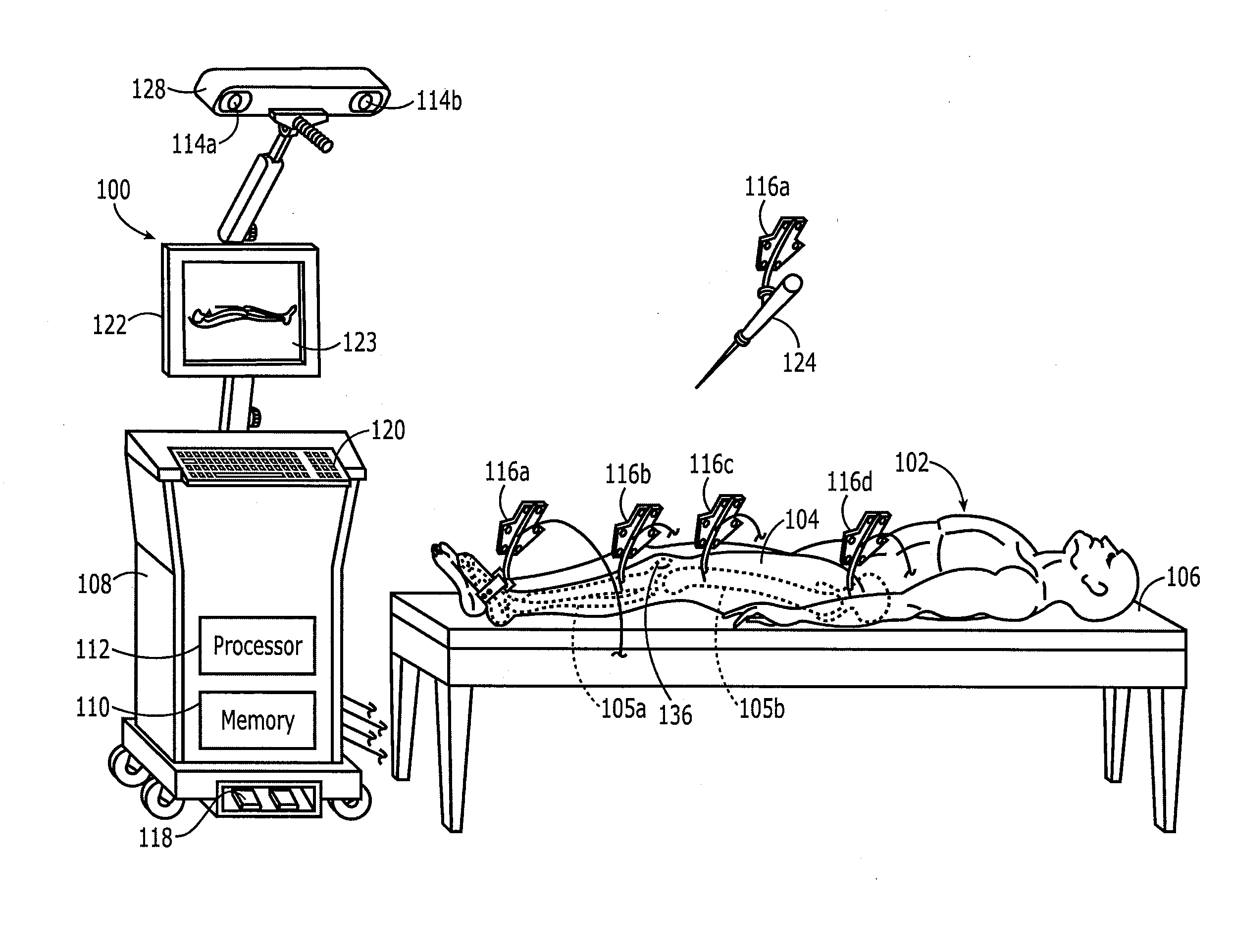
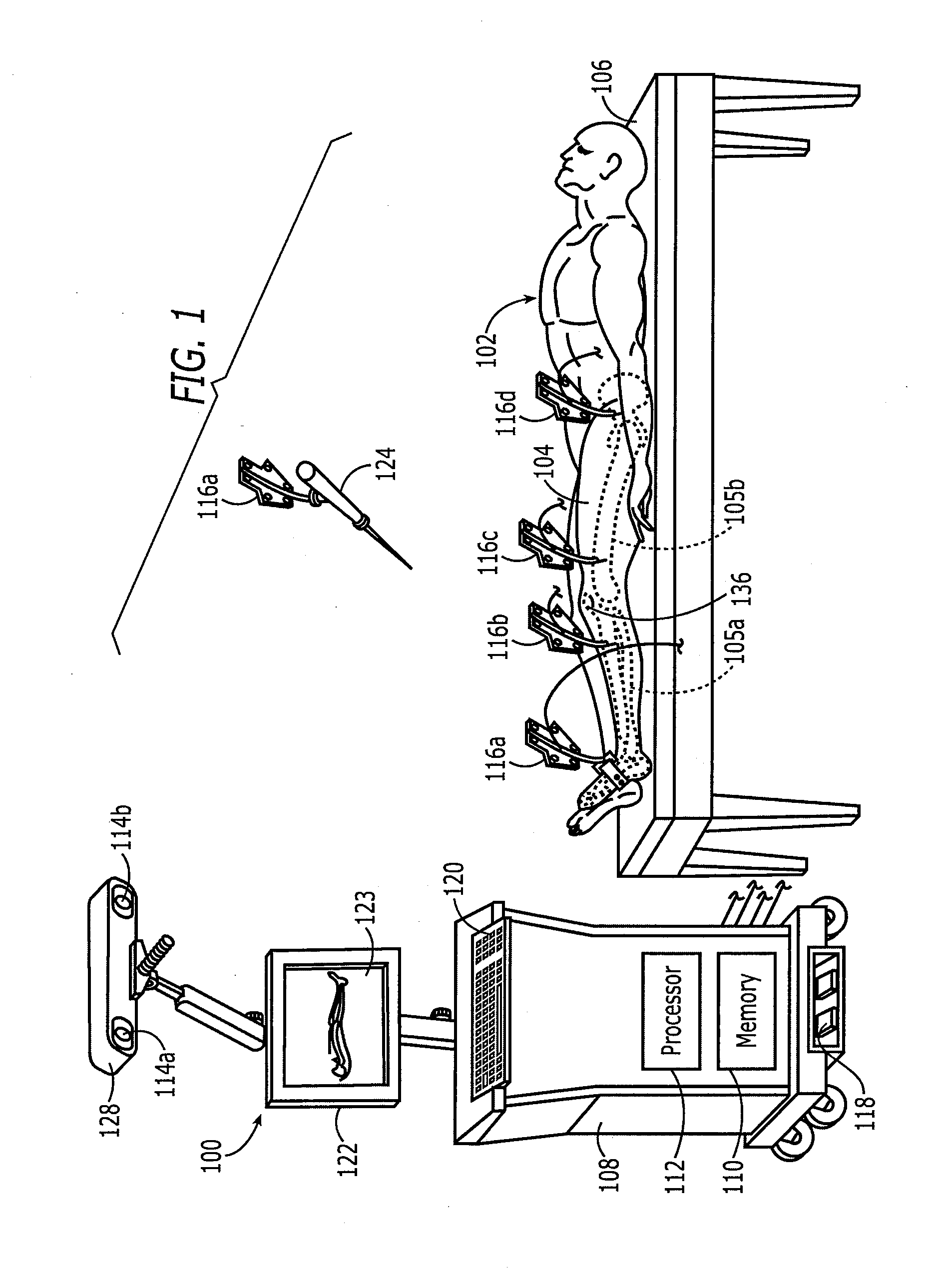
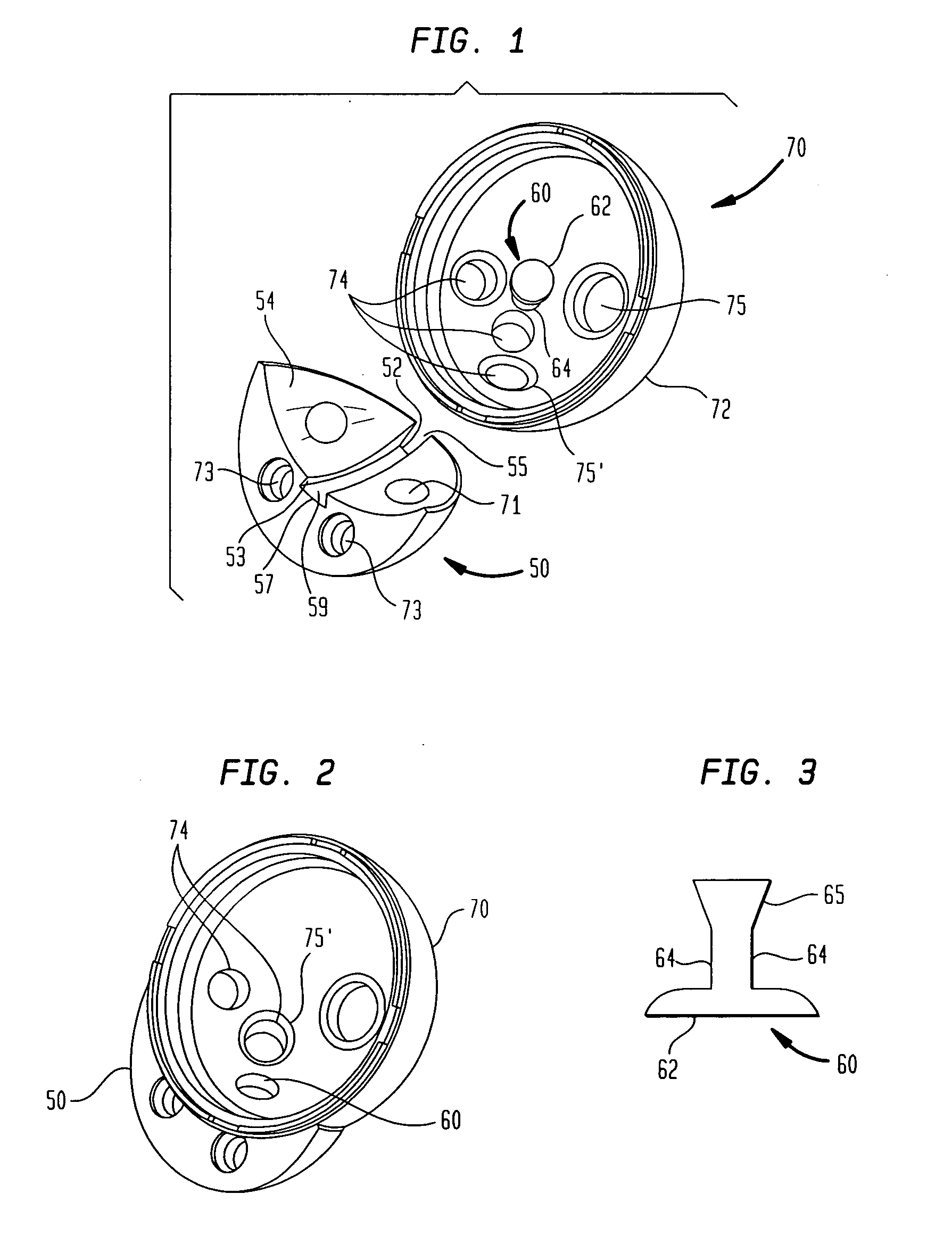
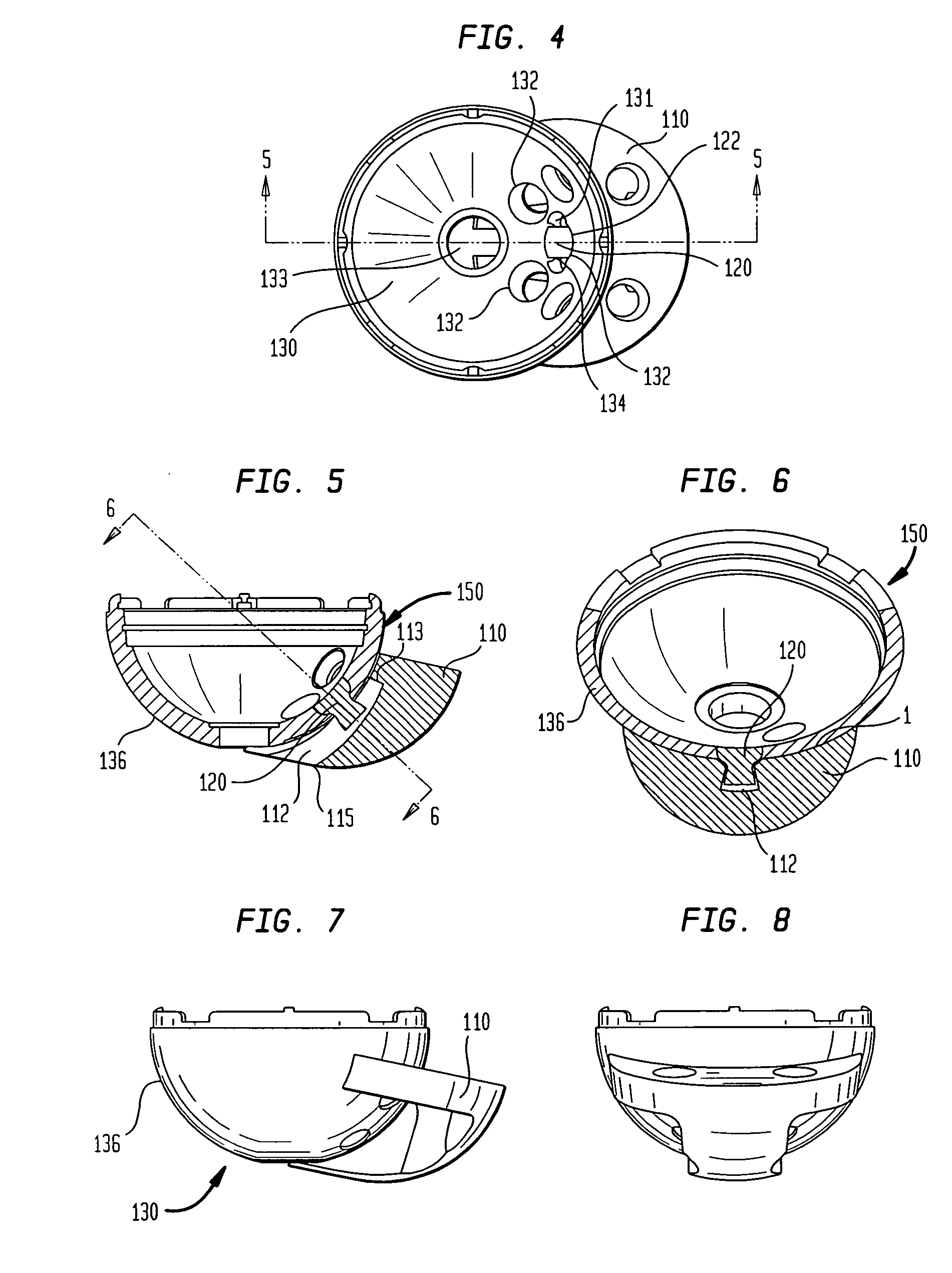
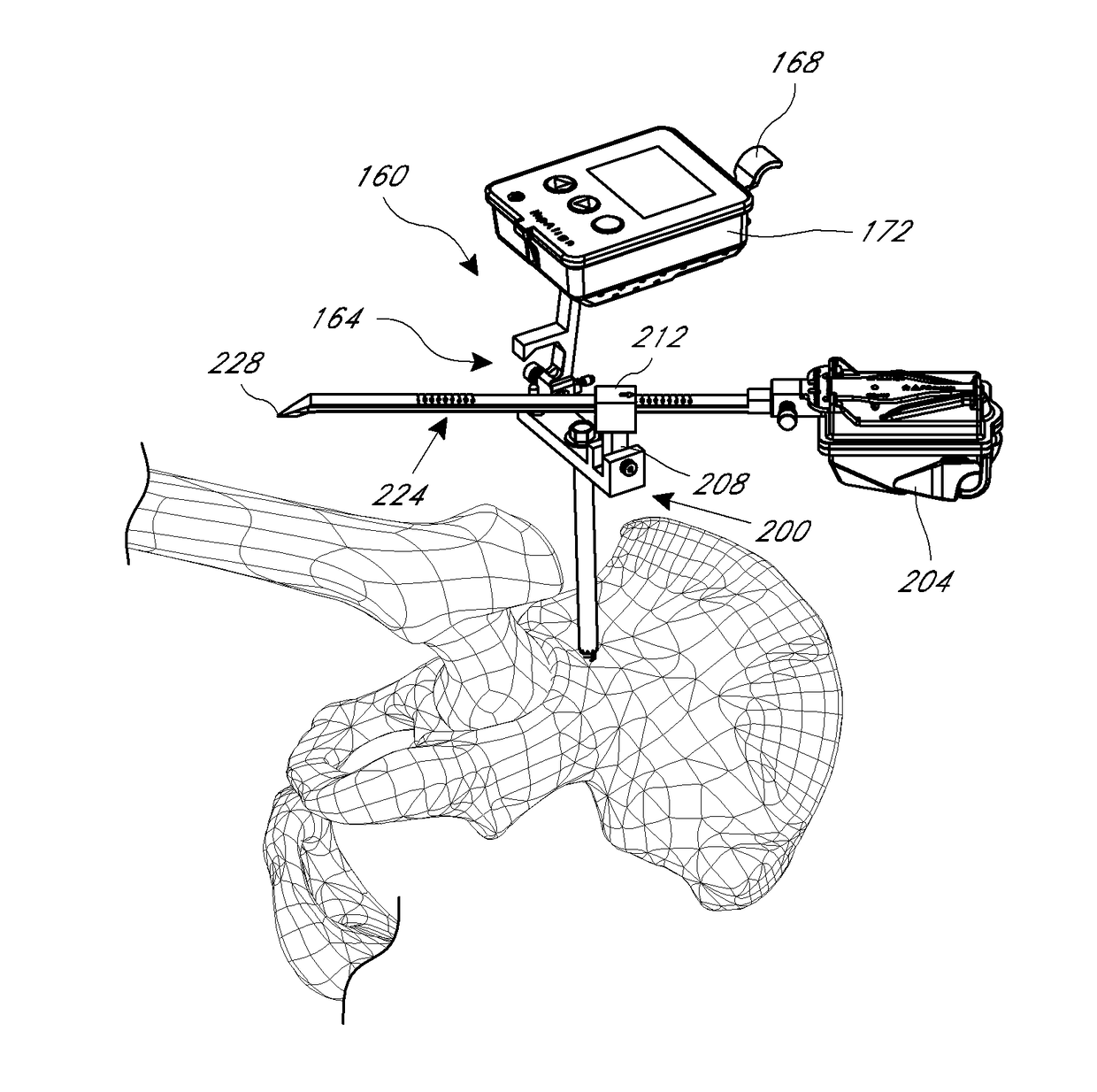
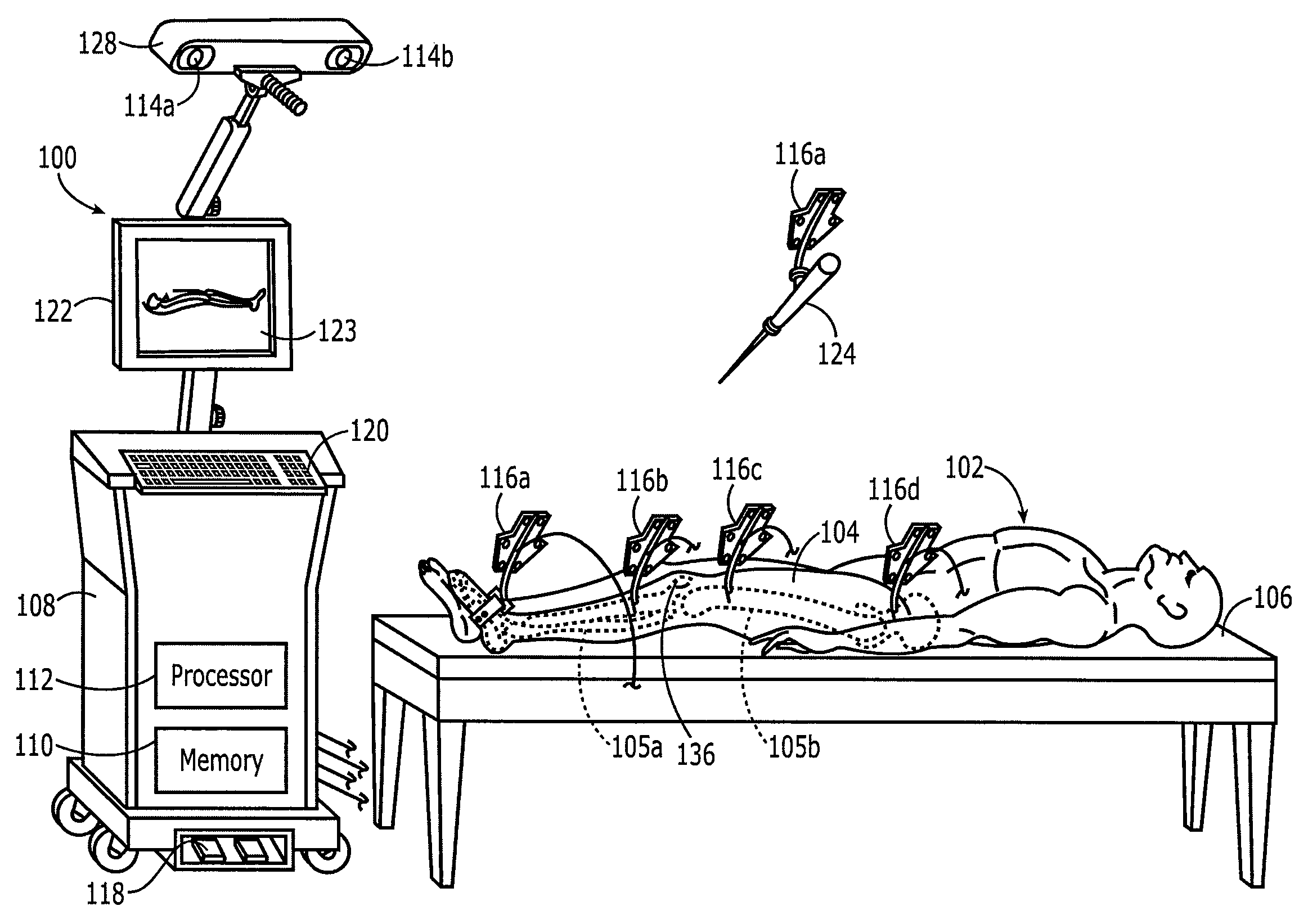
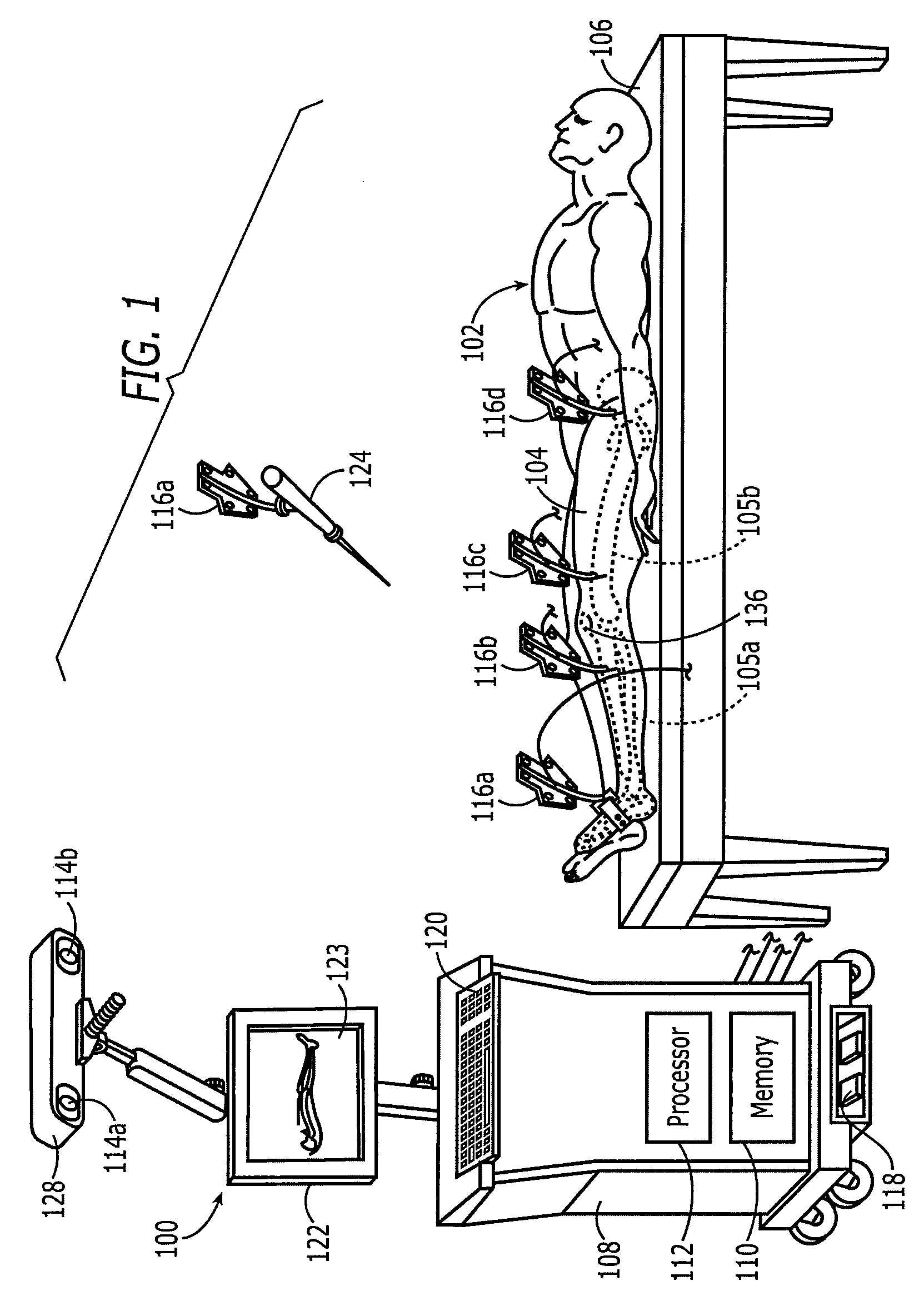
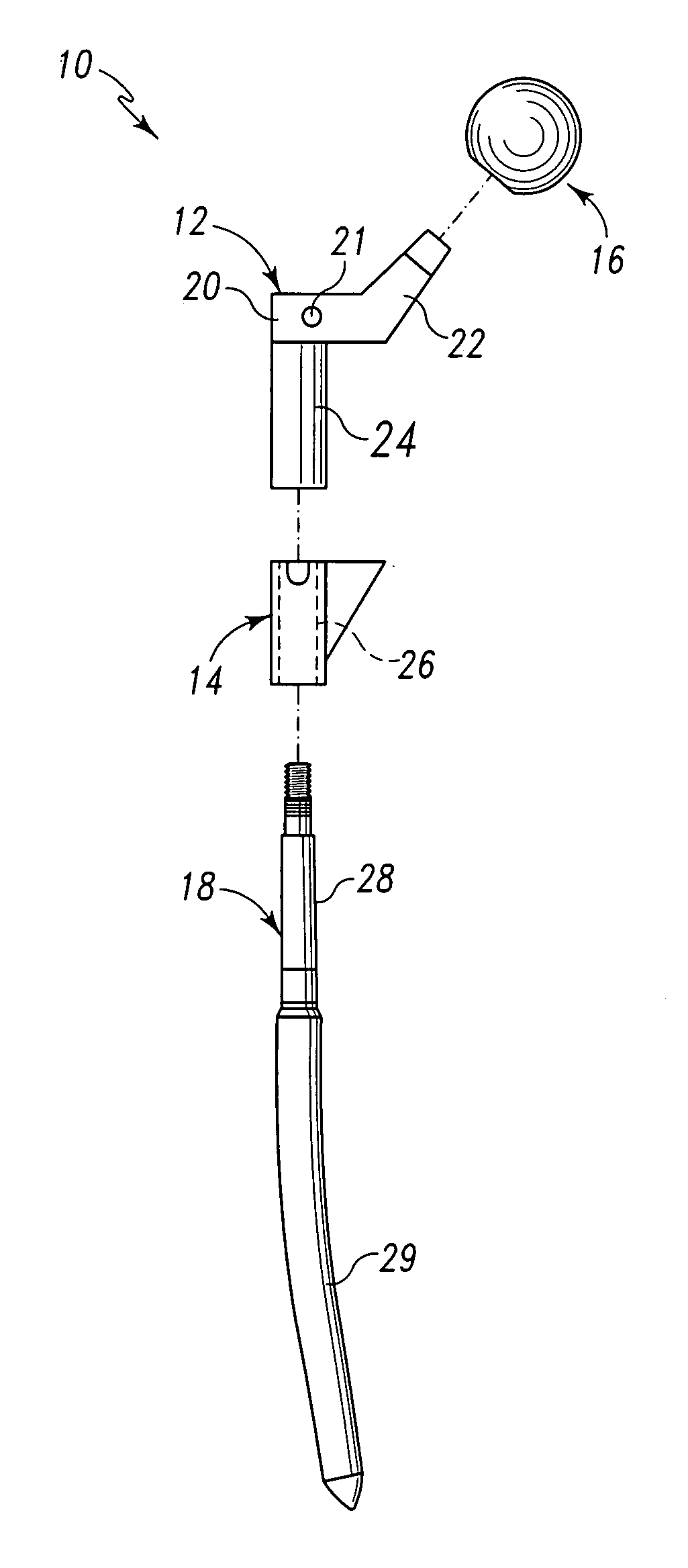
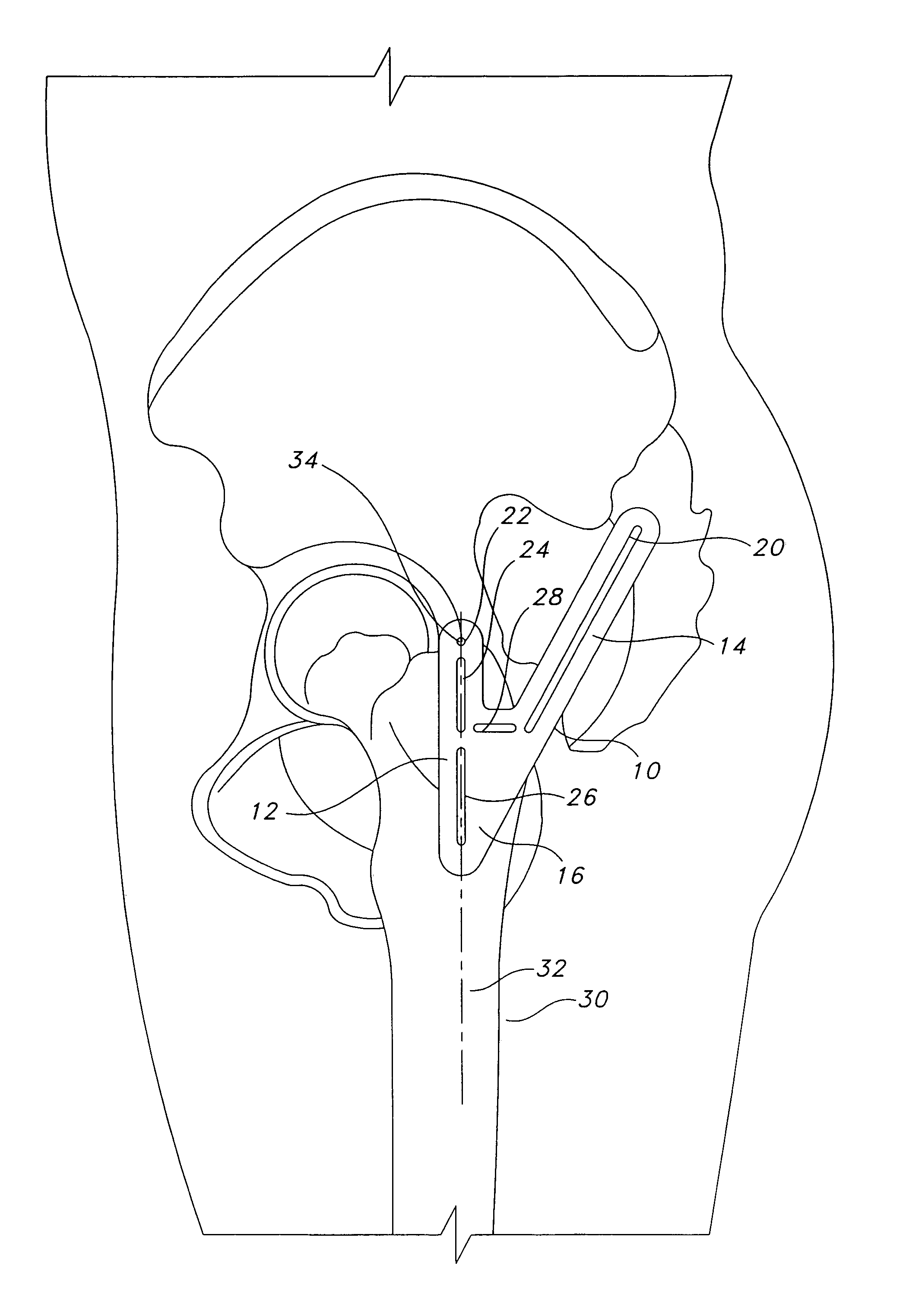
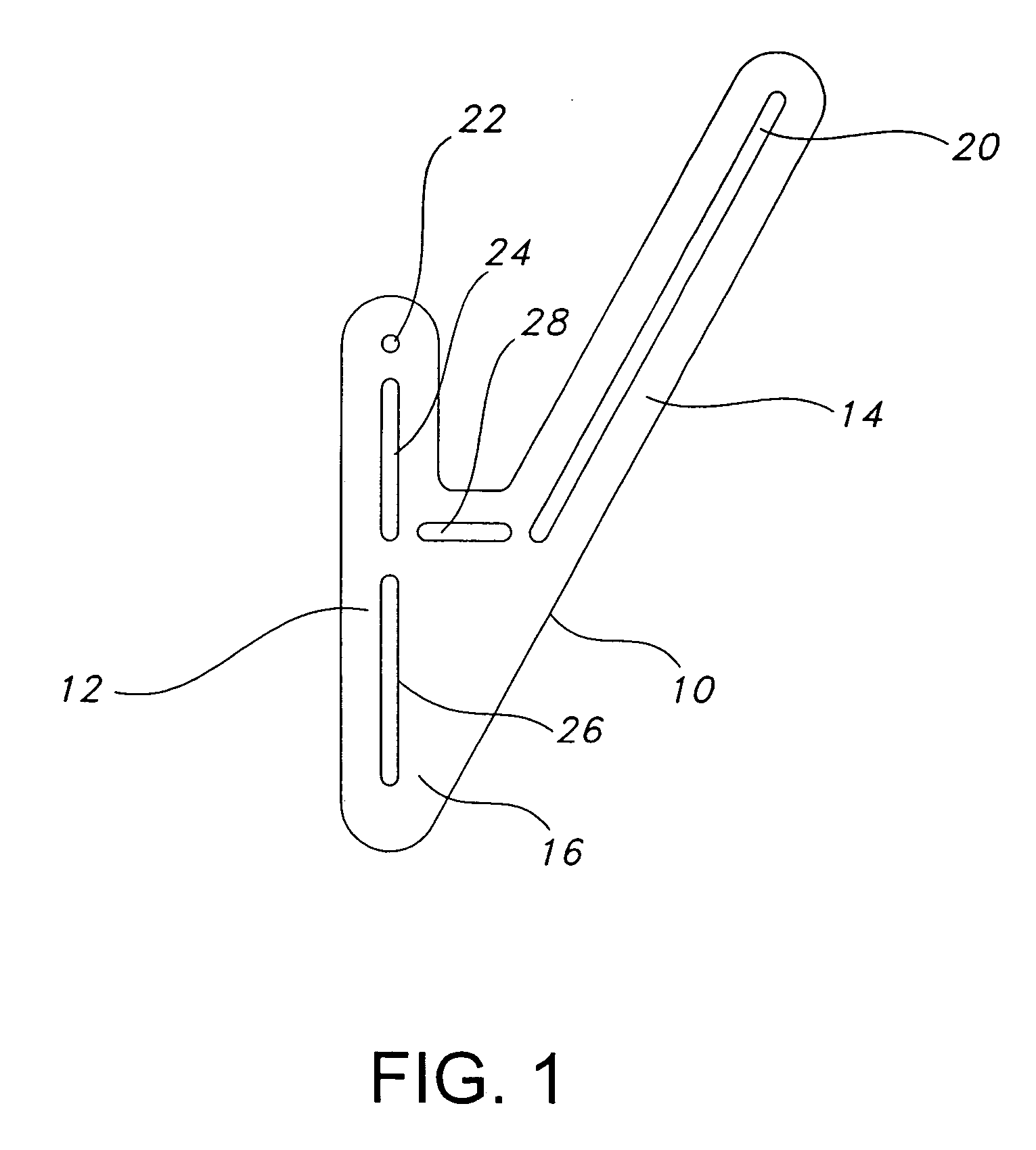
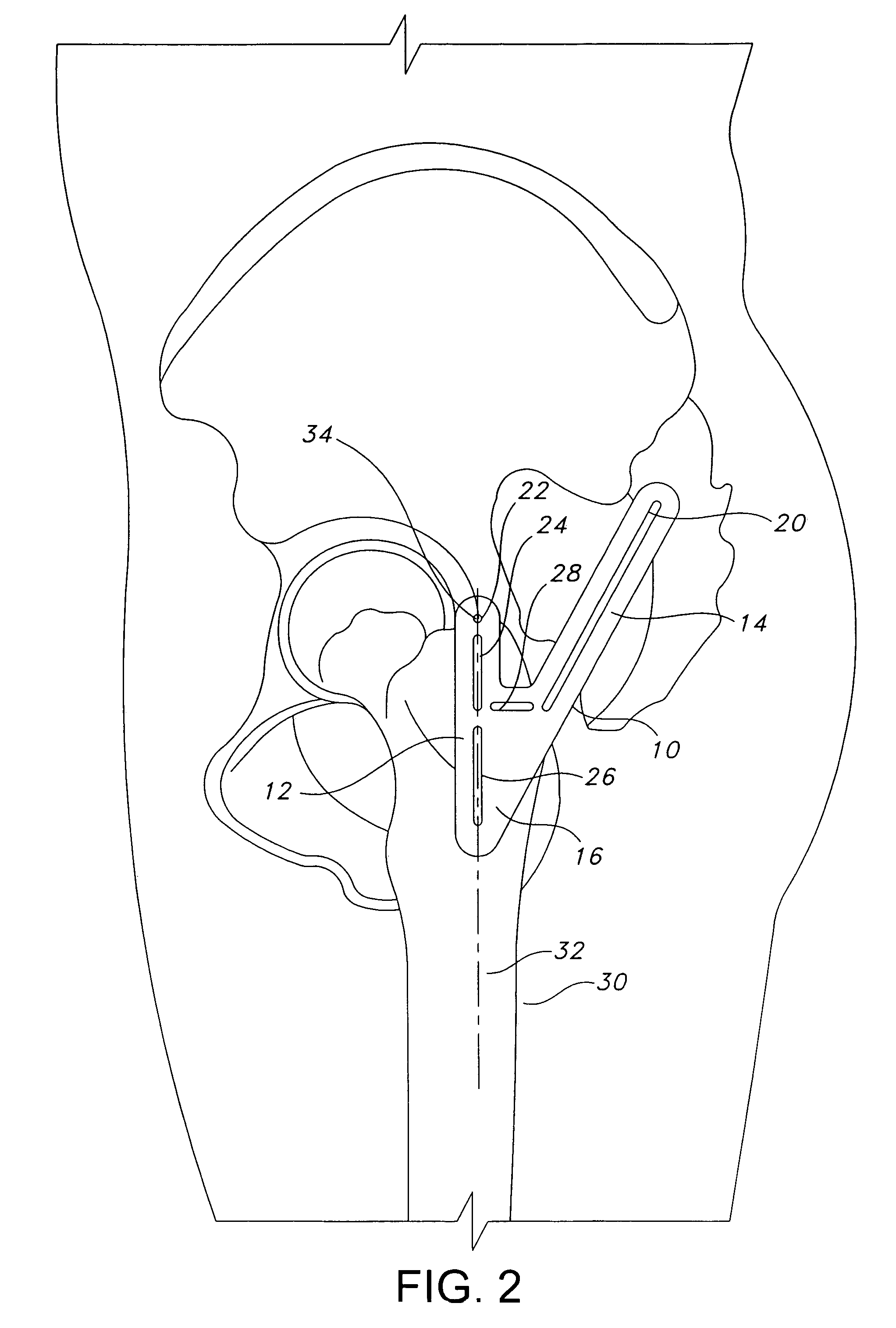
Method and apparatus for positioning a bone prosthesis using a localization system
InactiveUS20080051910A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceLocalization systemCoxal joint
Methods and apparatus using a surgical navigation system to position the femoral component of a prosthetic hip during hip joint replacement surgery without separately affixing a marker to the femur. The navigation system acquires the center of rotation of the hip joint as well as at least one point on the femur in the pelvic frame of reference. From these two points, the navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the hip joint and the point on the femur. Optionally, a second point on the femur that is not on the first line is palpated. The system can calculate the position and length of a second line that is perpendicular to the first line and that runs from the first line to the second palpated point on the femur. The prosthetic cup is implanted and its center of rotation is recorded. A tool for forming the bore within which the stem of the femoral implant component will be placed is tracked by the navigation system. While the tool is fixed to the femur, the surgeon re-palpates the same point(s) on the femur that were previously palpated. The navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the prosthetic cup and the re-palpated first point. If a second point on the femur was re-palpated, the navigation system also calculates the position and length of a perpendicular line between the first line and the second point. The surgical navigation system uses this information to calculate and display to the surgeon relevant information about the surgery, such as change in the patient's leg length and / or medialization / lateralization of the joint.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Expandable hip implant
InactiveUS6361565B1Reduce retentionReduce capacitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisProsthesisBody fluid
An implant is formed of an expandable material. An opening is formed in a bone in a patient's body. At least a portion of the implant is positioned in the opening in the bone in the patient's body. The implant is retained against movement relative to the bone in the patient's body by absorbing body fluid with the implant and expanding the implant while the implant is disposed in the opening in the bone in the patient's body. The implant may be a hip replacement member.
Owner:BONUTTI 2003 TRUST A THE +1
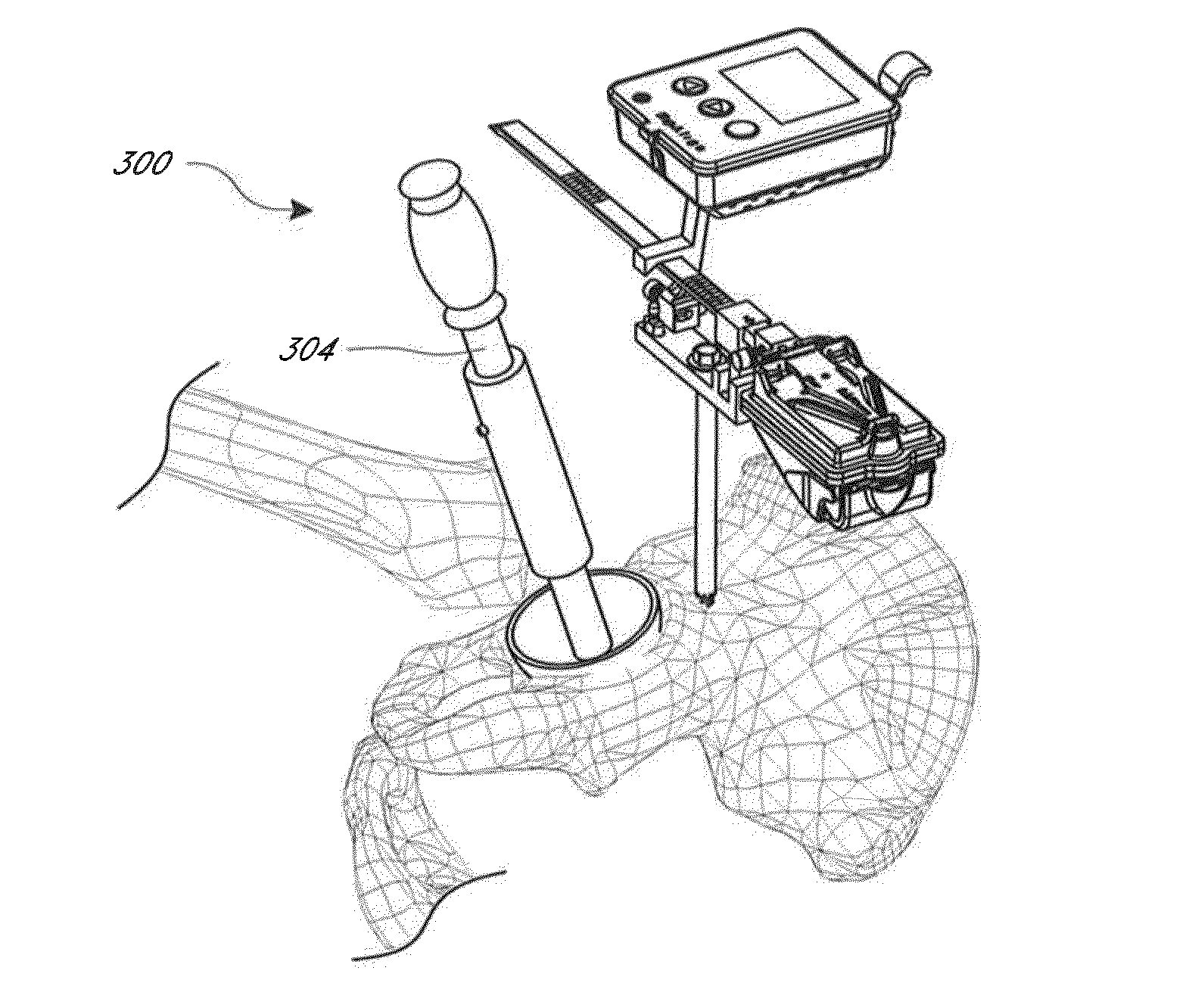
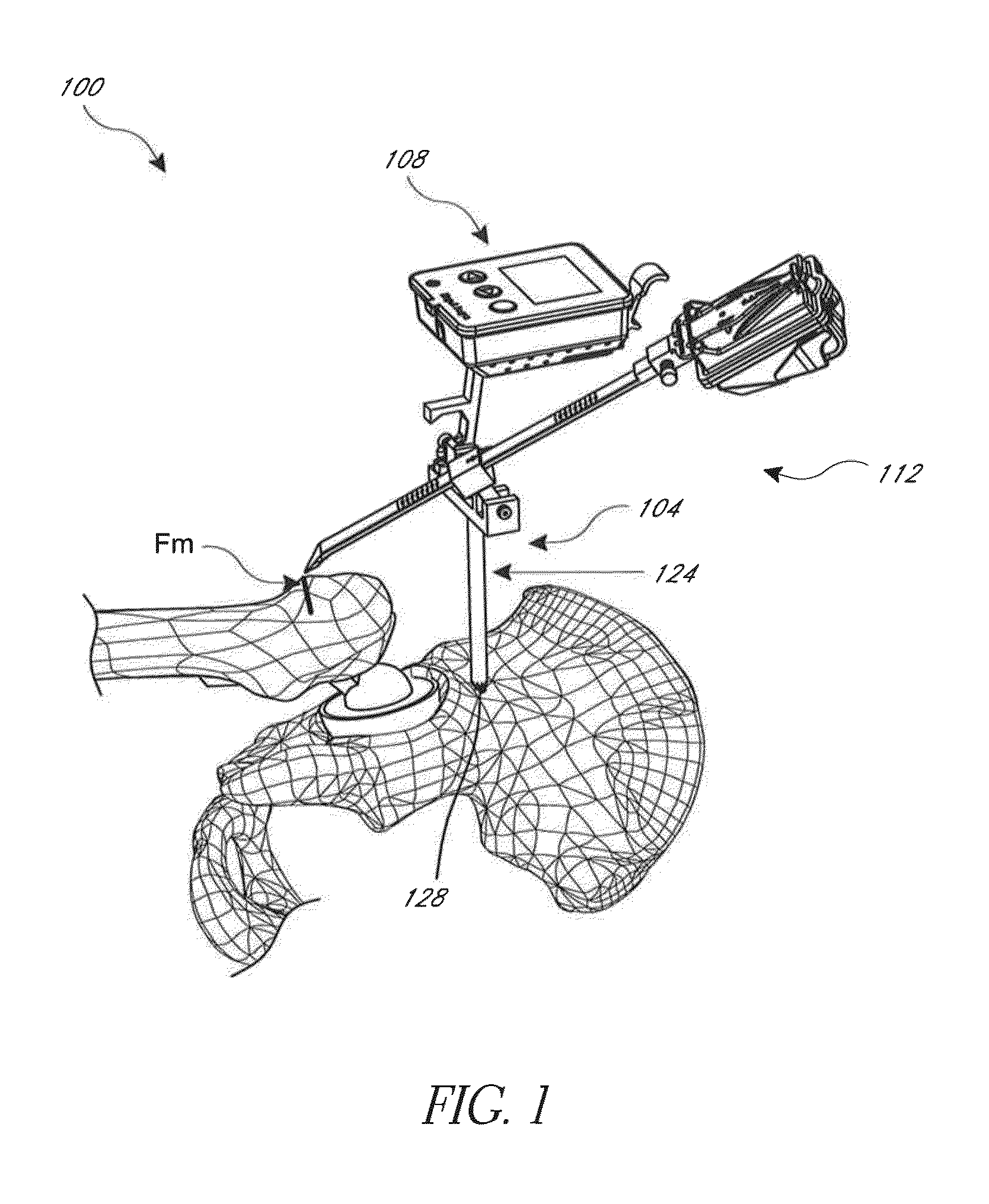
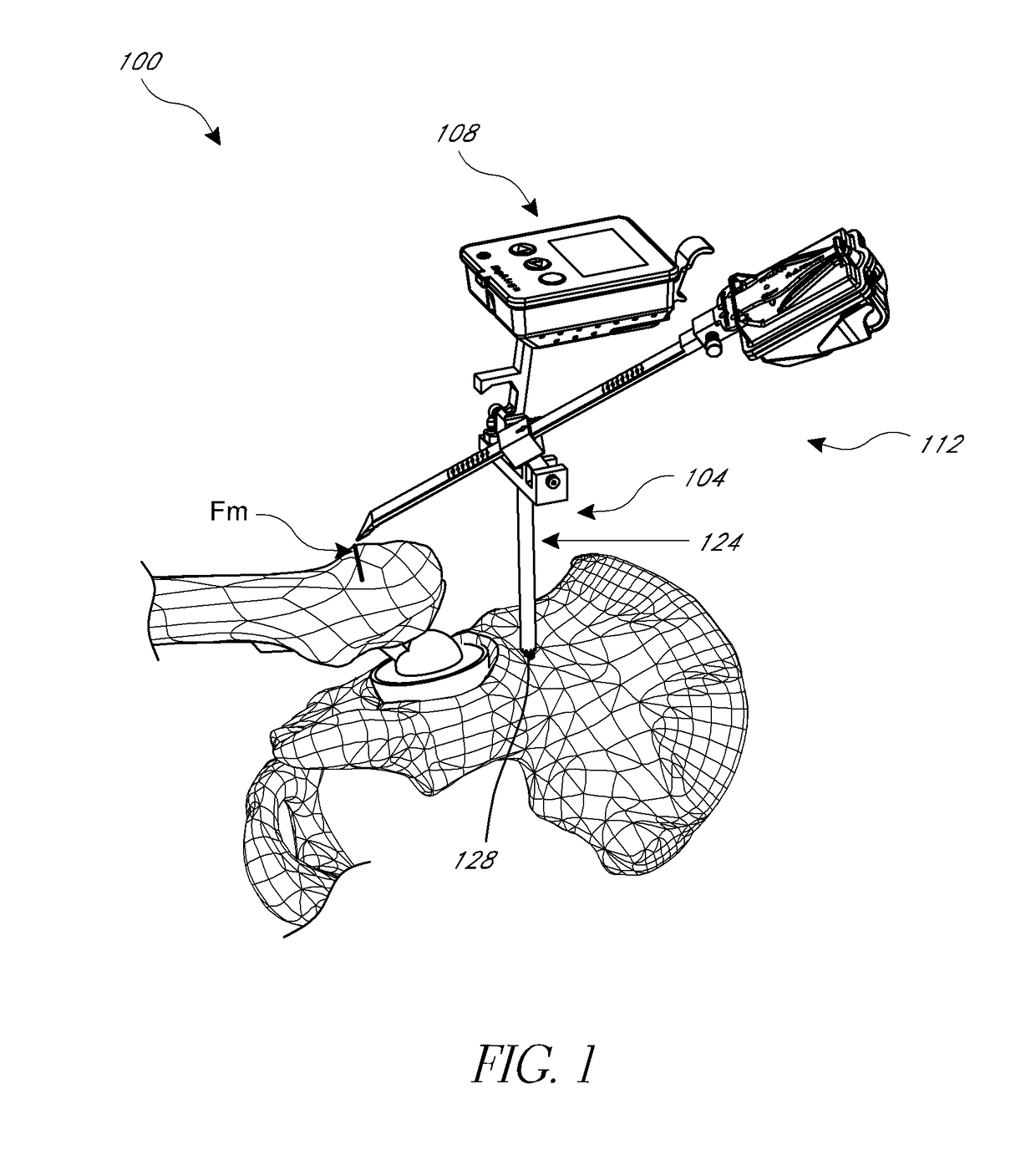
Hip replacement navigation system and method
ActiveUS20140052149A1Improve accuracyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsAnatomical landmarkMuscles of the hip
In another embodiment, a hip joint navigation jig is provided that includes an anatomical interface comprising a bone engagement portion. A registration jig is also provided that is coupled, e.g., removeably, with the anatomical interface. A rotatable member is provided for rotation about an axis that is not vertical when the jig is mounted to the bone adjacent to a hip joint and the registration jig is coupled with the anatomical interface. An anatomy engaging probe is coupled with the rotatable member for rotation about the axis and is translatable to enable the probe to be brought into contact with a plurality of anatomical landmarks during a procedure. An inertial sensor is coupled with the probe to indicate orientation related to the landmarks, the sensor being disposed in a different orientation relative to horizontal when the probe is in contact with the landmarks.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Non-spherical articulating surfaces in shoulder and hip replacement
An orthopedic device and method of use are provided that incorporate complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces to allow a greater available range of motion compared with existing artificial shoulder joint and artificial hip joints. According to some embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on a humeral head and / or glenoid of a shoulder prosthesis. In other embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on the acetabulum and / or femoral head of a hip prosthesis. These non-spherical surfaces can be used to adjust constraint, joint thickness, soft tissue tension, moment and arc of motion, and in doing so, influence motion.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
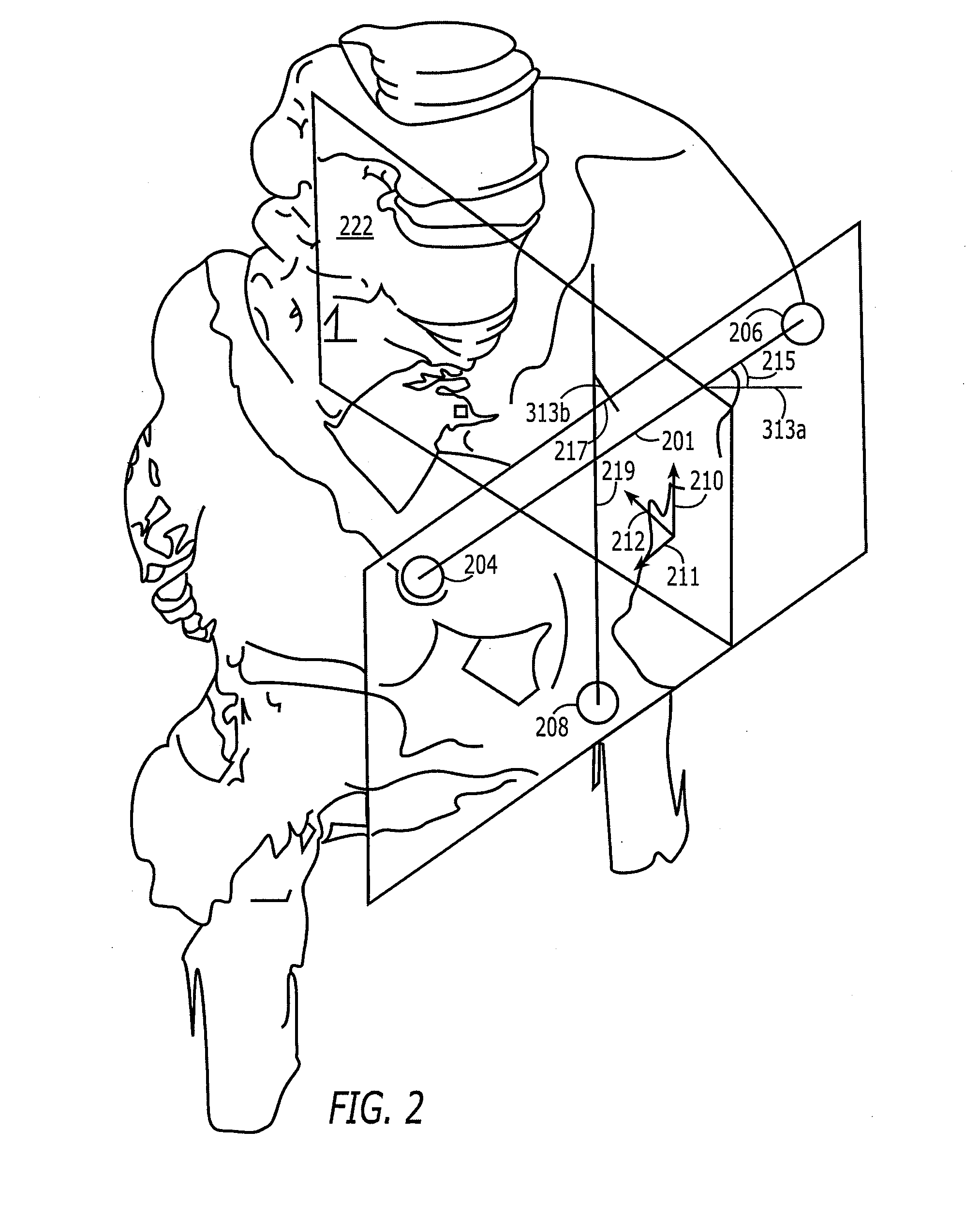
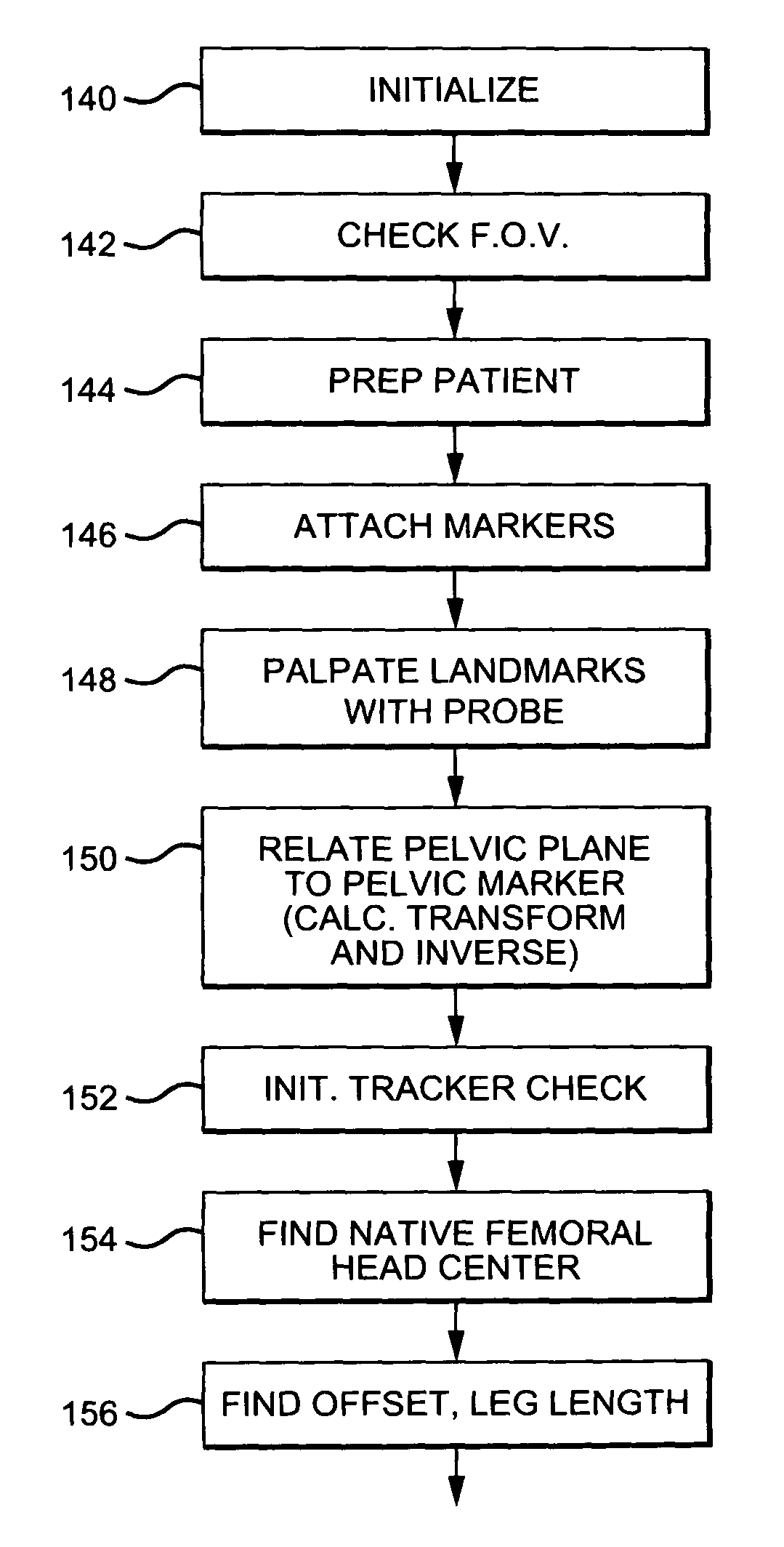
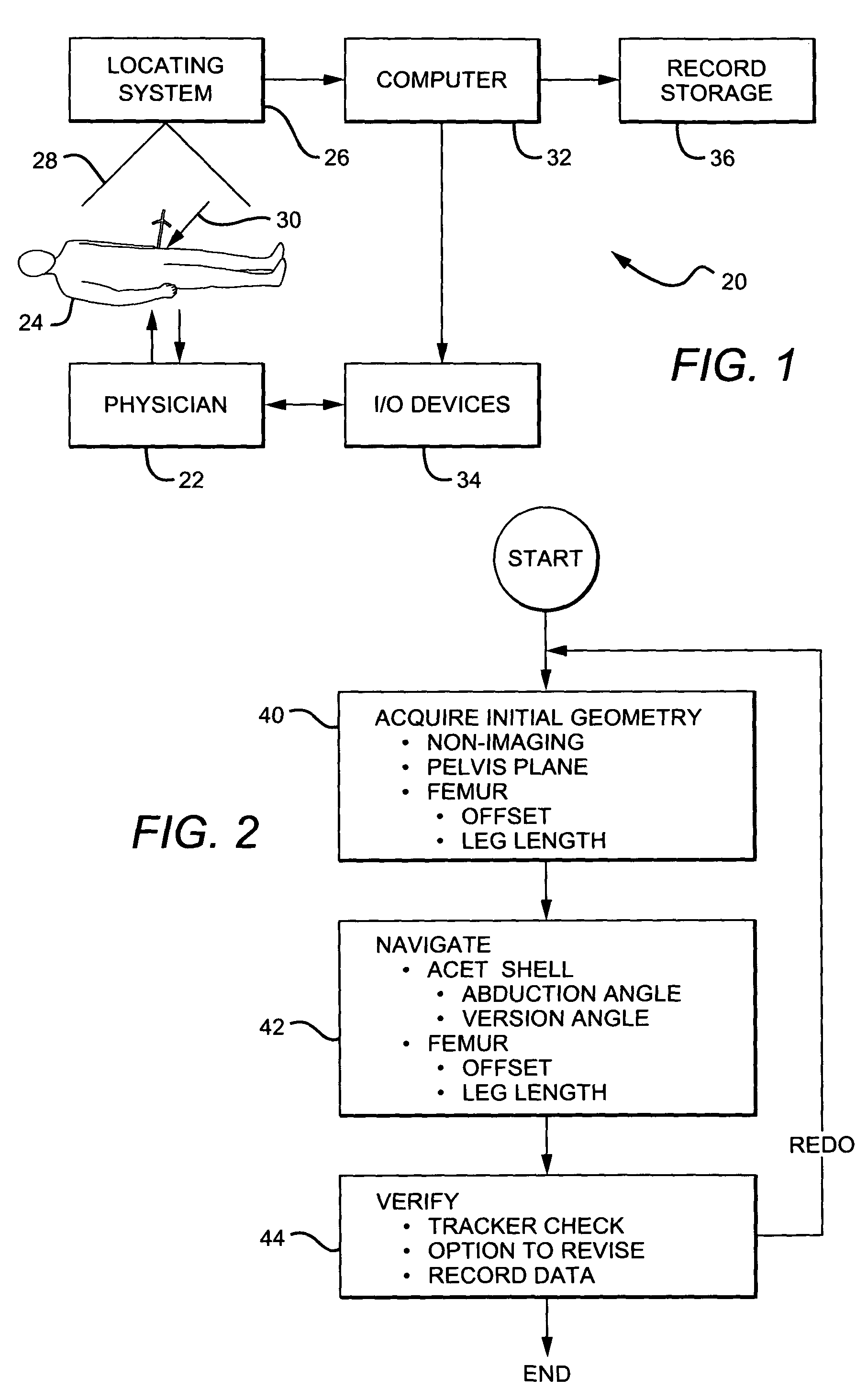
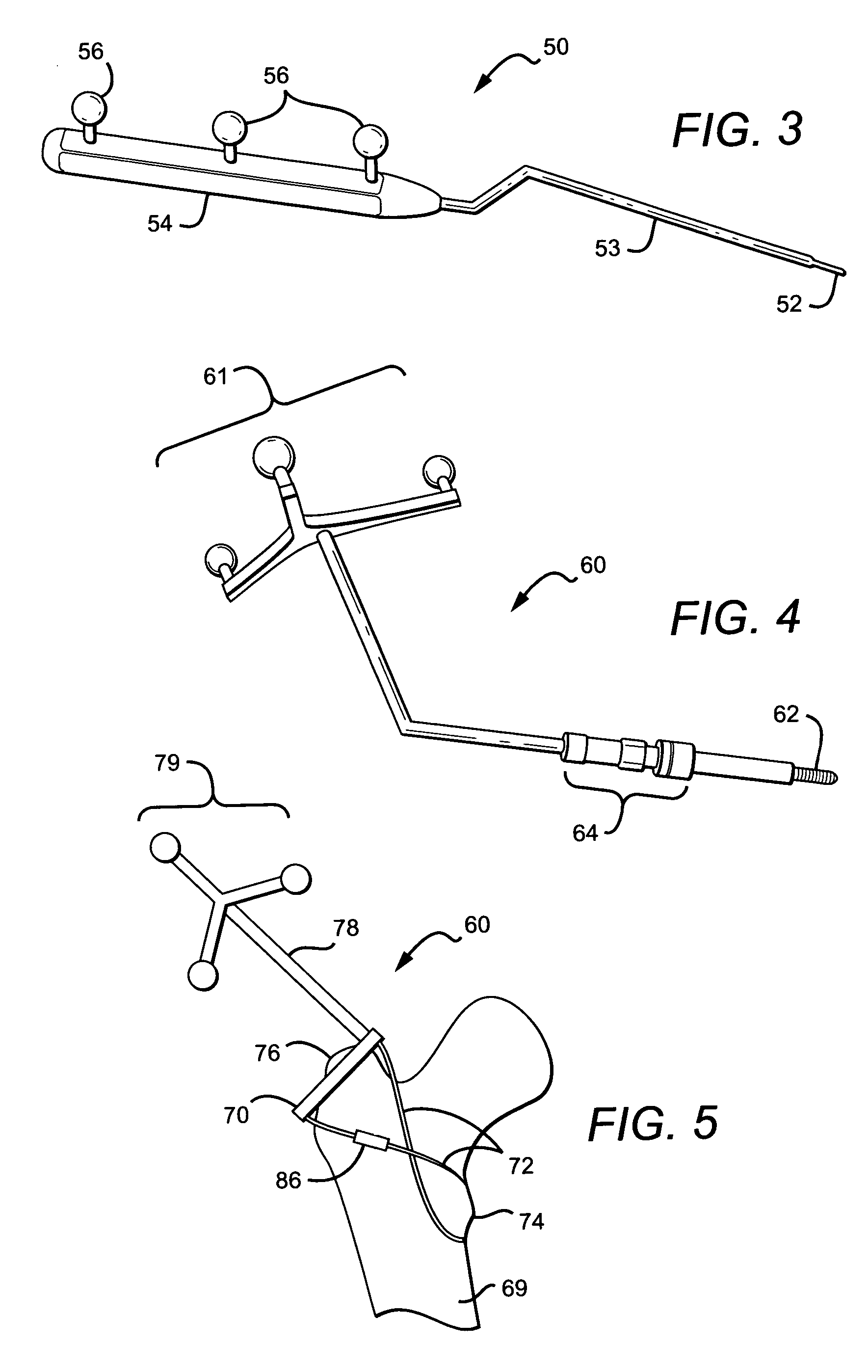
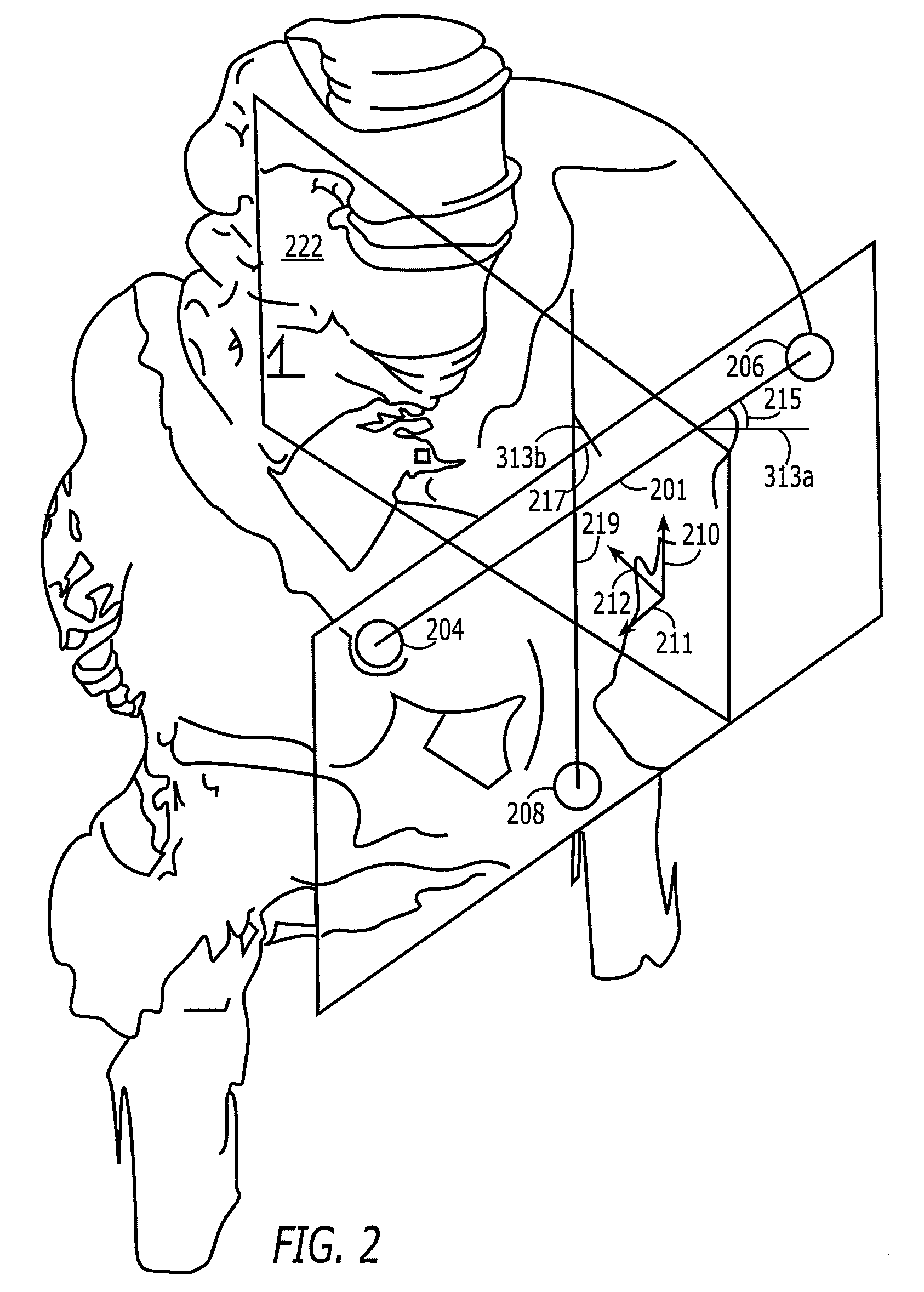
Non-imaging, computer assisted navigation system for hip replacement surgery
ActiveUS7780681B2Surgical navigation systemsJoint implantsHip joint replacement operationFemoral offset
The invention includes: a locating system; a computer, interfaced to the locating system and interpreting the positions of tracked objects in a generic computer model of a patient's hip geometry; a software module, executable on the computer, which defines the patient's pelvic plane without reference to previously obtained radiological data, by locating at least three pelvic landmarks; and a pelvic tracking marker, fixable to the pelvic bone and trackable by the locating system, to track in real time the orientation of the defined pelvic plane. Preferably, the system also includes a femoral tracking marker, securely attachable to a femur of the patient by a non-penetrating ligature and trackable by the locating system to detect changes in leg length and femoral offset.
Owner:KINAMED
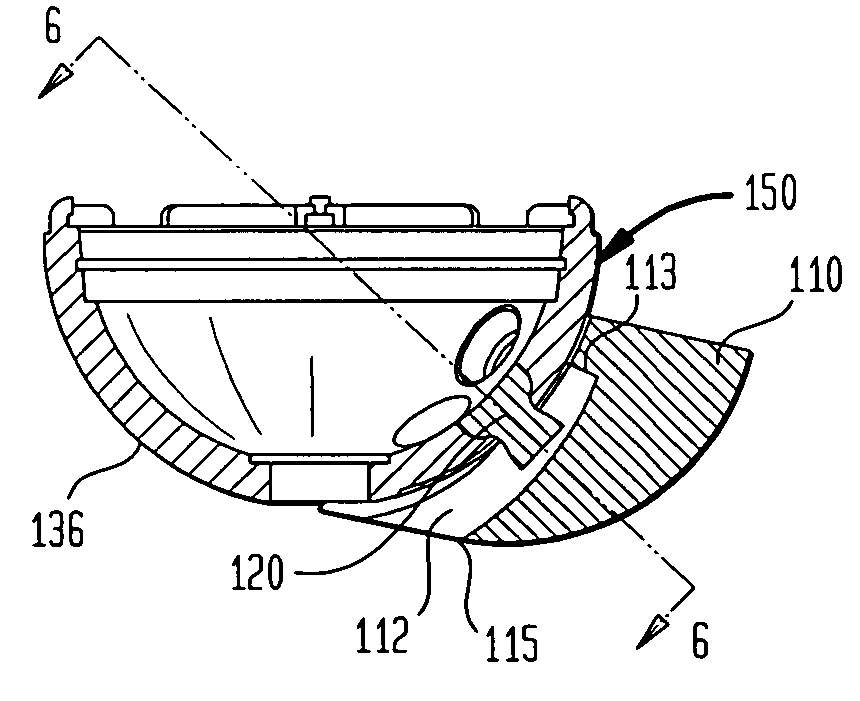
Acetabular cup augment system
InactiveUS20080021568A1Reduce decreaseSimplifies implant procedureJoint implantsAcetabular cupsCouplingEngineering
A modular prosthetic acetabular cup for use in restorative hip replacement has an augment which can be attached to an acetabular cup outer shell to provide an acetabular cup with a cross section of a desired configuration. The augment can be attached to the acetabular cup by a coupling element having an outer dovetail portion which slidably engages a groove formed within the augment preferably open to at least a first end thereof. The inner end of the coupling element can engage screw holes of the acetabular cup. The groove of the augment further includes a second end having a gradually increasing distance from the outer surface of the shell and the inner surface of the augment on moving towards the second end of the augment.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Hip replacement navigation system and method
ActiveUS20160242934A1Eliminate errorsDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsAnatomical landmarkAcetabular bone
A hip joint navigation system is provided that includes a base having at least one channel disposed therethrough for receiving a pin for mounting the base to the pelvis. A mount feature is disposed on a top surface. A registration jig is configured to couple with the base and to engage anatomical landmarks. In some aspects, a patient specific jig system for hip replacement is provided including an engagement surface formed to closely mate to acetabular bone contours of a specific patient and a registration feature configured to be in a pre-determined orientation relative to an acetabulum the patient when the jig is coupled with acetabular bone contours of the specific patient. In other aspects, methods of using the systems are provided.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Universal double offset surgical instrument
Instruments for use in anterior approach total hip arthroplasty. Instruments according to certain embodiments of the invention connect to a shaping member such as a broach, reamer or osteotome that is used to prepare the intramedullary canal of a desired femur or other bone for total hip arthroplasty. Such an instrument according to such embodiments can be configurable to allow operation on either the left or right leg, and in doing so to provide lateral offset and anterior offset of the instrument handle relative to the shaping member so that the patient's gut, musculature or other bodily portions may be avoided while still providing desired leverage and control over the shaping member to prepare the intramedullary canal.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Hip replacement navigation system and method
ActiveUS9649160B2Improve accuracySurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsAnatomical landmarkNavigation system
In another embodiment, a hip joint navigation jig is provided that includes an anatomical interface comprising a bone engagement portion. A registration jig is also provided that is coupled, e.g., removeably, with the anatomical interface. A rotatable member is provided for rotation about an axis that is not vertical when the jig is mounted to the bone adjacent to a hip joint and the registration jig is coupled with the anatomical interface. An anatomy engaging probe is coupled with the rotatable member for rotation about the axis and is translatable to enable the probe to be brought into contact with a plurality of anatomical landmarks during a procedure. An inertial sensor is coupled with the probe to indicate orientation related to the landmarks, the sensor being disposed in a different orientation relative to horizontal when the probe is in contact with the landmarks.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Diamond coated joint implant
A joint implant, which is not itself a femoral component for a conventional hip joint replacement prosthesis having a diamond or diamond like coated ball, has a diamond or diamond like coated articulating surface. The coating can be transitional in nature. The implant can be based on a suitable support material, for example, a metal, a ceramic, or a plastic, with the support material being coated with the diamond or diamond like substance. The implant may be, for instance, for a ginglymous type, an enarthrodial type, or a digital joint. Convex and / or concave articulating surface(s) of a prosthesis can have the coating.
Owner:BIOPRO
Hip replacement navigation system and method
A hip joint navigation system is provided that includes a base having at least one channel disposed therethrough for receiving a pin for mounting the base to the pelvis. A mount feature is disposed on a top surface. A registration jig is configured to couple with the base and to engage anatomical landmarks. In some aspects, a patient specific jig system for hip replacement is provided including an engagement surface formed to closely mate to acetabular bone contours of a specific patient and a registration feature configured to be in a pre-determined orientation relative to an acetabulum of the patient when the jig is coupled with acetabular bone contours of the specific patient. In other aspects, methods of using the systems are provided.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
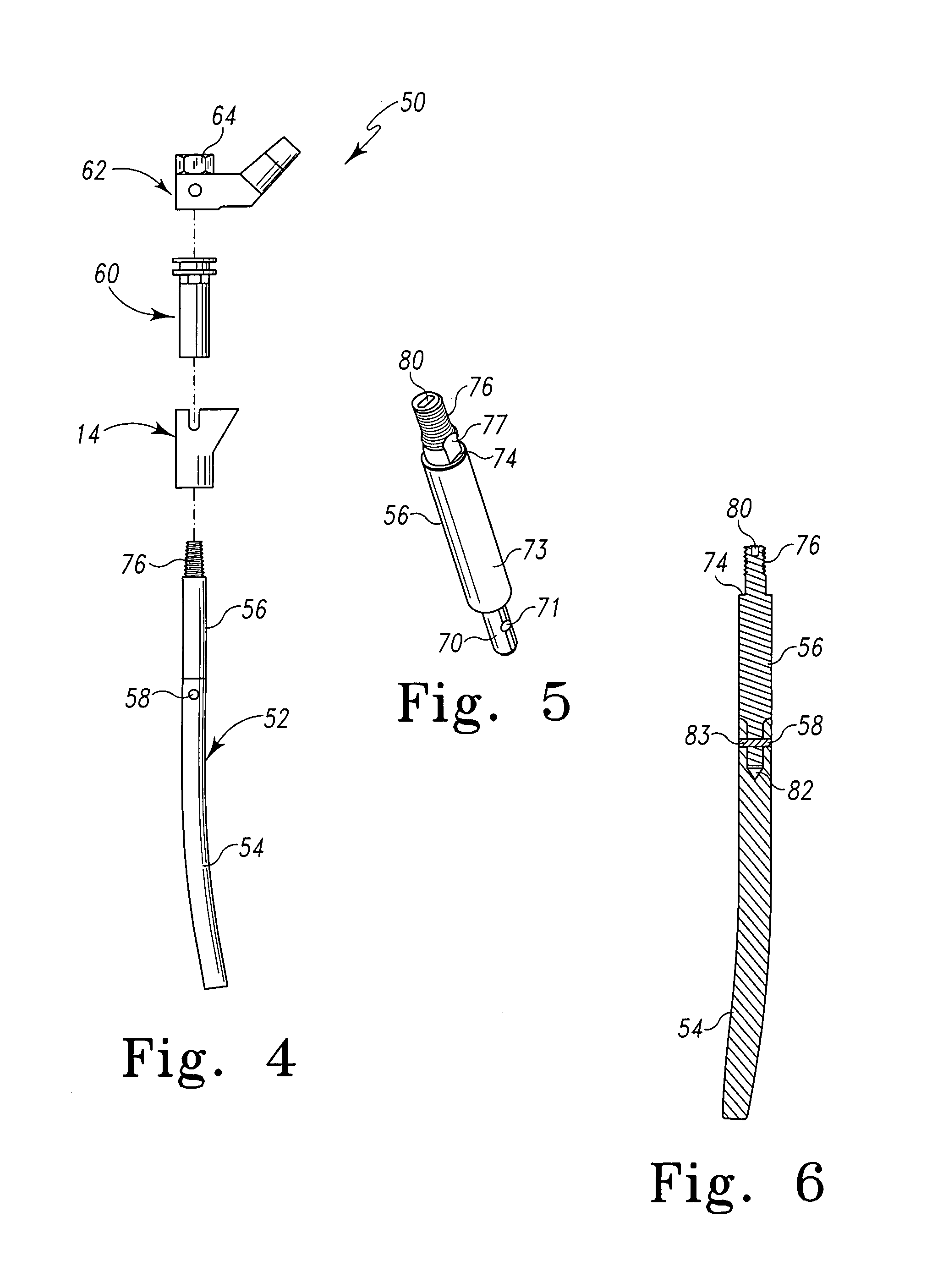
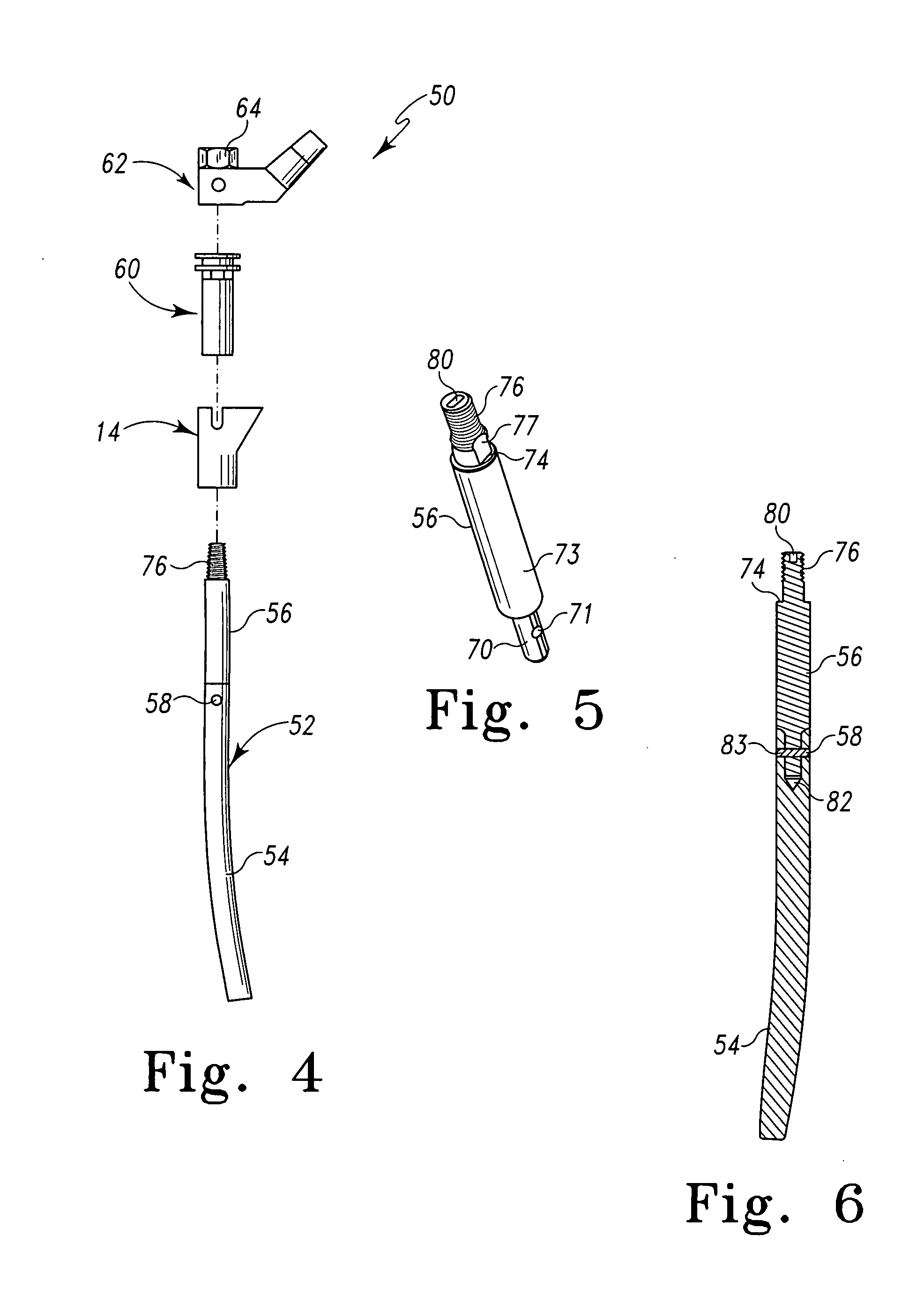
Modular hip stems and associated method of trialing
InactiveUS7235106B2Accurately approximatedReduce necessityJoint implantsFemoral headsMuscles of the hipModularity
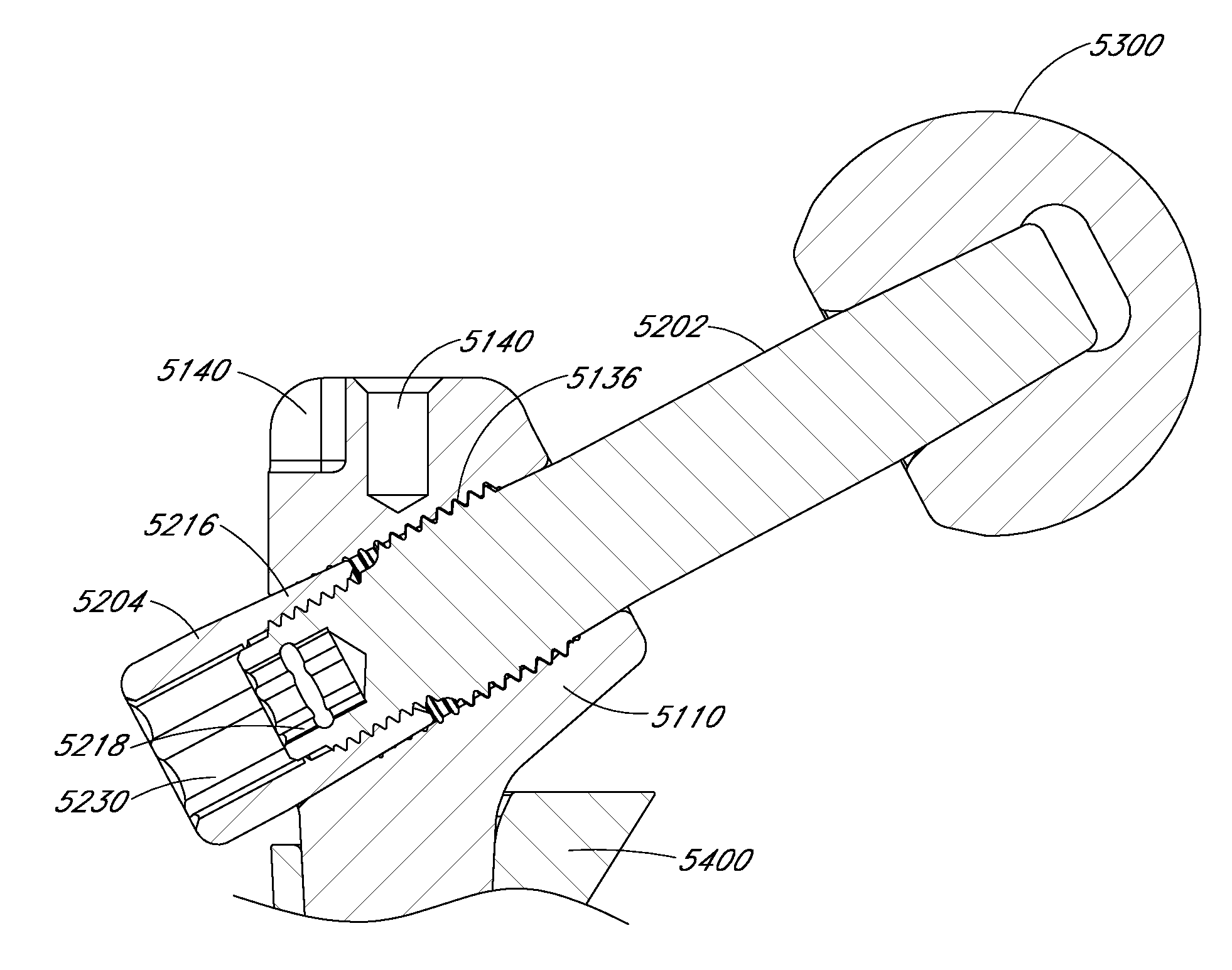
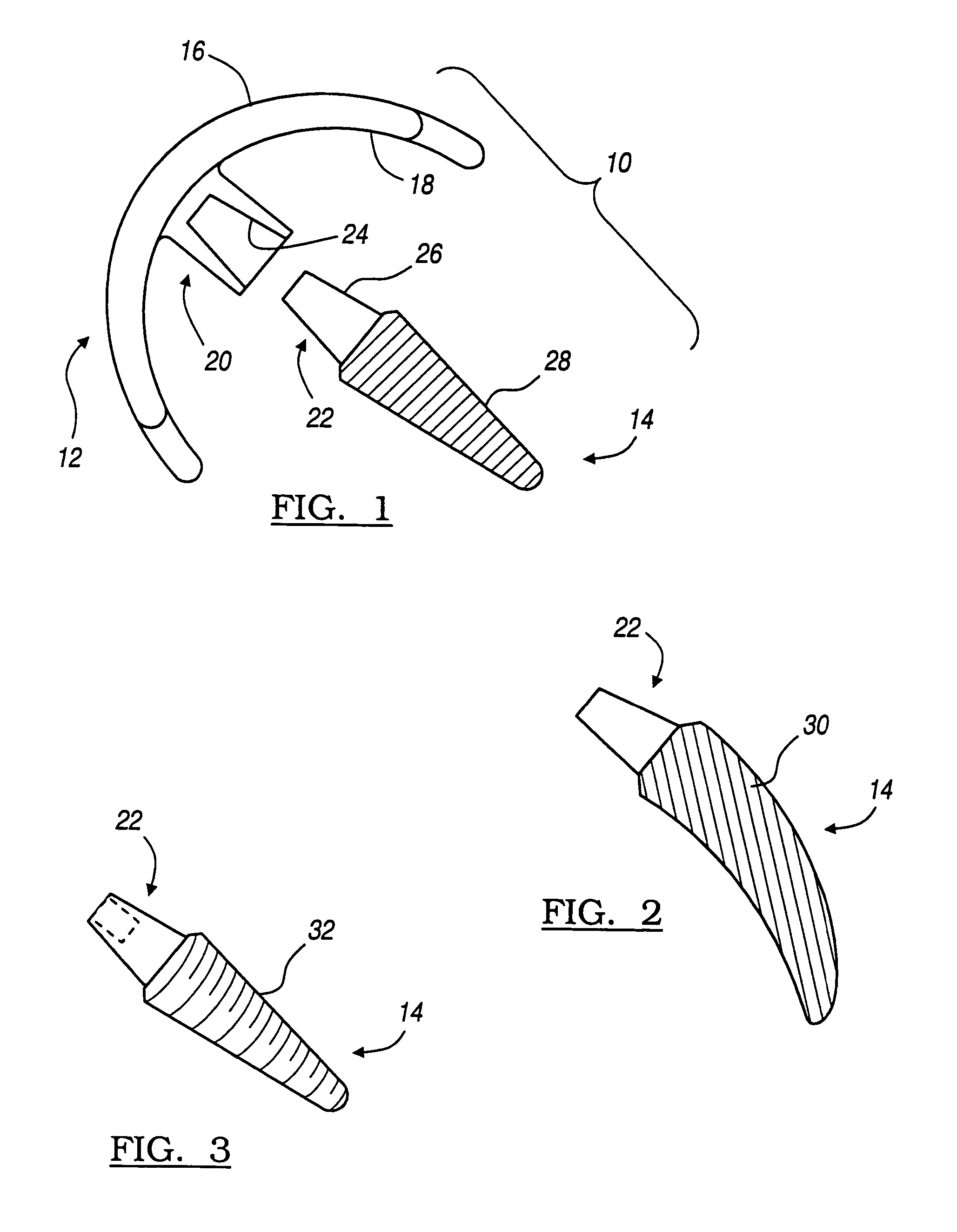
A system and method for trialing a modular hip replacement system (10) permits evaluation and replication of the anatomic anteversion rotational angle of the femur. A distal stem component (18) of the hip replacement system (10) includes a proximal portion (34) having a locator feature (35) that is externally accessible when the stem component is mounted within the femur. A proximal trial body assembly (60) is mounted on the proximal portion (34) of the distal stem component (18) to permit rotation of a trial neck component (62). The trial neck component (62) also includes a locator feature(126) that can be externally referenced to determine the anteversion angle.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
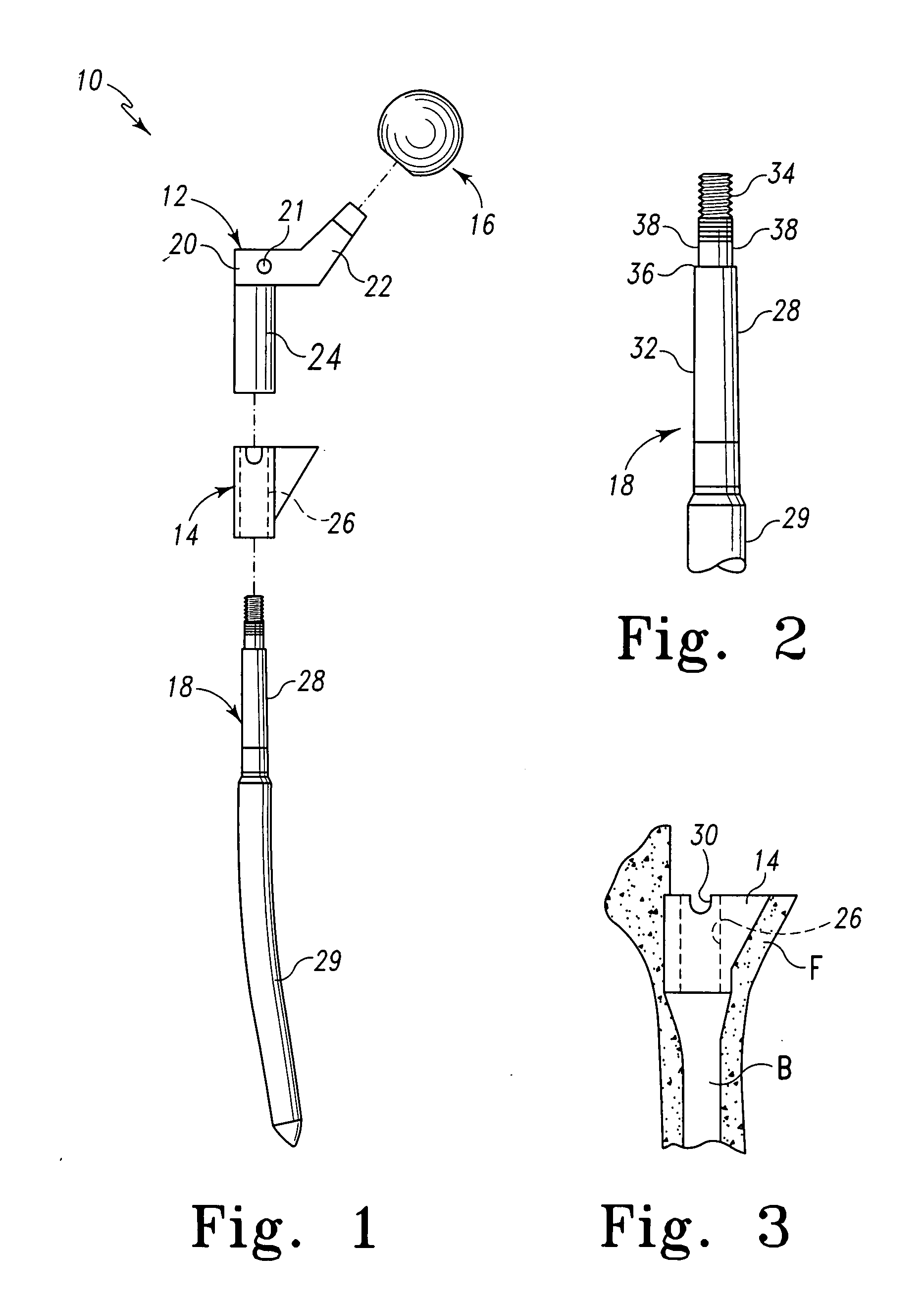
Method and apparatus for positioning a bone prosthesis using a localization system
InactiveUS7594933B2Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceHip joint replacement operationLocalization system
Methods and apparatus using a surgical navigation system during hip joint replacement surgery without separately affixing a marker to the femur. The navigation system acquires the center of rotation of the hip joint as well as at least one point on the femur in the pelvic frame of reference. From these two points, the navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the hip joint and the point on the femur. A prosthetic cup is implanted and its center of rotation is recorded. A tool for forming the bore within which the stem of the femoral implant component will be placed is tracked by the navigation system. The navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the prosthetic cup and the re-palpated first point. The surgical navigation system uses this information to calculate and display to the surgeon relevant information about the surgery.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Method and apparatus for hip replacement
InactiveUS20120130502A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInterference fitRight femoral head
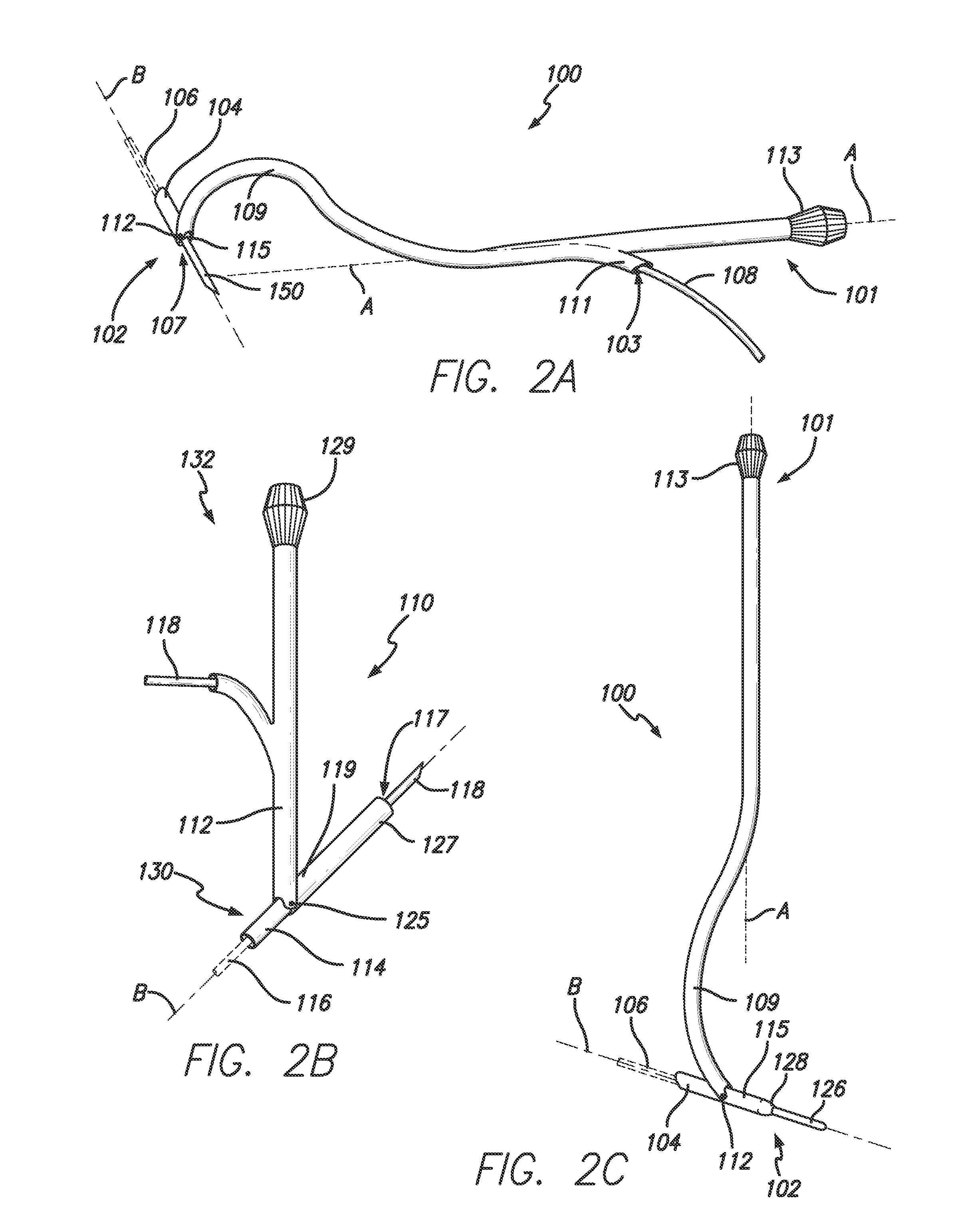
Methods and apparatus for orthopedic replacement of the hip through three incisions with a modular prosthetic system assembled in vivo while substantially preserving muscles and soft tissues around the hip joint resulting in reduced healing time and decreased risk of dislocation. A prosthetic femoral stem is inserted into the femur. A prosthetic femoral neck is inserted from a point along the side of the patient's body and into the side of the femur and through a lateral bore in the prosthetic femoral stem to join the prosthetic femoral head. The methods and apparatus include structures and techniques for fixing or enhancing interconnection of implant components, such as by increasing the interconnection in an interference fit with one or more tapers, threads, and / or cooling of components prior to assembly.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
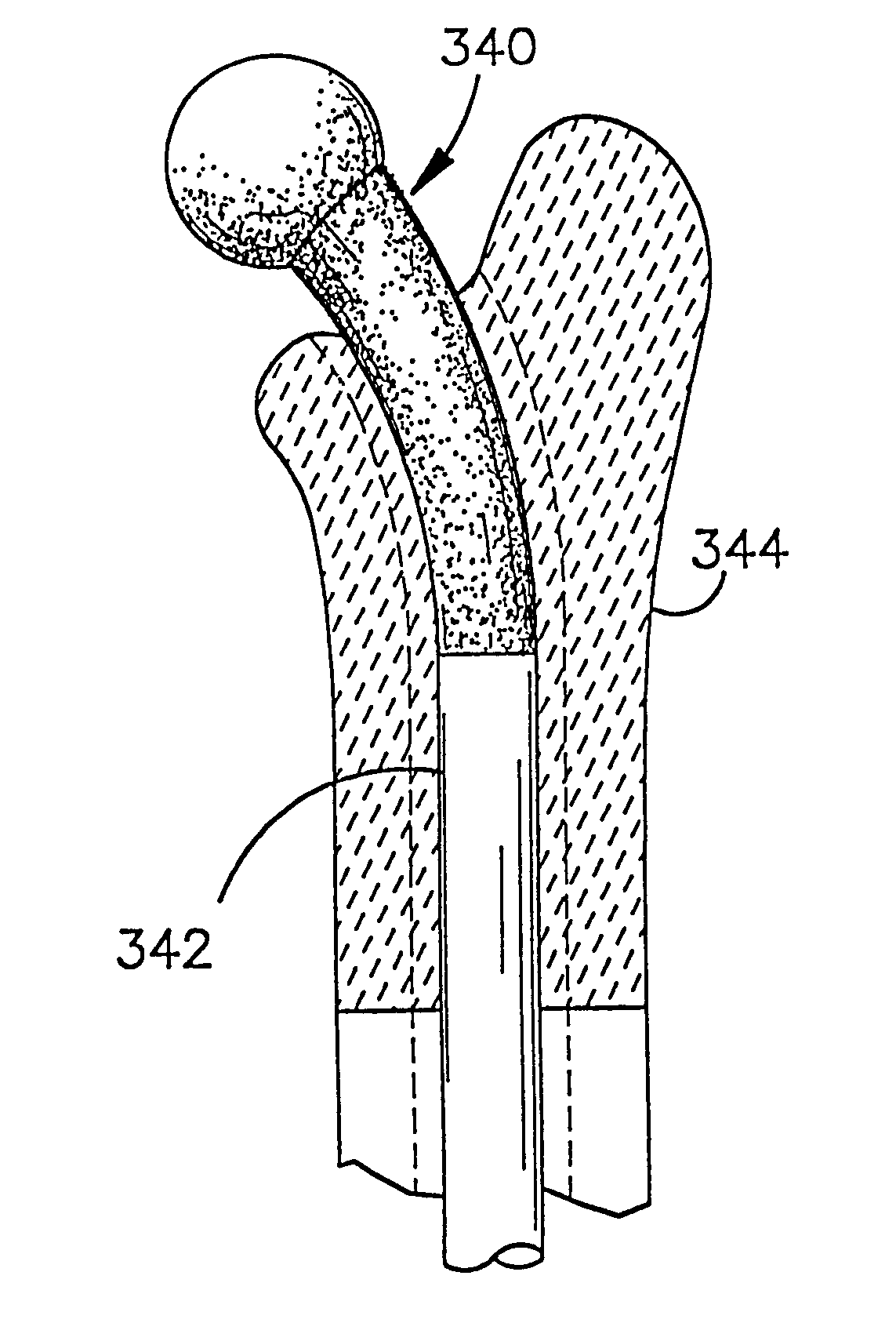
Periprosthetic bone plates
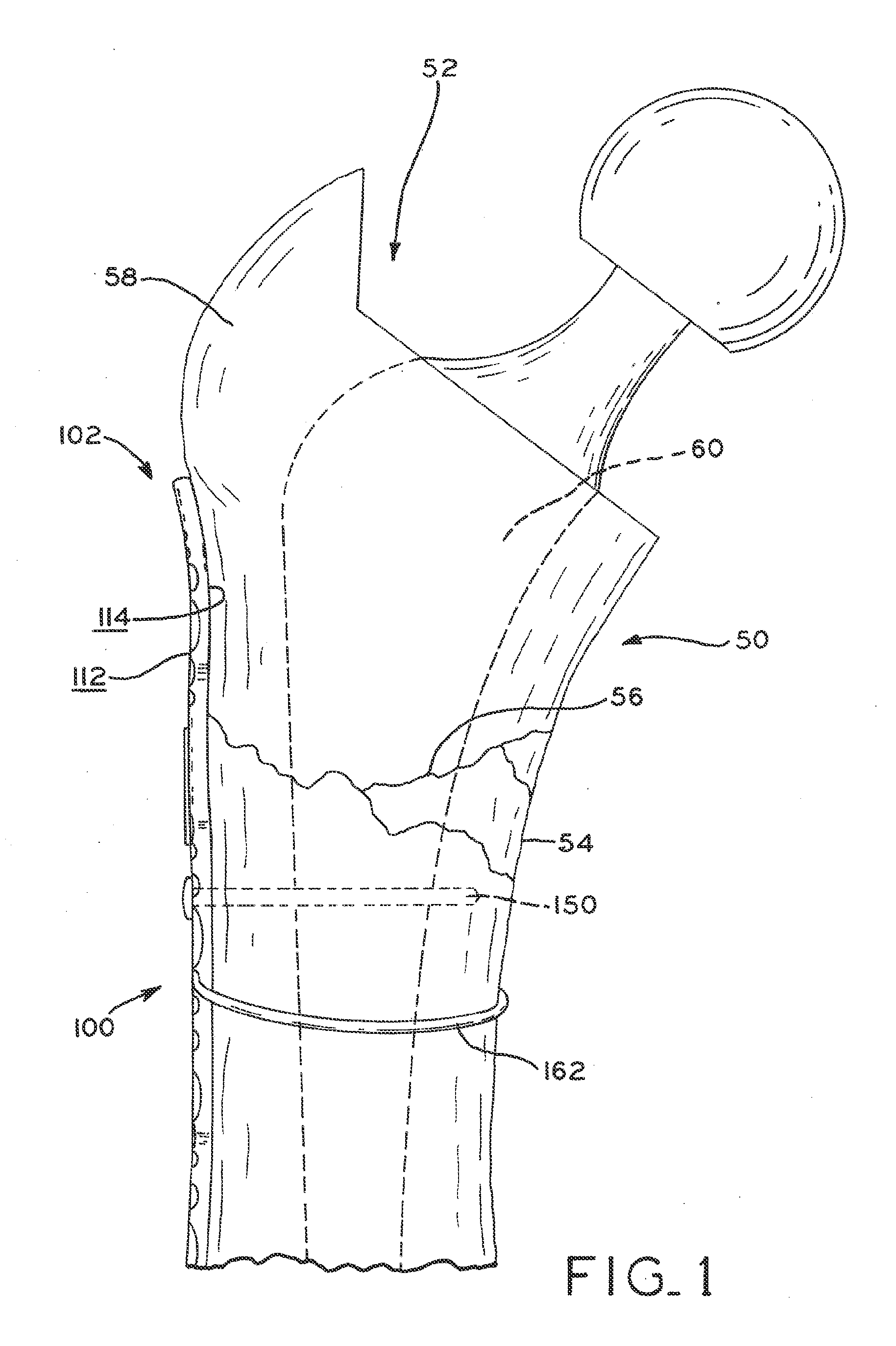
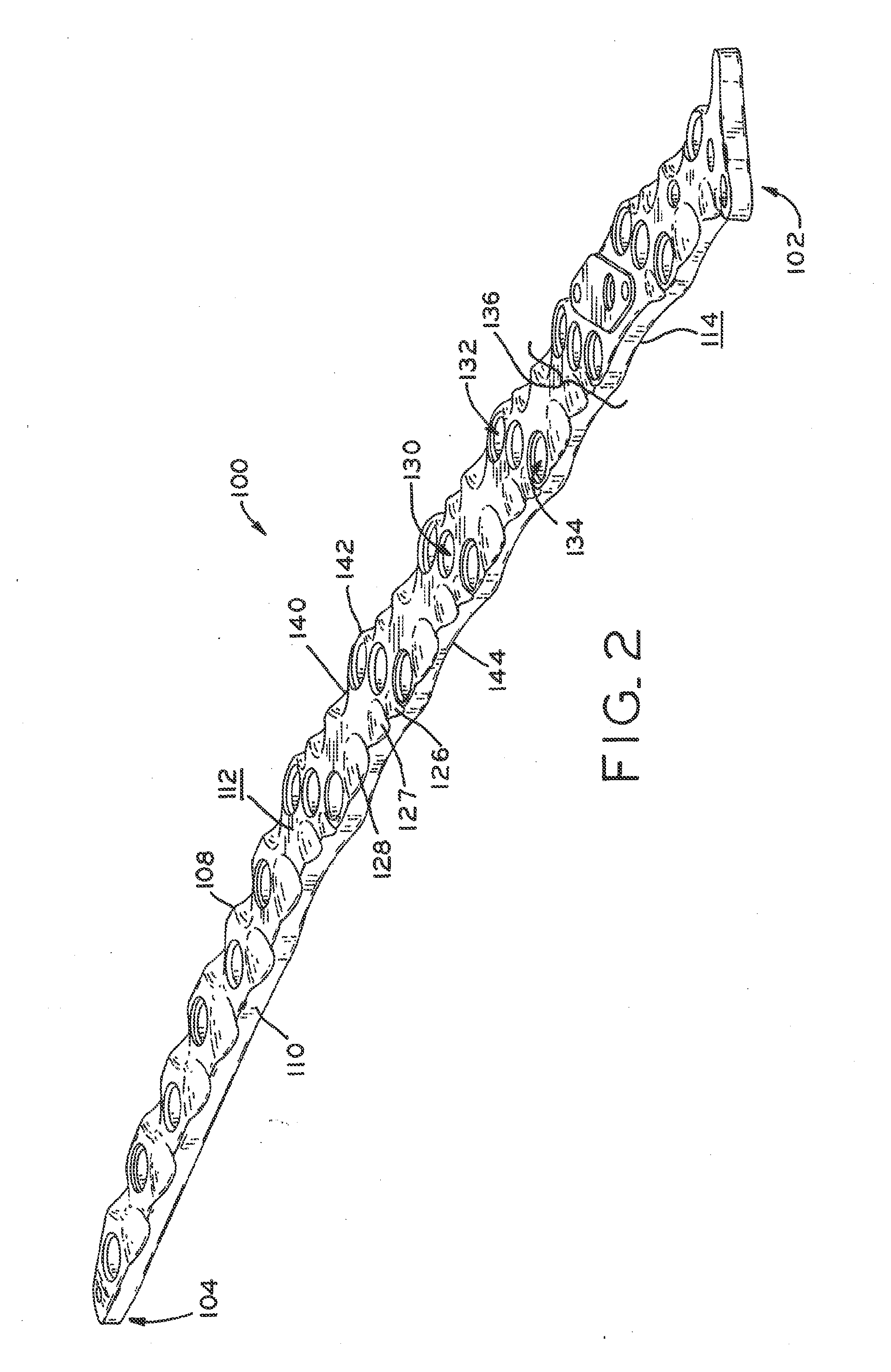
The present disclosure relates to bone plates that are configured for use with bones having periprosthetic fractures. For example, in the event that a proximal femur is fractured in an area that is adjacent to a prosthetic component, such as a femoral stem used in a hip replacement, the periprosthetic bone plates of the present invention may be used. In one exemplary embodiment, the periprosthetic bone plates include a periprosthetic zone having a plurality of central apertures and a plurality of outer apertures that are offset from the central apertures. The periprosthetic zone may further include a plurality of indentations, each indentation extending longitudinally between adjacent outer apertures to narrow a width of the bone plate.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Method and apparatus for hip replacement
InactiveUS8579985B2Enhance quality and reliability and compatibilityAvoid damageInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInterference fitRight femoral head
Methods and apparatus for orthopedic replacement of the hip through three incisions with a modular prosthetic system assembled in vivo while substantially preserving muscles and soft tissues around the hip joint resulting in reduced healing time and decreased risk of dislocation. A prosthetic femoral stem is inserted into the femur. A prosthetic femoral neck is inserted from a point along the side of the patient's body and into the side of the femur and through a lateral bore in the prosthetic femoral stem to join the prosthetic femoral head. The methods and apparatus include structures and techniques for fixing or enhancing interconnection of implant components, such as by increasing the interconnection in an interference fit with one or more tapers, threads, and / or cooling of components prior to assembly.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
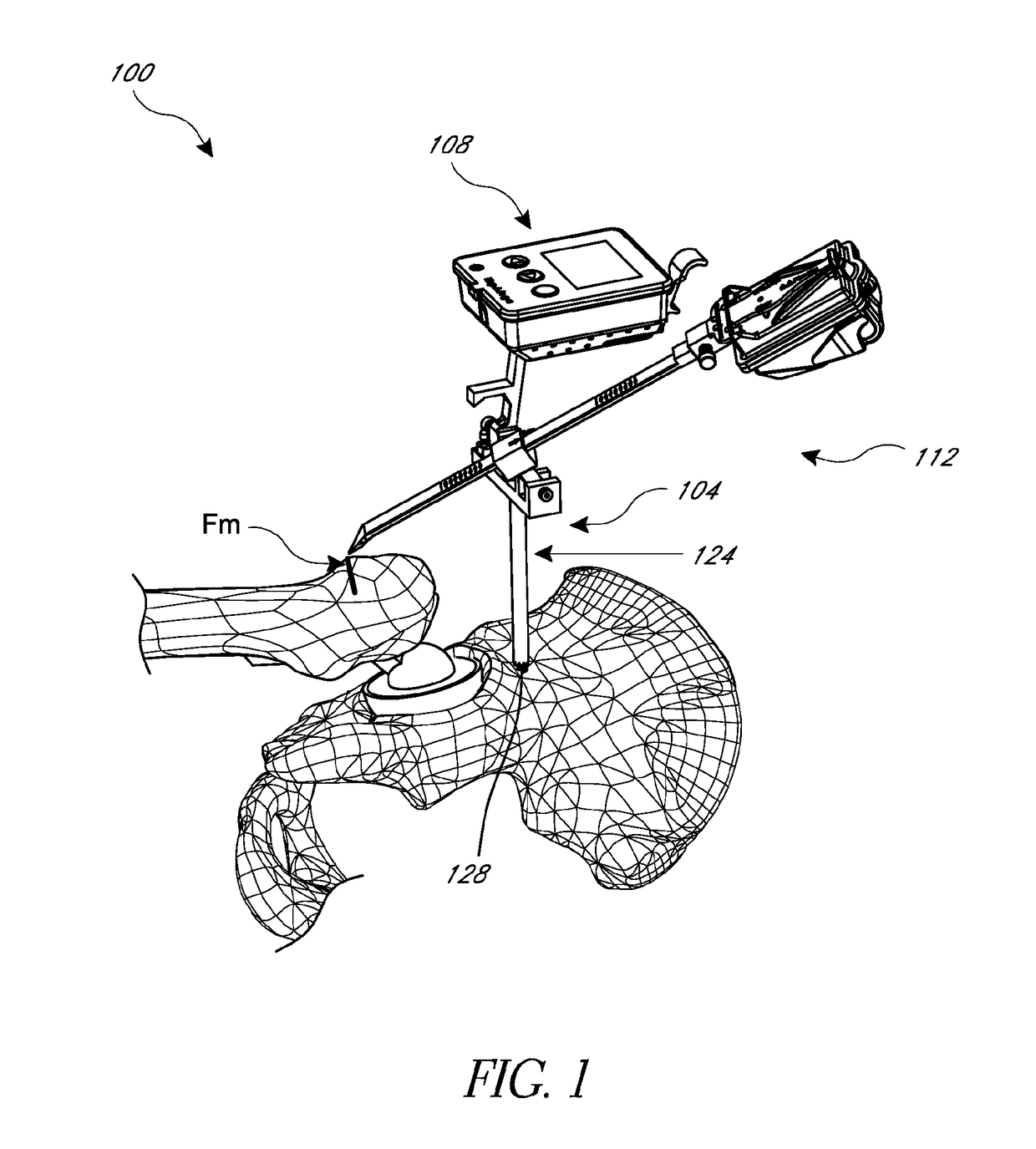
Operation assisting system
InactiveUS8400312B2Low costAccurate detectionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationPelvisJoints surgery
An operation assisting system. When an operator manipulates an operation instrument to perform an operation for a joint surgery including a hip replacement, the operation assisting system provides the operator with information on the orientation of a bone such as a pelvis and an appropriate direction of the operation instrument relative to the bone to assist the operator so as to complete the operation in an easy and accurate manner, which ensures a high degree of operation accuracy and reduces the cost of the system.
Owner:SAGA UNIVERSITY
Devices, systems and methods for monitoring hip replacements
InactiveUS20160029952A1Good adhesionEasy to mergePerson identificationJoint implantsAcetabular componentRight femoral head
Hip replacement prosthesis are provided, comprising a femoral stem, a femoral head coupled to the femoral stem, and an acetabular assembly coupled to the femoral head, and a plurality of sensors coupled to at least of the femoral stem, femoral head, and acetabular assembly.
Owner:CANARAY MEDICAL INC
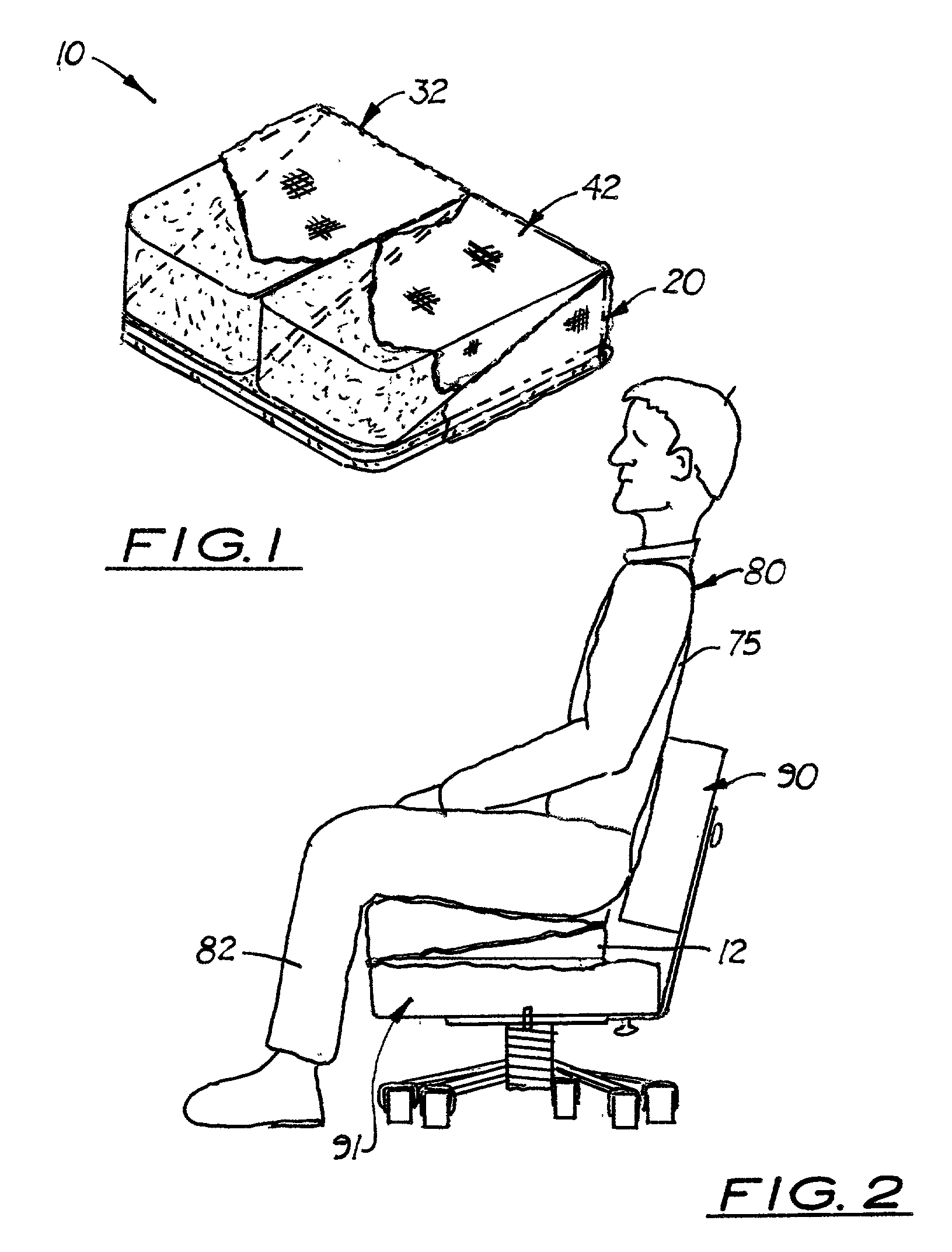
Adjustable split seat
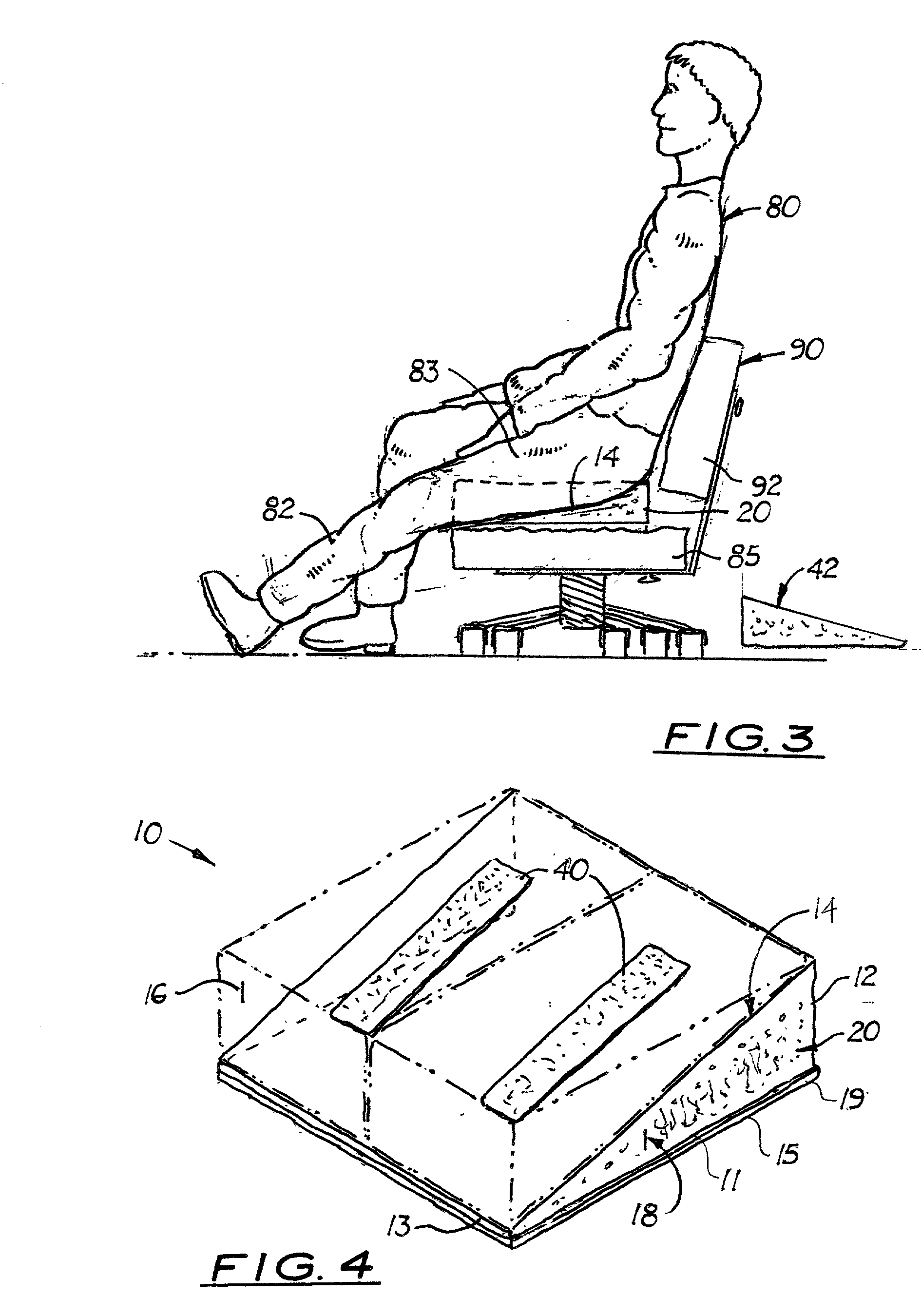
An adjustable seat that can be selectively adjusted to provide pressure relief for the back of the thighs and buttocks. The seat has two adjustable seat sections placed under the user's thighs. In one embodiment, the seat includes the main support body comprising a flat, horizontally aligned lower surface, a perpendicularly aligned, wide rear surface, a vertically aligned narrow front edge, a diagonally aligned upper support surface, and two equal vertically aligned side members. Disposed over the diagonally aligned support surface are two parallel, elastic wedge-shaped seat sections or two inflatable wedge-shaped seat sections. Each elastic or inflatable wedge-shaped seat section is complementary in shape and may create a flat seating surface on the seat accessory when the two wedge-shaped seat sections are longitudinally aligned over the diagonally aligned support surface. Each wedge-shaped seat section covers approximately one-half the diagonally aligned support surface. When one wedge-shaped seat section is removed from the main support body to accommodate the hip replacement patient's affected hip, which should not exceed 70° in flexion, the obtuse angle of the main support body supports the hip's approximate 70° angle of flexion. An optional attachment means is used to selectively connect each elastic wedge-shaped seat section to the main support body. With inflatable wedge seat sections, an air pump and control switch are also provided.
Owner:ODDERSON IB R
Resilient interpositional hip arthroplasty device
InactiveUS20130018479A1Preserve joint motionFree from painJoint implantsFemoral headsAnatomical structuresArticular surfaces
This disclosure is directed to a resilient interpositional arthroplasty implant for application into joints to pad cartilage defects, cushion joints, and replace or restore the articular surface, which may preserve joint integrity, reduce pain and improve function. The implant may endure variable joint compressive and shear forces and cyclic loads. The implant may repair, reconstruct, and regenerate joint anatomy, and thereby improve upon joint replacement alternatives. Rather than using periosteal harvesting for cell containment in joint resurfacing, the walls of this invention may capture, distribute and hold living cells until aggregation and hyaline cartilage regrowth occurs. The implant may be deployed into debrided joint spaces, molding and conforming to surrounding structures with sufficient stability to avoid extrusion or dislocation. Appendages of the implant may repair or reconstruct tendons or ligaments, and an interior of the implant that is inflatable may accommodate motions which mimic or approximate normal joint motion.
Owner:GROTZ R THOMAS
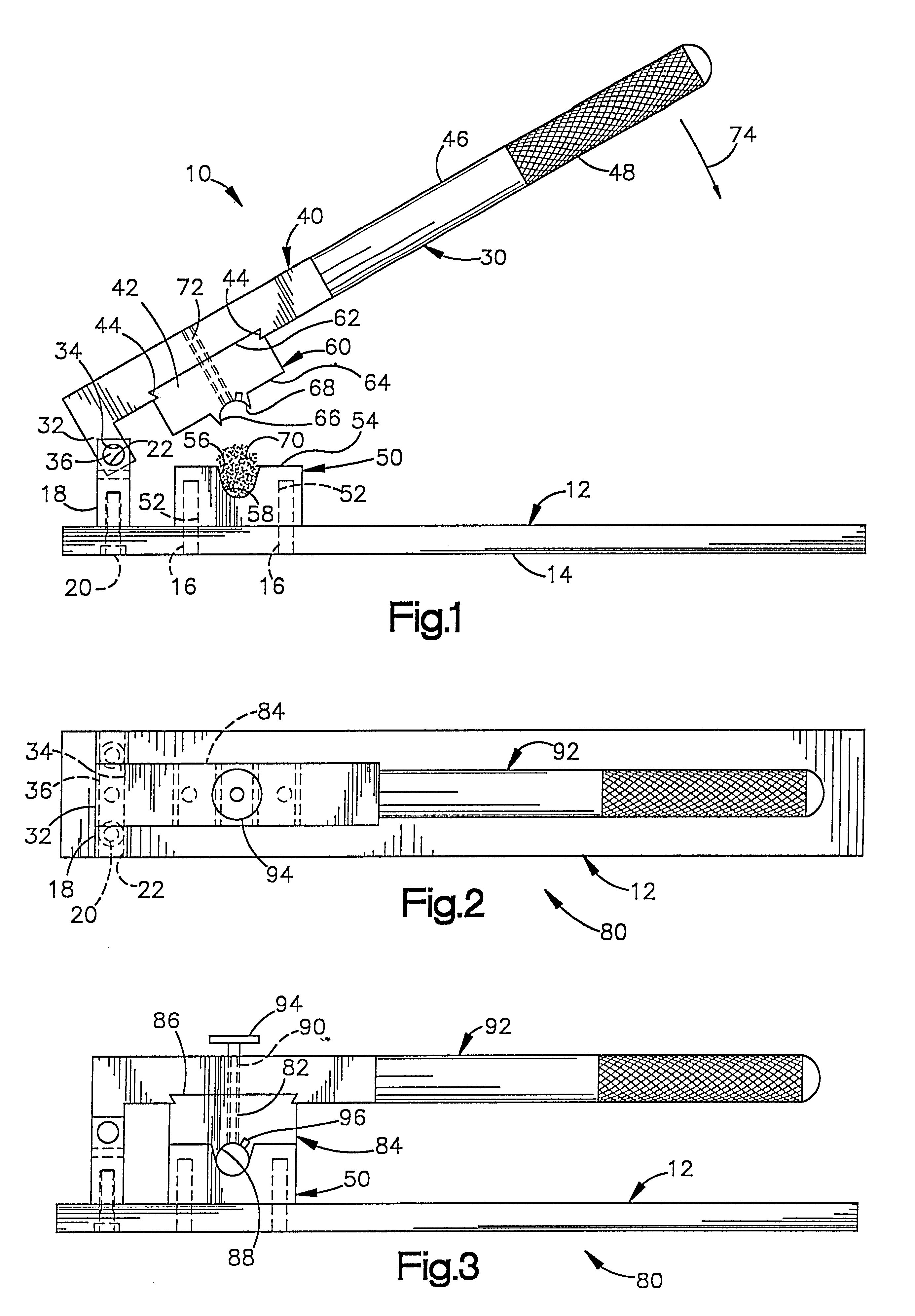
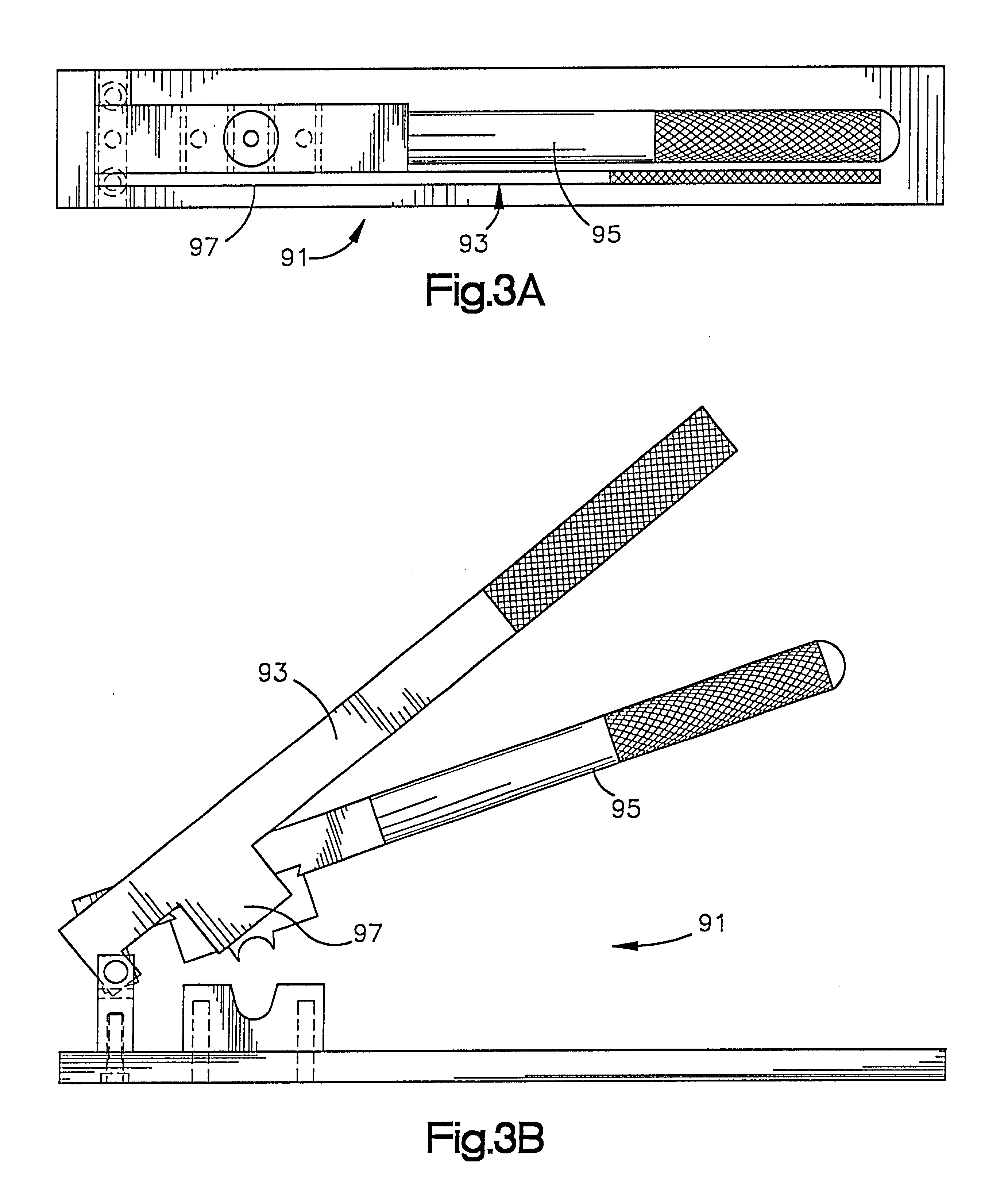
Hip replacement incision locator
ActiveUS7901411B2Precise alignmentAccurate locationIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsHip joint replacement operationSurgical incision
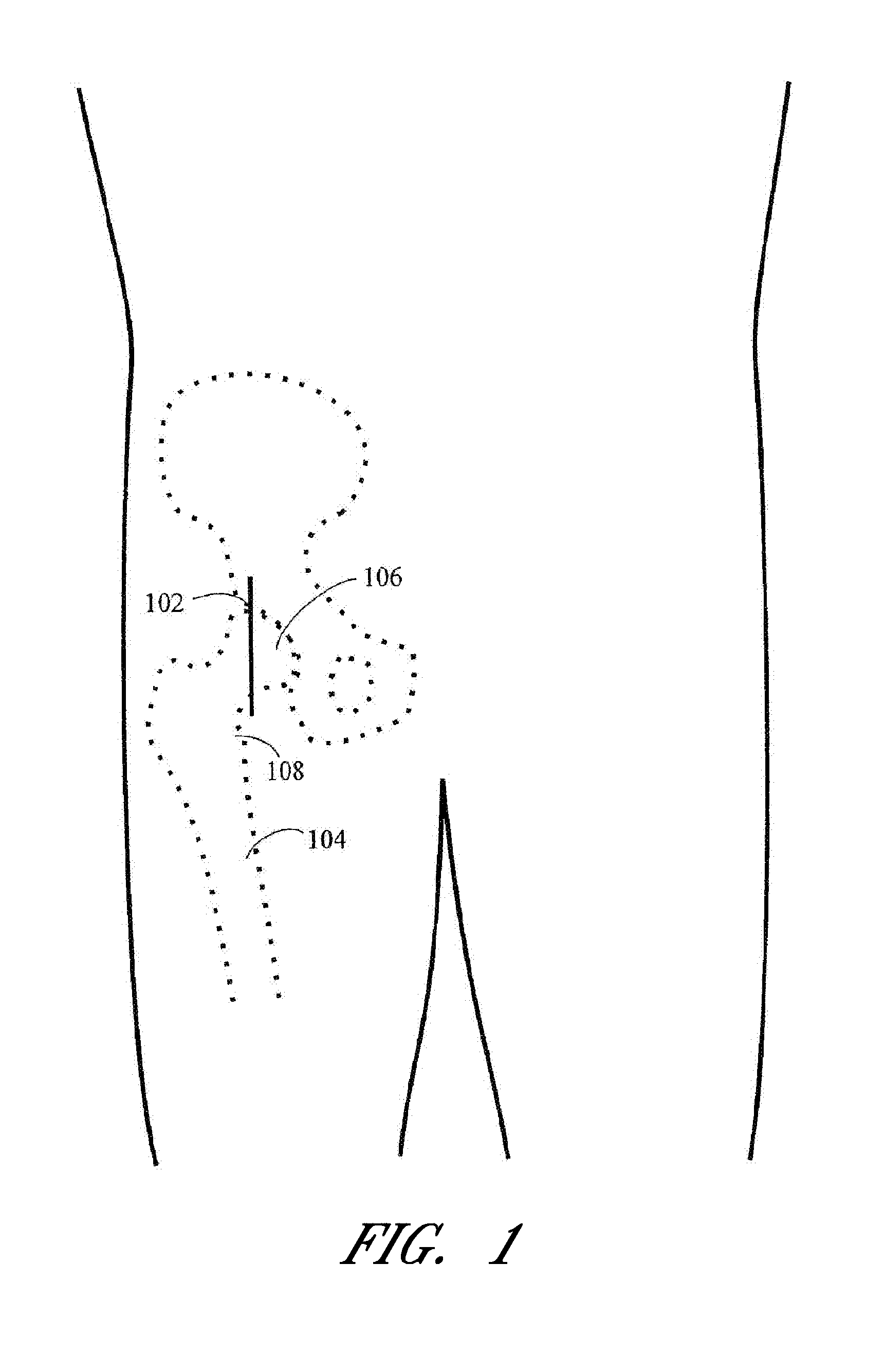
Methods and devices for performing hip replacement surgery are described. According to one embodiment, a method comprising providing an incision locator, the incision locator comprising at least one location indicator and at least one incision indicator, the location indicator configured to align with a central axis of the femur, and the incision indicator configured to guide a proper placement of a surgical incision when the location indicator is aligned, aligning the location indicator with at least one anatomical feature of the patient, making an incision in the proper location as guided by the incision indicator, and completing the surgical procedure is described.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Trialing system and method for modular hip joint replacement system
InactiveUS20070244566A1Easy to assembleAccurately approximatedJoint implantsFemoral headsModularityFemur
A system and method for trialing a modular hip replacement system (10) permits evaluation and replication of the anatomic anteversion rotational angle of the femur. A distal stem component (18) of the hip replacement system (10) includes a proximal portion (34) having a locator feature (35) that is externally accessible when the stem component is mounted within the femur. A proximal trial body assembly (60) is mounted on the proximal portion (34) of the distal stem component (18) to permit rotation of a trial neck component (62). The trial neck component (62) also includes a locator feature (126) that can be externally referenced to determine the anteversion angle.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Hip replacement navigation system and method
A hip joint navigation system is provided that includes a base having at least one channel disposed therethrough for receiving a pin for mounting the base to the pelvis. A mount feature is disposed on a top surface. A registration jig is configured to couple with the base and to engage anatomical landmarks. In some aspects, a patient specific jig system for hip replacement is provided including an engagement surface formed to closely mate to acetabular bone contours of a specific patient and a registration feature configured to be in a pre-determined orientation relative to an acetabulum the patient when the jig is coupled with acetabular bone contours of the specific patient. In other aspects, methods of using the systems are provided.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
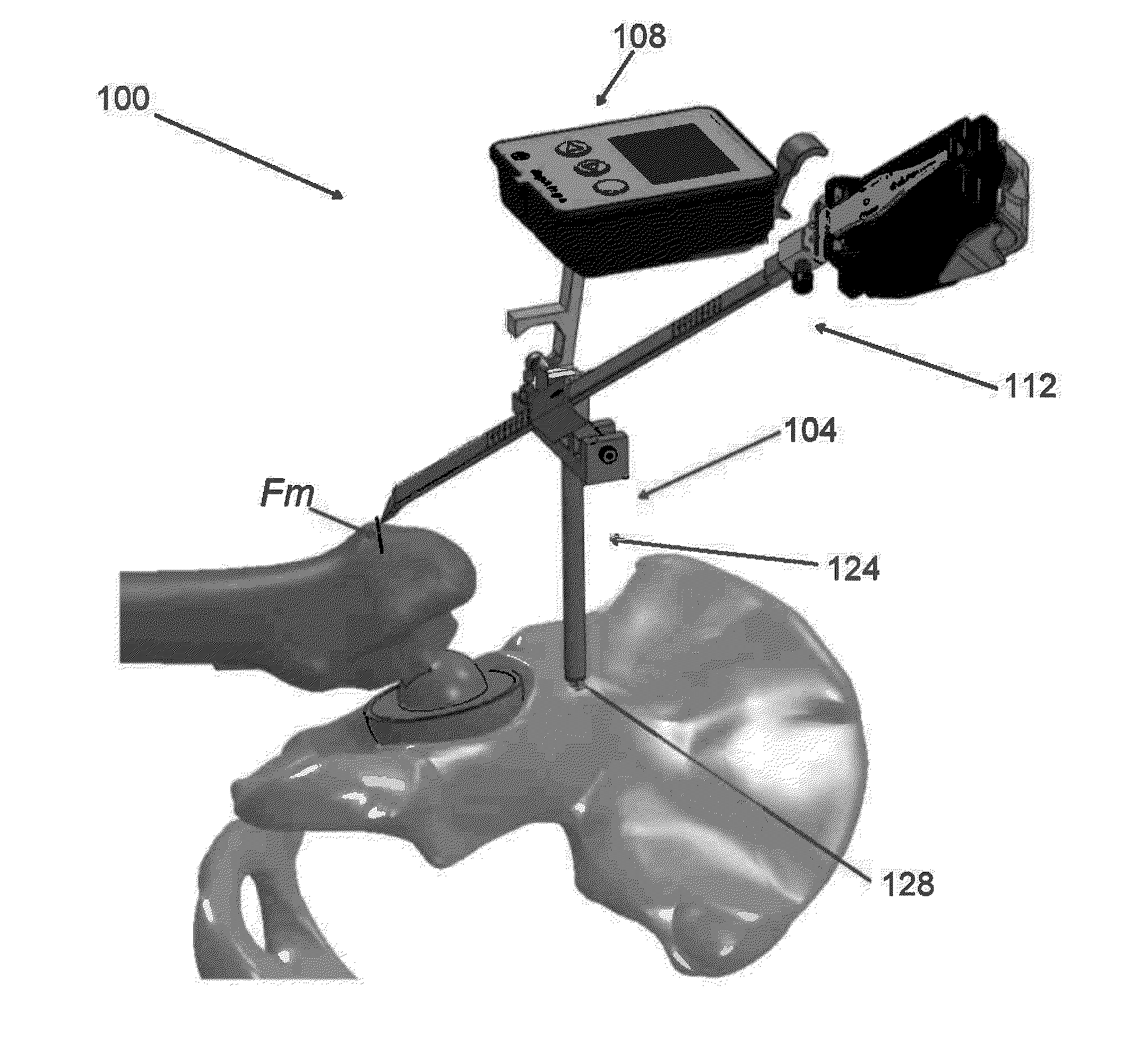
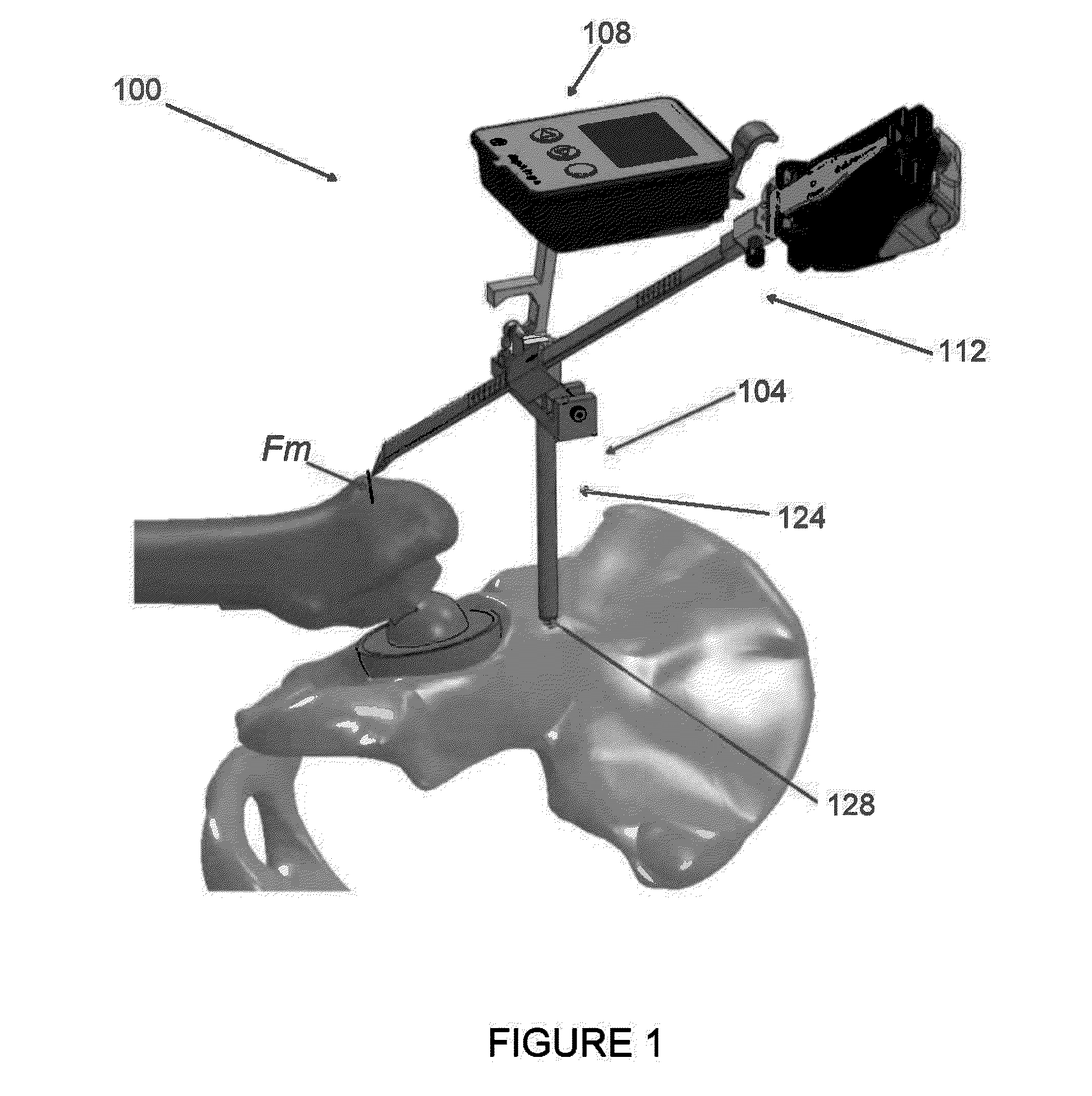
Precise femoral component positioning for hip replacement surgery
InactiveUS20130053904A1Precise alignmentPrecise positioningIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsHip joint replacement operationAcetabular component
A method for accurately positioning the acetabular cup in a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty (THA), comprising the steps of (a) placing the cup in roughly the correct position in the acetabulum using a acetabular component placement tool, (b) taking a first abduction reading and a first anteversion reading using a gyroscopic positioning unit aligned with the acetabular component placement tool, (c) taking an image of at least a portion of the cup using a radiography unit, (d) using the image to determine the actual orientation of the cup and required position of the cup to properly orient the acetabular component, (e) incrementally altering the position of the cup by using a striking tool, (f) taking new abduction and anteversion readings using the gyroscopic unit to determine the relative movement of the cup caused by the tapping, and (g) repeating any of the steps as necessary.
Owner:CRESCENT H TRUST
Modular resurfacing prosthetic
InactiveUS7621962B2Quantity minimizationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsAcetabular componentHip joint replacement operation
Femoral head modular resurfacing systems are described. The systems primarily include a head component and a stem component. The configuration of the head component and stem components allow for minimum invasiveness into the femur head region, thus conserving greater amounts of bone tissue than would be possible with conventional hip replacement systems. The systems also provide for various angles and offsets to be achieved between the systems and the femur head. The systems are useful in partial hip replacement procedures, as well as total hip replacement procedures, in which case an optional acetabular component would also be employed.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Metal bone supporter for necrosis of femoral head
InactiveUS20090287214A1Increase temperatureEasy to completeInternal osteosythesisBone implantBiomechanicsTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a metal bone supporter for medical bone substitute, which comprises a supporter and a connector component; every component of the metal bone supporter is functionally and structurally designed according to anatomical data and biomechanical data; the data of the supporter component is input to an electron beam melting fabrication device, and titanium alloy powders in the device is able be scanned, melted and molded through electron beams, to form a cylinder with the strength and elastic modulus similar to cancellous bones of human body; the supporter component is a porotic spongy body structure with threads on an end, and porous structure forms a rough surface; The connector component is made through mechanical treatment, with smooth surface and dense solid mass inside, and thread on an end, and is connected to the supporter component as a removable body. The invention has the porous structure for bone growing, high surface friction coefficient, stable structures and mechanical properties similar to bones, and is able to support the femoral head necrosis parts, slow down the necrosis speed and prolong or avoid the hip joint replacement. Thus, the invention is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:YU HAIYING
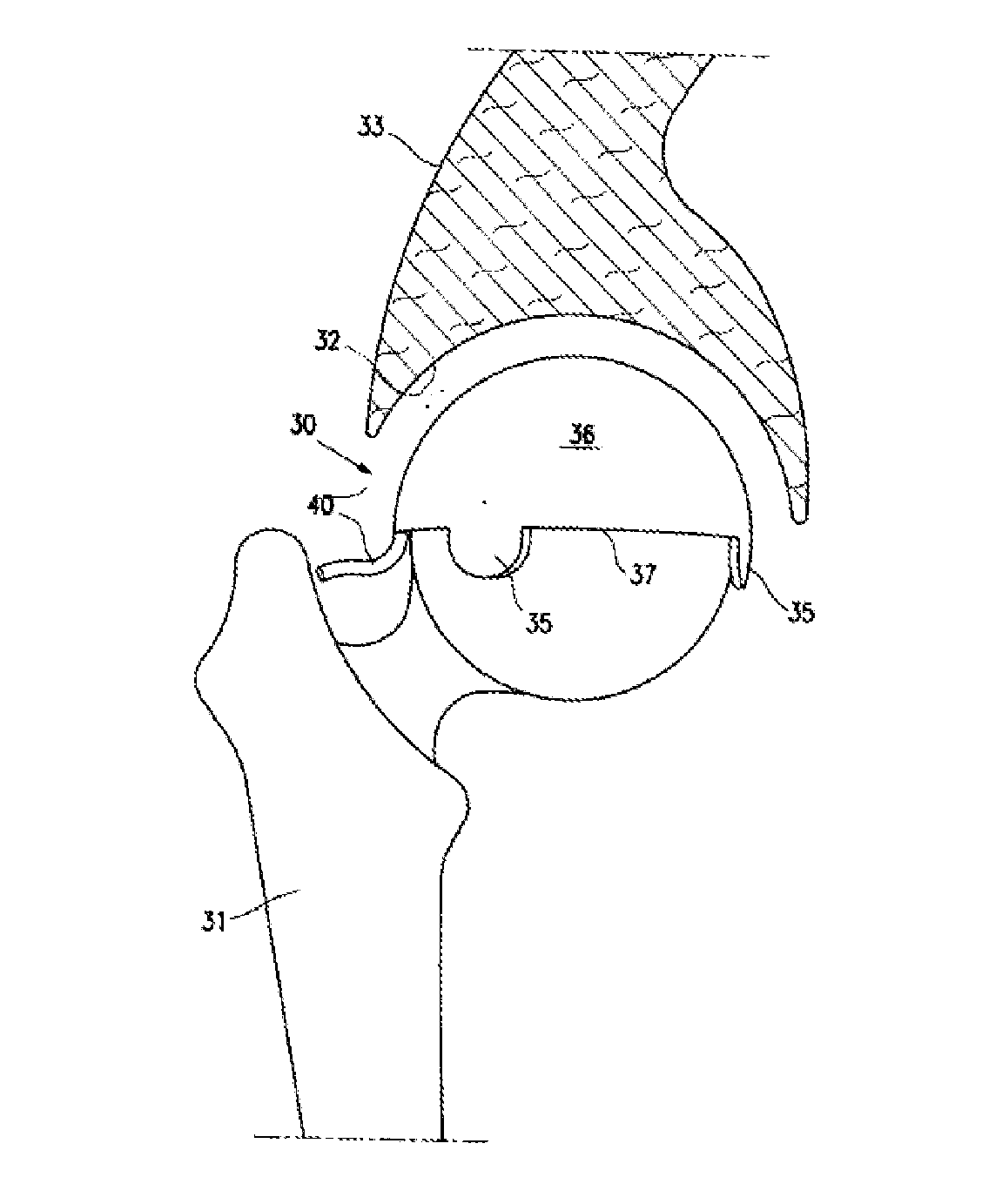
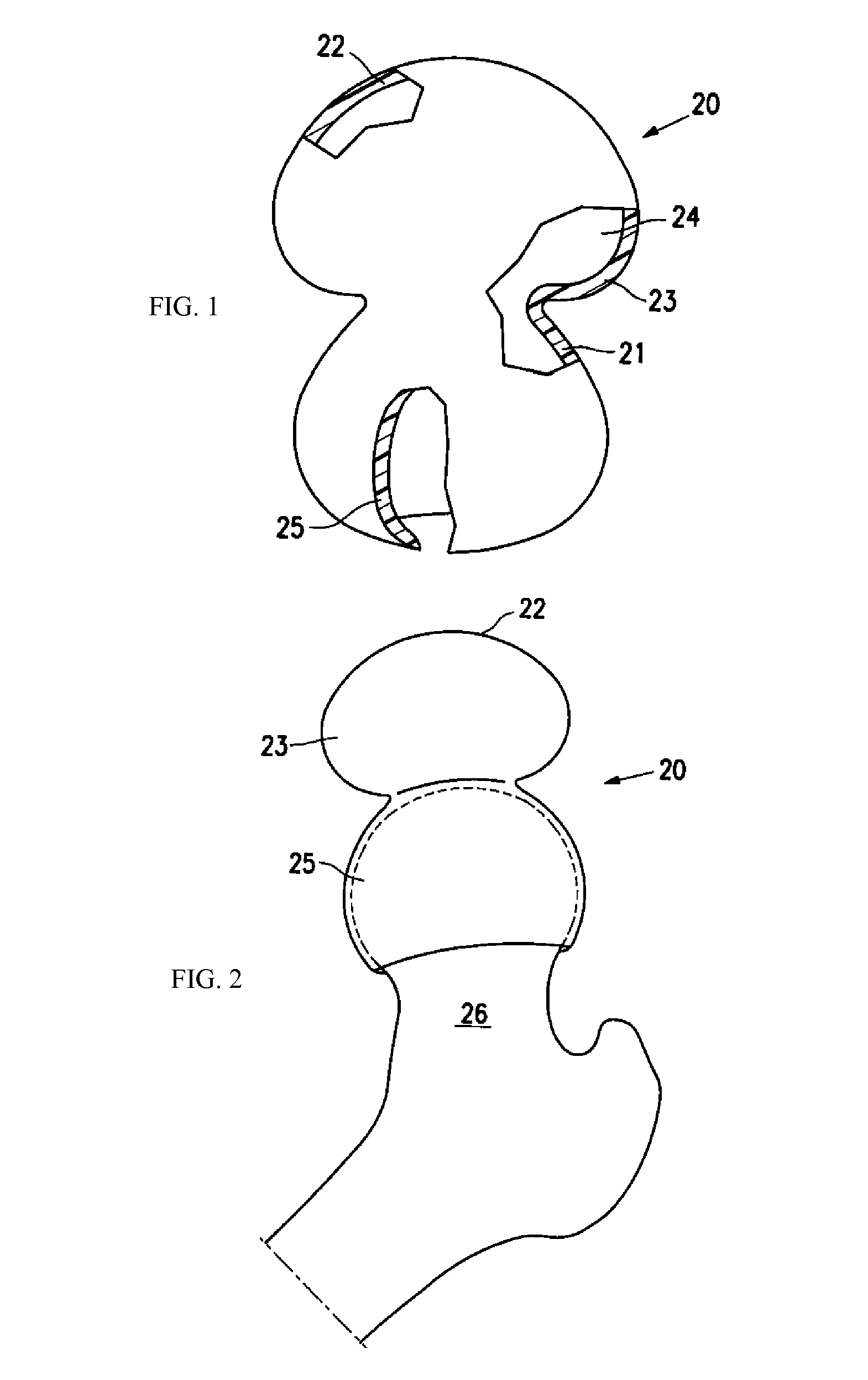
Snap-fitting, non-dislocating hip joint socket implant
InactiveUS6299647B1Improve proficiencyIncreased longevityJoint implantsFemoral headsAcetabular componentProsthesis
A hip joint socket implant for total hip replacement, can contain a modified surface configuration of its cement-fixable outer wall having small, widely dispersed cement spacer elevation members. The implant has a unique snap-fitted arrangement of the head-restraining marginal outlet of the acetabular component with posterior and anterior cut outs of the implant to avoid premature impingement against a prosthetic femoral neck, allowing a normal, non-dislocating range of unobstructed external and internal rotation of the hip, and a hood that is a marginally extended continuation of the superior one-half or so of the cup containment that is of a sufficient magnitude to reduce the overall dimension of the socket outlet to less than a hemisphere, which is especially pertinent to a conventional hip replacement acetabular cup prosthesis.
Owner:BIOPRO
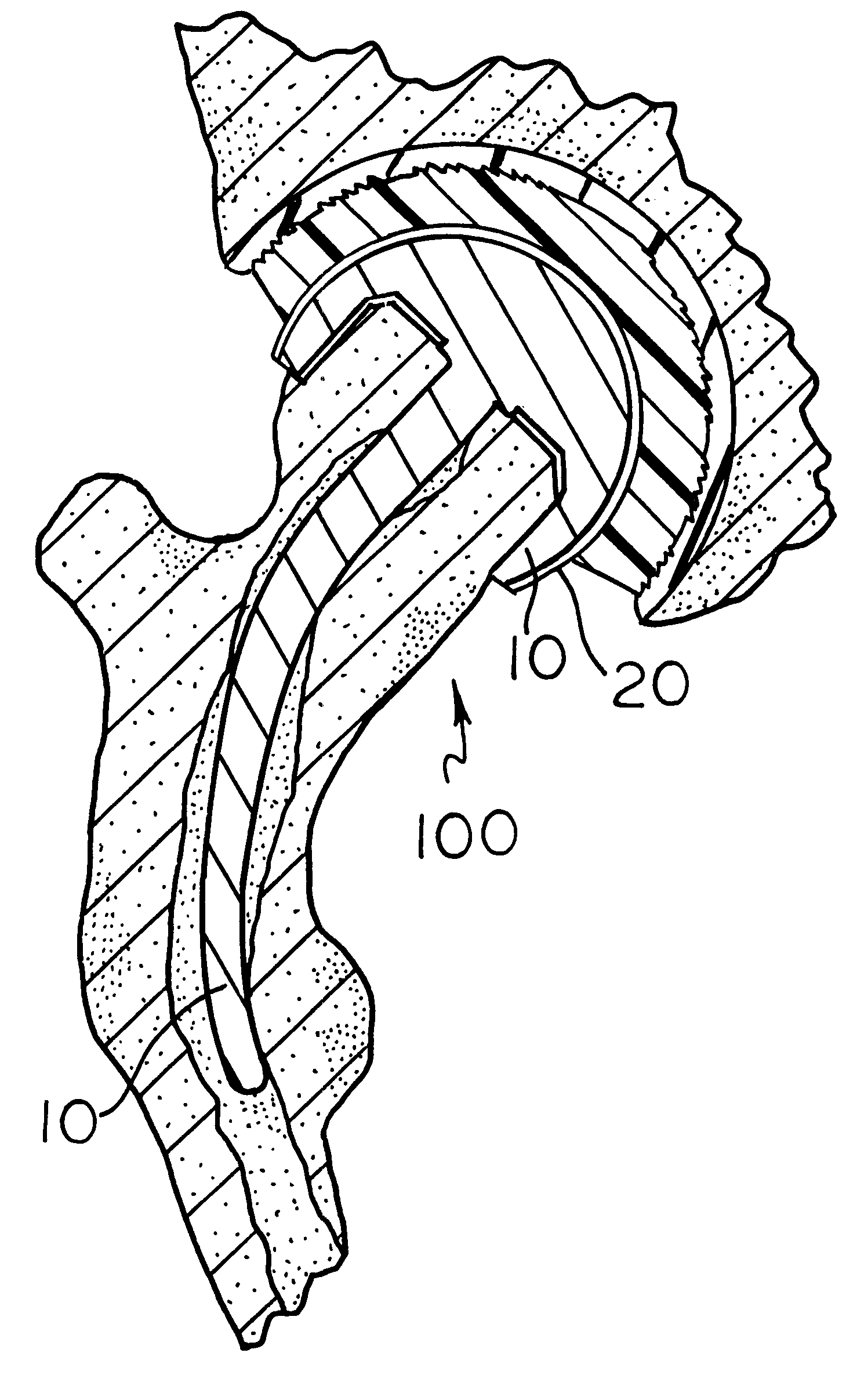
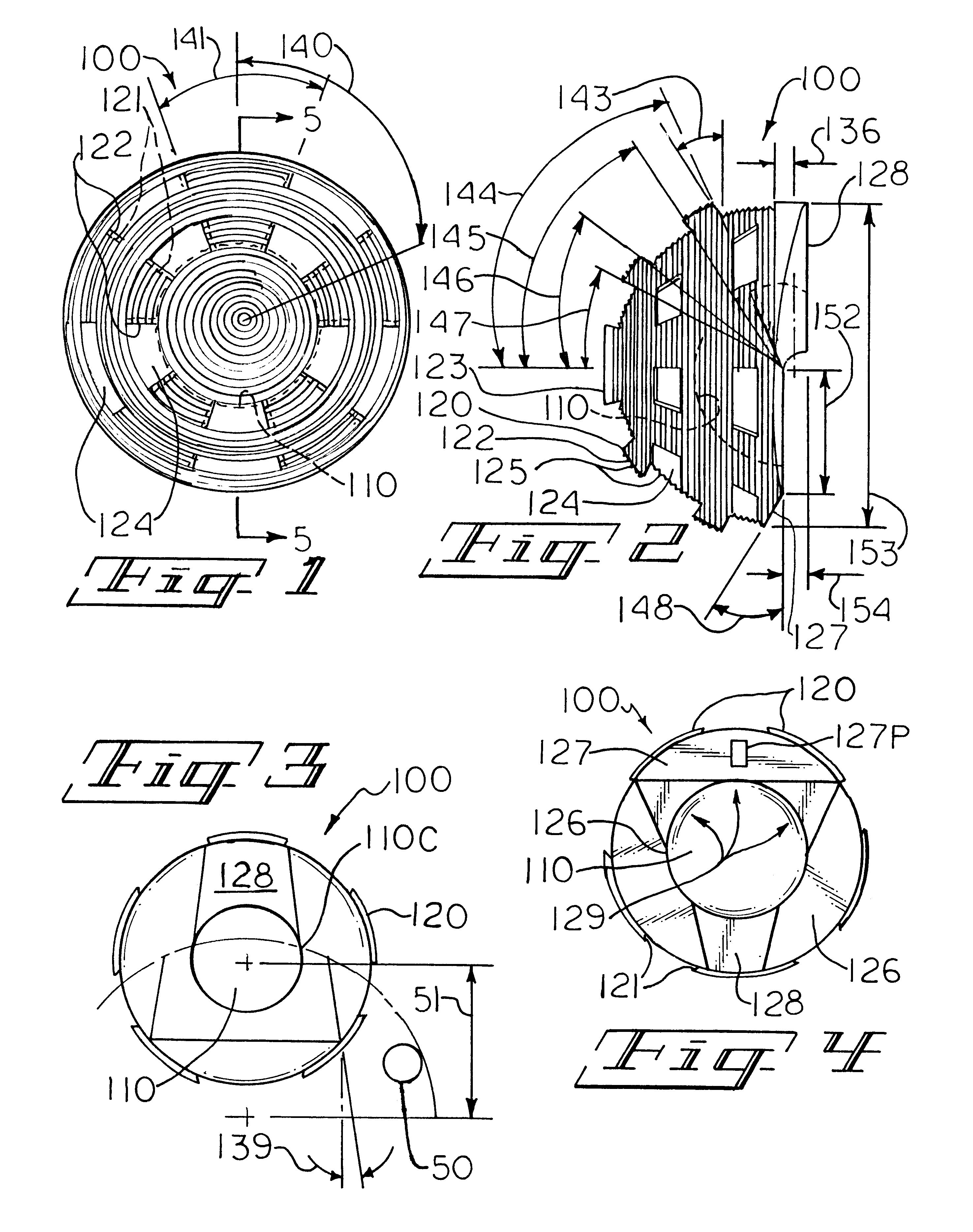
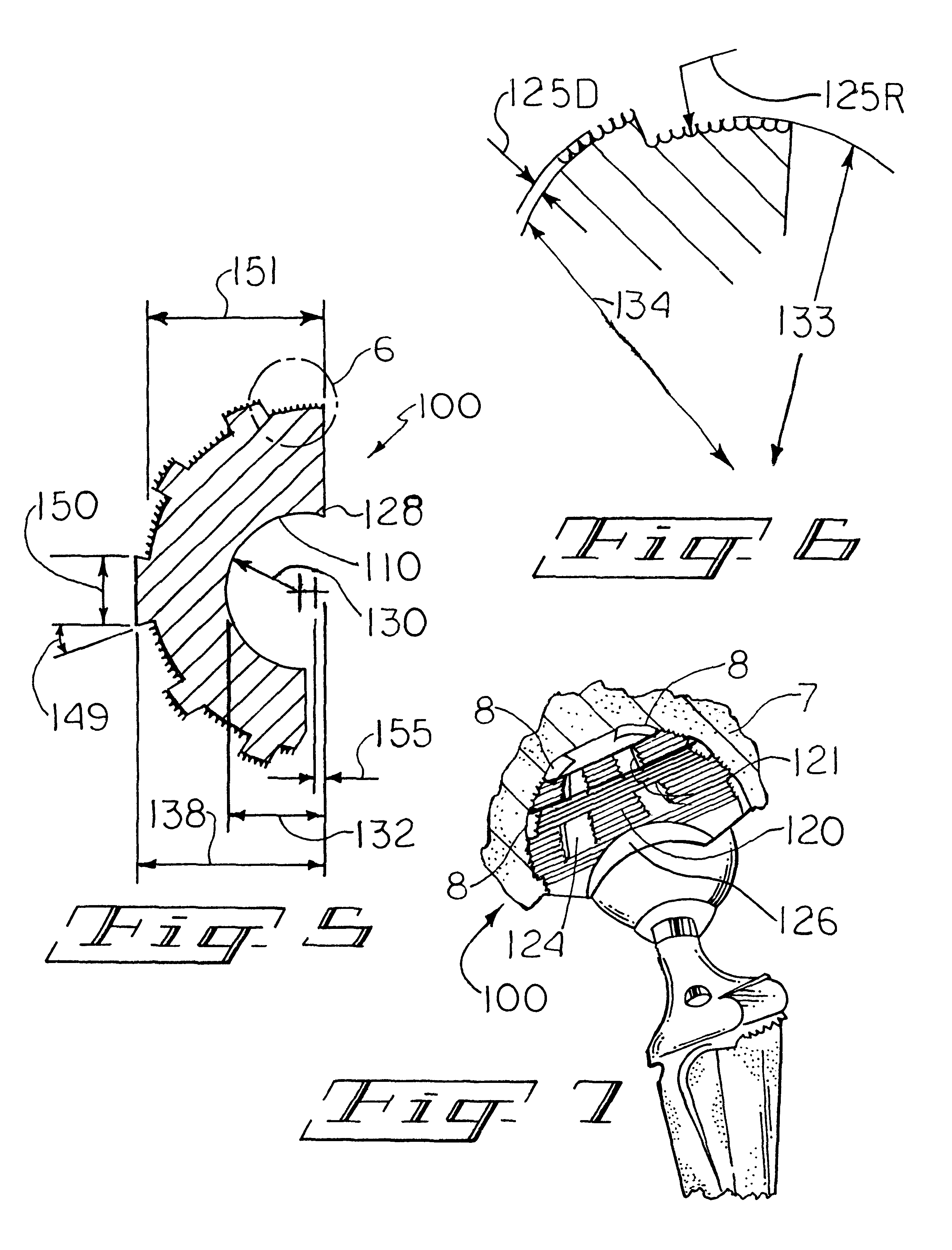
Femoral implant for hip arthroplasty
ActiveUS7060102B2Extended range of motionReduce morbidityJoint implantsFemoral headsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral bone
Owner:INST OF ORTHOPEDIC RES & EDUCATION
Prosthetic femoral joint
A prosthetic hip joint replacement system has a femoral component with a tapered trunion thereon. A modular head with a part-spherical outer surface terminating in a planar surface, engages the trunion. An acetabular cup member is provided for receiving the part-spherical head of a femoral implant, the cup member has a cavity having a part-spherical inner surface for receiving the modular head. The part-spherical inner surface of the cup defines a polar axis and an equator centered about a pole of the cavity. The cavity has a part-circular opening spaced from the pole a greater distance than the equator. Thus the inner part-spherical bearing surface extends beyond the 180° which the equator extends. The configuration of the part-spherical inner bearing surface causes a movement of translation of the head during rotation so that there is a crescent shaped retention area on each opposed side thereof. The opening has a non-circular or planar portion alignable with the planar head surface during insertion of the head in the cavity and a plane parallel to the non-circular portion through the center of the portion of the opening being offset from a parallel plane containing the polar axis of the cavity.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Hip replacement incision locator
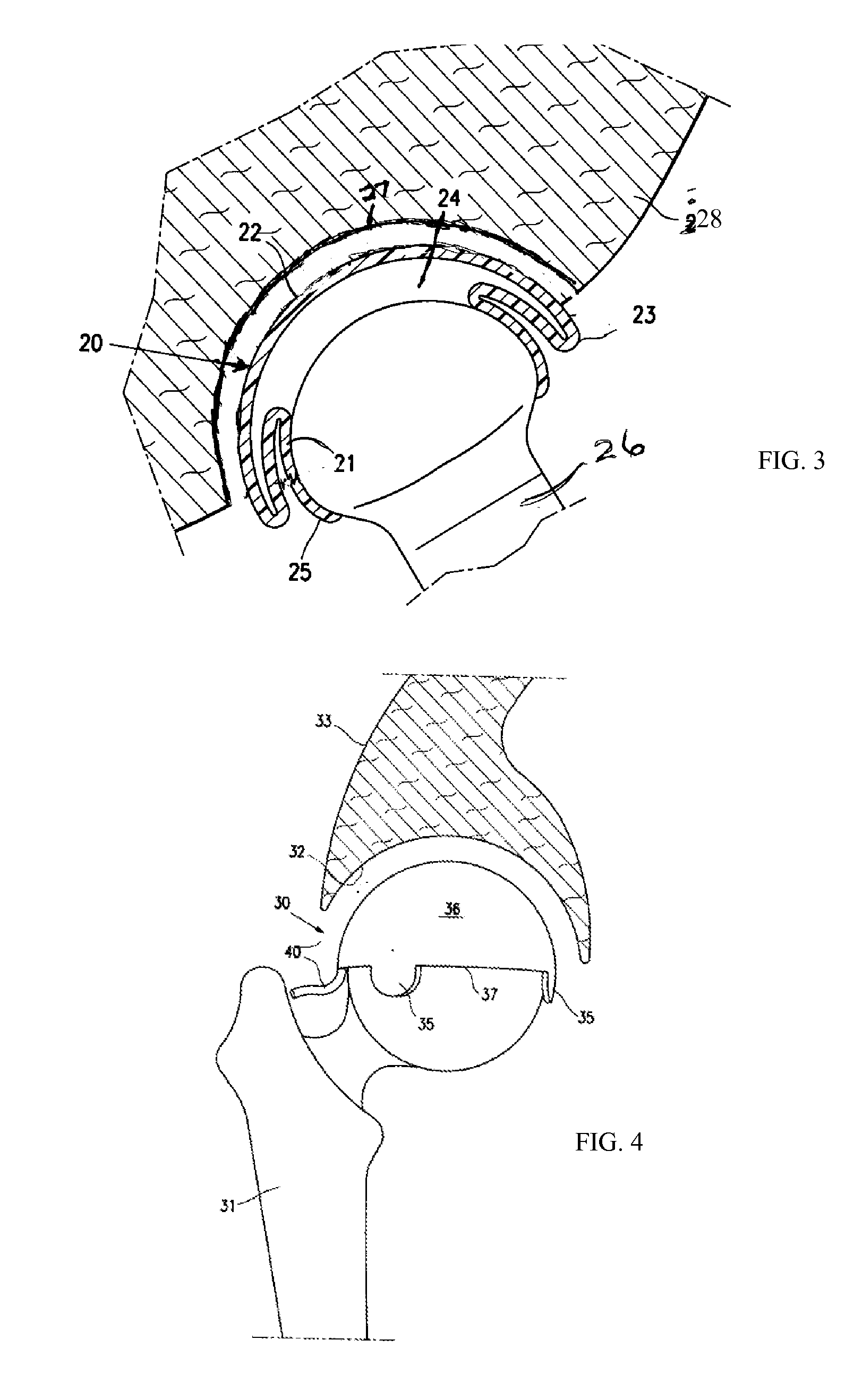
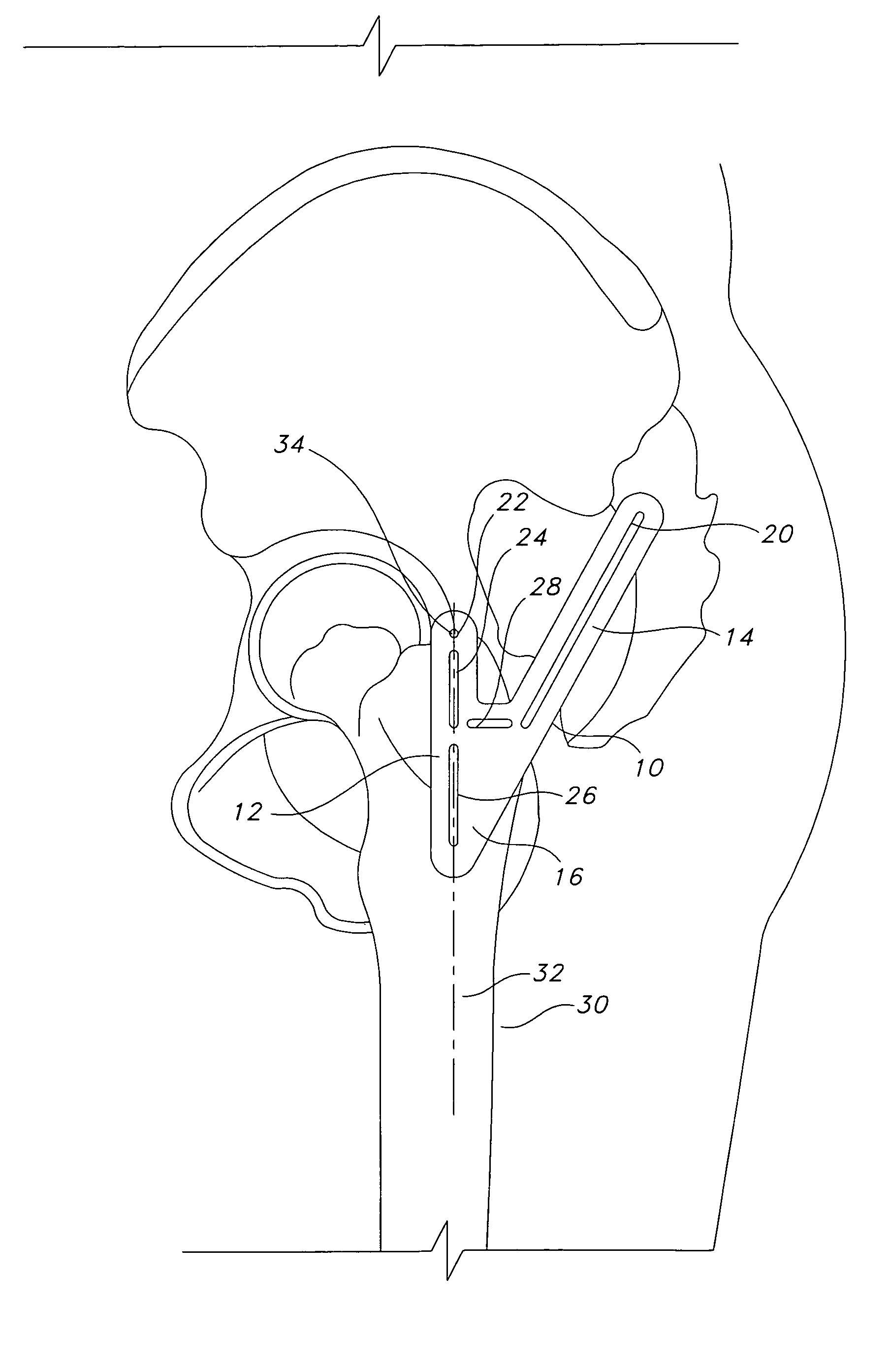
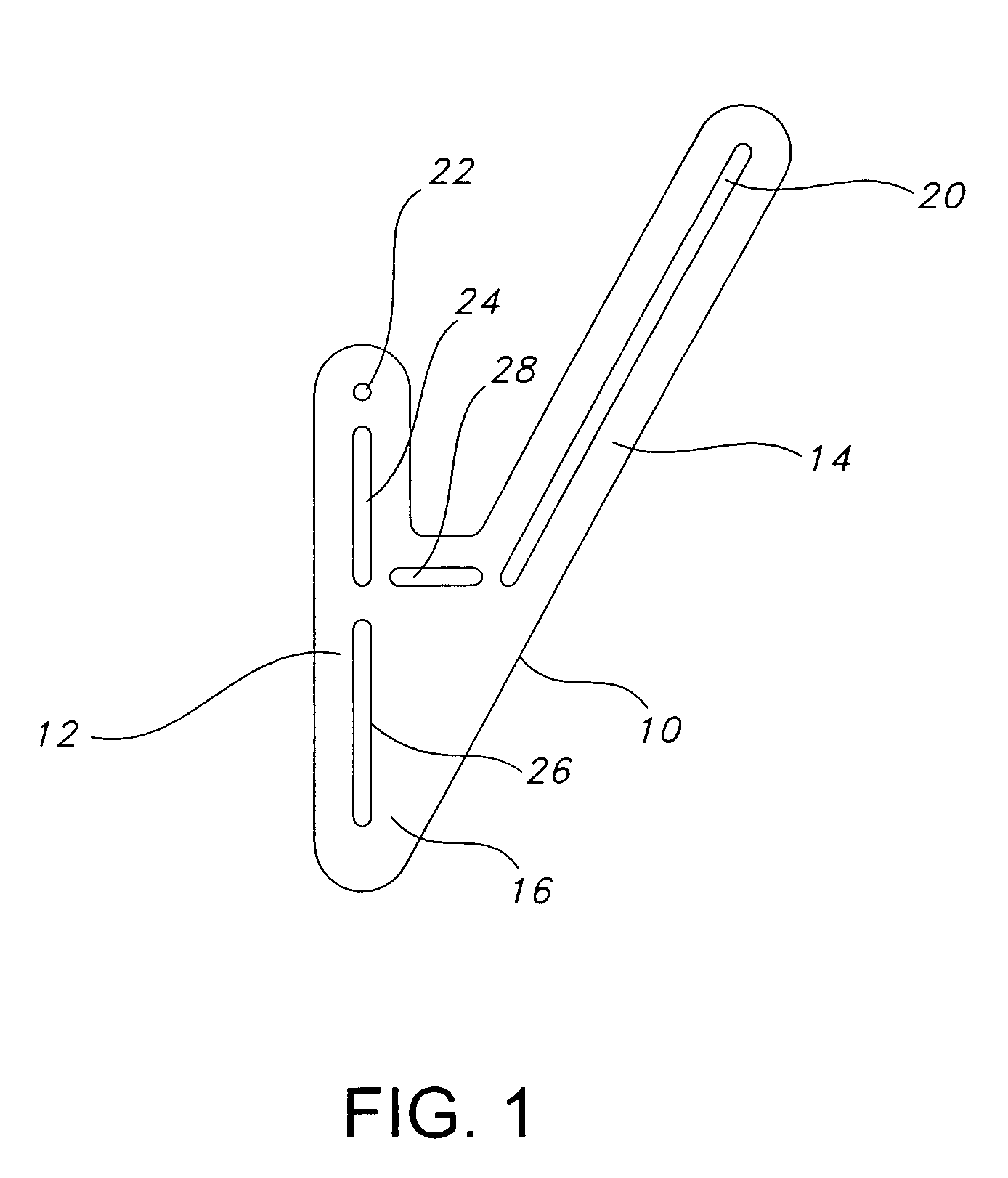
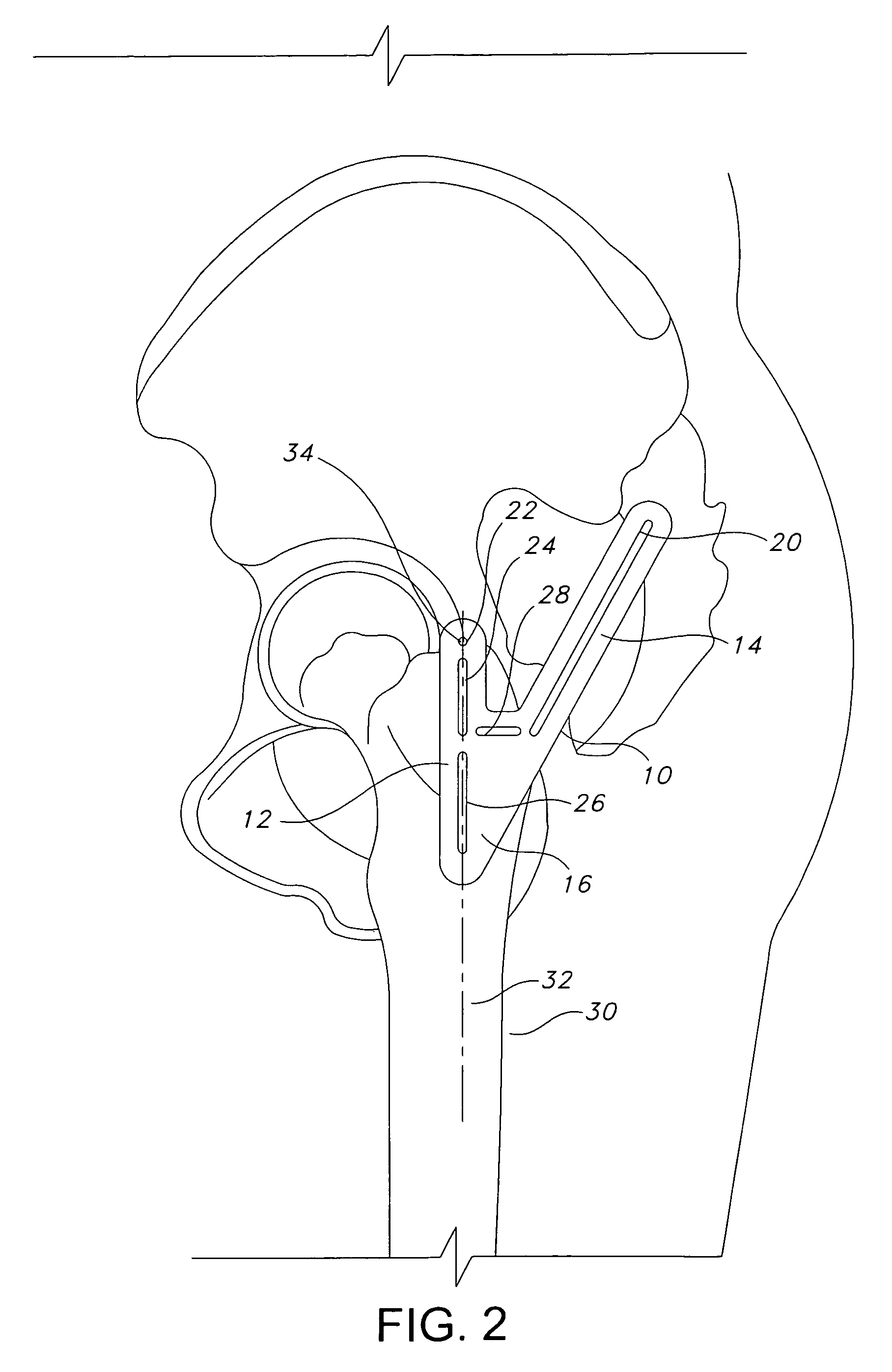
ActiveUS7160307B2Precise alignmentAccurate locationDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesHip joint replacement operationTrochanter
Methods and devices for performing hip replacement surgery are described. According to one embodiment, a method comprising providing an incision locator comprising a first wing and a second wing, the first wing adapted to be oriented generally along the femoral axis of a femur forming the hip on which the surgery is being conducted, positioning a proximal portion of the first wing adjacent to the greater trochanter, positioning other portions of first wing generally parallel to the femoral axis, indicating a proper placement of an incision based at least in part on the position of the second wing of the incision locator, performing an incision using at least one incision guide in at least one of the first and second wings, and completing the surgical procedure is described.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com