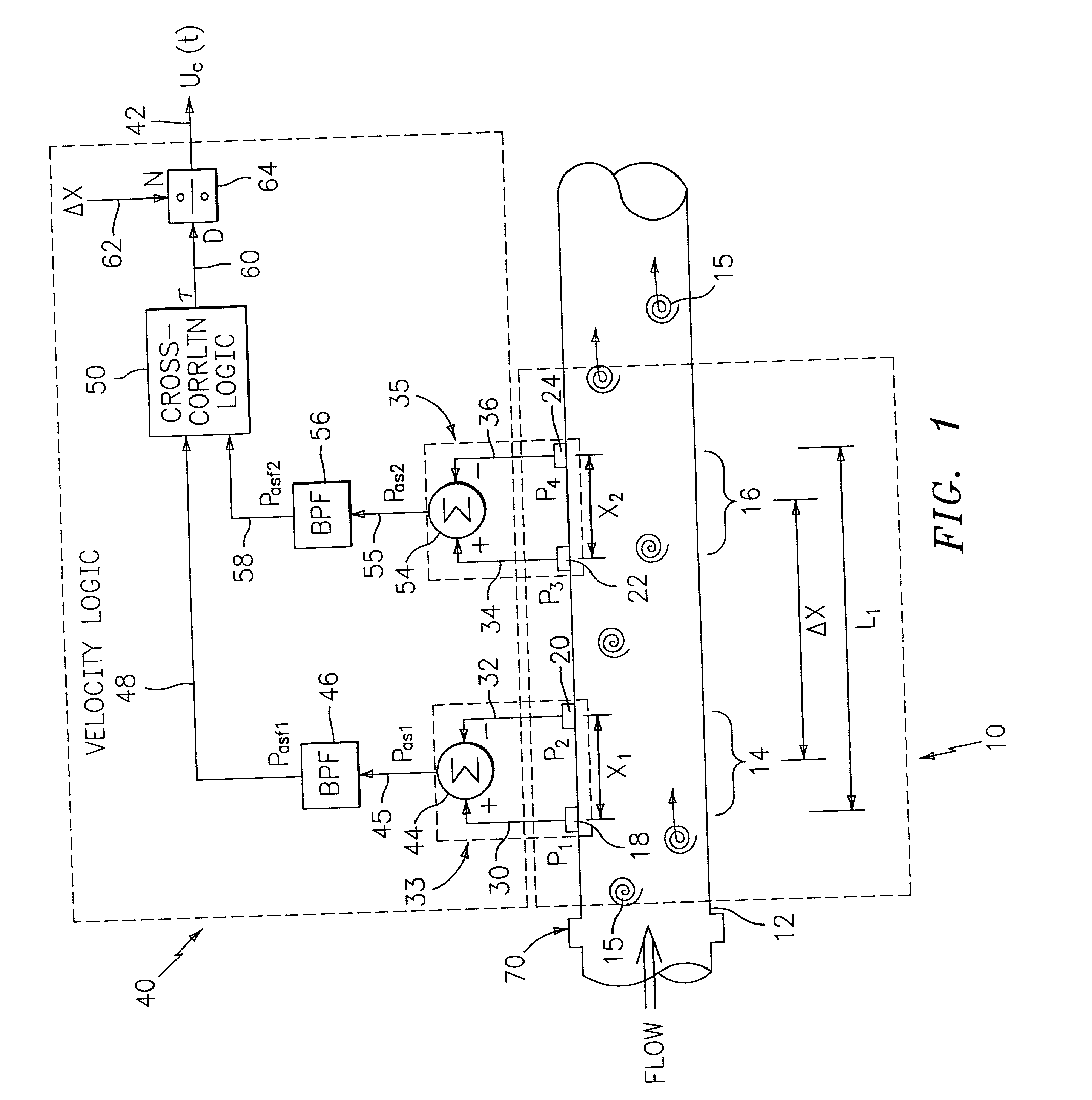Patents
Literature
1236 results about "Spatial filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A spatial filter is an optical device which uses the principles of Fourier optics to alter the structure of a beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation, typically coherent laser light. Spatial filtering is commonly used to "clean up" the output of lasers, removing aberrations in the beam due to imperfect, dirty, or damaged optics, or due to variations in the laser gain medium itself. This filtering can be applied to transmit a pure transverse mode from a multimode laser while blocking other modes emitted from the optical resonator. The term "filtering" indicates that the desirable structural features of the original source pass through the filter, while the undesirable features are blocked. Apparatus which follows the filter effectively sees a higher-quality but lower-powered image of the source, instead of the actual source directly. An example of the use of spatial filter can be seen in advanced setup of micro-Raman spectroscopy.
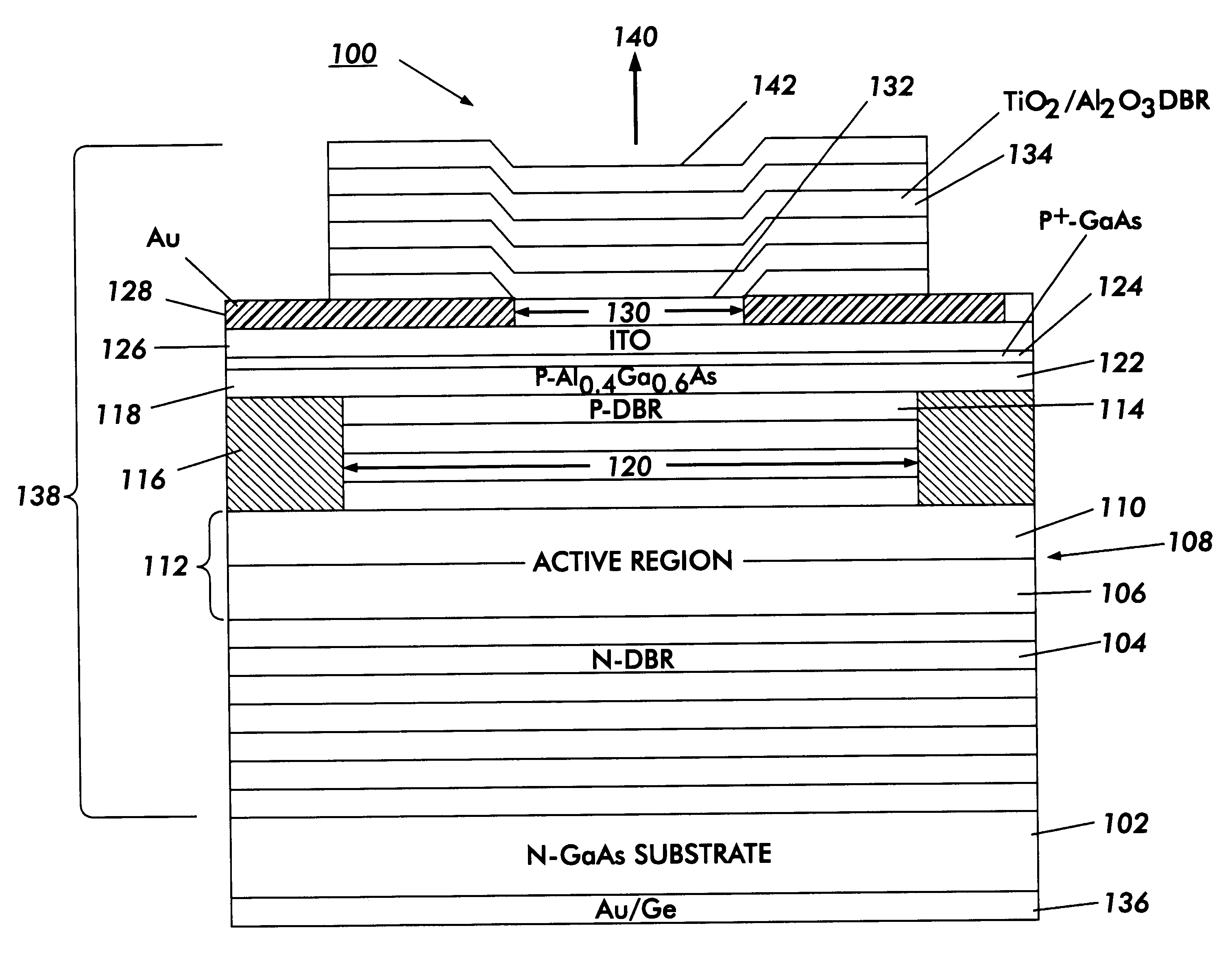
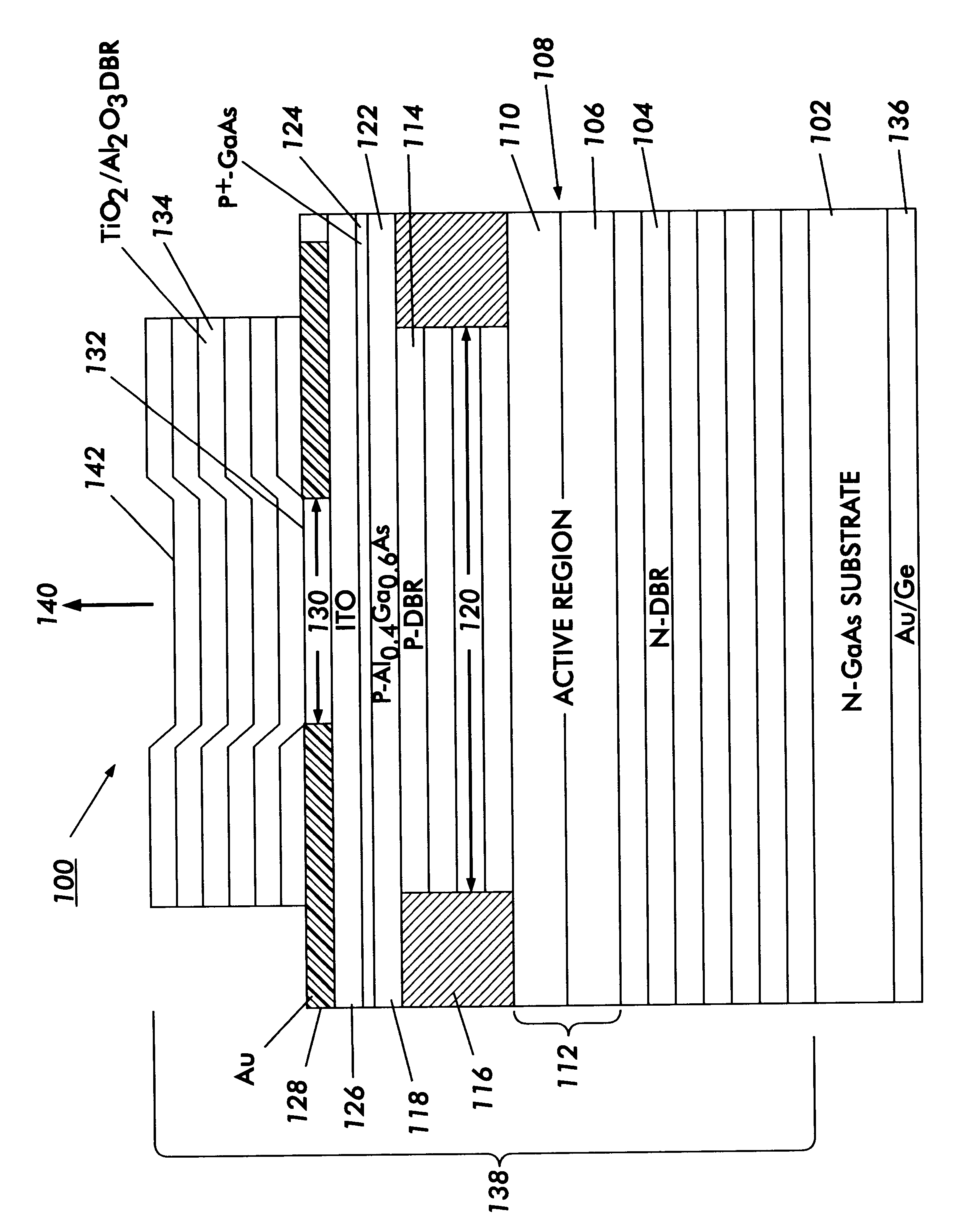
Metal spatial filter to enhance model reflectivity in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser
InactiveUS6185241B1Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
An annular metal layer is provided between a conductive oxide layer and a dielectric mirror in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The annular metal layer defines the output window for the laser cavity which matches the TEM.sub.00 fundamental mode of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL. The metal layer outside the output window provides modal reflectivity discrimination against high order transverse modes of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL.
Owner:XEROX CORP
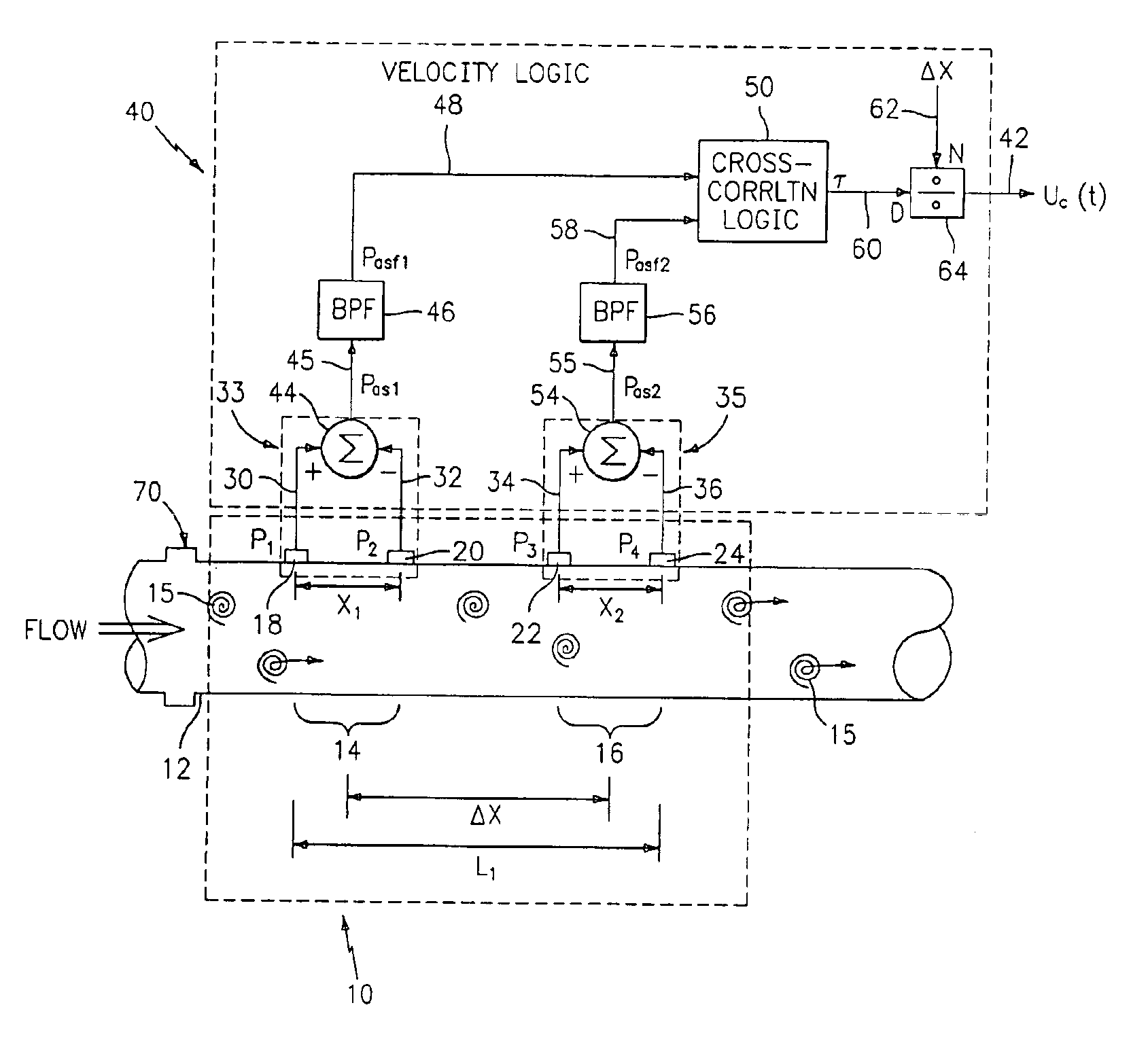
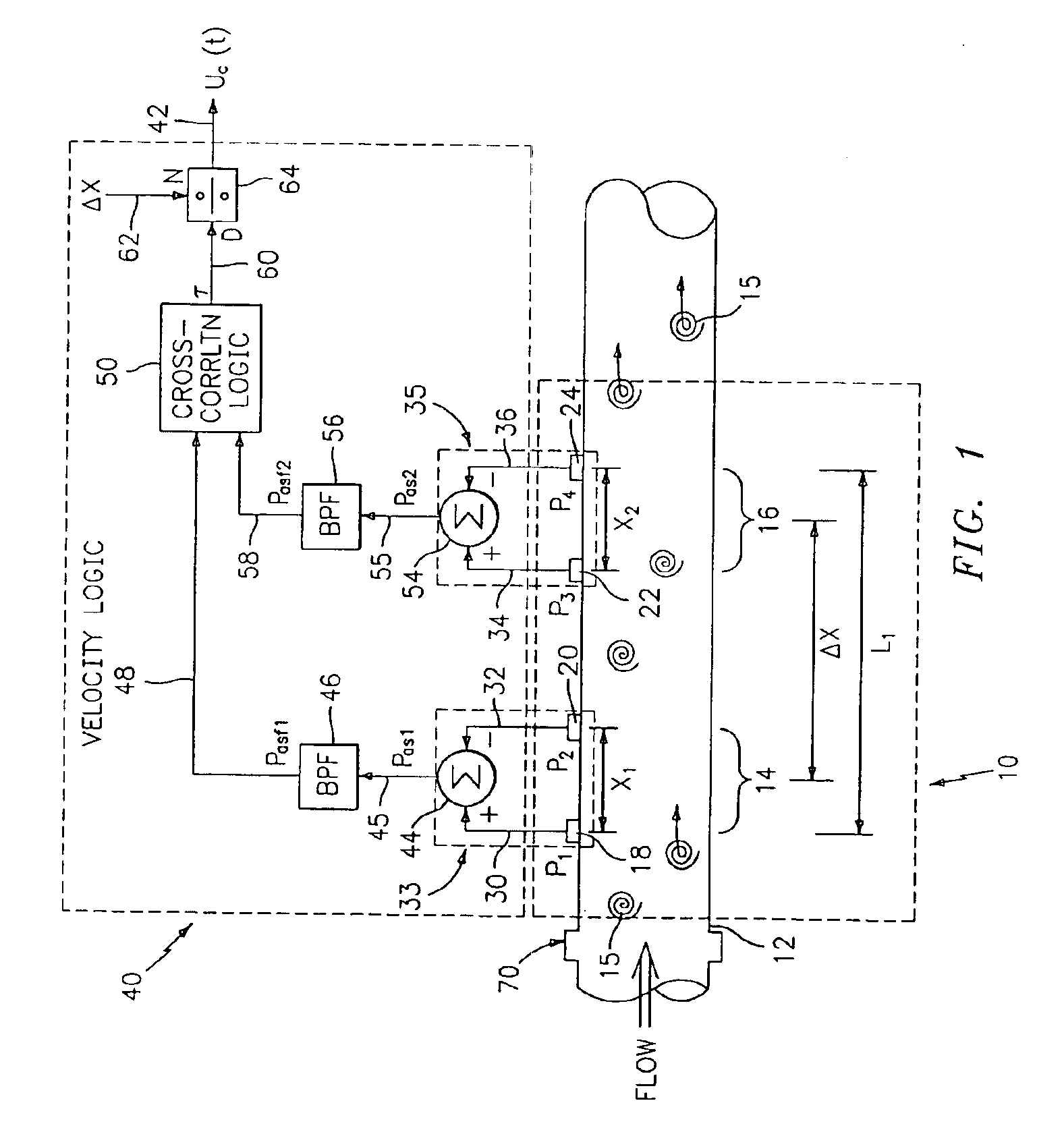
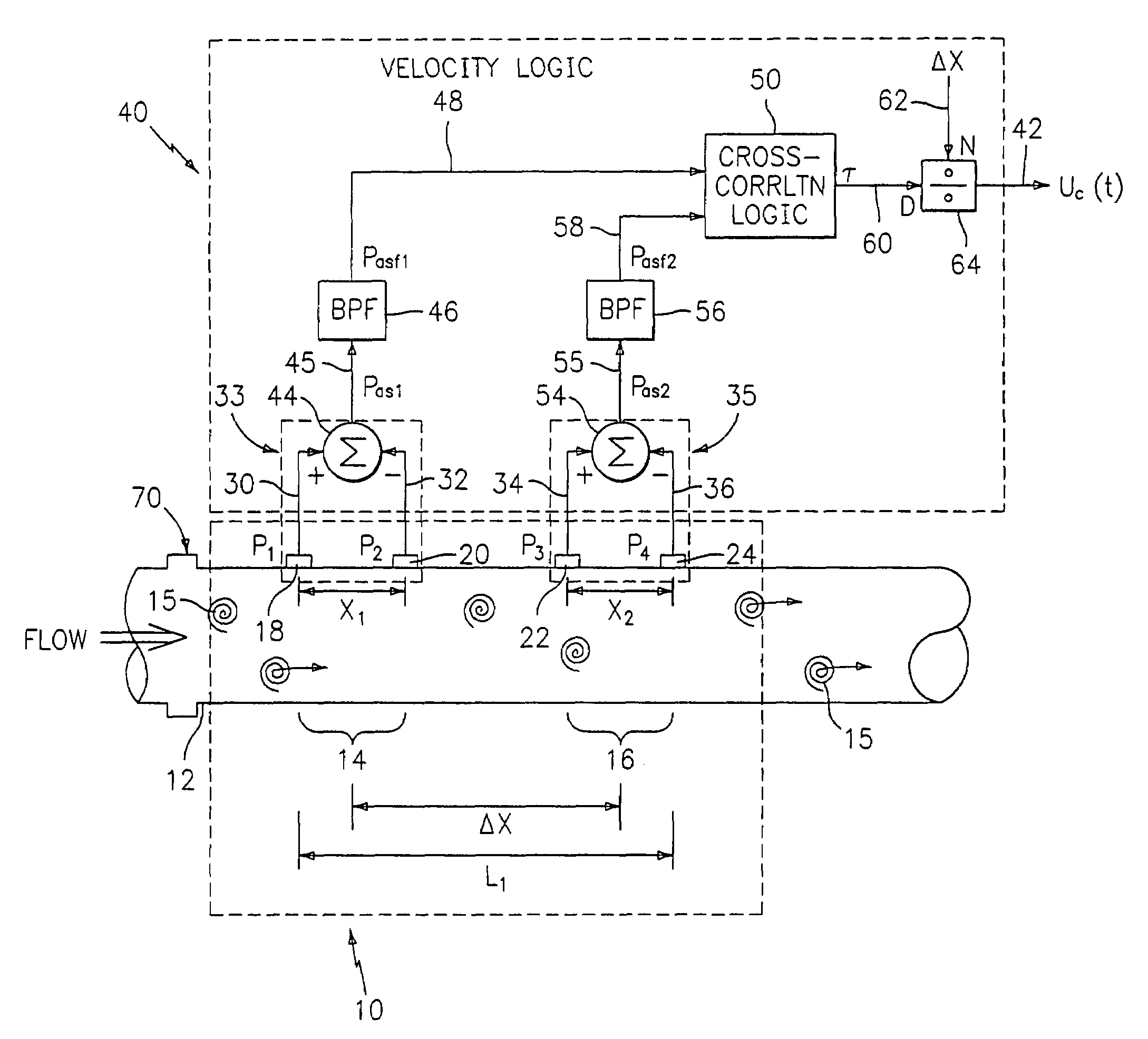
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
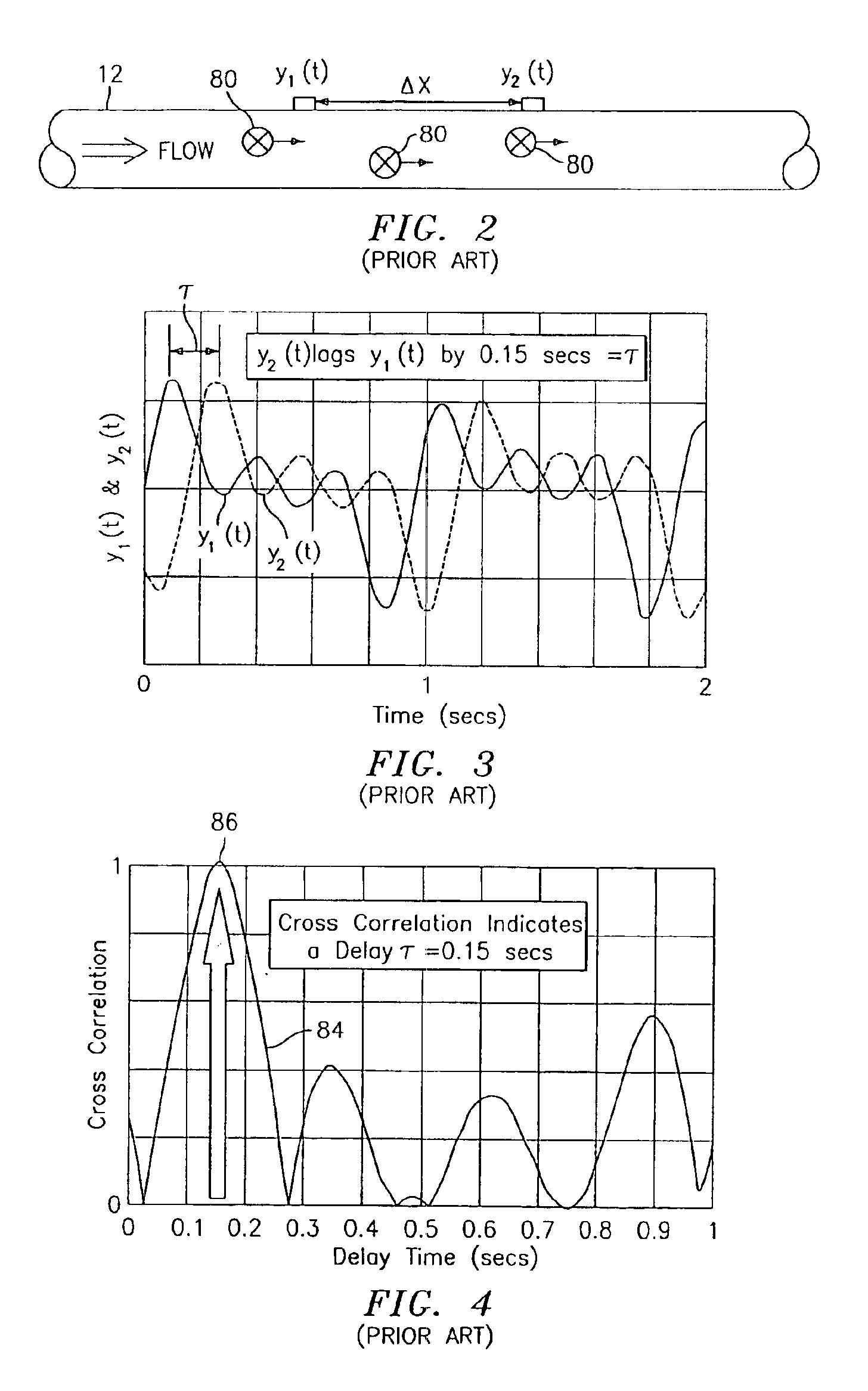
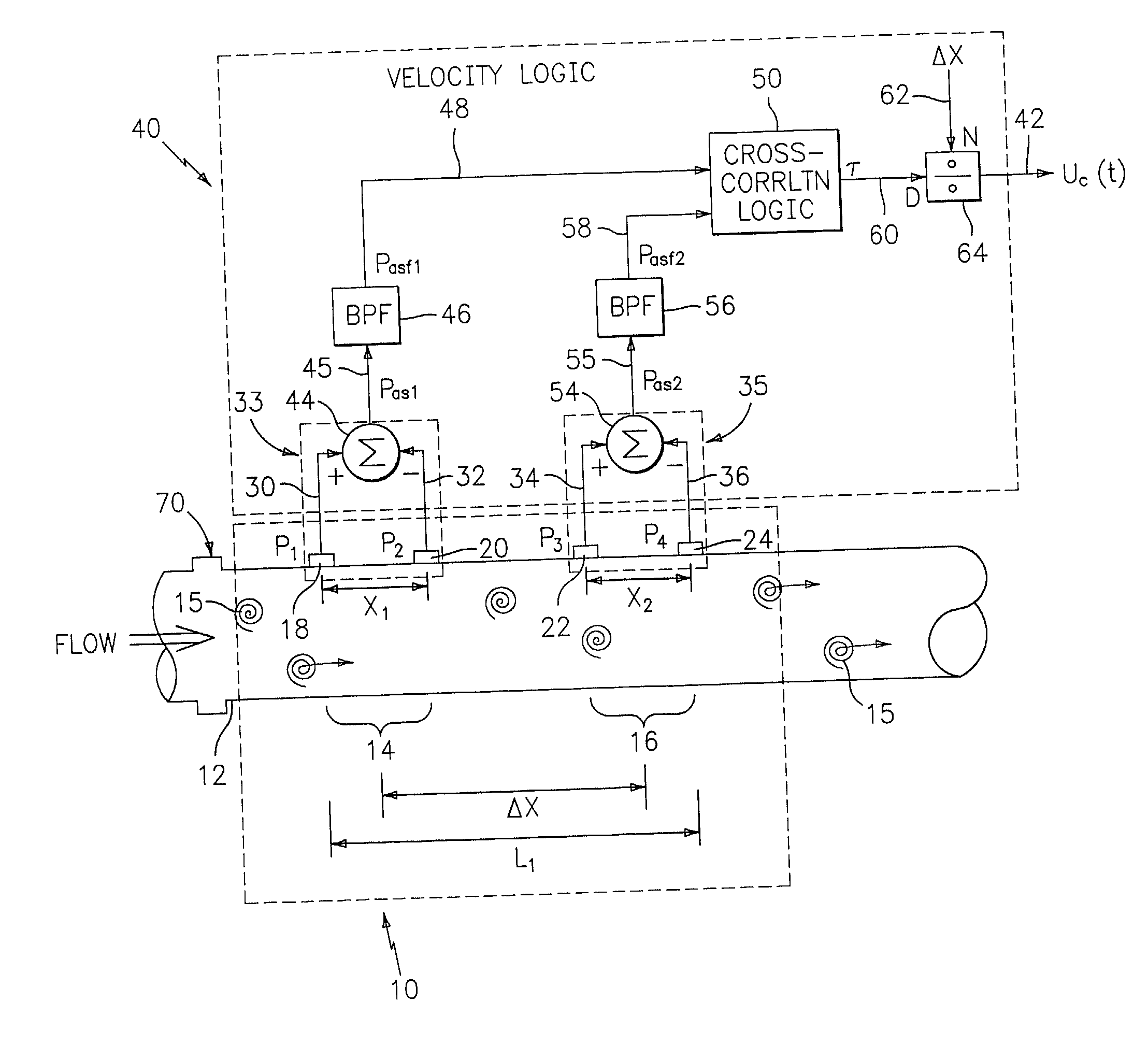
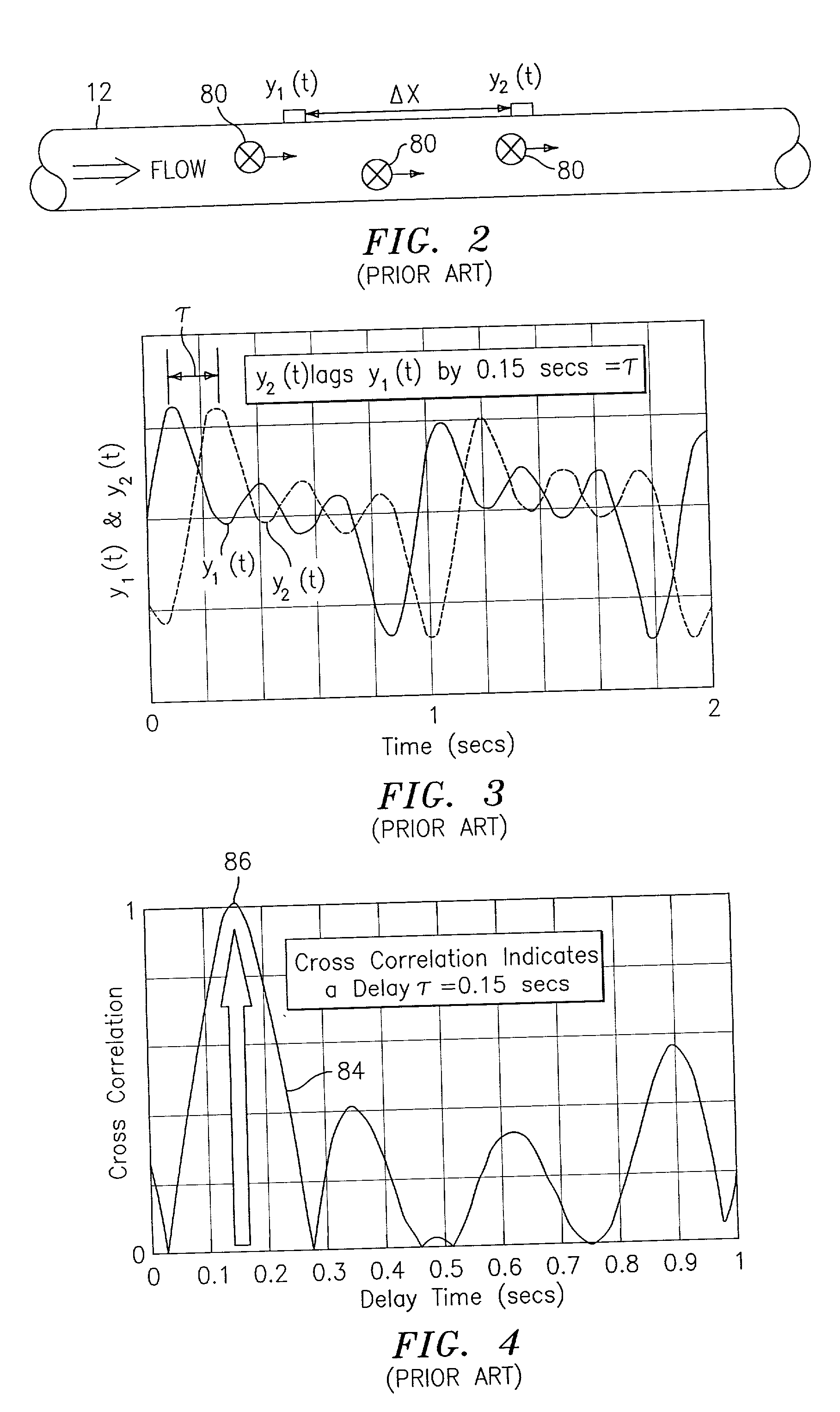
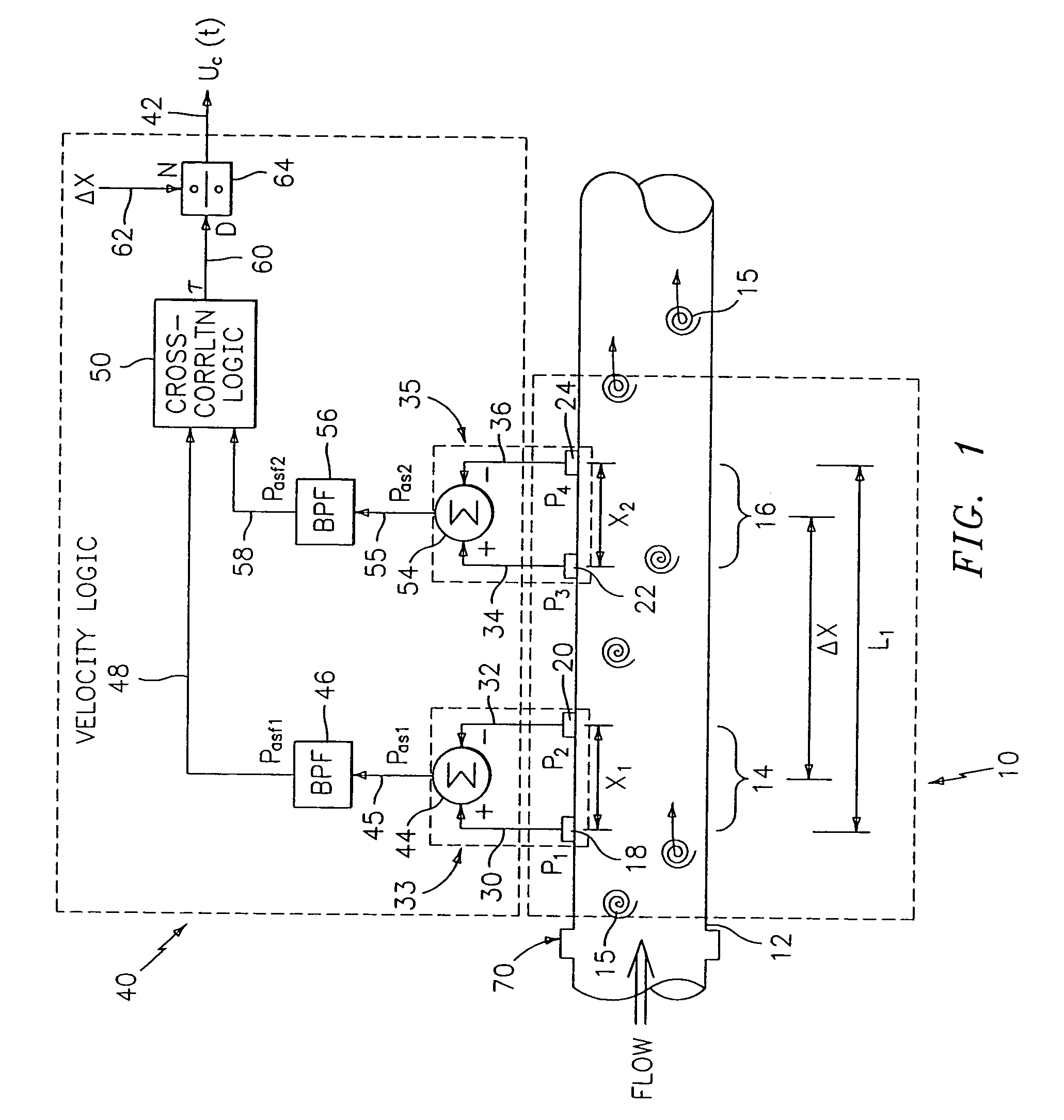
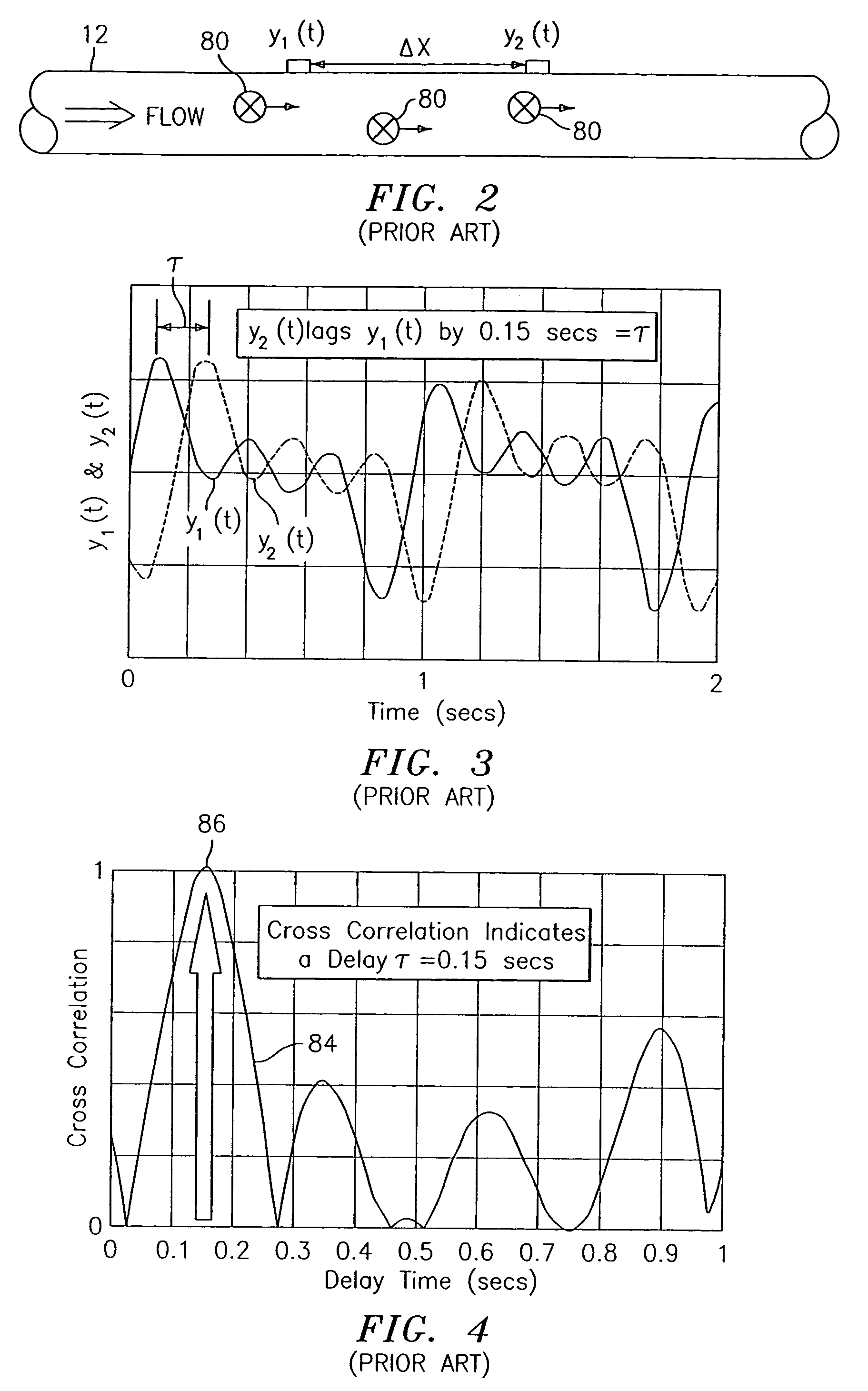
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical -dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
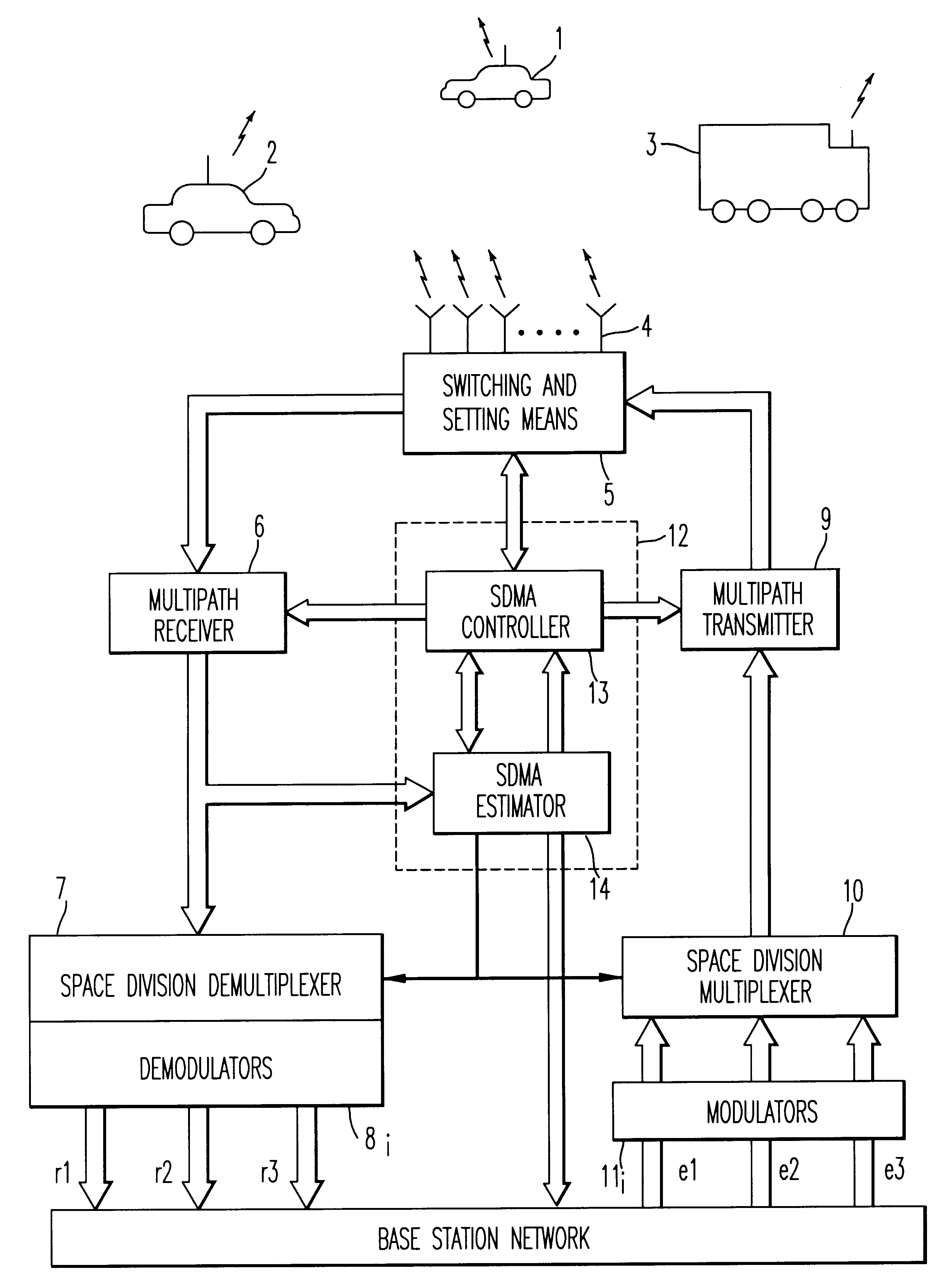
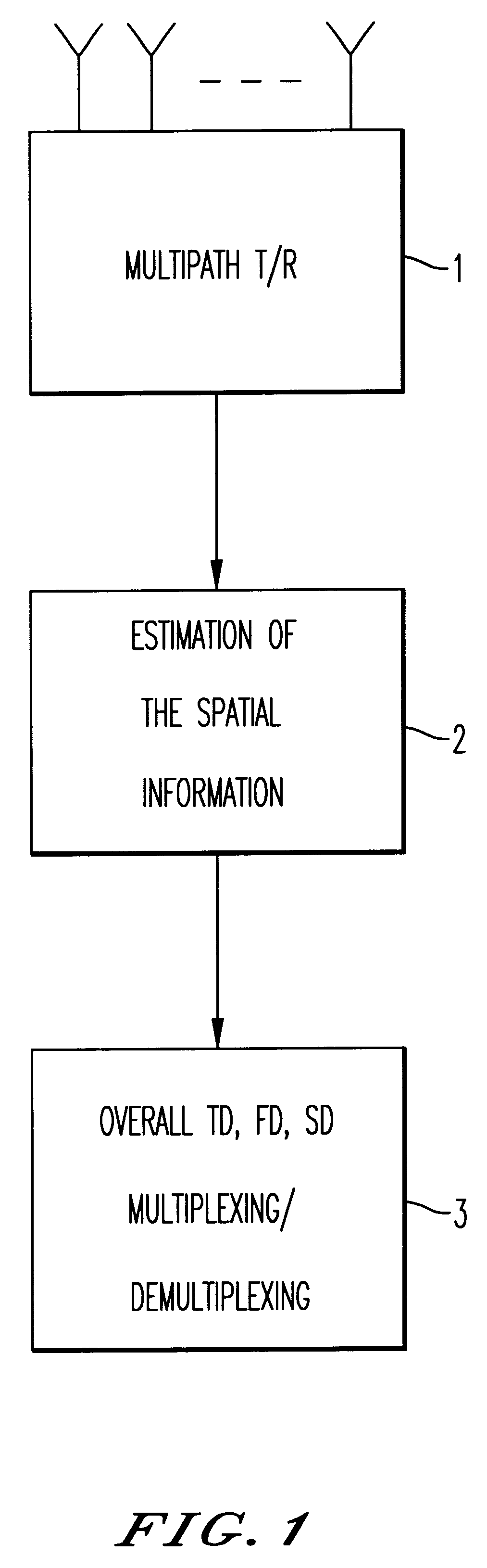
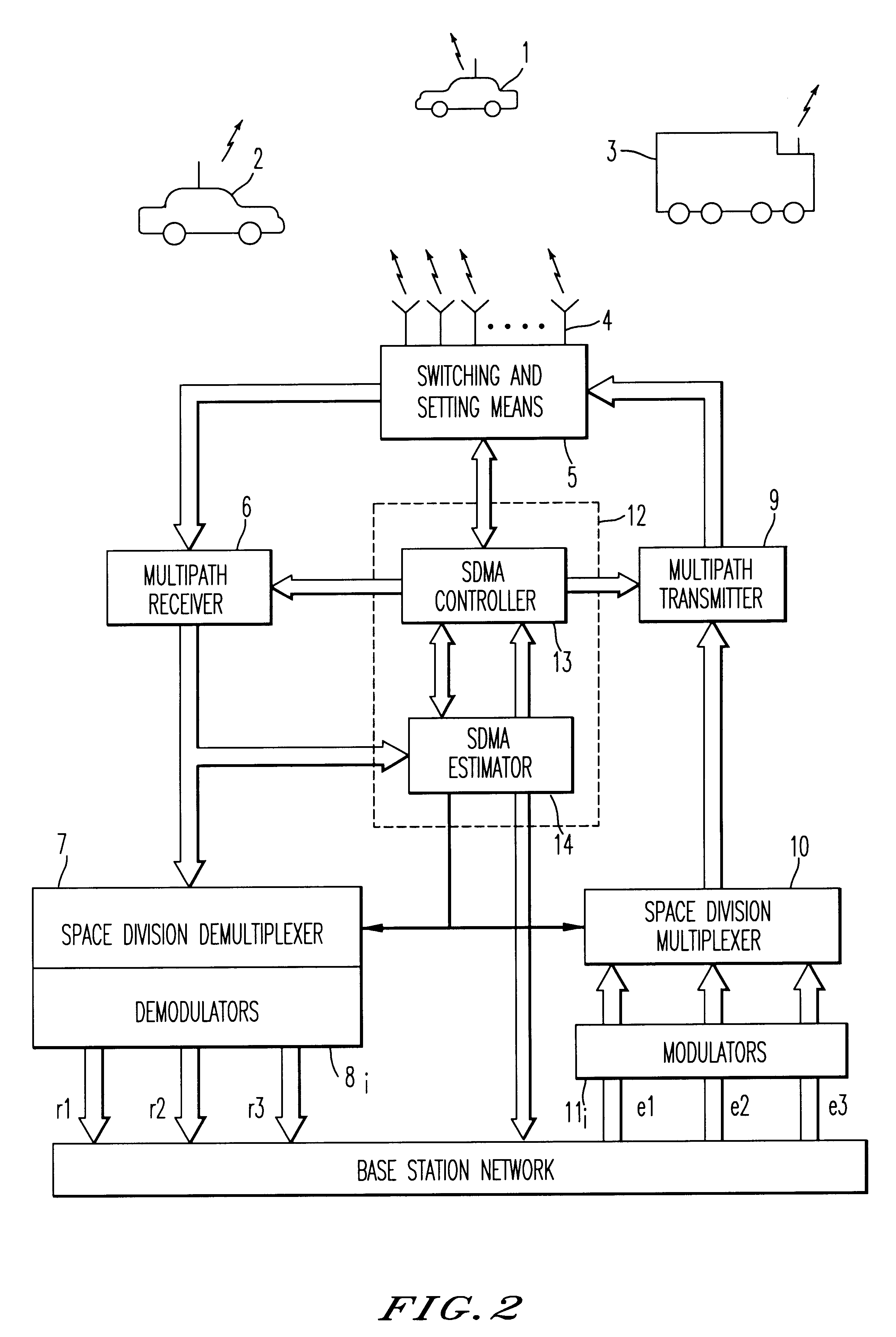
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
Method to control point spread function of an image
ActiveUS20060103951A1Guaranteed preservation qualityMore interferenceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityPoint spread function
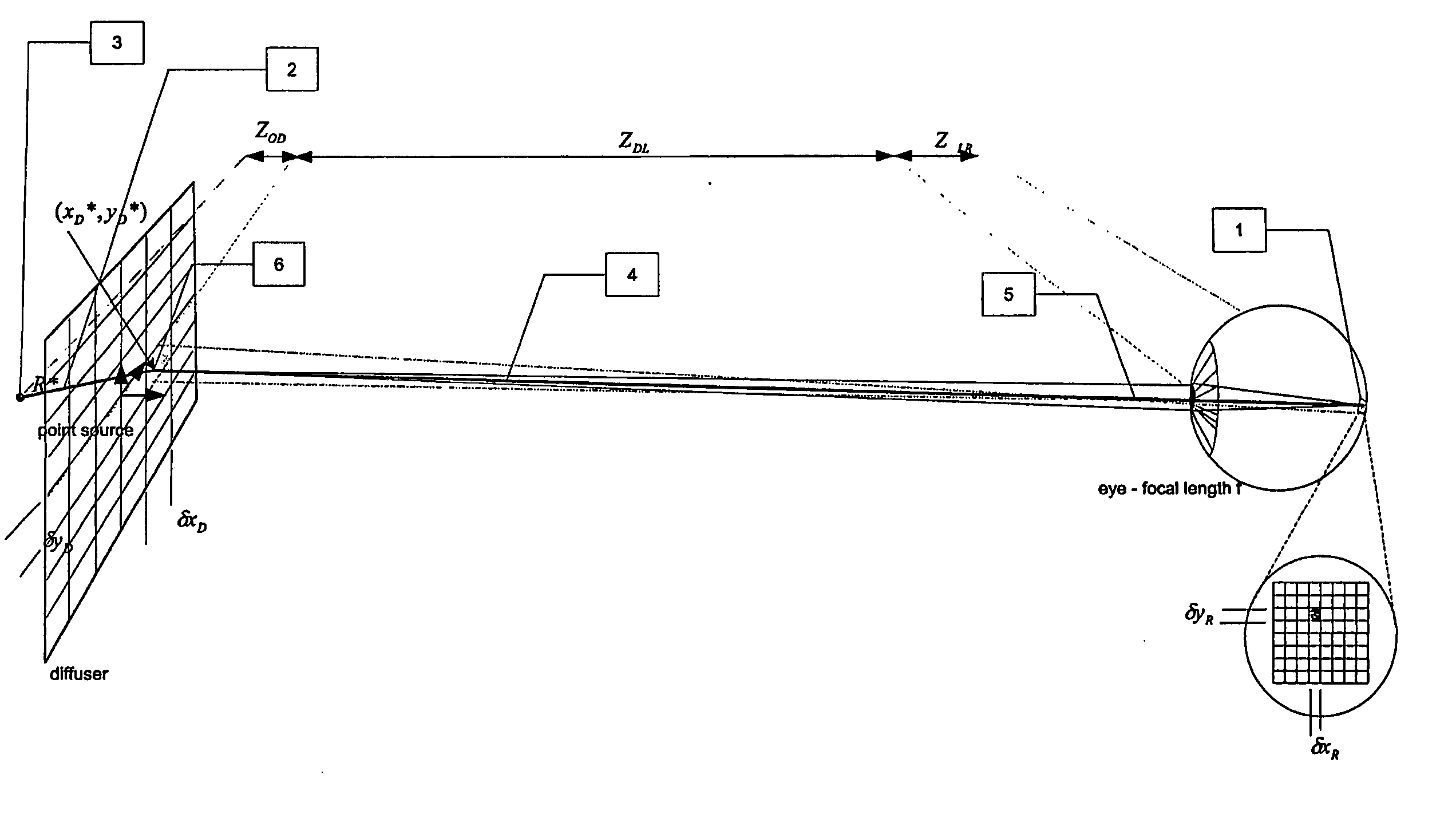
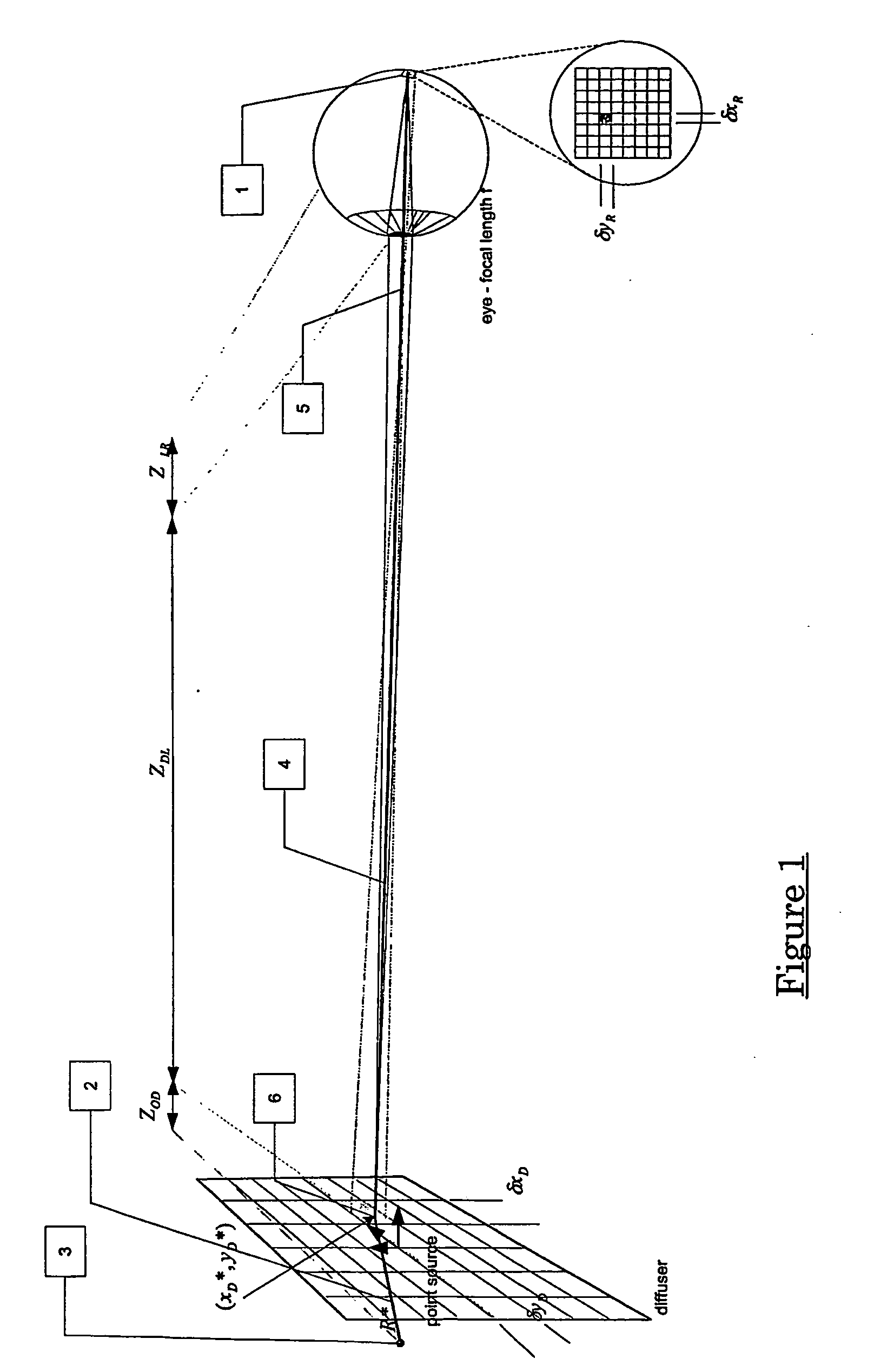
A method of controlling the point spread function of an image projected with said image being diffused by a filter; said point spread function is a result of the application of spatial filter(s) on said image; with said control of the point spread function effected by varying the distance between such image and said spatial filter(s) and varying the bidirectional scattering transmission function of the spatial filter(s). Said spatial filter may be a holographic diffuser, which by method of manufacture has a ell defined bi-directional scattering transmission spread function. Control of said spread function is particularly useful to maintain image quality while abating moiré interference in situations where two periodic patterns are layered causing moiré interference.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Telephony Device with Improved Noise Suppression
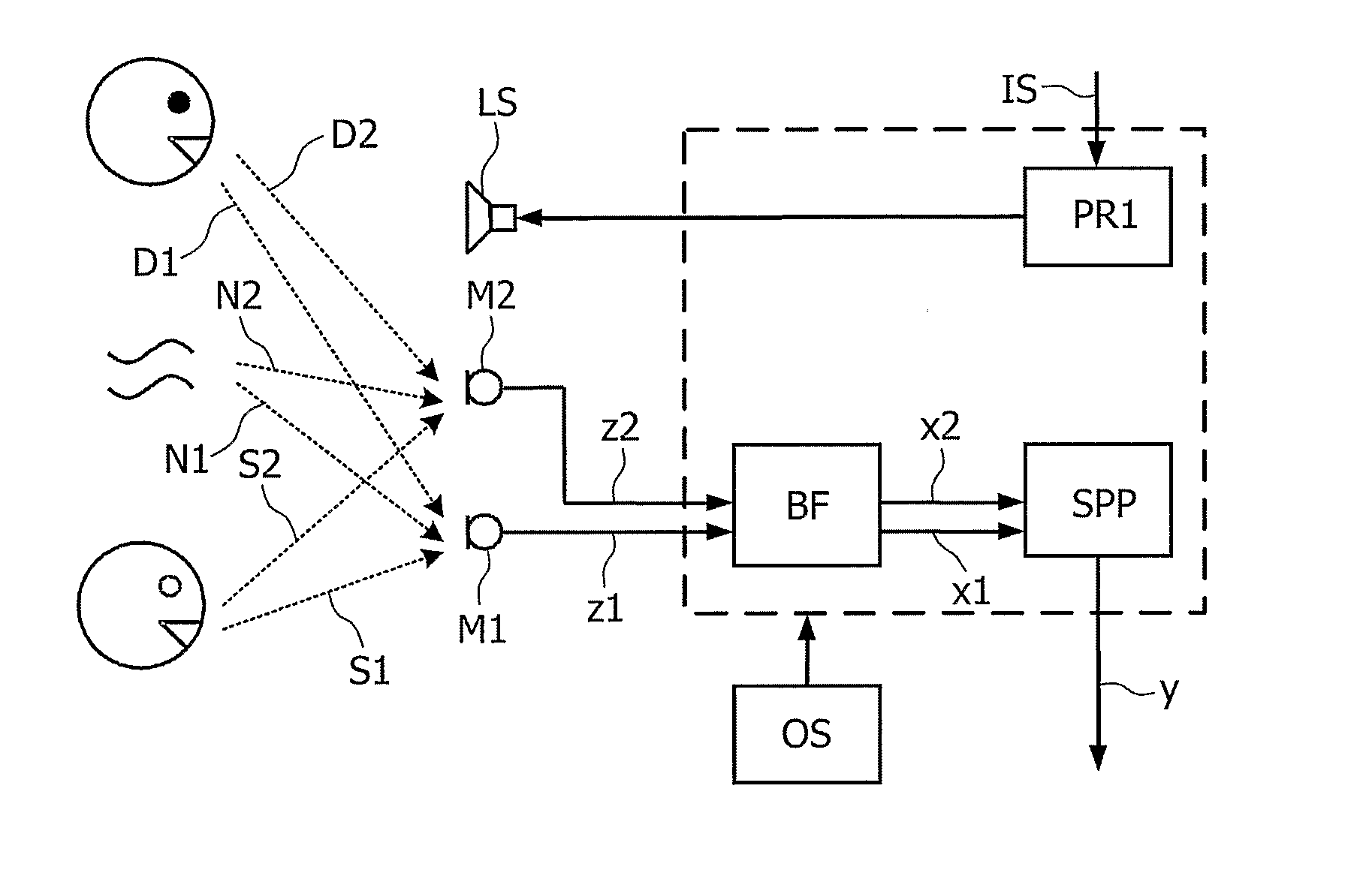
InactiveUS20070230712A1Unwanted noise signalMaximize qualityEar treatmentMicrophone structural associationFrequency spectrumPost processor
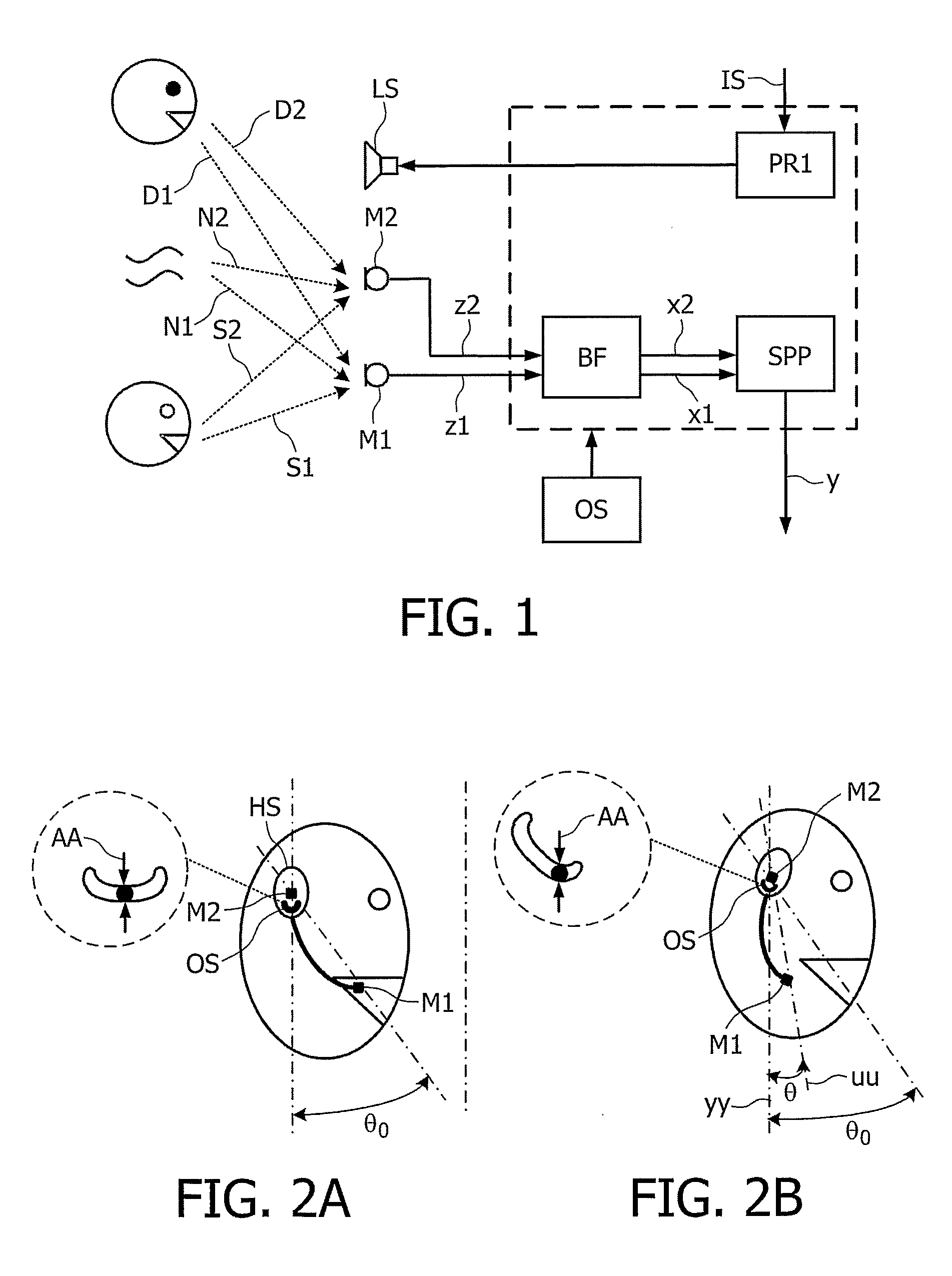
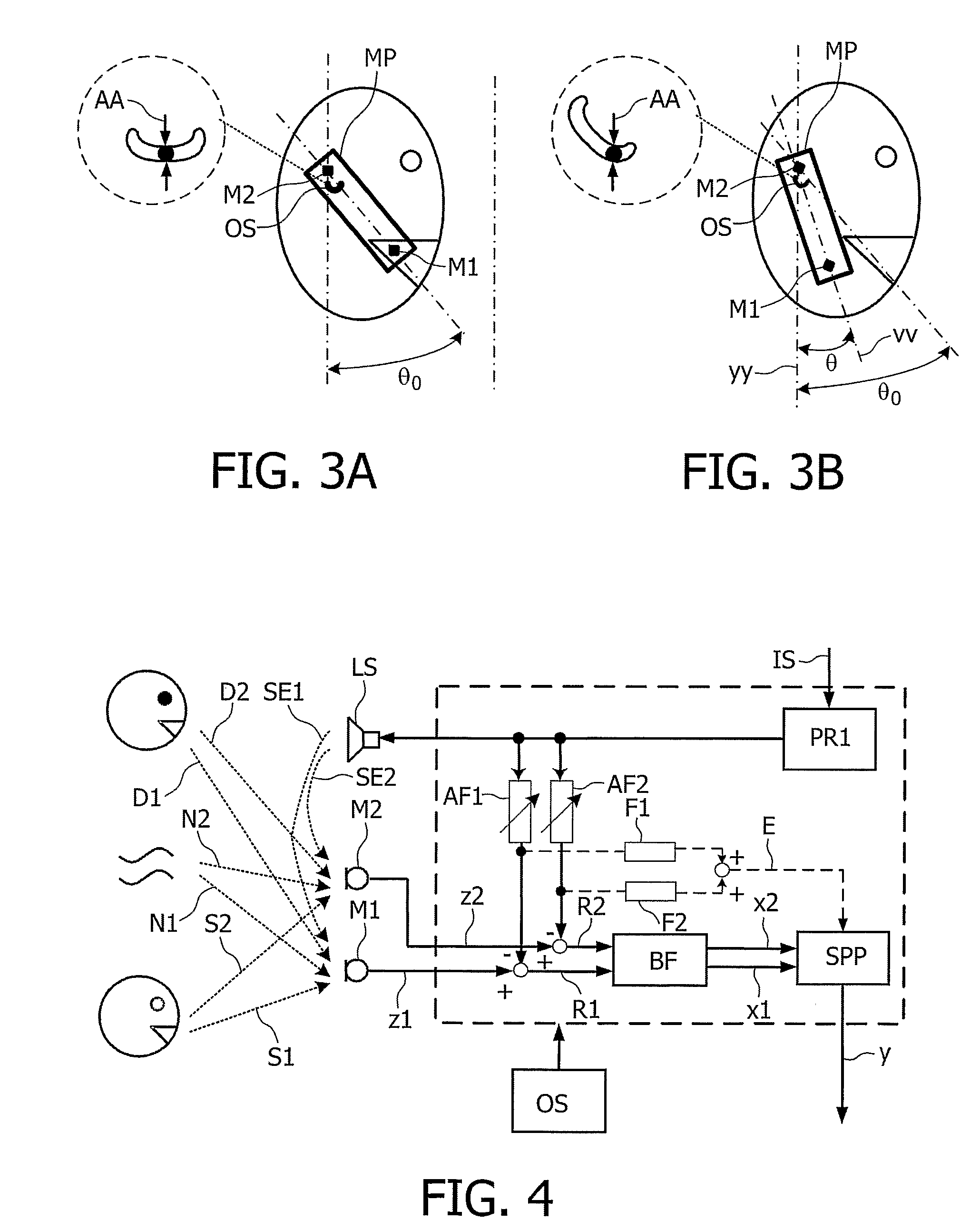
The present invention relates to a telephony device comprising a near-mouth microphone (M1) for picking up an input acoustic signal including the speaker's voice signal (S1) and an unwanted noise signal (N1,D1), a far-mouth microphone (M2) for picking up an unwanted noise signal (N2,D2) in addition to the near-end speaker's voice signal (S2), said speaker's voice signal being at a lower level than the near-mouth microphone, and an orientation sensor for measuring an orientation indication of said mobile device. The telephony device further comprises an audio processing unit comprising an adaptive beamformer (BF) coupled to the near-mouth and far-mouth microphones, including spatial filters for spatially filtering the input signals (z1,z2) delivered by the two microphones, and a spectral post-processor (SPP) for post-processing the signal delivered by the beam-former so as to separate the desired voice signal from the unwanted noise signal so as to deliver the output signal (y).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance .DELTA.X apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X.sub.1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X.sub.2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances P.sub.acoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances P.sub.vortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals P.sub.as1,P.sub.as2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The P.sub.vortical -dominated filtered signals P.sub.asf1,P.sub.asf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay .tau. between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance .DELTA.X to obtain a convection velocity U.sub.c(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
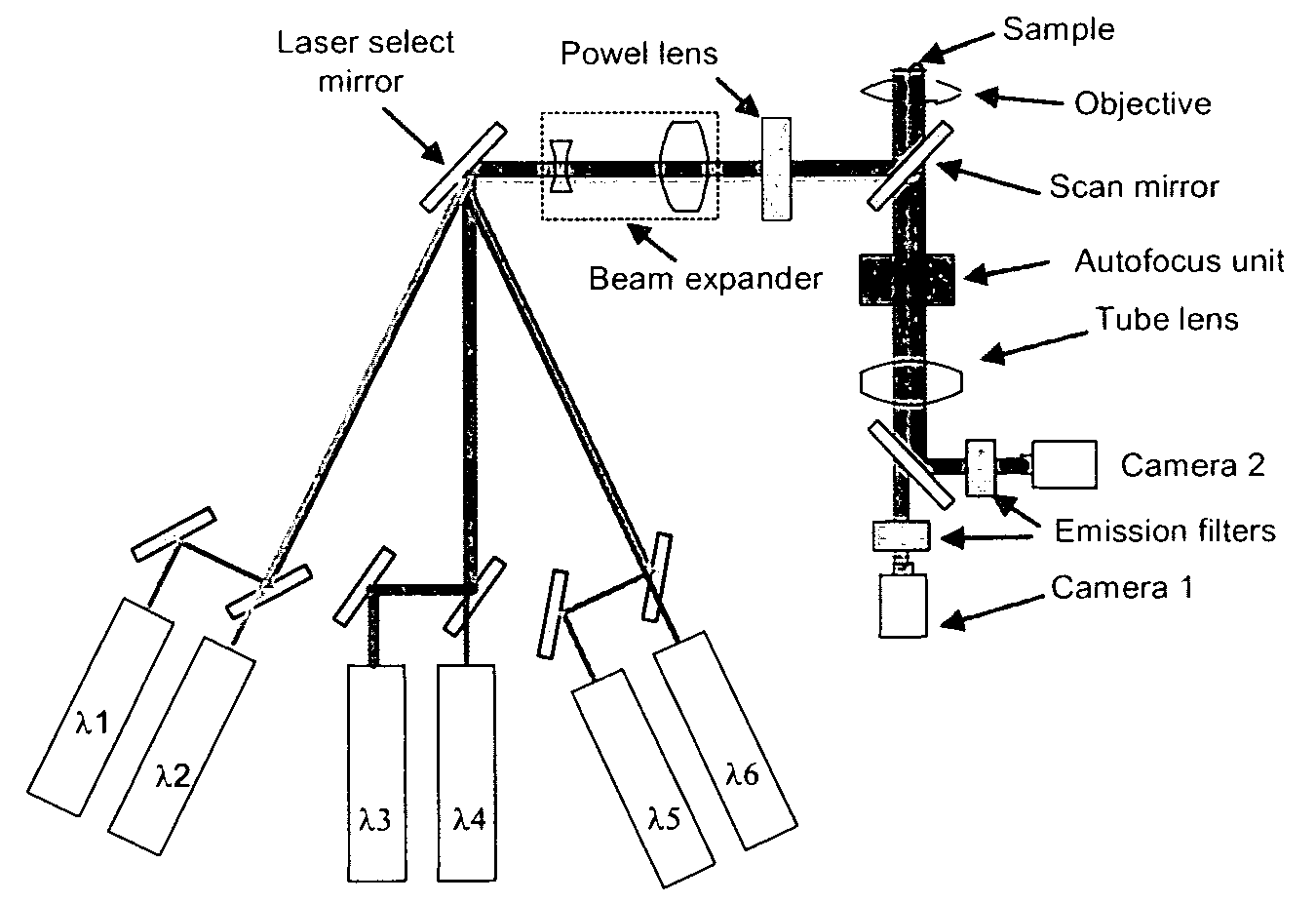
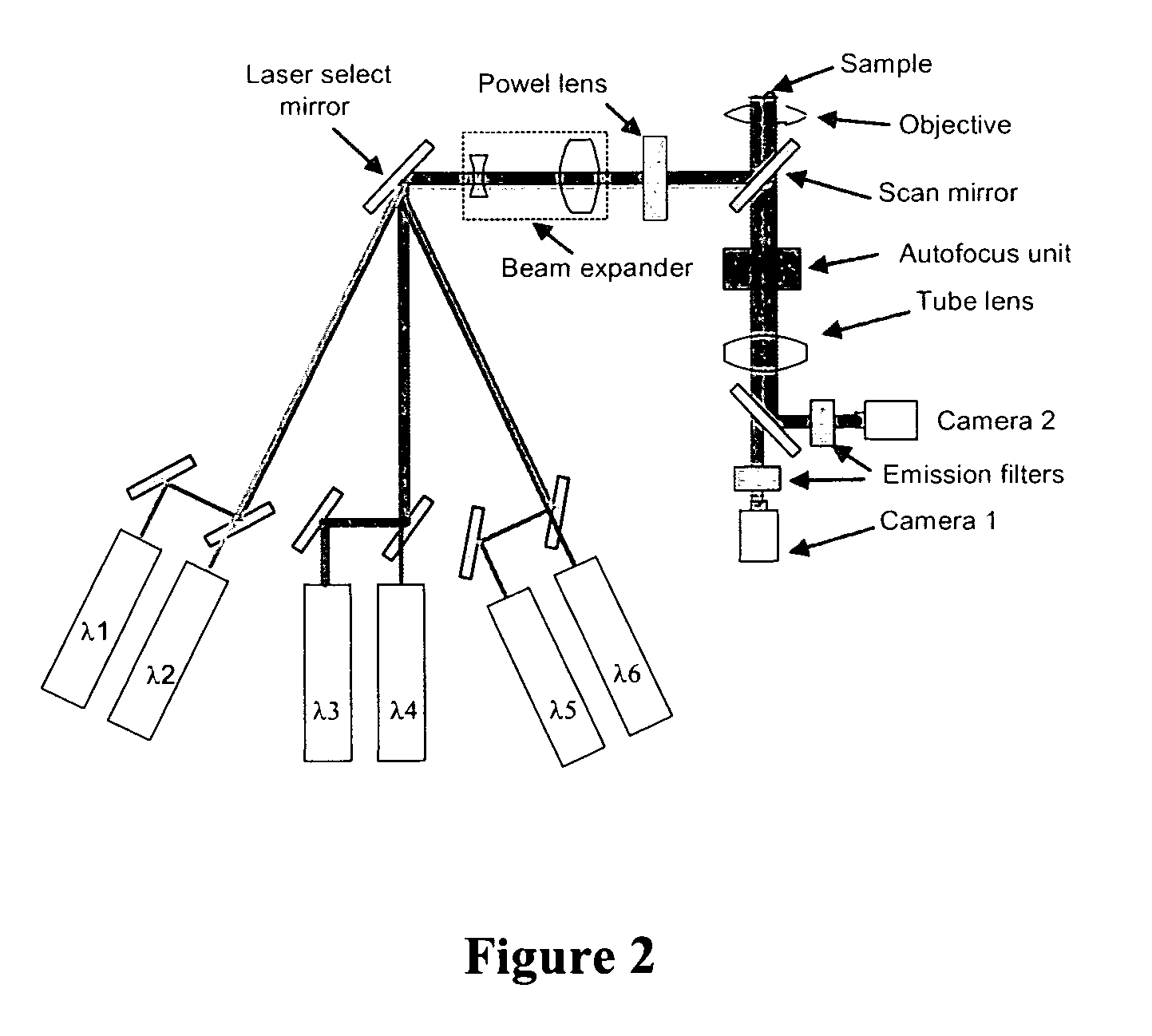
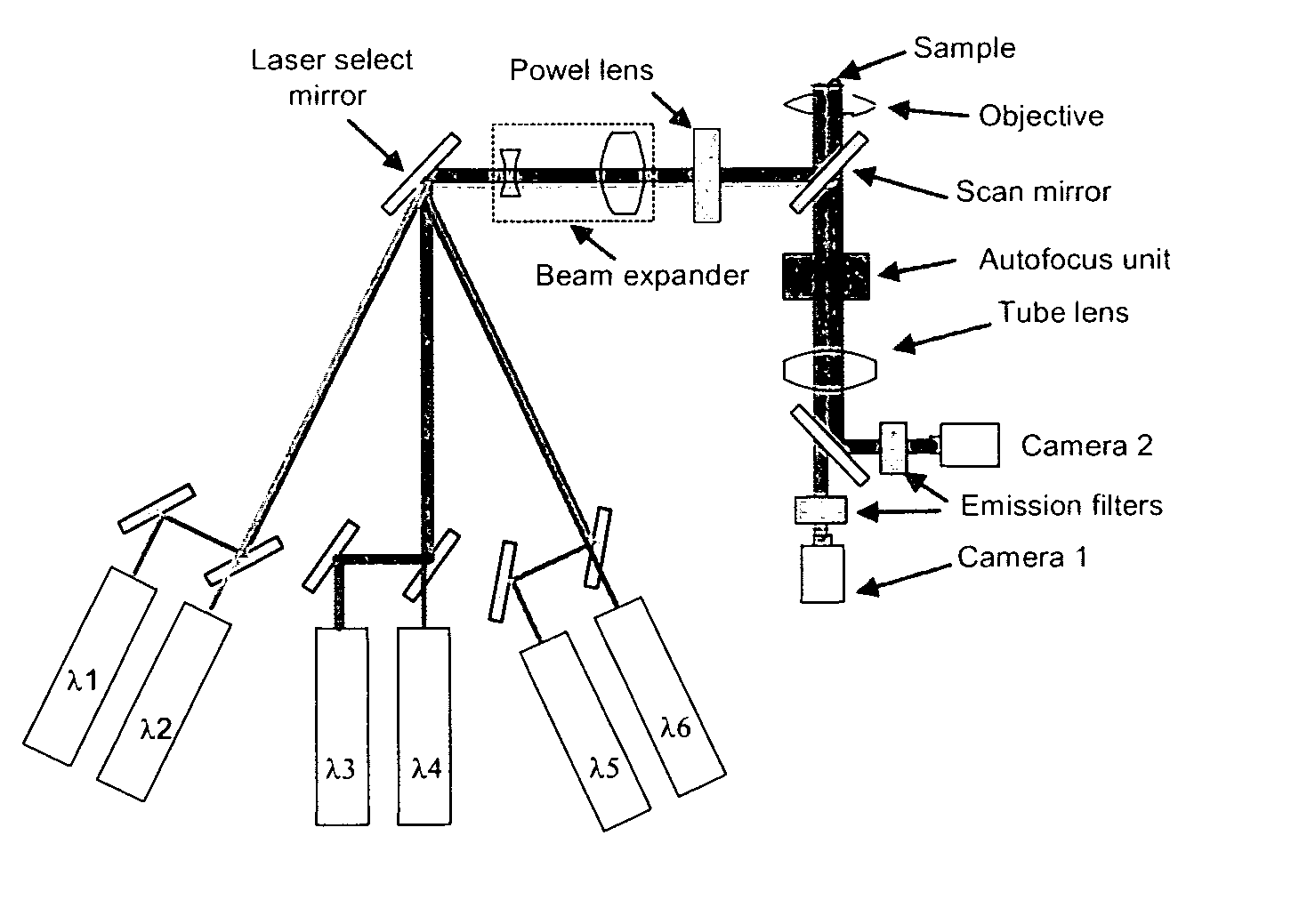
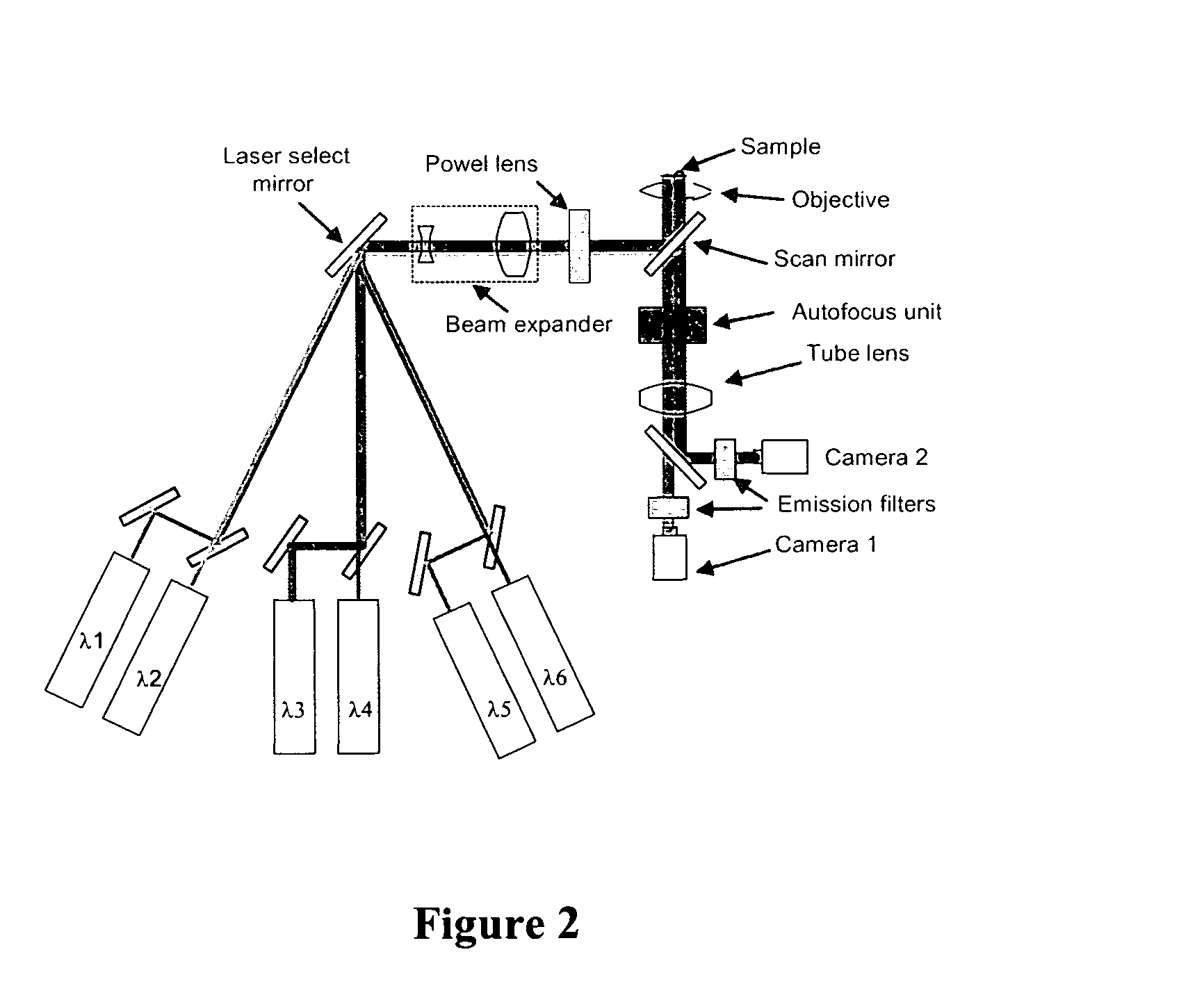
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS7335898B2Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
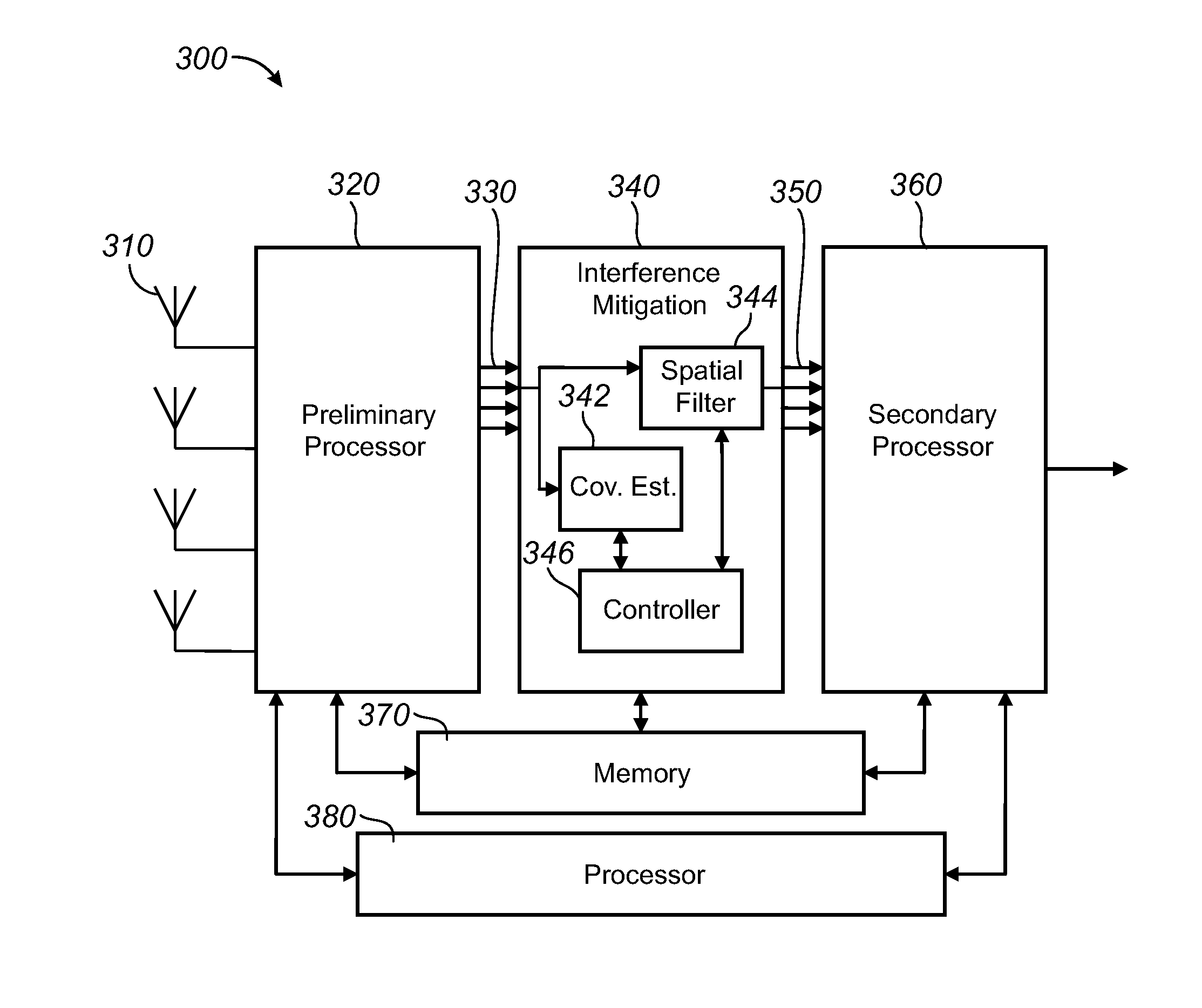
Wideband interference mitigation for devices with multiple receivers
ActiveUS20100303182A1Polarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemEngineering
Certain disclosed embodiments pertain to suppressing interference in a wireless communication system. For example, a method of suppressing interference can include receiving one or more first signals including components from a plurality of sub-channels. Each of the first signals can be converted into a respective plurality of first sub-band frequency components. A respective spatial filter can be determined for each frequency sub-band using one or more corresponding first sub-band components for each respective spatial filter. One or more second signals including components from the plurality of sub-channels can be received. Each of the second signals can be converted into a respective plurality of second sub-band frequency components. A corresponding plurality of filtered sub-band components can be generated by applying the respective spatial filters to the corresponding second sub-band components for each of the second signals.
Owner:SILVUS TECH
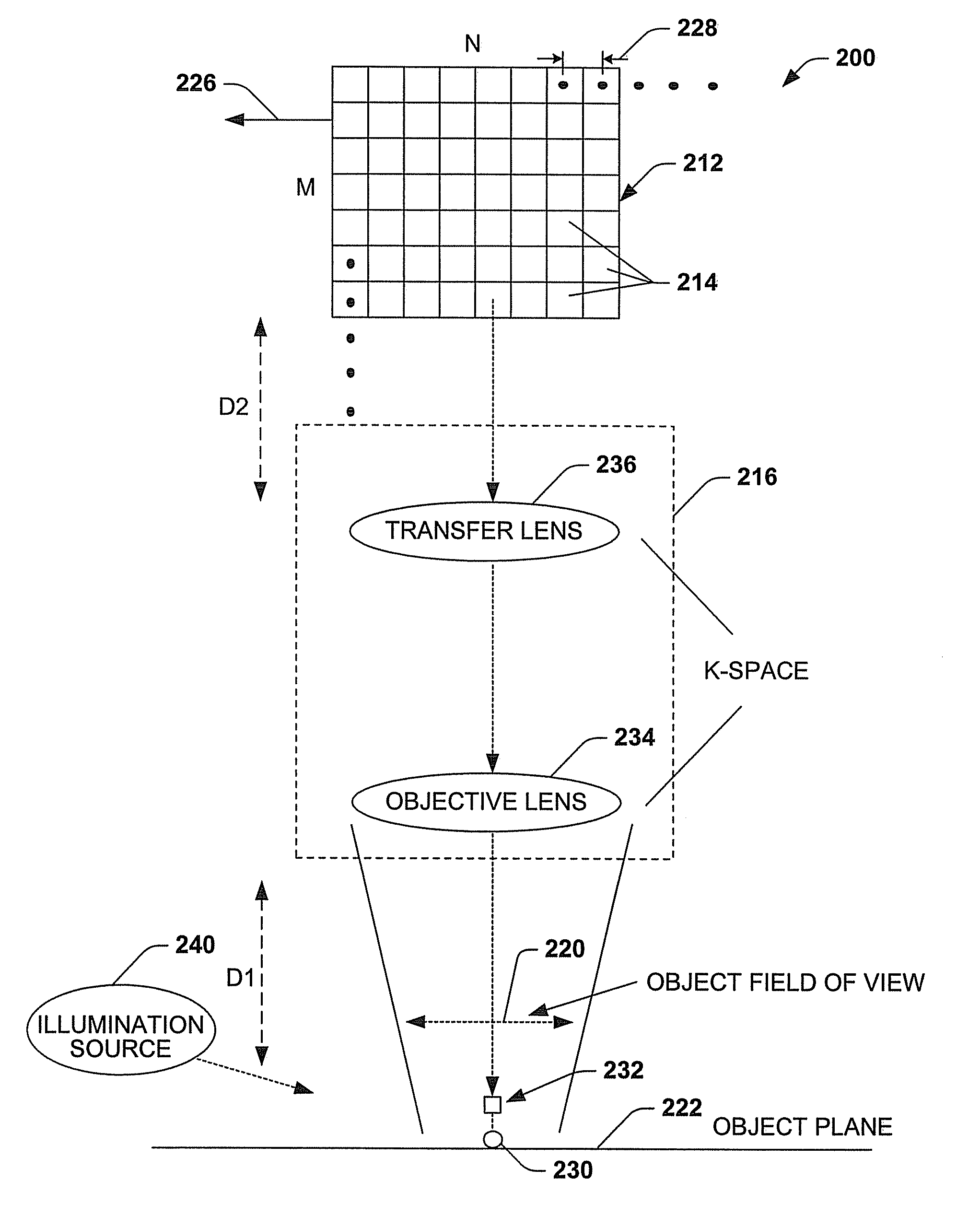
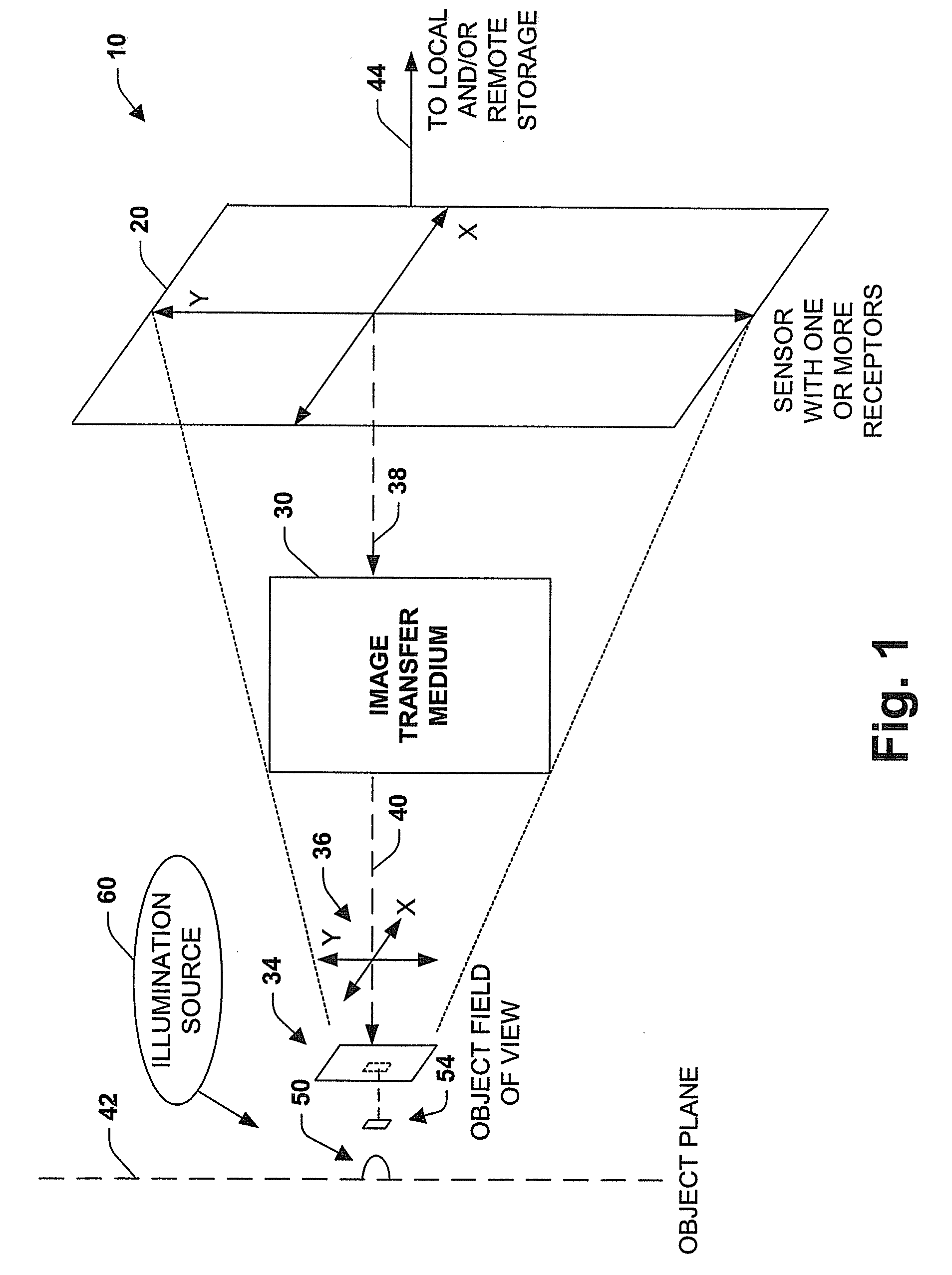
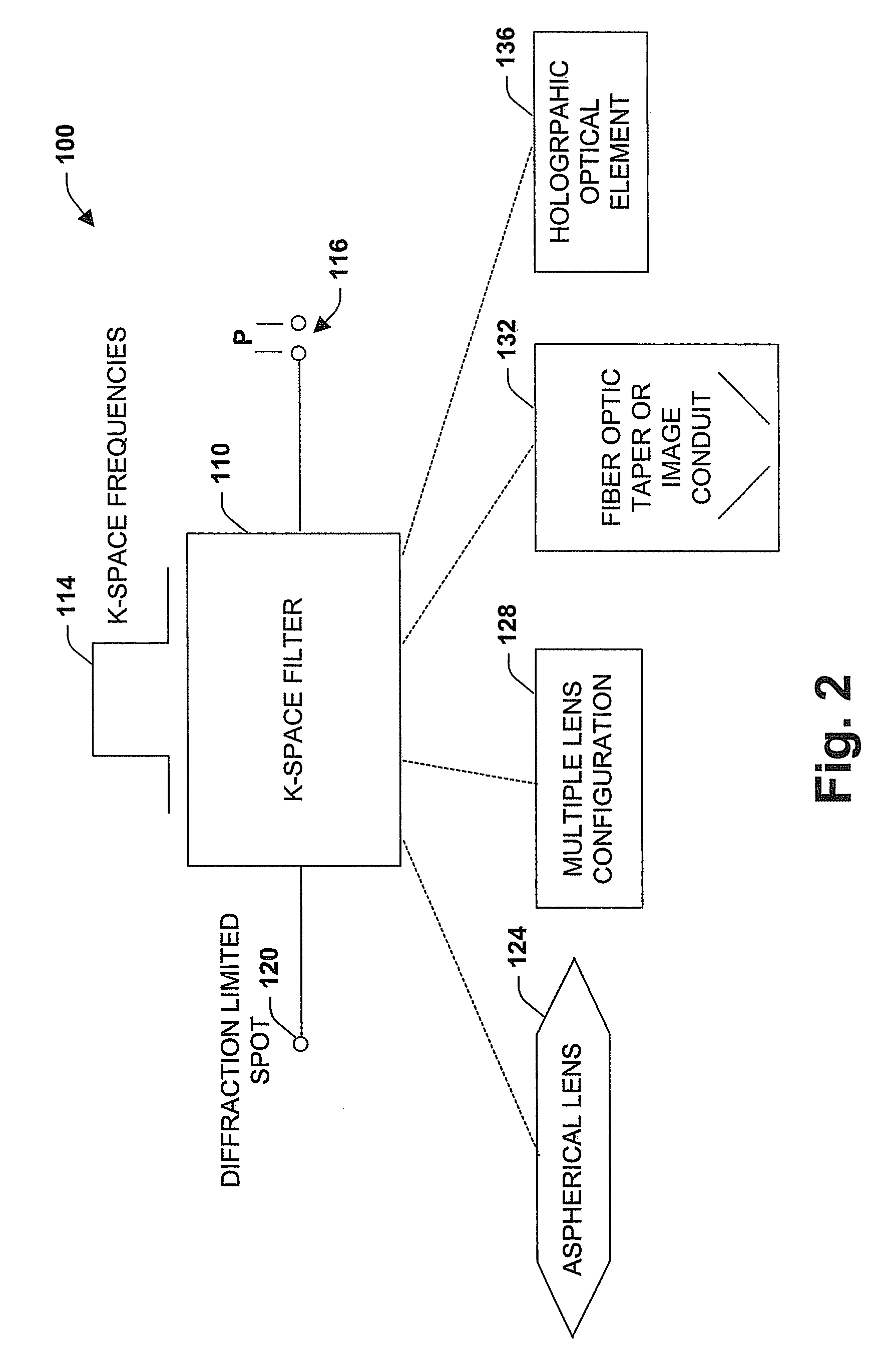
Imaging system and methodology
InactiveUS20070139541A1Improve performanceEffectively scaledTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage transferDisplay device
An imaging system, methodology, and various applications are provided to facilitate optical imaging performance. The system contains a sensor having one or more receptors and an image transfer medium to scale the sensor and receptors in accordance with resolvable characteristics of the medium, and as defined with certain ratios. A computer, memory, and / or display associated with the sensor provides storage and / or display of information relating to output from the receptors to produce and / or process an image, wherein a plurality of illumination sources can also be utilized in conjunction with the image transfer medium. The image transfer medium can be configured as a k-space filter that correlates projected receptor size to a diffraction-limited spot associated with the image transfer medium, wherein the projected receptor size can be unit-mapped within a certain ratio to the size of the diffraction-limited spot, both in the object plane.
Owner:PIXEL MATCHED HLDG
Projection exposure method and apparatus
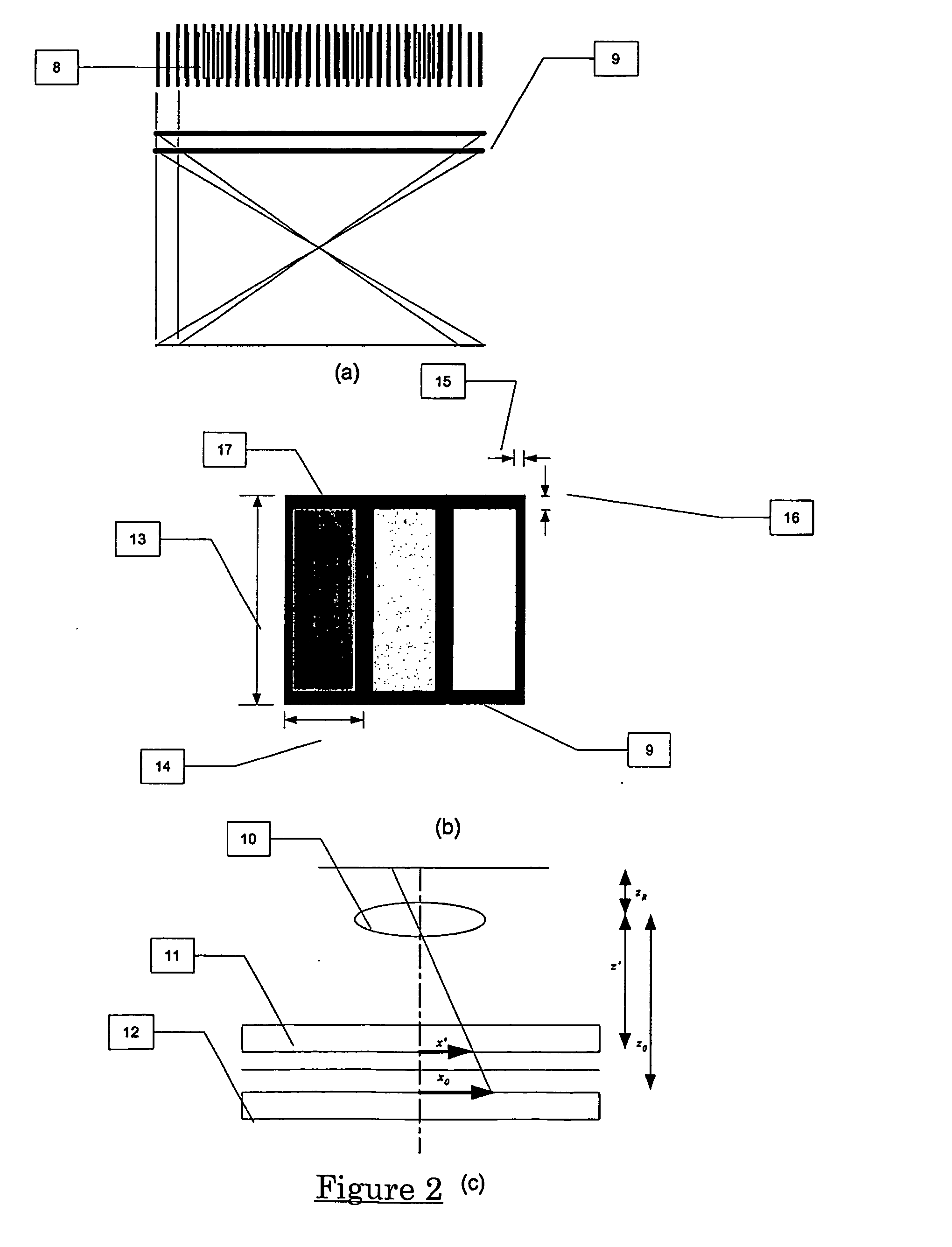
InactiveUS6310679B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
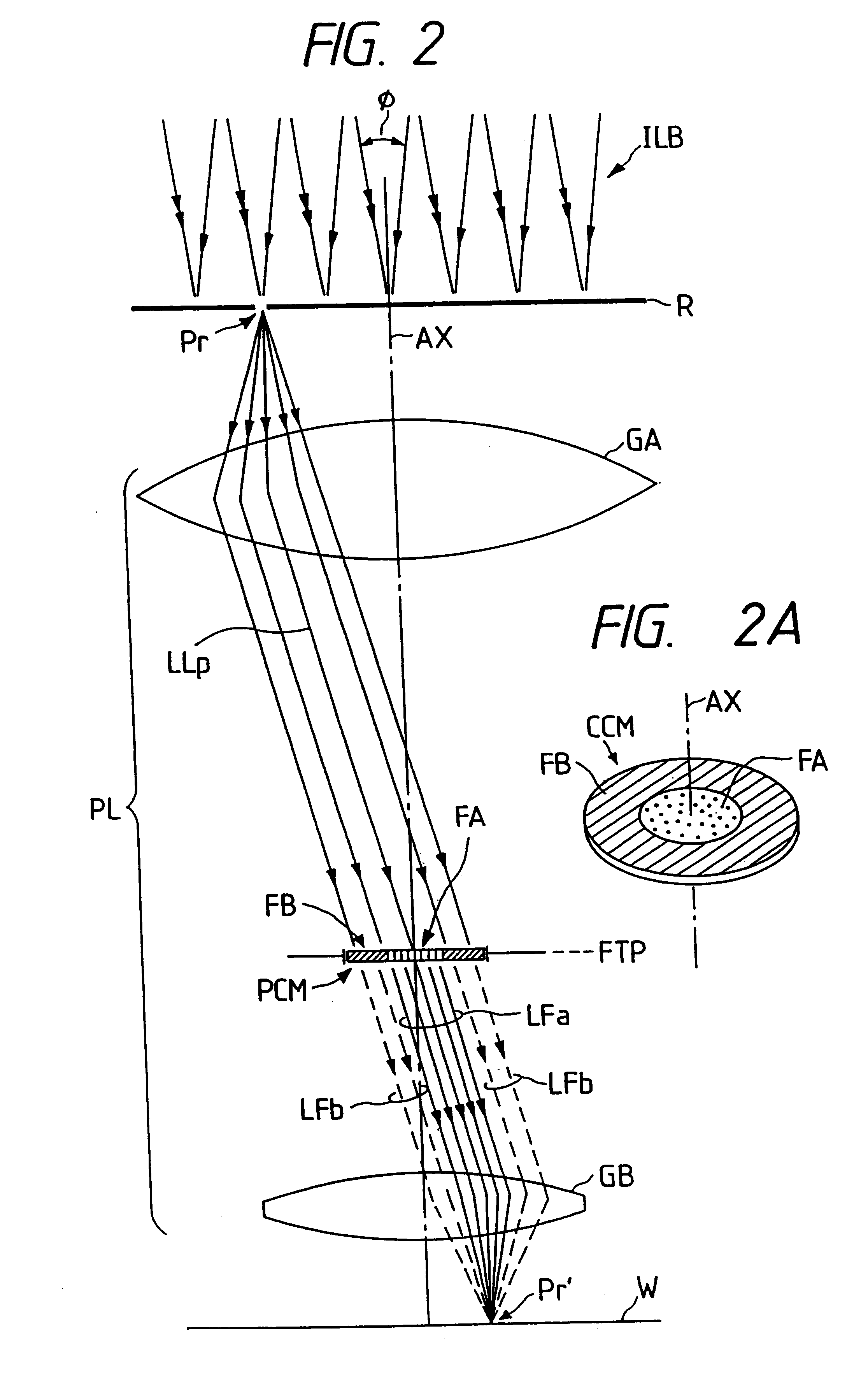
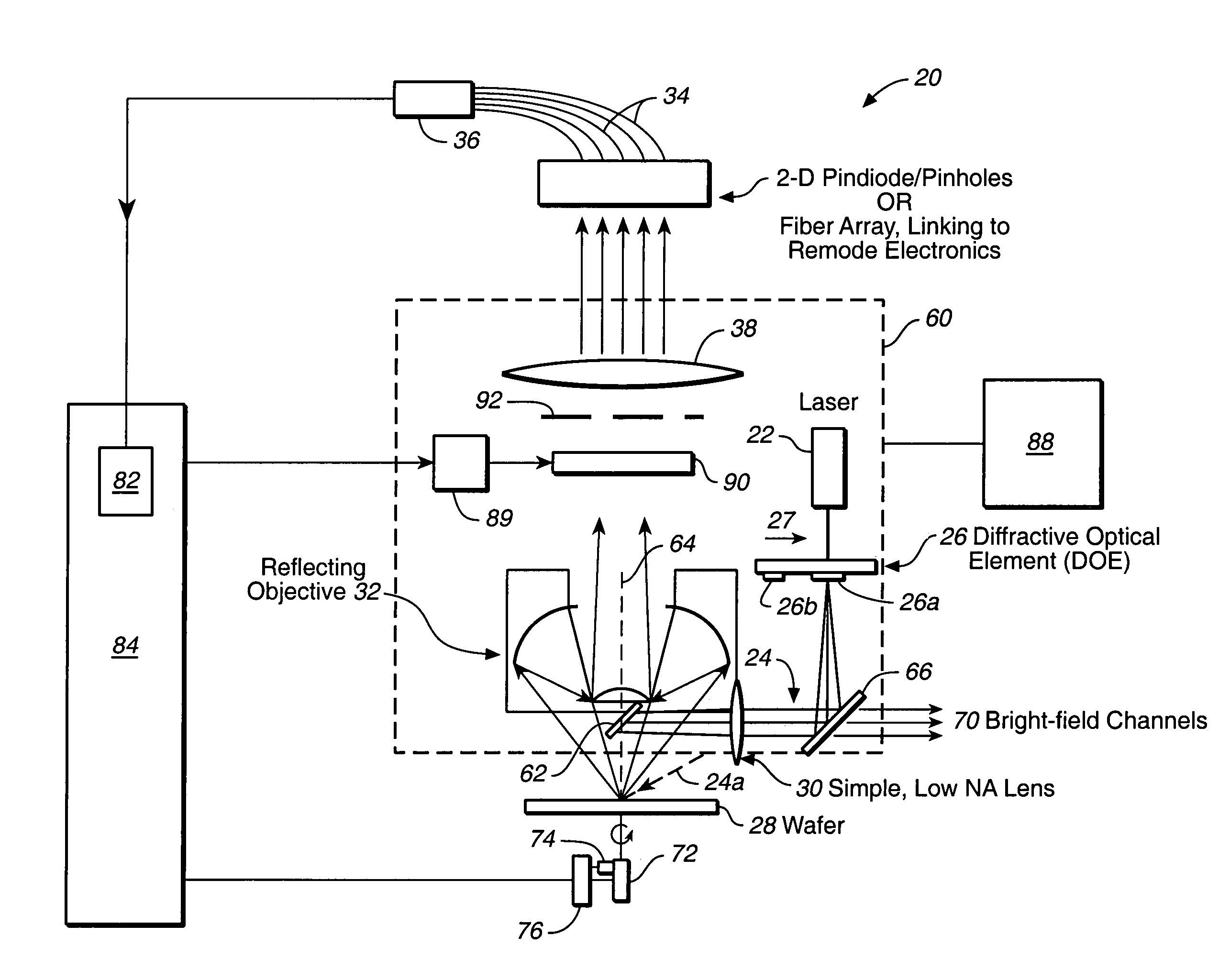
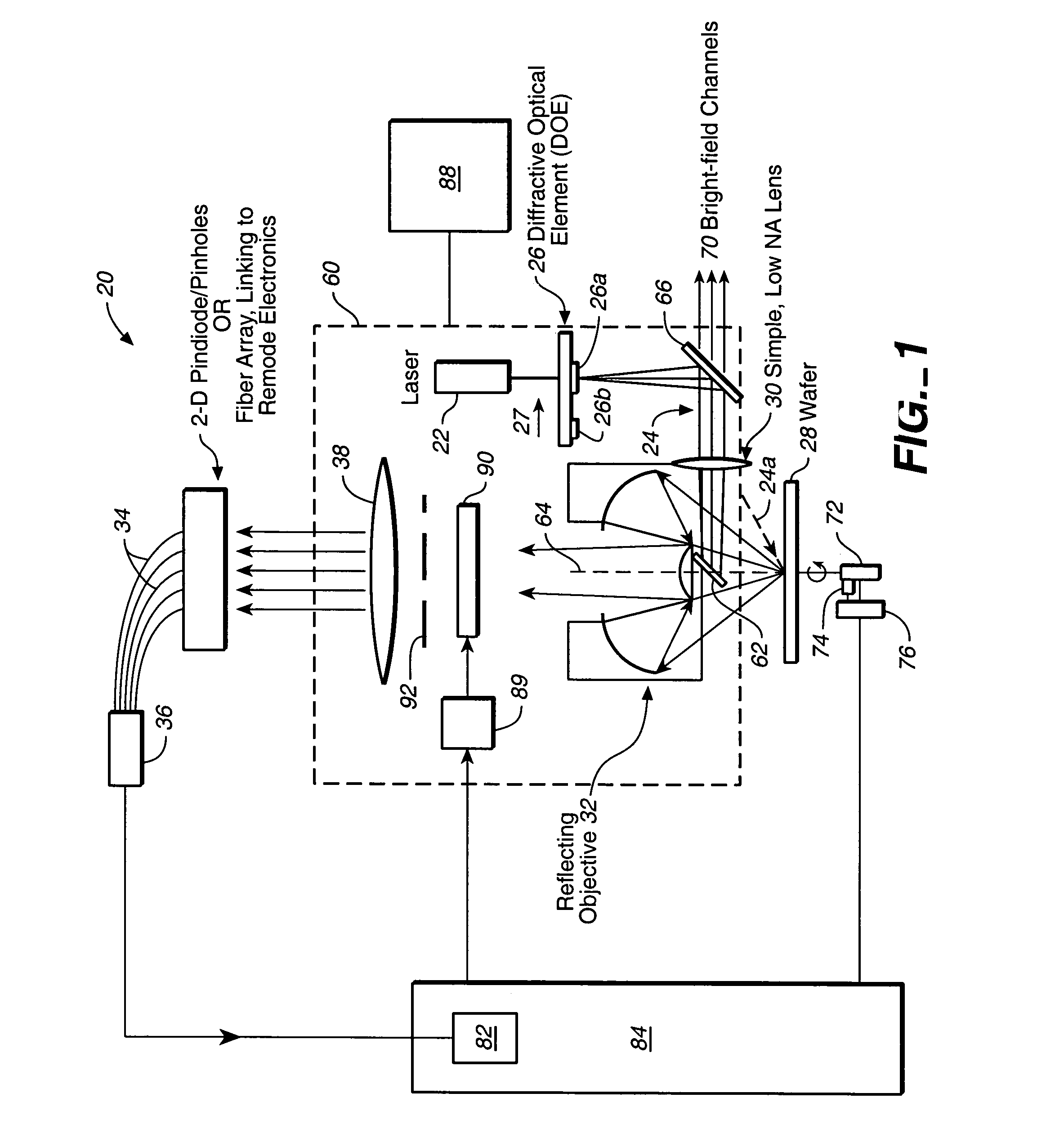
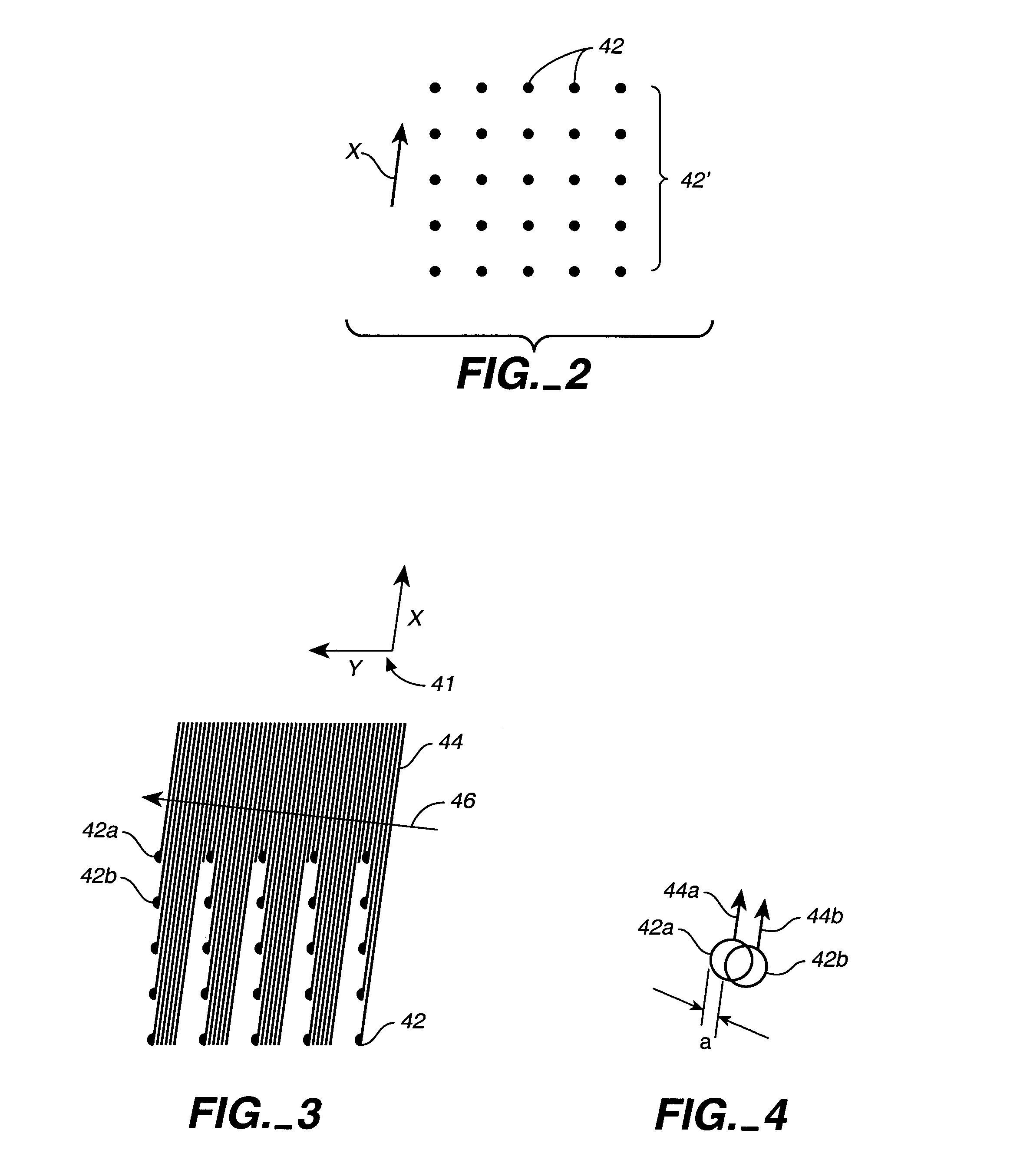
Simultaneous multi-spot inspection and imaging
InactiveUS7130039B2High detection sensitivityImprove performanceAnalysis by electrical excitationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayAnnular aperture
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
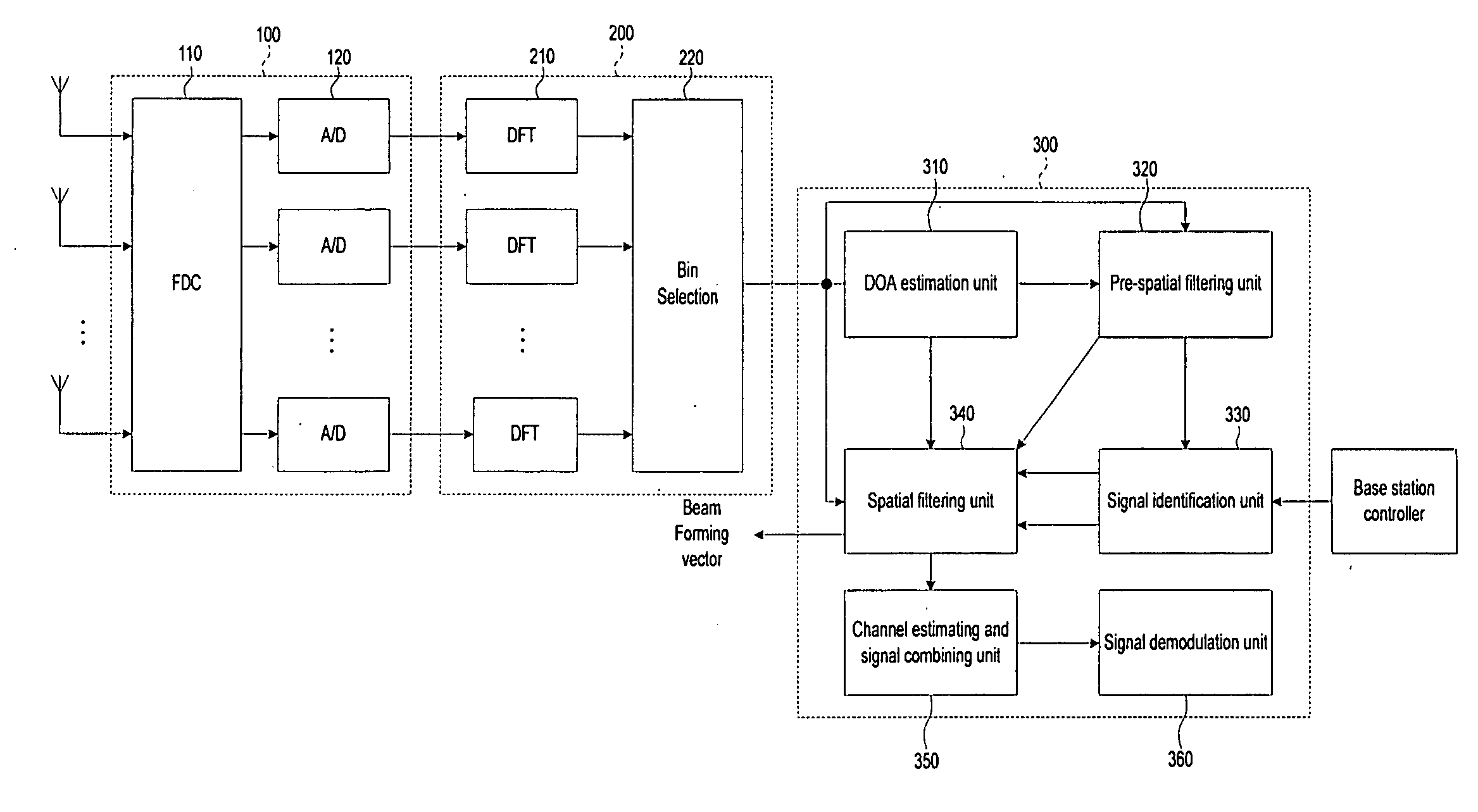
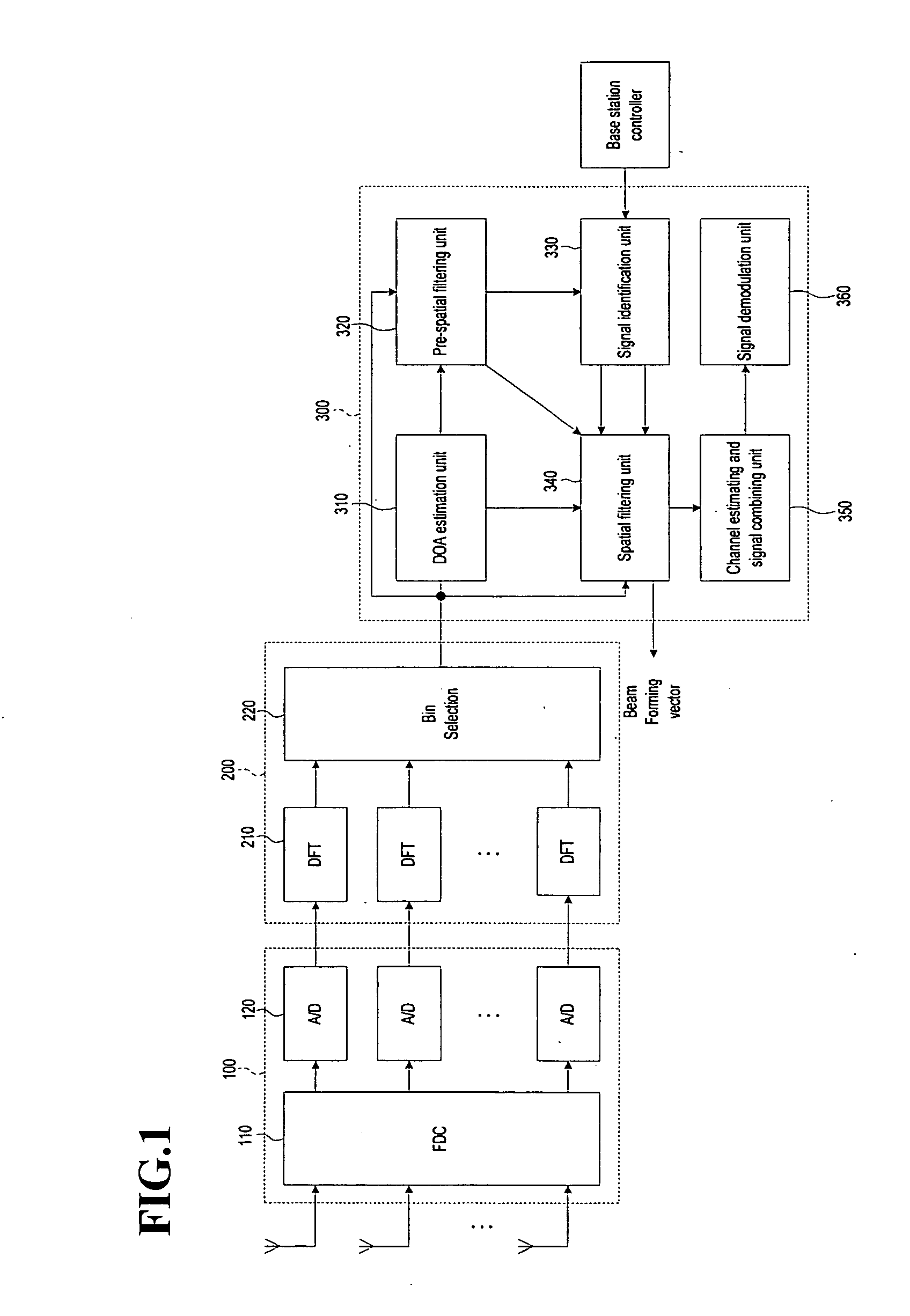
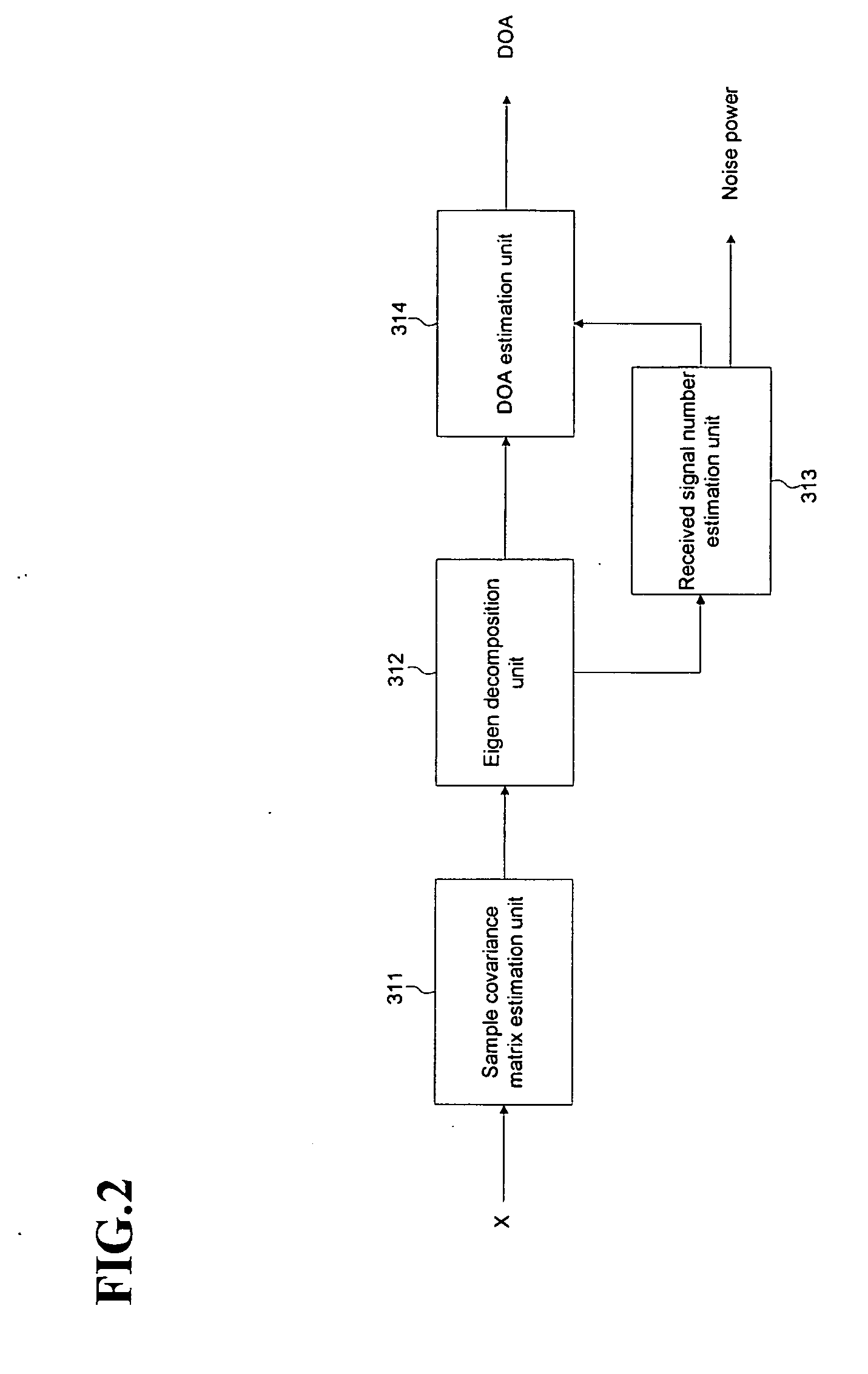
Smart antenna beamforming device in communication system and method thereof
ActiveUS20070164902A1Maximizing signal to interferenceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemSmart antenna
A beamforming device includes a Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation unit for estimating DOAs of the received signals based on a data subcarrier matrix; a pre-spatial filtering unit for using the estimated DOA, performing a filtering operation for the data subcarrier matrix, and generating filtering matrixes; a signal identification unit for using a data sequence, identifying original and interference signals, and generating the DOAs of the original and interference signals; a spatial filtering unit for generating an interference-plus-noise covariance matrix by using the DOA of the interference signal, eliminating the interference signal by using the covariance matrix and the DOA of the original signal, and forming final beams for the original signal; and a channel estimating and signal combining unit for performing a maximal ratio combining operation so that the final beams are combined as one combined final beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
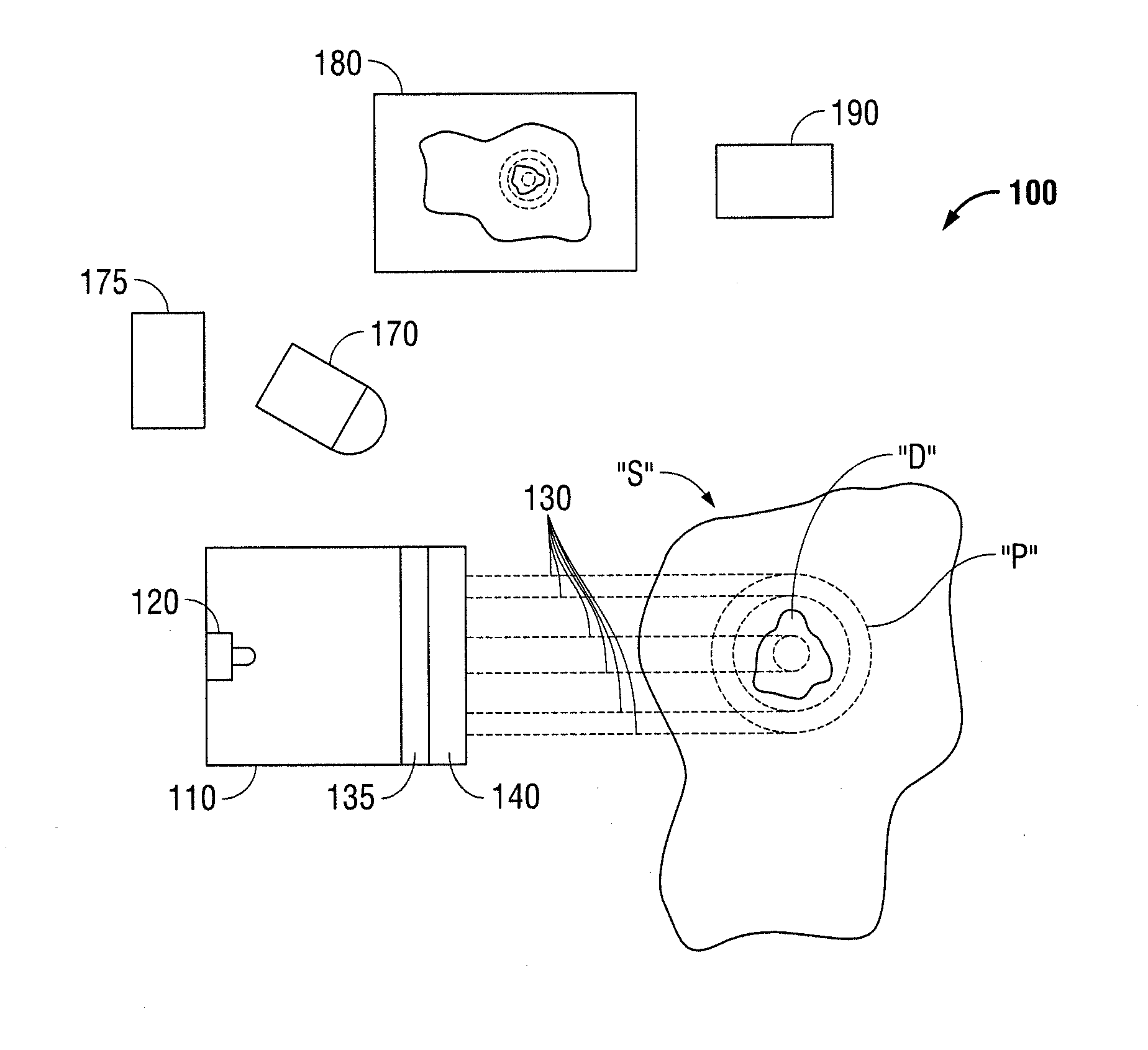
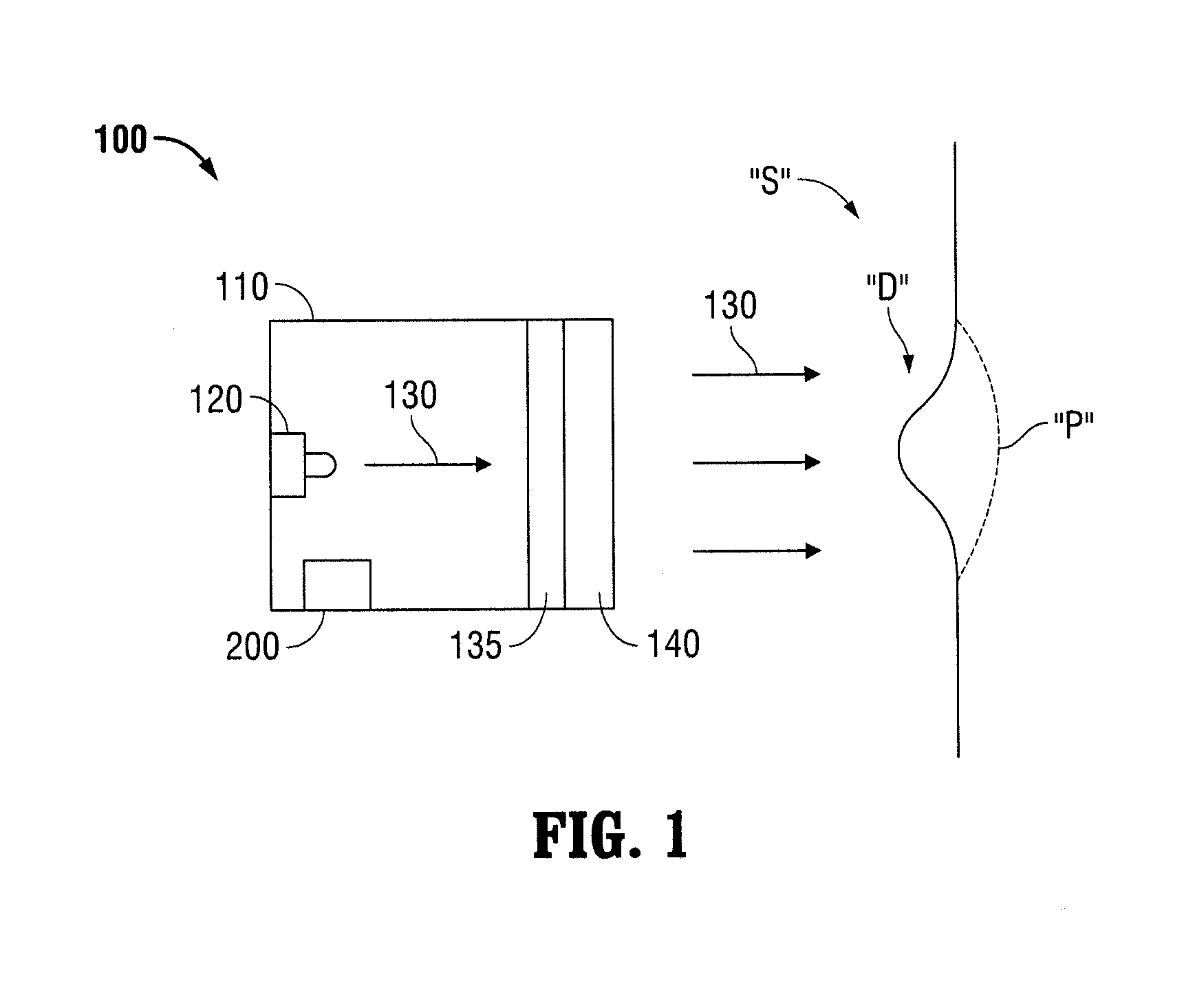
Telecentric Scale Projection System for Real-Time In-Situ Surgical Metrology
InactiveUS20140031665A1Superior in pointAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryMetrologySurgical site
A system and method for determining endoscopic dimensional measurements including a projector assembly comprising a light source for projecting light through a telecentric lens and into a surgical site, and a mask coupled to the projector assembly. Light projected from the light source projects through the mask. The projected light through the mask may be a collimated pattern which does not significantly change in size as a function of the distance to a projected plane. The projected light patterns may include multiple wavelengths of light for measurements of different features of tissue and may be produced using a laser in conjunction with a light shaping optical diffuser, or using a light emitting diode in conjunction with a light shaping optical diffuser, or using a spatial filter. The projected light patterns may take the form of concentric rings with each ring representing a radius of a given dimension.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
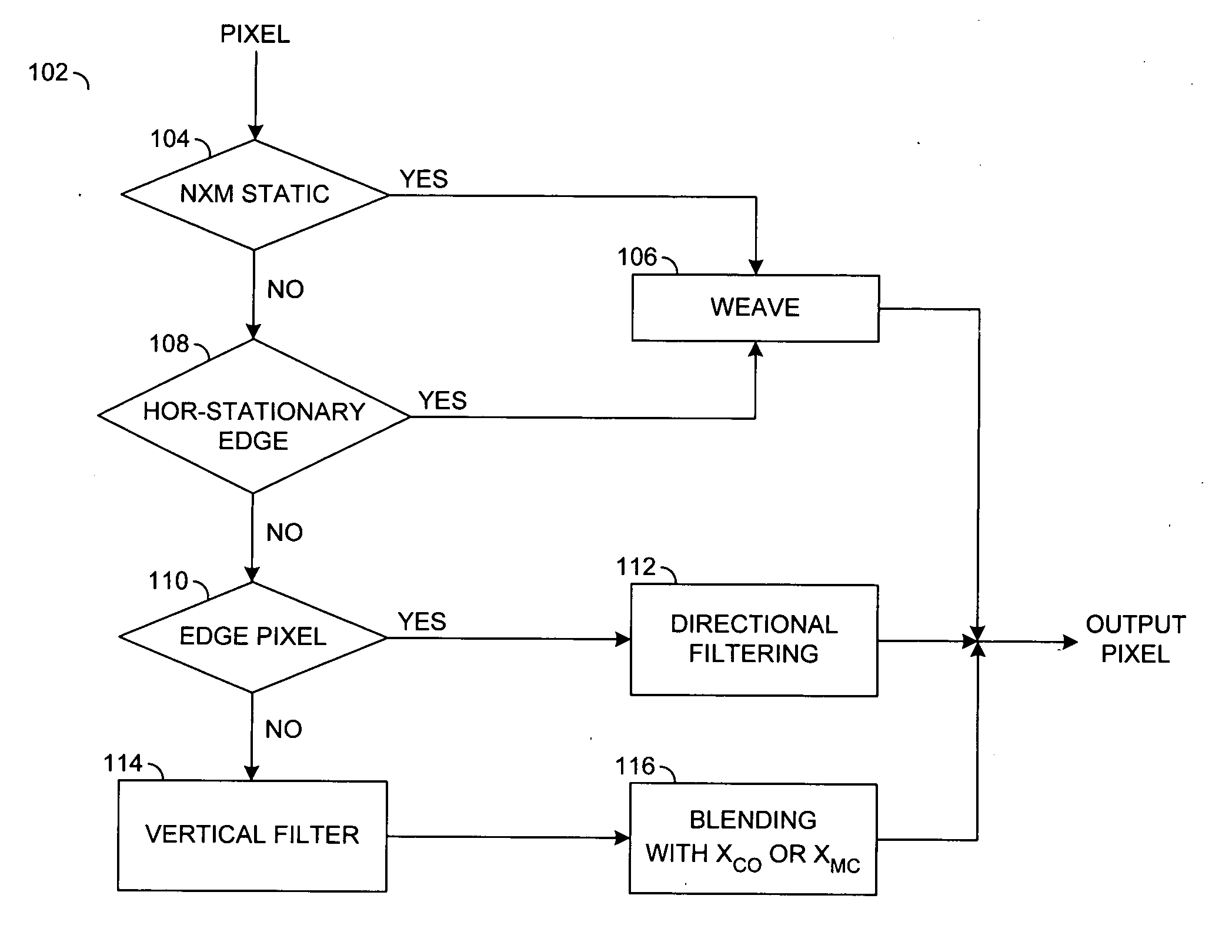
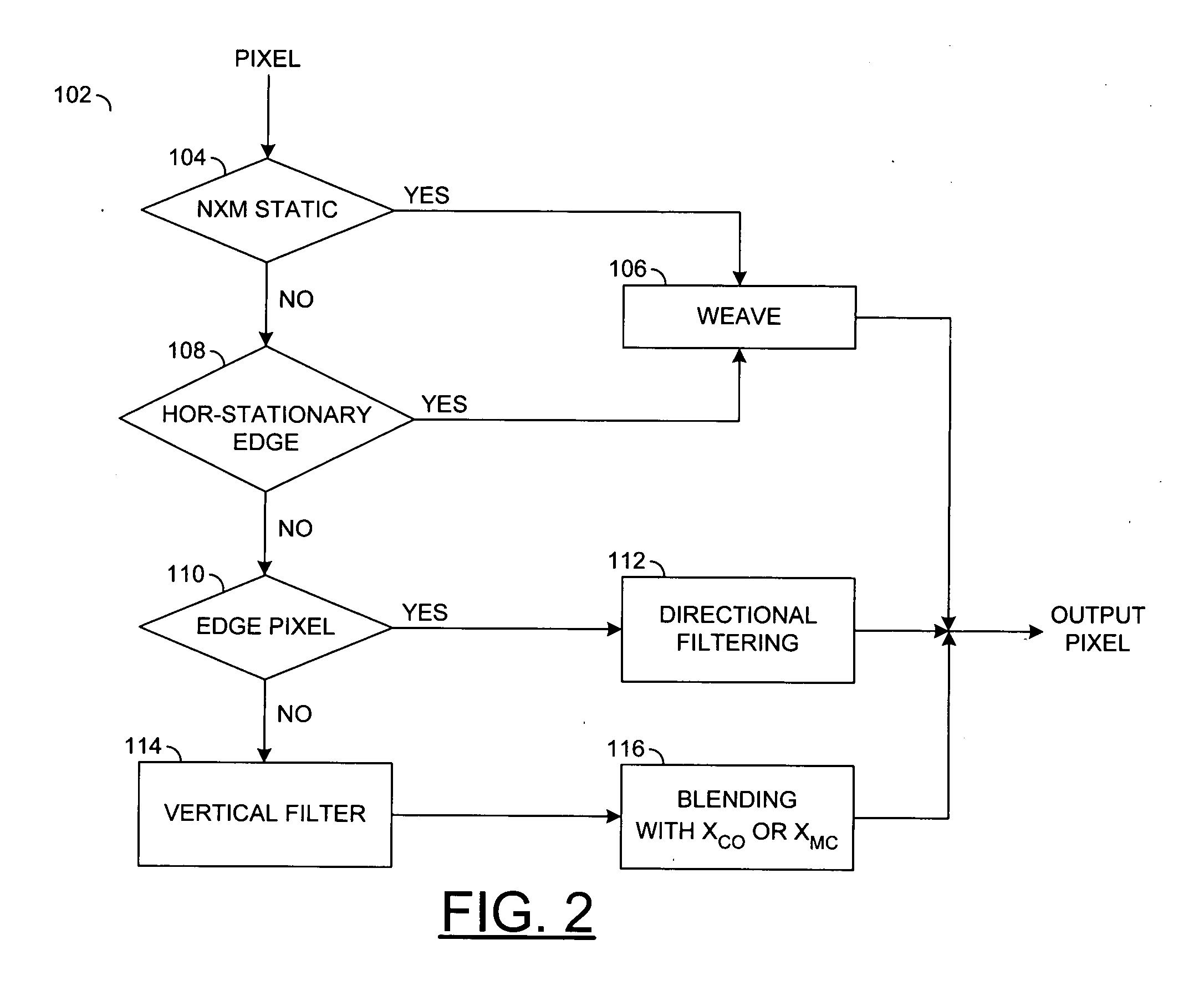
Method and apparatus for video deinterlacing and format conversion
ActiveUS20050134730A1Raise the confidence levelTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionInterlaced video
A method for deinterlacing a picture is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) determining a protection condition by performing a static check on the picture in a region around a location interlaced with a first field of the picture, (B) calculating an interpolated sample at the location by temporal averaging the first field with a second field in response to the protection condition indicating significant vertical activity and (C) calculating the interpolated sample at the location by spatial filtering the first field in response to the protection condition indicating insignificant vertical activity.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS20060017001A1Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Laser three-dimensional imaging device based on single-photon detector
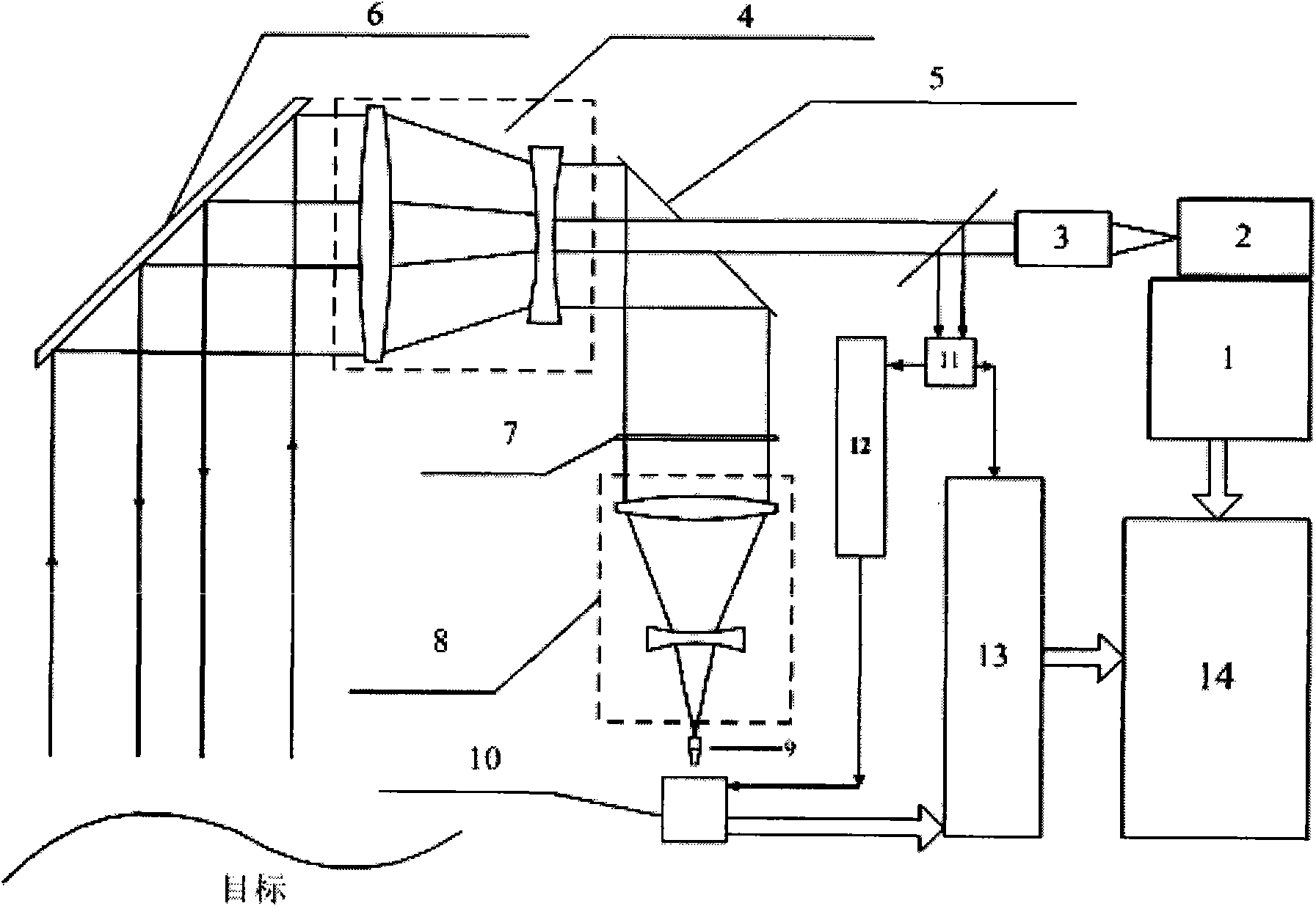
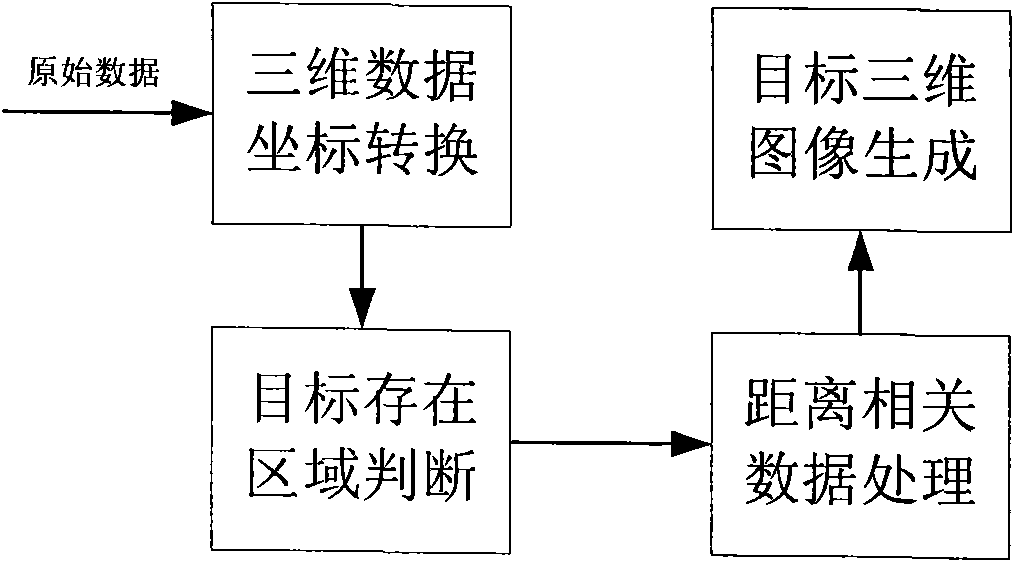
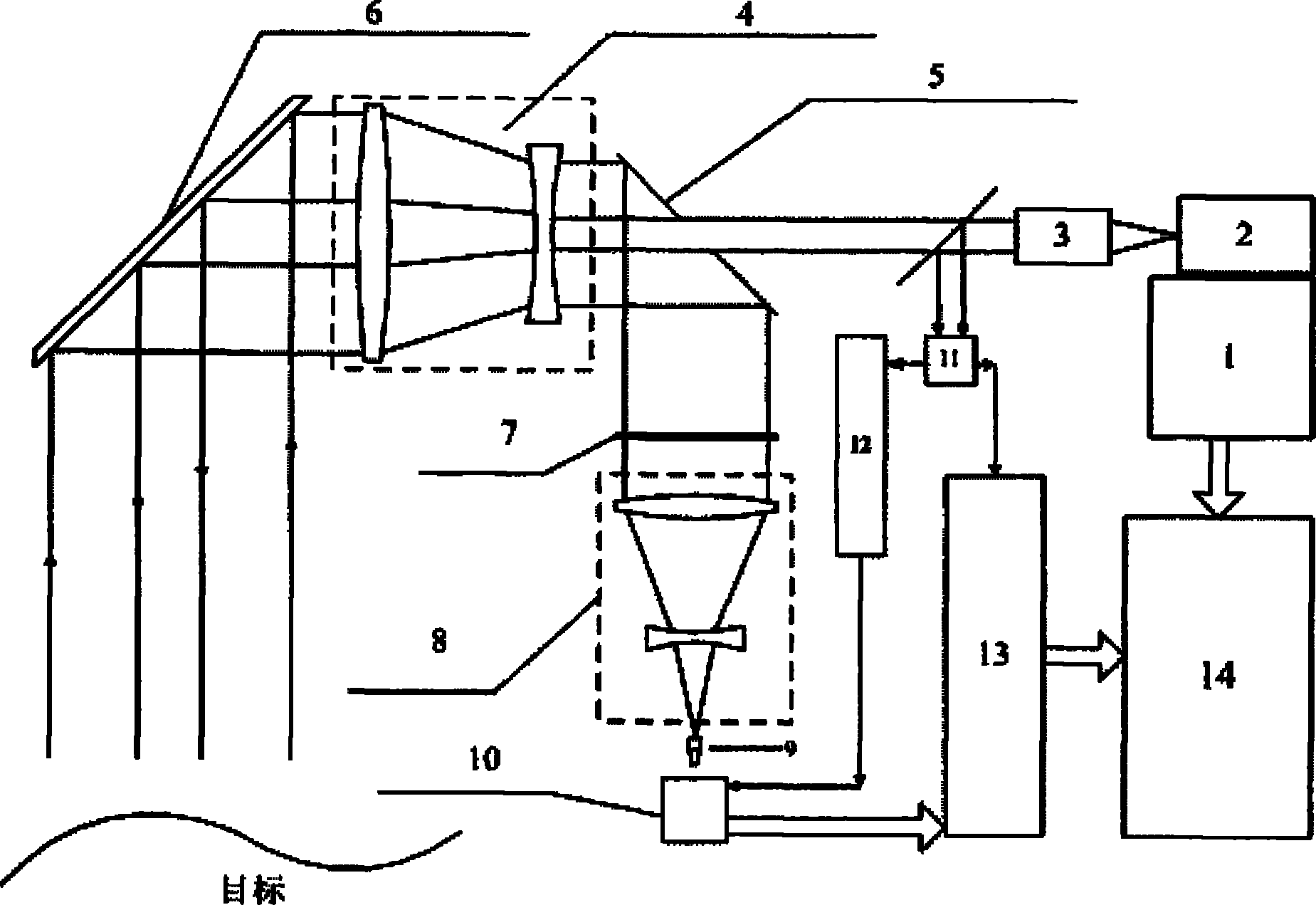
InactiveCN101776760AHigh sensitivityMiniaturizationElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsMeasurement pointFlight time
The invention discloses a laser three-dimensional imaging device based on a single-photon detector, belonging to the technical field of photoelectric instruments. A target to be detected is irradiated by the laser pulse emitted by a pulsed laser via a scanning system; the returning photons are received by a receiving / emitting co-axial optical system, i.e., the returning photons are received by a double-gating single-photon detecting module via a spectral filter and a spatial filter and an arriving pulse is outputted, so that the photon flight time of the target measuring point can be measured by combining the laser emission detection and the multi-photon arriving pulse time; and a data processing unit is used for carrying out the coordinate conversion based on the position and attitude data, scanning mirror targeting data, and photon flight time of the three-dimensional imaging device, de-noising and three-dimensional image construction and correction, so as to output the reliable target three-dimensional range image. The invention solves the problems that the existing laser three-dimensional imaging device is incapable of penetrating vegetation and camouflage and being miniaturized when conducting long-distance operations.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical-dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
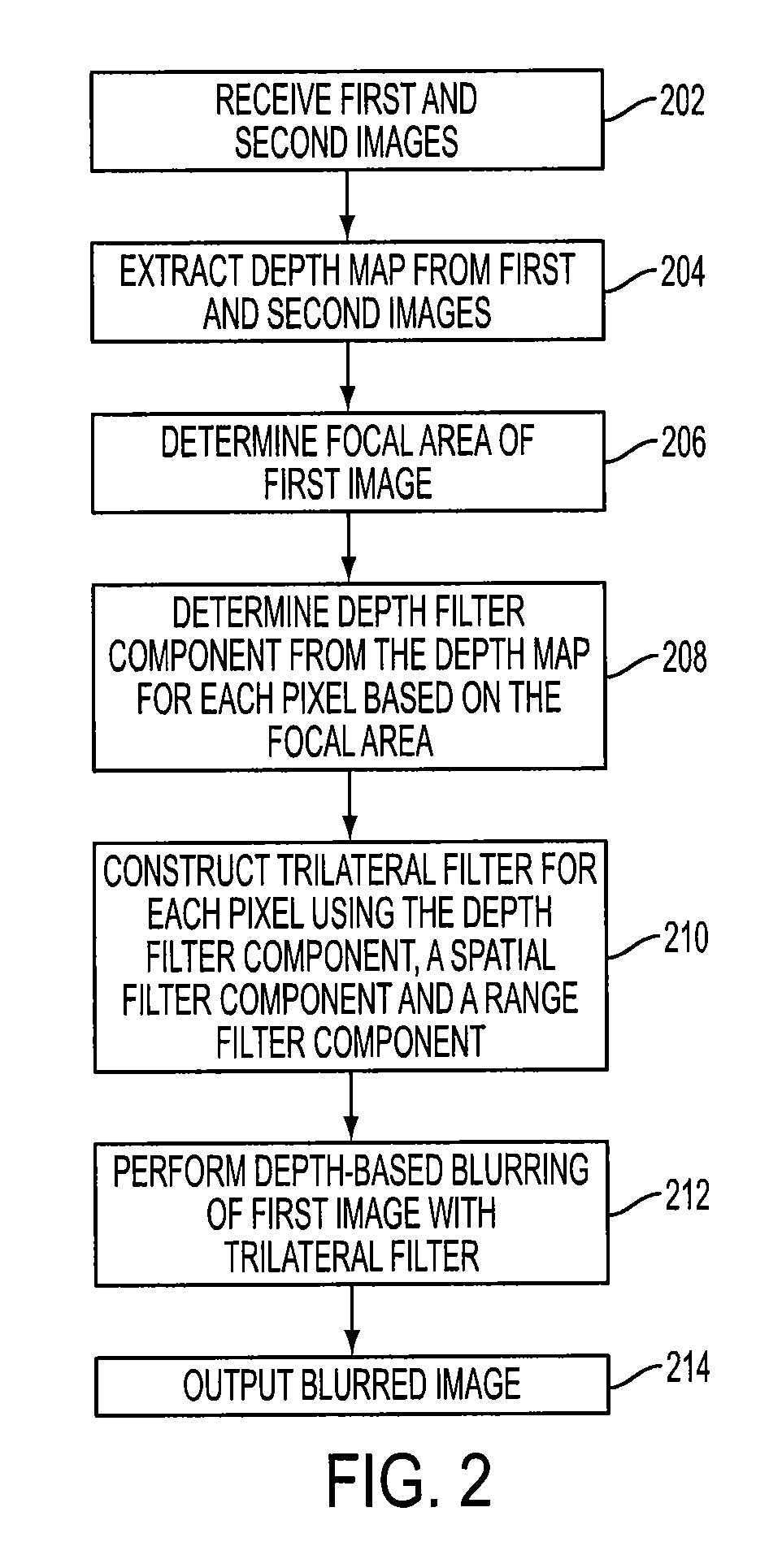
Method of depth-based imaging using an automatic trilateral filter for 3D stereo imagers
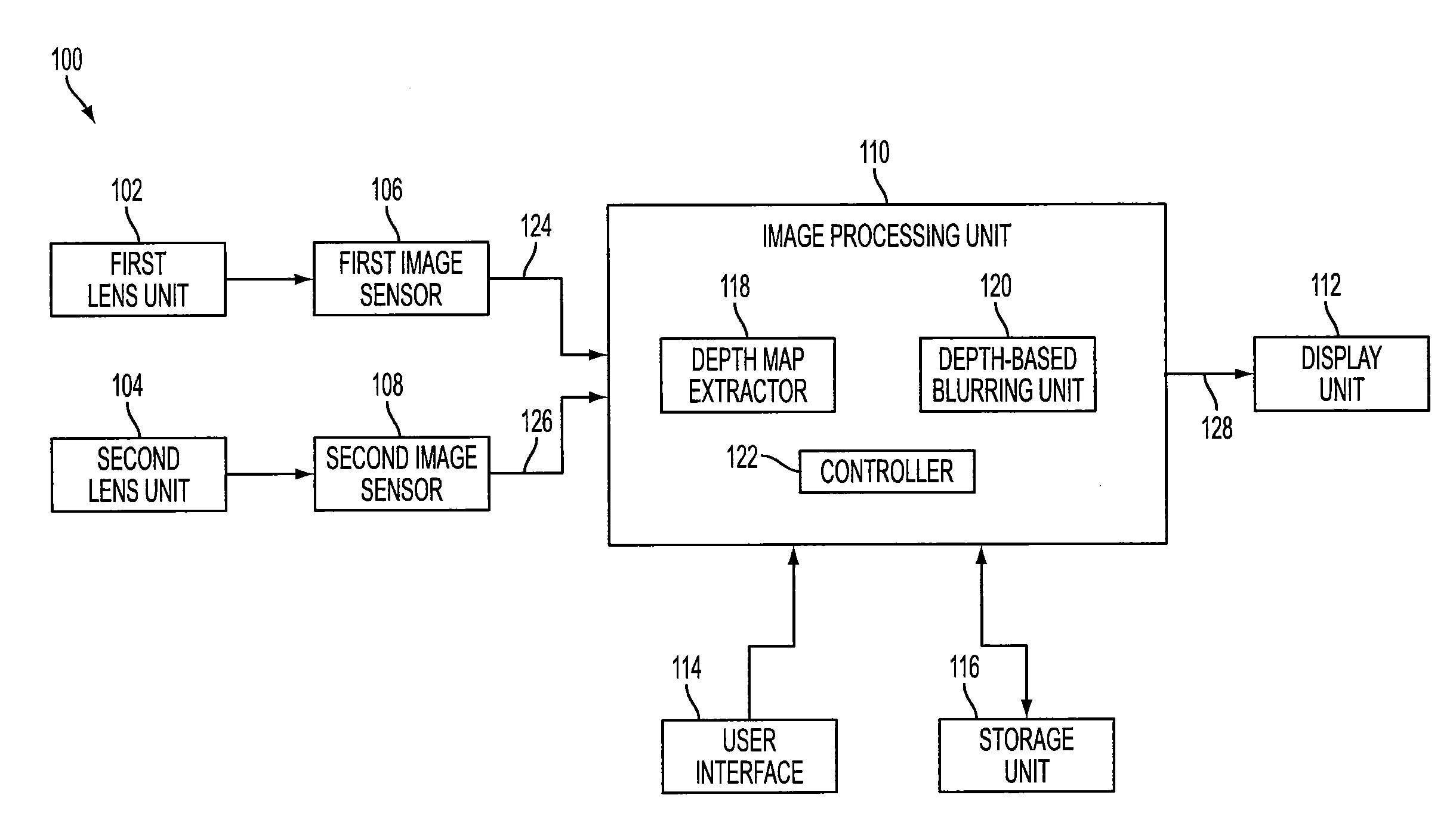
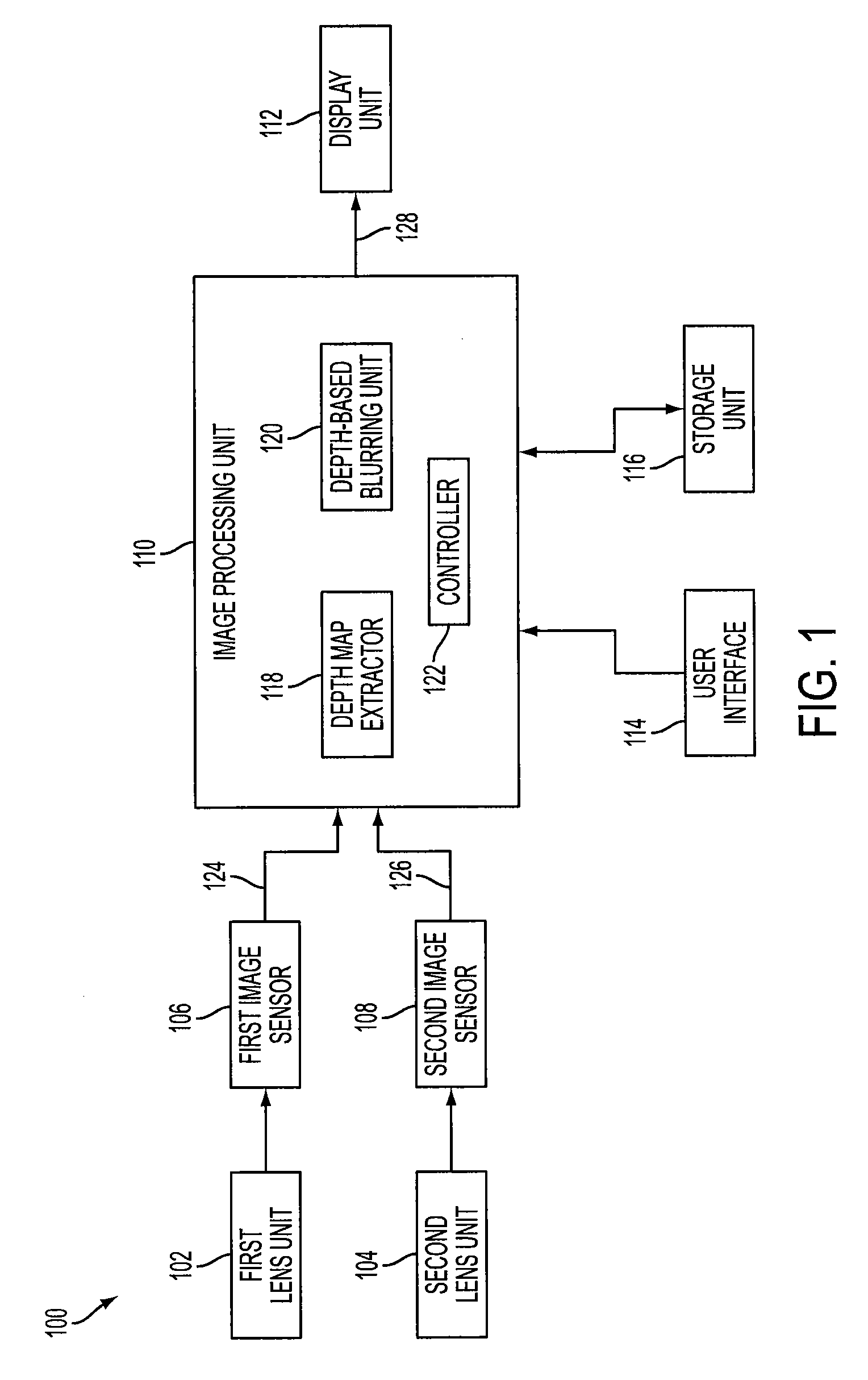
A system of stereo imagers, including image processing units and methods of blurring an image, is presented. The image is received from an image sensor. For each pixel of the image, a depth filter component is determined based on a focal area of the image and a depth map associated with the image. For each pixel of the image, a trilateral filter is generated that includes a spatial filter component, a range filter component and the depth filter component. The respective trilateral filter is applied to corresponding pixels of the image to blur the image outside of the focal area. A refocus area or position may be determined by imaging geometry or may be selected manually via a user interface.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Enhancing WLAN performance in the presence of interference
ActiveUS20100208712A1Easy to operateTransmission monitoringWireless commuication servicesEngineeringWireless access point
A wireless access point coherently receives signals transmitted from client devices and from interfering devices, measures noise and interference capture samples from the received signals, and computes a characterization of noise plus interference. Receive gains and threshold levels are adjusted based on the computed noise plus interference characterization. A set of weights for an interference suppression spatial filter are calculated from the measured noise and interference capture samples and used to produce a filtered signal by spatially filtering the received signals such that interference is spatially nulled in the filtered signal. The method may also include setting PHY parameters at the wireless access point based on the computed noise plus interference characterization. In some embodiments, a protection transmission is transmitted from the wireless access point, requesting connected client devices to suspend transmissions during a specified time period.
Owner:WAVION
Imaging system with low sensitivity to variation in scene illumination
InactiveUS6683645B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage detectionImage system
An imaging system comprises an image detection unit (52) and a filter unit (58). Pixel image signals are passed in parallel from the image detection unit (52) to the filter unit (58). Circuit elements within each pixel (56) generate pixel image signal whose amplitude is proportional to the logarithm of the image intensity at that pixel. The filter unit (58) carries out a spatial filtering operation and outputs the result.
Owner:FLIR SYSTEMS TRADING BELGIUM BVBA
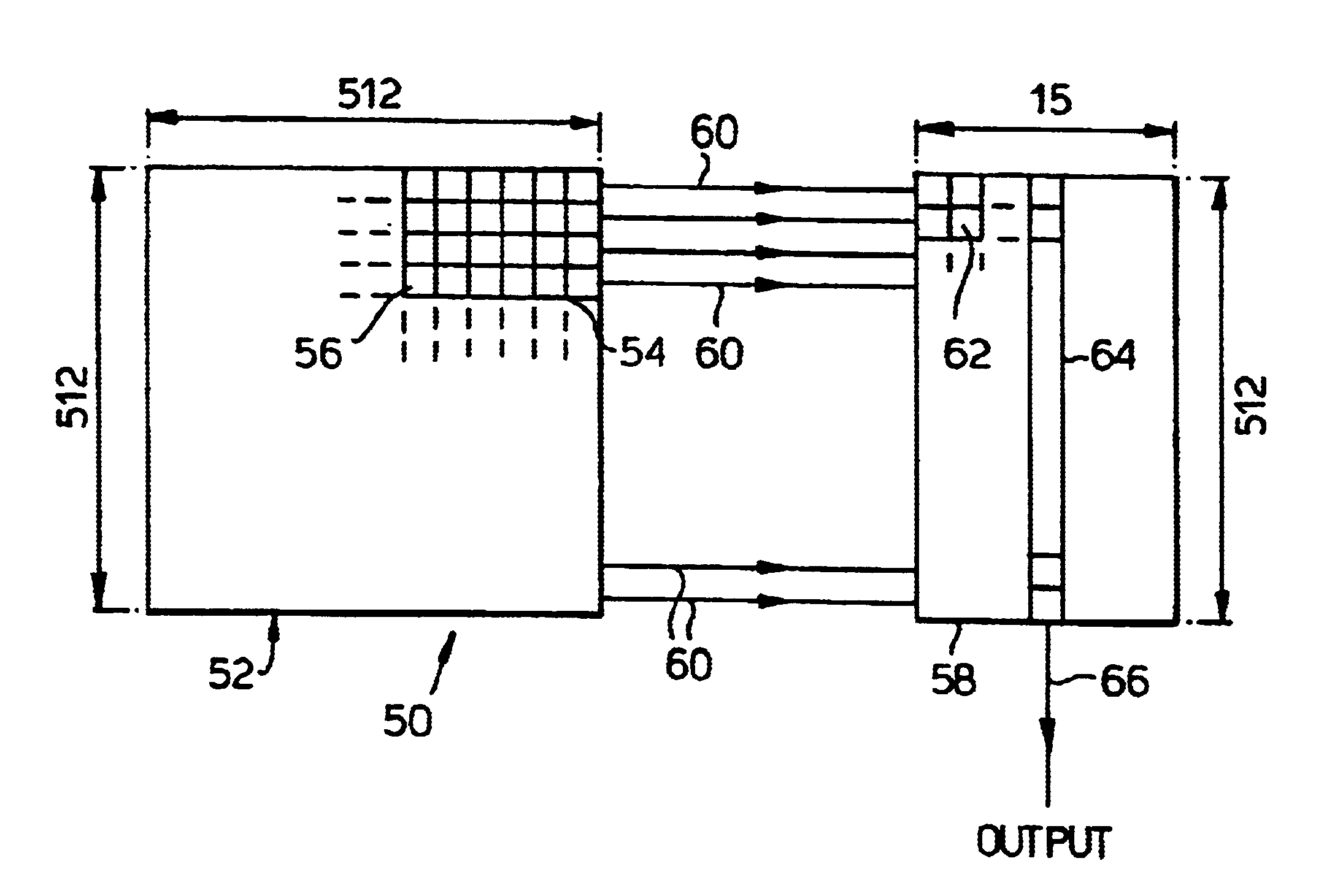
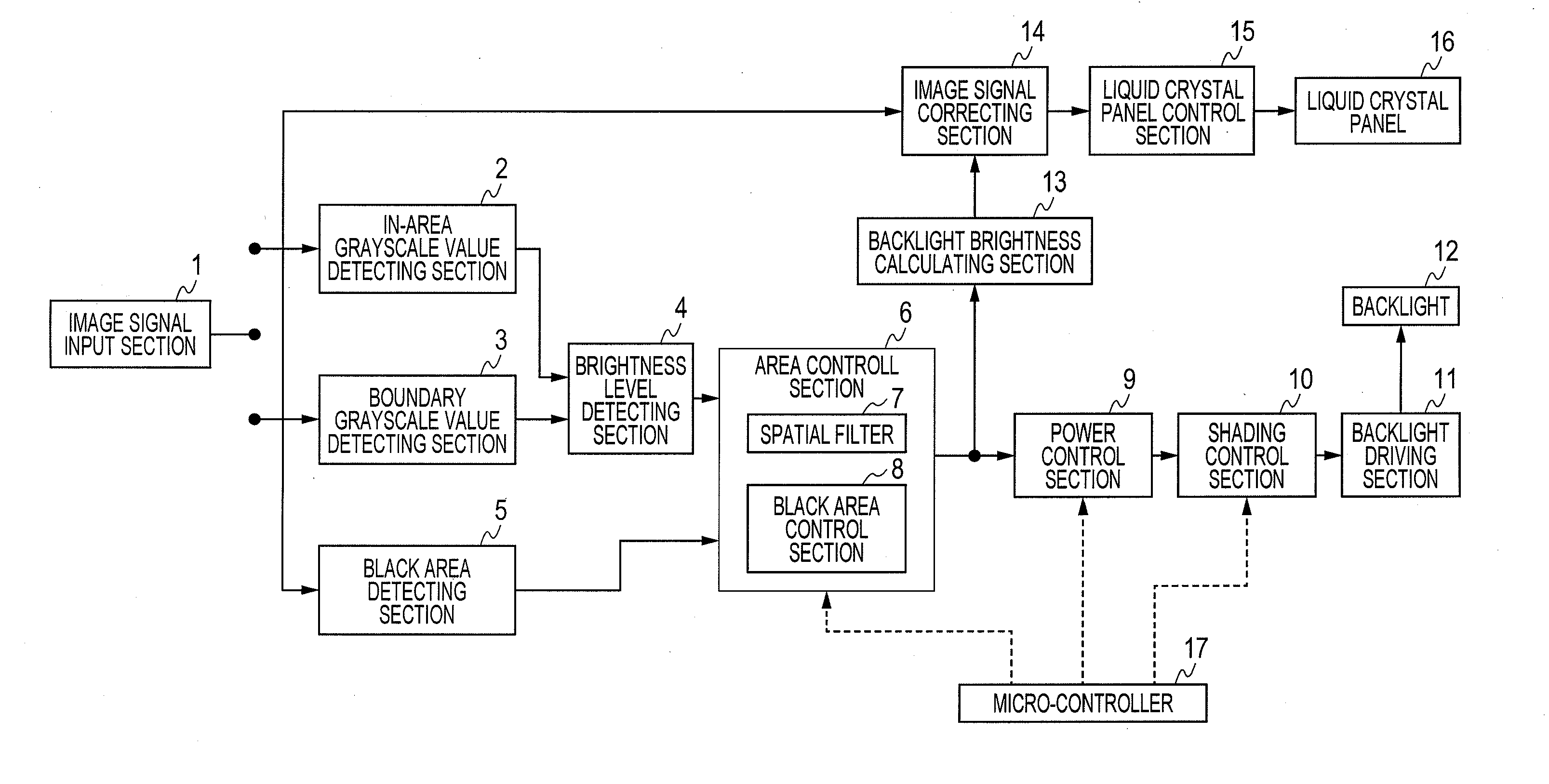
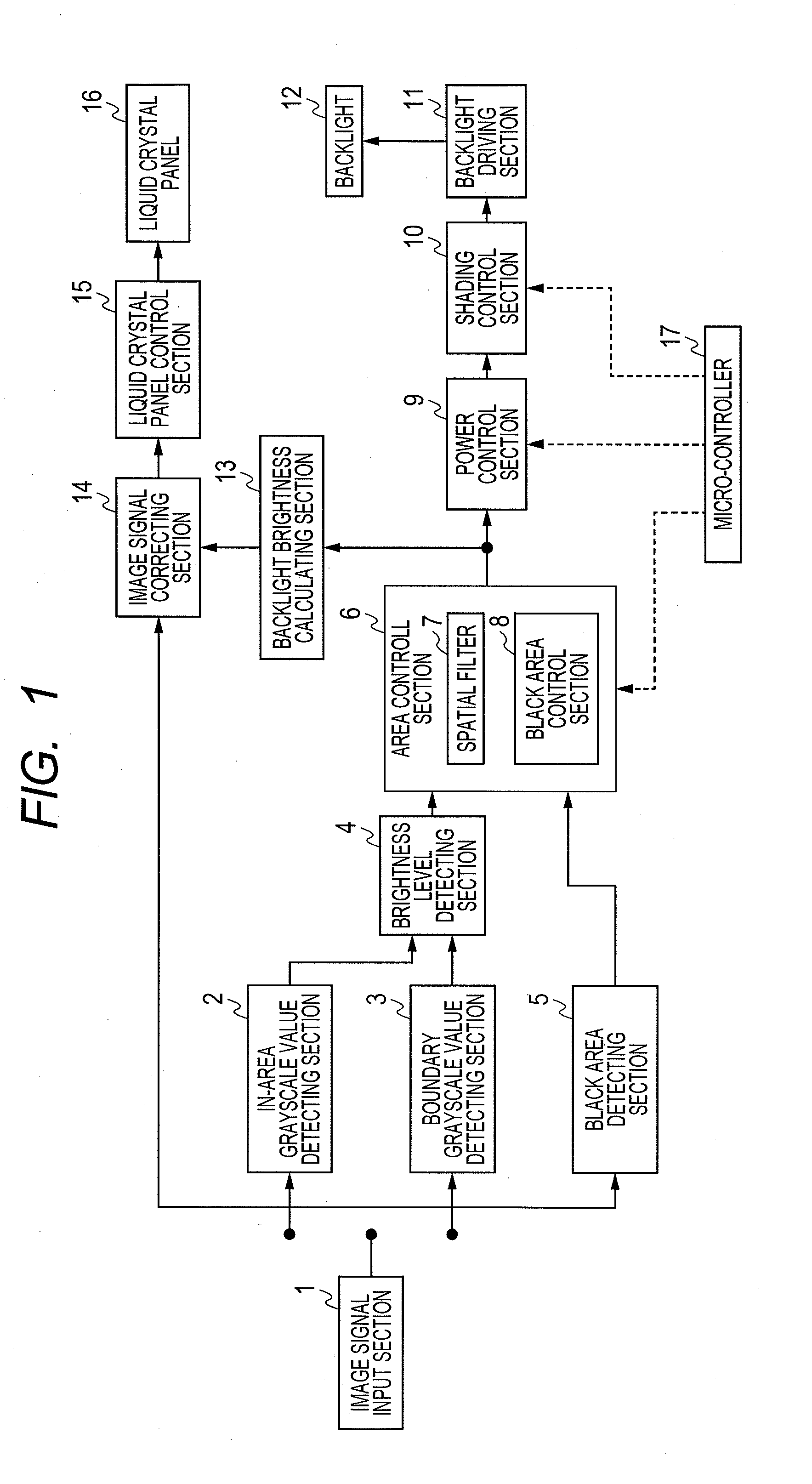
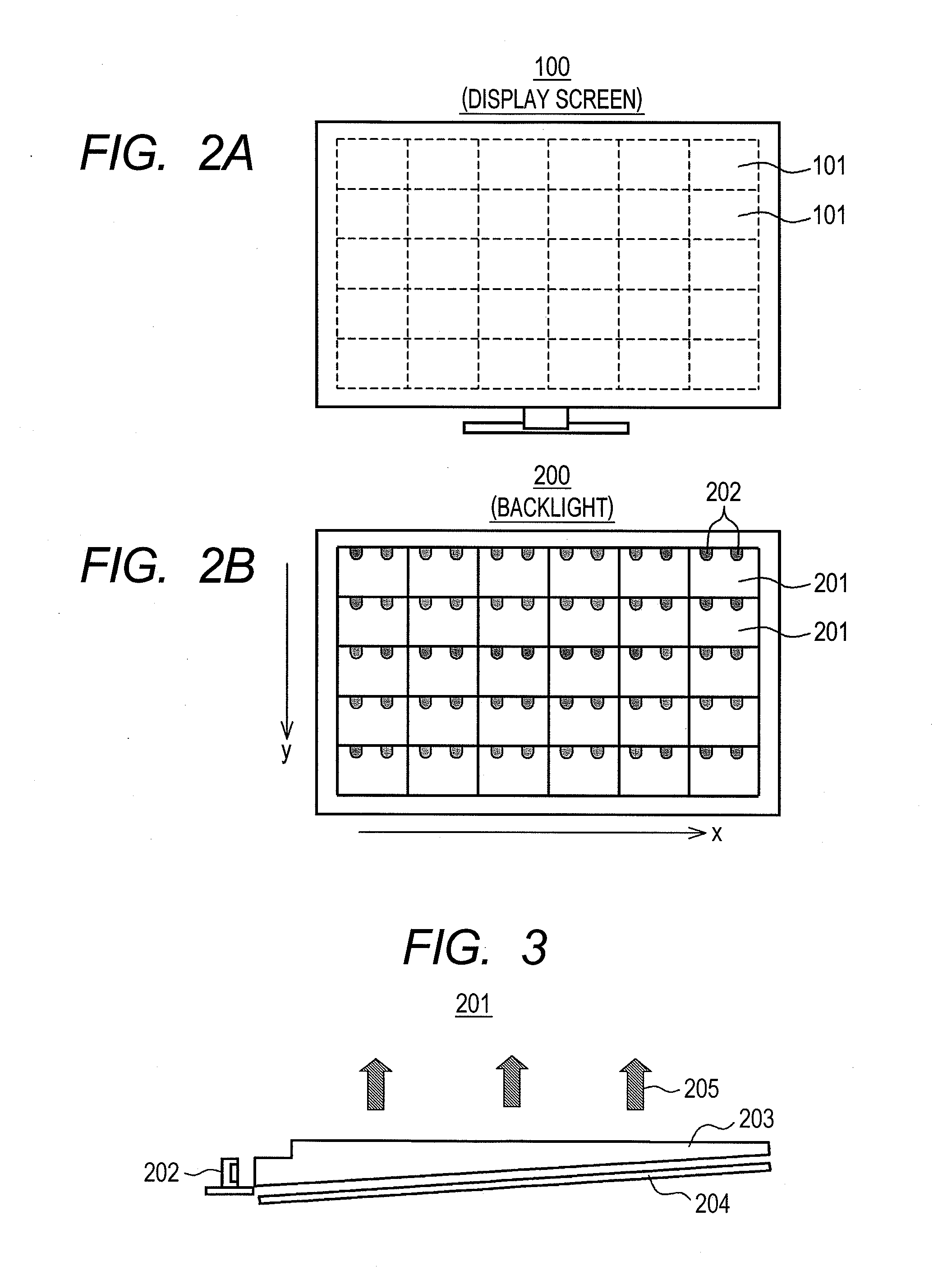
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20110292018A1Reduce brightnessEasy to set upCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayLimit value
An area control section individually sets illumination intensity (light control value) of each backlight cell corresponding to each area of the display screen. A spatial filter corrects the light control values so that spatial distribution of the light control values becomes more moderate between adjoining areas. A black area control section sets the minimum value of the light control value based on a “black area” in the screen. A power control section corrects the light control values so that power consumption of the backlight does not exceed a limit value. A shading control section corrects the light control values to relatively lower brightness in the peripheral part of the screen compared to the central part of the screen. A micro-controller switches the operations of the above light control value correcting sections according to an image display mode selected by the user.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
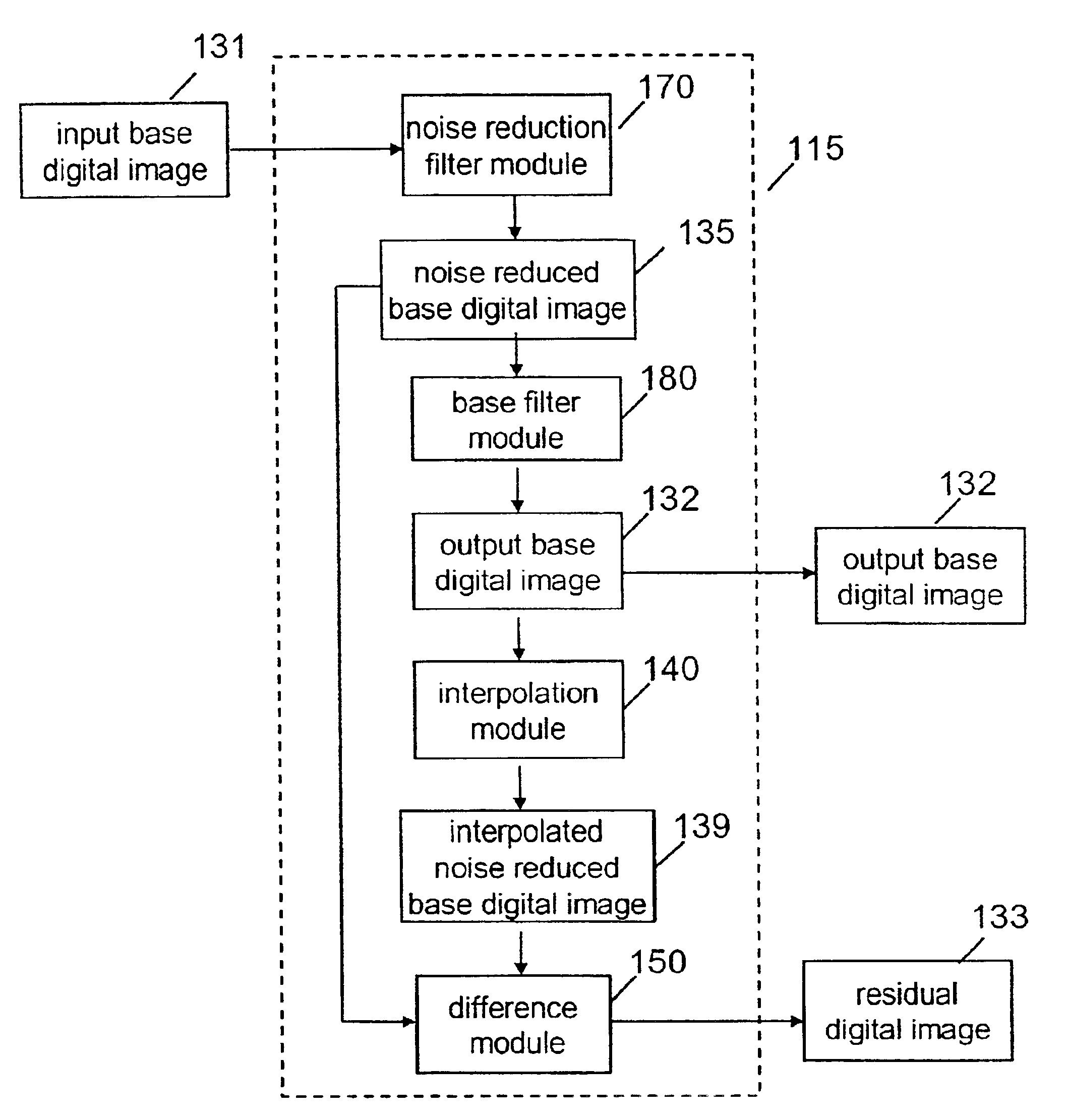
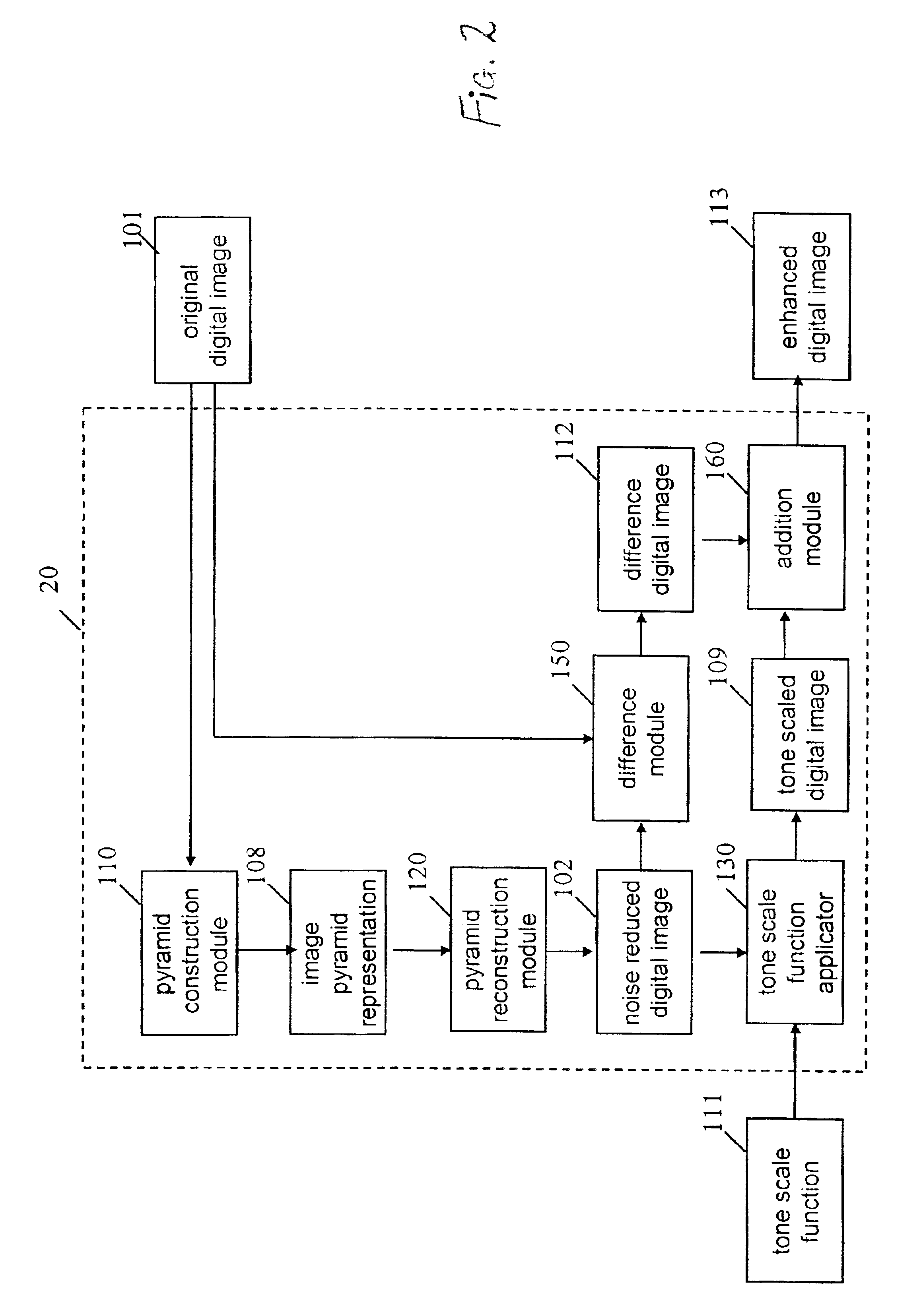
Method of enhancing the tone scale of a digital image to extend the linear response range without amplifying noise
A method of processing a digital image to improve contrast, the digital image being derived from an image captured by a recording medium having a nonlinear response to light, includes the steps of: applying a spatial filter to the digital image to produce a noise reduced digital image; subtracting the noise reduced digital image from the digital image to produce a difference digital image; applying a tone scale function to the noise reduced digital image to produce a tone scale adjusted digital image having the appearance of being derived from an image captured by a recording medium having a linear response; and combining the difference digital image with the tone scale adjusted digital image to produce a processed digital image, whereby the contrast of the digital image is improved without amplifying noise.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
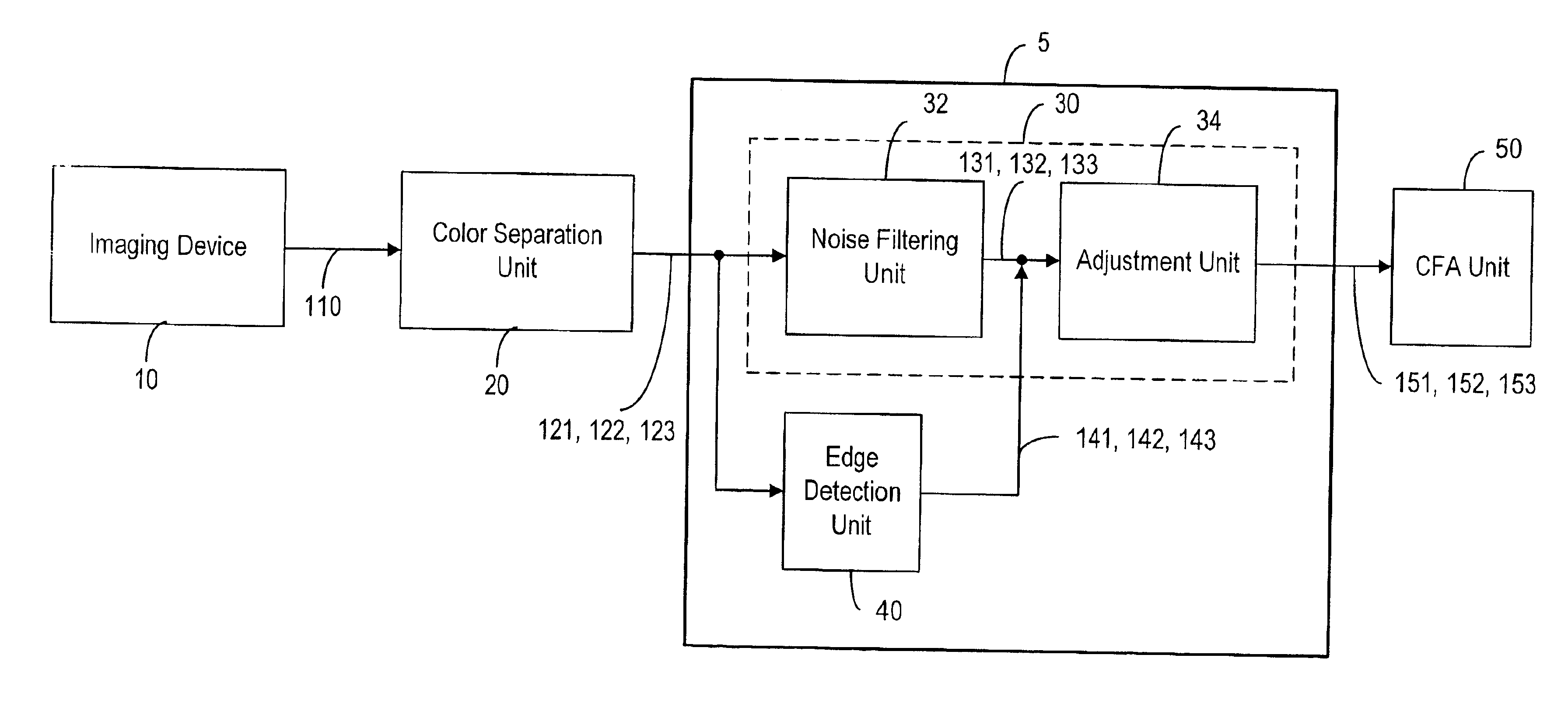
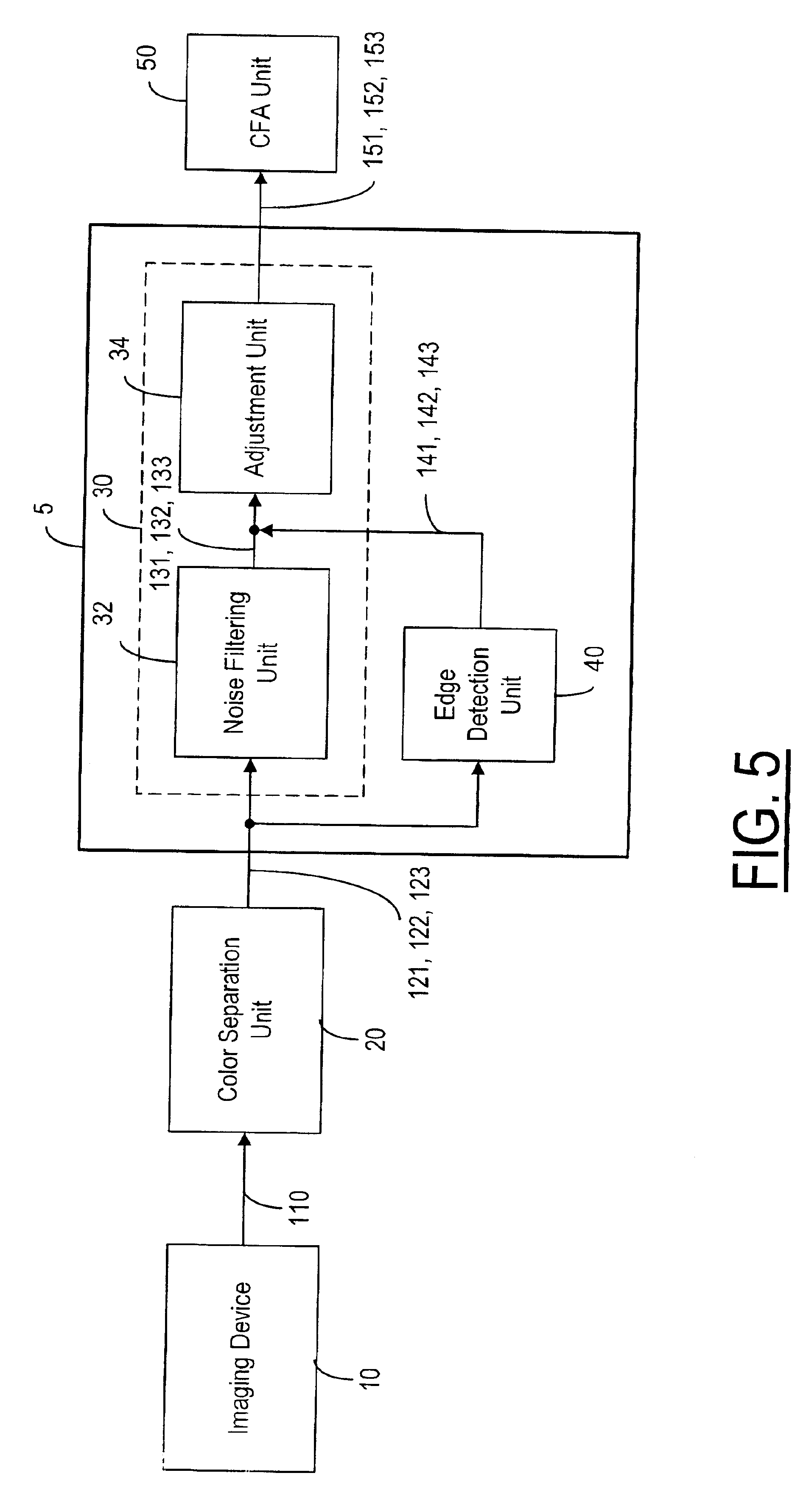
Method and system for improving color images
A method and system for improving a color image separable into three color components. A noise-filtering unit is used to filter the color components for providing noise-filtered color components. The edge information extracted from one color component is used to adjust the noise-filtered color component of a different color. The algorithm for noise filtering of color components can be based on linear spatial filters, non-linear filters or the combinations thereof. The algorithm for edge detection can be based on directional or non-directional spatial filters.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and apparatus for detecting defects
InactiveUS20070058164A1Quick selectionImproves grayscale depthOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansLength waveLight filter
This invention provides a defect inspection method and apparatus that can easily and quickly determine, from among a plurality of inspection conditions, a condition that allows for an inspection with high sensitivity. The inspection apparatus has a variety of optical functions to cover a variety of kinds of defects to be inspected (shape, material, nearby pattern, etc.). For each optical function, grayscale depths of defects that the operator wants detected and of pseudo defects that he or she wants undetected are accumulated for future use, so that conditions conducive to a higher sensitivity and a lower pseudo defect detection rate can be selected efficiently. Conditions that can be selected for optical systems include a bright-field illumination, a dark-field illumination and a bright- / dark-field composite illumination, illumination wavelength bands, polarization filters and spatial filters.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
System and method for preparing micro-pore array through femtosecond laser direct writing
InactiveCN103071930AEasy to operateTransformation is easy and feasibleLaser beam welding apparatusFrequency spectrumSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a system and a method for preparing a micro-pore array through femtosecond laser direct writing. The system comprises a femtosecond vector light field generation system, a spatial filtering component, a computer and a three-dimensional mobile platform, wherein a 1 / 2 wave plate, a Glan-laser polarizer, a beam expander and the femtosecond vector light field generation system are arranged on an output straight light path of a femtosecond laser device in sequence; a 4f system is arranged on a light path behind a reflective pure phase spatial light modulator after a holographic phase plate is loaded; a spatial filter is arranged on a frequency spectrum surface; and positive and negative levels of diffraction light which pass through the spatial filter pass through a 1 / 4 wave plate respectively and are combined into a beam of laser through a Rochi grating. A material is adjusted to a focal position through the spatial filtering component, an electronic diaphragm, a focusing lens and the three-dimensional mobile platform; and the spatial light modulator, the electronic diaphragm and the three-dimensional mobile platform are connected with a computer through data lines. The device has the advantages of simple structure, convenience in operation and capabilities of preparing the micro-pore array with various patterns and improving the machining efficiency.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Three-dimensional object information acquisition using patterned light projection with optimized image-thresholding
Techniques are disclosed of obtaining three-dimensional information pertaining to an object of interest, based on a light-pattern image acquired by digitally photographing the object with patterned light being projected onto the object, By an exemplary technique, a local adaptive spatial-filter is configured for the light-pattern image, based on a spatial frequency characteristic of the light-pattern image having a plurality of sub-areas, on a sub-area-by-sub-area basis, and local thresholds are set for the light-pattern image, based on image information acquired by locally applying the spatial filter to the light-pattern image, on a sub-area-by-sub-area basis.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
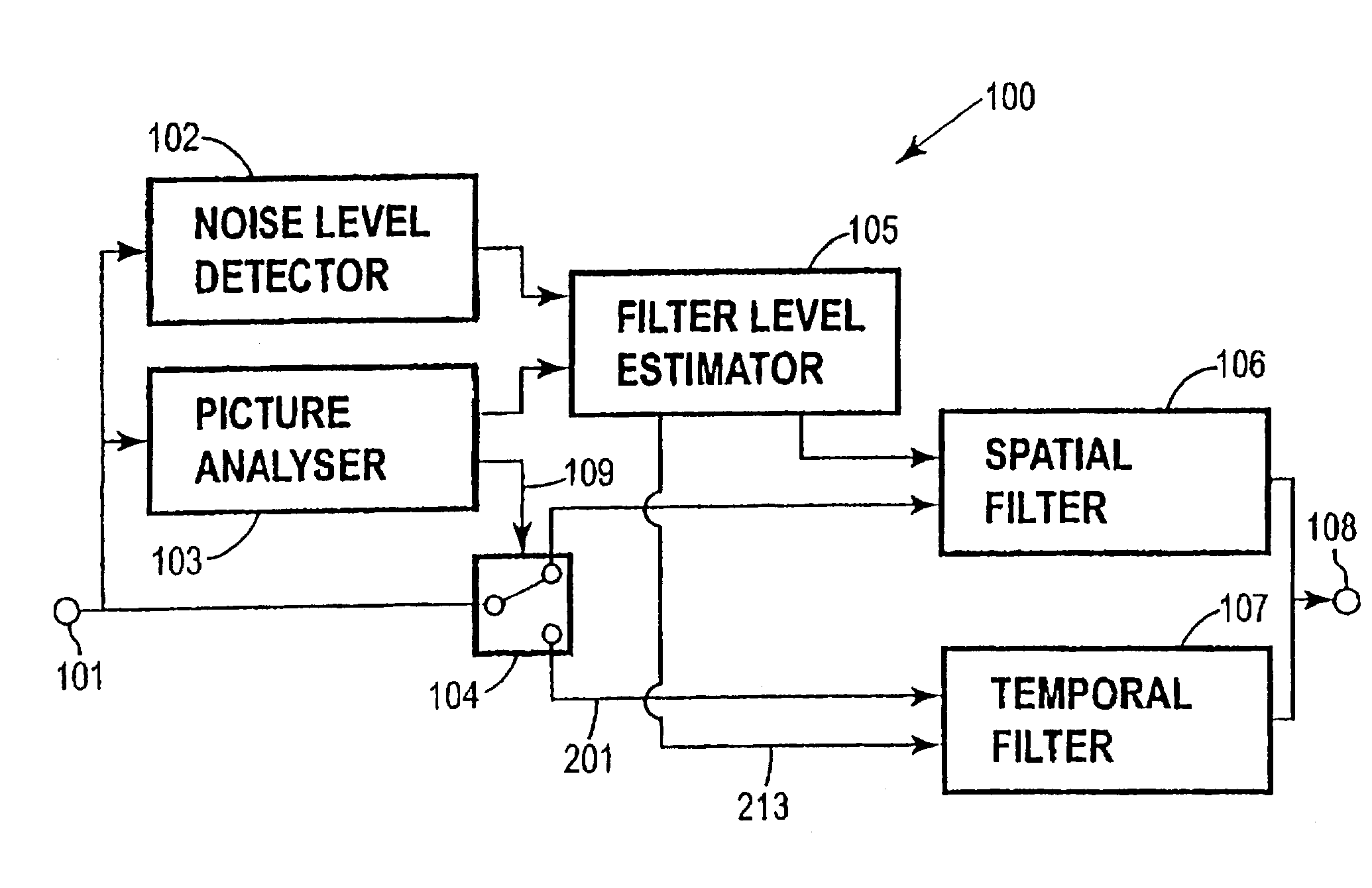
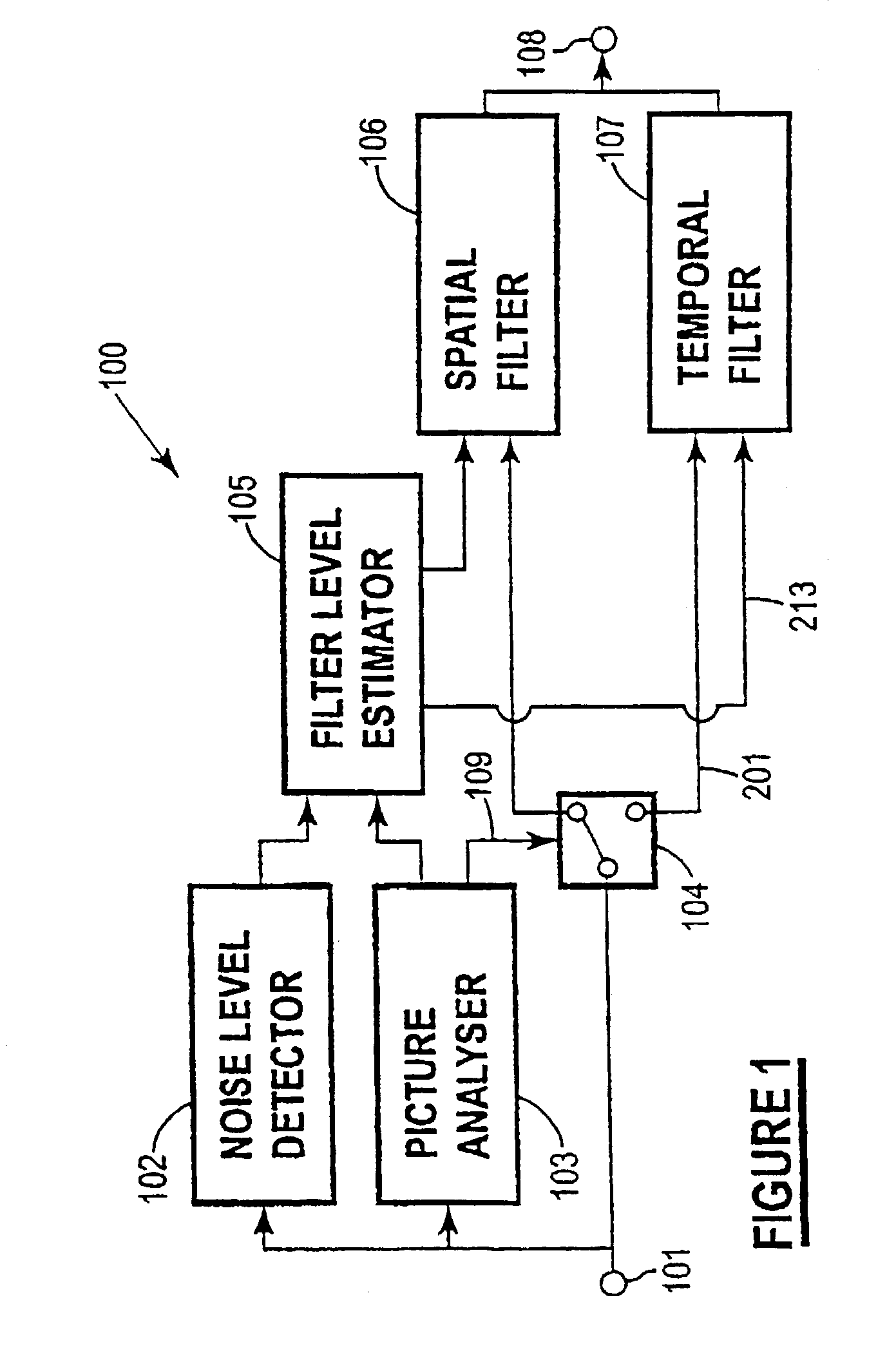
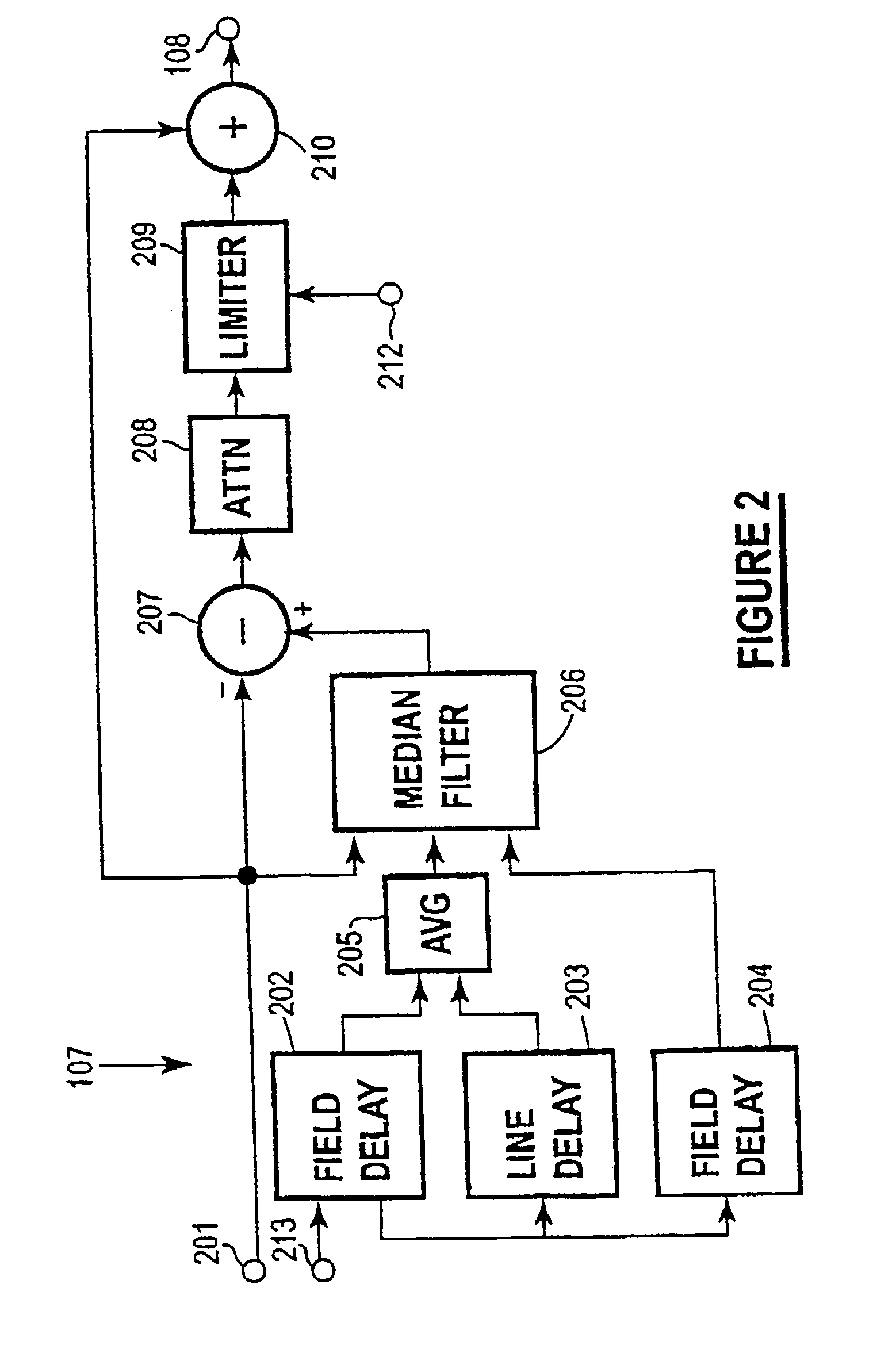
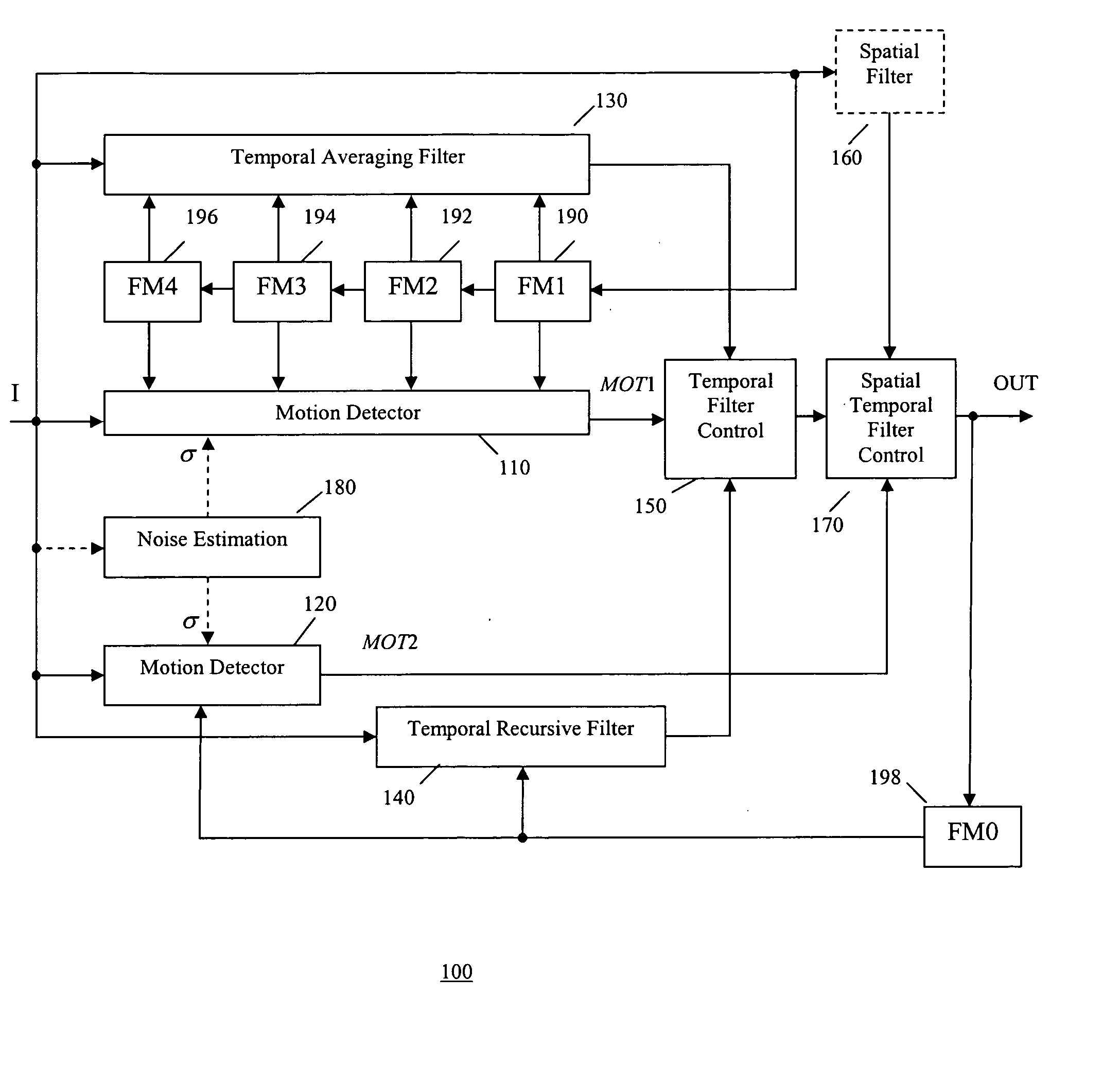
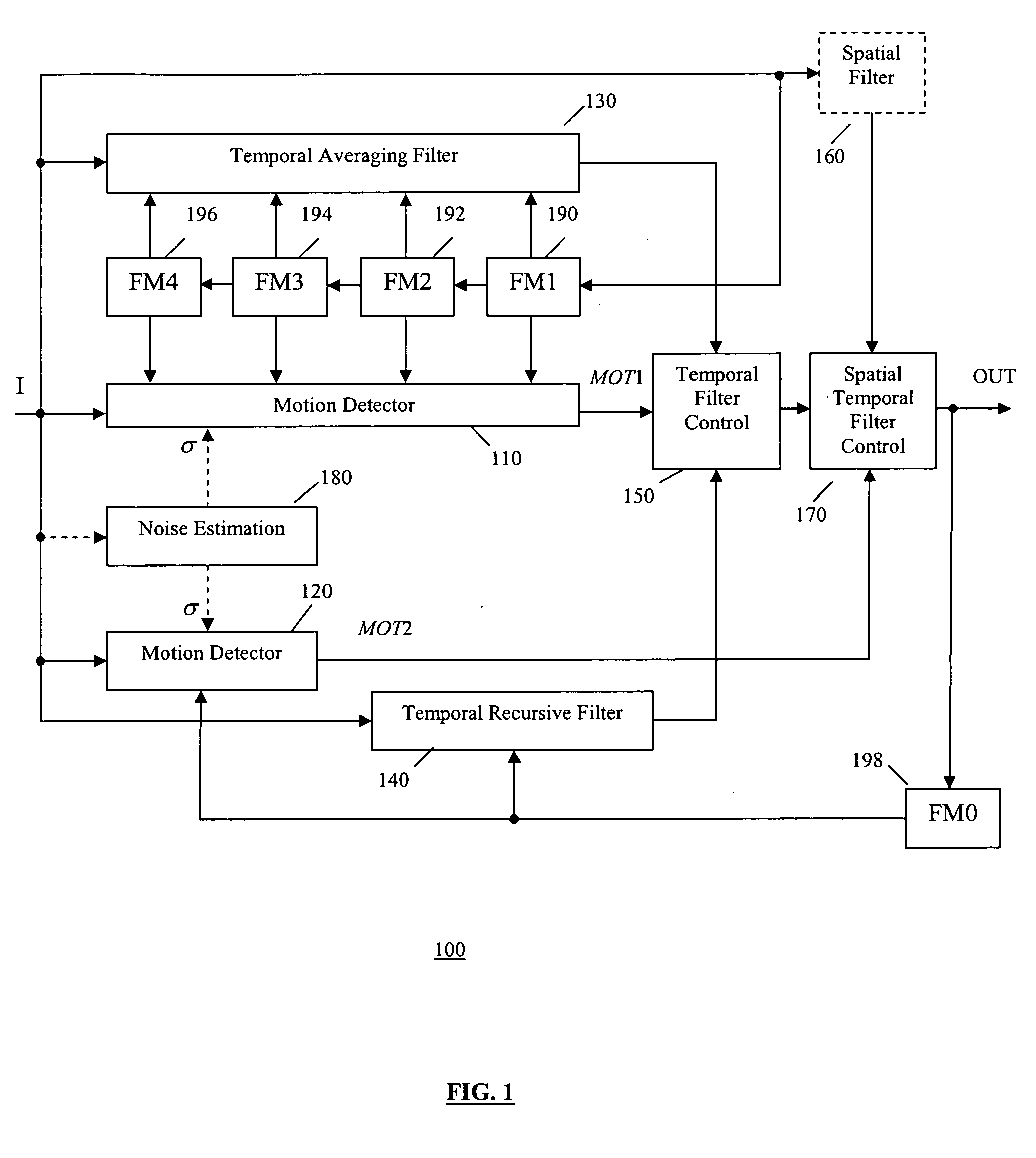
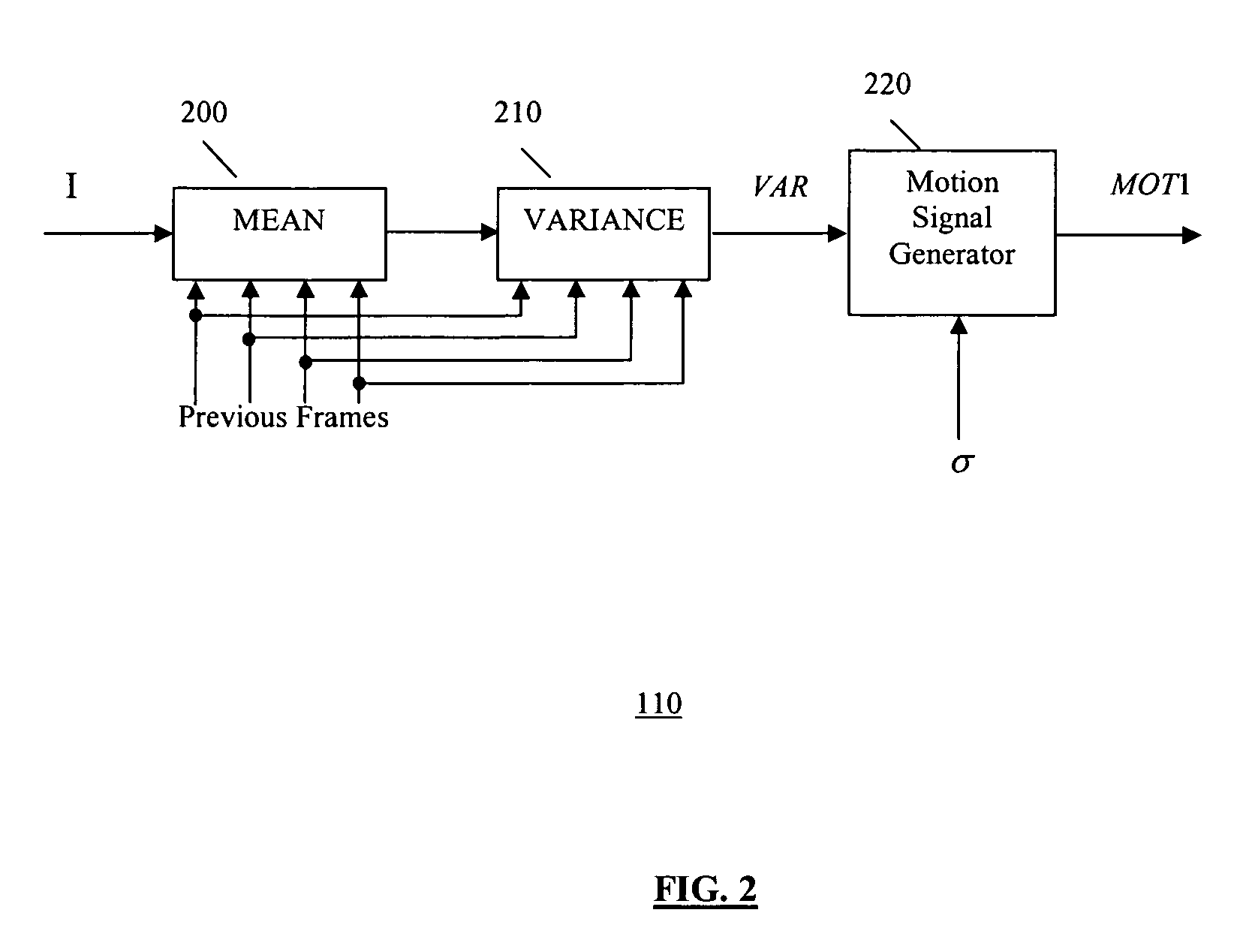
Spatio-temporal video noise reduction system
InactiveUS7145607B1Maximise noise reductionMinimize artefactTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionDigital video
A method and system for digital video noise reduction which includes a picture analyser (103) for analysing pictures in a video sequence to determine the amount of moving regions therein, a noise level detector (102) for estimating the noise level (N) in the video sequence, a filtering level estimator (105, 103) for determining a maximum filtering level (L) for each picture based on the amount of moving regions and the estimated noise level (N) and a spatial filter (106) and a temporal filter (107), the temporal filter being coupled to the filter level estimator for controlling the level of filtering of each picture in the sequence in accordance with the maximum filtering level.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Motion adaptive noise reduction apparatus and method for video signals
InactiveUS20050280739A1Optimal noise reductionIncrease the areaTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionSoft switching
A video noise reduction system for a set of video frames that computes a first motion signal using a current frame and multiple consecutive previous frames, computes a second motion signal using the current frame and the processed preceding frame; computes the multi-frame temporal average of the current frame and multiple consecutive previous frames; computes the recursive average of the current frame and the processed preceding frame; generates a temporal filtered signal by soft switching between the multi-frame temporal average and the recursive average based on the first motion signal; applies a spatial filter to the current frame to generate a spatial filtered signal; and combines the temporal filtered signal and the spatial filtered signal based on the second motion signal to generate a final noise reduced video output signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
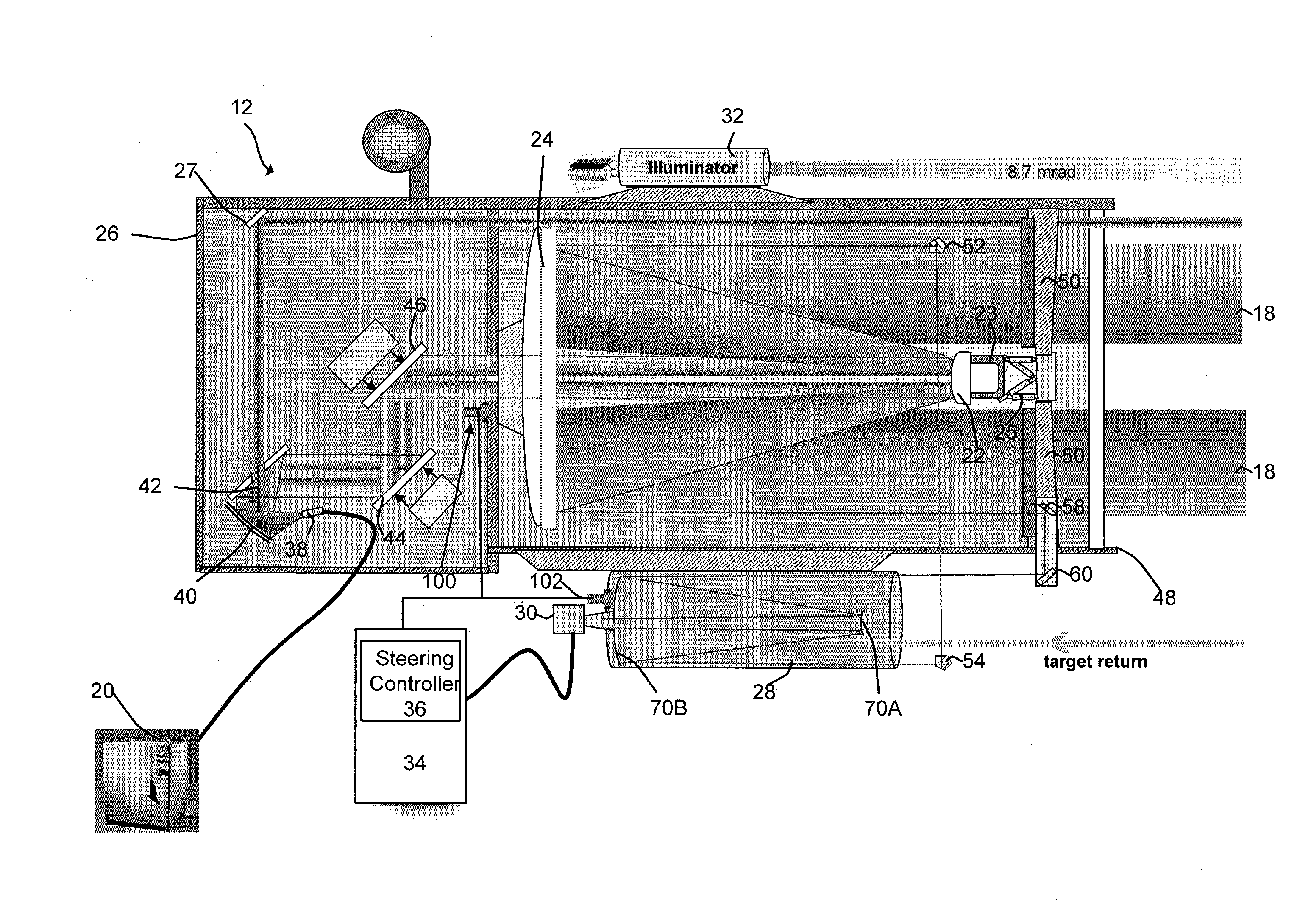
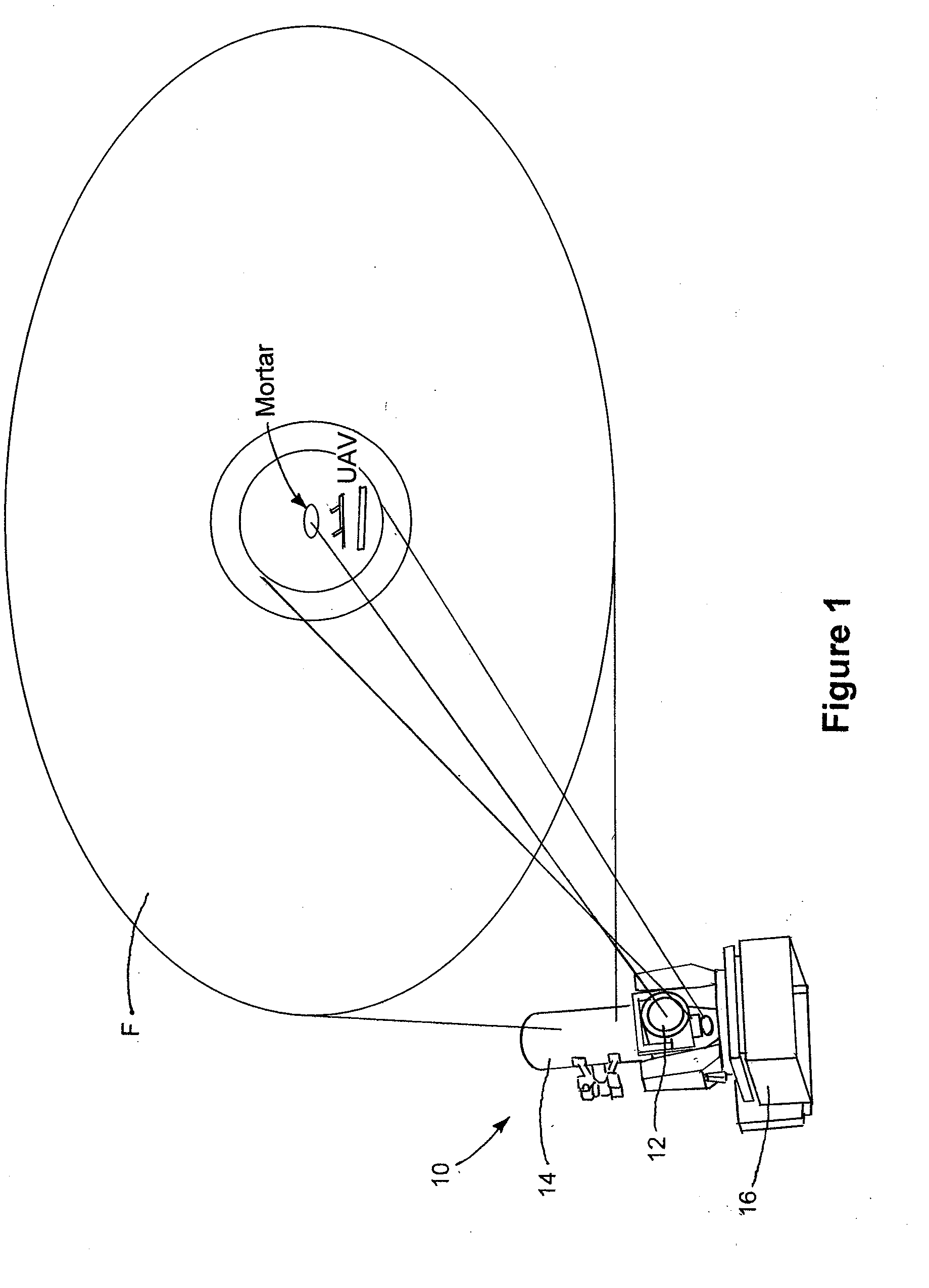
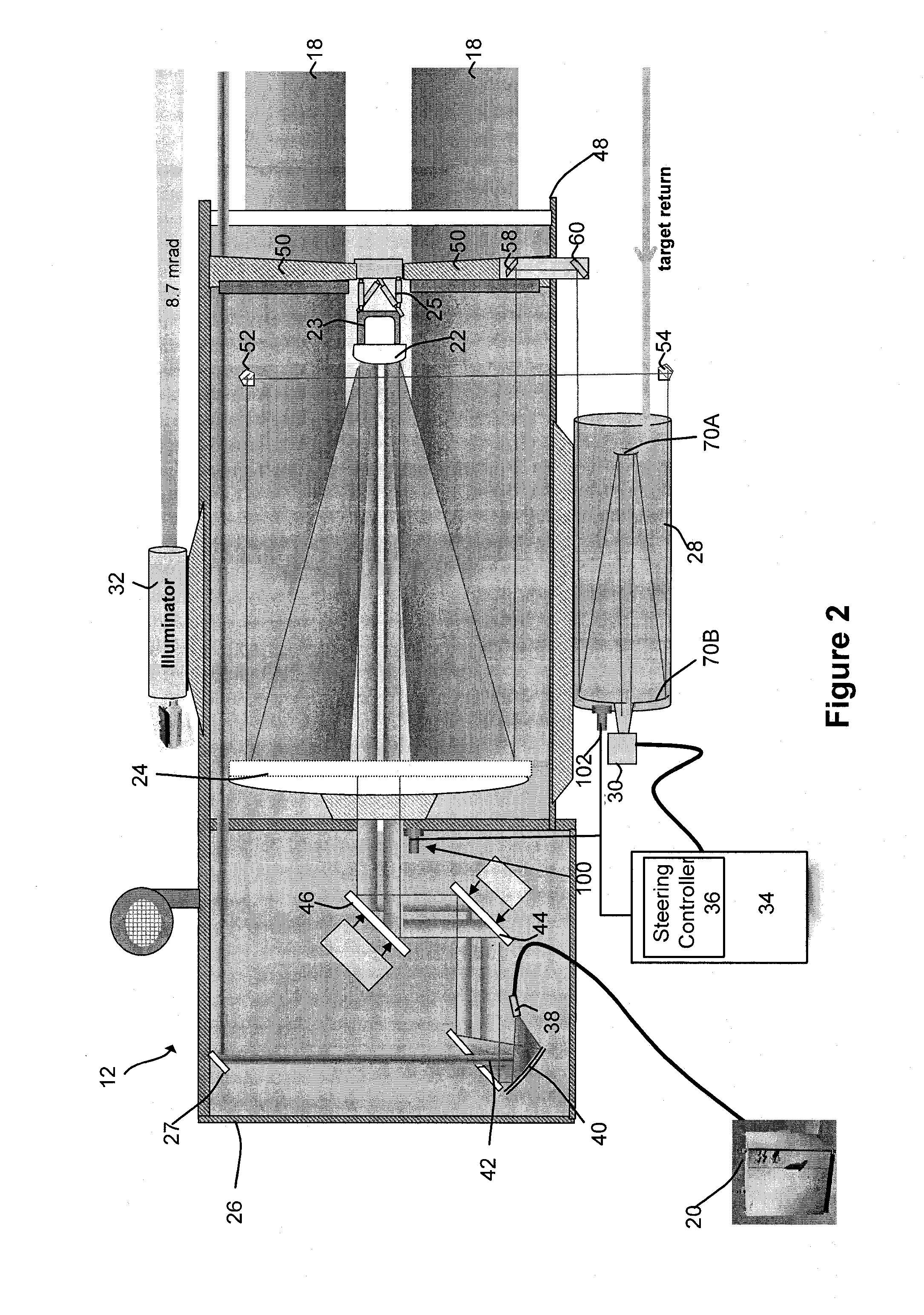
Semi-active optical tracking system
A system and method for tracking an airborne target including an illumination source (e.g., a diode laser array) is used to enhance a target signature and a detector (e.g., a passive high-speed camera) is used to detect to electromagnetic radiation (e.g., infrared radiation) reflected off the target. The received electromagnetic radiation may be processed by a digital computer and passed through a spatial filter that implements a band limited edge detection operation in the frequency domain. The filter may remove low spatial frequencies that attenuate soft edged clutter such as clouds and smoke as well as filter out artifacts and attenuated medium to high spatial frequencies to inhibit speckle noise from the detector as well as speckle from the laser return off the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
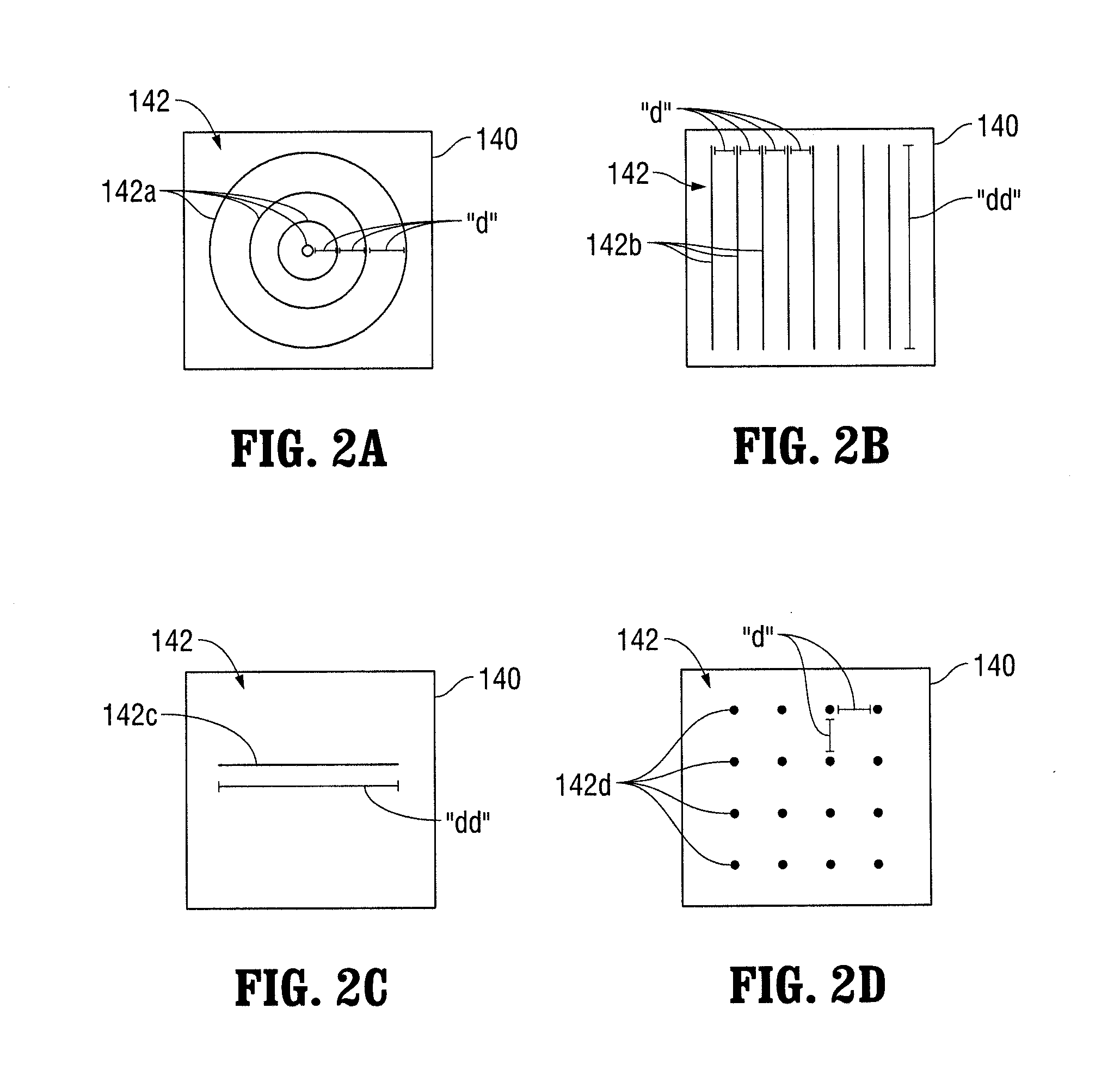
Programmable spatial filter for wafer inspection
InactiveUS20060012781A1Improve fill factorFacilitate transmissionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSpatial light modulatorLight beam
A programmable spatial filter for use as a Fourier plane filter in dark field wafer inspection systems, based on the use of MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) devices. In comparison with prior art systems, especially those using LCD's, the use of MEMS devices provide a number of potential advantages, including good transmission in the UV, a high fill factor, polarization independence and a high extinction ratio since the shutter is opaque when closed. The MEMS devices can be flap devices, artificial eyelid, or double shutter devices. Additionally, a novel spatial light modulator (SLM) assembly having a double layer of SLM arrays is described, in which the fill factor is increased in comparison to a single layer SLM using the same devices, by positioning the dead areas of the elements of both arrays collinearly in the modulated beam. This SLM assembly can be implemented using pixelated LCD arrays or MEMS arrays.
Owner:NEGEVTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com