Patents
Literature
418 results about "Bone marrow cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The medullary cavity (medulla, innermost part) is the central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow (adipose tissue) is stored; hence, the medullary cavity is also known as the marrow cavity.
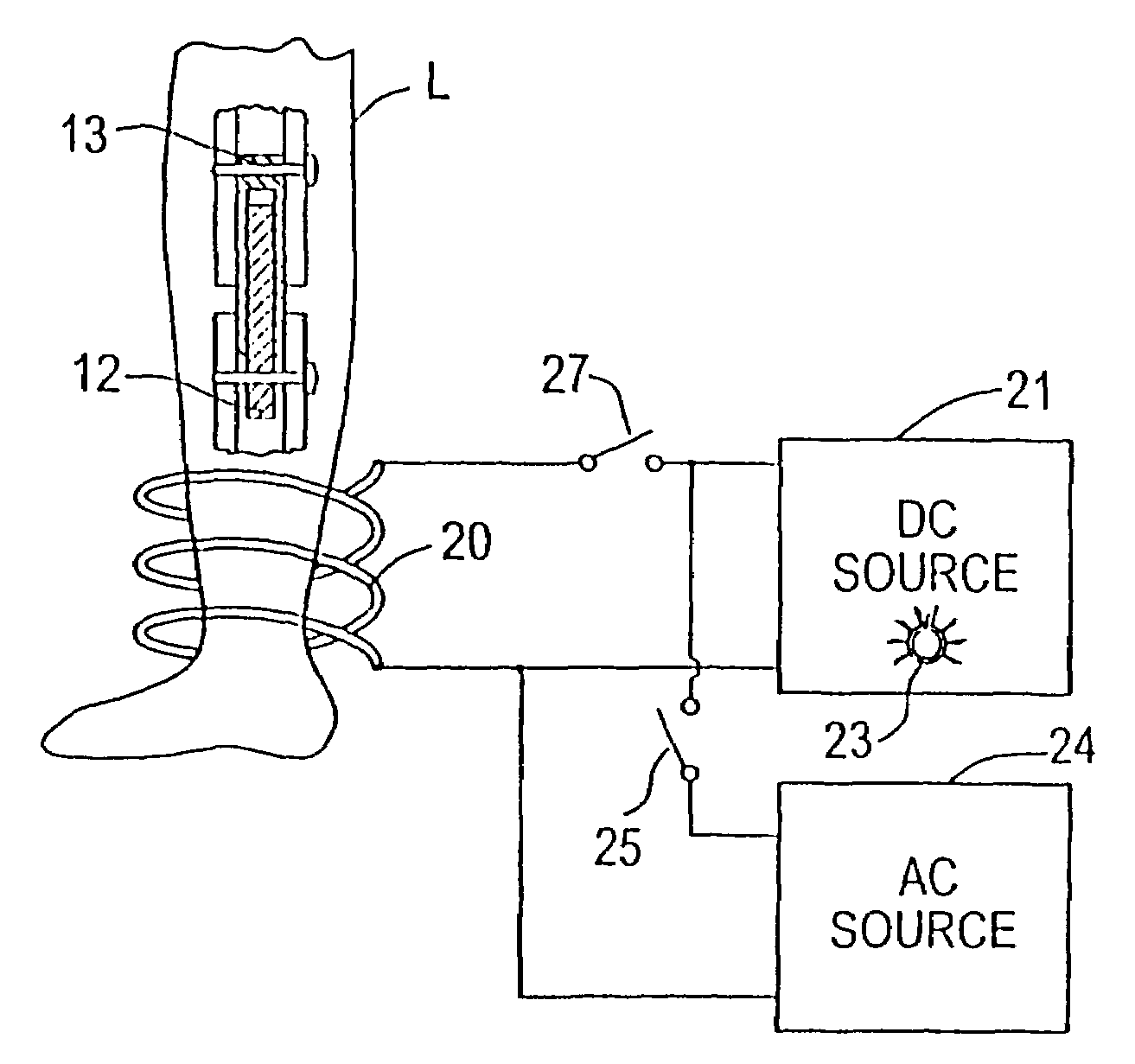
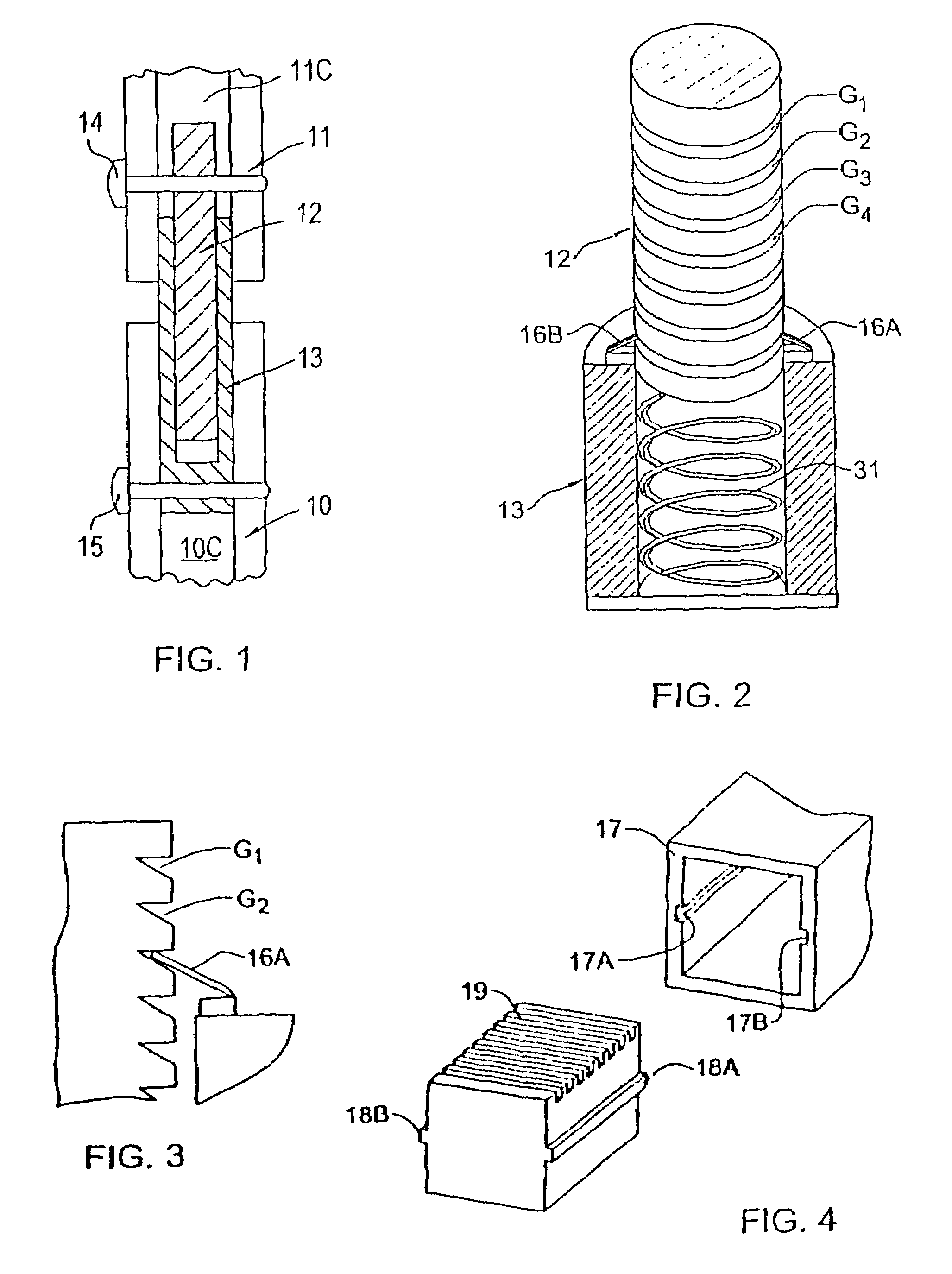
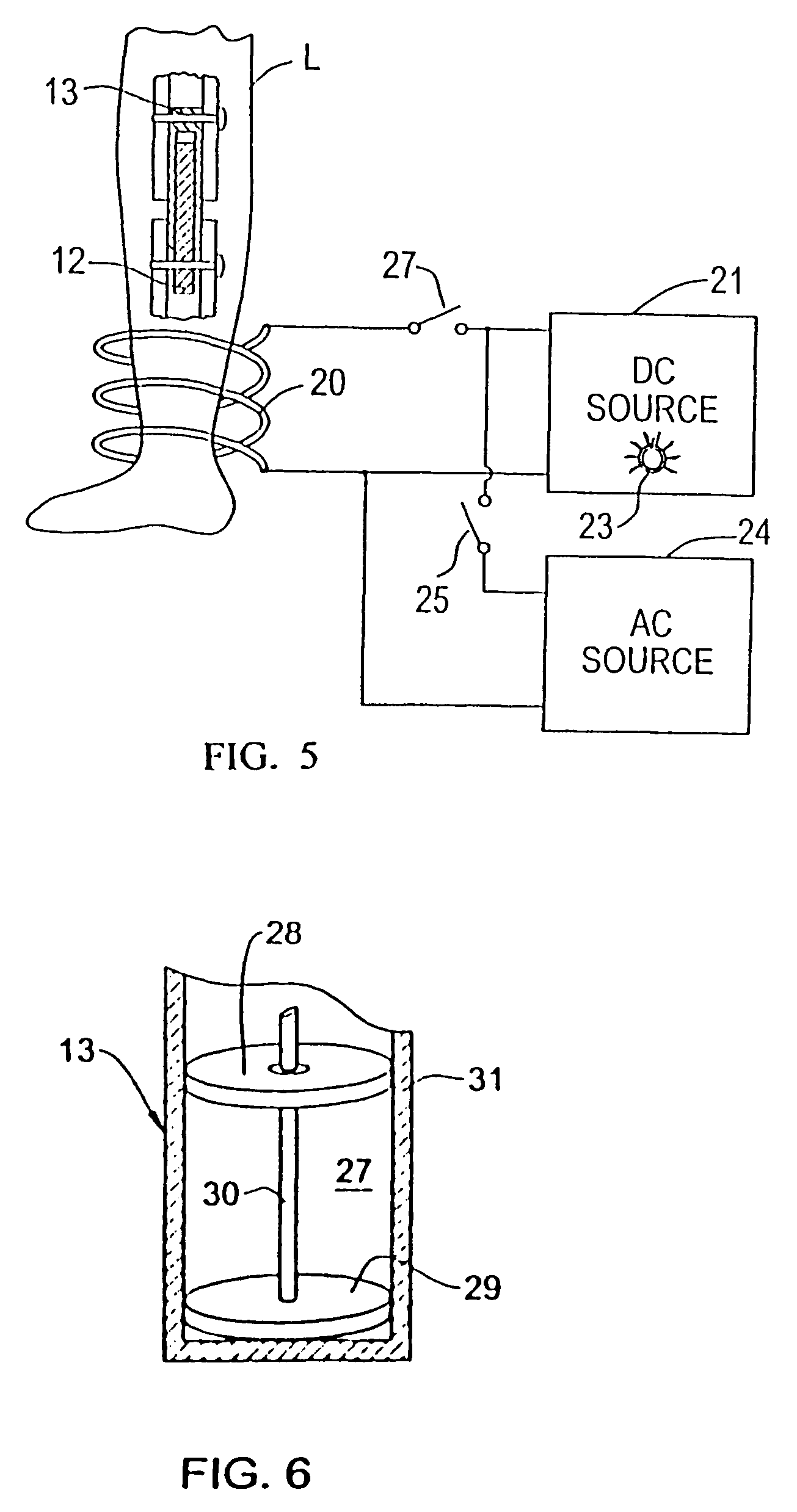
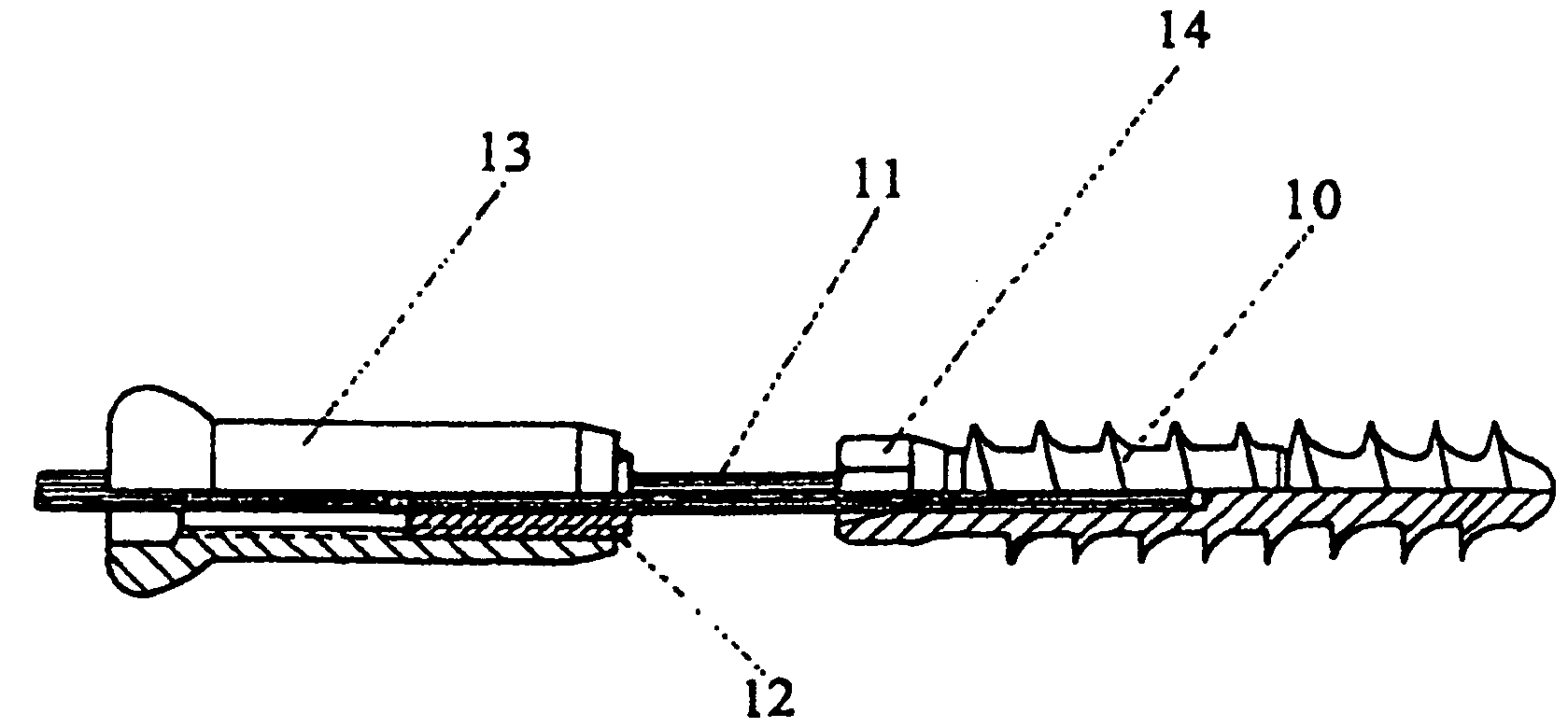
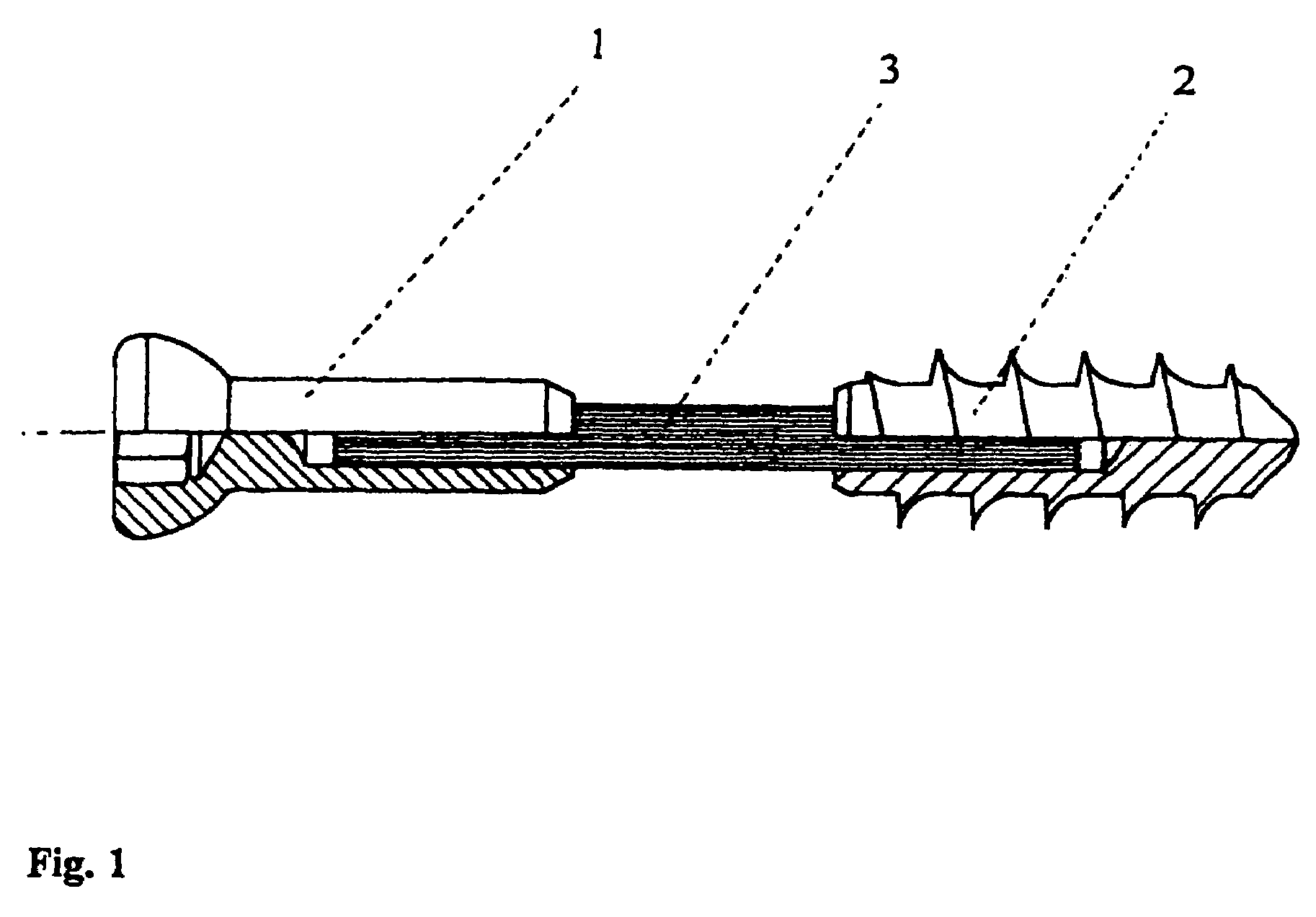
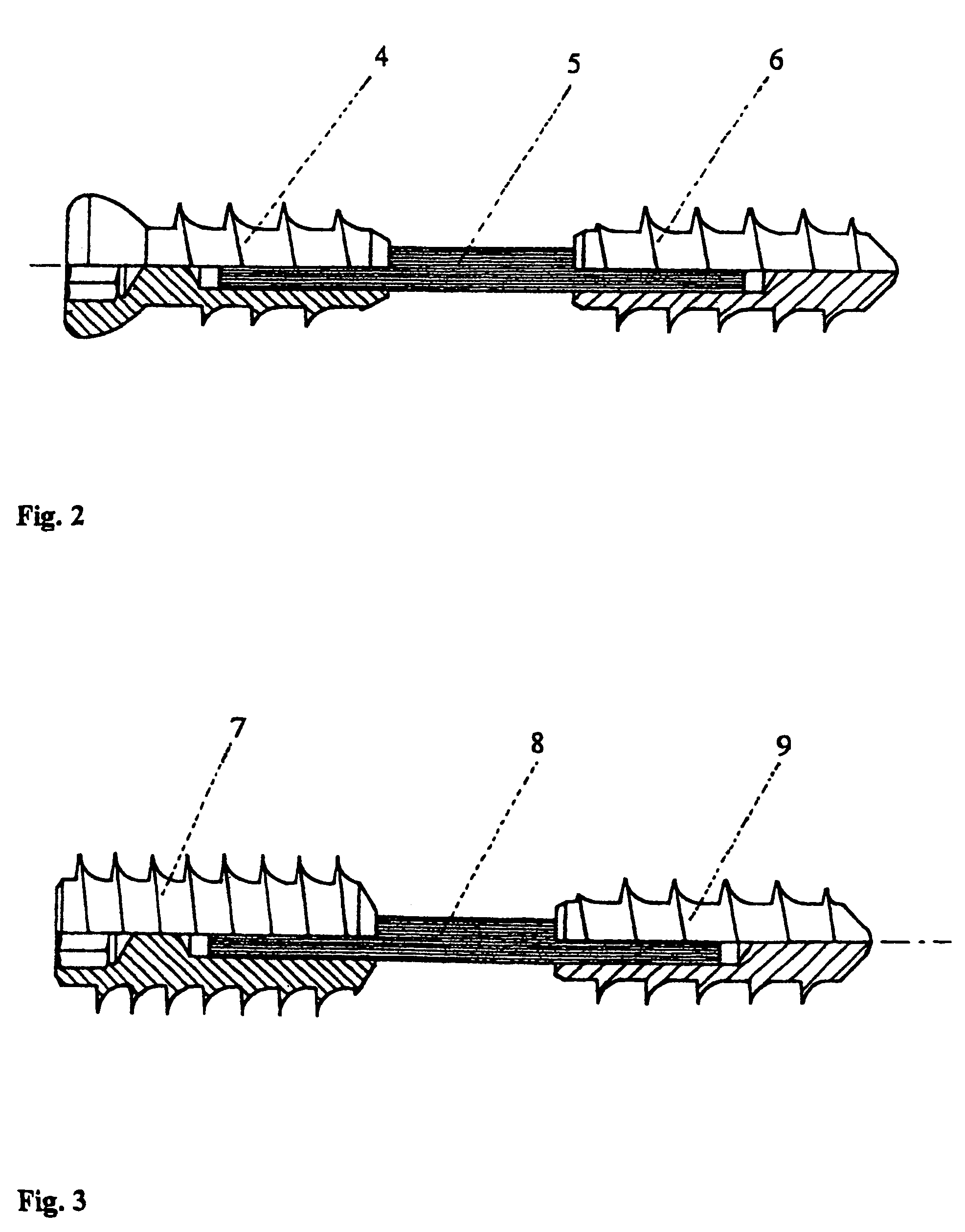
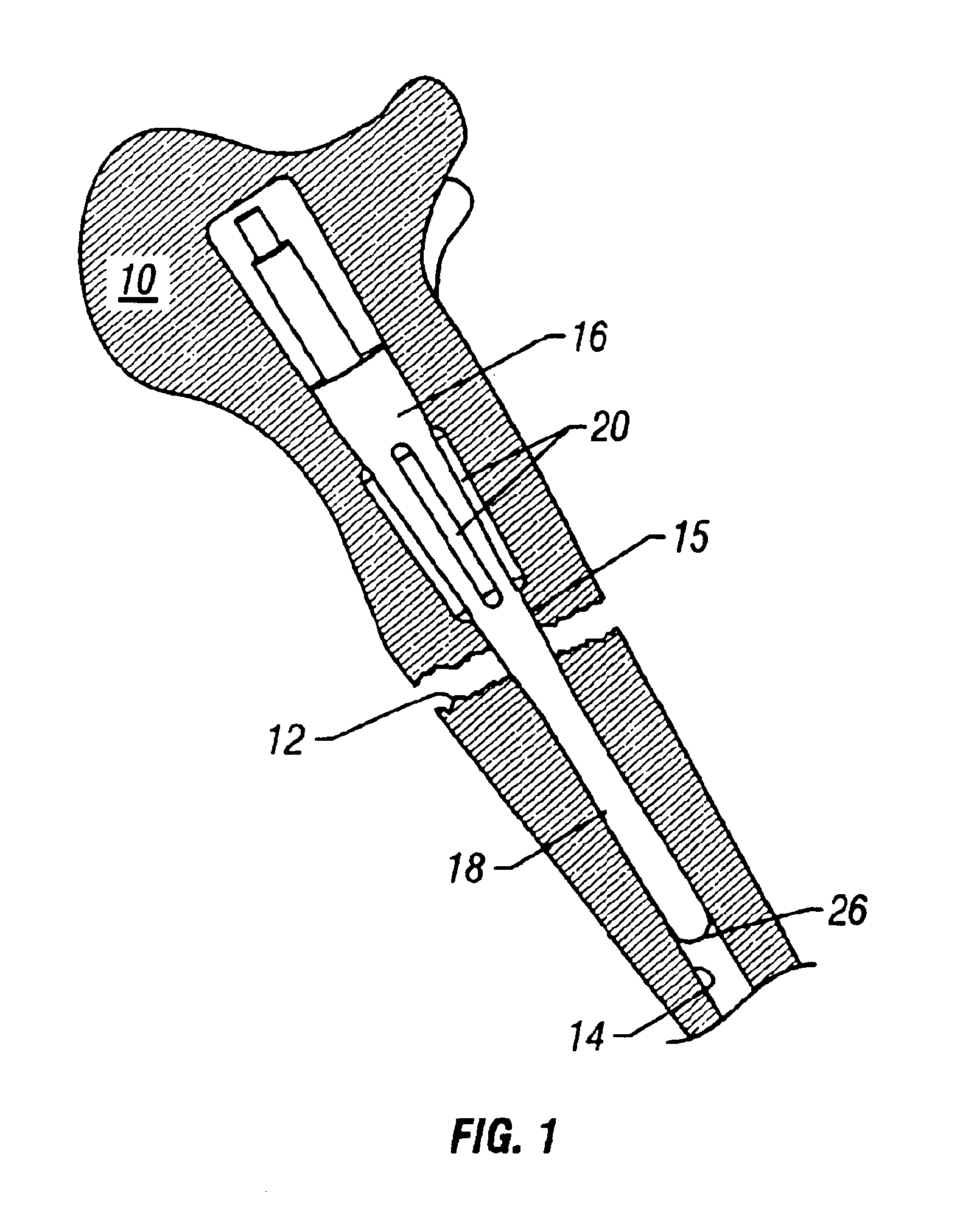
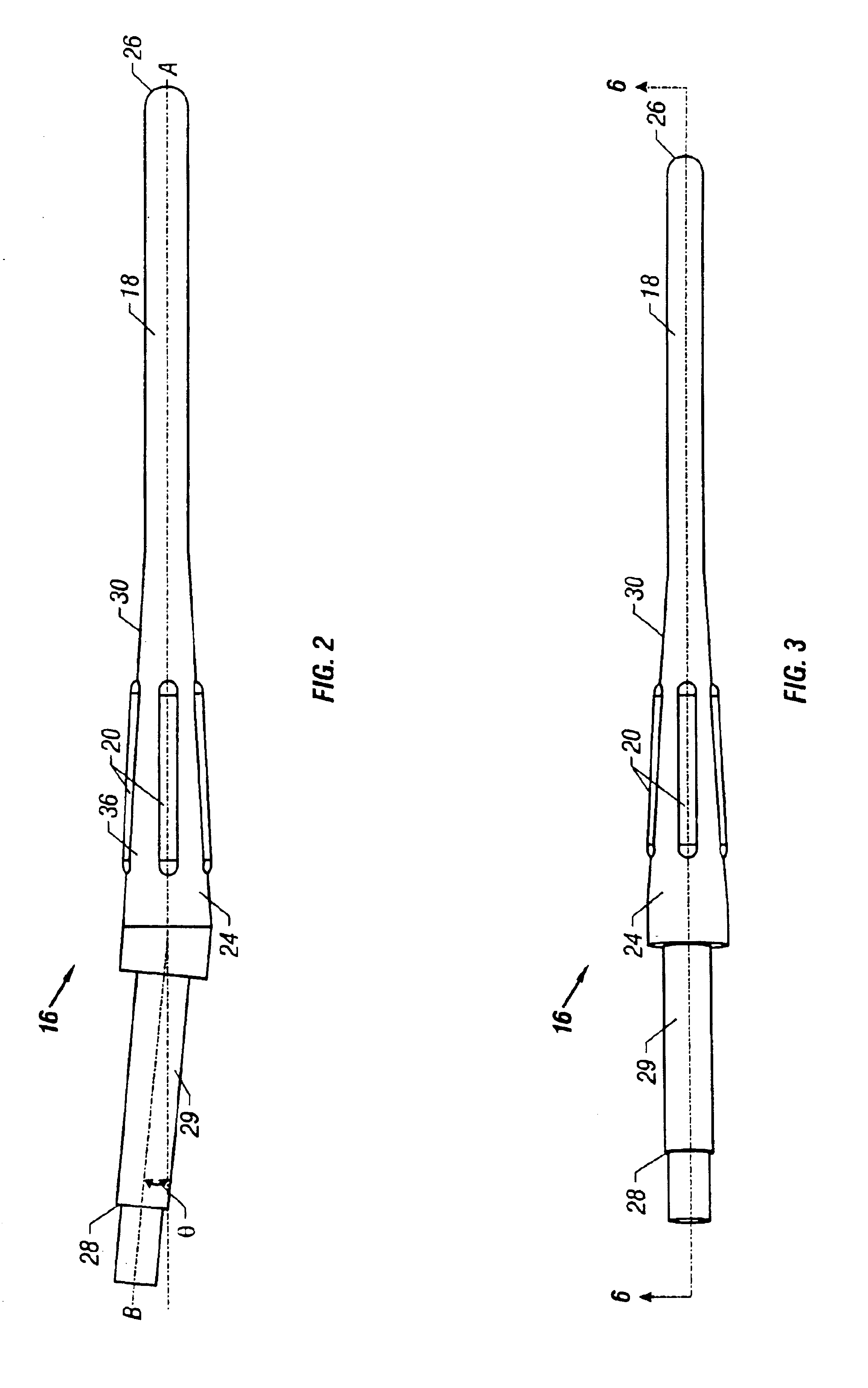
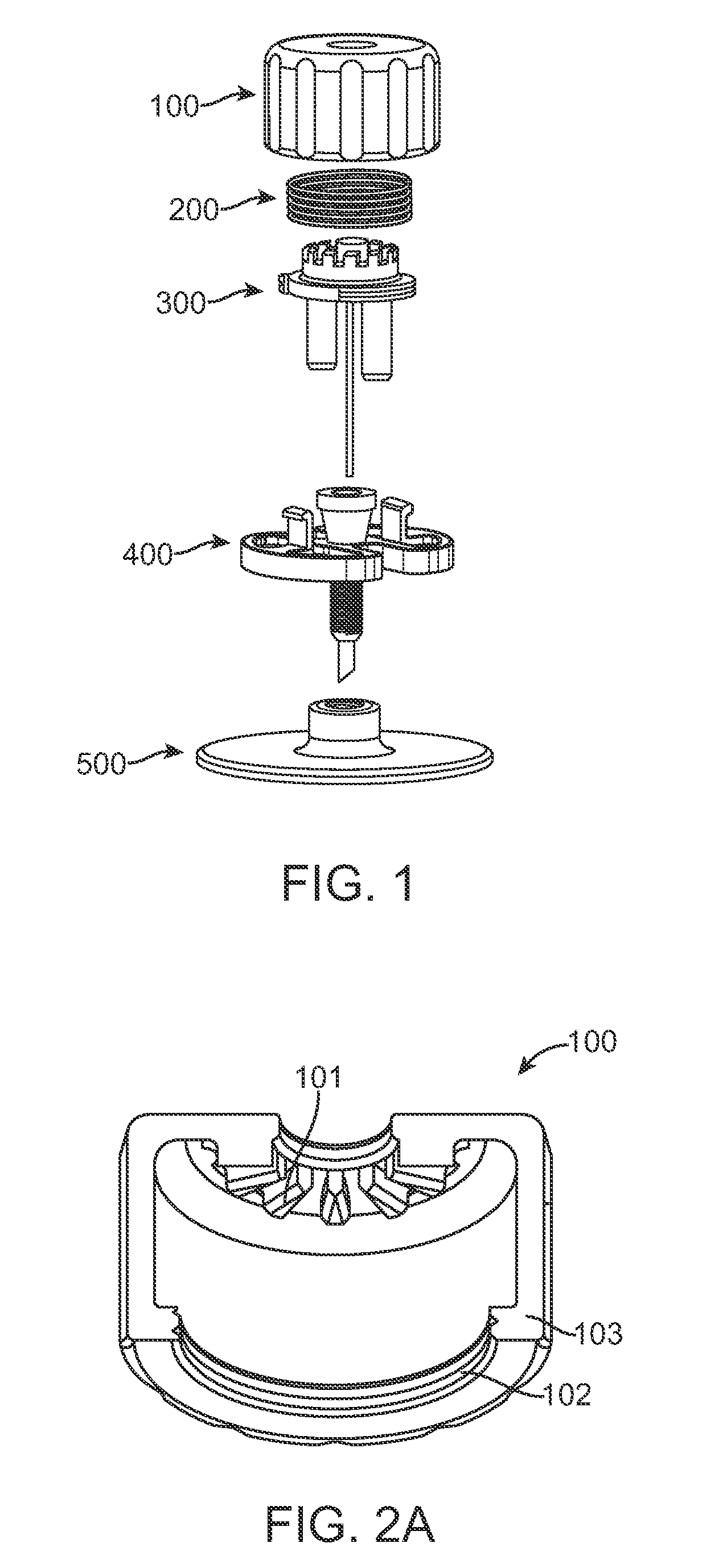
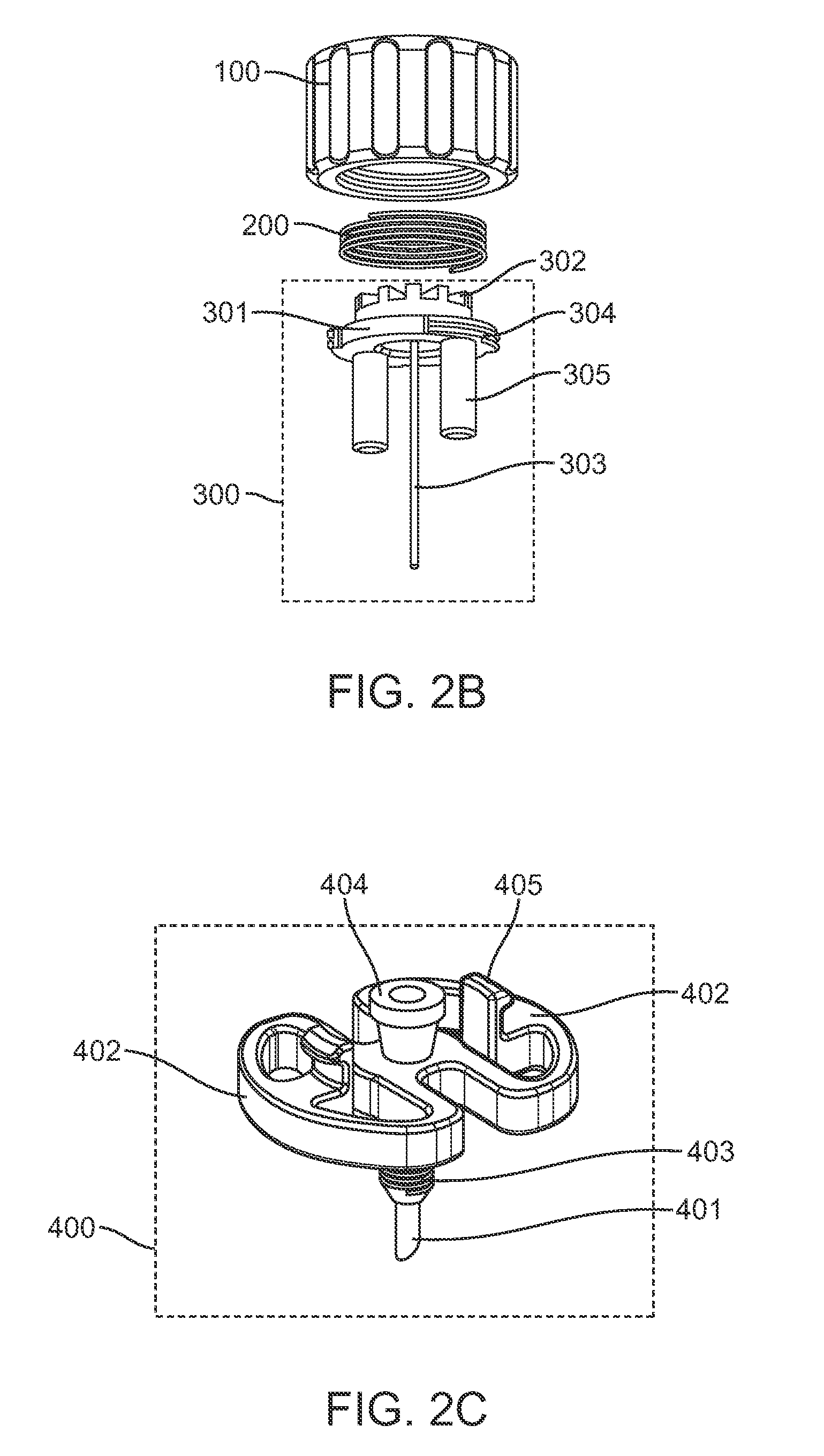
Magnetically-actuable intramedullary device
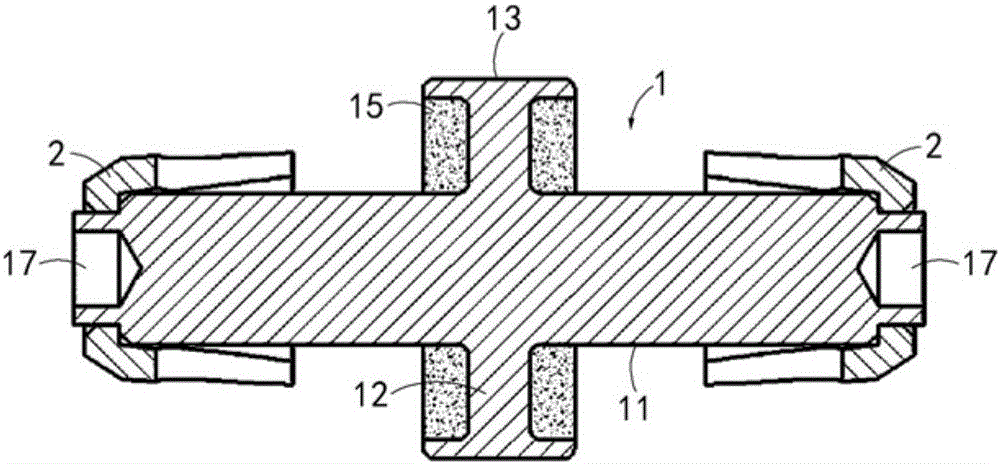
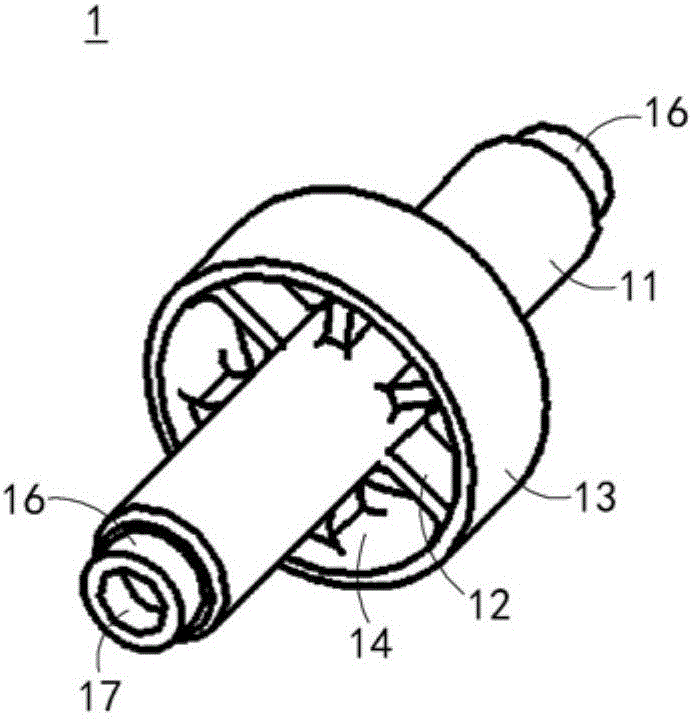
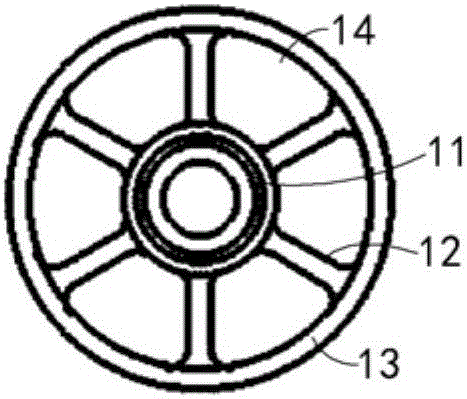
InactiveUS7135022B2Increase the lengthShorten the lengthInternal osteosythesisBone implantInterior spaceBone marrow cavity
The present invention provides a two-part telescopic intramedullary orthopedic device comprising a first section inserted into the medullary cavity of one of the fractured or severed bone ends, and secured thereto, and a second section inserted into the medullary cavity of the other fractured or severed bone end and secured thereto, wherein the first section is telescoped within the internal space of the second section, and wherein one of the sections comprises a ferromagnetic material and the other section is either constructed entirely of a non-magnetic material or comprises a ferromagnetic material, wherein the ferromagnetic section(s) are actuable by an external axially directed magnetic field, such that one section may be caused to move axially (either bidirectional or essentially unidirectional) in relation to the other section. In addition, the invention encompasses a method for changing bone length as well as a method for enhancing bone fracture healing.
Owner:ORTHOGON TECH 2003 LTD
Implantable screw for stabilization of a joint or a bone fracture
ActiveUS7625395B2Little or no impairment of the natural range of movement of the jointFirmly connectedSuture equipmentsLigamentsEngineeringBone marrow cavity
Owner:NOVOPLANT
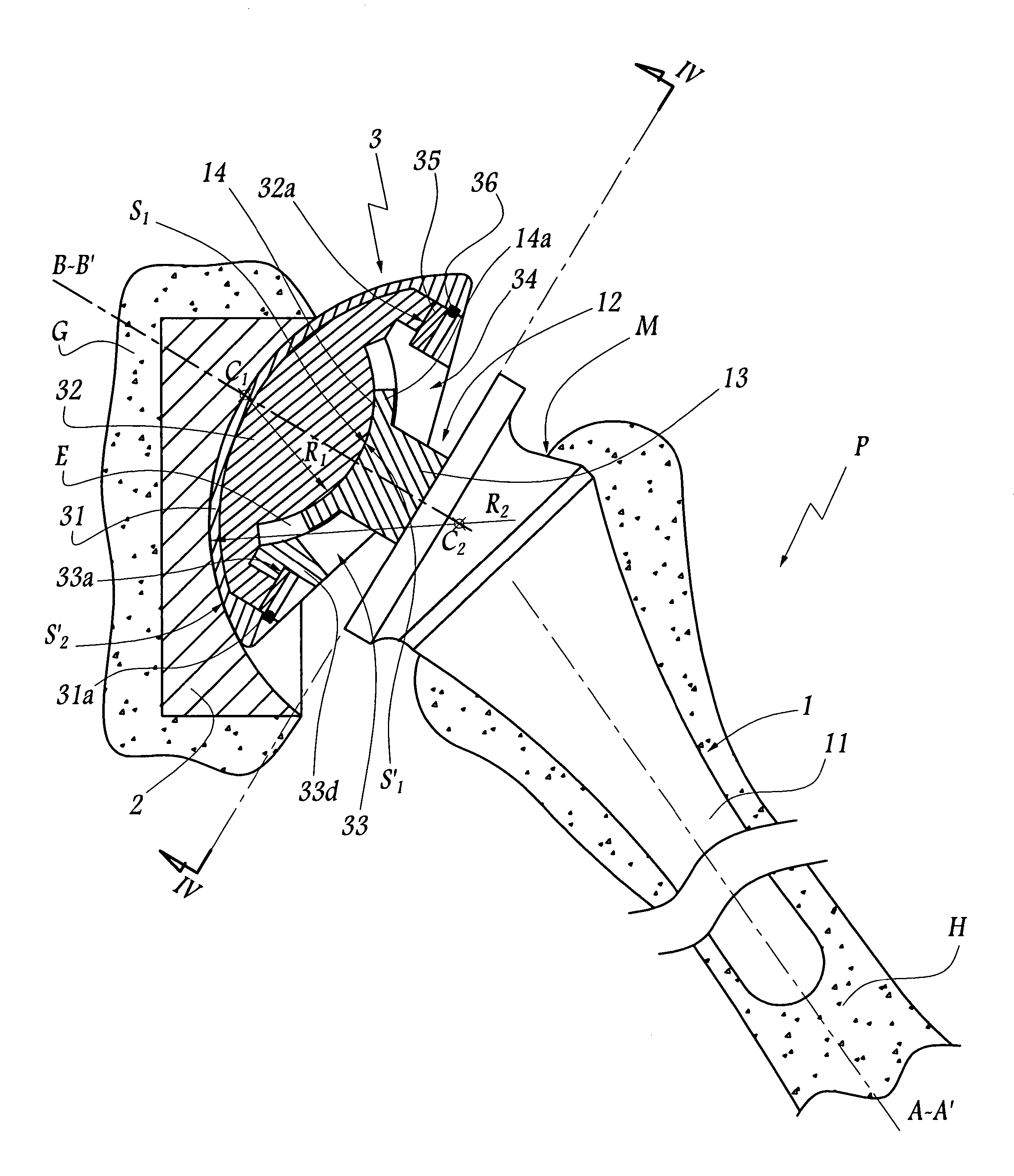
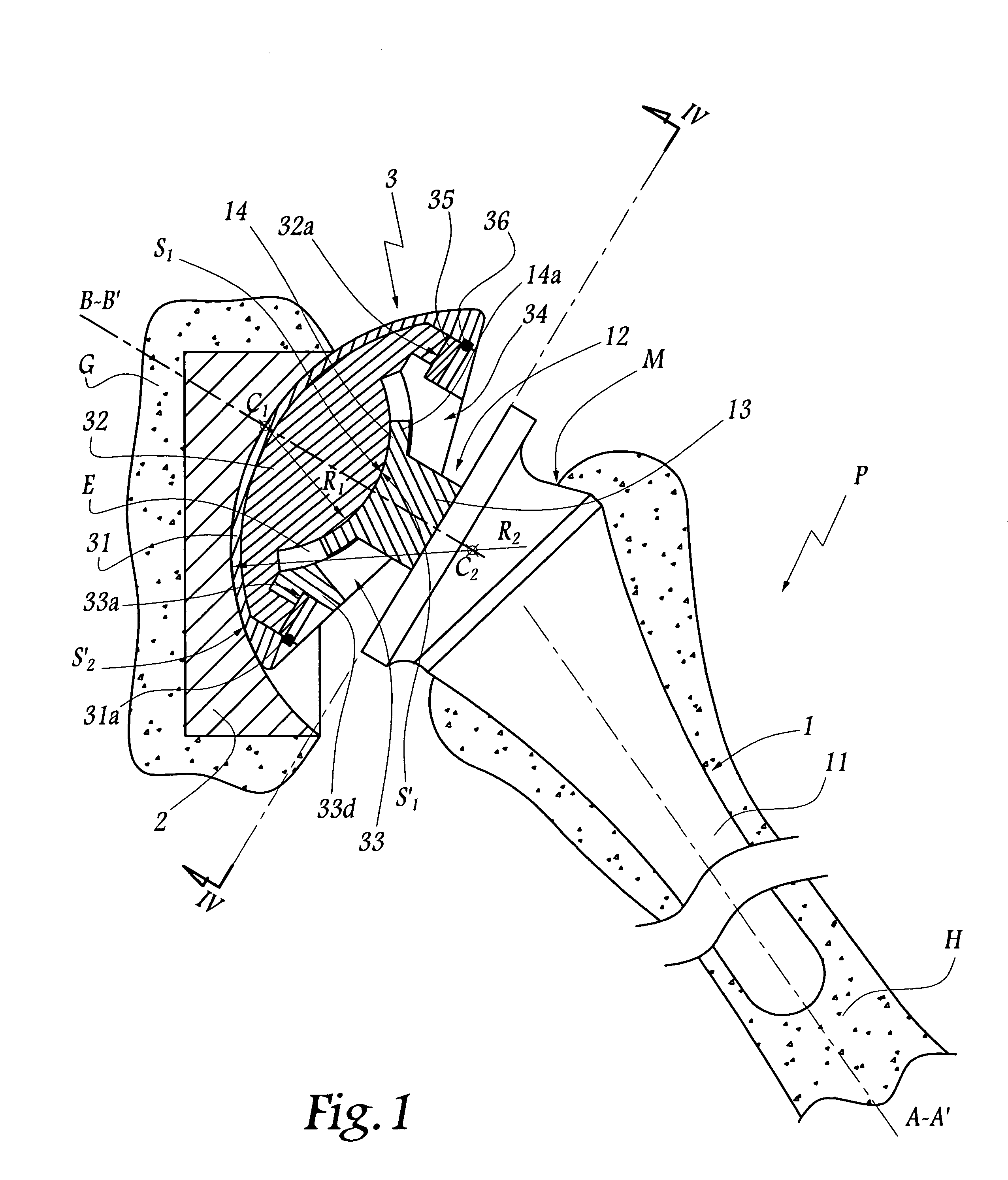
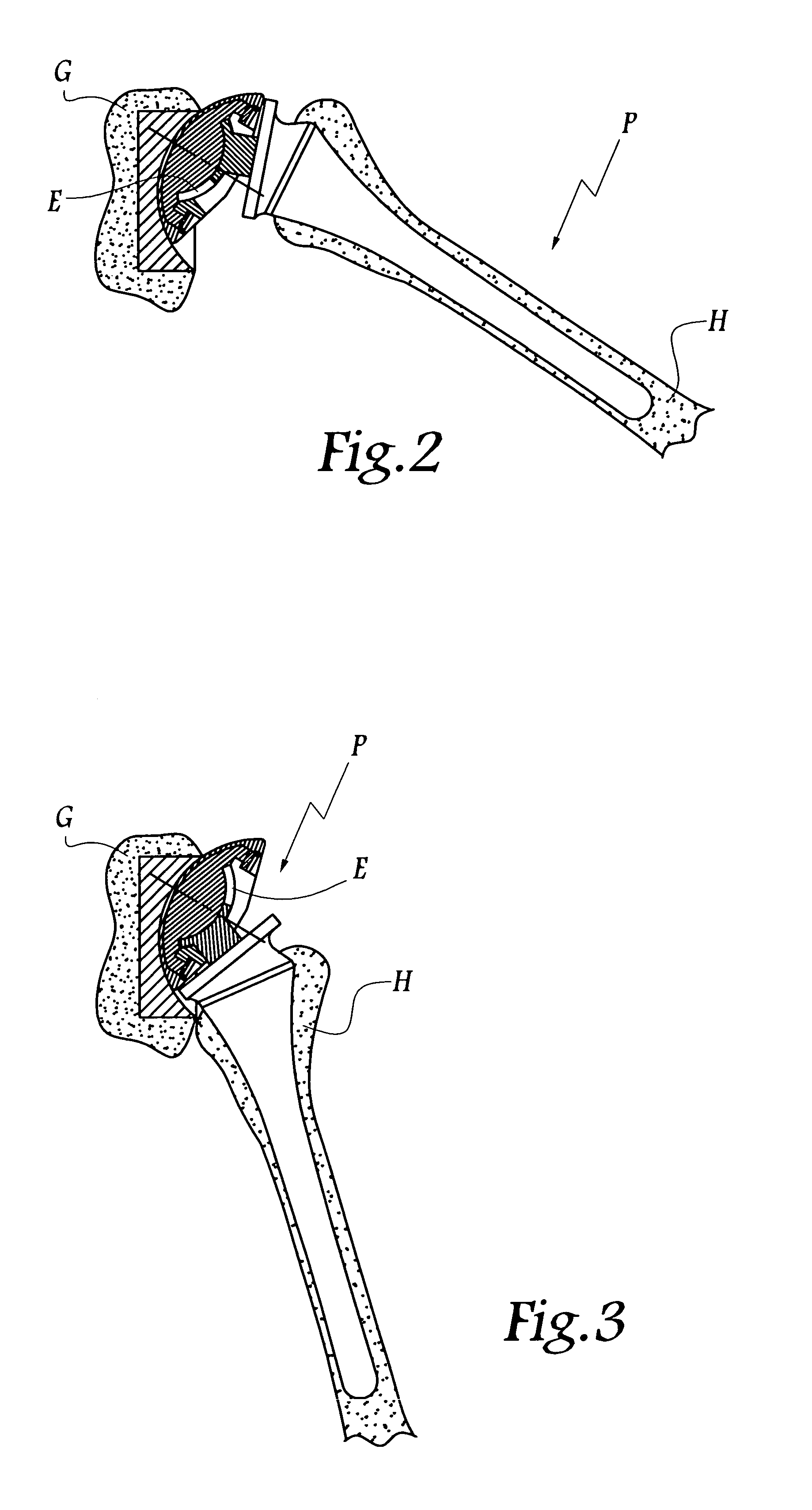
Shoulder or hip prosthesis and process for fitting same
InactiveUS20050165490A1Improve stabilityIncrease amplitudeJoint implantsFemoral headsMedicineAbutment
This prosthesis comprises a humeral or femoral component and an intermediate component. The concave surface of articulation of the humeral or femoral component is formed by a plate connected by a neck to a part of this component adapted to be anchored in the humeral or femoral medullary cavity. The intermediate component is provided with a member for retaining the humeral or femoral component in a position where the plate is in abutment against the first convex surface of the intermediate component. The retaining member defines a non-circular passage in which the neck is adapted to be displaced as a function of the movements of the humeral or femoral component with respect to the other components of the prosthesis. The retaining member defines with the first convex surface of articulation of the intermediate component a volume for receiving a part of the plate projecting radially with respect to the neck.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Implantable screw for stabilization of a joint or a bone fracture
ActiveUS20050177167A1Increase flexibilityLack of transferabilitySuture equipmentsLigamentsEngineeringBone marrow cavity
Owner:NOVOPLANT
Shoulder or hip prosthesis and process for fitting same
This prosthesis comprises a humeral or femoral component and an intermediate component. The concave surface of articulation of the humeral or femoral component is formed by a plate connected by a neck to a part of this component adapted to be anchored in the humeral or femoral medullary cavity. The intermediate component is provided with a member for retaining the humeral or femoral component in a position where the plate is in abutment against the first convex surface of the intermediate component. The retaining member defines a non-circular passage in which the neck is adapted to be displaced as a function of the movements of the humeral or femoral component with respect to the other components of the prosthesis. The retaining member defines with the first convex surface of articulation of the intermediate component a volume for receiving a part of the plate projecting radially with respect to the neck.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
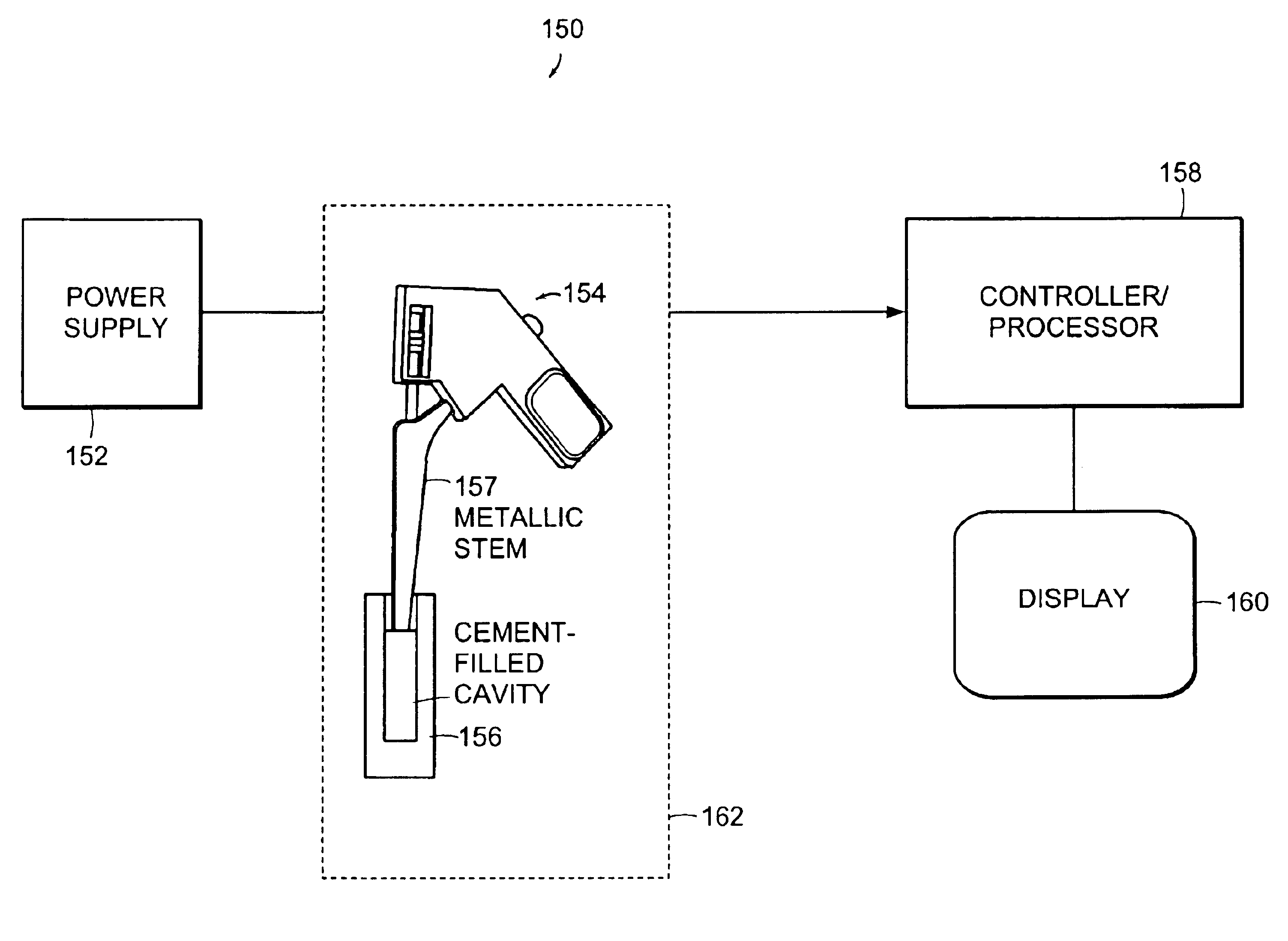
System and methods for reducing interfacial porosity in cements
InactiveUS6884264B2Reducing pores, or air pocketsReduce the possibilityUltrasound therapyBone implantPorosityHand held
The present invention provides a system and a method for reducing pores, or air pockets, that form at the interface between the material used to attach or adhere the surface of a component, such as a prosthesis, to a site.A preferred embodiment of the invention includes an actuator that controls a coupler which transmits energy to a prosthesis being inserted into a material to reduce porosity at an interface between the prosthesis and the material.The system of the present invention can include an oscillating hand-held device that vibrates the stem component of an orthopedic prosthesis at a particular frequency and amplitude. The device is typically held by the hand of the surgeon, who guides the vibrating prosthesis into the cement-filled medullary cavity.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE POLYMER GROUP
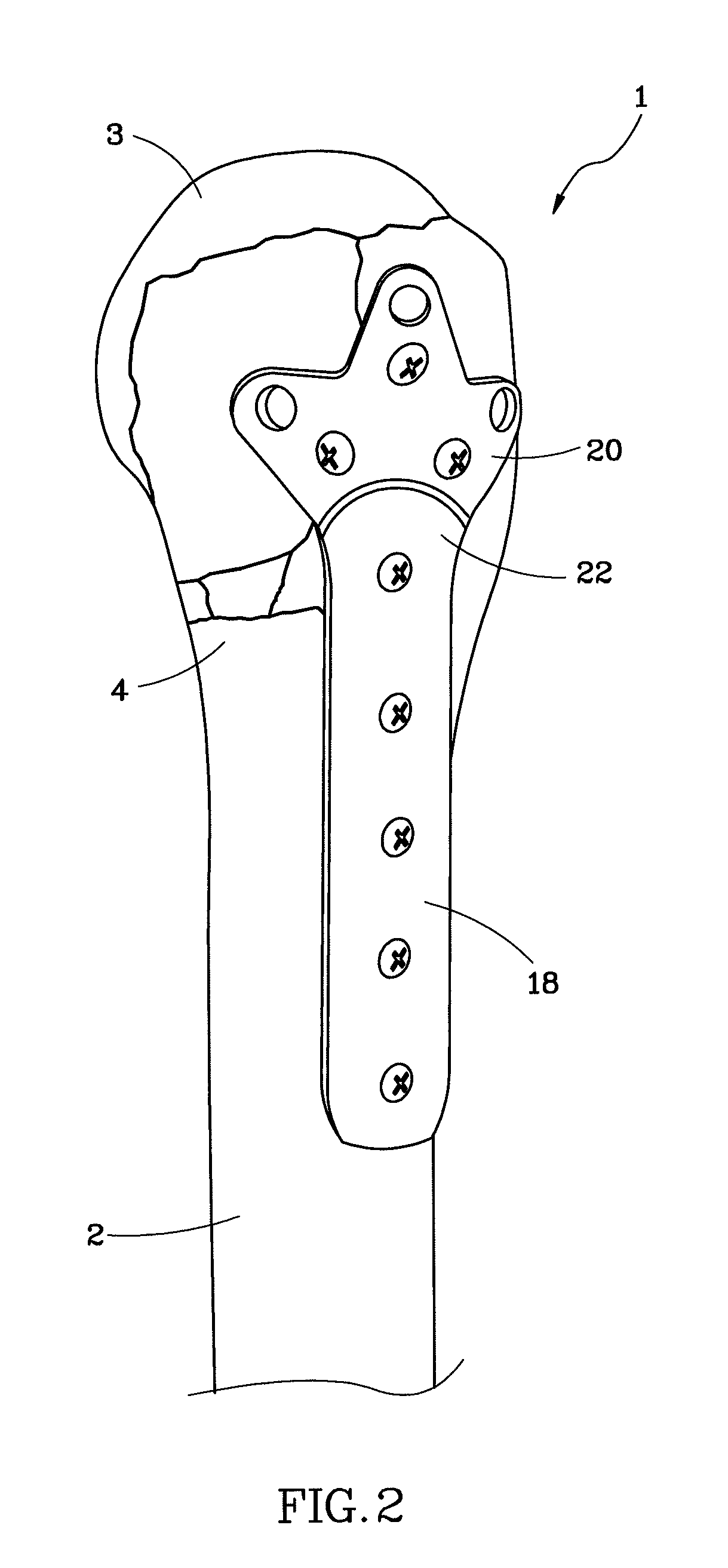
Interlocking bone plate system
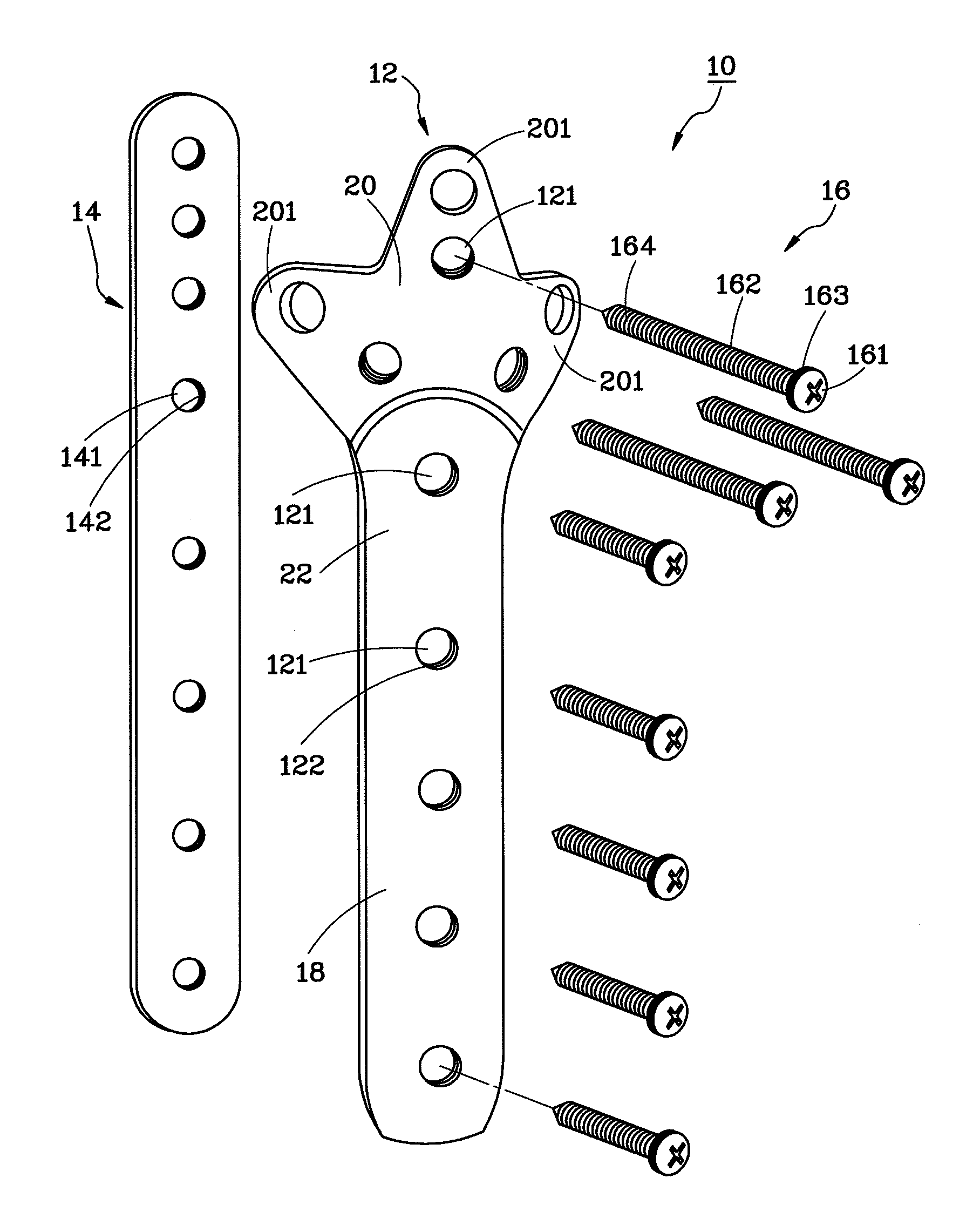
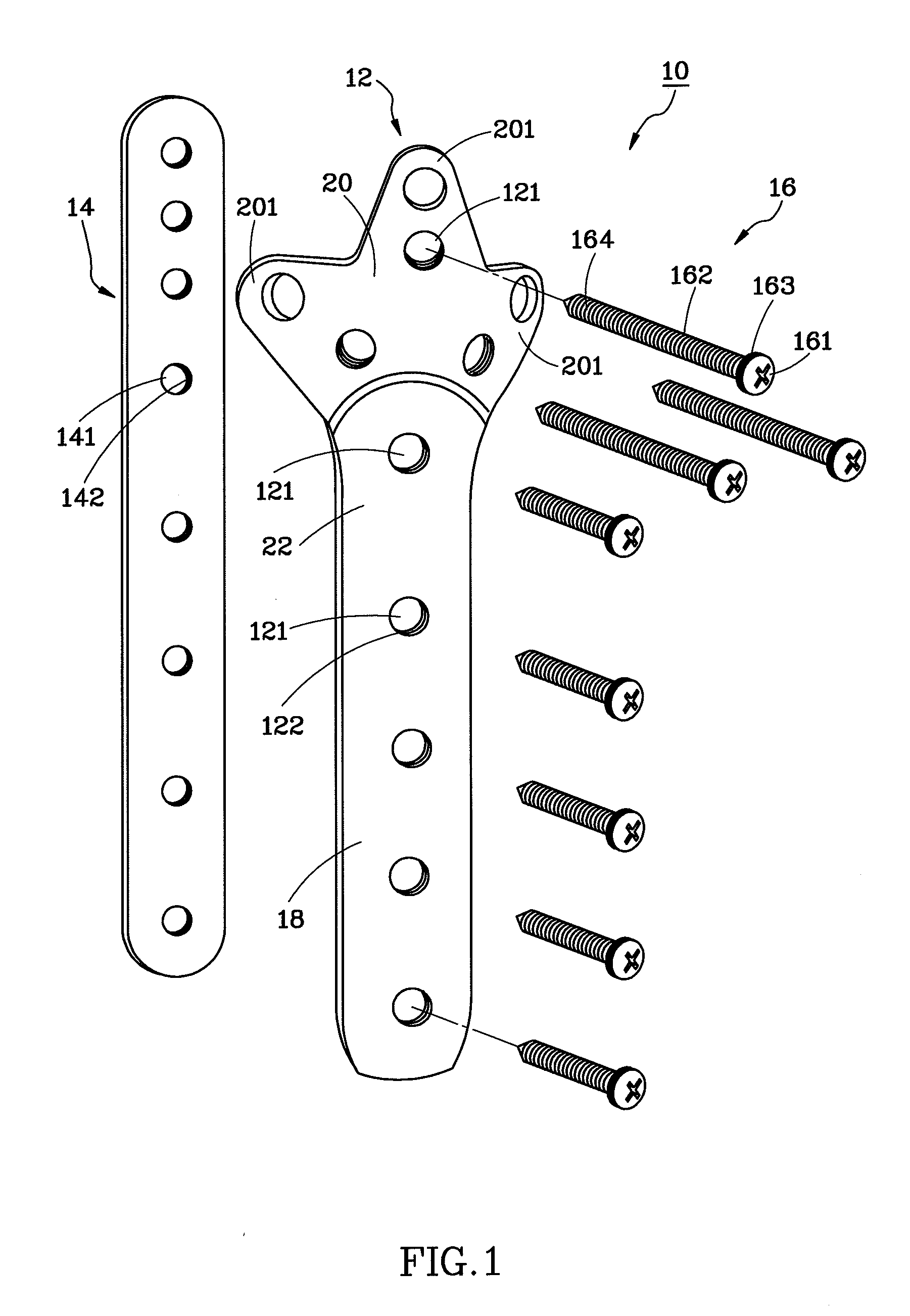
InactiveUS8911482B2Highly stable fixation structureReduce riskInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBone marrow cavityUltimate tensile strength
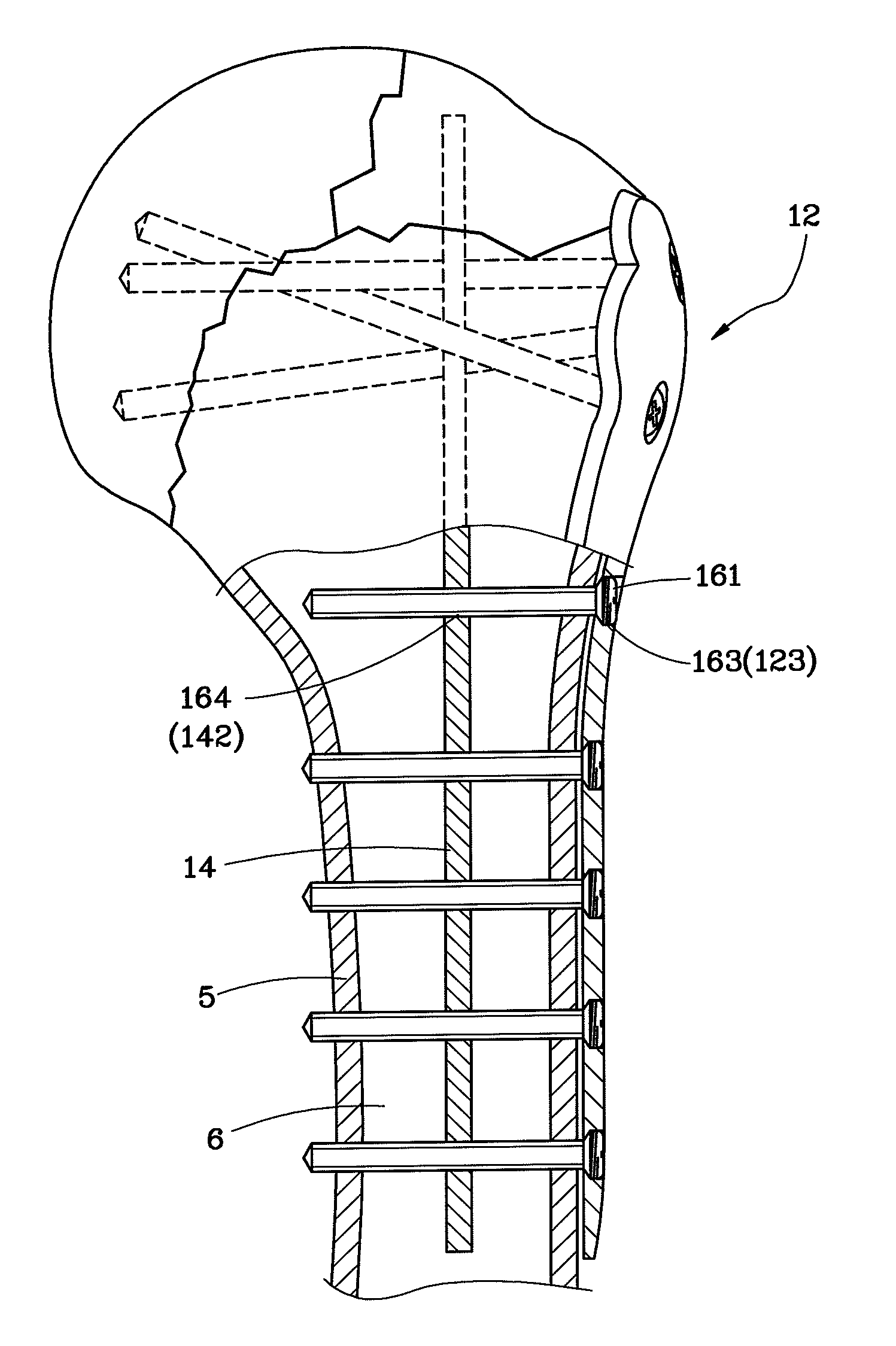
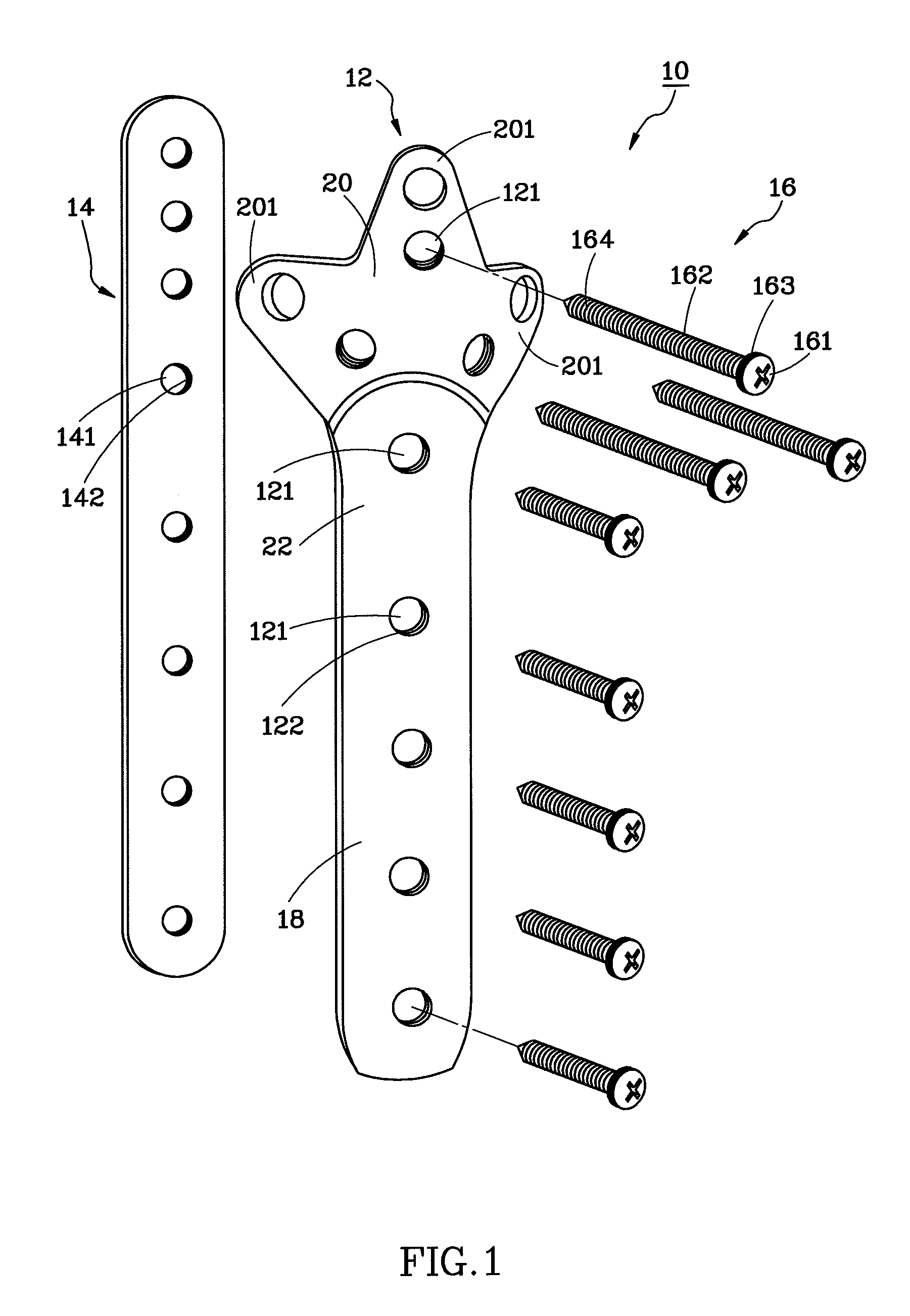
An interlocking bone plate system includes an outer bone plate for being arranged outside a broken bone, an inner bone plate for being installed inside the medullary cavity of the broken bone, and screws for being inserted through and engaged with the outer bone plate and the broken bone and then engaged with the inner bone plate so as to interlock the out and inner bone plates together. The inner bone plate provides an added support in addition to the support provided by the outer bone plate, enhancing the structural strength of the whole bone fixation structure and lowering the risk of failed surgery.
Owner:TAICHUNG VETERANS GENERAL HOSPITAL
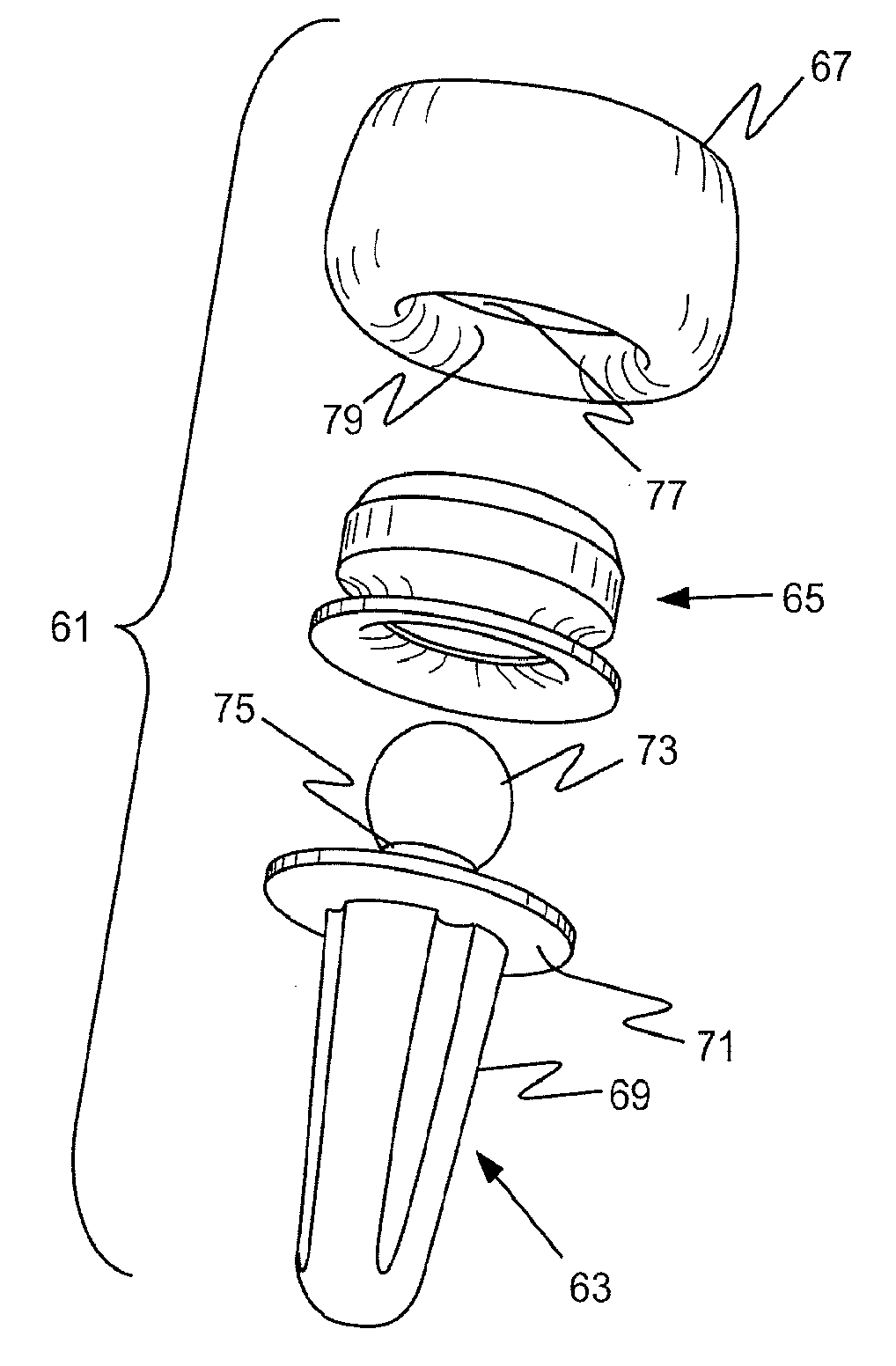
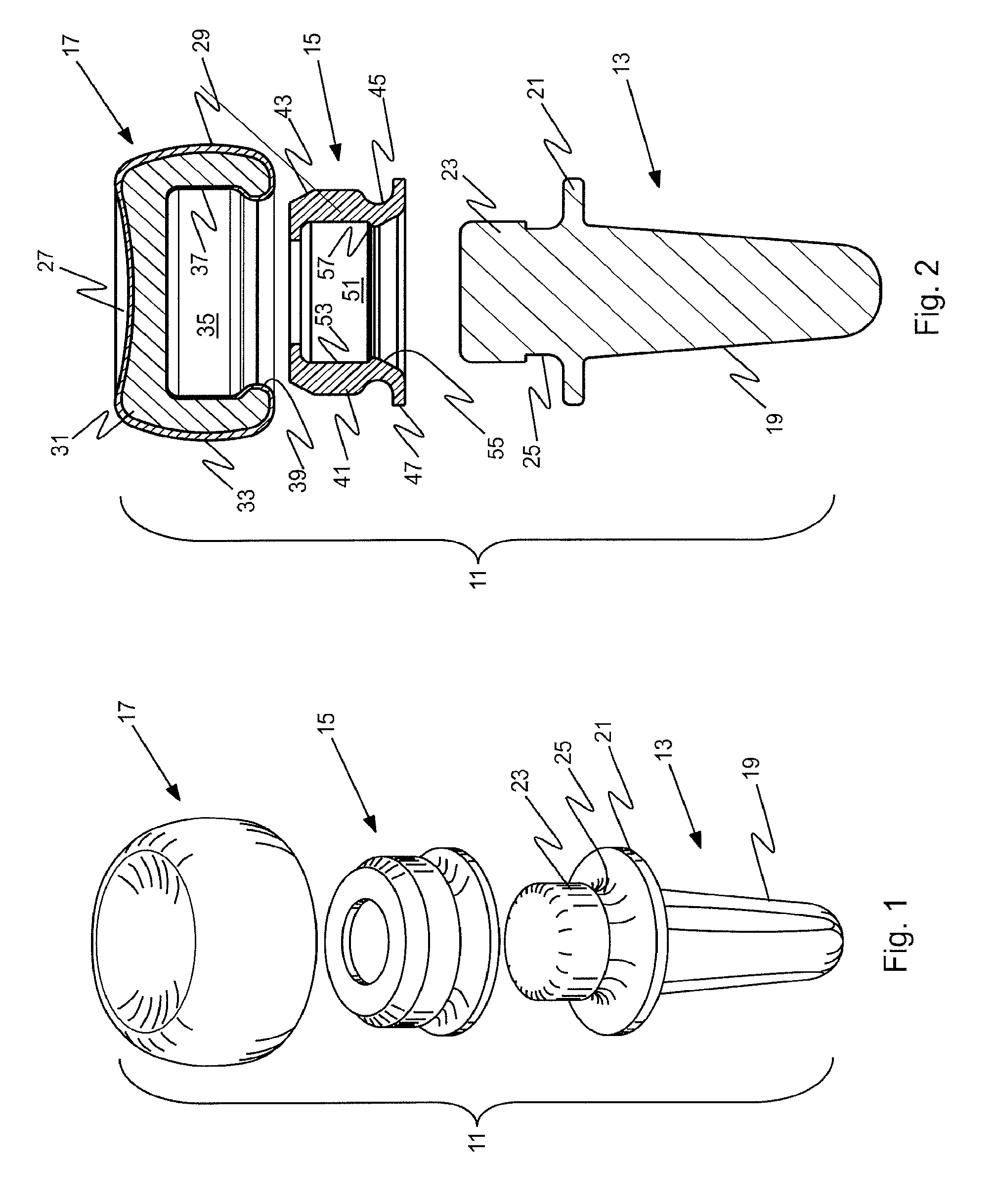
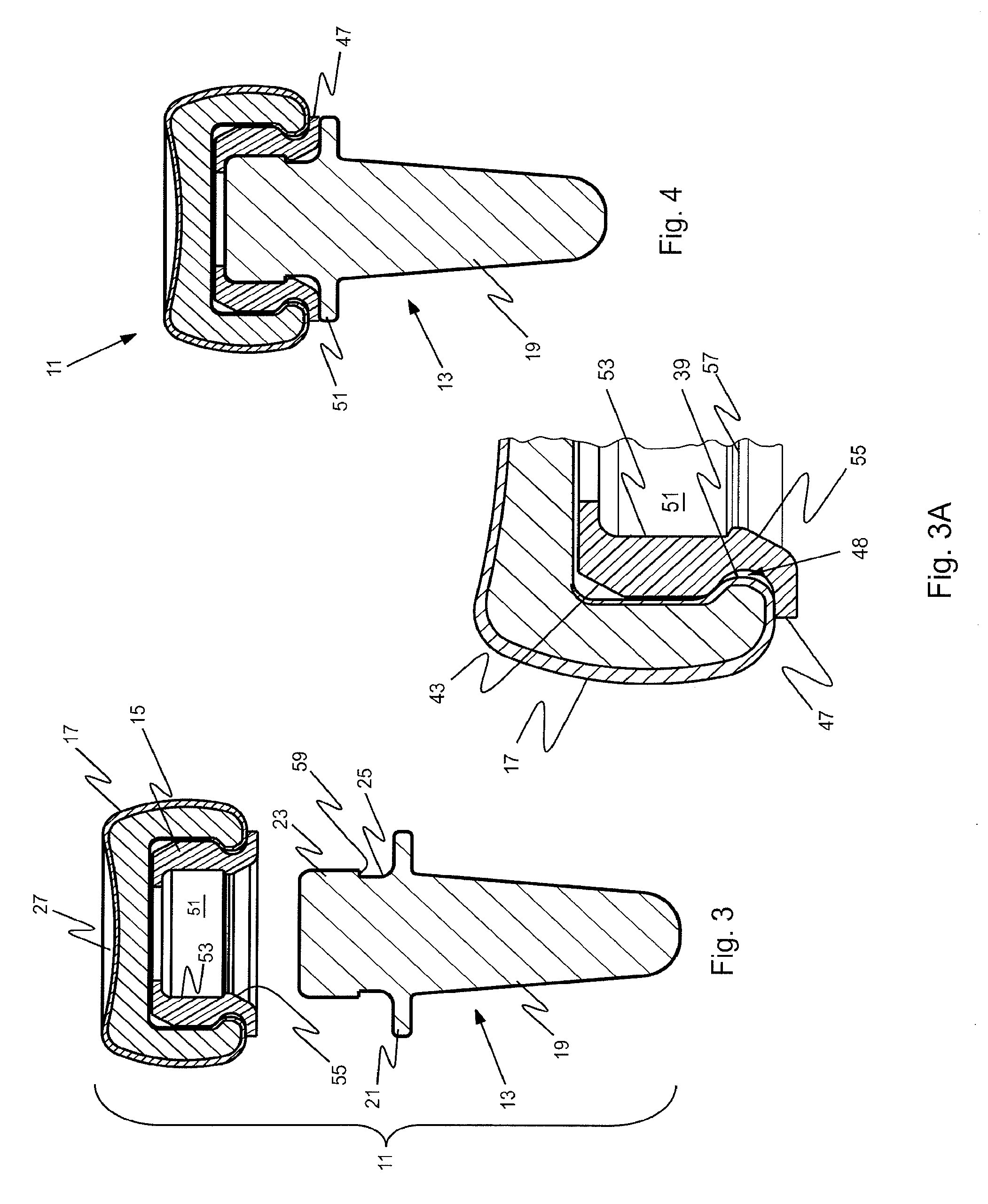
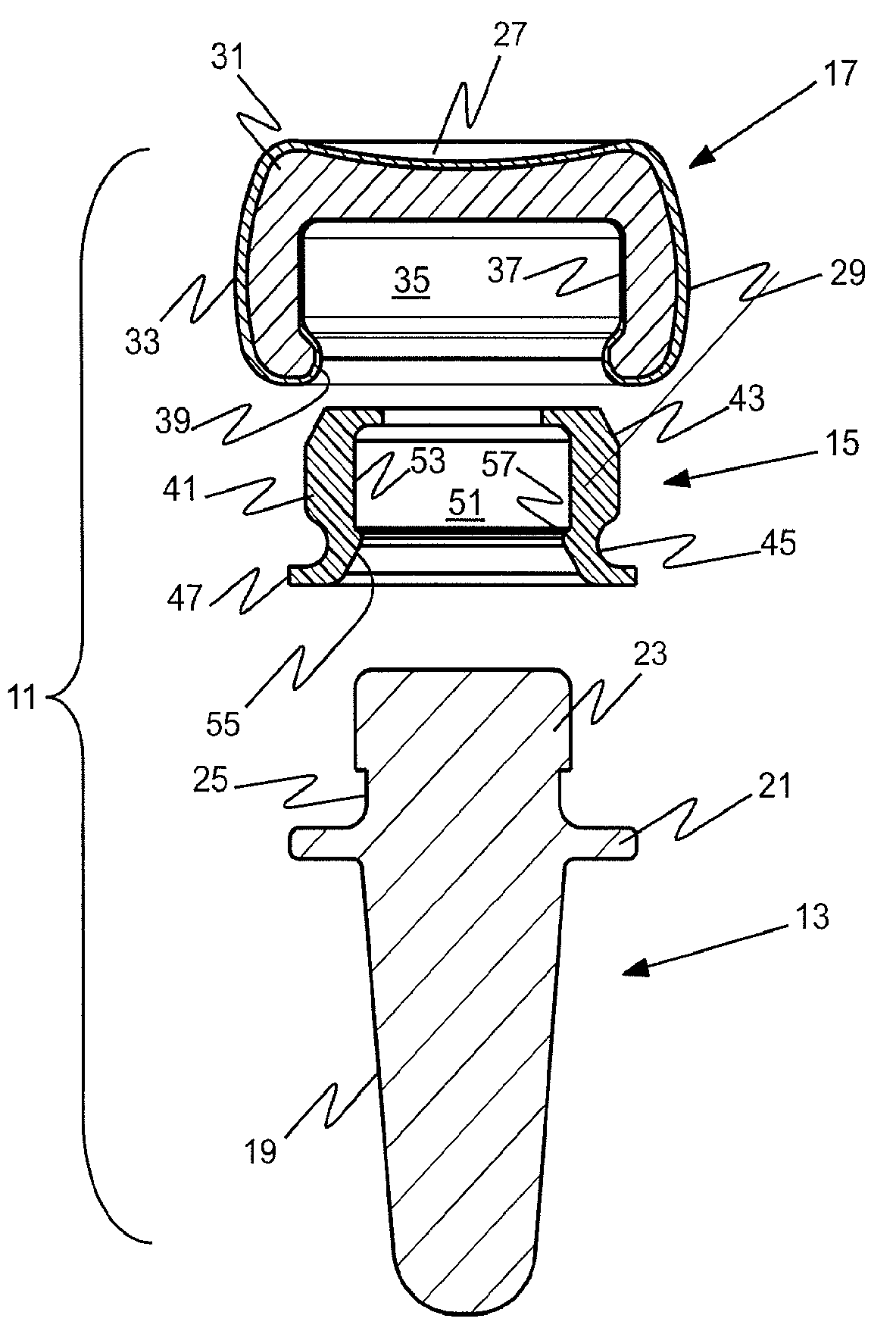
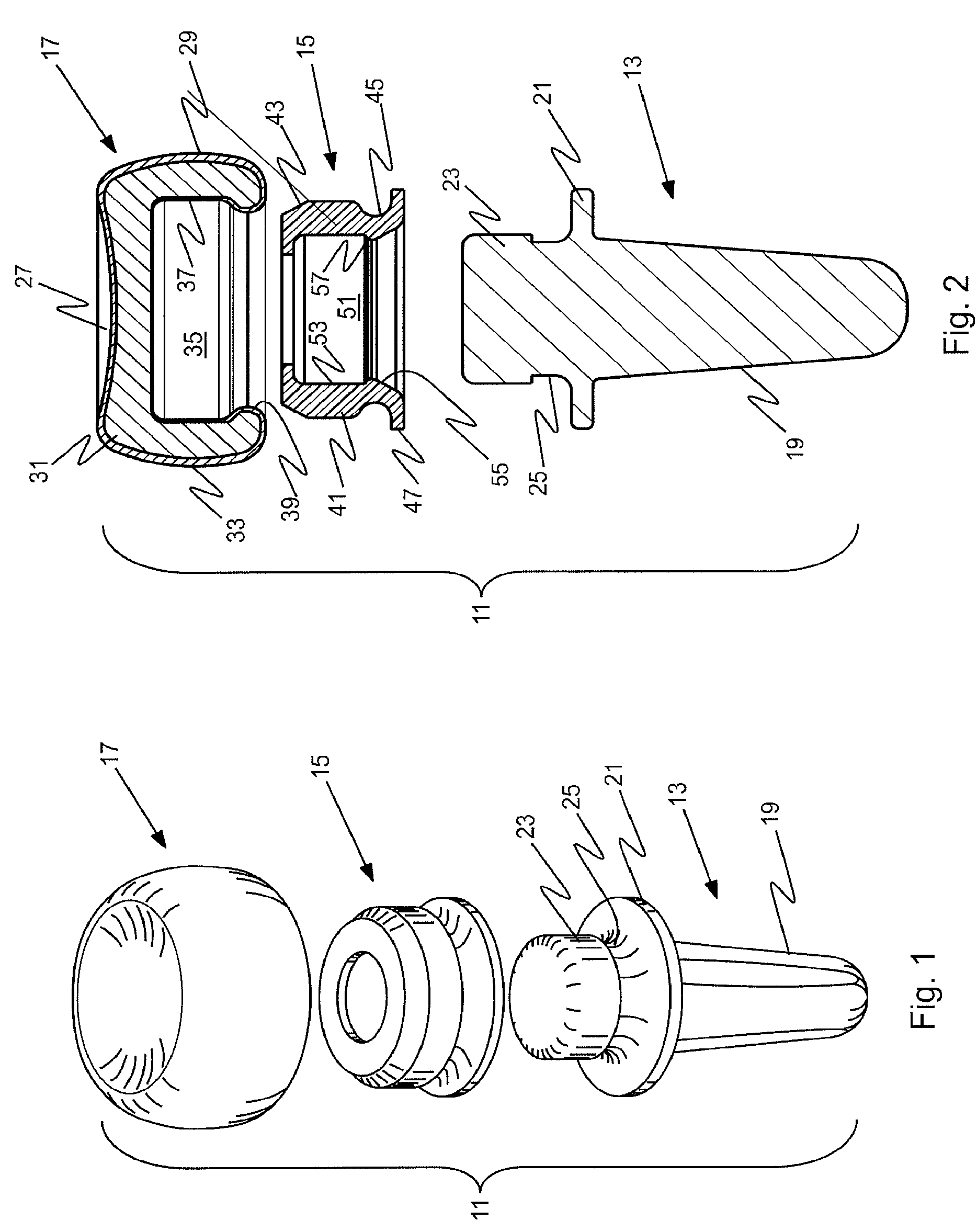
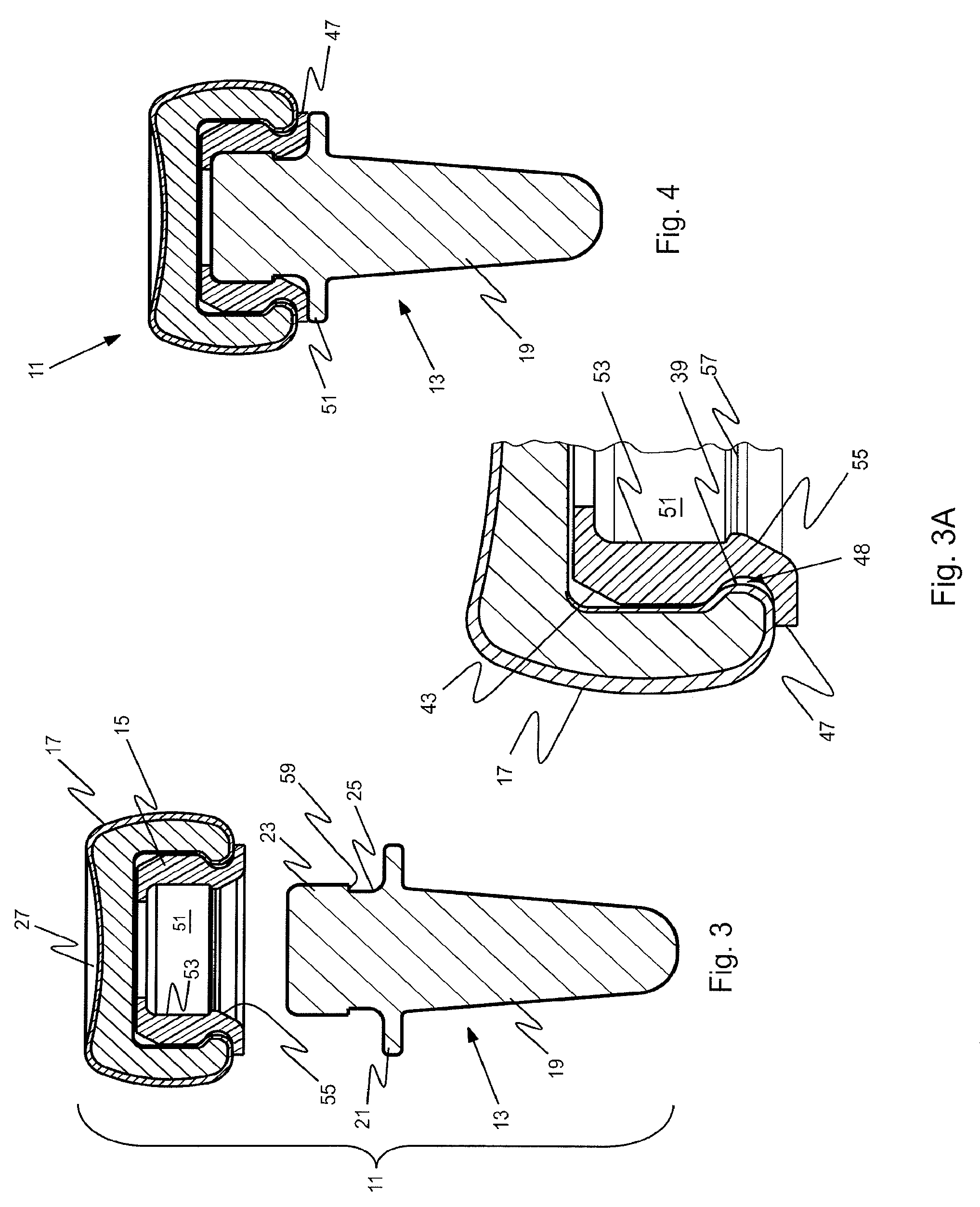
Prosthetic implant and assembly method
ActiveUS20090240336A1Small toleranceReduced diametric dimensionBone implantJoint implantsBone marrow cavityMedullary cavity
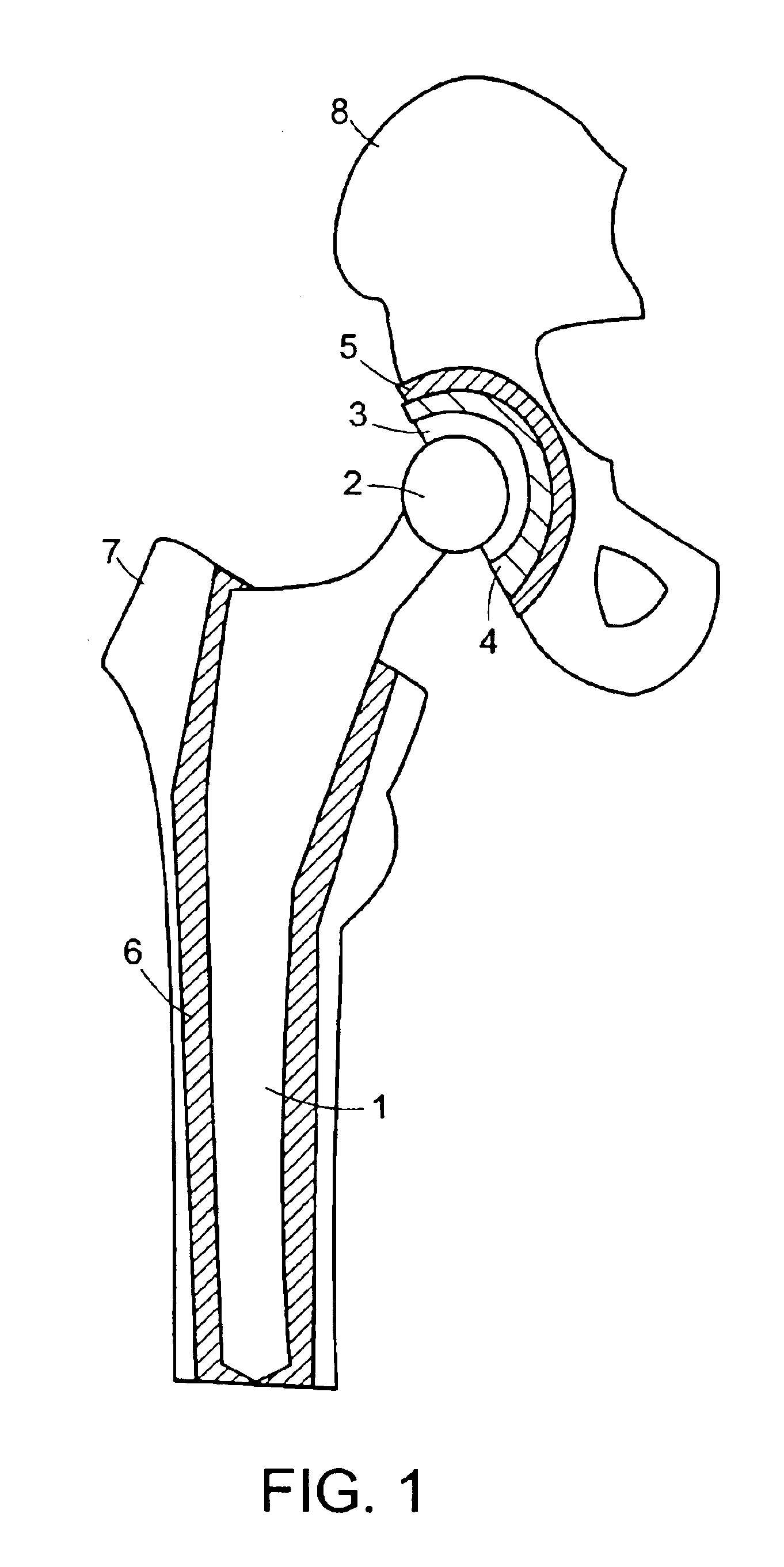
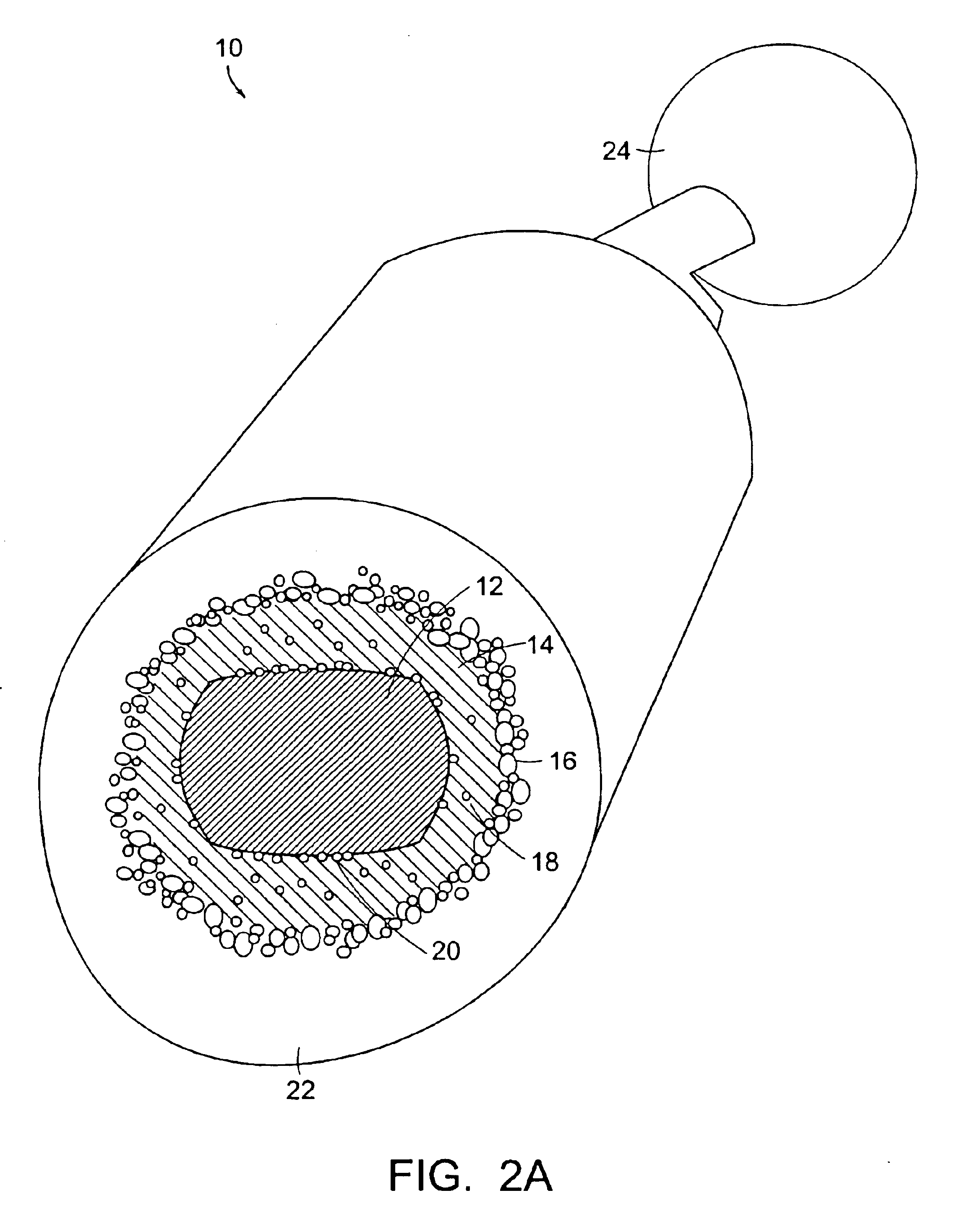
An orthopedic prosthetic implant comprises a metal alloy stem element (13, 63, 113), which has one end portion (19, 69, 119) constructed to reside in the medullary cavity of a bone and an integral connector (23, 73, 123) at the opposite end to which crystalline brittle head (17, 67, 117), preferably made of pyrocarbon-coated graphite, is joined. The head interfaces with human bone, and its effective joinder to the stem element is achieved through a polymeric insert (15, 65, 115) of proportional shape and design which has selected elastic properties. The design and material of the polymeric insert allow it to be securely received within an interior cavity (35, 77, 131) of the pyrocarbon-coated graphite head and mated to the stem connector in an either rigidly or bi-polar arrangement. The method of joinder allows the construction of composite implants that utilize the most desirable properties of metallic and brittle crystalline materials.
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
Intramedullary Arthrodesis Nail and Method of Use
ActiveUS20100130978A1Minimize excessive bone resectionMinimize tendon damageWrist jointsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisPost operative
A device is provided including a distal nail portion and a proximal nail portion that can be connected to each other to attain a rigid configuration. The device is to be placed internally within the medullary cavities of at least two bones forming a joint to accomplish arthrodesis of the joint. The device is placed intramedullarily in order to minimize incision size, excessive bone resection and post-operative tendon damage and tenderness. Additionally, one particular method for using the device is provided that includes placing and affixing the distal nail in a bone of a joint, placing the proximal nail in another bone of a joint, connecting the distal nail to the proximal nail, doing the desired geometrical adjustments, affixing the proximal nail to the distal nail by tightening the connection and affixing the proximal nail to the other bone of the joint to attain a rigid configuration.
Owner:SKELETAL DYNAMICS INC
Multi-functional orthopedic surgical instrument and method of using same
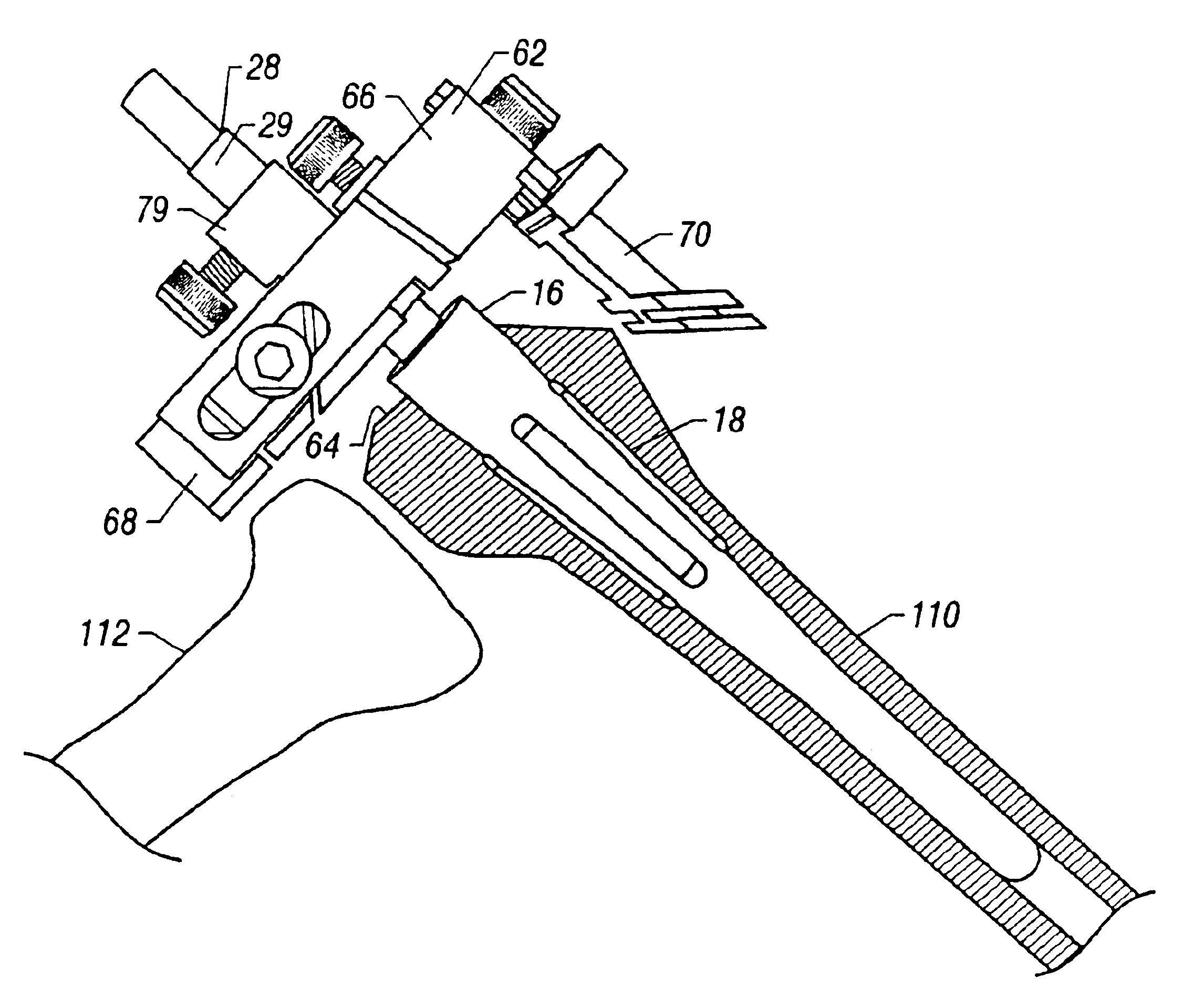
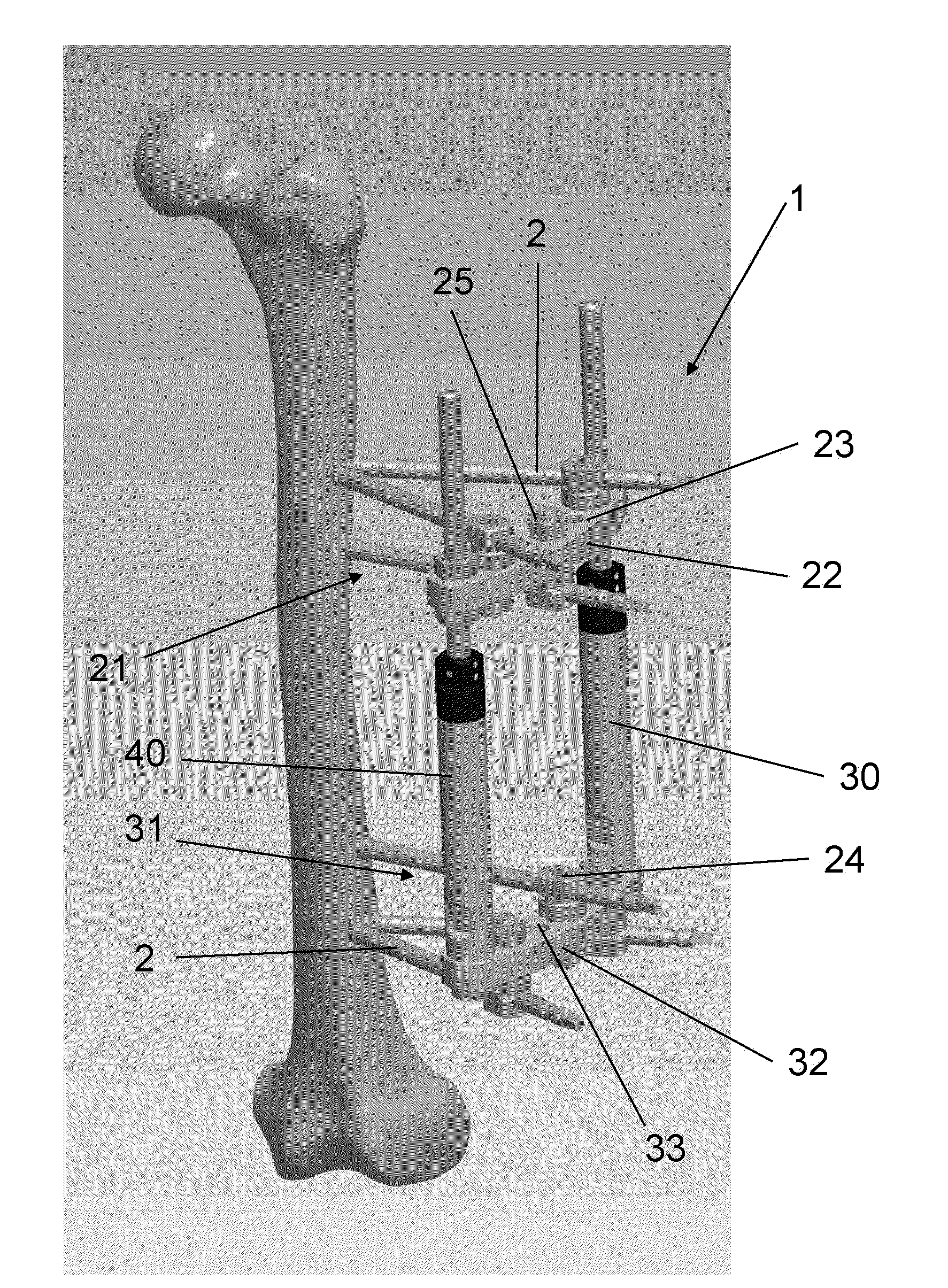
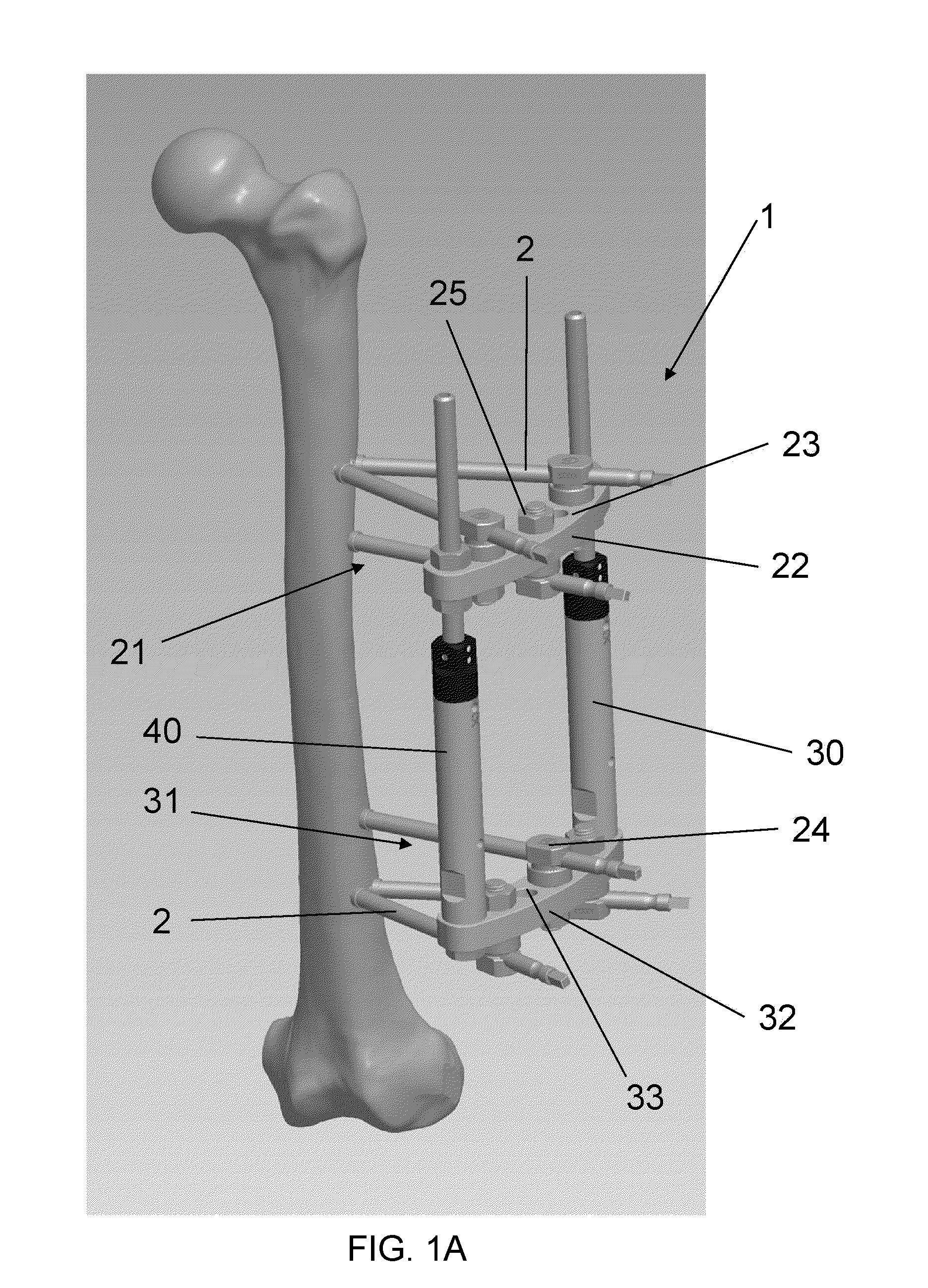
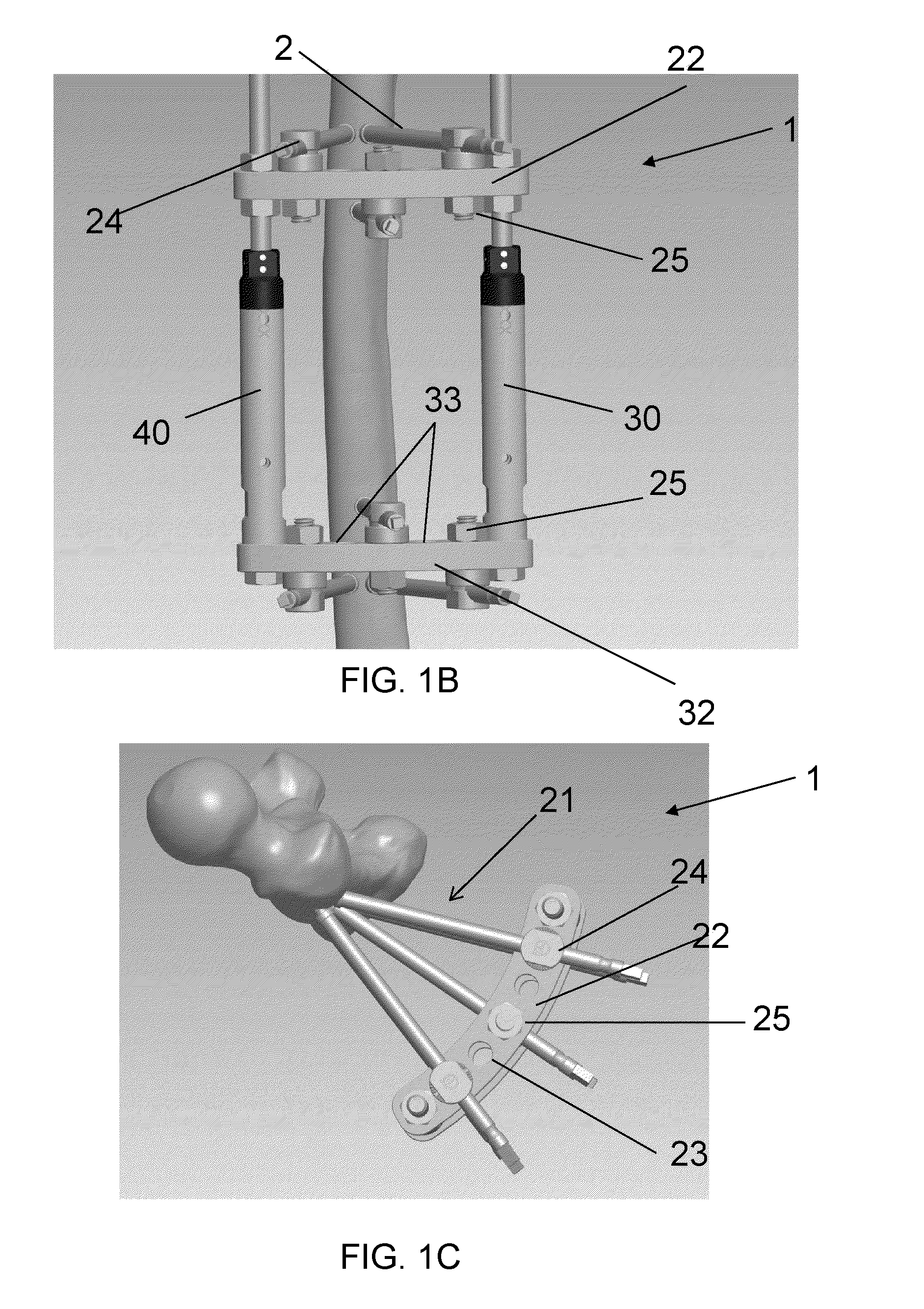
An apparatus has been developed to enable a surgeon to perform multiple orthopedic surgical operations, such as orthopedic surgical resectioning, total joint replacement and fixation of fractures, based on a single reference point. The apparatus is adjustable to conform to the needs and dimensions of individual patients and the surgical procedure(s) to be performed. The apparatus includes a support adapted for insertion into and alignment within the medullary cavity of a patient's bone. The support is capable of expanding into the bone so that the support is fixed within the bone and alignable to the bone. The support may be implanted to align a fractured bone, or extend a distance beyond its fixed position within the medullary cavity to provide a known surgical reference point. The apparatus includes one or more cutting guides mountable on the support and used in performing the desired surgical procedure(s). The cutting guides are positionable with respect to the known surgical reference point created by the support which enables the user to accurately position and secure various instruments at the desired position about the patient's anatomy.
Owner:KINNETT J GREGORY
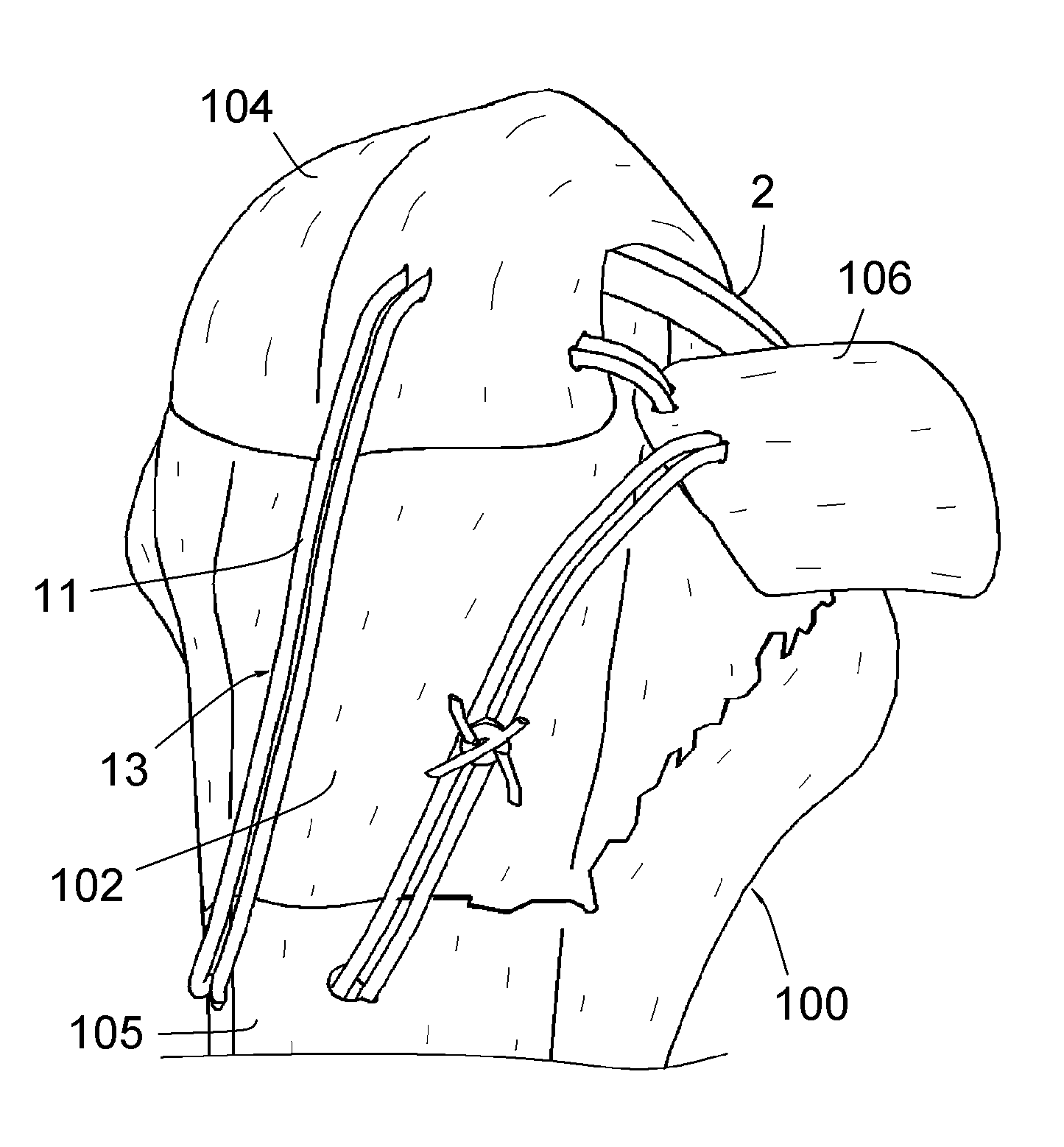
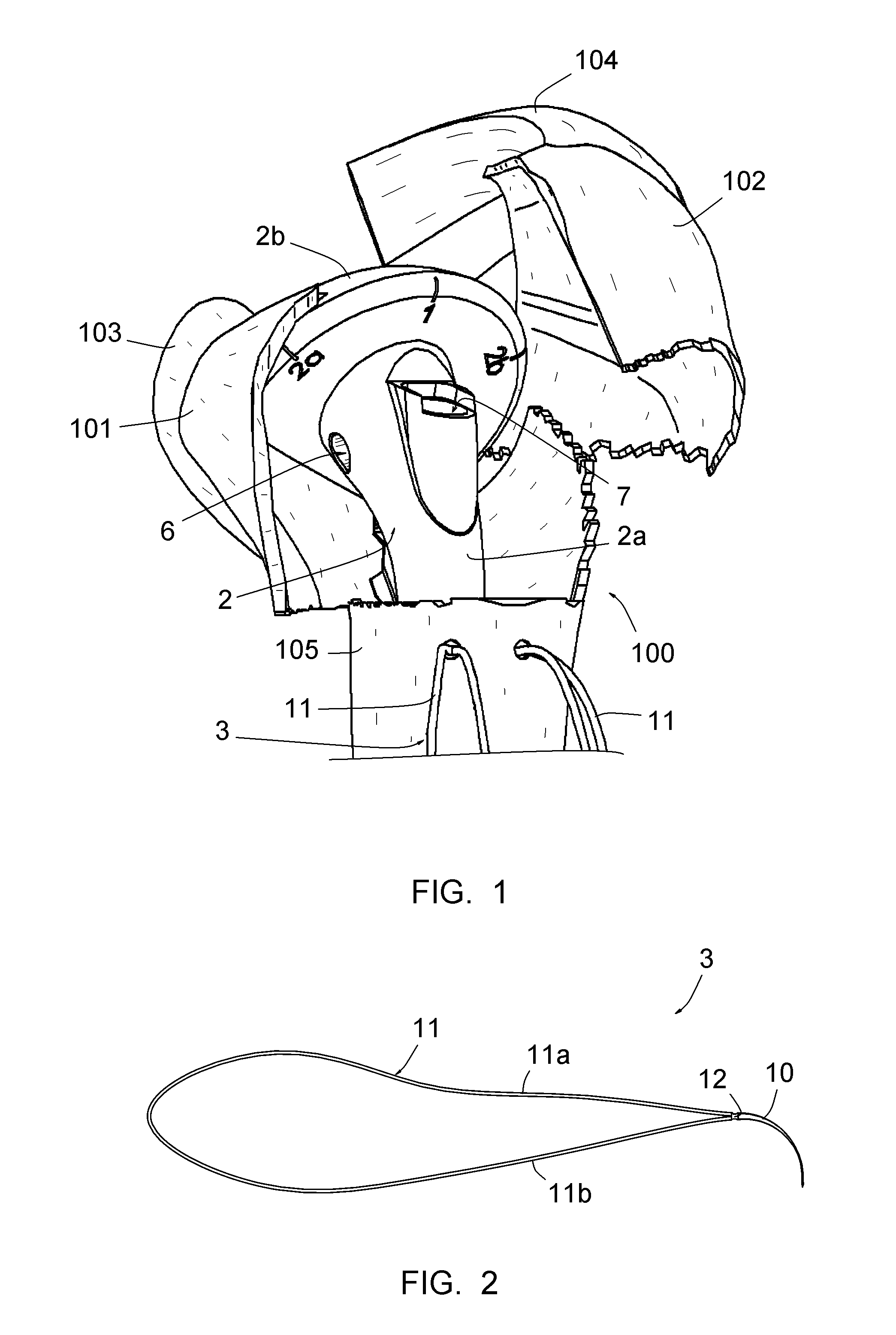
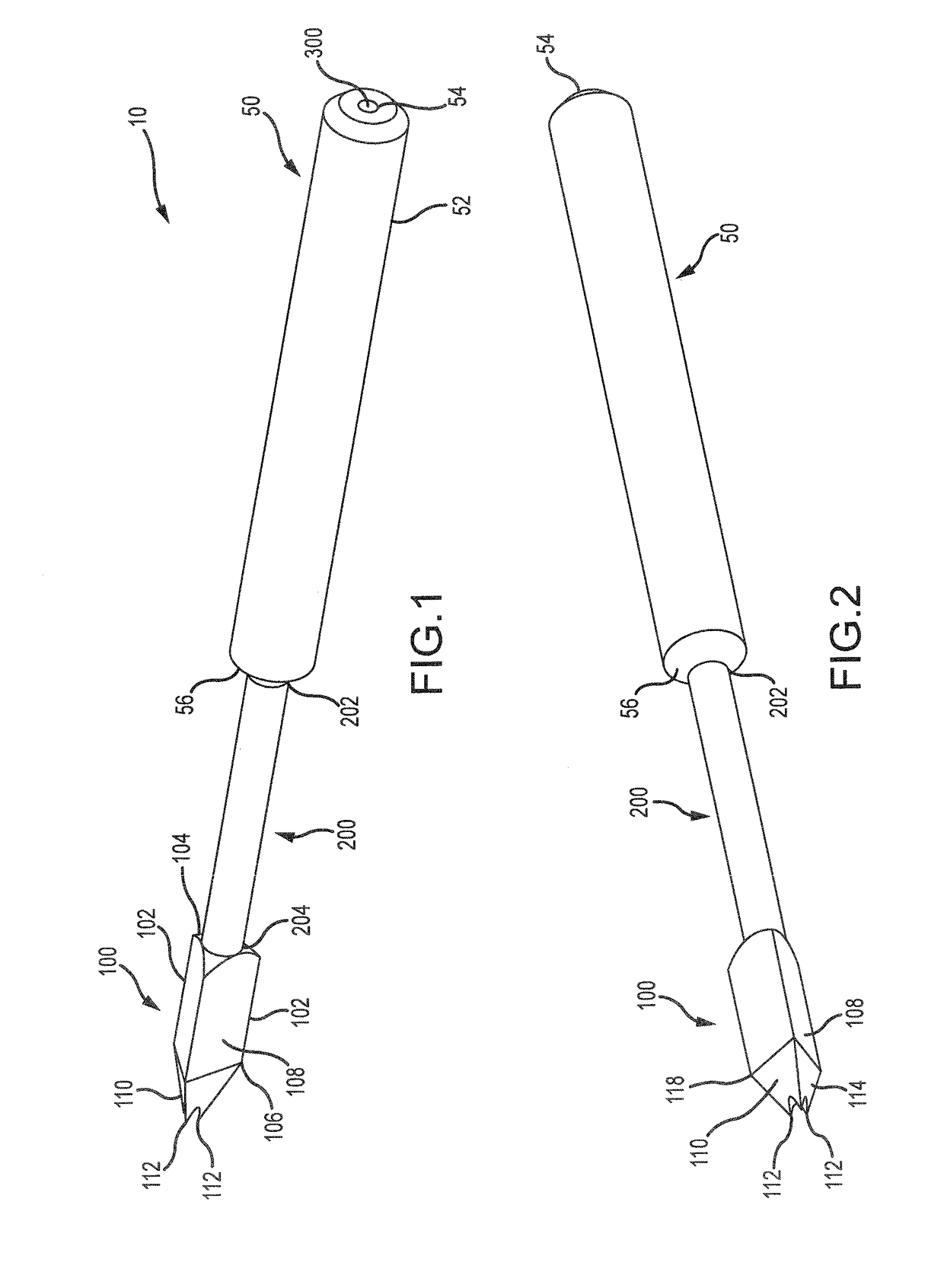
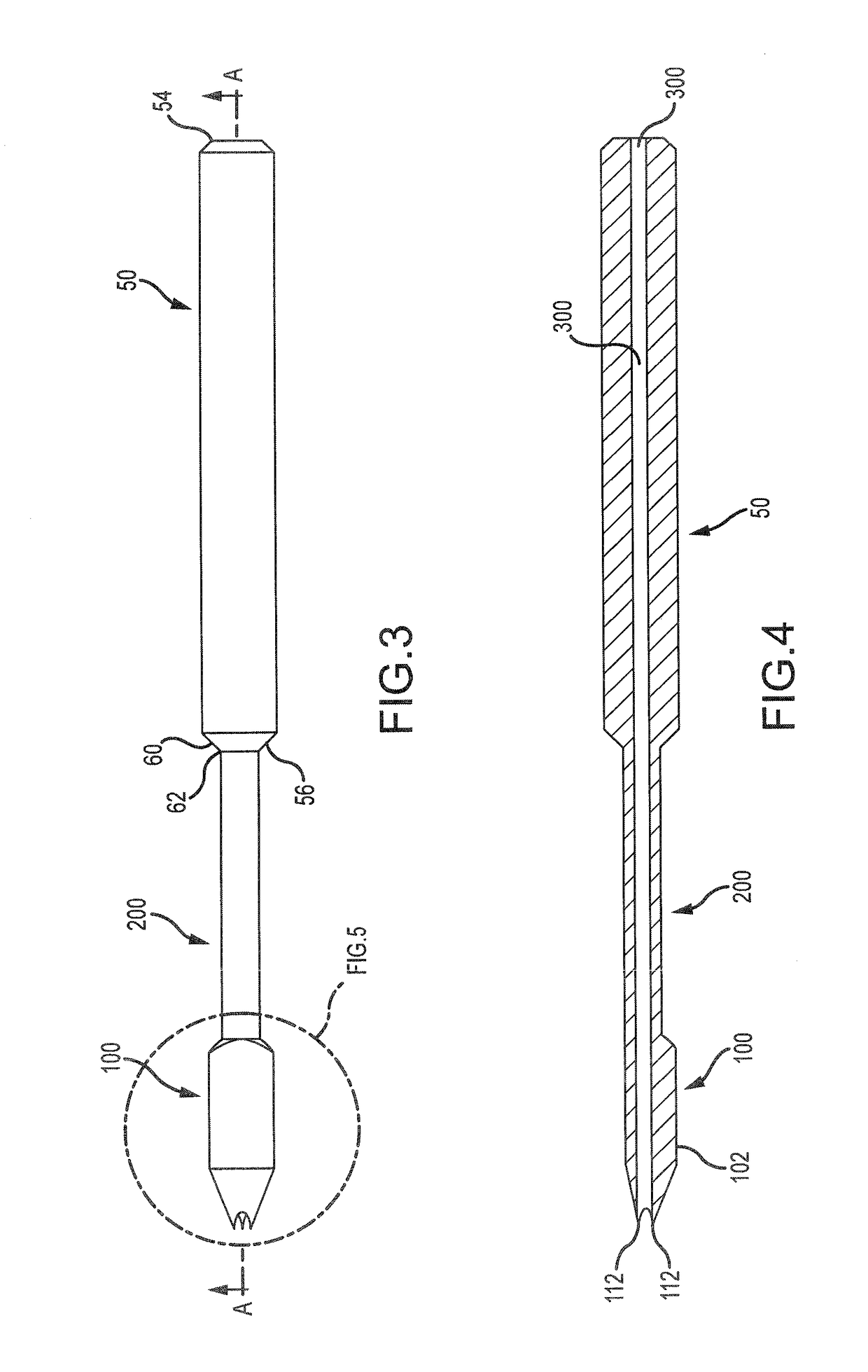
Surgical method for repairing a fractured shoulder joint
ActiveUS20120089143A1Good consolidationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone marrow cavityEngineering
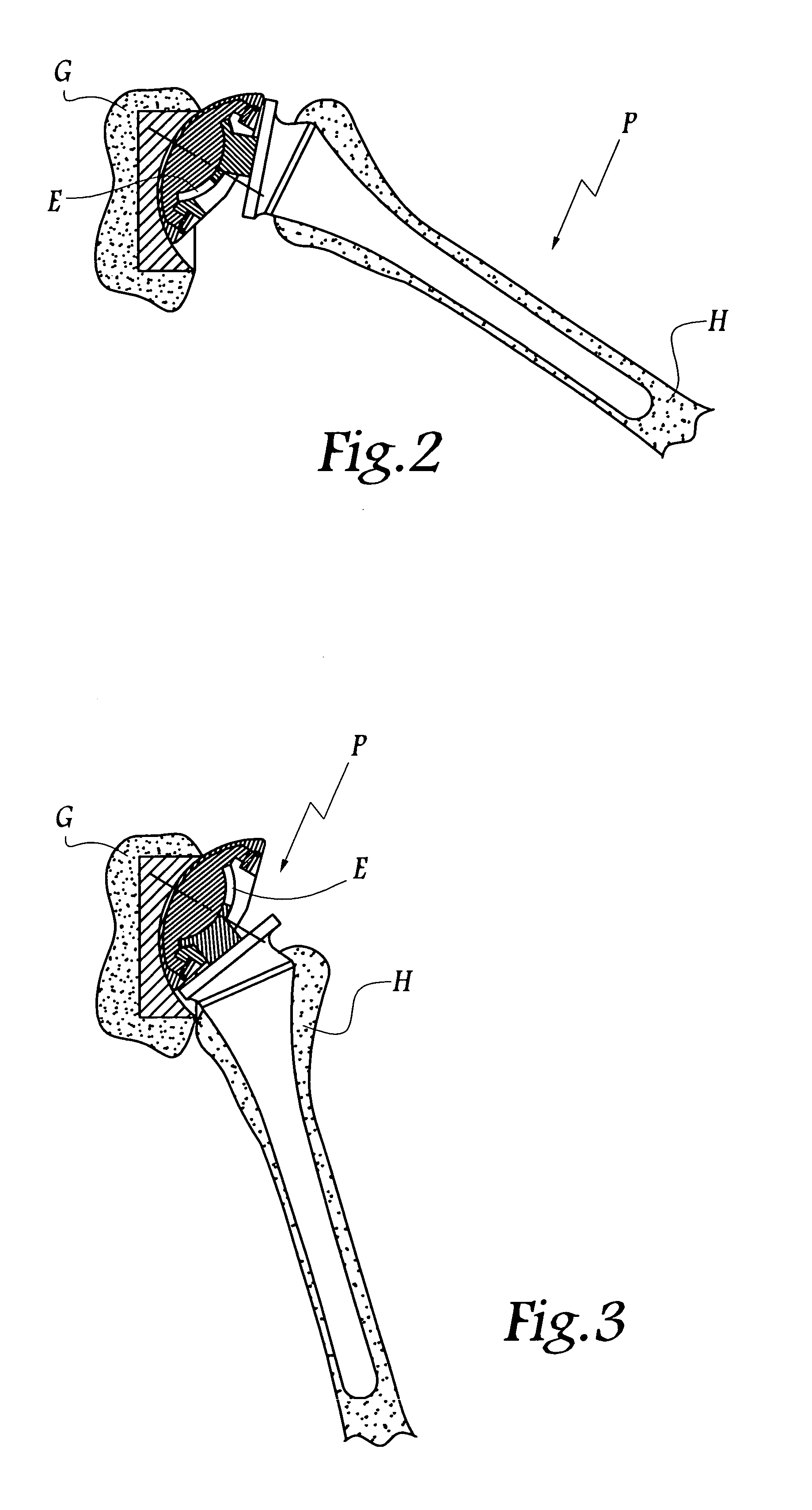
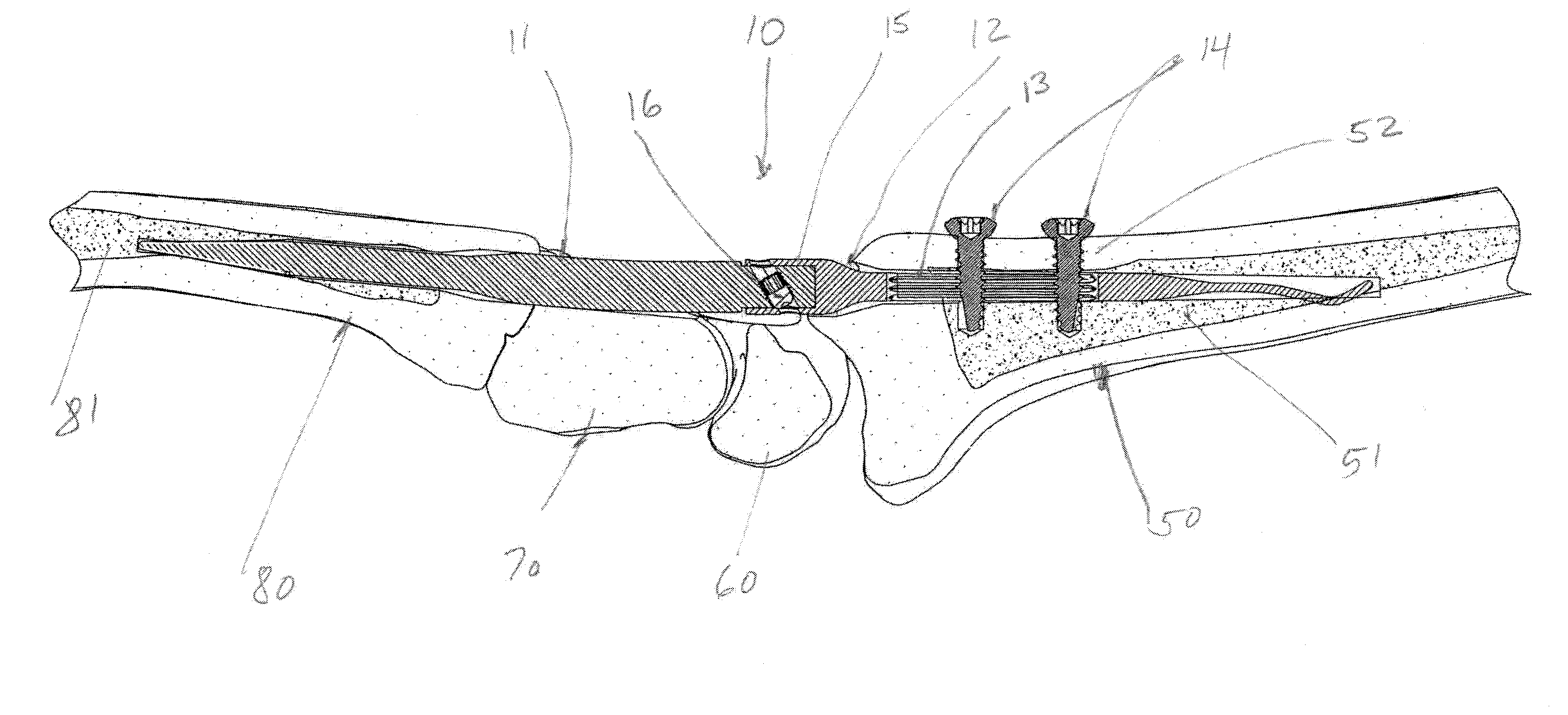
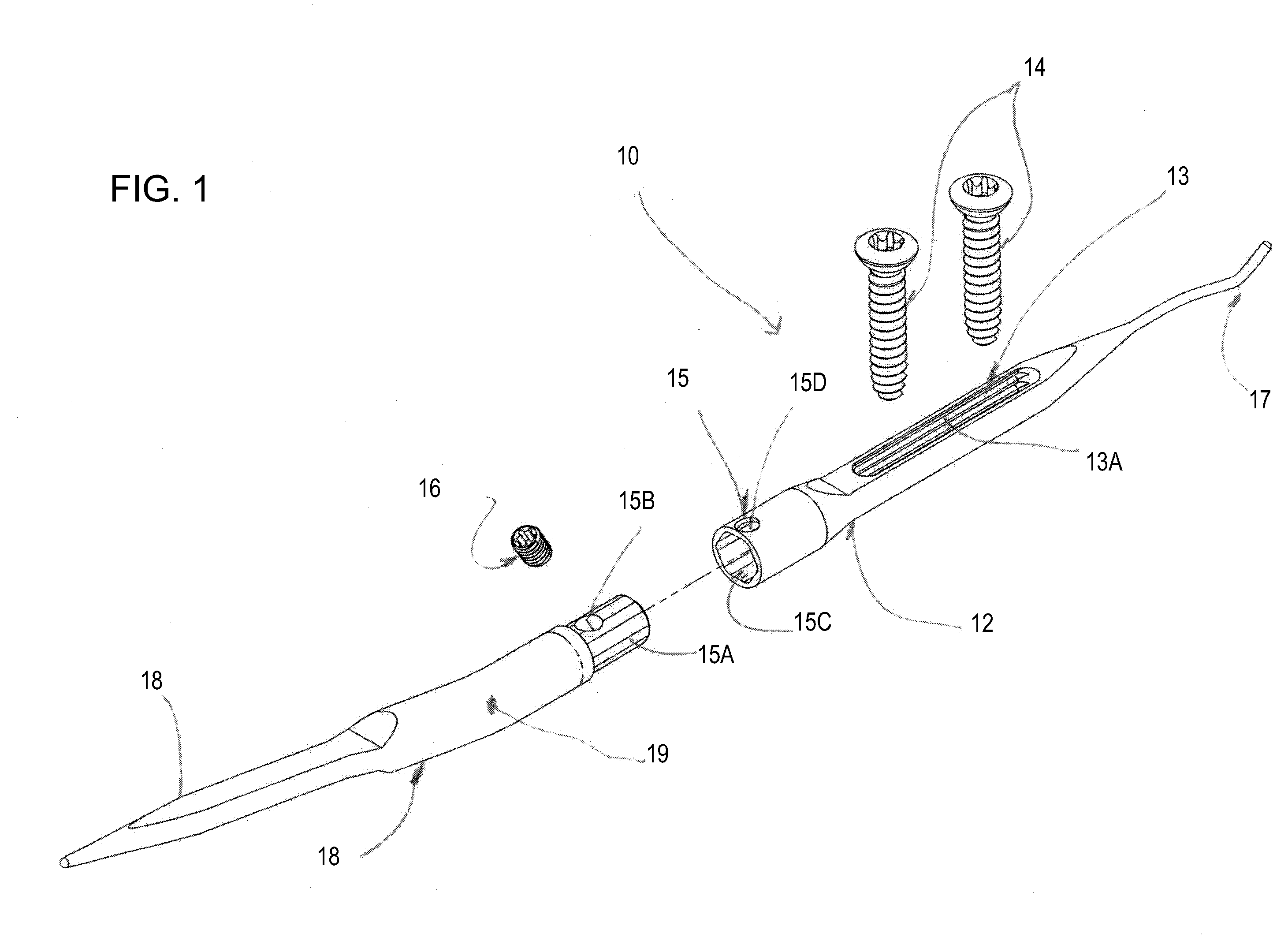
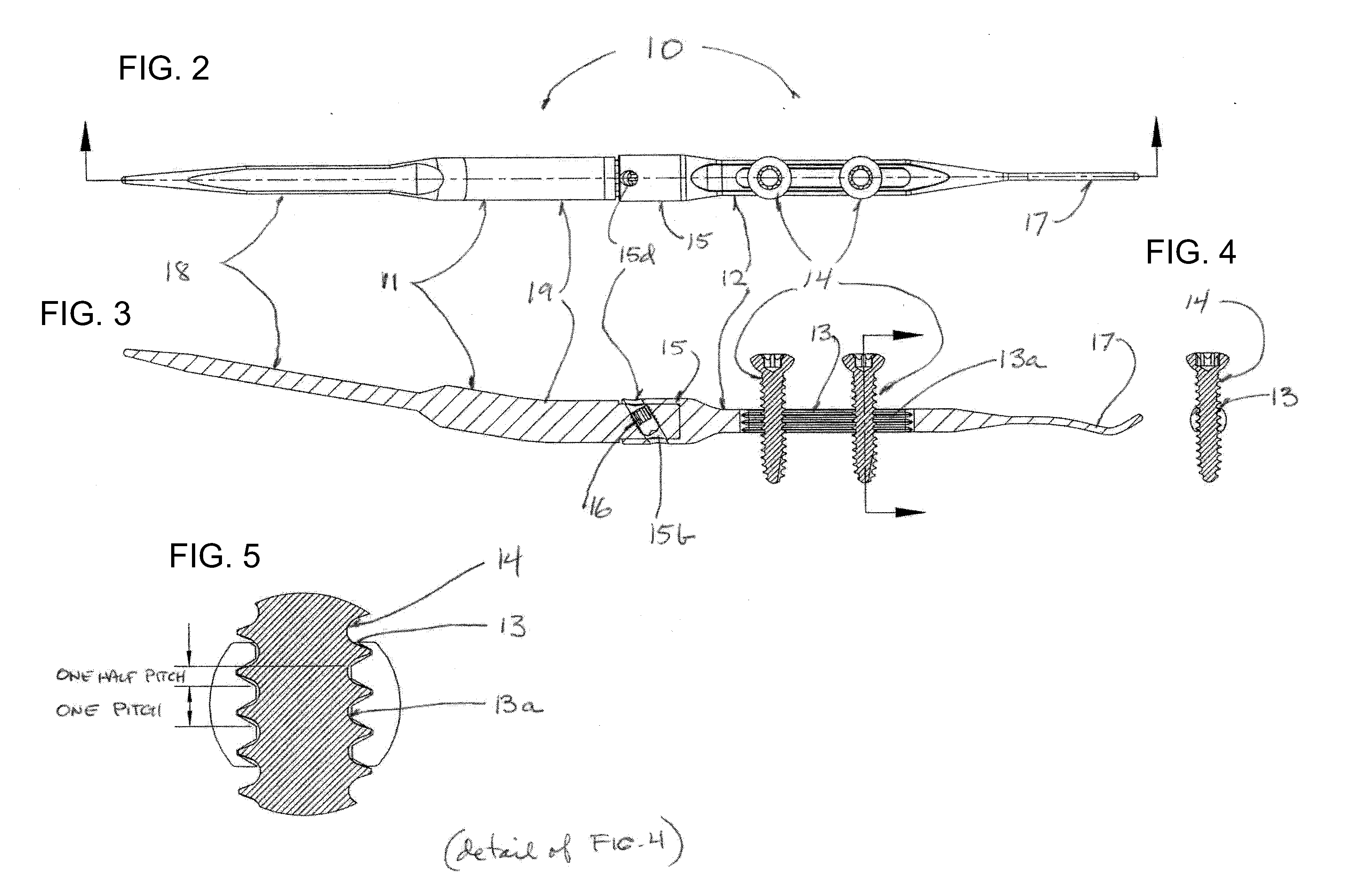
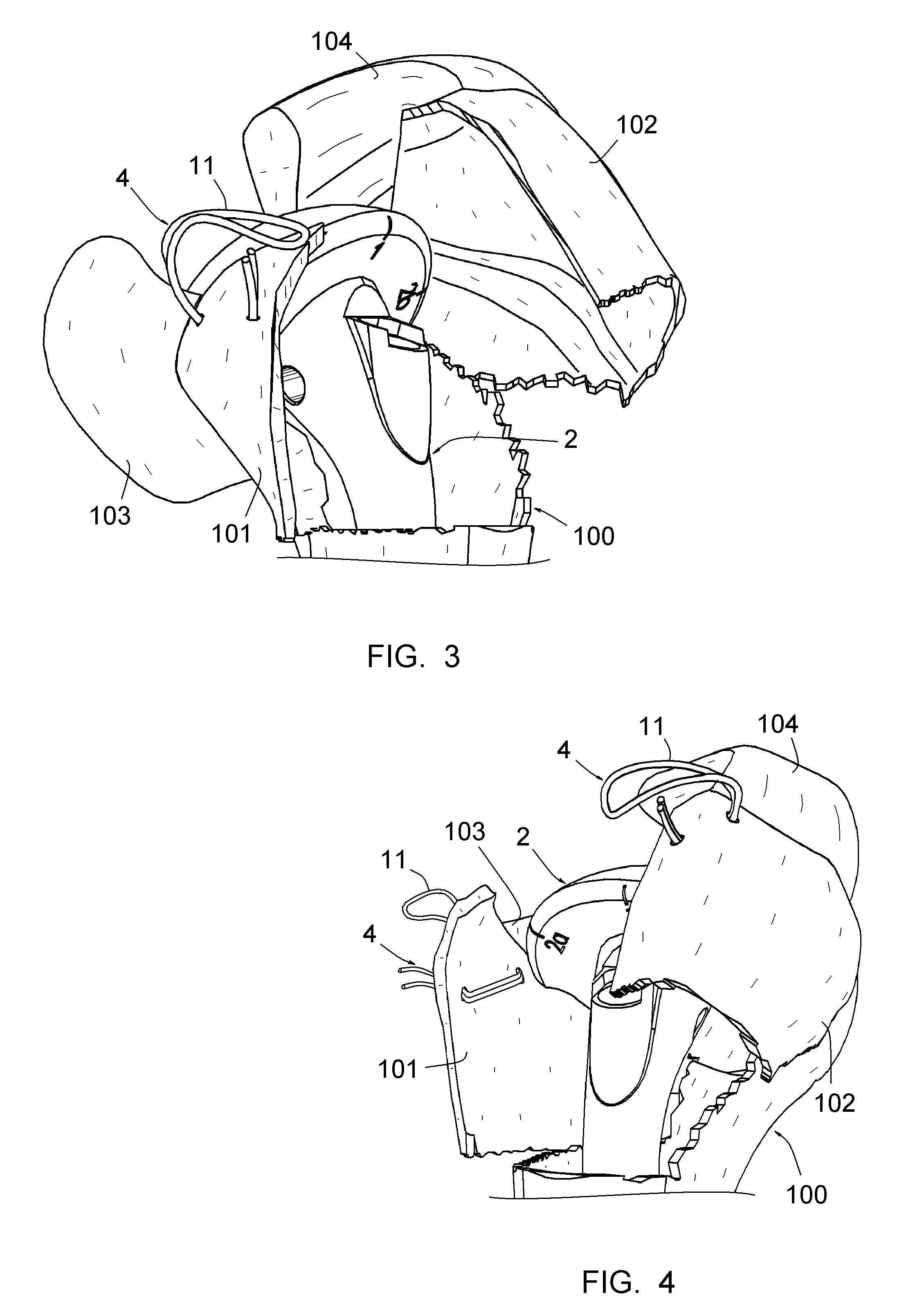
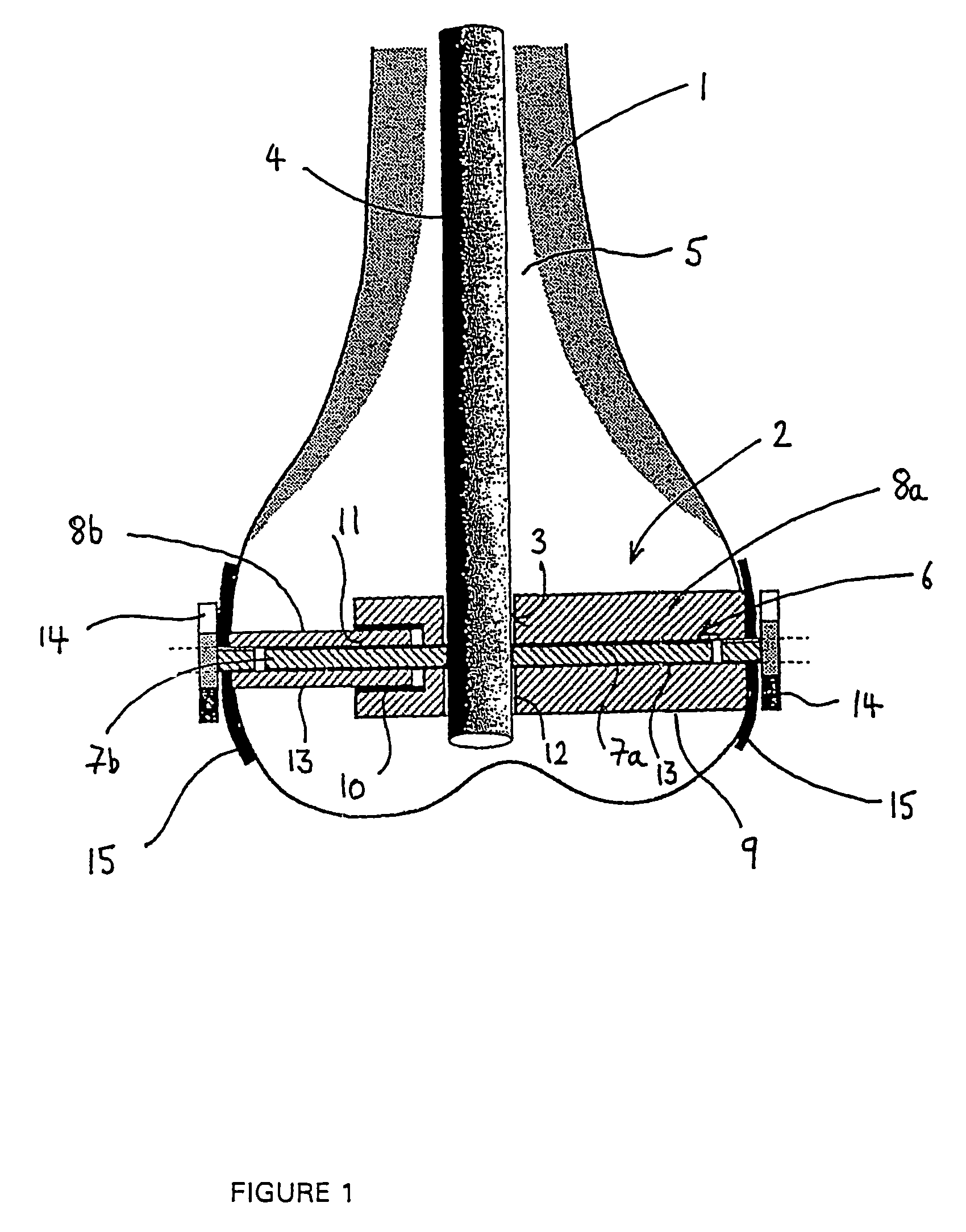
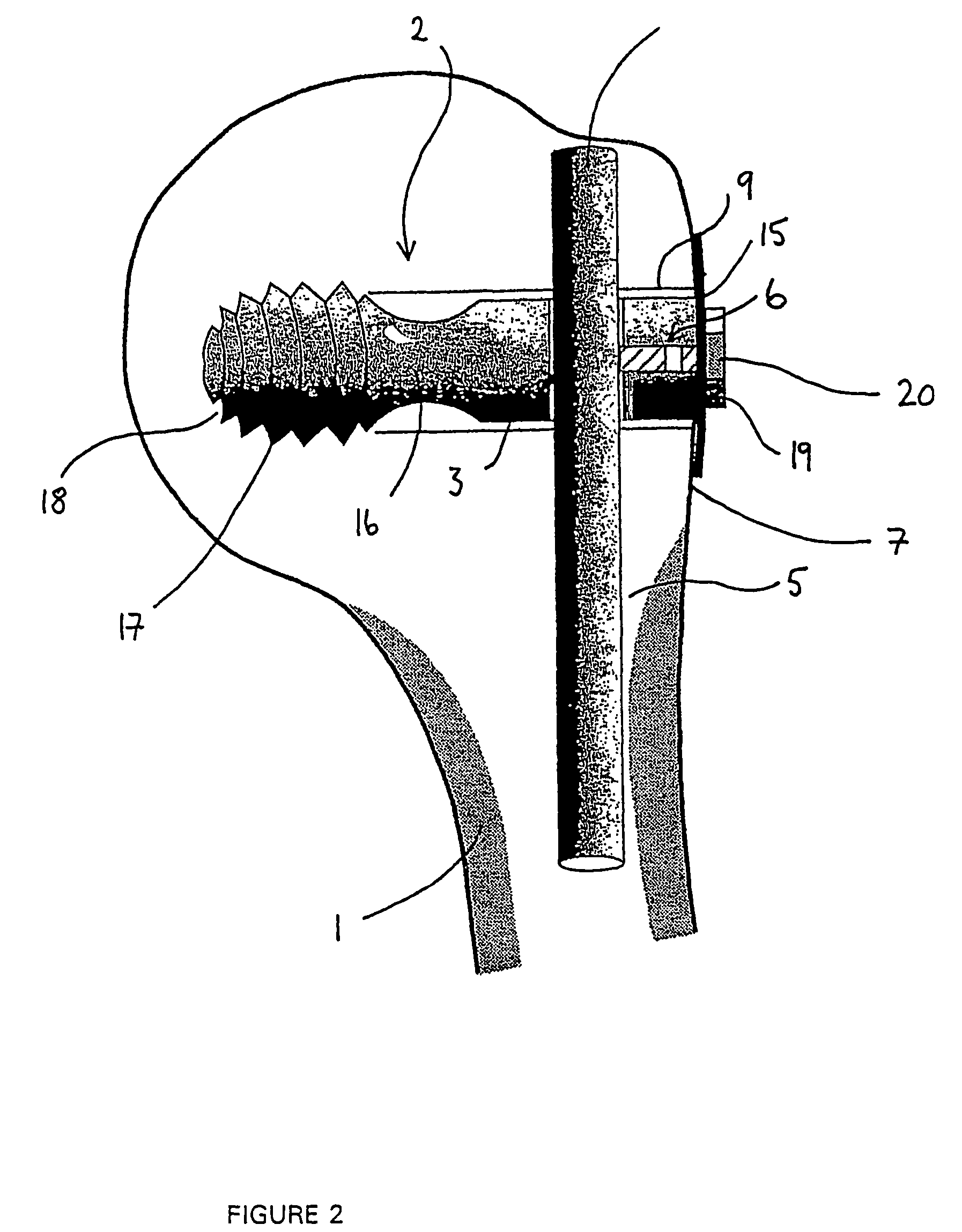
This method comprises the use of a repair equipment including a humeral rod (2) intended to be placed in the medullary cavity of the humerus, comprising at least one hole (6) for receiving a thread (11) for repositioning the tuberosities (101, 102) and for maintaining the latter with respect to the rest of the bone. Said hole (6) is formed in the metaphyseal portion of the humeral rod (2), in the anteroposterior direction thereof; and the repair equipment further comprises a so-called “guying” subassembly (3), to maintain the tuberosities (101, 102) when they re-installed, two second so-called “traction” subassemblies (4), for pulling of the tuberosities (101, 102) one toward the other, and two so-called third “pressing” subassemblies (5), for tackling the tuberosities (101, 102); each of these sub-assemblies comprises a needle and thread (11) connected to this needle, this thread (11) forming a loop.
Owner:FX SOLUTIONS
Methods for repair and regeneration of bone marrow
InactiveUS20090180965A1Promotes bone marrow regenerationPromotes stem cell growthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryProgenitorCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention is directed to a method for treating a tissue or organ in a subject by directly administering an effective amount of an exogenous, decellularized extracellular matrix or a mixture of extracellular matrix and mesenchymal stem cells into the intended site of activity, such as bone marrow cavity. In one embodiment, the invention provides methods of treating bone marrow to increase the number of circulating progenitor and stem cells. In some other embodiments of the invention, the decellularized extracellular matrix to be directly administered is configured to be a time released therapeutic.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices and methods for safely accessing bone marrow and other tissues
A device for safely accessing bone marrow and other tissues is disclosed. Such device comprises a needle assembly, a sensor mechanism, and an actuator configured to engage with the needle assembly via the sensor mechanism to advance a tissue penetrable needle through a first tissue region and into a second tissue region. In one aspect, the first tissue region is a bone cortex and the second tissue region is a bone marrow cavity. The sensor mechanism is configured to disengage the actuator from the needle once the needle has crossed the first tissue region (e.g., bone cortex) into the second tissue region (e.g., bone marrow cavity), thereby preventing the needle from advancing further into the second tissue region. In one aspect, the sensor mechanism is mechanical and comprises a pin assembly comprising a spring-loaded pin that extends through the needle. The pin assembly is configured such that advancement of the distal tip of the spring-loaded pin past the distal tip of the needle causes the actuator to disengage from the needle. The actuator is a rotatable actuator. A catheter-based embodiment of the device can be inserted in body passageways to access tissue internally within the body.
Owner:BEYHAN NIYAZI +2
Metal composite material capable of inducing bone growth and application thereof
ActiveCN103357063AHigh bonding strengthImprove biological activityProsthesisBone structureMetallic materials
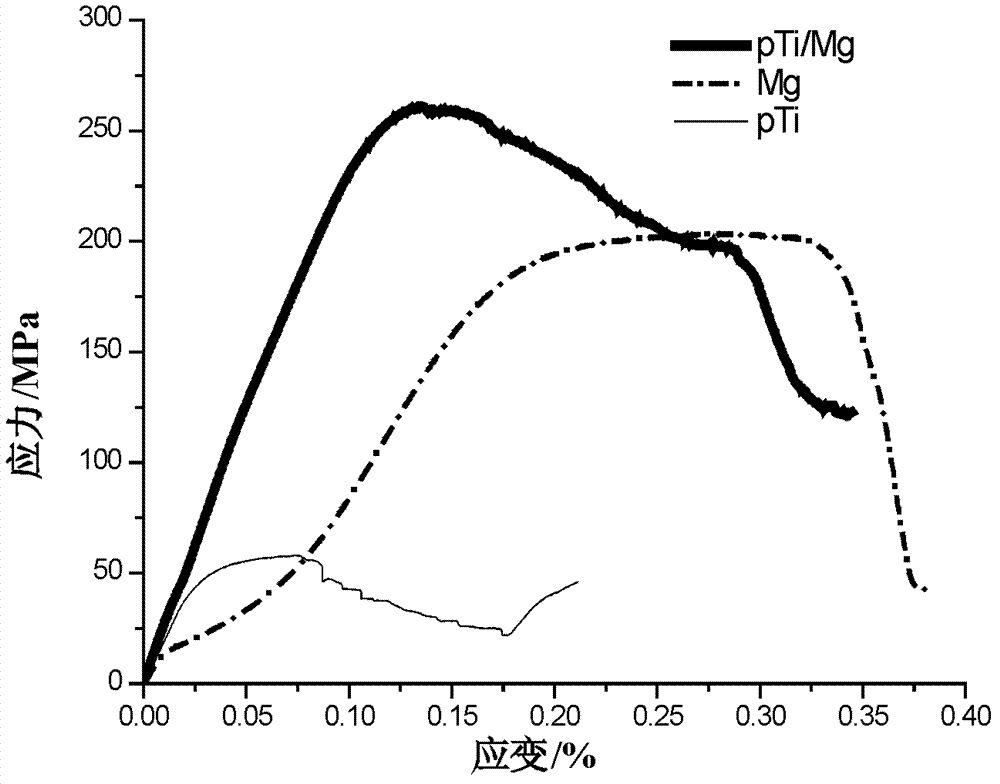
The invention discloses a metal composite material capable of inducing bone growth and an application thereof. The metal composite material is especially suitable for biomedical engineering for human hard tissue defect, comprising an artificial joint, artificial bone, a dental implant, a plastic surgery medical apparatus and instrument, a bone marrow cavity implant and the like. Specifically a double-phase composite material capable of inducing bone growth is provided, a cellular structure is prepared on a clinical medical metal material (titanium, titanium alloy, stainless steel, cobalt-base alloy, nickel-titanium shape memory alloy and the like), magnesium or a magnesium alloy capable of inducing bone growth is filled in the cellular structure, and the composite material in the structure can be used as a solid material, and as the surface / partial structure of a solid metal material. By virtue of the design of the composite material, the bioactivity of an existing medical metal implantable device can be improved; along with the continuous decomposition and bone induction effect of the magnesium or the magnesium alloy in a human body environment, and the bone structure is gradually induced to grow into the cellular structure to enhance the binding strength of the bone tissue with the implant so as to prevent the implant from getting separated, achieve good biological immobilization, and greatly improve the bone integration effect.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Orally implantable intraosseous port
InactiveUS20110076640A1Improve stabilityEliminates risk and necessityDental implantsTeeth fillingHypodermic needleBone marrow cavity
An apparatus for intrasosseous injection of medication to the medullary cavity of a jawbone and for the extraction of medullary bone contents is disclosed. It comprises an implant housing component, a drill bit component and a seal plug component. The implant housing component is implanted into the cortical bone of the mandible. The drill bit component produces a hole within the mandible that initiates the implanting of the implant housing component. The seal plug component that is removably attached to the distal end of the implant housing component allows for repeated access of a hypodermic needle into the mandible.
Owner:JONES ALLAN C
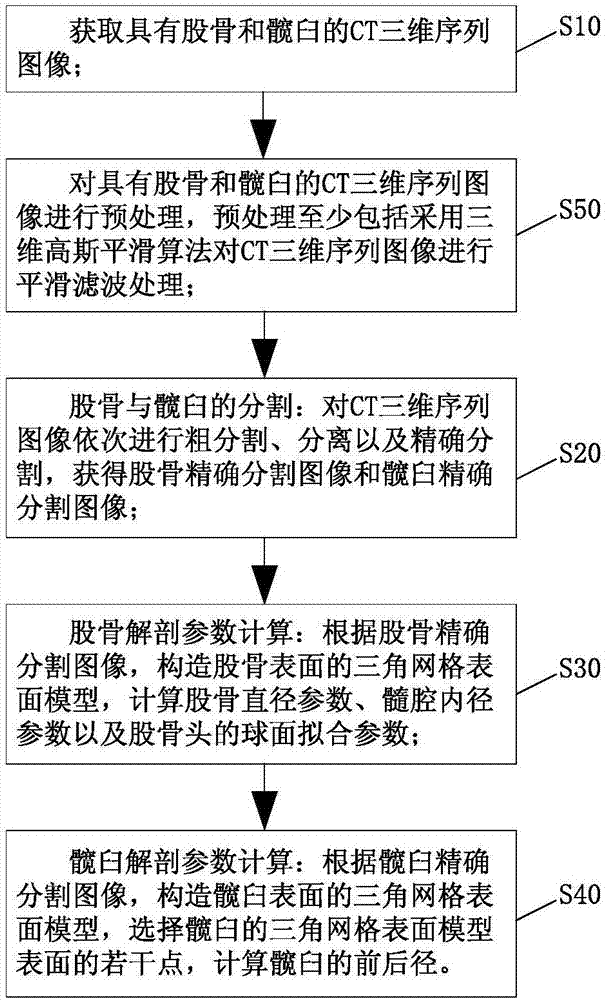
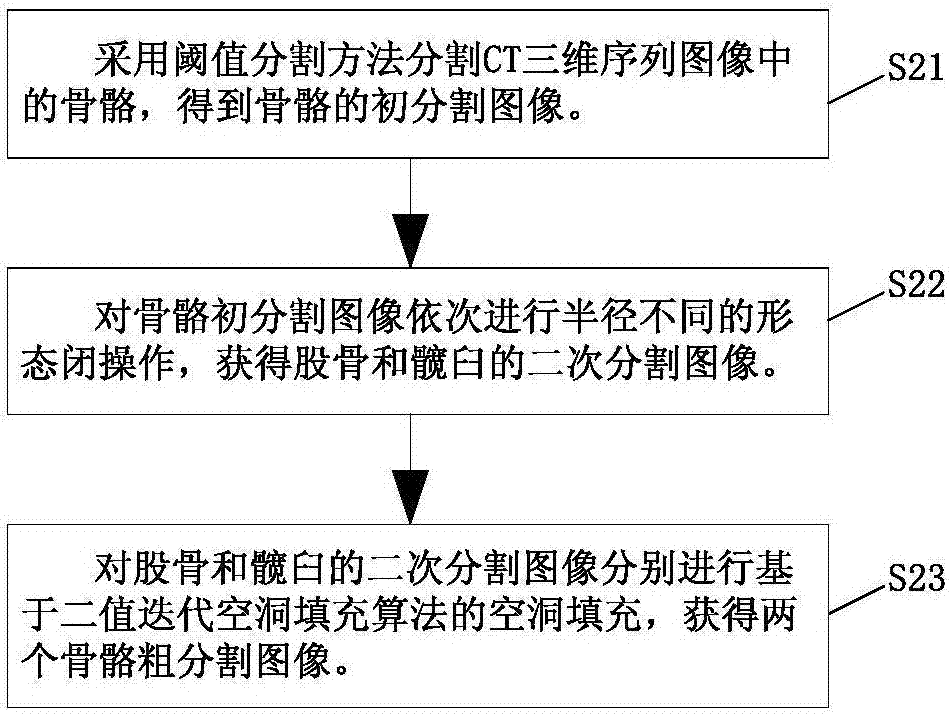
Acquisition method for anatomical parameters of femur and acetabulum based on CT three-dimensional sequence image
ActiveCN107274389AImprove the level of intelligenceImage enhancementImage analysisRight femoral headProsthesis
The present invention discloses an acquisition method for anatomical parameters of femur and acetabulum based on CT three-dimensional sequence image. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring a CT three-dimensional sequence image with femur and acetabulum; segmentation of the femur and the acetabulum: performing coarse segmentation, separation and precise segmentation on the CT three-dimensional sequence image sequentially, to obtain a femoral precise segmentation image and an acetabular precise segmentation image; calculation of anatomical parameter of femur: according to the femoral precise segmentation image, constructing a triangular mesh surface model of a femoral surface, calculating a femoral diameter parameter, a medullary cavity inner diameter parameter and a spherical fitting parameter of a femoral head; and calculation of anatomical parameter of acatabulum: selecting the acetabular precise segmentation image to construct multiple surface points of a triangular mesh surface model of an acetabular surface, and calculating anteroposterior diameter of the acetabulum. According to the method, the CT three-dimensional sequence image is directly processed, and precise segmentation of femur and acetabulum and acquisition of anatomical parameters are rapidly and automatically realized, so as to assist in individualized design and modeling of artificial bone prosthesis.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
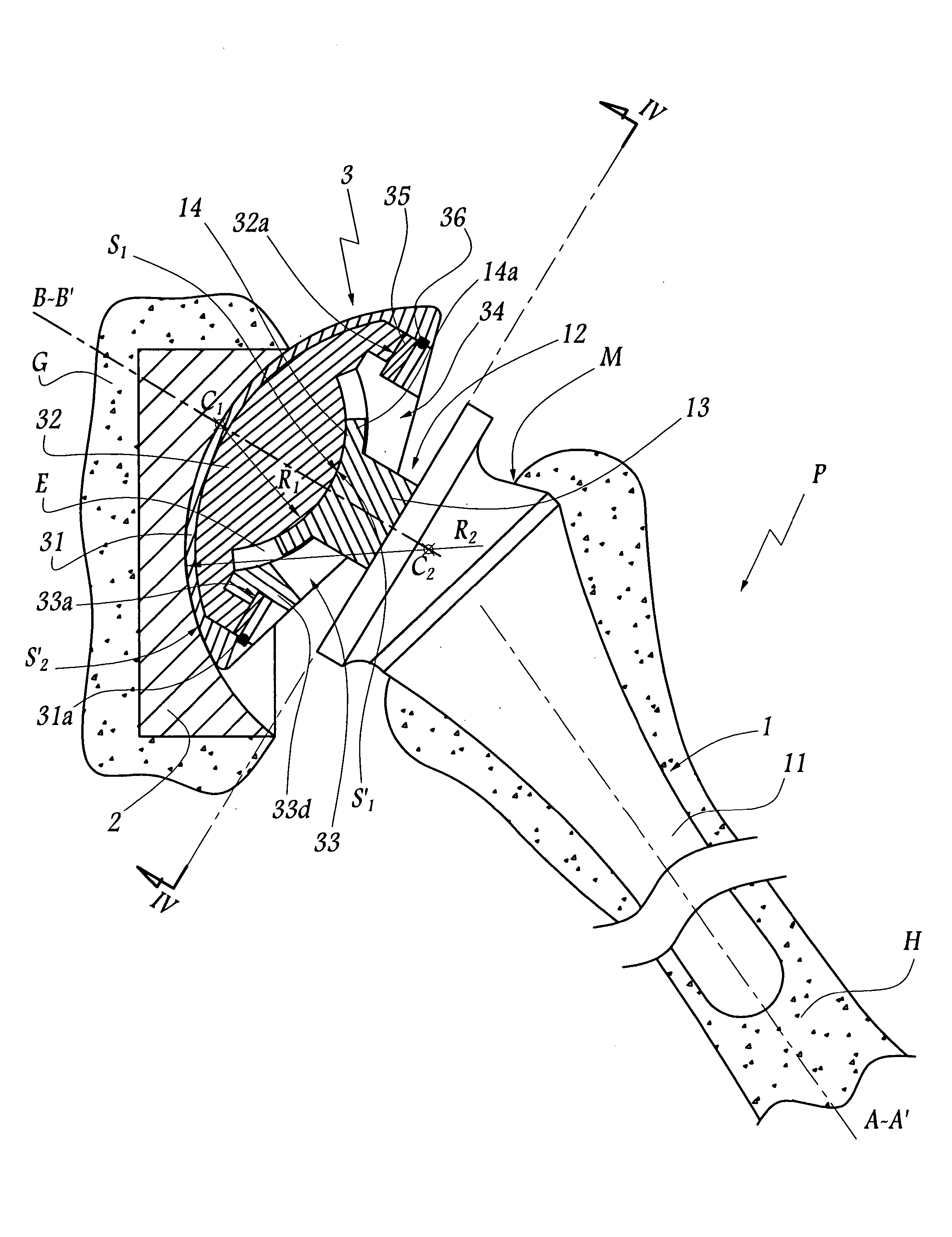
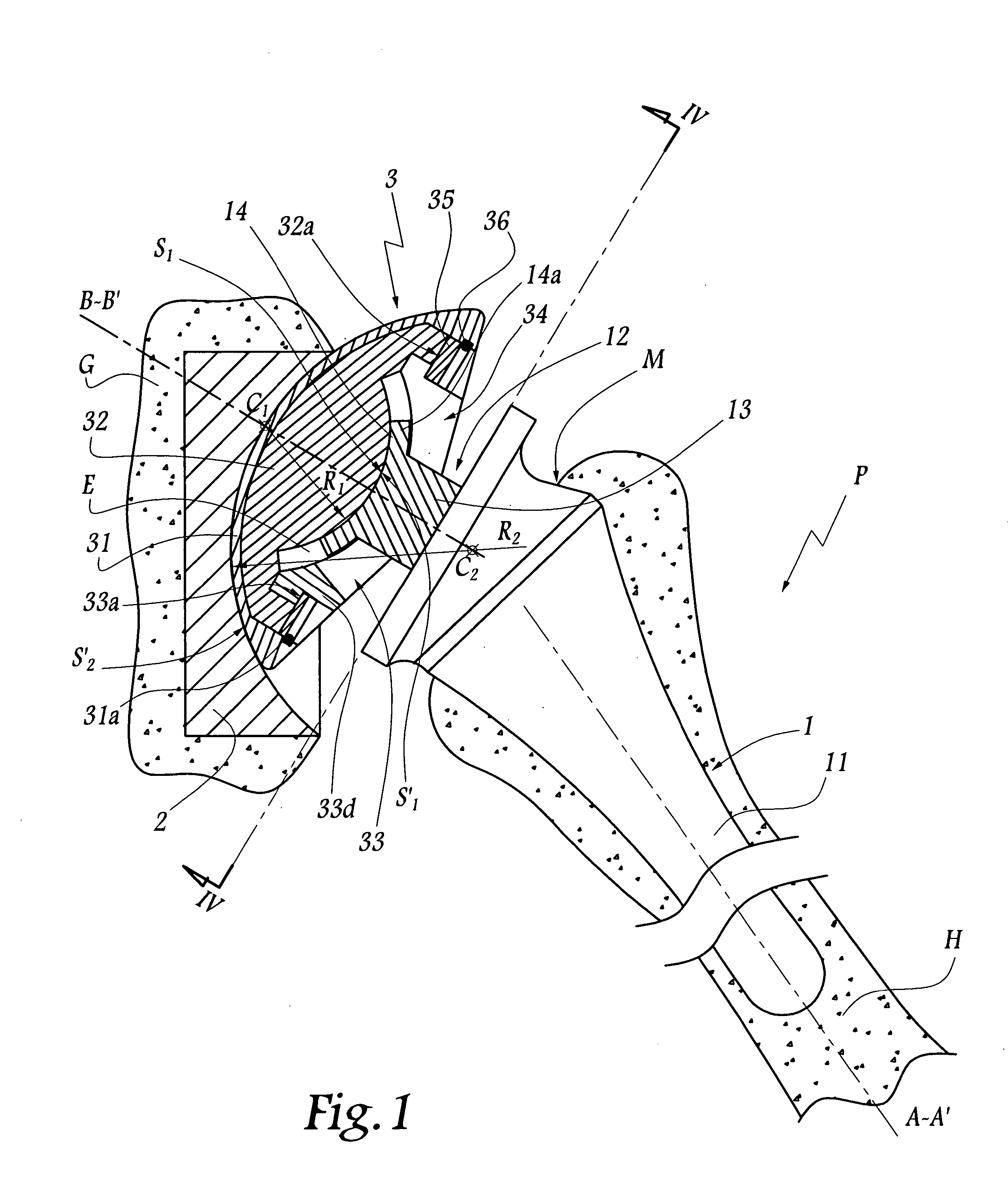
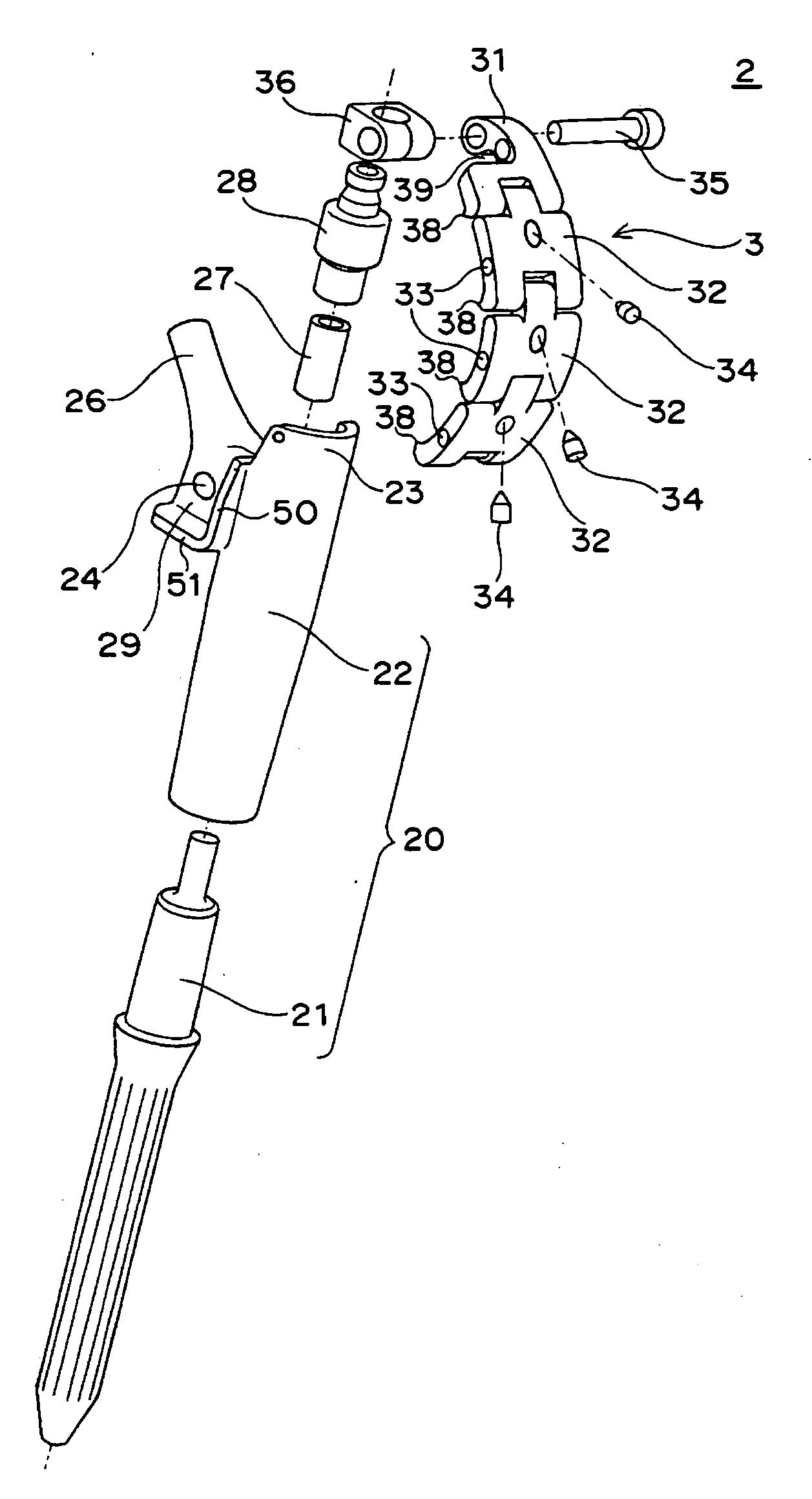
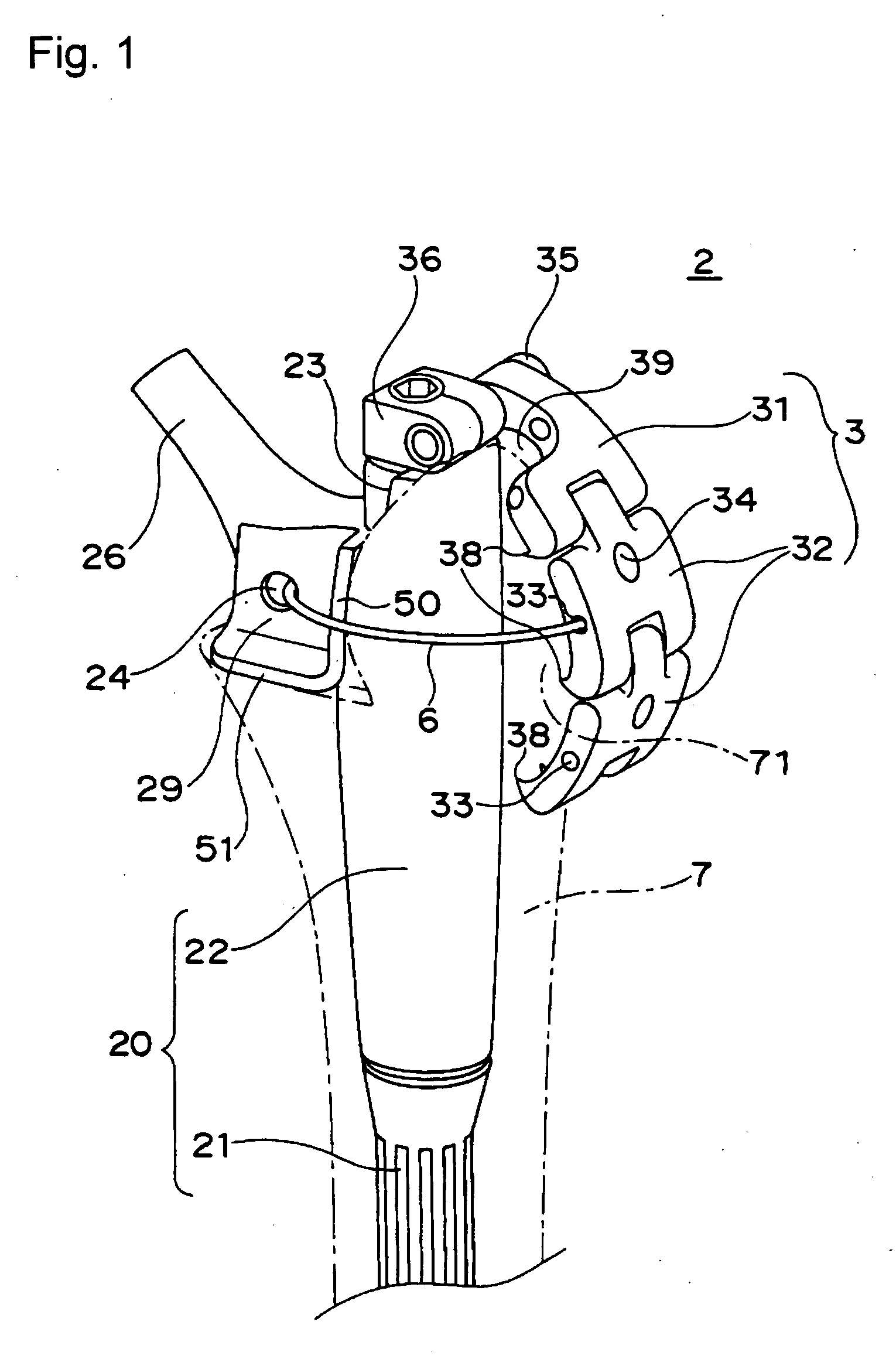
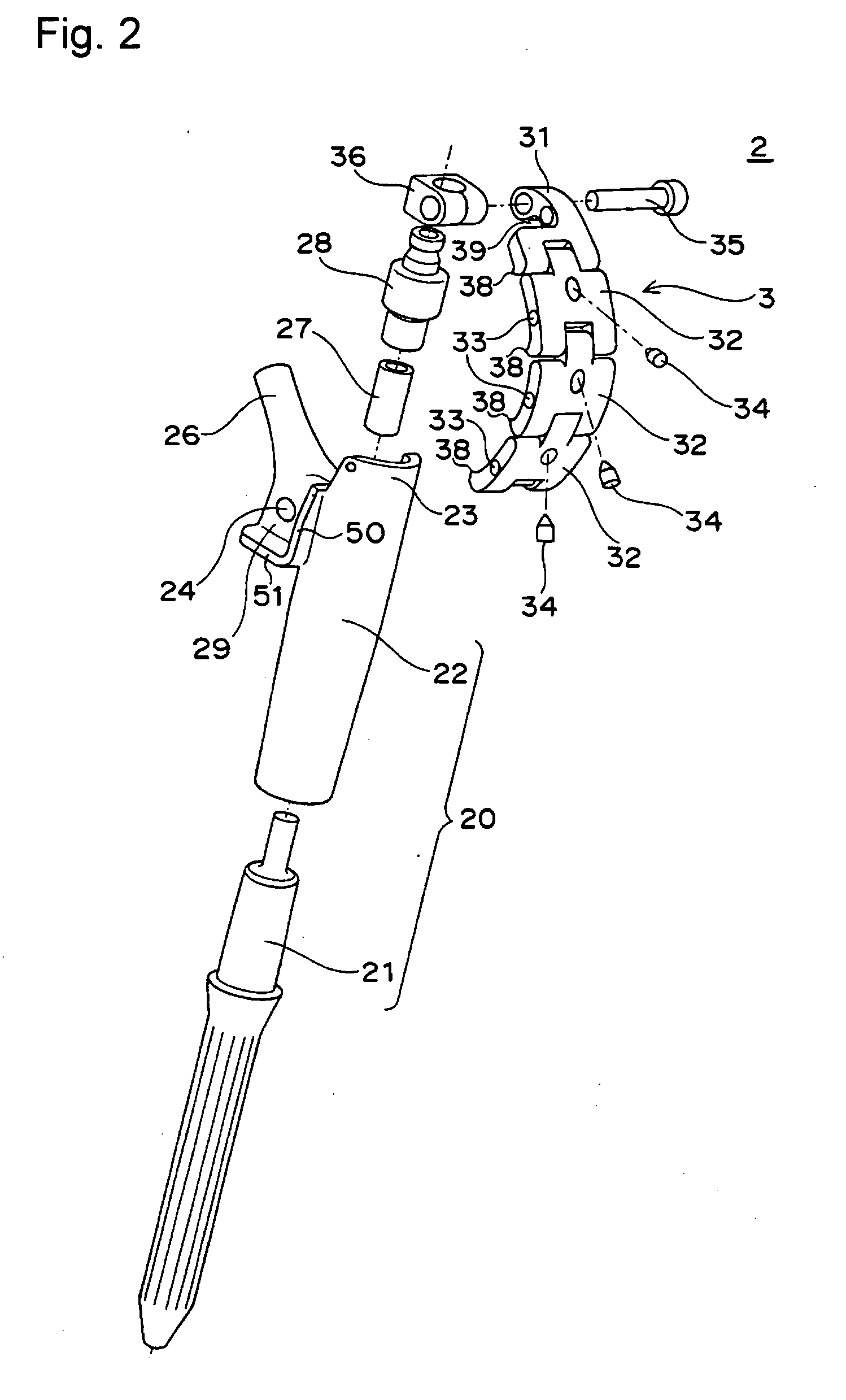
Femoral Stem for Artificial Hip Joint and Artificial Hip Joint Including the Same
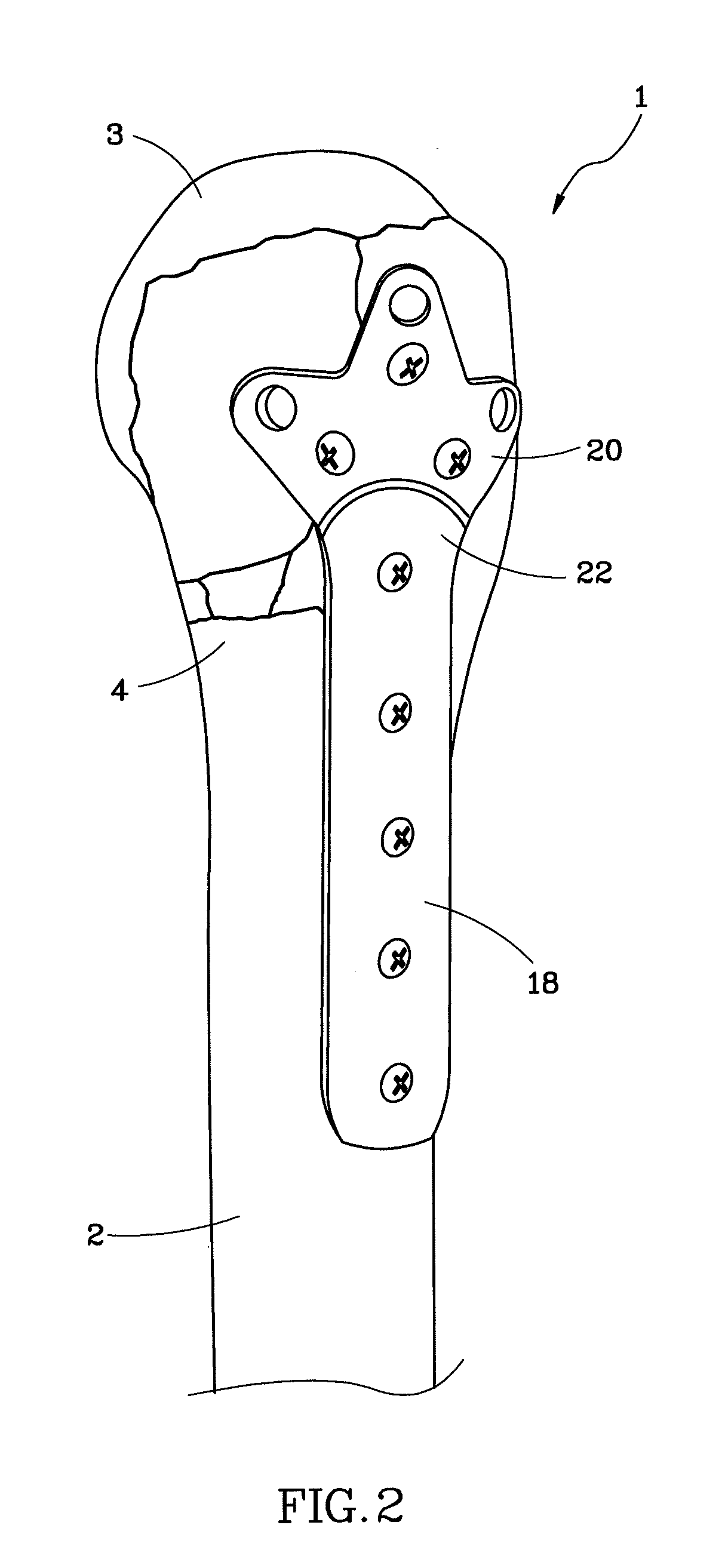
ActiveUS20090164026A1Suitable for treatmentEasy to fixJoint implantsFemoral headsArtificial hip jointsMedicine
A femoral stem 2 for artificial hip joint is provided that is capable of tightly fixing a greater trochanter and is suitable for treatment of transcervical fracture where it is necessary to fix the greater trochanter. The femoral stem 2 comprising: a stem member 20 including a distal part 21 of the stem member which is inserted in a medullary cavity of a femur and fixed therein and a proximal part 22 of the stem member which has a neck 26 for fixing an artificial head and is positioned at a proximal end of the distal part, the distal part and the proximal part being integrated or separable; a plate fixing portion 36 which is detachably attached at a top of the proximal part; and a greater trochanter plate 3 for depressing the greater trochanter 71, the greater trochanter being fixed to the plate fixing portion 36 at a certain angle or fixed to the plate fixing portion so as to adjust an angle. Since the greater trochanter plate 3 is fixed onto the femoral stem 2 of the present invention, the greater trochanter is tightly fixing and thus the fixation can be stabilized. Furthermore, since the greater trochanter plate 3 is fixed at the top of the proximal part 22, the greater trochanter plate 3 covers the top of the greater trochanter 71 when the greater trochanter 71 is fixed. Therefore upward displacement of the greater trochanter by a gluteus medius musculus can be effectively suppressed.
Owner:MIKAMI HIROSHI +1
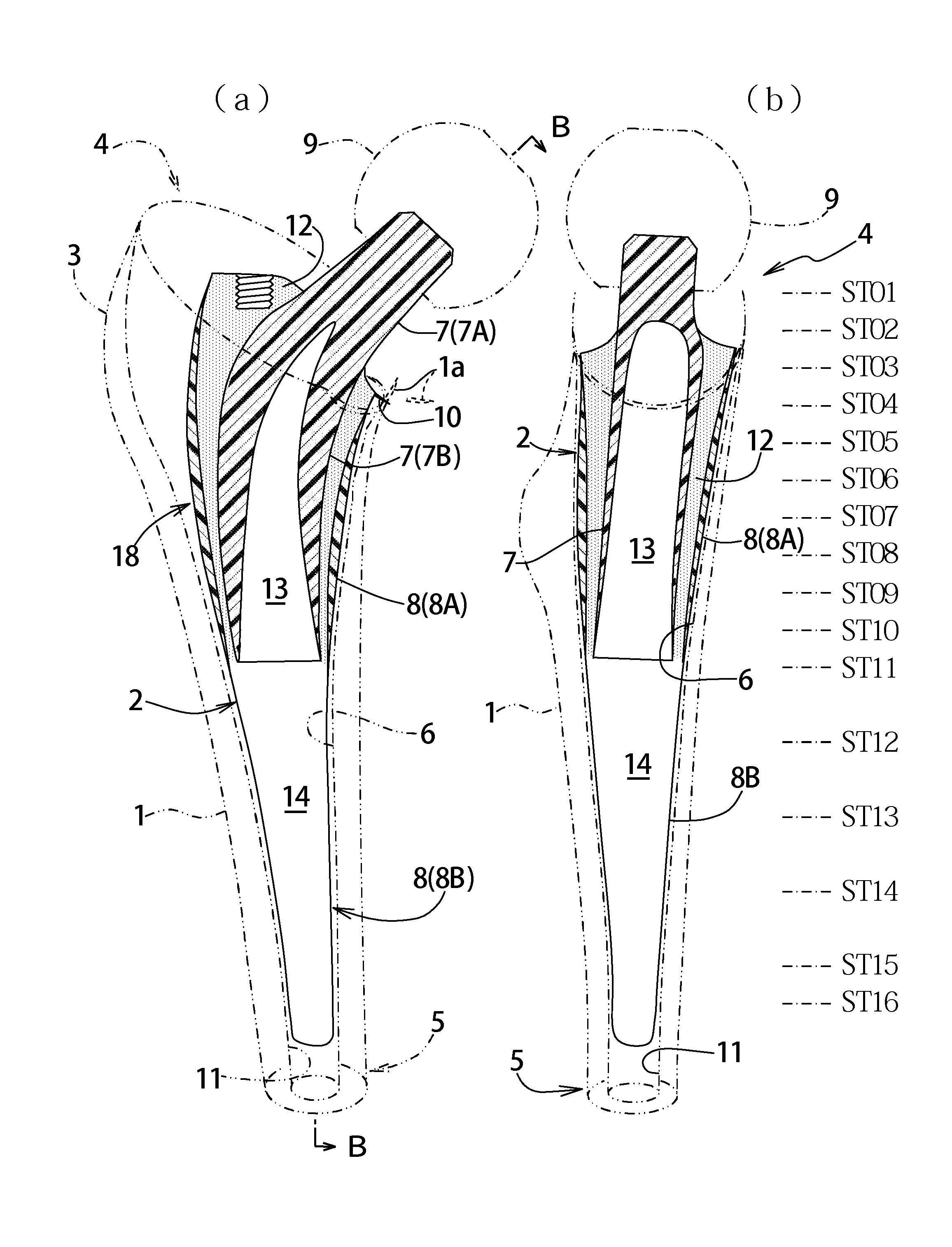
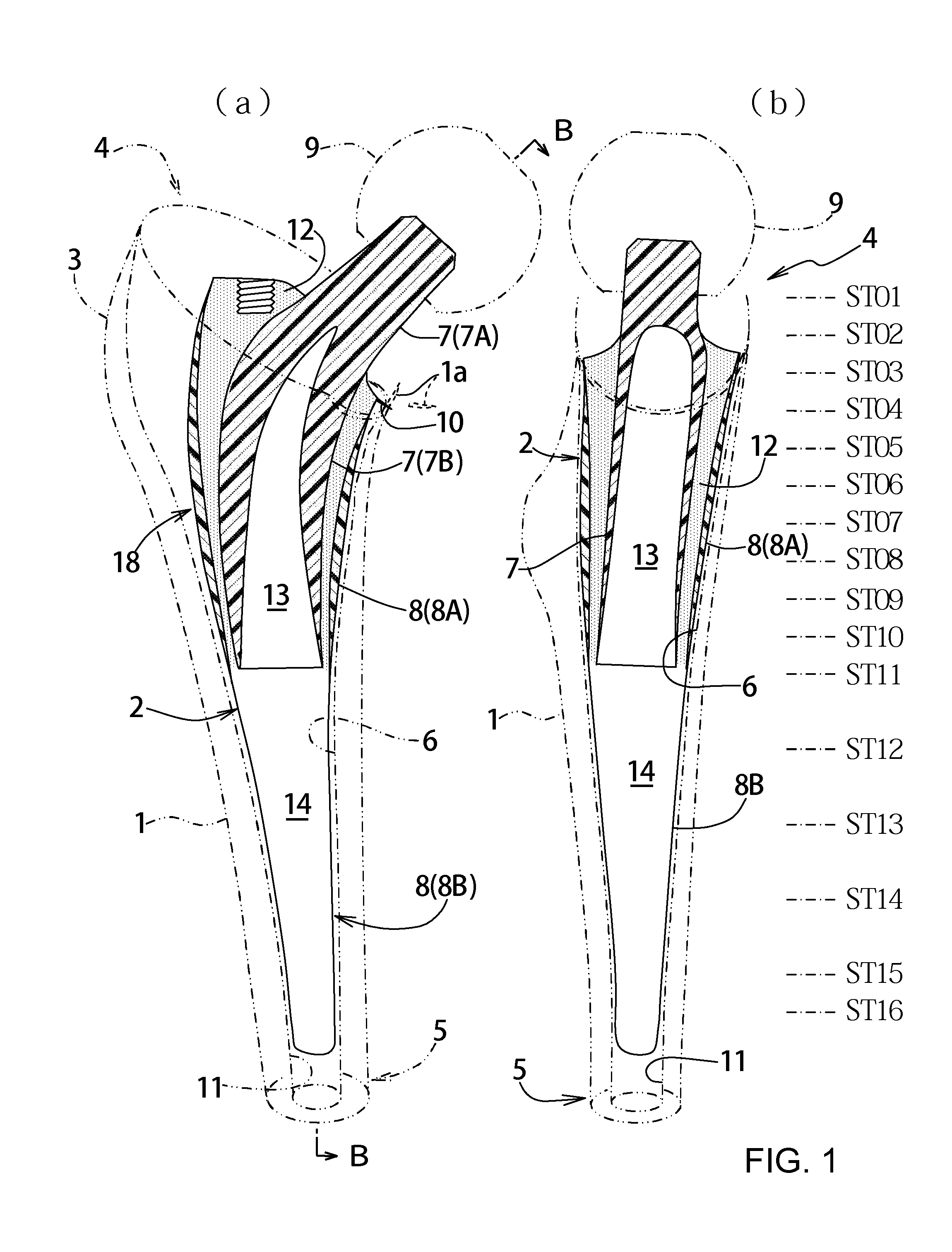
Artificial cementless hip prosthesis stem
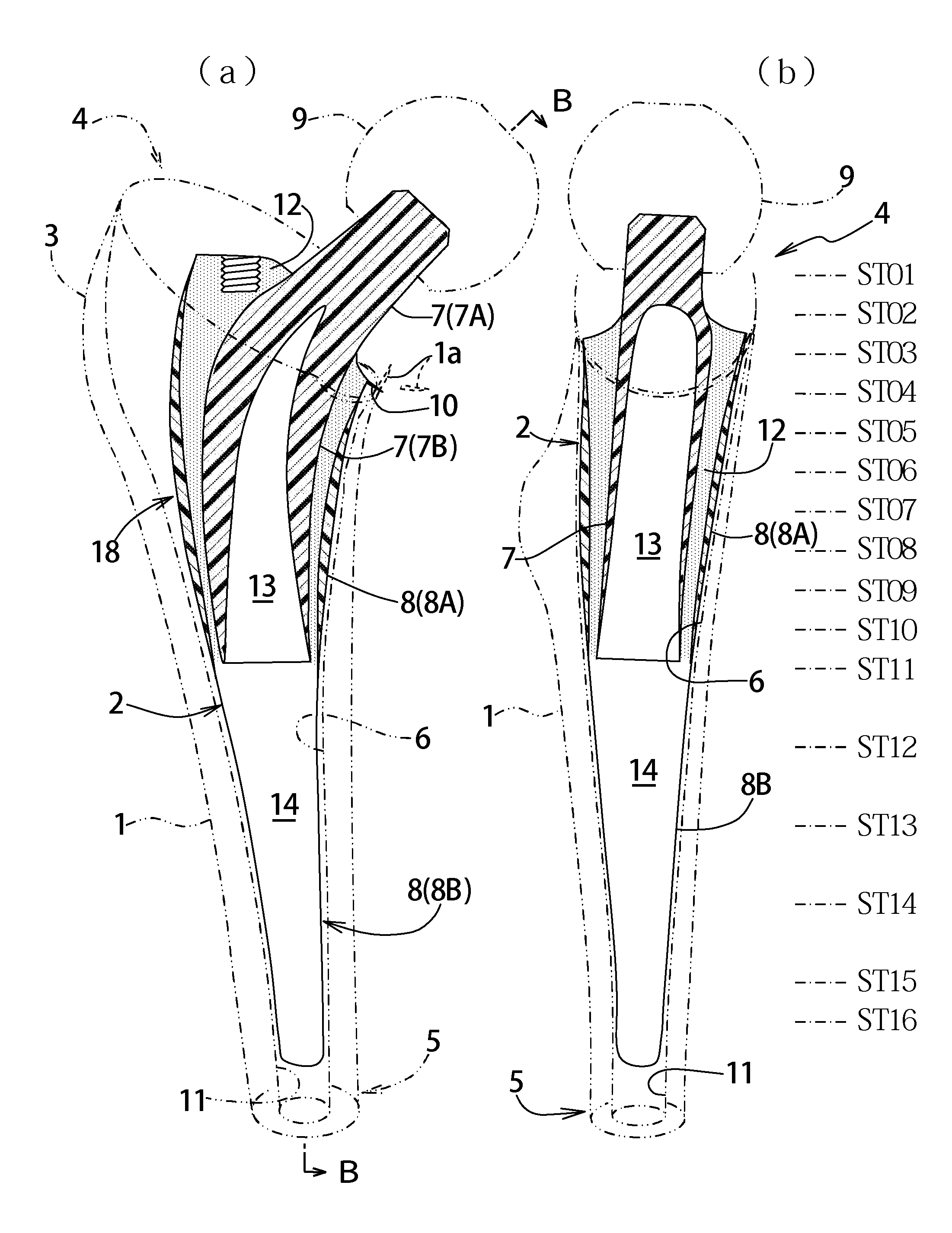
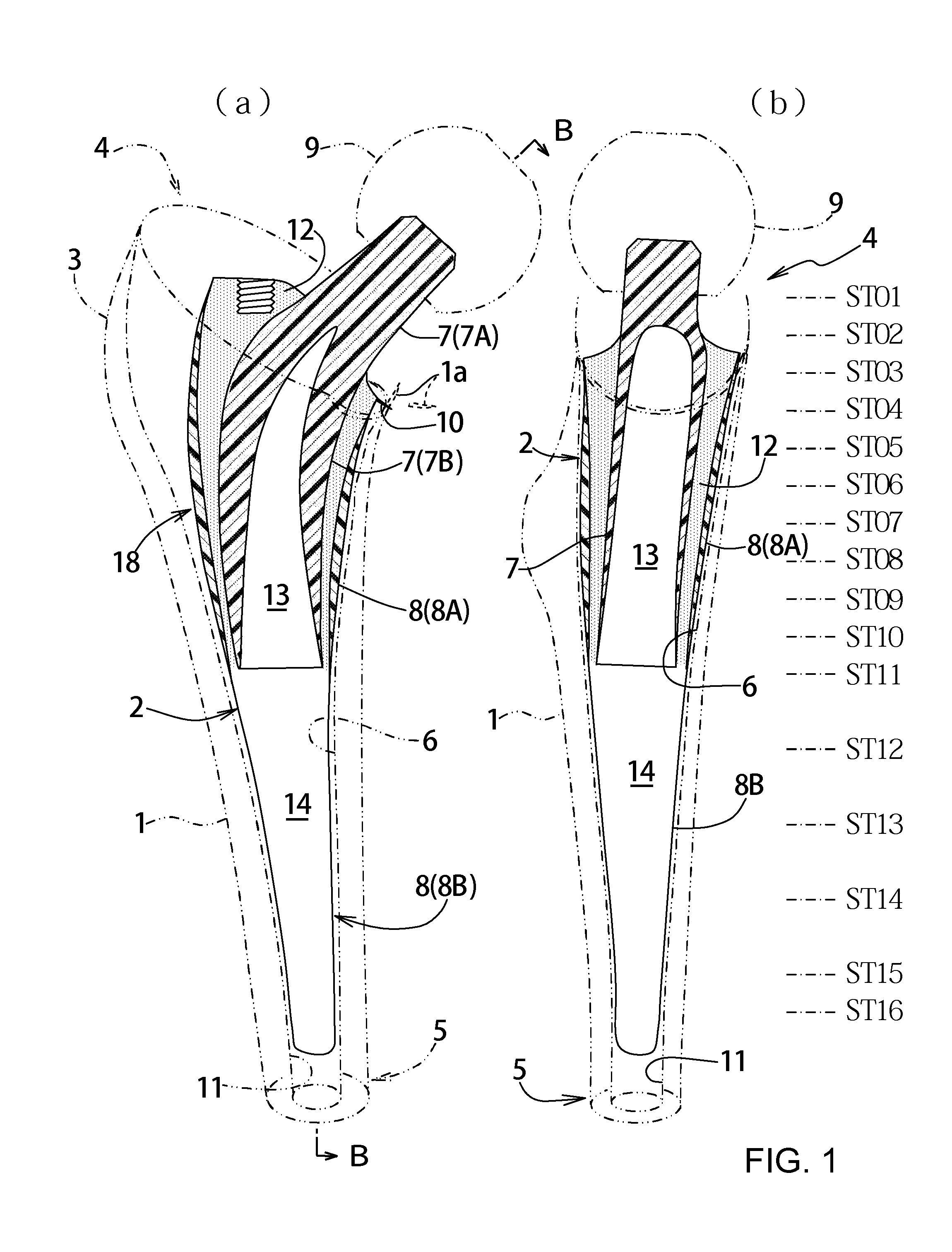
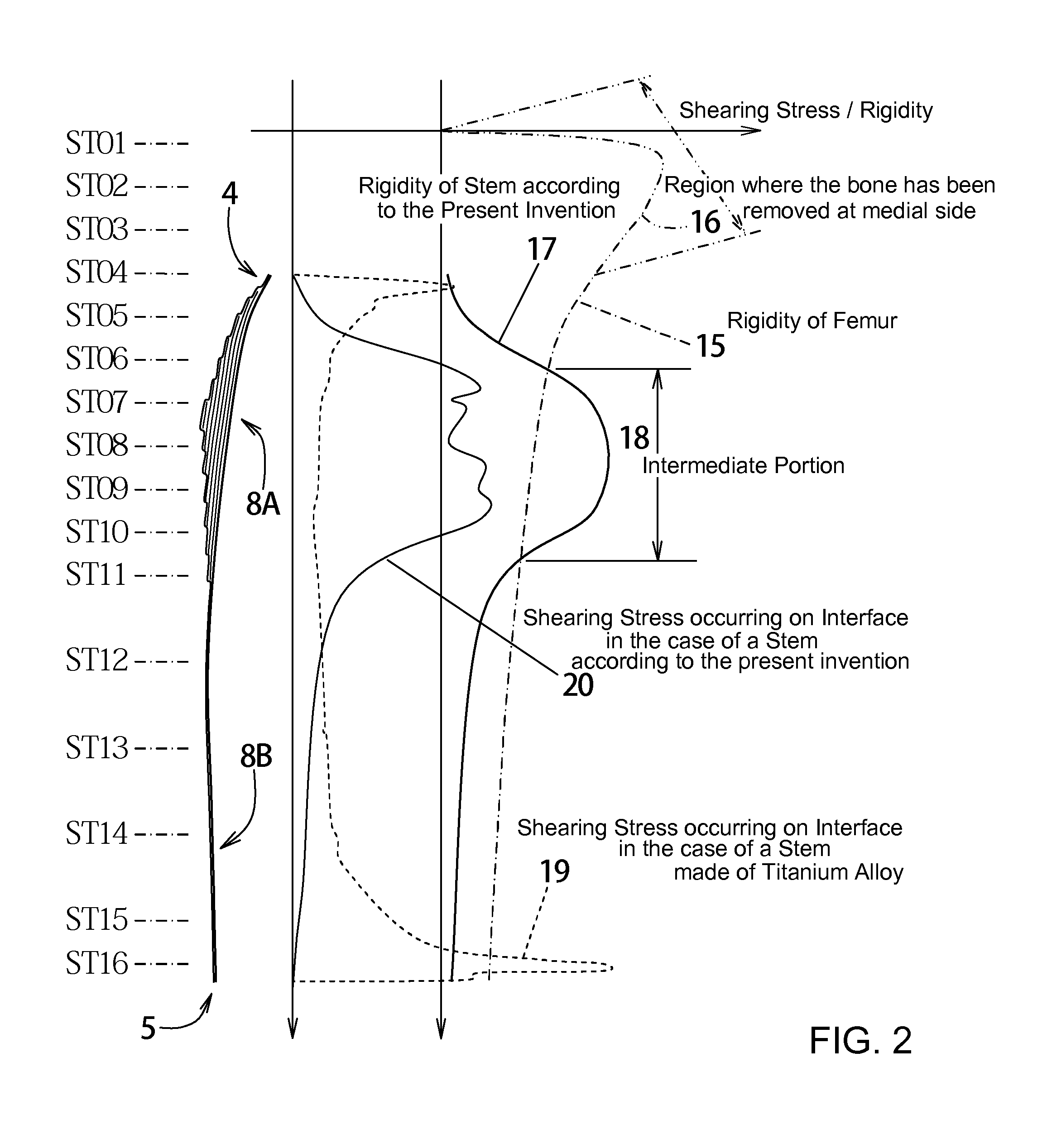
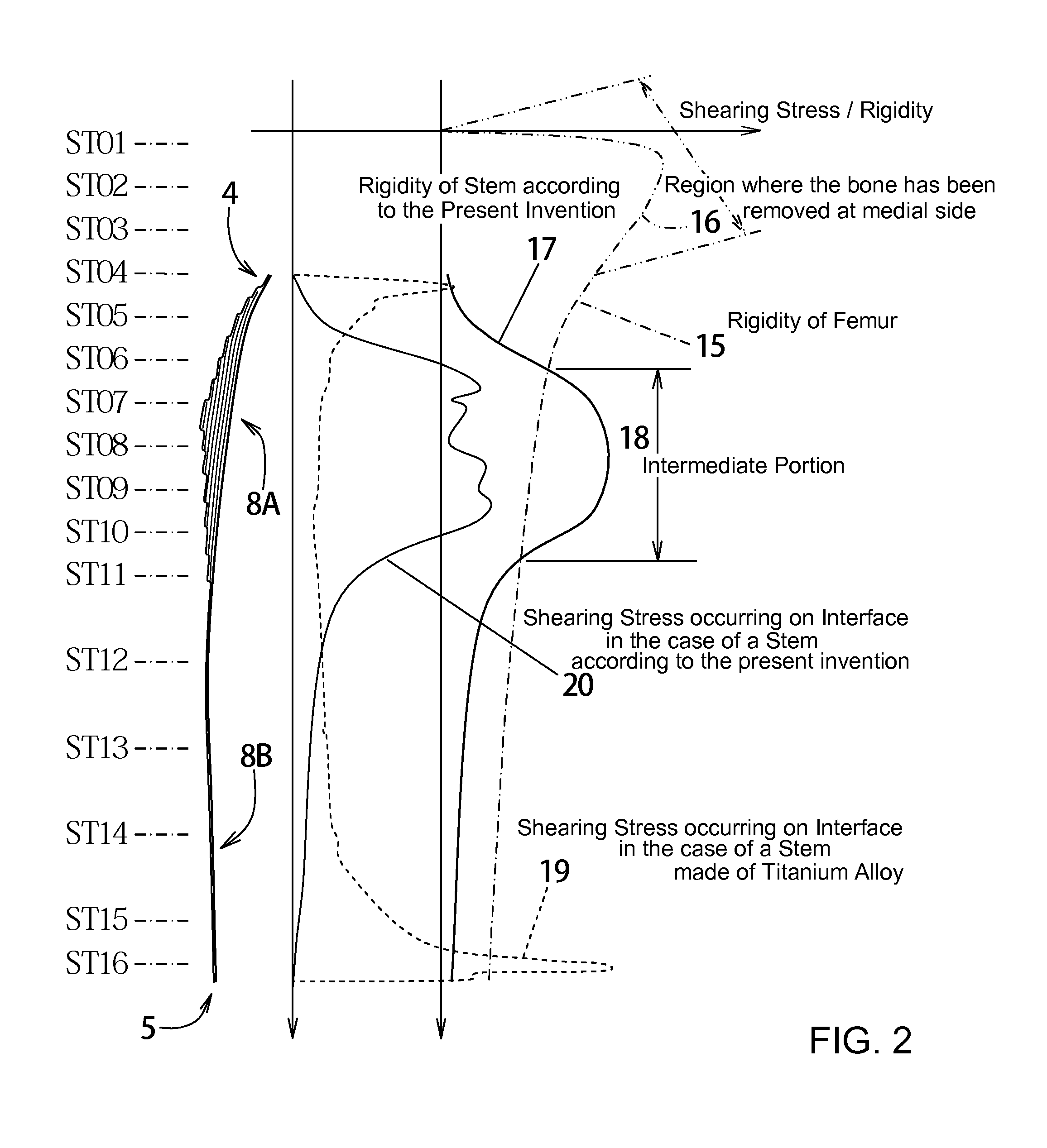
The purpose of the invention is to eliminate not only the shearing stress concentration occurring at a distal end of a stem but also that at a proximal end thereof so that a load acted on a hip joint can be distributed collectively on the proximal portion of the stem corresponding to transmission route in a normal state and the range of variation of the stress distribution on the proximal portion comes to be as narrow as possible on the whole. An artificial cement-less hip prosthesis stem which comprises an inner construct 7 reacted with the load acted on the hip joint and an outer construct 8 transmitting the load acted on the inner construct to a femur 1. The former construct has an inner body 7B reacted with the load transmitted from a neck 7A. The latter construct has both an outer body 8A which is bell mouth-shaped toward epiphysis so as to surround the inner body 7B and a leg 8B extending toward medullary cavity. The torsional rigidity given to the proximal end and the distal end of the outer body 8A and the leg 8B is regulated lower than the torsional rigidity given to the intermediate portion 18 of the outer body 8A,
Owner:B I TEC
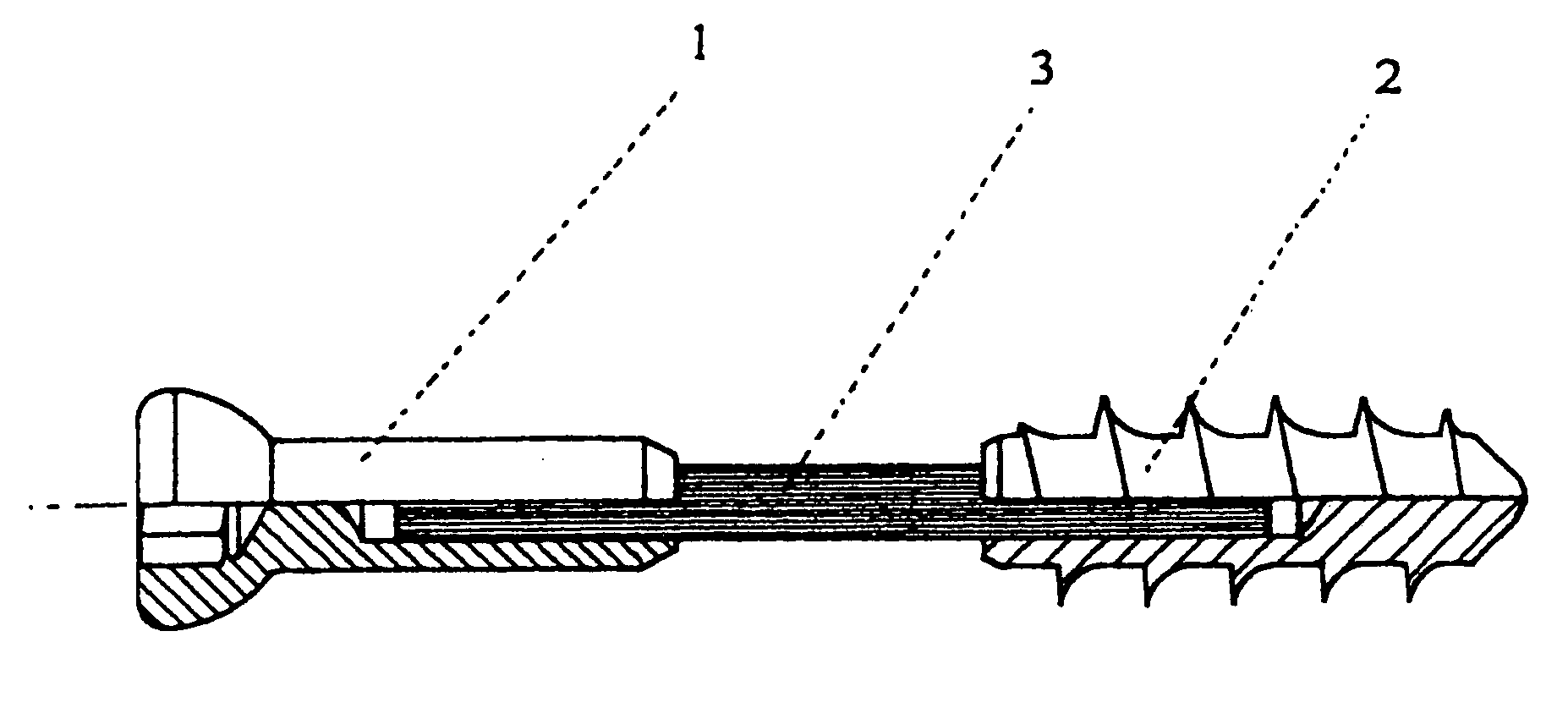
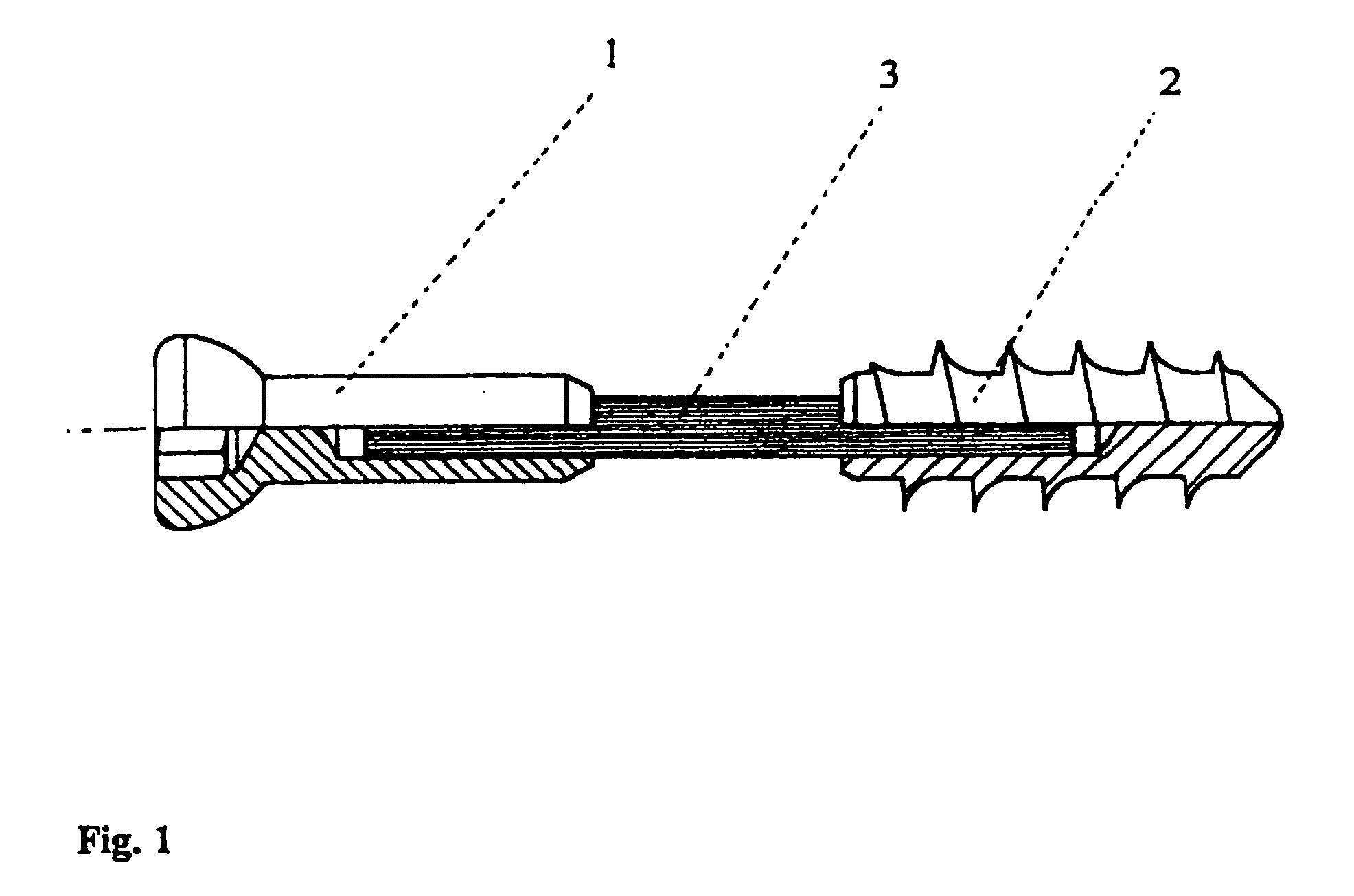
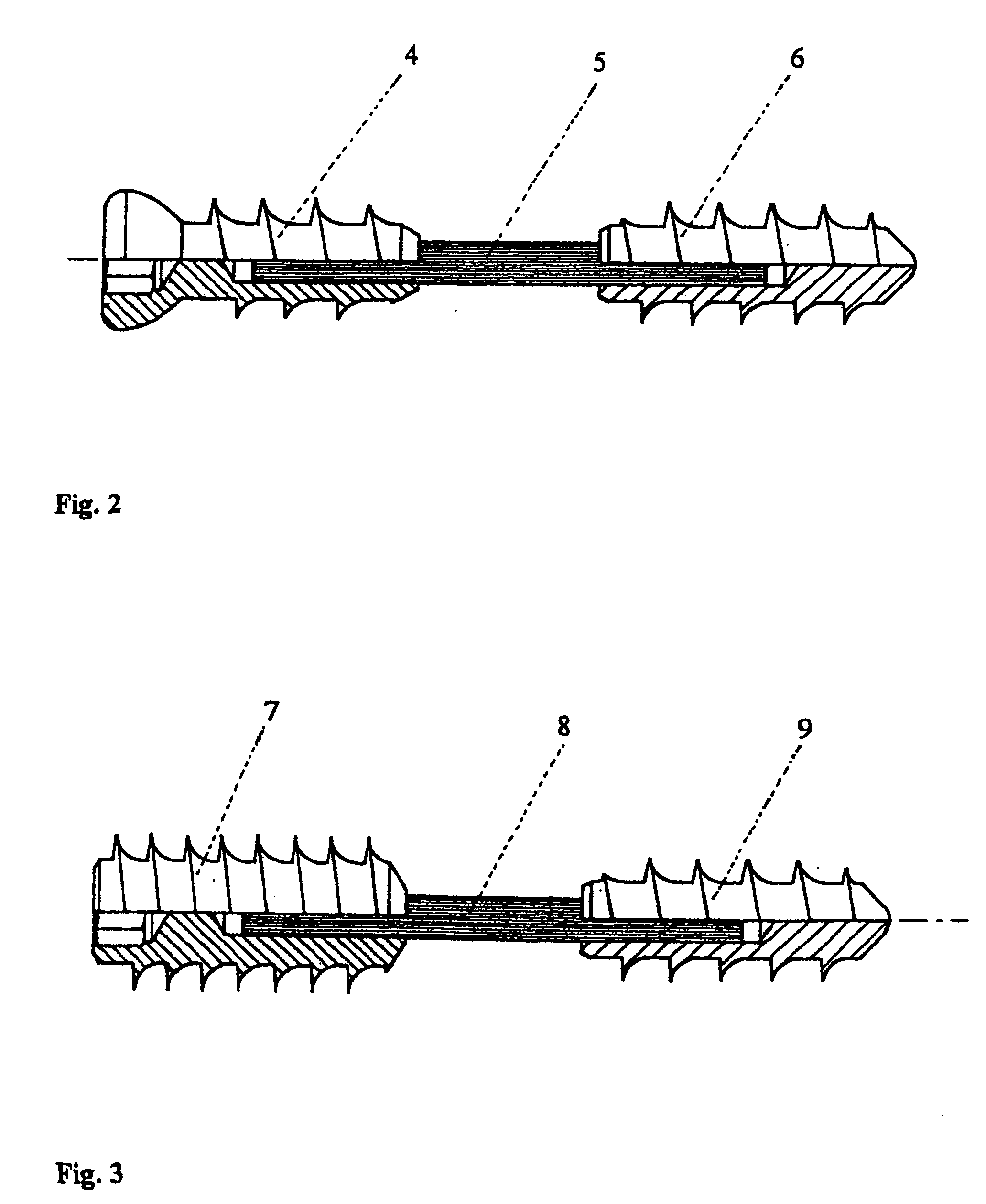
Method for Treating a Fracture of a Bone Having a Medullary Canal
A method for treating a fracture of a bone with a medullary canal. A first and a second group of three elongated monocortical pins are provided. Each pin has a stem with a first end portion having a conical shape with an external thread for insertion into a cortical portion of a bone. Each pin of the first and second group of three monocortical pins is inserted a predetermined distance from the bone fracture, and penetrates only into the cortical portion of the bone without reaching the medullary cavity, the pins of the first and second group being inserted such that they are not coplanar to each other. The stems of the pins of the first and groups are blocked to a first and a second common clamp element respectively. The first and second clamp elements are joined to a common rod to form a rigid external fixation system.
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
Femoral prosthesis component
InactiveUS20060229732A1Easy to disassembleJoint implantsFemoral headsTongue and grooveBone marrow cavity
A femoral prosthetic component of a replacement hip joint comprises a stem for fixing in a medullary cavity. A separate proximal element is provided with a neck for receiving a modular ball head or having an integral ball head. A dove tail-shaped system is provided for securing the proximal component to the stem which includes a sliding tongue and groove joint. The tongue being provided on the stem by an undercut rail which extends in a medial-lateral direction and the groove being provided in the separate proximal element. The tongue and groove being tapered along their lengths.
Owner:BENOIST GIRARD & CIE
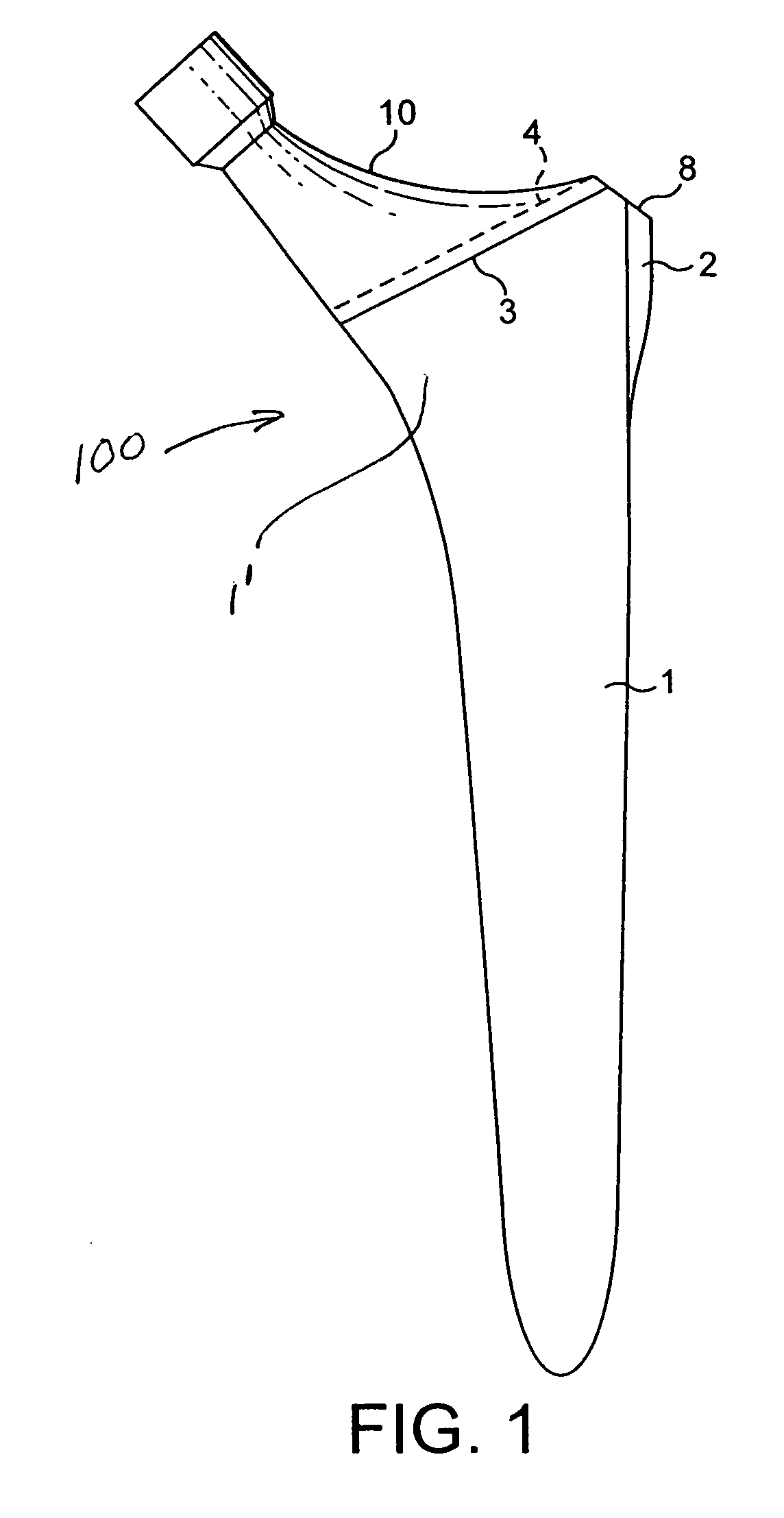
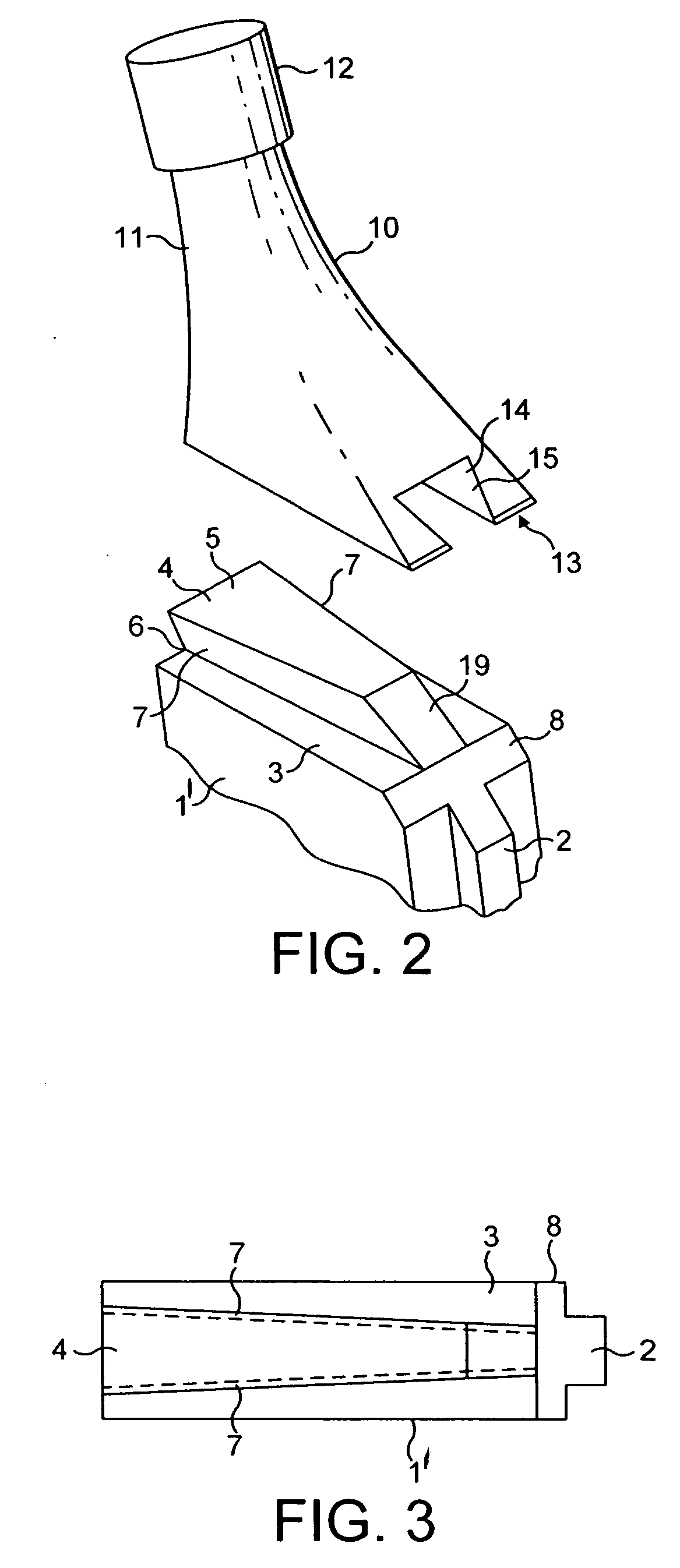
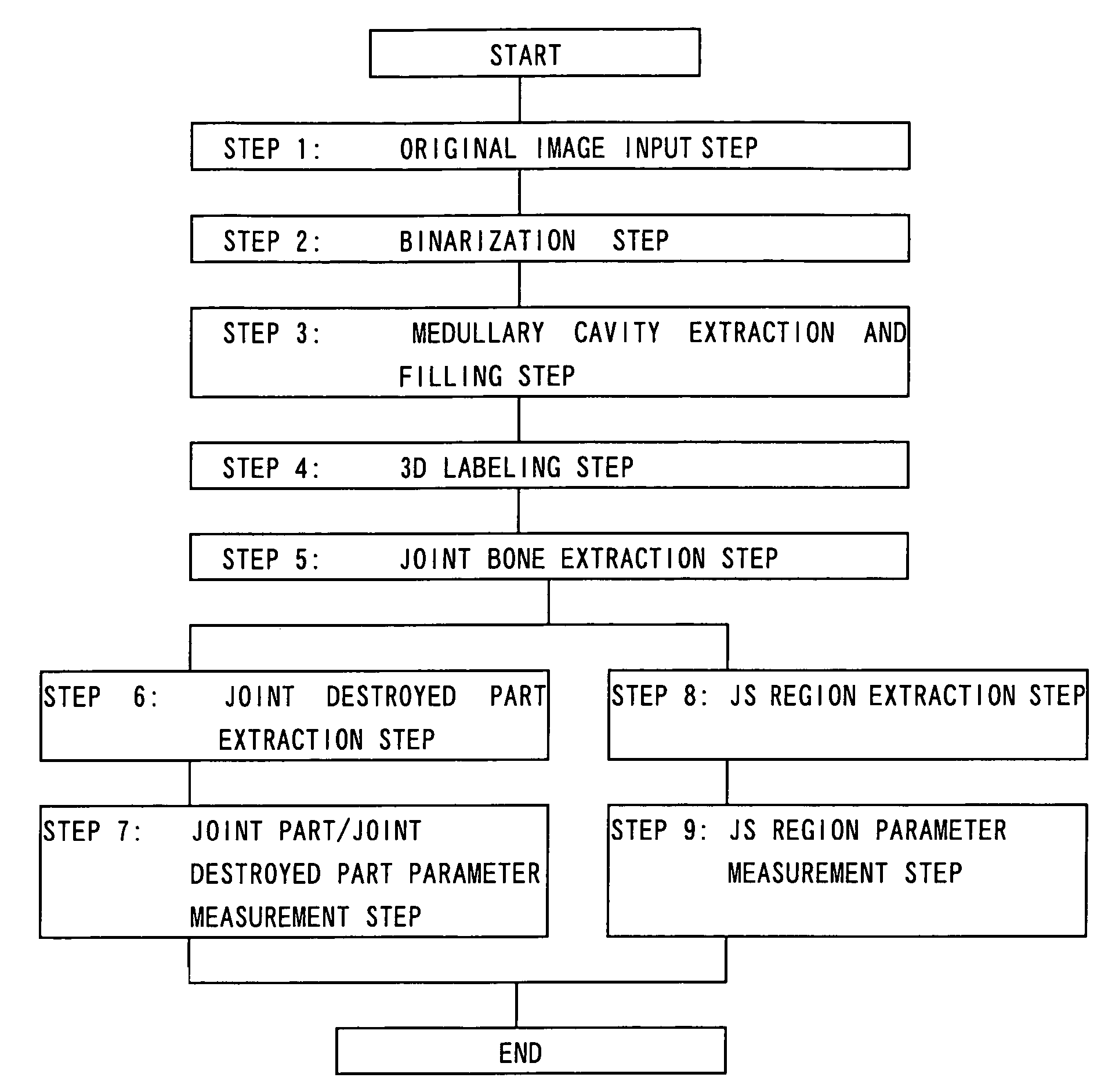
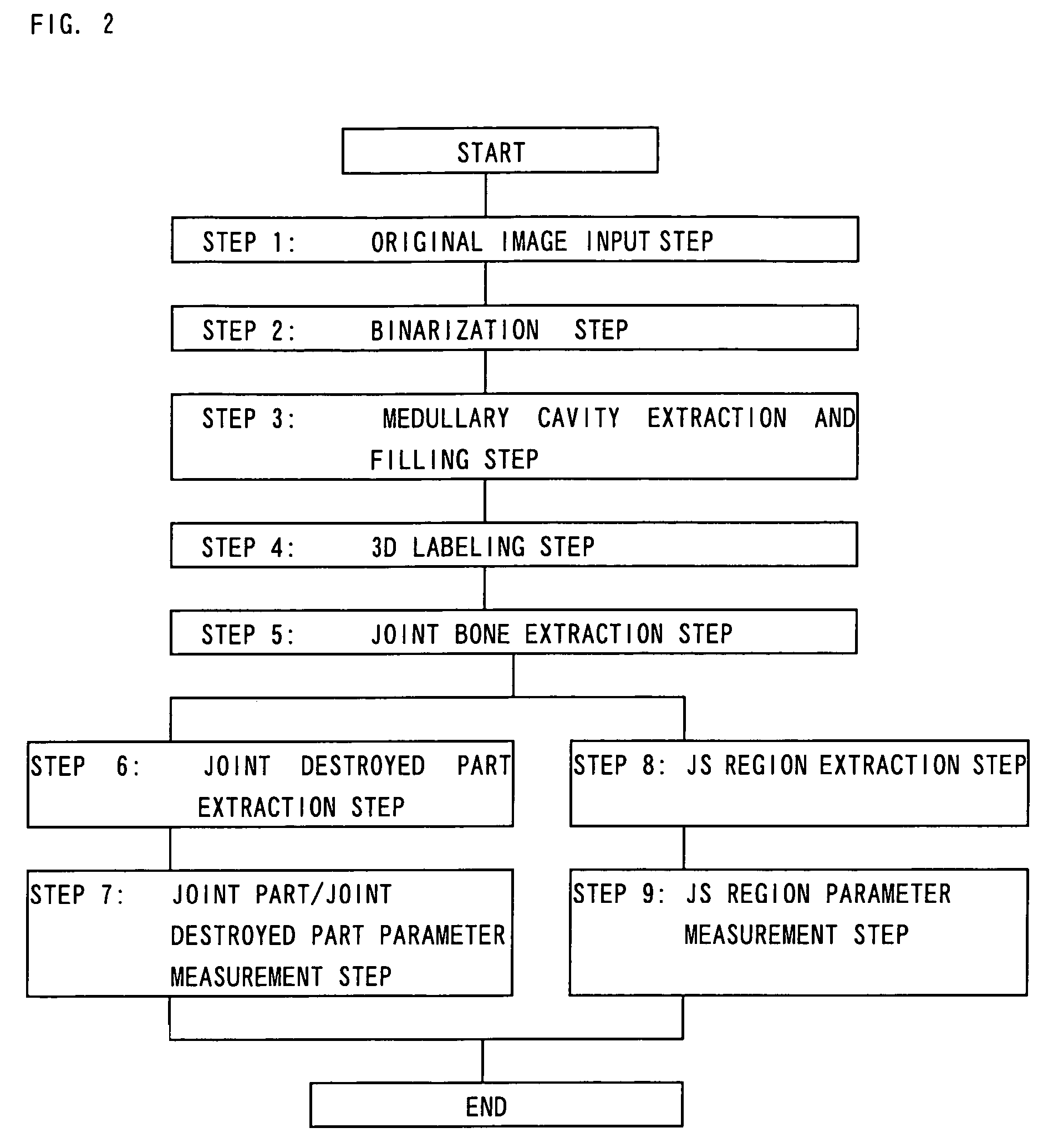
Three-dimensional joint structure measuring method
A method enabling a destroyed part of a joint or joint cartilage to be extracted accurately and at a high speed with a good repeatability and enabling quantitative and simple 3D analysis of the joint and the destroyed part, that is, a method of 3D image processing comprising filling in a medullary cavity region, comprised of a hollow region inside a joint, of a digitalized image of a cross-section of the examined joint using the Expansion and Shrinkage method, performing 3D labeling by a 3D image obtained by stacking digitalized images of cross-sections of the examined joint generated at a step of extracting a contour of the cross-sectional image of the joint or digitalized images of cross-sections of the examined joint not pre-processed, and defining the joint image to be evaluated.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
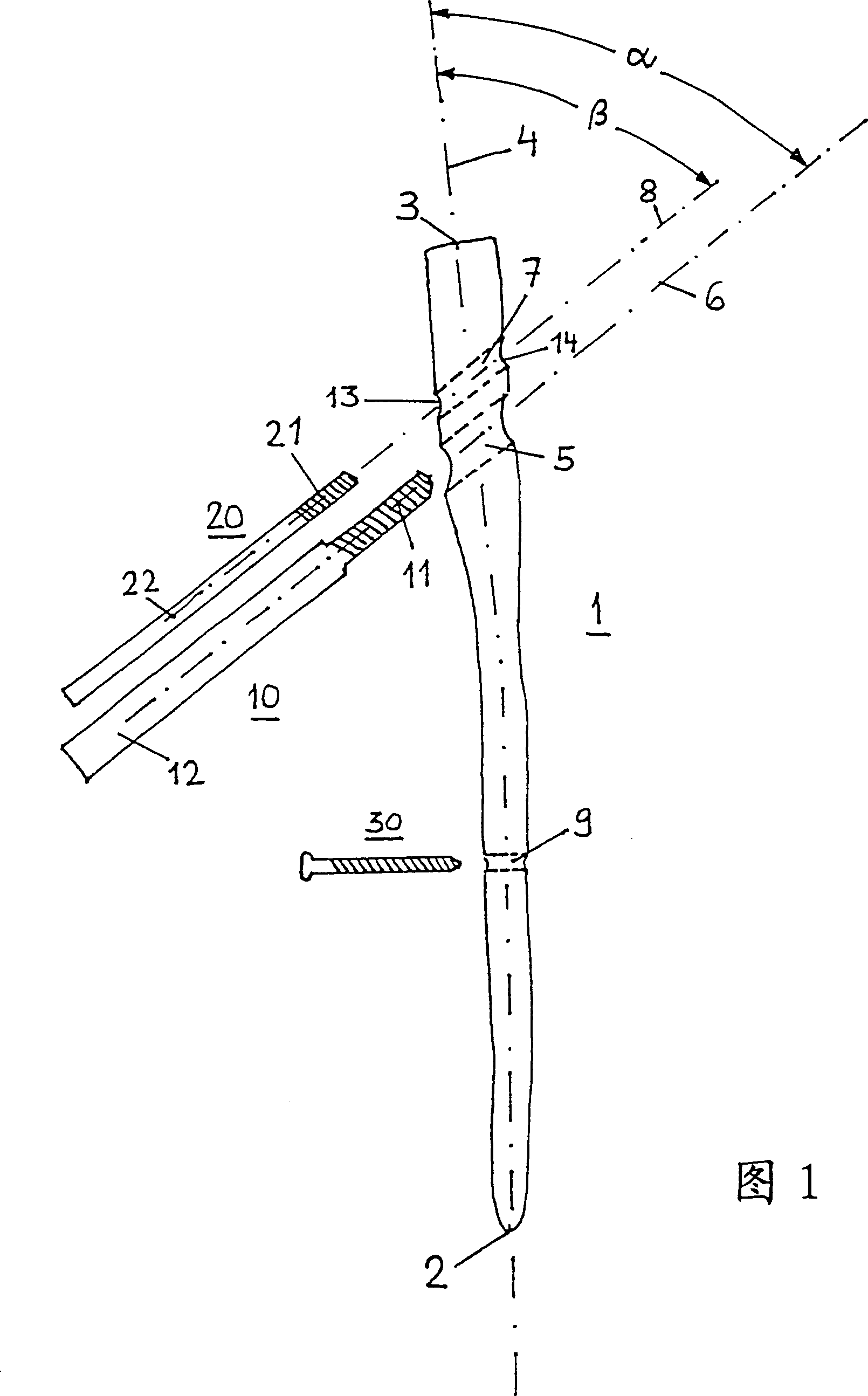
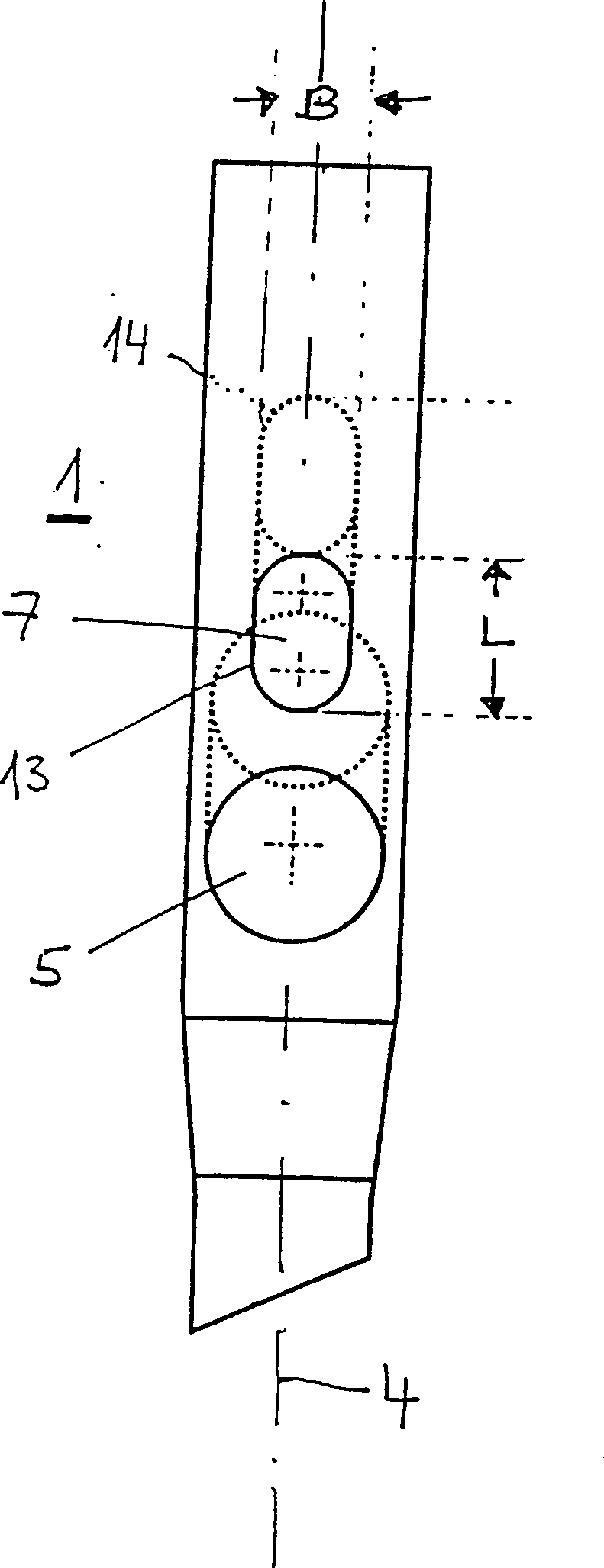
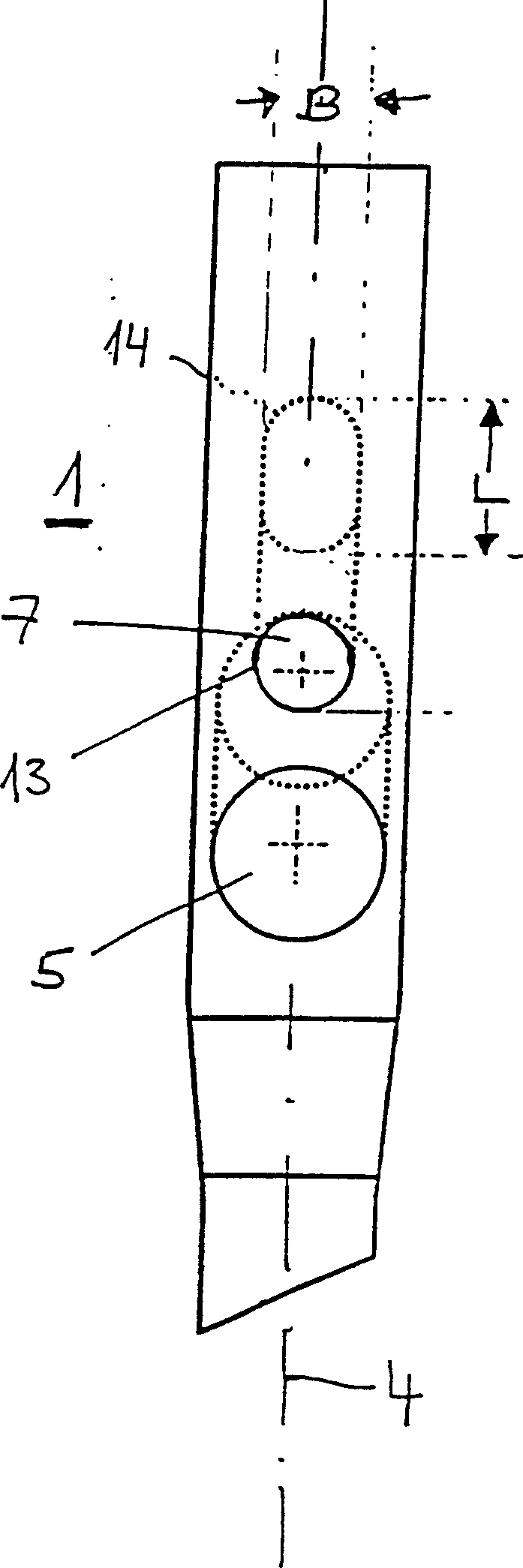
Intramedullary nail
Intramedullary nails (1) are used to treat femur fractures. It has a distal end (2) determined for insertion into the medullary canal, a proximal end (3) and a longitudinal axis (4). A first hole (5) near the proximal end (3) and transversely intersecting the longitudinal axis (4) is used to accommodate a femoral head screw (10), wherein the center line (6) of the first hole (5) is in line with the The longitudinal axes intersect at an angle of 110° to 150°. A second hole (7) located between the first hole (5) and the proximal end (3) and transverse to the longitudinal axis (4) receives a hip pin (20). The second hole (7) is at least partially formed as a long hole, which has a width B and a length L>B, wherein the length of the long hole is distributed along the direction of the longitudinal axis (4).
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Prosthetic implant and assembly method
ActiveUS8034116B2Small toleranceFacilitate the final mating of a subassemblyBone implantJoint implantsOrthopedic departmentEngineering
An orthopedic prosthetic implant comprises a metal alloy stem element (13, 63, 113), which has one end portion (19, 69, 119) constructed to reside in the medullary cavity of a bone and an integral connector (23, 73, 123) at the opposite end to which crystalline brittle head (17, 67, 117), preferably made of pyrocarbon-coated graphite, is joined. The head interfaces with human bone, and its effective joinder to the stem element is achieved through a polymeric insert (15, 65, 115) of proportional shape and design which has selected elastic properties. The design and material of the polymeric insert allow it to be securely received within an interior cavity (35, 77, 131) of the pyrocarbon-coated graphite head and mated to the stem connector in an either rigidly or bi-polar arrangement. The method of joinder allows the construction of composite implants that utilize the most desirable properties of metallic and brittle crystalline materials.
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
Bone fixture apparatus and jig
InactiveUS7347861B2Accurate locationStabilizing fractureInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsBone marrow cavityBone fixation devices
A bone fixture apparatus has an elongate fixture device intended to be inserted in a metaphysical region of a long bone. The device is inserted generally transversely of the direction of the medullary cavity in the bone. The fixture device includes an aperture extending laterally thereof and intended to accommodate an intramedullary nail inserted longitudinally therethrough into the cavity. The fixture device is further formed with an axial aperture intended to receive a securing element capable of insertion therein to firmly engage said nail with the fixture device. Also disclosed is a jig arrangement for locating, relative to a long bone, the bone fixture apparatus.
Owner:GRAMPIAN HEALTH BOARD
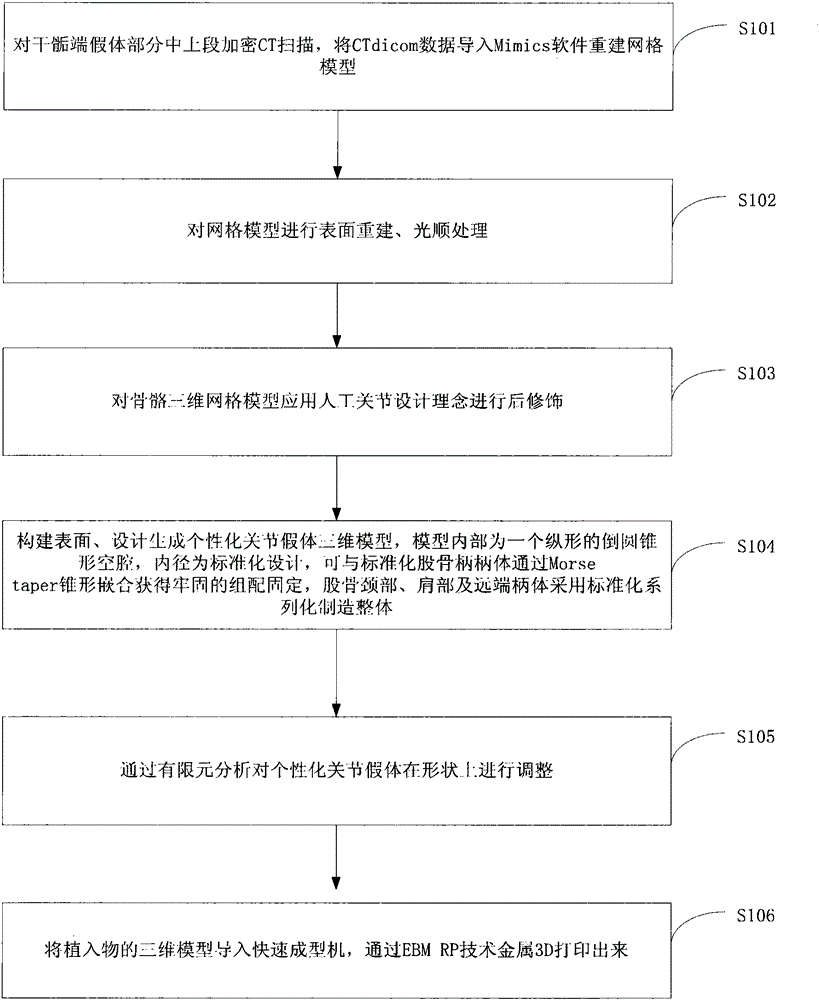
Method for performing EBM metal 3D printing on personalized human body thighbone prosthesis sleeve
InactiveCN105193527AGood initial fixationLong-term biological fixationProsthesisElement analysisBone marrow cavity
The invention discloses a method for performing EBM metal 3D printing on a personalized human body thighbone prosthesis sleeve. The method includes the steps that encrypted CT scanning is performed on the upper middle section of a metaphysis prosthesis part, and CTdicom data are input into Mimics software to reconstruct a grid model; surface reconstruction and smoothing processing are performed on the grid model; post-modification is performed on the bone three-dimensional grid model based on the joint prosthesis design concept; a personalized joint prosthesis three-dimensional model is generated through surface reconstruction and designing; the shape of a personalized joint prosthesis is adjusted through finite element analysis; the three-dimensional model of the implant is input into a rapid prototyping machine and printed through EBM RP technology metal 3D printing. The shape of the printed and manufactured finished product can be completely matched with that of the medullary cavity of the distal femoral metaphysic of every patient, the personalized thighbone prosthesis can be knocked to be implanted just through a few intra-operative medullary cavity files, and good initial fixation and long-time biological fixation can be achieved.
Owner:刘宏伟 +2
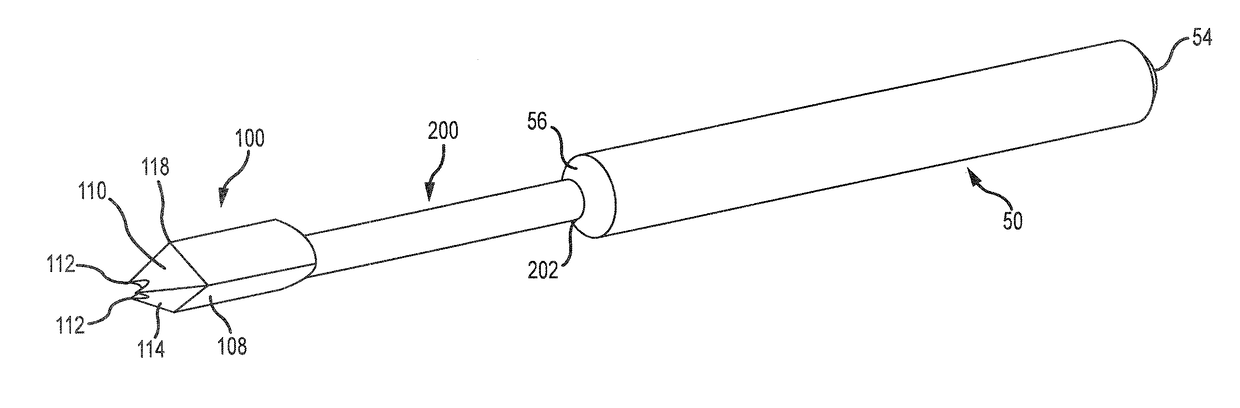
Tool for percutaneous joint cartilage destruction and preparation for joint fusion
A tool for scrubbing, removing tissue from the medullary cavity or joint cavity of a bone or removing cartilage and / or cortical bone from a joint cavity has a proximal end, a distal end, and a cannula extending therethrough. The distal end includes at least one scraping surface and / or cutting surface to soften marrow in the medullary cavity or joint cavity as the scraping and / or cutting surface(s) are rotated or otherwise moved relative to the medullary cavity or joint cavity. When used, the tool may be attached to a drill and the cannula receives a K-wire previously inserted into the medullary or joint cavity. The drill rotates the tool around the K-wire and pushes the tool over the K-wire into the medullary cavity or joint cavity.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
Artificial cementless hip prosthesis stem
An artificial cement-less hip prosthesis stem comprises an inner construct 7 which reacts with a load acting on a hip joint and an outer construct 8 for transmitting the load acting on the inner construct to a femur 1. The inner construct has an inner body 7B which reacts with the load transmitted from a neck 7A. The outer construct has both an outer body 8A which is bell mouth-shaped toward an epiphysis so as to surround the inner body 7B and a leg 8B extending toward a medullary cavity. The torsional rigidity given to the proximal end and the distal end of the outer body 8A and the leg 8B is regulated so as to be lower than the torsional rigidity given to an intermediate portion 18 of the outer body 8A.
Owner:B I TEC LTD
Hand and foot bone defect implant
ActiveCN105662655AAvoid the risk of amputationSome functions are reservedBone implantFoot BonesBone marrow cavity
The invention provides a hand and foot bone defect implant which comprises a defect compensation body and two supporting bodies. The defect compensation body comprises a central rod and an outer sleeve fixedly arranged on the central rod in a sleeving mode. The two ends of the central rod can be inserted in medullary cavities of broken bone on the two sides respectively. The end faces of the two ends of the outer sleeve can be connected with fracture surfaces of the broken bone on the two sides respectively. Cavities used for containing filler are formed in the end faces of the two ends of the outer sleeve. At least one part of the surface of the cavity on each end face is attached to the surface of cortical bone of the corresponding connected broken bone so that the corresponding filler can make contact with the cortical bone. The two supporting bodies are connected with the ends of the central rod respectively. The supporting bodies can make contact with the inner walls of the medullary cavities to support the central rod when the two ends of the central rod are inserted in the medullary cavities of the broken bone. By means of the hand and foot bone defect implant, hand and foot bone defect injuries can be repaired, and therefore the original length of the broken bone can be kept, the risk of amputation is avoided, and part of functions can be kept.
Owner:张黎 +1
Interlocking bone plate system
InactiveUS20130096630A1Highly stable fixation structureReduce riskInternal osteosythesisFastenersBone marrow cavityUltimate tensile strength
An interlocking bone plate system includes an outer bone plate for being arranged outside a broken bone, an inner bone plate for being installed inside the medullary cavity of the broken bone, and screws for being inserted through and engaged with the outer bone plate and the broken bone and then engaged with the inner bone plate so as to interlock the out and inner bone plates together. The inner bone plate provides an added support in addition to the support provided by the outer bone plate, enhancing the structural strength of the whole bone fixation structure and lowering the risk of failed surgery.
Owner:TAICHUNG VETERANS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Method and device for determining medullary cavity anatomical axis based on deep learning
ActiveCN111652888AImprove accuracyReduce failure rateImage enhancementImage analysisBone areaBone marrow cavity
The invention discloses a method and device for determining a medullary cavity anatomical axis based on deep learning, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the segmentation of a two-dimensional cross section image according to a preset segmentation neural network, and obtaining a bone region corresponding to a medullary cavity through segmentation; performing layer classification on the bone area according to a preset classification neural network, and separating out a medullary cavity layer; determining central points of all medullary cavity layers according to a central point calculation formula; carrying out straight line fitting on the center point, and determining the medullary cavity anatomical axis. The invention aims to provide a high-precision medullary cavity anatomical axis determination mode.
Owner:BEI JING LONGWOOD VALLEY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com