Optical fibers and optical fiber devices with total dispersion greater than material dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
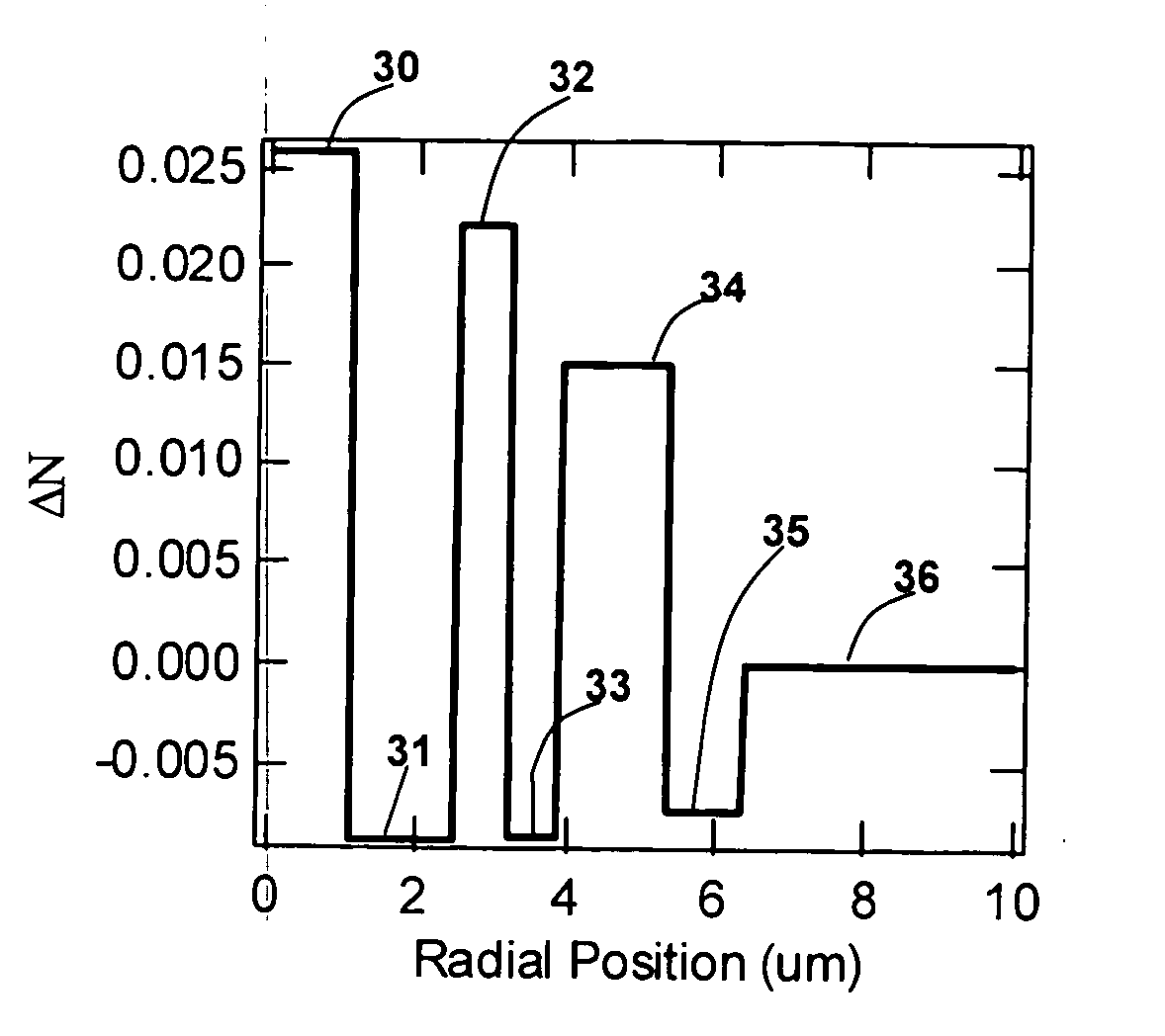
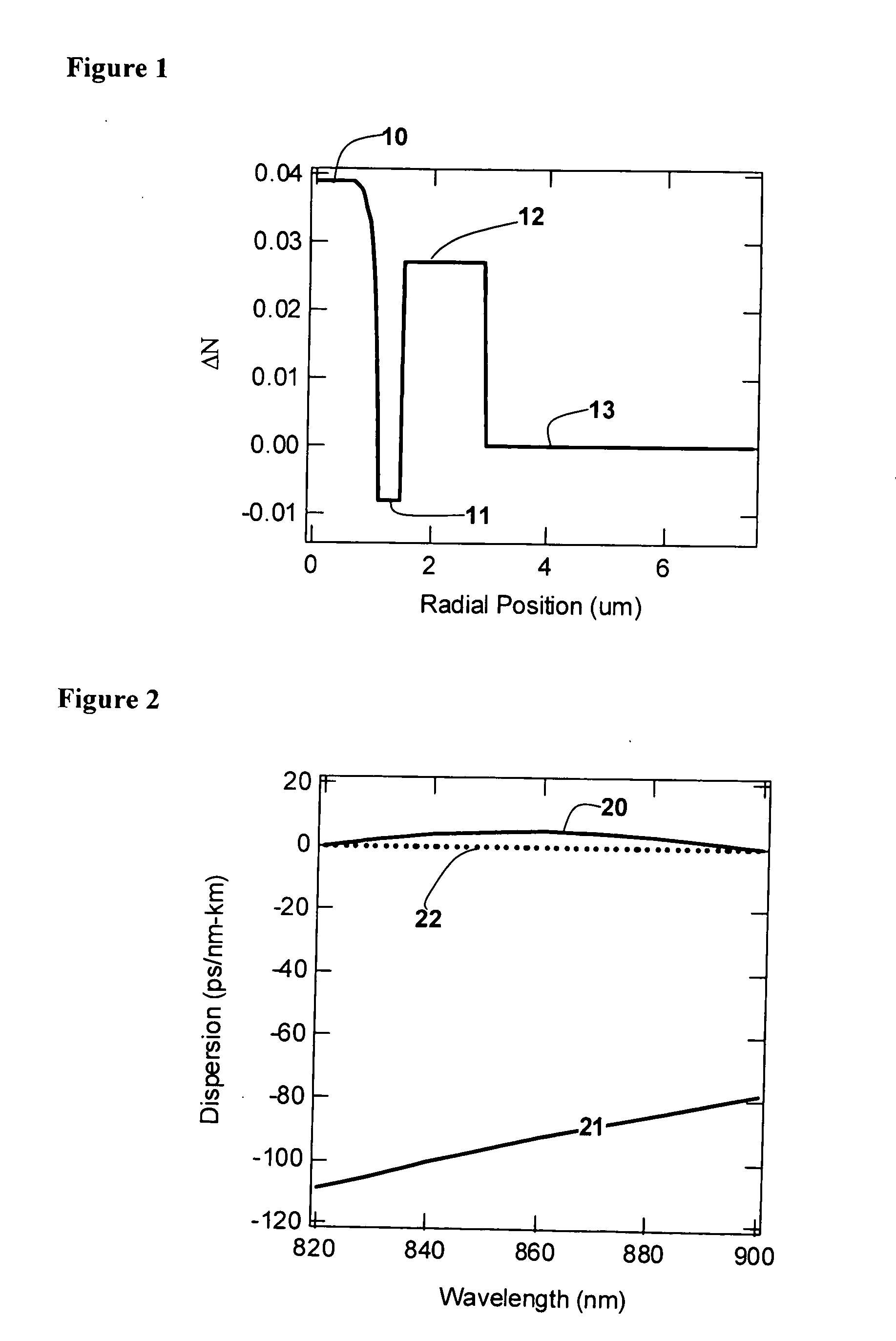
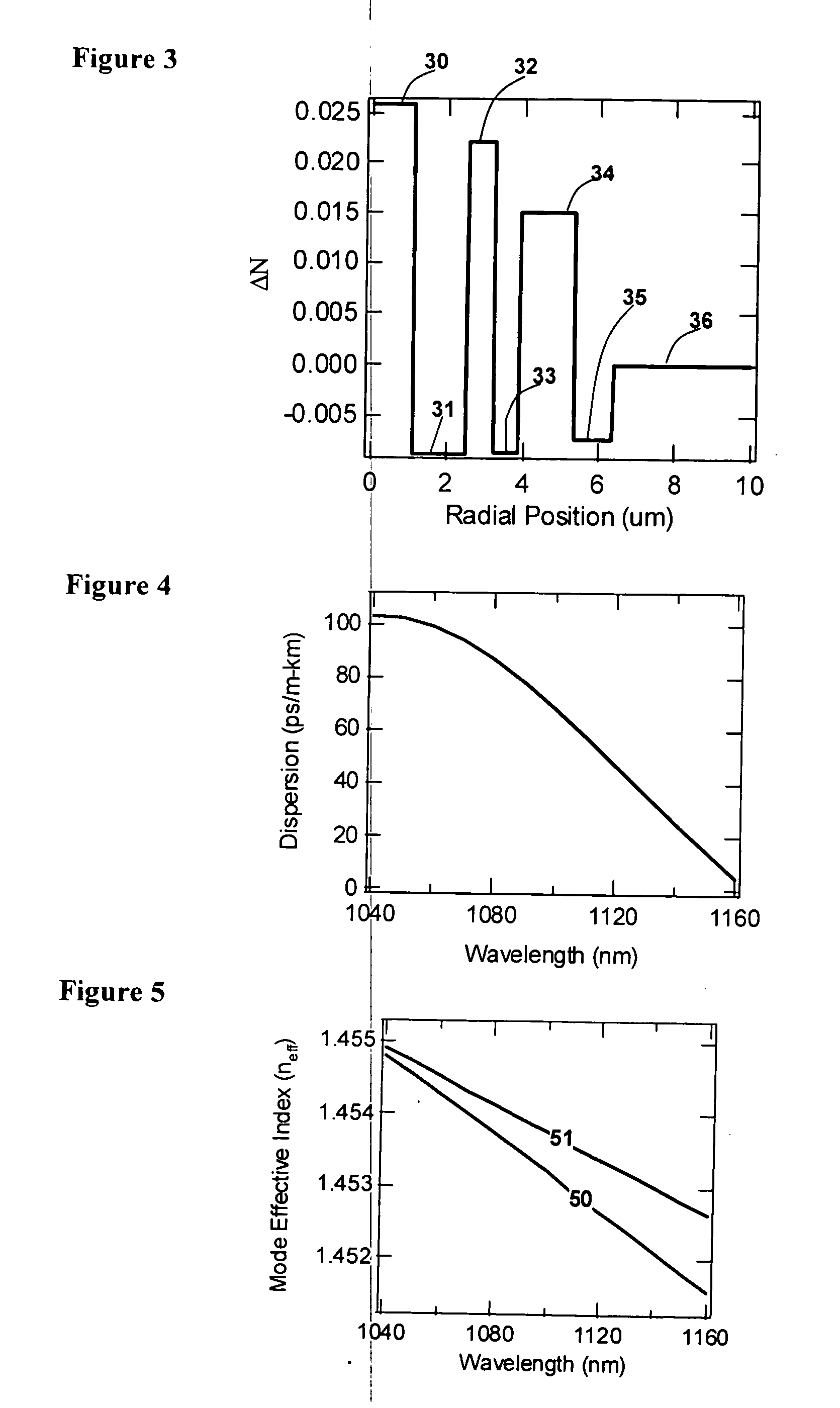
[0012]FIG. 1 shows the index profile of a fiber that supports more than one mode, but which is designed to yield desired the Dtotal for the LP02 mode. The refractive index profile comprises a core, 10, with ΔN of 0.039 extending to a radial position of 1 μm; followed by a trench region (down-doped ring), 11, with ΔN of −0.008 and a thickness of 0.5 □m; followed by an up-doped ring, 12, with ΔN of 0.027 and a thickness of 1.4 μm. Thereafter, the fiber cladding, consisting only of silica glass, 13, extends to the edge of the glass cladding of the fiber. For typical fibers, this extends to a radial position of 62.5 □m. The profile in FIG. 1 is shown only till a radial position of 7 μm because the rest of the fiber is merely an extension of the silica glass cladding. The refractive index profile is characterized in terms of ΔN, the difference in refractive index between the region of interest and the silica cladding.
[0013]FIG. 2 shows the dispersion as a function of wavelength, of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com