Patents
Literature
129 results about "Total hip replacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
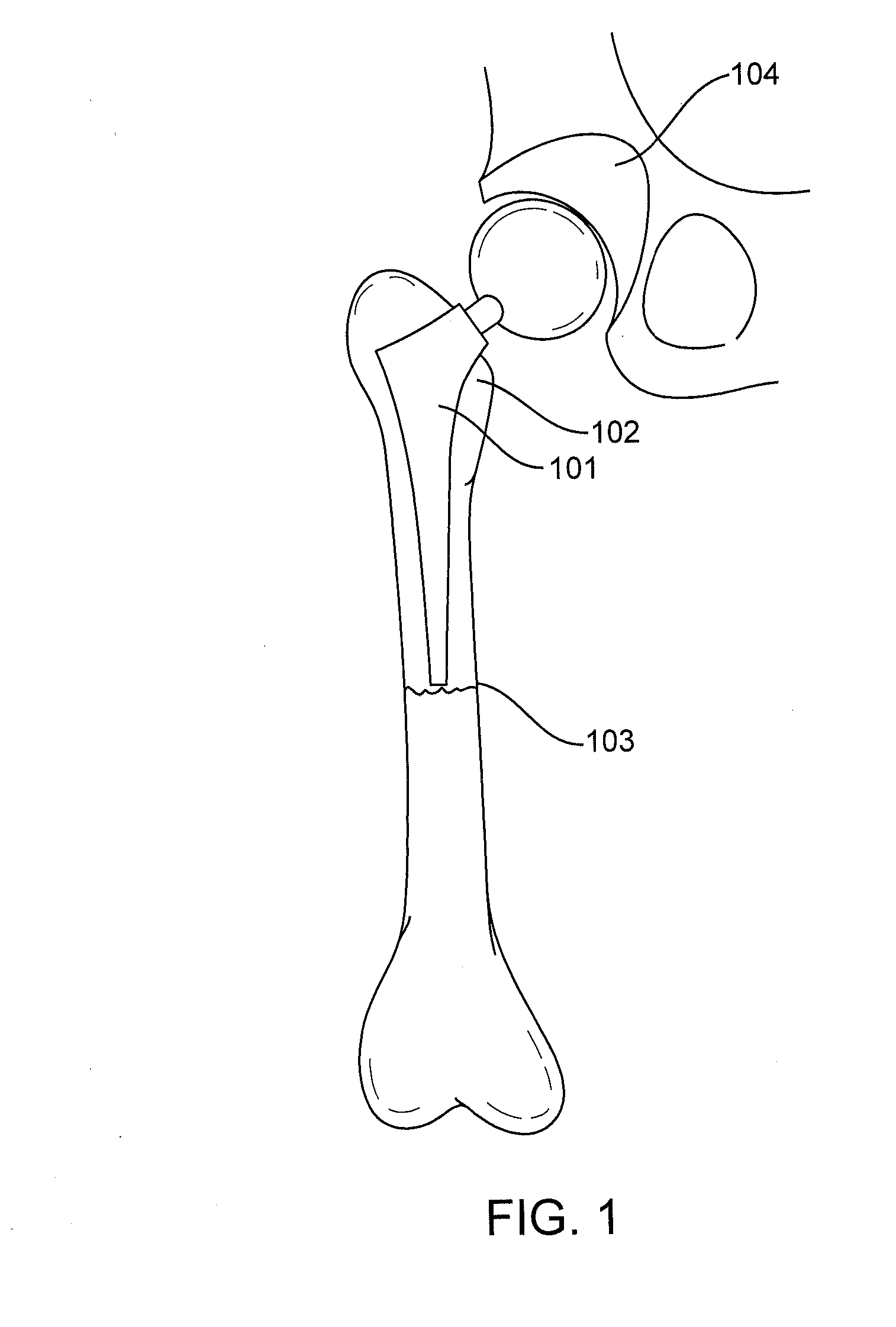
Total hip replacement (THR) is surgery to replace your hip joint damaged by wear, injury, or osteoarthritis. It is also called total hip arthroplasty. The hip joint is where the top of your femur (thigh bone) sits in the socket of your pelvic bone.
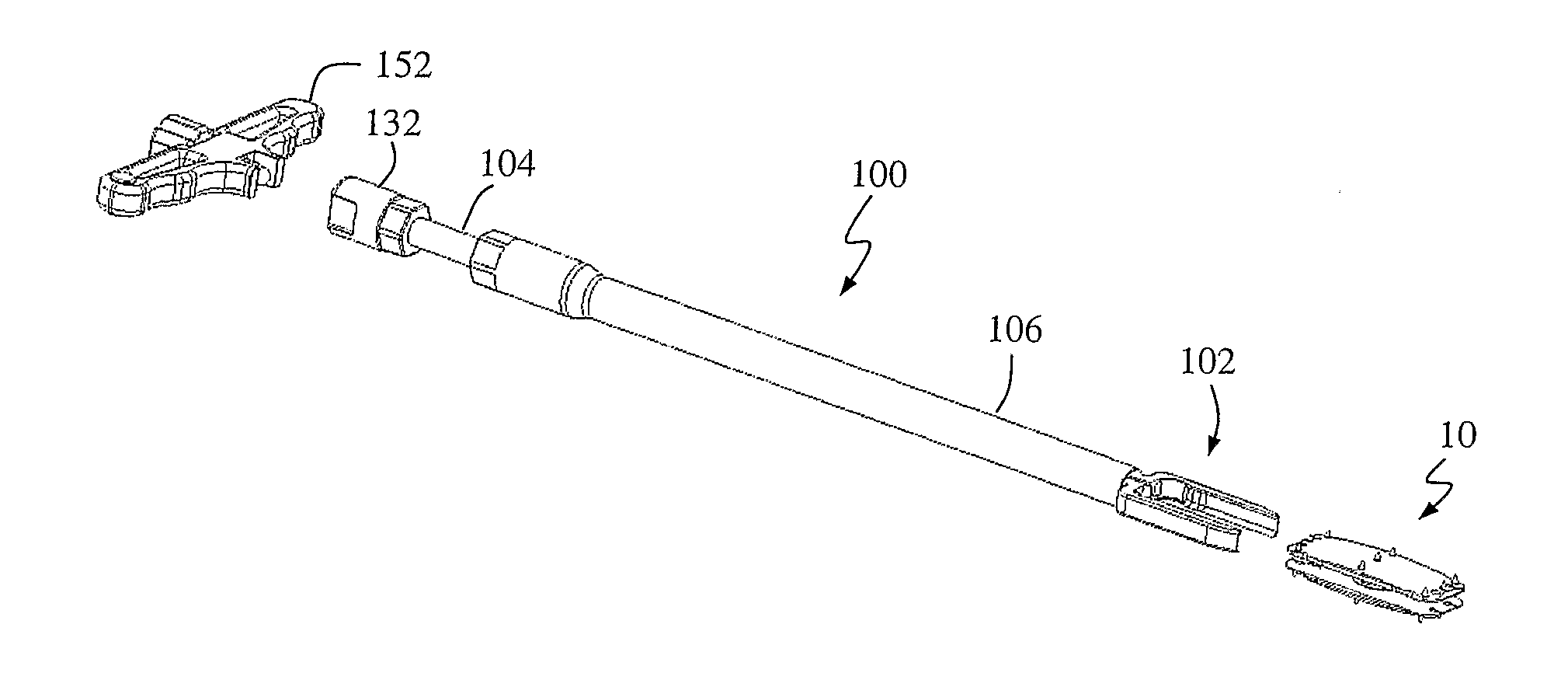
Device and method for achieving accurate positioning of acetabular cup during total hip replacement
InactiveUS20100274253A1DiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingMedical imaging dataHip resurfacing
A method and device are provided in order to achieve optimal or desired orientation of an acetabular cup for total hip replacement or hip resurfacing. The method and device utilize preoperative medical imaging such as CT or MRI scans, 3D computer modeling and a patient-specific alignment jig created from medical imaging data such as CT or MRI data and computer 3D modeling. The device allows accurate placement of a drill hole to establish an acetabular axis, and placement of an acetabular cup perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:URE KEITH J
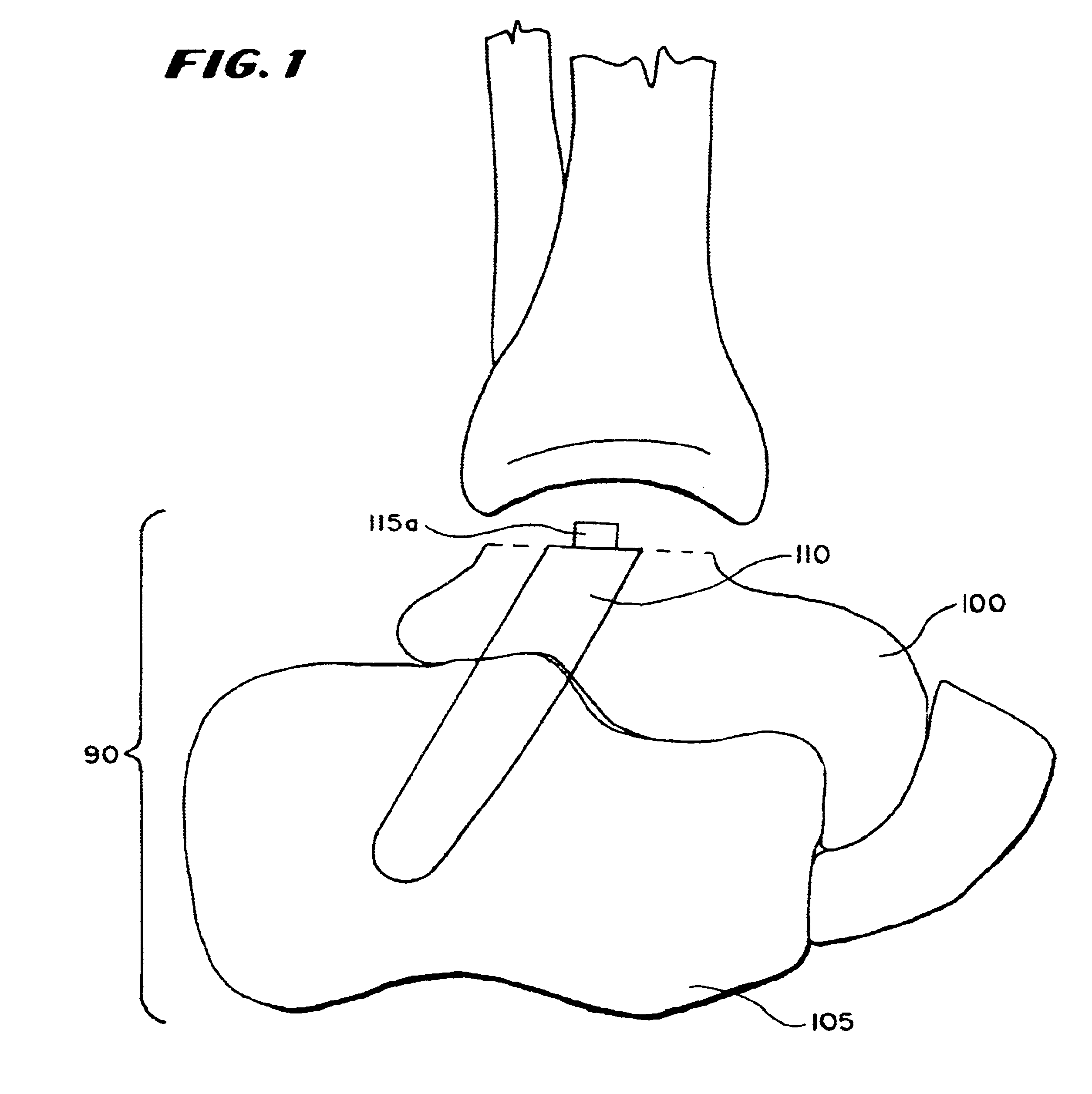
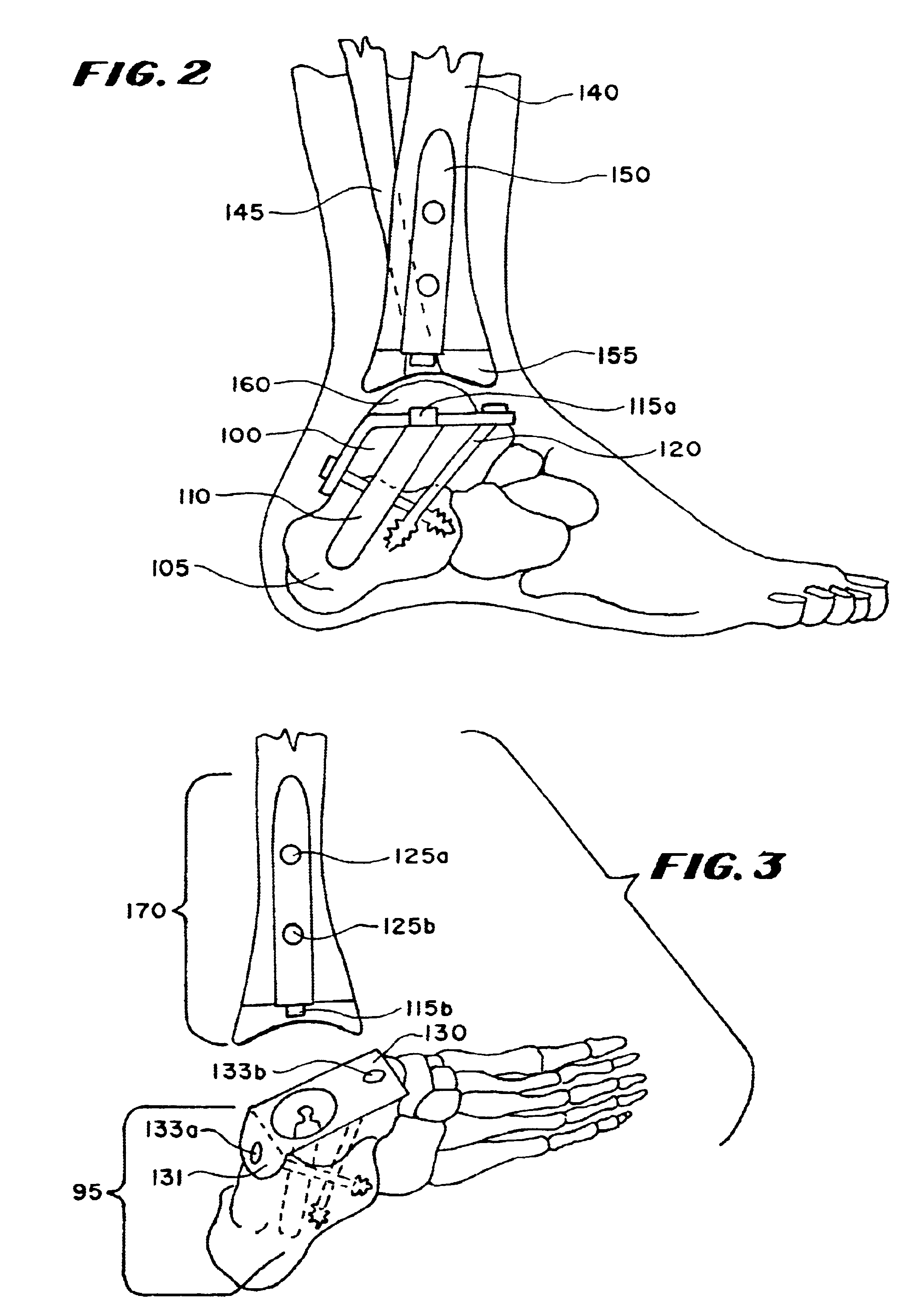
Ankle replacement system
A total ankle replacement system, novel surgical method for total ankle replacement, and novel surgical tools for performing the surgical method are described. The total ankle replacement system includes the calcaneus in fixation of a lower prosthesis body, thereby significantly increasing the amount of bone available for fixation of the lower prosthesis body and allowing the lower prosthesis body to be anchored with screws. The total ankle replacement system further includes a long tibial stem which can also be anchored into the tibia with, for example, screws, nails, anchors, or some other means of attachment. The novel surgical arthroscopic method allows introduction of ankle prostheses into the ankle joint through an exposure in the tibial tubercle. Various novel surgical instruments, such as a telescoping articulating reamer and a talo-calcaneal jig, which facilitate the novel surgical method, are also described.
Owner:INBONE TECH
Methods and apparatus for total disc replacements with oblique keels
Artificial disc replacement (ADR) systems with intradiscal components feature non anterior-posterior (A-P) or oblique-oriented keels such that the great vessels do not require as much retraction during insertion. The system may further include guides for aligning the ADR prior to insertion, and for cutting an oblique slot into a vertebral endplate to receive the keel. A screw adapted to penetrate a vertebral body may be used in conjunction with the keel. The screw and keel may converge, diverge or intersect. The screw may further include a mechanism providing a locking relationship with the keel. The system may further including a guide to direct drill bits and screws through holes in the keel. ADRs according to the invention may additionally, independently include a non-symmetrical endplate shaped so as to decrease the risk of injuring the great vessels. By virtue of the invention, a second ADR may be installed at a second level having a keel oriented differently from that of the ADR having an orientation other than anterior-to-posterior.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Total disc replacement system and related methods
ActiveUS20100286784A1Easy to insertQuick and direct and accurate placementJoint implantsSpinal implantsSurgical approachRadiology
Total disc replacement systems and related methods involving a lateral, trans-psoas surgical approach to the spine while performing at least one of continuous and intermittent intra-operative neural monitoring of the psoas muscle to avoid injury during introduction.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Total disc replacement system and related methods
ActiveUS7485146B1Convenient introductionInhibition of translationSpinal implantsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A total disc replacement (TDR) system for use in the spine and related methods, involving a first anchor plate having a first surface for engaging a first vertebra and a second surface including a semi-cylindrical surface, a second anchor plate having a first surface for engaging a second vertebra and a second surface including a semi-cylindrical surface, a pair of intradiscal liners, each having a first semi-cylindrical surface for engaging with said anchor plates and a second semi-cylindrical surface for engaging with an intradiscal element, and an intradiscal element including a first articular surface having a generally arcuate cross-section for articulating with said first intradiscal liner, and a second articular surface having a generally arcuate cross-section for articulating with said second intradiscal liner.
Owner:NUVASIVE
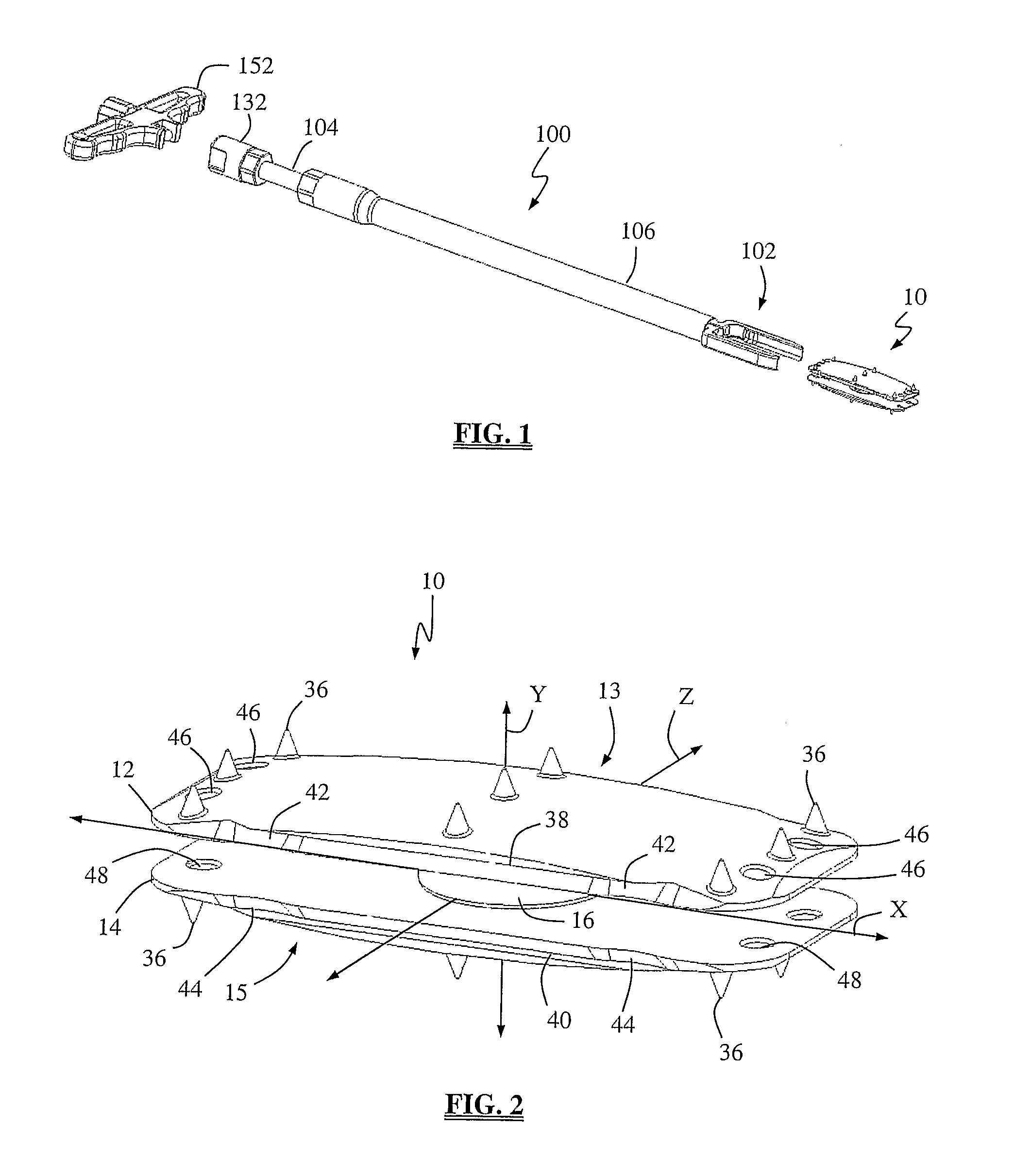
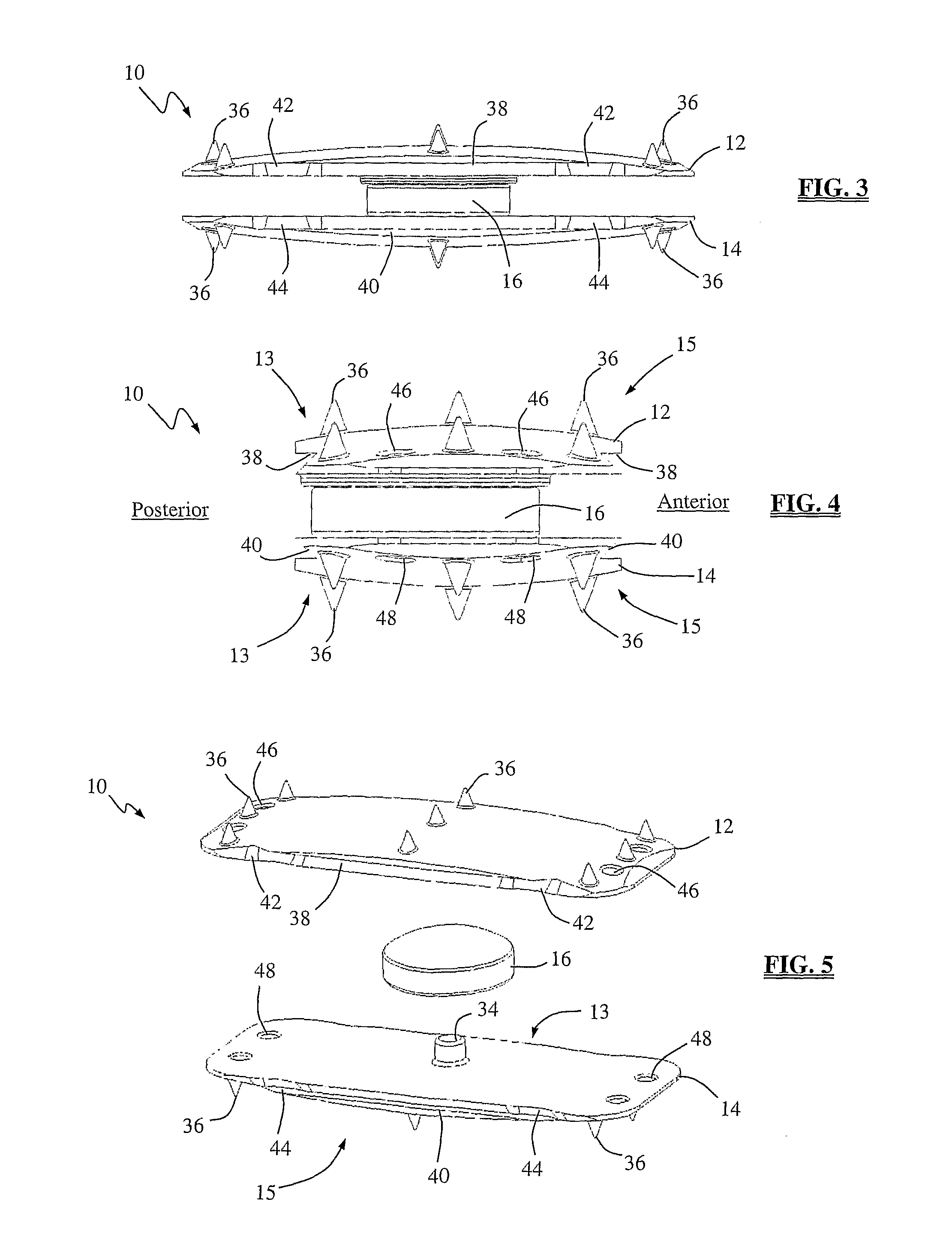
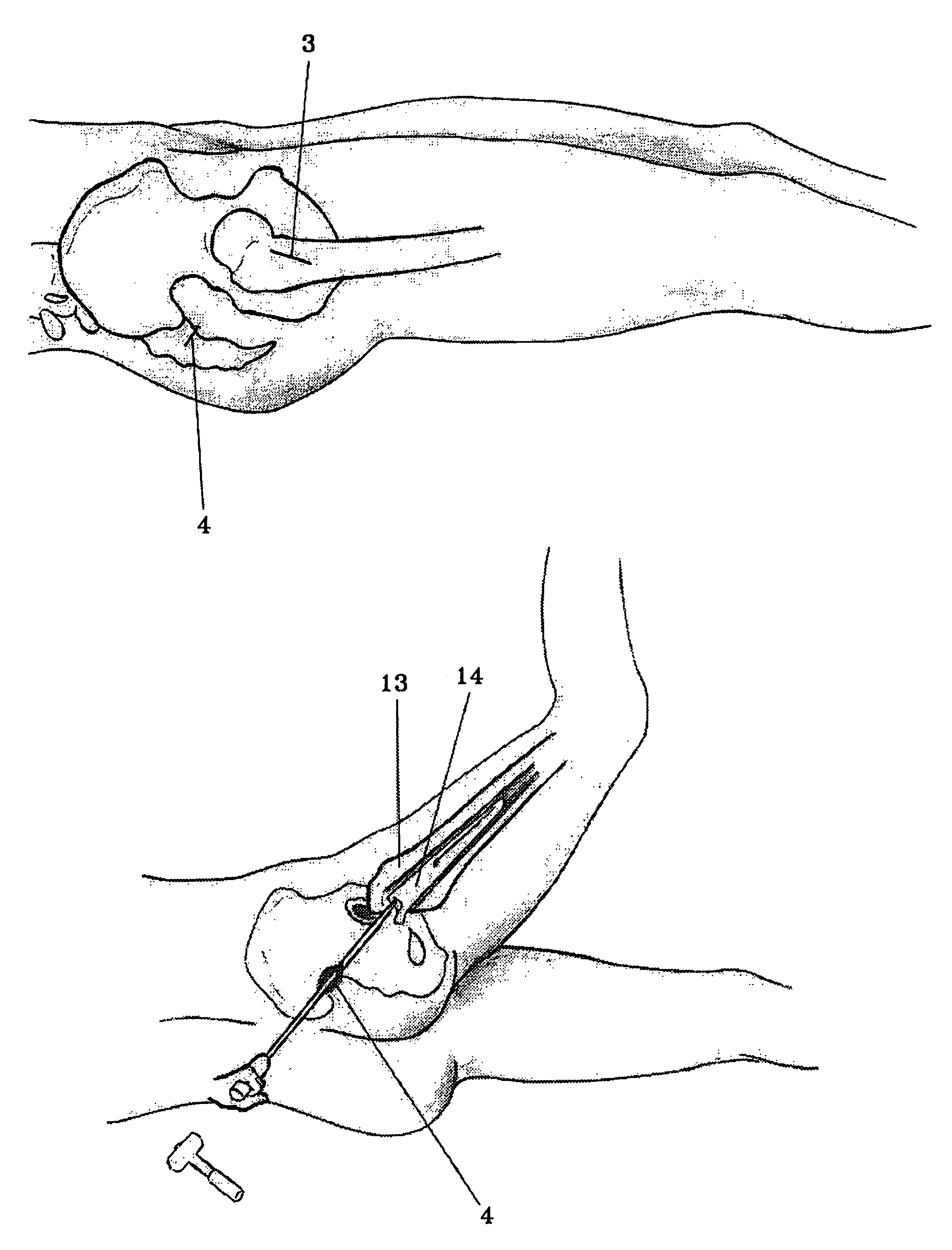
Constrained acetabular insert for total hip arthroplasty
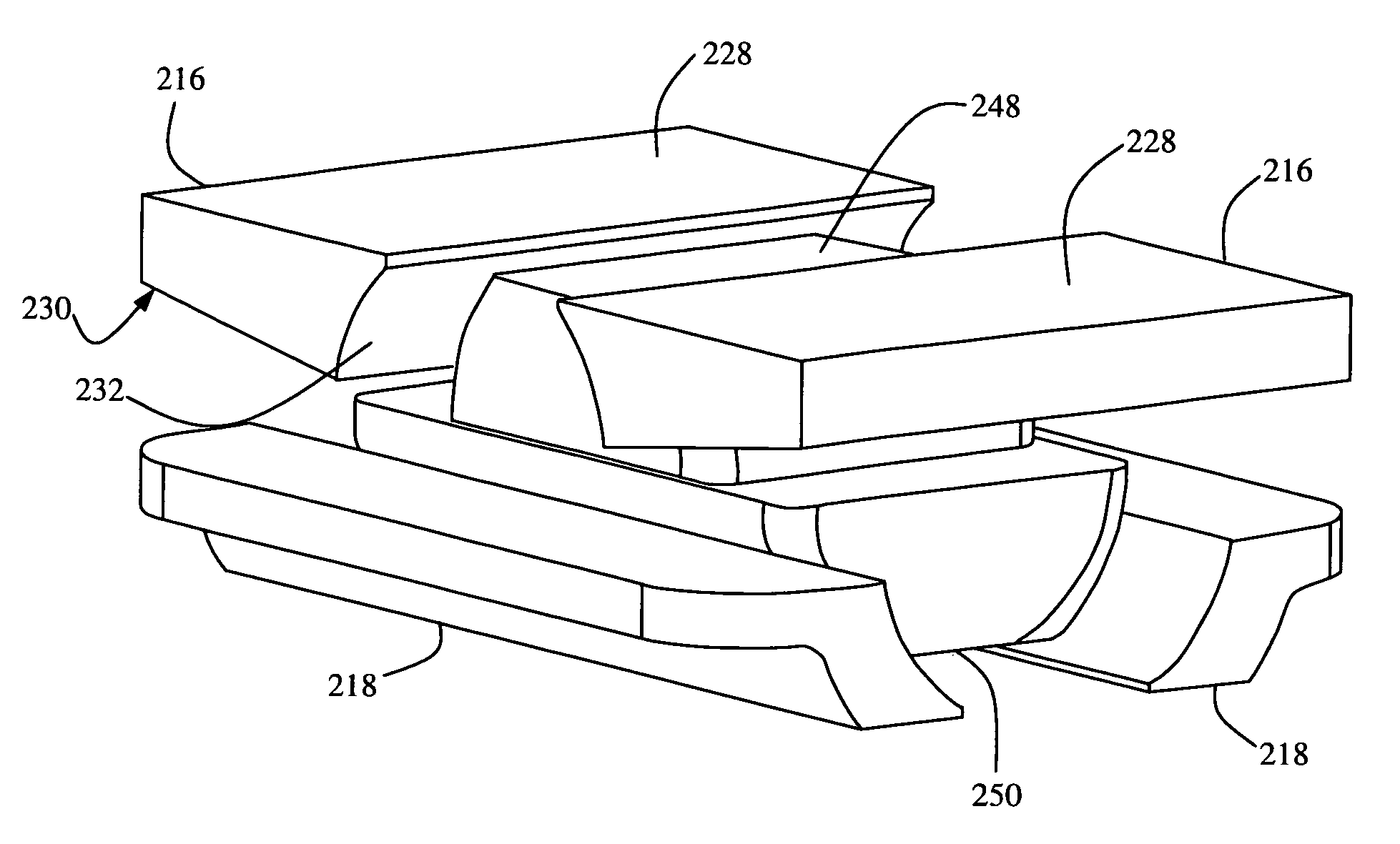
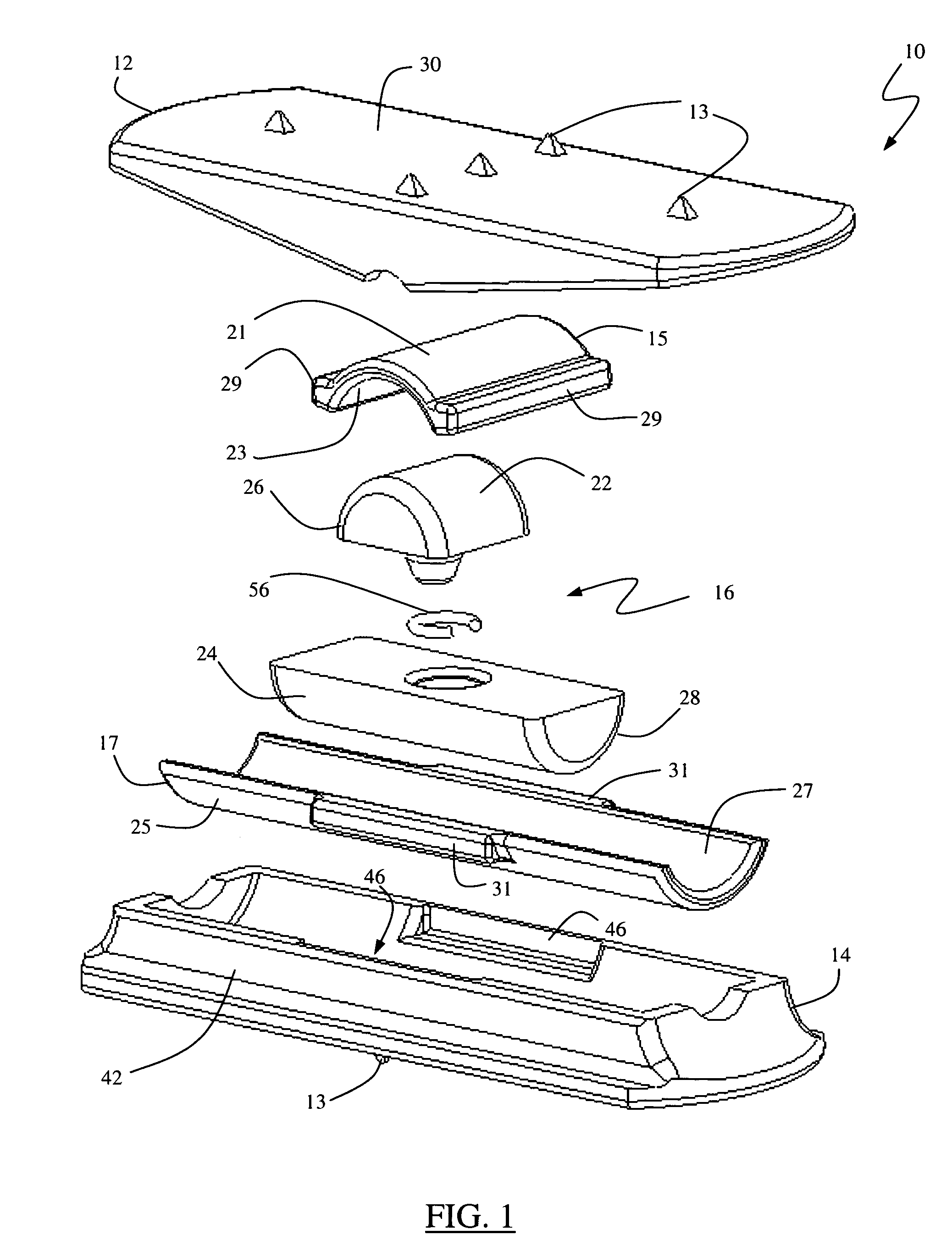
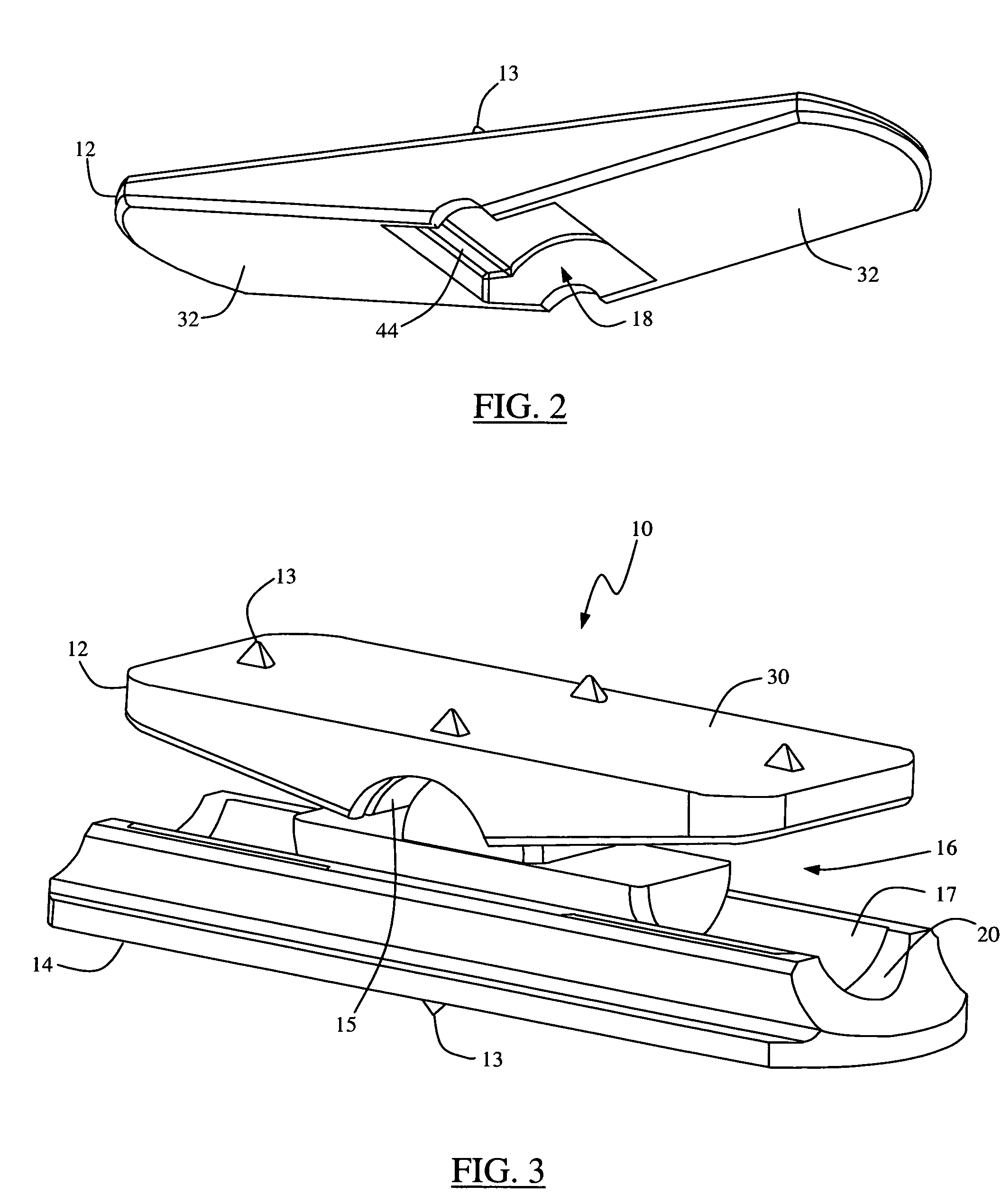
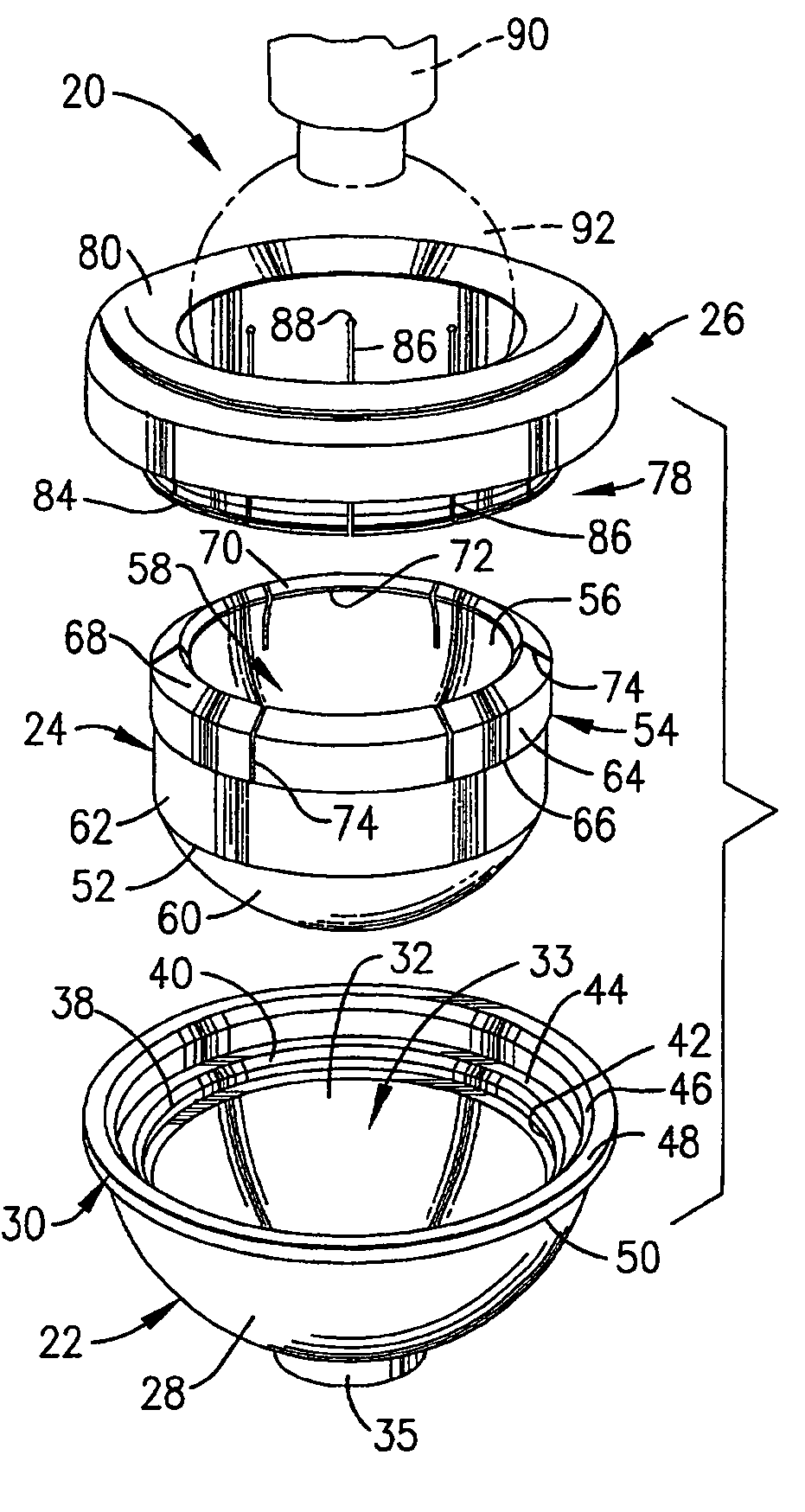
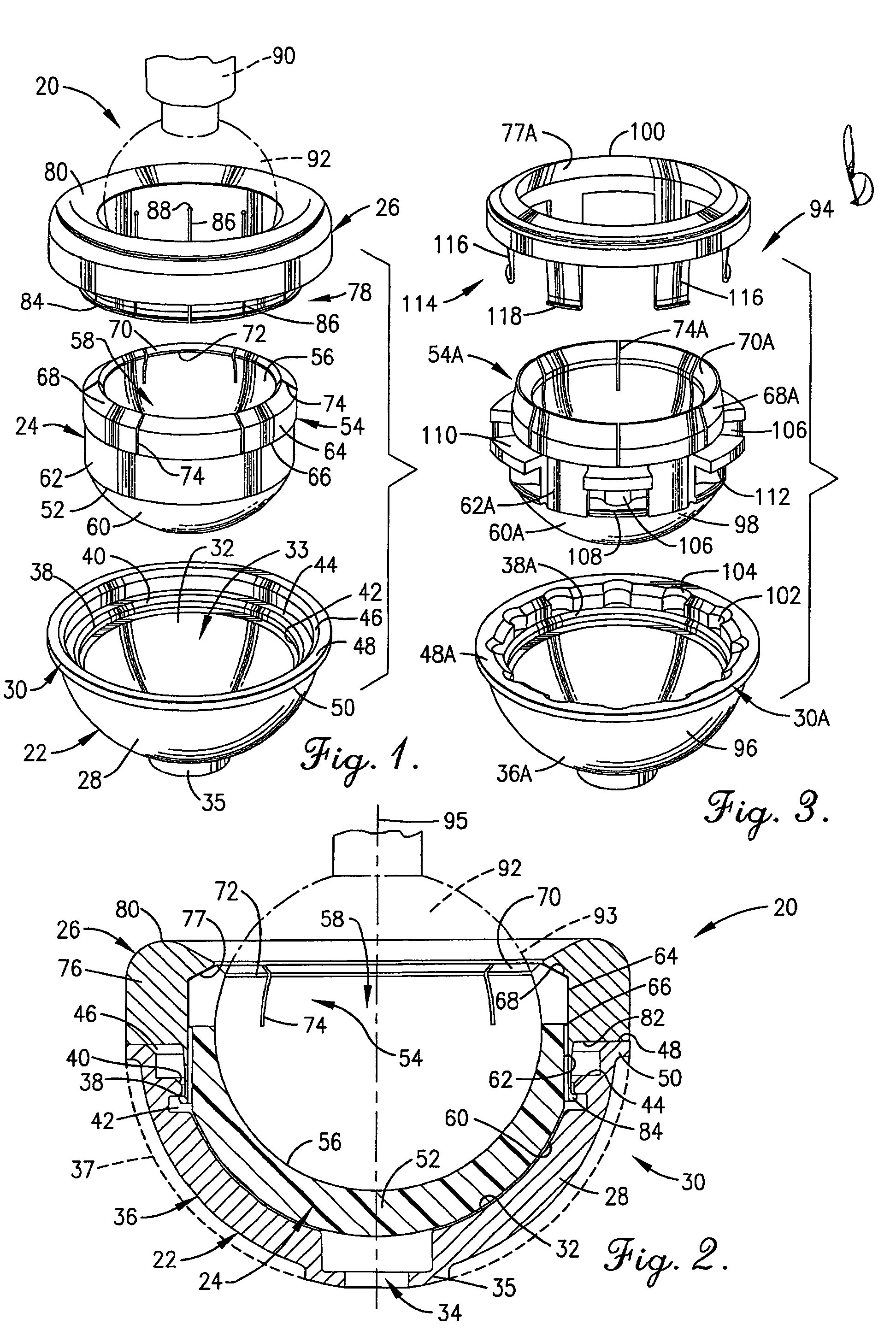
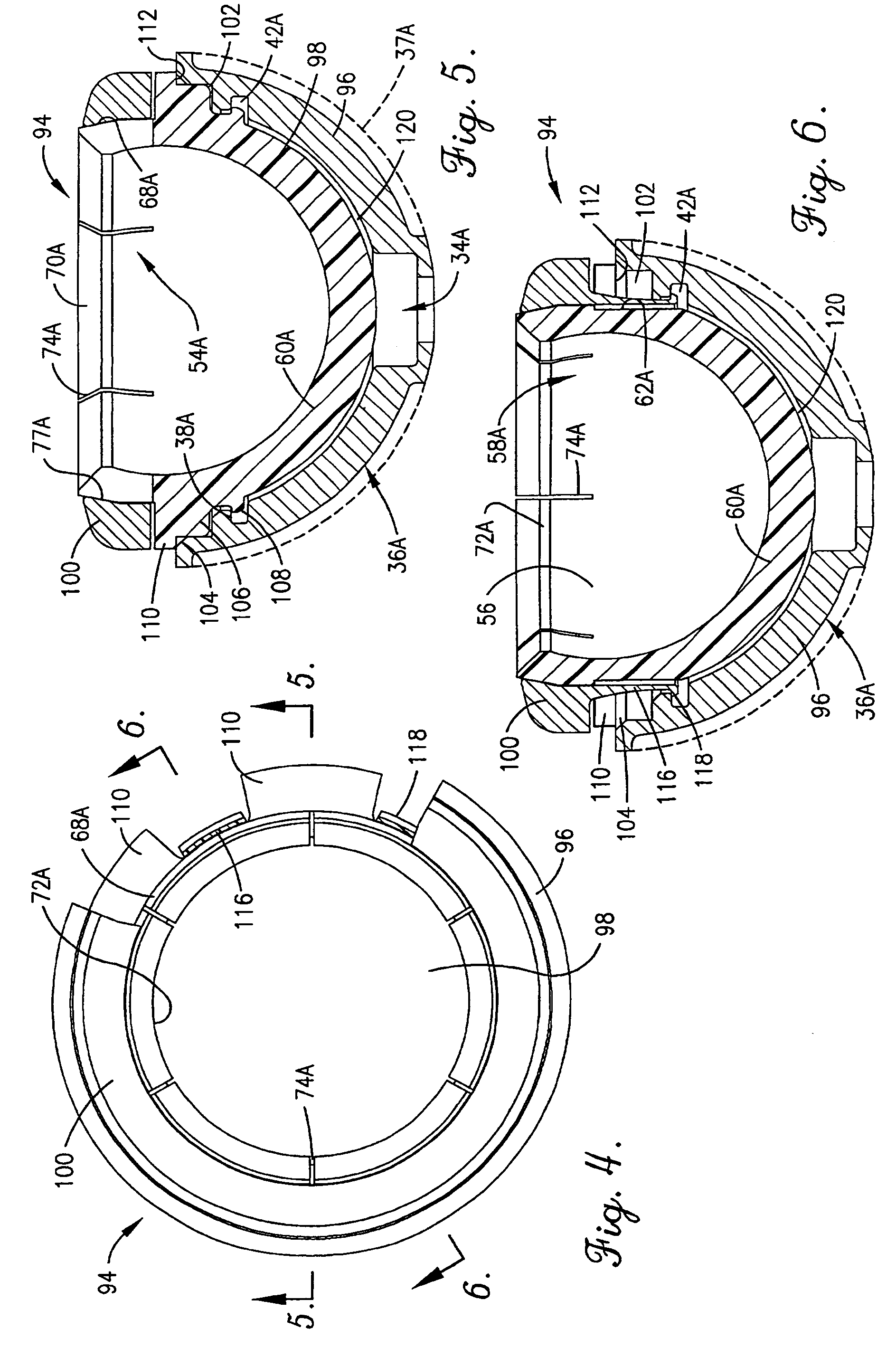
A hip prosthesis (20) having a shell (22), liner (24), and retainer ring (26) is utilized for hip arthroplasty. The liner (24) fits inside the shell (22), which is attached to a patient's pelvis, and the retainer ring (26) engages a terminal liner margin (54) to inhibit expansion of and decrease the size of a restricted liner opening (72) defined by the liner margin (54). By inhibiting expansion of the liner opening (72), the ball (92) of a patient's femur (90) is securely held in the liner (24). In one embodiment, the liner (98) is inhibited from rotation relative to the shell (96) by a plurality of protrusions (106) which mate with recesses (102) in the shell (96). In that embodiment, the liner (98) is provided with catch lips (108) to hold the liner (98) in the shell (96) and a positioning flange (110) which operates to form a relief gap (120) between the shell (96) and the liner (98). In another embodiment, the retainer ring comprises an attachment portion (128) and a retainer portion (130) with a threaded connection (132) between the attachment portion (128) and the retainer portion (130).
Owner:ORTHOPAEDIC RES INST
Modular hip stems and associated method of trialing
InactiveUS7235106B2Accurately approximatedReduce necessityJoint implantsFemoral headsMuscles of the hipModularity
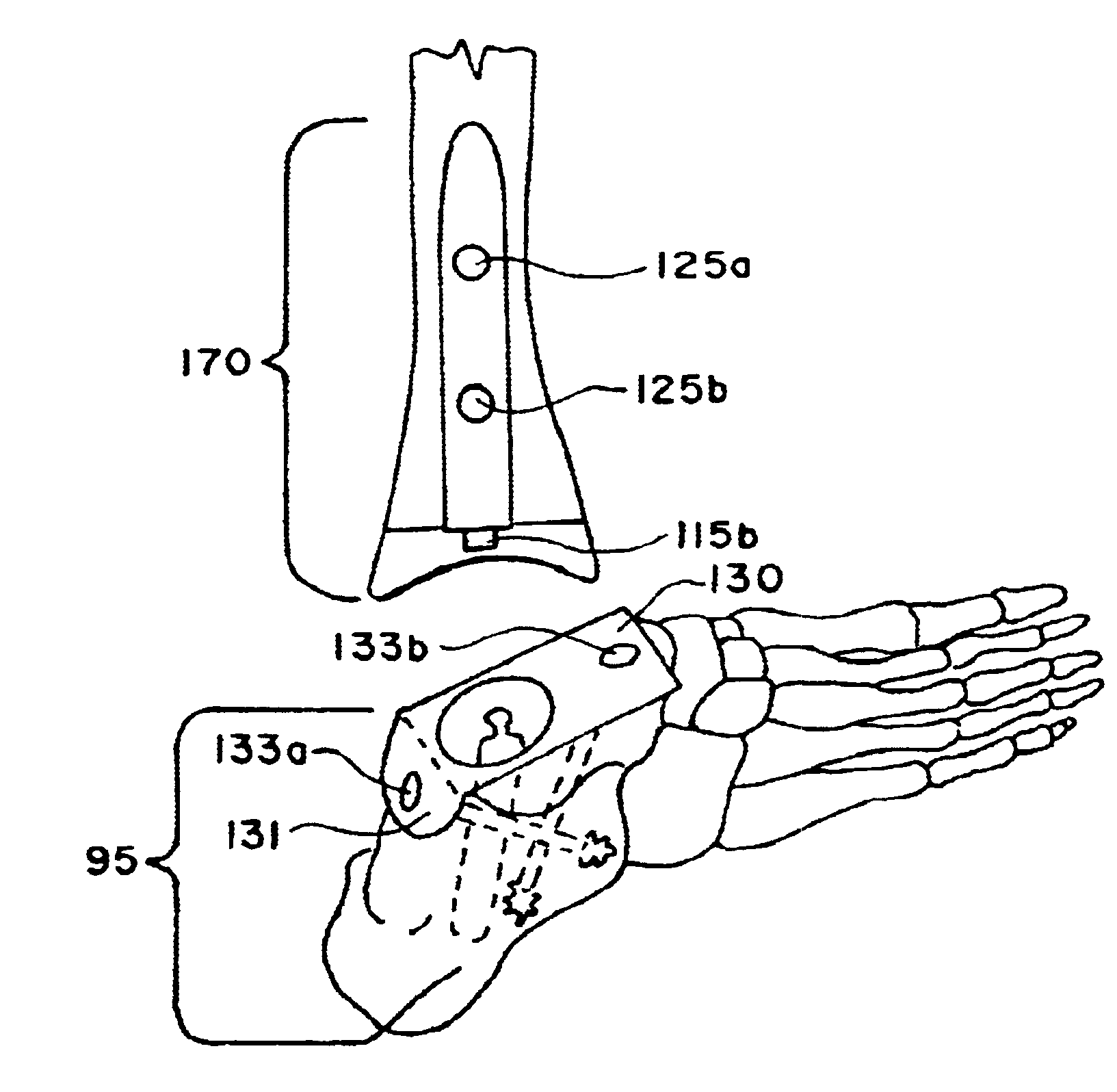
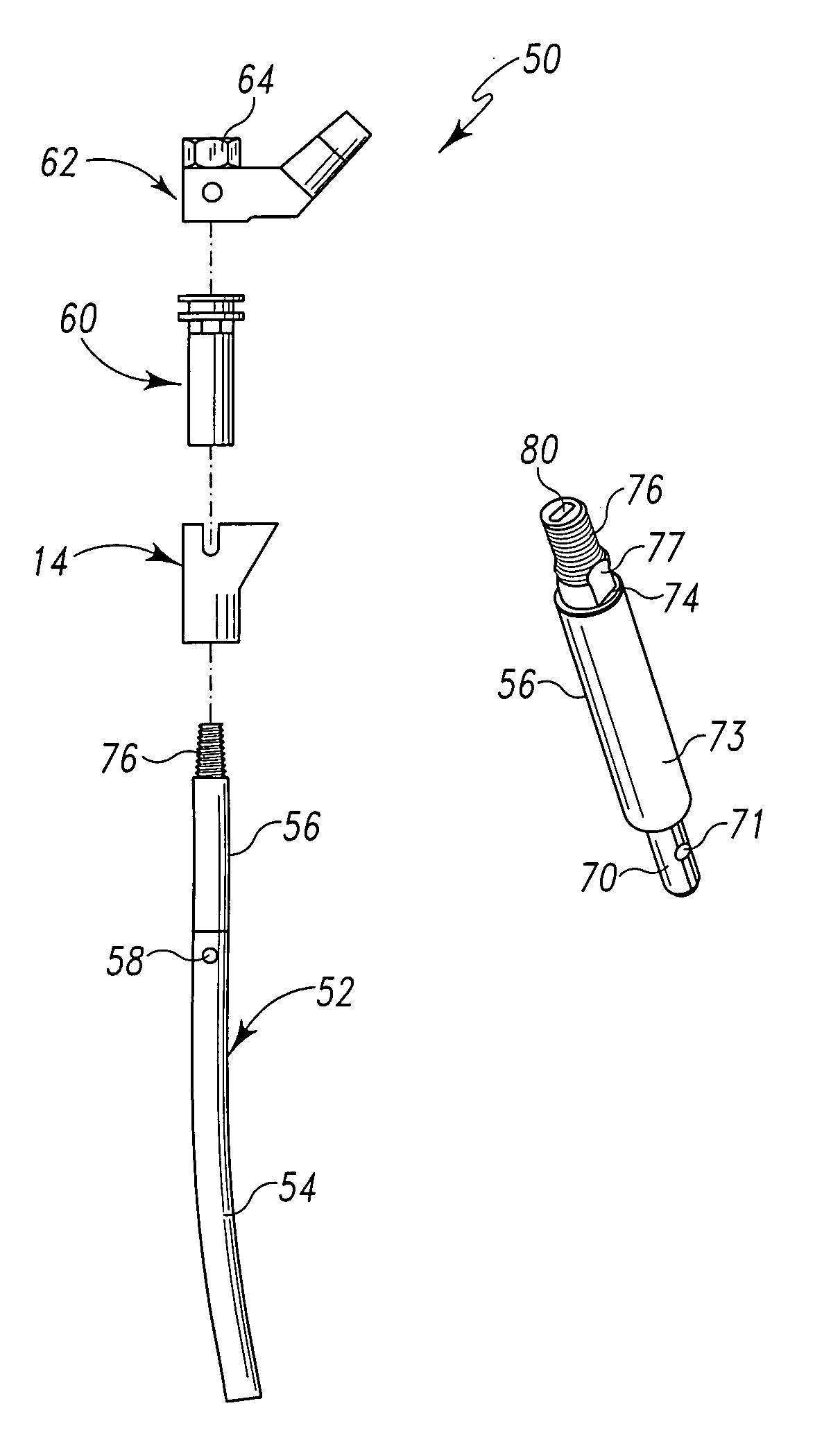
A system and method for trialing a modular hip replacement system (10) permits evaluation and replication of the anatomic anteversion rotational angle of the femur. A distal stem component (18) of the hip replacement system (10) includes a proximal portion (34) having a locator feature (35) that is externally accessible when the stem component is mounted within the femur. A proximal trial body assembly (60) is mounted on the proximal portion (34) of the distal stem component (18) to permit rotation of a trial neck component (62). The trial neck component (62) also includes a locator feature(126) that can be externally referenced to determine the anteversion angle.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
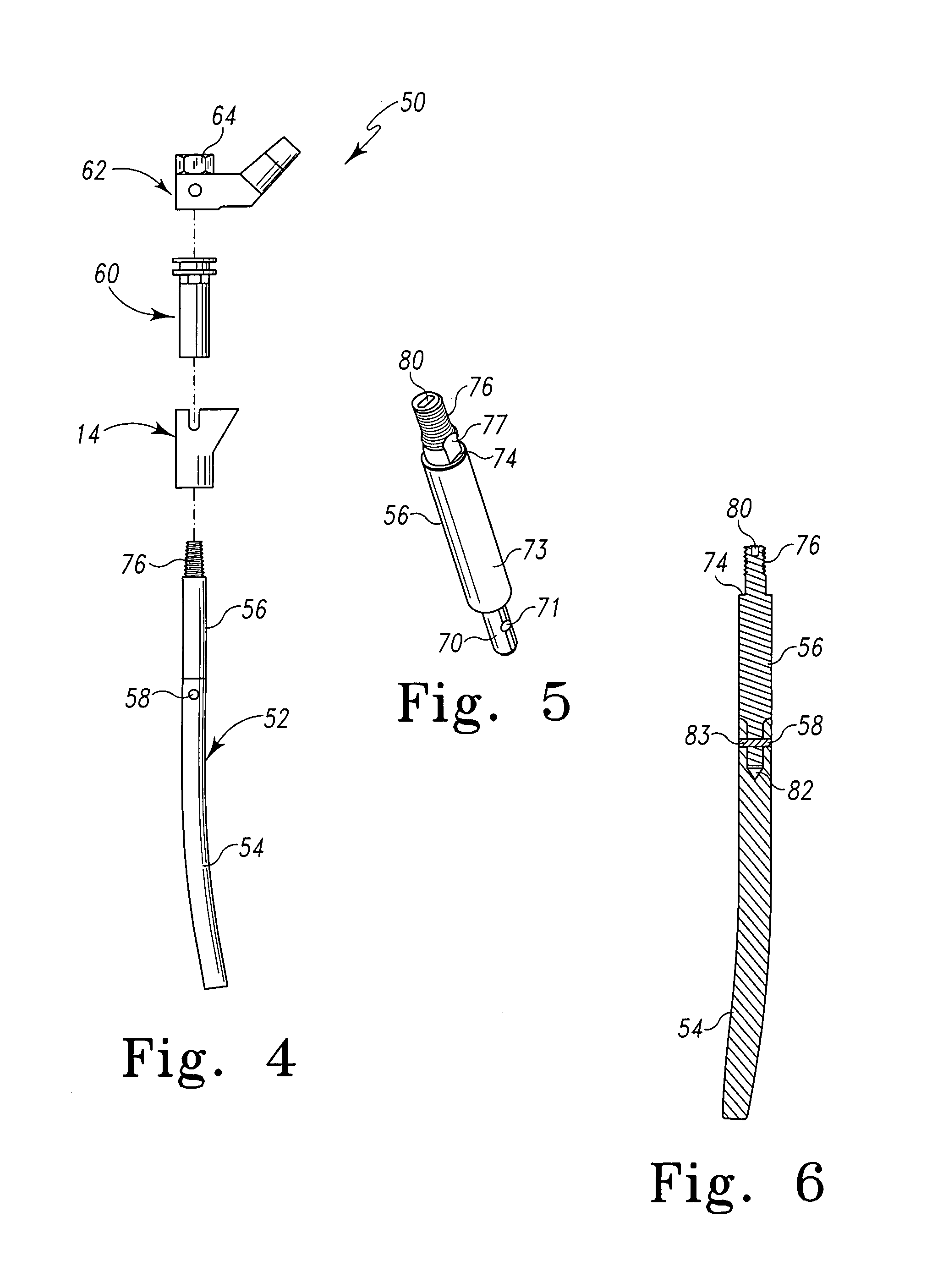
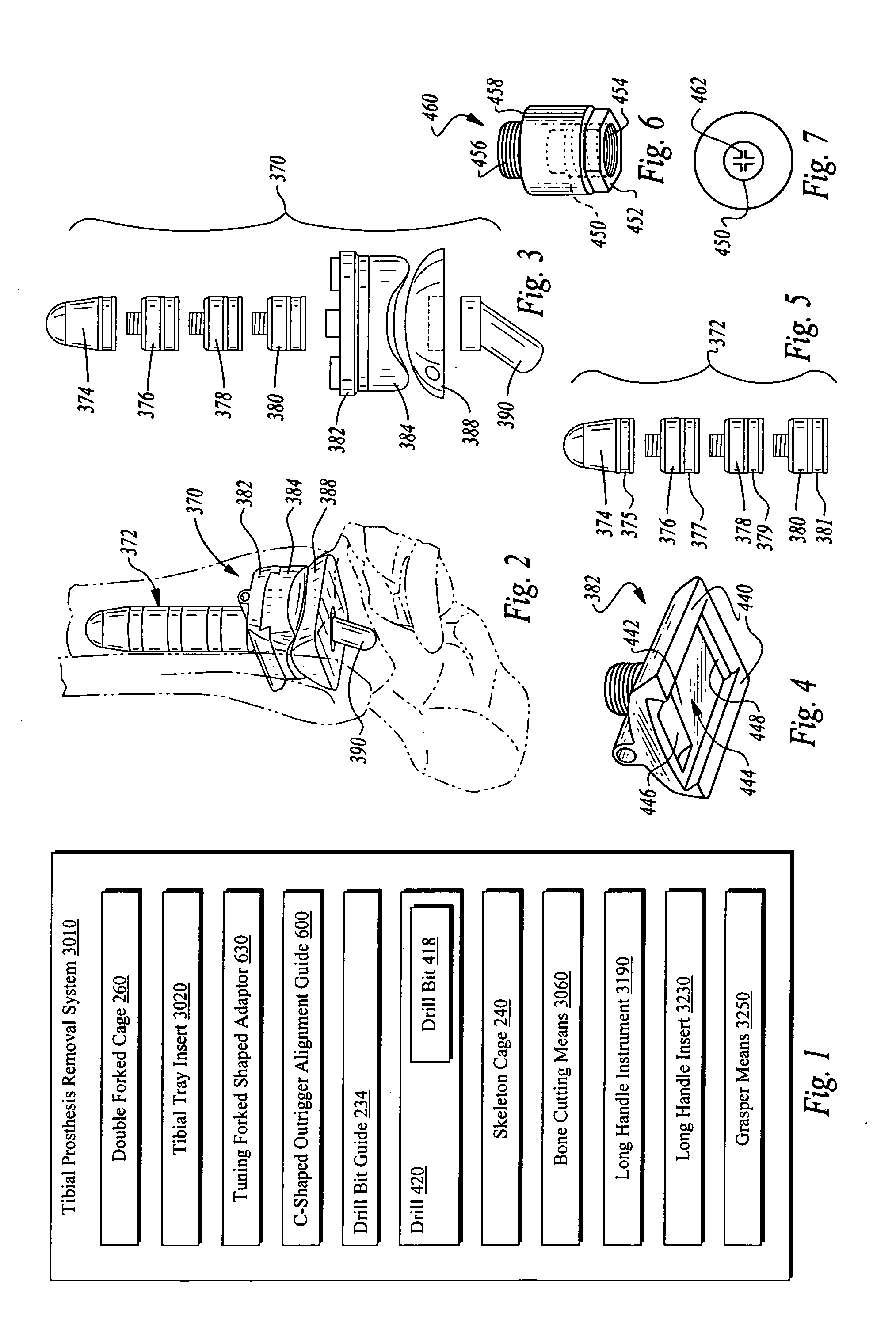
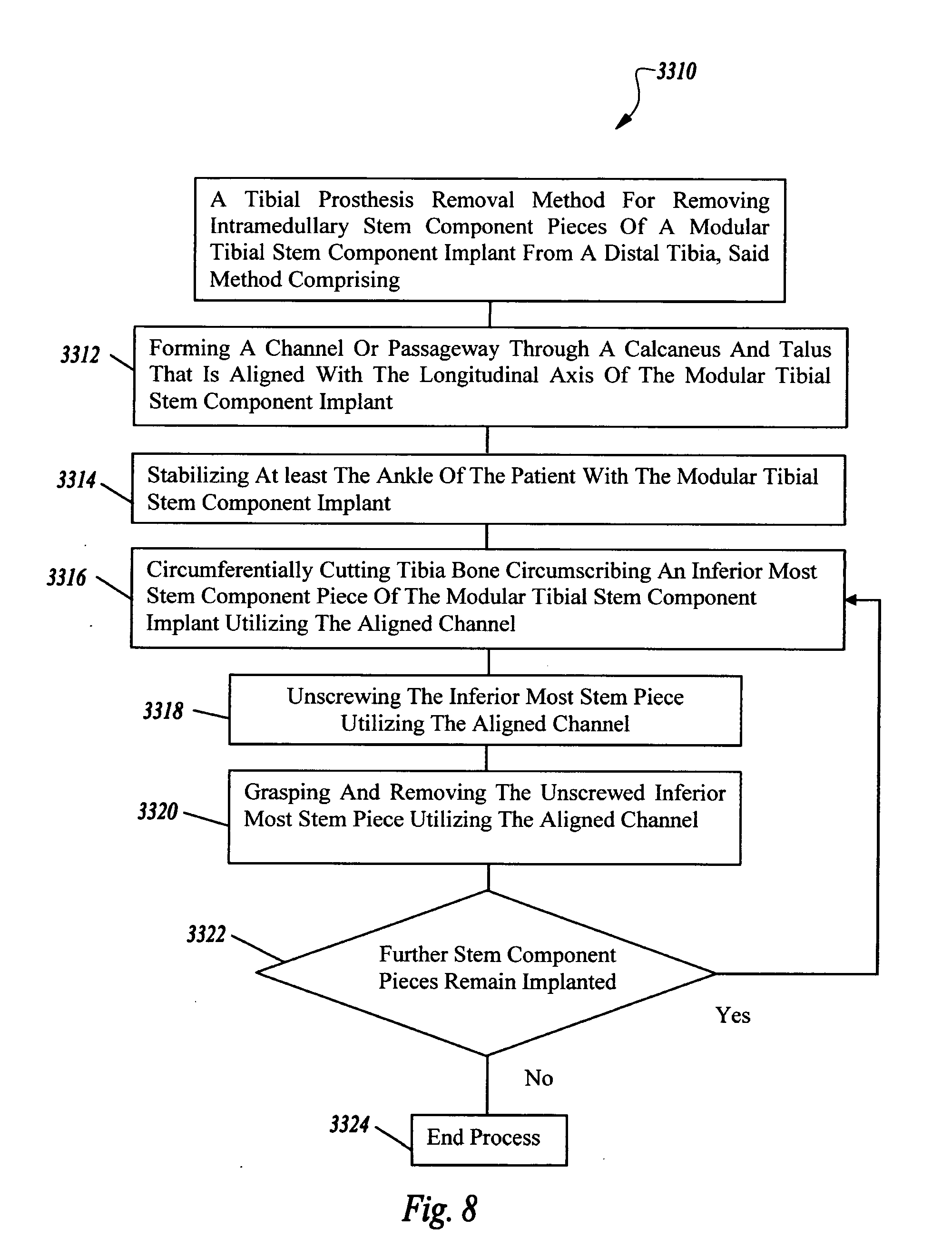
Systems and instrumentalities for use in removal of tibial prostheses of total ankle replacements
A system comprising instrumentalities and methods for removing intramedullary stem component pieces of a tibial implant from a distal tibia.
Owner:LIAN GEORGE JOHN
Method and apparatus for hip replacement
InactiveUS20120130502A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInterference fitRight femoral head
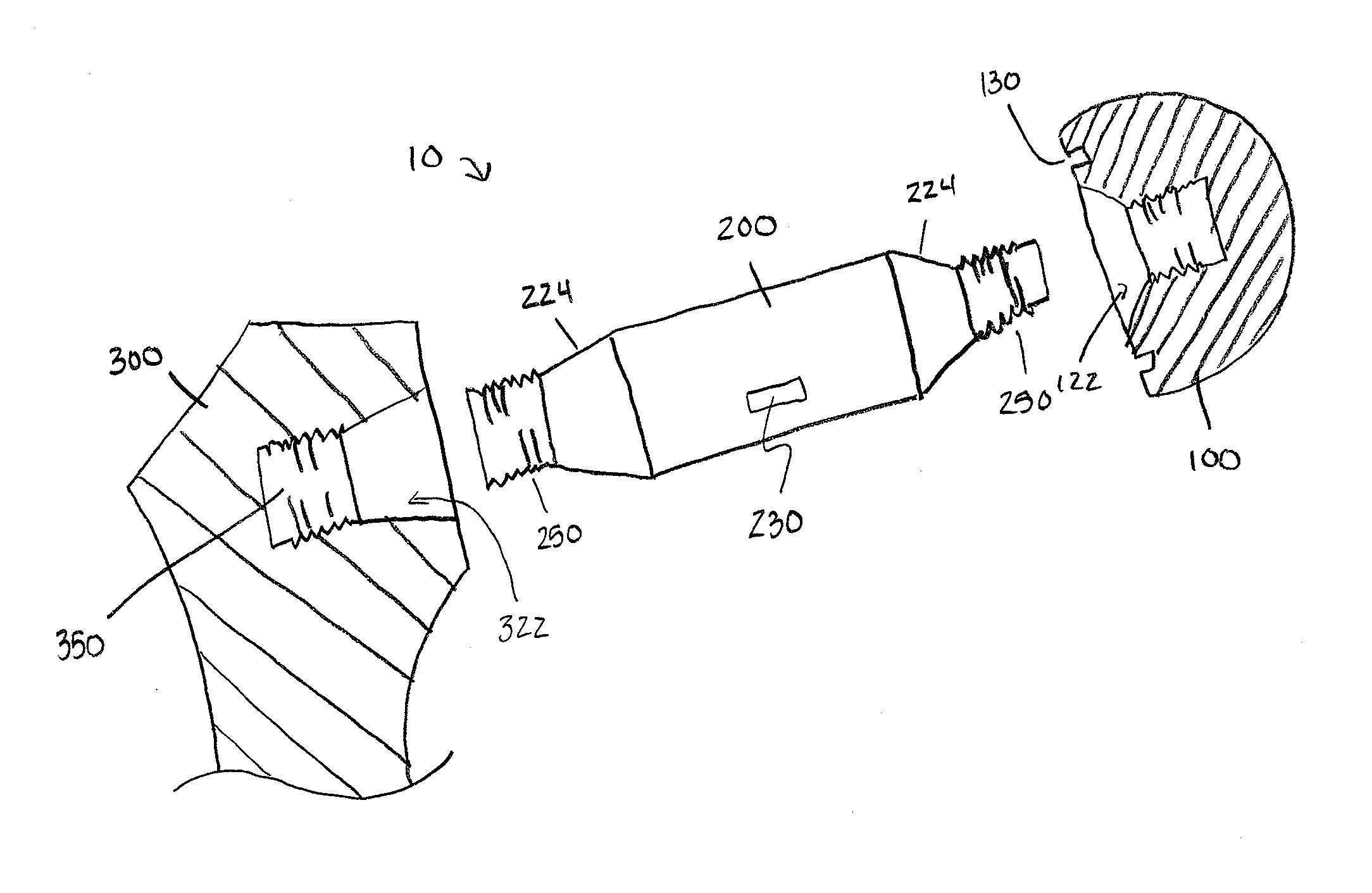
Methods and apparatus for orthopedic replacement of the hip through three incisions with a modular prosthetic system assembled in vivo while substantially preserving muscles and soft tissues around the hip joint resulting in reduced healing time and decreased risk of dislocation. A prosthetic femoral stem is inserted into the femur. A prosthetic femoral neck is inserted from a point along the side of the patient's body and into the side of the femur and through a lateral bore in the prosthetic femoral stem to join the prosthetic femoral head. The methods and apparatus include structures and techniques for fixing or enhancing interconnection of implant components, such as by increasing the interconnection in an interference fit with one or more tapers, threads, and / or cooling of components prior to assembly.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
Method and apparatus for hip replacement
InactiveUS8579985B2Enhance quality and reliability and compatibilityAvoid damageInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInterference fitRight femoral head
Methods and apparatus for orthopedic replacement of the hip through three incisions with a modular prosthetic system assembled in vivo while substantially preserving muscles and soft tissues around the hip joint resulting in reduced healing time and decreased risk of dislocation. A prosthetic femoral stem is inserted into the femur. A prosthetic femoral neck is inserted from a point along the side of the patient's body and into the side of the femur and through a lateral bore in the prosthetic femoral stem to join the prosthetic femoral head. The methods and apparatus include structures and techniques for fixing or enhancing interconnection of implant components, such as by increasing the interconnection in an interference fit with one or more tapers, threads, and / or cooling of components prior to assembly.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
Disc Implant
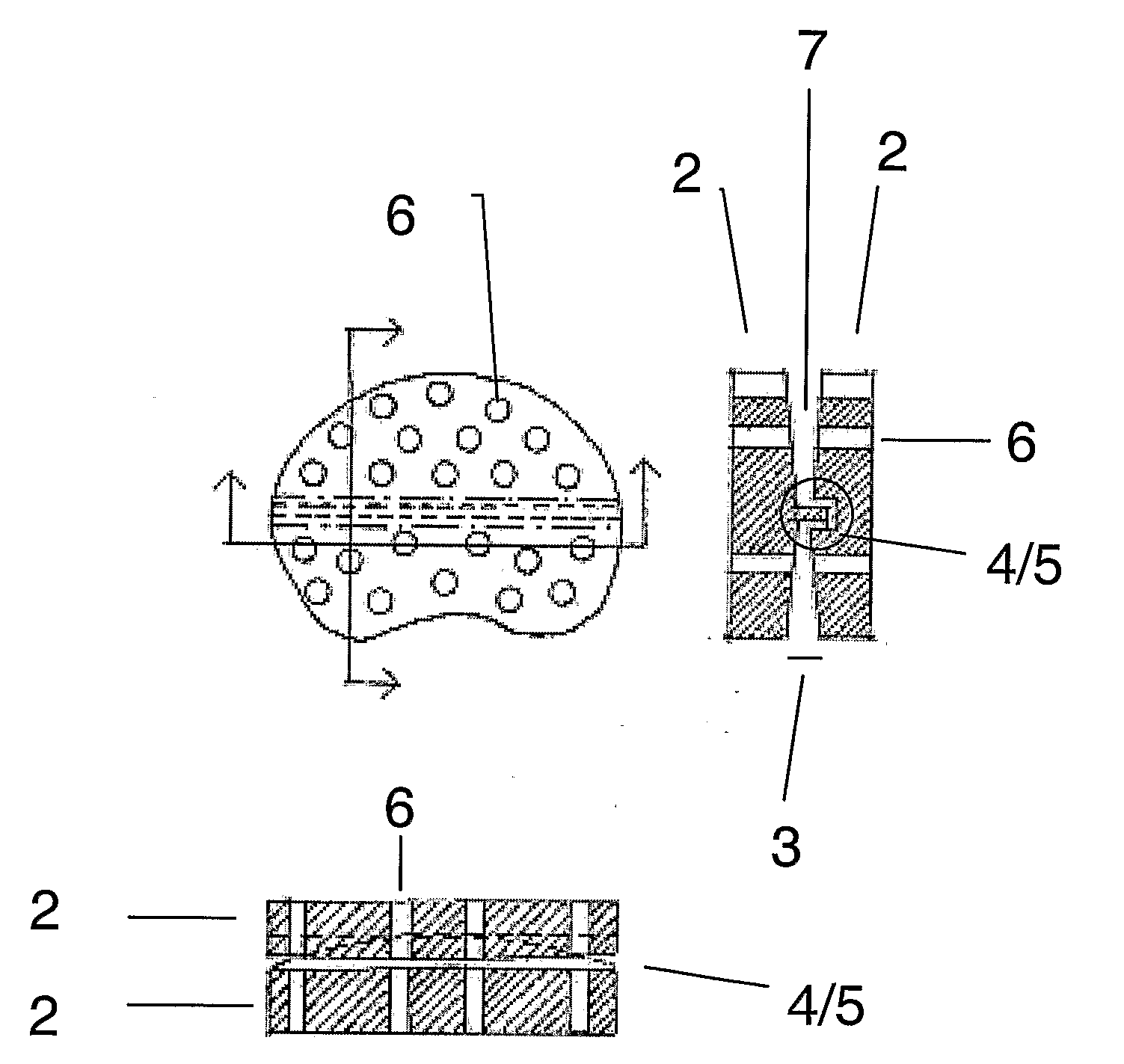
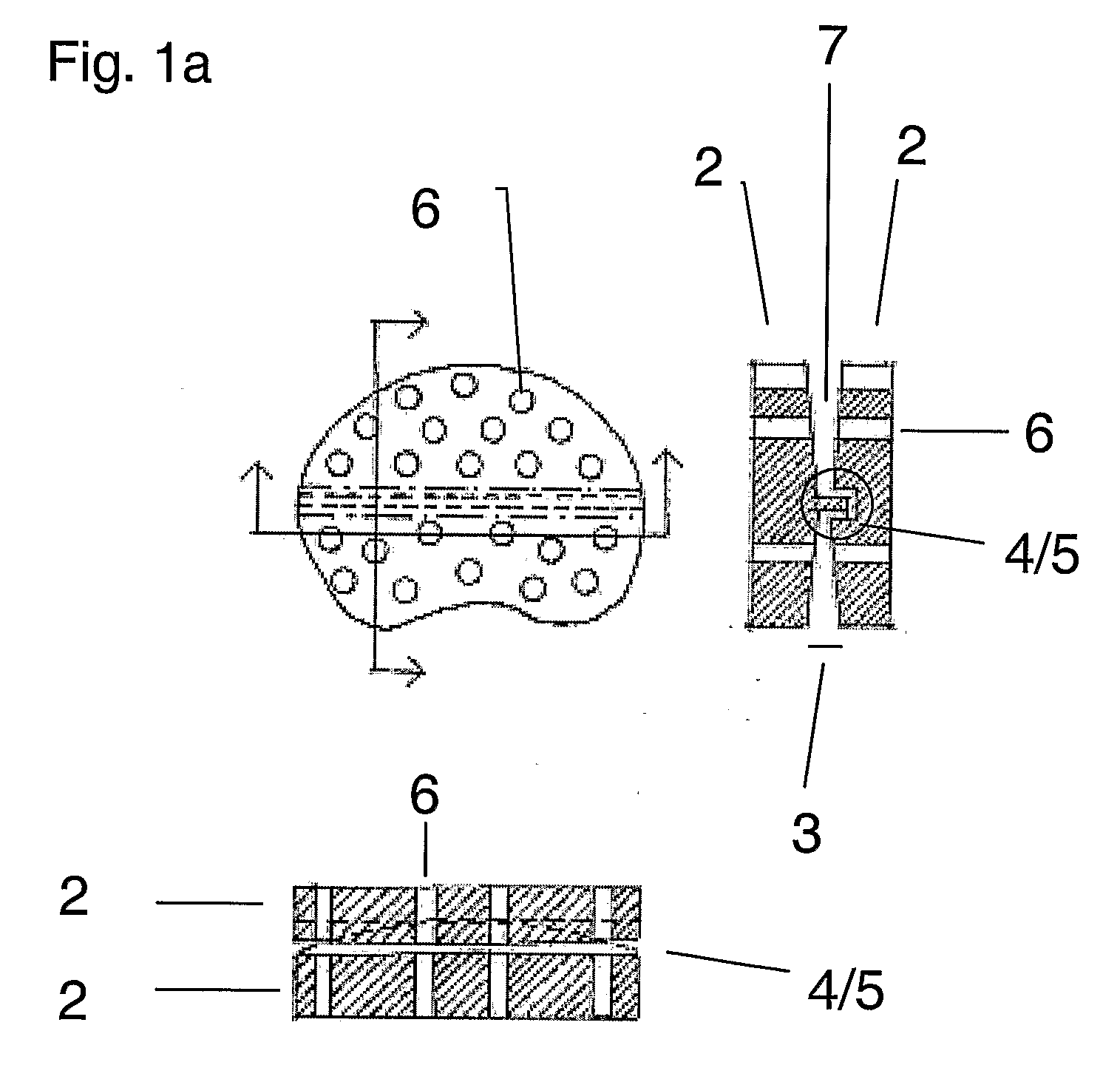
A problem with total disc implant surgery appears to be the positioning of the implant which if not correct may lead to pain and eventually new surgery. The present invention relates to an improved disc implant (1) for total disc replacement, comprising two inter-vertebral elements (2) which are flexibly connected via coupling means (4,5). Following surgery, the relative movability of said two inter-vertebral elements is decreased overtime, as bone ingrowth occurring around the implant and specifically through osseointegrative sections gradually degrease the movability of the elements relative to each other Following, the relative movability of the implant elements is replaced by fixation of the elements. The fixation has flowingly occurred in a position affected by the movement of the patient, and is thereby more acceptable to the patient.
Owner:FBCDEVICE
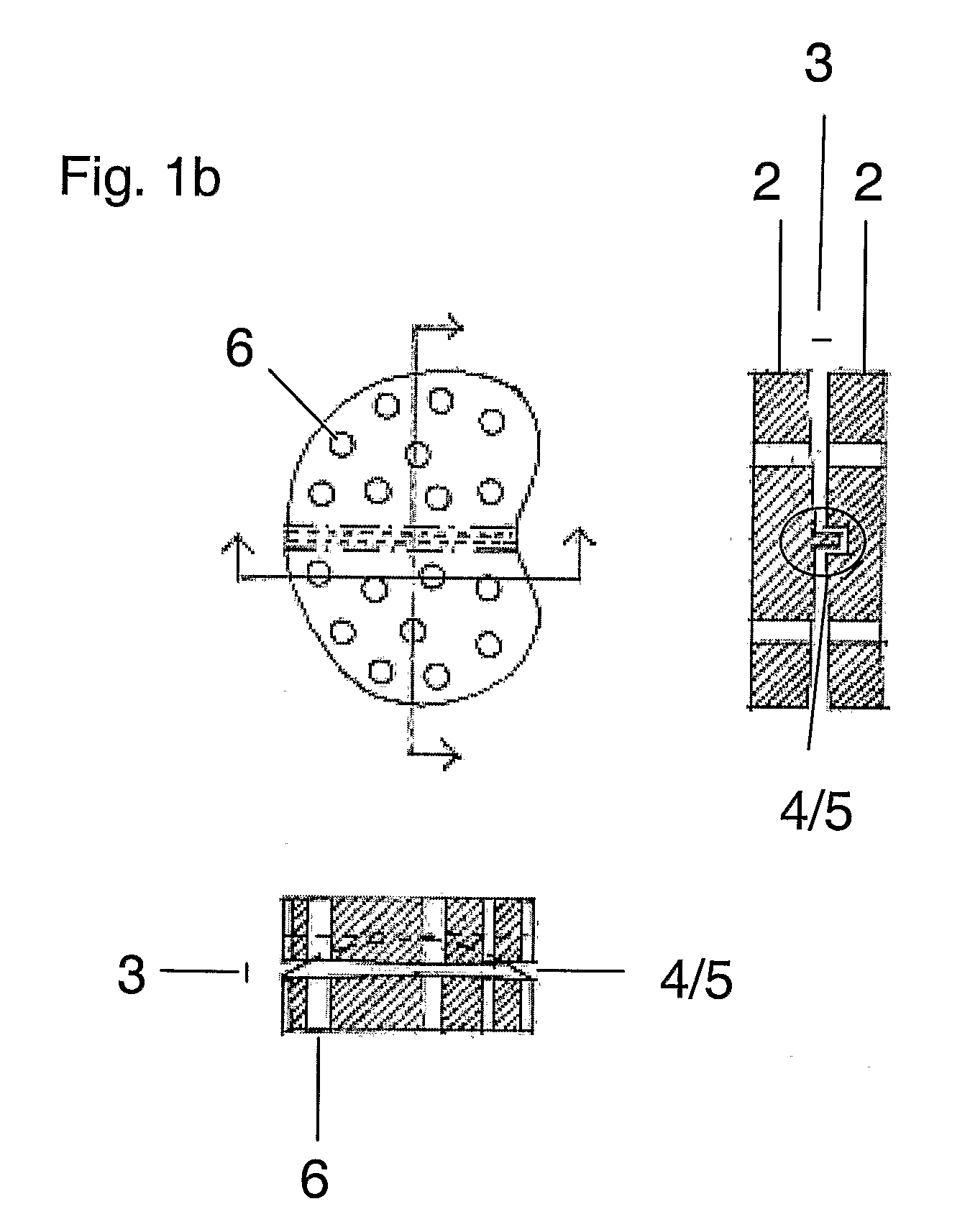
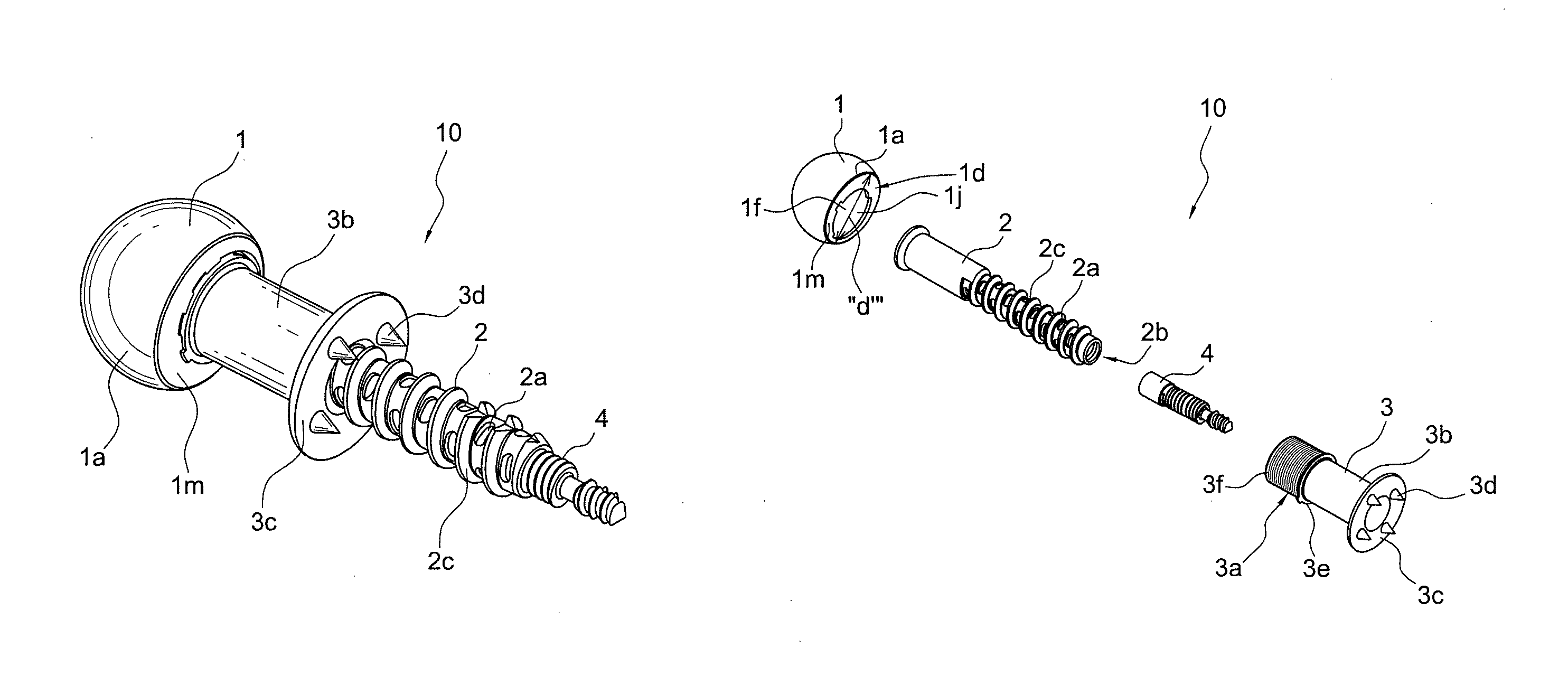
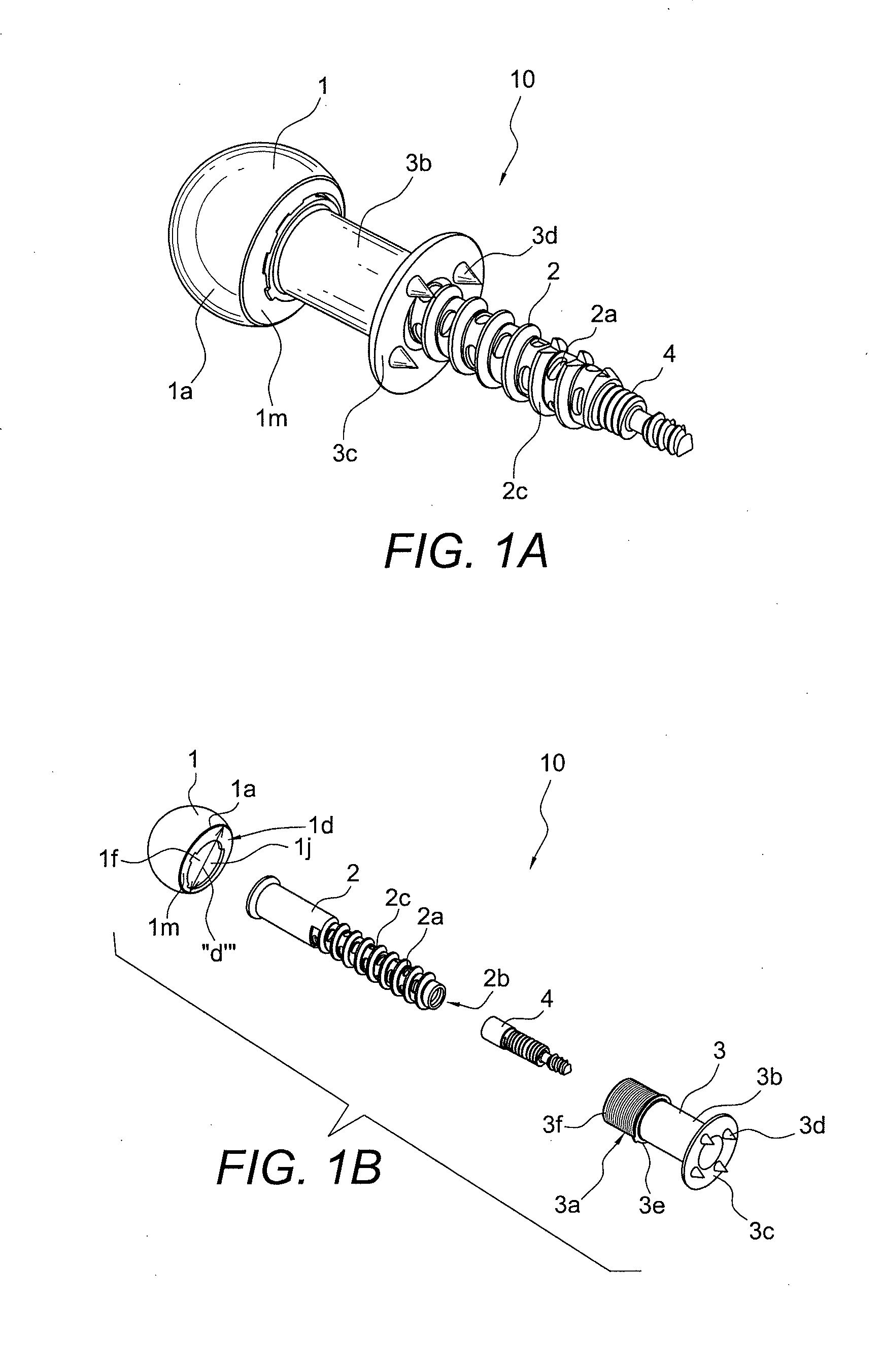
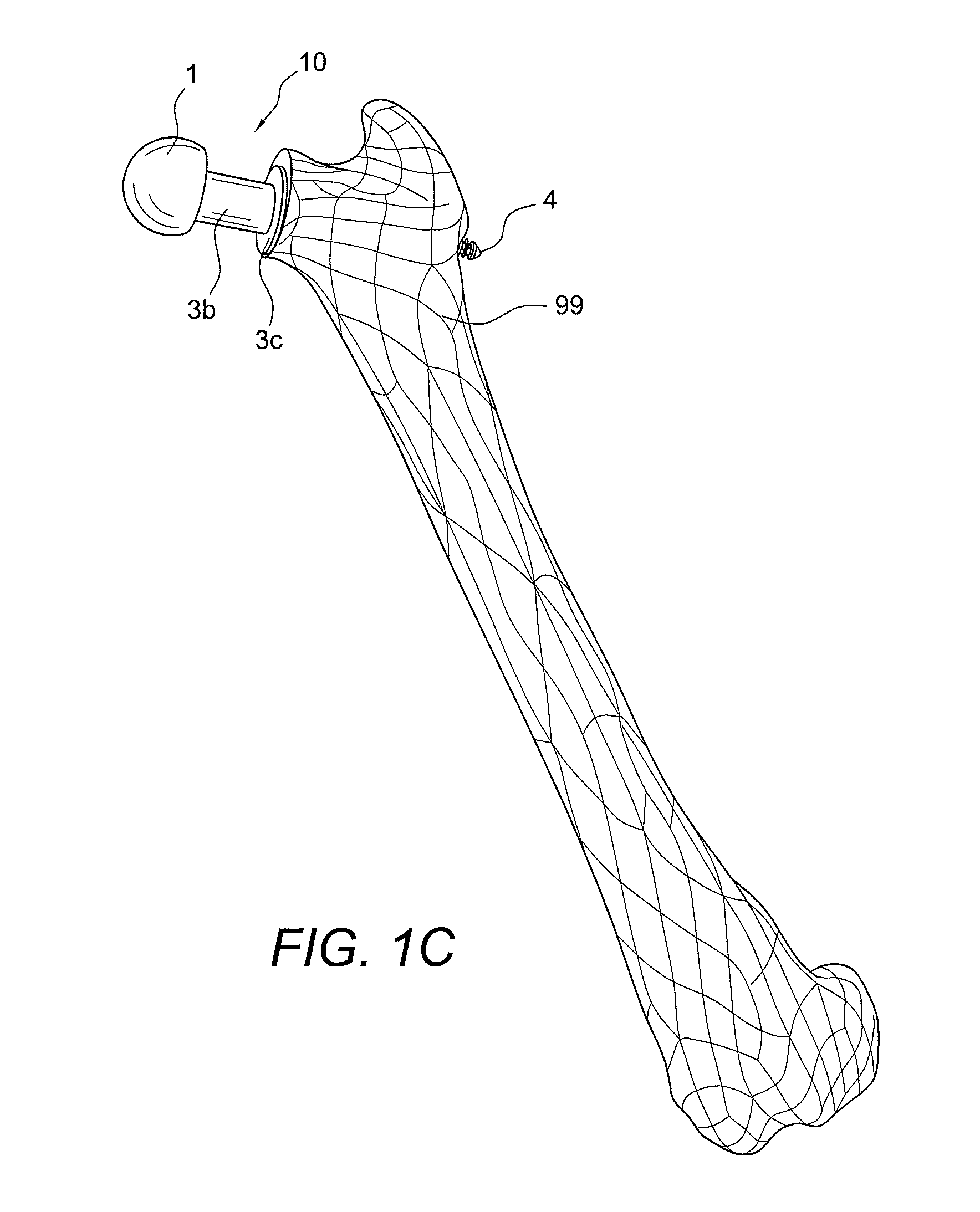
Minimally invasive total hip replacement
ActiveUS9295556B2Minimally invasiveMinimize stress transferredInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTotal hip replacementBiomedical engineering
A femoral implant for total hip replacement includes a cage screw, a femoral head and a base plate provided between the cage screw and the femoral head, to minimize the stress transferred from the femoral head to the bone. The femoral implant may optionally include devices for lateral fixation (for example, internal and / or external screws for lateral fixation) and a device for minimizing micro-motion that is integral to, and extends from, the cage screw.
Owner:ARTHREX
Total disc replacement system and related methods
ActiveUS8328851B2Quick and direct and accurate placementEasy to insertJoint implantsSpinal implantsSurgical approachRadiology
Total disc replacement systems and related methods involving a lateral, trans-psoas surgical approach to the spine while performing at least one of continuous and intermittent intra-operative neural monitoring of the psoas muscle to avoid injury during introduction.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Two-incision minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS7004972B2Avoid excessive injuryMore preservationDiagnosticsSurgeryMini invasive surgeryFemoral neck
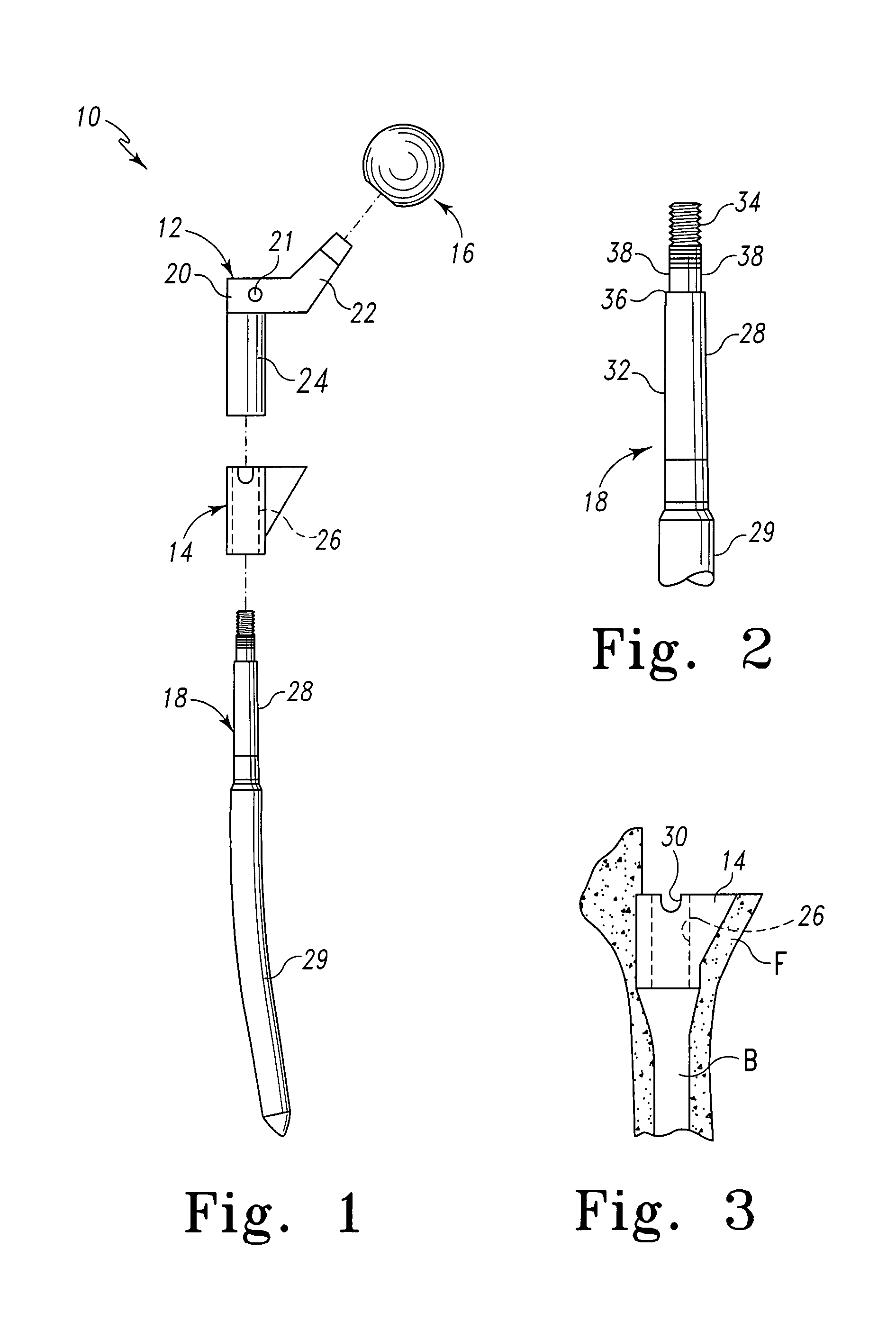
A surgical procedure for replacing a destructed hip joint with an artificial joint is disclosed. The present invention provides a two-incision minimally invasive surgery for total hip arthroplasty. This method comprises positioning of the patient on a lateral decubitus position and a series of surgical techniques including a first skin incision over the anterior side of the trochanteric area of the femur (ranging from 3 cm to 10 cm), intermuscular dissection between the Gluteus muscle (Gluteus minimus and medius) and Tensor fascia lata muscle, incision of the anterior joint capsule, osteotomy of the femoral neck, removal of the femoral head and neck, acetabular reaming and socket insertion, secondary skin incision over the Gluteus maximus muscle (ranging from 1 cm to 6 cm), dissection through the muscle fiber of the Gluteus maximus, intermuscular dissection between the Gluteus medius and Piriformis, partial incision of the joint capsule, femoral reaming, femoral stem insertion, femoral head insertion, joint capsule closure and skin closure.
Owner:YOON TAEK RIM
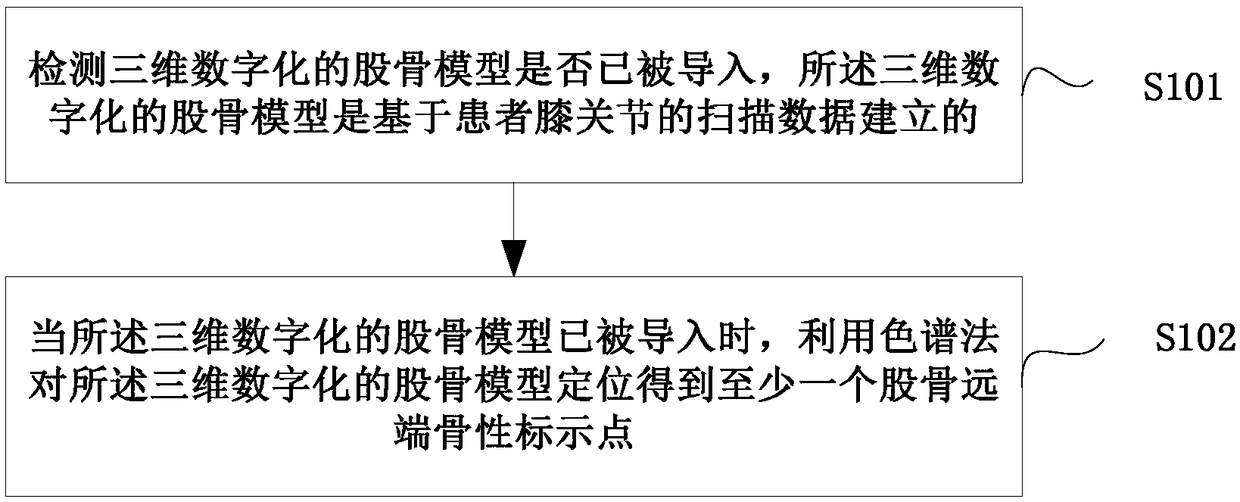
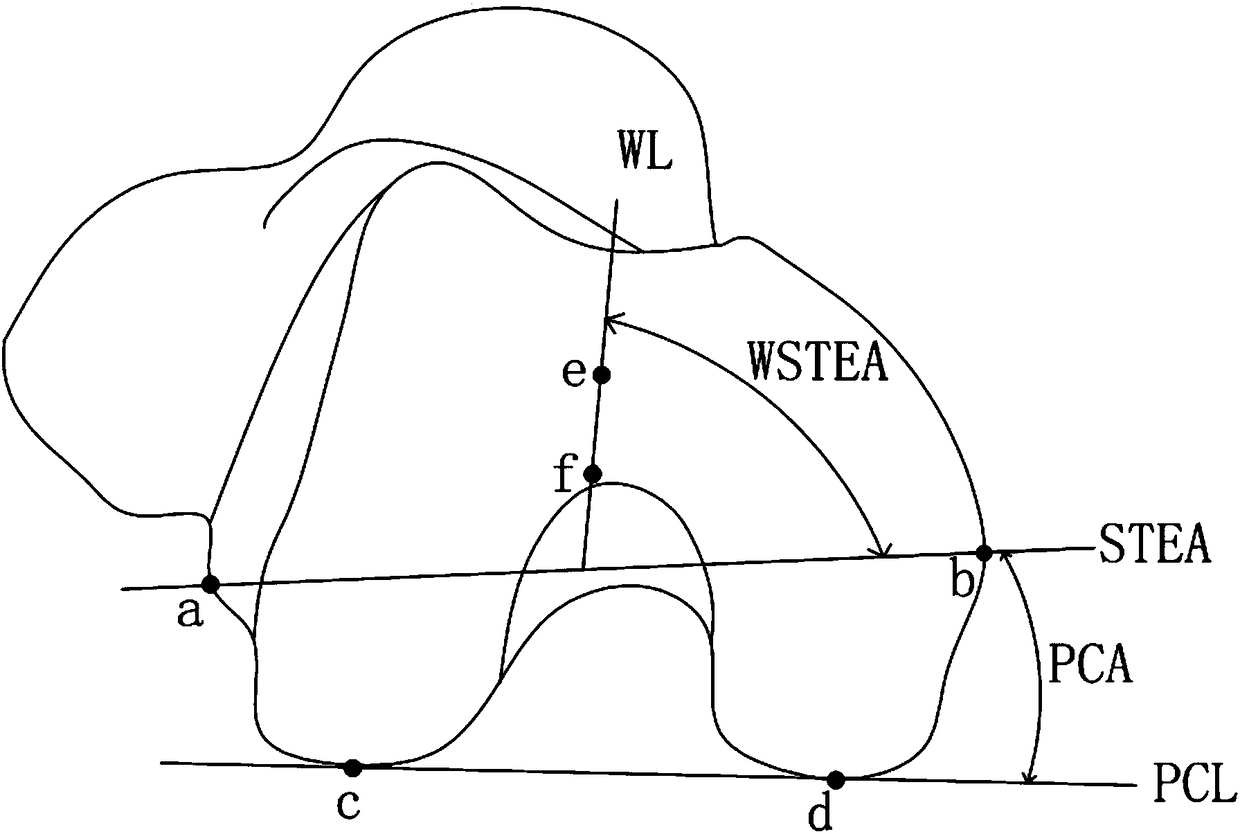
Femoral positioning method, personalized osteotomy guide plate and personalized prosthesis for total knee replacement
InactiveCN108478250AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityJoint implantsComputer-aided planning/modellingTotal knee replacementKnee Joint
The invention discloses a femoral positioning method, personalized osteotomy guide plate and personalized prosthesis for total knee replacement and relates to the technical field of total knee replacement. The femoral positioning method includes: detecting whether a three-dimensional digital femoral model is introduced in, wherein the three-dimensional digital femoral model is established based onscanning data of a patient's knee; if yes, using chromatography to position the three-dimensional digital femoral model to obtain at least one femoral distal osseous marker point. The femoral positioning method, personalized osteotomy guide plate and personalized prosthesis for total knee replacement can precisely position multiple osseous marker points at the distal end of the femur, and accuracy and repeatability are high; the personalized osteotomy guide plate is established according to the characteristics of femoral epicondylar axis and the three-dimensional reconstructed femoral distalsurface; the prosthesis is established by precise matching according to the characteristics of the femoral distal end after the personalized osteotomy guide plate is used to perform simulation osteotomy, and the prosthesis is applied to implementing of personal design.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Modular Femoral Head Surface Replacement, Modular Femoral Neck Stem, and Related Sleeve, Adapter, and Osteoconducting Rod
InactiveUS20090043397A1Relief the painRestore stabilityInternal osteosythesisBone implantEtiologyBody of femur
Disclosed therein is a big femoral head and femoral head surface replacement, which are used for hip osteoarthritis and vascular necrosis of femoral head. As a person get older and aged, the weight bearing hip joint is indispensably changed to osteoarthritis and sometimes showed avascular necrosis of the femoral head with unknown etiology. The deformed femoral head and hip joint should be replaced with the THA. Till now, the total hip replacement is performed in such a way that the necrosed femoral head and a healthy femoral neck are all removed and a femoral stem is inserted into the marrow cavity, and in this case, a small femoral head causes a reduction of a range of motion and dislocation of the hip joint occasionally, and osteolysis due to abrasion of plastic acetabular liner. In case of a conventional femoral head surface replacement (hereinafter, called “conventional FHSR”), a complication of femoral neck fracture and could not combined use with conventional THA. Recently, hard bearing system such as metal on metal THA or ceramic on ceramic THA without using plastic has been introduced to solve the problem of osteolysis due to abraded plastic particles generated when the THA is worn out as time goes. But there also have many problems as a limited range of motion, resected normal femoral neck and difficulties of rereplacement of the femoral stem. Because of the big femoral head or the FHSR can increase the range of motion and lower dislocation rate these devices are gradually widespread in young active person and Asian peoples. This invented design of the modularity gives the convenience to the surgeon and economically lower burden to patients to use of the FHSR and big femoral head system. The related accessory showed initial stability of the FHSR during operation and prevent from femoral neck fracture in follow-up periods.
Owner:PARK HYUNG BAE
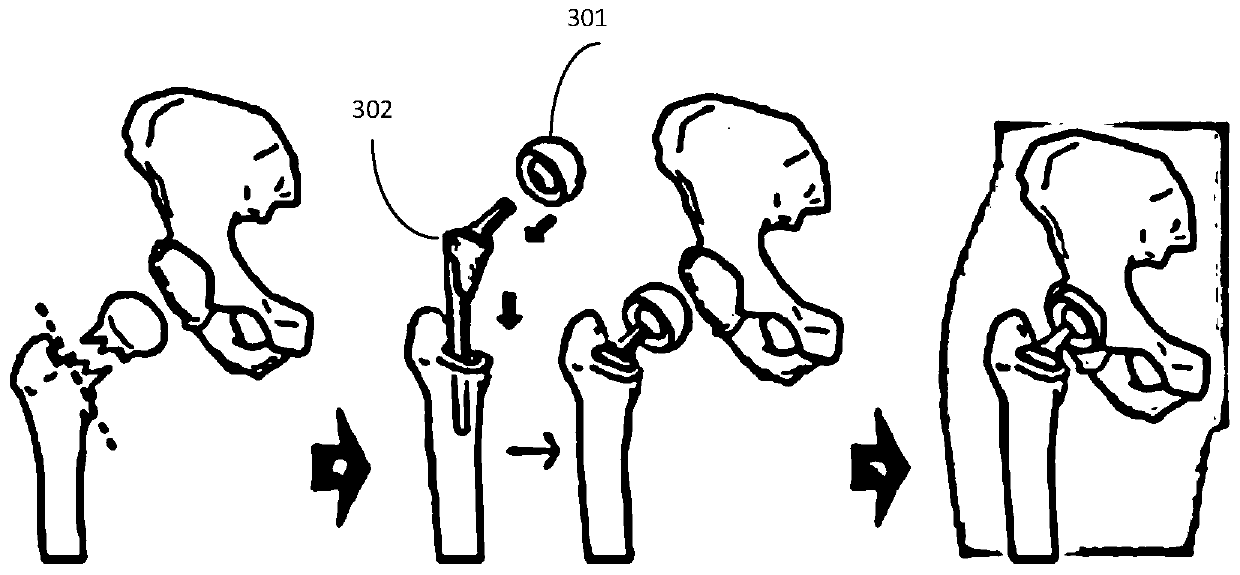
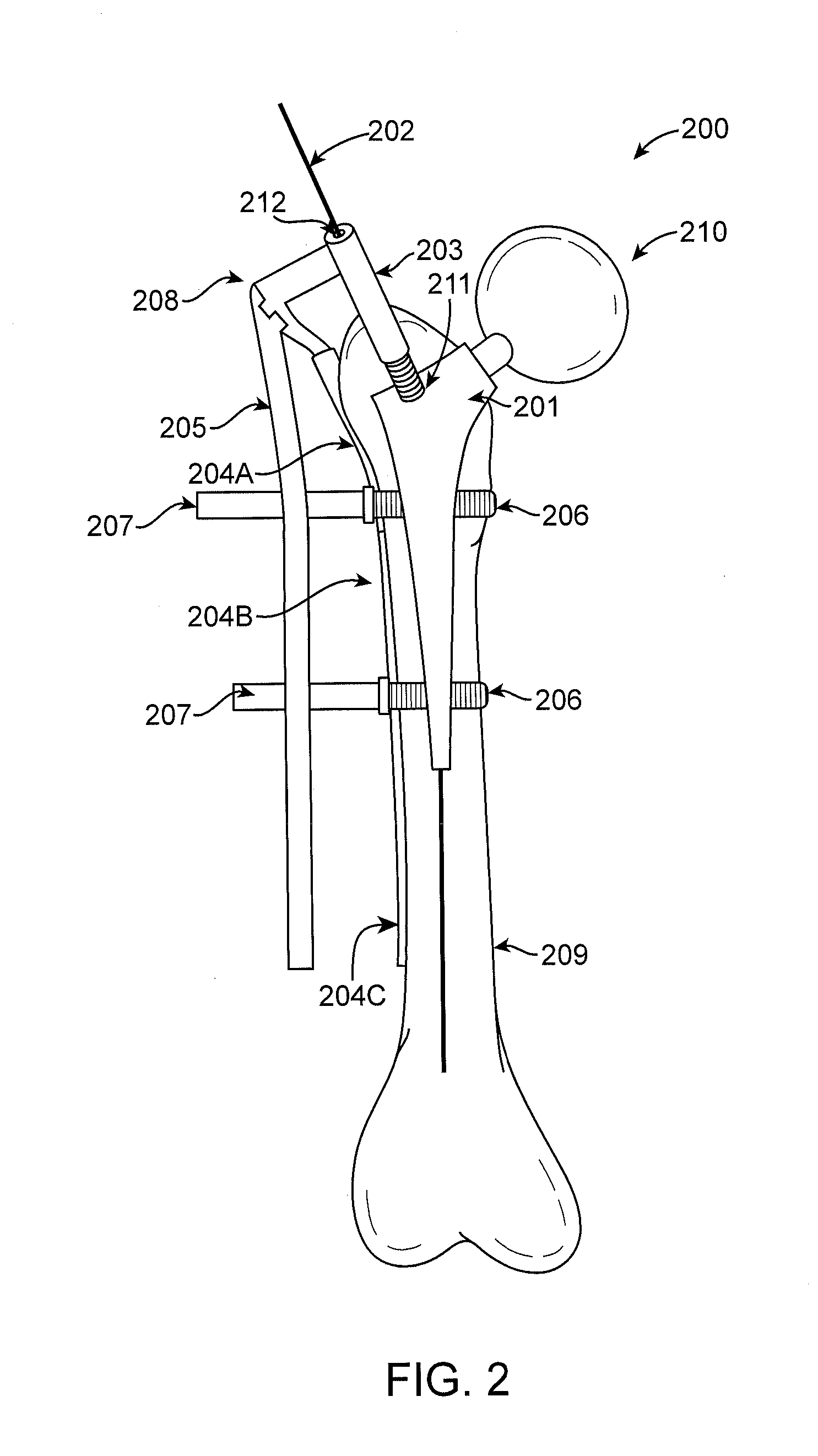
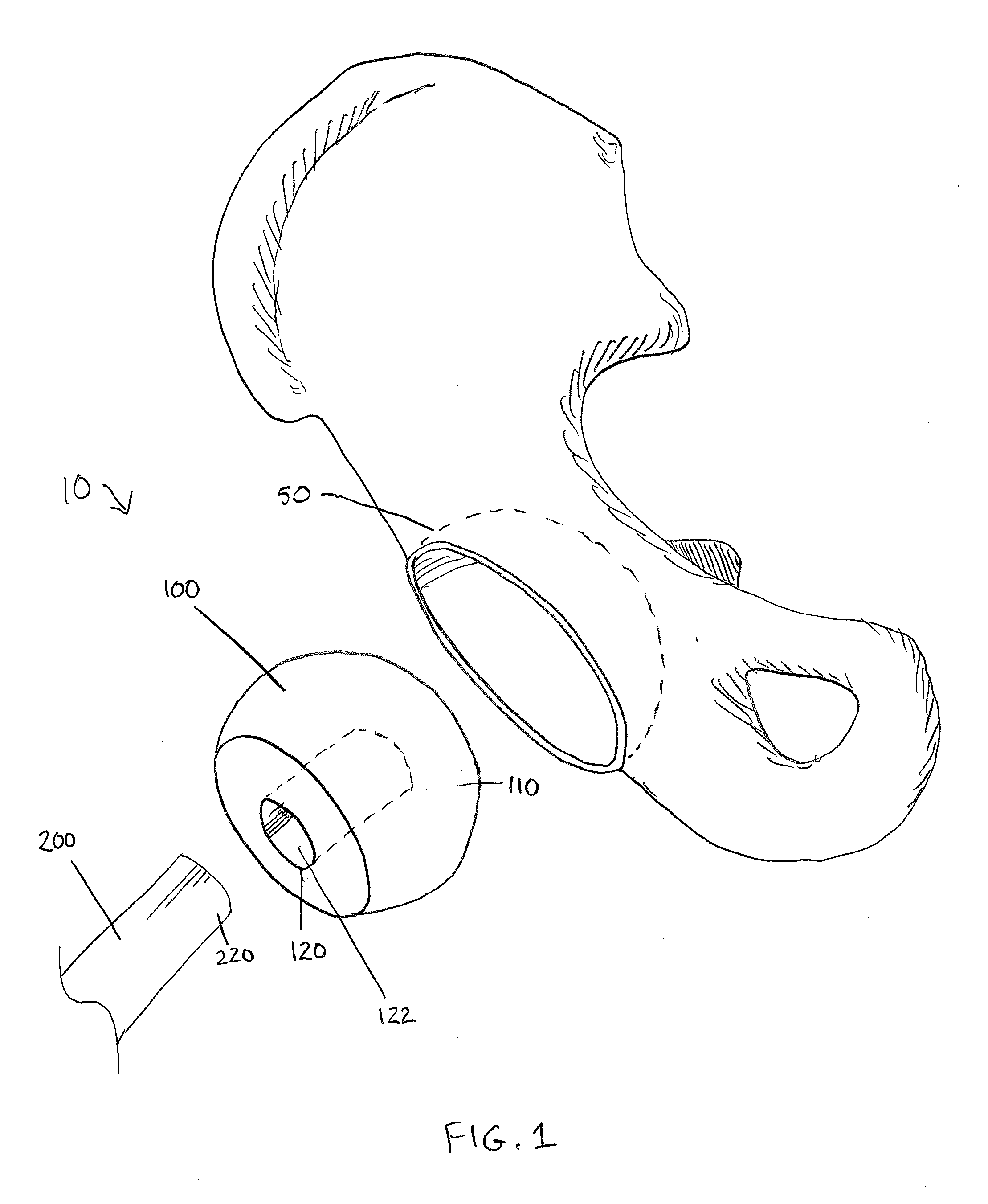
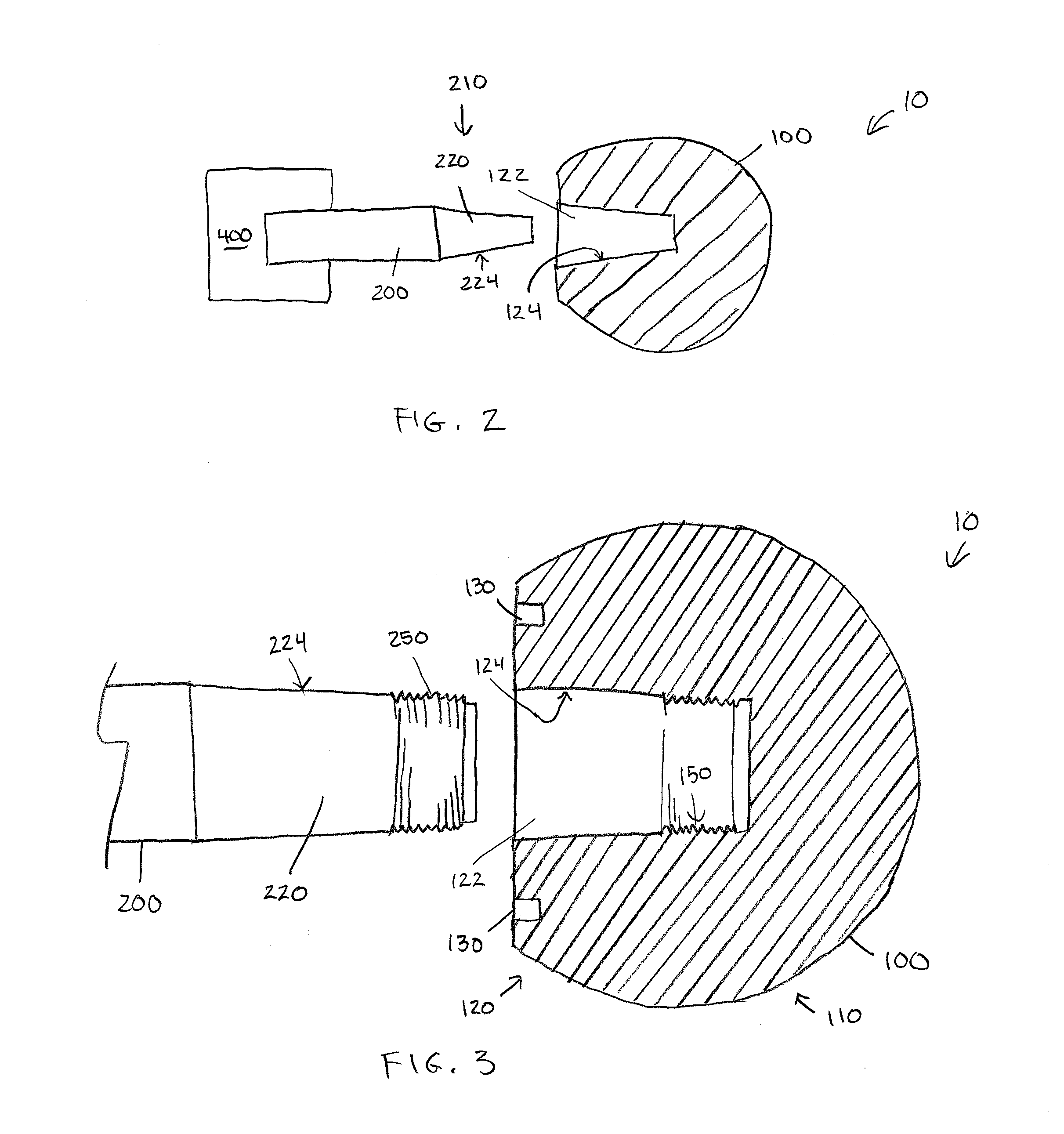
Method and apparatus for total hip replacement
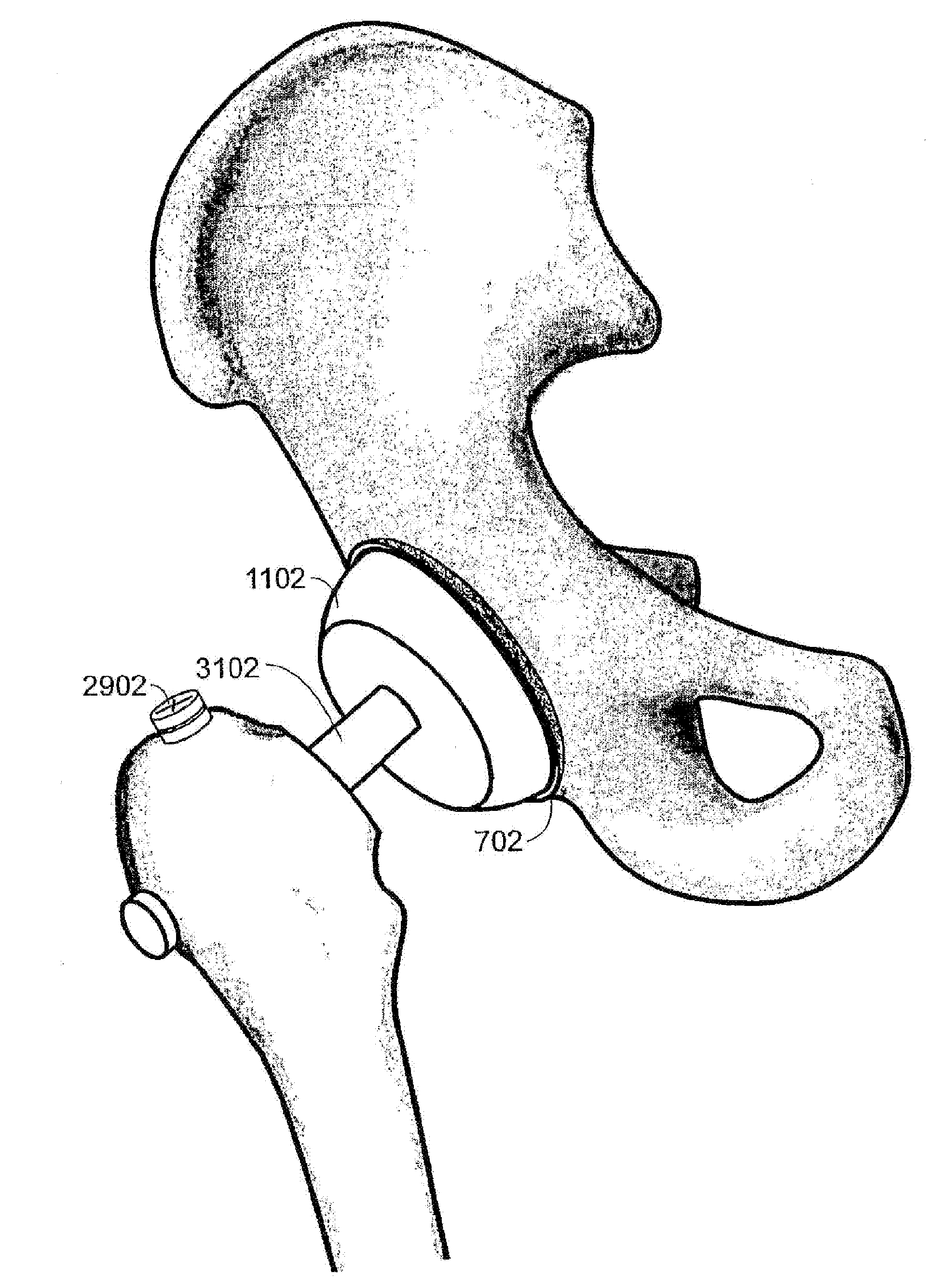
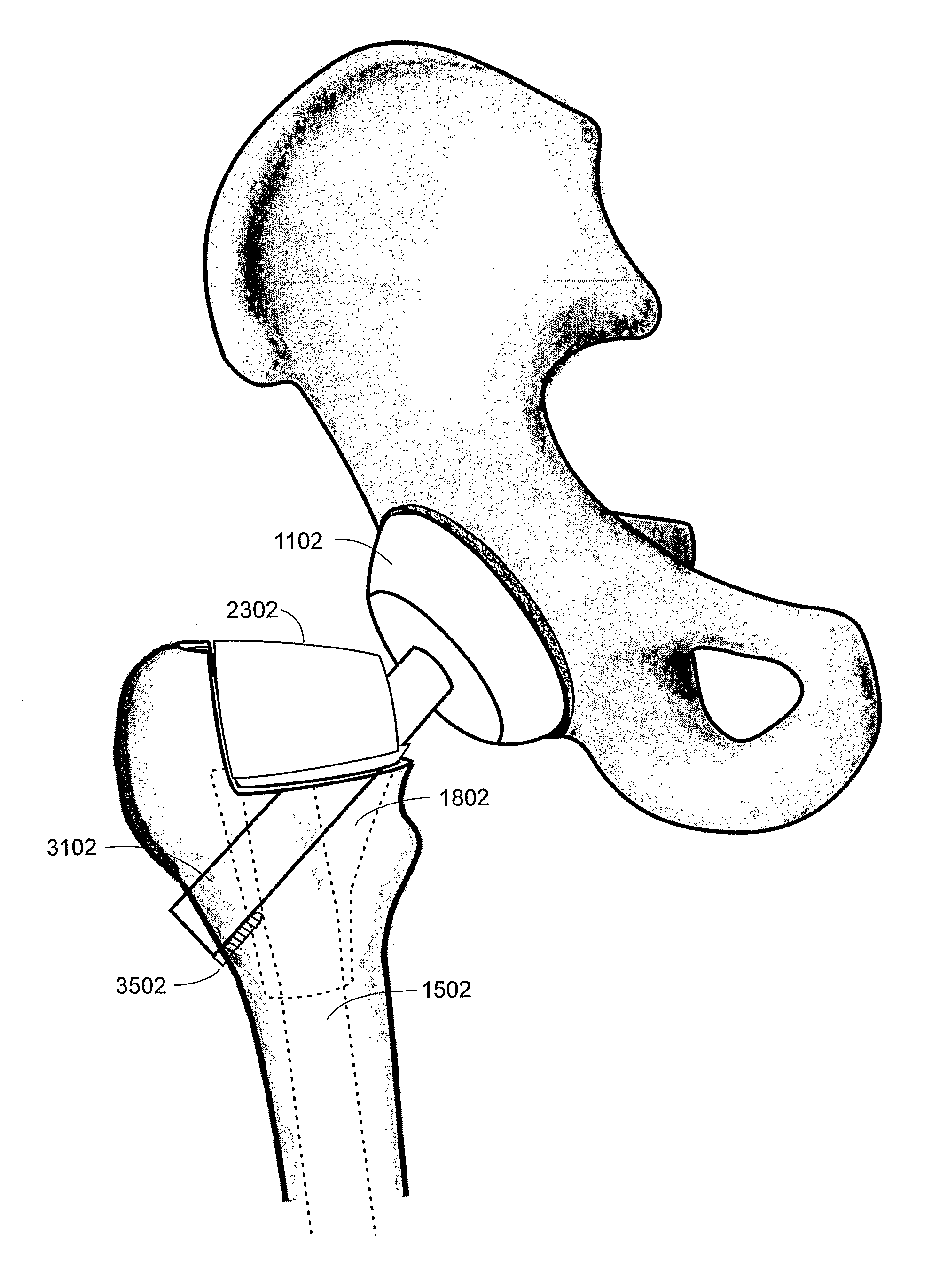
Methods and apparatus of the present invention provide for orthopedic total replacement of the hip while substantially preserving muscles and soft tissues around the hip joint resulting in reduced healing time and decreased risk of dislocation following the procedure. In an exemplary embodiment, the acetabulum is prepared and fitted with a prosthetic acetabular cup 702 and a prosthetic femoral head 1102 is fitted into the prosthetic acetabular cup 702. An intramedullary rod 1502 is inserted longitudinally into the femur. A prosthetic femoral neck 3102 is then inserted from a point along the side of the patient's body and into the side of the femur and through a pre-existing lateral bore in the intramedullary rod 1502 and through the remainder of the femur to join the prosthetic femoral head 1102. The methods and apparatus include structures and techniques for fixing the prosthetic femoral neck 3102 in relation to the intramedullary rod 1502.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
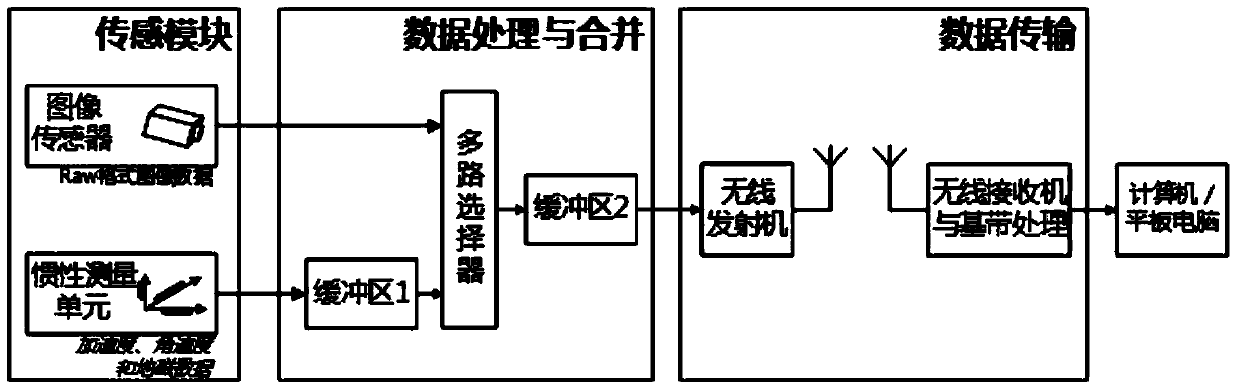
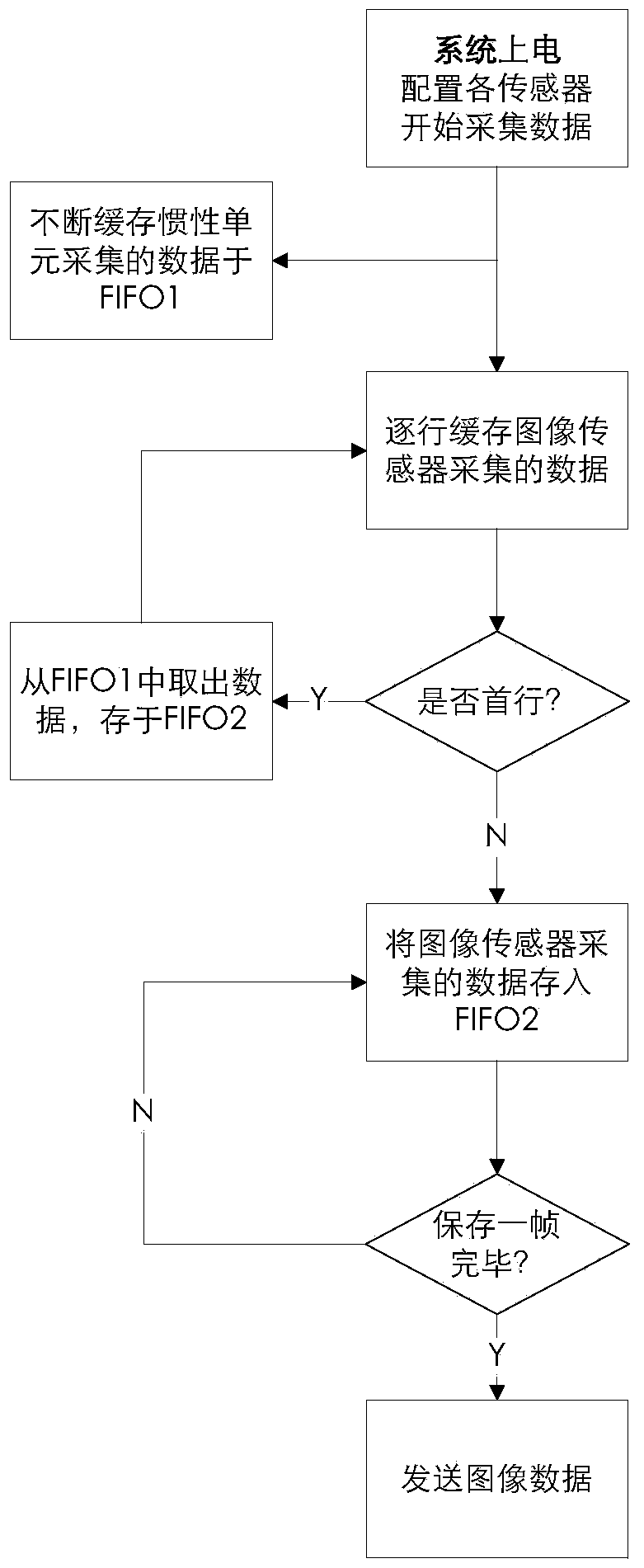
Real-time visualization assistant positioning system for interior of hip joint in total hip replacement arthroplasty
ActiveCN103735303AReduce the difficulty of surgeryImprove the success rate of surgerySurgeryFemoral headsData acquisitionPositioning system
A real-time visualization assistant positioning system for the interior of a hip joint in total hip replacement arthroplasty is divided into two portions of hardware and software, wherein the hardware can be divided into three modules of a sensing data gathering module, a data merging and processing module and a data transmission module according to functions, and takes charge of gathering information of images, accelerated speed and the like, encapsulating the information into data of an image, and transmitting the data of the image to a computer or a flat computer, and the software can be divided into four portions of a data extraction portion, a position and posture measurement and calculation module, a data fusion portion and a three dimensional (3D) display module, and takes charge of figuring out a relative position and a relative posture of an artificial thigh bone and acetabulum through various sensing data, improving precision and reliability of measurement and calculation through fusion of redundant data, and showing the relative position and the relative posture to a doctor in 3D mode. The real-time visualization assistant positioning system for the interior of the hip joint in the total hip replacement arthroplasty presents movement status of the thigh bone in the acetabulum and a relative position relation of the thigh bone and the acetabulum in real time, assists the doctor in visually observing installation status of the artificial thigh bone with the acetabulum during the operation process, and greatly improves success rate and operation curative effects of the total hip replacement arthroplasty.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
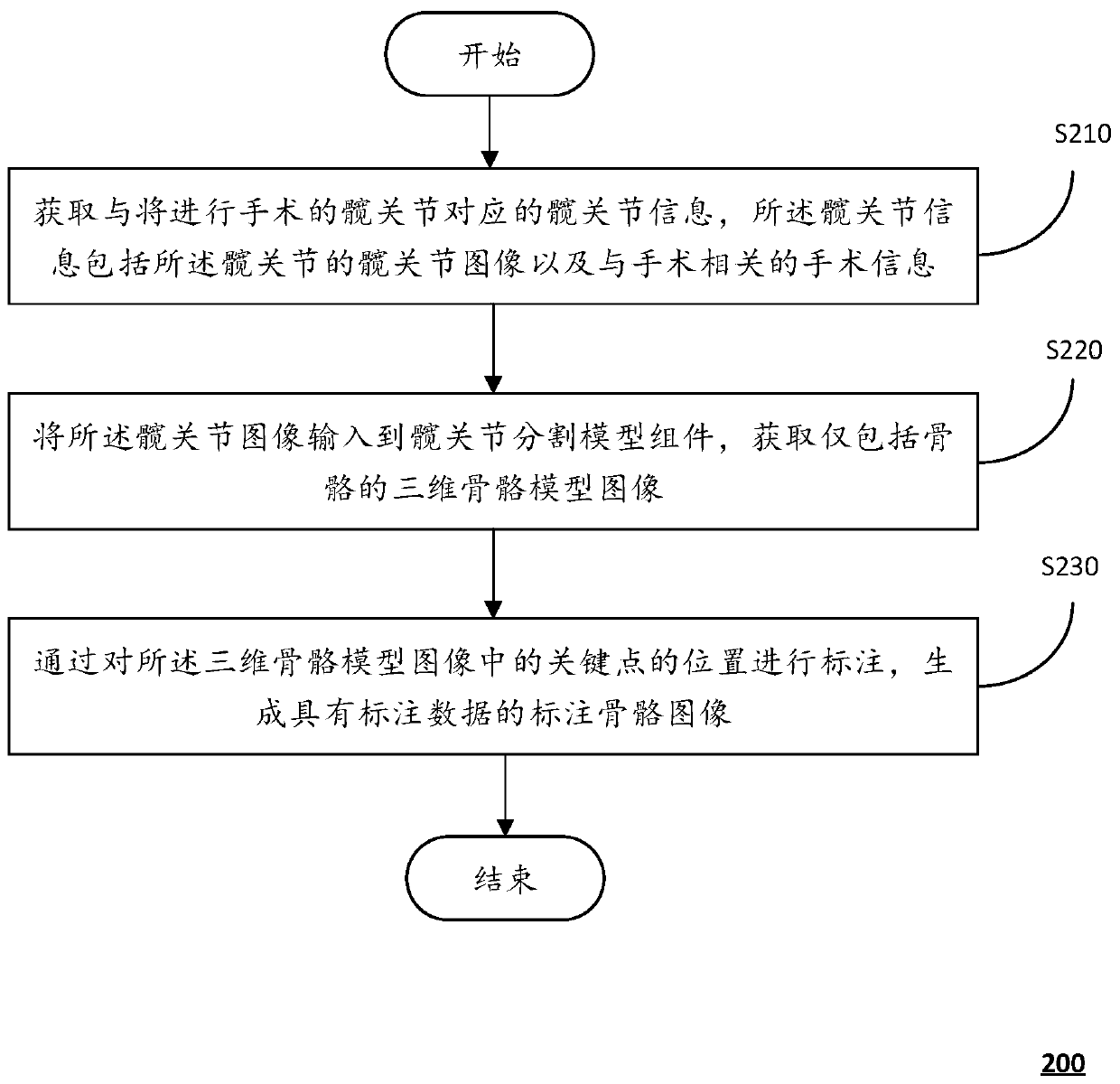
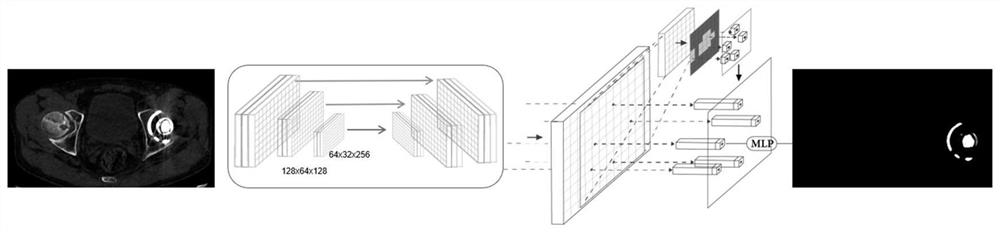
Hip joint image processing method based on deep learning and computing equipment
ActiveCN111179350AReduce dislocationReduce loosenessImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingThree dimensional measurement
The invention discloses a hip joint image processing method based on deep learning, and the method is suitable for being executed in computing equipment, and comprises the steps: obtaining hip joint information corresponding to a hip joint to be subjected to an operation, and enabling the hip joint information to comprise a hip joint image of the hip joint and operation information related to theoperation; inputting the hip joint image into a hip joint segmentation model assembly determined from the operation information, and obtaining a three-dimensional skeleton model image only comprisinga skeleton; labelling the positions of key points in a three-dimensional skeleton model image to generate a labeled skeleton image with labeled data. By the adoption of the three-dimensional measurement system and method, three-dimensional measurement data with high accuracy can be provided for prosthesis replacement before a total hip replacement operation is conducted.
Owner:张逸凌 +2
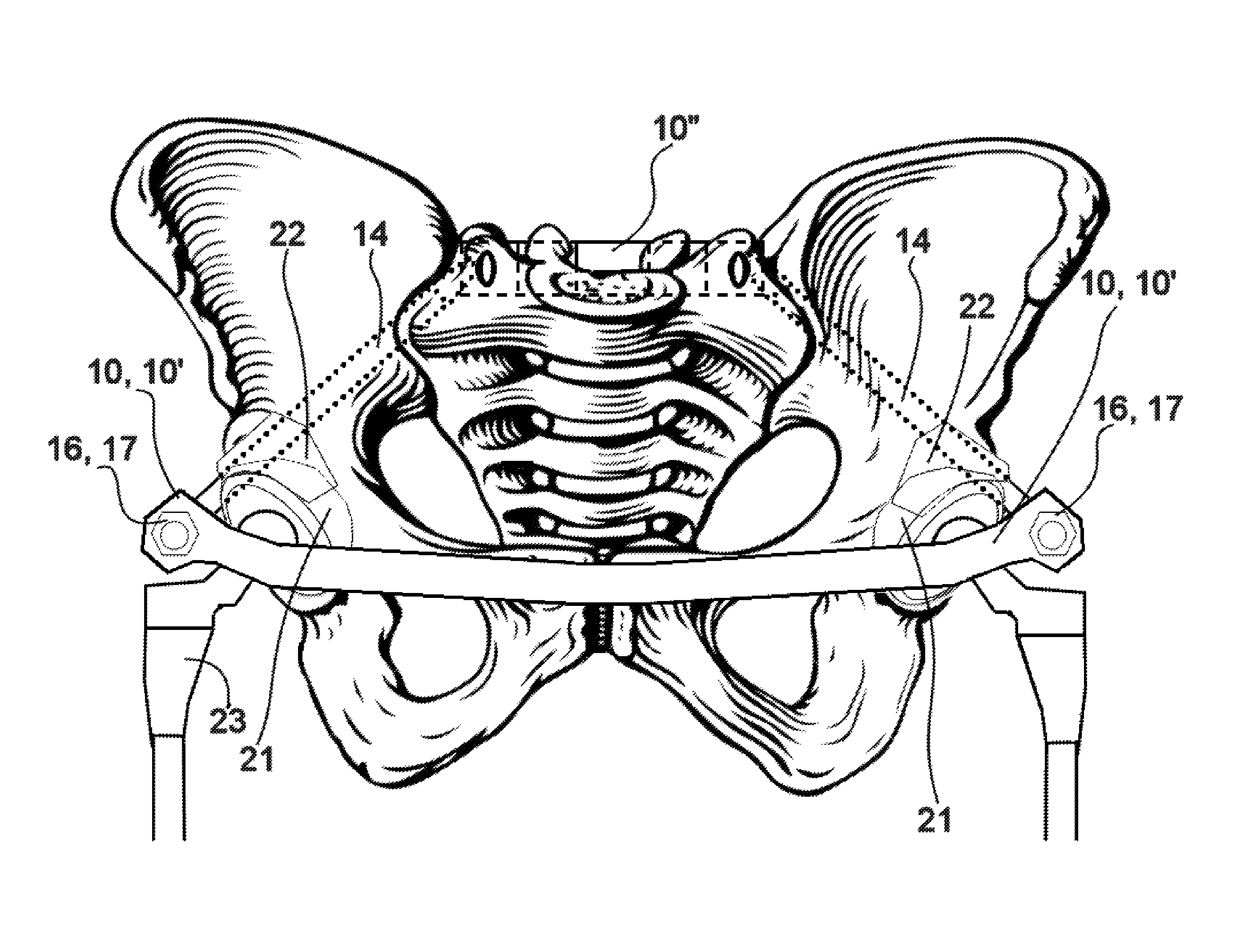
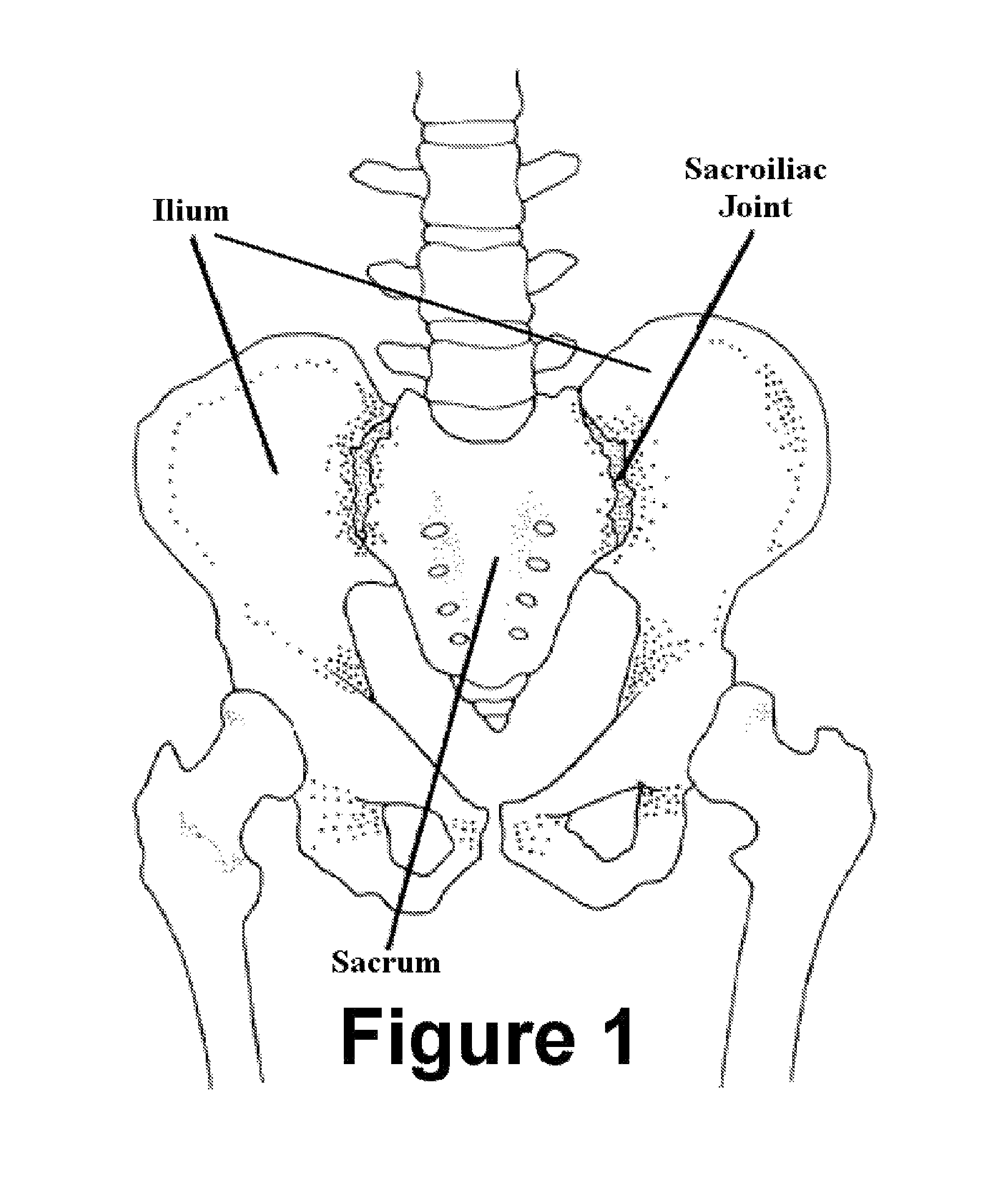
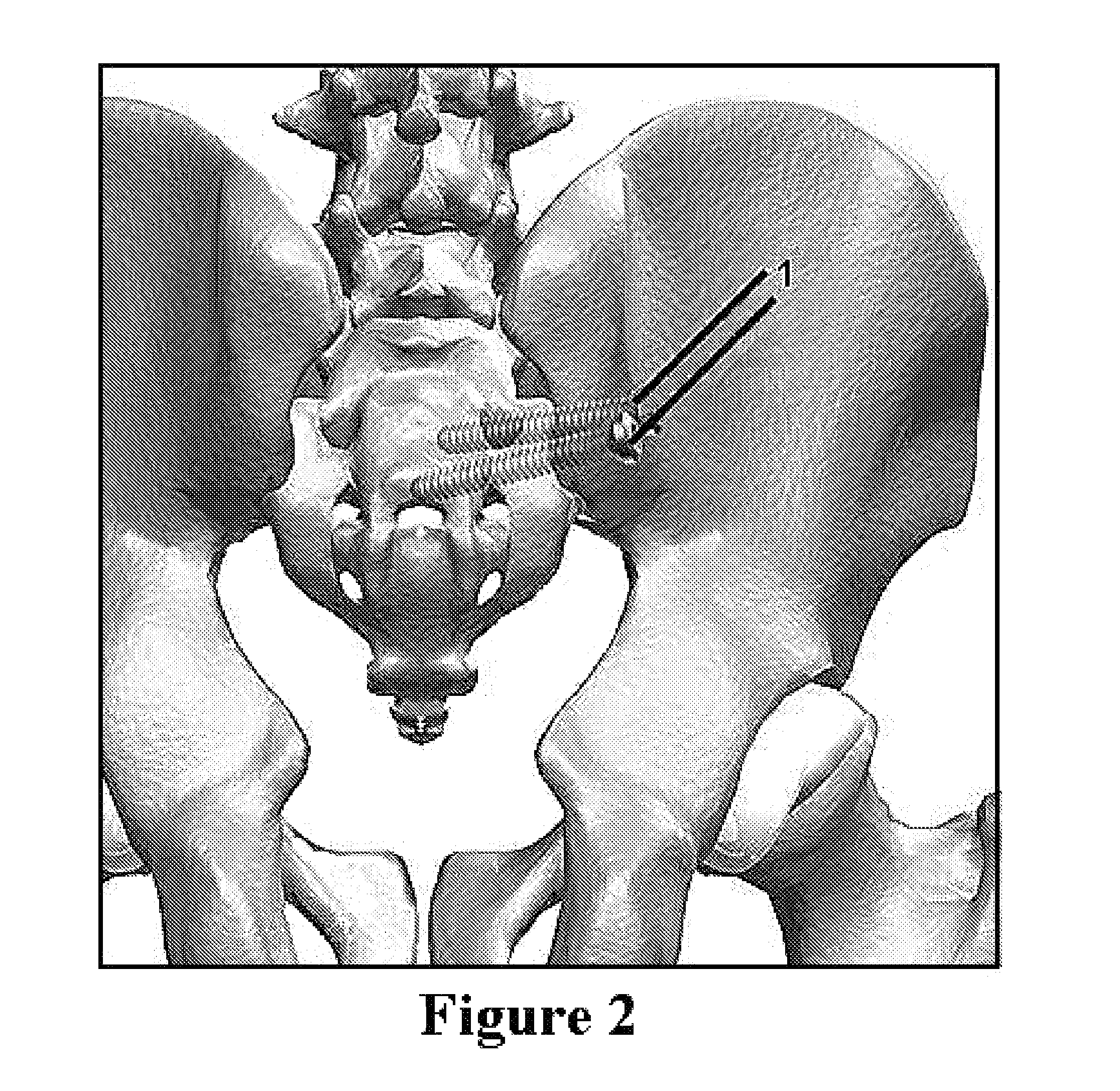
Method and apparatus for minimally invasive treatment of unstable pelvic ring injuries combined with hip arthroplasty
The instant invention is a novel method and apparatus for minimally invasive treatment of unstable pelvic ring injuries combined with fixation of acetabular cup assemblies for total hip arthroplasty. Fixation means and acetabular cup assemblies are affixed to the ilia and subcutaneous anteriorly bowed elongated rods / plate including possibly a subcutaneous posterior plate are connected between the fixation means.
Owner:VAIDYA RAHUL
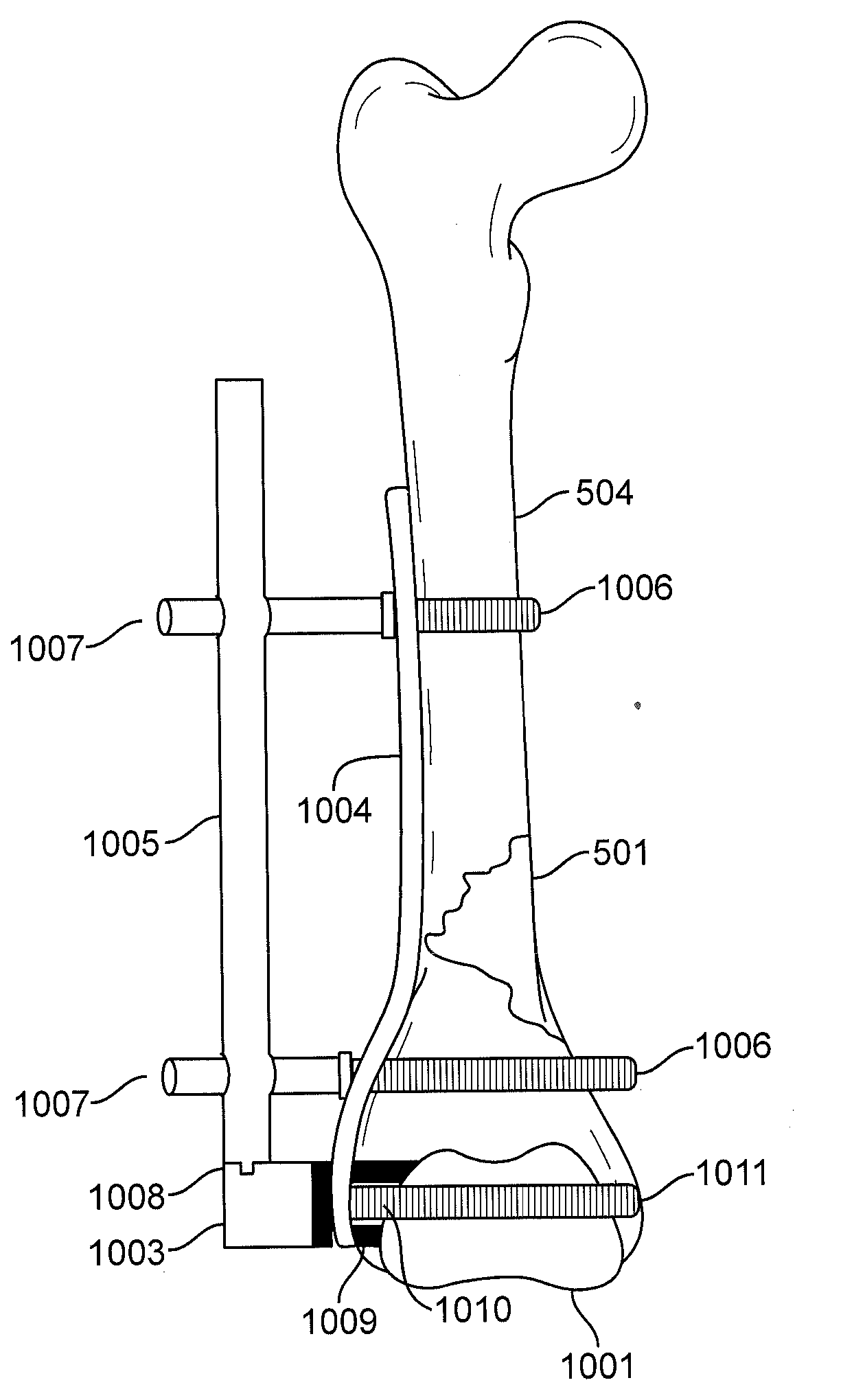
Periprosthetic Fracture Management Enhancements
A variety of options for for fracture fixation after total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty. The ability to pre-engineer fracture fixation contingent solutions into femoral or tibial components provides a distinct clinical advantage in the planning and execution for periprosthetic fracture fixation. Methods and apparatus include targeting devices allowing for intimate association of fixed angle locking screws in pre-drilled holes in an existing prosthetic, femoral nail, or other components including additional fixation components. Such apparatus and methods further include alignment devices and other components to allow for ease of repair of periprosthetic fractures utilizing the pre-engineered solutions.
Owner:GENESIS MEDICAL DEVICES
Method and apparatus for attachment in a modular hip replacement or fracture fixation device
InactiveUS20130204390A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityJoint implantsFemoral headsInterference fitRight femoral head
Methods and apparatus for orthopedic replacement of the hip and hip fracture fixation devices include structures and techniques for fixing or enhancing interconnection of implant components, such as by increasing the interconnection in an interference fit with one or more tapers, threads, and / or cooling of components prior to assembly. For example, a prosthetic femoral neck implant can include a thread and a Morse taper for lockable attachment to a prosthetic femoral head and / or intramedullary stem.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
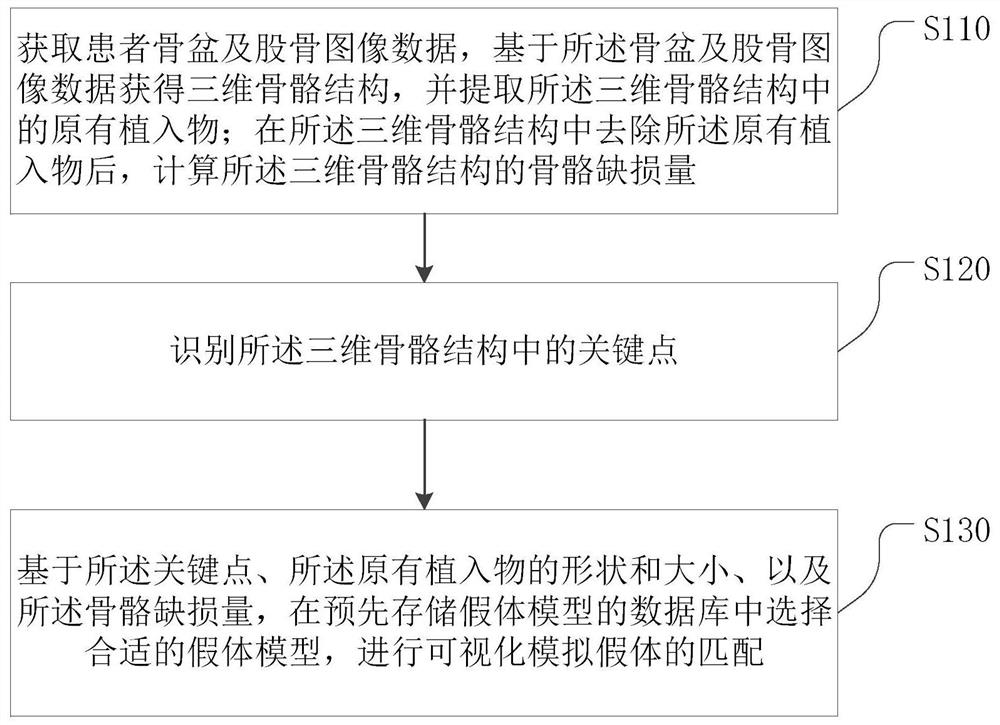
Total hip replacement revision preoperative planning method and equipment based on deep learning
The invention provides a total hip replacement revision preoperative planning method and equipment based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring pelvis and femur image data of a patient, acquiring a three-dimensional skeleton structure based on the pelvis and femur image data, and extracting an original implant in the three-dimensional skeleton structure; identifying key points in the three-dimensional skeleton structure; and based on the key points and the shape and size of the original implant, selecting a proper prosthesis model from a database in which prosthesis models are pre-stored, and carrying out visual simulation prosthesis matching. Technical support is provided for doctors to carry out total hip replacement revision, so that the surgical operation is more accurate and safer, and the development of the surgical operation towards the intelligent, precise and minimally invasive direction is promoted.
Owner:BEI JING LONGWOOD VALLEY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
Surgical process for anterior hip replacement
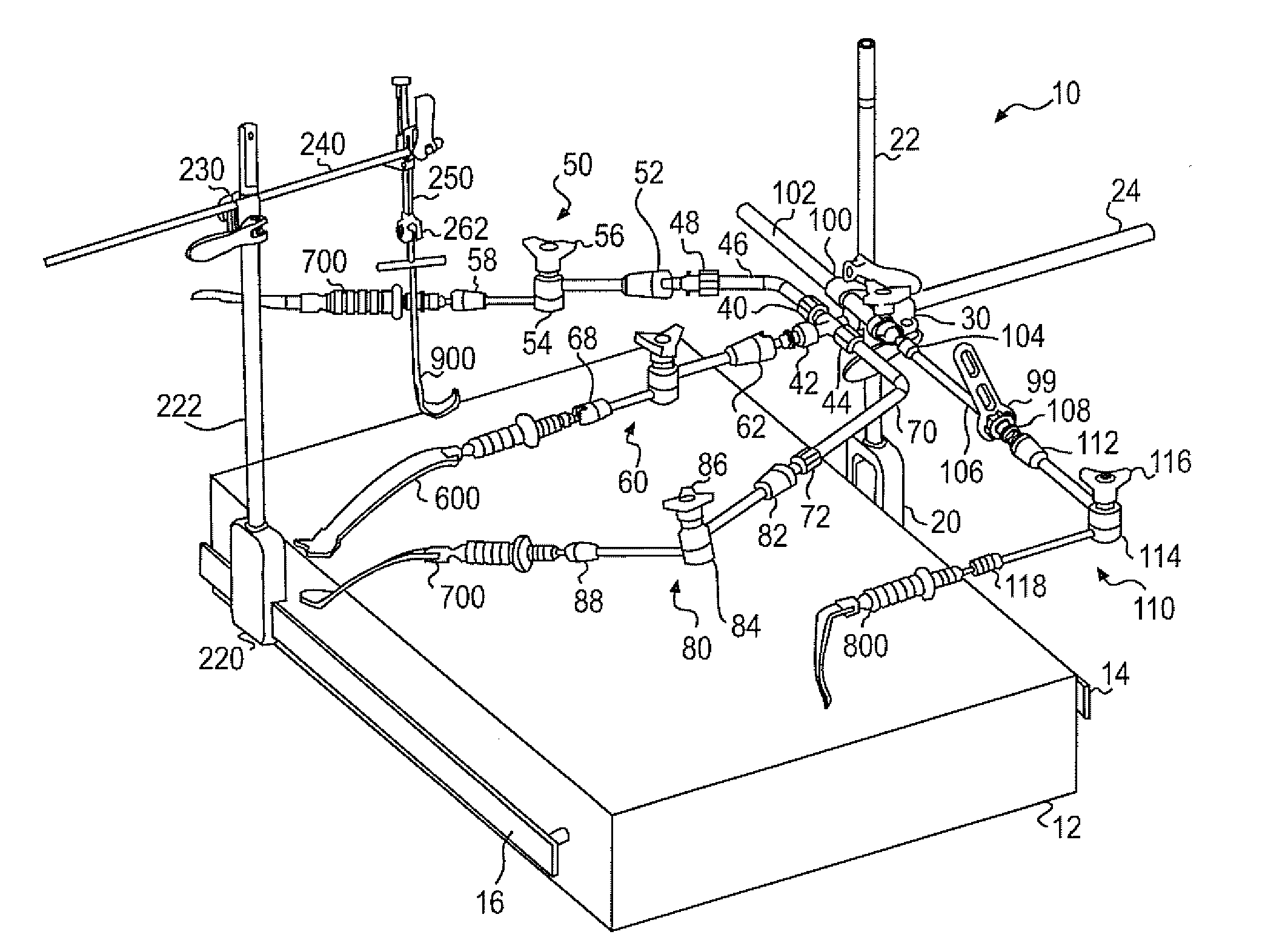
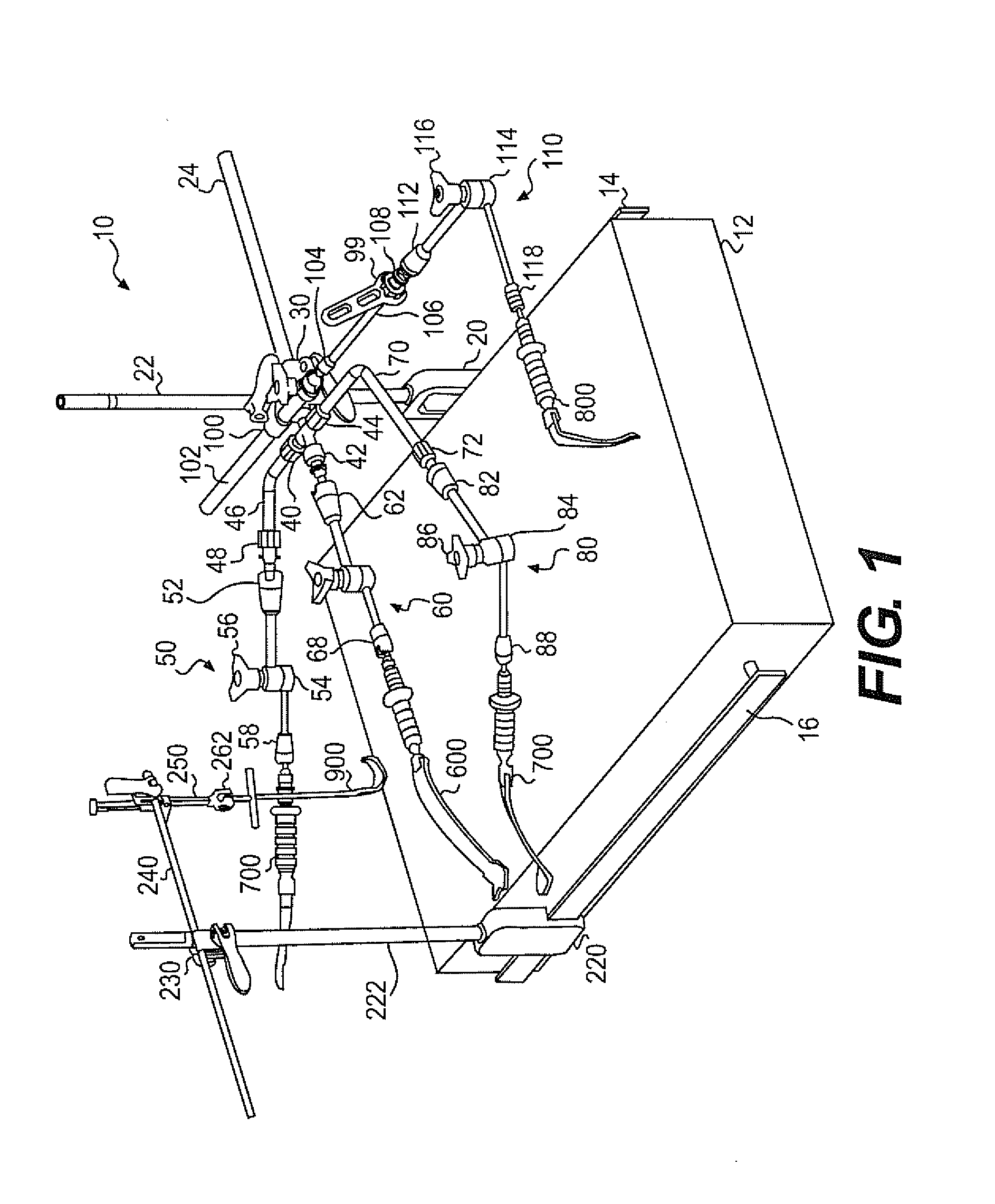
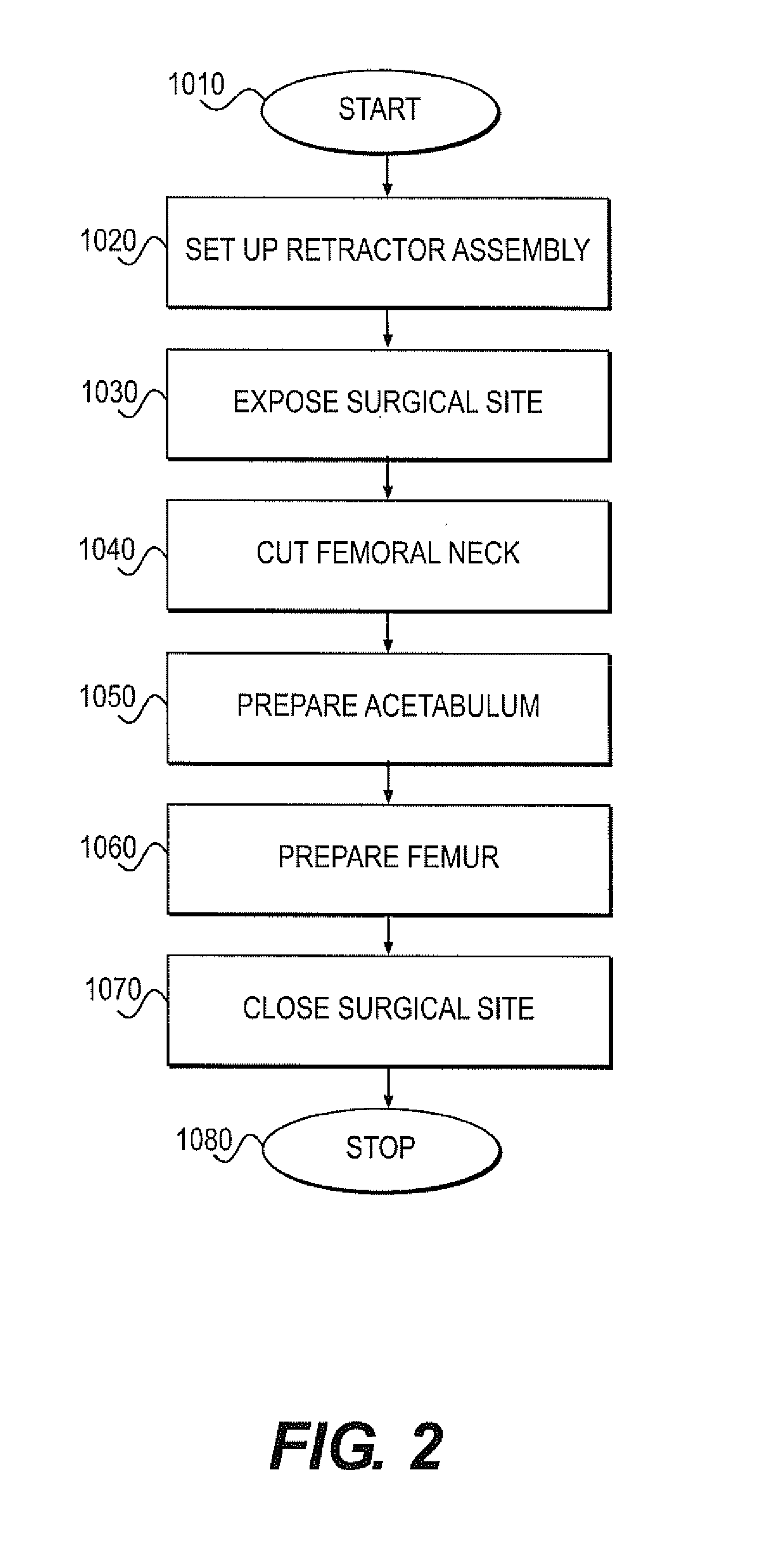
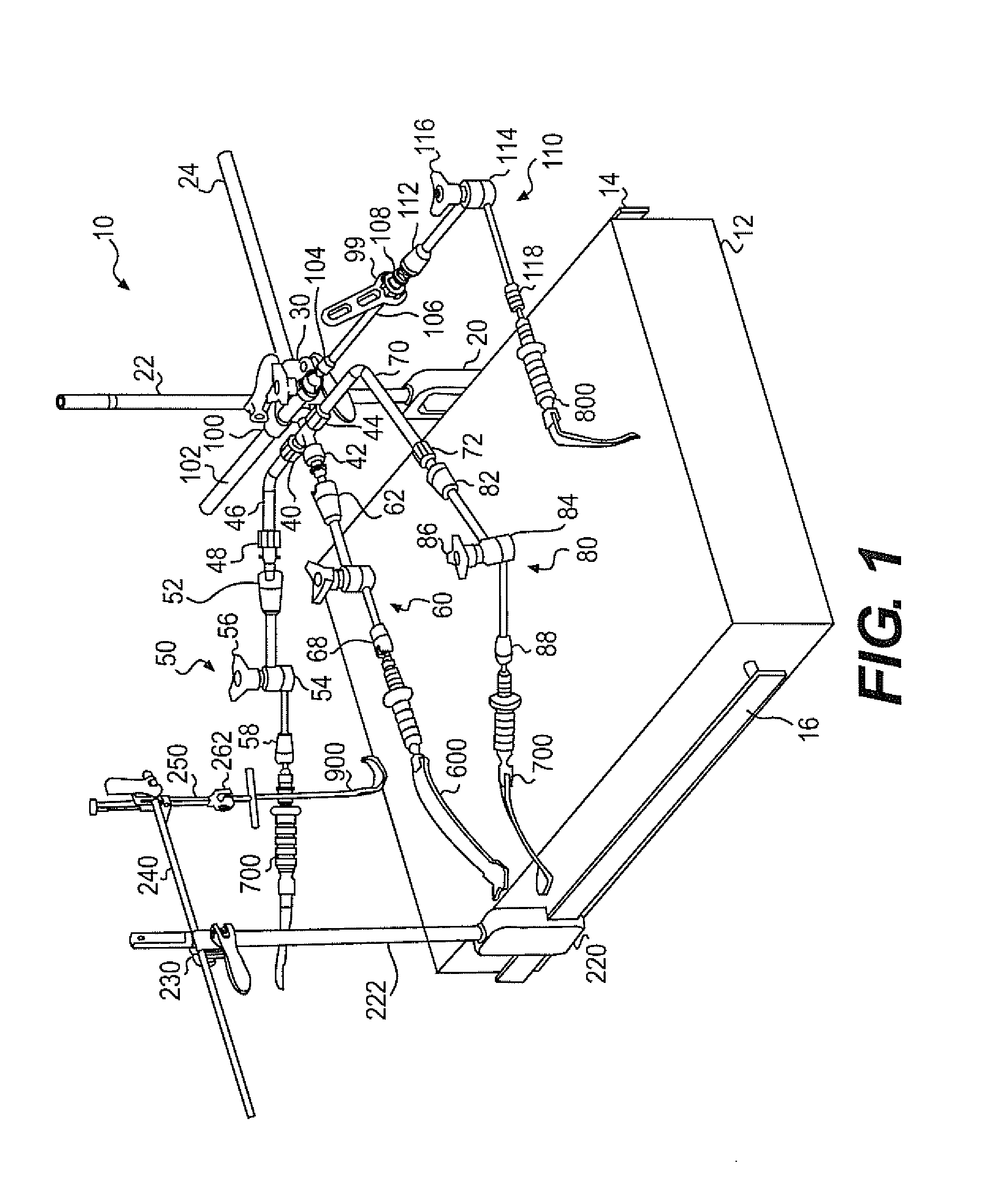
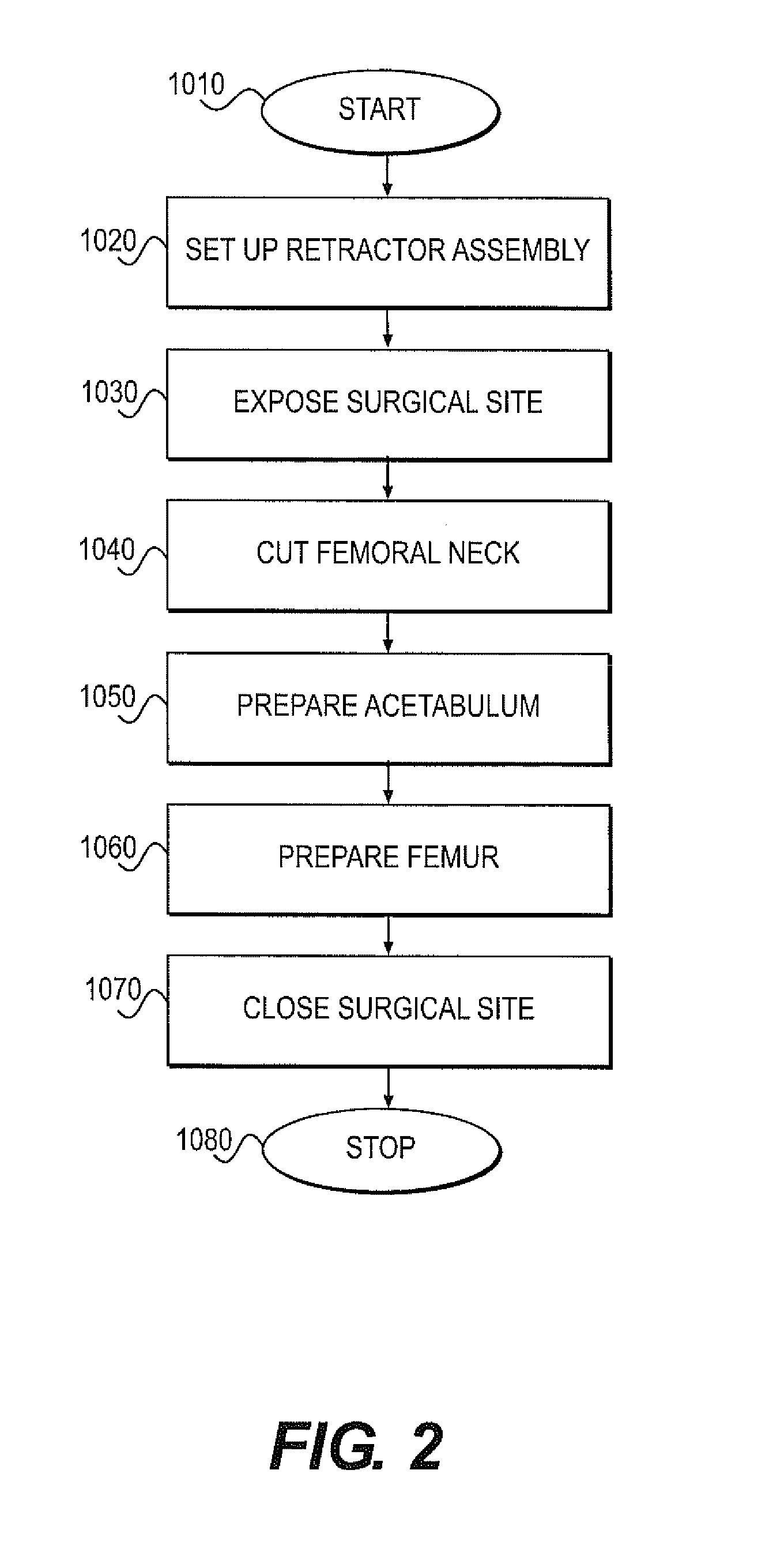
Various exemplary embodiments relate to a method of performing an anterior approach hip replacement using a retractor assembly. The method may include: providing a retractor assembly including a first vertical post, a plurality of accessory arms mounted to the first post, a second vertical post, and a femur distractor mounted to the second post; exposing a surgical site including the femoral neck and acetabulum using a plurality of retractors secured to the accessory arms; cutting the femoral neck to remove the femoral head; preparing the acetabulum for insertion of an acetabular cup; preparing the femur for insertion of a femoral implant by lifting the femur using a femur hook and the femur distractor; and closing the surgical site. In various alternative embodiments, the retractors may include a lesser trochanteric retractor coming from a direct medial approach and a greater trochanteric retractor coming from a lateral, posterior, proximal approach.
Owner:TEDAN SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
Individual biological type cushion block for bone defect in total knee replacement
The invention discloses an individual biological type cushion block for bone defect in total knee replacement. The individual biological type cushion block comprises a cushion block base body fixed to a bone bed through a fixing pile. The cushion block base body comprises a solid layer and a porous structure. The upper surface of the solid layer is fixed to a tibia support in a press fit contact mode. The cushion block base body and the fixing pile are integrally manufactured by adoption of a 3D printing technology. The individual biological type cushion block has the advantages of small osteotomy amount, good fixation in near and long term, smooth transition to surface of natural bone of the human body and no stress concentration.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Devices and methods for hip replacement
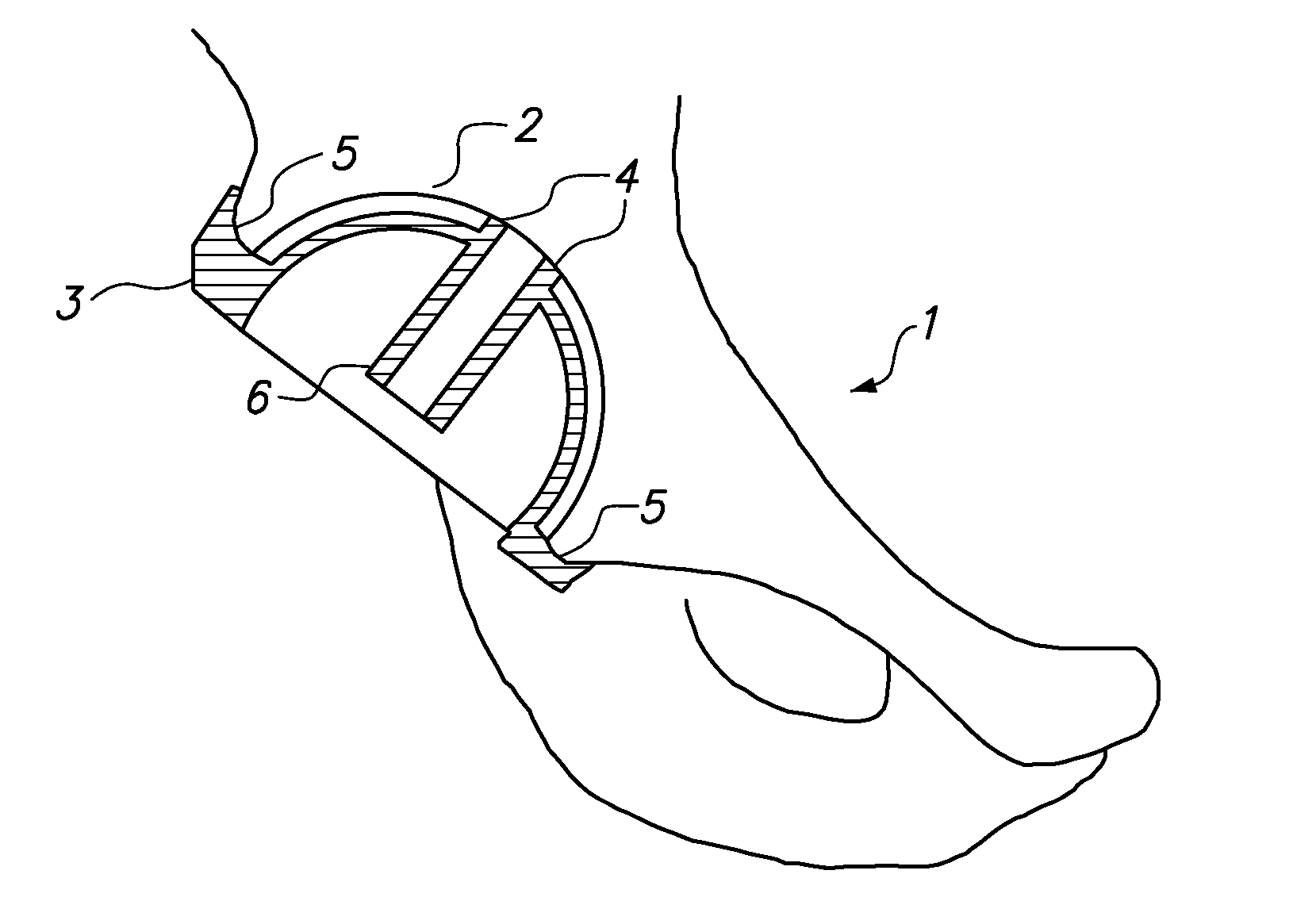
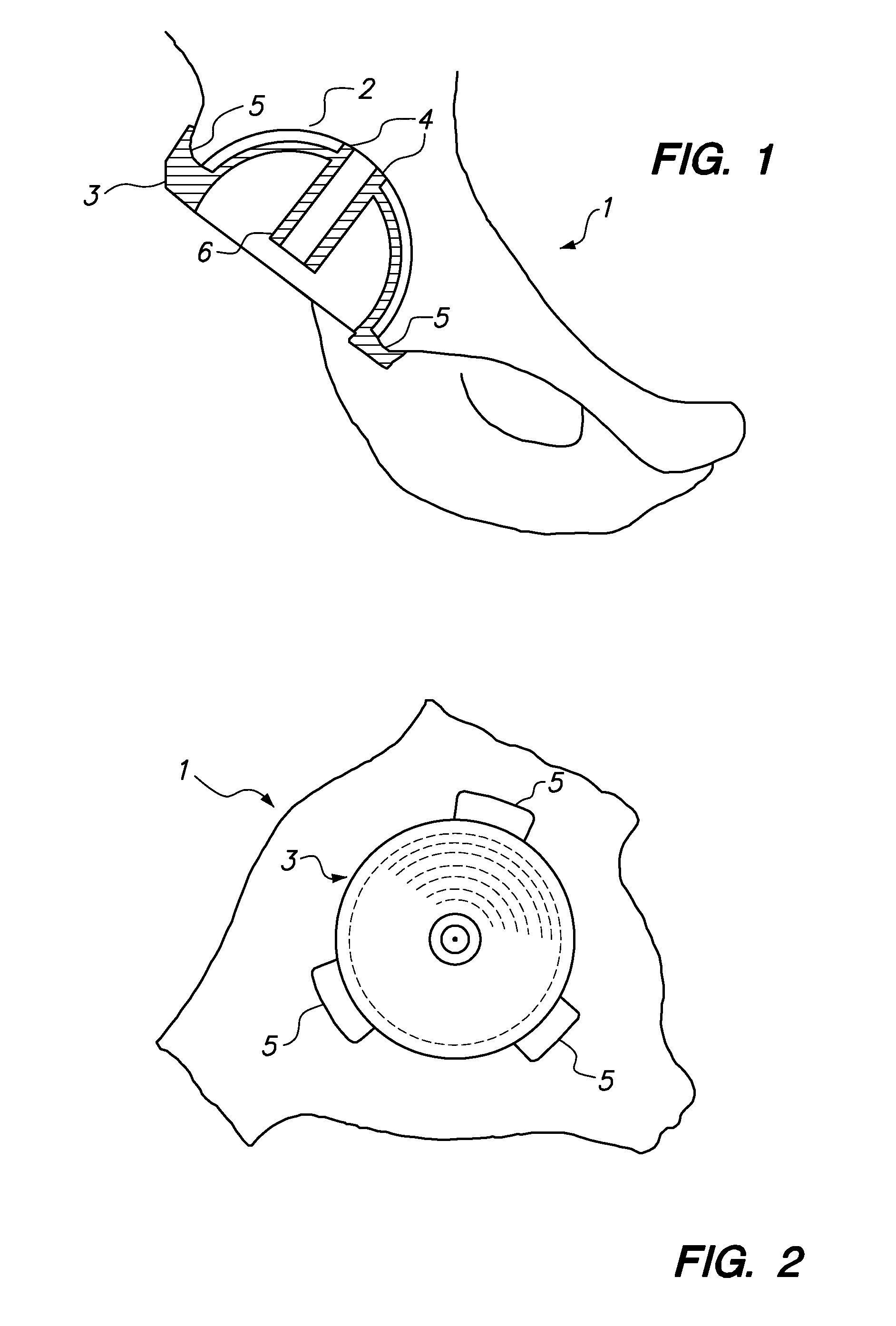
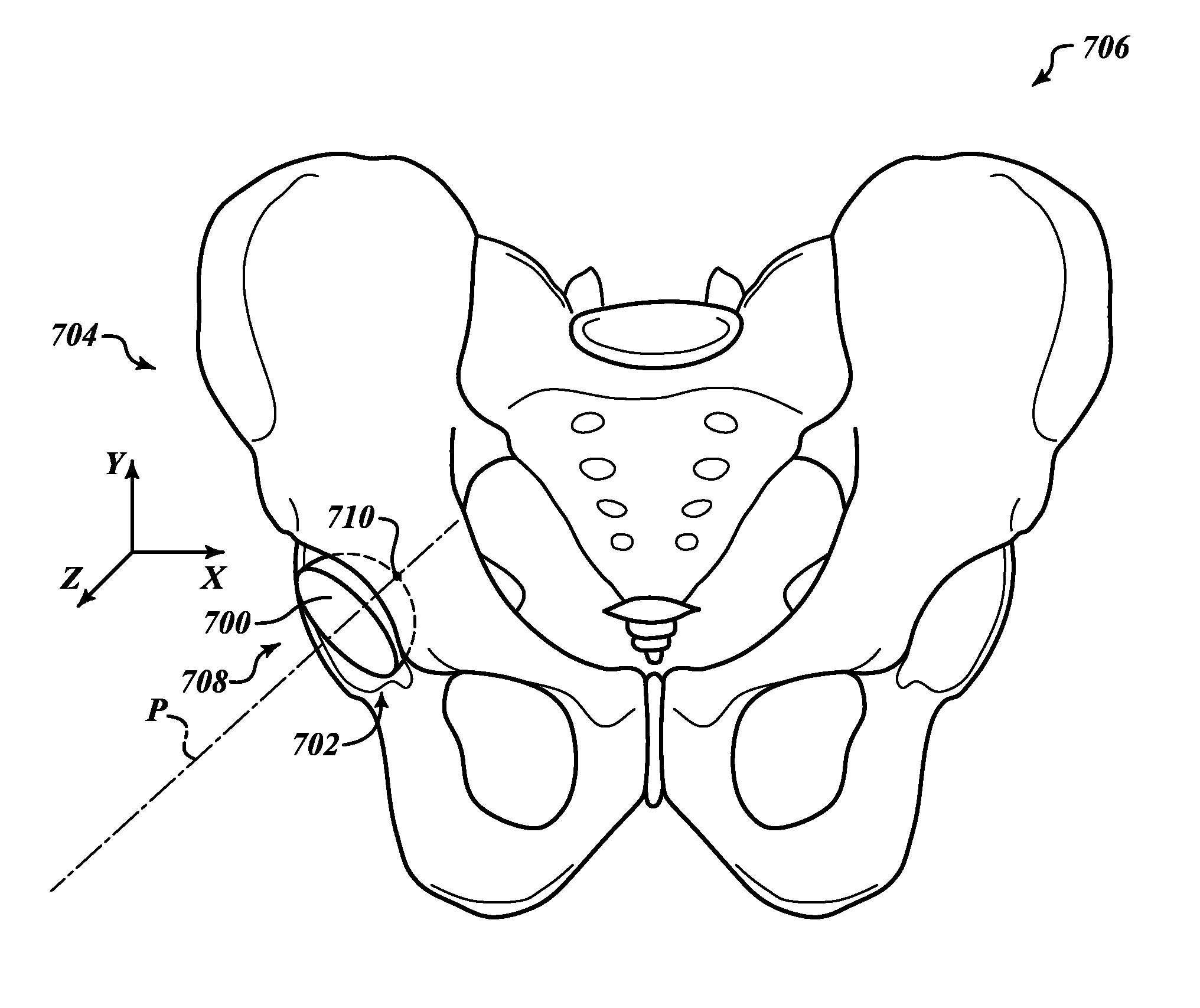
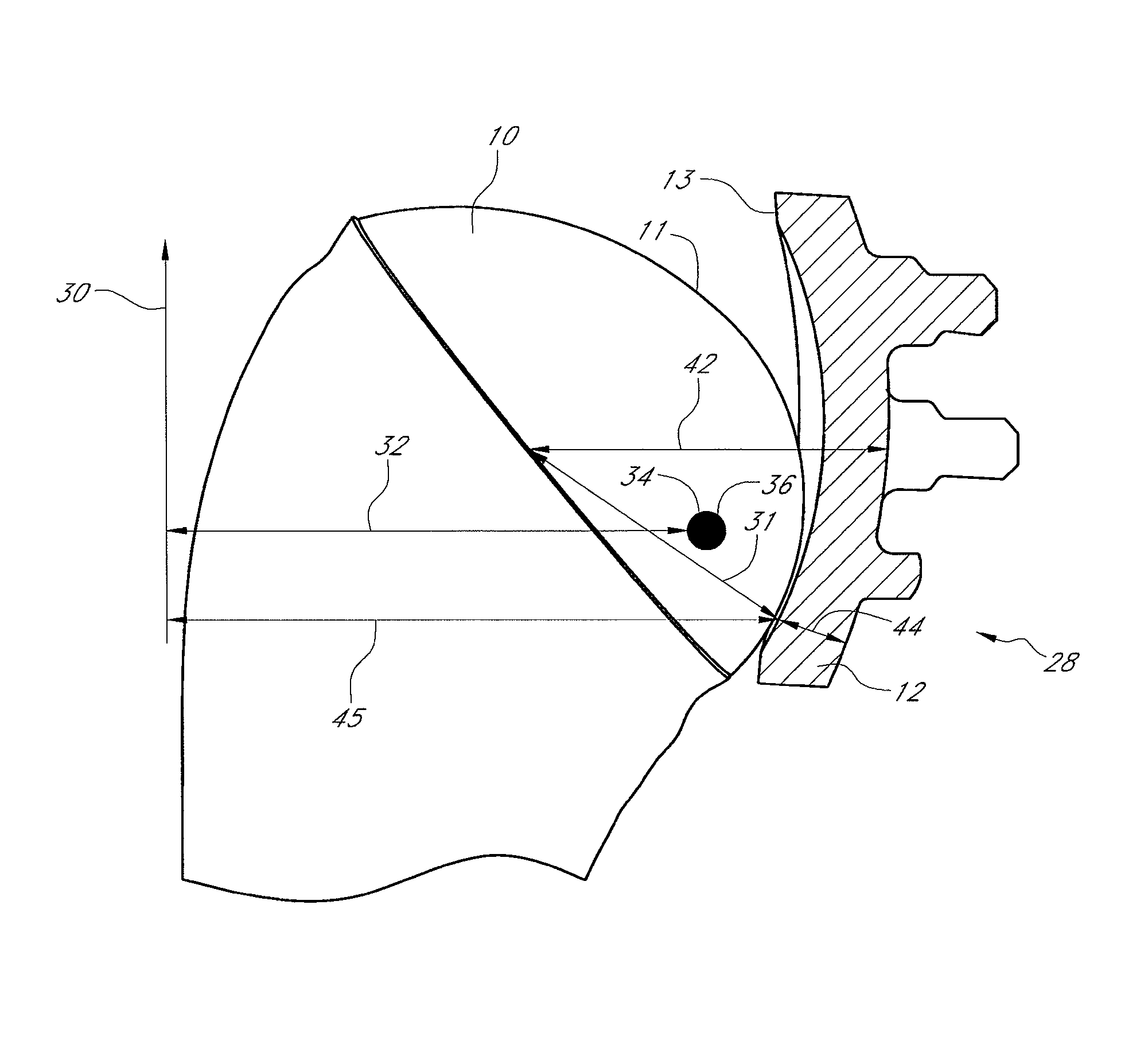
InactiveUS8998909B2Precise alignmentPrecise positioningImage analysisDiagnosticsHip joint replacement operationBone structures
Owner:BULLSEYE HIP REPLACEMENT
Non-spherical articulating surfaces in shoulder and hip replacement
An orthopedic device and method of use are provided that incorporate complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces to allow a greater available range of motion compared with existing artificial shoulder joint and artificial hip joints. According to some embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on a humeral head and / or glenoid of a shoulder prosthesis. In other embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on the acetabulum and / or femoral head of a hip prosthesis. These non-spherical surfaces can be used to adjust constraint, joint thickness, soft tissue tension, moment and arc of motion, and in doing so, influence motion.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Devices and methods for hip replacement
InactiveUS9211128B2Precise alignmentPrecise positioningJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesHip joint replacement operationBone structures
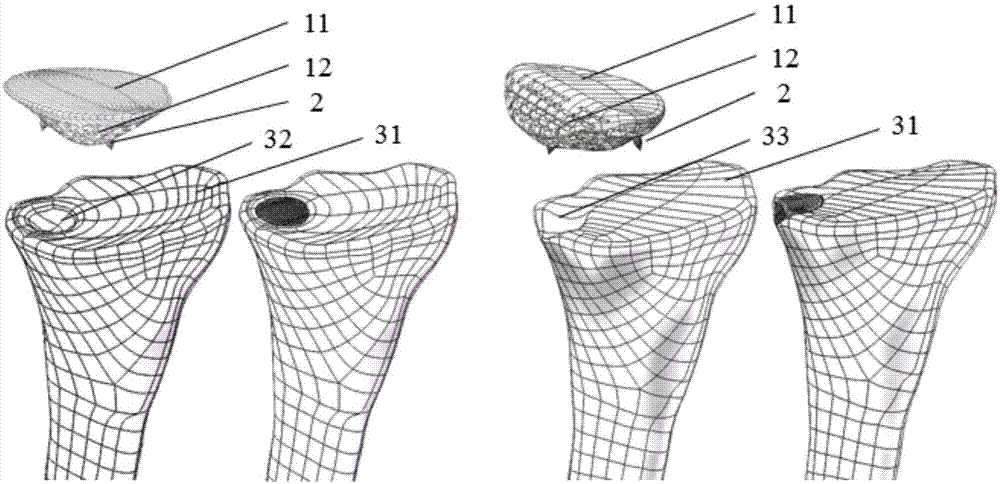
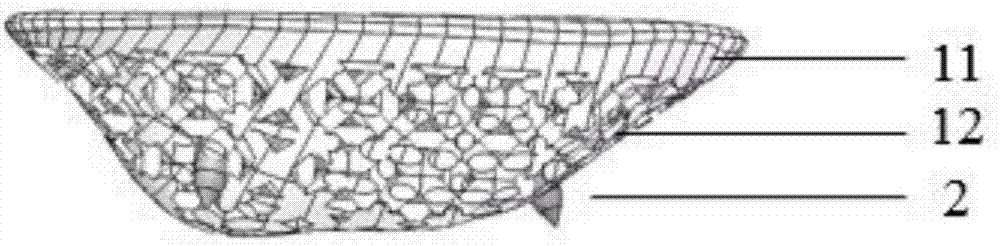
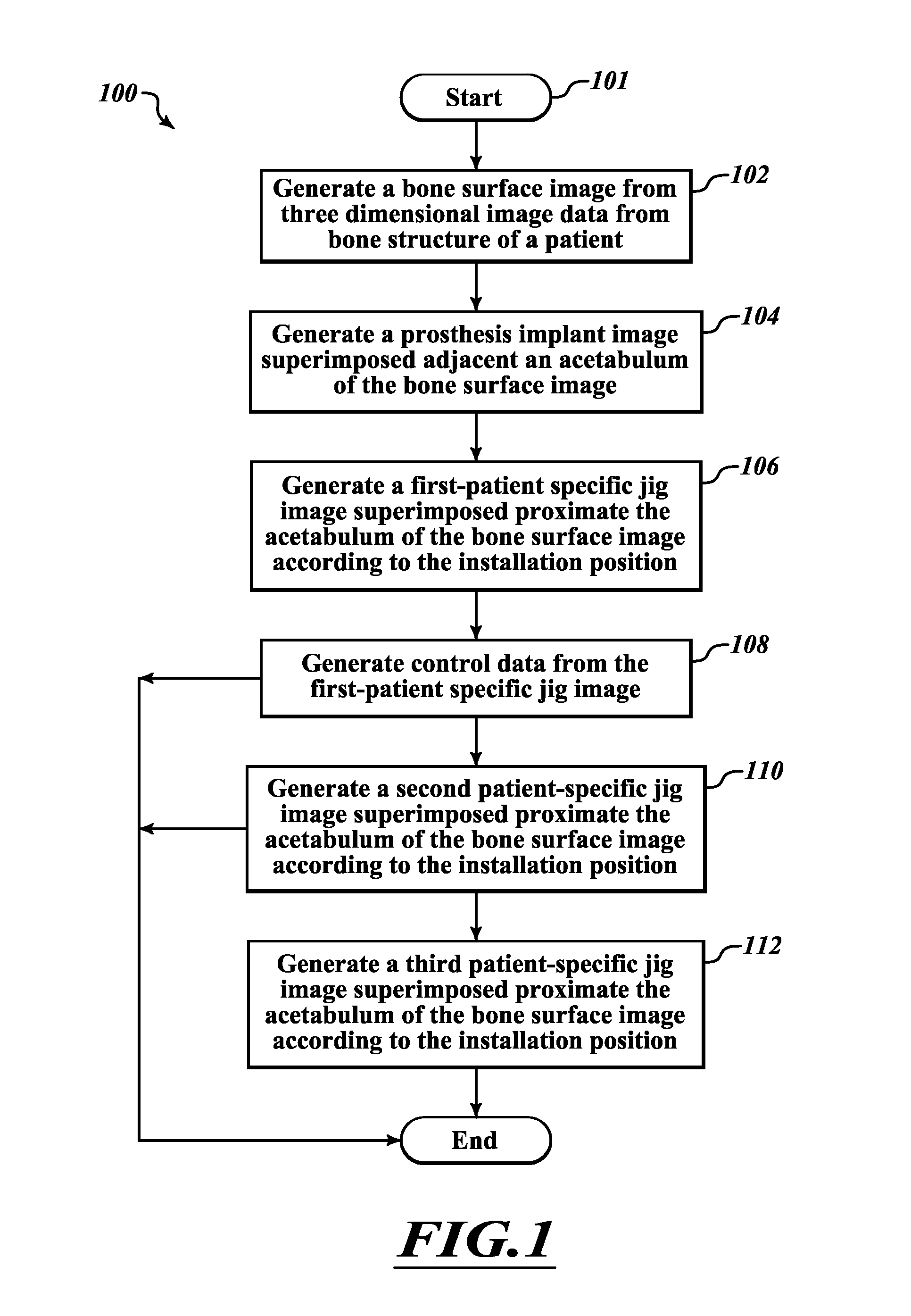
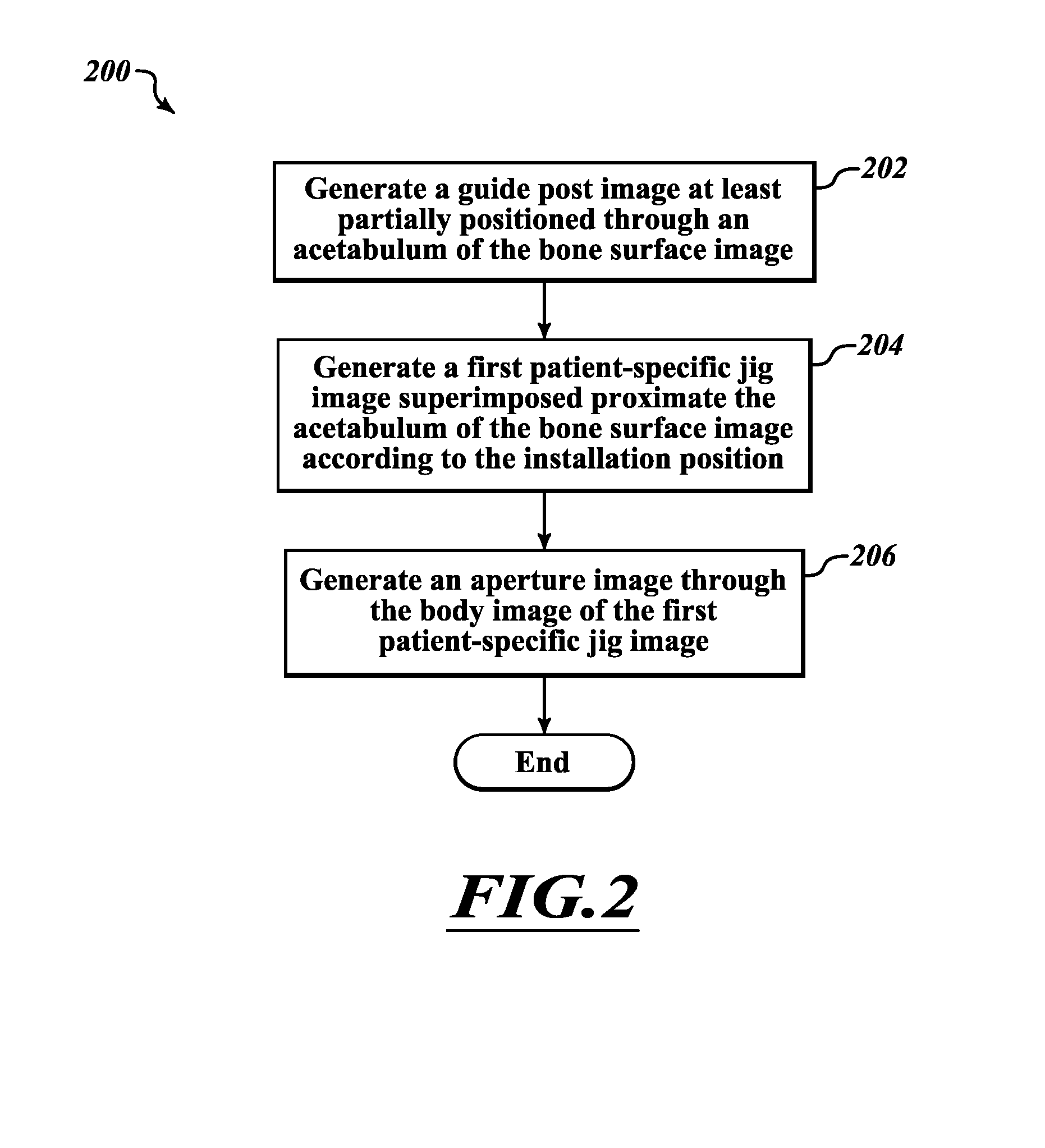
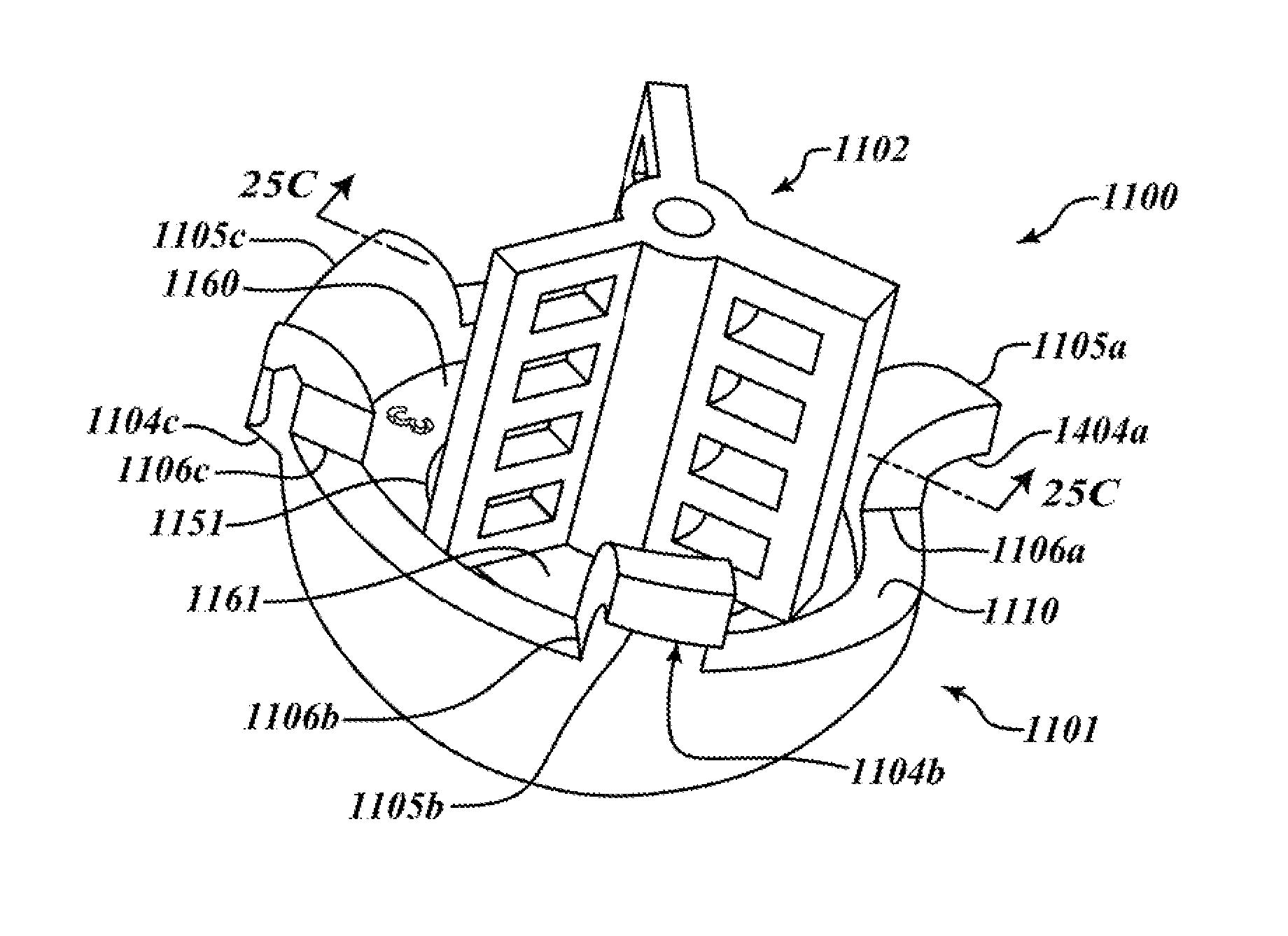
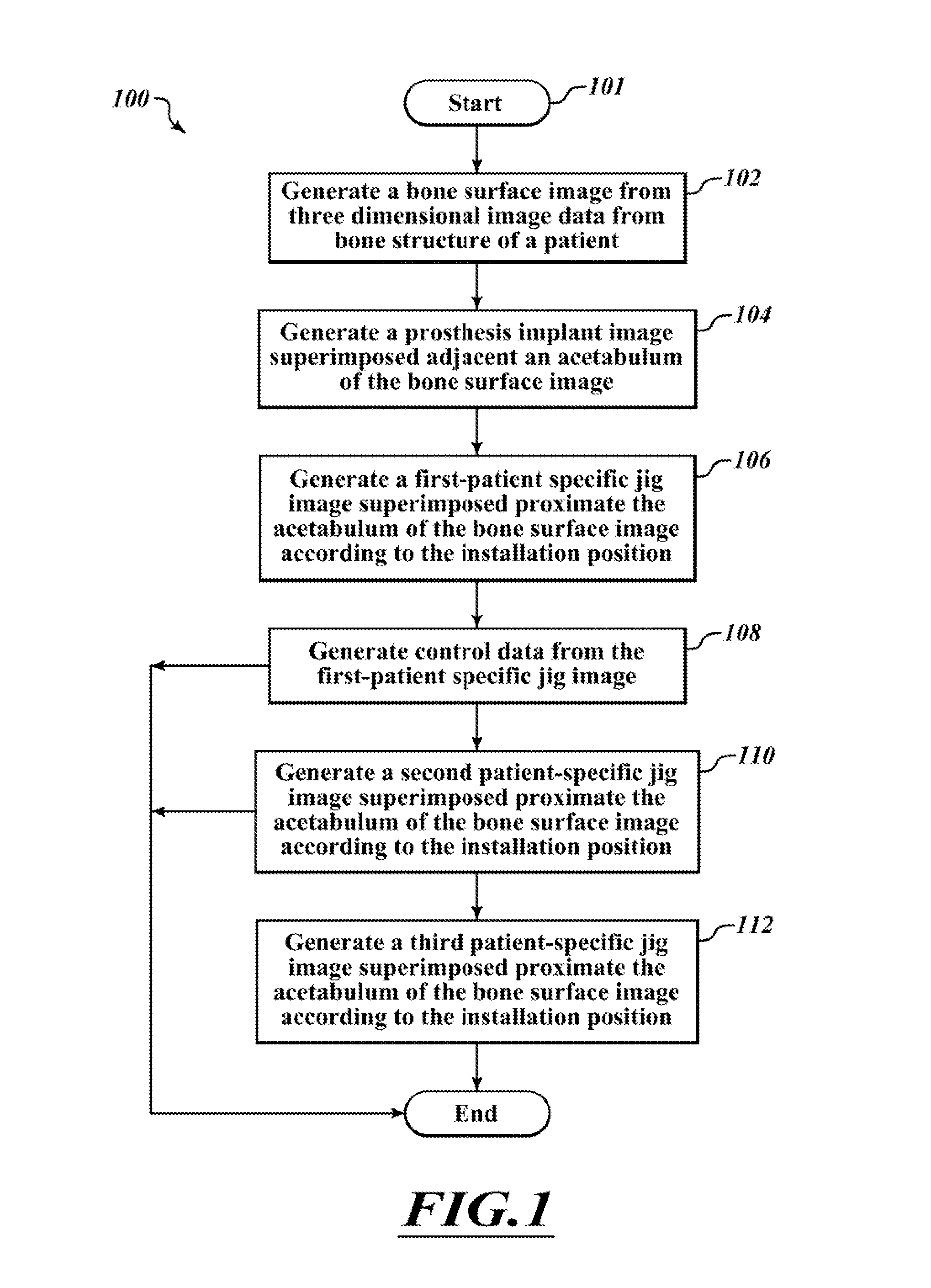
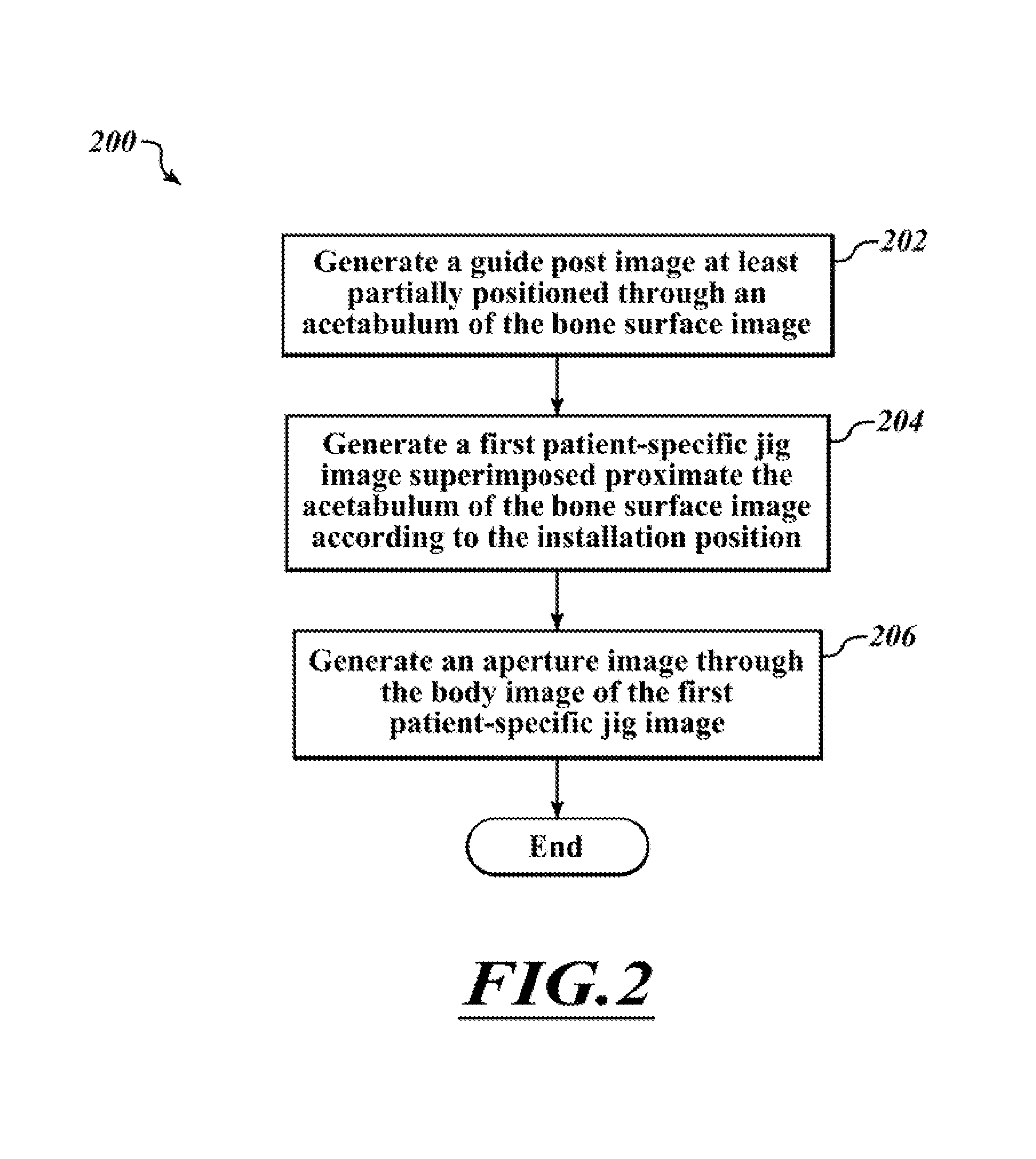
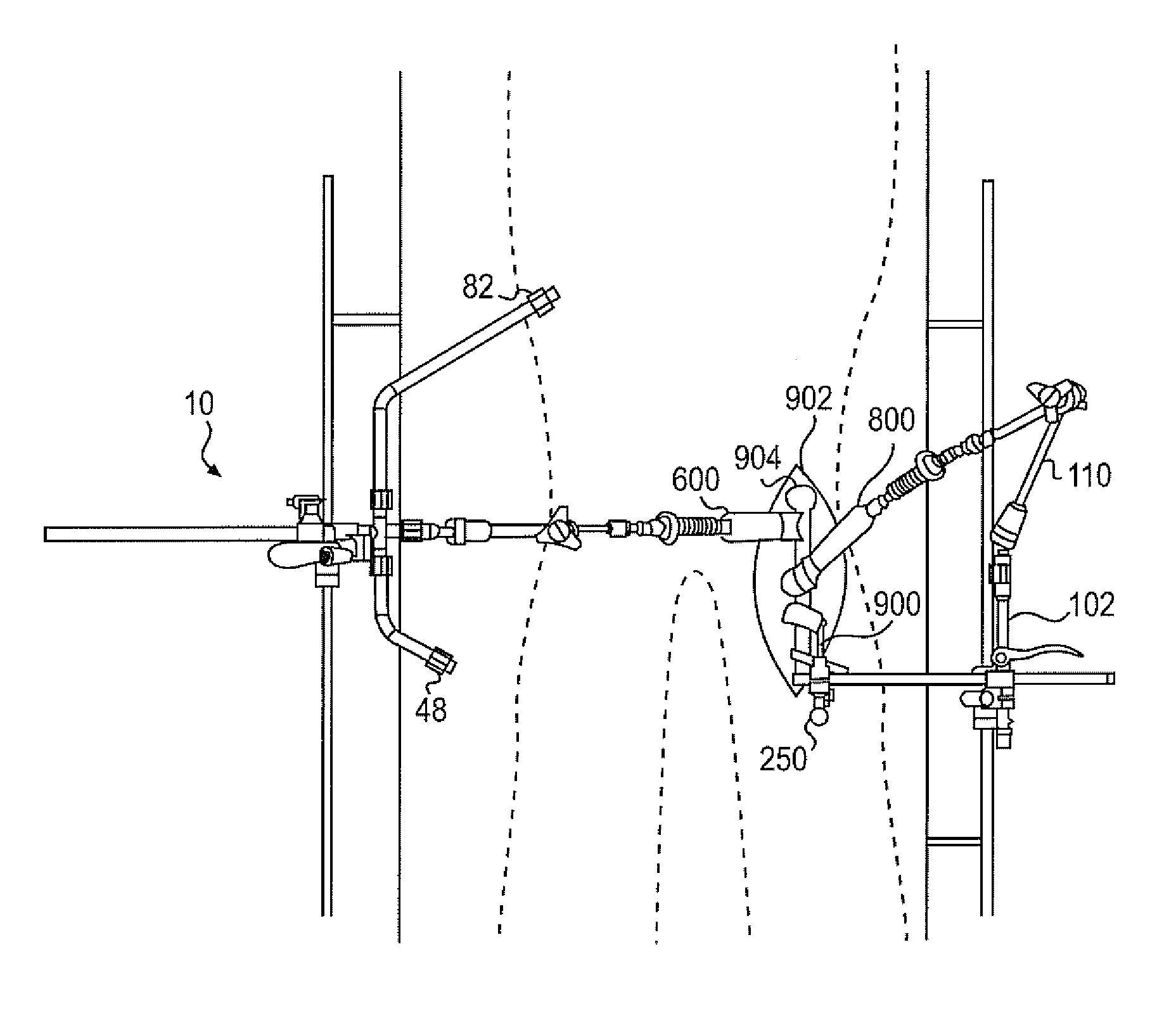
Devices and methods for use in hip replacement surgery can incorporate computer models of a patient's acetabulum and surrounding bone structure, a first patient-specific jig designed from the computer model and configured to correspond to a final installation position and orientation of a prosthetic hip implant, a second patient-specific jig, also designed from the computer model, configured to refine the procedure, if necessary, following use of the first patient-specific jig, and / or a third patient specific jig, designed from the computer model, configured to refine the procedure, if necessary, following use of the first and second patient-specific jigs, allowing the surgeon to properly position and orient the hip prosthesis. Also shown and described are novel devices for implanting an acetabular cup.
Owner:BULLSEYE HIP REPLACEMENT
Surgical process for anterior hip replacement
Owner:TEDAN SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
Cruciate replacing artificial knee
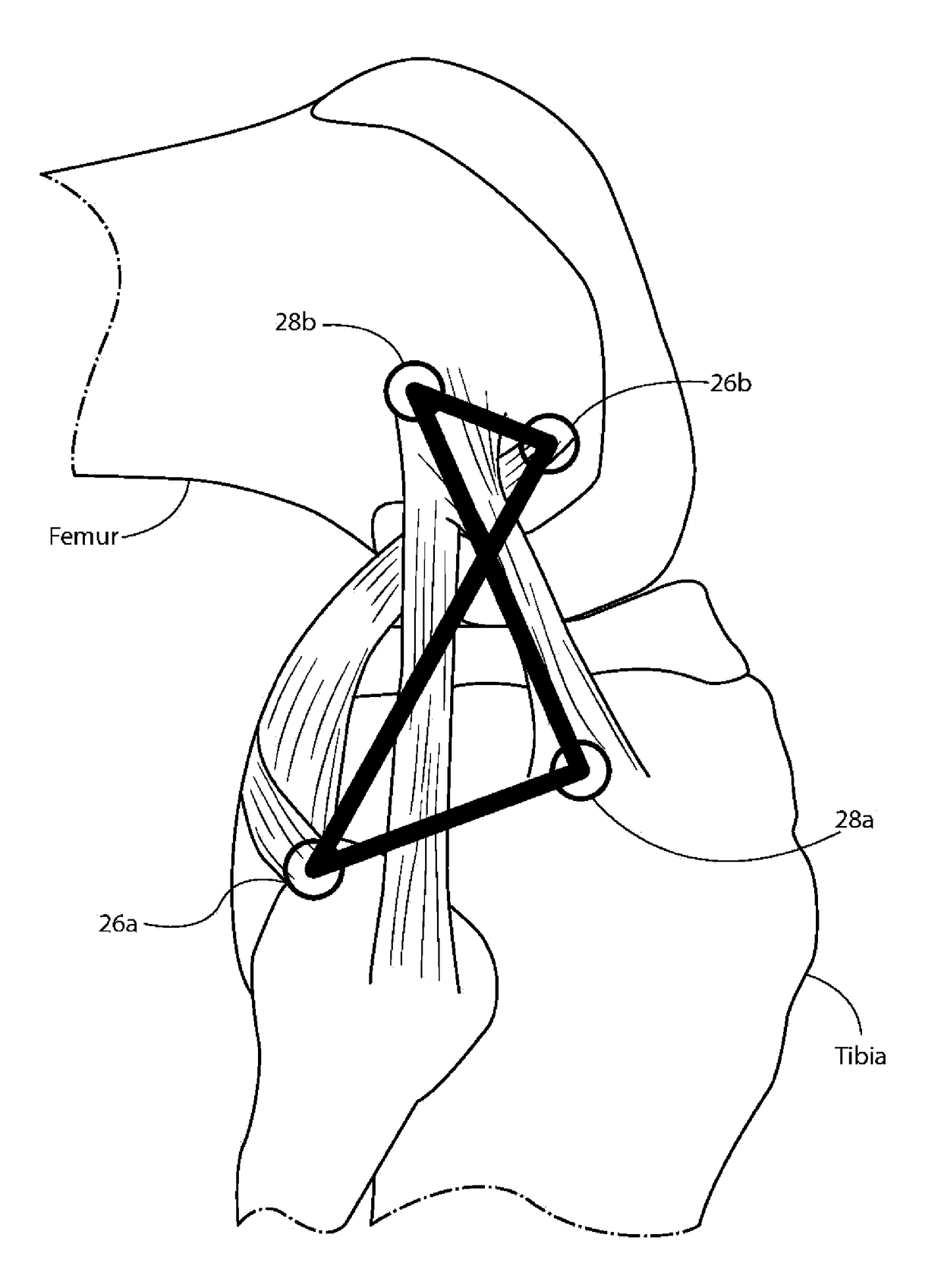
A prosthetic knee with an artificial ACL / PCL. The prosthetic knee includes a femoral component and a tibial component. The artificial ACL / PCL connects the femoral component and the tibial component and includes an anterior cruciate ligament portion connecting an anterior anchor point on the tibial component to a posterior anchor point on the femoral component, and a posterior cruciate ligament portion connecting a posterior anchor point on the tibial component to an anterior anchor point on the femoral component. The artificial ligament may be provided as single length of material and may be pre-assembled into an ACL / PCL module having portions that may be inserted into at least one of the femoral component or the tibial component. A system is also provided for total knee replacement that includes a selection of femoral components, tibial components, and one or more ACL / PCL modules of varying sizes,
Owner:GARINO JONATHAN P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com