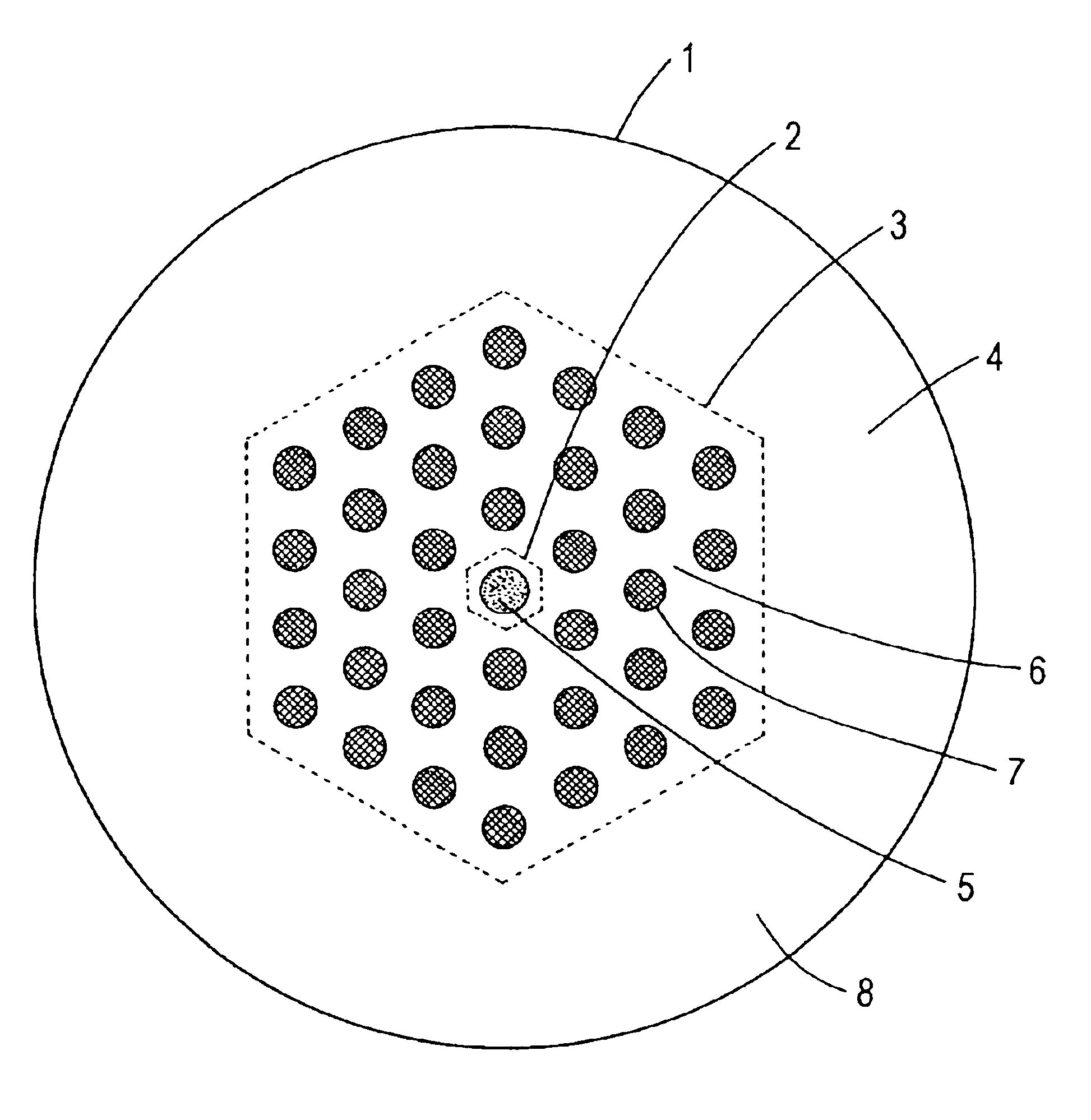
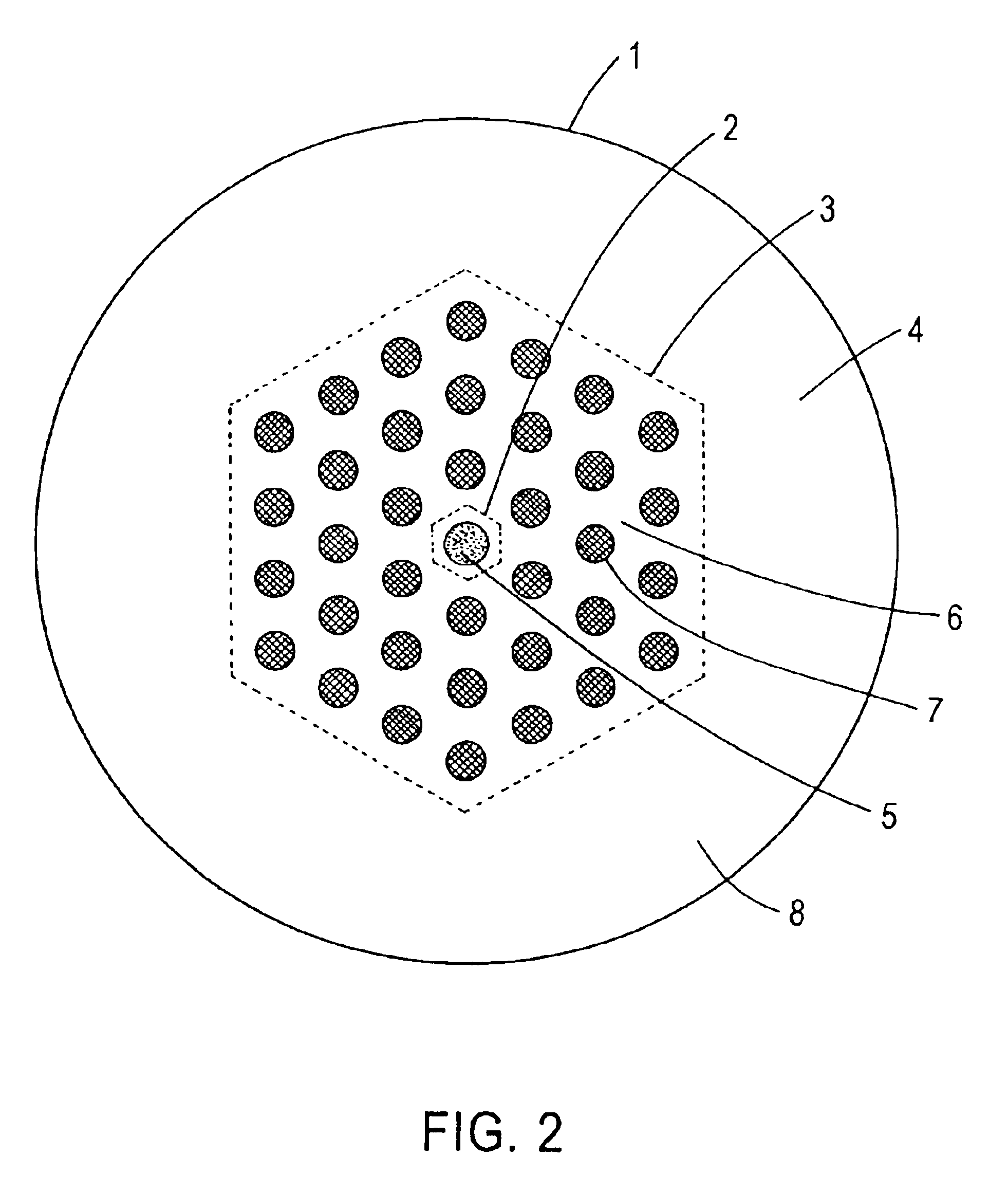
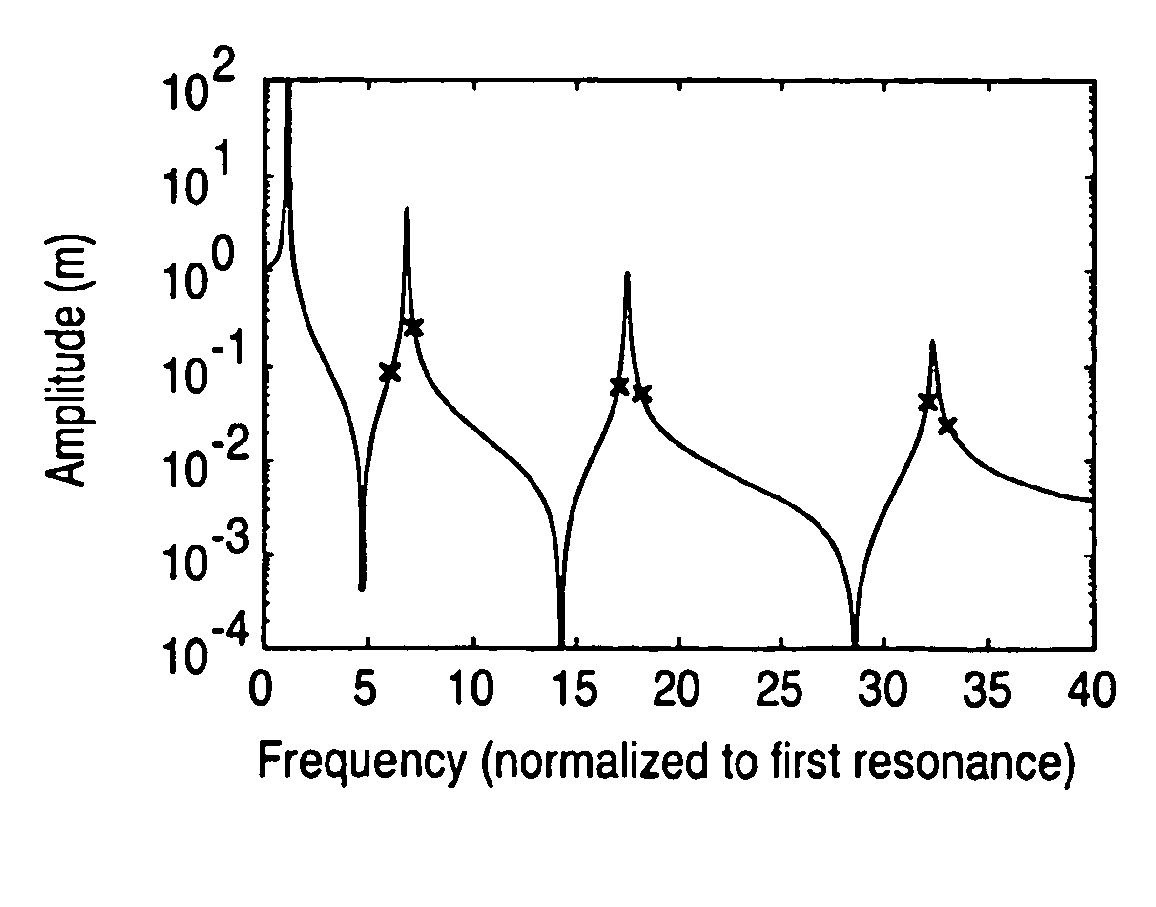
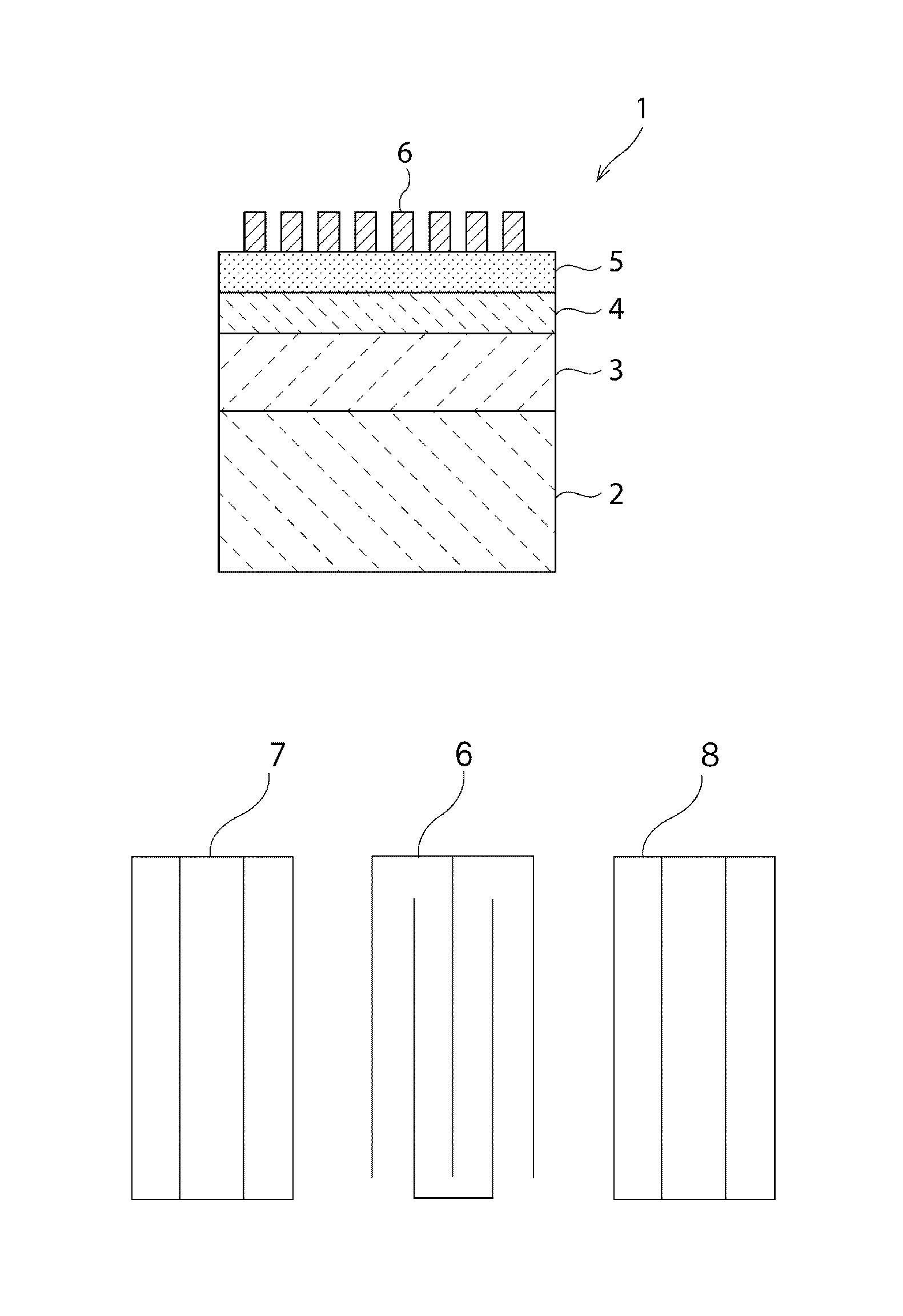
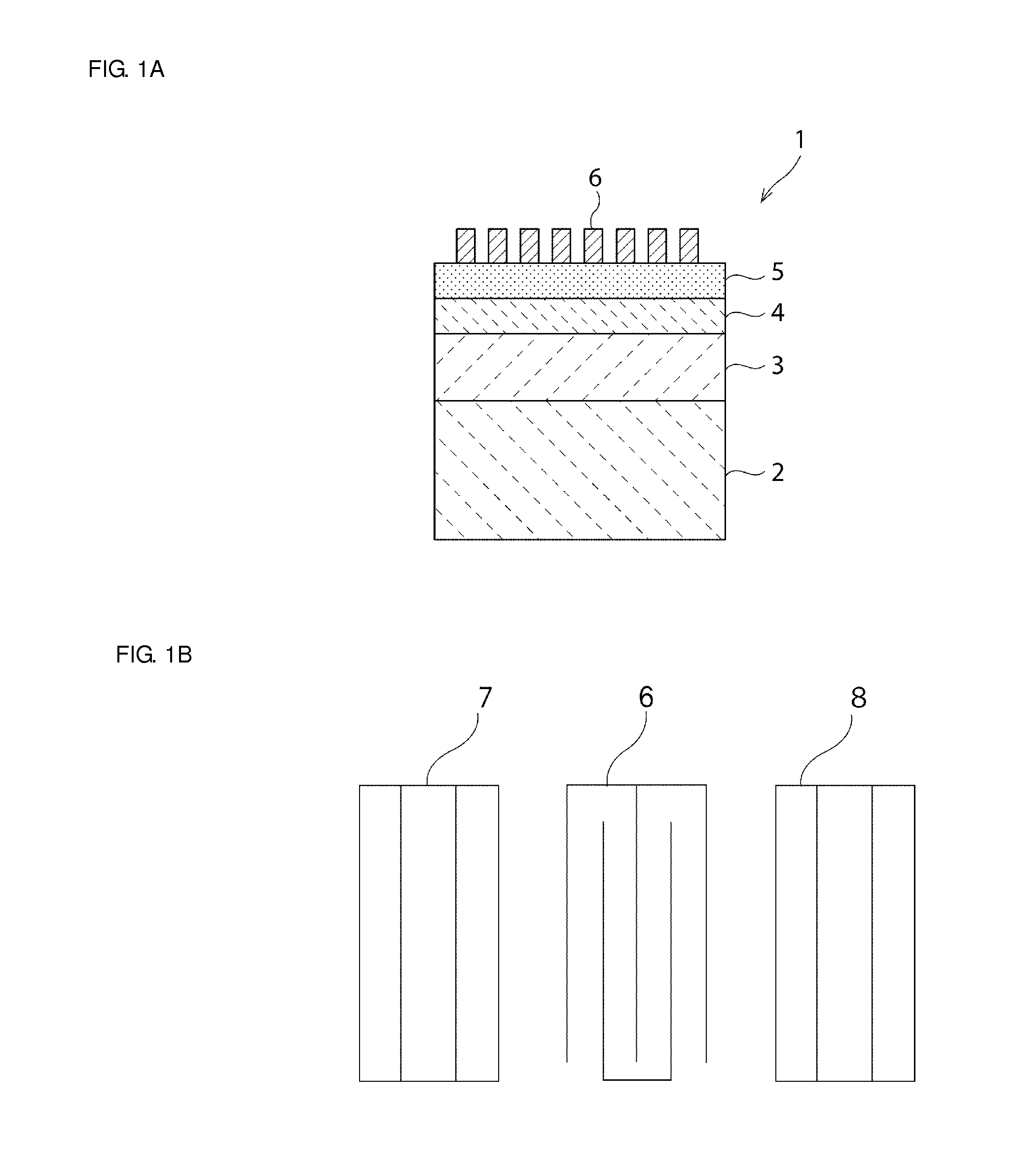
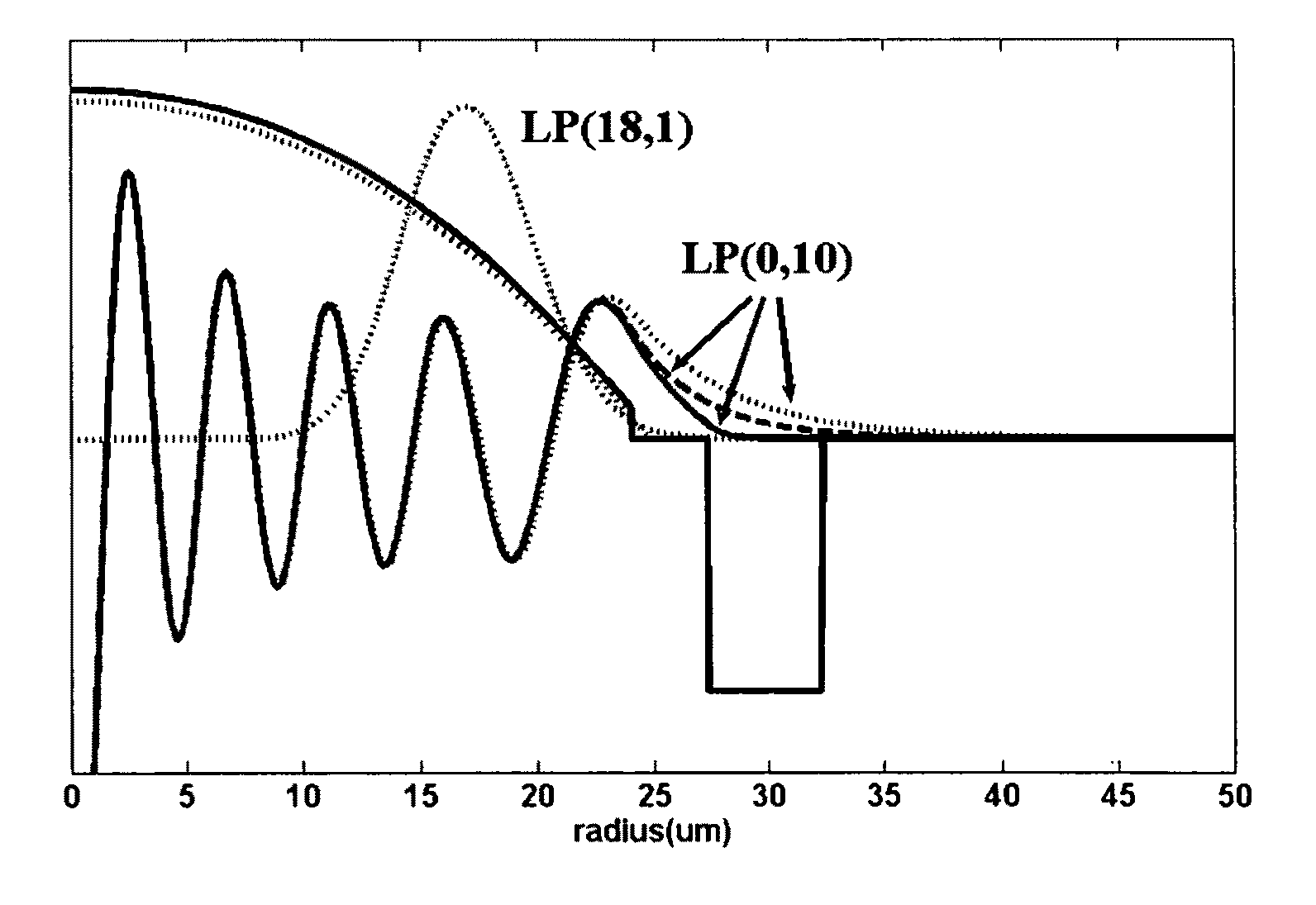
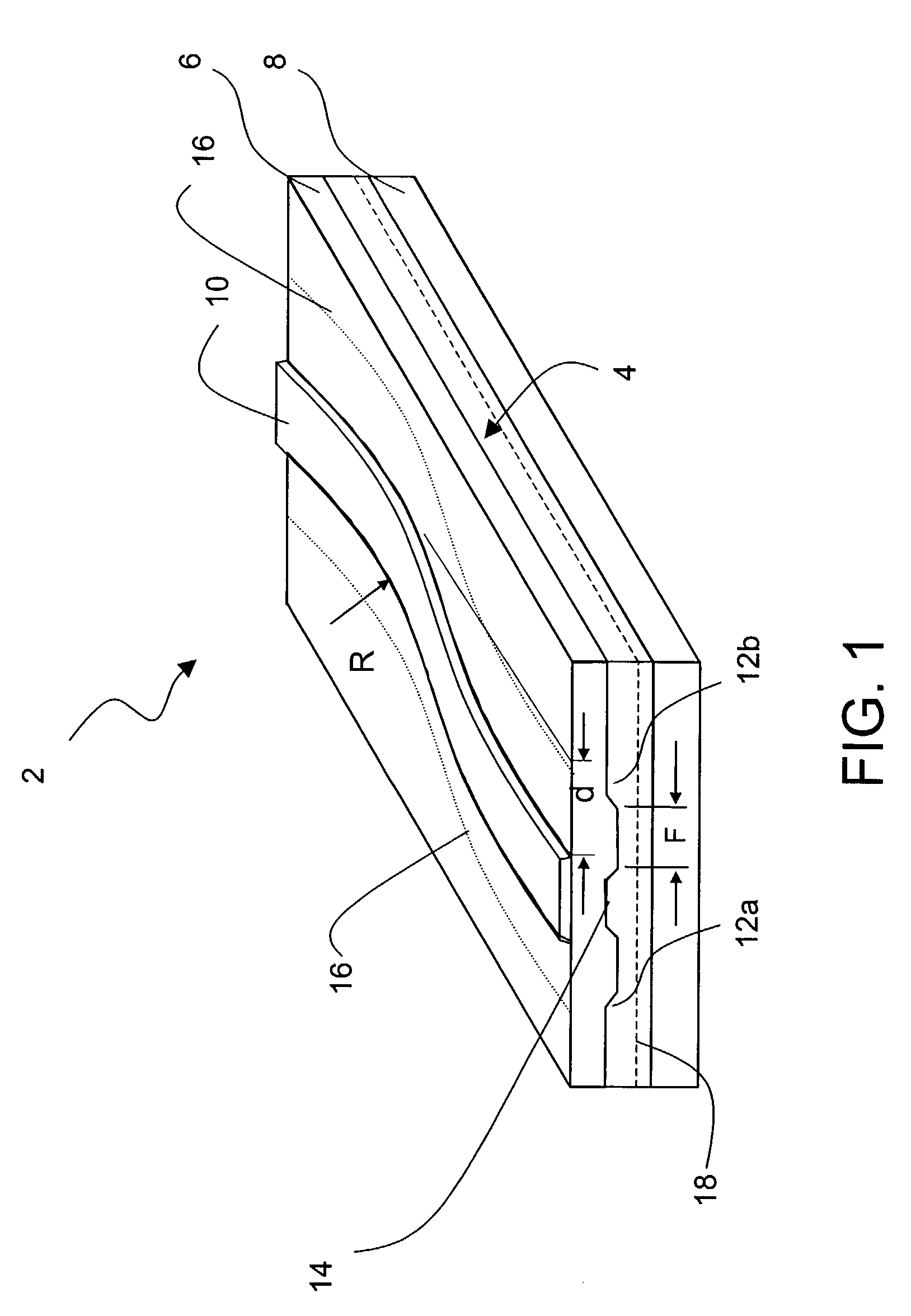
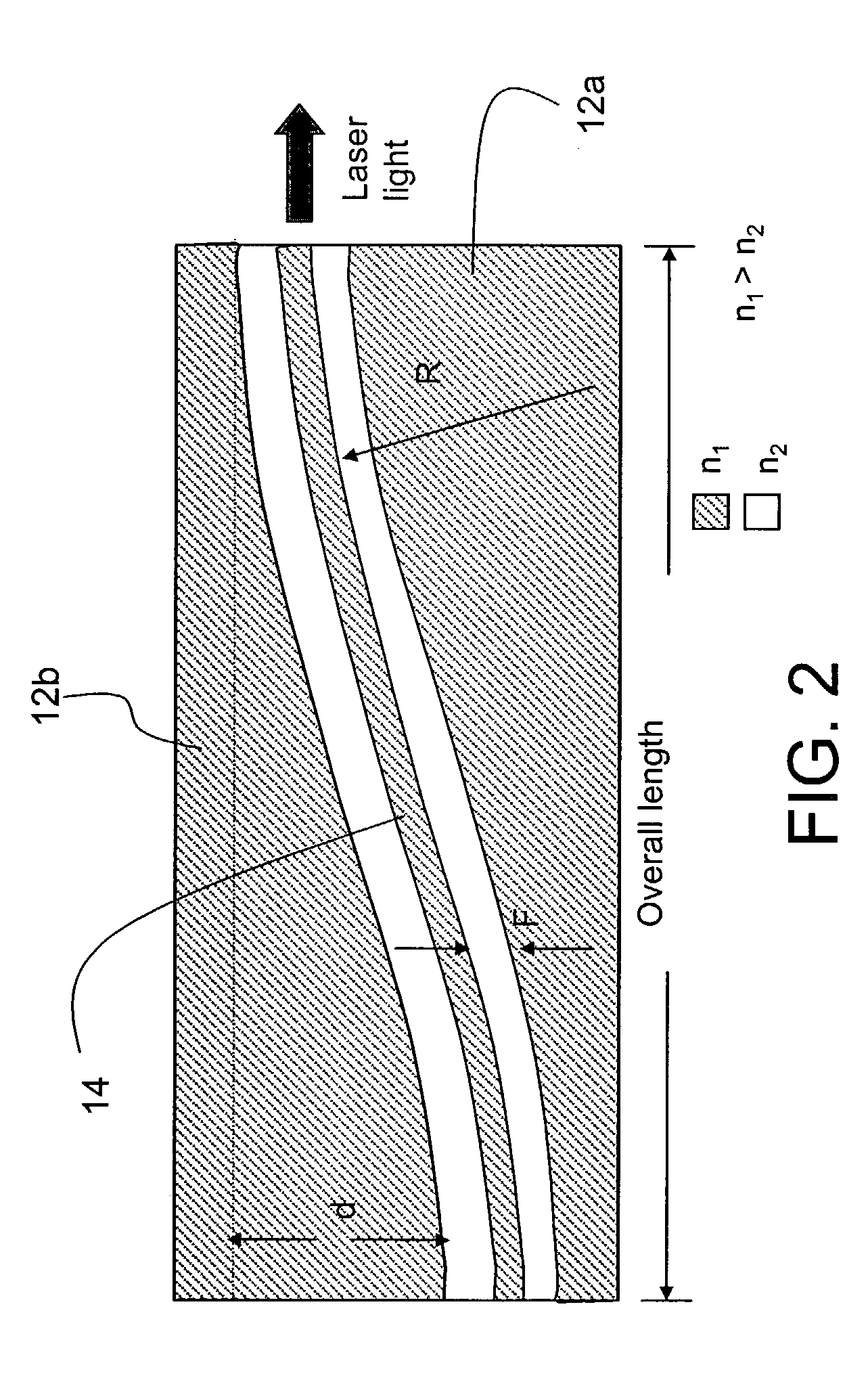
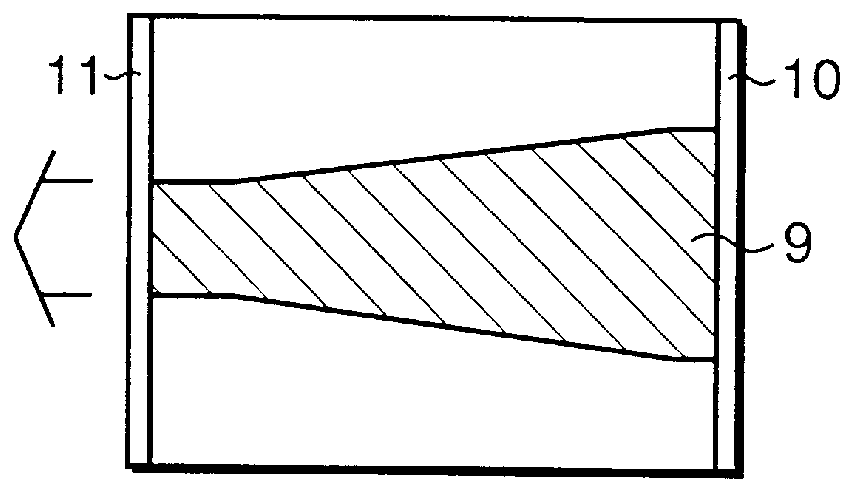
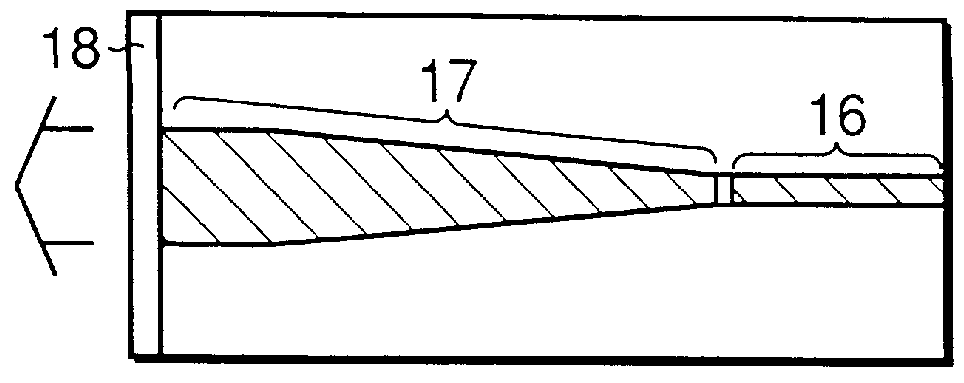
Patents
Literature
895 results about "Higher order mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
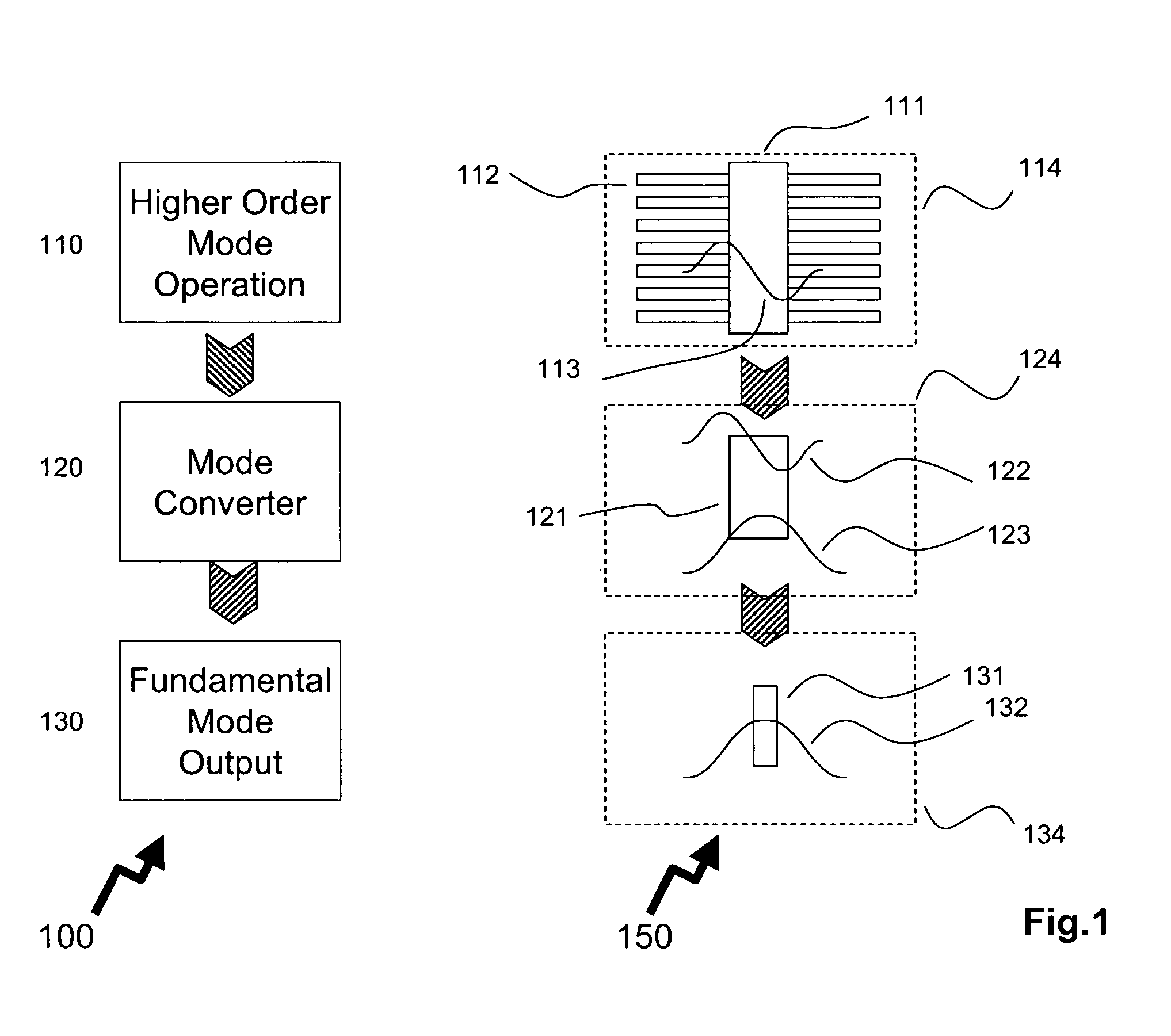
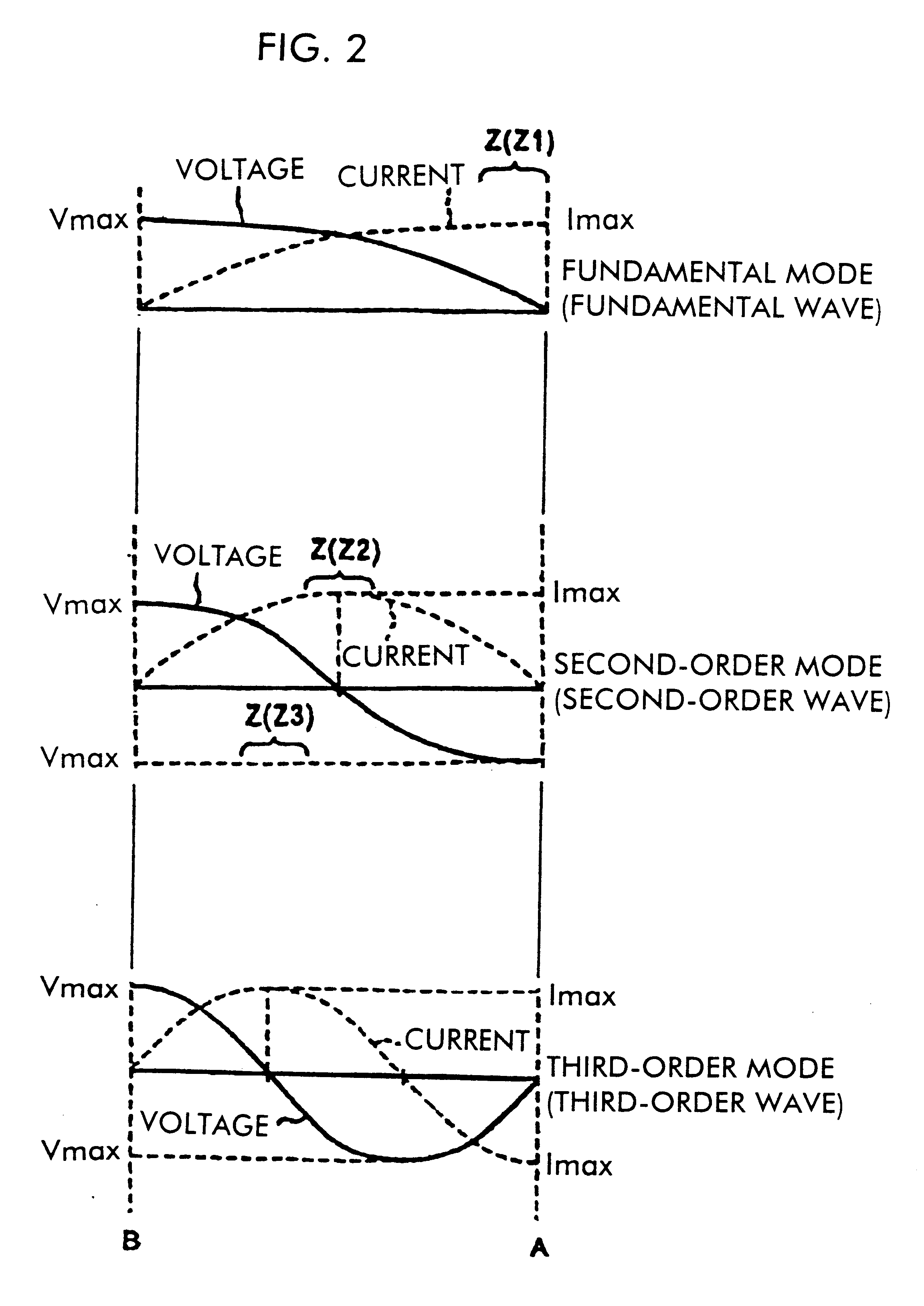
Higher-order Modes A mode is the spatial distribution of light inside an optical fiber. Traditionally, fibers have been engineered to be single-moded, since this is generally advantageous in optical communications. HOMs can be engineered to have special dispersion properties, making them ideal for certain tasks.
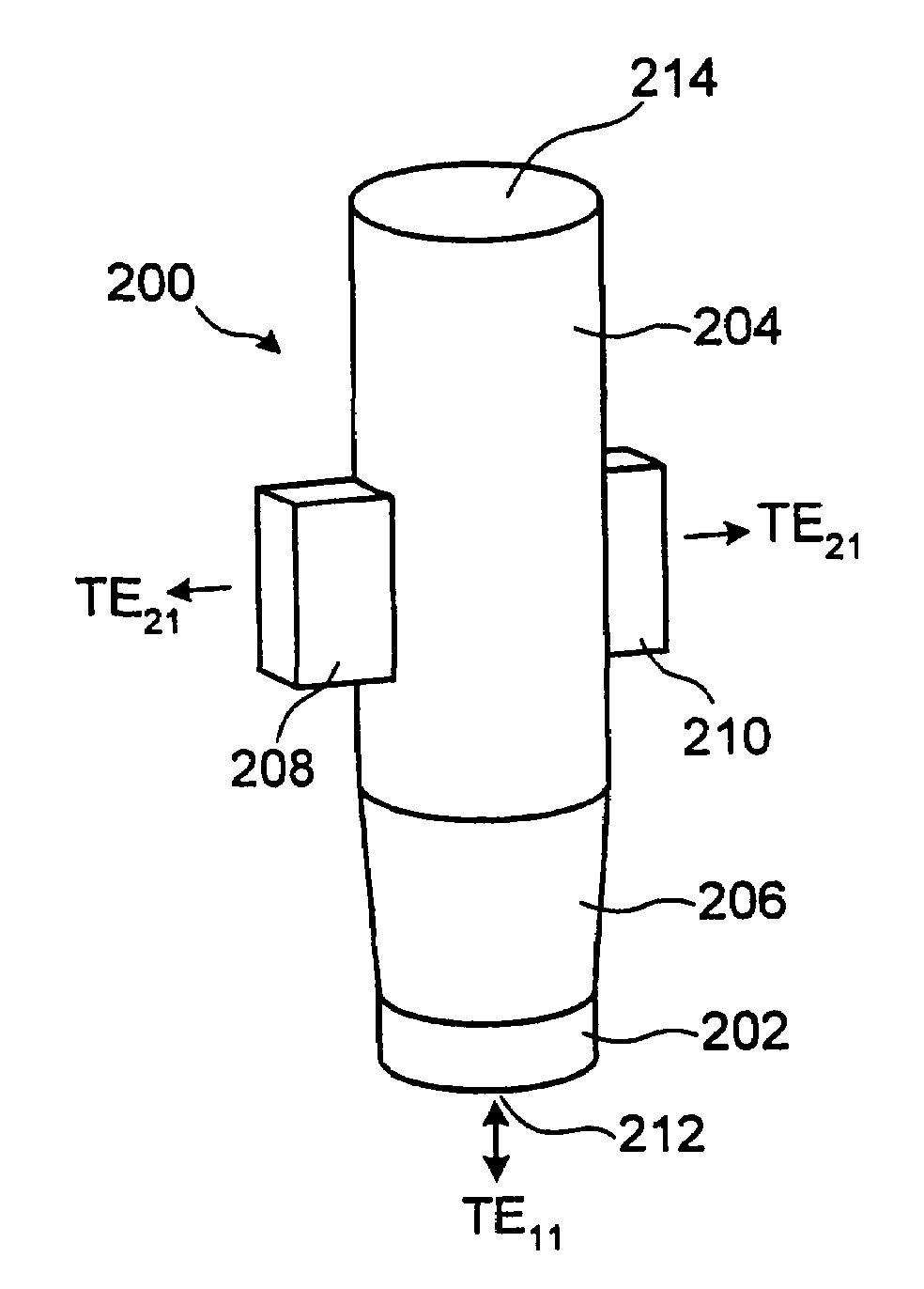
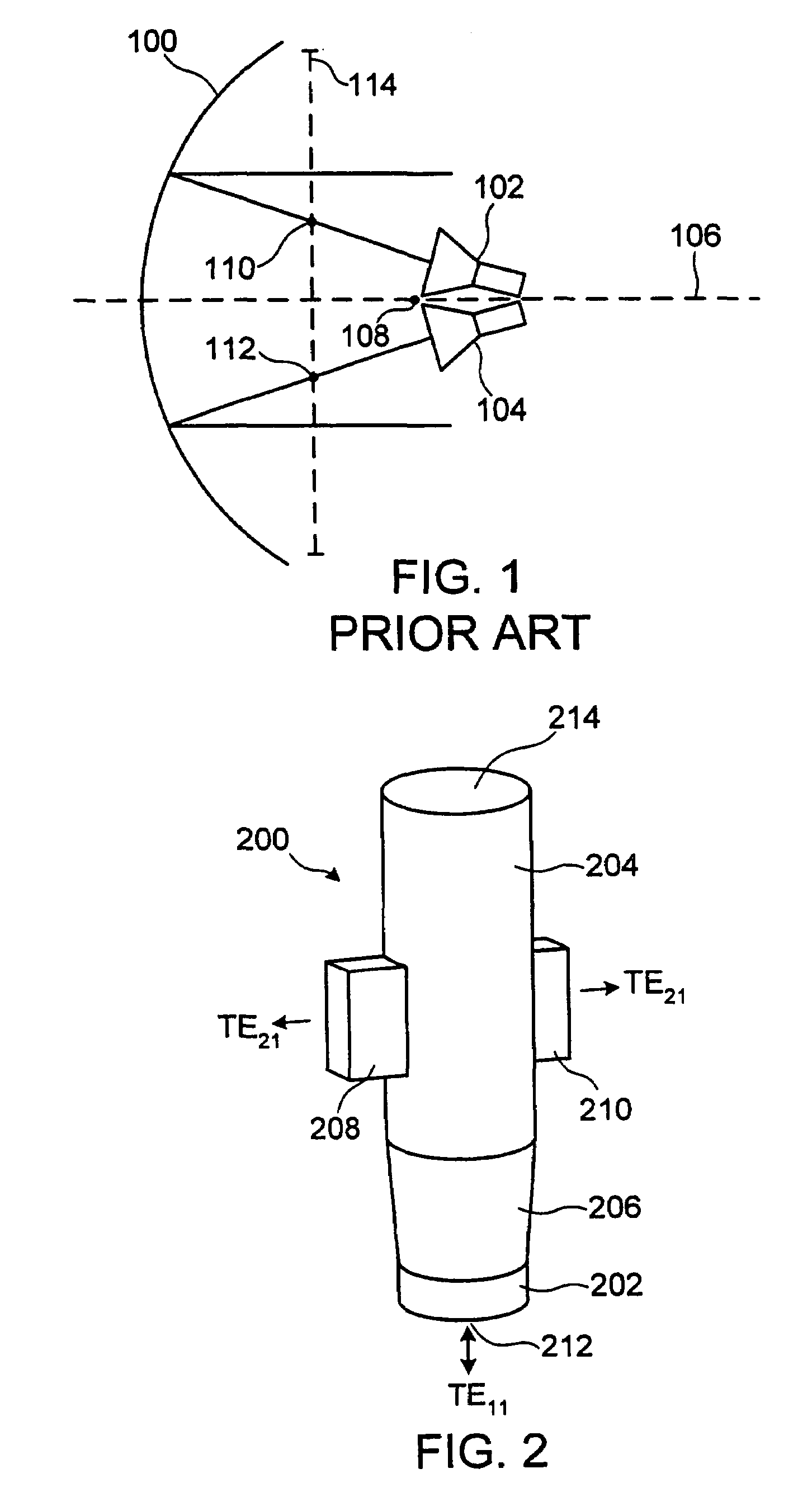
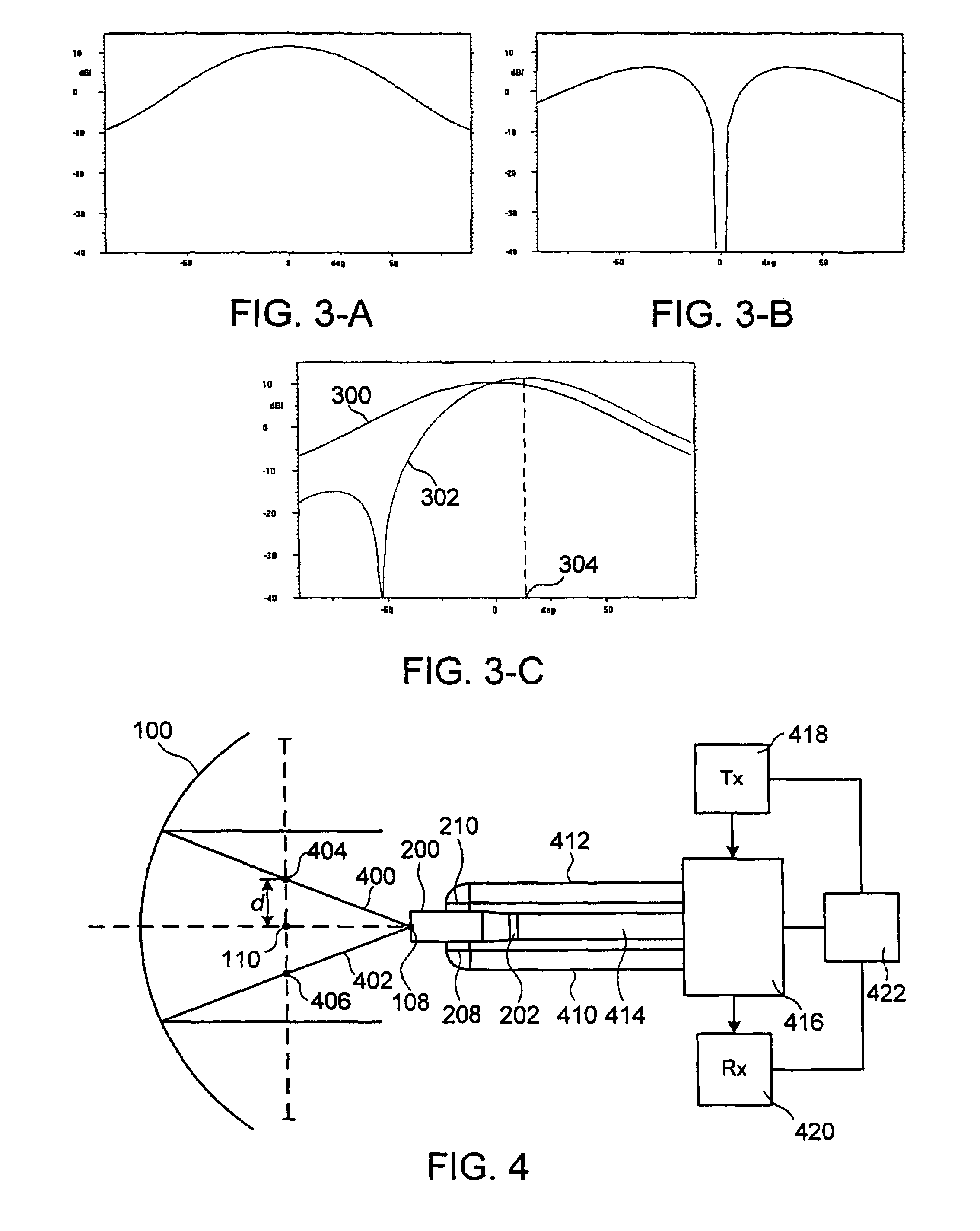
Multiple phase center feedhorn for reflector antenna
A feedhorn driving method and apparatus allows the establishment of multiple phase centers using only a single multimode feedhorn. At least two higher-order modes are extracted from the feedhorn and weighted in amplitude and phase. The phase center separation is established in accordance with an assigned weights. The feedhorn has application in i.a. moving target indication systems.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
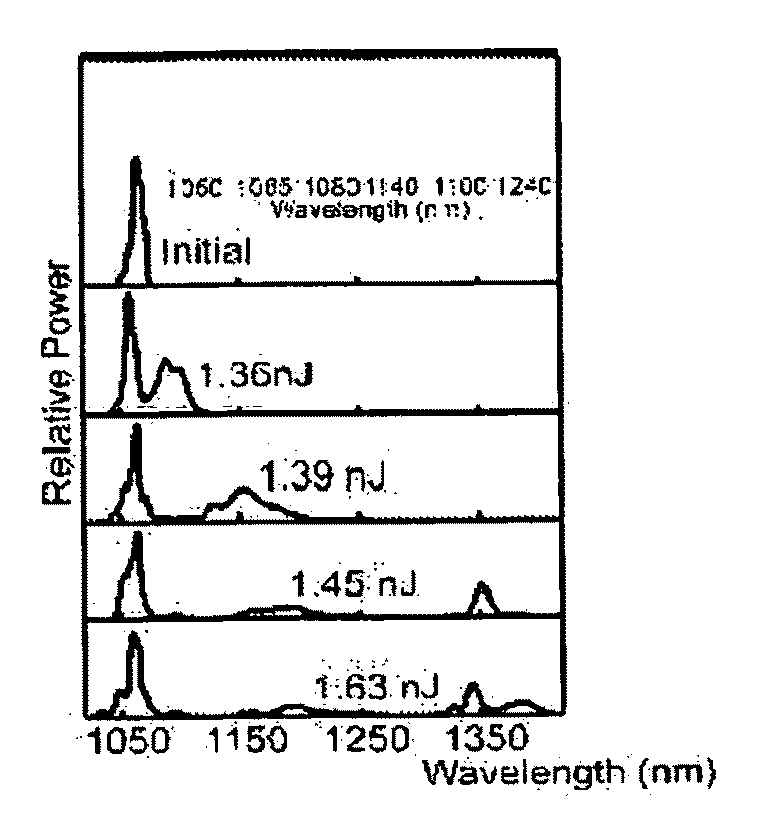
Production of optical pulses at a desired wavelength using solition self-frequency shift in higher-order-mode fiber
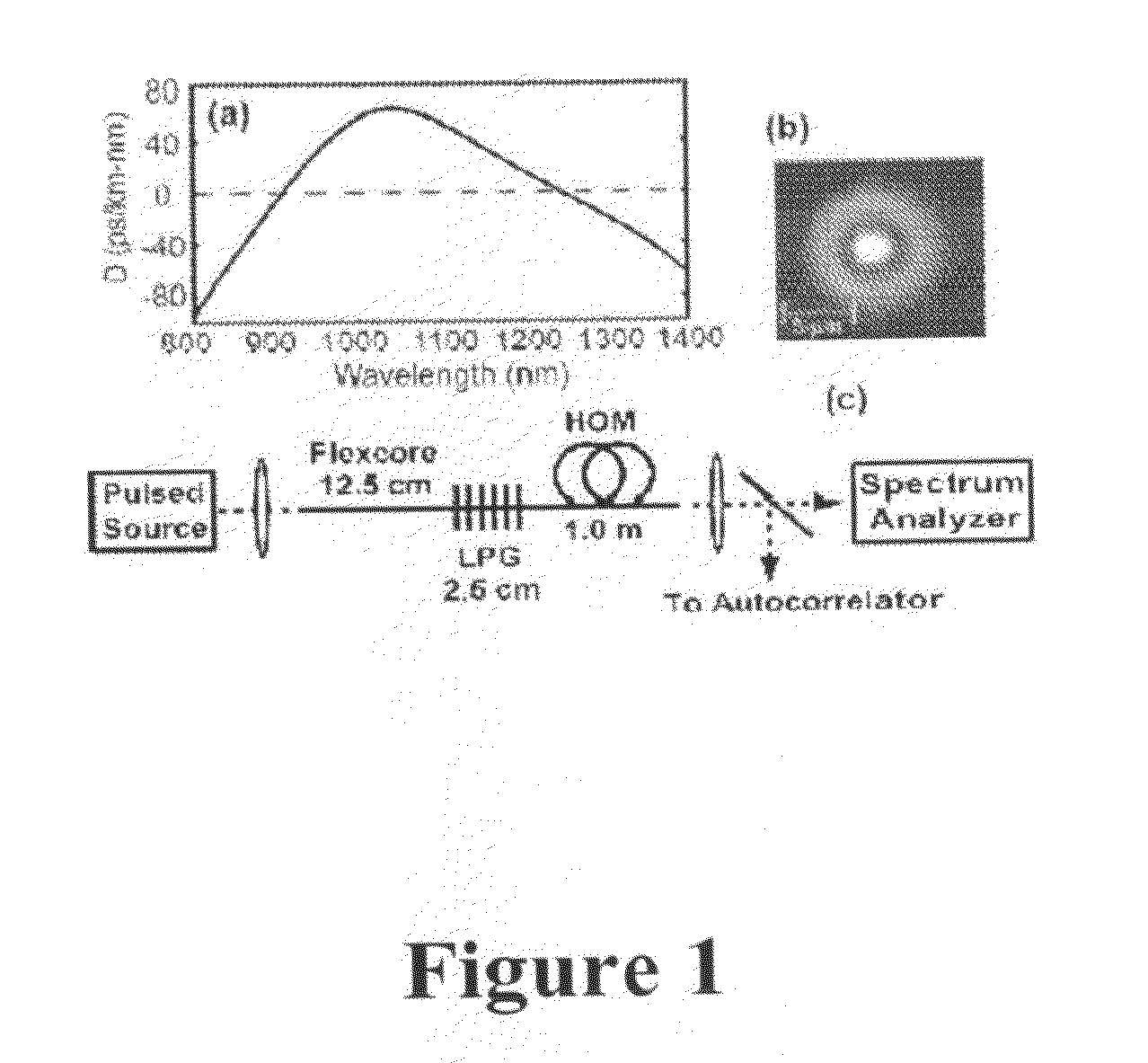
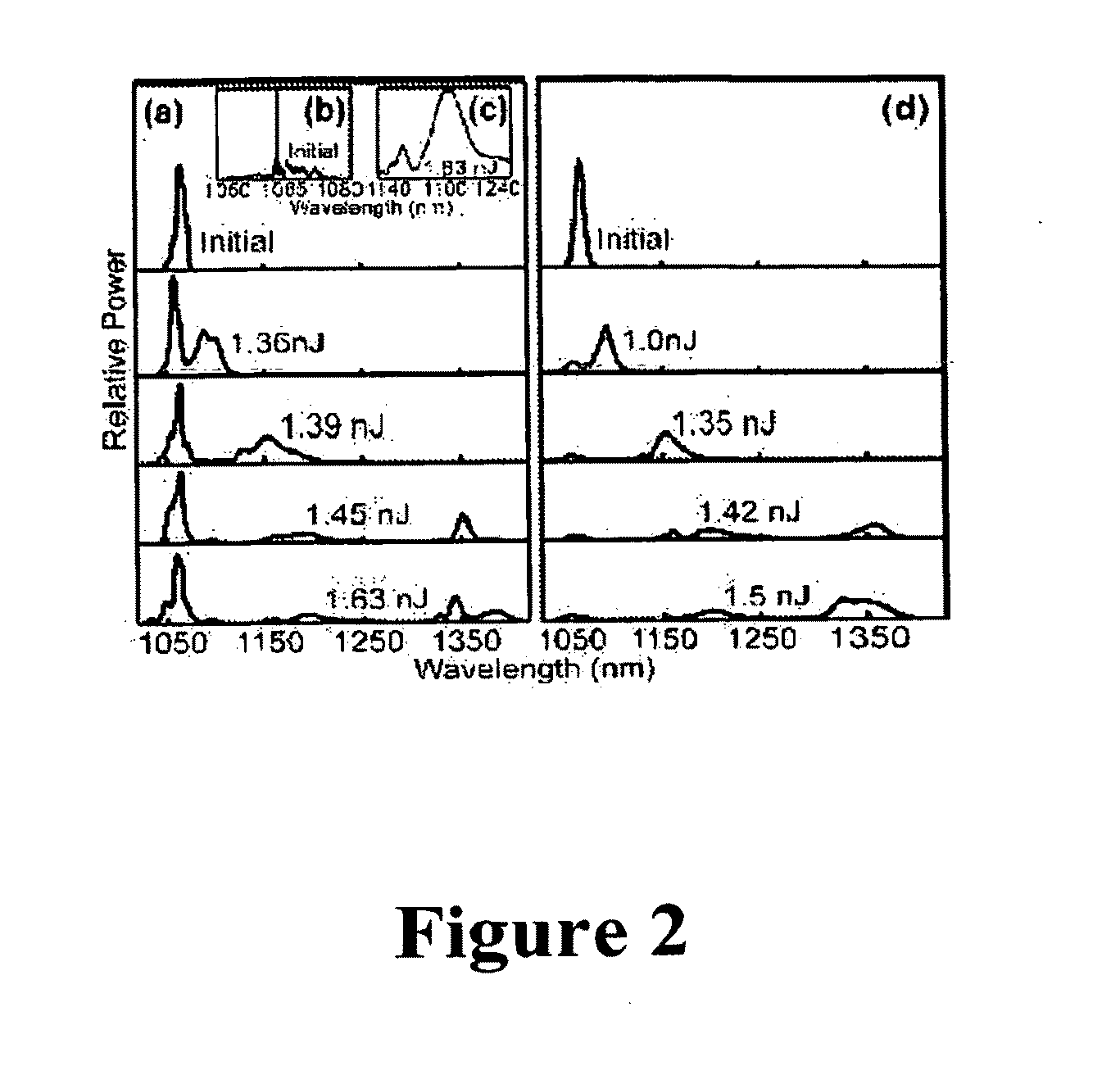
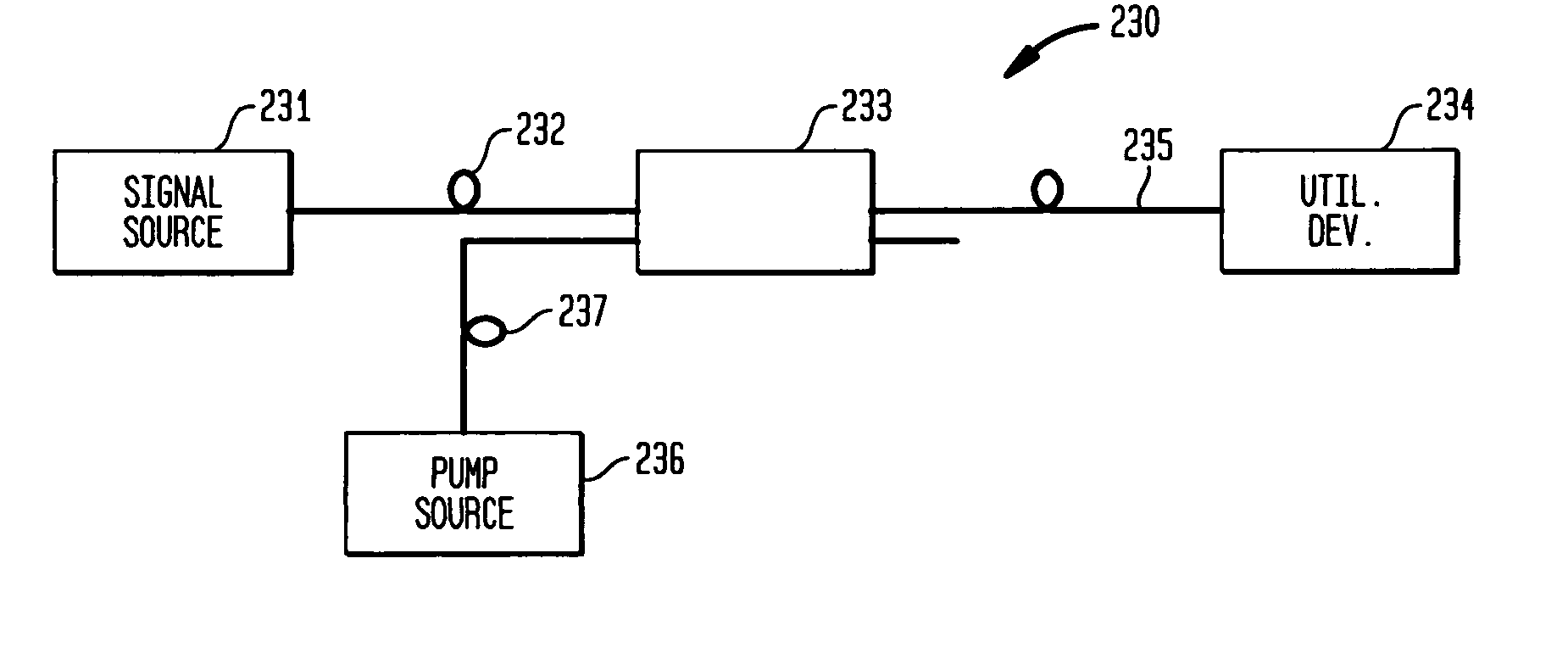
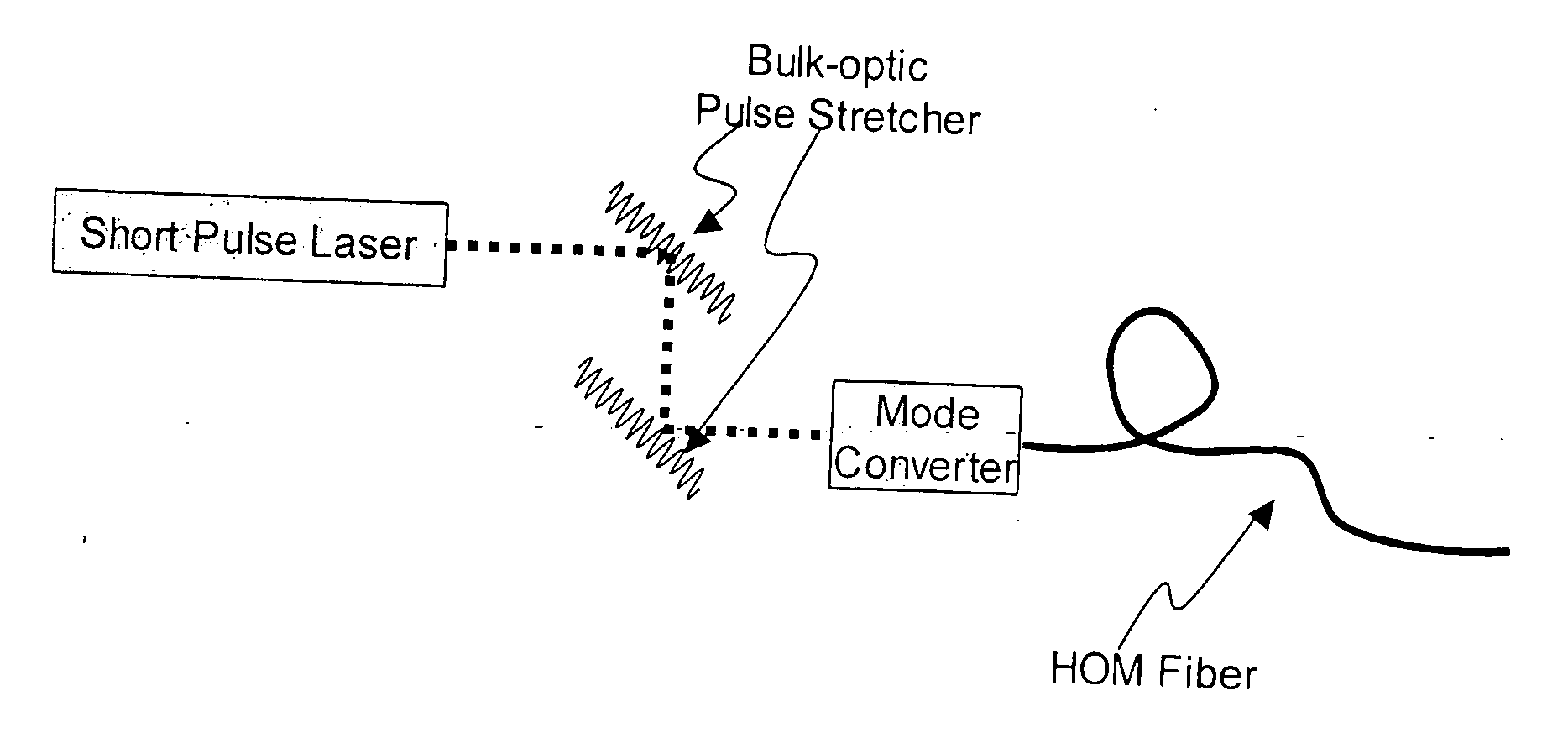
The present invention relates to an apparatus for producing optical pulses of a desired wavelength. The apparatus includes an optical pulse source operable to generate input optical pulses at a first wavelength. The apparatus further includes a higher-order-mode (HOM) fiber module operable to receive the input optical pulses at the first wavelength, and thereafter to produce output optical pulses at the desired wavelength by soliton self-frequency shift (SSFS). The present invention also relates to a method of producing optical pulses having a desired wavelength. This method includes generating input optical pulses using an optical pulse source, where the input optical pulses have a first wavelength and a first spatial mode. The input optical pulses are delivered into an HOM fiber module to alter the wavelength of the input optical pulses from the first wavelength to a desired wavelength by soliton self-frequency shift (SSFS) within the HOM fiber module, thereby producing output optical pulses having the desired wavelength.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
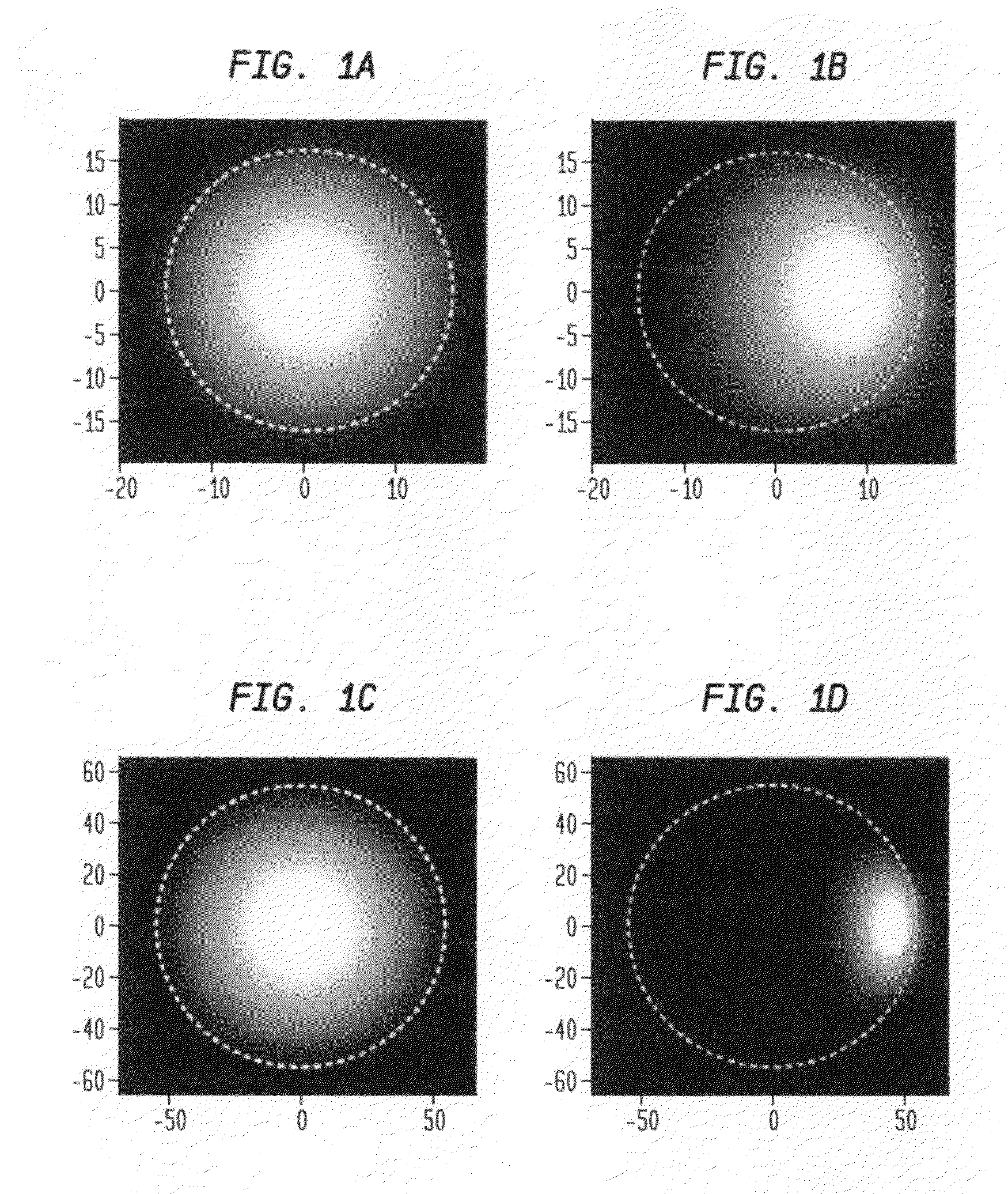
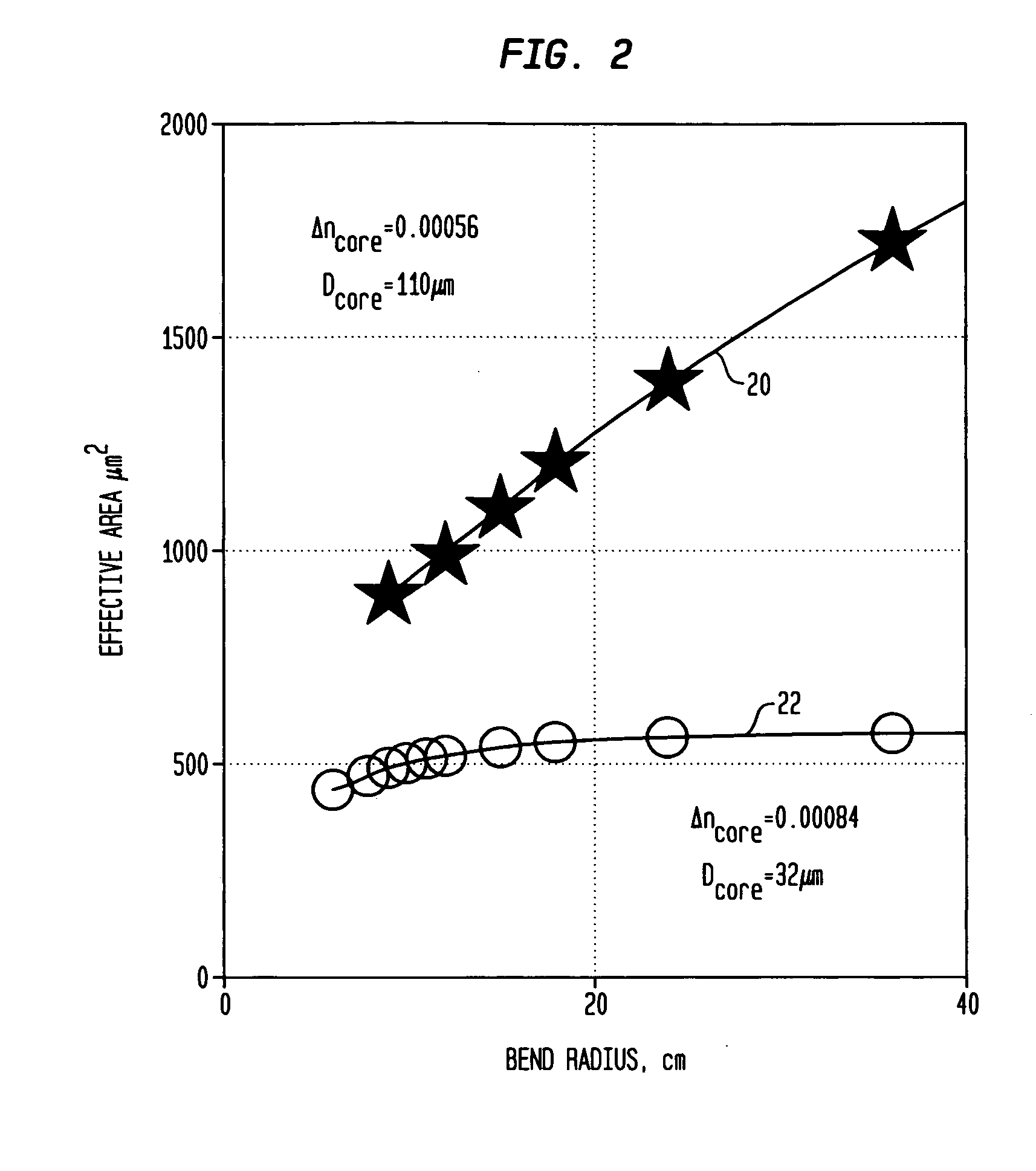
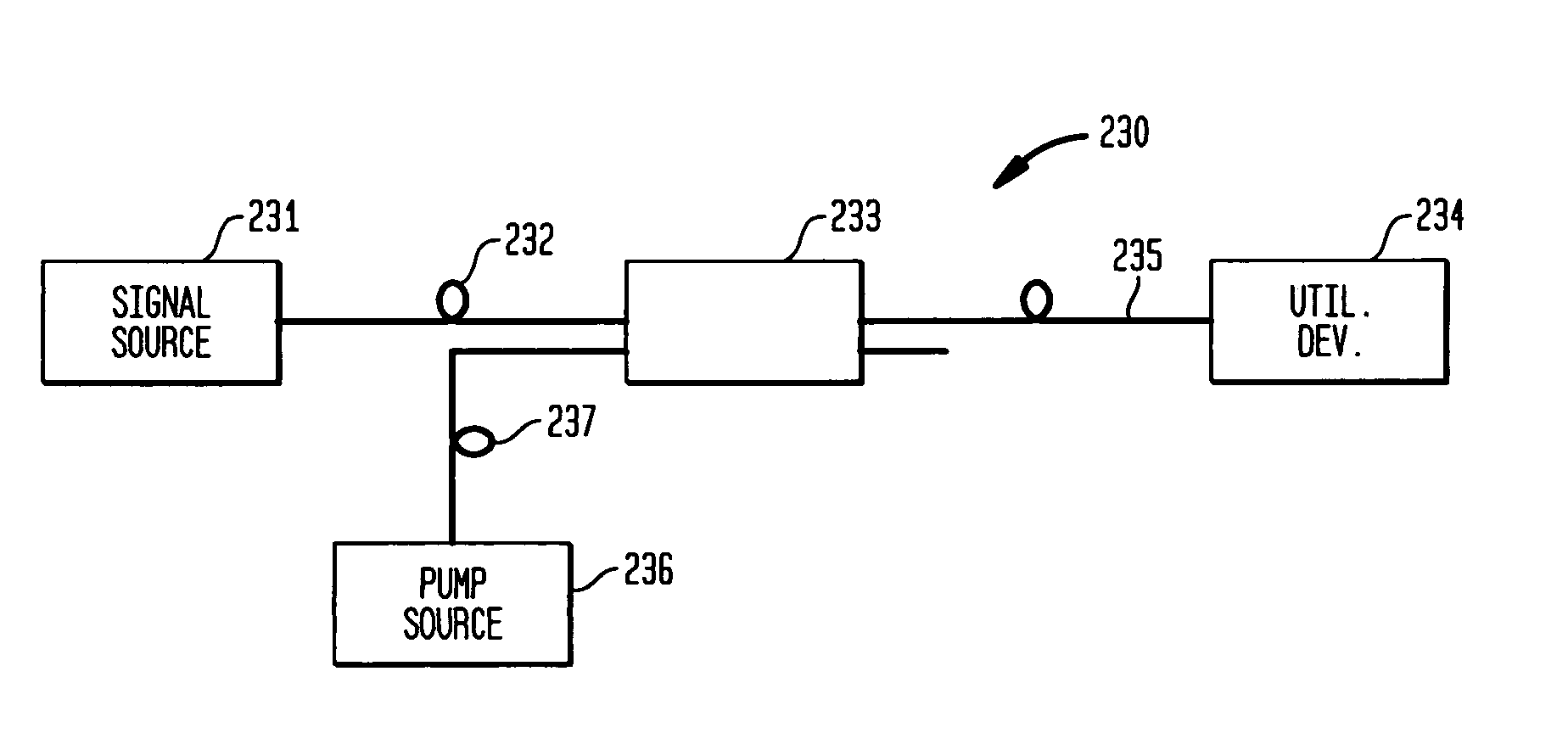
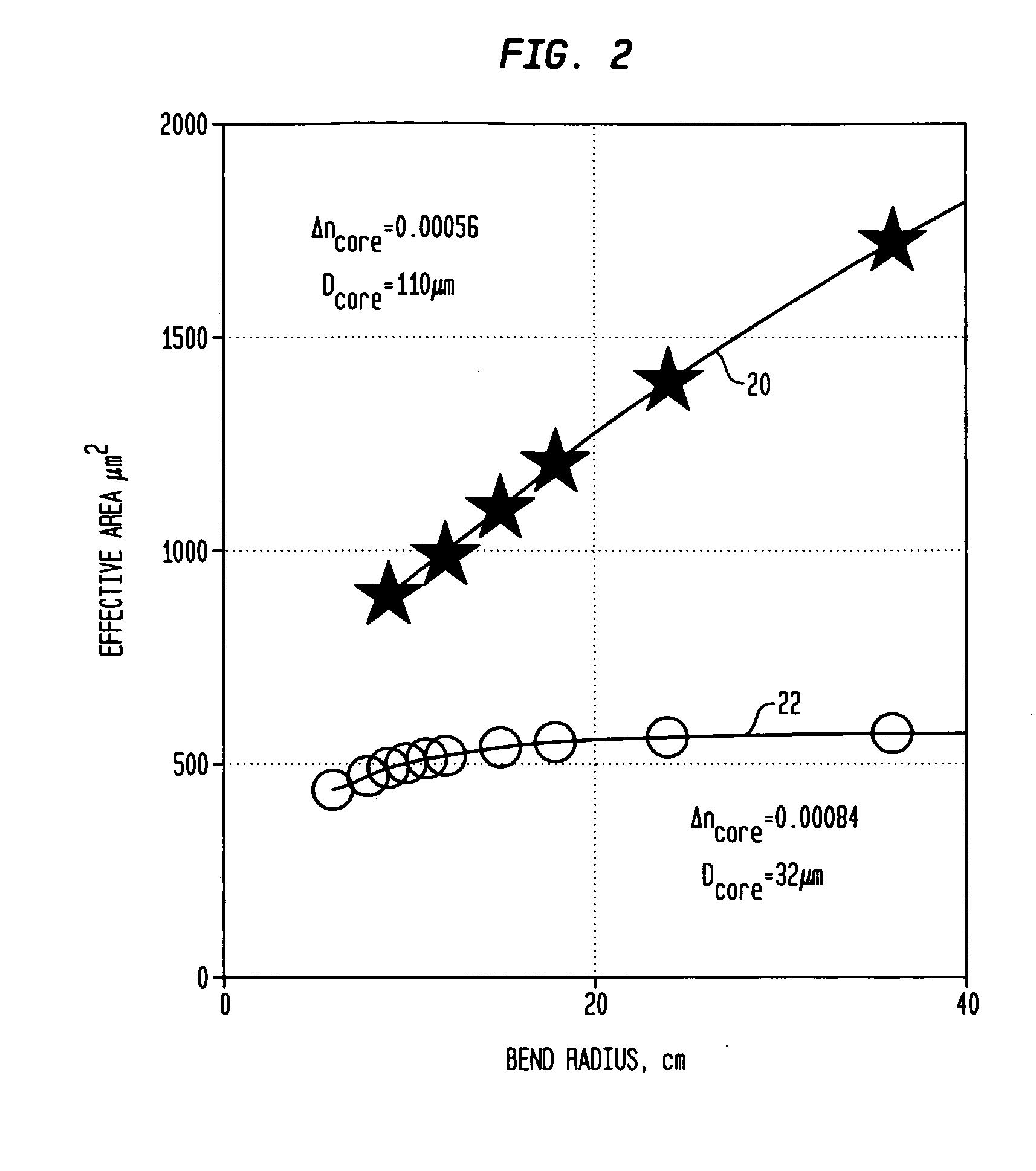
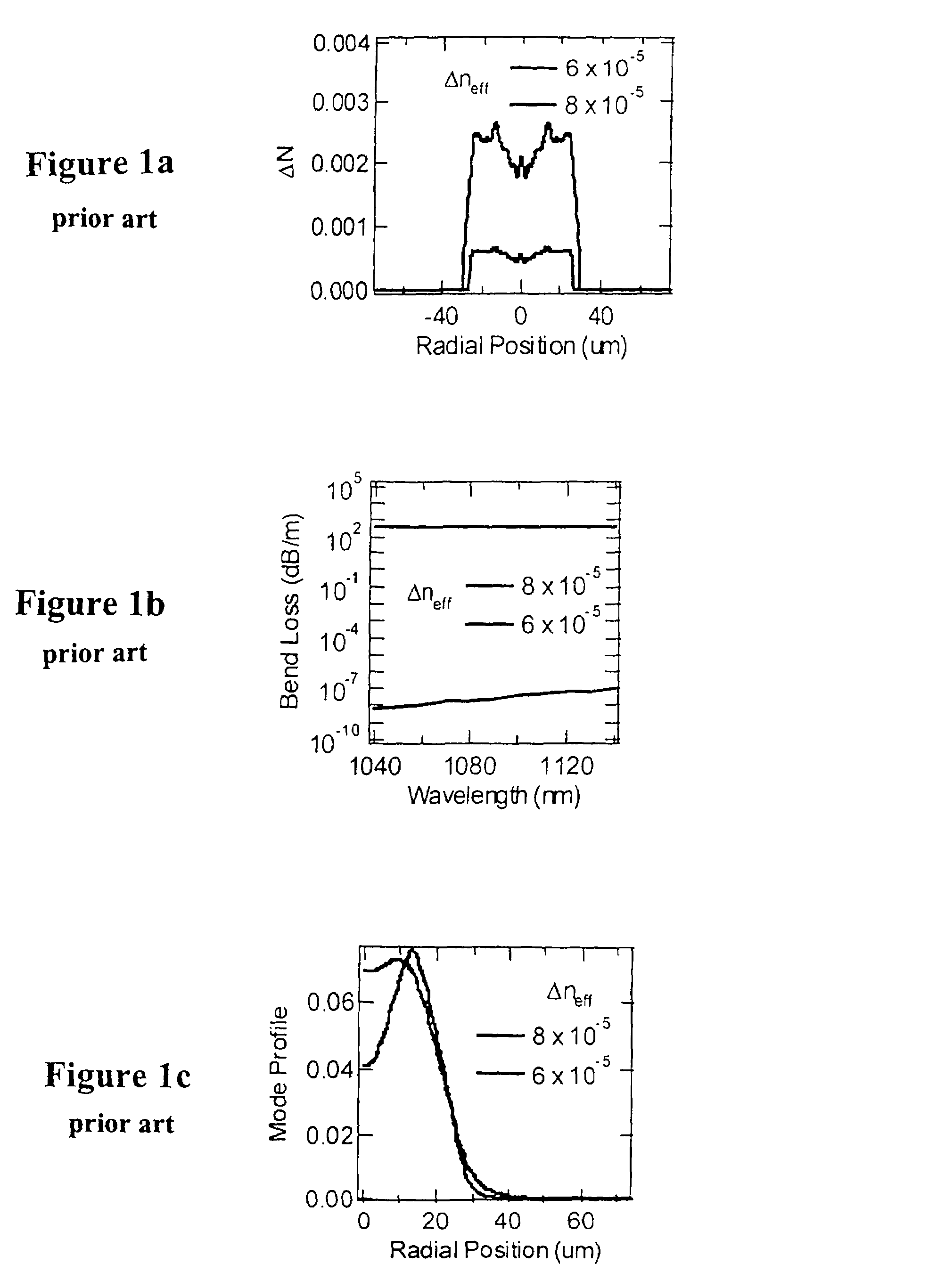
Large-mode-area optical fibers with reduced bend distortion
ActiveUS20090059353A1Reduces effective transverse mode areaReduce interactionGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsEngineeringBend radius
In a LMA optical fiber the index of the core region is graded (i.e., as viewed in a radial cross-section) and has a grading depth of Δng, as measured from a central maximum at or near the axis to a lower level that is not greater than the central maximum and not less than the index of the cladding region. When the fiber is to be bent at a bend radius, the grading depth, the radius of the core region, and the difference between the central maximum index and the cladding region index are configured to reduce bend distortion. They may also advantageously be configured to maximize the effective mode-field area of the fundamental mode, suppress higher order modes, and reduce bend loss. In a preferred embodiment, the core region includes a centralized gain region, which in turn includes a dark region that is no more than 30% of the area of the gain region. Also described is a method of making such LMA fibers.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
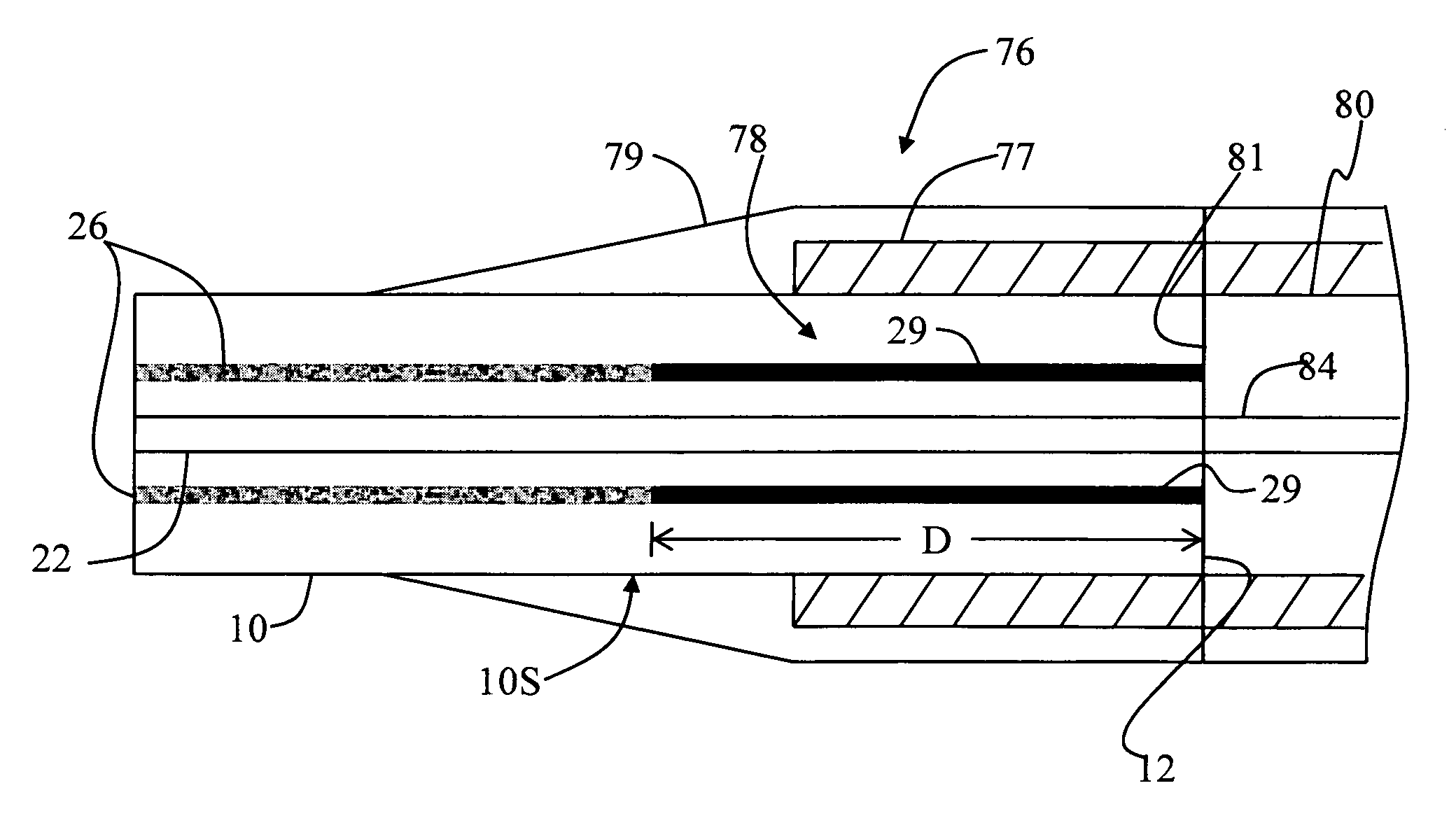
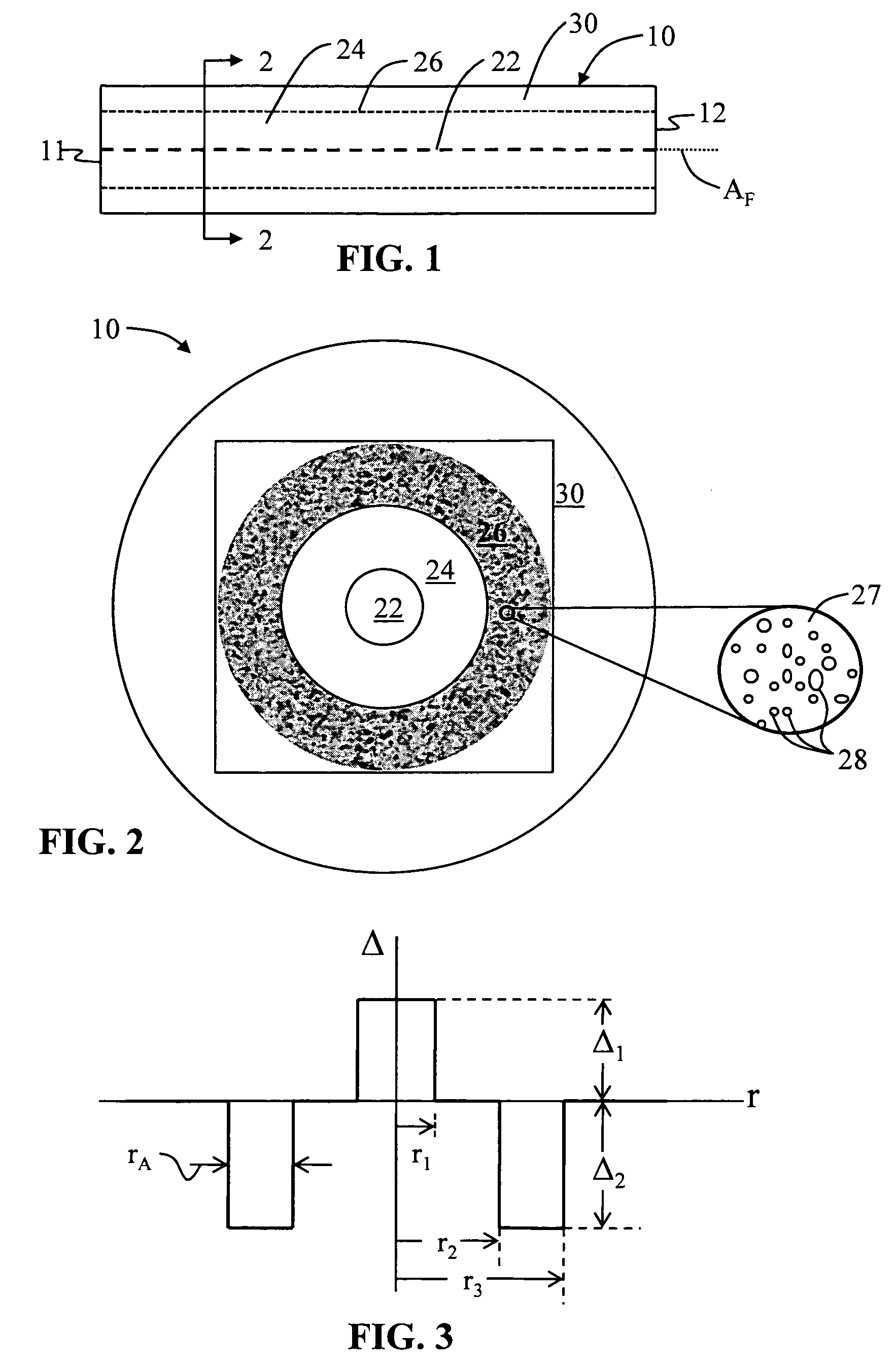
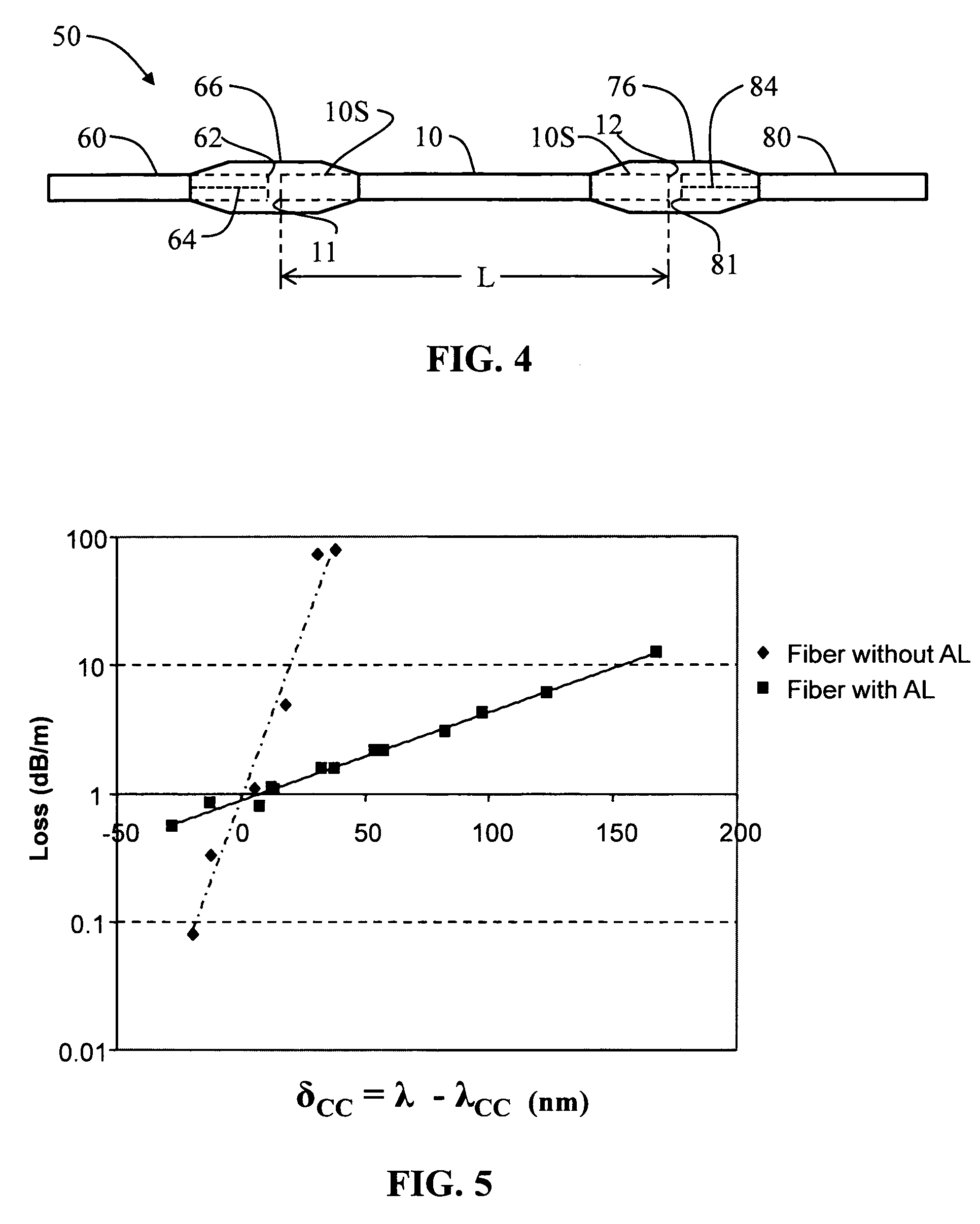
Airline optical fiber with reduced multipath interference and methods of forming same
InactiveUS7542645B1Reduce multipath interferenceReducing MPICladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFiberMultipath interference
An airline (AL) optical fiber (“AL fiber”) that has an AL region with airlines, with the AL region arranged relative to the fiber core so as to make the fiber bend insensitive. The AL region is capable of supporting one or more higher-order optical modes. One method of reducing multipath interference (MPI) includes accessing a section of the AL fiber and closing at least one of the airlines in the section. This serves to attenuate one or more higher-order modes, which reduces MPI. In one example, the AL fiber has an end section wherein the airlines are filled with a blocking material. An example blocking material is a curable adhesive that is wicked into the airlines via capillary action and then cured when the adhesive reaches a certain depth from the fiber end. In another example, the blocking material is formed by heating the AL fiber section to cause the section to melt and block the airlines, so that the melted AL fiber serves as the blocking material. The AL fiber with reduced MPI is particularly useful as a “jump” fiber, whose length is too short to rely on attenuating higher-order modes via a cable cut-off wavelength.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Microstructured optical fiber
An optical fiber suitable for use in a single fiber or multifiber optical connector or array is structured with a core region and a cladding region surrounding the core region, and exhibits a bending loss of a fundamental mode of the fiber at a wavelength λ is lower than 0.1 dB / m at a diameter of 15 mm, a mode-field diameter of the fundamental mode at an end of the fiber at the wavelength λ is between 8.0 μm and 50 λ, and a bending loss of a first higher-order mode at the wavelength λ is higher than 1 dB / m at a diameter of 30 mm. The fiber may be multistructured, wherein the cladding region comprises a main medium and a plurality of sub medium regions therein to form a spatially uniform average refractive index.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
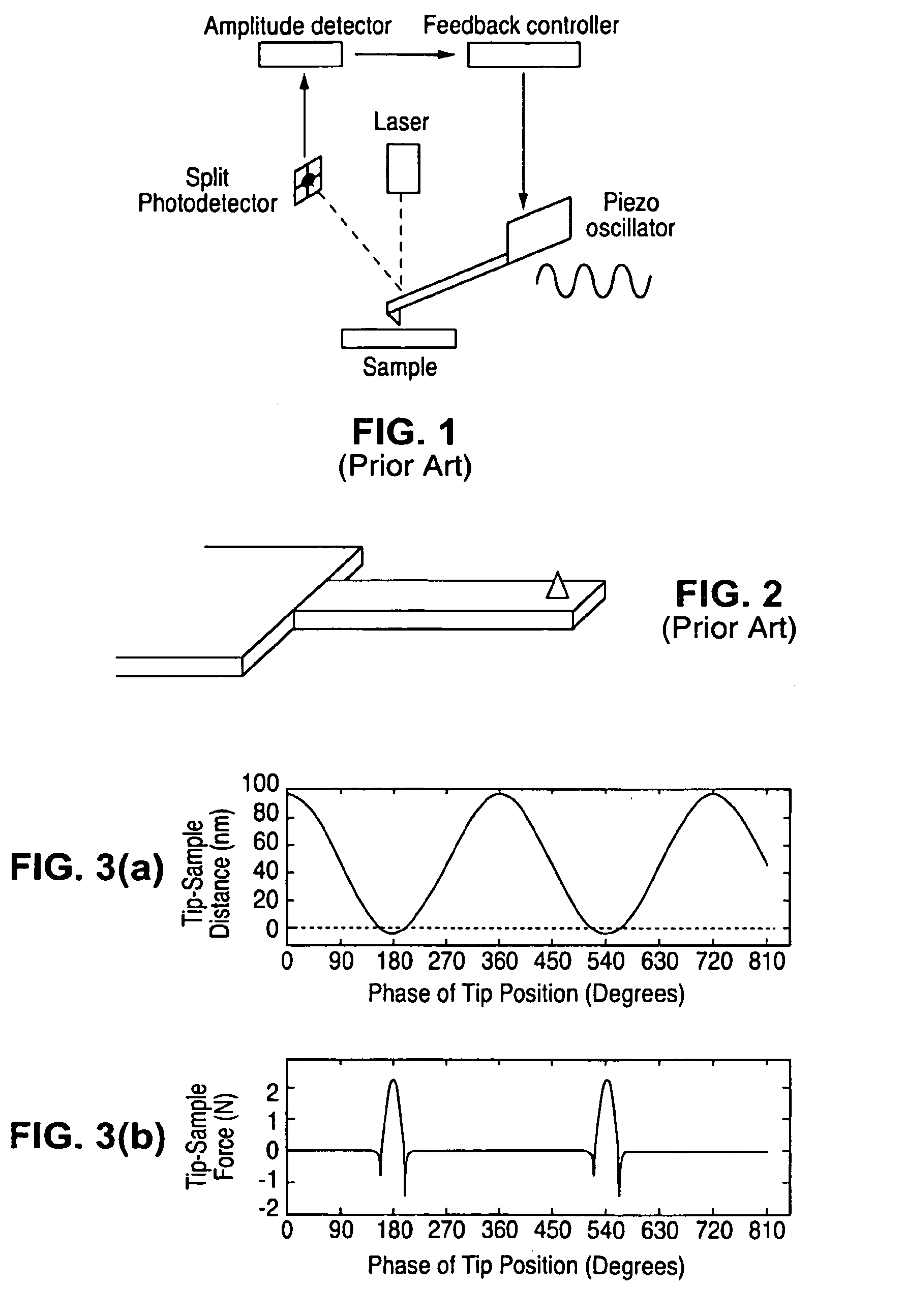
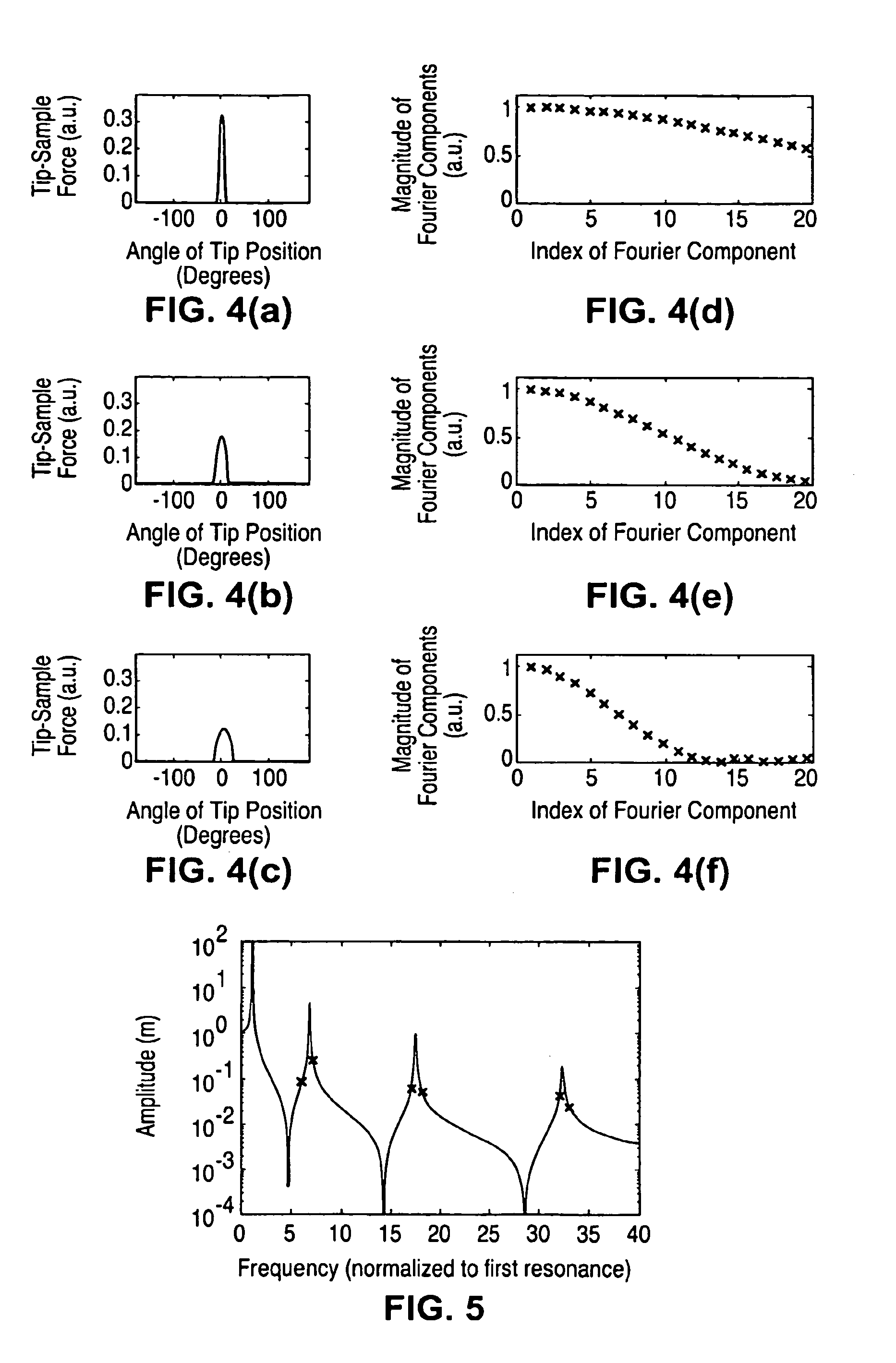
Harmonic cantilevers and imaging methods for atomic force microscopy
InactiveUS6935167B1Harmonic suppressionNanotechElectric discharge tubesAtomic force microscopyMagnetic force microscope
A harmonic cantilever for use in a tapping-mode atomic force microscope includes a cantilever arm and a probe tip. The cantilever arm has a shape selected to tune the fundamental resonance frequency or a resonance frequency of a selected higher order mode so that the fundamental and higher-order resonance frequencies have an integer ratio or near integer ratio. In one embodiment, the cantilever arm can be shaped to tune the fundamental resonance frequency. Alternately, the cantilever arm can include a geometric feature for tuning the resonance frequency of the fundamental mode or the selected higher order mode. An imaging method using the harmonic cantilever is disclosed whereby signals at the higher harmonics are measured to determine the material properties of a sample. In other embodiment, a cantilever includes a probe tip positioned at a location of minimum displacement of unwanted harmonics for suppressing signals associated with the unwanted harmonics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Optical waveguide structures
The purely bound electromagnetic modes of propagation supported by symmetric waveguide structures comprised of a thin lossy metal film of finite width embedded in an infinite homogeneous dielectric have been characterized at optical wavelengths. The modes supported are divided into four families depending on the symmetry of their fields. In addition to the four fundamental modes that exist, numerous higher order ones are supported as well. A nomenclature suitable for identifying all modes is discussed. The dispersion of the modes with film thickness and width has been assessed and the effects of varying the background permittivity on the characteristics of the modes determined. The frequency dependency of one of the modes has been investigated. The higher order modes have a cut-off width, below which they are no longer propagated and some of the modes have a cut-off thickness.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Large mode area fibers using higher order modes
ActiveUS20060103919A1Increase the areaImprove loss performanceLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberEngineering
The specification describes an optical fiber device wherein a LOM is converted to an HOM prior to entering the gain section. The gain section is a few mode fiber that supports the HOM. The output from the gain section, i.e. the HOM, may be utilized as is, or converted back to the LOM. With suitable design of the few mode fiber in the gain section of the device, the effective area, Aeff, may be greater than 1600 μm2. The large mode separation in the gain section reduces mode coupling, allowing greater design freedom and reducing the bend sensitivity of the optical fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Large-mode-area optical fibers with reduced bend distortion
ActiveUS7783149B2Reduces effective transverse mode areaReduce interactionLaser using scattering effectsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEngineeringBend radius
In a LMA optical fiber the index of the core region is graded (i.e., as viewed in a radial cross-section) and has a grading depth of Δng, as measured from a central maximum at or near the axis to a lower level that is not greater than the central maximum and not less than the index of the cladding region. When the fiber is to be bent at a bend radius, the grading depth, the radius of the core region, and the difference between the central maximum index and the cladding region index are configured to reduce bend distortion. They may also advantageously be configured to maximize the effective mode-field area of the fundamental mode, suppress higher order modes, and reduce bend loss. In a preferred embodiment, the core region includes a centralized gain region, which in turn includes a dark region that is no more than 30% of the area of the gain region. Also described is a method of making such LMA fibers.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Integrated lateral mode converter
ActiveUS7539373B1Minimal transmission lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesNon symmetricEngineering
The invention describes method and apparatus for a mode converter enabling an adiabatic transfer of a higher order mode into a lower order optical mode within a photonic integrated circuit exploiting integrated semiconductor ridge waveguide techniques. As disclosed by the invention, such a mode conversion is achievable by using an asymmetric coupler methodology. In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, the invention is used to provide a low insertion loss optical connection between laterally-coupled DFB laser operating in first order mode and passive waveguide operating in the zero order optical mode. The integrated arrangement fabricated by using one-step epitaxial growth allows for a launch of the laser's light into the waveguide circuitry operating in the zero order lateral mode or efficiently coupling it to single-mode fiber, an otherwise high loss interface due to the difference in laser and optical fiber modes.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
Optical fiber systems for delivering short high power pulses
InactiveUS20060233554A1Minimal distortionMinimum non-linear impairmentDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical light guidesNonlinear distortionFew mode fiber
Described is an optical fiber system for delivering ultrashort pulses with minimal distortions due to nonlinearity. The system is based on delivering the optical pulses in a higher order mode (HOM) of a few-moded fiber. The fiber is designed so that the dispersion for the HOM is very large. This results in a dispersion length LD for the delivery fiber that is exceptionally small, preferably less than the non-linear length LNL. Under these conditions the system may be designed so the optical pulses experience minimum non-linear impairment, and short pulse / high peak power levels are reproduced at the output of the delivery fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
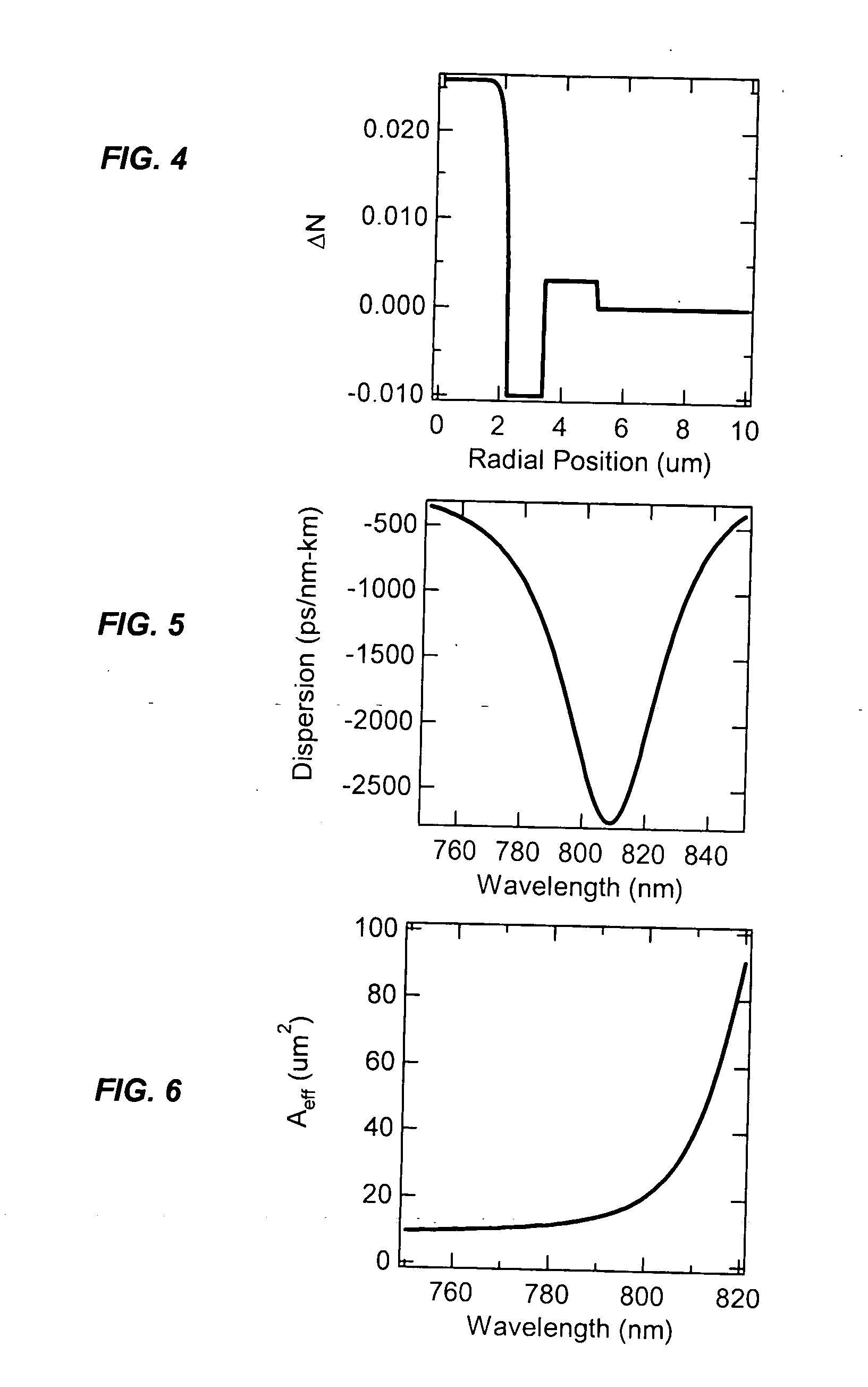
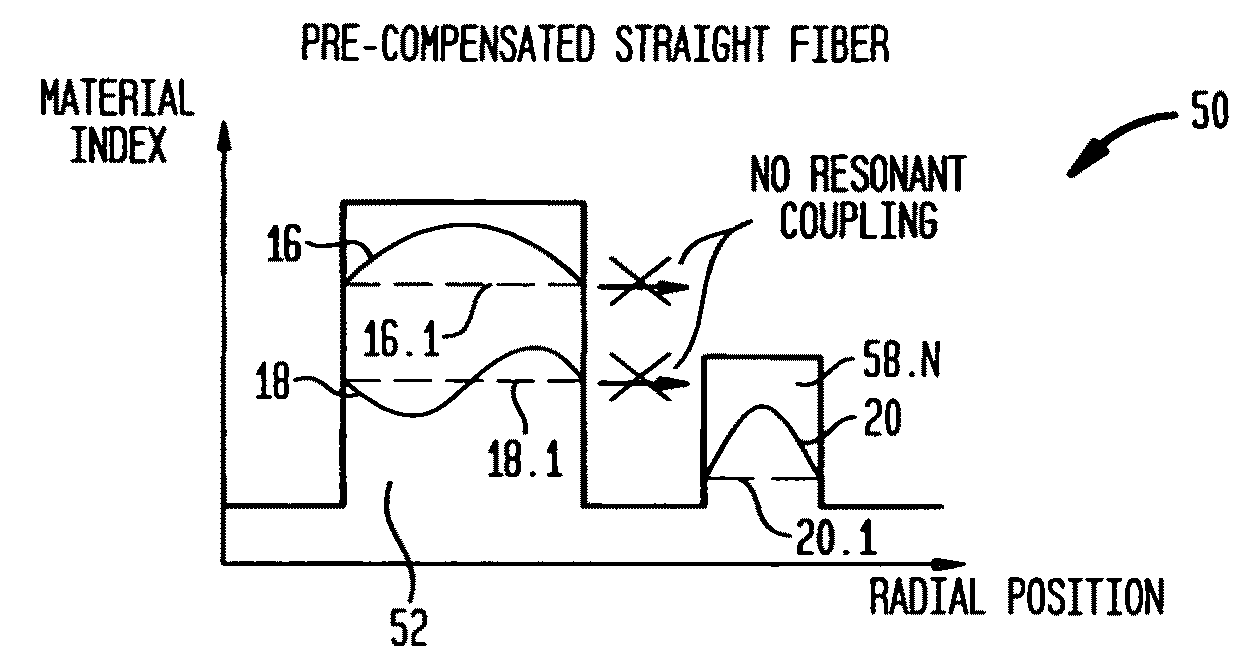
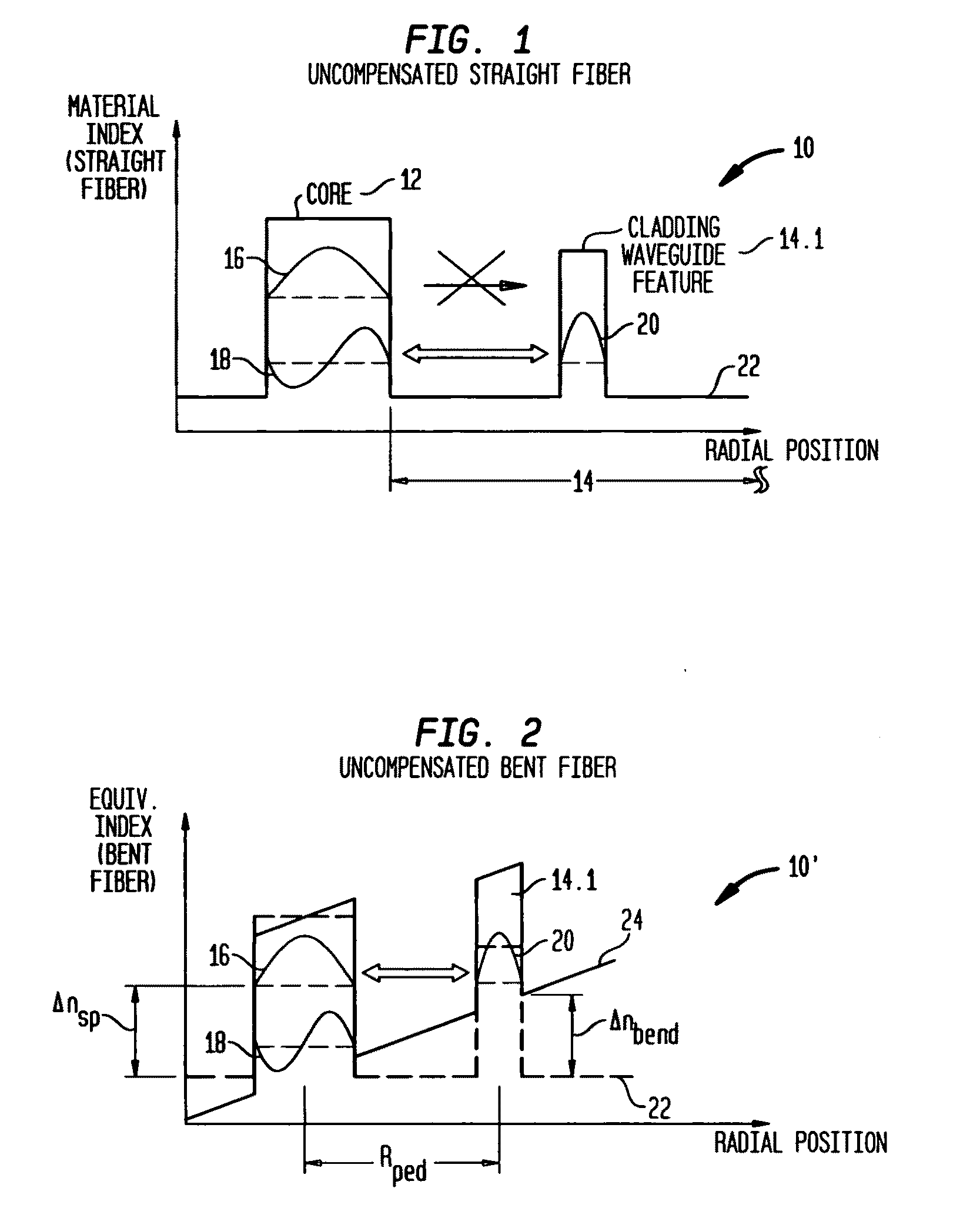
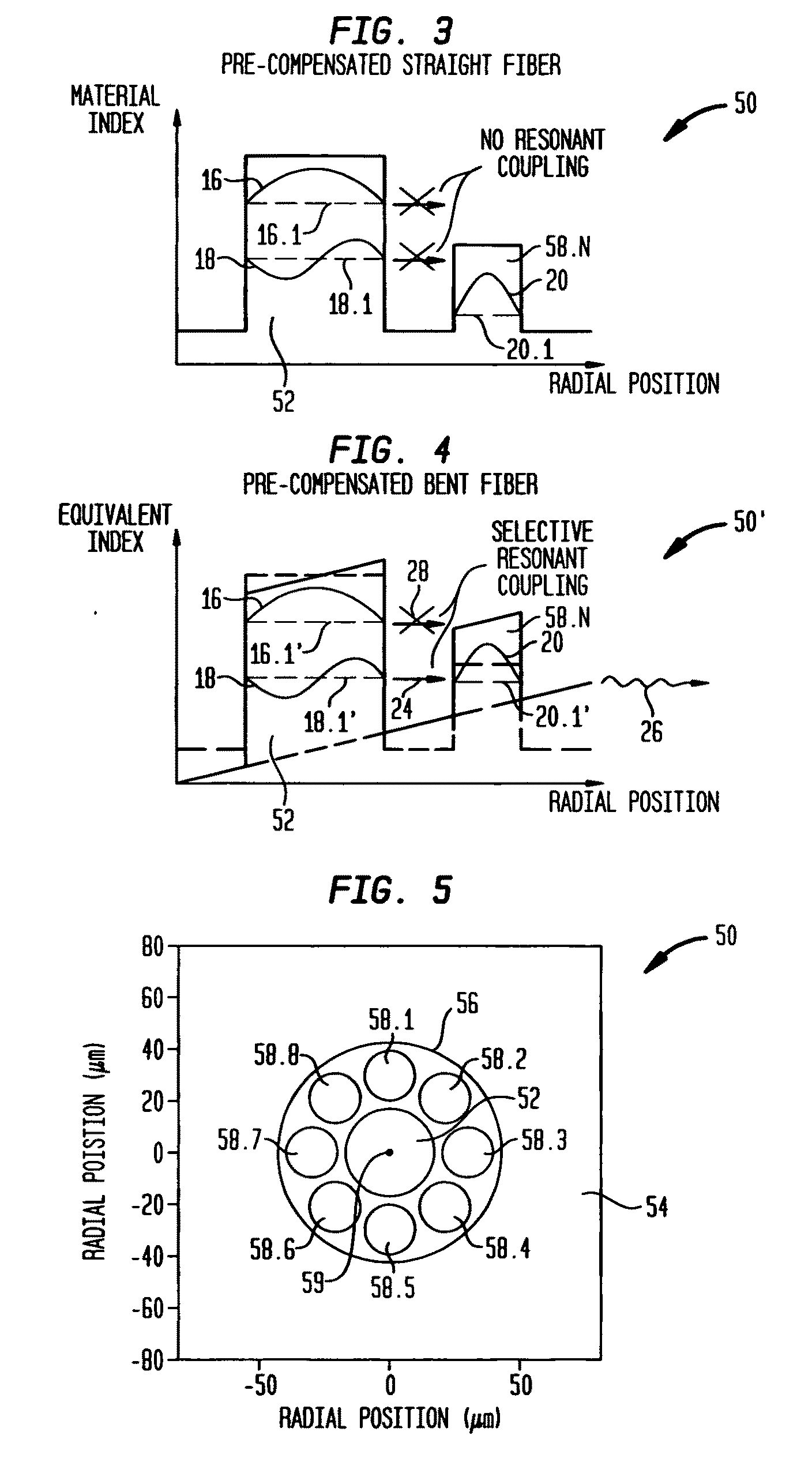
Suppression of higher-order modes by resonant coupling in bend-compensated optical fibers
ActiveUS20090034059A1High fundamental mode lossLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberCoupling
The effect of bending is anticipated in an optical fiber design, so that resonant coupling remains an effective strategy for suppressing HOMs. The index profile of the fiber and its bend radius are configured so that there is selective resonant coupling of at least one HOM, but not the fundamental mode, in the bent segment of the fiber. In an illustrative embodiment, the bend radius (or predetermined range of bend radii) of an optical fiber is known a priori. The core and cladding regions are configured to support (guide) the propagation of signal light in a fundamental transverse mode and at least one higher-order transverse mode in the core region. The cladding region includes an outer cladding region and an annular trench region. The trench region includes at least one axially extending, raised-index pedestal (waveguide) region having a refractive index higher than that of the outer cladding region. Within at least the bent segment the at least one pedestal region is configured (i) to support the propagation of at least one transverse mode and (ii) to resonantly couple at least one of the higher-order transverse modes (HOMs) of the core region to at least one transverse mode (e.g., the fundamental mode) of the pedestal region when the fiber is bent to a radius within the predetermined range of radii. In effect, the pedestal regions are configured so that the fiber is pre-compensated for the effect of bending; that is, an uncompensated bent fiber segment suffers high fundamental mode loss due to resonant coupling, whereas the pre-compensated bent fiber segment selectively couples any unwanted HOM from the core region into the pedestal region. In a preferred embodiment, the optical fiber is a LMA fiber incorporated in an optical fiber amplifier or laser package.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
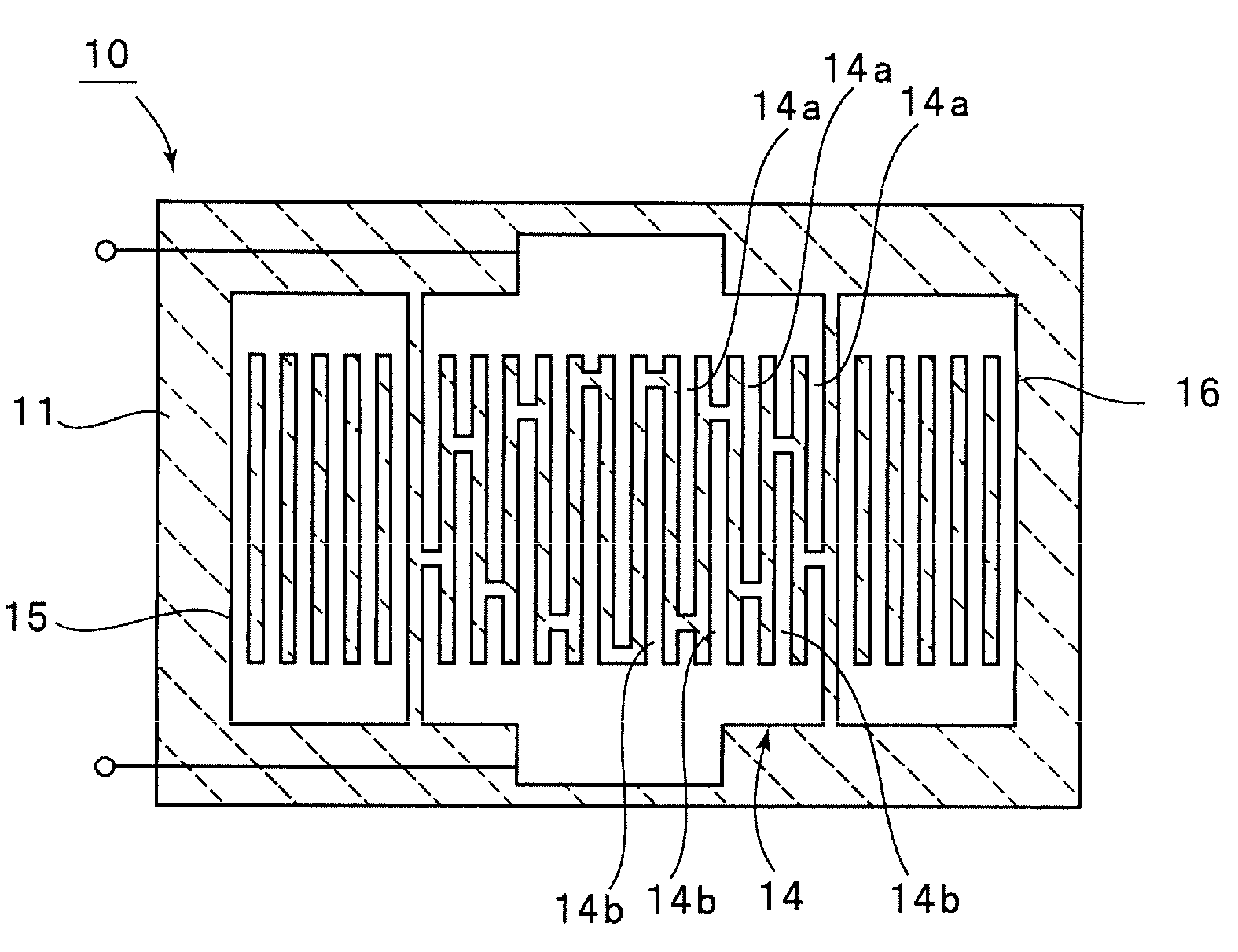
Elastic wave device
ActiveUS20150102705A1Suppress high order mode spuriousnessImprove resonance characteristicsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksConcentration ratioHigh pressure
An elastic wave device includes a high acoustic velocity film configured such that a bulk wave propagates at a higher acoustic velocity than an elastic wave that propagates in a piezoelectric film, a low acoustic velocity film configured such that a bulk wave propagates at a lower acoustic velocity than a bulk wave that propagates in the piezoelectric film is laminated on the high acoustic velocity film, the piezoelectric film is laminated on the low acoustic velocity film, and an IDT electrode is laminated on one surface of the piezoelectric film. In an upper structure section, an energy concentration ratio of a main mode which is an elastic wave is not less than about 99.9% and an energy concentration ratio of a high order mode which is spurious is not more than about 99.5%.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
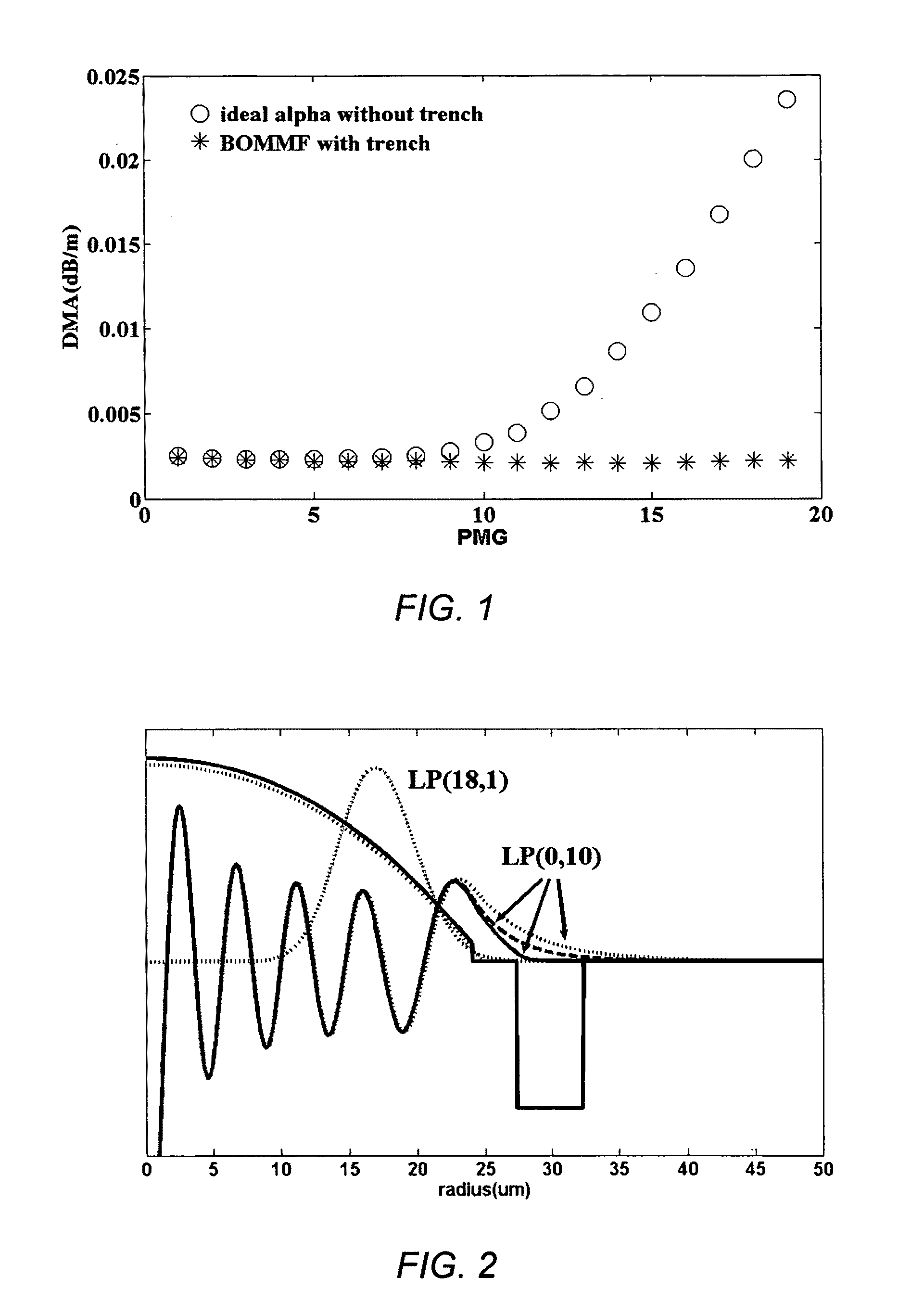
Equalizing modal delay of high order modes in bend insensitive multimode fiber
ActiveUS7865050B1RelaxingReducing bend lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingHigh bandwidthEngineering
Described are multimode optical fibers in which the differential in the mode delay for higher order modes is reduced for bending insensitive MMF. The result is preservation of low differential mode delay and high bandwidth while low bend loss is achieved. The designs are based on choosing a combination of a core profile and a cladding structure with a negative trench positioned at a radius related to the core profile. A feature of the preferred embodiments is a core with a hybrid refractive index profile. The hybrid refractive index profile is essentially a combination of a standard alpha profile and a step profile at the outer edge of the alpha profile.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Large mode area fibers using higher order modes
ActiveUS7171074B2Increase the areaImprove loss performanceLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberEngineering
The specification describes an optical fiber device wherein a LOM is converted to an HOM prior to entering the gain section. The gain section is a few mode fiber that supports the HOM. The output from the gain section, i.e. the HOM, may be utilized as is, or converted back to the LOM. With suitable design of the few mode fiber in the gain section of the device, the effective area, Aeff, may be greater than 1600 μm2. The large mode separation in the gain section reduces mode coupling, allowing greater design freedom and reducing the bend sensitivity of the optical fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Multimode optical fiber with low differential mode delay
ActiveUS7646955B2Manufacturing process compatibleMinimize differential mode delayOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiber couplerFiber
An optical multimode fiber including a graded index core and an extended gradient core which has a negative refractive index difference with respect to the cladding. The fiber improves the bandwidth, reliability and complexity of the telecommunication systems that are based on multimode fibers. The fiber reduces the differential mode delay among modes. The fiber thereby allows achieving large bandwidth even in the case when the highest order modes are excited. This has positive effects to the conditions that need to be fulfilled by the components such as optical sources, connectors, fiber couplers, other optical components, cables, etc. The fiber eliminates negative impact of the cladding that allows for reduction of fiber core size and the difference between the cladding and the core and thereby allows for achieving the larger bandwidth of optical fiber at lower fiber production cost.
Owner:CORNING INC
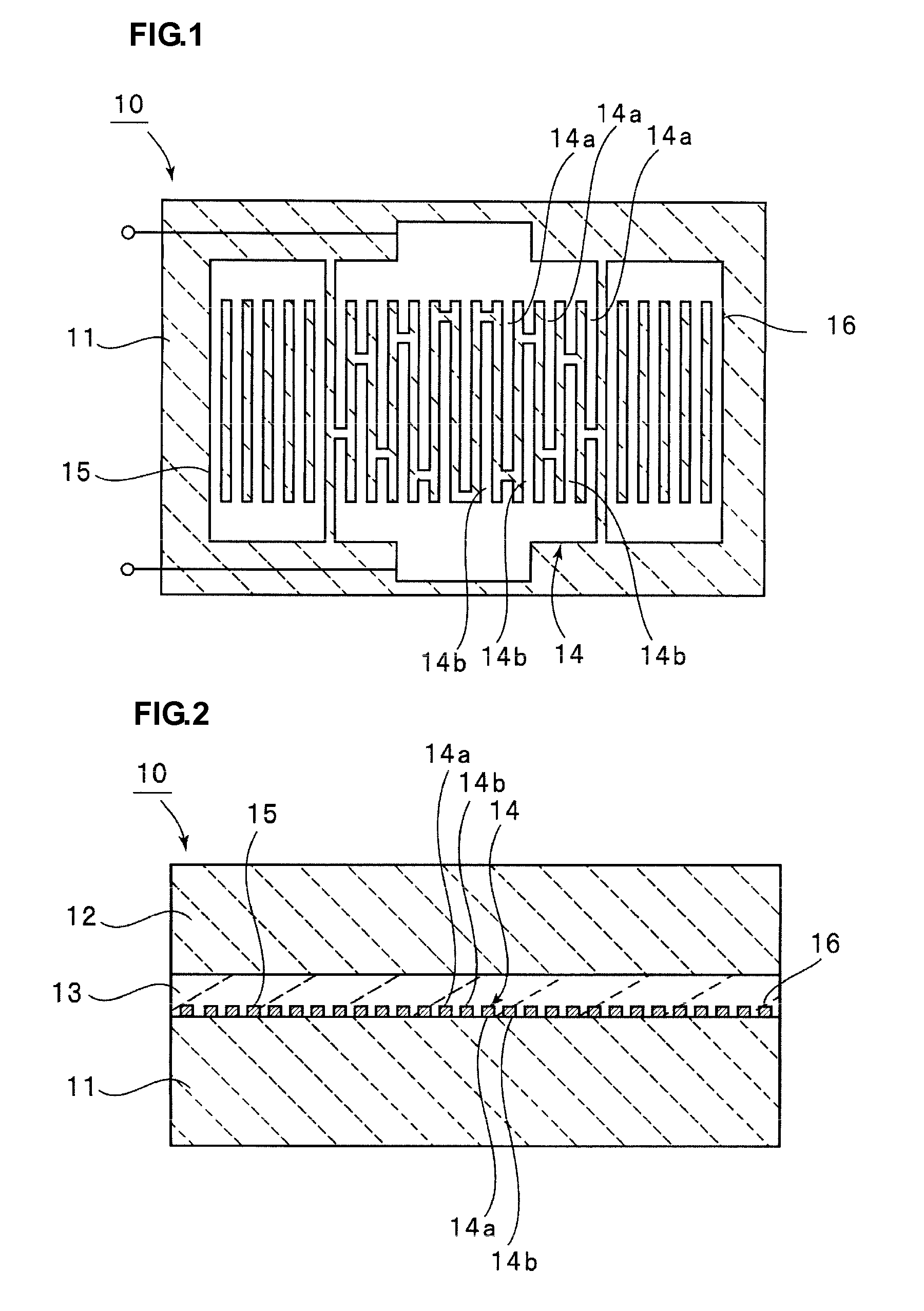
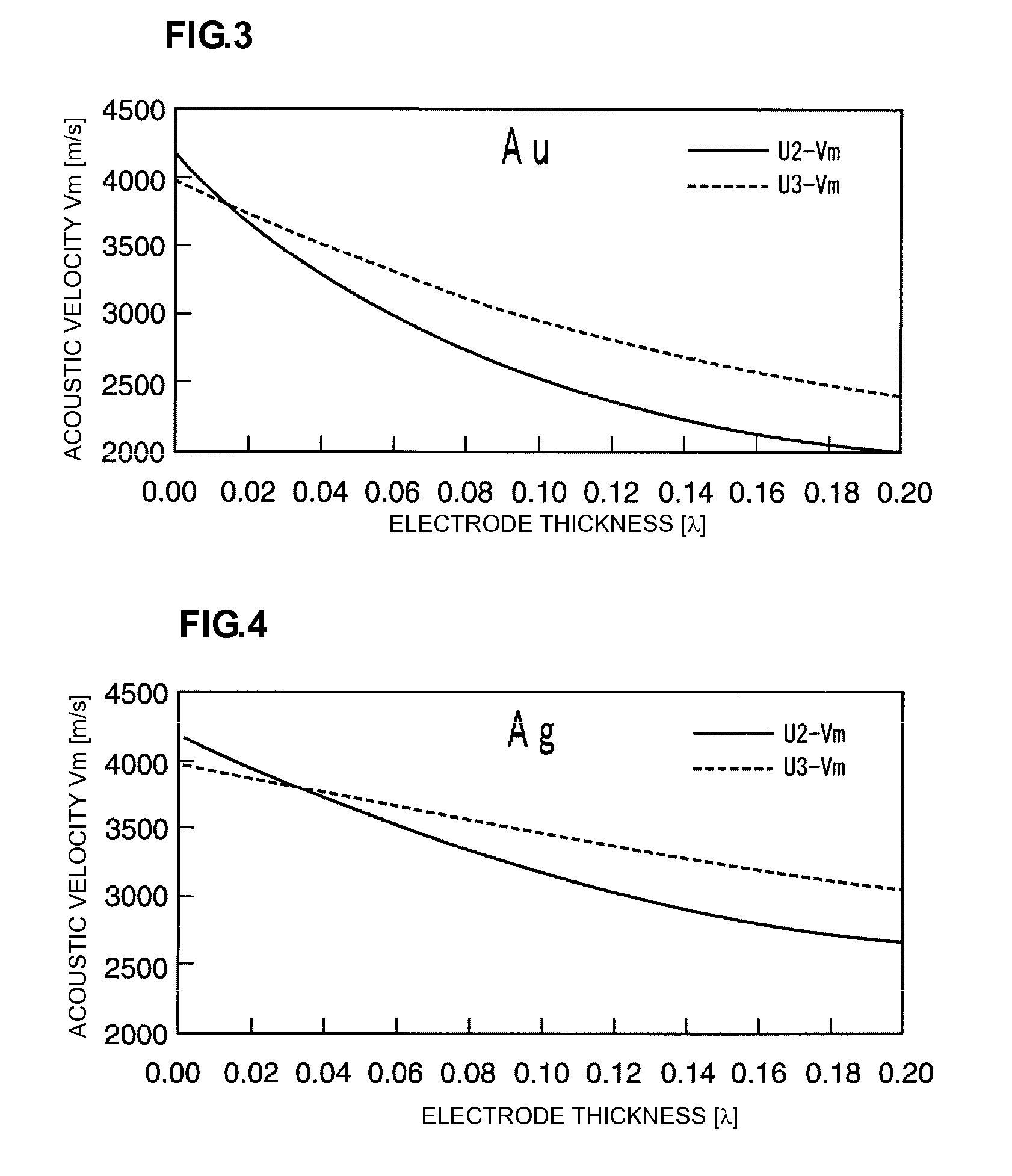
Boundary acoustic wave device
ActiveUS20090115287A1Efficiently vibrational energyLow boundary acoustic wave propagation lossImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectromechanical coupling coefficientAcoustic wave
A boundary acoustic wave device efficiently traps the vibrational energy of boundary acoustic waves and exhibits a high electromechanical coupling coefficient, and is consequently not affected by higher-order modes. The boundary acoustic wave device includes a first medium having piezoelectric characteristics, a non-electroconductive second medium, and a third medium through which slow transverse waves propagate at a lower acoustic velocity than slow transverse waves propagating through the first and second media. The first medium, the third medium, and the second medium are stacked in that order. An IDT is disposed between the first medium and the third medium. The IDT includes a metal layer made of a metal having a density ρ in the range of about 3000 kg / m3 to about 21500 kg / m3. The IDT has electrode fingers arranged at a pitch of λ and has a thickness H1 satisfying the relationship 0.006λ≦H1≦0.2λ, and the third medium has a thickness H2 satisfying the relationship H1<H2≦0.7λ.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
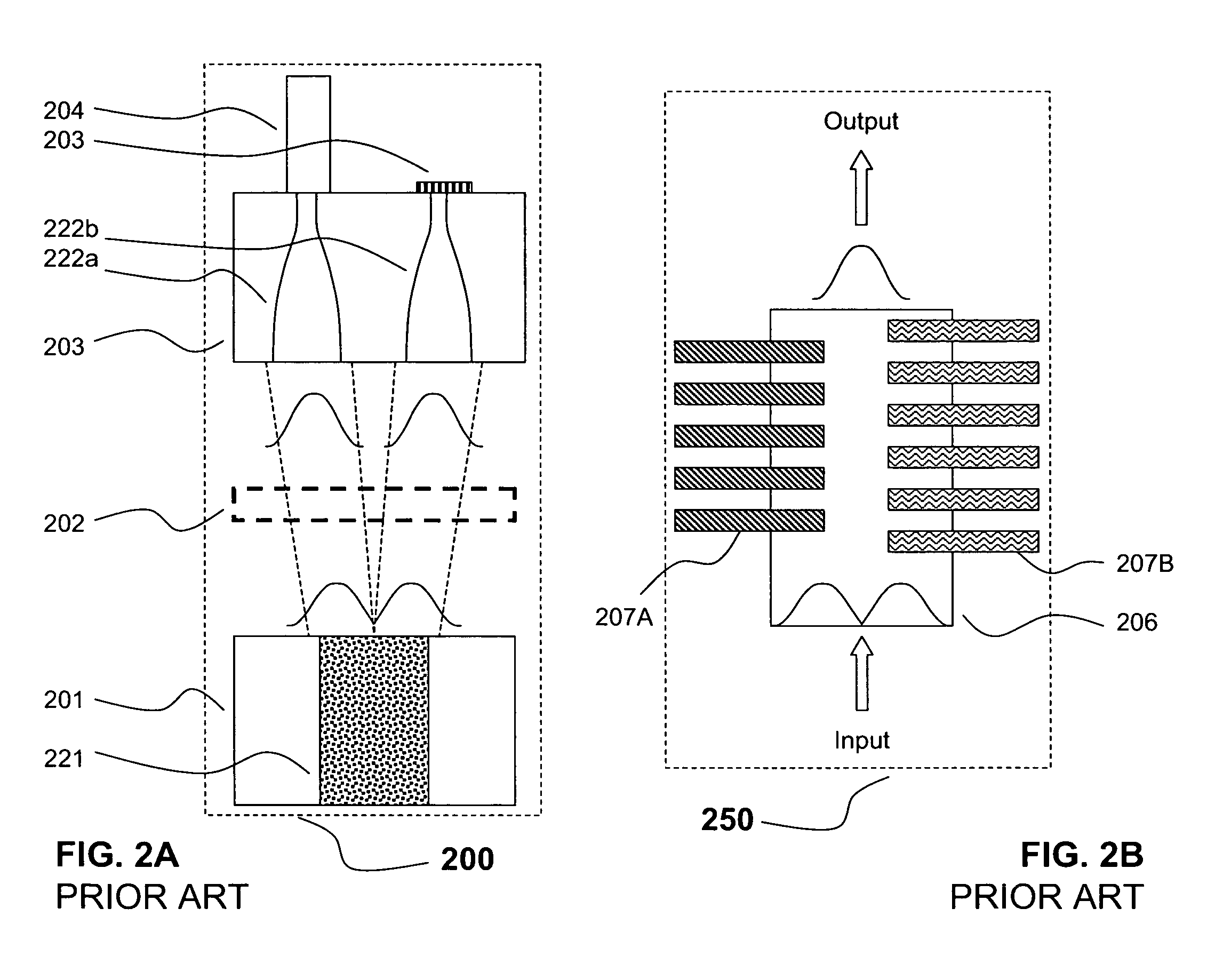
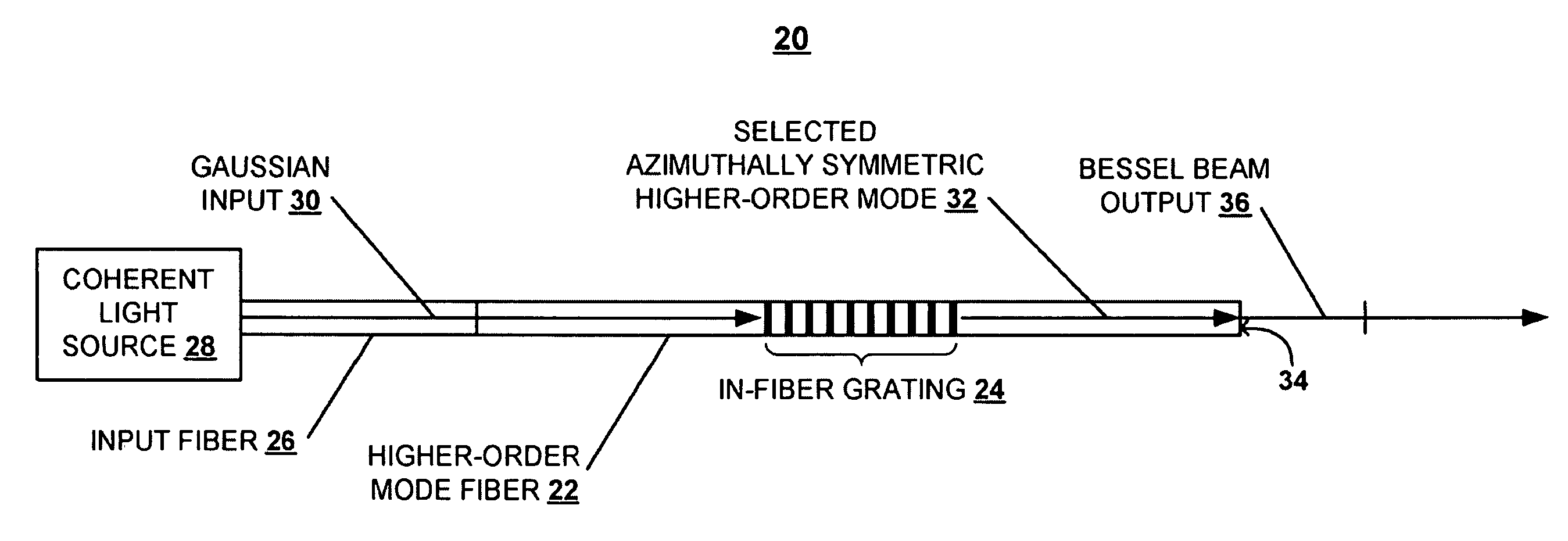
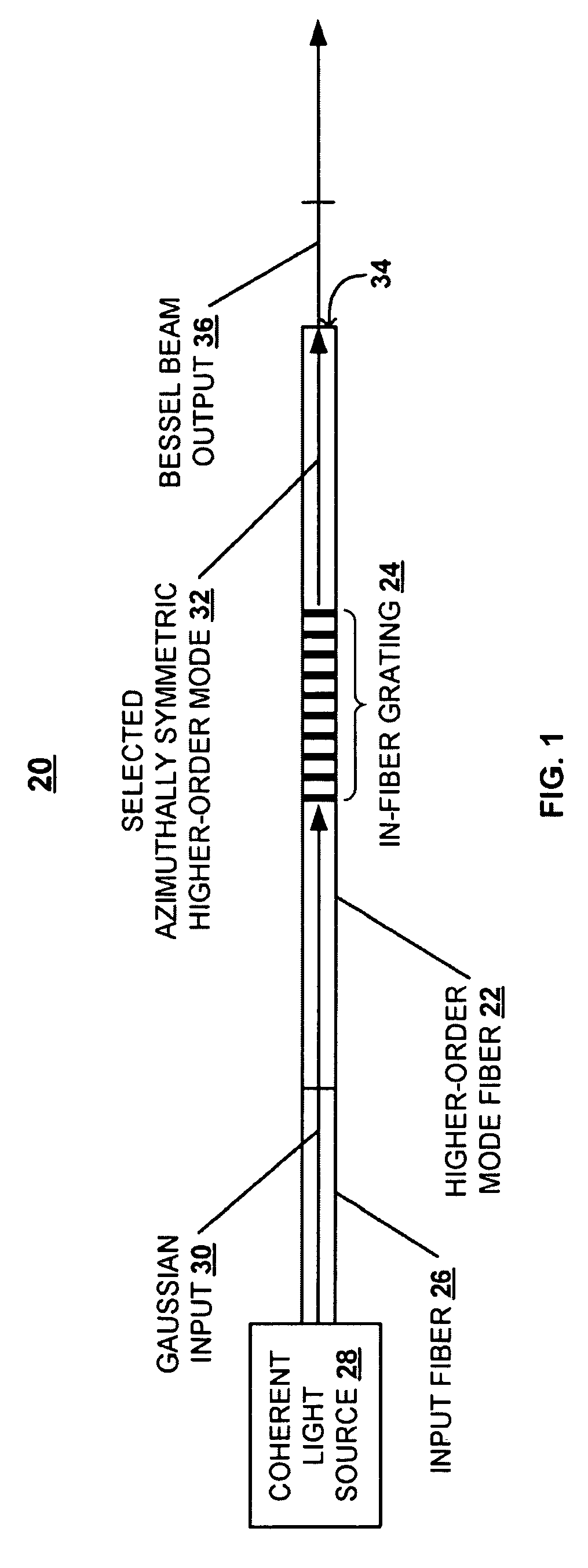
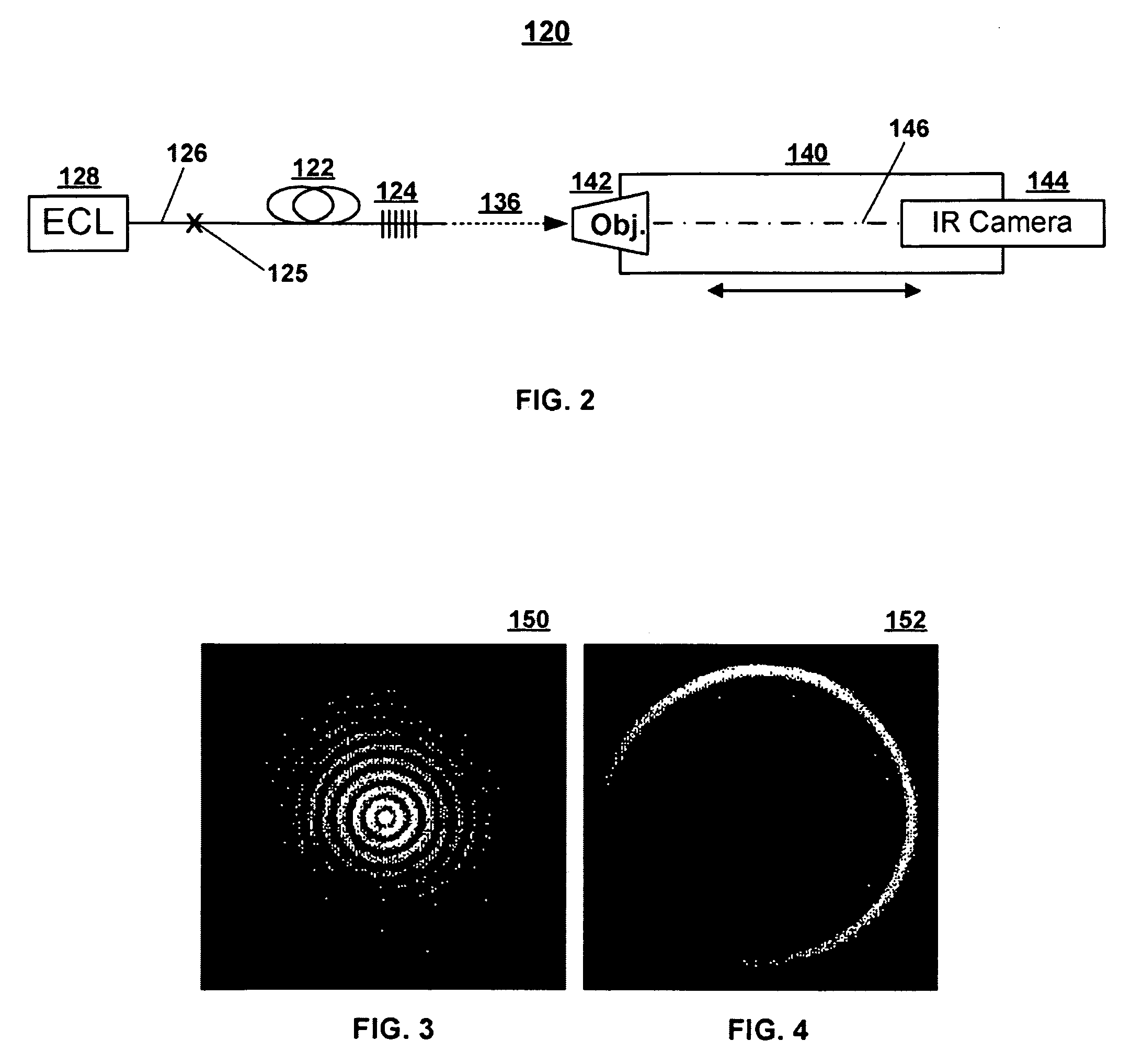
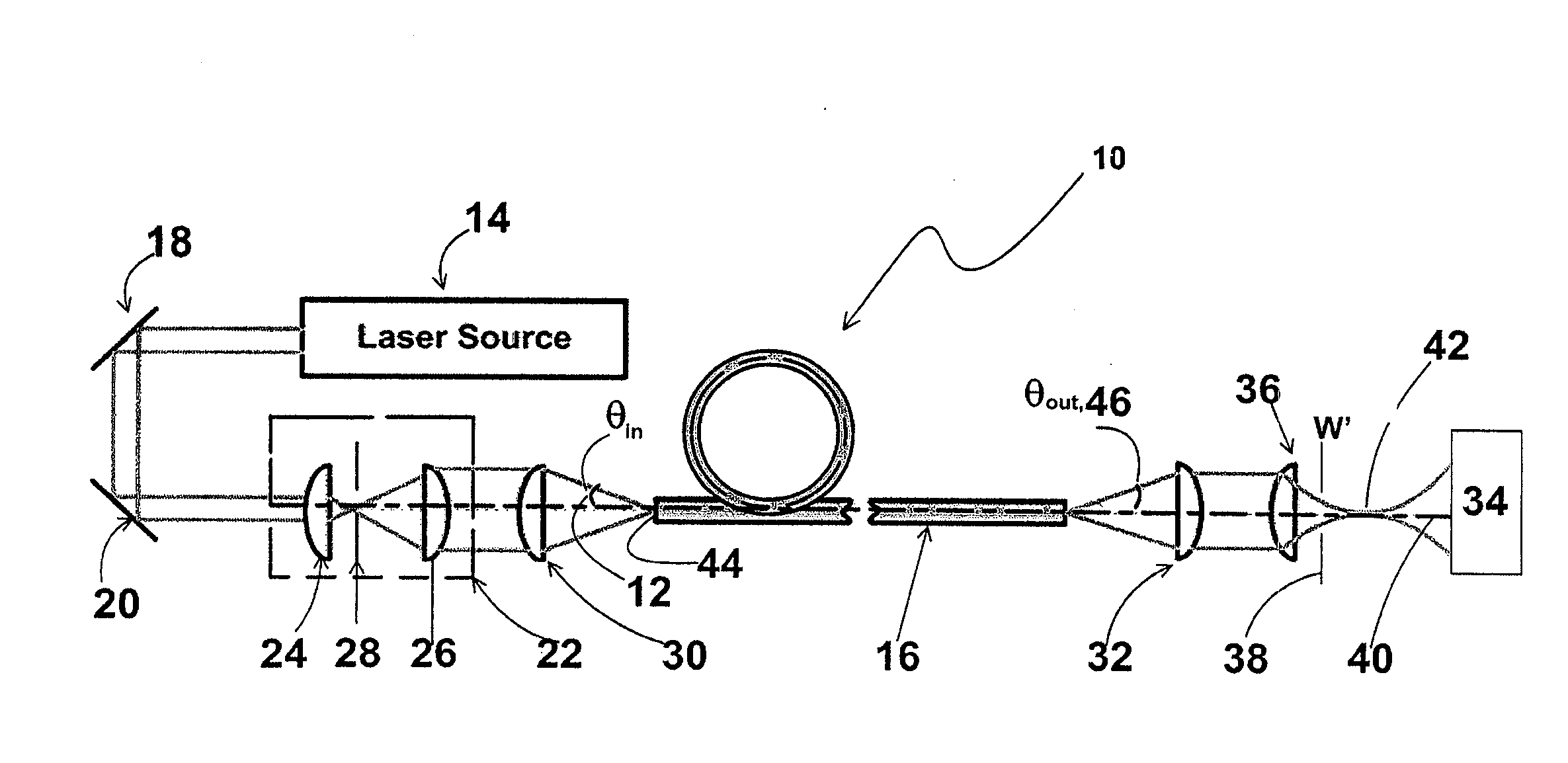
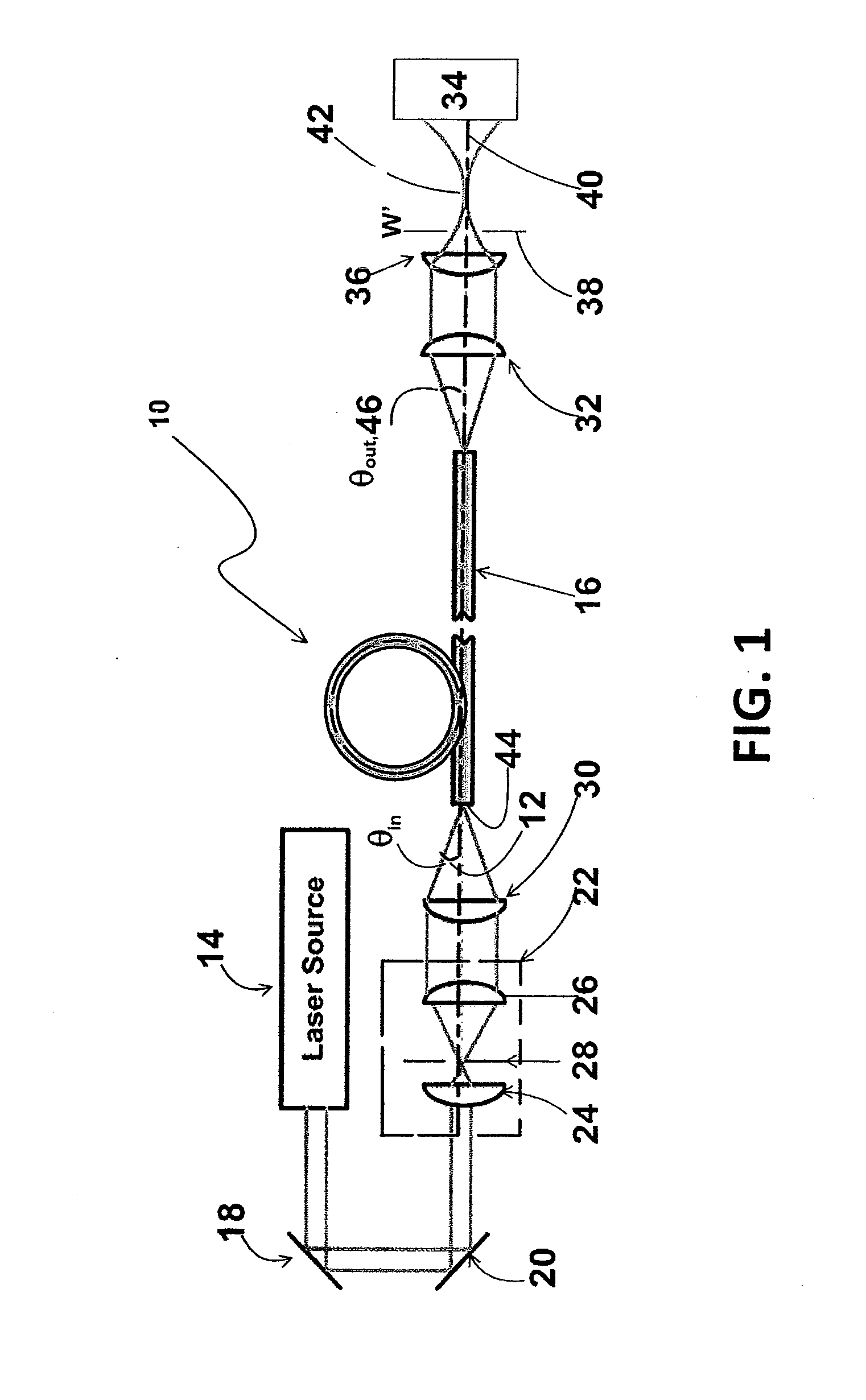
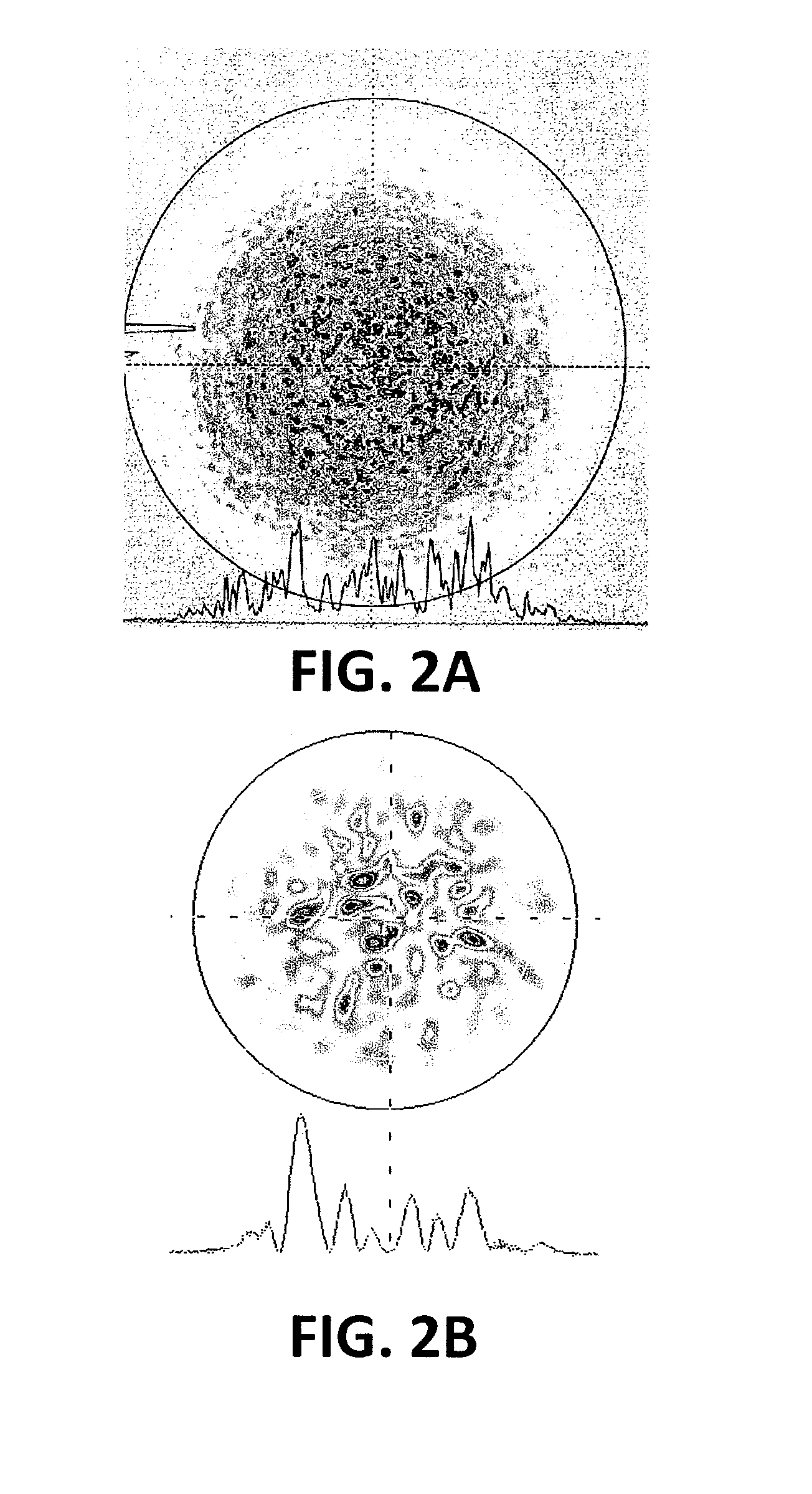
Systems and techniques for generating Bessel beams
A technique is described for generating a Bessel beam. An input optical fiber is provided that supports propagation in the fundamental mode. The input fiber is connected to a fiber mode converting device that provides phase matching, at a predetermined excitation wavelength, between the fundamental mode and a selected azimuthally symmetric higher-order mode. As an input to the fiber mode converting device, a coherent light beam is fed through the input optical fiber to provide a fundamental mode input at the excitation wavelength. The fiber mode converting device resonantly excites the selected azimuthally symmetric mode. The azimuthally symmetric mode is provided as a beam output from an endface of the fiber mode converting device to approximate a Bessel beam.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
High power single mode semiconductor laser device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20060193353A1Effective dispersionSuppress high order oscillationOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsActive layerLaser
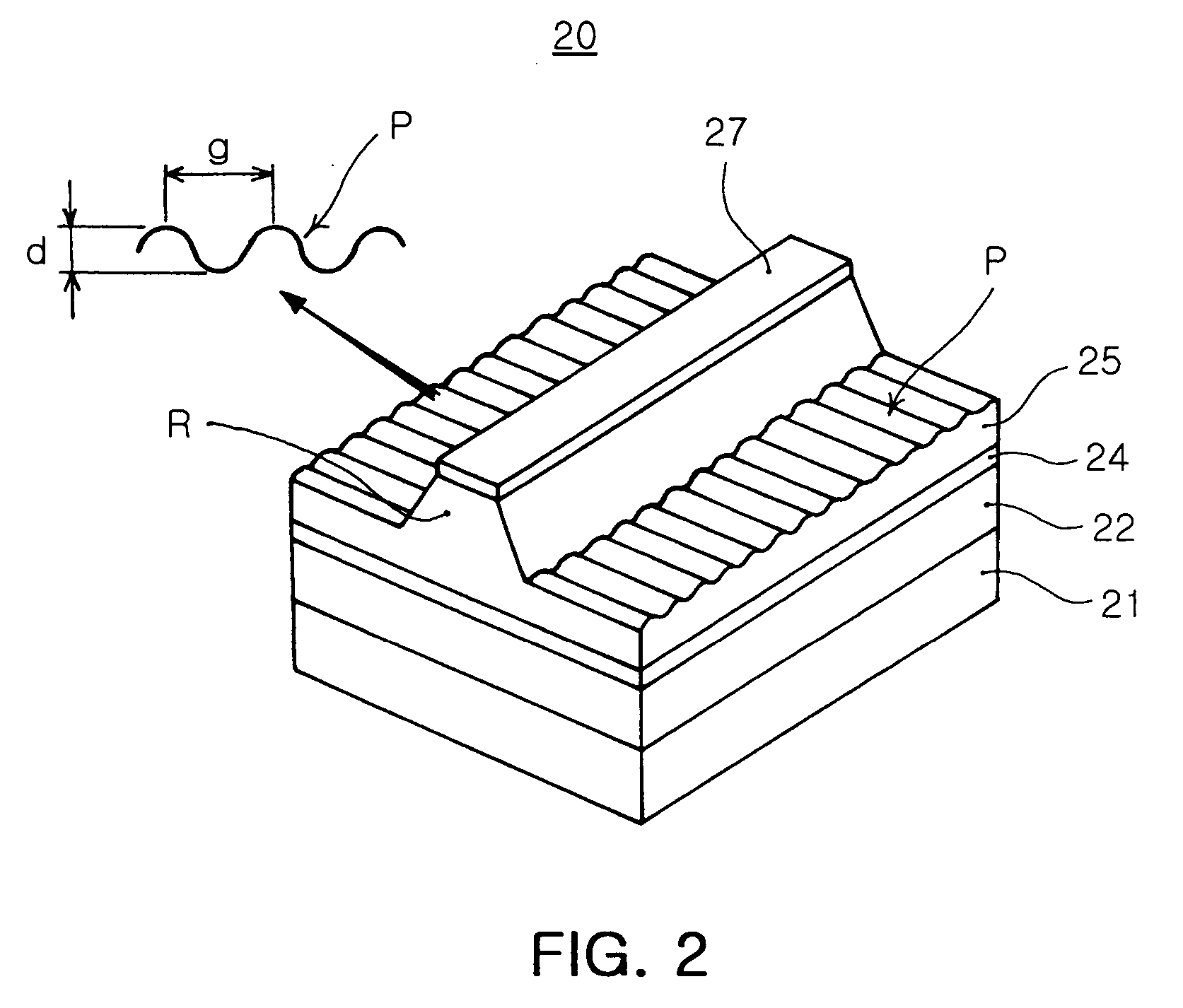
The present invention relates to a high-power single-mode semiconductor laser device, in which a first conductivity-type cladding layer is formed on a semiconductor substrate. An active layer is formed on the first conductivity-type cladding layer, and a second conductivity-type cladding layer is formed on the active layer, with a ridge protruding upward. The invention has corrugated parts formed on upper surfaces of the second conductivity-type cladding layer on both sides next to the ridge for scattering light in order to suppress high order mode oscillation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Optical fiber and integrated optic lasers with enhanced output power
InactiveUS6018533AEfficient pumpingIncrease powerCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsBasic modeLaser source
The invention describes a method of single-transverse-mode generation for waveguide lasers of various kinds having a large cross section of their active core and thus providing a possibility of efficient pump of the active core region. This results in a laser beam with enhanced power and high spatial quality for high efficiency coupling to standard single-mode optical fiber networks. It is found that a multimode waveguide having a central dip of special shape in the refractive index profile of its core is able to guide a higher order mode with sharp central peak of its field carrying the considerable part on the mode energy and whose width is well compatible with the width of the fundamental mode of standard single-mode fibers. The useful properties of this higher order mode can be employed to provide the single-transverse-mode regime of generation in optical fiber lasers, integrated optical micro-lasers and various semiconductor laser sources.
Owner:CERAMOPTEC IND INC
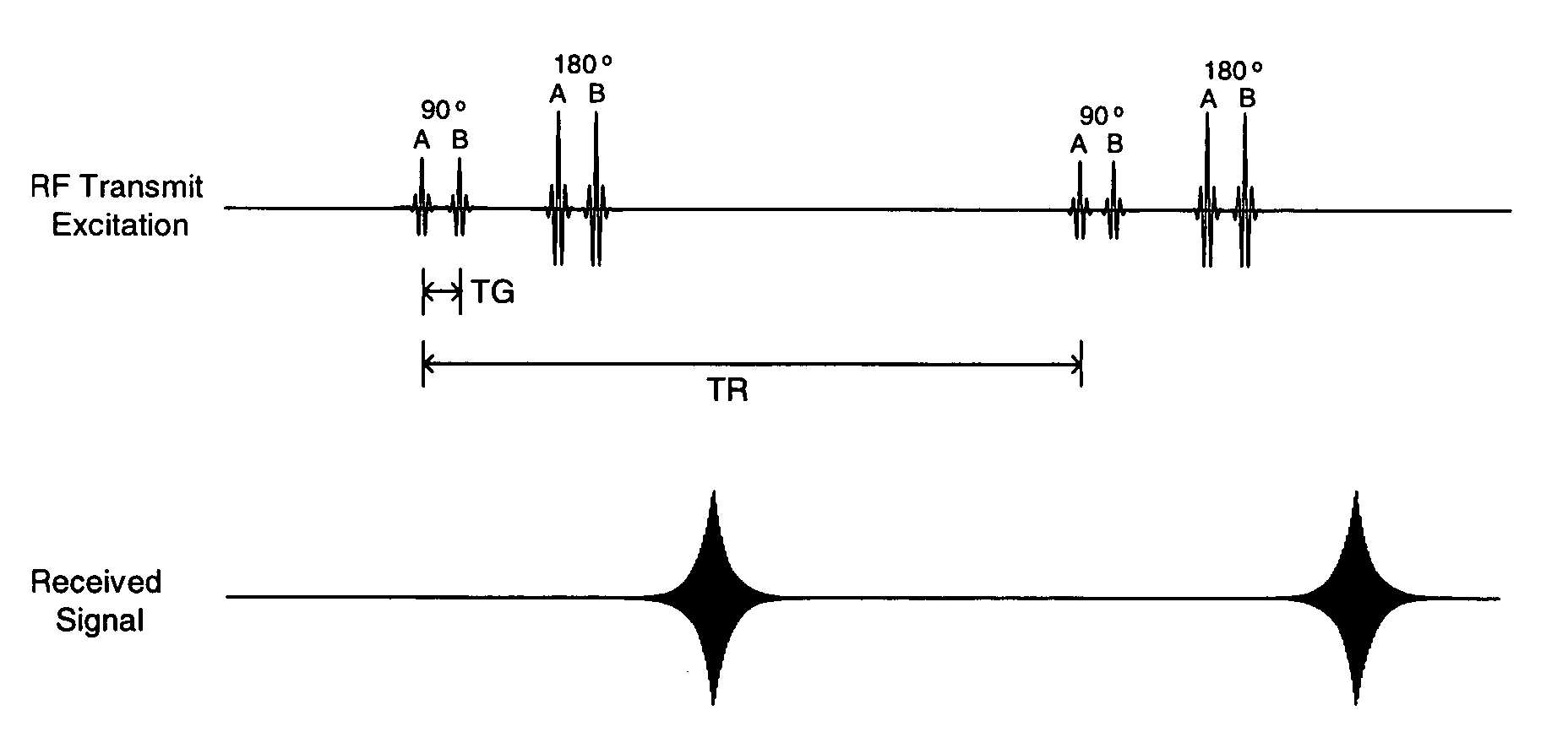
Methods for transmit excitation in magnetic resonance imaging using a transmit pulse with time varying spatial characteristics
ActiveUS6975114B1Optimize allocationEnhance excitationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSurface coilInductor
A method of inducing spin excitation by employing RF transmission fields of time-varying spatial characteristics in order to better control the overall distribution of spin excitation. The MRI transmit inductor system generates an RF transmission of particular spatial characteristics, followed by one or more additional RF transmissions with different spatial characteristics, where the additional RF transmissions alter the spin excitation produced by the first RF transmission. The spin excitation can be provided by a sequence of two or more discrete RF transmissions with different spatial characteristics, by a single RF transmission that has continuously varying spatial characteristics, by using successive RF transmissions of the primary and higher order modes of a volume coil, and / or by an RF transmission from a volume or surface coil followed by a second RF transmission from one or more local surface coils.
Owner:NOVA MEDICAL
Index guided laser structure
InactiveUS20030219053A1Limit and eliminate oscillationOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionClassical mechanicsLight beam
An index guide laser structure of the invention utilizes the combination of two spatial filter elements to limit or eliminate oscillation of high order lateral modes and beam steering. A preferred structure utilizes a frustrated and curved index guide to induce bend loss in higher order modes, and another preferred structure utilizes frustrating guides to introduce periodic interruptions of the refractive index outside the central guide to induce scattering loss in the higher order modes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Semiconductor laser with wide side of tapered light gain region
InactiveUS6075801AOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor packageLight beam
The semiconductor laser disclosed includes a first conductivity type buffer layer, an active layer and a second conductivity type cladding layer which are sequentially positioned on a first conductivity type semiconductor substrate. The active layer has a laser gain region to which an electric current is injected. The laser gain region having a width varying linearly along a resonating direction is disposed between a high reflection film provided on a facet of a wide side of the laser gain region of the active layer and a low reflection film provided on a facet of a narrow side of the laser gain region of the active layer. The facet of the narrow side is for outputting oscillation beams of a high order mode. This provides a high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency, and enables the outputting of a large output from a narrow light emission region.
Owner:NEC CORP
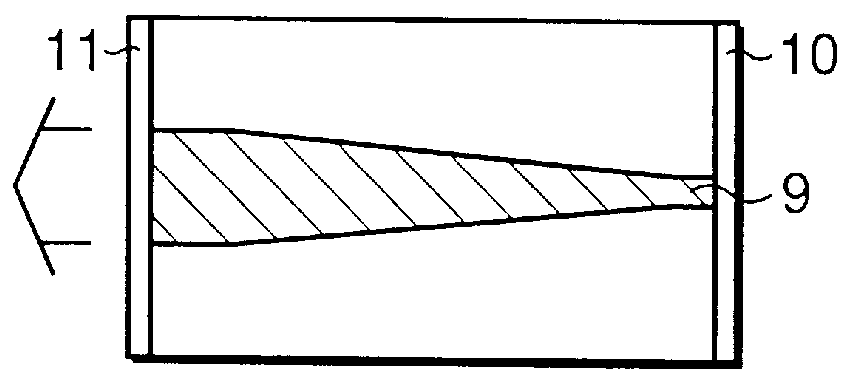
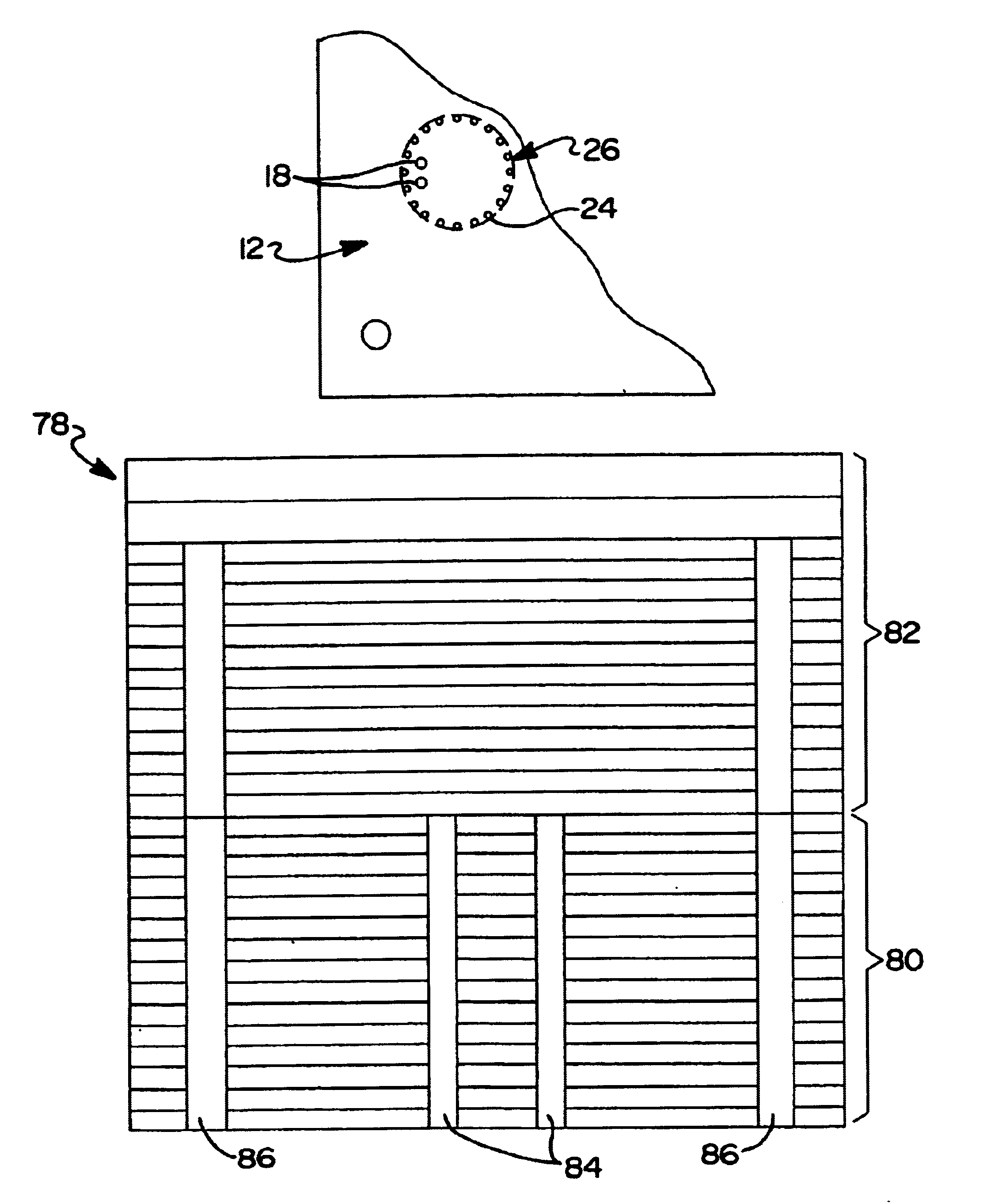
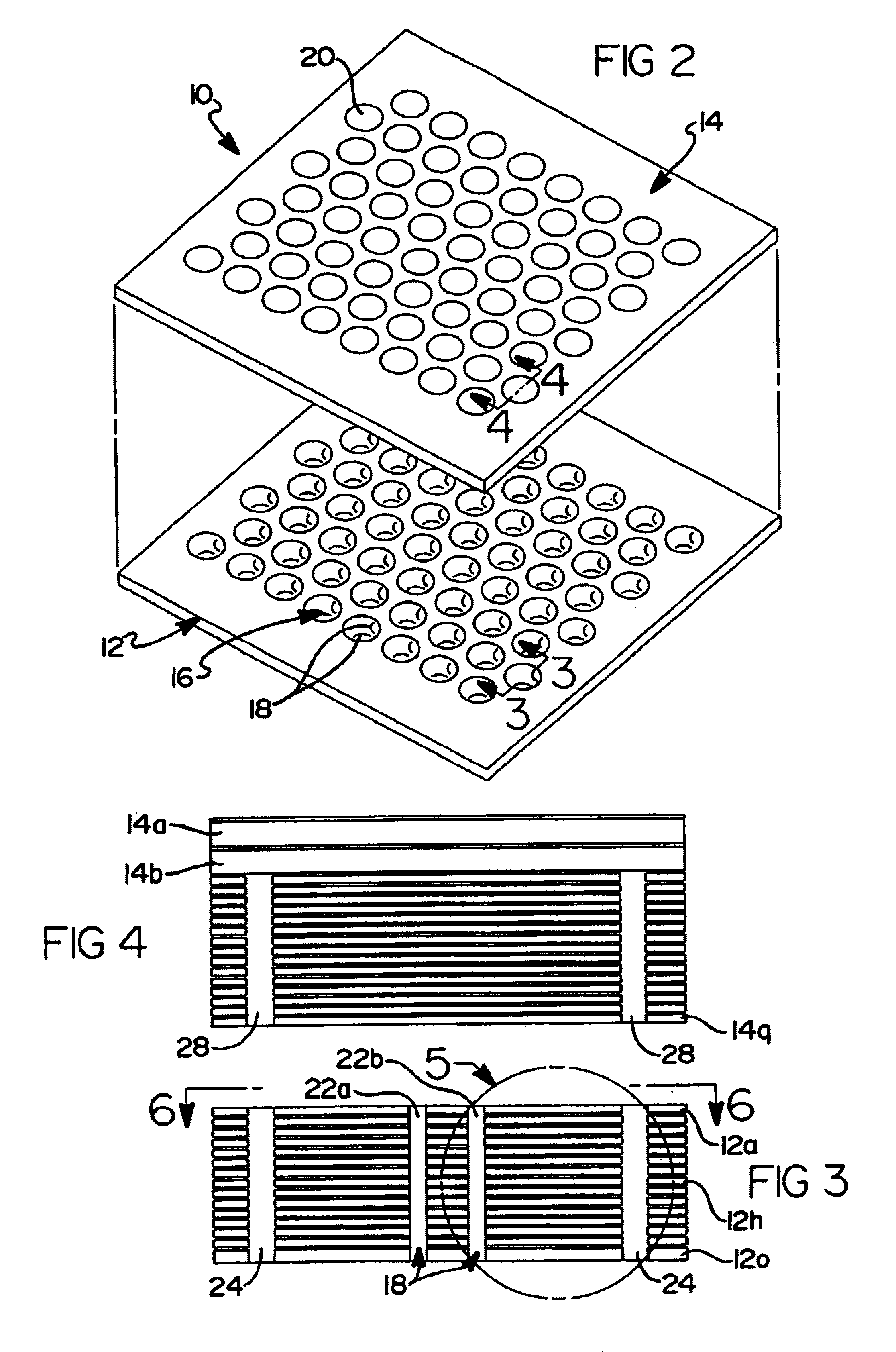
Antenna-integrated printed wiring board assembly for a phased array antenna system
InactiveUS6989791B2Reduces independent number of component partEasy to assembleSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsReturn loss bandwidthRF probe
A phased array antenna system including a plurality of metal, column-like elements formed adjacent the RF probes for improving the electrical performance of the system. In one embodiment a hole is formed in a multi-layer, probe-integrated printed wiring board of the system and metal material is plated thereon to fill the hole. The metal, column-like elements are each disposed generally in between associated pairs of the RF probes. The metal, column-like elements essentially form metal pins that improve the return loss bandwidth, probe-to-probe isolation, insertion loss bandwidth, higher order mode suppression and cross-polarization generation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High bandwidth multimode fiber
ActiveCN101738681AImprove bending resistanceHigh bandwidthOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingAccess networkUltrasound attenuation
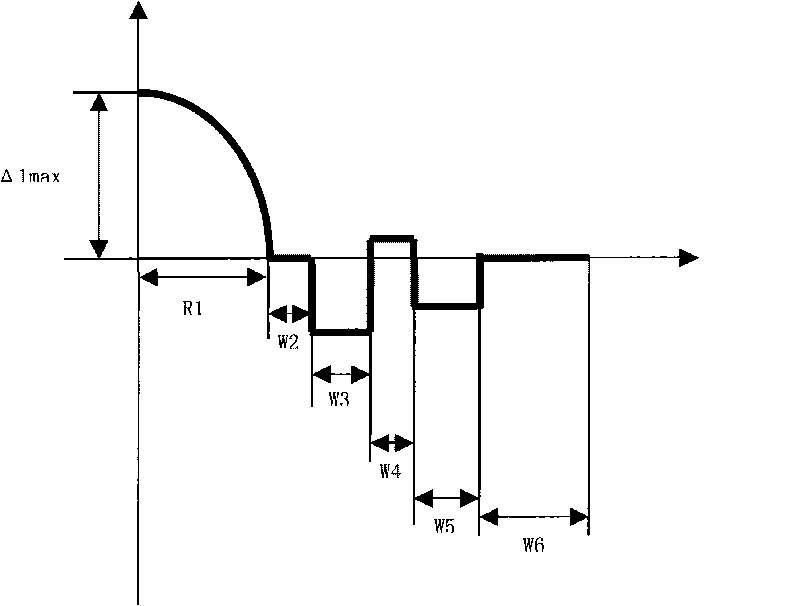
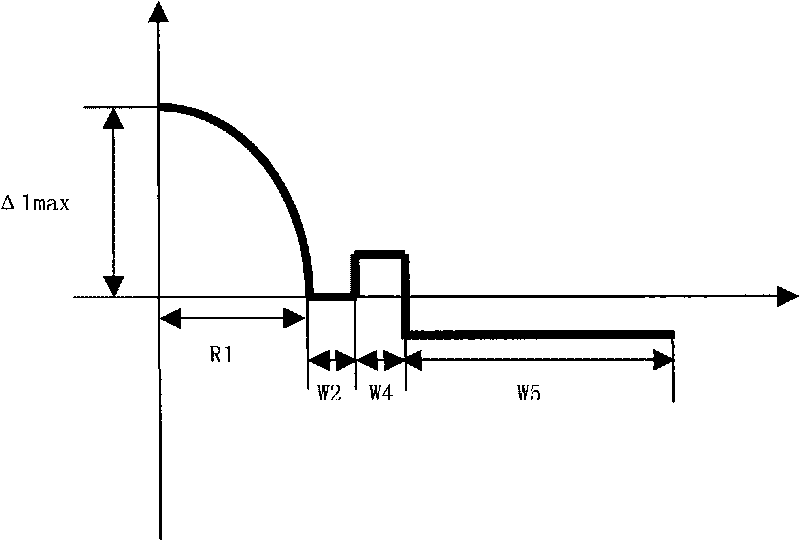
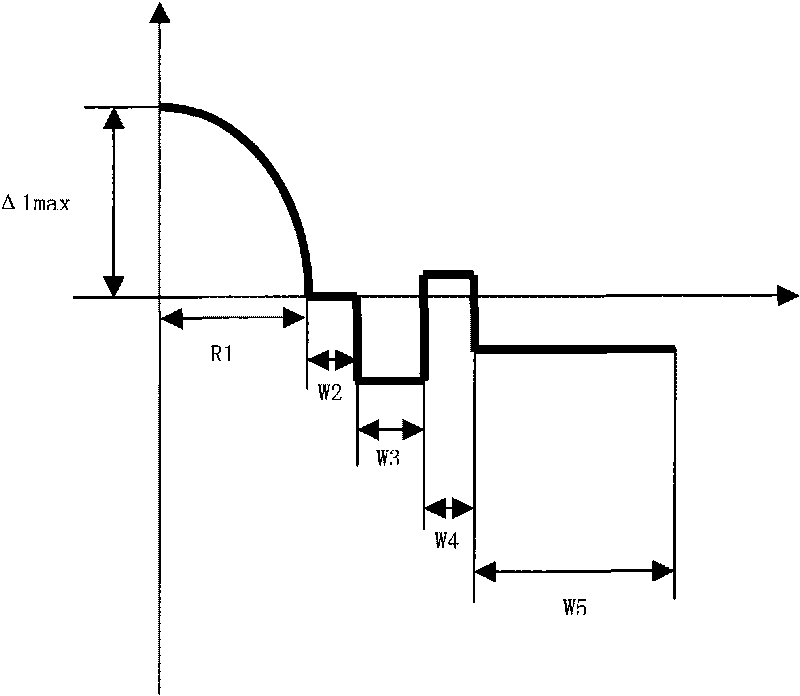
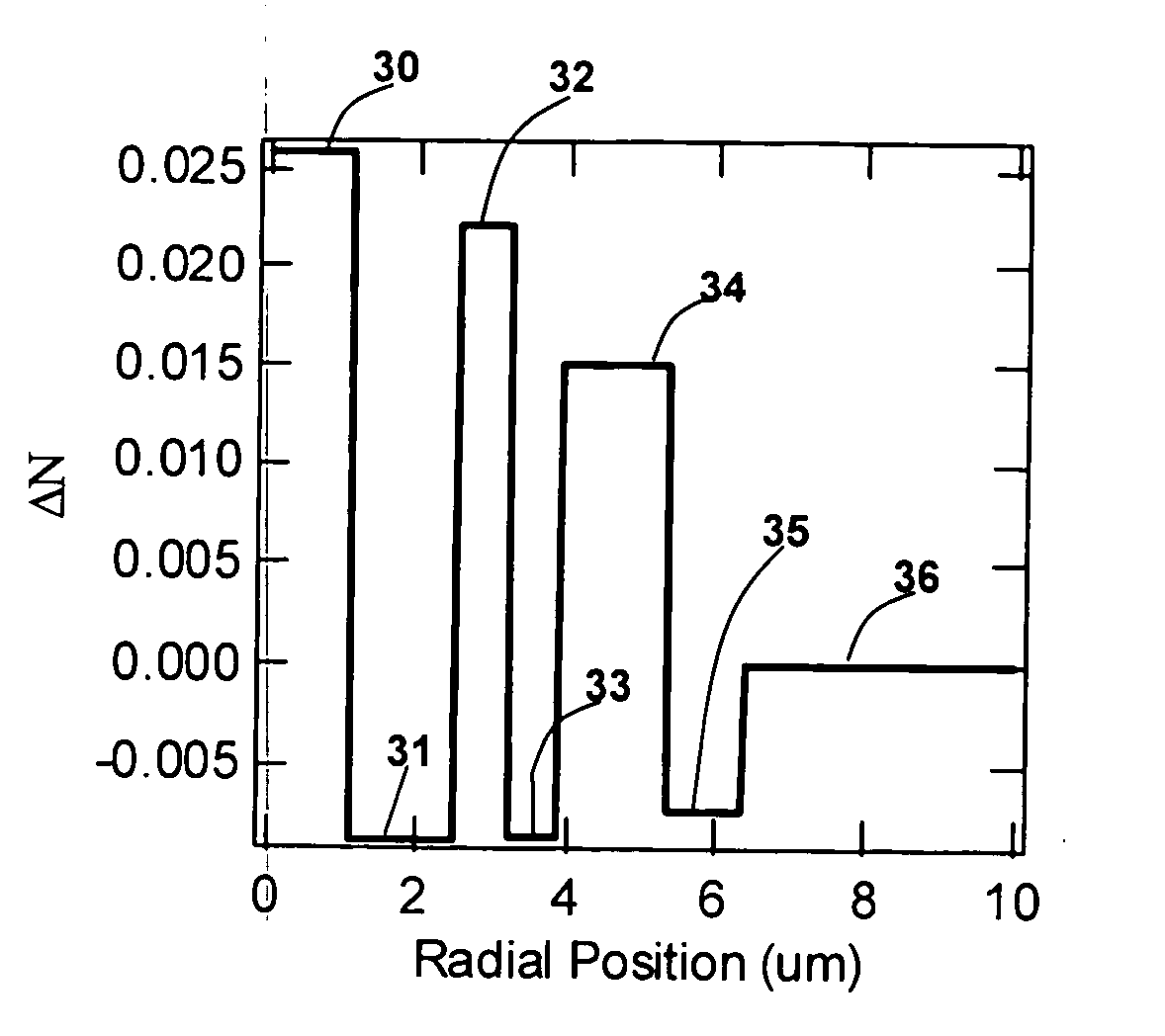
The invention relates to a high bandwidth multimode fiber used in an access network and a miniaturized optical device, which comprises a core layer and clad layers. The high bandwidth multimode fiber is characterized in that the radius of the core layer is 15 to 35 microns, the refractive index profile of the core layer is parabolic, and the maximum relative refractive index difference delta 1 percent max is over 0.8 percent; and the clad layers outside the core layer comprise an inner clad layer and / or a sunken inner clad layer, a rising ring and a sunken outer clad layer from the inside to the outside, and the relative refractive index difference of each layer satisfies the following relationships at the same time: delta 1 percent max is more than delta 2 percent which is more than delta 3 percent, delta 4 percent is more than delta 3 percent, the delta 4 percent is more than delta 5 percent, and the delta 4 percent is more than or equal to delta 2 percent. The macro-bending additional attenuation of the fiber is remarkably reduced, and the anti-bending performance of the fiber is improved; the fiber is provided with the rising ring so that the energy of some high-order mode of the core layer of the fiber is transferred or coupled to some mode of the rising ring from the core layer to effectively improve the bandwidth of the bending-insensitive multimode fiber; and the manufacturing method of the invention is simple, convenient and effective, and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
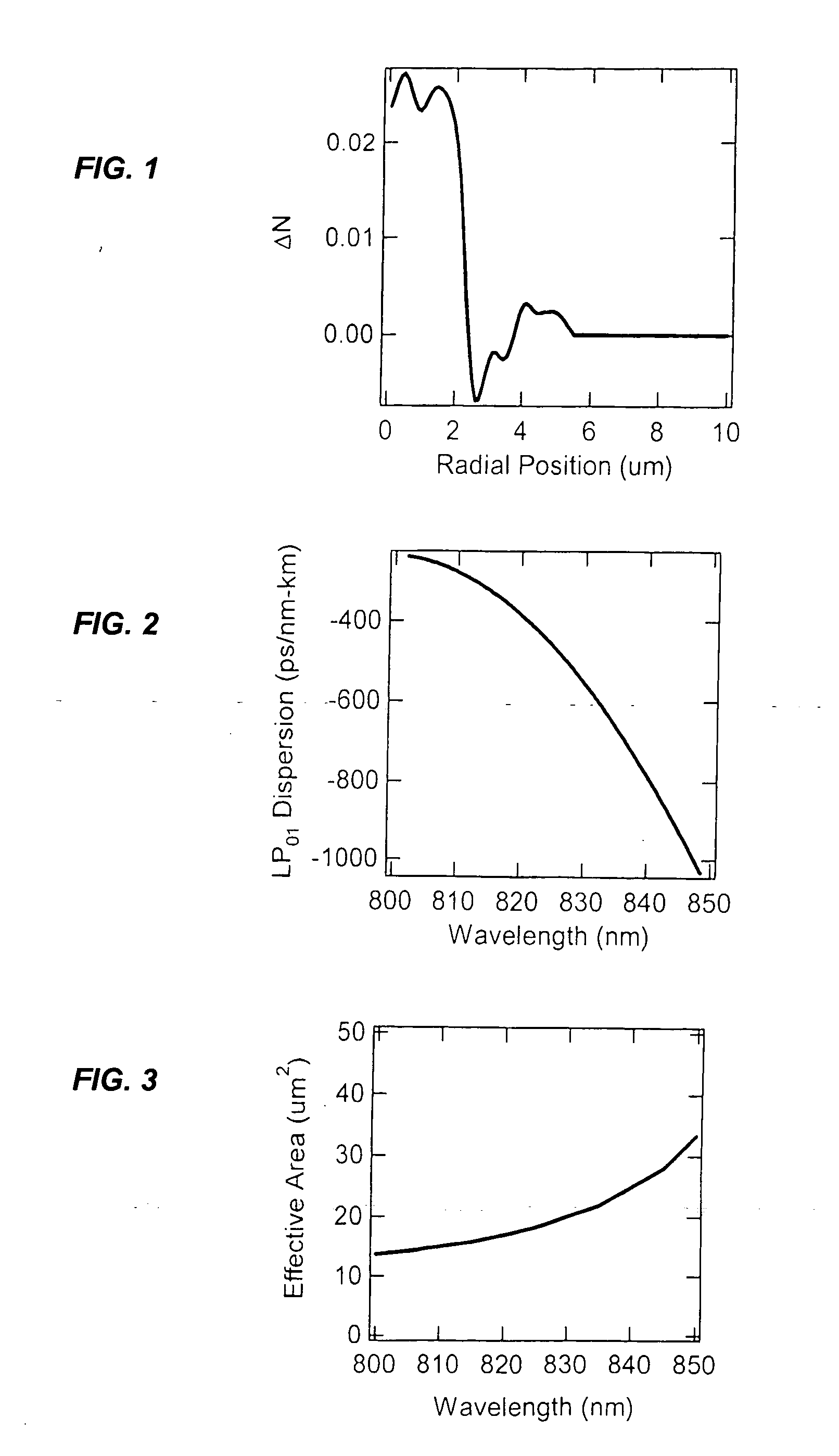
Optical fibers and optical fiber devices with total dispersion greater than material dispersion
InactiveUS20070206910A1Cladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFiberEffective refractive index
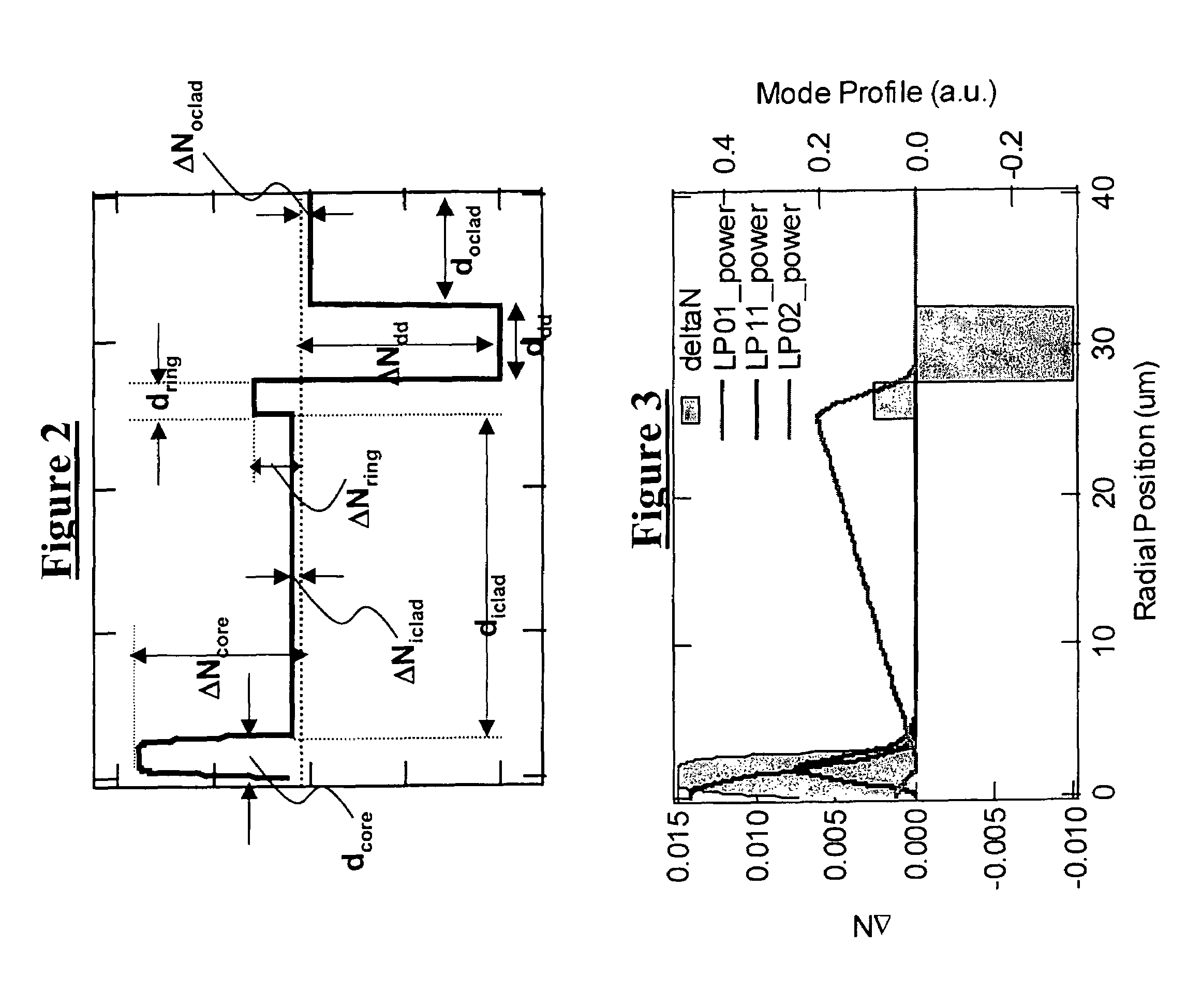
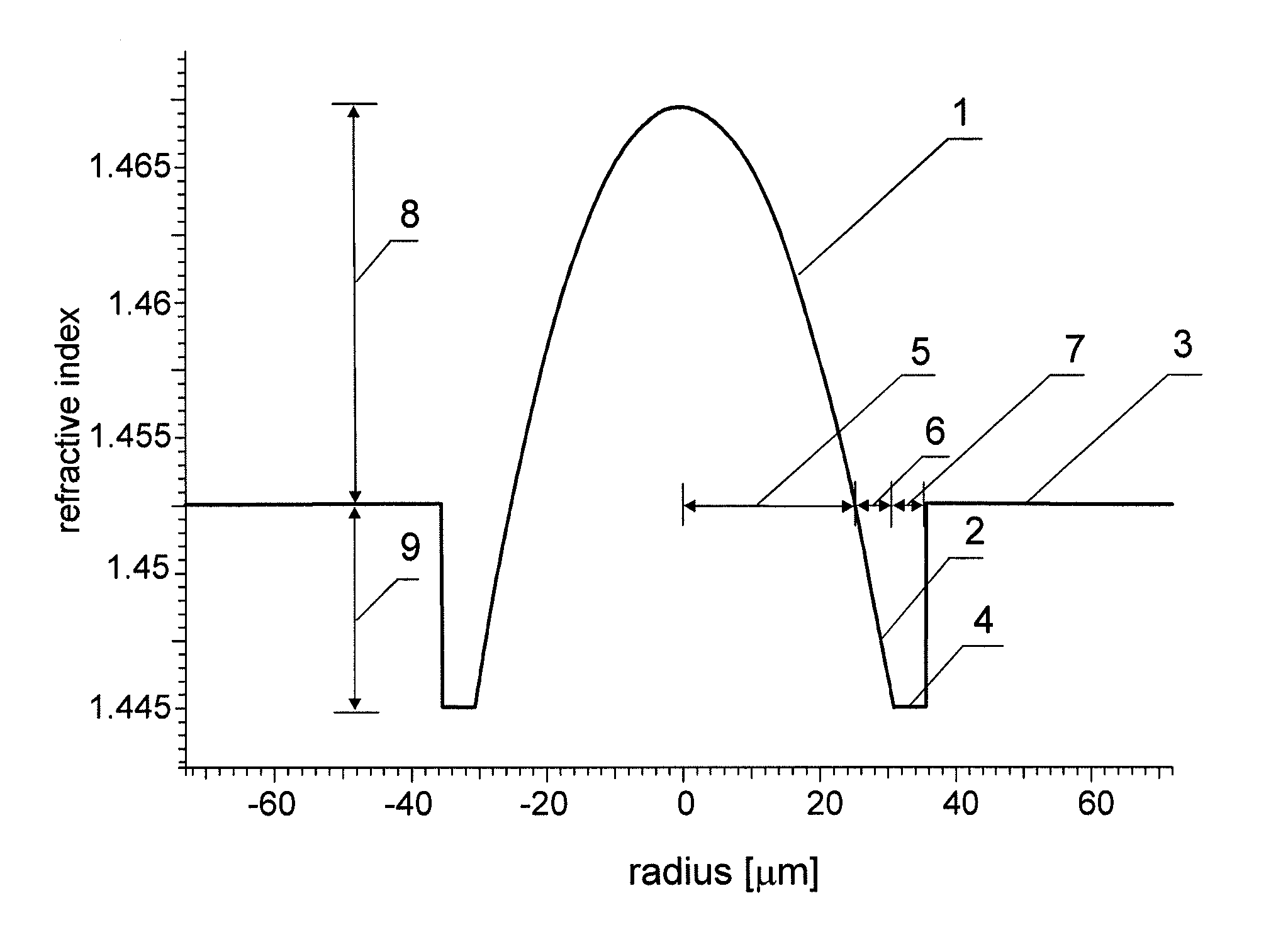
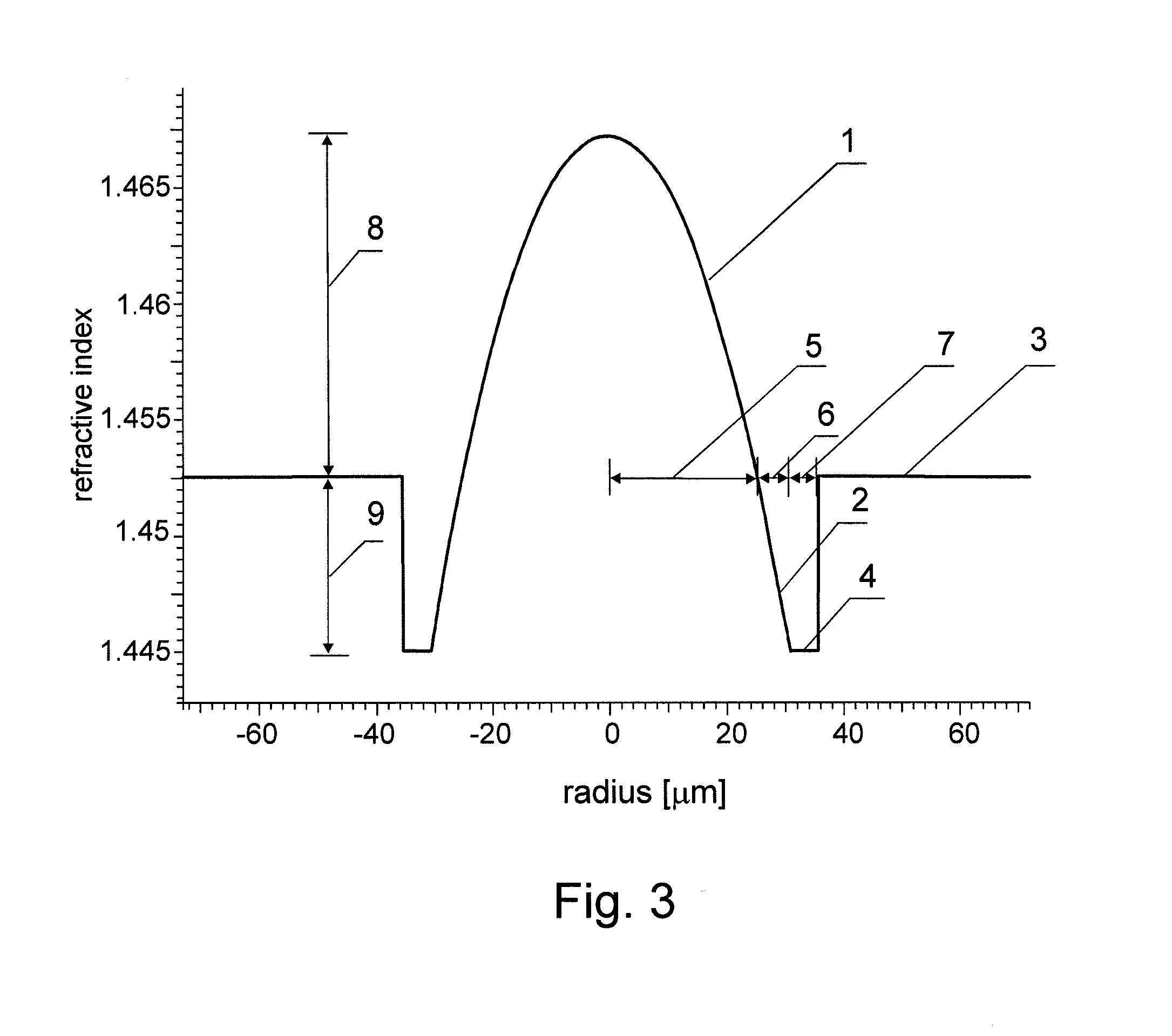
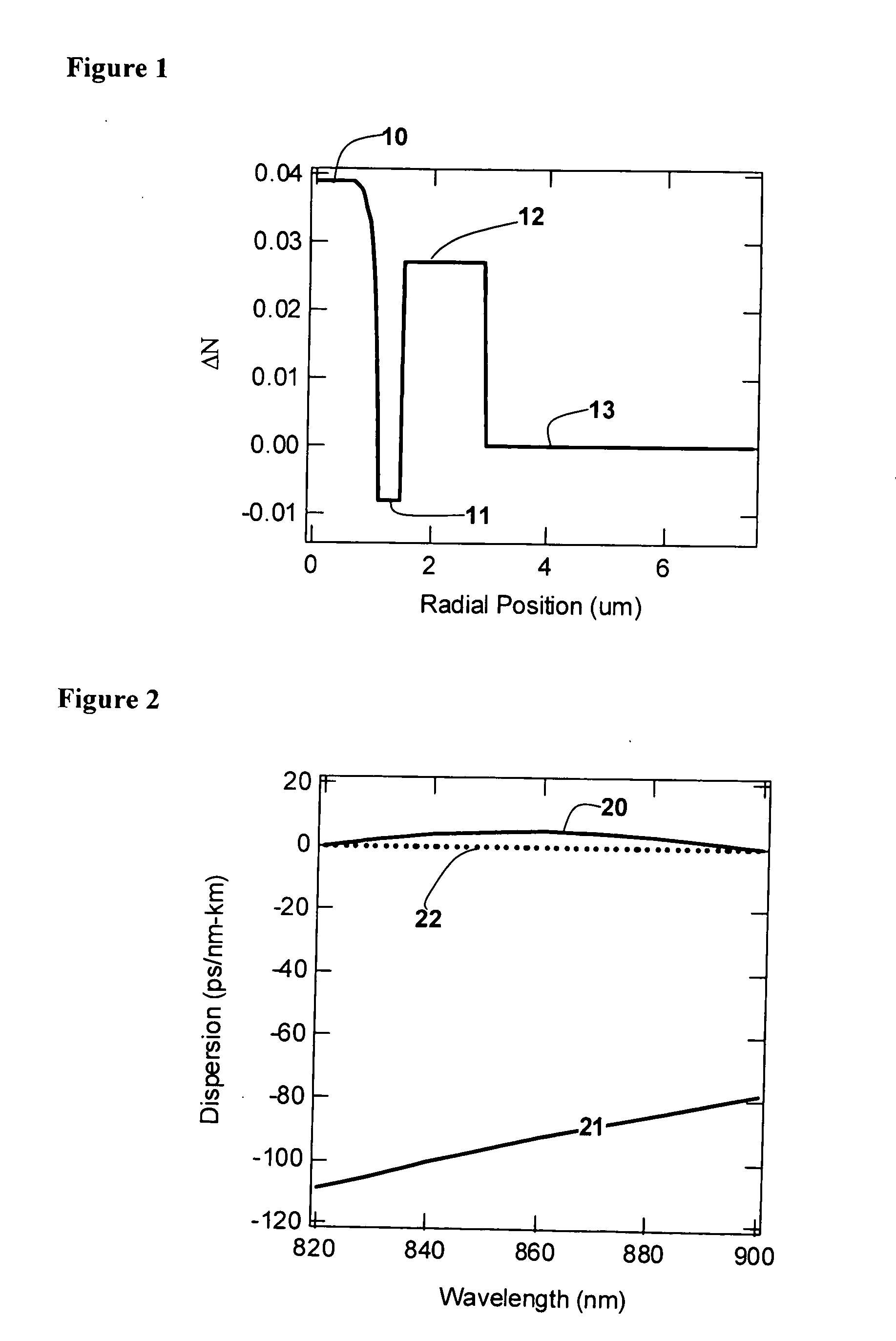
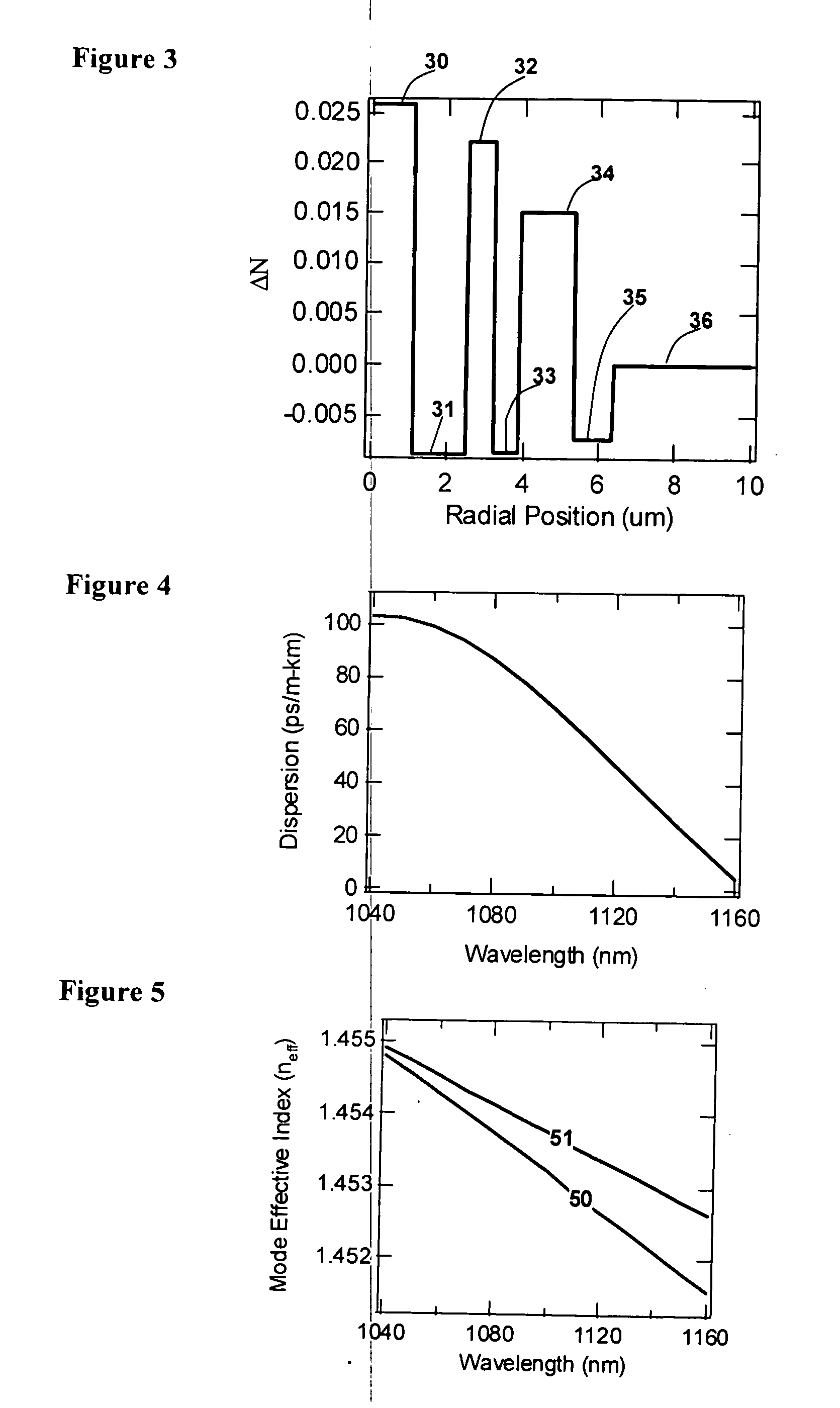
Disclosed are optical fiber devices incorporating optical fibers with total dispersion greater than material dispersion, and with preferred dispersion values less than +50 ps / nm-km. The desired dispersion values are obtained when light resides substantially in a single higher order mode (HOM) of the fiber, typically the LP02 mode. The optical fibers also preferably have substantial separation between the effective indices of the HOM and any other mode.
Owner:RAMACHANDRAN SIDDHARTH
Surface mount antenna and communication device including the same
InactiveUS6452548B2Increase electrical lengthChange frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandCommunication device
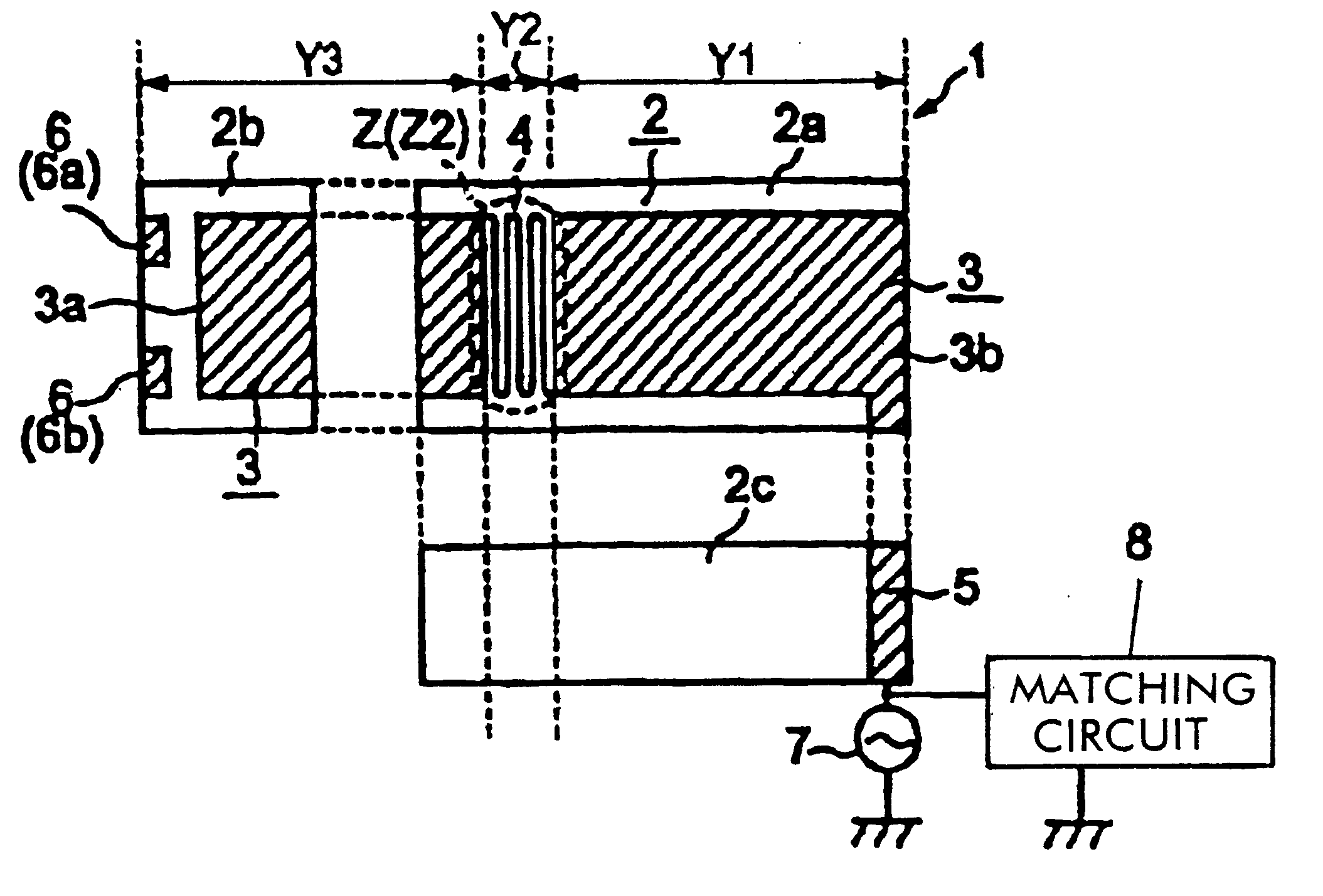
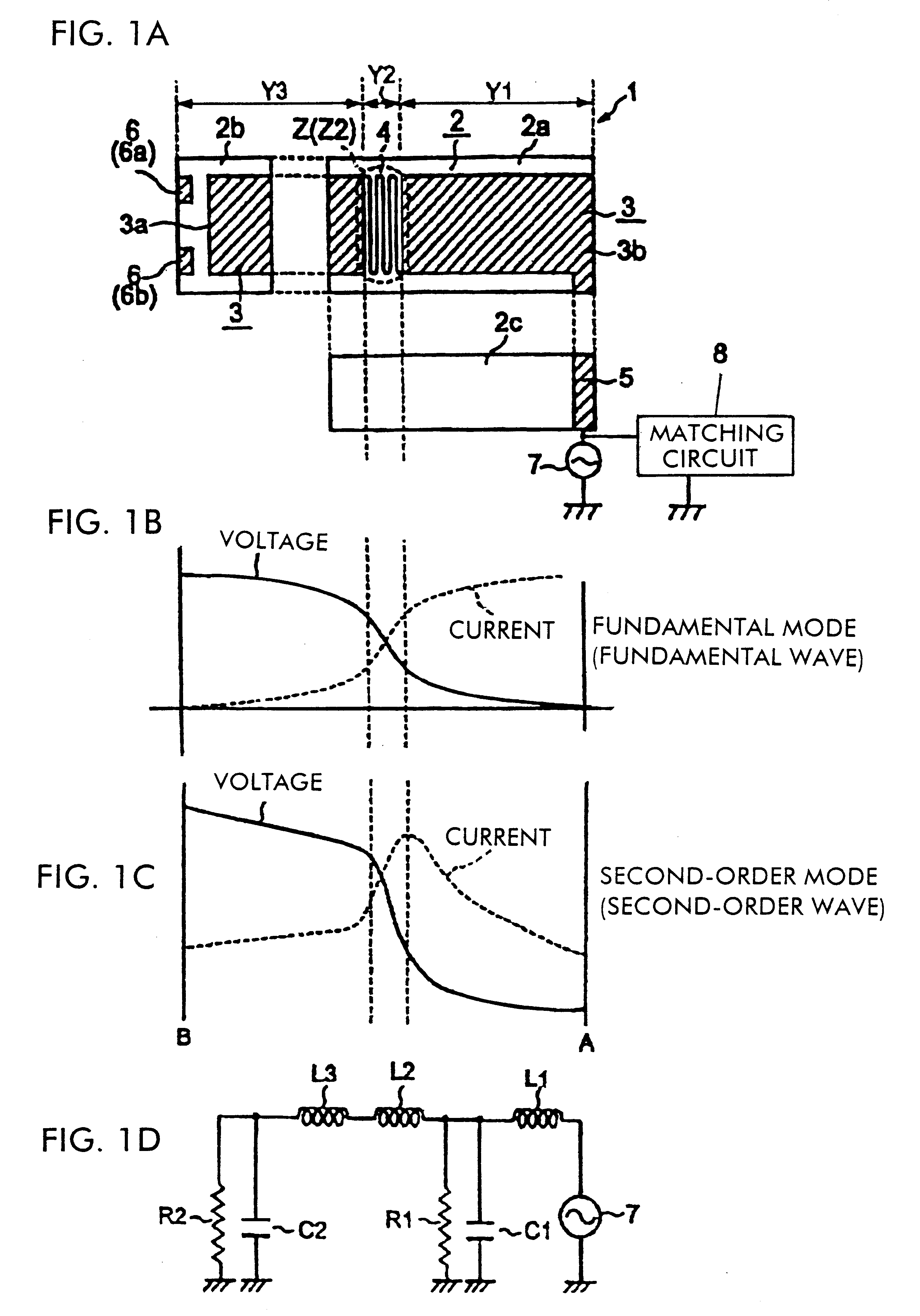
In a feeding radiation electrode of a surface mount antenna, a series inductance component such as a meander pattern is formed locally in a maximum resonance current part in a high-order mode (second-order mode) so as to locally form a series inductance component therein thereby making the maximum resonance current part have a greater electrical length per unit physical length than the other parts. This makes it possible to control the difference between the resonance frequency in a fundamental mode and the resonance frequency in the high-order mode over a large range. Furthermore, it is possible to vary the resonance frequency in the second-order mode independently of the resonance frequency in the fundamental mode by varying the number of lines or the line-to-line distance of the meander pattern thereby varying the value of the series inductance component. Thus, it is possible to easily and efficiently design a surface mount antenna having a frequency characteristic which satisfies requirements needed in multi-band applications without having to change the basic design.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Transmission of laser pulses with high output beam quality using step-index fibers having large cladding
InactiveUS20120051084A1Reduce couplingTighter focusingCosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical apparatusForming gasSilicon dioxide
An apparatus and method for transmission of laser pulses with high output beam quality using large core step-index silica optical fibers having thick cladding, are described. The thick cladding suppresses diffusion of modal power to higher order modes at the core-cladding interface, thereby enabling higher beam quality, M2, than are observed for large core, thin cladding optical fibers. For a given NA and core size, the thicker the cladding, the better the output beam quality. Mode coupling coefficients, D, has been found to scale approximately as the inverse square of the cladding dimension and the inverse square root of the wavelength. Output from a 2 m long silica optical fiber having a 100 μm core and a 660 μm cladding was found to be close to single mode, with an M2=1.6. Another thick cladding fiber (400 μm core and 720 μm clad) was used to transmit 1064 nm pulses of nanosecond duration with high beam quality to form gas sparks at the focused output (focused intensity of >100 GW / cm2), wherein the energy in the core was <6 mJ, and the duration of the laser pulses was about 6 ns. Extending the pulse duration provided the ability to increase the delivered pulse energy (>20 mJ delivered for 50 ns pulses) without damaging the silica fiber.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Multimode optical fiber with a higher order mode removing function
InactiveUS6535678B1Reduce lossLoss of sensitivityOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberClassical mechanics
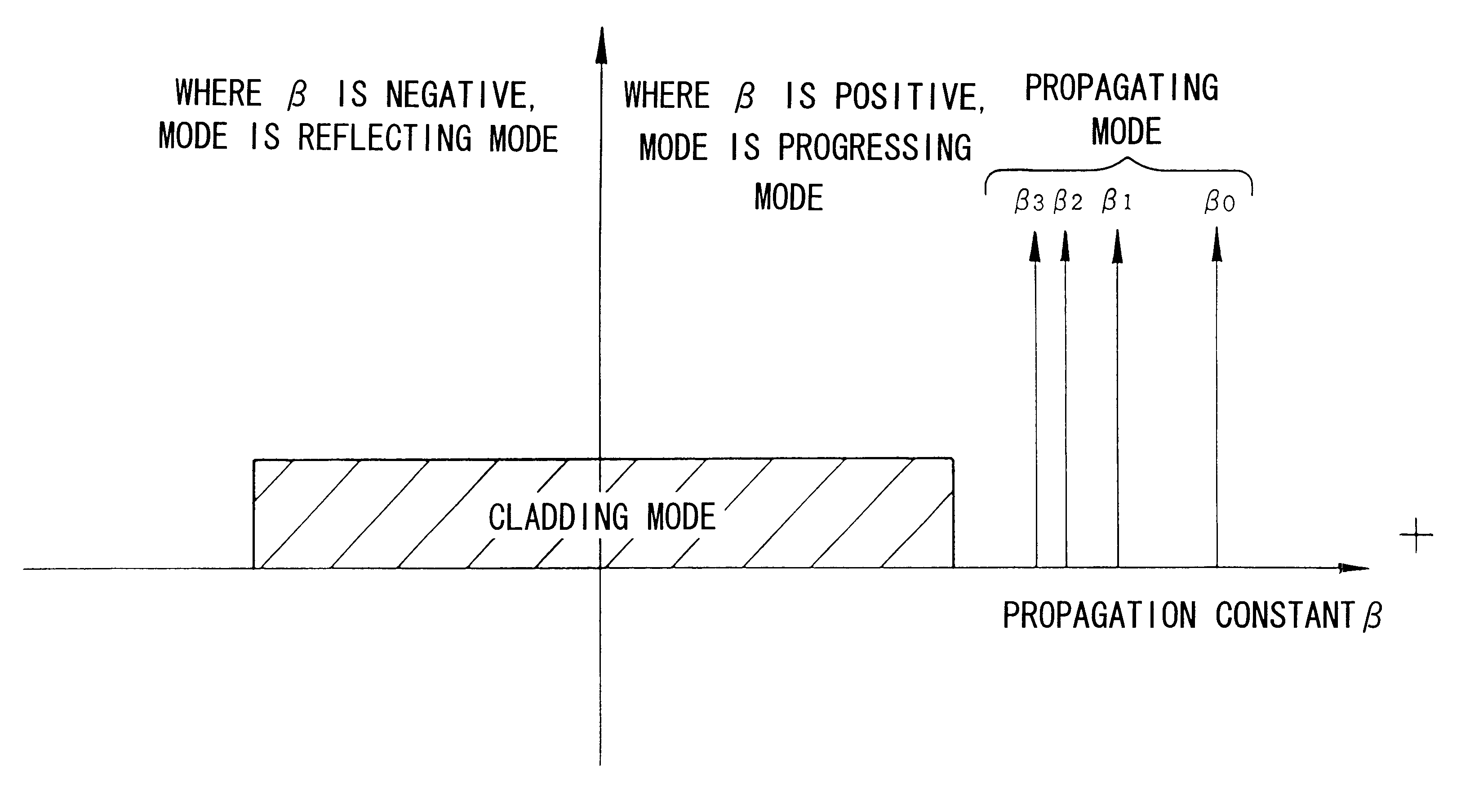
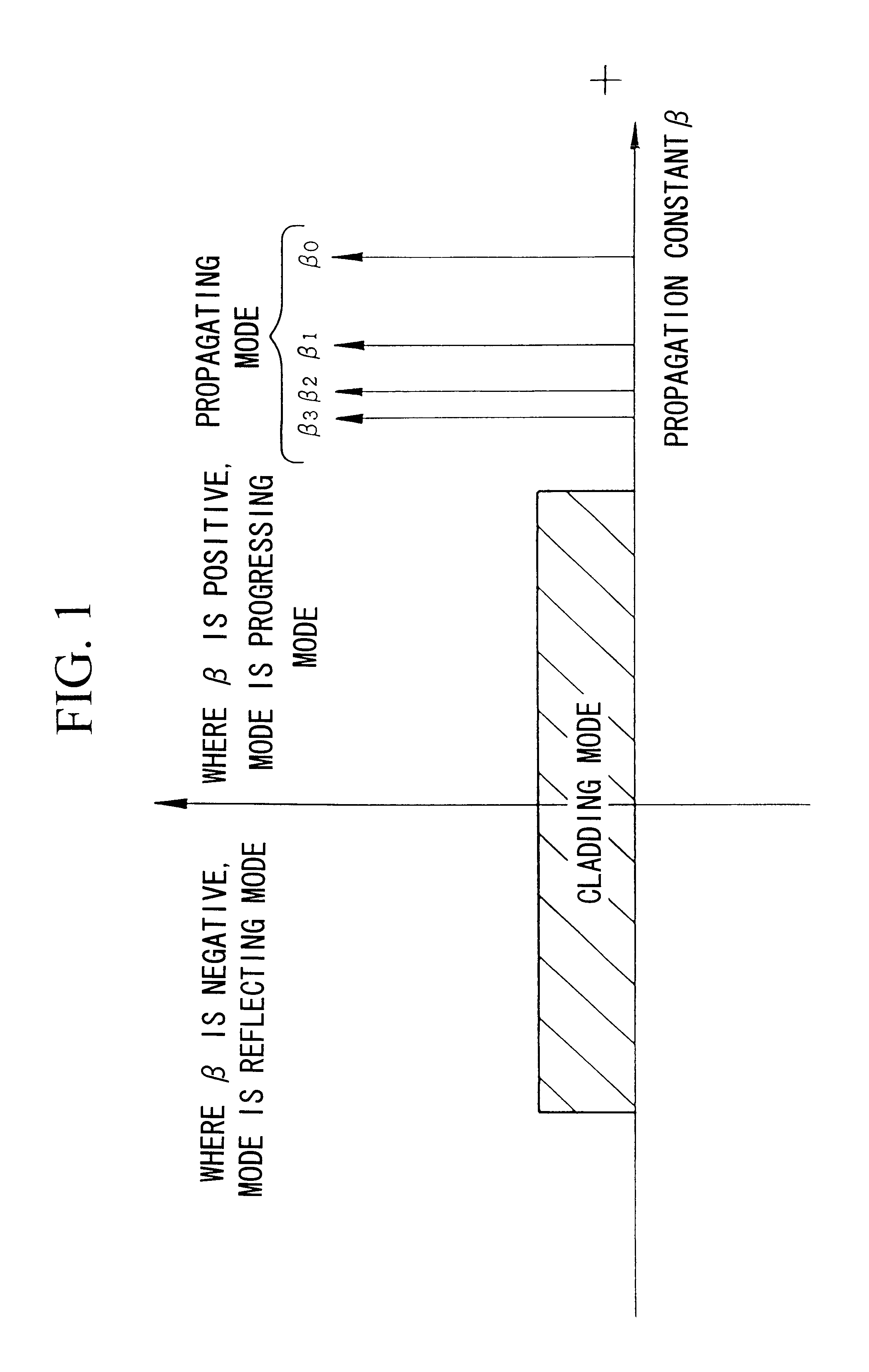
The present invention's multimode optical fiber is characterized in that the propagating modes include a mode the lowest and second or higher order modes; and the difference between the propagation constants of the lowest order mode and the second order mode is 2-fold or more than the difference between the propagation constants of adjacent modes that are second order or higher order modes. Due to this design, single mode propagation becomes possible once the modes have propagated over a specific distance. As a result, it is possible to relax the conventional single mode conditions, enabling the fiber parameters to be set relatively freely.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
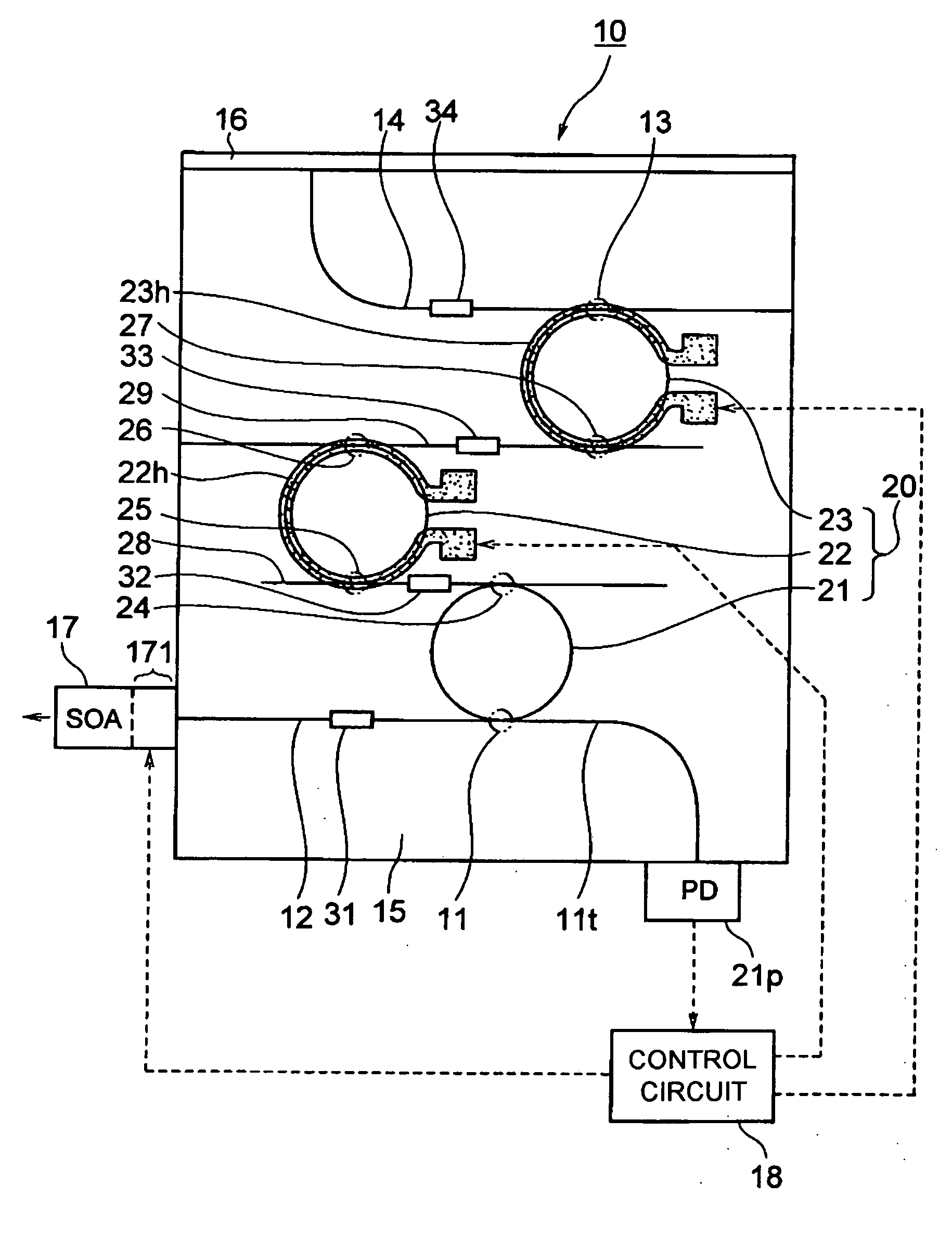
Tunable laser
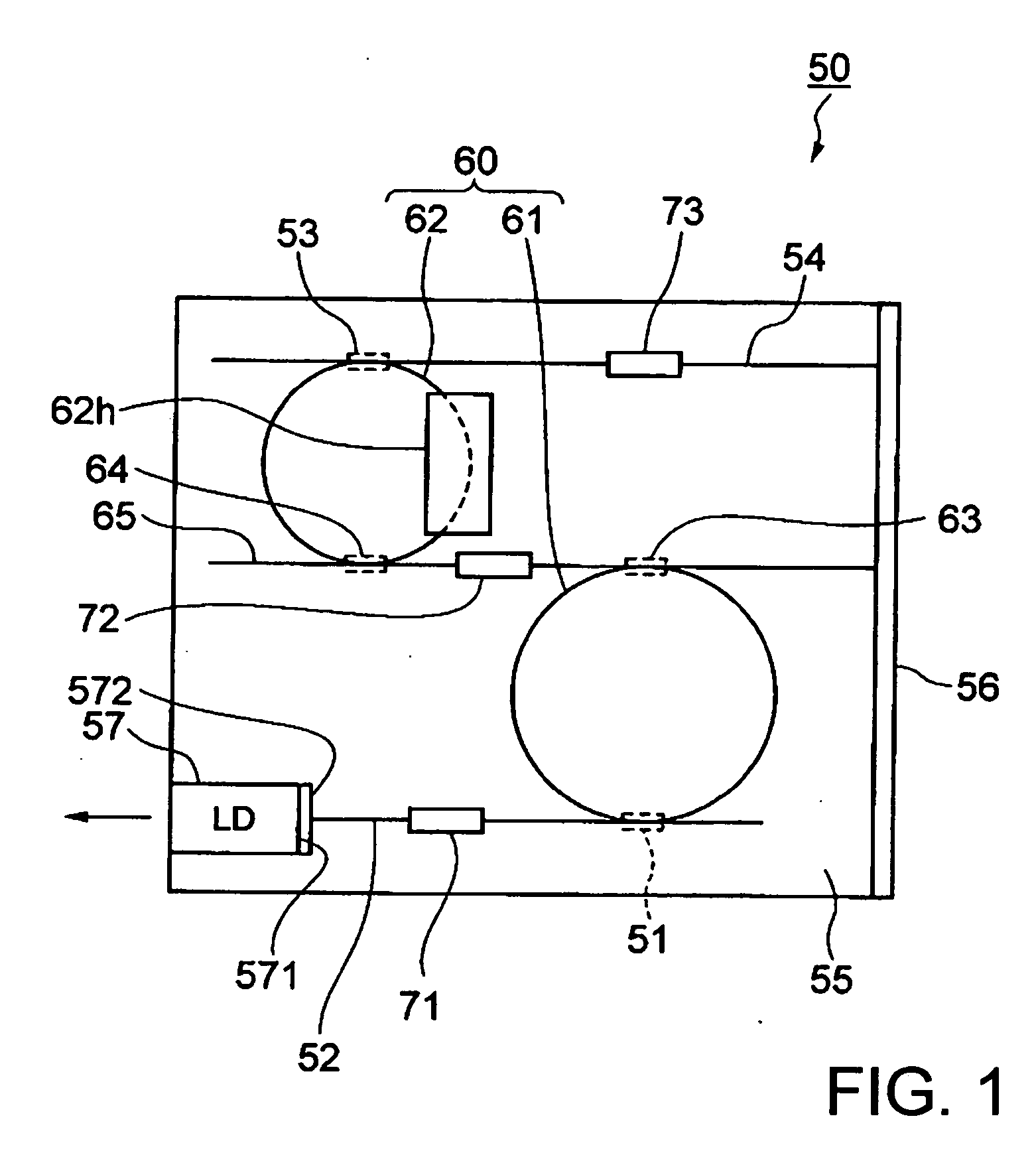
InactiveUS20060222038A1Improve reliabilityLow costLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLength waveWaveguide
A tunable laser has a multiple ring resonator comprising a plurality of ring resonators having respective ring-shaped waveguides and respective different optical path lengths, an input / output side optical waveguide coupled to the multiple ring resonator, an optical input / output device such as a laser diode coupled to the input / output side optical waveguide, a reflection side optical waveguide coupled to the multiple ring resonator, an optical reflector coupled to the reflection side optical waveguide, a wavelength varying mechanism for changing the resonant wavelength of the multiple ring resonator, and a filter for preventing light in high-order modes from being introduced into the multiple ring resonator and for propagating light in a fundamental mode in the multiple ring resonator.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com