Patents
Literature
2030results about "Mechanical record carriers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
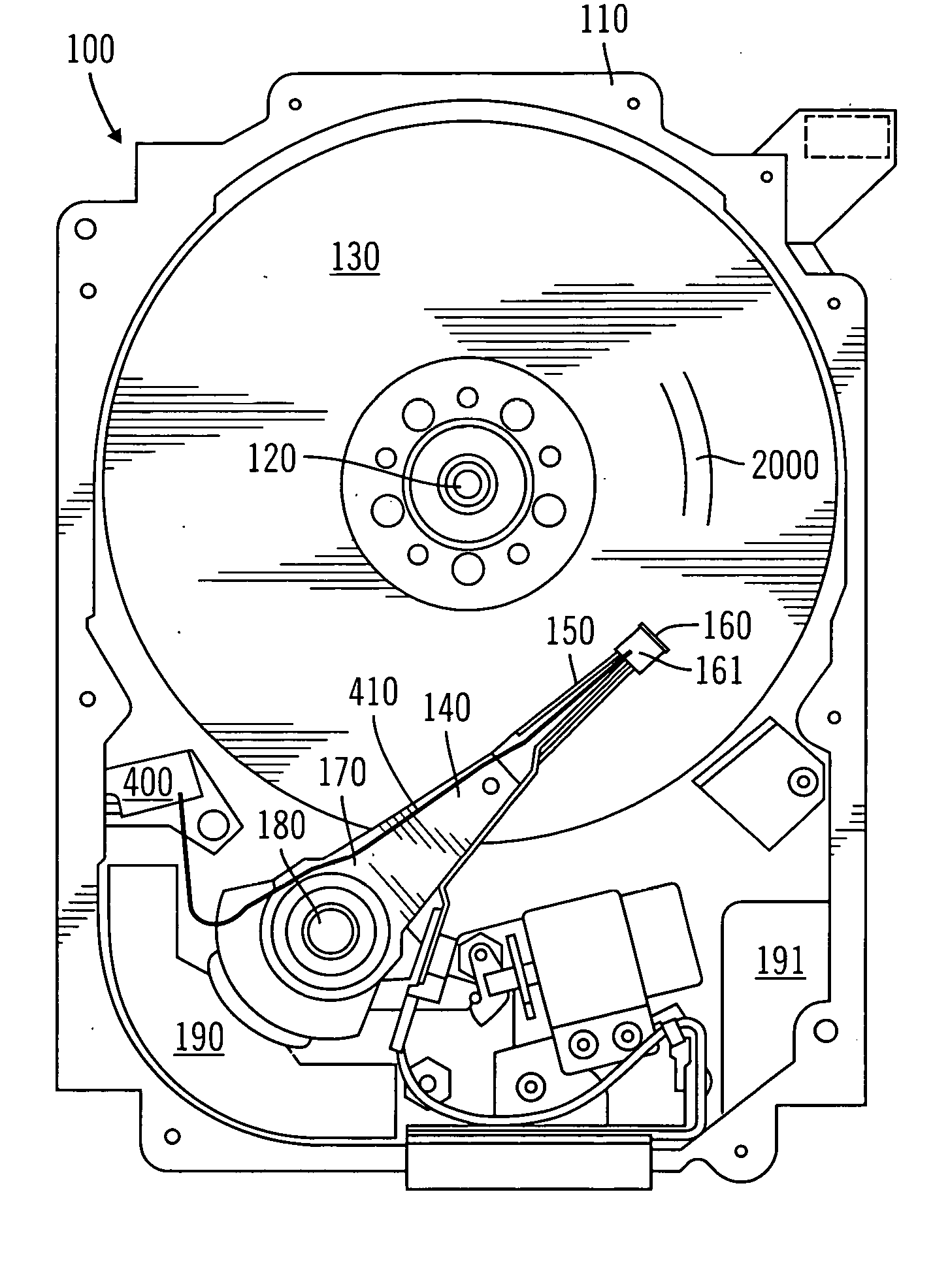
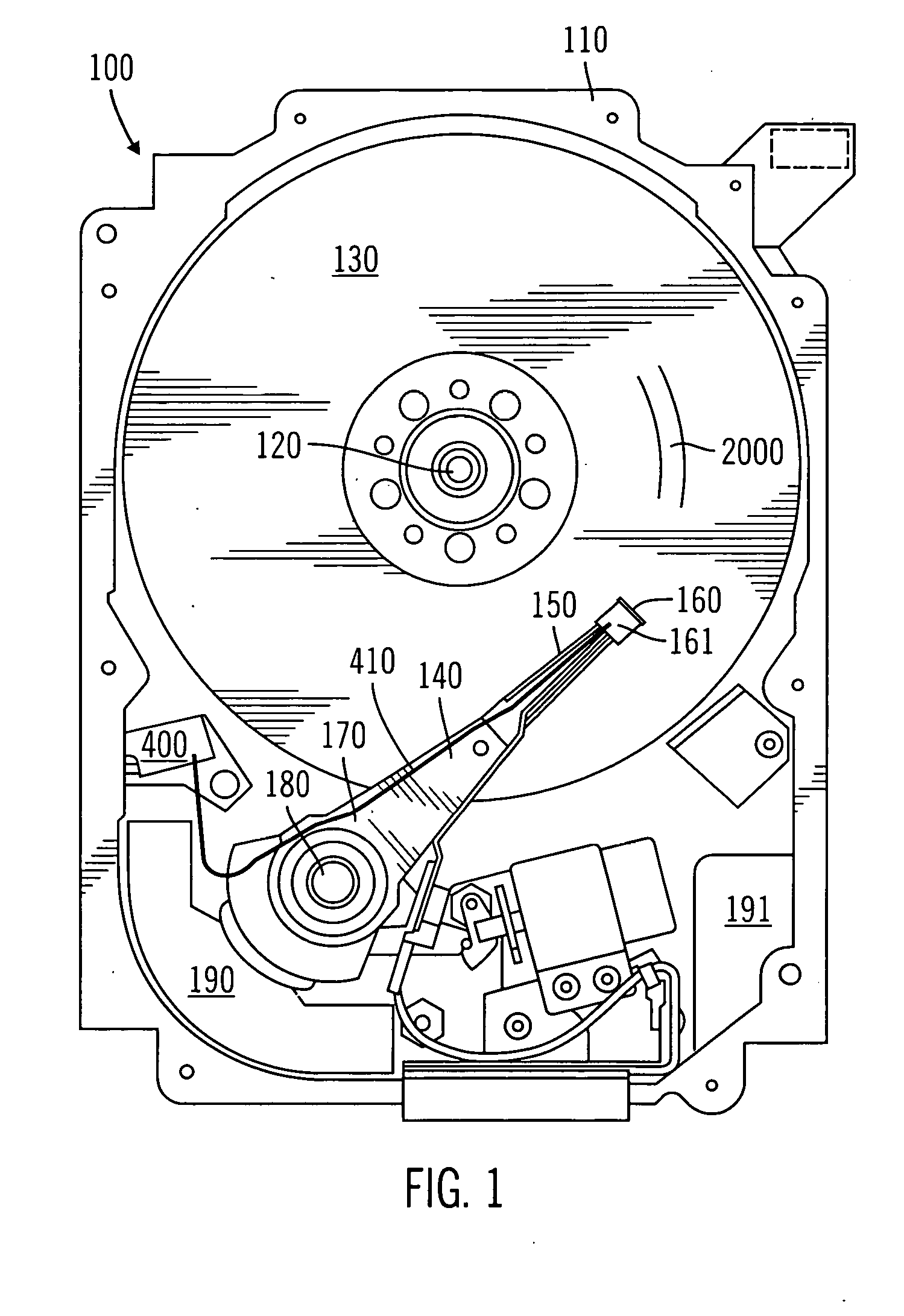
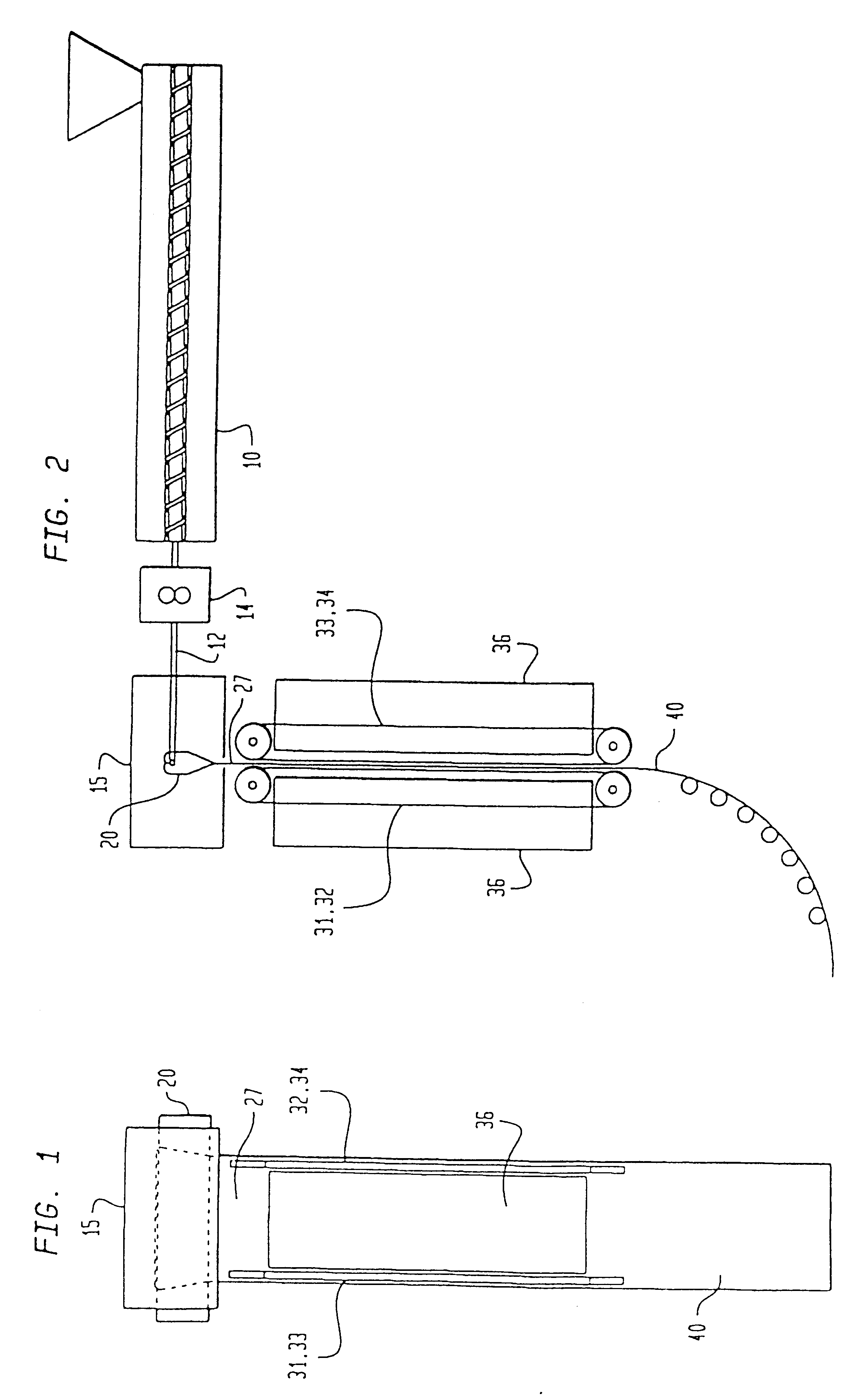
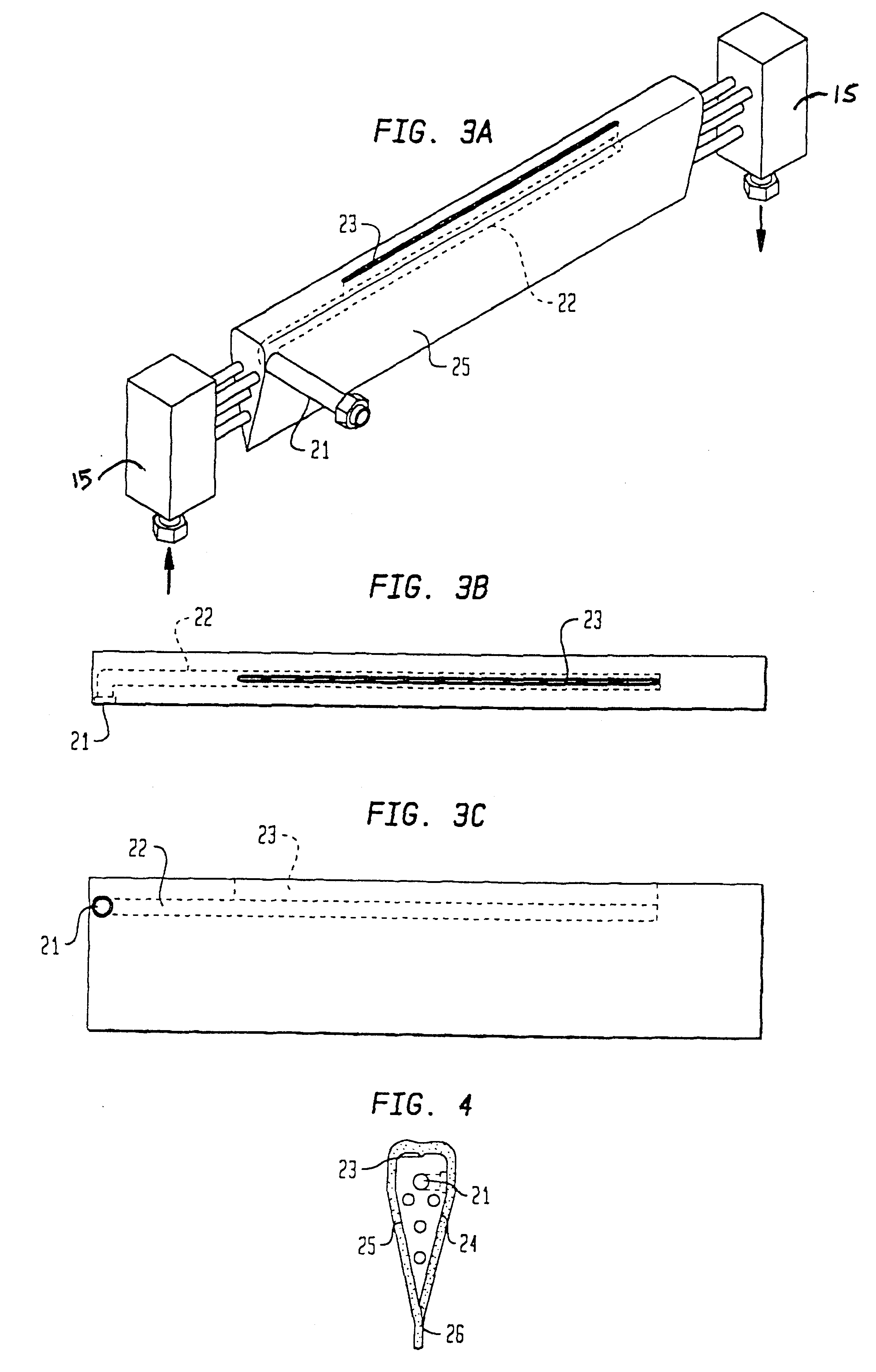
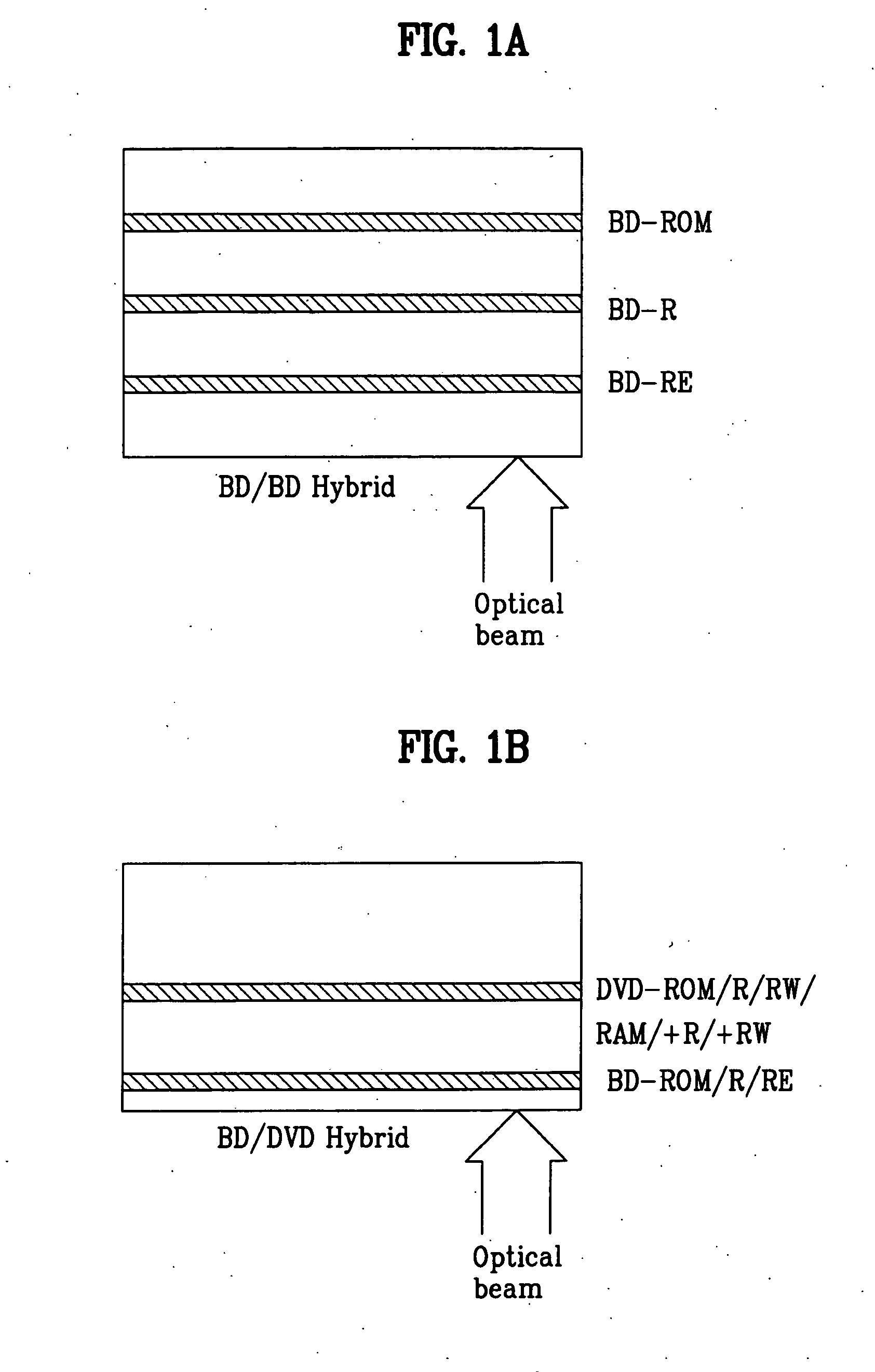
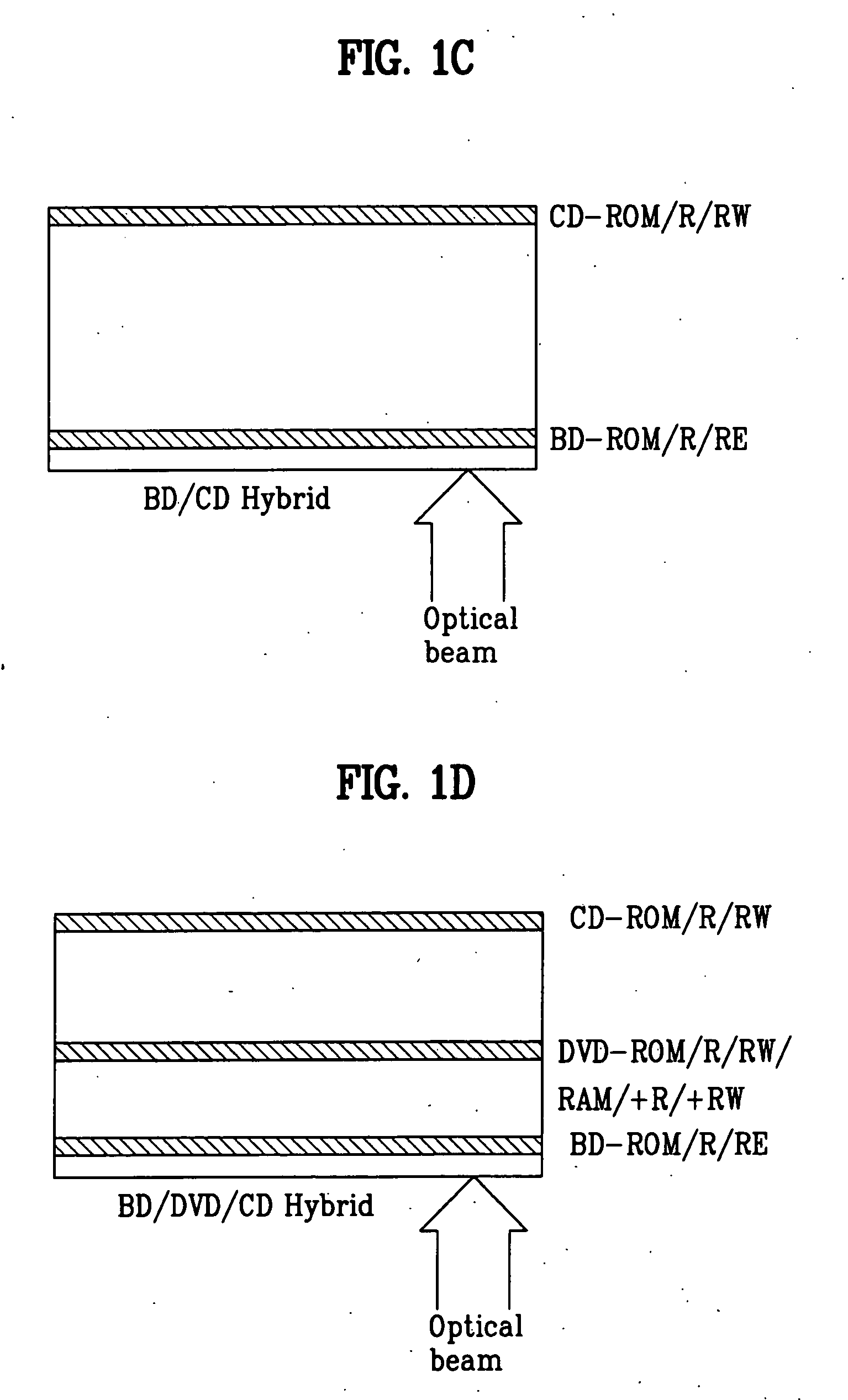
Optical disk, optical disk recording and reproducing apparatus, method for recording, reproducing and deleting data on optical disk, and information processing system
InactiveUS6938162B1Prevent unjust digital copyingImprove reliabilityAccessories for auxillary signalsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useInformation processingHandling system
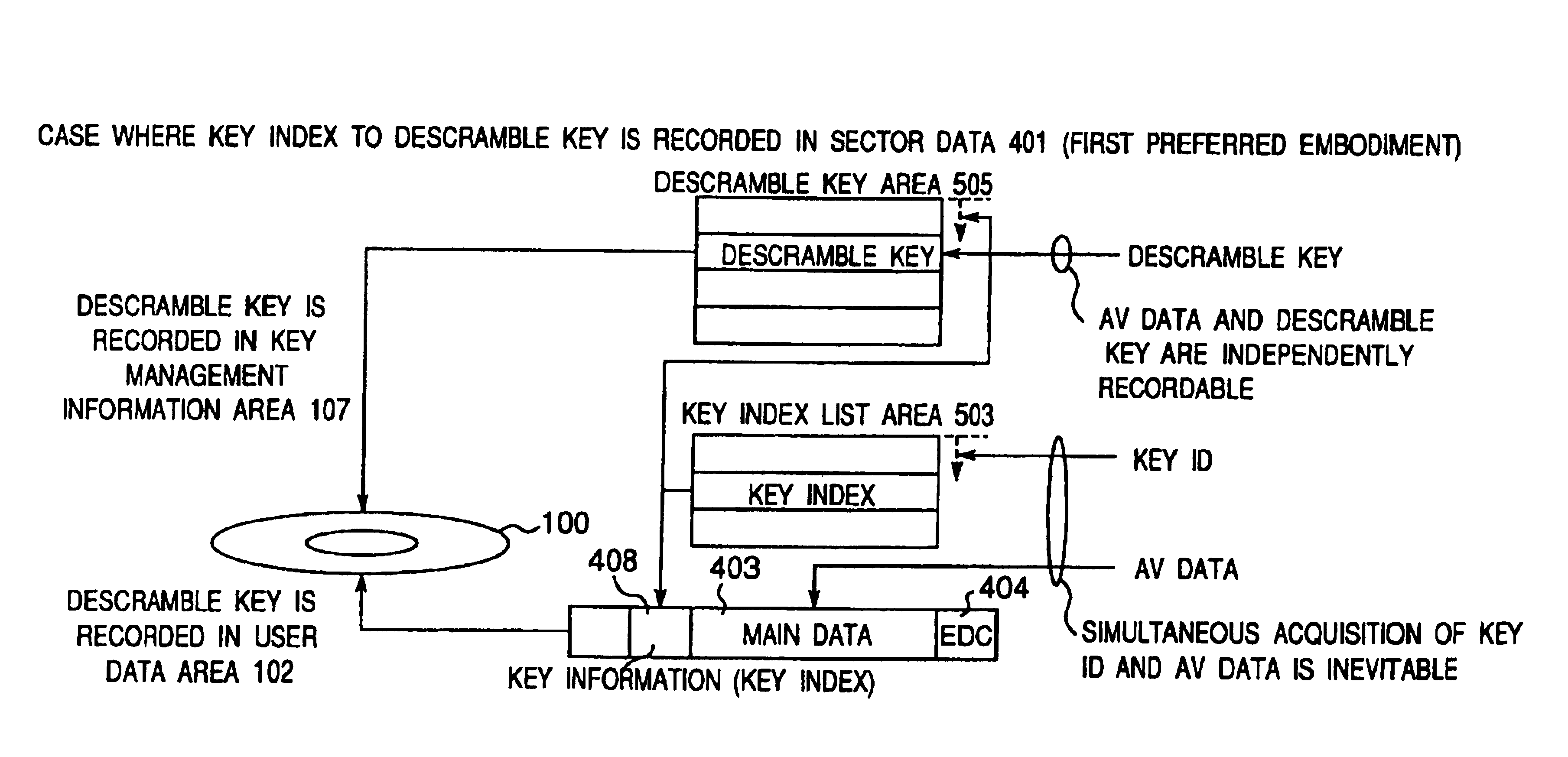
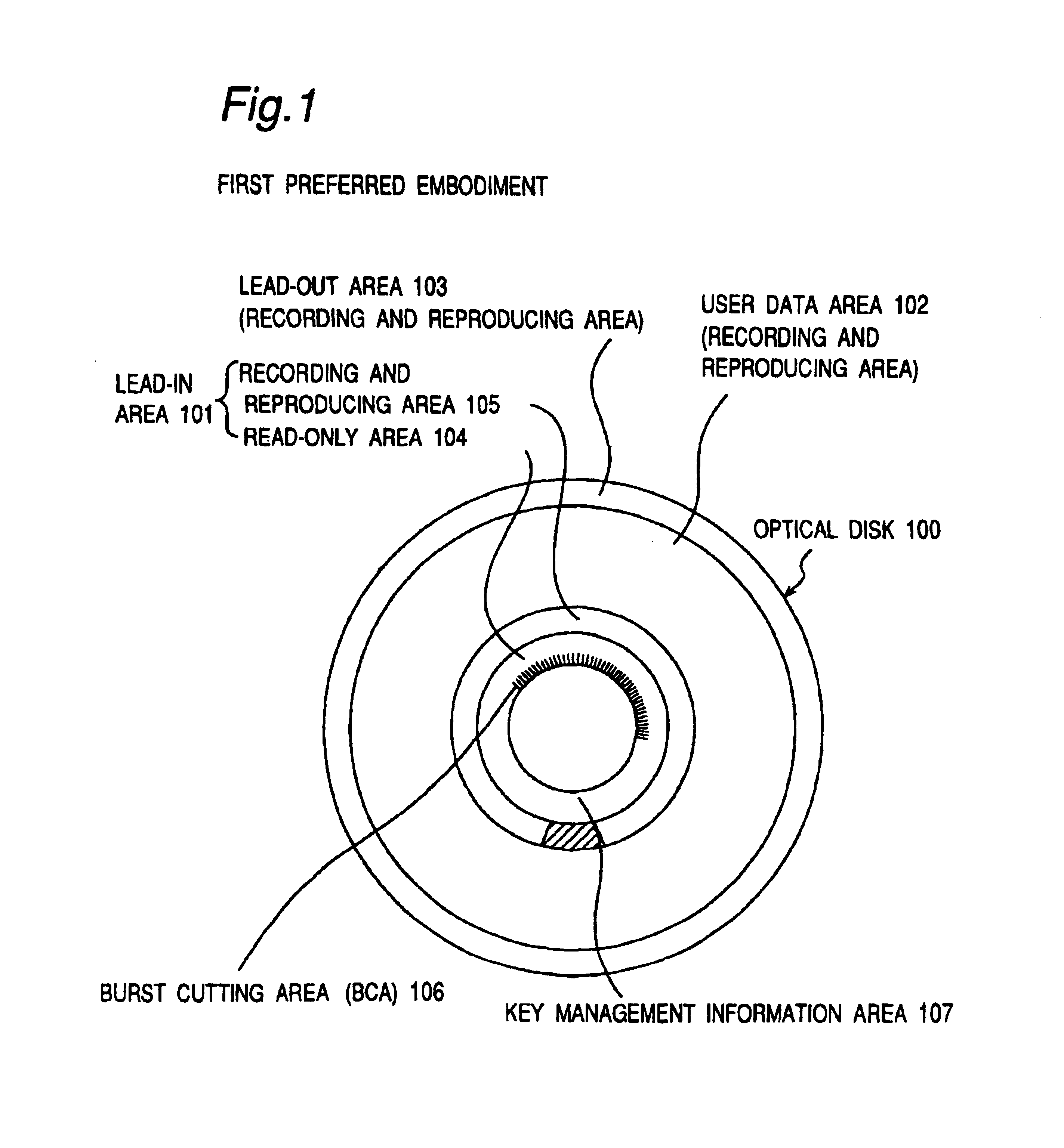
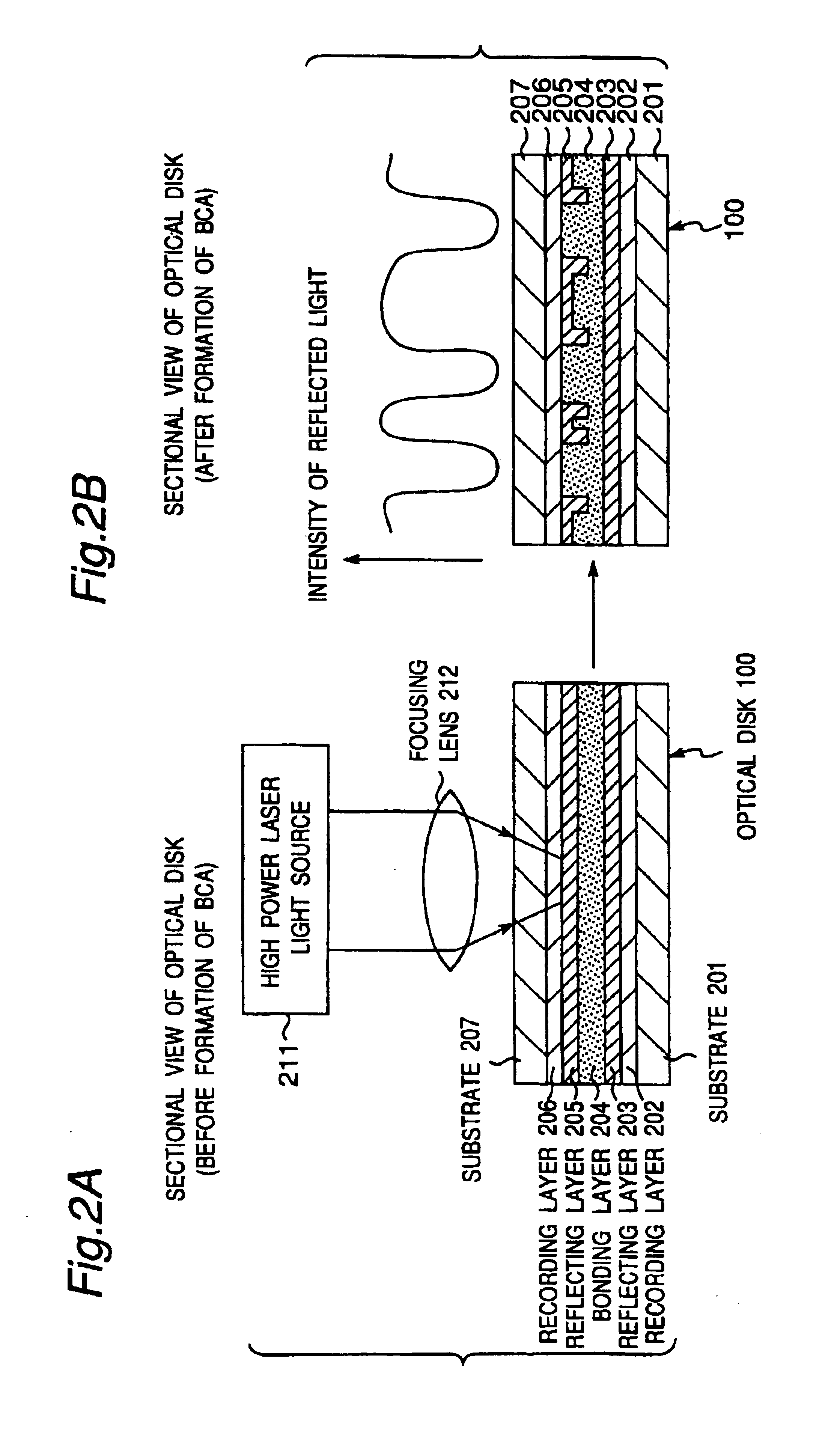
A recording type optical disk on which data is recordable includes a data recording and reproducing area for recording data therein and reproducing data therefrom, and a read-only disk identification information area for recording disk identification information for identifying the optical disk therein. In the optical disk, the disk identification information is formed by removing a reflection film that is formed on the optical disk in a strip shape. The disk identification information includes an inherent disk identifier for each optical disk, and the data recording and reproducing area includes an area for recording encrypted data therein. The encrypted data is encrypted by using information including the disk identification information for identifying the optical disk as a key.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
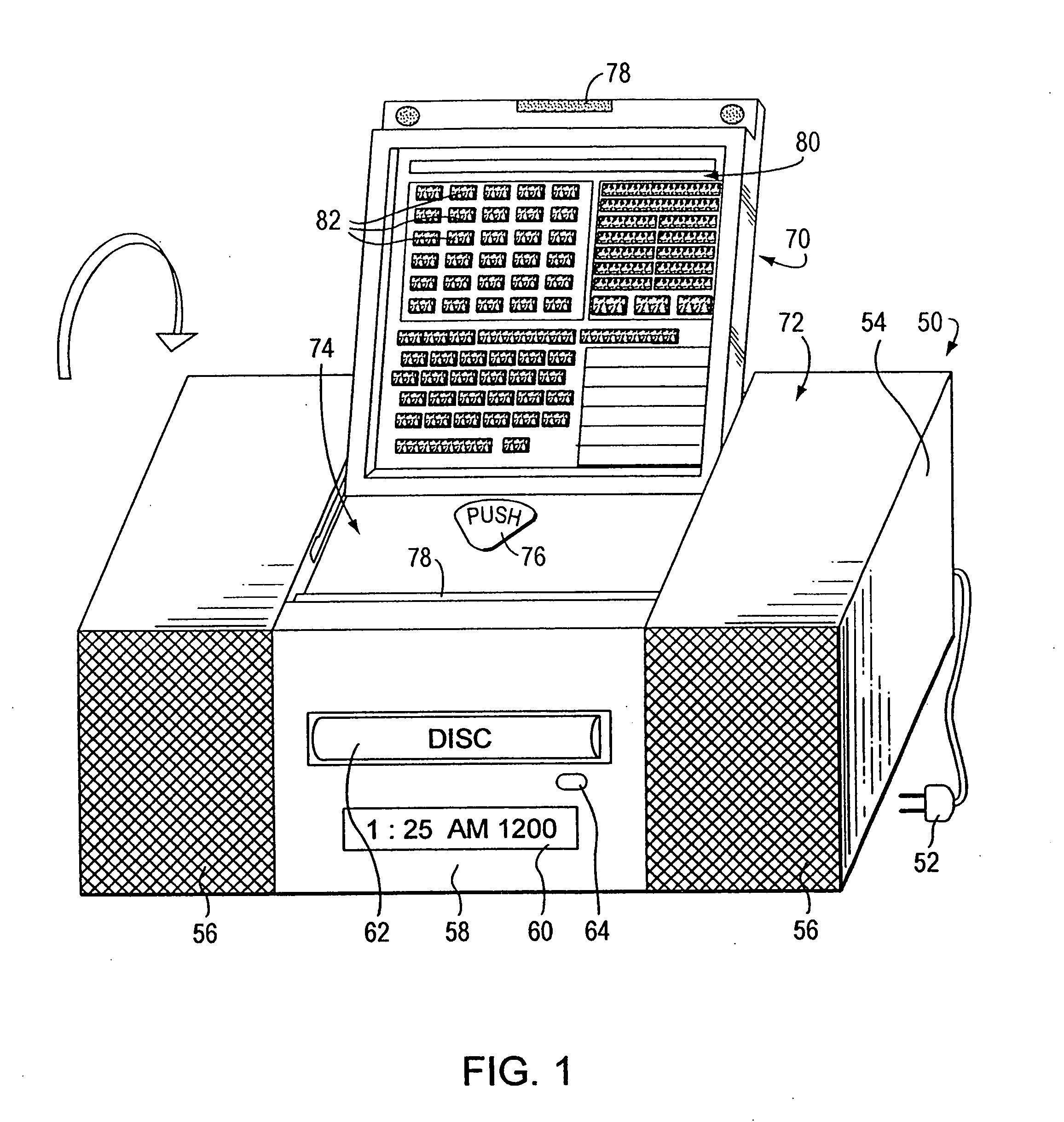
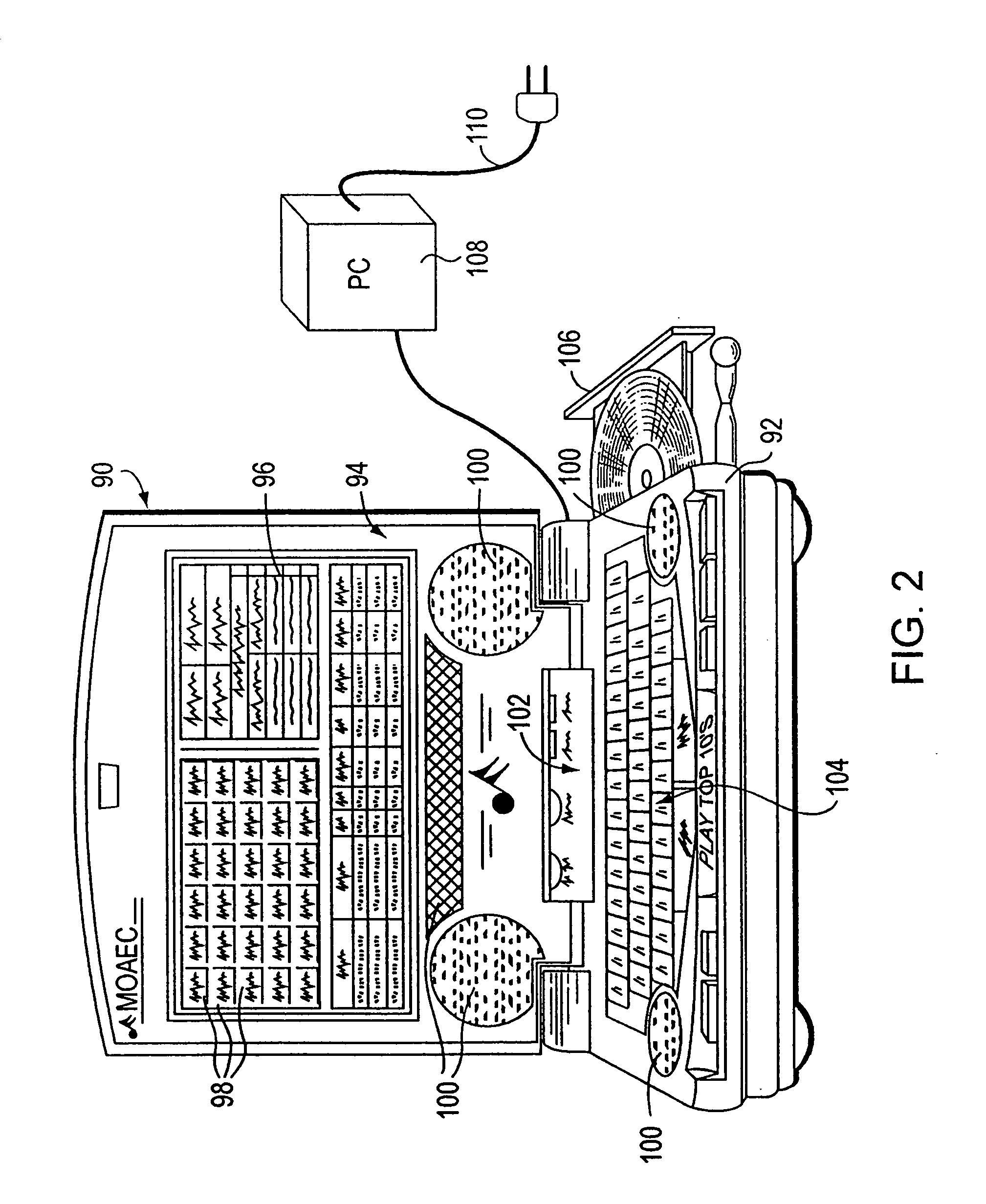
Media organizer and entertainment center
InactiveUS20050201254A1Control functionTelevision system detailsElectrophonic musical instrumentsAudio MediaData selection
A media organizer and entertainment center includes an importer for importing individual media / data selections and automatically assigning each selection at least one associated category flag pursuant to predetermined or user defined criteria. The center also includes a storage device for storing compressed data corresponding to the plurality of individual media / data selections and the associated category flags and a retriever for retrieving selections from the storage device based upon user selection of one or more of the associated category flags, and a data decompresser that translates the compressed data into playable digital or audio media data. With the center, playable digital or audio media data can be advantageously transported, organized, played or recorded through or on a variety of products or devices.
Owner:LOONEY PRODN
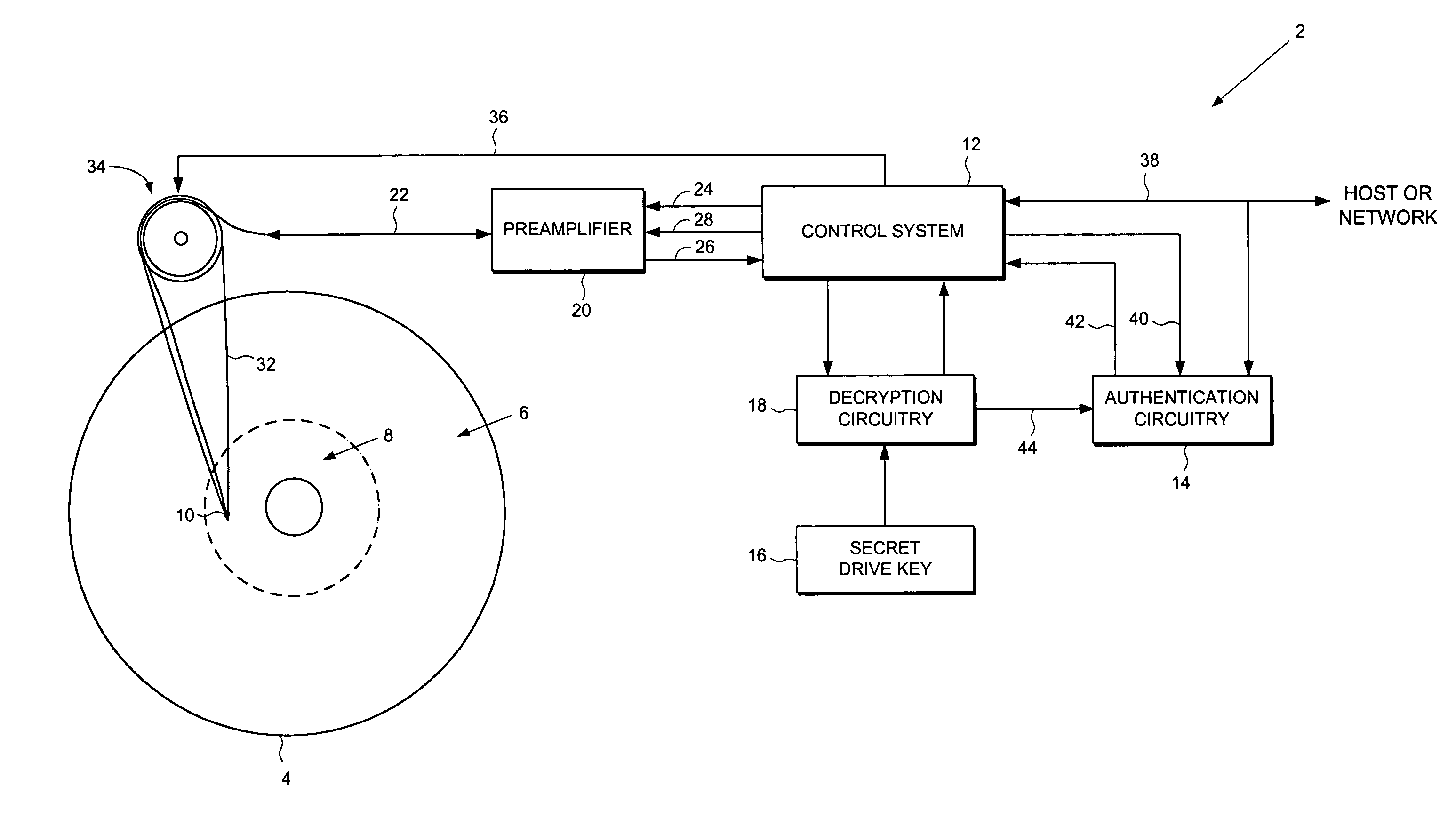
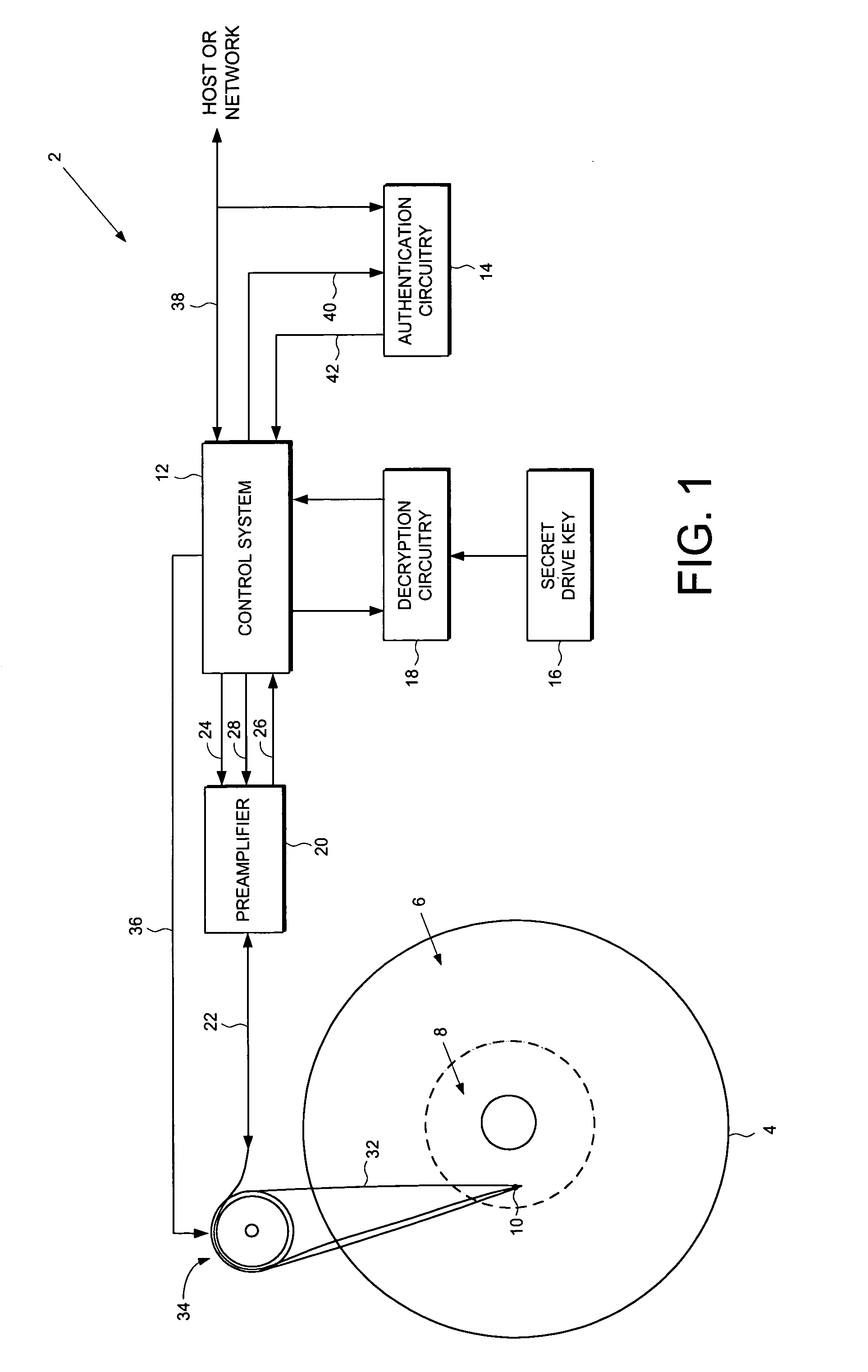
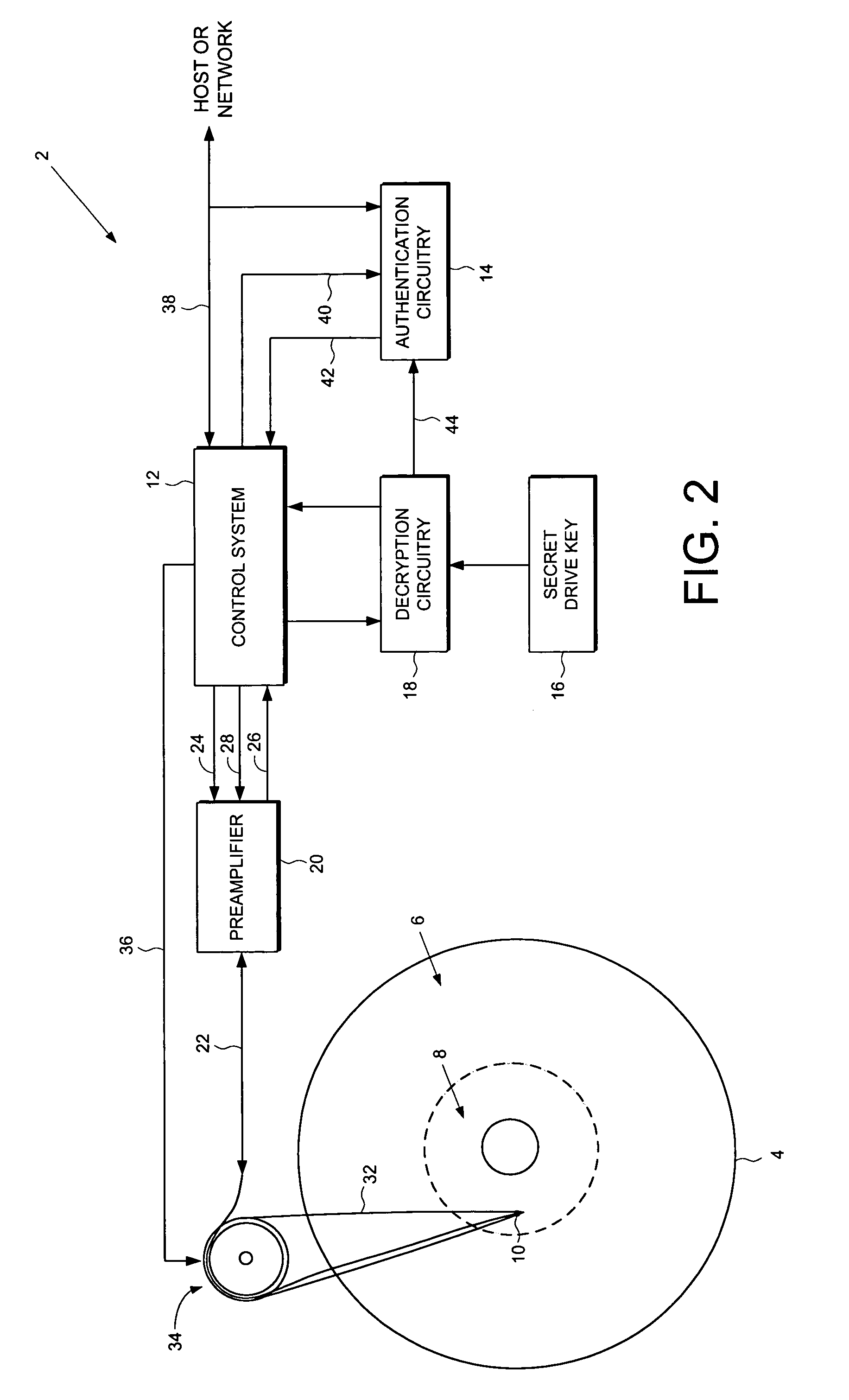
Disk drive employing a disk with a pristine area for storing encrypted data accessible only by trusted devices or clients to facilitate secure network communications
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk for storing data, the disk comprising a public area for storing plaintext data and a pristine area for storing encrypted data. The disk drive comprises a head for reading the encrypted data from the pristine area of the disk, and a control system for controlling access to the pristine area of the disk. Authentication circuitry within the disk drive is provided for authenticating a request received from an external entity to access the pristine area of the disk and for enabling the control system if the request is authenticated. The disk drive further comprises a secret drive key, and decryption circuitry responsive to the secret drive key, for decrypting the encrypted data stored in the pristine area of the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL VENTURES
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
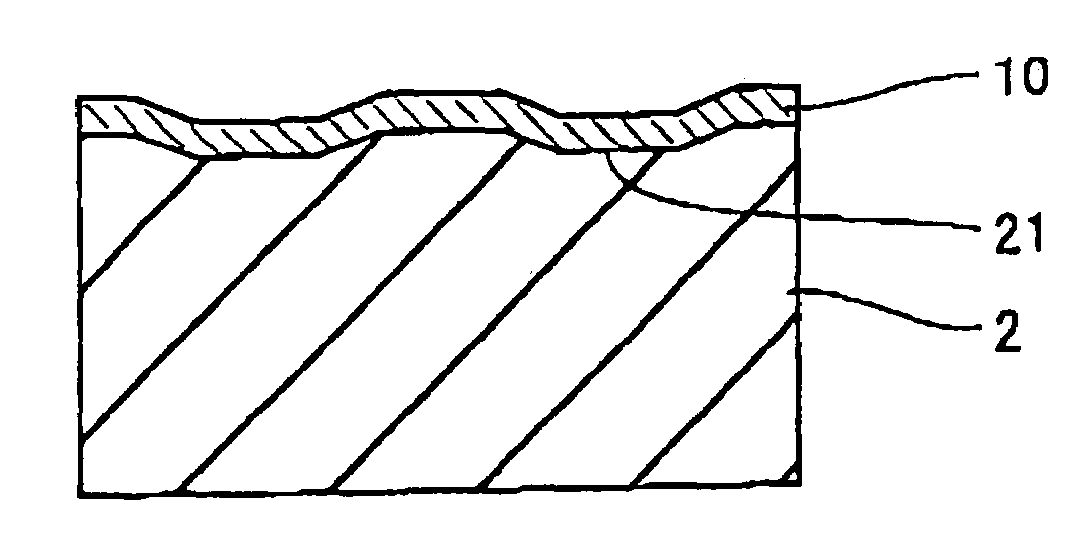
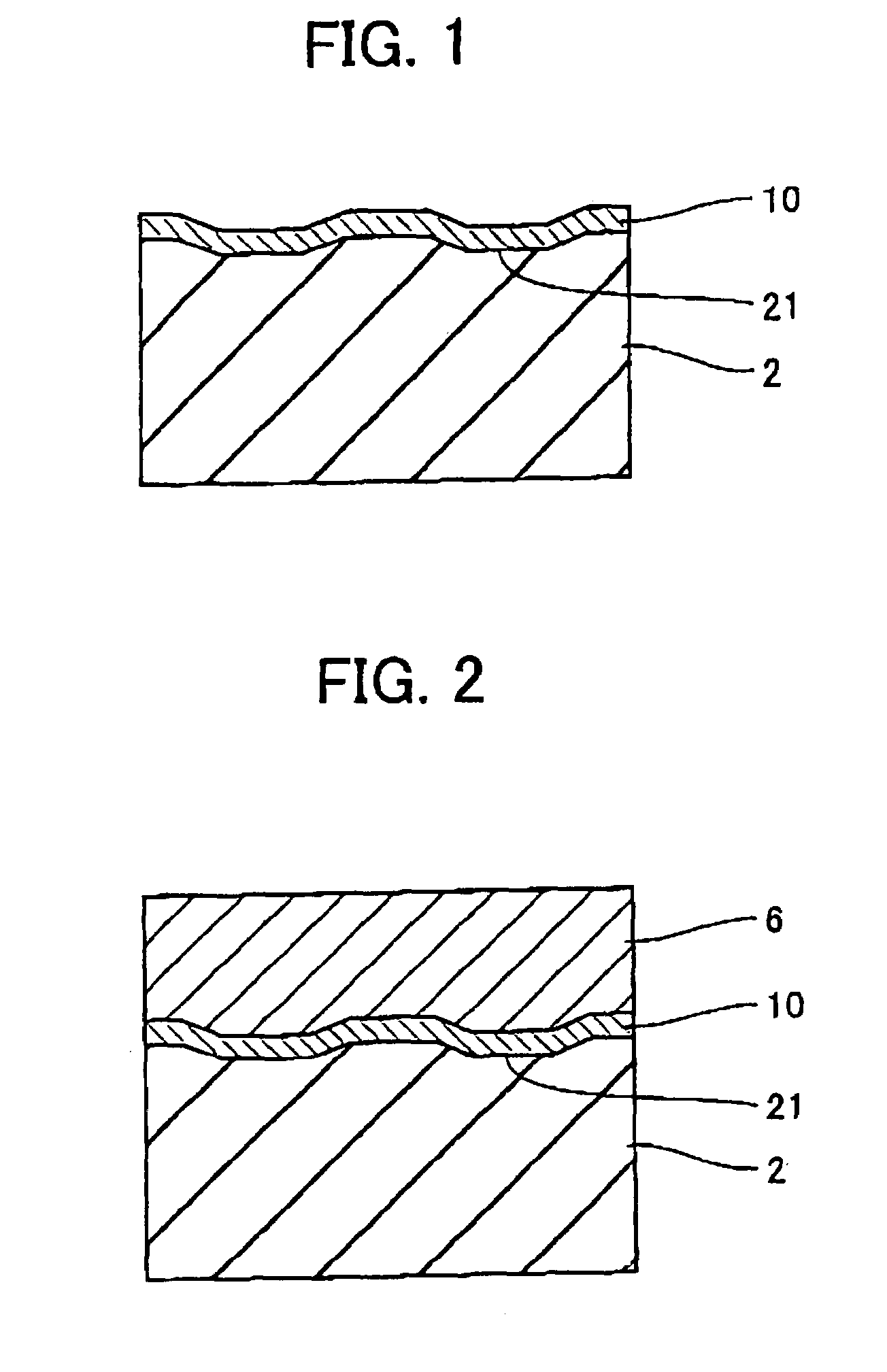
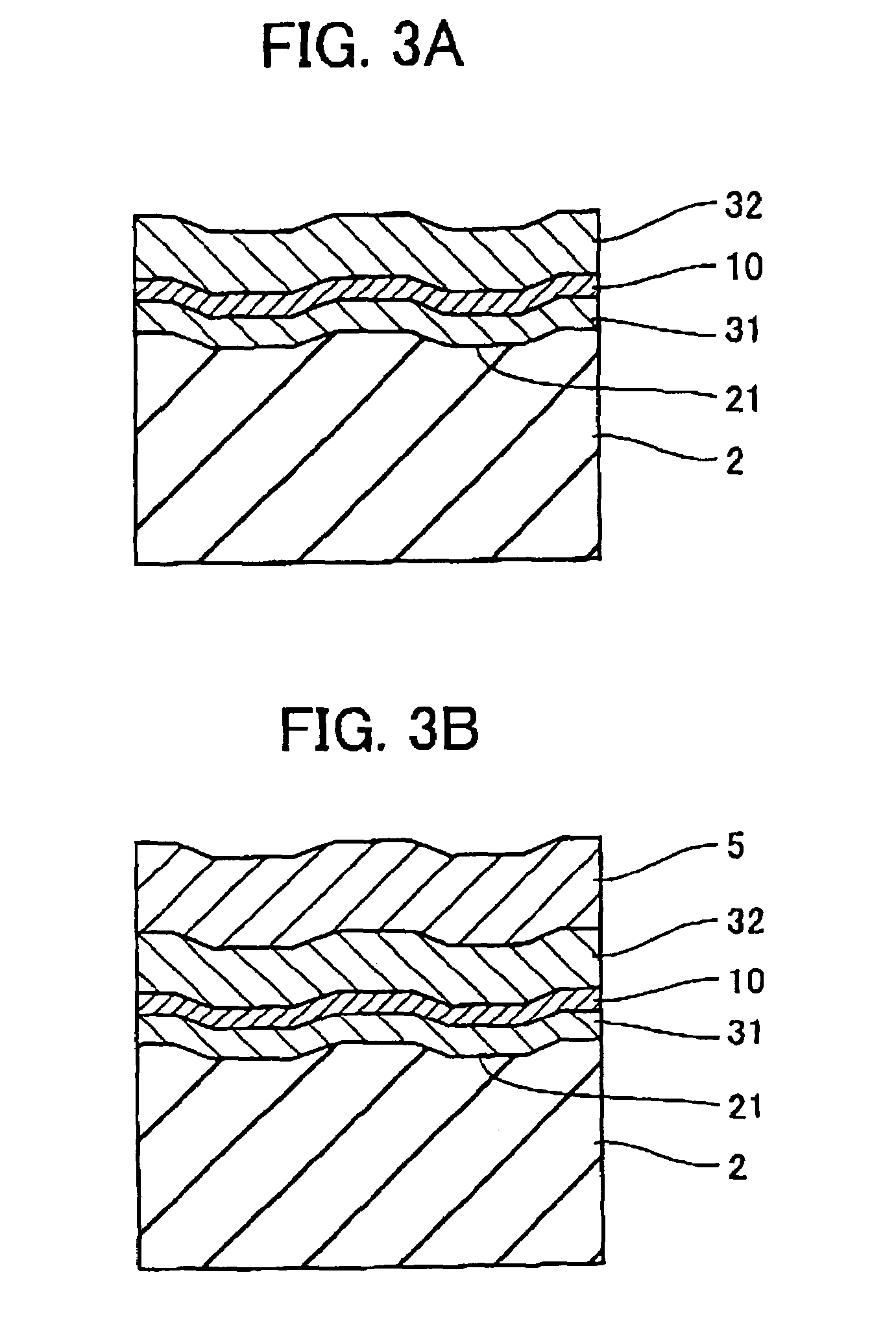
Information recording medium which indicates information according to the wobbling of a track and information recording and reproducing apparatus
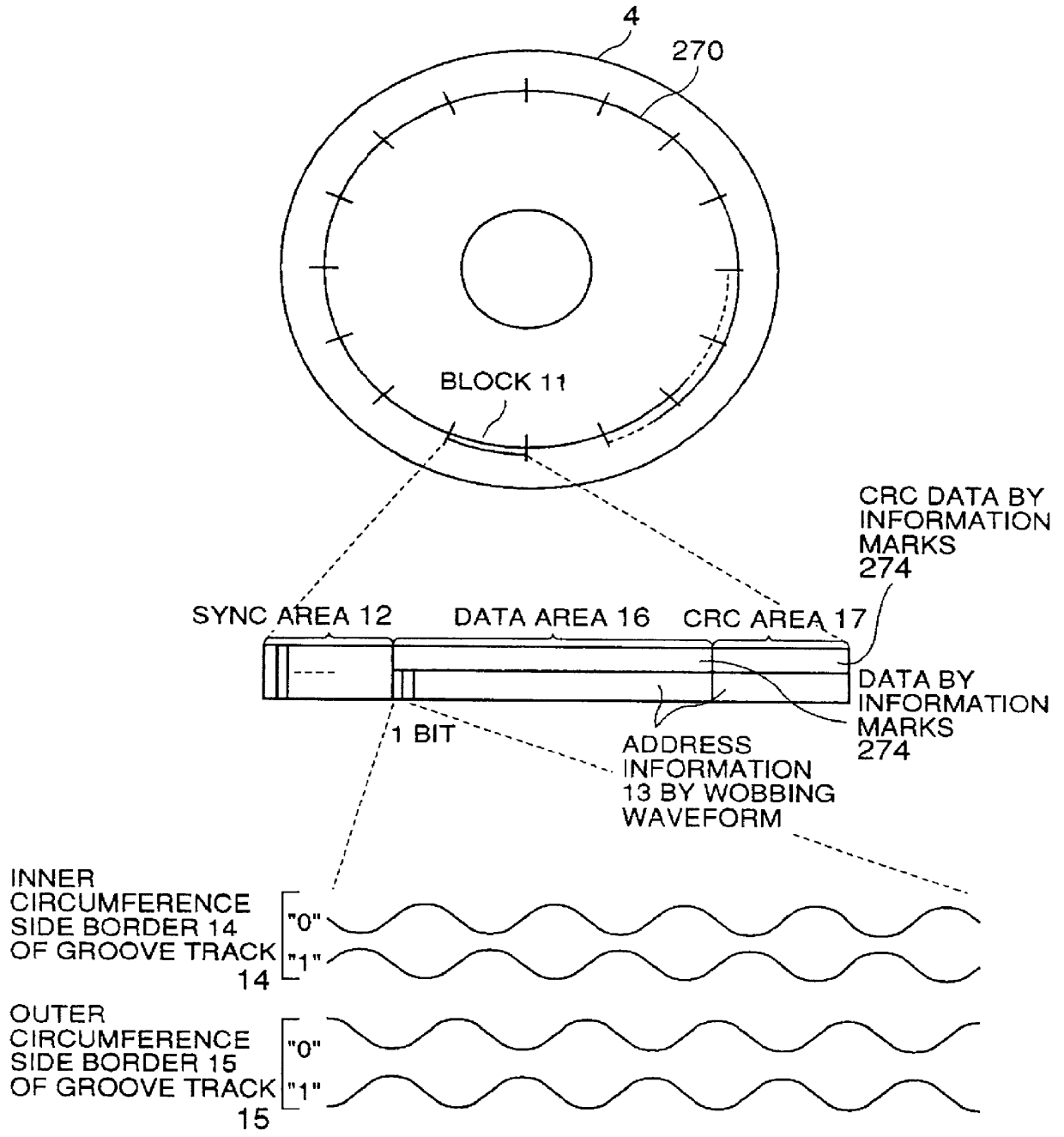
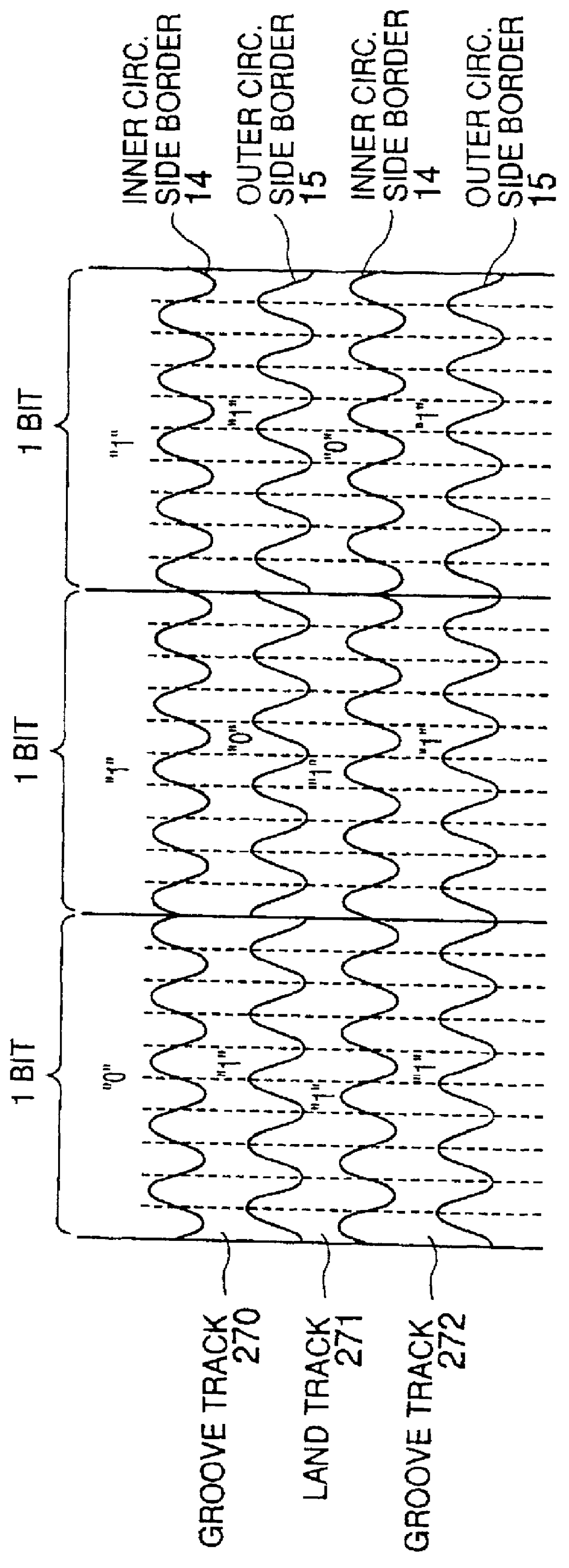
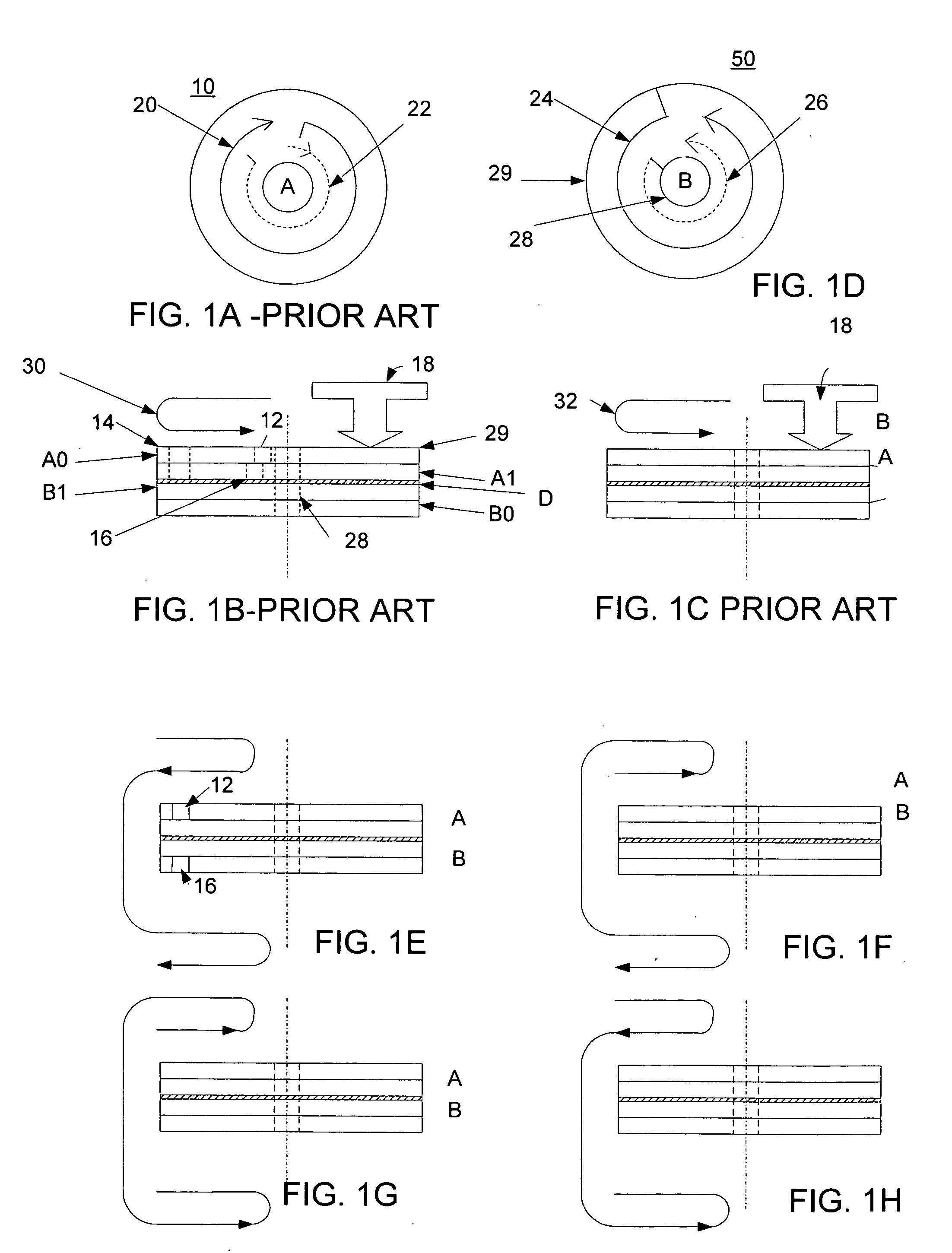
An optical disk comprising a substrate 4, and a plurality of tracks 269 to 273 formed on the substrate 4, wherein the plurality of tracks 269 to 273 include groove tracks 270, 272 consisting of a plurality of grooves mutually space apart by a fixed space, and land tracks 269, 271, 273 consisting of areas between the groove tracks, wherein the borders 14, 15 between the groove tracks and the land tracks represent information using the waveforms from their wobbling patterns, wherein the period of the wobbling waveforms of the borders 14, 15 are constant on each border, but the wobbling waveforms of the opposite portions of the borders across the track are shifted in phase by a predetermined phase difference.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
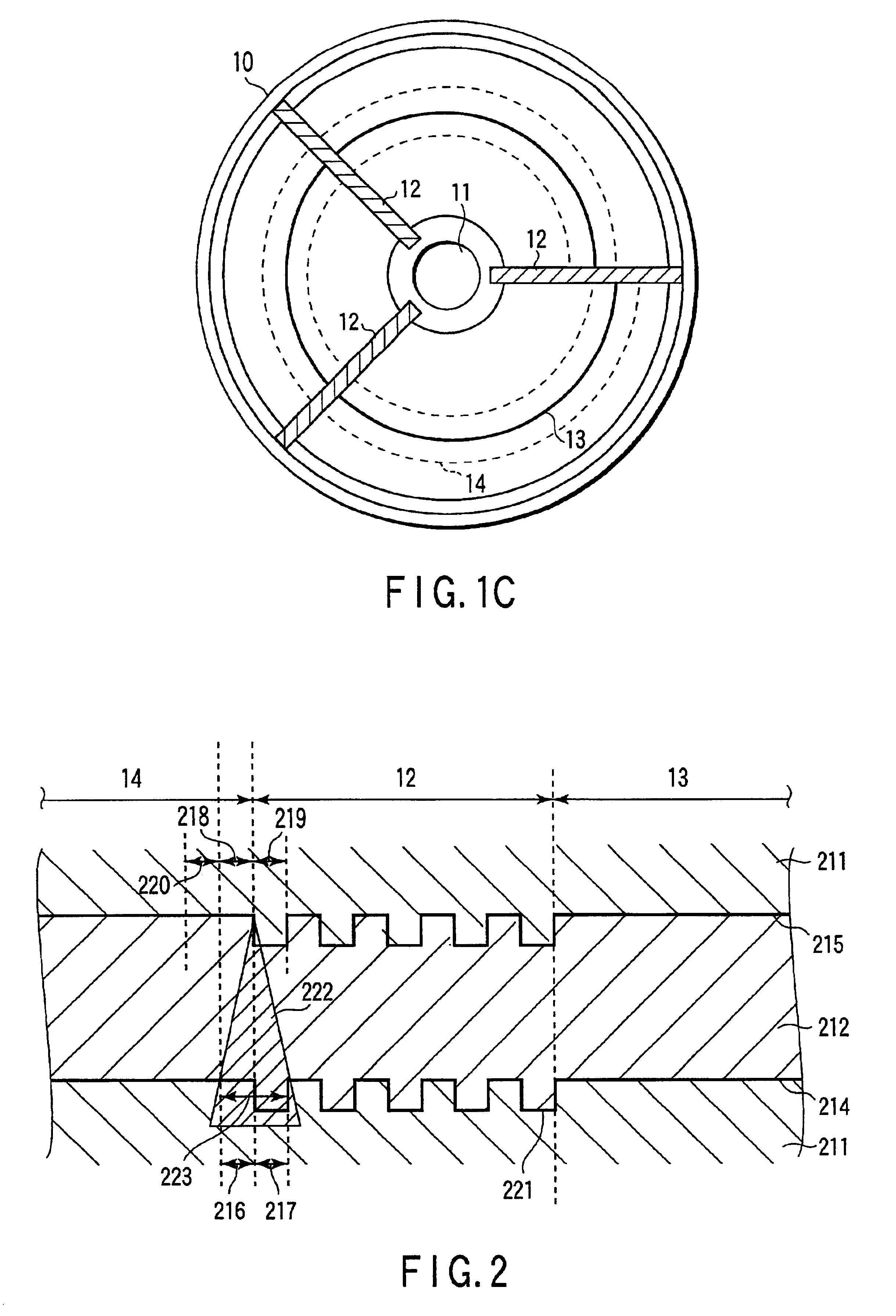
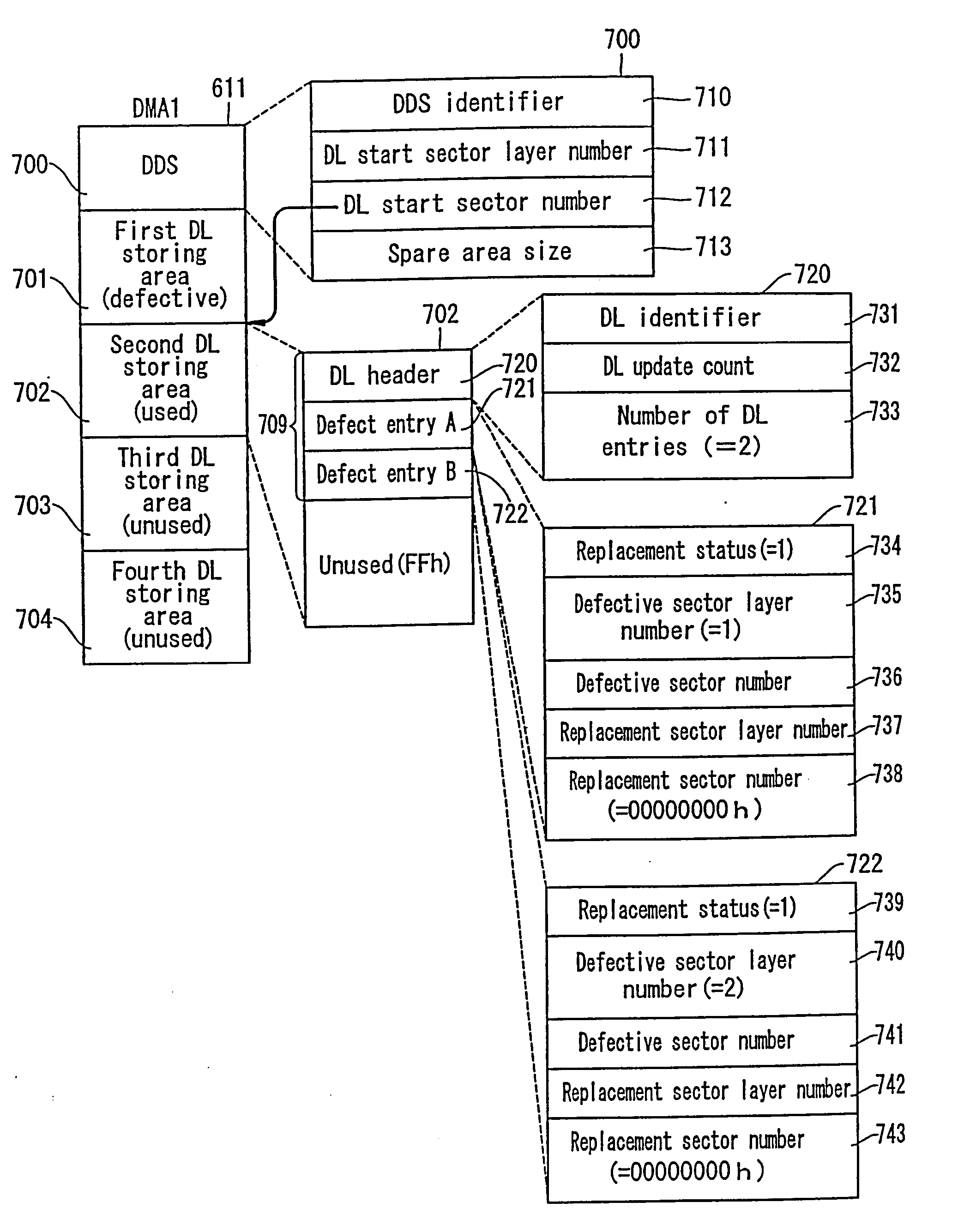
Multi-layered information recording medium with spare defect management areas
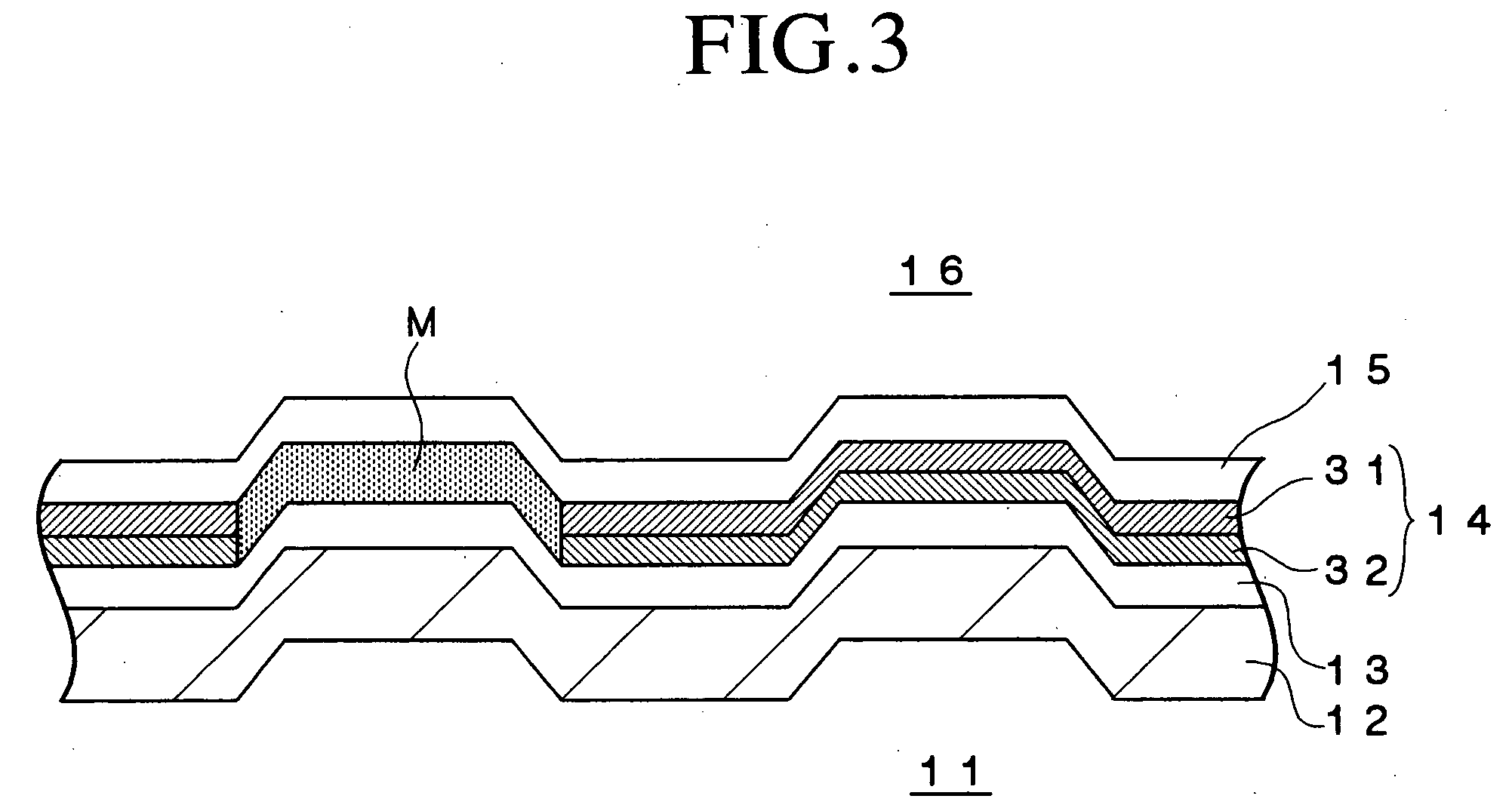
ActiveUS7123556B2Shorten the timeEfficient managementInput/output to record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareRecording layer
A multi-layered information recording medium comprising a plurality of recording layers, a user data area for recording user data, provided in at least two of the plurality of recording layers, and a defect list storing area for storing a defect list. When at least one defective area is detected in the user data area, the defect list is used to manage the at least one defective area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Incorporating a portable digital music player into a vehicle audio system
InactiveUS20060134959A1Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsMechanical record carriersMusic playerAudio frequency
A carriage receives and secures a portable digital music player in a vehicle audio system. The carriage is mechanically engagable with a dock of the vehicle audio system. Access and control over a portable digital music player received and secured by the vehicle audio system may be provided.
Owner:DASHJACK
Optical recording medium and method for recording optical information
The present invention provides an optical recording medium which incorporates an inorganic based recording layer which has a high reflectance, sufficient for reproduction compatibility on devices such as CD-ROM drives, as well as a high degree of modulation between the state prior to recording and that after recording, as well as an information recording method therefor. Accordingly, an optical recording medium comprises a substrate (2) which is substantially transparent with respect to a recording light beam and a reproduction light beam, a first recording layer (3) which is layered on top of the substrate (2) and which incorporates as the main constituent a metal which has a low melting point and a high reflectance, and a second recording layer (4) which is layered on top of the first recording layer (3) and which will, due to heat generated from irradiation of a light beam through the substrate (2), either mix, or alternatively react, with the first recording layer (3) to form an alloy of low reflectance as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby enabling the recording of information. Due to the heat generated from irradiation of a recording light beam through the substrate (2) the first recording layer (3) and the second recording layer (4) are either mixed, or alternatively reacted to form an alloy as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby recording information.
Owner:KAO CORP
Optimized media grain packing fraction for bit patterned magnetic recording media
InactiveUS20050157597A1Optimizes optical coupling efficiencyOptimizes medium grain packing fractionCombination recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringOptical coupling
A bit patterned magnetic recording medium for use in HAMR, which is optimized for optical coupling efficiencies and improved magnetic read-back coupling. The medium comprises bit-patterned magnetic recording elements, each corresponding to a magnetic data bit, and each comprising a cluster of discrete and separated magnetic grains. The desired packing fraction may be obtained by defining the number of grains within a bit, while bit-patterning provides efficient optical transmission. The grains have an effective packing fraction that enhances magnetic read-back signals, and the bits are distributed in a pattern having a packing fraction that enhances the optical coupling efficiency. The bits and / or the grains may be substantially thermally and optically isolated.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Process and apparatus for forming plastic sheet
InactiveUS6183829B1Avoid mistakesLow birefringenceRecord carriersPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Optical disk and method of integrating a high gain RFID antenna
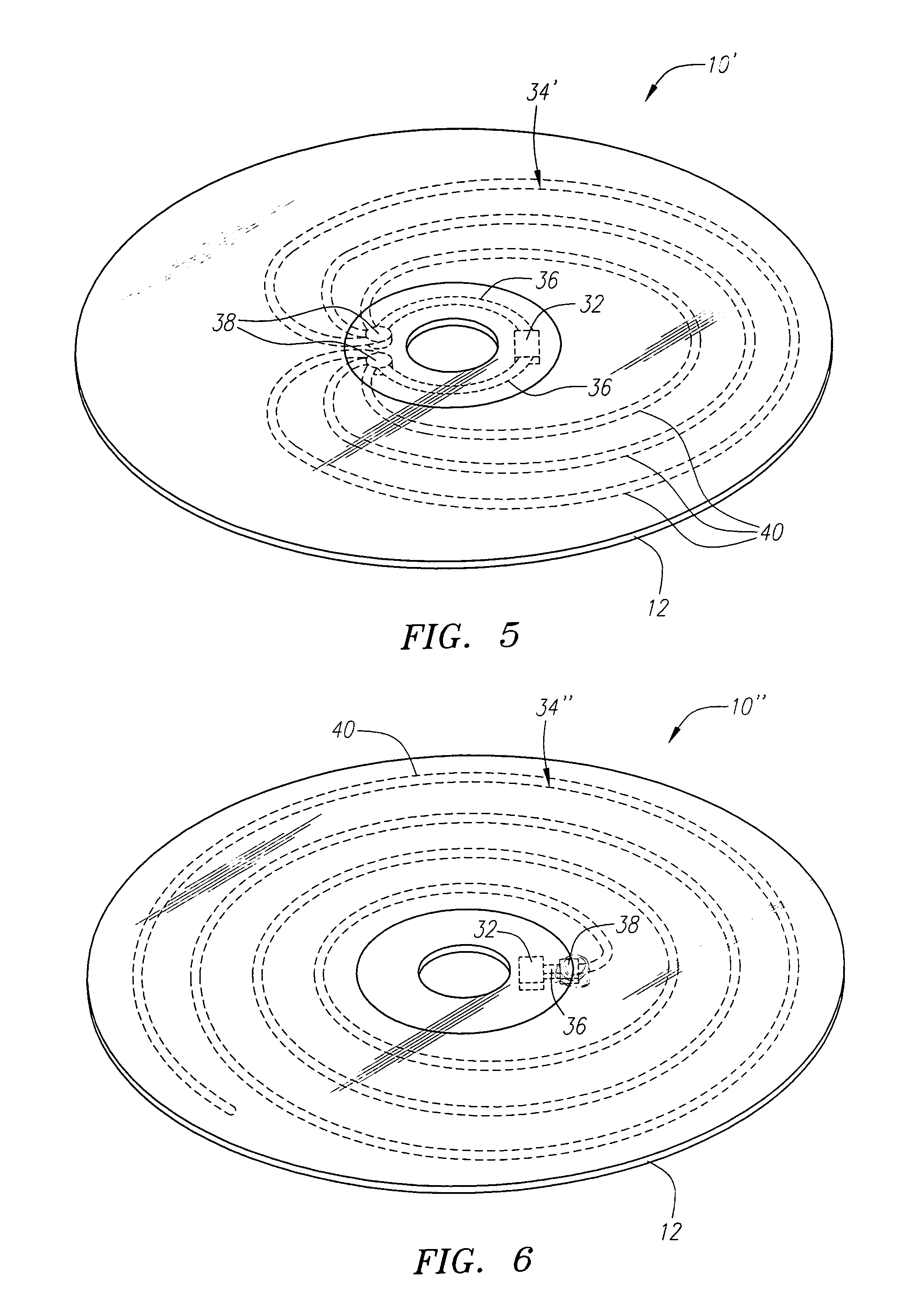
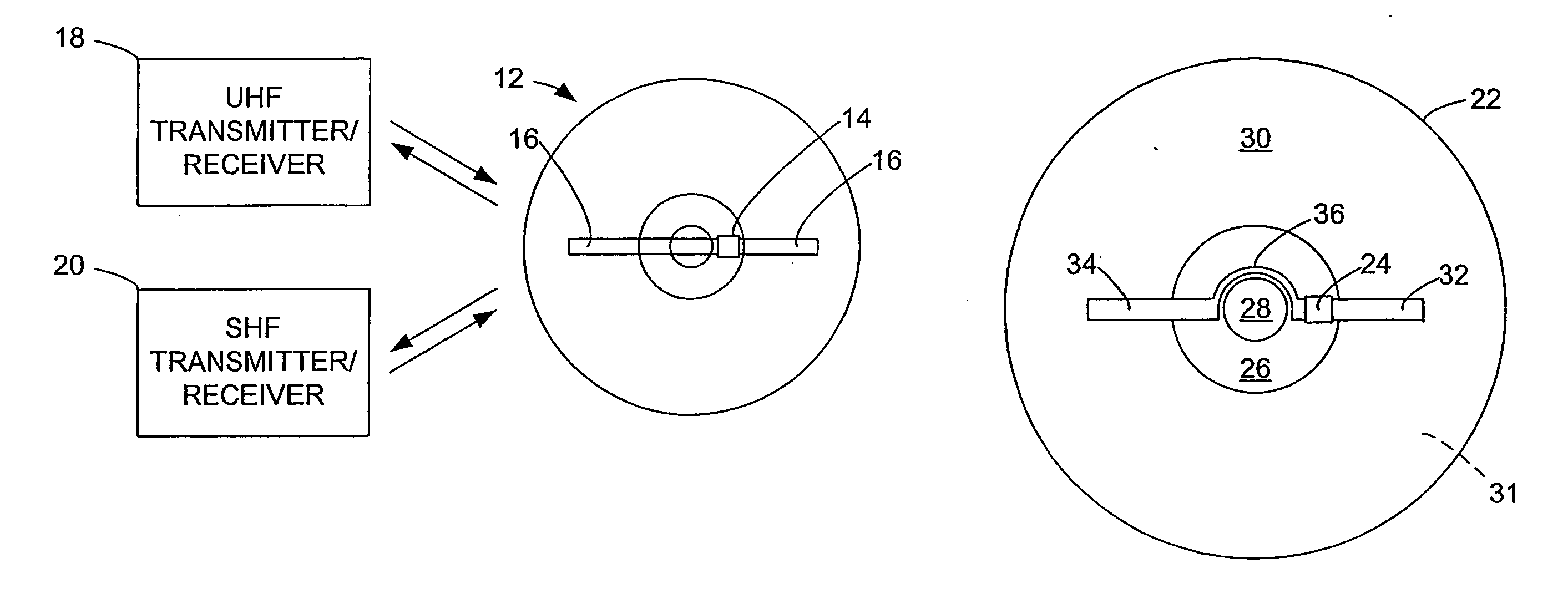
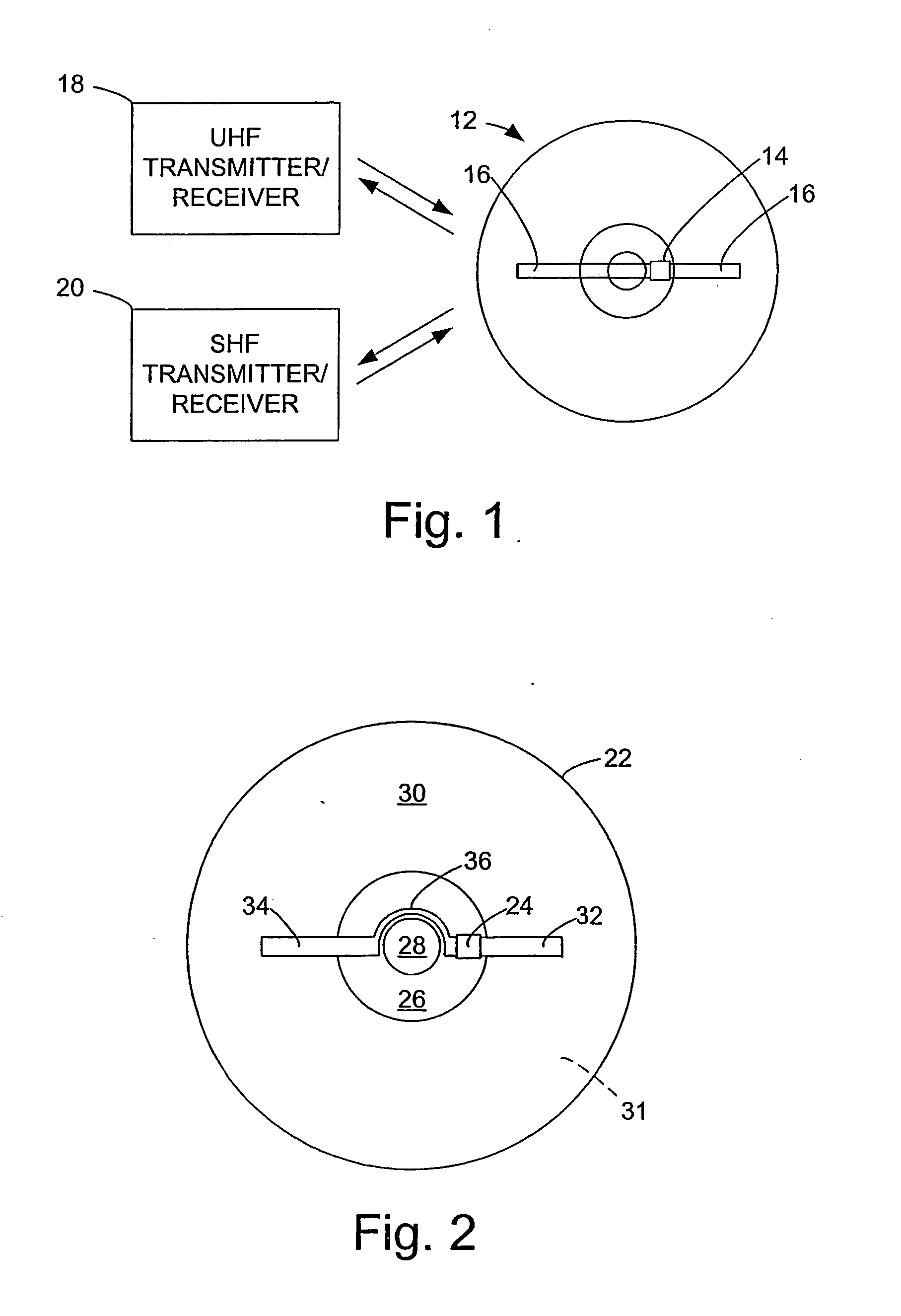
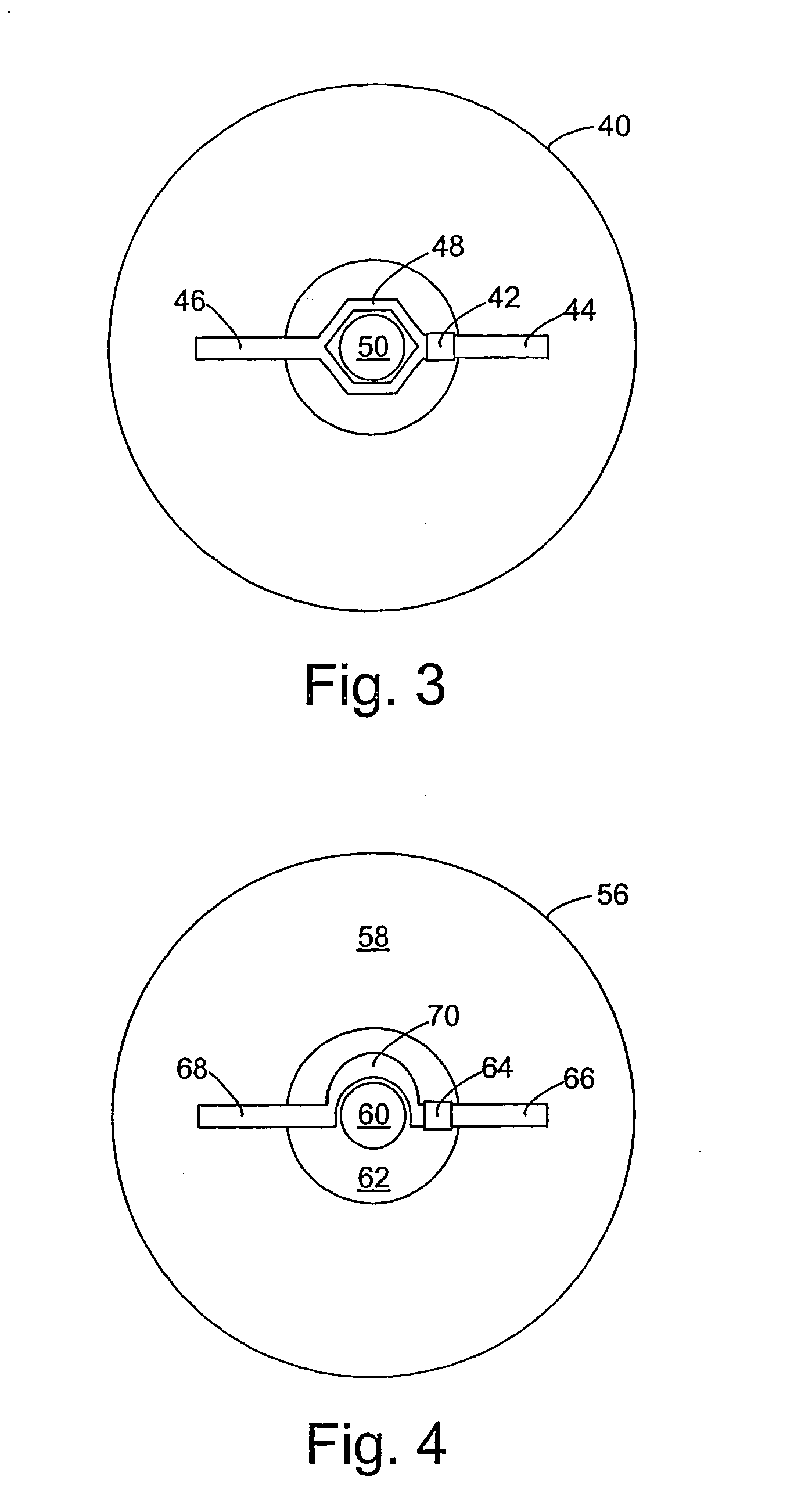
InactiveUS20060071795A1Easy to mergePrevent tamperingMechanical record carriersRecord information storageRadio frequency signalEngineering
An optical disk comprises a disk substrate having a hub and an annular optical metallicized data region extending radially outward from the hub. The optical disk further comprises a radio frequency identification (RFID) transponder affixed to the disk substrate, e.g., within the non-data containing hub region. The optical disk further comprises at least one linear antenna element coupled to the transponder, e.g., via pole lead(s), and extending within the data region. The antenna element(s) can be applied to the disk substrate as a patterned antenna layer over a metallicized data region, and can be electrically isolated from the data region. A method and system of identifying an optical disk is provided. A radio frequency (RF) signal can be transmitted to the optical disk at a range of at least five feet, and preferably at a range of at least ten feet. An RF signal with an identification code (e.g., a unique number) can be received from the optical disk in response to the transmitted RF signal. The activating RF signal can be transmitted by, and the identification RF signal can be received by, e.g., a handheld RF reader or an RF reader that is affixed to a building. The identification code can then be processed for many purposes, such as identifying the optical disk as a non-counterfeited optical disk, calculating a royalty, or tracking the location of the optical disk.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Extended range RFID system
InactiveUS20060028344A1Increase rangeAntenna supports/mountingsMechanical record carriersExtended coverageEngineering
A radio frequency identification (RFID) system for discs such as CDs, DVDs or minidiscs includes a special RFID transponder and antenna configuration. The discs normally include an outer metallized annular zone where information is stored, a central hole, and an inner annular zone between the hole and the outer annular zone. The transponder may be located in the inner annular zone, with antenna elements coupled to the transponder extending in opposite directions part way across the outer annular zone. Multilayer labels with a recess for the transponder chip, and antenna elements formed by conductive material may be employed to apply the RFID assembly to the discs. A monopole or dipole mode of antenna operation, prominently involving the metallized disc layer, results from the antenna configuration, and serves to more than double the range of the system.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
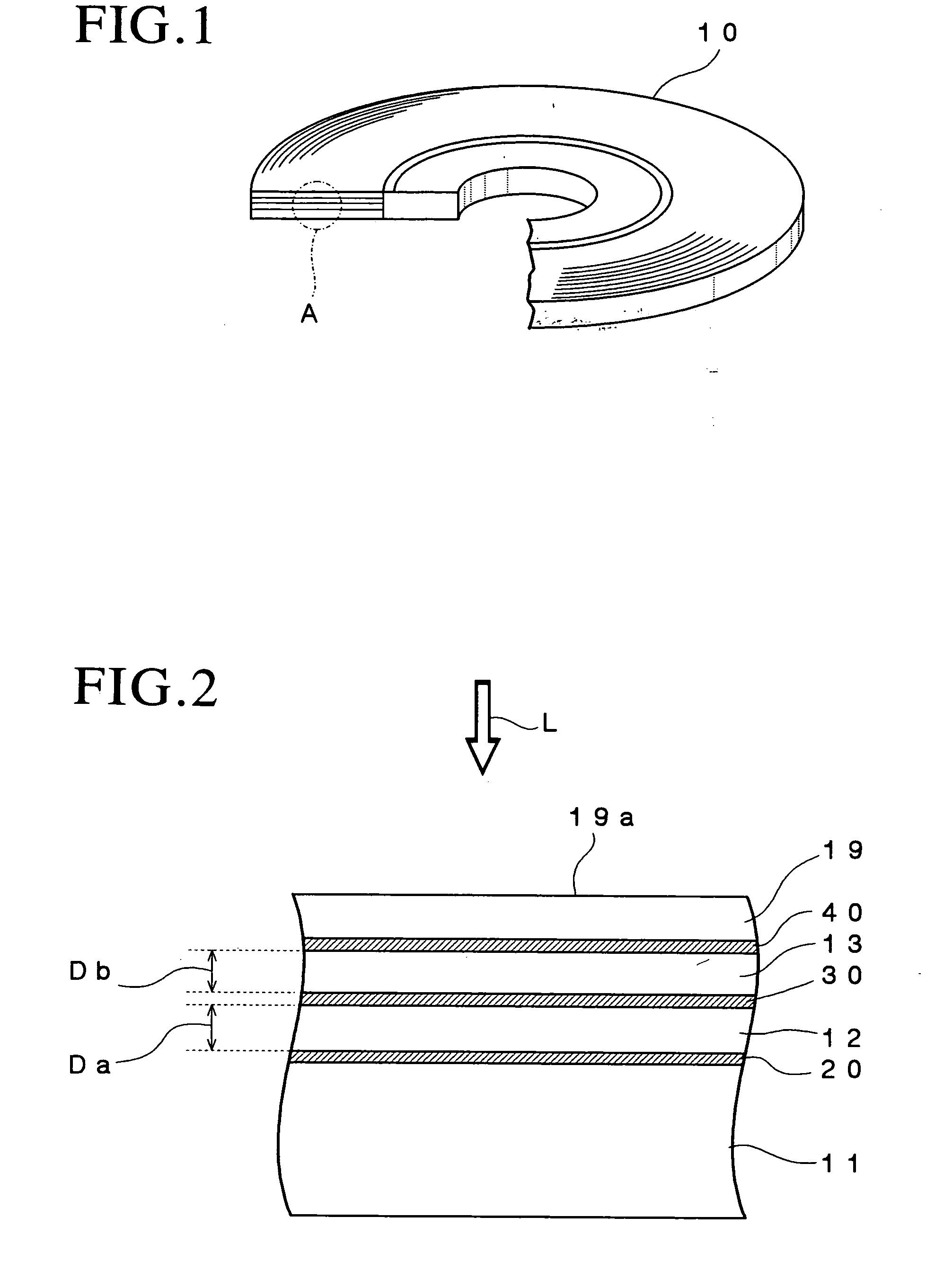
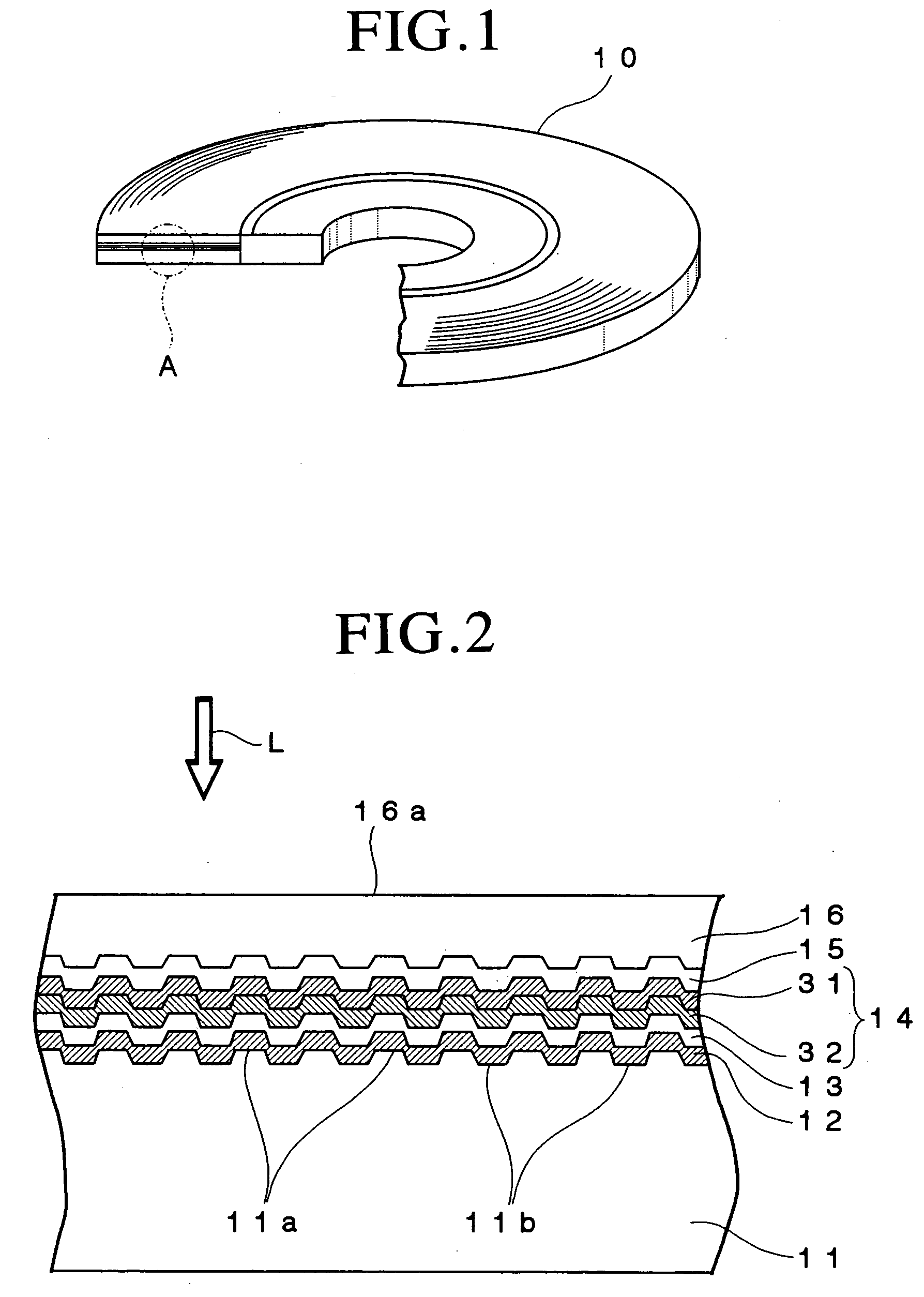
Information recording mediums, supporter used in the mediums, manufacture methods of the supporter, manufacturing apparatus of the supporter and stampers for producing the mediums
InactiveUS6254966B1Magnetic materials for record carriersLayered productsHigh densityManufactured apparatus
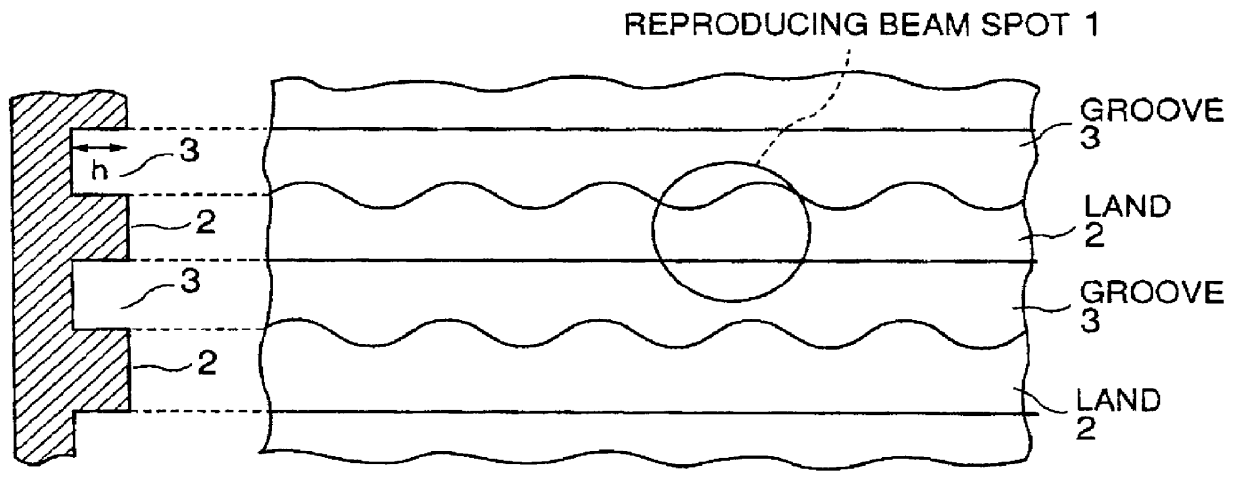
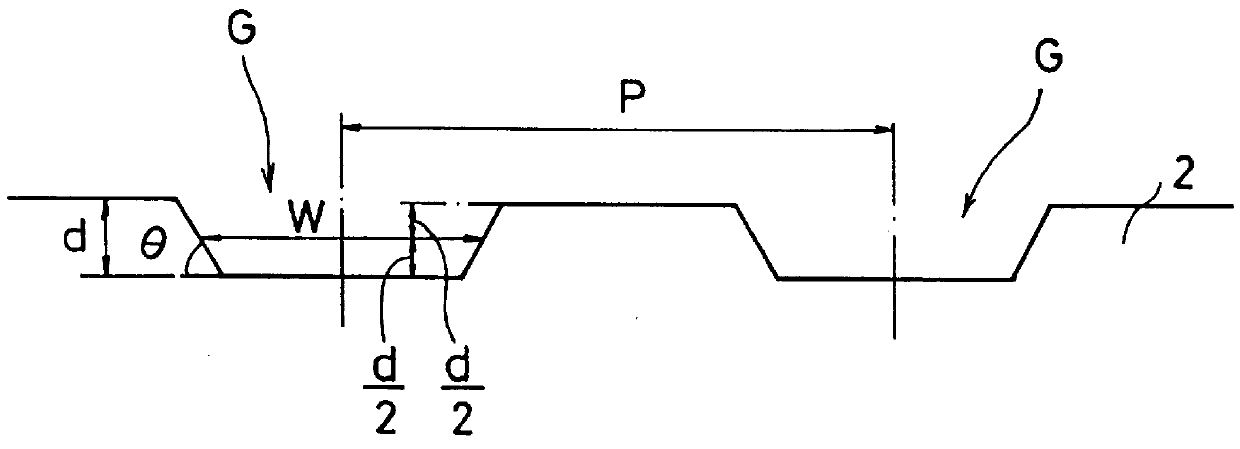
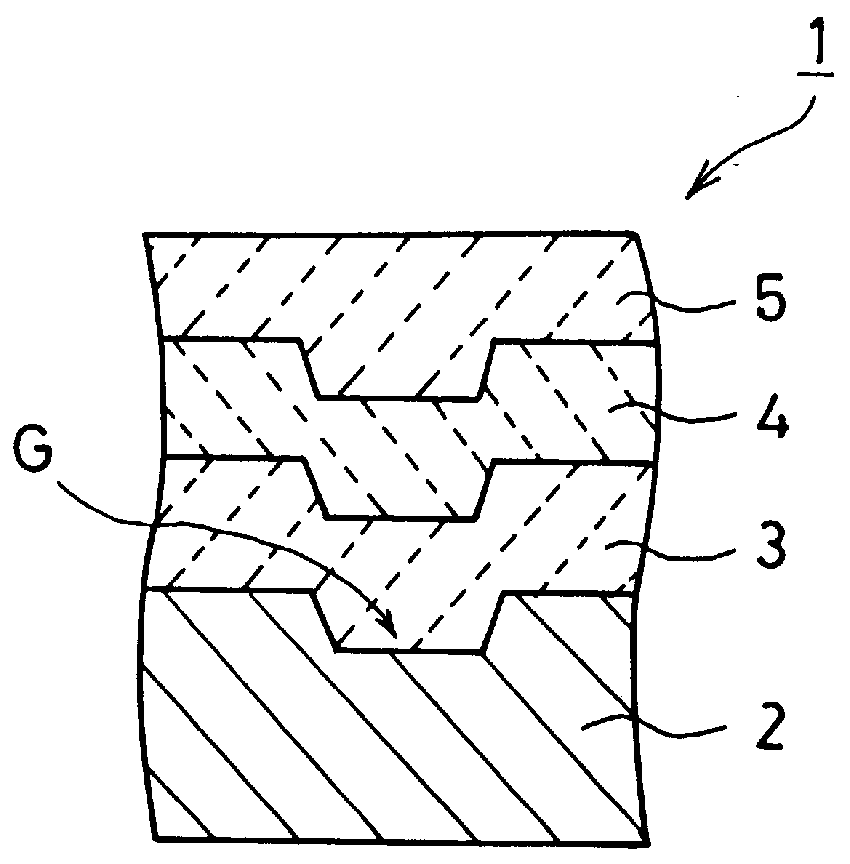
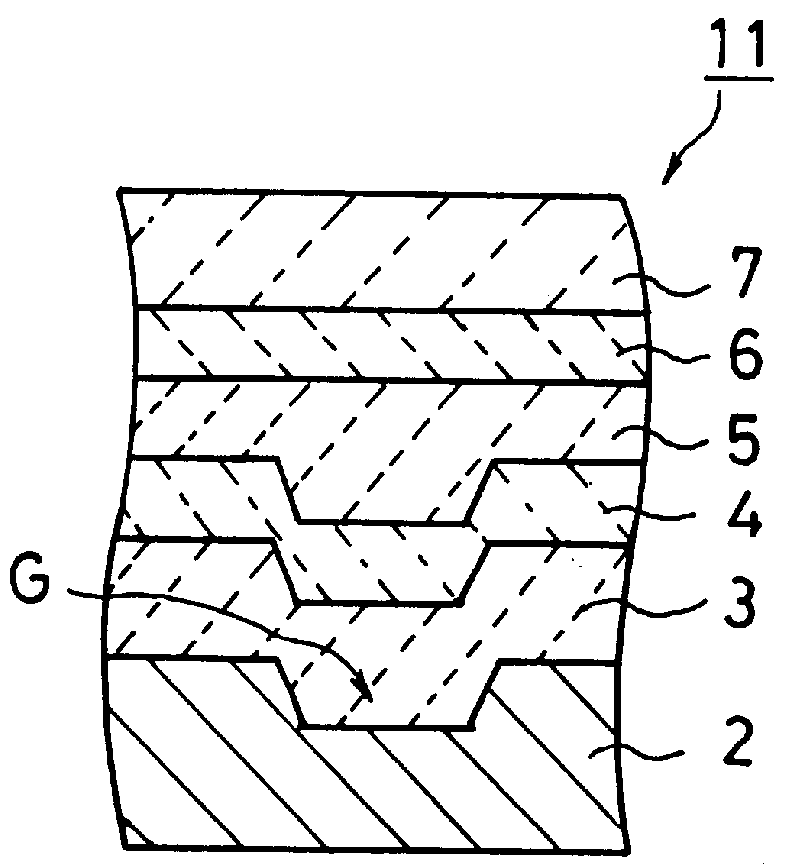
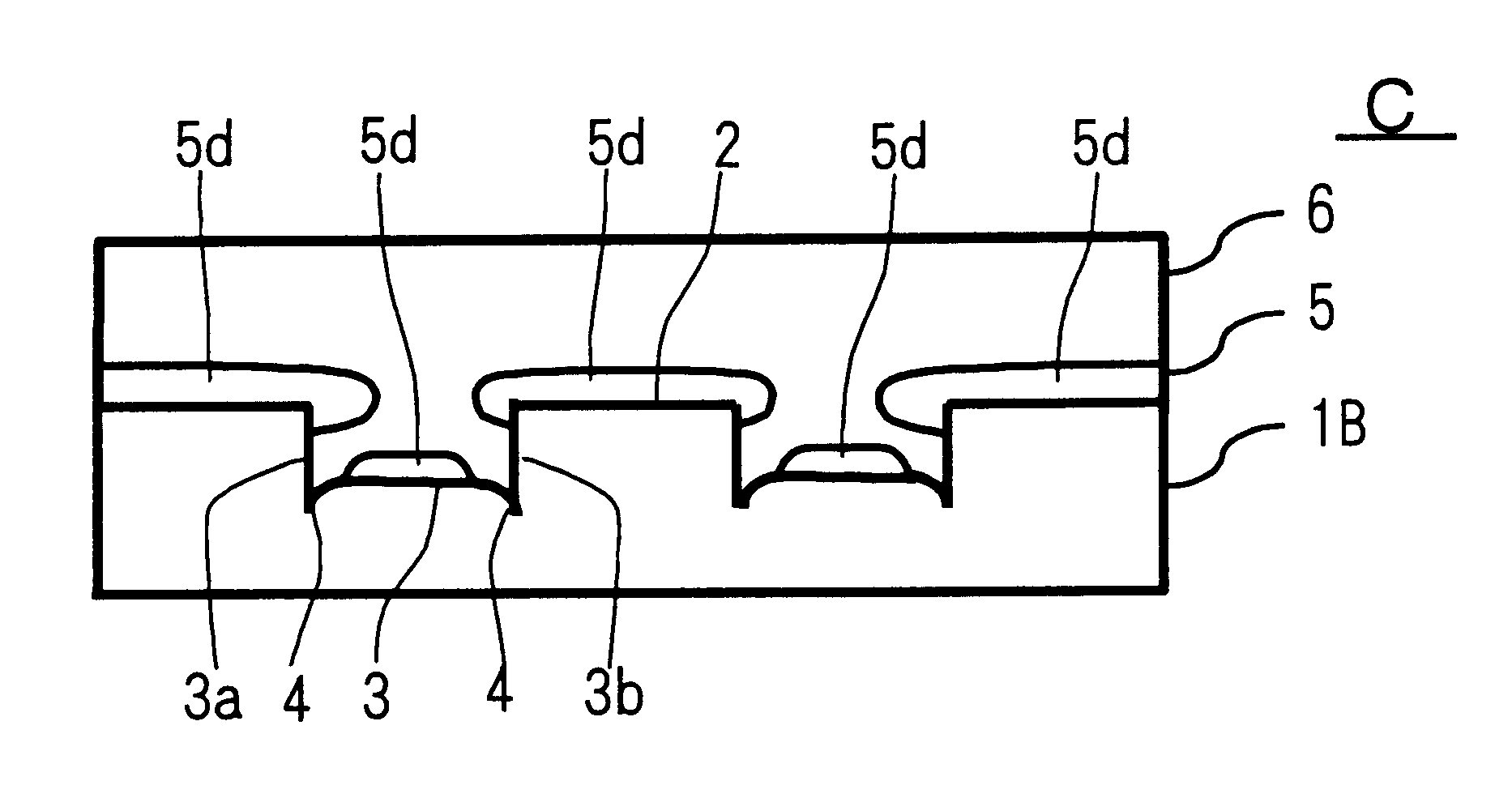
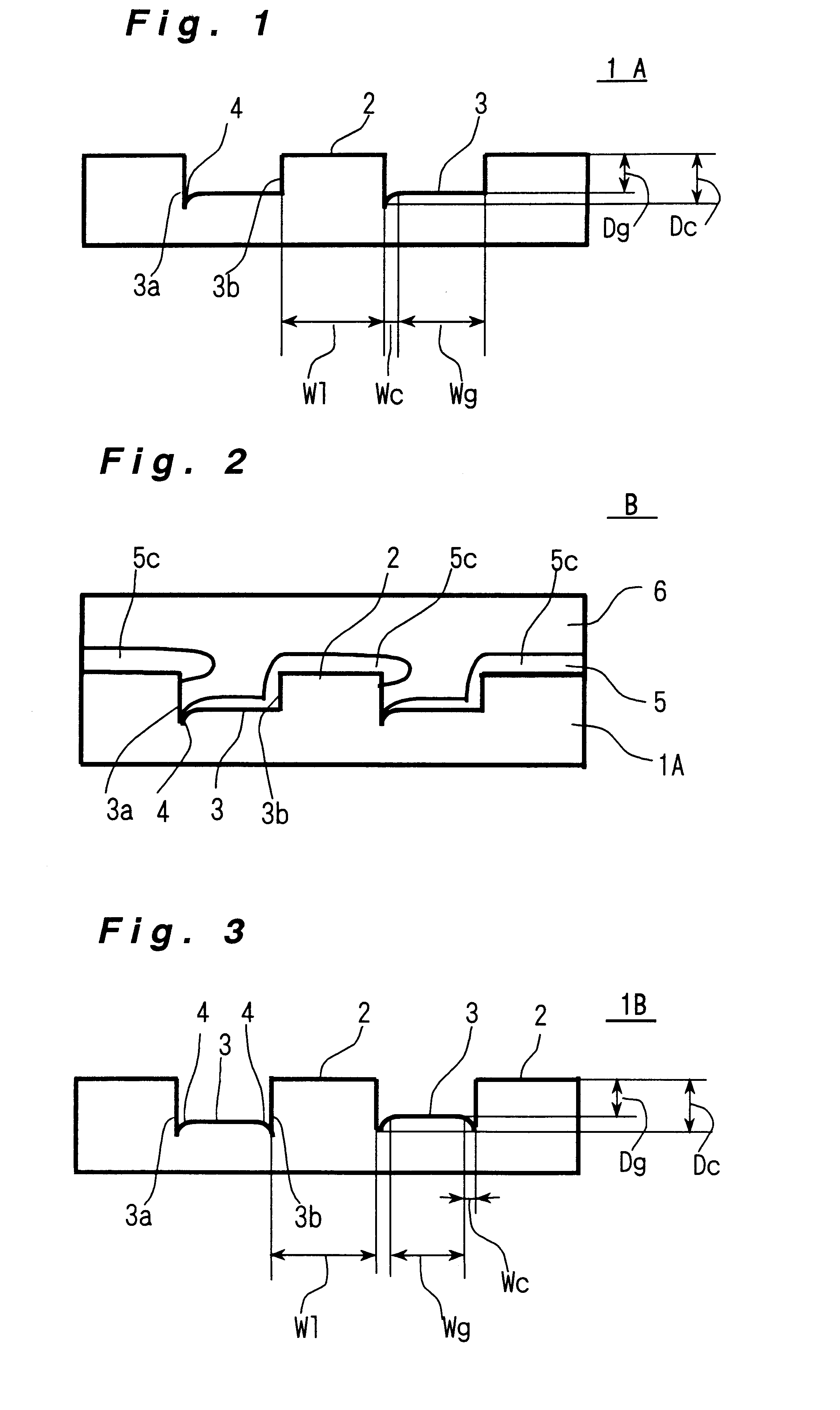
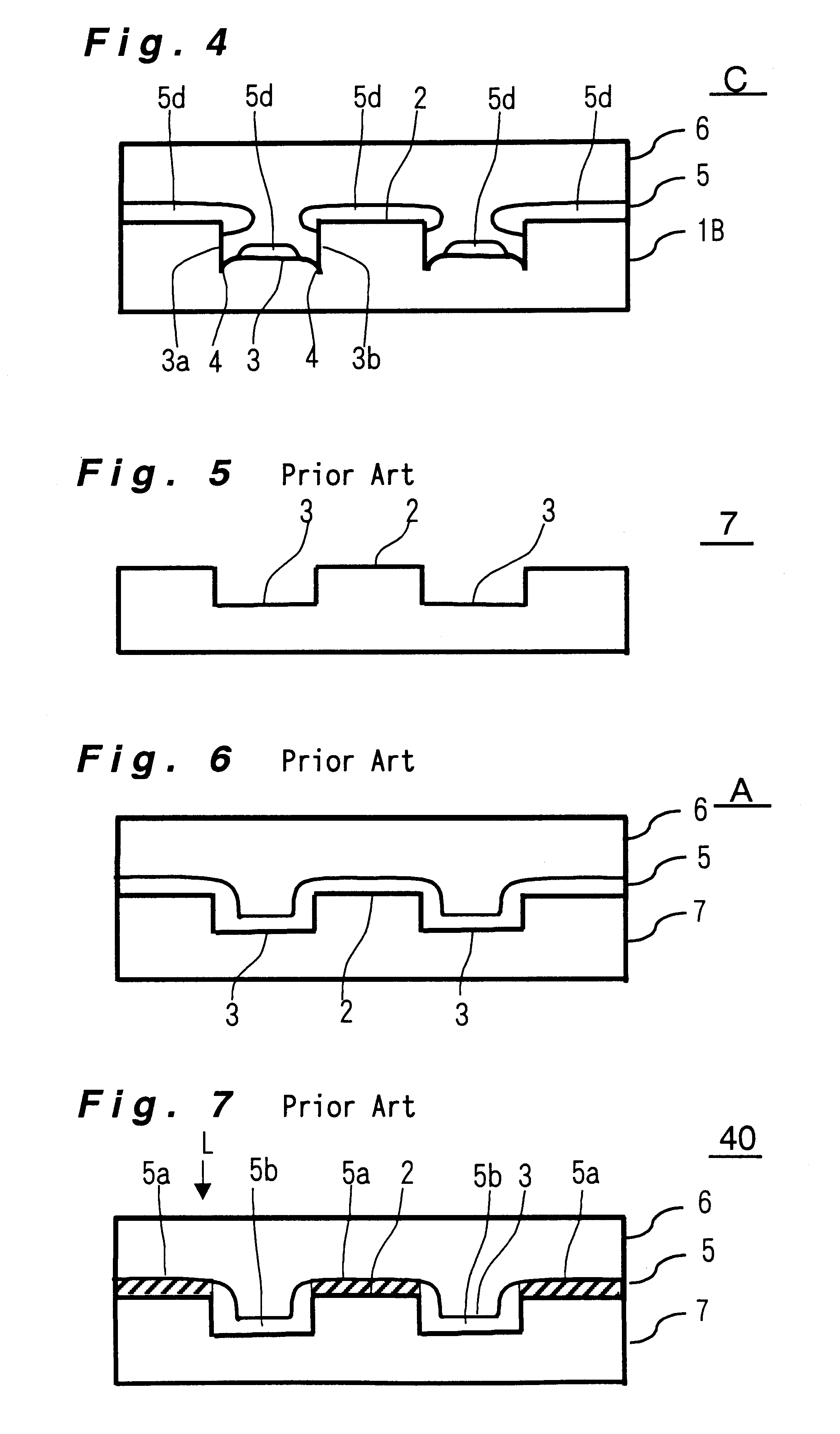
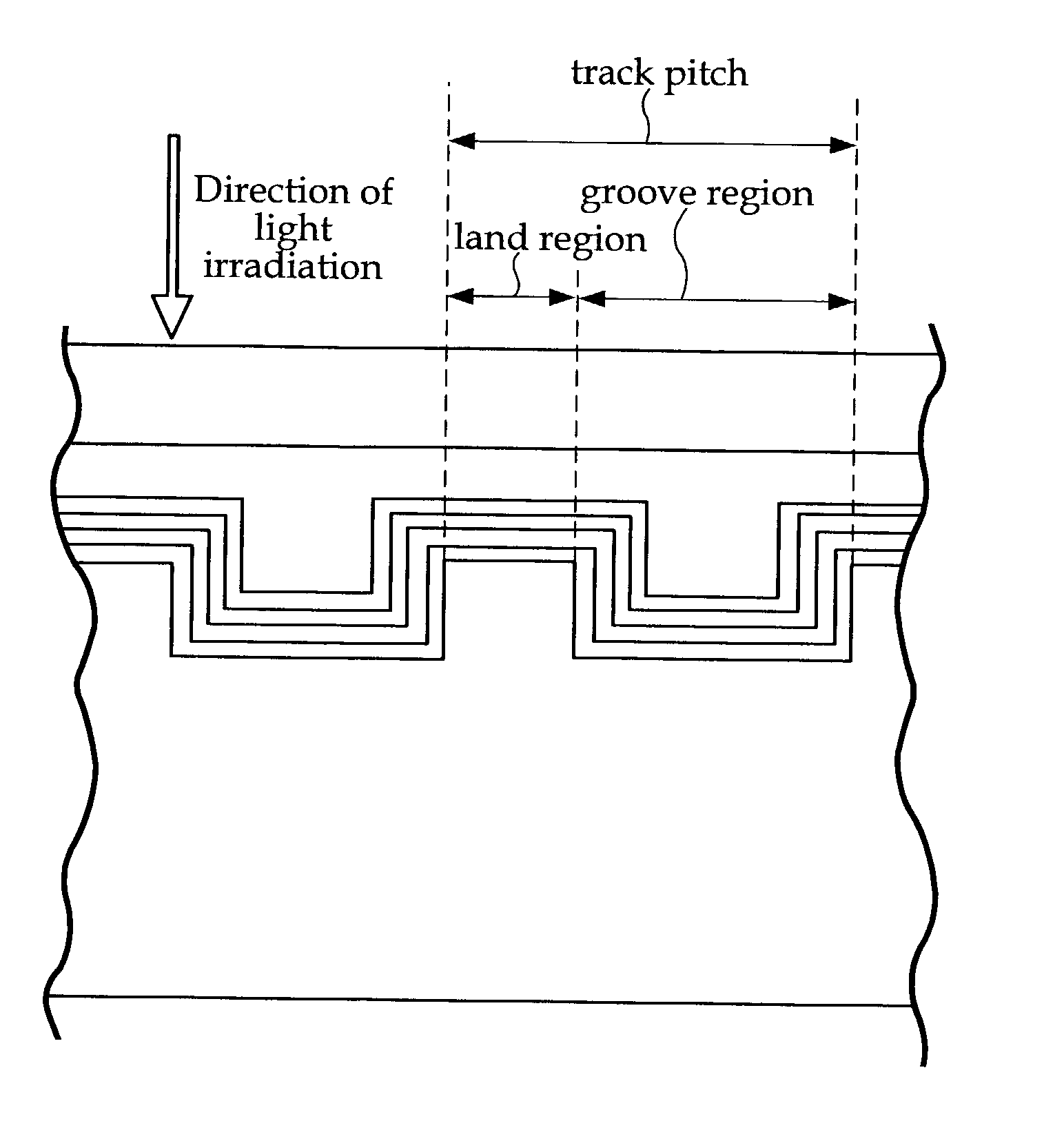
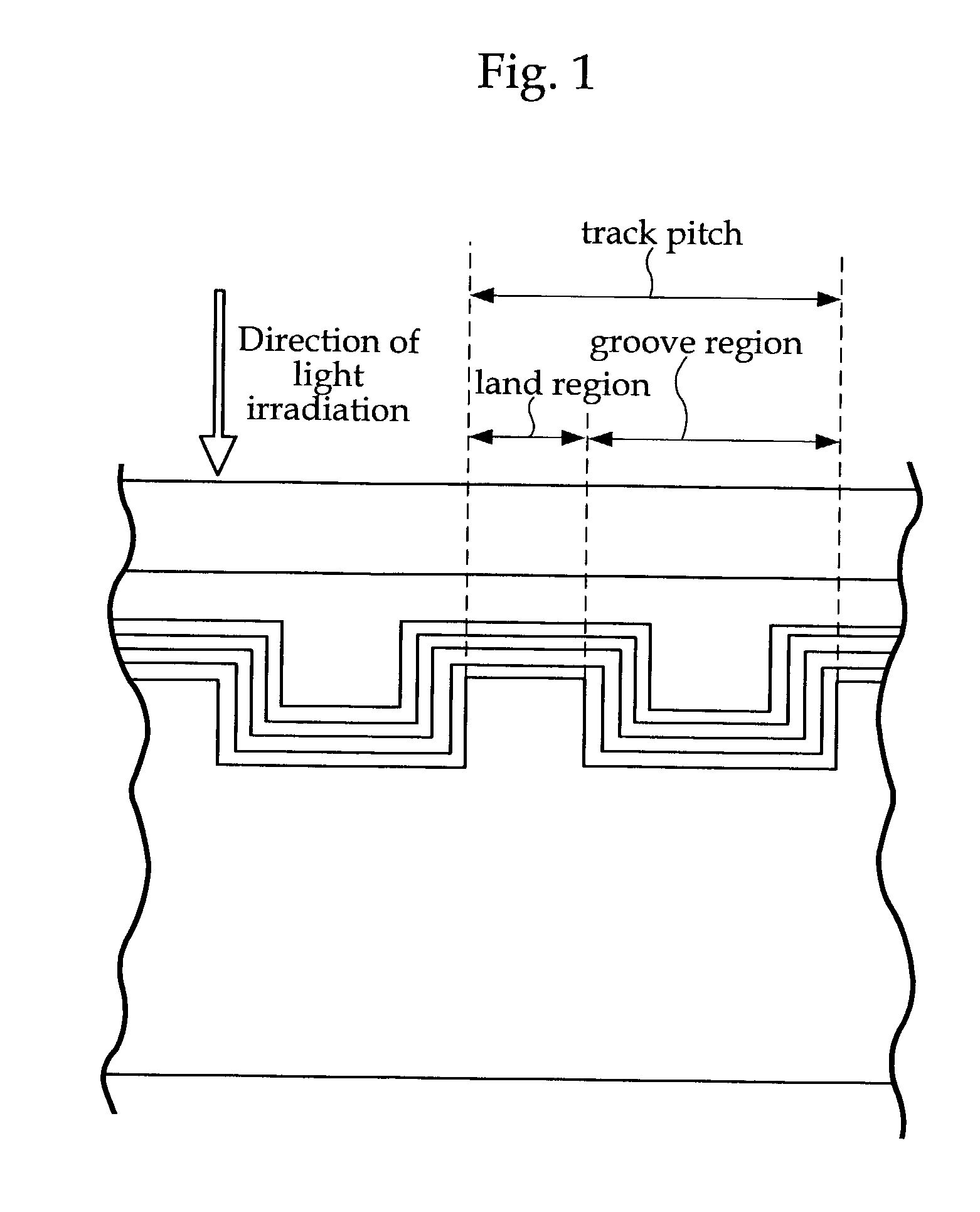
An information recording medium and a supporter used for the information recording medium capable of recording a land / groove recording by using a high density recording technique such as a super-resolution, resulting in a high density recording. An information recording medium B has a supporter 1A, on which a recording layer 5 is formed. On the supporter 1A, lands 2 and groove 3 are alternately formed as a minute track pattern. A crevice 4 having a depth Dc larger than a depth Dg of the respective grooves 3 is formed in the respective grooves 3 at one end of the respective grooves 3 in a width direction of the respective grooves.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Double-sided optical disc
A double-sided optical disc, is formed with data tracks on each layer. The tracks on one side follow one spiral while the tracks on the other side follow a second spiral, the two spirals being oriented in opposite directions as viewed from the respective sides, and therefore being mirror images of each other. This allows data to be read by a player seamlessly from both sides of the disc without changing the direction of rotation of the disc.
Owner:WARNER HOME VIDEO
Optical pickup apparatus, recording/reproducing apparatus provided with the optical pickup apparatus, optical element, and information recording/reproducing method
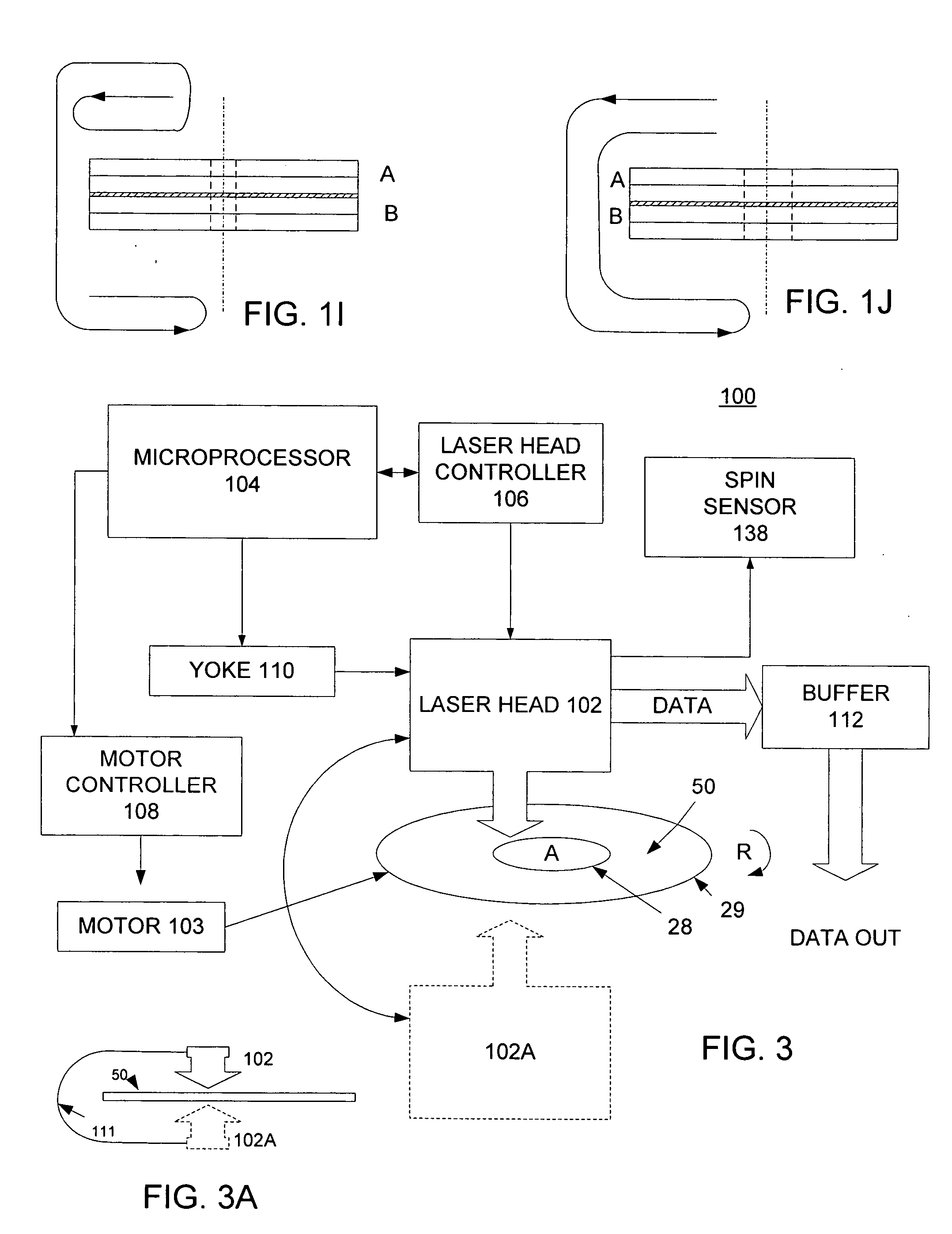
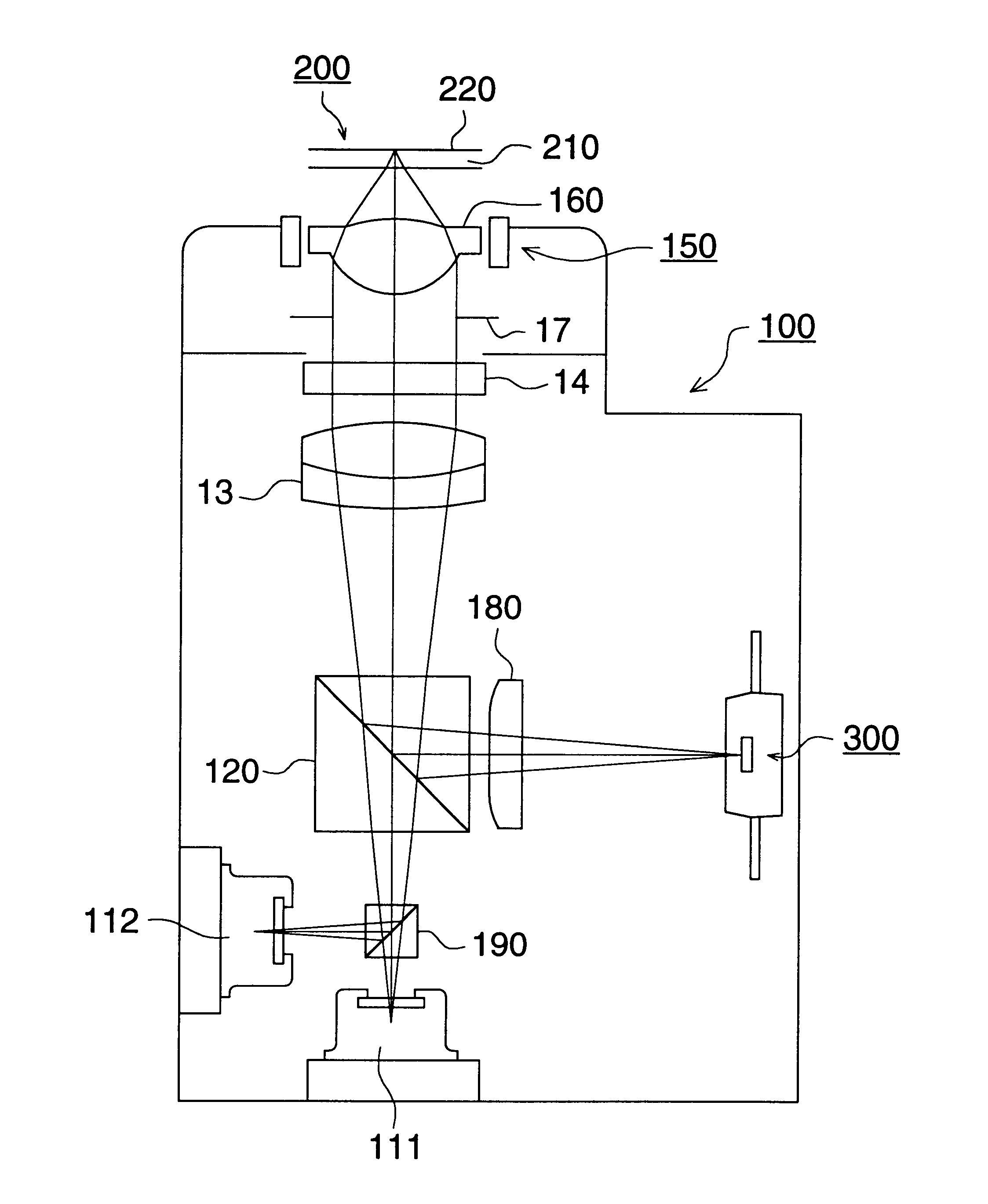
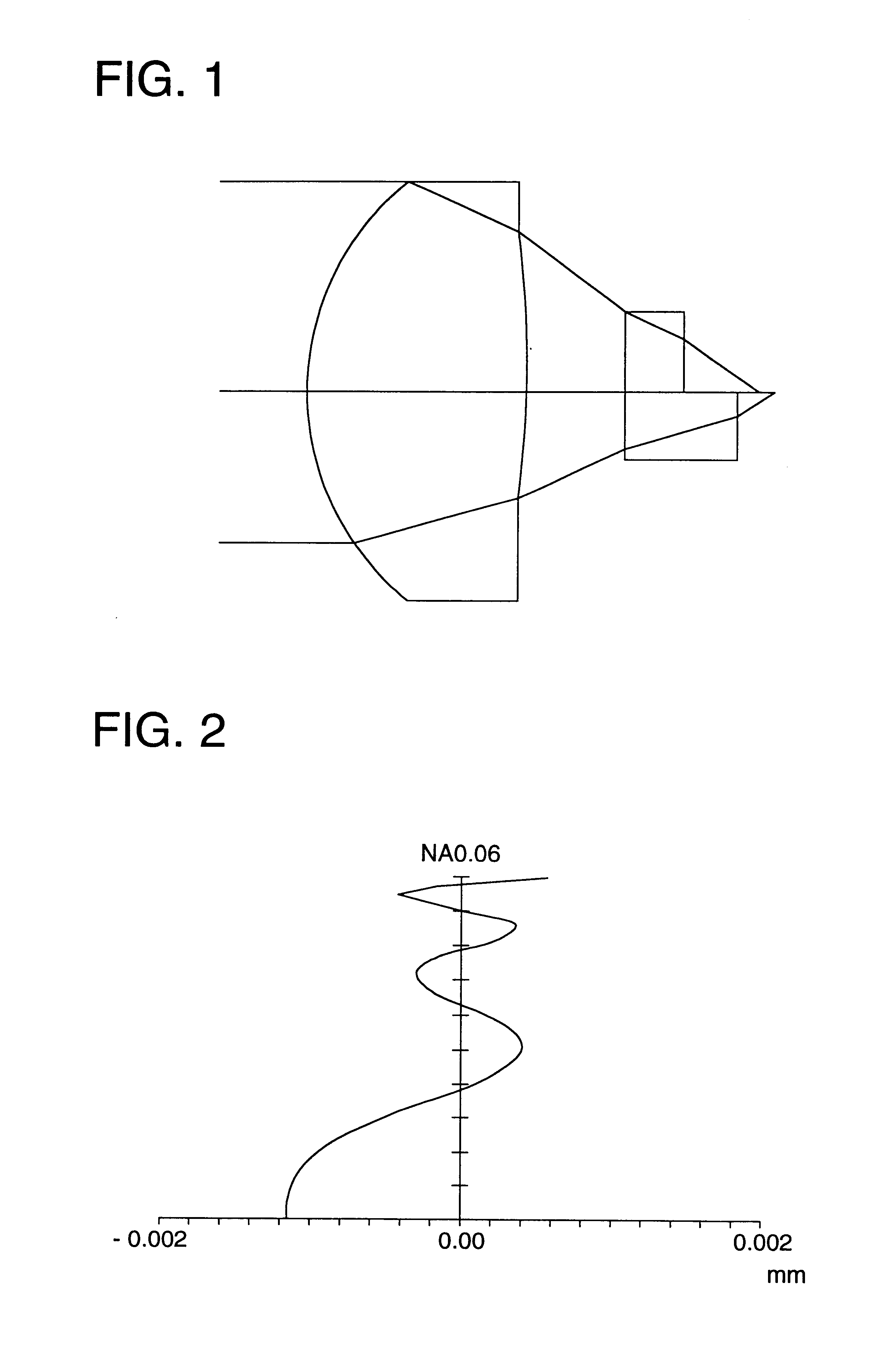
InactiveUS6870805B1Simple structureQuantity of light is lessOptical beam sourcesNon-mechanical controlsOptical pickupOptical axis
An optical pickup apparatus for reproducing information from an optical information recording medium or for recording information onto an optical information recording medium, is provided with a first light source for emitting first light flux having a first wavelength; a second light source for emitting second light flux having a second wavelength, the first wavelength being different from the second wavelength; a converging optical system having an optical axis and a diffractive portion, and a photo detector; wherein in case that the first light flux passes through the diffractive portion to generate at least one diffracted ray, an amount of n-th ordered diffracted ray of the first light flux is greater than that of any other ordered diffracted ray of the first light flux, and in case that the second light flux passes through the diffractive portion to generate at least one diffracted ray, an amount of n-th ordered diffracted ray of the second light flux is greater than that of any other ordered diffracted ray of the second light flux, where n stands for an integer other than zero.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Optical information recording medium, and substrate and manufacturing method for the optical information recording medium
InactiveUS6930977B1Interference minimizationMechanical record carriersRecord information storageRecord statusReflectivity
In an optical disk including at least a rewritable phase change material and comprising a recording layer having a reflectivity of more than 15%, an address output value as an address pit signal component occupying in a reproduced signal in a non recording state is prescribed to be 0.18 though 0.27 or a numerical aperture of an address pit signal occupying in a reproduced signal in a non recording state is prescribed to be more than 0.3.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Method of recording or reproducing data on or from high density multi-layer recording medium using variable light intensity
InactiveUS7009927B2Diminishing of dataDiminishing of surfaceOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageHigh densityData recording
A high-density optical recording medium and method of recording data on the optical recording medium. The optical recording medium includes a plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces having reflectances for light passing through a pit area, a land / groove area, and a land / groove area on which data are recorded, of a data recording / reproducing surface included between a light source for emitting light and a recording / reproducing surface selected from the plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces, the reflectances satisfy the expressions r1≧r2≧r3 and {(r1−r3) / r3}≦0.2, where r1, r2 and r3 are the reflectances of the pit area, the land / groove area and the land groove area on which data are recorded, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
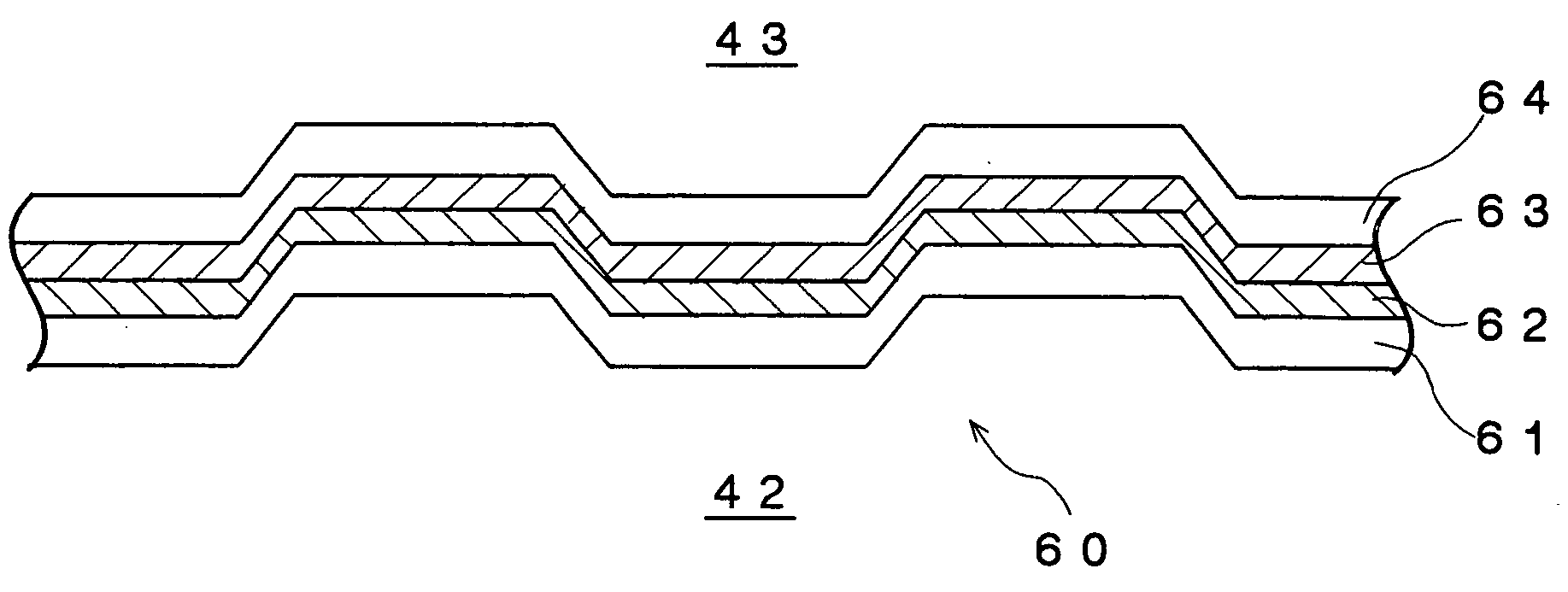
Recording medium, and method and apparatus for recording/reproducing data in/from the recording medium
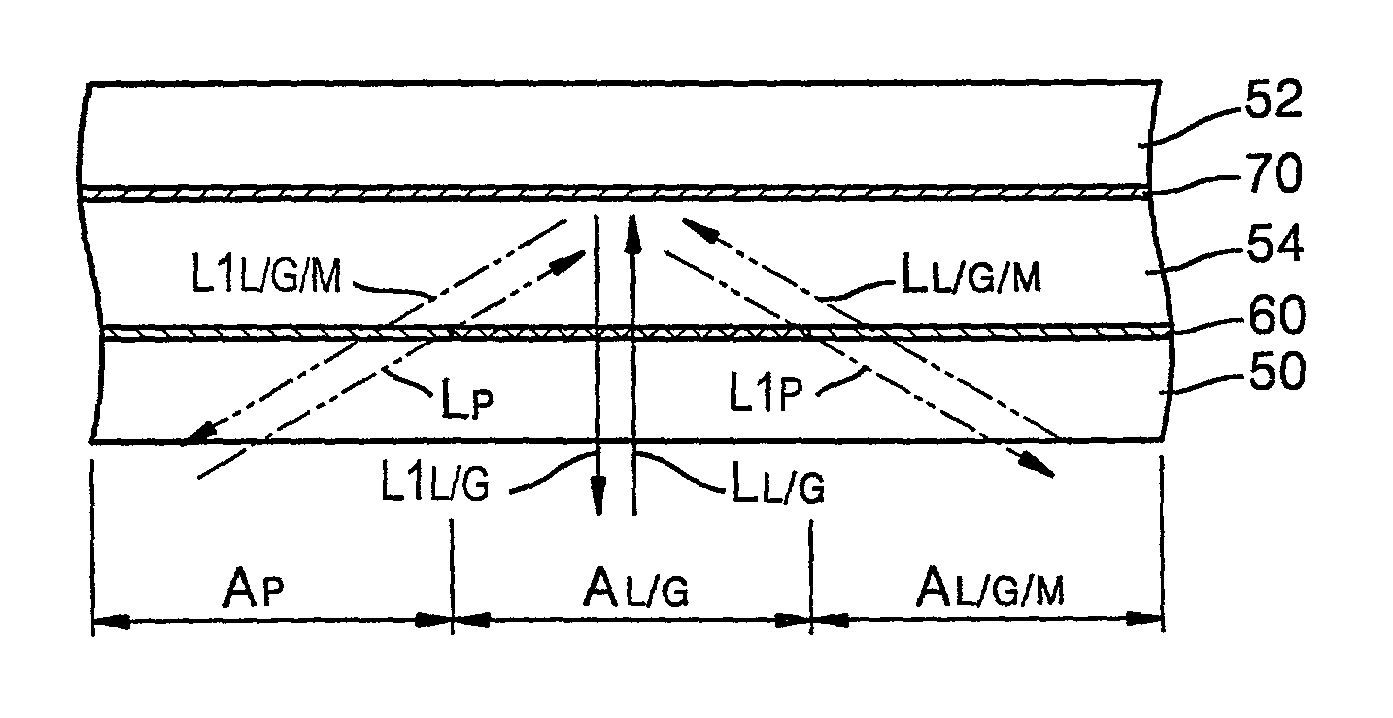
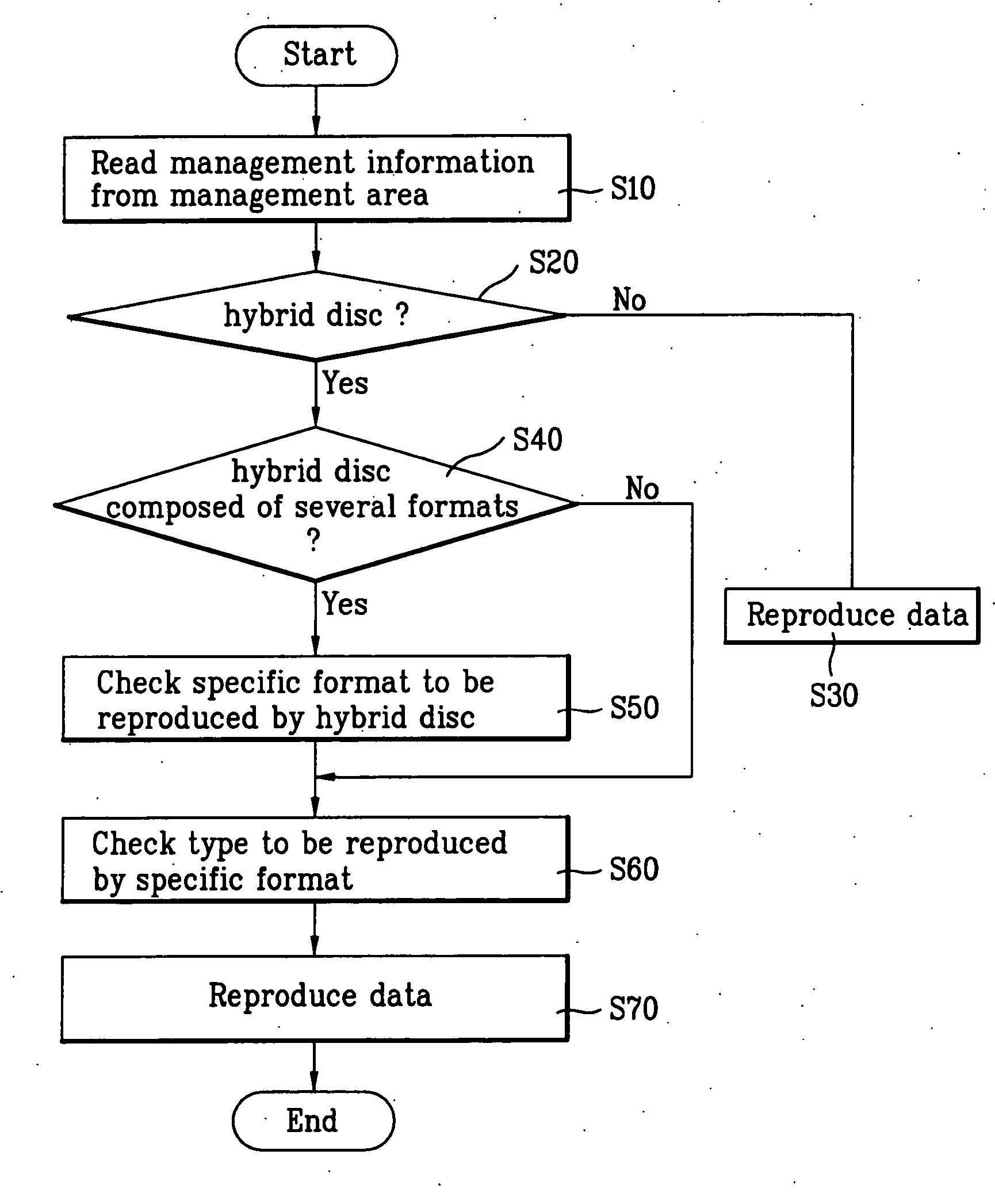
InactiveUS20070002699A1Discriminating a hybrid discTelevision system detailsRecord information storageComputer hardwareRecording layer
A recording medium, and a method and apparatus for recording / reproducing data in / from the recording medium are disclosed. The recording medium includes one or more recording layers, and a management area including management information, wherein the management information includes specific information indicating a presence of different format and type of recording layer in the recording medium. The management area is located at a specific recording layer. The format represents a different category in a recording layer and the type is classified by read-only or writable in a recording layer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
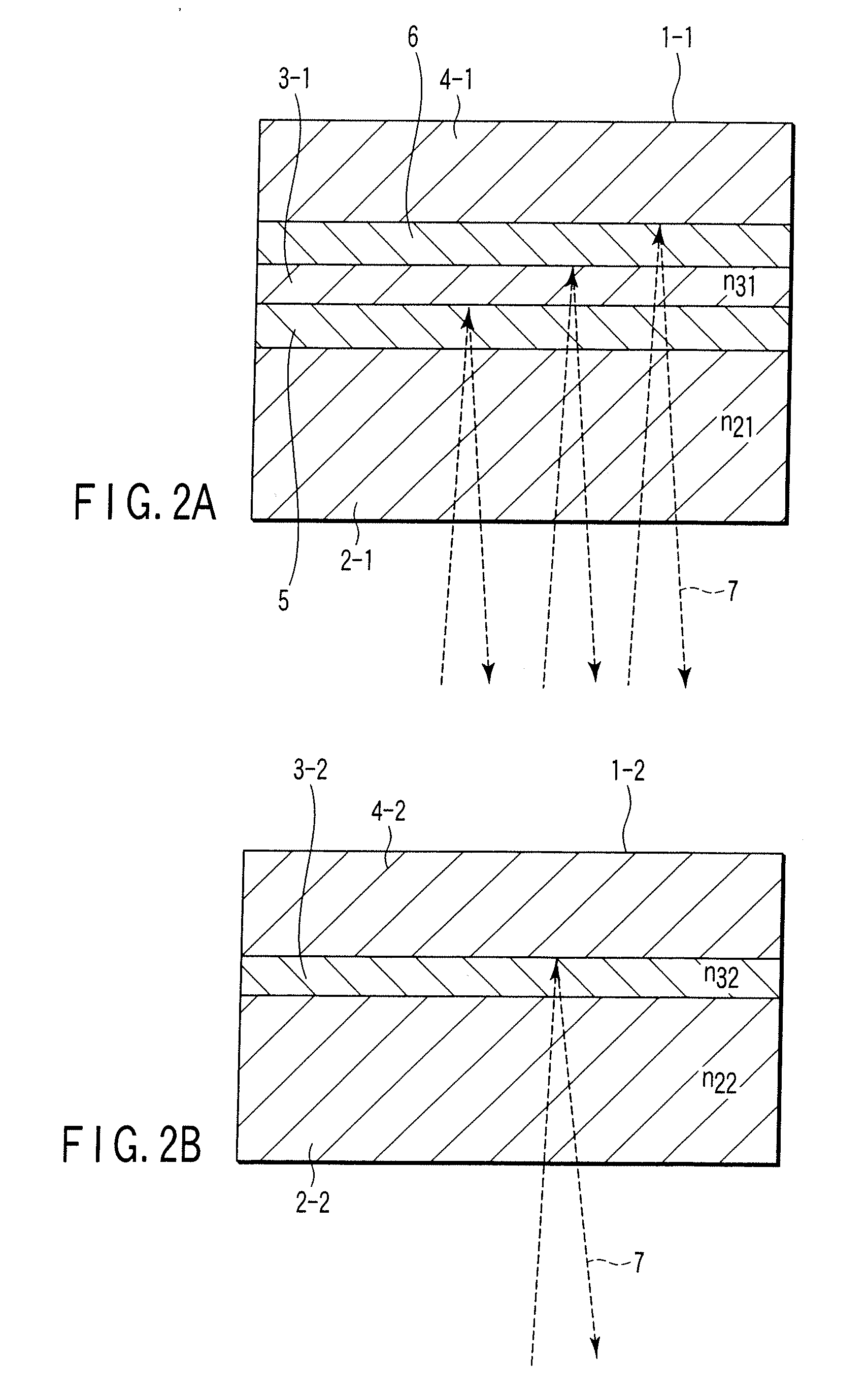
Optical recording medium
ActiveUS20040139459A1Avoid it happening againMechanical record carriersRecord information storageInter layerOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a protective layer, three or more information recording layers formed between the substrate and the protective layer and transparent intermediate layers each formed between neighboring information recording layers and capable of recording data in the three or more information recording layers and reproducing data recorded in the three or more information recording layers by projecting a laser beam onto the three or more information recording layers via a light incidence plane constituted by the surface of either the substrate or the protective layer, wherein neighboring transparent intermediate layers facing each other across an information recording layer have different thicknesses. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to reduce interlayer cross-talk.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
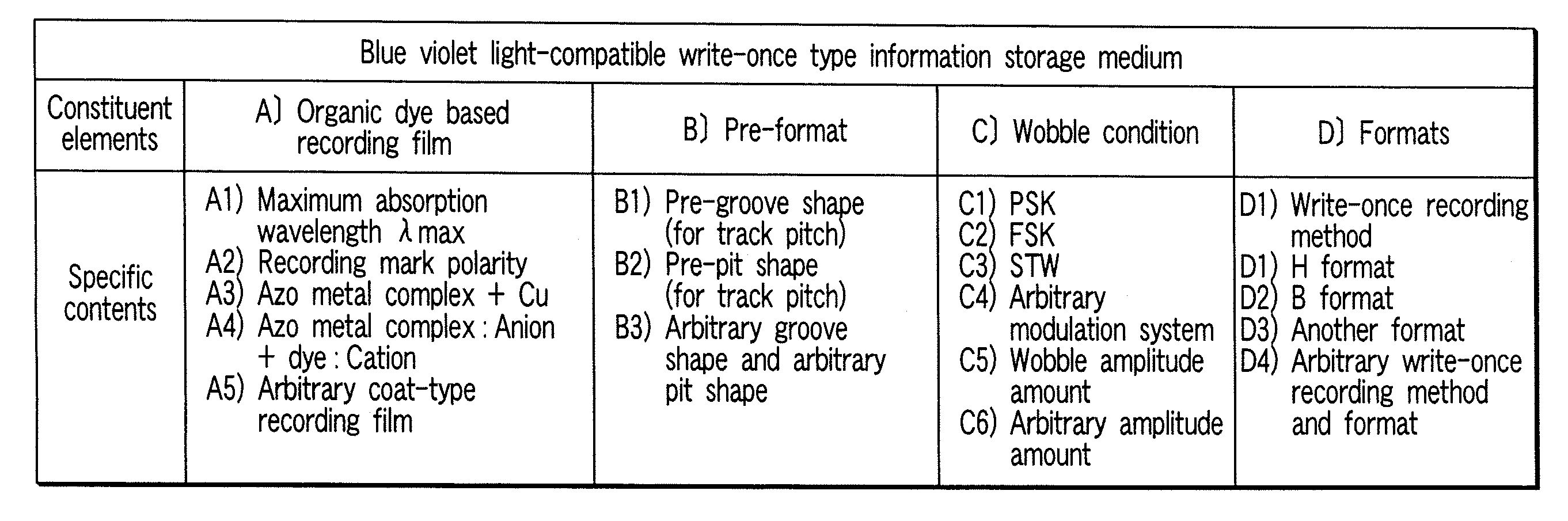
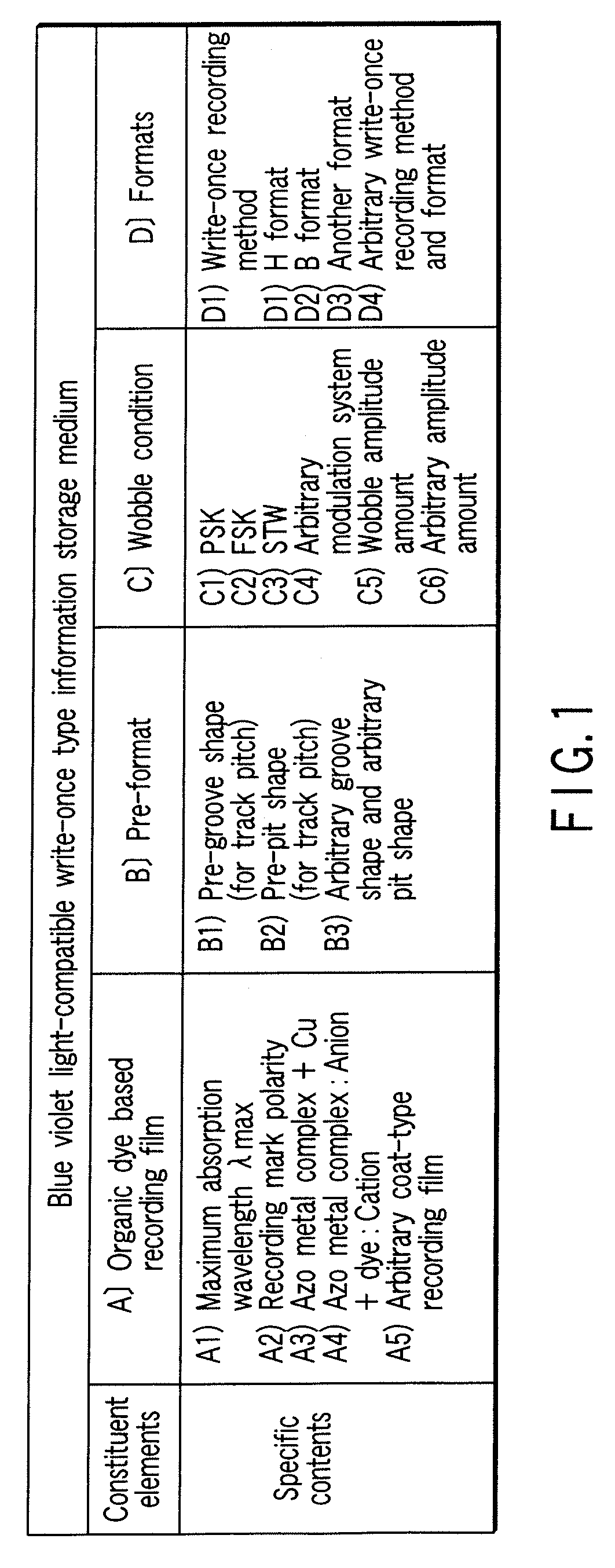
Recording material for medium
InactiveUS20050227178A1Reflection coefficientStyryl dyesLayered productsOptical reflectionLength wave
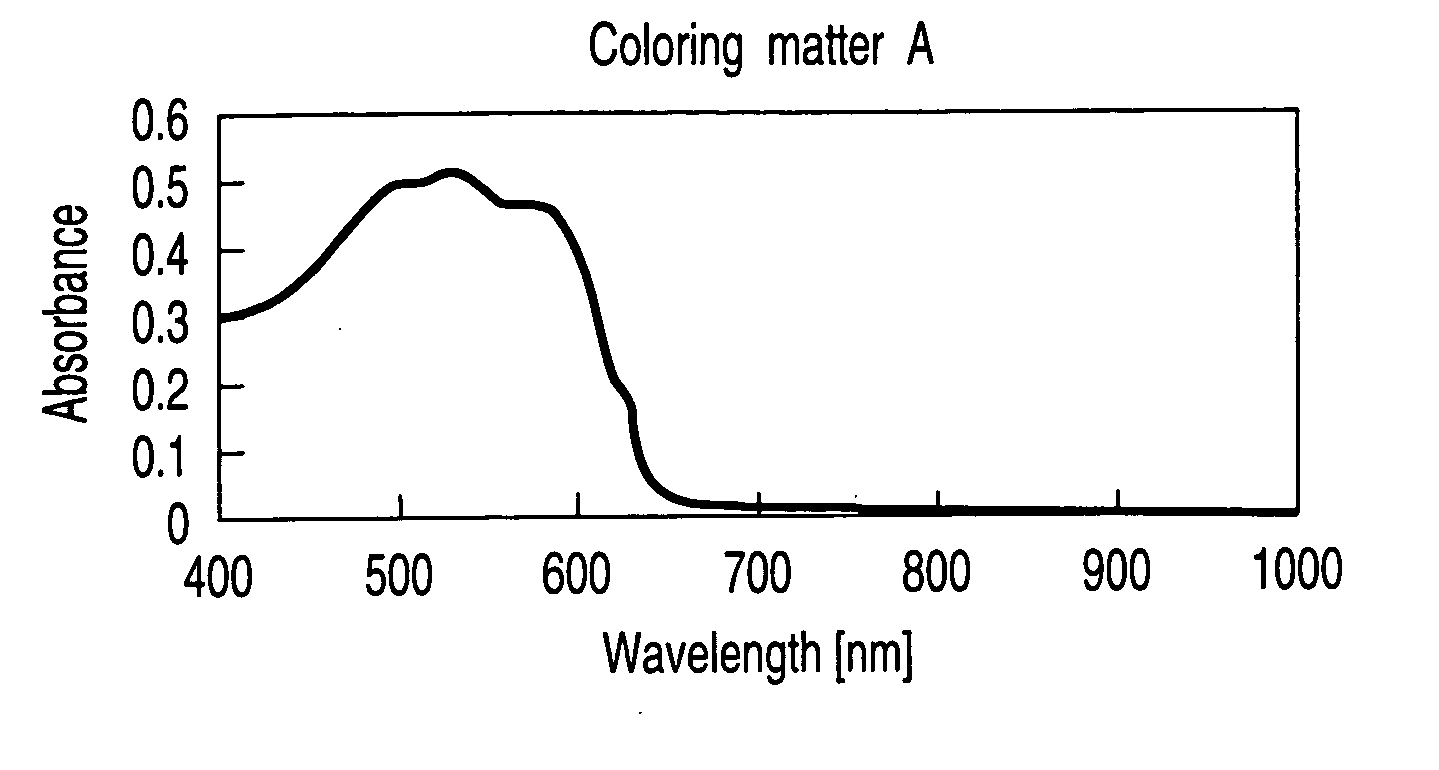
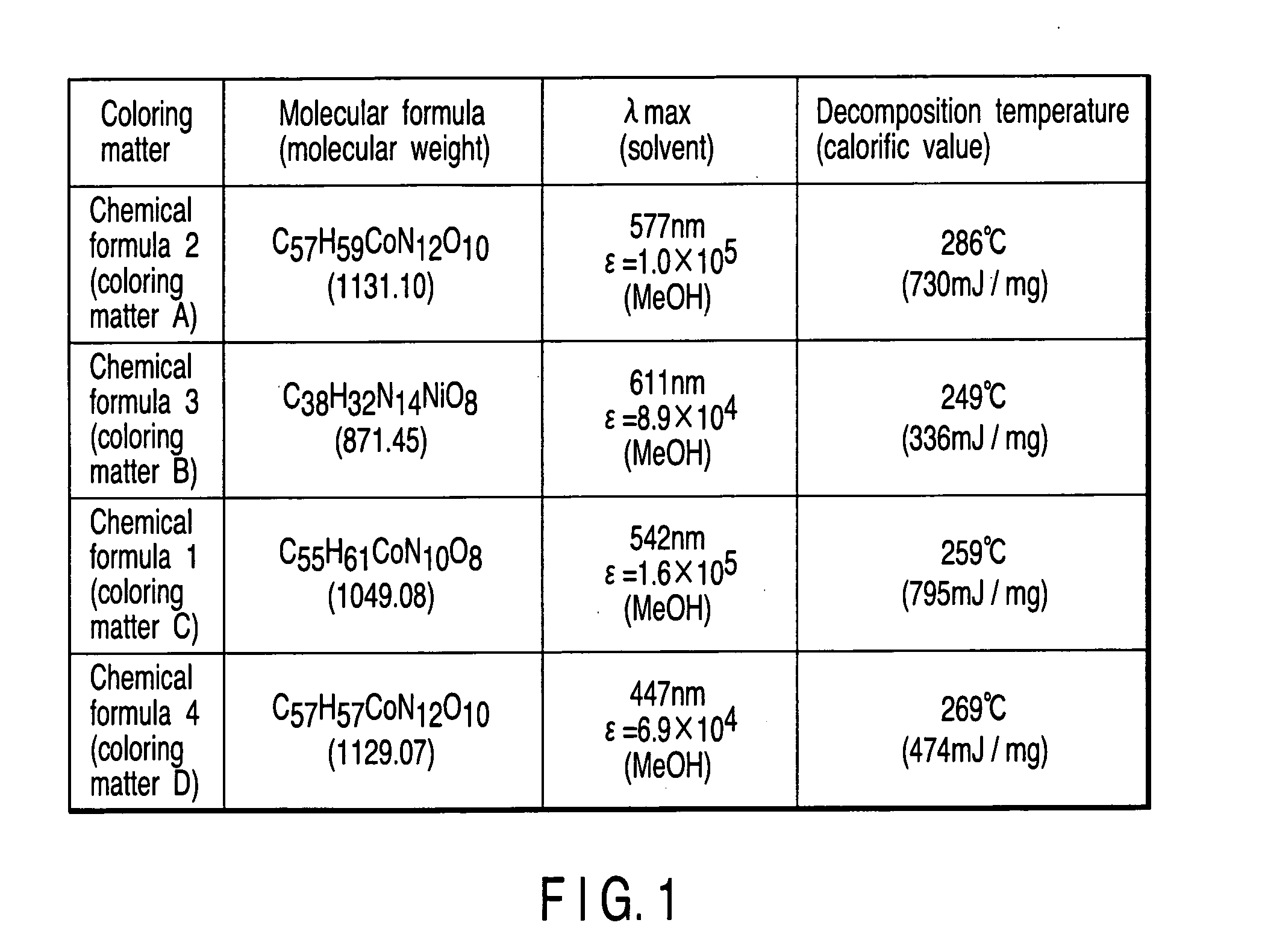
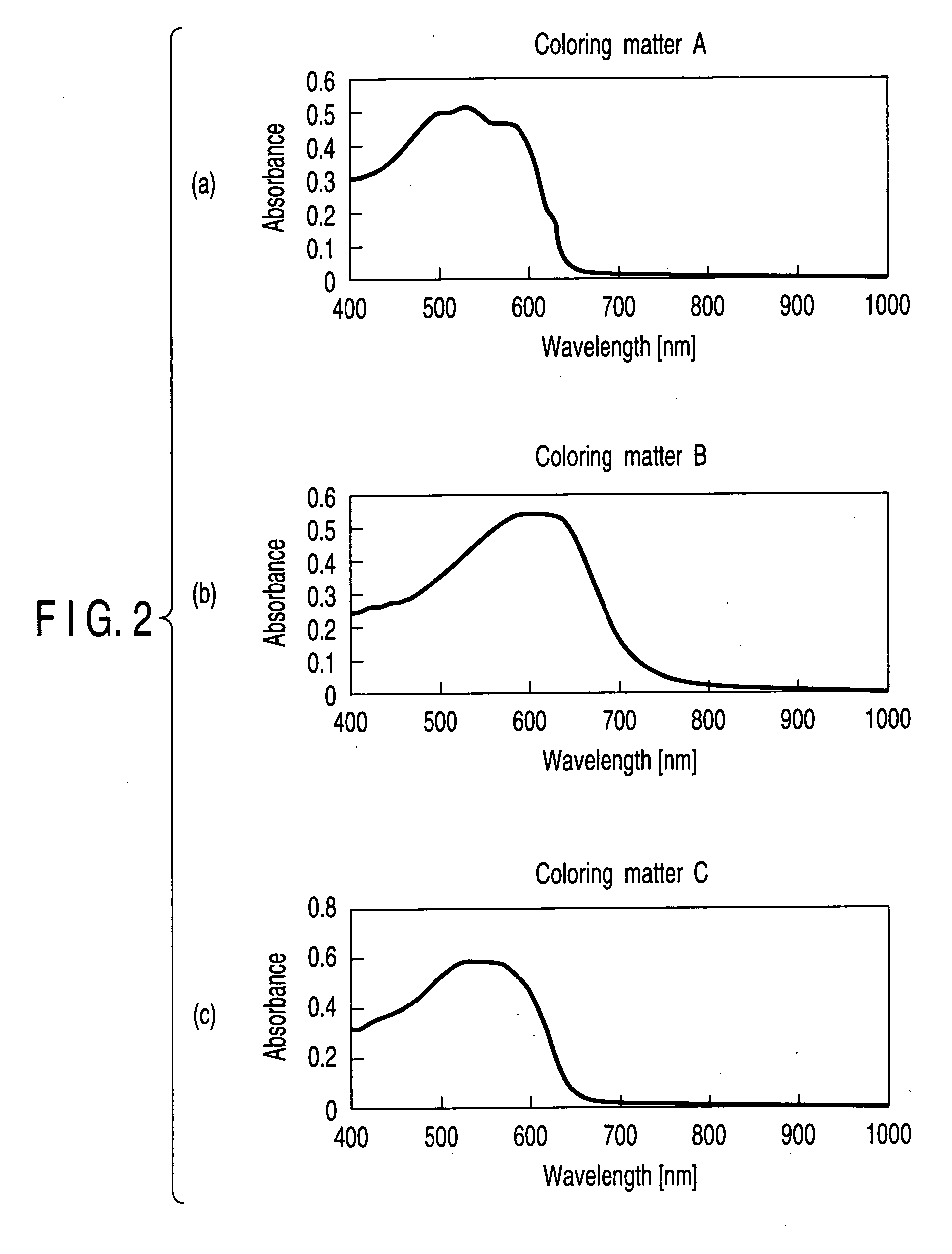
A recording material for a medium used for the recording film of a write-once type information recording disk equipped with a transparent resin substrate on which concentric or spiral grooves were formed and a recording film which was formed on the grooves, characterized in that it is formed by one organic coloring matter having an anion portion and a coloring matter portion in which the maximum absorption wavelength zone exists at a longer wavelength side than the wavelength of short wavelength laser beam irradiated on the recording film and forms a record mark on the recording film by irradiation of the short wavelength laser beam, and the record mark has a higher optical reflection coefficient than the optical reflection coefficient of the recording film before irradiation of the short wavelength laser beam. This material realizes so-called Low to High property.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Optical recording systems
InactiveUS6094413AIncrease contrastImprove signal-to-noise ratioNanoinformaticsOptical beam sourcesOptical storageOptical recording
An optical storage system suitable for optical storage and retrieval of information using a storage medium comprising a substrate, an active layer for retention of the data, and an overlying optical layer, or layers for double-sided. The optical layer serves to produce an evanescent field in or adjacent to the active layer in response to an incident beam of radiation. The evanescent field is frustrated or attenuated by the data in the active layer and produces a signal.
Owner:SENSHIN CAPITAL +1
Information recording medium with index header
InactiveUS6850469B2Accurately record informationAccurately reproduce informationTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersRecording layerMechanical engineering
An information recording medium has a plurality of stacked recording layers. Each recording layer has a spiral track which defines a plurality of rounds, and at least one index header aligned in the radial direction of the disk to partially intercept the spiral track. The index header has address data of each round of the spiral track, which is formed by embossed pits, and some or all of the index headers of the first and second recording layers are laid out to overlap each other when viewed from the predetermined surface.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Mutli-layered information recording medium, reproduction apparatus, recording apparatus, reproduction method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060195719A1Shorten the timeEfficient managementInput/output to record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareRecording layer
A multi-layered information recording medium comprising a plurality of recording layers, a user data area for recording user data, provided in at least two of the plurality of recording layers, and a defect list storing area for storing a defect list. When at least one defective area is detected in the user data area, the defect list is used to manage the at least one defective area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical information medium having high resolution beyond a diffraction limit and reading method
InactiveUS6965556B1Minimize dependenciesHigh resolutionNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersRefractive indexLength wave
In an optical information medium having an information bearing surface having projections and depressions and / or capable of forming recorded marks, a functional layer is added. The information borne on the information bearing surface can be read by using reading light of a wavelength longer than 4NA·PL wherein PL is the minimum size of the projections and depressions or the recorded marks and NA is the numerical aperture of a reading optical system, setting the power of the reading light within such a range that the functional layer does not change its complex index of refraction, and irradiating the reading light to the information bearing surface constructed by the functional layer or to the information bearing surface through the functional layer or to the functional layer through the information bearing surface. The medium enables reading at a high resolution beyond the diffraction limit.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20070098949A1High densityHigh sensitivityRecording strategiesLayered productsOrganic dyeLength wave
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium comprises an organic dye based recording material having sensitivity at a wavelength of 405 nm and at a recording wavelength in the range of 600 nm to 700 nm, wherein, when absorbance of a maximum absorption wavelength in the vicinity of 405 nm is defined as 1, the absorbance is 5% or more at any wavelength in the range of 600 nm to 700 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS20040157158A1High sensitivityReduce reproductionMechanical record carriersPhotomechanical apparatusRecording layerOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate and a recording layer in which data can be recorded by projecting a laser beam thereonto, the recording layer including a first recording film containing an element selected from the group consisting of Si, Ge, Sn, Mg, In, Zn, Bi and Al as a primary component and a second recording film containing Cu as a primary component and 10 to 30 atomic % of Al as an additive. The thus constituted optical recording medium has an excellent initial recording characteristic and can store recorded data in a good condition over the long term.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Information recording medium
InactiveUS20030081537A1Shorten speedHigh densityRadiation applicationsLayered productsLight irradiationLight reflection
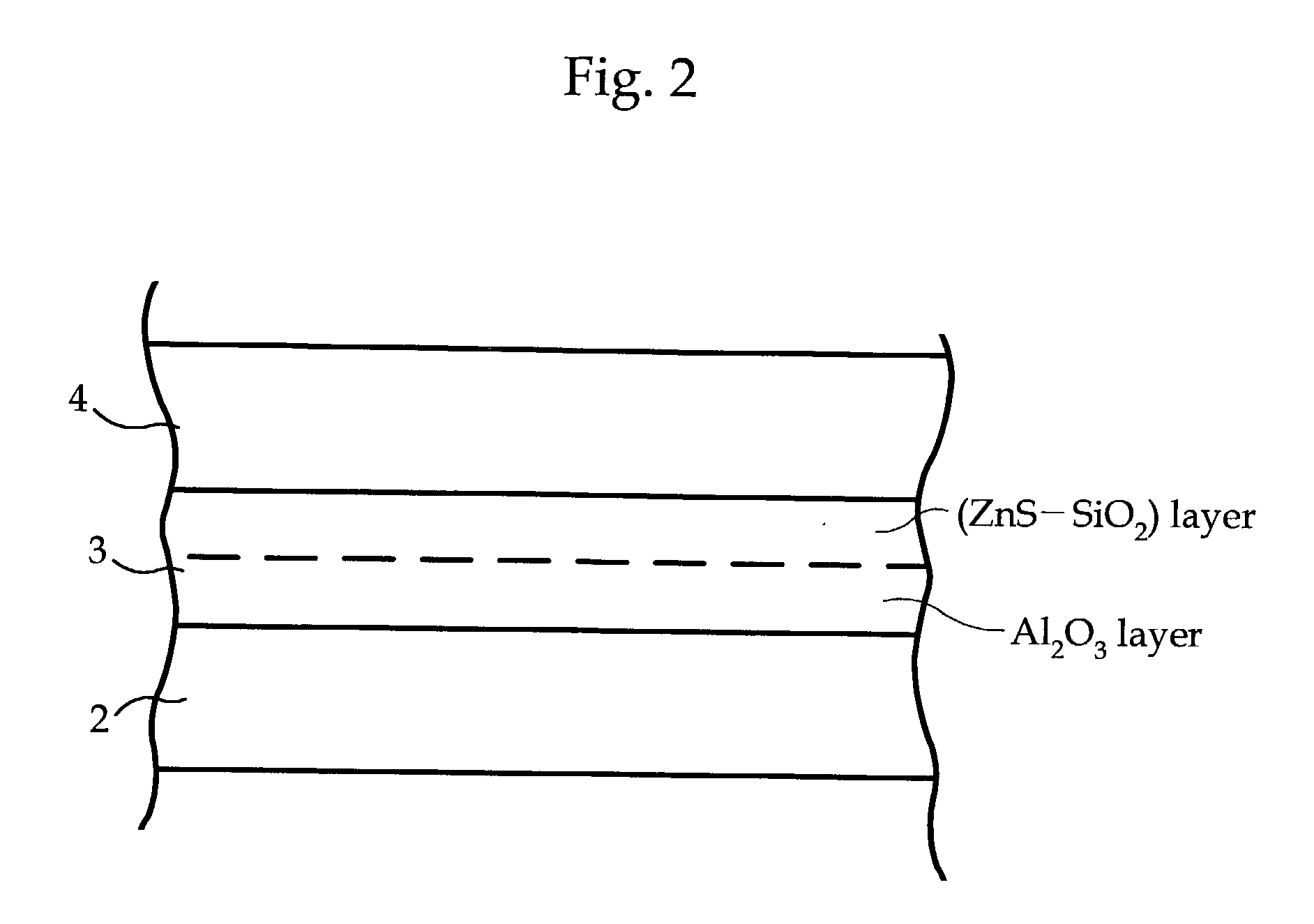
An optical recording medium configured with a light reflection layer; a first protection layer; a recording layer containing a phase-change material which changes between crystalline and amorphous phases by a light irradiation; a second protection layer; and one of a cover layer and a protective coating layer disposed on a substrate in this order; and in which the light reflection layer is formed of one of an Al alloy and an Ag alloy; the first protection layer has a ZnS-SiO2 mixture layer which contains a mixture of ZnS and SiO2, and a intermediate layer having higher thermal conductivity than the ZnS-SiO2 mixture layer; the intermediate layer is formed on the side of the light reflection layer; the recording layer comprises Ge, Sb, and Te as main elements; and the second protection layer comprises a mixture of ZnS and SiO2.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and apparatus for controlling access to storage media
InactiveUS20050083829A1Alters resultLimit installationMechanical record carriersRecord information storageOperating systemOptical medium
A method and apparatus for controlling access to a storage medium, such as an optically readable medium. Light sensitive or other materials that are adapted to change state and affect reading of a storage medium are used to control access to data that may be stored on optical medium and / or to control use of the medium.
Owner:SELINFREUND RICHARD H +3
Optical recording medium, manufacturing method thereof, method for recording data on optical recording medium, and data reproduction method
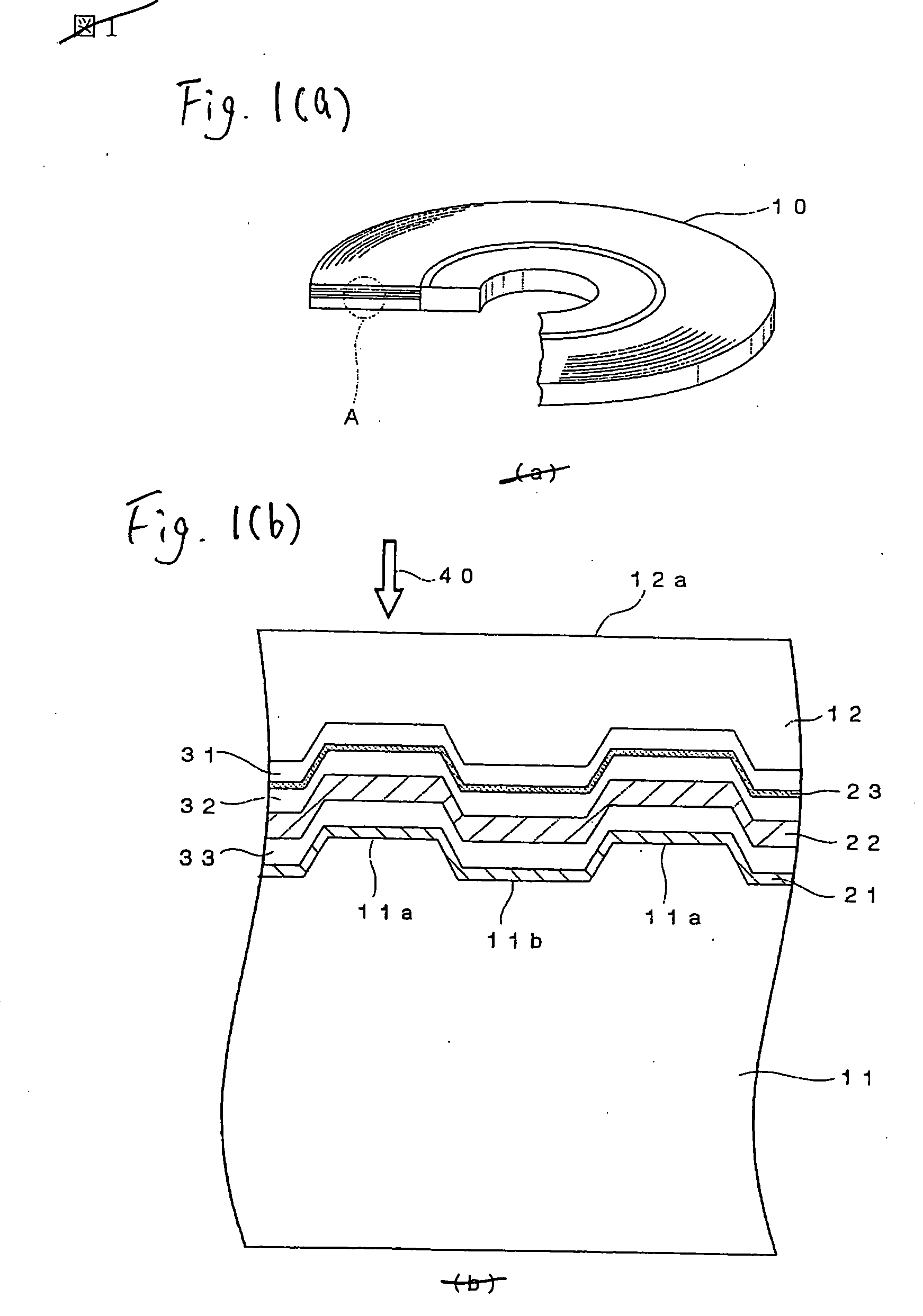
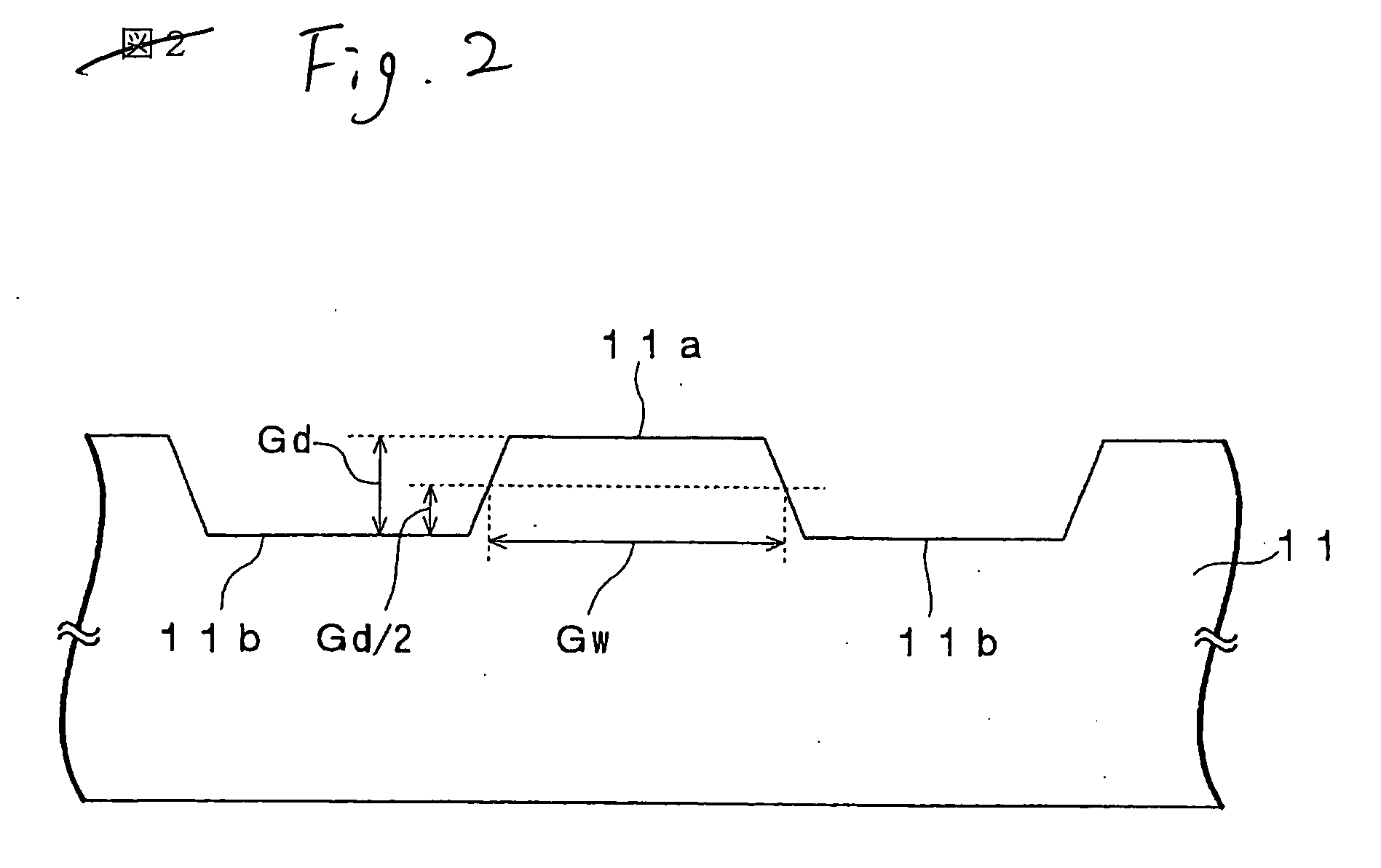
InactiveUS20070030795A1Excellent signal characteristicImprove featuresInformation arrangementMechanical record carriersRefractive indexPush pull
An optical recording medium 10 according to the present invention includes a supporting substrate 11 on which a groove 11a is formed, a light transmitting layer 12, a noble metal oxide layer 23 provided between the supporting substrate 11 and the light transmitting layer 12, wherein a depth of the groove 11a is set in excess of λ / 8 n but 60 nm or less, where n is a refractive index of the light transmitting layer 12 with respect to a light whose wavelength is λ. Thus, the good signal characteristics, especially a push-pull signal with an enough amplitude, can be obtained when the super-resolution recording and super-resolution reading are carried out by irradiating the laser beam onto the noble metal oxide layer 23. Also, since the depth of the groove is set to 60 nm or less, a grave difficulty never arises in producing a stamper used to manufacture the substrate.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
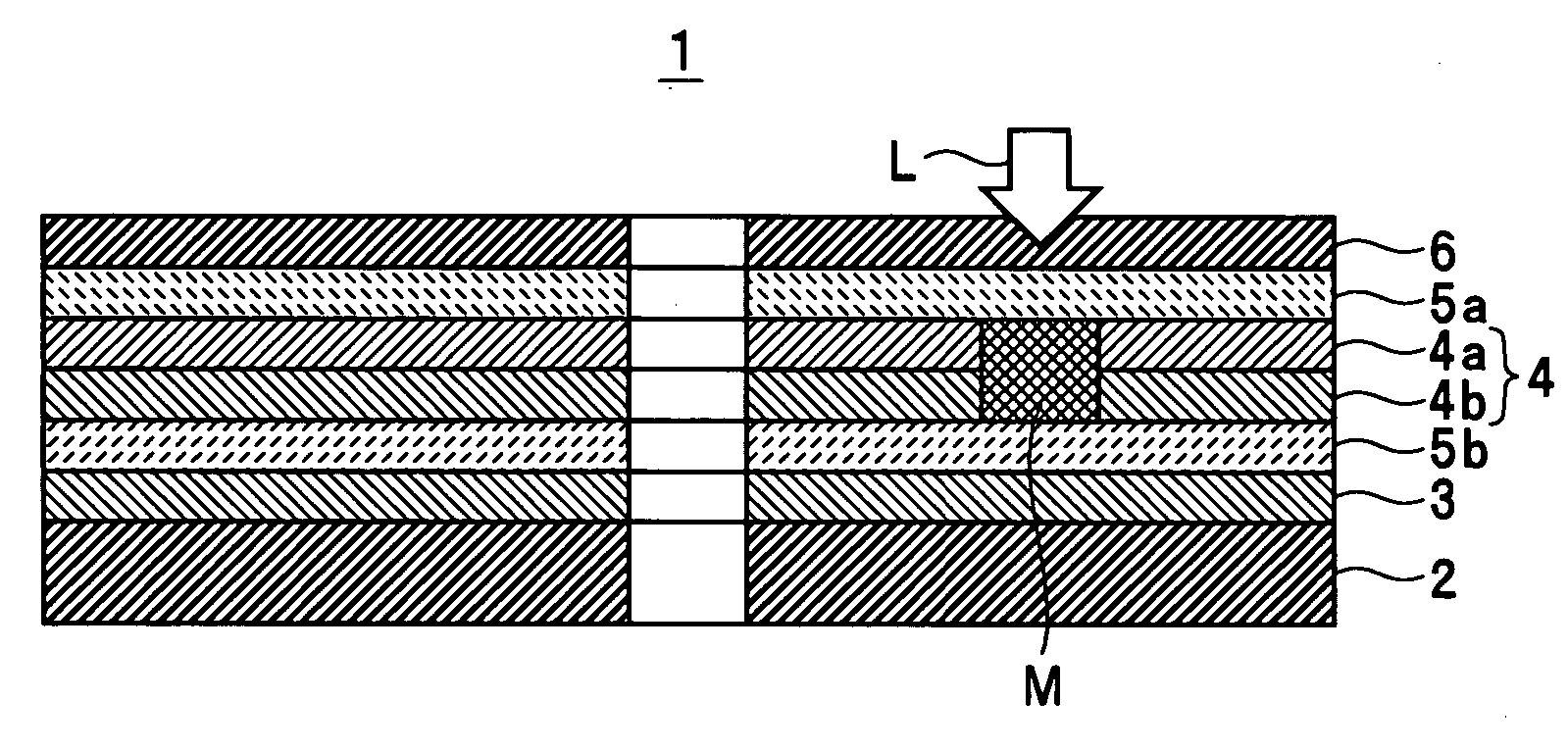
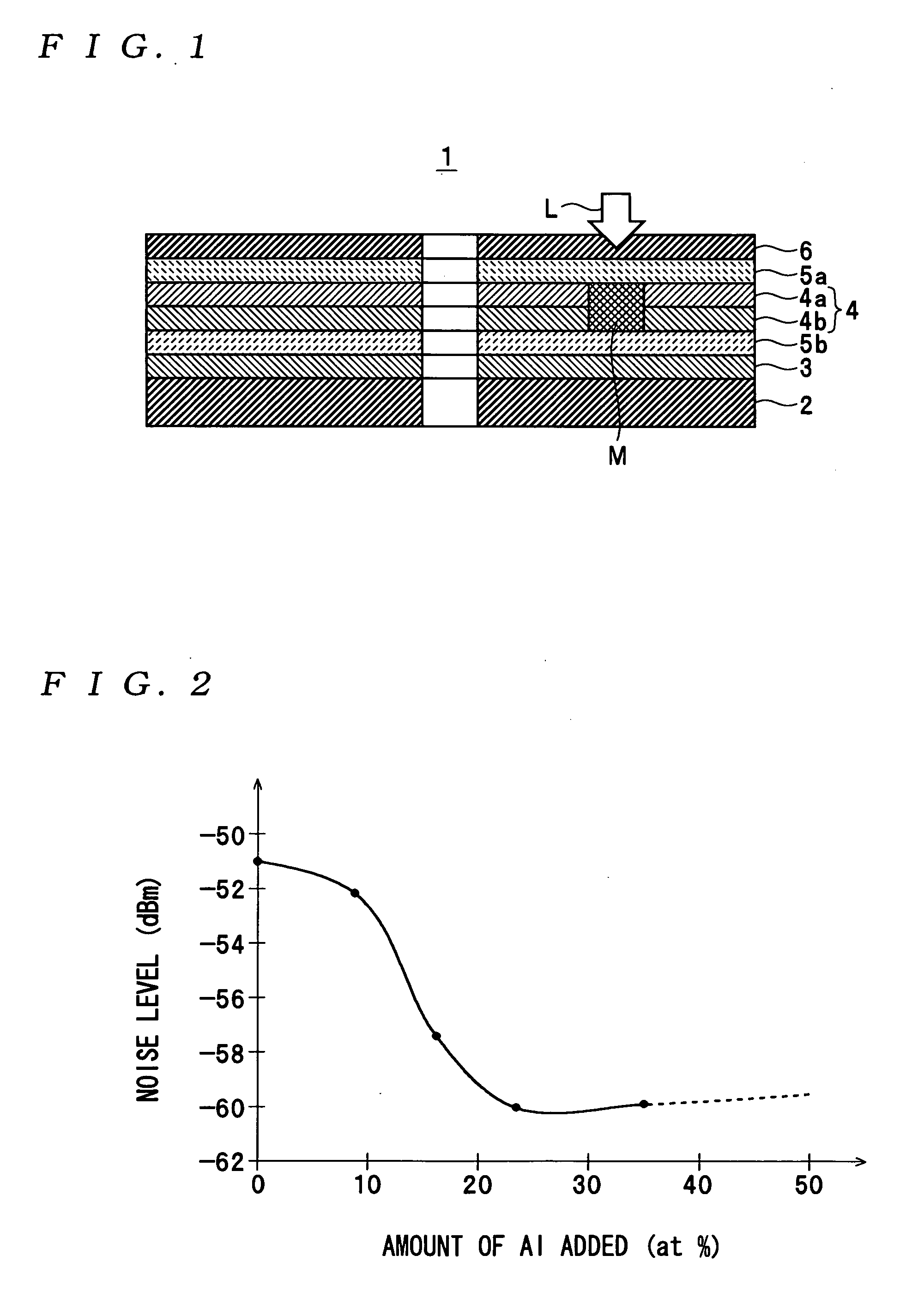
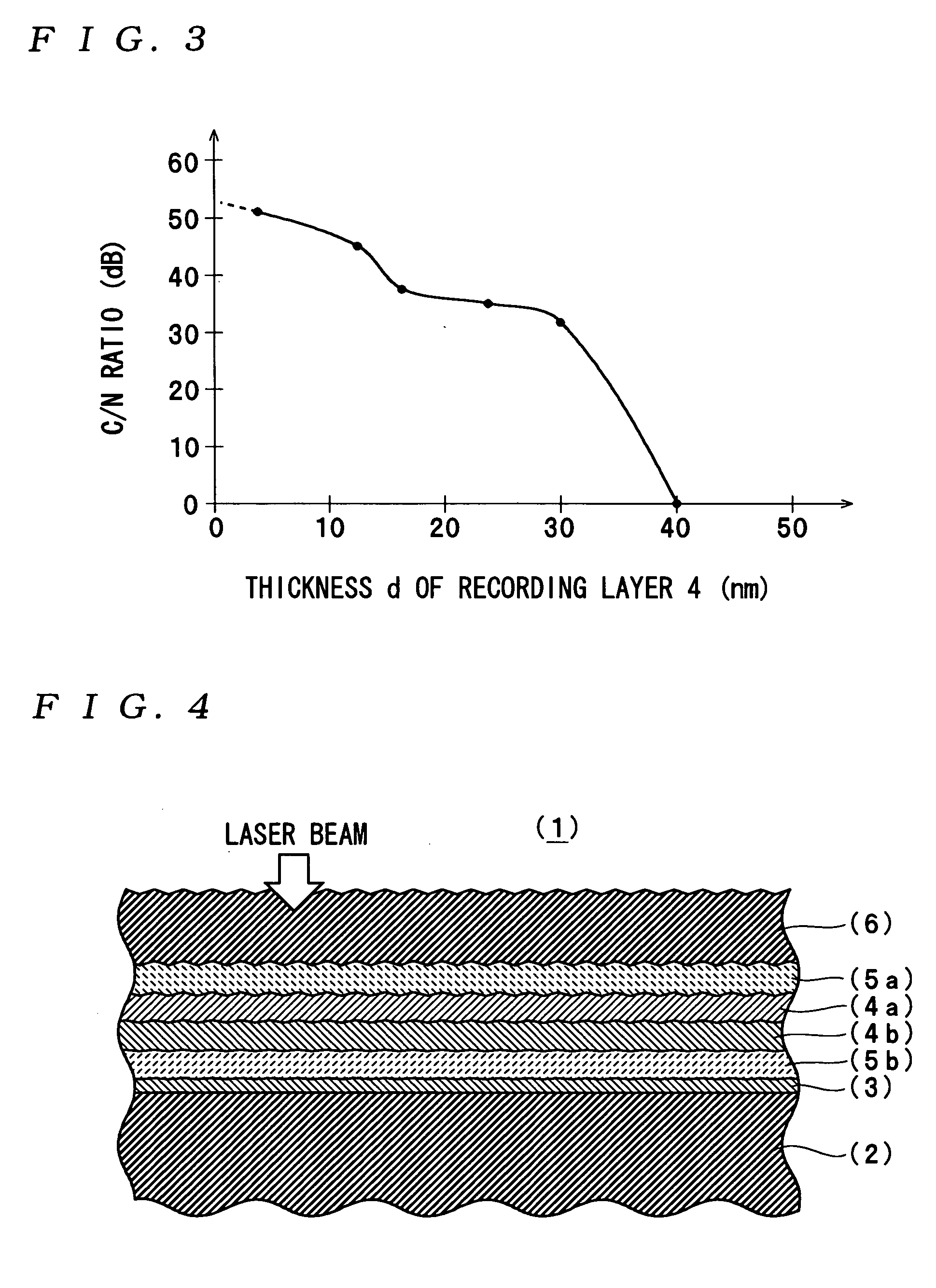
ActiveUS20050018590A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingMechanical record carriersNoise levelRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level and improve the C / N ratio. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproducing record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as a main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Zn as a main component and having Al added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com