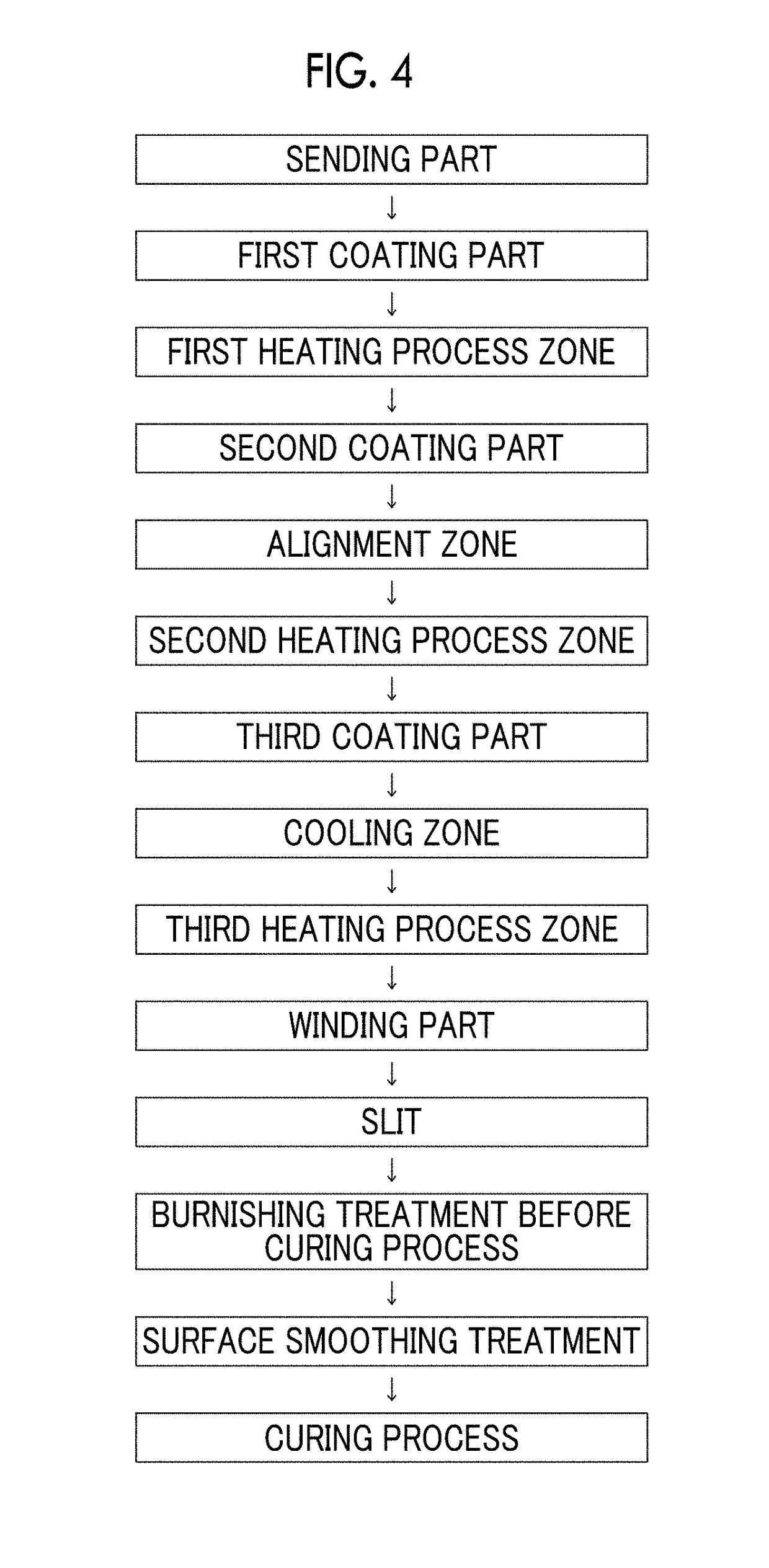
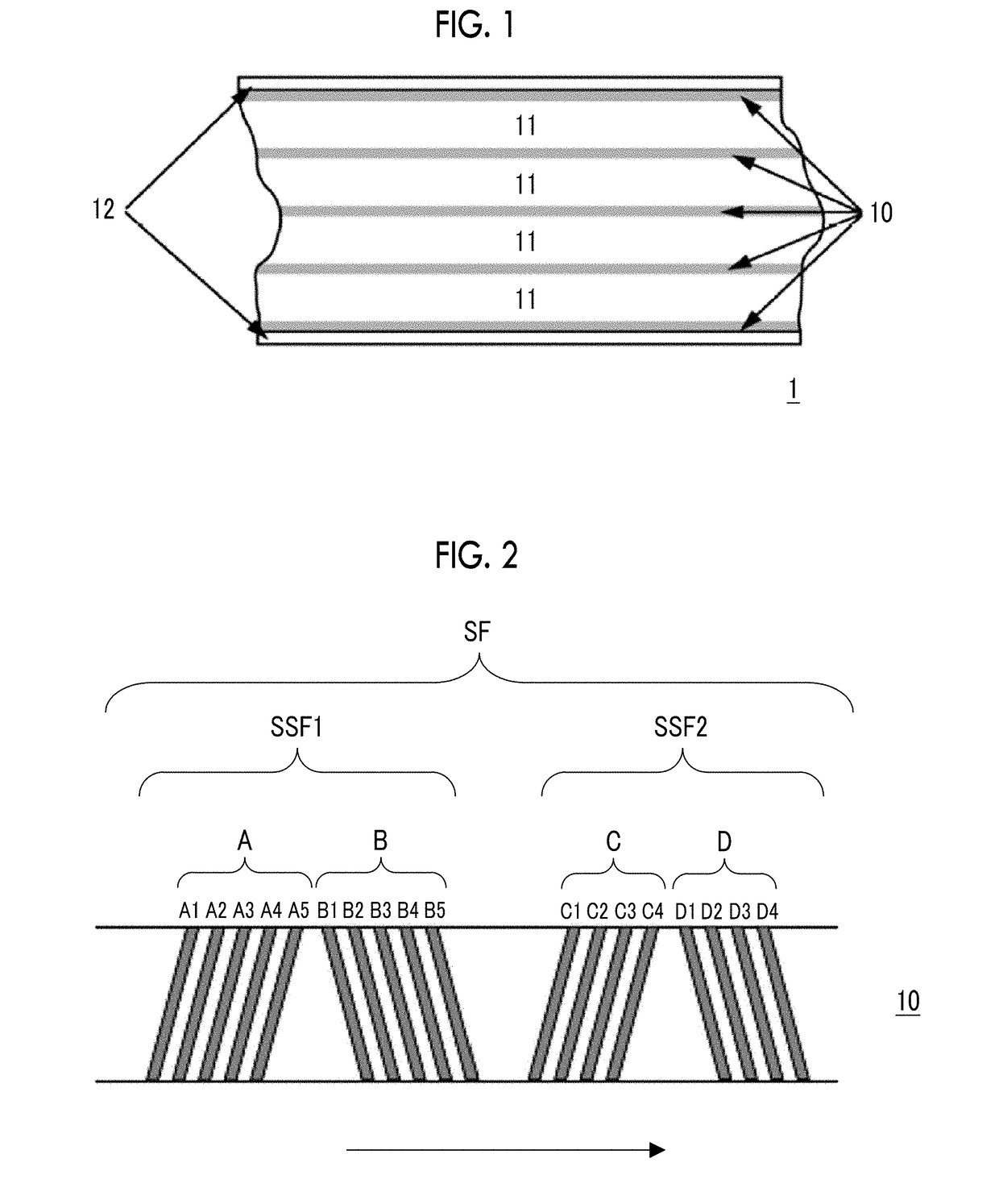
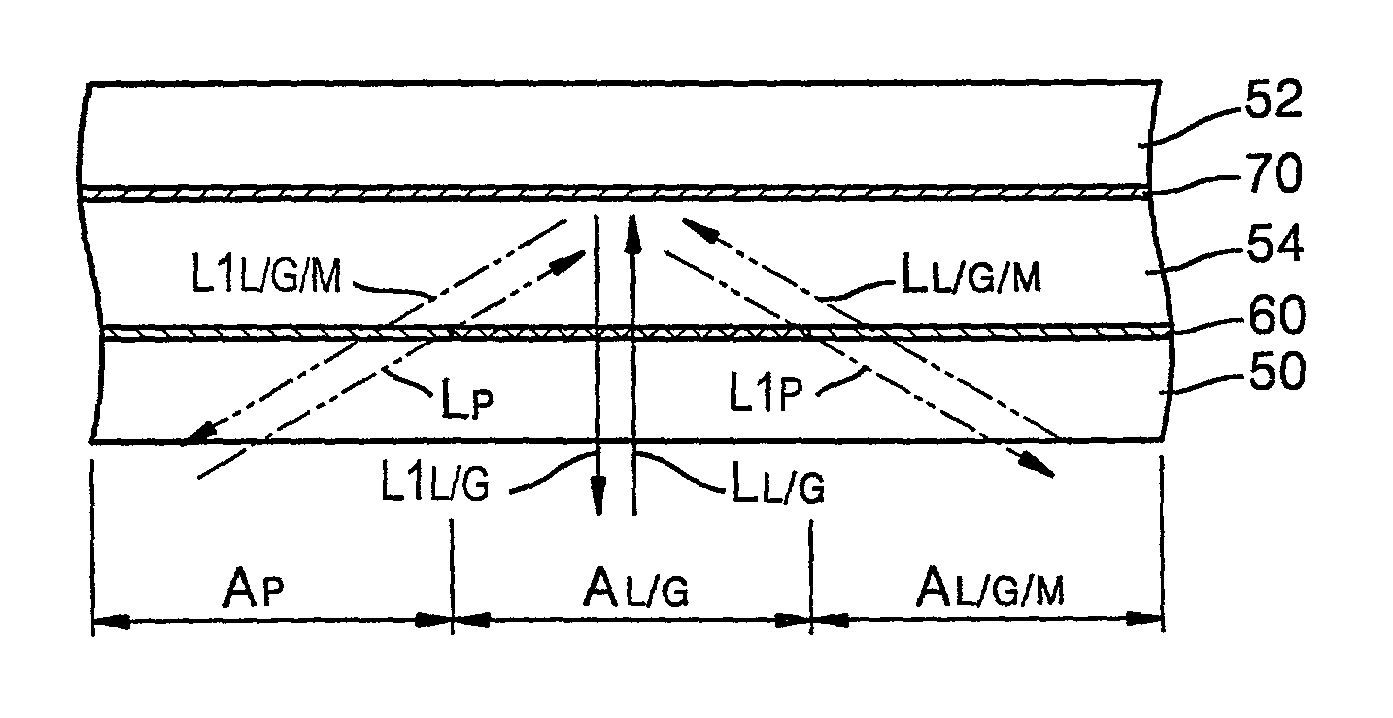
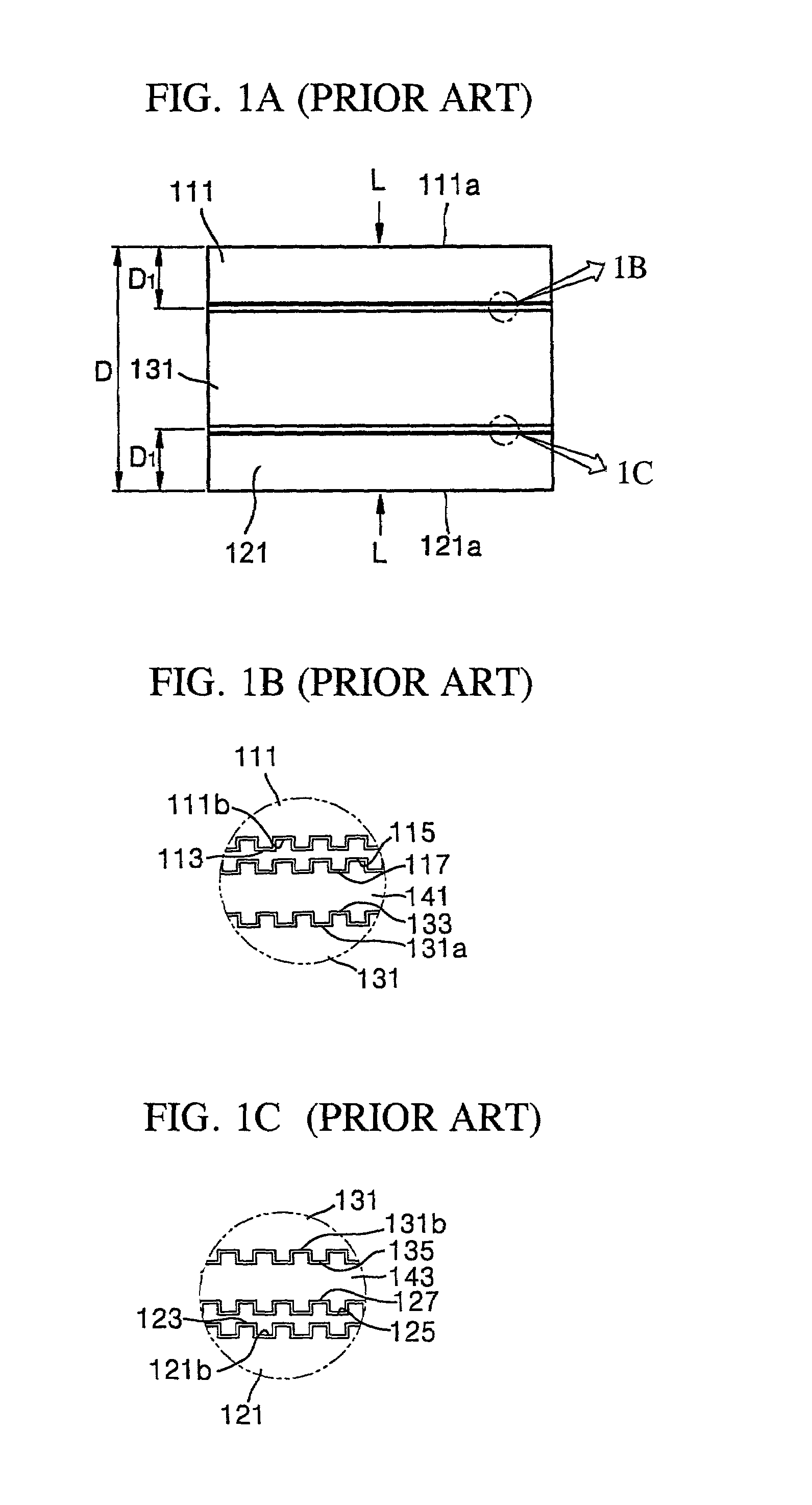
Patents
Literature
1964results about "Record carriers manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical disk, optical disk recording and reproducing apparatus, method for recording, reproducing and deleting data on optical disk, and information processing system
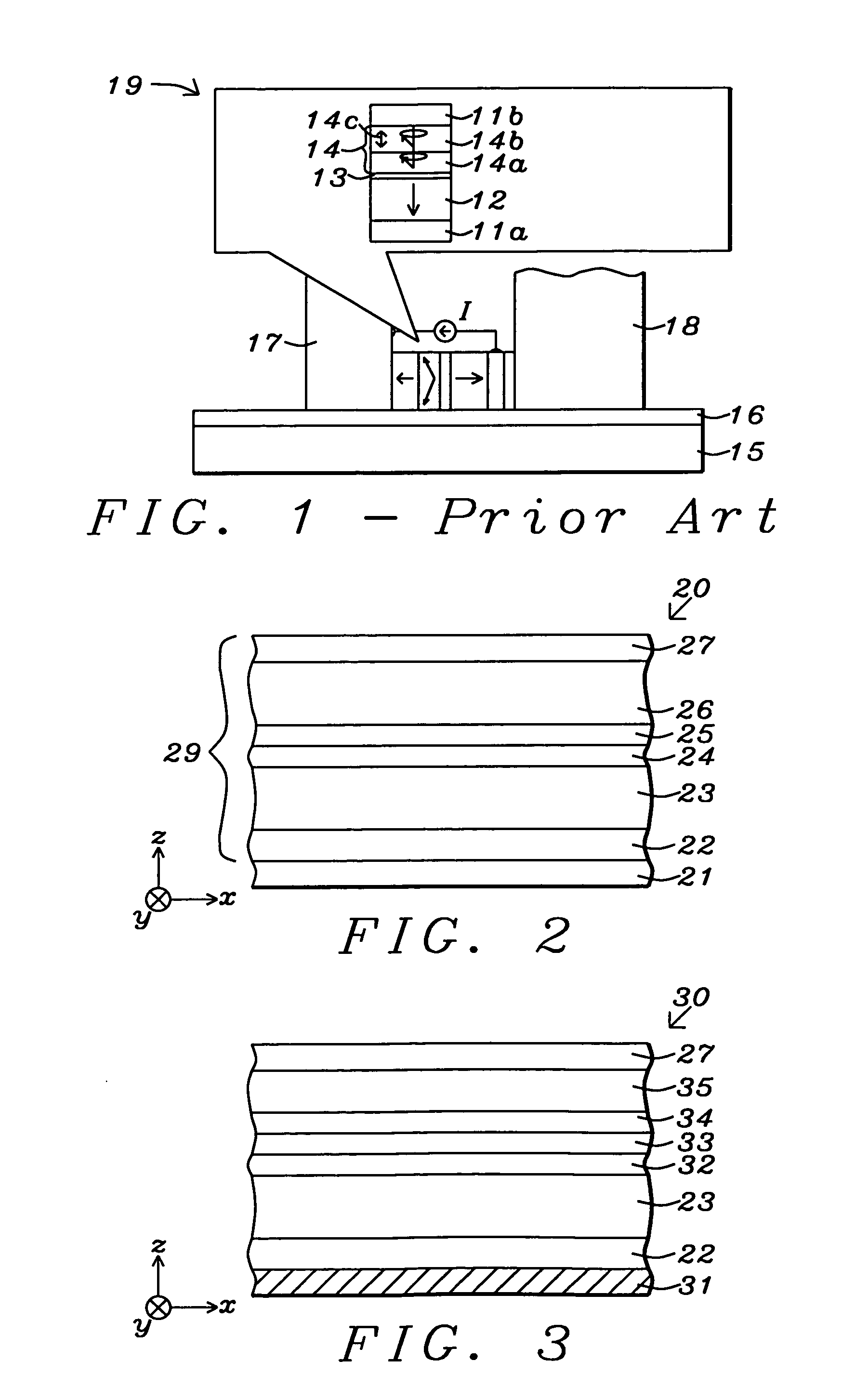
InactiveUS6938162B1Prevent unjust digital copyingImprove reliabilityAccessories for auxillary signalsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useInformation processingHandling system
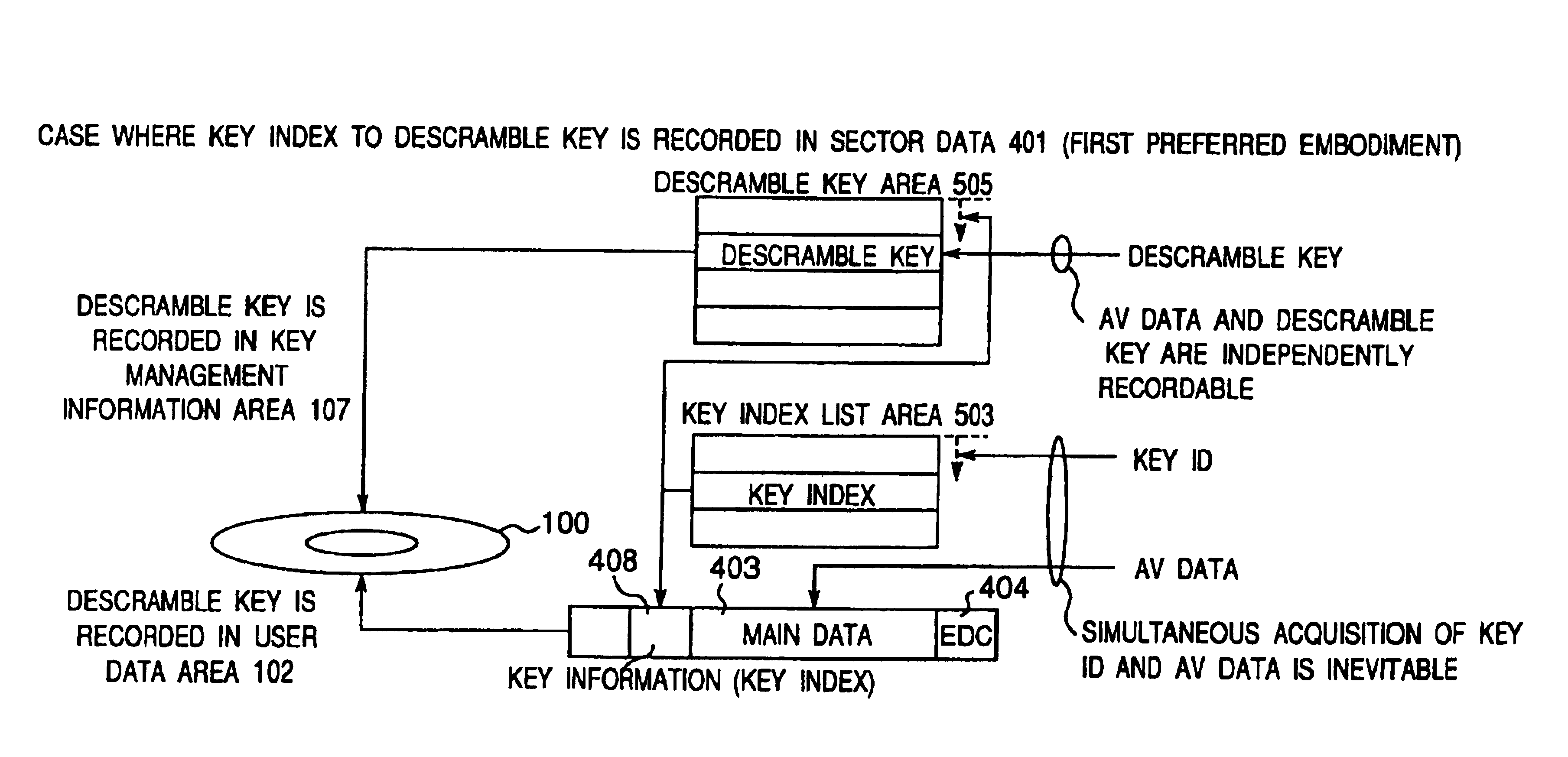
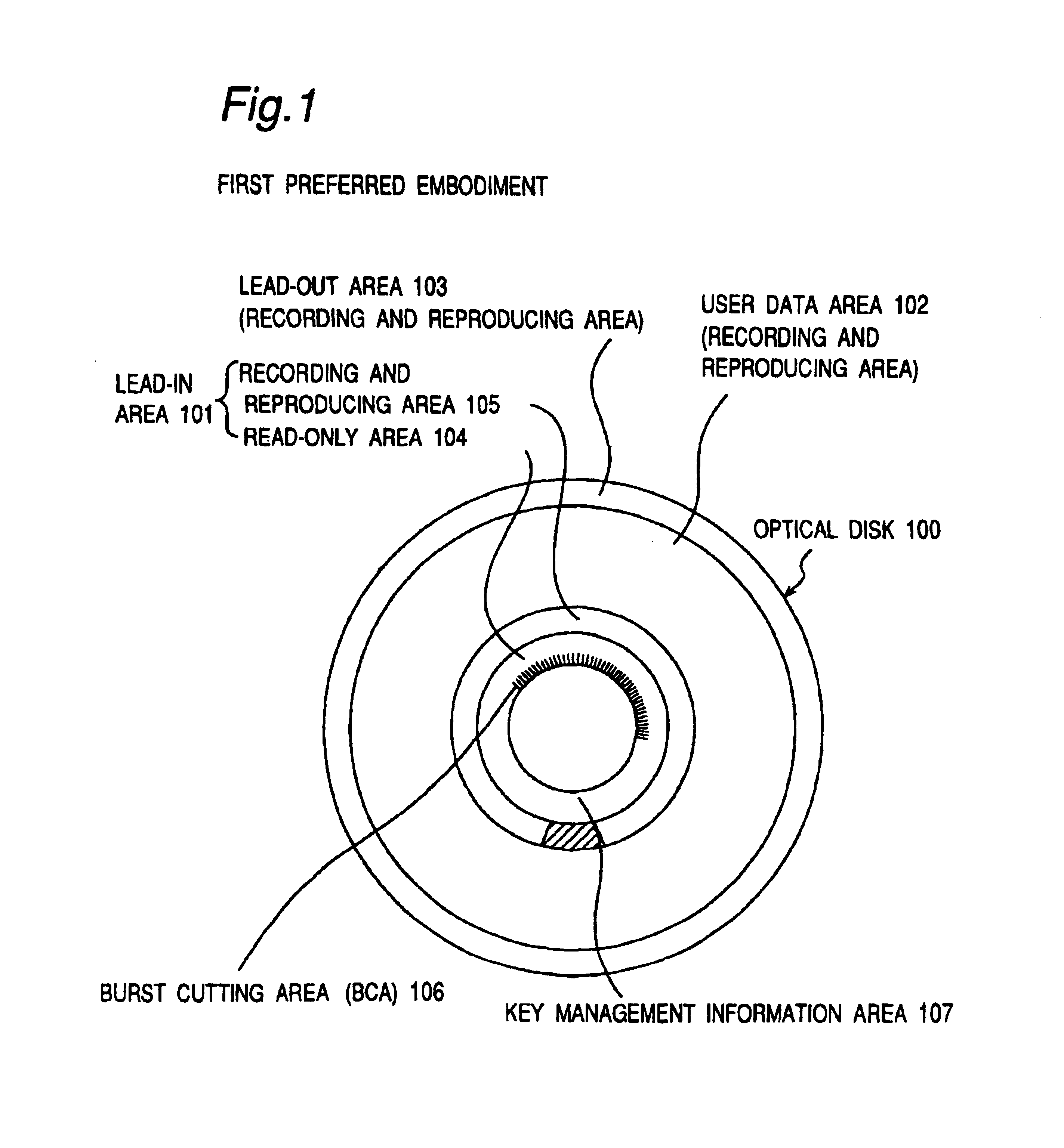
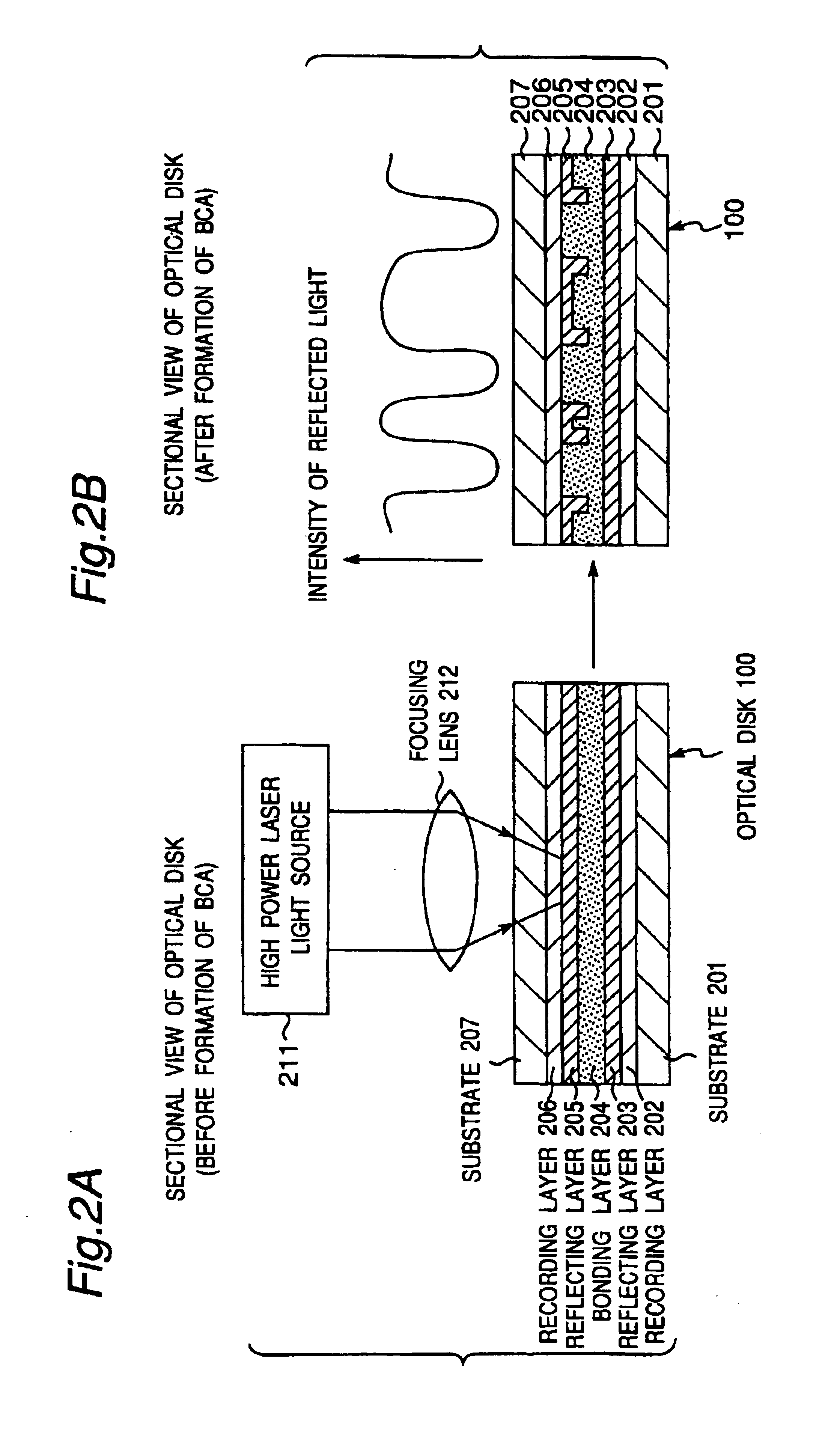
A recording type optical disk on which data is recordable includes a data recording and reproducing area for recording data therein and reproducing data therefrom, and a read-only disk identification information area for recording disk identification information for identifying the optical disk therein. In the optical disk, the disk identification information is formed by removing a reflection film that is formed on the optical disk in a strip shape. The disk identification information includes an inherent disk identifier for each optical disk, and the data recording and reproducing area includes an area for recording encrypted data therein. The encrypted data is encrypted by using information including the disk identification information for identifying the optical disk as a key.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of manufacturing a magnetoresistive-based device
ActiveUS8747680B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic reluctanceHard mask
A method of manufacturing a magnetoresistive-based device having magnetic material layers formed between a first electrically conductive layer and a second electrically conductive layer, the magnetic materials layers including a tunnel barrier layer formed between a first magnetic materials layer and a second magnetic materials layer, including removing the first electrically conductive layer and the first magnetic materials layer unprotected by a first hard mask, to form a first electrode and a first magnetic materials, respectively; and removing the tunnel barrier layer, second magnetic materials layer, and second electrically conductive layer unprotected by the second hard mask to form a tunnel barrier, second magnetic materials, and a second electrode.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
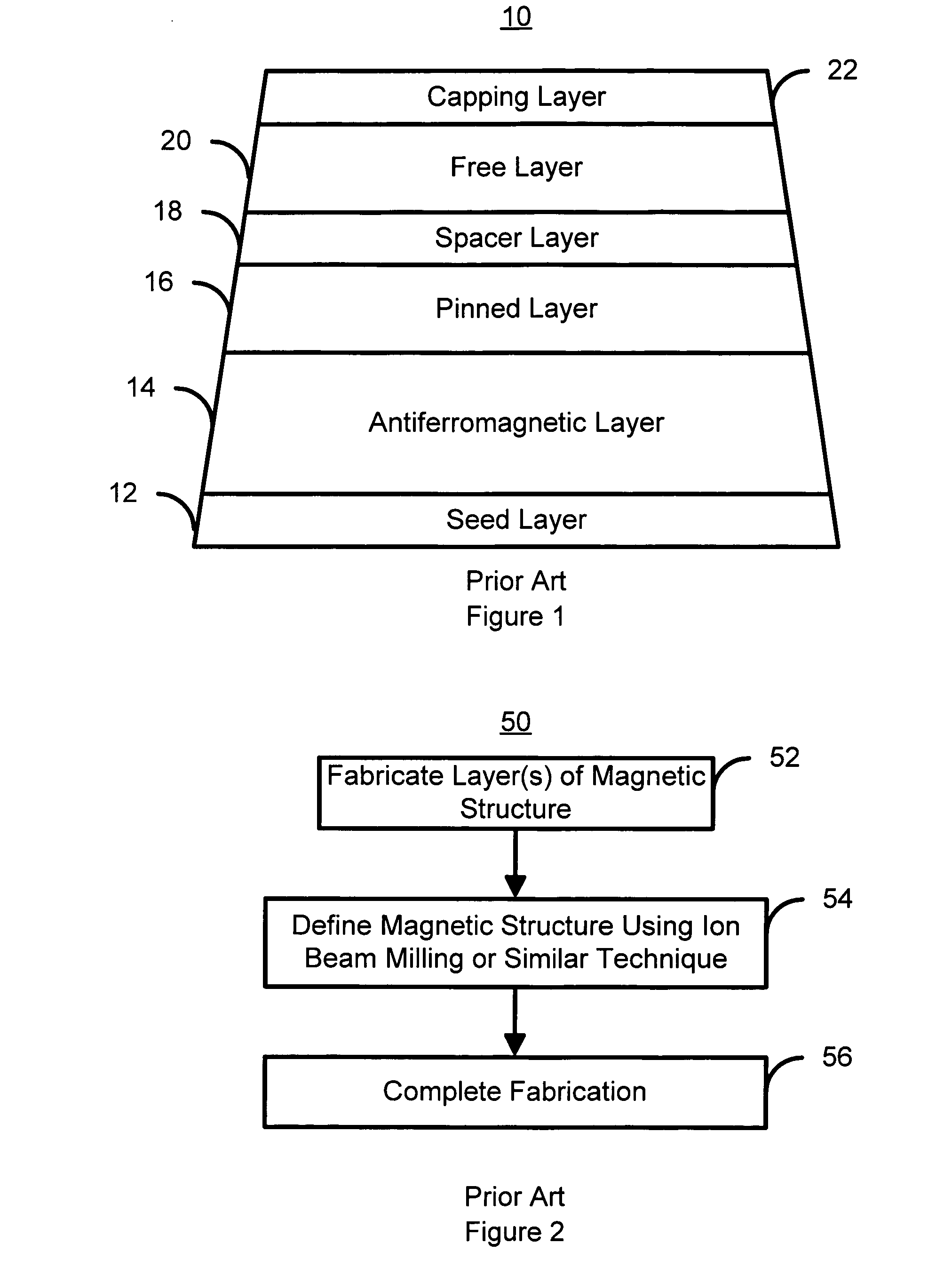
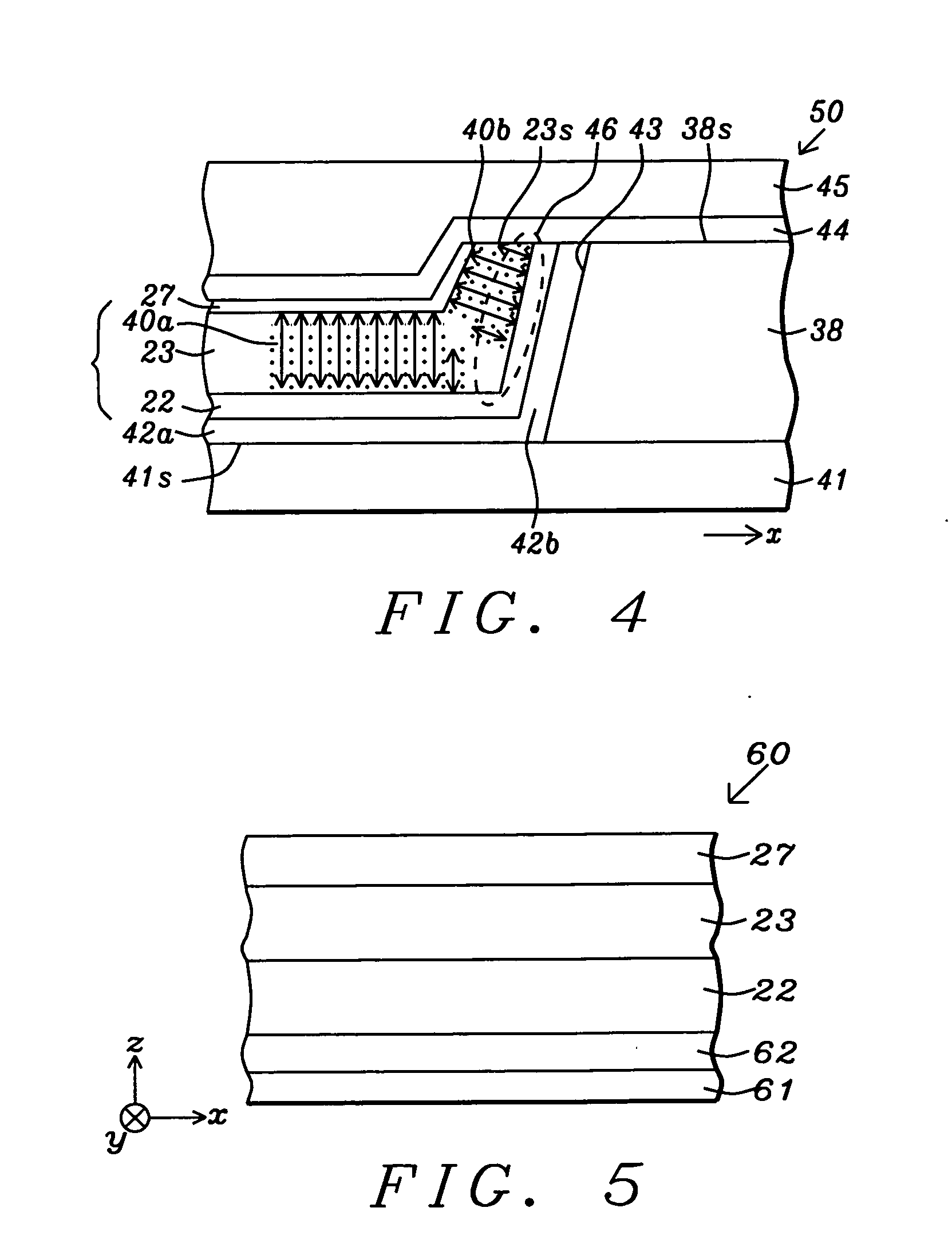
Method and system for providing magnetic tunneling junction elements having improved performance through capping layer induced perpendicular anisotropy and memories using such magnetic elements
ActiveUS20120155156A1Improve thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsElectricityPower flow
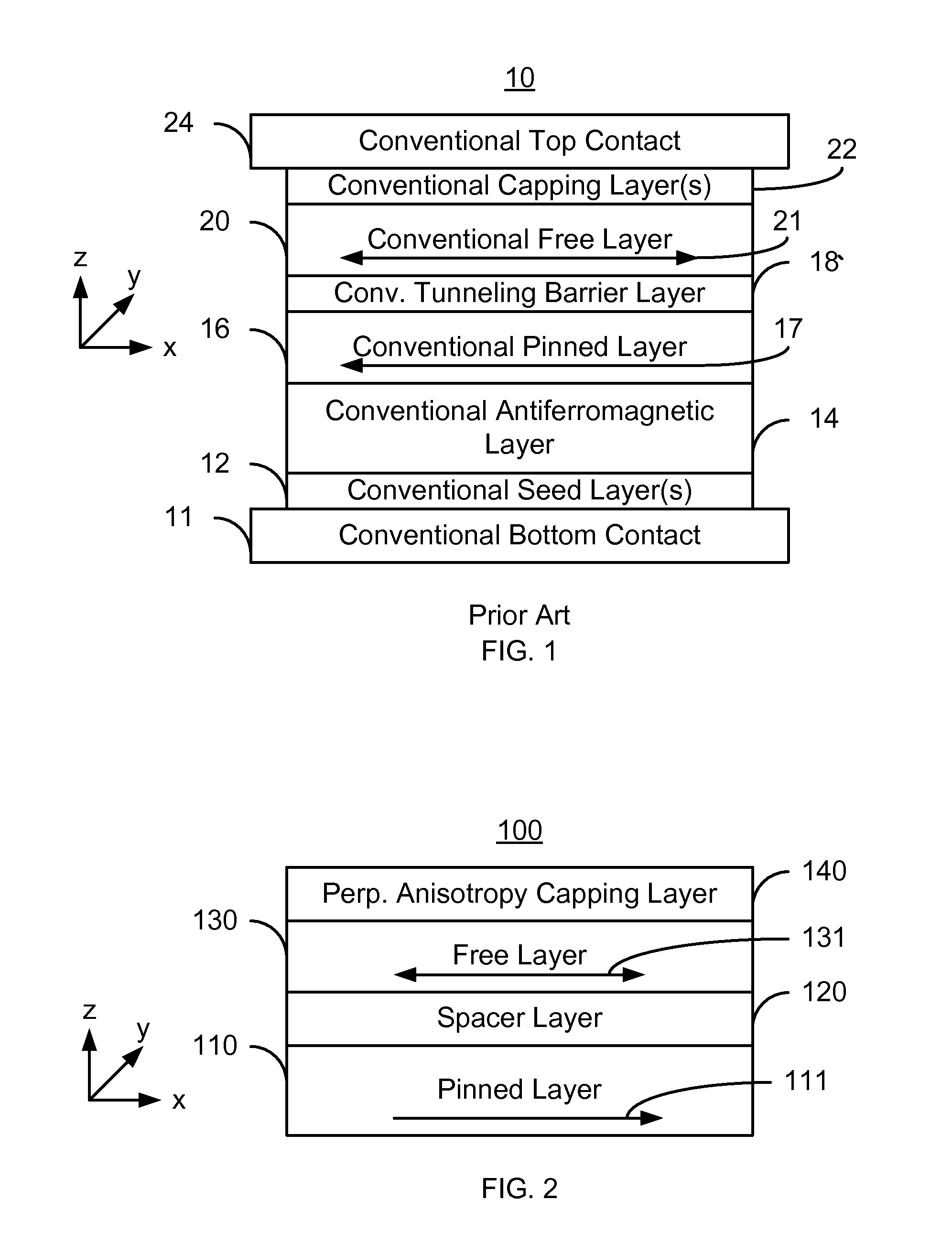
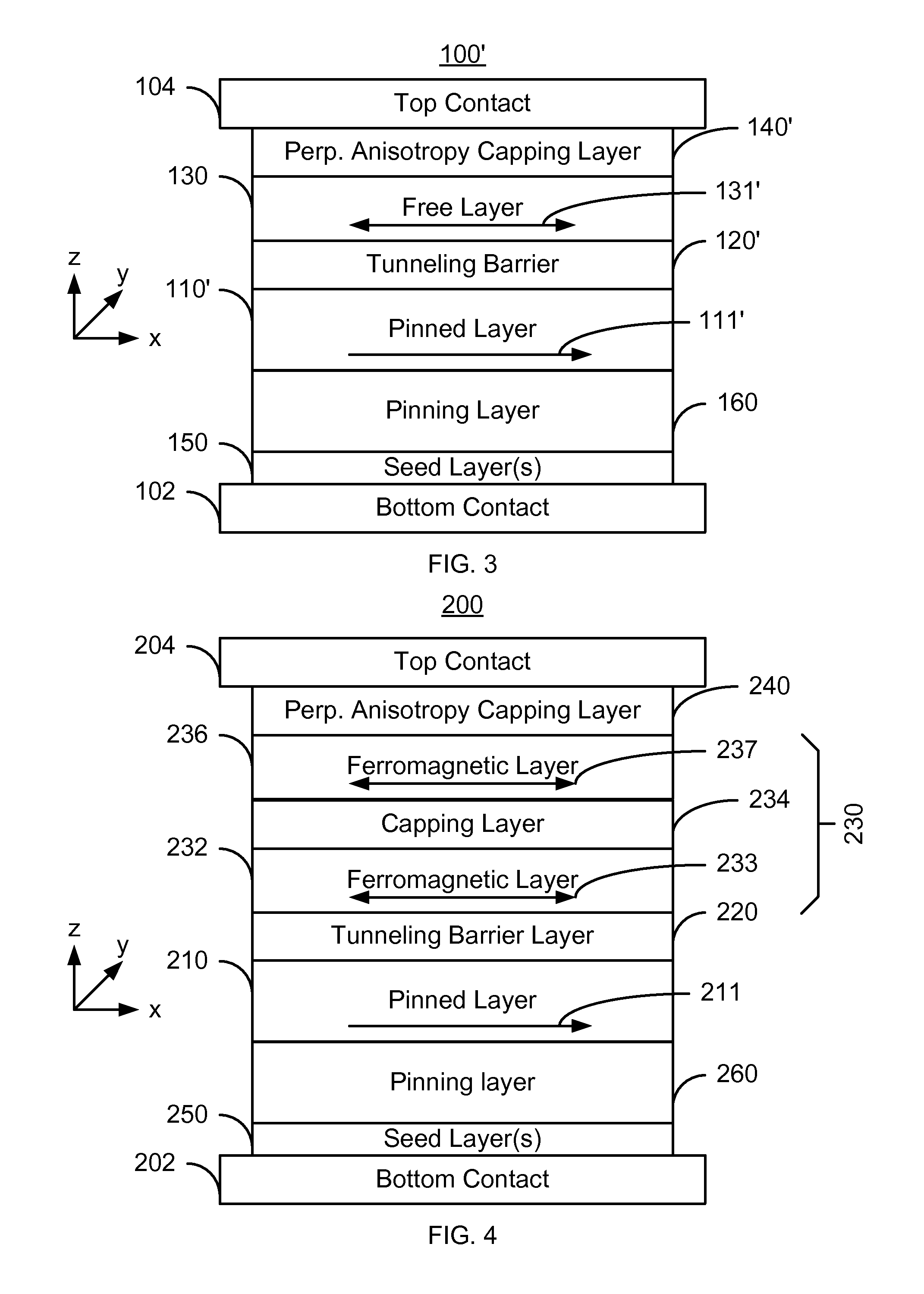
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and a magnetic memory utilizing the magnetic element are described. The magnetic element is used in a magnetic device that includes a contact electrically coupled to the magnetic element. The method and system include providing pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The free layer has an out-of-plane demagnetization energy and a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy corresponding to a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is less than the out-of-plane demagnetization energy. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned and free layers. The method and system also include providing a perpendicular capping layer adjoining the free layer and the contact. The perpendicular capping layer induces at least part of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in the free layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched between magnetic states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
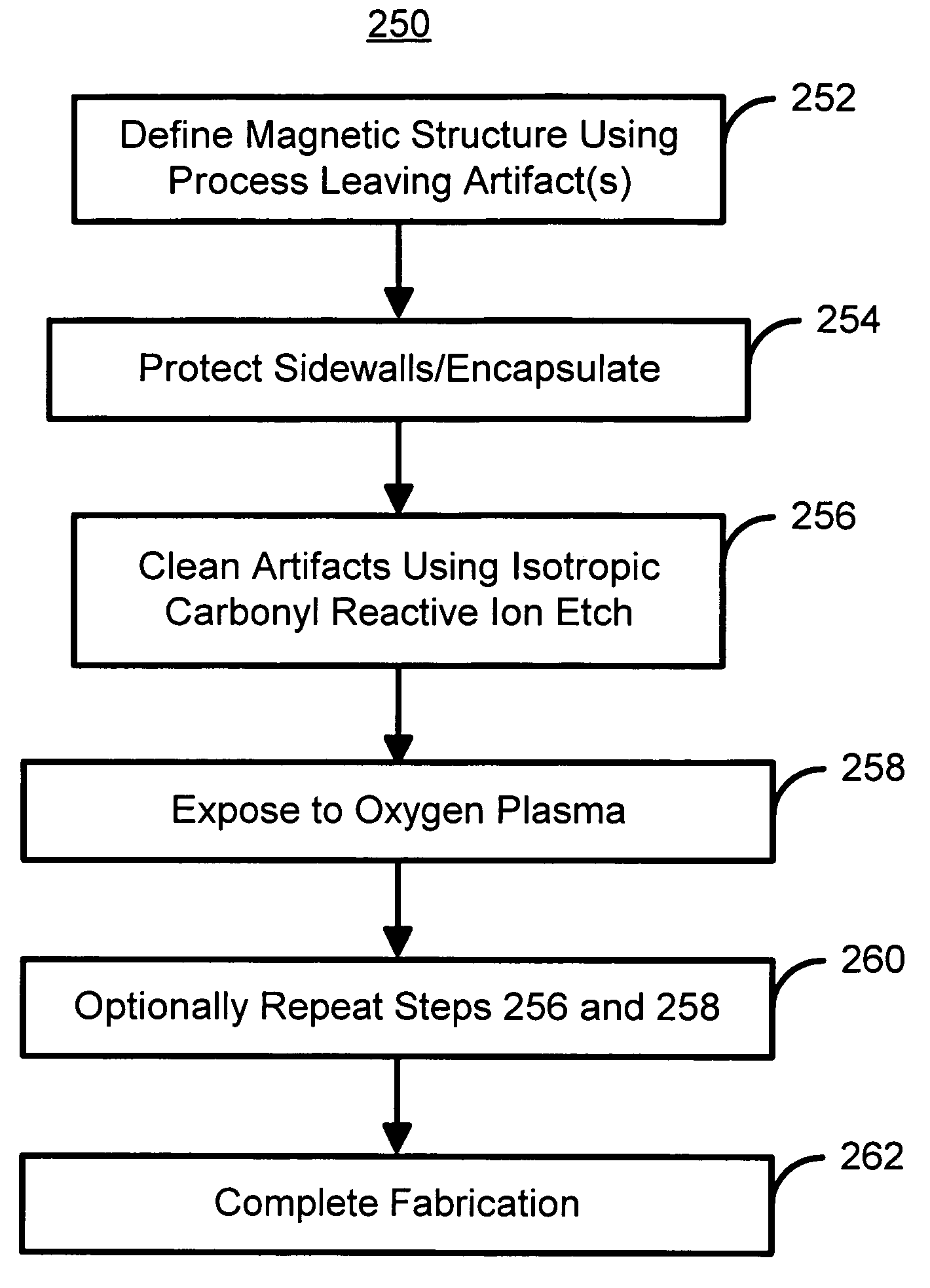
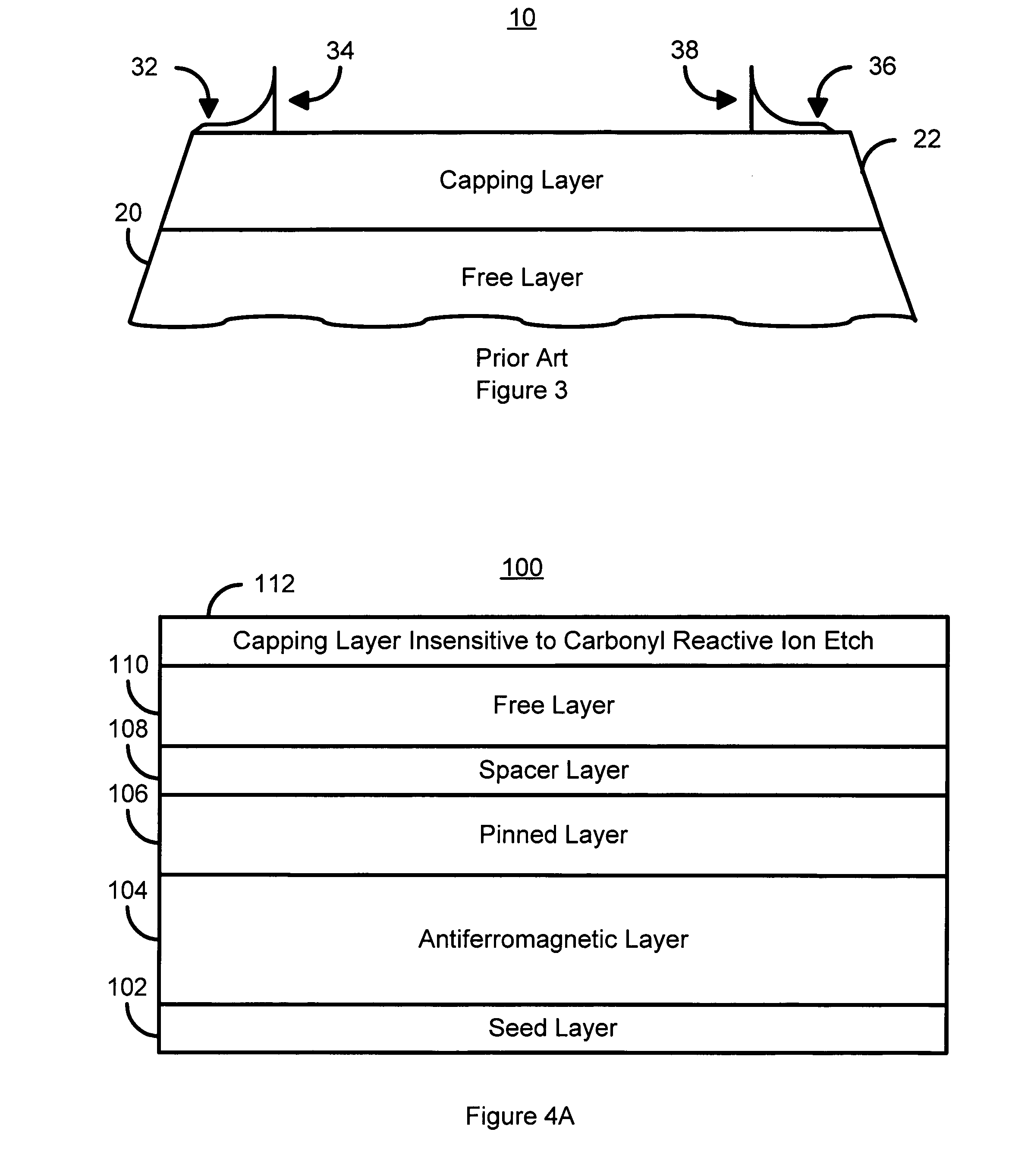
Method and system for cleaning magnetic artifacts using a carbonyl reactive ion etch
A method and system for providing a magnetic structure that includes at least one magnetic material is disclosed. The method and system include defining the magnetic structure. The magnetic structure also includes a top layer that is insensitive to an istroropic carbonyl reactive ion etch. The defining of the magnetic structure results in at least one artifact. The method and system further includes cleaning the at least one artifact using at least one isotropic carbonyl reactive ion etch.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Multilayer structure with high perpendicular anisotropy for device applications
ActiveUS20110293967A1Improve performanceLow costMagnetic measurementsPretreated surfacesPerpendicular anisotropyMagnetic media
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and Hc are enhanced in magnetic devices with a Ta / M1 / M2 seed layer where M1 is preferably Ti, and M2 is preferably Cu, and including an overlying (Co / Ni)X multilayer (x is 5 to 50) that is deposited with ultra high Ar pressure of >100 sccm to minimize impinging energy that could damage (Co / Ni)X interfaces. In one'embodiment, the seed layer is subjected to one or both of a low power plasma treatment and natural oxidation process to form a more uniform interface with the (Co / Ni)X multilayer. Furthermore, an oxygen surfactant layer may be formed at one or more interfaces between adjoining (Co / Ni)X layers in the multilayer stack. Annealing at temperatures between 180° C. and 400° C. also increases Hc but the upper limit depends on whether the magnetic device is MAMR, MRAM, a hard bias structure, or a perpendicular magnetic medium.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Method for forming a servo pattern on a magnetic tape
InactiveUS7029726B1Maintain alignmentTrack finding/aligningRadiation applicationsMagnetic tapeControl theory
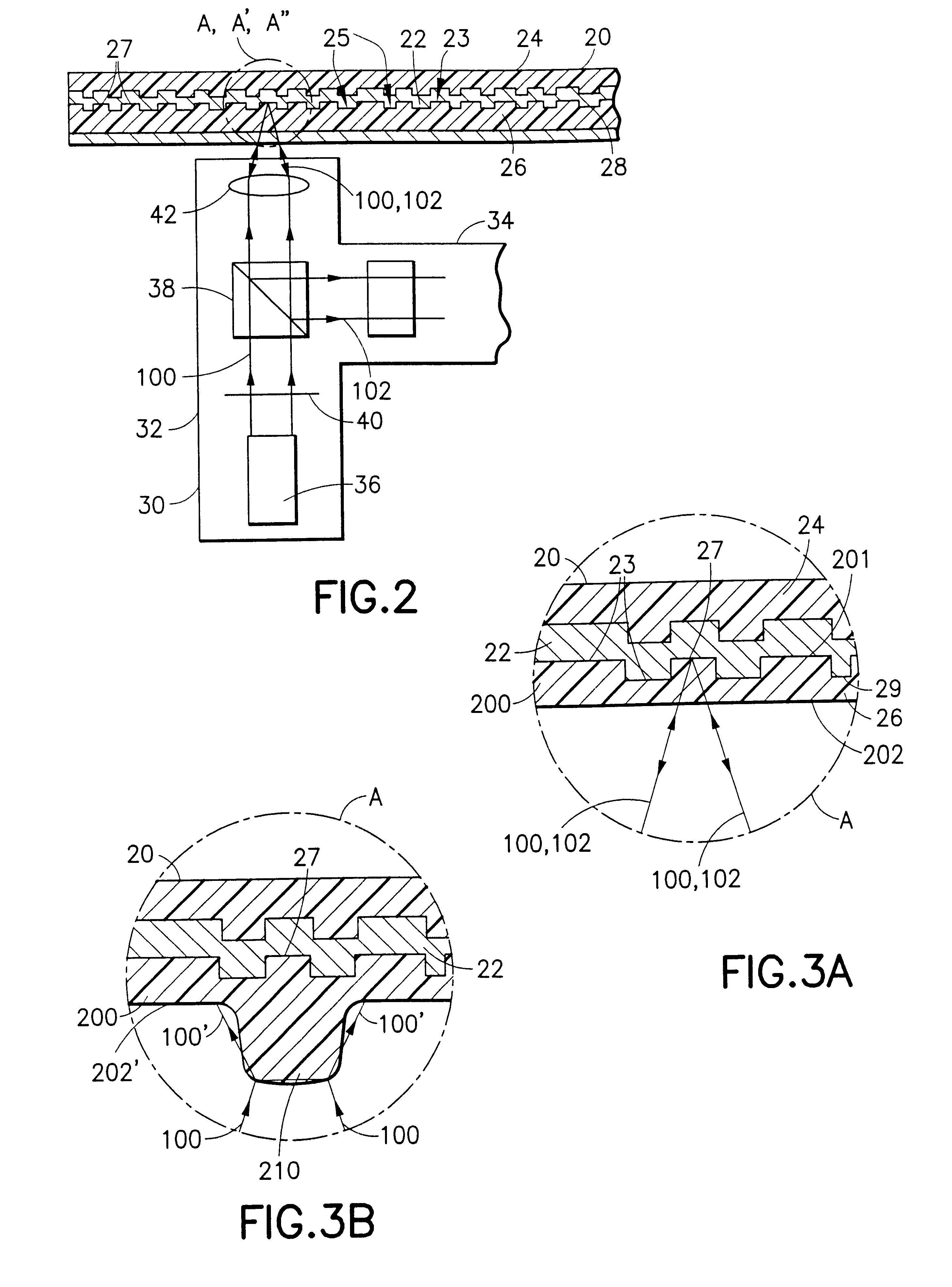
The systems, methods and products of the invention include systems and methods for manufacturing servo tracks on a magnetic tape. In one aspect, the invention includes systems for manufacturing magnetic tapes having servo tracks thereon wherein the servo tracks are optically detectable and are capable of being processed by a servo control system for maintaining alignment of a magnetic recording head with the data tracks on the recording side of the magnetic tape. In one practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the non-recording side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the non-recording side of the magnetic tape. In another practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the magnetic side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the magnetic side of the magnetic tape. Such engraved patterns can act as optical servo tracks for maintaining alignment of the recording head with the data tracks on the magnetic tape.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Multi-layered information recording medium with spare defect management areas
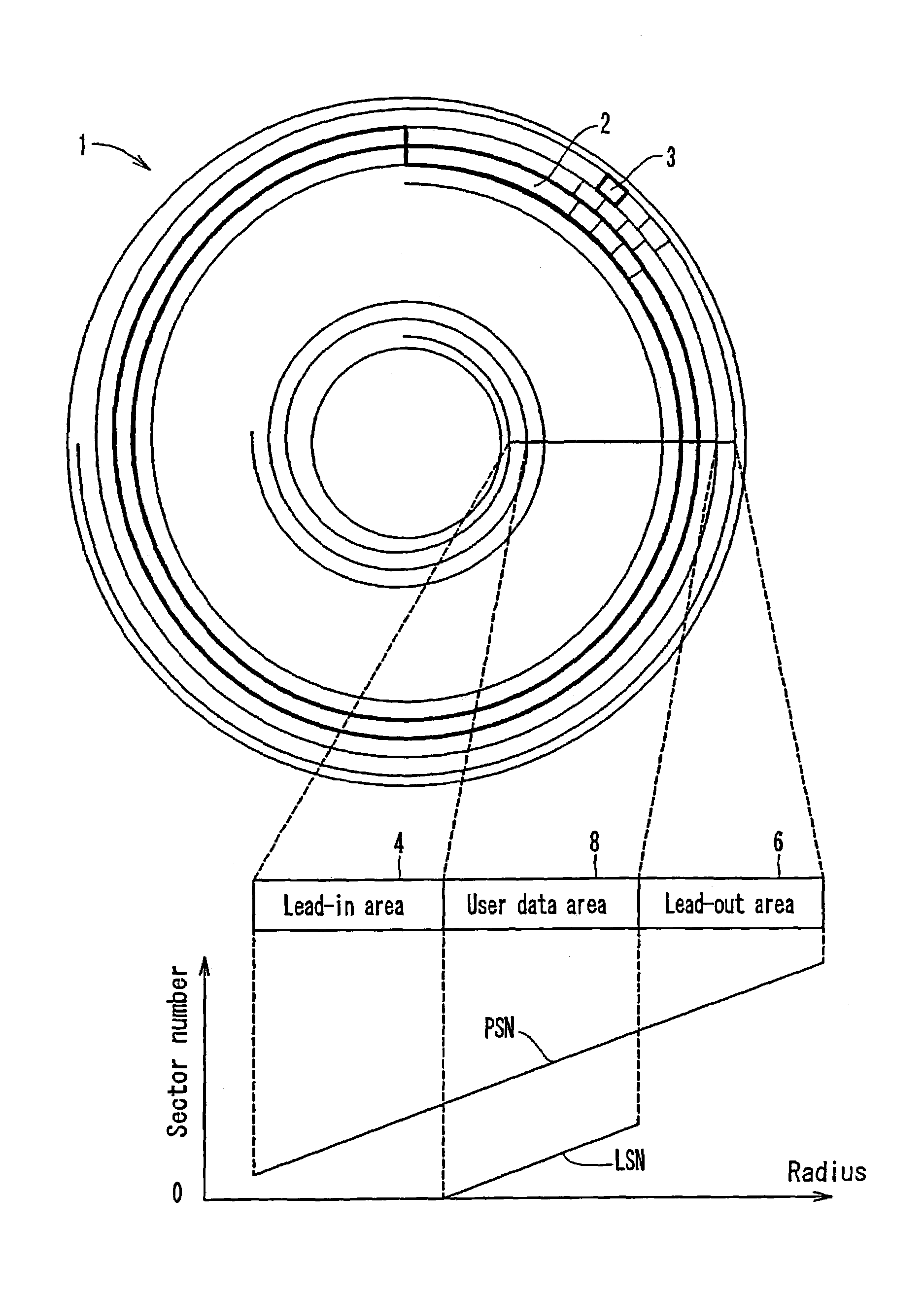
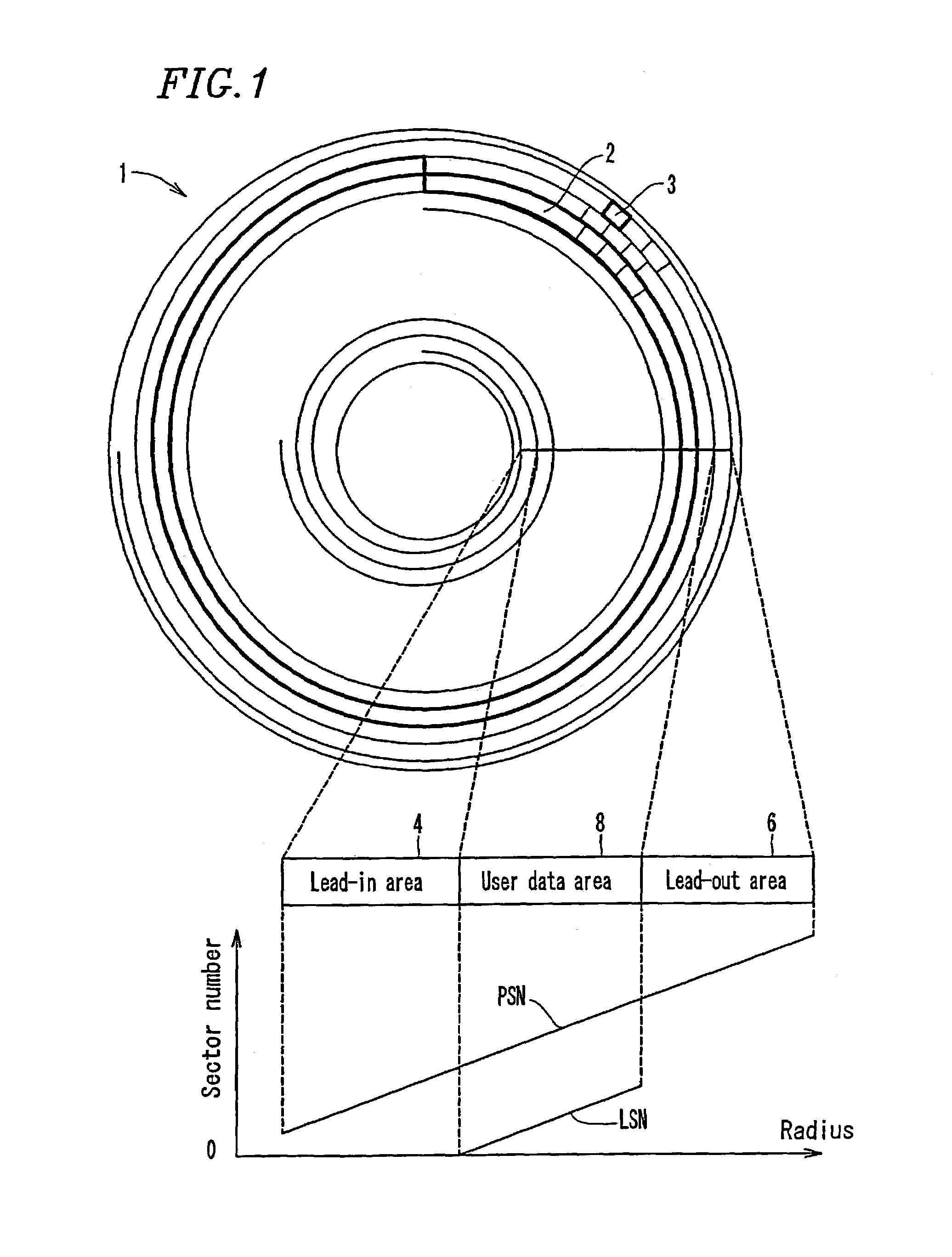
ActiveUS7123556B2Shorten the timeEfficient managementInput/output to record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareRecording layer
A multi-layered information recording medium comprising a plurality of recording layers, a user data area for recording user data, provided in at least two of the plurality of recording layers, and a defect list storing area for storing a defect list. When at least one defective area is detected in the user data area, the defect list is used to manage the at least one defective area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103133A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againMaterials with ironBase layers for recording layersIn planeX-ray
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes a ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio is 0.65 to 1.00, one or more kinds of component selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide is contained in a magnetic layer side portion on the non-magnetic support, a C—H derived C concentration of the magnetic layer is 45 atom % to 65 atom %, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103134A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againMaterials with ironProtective coatings for layersIn planeX-ray
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic recording medium is 0.65 to 1.00, a coefficient of friction measured regarding a base portion of a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.30, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
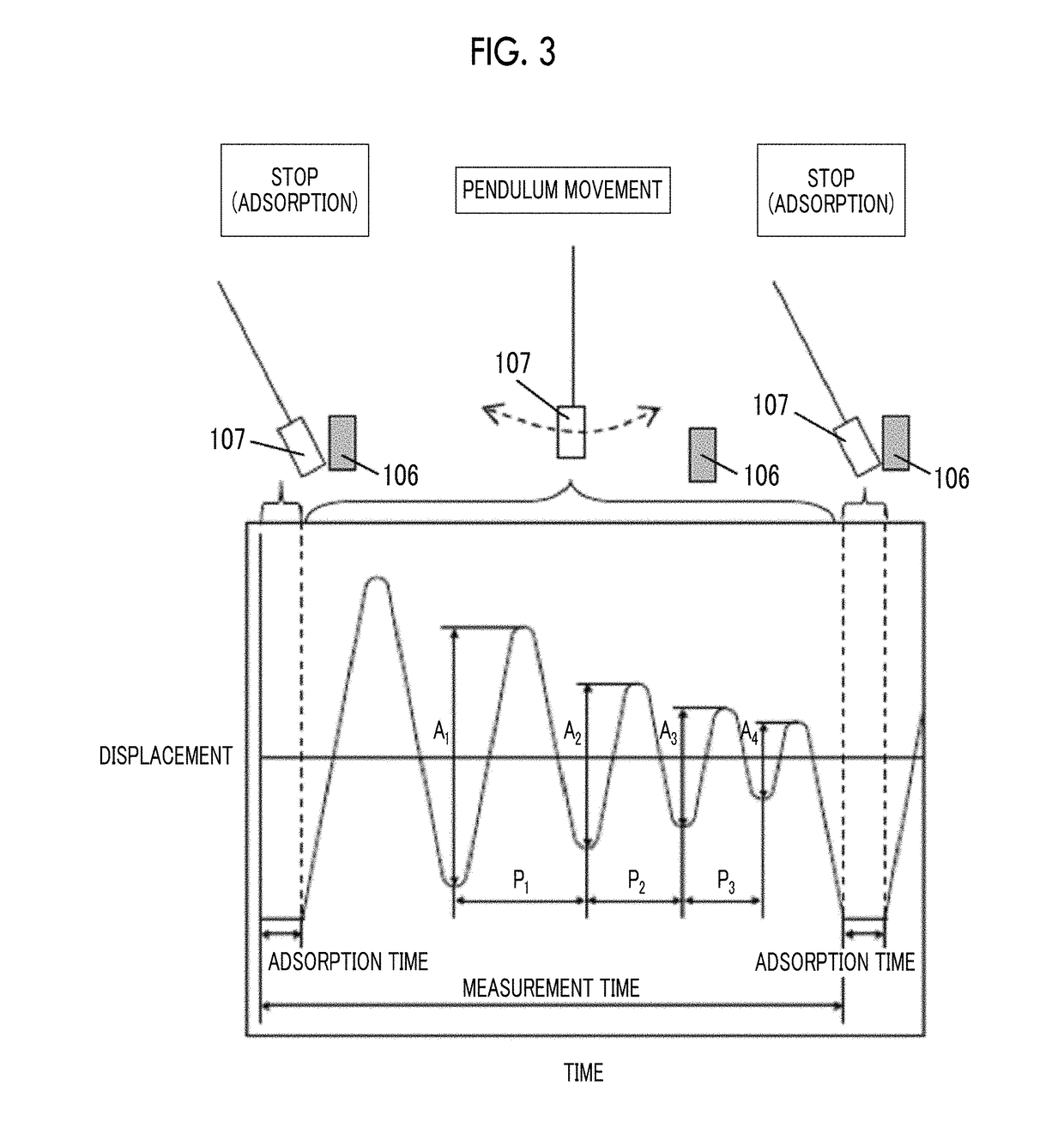
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS9972351B1Avoid it happening againImprove accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeEngineering
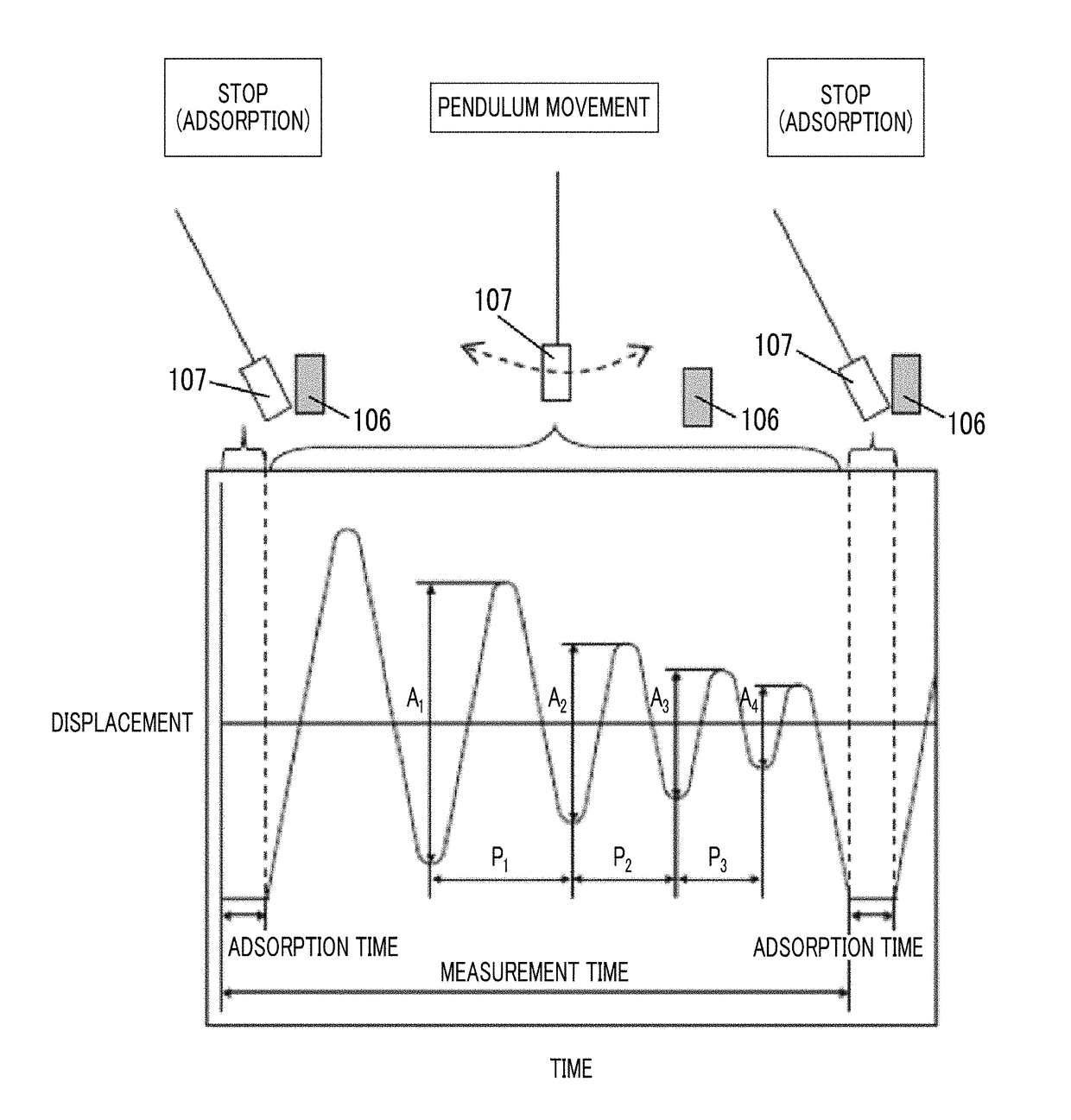
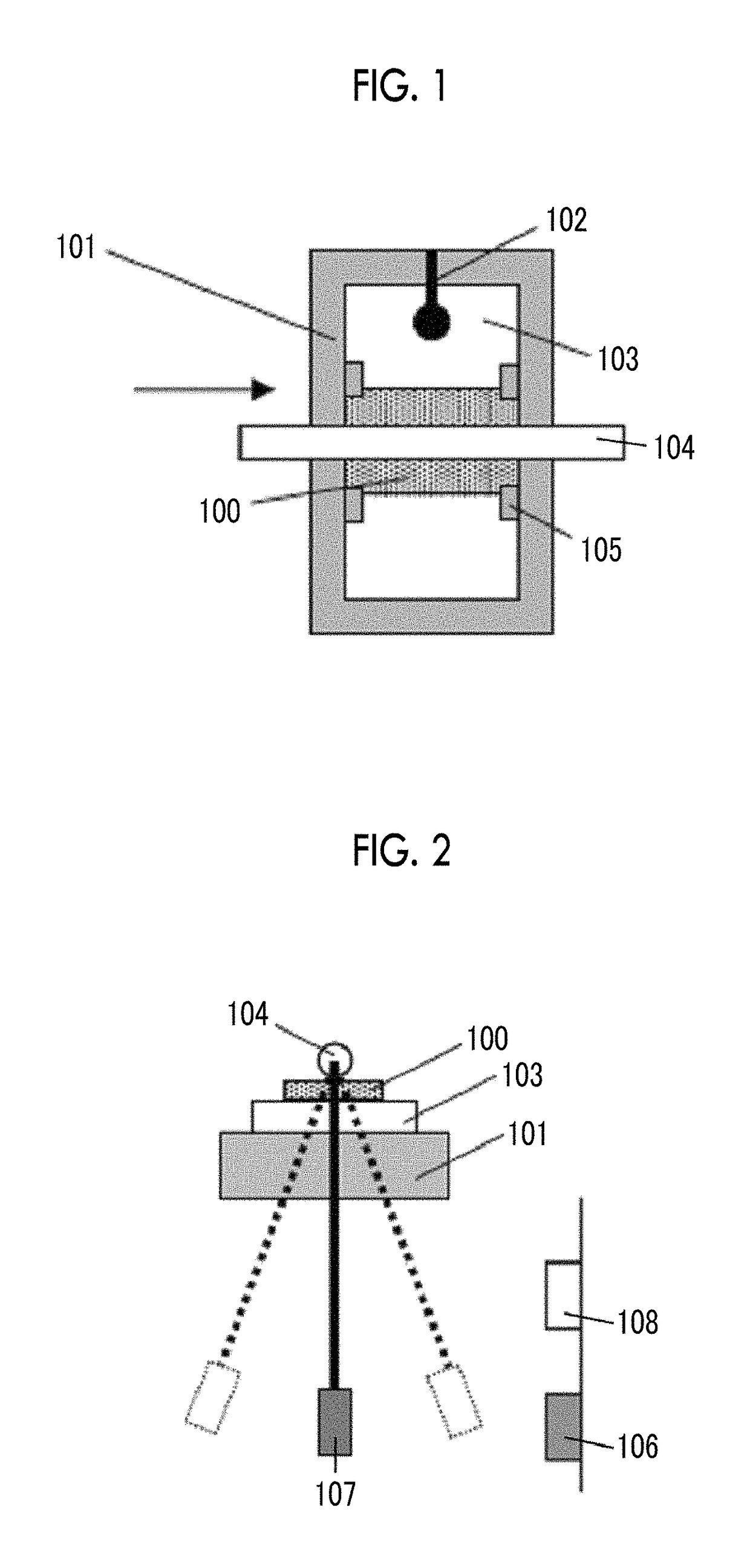
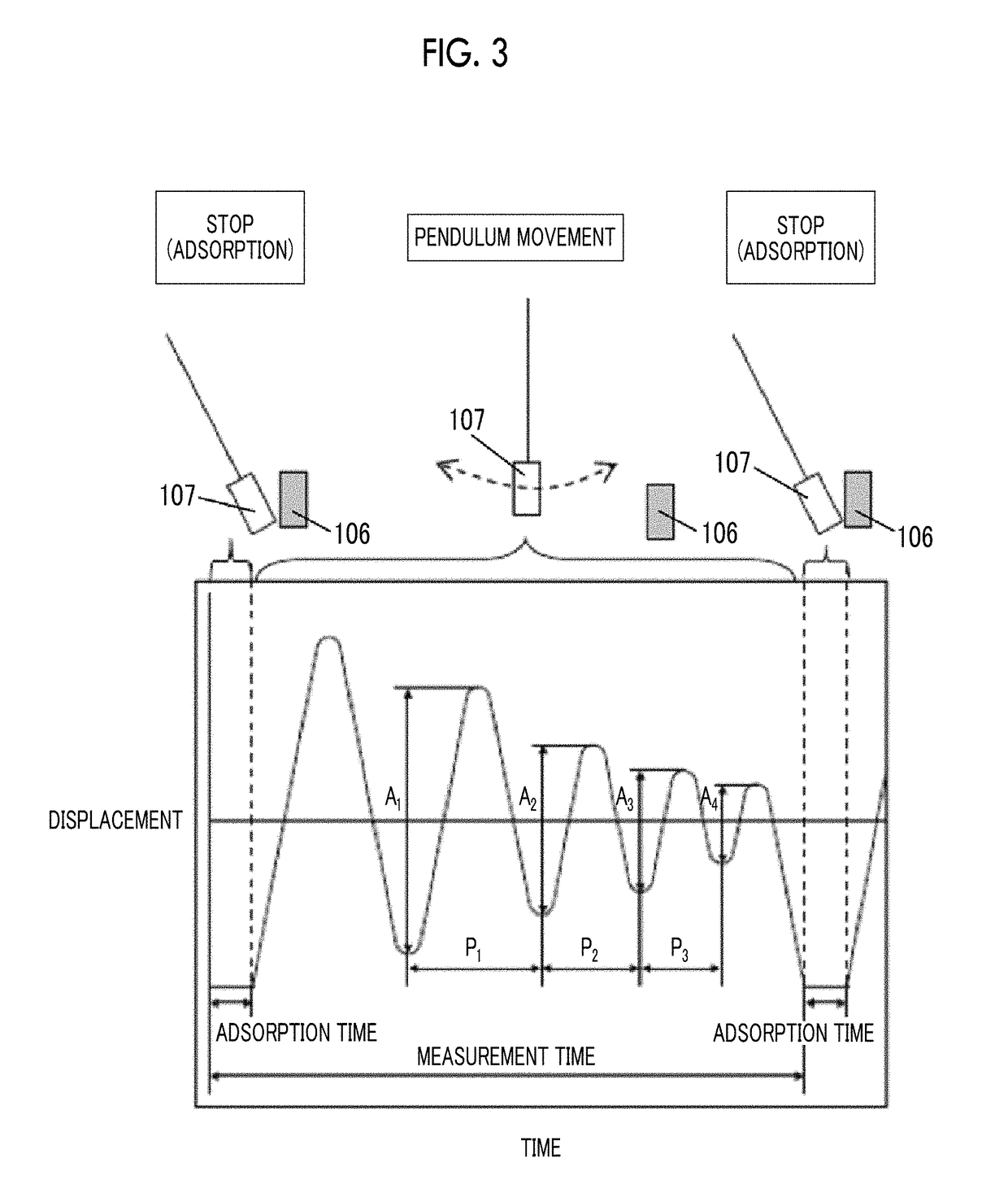
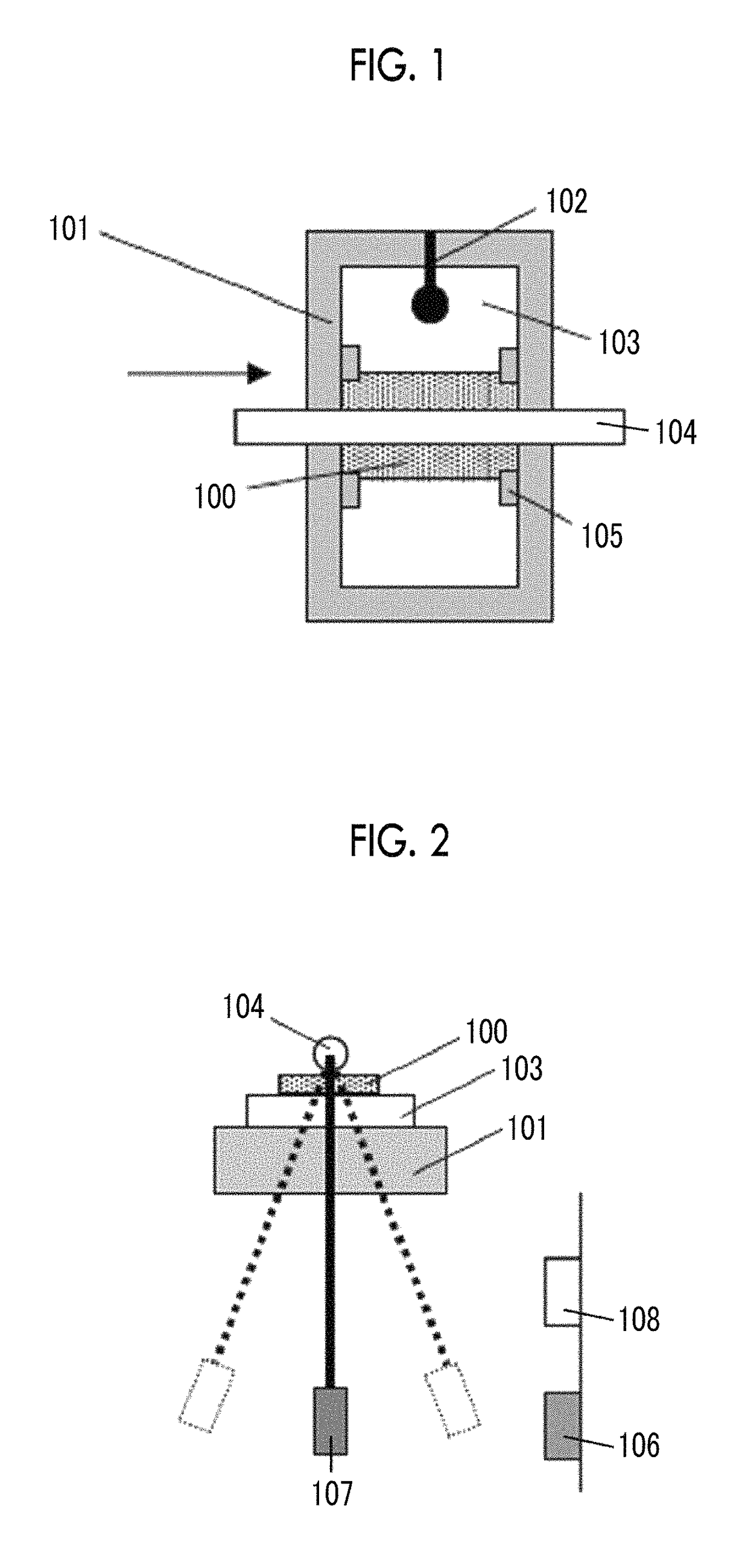
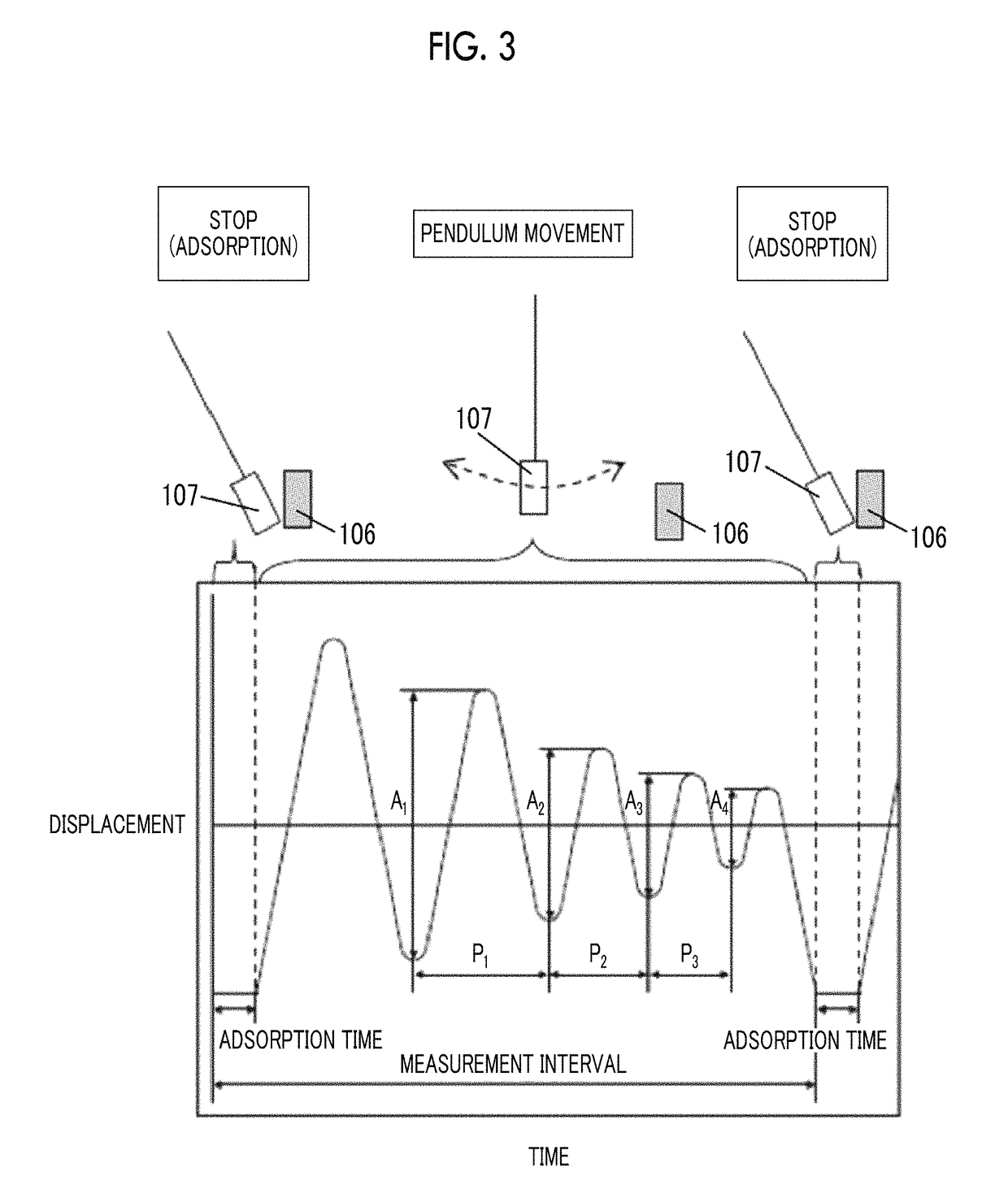
The magnetic tape device including: a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a magnetic head including a tunnel magnetoresistance effect type element as a servo pattern reading element, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, the magnetic layer includes a servo pattern, and logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10062403B1Improve accuracyExact reproductionTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a TMR head, the magnetic tape includes a servo pattern in the magnetic layer, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and a ratio (Sdc / Sac) of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
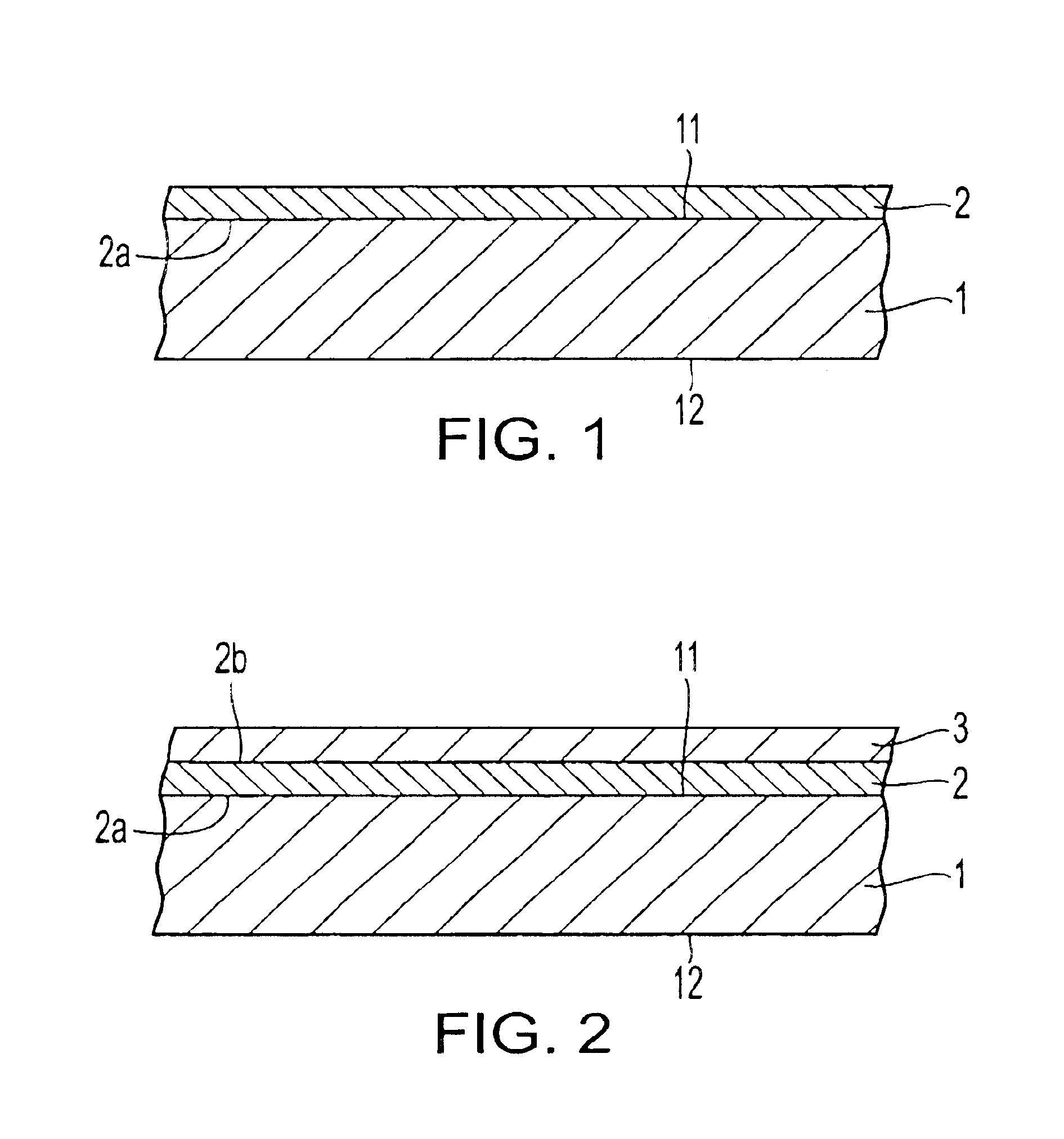
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20070009769A1Large recording capacityGood running durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeComputer data storage
A magnetic recording medium including a magnetic layer 93 containing ferromagnetic powder and a binder, a support 91, and a backcoat layer 94, provided in this order, and being obtained by slitting to width a magnetic material of broad width and continuous length. The magnetic recording medium has no ridge protruding above the surface plane of the magnetic layer along the slit edge thereof. The magnetic recording medium achieves large recording capacity, is free from the tape pack problems such as appearance of a radial pattern and the output reduction problem, produces no fine scrapings in high speed running, which would cause head clogging and dropouts, thereby exhibiting good running durability and electromagnetic characteristics, and is particularly useful for computer data storage applications.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Disk alignment apparatus and method for patterned media production
An apparatus and method for aligning a disk with an imprinting surface are described. In one embodiment, the apparatus has a die which includes an air-bearing mandrel having a tapered nose to engage an ID of the disk, a circular imprinting surface having a centerline concentric with the air-bearing mandrel, and an air-bearing cavity to position the disk. The axial movement of the top die towards the bottom die guides the ID of the disk into coincident alignment with the centerline of the top die.
Owner:WD MEDIA
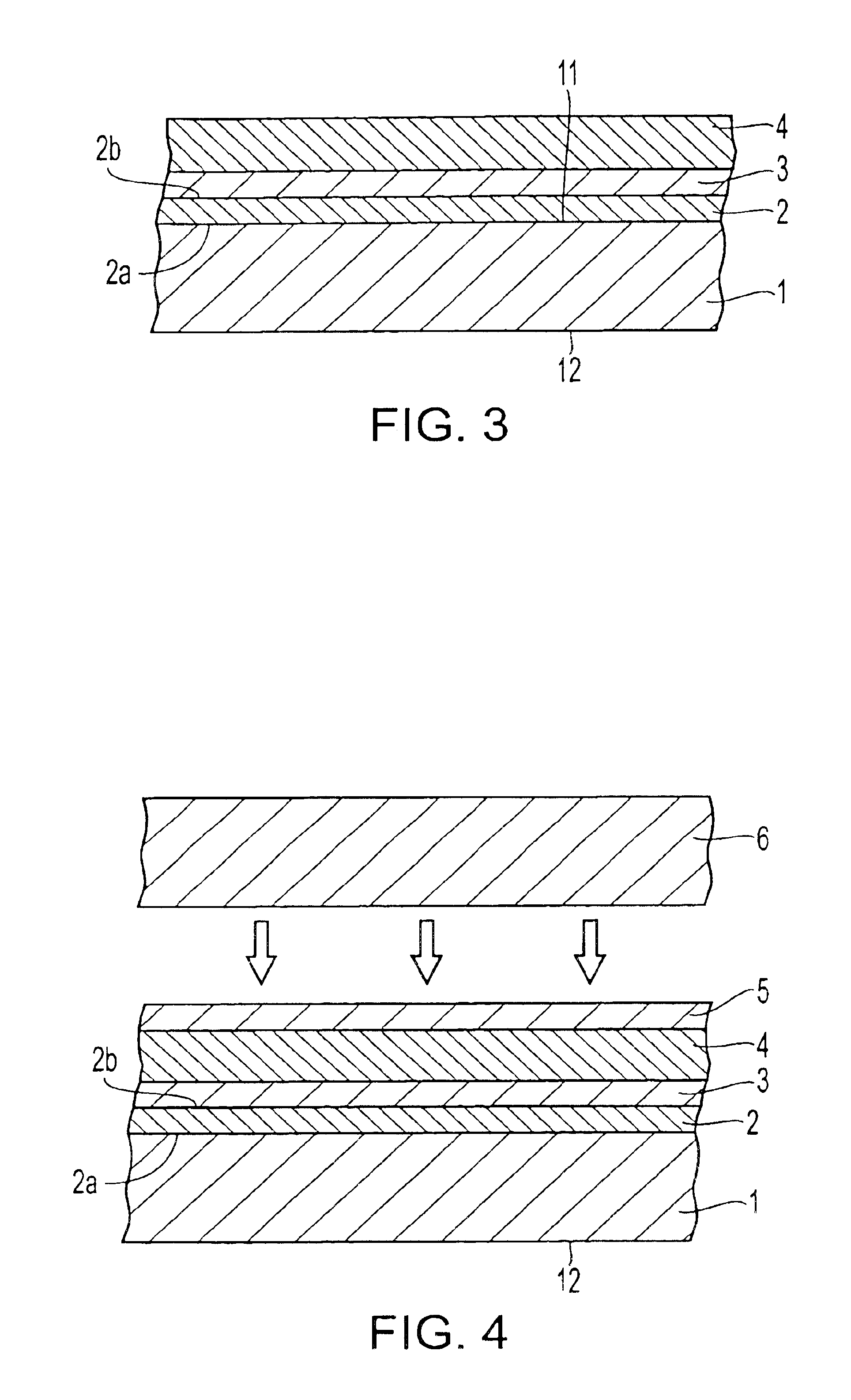
Magnetic recording medium and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20070231606A1Improve the overall coefficientHead contaminationMaterials with cobaltRecord information storageMetal powderCobalt
A magnetic recording medium comprising a substrate and a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic metal powder and a binder, wherein the ferromagnetic metal powder contains iron, cobalt and form 2 to 20 atom % of yttrium based on a total of iron and cobalt contained in the ferromagnetic metal powder and has an average length of 50 nm or smaller, and the magnetic recording medium has a test value of at least 100 passes in a magnetoresistive head resistance reduction test performed as defined herein.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
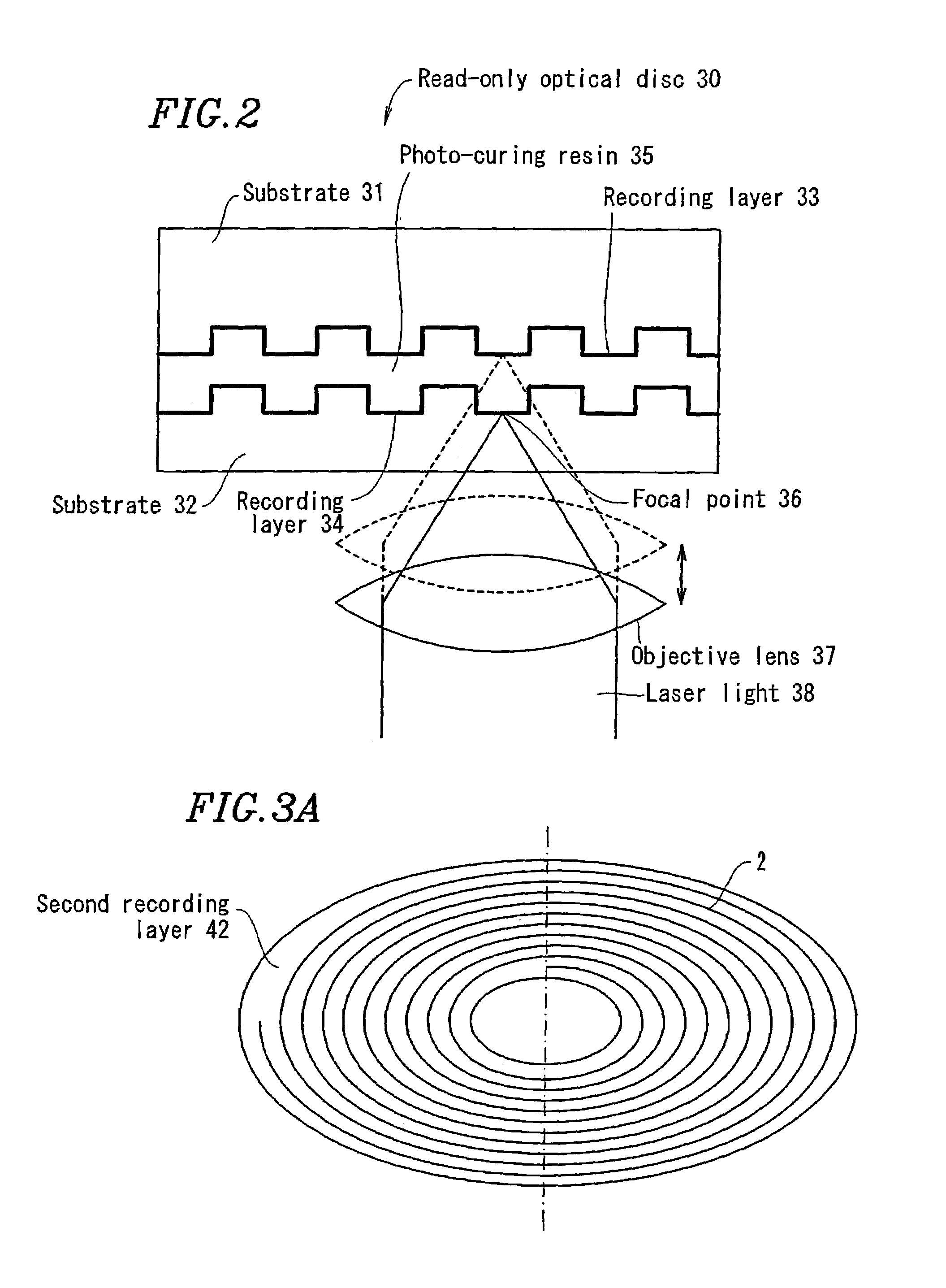
Optical recording medium and method for recording optical information
The present invention provides an optical recording medium which incorporates an inorganic based recording layer which has a high reflectance, sufficient for reproduction compatibility on devices such as CD-ROM drives, as well as a high degree of modulation between the state prior to recording and that after recording, as well as an information recording method therefor. Accordingly, an optical recording medium comprises a substrate (2) which is substantially transparent with respect to a recording light beam and a reproduction light beam, a first recording layer (3) which is layered on top of the substrate (2) and which incorporates as the main constituent a metal which has a low melting point and a high reflectance, and a second recording layer (4) which is layered on top of the first recording layer (3) and which will, due to heat generated from irradiation of a light beam through the substrate (2), either mix, or alternatively react, with the first recording layer (3) to form an alloy of low reflectance as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby enabling the recording of information. Due to the heat generated from irradiation of a recording light beam through the substrate (2) the first recording layer (3) and the second recording layer (4) are either mixed, or alternatively reacted to form an alloy as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby recording information.
Owner:KAO CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20190027181A1Improve surface smoothnessAvoid it happening againMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageIn planeCoated surface
Provided is a magnetic tape in which an Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, Int(110) / Int(114) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an XRD analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the back coating layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 10.0 nm, and a difference between the spacings measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the back coating layer before and after performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Process and apparatus for forming plastic sheet
InactiveUS6183829B1Avoid mistakesLow birefringenceRecord carriersPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Optical disk and method of integrating a high gain RFID antenna
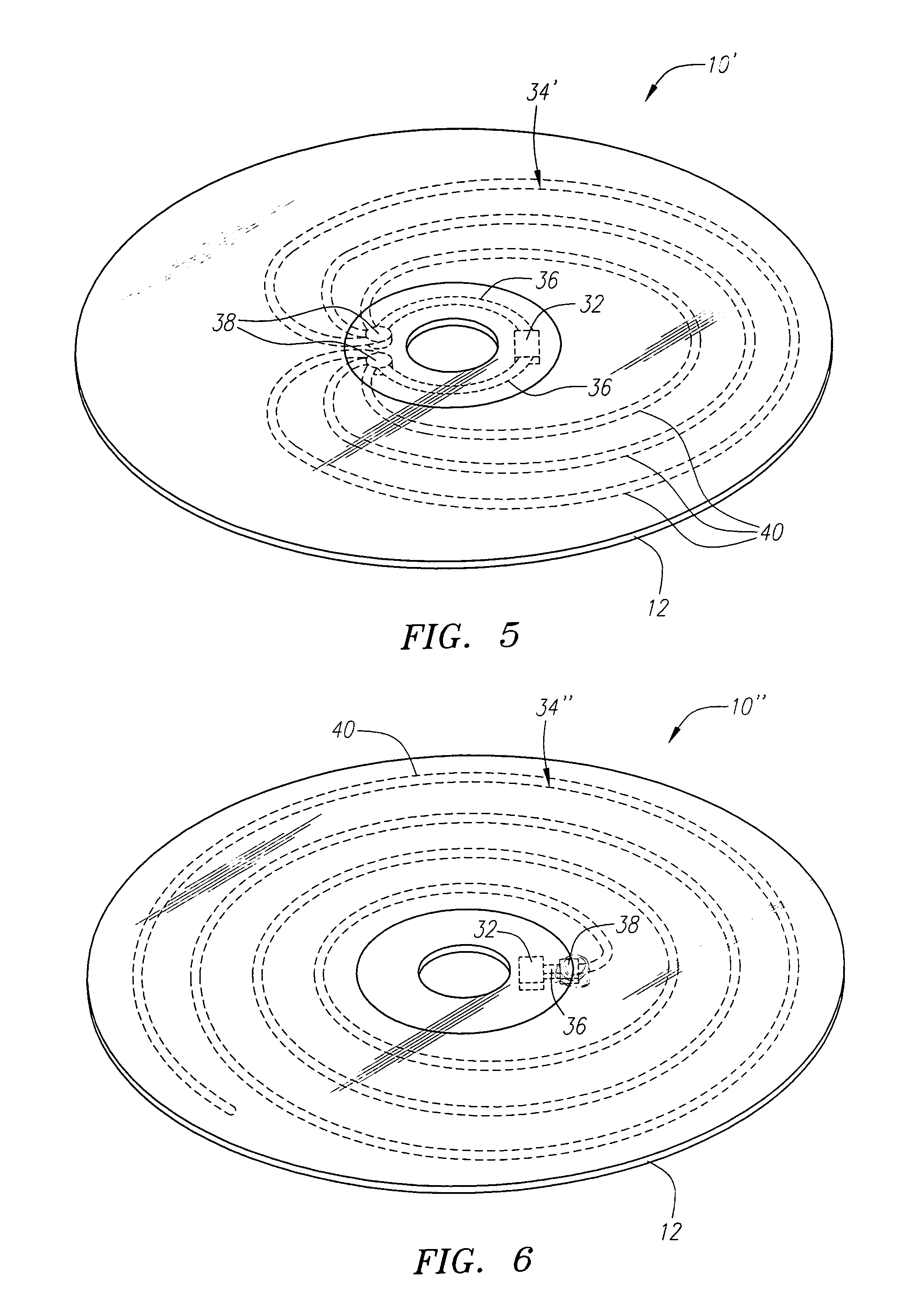
InactiveUS20060071795A1Easy to mergePrevent tamperingMechanical record carriersRecord information storageRadio frequency signalEngineering
An optical disk comprises a disk substrate having a hub and an annular optical metallicized data region extending radially outward from the hub. The optical disk further comprises a radio frequency identification (RFID) transponder affixed to the disk substrate, e.g., within the non-data containing hub region. The optical disk further comprises at least one linear antenna element coupled to the transponder, e.g., via pole lead(s), and extending within the data region. The antenna element(s) can be applied to the disk substrate as a patterned antenna layer over a metallicized data region, and can be electrically isolated from the data region. A method and system of identifying an optical disk is provided. A radio frequency (RF) signal can be transmitted to the optical disk at a range of at least five feet, and preferably at a range of at least ten feet. An RF signal with an identification code (e.g., a unique number) can be received from the optical disk in response to the transmitted RF signal. The activating RF signal can be transmitted by, and the identification RF signal can be received by, e.g., a handheld RF reader or an RF reader that is affixed to a building. The identification code can then be processed for many purposes, such as identifying the optical disk as a non-counterfeited optical disk, calculating a royalty, or tracking the location of the optical disk.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Extended range RFID system
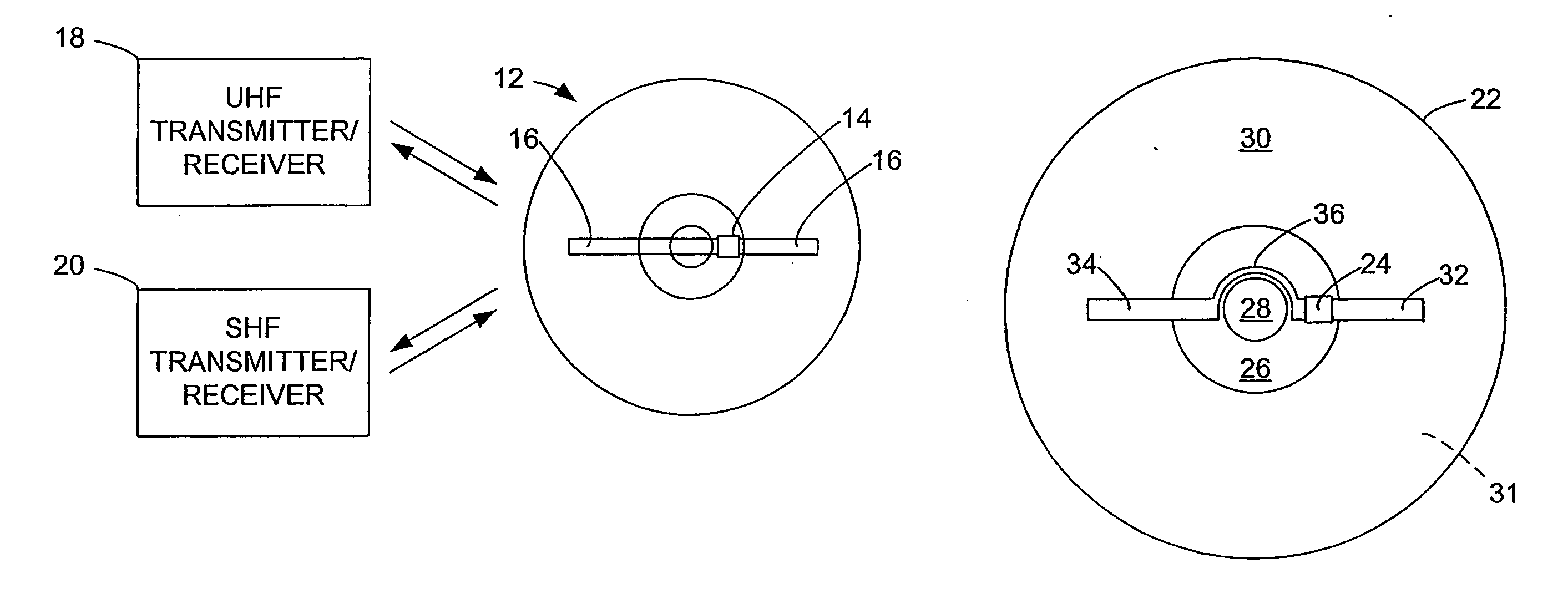
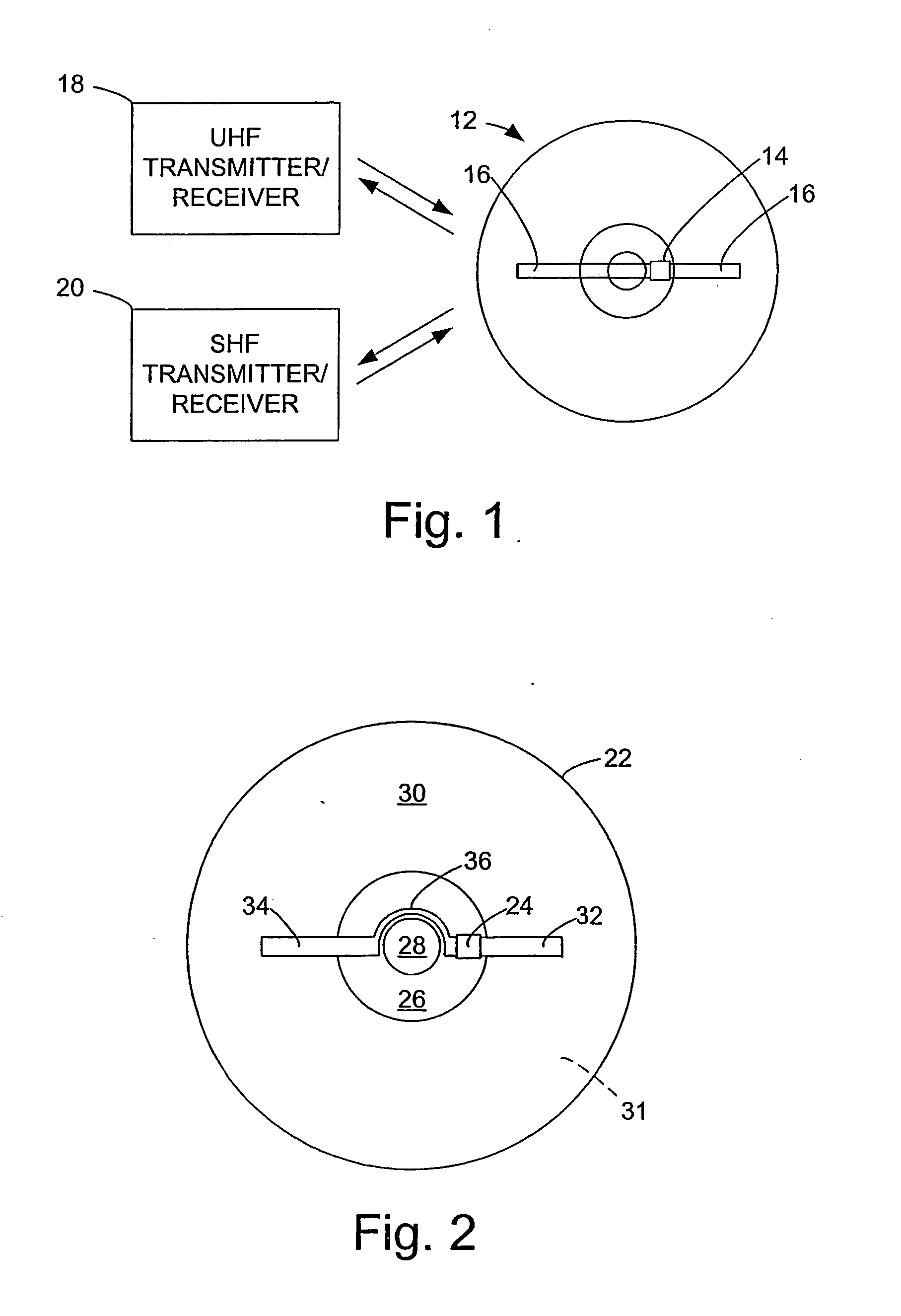
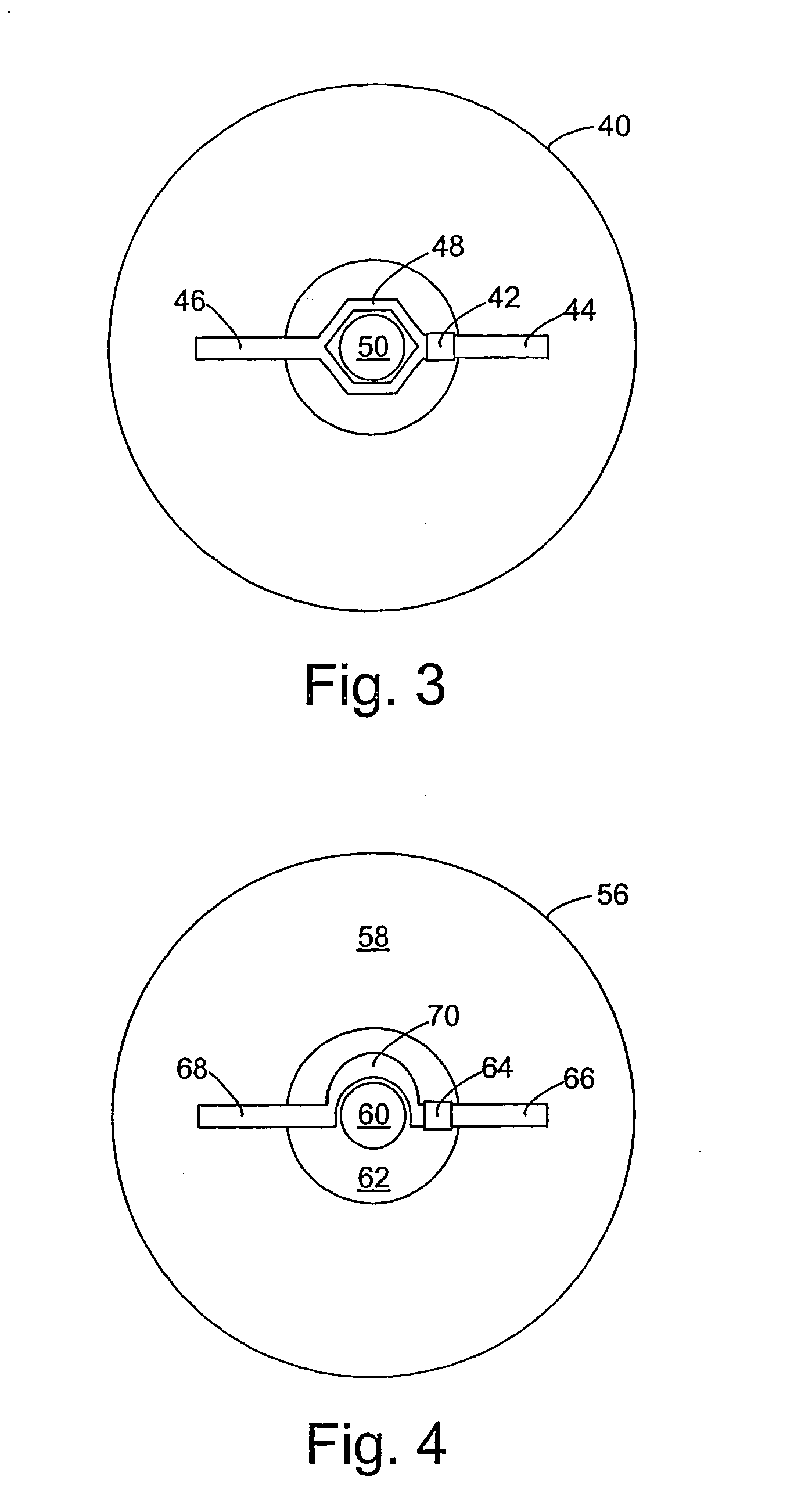
InactiveUS20060028344A1Increase rangeAntenna supports/mountingsMechanical record carriersExtended coverageEngineering
A radio frequency identification (RFID) system for discs such as CDs, DVDs or minidiscs includes a special RFID transponder and antenna configuration. The discs normally include an outer metallized annular zone where information is stored, a central hole, and an inner annular zone between the hole and the outer annular zone. The transponder may be located in the inner annular zone, with antenna elements coupled to the transponder extending in opposite directions part way across the outer annular zone. Multilayer labels with a recess for the transponder chip, and antenna elements formed by conductive material may be employed to apply the RFID assembly to the discs. A monopole or dipole mode of antenna operation, prominently involving the metallized disc layer, results from the antenna configuration, and serves to more than double the range of the system.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
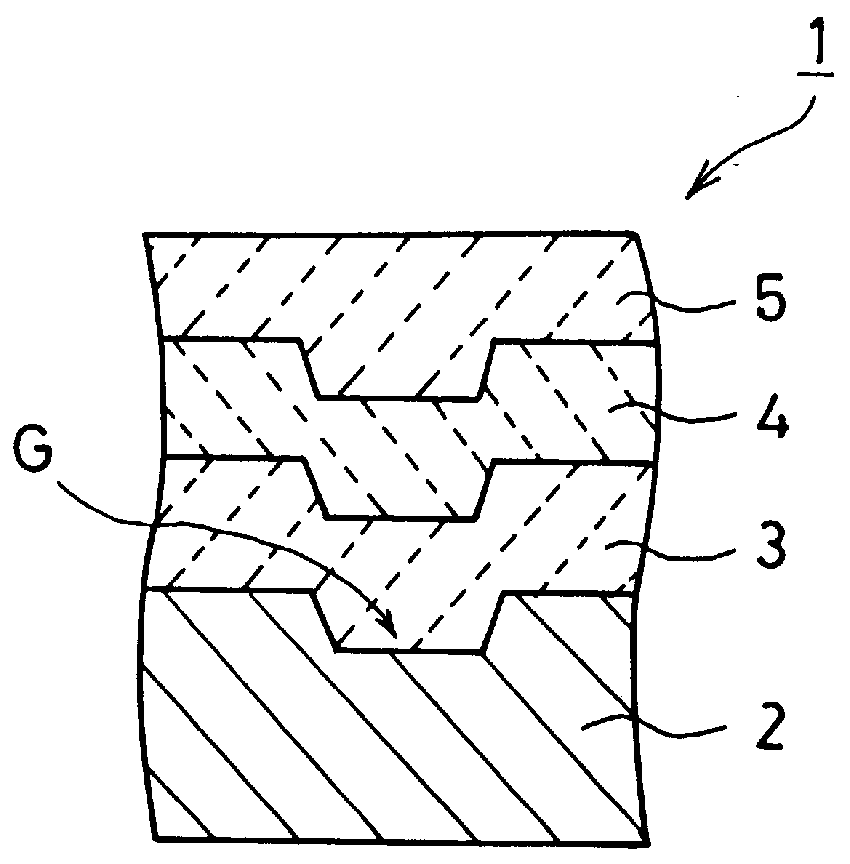
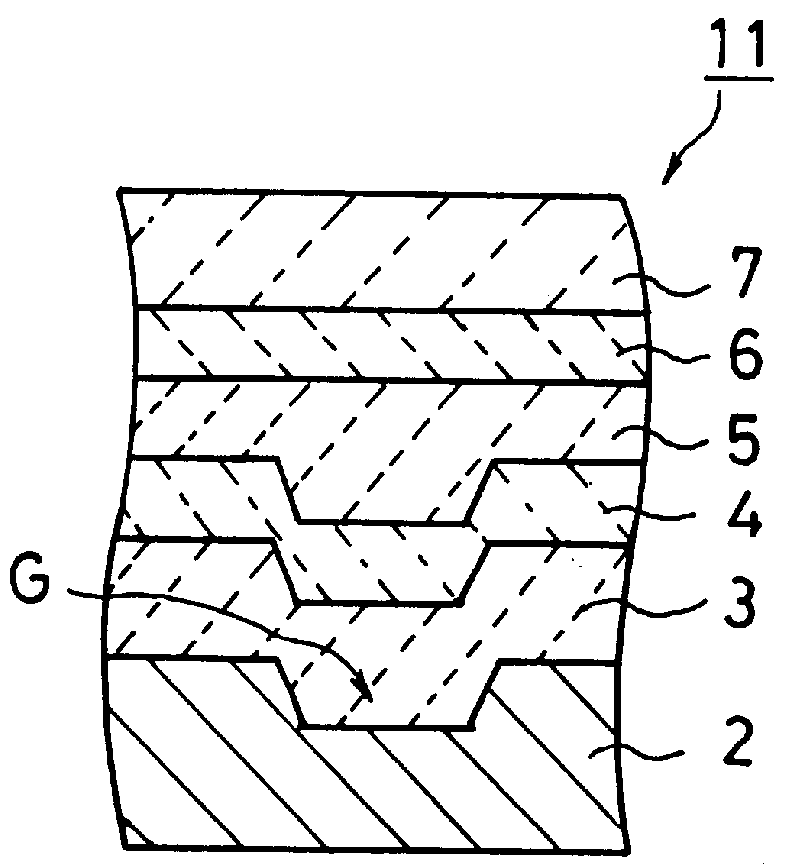
Information recording mediums, supporter used in the mediums, manufacture methods of the supporter, manufacturing apparatus of the supporter and stampers for producing the mediums
InactiveUS6254966B1Magnetic materials for record carriersLayered productsHigh densityManufactured apparatus
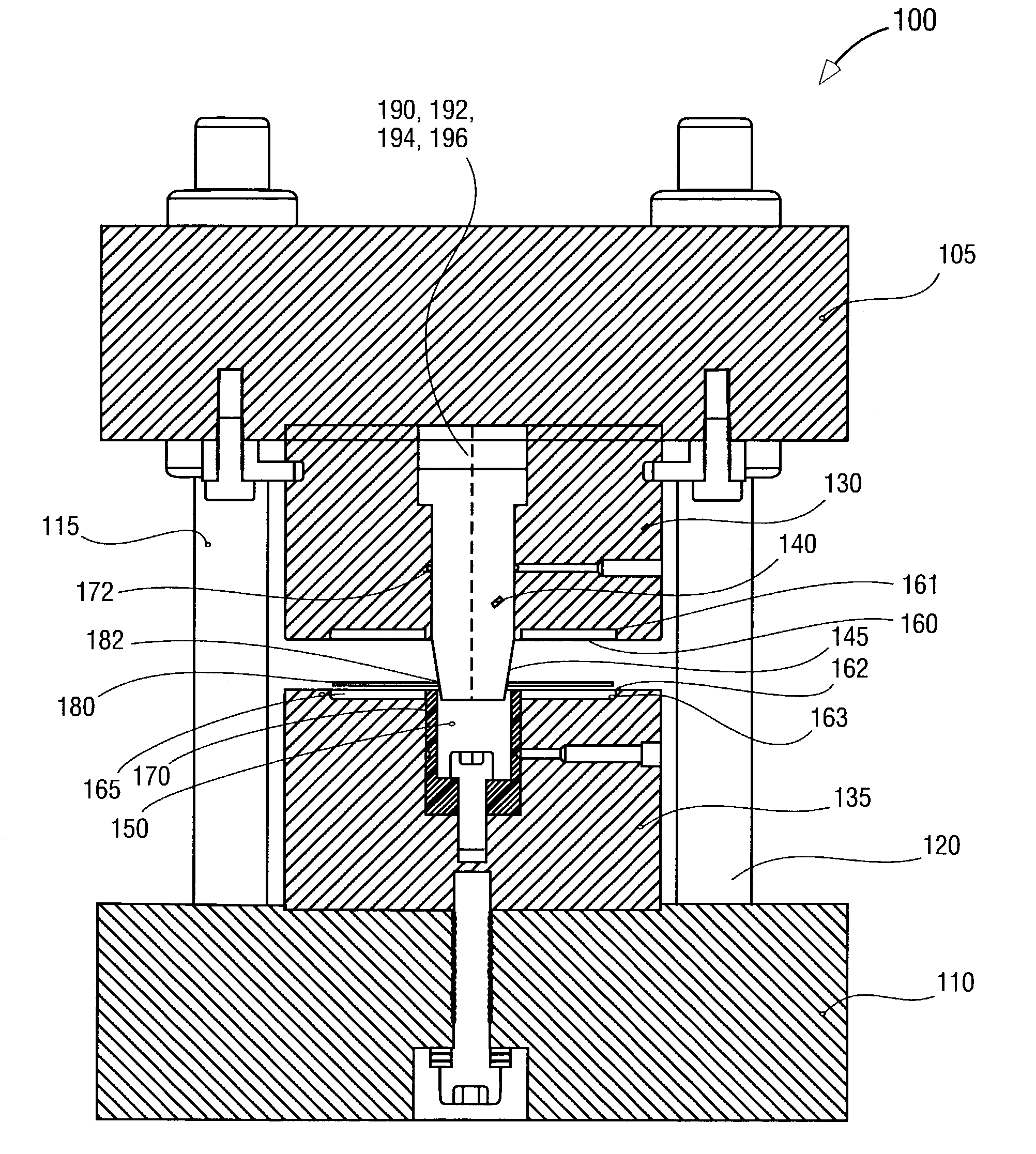
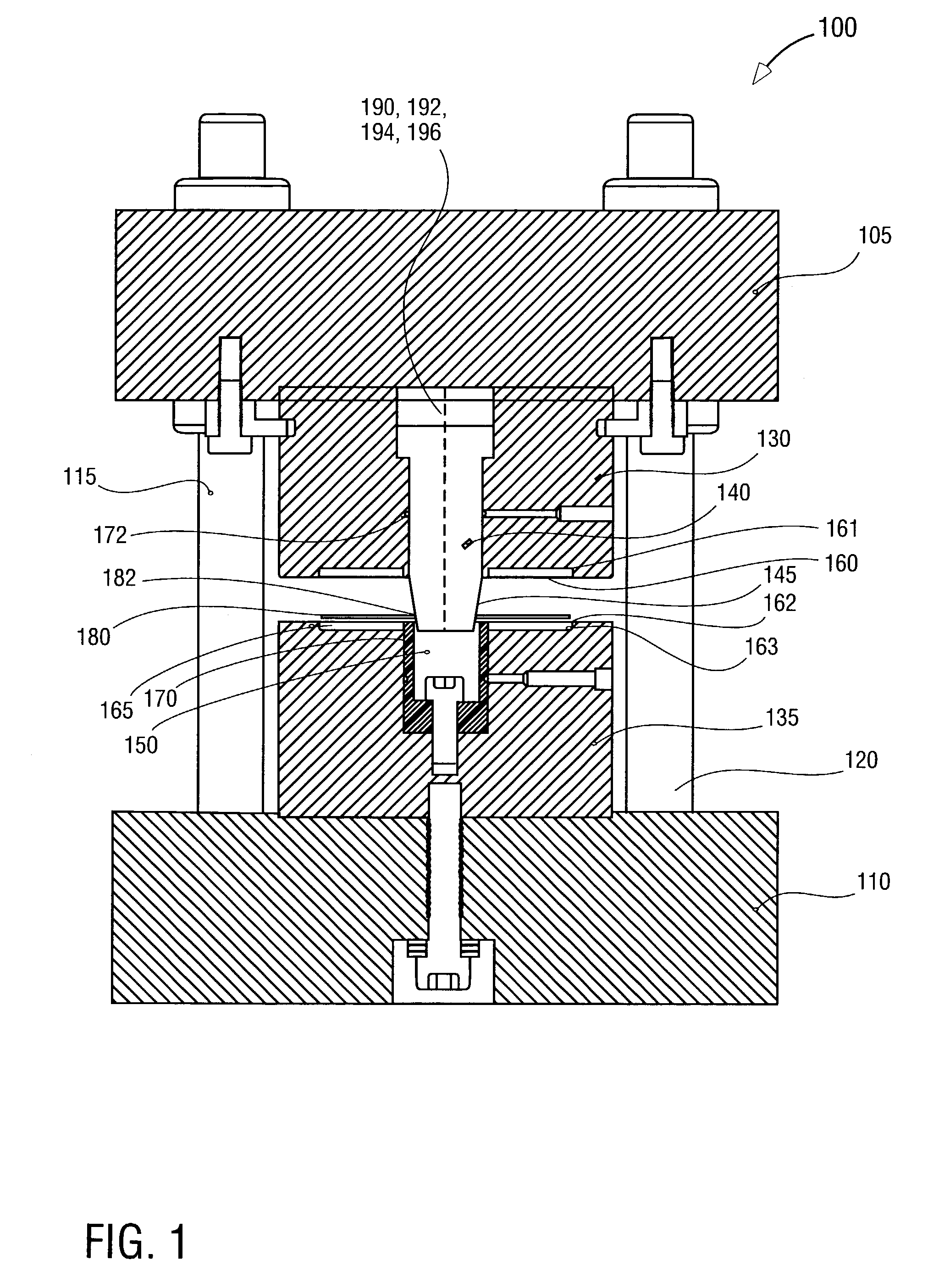
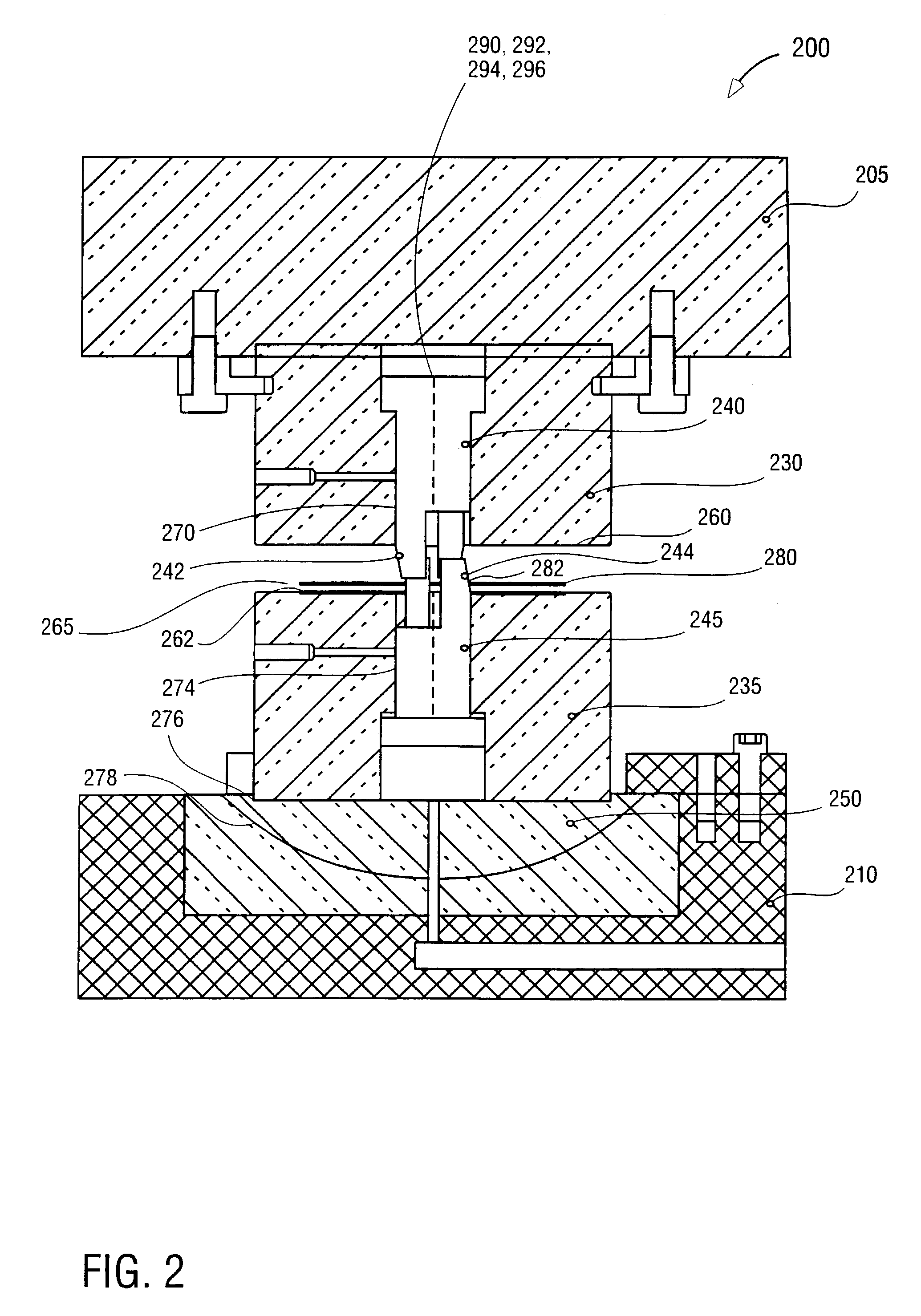
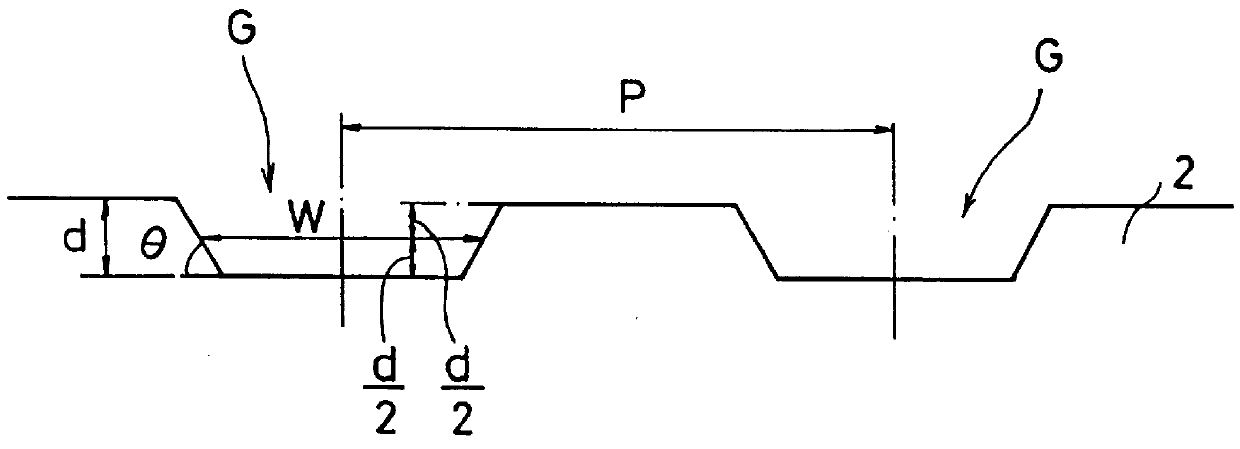
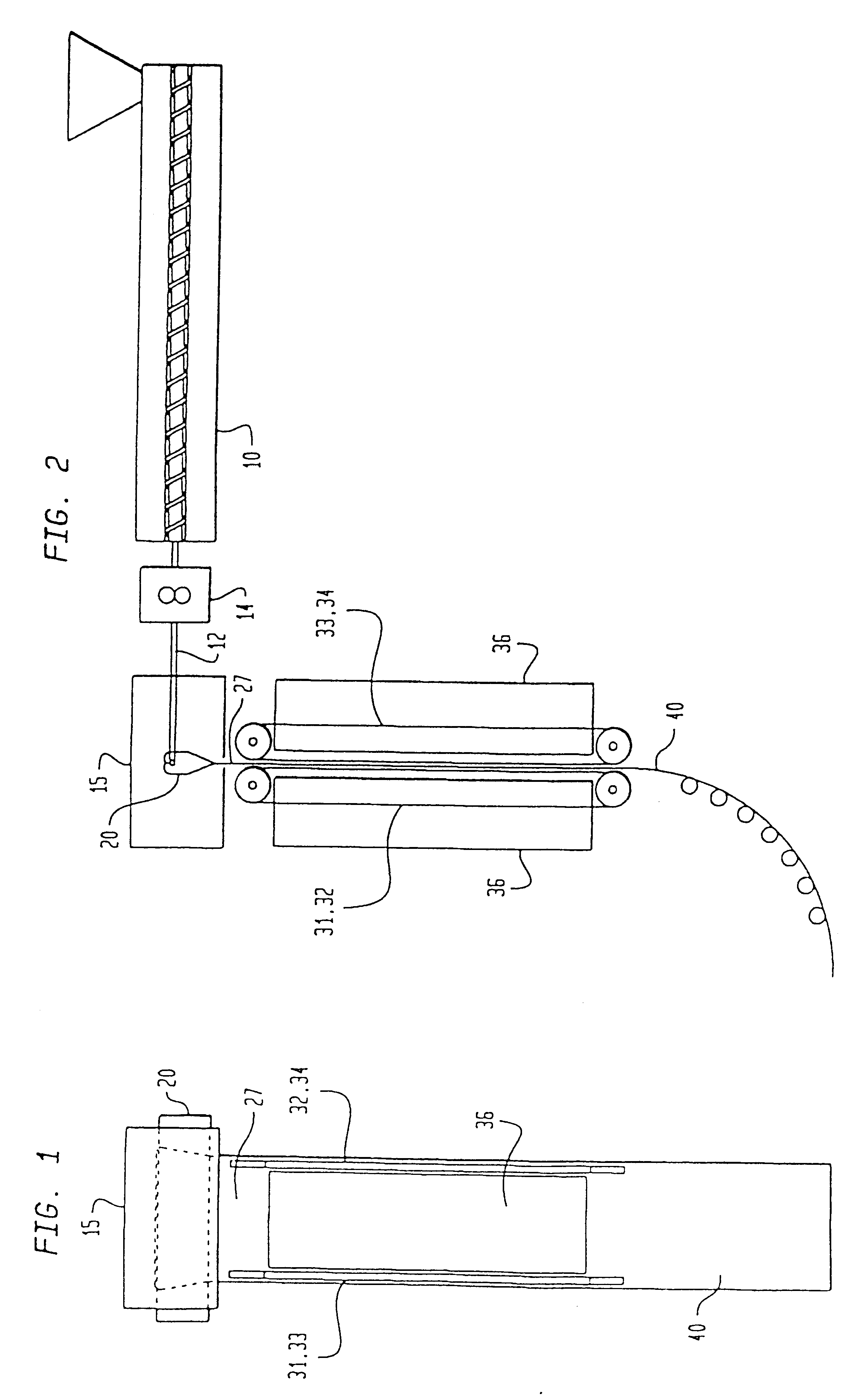
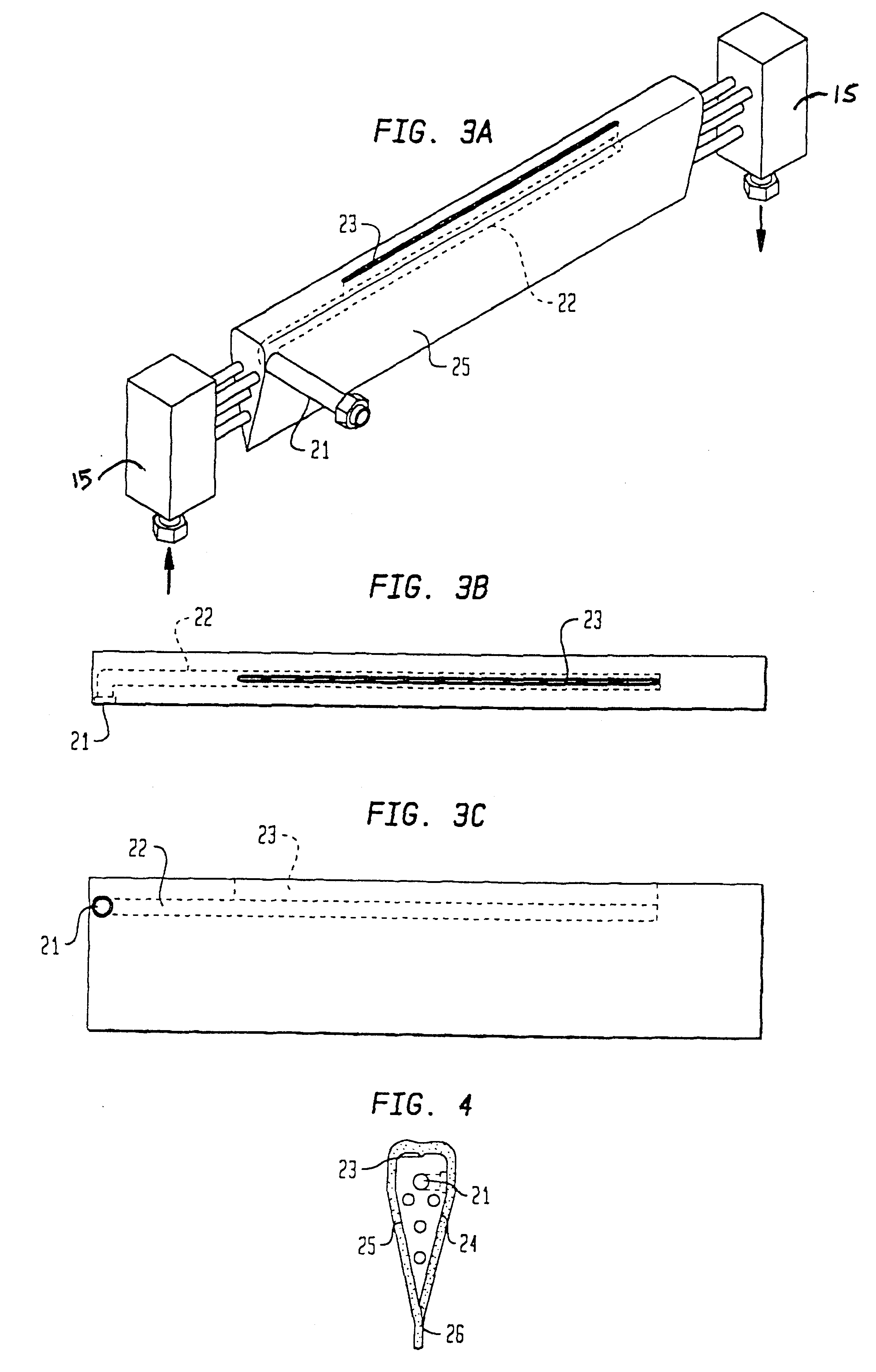
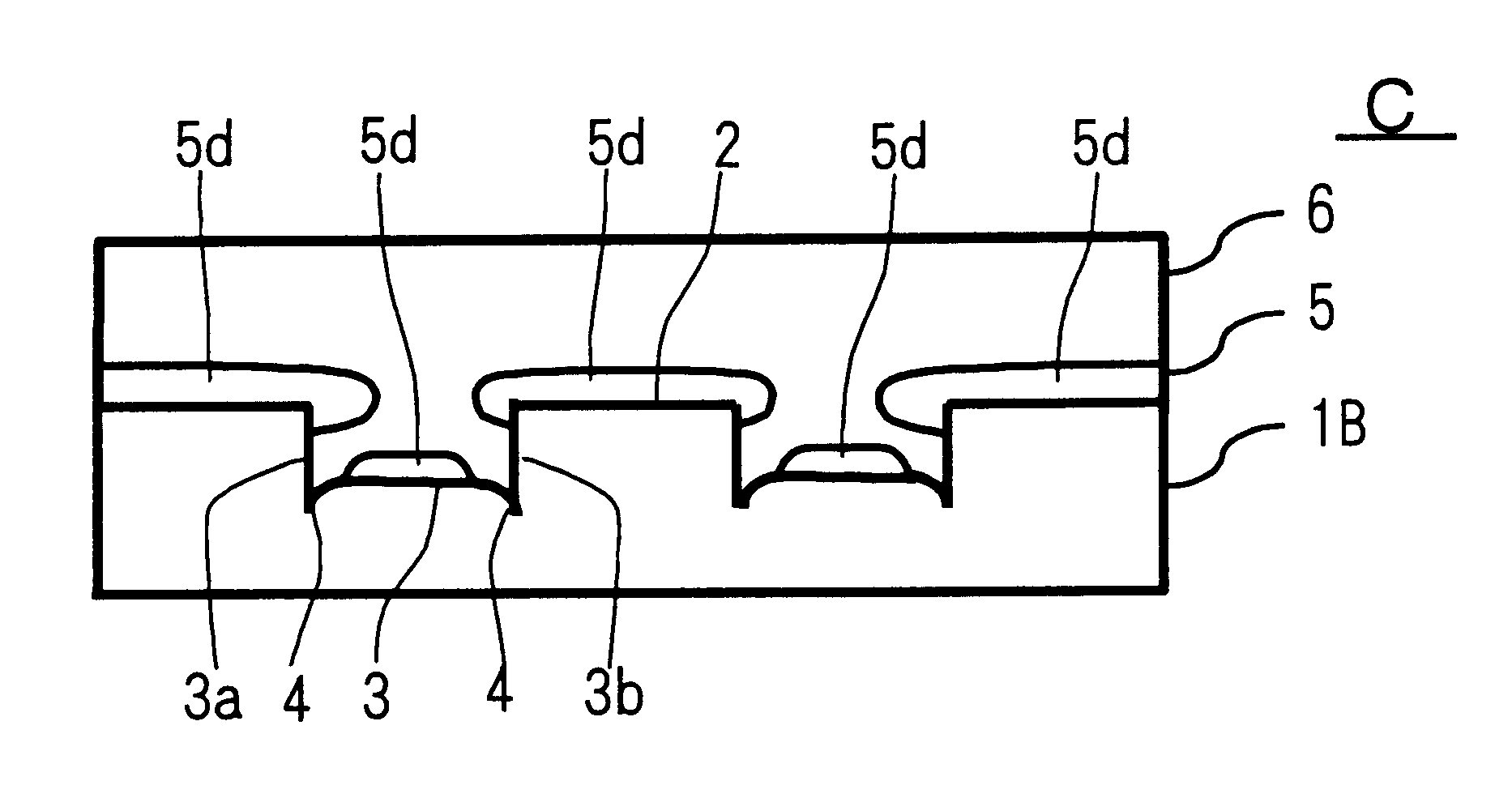
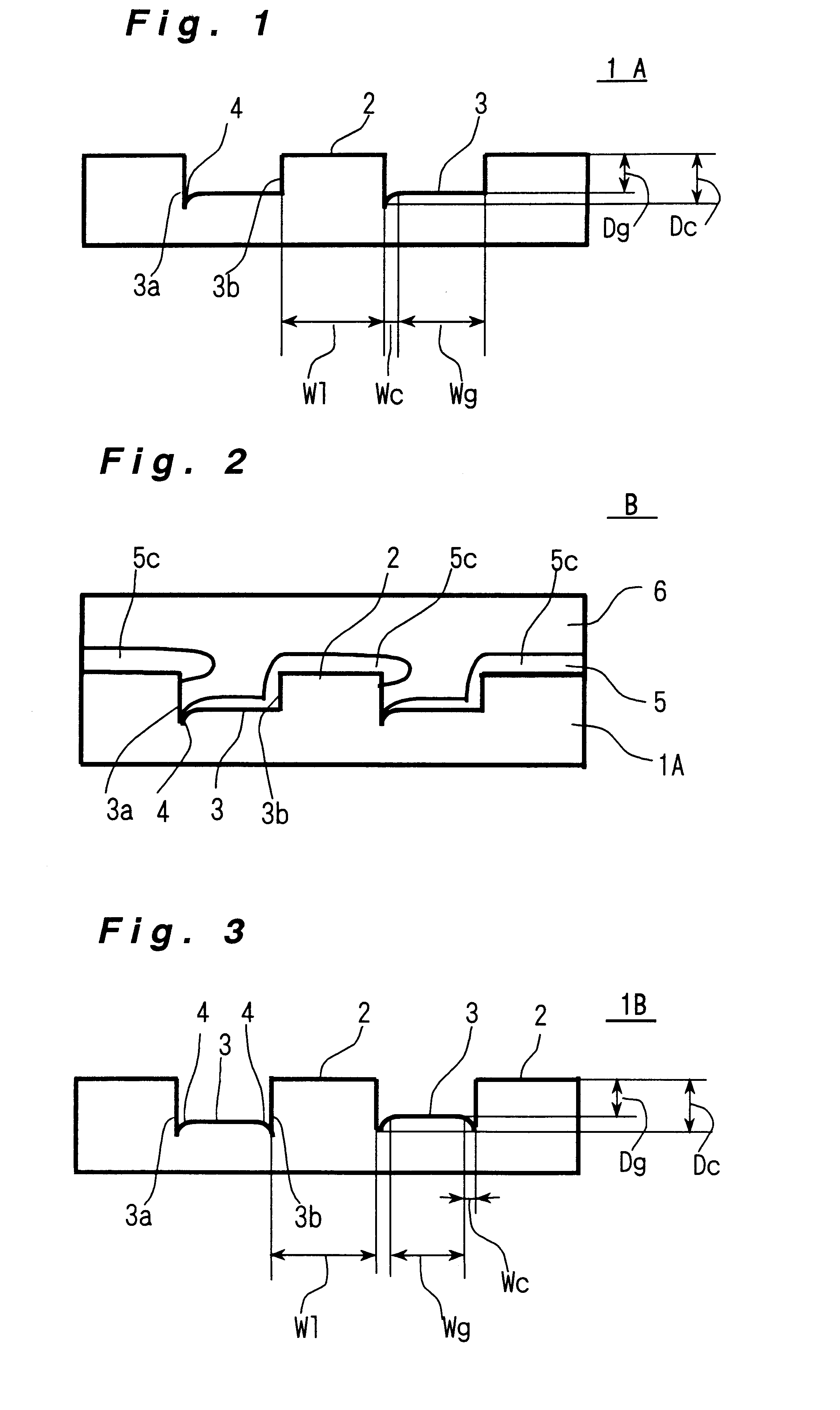
An information recording medium and a supporter used for the information recording medium capable of recording a land / groove recording by using a high density recording technique such as a super-resolution, resulting in a high density recording. An information recording medium B has a supporter 1A, on which a recording layer 5 is formed. On the supporter 1A, lands 2 and groove 3 are alternately formed as a minute track pattern. A crevice 4 having a depth Dc larger than a depth Dg of the respective grooves 3 is formed in the respective grooves 3 at one end of the respective grooves 3 in a width direction of the respective grooves.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20190027174A1Improve surface smoothnessAvoid it happening againRecord information storageTape carriersIn planeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape in which an Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, Int(110) / Int(114) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, the back coating layer includes one or more kinds of component selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the back coating layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 35 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20190027175A1Improve surface smoothnessAvoid it happening againRecord information storageTape carriersIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder, non-magnetic powder, and a binding agent and a back coating layer including non-magnetic powder and a binding agent, in which the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a center line average surface roughness measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and a contact angle with respect to 1-bromonaphthalene measured regarding a surface of the back coating layer is 15.0° to 30.0°.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Double-sided optical disc
A double-sided optical disc, is formed with data tracks on each layer. The tracks on one side follow one spiral while the tracks on the other side follow a second spiral, the two spirals being oriented in opposite directions as viewed from the respective sides, and therefore being mirror images of each other. This allows data to be read by a player seamlessly from both sides of the disc without changing the direction of rotation of the disc.
Owner:WARNER HOME VIDEO
Three-dimensional device
A memory IC includes a first substrate (substrate on the transfer destination side), and memory cell arrays deposited on the first substrate. The memory cell arrays are deposited from the bottom up by a method for transferring a thin film configuration. The transferring method includes the steps of forming a thin film device layer (memory cell array) on a second substrate with a separable layer therebetween, and irradiating the separable layer with light to cause a separation in the separable layer and / or at an interface so that the thin film device layer on the second substrate is transferred to the first substrate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20190027180A1Improve surface smoothnessAvoid it happening againMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder, non-magnetic powder, and a binding agent and a back coating layer including non-magnetic powder and a binding agent, in which the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, an Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the hack coating layer is equal to or smaller than 0.060.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20190027172A1Improve surface smoothnessImproved head positioning accuracyInorganic material magnetismRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
Provided are a magnetic tape including: a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer has a timing-based servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, and a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and a magnetic tape device including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of recording or reproducing data on or from high density multi-layer recording medium using variable light intensity
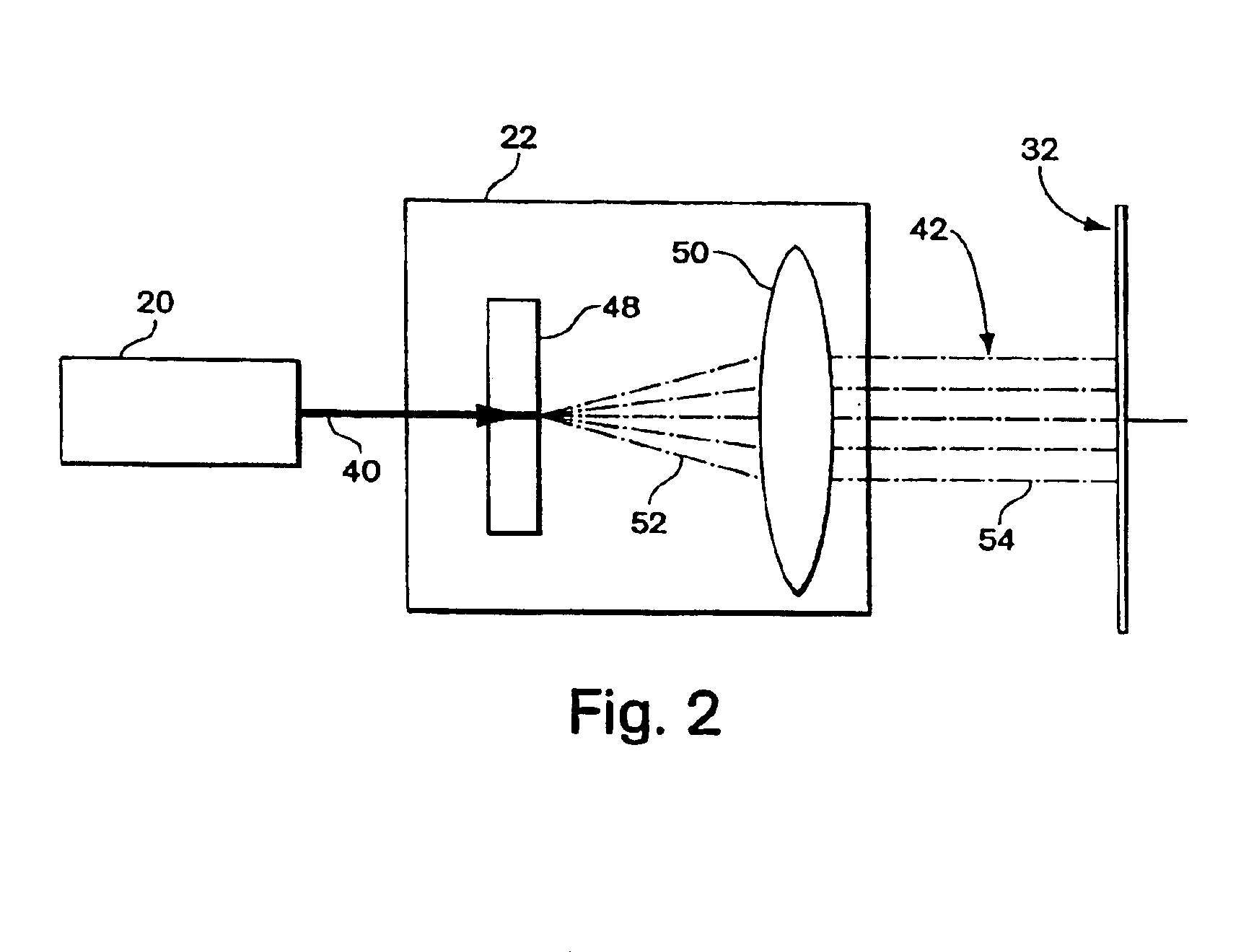
InactiveUS7009927B2Diminishing of dataDiminishing of surfaceOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageHigh densityData recording
A high-density optical recording medium and method of recording data on the optical recording medium. The optical recording medium includes a plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces having reflectances for light passing through a pit area, a land / groove area, and a land / groove area on which data are recorded, of a data recording / reproducing surface included between a light source for emitting light and a recording / reproducing surface selected from the plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces, the reflectances satisfy the expressions r1≧r2≧r3 and {(r1−r3) / r3}≦0.2, where r1, r2 and r3 are the reflectances of the pit area, the land / groove area and the land groove area on which data are recorded, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
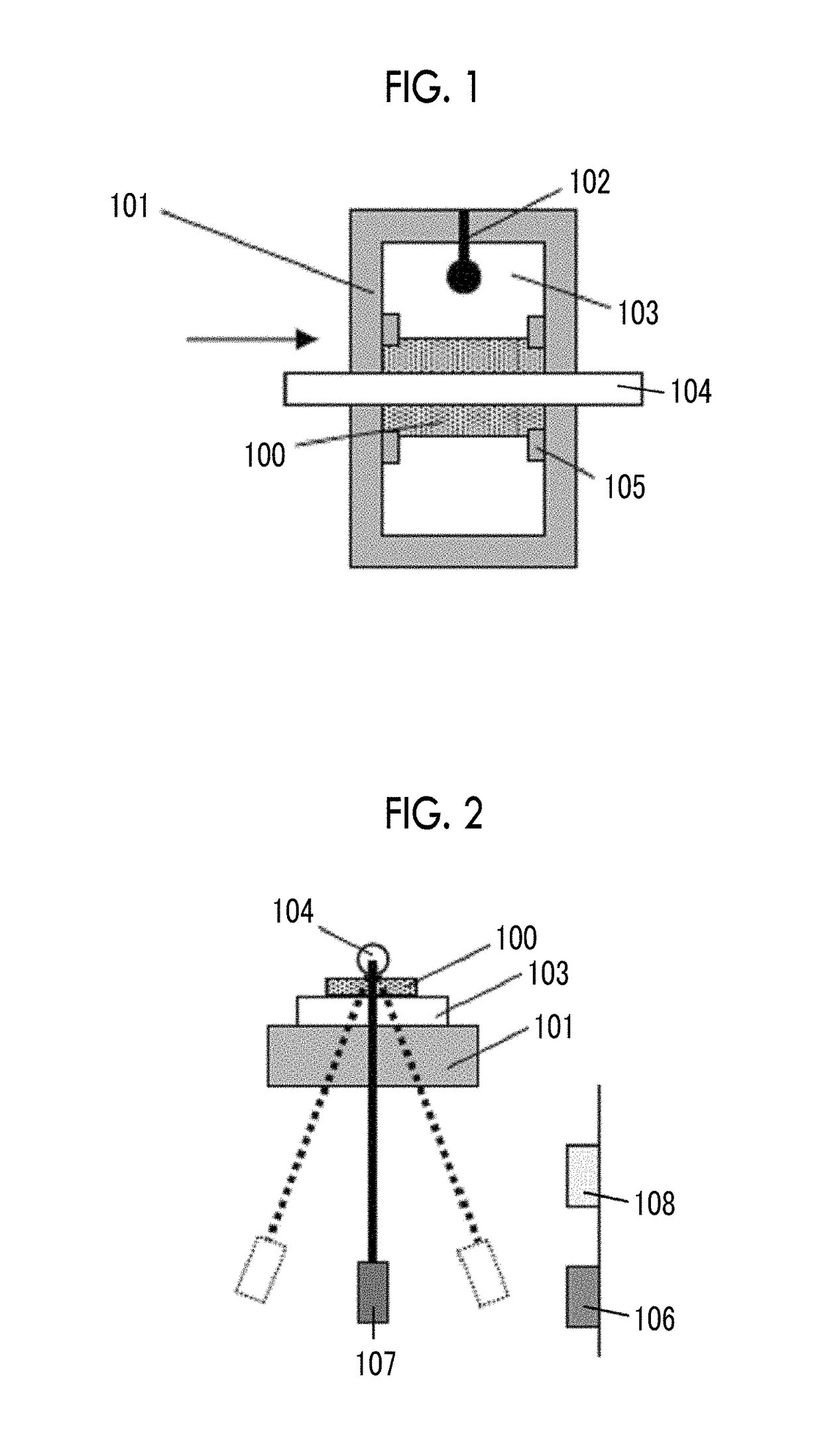
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and perpendicular magnetic recording medium manufacturing method
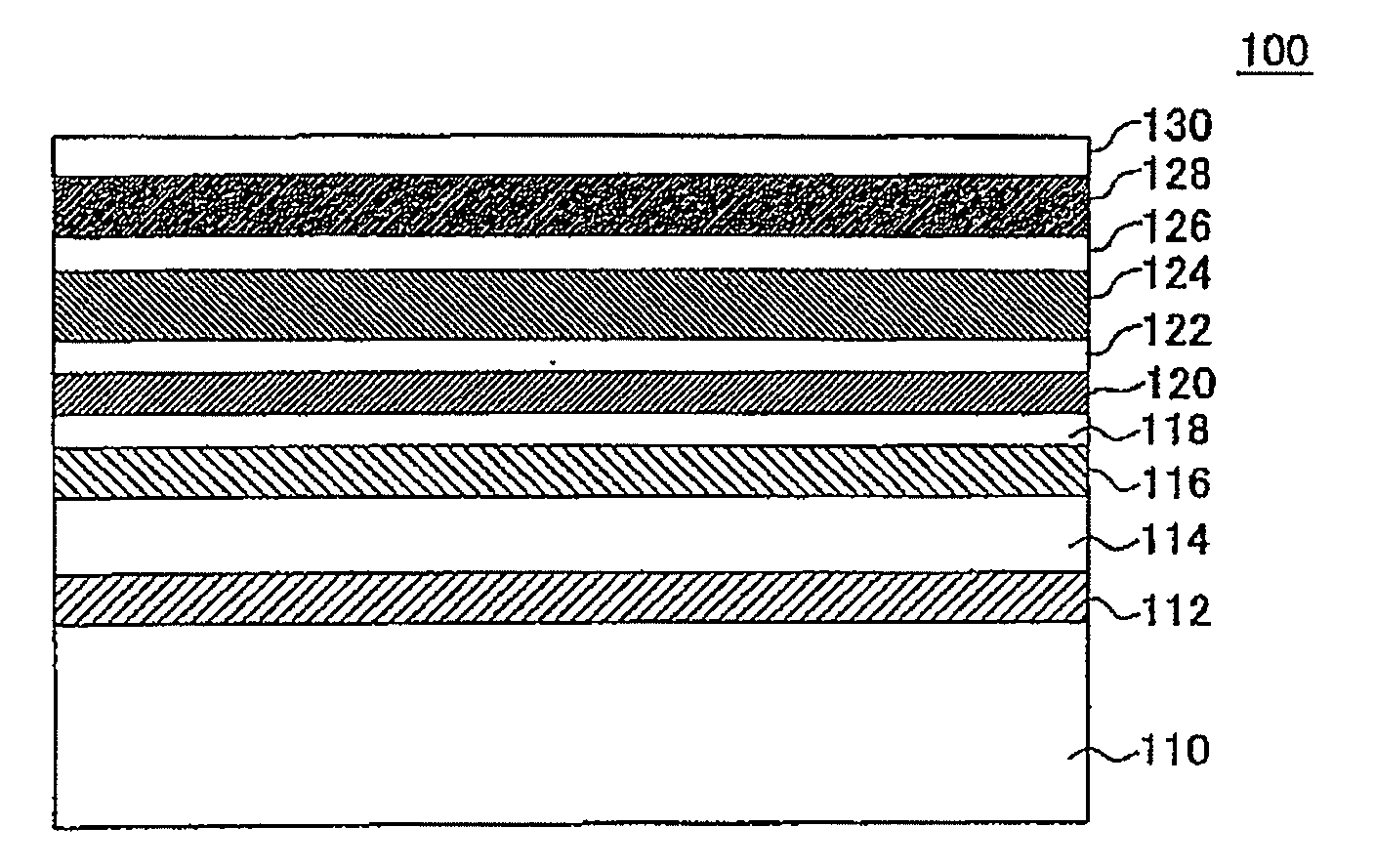
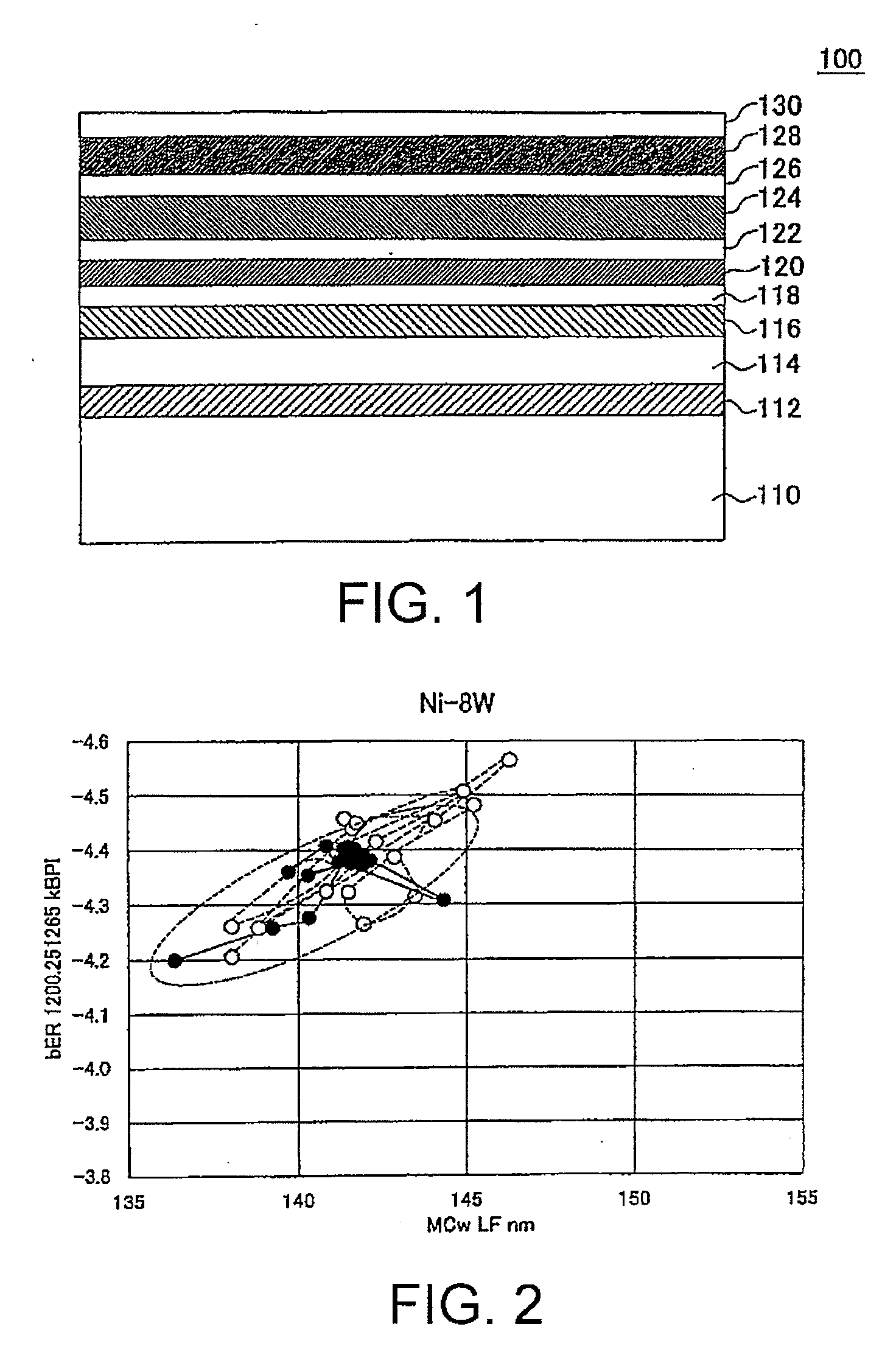
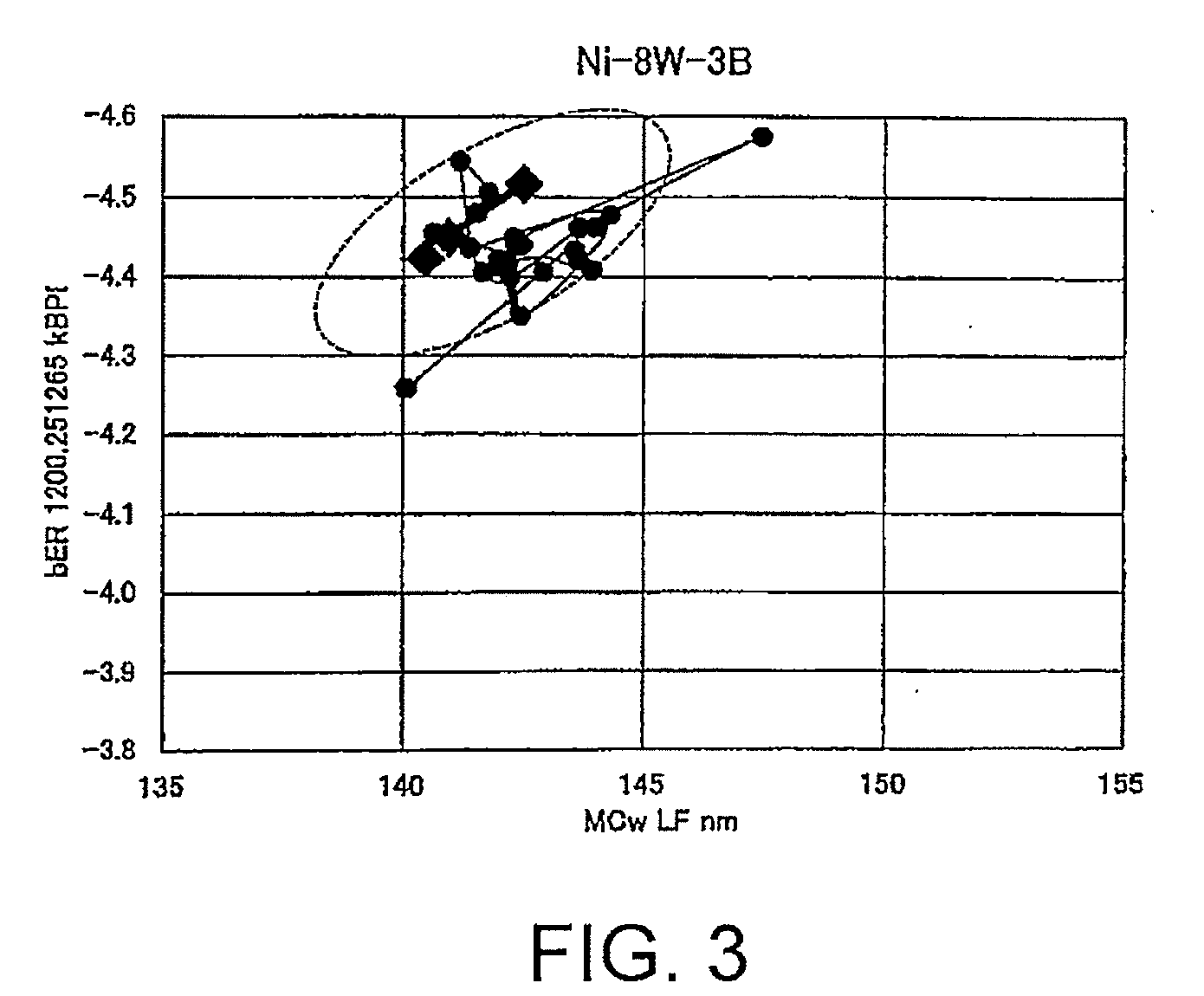
ActiveUS20100190035A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce write fringingRecord information storageCoatingsMagnetizationRecording layer
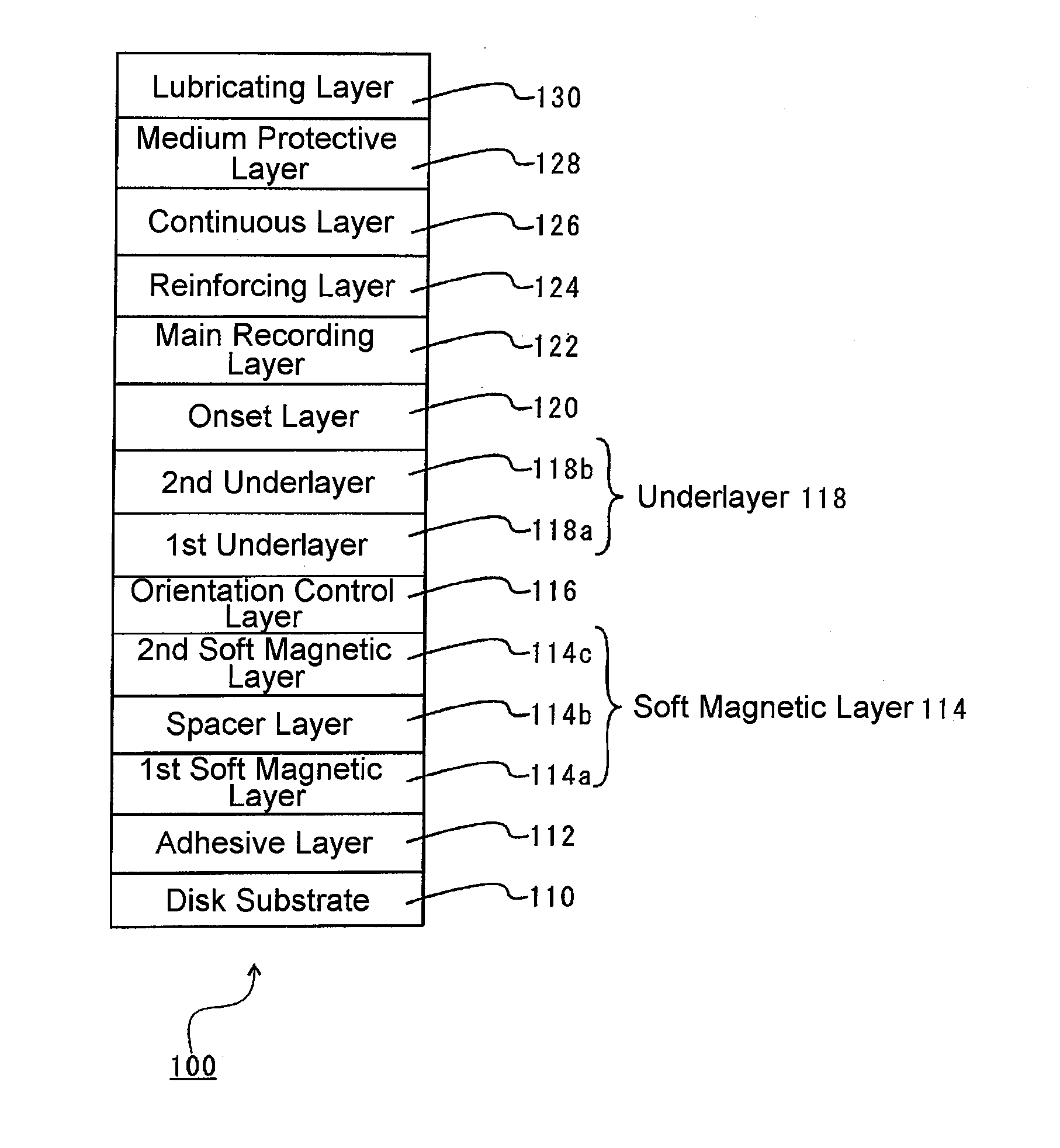
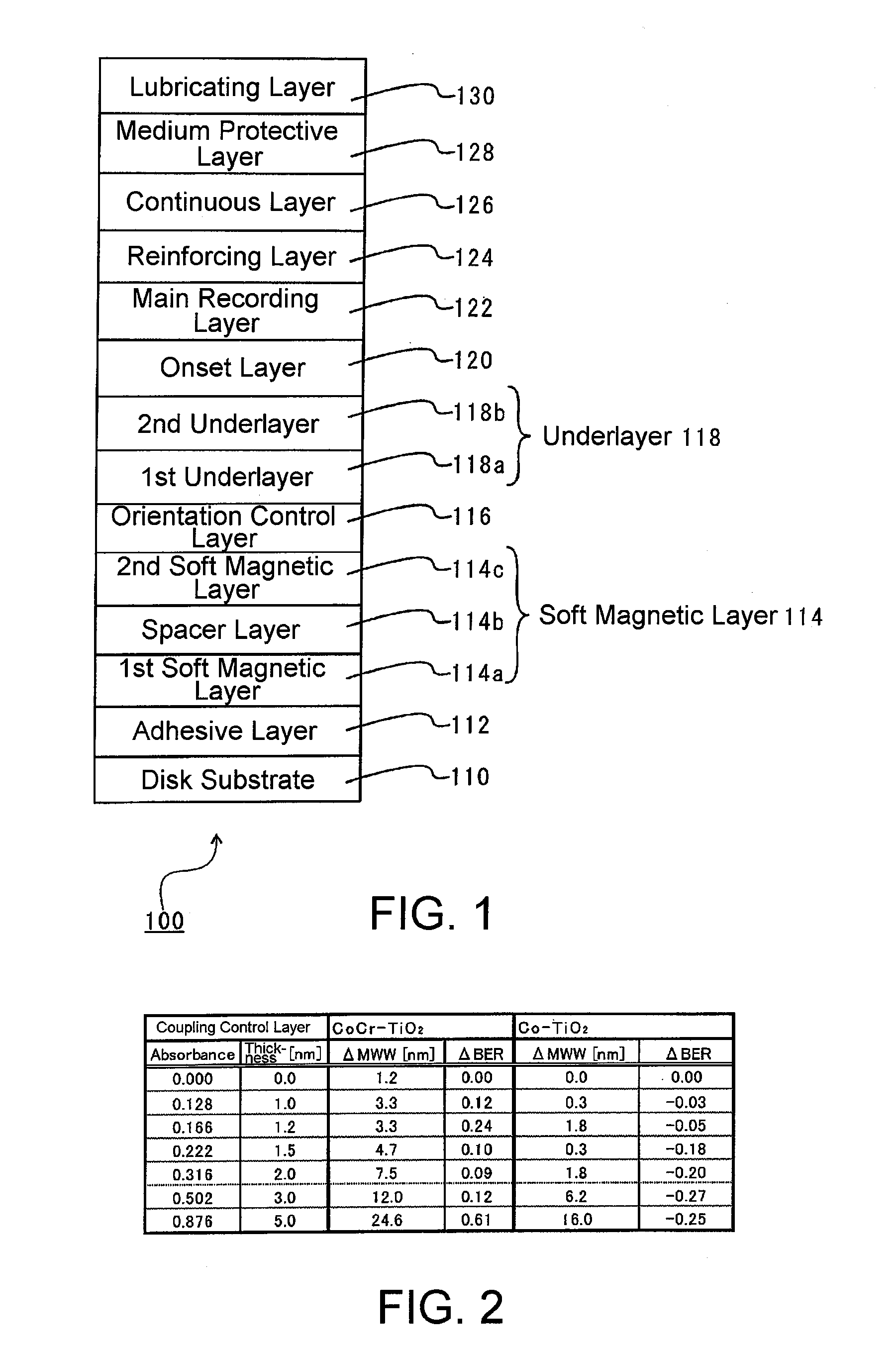
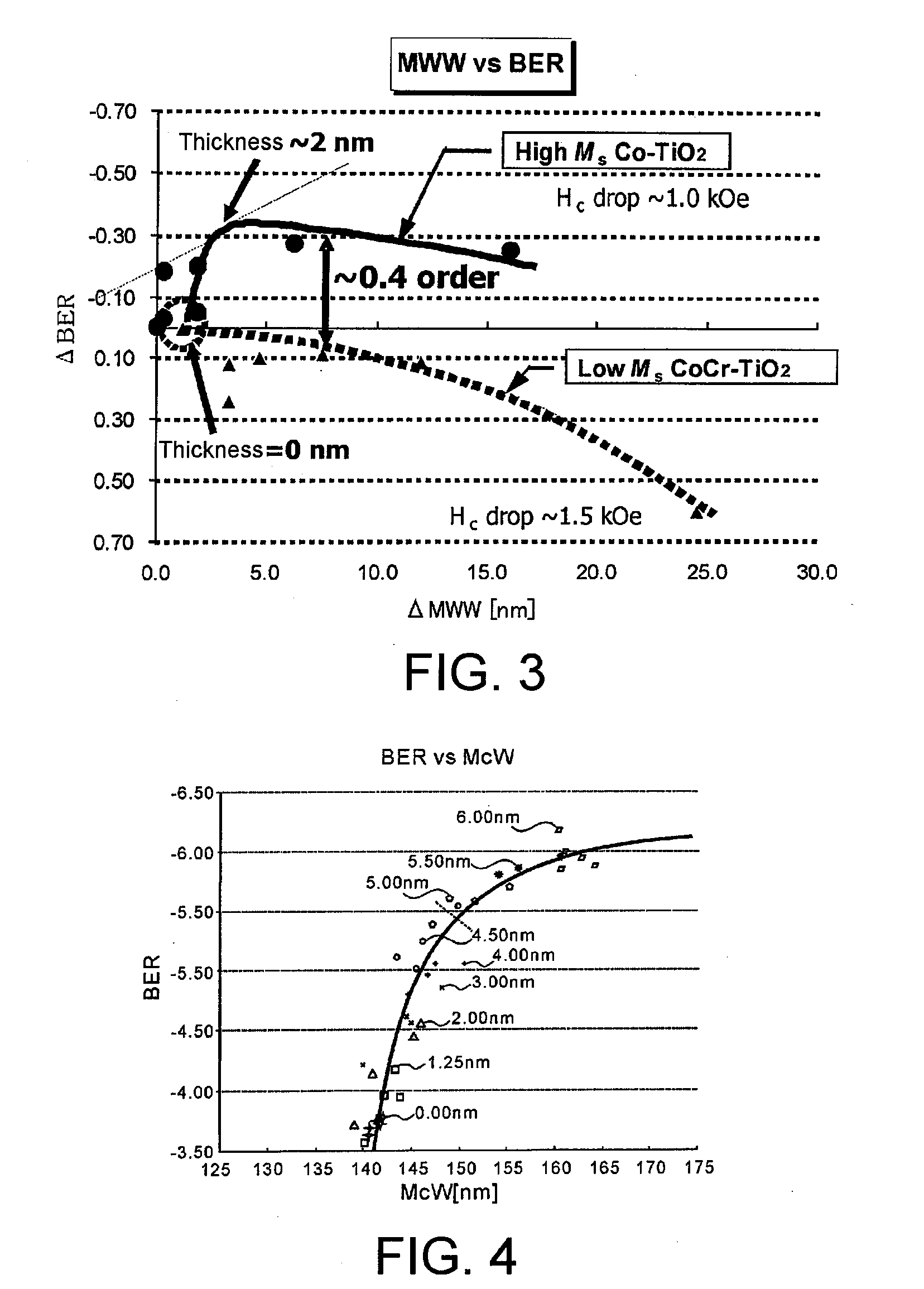
[Problems] To provide a reinforcing layer between a main recording layer and a continuous layer so as to improve the S / N ratio of a magnetic recording medium and reduce the write fringing effect by the new configuration.[Means for Solving Problems] A perpendicular magnetic recording medium (100) includes a substrate (110), and a main recording layer (122), a reinforcing layer (124), and a continuous layer (126) which are overlaid in this order on the substrate. The reinforcing layer (124) has a granular structure. The saturation magnetization Ms of the reinforcing layer (124) is higher than the saturation magnetization of the main recording layer (122).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100279151A1Improve recording densityImprove coercive forceRecord information storageCoatingsOptoelectronicsRecording layer
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, a soft magnetic layer, a pre-underlayer, an underlayer, and a main recording layer serving as a magnetic recording layer. The pre-underlayer contains seed crystal grains that serve as a base for crystal grains of the underlayer, and an addition substance that is added between the seed crystal grains and composed of an element having an atomic radius smaller than that of an element forming the seed crystal grains.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com