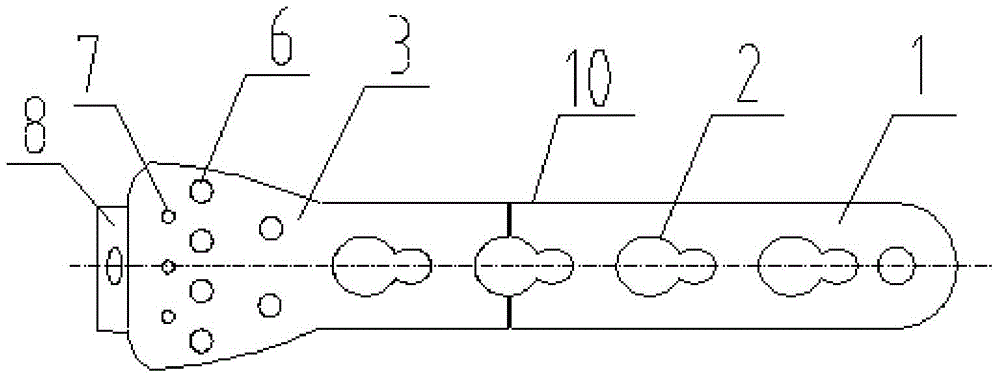
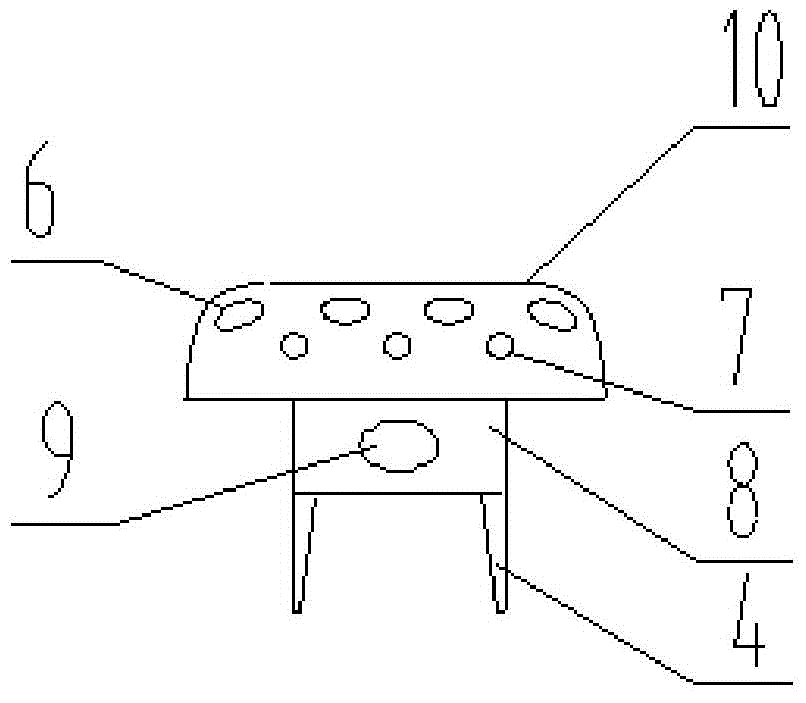
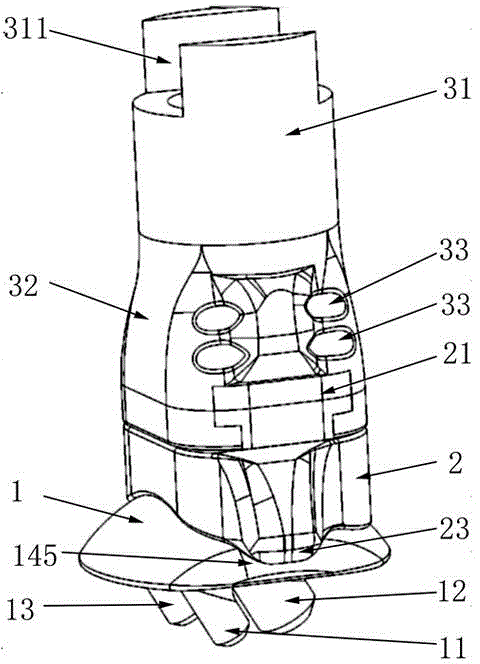
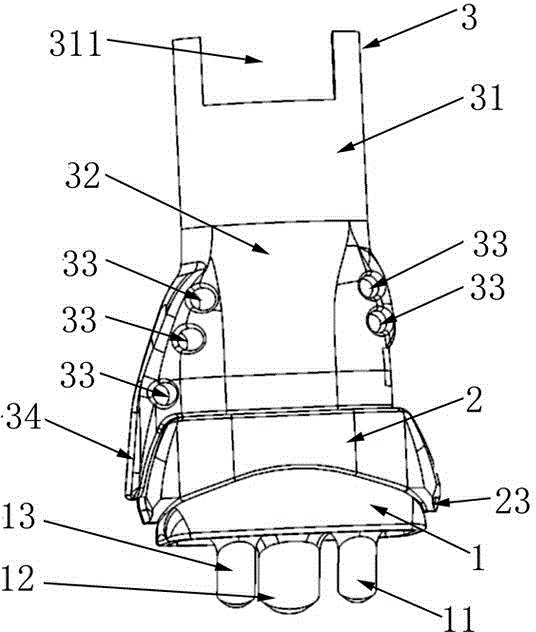
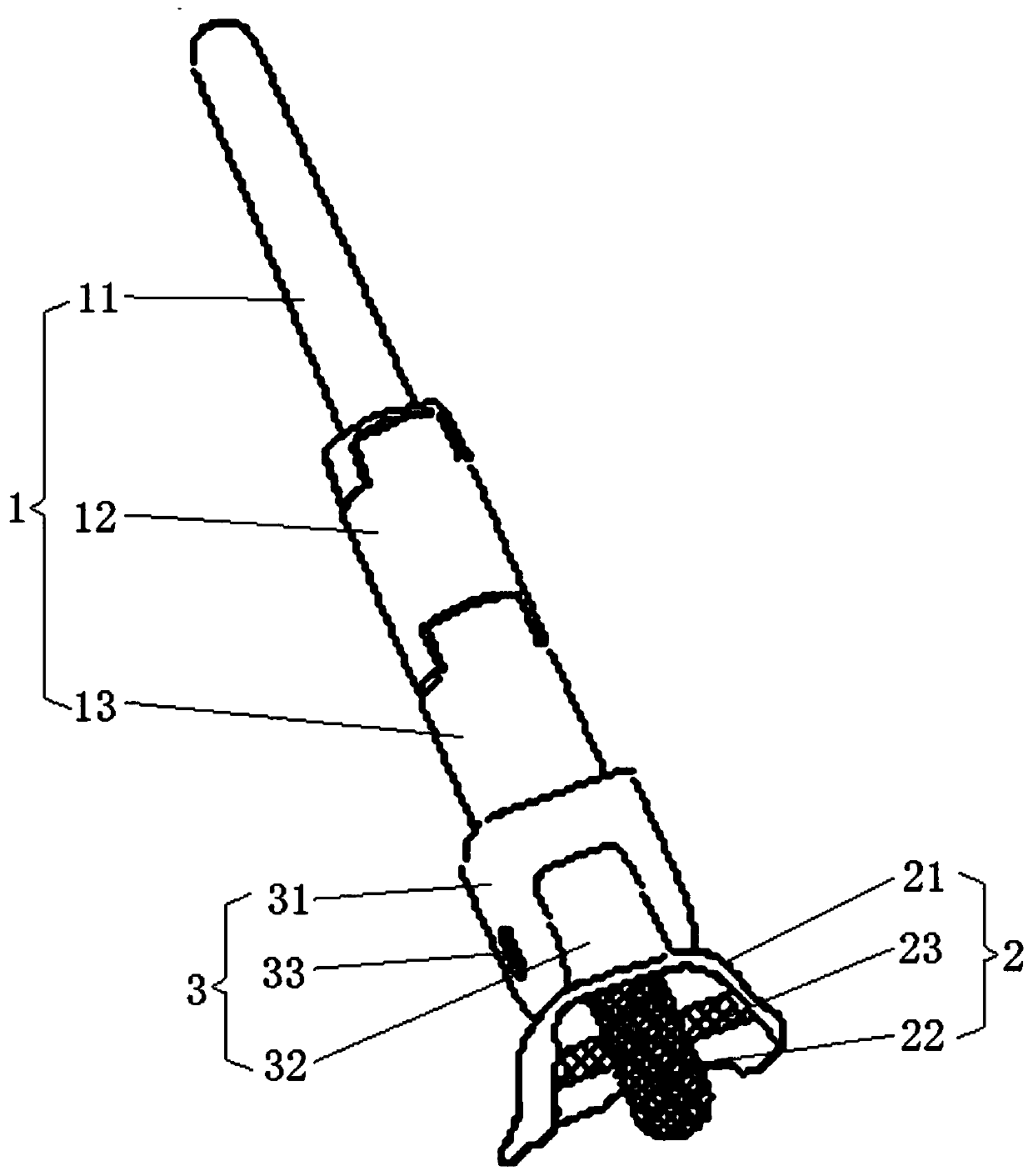
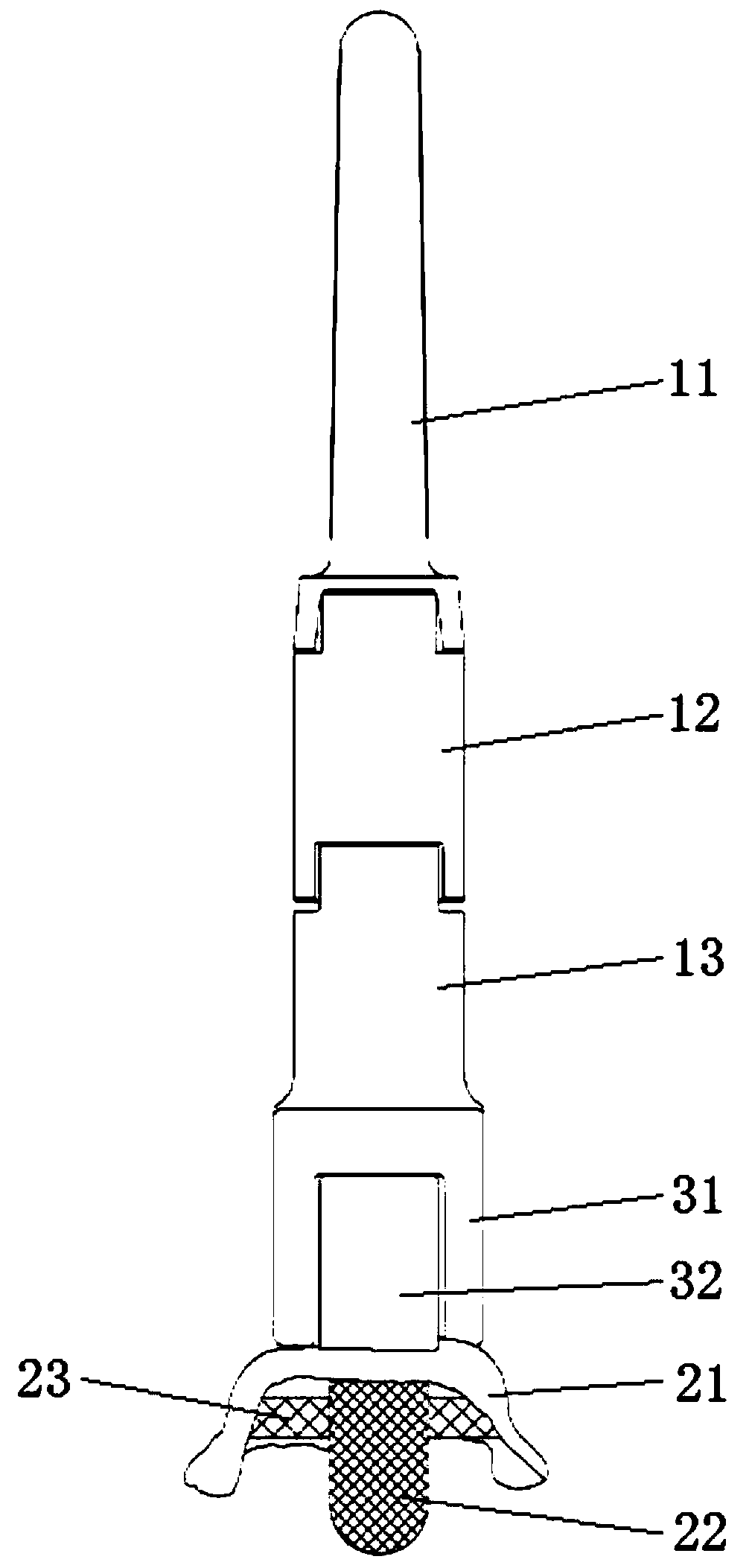
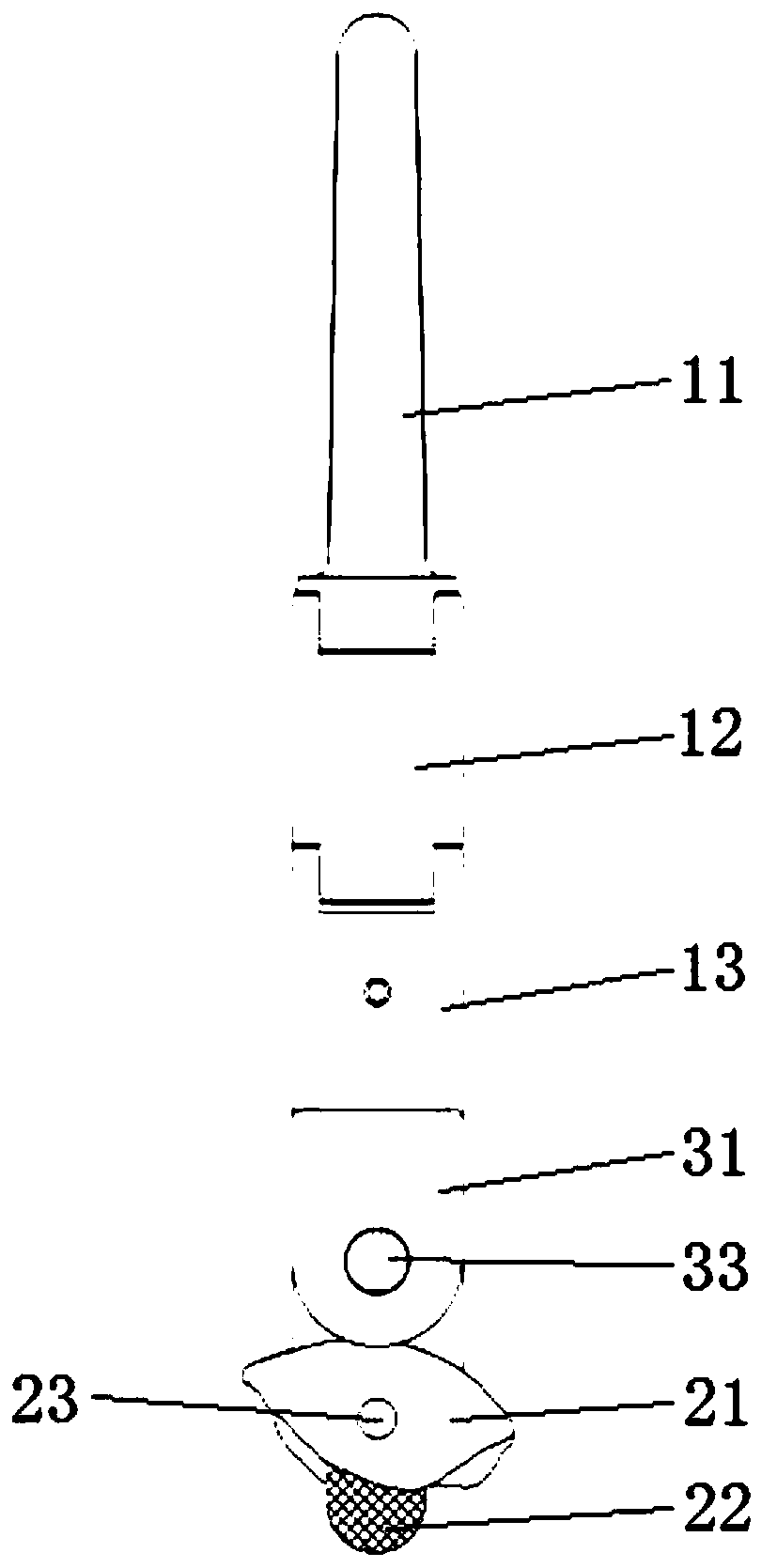
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Distal tibia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
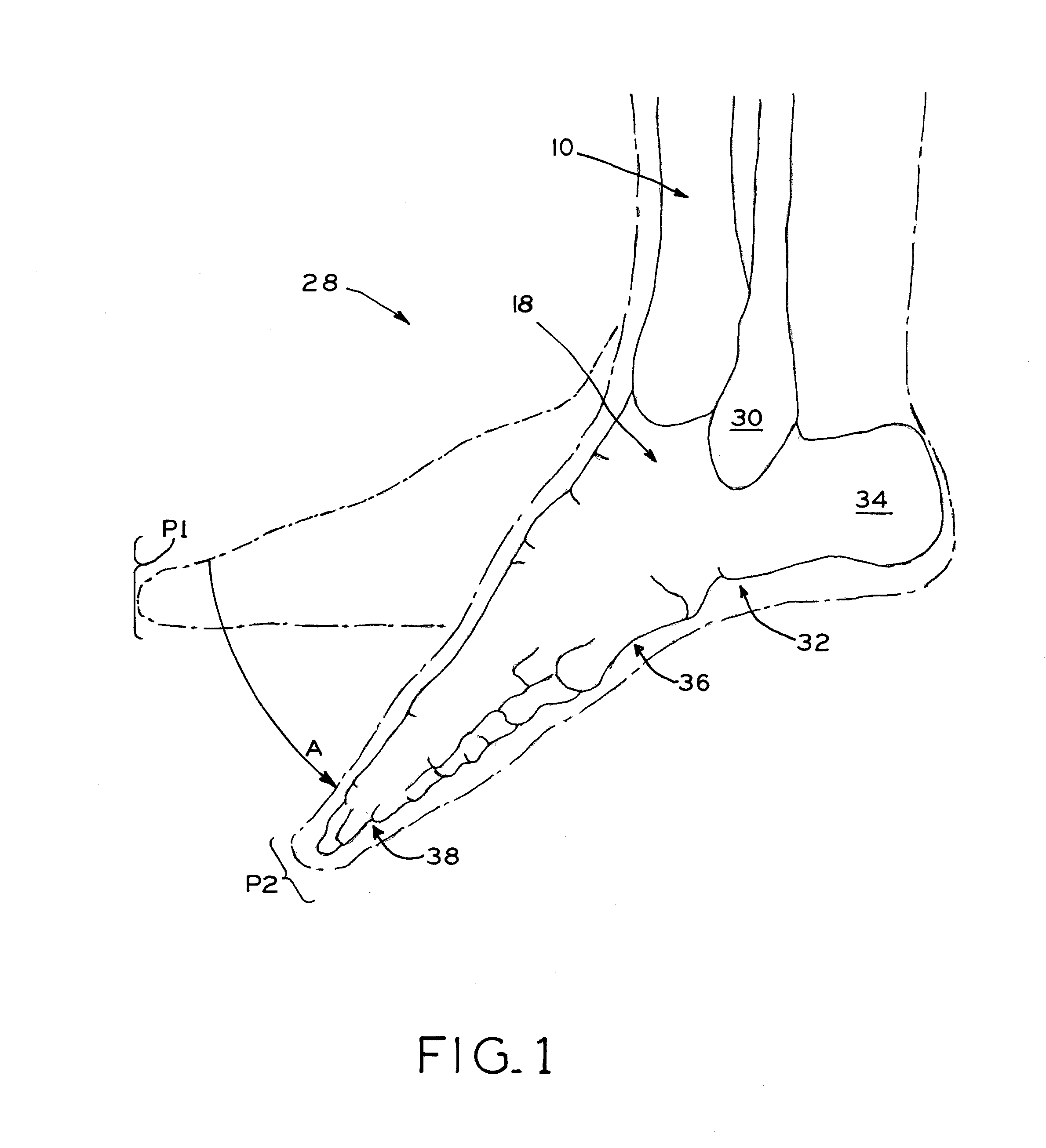
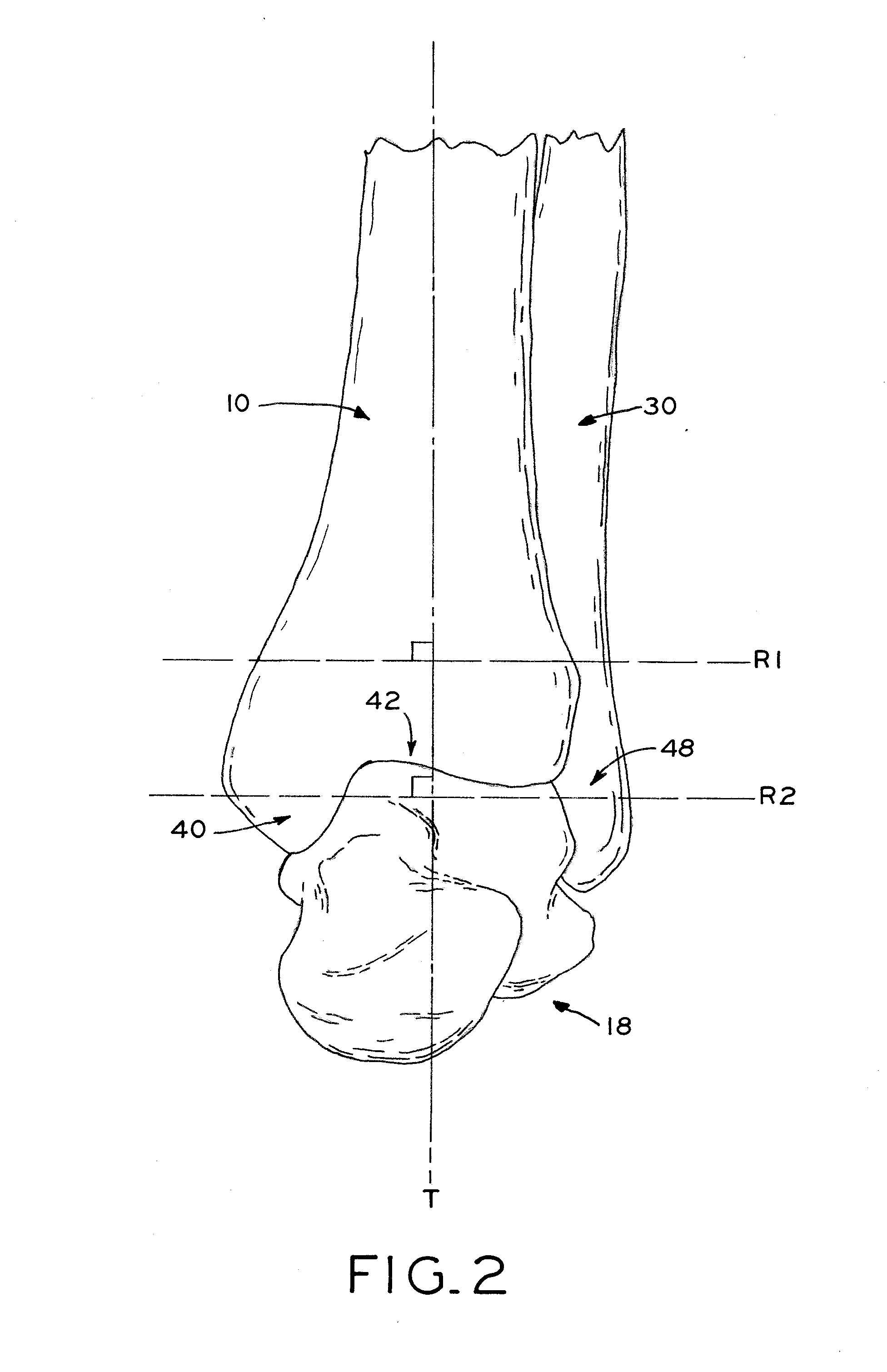
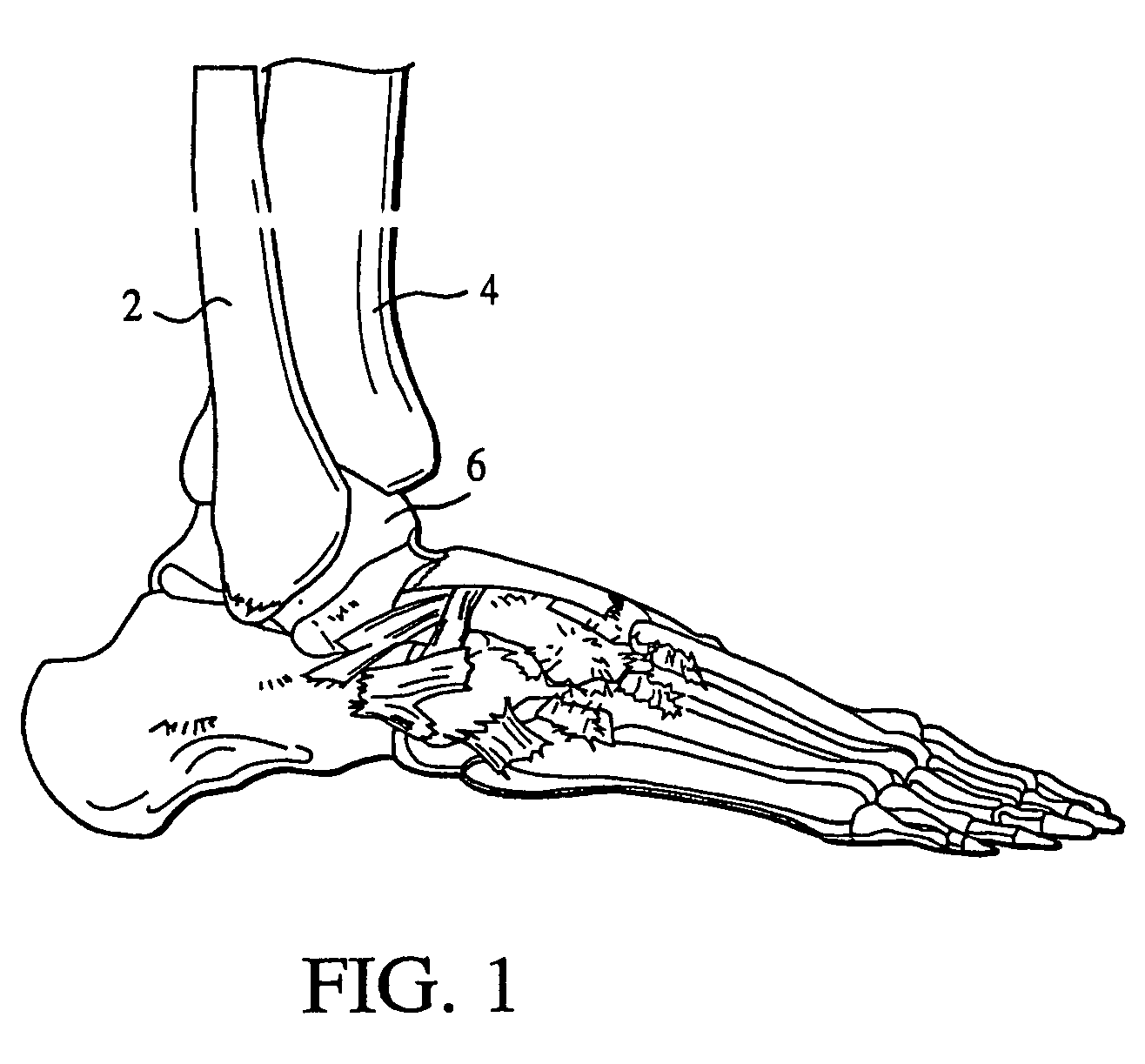
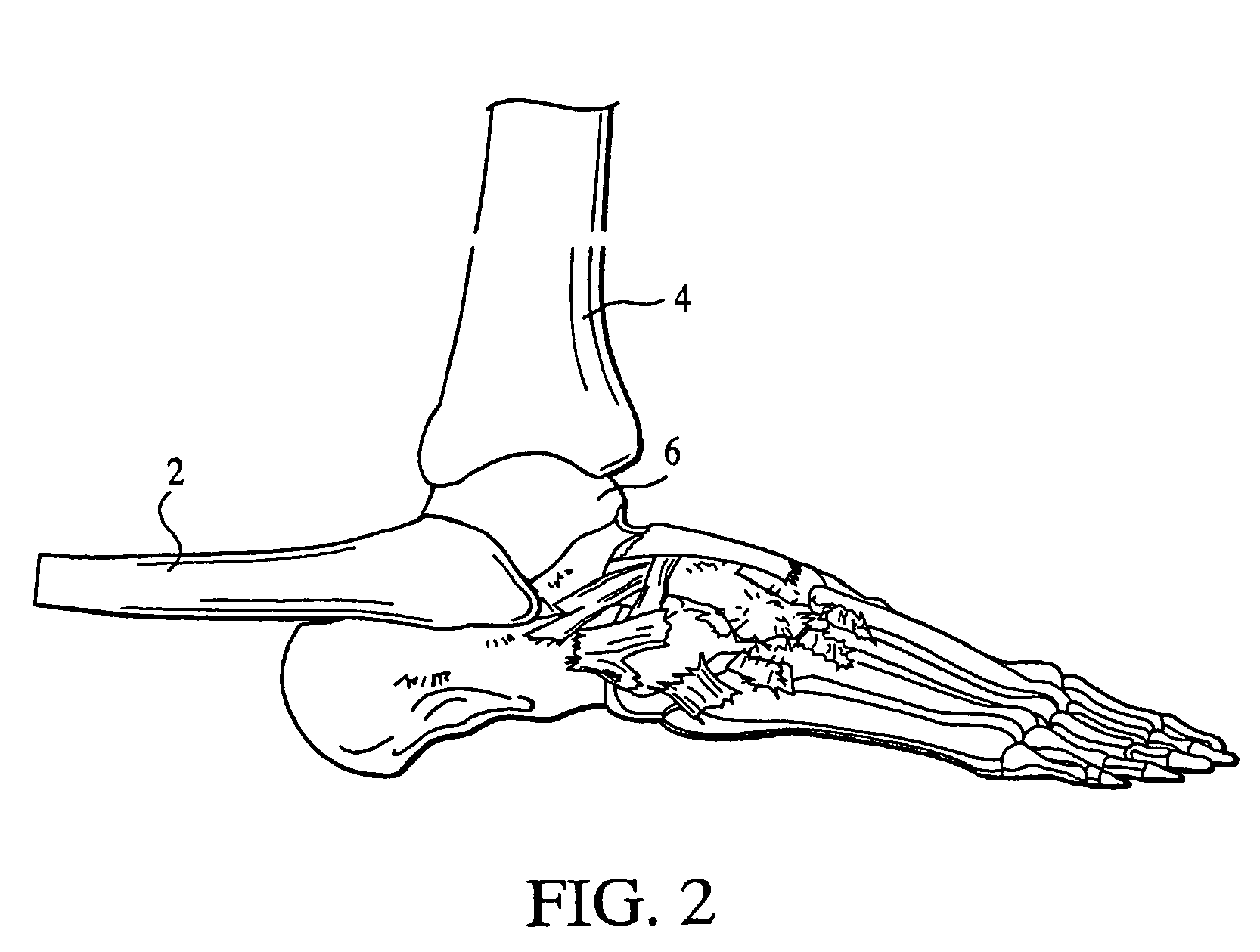
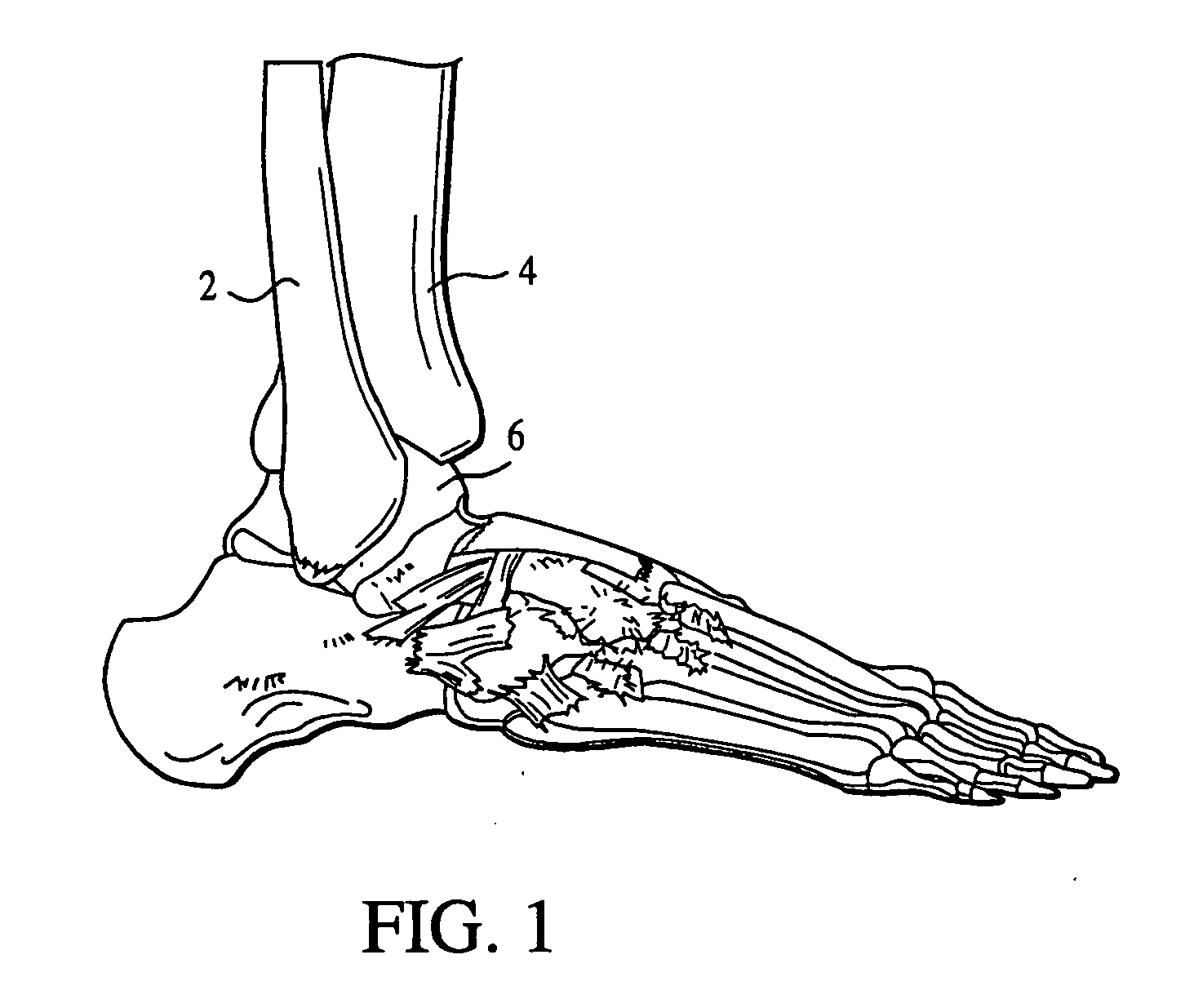
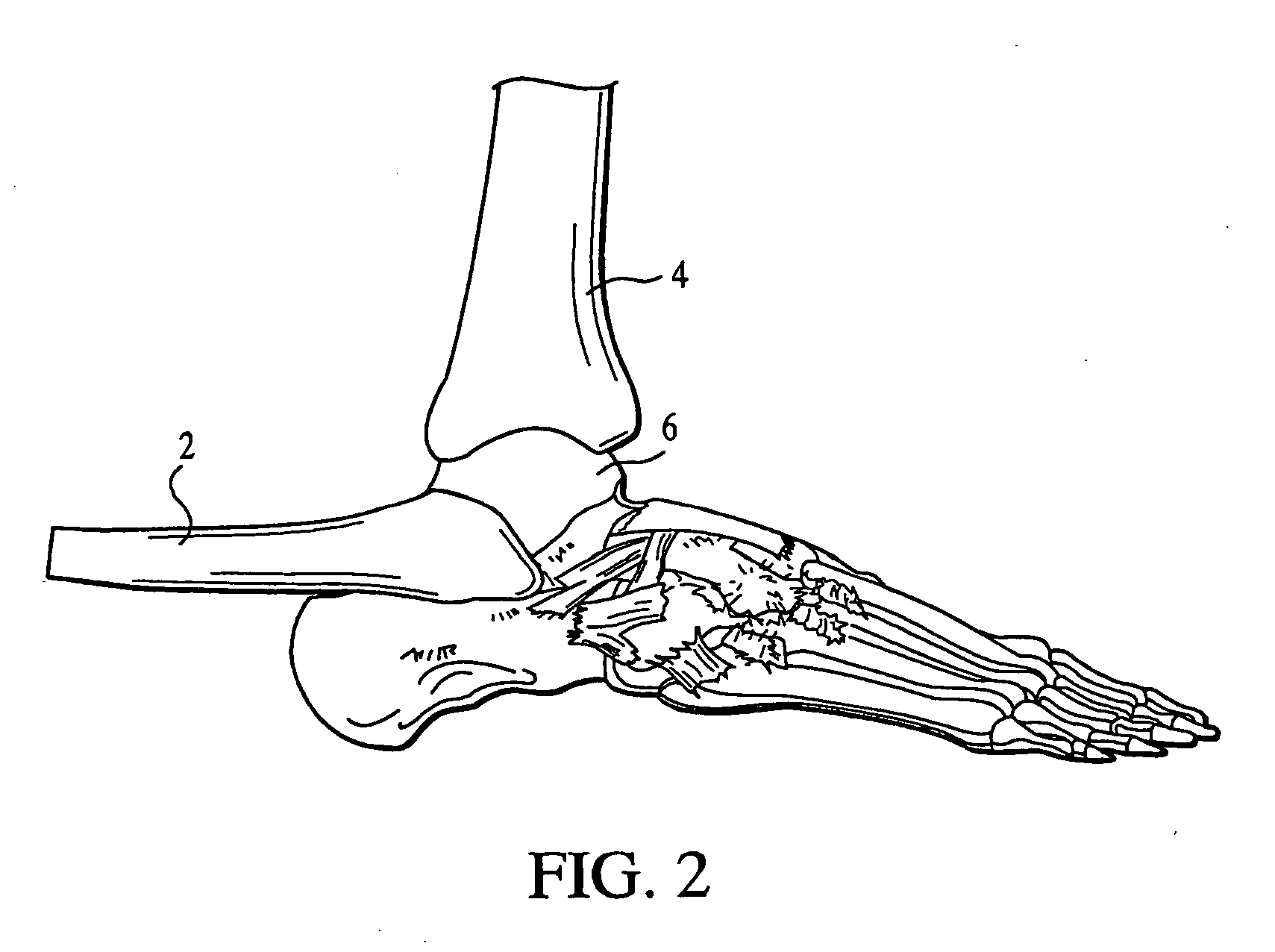
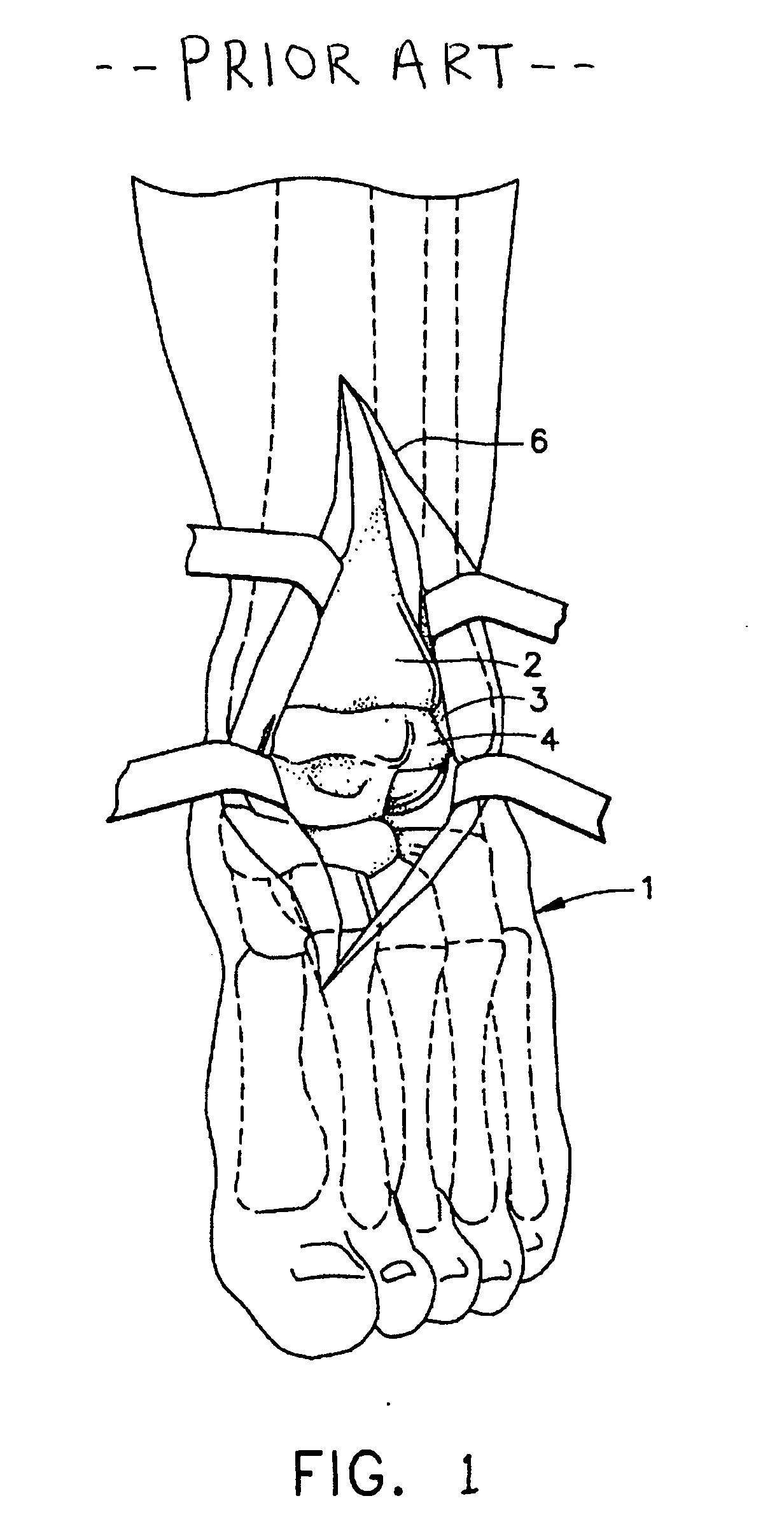
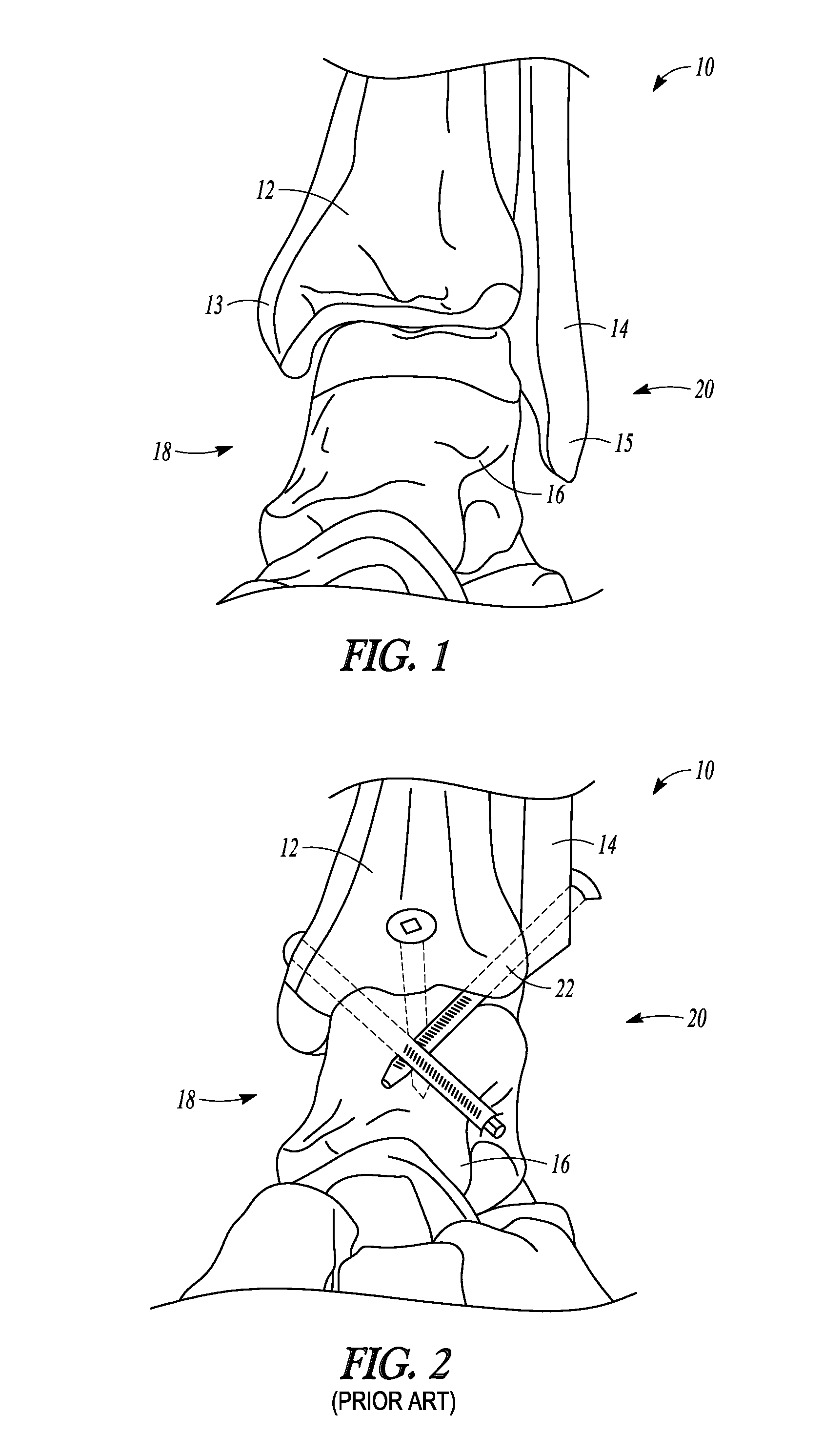
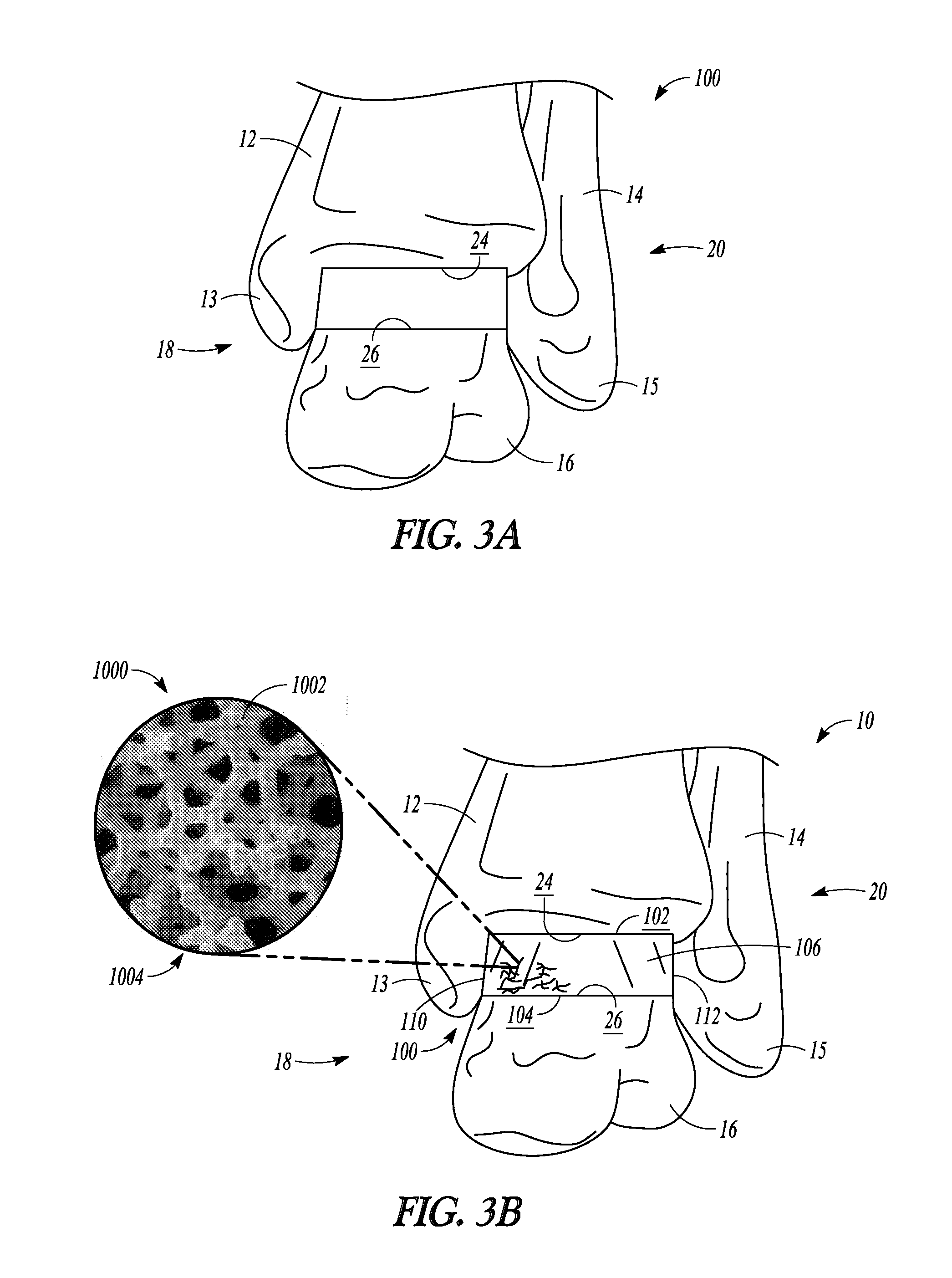
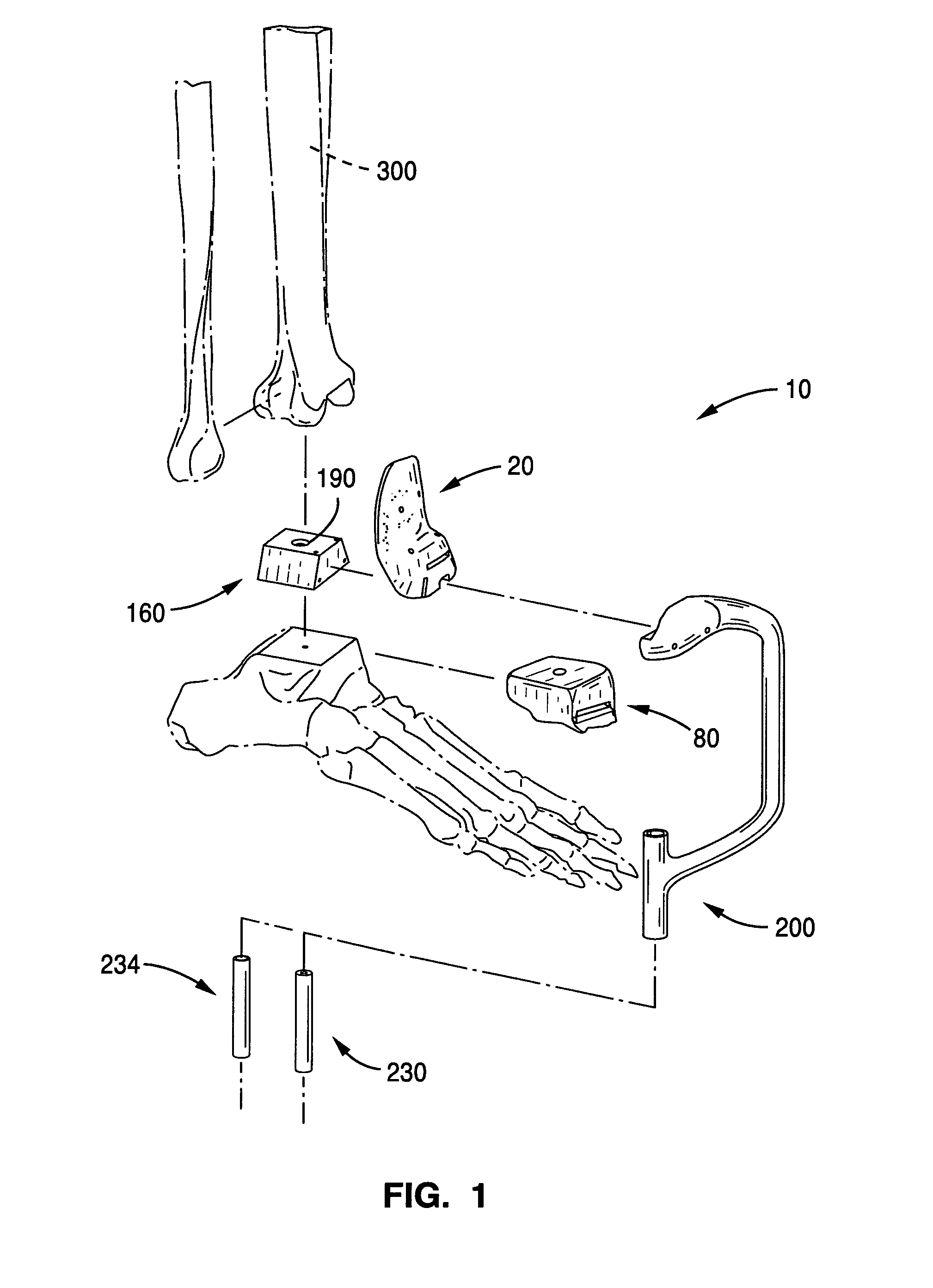
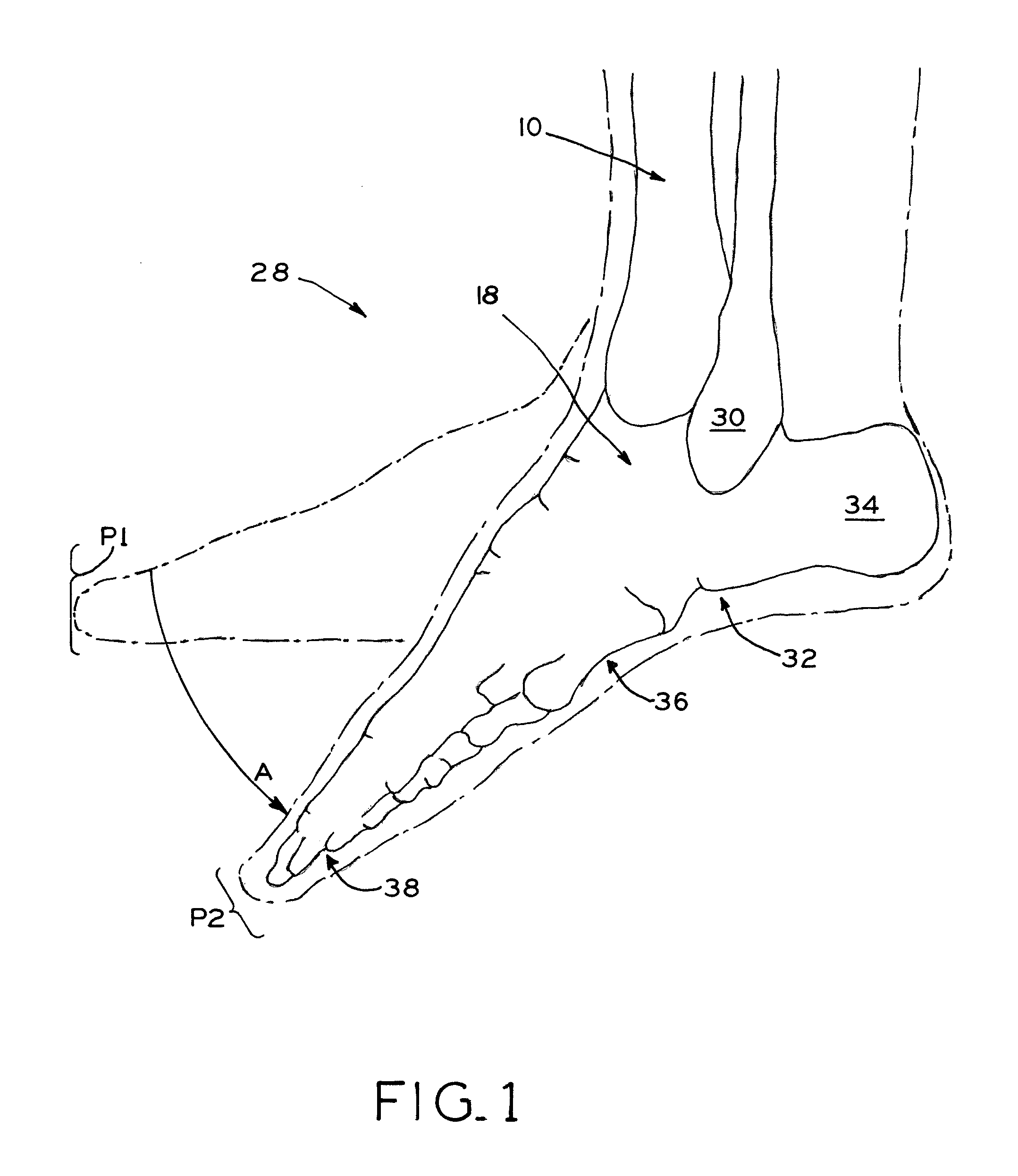
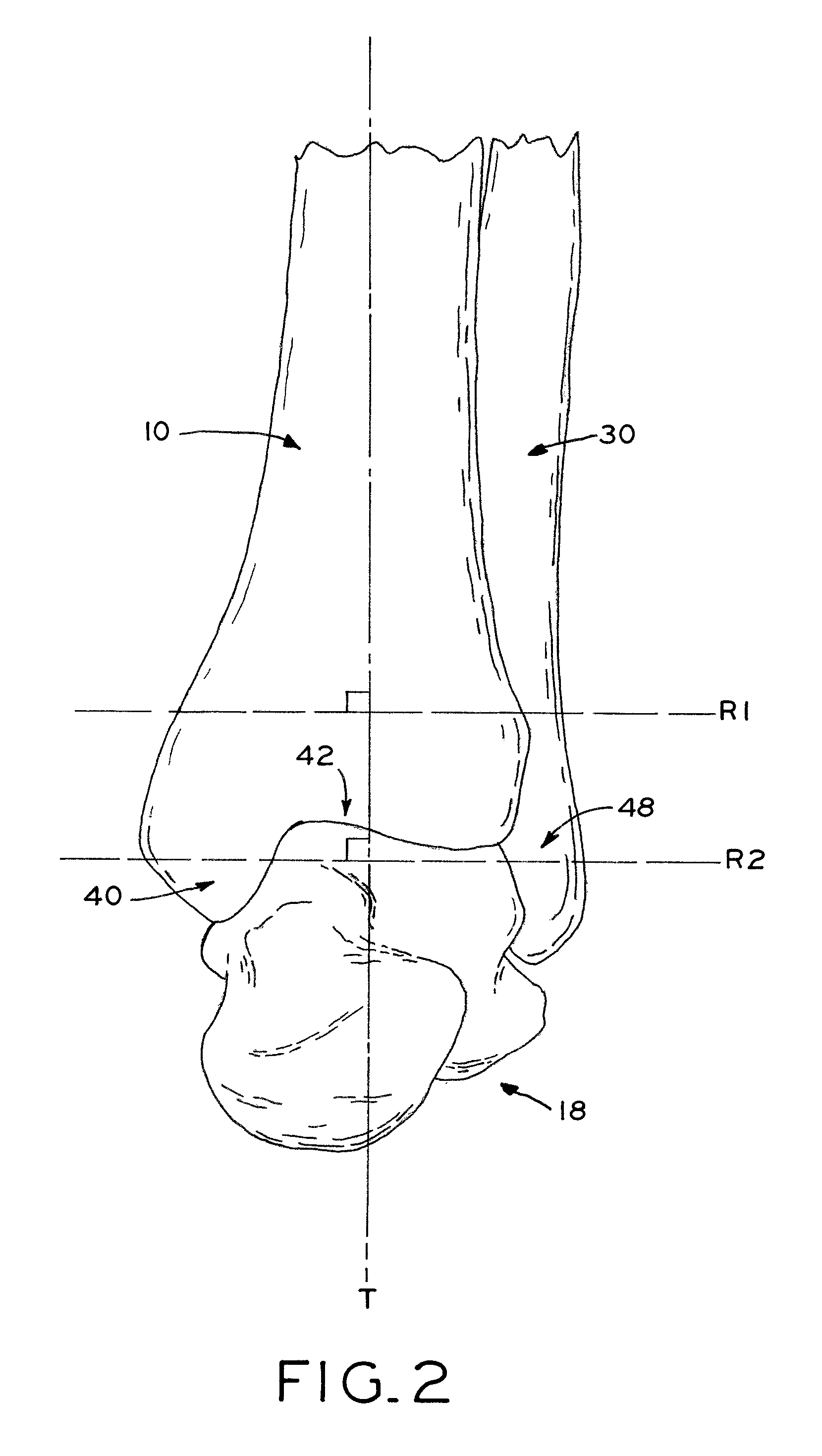
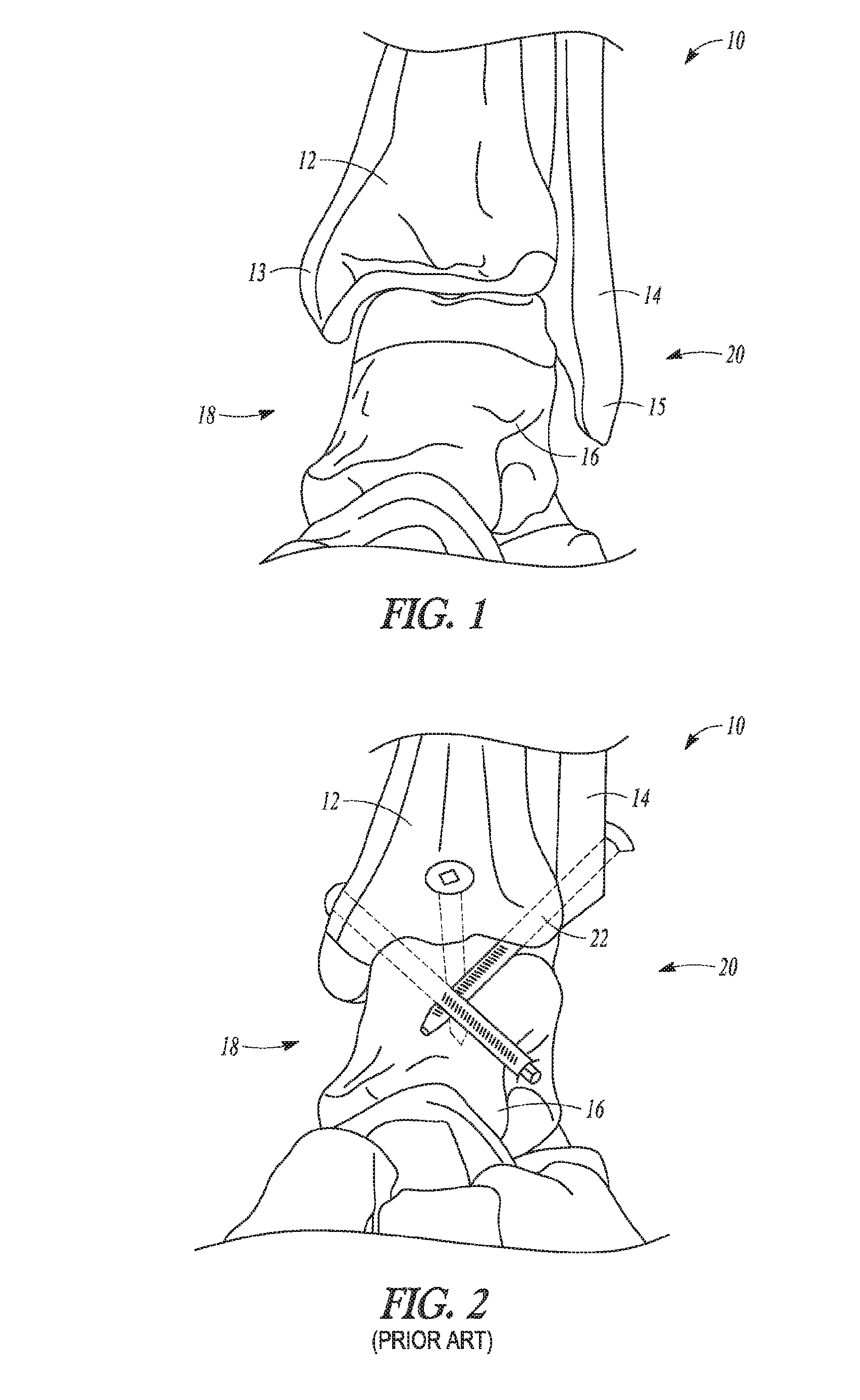
The distal end of the tibia is much smaller than the proximal end and presents five surfaces; it is prolonged downward on its medial side as a strong pyramidal process, the medial malleolus. The lower extremity of the tibia together with the fibula and talus forms the ankle joint.
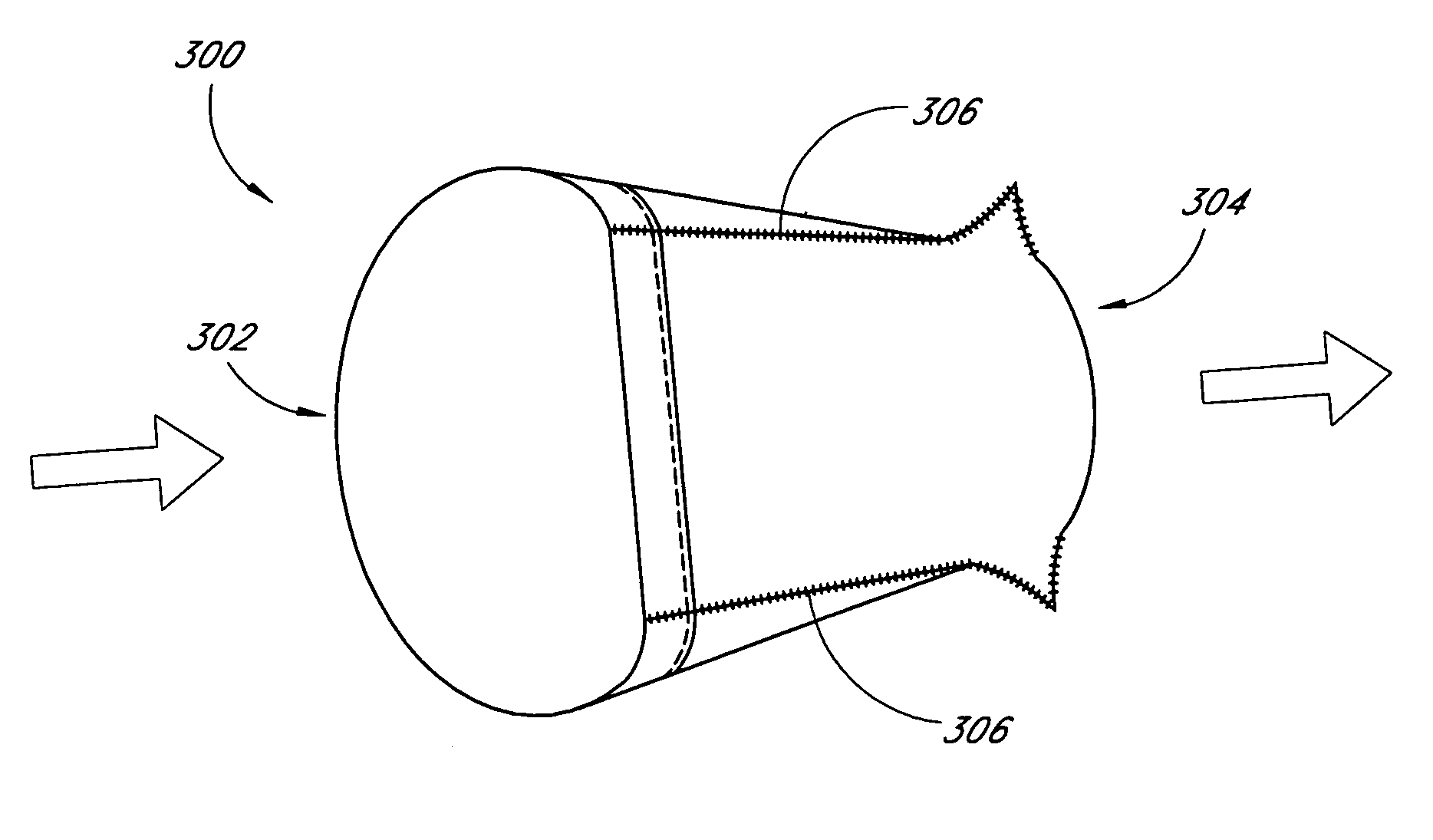
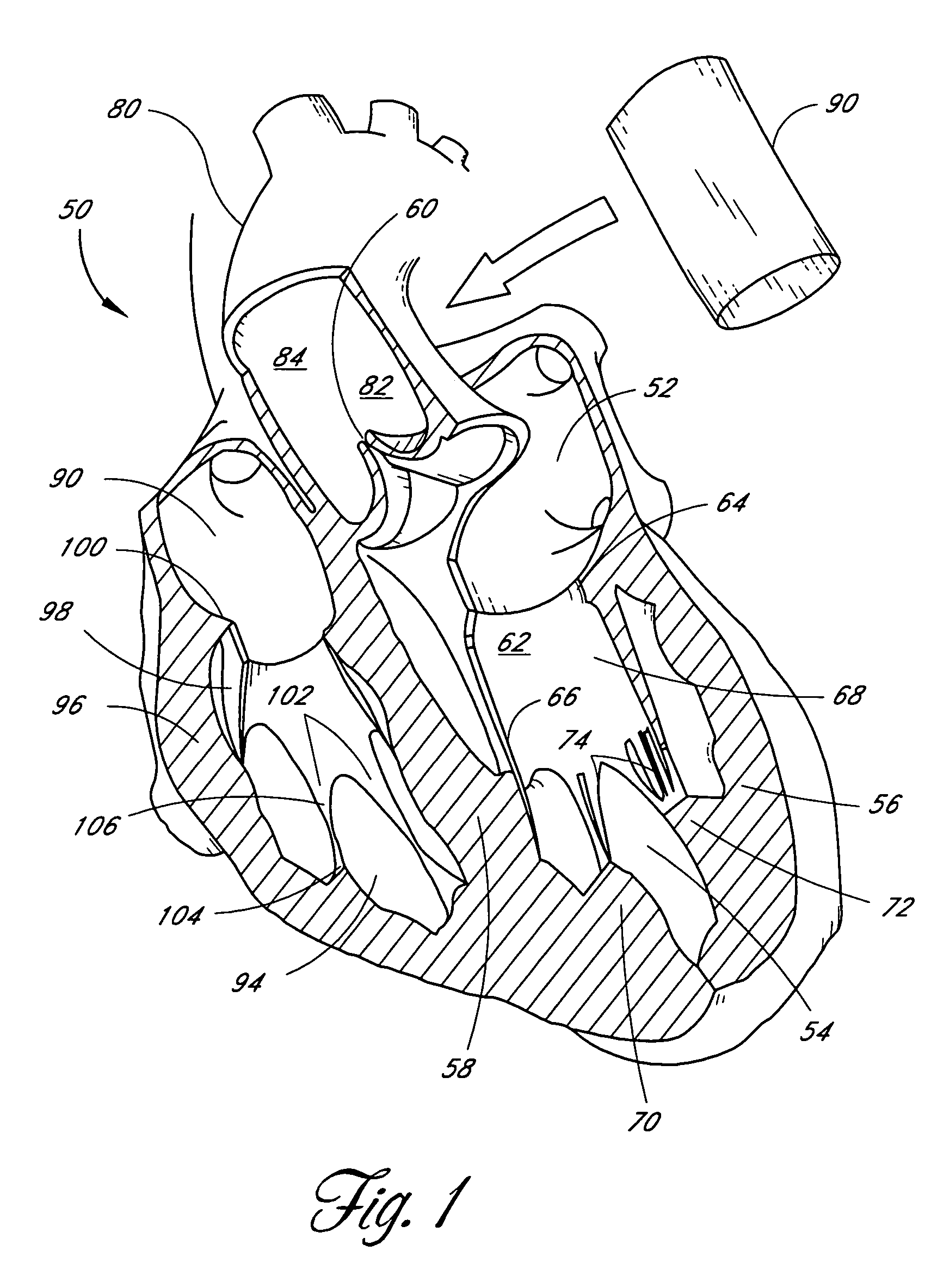
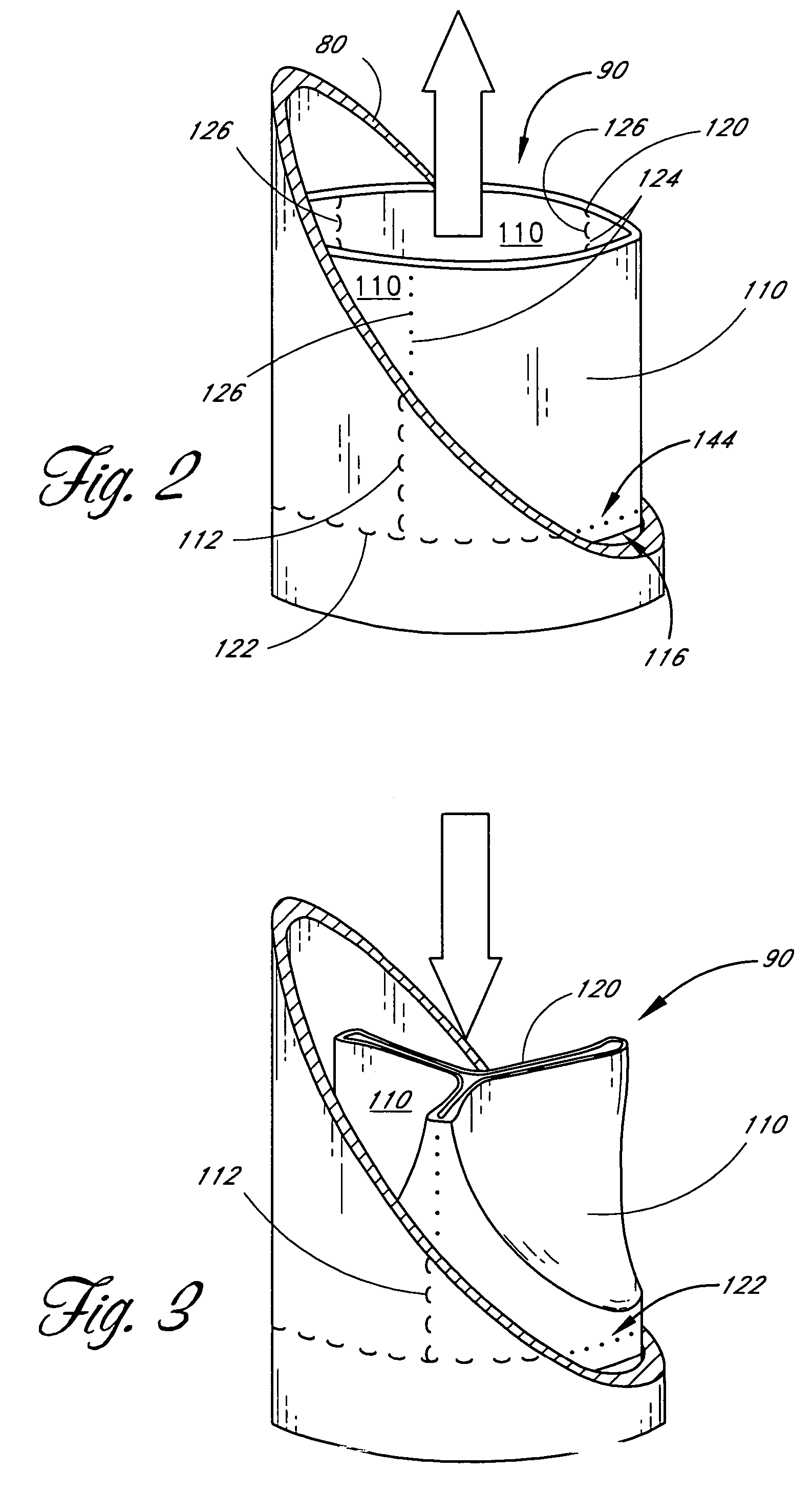
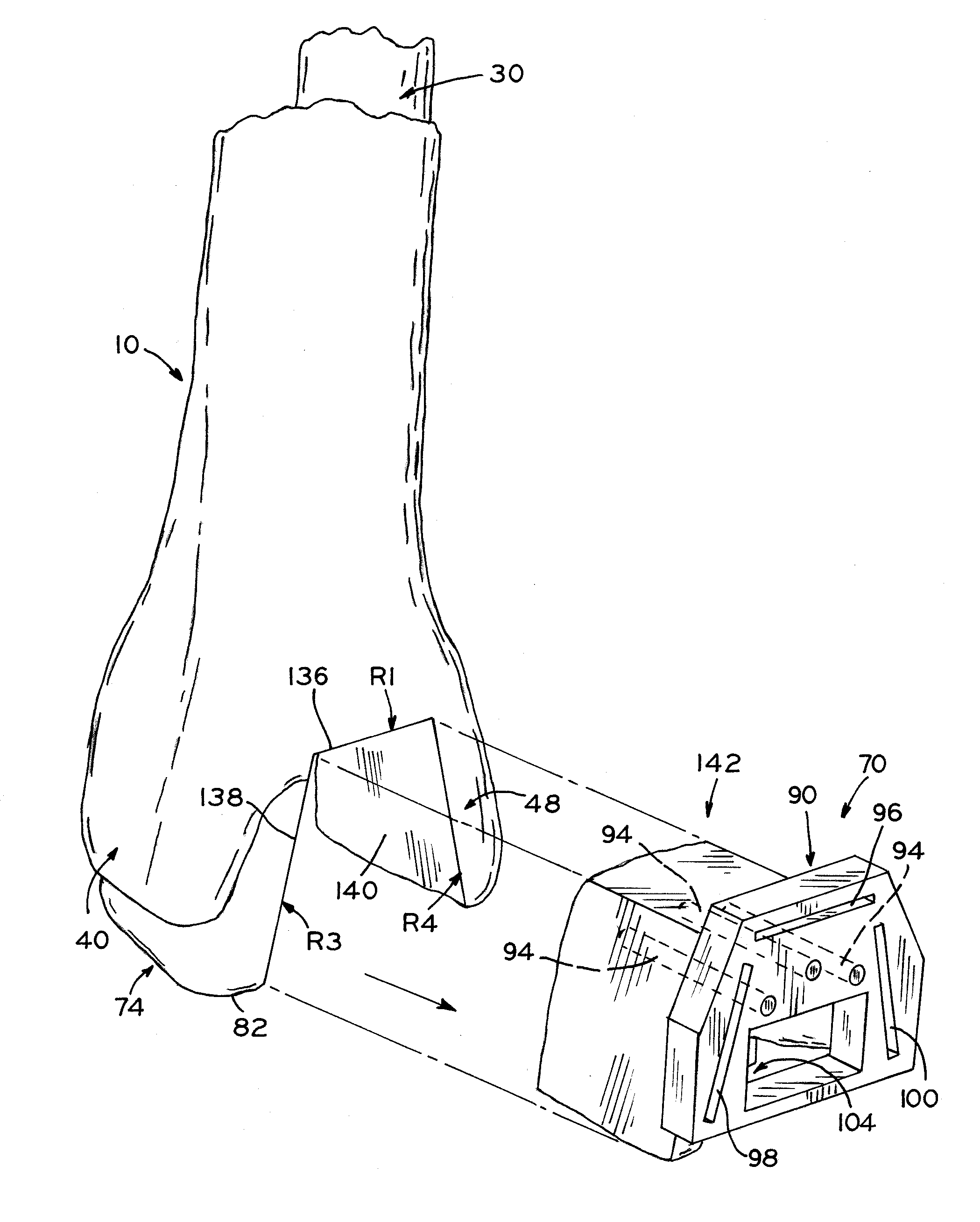
Prosthetic heart valve
InactiveUS7037333B2Increased durabilityImprove performanceHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic valvePapillary muscle
A tubular prosthetic semilunar or atrioventricular heart valve is formed by cutting flat, flexible leaflets according to a pattern. The valve is constructed by aligning the side edges of adjacent leaflets so that the leaflet inner faces engage each other, and then suturing the leaflets together with successive stitches along a fold line adjacent the side edges. The stitches are placed successively from a proximal in-flow end of each leaflet toward a distal out-flow end. During operation, when the leaflets open and close, the leaflets fold along the fold line. Distal tabs extend beyond the distal end of each leaflet. The successive stitches terminate proximal of the distal tab portion so that no locked stitches are placed along the distal portion of the fold line. The tab portions of adjacent leaflets are folded over each other and sewn together to form commissural attachment tabs. The commissural tabs provide commissural attachment points to accommodate sutures and the like in order to secure the tab to a vessel wall, if a semilunar valve, and papillary muscles and / or chordae tendineae if an atrioventricular valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Patient-specific instruments for total ankle arthroplasty
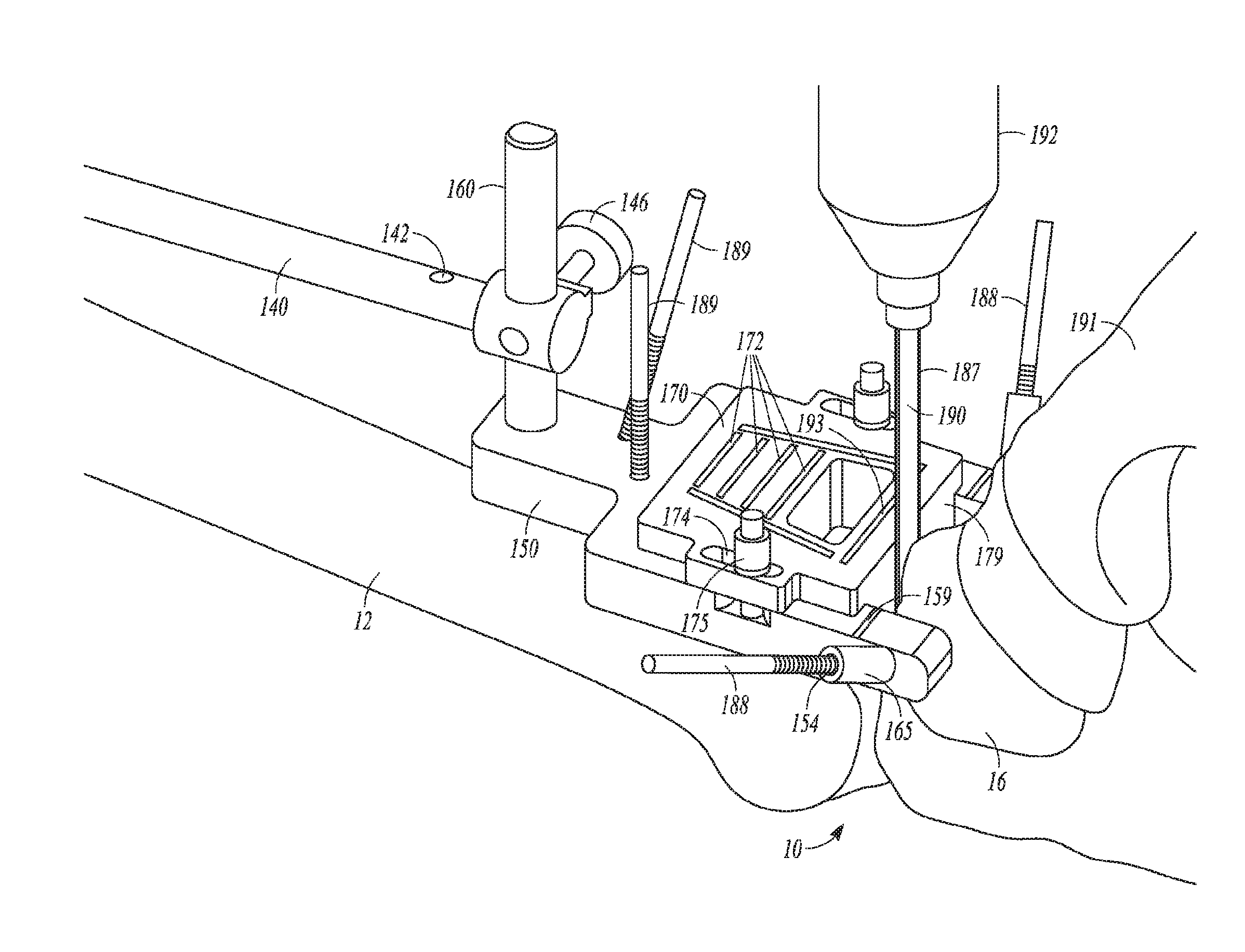
Patient-specific instruments for preparing bones for receipt of orthopedic prostheses, such as the distal tibia and the talus in a total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) procedure. A tibial guide and a talar guide are manufactured based on patient-specific anatomical data obtained using imaging technology, and each guide includes a surface conforming to selected anatomical surfaces or regions of the tibia or talus, respectively. Each guide includes at least one cut referencing surface, such as a cut slot, to guide a resection, and may also include a guide aperture sized to guide a reaming tool for reaming the distal tibia or talus. The guides may also include pin holes positioned within a periphery defined by the cut referencing surfaces such that, when the resections are made and the resected tibial bone portion or talus bone portion is removed, the guide and its associated pins are removed along with the resected bone portion. The guides may be designed to ensure that a proximal resected surface of the distal tibia is parallel to a resected surface of the talus, with the parallel resected surfaces perpendicular to the anatomical axis of the distal tibia.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Ankle joint prosthesis and its method of implantation
The ankle joint prosthesis adapted to involve the patient's distal tibia and talus has, according to the present invention, tibial, talar and mobile or semi-constrained bearing components that are laterally to medially implanted in the patient. The tibial component's top surface has convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the distal tibia; its bottom surface being approximately flat. The talar component's top surface has saddle-shaped, convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane, it's bottom surface has concave curvature and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the talus. The mobile or semi-constrained bearing components have embodiments that comprise a wide variety of geometric shapes. A method for implanting such a prosthesis is also disclosed.
Owner:CONCEPTS & MEDICINE III
Semi-constrained ankle joint prosthesis and its method of implantation
The ankle joint prosthesis adapted to involve the patient's distal tibia and talus has, according to the present invention, tibial, talar and mobile or semi-constrained bearing components that are laterally to medially implanted in the patient. The tibial component's top surface has convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the distal tibia; its bottom surface being approximately flat. The talar component's top surface has saddle-shaped, convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane, it's bottom surface has concave curvature and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the talus. The mobile or semi-constrained bearing components have embodiments that comprise a wide variety of geometric shapes. A method for implanting such a prosthesis is also disclosed.
Owner:SCHON LEW C +4
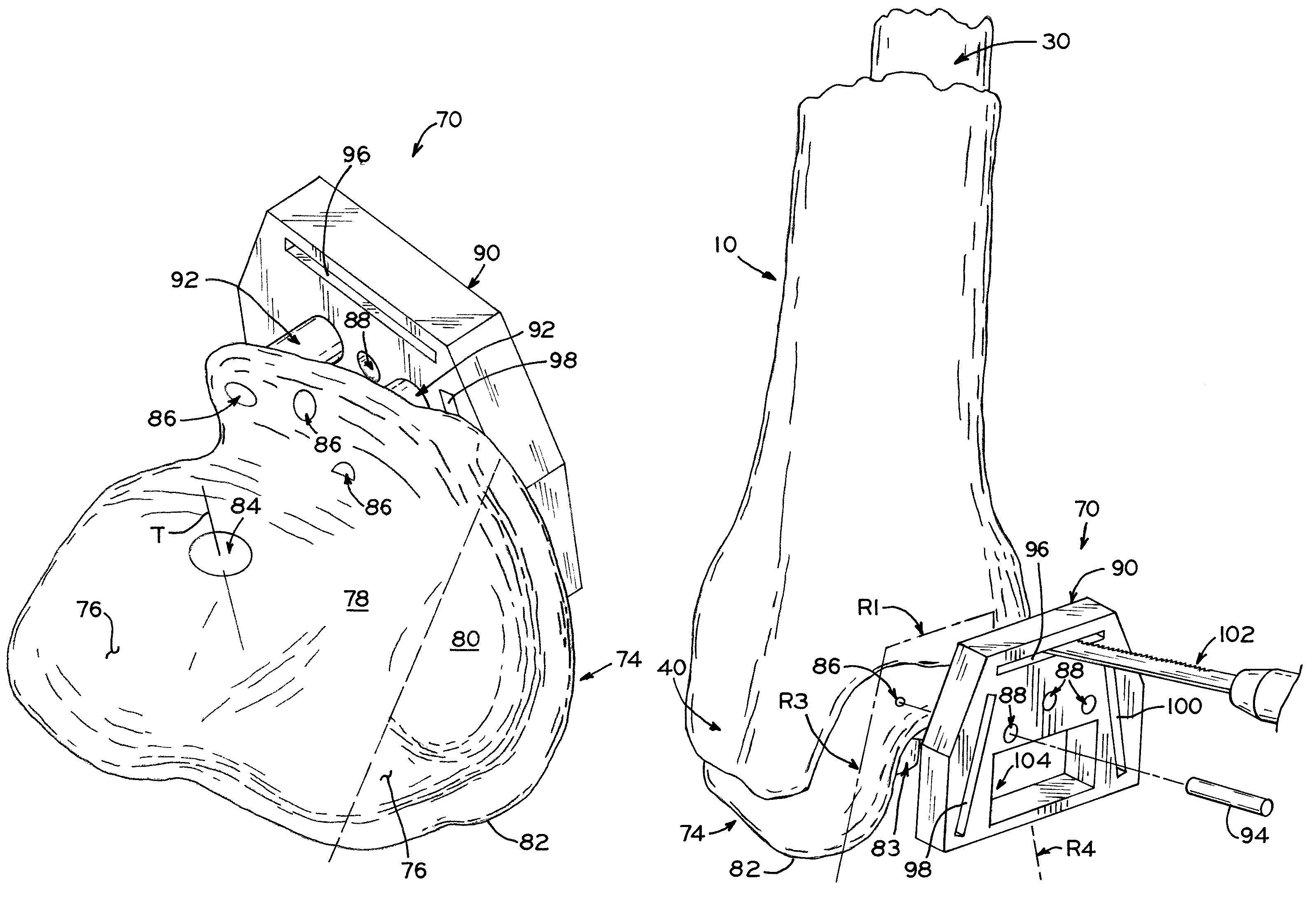
Osteotomy Guide and Method of Cutting the Medial Distal Tibia Employing the Same
InactiveUS20100069910A1Easy to replaceDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAnkle joint replacementDistal tibia
An osteotomy guide is provided for cutting a bone, such as the medial distal tibia, to facilitate an ankle replacement. The osteotomy guide includes a positioning device having a number of fixation points, a first guide member structured to align with a first portion of the bone, in order to perform a first procedure, thereon, and a second guide member structured to align with a second portion of the bone, in order to perform a second procedure thereon. The fixation points engage the bone and maintain alignment of the first guide member with respect to the first portion during the first procedure, and maintain alignment of the second guide member with respect to the second portion during the second procedure, in order that the first procedure and the second procedure are substantially reproducible.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Total ankle arthroplasty
A three-component system is used for total ankle arthroplasty in which a tibial prosthesis component is fixed to a distal tibia end, a talar prosthesis component is fixed to a talus, and a bearing component is positioned between and in contact with the tibial prosthesis component and the talar prosthesis component. In one embodiment, the natural curvature of the distal tibia end is maintained rather than creating a flat surface to which to adhere a prosthetic component. In still another embodiment, a lateral or medial incision is used to insert the prosthetic components of the total ankle arthroplasty.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lateral ankle fusion plate system and jig, and method for use therewith
ActiveUS20140107798A1Stable and strong and precise and comfortable for patientImprove operating conditionsAnkle jointsJoint implantsCalcaneusDistal tibia
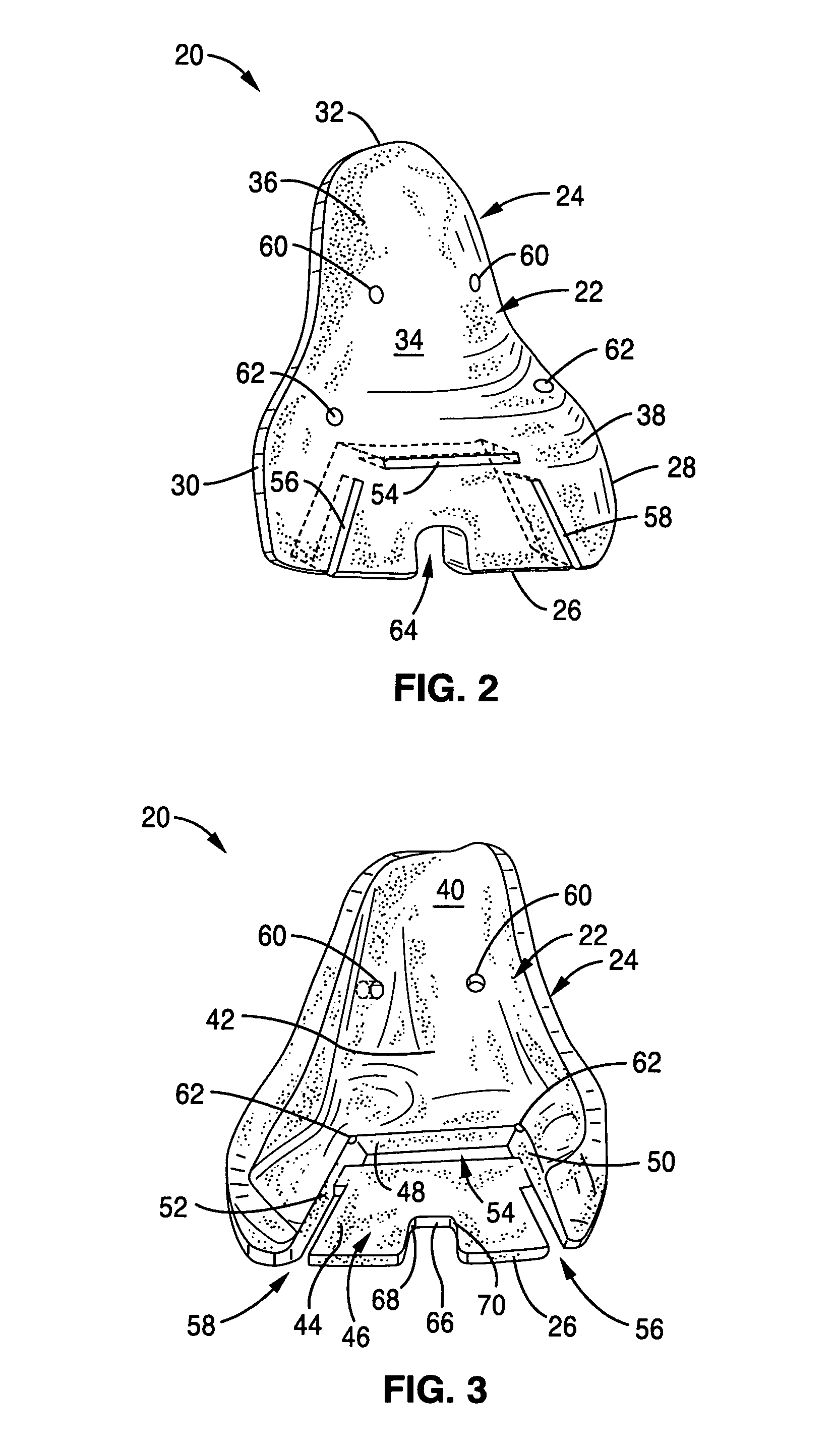
The invention comprises a lateral ankle fusion plate, a jig for use with the fusion plate and a method for ankle fusion of the joints between the tibia, the talus, and the calcaneus. In addition, a separate fusion screw from posterior to anterior through the calcaneal tuberosity into the distal tibia is useful and can be placed using the targeting jig of the invention. The plate includes a C-shaped stirrup portion that wraps the bottom of the calcaneus and is provided with a screw hole for a T-T-C-fusion screw. A C-shaped targeting jig is provided that interfaces with the plate to allow for placement of the calcaneal screw and has an additional attachment for placement of the independent fusion screw so as to avoid impingement with the plate, and plate screws. The invention also relates to a method of surgery that incorporates the use of the plate, the jig and the tibial / talar / calcaneal fusion screw for an arthrodesis of the ankle joint.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
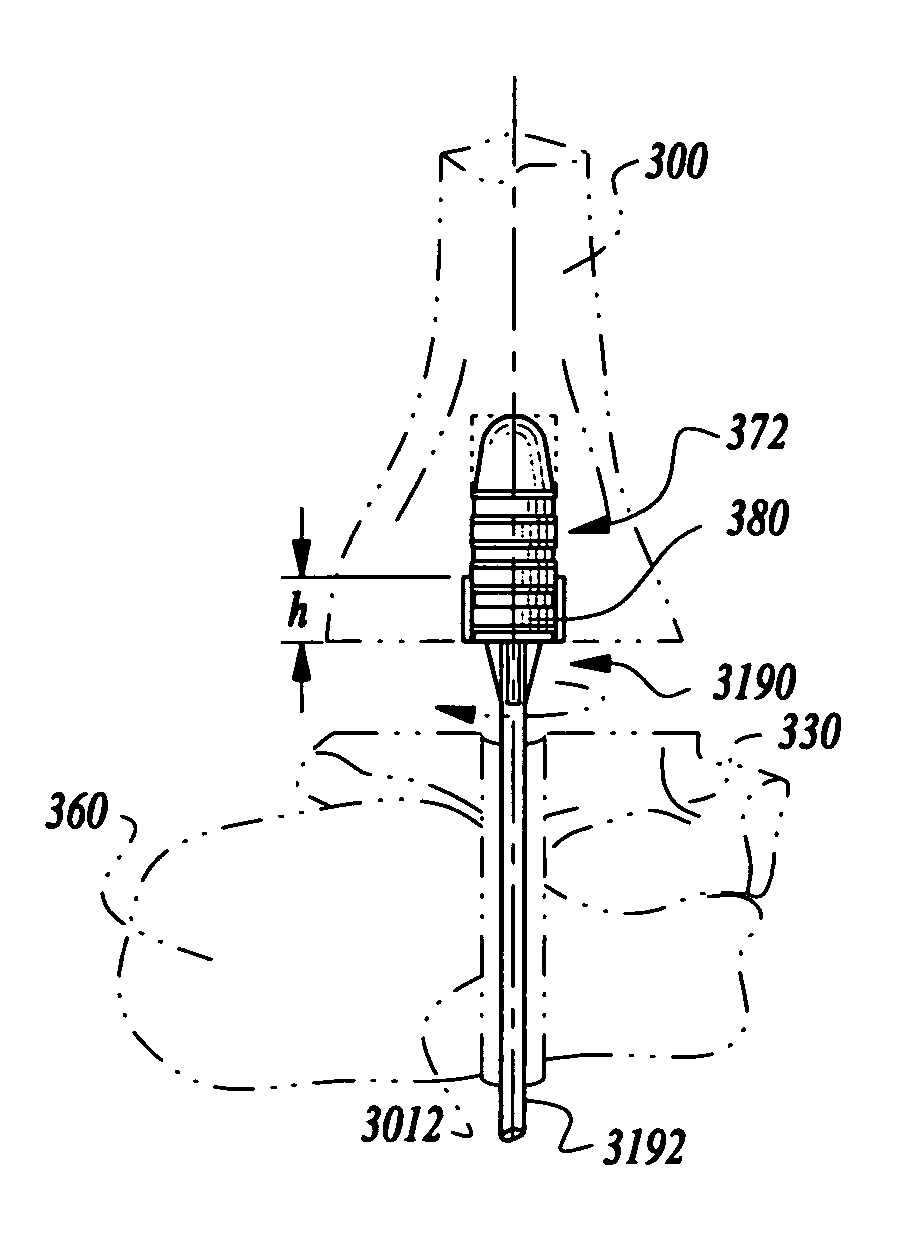
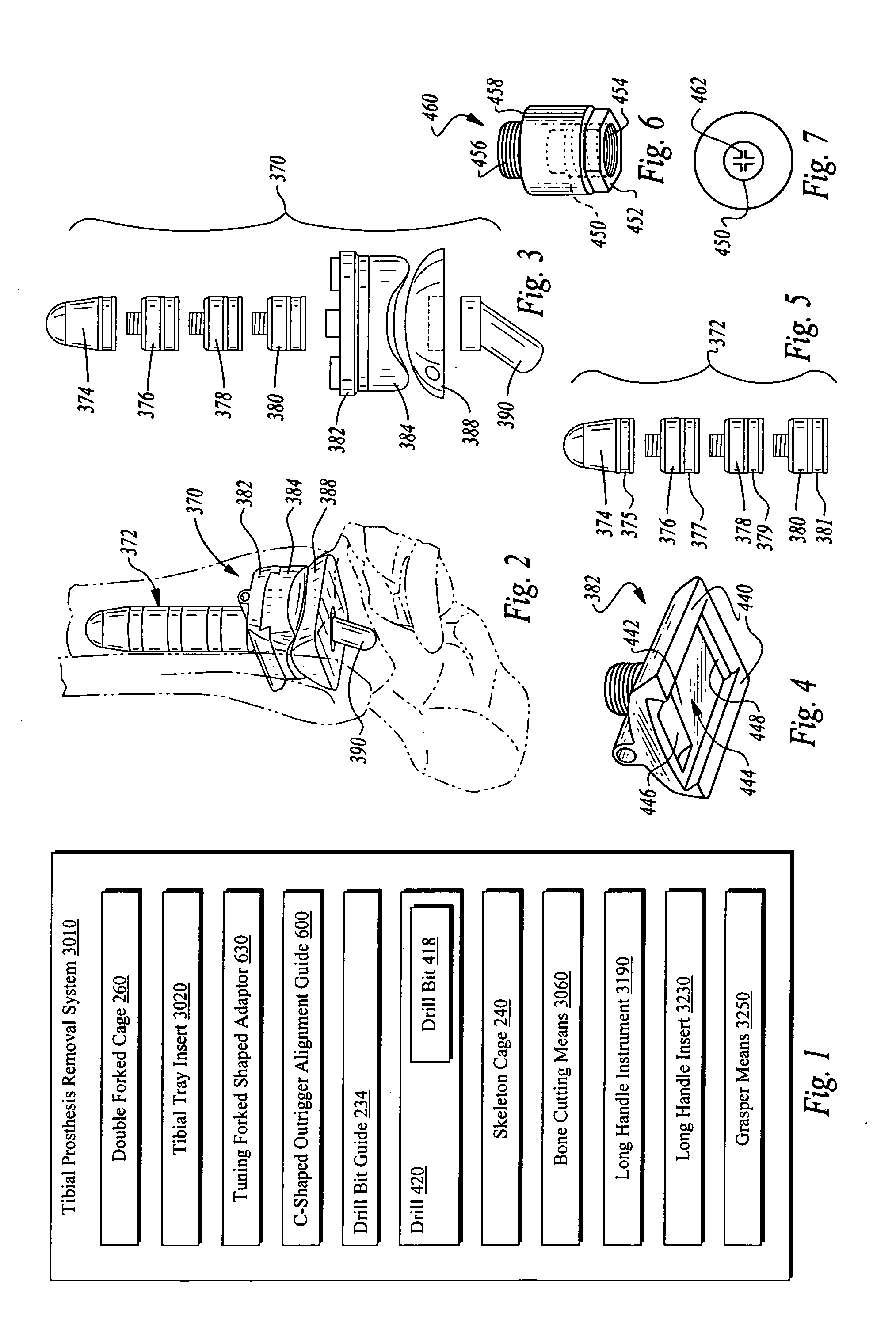
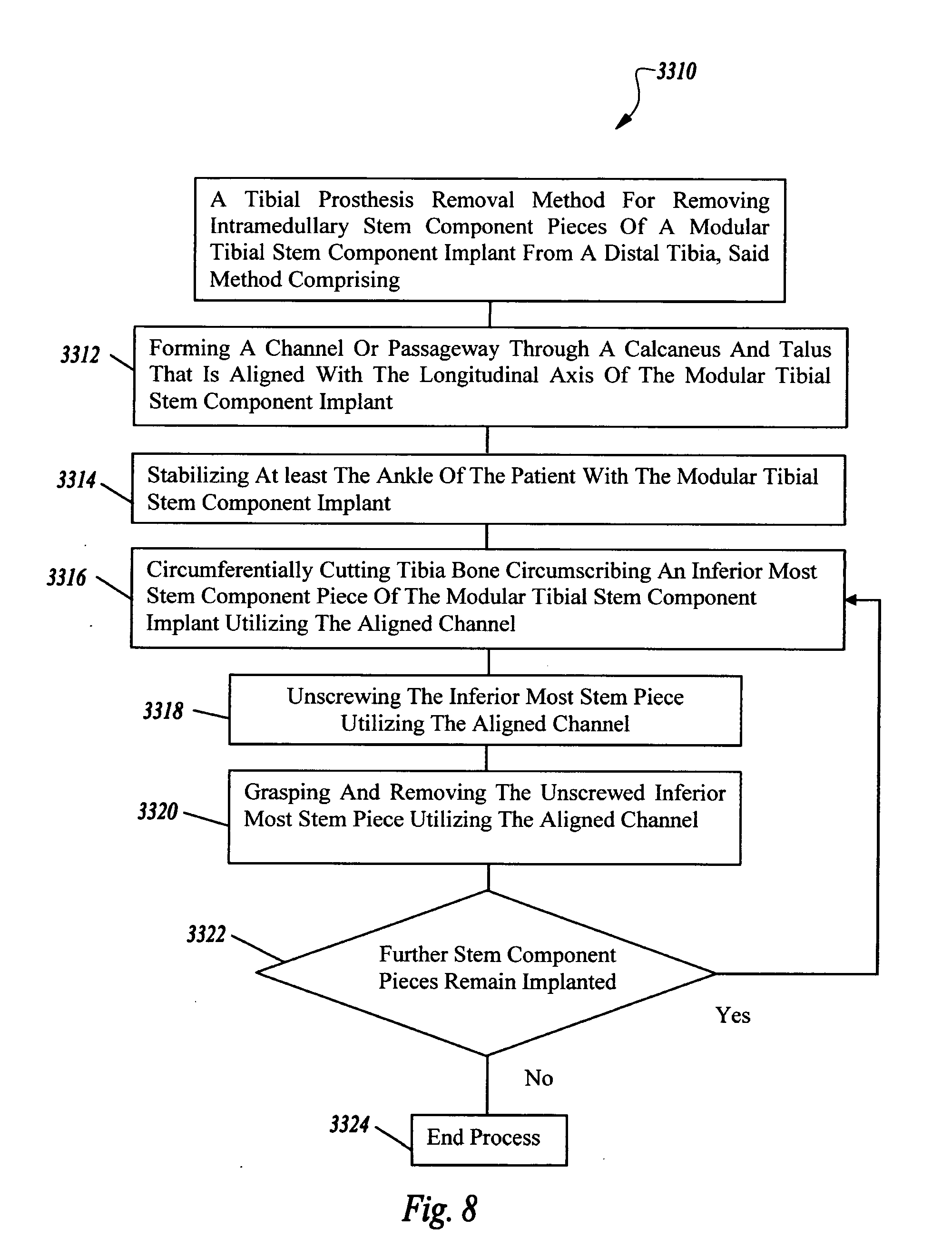
Systems and instrumentalities for use in removal of tibial prostheses of total ankle replacements
A system comprising instrumentalities and methods for removing intramedullary stem component pieces of a tibial implant from a distal tibia.
Owner:LIAN GEORGE JOHN
Porous spacers, instruments, and methods for foot and ankle fusion
ActiveUS20150057665A1Space is createdAnkle jointsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAnkle boneDistal tibia
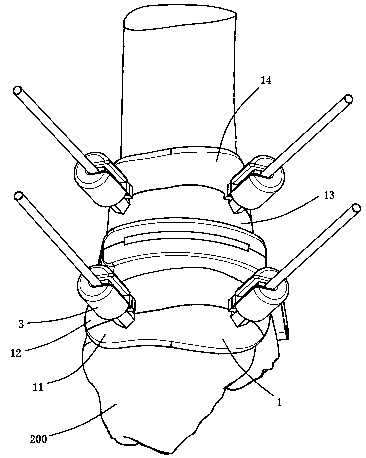
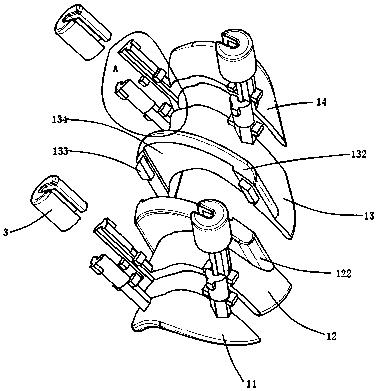
Porous spacers (100) are provided for foot and ankle fusion. The porous spacers disclosed herein may be implanted between separate bones of a joint or between two segments of a single bone following an osteotomy procedure. Such spacers may be used in conjunction with an ankle resection system which includes a resection frame (150) and a resection guide (170). The resection frame can be anchored to the distal tibia and / or the talus and provides an opening (155) through which a bone cutting element can pass for cutting underlying bone. The resection guide can include one or more cutting slots (169, 171, 172) and the resection guide can be coupled to the resection frame with the one or more cutting slots positioned over the opening in the resection frame so that the bone cutting element can pass through the one or more cutting slots and through the opening in the resection frame for cutting the distal tibia and / or the talus.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Systems and instrumentalities for use in total ankle replacement surgery
ActiveUS8475463B2High precisionSimplify operating proceduresWrist jointsAnkle jointsAnkle boneTotal ankle arthroplasty
Custom radiographically designed tibial and talar cutting guide system and instrumentalities including a tibial cutting guide position verification device is disclosed. A computer-based system and method for making the custom radiographically designed tibial and talar cutting guides is also disclosed. Further disclosed is an adjustable tibial reaming guide positioning system for allowing a position for reaming of a distal tibia to be adjusted during total ankle replacement surgery and, particularly, during total ankle arthroplasty for prostheses with an intramedullary stem.
Owner:LIAN GEORGE J
Lateral ankle fusion plate system and jig, and method for use therewith
InactiveUS20160354128A1Stable and strong and precise and comfortable for patientEasy to implantAnkle jointsJoint implantsCalcaneusDistal tibia
The invention comprises a lateral ankle fusion plate, a jig for use with the fusion plate and a method for ankle fusion of the joints between the tibia, the talus, and the calcaneus. In addition, a separate fusion screw from posterior to anterior through the calcaneal tuberosity into the distal tibia is useful and can be placed using the targeting jig of the invention. The plate includes a C-shaped stirrup portion that wraps the bottom of the calcaneus and is provided with a screw hole for a T-T-C-fusion screw. A C-shaped targeting jig is provided that interfaces with the plate to allow for placement of the calcaneal screw and has an additional attachment for placement of the independent fusion screw so as to avoid impingement with the plate, and plate screws. The invention also relates to a method of surgery that incorporates the use of the plate, the jig and the tibial / talar / calcaneal fusion screw for an arthrodesis of the ankle joint.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
Lateral ankle fusion plate system and jig, and method for use therewith
ActiveUS9421103B2Stable and strong and precise and comfortable for patientEasy to implantAnkle jointsJoint implantsCalcaneusJoint arthrodesis
The invention comprises a lateral ankle fusion plate, a jig for use with the fusion plate and a method for ankle fusion of the joints between the tibia, the talus, and the calcaneus. In addition, a separate fusion screw from posterior to anterior through the calcaneal tuberosity into the distal tibia is useful and can be placed using the targeting jig of the invention. The plate includes a C-shaped stirrup portion that wraps the bottom of the calcaneus and is provided with a screw hole for a T-T-C-fusion screw. A C-shaped targeting jig is provided that interfaces with the plate to allow for placement of the calcaneal screw and has an additional attachment for placement of the independent fusion screw so as to avoid impingement with the plate, and plate screws. The invention also relates to a method of surgery that incorporates the use of the plate, the jig and the tibial / talar / calcaneal fusion screw for an arthrodesis of the ankle joint.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
Lower limb traction device for intramedullary nail surgery
PendingCN110537964AImprove performanceDoes not affect the operationExternal osteosynthesisThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
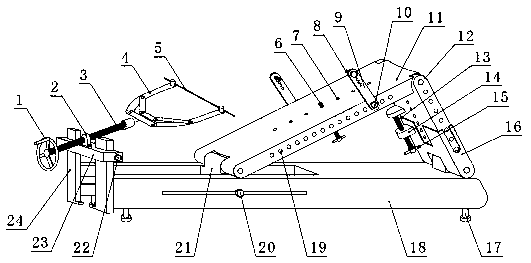
The invention discloses a lower limb traction device for an intramedullary nail surgery. The lower limb traction device includes a bottom beam, a shank support plate, a thigh backup plate, a sliding block, a traction needle, a traction bow and a pulling mechanism, the sliding block is installed on an axial sliding channel on the bottom beam and provided with sliding block locking screws, the shanksupport plate and the thigh backup plate are hinged in a Chinese character 'ren' shape, the lower end of the thigh backup plate is rotatably connected with the head end of the bottom beam, the lowerend of the shank support plate is rotatably connected with the sliding block, thighs and shanks of a patient respectively abut against the upper part of the thigh backup plate and the upper part of the shank support plate, the traction needle penetrates through the far-end of an anklebone or a shin bone of the patient and is connected between the two ends of the traction bow, and the bow back of the traction bow is connected with the tail end of the bottom beam through the pulling mechanism. According to the lower limb traction device, the patient can be kept in the state of curved leg, reliable traction of the shin bone of the patient can be achieved, all parts are not higher than lower limbs of the patient, and surgery operation is not affected; and according to the lower limb traction device, smooth operation of the intramedullary nail implantation surgery of a thigh bone and the shin bone can be ensured, and the surgical quality and the surgical efficiency are improved.
Owner:THE THIRD HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Method and apparatus for osteosynthesis
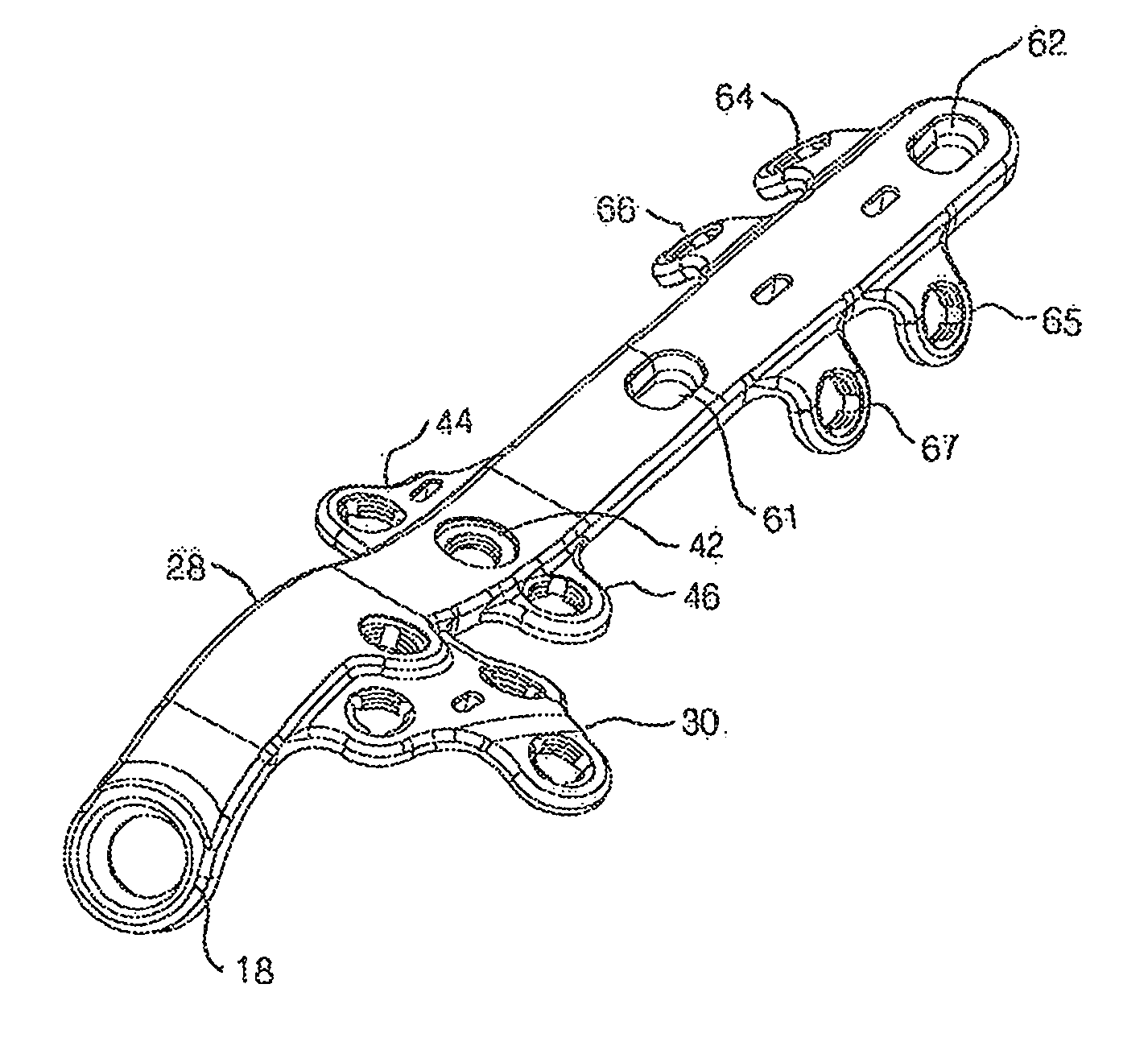
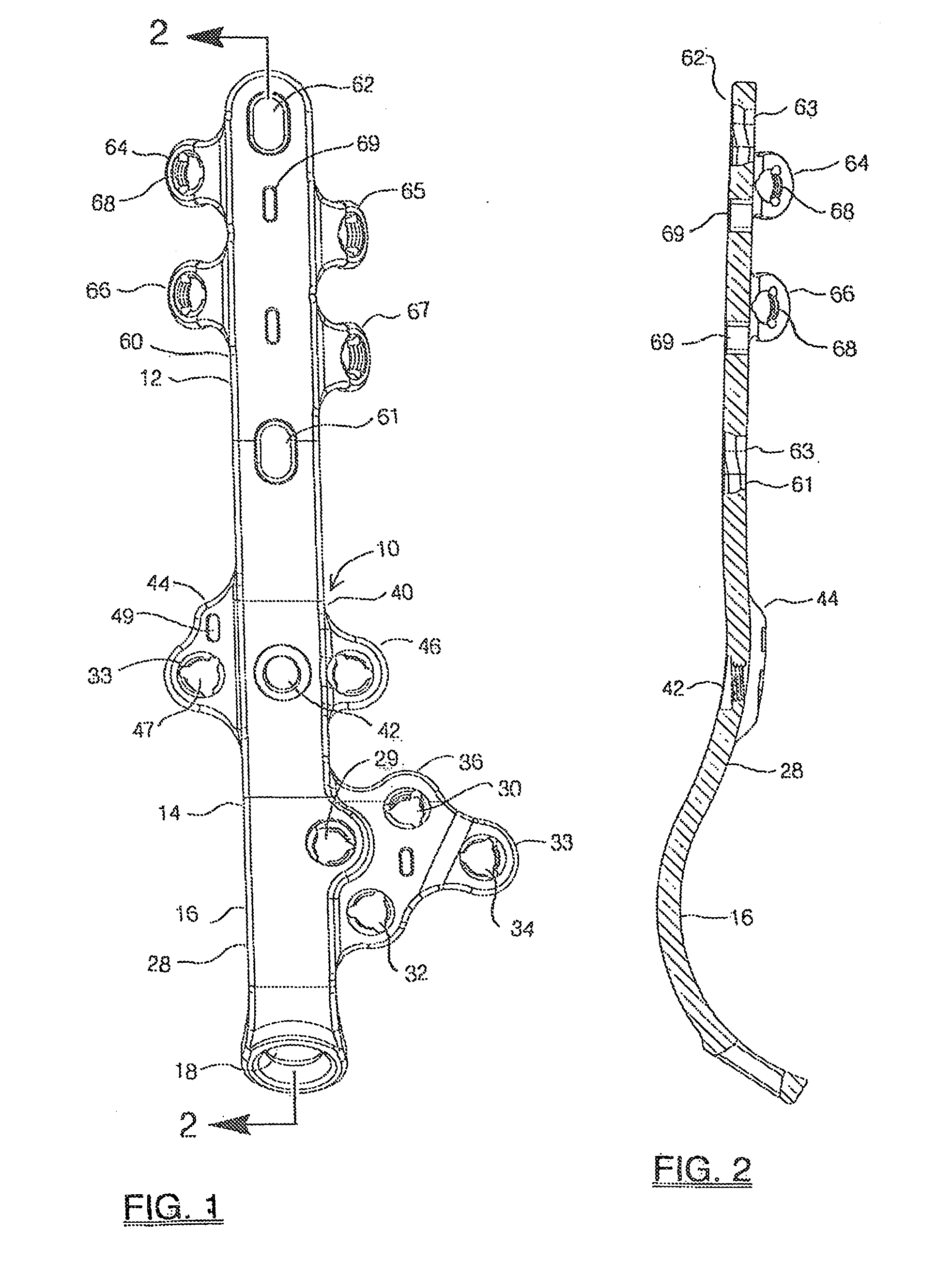
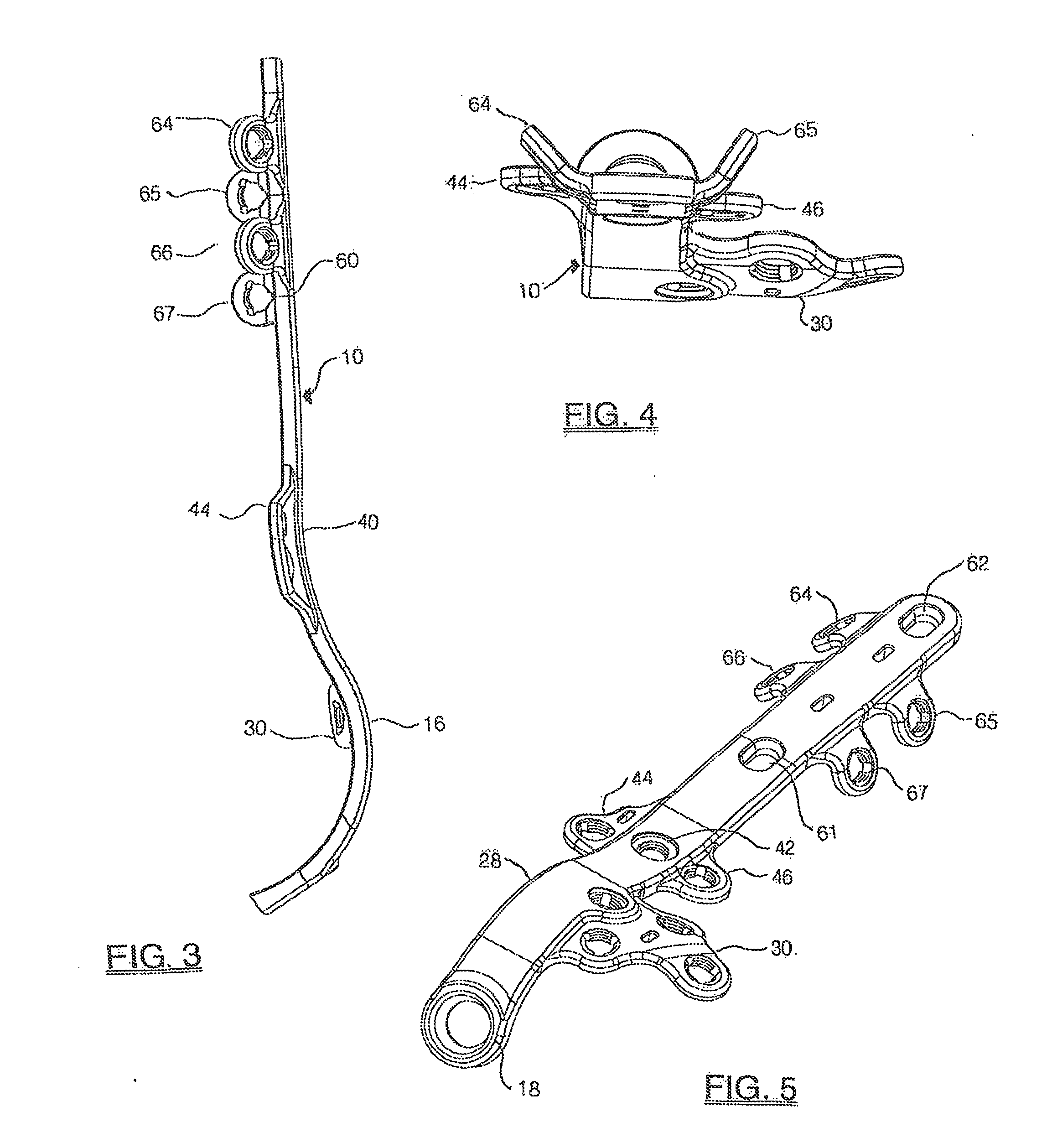
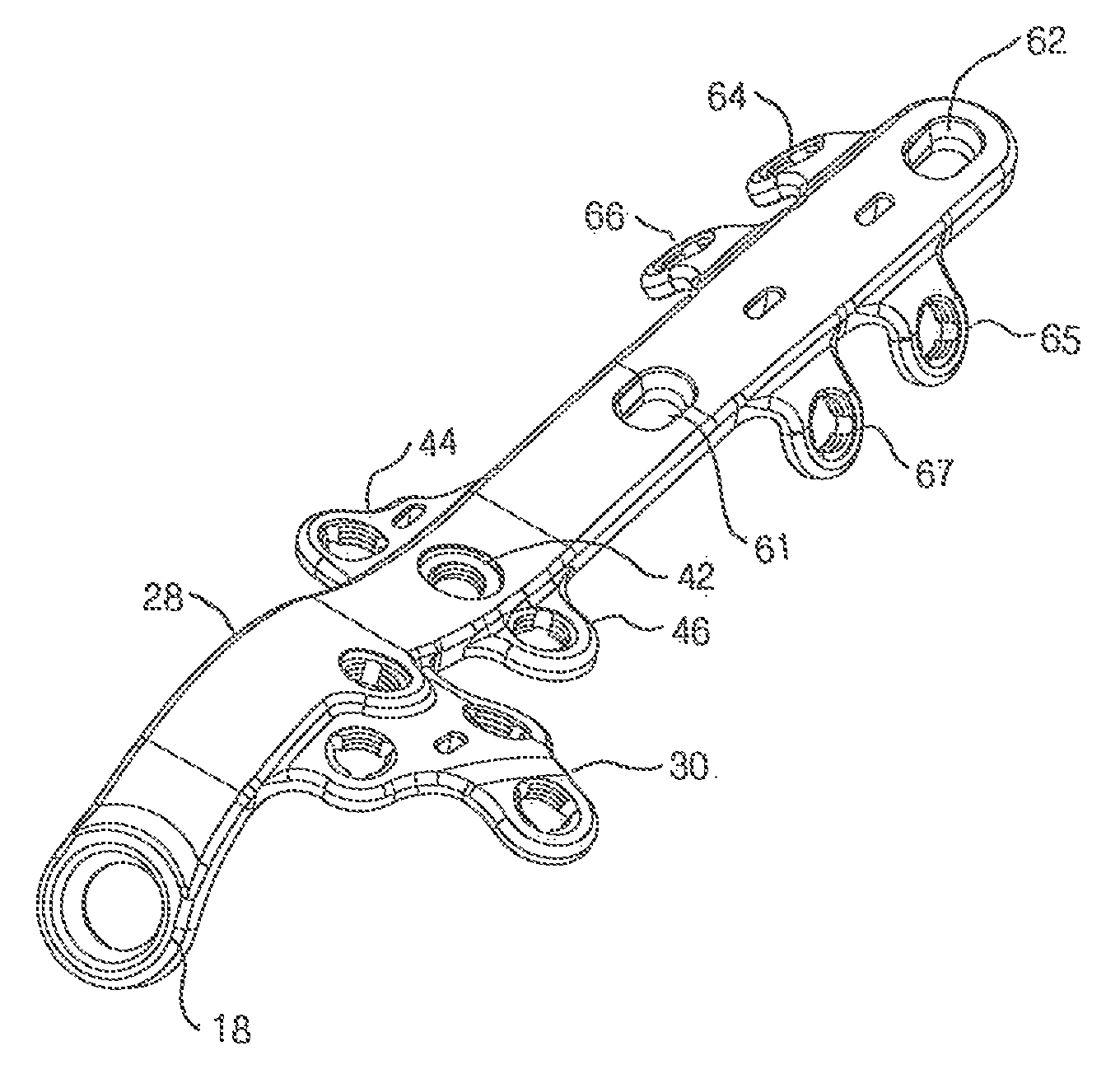
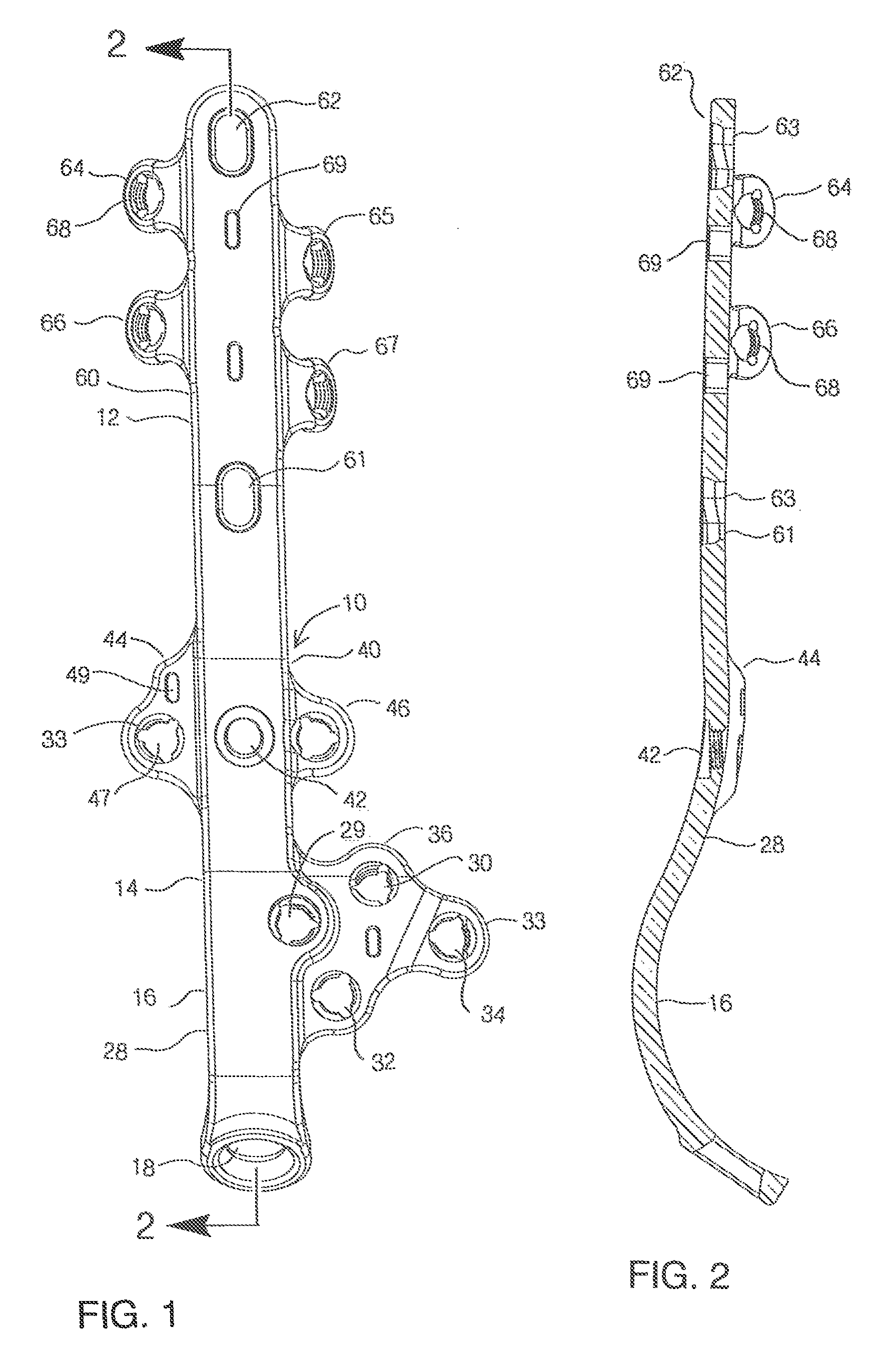
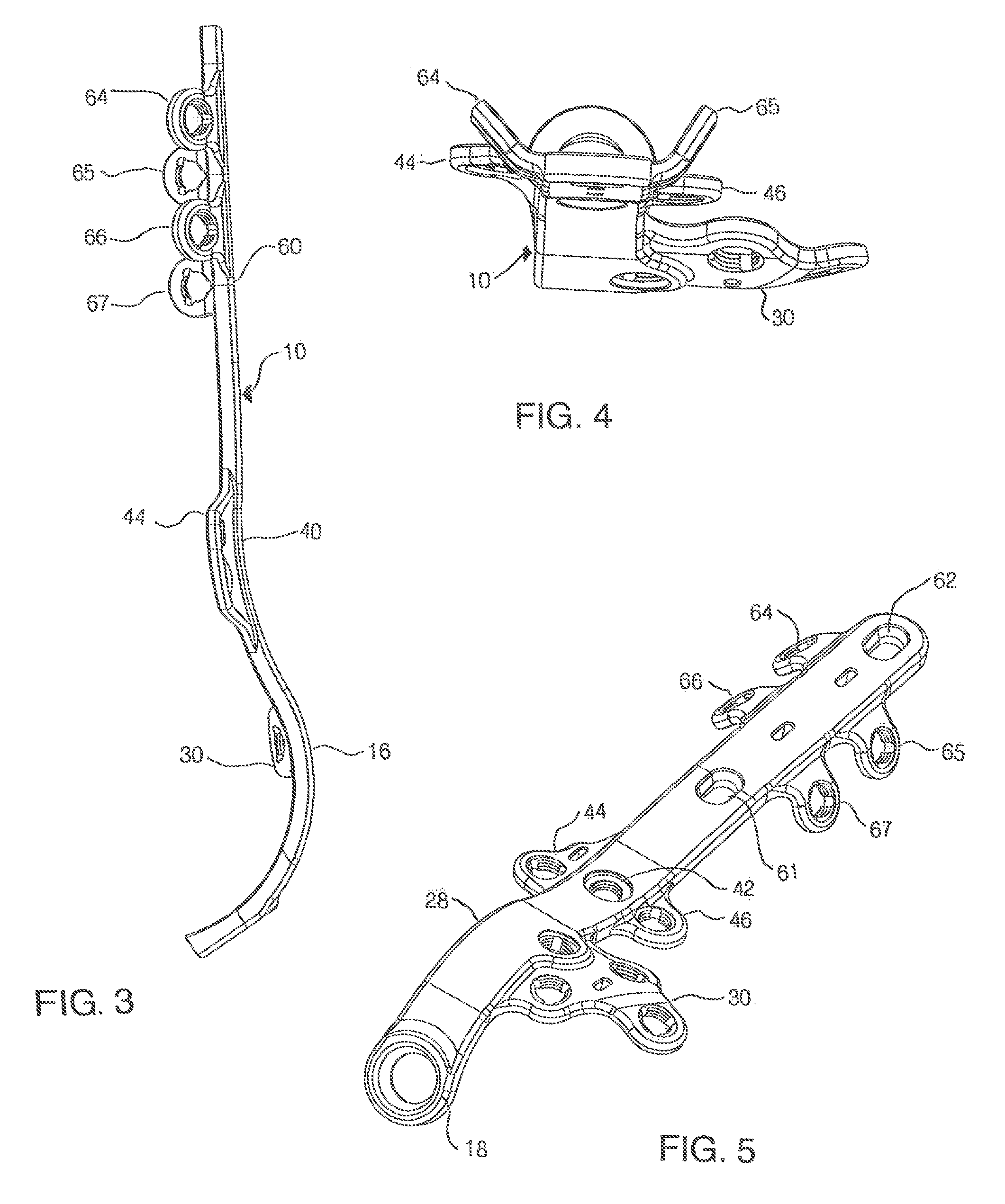
A bone plate assembly including a first plate, a coupler, a second plate, and a guide; the first plate defining a window and having a first major surface adapted to conform to a native bone structure. The coupler such as a beveled edge and / or slide mechanism can be formed on a second major surface of the first plate opposite the first major surface. The second plate can be adapted to engage the coupler, to cover the window, and to conform to the native bone structure. The second plate can include through holes adapted to receive bone screws. The guide can be adapted to engage the coupler and to guide at least one of a cutting tool and / or a dilation tool. The native bone structure is distal radius, proximal femur, distal femur, proximal tibia, distal tibia or calcaneus.
Owner:KIRITSIS PAUL
Patient-specific instruments for total ankle arthroplasty
Patient-specific instruments for preparing bones for receipt of orthopedic prostheses, such as the distal tibia and the talus in a total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) procedure. A tibial guide and a talar guide are manufactured based on patient-specific anatomical data obtained using imaging technology, and each guide includes a surface conforming to selected anatomical surfaces or regions of the tibia or talus, respectively. Each guide includes at least one cut referencing surface, such as a cut slot, to guide a resection, and may also include a guide aperture sized to guide a reaming tool for reaming the distal tibia or talus. The guides may also include pin holes positioned within a periphery defined by the cut referencing surfaces such that, when the resections are made and the resected tibial bone portion or talus bone portion is removed, the guide and its associated pins are removed along with the resected bone portion.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
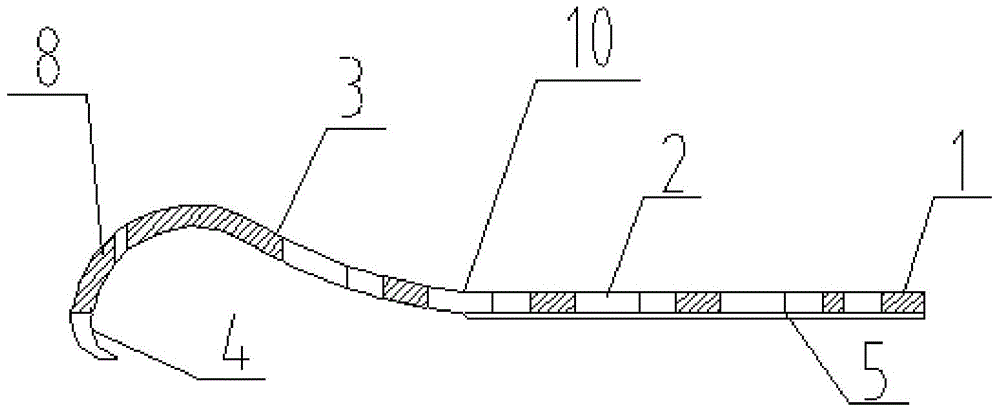
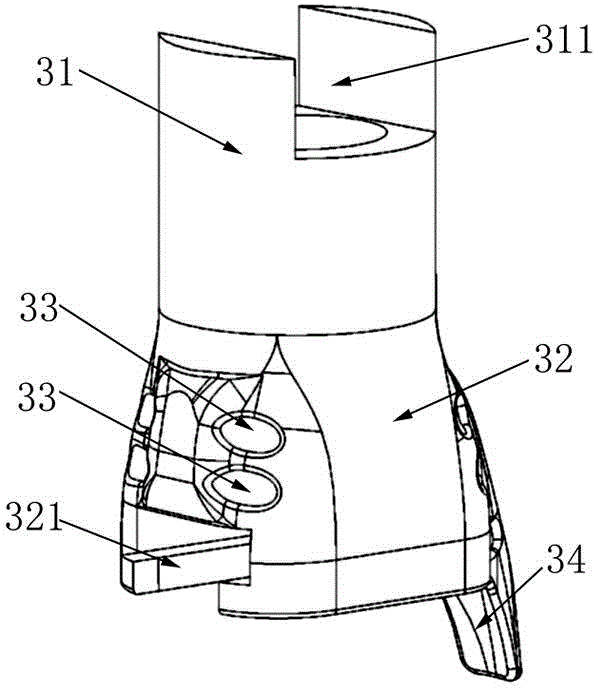
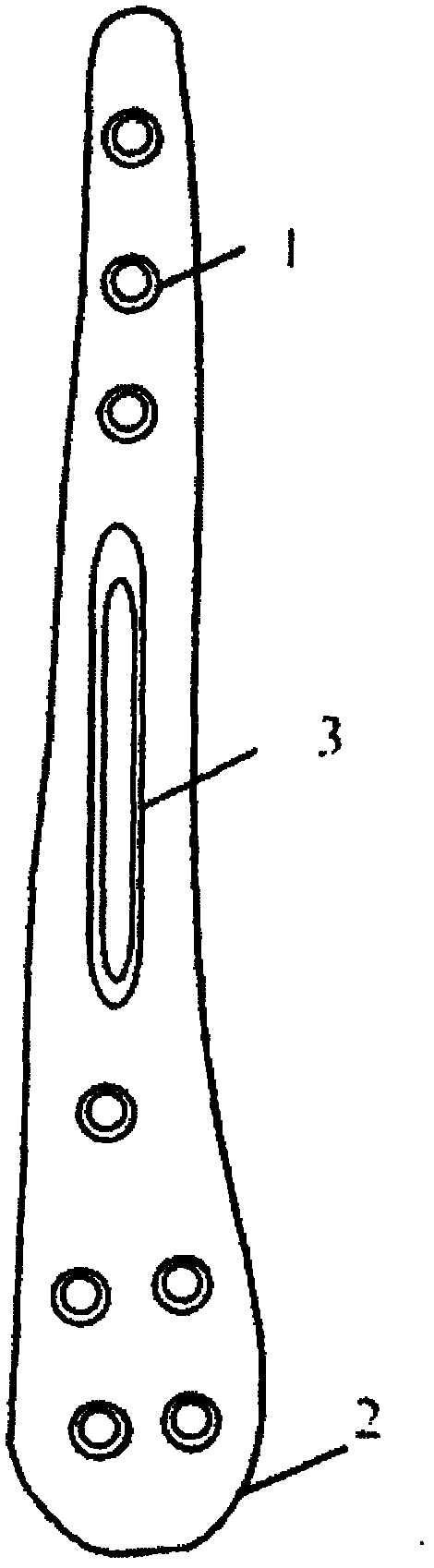
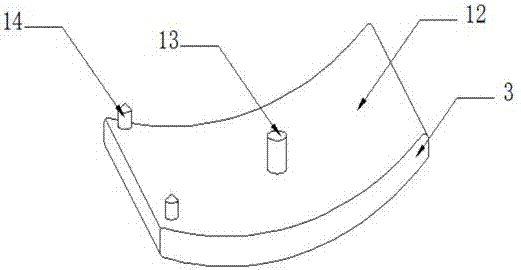
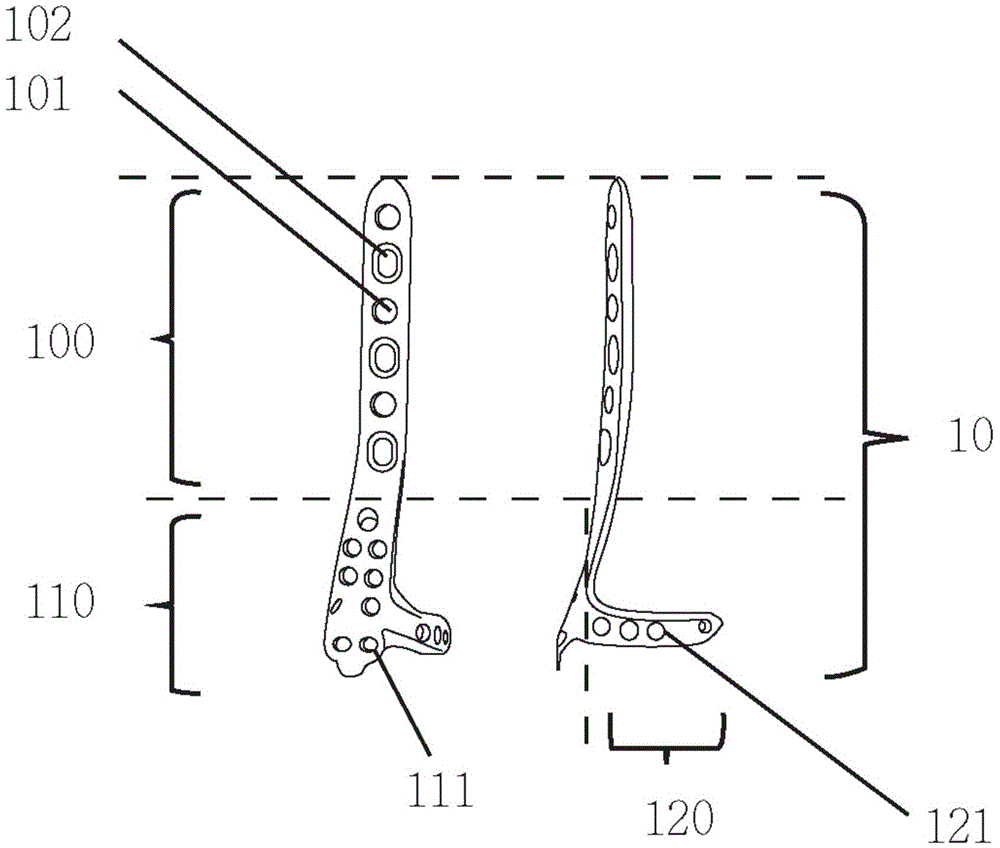
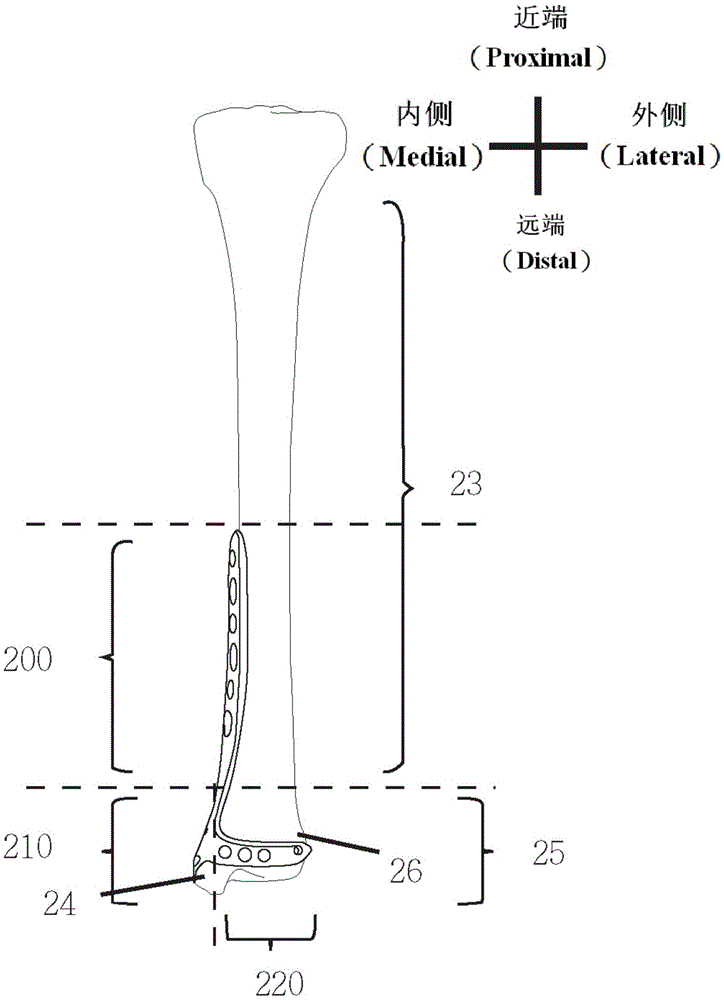
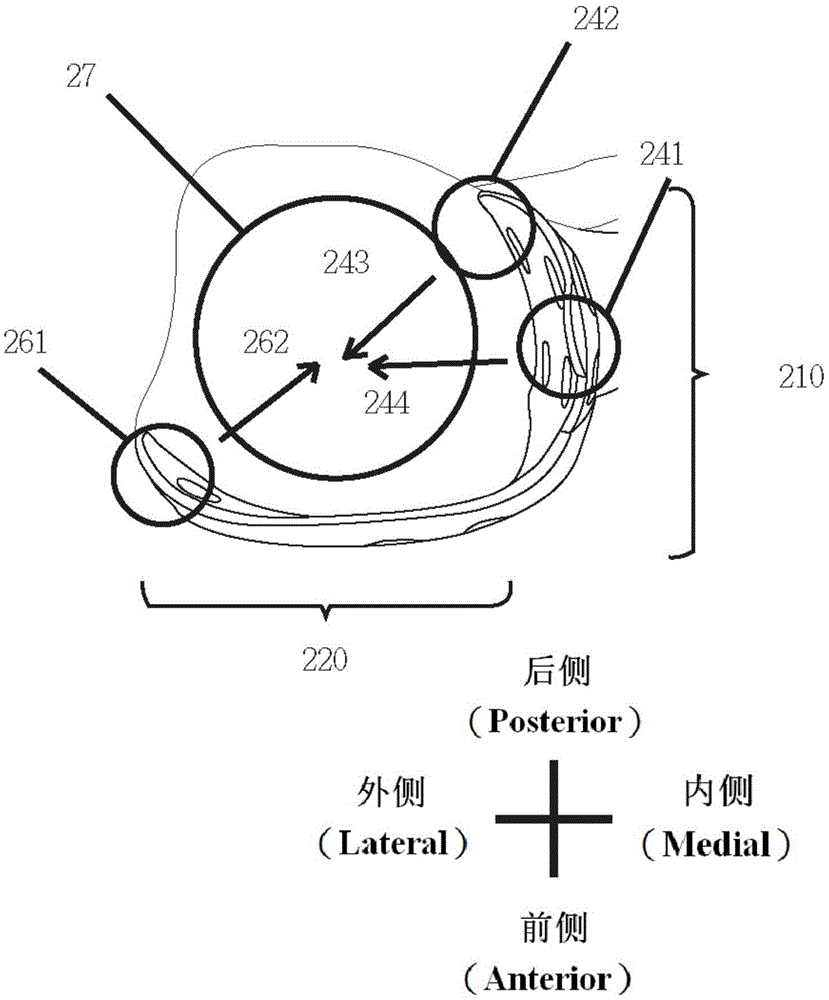
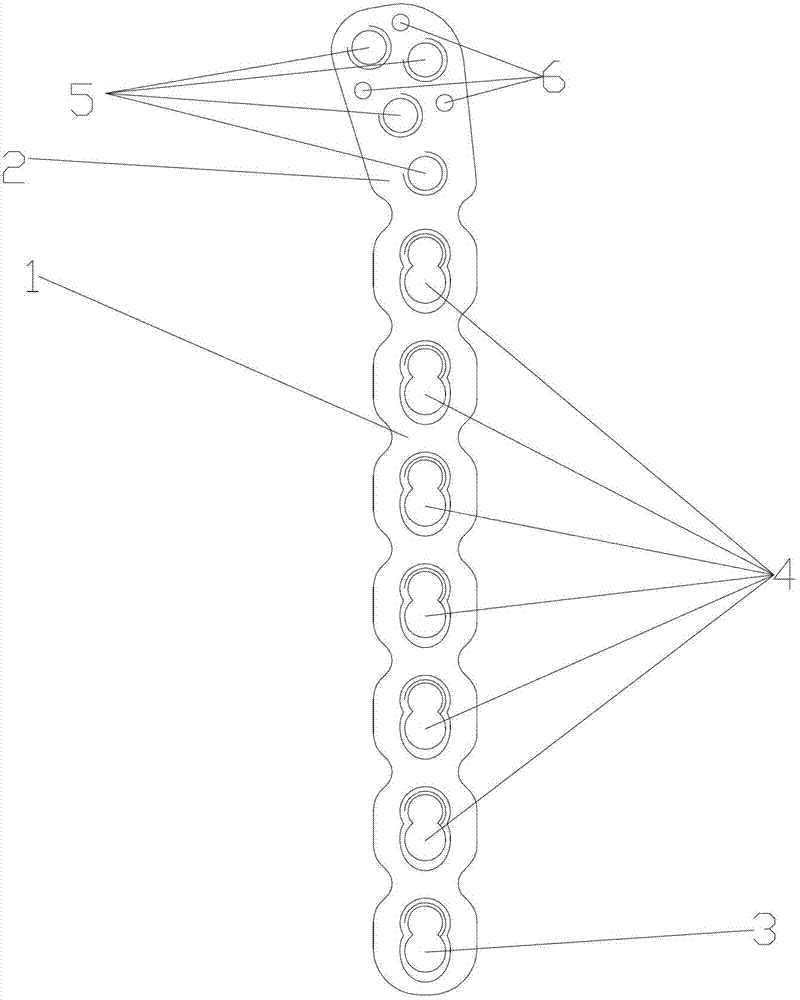
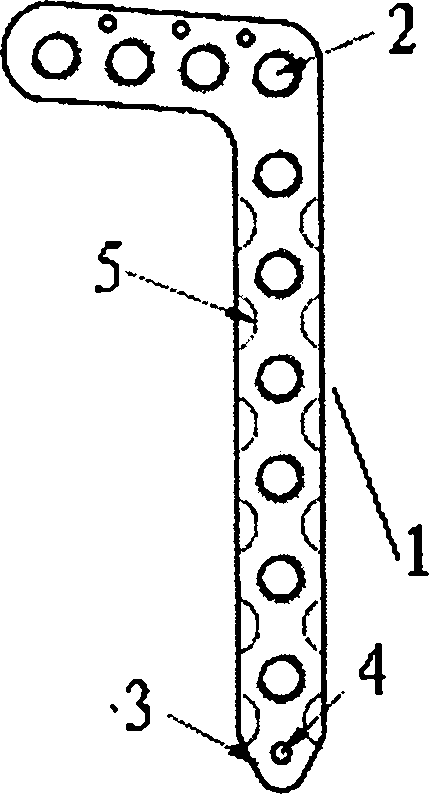
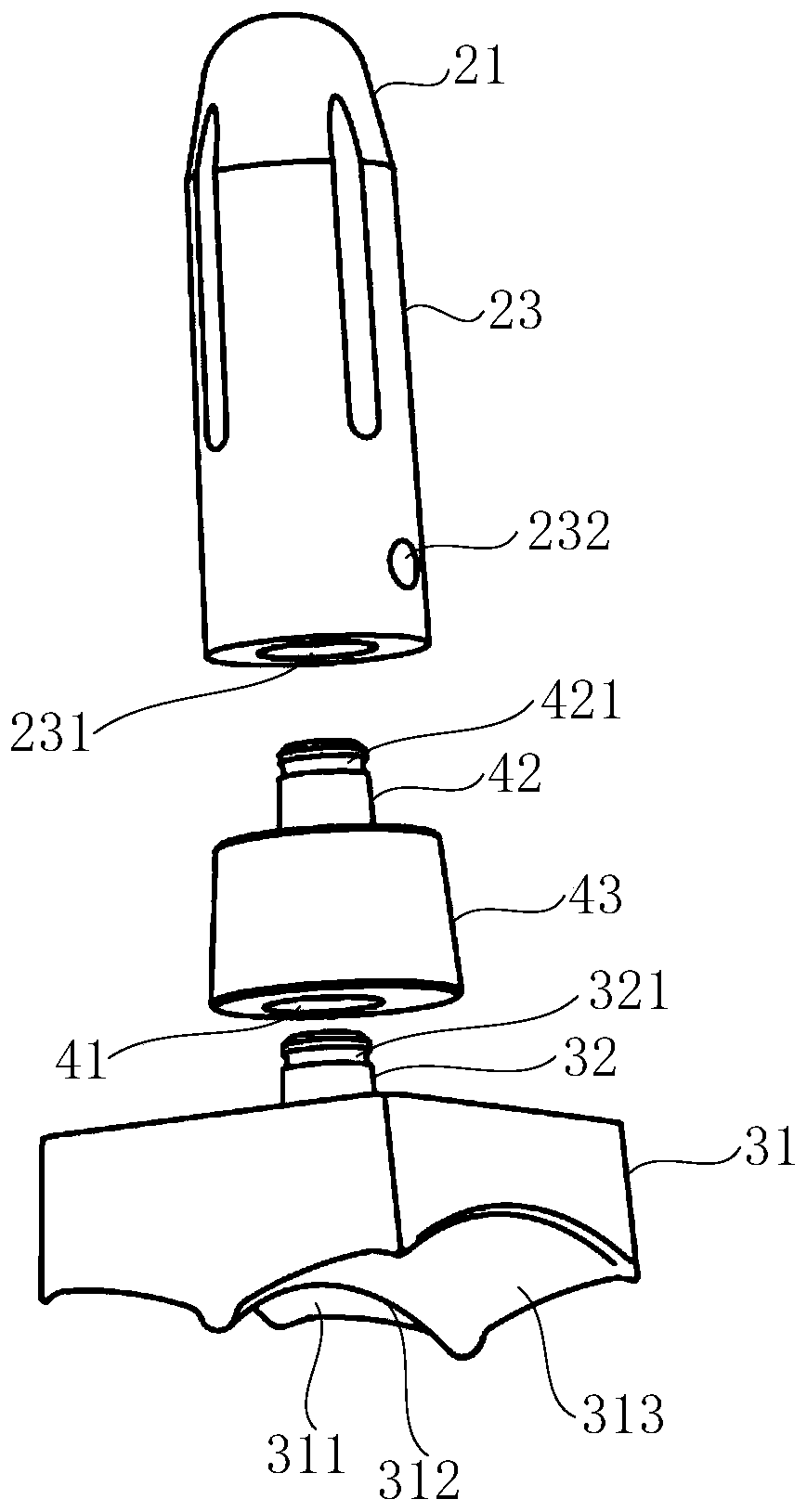
Distal tibia end inner side hook plate
InactiveCN104546104AAvoid displacementPrevent collapseBone platesArticular surfacesArticular surface
A distal tibia end inner side hook plate comprises a plate body and a hook body. The plate body comprises a proximal end portion and a distal end portion wider than the proximal end portion. The plate body is uniformly provided with adjustable screw holes in the axial direction. The hook body is connected to the distal end portion of the plate body and provided with two sharp hooks. The inner side surface of the plate body is recessed inwards. The distal end portion of the plate body is bent outwards. The hook body is bent inwards. The inner side surface of the plate body and the inner surface of the hook body are adapted to distal tibia end inner side bone in shape. The two sharp hooks of the hook body can be pressurized through hollow screws to enter the tip of the medial malleolus bone to form triangular multi-planar three-dimensional fixing at the distal fracture end, strengthen the anti-torsion capability, prevent the distal medial malleolus fracture end from shifting back and forth and reduce the risk of secondary reduction loss. The proximal end portion of the plate body is fixed through screws to serve as an anti-slipping plate for effectively preventing the displacement of the distal end bone. The hook plate used for fixing can also play a role of a supporting plate to prevent secondary collapse of the articular surface for a patient with medial malleolus superior angle articular cartilage lower bone compression.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Combined tumor-type ankle joint prosthesis
The invention relates to a combined tumor-type ankle joint prosthesis which comprises an ankle bone side component, a polyethylene liner and a top component. Three backward down inclined ridges are formed at the bottom of the ankle bone side component in a projecting manner, an arched sliding surface is formed at the top of the ankle bone side component, a T-shaped projection is transversely arranged at the top of the polyethylene liner, the bottom of the polyethylene liner is recessed inwards to form a joint fossa for containing the sliding surface, the top component is provided with an upper connecting surface for connecting the top component with a tibial prosthesis, a T-shaped groove for containing the projection is transversely formed in the bottom of the top component, five through holes for repairing ligaments on the inner side and the outer side of an ankle joint are formed in the top component in a front and rear penetrating manner, the inner side of the top component extends downwards to form a projecting ridge, and the projecting ridge is abutted to the inner side face of the polyethylene liner. The prosthesis is reasonable in structural design, preparation and surgical operation are facilitated, stability of an artificial ankle joint is enhanced, loading and moving functions of the ankle joint are restored, and the prosthesis is suitable for limb salvage treatment of distal tibial malignant tumors.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
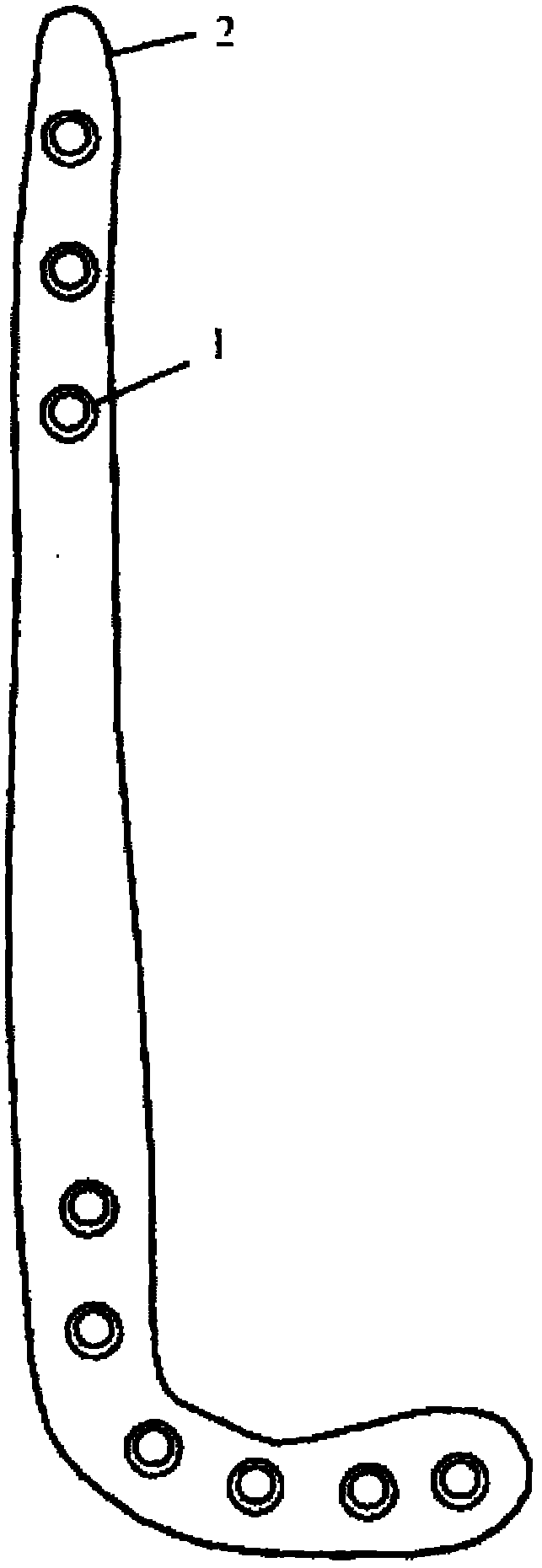
Anatomical tibia far-end outer-side bridge type bone fracture plate
The invention provides an anatomical tibia far-end outer-side bridge type bone fracture plate, belonging to the field of medical apparatuses, wherein the anatomical tibia far-end outer-side bridge type bone fracture plate comprises a top side surface, a bottom side surface and a group of screw holes, wherein the bottom side surface is used for being in contact with a bone, the screw holes are distributed at two ends of the anatomical tibia far-end outer-side bridge type bone fracture plate, the bottom side surface is of an anatomical shape of a tibia outer surface and is used for being adhered on a front side surface and an outer side surface of a far section and a middle section of a tibia. The anatomical tibia far-end outer-side bridge type bone fracture plate disclosed by the invention is suitable for tibia fracture, in particular for curing tibia far-end bone fracture through an MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis) technology, and can enable the bone fracture to be greatly healed up.
Owner:北京国人骨科医疗器械有限公司
Middle and distal tibia tumor type prosthesis and preparation device and method thereof
PendingCN109620476AGain intuitive knowledgeIntuitive knowledgeJoint implantsTomographyAnkle MortiseBone ingrowth
The invention relates to the technical field of auxiliary instruments, in particular to a middle and distal tibia tumor type prosthesis and a preparation device and method thereof. The preparation device comprises an image acquisition system for collecting tibia image data and a 3D printing system for printing a prosthesis model. The bilateral tibiofibula CT scanning is performed before an operation, the 3D tibiofibula of the affected side is reconstructed by reverse software, and the undercut range is expected corresponding to the tibia malignant tumor to make a middle and distal tibia tumortype prosthesis image to obtain intuitive understanding of the diseased tibia. The intraoperative prosthesis handle portion and the ankle mortise are compressed tightly with the host proximal tibia and the proximal talus osteotomy side, and fixed with multiple screws to complete the initial stabilization of the connection between two ends of the prosthesis and the host bone tissue. The porous surface of the proximal end of the prosthesis handle portion and the metal ankle mortise (a cavity at the ankle bone end) can promote the bone ingrowth, and the long-term postoperative stability is strengthened.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Osteotomy orthopaedic guide assembly on ankle
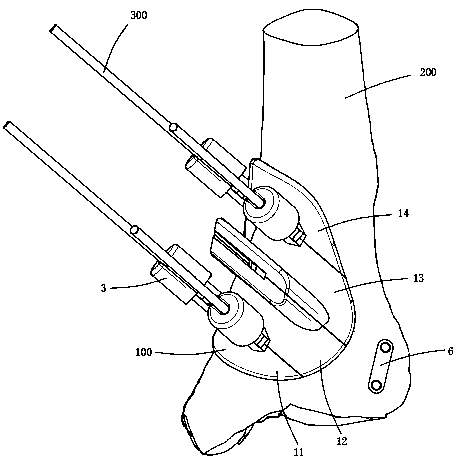
The invention provides an osteotomy orthopaedic guide assembly on an ankle. The assembly is arranged on a distal end of a tibia of a patient, to perform osteotomy and correction. The assembly includesa cutting guide that matches the patient's tibia, a locating block detachably snap to that cutting guide plate and a locking member for fastening the cutting guide plate and the locating block, The cutting guide plate is provided with a cutting groove and a bonding surface, the bonding surface is bonded with the surface of the corresponding position of the distal end of the tibia, the cutting guide plate comprises a plurality of positioning plates detachably arranged between each other, the locking member is sleeved on the plurality of positioning plates of the cutting guide plate, and the cutting guide plate is also provided with a through hole. The invention defines the angle and position of the distraction after osteotomy by a positioning block, improves the accuracy of the operation,reduces the difficulty of the operation and the dependence on the experience of the doctor, and avoids frequent X-ray fluoroscopy measurement during the operation. By setting the cutting guide plate as a detachable structure, the smooth disassembly of the cutting guide plate is facilitated, and the locking of the distraction position and the accuracy of the operation are ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINJIAN MEDICAL TECH
Tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis
PendingCN111870409AImprove stabilityPromote ingrowthAnkle jointsJoint implantsEntire tibiaBone marrow cavity
The invention provides a tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis. The tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis comprises a medullary cavity extension handle, a far-end ankle joint and a backbone extension section, wherein the backbone extension section is mounted between the medullary cavity extension handle and the far-end ankle joint, the medullary cavity extension handle is connected with a medullarycavity at the near end of a tibia, and a 3D printing bone trabecula structure is arranged on the contact surface of the far-end ankle joint, talus and fibula. A locking nail is inserted into the nailhole of the far-end ankle joint to be connected with the talus and the fibula, so that the far-end ankle joint is fixedly connected with the talus and the fibula. The tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis is suitable for ankle joint prosthesis replacement of a tibia far-end tumor excision patient, the 3D printing bone trabecula structure can effectively promote bone ingrowth, the prosthesis is morestable in combination with a locking nail, and the ankle joint prosthesis is high in initial bone ingrowth speed and good in medium and long term stability; And when the tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis is used, the whole tibia does not need to be replaced, the intact tibia is reserved, only the tibia with a focus is replaced, the length of the prosthesis is suitable for each patient due to the arrangement of the backbone extension section, and the manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING LIDAKANG TECH
Assembled tumor type artificial tibiotalar joint prosthesis
PendingCN111529139AAchieve stabilityRecovery lengthAnkle jointsJoint implantsTibiotalar jointTibial bone
The invention relates to an assembled tumor type artificial tibiotalar joint prosthesis. The assembled tumor type artificial tibiotalar joint prosthesis comprises a tibia assembly, a talus assembly and a tibiotalar hinge type connecting assembly, wherein the tibia assembly is connected with the human tibia; the talus assembly is mainly composed of a talus base, a talus connecting column and a locking screw; the talus base is of a shell type structure matched with the surface shape of the talus; the talus connecting column is integrally formed on the lower portion of the talus base and extendsdownwards along the vertical axis; the locking screw penetrates through the talus base, the talus connecting column and the human talus along the coronal axis; and the tibiotalar hinge type connectingassembly is rotationally connected between the tibia assembly and the talus assembly, so that the tibia assembly and the talus assembly can relatively rotate in a sagittal plane, and the plantar flexion and dorsal extension functions of the tibiotalar joint are recovered. The prosthesis can be widely applied to bone defect reconstruction of limb continuity interruption after tumor resection underthe condition that the far end of the tibia or the far end of the fibula seriously affects the tibia, the purpose of limb structure recovery can be achieved, meanwhile, perfect combination of immediate stability and long-term stability of the tibiotalar joint is achieved, and therefore the long-term tibiotalar joint function of a patient is remarkably improved.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Anatomical tibia far-end inner-side bridge-type bone fracture plate
The invention provides an anatomical tibia far-end inner-side bridge-type bone fracture plate and belongs to the field of medical apparatuses. The anatomical tibia far-end inner-side bridge-type bone fracture plate comprises a top side surface, a bottom side surface and a group of screw holes, wherein the bottom side surface is used for being in contact with a bone, the screw holes are distributed at two ends of the anatomical tibia far-end inner-side bridge-type bone fracture plate, and the bottom side surface of the anatomical tibia far-end inner-side bridge-type bone fracture plate is in an anatomical shape of a tibia inner side bone surface and is used for being adhered to the inner side bone surfaces of the far section and middle section of a tibia. The anatomical tibia far-end inner-side bridge-type bone fracture plate disclosed by the invention is suitable for tibia fracture, is especially used for treating tibia far-end bone fracture through an MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis) technology, and can enable the bone fracture to be healed up better.
Owner:北京国人骨科医疗器械有限公司
Anatomical ankle prosthesis with fixing pad
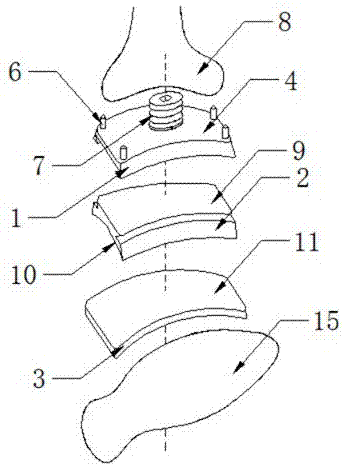
ActiveCN107374788ALight in massQuality improvementAnkle jointsJoint implantsArticular surfacesIsosceles trapezoid
The invention discloses an anatomical ankle prosthesis with a fixing pad. The anatomical ankle prosthesis comprises a tibia side component, the fixing pad and a talus side component and is characterized in that the top end of the tibia side component is provided with an upper supporting surface, four projection first dowels are fixedly arranged at four corners of the upper supporting surface respectively, and the middle of the tibia side component is fixedly connected to the bottom middle of an amputated tibia far end through a recess screw. The anatomical ankle prosthesis has advantages that the middle of the tibia side component is fixedly connected to a talus far end through the recess screw while the upper supporting surface are fixedly connected with the tibia far end through the four first dowels respectively, the four first dowels are in isosceles trapezoidal arrangement, stability in connection between the tibia side component and the amputated tibia far end is achieved, a lower slide surface at the bottom end of the fixing pad is in slide connection with an upper slide surface at the top end of the talus side component, and the upper supporting surface, the lower slide surface and the upper slide surface are all arc and matched with an articular surface of the tibia far end in radian to make the prosthesis better accord with a real human ankle structure.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Tibia remote end fixing device
InactiveCN105935312AEasy to fixImprove postoperative recoveryFastenersBone platesDistal tibiaSacroiliac joint
The invention discloses a tibia remote end fixing device including a bone fixing part capable of adhering to the tibia bone; a malleolus medialis fixing part extending from the bone fixing part in the tibia remote end direction and capable of adhering to the malleolus medialis; a fin part extending to a tibiofibula remote end joint from the malleolus medialis fixing part in the front direction of the tibia horizontally, wherein an arbitrary one of the bone fixing part, the malleolus medialis fixing part and the fin part is provided with at least one screw hole and a fixing bone nail and the malleolus medialis fixing part and the fin part can be embedded into the surface of the tibia remote end.
Owner:A PLUS BIOTECH
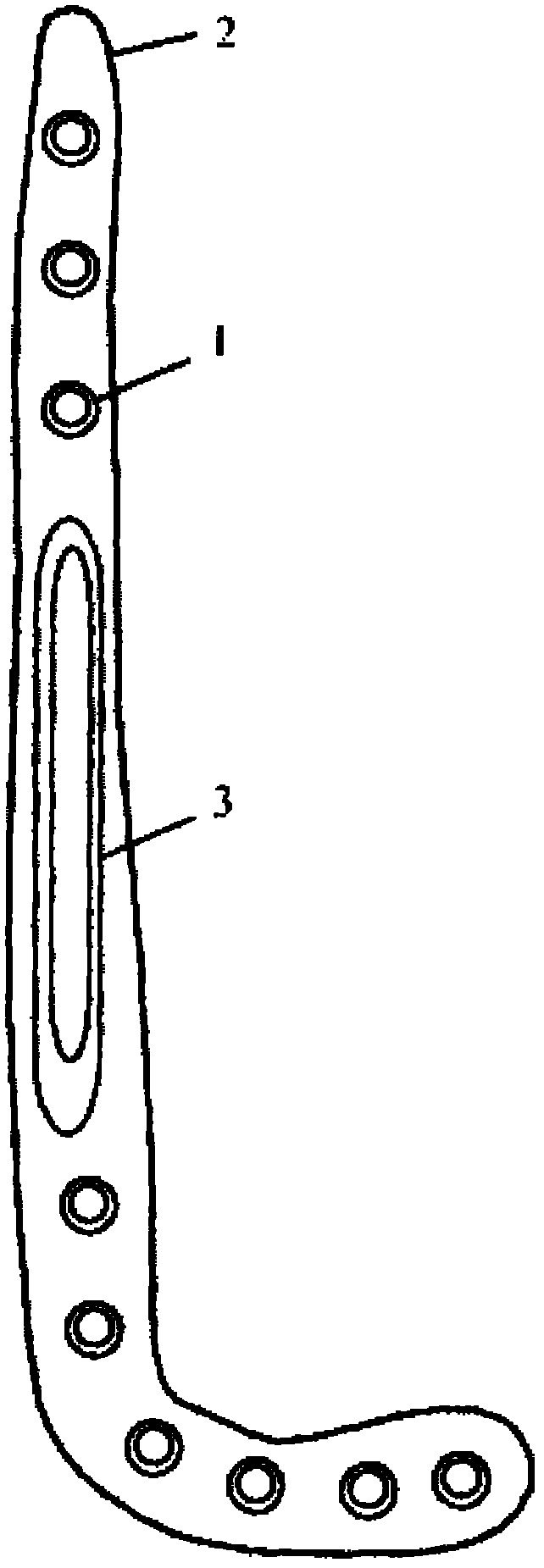
Inner side bone fracture plate for tibia far end
The invention relates to an inner side bone fracture plate for a tibia far end and belongs to the technical field of a medicine instrument. The inner side bone fracture plate comprises a bone fracture plate body and a thinned segment, wherein the bone fracture plate body is connected with the thinned segment, pressure device connecting holes and a plurality of combining holes are arranged in the bore fracture plate body, and a plurality of locking screw holes and auxiliary screw holes are arranged in the thinned segment; the space between every two adjacent combining holes is equal; the space between one pressure device connecting hole and the adjacent combining hole is smaller than the space between every two combining holes; and the space between one locking screw hole and the adjacent combining hole is smaller than the space between one pressure device connecting hole and the adjacent combining hole. The inner side bone fracture plate is applicable to tibia fracture and particularly applicable to the tibia far end fracture treated by MIPO (minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis) technology, the fracture is enabled to be better healed, and complications are effectively avoided; and the inner side bone fracture plate for tibia far end is simple, practical and is low in cost.
Owner:SUZHOU IDEAL MEDICAL APPLIANCE
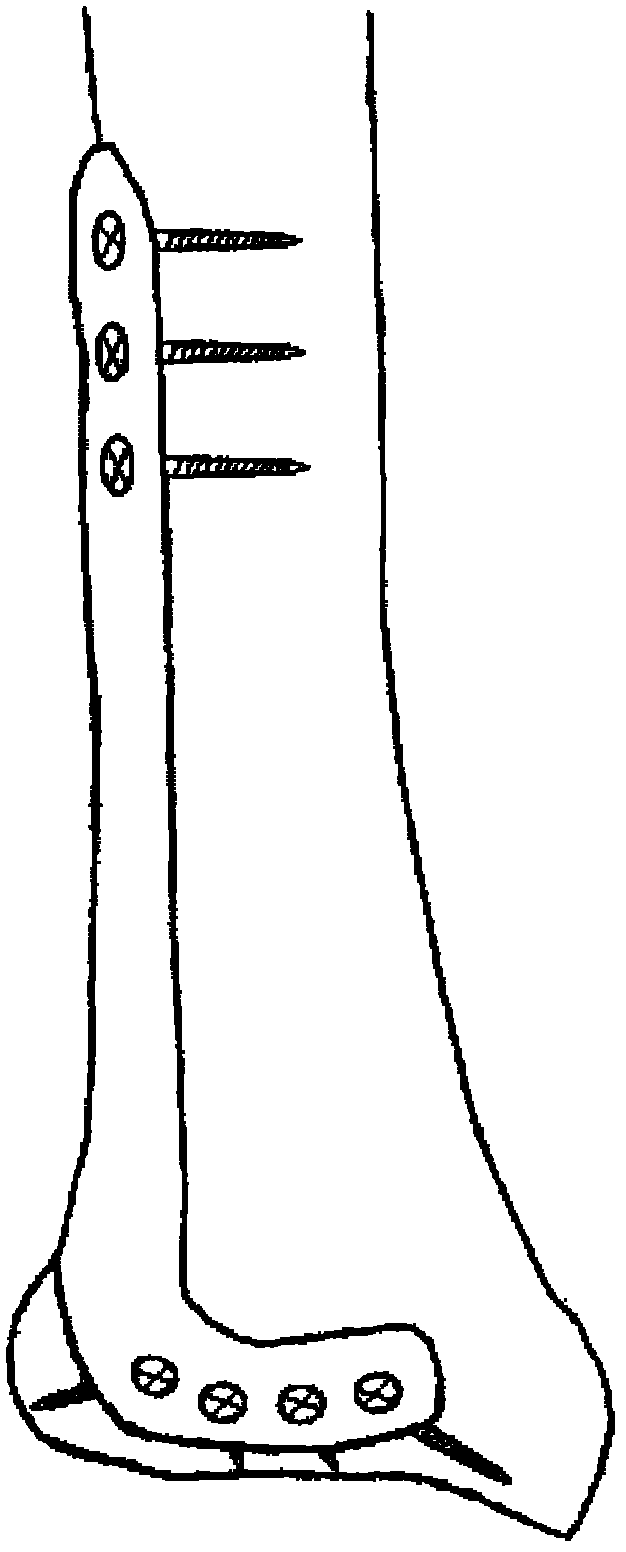
Lateral distal tibial locking plate
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical apparatuses and instruments, and particularly relates to a lateral distal tibial locking plate. The lateral distal tibial locking plate comprises an L-shaped plate body, wherein a plurality of locking holes are formed in the plate body, a minimally-invasive head portion used for reducing the stimulation caused to soft tissue when the plate body is implanted is arranged at one end of the plate body, and a kirschner wire hole for a doctor to conveniently conduct operation through a kirschner wire is formed in the minimally-invasive head portion. The minimally-invasive head portion used for reducing the stimulation caused to the soft tissue when the plate body is implanted is arranged at one end of the plate body, the kirschner wire hole for the doctor to conveniently conduct operation through the kirschner wire is formed in the minimally-invasive head portion, and therefore the operation of the doctor is facilitated, and the simulation caused to the soft tissue in the implanting process can be effectively reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN KANGER MEDICAL DEVICE
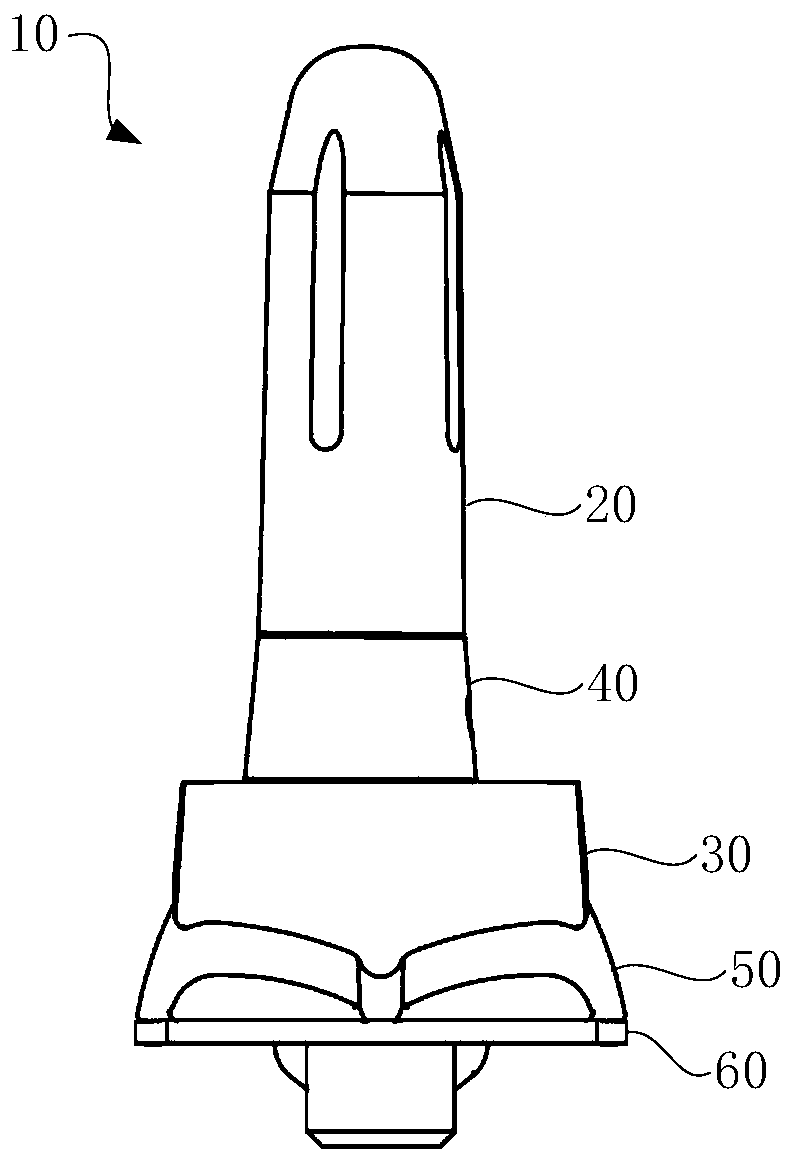
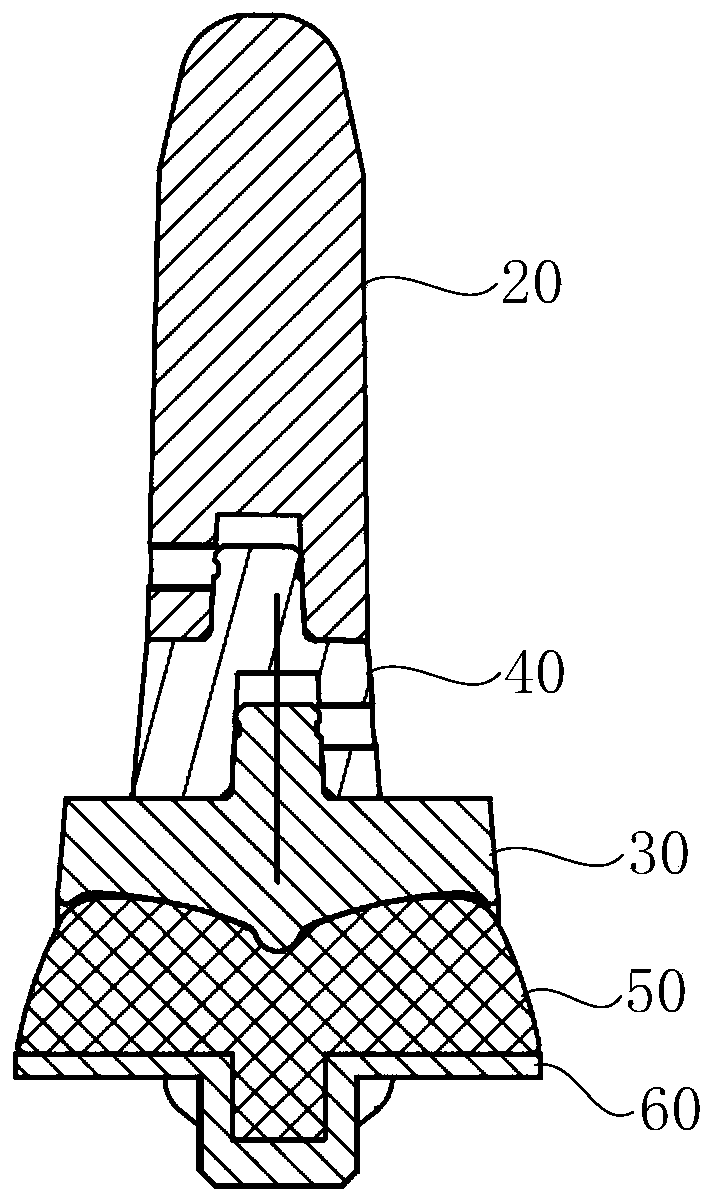
Ankle joint prosthesis
PendingCN110840635ASolve the problem of not being able to adapt to different tibial medullary cavity shapesImprove stabilityAnkle jointsJoint implantsHuman bodyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
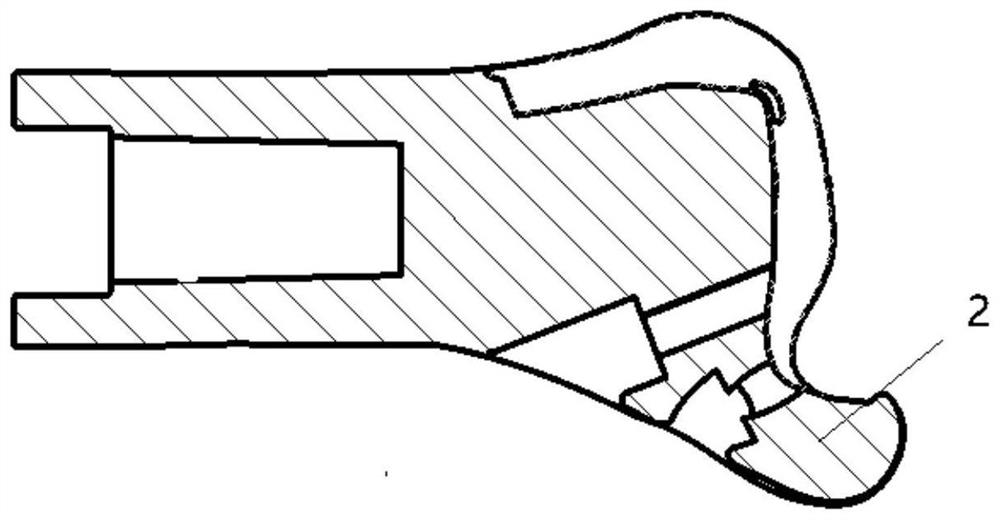
The invention provides an ankle joint prosthesis. The ankle joint prosthesis comprises a tibial stem, a distal tibial prosthesis and a tibial connector. The tibial stem is used for being disposed in atibial marrow cavity of a human body. The tibial connector is disposed between the tibial stem and the distal tibial prosthesis, so as to connect the tibial stem with the distal tibial prosthesis through the tibial connector. The tibial connector comprises a first connection portion and a second connection portion, the second connection portion is used for being connected with the tibial stem, and the first connection portion is used for being connected with the distal tibial prosthesis. A first center line of the first connection portion is parallel to a second center line of the second connection portion, the tibial connector is rotated relative to the distal tibial prosthesis to adjust the position of the second center line relative to a center line of the distal tibial prosthesis, theposition of the tibial stem relative to the distal tibial prosthesis is further adjusted, and accordingly, the tibial stem can well adapt to different bone marrow cavity shapes.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
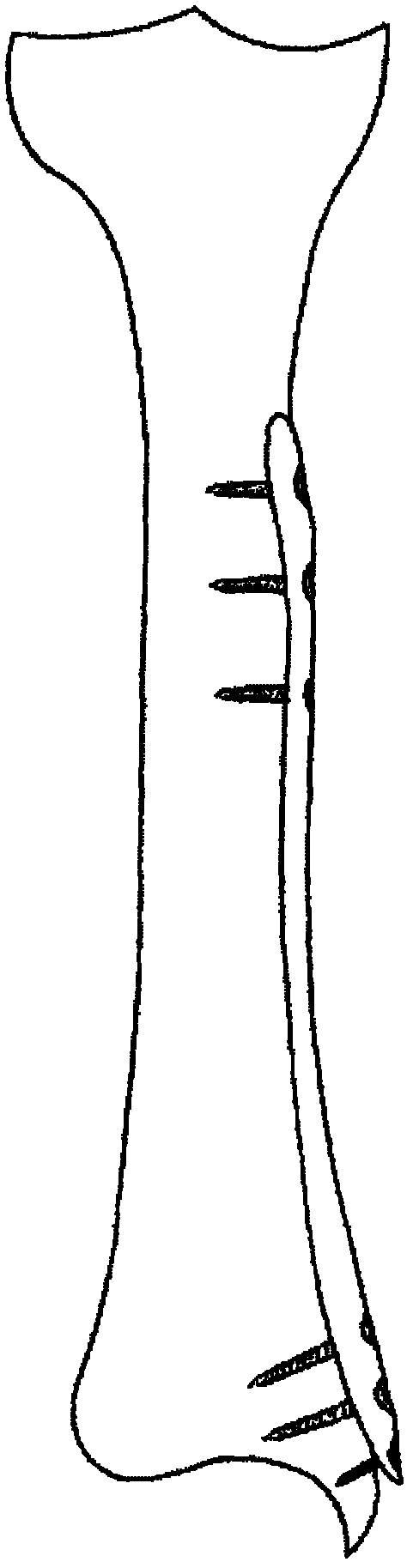
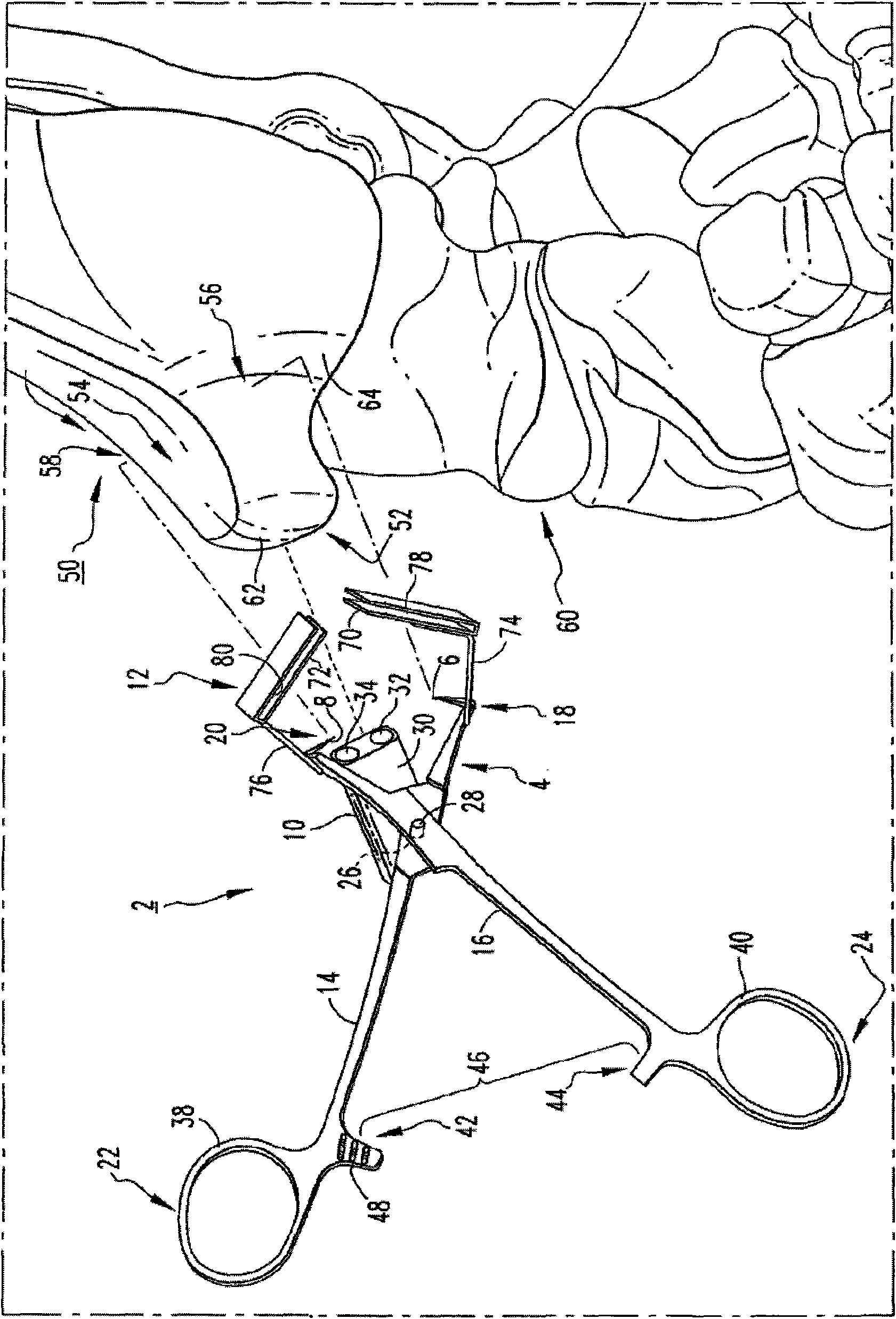
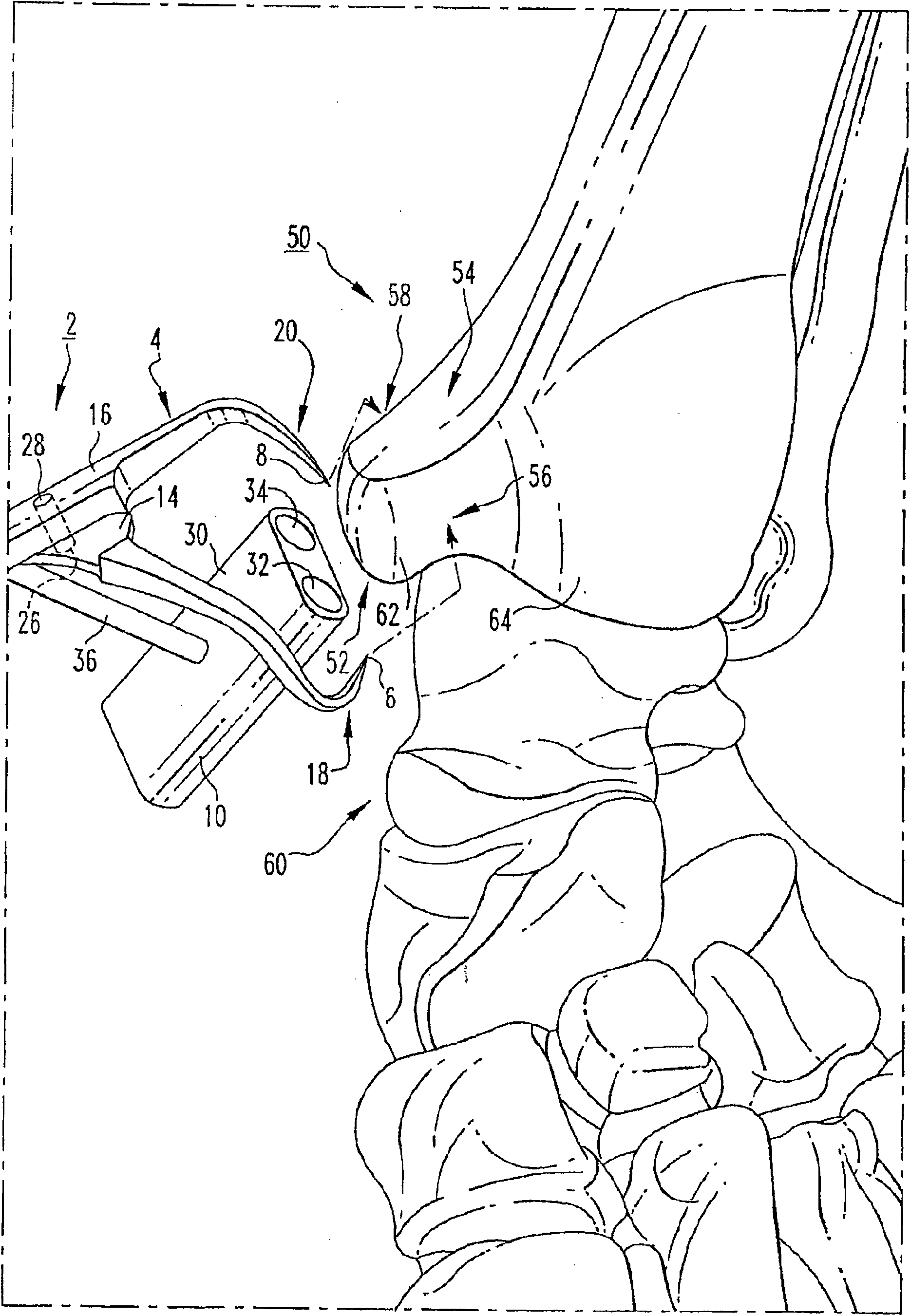
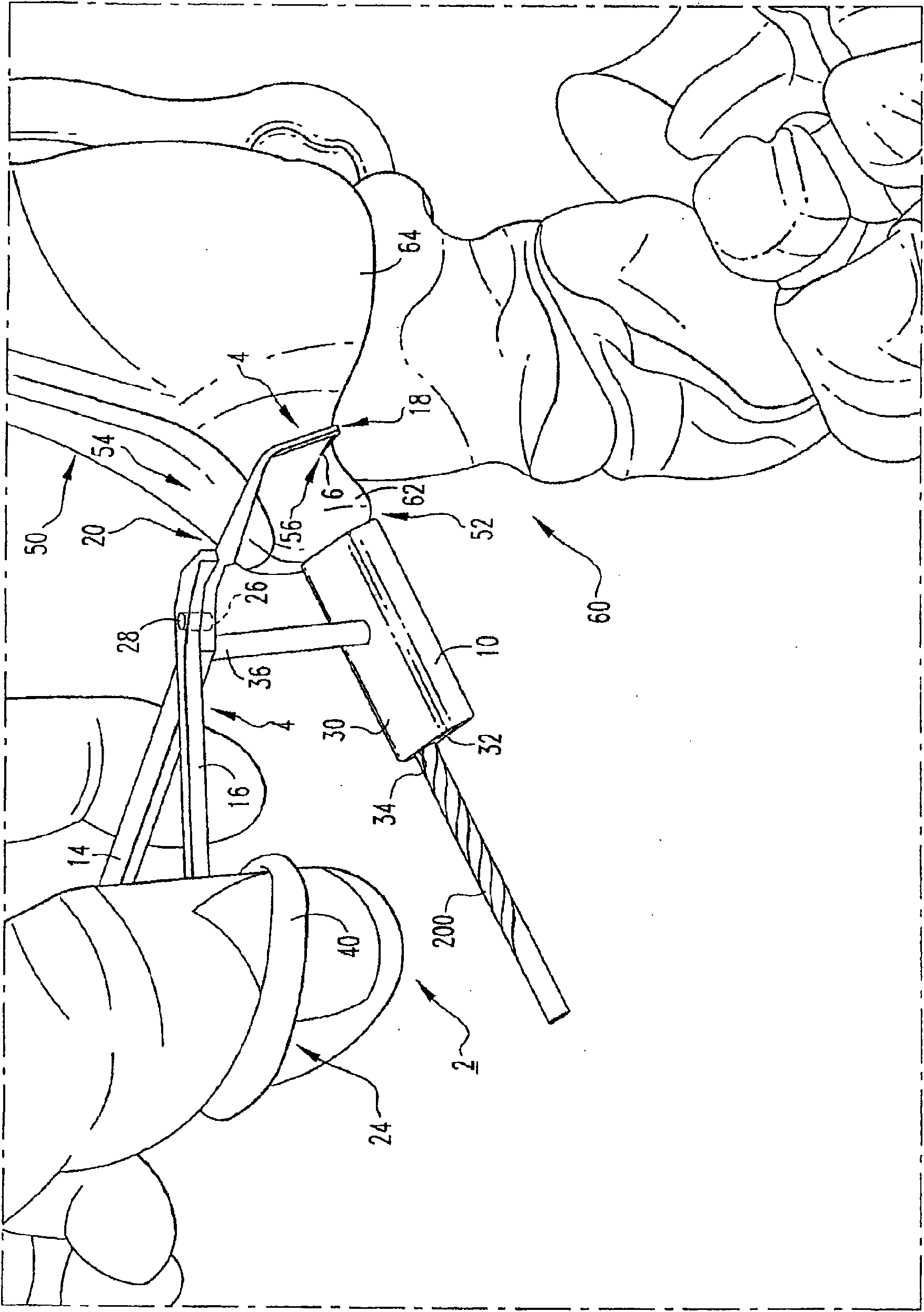
Osteotomy guide and method of cutting the medial distal tibia employing the same
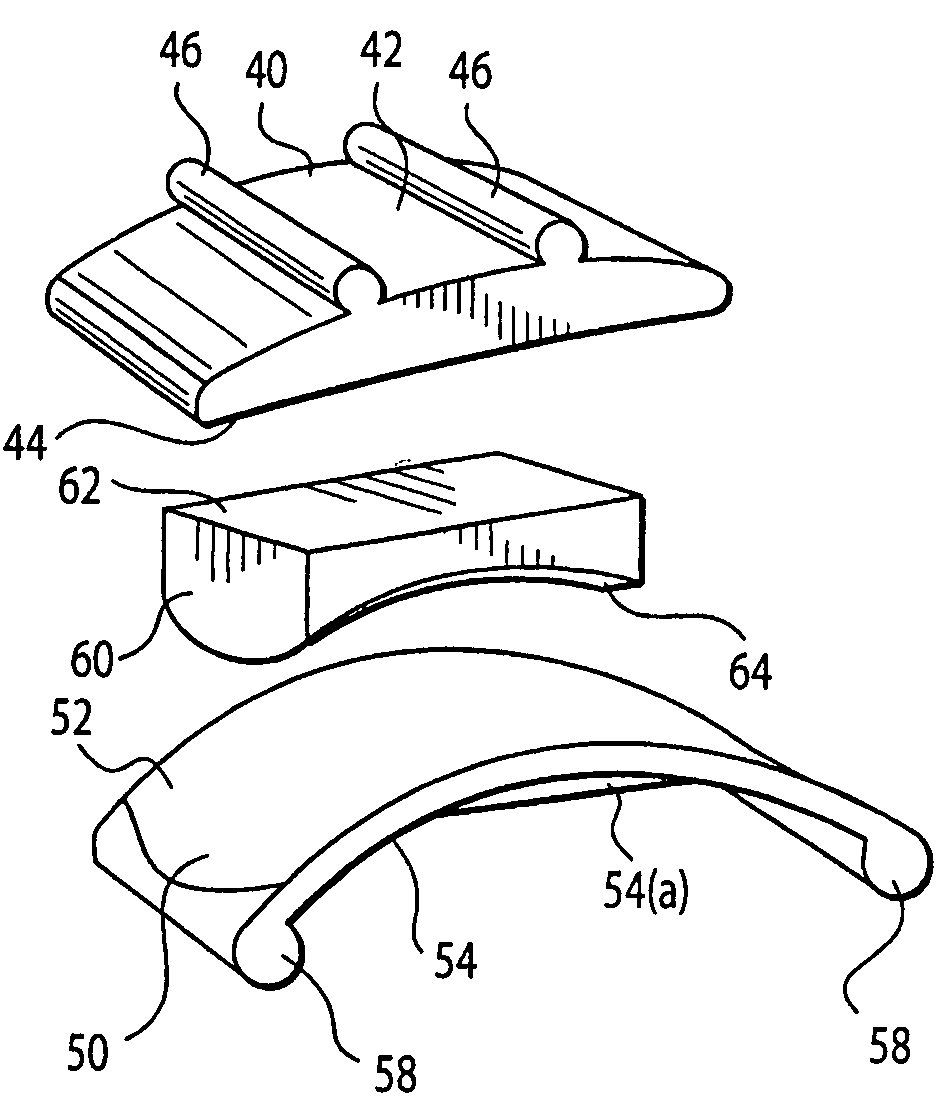
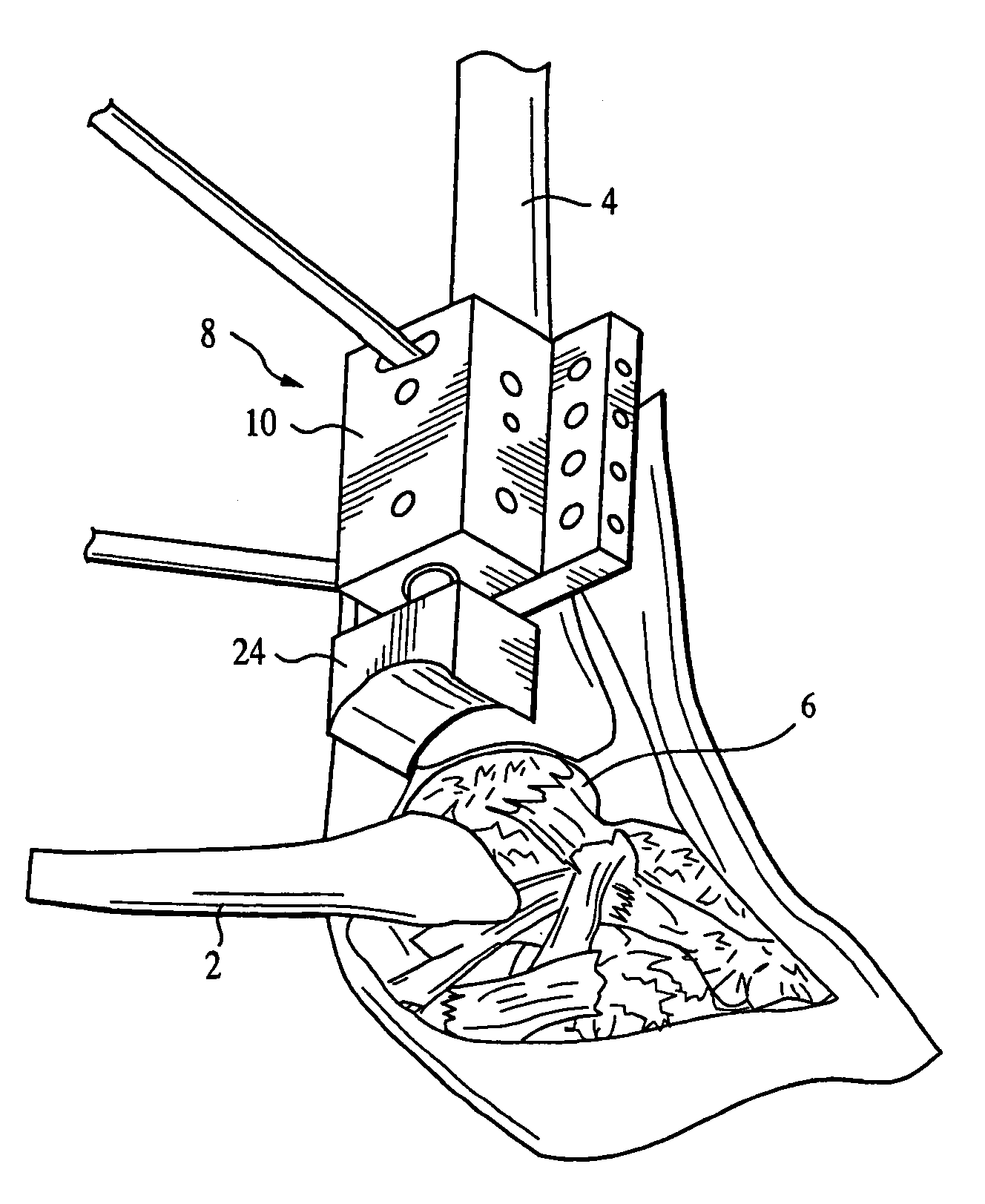
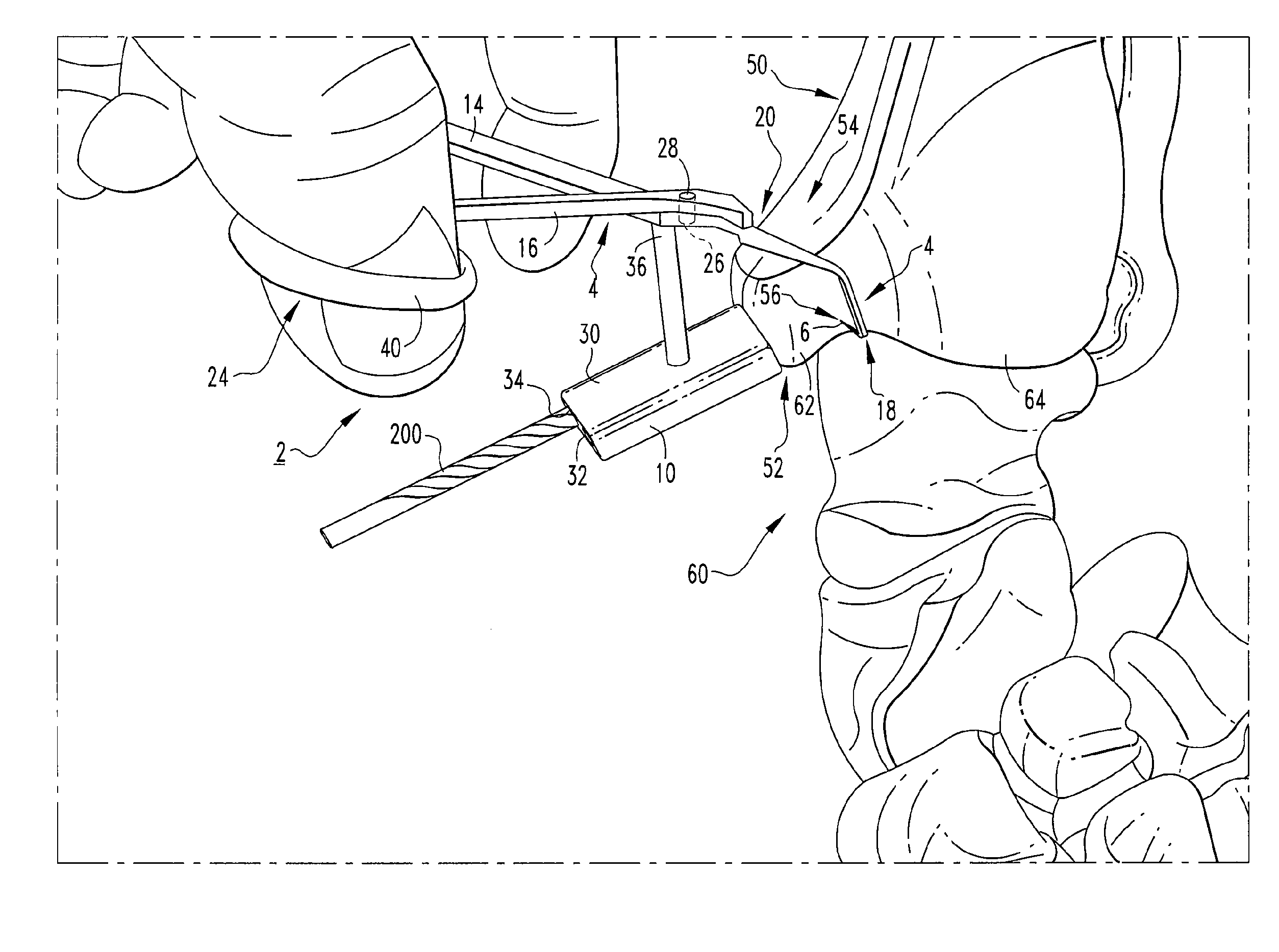
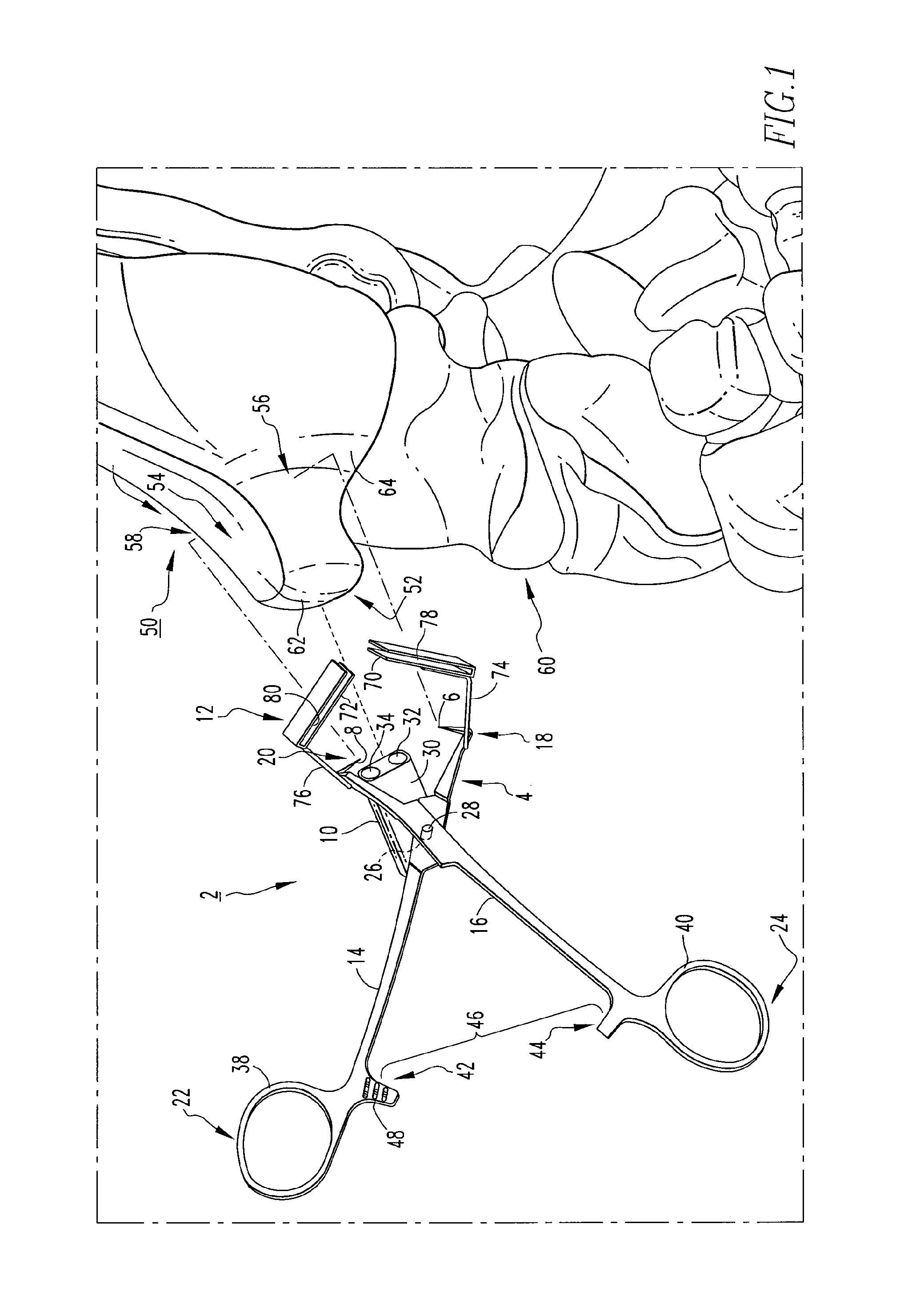
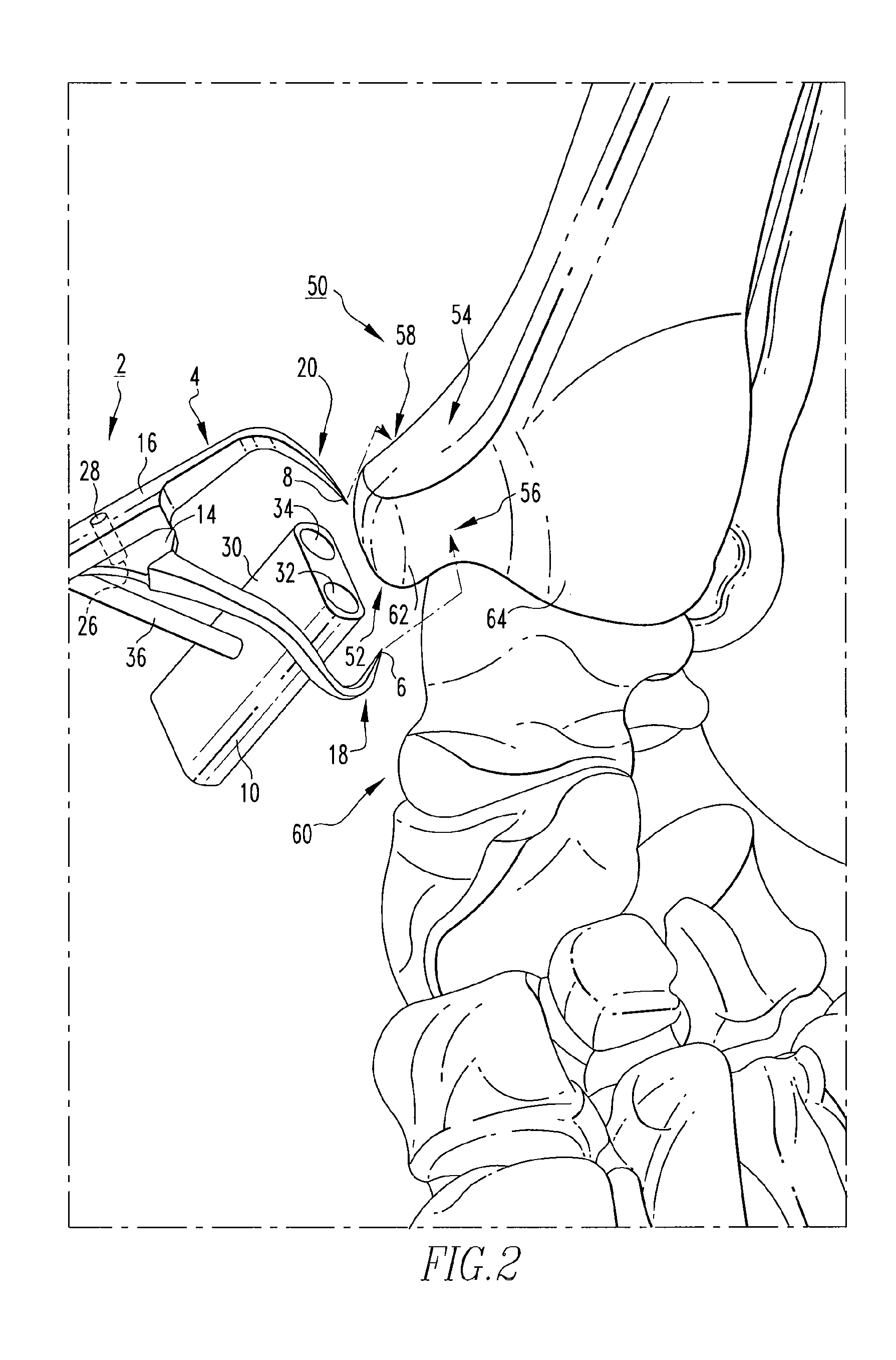
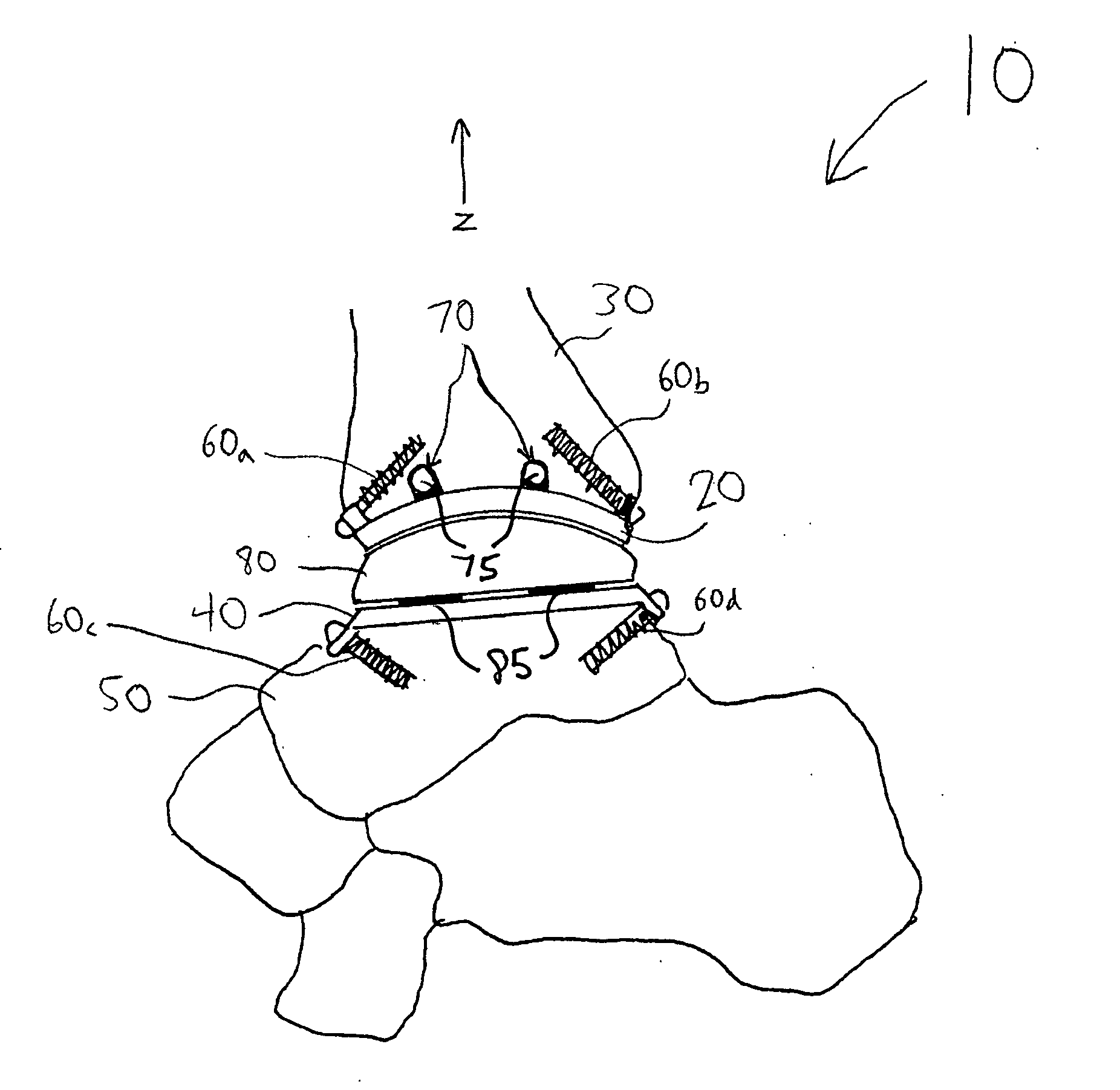
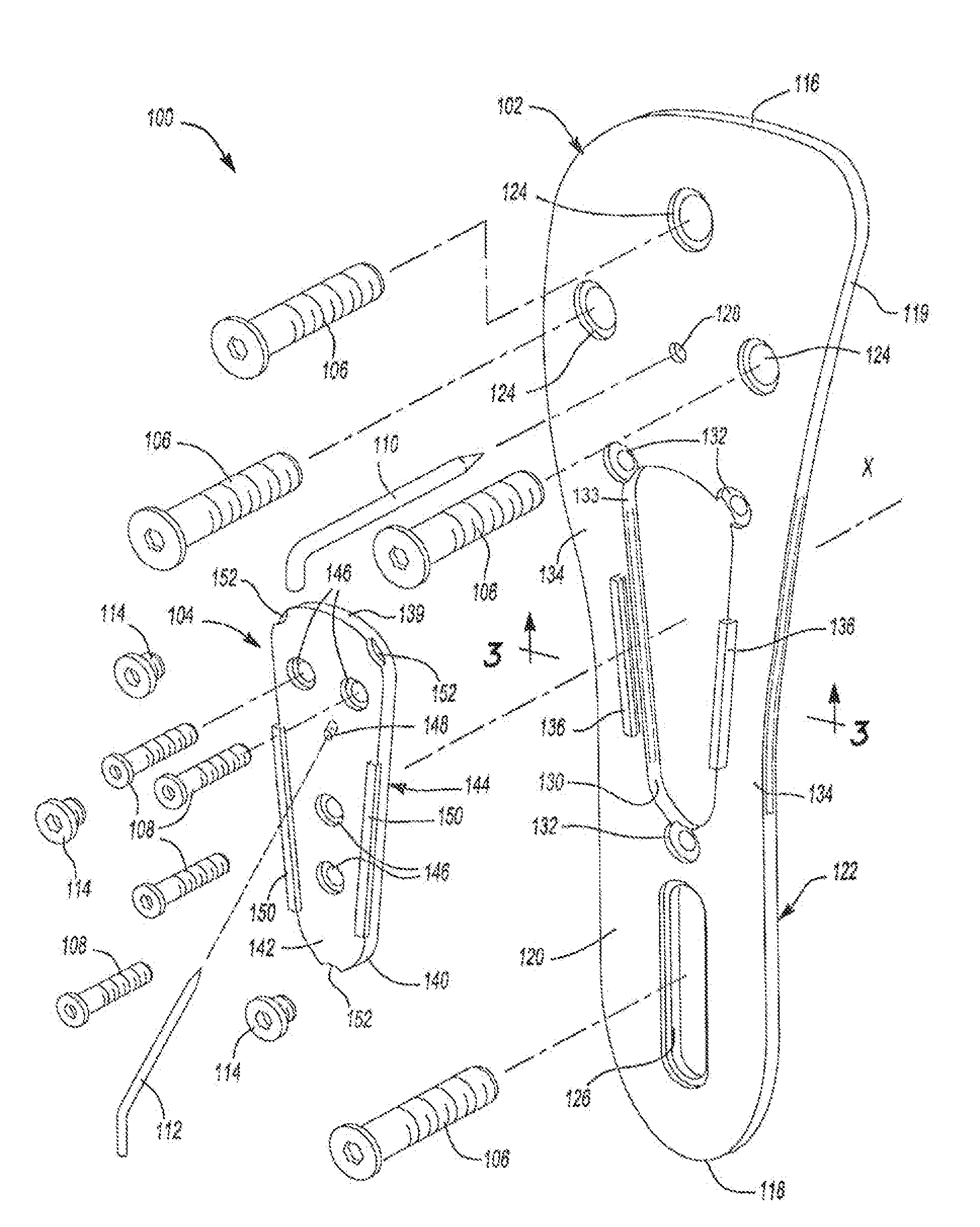
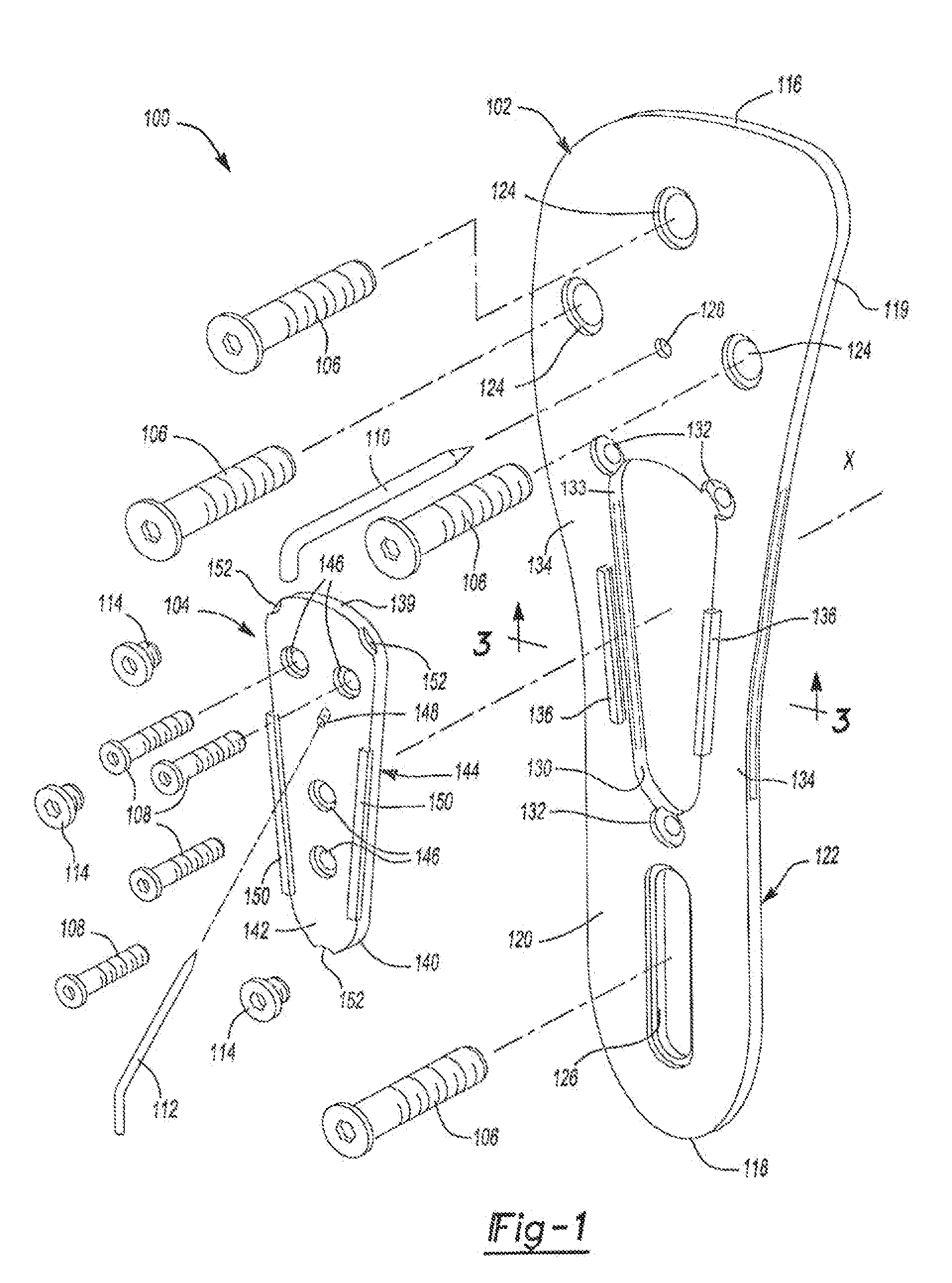
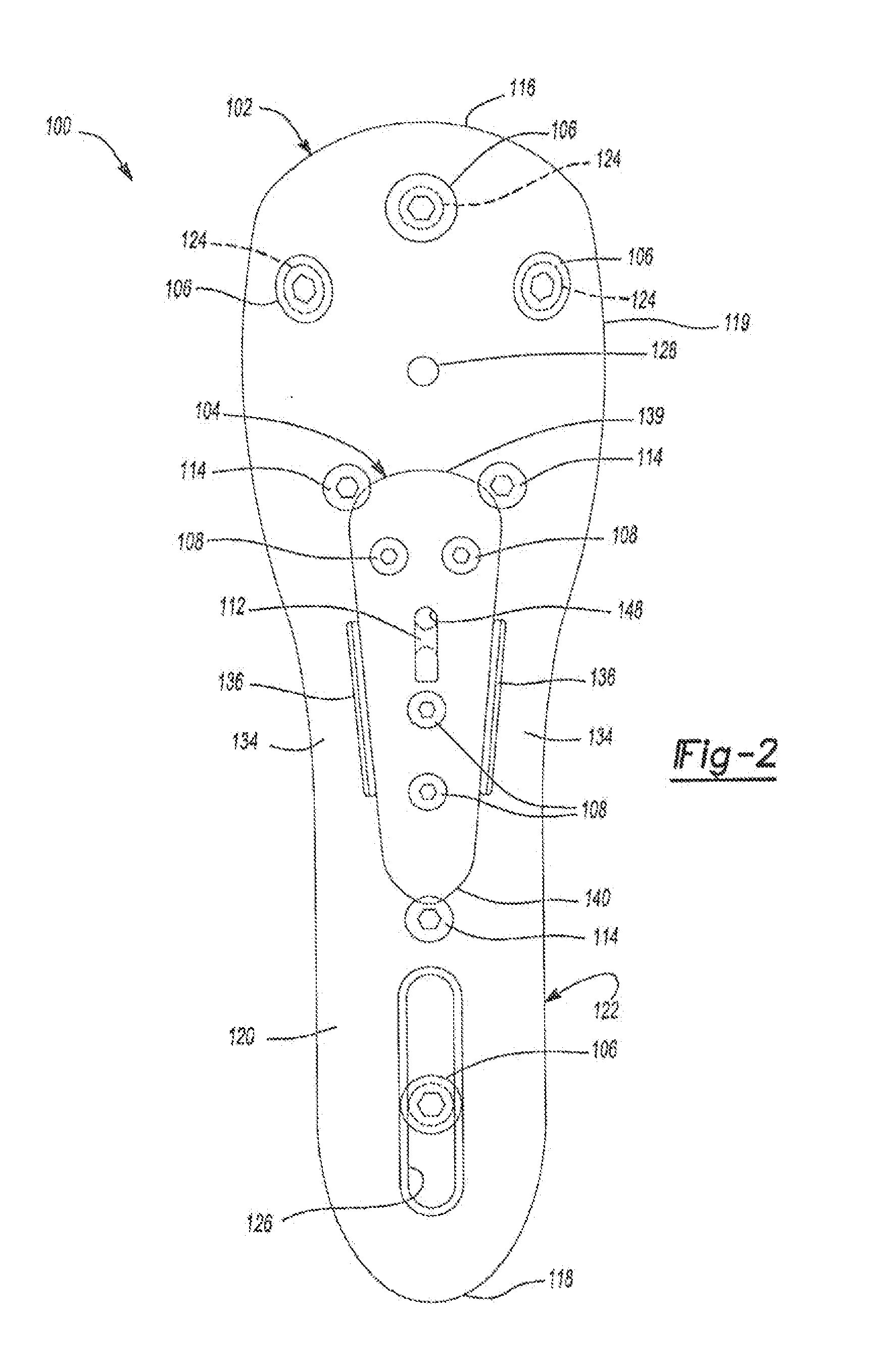
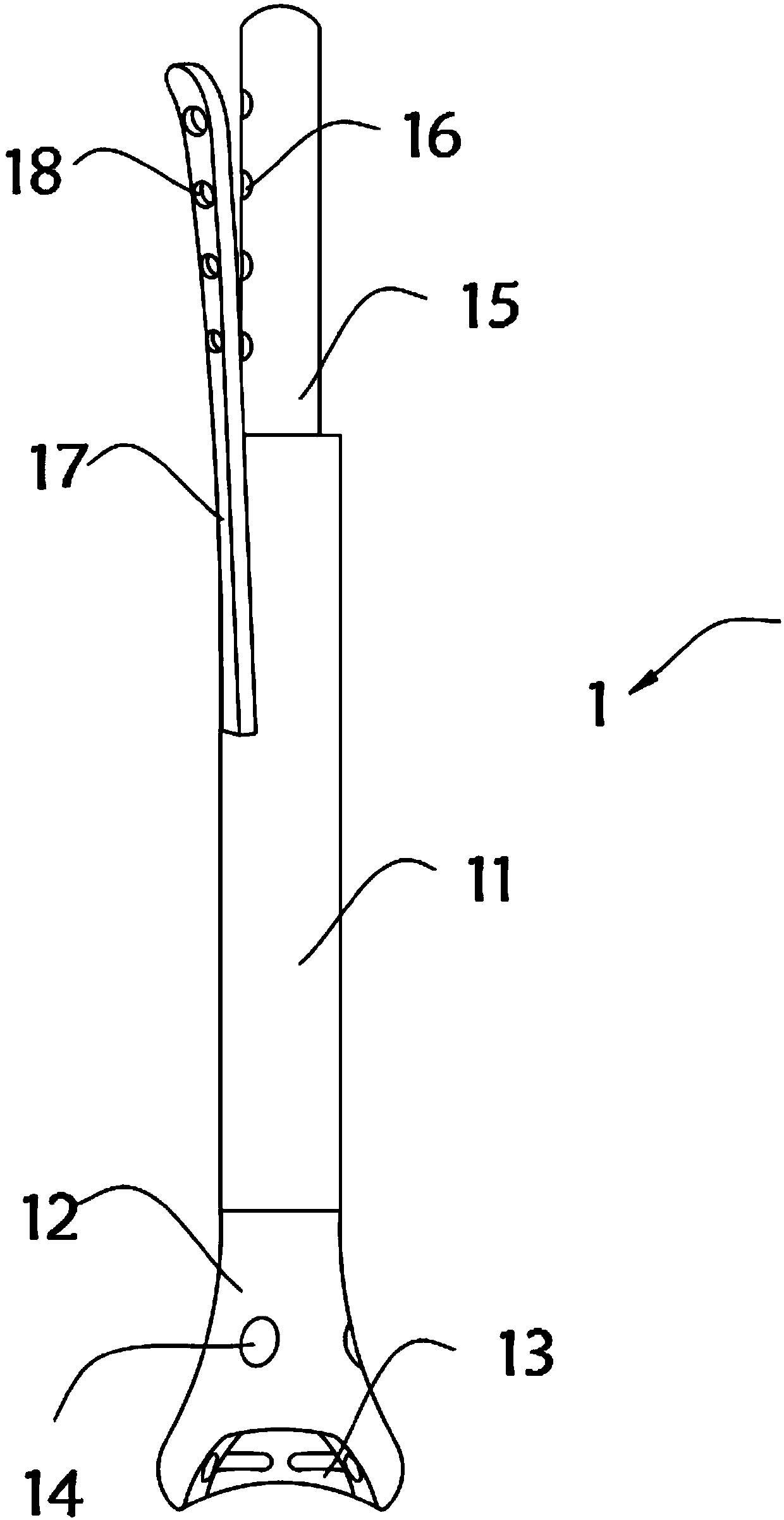
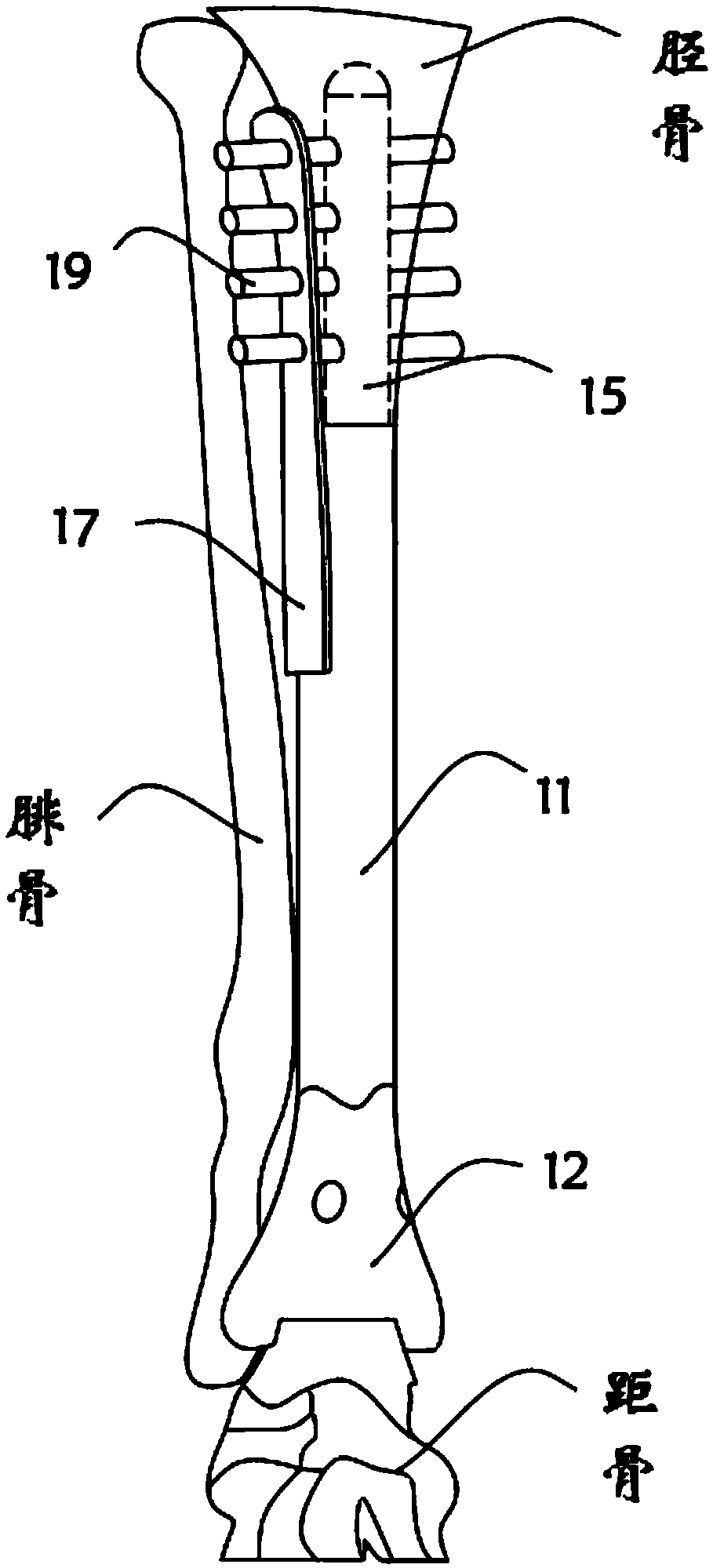
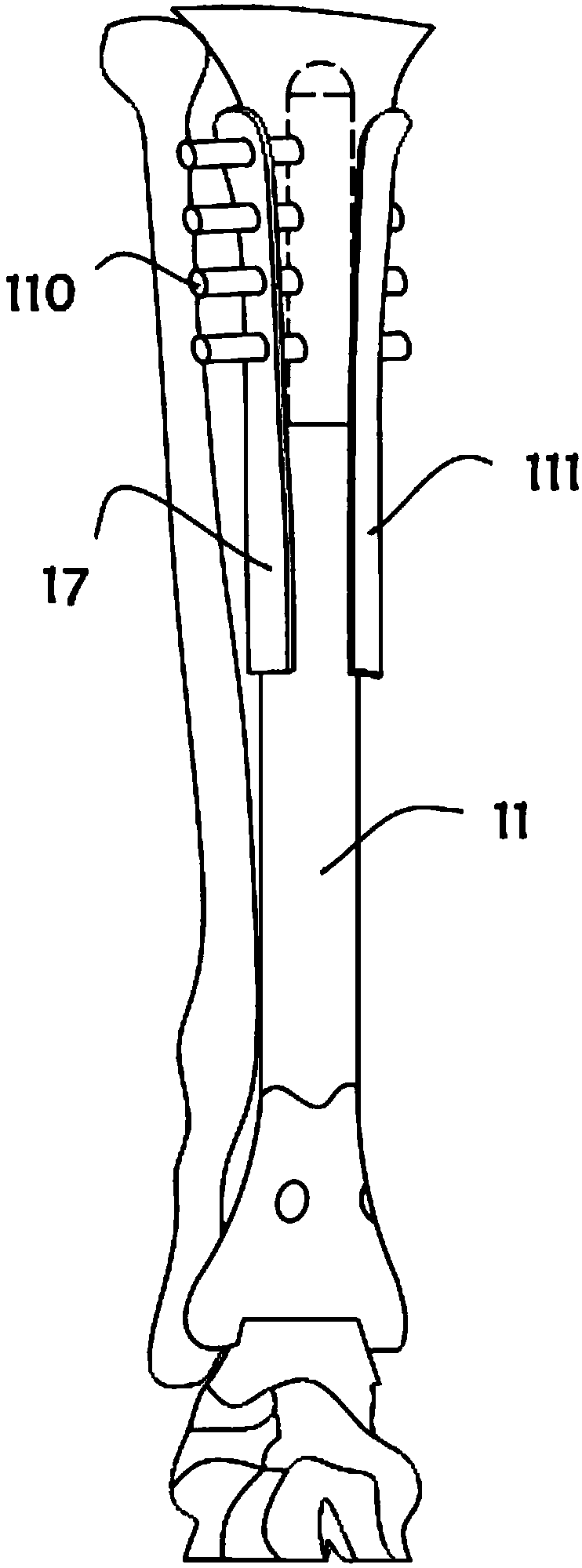
An osteotomy guide (2,102,302) is provided for cutting a bone, such as the medial distal tibia (50), for example, to facilitate an ankle replacement. The osteotomy guide (2,102,302) includes a positioning device (4,104,304) having a number of fixation points (6,8; 106, 108), a first guide member (10, 110) structured to align with a first portion (52) of the bone (50), in order to perform a first procedure on the first portion (52), and a second guide member (12,112,312) structured to align with a second portion (54) of the bone (50), in order to perform a second procedure on the second portion (54). The fixation points (6,8;106,108) engage the bone (50) and maintain alignment of the first guide member (10,110) with respect to the first portion (52) of the bone (50) during the first procedure, and maintain alignment of the second guide member (12,112,312) with respect to the second portion (54) of the bone (50) during the second procedure, in order that the first procedure and the second procedure are substantially reproducible.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com