Patents
Literature
233 results about "Magnetic force microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
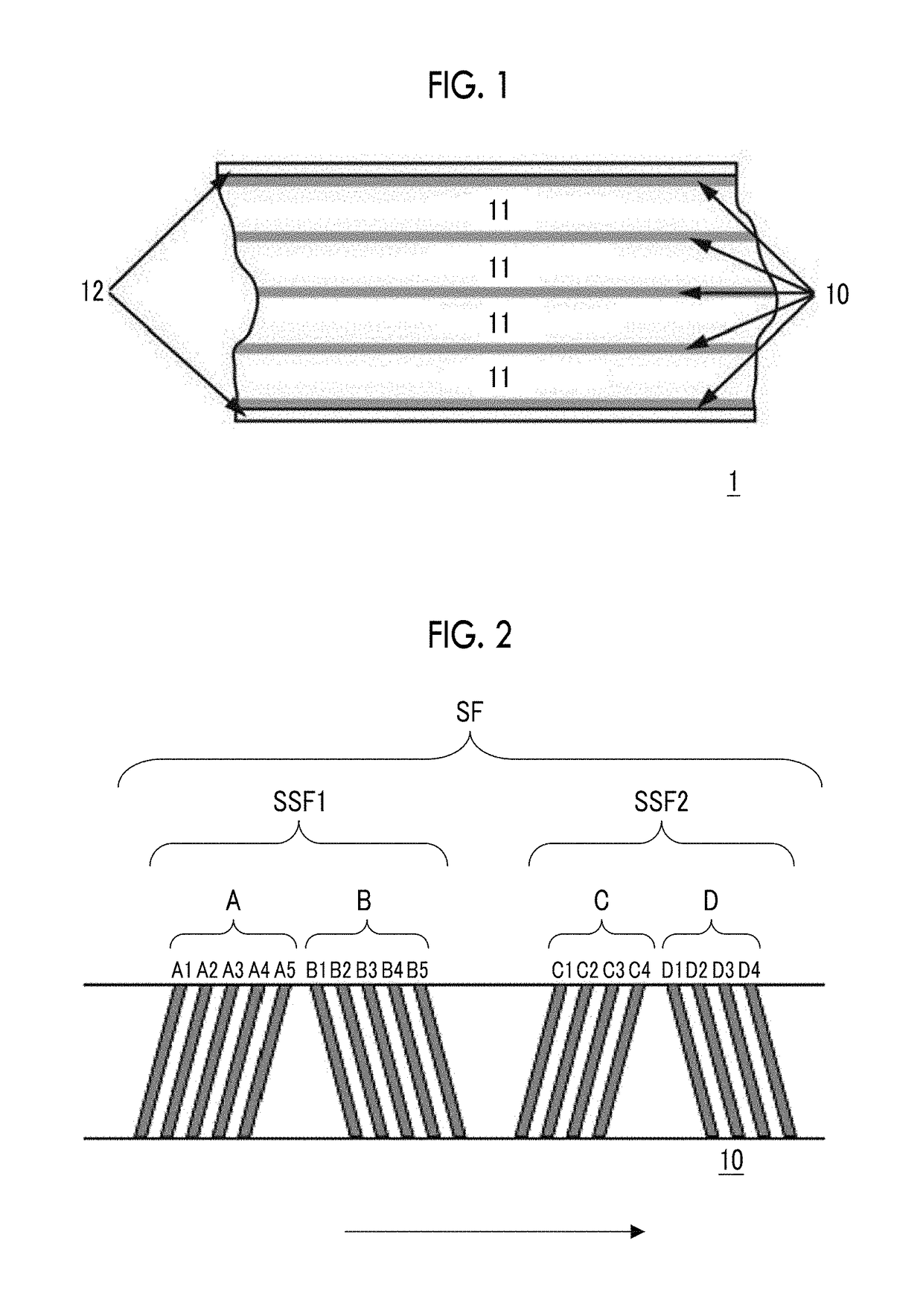
Magnetic force microscopy (MFM) is a variety of atomic force microscopy, in which a sharp magnetized tip scans a magnetic sample; the tip-sample magnetic interactions are detected and used to reconstruct the magnetic structure of the sample surface. Many kinds of magnetic interactions are measured by MFM, including magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. MFM scanning often uses non-contact AFM (NC-AFM) mode.
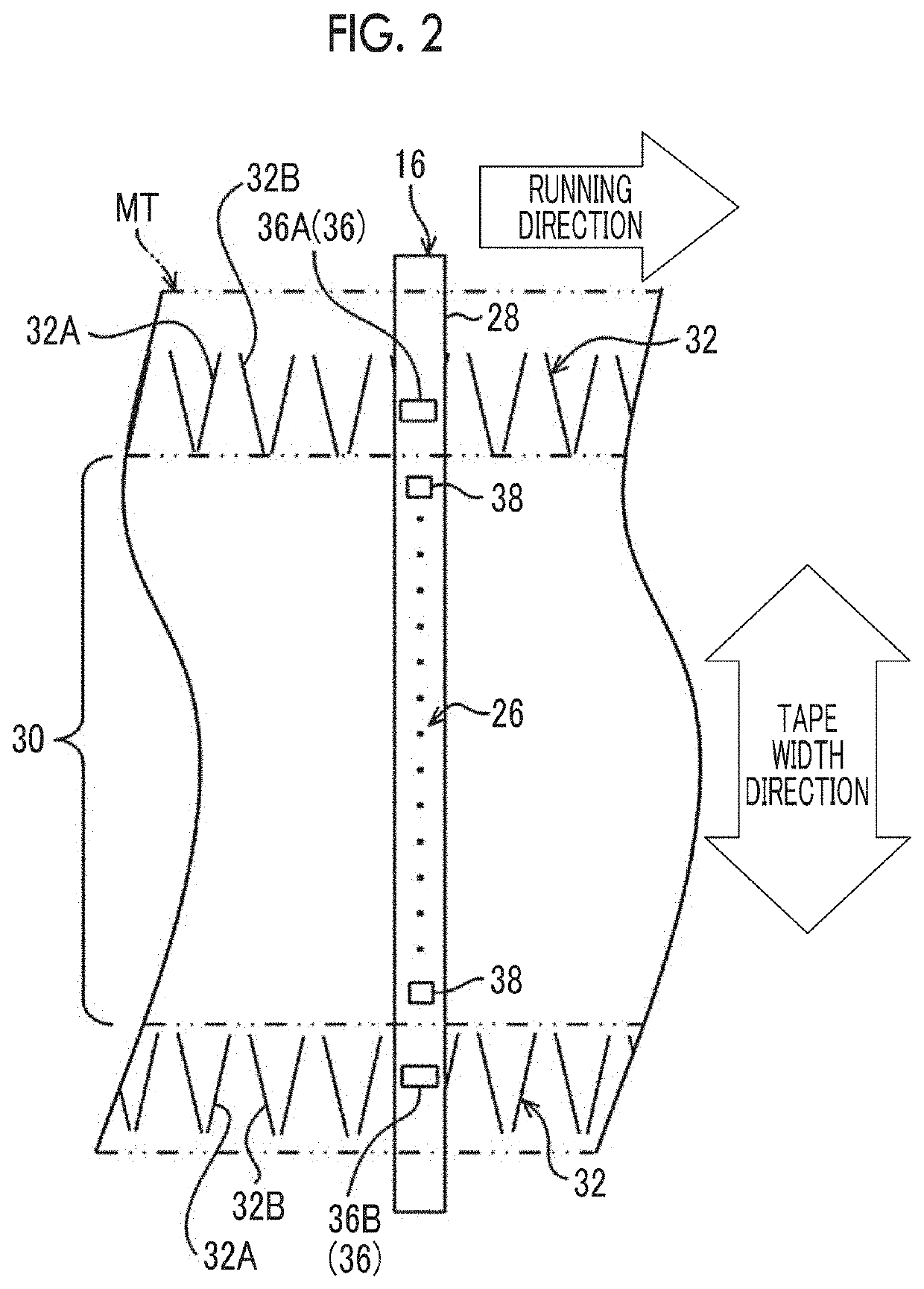
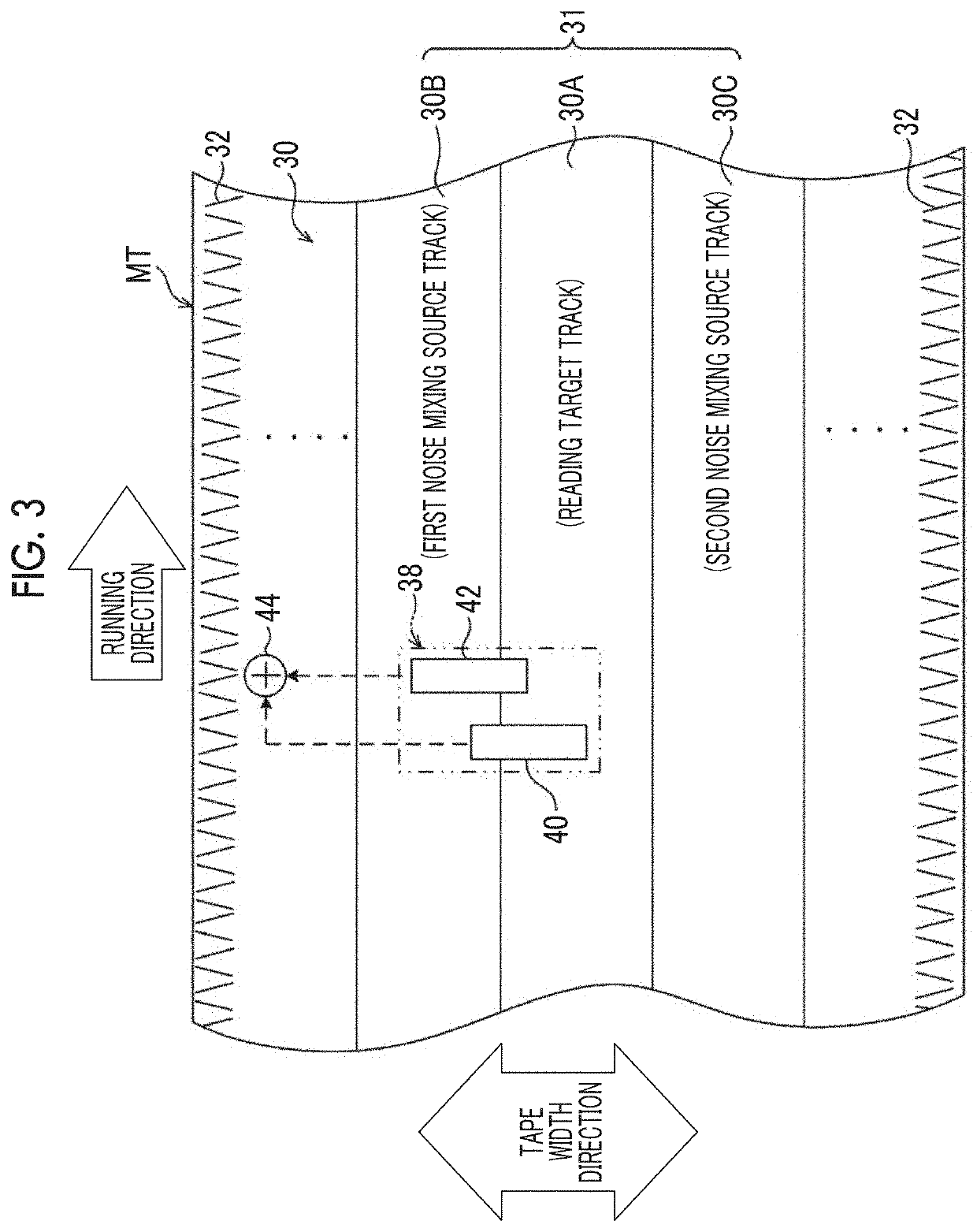
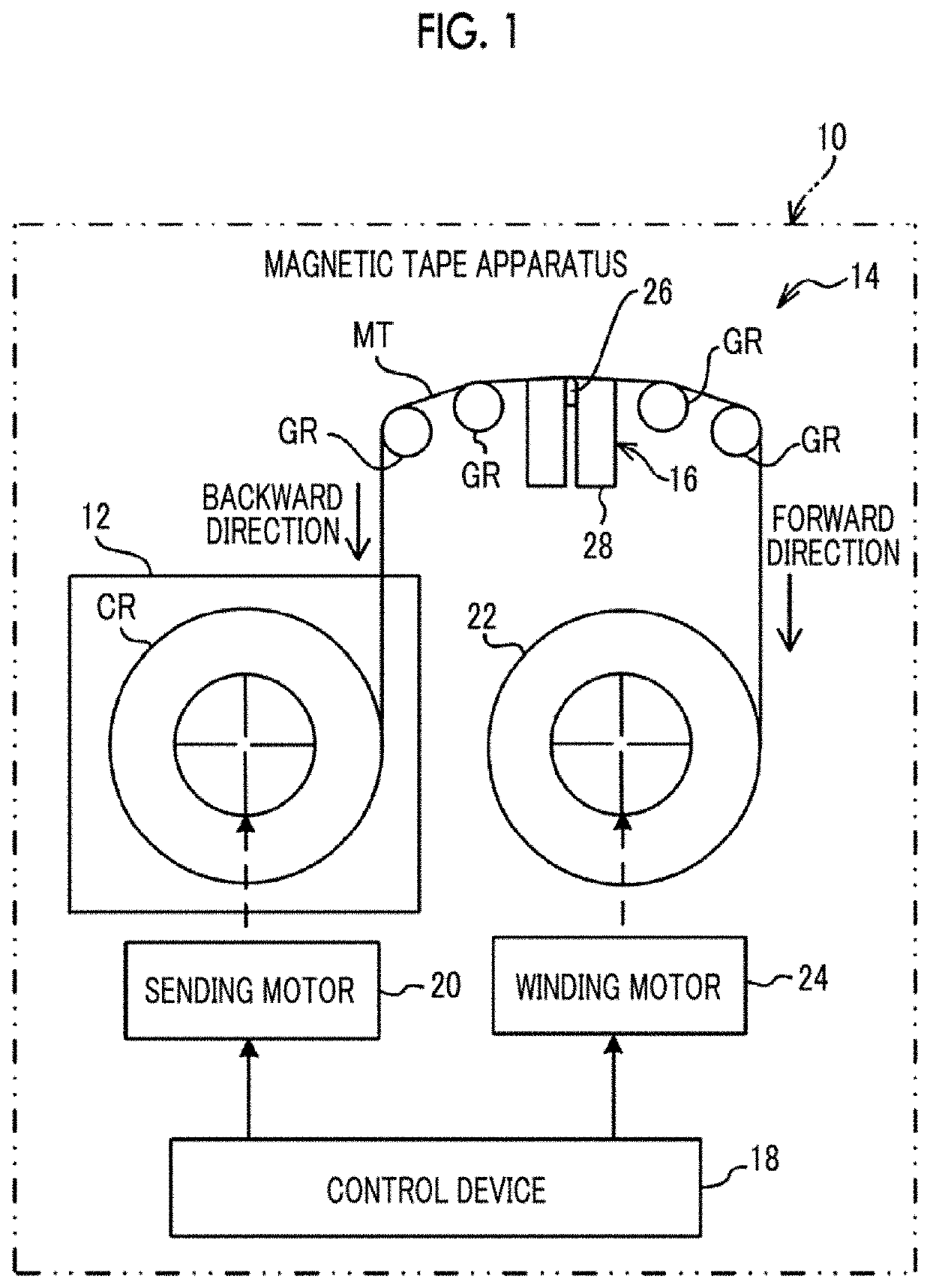
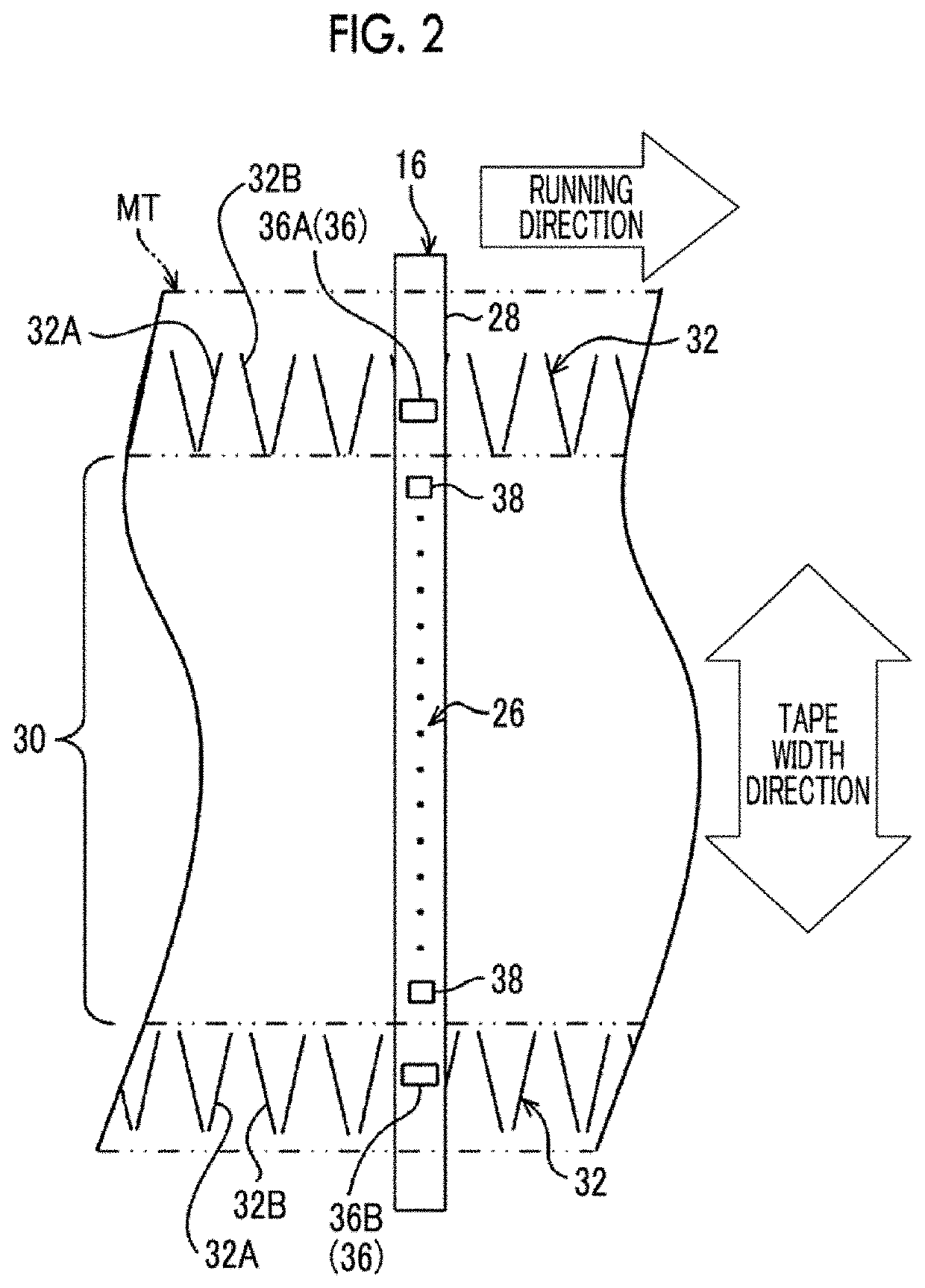
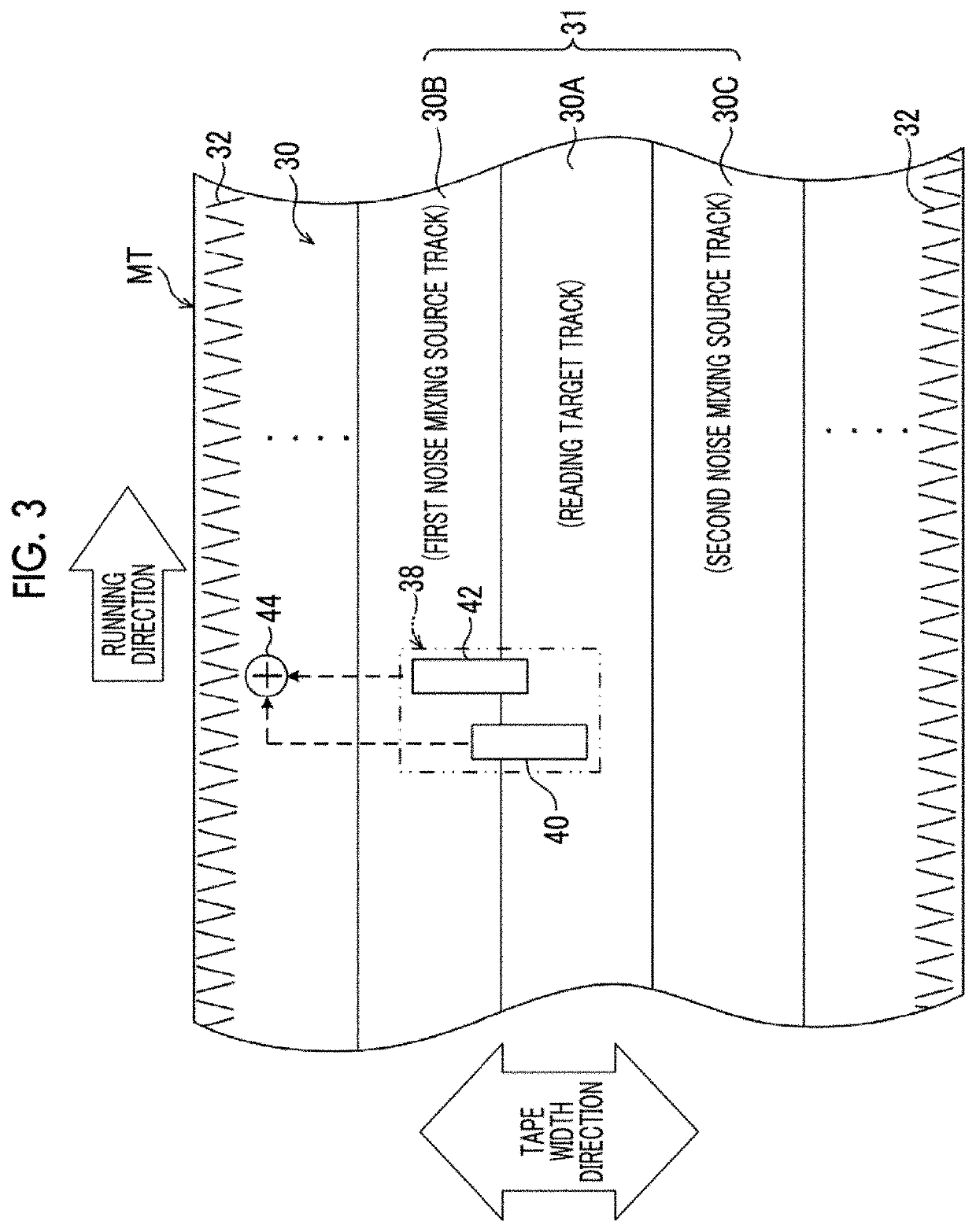
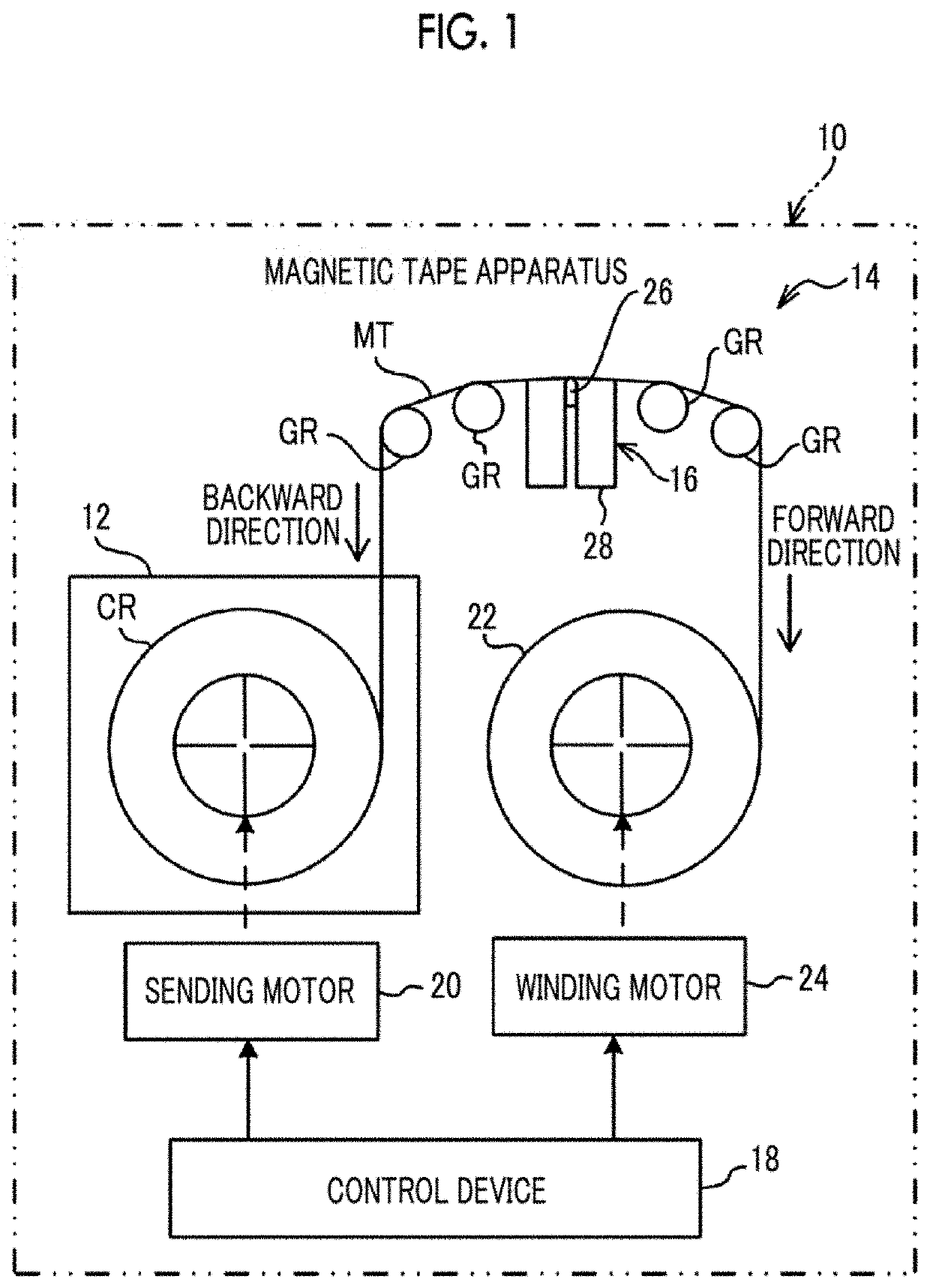
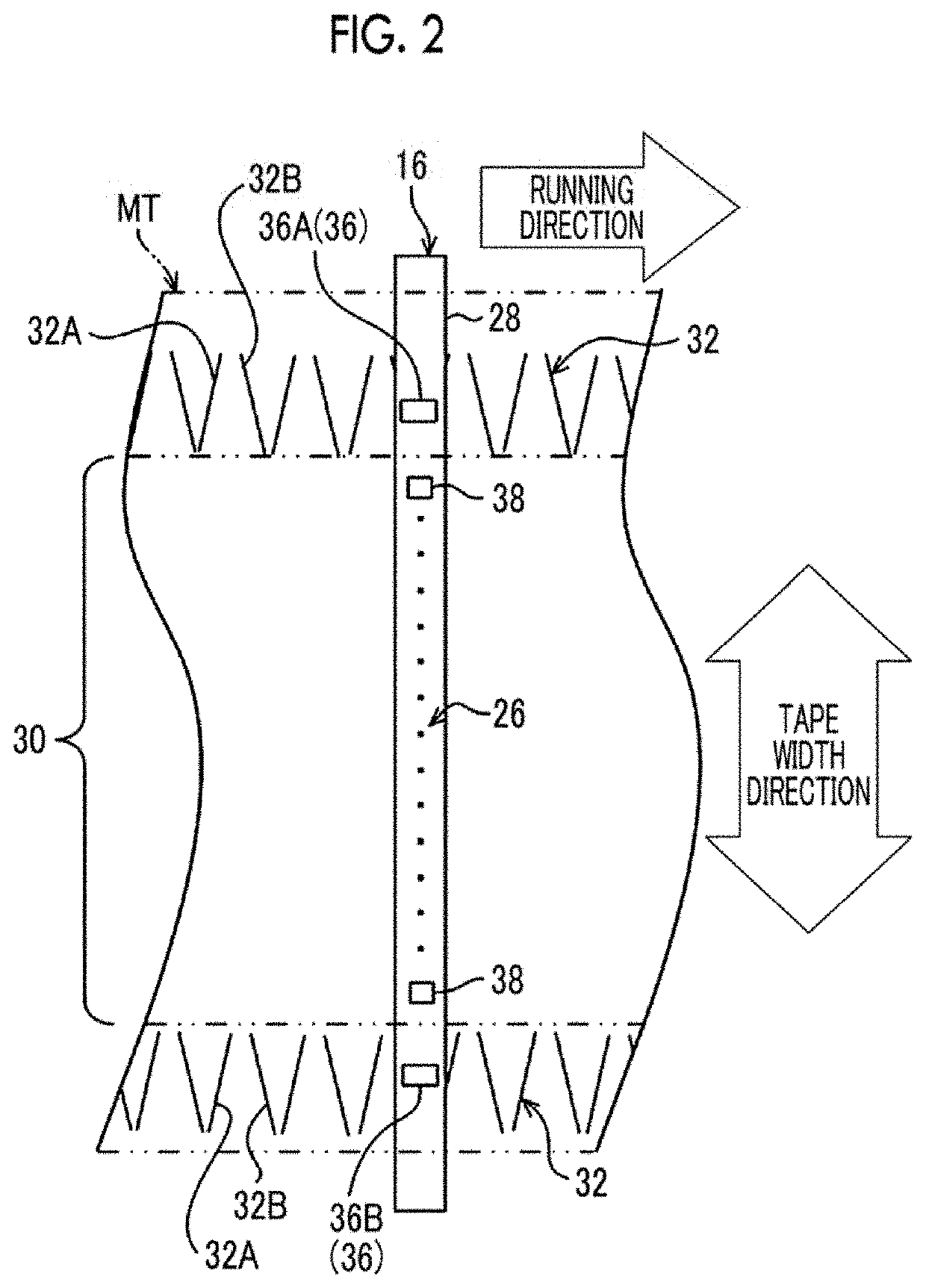
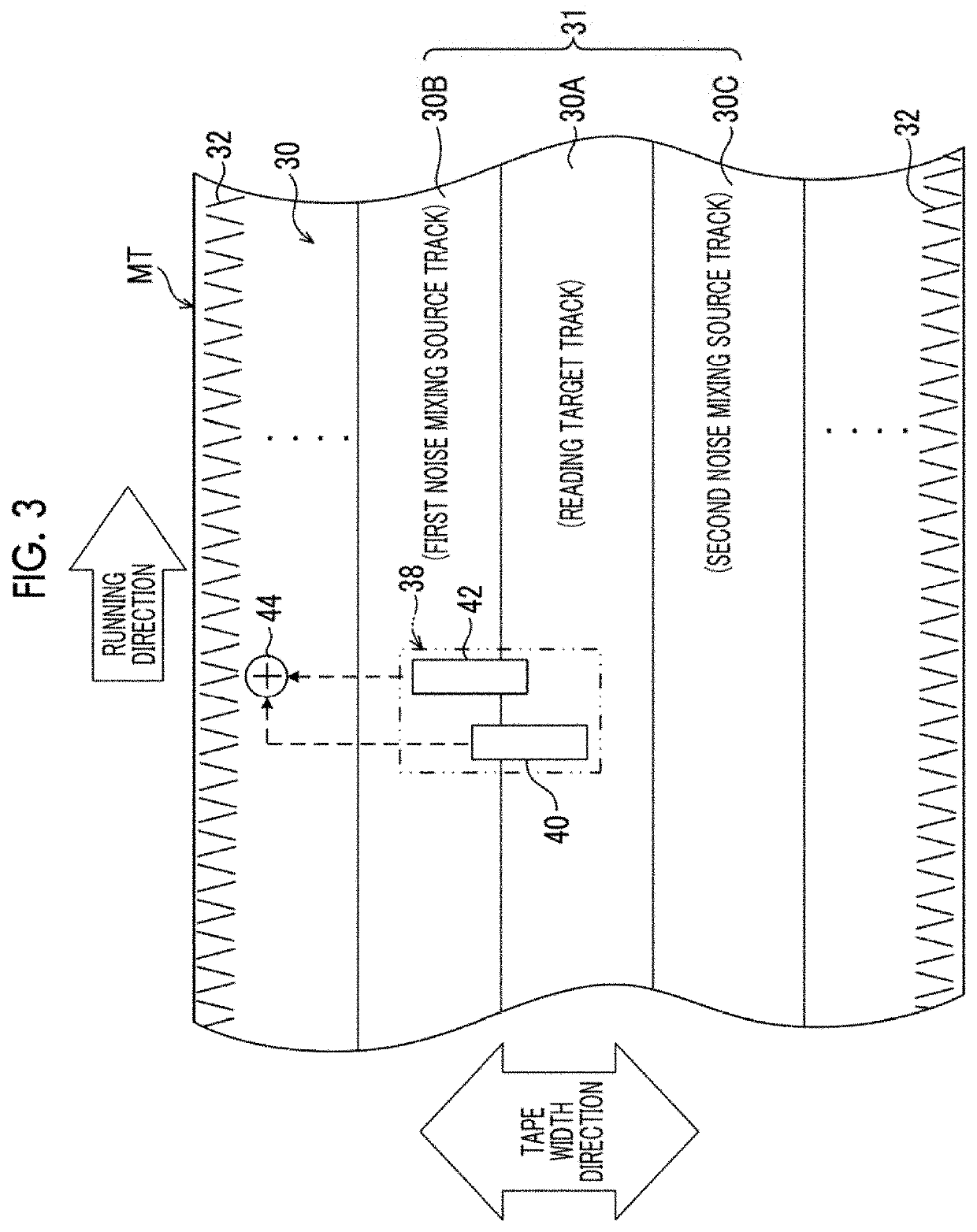
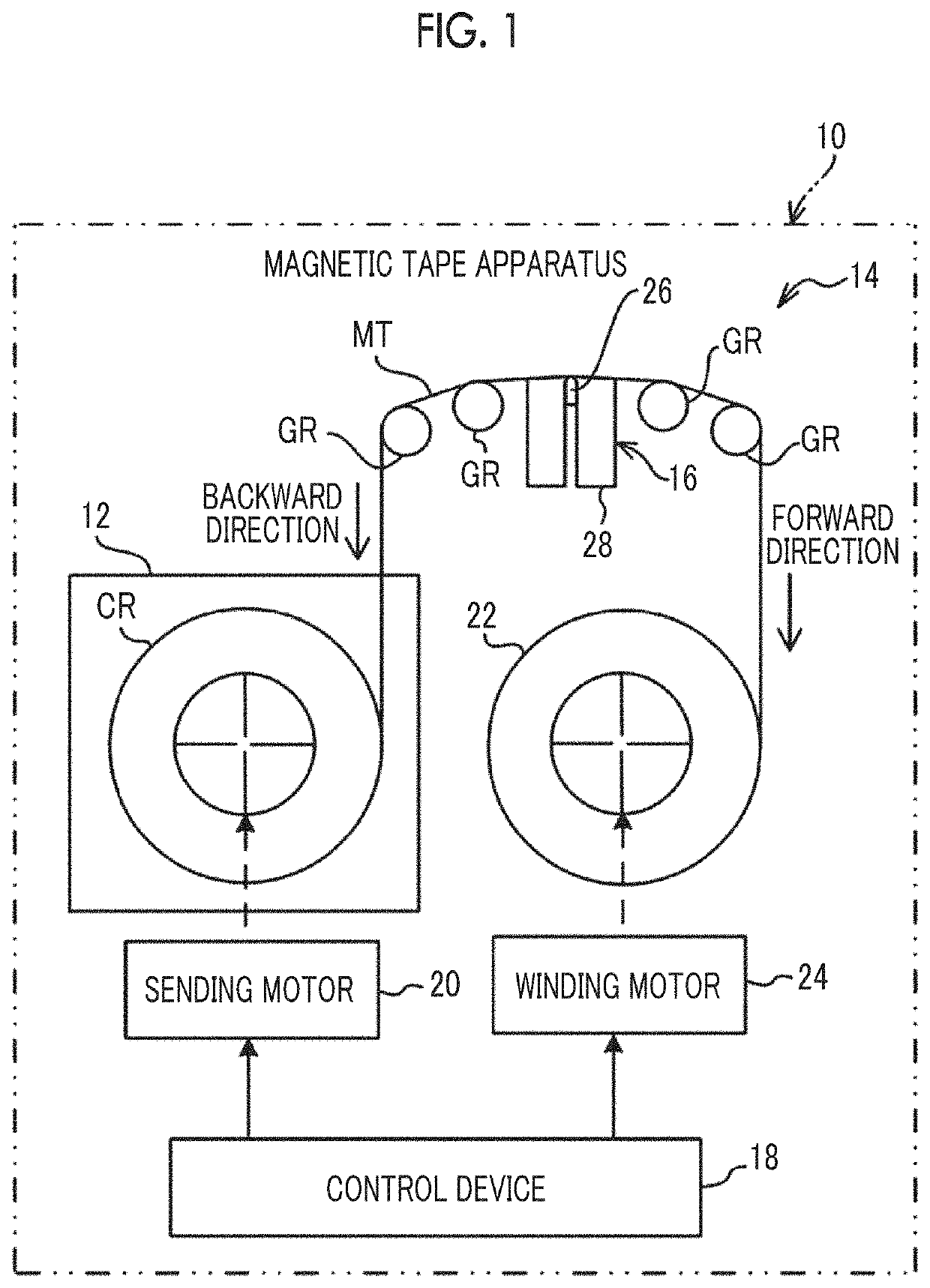
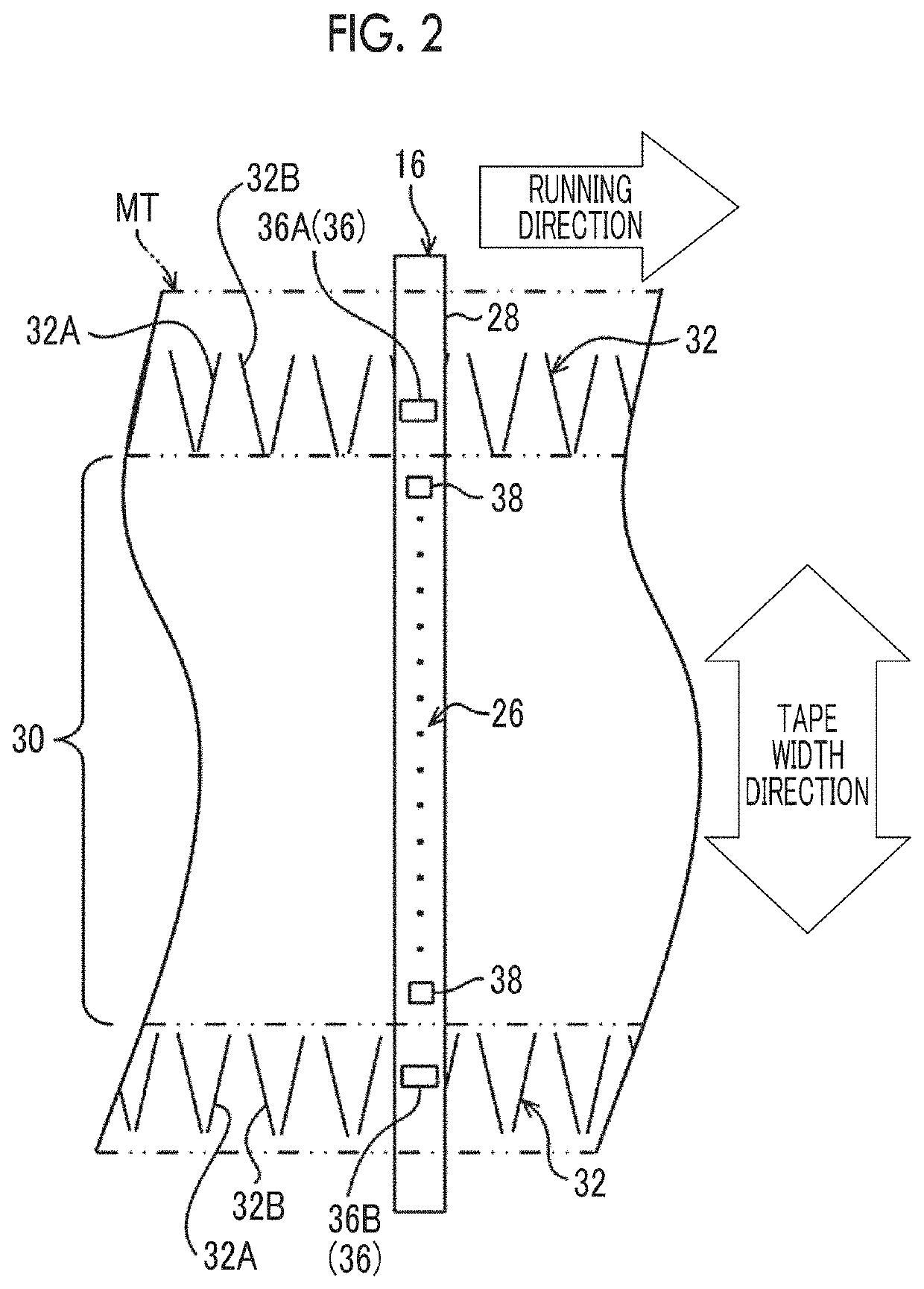
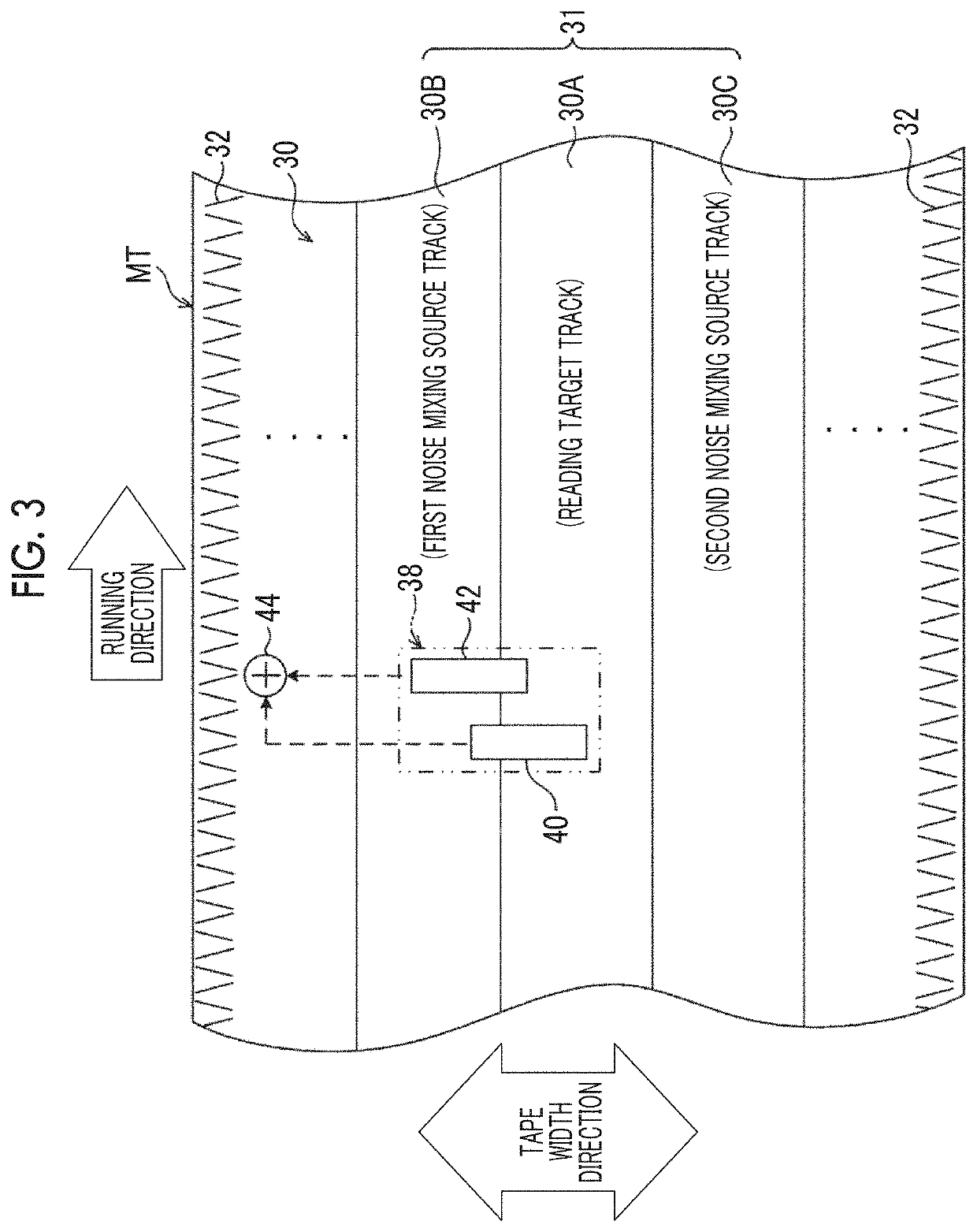
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
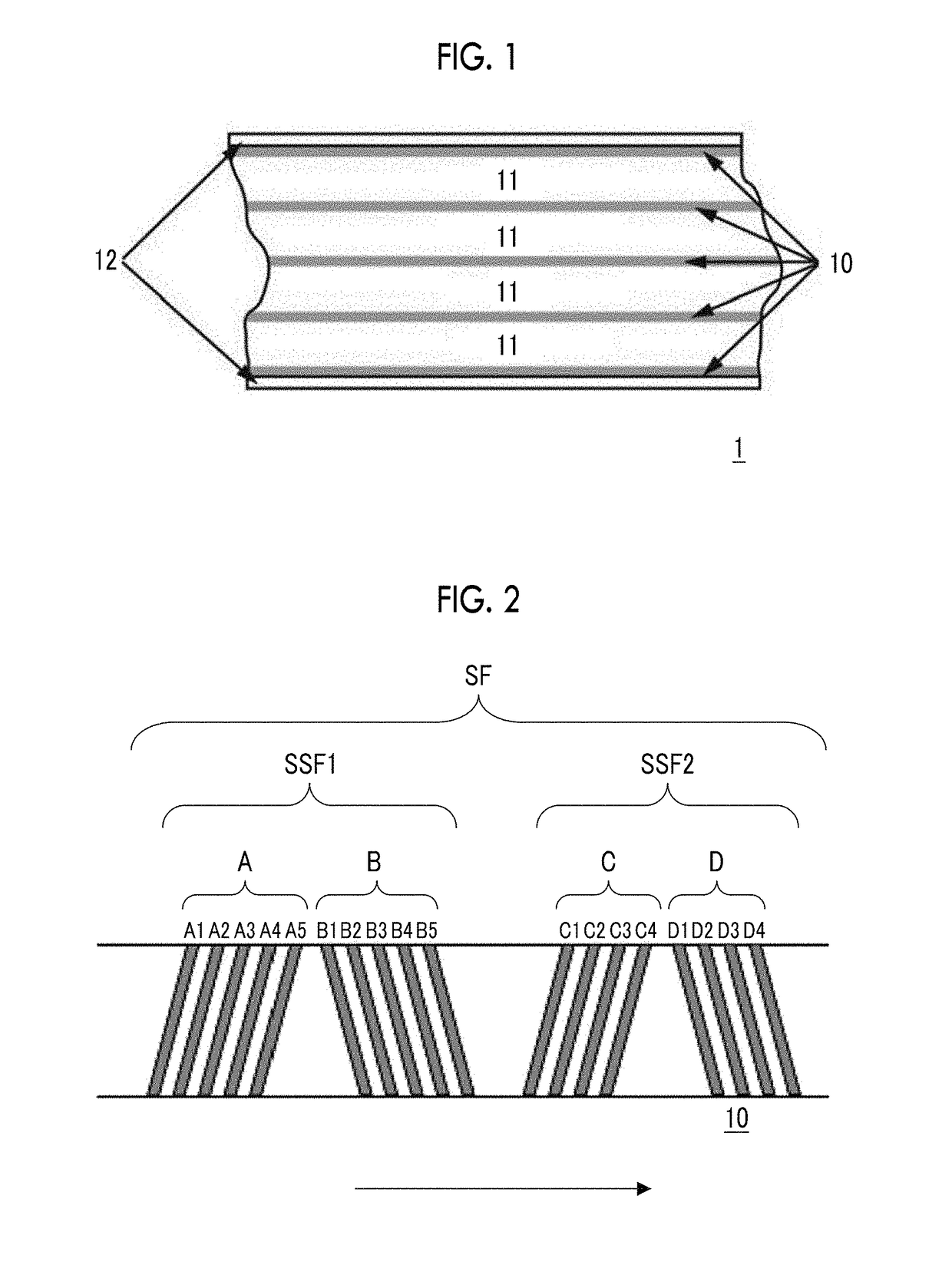
ActiveUS20170186460A1Increase capacityEnhance head positioningAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tension forceMagnetic force microscope
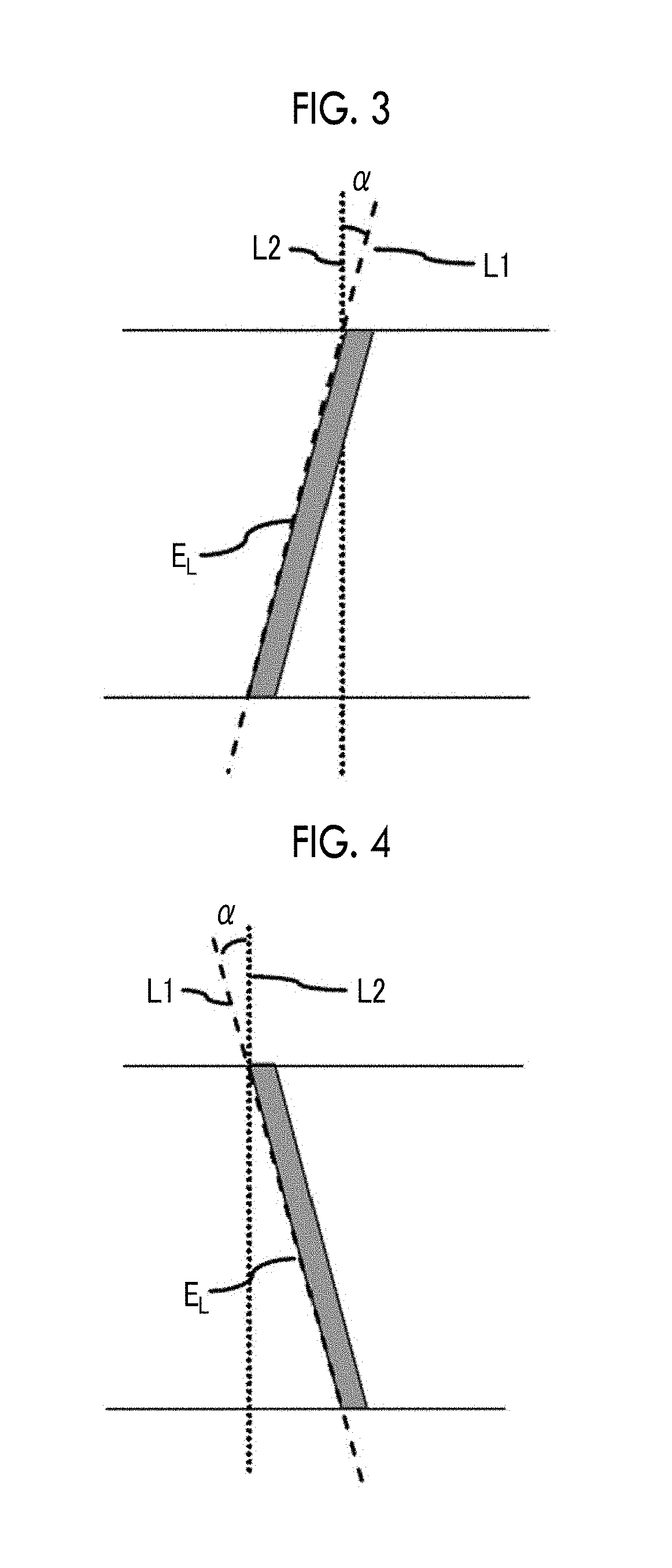
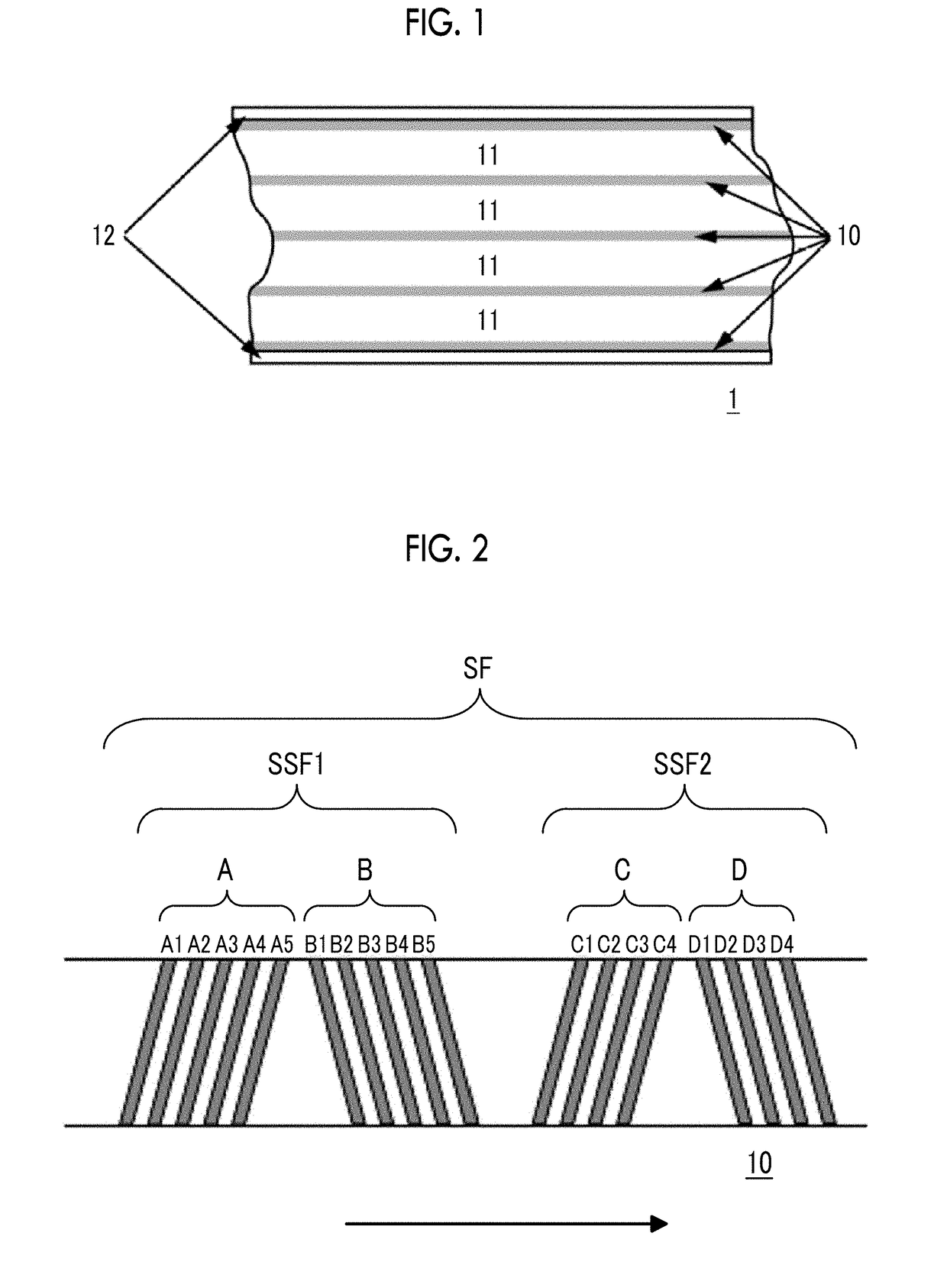
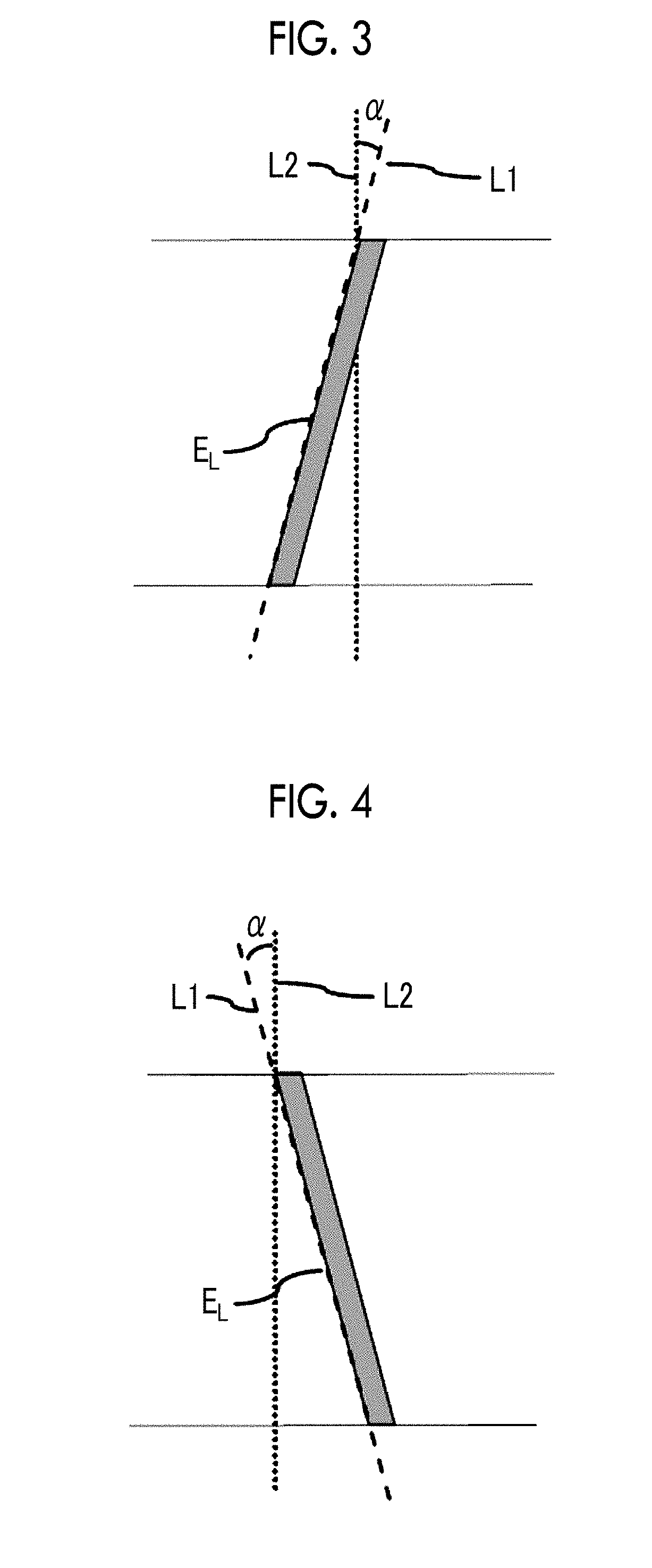
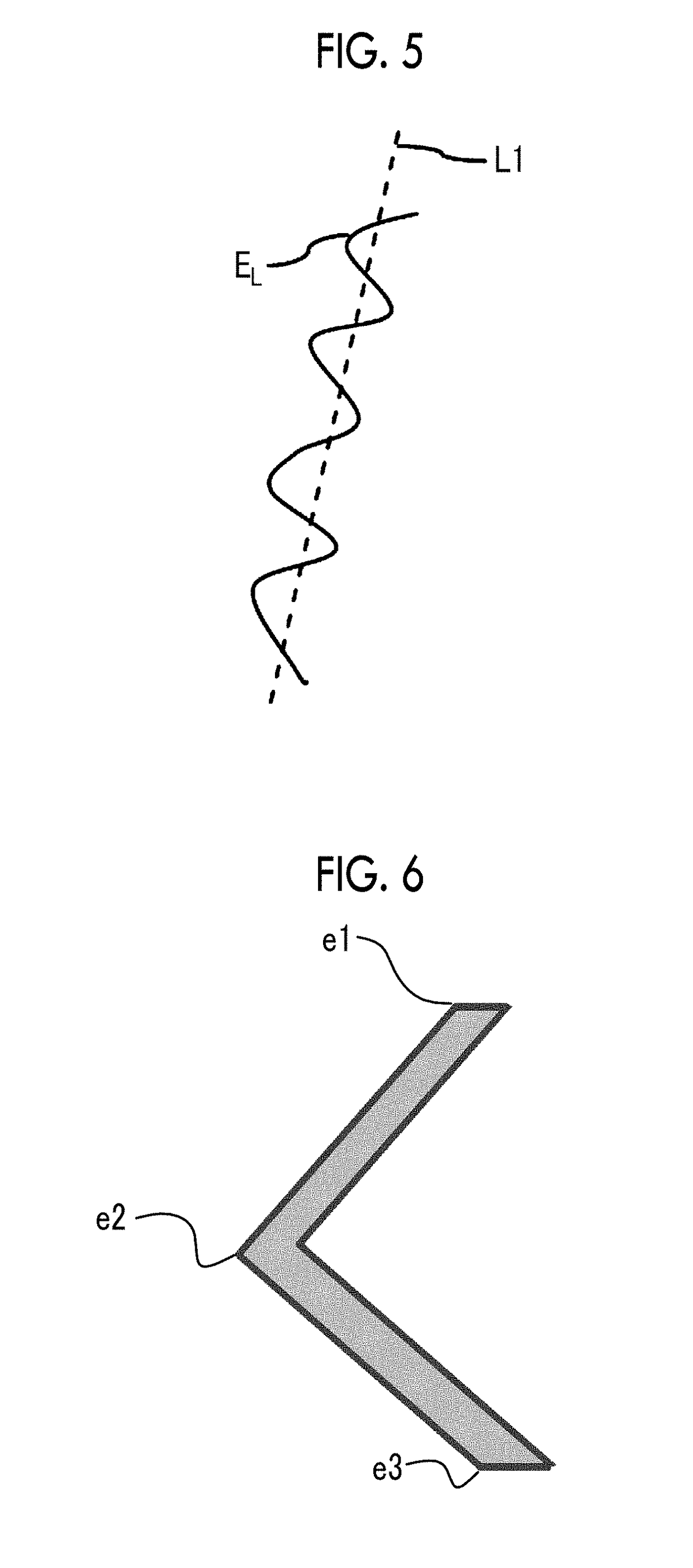
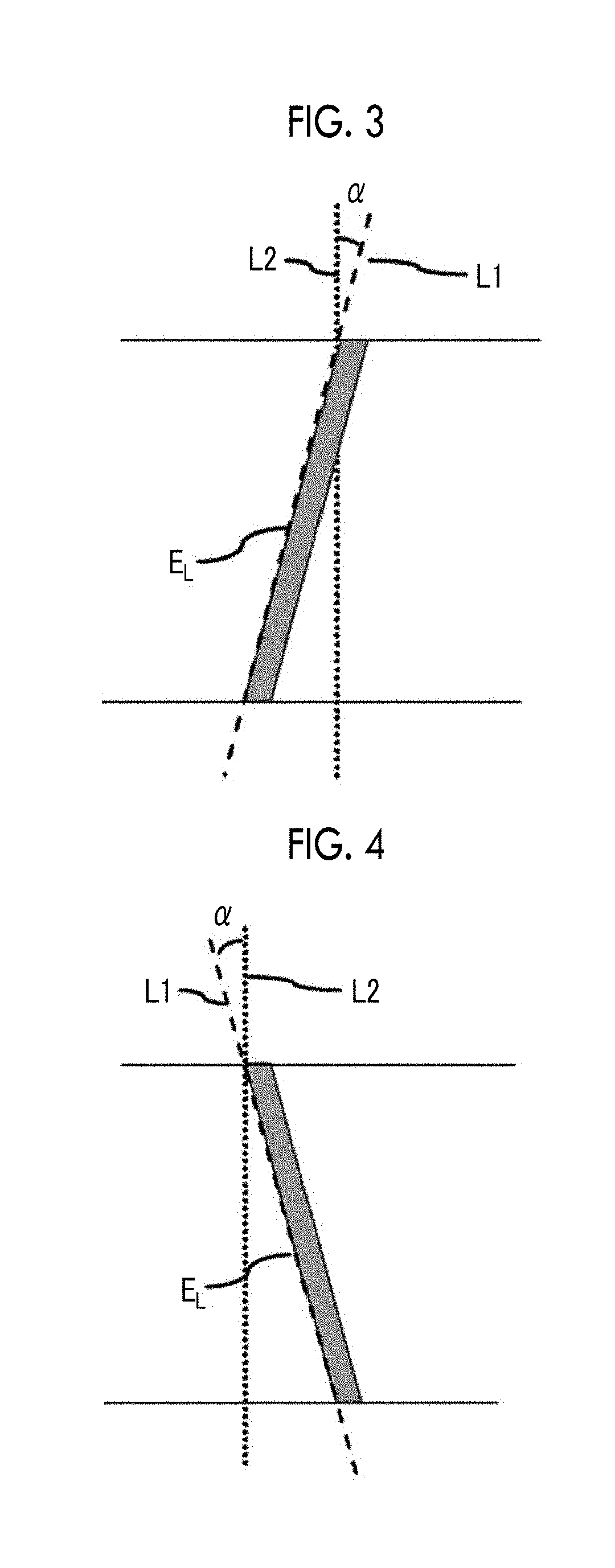
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the coercive force measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 167 kA / m, a timing-based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, and the edge shape specified by observing the timing-based servo pattern with a magnetic force microscope is a shape in which the difference between the value of the 99.9% cumulative distribution function of the width of misalignment from the ideal shape in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and the value L0.1 of the 0.1% cumulative distribution function, L99.9-L0.1, is less than or equal to 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS10074393B2Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tension force
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer having ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by a magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (l99.9−l0.1) between a value l99.9 of a cumulative frequency function of 99.9% of a position deviation width from an ideal shape in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and a value l0.1 of the cumulative frequency function of 0.1% thereof is equal to or smaller than 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20180374507A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesIn planeMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, an XRD intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (L99.9−L0.1) is equal to or smaller than 180 nm, and a magnetic tape device including the magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10062403B1Improve accuracyExact reproductionTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
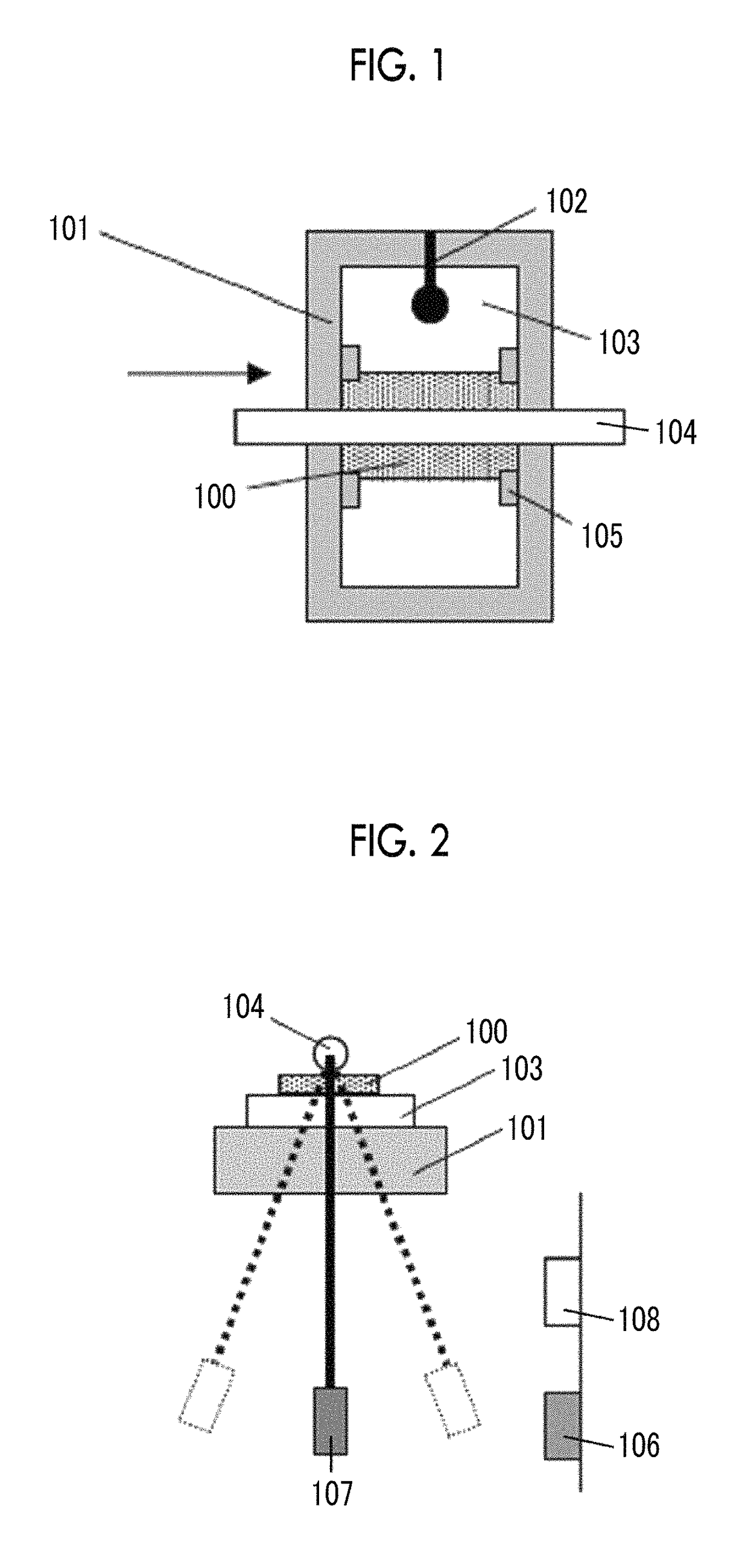
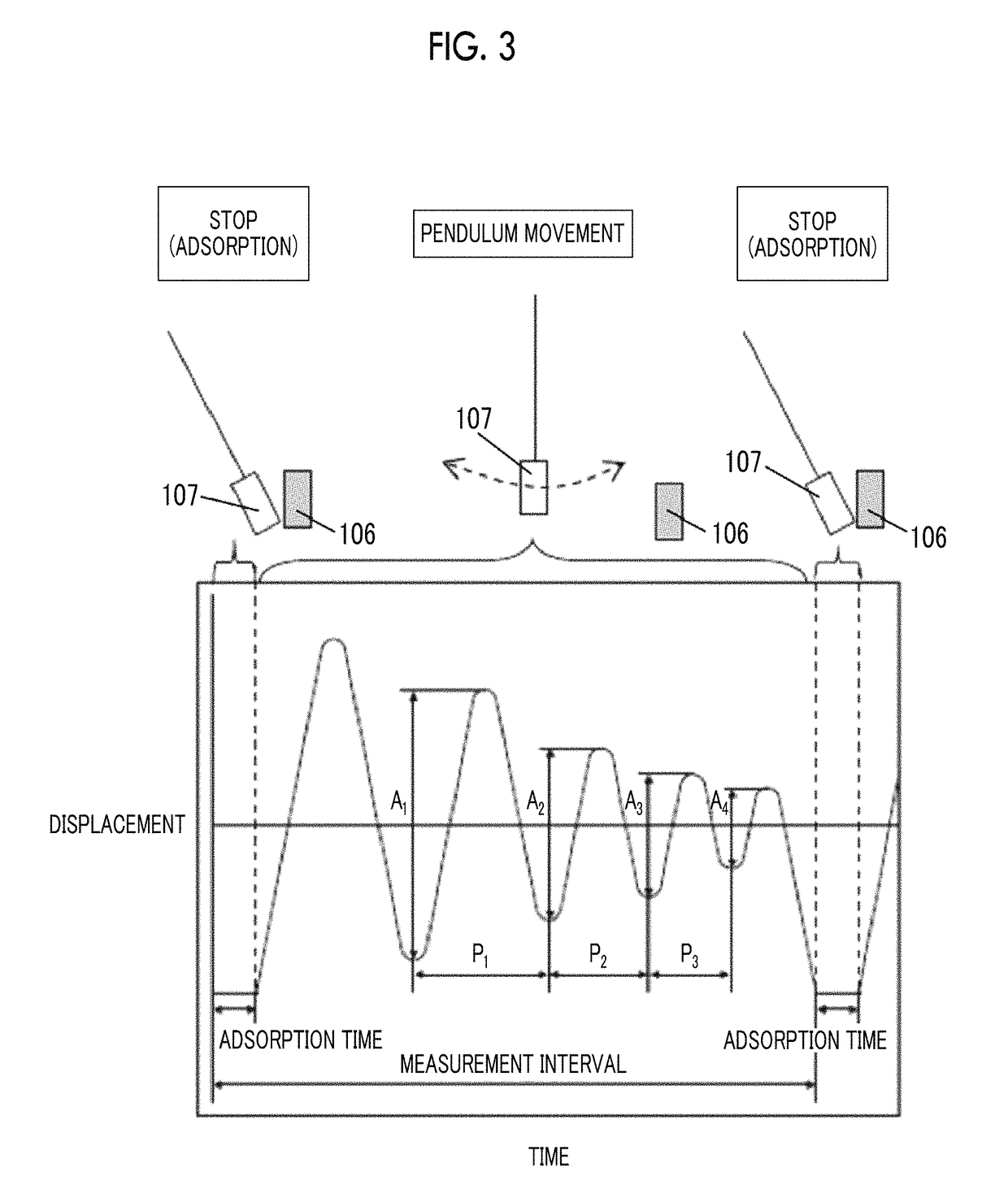
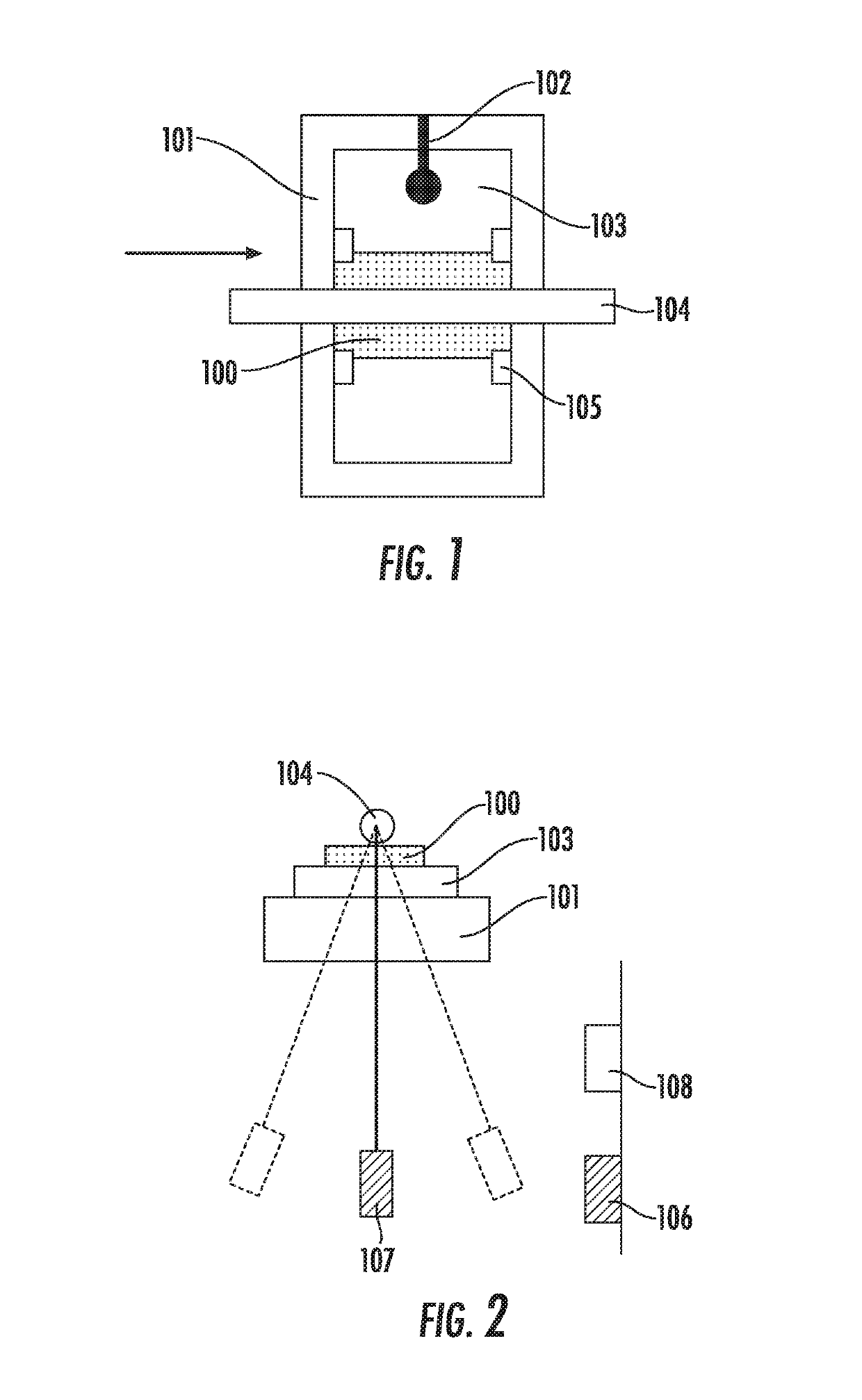
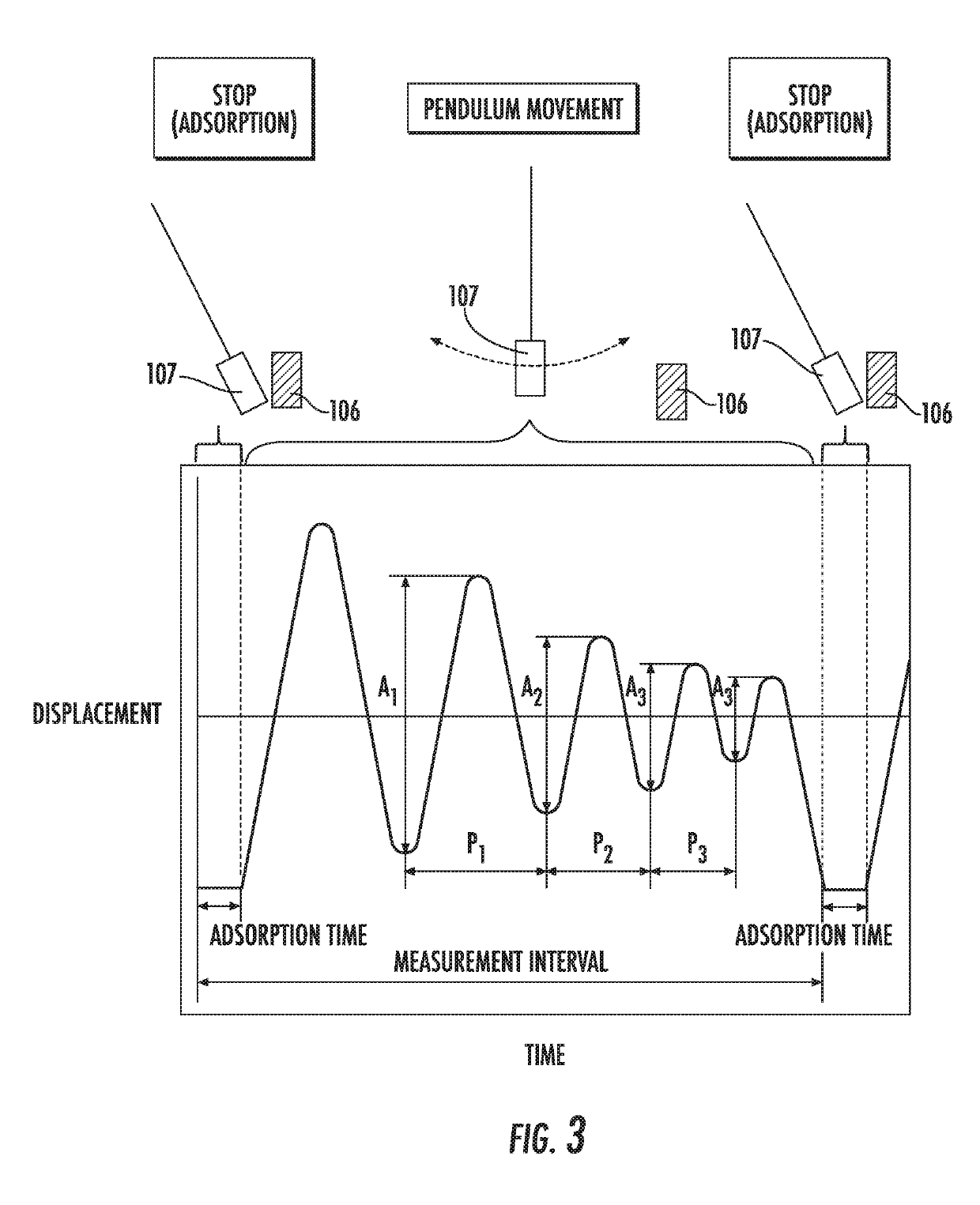
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a TMR head, the magnetic tape includes a servo pattern in the magnetic layer, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and a ratio (Sdc / Sac) of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape with specific servo pattern edge shape and magnetic tape device using same
ActiveUS9773519B2Accurate informationImprove positionAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tension forceMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the coercive force measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 167 kA / m, a timing-based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, and the edge shape specified by observing the timing-based servo pattern with a magnetic force microscope is a shape in which the difference between the value L99.9 of the 99.9% cumulative distribution function of the width of misalignment from the ideal shape in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and the value L0.1 of the 0.1% cumulative distribution function, L99.9−L0.1, is less than or equal to 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170355022A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer having ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by a magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (l99.9−l0.1) between a value l99.9 of a cumulative frequency function of 99.9% of a position deviation width from an ideal shape in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and a value l0.1 of the cumulative frequency function of 0.1% thereof is equal to or smaller than 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180286439A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head and a magnetic tape, in which the magnetic tape includes fatty acid ester in a magnetic layer, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is 2.0 nm or smaller, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding a surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and 7.0 nm or smaller, a difference between spacings before and after the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and 8.0 nm or smaller, and a ratio of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20090087689A1Improve high-speed running stabilityMaintain good propertiesMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageAtomic force microscopyMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support. In the magnetic recording medium, a number of protrusions equal to or greater than 10 nm in height on the magnetic layer surface, as measured by an atomic force microscope, ranges from 50 to 500 / 1,600 μm2, the binder comprises a polyurethane resin with a weight average molecular weight ranging from 100,000 to 200,000, and the magnetic layer further comprises a carbonic ester having a molecular weight ranging from 360 to 460.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducting method
ActiveUS20180240476A1Lower the resistance valueImprove smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a reproducing head, in which the reproducing head is a TMR head, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and a ratio (Sdc / Sac) of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10170144B2Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head and a magnetic tape, in which the magnetic tape includes fatty acid ester in a magnetic layer, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is 2.0 nm or smaller, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding a surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and 7.0 nm or smaller, a difference between spacings before and after the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and 8.0 nm or smaller, and a ratio of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Harmonic cantilevers and imaging methods for atomic force microscopy
InactiveUS6935167B1Harmonic suppressionNanotechElectric discharge tubesAtomic force microscopyMagnetic force microscope
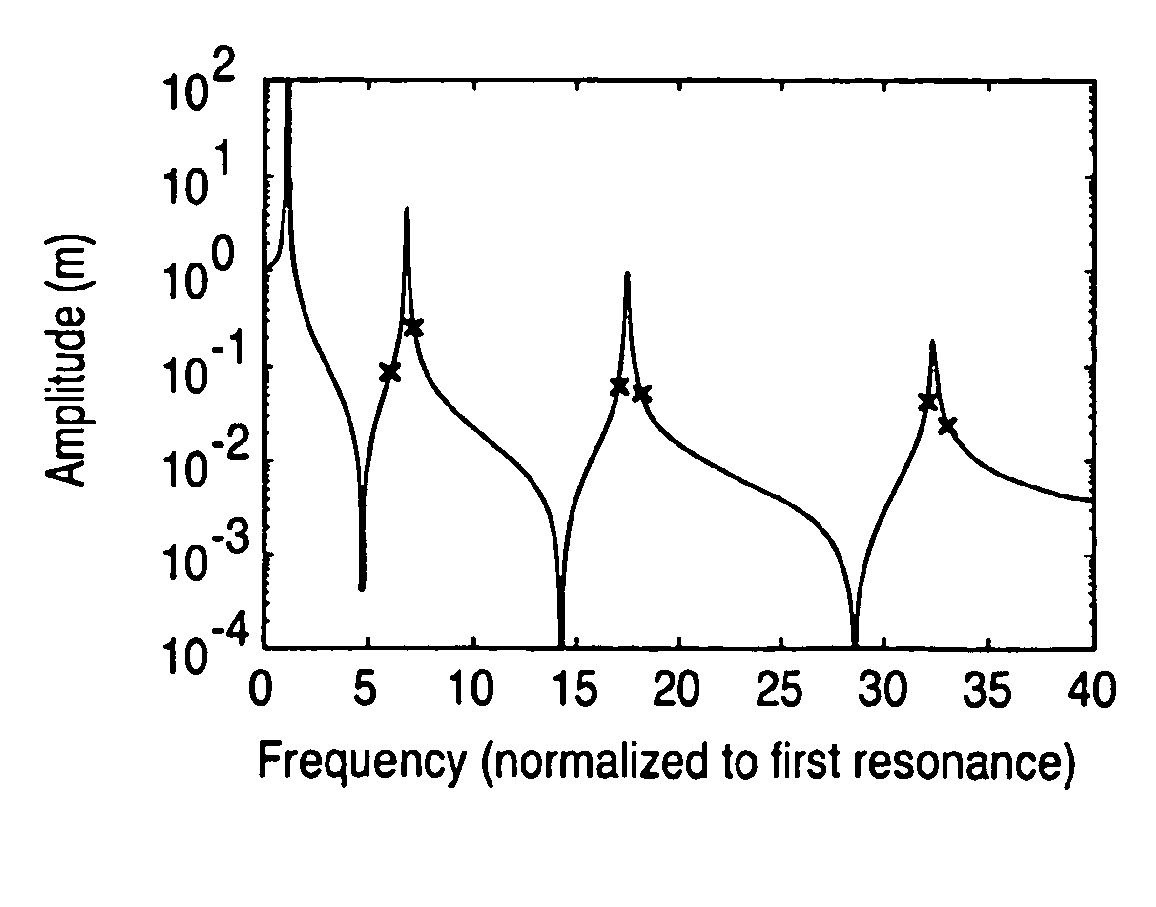
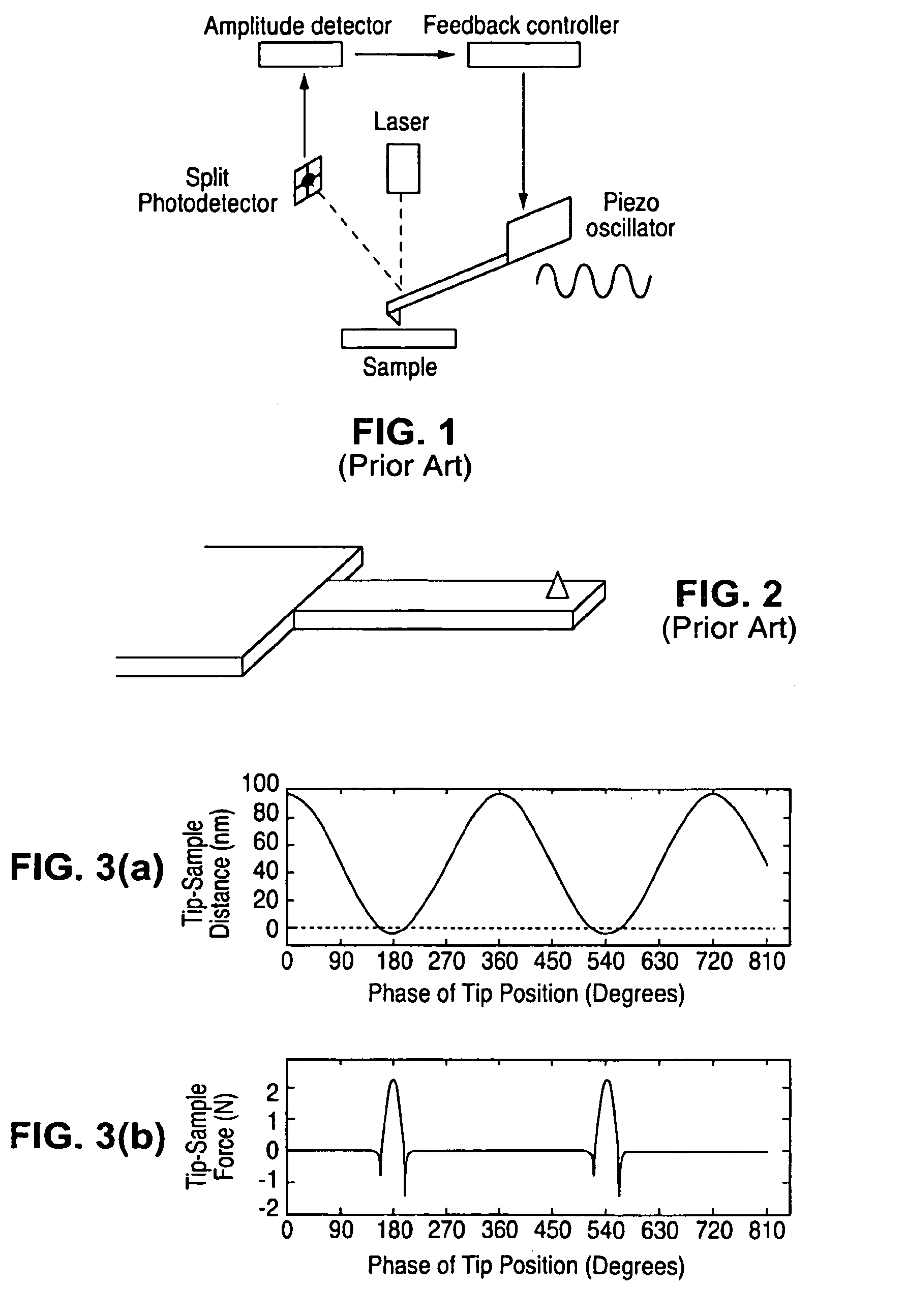
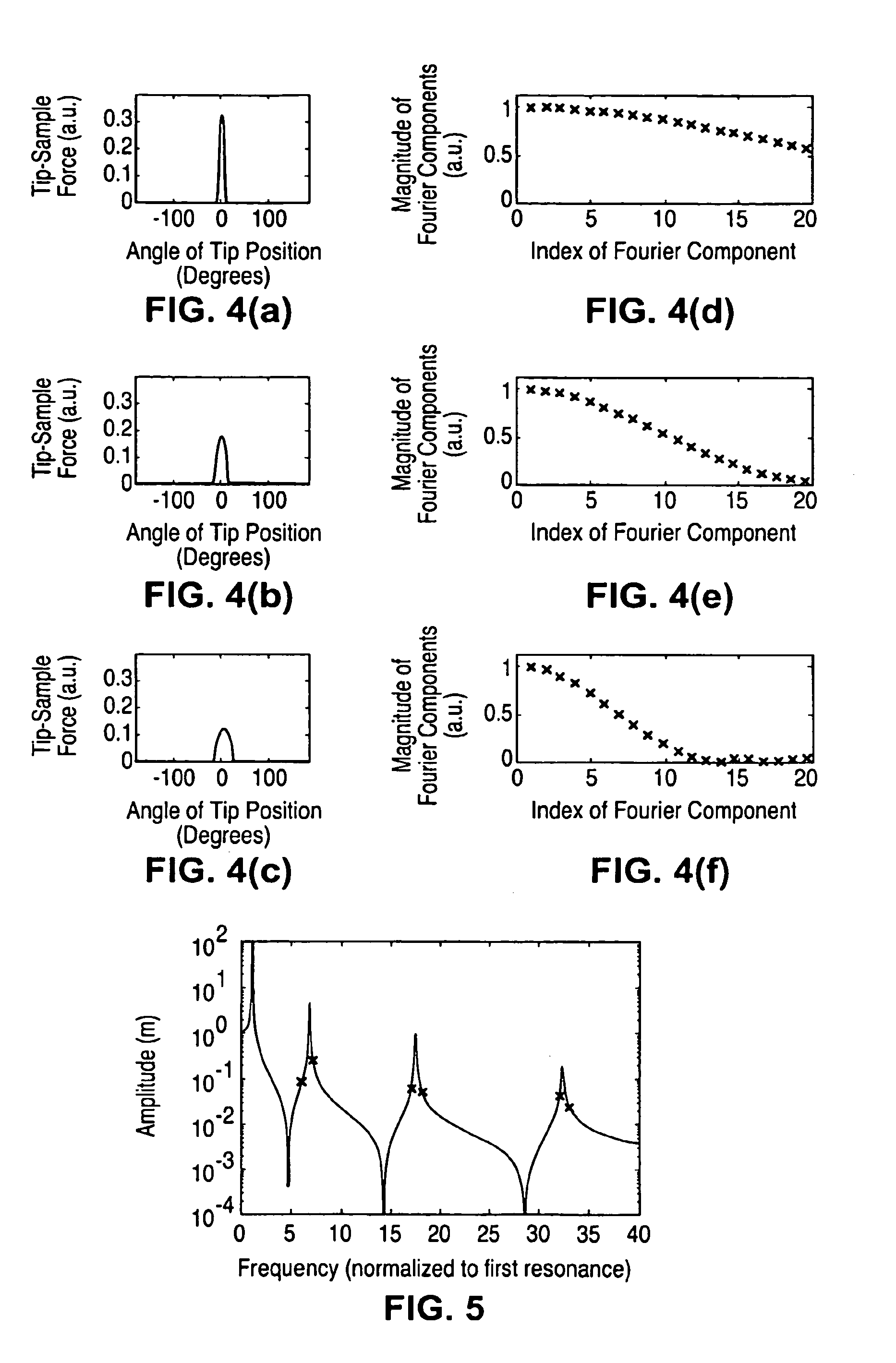
A harmonic cantilever for use in a tapping-mode atomic force microscope includes a cantilever arm and a probe tip. The cantilever arm has a shape selected to tune the fundamental resonance frequency or a resonance frequency of a selected higher order mode so that the fundamental and higher-order resonance frequencies have an integer ratio or near integer ratio. In one embodiment, the cantilever arm can be shaped to tune the fundamental resonance frequency. Alternately, the cantilever arm can include a geometric feature for tuning the resonance frequency of the fundamental mode or the selected higher order mode. An imaging method using the harmonic cantilever is disclosed whereby signals at the higher harmonics are measured to determine the material properties of a sample. In other embodiment, a cantilever includes a probe tip positioned at a location of minimum displacement of unwanted harmonics for suppressing signals associated with the unwanted harmonics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
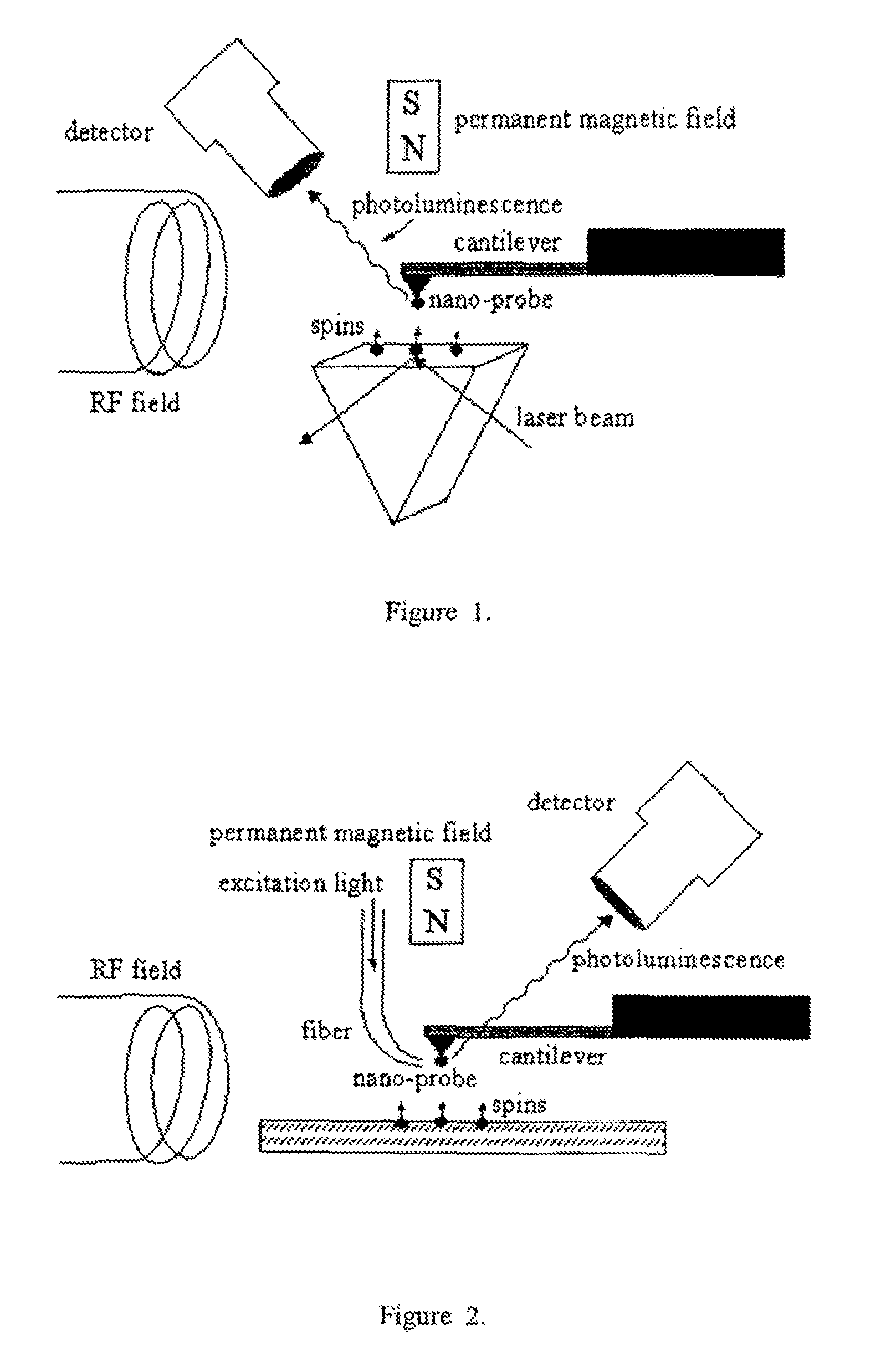
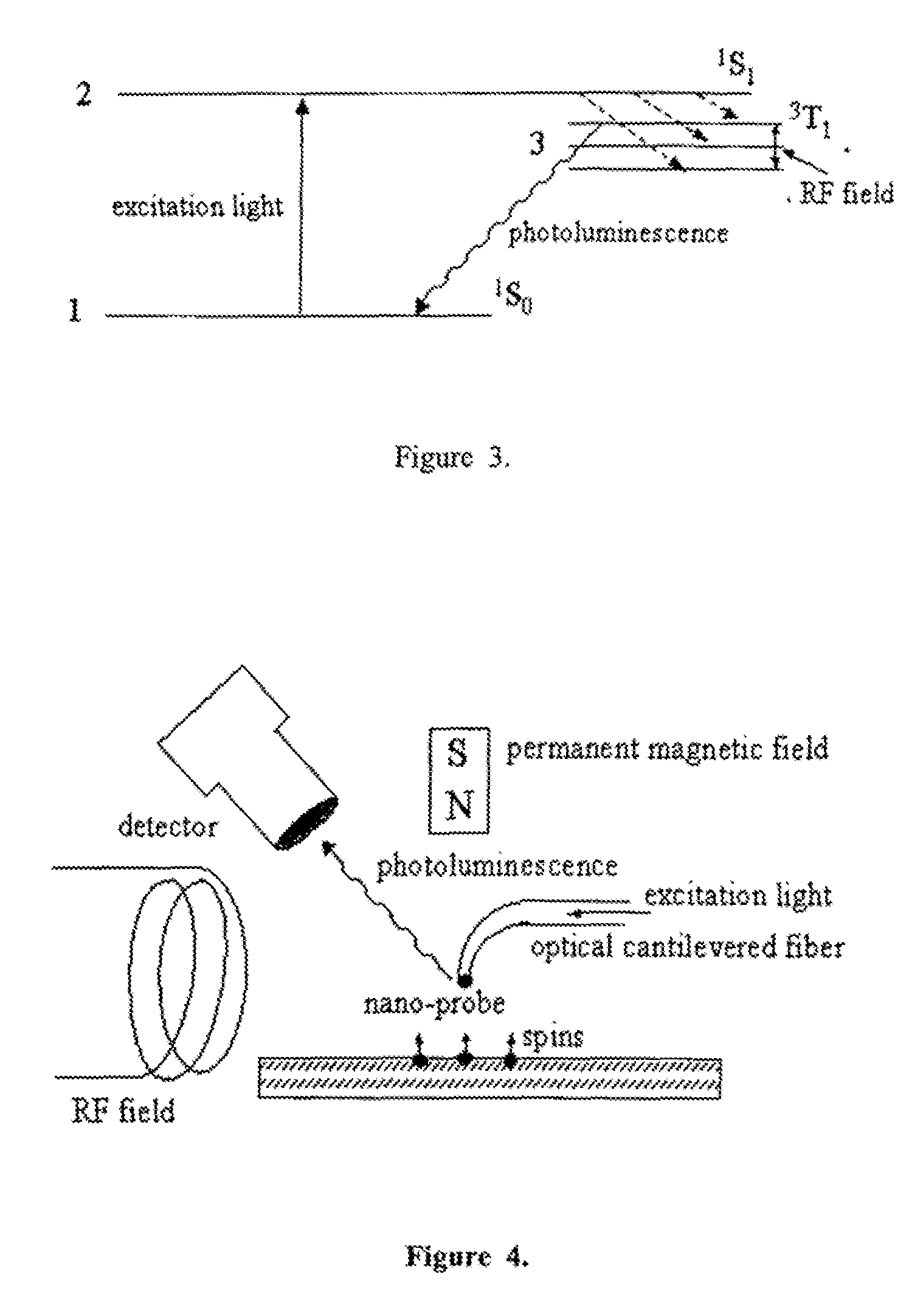
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
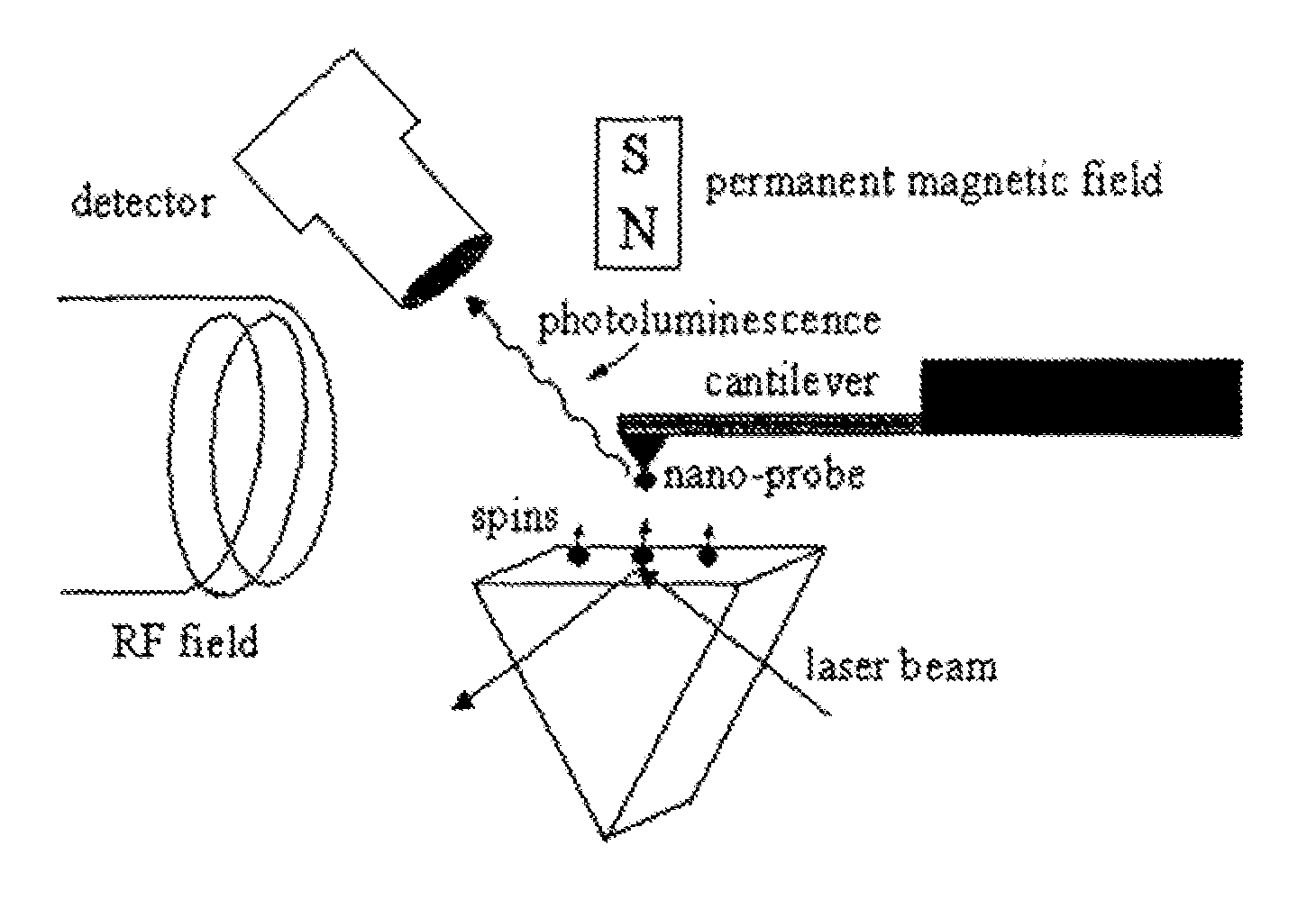
InactiveUS7608820B1NanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopePhotoluminescence
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of unpaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Probe of conducting atomic force microscope and measuring methods employing probe
ActiveCN102353817AImprove conductivityLow carrier injection potentialElectrical testingScanning probe microscopyMagnetic force microscopeConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a probe of a conducting atomic force microscope. The probe comprises: a substrate of a cantilever probe; a needle tip; and a conductive film, which is arranged at a surface of the needle tip. Besides, the material of the conductive film is graphene. Moreover, the invention provides a method that employs the probe to measure local conductivity of a semiconductor and a needle tip-free near-field optical detection method that employs the probe to measure a terahertz wave band. According to the invention, graphene is utilized, wherein the grapheme has the following characteristics that: the graphene is composed of carbon atoms and is thin to a monatomic layer; and the graphene is a semimetal two-dimensional thin material that has a zero gap; besides, the probe has advantages of good conductivity and high electron mobility; moreover, a Fermi surface can carry out self-adjustment with charging and discharging motions and a carrier injection potential is low. In addition, an electronic plasmon oscillating frequency of the graphene is just at a terahertz wave band; and the graphene has soft materials and strong stability on thermodynamics. The above-mentioned statements are physical bases on which the graphene is utilized to replace a traditional metal material as a plated film of a surface of an atomic force microscope probe, so that the above-mentioned limitations are broken through.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Head positioning of timing-based servo system for magnetic tape recording device
ActiveUS10366721B2Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeIn plane
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, an XRD intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (L99.9−L0.1) is equal to or smaller than 180 nm, and a magnetic tape device including the magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducting method employing TMR head and tape with characterized magnetic layer
ActiveUS10573338B2Increase resistanceReduce resistanceMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200251139A1High reproduction qualityPromote reproductionMagnetic materials for record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeZeta potential
The magnetic tape include a non-magnetic support and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent, in which the magnetic layer has a timing-based servo pattern, an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern, specified by magnetic force microscopy is a shape in which a difference (L99.9−L0.1) between a value L99.9 of a cumulative distribution function of 99.9% and a value L0.1 of a cumulative distribution function of 0.1% in a position deviation width from an ideal shape of the magnetic tape in a longitudinal direction is 180 nm or less, and an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the magnetic layer is 5.5 or more.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200251134A1High reproduction qualityPromote reproductionNanomagnetismElectronic editing analogue information signalsMagnetic force microscopeZeta potential
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent, in which the magnetic layer has a timing-based servo pattern, an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern, specified by magnetic force microscopy is a shape in which a difference (L99.9−L0.1) between a value L99.9 of a cumulative distribution function of 99.9% and a value L0.1 of a cumulative distribution function of 0.1% in a position deviation width from an ideal shape of the magnetic tape in a longitudinal direction is 180 nm or less, and an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the magnetic layer is 3.8 or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200251135A1High reproduction qualityPromote reproductionNanomagnetismElectronic editing analogue information signalsMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer, in which the magnetic layer has a timing-based servo pattern, an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern, specified by magnetic force microscopy is a shape in which a difference L99.9−L0.1 between a value L99.9 of a cumulative distribution function of 99.9% and a value L0.1 of a cumulative distribution function of 0.1% in a position deviation width from an ideal shape of the magnetic tape in a longitudinal direction is 180 nm or less, and an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy of the magnetic layer, measured in an in-plane direction and a refractive index Nz of the magnetic layer, measured in a thickness direction is 0.25 or more and 0.40 or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Characterization method of atomic force microscope for micro-pore structure of reservoir rock core
InactiveCN102183450APermeability/surface area analysisScanning probe microscopyMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a characterization method of an atomic force microscope for a micro-pore structure of a reservoir rock core. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing for a characterization sample to ensure that a reservoir rock sample adapts to the characterization of an atomic force microscope; (2) reconstructing a characterization apparatus to ensure that the atomic force microscope adapt to a characterization reservoir rock sample; and (3) analyzing the data of a characterization image, and analyzing the characterization image to obtain useful information to guide production practice. By using the method, the characterization method of the micro-pore structure of the rock can be more complete and accurate so that the characteristics of a nano-grade structure and a micron-grade structure of a reservoir stratum can be indicated three-dimensionally and clearly, and the method has important scientific and economic significances in evaluating reserves of an oil-gas field or the characteristics of the rock micro-pore structure of the oil-gas field to increase the yield of the oil-gas field.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Locally enhanced raman spectroscopy with an atomic force microscope
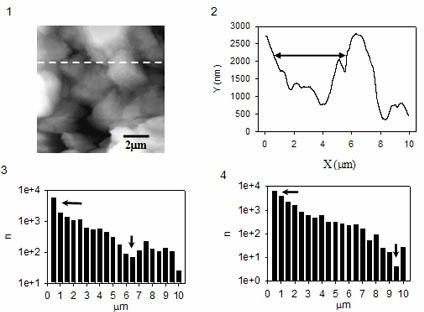
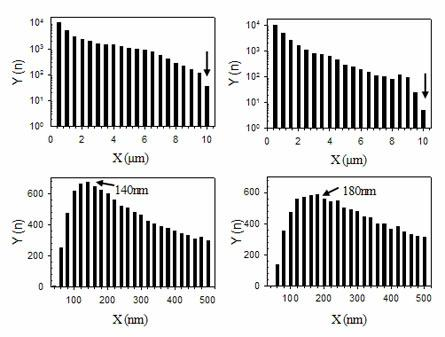
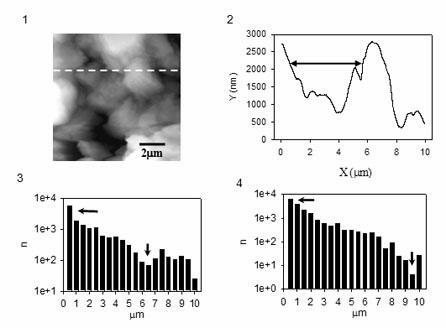
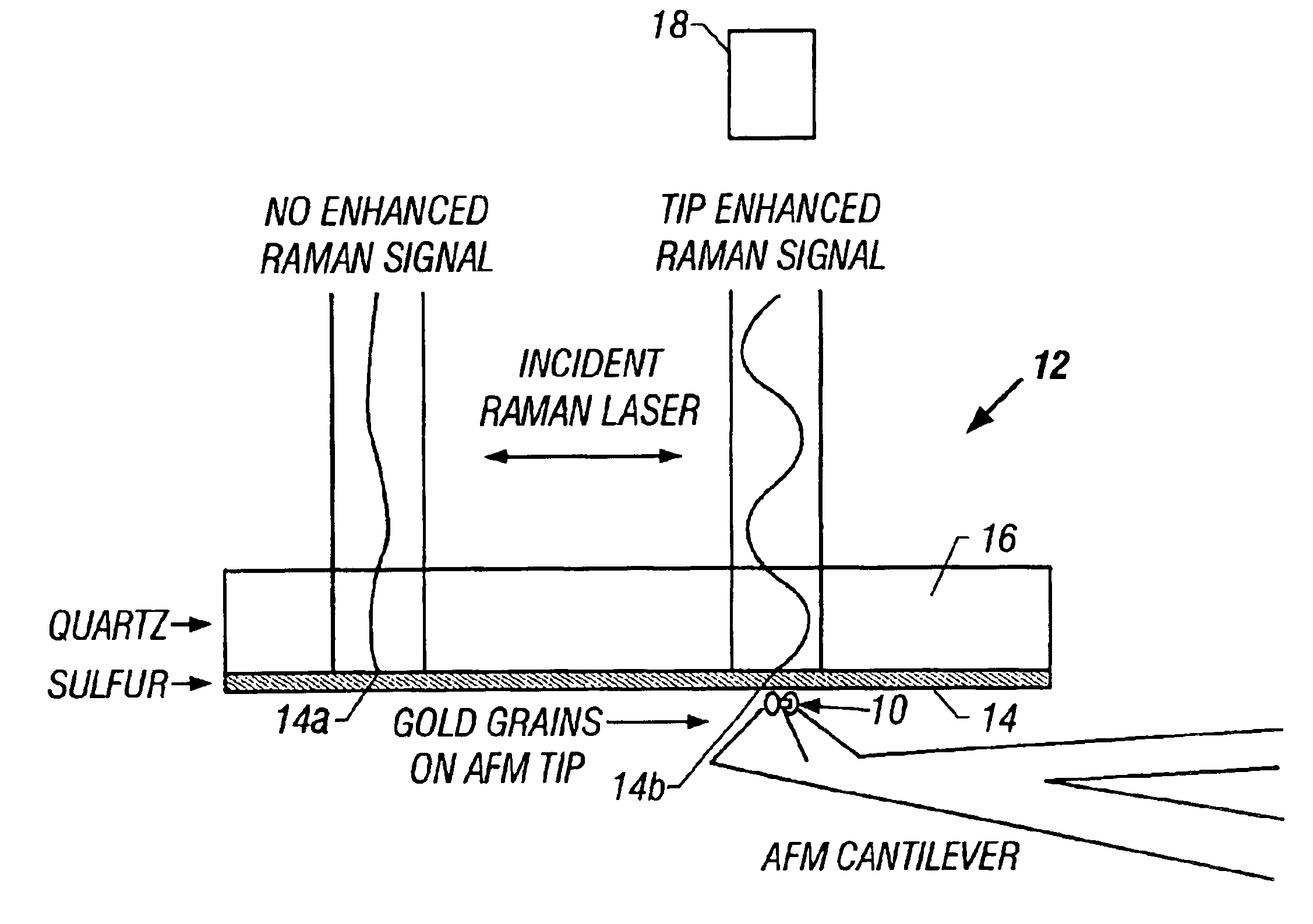
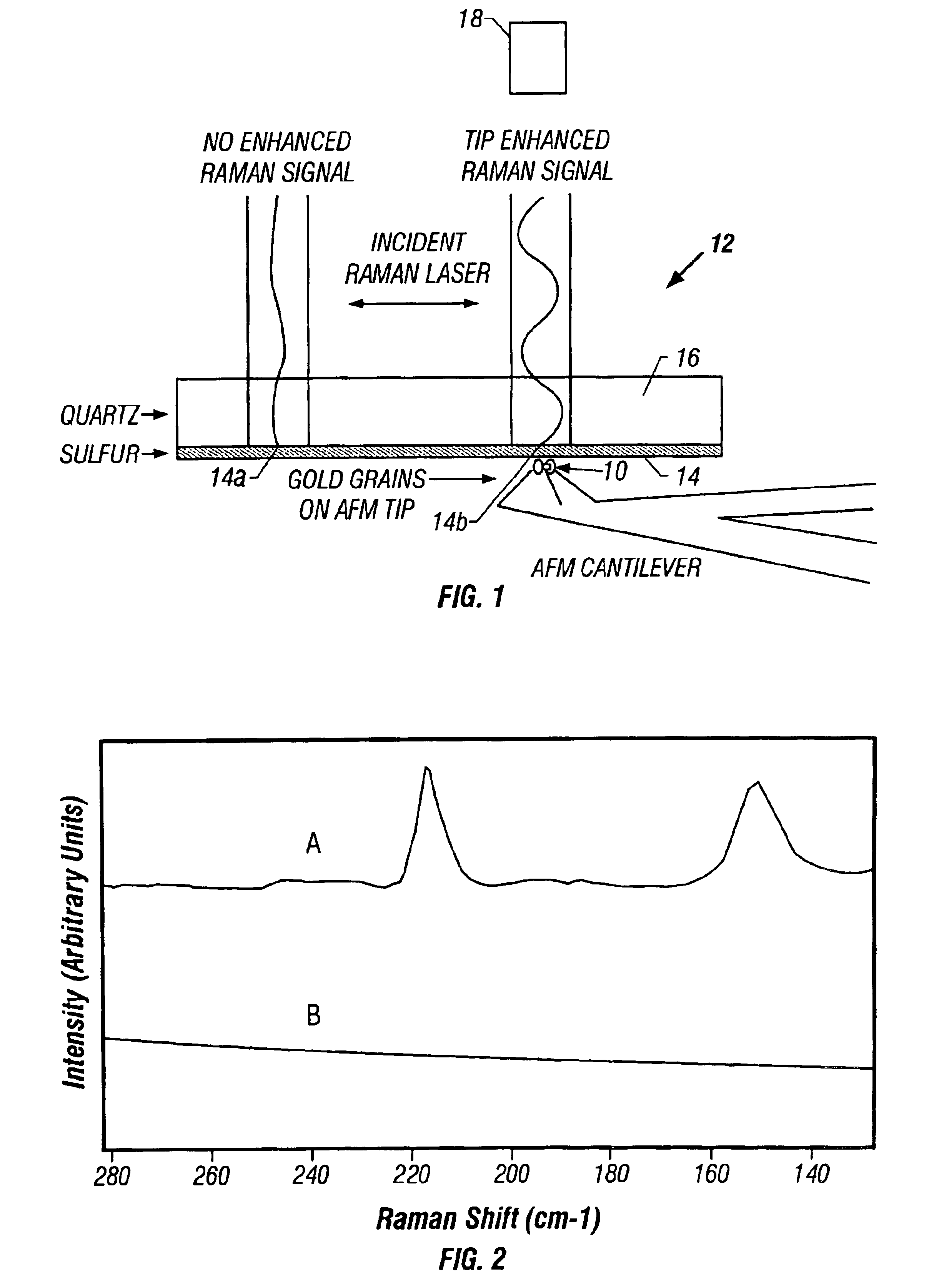
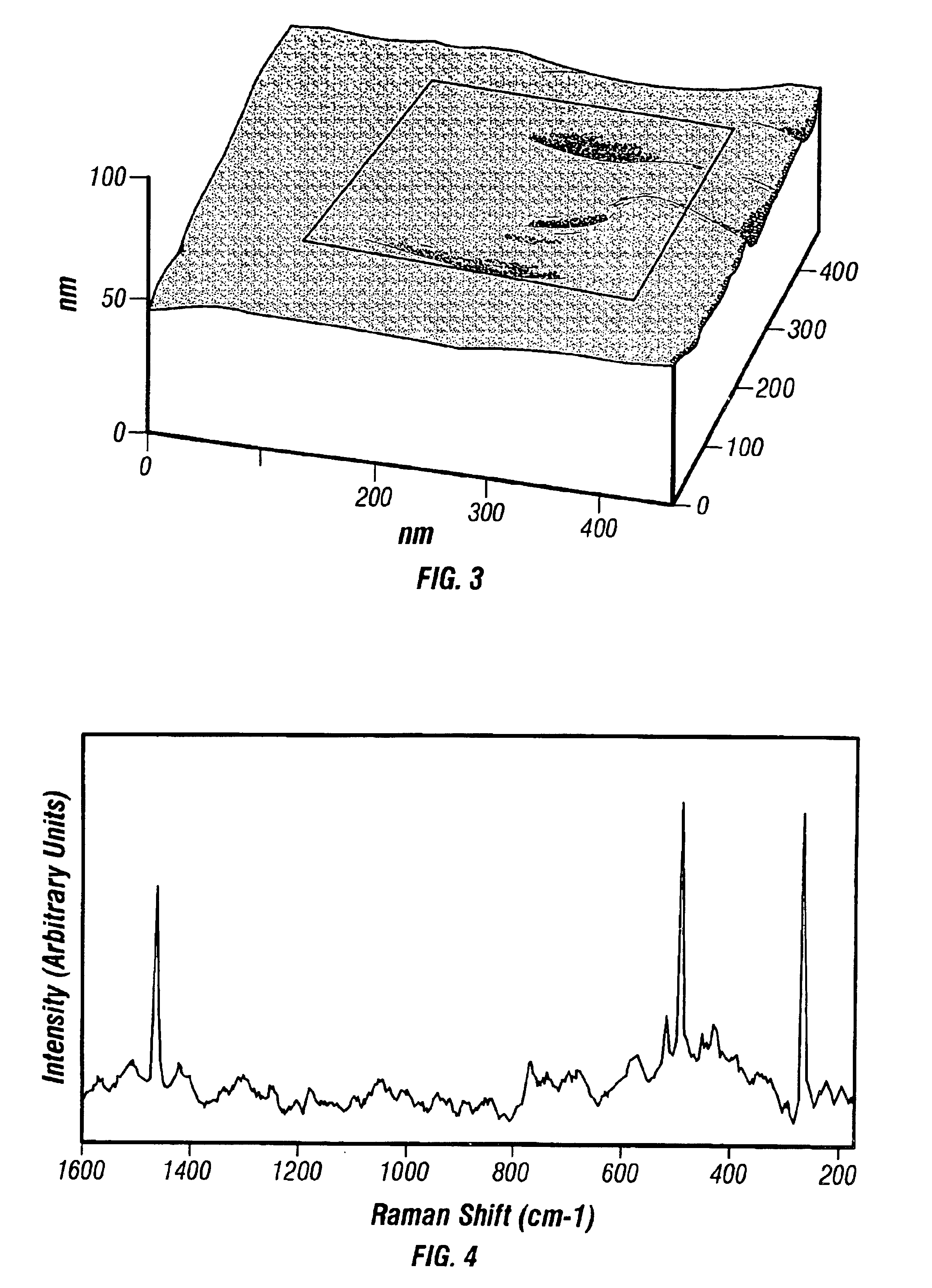
InactiveUS6850323B2Increase heightMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
An atomic force microscope (AFM) tip is used to selectively produce surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) for localized Raman spectroscopy. Spectra of thin films, undetectable with a Raman microprobe spectrometer alone, are readily acquired in contact with a suitably gold-coated AFM tip. Similarly, an AFM tip is used to remove sample layers at the nanometer scale and subsequently serve as a SERS substrate for ultra-trace analysis. This demonstrates the interface of an AFM with a Raman spectrometer that provides increases sensitivity, selectivity and spatial resolution over a conventional Raman microprobe. An AFM guiding the SERS effect has the potential for targeted single molecule spectroscopy.
Owner:NASA
Nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter in-situ quantitative characterization device based on atomic force microscope
ActiveCN102692427AExpand the evaluation functionHigh resolutionMaterial heat developmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansThermoelectric materialsAtomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a nano-thermoelectric energy material multi-parameter in-situ quantitative characterization device based on an atomic force microscope, which is used for detecting a micro-area heat conduction coefficient, a Seebeck coefficient and other thermoelectric property parameters of a detected nano-thermoelectric material sample. The device comprises a nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter atomic force microscope in-situ excitation platform and a nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter in-situ detection platform, wherein the nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter atomic force microscope in-situ excitation platform is used for providing a basic hardware platform required in nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter excitation and realizing in-situ simultaneous excitation of a micro-area frequency-tripled heat conduction signal and a micro-area stable-state Seebeck direct current voltage signal of a nano-thermoelectric material; and the nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter in-situ detection platform is used for realizing in-situ real-time detection and data processing of micro-area heat conduction and Seebeck voltage of the nano-thermoelectric material and realizing real-time display of the quantitative characterization results of the micro-area heat conduction coefficient and the Seebeck coefficient. According to the device disclosed by the invention, the nano-detection function of the atomic force microscope, the frequency tripling detection principle of macro-heat conductivity and the test principle of the macro-Seebeck coefficient are combined for establishing a nano in-situ evaluation device which is based on the commercial atomic force microscope and combines the properties of nano-scale heat excitation and thermoelectric multi-parameter detection.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
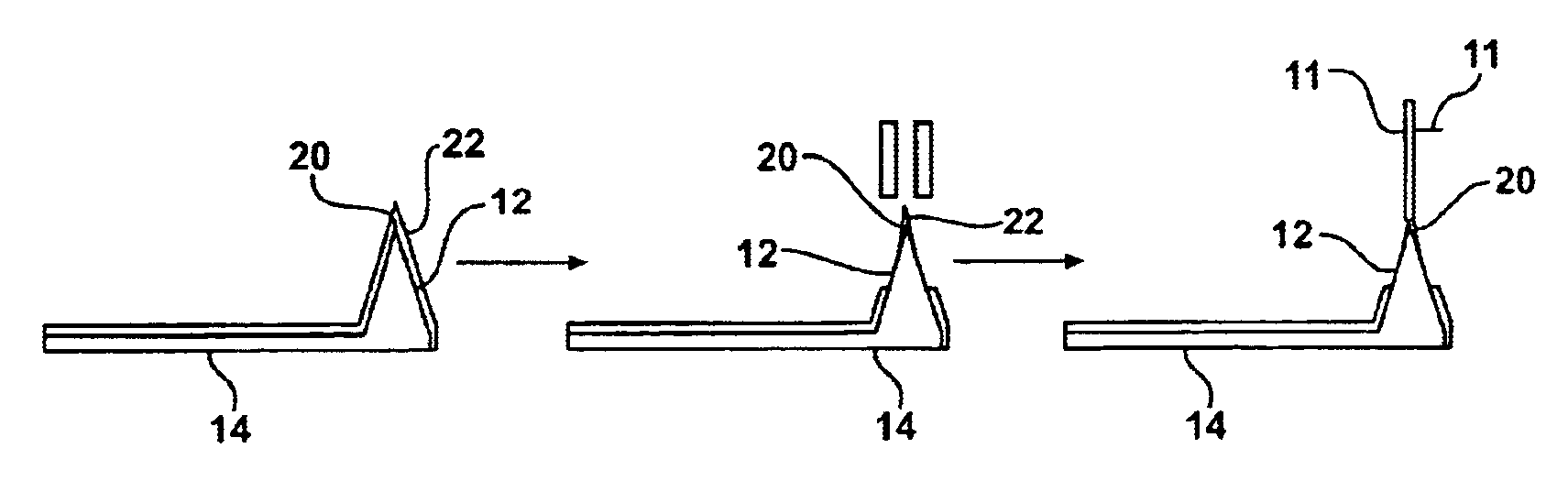
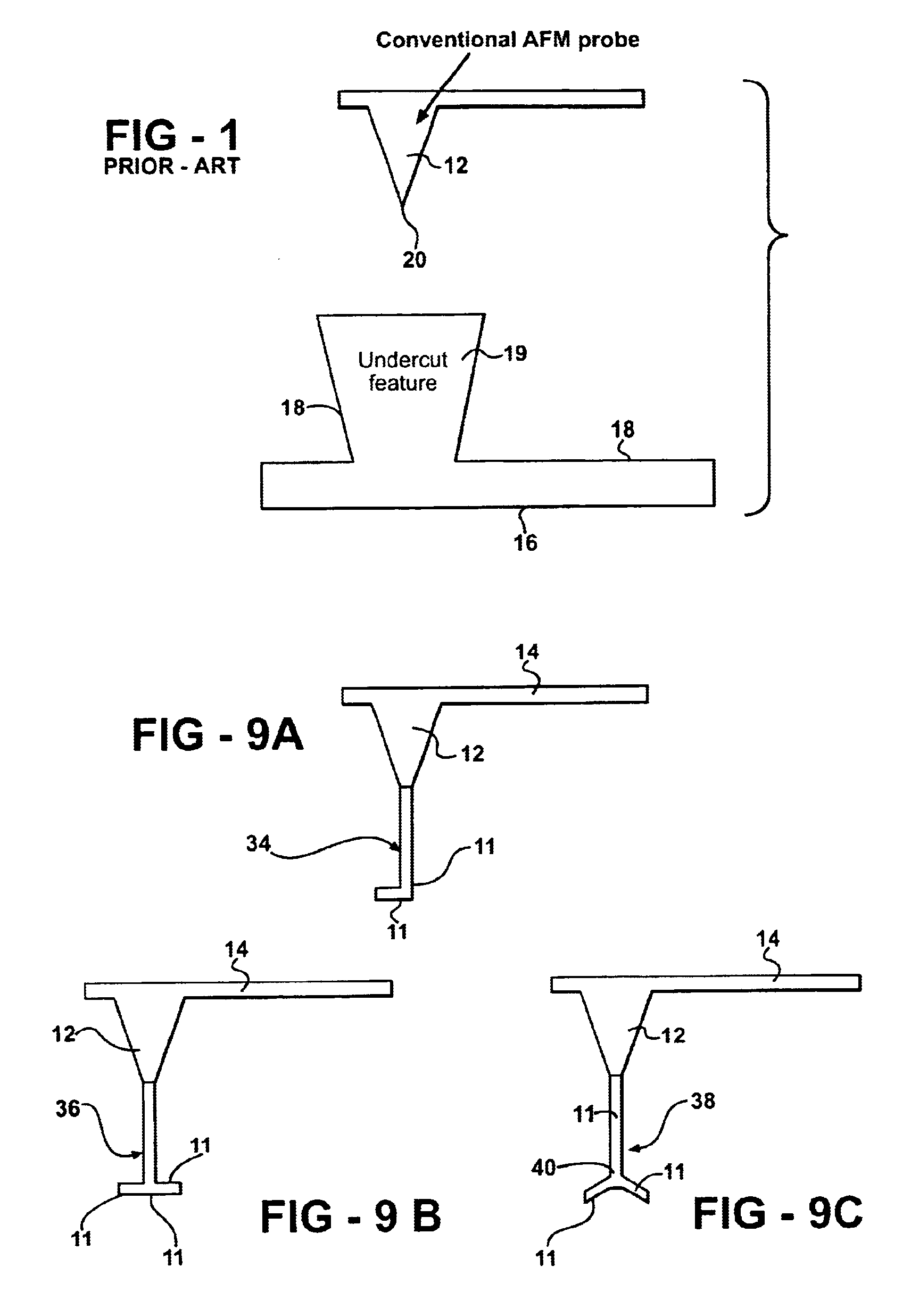
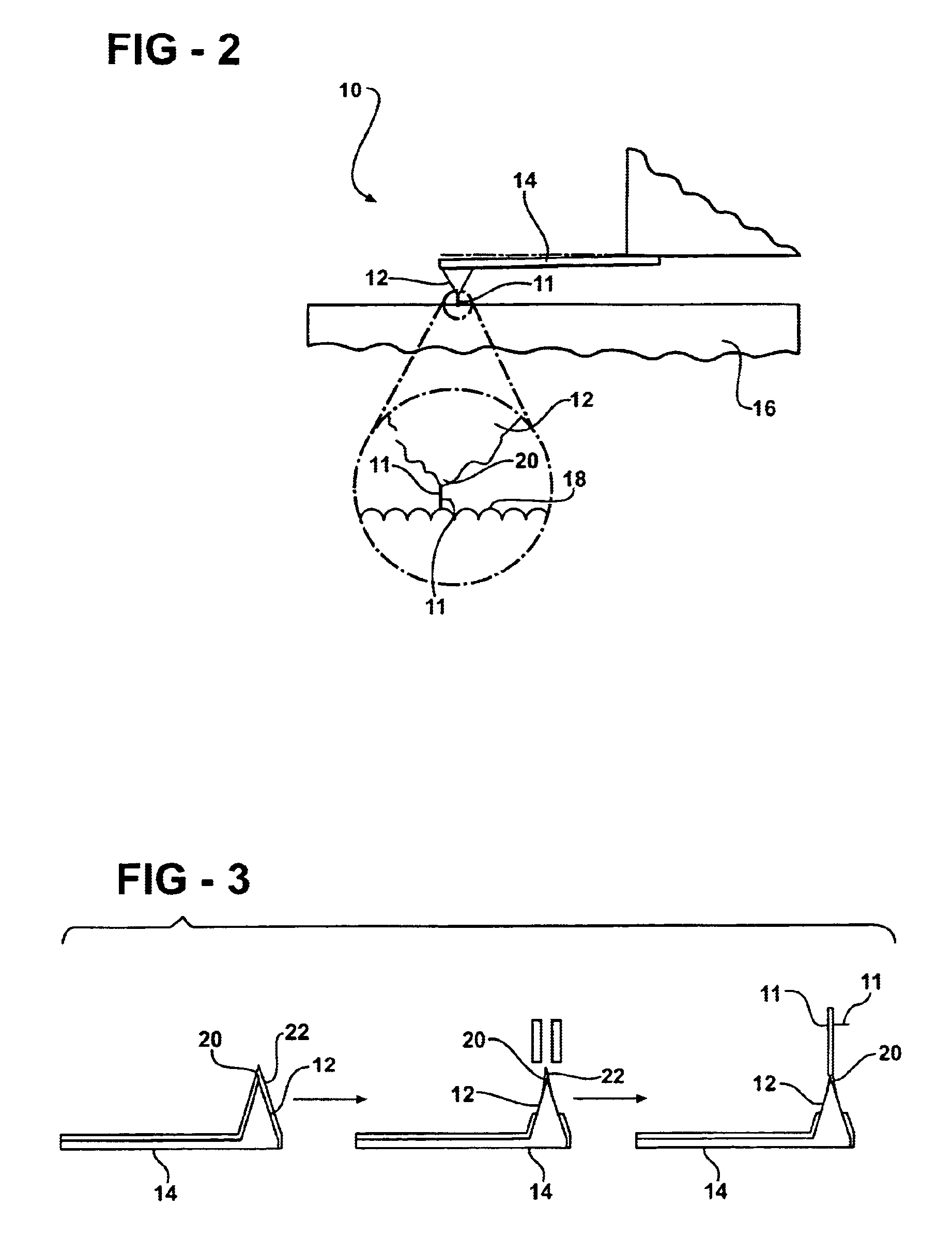
Method of producing a branched carbon nanotube for use with an atomic force microscope
InactiveUS6871528B2Extreme mechanical strengthImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
A method of producing a branched carbon nanotube (CNT) is disclosed. The branched CNT is used with an atomic force microscope having a cantilever and a tip and that is able to measure a surface of a substrate as well as an undercut feature of the substrate that protrudes from the surface. A catalytic material is deposited onto the tip of the microscope, and the catalytic material is subjected to chemical vapor deposition. This initiates growth of a primary branch of the branched carbon nanotube such that the primary branch extends from the tip. A secondary branch is then introduced to extend from the primary branch and produce the branched carbon nanotube. The primary branch interacts with the surface of the substrate and the secondary branch interacts with the undercut feature.
Owner:BOSTON COLLEGE +2
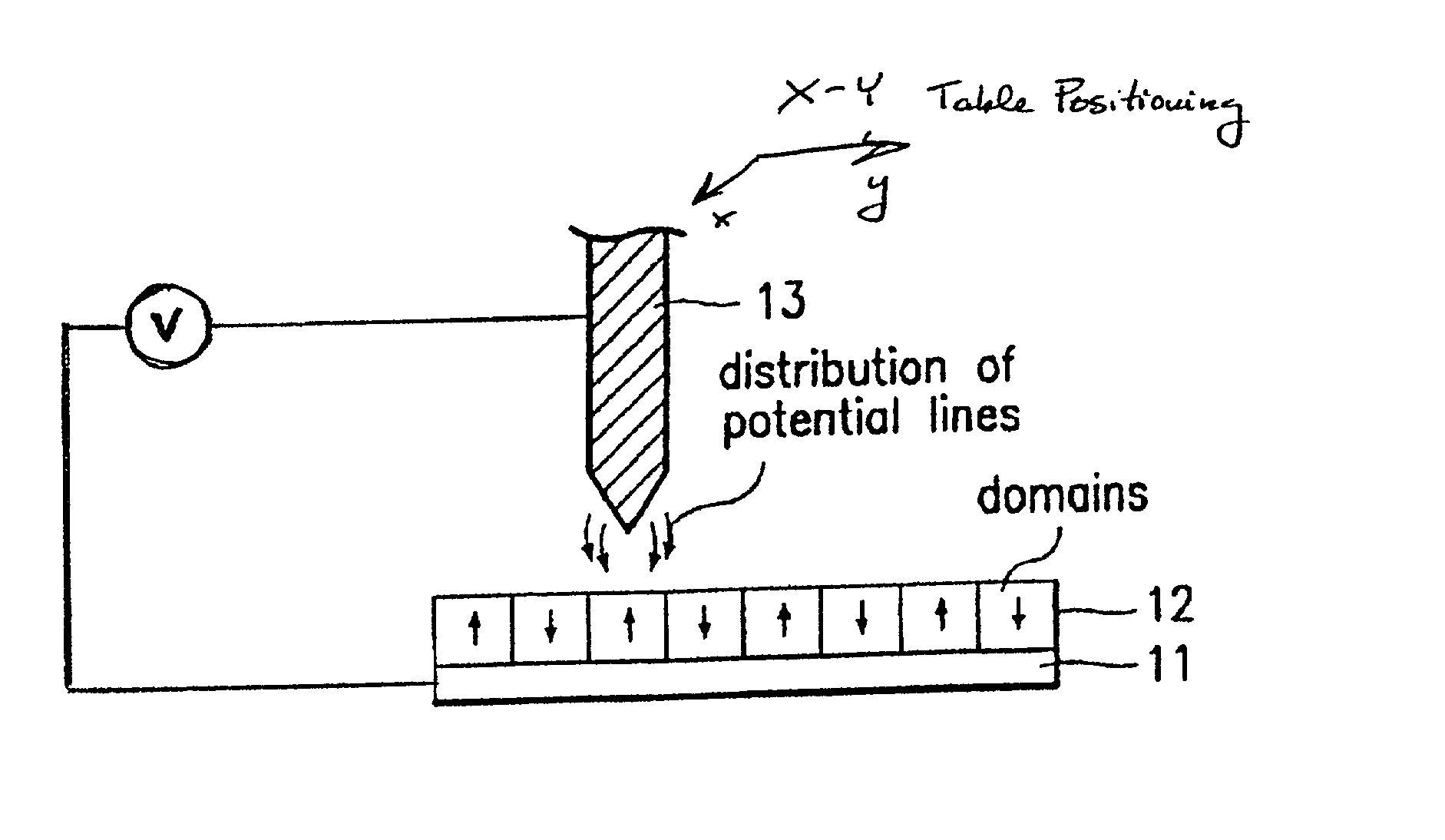
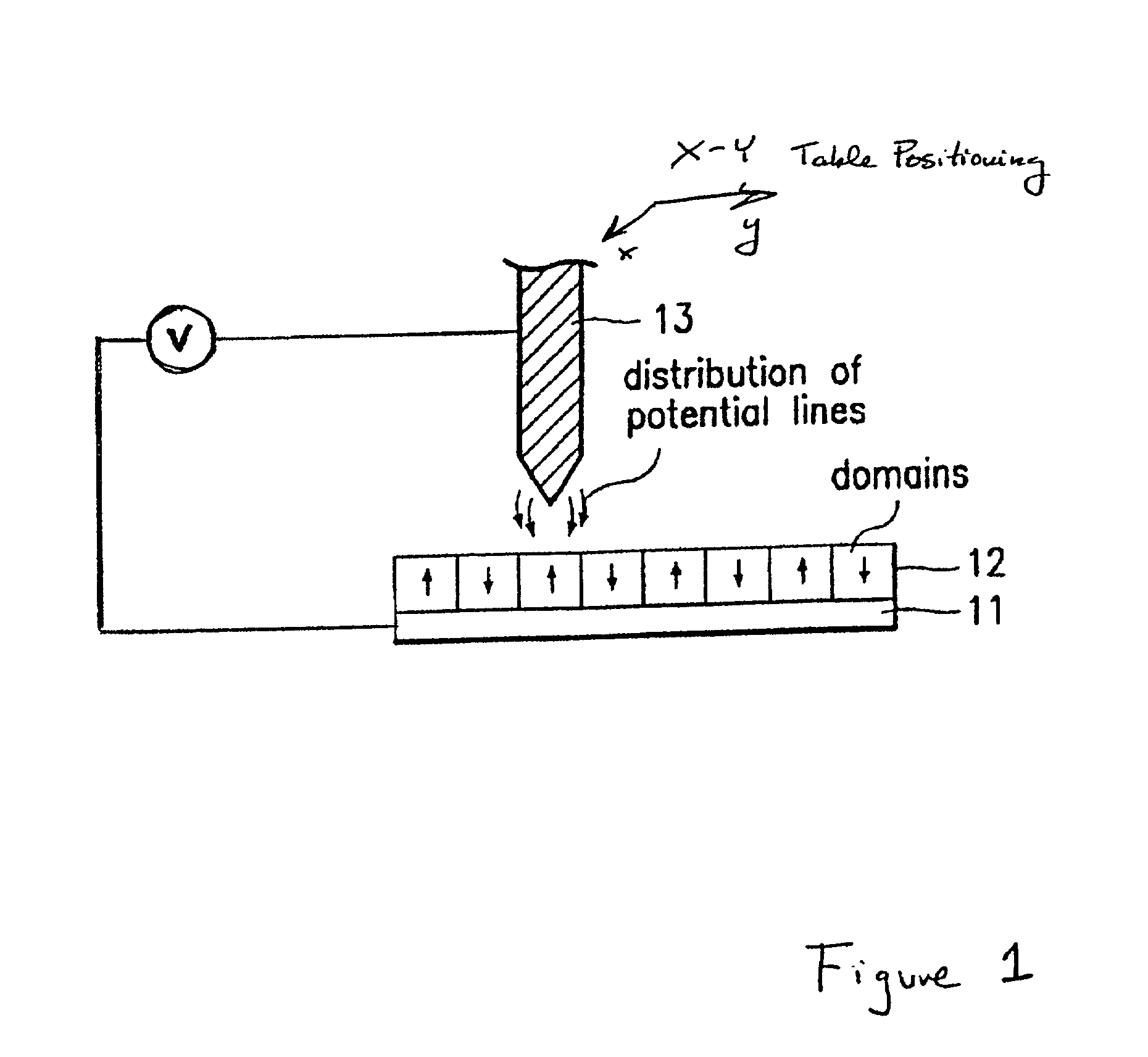
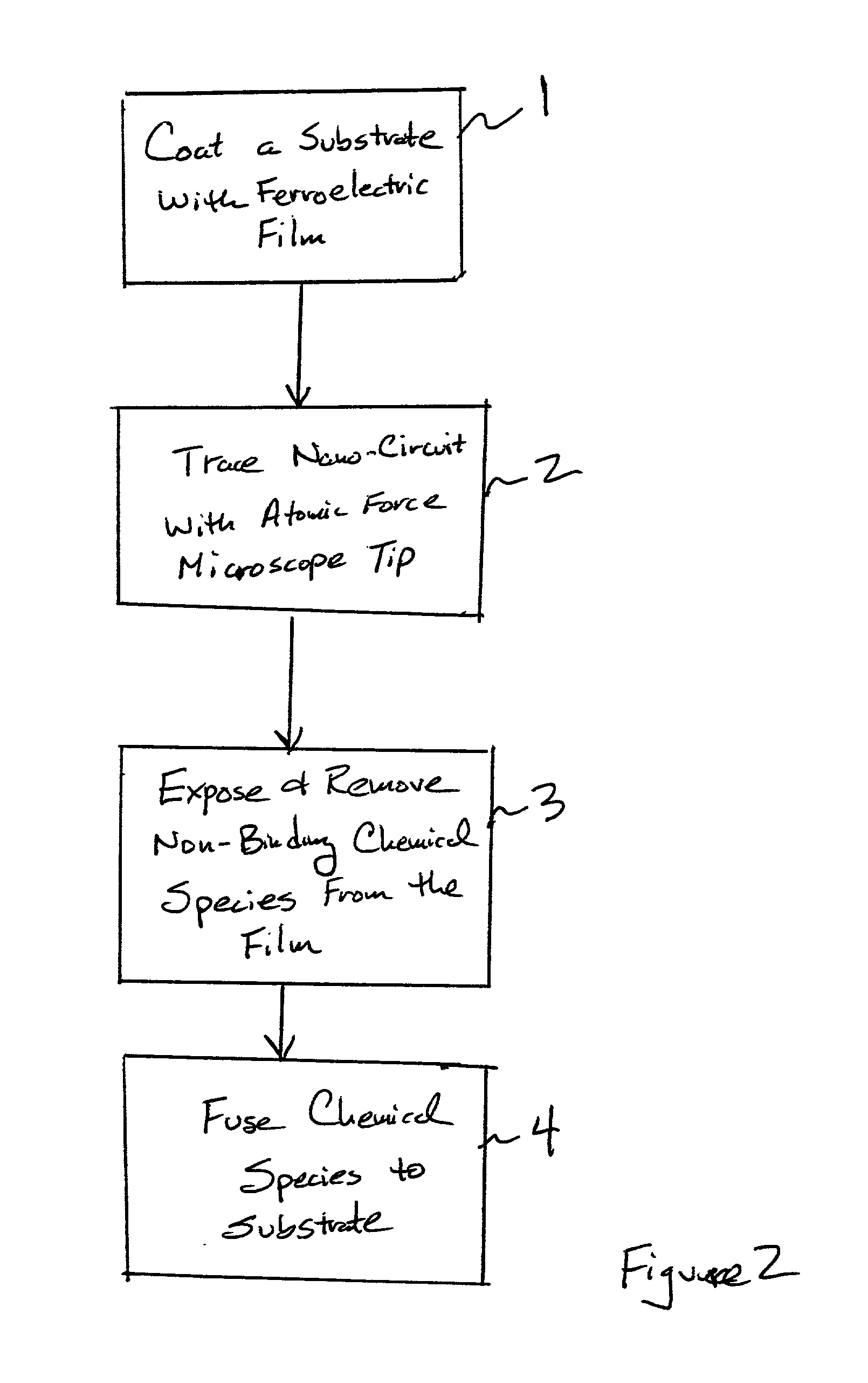
Assembling arrays of small particles using an atomic force microscope to define ferroelectric domains
InactiveUS20020118369A1Nanostructure manufactureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopeChemical species
A method of assembling arrays of small particles or molecules using an atomic force microscope to define ferroelectric domains includes depositing a ferroelectric thin film upon a substrate forming workpiece, then using an atomic force microscope having a conductive, tip for generating a pattern on this thin film to define desired nano-circuit patterns. Next, exposure of this thin film to a solution containing chemical species which selectively adsorb or accumulate under the influence of electrophoretic forces in selected regions of this thin film.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS10878846B2High reproduction qualityPromote reproductionMagnetic materials for record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeZeta potential
The magnetic tape include a non-magnetic support and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent, in which the magnetic layer has a timing-based servo pattern, an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern, specified by magnetic force microscopy is a shape in which a difference (L99.9−L0.1) between a value L99.9 of a cumulative distribution function of 99.9% and a value L0.1 of a cumulative distribution function of 0.1% in a position deviation width from an ideal shape of the magnetic tape in a longitudinal direction is 180 nm or less, and an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the magnetic layer is 5.5 or more.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
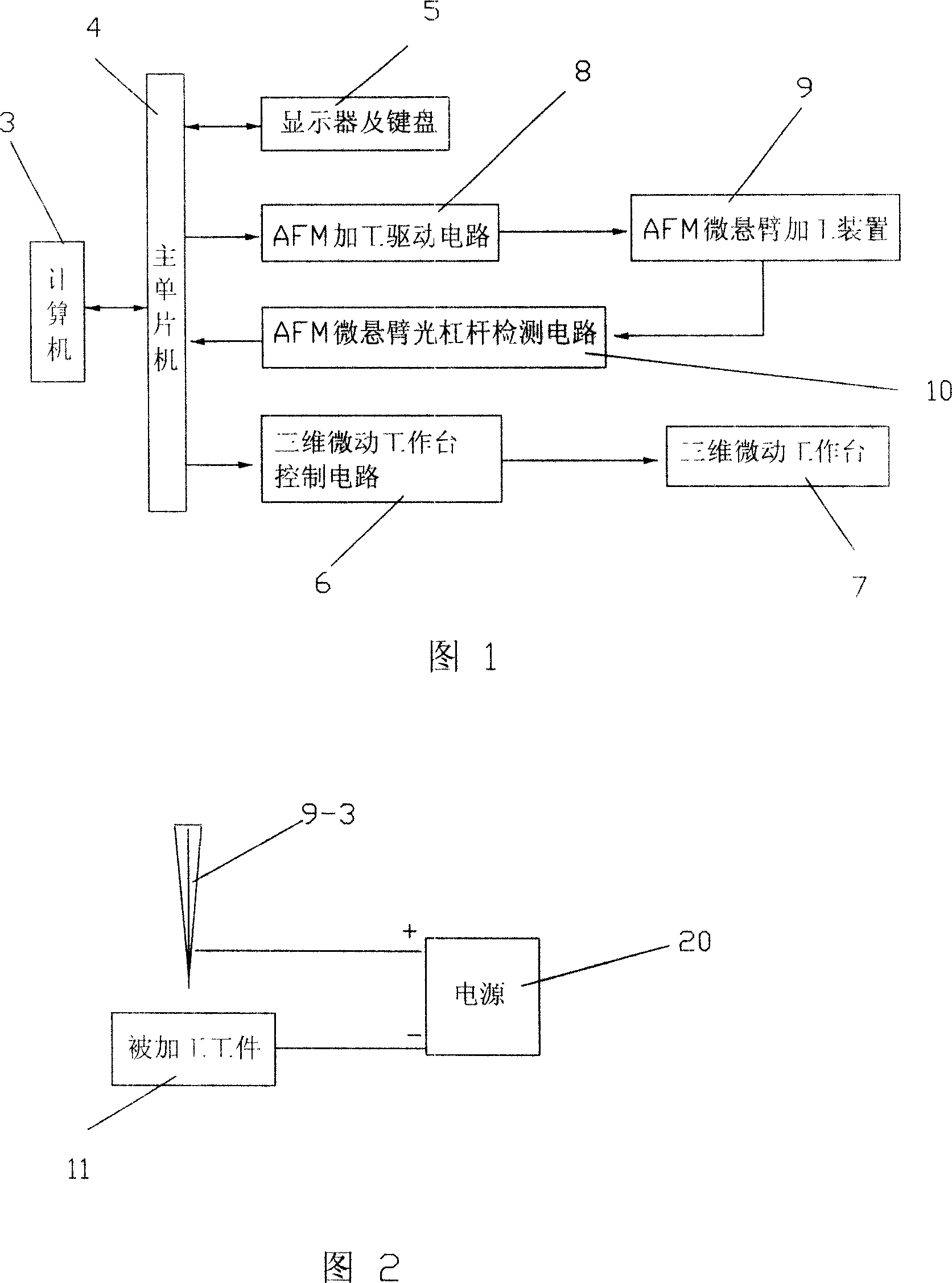
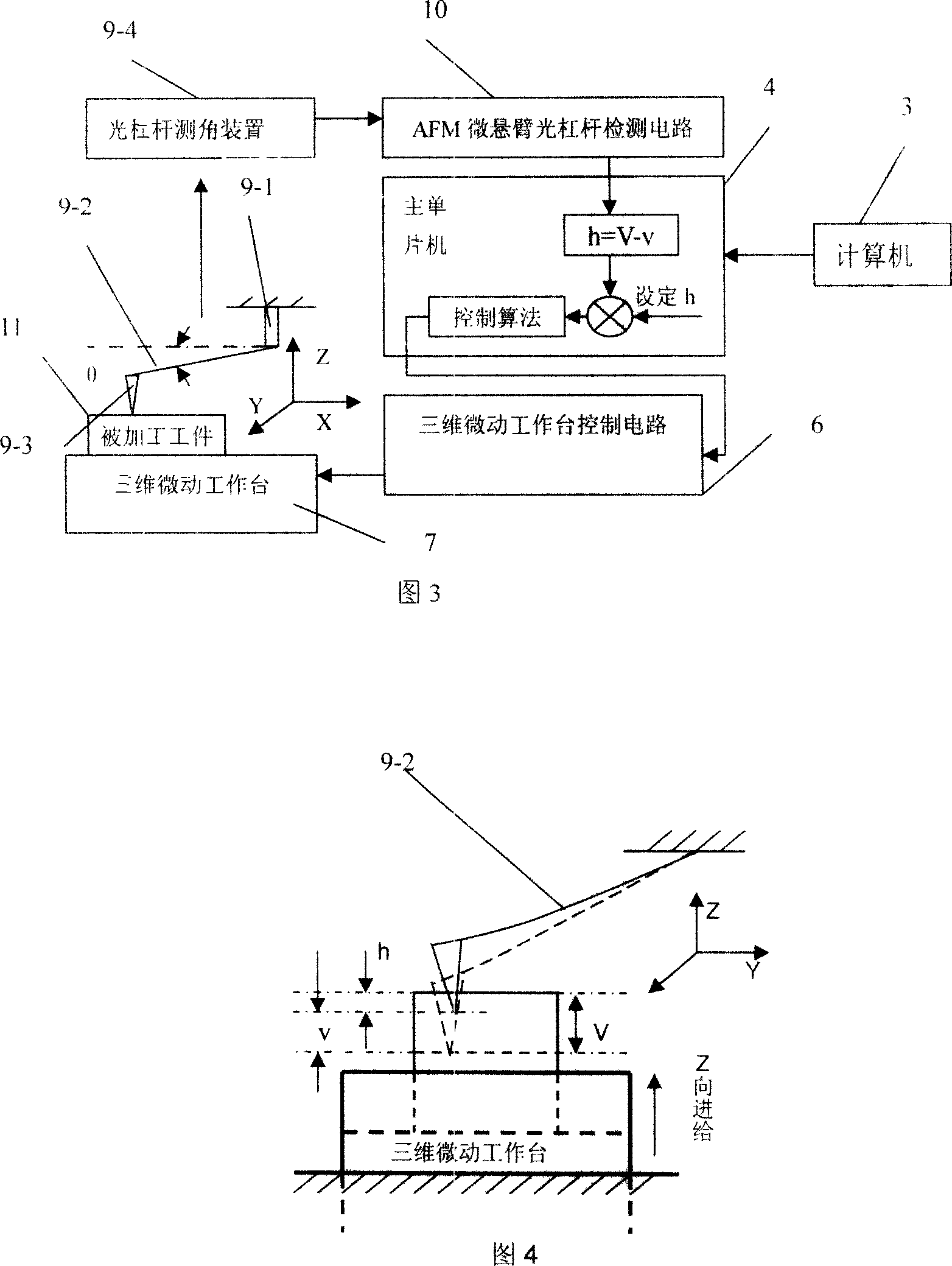
Method for making Nano microstructure based on constant height mode of atomic force microscope
InactiveCN101003356AOvercomes the drawback of a very limited size range for precise machiningAccuracy is easy to guaranteeNanostructure manufactureMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
A process based on the constant-height mode of atomic force microscope for preparing nano-class microstructure with controllable depth and large range of precise sizes features that 3D micro-motion bench and its control circuit is additionally used. The motion of said 3D micro-motion bench in height direction is driven by its control circuit to make the probe tip to prick into the surface of a workpiece to be processed. The deformation amount of cantilever caused by the reactive force received by said probe is detected by optical angular measurer and transmitted to single-chip computer. Said 3D bench is moving continuously in the height direction until the processed depth setting is equal to the difference between the motion amount of said 3D bench in height direction and said deformation amount of cantilever.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Micro-nano structure sidewall surface imaging device based on atomic force microscope (AFM) and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN104062466AAdd distance servo control programImprove usabilityScanning probe microscopyMagnetic force microscopeMicro nano
A micro-nano structure sidewall surface imaging device based on an atomic force microscope and an imaging method thereof relate to a technology of using an AFM to carry out scanning imaging on a micro-nano structure sidewall surface, and are used for solving the problem that the conventional AFM is very difficult to carry out scanning imaging on the micro-nano structure sidewall surface. The micro-nano structure sidewall surface imaging device based on the atomic force microscope of the present invention is characterized in that a probe rack is added on the basis of the original atomic force microscope, so that a probe can rotate around an X-axis direction; in addition, a distance servo control program of a sample table in an XZ scanning plane is also added, so that the sample table can approach the tip of the probe along a Y direction, and reach a distance which is set by users. The micro-nano structure sidewall surface imaging device based on the atomic force microscope and the imaging method thereof of the present invention can select the appropriate probe rotation angle according to different samples, can carry out scanning imaging on the sidewall surface of a sample and represent the sidewall surface of the sample under the premise of not damaging the sample, thereby realizing the accurate representation of the sidewall surfaces of different samples. The micro-nano structure sidewall surface imaging device based on the atomic force microscope and the imaging method thereof of the present invention are applicable to the micro-nano structure surface representation, and also can be used in the micro-nano manufacture and test fields.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Vacuum atomic force microscope and using method thereof
InactiveCN101625303ASolving Design DifficultiesRealize continuous measurementSurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsMagnetic force microscopeConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention discloses a vacuum atomic force microscope and a using method thereof, belonging to the field of micro-topography detecting equipment; the microscope comprises an electron beam launching device, a secondary electron detector, a probe with a cantilever, a piezoelectric ceramics scanner and a feedback controller. When in work, electron beams are irradiated to the cantilever of the probe; as the acting force between the probe and sample atoms causes the cantilever to become deformed; a secondary electron signal changes; the acting force between a pinpoint and the sample is controlled to be constant by the signal feedback; the pinpoint scans the surface of the sample point by point and can image surface topography of the sample. The currently common optical lever does not need to be drawn into the invention; the invention overcomes design difficulty brought about by the conventional atomic force microscope applied in vacuum environment, synthesizes two nanophase material characterization methods which are the advantages of the atomic force microscope and an electronic microscope, and can realize the continuous measuring on the material from millimeter size to the sub-nanometer size.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for making Nano microstructure based on constant force mode of atomic force microscope
InactiveCN101003357AAccuracy is easy to guaranteeHigh repeatability positioning accuracyNanostructure manufactureMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
A process based on the constant-force mode of atomic force microscope for preparing nano-class microstructure with controllable depth and large range of precise sizes features that 2D micro-motion bench and its control circuit is additionally used. The extension of scanning ceramic tube is driven by AFM driver circuit to make the probe tip to prick into the surface of a workpiece to be processed. The variation amount of scanning ceramic tube is detected by the real-time detection circuit and transmitted to single-chip computer. Said scanning ceramic tube is extended continuously in the relative direction until the processed depth setting is equal to the difference between the motion amount of said scanning ceramic tube in height direction and said deformation amount of cantilever.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic signal reproduction system and magnetic signal reproduction method
InactiveUS20090174969A1Good electromagnetic propertiesReduce noiseRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetic force microscopeNon magnetic
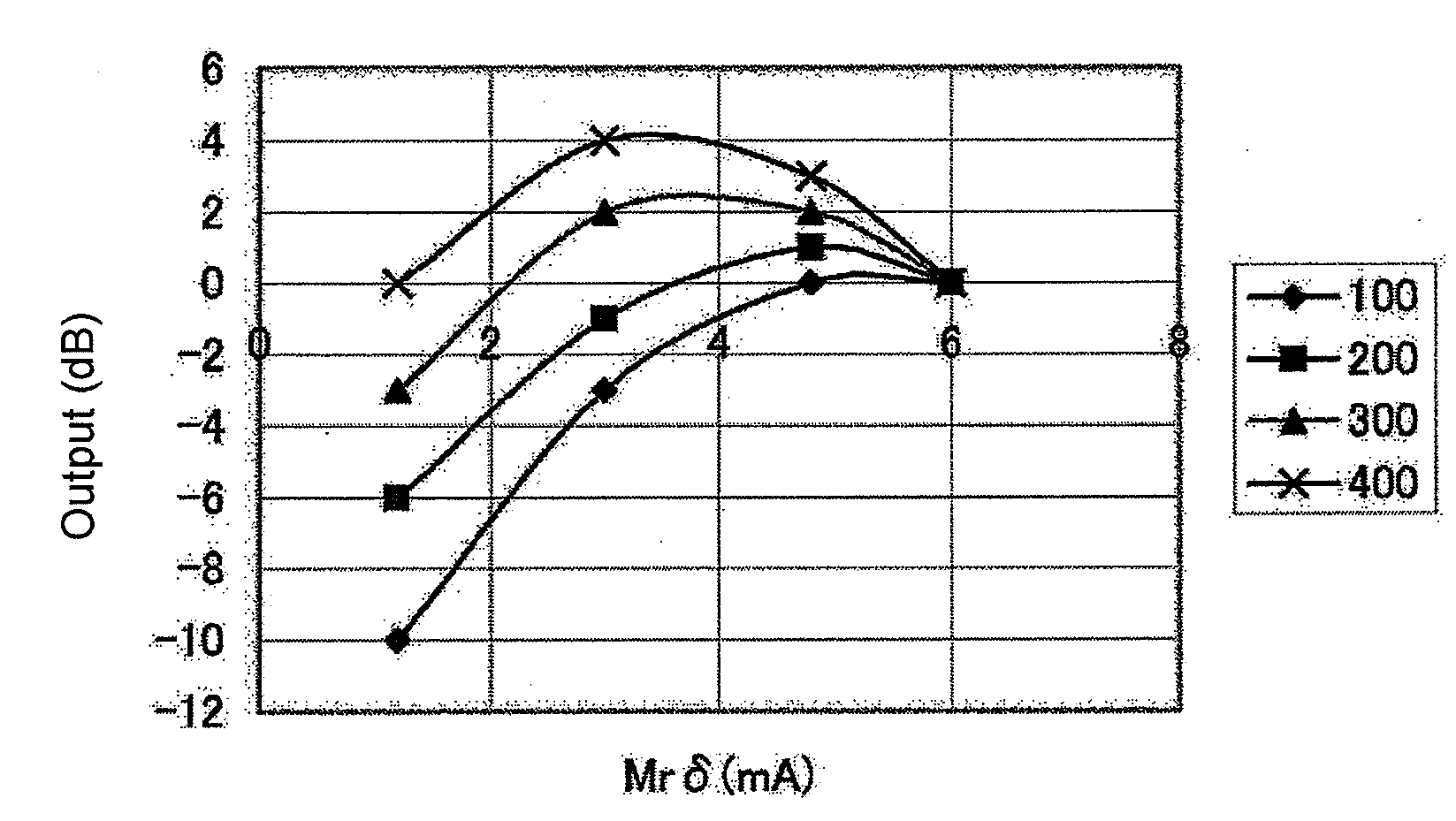
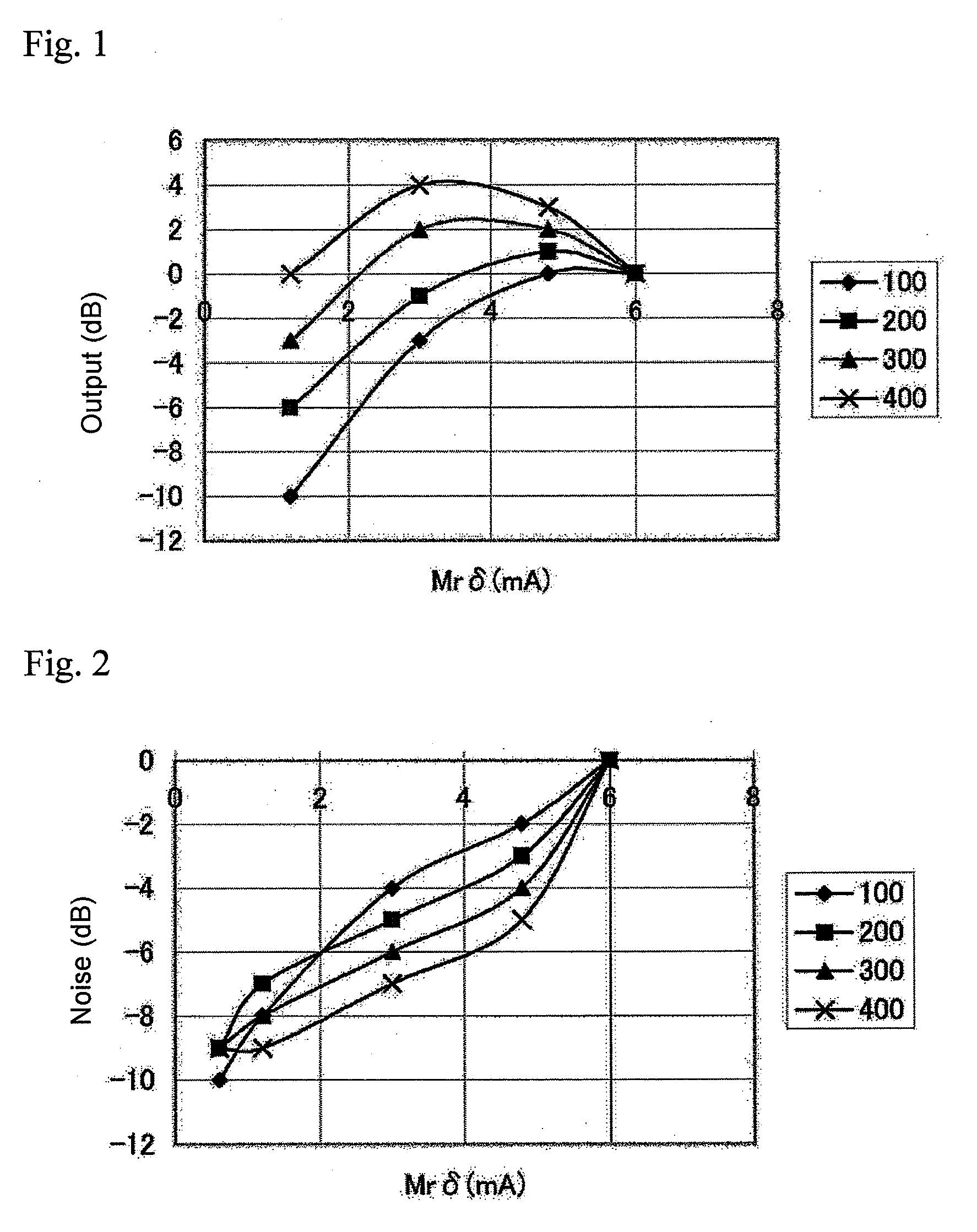
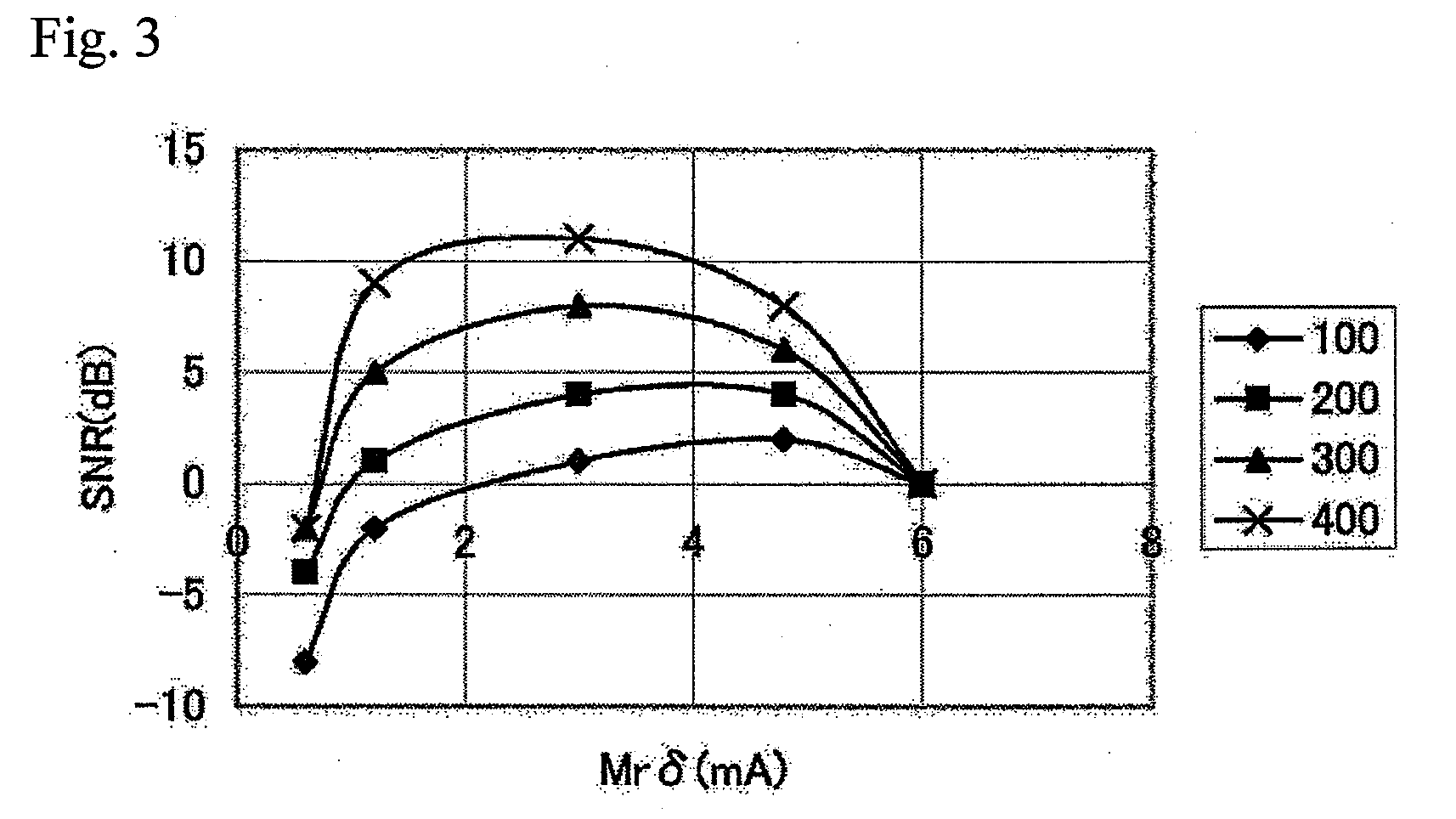
The present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the magnetic layer has a thickness δ ranging from 10 to 80 nm, a product, Mrδ, of a residual magnetization Mr of the magnetic layer and the thickness δ of the magnetic layer is equal to or greater than 1 mA but less than 5 mA, a ratio, Sdc / Sac, of an average area Sdc of magnetic clusters in a DC demagnetized state to an average area Sac of magnetic clusters in an AC demagnetized state as measured by a magnetic force microscope, MFM, ranges from 0.8 to 2.0.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Preparation method of colloid probe for atomic force microscope
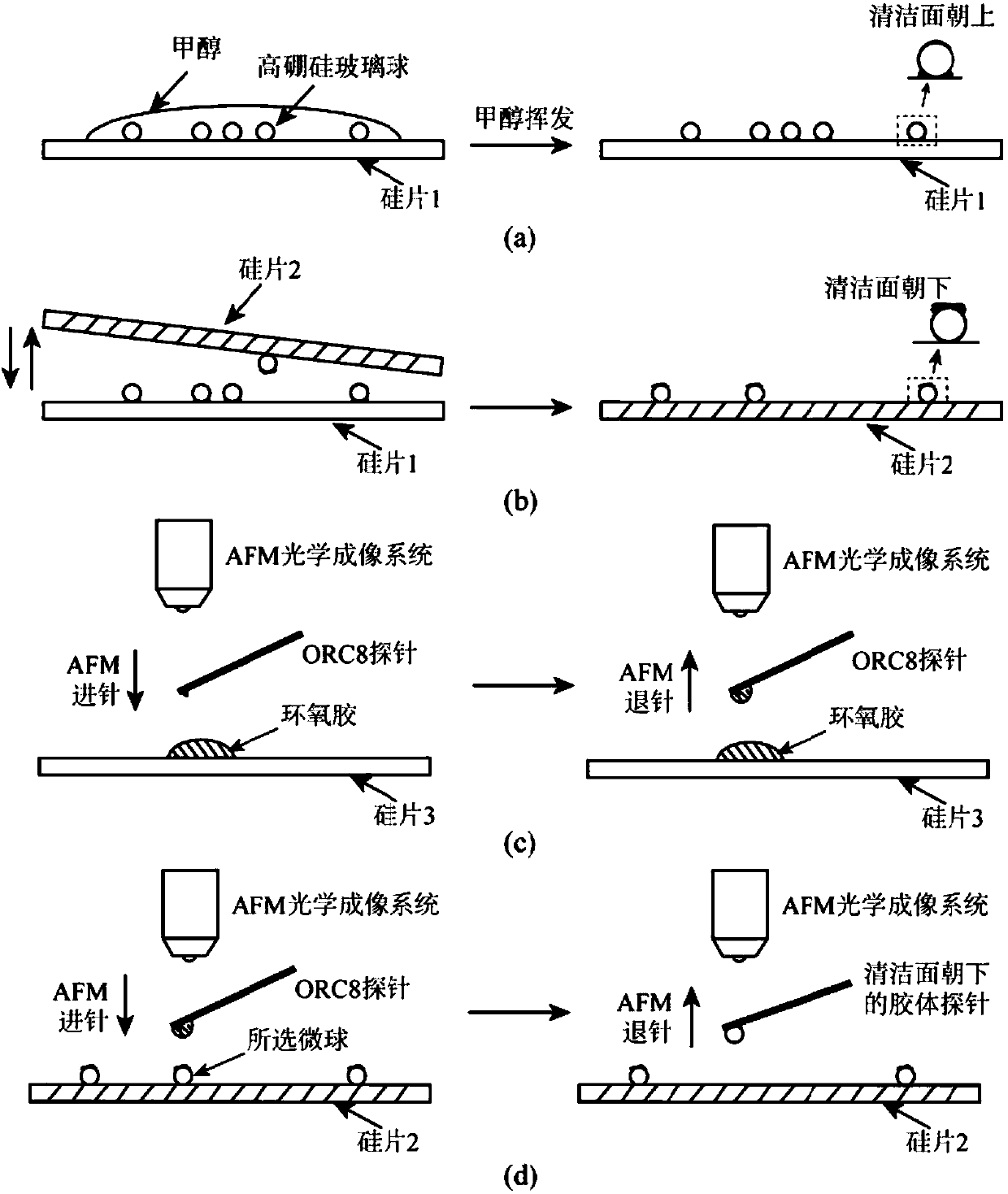
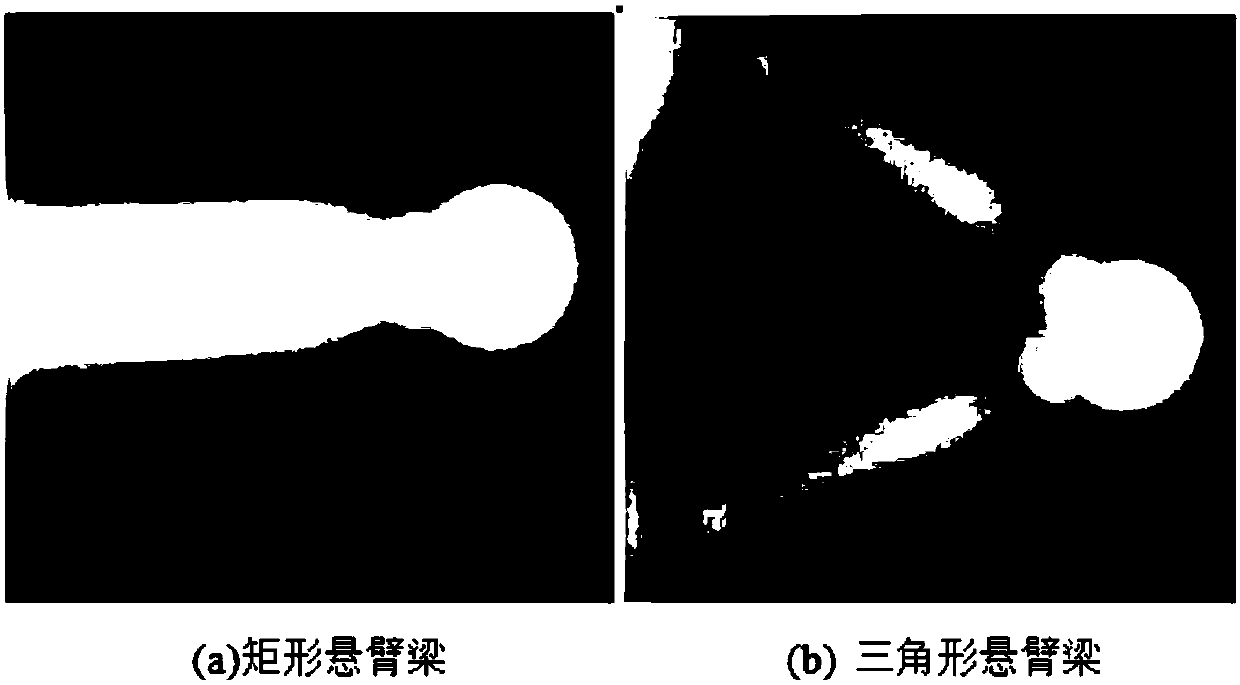
ActiveCN107796958AImprove machining accuracySignificant technological progressScanning probe microscopyMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
The invention provides a preparation method of a colloid probe for an atomic force microscope. Under the display function of an optical imaging system of an atomic force microscope, an epoxy adhesiveis pasted to the bottom of the front end of a microcantilever by using a motion control system of the atomic force microscope; and a cleaned microsphere is pasted to the center of the bottom of the front end of the microcantilever accurately by the epoxy adhesive to prepare a colloid probe. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, no special three-dimensional micro-motion operation platform is needed; the operation becomes simple and convenient; the practicability is high; the prepared colloid probe has a smooth and clean surface; and the preparation method is applied tobatched preparation of colloid probes in a laboratory.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com