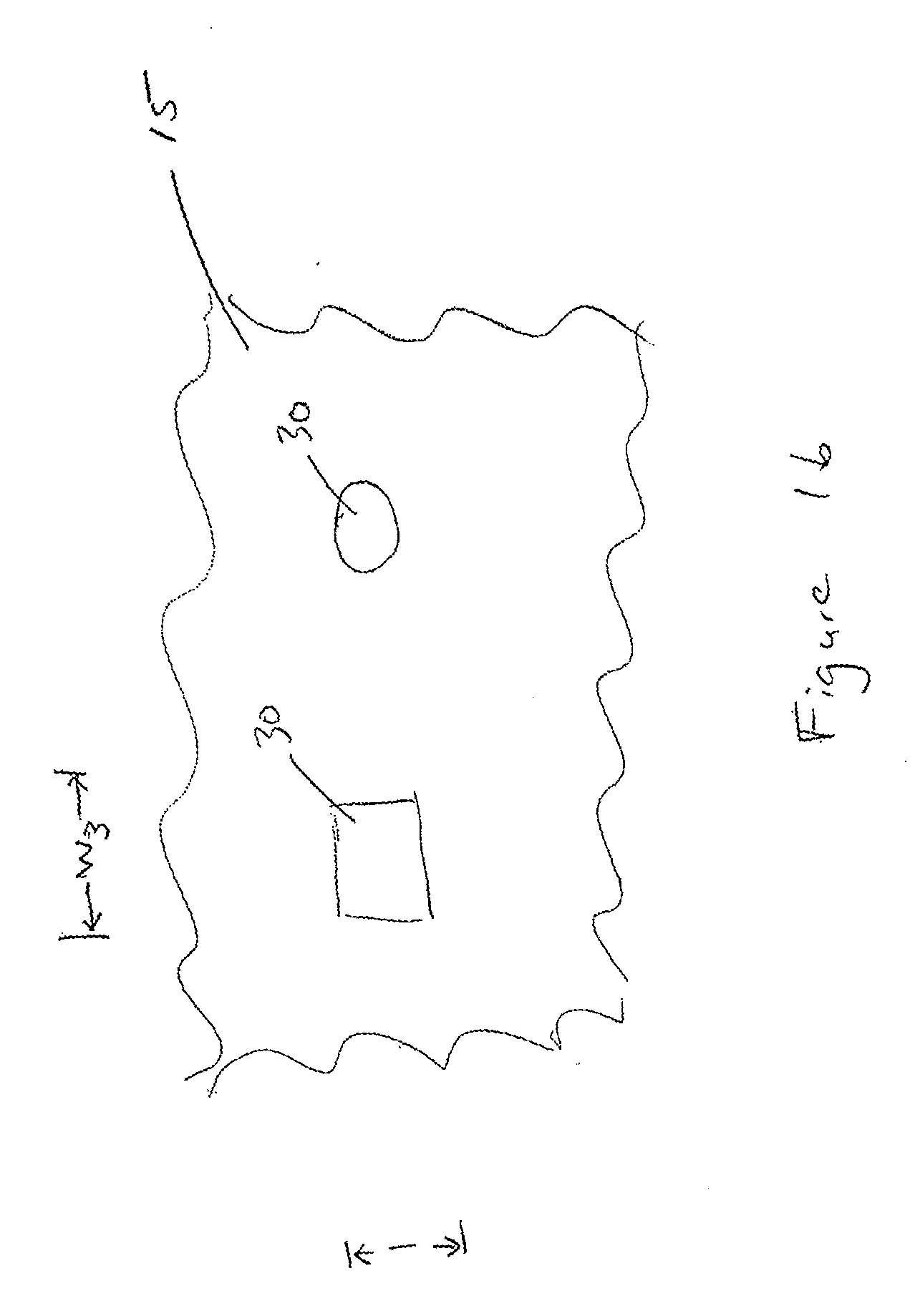
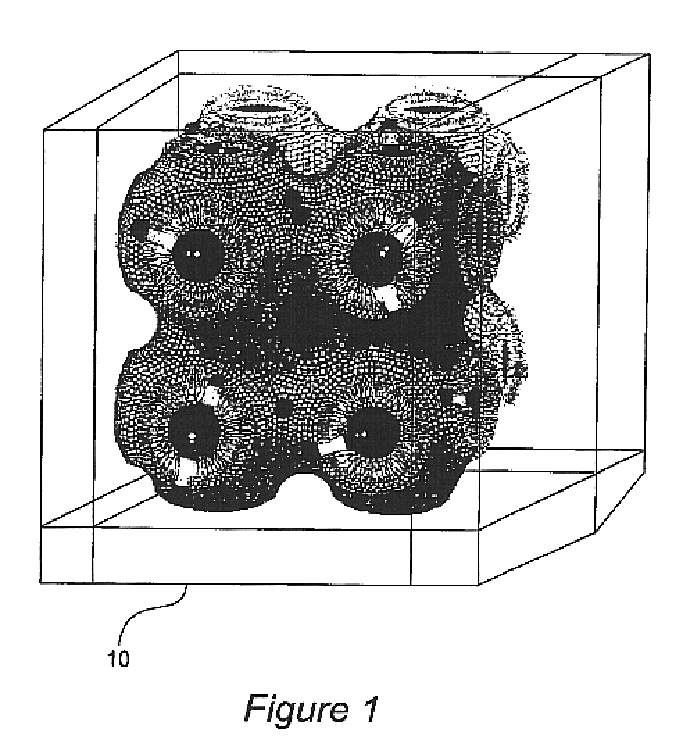
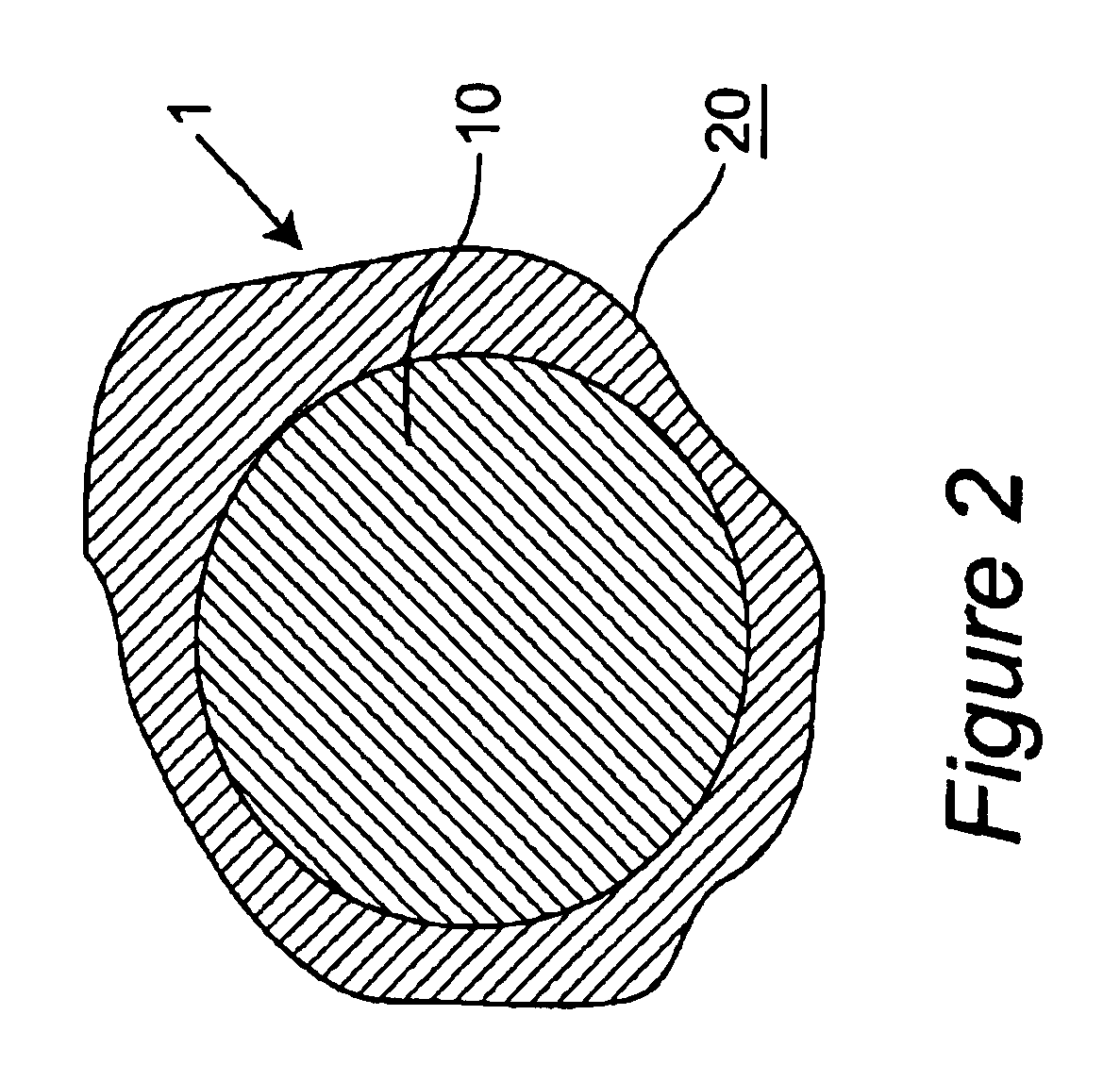
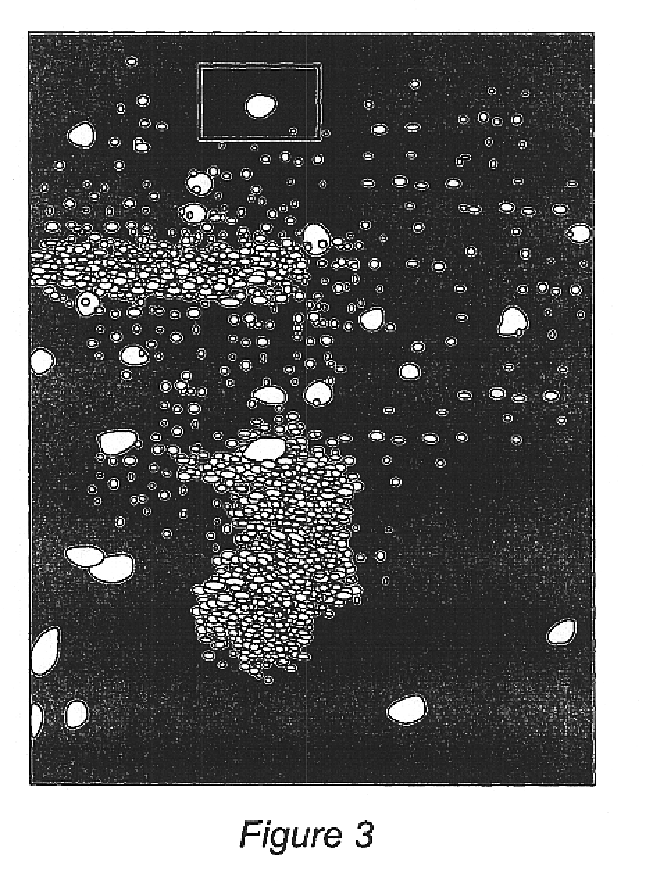
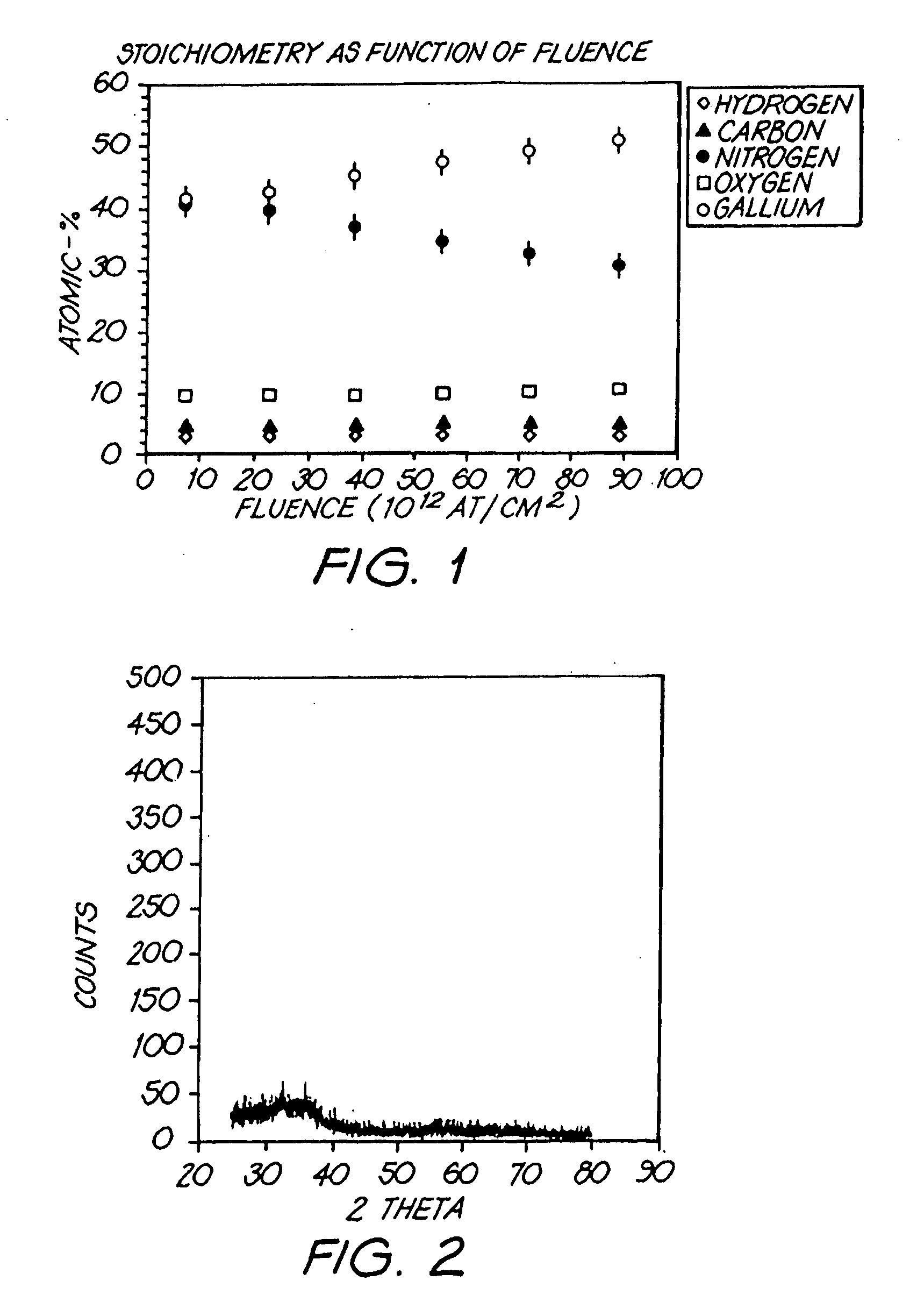
Patents
Literature
1381 results about "Crystalline materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Selective area epitaxy growth method and structure
InactiveUS20090309127A1Improve the level ofSmall sizePolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsIndiumPhotoluminescence
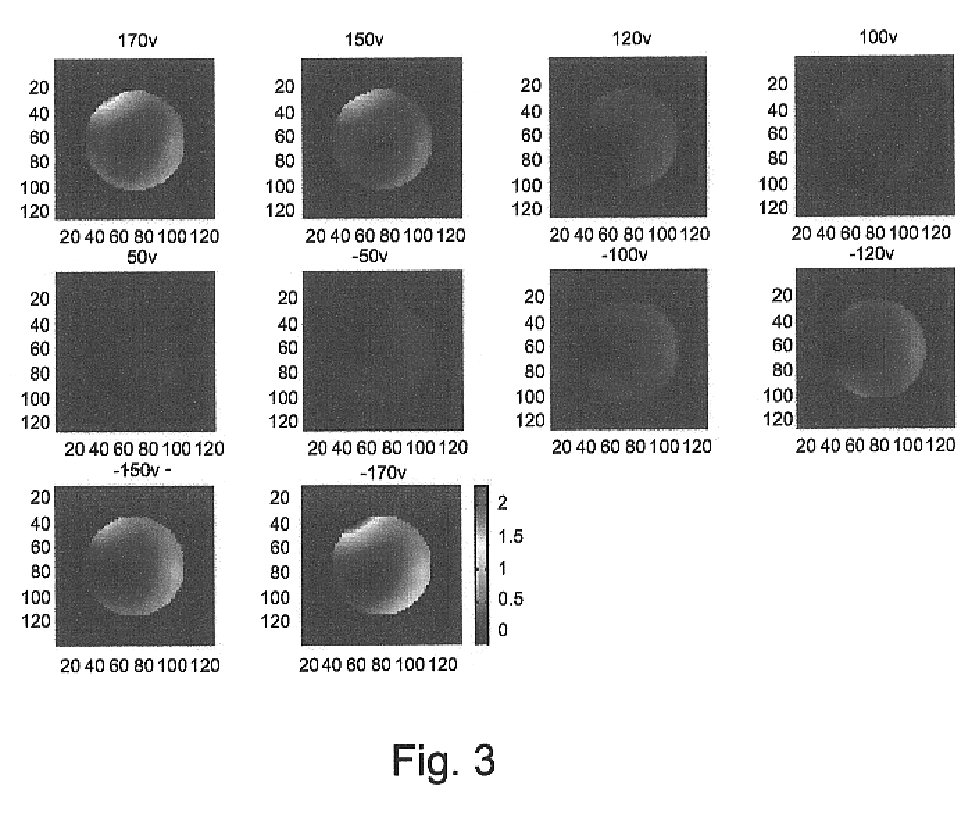
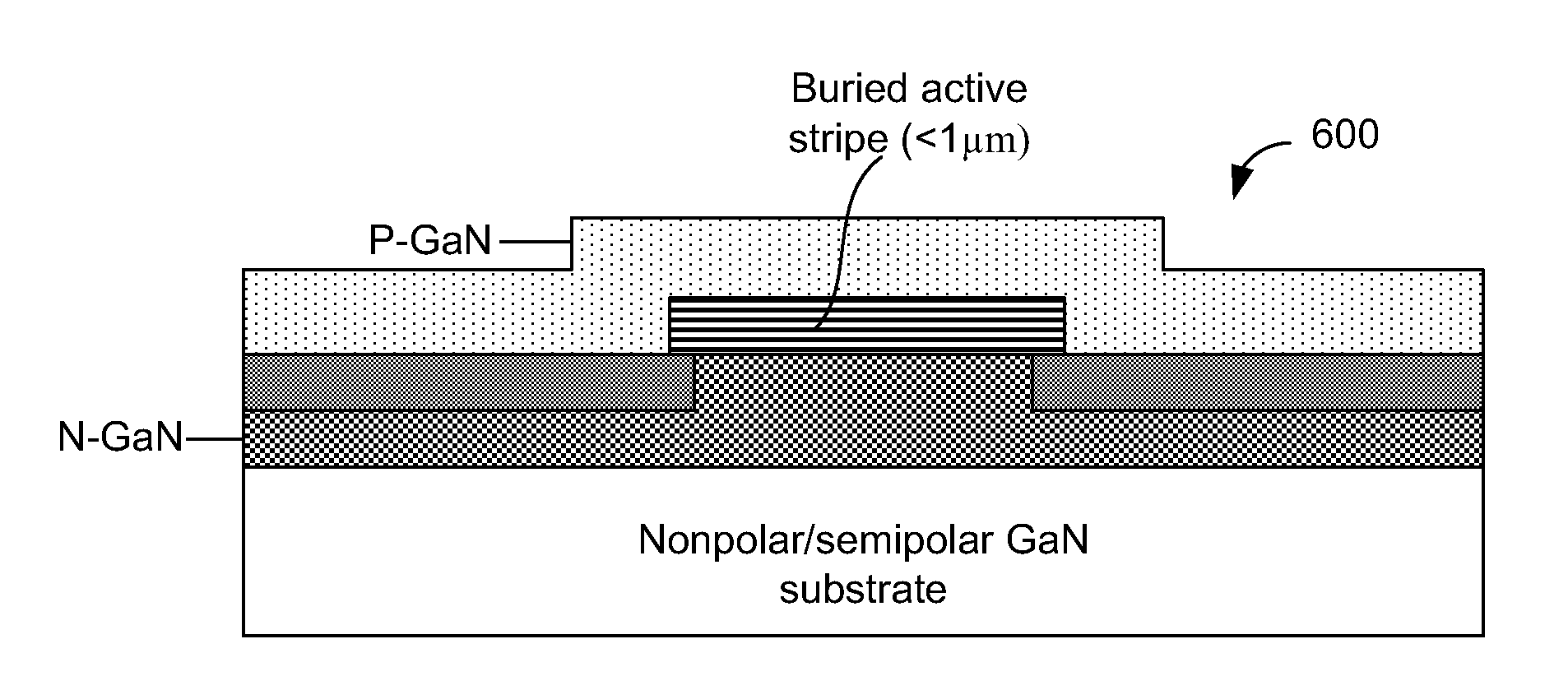
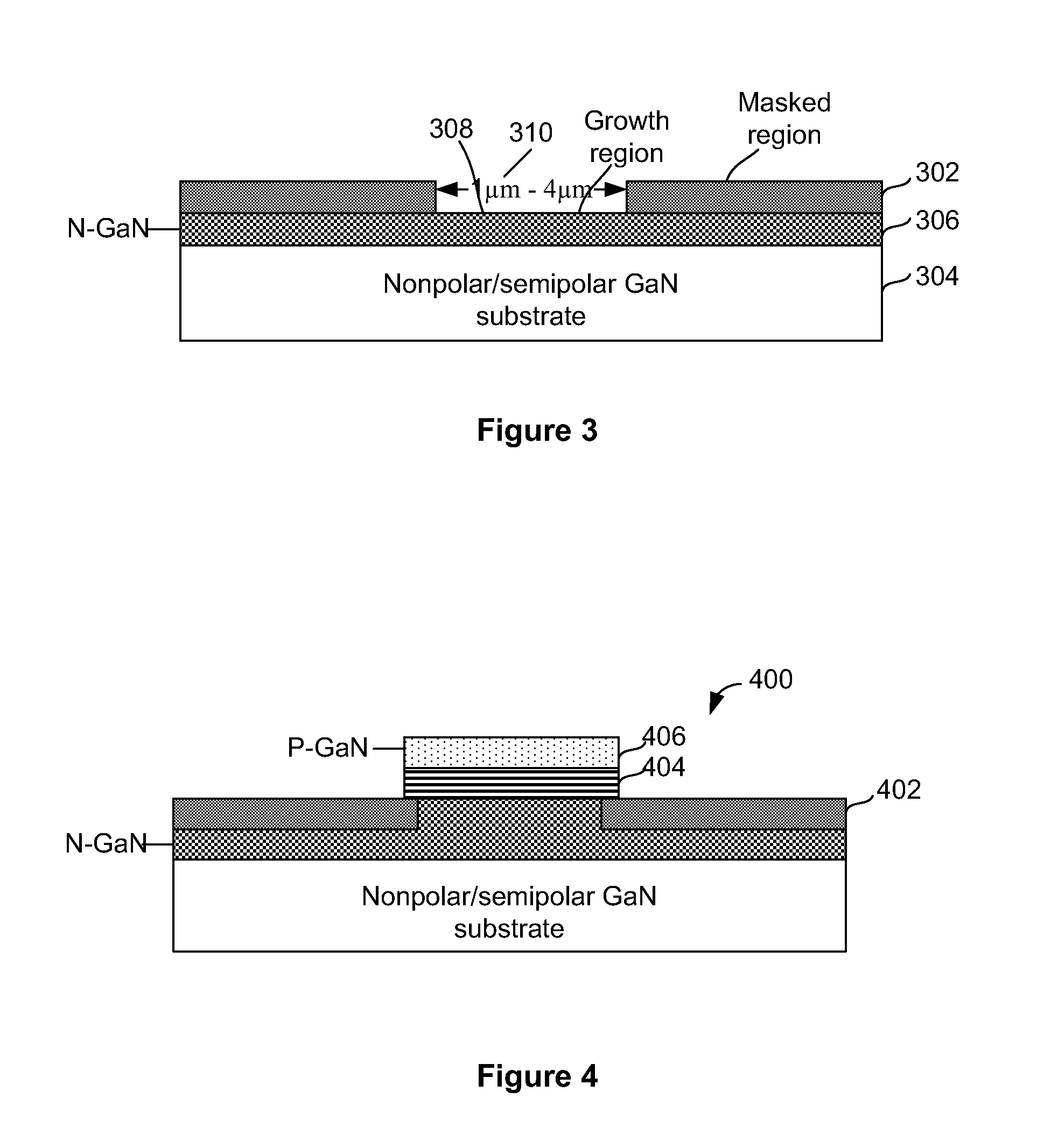
A gallium containing crystalline material. The material comprises a bulk semi-polar gallium indium containing crystalline material having a thickness of about 20 nanometers to about 1000 nanometers. The material includes a spatial width dimension of no greater than about 10 microns characterizing the thickness of the bulk semi-polar gallium indium containing crystalline material. The material includes a photoluminescent characteristic of the crystalline material having a first wavelength, which is at least five nanometers greater than a second wavelength, which is derived from an indium gallium containing crystalline material grown on a growth region of greater than about 15 microns.
Owner:SORAA +1
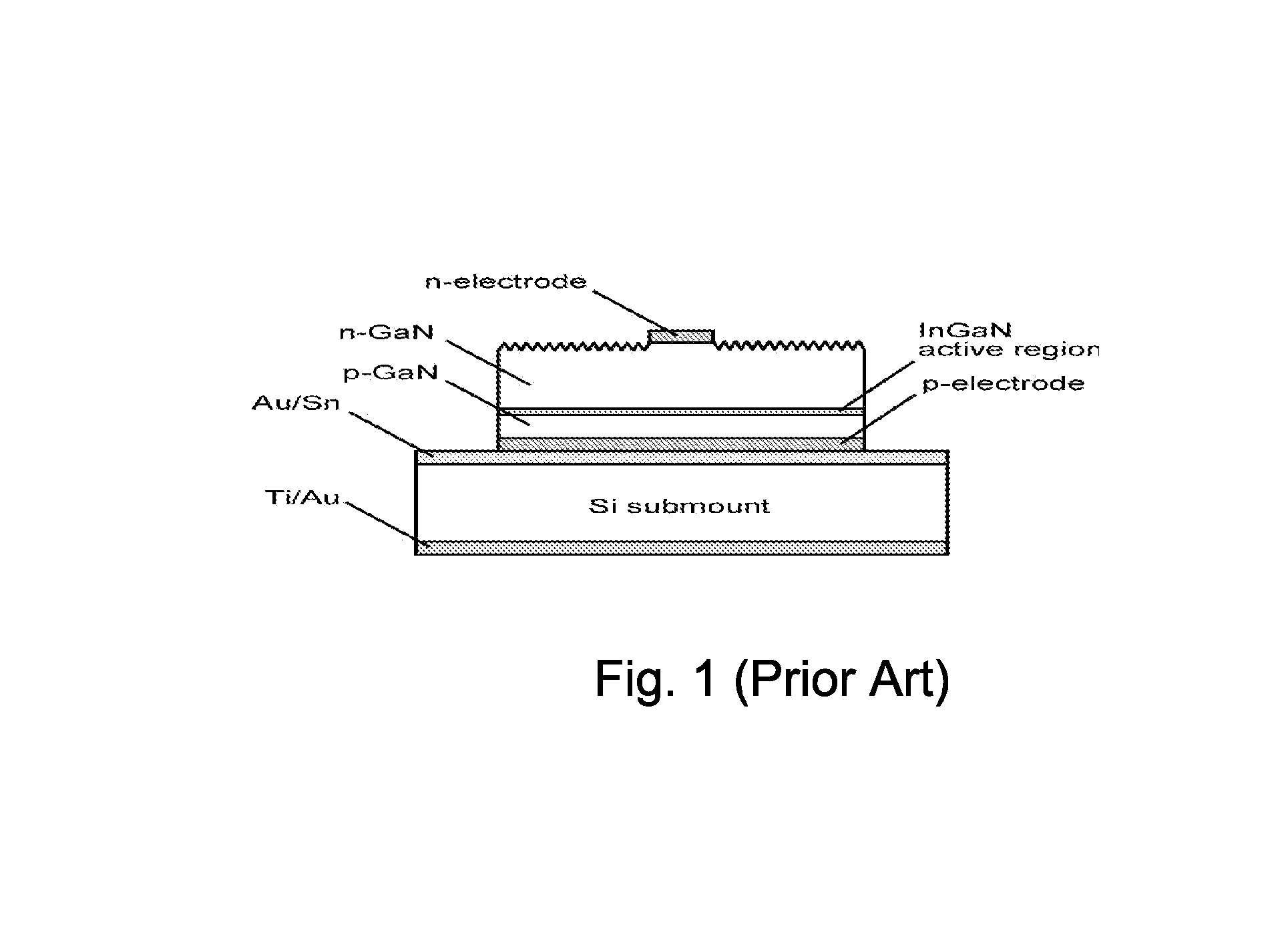
Method and structure for manufacture of light emitting diode devices using bulk GaN
ActiveUS8252662B1Minimize re-absorptionThickness minimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCrystalline materialsGallium nitride
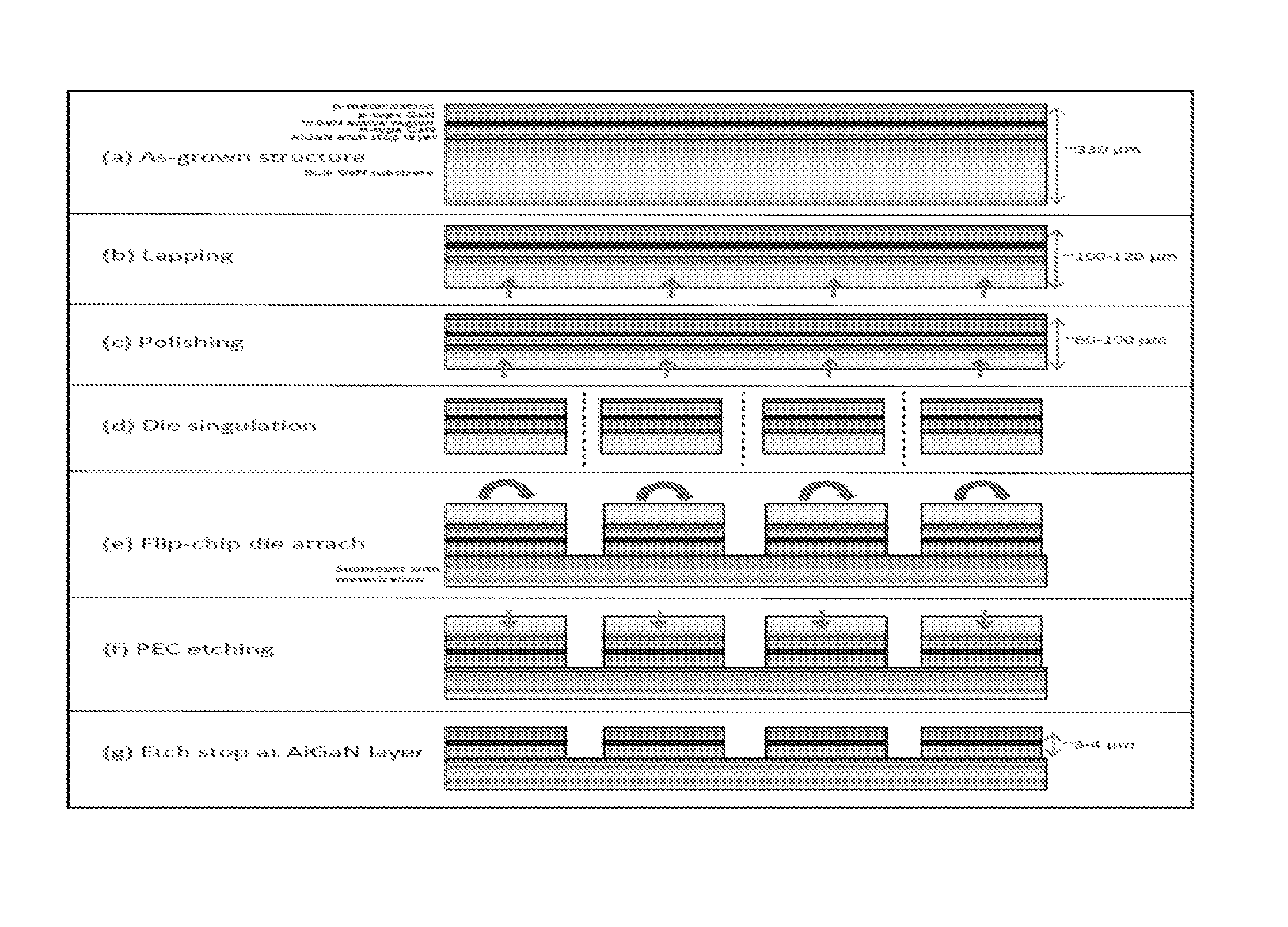
A method for manufacturing a plurality light emitting diodes includes providing a gallium nitride containing bulk crystalline substrate material configured in a non-polar or semi-polar crystallographic orientation, forming an etch stop layer, forming an n-type layer overlying the etch stop layer, forming an active region, a p-type layer, and forming a metallization. The method includes removing a thickness of material from the backside of the bulk gallium nitride containing substrate material. A plurality of individual LED devices are formed from at least a sandwich structure comprising portions of the metallization layer, the p-type layer, active layer, and the n-type layer. The LED devices are joined to a carrier structure. The method also includes subjecting the gallium nitride containing bulk crystalline substrate material to at least one etching process to selectively remove crystalline material underlying the etch stop layer, wherein the etch stop layer is exposed, and the etch stop layer remains substantially intact.
Owner:SLT TECH
Photovoltaics on silicon
ActiveUS20080257409A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystalline materialsSilicon
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
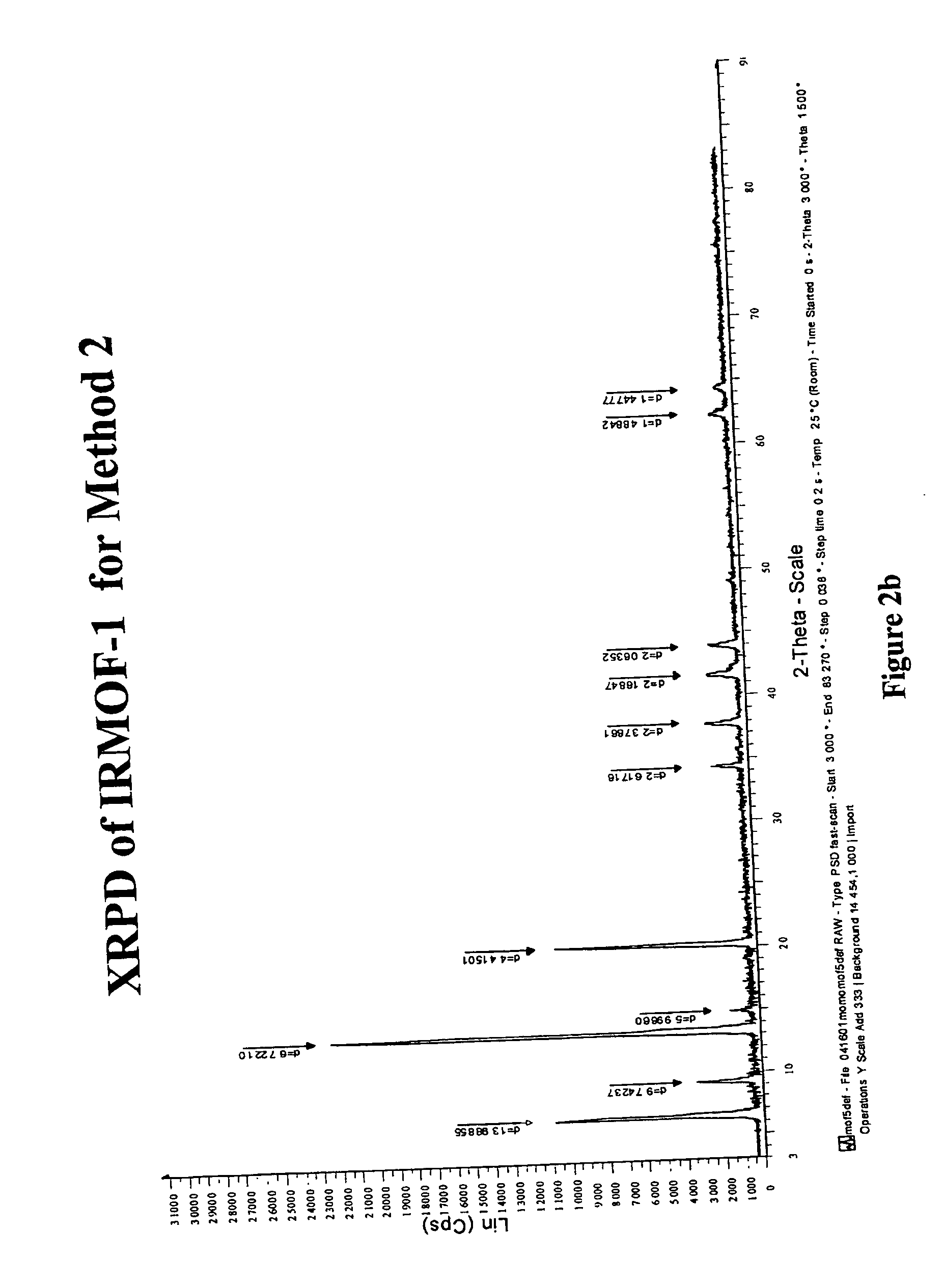
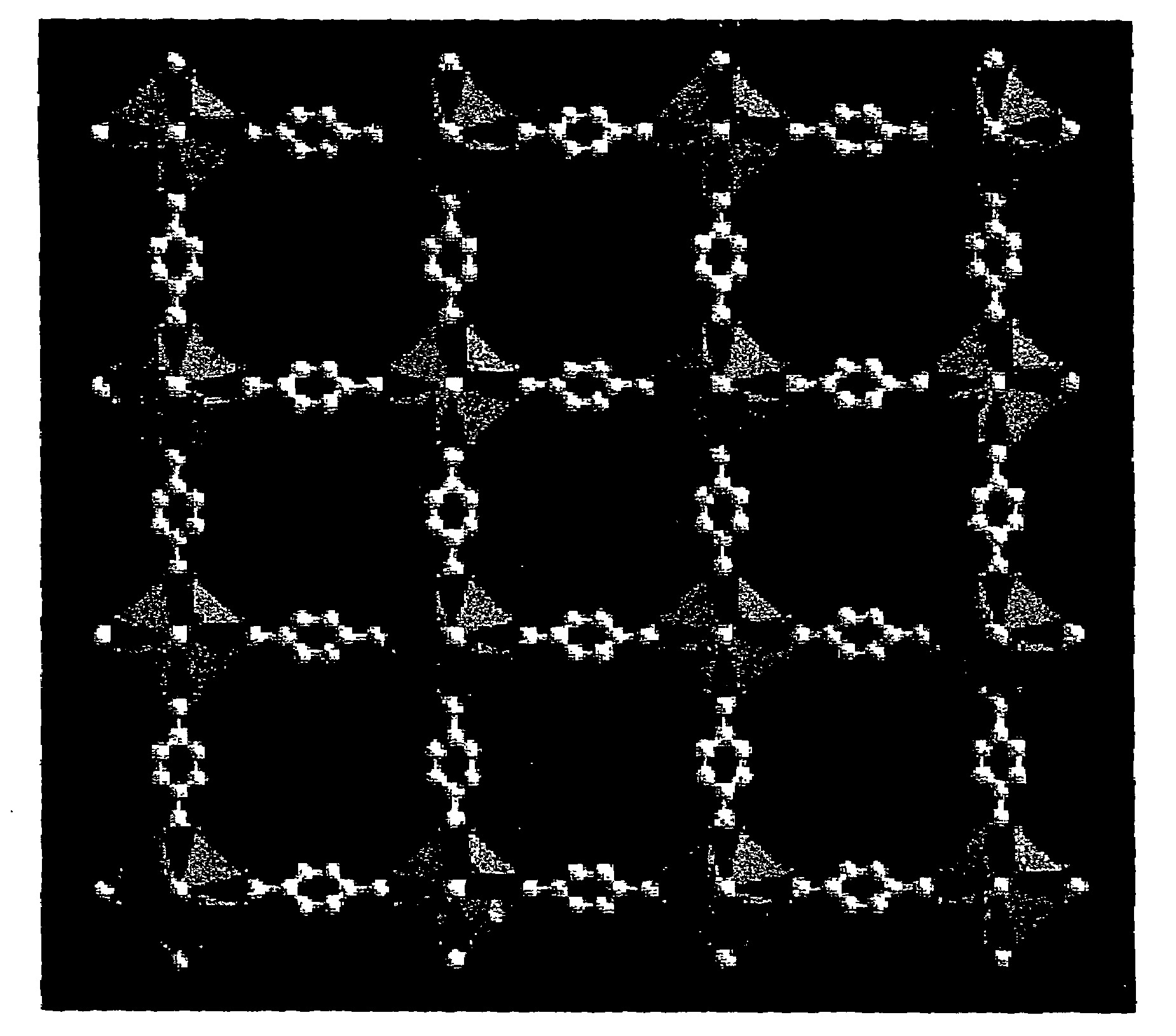
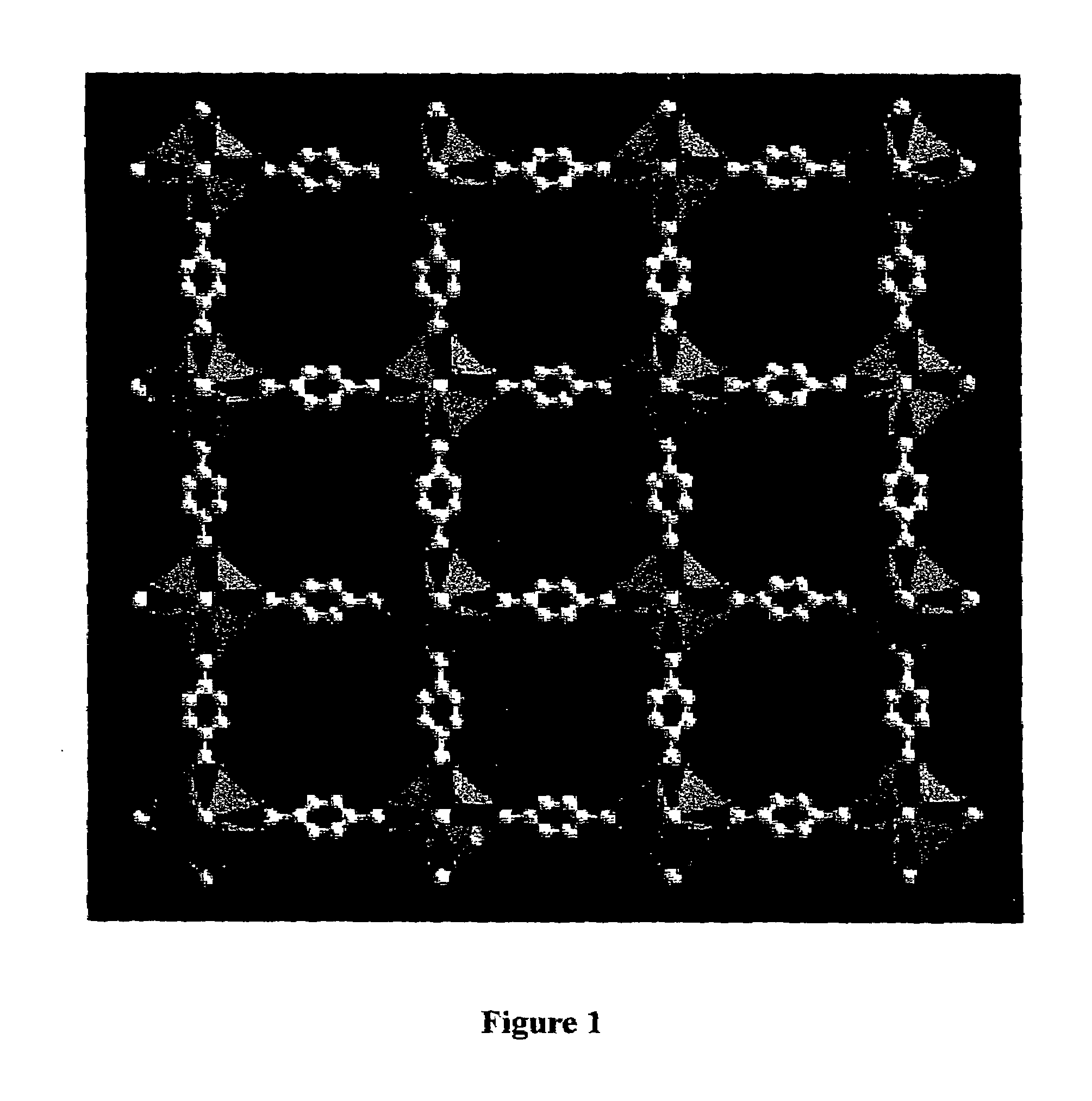
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS7196210B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSystems designMetal-organic framework
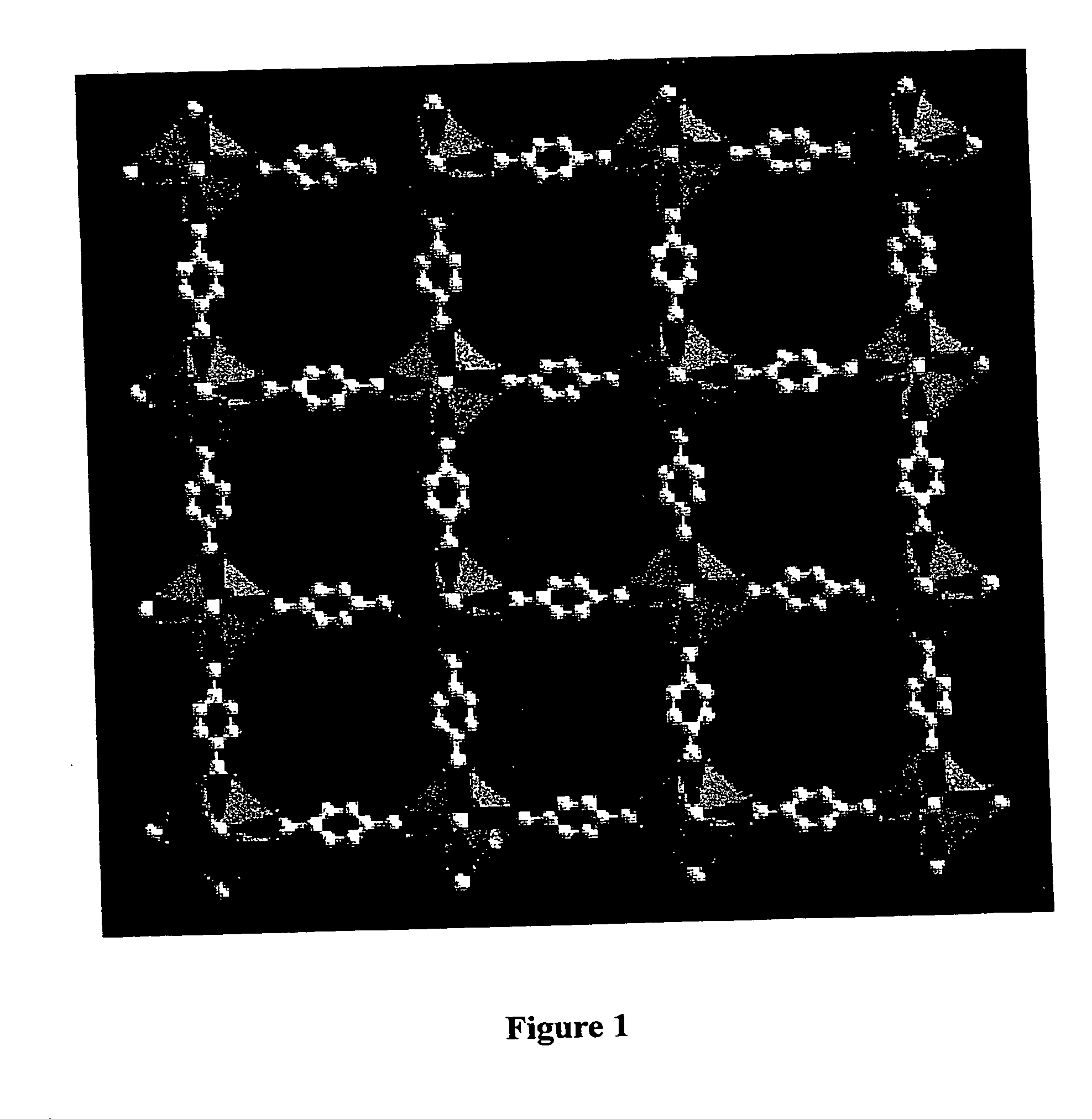
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
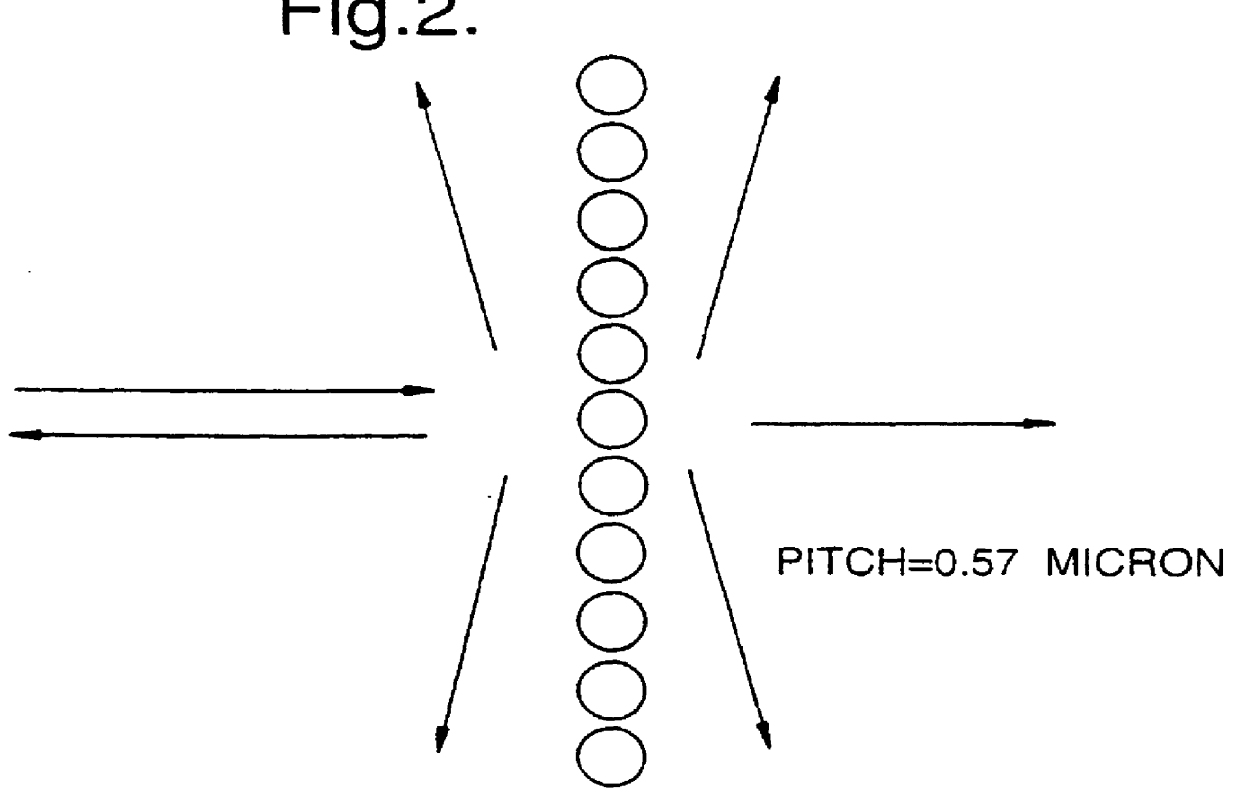
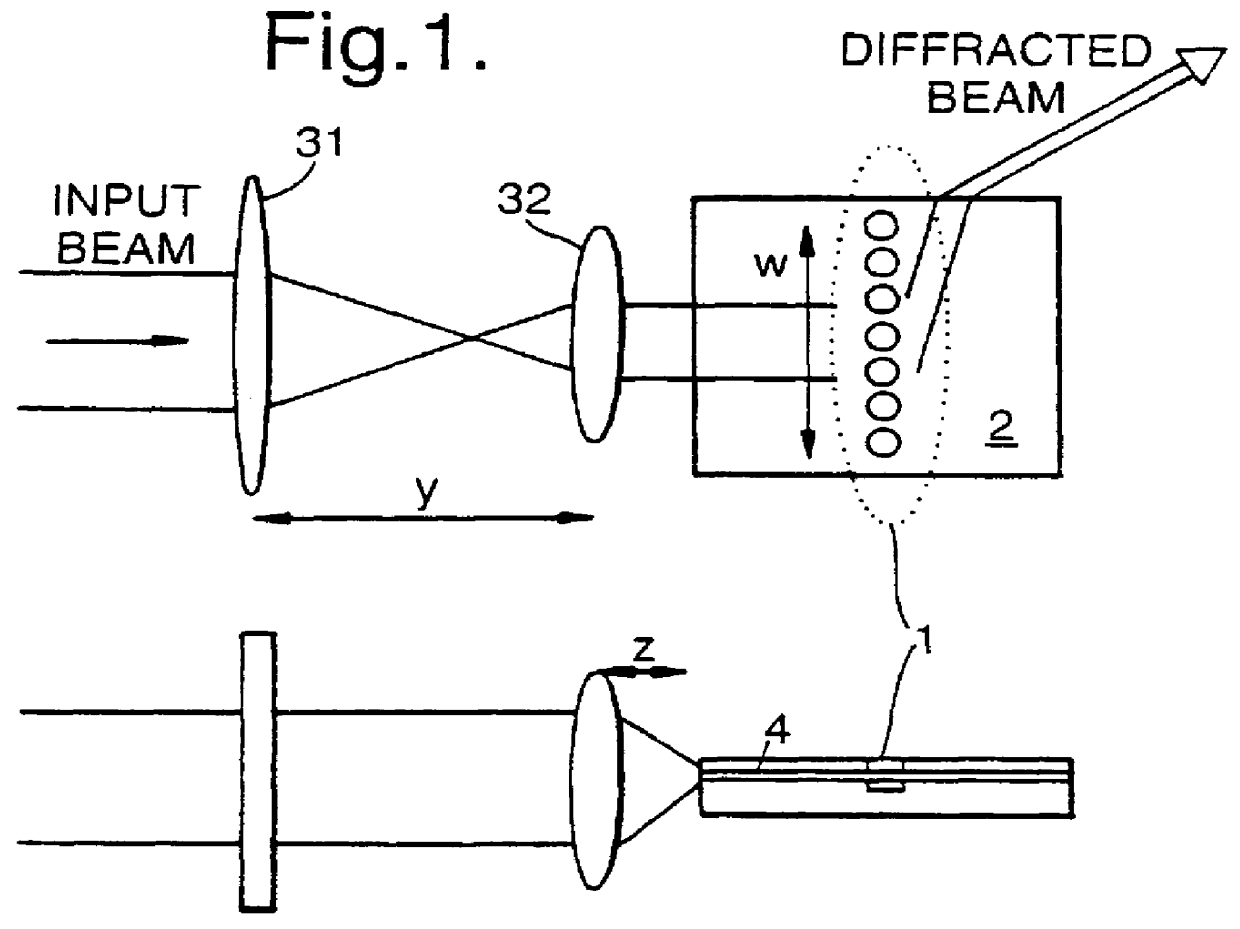
Optical diffraction grating
InactiveUS6052213ADiffraction gratingsOptical waveguide light guideOptical diffractionPhotonic crystal
PCT No. PCT / GB97 / 00817 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 13, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 13, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 24, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 36198 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 2, 1997An optical diffraction grating is formed from a region of photonic crystalline material Light is coupled into the photonic crystalline material, and the grazingly emergent output beam is collected. The photonic crystalline material may include an array of holes formed in a substrate of dielectric material, e.g., InP, and integrated with planar waveguide structures.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
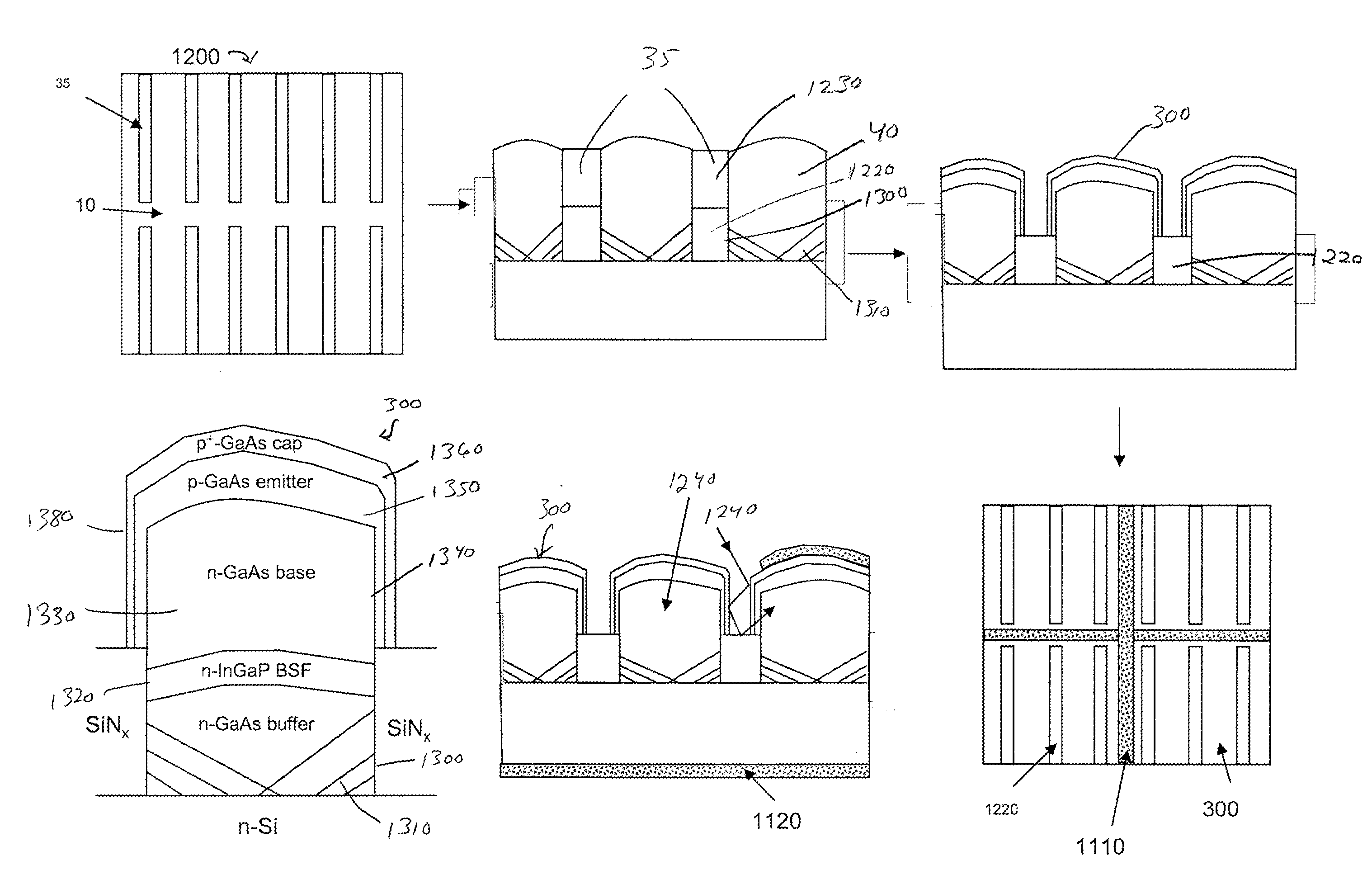
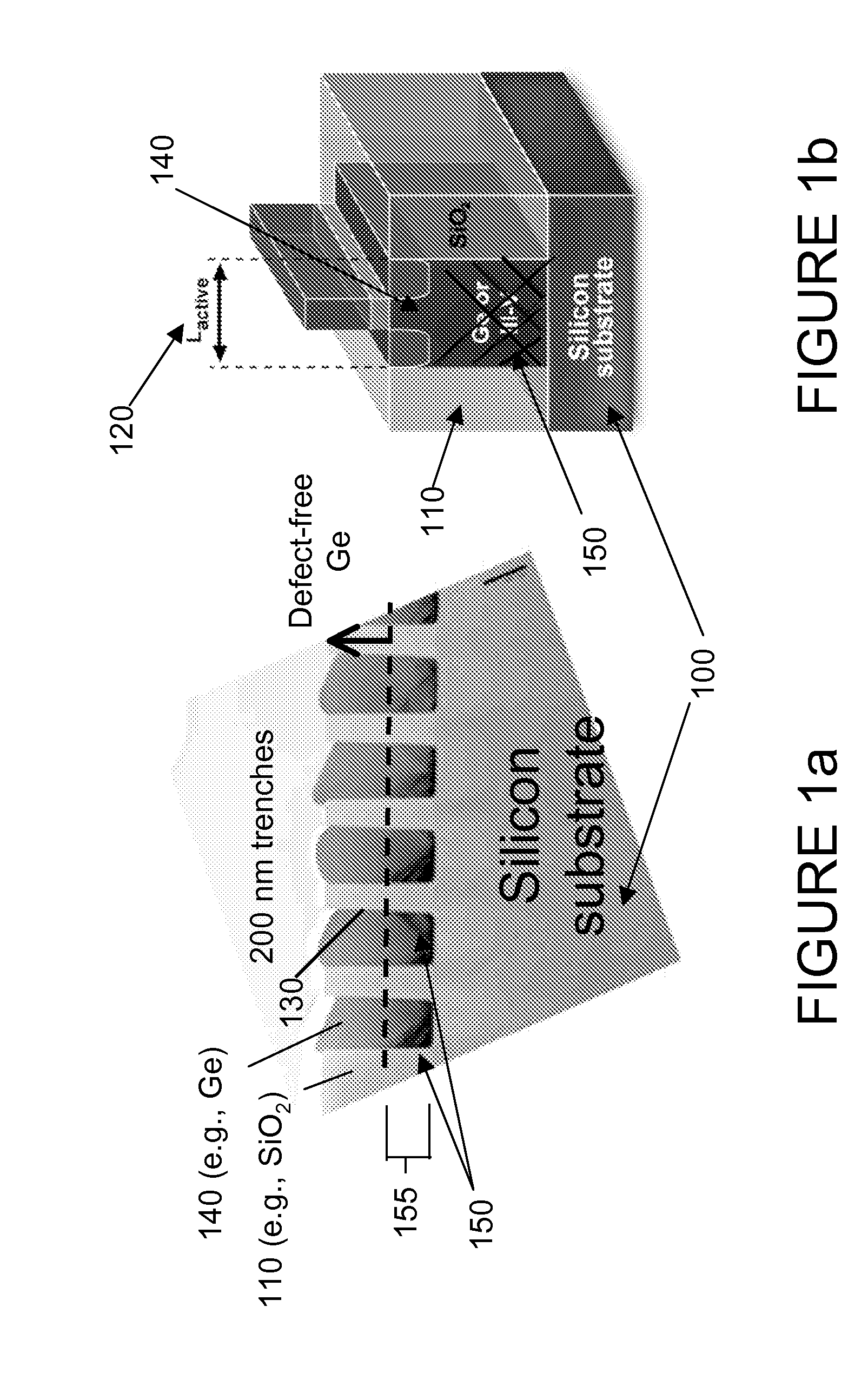
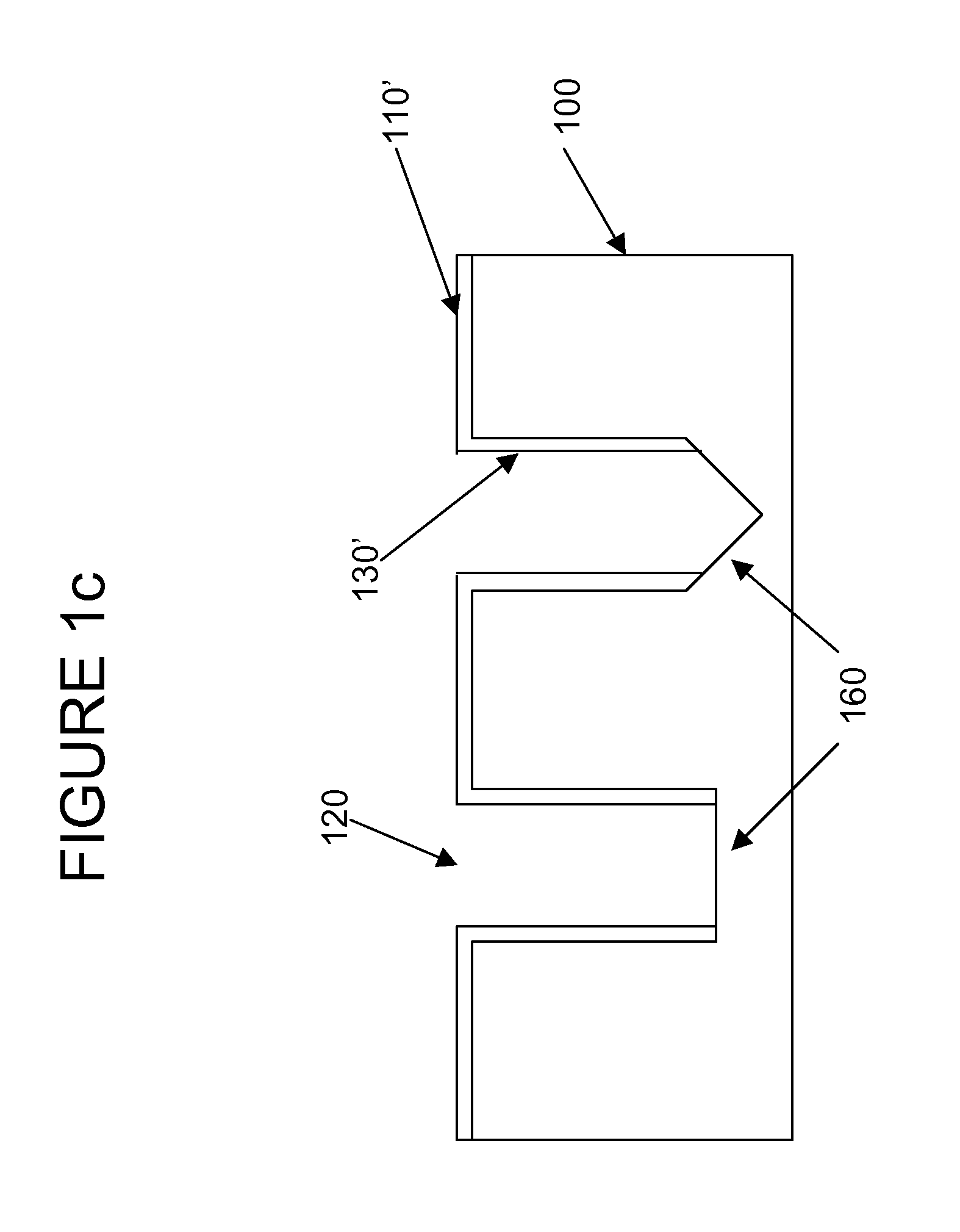
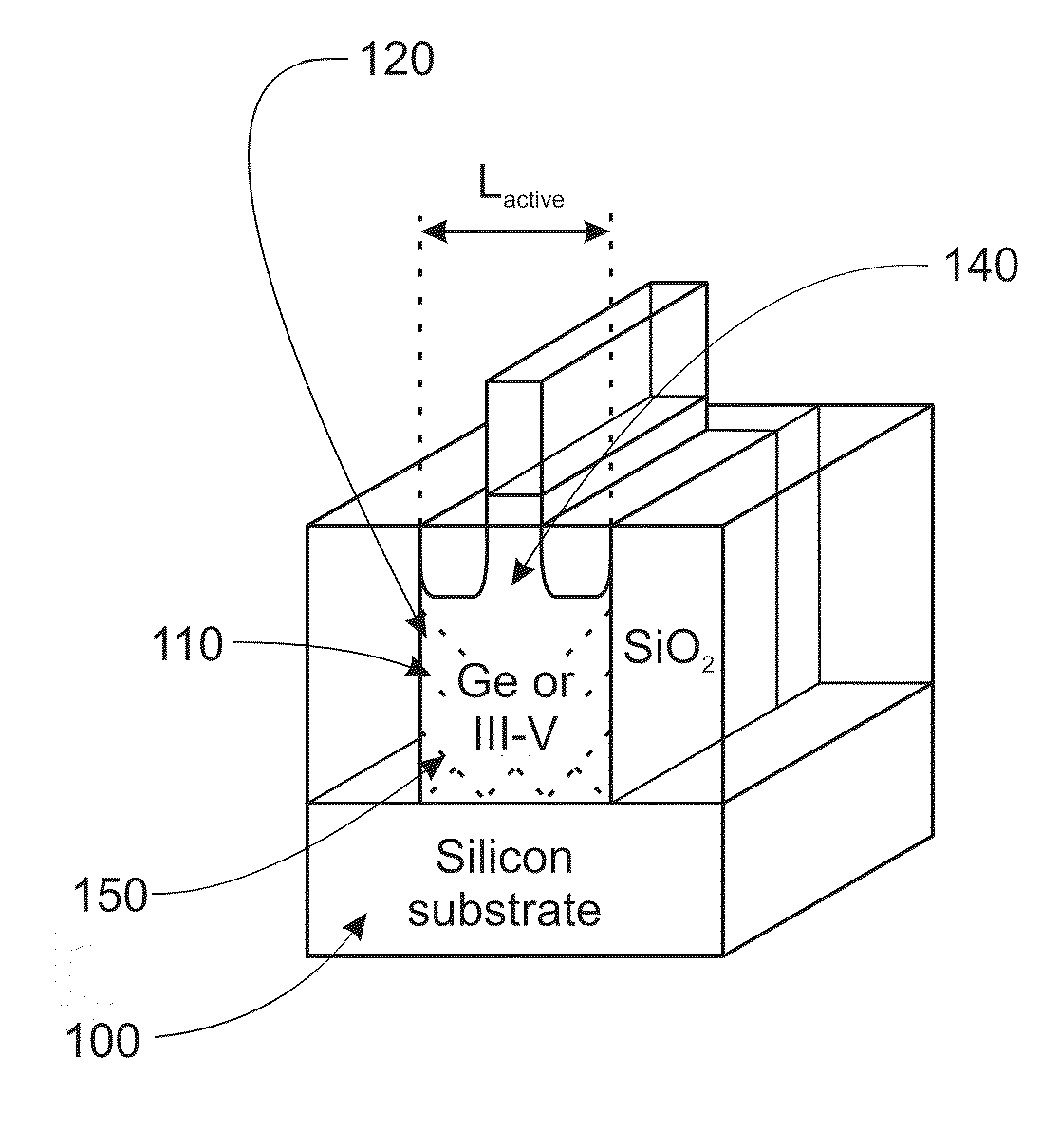
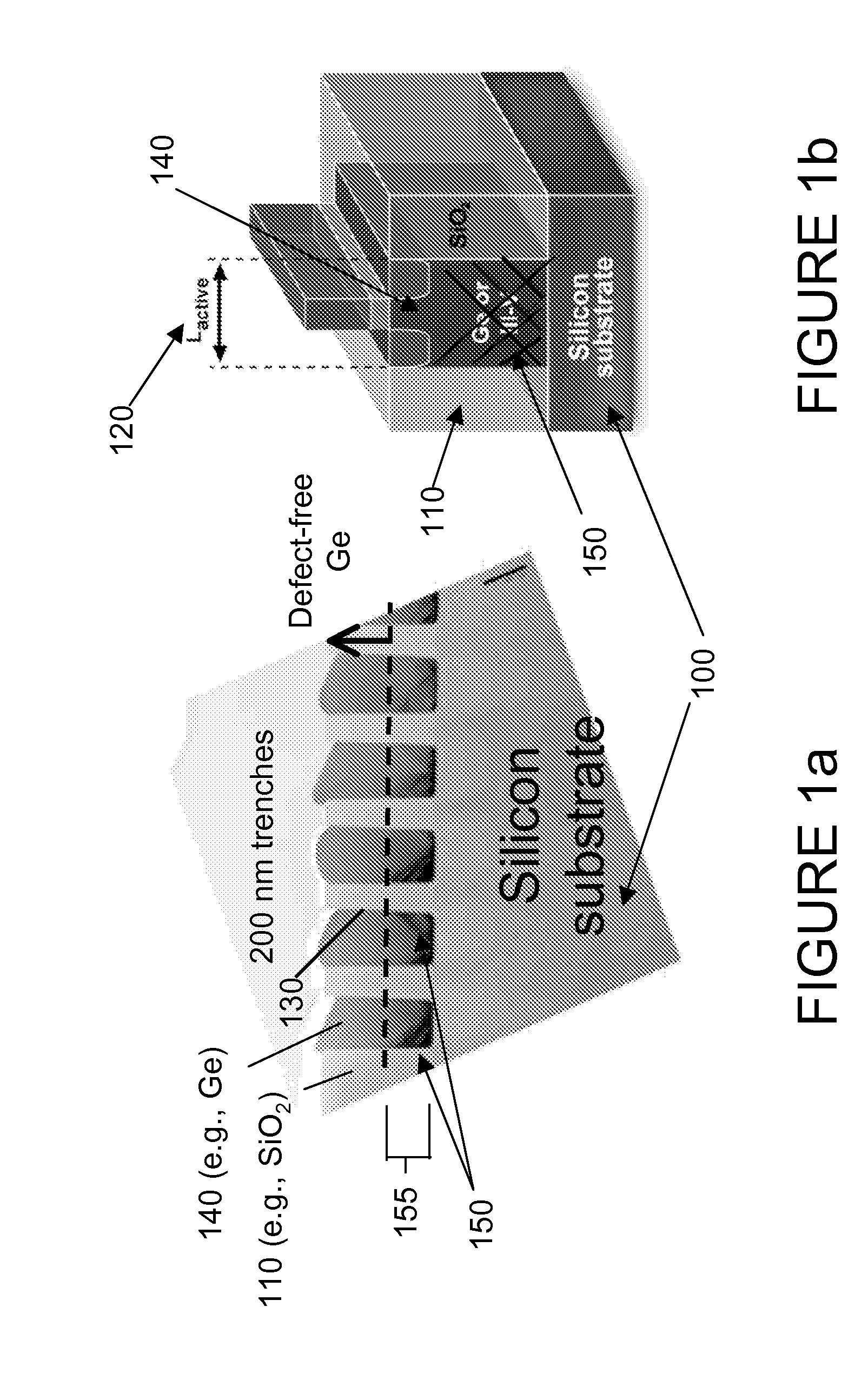
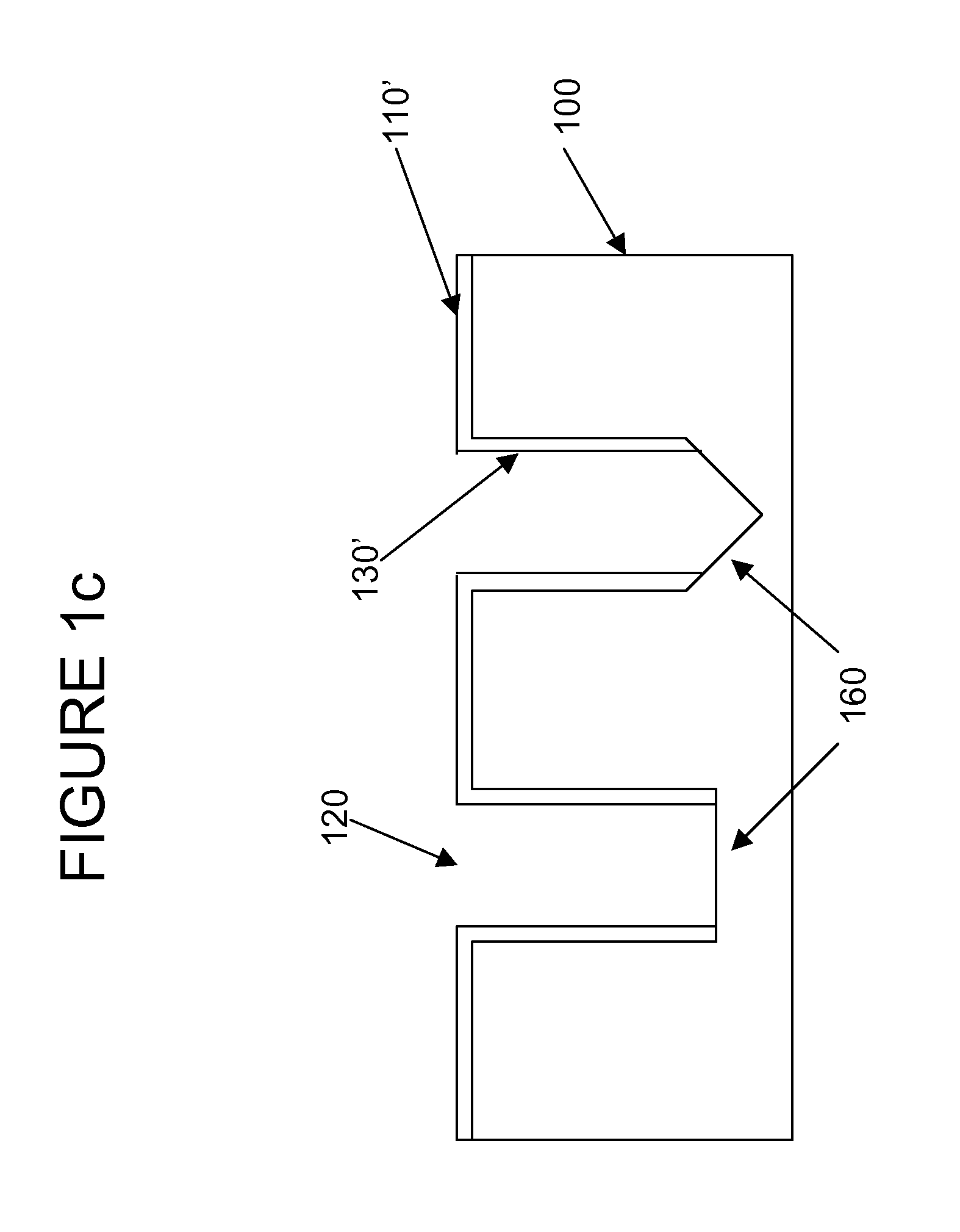
Semiconductor sensor structures with reduced dislocation defect densities and related methods for the same
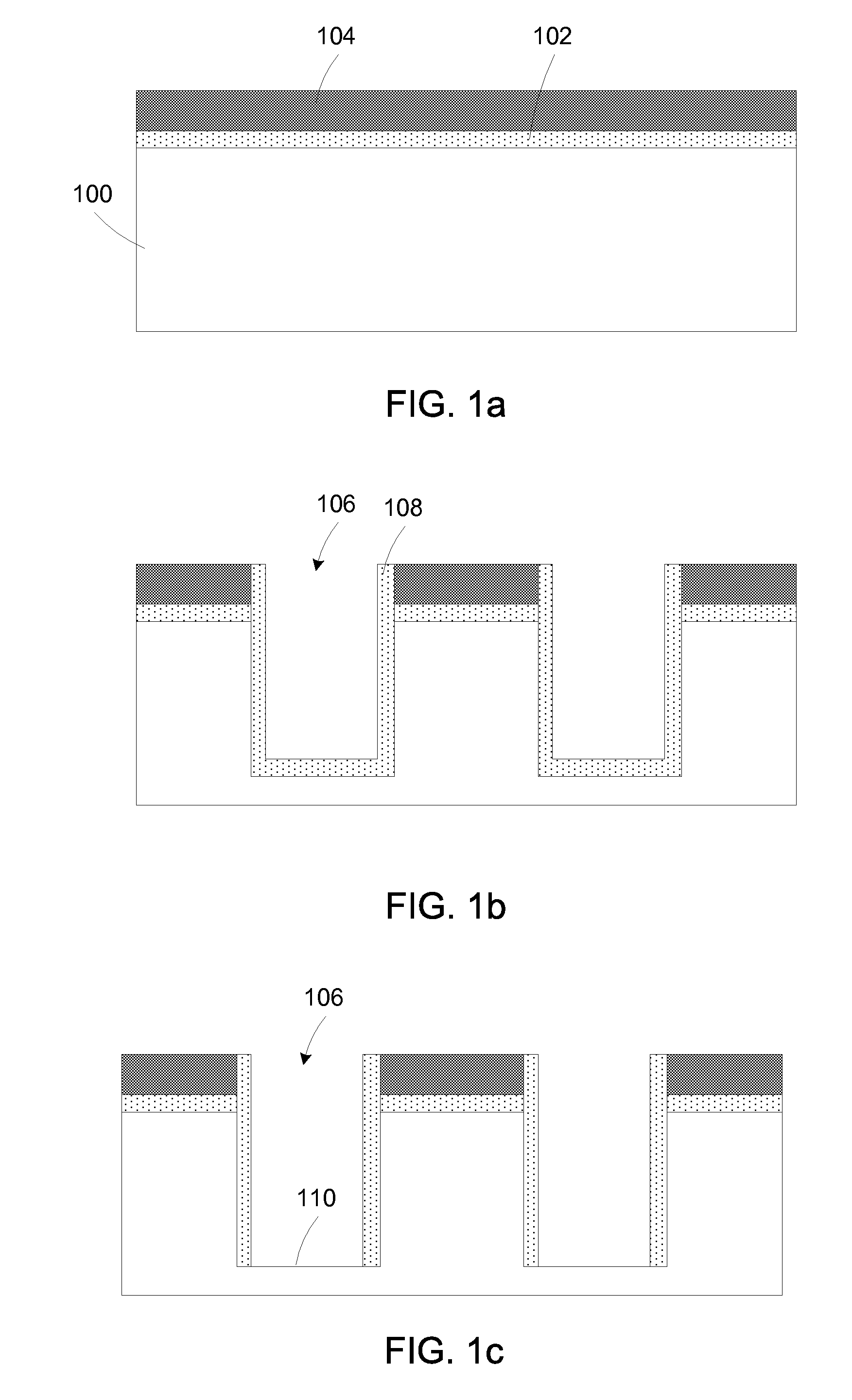
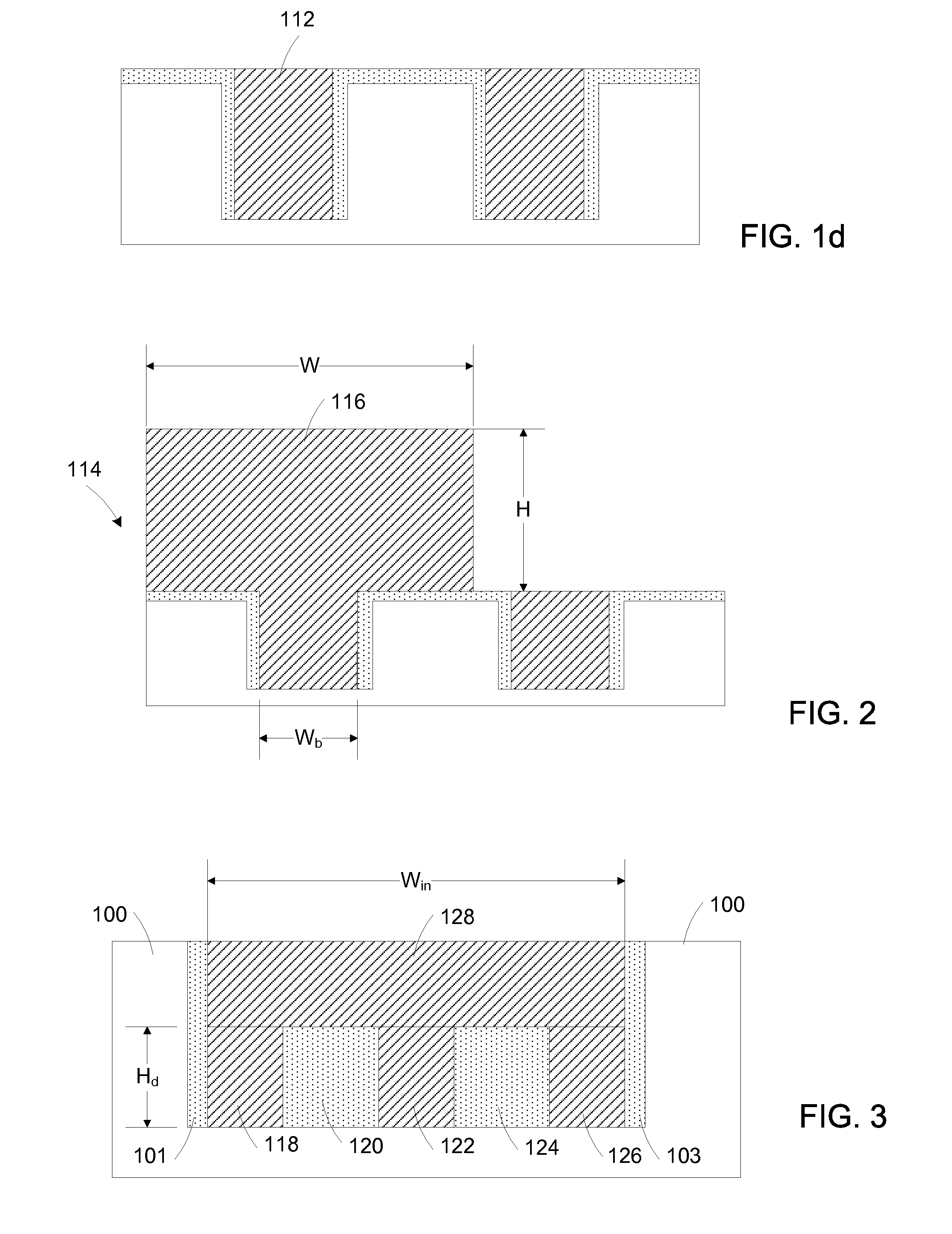
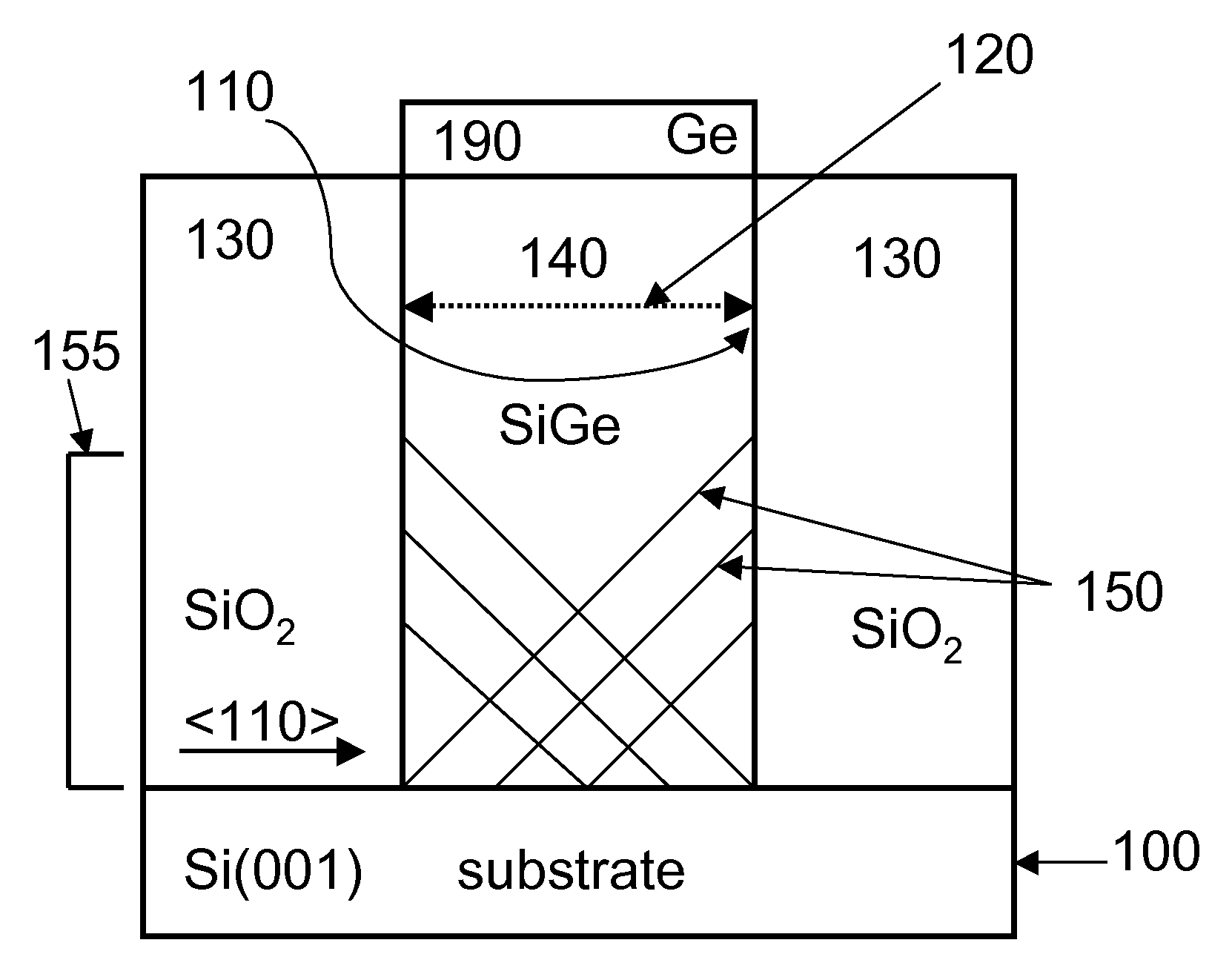
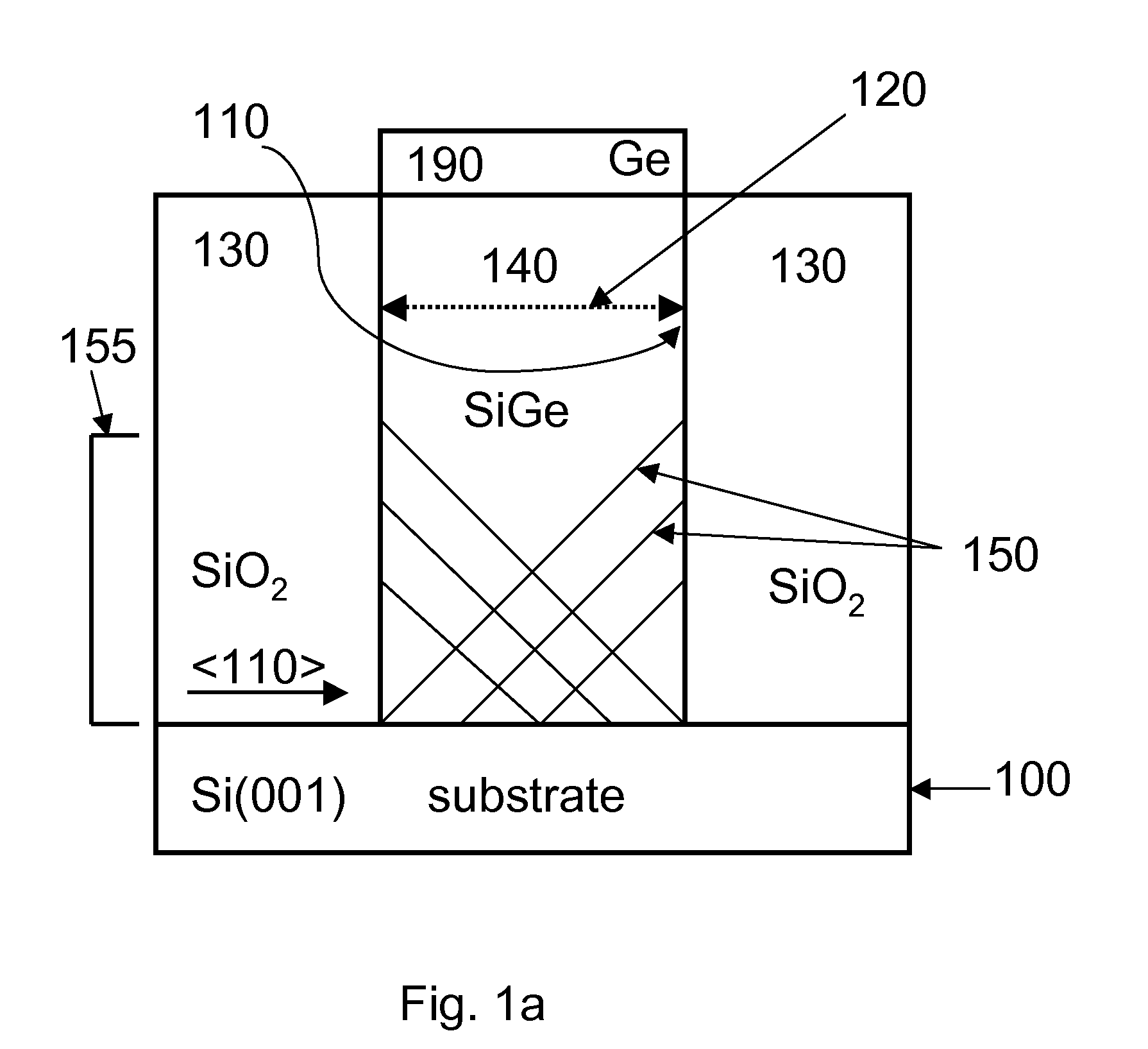
Non-silicon based semiconductor devices are integrated into silicon fabrication processes by using aspect-ratio-trapping materials. Non-silicon light-sensing devices in a least a portion of a crystalline material can output electrons generated by light absorption therein. Exemplary light-sensing devices can have relatively large micron dimensions. As an exemplary application, complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor photodetectors are formed on a silicon substrate by incorporating an aspect-ratio-trapping technique.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fabrication and structures of crystalline material
InactiveUS20100072515A1Reduce surface roughnessReduce the presence of impuritiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrappingCrystalline materials
A surface of the first semiconductor crystalline material has a reduced roughness. A semiconductor device includes a low defect, strained second semiconductor crystalline material over the surface of the first crystalline material. A surface of the strained second semiconductor crystalline material has a reduced roughness. One example includes obtaining a surface with reduced roughness by creating process parameters that reduce impurities at an interfacial boundary between the first and second semiconductor crystalline materials. In one embodiment, the first semiconductor crystalline material can be confined by an opening in an insulator having an aspect ratio sufficient to trap defects using Aspect Ratio Trapping techniques.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fabrication of strained heterojunction structures
ActiveUS20060134893A1Improve featuresHigh carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionLayer interface
Growth of multilayer films is carried out in a manner which allows close control of the strain in the grown layers and complete release of the grown films to allow mounting of the released multilayer structures on selected substrates. A layer of material, such as silicon-germanium, is grown onto a template layer, such as silicon, of a substrate having a sacrificial layer on which the template layer is formed. The grown layer has a lattice mismatch with the template layer so that it is strained as deposited. A top layer of crystalline material, such as silicon, is grown on the alloy layer to form a multilayer structure with the grown layer and the template layer. The sacrificial layer is preferentially etched away to release the multilayer structure from the sacrificial layer, relaxing the grown layer and straining the crystalline layers interfaced with it.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
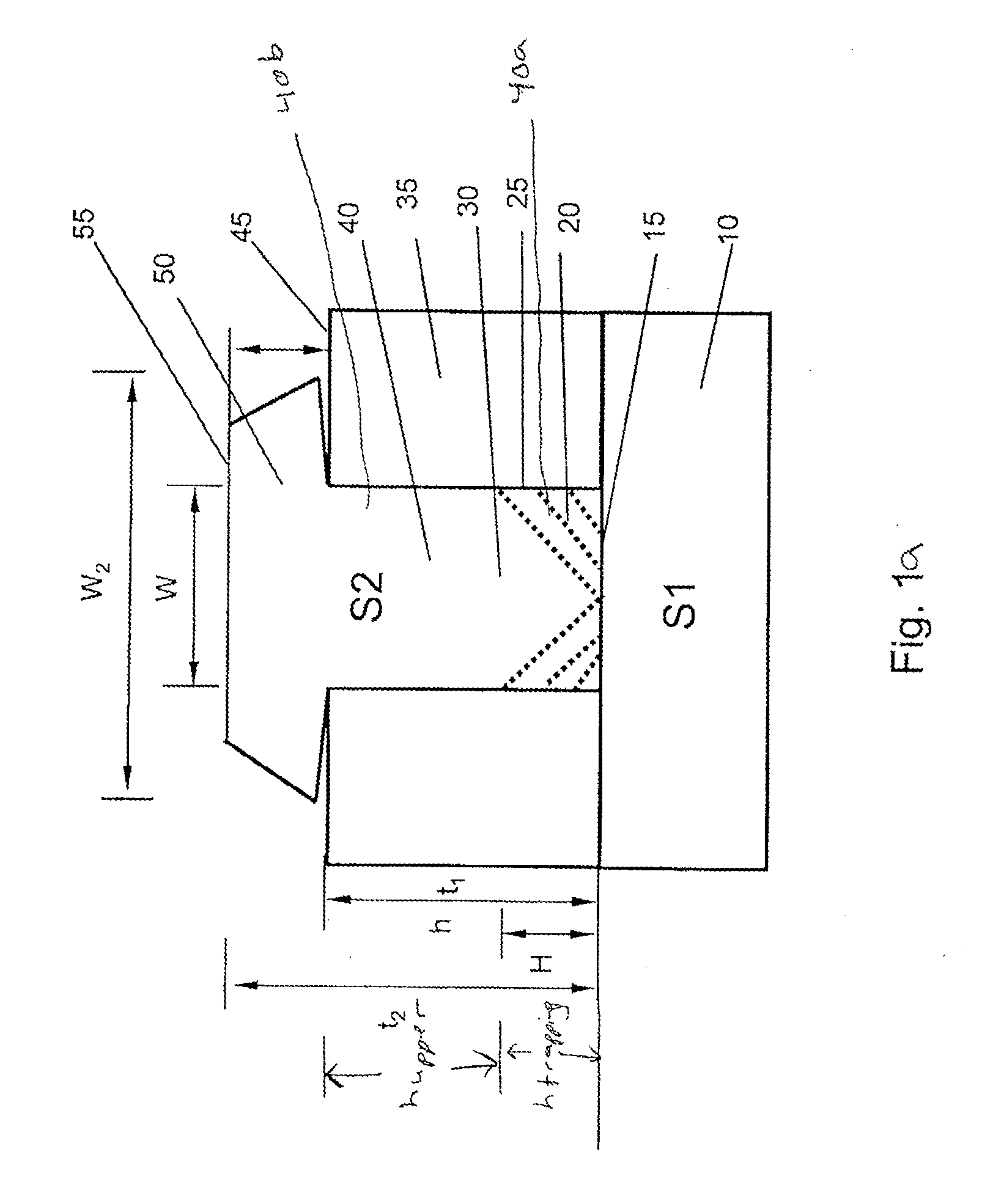
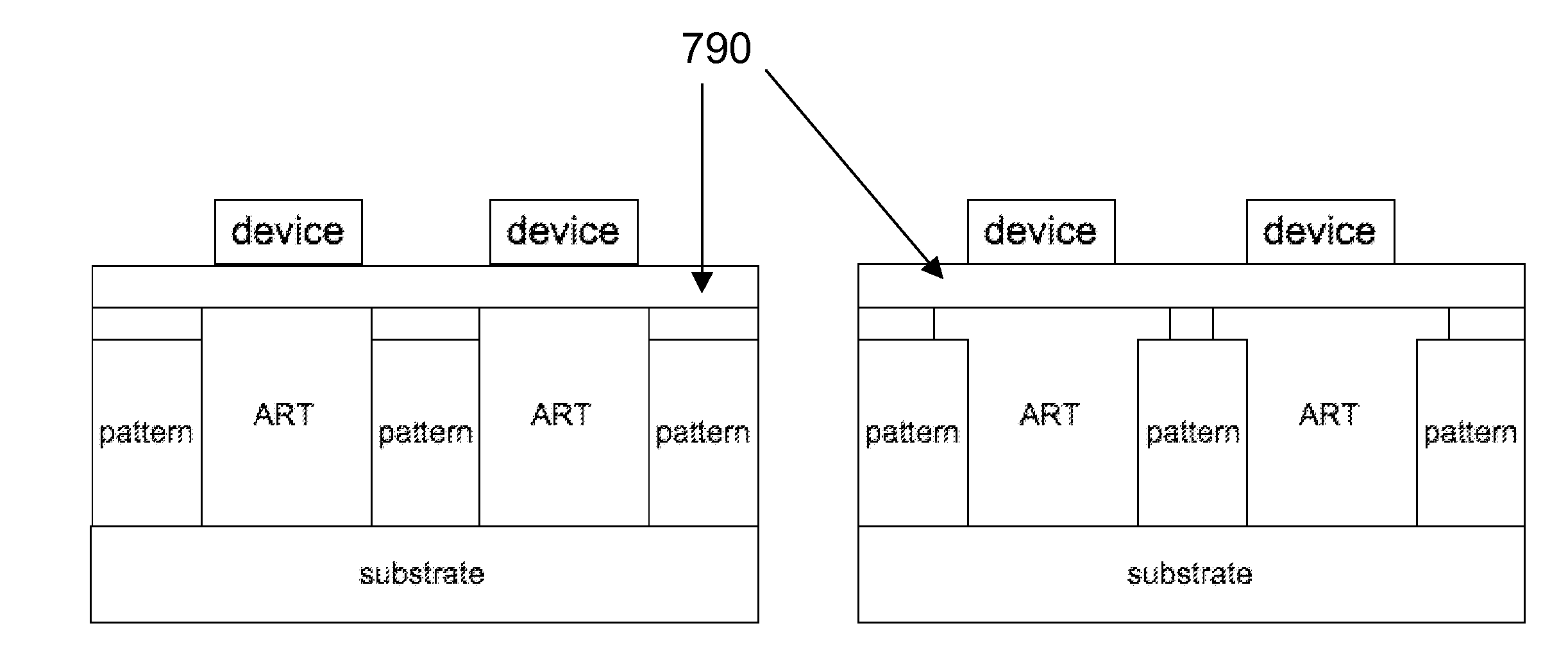
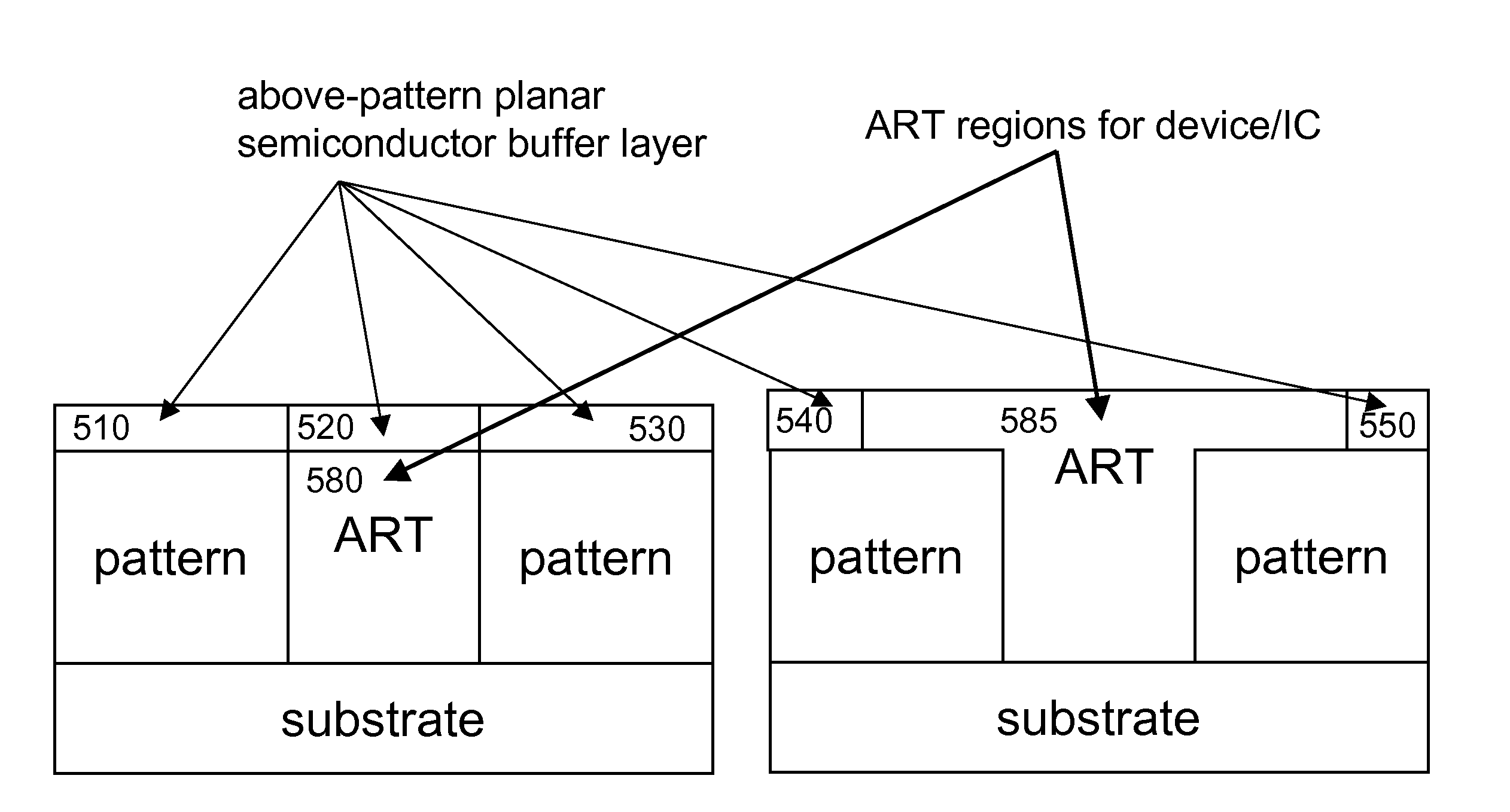
Reduction of edge effects from aspect ration trapping
ActiveUS20100025683A1Reduce edge effectsReduce disadvantagesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEdge effectsTrapping
A device includes a crystalline material within an area confined by an insulator. In one embodiment, the area confined by the insulator is an opening in the insulator having an aspect ratio sufficient to trap defects using an ART technique. Method and apparatus embodiments of the invention can reduce edge effects in semiconductor devices. Embodiments of the invention can provide a planar surface over a buffer layer between a plurality of uncoalesced ART structures.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Polishing of small composite semiconductor materials
ActiveUS20100012976A1Reduced and minimal dishingReduced and minimal and overpolishSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsCrystalline materials
A device includes a crystalline material within an area confined by an insulator. A surface of the crystalline material has a reduced roughness. One example includes obtaining a surface with reduced roughness by using a planarization process configured with a selectivity of the crystalline material to the insulator greater than one. In a preferred embodiment, the planarization process uses a composition including abrasive spherical silica, H2O2 and water. In a preferred embodiment, the area confined by the insulator is an opening in the insulator having an aspect ratio sufficient to trap defects using an ART technique.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
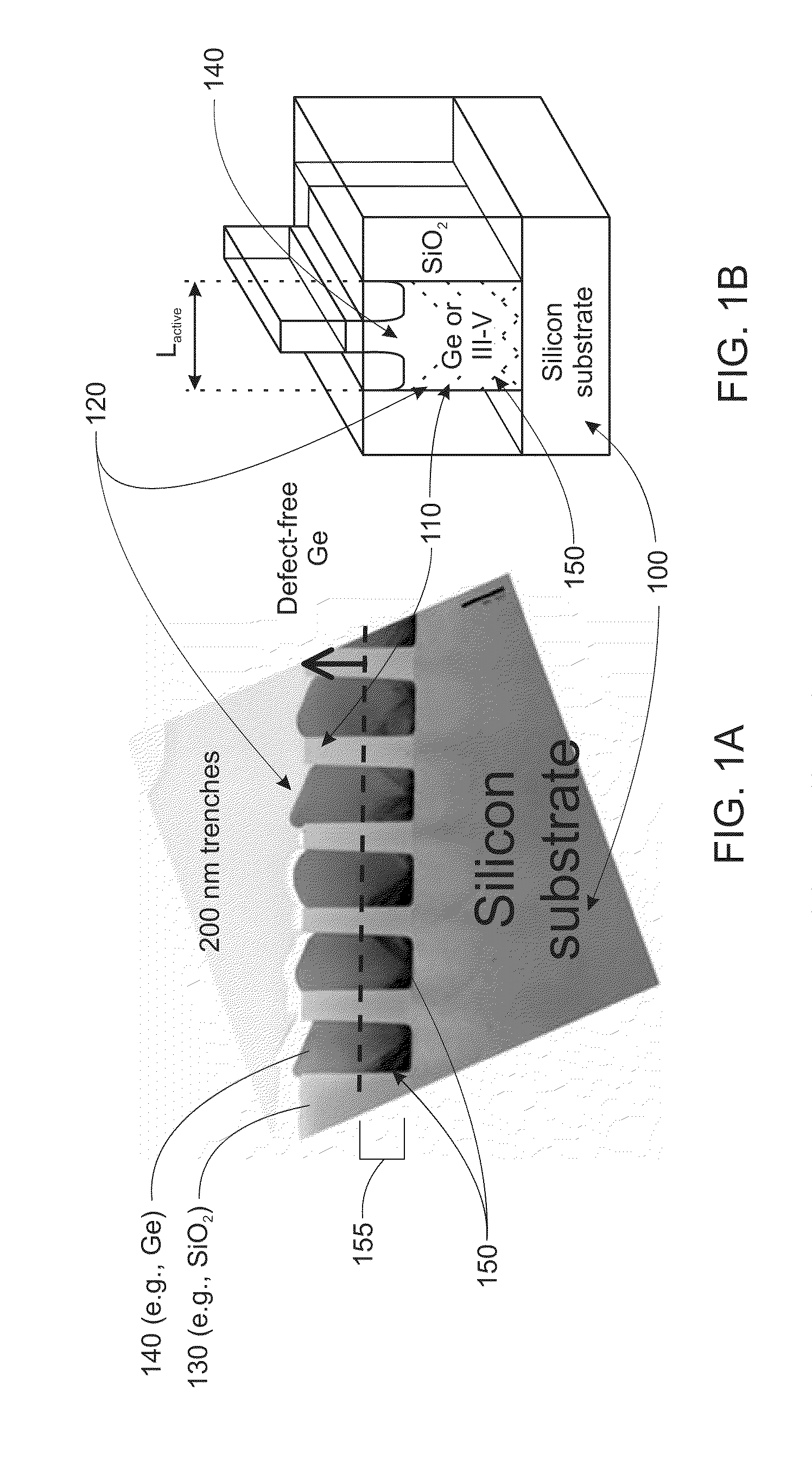
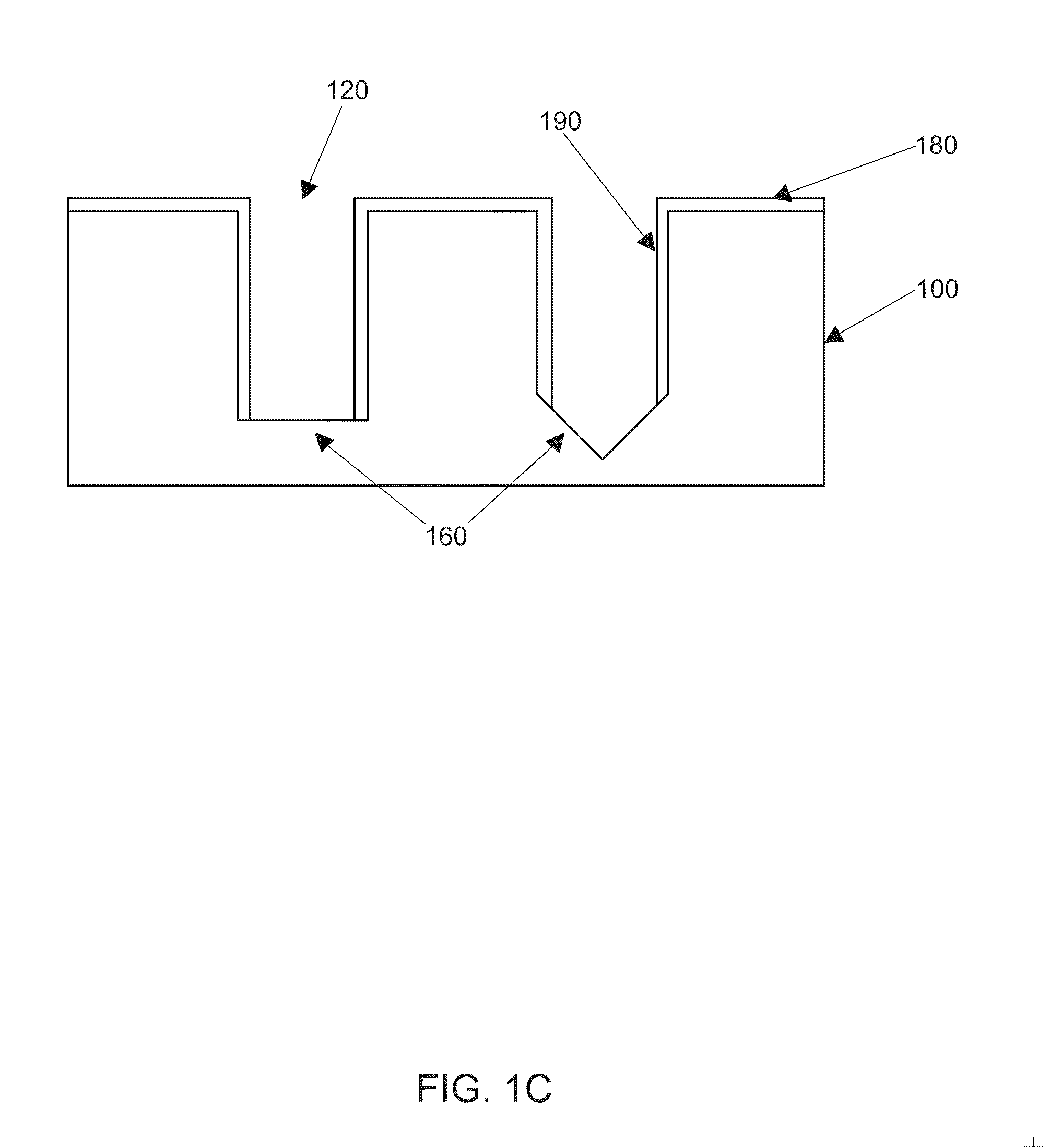
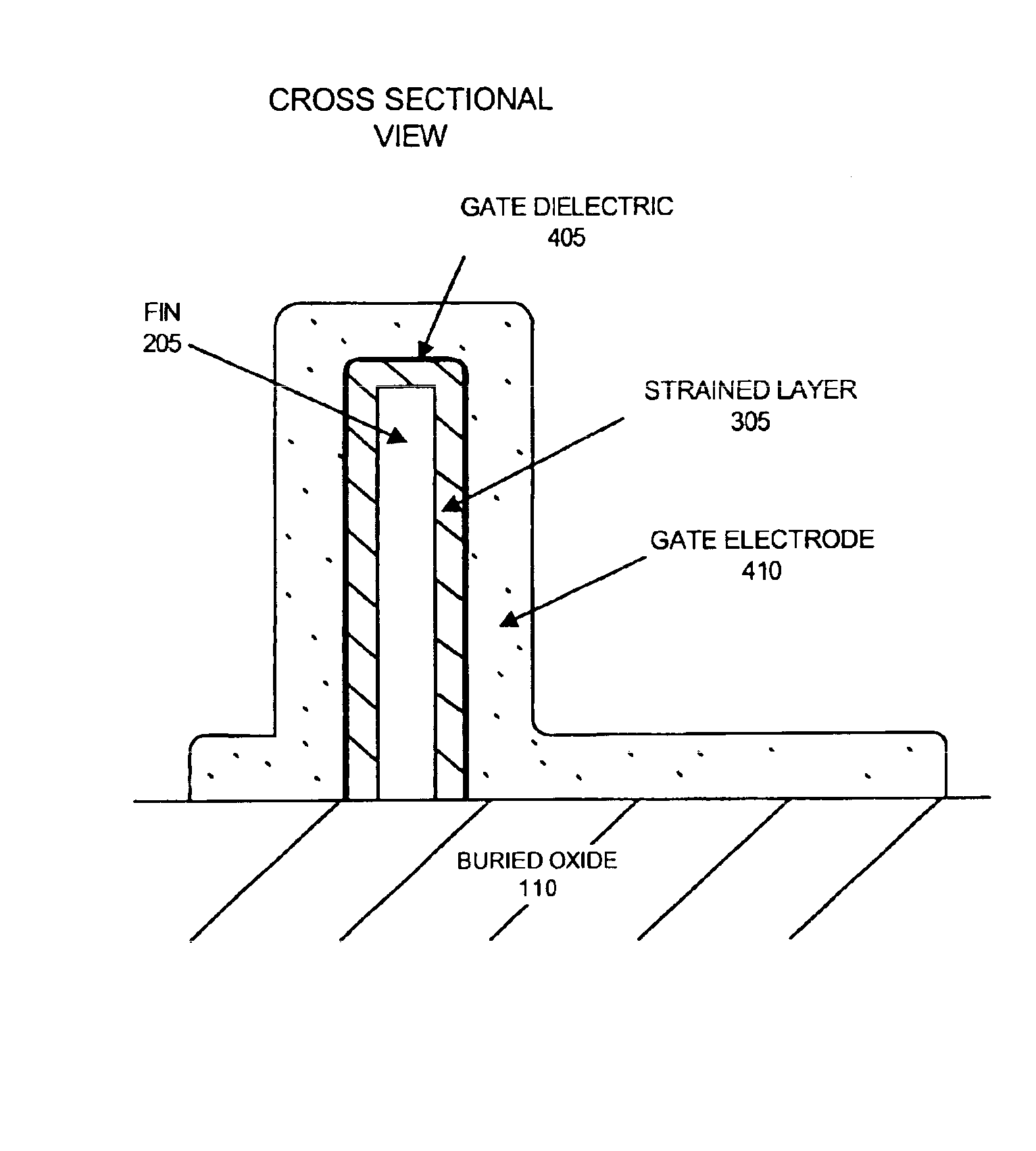
Strained channel FinFET
InactiveUS6897527B2High carrier mobilityImproving FinFET performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesTensile strainCrystalline materials
A semiconductor device includes a fin and a layer formed on at least a portion of the fin. The fin includes a first crystalline material. The layer includes a second crystalline material, where the first crystalline material has a larger lattice constant than the second crystalline material to induce tensile strain within the layer.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FOUNDRY TECH LLC
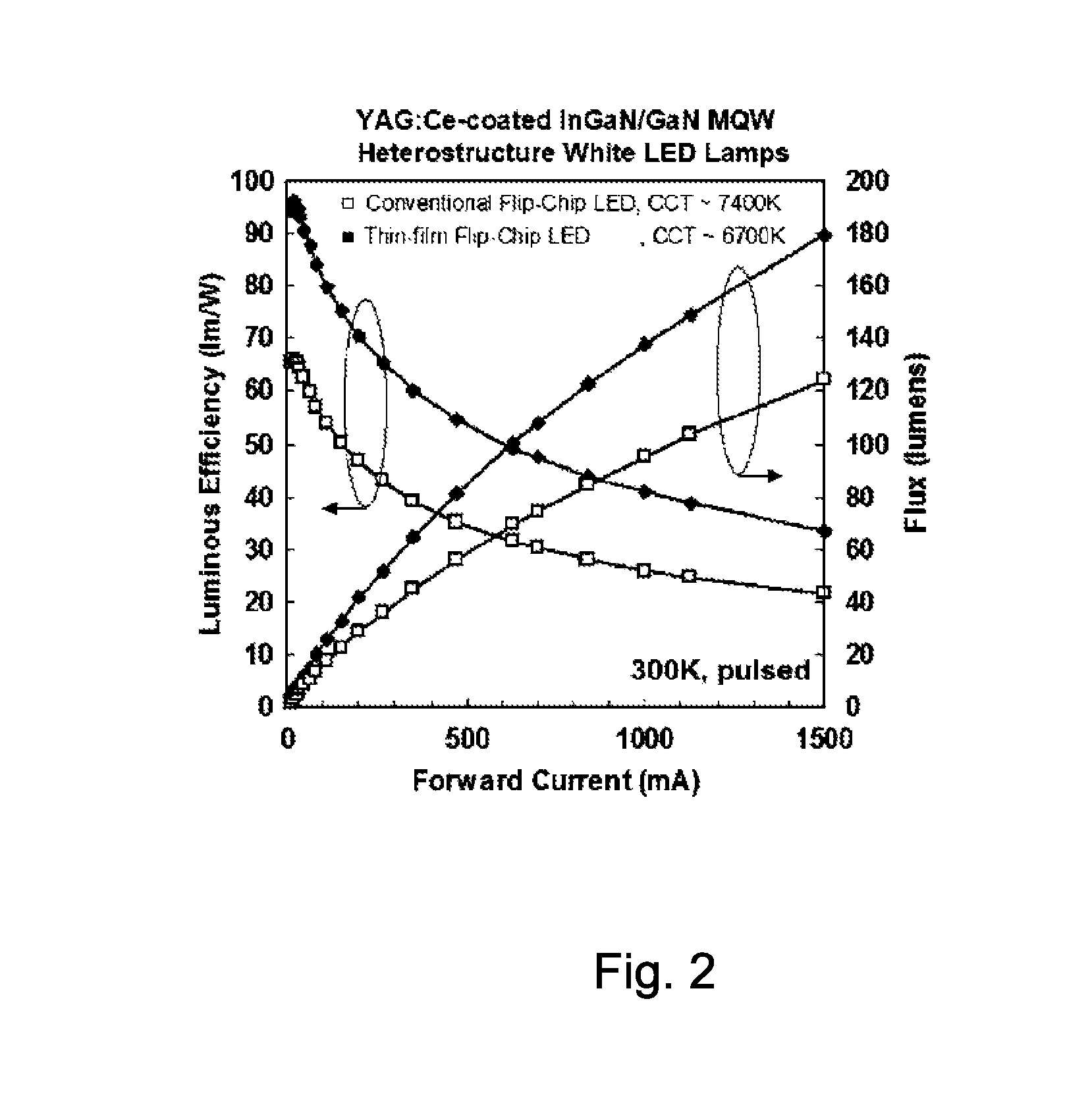
Thin film solar cell
InactiveUS20080078444A1Good choiceImprovement factorPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHigh energyUltraviolet
Optimal structures for high efficiency thin film silicon solar energy conversion devices and systems are disclosed. Thin film silicon active layer photoelectron conversion structures using ion implantation are disclosed. Thin film semiconductor devices optimized for exploiting the high energy and ultraviolet portion of the solar spectrum at the earths surface are also disclosed. Solar cell fabrication using high oxygen concentration single crystal silicon substrates formed using in preference the CZ method are used advantageously. Furthermore, the present invention discloses optical coatings for advantageous coupling of solar radiation into thin film solar cell devices via the use of rare-earth metal oxide (REOx), rare-earth metal oxynitride (REOxNy) and rare-earth metal oxy-phosphide (REOxPy) glasses and or crystalline material. The rare-earth metal is chosen from the group commonly known in the periodic table of elements as the lanthanide series.
Owner:IQE
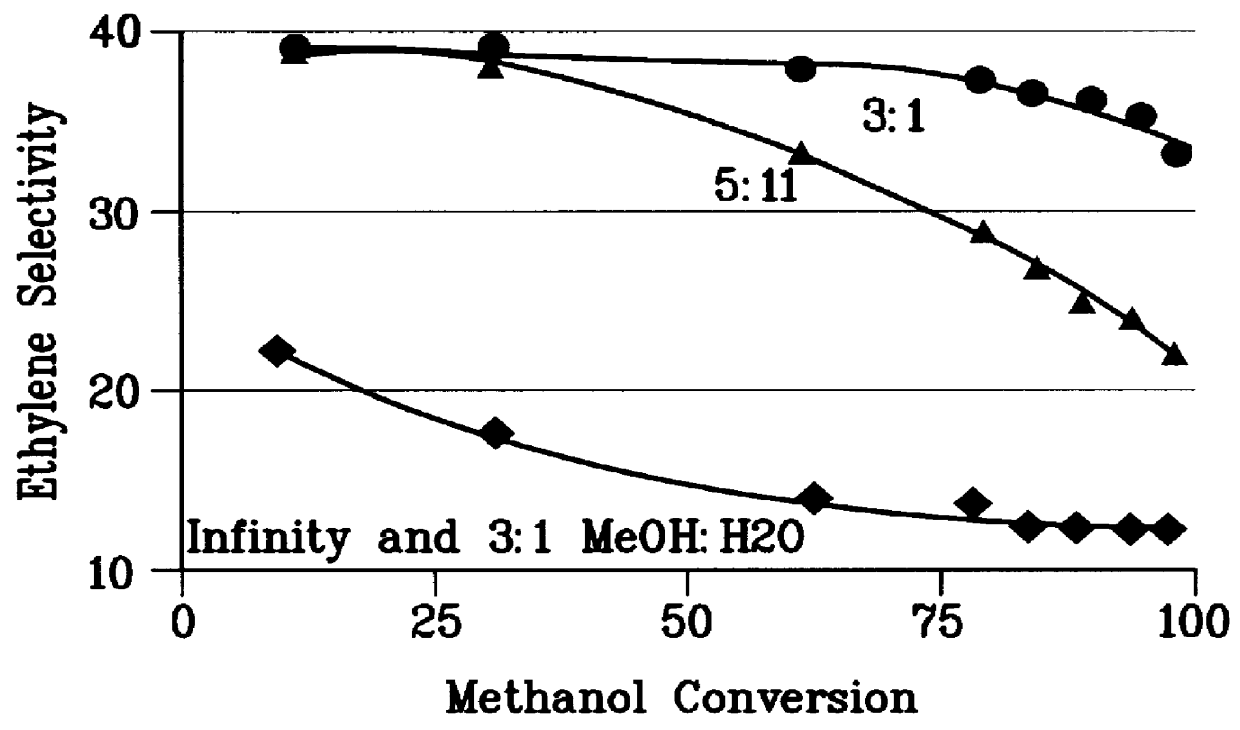
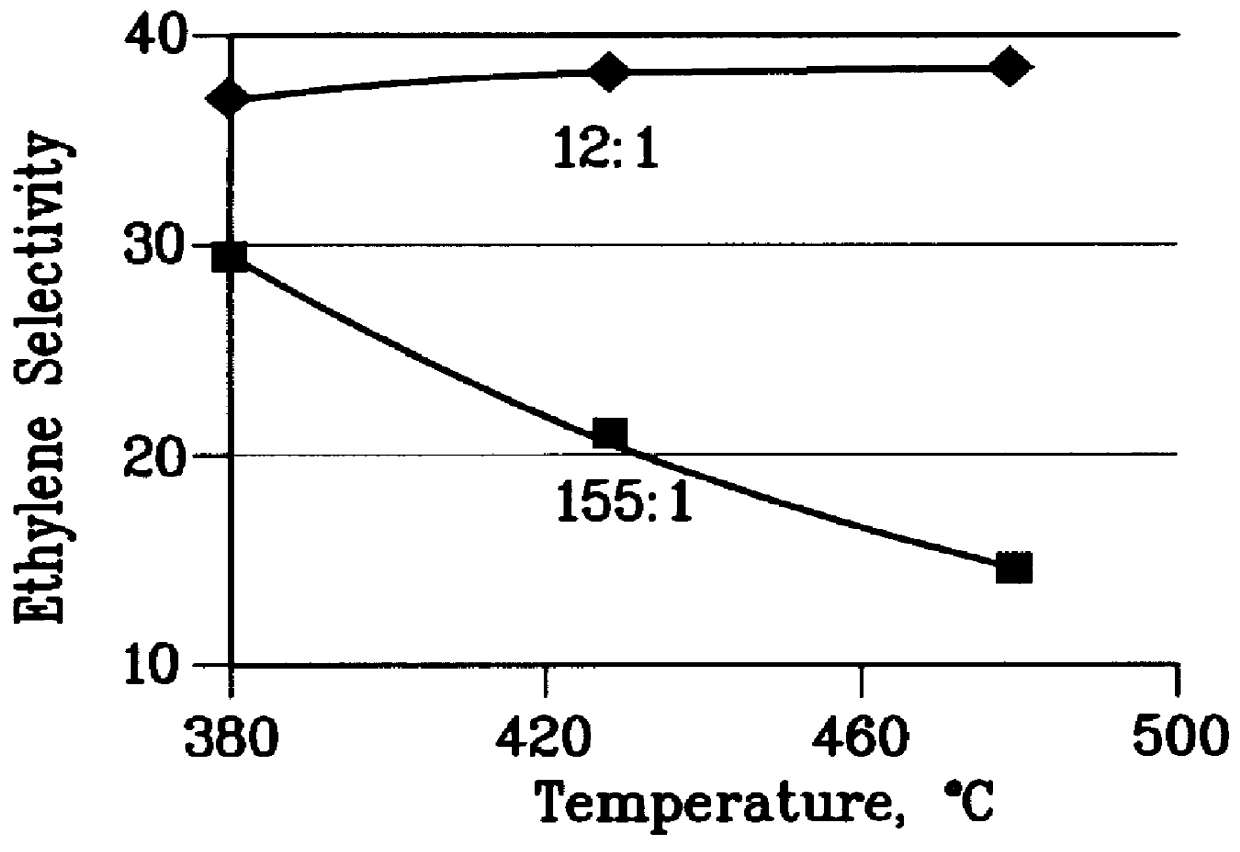
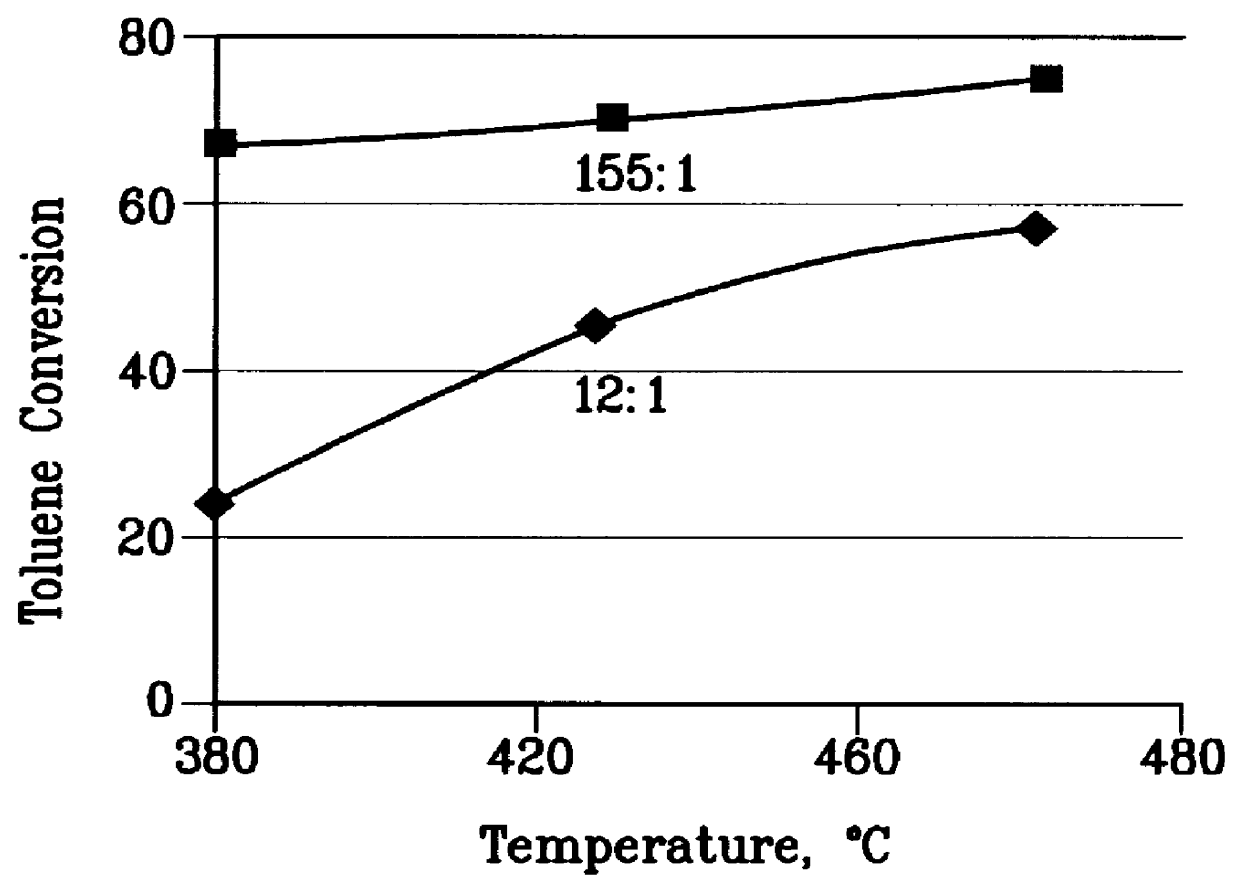
Process for producing light olefins
InactiveUS6046372AMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAlkyl transferCrystalline materials
There is provided a process for converting methanol and / or dimethyl ether to a product containing C2 to C4 olefins which comprises the step of contacting a feed which contains methanol and / or dimethyl ether with a catalyst comprising a porous crystalline material, said contacting step being conducted in the presence of an aromatic compound under conversion conditions including a temperature of 350 DEG C. to 480 DEG C. and a methanol partial pressure in excess of 10 psia (70 kPa), said porous crystalline material having a pore size greater than the critical diameter of the aromatic compound and the aromatic compound being capable of alkylation by the methanol and / or dimethyl ether under said conversion conditions.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
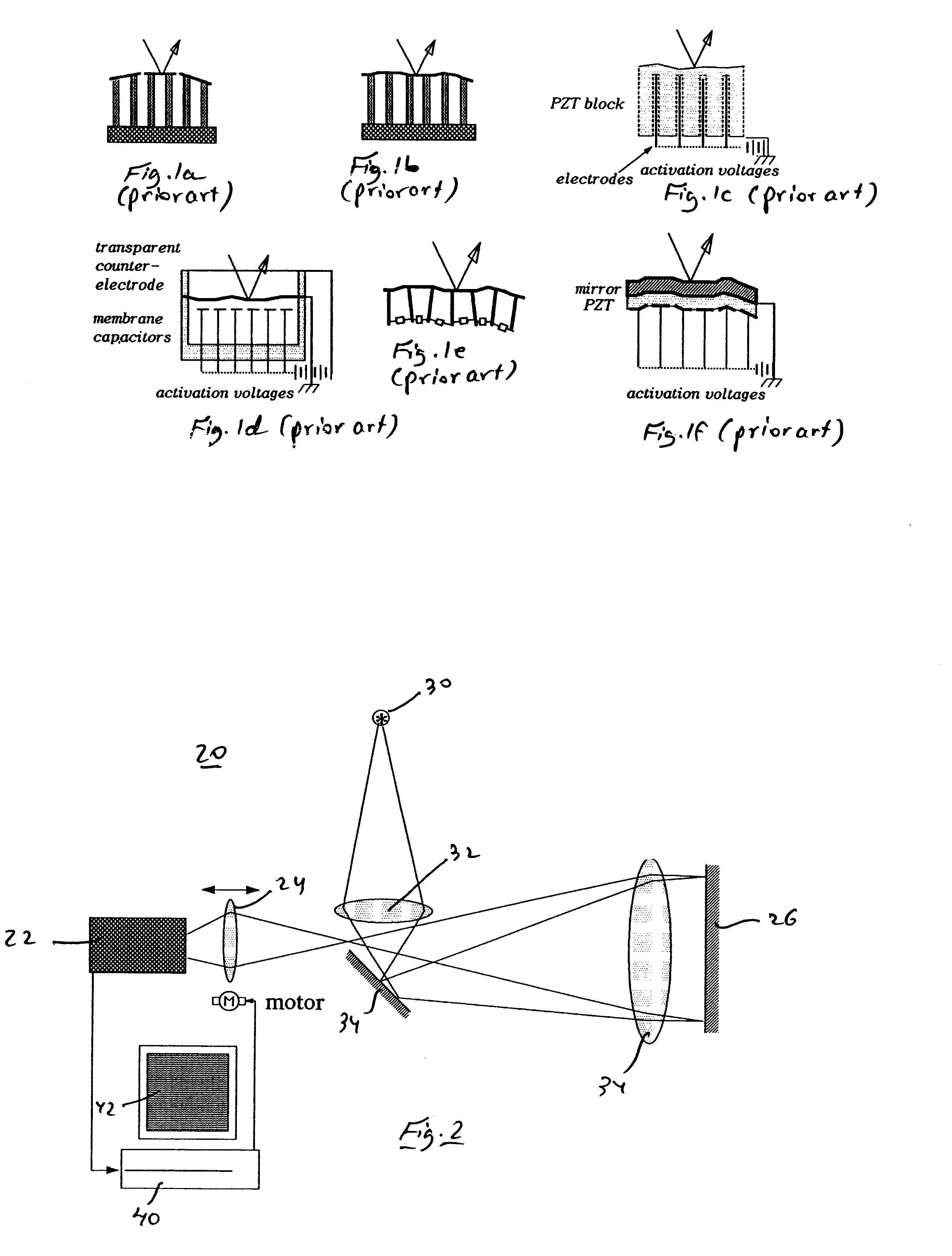
Voltage and light induced strains in porous crystalline materials and uses thereof
InactiveUS6728024B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionCrystalline materialsElectric potential
A piezoelectric device is disclosed, which includes a first element of porous crystalline material, a second element being attached to, or integrally formed with, the first element, and at least one electrode being in electrical contact with the first element, such that subjecting the first element to an electric potential via the at least one electrode results in a strain induced by the first element on the second element. Also disclosed is a piezooptic device which includes a first element of porous crystalline material, a second element being attached to, or integrally formed with, the first element, and a light source, such that subjecting the first element to light originating from the light source results in a strain induced by the first element on the second element.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Catalyst and process for converting methanol to hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6048816AMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystCrystalline materialsDimethyl ether
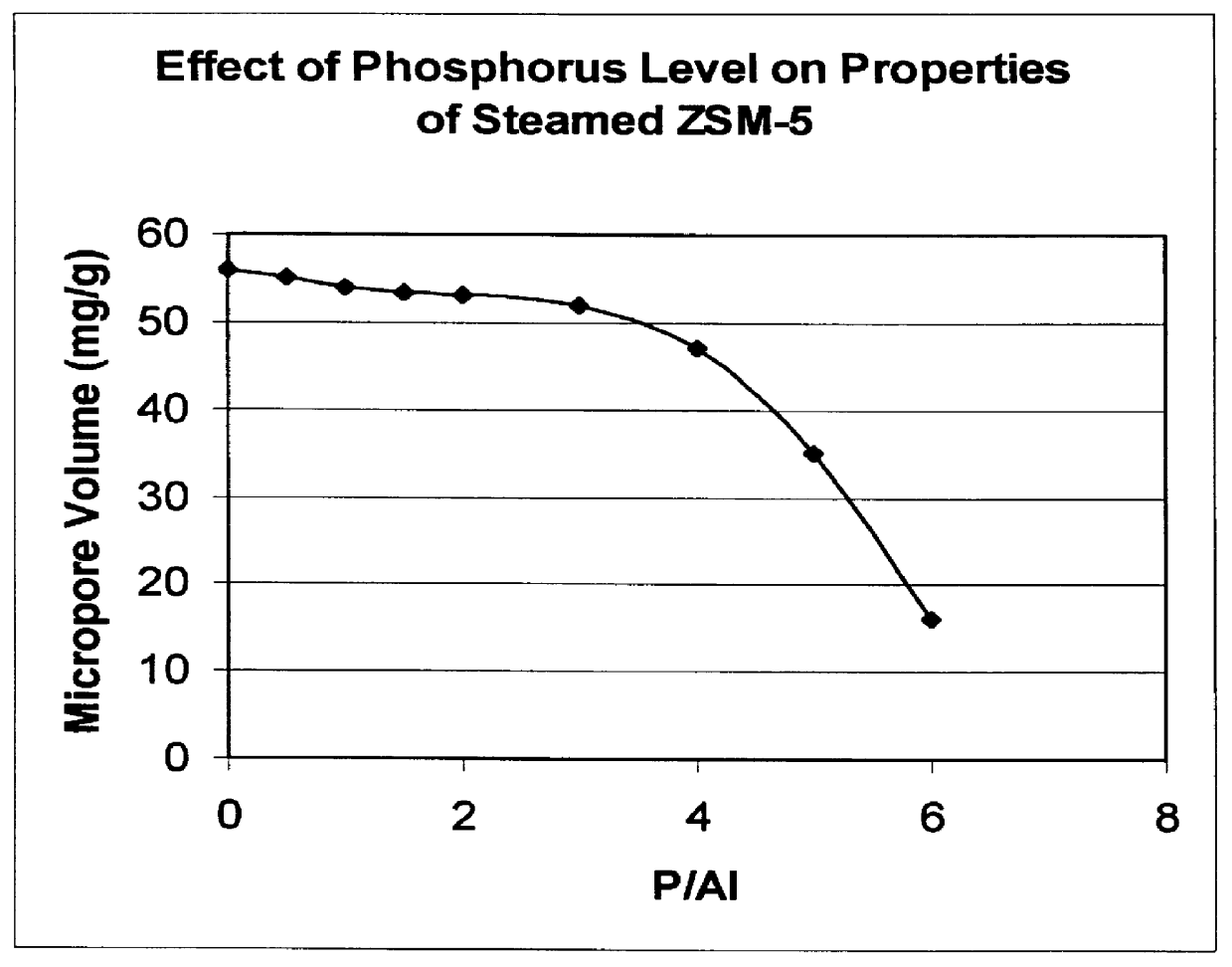
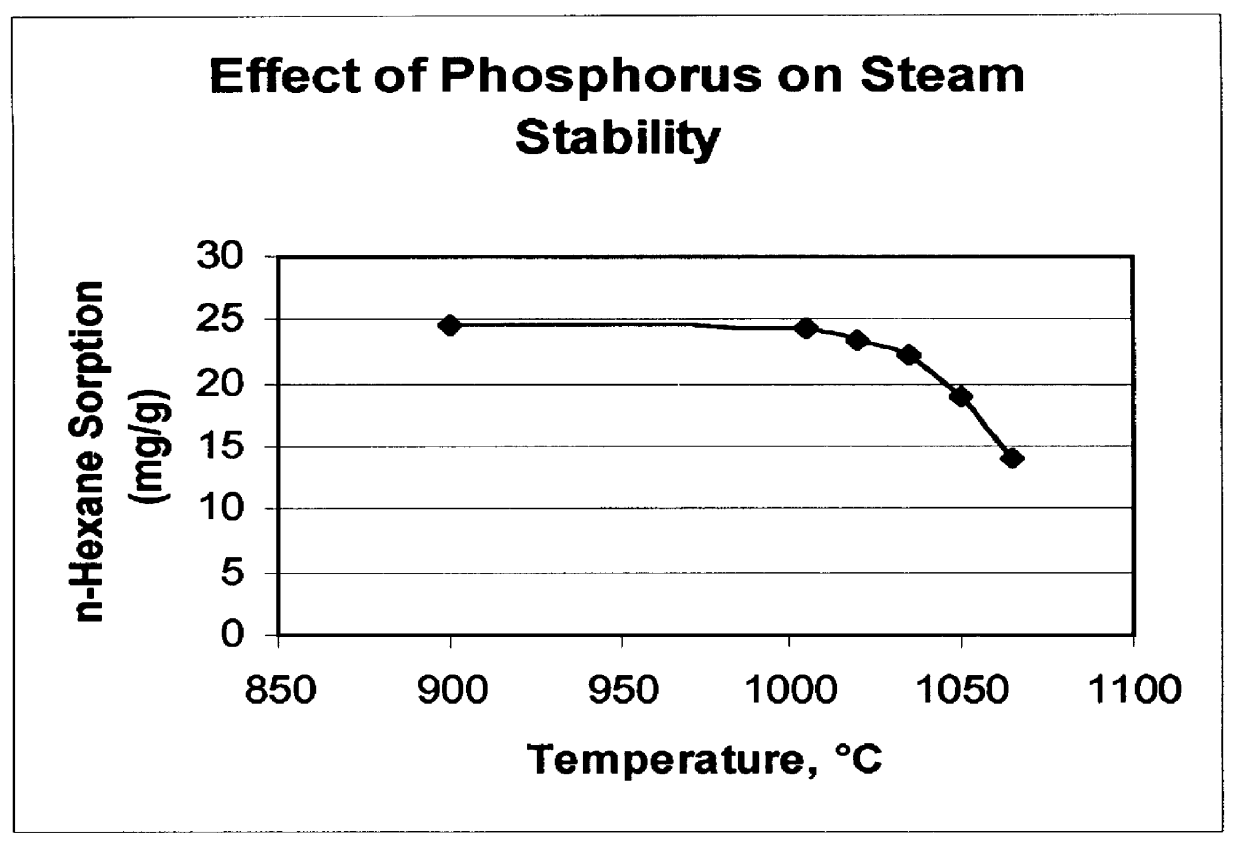
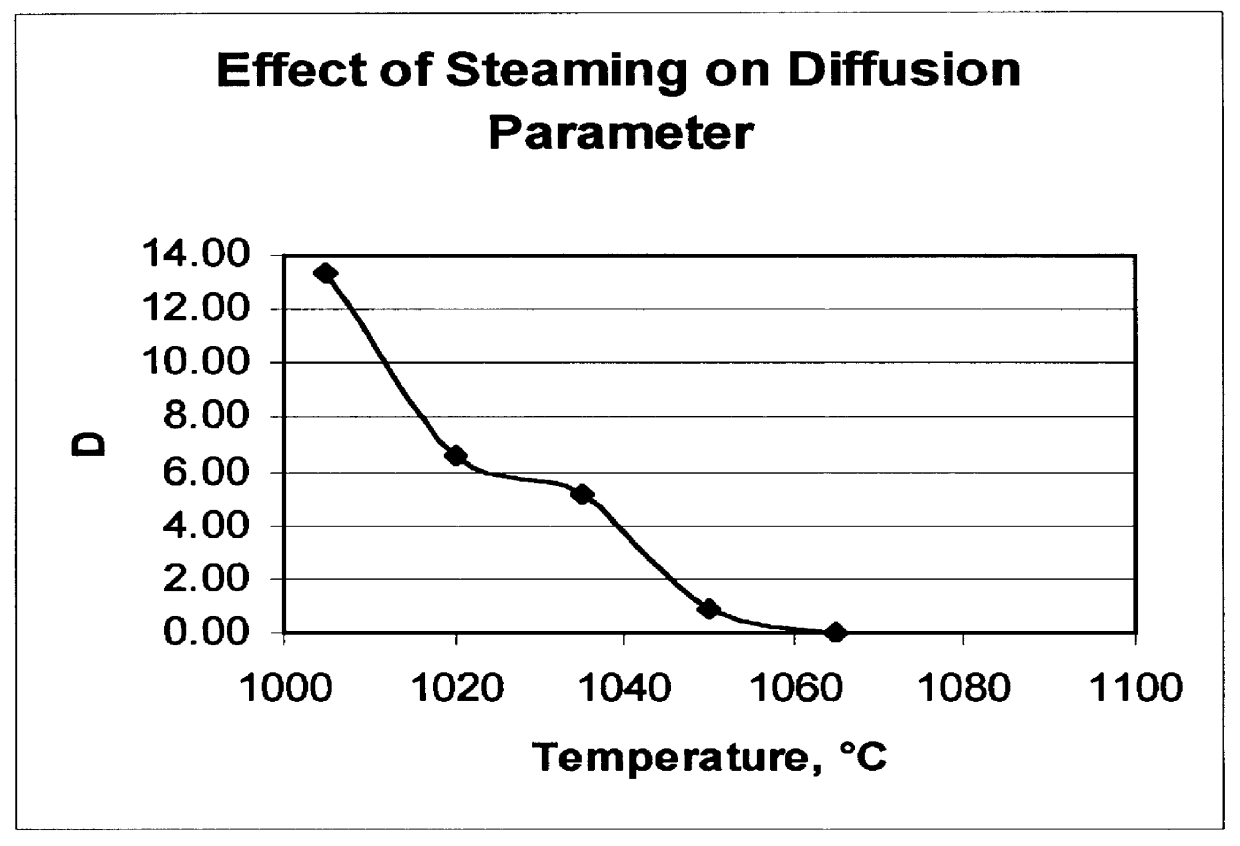
There is provided a catalyst and a process for converting methanol or dimethyl ether to a product containing C2 to C4 olefins. The catalyst comprises a porous crystalline material having a Diffusion Parameter for 2,2-dimethylbutane of about 0.1-20 sec-1 when measured at a temperature of 120 DEG C. and a 2,2-dimethylbutane pressure of 60 torr (8 kPa). In addition, the catalyst is characterized by a hydrothermal stability such that, after steaming the catalyst at 1025 DEG C. for 45 minutes in 1 atmosphere steam, the catalyst exhibits a methanol conversion activity of at least 50% when contacted with methanol at a methanol partial pressure of 1 atmosphere, a temperature of 430 DEG C. and 0.5 WHSV. The porous crystalline material is preferably a medium-pore zeolite, particularly ZSM-5, which contains phosphorus and has been severely steamed at a temperature of at least 950 DEG C.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Coated particles, methods of making and using
InactiveUS6989195B2Simple processOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryLiquid crystallineActive agent
A particle coated with a nonlamellar material such as a nonlamellar crystalline material, a nonlamellar amorphous material, or a nonlamellar semi-crystalline material includes an internal matrix core having at least one a nanostructured liquid phase, or at least on nanostructured liquid crystalline phase or a combination of the two is used for the delivery of active agents such as pharmaceuticals, nutrients, pesticides, etc. The coated particle can be fabricated by a variety of different techniques where the exterior coating is a nonlamellar material such as a nonlamellar crystalline material, a nonlamellar amorphous material, or a nonlamellar semi-crystalline material.
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
Aluminum oxide material for optical data storage
InactiveUS6846434B2Increase of write/read rateHigh data storage densityPolycrystalline material growthPhotosensitive materialsVacancy defectDopant
The present invention provides aluminum oxide crystalline materials including dopants and oxygen vacancy defects and methods of making such crystalline materials. The crystalline materials of the present invention have particular utility in optical data storage applications.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Epitazial growth of crystalline material
ActiveUS20090321882A1Reduce surface roughnessPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystalline materialsMaterials science
A device includes an epitaxially grown crystalline material within an area confined by an insulator. A surface of the crystalline material has a reduced roughness. One example includes obtaining a surface with reduced roughness by creating process parameters which result in the dominant growth component of the crystal to be supplied laterally from side walls of the insulator. In a preferred embodiment, the area confined by the insulator is an opening in the insulator having an aspect ratio sufficient to trap defects using an ART technique.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS20050192175A1Catalyst protectionMolecular sieve catalystsSystems designMetal-organic framework
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Process For Manufacturing A Gallium Rich Gallium Nitride Film
InactiveUS20080282978A1Improve conductivityLow resistivityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsGalliumGallium nitride
A process for the manufacture of a gallium rich gallium nitride film is described. The process comprises (a) preparing a reaction mixture containing a gallium species and a nitrogen species, the gallium species and the nitrogen species being selected such that, when they react with each other, gallium nitride is formed; and (b) growing the gallium rich gallium nitride film from the reaction mixture, by allowing the gallium species to react with the nitrogen species and to deposit gallium nitride on a substrate selected from the group consisting of silicon, glass, sapphire, quartz and crystalline materials having a lattice constant closely matched to gallium nitride, including zinc oxide, optionally with a zinc oxide buffer layer, at a temperature of from about 480° C. to about 900° C. and in the presence of a gaseous environment in which the partial pressure of oxygen is less than 10−4 Torr, wherein the ratio of gallium atoms to nitrogen atoms in the gallium rich gallium nitride film is from 1.01 to 1.20. The invention also provides the option of annealing the gallium rich gallium nitride film at a temperature of from about 20° C. to about 650° C. and for a time sufficient to decrease the resistivity of the film so that it becomes electrically conductive, for instance to a resistivity below 100 ohm.cm.
Owner:BUTCHER KENNETH SCOTT ALEXANDER +2
Methods to fabricate a photoactive substrate suitable for microfabrication
ActiveUS20110195360A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithium oxideGlass transition
Owner:3D GLASS SOLUTIONS INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20100247965A1Reduce surface roughnessImprove recording densityRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsCrystalline materialsNon magnetic
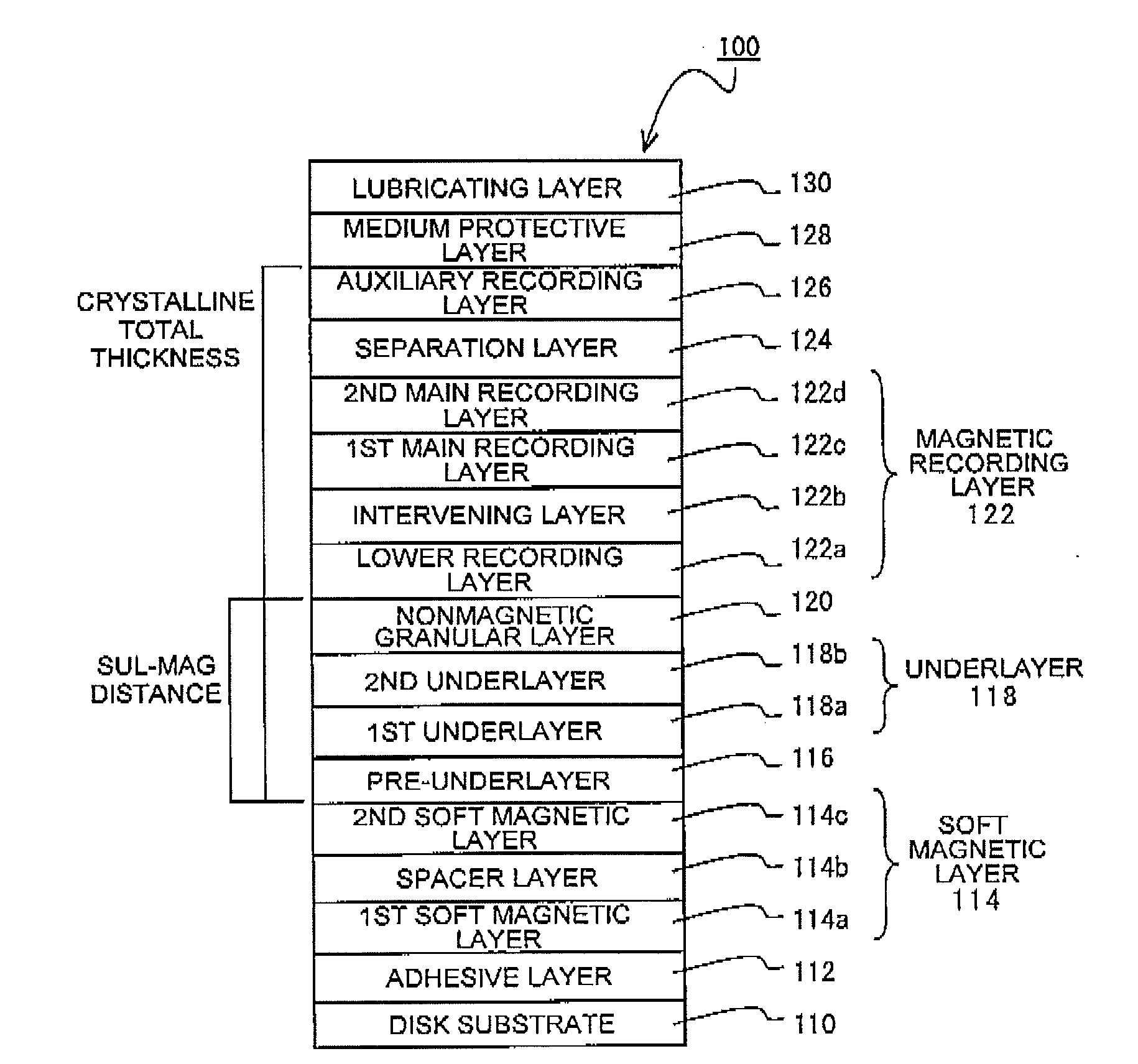
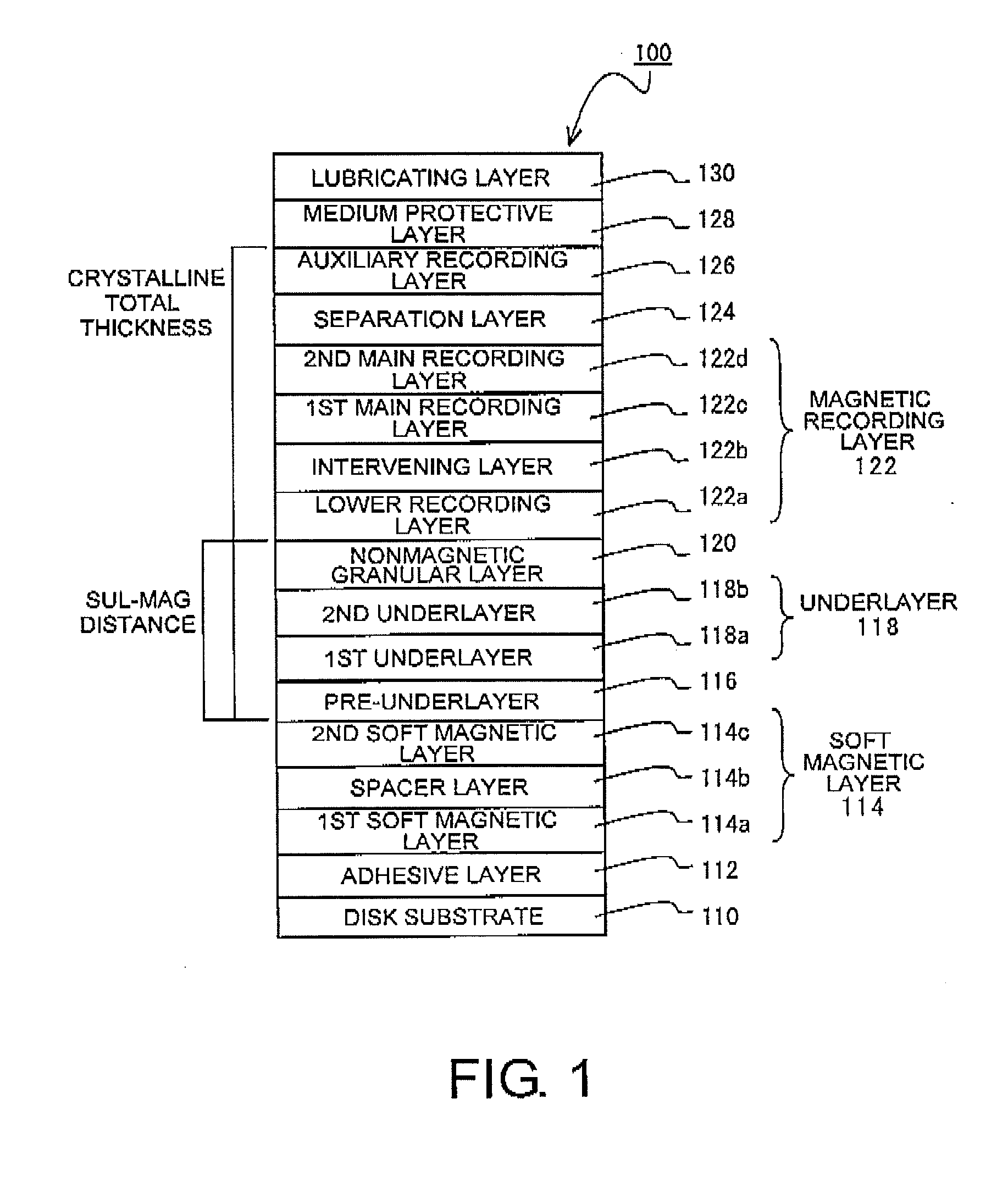
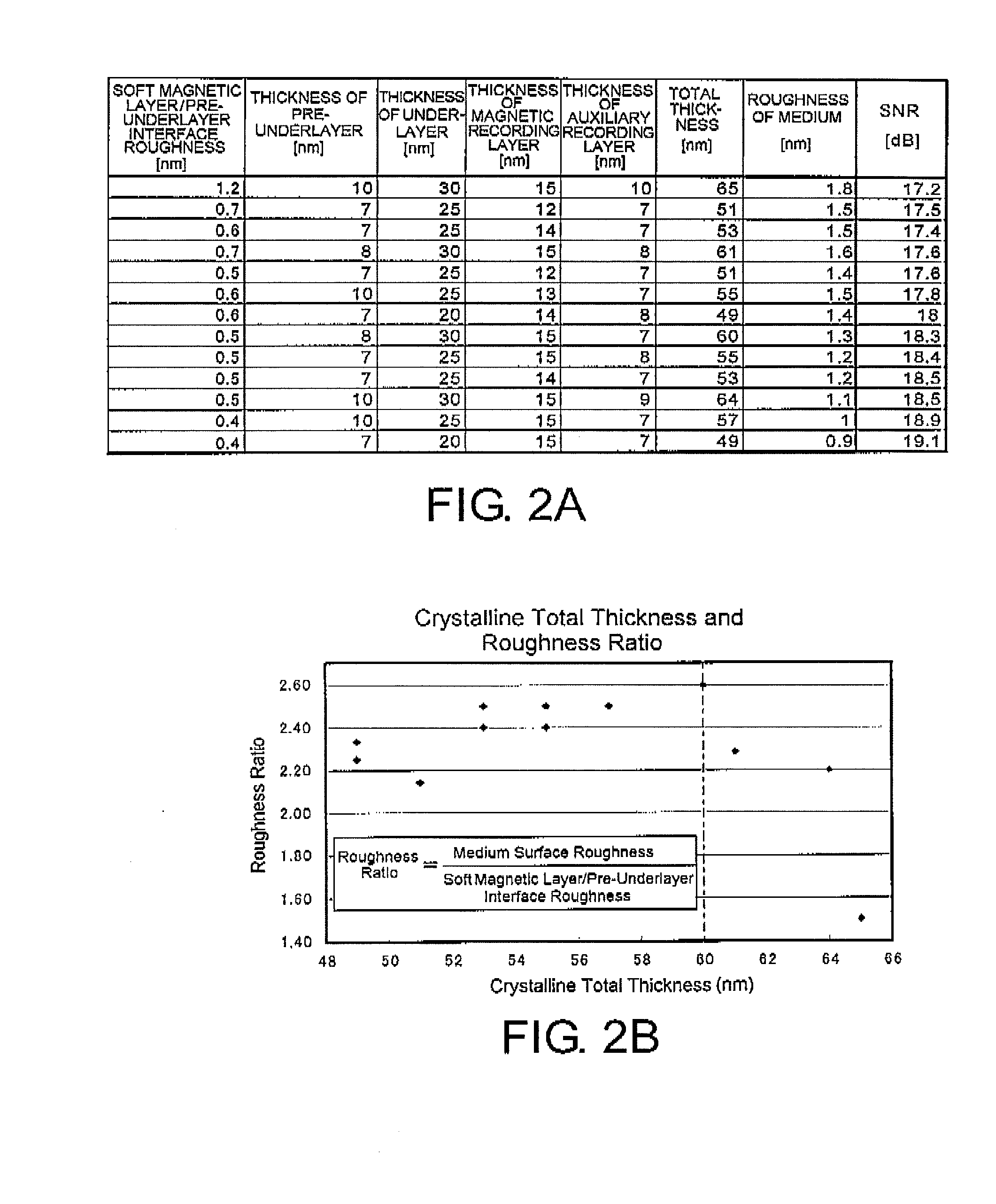
In a perpendicular magnetic recording medium having, over a substrate, a magnetic recording layer, an underlayer made of Ru or a Ru compound and provided below the magnetic recording layer, a pre-underlayer made of a nonmagnetic crystalline material, and a soft magnetic layer provided below the pre-underlayer, when the difference between the highest point and the lowest point of unevenness of the interface between the soft magnetic layer and the pre-underlayer, derived by a cross-sectional TEM image, is given as an interface roughness (nm) and the distance between the soft magnetic layer and the magnetic recording layer, excluding the soft magnetic layer and the magnetic recording layer, is given as a SUL-MAG distance (nm), interface roughness (nm)≦0.4 (nm) and interface roughness×SUL-MAG distance (nm)≦12 (nm) are satisfied.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System comprising a semiconductor device and structure
InactiveUS20110092030A1Reduced flexibilityReduce high cost of manufacturingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLogic cellCrystalline materials
A semiconductor device includes a first mono-crystallized layer including first transistors, and a first metal layer forming at least a portion of connections between the first transistors; and a second layer including second transistors, the second transistors including mono-crystalline material, the second layer overlying the first metal layer, wherein the first metal layer includes aluminum or copper, and wherein the second layer is less than one micron in thickness and includes logic cells.
Owner:MONOLITHIC 3D
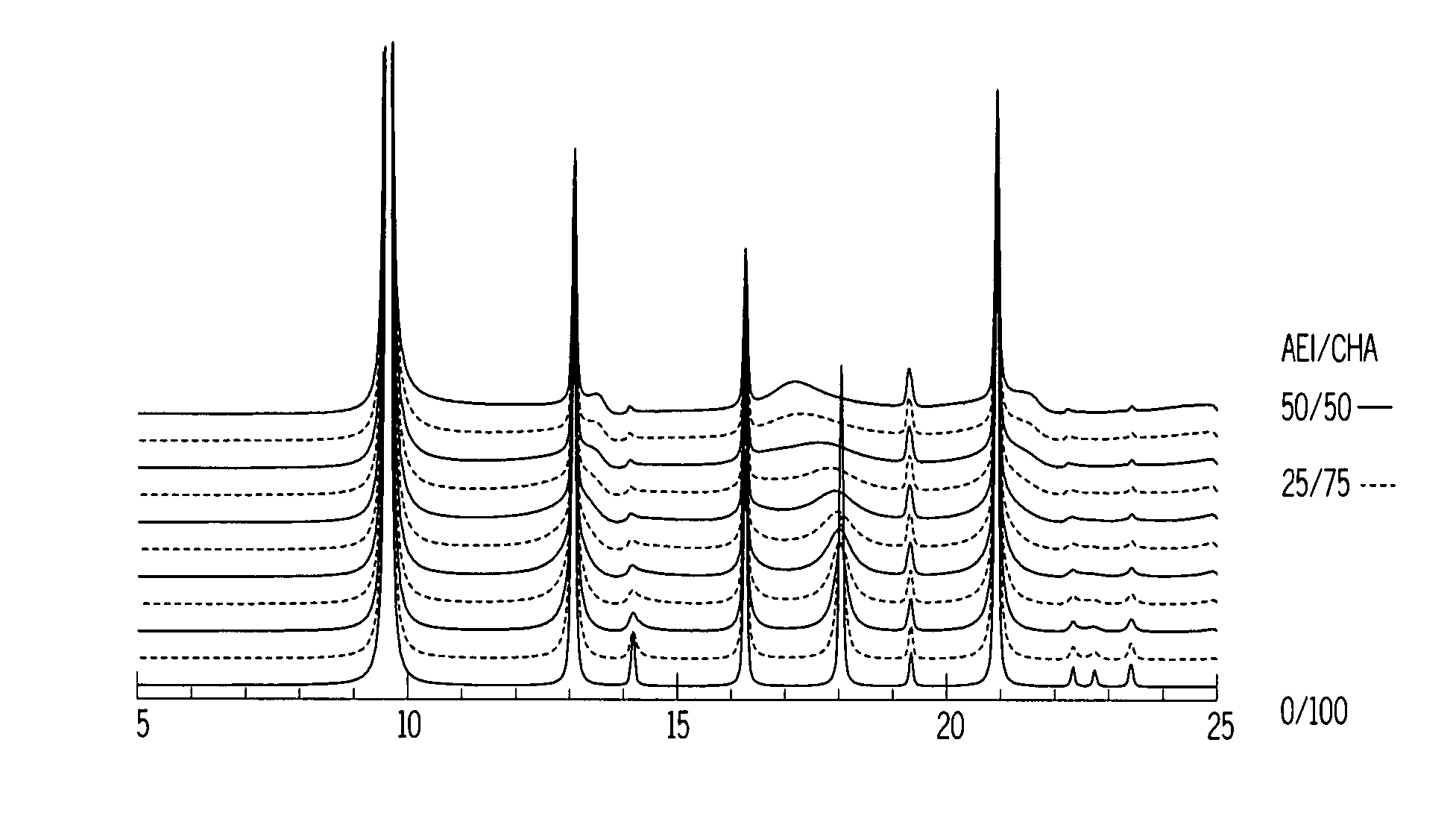
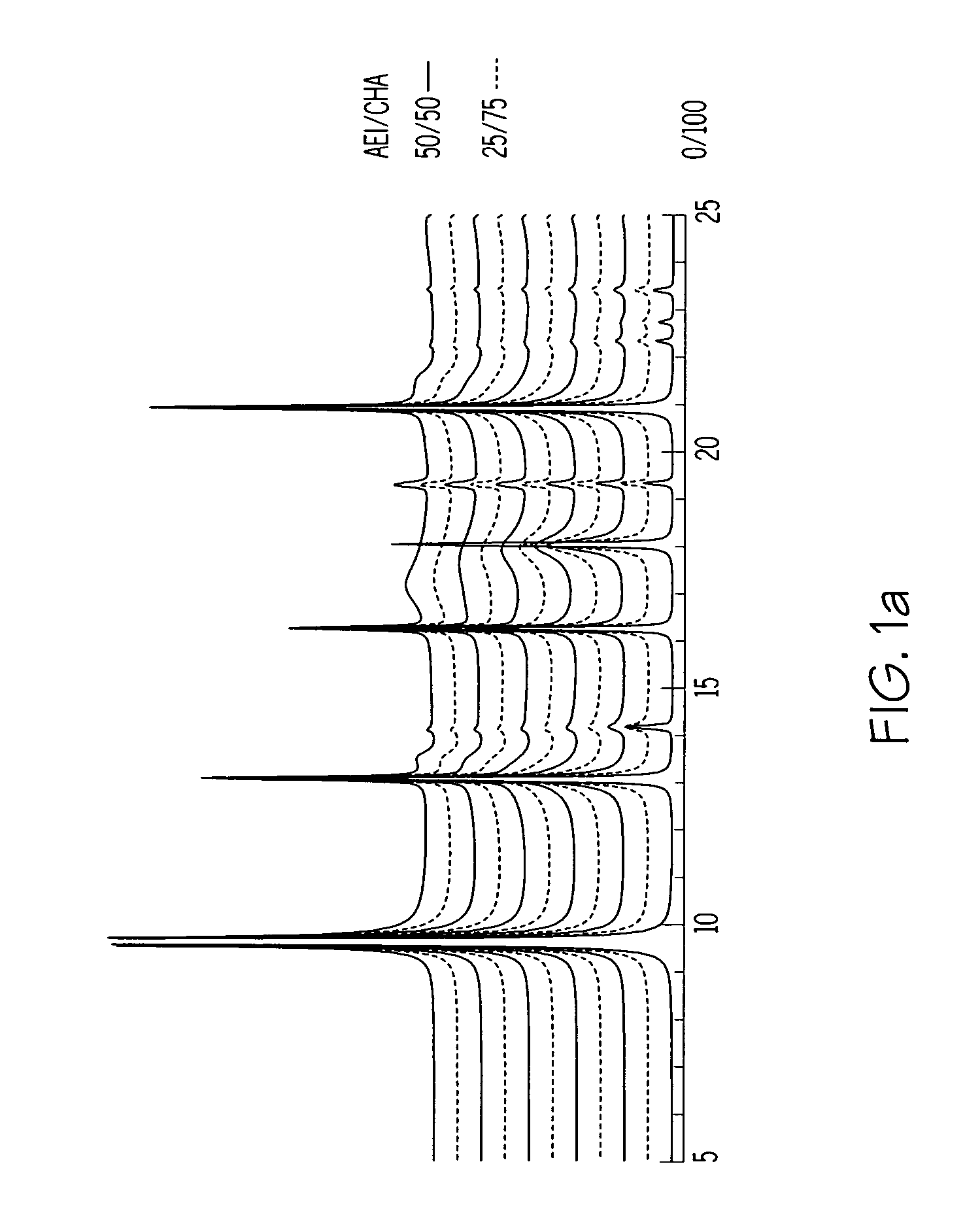
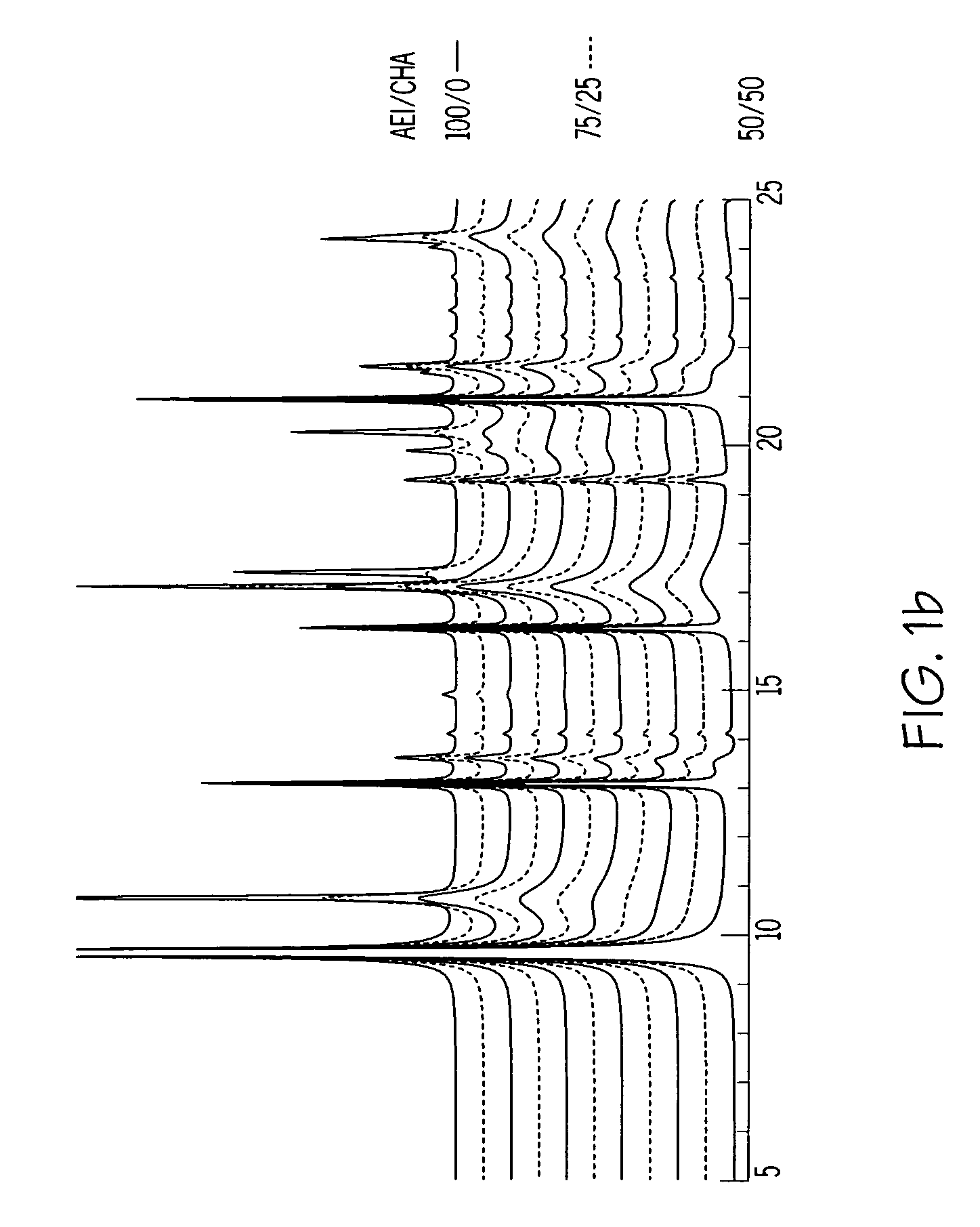
Chabazite-containing molecular sieve, its synthesis and its use in the conversion of oxygenates to olefins
A crystalline material substantially free of framework phosphorus and comprising a CHA framework type molecular sieve with stacking faults or at least one intergrown phase of a CHA framework type molecular sieve and an AEI framework type molecular sieve, wherein said material, in its calcined, anhydrous form, has a composition involving the molar relationship:(n)X2O3:YO2,wherein X is a trivalent element; Y is a tetravalent element; and n is from 0 to about 0.5. The material exhibits activity and selectivity in the conversion of methanol to lower olefins, especially ethylene and propylene.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
Reduction of edge effects from aspect ratio trapping
ActiveUS8274097B2Reduce edge effectsReduce disadvantagesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEdge effectsTrapping
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
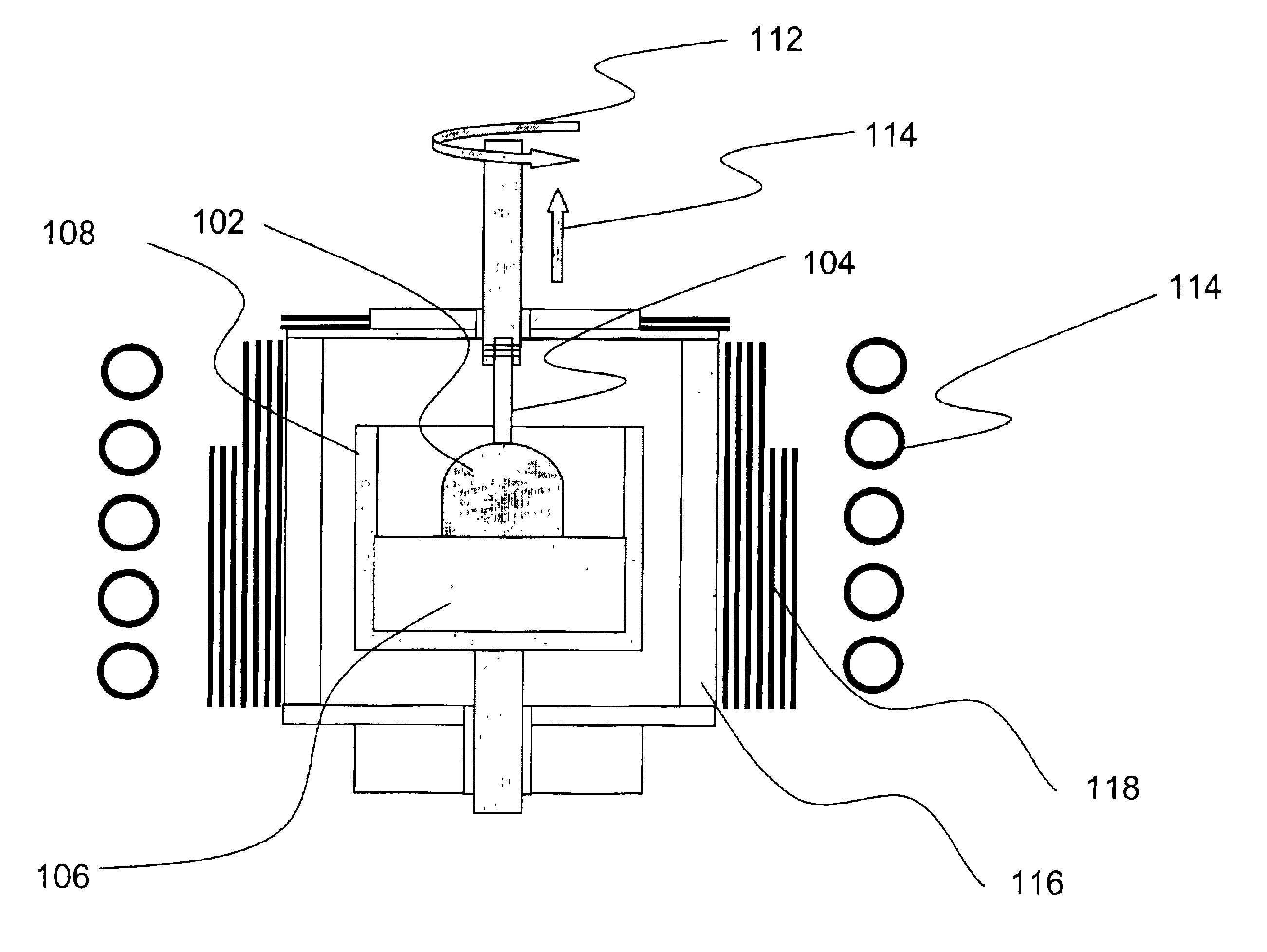
Heater device and method for high pressure processing of crystalline materials
InactiveUS20090320745A1ThinnerEasy to usePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsCost effectivenessMetallurgy
An improved heater for processing materials or growing crystals in supercritical fluids is provided. In a specific embodiment, the heater is scalable up to very large volumes and is cost effective. In conjunction with suitable high pressure apparatus, the heater is capable of processing materials at pressures and temperatures of 0.2-2 GPa and 400-1200° C., respectively.
Owner:SORAA
Methods to fabricate a photoactive substrate suitable for microfabrication
InactiveUS20110217657A1Improve performanceSmall layer thicknessContact member manufacturingPhotosensitive materialsLithium oxideSilicon dioxide
A method of fabrication and device with holes for electrical conduction made by preparing a photosensitive glass substrate comprising at least silica, lithium oxide, aluminum oxide, and cerium oxide, masking a design layout comprising one or more holes to form one or more electrical conduction paths on the photosensitive glass substrate, exposing at least one portion of the photosensitive glass substrate to an activating energy source, exposing the photosensitive glass substrate to a heating phase of at least ten minutes above its glass transition temperature, cooling the photosensitive glass substrate to transform at least part of the exposed glass to a crystalline material to form a glass-crystalline substrate and etching the glass-crystalline substrate with an etchant solution to form the one or more depressions or through holes for electrical conduction in the device.
Owner:LIFE BIOSCI
Microfluidic protein crystallography techniques
InactiveUS20050062196A1Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsDiffusionCrystalline materials
The present invention relates to microfluidic devices and methods facilitating the growth and analysis of crystallized materials such as proteins. In accordance with one embodiment, a crystal growth architecture is separated by a permeable membrane from an adjacent well having a much larger volume. The well may be configured to contain a fluid having an identity and concentration similar to the solvent and crystallizing agent employed in crystal growth, with diffusion across the membrane stabilizing that process. Alternatively, the well may be configured to contain a fluid having an identity calculated to affect the crystallization process. In accordance with the still other embodiment, the well may be configured to contain a material such as a cryo-protectant, which is useful in protecting the crystalline material once formed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Applications and equipment of substrate stiffness method and resulting devices for layer transfer processes on quartz or glass
ActiveUS20060205180A1Avoid the possibility of damageReduce temperature excursionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystalline materialsSurface roughness
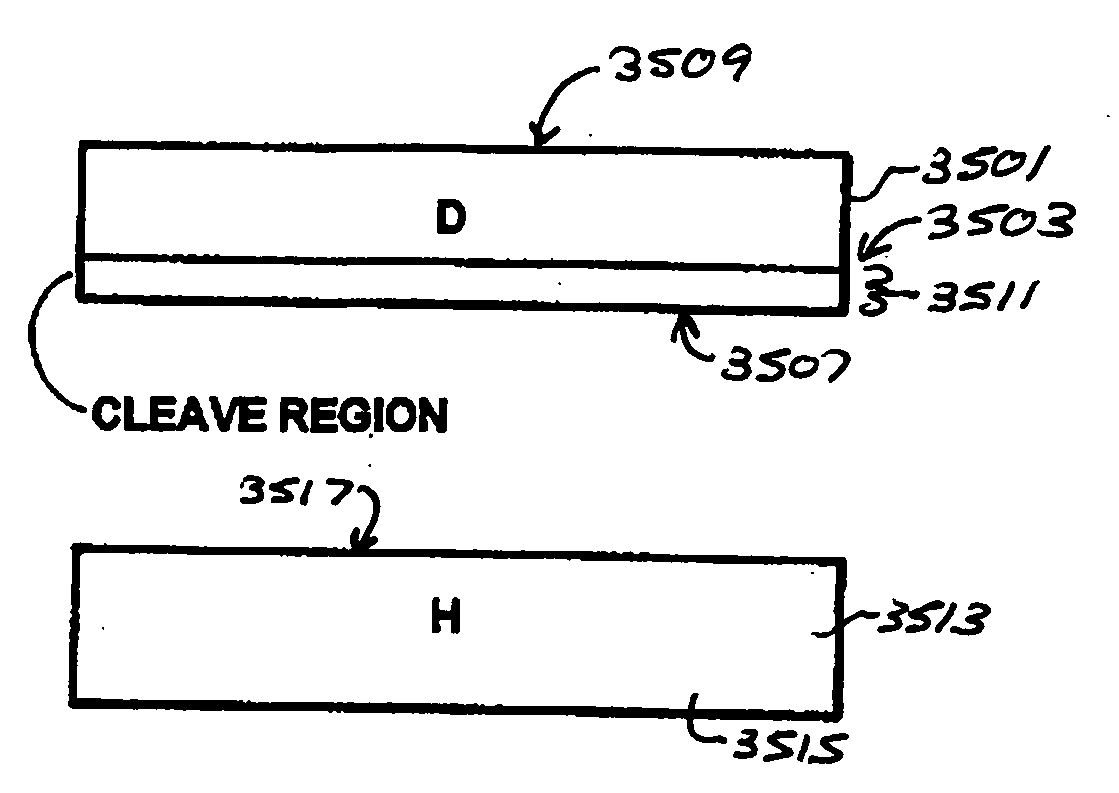
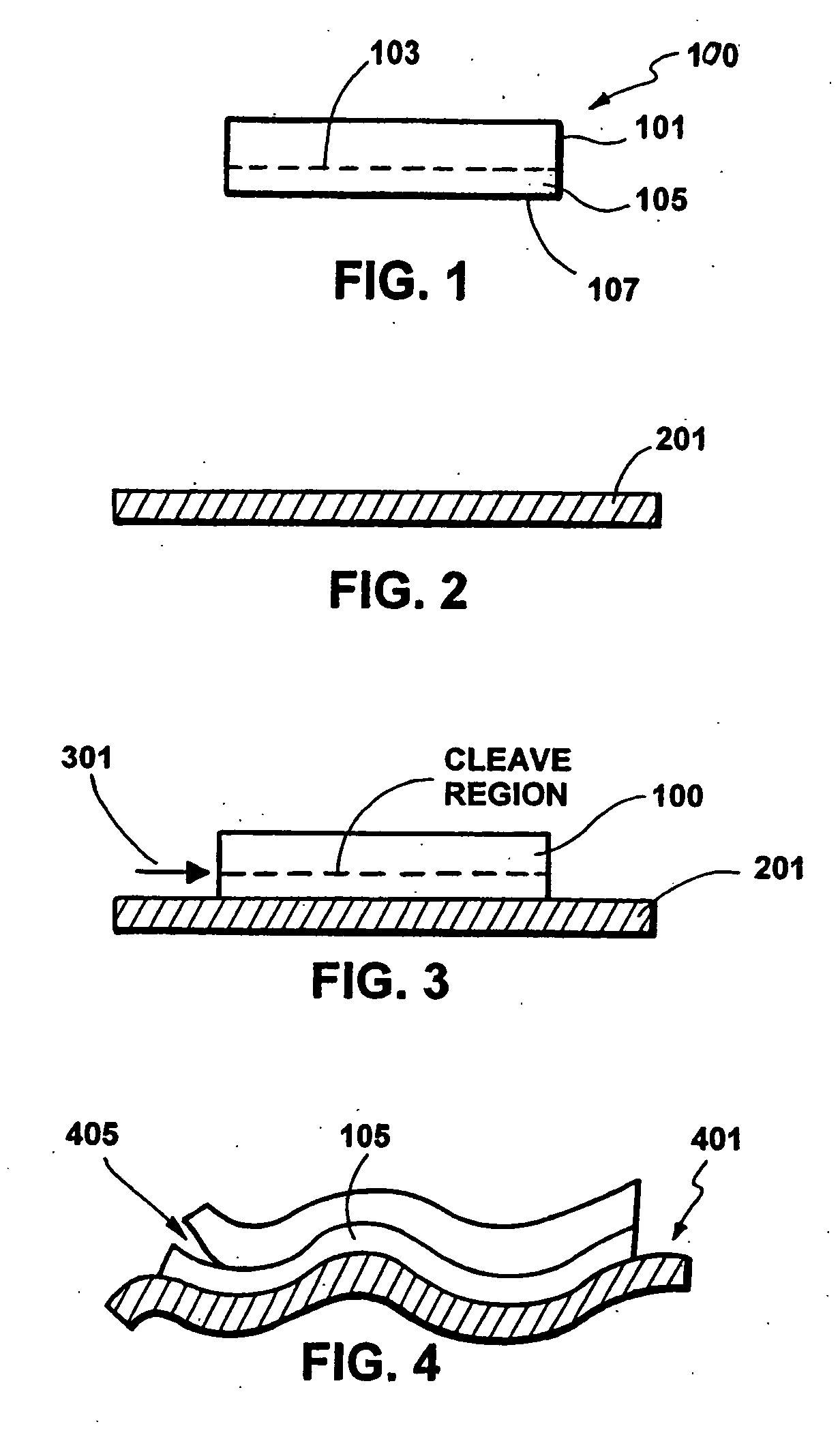
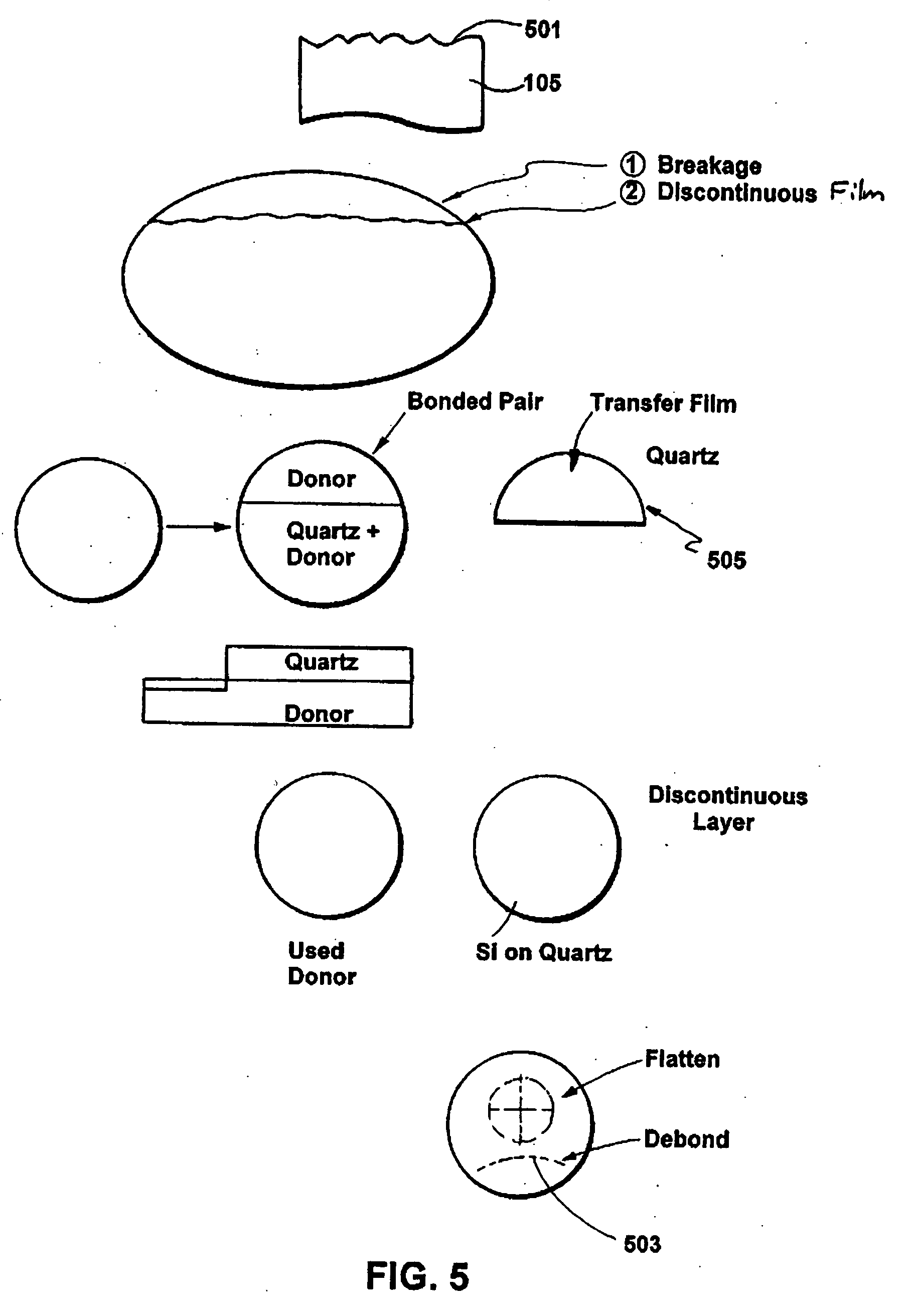
A multilayered substrate structure comprising one or more devices, e.g., optoelectronic, integrated circuit. The structure has a handle substrate, which is characterized by a predetermined thickness and a Young's modulus ranging from about 1 Mega Pascal to about 130 Giga Pascal. The structure also has a thickness of substantially crystalline material coupled to the handle substrate. Preferably, the thickness of substantially crystalline material ranges from about 100 microns to about 5 millimeters. The structure has a cleaved surface on the thickness of substantially crystalline material and a surface roughness characterizing the cleaved film of less than 200 Angstroms. At least one or more optoelectronic devices is provided on the thickness of material.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
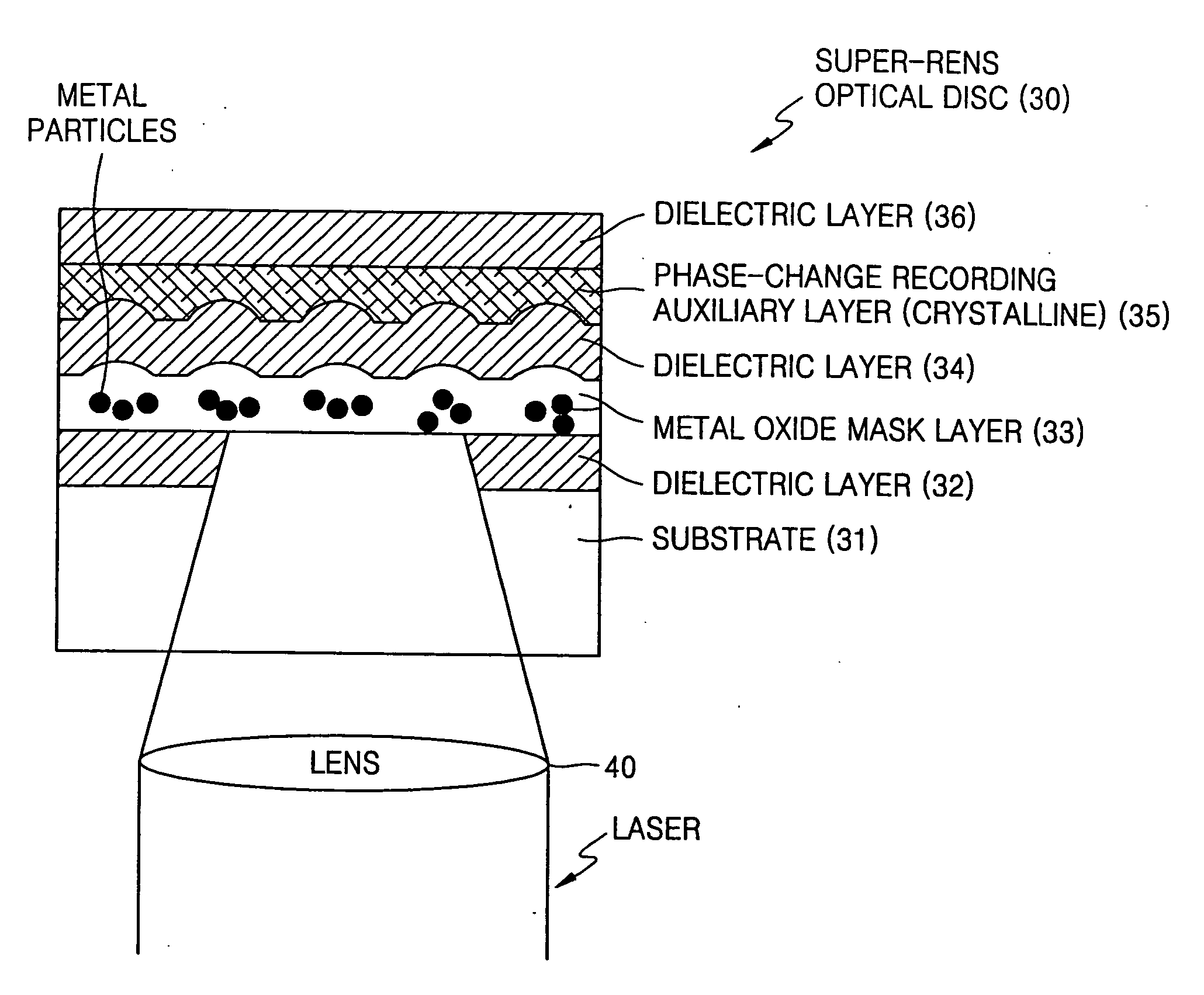
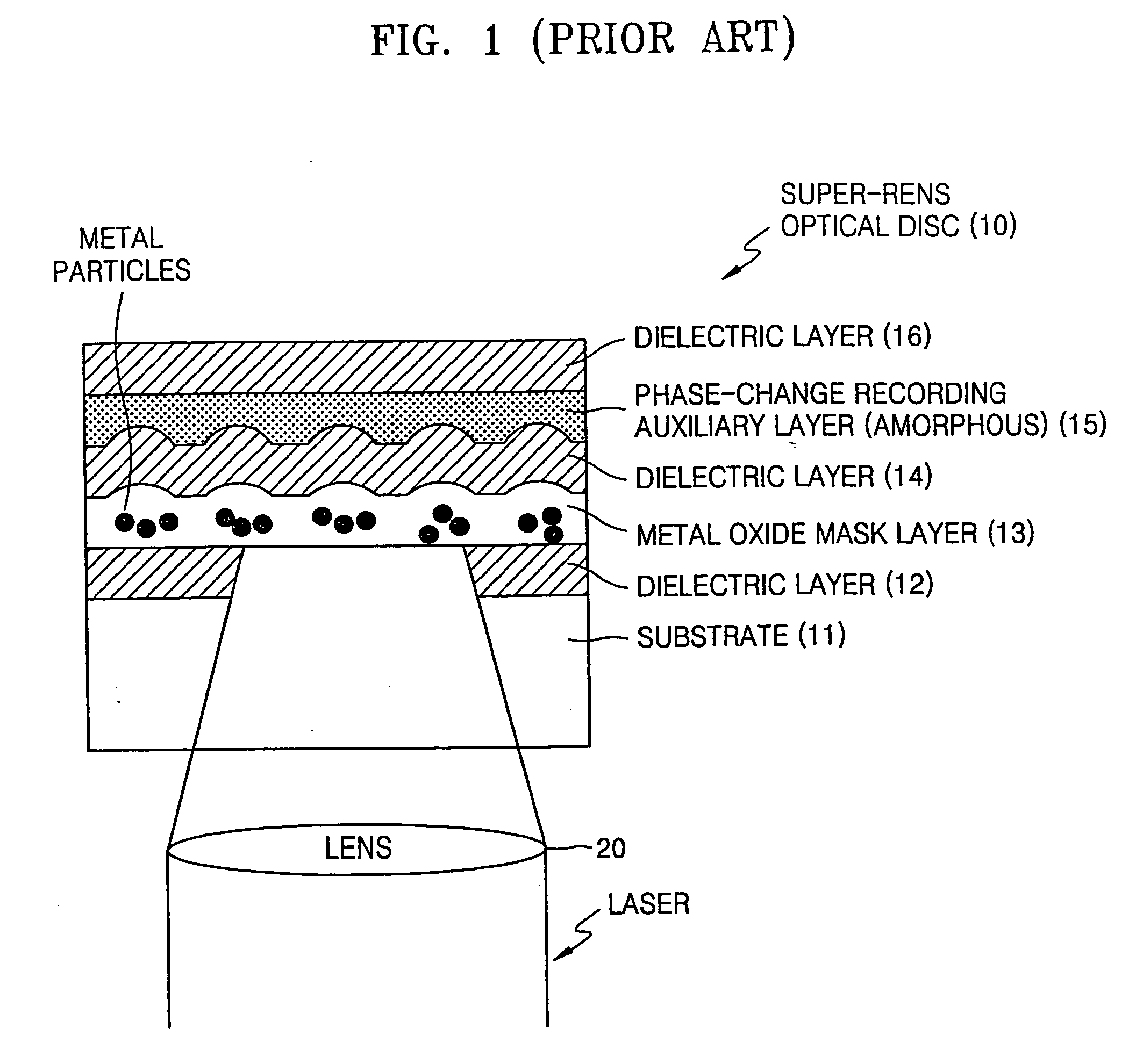
Optical disc with super-resolution near-field structure
A high-density optical disc with a super-resolution near-field structure (Super-RENS) on which information is written by a beam has multi-layers formed on a substrate. The disc includes one or more Super-RENS mask layers and one or more phase-change recording auxiliary layers, each containing a highly crystalline material. The Super-RENS optical disc allows high quality signal reproduction by eliminating signal instability and unevenness that may occur during reproduction after recording data as well as low manufacturing costs and high production yields.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com